39 |
40 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mdmeeuL4bTM "Introduction")
41 |
42 | This video presentation explains context information processing and advanced Big Data Analysis.
43 |
44 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
45 |
46 | Use of the Cosmos Flink Connector is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
47 |
48 | - [FIWARE 505: Real-time Processing and Big Data Analysis](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/big-data-flink.html)
49 | - [FIWARE 506: Real-time Processing and Big Data Analysis](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/big-data-spark.html)
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
Code Examples
54 |
55 | This GitHub repository exists containing a few examples for getting started with the cosmos flink connector is described
56 | in the following documentation:
57 |
58 | - [Cosmos Flink Examples](https://fiware-cosmos-flink-examples.readthedocs.io)
59 | - [Cosmos Spark Examples](https://github.com/ging/fiware-cosmos-orion-spark-connector-examples/)
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/core/cygnus.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Cygnus - Data Persistence using Apache Flume
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/core/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware-cygnus)
6 |
7 | Cygnus is a connector in charge of persisting context data sources into other third-party databases and storage systems,
8 | creating a historical view of the context. Internally, Cygnus is based on Apache Flume,
9 | [Flume](https://flume.apache.org/) is a data flow system based on the concepts of flow-based programming. It supports
10 | powerful and scalable directed graphs of data routing, transformation, and system mediation logic. It was built to
11 | automate the flow of data between systems. While the term 'dataflow' can be used in a variety of contexts, we use it
12 | here to mean the automated and managed flow of information between systems.
13 |
14 |  [Documentation](https://fiware-cygnus.rtfd.io)
15 |
16 |
Academy Courses
17 |
18 |
Lesson 1. Cygnus Introduction
19 |
20 | By following this course, you will learn about Cygnus, our connector able to create historics from Orion context data.
21 | FAQ, architecture, basic and advanced configuration, and detailed sink catalogue.
22 |
23 | - 
24 | [Lesson 1 - introduction to Cygnus](https://fiware-ops.github.io/docs.academy/cygnus/cygnus1.pdf)
25 |
26 |
Lesson 2. Persisting to HDFS using Cygnus
27 |
28 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q_TZKLDu4X0 "Cygnus HDFS")
29 |
30 | This video presentation explains how to use Cygnus to persist data for Big Data Analytics.
31 |
32 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
33 |
34 | Data Persistence using Cygnus is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
35 |
36 | - [FIWARE 301: Persisting Context Data using Apache Flume](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/historic-context-flume.html)
37 | (MongoDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL)
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/core/draco.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Draco - Data Persistence using Apache NIFI
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/core/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware-sth-comet)
6 |
7 | Draco is a connector in charge of persisting context data sources into other third-party databases and storage systems,
8 | creating a historical view of the context. Internally, Draco is based on Apache NiFi. [NiFi](https://nifi.apache.org) is
9 | a popular framework for data management and processing from multiple sources.
10 |
11 | Draco plays the role of a connector between the Orion Context Broker (which is an
12 | [NGSI](https://swagger.lab.fiware.org/?url=https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Fiware/specifications/master/OpenAPI/ngsiv2/ngsiv2-openapi.json)
13 | source of data) source of data) and a wide range of external systems such as MySQL, MongoDB etc. You can use Draco if
14 | you need to process and persist context data so that you can keep a historical record. Draco can also be used to filter
15 | and repost context data back into Orion.
16 |
17 |  [Documentation](https://fiware-draco.rtfd.io)
18 |
19 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
20 |
21 | Data Persistence using Draco is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
22 |
23 | - [FIWARE 302: Persisting Context Data using Apache NIFI](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/historic-context-nifi.html)
24 | (MongoDB, MySQL, PostgreSQL)
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/core/orion-ld.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Orion-LD - Linked Data Context Broker
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/core/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware)
6 |
7 | Orion-LD is an alternative
8 | [NGSI-LD](https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gs/CIM/001_099/009/01.08.01_60/gs_cim009v010801p.pdf) Context Broker written
9 | in C/C++. It is a standalone executable and therefore small, fast, lightweight and easy to handle. Context brokers allow
10 | for the management and requesting context of information in a structured manner based on linked data standards following
11 | the NGSI-LD specification. Orion-LD is more suitable for smaller installations or possibly in embedded environments - it
12 | currentlys supports only a subset of the standard NGSI-LD endpoints.
13 |
14 | 
15 | [Documentation](https://github.com/FIWARE/context.Orion-LD/tree/develop/doc/manuals-ld)
16 |
17 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
18 |
19 | Techniques for working with Linked Data using Orion-LD are described in the following step-by-step tutorials:
20 |
21 | - [FIWARE 601: Introduction to Linked Data](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/linked-data.html)
22 | - [FIWARE 602: Linked Data Relationships and Data Models](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/relationships-linked-data.html)
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/core/orion.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Orion - Context Broker
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/core/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware-orion)
6 |
7 | The Orion Context Broker is an implementation of the Publish/Subscribe Broker Generic Enabler.
8 |
9 | Orion Context Broker allows you to manage the entire lifecycle of context information including updates, queries,
10 | registrations and subscriptions. It is an NGSI v2 server implementation to manage context information and its
11 | availability. Using the Orion Context Broker, you are able to create context elements and manage them through updates
12 | and queries. In addition, you can subscribe to context information so when some condition occurs (e.g. the context
13 | elements have changed) you receive a notification.
14 |
15 |  [Documentation](https://fiware-orion.rtfd.io)
16 |
17 |
Academy Courses
18 |
19 |
Lesson 1. Orion Context Broker Basic
20 |
21 | Provides an introduction to Orion Context Broker and its basic API to manage context information. It also explains how
22 | to set Orion instances to start working with it.
23 |
24 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dn9PW43-rVg "Context Broker Basic")
25 |
26 | - 
27 | [Lesson 1 - Slides File](https://fiware-ops.github.io/docs.academy/orion/orion1.pdf)
28 |
29 |
Lesson 2. Orion Context Broker Advanced
30 | Describes advances Orion Context Broker topics, such as pagination, filtering, geo-location and much more.
31 |
32 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3qOXUcK0nCo "Context Broker Advanced")
33 |
34 | - 
35 | [Lesson 2 - Slides File](https://fiware-ops.github.io/docs.academy/orion/orion2.pdf)
36 |
37 |
Lesson 3. Upgrading from NGSI v1 to NGSI v2
38 |
39 | This document describes the novelties in NGSI v2 for people already familiar with NGSI v1. Thus, you would learn how to
40 | do the things you are familiar with NGSI v1 now in NGSI v2 as long as new and powerful capabilities of the new version
41 | of the API. Some knowledge in NGSI v1 API is required.
42 |
43 | - 
44 | [Lesson 3 - Slides File](https://fiware-ops.github.io/docs.academy/orion/orion3.pdf)
45 |
46 |
Lesson 4. Orion Context Broker Basic Exercises
47 |
48 | A set of basic-level exercises that you can use to exercise your knowledge on Orion.
49 |
50 | - 
51 | [Lesson 4 - Slides File](https://fiware-ops.github.io/docs.academy/orion/orion4.pdf)
52 |
53 |
Lesson 5. Orion Context Broker Advanced Exercises
54 | A set of advanced-level exercises that you can use to exercise your knowledge on Orion.
55 |
56 | - 
57 | [Lesson 5 - Slides File](https://fiware-ops.github.io/docs.academy/orion/orion5.pdf)
58 |
59 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
60 |
61 | These tutorials are an introduction to the FIWARE Context Broker, and are an essential first step when learning to use
62 | FIWARE:
63 |
64 | - [FIWARE 101: Getting Started](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/getting-started.html)
65 | - [FIWARE 102: Entity Relationships](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/entity-relationships.html)
66 | - [FIWARE 103: CRUD Operations](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/crud-operations.html)
67 | - [FIWARE 104: Context Providers](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/context-providers.html)
68 | - [FIWARE 105: Altering the Context Programmatically](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/accessing-context.html)
69 | - [FIWARE 106: Subscribing to Changes in Context](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/subscriptions.html)
70 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/core/quantum-leap.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
QuantumLeap - Times Series Data
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/core/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/search?q=%5Bfiware%5D+quantumleap)
6 |
7 | The QuantumLeap Generic Enabler focuses on persisting historical context data into
8 | [time-series databases](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Time_series_database) such as [CrateDB](https://crate.io/) with
9 | reference to maintaining a scalable architecture and compatibility with visualization tools such as
10 | [Grafana](https://www.grafana.com/)
11 |
12 |  [Documentation](https://quantumleap.rtfd.io/)
13 |
14 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
15 |
16 | Creating time series data using QuantumLeap is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
17 |
18 | - - [FIWARE 303: Querying Time Series Data](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/time-series-data.html)
19 | (Crate-DB)
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/core/scorpio.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Scorpio - Linked Data Context Broker
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/core/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware)
6 |
7 | Scorpio implements [NGSI-LD](https://www.etsi.org/deliver/etsi_gs/CIM/001_099/009/01.08.01_60/gs_cim009v010801p.pdf),
8 | which is the evolution of NGSI v2 and previous versions going back to the OMA NGSI context interfaces. This standardized
9 | version is based on the NGSI-LD specification published by the ETSI Industry Specification Group on Context Information
10 | Management.
11 |
12 | Scorpio supports different deployment configurations, which support scalability and extension of scenarios in an
13 | evolutionary way. For example two separate deployments can be combined or for scalability reasons different brokers can
14 | be used – completely transparent to Context Consumers that can still use a single point of access. Scorpio also
15 | implements the optional temporal NGSI-LD interface, so any updated context information can automatically be made
16 | available as history information through the temporal interface.
