├── html
└── cuda2glcore.JPG
├── src
├── gl_tools.h
├── shader_tools
│ ├── GLSLProgram.h
│ ├── GLSLShader.h
│ ├── shader_tools_common.h
│ ├── GLSLShader.cpp
│ └── GLSLProgram.cpp
├── glfw_tools.h
├── kernel.cu
├── main.cpp
└── libs
│ ├── helper_gl.h
│ ├── helper_cuda.h
│ └── helper_string.h
├── msvc
└── vs2019
│ ├── custom_includes.props
│ ├── cuda2GLCore.sln
│ ├── cuda2GLCore.vcxproj.filters
│ └── cuda2GLCore.vcxproj
├── README.md
├── .gitignore
└── LICENSE
/html/cuda2glcore.JPG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Forceflow/cuda2GLcore/HEAD/html/cuda2glcore.JPG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/gl_tools.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 |
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 |
6 | using namespace std;
7 |
8 | void printGlewInfo(){
9 | printf("GLEW: Glew version: %s \n", glewGetString(GLEW_VERSION));
10 | }
11 |
12 | void printGLInfo(){
13 | printf("OpenGL: GL version: %s \n", glGetString(GL_VERSION));
14 | printf("OpenGL: GLSL version: %s\n", glGetString(GL_SHADING_LANGUAGE_VERSION));
15 | printf("OpenGL: Vendor: %s\n", glGetString(GL_VENDOR));
16 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/shader_tools/GLSLProgram.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 | #include "shader_tools_common.h"
3 | #include "GLSLShader.h"
4 |
5 | class GLSLProgram {
6 | public:
7 | GLuint program;
8 | bool linked;
9 | private:
10 | GLSLShader* vertex_shader;
11 | GLSLShader* fragment_shader;
12 | public:
13 | GLSLProgram::GLSLProgram();
14 | GLSLProgram::GLSLProgram(GLSLShader* vertex, GLSLShader* fragment);
15 | void GLSLProgram::compile();
16 | void GLSLProgram::use();
17 | private:
18 | void GLSLProgram::printLinkError(GLuint program);
19 | };
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/glfw_tools.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 |
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 | #include
6 |
7 | using namespace std;
8 |
9 | void printGLFWInfo(GLFWwindow* w){
10 | int p = glfwGetWindowAttrib(w, GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE);
11 | string version = glfwGetVersionString();
12 | string opengl_profile = "";
13 | if(p == GLFW_OPENGL_COMPAT_PROFILE){
14 | opengl_profile = "OpenGL Compatibility Profile";
15 | }
16 | else if (p == GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE){
17 | opengl_profile = "OpenGL Core Profile";
18 | }
19 | printf("GLFW: %s \n", version.c_str());
20 | printf("GLFW: %s %i \n", opengl_profile.c_str(), p);
21 | }
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/shader_tools/GLSLShader.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 | #include "shader_tools_common.h"
3 |
4 | class GLSLShader {
5 | public:
6 | GLuint shader;
7 | GLint compiled;
8 | GLenum shadertype;
9 | std::string shader_name;
10 | private:
11 | std::string shader_src; // internal string representation of shader
12 |
13 | public:
14 | GLSLShader::GLSLShader();
15 | GLSLShader::GLSLShader(const std::string &shader_name, const char *shader_text, GLenum shadertype);
16 | GLSLShader::GLSLShader(const std::string &shader_name, const std::string &shader_text, GLenum shadertype);
17 | std::string GLSLShader::getSrc() const;
18 | void GLSLShader::setSrc(const std::string &new_source);
19 | void GLSLShader::setSrc(const char* new_source);
20 | void GLSLShader::compile();
21 |
22 | private:
23 | void GLSLShader::getCompilationError(GLuint shader);
24 | };
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/shader_tools/shader_tools_common.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #pragma once
2 |
3 | #ifndef GLEW_STATIC
4 | #define GLEW_STATIC
5 | #endif
6 |
7 | #include
8 | #include
9 | #include
10 | #include
11 | #include
12 |
13 | // Simple helper to switch between character arrays and C++ strings
14 | struct ShaderStringHelper{
15 | const char *p;
16 | ShaderStringHelper(const std::string& s) : p(s.c_str()) {}
17 | operator const char**() { return &p; }
18 | };
19 |
20 | // Function to load text from file
21 | // static, we only want this function to be available in this file's scope
22 | inline static std::string loadFileToString(const char *filename){
23 | std::ifstream file(filename, std::ios::in);
24 | std::string text;
25 | if (file){
26 | file.seekg(0, std::ios::end); // go to end
27 | text.resize(file.tellg()); // resize text buffer to file size
28 | file.seekg(0, std::ios::beg); // back to begin
29 | file.read(&text[0], text.size()); // read into buffer
30 | file.close();
31 | }
32 | else {
33 | std::string error_message = std::string("File not found: ") + filename;
34 | fprintf(stderr, error_message.c_str());
35 | throw std::runtime_error(error_message);
36 | }
37 | return text;
38 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/kernel.cu:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "cuda_runtime.h"
2 | #include
3 | #include
4 |
5 | cudaError_t cuda();
6 |
7 | __global__ void kernel(){
8 |
9 | }
10 |
11 | // clamp x to range [a, b]
12 | __device__ float clamp(float x, float a, float b)
13 | {
14 | return max(a, min(b, x));
15 | }
16 |
17 | __device__ int clamp(int x, int a, int b)
18 | {
19 | return max(a, min(b, x));
20 | }
21 |
22 | // convert floating point rgb color to 8-bit integer
23 | __device__ int rgbToInt(float r, float g, float b)
24 | {
25 | r = clamp(r, 0.0f, 255.0f);
26 | g = clamp(g, 0.0f, 255.0f);
27 | b = clamp(b, 0.0f, 255.0f);
28 | return (int(b) << 16) | (int(g) << 8) | int(r);
29 | }
30 |
31 | __global__ void
32 | cudaRender(unsigned int *g_odata, int imgw)
33 | {
34 | extern __shared__ uchar4 sdata[];
35 |
36 | int tx = threadIdx.x;
37 | int ty = threadIdx.y;
38 | int bw = blockDim.x;
39 | int bh = blockDim.y;
40 | int x = blockIdx.x*bw + tx;
41 | int y = blockIdx.y*bh + ty;
42 |
43 | uchar4 c4 = make_uchar4((x & 0x20) ? 100 : 0, 0, (y & 0x20) ? 100 : 0, 0);
44 | g_odata[y*imgw + x] = rgbToInt(c4.z, c4.y, c4.x);
45 | }
46 |
47 | extern "C" void
48 | launch_cudaRender(dim3 grid, dim3 block, int sbytes, unsigned int *g_odata, int imgw)
49 | {
50 | cudaRender << < grid, block, sbytes >> >(g_odata, imgw);
51 | }
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/msvc/vs2019/custom_includes.props:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 | D:\dev\libs\glfw
7 | D:\dev\libs\glew
8 |
9 |
10 | $(GLEW_DIR)\include;$(GLFW_DIR)\include;$(IncludePath)
11 | $(GLEW_DIR)\lib\Release\x64;$(GLFW_DIR)\lib-vc2015;$(LibraryPath)
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | glu32.lib;glew32s.lib;glfw3.lib;opengl32.lib;%(AdditionalDependencies)
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 | $(GLFW_DIR)
22 | true
23 |
24 |
25 | $(GLEW_DIR)
26 | true
27 |
28 |
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/msvc/vs2019/cuda2GLCore.sln:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Microsoft Visual Studio Solution File, Format Version 12.00
3 | # Visual Studio 15
4 | VisualStudioVersion = 15.0.26730.15
5 | MinimumVisualStudioVersion = 10.0.40219.1
6 | Project("{8BC9CEB8-8B4A-11D0-8D11-00A0C91BC942}") = "cuda2GLCore", "cuda2GLCore.vcxproj", "{6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}"
7 | EndProject
8 | Global
9 | GlobalSection(SolutionConfigurationPlatforms) = preSolution
10 | Debug|x64 = Debug|x64
11 | Debug|x86 = Debug|x86
12 | Release|x64 = Release|x64
13 | Release|x86 = Release|x86
14 | EndGlobalSection
15 | GlobalSection(ProjectConfigurationPlatforms) = postSolution
16 | {6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}.Debug|x64.ActiveCfg = Debug|x64
17 | {6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}.Debug|x64.Build.0 = Debug|x64
18 | {6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}.Debug|x86.ActiveCfg = Debug|Win32
19 | {6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}.Debug|x86.Build.0 = Debug|Win32
20 | {6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}.Release|x64.ActiveCfg = Release|x64
21 | {6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}.Release|x64.Build.0 = Release|x64
22 | {6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}.Release|x86.ActiveCfg = Release|Win32
23 | {6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}.Release|x86.Build.0 = Release|Win32
24 | EndGlobalSection
25 | GlobalSection(SolutionProperties) = preSolution
26 | HideSolutionNode = FALSE
27 | EndGlobalSection
28 | GlobalSection(ExtensibilityGlobals) = postSolution
29 | SolutionGuid = {6DF1FFA5-F510-483D-A8F0-F01E699EE79B}
30 | EndGlobalSection
31 | EndGlobal
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # cuda2GLcore
2 | This is an implementation of the *SimpleCuda2GL* sample provided in the [CUDA Samples by Nvidia](http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-samples/index.html). The project shows how to generate a texture in CUDA and use it in an [OpenGL](https://www.opengl.org/) context without copying it to main memory. The original implementation uses [Glut](https://www.opengl.org/resources/libraries/glut/) and OpenGL immediate mode to draw the resulting texture.
