 16 |
16 | 🤗 PEFT-MELO
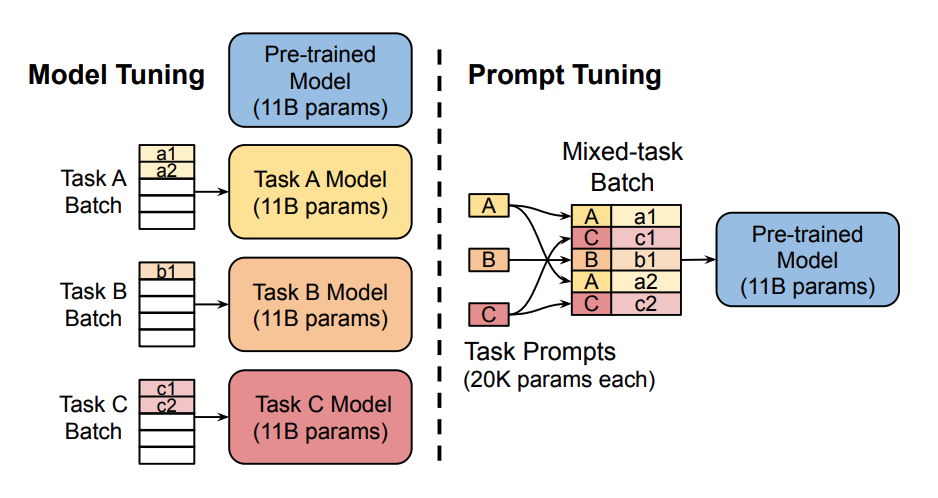
49 | 50 | ``` 51 | cd peft_egg 52 | pip install -e . 53 | ``` 54 | Detailed implementation of MELO is in `./peft_egg/src/tuners/melo.py` 55 | ## Prepare Datasets 56 | The zsRE experiments use data linked by the [MEND](https://github.com/eric-mitchell/mend) repository. Download the data for NQ and zsRE from their Google Drive link and unzip each sub-directory into ./melo/data. SCOTUS and Hallucination data are loaded through huggingface. 57 | 58 | ## Quick Start 59 | The location of inner vector database and dynamic LoRA target modules can be modified in `./melo/model/config` 60 | 61 | ### Editing GPT2-XL on Hallucination with MELO 62 | ``` 63 | cd melo 64 | python run.py +alg=lora +experiment=hallucination +model=gpt2xl 65 | ``` 66 | 67 | 68 | ### Editing BERT on SCOTUS with MELO 69 | ``` 70 | cd melo 71 | python run.py +alg=lora +experiment=scotus +model=scotus-bert 72 | ``` 73 | 74 | ### Editing T5 on zsRE with MELO 75 | ``` 76 | cd melo 77 | python run.py +alg=lora +experiment=qa +model=t5small 78 | ``` 79 | ## Important Tips 80 | * [Datasets](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1HDqh4ofYF7B-YkcU3CNlZMYAOJO0XxwX/view?usp=drive_link) for MELO's experiments can be downloaded through GoogleDrive now. Please extract the files and place them under `melo\data`. 81 | 82 | * The GPT2-XL model we use is fine-tuned in line with the work [GRACE](https://github.com/Thartvigsen/GRACE/blob/728a52ebcd328ddca0bb1ec975e79625eabfab2a/grace/main.py#L83). Please download the checkpoint with the [Google Drive](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1j_DvcUY8goksQVOBt4XqBe7z8fS-0zvI?usp=sharing) link, and place the files under `melo/scr/models--gpt2-xl` 83 | 84 | 85 | * Some [logs](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1UhlY1W8MUmvsxqIXlRFBfxuTXEQG8FJP?usp=sharing) recording the correct training and inference processes are released for checking hyper-parameters. 86 | 87 | * The settings of [torch.optim.lr_scheduler](https://github.com/BruthYU/MELO/blob/51c8322cc06faa2b7665c2d90236f1bd1b8d9575/melo/algs/lora.py#L135) vary on different tasks: 88 | ``` 89 | # T5-Small and T5-Large 90 | scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer,step_size=20,gamma=0.5) 91 | # SCOTUS-BERT and GPT2-XL 92 | scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer,step_size=30,gamma=0.5) 93 | ``` 94 | 95 | 96 | 97 | 98 | ## Acknowledgments 99 | We would like to thank the following individuals and organizations for their contributions to this project: 100 | ``` 101 | Huggingface: for their support of the PEFT community and their development of the PEFT framework (https://github.com/huggingface/peft) 102 | 103 | GRACE: for the development of the open-source library GRACE which inspired our work (https://github.com/Thartvigsen/GRACE) 104 | ``` 105 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /figures/bert.png: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ECNU-ICALK/MELO/ed097eb874aad866eefca881a97dba988247ab9c/figures/bert.png -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /figures/main_00.png: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ECNU-ICALK/MELO/ed097eb874aad866eefca881a97dba988247ab9c/figures/main_00.png -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /figures/table.png: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ECNU-ICALK/MELO/ed097eb874aad866eefca881a97dba988247ab9c/figures/table.png -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/algs/lora.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | from typing import List 2 | from omegaconf import OmegaConf 3 | import torch 4 | import copy 5 | import transformers 6 | import logging 7 | import os 8 | 9 | from torch.nn import Parameter 10 | 11 | from utils import * 12 | 13 | from peft import ( 14 | PeftModel, 15 | prepare_model_for_int8_training, 16 | MeloConfig, 17 | get_peft_model, 18 | get_peft_model_state_dict, 19 | ) 20 | from peft.tuners.melo import LoraLayer, GraceLayer 21 | from hooks import lora_backward_hook 22 | # from models import BertClassifier 23 | LOG = logging.getLogger(__name__) 24 | def translate_tokens(tokens, from_tok, to_tok): 25 | tokens = tokens.masked_fill(tokens == -100, from_tok.pad_token_id) 26 | text = from_tok.batch_decode(tokens, skip_special_tokens=True) 27 | return to_tok(text, return_tensors="pt")["input_ids"].to(tokens.device) 28 | 29 | class LORA(torch.nn.Module): 30 | def __init__(self, model, config, model_tok,scale=None): 31 | super(LORA, self).__init__() 32 | self.config = config 33 | 34 | '''Apply_lora 35 | ''' 36 | r_num = config.grace.num_block * config.grace.num_rank_per_block 37 | self.lora_config = MeloConfig( 38 | r = r_num, 39 | lora_alpha = r_num, 40 | target_modules= list(config.model.target_modules), 41 | lora_dropout = config.lora.lora_dropout, 42 | task_type = config.lora_task_type, 43 | fan_in_fan_out= config.model.fan_in_fan_out, 44 | grace_layer = config.model.grace_layer, 45 | grace_config= OmegaConf.to_object(config.grace) 46 | ) 47 | self.log_dict = {} 48 | 49 | '''Load 50 | ''' 51 | # self.original_model = model 52 | # self.model = model 53 | 54 | if not config.check_dir: 55 | self.model = get_peft_model(model, self.lora_config) 56 | else: 57 | save_path = os.path.join(config.base_dir, "checkpoint", config.check_dir) 58 | self.load_from_checkpoint(save_path) 59 | 60 | self.lora_list = self.named_lora_modules() 61 | self.grace_layer = self.named_grace_layer() 62 | # self.register_lora_backward_hooks(lora_backward_hook) 63 | 64 | '''Load Tokenizer 65 | ''' 66 | self.model_tok = model_tok 67 | self.classifier_tok = transformers.AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(config.lora.cls_name) 68 | 69 | '''Parameters to be optimized 70 | ''' 71 | self.opt_params = self.optim_parameters() 72 | pass 73 | 74 | 75 | def optim_parameters(self): 76 | for name, param in self.model.named_parameters(): 77 | if param.requires_grad==True and 'lora' not in name: 78 | param.requires_grad = False 79 | lora_params = list(filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad, self.model.parameters())) 80 | return lora_params 81 | 82 | 83 | 84 | 85 | #TODO 86 | def load_from_checkpoint(self, save_path): 87 | print(save_path) 88 | 89 | 90 | def save_classifier_weights(self,cls_dir): 91 | if not os.path.exists(cls_dir): 92 | os.makedirs(cls_dir,exist_ok=True) 93 | torch.save(self.classifier.state_dict(),f"{cls_dir}/classifier.pt") 94 | def save_lora_weights(self,lora_dir): 95 | self.model.save_pretrained(lora_dir+"/lora_checkpoint") 96 | 97 | 98 | def reset_lora(self): 99 | for key in self.lora_list: 100 | self.model.get_submodule(key).reset_lora_parameters('default') 101 | 102 | def named_lora_modules(self): 103 | module_list = [key for key,_ in self.model.named_modules()] 104 | lora_list = [] 105 | for key in module_list: 106 | if isinstance(self.model.get_submodule(key),LoraLayer): 107 | lora_list.append(key) 108 | return lora_list 109 | 110 | def named_grace_layer(self) -> str: 111 | module_list = [key for key, _ in self.model.named_modules()] 112 | grace_list = [] 113 | for key in module_list: 114 | if isinstance(self.model.get_submodule(key), GraceLayer): 115 | grace_list.append(key) 116 | assert len(grace_list) == 1, "At Most One Grace Layer" 117 | return grace_list[0] 118 | 119 | def register_lora_backward_hooks(self,backward_hook_fn): 120 | for key in self.lora_list: 121 | self.model.get_submodule(key).register_backward_hook(backward_hook_fn) 122 | 123 | 124 | def disable_melo(self): 125 | self.model.base_model.disable_adapter_layers() 126 | self.model.base_model.disable_grace_layer() 127 | 128 | def enable_melo(self): 129 | self.model.base_model.enable_adapter_layers() 130 | self.model.base_model.enable_grace_layer() 131 | 132 | 133 | def edit(self, tokens): 134 | optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(self.optim_parameters(), self.config.grace.edit_lr) 135 | scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer,step_size=20,gamma=0.5) 136 | # --- pass edit label, training mode, and key_id into GRACE --- 137 | setattr(self.model.get_submodule(self.grace_layer), "training", True) 138 | setattr(self.model.get_submodule(self.grace_layer), "edit_label", tokens["labels"]) 139 | 140 | self.losses = [] 141 | for i in range(self.config.grace.num_iter): 142 | # --- insert iteration into each layer (only initiate keys on first iteration) --- 143 | setattr(self.model.get_submodule(self.grace_layer), "batch_iter", i) 144 | 145 | # --- pass tokens through model (including through the GRACE layer) --- 146 | outputs = self.model.model(**tokens) 147 | loss = outputs.loss 148 | loss.backward() 149 | optimizer.step() 150 | optimizer.zero_grad() 151 | scheduler.step() 152 | self.losses.append(loss.detach().cpu().numpy()) 153 | LOG.info(f'batch loss in iter {i}: {loss.detach().cpu().numpy()}') 154 | self.loss = loss # Log final loss 155 | 156 | setattr(self.model.get_submodule(self.grace_layer), "training", False) 157 | 158 | 159 | 160 | 161 | def generate(self, *args, **kwargs): 162 | return self.model.model.generate(*args, **kwargs) 163 | 164 | def get_VecDB_info(self): 165 | VecDB_logdict = {} 166 | VecDB_logdict["num_cluster"] = len(getattr(self.model.get_submodule(self.grace_layer), "VecDB")) 167 | VecDB_logdict["conflict_num"] = getattr(self.model.get_submodule(self.grace_layer), "VecDB").conflict_num 168 | VecDB_logdict["forget_keys"] = len(getattr(self.model.get_submodule(self.grace_layer), "VecDB").forget_keys) 169 | return VecDB_logdict 170 | 171 | 172 | 173 | 174 | 175 | 176 | 177 | 178 | 179 | 180 | if __name__ == '__main__': 181 | pass 182 | 183 | 184 | 185 | 186 | 187 | 188 | 189 | 190 | 191 | 192 | 193 | 194 | 195 | 196 | 197 | 198 | 199 | 200 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/config/alg/lora.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # @package _global_ 2 | 3 | alg: lora 4 | lr: 1e-4 5 | train_base: False 6 | lr_lr: 1e-4 7 | lora: 8 | cls_name: distilbert-base-cased 9 | cls_class: AutoModel 10 | supervised: true 11 | cos: false 12 | freeze: null 13 | square: true 14 | bound_embeds: false 15 | use_all_negatives: false 16 | freeze_lora: false 17 | dist_heads: 1 18 | cross_attend: false 19 | soft_weighting: false 20 | checkpoint_grad: false 21 | lora_r: 64 22 | lora_alpha: 64 23 | lora_dropout: 0.0 24 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/config/config.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | alg: enn 2 | seed: 0 3 | debug: False 4 | model_save_pt: 5000 5 | edit_bs: 1 6 | silent: False 7 | max_iters: 200100 8 | log_interval: 100 9 | val_interval: 5000 10 | batch_size: 4 11 | val_batch_size: 4 12 | accumulate_bs: 10 13 | cedit: 0.2 14 | cloc: 1.0 15 | cbase: 1.0 16 | val_steps: 500 17 | device: cuda 18 | base_loss: distill 19 | oracle: False 20 | train: True 21 | train_base: True 22 | opt: Adam 23 | single_batch: False 24 | archive: null 25 | grad_clip: 100. 26 | ref: null 27 | early_stop_patience: 40000 28 | early_stop_key: "mixture/acc_val" 29 | dropout: 0.0 30 | tokenizer: null 31 | results_dir: null 32 | no_grad_layers: null 33 | eval_only: False 34 | half: False 35 | save: False 36 | log_errors: False 37 | unlikelihood: True 38 | check_dir: null 39 | batch_round: 10 40 | re_init_model: False 41 | max_n_edits: 5000 42 | 43 | model: 44 | pt: null 45 | 46 | data: 47 | path: null 48 | rephrase: true 49 | zsre_nq: false 50 | zsre_impl: false 51 | zsre_impl_path: ${hydra:runtime.cwd}/data/zsre/impl_{}.json 52 | zsre_yn: false 53 | zsre_yn_path: ${hydra:runtime.cwd}/data/zsre/zsre_yn_{}.txt 54 | zsre_eval_idxs: null 55 | zsre_path: ${hydra:runtime.cwd}/data/zsre/structured_zeroshot-{}-new_annotated_final.jsonl 56 | nq_path: ${hydra:runtime.cwd}/data/nq 57 | wiki_webtext: true 58 | n_edits: 1 59 | hard_neg: false 60 | hard_neg_neighbors: 100 61 | hard_neg_exclude: 25 62 | hard_neg_temp: 0.1 63 | hard_neg_prob: 0.5 64 | flip_inner_outer: false 65 | sent_eval_sample: false 66 | n_outer_max: null 67 | 68 | eval: 69 | verbose: True 70 | log_interval: 100 71 | final_eval: True 72 | 73 | hydra: 74 | run: 75 | dir: ./outputs/${now:%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S_%f${uuid:}} 76 | sweep: 77 | dir: ./outputs/${now:%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S_%f} 78 | subdir: ${hydra.job.num} 79 | 80 | 81 | 82 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/config/experiment/hallucination.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # @package _global_ 2 | task: hallucination 3 | lora_task_type: CAUSAL_LM 4 | grace: 5 | _name: grace 6 | num_iter: 50 7 | init_radius: 0.5 8 | dist_fn: euc # euc, mmd, cos 9 | val_init: cold # cold, warm 10 | val_train: sgd # sgd, pert 11 | val_reg: None # early 12 | reg: early_stop # early_stop 13 | replacement: replace_prompt # replace_last, replace_all, replace_prompt 14 | expand_mode: moving_avg # , moving_avg, decay 15 | num_pert: 8 # only matters when using perturbation training 16 | key_id: -1 17 | num_edit_per_block: 4 18 | num_block: 350 19 | num_rank_per_block: 2 20 | metric_period: 400 21 | edit_lr: 1e-3 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/config/experiment/qa.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # @package _global_ 2 | task: qa 3 | lora_task_type: SEQ_2_SEQ_LM 4 | grace: 5 | _name: grace 6 | num_iter: 50 7 | init_radius: 75 8 | dist_fn: euc # euc, mmd, cos 9 | val_init: cold # cold, warm 10 | val_train: sgd # sgd, pert 11 | val_reg: None # early 12 | reg: early_stop # early_stop 13 | replacement: replace_prompt # replace_last, replace_all, replace_prompt 14 | expand_mode: moving_avg # , moving_avg, decay 15 | num_pert: 8 # only matters when using perturbation training 16 | key_id: -1 17 | num_edit_per_block: 100 18 | num_block: 20 19 | num_rank_per_block: 2 20 | metric_period: 200 21 | edit_lr: 1e-2 22 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/config/experiment/scotus.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # @package _global_ 2 | task: scotus 3 | lora_task_type: SEQ_CLS 4 | grace: 5 | _name: grace 6 | num_iter: 50 7 | init_radius: 0.1 8 | dist_fn: euc # euc, mmd, cos 9 | val_init: cold # cold, warm 10 | val_train: sgd # sgd, pert 11 | val_reg: None # early 12 | reg: early_stop # early_stop 13 | replacement: replace_prompt # replace_last, replace_all, replace_prompt 14 | expand_mode: moving_avg # , moving_avg, decay 15 | num_pert: 8 # only matters when using perturbation training 16 | key_id: -1 17 | num_edit_per_block: 50 18 | num_block: 100 19 | num_rank_per_block: 4 20 | metric_period: 200 21 | edit_lr: 1e-2 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/config/model/gpt2xl.