17 |
18 |  [Documentation](https://scorpio.rtfd.io)
19 |
20 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
21 |
22 | Techniques for working with Linked Data using Scorpio are described in the following step-by-step tutorials:
23 |
24 | - [FIWARE 601: Introduction to Linked Data](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/linked-data.html)
25 | - [FIWARE 602: Linked Data Relationships and Data Models](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/relationships-linked-data.html)
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/core/sth-comet.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
STH Comet - Short Term History
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/core/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware-sth-comet)
6 |
7 | Short Time Historic (STH) - Comet is a component of the FIWARE ecosystem in charge of managing (storing and retrieving)
8 | historical raw and aggregated time series context information about the evolution in time of context data (i.e., entity
9 | attribute values) registered in an Orion Context Broker instance.
10 |
11 |  [Documentation](https://fiware-sth-comet.rtfd.io)
12 |
13 |
24 |
25 | Creating short-term historic data using STH-Comet is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
26 |
27 | - [FIWARE 302: Querying Time Series Data](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/short-term-history.html)
28 | (MongoDB)
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/data-publication/business-api.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Business API Ecosystem
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/data-publication/README.md)
5 |
6 | The **Business API Ecosystem** GE is the result of the collaboration between FIWARE and the TMForum. In this regard, the
7 | Business API Ecosystem GE is a joint component made up by integrating the FIWARE Business Framework with a set of
8 | standard APIs (and its reference implementations) provided by the TMForum in its TMF API ecosystem. This component
9 | allows the monetization of different kind of assets (both digital and physical) during the whole service life cycle,
10 | from offering creation to its charging, accounting and revenue settlement and sharing. In this way, the Business API
11 | Ecosystem provides sellers the means for managing, publishing, and generating revenue of they products, apps, data, and
12 | services.
13 |
14 |  [Documentation](https://business-api-ecosystem.rtfd.io/)
15 |
16 |
145 |
146 | This topic is intended for developers that want to create plug-ins for the Business API Ecosystem in order to extend its
147 | support for digital types of products. In particular, the current topic includes documentation about the plug-ins
148 | structure, existing events, and data models
149 |
150 | - To properly follow this topic it is required some knowledge on Python programming
151 |
152 | * API
153 | Specification File This document includes the reference of the REST API, including the possible interactions and
154 | the managed objects
155 |
156 | * Plugins
157 | Development These slides include the different concepts that are needed for creating a new asset plugin
158 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/data-publication/ckan.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Extensions to CKAN
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/data-publication/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/ckan)
6 |
7 | A set of CKAN extensions, developed within FIWARE, which integrates this data portal platform with the main FIWARE GEs,
8 | enhancing the default CKAN behaviour with improved access control, publication of right-time context data, and rich
9 | visualization features.
10 |
11 | - [CKAN User Guide](https://docs.ckan.org/en/latest/user-guide.html)
12 | - [CKAN API Guide](https://docs.ckan.org/en/latest/api/index.html)
13 | - [CKAN Sysadmin guide](https://docs.ckan.org/en/latest/sysadmin-guide.html)
14 |
15 |  [Documentation](https://fiware-ckan-extensions.rtfd.io/)
16 |
17 |
Academy Courses
18 |
19 |
Lesson 1. Managing data in CKAN
20 |
21 | This user guide covers using CKAN’s web interface to organize, publish and find data.
22 |
23 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PFe3Gv_-1wY ">Managing Data with CKAN")
24 |
25 |
Lesson 2. Monetize your APIs
26 |
27 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q_TZKLDu4X0 "CKAN")
28 |
29 | This video presentation explains how push data to CKAN for monetization.
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/data-publication/idra.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Idra
3 |
4 | [](https://www.fiware.org/developers/catalogue/)
5 | [](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware+idra+fiware-idra)
6 |
7 | Idra is a web application able to federate existing Open Data Management Systems (ODMS) based on different technologies,
8 | providing a unique access point to search and discover open datasets coming from heterogeneous sources. Idra uniforms
9 | metadata of collected open datasets, thanks to the adoption of international standards (DCAT-AP) and provides a set of
10 | RESTful APIs to be used by third-party applications.
11 |
12 | - [Idra general presentation](https://github.com/OPSILab/Idra/raw/master/docs/presentations/Idra_presentation_ENG.pdf)
13 | - [Idra user guide](https://idra.readthedocs.io/en/latest/user/enduser/)
14 | - [Idra installation and administration guide](https://docs.ckan.org/en/latest/sysadmin-guide.html)
15 | - [Idra API](https://idraopendata.docs.apiary.io/)
16 | - [Idra Demo](https://idra.eng.it/)
17 |
18 |
Academy Courses
19 |
20 |
Lesson 1. Idra portal - end user functionalities
21 | This video guide shows the main Idra portal functionalities for the end user.
22 |
23 | [](https://onedrive.live.com/embed?cid=F6FFB8A28077F737&resid=F6FFB8A28077F737%2113358&authkey=AO7rphVOtw7h5IE)
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
Lesson 2. Idra portal - administration dashboard
28 | This video guide shows the main functionalities of the Idra portal administration dashboard.
29 |
30 | [](https://onedrive.live.com/embed?cid=F6FFB8A28077F737&resid=F6FFB8A28077F737%2113357&authkey=AJ9ykXGuwT3Po9Q)
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 |
Lesson 3. Idra web scraping plugin and connector
35 | This video guide shows the usage of web scraping plugin and connector, to federate a generic open data portal (that does not provide API) in Idra.
36 |
37 | [](https://onedrive.live.com/embed?cid=F6FFB8A28077F737&resid=F6FFB8A28077F737%2113370&authkey=ALujfTjlixqI9vA)
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/img/favicon.ico:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FIWARE-Ops/docs.academy/d4503049abe8c74a3430ec44e8b5e9aa778d3644/docs/img/favicon.ico
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/img/favicon.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FIWARE-Ops/docs.academy/d4503049abe8c74a3430ec44e8b5e9aa778d3644/docs/img/favicon.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/img/fiware.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FIWARE-Ops/docs.academy/d4503049abe8c74a3430ec44e8b5e9aa778d3644/docs/img/fiware.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [FIWARE](https://www.fiware.org) is a curated framework of open source platform components which can be assembled
2 | together and with other third-party platform components to accelerate the development of Smart Solutions.
3 |
4 | The FIWARE Academy lists the video tutorials, slide decks and other training materials available for developers learning
5 | about the FIWARE Ecosystem. The training materials within the academy are arranged into a series of the chapters as
6 | defined within the [FIWARE catalogue](https://www.fiware.org/developers/catalogue/):
7 |
8 | 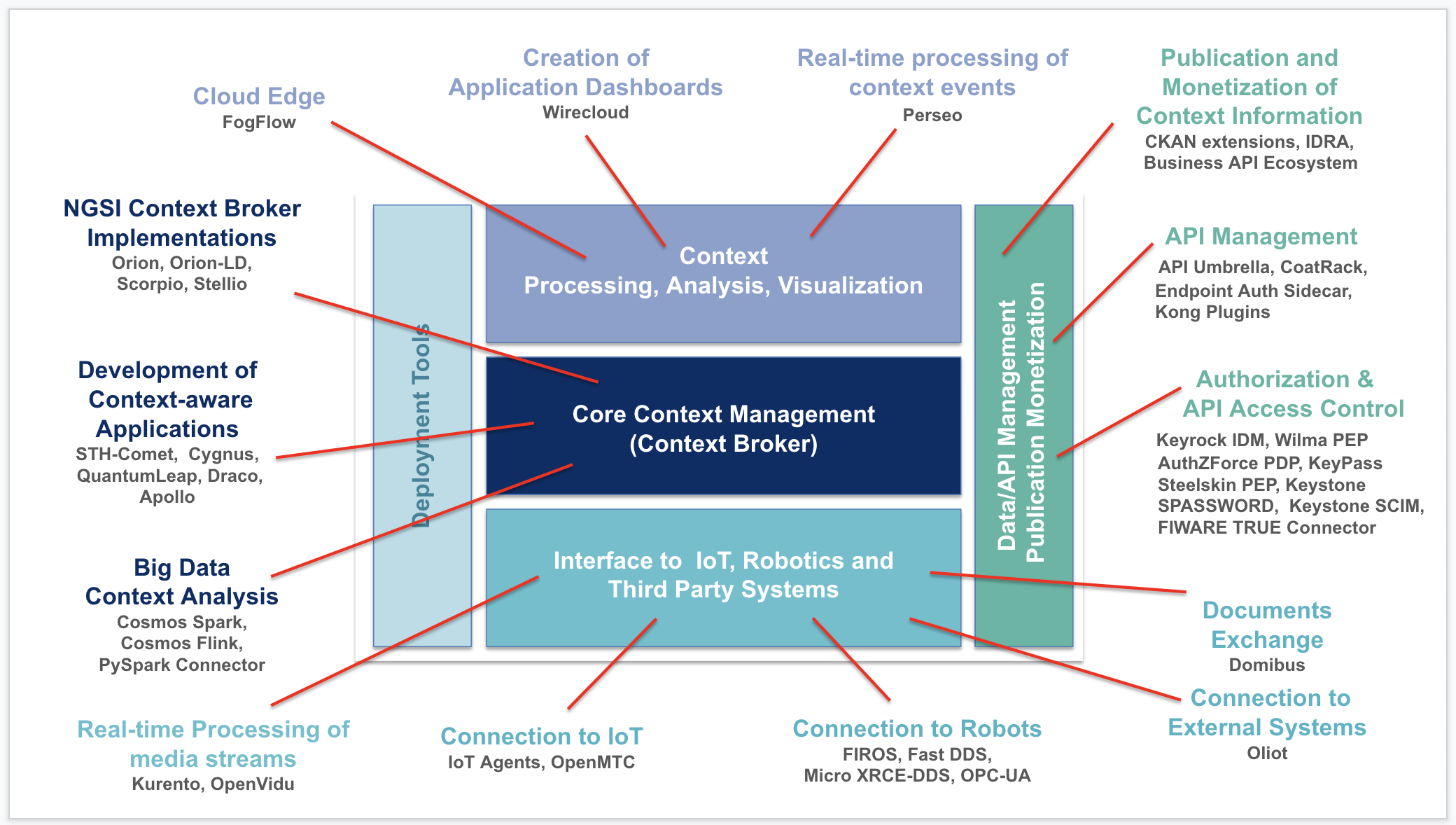
9 |
10 | - **Core Context Management** allows you to model, manage and gather context information at large scale enabling
11 | context-aware applications.