3 |
4 | This implementation improves on the original example by using [GLEW](http://glew.sourceforge.net/), [GLFW](http://www.glfw.org/) and OpenGL 4.5 core, using buffer objects, allowing your applications to be analyzed by excellent tools such as Renderdoc, which only support core OpenGL Profiles.
5 |
6 | **Note:** This example was based on the CUDA 8.0 samples and has been updated to work with newer CUDA versions. Since CUDA 11.0, the official NVIDIA sample has been problematic for me to run ([issue here](https://github.com/NVIDIA/cuda-samples/issues/61)). I'm working on pulling this example in line with the official samples. For now, this still seems like a good starting point, unless you're on OSX.
7 |
8 | # Usage
9 | In the `msvc` folder, there is a VS2017 and a VS2019 project (both have been tested using the VS Community Edition). Use the`custom_includes.props` file to define the locations of your GLEW and GLFW installations, then run the project.
10 |
11 | 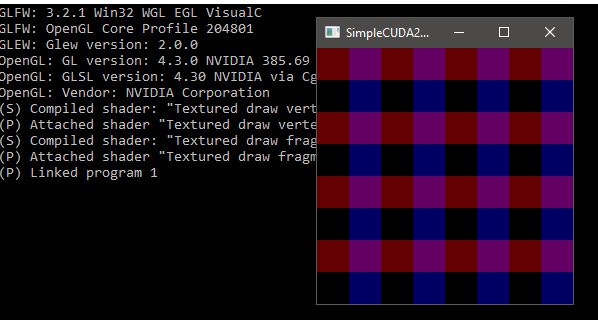
12 |
13 | # Notes
14 | * This code contains helper libraries by [Nvidia](http://docs.nvidia.com/cuda/cuda-samples/index.html). All of the code samples are available under a permissive license that allows you to freely incorporate them into your applications and create derivative works for commercial, academic, or personal use.
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/shader_tools/GLSLShader.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "GLSLShader.h"
2 |
3 | GLSLShader::GLSLShader() :
4 | shader(0), compiled(false), shadertype(0), shader_name(""), shader_src("") {
5 | }
6 |
7 | GLSLShader::GLSLShader(const std::string &shader_name, const char *shader_text, GLenum shadertype) :
8 | shader(0), compiled(false), shadertype(shadertype), shader_name(shader_name), shader_src(std::string(shader_text)) {
9 | }
10 |
11 | GLSLShader::GLSLShader(const std::string &shader_name, const std::string &shader_text, GLenum shadertype) :
12 | shader(0), compiled(false), shadertype(shadertype), shader_name(shader_name), shader_src(shader_text) {
13 | }
14 |
15 | std::string GLSLShader::getSrc() const {
16 | return shader_src;
17 | }
18 |
19 | void GLSLShader::setSrc(const std::string &new_source) {
20 | shader_src = new_source;
21 | compiled = false; // setting new source forces recompile
22 | }
23 |
24 | void GLSLShader::setSrc(const char* new_source) {
25 | shader_src = std::string(new_source);
26 | compiled = false; // setting new source forces recompile
27 | }
28 |
29 | void GLSLShader::compile() {
30 | printf("(S) Compiling shader \"%s\" ... ", this->shader_name.c_str());
31 | shader = glCreateShader(shadertype);
32 | glShaderSource(shader, 1, ShaderStringHelper(shader_src), NULL);
33 | glCompileShader(shader);
34 | // check if shader compiled
35 | glGetShaderiv(shader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &compiled);
36 | if (!compiled) {
37 | getCompilationError(shader);
38 | glDeleteShader(shader);
39 | compiled = false;
40 | }
41 | else {
42 | printf("OK - Shader ID: (%i) \n", shader);
43 | }
44 | }
45 |
46 | void GLSLShader::getCompilationError(GLuint shader) {
47 | int infologLength = 0;
48 | glGetShaderiv(shader, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, (GLint *)&infologLength);
49 | char* infoLog = (char *)malloc(infologLength);
50 | glGetShaderInfoLog(shader, infologLength, NULL, infoLog); // will include terminate char
51 | printf("(S) Shader compilation error:\n%s\n", infoLog);
52 | free(infoLog);
53 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/shader_tools/GLSLProgram.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "GLSLProgram.h"
2 |
3 | GLSLProgram::GLSLProgram() : program(0), vertex_shader(NULL), fragment_shader(NULL), linked(false) {}
4 |
5 | GLSLProgram::GLSLProgram(GLSLShader* vertex, GLSLShader* fragment) : program(0), vertex_shader(vertex), fragment_shader(fragment), linked(false) {}
6 |
7 | void GLSLProgram::compile() {
8 | // create empty program
9 | program = glCreateProgram();
10 | // try to attach all shaders
11 | GLSLShader* shaders[2] = { vertex_shader, fragment_shader };
12 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
13 | if (shaders[i] != NULL) {
14 | if (!shaders[i]->compiled) { shaders[i]->compile(); } // try to compile shader if not yet compiled
15 | if (shaders[i]->compiled) {
16 | glAttachShader(program, shaders[i]->shader);
17 | printf("(P) Attached shader \"%s\"(%i) to program (%i)\n", shaders[i]->shader_name.c_str(), shaders[i]->shader, program);
18 | }
19 | else {
20 | printf("(P) Failed to attach shader \"%s\"(%i) to program (%i)\n", shaders[i]->shader_name.c_str(), shaders[i]->shader, program);
21 | glDeleteProgram(program);
22 | return;
23 | }
24 | }
25 | }
26 | // try to link program
27 | glLinkProgram(program);
28 | GLint isLinked = 0;
29 | glGetProgramiv(program, GL_LINK_STATUS, &isLinked); // check if program linked
30 | if (isLinked == GL_FALSE) {
31 | printLinkError(program);
32 | glDeleteProgram(program);
33 | linked = false;
34 | }
35 | else {
36 | linked = true;
37 | printf("(P) Linked program %i \n", program);
38 | }
39 | }
40 |
41 | void GLSLProgram::use() {
42 | glUseProgram(this->program);
43 | }
44 |
45 | void GLSLProgram::printLinkError(GLuint program) {
46 | GLint infologLength = 0;
47 | glGetProgramiv(program, GL_INFO_LOG_LENGTH, (GLint *)&infologLength);
48 | char* infoLog = (char *)malloc(infologLength);
49 | glGetProgramInfoLog(program, infologLength, NULL, infoLog); // will include terminate char
50 | printf("(P) Program compilation error: %s\n", infoLog);
51 | free(infoLog);
52 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/msvc/vs2019/cuda2GLCore.vcxproj.filters:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | {e6709c1a-6cd6-4687-ad3f-68a303192e65}
6 |
7 |
8 | {0592dce3-c09a-4291-b67b-cd3a978ad025}
9 |
10 |
11 | {72c86a08-3efd-487c-998b-ce1d7e87365a}
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | shader_tools
17 |
18 |
19 | shader_tools
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 | shader_tools
26 |
27 |
28 | shader_tools
29 |
30 |
31 | shader_tools
32 |
33 |
34 | gl
35 |
36 |
37 | gl
38 |
39 |
40 | cuda
41 |
42 |
43 | cuda
44 |
45 |
46 | cuda
47 |
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Ignore Visual Studio temporary files, build results, and
2 | ## files generated by popular Visual Studio add-ons.