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: gpt2-xl 2 | class_name: GPT2LMHeadModel 3 | tokenizer_class: GPT2TokenizerFast 4 | tokenizer_name: gpt2-xl 5 | 6 | fan_in_fan_out: True 7 | target_modules: 8 | - transformer.h.36.mlp.c_fc 9 | - transformer.h.37.mlp.c_fc 10 | 11 | 12 | #pt: null 13 | pt: /home/yu/ECNU/MELO/melo/checkpoint # set this to 'hallucination' inside your checkpoint directory 14 | #model.base_model.h[35] 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | grace_layer: transformer.h.35.mlp.c_fc -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/config/model/scotus-bert.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: tomh/scotus-bert 2 | class_name: AutoModelForSequenceClassification 3 | tokenizer_class: AutoTokenizer 4 | tokenizer_name: bert-base-cased 5 | fan_in_fan_out: False 6 | target_modules: 7 | - bert.encoder.layer.9.output.dense 8 | - bert.encoder.layer.10.output.dense 9 | - bert.encoder.layer.11.output.dense 10 | grace_layer: bert.encoder.layer.4.output.dense 11 | 12 | pt: null -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/config/model/t5large.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: google/t5-large-ssm-nq 2 | class_name: AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM 3 | tokenizer_class: AutoTokenizer 4 | tokenizer_name: google/t5-large-ssm-nq 5 | fan_in_fan_out: False 6 | inner_params: 7 | - encoder.block.22.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi.weight 8 | - encoder.block.22.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo.weight 9 | - encoder.block.23.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi.weight 10 | - encoder.block.23.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo.weight 11 | - decoder.block.22.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wi.weight 12 | - decoder.block.22.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wo.weight 13 | - decoder.block.23.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wi.weight 14 | - decoder.block.23.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wo.weight 15 | 16 | 17 | target_modules: 18 | - encoder.block.22.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi 19 | - encoder.block.22.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo 20 | - encoder.block.23.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi 21 | - encoder.block.23.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo 22 | - decoder.block.22.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wi 23 | - decoder.block.22.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wo 24 | - decoder.block.23.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wi 25 | - decoder.block.23.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wo 26 | 27 | grace_layer: encoder.block.12.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo 28 | #alg.model.base_model.model.encoder.block[4].layer[1].DenseReluDense.wo 29 | #self.model.model.encoder.block[22].layer[1].DenseReluDense.wo.lora_B['default'][4:8] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/config/model/t5small.yaml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | name: google/t5-small-ssm-nq 2 | class_name: AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM 3 | tokenizer_class: AutoTokenizer 4 | tokenizer_name: google/t5-small-ssm-nq 5 | fan_in_fan_out: False 6 | target_modules: 7 | - encoder.block.5.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi 8 | - encoder.block.5.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo 9 | - decoder.block.5.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wi 10 | - decoder.block.5.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wo 11 | - encoder.block.6.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wi 12 | - encoder.block.6.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo 13 | - decoder.block.6.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wi 14 | - decoder.block.6.layer.2.DenseReluDense.wo 15 | 16 | pt: null 17 | 18 | grace_layer: encoder.block.4.layer.1.DenseReluDense.wo -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/grammar.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | import torch 2 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/hooks.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | def lora_backward_hook(lora_module, grad_in, grad_out): 2 | print("Module_name: ", lora_module) 3 | print("grad_in[0]_shape: ",grad_in[0].shape) 4 | print("grad_in[0]: ", grad_in[0]) 5 | print("grad_out[0]_shape: ", grad_out[0].shape) 6 | print("grad_out[0]: ", grad_out[0]) 7 | print("-------------------------------") -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/main.sh: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | +alg=lora +experiment=qa +model=t5small 2 | +alg=lora +experiment=hallucination +model=gpt2xl 3 | +alg=lora +experiment=scotus +model=scotus-bert 4 | 5 | 6 | CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=3 python few_shot_run.py +alg=lora +experiment=fnli +model=bert-base batch_size=10 val_batch_size=10 lora.cross_attend=True 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=3 python few_shot_run.py +alg=lora +experiment=qa +model=t5large batch_size=10 val_batch_size=10 data.zsre_impl=false data.zsre_yn=false data.hard_neg=false -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/metrics.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | import torch 2 | from utils import * 3 | import logging 4 | LOG = logging.getLogger(__name__) 5 | 6 | 7 | # DEPRECATED 8 | def sent_success(pre_edit_probs, post_edit_probs, pos_mask, eps=torch.finfo(torch.float32).eps, batch_size=20): 9 | assert False, "No longer used" 10 | # content_score = post_edit_probs[pos_mask].prod() ** (1/pos_mask.sum()) / (pre_edit_probs[pos_mask]. + eps) 11 | post_pos_avg = post_edit_probs[pos_mask].prod() ** (1 / pos_mask.sum()) 12 | pre_pos_avg = pre_edit_probs[pos_mask].prod() ** (1 / pos_mask.sum()) 13 | content_score = post_pos_avg / (pre_pos_avg + eps) 14 | z_content = min(1., content_score) 15 | 16 | # compute z_sent through a weighting objective 17 | # normalized_probs = post_edit_probs / (post_edit_probs.sum() + eps) 18 | # balancing_factor = 0.5 * ((~pos_mask).float().sum() / pos_mask.float().sum() + 1) 19 | # z_sent_weight = balancing_factor * normalized_probs.dot(pos_mask.float()) 20 | post_neg_avg = post_edit_probs[~pos_mask].prod() ** (1 / (~pos_mask).sum()) 21 | neg_over_pos = post_neg_avg / (eps + post_pos_avg) 22 | z_sent_weight = 1 / (1 + neg_over_pos) 23 | 24 | # compute z_sent through a ranking objective 25 | batch_mask = pos_mask.view(-1, batch_size).long() 26 | sort_idxs = post_edit_probs.view(-1, batch_size).sort(-1, descending=True).indices 27 | ranked_mask = batch_mask.gather(1, sort_idxs) 28 | true_mask = batch_mask.sort(-1, descending=True).values 29 | z_sent_rank = (ranked_mask == true_mask).float().mean() 30 | 31 | # compute the final success scores 32 | weight_success = (z_content * z_sent_weight) ** 0.5 33 | rank_success = (z_content * z_sent_rank) ** 0.5 34 | 35 | correct_probs = post_edit_probs[pos_mask].mean() 36 | wrong_probs = post_edit_probs[~pos_mask].mean() 37 | 38 | return { 39 | "acc_weight": weight_success, 40 | "acc_rank": rank_success, 41 | "rank_score": z_sent_rank, 42 | "weight_score": z_sent_weight, 43 | "content_score": content_score, 44 | "post_edit_probs": post_edit_probs.sum(), 45 | "pre_edit_probs": pre_edit_probs.sum(), 46 | "correct_probs": correct_probs, 47 | "wrong_probs": wrong_probs 48 | } 49 | 50 | 51 | 52 | # For zsRE and F-NLI 53 | def retain_rate(pre_logits, post_logits, mask=None): 54 | if pre_logits.shape[-1] == 1: 55 | pre_logits = pre_logits.squeeze(-1) 56 | if