├── .gitignore
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── data
├── toy_testing_data.npz
└── toy_training_data.npz
├── demo.py
├── resources
├── SML_diag.png
├── SUPERVISED_ONLINE_DIARIZATION_WITH_SAMPLE_MEAN_LOSS_FOR_MULTI_DOMAIN_DATA.pdf
└── uisrnn.gif
└── uisrnn
├── __init__.py
├── arguments.py
├── evals.py
├── loss_func.py
├── uisrnn.py
└── utils.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *~
2 | *.pyc
3 | .DS_Store
4 | *result.txt
5 | *.uisrnn
6 | build/*
7 | dist/*
8 | uisrnn.egg-info/*
9 | .coverage
10 | runs
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Apache License
3 | Version 2.0, January 2004
4 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/
5 |
6 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
7 |
8 | 1. Definitions.
9 |
10 | "License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
11 | and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
12 |
13 | "Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
14 | the copyright owner that is granting the License.
15 |
16 | "Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
17 | other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
18 | control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
19 | "control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
20 | direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
21 | otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
22 | outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
23 |
24 | "You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
25 | exercising permissions granted by this License.
26 |
27 | "Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
28 | including but not limited to software source code, documentation
29 | source, and configuration files.
30 |
31 | "Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
32 | transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
33 | not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
34 | and conversions to other media types.
35 |
36 | "Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
37 | Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
38 | copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
39 | (an example is provided in the Appendix below).
40 |
41 | "Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
42 | form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
43 | editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
44 | represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
45 | of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
46 | separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
47 | the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
48 |
49 | "Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
50 | the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
51 | to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
52 | submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
53 | or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
54 | the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
55 | means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
56 | to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
57 | communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
58 | and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
59 | Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
60 | excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
61 | designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
62 |
63 | "Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
64 | on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
65 | subsequently incorporated within the Work.
66 |
67 | 2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
68 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
69 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
70 | copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
71 | publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
72 | Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
73 |
74 | 3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
75 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
76 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
77 | (except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
78 | use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
79 | where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
80 | by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
81 | Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
82 | with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
83 | institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
84 | cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
85 | or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
86 | or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
87 | granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
88 | as of the date such litigation is filed.
89 |
90 | 4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
91 | Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
92 | modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
93 | meet the following conditions:
94 |
95 | (a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
96 | Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
97 |
98 | (b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
99 | stating that You changed the files; and
100 |
101 | (c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
102 | that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
103 | attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
104 | excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
105 | the Derivative Works; and
106 |
107 | (d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
108 | distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
109 | include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
110 | within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
111 | pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
112 | of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
113 | as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
114 | documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
115 | within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
116 | wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
117 | of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
118 | do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
119 | notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
120 | or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
121 | that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
122 | as modifying the License.
123 |
124 | You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
125 | may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
126 | for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
127 | for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
128 | reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
129 | the conditions stated in this License.
130 |
131 | 5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
132 | any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
133 | by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
134 | this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
135 | Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
136 | the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
137 | with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
138 |
139 | 6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
140 | names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
141 | except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
142 | origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
143 |
144 | 7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
145 | agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
146 | Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
147 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
148 | implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
149 | of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
150 | PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
151 | appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
152 | risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
153 |
154 | 8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
155 | whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
156 | unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
157 | negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
158 | liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
159 | incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
160 | result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
161 | Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
162 | work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
163 | other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
164 | has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
165 |
166 | 9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
167 | the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
168 | and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
169 | or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
170 | License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
171 | on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
172 | of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
173 | defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
174 | incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
175 | of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
176 |
177 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
178 |
179 | APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
180 |
181 | To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
182 | boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
183 | replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
184 | the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
185 | comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
186 | file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
187 | same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
188 | identification within third-party archives.
189 |
190 | Copyright [yyyy] [name of copyright owner]
191 |
192 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
193 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
194 | You may obtain a copy of the License at
195 |
196 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
197 |
198 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
199 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
200 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
201 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
202 | limitations under the License.
203 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Better, Faster, Stronger UIS-RNN
2 |
3 | This repository implements some useful features on top of the original [UIS-RNN repository](https://github.com/google/uis-rnn). Some of them are described in the following paper: [Supervised Online Diarization with Sample Mean Loss for Multi-Domain Data](https://arxiv.org/abs/1911.01266).
4 | Here is a list:
5 | * **Sample Mean Loss (SML)**, a loss function that improves performance and training efficiency. To learn more about it you can read our paper.
6 | * **Estimation of** `crp_alpha`, a parameter of the distance dependent Chinese Restaurant Process (ddCRP) that determines the probability of switching to a new speaker. Again, more info in our paper.
7 | * **Parallel prediction** using `torch.multiprocessing`, that mitigates the issue with slow decoding and enables higher GPU usage.
8 | * **Tensorboard** logging, for visualizing training.
9 |
10 | Here is a diagram of the Sample Mean Loss:
11 |
12 |
13 |  14 |
14 |
15 |
16 | The UIS-RNN was originally proposed in [Fully Supervised Speaker Diarization](https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.04719).
17 |
18 |
19 | 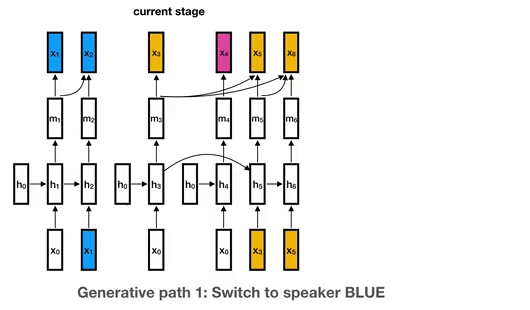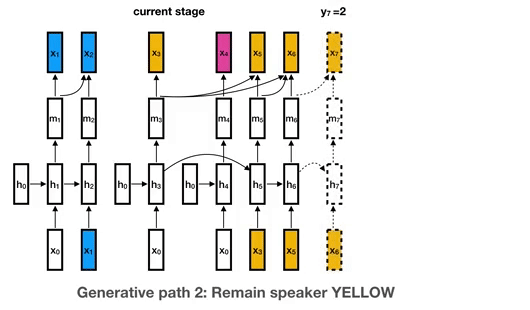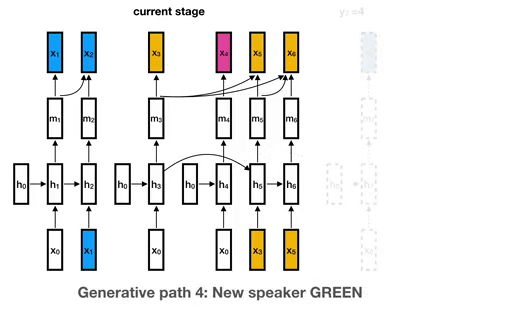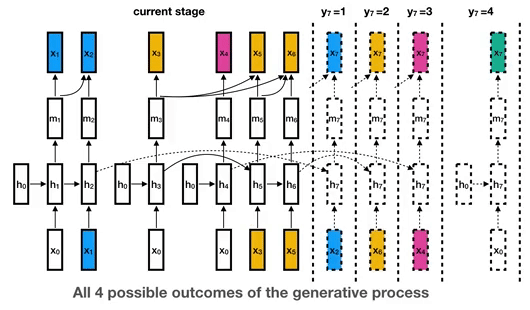 20 |
20 |
21 |
22 | ## Run the demo
23 |
24 | To get started, simply run this command:
25 |
26 | ```bash
27 | python3 demo.py --train_iteration=1000 -l=0.001
28 | ```
29 |
30 | This will train a UIS-RNN model using `data/toy_training_data.npz`,
31 | then store the model on disk, perform inference on `data/toy_testing_data.npz`,
32 | print the inference results, and save the averaged accuracy in a text file.
33 |
34 | P.S.: The files under `data/` are manually generated *toy data*,
35 | for demonstration purpose only.
36 | These data are very simple, so we are supposed to get 100% accuracy on the
37 | testing data.
38 |
39 | ## Arguments
40 |
41 | * `--loss_samples` the number of samples for the Sample Mean Loss. If `loss_samples <= 0` it will be ignored and the loss will be computed as per the original UIS-RNN
42 | * `--fc_depth`: the numebr of fully connected layers after the GRU.
43 | * `--non_lin`: whether to use non linearity (relu) in the fully connected layers.
44 | * `NUM_WORKERS`: the number of workers (processes) for multiprocessing. The argument can be found in `demo.py`.
