 10 |
10 | This documentation is for the archived version of TPOT, which is no longer maintained. For the latest version, click here.
5 | 6 |This documentation is for the archived version of TPOT, which is no longer maintained. For the latest version, click here.
5 | 6 | 10 |
10 |  18 |
18 | 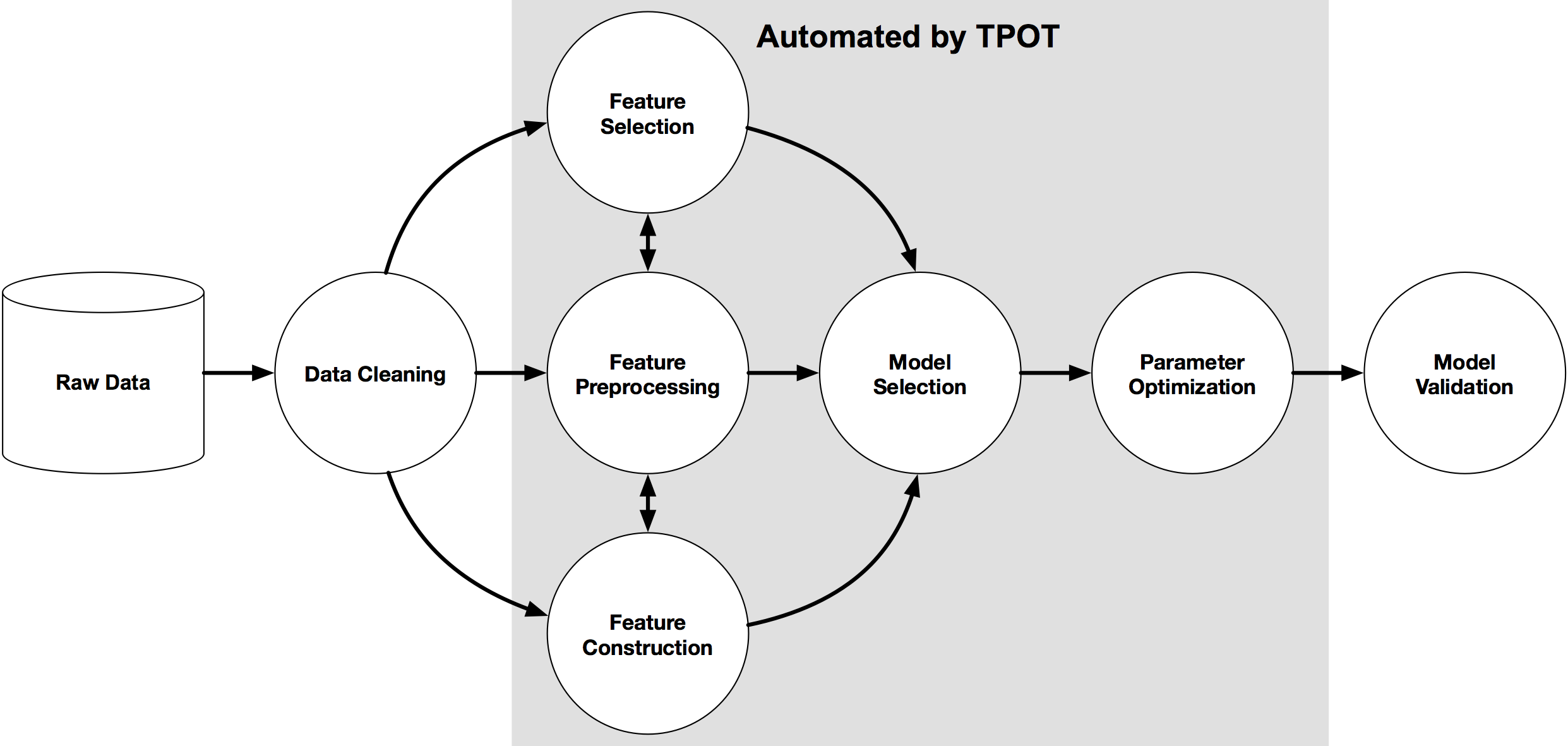 28 |
29 | An example machine learning pipeline
30 |
28 |