post_logits.shape[-1] == 1: 57 | post_logits = post_logits.squeeze(-1) 58 | 59 | assert pre_logits.shape == post_logits.shape 60 | assert pre_logits.shape[0] == mask.shape[0] 61 | 62 | if pre_logits.dim() == 1: 63 | # binary classification 64 | pre_preds = pre_logits > 0 65 | post_preds = post_logits > 0 66 | retain = (pre_preds == post_preds).float().mean() 67 | elif pre_logits.dim() == 3: 68 | # sequence modeling 69 | pre_preds = pre_logits.argmax(-1) 70 | post_preds = post_logits.argmax(-1) 71 | match = (pre_preds == post_preds) * mask 72 | retain = (match.sum(-1) == mask.sum(-1)).float().mean() 73 | else: 74 | raise NotImplementedError 75 | 76 | return retain.item() 77 | 78 | 79 | def is_acc_error(model, tokens): 80 | # Check whether or not the model's prediction for a batch element is correct 81 | labels = tokens["labels"] 82 | logits = model(**tokens).logits 83 | probs = torch.softmax(logits, -1).squeeze() 84 | argmaxs = torch.argmax(probs, dim=-1).squeeze() 85 | return labels != argmaxs 86 | 87 | 88 | def Accuracy(alg, tokens): 89 | labels = tokens["labels"] 90 | new_tokens = {f"{k}": v for k, v in tokens.items() if k != "labels"} 91 | logits = alg.model(**new_tokens).logits 92 | probs = torch.softmax(logits, -1).squeeze() 93 | argmaxs = torch.argmax(probs, dim=-1).squeeze() 94 | return (labels == argmaxs).float().mean() 95 | 96 | 97 | def is_qa_error(model, tokens): 98 | preds = model.generate(tokens["input_ids"], max_length=20).squeeze() # Run model to get its predictions 99 | labels = tokens["labels"] # [tokens["labels"] != -100] 100 | 101 | if (len(preds) != len(labels)) or ((preds == labels).sum() != len(preds)): 102 | return True 103 | else: 104 | return False 105 | 106 | 107 | def PPL(alg, batch): 108 | input_ids = batch["input_ids"][:, :1024] # .to(device) 109 | if "labels" not in batch: 110 | batch["labels"] = batch["input_ids"][:, :1024].clone() 111 | else: 112 | batch["labels"] = batch["labels"][:, :1024].clone() 113 | 114 | with torch.no_grad(): 115 | #outputs = alg.model.model(input_ids=input_ids, labels=target_ids) 116 | outputs = alg.model(**batch) 117 | nll = outputs.loss 118 | 119 | ppl = torch.exp(nll) # .clip(0, 100) 120 | return ppl 121 | 122 | 123 | 124 | def F1_ACC(alg, batch): 125 | try: 126 | preds = alg.generate(batch["input_ids"], max_length=20).squeeze() 127 | f1 = F1(preds, batch, alg.model_tok) 128 | acc = ACC(preds, batch, alg.model_tok) 129 | return f1, acc 130 | except Exception as e: 131 | raise e 132 | 133 | def F1(preds, batch, tok): 134 | try: 135 | f1_list = [] 136 | for p, g in zip(preds,batch["labels"]): 137 | p = p[p != tok.pad_token_id].cpu().squeeze() 138 | g = g[g != -100].cpu().squeeze() # -100 might be nonsense 139 | num_same = len(np.intersect1d(p, g)) 140 | len_pred = len(p) 141 | len_gold = len(g) 142 | precision = num_same / len_pred 143 | recall = 1.0 * num_same / len_gold 144 | f1 = (2 * precision * recall) / (precision + recall) 145 | f1_list.append(f1) 146 | except: 147 | return 0. 148 | 149 | return sum(f1_list) / len(f1_list) 150 | 151 | 152 | def ACC(preds, batch, tok): 153 | decode_preds = tok.batch_decode(preds,skip_special_tokens=True) 154 | gold_labels = batch['labels'] 155 | gold_labels = gold_labels.masked_fill(gold_labels == -100,tok.pad_token_id) 156 | decode_labels = tok.batch_decode(gold_labels,skip_special_tokens=True) 157 | assert len(decode_labels) == len(decode_preds), "Lengths of decode_preds and decode_labels should be the same" 158 | count = 0. 159 | for pred,label in zip(decode_preds, decode_labels): 160 | if pred == label: 161 | count = count + 1 162 | return count/len(decode_preds) 163 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/models.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | import transformers 2 | import torch 3 | import torch.nn as nn 4 | import re 5 | import logging 6 | # from torch.nn import FixableDropout 7 | from utils import scr 8 | 9 | 10 | LOG = logging.getLogger(__name__) 11 | 12 | 13 | class CastModule(nn.Module): 14 | def __init__(self, module: nn.Module, in_cast: torch.dtype = torch.float32, out_cast: torch.dtype = None): 15 | super().__init__() 16 | 17 | self.underlying = module 18 | self.in_cast = in_cast 19 | self.out_cast = out_cast 20 | 21 | def cast(self, obj, dtype): 22 | if dtype is None: 23 | return obj 24 | 25 | if isinstance(obj, torch.Tensor): 26 | return obj.to(dtype) 27 | else: 28 | return obj 29 | 30 | def forward(self, *args, **kwargs): 31 | args = tuple(self.cast(a, self.in_cast) for a in args) 32 | kwargs = {k: self.cast(v, self.in_cast) for k, v in kwargs.items()} 33 | outputs = self.underlying(*args, **kwargs) 34 | if isinstance(outputs, torch.Tensor): 35 | outputs = self.cast(outputs, self.out_cast) 36 | elif isinstance(outputs, tuple): 37 | outputs = tuple(self.cast(o, self.out_cast) for o in outputs) 38 | else: 39 | raise RuntimeError(f"Not sure how to cast type {type(outputs)}") 40 | return outputs 41 | 42 | def extra_repr(self): 43 | return f"in_cast: {self.in_cast}\nout_cast: {self.out_cast}" 44 | 45 | 46 | class BertClassifier(torch.nn.Module): 47 | def __init__(self, model_name, hidden_dim=768): 48 | super().__init__() 49 | if model_name.startswith("bert"): 50 | LOG.info(f"Loading model class {model_name}, cache dir {scr()}") 51 | self.model = transformers.BertModel.from_pretrained(model_name, cache_dir=scr()) 52 | else: 53 | self.model = transformers.AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name, cache_dir=scr()) 54 | self.classifier = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_dim, 1) 55 | 56 | @property 57 | def config(self): 58 | return self.model.config 59 | 60 | def forward(self, *args, **kwargs): 61 | filtered_kwargs = {k: v for k, v in kwargs.items() if k != "labels"} 62 | model_output = self.model(*args, **filtered_kwargs) 63 | if "pooler_output" in model_output.keys(): 64 | pred = self.classifier(model_output.pooler_output) 65 | else: 66 | pred = self.classifier(model_output.last_hidden_state[:, 0]) 67 | 68 | if "output_hidden_states" in kwargs and kwargs["output_hidden_states"]: 69 | last_hidden_state = model_output.last_hidden_state 70 | return pred, last_hidden_state 71 | else: 72 | return pred 73 | 74 | 75 | 76 | def get_hf_model(config): 77 | ModelClass = getattr(transformers, config.model.class_name) 78 | LOG.info(f"Loading model class {ModelClass} with name {config.model.name} from cache dir {scr()}") 79 | if config.model.pt is None: 80 | model = ModelClass.from_pretrained(config.model.name, cache_dir=scr()) 81 | elif config.re_init_model: 82 | print("Downloading untrained model.") 83 | model = ModelClass.from_pretrained(config.model.name) 84 | else: 85 | try: 86 | # try to load specified model from local dir 87 | model = ModelClass.from_pretrained(config.model.pt) 88 | print(f"Loaded model: {config.model.pt}") 89 | except: 90 | print("Couldn't load model: {config.model.pt}. Downloading new model.") 