45 |
46 | All the other arguments are the same as per the [original repository](https://github.com/google/uis-rnn)
47 |
48 | ## Citations
49 |
50 | Our paper is cited as:
51 |
52 | ```
53 | @article{fini2019supervised,
54 | title={Supervised online diarization with sample mean loss for multi-domain data},
55 | author={Fini, Enrico and Brutti, Alessio},
56 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1911.01266},
57 | year={2019}
58 | }
59 | ```
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/toy_testing_data.npz:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DonkeyShot21/uis-rnn-sml/820d8698b60c88683c5be15b8bf529afb3c886c9/data/toy_testing_data.npz
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/toy_training_data.npz:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DonkeyShot21/uis-rnn-sml/820d8698b60c88683c5be15b8bf529afb3c886c9/data/toy_training_data.npz
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2018 Google LLC
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | """A demo script showing how to use the uisrnn package on toy data."""
15 |
16 | import numpy as np
17 | from functools import partial
18 | from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
19 | import torch.multiprocessing as mp
20 | mp = mp.get_context('forkserver')
21 |
22 | import uisrnn
23 |
24 |
25 | SAVED_MODEL_NAME = 'saved_model.uisrnn'
26 | NUM_WORKERS = 2
27 |
28 |
29 | def diarization_experiment(model_args, training_args, inference_args):
30 | """Experiment pipeline.
31 |
32 | Load data --> train model --> test model --> output result
33 |
34 | Args:
35 | model_args: model configurations
36 | training_args: training configurations
37 | inference_args: inference configurations
38 | """
39 | # data loading
40 | train_data = np.load('./data/toy_training_data.npz', allow_pickle=True)
41 | test_data = np.load('./data/toy_testing_data.npz', allow_pickle=True)
42 | train_sequence = train_data['train_sequence']
43 | train_cluster_id = train_data['train_cluster_id']
44 | test_sequences = test_data['test_sequences'].tolist()
45 | test_cluster_ids = test_data['test_cluster_ids'].tolist()
46 |
47 | # model init
48 | model = uisrnn.UISRNN(model_args)
49 | # model.load(SAVED_MODEL_NAME) # to load a checkpoint
50 | # tensorboard writer init
51 | writer = SummaryWriter()
52 |
53 | # training
54 | for epoch in range(training_args.epochs):
55 | stats = model.fit(train_sequence, train_cluster_id, training_args)
56 | # add to tensorboard
57 | for loss, cur_iter in stats:
58 | for loss_name, loss_value in loss.items():
59 | writer.add_scalar('loss/' + loss_name, loss_value, cur_iter)
60 | # save the mdoel
61 | model.save(SAVED_MODEL_NAME)
62 |
63 | # testing
64 | predicted_cluster_ids = []
65 | test_record = []
66 | # predict sequences in parallel
67 | model.rnn_model.share_memory()
68 | pool = mp.Pool(NUM_WORKERS, maxtasksperchild=None)
69 | pred_gen = pool.imap(
70 | func=partial(model.predict, args=inference_args),
71 | iterable=test_sequences)
72 | # collect and score predicitons
73 | for idx, predicted_cluster_id in enumerate(pred_gen):
74 | accuracy = uisrnn.compute_sequence_match_accuracy(
75 | test_cluster_ids[idx], predicted_cluster_id)
76 | predicted_cluster_ids.append(predicted_cluster_id)
77 | test_record.append((accuracy, len(test_cluster_ids[idx])))
78 | print('Ground truth labels:')
79 | print(test_cluster_ids[idx])
80 | print('Predicted labels:')
81 | print(predicted_cluster_id)
82 | print('-' * 80)
83 |
84 | # close multiprocessing pool
85 | pool.close()
86 | # close tensorboard writer
87 | writer.close()
88 |
89 | print('Finished diarization experiment')
90 | print(uisrnn.output_result(model_args, training_args, test_record))
91 |
92 |
93 | def main():
94 | """The main function."""
95 | model_args, training_args, inference_args = uisrnn.parse_arguments()
96 | diarization_experiment(model_args, training_args, inference_args)
97 |
98 |
99 | if __name__ == '__main__':
100 | main()
101 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resources/SML_diag.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DonkeyShot21/uis-rnn-sml/820d8698b60c88683c5be15b8bf529afb3c886c9/resources/SML_diag.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resources/SUPERVISED_ONLINE_DIARIZATION_WITH_SAMPLE_MEAN_LOSS_FOR_MULTI_DOMAIN_DATA.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DonkeyShot21/uis-rnn-sml/820d8698b60c88683c5be15b8bf529afb3c886c9/resources/SUPERVISED_ONLINE_DIARIZATION_WITH_SAMPLE_MEAN_LOSS_FOR_MULTI_DOMAIN_DATA.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resources/uisrnn.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/DonkeyShot21/uis-rnn-sml/820d8698b60c88683c5be15b8bf529afb3c886c9/resources/uisrnn.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/uisrnn/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2018 Google LLC
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | """The module for Unbounded Interleaved-State Recurrent Neural Network.
15 |
16 | An introduction is available at [README.md].
17 |
18 | [README.md]: https://github.com/google/uis-rnn/blob/master/README.md
19 | """
20 |
21 | from . import arguments
22 | from . import evals
23 | from . import loss_func
24 | from . import uisrnn
25 | from . import utils
26 |
27 | #pylint: disable=C0103
28 | parse_arguments = arguments.parse_arguments
29 | compute_sequence_match_accuracy = evals.compute_sequence_match_accuracy
30 | output_result = utils.output_result
31 | UISRNN = uisrnn.UISRNN
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/uisrnn/arguments.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2018 Google LLC
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | """Arguments for UISRNN."""
15 |
16 | import argparse
17 |
18 | _DEFAULT_OBSERVATION_DIM = 256
19 |
20 |
21 | def str2bool(value):
22 | """A function to convert string to bool value."""
23 | if value.lower() in {'yes', 'true', 't', 'y', '1'}:
24 | return True
25 | if value.lower() in {'no', 'false', 'f', 'n', '0'}:
26 | return False
27 | raise argparse.ArgumentTypeError('Boolean value expected.')
28 |
29 |
30 | def parse_arguments():
31 | """Parse arguments.
32 |
33 | Returns:
34 | A tuple of:
35 |
36 | - `model_args`: model arguments
37 | - `training_args`: training arguments
38 | - `inference_args`: inference arguments
39 | """
40 | # model configurations
41 | model_parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
42 | description='Model configurations.', add_help=False)
43 |
44 | model_parser.add_argument(
45 | '--observation_dim',
46 | default=_DEFAULT_OBSERVATION_DIM,
47 | type=int,
48 | help='The dimension of the embeddings (e.g. d-vectors).')
49 |
50 | model_parser.add_argument(
51 | '--rnn_hidden_size',
52 | default=512,
53 | type=int,
54 | help='The number of nodes for each RNN layer.')
55 | model_parser.add_argument(
56 | '--rnn_depth',
57 | default=1,
58 | type=int,
59 | help='The number of RNN layers.')
60 | model_parser.add_argument(
61 | '--fc_depth',
62 | default=1,
63 | type=int,
64 | help='The number of fully connected layers.')
65 | model_parser.add_argument(
66 | '--rnn_dropout',
67 | default=0.2,
68 | type=float,
69 | help='The dropout rate for all RNN layers.')
70 | model_parser.add_argument(
71 | '--non_lin',
72 | default=True,
73 | type=str2bool,
74 | help='Whether to use non linearity after linear layers or not.')
75 | model_parser.add_argument(
76 | '--transition_bias',
77 | default=None,
78 | type=float,
79 | help='The value of p0, corresponding to Eq. (6) in the '
80 | 'paper. If the value is given, we will fix to this value. If the '
81 | 'value is None, we will estimate it from training data '
82 | 'using Eq. (13) in the paper.')
83 | model_parser.add_argument(
84 | '--crp_alpha',
85 | default=None,
86 | type=float,
87 | help='The value of alpha for the Chinese restaurant process (CRP), '
88 | 'corresponding to Eq. (7) in the paper. If the value is given,'
89 | 'we will fix to this value. If the value is None, we will estimate '
90 | 'it from training data.')
91 | model_parser.add_argument(
92 | '--sigma2',
93 | default=None,
94 | type=float,
95 | help='The value of sigma squared, corresponding to Eq. (11) in the '
96 | 'paper. If the value is given, we will fix to this value. If the '
97 | 'value is None, we will estimate it from training data.')
98 | model_parser.add_argument(
99 | '--verbosity',
100 | default=2,
101 | type=int,
102 | help='How verbose will the logging information be. Higher value '
103 | 'represents more verbose information. A general guideline: '
104 | '0 for errors; 1 for finishing important steps; '
105 | '2 for finishing less important steps; 3 or above for debugging '
106 | 'information.')