12 | - **Internet of Things (IoT), Robots and third-party systems**, defines interfaces for capturing updates on context
13 | information and translating required actuations.
14 | - **Context Data/API management, publication and monetization**, implementing the expected smart behaviour of
15 | applications and/or assisting end users in making smart decisions.
16 | - **Processing, analysis and visualization** of context information, bringing support to usage control and the
17 | opportunity to publish and monetize part of managed context data.
18 |
19 | In addition to the training materials for each individual enabler, two integrated courses have been recorded -
20 | [FIWARE Webinars](integrated-courses/webinars.md) and [CEF Smart Cities](integrated-courses/cef-smart-cities.md)
21 |
22 |
Lesson 1. Introduction to FIWARE
23 |
24 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=97JsnnpPLrA "Introduction")
25 |
26 | This video presentation is a basic introduction describing what FIWARE is, why you need it and how the elements of the
27 | FIWARE Catalogue can help accelerate the development of your Smart Solution.
28 |
29 | 🇯🇵 このビデオ・プレゼンテーションは
30 | [日本語字幕](https://www.youtube.com/embed/97JsnnpPLrA?cc_load_policy=1&cc_lang_pref=ja)でご覧いただけます。 🇪🇸
31 | Este webinar está disponible con subtítulos en
32 | [español](https://www.youtube.com/embed/97JsnnpPLrA?cc_load_policy=1&cc_lang_pref=es).
33 |
34 |
Lesson 2. FIWARE Basics
35 |
36 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=laDTBcLziB8 "Basics")
37 |
38 | A video presenation for a non-technical audience describing the terminology used in FIWARE, explaining the benefits in
39 | using open standards and demystifying the terms used by software developers.
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/integrated-courses/cef-smart-cities.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
CEF Smart Cities Webinars
2 |
3 | The digital arm of the Connecting Europe Facility improves the daily lives of European citizens via investments in
4 | digital Building Blocks, cross-border digital infrastructures, and broadband networks. It facilitates the cross-border
5 | interaction between public administrations, businesses or citizens. It promotes economic growth and supports the
6 | completion and functioning of the internal market, enhancing the competitiveness of the European economy. CEF-supported
7 | projects help create and maintain a European ecosystem of interoperable and interconnected digital services and thus
8 | help sustain the Digital Single Market.
9 |
10 | In August 2018, the CEF Programme successfully went live with the Context Broker Building Block. The Context Broker is
11 | the core component of the FIWARE platform. The Context Broker, which is able to handle context information on a large
12 | scale by implementing standard REST APIs, has been added to the European Data Portal and its core service platform as a
13 | new functionality. This allows the European Data Model and EU Member States to collect, manage, use, and share data.
14 |
15 | #### 1. Meet Context Broker, the new CEF Building Block
16 |
17 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1Cqcrnj9id4)
18 |
19 | The FIWARE Context Broker, which is able to handle context information on a large scale by implementing standard REST
20 | APIs, has been added to the European Data Portal and its core service platform as a new functionality, allowing the
21 | European Data Model and EU Member States to collect, manage, use, and share real-time data. In addition, the platform
22 | will provide governments with a sandbox environment, allowing them to test the use of real-time data.
23 |
24 | Thus, for example, Smart Cities can share information about what is happening in streets (e.g., traffic status, quality
25 | of air data, available parking slots, location). Similarly, a packet delivery service company may share data about
26 | orders (e.g., current location and expected delivery time). This information describing what is currently happening is
27 | referred as “context information”.
28 |
29 | #### 2. Introduction: Smart Cities and the EC
30 |
31 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GoqLmkwHwbI)
32 |
33 | Cristina Martinez - Deputy Head of Unit, Smart Mobility and Living (CNECT - European Commission)
34 |
35 | #### 3. Smart Cities and the CEF Building Blocks
36 |
37 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5wWPFTAKwH8)
38 |
39 | Joao Rodrigues Frade - Head of Sector, Building Blocks (DIGIT - European Commission)
40 |
41 | #### 4. City as Platform Manifesto
42 |
43 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2mpowkOa3zw)
44 |
45 | Carl Piva - Senior Advisor to governments, cities and ICT companies
46 |
47 | #### 5. CEF Building Blocks in the context of Smart Cities
48 |
49 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TbA5tYxTJpk)
50 |
51 | Ulrich Ahle - CEO, FIWARE Foundation
52 |
53 | #### 6. Closing Words and final Q&A
54 |
55 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KzEGOlG_mVg)
56 |
57 | Kelly Liljemo - Project Officer, Building Blocks (DIGIT - European Commission)
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/integrated-courses/fiware-training.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
FIWARE Training
2 |
3 | An online training course run by the FIWARE Foundation in conjunction with the i4Trust project. The core part of this
4 | virtual training camp (21-24 June 2021) covered all the necessary skills to develop smart solutions powered by FIWARE.
5 | It introduces the basis of Digital Twin programming using linked data concepts - JSON-LD and NGSI-LD and combines these
6 | with common smart data models for the sharing and augmentation of context data.
7 |
8 | In addition, it will covers the supplementary FIWARE technologies used to implement the common functions typically
9 | required when architecting a complete smart solution: Identity and Access Management (IAM) functions to secure access to
10 | digital twin data and functions enabling the interface with IoT and 3rd systems, or the connection with different tools
11 | for processing and monitoring current and historical big data.
12 |
13 | This 12 hour online training course can be used to obtain a good understanding of FIWARE and NGSI Interfaces and form
14 | the basis of studying for the FIWARE expert certification.
15 |
16 | Extending this core part, the virtual training camp adds introductory and deep-dive sessions on how FIWARE and iSHARE
17 | technologies, brought together under the umbrella of the i4Trust initiative, can be combined to provide the means for
18 | the creation of data spaces in which multiple organizations can exchange digital twin data in a trusted and efficient
19 | manner, collaborating in the creation of innovative services based on data sharing. In addition, SMEs and Digital
20 | Innovation Hubs (DIHs) that go through this complete training and are located in countries eligible under Horizon 2020
21 | will be equipped with the necessary know-how to apply to the recently launched i4Trust Open Call.
22 |
23 | #### 1. JSON-LD, NGSI-LD, Digital Twins and Smart Data Models
24 |
25 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dfigPKx99Bs)
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 | - FIWARE in a nutshell
30 | - Rationale behind NGSI-LD (Why linked data)
31 | - NGSI-v2 to NGSI-LD
32 | - Basic CRUD Properties
33 | - Basic CRUD Relationships
34 | - IRI attributes
35 | - Subscriptions
36 | - Registrations
37 | - Data Models
38 |
39 | This session consists of two parts. In the first part you will get introduced to NGSI-LD: the basic model/concept behind
40 | and basic operations allowing you to start developing applications with the API. In the second part, you will get
41 | introduced to the Smart Data Models initiative.
42 |
43 | - 
44 | [Lesson 1a - Slides File](https://www.slideshare.net/FI-WARE/fiware-training-jsonld-and-ngsild)
45 | - 
46 | [Lesson 1b - Slides File](https://www.slideshare.net/FI-WARE/fiware-training-ngsild-introduction)
47 | - 
48 | [Lesson 1c - Slides File](https://www.slideshare.net/FI-WARE/fiware-training-smart-data-models)
49 |
50 | #### 2. Advanced NGSI-LD Operations
51 |
52 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tcfJOx7g7jI)
53 |
54 | - NGSI-LD Specific Headers
55 | - Temporal Queries
56 | - NGSI-LD Language Maps
57 | - Expansion and Compaction
58 | - Filtering entity queries
59 | - Filtering using the q parameter
60 | - The geoQ parameters
61 | - The temporalQ parameters
62 | - Connecting Data Providers
63 | - Data Models
64 |
65 | This session covers advanced NGSI-LD operations beyond basic CRUD, registration and subscriptions. It also includes
66 | exercises on creating data models and connecting disparate data providers in a trusted fashion.
67 |
68 | - 
69 | [Lesson 2 - Slides File](https://www.slideshare.net/FI-WARE/fiware-training-ngsi-ld-advanced-operationspptx)
70 |
71 | #### 3. NGSI-LD IoT Agents & Interfacing with third-party systems
72 |
73 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H2DIGqzO62k)
74 |
75 | The session will explain about how to connect to legacy systems, IoT, etc. Also includes information on data persistence
76 | of NGSI-LD context data
77 |
78 | - 
79 | [Lesson 3 - Slides File](https://www.slideshare.net/FI-WARE/fiware-training-iot-and-legacy)
80 |
81 | #### 4. Identity and Access Management Components
82 |
83 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LFTpuE_2ANU)
84 |
85 | This session consists of two parts. The first part of the session will introduce you to i4Trust IAM components in detail
86 | while the second will introduce i4Trust Marketplace Services.
87 |
88 | - 
89 | [Lesson 4a - Slides File](https://www.slideshare.net/FI-WARE/fiware-training-api-umbrella)
90 | - 
91 | [Lesson 4b - Slides File](https://www.slideshare.net/FI-WARE/fiware-training-identity-management-access-control)
92 | - 
93 | [Lesson 4c - Slides File](https://www.slideshare.net/FI-WARE/fiware-training-fiware-training-i4trust-marketplace)
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/integrated-courses/i4Trust.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
i4Trust: Train the Trainers
2 |
3 | i4Trust is looking for DIHs to engage in a process of collective learning and human endeavor that will grow and scale
4 | the ideas of SMEs in their regions, unleashing the potential of data sharing and enabling cross-domain data value
5 | chains.