91 | model = ModelClass.from_pretrained(config.model.name, cache_dir=scr()) 92 | 93 | 94 | if config.dropout is not None: 95 | n_reset = 0 96 | for m in model.modules(): 97 | if isinstance(m, nn.Dropout): 98 | m.p = config.dropout 99 | n_reset += 1 100 | 101 | if hasattr(m, "dropout"): # Requires for BART, which uses F.dropout 102 | if isinstance(m.dropout, float): 103 | m.dropout = config.dropout 104 | n_reset += 1 105 | 106 | if hasattr(m, "activation_dropout"): # Requires for BART, which uses F.dropout 107 | if isinstance(m.activation_dropout, float): 108 | m.activation_dropout = config.dropout 109 | n_reset += 1 110 | 111 | LOG.info(f"Set {n_reset} dropout modules to p={config.dropout}") 112 | return model 113 | 114 | 115 | 116 | def get_tokenizer(config): 117 | tok_name = config.model.tokenizer_name if config.model.tokenizer_name is not None else config.model.name 118 | tokenizer = getattr(transformers, config.model.tokenizer_class).from_pretrained(tok_name, cache_dir=scr()) 119 | if not tokenizer.pad_token: 120 | tokenizer.pad_token = tokenizer.eos_token 121 | return tokenizer 122 | 123 | def get_processor(config): 124 | processor_name = config.model.processor_name if config.model.processor_name is not None else config.model.name 125 | processor = getattr(transformers, config.model.processor_class).from_pretrained(processor_name, cache_dir = scr()) 126 | return processor 127 | 128 | 129 | if __name__ == '__main__': 130 | m = BertClassifier("bert-base-uncased") 131 | m(torch.arange(5)[None, :]) 132 | import pdb; pdb.set_trace() 133 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/run.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | import copy 2 | import random 3 | import importlib 4 | import logging 5 | from time import time 6 | import hydra 7 | from omegaconf import OmegaConf,open_dict 8 | import numpy as np 9 | import torch 10 | from utils import * 11 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader 12 | from tqdm import tqdm 13 | import pickle 14 | import models 15 | from trainer import zsre_trainer, hallucination_trainer, scotus_trainer 16 | #TODO 17 | #SUPPORT MELO CONV1D fan_in_fan_out 18 | 19 | # os.environ['http_proxy'] = '127.0.0.1:7890' 20 | # os.environ['https_proxy'] = '127.0.0.1:7890' 21 | OmegaConf.register_new_resolver("uuid", lambda: uuid()) 22 | LOG = logging.getLogger(__name__) 23 | @hydra.main(config_path='config', config_name='config') 24 | def run(config): 25 | grace_config_keys = ['edit_lr','init_radius','expand_mode','key_id','num_edit_per_block','num_block','num_rank_per_block'] 26 | model_config_keys = ['target_modules','grace_layer'] 27 | GRACE_CONFIG = dict(config.grace) 28 | MODEL_CONFIG = dict(config.model) 29 | 30 | for k in grace_config_keys: 31 | LOG.info(f'[-GRACE CONFIG-] {k}: {GRACE_CONFIG[k]}') 32 | for k in model_config_keys: 33 | LOG.info(f'[-MODEL CONFIG-] {k}: {MODEL_CONFIG[k]}') 34 | 35 | base_dir = hydra.utils.get_original_cwd() 36 | with open_dict(config): 37 | config.base_dir = base_dir 38 | 39 | random.seed(config.seed) 40 | np.random.seed(config.seed) 41 | torch.manual_seed(config.seed) 42 | 43 | if config.task == "qa" or config.task == "zsre": 44 | model = models.get_hf_model(config) 45 | elif config.task == "hallucination": 46 | model = models.get_hf_model(config) 47 | elif config.task == "scotus": 48 | model = models.get_hf_model(config) 49 | else: 50 | print(f"{config.task} task not found") 51 | 52 | 53 | 54 | model.to(config.device) 55 | tokenizer = models.get_tokenizer(config) 56 | 57 | 58 | ''' 59 | Load Dataset 60 | ''' 61 | if config.task == "qa" or config.task == "zsre": 62 | from dataset import NQ, zsRE, zsRE_balanced 63 | from metrics import F1_ACC, is_qa_error 64 | upstream = NQ() 65 | edits = zsRE_balanced(split="edit", n_edits=1000) 66 | edit_holdouts = zsRE_balanced(split="holdout", n_edits=1000) 67 | 68 | '''Get Loaders 69 | ''' 70 | batch_size = config.grace.num_edit_per_block 71 | edit_loader = DataLoader(edits, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True) 72 | edit_holdout_loader = DataLoader(edit_holdouts, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) 73 | upstream_loader = DataLoader(upstream, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) 74 | hold_out = 0 75 | '''Define Metrics 76 | ''' 77 | metric = F1_ACC # Measure QA F1 78 | is_error = is_qa_error 79 | tokenize = tokenize_qa 80 | 81 | elif config.task == "hallucination": 82 | from dataset import Hallucination, WebText10k 83 | from metrics import PPL 84 | upstream = WebText10k() 85 | edits = Hallucination(split="edit") 86 | accurate_dataset = Hallucination(split="accurate") 87 | 88 | '''Get Loaders 89 | ''' 90 | batch_size = config.grace.num_edit_per_block 91 | edit_loader = DataLoader(edits, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) 92 | accurate_loader = DataLoader(accurate_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) 93 | upstream_loader = DataLoader(upstream, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) 94 | '''Define Metrics 95 | ''' 96 | metric = PPL # Measure QA F1 97 | tokenize = tokenize_gpt 98 | elif config.task == 'scotus': 99 | from dataset import SCOTUS 100 | from metrics import Accuracy 101 | upstream = SCOTUS("train") 102 | edits = SCOTUS("edit") 103 | 104 | '''Get Loaders 105 | ''' 106 | batch_size = config.grace.num_edit_per_block 107 | edit_loader = DataLoader(edits, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) 108 | upstream_loader = DataLoader(upstream, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False) 109 | '''Define Metrics 110 | ''' 111 | metric = Accuracy 112 | tokenize = tokenize_clf 113 | else: 114 | print(f"{config.task} task not found") 115 | 116 | alg_module = importlib.import_module(f'algs.{config.alg}') 117 | AlgClass = getattr(alg_module,config.alg.upper()) 118 | alg = AlgClass(model,config,tokenizer) 119 | alg.to(config.device) 120 | 121 | # Trainer 122 | if config.task == "qa" or config.task == "zsre": 123 | trainer = zsre_trainer(config,alg,tokenize,metric,edit_loader,upstream_loader,edit_holdout_loader) 124 | elif config.task == "hallucination": 125 | trainer = hallucination_trainer(config,alg,tokenize,metric,edit_loader,upstream_loader,accurate_loader) 126 | elif config.task == "scotus": 127 | trainer = scotus_trainer(config,alg,tokenize,metric,edit_loader,upstream_loader) 128 | 129 | # trainer.pre_editing_analyse() 130 | torch.cuda.empty_cache() 131 | trainer.run_edit() 132 | 133 | 134 | if __name__ == '__main__': 135 | run() -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/utils.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | import transformers 2 | import torch 3 | import os 4 | import numpy as np 5 | import datetime 6 | import struct 7 | from torch.nn.utils.rnn import pad_sequence 8 | import torch.nn.functional as F 9 | import wandb 10 | import hydra 11 | 12 | def get_inner_params(named_parameters, inner_names): 13 | param_dict = dict(named_parameters) 14 | return [(n, param_dict[n]) for n in inner_names] 15 | 16 | 17 | def param_subset(named_parameters, inner_names): 18 | param_dict = dict(named_parameters) 19 | return [param_dict[n] for n in inner_names] 20 | 21 | 22 | def parent_module(model, pname): 23 | components = pname.split('.') 