107 | model_parser.add_argument(
108 | '--enable_cuda',
109 | default=True,
110 | type=str2bool,
111 | help='Whether we should use CUDA if it is avaiable. If False, we will '
112 | 'always use CPU.')
113 |
114 | # training configurations
115 | training_parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
116 | description='Training configurations.', add_help=False)
117 |
118 | training_parser.add_argument(
119 | '--optimizer',
120 | '-o',
121 | default='adam',
122 | choices=['adam'],
123 | help='The optimizer for training.')
124 | training_parser.add_argument(
125 | '--learning_rate',
126 | '-l',
127 | default=1e-3,
128 | type=float,
129 | help='The leaning rate for training.')
130 | training_parser.add_argument(
131 | '--train_iteration',
132 | '-t',
133 | default=20000,
134 | type=int,
135 | help='The total number of training iterations.')
136 | training_parser.add_argument(
137 | '--epochs',
138 | '-e',
139 | default=10,
140 | type=int,
141 | help='The total number of training epochs.')
142 | training_parser.add_argument(
143 | '--batch_size',
144 | '-b',
145 | default=10,
146 | type=int,
147 | help='The batch size for training.')
148 | training_parser.add_argument(
149 | '--num_permutations',
150 | default=10,
151 | type=int,
152 | help='The number of permutations per utterance sampled in the training '
153 | 'data.')
154 | training_parser.add_argument(
155 | '--sigma_alpha',
156 | default=1.0,
157 | type=float,
158 | help='The inverse gamma shape for estimating sigma2. This value is only '
159 | 'meaningful when sigma2 is not given, and estimated from data.')
160 | training_parser.add_argument(
161 | '--sigma_beta',
162 | default=1.0,
163 | type=float,
164 | help='The inverse gamma scale for estimating sigma2. This value is only '
165 | 'meaningful when sigma2 is not given, and estimated from data.')
166 | training_parser.add_argument(
167 | '--regularization_weight',
168 | '-r',
169 | default=1e-5,
170 | type=float,
171 | help='The network regularization multiplicative.')
172 | training_parser.add_argument(
173 | '--grad_max_norm',
174 | default=5.0,
175 | type=float,
176 | help='Max norm of the gradient.')
177 | training_parser.add_argument(
178 | '--enforce_cluster_id_uniqueness',
179 | default=True,
180 | type=str2bool,
181 | help='Whether to enforce cluster ID uniqueness across different '
182 | 'training sequences. Only effective when the first input to fit() '
183 | 'is a list of sequences. In general, assume the cluster IDs for two '
184 | 'sequences are [a, b] and [a, c]. If the `a` from the two sequences '
185 | 'are not the same label, then this arg should be True.')
186 | training_parser.add_argument(
187 | '--loss_samples',
188 | default=-1,
189 | type=int,
190 | help='if loss_samples > 0 then it represents the number of embeddings '
191 | 'to be sampled in the Sample Mean Loss otherwise it will be ignored '
192 | 'and the loss will be computed as per the original UIS-RNN')
193 |
194 | # inference configurations
195 | inference_parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
196 | description='Inference configurations.', add_help=False)
197 |
198 | inference_parser.add_argument(
199 | '--beam_size',
200 | '-s',
201 | default=10,
202 | type=int,
203 | help='The beam search size for inference.')
204 | inference_parser.add_argument(
205 | '--look_ahead',
206 | default=1,
207 | type=int,
208 | help='The number of look ahead steps during inference.')
209 | inference_parser.add_argument(
210 | '--test_iteration',
211 | default=2,
212 | type=int,
213 | help='During inference, we concatenate M duplicates of the test '
214 | 'sequence, and run inference on this concatenated sequence. '
215 | 'Then we return the inference results on the last duplicate as the '
216 | 'final prediction for the test sequence.')
217 |
218 | # a super parser for sanity checks
219 | super_parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
220 | parents=[model_parser, training_parser, inference_parser])
221 |
222 | # get arguments
223 | super_parser.parse_args()
224 | model_args, _ = model_parser.parse_known_args()
225 | training_args, _ = training_parser.parse_known_args()
226 | inference_args, _ = inference_parser.parse_known_args()
227 |
228 | return (model_args, training_args, inference_args)
229 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/uisrnn/evals.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2018 Google LLC
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | """Utils for model evaluation."""
15 |
16 | from scipy import optimize
17 | import numpy as np
18 |
19 |
20 | def get_list_inverse_index(unique_ids):
21 | """Get value to position index from a list of unique ids.
22 |
23 | Args:
24 | unique_ids: A list of unique integers of strings.
25 |
26 | Returns:
27 | result: a dict from value to position
28 |
29 | Raises:
30 | TypeError: If unique_ids is not a list.
31 | """
32 | if not isinstance(unique_ids, list):
33 | raise TypeError('unique_ids must be a list')
34 | result = dict()
35 | for i, unique_id in enumerate(unique_ids):
36 | result[unique_id] = i
37 | return result
38 |
39 |
40 | def compute_sequence_match_accuracy(sequence1, sequence2):
41 | """Compute the accuracy between two sequences by finding optimal matching.
42 |
43 | Args:
44 | sequence1: A list of integers or strings.
45 | sequence2: A list of integers or strings.
46 |
47 | Returns:
48 | accuracy: sequence matching accuracy as a number in [0.0, 1.0]
49 |
50 | Raises:
51 | TypeError: If sequence1 or sequence2 is not list.
52 | ValueError: If sequence1 and sequence2 are not same size.
53 | """
54 | if not isinstance(sequence1, list) or not isinstance(sequence2, list):
55 | raise TypeError('sequence1 and sequence2 must be lists')
56 | if not sequence1 or len(sequence1) != len(sequence2):
57 | raise ValueError(
58 | 'sequence1 and sequence2 must have the same non-zero length')
59 | # get unique ids from sequences
60 | unique_ids1 = sorted(set(sequence1))
61 | unique_ids2 = sorted(set(sequence2))
62 | inverse_index1 = get_list_inverse_index(unique_ids1)
63 | inverse_index2 = get_list_inverse_index(unique_ids2)
64 | # get the count matrix
65 | count_matrix = np.zeros((len(unique_ids1), len(unique_ids2)))
66 | for item1, item2 in zip(sequence1, sequence2):
67 | index1 = inverse_index1[item1]
68 | index2 = inverse_index2[item2]
69 | count_matrix[index1, index2] += 1.0
70 | row_index, col_index = optimize.linear_sum_assignment(-count_matrix)
71 | optimal_match_count = count_matrix[row_index, col_index].sum()
72 | accuracy = optimal_match_count / len(sequence1)
73 | return accuracy
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/uisrnn/loss_func.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2018 Google LLC
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | """Loss functions for training."""
15 |
16 | import torch
17 |
18 |
19 | def weighted_mse_loss(input_tensor, target_tensor, weight=1):
20 | """Compute weighted MSE loss.
21 |
22 | Note that we are doing weighted loss that only sum up over non-zero entries.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | input_tensor: input tensor
26 | target_tensor: target tensor
27 | weight: weight tensor, in this case 1/sigma^2
28 |
29 | Returns:
30 | the weighted MSE loss
31 | """
32 | observation_dim = input_tensor.size()[-1]
33 | streched_tensor = ((input_tensor - target_tensor) ** 2).view(
34 | -1, observation_dim)
35 | entry_num = float(streched_tensor.size()[0])
36 | non_zero_entry_num = torch.sum(streched_tensor[:, 0] != 0).float()
37 | weighted_tensor = torch.mm(
38 | ((input_tensor - target_tensor)**2).view(-1, observation_dim),
39 | (torch.diag(weight.float().view(-1))))
40 | return torch.mean(
41 | weighted_tensor) * weight.nelement() * entry_num / non_zero_entry_num
42 |
43 |
44 | def sigma2_prior_loss(num_non_zero, sigma_alpha, sigma_beta, sigma2):
45 | """Compute sigma2 prior loss.
46 |
47 | Args:
48 | num_non_zero: since rnn_truth is a collection of different length sequences
49 | padded with zeros to fit them into a tensor, we count the sum of
50 | 'real lengths' of all sequences
51 | sigma_alpha: inverse gamma shape
52 | sigma_beta: inverse gamma scale
53 | sigma2: sigma squared
54 |
55 | Returns:
56 | the sigma2 prior loss
57 | """
58 | return ((2 * sigma_alpha + num_non_zero + 2) /
59 | (2 * num_non_zero) * torch.log(sigma2)).sum() + (
60 | sigma_beta / (sigma2 * num_non_zero)).sum()
61 |
62 |
63 | def regularization_loss(params, weight):
64 | """Compute regularization loss.