29 | An example machine learning pipeline
30 | 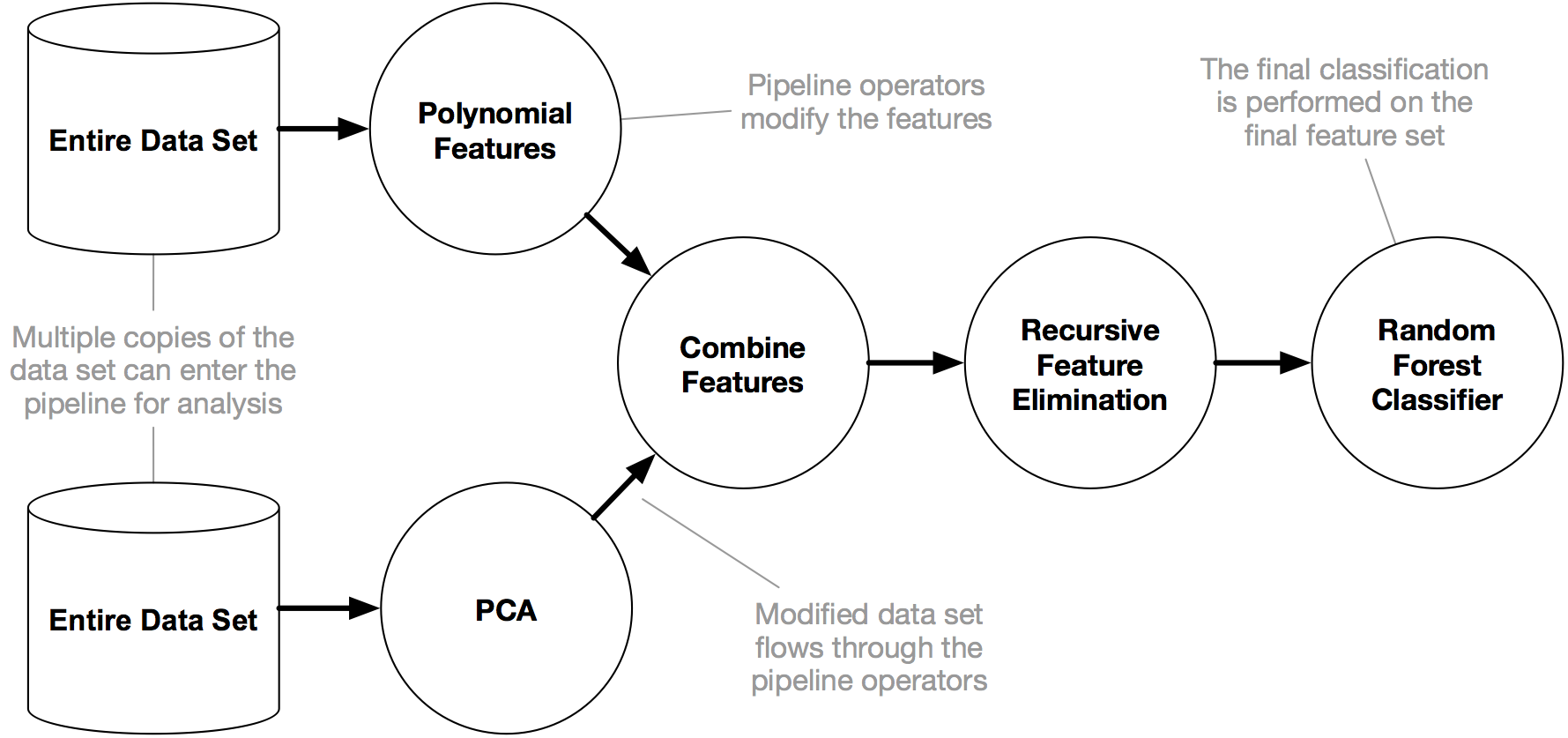 40 |
41 | An example TPOT pipeline
42 |
40 |
41 | An example TPOT pipeline
42 | This documentation is for the archived version of TPOT, which is no longer maintained. For the latest version, click here.
5 | 6 |This documentation is for the archived version of TPOT, which is no longer maintained. For the latest version, click here.
