├── __init__.py
├── pybert
├── __init__.py
├── io
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── utils.py
│ ├── task_data.py
│ ├── vocabulary.py
│ ├── albert_processor.py
│ ├── bert_processor.py
│ └── xlnet_processor.py
├── test
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── predictor.py
├── callback
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── optimizater
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── planradam.py
│ │ ├── novograd.py
│ │ ├── sgdw.py
│ │ ├── lars.py
│ │ ├── radam.py
│ │ ├── nadam.py
│ │ ├── adamw.py
│ │ ├── ralamb.py
│ │ ├── lookahead.py
│ │ ├── lamb.py
│ │ ├── ralars.py
│ │ ├── adabound.py
│ │ └── adafactor.py
│ ├── progressbar.py
│ ├── trainingmonitor.py
│ ├── earlystopping.py
│ └── modelcheckpoint.py
├── configs
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── basic_config.py
├── dataset
│ └── __init__.py
├── model
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── albert
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── configuration_bert.py
│ │ ├── configuration_albert.py
│ │ ├── configuration_utils.py
│ │ └── file_utils.py
│ ├── albert_for_multi_label.py
│ ├── xlnet_for_multi_label.py
│ └── bert_for_multi_label.py
├── output
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── feature
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── figure
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── log
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── result
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── checkpoints
│ │ └── __init__.py
│ └── embedding
│ │ └── __init__.py
├── pretrain
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── albert
│ │ └── albert-base
│ │ │ └── __init__.py
│ ├── bert
│ │ └── base-uncased
│ │ │ └── __init__.py
│ └── xlnet
│ │ └── base-cased
│ │ └── __init__.py
├── train
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── losses.py
│ ├── trainer.py
│ └── metrics.py
└── preprocessing
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── augmentation.py
│ └── preprocessor.py
├── .idea
├── .gitignore
├── encodings.xml
├── misc.xml
├── vcs.xml
├── inspectionProfiles
│ └── profiles_settings.xml
├── modules.xml
├── Bert-Multi-Label-Text-Classification.iml
└── deployment.xml
├── Pipfile
├── requirements.txt
├── LICENSE
├── predict_one.py
├── .gitignore
├── README.md
├── run_albert.py
└── run_xlnet.py
/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/test/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/configs/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/dataset/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/pretrain/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/train/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/albert/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/feature/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/figure/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/log/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/result/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/preprocessing/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/checkpoints/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/output/embedding/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Default ignored files
3 | /workspace.xml
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/pretrain/albert/albert-base/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/pretrain/bert/base-uncased/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/pretrain/xlnet/base-cased/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/encodings.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/misc.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/vcs.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/inspectionProfiles/profiles_settings.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Pipfile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [[source]]
2 | name = "pypi"
3 | url = "https://pypi.org/simple"
4 | verify_ssl = true
5 |
6 | [dev-packages]
7 |
8 | [packages]
9 | torch = "==1.1.0"
10 | transformers = "==2.5.1"
11 | tqdm = "*"
12 | numpy = "*"
13 | scikit-learn = "*"
14 | matplotlib = "*"
15 | pandas = "*"
16 |
17 | [requires]
18 | python_version = "3.7"
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/modules.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | boto3==1.9.227
2 | botocore==1.12.227
3 | certifi==2019.9.11
4 | chardet==3.0.4
5 | Click==7.0
6 | cycler==0.10.0
7 | docutils==0.15.2
8 | idna==2.8
9 | jmespath==0.9.4
10 | joblib==0.13.2
11 | kiwisolver==1.1.0
12 | matplotlib==3.1.1
13 | numpy==1.17.2
14 | pandas==0.25.1
15 | pillow>=6.2.0
16 | pyparsing==2.4.2
17 | python-dateutil==2.8.0
18 | transformers==2.5.1
19 | pytz==2019.2
20 | regex==2019.8.19
21 | requests==2.22.0
22 | s3transfer==0.2.1
23 | sacremoses==0.0.33
24 | scikit-learn==0.21.3
25 | scipy==1.3.1
26 | sentencepiece==0.1.83
27 | six==1.12.0
28 | torch==1.0.1
29 | tqdm==4.35.0
30 | urllib3==1.25.3
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/Bert-Multi-Label-Text-Classification.iml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/train/losses.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from torch.nn import CrossEntropyLoss
2 | from torch.nn import BCEWithLogitsLoss
3 |
4 |
5 | __call__ = ['CrossEntropy','BCEWithLogLoss']
6 |
7 | class CrossEntropy(object):
8 | def __init__(self):
9 | self.loss_f = CrossEntropyLoss()
10 |
11 | def __call__(self, output, target):
12 | loss = self.loss_f(input=output, target=target)
13 | return loss
14 |
15 | class BCEWithLogLoss(object):
16 | def __init__(self):
17 | self.loss_fn = BCEWithLogitsLoss()
18 |
19 | def __call__(self,output,target):
20 | output = output.float()
21 | target = target.float()
22 | loss = self.loss_fn(input = output,target = target)
23 | return loss
24 |
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/albert_for_multi_label.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | from .albert.modeling_albert import AlbertPreTrainedModel, AlbertModel
3 |
4 | class AlbertForMultiLable(AlbertPreTrainedModel):
5 | def __init__(self, config):
6 | super(AlbertForMultiLable, self).__init__(config)
7 | self.bert = AlbertModel(config)
8 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
9 | self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_labels)
10 | self.init_weights()
11 |
12 | def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=None,head_mask=None):
13 | outputs = self.bert(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids,attention_mask=attention_mask, head_mask=head_mask)
14 | pooled_output = outputs[1]
15 | pooled_output = self.dropout(pooled_output)
16 | logits = self.classifier(pooled_output)
17 | return logits
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.idea/deployment.xml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2019 lonePatinet
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | def collate_fn(batch):
3 | """
4 | batch should be a list of (sequence, target, length) tuples...
5 | Returns a padded tensor of sequences sorted from longest to shortest,
6 | """
7 | all_input_ids, all_input_mask, all_segment_ids, all_label_ids,all_input_lens = map(torch.stack, zip(*batch))
8 | max_len = max(all_input_lens).item()
9 | all_input_ids = all_input_ids[:, :max_len]
10 | all_input_mask = all_input_mask[:, :max_len]
11 | all_segment_ids = all_segment_ids[:, :max_len]
12 | return all_input_ids, all_input_mask, all_segment_ids, all_label_ids
13 |
14 | def xlnet_collate_fn(batch):
15 | """
16 | batch should be a list of (sequence, target, length) tuples...
17 | Returns a padded tensor of sequences sorted from longest to shortest,
18 | """
19 | all_input_ids, all_input_mask, all_segment_ids, all_label_ids,all_input_lens = map(torch.stack, zip(*batch))
20 | max_len = max(all_input_lens).item()
21 | all_input_ids = all_input_ids[:, -max_len:]
22 | all_input_mask = all_input_mask[:, -max_len:]
23 | all_segment_ids = all_segment_ids[:, -max_len:]
24 | return all_input_ids, all_input_mask, all_segment_ids, all_label_ids
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/xlnet_for_multi_label.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | from transformers.modeling_xlnet import XLNetPreTrainedModel, XLNetModel,SequenceSummary
3 |
4 | class XlnetForMultiLable(XLNetPreTrainedModel):
5 | def __init__(self, config):
6 |
7 | super(XlnetForMultiLable, self).__init__(config)
8 | self.transformer = XLNetModel(config)
9 | self.sequence_summary = SequenceSummary(config)
10 | self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_labels)
11 | self.init_weights()
12 |
13 | def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids=None, input_mask=None,attention_mask=None,
14 | mems=None, perm_mask=None, target_mapping=None,head_mask=None):
15 | # XLM don't use segment_ids
16 | token_type_ids = None
17 | transformer_outputs = self.transformer(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids,
18 | input_mask=input_mask, attention_mask=attention_mask,
19 | mems=mems, perm_mask=perm_mask, target_mapping=target_mapping,
20 | head_mask=head_mask)
21 | output = transformer_outputs[0]
22 | output = self.sequence_summary(output)
23 | logits = self.classifier(output)
24 | return logits
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/test/predictor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
2 | import torch
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from ..common.tools import model_device
5 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
6 |
7 | class Predictor(object):
8 | def __init__(self,model,logger,n_gpu):
9 | self.model = model
10 | self.logger = logger
11 | self.model, self.device = model_device(n_gpu= n_gpu, model=self.model)
12 |
13 | def predict(self,data):
14 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(data),desc='Testing')
15 | all_logits = None
16 | for step, batch in enumerate(data):
17 | self.model.eval()
18 | batch = tuple(t.to(self.device) for t in batch)
19 | with torch.no_grad():
20 | input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids = batch
21 | logits = self.model(input_ids, segment_ids, input_mask)
22 | logits = logits.sigmoid()
23 | if all_logits is None:
24 | all_logits = logits.detach().cpu().numpy()
25 | else:
26 | all_logits = np.concatenate([all_logits,logits.detach().cpu().numpy()],axis = 0)
27 | pbar(step=step)
28 | if 'cuda' in str(self.device):
29 | torch.cuda.empty_cache()
30 | return all_logits
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/configs/basic_config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from pathlib import Path
3 | BASE_DIR = Path('pybert')
4 | config = {
5 | 'raw_data_path': BASE_DIR / 'dataset/train_sample.csv',
6 | 'test_path': BASE_DIR / 'dataset/test.csv',
7 |
8 | 'data_dir': BASE_DIR / 'dataset',
9 | 'log_dir': BASE_DIR / 'output/log',
10 | 'writer_dir': BASE_DIR / "output/TSboard",
11 | 'figure_dir': BASE_DIR / "output/figure",
12 | 'checkpoint_dir': BASE_DIR / "output/checkpoints",
13 | 'cache_dir': BASE_DIR / 'model/',
14 | 'result': BASE_DIR / "output/result",
15 |
16 | 'bert_vocab_path': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/bert/base-uncased/bert_vocab.txt',
17 | 'bert_config_file': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/bert/base-uncased/config.json',
18 | 'bert_model_dir': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/bert/base-uncased',
19 |
20 | 'xlnet_vocab_path': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/xlnet/base-cased/spiece.model',
21 | 'xlnet_config_file': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/xlnet/base-cased/config.json',
22 | 'xlnet_model_dir': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/xlnet/base-cased',
23 |
24 | 'albert_vocab_path': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/albert/albert-base/30k-clean.model',
25 | 'albert_config_file': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/albert/albert-base/config.json',
26 | 'albert_model_dir': BASE_DIR / 'pretrain/albert/albert-base'
27 |
28 |
29 | }
30 |
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/preprocessing/augmentation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import random
4 |
5 | class Augmentator(object):
6 | def __init__(self,is_train_mode = True, proba = 0.5):
7 | self.mode = is_train_mode
8 | self.proba = proba
9 | self.augs = []
10 | self._reset()
11 |
12 |
13 | def _reset(self):
14 | self.augs.append(lambda text: self._shuffle(text))
15 | self.augs.append(lambda text: self._dropout(text,p = 0.5))
16 |
17 |
18 | def _shuffle(self, text):
19 | text = np.random.permutation(text.strip().split())
20 | return ' '.join(text)
21 |
22 |
23 | def _dropout(self, text, p=0.5):
24 | # random delete some text
25 | text = text.strip().split()
26 | len_ = len(text)
27 | indexs = np.random.choice(len_, int(len_ * p))
28 | for i in indexs:
29 | text[i] = ''
30 | return ' '.join(text)
31 |
32 | def __call__(self,text,aug_type):
33 | '''
34 | 用aug_type区分数据
35 | '''
36 | # TTA模式
37 | if 0 <= aug_type <= 2:
38 | pass
39 | # 训练模式
40 | if self.mode and random.random() < self.proba:
41 | aug = random.choice(self.augs)
42 | text = aug(text)
43 | return text
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/predict_one.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from pybert.configs.basic_config import config
3 | from pybert.io.bert_processor import BertProcessor
4 | from pybert.model.bert_for_multi_label import BertForMultiLable
5 |
6 | def main(text,arch,max_seq_length,do_lower_case):
7 | processor = BertProcessor(vocab_path=config['bert_vocab_path'], do_lower_case=do_lower_case)
8 | label_list = processor.get_labels()
9 | id2label = {i: label for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
10 | model = BertForMultiLable.from_pretrained(config['checkpoint_dir'] /f'{arch}', num_labels=len(label_list))
11 | tokens = processor.tokenizer.tokenize(text)
12 | if len(tokens) > max_seq_length - 2:
13 | tokens = tokens[:max_seq_length - 2]
14 | tokens = ['[CLS]'] + tokens + ['[SEP]']
15 | input_ids = processor.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
16 | input_ids = torch.tensor(input_ids).unsqueeze(0) # Batch size 1, 2 choices
17 | logits = model(input_ids)
18 | probs = logits.sigmoid()
19 | return probs.cpu().detach().numpy()[0]
20 |
21 | if __name__ == "__main__":
22 | text = ''''"FUCK YOUR FILTHY MOTHER IN THE ASS, DRY!"'''
23 | max_seq_length = 256
24 | do_loer_case = True
25 | arch = 'bert'
26 | probs = main(text,arch,max_seq_length,do_loer_case)
27 | print(probs)
28 |
29 | '''
30 | #output
31 | [0.98304486 0.40958735 0.9851305 0.04566246 0.8630512 0.07316463]
32 | '''
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | build/
12 | develop-eggs/
13 | dist/
14 | downloads/
15 | eggs/
16 | .eggs/
17 | lib/
18 | lib64/
19 | parts/
20 | sdist/
21 | var/
22 | wheels/
23 | *.egg-info/
24 | .installed.cfg
25 | *.egg
26 | MANIFEST
27 |
28 | # PyInstaller
29 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
30 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
31 | *.manifest
32 | *.spec
33 |
34 | # Installer logs
35 | pip-log.txt
36 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
37 |
38 | # Unit test / coverage reports
39 | htmlcov/
40 | .tox/
41 | .coverage
42 | .coverage.*
43 | .cache
44 | nosetests.xml
45 | coverage.xml
46 | *.cover
47 | .hypothesis/
48 | .pytest_cache/
49 |
50 | # Translations
51 | *.mo
52 | *.pot
53 |
54 | # Django stuff:
55 | *.log
56 | local_settings.py
57 | db.sqlite3
58 |
59 | # Flask stuff:
60 | instance/
61 | .webassets-cache
62 |
63 | # Scrapy stuff:
64 | .scrapy
65 |
66 | # Sphinx documentation
67 | docs/_build/
68 |
69 | # PyBuilder
70 | target/
71 |
72 | # Jupyter Notebook
73 | .ipynb_checkpoints
74 |
75 | # pyenv
76 | .python-version
77 |
78 | # celery beat schedule file
79 | celerybeat-schedule
80 |
81 | # SageMath parsed files
82 | *.sage.py
83 |
84 | # Environments
85 | .env
86 | .venv
87 | env/
88 | venv/
89 | ENV/
90 | env.bak/
91 | venv.bak/
92 |
93 | # Spyder project settings
94 | .spyderproject
95 | .spyproject
96 |
97 | # Rope project settings
98 | .ropeproject
99 |
100 | # mkdocs documentation
101 | /site
102 |
103 | # mypy
104 | .mypy_cache/
105 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/bert_for_multi_label.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | from transformers.modeling_bert import BertPreTrainedModel, BertModel
3 |
4 | class BertForMultiLable(BertPreTrainedModel):
5 | def __init__(self, config):
6 | super(BertForMultiLable, self).__init__(config)
7 | self.bert = BertModel(config)
8 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(config.hidden_dropout_prob)
9 | self.classifier = nn.Linear(config.hidden_size, config.num_labels)
10 | self.init_weights()
11 |
12 | def forward(self, input_ids, token_type_ids=None, attention_mask=None,head_mask=None):
13 | outputs = self.bert(input_ids, token_type_ids=token_type_ids,attention_mask=attention_mask, head_mask=head_mask)
14 | pooled_output = outputs[1]
15 | pooled_output = self.dropout(pooled_output)
16 | logits = self.classifier(pooled_output)
17 | return logits
18 |
19 | def unfreeze(self,start_layer,end_layer):
20 | def children(m):
21 | return m if isinstance(m, (list, tuple)) else list(m.children())
22 | def set_trainable_attr(m, b):
23 | m.trainable = b
24 | for p in m.parameters():
25 | p.requires_grad = b
26 | def apply_leaf(m, f):
27 | c = children(m)
28 | if isinstance(m, nn.Module):
29 | f(m)
30 | if len(c) > 0:
31 | for l in c:
32 | apply_leaf(l, f)
33 | def set_trainable(l, b):
34 | apply_leaf(l, lambda m: set_trainable_attr(m, b))
35 |
36 | # You can unfreeze the last layer of bert by calling set_trainable(model.bert.encoder.layer[23], True)
37 | set_trainable(self.bert, False)
38 | for i in range(start_layer, end_layer+1):
39 | set_trainable(self.bert.encoder.layer[i], True)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/progressbar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import time
2 | class ProgressBar(object):
3 | '''
4 | custom progress bar
5 | Example:
6 | >>> pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=30,desc='training')
7 | >>> step = 2
8 | >>> pbar(step=step)
9 | '''
10 | def __init__(self, n_total,width=30,desc = 'Training'):
11 | self.width = width
12 | self.n_total = n_total
13 | self.start_time = time.time()
14 | self.desc = desc
15 |
16 | def __call__(self, step, info={}):
17 | now = time.time()
18 | current = step + 1
19 | recv_per = current / self.n_total
20 | bar = f'[{self.desc}] {current}/{self.n_total} ['
21 | if recv_per >= 1:
22 | recv_per = 1
23 | prog_width = int(self.width * recv_per)
24 | if prog_width > 0:
25 | bar += '=' * (prog_width - 1)
26 | if current< self.n_total:
27 | bar += ">"
28 | else:
29 | bar += '='
30 | bar += '.' * (self.width - prog_width)
31 | bar += ']'
32 | show_bar = f"\r{bar}"
33 | time_per_unit = (now - self.start_time) / current
34 | if current < self.n_total:
35 | eta = time_per_unit * (self.n_total - current)
36 | if eta > 3600:
37 | eta_format = ('%d:%02d:%02d' %
38 | (eta // 3600, (eta % 3600) // 60, eta % 60))
39 | elif eta > 60:
40 | eta_format = '%d:%02d' % (eta // 60, eta % 60)
41 | else:
42 | eta_format = '%ds' % eta
43 | time_info = f' - ETA: {eta_format}'
44 | else:
45 | if time_per_unit >= 1:
46 | time_info = f' {time_per_unit:.1f}s/step'
47 | elif time_per_unit >= 1e-3:
48 | time_info = f' {time_per_unit * 1e3:.1f}ms/step'
49 | else:
50 | time_info = f' {time_per_unit * 1e6:.1f}us/step'
51 |
52 | show_bar += time_info
53 | if len(info) != 0:
54 | show_info = f'{show_bar} ' + \
55 | "-".join([f' {key}: {value:.4f} ' for key, value in info.items()])
56 | print(show_info, end='')
57 | else:
58 | print(show_bar, end='')
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/trainingmonitor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # encoding:utf-8
2 | import numpy as np
3 | from pathlib import Path
4 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
5 | from ..common.tools import load_json
6 | from ..common.tools import save_json
7 | plt.switch_backend('agg')
8 |
9 |
10 | class TrainingMonitor():
11 | def __init__(self, file_dir, arch, add_test=False):
12 | '''
13 | :param startAt: 重新开始训练的epoch点
14 | '''
15 | if isinstance(file_dir, Path):
16 | pass
17 | else:
18 | file_dir = Path(file_dir)
19 | file_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
20 |
21 | self.arch = arch
22 | self.file_dir = file_dir
23 | self.H = {}
24 | self.add_test = add_test
25 | self.json_path = file_dir / (arch + "_training_monitor.json")
26 |
27 | def reset(self,start_at):
28 | if start_at > 0:
29 | if self.json_path is not None:
30 | if self.json_path.exists():
31 | self.H = load_json(self.json_path)
32 | for k in self.H.keys():
33 | self.H[k] = self.H[k][:start_at]
34 |
35 | def epoch_step(self, logs={}):
36 | for (k, v) in logs.items():
37 | l = self.H.get(k, [])
38 | # np.float32会报错
39 | if not isinstance(v, np.float):
40 | v = round(float(v), 4)
41 | l.append(v)
42 | self.H[k] = l
43 |
44 | # 写入文件
45 | if self.json_path is not None:
46 | save_json(data = self.H,file_path=self.json_path)
47 |
48 | # 保存train图像
49 | if len(self.H["loss"]) == 1:
50 | self.paths = {key: self.file_dir / (self.arch + f'_{key.upper()}') for key in self.H.keys()}
51 |
52 | if len(self.H["loss"]) > 1:
53 | # 指标变化
54 | # 曲线
55 | # 需要成对出现
56 | keys = [key for key, _ in self.H.items() if '_' not in key]
57 | for key in keys:
58 | N = np.arange(0, len(self.H[key]))
59 | plt.style.use("ggplot")
60 | plt.figure()
61 | plt.plot(N, self.H[key], label=f"train_{key}")
62 | plt.plot(N, self.H[f"valid_{key}"], label=f"valid_{key}")
63 | if self.add_test:
64 | plt.plot(N, self.H[f"test_{key}"], label=f"test_{key}")
65 | plt.legend()
66 | plt.xlabel("Epoch #")
67 | plt.ylabel(key)
68 | plt.title(f"Training {key} [Epoch {len(self.H[key])}]")
69 | plt.savefig(str(self.paths[key]))
70 | plt.close()
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/planradam.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import math
3 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
4 | class PlainRAdam(Optimizer):
5 |
6 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0):
7 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay)
8 |
9 | super(PlainRAdam, self).__init__(params, defaults)
10 |
11 | def __setstate__(self, state):
12 | super(PlainRAdam, self).__setstate__(state)
13 |
14 | def step(self, closure=None):
15 |
16 | loss = None
17 | if closure is not None:
18 | loss = closure()
19 |
20 | for group in self.param_groups:
21 |
22 | for p in group['params']:
23 | if p.grad is None:
24 | continue
25 | grad = p.grad.data.float()
26 | if grad.is_sparse:
27 | raise RuntimeError('RAdam does not support sparse gradients')
28 |
29 | p_data_fp32 = p.data.float()
30 |
31 | state = self.state[p]
32 |
33 | if len(state) == 0:
34 | state['step'] = 0
35 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p_data_fp32)
36 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p_data_fp32)
37 | else:
38 | state['exp_avg'] = state['exp_avg'].type_as(p_data_fp32)
39 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = state['exp_avg_sq'].type_as(p_data_fp32)
40 |
41 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
42 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
43 |
44 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1 - beta2, grad, grad)
45 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1 - beta1, grad)
46 |
47 | state['step'] += 1
48 | beta2_t = beta2 ** state['step']
49 | N_sma_max = 2 / (1 - beta2) - 1
50 | N_sma = N_sma_max - 2 * state['step'] * beta2_t / (1 - beta2_t)
51 |
52 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
53 | p_data_fp32.add_(-group['weight_decay'] * group['lr'], p_data_fp32)
54 |
55 | # more conservative since it's an approximated value
56 | if N_sma >= 5:
57 | step_size = group['lr'] * math.sqrt((1 - beta2_t) * (N_sma - 4) / (N_sma_max - 4) * (N_sma - 2) / N_sma * N_sma_max / (N_sma_max - 2)) / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
58 | denom = exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
59 | p_data_fp32.addcdiv_(-step_size, exp_avg, denom)
60 | else:
61 | step_size = group['lr'] / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
62 | p_data_fp32.add_(-step_size, exp_avg)
63 |
64 | p.data.copy_(p_data_fp32)
65 |
66 | return loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/task_data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import random
2 | import pandas as pd
3 | from tqdm import tqdm
4 | from ..common.tools import save_pickle
5 | from ..common.tools import logger
6 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
7 |
8 | class TaskData(object):
9 | def __init__(self):
10 | pass
11 | def train_val_split(self,X, y,valid_size,stratify=False,shuffle=True,save = True,
12 | seed = None,data_name = None,data_dir = None):
13 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(X),desc='bucket')
14 | logger.info('split raw data into train and valid')
15 | if stratify:
16 | num_classes = len(list(set(y)))
17 | train, valid = [], []
18 | bucket = [[] for _ in range(num_classes)]
19 | for step,(data_x, data_y) in enumerate(zip(X, y)):
20 | bucket[int(data_y)].append((data_x, data_y))
21 | pbar(step=step)
22 | del X, y
23 | for bt in tqdm(bucket, desc='split'):
24 | N = len(bt)
25 | if N == 0:
26 | continue
27 | test_size = int(N * valid_size)
28 | if shuffle:
29 | random.seed(seed)
30 | random.shuffle(bt)
31 | valid.extend(bt[:test_size])
32 | train.extend(bt[test_size:])
33 | if shuffle:
34 | random.seed(seed)
35 | random.shuffle(train)
36 | else:
37 | data = []
38 | for step,(data_x, data_y) in enumerate(zip(X, y)):
39 | data.append((data_x, data_y))
40 | pbar(step=step)
41 | del X, y
42 | N = len(data)
43 | test_size = int(N * valid_size)
44 | if shuffle:
45 | random.seed(seed)
46 | random.shuffle(data)
47 | valid = data[:test_size]
48 | train = data[test_size:]
49 | # 混洗train数据集
50 | if shuffle:
51 | random.seed(seed)
52 | random.shuffle(train)
53 | if save:
54 | train_path = data_dir / f"{data_name}.train.pkl"
55 | valid_path = data_dir / f"{data_name}.valid.pkl"
56 | save_pickle(data=train,file_path=train_path)
57 | save_pickle(data = valid,file_path=valid_path)
58 | return train, valid
59 |
60 | def read_data(self,raw_data_path,preprocessor = None,is_train=True):
61 | '''
62 | :param raw_data_path:
63 | :param skip_header:
64 | :param preprocessor:
65 | :return:
66 | '''
67 | targets, sentences = [], []
68 | data = pd.read_csv(raw_data_path)
69 | for row in data.values:
70 | if is_train:
71 | target = row[2:]
72 | else:
73 | target = [-1,-1,-1,-1,-1,-1]
74 | sentence = str(row[1])
75 | if preprocessor:
76 | sentence = preprocessor(sentence)
77 | if sentence:
78 | targets.append(target)
79 | sentences.append(sentence)
80 | return targets,sentences
81 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/earlystopping.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from ..common.tools import logger
3 | class EarlyStopping(object):
4 | '''
5 | """Stop training when a monitored quantity has stopped improving.