65 |
66 | Args:
67 | params: iterable of all parameters
68 | weight: weight for the regularization term
69 |
70 | Returns:
71 | the regularization loss
72 | """
73 | l2_reg = 0
74 | for param in params:
75 | l2_reg += torch.norm(param)
76 | return weight * l2_reg
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/uisrnn/uisrnn.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2018 Google LLC
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | """The UIS-RNN model."""
15 |
16 | import numpy as np
17 | import torch
18 | from torch import autograd
19 | from torch import nn
20 | from torch import optim
21 | import torch.nn.functional as F
22 |
23 | from uisrnn import loss_func
24 | from uisrnn import utils
25 |
26 | _INITIAL_SIGMA2_VALUE = 0.1
27 |
28 |
29 | class CoreRNN(nn.Module):
30 | """The core Recurent Neural Network used by UIS-RNN."""
31 |
32 | def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_size, rnn_depth, fc_depth,
33 | observation_dim, dropout=0, non_lin=True):
34 | super(CoreRNN, self).__init__()
35 | self.hidden_size = hidden_size
36 | self.non_lin = non_lin
37 | if rnn_depth >= 2:
38 | self.gru = nn.GRU(input_dim, hidden_size, rnn_depth, dropout=dropout)
39 | else:
40 | self.gru = nn.GRU(input_dim, hidden_size, rnn_depth)
41 | self.linears = nn.ModuleList(
42 | [nn.Linear(hidden_size, hidden_size) for _ in range(fc_depth)])
43 | self.last_linear = nn.Linear(hidden_size, observation_dim)
44 |
45 | def forward(self, input_seq, hidden=None):
46 | out, hidden = self.gru(input_seq, hidden)
47 | if isinstance(out, torch.nn.utils.rnn.PackedSequence):
48 | out, _ = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_packed_sequence(out, batch_first=False)
49 | for layer in self.linears:
50 | out = layer(out)
51 | if self.non_lin:
52 | out = F.relu(out)
53 | mean = self.last_linear(out)
54 | return mean, hidden
55 |
56 |
57 | class BeamState:
58 | """Structure that contains necessary states for beam search."""
59 |
60 | def __init__(self, source=None):
61 | if not source:
62 | self.mean_set = []
63 | self.hidden_set = []
64 | self.neg_likelihood = 0
65 | self.trace = []
66 | self.block_counts = []
67 | else:
68 | self.mean_set = source.mean_set.copy()
69 | self.hidden_set = source.hidden_set.copy()
70 | self.trace = source.trace.copy()
71 | self.block_counts = source.block_counts.copy()
72 | self.neg_likelihood = source.neg_likelihood
73 |
74 | def append(self, mean, hidden, cluster):
75 | """Append new item to the BeamState."""
76 | self.mean_set.append(mean.clone())
77 | self.hidden_set.append(hidden.clone())
78 | self.block_counts.append(1)
79 | self.trace.append(cluster)
80 |
81 |
82 | class UISRNN:
83 | """Unbounded Interleaved-State Recurrent Neural Networks."""
84 |
85 | def __init__(self, args):
86 | """Construct the UISRNN object.
87 |
88 | Args:
89 | args: Model configurations. See `arguments.py` for details.
90 | """
91 | self.observation_dim = args.observation_dim
92 | self.device = torch.device(
93 | 'cuda:0' if (torch.cuda.is_available() and args.enable_cuda) else 'cpu')
94 | self.rnn_model = CoreRNN(self.observation_dim, args.rnn_hidden_size,
95 | args.rnn_depth, args.fc_depth,
96 | self.observation_dim, args.rnn_dropout,
97 | args.non_lin).to(self.device)
98 | self.rnn_init_hidden = nn.Parameter(
99 | torch.zeros(args.rnn_depth, 1, args.rnn_hidden_size).to(self.device))
100 | # booleans indicating which variables are trainable
101 | self.estimate_sigma2 = (args.sigma2 is None)
102 | self.estimate_transition_bias = (args.transition_bias is None)
103 | self.estimate_crp_alpha = (args.crp_alpha is None)
104 | # initial values of variables
105 | sigma2 = _INITIAL_SIGMA2_VALUE if self.estimate_sigma2 else args.sigma2
106 | self.sigma2 = nn.Parameter(
107 | sigma2 * torch.ones(self.observation_dim).to(self.device))
108 | self.transition_bias = args.transition_bias
109 | self.transition_bias_denominator = 0.0
110 | self.crp_alpha = args.crp_alpha
111 | self.crp_alpha_denominator = 0.0
112 | self.logger = utils.Logger(args.verbosity)
113 | self.current_iter = 0
114 |
115 |
116 | def _get_optimizer(self, optimizer, learning_rate):
117 | """Get optimizer for UISRNN.
118 |
119 | Args:
120 | optimizer: string - name of the optimizer.
121 | learning_rate: - learning rate for the entire model.
122 | We do not customize learning rate for separate parts.
123 |
124 | Returns:
125 | a pytorch "optim" object
126 | """
127 | params = [
128 | {
129 | 'params': self.rnn_model.parameters()
130 | }, # rnn parameters
131 | {
132 | 'params': self.rnn_init_hidden
133 | } # rnn initial hidden state
134 | ]
135 | if self.estimate_sigma2: # train sigma2
136 | params.append({
137 | 'params': self.sigma2
138 | }) # variance parameters
139 | assert optimizer == 'adam', 'Only adam optimizer is supported.'
140 | return optim.Adam(params, lr=learning_rate)
141 |
142 | def save(self, filepath):
143 | """Save the model to a file.
144 |
145 | Args:
146 | filepath: the path of the file.
147 | """
148 | torch.save({
149 | 'rnn_state_dict': self.rnn_model.state_dict(),
150 | 'rnn_init_hidden': self.rnn_init_hidden.detach().cpu().numpy(),
151 | 'transition_bias': self.transition_bias,
152 | 'transition_bias_denominator': self.transition_bias_denominator,
153 | 'crp_alpha': self.crp_alpha,
154 | 'crp_alpha_denominator': self.crp_alpha_denominator,
155 | 'sigma2': self.sigma2.detach().cpu().numpy(),
156 | 'current_iter': self.current_iter}, filepath)
157 |
158 | def load(self, filepath):
159 | """Load the model from a file.
160 |
161 | Args:
162 | filepath: the path of the file.
163 | """
164 | var_dict = torch.load(filepath)
165 | self.rnn_model.load_state_dict(var_dict['rnn_state_dict'])
166 | self.rnn_init_hidden = nn.Parameter(
167 | torch.from_numpy(var_dict['rnn_init_hidden']).to(self.device))
168 | self.transition_bias = float(var_dict['transition_bias'])
169 | self.transition_bias_denominator = float(
170 | var_dict['transition_bias_denominator'])
171 | self.crp_alpha = float(var_dict['crp_alpha'])
172 | self.crp_alpha_denominator = float(var_dict['crp_alpha_denominator'])
173 | self.sigma2 = nn.Parameter(
174 | torch.from_numpy(var_dict['sigma2']).to(self.device))
175 | self.current_iter = int(var_dict['current_iter'])
176 |
177 | self.logger.print(
178 | 3, 'Loaded model with transition_bias={}, crp_alpha={}, sigma2={}, '
179 | 'rnn_init_hidden={}'.format(
180 | self.transition_bias, self.crp_alpha, var_dict['sigma2'],
181 | var_dict['rnn_init_hidden']))
182 |
183 | def fit_concatenated(self, train_sequence, train_cluster_id, args):
184 | """Fit UISRNN model to concatenated sequence and cluster_id.
185 |
186 | Args:
187 | train_sequence: the training observation sequence, which is a
188 | 2-dim numpy array of real numbers, of size `N * D`.
189 |
190 | - `N`: summation of lengths of all utterances.
191 | - `D`: observation dimension.
192 |
193 | For example,
194 | ```
195 | train_sequence =
196 | [[1.2 3.0 -4.1 6.0] --> an entry of speaker #0 from utterance 'iaaa'
197 | [0.8 -1.1 0.4 0.5] --> an entry of speaker #1 from utterance 'iaaa'
198 | [-0.2 1.0 3.8 5.7] --> an entry of speaker #0 from utterance 'iaaa'
199 | [3.8 -0.1 1.5 2.3] --> an entry of speaker #0 from utterance 'ibbb'
200 | [1.2 1.4 3.6 -2.7]] --> an entry of speaker #0 from utterance 'ibbb'
201 | ```
202 | Here `N=5`, `D=4`.