24 | parent = model 25 | 26 | for component in components[:-1]: 27 | if hasattr(parent, component): 28 | parent = getattr(parent, component) 29 | elif component.isdigit(): 30 | parent = parent[int(component)] 31 | else: 32 | raise RuntimeError(f"Couldn't find child module {component}") 33 | 34 | if not hasattr(parent, components[-1]): 35 | raise RuntimeError(f"Couldn't find child module {components[-1]}") 36 | 37 | return parent 38 | 39 | 40 | def uuid(digits=4): 41 | if not hasattr(uuid, "uuid_value"): 42 | uuid.uuid_value = struct.unpack('I', os.urandom(4))[0] % int(10 ** digits) 43 | 44 | return uuid.uuid_value 45 | 46 | def scr(): 47 | base_dir = hydra.utils.get_original_cwd() 48 | if os.path.exists(os.path.join(base_dir,"scr-ssd")): 49 | scr_dir = os.path.join(base_dir,"scr-ssd") 50 | else: 51 | scr_dir = os.path.join(base_dir,"scr") 52 | 53 | if not os.path.exists(scr_dir): 54 | os.makedirs(scr_dir) 55 | 56 | return scr_dir 57 | def ckpt_dir(): 58 | """returns the directory in which to store model checkpoints""" 59 | path = "./ckpts/" 60 | if not os.path.exists(path): 61 | os.makedirs(path) 62 | return path 63 | 64 | 65 | def brackets_to_periods(name): 66 | return name.replace("[", ".").replace("]", "") 67 | 68 | 69 | def get_params(model): 70 | return model.state_dict() 71 | 72 | 73 | def get_shape(p, model): 74 | # We need to flip the shapes since OpenAI gpt2 uses convs instead of linear 75 | return p.shape if isinstance(model, transformers.GPT2LMHeadModel) else (p.shape[1], p.shape[0]) 76 | 77 | 78 | def get_logits(x): 79 | return x.logits if hasattr(x, "logits") else x 80 | 81 | 82 | def tokenize_gpt(batch, tokenizer, device, test=False): 83 | prompt, label = batch["text"], batch["labels"] 84 | mask_token = -100 # ignore_index of CrossEntropyLoss 85 | if test or not label: 86 | tokens = tokenizer(list(prompt), return_tensors="pt", padding=True, truncation=True) 87 | tokens["labels"] = tokens["input_ids"].clone() 88 | tokens["labels"][tokens["input_ids"] == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = mask_token 89 | 90 | else: 91 | full_prompt = [f"{p} {l} <|endoftext|>" for p, l in zip(prompt, label)] 92 | # full_prompt = [f"{p} {l} {tokenizer.eos_token}" for p, l in zip(prompt, label)] 93 | prompt_ids = tokenizer(list(prompt), return_tensors="pt", padding=True, truncation=True)["input_ids"] 94 | num_prompt_toks = [int((i != tokenizer.pad_token_id).sum()) for i in prompt_ids] 95 | tokens = tokenizer(full_prompt, return_tensors="pt", padding=True, truncation=True) 96 | tokens["labels"] = tokens["input_ids"].clone() 97 | for i in range(len(prompt)): 98 | tokens["labels"][i][:num_prompt_toks[i]] = mask_token 99 | 100 | tokens["labels"][tokens["input_ids"] == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = mask_token # What is this doing? 101 | 102 | tokens = {f"{k1}": v1.to(device) for k1, v1 in tokens.items()} 103 | return tokens 104 | 105 | 106 | def tokenize_qa(batch, tokenizer, device, **kwargs): 107 | input_sequences, output_sequences = batch["text"], batch["labels"] 108 | 109 | input_encoding = tokenizer( 110 | list(input_sequences), 111 | padding="longest", 112 | max_length=20, 113 | truncation=True, 114 | return_tensors="pt", 115 | ) 116 | 117 | input_ids, attention_mask = input_encoding.input_ids, input_encoding.attention_mask 118 | 119 | target_encoding = tokenizer( 120 | list(output_sequences), 121 | padding="longest", 122 | max_length=20, 123 | truncation=True, 124 | return_tensors="pt", 125 | ) 126 | 127 | labels = target_encoding.input_ids 128 | labels[labels == tokenizer.pad_token_id] = -100 129 | 130 | tokens = { 131 | "input_ids": input_ids, 132 | "attention_mask": attention_mask, 133 | "labels": labels 134 | } 135 | 136 | tokens = {f"{k1}": v1.to(device) for k1, v1 in tokens.items()} 137 | return tokens 138 | 139 | 140 | def tokenize_clf(batch, tokenizer, device, **kwargs): 141 | input_sequences, labels = batch["text"], batch["labels"] 142 | 143 | tokens = tokenizer(input_sequences, truncation=True, padding="max_length", return_tensors="pt") 144 | tokens["labels"] = labels 145 | tokens = {f"{k1}": v1.to(device) for k1, v1 in tokens.items()} 146 | return tokens 147 | 148 | 149 | 150 | 151 | 152 | 153 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /melo/wiki_bio_concepts.txt: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | john russell reynolds 2 | matthew aylmer , 1st baron aylmer 3 | rick mahler 4 | james blair south carolina 5 | tim finchem 6 | akila dananjaya 7 | derek king australian footballer 8 | wilhelm windelband 9 | freddie frith 10 | marshall manesh 11 | eleanor arnason 12 | carter harrison , sr. . 13 | winnebago deal 14 | noel hogan 15 | dawn landes 16 | bill quinn 17 | carol huston 18 | gia carangi 19 | nigel milsom 20 | rod morgenstein 21 | terry alderman 22 | frank a. mclain 23 | rich williams 24 | torry castellano 25 | albert i , margrave of meissen 26 | sirið stenberg 27 | thomas harriot 28 | tadeusz szeligowski 29 | gordon strachan 30 | steven threet 31 | archie baird 32 | peter breen politician 33 | adja yunkers 34 | the blood divine 35 | king zhuang of chu 36 | william j. flanagan , jr. 37 | k. s. manilal 38 | jeannine riley 39 | seyi shay 40 | hilda kuper 41 | stuart scott 42 | mark fite 43 | philippe dodard 44 | rudy fernandez labor leader 45 | mackenzie caquatto 46 | twila shively 47 | lionel aldridge 48 | irena sendler 49 | ronnie barker 50 | honoré iii , prince of monaco 51 | emily gielnik 52 | choi jae-bong 53 | tom izzo 54 | tommy nutter 55 | jearl walker 56 | steve ridzik 57 | achille-ferdinand carrier 58 | tera van beilen 59 | harry kennedy 60 | david kappos 61 | pattern is movement 62 | kévin gameiro 63 | lee hsien loong 64 | lucien turcotte pacaud 65 | makiko esumi 66 | kate deines 67 | c. v. ananda bose 68 | anthony dimond 69 | honoré iv , prince of monaco 70 | tristan rogers 71 | john burnham cricketer 72 | nate saint 73 | thutmose iii 74 | john loder sound engineer 75 | a. p. j. abdul kalam 76 | john reed , jr. . 77 | paul elliott politician 78 | moisés kaufman 79 | robert holgate 80 | duncan mackay footballer 81 | saul david 82 | tomasz lis 83 | véra korène 84 | nodar kumaritashvili 85 | leana de bruin 86 | alfred fischer ss officer 87 | kermit davis 88 | daniel ménard 89 | modibo adama 90 | bert deacon 91 | mushahid hussain syed 92 | kia joorabchian 93 | vitaliano brancati 94 | emperor wenxuan of northern qi 95 | johan christian dahl 96 | steve cooper footballer , born 1964 97 | ernest miller cinematographer 98 | david king australian rules footballer 99 | danny smith coach 100 | hope cooke 101 | tathagata satpathy 102 | michel mathieu canadian politician 103 | mario monti 104 | pino palladino 105 | tony la russa 106 | murray g. ross 107 | malcolm brogdon 108 | john les 109 | evan rachel wood 110 | frank abagnale 111 | reezal merican naina merican 112 | dan stearns 113 | lindsay crouse 114 | clay timpner 115 | yaakov israel ifargan 116 | ha jung-woo 117 | charles lee basketball 118 | stereophonics 119 | don r. swanson 120 | roy beggs , jr. . 121 | adiele afigbo 122 | brian petrovek 123 | john cushnahan 124 | ron meagher 125 | george milne cricketer 126 | bill tobin american football 127 | william luther pierce 128 | martina sorbara 129 | tom wise 130 | frederick thomas brentnall 131 | bill brown goalkeeper 132 | eden natan-zada 133 | richard carpenter screenwriter 134 | joe brown utility player 135 | wayne allyn root 136 | assassination of robert f. kennedy 137 | paul caddis 138 | paul taylor winger 139 | linda hunt 140 | jerry leger 141 | 3rd dalai lama 142 | james clarke vc 143 | jack straw 144 | syd rapson 145 | billy barnie 146 | catherine johnson playwright 147 | sara montiel 148 | lucy akhurst 149 | william allan neilson 150 | elisha brown 151 | joe walsh rugby league 152 | josiah mason 153 | balbir singh kullar 154 | george bovell 155 | fei-ping hsu 156 | anne de gaulle 157 | rusty stevens 158 | john cameron alberta politician 159 | carole gist 160 | david collings 161 | matt striebel 162 | bob miller american football 163 | bryan mcclendon 164 | royce campbell 165 | carlos arniches 166 | geoff griffin 167 | frankie lymon 168 | raymond harry brown 169 | george roll 170 | ayn rand 171 | richard allen epstein 172 | tom butler