3 |
4 | # User-specific files
5 | *.suo
6 | *.user
7 | *.userosscache
8 | *.sln.docstates
9 |
10 | # User-specific files (MonoDevelop/Xamarin Studio)
11 | *.userprefs
12 |
13 | # Build results
14 | [Dd]ebug/
15 | [Dd]ebugPublic/
16 | [Rr]elease/
17 | [Rr]eleases/
18 | x64/
19 | x86/
20 | build/
21 | bld/
22 | [Bb]in/
23 | [Oo]bj/
24 |
25 | # Visual Studio 2015 cache/options directory
26 | .vs/
27 |
28 | # MSTest test Results
29 | [Tt]est[Rr]esult*/
30 | [Bb]uild[Ll]og.*
31 |
32 | # NUNIT
33 | *.VisualState.xml
34 | TestResult.xml
35 |
36 | # Build Results of an ATL Project
37 | [Dd]ebugPS/
38 | [Rr]eleasePS/
39 | dlldata.c
40 |
41 | # DNX
42 | project.lock.json
43 | artifacts/
44 |
45 | *_i.c
46 | *_p.c
47 | *_i.h
48 | *.ilk
49 | *.meta
50 | *.obj
51 | *.pch
52 | *.pdb
53 | *.pgc
54 | *.pgd
55 | *.rsp
56 | *.sbr
57 | *.tlb
58 | *.tli
59 | *.tlh
60 | *.tmp
61 | *.tmp_proj
62 | *.log
63 | *.vspscc
64 | *.vssscc
65 | .builds
66 | *.pidb
67 | *.svclog
68 | *.scc
69 |
70 | # Chutzpah Test files
71 | _Chutzpah*
72 |
73 | # Visual C++ cache files
74 | ipch/
75 | *.aps
76 | *.ncb
77 | *.opensdf
78 | *.sdf
79 | *.cachefile
80 |
81 | # Visual Studio profiler
82 | *.psess
83 | *.vsp
84 | *.vspx
85 |
86 | # TFS 2012 Local Workspace
87 | $tf/
88 |
89 | # Guidance Automation Toolkit
90 | *.gpState
91 |
92 | # ReSharper is a .NET coding add-in
93 | _ReSharper*/
94 | *.[Rr]e[Ss]harper
95 | *.DotSettings.user
96 |
97 | # JustCode is a .NET coding add-in
98 | .JustCode
99 |
100 | # TeamCity is a build add-in
101 | _TeamCity*
102 |
103 | # DotCover is a Code Coverage Tool
104 | *.dotCover
105 |
106 | # NCrunch
107 | _NCrunch_*
108 | .*crunch*.local.xml
109 |
110 | # MightyMoose
111 | *.mm.*
112 | AutoTest.Net/
113 |
114 | # Web workbench (sass)
115 | .sass-cache/
116 |
117 | # Installshield output folder
118 | [Ee]xpress/
119 |
120 | # DocProject is a documentation generator add-in
121 | DocProject/buildhelp/
122 | DocProject/Help/*.HxT
123 | DocProject/Help/*.HxC
124 | DocProject/Help/*.hhc
125 | DocProject/Help/*.hhk
126 | DocProject/Help/*.hhp
127 | DocProject/Help/Html2
128 | DocProject/Help/html
129 |
130 | # Click-Once directory
131 | publish/
132 |
133 | # Publish Web Output
134 | *.[Pp]ublish.xml
135 | *.azurePubxml
136 | ## TODO: Comment the next line if you want to checkin your
137 | ## web deploy settings but do note that will include unencrypted
138 | ## passwords
139 | #*.pubxml
140 |
141 | *.publishproj
142 |
143 | # NuGet Packages
144 | *.nupkg
145 | # The packages folder can be ignored because of Package Restore
146 | **/packages/*
147 | # except build/, which is used as an MSBuild target.
148 | !**/packages/build/
149 | # Uncomment if necessary however generally it will be regenerated when needed
150 | #!**/packages/repositories.config
151 |
152 | # Windows Azure Build Output
153 | csx/
154 | *.build.csdef
155 |
156 | # Windows Store app package directory
157 | AppPackages/
158 |
159 | # Visual Studio cache files
160 | # files ending in .cache can be ignored
161 | *.[Cc]ache
162 | # but keep track of directories ending in .cache
163 | !*.[Cc]ache/
164 |
165 | # Others
166 | ClientBin/
167 | [Ss]tyle[Cc]op.*
168 | ~$*
169 | *~
170 | *.dbmdl
171 | *.dbproj.schemaview
172 | *.pfx
173 | *.publishsettings
174 | node_modules/
175 | orleans.codegen.cs
176 |
177 | # RIA/Silverlight projects
178 | Generated_Code/
179 |
180 | # Backup & report files from converting an old project file
181 | # to a newer Visual Studio version. Backup files are not needed,
182 | # because we have git ;-)
183 | _UpgradeReport_Files/
184 | Backup*/
185 | UpgradeLog*.XML
186 | UpgradeLog*.htm
187 |
188 | # SQL Server files
189 | *.mdf
190 | *.ldf
191 |
192 | # Business Intelligence projects
193 | *.rdl.data
194 | *.bim.layout
195 | *.bim_*.settings
196 |
197 | # Microsoft Fakes
198 | FakesAssemblies/
199 |
200 | # Node.js Tools for Visual Studio
201 | .ntvs_analysis.dat
202 |
203 | # Visual Studio 6 build log
204 | *.plg
205 |
206 | # Visual Studio 6 workspace options file
207 | *.opt
208 |
209 | # LightSwitch generated files
210 | GeneratedArtifacts/
211 | _Pvt_Extensions/
212 | ModelManifest.xml
213 | /msvc/cuda_raytracer.VC.VC.opendb
214 | /msvc/cuda_raytracer.VC.db
215 |
216 | #nSight
217 | *.nvvp
218 | *.nvprof
219 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/main.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // Implementation of CUDA simpleCUDA2GL sample - based on Cuda Samples 9.0
2 | // Dependencies: GLFW, GLEW
3 |
4 | #ifndef GLEW_STATIC
5 | #define GLEW_STATIC
6 | #endif
7 |
8 | // OpenGL
9 | #include // Take care: GLEW should be included before GLFW
10 | #include
11 | // CUDA
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 | #include "libs/helper_cuda.h"
15 | #include "libs/helper_gl.h"
16 | // C++ libs
17 | #include
18 | #include
19 | #include "shader_tools/GLSLProgram.h"
20 | #include "shader_tools/GLSLShader.h"
21 | #include "gl_tools.h"
22 | #include "glfw_tools.h"
23 |
24 | using namespace std;
25 |
26 | // GLFW
27 | GLFWwindow* window;
28 | int WIDTH = 256;
29 | int HEIGHT = 256;
30 |
31 | // OpenGL
32 | GLuint VBO, VAO, EBO;
33 | GLSLShader drawtex_f; // GLSL fragment shader
34 | GLSLShader drawtex_v; // GLSL fragment shader
35 | GLSLProgram shdrawtex; // GLSLS program for textured draw
36 |
37 | // Cuda <-> OpenGl interop resources
38 | void* cuda_dev_render_buffer; // Cuda buffer for initial render
39 | struct cudaGraphicsResource* cuda_tex_resource;
40 | GLuint opengl_tex_cuda; // OpenGL Texture for cuda result
41 | extern "C" void
42 | // Forward declaration of CUDA render
43 | launch_cudaRender(dim3 grid, dim3 block, int sbytes, unsigned int *g_odata, int imgw);
44 |
45 | // CUDA
46 | size_t size_tex_data;
47 | unsigned int num_texels;
48 | unsigned int num_values;
49 |
50 | static const char *glsl_drawtex_vertshader_src =
51 | "#version 330 core\n"
52 | "layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;\n"
53 | "layout (location = 1) in vec3 color;\n"
54 | "layout (location = 2) in vec2 texCoord;\n"
55 | "\n"
56 | "out vec3 ourColor;\n"
57 | "out vec2 ourTexCoord;\n"
58 | "\n"
59 | "void main()\n"
60 | "{\n"
61 | " gl_Position = vec4(position, 1.0f);\n"
62 | " ourColor = color;\n"
63 | " ourTexCoord = texCoord;\n"
64 | "}\n";
65 |
66 | static const char *glsl_drawtex_fragshader_src =
67 | "#version 330 core\n"
68 | "uniform usampler2D tex;\n"
69 | "in vec3 ourColor;\n"
70 | "in vec2 ourTexCoord;\n"
71 | "out vec4 color;\n"
72 | "void main()\n"
73 | "{\n"
74 | " vec4 c = texture(tex, ourTexCoord);\n"
75 | " color = c / 255.0;\n"
76 | "}\n";
77 |
78 | // QUAD GEOMETRY
79 | GLfloat vertices[] = {
80 | // Positions // Colors // Texture Coords
81 | 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f, // Top Right
82 | 1.0f, -1.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, // Bottom Right
83 | -1.0f, -1.0f, 0.5f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, // Bottom Left
84 | -1.0f, 1.0f, 0.5f, 1.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f // Top Left
85 | };
86 | // you can also put positions, colors and coordinates in seperate VBO's
87 | GLuint indices[] = { // Note that we start from 0!