203 |
204 | We concatenate all training utterances into this single sequence.
205 | train_cluster_id: the speaker id sequence, which is 1-dim list or
206 | numpy array of strings, of size `N`.
207 | For example,
208 | ```
209 | train_cluster_id =
210 | ['iaaa_0', 'iaaa_1', 'iaaa_0', 'ibbb_0', 'ibbb_0']
211 | ```
212 | 'iaaa_0' means the entry belongs to speaker #0 in utterance 'iaaa'.
213 |
214 | Note that the order of entries within an utterance are preserved,
215 | and all utterances are simply concatenated together.
216 | args: Training configurations. See `arguments.py` for details.
217 |
218 | Raises:
219 | TypeError: If train_sequence or train_cluster_id is of wrong type.
220 | ValueError: If train_sequence or train_cluster_id has wrong dimension.
221 | """
222 | # check type
223 | if (not isinstance(train_sequence, np.ndarray) or
224 | train_sequence.dtype != float):
225 | raise TypeError('train_sequence should be a numpy array of float type.')
226 | if isinstance(train_cluster_id, list):
227 | train_cluster_id = np.array(train_cluster_id)
228 | if (not isinstance(train_cluster_id, np.ndarray) or
229 | not train_cluster_id.dtype.name.startswith(('str', 'unicode'))):
230 | raise TypeError('train_cluster_id type be a numpy array of strings.')
231 | # check dimension
232 | if train_sequence.ndim != 2:
233 | raise ValueError('train_sequence must be 2-dim array.')
234 | if train_cluster_id.ndim != 1:
235 | raise ValueError('train_cluster_id must be 1-dim array.')
236 | # check length and size
237 | train_total_length, observation_dim = train_sequence.shape
238 | if observation_dim != self.observation_dim:
239 | raise ValueError('train_sequence does not match the dimension specified '
240 | 'by args.observation_dim.')
241 | if train_total_length != len(train_cluster_id):
242 | raise ValueError('train_sequence length is not equal to '
243 | 'train_cluster_id length.')
244 |
245 | self.rnn_model.train()
246 | optimizer = self._get_optimizer(optimizer=args.optimizer,
247 | learning_rate=args.learning_rate)
248 |
249 | sub_sequences, seq_lengths = utils.resize_sequence(
250 | sequence=train_sequence,
251 | cluster_id=train_cluster_id,
252 | num_permutations=args.num_permutations)
253 |
254 | # For batch learning, pack the entire dataset.
255 | if args.batch_size is None:
256 | packed_train_sequence, rnn_truth = utils.pack_sequence(
257 | sub_sequences,
258 | seq_lengths,
259 | args.batch_size,
260 | self.observation_dim,
261 | self.device,
262 | args.loss_samples)
263 | train_loss = []
264 | for _ in range(args.train_iteration):
265 | self.current_iter += 1
266 | optimizer.zero_grad()
267 | # For online learning, pack a subset in each iteration.
268 | if args.batch_size is not None:
269 | packed_train_sequence, rnn_truth = utils.pack_sequence(
270 | sub_sequences,
271 | seq_lengths,
272 | args.batch_size,
273 | self.observation_dim,
274 | self.device,
275 | args.loss_samples)
276 | hidden = self.rnn_init_hidden.repeat(1, args.batch_size, 1)
277 | mean, _ = self.rnn_model(packed_train_sequence, hidden)
278 | # use mean to predict
279 | mean = torch.cumsum(mean, dim=0)
280 | mean_size = mean.size()
281 | mean = torch.mm(
282 | torch.diag(
283 | 1.0 / torch.arange(1, mean_size[0] + 1).float().to(self.device)),
284 | mean.view(mean_size[0], -1))
285 | mean = mean.view(mean_size)
286 |
287 | # Likelihood part.
288 | loss1 = loss_func.weighted_mse_loss(
289 | input_tensor=(rnn_truth != 0).float() * mean[:-1, :, :],
290 | target_tensor=rnn_truth,
291 | weight=1 / (2 * self.sigma2))
292 |
293 | # Sigma2 prior part.
294 | weight = (((rnn_truth != 0).float() * mean[:-1, :, :] - rnn_truth)
295 | ** 2).view(-1, observation_dim)
296 | num_non_zero = torch.sum((weight != 0).float(), dim=0).squeeze()
297 | loss2 = loss_func.sigma2_prior_loss(
298 | num_non_zero, args.sigma_alpha, args.sigma_beta, self.sigma2)
299 |
300 | # Regularization part.
301 | loss3 = loss_func.regularization_loss(
302 | self.rnn_model.parameters(), args.regularization_weight)
303 |
304 | loss = loss1 + loss2 + loss3
305 | loss.backward()
306 | nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.rnn_model.parameters(), args.grad_max_norm)
307 | optimizer.step()
308 | # avoid numerical issues
309 | self.sigma2.data.clamp_(min=1e-6)
310 |
311 | if (np.remainder(self.current_iter, 10) == 0 or
312 | self.current_iter == args.train_iteration - 1):
313 | self.logger.print(
314 | 2,
315 | 'Iter: {:d} \t'
316 | 'Training Loss: {:.4f} \n'
317 | ' Negative Log Likelihood: {:.4f}\t'
318 | 'Sigma2 Prior: {:.4f}\t'
319 | 'Regularization: {:.4f}'.format(
320 | self.current_iter,
321 | float(loss.data),
322 | float(loss1.data),
323 | float(loss2.data),
324 | float(loss3.data)))
325 | yield {'total': loss.data,
326 | 'nll': loss1.data,
327 | 's2p': loss2.data,
328 | 'regular': loss3.data}, self.current_iter
329 | train_loss.append(float(loss1.data)) # only save the likelihood part
330 | self.logger.print(
331 | 1, 'Done training with {} iterations'.format(args.train_iteration))
332 |
333 |
334 | def fit(self, train_sequences, train_cluster_ids, args):
335 | """Fit UISRNN model.
336 |
337 | Args:
338 | train_sequences: Either a list of training sequences, or a single
339 | concatenated training sequence:
340 |
341 | 1. train_sequences is list, and each element is a 2-dim numpy array
342 | of real numbers, of size: `length * D`.
343 | The length varies among different sequences, but the D is the same.
344 | In speaker diarization, each sequence is the sequence of speaker
345 | embeddings of one utterance.
346 | 2. train_sequences is a single concatenated sequence, which is a
347 | 2-dim numpy array of real numbers. See `fit_concatenated()`
348 | for more details.
349 | train_cluster_ids: Ground truth labels for train_sequences:
350 |
351 | 1. if train_sequences is a list, this must also be a list of the same
352 | size, each element being a 1-dim list or numpy array of strings.
353 | 2. if train_sequences is a single concatenated sequence, this
354 | must also be the concatenated 1-dim list or numpy array of strings
355 | args: Training configurations. See `arguments.py` for details.
356 |
357 | Raises:
358 | TypeError: If train_sequences or train_cluster_ids is of wrong type.
359 | """
360 | if isinstance(train_sequences, np.ndarray):
361 | # train_sequences is already the concatenated sequence
362 | if self.estimate_transition_bias:
363 | # see issue #55: https://github.com/google/uis-rnn/issues/55
364 | self.logger.print(
365 | 2,
366 | 'Warning: transition_bias cannot be correctly estimated from a '
367 | 'concatenated sequence; train_sequences will be treated as a '
368 | 'single sequence. This can lead to inaccurate estimation of '
369 | 'transition_bias. Please, consider estimating transition_bias '
370 | 'before concatenating the sequences and passing it as argument.')