5 | 6 || Name | 13 |Language | 14 |License | 15 |Description | 16 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto-WEKA | 19 |Java | 20 |GPL-v3 | 21 |Automated model selection and hyper-parameter tuning for Weka models. | 22 |
| auto-sklearn | 25 |Python | 26 |BSD-3-Clause | 27 |An automated machine learning toolkit and a drop-in replacement for a scikit-learn estimator. | 28 |
| auto_ml | 31 |Python | 32 |MIT | 33 |Automated machine learning for analytics & production. Supports manual feature type declarations. | 34 |
| H2O AutoML | 37 |Java with Python, Scala & R APIs and web GUI | 38 |Apache 2.0 | 39 |Automated: data prep, hyperparameter tuning, random grid search and stacked ensembles in a distributed ML platform. | 40 |
| devol | 43 |Python | 44 |MIT | 45 |Automated deep neural network design via genetic programming. | 46 |
| MLBox | 49 |Python | 50 |BSD-3-Clause | 51 |Accurate hyper-parameter optimization in high-dimensional space with support for distributed computing. | 52 |
| Recipe | 55 |C | 56 |GPL-v3 | 57 |Machine-learning pipeline optimization through genetic programming. Uses grammars to define pipeline structure. | 58 |
| Xcessiv | 61 |Python | 62 |Apache 2.0 | 63 |A web-based application for quick, scalable, and automated hyper-parameter tuning and stacked ensembling in Python. | 64 |
| GAMA | 67 |Python | 68 |Apache 2.0 | 69 |Machine-learning pipeline optimization through asynchronous evaluation based genetic programming. | 70 |
This documentation is for the archived version of TPOT, which is no longer maintained. For the latest version, click here.
5 | 6 || Name | 6 |Language | 7 |License | 8 |Description | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Auto-WEKA | 12 |Java | 13 |GPL-v3 | 14 |Automated model selection and hyper-parameter tuning for Weka models. | 15 |
| auto-sklearn | 18 |Python | 19 |BSD-3-Clause | 20 |An automated machine learning toolkit and a drop-in replacement for a scikit-learn estimator. | 21 |
| auto_ml | 24 |Python | 25 |MIT | 26 |Automated machine learning for analytics & production. Supports manual feature type declarations. | 27 |
| H2O AutoML | 30 |Java with Python, Scala & R APIs and web GUI | 31 |Apache 2.0 | 32 |Automated: data prep, hyperparameter tuning, random grid search and stacked ensembles in a distributed ML platform. | 33 |
| devol | 36 |Python | 37 |MIT | 38 |Automated deep neural network design via genetic programming. | 39 |
| MLBox | 42 |Python | 43 |BSD-3-Clause | 44 |Accurate hyper-parameter optimization in high-dimensional space with support for distributed computing. | 45 |
| Recipe | 48 |C | 49 |GPL-v3 | 50 |Machine-learning pipeline optimization through genetic programming. Uses grammars to define pipeline structure. | 51 |
| Xcessiv | 54 |Python | 55 |Apache 2.0 | 56 |A web-based application for quick, scalable, and automated hyper-parameter tuning and stacked ensembling in Python. | 57 |
| GAMA | 60 |Python | 61 |Apache 2.0 | 62 |Machine-learning pipeline optimization through asynchronous evaluation based genetic programming. | 63 |
| PyMoo | 66 |Python | 67 |Apache 2.0 | 68 |Multi-objective optimization in Python. | 69 |
| Karoo GP | 72 |Python | 73 |MIT | 74 |A Python based genetic programming application suite with support for symbolic regression and classification. | 75 |
| MABE | 78 |C++ | 79 |See here | 80 |A Python based genetic programming application suite with support for symbolic regression and classification. | 81 |
| SBBFramework | 84 |Python | 85 |BSD-2-Clause | 86 |Python implementation of Symbiotic Bid-Based (SBB) framework for problem decomposition using Genetic Programming (GP). | 87 |
| Tiny GP | 90 |Python | 91 |GPL-v3 | 92 |A minimalistic program implementing Koza-style (tree-based) genetic programming to solve a symbolic regression problem. | 93 |
| Baikal | 96 |Python | 97 |BSD-3-Clause | 98 |A graph-based functional API for building complex scikit-learn pipelines. | 99 |
| skdag | 102 |Python | 103 |MIT | 104 |A more flexible alternative to scikit-learn Pipelines. | 105 |
| d6tflow | 108 |Python | 109 |MIT | 110 |A python library which makes building complex data science workflows easy, fast and intuitive. | 111 |