88 | 0, 1, 3, // First Triangle
89 | 1, 2, 3 // Second Triangle
90 | };
91 |
92 | // Create 2D OpenGL texture in gl_tex and bind it to CUDA in cuda_tex
93 | void createGLTextureForCUDA(GLuint* gl_tex, cudaGraphicsResource** cuda_tex, unsigned int size_x, unsigned int size_y)
94 | {
95 | // create an OpenGL texture
96 | glGenTextures(1, gl_tex); // generate 1 texture
97 | glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, *gl_tex); // set it as current target
98 | // set basic texture parameters
99 | glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); // clamp s coordinate
100 | glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T, GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE); // clamp t coordinate
101 | glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
102 | glTexParameteri(GL_TEXTURE_2D, GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER, GL_NEAREST);
103 | // Specify 2D texture
104 | glTexImage2D(GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, GL_RGBA8UI_EXT, size_x, size_y, 0, GL_RGBA_INTEGER_EXT, GL_UNSIGNED_BYTE, NULL);
105 | // Register this texture with CUDA
106 | checkCudaErrors(cudaGraphicsGLRegisterImage(cuda_tex, *gl_tex, GL_TEXTURE_2D, cudaGraphicsRegisterFlagsWriteDiscard));
107 | SDK_CHECK_ERROR_GL();
108 | }
109 |
110 | void initGLBuffers()
111 | {
112 | // create texture that will receive the result of cuda kernel
113 | createGLTextureForCUDA(&opengl_tex_cuda, &cuda_tex_resource, WIDTH, HEIGHT);
114 | // create shader program
115 | drawtex_v = GLSLShader("Textured draw vertex shader", glsl_drawtex_vertshader_src, GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
116 | drawtex_f = GLSLShader("Textured draw fragment shader", glsl_drawtex_fragshader_src, GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
117 | shdrawtex = GLSLProgram(&drawtex_v, &drawtex_f);
118 | shdrawtex.compile();
119 | SDK_CHECK_ERROR_GL();
120 | }
121 |
122 | // Keyboard
123 | void keyboardfunc(GLFWwindow* window, int key, int scancode, int action, int mods){
124 | }
125 |
126 | bool initGL(){
127 | glewExperimental = GL_TRUE; // need this to enforce core profile
128 | GLenum err = glewInit();
129 | glGetError(); // parse first error
130 | if (err != GLEW_OK) {// Problem: glewInit failed, something is seriously wrong.
131 | printf("glewInit failed: %s /n", glewGetErrorString(err));
132 | exit(1);
133 | }
134 | glViewport(0, 0, WIDTH, HEIGHT); // viewport for x,y to normalized device coordinates transformation
135 | SDK_CHECK_ERROR_GL();
136 | return true;
137 | }
138 |
139 | void initCUDABuffers()
140 | {
141 | // set up vertex data parameters
142 | num_texels = WIDTH * WIDTH;
143 | num_values = num_texels * 4;
144 | size_tex_data = sizeof(GLubyte) * num_values;
145 | // We don't want to use cudaMallocManaged here - since we definitely want
146 | checkCudaErrors(cudaMalloc(&cuda_dev_render_buffer, size_tex_data)); // Allocate CUDA memory for color output
147 | }
148 |
149 | bool initGLFW(){
150 | if (!glfwInit()) exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
151 | // These hints switch the OpenGL profile to core
152 | glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 4);
153 | glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
154 | glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_FORWARD_COMPAT, GL_TRUE);
155 | glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
156 | window = glfwCreateWindow(WIDTH, WIDTH, "SimpleCUDA2GL Modern OpenGL", NULL, NULL);
157 | if (!window){ glfwTerminate(); exit(EXIT_FAILURE); }
158 | glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
159 | glfwSwapInterval(1);
160 | glfwSetKeyCallback(window, keyboardfunc);
161 | return true;
162 | }
163 |
164 | void generateCUDAImage()
165 | {
166 | // calculate grid size
167 | dim3 block(16, 16, 1);
168 | dim3 grid(WIDTH / block.x, HEIGHT / block.y, 1); // 2D grid, every thread will compute a pixel
169 | launch_cudaRender(grid, block, 0, (unsigned int *) cuda_dev_render_buffer, WIDTH); // launch with 0 additional shared memory allocated
170 |
171 | // We want to copy cuda_dev_render_buffer data to the texture
172 | // Map buffer objects to get CUDA device pointers
173 | cudaArray *texture_ptr;
174 | checkCudaErrors(cudaGraphicsMapResources(1, &cuda_tex_resource, 0));
175 | checkCudaErrors(cudaGraphicsSubResourceGetMappedArray(&texture_ptr, cuda_tex_resource, 0, 0));
176 |
177 | int num_texels = WIDTH * HEIGHT;
178 | int num_values = num_texels * 4;
179 | int size_tex_data = sizeof(GLubyte) * num_values;
180 | checkCudaErrors(cudaMemcpyToArray(texture_ptr, 0, 0, cuda_dev_render_buffer, size_tex_data, cudaMemcpyDeviceToDevice));
181 | checkCudaErrors(cudaGraphicsUnmapResources(1, &cuda_tex_resource, 0));
182 | }
183 |
184 | void display(void) {
185 | generateCUDAImage();
186 | glfwPollEvents();
187 | // Clear the color buffer
188 | glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
189 | glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
190 |
191 | glActiveTexture(GL_TEXTURE0);
192 | glBindTexture(GL_TEXTURE_2D, opengl_tex_cuda);
193 |
194 | shdrawtex.use(); // we gonna use this compiled GLSL program
195 | glUniform1i(glGetUniformLocation(shdrawtex.program, "tex"), 0);
196 |
197 | glBindVertexArray(VAO); // binding VAO automatically binds EBO
198 | glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 6, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
199 | glBindVertexArray(0); // unbind VAO
200 |
201 | SDK_CHECK_ERROR_GL();
202 |
203 | // Swap the screen buffers
204 | glfwSwapBuffers(window);
205 | }
206 |
207 | int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
208 | initGLFW();
209 | initGL();
210 |
211 | printGLFWInfo(window);
212 | printGlewInfo();
213 | printGLInfo();
214 |
215 | findCudaDevice(argc, (const char **)argv);
216 | initGLBuffers();
217 | initCUDABuffers();
218 |
219 | // Generate buffers
220 | glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
221 | glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
222 | glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);
223 |
224 | // Buffer setup
225 | // Bind the Vertex Array Object first, then bind and set vertex buffer(s) and attribute pointer(s).