371 | train_sequences = [train_sequences]
372 | train_cluster_ids = [train_cluster_ids]
373 | elif isinstance(train_sequences, list):
374 | # train_sequences is a list of un-concatenated sequences
375 | # we will concatenate it later, after estimating transition_bias
376 | pass
377 | else:
378 | raise TypeError('train_sequences must be a list or numpy.ndarray')
379 |
380 | # estimate transition_bias
381 | if self.estimate_transition_bias:
382 | (transition_bias,
383 | transition_bias_denominator) = utils.estimate_transition_bias(
384 | train_cluster_ids)
385 | # set or update transition_bias
386 | if self.transition_bias is None:
387 | self.transition_bias = transition_bias
388 | self.transition_bias_denominator = transition_bias_denominator
389 | else:
390 | self.transition_bias = (
391 | self.transition_bias * self.transition_bias_denominator +
392 | transition_bias * transition_bias_denominator) / (
393 | self.transition_bias_denominator + transition_bias_denominator)
394 | self.transition_bias_denominator += transition_bias_denominator
395 |
396 | # estimate crp_alpha
397 | if self.estimate_crp_alpha:
398 | (crp_alpha,
399 | crp_alpha_denominator) = utils.estimate_crp_alpha(train_cluster_ids)
400 | # set or update crp_alpha
401 | if self.crp_alpha is None:
402 | self.crp_alpha = crp_alpha
403 | self.crp_alpha_denominator = crp_alpha_denominator
404 | else:
405 | self.crp_alpha = (
406 | self.crp_alpha * self.crp_alpha_denominator +
407 | crp_alpha * crp_alpha_denominator) / (
408 | self.crp_alpha_denominator + crp_alpha)
409 | self.crp_alpha_denominator += crp_alpha_denominator
410 |
411 | # concatenate train_sequences
412 | (concatenated_train_sequence,
413 | concatenated_train_cluster_id) = utils.concatenate_training_data(
414 | train_sequences,
415 | train_cluster_ids,
416 | args.enforce_cluster_id_uniqueness,
417 | True)
418 |
419 | return self.fit_concatenated(
420 | concatenated_train_sequence, concatenated_train_cluster_id, args)
421 |
422 | def _update_beam_state(self, beam_state, look_ahead_seq, cluster_seq):
423 | """Update a beam state given a look ahead sequence and known cluster
424 | assignments.
425 |
426 | Args:
427 | beam_state: A BeamState object.
428 | look_ahead_seq: Look ahead sequence, size: look_ahead*D.
429 | look_ahead: number of step to look ahead in the beam search.
430 | D: observation dimension
431 | cluster_seq: Cluster assignment sequence for look_ahead_seq.
432 |
433 | Returns:
434 | new_beam_state: An updated BeamState object.
435 | """
436 |
437 | loss = 0
438 | new_beam_state = BeamState(beam_state)
439 | for sub_idx, cluster in enumerate(cluster_seq):
440 | if cluster > len(new_beam_state.mean_set): # invalid trace
441 | new_beam_state.neg_likelihood = float('inf')
442 | break
443 | elif cluster < len(new_beam_state.mean_set): # existing cluster
444 | last_cluster = new_beam_state.trace[-1]
445 | loss = loss_func.weighted_mse_loss(
446 | input_tensor=torch.squeeze(new_beam_state.mean_set[cluster]),
447 | target_tensor=look_ahead_seq[sub_idx, :],
448 | weight=1 / (2 * self.sigma2)).cpu().detach().numpy()
449 | if cluster == last_cluster:
450 | loss -= np.log(1 - self.transition_bias)
451 | else:
452 | loss -= np.log(self.transition_bias) + np.log(
453 | new_beam_state.block_counts[cluster]) - np.log(
454 | sum(new_beam_state.block_counts) + self.crp_alpha)
455 | # update new mean and new hidden
456 | mean, hidden = self.rnn_model(
457 | look_ahead_seq[sub_idx, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0),
458 | new_beam_state.hidden_set[cluster])
459 | new_beam_state.mean_set[cluster] = (new_beam_state.mean_set[cluster]*(
460 | (np.array(new_beam_state.trace) == cluster).sum() -
461 | 1).astype(float) + mean.clone()) / (
462 | np.array(new_beam_state.trace) == cluster).sum().astype(
463 | float) # use mean to predict
464 | new_beam_state.hidden_set[cluster] = hidden.clone()
465 | if cluster != last_cluster:
466 | new_beam_state.block_counts[cluster] += 1
467 | new_beam_state.trace.append(cluster)
468 | else: # new cluster
469 | init_input = autograd.Variable(
470 | torch.zeros(self.observation_dim)
471 | ).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device)
472 | mean, hidden = self.rnn_model(init_input,
473 | self.rnn_init_hidden)
474 | loss = loss_func.weighted_mse_loss(
475 | input_tensor=torch.squeeze(mean),
476 | target_tensor=look_ahead_seq[sub_idx, :],
477 | weight=1 / (2 * self.sigma2)).cpu().detach().numpy()
478 | loss -= np.log(self.transition_bias) + np.log(
479 | self.crp_alpha) - np.log(
480 | sum(new_beam_state.block_counts) + self.crp_alpha)
481 | # update new min and new hidden
482 | mean, hidden = self.rnn_model(
483 | look_ahead_seq[sub_idx, :].unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0),
484 | hidden)
485 | new_beam_state.append(mean, hidden, cluster)
486 | new_beam_state.neg_likelihood += loss
487 | return new_beam_state
488 |
489 | def _calculate_score(self, beam_state, look_ahead_seq):
490 | """Calculate negative log likelihoods for all possible state allocations
491 | of a look ahead sequence, according to the current beam state.
492 |
493 | Args:
494 | beam_state: A BeamState object.
495 | look_ahead_seq: Look ahead sequence, size: look_ahead*D.
496 | look_ahead: number of step to look ahead in the beam search.
497 | D: observation dimension
498 |
499 | Returns:
500 | beam_score_set: a set of scores for each possible state allocation.
501 | """
502 |
503 | look_ahead, _ = look_ahead_seq.shape
504 | beam_num_clusters = len(beam_state.mean_set)
505 | beam_score_set = float('inf') * np.ones(
506 | beam_num_clusters + 1 + np.arange(look_ahead))
507 | for cluster_seq, _ in np.ndenumerate(beam_score_set):
508 | updated_beam_state = self._update_beam_state(beam_state,
509 | look_ahead_seq, cluster_seq)
510 | beam_score_set[cluster_seq] = updated_beam_state.neg_likelihood
511 | return beam_score_set
512 |
513 | def predict_single(self, test_sequence, args):
514 | """Predict labels for a single test sequence using UISRNN model.
515 |
516 | Args:
517 | test_sequence: the test observation sequence, which is 2-dim numpy array
518 | of real numbers, of size `N * D`.
519 |
520 | - `N`: length of one test utterance.
521 | - `D` : observation dimension.
522 |
523 | For example:
524 | ```
525 | test_sequence =
526 | [[2.2 -1.0 3.0 5.6] --> 1st entry of utterance 'iccc'
527 | [0.5 1.8 -3.2 0.4] --> 2nd entry of utterance 'iccc'
528 | [-2.2 5.0 1.8 3.7] --> 3rd entry of utterance 'iccc'
529 | [-3.8 0.1 1.4 3.3] --> 4th entry of utterance 'iccc'
530 | [0.1 2.7 3.5 -1.7]] --> 5th entry of utterance 'iccc'
531 | ```
532 | Here `N=5`, `D=4`.
533 | args: Inference configurations. See `arguments.py` for details.
534 |
535 | Returns:
536 | predicted_cluster_id: predicted speaker id sequence, which is
537 | an array of integers, of size `N`.
538 | For example, `predicted_cluster_id = [0, 1, 0, 0, 1]`
539 |
540 | Raises:
541 | TypeError: If test_sequence is of wrong type.
542 | ValueError: If test_sequence has wrong dimension.
543 | """
544 | # check type
545 | if (not isinstance(test_sequence, np.ndarray) or
546 | test_sequence.dtype != float):
547 | raise TypeError('test_sequence should be a numpy array of float type.')
548 | # check dimension
549 | if test_sequence.ndim != 2:
550 | raise ValueError('test_sequence must be 2-dim array.')
551 | # check size
552 | test_sequence_length, observation_dim = test_sequence.shape
553 | if observation_dim != self.observation_dim:
554 | raise ValueError('test_sequence does not match the dimension specified '
555 | 'by args.observation_dim.')
