 59 |
60 | [Github](https://github.com/kipgparker/soft-prompt-tuning) source for soft prompt tuning.
61 |
62 | ## DART Implementation (???)
63 |
64 | Refer to soft prompt tuning. The methodology seems exactly the same, except that DART can be applied to any language
65 | model, and they added fluency constraint objectives to the model training to ensure the differentiable prompts retain
66 | association between template tokens.
67 |
68 | Differentiable prompts [DART](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.13161.pdf) except we adapt it from MLM to CLM. Instead of
69 | labels based on a the output of a single [MASK] token we generate a whole sequence and evaluate the semantic similarity
70 | of the output sequence.
71 |
72 | The input prompt when fed into an MLM model looks like this:
73 | Xprompt = [CLS] Xin [SEP] T [SEP]
74 |
75 | where T is the template prompt with containing single [MASK] token, of the form:
76 | {h0,...,hi,w([MASK]),hi+1,...,hm}
77 |
78 | Since OPT as a decoder is autoregressive, we alter T as such (predk are predicted tokens from previous k
79 | iterations):
80 | {h0,...,hi,pred0,...,predk,w([MASK])}
81 |
82 | Prompt embeddings that come after w([MASK]) will be masked and ignored anyway, hence we omit them in this
83 | implementation. The input prompt when fed into OPT (formatted similarly to GPT2's tokenizer) will then look like this:
84 | Xprompt = [EOS] Xin [BOS/EOS] {h0,...,hi,pred0,...,pred
85 | k,w([MASK])}
86 |
87 | We then iterate through multiple forward passes until we reach an eos_token output by the model or max length of the
88 | sequence.
89 |
90 | # ERROR SHEET
91 |
92 | Some errors may pop up when trying to run the program. "But it works on my machine" yeah it will work on your machine
93 | when you do these things.
94 |
95 | ### PyGraphViz Installation Errors (Especially on Windows)
96 | https://pygraphviz.github.io/documentation/stable/install.html#install
97 | Cancer. Follow the instructions. Use powershell or anaconda powershell. Restart the terminal/editor.
98 |
99 |
100 | ### Memory Errors
101 | Who doesn't love training large models? Some errors aren't due to the large model though. Like this one, this one occurs
102 | if the batch size is too large. Reduce the batch size because huggingface is trying to allocate a continguous block of
103 | gpu memory to compare the logits, and if the batch size is too large the logits are as a result too large to fit in the
104 | gpu.
105 |
106 | ```commandline
107 | File "/opt/conda/envs/OPT/lib/python3.10/site-packages/transformers/models/opt/modeling_opt.py", line 951, in forward
108 | shift_logits = logits[..., :-1, :].contiguous()
109 | RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate 2.11 GiB (GPU 0; 39.59 GiB total capacity; 36.18 GiB already allocated; 910.19 MiB free; 36.66 GiB reserved in total by PyTorch) If reserved memory is >> allocated memory try setting max_split_size_mb to avoid fragmentation. See documentation for Memory Management and PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF
110 | ```
111 |
112 |
113 | ### protobuf error
114 |
115 | Might encounter an error with protobuf apparently one of google's updates broke it so its incompatible with pytorch
116 | lightning. Quick fix is to downgrade it to an older version:
117 |
118 | ```buildoutcfg
119 | pip install protobuf==3.20.1
120 | ```
121 |
122 | # GCloud Compute CLI Cheatsheet
123 |
124 | ## ssh
125 | ```commandline
126 | gcloud compute instances start liewweipyn
127 | gcloud compute ssh liewweipyn
128 | gcloud compute instances stop liewweipyn
129 | ```
130 |
131 | ## tmux
132 | To detach sessions from the ssh shell, so we can close the ssh client without ending the training.
133 | Use ctrl + b + d to exit a session.
134 | ```commandline
135 | tmux new // create new session
136 | tmux ls // look at all created sessions
137 | tmux attach -t 0 // reattach to a detached session
138 | ```
139 |
140 | ## scp
141 | To transfer files between google cloud compute and desktop, works both ways.
142 | ```
143 | gcloud compute scp liewweipyn:
59 |
60 | [Github](https://github.com/kipgparker/soft-prompt-tuning) source for soft prompt tuning.
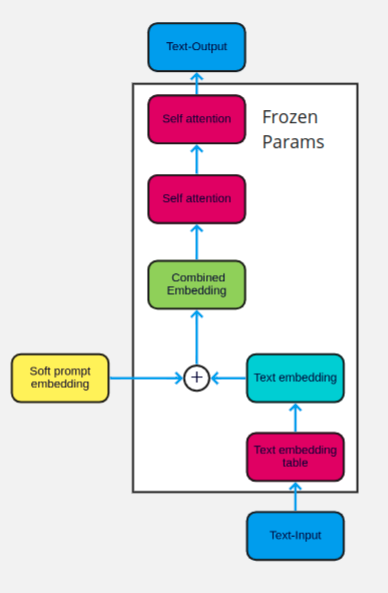
61 |
62 | ## DART Implementation (???)
63 |
64 | Refer to soft prompt tuning. The methodology seems exactly the same, except that DART can be applied to any language
65 | model, and they added fluency constraint objectives to the model training to ensure the differentiable prompts retain
66 | association between template tokens.
67 |
68 | Differentiable prompts [DART](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.13161.pdf) except we adapt it from MLM to CLM. Instead of
69 | labels based on a the output of a single [MASK] token we generate a whole sequence and evaluate the semantic similarity
70 | of the output sequence.
71 |
72 | The input prompt when fed into an MLM model looks like this:
73 | Xprompt = [CLS] Xin [SEP] T [SEP]
74 |
75 | where T is the template prompt with containing single [MASK] token, of the form:
76 | {h0,...,hi,w([MASK]),hi+1,...,hm}
77 |
78 | Since OPT as a decoder is autoregressive, we alter T as such (predk are predicted tokens from previous k
79 | iterations):
80 | {h0,...,hi,pred0,...,predk,w([MASK])}
81 |
82 | Prompt embeddings that come after w([MASK]) will be masked and ignored anyway, hence we omit them in this
83 | implementation. The input prompt when fed into OPT (formatted similarly to GPT2's tokenizer) will then look like this:
84 | Xprompt = [EOS] Xin [BOS/EOS] {h0,...,hi,pred0,...,pred
85 | k,w([MASK])}
86 |
87 | We then iterate through multiple forward passes until we reach an eos_token output by the model or max length of the
88 | sequence.
89 |
90 | # ERROR SHEET
91 |
92 | Some errors may pop up when trying to run the program. "But it works on my machine" yeah it will work on your machine
93 | when you do these things.
94 |
95 | ### PyGraphViz Installation Errors (Especially on Windows)
96 | https://pygraphviz.github.io/documentation/stable/install.html#install
97 | Cancer. Follow the instructions. Use powershell or anaconda powershell. Restart the terminal/editor.
98 |
99 |
100 | ### Memory Errors
101 | Who doesn't love training large models? Some errors aren't due to the large model though. Like this one, this one occurs
102 | if the batch size is too large. Reduce the batch size because huggingface is trying to allocate a continguous block of
103 | gpu memory to compare the logits, and if the batch size is too large the logits are as a result too large to fit in the
104 | gpu.
