├── README.md
├── SCNet_arch.py
├── basicsr
├── __init__.py
├── archs
│ ├── SCNet_arch.py
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── arch_util.py
│ └── vgg_arch.py
├── data
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── data_sampler.py
│ ├── data_util.py
│ ├── degradations.py
│ ├── ffhq_dataset.py
│ ├── meta_info
│ │ ├── meta_info_DIV2K800sub_GT.txt
│ │ ├── meta_info_REDS4_test_GT.txt
│ │ ├── meta_info_REDS_GT.txt
│ │ ├── meta_info_REDSofficial4_test_GT.txt
│ │ ├── meta_info_REDSval_official_test_GT.txt
│ │ ├── meta_info_Vimeo90K_test_GT.txt
│ │ ├── meta_info_Vimeo90K_test_fast_GT.txt
│ │ ├── meta_info_Vimeo90K_test_medium_GT.txt
│ │ ├── meta_info_Vimeo90K_test_slow_GT.txt
│ │ └── meta_info_Vimeo90K_train_GT.txt
│ ├── paired_image_dataset.py
│ ├── prefetch_dataloader.py
│ ├── realesrgan_dataset.py
│ ├── realesrgan_paired_dataset.py
│ ├── reds_dataset.py
│ ├── single_image_dataset.py
│ ├── transforms.py
│ ├── video_test_dataset.py
│ └── vimeo90k_dataset.py
├── losses
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── basic_loss.py
│ ├── gan_loss.py
│ └── loss_util.py
├── metrics
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── README_CN.md
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── fid.py
│ ├── metric_util.py
│ ├── niqe.py
│ ├── niqe_pris_params.npz
│ ├── psnr_ssim.py
│ └── test_metrics
│ │ └── test_psnr_ssim.py
├── models
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── base_model.py
│ ├── lr_scheduler.py
│ └── sr_model.py
├── ops
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── dcn
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── deform_conv.py
│ │ └── src
│ │ │ ├── deform_conv_cuda.cpp
│ │ │ ├── deform_conv_cuda_kernel.cu
│ │ │ └── deform_conv_ext.cpp
│ ├── fused_act
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── fused_act.py
│ │ └── src
│ │ │ ├── fused_bias_act.cpp
│ │ │ └── fused_bias_act_kernel.cu
│ └── upfirdn2d
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── src
│ │ ├── upfirdn2d.cpp
│ │ └── upfirdn2d_kernel.cu
│ │ └── upfirdn2d.py
├── test.py
├── train.py
└── utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── color_util.py
│ ├── diffjpeg.py
│ ├── dist_util.py
│ ├── download_util.py
│ ├── file_client.py
│ ├── flow_util.py
│ ├── img_process_util.py
│ ├── img_util.py
│ ├── lmdb_util.py
│ ├── logger.py
│ ├── matlab_functions.py
│ ├── misc.py
│ ├── options.py
│ ├── plot_util.py
│ └── registry.py
└── options
├── test
└── SCNet
│ ├── SCNet-T-x4-PS.yml
│ └── SCNet-T-x4.yml
└── train
└── SCNet
└── SCNet-T-x4.yml
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | # Fully 1x1 Convolutional Network for Lightweight Image Super-Resolution
4 |
5 | [Gang Wu](https://scholar.google.com/citations?user=JSqb7QIAAAAJ), [Junjun Jiang](http://homepage.hit.edu.cn/jiangjunjun), [Kui Jiang](https://github.com/kuijiang94), and [Xianming Liu](http://homepage.hit.edu.cn/xmliu)
6 |
7 | [AIIA Lab](https://aiialabhit.github.io/team/), Harbin Institute of Technology.
8 |
9 | ---
10 |
11 |
12 | [](https://arxiv.org/abs/2307.16140)
13 | [](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1eUqL_8a9DQXZ2uCVyKeWB-6fO1ZdJciG?usp=sharing)
14 | [](https://pan.baidu.com/s/13_syaIXmG3lVnoMgzOS2Ag?pwd=SCSR)
15 | [](https://hits.sh/github.com/Aitical/SCNet/)
16 |
17 |
18 | This repository is the official PyTorch implementation of "Fully 1×1 Convolutional Network for Lightweight Image Super-Resolution". If our work helps your research or work, please cite it.