6 | # Arguments
7 | monitor: quantity to be monitored.
8 | min_delta: minimum change in the monitored quantity
9 | to qualify as an improvement, i.e. an absolute
10 | change of less than min_delta, will count as no
11 | improvement.
12 | patience: number of epochs with no improvement
13 | after which training will be stopped.
14 | verbose: verbosity mode.
15 | mode: one of {auto, min, max}. In `min` mode,
16 | training will stop when the quantity
17 | monitored has stopped decreasing; in `max`
18 | mode it will stop when the quantity
19 | monitored has stopped increasing; in `auto`
20 | mode, the direction is automatically inferred
21 | from the name of the monitored quantity.
22 | baseline: Baseline value for the monitored quantity to reach.
23 | Training will stop if the model doesn't show improvement
24 | over the baseline.
25 | restore_best_weights: whether to restore model weights from
26 | the epoch with the best value of the monitored quantity.
27 | If False, the model weights obtained at the last step of
28 | training are used.
29 |
30 | # Arguments
31 | min_delta: 最小变化
32 | patience: 多少个epoch未提高,就停止训练
33 | verbose: 信息大于,默认打印信息
34 | mode: 计算模式
35 | monitor: 计算指标
36 | baseline: 基线
37 | '''
38 | def __init__(self,
39 | min_delta = 0,
40 | patience = 10,
41 | verbose = 1,
42 | mode = 'min',
43 | monitor = 'loss',
44 | baseline = None):
45 |
46 | self.baseline = baseline
47 | self.patience = patience
48 | self.verbose = verbose
49 | self.min_delta = min_delta
50 | self.monitor = monitor
51 |
52 | assert mode in ['min','max']
53 |
54 | if mode == 'min':
55 | self.monitor_op = np.less
56 | elif mode == 'max':
57 | self.monitor_op = np.greater
58 | if self.monitor_op == np.greater:
59 | self.min_delta *= 1
60 | else:
61 | self.min_delta *= -1
62 | self.reset()
63 |
64 | def reset(self):
65 | # Allow instances to be re-used
66 | self.wait = 0
67 | self.stop_training = False
68 | if self.baseline is not None:
69 | self.best = self.baseline
70 | else:
71 | self.best = np.Inf if self.monitor_op == np.less else -np.Inf
72 |
73 | def epoch_step(self,current):
74 | if self.monitor_op(current - self.min_delta, self.best):
75 | self.best = current
76 | self.wait = 0
77 | else:
78 | self.wait += 1
79 | if self.wait >= self.patience:
80 | if self.verbose >0:
81 | logger.info(f"{self.patience} epochs with no improvement after which training will be stopped")
82 | self.stop_training = True
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/novograd.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import math
3 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
4 |
5 |
6 | class NovoGrad(Optimizer):
7 | """Implements NovoGrad algorithm.
8 | Arguments:
9 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
10 | parameter groups
11 | lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 1e-2)
12 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
13 | running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.95, 0.98))
14 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
15 | numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
16 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
17 | Example:
18 | >>> model = ResNet()
19 | >>> optimizer = NovoGrad(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2, weight_decay=1e-5)
20 | """
21 |
22 | def __init__(self, params, lr=0.01, betas=(0.95, 0.98), eps=1e-8,
23 | weight_decay=0, grad_averaging=False):
24 | if lr < 0.0:
25 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
26 | if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
27 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
28 | if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
29 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
30 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay, grad_averaging=grad_averaging)
31 | super().__init__(params, defaults)
32 |
33 | def step(self, closure=None):
34 | loss = None
35 | if closure is not None:
36 | loss = closure()
37 | for group in self.param_groups:
38 | for p in group['params']:
39 | if p.grad is None:
40 | continue
41 | grad = p.grad.data
42 | if grad.is_sparse:
43 | raise RuntimeError('NovoGrad does not support sparse gradients')
44 | state = self.state[p]
45 | g_2 = torch.sum(grad ** 2)
46 | if len(state) == 0:
47 | state['step'] = 0
48 | state['moments'] = grad.div(g_2.sqrt() + group['eps']) + \
49 | group['weight_decay'] * p.data
50 | state['grads_ema'] = g_2
51 | moments = state['moments']
52 | grads_ema = state['grads_ema']
53 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
54 | state['step'] += 1
55 | grads_ema.mul_(beta2).add_(1 - beta2, g_2)
56 |
57 | denom = grads_ema.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
58 | grad.div_(denom)
59 | # weight decay
60 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
61 | decayed_weights = torch.mul(p.data, group['weight_decay'])
62 | grad.add_(decayed_weights)
63 |
64 | # Momentum --> SAG
65 | if group['grad_averaging']:
66 | grad.mul_(1.0 - beta1)
67 |
68 | moments.mul_(beta1).add_(grad) # velocity
69 |
70 | bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
71 | bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
72 | step_size = group['lr'] * math.sqrt(bias_correction2) / bias_correction1
73 | p.data.add_(-step_size, moments)
74 |
75 | return loss
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/sgdw.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
3 |
4 | class SGDW(Optimizer):
5 | r"""Implements stochastic gradient descent (optionally with momentum) with
6 | weight decay from the paper `Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam`_.
7 |
8 | Nesterov momentum is based on the formula from
9 | `On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning`__.
10 |
11 | Args:
12 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
13 | parameter groups
14 | lr (float): learning rate
15 | momentum (float, optional): momentum factor (default: 0)
16 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay factor (default: 0)
17 | dampening (float, optional): dampening for momentum (default: 0)
18 | nesterov (bool, optional): enables Nesterov momentum (default: False)
19 |
20 | .. _Fixing Weight Decay Regularization in Adam:
21 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101
22 |
23 | Example:
24 | >>> model = LSTM()
25 | >>> optimizer = SGDW(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9,weight_decay=1e-5)
26 | """
27 | def __init__(self, params, lr=0.1, momentum=0, dampening=0,
28 | weight_decay=0, nesterov=False):
29 | if lr < 0.0:
30 | raise ValueError(f"Invalid learning rate: {lr}")
31 | if momentum < 0.0:
32 | raise ValueError(f"Invalid momentum value: {momentum}")
33 | if weight_decay < 0.0:
34 | raise ValueError(f"Invalid weight_decay value: {weight_decay}")
35 |
36 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, momentum=momentum, dampening=dampening,
37 | weight_decay=weight_decay, nesterov=nesterov)
38 | if nesterov and (momentum <= 0 or dampening != 0):
39 | raise ValueError("Nesterov momentum requires a momentum and zero dampening")
40 | super(SGDW, self).__init__(params, defaults)
41 |
42 | def __setstate__(self, state):
43 | super(SGDW, self).__setstate__(state)
44 | for group in self.param_groups:
45 | group.setdefault('nesterov', False)
46 |
47 | def step(self, closure=None):
48 | """Performs a single optimization step.
49 |
50 | Arguments:
51 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
52 | and returns the loss.
53 | """
54 | loss = None
55 | if closure is not None:
56 | loss = closure()
57 |
58 | for group in self.param_groups:
59 | weight_decay = group['weight_decay']
60 | momentum = group['momentum']
61 | dampening = group['dampening']
62 | nesterov = group['nesterov']
63 | for p in group['params']:
64 | if p.grad is None:
65 | continue
66 | d_p = p.grad.data
67 | if momentum != 0:
68 | param_state = self.state[p]
69 | if 'momentum_buffer' not in param_state:
70 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
71 | buf.mul_(momentum).add_(d_p)
72 | else:
73 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer']
74 | buf.mul_(momentum).add_(1 - dampening, d_p)
75 | if nesterov:
76 | d_p = d_p.add(momentum, buf)
77 | else:
78 | d_p = buf
79 | if weight_decay != 0:
80 | p.data.add_(-weight_decay, p.data)
81 | p.data.add_(-group['lr'], d_p)
82 | return loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/lars.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
3 |
4 | class Lars(Optimizer):
5 | r"""Implements the LARS optimizer from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.03888.pdf
6 |
7 | Args:
8 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
9 | parameter groups
10 | lr (float): learning rate
11 | momentum (float, optional): momentum factor (default: 0)
12 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
13 | dampening (float, optional): dampening for momentum (default: 0)
14 | nesterov (bool, optional): enables Nesterov momentum (default: False)
15 | scale_clip (tuple, optional): the lower and upper bounds for the weight norm in local LR of LARS
16 | Example:
17 | >>> model = ResNet()
18 | >>> optimizer = Lars(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2, weight_decay=1e-5)
19 | """
20 |
21 | def __init__(self, params, lr, momentum=0, dampening=0,
22 | weight_decay=0, nesterov=False, scale_clip=None):
23 | if lr < 0.0:
24 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
25 | if momentum < 0.0:
26 | raise ValueError("Invalid momentum value: {}".format(momentum))
27 | if weight_decay < 0.0:
28 | raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
29 |
30 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, momentum=momentum, dampening=dampening,
31 | weight_decay=weight_decay, nesterov=nesterov)
32 | if nesterov and (momentum <= 0 or dampening != 0):
33 | raise ValueError("Nesterov momentum requires a momentum and zero dampening")
34 | super(Lars, self).__init__(params, defaults)
35 | # LARS arguments
36 | self.scale_clip = scale_clip
37 | if self.scale_clip is None:
38 | self.scale_clip = (0, 10)
39 |
40 | def __setstate__(self, state):
41 | super(Lars, self).__setstate__(state)
42 | for group in self.param_groups:
43 | group.setdefault('nesterov', False)
44 |
45 | def step(self, closure=None):
46 | """Performs a single optimization step.
47 |
48 | Arguments:
49 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
50 | and returns the loss.
51 | """
52 | loss = None
53 | if closure is not None:
54 | loss = closure()
55 |
56 | for group in self.param_groups:
57 | weight_decay = group['weight_decay']
58 | momentum = group['momentum']
59 | dampening = group['dampening']
60 | nesterov = group['nesterov']
61 |
62 | for p in group['params']:
63 | if p.grad is None:
64 | continue
65 | d_p = p.grad.data
66 | if weight_decay != 0:
67 | d_p.add_(weight_decay, p.data)
68 | if momentum != 0:
69 | param_state = self.state[p]
70 | if 'momentum_buffer' not in param_state:
71 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer'] = torch.clone(d_p).detach()
72 | else:
73 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer']
74 | buf.mul_(momentum).add_(1 - dampening, d_p)
75 | if nesterov:
76 | d_p = d_p.add(momentum, buf)
77 | else:
78 | d_p = buf
79 |
80 | # LARS
81 | p_norm = p.data.pow(2).sum().sqrt()
82 | update_norm = d_p.pow(2).sum().sqrt()
83 | # Compute the local LR
84 | if p_norm == 0 or update_norm == 0:
85 | local_lr = 1
86 | else:
87 | local_lr = p_norm / update_norm
88 |
89 | p.data.add_(-group['lr'] * local_lr, d_p)
90 |
91 | return loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/radam.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import math
3 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
4 | class RAdam(Optimizer):
5 | """Implements the RAdam optimizer from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03265.pdf
6 | Args:
7 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining parameter groups
8 | lr (float, optional): learning rate
9 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.9, 0.999))
10 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
11 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
12 | Example:
13 | >>> model = ResNet()
14 | >>> optimizer = RAdam(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
15 | """
16 |
17 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0):
18 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay)
19 | self.buffer = [[None, None, None] for ind in range(10)]
20 | super(RAdam, self).__init__(params, defaults)
21 |
22 | def __setstate__(self, state):
23 | super(RAdam, self).__setstate__(state)
24 |
25 | def step(self, closure=None):
26 |
27 | loss = None
28 | if closure is not None:
29 | loss = closure()
30 |
31 | for group in self.param_groups:
32 |
33 | for p in group['params']:
34 | if p.grad is None:
35 | continue
36 | grad = p.grad.data.float()
37 | if grad.is_sparse:
38 | raise RuntimeError('RAdam does not support sparse gradients')
39 |
40 | p_data_fp32 = p.data.float()
41 |
42 | state = self.state[p]
43 |
44 | if len(state) == 0:
45 | state['step'] = 0
46 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p_data_fp32)
47 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p_data_fp32)
48 | else:
49 | state['exp_avg'] = state['exp_avg'].type_as(p_data_fp32)
50 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = state['exp_avg_sq'].type_as(p_data_fp32)
51 |
52 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
53 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
54 |
55 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1 - beta2, grad, grad)
56 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1 - beta1, grad)
57 |
58 | state['step'] += 1
59 | buffered = self.buffer[int(state['step'] % 10)]
60 | if state['step'] == buffered[0]:
61 | N_sma, step_size = buffered[1], buffered[2]
62 | else:
63 | buffered[0] = state['step']
64 | beta2_t = beta2 ** state['step']
65 | N_sma_max = 2 / (1 - beta2) - 1
66 | N_sma = N_sma_max - 2 * state['step'] * beta2_t / (1 - beta2_t)
67 | buffered[1] = N_sma
68 |
69 | # more conservative since it's an approximated value
70 | if N_sma >= 5:
71 | step_size = math.sqrt((1 - beta2_t) * (N_sma - 4) / (N_sma_max - 4) * (N_sma - 2) / N_sma * N_sma_max / (N_sma_max - 2)) / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
72 | else:
73 | step_size = 1.0 / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
74 | buffered[2] = step_size
75 |
76 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
77 | p_data_fp32.add_(-group['weight_decay'] * group['lr'], p_data_fp32)
78 |
79 | # more conservative since it's an approximated value
80 | if N_sma >= 5:
81 | denom = exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
82 | p_data_fp32.addcdiv_(-step_size * group['lr'], exp_avg, denom)
83 | else:
84 | p_data_fp32.add_(-step_size * group['lr'], exp_avg)
85 |
86 | p.data.copy_(p_data_fp32)
87 |
88 | return loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/albert/configuration_bert.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | """ BERT model configuration """
3 |
4 | from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
5 |
6 | import json
7 | import logging
8 | import sys
9 | from io import open
10 |
11 | from .configuration_utils import PretrainedConfig
12 |
13 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
14 |
15 | BERT_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP = {}
16 | class BertConfig(PretrainedConfig):
17 | r"""
18 | :class:`~pytorch_transformers.BertConfig` is the configuration class to store the configuration of a
19 | `BertModel`.
20 |
21 |
22 | Arguments:
23 | vocab_size_or_config_json_file: Vocabulary size of `inputs_ids` in `BertModel`.
24 | hidden_size: Size of the encoder layers and the pooler layer.
25 | num_hidden_layers: Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder.
26 | num_attention_heads: Number of attention heads for each attention layer in
27 | the Transformer encoder.
28 | intermediate_size: The size of the "intermediate" (i.e., feed-forward)
29 | layer in the Transformer encoder.
30 | hidden_act: The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the
31 | encoder and pooler. If string, "gelu", "relu" and "swish" are supported.
32 | hidden_dropout_prob: The dropout probabilitiy for all fully connected
33 | layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler.
34 | attention_probs_dropout_prob: The dropout ratio for the attention
35 | probabilities.
36 | max_position_embeddings: The maximum sequence length that this model might
37 | ever be used with. Typically set this to something large just in case
38 | (e.g., 512 or 1024 or 2048).
39 | type_vocab_size: The vocabulary size of the `token_type_ids` passed into
40 | `BertModel`.
41 | initializer_range: The sttdev of the truncated_normal_initializer for
42 | initializing all weight matrices.
43 | layer_norm_eps: The epsilon used by LayerNorm.
44 | """
45 | pretrained_config_archive_map = BERT_PRETRAINED_CONFIG_ARCHIVE_MAP
46 |
47 | def __init__(self,
48 | vocab_size_or_config_json_file=30522,
49 | hidden_size=768,
50 | num_hidden_layers=12,
51 | num_attention_heads=12,
52 | intermediate_size=3072,
53 | hidden_act="gelu",
54 | hidden_dropout_prob=0.1,
55 | attention_probs_dropout_prob=0.1,
56 | max_position_embeddings=512,
57 | type_vocab_size=2,
58 | initializer_range=0.02,
59 | layer_norm_eps=1e-12,
60 | **kwargs):
61 | super(BertConfig, self).__init__(**kwargs)
62 | if isinstance(vocab_size_or_config_json_file, str) or (sys.version_info[0] == 2
63 | and isinstance(vocab_size_or_config_json_file, unicode)):
64 | with open(vocab_size_or_config_json_file, "r", encoding='utf-8') as reader:
65 | json_config = json.loads(reader.read())
66 | for key, value in json_config.items():
67 | self.__dict__[key] = value
68 | elif isinstance(vocab_size_or_config_json_file, int):
69 | self.vocab_size = vocab_size_or_config_json_file
70 | self.hidden_size = hidden_size
71 | self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
72 | self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
73 | self.hidden_act = hidden_act
74 | self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
75 | self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
76 | self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
77 | self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
78 | self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
79 | self.initializer_range = initializer_range
80 | self.layer_norm_eps = layer_norm_eps
81 | else:
82 | raise ValueError("First argument must be either a vocabulary size (int)"
83 | " or the path to a pretrained model config file (str)")
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/albert/configuration_albert.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """ BERT model configuration """
2 | from __future__ import absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals
3 |
4 | import json
5 | import logging
6 | import sys
7 | from io import open
8 |
9 | from .configuration_utils import PretrainedConfig
10 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
11 |
12 | class AlbertConfig(PretrainedConfig):
13 | r"""
14 | Arguments:
15 | vocab_size_or_config_json_file: Vocabulary size of `inputs_ids` in `BertModel`.
16 | hidden_size: Size of the encoder layers and the pooler layer.
17 | num_hidden_layers: Number of hidden layers in the Transformer encoder.
18 | num_attention_heads: Number of attention heads for each attention layer in
19 | the Transformer encoder.
20 | intermediate_size: The size of the "intermediate" (i.e., feed-forward)
21 | layer in the Transformer encoder.
22 | hidden_act: The non-linear activation function (function or string) in the
23 | encoder and pooler. If string, "gelu", "relu" and "swish" are supported.
24 | hidden_dropout_prob: The dropout probabilitiy for all fully connected
25 | layers in the embeddings, encoder, and pooler.
26 | attention_probs_dropout_prob: The dropout ratio for the attention
27 | probabilities.
28 | max_position_embeddings: The maximum sequence length that this model might
29 | ever be used with. Typically set this to something large just in case
30 | (e.g., 512 or 1024 or 2048).
31 | type_vocab_size: The vocabulary size of the `token_type_ids` passed into
32 | `BertModel`.
33 | initializer_range: The sttdev of the truncated_normal_initializer for
34 | initializing all weight matrices.
35 | layer_norm_eps: The epsilon used by LayerNorm.
36 | """
37 | def __init__(self,
38 | vocab_size_or_config_json_file=30000,
39 | embedding_size=128,
40 | hidden_size=4096,
41 | num_hidden_layers=12,
42 | num_hidden_groups=1,
43 | num_attention_heads=64,
44 | intermediate_size=16384,
45 | inner_group_num=1,
46 | hidden_act="gelu_new",
47 | hidden_dropout_prob=0,
48 | attention_probs_dropout_prob=0,
49 | max_position_embeddings=512,
50 | type_vocab_size=2,
51 | initializer_range=0.02,
52 | layer_norm_eps=1e-12,
53 | **kwargs):
54 | super(AlbertConfig, self).__init__(**kwargs)
55 | if isinstance(vocab_size_or_config_json_file, str) or (sys.version_info[0] == 2
56 | and isinstance(vocab_size_or_config_json_file, unicode)):
57 | with open(vocab_size_or_config_json_file, "r", encoding='utf-8') as reader:
58 | json_config = json.loads(reader.read())
59 | for key, value in json_config.items():
60 | self.__dict__[key] = value
61 | elif isinstance(vocab_size_or_config_json_file, int):
62 | self.vocab_size = vocab_size_or_config_json_file
63 | self.hidden_size = hidden_size
64 | self.num_hidden_layers = num_hidden_layers
65 | self.num_attention_heads = num_attention_heads
66 | self.hidden_act = hidden_act
67 | self.intermediate_size = intermediate_size
68 | self.hidden_dropout_prob = hidden_dropout_prob
69 | self.attention_probs_dropout_prob = attention_probs_dropout_prob
70 | self.max_position_embeddings = max_position_embeddings
71 | self.type_vocab_size = type_vocab_size
72 | self.initializer_range = initializer_range
73 | self.layer_norm_eps = layer_norm_eps
74 | self.embedding_size = embedding_size
75 | self.inner_group_num = inner_group_num
76 | self.num_hidden_groups = num_hidden_groups
77 | else:
78 | raise ValueError("First argument must be either a vocabulary size (int)"
79 | " or the path to a pretrained model config file (str)")
80 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/nadam.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import math
3 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
4 |
5 | class Nadam(Optimizer):
6 | """Implements Nadam algorithm (a variant of Adam based on Nesterov momentum).