226 | glBindVertexArray(VAO); // all next calls wil use this VAO (descriptor for VBO)
227 |
228 | glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
229 | glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
230 |
231 | glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
232 | glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(indices), indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
233 |
234 | // Position attribute (3 floats)
235 | glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)0);
236 | glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
237 | // Color attribute (3 floats)
238 | glVertexAttribPointer(1, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(3 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
239 | glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
240 | // Texture attribute (2 floats)
241 | glVertexAttribPointer(2, 2, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 8 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)(6 * sizeof(GLfloat)));
242 | glEnableVertexAttribArray(2);
243 |
244 | glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0);
245 | // Note that this is allowed, the call to glVertexAttribPointer registered VBO as the currently bound
246 | // vertex buffer object so afterwards we can safely unbind
247 | glBindVertexArray(0);
248 |
249 | // Unbind VAO (it's always a good thing to unbind any buffer/array to prevent strange bugs), remember: do NOT unbind the EBO, keep it bound to this VAO
250 | // A VAO stores the glBindBuffer calls when the target is GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER.
251 | // This also means it stores its unbind calls so make sure you don't unbind the element array buffer before unbinding your VAO, otherwise it doesn't have an EBO configured.
252 |
253 | while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
254 | {
255 | display();
256 | glfwWaitEvents();
257 | }
258 |
259 | glfwDestroyWindow(window);
260 | glfwTerminate();
261 | exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
262 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/msvc/vs2019/cuda2GLCore.vcxproj:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | Debug
6 | Win32
7 |
8 |
9 | Debug
10 | x64
11 |
12 |
13 | Release
14 | Win32
15 |
16 |
17 | Release
18 | x64
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 | {6539033A-8268-48FE-AEFA-BF1FF83DA9A5}
41 | cuda2GLCore
42 | 10.0
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 | Application
47 | true
48 | MultiByte
49 | v142
50 |
51 |
52 | Application
53 | true
54 | MultiByte
55 | v142
56 |
57 |
58 | Application
59 | false
60 | true
61 | MultiByte
62 | v142
63 |
64 |
65 | Application
66 | false
67 | true
68 | MultiByte
69 | v142
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 |
82 |
83 |
84 |
85 |
86 |
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 |
92 |
93 | true
94 |
95 |
96 | true
97 |
98 |
99 |
100 | Level3
101 | Disabled
102 | WIN32;_DEBUG;_CONSOLE;%(PreprocessorDefinitions)
103 |
104 |
105 | true
106 | Console
107 | cudart.lib;kernel32.lib;user32.lib;gdi32.lib;winspool.lib;comdlg32.lib;advapi32.lib;shell32.lib;ole32.lib;oleaut32.lib;uuid.lib;odbc32.lib;odbccp32.lib;%(AdditionalDependencies)
108 |
109 |
110 | echo copy "$(CudaToolkitBinDir)\cudart*.dll" "$(OutDir)"
111 | copy "$(CudaToolkitBinDir)\cudart*.dll" "$(OutDir)"
112 |
113 |
114 |
115 |
116 | Level3
117 | Disabled
118 | WIN32;WIN64;_DEBUG;_CONSOLE;%(PreprocessorDefinitions)
119 | -Bv %(AdditionalOptions)
120 |
121 |
122 | true
123 | Console
124 | cudart.lib;kernel32.lib;user32.lib;gdi32.lib;winspool.lib;comdlg32.lib;advapi32.lib;shell32.lib;ole32.lib;oleaut32.lib;uuid.lib;odbc32.lib;odbccp32.lib;%(AdditionalDependencies)
125 |
126 |
127 | echo copy "$(CudaToolkitBinDir)\cudart*.dll" "$(OutDir)"
128 | copy "$(CudaToolkitBinDir)\cudart*.dll" "$(OutDir)"
129 |
130 |
131 | 64
132 |
133 |
134 |
135 |
136 | Level3
137 | MaxSpeed
138 | true
139 | true
140 | WIN32;NDEBUG;_CONSOLE;%(PreprocessorDefinitions)
141 |
142 |
143 | true
144 | true
145 | true
146 | Console
147 | cudart.lib;kernel32.lib;user32.lib;gdi32.lib;winspool.lib;comdlg32.lib;advapi32.lib;shell32.lib;ole32.lib;oleaut32.lib;uuid.lib;odbc32.lib;odbccp32.lib;%(AdditionalDependencies)
148 |
149 |
150 | echo copy "$(CudaToolkitBinDir)\cudart*.dll" "$(OutDir)"
151 | copy "$(CudaToolkitBinDir)\cudart*.dll" "$(OutDir)"
152 |
153 |
154 |
155 |
156 | Level3
157 | MaxSpeed
158 | true
159 | true
160 | WIN32;WIN64;NDEBUG;_CONSOLE;%(PreprocessorDefinitions)
161 | -Bv %(AdditionalOptions)
162 |
163 |
164 | true
165 | true
166 | true
167 | Console
168 | cudart.lib;kernel32.lib;user32.lib;gdi32.lib;winspool.lib;comdlg32.lib;advapi32.lib;shell32.lib;ole32.lib;oleaut32.lib;uuid.lib;odbc32.lib;odbccp32.lib;%(AdditionalDependencies)
169 |
170 |
171 | echo copy "$(CudaToolkitBinDir)\cudart*.dll" "$(OutDir)"
172 | copy "$(CudaToolkitBinDir)\cudart*.dll" "$(OutDir)"
173 |
174 |
175 | 64
176 |
177 |
178 |
179 |
180 |
181 |
182 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/libs/helper_gl.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /**
2 | * Copyright 2014 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | *
4 | * Please refer to the NVIDIA end user license agreement (EULA) associated
5 | * with this source code for terms and conditions that govern your use of
6 | * this software. Any use, reproduction, disclosure, or distribution of
7 | * this software and related documentation outside the terms of the EULA
8 | * is strictly prohibited.
