├── .gitignore
├── 00091.png
├── README.md
├── data.py
├── losses.py
├── model.py
├── test.py
└── train.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *png
2 | *jpg
3 | *pth
4 | *pt
5 | *pyc
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/00091.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/AakashKT/pytorch-recurrent-ae-siggraph17/5fd5aa445fc6782aab62365fb65c387391c90e39/00091.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Interactive Reconstruction of Monte Carlo Image Sequences using a Recurrent Denoising Autoencoder , PyTorch implementation
2 | Link to original paper (SIGGRAPH '17) : https://research.nvidia.com/publication/interactive-reconstruction-monte-carlo-image-sequences-using-recurrent-denoising
3 |
4 | This is the unofficial PyTorch implementation of the above paper.
5 |
6 | # Dataset Preparation
7 | The input to this network is :
8 | * Albedo demodulated 1spp RGB image
9 | * Render a scene using any standart path tracer, and divide it by the albedo image of the same scene. Albedo image is usually obtained by adding the 'DiffuseColor' and 'GlossyColor' passes from the renderer.
10 | * Depth (Z-buffer)
11 | * Normal Map
12 | * Material roughness Map
13 | * Add the 'GlossyDirect' and 'GlossyIndirect' components from the renderer. Take the inverse of this image.
14 |
15 | The output of this network is :
16 | * Albedo demodulated 250spp RGB image
17 |
18 | Construct the input as one image, as follows :
19 | 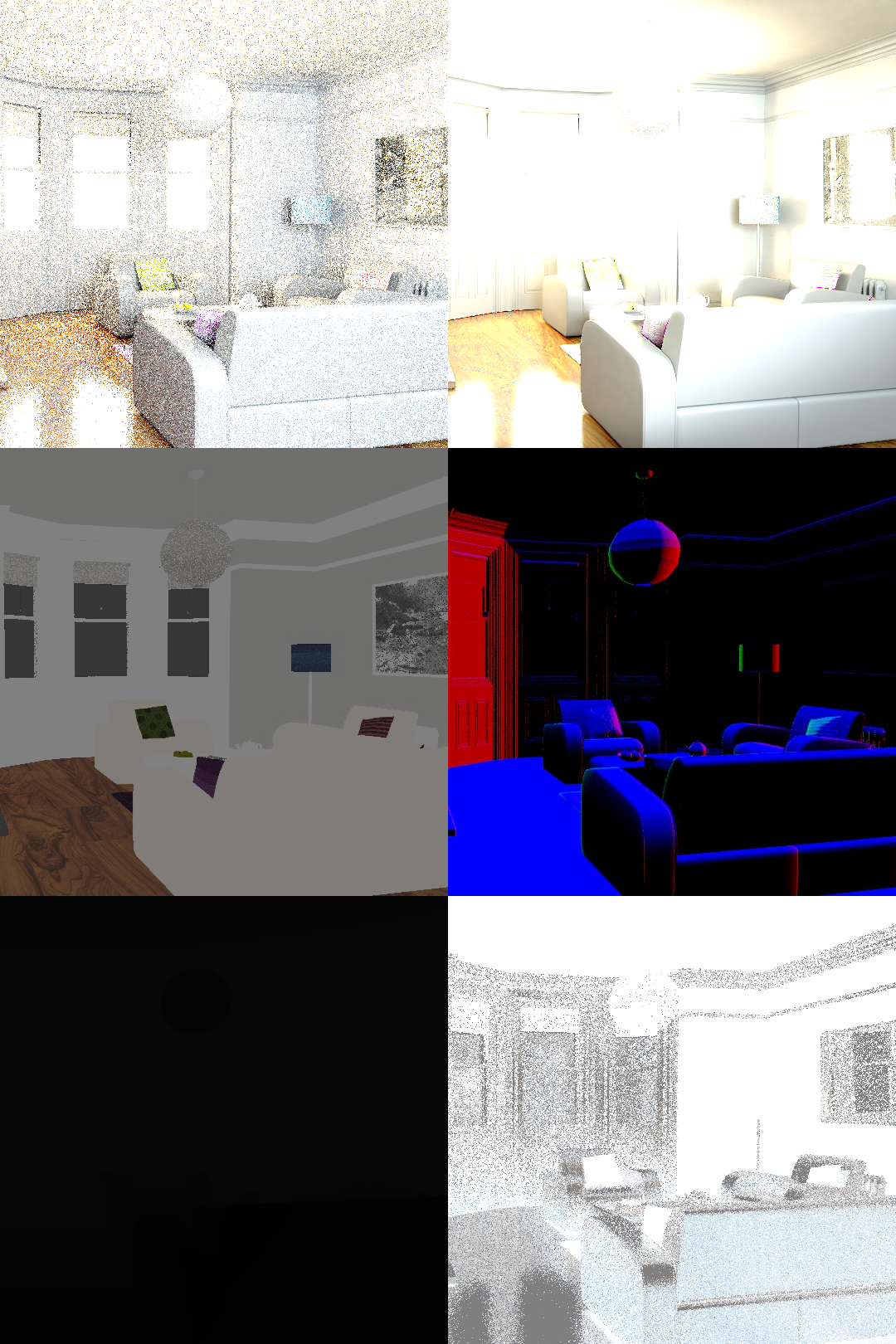 20 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 | | Column 1 |