6 |
7 | A comprehensive Train the Trainers program, created by the i4Trust experts in data sharing from the FIWARE Foundation
8 | and iSHARE Foundation, will help to equip DIH local experts with the necessary i4Trust know-how to support the selected
9 | experiments in the first Open Call and their transference to the market.
10 |
11 | #### 1. Introduction to i4Trust Data Spaces
12 |
13 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qk7HSd_p5eQ)
14 |
15 | This session will elaborate on the i4Trust overall mission and vision and introduce you to data spaces: how they enable
16 | the development of innovative services and what building blocks are required to build data spaces. It will elaborate on
17 | what i4Trust is aiming at beyond building blocks which is the creation of a vibrant community. In addition, there will
18 | be an introduction to the role of DIHs and to i4Trust open calls. The session for Local Experts in Data Sharing (LEBDs)
19 | & Ambassadors.
20 |
21 | #### 2. NGSI-LD primer & Smart Data Models
22 |
23 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zkRCk8n1YZk)
24 |
25 | This session consists of two parts. In the first part you will get introduced to NGSI-LD: the basic model/concept behind
26 | and basic operations allowing you to start developing applications with the API. In the second part, you will get
27 | introduced to the Smart Data Models initiative. Technical Session for Local Experts in Data Sharing (LEBDs)
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 | - FIWARE in a nutshell
32 | - Rationale behind NGSI-LD (Why linked data)
33 | - NGSI-v2 to NGSI-LD
34 | - Basic CRUD Properties
35 | - Basic CRUD Relationships
36 | - IRI attributes
37 | - Subscriptions
38 | - Registrations
39 | - Data Models
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 | #### 3. i4Trust components for Identity Management and Access Control
44 |
45 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=kVMXoN8wUKk)
46 |
47 | This session consists of two parts. The first part of the session will introduce you to i4Trust IAM components in detail
48 | while the second will introduce i4Trust Marketplace Services. Technical session for Local Experts in Data Sharing
49 | (LEBDs)
50 |
51 | #### 4. Bringing the pieces together - Detailed review of a reference example
52 |
53 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t_MrBTAGPf4)
54 |
55 | This session will explain how everything comes together under i4Trust using a reference example and then explain that
56 | example in detail. It will be bringing the pieces together: Detailed technical review of a reference example: the
57 | prerequisites, creating an offering, acquiring rights/activation, & consumption. And the setup of components of the
58 | i4Trust experimentation framework. The technical session for Local Experts in Data Sharing (LEBDs).
59 |
60 | #### 5. NGSI-LD Advanced Operations
61 |
62 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ll-t8Vi9i50)
63 |
64 | - NGSI-LD Specific Headers
65 | - Temporal Queries
66 | - NGSI-LD Language Maps
67 | - Expansion and Compaction
68 | - Filtering entity queries
69 | - Filtering using the q parameter
70 | - The geoQ parameters
71 | - The temporalQ parameters
72 | - Connecting Data Providers
73 | - Data Models
74 |
75 | #### 6. Ecosystem Building & the role of DIHs
76 |
77 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0bDu1SItYDA)
78 |
79 | This session consists of two parts. The first part will elaborate on the approach adopted towards building the i4Trust
80 | Community and the second will elaborate on the OnBoarding: the role of DIHs.
81 |
82 | #### 7. Connecting to Legacy Systems,IoT and other Systems
83 |
84 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0bDu1SItYDA)
85 |
86 | Session for Local Experts in Data Sharing (LEBDs), the session will explain about how to connect to legacy systems, IoT,
87 | etc.
88 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/iot-agents/idas.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
IoT Agents
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/iot-agents/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware+iot)
6 |
7 | The IoT Agent component is an implementation of the Backend Device Management GE, according to the FIWARE reference
8 | architecture. You are here because you need to connect objects to gather data or interact with them, typical IoT use
9 | case scenario . If so, you need to use one of the existing IoT Agents that are part of IDAS.
10 |
11 | You need this component if you plan to connect IoT devices/gateways to FIWARE-based ecosystems. IoT Agents translate
12 | IoT-specific protocols into the NGSI context information protocol, that is the FIWARE standard data exchange model. You
13 | do not need this component if your devices or gateways natively support the NGSI API.
14 |
15 |
44 |
45 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G-3PGEibDuY "OMA Lightweight M2M")
46 |
47 | This video presentation explains how to connect to the internet of Things using the OMA Lightweight M2M protocol.
48 |
49 |
24 |
25 | The Open MTC GitHub repository contains a series examples for getting started with Open MTC:
26 |
27 | - [IPE-Sensors Demo App](https://fiware-openmtc.readthedocs.io/en/latest/training/training-ipe-sensors)
28 | - [Orion Context Broker Integration](https://github.com/OpenMTC/OpenMTC/tree/master/apps/OrionContextBroker)
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/processing/fogflow.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
FogFlow
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/processing/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/search?q=fogflow)
6 |
7 | FogFlow is an IoT edge computing framework to orchestrate dynamic processing flows over cloud and edges. It can
8 | dynamically and automatically composite multiple NGSI-based data processing tasks to form high level IoT services, and
9 | then orchestrate and optimize the deployment of those services within a shared cloud-edge environment, with regards to
10 | the availability, locality, and mobility of IoT devices.
11 |
12 |
13 |
14 | - [Documentation](https://fogflow.rtfd.io/)
15 |
16 |
24 |
25 | Use of FogFlow is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
26 |
27 | - [FIWARE 507: Cloud-Edge Computing](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/edge-computing.html)
28 |
29 |
Code Examples
30 |
31 | The Smart Parking repository contains a series examples for getting started with FogFlow:
32 |
33 | - [FogFlow Examples](https://github.com/smartfog/fogflow/tree/master/application/operator/smartparking)
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/processing/knowage.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Knowage - Business Intellegence
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/processing/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware-knowage)
6 |
7 | Knowage is the full capabilities open source suite for business analytics that ensures the freedom to access source code
8 | and collaborate in an international community, while letting you build your own business solution that ensure strategic
9 | decision-making and improved productivity. It provides different products, each one focused on a specific domain but
10 | mutually combinable to ensure comprehensive support to rich and multi-source data analysis. A full set of features, such
11 | as data federation, mash-up, data/text mining and advanced data visualization, give special focus on big data analytics
12 | and comprehensive support to rich and multi-source data analysis.
13 |
14 | - [Documentation](https://knowage.rtfd.io/)
15 | - [Site](https://www.knowage-suite.com/site/home/)
16 |
17 |
Academy Courses
18 |
19 |
Lesson 1. Introduction to Knowage
20 |
21 | This course depicts the global vision of Knowage Suite, the policy it carries out, its usage and its main features.
22 |
23 | - 
24 | [Lesson 1 - Introduction to Knowage](https://fiware-ops.github.io/docs.academy/knowage/course1)
25 |
26 |
Lesson 2. Knowage Report Designer
27 |
28 | BIRT technology platform is one of the most broadly employed data visualization and reporting technologies. Knowage open
29 | source project embedded BIRT technology platform into its products. Precisely, Knowage Report Designer contains a visual
30 | report designer for creating BIRT Designs while Knowage Server contains the runtime engine for generating those designs
31 | that can be deployed to any Java environment.
32 |
33 | - 
34 | [Lesson 2 - My First Report](https://fiware-ops.github.io/docs.academy/knowage/course2)
35 |
36 | This course aims at offering assistance to create a simple Report with Birt. We focused the attention on crucial steps
37 | from installation to the development of the document and finally show how the report can be transferred on server.
38 |
39 |
Lesson 3. Basics on the concept of Analytical Driver and LOV
40 |
41 | Knowage Server allows the user to set parameters to any analytical document by means of analytical drivers and LOVs. An
42 | analytical driver (AD) is an autonomous entity that models a business concept in order to use it as a discriminating
43 | criterion in the global data context, according to the different end user roles. LOV stands for List of Values. They
44 | represent the valid values for an analytical driver.
45 |
46 | - 
47 | [Lesson 3 - Parametric Report](https://fiware-ops.github.io/docs.academy/knowage/course3)
48 |
49 | In this course we see how parameters can be set on analytical documents stored on Knowage Server. The delineation of
50 | them is realised by means of LOV and AD. We illustrate the procedure step by step, in particular we show how these two
51 | tools comunicate with each other.
52 |
53 |
Lesson 4. Installing Knowage
54 |
55 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gqBBLOTi07Y "Installion on Windows")
56 |
57 | This video presentation explains how to install Knowage on Windows
58 |
59 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uK_C_bQSAaU "Installion on Linux")
60 |
61 | This video presentation explains how to install Knowage on Linux
62 |
63 |
Lesson 5. Online Demonstrations
64 |
65 | The following videos are without sound:
66 |
67 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=tgnVUAWs1kI "Overview")
68 |
69 | This video presentation gives an overview of the main analytical documents provided by the suite: traditional and
70 | advanced charts, reports, maps, OLAP, KPIs and interactive cockpits
71 |
72 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8FOiT7fhyf8 "Data federation")
73 |
74 | This video presentation shows how to upload private files, use external open data sets (ckan), relate both with
75 | enterprise data using a federated model.
76 |
77 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Rk9slySowO0 "Free Inquiry")
78 |
79 | This video presentation demonstrates the drag & drop query builder, to freely inquire traditional data source and big
80 | data systems, producing custom data sets
81 |
82 | [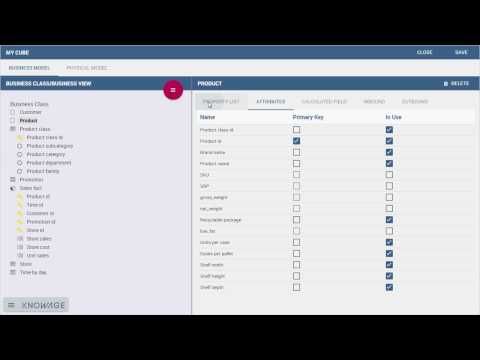](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ueUfgYHT_CA "Meta Model")
83 |
84 | This video presentation describes how to create a business metamodel over a traditional data source or big data
85 | systems/NoSQL databases that provide a metadata catalogue.