9 | *
10 | */
11 |
12 | // These are helper functions for the SDK samples (OpenGL)
13 | #ifndef HELPER_GL_H
14 | #define HELPER_GL_H
15 |
16 | #if defined(WIN32) || defined(_WIN32) || defined(WIN64) || defined(_WIN64)
17 | #include
18 | #endif
19 |
20 | #if defined(__APPLE__) || defined(MACOSX)
21 | #include
22 | #else
23 | #include
24 | #ifdef __linux__
25 | #include
26 | #endif /* __linux__ */
27 | #endif
28 |
29 | #include
30 | #include
31 | #include
32 | #include
33 | #include
34 | #include
35 | #include
36 | #include
37 |
38 |
39 | /* Prototypes */
40 | namespace __HelperGL {
41 | static int isGLVersionSupported(unsigned reqMajor, unsigned reqMinor);
42 | static int areGLExtensionsSupported(const std::string &);
43 | #ifdef __linux__
44 |
45 | #ifndef HELPERGL_EXTERN_GL_FUNC_IMPLEMENTATION
46 | #define USE_GL_FUNC(name, proto) proto name = (proto) glXGetProcAddress ((const GLubyte *)#name)
47 | #else
48 | #define USE_GL_FUNC(name, proto) extern proto name
49 | #endif
50 |
51 | USE_GL_FUNC(glBindBuffer, PFNGLBINDBUFFERPROC);
52 | USE_GL_FUNC(glDeleteBuffers, PFNGLDELETEBUFFERSPROC);
53 | USE_GL_FUNC(glBufferData, PFNGLBUFFERDATAPROC);
54 | USE_GL_FUNC(glBufferSubData, PFNGLBUFFERSUBDATAPROC);
55 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGenBuffers, PFNGLGENBUFFERSPROC);
56 | USE_GL_FUNC(glCreateProgram, PFNGLCREATEPROGRAMPROC);
57 | USE_GL_FUNC(glBindProgramARB, PFNGLBINDPROGRAMARBPROC);
58 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGenProgramsARB, PFNGLGENPROGRAMSARBPROC);
59 | USE_GL_FUNC(glDeleteProgramsARB, PFNGLDELETEPROGRAMSARBPROC);
60 | USE_GL_FUNC(glDeleteProgram, PFNGLDELETEPROGRAMPROC);
61 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGetProgramInfoLog, PFNGLGETPROGRAMINFOLOGPROC);
62 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGetProgramiv, PFNGLGETPROGRAMIVPROC);
63 | USE_GL_FUNC(glProgramParameteriEXT, PFNGLPROGRAMPARAMETERIEXTPROC);
64 | USE_GL_FUNC(glProgramStringARB, PFNGLPROGRAMSTRINGARBPROC);
65 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUnmapBuffer, PFNGLUNMAPBUFFERPROC);
66 | USE_GL_FUNC(glMapBuffer, PFNGLMAPBUFFERPROC);
67 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGetBufferParameteriv, PFNGLGETBUFFERPARAMETERIVPROC);
68 | USE_GL_FUNC(glLinkProgram, PFNGLLINKPROGRAMPROC);
69 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUseProgram, PFNGLUSEPROGRAMPROC);
70 | USE_GL_FUNC(glAttachShader, PFNGLATTACHSHADERPROC);
71 | USE_GL_FUNC(glCreateShader, PFNGLCREATESHADERPROC);
72 | USE_GL_FUNC(glShaderSource, PFNGLSHADERSOURCEPROC);
73 | USE_GL_FUNC(glCompileShader, PFNGLCOMPILESHADERPROC);
74 | USE_GL_FUNC(glDeleteShader, PFNGLDELETESHADERPROC);
75 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGetShaderInfoLog, PFNGLGETSHADERINFOLOGPROC);
76 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGetShaderiv, PFNGLGETSHADERIVPROC);
77 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniform1i, PFNGLUNIFORM1IPROC);
78 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniform1f, PFNGLUNIFORM1FPROC);
79 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniform2f, PFNGLUNIFORM2FPROC);
80 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniform3f, PFNGLUNIFORM3FPROC);
81 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniform4f, PFNGLUNIFORM4FPROC);
82 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniform1fv, PFNGLUNIFORM1FVPROC);
83 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniform2fv, PFNGLUNIFORM2FVPROC);
84 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniform3fv, PFNGLUNIFORM3FVPROC);
85 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniform4fv, PFNGLUNIFORM4FVPROC);
86 | USE_GL_FUNC(glUniformMatrix4fv, PFNGLUNIFORMMATRIX4FVPROC);
87 | USE_GL_FUNC(glSecondaryColor3fv, PFNGLSECONDARYCOLOR3FVPROC);
88 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGetUniformLocation, PFNGLGETUNIFORMLOCATIONPROC);
89 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGenFramebuffersEXT, PFNGLGENFRAMEBUFFERSEXTPROC);
90 | USE_GL_FUNC(glBindFramebufferEXT, PFNGLBINDFRAMEBUFFEREXTPROC);
91 | USE_GL_FUNC(glDeleteFramebuffersEXT, PFNGLDELETEFRAMEBUFFERSEXTPROC);
92 | USE_GL_FUNC(glCheckFramebufferStatusEXT, PFNGLCHECKFRAMEBUFFERSTATUSEXTPROC);
93 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGetFramebufferAttachmentParameterivEXT, PFNGLGETFRAMEBUFFERATTACHMENTPARAMETERIVEXTPROC);
94 | USE_GL_FUNC(glFramebufferTexture1DEXT, PFNGLFRAMEBUFFERTEXTURE1DEXTPROC);
95 | USE_GL_FUNC(glFramebufferTexture2DEXT, PFNGLFRAMEBUFFERTEXTURE2DEXTPROC);
96 | USE_GL_FUNC(glFramebufferTexture3DEXT, PFNGLFRAMEBUFFERTEXTURE3DEXTPROC);
97 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGenerateMipmapEXT, PFNGLGENERATEMIPMAPEXTPROC);
98 | USE_GL_FUNC(glGenRenderbuffersEXT, PFNGLGENRENDERBUFFERSEXTPROC);
99 | USE_GL_FUNC(glDeleteRenderbuffersEXT, PFNGLDELETERENDERBUFFERSEXTPROC);
100 | USE_GL_FUNC(glBindRenderbufferEXT, PFNGLBINDRENDERBUFFEREXTPROC);
101 | USE_GL_FUNC(glRenderbufferStorageEXT, PFNGLRENDERBUFFERSTORAGEEXTPROC);
102 | USE_GL_FUNC(glFramebufferRenderbufferEXT, PFNGLFRAMEBUFFERRENDERBUFFEREXTPROC);
103 | USE_GL_FUNC(glClampColorARB, PFNGLCLAMPCOLORARBPROC);
104 | USE_GL_FUNC(glBindFragDataLocationEXT, PFNGLBINDFRAGDATALOCATIONEXTPROC);
105 |
106 | #if !defined(GLX_EXTENSION_NAME) || !defined(GL_VERSION_1_3)
107 | USE_GL_FUNC(glActiveTexture, PFNGLACTIVETEXTUREPROC);
108 | USE_GL_FUNC(glClientActiveTexture, PFNGLACTIVETEXTUREPROC);
109 | #endif
110 |
111 | #undef USE_GL_FUNC
112 | #endif /*__linux__ */
113 | }
114 |
115 |
116 | namespace __HelperGL {
117 | namespace __Int {
118 | static std::vector split(const std::string &str)
119 | {
120 | std::istringstream ss(str);
121 | std::istream_iterator it(ss);
122 | return std::vector (it, std::istream_iterator());
123 | }
124 |
125 | /* Sort the vector passed by reference */
126 | template static inline void sort(std::vector &a)
127 | {
128 | std::sort(a.begin(), a.end());
129 | }
130 |
131 | /* Compare two vectors */
132 | template static int equals(std::vector a, std::vector b)
133 | {
134 | if (a.size() != b.size()) return 0;
135 | sort(a);
136 | sort(b);
137 |
138 | return std::equal(a.begin(), a.end(), b.begin());
139 | }
140 |
141 | template static std::vector getIntersection(std::vector a, std::vector b)
142 | {
143 | sort(a);
144 | sort(b);
145 |
146 | std::vector rc;
147 | std::set_intersection(a.begin(), a.end(), b.begin(), b.end(),
148 | std::back_inserter >(rc));
149 | return rc;
150 | }
151 |
152 | static std::vector getGLExtensions()
153 | {
154 | std::string extensionsStr( (const char *)glGetString(GL_EXTENSIONS));
155 | return split (extensionsStr);
156 | }
157 | }
158 |
159 | static int areGLExtensionsSupported(const std::string &extensions)
160 | {
161 | std::vector all = __Int::getGLExtensions();
162 |
163 | std::vector requested = __Int::split(extensions);
164 | std::vector matched = __Int::getIntersection(all, requested);
165 |
166 | return __Int::equals(matched, requested);
167 | }
168 |
169 | static int isGLVersionSupported(unsigned reqMajor, unsigned reqMinor)
170 | {
171 | #if defined(WIN32) || defined(_WIN32) || defined(WIN64) || defined(_WIN64)
172 | if (glewInit() != GLEW_OK)
173 | {
174 | std::cerr << "glewInit() failed!" << std::endl;
175 | return 0;
176 | }
177 | #endif
178 | std::string version ((const char *) glGetString (GL_VERSION));
179 | std::stringstream stream (version);
180 | unsigned major, minor;
181 | char dot;
182 |
183 | stream >> major >> dot >> minor;
184 |
185 | assert (dot == '.');
186 | return major > reqMajor || (major == reqMajor && minor >= reqMinor);
187 | }
188 |
189 | static inline const char* glErrorToString(GLenum err)
190 | {
191 | #define CASE_RETURN_MACRO(arg) case arg: return #arg
192 | switch(err)
193 | {
194 | CASE_RETURN_MACRO(GL_NO_ERROR);
195 | CASE_RETURN_MACRO(GL_INVALID_ENUM);
196 | CASE_RETURN_MACRO(GL_INVALID_VALUE);
197 | CASE_RETURN_MACRO(GL_INVALID_OPERATION);
198 | CASE_RETURN_MACRO(GL_OUT_OF_MEMORY);
199 | CASE_RETURN_MACRO(GL_STACK_UNDERFLOW);
200 | CASE_RETURN_MACRO(GL_STACK_OVERFLOW);
201 | #ifdef GL_INVALID_FRAMEBUFFER_OPERATION
202 | CASE_RETURN_MACRO(GL_INVALID_FRAMEBUFFER_OPERATION);
203 | #endif
204 | default: break;
205 | }
206 | #undef CASE_RETURN_MACRO
207 | return "*UNKNOWN*";
208 | }
209 |
210 | ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
211 | //! Check for OpenGL error
212 | //! @return bool if no GL error has been encountered, otherwise 0
213 | //! @param file __FILE__ macro
214 | //! @param line __LINE__ macro
215 | //! @note The GL error is listed on stderr
216 | //! @note This function should be used via the CHECK_ERROR_GL() macro
217 | ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
218 | inline bool sdkCheckErrorGL(const char *file, const int line)
219 | {
220 | bool ret_val = true;
221 |
222 | // check for error
223 | GLenum gl_error = glGetError();
224 |
225 | if (gl_error != GL_NO_ERROR)
226 | {
227 | #if defined(WIN32) || defined(_WIN32) || defined(WIN64) || defined(_WIN64)
228 | char tmpStr[512];
229 | // NOTE: "%s(%i) : " allows Visual Studio to directly jump to the file at the right line
230 | // when the user double clicks on the error line in the Output pane. Like any compile error.