7 |
8 | It has been proposed in `Incorporating Nesterov Momentum into Adam`__.
9 |
10 | Arguments:
11 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
12 | parameter groups
13 | lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 2e-3)
14 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
15 | running averages of gradient and its square
16 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
17 | numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
18 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
19 | schedule_decay (float, optional): momentum schedule decay (default: 4e-3)
20 |
21 | __ http://cs229.stanford.edu/proj2015/054_report.pdf
22 | __ http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~fritz/absps/momentum.pdf
23 |
24 | Originally taken from: https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/pull/1408
25 | NOTE: Has potential issues but does work well on some problems.
26 | Example:
27 | >>> model = LSTM()
28 | >>> optimizer = Nadam(model.parameters())
29 | """
30 |
31 | def __init__(self, params, lr=2e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8,
32 | weight_decay=0, schedule_decay=4e-3):
33 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps,
34 | weight_decay=weight_decay, schedule_decay=schedule_decay)
35 | super(Nadam, self).__init__(params, defaults)
36 |
37 | def step(self, closure=None):
38 | """Performs a single optimization step.
39 |
40 | Arguments:
41 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
42 | and returns the loss.
43 | """
44 | loss = None
45 | if closure is not None:
46 | loss = closure()
47 |
48 | for group in self.param_groups:
49 | for p in group['params']:
50 | if p.grad is None:
51 | continue
52 | grad = p.grad.data
53 | state = self.state[p]
54 |
55 | # State initialization
56 | if len(state) == 0:
57 | state['step'] = 0
58 | state['m_schedule'] = 1.
59 | state['exp_avg'] = grad.new().resize_as_(grad).zero_()
60 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = grad.new().resize_as_(grad).zero_()
61 |
62 | # Warming momentum schedule
63 | m_schedule = state['m_schedule']
64 | schedule_decay = group['schedule_decay']
65 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
66 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
67 | eps = group['eps']
68 | state['step'] += 1
69 | t = state['step']
70 |
71 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
72 | grad = grad.add(group['weight_decay'], p.data)
73 |
74 | momentum_cache_t = beta1 * \
75 | (1. - 0.5 * (0.96 ** (t * schedule_decay)))
76 | momentum_cache_t_1 = beta1 * \
77 | (1. - 0.5 * (0.96 ** ((t + 1) * schedule_decay)))
78 | m_schedule_new = m_schedule * momentum_cache_t
79 | m_schedule_next = m_schedule * momentum_cache_t * momentum_cache_t_1
80 | state['m_schedule'] = m_schedule_new
81 |
82 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
83 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1. - beta1, grad)
84 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1. - beta2, grad, grad)
85 | exp_avg_sq_prime = exp_avg_sq / (1. - beta2 ** t)
86 | denom = exp_avg_sq_prime.sqrt_().add_(eps)
87 |
88 | p.data.addcdiv_(-group['lr'] * (1. - momentum_cache_t) / (1. - m_schedule_new), grad, denom)
89 | p.data.addcdiv_(-group['lr'] * momentum_cache_t_1 / (1. - m_schedule_next), exp_avg, denom)
90 |
91 | return loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/adamw.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import math
3 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
4 |
5 | class AdamW(Optimizer):
6 | """ Implements Adam algorithm with weight decay fix.
7 |
8 | Parameters:
9 | lr (float): learning rate. Default 1e-3.
10 | betas (tuple of 2 floats): Adams beta parameters (b1, b2). Default: (0.9, 0.999)
11 | eps (float): Adams epsilon. Default: 1e-6
12 | weight_decay (float): Weight decay. Default: 0.0
13 | correct_bias (bool): can be set to False to avoid correcting bias in Adam (e.g. like in Bert TF repository). Default True.
14 | Example:
15 | >>> model = LSTM()
16 | >>> optimizer = AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3, weight_decay=1e-5)
17 | """
18 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-6, weight_decay=0.0, correct_bias=True):
19 | if lr < 0.0:
20 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {} - should be >= 0.0".format(lr))
21 | if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
22 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter: {} - should be in [0.0, 1.0[".format(betas[0]))
23 | if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
24 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter: {} - should be in [0.0, 1.0[".format(betas[1]))
25 | if not 0.0 <= eps:
26 | raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {} - should be >= 0.0".format(eps))
27 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay,
28 | correct_bias=correct_bias)
29 | super(AdamW, self).__init__(params, defaults)
30 |
31 | def step(self, closure=None):
32 | """Performs a single optimization step.
33 |
34 | Arguments:
35 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
36 | and returns the loss.
37 | """
38 | loss = None
39 | if closure is not None:
40 | loss = closure()
41 |
42 | for group in self.param_groups:
43 | for p in group['params']:
44 | if p.grad is None:
45 | continue
46 | grad = p.grad.data
47 | if grad.is_sparse:
48 | raise RuntimeError('Adam does not support sparse gradients, please consider SparseAdam instead')
49 |
50 | state = self.state[p]
51 |
52 | # State initialization
53 | if len(state) == 0:
54 | state['step'] = 0
55 | # Exponential moving average of gradient values
56 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
57 | # Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
58 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
59 |
60 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
61 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
62 |
63 | state['step'] += 1
64 |
65 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
66 | # In-place operations to update the averages at the same time
67 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1.0 - beta1, grad)
68 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1.0 - beta2, grad, grad)
69 | denom = exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
70 |
71 | step_size = group['lr']
72 | if group['correct_bias']: # No bias correction for Bert
73 | bias_correction1 = 1.0 - beta1 ** state['step']
74 | bias_correction2 = 1.0 - beta2 ** state['step']
75 | step_size = step_size * math.sqrt(bias_correction2) / bias_correction1
76 |
77 | p.data.addcdiv_(-step_size, exp_avg, denom)
78 |
79 | # Just adding the square of the weights to the loss function is *not*
80 | # the correct way of using L2 regularization/weight decay with Adam,
81 | # since that will interact with the m and v parameters in strange ways.
82 | #
83 | # Instead we want to decay the weights in a manner that doesn't interact
84 | # with the m/v parameters. This is equivalent to adding the square
85 | # of the weights to the loss with plain (non-momentum) SGD.
86 | # Add weight decay at the end (fixed version)
87 | if group['weight_decay'] > 0.0:
88 | p.data.add_(-group['lr'] * group['weight_decay'], p.data)
89 |
90 | return loss
91 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/ralamb.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
4 |
5 | class Ralamb(Optimizer):
6 | '''
7 | RAdam + LARS
8 | Example:
9 | >>> model = ResNet()
10 | >>> optimizer = Ralamb(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
11 | '''
12 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0):
13 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay)
14 | self.buffer = [[None, None, None] for ind in range(10)]
15 | super(Ralamb, self).__init__(params, defaults)
16 |
17 | def __setstate__(self, state):
18 | super(Ralamb, self).__setstate__(state)
19 |
20 | def step(self, closure=None):
21 |
22 | loss = None
23 | if closure is not None:
24 | loss = closure()
25 |
26 | for group in self.param_groups:
27 |
28 | for p in group['params']:
29 | if p.grad is None:
30 | continue
31 | grad = p.grad.data.float()
32 | if grad.is_sparse:
33 | raise RuntimeError('Ralamb does not support sparse gradients')
34 |
35 | p_data_fp32 = p.data.float()
36 |
37 | state = self.state[p]
38 |
39 | if len(state) == 0:
40 | state['step'] = 0
41 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p_data_fp32)
42 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p_data_fp32)
43 | else:
44 | state['exp_avg'] = state['exp_avg'].type_as(p_data_fp32)
45 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = state['exp_avg_sq'].type_as(p_data_fp32)
46 |
47 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
48 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
49 |
50 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
51 | # m_t
52 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1 - beta1, grad)
53 | # v_t
54 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1 - beta2, grad, grad)
55 |
56 | state['step'] += 1
57 | buffered = self.buffer[int(state['step'] % 10)]
58 |
59 | if state['step'] == buffered[0]:
60 | N_sma, radam_step_size = buffered[1], buffered[2]
61 | else:
62 | buffered[0] = state['step']
63 | beta2_t = beta2 ** state['step']
64 | N_sma_max = 2 / (1 - beta2) - 1
65 | N_sma = N_sma_max - 2 * state['step'] * beta2_t / (1 - beta2_t)
66 | buffered[1] = N_sma
67 |
68 | # more conservative since it's an approximated value
69 | if N_sma >= 5:
70 | radam_step_size = math.sqrt((1 - beta2_t) * (N_sma - 4) / (N_sma_max - 4) * (N_sma - 2) / N_sma * N_sma_max / (N_sma_max - 2)) / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
71 | else:
72 | radam_step_size = 1.0 / (1 - beta1 ** state['step'])
73 | buffered[2] = radam_step_size
74 |
75 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
76 | p_data_fp32.add_(-group['weight_decay'] * group['lr'], p_data_fp32)
77 |
78 | # more conservative since it's an approximated value
79 | radam_step = p_data_fp32.clone()
80 | if N_sma >= 5:
81 | denom = exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
82 | radam_step.addcdiv_(-radam_step_size * group['lr'], exp_avg, denom)
83 | else:
84 | radam_step.add_(-radam_step_size * group['lr'], exp_avg)
85 |
86 | radam_norm = radam_step.pow(2).sum().sqrt()
87 | weight_norm = p.data.pow(2).sum().sqrt().clamp(0, 10)
88 | if weight_norm == 0 or radam_norm == 0:
89 | trust_ratio = 1
90 | else:
91 | trust_ratio = weight_norm / radam_norm
92 |
93 | state['weight_norm'] = weight_norm
94 | state['adam_norm'] = radam_norm
95 | state['trust_ratio'] = trust_ratio
96 |
97 | if N_sma >= 5:
98 | p_data_fp32.addcdiv_(-radam_step_size * group['lr'] * trust_ratio, exp_avg, denom)
99 | else:
100 | p_data_fp32.add_(-radam_step_size * group['lr'] * trust_ratio, exp_avg)
101 |
102 | p.data.copy_(p_data_fp32)
103 |
104 | return loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/modelcheckpoint.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from pathlib import Path
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import torch
4 | from ..common.tools import logger
5 |
6 | class ModelCheckpoint(object):
7 | """Save the model after every epoch.
8 | # Arguments
9 | checkpoint_dir: string, path to save the model file.
10 | monitor: quantity to monitor.
11 | verbose: verbosity mode, 0 or 1.
12 | save_best_only: if `save_best_only=True`,
13 | the latest best model according to
14 | the quantity monitored will not be overwritten.
15 | mode: one of {auto, min, max}.
16 | If `save_best_only=True`, the decision
17 | to overwrite the current save file is made
18 | based on either the maximization or the
19 | minimization of the monitored quantity. For `val_acc`,
20 | this should be `max`, for `val_loss` this should
21 | be `min`, etc. In `auto` mode, the direction is
22 | automatically inferred from the name of the monitored quantity.
23 | """
24 | def __init__(self, checkpoint_dir,
25 | monitor,
26 | arch,
27 | mode='min',
28 | epoch_freq=1,
29 | best = None,
30 | save_best_only = True):
31 | if isinstance(checkpoint_dir,Path):
32 | checkpoint_dir = checkpoint_dir
33 | else:
34 | checkpoint_dir = Path(checkpoint_dir)
35 | assert checkpoint_dir.is_dir()
36 | checkpoint_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
37 | self.base_path = checkpoint_dir
38 | self.arch = arch
39 | self.monitor = monitor
40 | self.epoch_freq = epoch_freq
41 | self.save_best_only = save_best_only
42 |
43 | # 计算模式
44 | if mode == 'min':
45 | self.monitor_op = np.less
46 | self.best = np.Inf
47 |
48 | elif mode == 'max':
49 | self.monitor_op = np.greater
50 | self.best = -np.Inf
51 | # 这里主要重新加载模型时候
52 | #对best重新赋值
53 | if best:
54 | self.best = best
55 |
56 | if save_best_only:
57 | self.model_name = f"BEST_{arch}_MODEL.pth"
58 |
59 | def epoch_step(self, state,current):
60 | '''
61 | :param state: 需要保存的信息
62 | :param current: 当前判断指标
63 | :return:
64 | '''
65 | if self.save_best_only:
66 | if self.monitor_op(current, self.best):
67 | logger.info(f"\nEpoch {state['epoch']}: {self.monitor} improved from {self.best:.5f} to {current:.5f}")
68 | self.best = current
69 | state['best'] = self.best
70 | best_path = self.base_path/ self.model_name
71 | torch.save(state, str(best_path))
72 |
73 | else:
74 | filename = self.base_path / f"epoch_{state['epoch']}_{state[self.monitor]}_{self.arch}_model.bin"
75 | if state['epoch'] % self.epoch_freq == 0:
76 | logger.info(f"\nEpoch {state['epoch']}: save model to disk.")
77 | torch.save(state, str(filename))
78 |
79 | def bert_epoch_step(self, state,current):
80 | model_to_save = state['model']
81 | if self.save_best_only:
82 | if self.monitor_op(current, self.best):
83 | logger.info(f"\nEpoch {state['epoch']}: {self.monitor} improved from {self.best:.5f} to {current:.5f}")
84 | self.best = current
85 | state['best'] = self.best
86 | model_to_save.save_pretrained(str(self.base_path))
87 | output_config_file = self.base_path / 'config.json'
88 | with open(str(output_config_file), 'w') as f:
89 | f.write(model_to_save.config.to_json_string())
90 | state.pop("model")
91 | torch.save(state,self.base_path / 'checkpoint_info.bin')
92 |
93 | else:
94 | if state['epoch'] % self.epoch_freq == 0:
95 | save_path = self.base_path / f"checkpoint-epoch-{state['epoch']}"
96 | save_path.mkdir(exist_ok=True)
97 | logger.info(f"\nEpoch {state['epoch']}: save model to disk.")
98 | model_to_save.save_pretrained(save_path)
99 | output_config_file = save_path / 'config.json'
100 | with open(str(output_config_file), 'w') as f:
101 | f.write(model_to_save.config.to_json_string())
102 | state.pop("model")
103 | torch.save(state, save_path / 'checkpoint_info.bin')
104 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/lookahead.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch.optim import Optimizer
3 | from collections import defaultdict
4 |
5 | class Lookahead(Optimizer):
6 | '''
7 | PyTorch implementation of the lookahead wrapper.
8 | Lookahead Optimizer: https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.08610
9 |
10 | We found that evaluation performance is typically better using the slow weights.
11 | This can be done in PyTorch with something like this in your eval loop:
12 | if args.lookahead:
13 | optimizer._backup_and_load_cache()
14 | val_loss = eval_func(model)
15 | optimizer._clear_and_load_backup()
16 | '''
17 | def __init__(self, optimizer,alpha=0.5, k=6,pullback_momentum="none"):
18 | '''
19 | :param optimizer:inner optimizer
20 | :param k (int): number of lookahead steps
21 | :param alpha(float): linear interpolation factor. 1.0 recovers the inner optimizer.
22 | :param pullback_momentum (str): change to inner optimizer momentum on interpolation update
23 | '''
24 | if not 0.0 <= alpha <= 1.0:
25 | raise ValueError(f'Invalid slow update rate: {alpha}')
26 | if not 1 <= k:
27 | raise ValueError(f'Invalid lookahead steps: {k}')
28 | self.optimizer = optimizer
29 | self.param_groups = self.optimizer.param_groups
30 | self.alpha = alpha
31 | self.k = k
32 | self.step_counter = 0
33 | assert pullback_momentum in ["reset", "pullback", "none"]
34 | self.pullback_momentum = pullback_momentum
35 | self.state = defaultdict(dict)
36 |
37 | # Cache the current optimizer parameters
38 | for group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
39 | for p in group['params']:
40 | param_state = self.state[p]
41 | param_state['cached_params'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
42 | param_state['cached_params'].copy_(p.data)
43 |
44 | def __getstate__(self):
45 | return {
46 | 'state': self.state,
47 | 'optimizer': self.optimizer,
48 | 'alpha': self.alpha,
49 | 'step_counter': self.step_counter,
50 | 'k':self.k,
51 | 'pullback_momentum': self.pullback_momentum
52 | }
53 |
54 | def zero_grad(self):
55 | self.optimizer.zero_grad()
56 |
57 | def state_dict(self):
58 | return self.optimizer.state_dict()
59 |
60 | def load_state_dict(self, state_dict):
61 | self.optimizer.load_state_dict(state_dict)
62 |
63 | def _backup_and_load_cache(self):
64 | """Useful for performing evaluation on the slow weights (which typically generalize better)
65 | """
66 | for group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
67 | for p in group['params']:
68 | param_state = self.state[p]
69 | param_state['backup_params'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
70 | param_state['backup_params'].copy_(p.data)
71 | p.data.copy_(param_state['cached_params'])
72 |
73 | def _clear_and_load_backup(self):
74 | for group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
75 | for p in group['params']:
76 | param_state = self.state[p]
77 | p.data.copy_(param_state['backup_params'])
78 | del param_state['backup_params']
79 |
80 | def step(self, closure=None):
81 | """Performs a single Lookahead optimization step.
82 | Arguments:
83 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
84 | and returns the loss.
85 | """
86 | loss = self.optimizer.step(closure)
87 | self.step_counter += 1
88 |
89 | if self.step_counter >= self.k:
90 | self.step_counter = 0
91 | # Lookahead and cache the current optimizer parameters
92 | for group in self.optimizer.param_groups:
93 | for p in group['params']:
94 | param_state = self.state[p]
95 | p.data.mul_(self.alpha).add_(1.0 - self.alpha, param_state['cached_params']) # crucial line
96 | param_state['cached_params'].copy_(p.data)
97 | if self.pullback_momentum == "pullback":
98 | internal_momentum = self.optimizer.state[p]["momentum_buffer"]
99 | self.optimizer.state[p]["momentum_buffer"] = internal_momentum.mul_(self.alpha).add_(
100 | 1.0 - self.alpha, param_state["cached_mom"])
101 | param_state["cached_mom"] = self.optimizer.state[p]["momentum_buffer"]
102 | elif self.pullback_momentum == "reset":
103 | self.optimizer.state[p]["momentum_buffer"] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
104 |
105 | return loss
106 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/lamb.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
3 |
4 |
5 | class Lamb(Optimizer):
6 | r"""Implements Lamb algorithm.
7 | It has been proposed in `Large Batch Optimization for Deep Learning: Training BERT in 76 minutes`_.
8 | Arguments:
9 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
10 | parameter groups
11 | lr (float, optional): learning rate (default: 1e-3)
12 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
13 | running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.9, 0.999))
14 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
15 | numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
16 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
17 | adam (bool, optional): always use trust ratio = 1, which turns this into
18 | Adam. Useful for comparison purposes.
19 | .. _Large Batch Optimization for Deep Learning: Training BERT in 76 minutes:
20 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.00962
21 | Example:
22 | >>> model = ResNet()
23 | >>> optimizer = Lamb(model.parameters(), lr=1e-2, weight_decay=1e-5)
24 | """
25 |
26 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-6,
27 | weight_decay=0, adam=False):
28 | if not 0.0 <= lr:
29 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
30 | if not 0.0 <= eps:
31 | raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
32 | if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
33 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
34 | if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
35 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
36 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps,
37 | weight_decay=weight_decay)
38 | self.adam = adam
39 | super(Lamb, self).__init__(params, defaults)
40 |
41 | def step(self, closure=None):
42 | """Performs a single optimization step.
43 | Arguments:
44 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
45 | and returns the loss.
46 | """
47 | loss = None
48 | if closure is not None:
49 | loss = closure()
50 |
51 | for group in self.param_groups:
52 | for p in group['params']:
53 | if p.grad is None:
54 | continue
55 | grad = p.grad.data
56 | if grad.is_sparse:
57 | raise RuntimeError('Lamb does not support sparse gradients, consider SparseAdam instad.')
58 |
59 | state = self.state[p]
60 |
61 | # State initialization
62 | if len(state) == 0:
63 | state['step'] = 0
64 | # Exponential moving average of gradient values
65 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
66 | # Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
67 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
68 |
69 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
70 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
71 |
72 | state['step'] += 1
73 |
74 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
75 | # m_t
76 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1 - beta1, grad)
77 | # v_t
78 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1 - beta2, grad, grad)
79 |
80 | # Paper v3 does not use debiasing.
81 | # bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
82 | # bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
83 | # Apply bias to lr to avoid broadcast.
84 | step_size = group['lr'] # * math.sqrt(bias_correction2) / bias_correction1
85 |
86 | weight_norm = p.data.pow(2).sum().sqrt().clamp(0, 10)
87 |
88 | adam_step = exp_avg / exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add(group['eps'])
89 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
90 | adam_step.add_(group['weight_decay'], p.data)
91 |
92 | adam_norm = adam_step.pow(2).sum().sqrt()
93 | if weight_norm == 0 or adam_norm == 0:
94 | trust_ratio = 1
95 | else:
96 | trust_ratio = weight_norm / adam_norm
97 | state['weight_norm'] = weight_norm
98 | state['adam_norm'] = adam_norm
99 | state['trust_ratio'] = trust_ratio
100 | if self.adam:
101 | trust_ratio = 1
102 |
103 | p.data.add_(-step_size * trust_ratio, adam_step)
104 |
105 | return loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Bert multi-label text classification by PyTorch
2 |
3 | This repo contains a PyTorch implementation of the pretrained BERT and XLNET model for multi-label text classification.
4 |
5 | ### Structure of the code
6 |
7 | At the root of the project, you will see:
8 |
9 | ```text
10 | ├── pybert
11 | | └── callback
12 | | | └── lrscheduler.py
13 | | | └── trainingmonitor.py
14 | | | └── ...
15 | | └── config
16 | | | └── basic_config.py #a configuration file for storing model parameters
17 | | └── dataset
18 | | └── io
19 | | | └── dataset.py
20 | | | └── data_transformer.py
21 | | └── model
22 | | | └── nn
23 | | | └── pretrain
24 | | └── output #save the ouput of model
25 | | └── preprocessing #text preprocessing
26 | | └── train #used for training a model
27 | | | └── trainer.py
28 | | | └── ...
29 | | └── common # a set of utility functions
30 | ├── run_bert.py
31 | ├── run_xlnet.py
32 | ```
33 | ### Dependencies
34 |
35 | - csv
36 | - tqdm
37 | - numpy
38 | - pickle
39 | - scikit-learn
40 | - PyTorch 1.1+
41 | - matplotlib
42 | - pandas
43 | - transformers=2.5.1
44 |
45 | ### How to use the code
46 |
47 | you need download pretrained bert model and xlnet model.