24 | Column 2 |
25 |
26 |
27 | | 1 spp input |
28 | 250 spp output |
29 |
30 |
31 | | Albedo Image |
32 | Normal Map |
33 |
34 |
35 | | Depth Map |
36 | Roughness Map |
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 | Directory structure
41 | Make batches of batch size 7 of continuous frames, and put them in a directory (seq_0, seq_1 ..). Do this for all frames.
42 | Split the resulting directories into test and train.
43 |
44 | Note : The data directory must contain 'train' and 'test' directories, and these directories much contain directories where the sequence is stored.
45 |
46 | * [DATA_DIRECTORY]/train
47 | * [DATA_DIRECTORY]/train/seq_0/
48 | * [DATA_DIRECTORY]/train/seq_1/
49 | * ....
50 | * [DATA_DIRECTORY]/test
51 | * [DATA_DIRECTORY]/test/seq_0/
52 | * [DATA_DIRECTORY]/test/seq_1/
53 | * ....
54 |
55 | # Training the network
56 | To train the network, run the following command :
57 |
58 | ```
59 | python train.py --data_dir [PATH_TO_DATA_DIRECTORY] --name [EXP_NAME] --save_dir [PATH_TO_SAVE_CHECKPOINTS] --epochs 500
60 | ```
61 |
62 | # Running a trained network
63 | To test the network, run the following command :
64 |
65 | ```
66 | python test.py --data_dir [PATH_TO_DATA_DIRECTORY] --output_dir [PATH_TO_SAVE_RESULTS] --checkpoint [PATH_TO_CHECKPOINT].pt
67 | ```
68 |
69 | # TODO / Possible faults
70 | * Can we get the demodulated albedo directly from the renderer?
71 | * The network denoises the demodulated albedo perfectly. But while reconstructing the textured image, by multiplication with albedo, it looses a lot of detail. FIX THIS.