105 |
106 | ```commandline
107 | File "/opt/conda/envs/OPT/lib/python3.10/site-packages/transformers/models/opt/modeling_opt.py", line 951, in forward
108 | shift_logits = logits[..., :-1, :].contiguous()
109 | RuntimeError: CUDA out of memory. Tried to allocate 2.11 GiB (GPU 0; 39.59 GiB total capacity; 36.18 GiB already allocated; 910.19 MiB free; 36.66 GiB reserved in total by PyTorch) If reserved memory is >> allocated memory try setting max_split_size_mb to avoid fragmentation. See documentation for Memory Management and PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF
110 | ```
111 |
112 |
113 | ### protobuf error
114 |
115 | Might encounter an error with protobuf apparently one of google's updates broke it so its incompatible with pytorch
116 | lightning. Quick fix is to downgrade it to an older version:
117 |
118 | ```buildoutcfg
119 | pip install protobuf==3.20.1
120 | ```
121 |
122 | # GCloud Compute CLI Cheatsheet
123 |
124 | ## ssh
125 | ```commandline
126 | gcloud compute instances start liewweipyn
127 | gcloud compute ssh liewweipyn
128 | gcloud compute instances stop liewweipyn
129 | ```
130 |
131 | ## tmux
132 | To detach sessions from the ssh shell, so we can close the ssh client without ending the training.
133 | Use ctrl + b + d to exit a session.
134 | ```commandline
135 | tmux new // create new session
136 | tmux ls // look at all created sessions
137 | tmux attach -t 0 // reattach to a detached session
138 | ```
139 |
140 | ## scp
141 | To transfer files between google cloud compute and desktop, works both ways.
142 | ```
143 | gcloud compute scp liewweipyn:-
5 |
-
210 |
- 211 |
- 212 |
- 213 |
- 214 |
- 215 |
- 216 |
-
219 |
- 220 |
- 221 |
- 222 |
- 223 |
- 224 |
 51 |
52 | The learnable tokens can be thought of as passing conceptual notions to the model in an attempt to get it to better
53 | understand the task that is requested. As the models represent words as numbers in a high dimensional space,
54 | we need not restrict our prompts to discrete words, and can search in the space between words to find the most
55 | suitable prompts to feed into the model.
56 |
57 | These prompts are very efficient in terms of memory and compute, requiring just 0.2% of the size of a complete model
58 | checkpoint which would store fine-tuned model parameters, as well as being capable of achieving good results in
59 | less training time.
60 |
61 |
62 | ## Datasets
63 | Two popular paraphrasic datasets were used in soft prompt training of the models.
64 | [ParaBank 2.0](https://nlp.jhu.edu/parabank/) and [ParaNMT-50M](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.05732.pdf),
65 | both datasets generated through automatic translation of large amounts of bilingual textual data, translating a
66 | foreign language to english to obtain english-english paraphrase pairs.
67 |
68 | For example, the ParaNMT-50M dataset used Czech-English parallel pairs and applied a Czech to English
69 | pretrained model for translation on the czech pairs.
70 |
71 | As the datasets are incredibly large, we utilised HuggingFace's [dataset streaming](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/stream)
72 | feature to progressively feed training data to the model.
73 |
74 | Initially the baseline 20 token model was trained on a 35%-65% split of Parabank 2.0 and ParaNMT-50M respectively,
75 | however for parameter optimization, all further models were trained on a 50%-50% split of Parabank 2.0 and ParaNMT-50M
76 | respectively.
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | ## Implementation
81 | The model was implemented using the OPT model provided by the HuggingFace team, organising the
82 | training logic with Pytorch Lightning, tracking the model performance with Weights and Biases, and
83 | multiple visualisations using Streamlit and Graphistry.
84 |
85 |
86 | ### HuggingFace Model Wrapper
87 | The implementation of the soft prompts follows nearly identical to the
88 | [Github here](https://github.com/kipgparker/soft-prompt-tuning) where the soft prompts are
89 | simply float tensors duplicated from existing vocabulary and adding them to the module's list of
90 | parameters, to be considered backpropagatable tensors.
91 |
92 | The relevant code snippet is shown below, and the full implementation is
93 | [here](https://github.com/Clyde013/Paraphrase-OPT/blob/fb8f59d6987e3902baf05fa375c856f86e139bb3/soft_prompt_tuning/soft_embedding.py#L26-L44).
94 | ```python
95 | self.learned_embedding = nn.parameter.Parameter(self.initialize_embedding(wte,
96 | n_tokens,
97 | random_range,
98 | initialize_from_vocab))
99 |
100 | def initialize_embedding(self,
101 | wte: nn.Embedding,
102 | n_tokens: int = 10,
103 | random_range: float = 0.5,
104 | initialize_from_vocab: bool = True) -> torch.Tensor:
105 | """initializes learned embedding
106 | Args:
107 | same as __init__
108 | Returns:
109 | torch.float: initialized using original schemes
110 | """
111 | if initialize_from_vocab:
112 | return self.wte.weight[:n_tokens].clone().detach()
113 | return torch.FloatTensor(n_tokens, wte.weight.size(1)).uniform_(-random_range, random_range)
114 | ```
115 |
116 | We then subclass the HuggingFace's [`OPTForCausalLM`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/opt#transformers.OPTForCausalLM)
117 | class, initialise a new soft embedding and
118 | [override the forward pass](https://github.com/Clyde013/Paraphrase-OPT/blob/fb8f59d6987e3902baf05fa375c856f86e139bb3/soft_prompt_tuning/soft_prompt_opt.py#L44-L64)
119 | to prepend our learned embeddings in front of the input.
120 |
121 | ```python
122 | def forward(self,
123 | input_ids: torch.LongTensor = None,
124 | attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
125 | labels: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
126 | **kwargs):
127 | batch_size = input_ids.shape[0]
128 | # Note: concatenation of tensors have to happen on the same device
129 | # concat padding representing our learned embedding tokens for batched inputs
130 | # inputs come in as (batch_size, seq_len) and are padded to be (batch_size, n_tokens + seq_len)
131 | input_ids = torch.cat([torch.full((batch_size, self.n_tokens), 50256).to(input_ids.device), input_ids], dim=1)
132 | attention_mask = torch.cat(
133 | [torch.full((batch_size, self.n_tokens), 1).to(attention_mask.device), attention_mask], dim=1)
134 | if labels is not None:
135 | labels = torch.cat([torch.full((batch_size, self.n_tokens), 50256).to(labels.device), labels], dim=1)
136 |
137 | return super().forward(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, labels=labels, **kwargs)
138 | ```
139 |
140 |
141 | ### Training
142 | Training was done on the OPT1.3B variant, and hyperparameter search for the optimal number of soft tokens
143 | using Optuna.
144 |
145 | All models were trained for 8000 steps per epoch with batch size of 32, and some early stopping applied to
146 | prune under performing models.
147 |
148 | It was clear early on that Adam optimizer performed better than Stochastic Gradient Descent, and as such all
149 | further trials were done using the Adam optimizer.
150 |
151 | Below are a few selected runs that show a very clear trend.