86 |
87 | [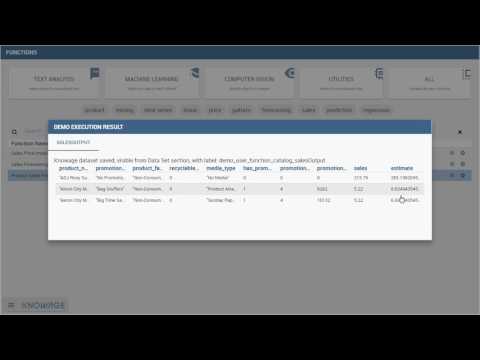](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=VZHBkfifW2c "Function catalogue")
88 |
89 | This video presentation describes how to use advanced analytics over private data in an easy way (prevision using R
90 | script)
91 |
92 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=f9dp8A74F7w "Cockpit Creation")
93 |
94 | This video presentation describes how to create an interactive cockpit in a few clicks without technical skills.
95 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/processing/kurento.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Kurento- Media Server
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/processing/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/kurento)
6 |
7 | The Kurento Media Server is a Stream-oriented Generic Enabler which provides a framework devoted to simplify the
8 | development of complex interactive multimedia applications through a rich family of APIs and toolboxes. Thanks to these,
9 | the Stream Oriented Generic Enabler provides developers with a set of robust end-to-end interoperable multimedia
10 | communication capabilities to deal with the complexity of transport, encoding/decoding, processing and rendering tasks
11 | in an easy and efficient way. Kurento is an implementation of the FIWARE Stream Oriented Generic Enabler. In summary,
12 | Kurento makes possible the development of complex interactive multimedia communications in a fast, simple and easy way.
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | - [Documentation](https://kurento.rtfd.io/)
17 | - [Site](https://www.kurento.org/)
18 |
19 |
54 |
55 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KpmOxTMb8Iw "Media Streams")
56 |
57 | This video presentation explains real-time media stream processing using the Kurento Media Server.
58 |
59 |
Code Examples
60 |
61 | Moreover, other tutorials can be done using the Stream Oriented GE (Kurento), for example:
62 |
63 | - Hello-world application.
64 | This application implements a WebRTC loopback (a WebRTC media stream going from client to Kurento and back to the
65 | client).
66 | - One to many
67 | video call application. This web application consists video broadcasting with WebRTC. One peer transmits a video
68 | stream and N peers receives it.
69 | - One to one
70 | video call. This application is a soft phone based on WebRTC.
71 | - Advanced
72 | one to one video call application. This is an enhanced version of the previous application recording of the
73 | video communication, and also integration with an augmented reality filter.
74 |
75 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
76 |
77 | Kurento is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
78 |
79 | - [FIWARE 503: Introduction to Media Streams](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/media-streams.html)
80 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/processing/wirecloud.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
WireCloud - Application Mashup
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/processing/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware-wirecloud)
6 |
7 | Wirecloud is a web mashup tool designed to ease the development of operational dashboards. This allows end users to
8 | easily create web applications and dashboards without programming skills and to visualize data of interest and control
9 | their environment.
10 |
11 | - [Documentation](https://wirecloud.rtfd.io/)
12 |
13 |
Academy Courses
14 |
15 |
Video 1. Wirecloud Training
16 |
17 | Recording of the Workshop about WireCloud delivered in the Developers' week at Madrid. This video presents an
18 | introduction on WireCloud and also presents some practical examples of how to use it for Data/Application Visualization
19 | and for building custom dashboards.
20 |
21 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=35npcYlnJpM "Wirecloud Training")
22 |
23 |
Video 2. FI-PPP Liaison Workshop about WireCloud
24 |
25 | Recording of the IMDEA FI-PPP Liaison Workshop about WireCloud. This video presents an introduction on WireCloud and
26 | also presents some practical examples of developing a simple chat widget using the WireCloud APIs.
27 |
28 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=q9smyuI-Yug "IMDEA FI-PPP Liaison")
29 |
30 |
51 | In this section you will learn how to use WireCloud from the point of view of a component developer. That is, you will learn how to develop Mashable Application Components (widgets and operators).
52 |
53 |
121 |
122 | Wirecloud is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
123 |
124 | - [FIWARE 501: Creating Application Mashups](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/application-mashups.html)
125 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | mkdocs==1.4.1
2 | Pygments==2.15.0
3 | Markdown==3.3.4
4 | jinja2==3.1.4
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/robotics/fast-rtps.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Fast-RTPS
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/robotics/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware)
6 |
7 | eProsima Fast RTPS is a C++ implementation of the RTPS (Real Time Publish Subscribe) protocol, which provides
8 | publisher-subscriber communications over unreliable transports such as UDP, as defined and maintained by the Object
9 | Management Group (OMG) consortium. RTPS is also the wire interoperability protocol defined for the Data Distribution
10 | Service (DDS) standard, again by the OMG.
11 |
12 |  [Documentation](https://fast-rtps.docs.eprosima.com/en/latest/)
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/security/apinf.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
APInf - API Management Framework
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/data-publication/README.md)
5 |
6 | The APInf API Management Framework is a Smart City orchestrator to be used together with other FIWARE enablers. APInf
7 | integrates with FIWARE core technologies, such as Identity Management, NGSI v2 and Business API Ecosystem along with API
8 | Umbrella to offer a comprehensive toolset to let various API Owners to run business with their APIs. Public market place
9 | is one of the essential GUI tools to help API Owners to reach their customer with the showcase.
10 |
11 | 
12 | [Documentation](https://github.com/apinf/platform/blob/develop/README.md)
13 |
14 |
Academy Courses
15 |
16 |
Lesson 1. Quick Start
17 |
18 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yCR6pCnTm5w "Quick Start")
19 |
20 | This video presentation shows how to get started with APInf API platform. It covers basic usage, and simple processes
21 | such as creating an account, adding a proxy and adding an API
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/security/authzforce.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
AuthzForce - XACML PDP
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/security/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/authzforce)
6 |
7 | **AuthzForce** is the reference implementation of the Authorization PDP Generic Enabler (formerly called Access Control
8 | GE). Indeed, as mandated by the GE specification, this implementation provides an API to get authorization decisions
9 | based on authorization policies, and authorization requests from PEPs. The API follows the REST architecture style, and
10 | complies with XACML v3.0.
11 |
12 |  [Documentation](https://authzforce-ce-fiware.rtfd.io/)
13 |
14 |
Academy Courses
15 |
16 |
Lesson 1. Introduction to Authorization PDP GE and AuthzForce GEri
Lesson 2. Introduction to the API of Authorization PDP GE
25 |
26 | In this lesson, you will learn how to use the common API (Application Programming Interface) of Authorization PDP
27 | Generic Enabler implementations, as defined in FIWARE Open Specification, including the reference implementation
28 | AuthzForce.
29 |
30 | - 
31 | Lesson 2 - Slides with audio
32 |
33 |
Lesson 3. Introduction to AuthzForce
34 |
35 | In this lesson, you will learn about AuthzForce - the Authorization PDP GEri:
36 |
37 | - Features, including extra API enhancements (not in the GE specification);
38 | - How to install;
39 | - How to administer;
40 | - How to use and program with AuthzForce API.
41 |
42 |
43 |
44 | - 
45 | Lesson 3 - Slides with audio
46 |
47 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
48 |
49 | Use of Authzforce is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
50 |
51 | - [FIWARE 405: XACML Rules-based Permissions](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/xacml-access-rules.html)
52 | - [FIWARE 406: Administrating XACML via a PAP](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/administrating-xacml.html)
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/security/keyrock.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Keyrock - Identity Management
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/security/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/search?q=%5Bfiware%5D+keyrock)
6 |
7 | Identity Management covers a number of aspects involving users' access to networks, services and applications, including
8 | secure and private authentication from users to devices, networks and services, authorization & trust management,
9 | user profile management, privacy-preserving disposition of personal data, Single Sign-On (SSO) to service domains and
10 | Identity Federation towards applications.
11 |
12 | The Identity Manager is the central component that provides a bridge between IdM systems at connectivity-level and
13 | application-level. Furthermore, Identity Management is used for authorising foreign services to access personal data
14 | stored in a secure environment. Hereby usually the owner of the data must give consent to access the data; the
15 | consent-giving procedure also implies certain user authentication.
16 |
17 |  [Documentation](https://fiware-idm.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
18 |
19 |
Academy Courses
20 |
21 |
Lesson 1. Introduction
22 | This lesson is an introduction of the functionalities that Keyrock offers you and an overview of how this course is structured.
23 |
24 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dHyVTan6bUY "Introduction")
25 |
26 | - 
27 | Lesson 1 - Slides
28 |
29 |
Lesson 2. Keyrock overview. Accounts and organizations.
30 | In this lesson you will learn how to manage accounts and organizations in Keyrock.
31 |
32 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dtKsjGbJ7Xc "Accounts and Organizations")
33 |
34 | - 
35 | Lesson 2 - Slides
36 |
37 |
Lesson 3. Applications. How to create OAuth2 tokens.
38 | In this lesson you will learn how to manage applications and how to create OAuth2 tokens with Keyrock.
39 |
40 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=pjsl0eHpFww "OAuth2 Tokens")
41 |
42 | - 
43 | Lesson 3 - Slides
44 |
45 |
Lesson 4. How to authorize users in your Cloud organization
46 | In this lesson you will learn how to authorize other users inside your organization in order to allow them to access your cloud resources.