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch, os, sys, cv2
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from torch.nn import init
4 | import functools
5 | import torch.optim as optim
6 |
7 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
8 | from torch.nn import functional as func
9 | from PIL import Image
10 |
11 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import torch
14 |
15 |
16 | class RAEData(Dataset):
17 |
18 | def __init__(self, input_dir, size):
19 | super(RAEData, self).__init__()
20 |
21 | self.input_dir = input_dir
22 | self.images = sorted(os.listdir(self.input_dir))
23 |
24 | self.width = size[0]
25 | self.height = size[1]
26 |
27 | def __getitem__(self, index):
28 | # 10spp_shading ray_shading
29 | # 10spp_albedo normal
30 | # depth roughness
31 | #-----------------------------
32 |
33 | A = np.zeros((7, self.height, self.width, 8), dtype=np.float)
34 | B = np.zeros((7, self.height, self.width, 3), dtype=np.float)
35 | ALBEDO = np.zeros((7, self.height, self.width, 3), dtype=np.float)
36 |
37 | seq_images = sorted(os.listdir('%s/%s' % (self.input_dir, self.images[index])))
38 | for i, item in enumerate(seq_images):
39 | img = cv2.imread('%s/%s/%s' % (self.input_dir, self.images[index], item))
40 | img = cv2.resize(img, (self.width * 2, self.height * 3))
41 |
42 | shading = img[:self.height, :self.width, :]
43 | ray_shading = img[:self.height, self.width:, :]
44 | albedo = img[self.height:self.height * 2, :self.width, :]
45 | normal = img[self.height:self.height * 2, self.width:, :]
46 | depth = (img[self.height * 2:, :self.width, 0] + img[self.height * 2:, :self.width, 1] \
47 | + img[self.height * 2:, :self.width, 2]) / 3
48 | roughness = (img[self.height * 2:, self.width:, 0] + img[self.height * 2:, self.width:, 1] \
49 | + img[self.height * 2:, self.width:, 2]) / 3
50 | depth = np.expand_dims(depth, axis=2)
51 | roughness = np.expand_dims(roughness, axis=2)
52 |
53 | ray_shading = ray_shading.astype(np.float) / 255.0
54 | shading = shading.astype(np.float) / 255.0
55 | normal = normal.astype(np.float) / 255.0
56 | albedo = albedo.astype(np.float) / 255.0
57 | depth = depth.astype(np.float) / 255.0
58 | roughness = roughness.astype(np.float) / 255.0
59 |
60 | A[i, :, :, :3] = shading
61 | A[i, :, :, 3:6] = normal
62 | A[i, :, :, 6:7] = depth
63 | A[i, :, :, 7:8] = roughness
64 |
65 | B[i, :, :, :] = ray_shading
66 | ALBEDO[i, :, :, :] = albedo
67 |
68 | A = torch.from_numpy(A)
69 | B = torch.from_numpy(B)
70 | ALBEDO = torch.from_numpy(ALBEDO)
71 |
72 | A = A.permute((0, 3, 1, 2))
73 | B = B.permute((0, 3, 1, 2))
74 | ALBEDO = ALBEDO.permute((0, 3, 1, 2))
75 |
76 | return {
77 | 'A': A.type(torch.float).to('cuda:0'),
78 | 'B': B.type(torch.float).to('cuda:0'),
79 | 'ALBEDO': ALBEDO.type(torch.float).to('cuda:0')
80 | }
81 |
82 |
83 | def __len__(self):
84 | return len(self.images)
85 |
86 | def np_normalize(self, img):
87 | return (img - img.min()) / (img.max() - img.min())
88 |
89 | def save_image(self, img, img_name):
90 | img = torch.squeeze(img.detach(), dim=0) * 255.0
91 | img = img.permute((1, 2, 0))
92 | img = img.cpu().numpy().astype(np.uint8)
93 |
94 | cv2.imwrite(img_name, img)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/losses.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch, os, sys, cv2
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from torch.nn import init
4 | import functools
5 | import torch.optim as optim
6 |
7 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
8 | from torch.nn import functional as func
9 | from PIL import Image
10 |