152 | 
153 |
154 |
155 | ## Results
156 | The models were allowed to run on a small subset of the dataset and their outputs saved, as expected the
157 | results are not fantastic. The model is comparatively small, with only 1.3 billion parameters, and as such
158 | soft prompt tuning will not achieve state of the art performance. Nevertheless, it is observed that at
159 | semantic similarity is maintained, instead of the usual action of OPT continuing to generate the sentence.
160 | Unfortunately the model is unable to comprehend that it should be paraphrasing, and thus changing lexical components
161 | of the input, however as model size increases, it is reasonable to assume that performance will get better. The
162 | following is a selection of some of the better paraphrased results from the model.
163 |
164 | | model preds | target |
165 | |:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
166 | | for the movie that's being shot in 1 5 minutes? | for the movie that we 're shooting in about 1 5 minutes ? |
167 | | adler took a moment to consider that, and nodded. | adler took a few seconds to consider that , then nodded thoughtfully . |
168 | | david schwartz was unaware of the fact that he was only narrowly avoided a permanent dent in his ego. | david schwartz was unaware of how narrowly he had escaped crippling and a permanent dent in his ego . |
169 | | i had no idea you were a stunt performer. | i had no idea you did stunt work . |
170 | | seldon was no longer traveling around only when accompanied. | seldon no longer traveled around only if accompanied . |
171 |
172 | The next question that comes to mind is how do we evaluate their predictions?
173 |
174 |
175 | ### Metrics
176 | In order to evaluate our model, we employ multiple different metrics. Traditional metrics such as BLEU and ROUGE might
177 | not be suitable to evaluate our model directly as good paraphrases usually do not share the same vocabulary, and thus
178 | would attain a lower ROUGE score, despite being semantically equivalent.
179 |
180 | Many alternative metrics are available to tackle this problem, and one of them is
181 | [BARTScore](https://github.com/neulab/BARTScore). BARTScore leverages a pretrained BART model for
182 | paraphrase generation to score sentence pairs. A generated sentence is scored by the BART model based
183 | on its probability that the model itself would generate the same sentence, gauging the quality
184 | of the paraphrase sentence according to how much the BART model agrees with it.
185 |
186 | Below are tabulated results of some selected models, compared to the baselines of OPT1.3B with their weights
187 | directly fine tuned for the task of paraphrasing, and the BART model fine tuned for paraphrasing.
188 |
189 | | | soft prompt 20 tokens | soft prompt 111 tokens | soft prompt 163 tokens | fine tuned | bart fine tuned |
190 | |:--------------------|------------------------:|-------------------------:|-------------------------:|-------------:|------------------:|
191 | | bartscore | -3.02511 | -2.15795 | -2.19397 | -4.32509 | -2.65748 |
192 | | bleuscore | 0.246091 | 0.342787 | 0.316936 | 0.0251696 | 0.0833621 |
193 | | rouge1_fmeasure | 0.632655 | 0.835004 | 0.834778 | 0.315754 | 0.316741 |
194 | | rouge1_precision | 0.70008 | 0.856809 | 0.850439 | 0.304833 | 0.207854 |
195 | | rouge1_recall | 0.636459 | 0.838207 | 0.833884 | 0.374748 | 0.935199 |
196 | | rouge2_fmeasure | 0.538138 | 0.737537 | 0.721758 | 0.140419 | 0.251569 |
197 | | rouge2_precision | 0.590409 | 0.756071 | 0.734675 | 0.130611 | 0.164845 |
198 | | rouge2_recall | 0.540979 | 0.743406 | 0.722555 | 0.178818 | 0.816269 |
199 | | rougeL_fmeasure | 0.626995 | 0.83046 | 0.829546 | 0.300252 | 0.301592 |
200 | | rougeL_precision | 0.693667 | 0.852231 | 0.845049 | 0.288716 | 0.197495 |
201 | | rougeL_recall | 0.630616 | 0.83334 | 0.828588 | 0.358478 | 0.900656 |
202 | | rougeLsum_fmeasure | 0.626495 | 0.830814 | 0.82999 | 0.302298 | 0.309371 |
203 | | rougeLsum_precision | 0.693297 | 0.852436 | 0.845449 | 0.290669 | 0.202609 |
204 | | rougeLsum_recall | 0.629847 | 0.833801 | 0.829088 | 0.360918 | 0.920124 |
205 |
206 |
207 |
208 | ### Visualisation
209 | The next step might be to visualise the meanings of the soft prompts with respect to where in the model's
210 | embedding space they end up in, for example in the original paper it was found that clusters of nearest neighbours
211 | maintained high lexical and semantic similarities, and that several prompt tokens end up in the vicinity of each other.
212 |
213 | The numerical representation of word tokens are of high dimensionality, and with the specific instance of
214 | OPT1.3B being used, has a hidden size of 2048. That is 2048 dimensions, incomprehensible to the human mind, and
215 | while traditional methods such as PCA and TSNE can produce viable results, lots of information is lost when decomposing
216 | a high dimensional space into 2 dimensions for us to view. In addition, the TSNE algorithm is stochastic and multiple
217 | restarts with different seeds can yield different embeddings, hence we have no way to directly compare two embedding
218 | spaces.
219 |
220 | The visualisation below is produced through the use of a data structure called a locality sensitive hash forest
221 | and a graph visualisation tool graphistry. However, this technique does suffer from information loss
222 | and is even stochastic to a certain extent. We mitigate this issue by utilising the fixed
223 | embeddings as anchor points, such that they always end up in the same position in the visualisation (determined by an
224 | initial random seed), and then fit the learned embeddings onto the generated anchor points.
225 |
226 | If the graph renders as a multicoloured tree, you might need to reload the page as it is a little buggy with 50k
227 | visualisation points :). The visualisation is also available
228 | [here](https://hub.graphistry.com/graph/graph.html?dataset=05a0c49697bd4a5ebe88c624d709d87f&type=arrow&splashAfter=false&info=False&play=0&menu=True&showArrows=False&pointSize=0.07&edgeCurvature=0.01&edgeSize=1.0&edgeOpacity=0.5&pointOpacity=0.9&lockedX=True&lockedY=True&lockedR=False&linLog=False&strongGravity=False&dissuadeHubs=False&edgeInfluence=1.0&precisionVsSpeed=1.0&gravity=1.0&scalingRatio=0.5&showLabels=True&showLabelOnHover=True&showPointsOfInterest=False&showPointsOfInterestLabel=False&showLabelPropertiesOnHover=True&pointsOfInterestMax=0).
229 | In the graph, red points are the default embeddings, blue points belong to the prompt of 59 prepended tokens, and green
230 | points belong to the prompt of 111 prepended tokens.
231 |
51 |
52 | The learnable tokens can be thought of as passing conceptual notions to the model in an attempt to get it to better
53 | understand the task that is requested. As the models represent words as numbers in a high dimensional space,
54 | we need not restrict our prompts to discrete words, and can search in the space between words to find the most
55 | suitable prompts to feed into the model.
56 |
57 | These prompts are very efficient in terms of memory and compute, requiring just 0.2% of the size of a complete model
58 | checkpoint which would store fine-tuned model parameters, as well as being capable of achieving good results in
59 | less training time.