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 | 1. Download the Bert pretrained model from [s3](https://s3.amazonaws.com/models.huggingface.co/bert/bert-base-uncased-pytorch_model.bin)
54 | 2. Download the Bert config file from [s3](https://s3.amazonaws.com/models.huggingface.co/bert/bert-base-uncased-config.json)
55 | 3. Download the Bert vocab file from [s3](https://s3.amazonaws.com/models.huggingface.co/bert/bert-base-uncased-vocab.txt)
56 | 4. Rename:
57 |
58 | - `bert-base-uncased-pytorch_model.bin` to `pytorch_model.bin`
59 | - `bert-base-uncased-config.json` to `config.json`
60 | - `bert-base-uncased-vocab.txt` to `bert_vocab.txt`
61 | 5. Place `model` ,`config` and `vocab` file into the `/pybert/pretrain/bert/base-uncased` directory.
62 | 6. `pip install pytorch-transformers` from [github](https://github.com/huggingface/pytorch-transformers).
63 | 7. Download [kaggle data](https://www.kaggle.com/c/jigsaw-toxic-comment-classification-challenge/data) and place in `pybert/dataset`.
64 | - you can modify the `io.task_data.py` to adapt your data.
65 | 8. Modify configuration information in `pybert/configs/basic_config.py`(the path of data,...).
66 | 9. Run `python run_bert.py --do_data` to preprocess data.
67 | 10. Run `python run_bert.py --do_train --save_best --do_lower_case` to fine tuning bert model.
68 | 11. Run `run_bert.py --do_test --do_lower_case` to predict new data.
69 |
70 | ### training
71 |
72 | ```text
73 | [training] 8511/8511 [>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>] -0.8s/step- loss: 0.0640
74 | training result:
75 | [2019-01-14 04:01:05]: bert-multi-label trainer.py[line:176] INFO
76 | Epoch: 2 - loss: 0.0338 - val_loss: 0.0373 - val_auc: 0.9922
77 | ```
78 | ### training figure
79 |
80 | 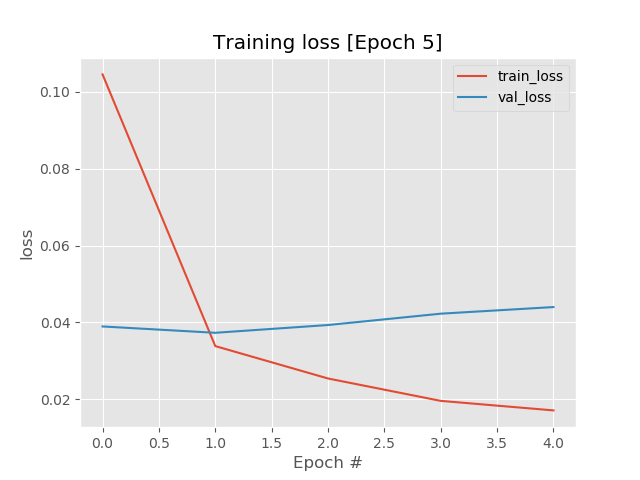
81 |
82 | ### result
83 |
84 | ```python
85 | ---- train report every label -----
86 | Label: toxic - auc: 0.9903
87 | Label: severe_toxic - auc: 0.9913
88 | Label: obscene - auc: 0.9951
89 | Label: threat - auc: 0.9898
90 | Label: insult - auc: 0.9911
91 | Label: identity_hate - auc: 0.9910
92 | ---- valid report every label -----
93 | Label: toxic - auc: 0.9892
94 | Label: severe_toxic - auc: 0.9911
95 | Label: obscene - auc: 0.9945
96 | Label: threat - auc: 0.9955
97 | Label: insult - auc: 0.9903
98 | Label: identity_hate - auc: 0.9927
99 | ```
100 |
101 | ## Tips
102 |
103 | - When converting the tensorflow checkpoint into the pytorch, it's expected to choice the "bert_model.ckpt", instead of "bert_model.ckpt.index", as the input file. Otherwise, you will see that the model can learn nothing and give almost same random outputs for any inputs. This means, in fact, you have not loaded the true ckpt for your model
104 | - When using multiple GPUs, the non-tensor calculations, such as accuracy and f1_score, are not supported by DataParallel instance
105 | - As recommanded by Jocob in his paper https://arxiv.org/pdf/1810.04805.pdf, in fine-tuning tasks, the hyperparameters are expected to set as following: **Batch_size**: 16 or 32, **learning_rate**: 5e-5 or 2e-5 or 3e-5, **num_train_epoch**: 3 or 4
106 | - The pretrained model has a limit for the sentence of input that its length should is not larger than 512, the max position embedding dim. The data flows into the model as: Raw_data -> WordPieces -> Model. Note that the length of wordPieces is generally larger than that of raw_data, so a safe max length of raw_data is at ~128 - 256
107 | - Upon testing, we found that fine-tuning all layers could get much better results than those of only fine-tuning the last classfier layer. The latter is actually a feature-based way
108 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/vocabulary.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from collections import Counter
2 | from ..common.tools import save_pickle
3 | from ..common.tools import load_pickle
4 | from ..common.tools import logger
5 |
6 | class Vocabulary(object):
7 | def __init__(self, max_size=None,
8 | min_freq=None,
9 | pad_token="[PAD]",
10 | unk_token = "[UNK]",
11 | cls_token = "[CLS]",
12 | sep_token = "[SEP]",
13 | mask_token = "[MASK]",
14 | add_unused = False):
15 | self.max_size = max_size
16 | self.min_freq = min_freq
17 | self.cls_token = cls_token
18 | self.sep_token = sep_token
19 | self.pad_token = pad_token
20 | self.mask_token = mask_token
21 | self.unk_token = unk_token
22 | self.word2id = {}
23 | self.id2word = None
24 | self.rebuild = True
25 | self.add_unused = add_unused
26 | self.word_counter = Counter()
27 | self.reset()
28 |
29 | def reset(self):
30 | ctrl_symbols = [self.pad_token,self.unk_token,self.cls_token,self.sep_token,self.mask_token]
31 | for index,syb in enumerate(ctrl_symbols):
32 | self.word2id[syb] = index
33 |
34 | if self.add_unused:
35 | for i in range(20):
36 | self.word2id[f'[UNUSED{i}]'] = len(self.word2id)
37 |
38 | def update(self, word_list):
39 | '''
40 | 依次增加序列中词在词典中的出现频率
41 | :param word_list:
42 | :return:
43 | '''
44 | self.word_counter.update(word_list)
45 |
46 | def add(self, word):
47 | '''
48 | 增加一个新词在词典中的出现频率
49 | :param word:
50 | :return:
51 | '''
52 | self.word_counter[word] += 1
53 |
54 | def has_word(self, word):
55 | '''
56 | 检查词是否被记录
57 | :param word:
58 | :return:
59 | '''
60 | return word in self.word2id
61 |
62 | def to_index(self, word):
63 | '''
64 | 将词转为数字. 若词不再词典中被记录, 将视为 unknown, 若 ``unknown=None`` , 将抛出
65 | :param word:
66 | :return:
67 | '''
68 | if word in self.word2id:
69 | return self.word2id[word]
70 | if self.unk_token is not None:
71 | return self.word2id[self.unk_token]
72 | else:
73 | raise ValueError("word {} not in vocabulary".format(word))
74 |
75 | def unknown_idx(self):
76 | """
77 | unknown 对应的数字.
78 | """
79 | if self.unk_token is None:
80 | return None
81 | return self.word2id[self.unk_token]
82 |
83 | def padding_idx(self):
84 | """
85 | padding 对应的数字
86 | """
87 | if self.pad_token is None:
88 | return None
89 | return self.word2id[self.pad_token]
90 |
91 | def to_word(self, idx):
92 | """
93 | 给定一个数字, 将其转为对应的词.
94 |
95 | :param int idx: the index
96 | :return str word: the word
97 | """
98 | return self.id2word[idx]
99 |
100 | def build_vocab(self):
101 | max_size = min(self.max_size, len(self.word_counter)) if self.max_size else None
102 | words = self.word_counter.most_common(max_size)
103 | if self.min_freq is not None:
104 | words = filter(lambda kv: kv[1] >= self.min_freq, words)
105 | if self.word2id:
106 | words = filter(lambda kv: kv[0] not in self.word2id, words)
107 | start_idx = len(self.word2id)
108 | self.word2id.update({w: i + start_idx for i, (w, _) in enumerate(words)})
109 | logger.info(f"The size of vocab is: {len(self.word2id)}")
110 | self.build_reverse_vocab()
111 | self.rebuild = False
112 |
113 | def save(self, file_path):
114 | '''
115 | 保存vocab
116 | :param file_name:
117 | :param pickle_path:
118 | :return:
119 | '''
120 | mappings = {
121 | "word2id": self.word2id,
122 | 'id2word': self.id2word
123 | }
124 | save_pickle(data=mappings, file_path=file_path)
125 |
126 | def save_bert_vocab(self,file_path):
127 | bert_vocab = [x for x,y in self.word2id.items()]
128 | with open(str(file_path),'w') as fo:
129 | for token in bert_vocab:
130 | fo.write(token+"\n")
131 |
132 | def load_from_file(self, file_path):
133 | '''
134 | 从文件组红加载vocab
135 | :param file_name:
136 | :param pickle_path:
137 | :return:
138 | '''
139 | mappings = load_pickle(input_file=file_path)
140 | self.id2word = mappings['id2word']
141 | self.word2id = mappings['word2id']
142 |
143 | def build_reverse_vocab(self):
144 | self.id2word = {i: w for w, i in self.word2id.items()}
145 |
146 | def clear(self):
147 | """
148 | 删除Vocabulary中的词表数据。相当于重新初始化一下。
149 | :return:
150 | """
151 | self.word_counter.clear()
152 | self.word2id = None
153 | self.id2word = None
154 | self.rebuild = True
155 | self.reset()
156 |
157 | def __len__(self):
158 | return len(self.id2word)
159 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/ralars.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
4 |
5 |
6 | class RaLars(Optimizer):
7 | """Implements the RAdam optimizer from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1908.03265.pdf
8 | with optional Layer-wise adaptive Scaling from https://arxiv.org/pdf/1708.03888.pdf
9 |
10 | Args:
11 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining parameter groups
12 | lr (float, optional): learning rate
13 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.9, 0.999))
14 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
15 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
16 | scale_clip (float, optional): the maximal upper bound for the scale factor of LARS
17 | Example:
18 | >>> model = ResNet()
19 | >>> optimizer = RaLars(model.parameters(), lr=0.001)
20 | """
21 |
22 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0,
23 | scale_clip=None):
24 | if not 0.0 <= lr:
25 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
26 | if not 0.0 <= eps:
27 | raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
28 | if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
29 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
30 | if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
31 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
32 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps, weight_decay=weight_decay)
33 | super(RaLars, self).__init__(params, defaults)
34 | # LARS arguments
35 | self.scale_clip = scale_clip
36 | if self.scale_clip is None:
37 | self.scale_clip = (0, 10)
38 |
39 | def step(self, closure=None):
40 | """Performs a single optimization step.
41 | Arguments:
42 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
43 | and returns the loss.
44 | """
45 | loss = None
46 | if closure is not None:
47 | loss = closure()
48 |
49 | for group in self.param_groups:
50 |
51 | # Get group-shared variables
52 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
53 | sma_inf = group.get('sma_inf')
54 | # Compute max length of SMA on first step
55 | if not isinstance(sma_inf, float):
56 | group['sma_inf'] = 2 / (1 - beta2) - 1
57 | sma_inf = group.get('sma_inf')
58 |
59 | for p in group['params']:
60 | if p.grad is None:
61 | continue
62 | grad = p.grad.data
63 | if grad.is_sparse:
64 | raise RuntimeError('RAdam does not support sparse gradients')
65 |
66 | state = self.state[p]
67 |
68 | # State initialization
69 | if len(state) == 0:
70 | state['step'] = 0
71 | # Exponential moving average of gradient values
72 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
73 | # Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
74 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
75 |
76 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
77 |
78 | state['step'] += 1
79 |
80 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
81 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1 - beta1, grad)
82 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1 - beta2, grad, grad)
83 |
84 | # Bias correction
85 | bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
86 | bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
87 |
88 | # Compute length of SMA
89 | sma_t = sma_inf - 2 * state['step'] * (1 - bias_correction2) / bias_correction2
90 |
91 | update = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
92 | if sma_t > 4:
93 | # Variance rectification term
94 | r_t = math.sqrt((sma_t - 4) * (sma_t - 2) * sma_inf / ((sma_inf - 4) * (sma_inf - 2) * sma_t))
95 | # Adaptive momentum
96 | update.addcdiv_(r_t, exp_avg / bias_correction1,
97 | (exp_avg_sq / bias_correction2).sqrt().add_(group['eps']))
98 | else:
99 | # Unadapted momentum
100 | update.add_(exp_avg / bias_correction1)
101 |
102 | # Weight decay
103 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
104 | update.add_(group['weight_decay'], p.data)
105 |
106 | # LARS
107 | p_norm = p.data.pow(2).sum().sqrt()
108 | update_norm = update.pow(2).sum().sqrt()
109 | phi_p = p_norm.clamp(*self.scale_clip)
110 | # Compute the local LR
111 | if phi_p == 0 or update_norm == 0:
112 | local_lr = 1
113 | else:
114 | local_lr = phi_p / update_norm
115 |
116 | state['local_lr'] = local_lr
117 |
118 | p.data.add_(-group['lr'] * local_lr, update)
119 |
120 | return loss
121 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/adabound.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import math
3 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
4 |
5 | class AdaBound(Optimizer):
6 | """Implements AdaBound algorithm.
7 | It has been proposed in `Adaptive Gradient Methods with Dynamic Bound of Learning Rate`_.
8 | Arguments:
9 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize or dicts defining
10 | parameter groups
11 | lr (float, optional): Adam learning rate (default: 1e-3)
12 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
13 | running averages of gradient and its square (default: (0.9, 0.999))
14 | final_lr (float, optional): final (SGD) learning rate (default: 0.1)
15 | gamma (float, optional): convergence speed of the bound functions (default: 1e-3)
16 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
17 | numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
18 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: 0)
19 | amsbound (boolean, optional): whether to use the AMSBound variant of this algorithm
20 | .. Adaptive Gradient Methods with Dynamic Bound of Learning Rate:
21 | https://openreview.net/forum?id=Bkg3g2R9FX
22 | Example:
23 | >>> model = LSTM()
24 | >>> optimizer = AdaBound(model.parameters())
25 | """
26 |
27 | def __init__(self, params, lr=1e-3, betas=(0.9, 0.999), final_lr=0.1, gamma=1e-3,
28 | eps=1e-8, weight_decay=0, amsbound=False):
29 | if not 0.0 <= lr:
30 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
31 | if not 0.0 <= eps:
32 | raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
33 | if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
34 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
35 | if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
36 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
37 | if not 0.0 <= final_lr:
38 | raise ValueError("Invalid final learning rate: {}".format(final_lr))
39 | if not 0.0 <= gamma < 1.0:
40 | raise ValueError("Invalid gamma parameter: {}".format(gamma))
41 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, final_lr=final_lr, gamma=gamma, eps=eps,
42 | weight_decay=weight_decay, amsbound=amsbound)
43 | super(AdaBound, self).__init__(params, defaults)
44 |
45 | self.base_lrs = list(map(lambda group: group['lr'], self.param_groups))
46 |
47 | def __setstate__(self, state):
48 | super(AdaBound, self).__setstate__(state)
49 | for group in self.param_groups:
50 | group.setdefault('amsbound', False)
51 |
52 | def step(self, closure=None):
53 | """Performs a single optimization step.
54 | Arguments:
55 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
56 | and returns the loss.
57 | """
58 | loss = None
59 | if closure is not None:
60 | loss = closure()
61 | for group, base_lr in zip(self.param_groups, self.base_lrs):
62 | for p in group['params']:
63 | if p.grad is None:
64 | continue
65 | grad = p.grad.data
66 | if grad.is_sparse:
67 | raise RuntimeError(
68 | 'Adam does not support sparse gradients, please consider SparseAdam instead')
69 | amsbound = group['amsbound']
70 | state = self.state[p]
71 | # State initialization
72 | if len(state) == 0:
73 | state['step'] = 0
74 | # Exponential moving average of gradient values
75 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
76 | # Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
77 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
78 | if amsbound:
79 | # Maintains max of all exp. moving avg. of sq. grad. values
80 | state['max_exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p.data)
81 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
82 | if amsbound:
83 | max_exp_avg_sq = state['max_exp_avg_sq']
84 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
85 | state['step'] += 1
86 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
87 | grad = grad.add(group['weight_decay'], p.data)
88 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
89 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(1 - beta1, grad)
90 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(1 - beta2, grad, grad)
91 | if amsbound:
92 | # Maintains the maximum of all 2nd moment running avg. till now
93 | torch.max(max_exp_avg_sq, exp_avg_sq, out=max_exp_avg_sq)
94 | # Use the max. for normalizing running avg. of gradient
95 | denom = max_exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
96 | else:
97 | denom = exp_avg_sq.sqrt().add_(group['eps'])
98 |
99 | bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
100 | bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
101 | step_size = group['lr'] * math.sqrt(bias_correction2) / bias_correction1
102 |
103 | # Applies bounds on actual learning rate
104 | # lr_scheduler cannot affect final_lr, this is a workaround to apply lr decay
105 | final_lr = group['final_lr'] * group['lr'] / base_lr
106 | lower_bound = final_lr * (1 - 1 / (group['gamma'] * state['step'] + 1))
107 | upper_bound = final_lr * (1 + 1 / (group['gamma'] * state['step']))
108 | step_size = torch.full_like(denom, step_size)
109 | step_size.div_(denom).clamp_(lower_bound, upper_bound).mul_(exp_avg)
110 | p.data.add_(-step_size)
111 | return loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/preprocessing/preprocessor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #encoding:utf-8
2 | import re
3 |
4 | replacement = {
5 | "aren't" : "are not",
6 | "can't" : "cannot",
7 | "couldn't" : "could not",
8 | "didn't" : "did not",
9 | "doesn't" : "does not",
10 | "don't" : "do not",
11 | "hadn't" : "had not",
12 | "hasn't" : "has not",
13 | "haven't" : "have not",
14 | "he'd" : "he would",
15 | "he'll" : "he will",
16 | "he's" : "he is",
17 | "i'd" : "I would",
18 | "i'll" : "I will",
19 | "i'm" : "I am",
20 | "isn't" : "is not",
21 | "it's" : "it is",
22 | "it'll":"it will",
23 | "i've" : "I have",
24 | "let's" : "let us",
25 | "mightn't" : "might not",
26 | "mustn't" : "must not",
27 | "shan't" : "shall not",
28 | "she'd" : "she would",
29 | "she'll" : "she will",
30 | "she's" : "she is",
31 | "shouldn't" : "should not",
32 | "that's" : "that is",
33 | "there's" : "there is",
34 | "they'd" : "they would",
35 | "they'll" : "they will",
36 | "they're" : "they are",
37 | "they've" : "they have",
38 | "we'd" : "we would",
39 | "we're" : "we are",
40 | "weren't" : "were not",
41 | "we've" : "we have",
42 | "what'll" : "what will",
43 | "what're" : "what are",
44 | "what's" : "what is",
45 | "what've" : "what have",
46 | "where's" : "where is",
47 | "who'd" : "who would",
48 | "who'll" : "who will",
49 | "who're" : "who are",
50 | "who's" : "who is",
51 | "who've" : "who have",
52 | "won't" : "will not",
53 | "wouldn't" : "would not",
54 | "you'd" : "you would",
55 | "you'll" : "you will",
56 | "you're" : "you are",
57 | "you've" : "you have",
58 | "'re": " are",
59 | "wasn't": "was not",
60 | "we'll":" will",
61 | "tryin'":"trying",
62 | }
63 |
64 | class EnglishPreProcessor(object):
65 | def __init__(self,min_len = 2,stopwords_path = None):
66 | self.min_len = min_len
67 | self.stopwords_path = stopwords_path
68 | self.reset()
69 |
70 | def lower(self,sentence):
71 | '''
72 | 大写转化为小写
73 | :param sentence:
74 | :return:
75 | '''
76 | return sentence.lower()
77 |
78 | def reset(self):
79 | '''
80 | 加载停用词
81 | :return:
82 | '''
83 | if self.stopwords_path:
84 | with open(self.stopwords_path,'r') as fr:
85 | self.stopwords = {}
86 | for line in fr:
87 | word = line.strip(' ').strip('\n')
88 | self.stopwords[word] = 1
89 |
90 |
91 | def clean_length(self,sentence):
92 | '''
93 | 去除长度小于min_len的文本
94 | :param sentence:
95 | :return:
96 | '''
97 | if len([x for x in sentence]) >= self.min_len:
98 | return sentence
99 |
100 | def replace(self,sentence):
101 | '''
102 | 一些特殊缩写替换
103 | :param sentence:
104 | :return:
105 | '''
106 | # Replace words like gooood to good
107 | sentence = re.sub(r'(\w)\1{2,}', r'\1\1', sentence)
108 | # Normalize common abbreviations
109 | words = sentence.split(' ')
110 | words = [replacement[word] if word in replacement else word for word in words]
111 | sentence_repl = " ".join(words)
112 | return sentence_repl
113 |
114 | def remove_website(self,sentence):
115 | '''
116 | 处理网址符号
117 | :param sentence:
118 | :return:
119 | '''
120 | sentence_repl = sentence.replace(r"http\S+", "")
121 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r"https\S+", "")
122 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r"http", "")
123 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r"https", "")
124 | return sentence_repl
125 |
126 | def remove_name_tag(self,sentence):
127 | # Remove name tag
128 | sentence_repl = sentence.replace(r"@\S+", "")
129 | return sentence_repl
130 |
131 | def remove_time(self,sentence):
132 | '''
133 | 特殊数据处理
134 | :param sentence:
135 | :return:
136 | '''
137 | # Remove time related text
138 | sentence_repl = sentence.replace(r'\w{3}[+-][0-9]{1,2}\:[0-9]{2}\b', "") # e.g. UTC+09:00
139 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r'\d{1,2}\:\d{2}\:\d{2}', "") # e.g. 18:09:01
140 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r'\d{1,2}\:\d{2}', "") # e.g. 18:09
141 | # Remove date related text
142 | # e.g. 11/12/19, 11-1-19, 1.12.19, 11/12/2019
143 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r'\d{1,2}(?:\/|\-|\.)\d{1,2}(?:\/|\-|\.)\d{2,4}', "")
144 | # e.g. 11 dec, 2019 11 dec 2019 dec 11, 2019
145 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(
146 | r"([\d]{1,2}\s(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)|(jan|feb|mar|apr|may|jun|jul|aug|sep|oct|nov|dec)\s[\d]{1,2})(\s|\,|\,\s|\s\,)[\d]{2,4}",
147 | "")
148 | # e.g. 11 december, 2019 11 december 2019 december 11, 2019
149 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(
150 | r"[\d]{1,2}\s(january|february|march|april|may|june|july|august|september|october|november|december)(\s|\,|\,\s|\s\,)[\d]{2,4}",
151 | "")
152 | return sentence_repl
153 |
154 | def remove_breaks(self,sentence):
155 | # Remove line breaks
156 | sentence_repl = sentence.replace("\r", "")
157 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace("\n", "")
158 | sentence_repl = re.sub(r"\\n\n", ".", sentence_repl)
159 | return sentence_repl
160 |
161 | def remove_ip(self,sentence):
162 | # Remove phone number and IP address
163 | sentence_repl = sentence.replace(r'\d{8,}', "")
164 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r'\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}\.\d{1,3}', "")
165 | return sentence_repl
166 |
167 | def adjust_common(self,sentence):
168 | # Adjust common abbreviation
169 | sentence_repl = sentence.replace(r" you re ", " you are ")
170 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r" we re ", " we are ")
171 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r" they re ", " they are ")
172 | sentence_repl = sentence_repl.replace(r"@", "at")
173 | return sentence_repl
174 |
175 | def remove_chinese(self,sentence):
176 | # Chinese bad word
177 | sentence_repl = re.sub(r"fucksex", "fuck sex", sentence)
178 | sentence_repl = re.sub(r"f u c k", "fuck", sentence_repl)
179 | sentence_repl = re.sub(r"幹", "fuck", sentence_repl)
180 | sentence_repl = re.sub(r"死", "die", sentence_repl)
181 | sentence_repl = re.sub(r"他妈的", "fuck", sentence_repl)
182 | sentence_repl = re.sub(r"去你妈的", "fuck off", sentence_repl)
183 | sentence_repl = re.sub(r"肏你妈", "fuck your mother", sentence_repl)
184 | sentence_repl = re.sub(r"肏你祖宗十八代", "your ancestors to the 18th generation", sentence_repl)
185 | return sentence_repl
186 |
187 | def full2half(self,sentence):
188 | '''
189 | 全角转化为半角
190 | :param sentence:
191 | :return:
192 | '''
193 | ret_str = ''
194 | for i in sentence:
195 | if ord(i) >= 33 + 65248 and ord(i) <= 126 + 65248:
196 | ret_str += chr(ord(i) - 65248)
197 | else:
198 | ret_str += i
199 | return ret_str
200 |
201 | def remove_stopword(self,sentence):
202 | '''
203 | 去除停用词
204 | :param sentence:
205 | :return:
206 | '''
207 | words = sentence.split()
208 | x = [word for word in words if word not in self.stopwords]
209 | return " ".join(x)
210 |
211 | # 主函数
212 | def __call__(self, sentence):
213 | x = sentence
214 | # x = self.lower(x)
215 | x = self.replace(x)
216 | x = self.remove_website(x)
217 | x = self.remove_name_tag(x)
218 | x = self.remove_time(x)
219 | x = self.remove_breaks(x)
220 | x = self.remove_ip(x)
221 | x = self.adjust_common(x)
222 | x = self.remove_chinese(x)
223 | return x
224 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/train/trainer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
3 | from ..common.tools import model_device
4 | from ..common.tools import summary
5 | from ..common.tools import seed_everything
6 | from ..common.tools import AverageMeter
7 | from torch.nn.utils import clip_grad_norm_
8 |
9 | class Trainer(object):
10 | def __init__(self,args,model,logger,criterion,optimizer,scheduler,early_stopping,epoch_metrics,
11 | batch_metrics,verbose = 1,training_monitor = None,model_checkpoint = None
12 | ):
13 | self.args = args
14 | self.model = model
15 | self.logger =logger
16 | self.verbose = verbose
17 | self.criterion = criterion
18 | self.optimizer = optimizer
19 | self.scheduler = scheduler
20 | self.early_stopping = early_stopping
21 | self.epoch_metrics = epoch_metrics
22 | self.batch_metrics = batch_metrics
23 | self.model_checkpoint = model_checkpoint
24 | self.training_monitor = training_monitor
25 | self.start_epoch = 1
26 | self.global_step = 0
27 | self.model, self.device = model_device(n_gpu = args.n_gpu, model=self.model)
28 | if args.fp16:
29 | try:
30 | from apex import amp
31 | except ImportError:
32 | raise ImportError("Please install apex from https://www.github.com/nvidia/apex to use fp16 training.")