47 |
48 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9h4edPsdANA "Authorize Users")
49 |
50 | - 
51 | Lesson 4 - Slides
52 |
53 |
Lesson 5. Installing Keyrock in your own infrastructure
Lesson 6. How to register your sensors in account portal
62 |
63 | In this lesson you will learn how to register IoT sensors in your FIWARE Lab applications
64 |
65 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Kbpx5CbQL74 "Register Sensors")
66 |
67 | - 
68 | Lesson 6 - Slides
69 |
70 |
Lesson 7. Adding Identity Manager and Access Control
71 |
72 | End-to-end example for IdM and Access Control. Training at Madrid Developers Week 2015.
73 |
74 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DzmtvEztcSY "Access Control")
75 |
76 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
77 |
78 | Use of the Keyrock Identity Manager is described in the following step-by-step tutorials:
79 |
80 | - [FIWARE 401: Administrating Users and Organizations](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/identity-management.html)
81 | - [FIWARE 402: Managing Roles and Permissions](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/.html)
82 | - [FIWARE 403: Securing Application Access](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/securing-access.html)
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/security/wilma.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Wilma - PEP Proxy
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/security/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware-wilma)
6 |
7 | The Wilma PEP Proxy in combination with Identity Management and Authorization PDP GEs, adds authentication and
8 | authorization security to your backend applications. Thus, only FIWARE users will be able to access your Generic
9 | Enablers and other REST services. The PEP Proxy allows you to programmatially manage specific permissions and policies
10 | to your resources allowing different access levels to your users.
11 |
12 |  [Documentation](https://fiware-pep-proxy.rtfd.io/)
13 |
14 |
Academy Courses
15 |
Lesson 1. Introduction
16 |
17 | This lesson introduces the main concepts needed to understand the architecture and the goals of Wilma.
18 |
19 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8tGbUI18udM "Introduction")
20 |
21 | - 
22 | Lesson 1 - Slides
23 |
24 |
Lesson 2. Installing, registering and configuring Wilma
33 | This lesson presents the way in which you can secure your REST APIs and shows practical examples with a real backend.
34 |
35 | [](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=coxFQEY0_So "Securing a REST API")
36 |
37 | - Lesson
38 | 3 - Slides
39 |
40 |
Step-by-Step Tutorials
41 |
42 | Use of the Wilma PEP Proxy is described in the following step-by-step tutorial:
43 |
44 | - [FIWARE 404: Securing Microservices with a PEP Proxy](https://fiware-tutorials.readthedocs.io/en/latest/pep-proxy.html)
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/third-party/domibus.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
Domibus - Electronic Data Exchange
3 |
4 | [](https://github.com/FIWARE/catalogue/blob/master/third-party/README.md)
5 | [](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/fiware)
6 |
7 | Domibus is a sample implementation of a
8 | [CEF eDelivery Access Point](https://ec.europa.eu/cefdigital/wiki/display/CEFDIGITAL/Access+Point+software). CEF
9 | eDelivery helps users to exchange electronic data and documents with one another in a reliable and trusted way. The CEF
10 | eDelivery solution is based on a distributed model called the “4-corner model”. In this model, the backend systems of
11 | the users don’t exchange data directly with each other but do this through Access Points. These Access Points are
12 | conformant to the same technical specifications and therefore capable of communicating with each other. As a result of
13 | this, users adopting CEF eDelivery can easily and safely exchange data even if their IT systems were developed
14 | independently from each other.
15 |
16 | 
17 | [Documentation](https://ec.europa.eu/cefdigital/wiki/display/CEFDIGITAL/Domibus)
18 |
19 |
Academy Courses
20 |
21 |
Lesson 1. Message Exchange Infrastructures
22 |
23 | The course explains how to design a Message Exchange Infrastructure putting together a message exchange model, discovery
24 | model and security model. Furthermore, it provides information on the specifications underpinning CEF eDelivery and its
25 | sample implementations.
26 |
27 | - 
28 | Lesson 1- Introdution to eDelivery
29 |
30 |
Lesson 2. Domibus Installation Tutorial PART I (Tomcat, Mysql, Linux)
10 |
11 | Good morning everybody. The subject of today's webinar is an overview to FIWARE itself. It assumes no prior knowledge of
12 | FIWARE and will introduce all the concepts you need to know.
13 |
14 | The learning goals for this particular session are as follows: you will try to understand what is context data in the
15 | realms of FIWARE; how is context data used within smart applications and how can FIWARE help; what is NGSI - it's a term
16 | which is fairly common when you're talking about FIWARE and then finally three things about aspects of FIWARE itself -
17 | the FIWARE catalog FIWARE marketplace and what is the overall role of the FIWARE Foundation itself, because sometimes
18 | the word _"FIWARE"_ can be used to mean the technologies and sometimes it can be meant to be the actual FIWARE
19 | Foundation. As you well know, the Internet has been changing over the years we've gone from very simple client-server
20 | applications through to much more complex and rich ecosystem the idea that you can have interaction with your business
21 | to business or things like social media you would have been completely unknown 5-10 years ago and you can see that the
22 | amount of information we are getting is increasing all the time we've gone from simple b2b moving up to actually getting
23 | people to talk to each other over the web, explain what they're doing and what-have-you and now it's a situation where
24 | machines, devices, robots are able to talk to the internet explain what is going on and this is the idea behind smart
25 | life.
26 |
27 | The background to all these things is _"context data"_. Context data describes what is going on where when and why. The
28 | way I prefer to describe it is that there are three vital questions you need to ask any device or any context entity and
29 | these are: _"Who are you?""_ - in other words you must have some sort of unique ID within your system. _"What are
30 | you?"_ - in other words there should be a type of the entity which will describe the data model which holds the data,
31 | and finally you need to ask _"How are you feeling today?"_ - in other words what are the attributes which are associated
32 | this entity. Now there is one obvious attribute which is _"location"_ which is dealt with differently within FIWARE
33 | because that means you can then do things like geofencing and what-have-you but the vast majority of attributes it will
34 | depend entirely on what you actually are - so for example a weather forecast would have the idea of _"temperature"_ or
35 | _"whether it's cloudy"_ or what-have-you whereas a coffee-shop would have a _"location"_ like where it is but also
36 | things like the _"opening times"_ or even possibly the prices of the coffee or what-have-you and with the cars it could
37 | have been a car with the GPS in it would have a _"location"_ or would have a _"number plate"_ and so on and so forth. So
38 | you can see the actual context data will depend on the elements you are talking about rather than being consistent
39 | across all devices - what this means is that we have more and more data which is coming from a wide variety of
40 | locations, a wide variety of sources and we want to make sure that such data is accessible outside of the information
41 | silo. You don't want to have all your mobility data completely separate from all of your building data - you want to be
42 | able to access elements as necessary - you want to be able to get information from additional web services - you want to
43 | be able to get information from social media - you obviously want to get information from IoT as well. It's also
44 | different locations where you can get the information about context.
45 |
46 | Now, this means that you have a situation where it is possible to retrieve information over a large amount of data so
47 | you can get a better position on what you should be doing within your smart system. The whole point about a smart
48 | solution is that you need to gather these sources, analyze these sources and then change the real world. The whole point
49 | about a smart solution is that smart solutions are not isolated into a single place - its a case of I have a model of
50 | the world, I modify that model of the world by processing my data saying what should I do next, and thereafter this will
51 | actuate real devices - it will change the state of the world. The state of the world will then be retrieved from sensors
52 | so that it will go back into the system, and you get this feedback to loop across here so you go process, capture -
53 | actually capture, process, actuate, capture, process, actuate so you're constantly changing the state of the smart
54 | solution. That is what is meant by a _"smart solution"_ - as you can see you can get this information in different
55 | domains within the domain of smart cities you would have things like a shop, with a location or business name or a bus,
56 | where its moving around and the driver would change or the number of passengers and how full it is would change but it's
57 | not just about smart cities - it's applicable to multiple verticals you can have the same situation in agri-food where
58 | you could have tractors, which obviously have a location like a bus, with of a location but you could also have crops,
59 | which would have things like the humidity or whatever - you can see that the idea is that you have an entity, which is
60 | covering something. It is covering something in the real world. Finally, another example, you within industry, you could
61 | have tankers, you could have the amount of space and a gas tank and so on and so forth.You can see this can apply to
62 | multiple domains.
63 |
64 | So what's the concept of FIWARE? What if there were a standard API for accessing context information? A universal
65 | standard for context information. You will have a situation where if you are supplying data in a neutral standard, you
66 | could have two separate cities (both of these cities happen to have a FIWARE web-based solution) who are offering their
67 | data to third parties, which would then be able to know that the data is in a standard format. So if you, in this case
68 | you're trying to solve the _"final mile problem"_ where you don't know where to go because you don't know where the
69 | parking spaces are or if parking spaces could be defined in a vendor-neutral standard, it doesn't matter what the
70 | low-level sensors are - whether they're different in these two cities - it means that you have an overall idea of this
71 | is how things are overall in this system - so that when your mobile phone goes to one of these two cities, you can say,
72 | okay, switching on where the car parking spaces - tell me what's going on. You can also get a situation where we don't
73 | care within FIWARE what the low level IoT protocol is being used. There are different competing IoT platforms which have
74 | got perfectly valid reasons to exist, because they might be low energy, they might be specific to domains, they might be
75 | solving a specific problem, however, if you can have an overriding context data layer above it - then you can get things
76 | like this one API call which we've got on the top of the screen - saying we can get data by just having stuff on a
77 | well-known endpoint - v2 - entities - slash - then the name of the entity itself, its ID, followed by the rest of the
78 | information. So this is getting the present sensor value of that lamp1 - this URL is part of the NGSI v2 definition,
79 | which is an open API specification for context data. The whole point being that you can use this standard, so you will
80 | be able to retrieve values from a sensor. We're just making a GET request which is obviously very simple if you're a web
81 | developer. Similarly if you want to actuate devices it's just simply a PUT request. It's not difficult to get these sort
82 | of things to happen, we can just switch on a water sprinkler by doing again an NGSI call using HTTP - just a standard
83 | PUT HTTP verb, and it's got a well-known URL saying for this particular attribute, of that particular entity, change
84 | that value. So activation becomes a side-effect effectively of just changing whatever we're doing with the end user
85 | interface. it means you have a very simple API. if we have this situation where you have a common context layer, you are
86 | able to interchange the information around the system quite easily, and you are reducing the silos within our system. So
87 | you have a situation where you can have common authorization policies, you can have possibilities of selling your data
88 | (if you wish) because you'll be doing it from the NGSI standards to whatever data standard you're using for
89 | monetization.