11 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import torch
14 |
15 |
16 | def LoG(img):
17 | weight = [
18 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
19 | [0, 1, 2, 1, 0],
20 | [1, 2, -16, 2, 1],
21 | [0, 1, 2, 1, 0],
22 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0]
23 | ]
24 | weight = np.array(weight)
25 |
26 | weight_np = np.zeros((1, 1, 5, 5))
27 | weight_np[0, 0, :, :] = weight
28 | weight_np = np.repeat(weight_np, img.shape[1], axis=1)
29 | weight_np = np.repeat(weight_np, img.shape[0], axis=0)
30 |
31 | weight = torch.from_numpy(weight_np).type(torch.FloatTensor).to('cuda:0')
32 |
33 | return func.conv2d(img, weight, padding=1)
34 |
35 | def HFEN(output, target):
36 | return torch.sum(torch.pow(LoG(output) - LoG(target), 2)) / torch.sum(torch.pow(LoG(target), 2))
37 |
38 |
39 | def l1_norm(output, target):
40 | return torch.sum(torch.abs(output - target)) / torch.numel(output)
41 |
42 | def get_temporal_data(output, target):
43 | final_output = output.clone()
44 | final_target = target.clone()
45 | final_output.fill_(0)
46 | final_target.fill_(0)
47 |
48 | for i in range(1, 7):
49 | final_output[:, i, :, :, :] = output[:, i, :, :] - output[:, i-1, :, :]
50 | final_target[:, i, :, :, :] = target[:, i, :, :] - target[:, i-1, :, :]
51 |
52 | return final_output, final_target
53 |
54 | def temporal_norm(output, target):
55 | return torch.sum(torch.abs(output - target)) / torch.numel(output)
56 |
57 | def loss_func(output, temporal_output, target, temporal_target):
58 | ls = l1_norm(output, target)
59 | lg = HFEN(output, target)
60 | lt = temporal_norm(temporal_output, temporal_target)
61 |
62 | return 0.8 * ls + 0.1 * lg + 0.1 * lt, ls, lg, lt
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch, os, sys, cv2
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from torch.nn import init
4 | import functools
5 | import torch.optim as optim
6 |
7 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
8 | from torch.nn import functional as func
9 | from PIL import Image
10 |
11 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import torch
14 |
15 |
16 | class RecurrentBlock(nn.Module):
17 |
18 | def __init__(self, input_nc, output_nc, downsampling=False, bottleneck=False, upsampling=False):
19 | super(RecurrentBlock, self).__init__()
20 |
21 | self.input_nc = input_nc
22 | self.output_nc = output_nc
23 |
24 | self.downsampling = downsampling
25 | self.upsampling = upsampling
26 | self.bottleneck = bottleneck
27 |
28 | self.hidden = None
29 |
30 | if self.downsampling:
31 | self.l1 = nn.Sequential(
32 | nn.Conv2d(input_nc, output_nc, 3, padding=1),
33 | nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)
34 | )
35 | self.l2 = nn.Sequential(
36 | nn.Conv2d(2 * output_nc, output_nc, 3, padding=1),
37 | nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1),
38 | nn.Conv2d(output_nc, output_nc, 3, padding=1),
39 | nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1),
40 | )
41 | elif self.upsampling:
42 | self.l1 = nn.Sequential(
43 | nn.Upsample(scale_factor=2, mode='nearest'),
44 | nn.Conv2d(2 * input_nc, output_nc, 3, padding=1),
45 | nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1),
46 | nn.Conv2d(output_nc, output_nc, 3, padding=1),
47 | nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1),
48 | )
49 | elif self.bottleneck:
50 | self.l1 = nn.Sequential(
51 | nn.Conv2d(input_nc, output_nc, 3, padding=1),
52 | nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)
53 | )
54 | self.l2 = nn.Sequential(
55 | nn.Conv2d(2 * output_nc, output_nc, 3, padding=1),