60 |
61 |
62 | ## Datasets
63 | Two popular paraphrasic datasets were used in soft prompt training of the models.
64 | [ParaBank 2.0](https://nlp.jhu.edu/parabank/) and [ParaNMT-50M](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1711.05732.pdf),
65 | both datasets generated through automatic translation of large amounts of bilingual textual data, translating a
66 | foreign language to english to obtain english-english paraphrase pairs.
67 |
68 | For example, the ParaNMT-50M dataset used Czech-English parallel pairs and applied a Czech to English
69 | pretrained model for translation on the czech pairs.
70 |
71 | As the datasets are incredibly large, we utilised HuggingFace's [dataset streaming](https://huggingface.co/docs/datasets/stream)
72 | feature to progressively feed training data to the model.
73 |
74 | Initially the baseline 20 token model was trained on a 35%-65% split of Parabank 2.0 and ParaNMT-50M respectively,
75 | however for parameter optimization, all further models were trained on a 50%-50% split of Parabank 2.0 and ParaNMT-50M
76 | respectively.
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | ## Implementation
81 | The model was implemented using the OPT model provided by the HuggingFace team, organising the
82 | training logic with Pytorch Lightning, tracking the model performance with Weights and Biases, and
83 | multiple visualisations using Streamlit and Graphistry.
84 |
85 |
86 | ### HuggingFace Model Wrapper
87 | The implementation of the soft prompts follows nearly identical to the
88 | [Github here](https://github.com/kipgparker/soft-prompt-tuning) where the soft prompts are
89 | simply float tensors duplicated from existing vocabulary and adding them to the module's list of
90 | parameters, to be considered backpropagatable tensors.
91 |
92 | The relevant code snippet is shown below, and the full implementation is
93 | [here](https://github.com/Clyde013/Paraphrase-OPT/blob/fb8f59d6987e3902baf05fa375c856f86e139bb3/soft_prompt_tuning/soft_embedding.py#L26-L44).
94 | ```python
95 | self.learned_embedding = nn.parameter.Parameter(self.initialize_embedding(wte,
96 | n_tokens,
97 | random_range,
98 | initialize_from_vocab))
99 |
100 | def initialize_embedding(self,
101 | wte: nn.Embedding,
102 | n_tokens: int = 10,
103 | random_range: float = 0.5,
104 | initialize_from_vocab: bool = True) -> torch.Tensor:
105 | """initializes learned embedding
106 | Args:
107 | same as __init__
108 | Returns:
109 | torch.float: initialized using original schemes
110 | """
111 | if initialize_from_vocab:
112 | return self.wte.weight[:n_tokens].clone().detach()
113 | return torch.FloatTensor(n_tokens, wte.weight.size(1)).uniform_(-random_range, random_range)
114 | ```
115 |
116 | We then subclass the HuggingFace's [`OPTForCausalLM`](https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/model_doc/opt#transformers.OPTForCausalLM)
117 | class, initialise a new soft embedding and
118 | [override the forward pass](https://github.com/Clyde013/Paraphrase-OPT/blob/fb8f59d6987e3902baf05fa375c856f86e139bb3/soft_prompt_tuning/soft_prompt_opt.py#L44-L64)
119 | to prepend our learned embeddings in front of the input.
120 |
121 | ```python
122 | def forward(self,
123 | input_ids: torch.LongTensor = None,
124 | attention_mask: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
125 | labels: Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None,
126 | **kwargs):
127 | batch_size = input_ids.shape[0]
128 | # Note: concatenation of tensors have to happen on the same device
129 | # concat padding representing our learned embedding tokens for batched inputs
130 | # inputs come in as (batch_size, seq_len) and are padded to be (batch_size, n_tokens + seq_len)
131 | input_ids = torch.cat([torch.full((batch_size, self.n_tokens), 50256).to(input_ids.device), input_ids], dim=1)
132 | attention_mask = torch.cat(
133 | [torch.full((batch_size, self.n_tokens), 1).to(attention_mask.device), attention_mask], dim=1)
134 | if labels is not None:
135 | labels = torch.cat([torch.full((batch_size, self.n_tokens), 50256).to(labels.device), labels], dim=1)
136 |
137 | return super().forward(input_ids=input_ids, attention_mask=attention_mask, labels=labels, **kwargs)
138 | ```
139 |
140 |
141 | ### Training
142 | Training was done on the OPT1.3B variant, and hyperparameter search for the optimal number of soft tokens
143 | using Optuna.
144 |
145 | All models were trained for 8000 steps per epoch with batch size of 32, and some early stopping applied to
146 | prune under performing models.
147 |
148 | It was clear early on that Adam optimizer performed better than Stochastic Gradient Descent, and as such all
149 | further trials were done using the Adam optimizer.
150 |
151 | Below are a few selected runs that show a very clear trend.
152 | 
153 |
154 |
155 | ## Results
156 | The models were allowed to run on a small subset of the dataset and their outputs saved, as expected the
157 | results are not fantastic. The model is comparatively small, with only 1.3 billion parameters, and as such
158 | soft prompt tuning will not achieve state of the art performance. Nevertheless, it is observed that at
159 | semantic similarity is maintained, instead of the usual action of OPT continuing to generate the sentence.
160 | Unfortunately the model is unable to comprehend that it should be paraphrasing, and thus changing lexical components
161 | of the input, however as model size increases, it is reasonable to assume that performance will get better. The
162 | following is a selection of some of the better paraphrased results from the model.
163 |
164 | | model preds | target |
165 | |:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|:------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
166 | | for the movie that's being shot in 1 5 minutes? | for the movie that we 're shooting in about 1 5 minutes ? |
167 | | adler took a moment to consider that, and nodded. | adler took a few seconds to consider that , then nodded thoughtfully . |
168 | | david schwartz was unaware of the fact that he was only narrowly avoided a permanent dent in his ego. | david schwartz was unaware of how narrowly he had escaped crippling and a permanent dent in his ego . |
169 | | i had no idea you were a stunt performer. | i had no idea you did stunt work . |
170 | | seldon was no longer traveling around only when accompanied. | seldon no longer traveled around only if accompanied . |
171 |
172 | The next question that comes to mind is how do we evaluate their predictions?
173 |
174 |
175 | ### Metrics
176 | In order to evaluate our model, we employ multiple different metrics. Traditional metrics such as BLEU and ROUGE might
177 | not be suitable to evaluate our model directly as good paraphrases usually do not share the same vocabulary, and thus
178 | would attain a lower ROUGE score, despite being semantically equivalent.
179 |
180 | Many alternative metrics are available to tackle this problem, and one of them is
181 | [BARTScore](https://github.com/neulab/BARTScore). BARTScore leverages a pretrained BART model for
182 | paraphrase generation to score sentence pairs. A generated sentence is scored by the BART model based
183 | on its probability that the model itself would generate the same sentence, gauging the quality
184 | of the paraphrase sentence according to how much the BART model agrees with it.
185 |
186 | Below are tabulated results of some selected models, compared to the baselines of OPT1.3B with their weights
187 | directly fine tuned for the task of paraphrasing, and the BART model fine tuned for paraphrasing.