19 | ```
20 | @article{wu2023fully,
21 | title={Fully $1\times1$ Convolutional Network for Lightweight Image Super-Resolution},
22 | author={Gang Wu and Junjun Jiang and Kui Jiang and Xianming Liu},
23 | year={2023},
24 | journal={Machine Intelligence Research},
25 | doi={10.1007/s11633-024-1401-z},
26 | }
27 | ```
28 | >Wu, Gang, Junjun Jiang, Kui Jiang and Xianming Liu. “Fully 1×1 Convolutional Network for Lightweight Image Super-Resolution.” Machine Intelligence Research.
29 |
30 | ## News
31 |
32 | - [x] Update implementation codes.
33 |
34 | - [x] Upload pre-trained weights utilized in manuscript. You can download from [Google Drive](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1eUqL_8a9DQXZ2uCVyKeWB-6fO1ZdJciG?usp=sharing) or [Baidu Netdisk](https://pan.baidu.com/s/13_syaIXmG3lVnoMgzOS2Ag?pwd=SCSR) with password `SCSR`.
35 |
36 | ## Overview
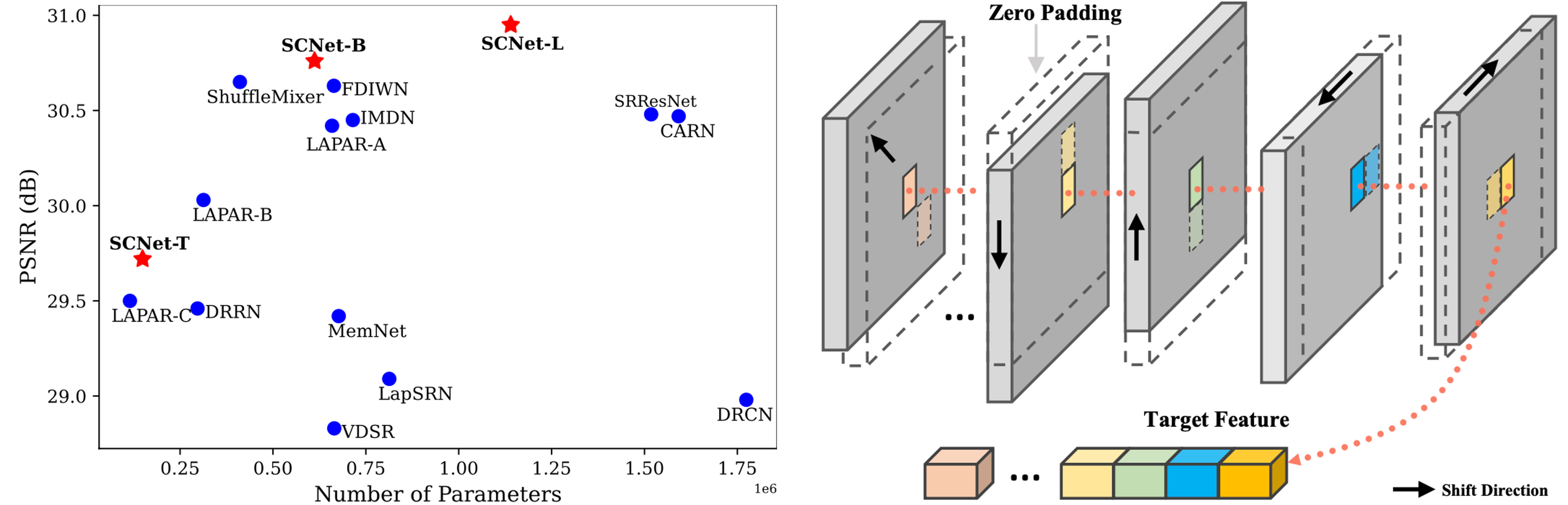
37 | >Deep models have achieved significant process on single image super-resolution (SISR) tasks, in particular large models with large kernel (3×3 or more). However, the heavy computational footprint of such models prevents their deployment in real-time, resource-constrained environments. Conversely, 1×1 convolutions bring substantial computational efficiency, but struggle with aggregating local spatial representations, an essential capability to SISR models. In response to this dichotomy, we propose to harmonize the merits of both 3×3 and 1×1 kernels, and exploit a great potential for lightweight SISR tasks. Specifically, we propose a simple yet effective fully 1×1 convolutional network, named Shift-Conv-based Network (SCNet). By incorporating a parameter-free spatial-shift operation, it equips the fully 1×1 convolutional network with powerful representation capability while impressive computational efficiency. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SCNets, despite its fully 1×1 convolutional structure, consistently matches or even surpasses the performance of existing lightweight SR models that employ regular convolutions.
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 |
 41 |
41 |  41 |
41 |