56 | nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1),
57 | nn.Conv2d(output_nc, output_nc, 3, padding=1),
58 | nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1),
59 | )
60 |
61 | def forward(self, inp):
62 |
63 | if self.downsampling:
64 | op1 = self.l1(inp)
65 | op2 = self.l2(torch.cat((op1, self.hidden), dim=1))
66 |
67 | self.hidden = op2
68 |
69 | return op2
70 | elif self.upsampling:
71 | op1 = self.l1(inp)
72 |
73 | return op1
74 | elif self.bottleneck:
75 | op1 = self.l1(inp)
76 | op2 = self.l2(torch.cat((op1, self.hidden), dim=1))
77 |
78 | self.hidden = op2
79 |
80 | return op2
81 |
82 | def reset_hidden(self, inp, dfac):
83 | size = list(inp.size())
84 | size[1] = self.output_nc
85 | size[2] /= dfac
86 | size[3] /= dfac
87 |
88 | self.hidden_size = size
89 | self.hidden = torch.zeros(*(size)).to('cuda:0')
90 |
91 |
92 |
93 | class RecurrentAE(nn.Module):
94 |
95 | def __init__(self, input_nc):
96 | super(RecurrentAE, self).__init__()
97 |
98 | self.d1 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=input_nc, output_nc=32, downsampling=True)
99 | self.d2 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=32, output_nc=43, downsampling=True)
100 | self.d3 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=43, output_nc=57, downsampling=True)
101 | self.d4 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=57, output_nc=76, downsampling=True)
102 | self.d5 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=76, output_nc=101, downsampling=True)
103 |
104 | self.bottleneck = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=101, output_nc=101, bottleneck=True)
105 |
106 | self.u5 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=101, output_nc=76, upsampling=True)
107 | self.u4 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=76, output_nc=57, upsampling=True)
108 | self.u3 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=57, output_nc=43, upsampling=True)
109 | self.u2 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=43, output_nc=32, upsampling=True)
110 | self.u1 = RecurrentBlock(input_nc=32, output_nc=3, upsampling=True)
111 |
112 | def set_input(self, inp):
113 | self.inp = inp['A']
114 |
115 | def forward(self):
116 | d1 = func.max_pool2d(input=self.d1(self.inp), kernel_size=2)
117 | d2 = func.max_pool2d(input=self.d2(d1), kernel_size=2)
118 | d3 = func.max_pool2d(input=self.d3(d2), kernel_size=2)
119 | d4 = func.max_pool2d(input=self.d4(d3), kernel_size=2)
120 | d5 = func.max_pool2d(input=self.d5(d4), kernel_size=2)
121 |
122 | b = self.bottleneck(d5)
123 |
124 | u5 = self.u5(torch.cat((b, d5), dim=1))
125 | u4 = self.u4(torch.cat((u5, d4), dim=1))
126 | u3 = self.u3(torch.cat((u4, d3), dim=1))
127 | u2 = self.u2(torch.cat((u3, d2), dim=1))
128 | u1 = self.u1(torch.cat((u2, d1), dim=1))
129 |
130 | return u1
131 |
132 | def reset_hidden(self):
133 | self.d1.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=1)
134 | self.d2.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=2)
135 | self.d3.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=4)
136 | self.d4.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=8)
137 | self.d5.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=16)
138 |
139 | self.bottleneck.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=32)
140 |
141 | self.u4.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=16)
142 | self.u3.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=8)
143 | self.u5.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=4)
144 | self.u2.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=2)