188 |
189 | | | soft prompt 20 tokens | soft prompt 111 tokens | soft prompt 163 tokens | fine tuned | bart fine tuned |
190 | |:--------------------|------------------------:|-------------------------:|-------------------------:|-------------:|------------------:|
191 | | bartscore | -3.02511 | -2.15795 | -2.19397 | -4.32509 | -2.65748 |
192 | | bleuscore | 0.246091 | 0.342787 | 0.316936 | 0.0251696 | 0.0833621 |
193 | | rouge1_fmeasure | 0.632655 | 0.835004 | 0.834778 | 0.315754 | 0.316741 |
194 | | rouge1_precision | 0.70008 | 0.856809 | 0.850439 | 0.304833 | 0.207854 |
195 | | rouge1_recall | 0.636459 | 0.838207 | 0.833884 | 0.374748 | 0.935199 |
196 | | rouge2_fmeasure | 0.538138 | 0.737537 | 0.721758 | 0.140419 | 0.251569 |
197 | | rouge2_precision | 0.590409 | 0.756071 | 0.734675 | 0.130611 | 0.164845 |
198 | | rouge2_recall | 0.540979 | 0.743406 | 0.722555 | 0.178818 | 0.816269 |
199 | | rougeL_fmeasure | 0.626995 | 0.83046 | 0.829546 | 0.300252 | 0.301592 |
200 | | rougeL_precision | 0.693667 | 0.852231 | 0.845049 | 0.288716 | 0.197495 |
201 | | rougeL_recall | 0.630616 | 0.83334 | 0.828588 | 0.358478 | 0.900656 |
202 | | rougeLsum_fmeasure | 0.626495 | 0.830814 | 0.82999 | 0.302298 | 0.309371 |
203 | | rougeLsum_precision | 0.693297 | 0.852436 | 0.845449 | 0.290669 | 0.202609 |
204 | | rougeLsum_recall | 0.629847 | 0.833801 | 0.829088 | 0.360918 | 0.920124 |
205 |
206 |
207 |
208 | ### Visualisation
209 | The next step might be to visualise the meanings of the soft prompts with respect to where in the model's
210 | embedding space they end up in, for example in the original paper it was found that clusters of nearest neighbours
211 | maintained high lexical and semantic similarities, and that several prompt tokens end up in the vicinity of each other.
212 |
213 | The numerical representation of word tokens are of high dimensionality, and with the specific instance of
214 | OPT1.3B being used, has a hidden size of 2048. That is 2048 dimensions, incomprehensible to the human mind, and
215 | while traditional methods such as PCA and TSNE can produce viable results, lots of information is lost when decomposing
216 | a high dimensional space into 2 dimensions for us to view. In addition, the TSNE algorithm is stochastic and multiple
217 | restarts with different seeds can yield different embeddings, hence we have no way to directly compare two embedding
218 | spaces.
219 |
220 | The visualisation below is produced through the use of a data structure called a locality sensitive hash forest
221 | and a graph visualisation tool graphistry. However, this technique does suffer from information loss
222 | and is even stochastic to a certain extent. We mitigate this issue by utilising the fixed
223 | embeddings as anchor points, such that they always end up in the same position in the visualisation (determined by an
224 | initial random seed), and then fit the learned embeddings onto the generated anchor points.
225 |
226 | If the graph renders as a multicoloured tree, you might need to reload the page as it is a little buggy with 50k
227 | visualisation points :). The visualisation is also available
228 | [here](https://hub.graphistry.com/graph/graph.html?dataset=05a0c49697bd4a5ebe88c624d709d87f&type=arrow&splashAfter=false&info=False&play=0&menu=True&showArrows=False&pointSize=0.07&edgeCurvature=0.01&edgeSize=1.0&edgeOpacity=0.5&pointOpacity=0.9&lockedX=True&lockedY=True&lockedR=False&linLog=False&strongGravity=False&dissuadeHubs=False&edgeInfluence=1.0&precisionVsSpeed=1.0&gravity=1.0&scalingRatio=0.5&showLabels=True&showLabelOnHover=True&showPointsOfInterest=False&showPointsOfInterestLabel=False&showLabelPropertiesOnHover=True&pointsOfInterestMax=0).
229 | In the graph, red points are the default embeddings, blue points belong to the prompt of 59 prepended tokens, and green
230 | points belong to the prompt of 111 prepended tokens.
231 |
232 |
233 |
234 |
235 |
236 | ## Conclusion
237 | We've taught OPT1.3B to paraphrase!
238 |
239 | Much of the results of this implementation agree with the conclusions of the original prompt tuning paper authors.
240 | 1. Increasing model size improves soft prompt performance.
241 | 2. Increasing the length of the soft prompts improves model performance.
242 | 3. This method largely outperforms zero-shot prompting (i.e. "paraphrase the following:"), at least when tested on
243 | OPT1.3B.
244 |
245 | Furthermore, some exciting facets of exploration are:
246 | 1. Training the full OPT175B model.
247 | 2. Distilling the large prepended soft prompt model into a smaller model without need for prepended prompts.
248 | 3. Prompting to achieve better chain of thought intermediate responses, thereby improving the final response.
249 |
250 | Code is all available publicly on the github here:
251 | https://github.com/Clyde013/Paraphrase-OPT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.ipynb_checkpoints/EDA_benchmarking-checkpoint.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "id": "ce5f4e17-2400-4b69-8933-e3234d70b104",
7 | "metadata": {},
8 | "outputs": [],
9 | "source": [
10 | "import pandas as pd"
11 | ]
12 | },
13 | {
14 | "cell_type": "code",
15 | "execution_count": 3,
16 | "id": "5777276a-0e78-4151-8fa0-c73f18c37af6",
17 | "metadata": {},
18 | "outputs": [
19 | {
20 | "data": {
21 | "text/html": [
22 | "\n",
23 | "\n",
36 | "\n",
37 | " \n",
38 | "
\n",
270 | "
"
272 | ],
273 | "text/plain": [
274 | " src \\\n",
275 | "0 david schwartz was unaware of the fact that he... \n",
276 | "1 we 'll be safe here. \n",
277 | "2 we 'll talk about it. \n",
278 | "3 What was your plan? \n",
279 | "4 historians can make a credible case that the p... \n",