33 | if args.resume_path:
34 | self.logger.info(f"\nLoading checkpoint: {args.resume_path}")
35 | resume_dict = torch.load(args.resume_path / 'checkpoint_info.bin')
36 | best = resume_dict['best']
37 | self.start_epoch = resume_dict['epoch']
38 | if self.model_checkpoint:
39 | self.model_checkpoint.best = best
40 | self.logger.info(f"\nCheckpoint '{args.resume_path}' and epoch {self.start_epoch} loaded")
41 |
42 | def epoch_reset(self):
43 | self.outputs = []
44 | self.targets = []
45 | self.result = {}
46 | for metric in self.epoch_metrics:
47 | metric.reset()
48 |
49 | def batch_reset(self):
50 | self.info = {}
51 | for metric in self.batch_metrics:
52 | metric.reset()
53 |
54 | def save_info(self,epoch,best):
55 | model_save = self.model.module if hasattr(self.model, 'module') else self.model
56 | state = {"model":model_save,
57 | 'epoch':epoch,
58 | 'best':best}
59 | return state
60 |
61 | def valid_epoch(self,data):
62 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(data),desc="Evaluating")
63 | self.epoch_reset()
64 | for step, batch in enumerate(data):
65 | self.model.eval()
66 | batch = tuple(t.to(self.device) for t in batch)
67 | with torch.no_grad():
68 | input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids = batch
69 | logits = self.model(input_ids, segment_ids,input_mask)
70 | self.outputs.append(logits.cpu().detach())
71 | self.targets.append(label_ids.cpu().detach())
72 | pbar(step=step)
73 | self.outputs = torch.cat(self.outputs, dim = 0).cpu().detach()
74 | self.targets = torch.cat(self.targets, dim = 0).cpu().detach()
75 | loss = self.criterion(target = self.targets, output=self.outputs)
76 | self.result['valid_loss'] = loss.item()
77 | print("------------- valid result --------------")
78 | if self.epoch_metrics:
79 | for metric in self.epoch_metrics:
80 | metric(logits=self.outputs, target=self.targets)
81 | value = metric.value()
82 | if value:
83 | self.result[f'valid_{metric.name()}'] = value
84 | if 'cuda' in str(self.device):
85 | torch.cuda.empty_cache()
86 | return self.result
87 |
88 | def train_epoch(self,data):
89 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total = len(data),desc='Training')
90 | tr_loss = AverageMeter()
91 | self.epoch_reset()
92 | for step, batch in enumerate(data):
93 | self.batch_reset()
94 | self.model.train()
95 | batch = tuple(t.to(self.device) for t in batch)
96 | input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids = batch
97 | logits = self.model(input_ids, segment_ids,input_mask)
98 | loss = self.criterion(output=logits,target=label_ids)
99 | if len(self.args.n_gpu) >= 2:
100 | loss = loss.mean()
101 | if self.args.gradient_accumulation_steps > 1:
102 | loss = loss / self.args.gradient_accumulation_steps
103 | if self.args.fp16:
104 | with amp.scale_loss(loss, self.optimizer) as scaled_loss:
105 | scaled_loss.backward()
106 | clip_grad_norm_(amp.master_params(self.optimizer), self.args.grad_clip)
107 | else:
108 | loss.backward()
109 | clip_grad_norm_(self.model.parameters(), self.args.grad_clip)
110 | if (step + 1) % self.args.gradient_accumulation_steps == 0:
111 | self.scheduler.step()
112 | self.optimizer.step()
113 | self.optimizer.zero_grad()
114 | self.global_step += 1
115 | if self.batch_metrics:
116 | for metric in self.batch_metrics:
117 | metric(logits = logits,target = label_ids)
118 | self.info[metric.name()] = metric.value()
119 | self.info['loss'] = loss.item()
120 | tr_loss.update(loss.item(),n = 1)
121 | if self.verbose >= 1:
122 | pbar(step= step,info = self.info)
123 | self.outputs.append(logits.cpu().detach())
124 | self.targets.append(label_ids.cpu().detach())
125 | print("\n------------- train result --------------")
126 | # epoch metric
127 | self.outputs = torch.cat(self.outputs, dim =0).cpu().detach()
128 | self.targets = torch.cat(self.targets, dim =0).cpu().detach()
129 | self.result['loss'] = tr_loss.avg
130 | if self.epoch_metrics:
131 | for metric in self.epoch_metrics:
132 | metric(logits=self.outputs, target=self.targets)
133 | value = metric.value()
134 | if value:
135 | self.result[f'{metric.name()}'] = value
136 | if "cuda" in str(self.device):
137 | torch.cuda.empty_cache()
138 | return self.result
139 |
140 | def train(self,train_data,valid_data):
141 | # print("model summary info: ")
142 | # for step, (input_ids, input_mask, segment_ids, label_ids) in enumerate(train_data):
143 | # input_ids = input_ids.to(self.device)
144 | # input_mask = input_mask.to(self.device)
145 | # segment_ids = segment_ids.to(self.device)
146 | # summary(self.model,*(input_ids, segment_ids,input_mask),show_input=True)
147 | # break
148 | # ***************************************************************
149 | self.model.zero_grad()
150 | seed_everything(self.args.seed) # Added here for reproductibility (even between python 2 a
151 | for epoch in range(self.start_epoch,self.start_epoch+self.args.epochs):
152 | self.logger.info(f"Epoch {epoch}/{self.args.epochs}")
153 | train_log = self.train_epoch(train_data)
154 | valid_log = self.valid_epoch(valid_data)
155 |
156 | logs = dict(train_log,**valid_log)
157 | show_info = f'\nEpoch: {epoch} - ' + "-".join([f' {key}: {value:.4f} ' for key,value in logs.items()])
158 | self.logger.info(show_info)
159 |
160 | # save
161 | if self.training_monitor:
162 | self.training_monitor.epoch_step(logs)
163 |
164 | # save model
165 | if self.model_checkpoint:
166 | state = self.save_info(epoch,best=logs[self.model_checkpoint.monitor])
167 | self.model_checkpoint.bert_epoch_step(current=logs[self.model_checkpoint.monitor],state = state)
168 |
169 | # early_stopping
170 | if self.early_stopping:
171 | self.early_stopping.epoch_step(epoch=epoch, current=logs[self.early_stopping.monitor])
172 | if self.early_stopping.stop_training:
173 | break
174 |
175 |
176 |
177 |
178 |
179 |
180 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/callback/optimizater/adafactor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import operator
2 | import torch
3 | from copy import copy
4 | import functools
5 | from math import sqrt
6 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer
7 |
8 |
9 | class AdaFactor(Optimizer):
10 | '''
11 | # Code below is an implementation of https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.04235.pdf
12 | # inspired but modified from https://github.com/DeadAt0m/adafactor-pytorch
13 | Example:
14 | >>> model = LSTM()
15 | >>> optimizer = AdaFactor(model.parameters(),lr= lr)
16 | '''
17 |
18 | def __init__(self, params, lr=None, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.999, eps1=1e-30,
19 | eps2=1e-3, cliping_threshold=1, non_constant_decay=True,
20 | enable_factorization=True, ams_grad=True, weight_decay=0):
21 |
22 | enable_momentum = beta1 != 0
23 | if non_constant_decay:
24 | ams_grad = False
25 |
26 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, beta1=beta1, beta2=beta2, eps1=eps1,
27 | eps2=eps2, cliping_threshold=cliping_threshold,
28 | weight_decay=weight_decay, ams_grad=ams_grad,
29 | enable_factorization=enable_factorization,
30 | enable_momentum=enable_momentum,
31 | non_constant_decay=non_constant_decay)
32 |
33 | super(AdaFactor, self).__init__(params, defaults)
34 |
35 | def __setstate__(self, state):
36 | super(AdaFactor, self).__setstate__(state)
37 |
38 | def _experimental_reshape(self, shape):
39 | temp_shape = shape[2:]
40 | if len(temp_shape) == 1:
41 | new_shape = (shape[0], shape[1] * shape[2])
42 | else:
43 | tmp_div = len(temp_shape) // 2 + len(temp_shape) % 2
44 | new_shape = (shape[0] * functools.reduce(operator.mul,
45 | temp_shape[tmp_div:], 1),
46 | shape[1] * functools.reduce(operator.mul,
47 | temp_shape[:tmp_div], 1))
48 | return new_shape, copy(shape)
49 |
50 | def _check_shape(self, shape):
51 | '''
52 | output1 - True - algorithm for matrix, False - vector;
53 | output2 - need reshape
54 | '''
55 | if len(shape) > 2:
56 | return True, True
57 | elif len(shape) == 2:
58 | return True, False
59 | elif len(shape) == 2 and (shape[0] == 1 or shape[1] == 1):
60 | return False, False
61 | else:
62 | return False, False
63 |
64 | def _rms(self, x):
65 | return sqrt(torch.mean(x.pow(2)))
66 |
67 | def step(self, closure=None):
68 | loss = None
69 | if closure is not None:
70 | loss = closure()
71 | for group in self.param_groups:
72 | for p in group['params']:
73 | if p.grad is None:
74 | continue
75 | grad = p.grad.data
76 |
77 | if grad.is_sparse:
78 | raise RuntimeError('Adam does not support sparse \
79 | gradients, use SparseAdam instead')
80 |
81 | is_matrix, is_need_reshape = self._check_shape(grad.size())
82 | new_shape = p.data.size()
83 | if is_need_reshape and group['enable_factorization']:
84 | new_shape, old_shape = \
85 | self._experimental_reshape(p.data.size())
86 | grad = grad.view(new_shape)
87 |
88 | state = self.state[p]
89 | if len(state) == 0:
90 | state['step'] = 0
91 | if group['enable_momentum']:
92 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros(new_shape,
93 | dtype=torch.float32,
94 | device=p.grad.device)
95 |
96 | if is_matrix and group['enable_factorization']:
97 | state['exp_avg_sq_R'] = \
98 | torch.zeros((1, new_shape[1]),
99 | dtype=torch.float32,
100 | device=p.grad.device)
101 | state['exp_avg_sq_C'] = \
102 | torch.zeros((new_shape[0], 1),
103 | dtype=torch.float32,
104 | device=p.grad.device)
105 | else:
106 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros(new_shape,
107 | dtype=torch.float32,
108 | device=p.grad.device)
109 | if group['ams_grad']:
110 | state['exp_avg_sq_hat'] = \
111 | torch.zeros(new_shape, dtype=torch.float32,
112 | device=p.grad.device)
113 |
114 | if group['enable_momentum']:
115 | exp_avg = state['exp_avg']
116 |
117 | if is_matrix and group['enable_factorization']:
118 | exp_avg_sq_r = state['exp_avg_sq_R']
119 | exp_avg_sq_c = state['exp_avg_sq_C']
120 | else:
121 | exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg_sq']
122 |
123 | if group['ams_grad']:
124 | exp_avg_sq_hat = state['exp_avg_sq_hat']
125 |
126 | state['step'] += 1
127 | lr_t = group['lr']
128 | lr_t *= max(group['eps2'], self._rms(p.data))
129 |
130 | if group['enable_momentum']:
131 | if group['non_constant_decay']:
132 | beta1_t = group['beta1'] * \
133 | (1 - group['beta1'] ** (state['step'] - 1)) \
134 | / (1 - group['beta1'] ** state['step'])
135 | else:
136 | beta1_t = group['beta1']
137 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1_t).add_(1 - beta1_t, grad)
138 |
139 | if group['non_constant_decay']:
140 | beta2_t = group['beta2'] * \
141 | (1 - group['beta2'] ** (state['step'] - 1)) / \
142 | (1 - group['beta2'] ** state['step'])
143 | else:
144 | beta2_t = group['beta2']
145 |
146 | if is_matrix and group['enable_factorization']:
147 | exp_avg_sq_r.mul_(beta2_t). \
148 | add_(1 - beta2_t, torch.sum(torch.mul(grad, grad).
149 | add_(group['eps1']),
150 | dim=0, keepdim=True))
151 | exp_avg_sq_c.mul_(beta2_t). \
152 | add_(1 - beta2_t, torch.sum(torch.mul(grad, grad).
153 | add_(group['eps1']),
154 | dim=1, keepdim=True))
155 | v = torch.mul(exp_avg_sq_c,
156 | exp_avg_sq_r).div_(torch.sum(exp_avg_sq_r))
157 | else:
158 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2_t). \
159 | addcmul_(1 - beta2_t, grad, grad). \
160 | add_((1 - beta2_t) * group['eps1'])
161 | v = exp_avg_sq
162 | g = grad
163 | if group['enable_momentum']:
164 | g = torch.div(exp_avg, 1 - beta1_t ** state['step'])
165 | if group['ams_grad']:
166 | torch.max(exp_avg_sq_hat, v, out=exp_avg_sq_hat)
167 | v = exp_avg_sq_hat
168 | u = torch.div(g, (torch.div(v, 1 - beta2_t **
169 | state['step'])).sqrt().add_(group['eps1']))
170 | else:
171 | u = torch.div(g, v.sqrt())
172 | u.div_(max(1, self._rms(u) / group['cliping_threshold']))
173 | p.data.add_(-lr_t * (u.view(old_shape) if is_need_reshape and
174 | group['enable_factorization'] else u))
175 | if group['weight_decay'] != 0:
176 | p.data.add_(-group['weight_decay'] * lr_t, p.data)
177 | return loss
178 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/albert_processor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import numpy as np
3 | from ..common.tools import load_pickle
4 | from ..common.tools import logger
5 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
6 | from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
7 | from pybert.model.albert.tokenization_albert import FullTokenizer
8 |
9 | class InputExample(object):
10 | def __init__(self, guid, text_a, text_b=None, label=None):
11 | """Constructs a InputExample.
12 | Args:
13 | guid: Unique id for the example.
14 | text_a: string. The untokenized text of the first sequence. For single
15 | sequence tasks, only this sequence must be specified.
16 | text_b: (Optional) string. The untokenized text of the second sequence.
17 | Only must be specified for sequence pair tasks.
18 | label: (Optional) string. The label of the example. This should be
19 | specified for train and dev examples, but not for test examples.
20 | """
21 | self.guid = guid
22 | self.text_a = text_a
23 | self.text_b = text_b
24 | self.label = label
25 |
26 | class InputFeature(object):
27 | '''
28 | A single set of features of data.
29 | '''
30 | def __init__(self,input_ids,input_mask,segment_ids,label_id,input_len):
31 | self.input_ids = input_ids
32 | self.input_mask = input_mask
33 | self.segment_ids = segment_ids
34 | self.label_id = label_id
35 | self.input_len = input_len
36 |
37 | class AlbertProcessor(object):
38 | """Base class for data converters for sequence classification data sets."""
39 |
40 | def __init__(self,vocab_file,spm_model_file,do_lower_case):
41 | self.tokenizer = FullTokenizer(vocab_file=vocab_file,spm_model_file=spm_model_file,do_lower_case=do_lower_case)
42 |
43 | def get_train(self, data_file):
44 | """Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the train set."""
45 | return self.read_data(data_file)
46 |
47 | def get_dev(self, data_file):
48 | """Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the dev set."""
49 | return self.read_data(data_file)
50 |
51 | def get_test(self,lines):
52 | return lines
53 |
54 | def get_labels(self):
55 | """Gets the list of labels for this data set."""
56 | return ["toxic","severe_toxic","obscene","threat","insult","identity_hate"]
57 |
58 | @classmethod
59 | def read_data(cls, input_file,quotechar = None):
60 | """Reads a tab separated value file."""
61 | if 'pkl' in str(input_file):
62 | lines = load_pickle(input_file)
63 | else:
64 | lines = input_file
65 | return lines
66 |
67 | def truncate_seq_pair(self,tokens_a,tokens_b,max_length):
68 | # This is a simple heuristic which will always truncate the longer sequence
69 | # one token at a time. This makes more sense than truncating an equal percent
70 | # of tokens from each, since if one sequence is very short then each token
71 | # that's truncated likely contains more information than a longer sequence.
72 | while True:
73 | total_length = len(tokens_a) + len(tokens_b)
74 | if total_length <= max_length:
75 | break
76 | if len(tokens_a) > len(tokens_b):
77 | tokens_a.pop()
78 | else:
79 | tokens_b.pop()
80 |
81 | def create_examples(self,lines,example_type,cached_examples_file):
82 | '''
83 | Creates examples for data
84 | '''
85 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total = len(lines),desc='create examples')
86 | if cached_examples_file.exists():
87 | logger.info("Loading examples from cached file %s", cached_examples_file)
88 | examples = torch.load(cached_examples_file)
89 | else:
90 | examples = []
91 | for i,line in enumerate(lines):
92 | guid = '%s-%d'%(example_type,i)
93 | text_a = line[0]
94 | label = line[1]
95 | if isinstance(label,str):
96 | label = [np.float(x) for x in label.split(",")]
97 | else:
98 | label = [np.float(x) for x in list(label)]
99 | text_b = None
100 | example = InputExample(guid = guid,text_a = text_a,text_b=text_b,label= label)
101 | examples.append(example)
102 | pbar(step=i)
103 | logger.info("Saving examples into cached file %s", cached_examples_file)
104 | torch.save(examples, cached_examples_file)
105 | return examples
106 |
107 | def create_features(self,examples,max_seq_len,cached_features_file):
108 | '''
109 | # The convention in BERT is:
110 | # (a) For sequence pairs:
111 | # tokens: [CLS] is this jack ##son ##ville ? [SEP] no it is not . [SEP]
112 | # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
113 | # (b) For single sequences:
114 | # tokens: [CLS] the dog is hairy . [SEP]
115 | # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
116 | '''
117 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(examples),desc='create features')
118 | if cached_features_file.exists():
119 | logger.info("Loading features from cached file %s", cached_features_file)
120 | features = torch.load(cached_features_file)
121 | else:
122 | features = []
123 | for ex_id,example in enumerate(examples):
124 | tokens_a = self.tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_a)
125 | tokens_b = None
126 | label_id = example.label
127 |
128 | if example.text_b:
129 | tokens_b = self.tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_b)
130 | # Modifies `tokens_a` and `tokens_b` in place so that the total
131 | # length is less than the specified length.