145 | self.u1.reset_hidden(self.inp, dfac=1)
146 |
147 |
148 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch, os, sys, cv2
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from torch.nn import init
4 | import functools
5 | import torch.optim as optim
6 |
7 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
8 | from torch.nn import functional as func
9 | from PIL import Image
10 |
11 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import torch, argparse, pdb
14 |
15 | from model import *
16 | from data import *
17 | from losses import *
18 |
19 |
20 | def load_checkpoint(filename):
21 | chkpoint = torch.load(filename);
22 | model = RecurrentAE(8);
23 | model.to('cuda:0');
24 | optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001, betas=(0.9, 0.99))
25 |
26 | epoch = chkpoint['epoch'];
27 | model.load_state_dict(chkpoint['state_dict']);
28 | optimizer.load_state_dict(chkpoint['optimizer']);
29 |
30 | return model, optimizer, int(epoch);
31 |
32 |
33 | if __name__ == '__main__':
34 |
35 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='RecurentAE, SIGGRAPH \'17')
36 | parser.add_argument('--data_dir', type=str, help='Data directory')
37 | parser.add_argument('--output_dir', type=str, help='Directory to save output')
38 | parser.add_argument('--checkpoint', type=str, help='Checkpoint to load')
39 |
40 | args = parser.parse_args()
41 |
42 | model, optimizer, epoch = load_checkpoint(args.checkpoint)
43 |
44 | size = (256, 256)
45 | width = size[0]
46 | height = size[1]
47 |
48 | data_loader = RAEData('%s/test' % args.data_dir, size)
49 | dataset = DataLoader(data_loader, batch_size=1, num_workers=0, shuffle=False)
50 |
51 | for i, item in enumerate(dataset):
52 |
53 | os.system('mkdir -p %s/seq_%s' % (args.output_dir, i))
54 | for j in range(0, 7):
55 | inp = item['A']
56 | gt = item['B']
57 |
58 | inp = inp[:, j, :, :, :]
59 | gt = gt[:, j, :, :, :]
60 |
61 | final_inp = {
62 | 'A': inp,
63 | 'B': gt
64 | }
65 |
66 | model.set_input(final_inp)
67 | if j == 0:
68 | model.reset_hidden()
69 |
70 | output = model()
71 |
72 | albedo = item['ALBEDO'].clone()
73 | albedo = albedo[:, j, :, :, :]
74 | albedo = torch.squeeze(albedo.detach(), dim=0) * 255.0
75 | albedo = albedo.permute((1, 2, 0))
76 | albedo = albedo.cpu().numpy()
77 |
78 | ray = final_inp['B'].clone()
79 | ray = torch.squeeze(ray, dim=0)
80 | ray = ray[:3, :, :]
81 | ray = ray.permute((1, 2, 0))
82 | ray = ray.cpu().numpy()
83 | ray *= 255.0
84 |
85 | output = torch.squeeze(output.detach(), dim=0)
86 | output = output.permute((1, 2, 0))
87 | output = output.cpu().numpy()
88 | output *= 255.0
89 |
90 | og = final_inp['A']
91 | og = torch.squeeze(og.detach(), dim=0) * 255.0
92 | og = og.permute((1, 2, 0))
93 | og = og.cpu().numpy()
94 |
95 | final = np.zeros((height, width * 4, 3), dtype=np.float)
96 | final[:, :width, :] = og[:, :, :3]
97 | final[:, width:width * 2, :] = albedo
98 | final[:, width * 2:width * 3, :] = output
99 | final[:, width * 3:width * 4, :] = ray
100 |
101 | cv2.imwrite('%s/seq_%s/%s.png' % (args.output_dir, i, j), final)
102 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch, os, sys, cv2
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from torch.nn import init
4 | import functools
5 | import torch.optim as optim
6 |
7 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
8 | from torch.nn import functional as func
9 | from PIL import Image
10 |
11 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import torch, argparse, pdb
14 |
15 | from model import *
16 | from data import *
17 | from losses import *
18 |
19 |