280 | ".. ... \n",
281 | "495 adler took a moment to consider that, and nodded. \n",
282 | "496 Five minutes. \n",
283 | "497 i, uh -- i brought you, uh -- i brought you. \n",
284 | "498 Every child is different. \n",
285 | "499 Qatar motorcycle Grand Prix \n",
286 | "\n",
287 | " target bartscore bleuscore \\\n",
288 | "0 david schwartz was unaware of how narrowly he ... -2.400615 0.396709 \n",
289 | "1 we'il be safe here . -3.485580 0.000000 \n",
290 | "2 why do n't you come in and we 'll talk about it . -3.939687 0.135016 \n",
291 | "3 What was your plan? -0.602847 1.000000 \n",
292 | "4 historians can make a credible case that perio... -2.147272 0.353486 \n",
293 | ".. ... ... ... \n",
294 | "495 adler took a few seconds to consider that , th... -2.633909 0.000000 \n",
295 | "496 Ladies and gentlemen, five minutes. -2.346147 0.000000 \n",
296 | "497 i , uh -- i brought you , uh -- -2.529754 0.289978 \n",
297 | "498 Every child is different. -0.453974 1.000000 \n",
298 | "499 Qatar motorcycle Grand Prix -1.097775 1.000000 \n",
299 | "\n",
300 | " rouge1_fmeasure rouge1_precision rouge1_recall rouge2_fmeasure \\\n",
301 | "0 0.702703 0.684211 0.722222 0.514286 \n",
302 | "1 0.800000 0.800000 0.800000 0.500000 \n",
303 | "2 0.555556 1.000000 0.384615 0.500000 \n",
304 | "3 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 \n",
305 | "4 0.745098 0.791667 0.703704 0.571429 \n",
306 | ".. ... ... ... ... \n",
307 | "495 0.700000 0.777778 0.636364 0.444444 \n",
308 | "496 0.571429 1.000000 0.400000 0.400000 \n",
309 | "497 0.800000 0.666667 1.000000 0.769231 \n",
310 | "498 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 \n",
311 | "499 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 \n",
312 | "\n",
313 | " rouge2_precision rouge2_recall rougeL_fmeasure rougeL_precision \\\n",
314 | "0 0.500000 0.529412 0.648649 0.631579 \n",
315 | "1 0.500000 0.500000 0.800000 0.800000 \n",
316 | "2 1.000000 0.333333 0.555556 1.000000 \n",
317 | "3 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 \n",
318 | "4 0.608696 0.538462 0.705882 0.750000 \n",
319 | ".. ... ... ... ... \n",
320 | "495 0.500000 0.400000 0.700000 0.777778 \n",
321 | "496 1.000000 0.250000 0.571429 1.000000 \n",
322 | "497 0.625000 1.000000 0.800000 0.666667 \n",
323 | "498 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 \n",
324 | "499 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 \n",
325 | "\n",
326 | " rougeL_recall rougeLsum_fmeasure rougeLsum_precision rougeLsum_recall \n",
327 | "0 0.666667 0.648649 0.631579 0.666667 \n",
328 | "1 0.800000 0.800000 0.800000 0.800000 \n",
329 | "2 0.384615 0.555556 1.000000 0.384615 \n",
330 | "3 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 \n",
331 | "4 0.666667 0.705882 0.750000 0.666667 \n",
332 | ".. ... ... ... ... \n",
333 | "495 0.636364 0.700000 0.777778 0.636364 \n",
334 | "496 0.400000 0.571429 1.000000 0.400000 \n",
335 | "497 1.000000 0.800000 0.666667 1.000000 \n",
336 | "498 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 \n",
337 | "499 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 1.000000 \n",
338 | "\n",
339 | "[500 rows x 16 columns]"
340 | ]
341 | },
342 | "execution_count": 3,
343 | "metadata": {},
344 | "output_type": "execute_result"
345 | }
346 | ],
347 | "source": [
348 | "filepath = r\"metrics/benchmark_runs/model_benchmarked_results/1.3b-optimized-tokens=111-samples=500.pkl\"\n",
349 | "df = pd.read_pickle(filepath)\n",
350 | "df"
351 | ]
352 | },
353 | {
354 | "cell_type": "code",
355 | "execution_count": 5,
356 | "id": "0a785aa1-1893-4a5b-bba6-781e284cea48",
357 | "metadata": {},
358 | "outputs": [
359 | {
360 | "name": "stderr",
361 | "output_type": "stream",
362 | "text": [
363 | "C:\\Users\\weipy\\AppData\\Local\\Temp\\ipykernel_5208\\3698961737.py:1: FutureWarning: Dropping of nuisance columns in DataFrame reductions (with 'numeric_only=None') is deprecated; in a future version this will raise TypeError. Select only valid columns before calling the reduction.\n",
364 | " df.mean()\n"
365 | ]
366 | },
367 | {
368 | "data": {
369 | "text/plain": [
370 | "bartscore -2.157947\n",
371 | "bleuscore 0.342787\n",
372 | "rouge1_fmeasure 0.835004\n",
373 | "rouge1_precision 0.856809\n",
374 | "rouge1_recall 0.838207\n",
375 | "rouge2_fmeasure 0.737537\n",
376 | "rouge2_precision 0.756071\n",
377 | "rouge2_recall 0.743406\n",
378 | "rougeL_fmeasure 0.830460\n",
379 | "rougeL_precision 0.852231\n",
380 | "rougeL_recall 0.833340\n",
381 | "rougeLsum_fmeasure 0.830814\n",
382 | "rougeLsum_precision 0.852436\n",
383 | "rougeLsum_recall 0.833801\n",
384 | "dtype: float64"
385 | ]
386 | },
387 | "execution_count": 5,
388 | "metadata": {},
389 | "output_type": "execute_result"
390 | }
391 | ],
392 | "source": [
393 | "df.mean()"
394 | ]
395 | },
396 | {
397 | "cell_type": "code",
398 | "execution_count": null,
399 | "id": "275fe94e-476a-436b-ac24-1c5eefac27c7",
400 | "metadata": {},
401 | "outputs": [],
402 | "source": [
403 | "filepath = r\"metrics/benchmark_runs/model_benchmarked_results/1.3b-fine-tuned-samples=500.pkl\"\n",
404 | "df = pd.read_pickle(filepath)\n",
405 | "df"
406 | ]
407 | }
408 | ],
409 | "metadata": {
410 | "kernelspec": {
411 | "display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
412 | "language": "python",
413 | "name": "python3"
414 | },
415 | "language_info": {
416 | "codemirror_mode": {
417 | "name": "ipython",
418 | "version": 3
419 | },
420 | "file_extension": ".py",
421 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
422 | "name": "python",
423 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
424 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