556 |
557 | self.rnn_model.eval()
558 | test_sequence = np.tile(test_sequence, (args.test_iteration, 1))
559 | test_sequence = autograd.Variable(
560 | torch.from_numpy(test_sequence).float()).to(self.device)
561 | # bookkeeping for beam search
562 | beam_set = [BeamState()]
563 | for num_iter in np.arange(0, args.test_iteration * test_sequence_length,
564 | args.look_ahead):
565 | max_clusters = max([len(beam_state.mean_set) for beam_state in beam_set])
566 | look_ahead_seq = test_sequence[num_iter: num_iter + args.look_ahead, :]
567 | look_ahead_seq_length = look_ahead_seq.shape[0]
568 | score_set = float('inf') * np.ones(
569 | np.append(
570 | args.beam_size, max_clusters + 1 + np.arange(
571 | look_ahead_seq_length)))
572 | for beam_rank, beam_state in enumerate(beam_set):
573 | beam_score_set = self._calculate_score(beam_state, look_ahead_seq)
574 | score_set[beam_rank, :] = np.pad(
575 | beam_score_set,
576 | np.tile([[0, max_clusters - len(beam_state.mean_set)]],
577 | (look_ahead_seq_length, 1)), 'constant',
578 | constant_values=float('inf'))
579 | # find top scores
580 | score_ranked = np.sort(score_set, axis=None)
581 | score_ranked[score_ranked == float('inf')] = 0
582 | score_ranked = np.trim_zeros(score_ranked)
583 | idx_ranked = np.argsort(score_set, axis=None)
584 | updated_beam_set = []
585 | for new_beam_rank in range(
586 | np.min((len(score_ranked), args.beam_size))):
587 | total_idx = np.unravel_index(idx_ranked[new_beam_rank],
588 | score_set.shape)
589 | prev_beam_rank = total_idx[0]
590 | cluster_seq = total_idx[1:]
591 | updated_beam_state = self._update_beam_state(
592 | beam_set[prev_beam_rank], look_ahead_seq, cluster_seq)
593 | updated_beam_set.append(updated_beam_state)
594 | beam_set = updated_beam_set
595 | predicted_cluster_id = beam_set[0].trace[-test_sequence_length:]
596 | return predicted_cluster_id
597 |
598 | def predict(self, test_sequences, args):
599 | """Predict labels for a single or many test sequences using UISRNN model.
600 |
601 | Args:
602 | test_sequences: Either a list of test sequences, or a single test
603 | sequence. Each test sequence is a 2-dim numpy array
604 | of real numbers. See `predict_single()` for details.
605 | args: Inference configurations. See `arguments.py` for details.
606 |
607 | Returns:
608 | predicted_cluster_ids: Predicted labels for test_sequences.
609 |
610 | 1. if test_sequences is a list, predicted_cluster_ids will be a list
611 | of the same size, where each element being a 1-dim list of strings.
612 | 2. if test_sequences is a single sequence, predicted_cluster_ids will
613 | be a 1-dim list of strings
614 |
615 | Raises:
616 | TypeError: If test_sequences is of wrong type.
617 | """
618 | # check type
619 | if isinstance(test_sequences, np.ndarray):
620 | return self.predict_single(test_sequences, args)
621 | if isinstance(test_sequences, list):
622 | return [self.predict_single(test_sequence, args)
623 | for test_sequence in test_sequences]
624 | raise TypeError('test_sequences should be either a list or numpy array.')
625 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/uisrnn/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2018 Google LLC
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | """Utils for UIS-RNN."""
15 |
16 | import random
17 | import string
18 |
19 | import numpy as np
20 | import torch
21 | from torch import autograd
22 |
23 |
24 | class Logger:
25 | """A class for printing logging information to screen."""
26 |
27 | def __init__(self, verbosity):
28 | self._verbosity = verbosity
29 |
30 | def print(self, level, message):
31 | """Print a message if level is not higher than verbosity.
32 |
33 | Args:
34 | level: the level of this message, smaller value means more important
35 | message: the message to be printed
36 | """
37 | if level <= self._verbosity:
38 | print(message)
39 |
40 |
41 | def generate_random_string(length=6):
42 | """Generate a random string of upper case letters and digits.
43 |
44 | Args:
45 | length: length of the generated string
46 |
47 | Returns:
48 | the generated string
49 | """
50 | return ''.join([
51 | random.choice(string.ascii_uppercase + string.digits)
52 | for _ in range(length)])
53 |
54 |
55 | def enforce_cluster_id_uniqueness(cluster_ids):
56 | """Enforce uniqueness of cluster id across sequences.
57 |
58 | Args:
59 | cluster_ids: a list of 1-dim list/numpy.ndarray of strings
60 |
61 | Returns:
62 | a new list with same length of cluster_ids
63 |
64 | Raises:
65 | TypeError: if cluster_ids or its element has wrong type
66 | """
67 | if not isinstance(cluster_ids, list):
68 | raise TypeError('cluster_ids must be a list')
69 | new_cluster_ids = []
70 | for cluster_id in cluster_ids:
71 | sequence_id = generate_random_string()
72 | if isinstance(cluster_id, np.ndarray):
73 | cluster_id = cluster_id.tolist()
74 | if not isinstance(cluster_id, list):
75 | raise TypeError('Elements of cluster_ids must be list or numpy.ndarray')
76 | new_cluster_id = ['_'.join([sequence_id, s]) for s in cluster_id]
77 | new_cluster_ids.append(new_cluster_id)
78 | return new_cluster_ids
79 |
80 |
81 | def concatenate_training_data(train_sequences, train_cluster_ids,
82 | enforce_uniqueness=True, shuffle=True):
83 | """Concatenate training data.
84 |
85 | Args:
86 | train_sequences: a list of 2-dim numpy arrays to be concatenated
87 | train_cluster_ids: a list of 1-dim list/numpy.ndarray of strings
88 | enforce_uniqueness: a boolean indicated whether we should enfore uniqueness
89 | to train_cluster_ids
90 | shuffle: whether to randomly shuffle input order
91 |
92 | Returns:
93 | concatenated_train_sequence: a 2-dim numpy array
94 | concatenated_train_cluster_id: a list of strings
95 |
96 | Raises:
97 | TypeError: if input has wrong type
98 | ValueError: if sizes/dimensions of input or their elements are incorrect
99 | """
100 | # check input
101 | if not isinstance(train_sequences, list) or not isinstance(
102 | train_cluster_ids, list):
103 | raise TypeError('train_sequences and train_cluster_ids must be lists')
104 | if len(train_sequences) != len(train_cluster_ids):
105 | raise ValueError(
106 | 'train_sequences and train_cluster_ids must have same size')
107 | train_cluster_ids = [
108 | x.tolist() if isinstance(x, np.ndarray) else x
109 | for x in train_cluster_ids]
110 | global_observation_dim = None
111 | for i, (train_sequence, train_cluster_id) in enumerate(
112 | zip(train_sequences, train_cluster_ids)):
113 | train_length, observation_dim = train_sequence.shape
114 | if i == 0:
115 | global_observation_dim = observation_dim
116 | elif global_observation_dim != observation_dim:
117 | raise ValueError(
118 | 'train_sequences must have consistent observation dimension')
119 | if not isinstance(train_cluster_id, list):
120 | raise TypeError(
121 | 'Elements of train_cluster_ids must be list or numpy.ndarray')
122 | if len(train_cluster_id) != train_length:
123 | raise ValueError(
124 | 'Each train_sequence and its train_cluster_id must have same length')
125 |
126 | # enforce uniqueness
127 | if enforce_uniqueness:
128 | train_cluster_ids = enforce_cluster_id_uniqueness(train_cluster_ids)
129 |
130 | # random shuffle
131 | if shuffle:
132 | zipped_input = list(zip(train_sequences, train_cluster_ids))
133 | random.shuffle(zipped_input)
134 | train_sequences, train_cluster_ids = zip(*zipped_input)
135 |
136 | # concatenate
137 | concatenated_train_sequence = np.concatenate(train_sequences, axis=0)
138 | concatenated_train_cluster_id = [x for train_cluster_id in train_cluster_ids
139 | for x in train_cluster_id]
140 | return concatenated_train_sequence, concatenated_train_cluster_id
141 |
142 |
143 | def sample_permuted_segments(index_sequence, number_samples):
144 | """Sample sequences with permuted blocks.
145 |
146 | Args:
147 | index_sequence: (integer array, size: L)
148 | - subsequence index
149 | For example, index_sequence = [1,2,6,10,11,12].
150 | number_samples: (integer)
151 | - number of subsampled block-preserving permuted sequences.
152 | For example, number_samples = 5
153 |
154 | Returns:
155 | sampled_index_sequences: (a list of numpy arrays) - a list of subsampled
156 | block-preserving permuted sequences. For example,
157 | ```
158 | sampled_index_sequences =
159 | [[10,11,12,1,2,6],
160 | [6,1,2,10,11,12],
161 | [1,2,10,11,12,6],
162 | [6,1,2,10,11,12],
163 | [1,2,6,10,11,12]]
164 | ```
165 | The length of "sampled_index_sequences" is "number_samples".
166 | """
167 | segments = []
168 | if len(index_sequence) == 1:
169 | segments.append(index_sequence)
170 | else:
171 | prev = 0
172 | for i in range(len(index_sequence) - 1):
173 | if index_sequence[i + 1] != index_sequence[i] + 1:
174 | segments.append(index_sequence[prev:(i + 1)])
175 | prev = i + 1
176 | if i + 1 == len(index_sequence) - 1:
177 | segments.append(index_sequence[prev:])
178 | # sample permutations
179 | sampled_index_sequences = []
180 | for _ in range(number_samples):
181 | segments_array = []
182 | permutation = np.random.permutation(len(segments))
183 | for permutation_item in permutation:
184 | segments_array.append(segments[permutation_item])
185 | sampled_index_sequences.append(np.concatenate(segments_array))
186 | return sampled_index_sequences
187 |
188 |
189 | def resize_sequence(sequence, cluster_id, num_permutations=None):
190 | """Resize sequences for packing and batching.