132 | # Account for [CLS], [SEP], [SEP] with "- 3"
133 | self.truncate_seq_pair(tokens_a,tokens_b,max_length = max_seq_len - 3)
134 | else:
135 | # Account for [CLS] and [SEP] with '-2'
136 | if len(tokens_a) > max_seq_len - 2:
137 | tokens_a = tokens_a[:max_seq_len - 2]
138 | tokens = ['[CLS]'] + tokens_a + ['[SEP]']
139 | segment_ids = [0] * len(tokens)
140 | if tokens_b:
141 | tokens += tokens_b + ['[SEP]']
142 | segment_ids += [1] * (len(tokens_b) + 1)
143 |
144 | input_ids = self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
145 | input_mask = [1] * len(input_ids)
146 | padding = [0] * (max_seq_len - len(input_ids))
147 | input_len = len(input_ids)
148 |
149 | input_ids += padding
150 | input_mask += padding
151 | segment_ids += padding
152 |
153 | assert len(input_ids) == max_seq_len
154 | assert len(input_mask) == max_seq_len
155 | assert len(segment_ids) == max_seq_len
156 |
157 | if ex_id < 2:
158 | logger.info("*** Example ***")
159 | logger.info(f"guid: {example.guid}" % ())
160 | logger.info(f"tokens: {' '.join([str(x) for x in tokens])}")
161 | logger.info(f"input_ids: {' '.join([str(x) for x in input_ids])}")
162 | logger.info(f"input_mask: {' '.join([str(x) for x in input_mask])}")
163 | logger.info(f"segment_ids: {' '.join([str(x) for x in segment_ids])}")
164 |
165 | feature = InputFeature(input_ids = input_ids,
166 | input_mask = input_mask,
167 | segment_ids = segment_ids,
168 | label_id = label_id,
169 | input_len = input_len)
170 | features.append(feature)
171 | pbar(step=ex_id)
172 | logger.info("Saving features into cached file %s", cached_features_file)
173 | torch.save(features, cached_features_file)
174 | return features
175 |
176 | def create_dataset(self,features,is_sorted = False):
177 | # Convert to Tensors and build dataset
178 | if is_sorted:
179 | logger.info("sorted data by th length of input")
180 | features = sorted(features,key=lambda x:x.input_len,reverse=True)
181 | all_input_ids = torch.tensor([f.input_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
182 | all_input_mask = torch.tensor([f.input_mask for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
183 | all_segment_ids = torch.tensor([f.segment_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
184 | all_label_ids = torch.tensor([f.label_id for f in features],dtype=torch.long)
185 | all_input_lens = torch.tensor([f.input_len for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
186 | dataset = TensorDataset(all_input_ids, all_input_mask, all_segment_ids, all_label_ids,all_input_lens)
187 | return dataset
188 |
189 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/bert_processor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import csv
2 | import torch
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from ..common.tools import load_pickle
5 | from ..common.tools import logger
6 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
7 | from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
8 | from transformers import BertTokenizer
9 |
10 | class InputExample(object):
11 | def __init__(self, guid, text_a, text_b=None, label=None):
12 | """Constructs a InputExample.
13 | Args:
14 | guid: Unique id for the example.
15 | text_a: string. The untokenized text of the first sequence. For single
16 | sequence tasks, only this sequence must be specified.
17 | text_b: (Optional) string. The untokenized text of the second sequence.
18 | Only must be specified for sequence pair tasks.
19 | label: (Optional) string. The label of the example. This should be
20 | specified for train and dev examples, but not for test examples.
21 | """
22 | self.guid = guid
23 | self.text_a = text_a
24 | self.text_b = text_b
25 | self.label = label
26 |
27 | class InputFeature(object):
28 | '''
29 | A single set of features of data.
30 | '''
31 | def __init__(self,input_ids,input_mask,segment_ids,label_id,input_len):
32 | self.input_ids = input_ids
33 | self.input_mask = input_mask
34 | self.segment_ids = segment_ids
35 | self.label_id = label_id
36 | self.input_len = input_len
37 |
38 | class BertProcessor(object):
39 | """Base class for data converters for sequence classification data sets."""
40 |
41 | def __init__(self,vocab_path,do_lower_case):
42 | self.tokenizer = BertTokenizer(vocab_path,do_lower_case)
43 |
44 | def get_train(self, data_file):
45 | """Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the train set."""
46 | return self.read_data(data_file)
47 |
48 | def get_dev(self, data_file):
49 | """Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the dev set."""
50 | return self.read_data(data_file)
51 |
52 | def get_test(self,lines):
53 | return lines
54 |
55 | def get_labels(self):
56 | """Gets the list of labels for this data set."""
57 | return ["toxic","severe_toxic","obscene","threat","insult","identity_hate"]
58 |
59 | @classmethod
60 | def read_data(cls, input_file,quotechar = None):
61 | """Reads a tab separated value file."""
62 | if 'pkl' in str(input_file):
63 | lines = load_pickle(input_file)
64 | else:
65 | lines = input_file
66 | return lines
67 |
68 | def truncate_seq_pair(self,tokens_a,tokens_b,max_length):
69 | # This is a simple heuristic which will always truncate the longer sequence
70 | # one token at a time. This makes more sense than truncating an equal percent
71 | # of tokens from each, since if one sequence is very short then each token
72 | # that's truncated likely contains more information than a longer sequence.
73 | while True:
74 | total_length = len(tokens_a) + len(tokens_b)
75 | if total_length <= max_length:
76 | break
77 | if len(tokens_a) > len(tokens_b):
78 | tokens_a.pop()
79 | else:
80 | tokens_b.pop()
81 |
82 | def create_examples(self,lines,example_type,cached_examples_file):
83 | '''
84 | Creates examples for data
85 | '''
86 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total = len(lines),desc='create examples')
87 | if cached_examples_file.exists():
88 | logger.info("Loading examples from cached file %s", cached_examples_file)
89 | examples = torch.load(cached_examples_file)
90 | else:
91 | examples = []
92 | for i,line in enumerate(lines):
93 | guid = '%s-%d'%(example_type,i)
94 | text_a = line[0]
95 | label = line[1]
96 | if isinstance(label,str):
97 | label = [np.float(x) for x in label.split(",")]
98 | else:
99 | label = [np.float(x) for x in list(label)]
100 | text_b = None
101 | example = InputExample(guid = guid,text_a = text_a,text_b=text_b,label= label)
102 | examples.append(example)
103 | pbar(step=i)
104 | logger.info("Saving examples into cached file %s", cached_examples_file)
105 | torch.save(examples, cached_examples_file)
106 | return examples
107 |
108 | def create_features(self,examples,max_seq_len,cached_features_file):
109 | '''
110 | # The convention in BERT is:
111 | # (a) For sequence pairs:
112 | # tokens: [CLS] is this jack ##son ##ville ? [SEP] no it is not . [SEP]
113 | # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
114 | # (b) For single sequences:
115 | # tokens: [CLS] the dog is hairy . [SEP]
116 | # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
117 | '''
118 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(examples),desc='create features')
119 | if cached_features_file.exists():
120 | logger.info("Loading features from cached file %s", cached_features_file)
121 | features = torch.load(cached_features_file)
122 | else:
123 | features = []
124 | for ex_id,example in enumerate(examples):
125 | tokens_a = self.tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_a)
126 | tokens_b = None
127 | label_id = example.label
128 |
129 | if example.text_b:
130 | tokens_b = self.tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_b)
131 | # Modifies `tokens_a` and `tokens_b` in place so that the total
132 | # length is less than the specified length.
133 | # Account for [CLS], [SEP], [SEP] with "- 3"
134 | self.truncate_seq_pair(tokens_a,tokens_b,max_length = max_seq_len - 3)
135 | else:
136 | # Account for [CLS] and [SEP] with '-2'
137 | if len(tokens_a) > max_seq_len - 2:
138 | tokens_a = tokens_a[:max_seq_len - 2]
139 | tokens = ['[CLS]'] + tokens_a + ['[SEP]']
140 | segment_ids = [0] * len(tokens)
141 | if tokens_b:
142 | tokens += tokens_b + ['[SEP]']
143 | segment_ids += [1] * (len(tokens_b) + 1)
144 |
145 | input_ids = self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
146 | input_mask = [1] * len(input_ids)
147 | padding = [0] * (max_seq_len - len(input_ids))
148 | input_len = len(input_ids)
149 |
150 | input_ids += padding
151 | input_mask += padding
152 | segment_ids += padding
153 |
154 | assert len(input_ids) == max_seq_len
155 | assert len(input_mask) == max_seq_len
156 | assert len(segment_ids) == max_seq_len
157 |
158 | if ex_id < 2:
159 | logger.info("*** Example ***")
160 | logger.info(f"guid: {example.guid}" % ())
161 | logger.info(f"tokens: {' '.join([str(x) for x in tokens])}")
162 | logger.info(f"input_ids: {' '.join([str(x) for x in input_ids])}")
163 | logger.info(f"input_mask: {' '.join([str(x) for x in input_mask])}")
164 | logger.info(f"segment_ids: {' '.join([str(x) for x in segment_ids])}")
165 |
166 | feature = InputFeature(input_ids = input_ids,
167 | input_mask = input_mask,
168 | segment_ids = segment_ids,
169 | label_id = label_id,
170 | input_len = input_len)
171 | features.append(feature)
172 | pbar(step=ex_id)
173 | logger.info("Saving features into cached file %s", cached_features_file)
174 | torch.save(features, cached_features_file)
175 | return features
176 |
177 | def create_dataset(self,features,is_sorted = False):
178 | # Convert to Tensors and build dataset
179 | if is_sorted:
180 | logger.info("sorted data by th length of input")
181 | features = sorted(features,key=lambda x:x.input_len,reverse=True)
182 | all_input_ids = torch.tensor([f.input_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
183 | all_input_mask = torch.tensor([f.input_mask for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
184 | all_segment_ids = torch.tensor([f.segment_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
185 | all_label_ids = torch.tensor([f.label_id for f in features],dtype=torch.long)
186 | all_input_lens = torch.tensor([f.input_len for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
187 | dataset = TensorDataset(all_input_ids, all_input_mask, all_segment_ids, all_label_ids,all_input_lens)
188 | return dataset
189 |
190 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/io/xlnet_processor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import csv
2 | import torch
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from ..common.tools import load_pickle
5 | from ..common.tools import logger
6 | from ..callback.progressbar import ProgressBar
7 | from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset
8 | from transformers import XLNetTokenizer
9 |
10 | class InputExample(object):
11 | def __init__(self, guid, text_a, text_b=None, label=None):
12 | """Constructs a InputExample.
13 | Args:
14 | guid: Unique id for the example.
15 | text_a: string. The untokenized text of the first sequence. For single
16 | sequence tasks, only this sequence must be specified.
17 | text_b: (Optional) string. The untokenized text of the second sequence.
18 | Only must be specified for sequence pair tasks.
19 | label: (Optional) string. The label of the example. This should be
20 | specified for train and dev examples, but not for test examples.
21 | """
22 | self.guid = guid
23 | self.text_a = text_a
24 | self.text_b = text_b
25 | self.label = label
26 |
27 | class InputFeature(object):
28 | '''
29 | A single set of features of data.
30 | '''
31 | def __init__(self,input_ids,input_mask,segment_ids,label_id,input_len):
32 | self.input_ids = input_ids
33 | self.input_mask = input_mask
34 | self.segment_ids = segment_ids
35 | self.label_id = label_id
36 | self.input_len = input_len
37 |
38 | class XlnetProcessor(object):
39 | """Base class for data converters for sequence classification data sets."""
40 |
41 | def __init__(self,vocab_path,do_lower_case):
42 | self.tokenizer = XLNetTokenizer(vocab_path,do_lower_case)
43 |
44 | def get_train(self, data_file):
45 | """Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the train set."""
46 | return self.read_data(data_file)
47 |
48 | def get_dev(self, data_file):
49 | """Gets a collection of `InputExample`s for the dev set."""
50 | return self.read_data(data_file)
51 |
52 | def get_test(self,lines):
53 | return lines
54 |
55 | def get_labels(self):
56 | """Gets the list of labels for this data set."""
57 | return ["toxic","severe_toxic","obscene","threat","insult","identity_hate"]
58 |
59 | @classmethod
60 | def read_data(cls, input_file,quotechar = None):
61 | """Reads a tab separated value file."""
62 | if 'pkl' in str(input_file):
63 | lines = load_pickle(input_file)
64 | else:
65 | lines = input_file
66 | return lines
67 |
68 | def truncate_seq_pair(self,tokens_a,tokens_b,max_length):
69 | # This is a simple heuristic which will always truncate the longer sequence
70 | # one token at a time. This makes more sense than truncating an equal percent
71 | # of tokens from each, since if one sequence is very short then each token
72 | # that's truncated likely contains more information than a longer sequence.
73 | while True:
74 | total_length = len(tokens_a) + len(tokens_b)
75 | if total_length <= max_length:
76 | break
77 | if len(tokens_a) > len(tokens_b):
78 | tokens_a.pop()
79 | else:
80 | tokens_b.pop()
81 |
82 | def create_examples(self,lines,example_type,cached_examples_file):
83 | '''
84 | Creates examples for data
85 | '''
86 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(lines),desc='create examples')
87 | if cached_examples_file.exists():
88 | logger.info("Loading examples from cached file %s", cached_examples_file)
89 | examples = torch.load(cached_examples_file)
90 | else:
91 | examples = []
92 | for i,line in enumerate(lines):
93 | guid = '%s-%d'%(example_type,i)
94 | text_a = line[0]
95 | label = line[1]
96 | if isinstance(label,str):
97 | label = [np.float(x) for x in label.split(",")]
98 | else:
99 | label = [np.float(x) for x in list(label)]
100 | text_b = None
101 | example = InputExample(guid = guid,text_a = text_a,text_b=text_b,label= label)
102 | examples.append(example)
103 | pbar(step = i)
104 | logger.info("Saving examples into cached file %s", cached_examples_file)
105 | torch.save(examples, cached_examples_file)
106 | return examples
107 |
108 | def create_features(self,examples,max_seq_len,cached_features_file):
109 | '''
110 | # The convention in BERT is:
111 | # (a) For sequence pairs:
112 | # tokens: [CLS] is this jack ##son ##ville ? [SEP] no it is not . [SEP]
113 | # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1 1
114 | # (b) For single sequences:
115 | # tokens: [CLS] the dog is hairy . [SEP]
116 | # type_ids: 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
117 | '''
118 | # Load data features from cache or dataset file
119 | pbar = ProgressBar(n_total=len(examples),desc='create features')
120 | if cached_features_file.exists():
121 | logger.info("Loading features from cached file %s", cached_features_file)
122 | features = torch.load(cached_features_file)
123 | else:
124 | features = []
125 | pad_token = self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids([self.tokenizer.pad_token])[0]
126 | cls_token = self.tokenizer.cls_token
127 | sep_token = self.tokenizer.sep_token
128 | cls_token_segment_id = 2
129 | pad_token_segment_id = 4
130 |
131 | for ex_id,example in enumerate(examples):
132 | tokens_a = self.tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_a)
133 | tokens_b = None
134 | label_id = example.label
135 |
136 | if example.text_b:
137 | tokens_b = self.tokenizer.tokenize(example.text_b)
138 | # Modifies `tokens_a` and `tokens_b` in place so that the total
139 | # length is less than the specified length.
140 | # Account for [CLS], [SEP], [SEP] with "- 3"
141 | self.truncate_seq_pair(tokens_a,tokens_b,max_length = max_seq_len - 3)
142 | else:
143 | # Account for [CLS] and [SEP] with '-2'
144 | if len(tokens_a) > max_seq_len - 2:
145 | tokens_a = tokens_a[:max_seq_len - 2]
146 |
147 | # xlnet has a cls token at the end
148 | tokens = tokens_a + [sep_token]
149 | segment_ids = [0] * len(tokens)
150 | if tokens_b:
151 | tokens += tokens_b + [sep_token]
152 | segment_ids += [1] * (len(tokens_b) + 1)
153 | tokens += [cls_token]
154 | segment_ids += [cls_token_segment_id]
155 |
156 | input_ids = self.tokenizer.convert_tokens_to_ids(tokens)
157 | input_mask = [1] * len(input_ids)
158 | input_len = len(input_ids)
159 | padding_len = max_seq_len - len(input_ids)
160 |
161 | # pad on the left for xlnet
162 | input_ids = ([pad_token] * padding_len) + input_ids
163 | input_mask = ([0 ] * padding_len) + input_mask
164 | segment_ids = ([pad_token_segment_id] * padding_len) + segment_ids
165 |
166 | assert len(input_ids) == max_seq_len
167 | assert len(input_mask) == max_seq_len
168 | assert len(segment_ids) == max_seq_len
169 |
170 | if ex_id < 2:
171 | logger.info("*** Example ***")
172 | logger.info(f"guid: {example.guid}" % ())
173 | logger.info(f"tokens: {' '.join([str(x) for x in tokens])}")
174 | logger.info(f"input_ids: {' '.join([str(x) for x in input_ids])}")
175 | logger.info(f"input_mask: {' '.join([str(x) for x in input_mask])}")
176 | logger.info(f"segment_ids: {' '.join([str(x) for x in segment_ids])}")
177 |
178 | feature = InputFeature(input_ids = input_ids,
179 | input_mask = input_mask,
180 | segment_ids = segment_ids,
181 | label_id = label_id,
182 | input_len = input_len)
183 | features.append(feature)
184 | pbar(step=ex_id)
185 | logger.info("Saving features into cached file %s", cached_features_file)
186 | torch.save(features, cached_features_file)
187 | return features
188 |
189 | def create_dataset(self,features,is_sorted = False):
190 | # Convert to Tensors and build dataset
191 | if is_sorted:
192 | logger.info("sorted data by th length of input")
193 | features = sorted(features,key=lambda x:x.input_len,reverse=True)
194 | all_input_ids = torch.tensor([f.input_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
195 | all_input_mask = torch.tensor([f.input_mask for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
196 | all_segment_ids = torch.tensor([f.segment_ids for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
197 | all_label_ids = torch.tensor([f.label_id for f in features],dtype=torch.long)
198 | all_input_lens = torch.tensor([f.input_len for f in features], dtype=torch.long)
199 | dataset = TensorDataset(all_input_ids, all_input_mask, all_segment_ids, all_label_ids,all_input_lens)
200 | return dataset
201 |
202 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/train/metrics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | r"""Functional interface"""
2 | import torch
3 | from tqdm import tqdm
4 | import numpy as np
5 | from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
6 | from sklearn.metrics import f1_score, classification_report
7 |
8 | __call__ = ['Accuracy','AUC','F1Score','EntityScore','ClassReport','MultiLabelReport','AccuracyThresh']
9 |
10 | class Metric:
11 | def __init__(self):
12 | pass
13 |
14 | def __call__(self, outputs, target):
15 | raise NotImplementedError
16 |
17 | def reset(self):
18 | raise NotImplementedError
19 |
20 | def value(self):
21 | raise NotImplementedError
22 |
23 | def name(self):
24 | raise NotImplementedError
25 |
26 | class Accuracy(Metric):
27 | '''
28 | 计算准确度
29 | 可以使用topK参数设定计算K准确度
30 | Examples:
31 | >>> metric = Accuracy(**)
32 | >>> for epoch in range(epochs):
33 | >>> metric.reset()
34 | >>> for batch in batchs:
35 | >>> logits = model()
36 | >>> metric(logits,target)
37 | >>> print(metric.name(),metric.value())
38 | '''
39 | def __init__(self,topK):
40 | super(Accuracy,self).__init__()
41 | self.topK = topK
42 | self.reset()
43 |
44 | def __call__(self, logits, target):
45 | _, pred = logits.topk(self.topK, 1, True, True)
46 | pred = pred.t()
47 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
48 | self.correct_k = correct[:self.topK].view(-1).float().sum(0)
49 | self.total = target.size(0)
50 |
51 | def reset(self):
52 | self.correct_k = 0
53 | self.total = 0
54 |
55 | def value(self):
56 | return float(self.correct_k) / self.total
57 |
58 | def name(self):
59 | return 'accuracy'
60 |
61 |
62 | class AccuracyThresh(Metric):
63 | '''
64 | 计算准确度
65 | 可以使用topK参数设定计算K准确度
66 | Example:
67 | >>> metric = AccuracyThresh(**)
68 | >>> for epoch in range(epochs):
69 | >>> metric.reset()
70 | >>> for batch in batchs:
71 | >>> logits = model()
72 | >>> metric(logits,target)
73 | >>> print(metric.name(),metric.value())
74 | '''
75 | def __init__(self,thresh = 0.5):
76 | super(AccuracyThresh,self).__init__()
77 | self.thresh = thresh
78 | self.reset()
79 |
80 | def __call__(self, logits, target):
81 | self.y_pred = logits.sigmoid()
82 | self.y_true = target
83 |
84 | def reset(self):
85 | self.correct_k = 0
86 | self.total = 0
87 |
88 | def value(self):
89 | data_size = self.y_pred.size(0)
90 | acc = np.mean(((self.y_pred>self.thresh)==self.y_true.byte()).float().cpu().numpy(), axis=1).sum()
91 | return acc / data_size
92 |
93 | def name(self):
94 | return 'accuracy'
95 |
96 |
97 | class AUC(Metric):
98 | '''
99 | AUC score
100 | micro:
101 | Calculate metrics globally by considering each element of the label
102 | indicator matrix as a label.
103 | macro:
104 | Calculate metrics for each label, and find their unweighted
105 | mean. This does not take label imbalance into account.
106 | weighted:
107 | Calculate metrics for each label, and find their average, weighted
108 | by support (the number of true instances for each label).
109 | samples:
110 | Calculate metrics for each instance, and find their average.
111 | Example:
112 | >>> metric = AUC(**)
113 | >>> for epoch in range(epochs):
114 | >>> metric.reset()
115 | >>> for batch in batchs:
116 | >>> logits = model()
117 | >>> metric(logits,target)
118 | >>> print(metric.name(),metric.value())
119 | '''
120 |
121 | def __init__(self,task_type = 'binary',average = 'binary'):
122 | super(AUC, self).__init__()
123 |
124 | assert task_type in ['binary','multiclass']
125 | assert average in ['binary','micro', 'macro', 'samples', 'weighted']
126 |
127 | self.task_type = task_type
128 | self.average = average
129 |
130 | def __call__(self,logits,target):
131 | '''
132 | 计算整个结果
133 | '''
134 | if self.task_type == 'binary':
135 | self.y_prob = logits.sigmoid().data.cpu().numpy()
136 | else:
137 | self.y_prob = logits.softmax(-1).data.cpu().detach().numpy()
138 | self.y_true = target.cpu().numpy()
139 |
140 | def reset(self):
141 | self.y_prob = 0
142 | self.y_true = 0
143 |
144 | def value(self):
145 | '''
146 | 计算指标得分
147 | '''
148 | auc = roc_auc_score(y_score=self.y_prob, y_true=self.y_true, average=self.average)
149 | return auc
150 |
151 | def name(self):
152 | return 'auc'
153 |
154 | class F1Score(Metric):
155 | '''
156 | F1 Score
157 | binary:
158 | Only report results for the class specified by ``pos_label``.
159 | This is applicable only if targets (``y_{true,pred}``) are binary.
160 | micro:
161 | Calculate metrics globally by considering each element of the label
162 | indicator matrix as a label.
163 | macro:
164 | Calculate metrics for each label, and find their unweighted
165 | mean. This does not take label imbalance into account.
166 | weighted:
167 | Calculate metrics for each label, and find their average, weighted
168 | by support (the number of true instances for each label).
169 | samples:
170 | Calculate metrics for each instance, and find their average.