425 | "version": "3.10.4"
426 | }
427 | },
428 | "nbformat": 4,
429 | "nbformat_minor": 5
430 | }
431 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/EDA_embedding.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 2,
6 | "id": "b7e011c3-5eb8-454e-b54e-24f5b96bf80c",
7 | "metadata": {
8 | "pycharm": {
9 | "name": "#%%\n"
10 | }
11 | },
12 | "outputs": [],
13 | "source": [
14 | "import tmap as tm\n",
15 | "import torch\n",
16 | "import time\n",
17 | "import numpy as np\n",
18 | "from numpy.random import RandomState\n",
19 | "import pandas as pd\n",
20 | "import re\n",
21 | "\n",
22 | "import graphistry\n",
23 | "\n",
24 | "import os\n",
25 | "from dotenv import load_dotenv\n",
26 | "load_dotenv() # take environment variables from .env.\n",
27 | "\n",
28 | "from pyvis import network as net\n",
29 | "import networkx as nx\n",
30 | "from sklearn import manifold\n",
31 | "from sklearn.decomposition import PCA\n",
32 | "\n",
33 | "%matplotlib inline\n",
34 | "import matplotlib.pyplot as plt\n",
35 | "from matplotlib import ticker\n",
36 | "plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = [20, 20]"
37 | ]
38 | },
39 | {
40 | "cell_type": "code",
41 | "execution_count": 3,
42 | "id": "8e0a7d83-dfc6-45ac-9cfa-b02e4bd401e6",
43 | "metadata": {
44 | "pycharm": {
45 | "name": "#%%\n"
46 | }
47 | },
48 | "outputs": [],
49 | "source": [
50 | "graphistry.register(api=3, protocol=\"https\", server=\"hub.graphistry.com\", username=os.environ['GRAPHISTRY_USERNAME'], password=os.environ['GRAPHISTRY_PASSWORD'])"
51 | ]
52 | },
53 | {
54 | "cell_type": "code",
55 | "execution_count": 4,
56 | "id": "946c923d-2778-400b-a80b-4f4bf3d1344b",
57 | "metadata": {
58 | "pycharm": {
59 | "name": "#%%\n"
60 | }
61 | },
62 | "outputs": [],
63 | "source": [
64 | "import wandb\n",
65 | "from transformers import GPT2Tokenizer\n",
66 | "from soft_prompt_tuning.soft_prompt_opt import ParaphraseOPT"
67 | ]
68 | },
69 | {
70 | "cell_type": "markdown",
71 | "id": "c88b40fa-726c-4062-95d6-3f14fc4cc60d",
72 | "metadata": {
73 | "pycharm": {
74 | "name": "#%% md\n"
75 | }
76 | },
77 | "source": [
78 | "# Init embedding space"
79 | ]
80 | },
81 | {
82 | "cell_type": "code",
83 | "execution_count": 5,
84 | "id": "24cd0cac-59b8-4d04-9b8a-32e1eef717c3",
85 | "metadata": {
86 | "pycharm": {
87 | "name": "#%%\n"
88 | }
89 | },
90 | "outputs": [
91 | {
92 | "name": "stderr",
93 | "output_type": "stream",
94 | "text": [
95 | "\u001B[34m\u001B[1mwandb\u001B[0m: Currently logged in as: \u001B[33mclyde013\u001B[0m. Use \u001B[1m`wandb login --relogin`\u001B[0m to force relogin\n"
96 | ]
97 | },
98 | {
99 | "data": {
100 | "text/html": [
101 | "wandb version 0.12.18 is available! To upgrade, please run:\n",
102 | " $ pip install wandb --upgrade"
103 | ],
104 | "text/plain": [
105 | "| \n", 40 | " | src | \n", 41 | "target | \n", 42 | "bartscore | \n", 43 | "bleuscore | \n", 44 | "rouge1_fmeasure | \n", 45 | "rouge1_precision | \n", 46 | "rouge1_recall | \n", 47 | "rouge2_fmeasure | \n", 48 | "rouge2_precision | \n", 49 | "rouge2_recall | \n", 50 | "rougeL_fmeasure | \n", 51 | "rougeL_precision | \n", 52 | "rougeL_recall | \n", 53 | "rougeLsum_fmeasure | \n", 54 | "rougeLsum_precision | \n", 55 | "rougeLsum_recall | \n", 56 | "
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | \n", 61 | "david schwartz was unaware of the fact that he... | \n", 62 | "david schwartz was unaware of how narrowly he ... | \n", 63 | "-2.400615 | \n", 64 | "0.396709 | \n", 65 | "0.702703 | \n", 66 | "0.684211 | \n", 67 | "0.722222 | \n", 68 | "0.514286 | \n", 69 | "0.500000 | \n", 70 | "0.529412 | \n", 71 | "0.648649 | \n", 72 | "0.631579 | \n", 73 | "0.666667 | \n", 74 | "0.648649 | \n", 75 | "0.631579 | \n", 76 | "0.666667 | \n", 77 | "
| 1 | \n", 80 | "we 'll be safe here. | \n", 81 | "we'il be safe here . | \n", 82 | "-3.485580 | \n", 83 | "0.000000 | \n", 84 | "0.800000 | \n", 85 | "0.800000 | \n", 86 | "0.800000 | \n", 87 | "0.500000 | \n", 88 | "0.500000 | \n", 89 | "0.500000 | \n", 90 | "0.800000 | \n", 91 | "0.800000 | \n", 92 | "0.800000 | \n", 93 | "0.800000 | \n", 94 | "0.800000 | \n", 95 | "0.800000 | \n", 96 | "
| 2 | \n", 99 | "we 'll talk about it. | \n", 100 | "why do n't you come in and we 'll talk about it . | \n", 101 | "-3.939687 | \n", 102 | "0.135016 | \n", 103 | "0.555556 | \n", 104 | "1.000000 | \n", 105 | "0.384615 | \n", 106 | "0.500000 | \n", 107 | "1.000000 | \n", 108 | "0.333333 | \n", 109 | "0.555556 | \n", 110 | "1.000000 | \n", 111 | "0.384615 | \n", 112 | "0.555556 | \n", 113 | "1.000000 | \n", 114 | "0.384615 | \n", 115 | "
| 3 | \n", 118 | "What was your plan? | \n", 119 | "What was your plan? | \n", 120 | "-0.602847 | \n", 121 | "1.000000 | \n", 122 | "1.000000 | \n", 123 | "1.000000 | \n", 124 | "1.000000 | \n", 125 | "1.000000 | \n", 126 | "1.000000 | \n", 127 | "1.000000 | \n", 128 | "1.000000 | \n", 129 | "1.000000 | \n", 130 | "1.000000 | \n", 131 | "1.000000 | \n", 132 | "1.000000 | \n", 133 | "1.000000 | \n", 134 | "
| 4 | \n", 137 | "historians can make a credible case that the p... | \n", 138 | "historians can make a credible case that perio... | \n", 139 | "-2.147272 | \n", 140 | "0.353486 | \n", 141 | "0.745098 | \n", 142 | "0.791667 | \n", 143 | "0.703704 | \n", 144 | "0.571429 | \n", 145 | "0.608696 | \n", 146 | "0.538462 | \n", 147 | "0.705882 | \n", 148 | "0.750000 | \n", 149 | "0.666667 | \n", 150 | "0.705882 | \n", 151 | "0.750000 | \n", 152 | "0.666667 | \n", 153 | "
| ... | \n", 156 | "... | \n", 157 | "... | \n", 158 | "... | \n", 159 | "... | \n", 160 | "... | \n", 161 | "... | \n", 162 | "... | \n", 163 | "... | \n", 164 | "... | \n", 165 | "... | \n", 166 | "... | \n", 167 | "... | \n", 168 | "... | \n", 169 | "... | \n", 170 | "... | \n", 171 | "... | \n", 172 | "