191 |
192 | Args:
193 | sequence: (real numpy matrix, size: seq_len*obs_size) - observed sequence
194 | cluster_id: (numpy vector, size: seq_len) - cluster indicator sequence
195 | num_permutations: int - Number of permutations per utterance sampled.
196 |
197 | Returns:
198 | sub_sequences: A list of numpy array, with obsevation vector from the same
199 | cluster in the same list.
200 | seq_lengths: The length of each cluster (+1).
201 | """
202 | # merge sub-sequences that belong to a single cluster to a single sequence
203 | unique_id = np.unique(cluster_id)
204 | sub_sequences = []
205 | seq_lengths = []
206 | if num_permutations and num_permutations > 1:
207 | for i in unique_id:
208 | idx_set = np.where(cluster_id == i)[0]
209 | sampled_idx_sets = sample_permuted_segments(idx_set, num_permutations)
210 | for j in range(num_permutations):
211 | sub_sequences.append(sequence[sampled_idx_sets[j], :])
212 | seq_lengths.append(len(idx_set) + 1)
213 | else:
214 | for i in unique_id:
215 | idx_set = np.where(cluster_id == i)
216 | sub_sequences.append(sequence[idx_set, :][0])
217 | seq_lengths.append(len(idx_set[0]) + 1)
218 | return sub_sequences, seq_lengths
219 |
220 |
221 | def pack_sequence(sub_sequences, seq_lengths, batch_size, observation_dim,
222 | device, loss_samples):
223 | """Pack sequences for training.
224 |
225 | Args:
226 | sub_sequences: A list of numpy array, with obsevation vector from the same
227 | cluster in the same list.
228 | seq_lengths: The length of each cluster (+1).
229 | batch_size: int or None - Run batch learning if batch_size is None. Else,
230 | run online learning with specified batch size.
231 | observation_dim: int - dimension for observation vectors
232 | device: str - Your device. E.g., `cuda:0` or `cpu`.
233 |
234 | Returns:
235 | packed_rnn_input: (PackedSequence object) packed rnn input
236 | rnn_truth: ground truth
237 | """
238 | num_clusters = len(seq_lengths)
239 | sorted_seq_lengths = np.sort(seq_lengths)[::-1]
240 | permute_index = np.argsort(seq_lengths)[::-1]
241 |
242 | if batch_size is None:
243 | rnn_input = np.zeros((sorted_seq_lengths[0],
244 | num_clusters,
245 | observation_dim))
246 | for i in range(num_clusters):
247 | rnn_input[1:sorted_seq_lengths[i], i,
248 | :] = sub_sequences[permute_index[i]]
249 | rnn_input_tensor = autograd.Variable(
250 | torch.from_numpy(rnn_input).float()).to(device)
251 | packed_rnn_input = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence(
252 | rnn_input_tensor, sorted_seq_lengths, batch_first=False)
253 | else:
254 | mini_batch = np.sort(np.random.choice(num_clusters, batch_size))
255 | rnn_input = np.zeros((sorted_seq_lengths[mini_batch[0]],
256 | batch_size,
257 | observation_dim))
258 | for i in range(batch_size):
259 | rnn_input[1:sorted_seq_lengths[mini_batch[i]],
260 | i, :] = sub_sequences[permute_index[mini_batch[i]]]
261 | rnn_input_tensor = autograd.Variable(
262 | torch.from_numpy(rnn_input).float()).to(device)
263 | packed_rnn_input = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pack_padded_sequence(
264 | rnn_input_tensor, sorted_seq_lengths[mini_batch], batch_first=False)
265 | # build ground truth
266 | if loss_samples > 0: #
267 | rnn_truth = np.zeros_like(rnn_input[1:,:,:])
268 | for i in range(batch_size):
269 | for j in range(sorted_seq_lengths[mini_batch[i]] - 1):
270 | samples_idx = np.random.randint(
271 | low=j + 1,
272 | high=sorted_seq_lengths[mini_batch[i]],
273 | size=min(loss_samples, sorted_seq_lengths[mini_batch[i]]-j-1))
274 | rnn_truth[j] = np.mean(rnn_input[samples_idx, i, :], axis=0)
275 | else:
276 | rnn_truth = rnn_input[1:, :, :]
277 | rnn_truth = torch.from_numpy(rnn_truth).float().to(device)
278 | return packed_rnn_input, rnn_truth
279 |
280 |
281 | def output_result(model_args, training_args, test_record):
282 | """Produce a string to summarize the experiment."""
283 | accuracy_array, _ = zip(*test_record)
284 | total_accuracy = np.mean(accuracy_array)
285 | output_string = """
286 | Config:
287 | sigma_alpha: {}
288 | sigma_beta: {}
289 | crp_alpha: {}
290 | learning rate: {}
291 | regularization: {}
292 | batch size: {}
293 |
294 | Performance:
295 | averaged accuracy: {:.6f}
296 | accuracy numbers for all testing sequences:
297 | """.strip().format(
298 | training_args.sigma_alpha,
299 | training_args.sigma_beta,
300 | model_args.crp_alpha,
301 | training_args.learning_rate,
302 | training_args.regularization_weight,
303 | training_args.batch_size,
304 | total_accuracy)
305 | for accuracy in accuracy_array:
306 | output_string += '\n {:.6f}'.format(accuracy)
307 | output_string += '\n' + '=' * 80 + '\n'
308 | filename = 'layer_{}_{}_{:.1f}_result.txt'.format(
309 | model_args.rnn_hidden_size,
310 | model_args.rnn_depth, model_args.rnn_dropout)
311 | with open(filename, 'a') as file_object:
312 | file_object.write(output_string)
313 | return output_string
314 |
315 |
316 | def estimate_transition_bias(cluster_ids, smooth=1):
317 | """Estimate the transition bias.
318 |
319 | Args:
320 | cluster_id: Either a list of cluster indicator sequences, or a single
321 | concatenated sequence. The former is strongly preferred, since the
322 | transition_bias estimated from the latter will be inaccurate.
323 | smooth: int or float - Smoothing coefficient, avoids -inf value in np.log
324 | in the case of a sequence with a single speaker and division by 0 in the
325 | case of empty sequences. Using a small value for smooth decreases the
326 | bias in the calculation of transition_bias but can also lead to underflow
327 | in some remote cases, larger values are safer but less accurate.
328 |
329 | Returns:
330 | bias: Flipping coin head probability.
331 | bias_denominator: The denominator of the bias, used for multiple calls to
332 | fit().
333 | """
334 | transit_num = smooth
335 | bias_denominator = 2 * smooth
336 | for cluster_id_seq in cluster_ids:
337 | for entry in range(len(cluster_id_seq) - 1):
338 | transit_num += (cluster_id_seq[entry] != cluster_id_seq[entry + 1])
339 | bias_denominator += 1
340 | bias = transit_num / bias_denominator
341 | return bias, bias_denominator
342 |
343 |
344 | def estimate_crp_alpha(cluster_ids, smooth=1):
345 | """Estimate the transition bias.
346 |
347 | Args:
348 | cluster_id: Either a list of cluster indicator sequences, or a single
349 | concatenated sequence. The former is strongly preferred, since the
350 | transition_bias estimated from the latter will be inaccurate.
351 | smooth: int or float - Smoothing coefficient, avoids -inf value in np.log
352 | in the case of a sequence with a single speaker and division by 0 in the
353 | case of empty sequences. Using a small value for smooth decreases the
354 | bias in the calculation of transition_bias but can also lead to underflow
355 | in some remote cases, larger values are safer but less accurate.
356 |
357 | Returns:
358 | crp_alpha: alpha parameter of the ddCRP that quentifies the probability
359 | of a new speaker joining the conversation.
360 | crp_alpha_denominator: The denominator of for crp_alpha, used for
361 | multiple calls to fit().
362 | """
363 | speaker_joins = sum(len(set(seq)) - 1 for seq in cluster_ids) + smooth
364 | speaker_changes = 2 * smooth
365 | for cluster_id_seq in cluster_ids:
366 | for entry in range(len(cluster_id_seq) - 1):
367 | speaker_changes += (cluster_id_seq[entry] != cluster_id_seq[entry + 1])
368 | return speaker_joins / speaker_changes, speaker_changes
369 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 14 |
14 |  14 |
14 |  20 |
20 |