actor 173 | kenan hasagić 174 | gordon hogg 175 | vagos motorcycle club 176 | katie ledecky 177 | michael savage 178 | john howe illustrator 179 | alana davis 180 | arthur sewall 181 | stan heal 182 | ithamara koorax 183 | thomas wolfe 184 | john russell vc 185 | cicero hunt lewis 186 | philip of france 1116 -- 1131 187 | brian hughes musician 188 | rickey paulding 189 | charles melville hays 190 | lee naylor footballer 191 | bane band 192 | adam collis 193 | alan dinehart 194 | sylvain barrier 195 | kirill karabits 196 | b. k. anand 197 | robert emmett keane 198 | charlotte rae 199 | riccardo tisci 200 | lester germer 201 | laurent koscielny 202 | bridget moynahan 203 | george hubbard clapp 204 | merle oberon 205 | mayhew foster 206 | hephaestion 207 | thomas biagi 208 | susan pedersen swimmer 209 | tetsuzō iwamoto 210 | donald alexander mackinnon 211 | joe holland basketball 212 | casey serin 213 | jean hugo 214 | heinz christian pander 215 | arthur tedder , 1st baron tedder 216 | cindy kleine 217 | willie naulls 218 | john holman chemist 219 | paul y. r. waddington 220 | andy hurley 221 | dara torres 222 | john hughes archbishop of new york 223 | millicent shelton 224 | whitey kurowski 225 | nofx 226 | hisashi iwakuma 227 | virginia bottomley 228 | john liscio 229 | john vallely 230 | johannes andreas august grabau 231 | guðlaugur Þór Þórðarson 232 | laurier lévesque 233 | micky moody 234 | gündüz kılıç 235 | michael replogle 236 | billy burke golfer 237 | ted childs 238 | edward synge archbishop of tuam -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /peft_egg/.gitignore: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files 2 | __pycache__/ 3 | *.py[cod] 4 | *$py.class 5 | 6 | # C extensions 7 | *.so 8 | 9 | # Distribution / packaging 10 | .Python 11 | build/ 12 | develop-eggs/ 13 | dist/ 14 | downloads/ 15 | eggs/ 16 | .eggs/ 17 | lib/ 18 | lib64/ 19 | parts/ 20 | sdist/ 21 | var/ 22 | wheels/ 23 | pip-wheel-metadata/ 24 | share/python-wheels/ 25 | *.egg-info/ 26 | .installed.cfg 27 | *.egg 28 | MANIFEST 29 | 30 | # PyInstaller 31 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template 32 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it. 33 | *.manifest 34 | *.spec 35 | 36 | # Installer logs 37 | pip-log.txt 38 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt 39 | 40 | # Unit test / coverage reports 41 | htmlcov/ 42 | .tox/ 43 | .nox/ 44 | .coverage 45 | .coverage.* 46 | .cache 47 | nosetests.xml 48 | coverage.xml 49 | *.cover 50 | *.py,cover 51 | .hypothesis/ 52 | .pytest_cache/ 53 | 54 | # Translations 55 | *.mo 56 | *.pot 57 | 58 | # Django stuff: 59 | *.log 60 | local_settings.py 61 | db.sqlite3 62 | db.sqlite3-journal 63 | 64 | # Flask stuff: 65 | instance/ 66 | .webassets-cache 67 | 68 | # Scrapy stuff: 69 | .scrapy 70 | 71 | # Sphinx documentation 72 | docs/_build/ 73 | 74 | # PyBuilder 75 | target/ 76 | 77 | # Jupyter Notebook 78 | .ipynb_checkpoints 79 | 80 | # IPython 81 | profile_default/ 82 | ipython_config.py 83 | 84 | # pyenv 85 | .python-version 86 | 87 | # pipenv 88 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control. 89 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies 90 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not 91 | # install all needed dependencies. 92 | #Pipfile.lock 93 | 94 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow 95 | __pypackages__/ 96 | 97 | # Celery stuff 98 | celerybeat-schedule 99 | celerybeat.pid 100 | 101 | # SageMath parsed files 102 | *.sage.py 103 | 104 | # Environments 105 | .env 106 | .venv 107 | env/ 108 | venv/ 109 | ENV/ 110 | env.bak/ 111 | venv.bak/ 112 | 113 | # Spyder project settings 114 | .spyderproject 115 | .spyproject 116 | 117 | # Rope project settings 118 | .ropeproject 119 | 120 | # mkdocs documentation 121 | /site 122 | 123 | # mypy 124 | .mypy_cache/ 125 | .dmypy.json 126 | dmypy.json 127 | 128 | # Pyre type checker 129 | .pyre/ 130 | 131 | # VSCode 132 | .vscode 133 | 134 | # IntelliJ 135 | .idea 136 | 137 | # Mac .DS_Store 138 | .DS_Store 139 | 140 | # More test things 141 | wandb -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /peft_egg/Makefile: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | .PHONY: quality style test docs 2 | 3 | check_dirs := src tests examples docs 4 | 5 | # Check that source code meets quality standards 6 | 7 | # this target runs checks on all files 8 | quality: 9 | black --check $(check_dirs) 10 | ruff $(check_dirs) 11 | doc-builder style src/peft tests docs/source --max_len 119 --check_only 12 | 13 | # Format source code automatically and check is there are any problems left that need manual fixing 14 | style: 15 | black $(check_dirs) 16 | ruff $(check_dirs) --fix 17 | doc-builder style src/peft tests docs/source --max_len 119 18 | 19 | test: 20 | python -m pytest -n 3 tests/ $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "ci_tests.log",) 21 | 22 | tests_examples_multi_gpu: 23 | python -m pytest -m multi_gpu_tests tests/test_gpu_examples.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "multi_gpu_examples.log",) 24 | 25 | tests_examples_single_gpu: 26 | python -m pytest -m single_gpu_tests tests/test_gpu_examples.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "single_gpu_examples.log",) 27 | 28 | tests_core_multi_gpu: 29 | python -m pytest -m multi_gpu_tests tests/test_common_gpu.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "core_multi_gpu.log",) 30 | 31 | tests_core_single_gpu: 32 | python -m pytest -m single_gpu_tests tests/test_common_gpu.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "core_single_gpu.log",) 33 | 34 | tests_common_gpu: 35 | python -m pytest tests/test_decoder_models.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "common_decoder.log",) 36 | python -m pytest tests/test_encoder_decoder_models.py $(if $(IS_GITHUB_CI),--report-log "common_encoder_decoder.log",) 37 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /peft_egg/docker/peft-cpu/Dockerfile: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Builds GPU docker image of PyTorch 2 | # Uses multi-staged approach to reduce size 3 | # Stage 1 4 | # Use base conda image to reduce time 5 | FROM continuumio/miniconda3:latest AS compile-image 6 | # Specify py version 7 | ENV PYTHON_VERSION=3.8 8 | # Install apt libs - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile 9 | RUN apt-get update && \ 10 | apt-get install -y curl git wget software-properties-common git-lfs && \ 11 | apt-get clean && \ 12 | rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists* 13 | 14 | # Install audio-related libraries 15 | RUN apt-get update && \ 16 | apt install -y ffmpeg 17 | 18 | RUN apt install -y libsndfile1-dev 19 | RUN git lfs install 20 | 21 | # Create our conda env - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile 22 | RUN conda create --name peft python=${PYTHON_VERSION} ipython jupyter pip 23 | RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip 24 | 25 | # Below is copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile 26 | # We don't install pytorch here yet since CUDA isn't available 27 | # instead we use the direct torch wheel 28 | ENV PATH /opt/conda/envs/peft/bin:$PATH 29 | # Activate our bash shell 30 | RUN chsh -s /bin/bash 31 | SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"] 32 | # Activate the conda env and install transformers + accelerate from source 33 | RUN source activate peft && \ 34 | python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \ 35 | librosa \ 36 | "soundfile>=0.12.1" \ 37 | scipy \ 38 | git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers \ 39 | git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate \ 40 | peft[test]@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft 41 | 42 | # Install apt libs 43 | RUN apt-get update && \ 44 | apt-get install -y curl git wget && \ 45 | apt-get clean && \ 46 | rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists* 47 | 48 | RUN echo "source activate peft" >> ~/.profile 49 | 50 | # Activate the virtualenv 51 | CMD ["/bin/bash"] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /peft_egg/docker/peft-gpu/Dockerfile: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Builds GPU docker image of PyTorch 2 | # Uses multi-staged approach to reduce size 3 | # Stage 1 4 | # Use base conda image to reduce time 5 | FROM continuumio/miniconda3:latest AS compile-image 6 | # Specify py version 7 | ENV PYTHON_VERSION=3.8 8 | # Install apt libs - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile 9 | RUN apt-get update && \ 10 | apt-get install -y curl git wget software-properties-common git-lfs && \ 11 | apt-get clean && \ 12 | rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists* 13 | 14 | # Install audio-related libraries 15 | RUN apt-get update && \ 16 | apt install -y ffmpeg 17 | 18 | RUN apt install -y libsndfile1-dev 19 | RUN git lfs install 20 | 21 | # Create our conda env - copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile 22 | RUN conda create --name peft python=${PYTHON_VERSION} ipython jupyter pip 23 | RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir --upgrade pip 24 | 25 | # Below is copied from https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate/blob/main/docker/accelerate-gpu/Dockerfile 26 | # We don't install pytorch here yet since CUDA isn't available 27 | # instead we use the direct torch wheel 28 | ENV PATH /opt/conda/envs/peft/bin:$PATH 29 | # Activate our bash shell 30 | RUN chsh -s /bin/bash 31 | SHELL ["/bin/bash", "-c"] 32 | # Activate the conda env and install transformers + accelerate from source 33 | RUN source activate peft && \ 34 | python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir \ 35 | librosa \ 36 | "soundfile>=0.12.1" \ 37 | scipy \ 38 | git+https://github.com/huggingface/transformers \ 39 | git+https://github.com/huggingface/accelerate \ 40 | peft[test]@git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft 41 | 42 | RUN python3 -m pip install --no-cache-dir bitsandbytes 43 | 44 | # Stage 2 45 | FROM nvidia/cuda:11.2.2-cudnn8-devel-ubuntu20.04 AS build-image 46 | COPY --from=compile-image /opt/conda /opt/conda 47 | ENV PATH /opt/conda/bin:$PATH 48 | 49 | # Install apt libs 50 | RUN apt-get update && \ 51 | apt-get install -y curl git wget && \ 52 | apt-get clean && \ 53 | rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists* 54 | 55 | RUN echo "source activate peft" >> ~/.profile 56 | 57 | # Activate the virtualenv 58 | CMD ["/bin/bash"] -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /peft_egg/docs/Makefile: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Minimal makefile for Sphinx documentation 2 | # 3 | 4 | # You can set these variables from the command line. 5 | SPHINXOPTS = 6 | SPHINXBUILD = sphinx-build 7 | SOURCEDIR = source 8 | BUILDDIR = _build 9 | 10 | # Put it first so that "make" without argument is like "make help". 11 | help: 12 | @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M help "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O) 13 | 14 | .PHONY: help Makefile 15 | 16 | # Catch-all target: route all unknown targets to Sphinx using the new 17 | # "make mode" option. $(O) is meant as a shortcut for $(SPHINXOPTS). 18 | %: Makefile 19 | @$(SPHINXBUILD) -M $@ "$(SOURCEDIR)" "$(BUILDDIR)" $(SPHINXOPTS) $(O) -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /peft_egg/docs/source/_config.py: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # docstyle-ignore 2 | INSTALL_CONTENT = """ 3 | # PEFT installation 4 | ! pip install peft accelerate transformers 5 | # To install from source instead of the last release, comment the command above and uncomment the following one. 6 | # ! pip install git+https://github.com/huggingface/peft.git 7 | """ 8 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /peft_egg/docs/source/_toctree.yml: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | - title: Get started 2 | sections: 3 | - local: index 4 | title: 🤗 PEFT 5 | - local: quicktour 6 | title: Quicktour 7 | - local: install 8 | title: Installation 9 | 10 | - title: Task guides 11 | sections: 12 | - local: task_guides/image_classification_lora 13 | title: Image classification using LoRA 14 | - local: task_guides/seq2seq-prefix-tuning 15 | title: Prefix tuning for conditional generation 16 | - local: task_guides/clm-prompt-tuning 17 | title: Prompt tuning for causal language modeling 18 | - local: task_guides/semantic_segmentation_lora 19 | title: Semantic segmentation using LoRA 20 | - local: task_guides/ptuning-seq-classification 21 | title: P-tuning for sequence classification 22 | - local: task_guides/dreambooth_lora 23 | title: Dreambooth fine-tuning with LoRA 24 | - local: task_guides/token-classification-lora 25 | title: LoRA for token classification 26 | - local: task_guides/int8-asr 27 | title: int8 training for automatic speech recognition 28 | 29 | - title: 🤗 Accelerate integrations 30 | sections: 31 | - local: accelerate/deepspeed-zero3-offload 32 | title: DeepSpeed 33 | - local: accelerate/fsdp 34 | title: Fully Sharded Data Parallel 35 | 36 | - title: Conceptual guides 37 | sections: 38 | - local: conceptual_guides/lora 39 | title: LoRA 40 | - local: conceptual_guides/prompting 41 | title: Prompting 42 | 43 | - title: Reference 44 | sections: 45 | - local: package_reference/peft_model 46 | title: PEFT model 47 | - local: package_reference/config 48 | title: Configuration 49 | - local: package_reference/tuners 50 | title: Tuners -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- /peft_egg/docs/source/accelerate/fsdp.mdx: -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 | # Fully Sharded Data Parallel 2 | 3 | [Fully sharded data parallel](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/fsdp.html) (FSDP) is developed for distributed training of large pretrained models up to 1T parameters. FSDP achieves this by sharding the model parameters, gradients, and optimizer states across data parallel processes and it can also offload sharded model parameters to a CPU. The memory efficiency afforded by FSDP allows you to scale training to larger batch or model sizes. 4 | 5 | 16 |
16 | 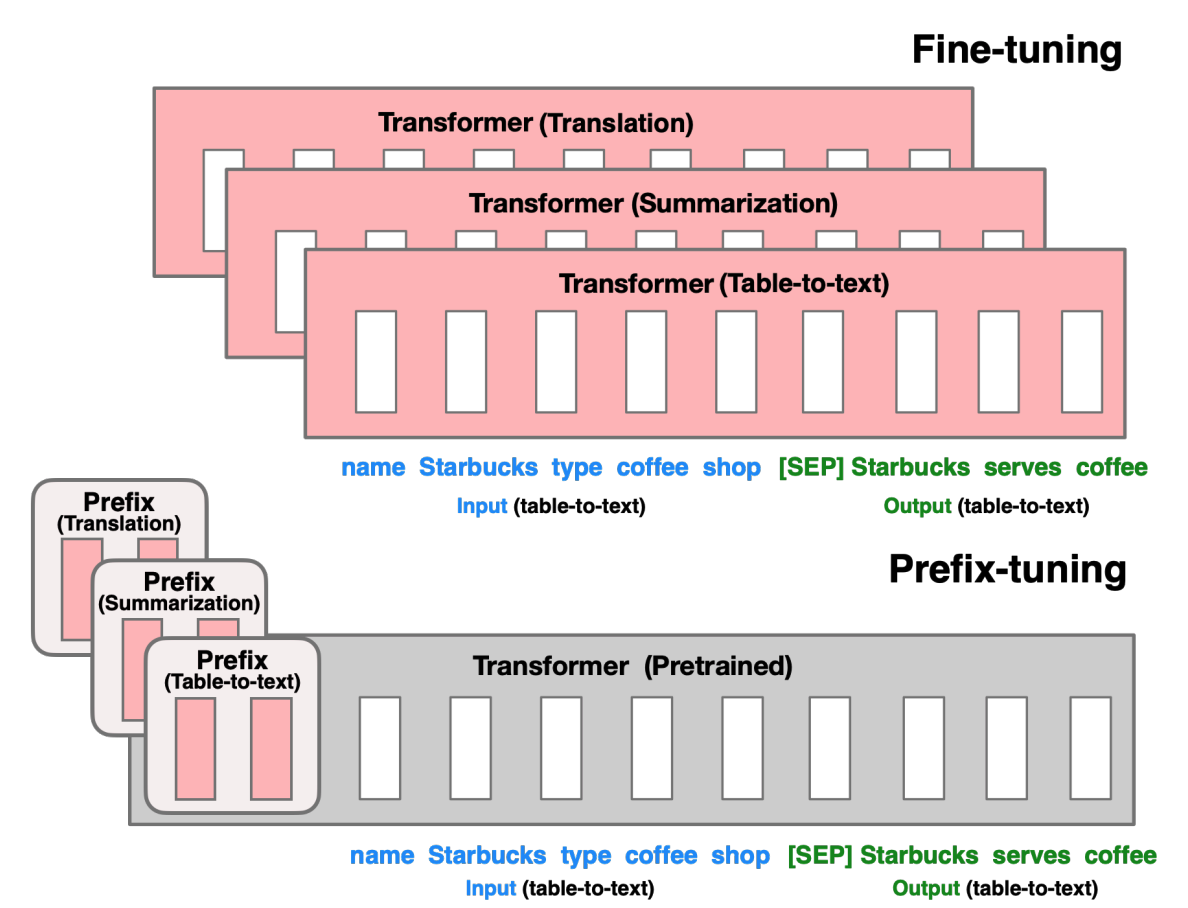 29 |
29 | 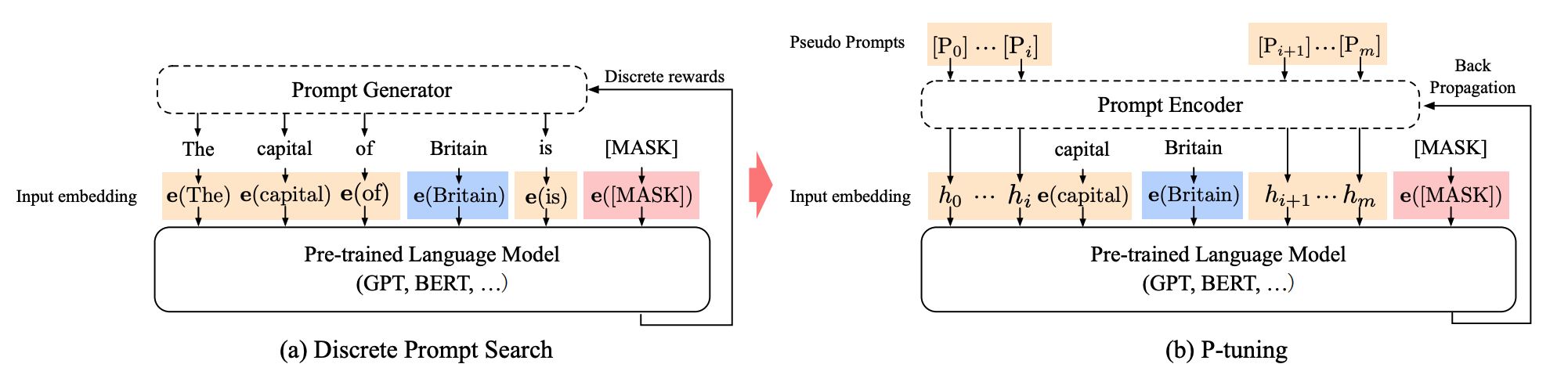 44 |
44 | Start here if you're new to 🤗 PEFT to get an overview of the library's main features, and how to train a model with a PEFT method.
26 | 27 |Practical guides demonstrating how to apply various PEFT methods across different types of tasks like image classification, causal language modeling, automatic speech recognition, and more. Learn how to use 🤗 PEFT with the DeepSpeed and Fully Sharded Data Parallel scripts.
30 | 31 |Get a better theoretical understanding of how LoRA and various soft prompting methods help reduce the number of trainable parameters to make training more efficient.
34 | 35 |Technical descriptions of how 🤗 PEFT classes and methods work.
38 | 39 |