90 |
91 | Now the concept here has been picked up by the European Commission and we've been given a rubber stamp as one of the
92 | building blocks for connecting Europe facility - which means that someone out there thinks that actually this idea is
93 | rather good. It's already got a lot of traction in smart cities, we're growing in other verticals as we speak, so it
94 | means that you have a system where there are ways of getting the data which are open to other users rather than have to
95 | do all your development proprietarily in-house. if you are offering your data in this standard, or offering this
96 | interface in a standard, it means that other SMEs, other companies are able to access this data, and do the work for
97 | you. and do the work only once. if you are a SME if you can make your application _"FIWARE ready"_ - in other words it's
98 | able to talk this language - it means you can plug into any system similarly. if you have a processing layer which is
99 | talking NSGI, it can pass information down to devices which are _"FIWARE ready"_ - any device - regardless of the actual
100 | platform so it means that the whole system avoids vendor lock-in. FIWARE has been promoting a public royalty-free
101 | standard for context information management. This is a simple REST API this is NGSI v2, which I've mentioned already
102 | (and obviously with the v2 you can see that there was a v1 it's in the process of adapting as time goes by) The next
103 | generation we call NGSI-LD which adds in linked data concepts, such that you can have one entity, and then you can get
104 | information about another entity from it, so you have a application using this NGSI or FIWARE end user system and you
105 | can get the attributes from elsewhere. Once again you have your entities with your attributes - it's seen as a good idea
106 | this whole NGSI system has been rubber-stamped by a series of relevant standards bodies such as GSMA, CEF which I
107 | mentioned earlier, and the ETSI standard has recently been completed, and this is covering things like mobile operators,
108 | like your configured context data and information for smart cities. Furthermore there are other bodies such as OASC -
109 | we've got a large number of smart cities which are using this thing. In FIWARE we are developing common data models,
110 | such that the information can be passed from one system smoothly to another one - in concert with other standards bodies
111 | like a TM Forum and so on and so forth. And there's more! We have an agreement with IDSA, which is in the robotics
112 | domain for trying to get an open source implementation reference architecture here.
113 |
114 | Now, the idea here, is that because we are a middle layer, you need to find the appropriate player in the vertical to
115 | try and help you define the correct interface for that particular domain, because we're not experts in everything - we
116 | are obviously partnering with other systems as necessary. So this is the simple overview as to what the FIWARE web
117 | platform looks like. It consists of normally five blocks where you can get components from the different layers which
118 | can talk to each other. The only mandatory part is you must have a context broker. The context broker receives
119 | information in NGSI v2 format, holds the current context only, and then is able to pass information onto other layers.
120 | You may well want to get your information in using a component - you can send this stuff directly of course if you're
121 | doing HTTP calls and you almost certainly will want to get information out for either processing, visualization analysis
122 | and so and so forth. The other thing which goes in the core layer is that you can do things like data persistence and
123 | short term history and what-have-you, but the only mandatory thing is the context broker, to take the security part as
124 | an example, on the right hand side we keep the security components - obviously you want to have a secure system, but you
125 | don't have to take our security system - you can take an alternative security system. Similarly we have a set of
126 | visualization components, you can easily slot that in. You can just use ours, if it's not appropriate for your system
127 | ,you can create a receiving endpoint which will then do your own visualization. It's not all about _"take the whole
128 | lot"_ - just take the bits you need, but all you really need is a context broker. The context broker holds the current
129 | state of the overall smart system. This is the current set of FIWARE generic enablers. These are the free bits of
130 | software. The items in yellow are the incubated enablers, which are in the process of being accepted within the
131 | community. The items in white are full members who have achieved a certain level of traction within FIWARE. As you can
132 | see we have a wide range of elements across the entire system and I will go into detail with some of them going forward.
133 | You can see we've got things like big data analysis, we've got things like getting a connection to robots, document
134 | exchange, getting information from Internet of Things and so on and so forth. Looking in the core area, apart from the
135 | context broker itself, we have got several elements which are used for putting data into databases or to retrieve
136 | information on short term history so you can get a timeline. You can get information on trends, or you can get
137 | information posted into a large number of different databases. Again if you want this sort of thing, you just take it
138 | off the shelf, plug it in, it'll work in five minutes. For Comet, which the short-term history element you can get a
139 | timeline. There's an alternative for Comet called Quantum Leap which will do it into a Crate-DB rather than a MongoDB
140 | database, similarly there is an alternative to Cygnus called Draco which will use Apache NIFI rather than Apache Flume -
141 | as I said even within our system it's not _"take everything"_ - you take the bits you want if you're an expert in Flume
142 | then obviously you'd prefer Cygnus - it's up to you. Coming in from the bottom we need to be able to cope with
143 | proprietary systems, other IoT platforms so on and so forth and the way this is done is through creating a series of IoT
144 | agents. An IoT agent talks whatever language it is, whatever format it is below the line from the South port. For
145 | example OPC-UA is an example, but on the north port it talks pure NGSI v2 ,so it is a translation layer, you know, which
146 | can be configured using an API as you'd expect. So it's a microservice, and it can also talk through various different
147 | transports - you can either talk directly using HTTP, you can use MQTT, you can use Rabbit MQ and of course there are a
148 | wide range and growing range of IoT platforms which are supported. So this is our way of getting around the standards of
149 | the IoT level in other words we stay on top. We also have the ability to get data out of stream information video
150 | information this is the Kurento component. with Kurento you would be able to retrieve a video stream and then look into
151 | the images so that you can actually get some context data out of it. It also does a large number of other elements which
152 | are not strictly speaking context data related, but within our system you'd want to get context in and out of your data.
153 | With any of these systems you want to be able to display and then activate the system and one of the components here is
154 | called Wirecloud. Wirecloud is a mash-up visualization tool which reads the data from the NGSI format and then puts it
155 | out in whichever graphically pleasing method you want. You're able to add in additional custom widgets as necessary, so
156 | that and you can share them as well, so that you can get the data in the right format, so you can make the right
157 | analysis. Another more extensive tool is Knowage, this is a business intelligence suite, which again you're able to
158 | retrieve the data and do a wide range of queries based on what is the state of our smart system. Furthermore, we are
159 | able to connect to big data - as you would expect you're able to extract out data and put it into some sort of system
160 | for big data analysis. You may well be in a situation where you want to be able to sell the your data. Your data is
161 | valuable, and obviously you need to have sovereignty on it, and you need to be able to make money as necessary, and give
162 | people access as necessary. The components here are extended CKAN and the business framework API. The business framework
163 | will take the money for you, extended CKAN will offer your data set as a CKAN data set, but it is actually the current
164 | context data which is in the system - so that you are able to pass information out to other systems.
165 |
166 | Now as I said, we have a series of access control components, where as you would expect you make a request of some sort,
167 | there is some sort of gatekeeping components (this is Wilma which is a PEP proxy - which is a policy execution point in
168 | the jargon) and that will then talk to an IDM which is an identity manager saying _"okay, who is this?"_ because they
169 | have already supplied some sort of token in their request the IDM will give information including roles or including the
170 | name of the person what have you, and then you can either ask Keyrock to adjudicate or more likely for a complex
171 | scenario you can ask Authzforce to adjudicate which is a policy decision point saying _"based on the information I have,
172 | should I let this user through or not?"_ It's a fairly standard architecture for securing your services - in the case
173 | where you were doing monetization, what you would need to do is, you set up the system where you would have a PEP proxy
174 | in front of the accounting framework, which would say _"can this user get hold of this thing?"_ - _"is he going to let
175 | this GET request be allowed through?""_ and then once information is being passed to the proxy it would also then get
176 | the business framework to talk to CKAN. CKQN would then also request the information saying _"is this OK? am I really
177 | allowed to send this out?"_ and then pass the information on. So you can see that the various components we have are
178 | able to talk amongst themselves to cover the scenarios which are required of it. We have a series of developer
179 |
180 |
181 |
182 | information on our website - if there any questions beyond the webinar today the answer is usually on fiware.org.
183 |
184 |
185 |
186 | Now for our reference architecture - we take that five box system - obviously deployment is not necessary for these
187 | architecture, and again you have the context broker there in the middle - which is receiving data from the data
188 | acquisition layer, and then you are processing on the top. With in this particular diagram we're doing an agricultural
189 | system - as you can see you get information from your machines or from your crops it goes through the adaption layer -
190 | so that means that it's no longer proprietary stuff - it's NGSI and from the context broker onwards everything is NGSI,
191 | and covers our system so you can use our access control to let people in or out if it's necessary, and then we can talk
192 | to other processing layers on top so we can also retrieve information from third parties, such as weather web services
193 | to augment the existing context information. So that when you are receiving the information on the top layer, you've got
194 | an overall view of the context, not just or not necessarily just what's in the devices themselves. You will see that the
195 | reference architecture is very similar depending on which system you are looking at. There are various examples of
196 | systems out there which are already using FIWARE. they are already _"FIWARE ready"_. This is an example in the cities
197 | domain which is a _"FIWARE ready"_ solution which is able to retrieve noise information - obviously that would then be
198 | changed in NGSI and it will be pushed on the screen in an appropriate manner - again you've got visualization it's the
199 | same thing. You have other examples of FIWARE, which would be say, using industry or preventative maintenance - once
200 | again you have elements which are things like GPS or you have devices in the in the vehicle which would then be able to
201 | pass that as context information up to the system and you do appropriate processing. Similarly there are elements in the
202 | agricultural domain where you could have a collar around the an animal and that once again would give you information
203 | using the say the sigfox IoT agent which passes information up into the context data . You'd know where your animals
204 | are, even how they are feeling and you are protecting your assets. ... and again another one - with the idea of trying
205 | to make sure that your information in the silo is passed into the system it's a method of analyzing grain silos to see
206 | how much it is left in there and it's just purely battery-powered ... and there's more stuff at the FIWARE health domain
207 | as well. You can see that we are covering a wide range of areas. We can also use FIWARE as the basis of a
208 | system-of-systems approach because we are able to retrieve information from other contexts brokers - as information
209 | which is relevant for my entity - so I can augment my entity with information from other systems. So we can take
210 | information from, say a silo, a pest management system and so on and so forth to come up with an overall integrated
211 | version of the farm. Within smart cities again, it's the same architecture - you've got the Orion context broker in the
212 | middle, you've got your devices at the bottom, you've got your IoT agent in the middle and you've got your governing
213 | system the top - obviously it's either at the top where you've got the processing stuff all right at the bottom where
214 | you will be able to supply your unique intellectual property so that's where companies are able to make you make money
215 | out of this system .. and for same similar picture and factory - similar picture everything is coming in the same idea -
216 | you have your devices at the bottom - you have some sort of translation layer, you get the context broker and keep
217 | moving it up to the processing layer. So, I've already mentioned the stuff about the car navigators, but the point here
218 | is that you can actually get information coming out in a fashion that other users, other third-party users, are able to
219 | go retrieve.