231 | sprintf_s(tmpStr, 255, "\n%s(%i) : GL Error : %s\n\n", file, line, glErrorToString(gl_error));
232 | fprintf(stderr, "%s", tmpStr);
233 | #endif
234 | fprintf(stderr, "GL Error in file '%s' in line %d :\n", file, line);
235 | fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", glErrorToString(gl_error));
236 | ret_val = false;
237 | }
238 |
239 | return ret_val;
240 | }
241 |
242 | #define SDK_CHECK_ERROR_GL() \
243 | if( false == sdkCheckErrorGL( __FILE__, __LINE__)) { \
244 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE); \
245 | }
246 |
247 | } /* of namespace __HelperGL*/
248 |
249 | using namespace __HelperGL;
250 |
251 | #endif /*HELPER_GL_H*/
252 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/libs/helper_cuda.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /**
2 | * Copyright 1993-2017 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | *
4 | * Please refer to the NVIDIA end user license agreement (EULA) associated
5 | * with this source code for terms and conditions that govern your use of
6 | * this software. Any use, reproduction, disclosure, or distribution of
7 | * this software and related documentation outside the terms of the EULA
8 | * is strictly prohibited.
9 | *
10 | */
11 |
12 | ////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
13 | // These are CUDA Helper functions for initialization and error checking
14 |
15 | #ifndef COMMON_HELPER_CUDA_H_
16 | #define COMMON_HELPER_CUDA_H_
17 |
18 | #pragma once
19 |
20 | #include
21 | #include
22 | #include
23 | #include
24 |
25 | #include "helper_string.h"
26 |
27 | #ifndef EXIT_WAIVED
28 | #define EXIT_WAIVED 2
29 | #endif
30 |
31 | // Note, it is required that your SDK sample to include the proper header
32 | // files, please refer the CUDA examples for examples of the needed CUDA
33 | // headers, which may change depending on which CUDA functions are used.
34 |
35 | // CUDA Runtime error messages
36 | #ifdef __DRIVER_TYPES_H__
37 | static const char *_cudaGetErrorEnum(cudaError_t error) {
38 | return cudaGetErrorName(error);
39 | }
40 | #endif
41 |
42 | #ifdef CUDA_DRIVER_API
43 | // CUDA Driver API errors
44 | static const char *_cudaGetErrorEnum(CUresult error) {
45 | static char unknown[] = "";
46 | const char *ret = NULL;
47 | cuGetErrorName(error, &ret);
48 | return ret ? ret : unknown;
49 | }
50 | #endif
51 |
52 | #ifdef CUBLAS_API_H_
53 | // cuBLAS API errors
54 | static const char *_cudaGetErrorEnum(cublasStatus_t error) {
55 | switch (error) {
56 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_SUCCESS:
57 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_SUCCESS";
58 |
59 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED:
60 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED";
61 |
62 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_ALLOC_FAILED:
63 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_ALLOC_FAILED";
64 |
65 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_INVALID_VALUE:
66 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_INVALID_VALUE";
67 |
68 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH:
69 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH";
70 |
71 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_MAPPING_ERROR:
72 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_MAPPING_ERROR";
73 |
74 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED:
75 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED";
76 |
77 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR:
78 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR";
79 |
80 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED:
81 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED";
82 |
83 | case CUBLAS_STATUS_LICENSE_ERROR:
84 | return "CUBLAS_STATUS_LICENSE_ERROR";
85 | }
86 |
87 | return "";
88 | }
89 | #endif
90 |
91 | #ifdef _CUFFT_H_
92 | // cuFFT API errors
93 | static const char *_cudaGetErrorEnum(cufftResult error) {
94 | switch (error) {
95 | case CUFFT_SUCCESS:
96 | return "CUFFT_SUCCESS";
97 |
98 | case CUFFT_INVALID_PLAN:
99 | return "CUFFT_INVALID_PLAN";
100 |
101 | case CUFFT_ALLOC_FAILED:
102 | return "CUFFT_ALLOC_FAILED";
103 |
104 | case CUFFT_INVALID_TYPE:
105 | return "CUFFT_INVALID_TYPE";
106 |
107 | case CUFFT_INVALID_VALUE:
108 | return "CUFFT_INVALID_VALUE";
109 |
110 | case CUFFT_INTERNAL_ERROR:
111 | return "CUFFT_INTERNAL_ERROR";
112 |
113 | case CUFFT_EXEC_FAILED:
114 | return "CUFFT_EXEC_FAILED";
115 |
116 | case CUFFT_SETUP_FAILED:
117 | return "CUFFT_SETUP_FAILED";
118 |
119 | case CUFFT_INVALID_SIZE:
120 | return "CUFFT_INVALID_SIZE";
121 |
122 | case CUFFT_UNALIGNED_DATA:
123 | return "CUFFT_UNALIGNED_DATA";
124 |
125 | case CUFFT_INCOMPLETE_PARAMETER_LIST:
126 | return "CUFFT_INCOMPLETE_PARAMETER_LIST";
127 |
128 | case CUFFT_INVALID_DEVICE:
129 | return "CUFFT_INVALID_DEVICE";
130 |
131 | case CUFFT_PARSE_ERROR:
132 | return "CUFFT_PARSE_ERROR";
133 |
134 | case CUFFT_NO_WORKSPACE:
135 | return "CUFFT_NO_WORKSPACE";
136 |
137 | case CUFFT_NOT_IMPLEMENTED:
138 | return "CUFFT_NOT_IMPLEMENTED";
139 |
140 | case CUFFT_LICENSE_ERROR:
141 | return "CUFFT_LICENSE_ERROR";
142 |
143 | case CUFFT_NOT_SUPPORTED:
144 | return "CUFFT_NOT_SUPPORTED";
145 | }
146 |
147 | return "";
148 | }
149 | #endif
150 |
151 | #ifdef CUSPARSEAPI
152 | // cuSPARSE API errors
153 | static const char *_cudaGetErrorEnum(cusparseStatus_t error) {
154 | switch (error) {
155 | case CUSPARSE_STATUS_SUCCESS:
156 | return "CUSPARSE_STATUS_SUCCESS";
157 |
158 | case CUSPARSE_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED:
159 | return "CUSPARSE_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED";
160 |
161 | case CUSPARSE_STATUS_ALLOC_FAILED:
162 | return "CUSPARSE_STATUS_ALLOC_FAILED";
163 |
164 | case CUSPARSE_STATUS_INVALID_VALUE:
165 | return "CUSPARSE_STATUS_INVALID_VALUE";
166 |
167 | case CUSPARSE_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH:
168 | return "CUSPARSE_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH";
169 |
170 | case CUSPARSE_STATUS_MAPPING_ERROR:
171 | return "CUSPARSE_STATUS_MAPPING_ERROR";
172 |
173 | case CUSPARSE_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED:
174 | return "CUSPARSE_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED";
175 |
176 | case CUSPARSE_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR:
177 | return "CUSPARSE_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR";
178 |
179 | case CUSPARSE_STATUS_MATRIX_TYPE_NOT_SUPPORTED:
180 | return "CUSPARSE_STATUS_MATRIX_TYPE_NOT_SUPPORTED";