171 | Example:
172 | >>> metric = F1Score(**)
173 | >>> for epoch in range(epochs):
174 | >>> metric.reset()
175 | >>> for batch in batchs:
176 | >>> logits = model()
177 | >>> metric(logits,target)
178 | >>> print(metric.name(),metric.value())
179 | '''
180 | def __init__(self,thresh = 0.5, normalizate = True,task_type = 'binary',average = 'binary',search_thresh = False):
181 | super(F1Score).__init__()
182 | assert task_type in ['binary','multiclass']
183 | assert average in ['binary','micro', 'macro', 'samples', 'weighted']
184 |
185 | self.thresh = thresh
186 | self.task_type = task_type
187 | self.normalizate = normalizate
188 | self.search_thresh = search_thresh
189 | self.average = average
190 |
191 | def thresh_search(self,y_prob):
192 | '''
193 | 对于f1评分的指标,一般我们需要对阈值进行调整,一般不会使用默认的0.5值,因此
194 | 这里我们队Thresh进行优化
195 | :return:
196 | '''
197 | best_threshold = 0
198 | best_score = 0
199 | for threshold in tqdm([i * 0.01 for i in range(100)], disable=True):
200 | self.y_pred = y_prob > threshold
201 | score = self.value()
202 | if score > best_score:
203 | best_threshold = threshold
204 | best_score = score
205 | return best_threshold,best_score
206 |
207 | def __call__(self,logits,target):
208 | '''
209 | 计算整个结果
210 | :return:
211 | '''
212 | self.y_true = target.cpu().numpy()
213 | if self.normalizate and self.task_type == 'binary':
214 | y_prob = logits.sigmoid().data.cpu().numpy()
215 | elif self.normalizate and self.task_type == 'multiclass':
216 | y_prob = logits.softmax(-1).data.cpu().detach().numpy()
217 | else:
218 | y_prob = logits.cpu().detach().numpy()
219 |
220 | if self.task_type == 'binary':
221 | if self.thresh and self.search_thresh == False:
222 | self.y_pred = (y_prob > self.thresh ).astype(int)
223 | self.value()
224 | else:
225 | thresh,f1 = self.thresh_search(y_prob = y_prob)
226 | print(f"Best thresh: {thresh:.4f} - F1 Score: {f1:.4f}")
227 |
228 | if self.task_type == 'multiclass':
229 | self.y_pred = np.argmax(y_prob, 1)
230 |
231 | def reset(self):
232 | self.y_pred = 0
233 | self.y_true = 0
234 |
235 | def value(self):
236 | '''
237 | 计算指标得分
238 | '''
239 | f1 = f1_score(y_true=self.y_true, y_pred=self.y_pred, average=self.average)
240 | return f1
241 |
242 | def name(self):
243 | return 'f1'
244 |
245 | class ClassReport(Metric):
246 | '''
247 | class report
248 | '''
249 | def __init__(self,target_names = None):
250 | super(ClassReport).__init__()
251 | self.target_names = target_names
252 |
253 | def reset(self):
254 | self.y_pred = 0
255 | self.y_true = 0
256 |
257 | def value(self):
258 | '''
259 | 计算指标得分
260 | '''
261 | score = classification_report(y_true = self.y_true,
262 | y_pred = self.y_pred,
263 | target_names=self.target_names)
264 | print(f"\n\n classification report: {score}")
265 |
266 | def __call__(self,logits,target):
267 | _, y_pred = torch.max(logits.data, 1)
268 | self.y_pred = y_pred.cpu().numpy()
269 | self.y_true = target.cpu().numpy()
270 |
271 | def name(self):
272 | return "class_report"
273 |
274 | class MultiLabelReport(Metric):
275 | '''
276 | multi label report
277 | '''
278 | def __init__(self,id2label = None):
279 | super(MultiLabelReport).__init__()
280 | self.id2label = id2label
281 |
282 | def reset(self):
283 | self.y_prob = 0
284 | self.y_true = 0
285 |
286 | def __call__(self,logits,target):
287 |
288 | self.y_prob = logits.sigmoid().data.cpu().detach().numpy()
289 | self.y_true = target.cpu().numpy()
290 |
291 | def value(self):
292 | '''
293 | 计算指标得分
294 | '''
295 | for i, label in self.id2label.items():
296 | auc = roc_auc_score(y_score=self.y_prob[:, i], y_true=self.y_true[:, i])
297 | print(f"label:{label} - auc: {auc:.4f}")
298 |
299 | def name(self):
300 | return "multilabel_report"
301 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/albert/configuration_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 | # Copyright 2018 The Google AI Language Team Authors and The HuggingFace Inc. team.
3 | # Copyright (c) 2018, NVIDIA CORPORATION. All rights reserved.
4 | #
5 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
6 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
7 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
8 | #
9 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
10 | #
11 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
12 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
13 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
14 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
15 | # limitations under the License.
16 | """ Configuration base class and utilities."""
17 |
18 | from __future__ import (absolute_import, division, print_function,
19 | unicode_literals)
20 |
21 | import copy
22 | import json
23 | import logging
24 | import os
25 | from io import open
26 |
27 | from .file_utils import cached_path, CONFIG_NAME
28 |
29 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
30 |
31 | class PretrainedConfig(object):
32 | r""" Base class for all configuration classes.
33 | Handles a few parameters tools to all models' configurations as well as methods for loading/downloading/saving configurations.
34 |
35 | Note:
36 | A configuration file can be loaded and saved to disk. Loading the configuration file and using this file to initialize a model does **not** load the model weights.
37 | It only affects the model's configuration.
38 |
39 | Class attributes (overridden by derived classes):
40 | - ``pretrained_config_archive_map``: a python ``dict`` of with `short-cut-names` (string) as keys and `url` (string) of associated pretrained model configurations as values.
41 |
42 | Parameters:
43 | ``finetuning_task``: string, default `None`. Name of the task used to fine-tune the model. This can be used when converting from an original (TensorFlow or PyTorch) checkpoint.
44 | ``num_labels``: integer, default `2`. Number of classes to use when the model is a classification model (sequences/tokens)
45 | ``output_attentions``: boolean, default `False`. Should the model returns attentions weights.
46 | ``output_hidden_states``: string, default `False`. Should the model returns all hidden-states.
47 | ``torchscript``: string, default `False`. Is the model used with Torchscript.
48 | """
49 | pretrained_config_archive_map = {}
50 |
51 | def __init__(self, **kwargs):
52 | self.finetuning_task = kwargs.pop('finetuning_task', None)
53 | self.num_labels = kwargs.pop('num_labels', 2)
54 | self.output_attentions = kwargs.pop('output_attentions', False)
55 | self.output_hidden_states = kwargs.pop('output_hidden_states', False)
56 | self.torchscript = kwargs.pop('torchscript', False)
57 | self.pruned_heads = kwargs.pop('pruned_heads', {})
58 |
59 | def save_pretrained(self, save_directory):
60 | """ Save a configuration object to the directory `save_directory`, so that it
61 | can be re-loaded using the :func:`~pytorch_transformers.PretrainedConfig.from_pretrained` class method.
62 | """
63 | assert os.path.isdir(save_directory), "Saving path should be a directory where the model and configuration can be saved"
64 |
65 | # If we save using the predefined names, we can load using `from_pretrained`
66 | output_config_file = os.path.join(save_directory, CONFIG_NAME)
67 |
68 | self.to_json_file(output_config_file)
69 |
70 | @classmethod
71 | def from_pretrained(cls, pretrained_model_name_or_path, **kwargs):
72 | r""" Instantiate a :class:`~pytorch_transformers.PretrainedConfig` (or a derived class) from a pre-trained model configuration.
73 |
74 | Parameters:
75 | pretrained_model_name_or_path: either:
76 |
77 | - a string with the `shortcut name` of a pre-trained model configuration to load from cache or download, e.g.: ``bert-base-uncased``.
78 | - a path to a `directory` containing a configuration file saved using the :func:`~pytorch_transformers.PretrainedConfig.save_pretrained` method, e.g.: ``./my_model_directory/``.
79 | - a path or url to a saved configuration JSON `file`, e.g.: ``./my_model_directory/configuration.json``.
80 |
81 | cache_dir: (`optional`) string:
82 | Path to a directory in which a downloaded pre-trained model
83 | configuration should be cached if the standard cache should not be used.
84 |
85 | kwargs: (`optional`) dict: key/value pairs with which to update the configuration object after loading.
86 |
87 | - The values in kwargs of any keys which are configuration attributes will be used to override the loaded values.
88 | - Behavior concerning key/value pairs whose keys are *not* configuration attributes is controlled by the `return_unused_kwargs` keyword parameter.
89 |
90 | force_download: (`optional`) boolean, default False:
91 | Force to (re-)download the model weights and configuration files and override the cached versions if they exists.
92 |
93 | proxies: (`optional`) dict, default None:
94 | A dictionary of proxy servers to use by protocol or endpoint, e.g.: {'http': 'foo.bar:3128', 'http://hostname': 'foo.bar:4012'}.
95 | The proxies are used on each request.
96 |
97 | return_unused_kwargs: (`optional`) bool:
98 |
99 | - If False, then this function returns just the final configuration object.
100 | - If True, then this functions returns a tuple `(config, unused_kwargs)` where `unused_kwargs` is a dictionary consisting of the key/value pairs whose keys are not configuration attributes: ie the part of kwargs which has not been used to update `config` and is otherwise ignored.
101 |
102 | Examples::
103 |
104 | # We can't instantiate directly the base class `PretrainedConfig` so let's show the examples on a
105 | # derived class: BertConfig
106 | config = BertConfig.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased') # Download configuration from S3 and cache.
107 | config = BertConfig.from_pretrained('./test/saved_model/') # E.g. config (or model) was saved using `save_pretrained('./test/saved_model/')`
108 | config = BertConfig.from_pretrained('./test/saved_model/my_configuration.json')
109 | config = BertConfig.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased', output_attention=True, foo=False)
110 | assert config.output_attention == True
111 | config, unused_kwargs = BertConfig.from_pretrained('bert-base-uncased', output_attention=True,
112 | foo=False, return_unused_kwargs=True)
113 | assert config.output_attention == True
114 | assert unused_kwargs == {'foo': False}
115 |
116 | """
117 | cache_dir = kwargs.pop('cache_dir', None)
118 | force_download = kwargs.pop('force_download', False)
119 | proxies = kwargs.pop('proxies', None)
120 | return_unused_kwargs = kwargs.pop('return_unused_kwargs', False)
121 |
122 | if pretrained_model_name_or_path in cls.pretrained_config_archive_map:
123 | config_file = cls.pretrained_config_archive_map[pretrained_model_name_or_path]
124 | elif os.path.isdir(pretrained_model_name_or_path):
125 | config_file = os.path.join(pretrained_model_name_or_path, CONFIG_NAME)
126 | else:
127 | config_file = pretrained_model_name_or_path
128 | # redirect to the cache, if necessary
129 | try:
130 | resolved_config_file = cached_path(config_file, cache_dir=cache_dir, force_download=force_download, proxies=proxies)
131 | except EnvironmentError as e:
132 | if pretrained_model_name_or_path in cls.pretrained_config_archive_map:
133 | logger.error(
134 | "Couldn't reach server at '{}' to download pretrained model configuration file.".format(
135 | config_file))
136 | else:
137 | logger.error(
138 | "Model name '{}' was not found in model name list ({}). "
139 | "We assumed '{}' was a path or url but couldn't find any file "
140 | "associated to this path or url.".format(
141 | pretrained_model_name_or_path,
142 | ', '.join(cls.pretrained_config_archive_map.keys()),
143 | config_file))
144 | raise e
145 | if resolved_config_file == config_file:
146 | logger.info("loading configuration file {}".format(config_file))
147 | else:
148 | logger.info("loading configuration file {} from cache at {}".format(
149 | config_file, resolved_config_file))
150 |
151 | # Load config
152 | config = cls.from_json_file(resolved_config_file)
153 |
154 | if hasattr(config, 'pruned_heads'):
155 | config.pruned_heads = dict((int(key), set(value)) for key, value in config.pruned_heads.items())
156 |
157 | # Update config with kwargs if needed
158 | to_remove = []
159 | for key, value in kwargs.items():
160 | if hasattr(config, key):
161 | setattr(config, key, value)
162 | to_remove.append(key)
163 | else:
164 | setattr(config,key,value)
165 | for key in to_remove:
166 | kwargs.pop(key, None)
167 |
168 | logger.info("Model config %s", config)
169 | if return_unused_kwargs:
170 | return config, kwargs
171 | else:
172 | return config
173 |
174 | @classmethod
175 | def from_dict(cls, json_object):
176 | """Constructs a `Config` from a Python dictionary of parameters."""
177 | config = cls(vocab_size_or_config_json_file=-1)
178 | for key, value in json_object.items():
179 | config.__dict__[key] = value
180 | return config
181 |
182 | @classmethod
183 | def from_json_file(cls, json_file):
184 | """Constructs a `BertConfig` from a json file of parameters."""
185 | with open(json_file, "r", encoding='utf-8') as reader:
186 | text = reader.read()
187 | return cls.from_dict(json.loads(text))
188 |
189 | def __eq__(self, other):
190 | return self.__dict__ == other.__dict__
191 |
192 | def __repr__(self):
193 | return str(self.to_json_string())
194 |
195 | def to_dict(self):
196 | """Serializes this instance to a Python dictionary."""
197 | output = copy.deepcopy(self.__dict__)
198 | return output
199 |
200 | def to_json_string(self):
201 | """Serializes this instance to a JSON string."""
202 | return json.dumps(self.to_dict(), indent=2, sort_keys=True) + "\n"
203 |
204 | def to_json_file(self, json_file_path):
205 | """ Save this instance to a json file."""
206 | with open(json_file_path, "w", encoding='utf-8') as writer:
207 | writer.write(self.to_json_string())
208 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pybert/model/albert/file_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utilities for working with the local dataset cache.
3 | This file is adapted from the AllenNLP library at https://github.com/allenai/allennlp
4 | Copyright by the AllenNLP authors.
5 | """
6 | from __future__ import (absolute_import, division, print_function, unicode_literals)
7 |
8 | import sys
9 | import json
10 | import logging
11 | import os
12 | import six
13 | import shutil
14 | import tempfile
15 | import fnmatch
16 | from functools import wraps
17 | from hashlib import sha256
18 | from io import open
19 |
20 | import boto3
21 | from botocore.config import Config
22 | from botocore.exceptions import ClientError
23 | import requests
24 | from tqdm import tqdm
25 |
26 | try:
27 | from torch.hub import _get_torch_home
28 | torch_cache_home = _get_torch_home()
29 | except ImportError:
30 | torch_cache_home = os.path.expanduser(
31 | os.getenv('TORCH_HOME', os.path.join(
32 | os.getenv('XDG_CACHE_HOME', '~/.cache'), 'torch')))
33 | default_cache_path = os.path.join(torch_cache_home, 'pytorch_transformers')
34 |
35 | try:
36 | from urllib.parse import urlparse
37 | except ImportError:
38 | from urlparse import urlparse
39 |
40 | try:
41 | from pathlib import Path
42 | PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE = Path(
43 | os.getenv('PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE', os.getenv('PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE', default_cache_path)))
44 | except (AttributeError, ImportError):
45 | PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE = os.getenv('PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE',
46 | os.getenv('PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE',
47 | default_cache_path))
48 |
49 | PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE = PYTORCH_PRETRAINED_BERT_CACHE # Kept for backward compatibility
50 |
51 | WEIGHTS_NAME = "pytorch_model.bin"
52 | TF_WEIGHTS_NAME = 'model.ckpt'
53 | CONFIG_NAME = "config.json"
54 |
55 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__) # pylint: disable=invalid-name
56 |
57 | if not six.PY2:
58 | def add_start_docstrings(*docstr):
59 | def docstring_decorator(fn):
60 | fn.__doc__ = ''.join(docstr) + fn.__doc__
61 | return fn
62 | return docstring_decorator
63 |
64 | def add_end_docstrings(*docstr):
65 | def docstring_decorator(fn):
66 | fn.__doc__ = fn.__doc__ + ''.join(docstr)
67 | return fn
68 | return docstring_decorator
69 | else:
70 | # Not possible to update class docstrings on python2
71 | def add_start_docstrings(*docstr):
72 | def docstring_decorator(fn):
73 | return fn
74 | return docstring_decorator
75 |
76 | def add_end_docstrings(*docstr):
77 | def docstring_decorator(fn):
78 | return fn
79 | return docstring_decorator
80 |
81 | def url_to_filename(url, etag=None):
82 | """
83 | Convert `url` into a hashed filename in a repeatable way.
84 | If `etag` is specified, append its hash to the url's, delimited
85 | by a period.
86 | """
87 | url_bytes = url.encode('utf-8')
88 | url_hash = sha256(url_bytes)
89 | filename = url_hash.hexdigest()
90 |
91 | if etag:
92 | etag_bytes = etag.encode('utf-8')
93 | etag_hash = sha256(etag_bytes)
94 | filename += '.' + etag_hash.hexdigest()
95 |
96 | return filename
97 |
98 |
99 | def filename_to_url(filename, cache_dir=None):
100 | """
101 | Return the url and etag (which may be ``None``) stored for `filename`.
102 | Raise ``EnvironmentError`` if `filename` or its stored metadata do not exist.
103 | """
104 | if cache_dir is None:
105 | cache_dir = PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE
106 | if sys.version_info[0] == 3 and isinstance(cache_dir, Path):
107 | cache_dir = str(cache_dir)
108 |
109 | cache_path = os.path.join(cache_dir, filename)
110 | if not os.path.exists(cache_path):
111 | raise EnvironmentError("file {} not found".format(cache_path))
112 |
113 | meta_path = cache_path + '.json'
114 | if not os.path.exists(meta_path):
115 | raise EnvironmentError("file {} not found".format(meta_path))
116 |
117 | with open(meta_path, encoding="utf-8") as meta_file:
118 | metadata = json.load(meta_file)
119 | url = metadata['url']
120 | etag = metadata['etag']
121 |
122 | return url, etag
123 |
124 |
125 | def cached_path(url_or_filename, cache_dir=None, force_download=False, proxies=None):
126 | """
127 | Given something that might be a URL (or might be a local path),
128 | determine which. If it's a URL, download the file and cache it, and
129 | return the path to the cached file. If it's already a local path,
130 | make sure the file exists and then return the path.
131 | Args:
132 | cache_dir: specify a cache directory to save the file to (overwrite the default cache dir).
133 | force_download: if True, re-dowload the file even if it's already cached in the cache dir.
134 | """
135 | if cache_dir is None:
136 | cache_dir = PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE
137 | if sys.version_info[0] == 3 and isinstance(url_or_filename, Path):
138 | url_or_filename = str(url_or_filename)
139 | if sys.version_info[0] == 3 and isinstance(cache_dir, Path):
140 | cache_dir = str(cache_dir)
141 |
142 | parsed = urlparse(url_or_filename)
143 |
144 | if parsed.scheme in ('http', 'https', 's3'):
145 | # URL, so get it from the cache (downloading if necessary)
146 | return get_from_cache(url_or_filename, cache_dir=cache_dir, force_download=force_download, proxies=proxies)
147 | elif os.path.exists(url_or_filename):
148 | # File, and it exists.
149 | return url_or_filename
150 | elif parsed.scheme == '':
151 | # File, but it doesn't exist.
152 | raise EnvironmentError("file {} not found".format(url_or_filename))
153 | else:
154 | # Something unknown
155 | raise ValueError("unable to parse {} as a URL or as a local path".format(url_or_filename))
156 |
157 |
158 | def split_s3_path(url):
159 | """Split a full s3 path into the bucket name and path."""
160 | parsed = urlparse(url)
161 | if not parsed.netloc or not parsed.path:
162 | raise ValueError("bad s3 path {}".format(url))
163 | bucket_name = parsed.netloc
164 | s3_path = parsed.path
165 | # Remove '/' at beginning of path.
166 | if s3_path.startswith("/"):
167 | s3_path = s3_path[1:]
168 | return bucket_name, s3_path
169 |
170 |
171 | def s3_request(func):
172 | """
173 | Wrapper function for s3 requests in order to create more helpful error
174 | messages.
175 | """
176 |
177 | @wraps(func)
178 | def wrapper(url, *args, **kwargs):
179 | try:
180 | return func(url, *args, **kwargs)
181 | except ClientError as exc:
182 | if int(exc.response["Error"]["Code"]) == 404:
183 | raise EnvironmentError("file {} not found".format(url))
184 | else:
185 | raise
186 |
187 | return wrapper
188 |
189 |
190 | @s3_request
191 | def s3_etag(url, proxies=None):
192 | """Check ETag on S3 object."""
193 | s3_resource = boto3.resource("s3", config=Config(proxies=proxies))
194 | bucket_name, s3_path = split_s3_path(url)
195 | s3_object = s3_resource.Object(bucket_name, s3_path)
196 | return s3_object.e_tag
197 |
198 |
199 | @s3_request
200 | def s3_get(url, temp_file, proxies=None):
201 | """Pull a file directly from S3."""
202 | s3_resource = boto3.resource("s3", config=Config(proxies=proxies))
203 | bucket_name, s3_path = split_s3_path(url)
204 | s3_resource.Bucket(bucket_name).download_fileobj(s3_path, temp_file)
205 |
206 |
207 | def http_get(url, temp_file, proxies=None):
208 | req = requests.get(url, stream=True, proxies=proxies)
209 | content_length = req.headers.get('Content-Length')
210 | total = int(content_length) if content_length is not None else None
211 | progress = tqdm(unit="B", total=total)
212 | for chunk in req.iter_content(chunk_size=1024):
213 | if chunk: # filter out keep-alive new chunks
214 | progress.update(len(chunk))
215 | temp_file.write(chunk)
216 | progress.close()
217 |
218 |
219 | def get_from_cache(url, cache_dir=None, force_download=False, proxies=None):
220 | """
221 | Given a URL, look for the corresponding dataset in the local cache.
222 | If it's not there, download it. Then return the path to the cached file.
223 | """
224 | if cache_dir is None:
225 | cache_dir = PYTORCH_TRANSFORMERS_CACHE
226 | if sys.version_info[0] == 3 and isinstance(cache_dir, Path):
227 | cache_dir = str(cache_dir)
228 | if sys.version_info[0] == 2 and not isinstance(cache_dir, str):
229 | cache_dir = str(cache_dir)
230 |
231 | if not os.path.exists(cache_dir):
232 | os.makedirs(cache_dir)
233 |
234 | # Get eTag to add to filename, if it exists.
235 | if url.startswith("s3://"):
236 | etag = s3_etag(url, proxies=proxies)
237 | else:
238 | try:
239 | response = requests.head(url, allow_redirects=True, proxies=proxies)
240 | if response.status_code != 200:
241 | etag = None
242 | else:
243 | etag = response.headers.get("ETag")
244 | except EnvironmentError:
245 | etag = None
246 |
247 | if sys.version_info[0] == 2 and etag is not None:
248 | etag = etag.decode('utf-8')
249 | filename = url_to_filename(url, etag)
250 |
251 | # get cache path to put the file
252 | cache_path = os.path.join(cache_dir, filename)
253 |
254 | # If we don't have a connection (etag is None) and can't identify the file
255 | # try to get the last downloaded one
256 | if not os.path.exists(cache_path) and etag is None:
257 | matching_files = fnmatch.filter(os.listdir(cache_dir), filename + '.*')
258 | matching_files = list(filter(lambda s: not s.endswith('.json'), matching_files))
259 | if matching_files:
260 | cache_path = os.path.join(cache_dir, matching_files[-1])
261 |
262 | if not os.path.exists(cache_path) or force_download:
263 | # Download to temporary file, then copy to cache dir once finished.
264 | # Otherwise you get corrupt cache entries if the download gets interrupted.