20 | def save_checkpoint(state, filename):
21 | torch.save(state, filename);
22 |
23 | def train_sequence(model, sequence):
24 | output_final = sequence['B'].clone()
25 | output_final.fill_(0)
26 | target_final = sequence['B'].clone()
27 | target_final.fill_(0)
28 |
29 | inp = sequence['A']
30 | target = sequence['B']
31 |
32 | loss_final = 0
33 | ls_final = 0
34 | lg_final = 0
35 | lt_final = 0
36 |
37 | for j in range(0, 7):
38 | inpi = inp[:, j, :, :, :]
39 | gti = target[:, j, :, :, :]
40 |
41 | final_inp = {
42 | 'A': inpi,
43 | 'B': gti
44 | }
45 |
46 | model.set_input(final_inp)
47 | if j == 0:
48 | model.reset_hidden()
49 |
50 | output = model()
51 | output_final[:, j, :, :, :] = output
52 | target_final[:, j, :, :, :] = gti
53 |
54 | temporal_output, temporal_target = get_temporal_data(output_final, target_final)
55 |
56 | for j in range(0, 7):
57 | output = output_final[:, j, :, :, :]
58 | target = target_final[:, j, :, :, :]
59 | t_output = temporal_output[:, j, :, :, :]
60 | t_target = temporal_target[:, j, :, :, :]
61 |
62 | l, ls, lg, lt = loss_func(output, t_output, target, t_target)
63 | loss_final += l
64 | ls_final += ls
65 | lg_final += lg
66 | lt_final += lt
67 |
68 | return loss_final, ls_final, lg_final, lt_final
69 |
70 |
71 | def train(model, dataset, optimizer, epoch):
72 |
73 | total_loss = 0
74 | total_loss_num = 0
75 |
76 | for i, item in enumerate(dataset):
77 | optimizer.zero_grad()
78 | loss_final, ls_final, lg_final, lt_final = train_sequence(model, item)
79 |
80 | loss_final.backward(retain_graph=False)
81 | optimizer.step()
82 |
83 | total_loss += loss_final.item()
84 | total_loss_num += 1
85 |
86 | if i % 50 == 0:
87 | print('[Epoch : %s] [%s/%s] Loss => %s , L1 => %s , HFEN => %s , TEMPORAL => %s' % \
88 | (epoch+1, (i+1), len(data_loader), loss_final.item(), ls_final.item(), \
89 | lg_final.item(), lt_final.item()))
90 | sys.stdout.flush()
91 |
92 | total_loss /= total_loss_num
93 |
94 | return total_loss
95 |
96 |
97 |
98 | if __name__ == '__main__':
99 |
100 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='RecurentAE, SIGGRAPH \'17')
101 | parser.add_argument('--data_dir', type=str, help='Data directory')
102 | parser.add_argument('--save_dir', type=str, help='Model chekpoint saving directory')
103 | parser.add_argument('--name', type=str, help='Experiment Name')
104 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, help='Number of epochs to train')
105 |
106 | args = parser.parse_args()
107 |
108 | data_loader = RAEData('%s/train' % args.data_dir, (256, 256))
109 | dataset = DataLoader(data_loader, batch_size=1, num_workers=0, shuffle=True)
110 |
111 | model = RecurrentAE(8)
112 | model.to('cuda:0')
113 | print(model)
114 |
115 | optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=0.0001, betas=(0.9, 0.99))
116 |
117 | for epoch in range(args.epochs):
118 | print('\nEpoch %s' % (epoch+1))
119 |
120 | total_loss = train(model, dataset, optimizer, epoch)
121 |
122 | print('Epoch %s loss => %s' % (epoch+1, total_loss))
123 | sys.stdout.flush()
124 |
125 | if epoch % 100 == 0:
126 | print('SAVING MODEL AT EPOCH %s' % (epoch+1))
127 | save_checkpoint({
128 | 'epoch': epoch+1,
129 | 'state_dict':model.state_dict(),
130 | 'optimizer':optimizer.state_dict(),
131 | }, '%s/%s_%s.pt' % (args.save_dir, args.name, epoch+1))
132 |
133 |
134 | save_checkpoint({
135 | 'epoch': args.epochs,
136 | 'state_dict':model.state_dict(),
137 | 'optimizer':optimizer.state_dict(),
138 | }, '%s/%s_%s.pt' % (args.save_dir, args.name, args.epochs))
139 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 20 |
20 |