| 495 | \n", 175 | "adler took a moment to consider that, and nodded. | \n", 176 | "adler took a few seconds to consider that , th... | \n", 177 | "-2.633909 | \n", 178 | "0.000000 | \n", 179 | "0.700000 | \n", 180 | "0.777778 | \n", 181 | "0.636364 | \n", 182 | "0.444444 | \n", 183 | "0.500000 | \n", 184 | "0.400000 | \n", 185 | "0.700000 | \n", 186 | "0.777778 | \n", 187 | "0.636364 | \n", 188 | "0.700000 | \n", 189 | "0.777778 | \n", 190 | "0.636364 | \n", 191 | "
| 496 | \n", 194 | "Five minutes. | \n", 195 | "Ladies and gentlemen, five minutes. | \n", 196 | "-2.346147 | \n", 197 | "0.000000 | \n", 198 | "0.571429 | \n", 199 | "1.000000 | \n", 200 | "0.400000 | \n", 201 | "0.400000 | \n", 202 | "1.000000 | \n", 203 | "0.250000 | \n", 204 | "0.571429 | \n", 205 | "1.000000 | \n", 206 | "0.400000 | \n", 207 | "0.571429 | \n", 208 | "1.000000 | \n", 209 | "0.400000 | \n", 210 | "
| 497 | \n", 213 | "i, uh -- i brought you, uh -- i brought you. | \n", 214 | "i , uh -- i brought you , uh -- | \n", 215 | "-2.529754 | \n", 216 | "0.289978 | \n", 217 | "0.800000 | \n", 218 | "0.666667 | \n", 219 | "1.000000 | \n", 220 | "0.769231 | \n", 221 | "0.625000 | \n", 222 | "1.000000 | \n", 223 | "0.800000 | \n", 224 | "0.666667 | \n", 225 | "1.000000 | \n", 226 | "0.800000 | \n", 227 | "0.666667 | \n", 228 | "1.000000 | \n", 229 | "
| 498 | \n", 232 | "Every child is different. | \n", 233 | "Every child is different. | \n", 234 | "-0.453974 | \n", 235 | "1.000000 | \n", 236 | "1.000000 | \n", 237 | "1.000000 | \n", 238 | "1.000000 | \n", 239 | "1.000000 | \n", 240 | "1.000000 | \n", 241 | "1.000000 | \n", 242 | "1.000000 | \n", 243 | "1.000000 | \n", 244 | "1.000000 | \n", 245 | "1.000000 | \n", 246 | "1.000000 | \n", 247 | "1.000000 | \n", 248 | "
| 499 | \n", 251 | "Qatar motorcycle Grand Prix | \n", 252 | "Qatar motorcycle Grand Prix | \n", 253 | "-1.097775 | \n", 254 | "1.000000 | \n", 255 | "1.000000 | \n", 256 | "1.000000 | \n", 257 | "1.000000 | \n", 258 | "1.000000 | \n", 259 | "1.000000 | \n", 260 | "1.000000 | \n", 261 | "1.000000 | \n", 262 | "1.000000 | \n", 263 | "1.000000 | \n", 264 | "1.000000 | \n", 265 | "1.000000 | \n", 266 | "1.000000 | \n", 267 | "
500 rows × 16 columns
\n", 271 | "C:\\Users\\weipy\\OneDrive\\Documents\\GitHub\\Paraphrase-OPT\\wandb\\run-20220622_165114-37zd2lmm"
127 | ],
128 | "text/plain": [
129 | "" 139 | ], 140 | "text/plain": [ 141 | "
| \n", 329 | " | index | \n", 330 | "x | \n", 331 | "y | \n", 332 | "title | \n", 333 | "
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | \n", 338 | "0 | \n", 339 | "0.516557 | \n", 340 | "87.041412 | \n", 341 | "0 | \n", 342 | "
| 1 | \n", 345 | "1 | \n", 346 | "1.971469 | \n", 347 | "80.593559 | \n", 348 | "0 | \n", 349 | "
| 2 | \n", 352 | "2 | \n", 353 | "70.881744 | \n", 354 | "-50.733025 | \n", 355 | "0 | \n", 356 | "
| 3 | \n", 359 | "3 | \n", 360 | "1.032740 | \n", 361 | "87.292603 | \n", 362 | "0 | \n", 363 | "
| 4 | \n", 366 | "4 | \n", 367 | "73.105972 | \n", 368 | "-49.037640 | \n", 369 | "0 | \n", 370 | "
| ... | \n", 373 | "... | \n", 374 | "... | \n", 375 | "... | \n", 376 | "... | \n", 377 | "
| 50437 | \n", 380 | "50437 | \n", 381 | "75.097878 | \n", 382 | "-53.299850 | \n", 383 | "2 | \n", 384 | "
| 50438 | \n", 387 | "50438 | \n", 388 | "53.052044 | \n", 389 | "69.566902 | \n", 390 | "2 | \n", 391 | "
| 50439 | \n", 394 | "50439 | \n", 395 | "73.531258 | \n", 396 | "-49.463772 | \n", 397 | "2 | \n", 398 | "
| 50440 | \n", 401 | "50440 | \n", 402 | "46.075760 | \n", 403 | "54.189522 | \n", 404 | "2 | \n", 405 | "
| 50441 | \n", 408 | "50441 | \n", 409 | "73.672615 | \n", 410 | "-47.943157 | \n", 411 | "2 | \n", 412 | "
50442 rows × 4 columns
\n", 416 | "" 417 | ], 418 | "text/plain": [ 419 | " index x y title\n", 420 | "0 0 0.516557 87.041412 0\n", 421 | "1 1 1.971469 80.593559 0\n", 422 | "2 2 70.881744 -50.733025 0\n", 423 | "3 3 1.032740 87.292603 0\n", 424 | "4 4 73.105972 -49.037640 0\n", 425 | "... ... ... ... ...\n", 426 | "50437 50437 75.097878 -53.299850 2\n", 427 | "50438 50438 53.052044 69.566902 2\n", 428 | "50439 50439 73.531258 -49.463772 2\n", 429 | "50440 50440 46.075760 54.189522 2\n", 430 | "50441 50441 73.672615 -47.943157 2\n", 431 | "\n", 432 | "[50442 rows x 4 columns]" 433 | ] 434 | }, 435 | "execution_count": 33, 436 | "metadata": {}, 437 | "output_type": "execute_result" 438 | } 439 | ], 440 | "source": [ 441 | "df = pd.DataFrame(embedded, columns=['x', 'y']).reset_index()\n", 442 | "df[\"title\"] = np.concatenate([np.zeros(50272), np.ones(111), np.full(59, 2)])\n", 443 | "df[\"title\"] = df[\"title\"].astype(int)\n", 444 | "df" 445 | ] 446 | }, 447 | { 448 | "cell_type": "code", 449 | "execution_count": 34, 450 | "id": "b0e899b1", 451 | "metadata": {}, 452 | "outputs": [ 453 | { 454 | "data": { 455 | "text/html": [ 456 | "\n",
457 | "\n",
470 | "\n",
471 | " \n",
472 | "
\n",
486 | "
"
487 | ],
488 | "text/plain": [
489 | " source target\n",
490 | "0 0 0"
491 | ]
492 | },
493 | "execution_count": 34,
494 | "metadata": {},
495 | "output_type": "execute_result"
496 | }
497 | ],
498 | "source": [
499 | "df_edges = pd.DataFrame({'source':[0], 'target':[0]})\n",
500 | "df_edges"
501 | ]
502 | },
503 | {
504 | "cell_type": "code",
505 | "execution_count": 35,
506 | "id": "9c922176",
507 | "metadata": {},
508 | "outputs": [
509 | {
510 | "data": {
511 | "text/html": [
512 | "\n",
513 | " \n",
520 | " \n",
521 | " \n",
526 | " "
527 | ],
528 | "text/plain": [
529 | "| \n", 474 | " | source | \n", 475 | "target | \n", 476 | "
|---|---|---|
| 0 | \n", 481 | "0 | \n", 482 | "0 | \n", 483 | "