265 | with tempfile.NamedTemporaryFile() as temp_file:
266 | logger.info("%s not found in cache or force_download set to True, downloading to %s", url, temp_file.name)
267 |
268 | # GET file object
269 | if url.startswith("s3://"):
270 | s3_get(url, temp_file, proxies=proxies)
271 | else:
272 | http_get(url, temp_file, proxies=proxies)
273 |
274 | # we are copying the file before closing it, so flush to avoid truncation
275 | temp_file.flush()
276 | # shutil.copyfileobj() starts at the current position, so go to the start
277 | temp_file.seek(0)
278 |
279 | logger.info("copying %s to cache at %s", temp_file.name, cache_path)
280 | with open(cache_path, 'wb') as cache_file:
281 | shutil.copyfileobj(temp_file, cache_file)
282 |
283 | logger.info("creating metadata file for %s", cache_path)
284 | meta = {'url': url, 'etag': etag}
285 | meta_path = cache_path + '.json'
286 | with open(meta_path, 'w') as meta_file:
287 | output_string = json.dumps(meta)
288 | if sys.version_info[0] == 2 and isinstance(output_string, str):
289 | output_string = unicode(output_string, 'utf-8') # The beauty of python 2
290 | meta_file.write(output_string)
291 |
292 | logger.info("removing temp file %s", temp_file.name)
293 |
294 | return cache_path
295 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/run_albert.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import time
3 | import warnings
4 | from pathlib import Path
5 | from argparse import ArgumentParser
6 | from pybert.train.losses import BCEWithLogLoss
7 | from pybert.train.trainer import Trainer
8 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
9 |
10 | from pybert.common.tools import init_logger, logger
11 | from pybert.common.tools import seed_everything
12 | from pybert.configs.basic_config import config
13 | from pybert.io.albert_processor import AlbertProcessor
14 | from pybert.io.utils import collate_fn
15 | from pybert.model.albert_for_multi_label import AlbertForMultiLable
16 | from pybert.preprocessing.preprocessor import EnglishPreProcessor
17 | from pybert.callback.modelcheckpoint import ModelCheckpoint
18 | from pybert.callback.trainingmonitor import TrainingMonitor
19 | from pybert.train.metrics import AUC, AccuracyThresh, MultiLabelReport
20 | from pybert.callback.optimizater.adamw import AdamW
21 | from pybert.callback.lr_schedulers import get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
22 | from torch.utils.data import RandomSampler, SequentialSampler
23 | warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
24 |
25 | def run_train(args):
26 | # --------- data
27 | processor = AlbertProcessor(spm_model_file=config['albert_vocab_path'], do_lower_case=args.do_lower_case,
28 | vocab_file=None)
29 | label_list = processor.get_labels()
30 | label2id = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
31 | id2label = {i: label for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
32 |
33 | train_data = processor.get_train(config['data_dir'] / f"{args.data_name}.train.pkl")
34 | train_examples = processor.create_examples(lines=train_data,
35 | example_type='train',
36 | cached_examples_file=config[
37 | 'data_dir'] / f"cached_train_examples_{args.arch}")
38 | train_features = processor.create_features(examples=train_examples,
39 | max_seq_len=args.train_max_seq_len,
40 | cached_features_file=config[
41 | 'data_dir'] / "cached_train_features_{}_{}".format(
42 | args.train_max_seq_len, args.arch
43 | ))
44 | train_dataset = processor.create_dataset(train_features, is_sorted=args.sorted)
45 | if args.sorted:
46 | train_sampler = SequentialSampler(train_dataset)
47 | else:
48 | train_sampler = RandomSampler(train_dataset)
49 | train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, sampler=train_sampler, batch_size=args.train_batch_size,
50 | collate_fn=collate_fn)
51 | valid_data = processor.get_dev(config['data_dir'] / f"{args.data_name}.valid.pkl")
52 | valid_examples = processor.create_examples(lines=valid_data,
53 | example_type='valid',
54 | cached_examples_file=config[
55 | 'data_dir'] / f"cached_valid_examples_{args.arch}")
56 |
57 | valid_features = processor.create_features(examples=valid_examples,
58 | max_seq_len=args.eval_max_seq_len,
59 | cached_features_file=config[
60 | 'data_dir'] / "cached_valid_features_{}_{}".format(
61 | args.eval_max_seq_len, args.arch
62 | ))
63 | valid_dataset = processor.create_dataset(valid_features)
64 | valid_sampler = SequentialSampler(valid_dataset)
65 | valid_dataloader = DataLoader(valid_dataset, sampler=valid_sampler, batch_size=args.eval_batch_size,
66 | collate_fn=collate_fn)
67 |
68 | # ------- model
69 | logger.info("initializing model")
70 | if args.resume_path:
71 | args.resume_path = Path(args.resume_path)
72 | model = AlbertForMultiLable.from_pretrained(args.resume_path, num_labels=len(label_list))
73 | else:
74 | model = AlbertForMultiLable.from_pretrained(config['albert_model_dir'], num_labels=len(label_list))
75 | t_total = int(len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps * args.epochs)
76 |
77 | param_optimizer = list(model.named_parameters())
78 | no_decay = ['bias', 'LayerNorm.weight']
79 | optimizer_grouped_parameters = [
80 | {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],'weight_decay': args.weight_decay},
81 | {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)], 'weight_decay': 0.0}
82 | ]
83 | warmup_steps = int(t_total * args.warmup_proportion)
84 | optimizer = AdamW(optimizer_grouped_parameters, lr=args.learning_rate, eps=args.adam_epsilon)
85 | scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer, num_warmup_steps=warmup_steps,
86 | num_training_steps=t_total)
87 | if args.fp16:
88 | try:
89 | from apex import amp
90 | except ImportError:
91 | raise ImportError("Please install apex from https://www.github.com/nvidia/apex to use fp16 training.")
92 | model, optimizer = amp.initialize(model, optimizer, opt_level=args.fp16_opt_level)
93 | # ---- callbacks
94 | logger.info("initializing callbacks")
95 | train_monitor = TrainingMonitor(file_dir=config['figure_dir'], arch=args.arch)
96 | model_checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(checkpoint_dir=config['checkpoint_dir'],mode=args.mode,
97 | monitor=args.monitor,arch=args.arch,
98 | save_best_only=args.save_best)
99 |
100 | # **************************** training model ***********************
101 | logger.info("***** Running training *****")
102 | logger.info(" Num examples = %d", len(train_examples))
103 | logger.info(" Num Epochs = %d", args.epochs)
104 | logger.info(" Total train batch size (w. parallel, distributed & accumulation) = %d",
105 | args.train_batch_size * args.gradient_accumulation_steps * (
106 | torch.distributed.get_world_size() if args.local_rank != -1 else 1))
107 | logger.info(" Gradient Accumulation steps = %d", args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
108 | logger.info(" Total optimization steps = %d", t_total)
109 |
110 | trainer = Trainer(args= args,model=model,logger=logger,criterion=BCEWithLogLoss(),optimizer=optimizer,
111 | scheduler=scheduler,early_stopping=None,training_monitor=train_monitor,
112 | model_checkpoint=model_checkpoint,
113 | batch_metrics=[AccuracyThresh(thresh=0.5)],
114 | epoch_metrics=[AUC(average='micro', task_type='binary'),
115 | MultiLabelReport(id2label=id2label)])
116 | trainer.train(train_data=train_dataloader, valid_data=valid_dataloader)
117 |
118 | def run_test(args):
119 | from pybert.io.task_data import TaskData
120 | from pybert.test.predictor import Predictor
121 | data = TaskData()
122 | targets, sentences = data.read_data(raw_data_path=config['test_path'],
123 | preprocessor=EnglishPreProcessor(),
124 | is_train=False)
125 | lines = list(zip(sentences, targets))
126 | processor = AlbertProcessor(spm_model_file=config['albert_vocab_path'], do_lower_case=args.do_lower_case,
127 | vocab_file=None)
128 | label_list = processor.get_labels()
129 | id2label = {i: label for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
130 |
131 | test_data = processor.get_test(lines=lines)
132 | test_examples = processor.create_examples(lines=test_data,
133 | example_type='test',
134 | cached_examples_file=config[
135 | 'data_dir'] / f"cached_test_examples_{args.arch}")
136 | test_features = processor.create_features(examples=test_examples,
137 | max_seq_len=args.eval_max_seq_len,
138 | cached_features_file=config[
139 | 'data_dir'] / "cached_test_features_{}_{}".format(
140 | args.eval_max_seq_len, args.arch
141 | ))
142 | test_dataset = processor.create_dataset(test_features)
143 | test_sampler = SequentialSampler(test_dataset)
144 | test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_dataset, sampler=test_sampler, batch_size=args.train_batch_size,
145 | collate_fn=collate_fn)
146 | model = AlbertForMultiLable.from_pretrained(config['checkpoint_dir'], num_labels=len(label_list))
147 |
148 | # ----------- predicting
149 | logger.info('model predicting....')
150 | predictor = Predictor(model=model,logger=logger,n_gpu=args.n_gpu)
151 | result = predictor.predict(data=test_dataloader)
152 | print(result)
153 |
154 |
155 | def main():
156 | parser = ArgumentParser()
157 | parser.add_argument("--arch", default='albert', type=str)
158 | parser.add_argument("--do_data", action='store_true')
159 | parser.add_argument("--do_train", action='store_true')
160 | parser.add_argument("--do_test", action='store_true')
161 | parser.add_argument("--save_best", action='store_true')
162 | parser.add_argument("--do_lower_case", action='store_true')
163 | parser.add_argument('--data_name', default='kaggle', type=str)
164 | parser.add_argument("--mode", default='min', type=str)
165 | parser.add_argument("--monitor", default='valid_loss', type=str)
166 |
167 | parser.add_argument("--epochs", default=6, type=int)
168 | parser.add_argument("--resume_path", default='', type=str)
169 | parser.add_argument("--valid_size", default=0.2, type=float)
170 | parser.add_argument("--local_rank", type=int, default=-1)
171 | parser.add_argument("--sorted", default=1, type=int, help='1 : True 0:False ')
172 | parser.add_argument("--n_gpu", type=str, default='0', help='"0,1,.." or "0" or "" ')
173 | parser.add_argument('--gradient_accumulation_steps', type=int, default=1)
174 | parser.add_argument("--train_batch_size", default=16, type=int)
175 | parser.add_argument('--eval_batch_size', default=16, type=int)
176 | parser.add_argument("--train_max_seq_len", default=256, type=int)
177 | parser.add_argument("--eval_max_seq_len", default=256, type=int)
178 | parser.add_argument('--loss_scale', type=float, default=0)
179 | parser.add_argument("--warmup_proportion", default=0.1, type=float)
180 | parser.add_argument("--weight_decay", default=0.01, type=float)
181 | parser.add_argument("--adam_epsilon", default=1e-8, type=float)
182 | parser.add_argument("--grad_clip", default=1.0, type=float)
183 | parser.add_argument("--learning_rate", default=1e-5, type=float)
184 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=42)
185 | parser.add_argument('--fp16', action='store_true')
186 | parser.add_argument('--fp16_opt_level', type=str, default='O1')
187 | args = parser.parse_args()
188 |
189 | init_logger(log_file=config['log_dir'] / f'{args.arch}-{time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H:%M:%S", time.localtime())}.log')
190 | config['checkpoint_dir'] = config['checkpoint_dir'] / args.arch
191 | config['checkpoint_dir'].mkdir(exist_ok=True)
192 | # Good practice: save your training arguments together with the trained model
193 | torch.save(args, config['checkpoint_dir'] / 'training_args.bin')
194 | seed_everything(args.seed)
195 | logger.info("Training/evaluation parameters %s", args)
196 | if args.do_data:
197 | from pybert.io.task_data import TaskData
198 | data = TaskData()
199 | targets, sentences = data.read_data(raw_data_path=config['raw_data_path'],
200 | preprocessor=EnglishPreProcessor(),
201 | is_train=True)
202 | data.train_val_split(X=sentences, y=targets, shuffle=True, stratify=False,
203 | valid_size=args.valid_size, data_dir=config['data_dir'],
204 | data_name=args.data_name)
205 | if args.do_train:
206 | run_train(args)
207 |
208 | if args.do_test:
209 | run_test(args)
210 |
211 |
212 | if __name__ == '__main__':
213 | main()
214 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/run_xlnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import time
3 | import warnings
4 | from pathlib import Path
5 | from argparse import ArgumentParser
6 | from pybert.train.losses import BCEWithLogLoss
7 | from pybert.train.trainer import Trainer
8 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
9 | from pybert.io.utils import xlnet_collate_fn as collate_fn
10 | from pybert.io.xlnet_processor import XlnetProcessor
11 | from pybert.common.tools import init_logger, logger
12 | from pybert.common.tools import seed_everything
13 | from pybert.configs.basic_config import config
14 | from pybert.model.xlnet_for_multi_label import XlnetForMultiLable
15 | from pybert.preprocessing.preprocessor import EnglishPreProcessor
16 | from pybert.callback.modelcheckpoint import ModelCheckpoint
17 | from pybert.callback.trainingmonitor import TrainingMonitor
18 | from pybert.train.metrics import AUC, AccuracyThresh, MultiLabelReport
19 | from pybert.callback.optimizater.adamw import AdamW
20 | from pybert.callback.lr_schedulers import get_linear_schedule_with_warmup
21 | from torch.utils.data import RandomSampler, SequentialSampler
22 | warnings.filterwarnings("ignore")
23 |
24 |
25 | def run_train(args):
26 | # --------- data
27 | processor = XlnetProcessor(vocab_path=str(config['xlnet_vocab_path']), do_lower_case=args.do_lower_case)
28 | label_list = processor.get_labels()
29 | label2id = {label: i for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
30 | id2label = {i: label for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
31 |
32 | train_data = processor.get_train(config['data_dir'] / f"{args.data_name}.train.pkl")
33 | train_examples = processor.create_examples(lines=train_data,
34 | example_type='train',
35 | cached_examples_file=config[
36 | 'data_dir'] / f"cached_train_examples_{args.arch}")
37 | train_features = processor.create_features(examples=train_examples,
38 | max_seq_len=args.train_max_seq_len,
39 | cached_features_file=config[
40 | 'data_dir'] / "cached_train_features_{}_{}".format(
41 | args.train_max_seq_len, args.arch
42 | ))
43 | train_dataset = processor.create_dataset(train_features, is_sorted=args.sorted)
44 | if args.sorted:
45 | train_sampler = SequentialSampler(train_dataset)
46 | else:
47 | train_sampler = RandomSampler(train_dataset)
48 | train_dataloader = DataLoader(train_dataset, sampler=train_sampler, batch_size=args.train_batch_size,
49 | collate_fn=collate_fn)
50 |
51 | valid_data = processor.get_dev(config['data_dir'] / f"{args.data_name}.valid.pkl")
52 | valid_examples = processor.create_examples(lines=valid_data,
53 | example_type='valid',
54 | cached_examples_file=config[
55 | 'data_dir'] / f"cached_valid_examples_{args.arch}")
56 |
57 | valid_features = processor.create_features(examples=valid_examples,
58 | max_seq_len=args.eval_max_seq_len,
59 | cached_features_file=config[
60 | 'data_dir'] / "cached_valid_features_{}_{}".format(
61 | args.eval_max_seq_len, args.arch
62 | ))
63 | valid_dataset = processor.create_dataset(valid_features)
64 | valid_sampler = SequentialSampler(valid_dataset)
65 | valid_dataloader = DataLoader(valid_dataset, sampler=valid_sampler, batch_size=args.eval_batch_size,
66 | collate_fn=collate_fn)
67 |
68 | # ------- model
69 | logger.info("initializing model")
70 | if args.resume_path:
71 | args.resume_path = Path(args.resume_path)
72 | model = XlnetForMultiLable.from_pretrained(args.resume_path, num_labels=len(label_list))
73 | else:
74 | model = XlnetForMultiLable.from_pretrained(config['xlnet_model_dir'], num_labels=len(label_list))
75 | t_total = int(len(train_dataloader) / args.gradient_accumulation_steps * args.epochs)
76 |
77 | # Prepare optimizer and schedule (linear warmup and decay)
78 | param_optimizer = list(model.named_parameters())
79 | no_decay = ['bias', 'LayerNorm.weight']
80 | optimizer_grouped_parameters = [
81 | {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if not any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)],
82 | 'weight_decay': args.weight_decay},
83 | {'params': [p for n, p in param_optimizer if any(nd in n for nd in no_decay)], 'weight_decay': 0.0}
84 | ]
85 | warmup_steps = int(t_total * args.warmup_proportion)
86 | optimizer = AdamW(optimizer_grouped_parameters, lr=args.learning_rate, eps=args.adam_epsilon)
87 | scheduler = get_linear_schedule_with_warmup(optimizer, num_warmup_steps=warmup_steps,
88 | num_training_steps=t_total)
89 |
90 | if args.fp16:
91 | try:
92 | from apex import amp
93 | except ImportError:
94 | raise ImportError("Please install apex from https://www.github.com/nvidia/apex to use fp16 training.")
95 | model, optimizer = amp.initialize(model, optimizer, opt_level=args.fp16_opt_level)
96 |
97 | # ---- callbacks
98 | logger.info("initializing callbacks")
99 | train_monitor = TrainingMonitor(file_dir=config['figure_dir'], arch=args.arch)
100 | model_checkpoint = ModelCheckpoint(checkpoint_dir=config['checkpoint_dir'],
101 | mode=args.mode,
102 | monitor=args.monitor,
103 | arch=args.arch,
104 | save_best_only=args.save_best)
105 |
106 | # **************************** training model ***********************
107 | logger.info("***** Running training *****")
108 | logger.info(" Num examples = %d", len(train_examples))
109 | logger.info(" Num Epochs = %d", args.epochs)
110 | logger.info(" Total train batch size (w. parallel, distributed & accumulation) = %d",
111 | args.train_batch_size * args.gradient_accumulation_steps * (
112 | torch.distributed.get_world_size() if args.local_rank != -1 else 1))
113 | logger.info(" Gradient Accumulation steps = %d", args.gradient_accumulation_steps)
114 | logger.info(" Total optimization steps = %d", t_total)
115 |
116 | trainer = Trainer(args= args,model=model,logger=logger,criterion=BCEWithLogLoss(),optimizer=optimizer,
117 | scheduler=scheduler,early_stopping=None,training_monitor=train_monitor,
118 | model_checkpoint=model_checkpoint,
119 | batch_metrics=[AccuracyThresh(thresh=0.5)],
120 | epoch_metrics=[AUC(average='micro', task_type='binary'),
121 | MultiLabelReport(id2label=id2label)])
122 | trainer.train(train_data=train_dataloader, valid_data=valid_dataloader)
123 |
124 |
125 | def run_test(args):
126 | from pybert.io.task_data import TaskData
127 | from pybert.test.predictor import Predictor
128 | data = TaskData()
129 | targets, sentences = data.read_data(raw_data_path=config['test_path'],
130 | preprocessor=EnglishPreProcessor(),
131 | is_train=True)
132 | lines = zip(sentences, targets)
133 | processor = XlnetProcessor(vocab_path=config['xlnet_vocab_path'], do_lower_case=args.do_lower_case)
134 | label_list = processor.get_labels()
135 | id2label = {i: label for i, label in enumerate(label_list)}
136 |
137 | test_data = processor.get_test(lines=lines)
138 | test_examples = processor.create_examples(lines=test_data,
139 | example_type='test',
140 | cached_examples_file=config[
141 | 'data_dir'] / f"cached_test_examples_{args.arch}")
142 | test_features = processor.create_features(examples=test_examples,
143 | max_seq_len=args.eval_max_seq_len,
144 | cached_features_file=config[
145 | 'data_dir'] / "cached_test_features_{}_{}".format(
146 | args.eval_max_seq_len, args.arch
147 | ))
148 | test_dataset = processor.create_dataset(test_features)
149 | test_sampler = SequentialSampler(test_dataset)
150 | test_dataloader = DataLoader(test_dataset, sampler=test_sampler, batch_size=args.train_batch_size,
151 | collate_fn=collate_fn)
152 | model = XlnetForMultiLable.from_pretrained(config['checkpoint_dir'], num_labels=len(label_list))
153 | # ----------- predicting
154 | logger.info('model predicting....')
155 | predictor = Predictor(model=model,logger=logger,n_gpu=args.n_gpu)
156 | result = predictor.predict(data=test_dataloader)
157 | print(result)
158 |
159 | def main():
160 | parser = ArgumentParser()
161 | parser.add_argument("--arch", default='xlnet', type=str)
162 | parser.add_argument("--do_data", action='store_true')
163 | parser.add_argument("--do_train", action='store_true')
164 | parser.add_argument("--do_test", action='store_true')
165 | parser.add_argument("--save_best", action='store_true')
166 | parser.add_argument("--do_lower_case", action='store_true')
167 | parser.add_argument('--data_name', default='kaggle', type=str)
168 | parser.add_argument("--epochs", default=6, type=int)
169 | parser.add_argument("--resume_path", default='', type=str)
170 | parser.add_argument("--mode", default='min', type=str)
171 | parser.add_argument("--monitor", default='valid_loss', type=str)
172 | parser.add_argument("--valid_size", default=0.2, type=float)
173 | parser.add_argument("--local_rank", type=int, default=-1)
174 | parser.add_argument("--sorted", default=1, type=int, help='1 : True 0:False ')
175 | parser.add_argument("--n_gpu", type=str, default='0', help='"0,1,.." or "0" or "" ')
176 | parser.add_argument('--gradient_accumulation_steps', type=int, default=1)
177 | parser.add_argument("--train_batch_size", default=8, type=int)
178 | parser.add_argument('--eval_batch_size', default=8, type=int)
179 | parser.add_argument("--train_max_seq_len", default=256, type=int)
180 | parser.add_argument("--eval_max_seq_len", default=256, type=int)
181 | parser.add_argument('--loss_scale', type=float, default=0)
182 | parser.add_argument("--warmup_proportion", default=0.1, type=int, )
183 | parser.add_argument("--weight_decay", default=0.01, type=float)
184 | parser.add_argument("--adam_epsilon", default=1e-8, type=float)
185 | parser.add_argument("--grad_clip", default=1.0, type=float)
186 | parser.add_argument("--learning_rate", default=2e-5, type=float)
187 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=42)
188 | parser.add_argument('--fp16', action='store_true')
189 | parser.add_argument('--fp16_opt_level', type=str, default='O1')
190 | args = parser.parse_args()
191 | init_logger(log_file=config['log_dir'] / f'{args.arch}-{time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H:%M:%S", time.localtime())}.log')
192 | config['checkpoint_dir'] = config['checkpoint_dir'] / args.arch
193 | config['checkpoint_dir'].mkdir(exist_ok=True)
194 | # Good practice: save your training arguments together with the trained model
195 | torch.save(args, config['checkpoint_dir'] / 'training_args.bin')
196 | seed_everything(args.seed)
197 | logger.info("Training/evaluation parameters %s", args)
198 | if args.do_data:
199 | from pybert.io.task_data import TaskData
200 | data = TaskData()
201 | targets, sentences = data.read_data(raw_data_path=config['raw_data_path'],
202 | preprocessor=EnglishPreProcessor(),
203 | is_train=True)
204 | data.train_val_split(X=sentences, y=targets, shuffle=True, stratify=False,
205 | valid_size=args.valid_size, data_dir=config['data_dir'],
206 | data_name=args.data_name)
207 | if args.do_train:
208 | run_train(args)
209 |
210 | if args.do_test:
211 | run_test(args)
212 |
213 | if __name__ == '__main__':
214 | main()
215 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------