220 |
221 | So we're not just about the technology. The FIWARE Foundation is about promoting this technology and covers a wider
222 | range of elements than just doing the technology itself. Ee don't actually create the software ourselves, we are
223 | promoting and doing it. We are trying to create a sustainable ecosystem here, which is obviously from a wide variety of
224 | users. We offer a marketplace which is usable for any system which is _"powered by FIWARE"_ or _"FIWARE ready"_.
225 | _"Powered by FIWARE"_ means that you've got something using the context broker. _"FIWARE ready"_ means that you're able
226 | to connect to the context broker. You can see that solutions are able to go end-to-end, but you're also able to offer
227 | information about devices, so you can say, this device will plug into any FIWARE solution. And of course you can also
228 |
229 |
230 |
231 | offer training or consultancy services and so on and so forth. There is also the FIWARE lab. It is a experimental area
232 |
233 |
234 |
235 | where you can actually upload and fiddle around with your architecture for free and we have another area called FIWARE
236 | Mundus which is doing things worldwide and there are a series of FIWARE iHubs where you can get technical information
237 | local to you and we have accelerator program. In summary, there are six areas - the overall mission is to create this
238 | sustainable ecosystem around these royalty-free things using these five pillars. So that is FIWARE. In summary:
239 | _"context data"_ represents the state of a physical or conceptual object which exists in the real world. You have smart
240 | solutions which are able to read information from sensors and other sources and analyze that information to actuate
241 | devices - this is a continuous feedback loop. _"FIWARE"_ itself is an open source initiative, which we are driving the
242 | definition of the universal set of standards for context data management - if you haven't got context data in your
243 | system you shouldn't use us, use somebody else.
244 |
245 | Now, the name of this standard is called _"NGSI v2"_, and it is vendor-neutral so that no one company has got control of
246 | it. That is why we are a spin-off Foundation and it is usable for all interactions within the FIWARE technology. FIWARE
247 | also has a catalog which is a curated framework of open-source platform components which can be added to one another and
248 | you only take the bits you want, so you get free software and the right bit of free software for you, and the only one
249 | which is essential is the context broker. You can use other components, you can use third-party components to cover that
250 | area - and the whole point here is to accelerate the development of your smart solution. You don't have to write
251 | everything from scratch you can get 90% of it for free. Once you've created a solution we have a marketplace, which is
252 | able to promote your existing commercial offerings. ... and the FIWARE Foundation, which is a legally independent body
253 | is able to protect FIWARE itself and it has these five pillars of the FIWARE lab, the iHubs, the Accelerator, Mundus and
254 | everything else which has been there covered this morning. So that, in summary, is a brief introduction to FIWARE, and I
255 | thank you very much and I hope you have a good day.
256 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/doc.svg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
5 | ]>
6 |
113 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/favicon.ico:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FIWARE-Ops/docs.academy/d4503049abe8c74a3430ec44e8b5e9aa778d3644/img/favicon.ico
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/favicon.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FIWARE-Ops/docs.academy/d4503049abe8c74a3430ec44e8b5e9aa778d3644/img/favicon.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/link.svg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
5 | ]>
6 |
486 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/logo.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FIWARE-Ops/docs.academy/d4503049abe8c74a3430ec44e8b5e9aa778d3644/img/logo.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/pdf.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FIWARE-Ops/docs.academy/d4503049abe8c74a3430ec44e8b5e9aa778d3644/img/pdf.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mkdocs.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | site_name: Academy
2 | site_url: https://fiware-academy.readthedocs.org
3 | repo_url: https://github.com/fiware-ops/docs.academy
4 | site_description: FIWARE Academy
5 | docs_dir: docs
6 | site_dir: html
7 | use_directory_urls: false
8 | theme: readthedocs
9 | google_analytics: ["UA-83719923-1", 'fiware-academy.readthedocs.io']
10 | extra_css: ["https://www.fiware.org/style/fiware_readthedocs.css", "https://www.fiware.org/style/fiware_readthedocs_neutral.css"]
11 | nav:
12 | - Home: 'index.md'
13 | - 'Integrated Courses':
14 | - 'FIWARE Webinars': 'integrated-courses/webinars.md'
15 | - 'FIWARE Training': 'integrated-courses/fiware-training.md'
16 | - 'i4Trust: Train the Trainers': 'integrated-courses/i4Trust.md'
17 | - 'CEF Smart Cities': 'integrated-courses/cef-smart-cities.md'
18 | - 'Core Context Managment':
19 | - 'Cosmos': 'core/cosmos.md'
20 | - 'Cygnus': 'core/cygnus.md'
21 | - 'Draco': 'core/draco.md'
22 | - 'Orion': 'core/orion.md'
23 | - 'Orion-LD': 'core/orion-ld.md'
24 | - 'QuantumLeap': 'core/quantum-leap.md'
25 | - 'Scorpio': 'core/scorpio.md'
26 | - 'STH-Comet': 'core/sth-comet.md'
27 | - 'IoT Agents, Robots & Third Party Systems':
28 | - 'Domibus': 'third-party/domibus.md'
29 | - 'Fast-RTPS': 'robotics/fast-rtps.md'
30 | - 'IoT Agents': 'iot-agents/idas.md'
31 | - 'Open MTC': 'iot-agents/open-mtc.md'
32 | - 'Security':
33 | - 'APInf': 'security/apinf.md'
34 | - 'Authzforce': 'security/authzforce.md'
35 | - 'Keyrock': 'security/keyrock.md'
36 | - 'Wilma': 'security/wilma.md'
37 | - 'Processing, Analysis and Visualization':
38 | - 'FogFlow': 'processing/fogflow.md'
39 | - 'Knowage': 'processing/knowage.md'
40 | - 'Kurento': 'processing/kurento.md'
41 | - 'Wirecloud': 'processing/wirecloud.md'
42 | - 'Data Publication':
43 | - 'Biz Ecosystem': 'data-publication/business-api.md'
44 | - 'CKAN': 'data-publication/ckan.md'
45 | - 'Idra': 'data-publication/idra.md'
46 | - 'Appendix: Transcripts':
47 | - 'Introduction to FIWARE': 'transcripts/introduction-to-fiware.md'
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "name": "fiware-academy",
3 | "version": "8.2.0",
4 | "description": "Video tutorials, slide decks and other training materials for developers learning about the FIWARE ecosystem.",
5 | "keywords": [
6 | "node",
7 | "fiware",
8 | "tutorials",
9 | "validator",
10 | "ngsi"
11 | ],
12 | "license": "CC-BY-4.0",
13 | "repository": {
14 | "type": "git",
15 | "url": "https://github.com/fiware/academy"
16 | },
17 | "homepage": "https://fiware-academy.readthedocs.io/en/latest/",
18 | "devDependencies": {
19 | "eslint": "^8.9.0",
20 | "eslint-config-tamia": "^7.2.7",
21 | "eslint-plugin-prettier": "^4.0.0",
22 | "husky": "^7.0.4",
23 | "lint-staged": "^13.2.1",
24 | "memfs": "3.4.1",
25 | "prettier": "^2.5.1",
26 | "remark-cli": "^10.0.1",
27 | "remark-preset-lint-recommended": "^6.1.2",
28 | "textlint": "^12.1.0",
29 | "textlint-filter-rule-comments": "^1.2.2",
30 | "textlint-rule-common-misspellings": "^1.0.1",
31 | "textlint-rule-terminology": "^2.1.5",
32 | "textlint-rule-write-good": "^2.0.0"
33 | },
34 | "engines": {
35 | "node": ">=16"
36 | },
37 | "scripts": {
38 | "start": "mkdocs serve",
39 | "pre-commit": "lint-staged",
40 | "lint:text": "textlint 'README.md' 'docs/*.md' 'docs/**/*.md'",
41 | "lint:md": "remark -f 'README.md' 'docs'",
42 | "prettier:text": "prettier 'README.md' 'docs/*.md' 'docs/**/*.md' --no-config --tab-width 4 --print-width 120 --write --prose-wrap always",
43 | "prepare": "husky install"
44 | },
45 | "lint-staged": {
46 | "*.md": [
47 | "prettier --no-config --tab-width 4 --print-width 120 --write --prose-wrap always"
48 | ]
49 | },
50 | "remarkConfig": {
51 | "settings": {
52 | "bullet": "-",
53 | "paddedTable": true
54 | },
55 | "plugins": [
56 | "remark-preset-lint-recommended"
57 | ]
58 | }
59 | }
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------