181 | }
182 |
183 | return "";
184 | }
185 | #endif
186 |
187 | #ifdef CUSOLVER_COMMON_H_
188 | // cuSOLVER API errors
189 | static const char *_cudaGetErrorEnum(cusolverStatus_t error) {
190 | switch (error) {
191 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_SUCCESS:
192 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_SUCCESS";
193 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED:
194 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED";
195 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_ALLOC_FAILED:
196 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_ALLOC_FAILED";
197 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_INVALID_VALUE:
198 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_INVALID_VALUE";
199 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH:
200 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH";
201 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_MAPPING_ERROR:
202 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_MAPPING_ERROR";
203 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED:
204 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED";
205 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR:
206 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR";
207 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_MATRIX_TYPE_NOT_SUPPORTED:
208 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_MATRIX_TYPE_NOT_SUPPORTED";
209 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED:
210 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_NOT_SUPPORTED ";
211 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_ZERO_PIVOT:
212 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_ZERO_PIVOT";
213 | case CUSOLVER_STATUS_INVALID_LICENSE:
214 | return "CUSOLVER_STATUS_INVALID_LICENSE";
215 | }
216 |
217 | return "";
218 | }
219 | #endif
220 |
221 | #ifdef CURAND_H_
222 | // cuRAND API errors
223 | static const char *_cudaGetErrorEnum(curandStatus_t error) {
224 | switch (error) {
225 | case CURAND_STATUS_SUCCESS:
226 | return "CURAND_STATUS_SUCCESS";
227 |
228 | case CURAND_STATUS_VERSION_MISMATCH:
229 | return "CURAND_STATUS_VERSION_MISMATCH";
230 |
231 | case CURAND_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED:
232 | return "CURAND_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED";
233 |
234 | case CURAND_STATUS_ALLOCATION_FAILED:
235 | return "CURAND_STATUS_ALLOCATION_FAILED";
236 |
237 | case CURAND_STATUS_TYPE_ERROR:
238 | return "CURAND_STATUS_TYPE_ERROR";
239 |
240 | case CURAND_STATUS_OUT_OF_RANGE:
241 | return "CURAND_STATUS_OUT_OF_RANGE";
242 |
243 | case CURAND_STATUS_LENGTH_NOT_MULTIPLE:
244 | return "CURAND_STATUS_LENGTH_NOT_MULTIPLE";
245 |
246 | case CURAND_STATUS_DOUBLE_PRECISION_REQUIRED:
247 | return "CURAND_STATUS_DOUBLE_PRECISION_REQUIRED";
248 |
249 | case CURAND_STATUS_LAUNCH_FAILURE:
250 | return "CURAND_STATUS_LAUNCH_FAILURE";
251 |
252 | case CURAND_STATUS_PREEXISTING_FAILURE:
253 | return "CURAND_STATUS_PREEXISTING_FAILURE";
254 |
255 | case CURAND_STATUS_INITIALIZATION_FAILED:
256 | return "CURAND_STATUS_INITIALIZATION_FAILED";
257 |
258 | case CURAND_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH:
259 | return "CURAND_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH";
260 |
261 | case CURAND_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR:
262 | return "CURAND_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR";
263 | }
264 |
265 | return "";
266 | }
267 | #endif
268 |
269 | #ifdef NVJPEGAPI
270 | // nvJPEG API errors
271 | static const char *_cudaGetErrorEnum(nvjpegStatus_t error) {
272 | switch (error) {
273 | case NVJPEG_STATUS_SUCCESS:
274 | return "NVJPEG_STATUS_SUCCESS";
275 |
276 | case NVJPEG_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED:
277 | return "NVJPEG_STATUS_NOT_INITIALIZED";
278 |
279 | case NVJPEG_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER:
280 | return "NVJPEG_STATUS_INVALID_PARAMETER";
281 |
282 | case NVJPEG_STATUS_BAD_JPEG:
283 | return "NVJPEG_STATUS_BAD_JPEG";
284 |
285 | case NVJPEG_STATUS_JPEG_NOT_SUPPORTED:
286 | return "NVJPEG_STATUS_JPEG_NOT_SUPPORTED";
287 |
288 | case NVJPEG_STATUS_ALLOCATOR_FAILURE:
289 | return "NVJPEG_STATUS_ALLOCATOR_FAILURE";
290 |
291 | case NVJPEG_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED:
292 | return "NVJPEG_STATUS_EXECUTION_FAILED";
293 |
294 | case NVJPEG_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH:
295 | return "NVJPEG_STATUS_ARCH_MISMATCH";
296 |
297 | case NVJPEG_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR:
298 | return "NVJPEG_STATUS_INTERNAL_ERROR";
299 | }
300 |
301 | return "";
302 | }
303 | #endif
304 |
305 | #ifdef NV_NPPIDEFS_H
306 | // NPP API errors
307 | static const char *_cudaGetErrorEnum(NppStatus error) {
308 | switch (error) {
309 | case NPP_NOT_SUPPORTED_MODE_ERROR:
310 | return "NPP_NOT_SUPPORTED_MODE_ERROR";
311 |
312 | case NPP_ROUND_MODE_NOT_SUPPORTED_ERROR:
313 | return "NPP_ROUND_MODE_NOT_SUPPORTED_ERROR";
314 |
315 | case NPP_RESIZE_NO_OPERATION_ERROR:
316 | return "NPP_RESIZE_NO_OPERATION_ERROR";
317 |
318 | case NPP_NOT_SUFFICIENT_COMPUTE_CAPABILITY:
319 | return "NPP_NOT_SUFFICIENT_COMPUTE_CAPABILITY";
320 |
321 | #if ((NPP_VERSION_MAJOR << 12) + (NPP_VERSION_MINOR << 4)) <= 0x5000
322 |
323 | case NPP_BAD_ARG_ERROR:
324 | return "NPP_BAD_ARGUMENT_ERROR";
325 |
326 | case NPP_COEFF_ERROR:
327 | return "NPP_COEFFICIENT_ERROR";
328 |
329 | case NPP_RECT_ERROR:
330 | return "NPP_RECTANGLE_ERROR";
331 |
332 | case NPP_QUAD_ERROR:
333 | return "NPP_QUADRANGLE_ERROR";
334 |
335 | case NPP_MEM_ALLOC_ERR:
336 | return "NPP_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_ERROR";
337 |
338 | case NPP_HISTO_NUMBER_OF_LEVELS_ERROR:
339 | return "NPP_HISTOGRAM_NUMBER_OF_LEVELS_ERROR";
340 |
341 | case NPP_INVALID_INPUT:
342 | return "NPP_INVALID_INPUT";
343 |
344 | case NPP_POINTER_ERROR:
345 | return "NPP_POINTER_ERROR";
346 |
347 | case NPP_WARNING:
348 | return "NPP_WARNING";
349 |
350 | case NPP_ODD_ROI_WARNING:
351 | return "NPP_ODD_ROI_WARNING";
352 | #else
353 |
354 | // These are for CUDA 5.5 or higher
355 | case NPP_BAD_ARGUMENT_ERROR:
356 | return "NPP_BAD_ARGUMENT_ERROR";
357 |
358 | case NPP_COEFFICIENT_ERROR:
359 | return "NPP_COEFFICIENT_ERROR";
360 |
361 | case NPP_RECTANGLE_ERROR:
362 | return "NPP_RECTANGLE_ERROR";
363 |
364 | case NPP_QUADRANGLE_ERROR:
365 | return "NPP_QUADRANGLE_ERROR";
366 |
367 | case NPP_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_ERR:
368 | return "NPP_MEMORY_ALLOCATION_ERROR";
369 |
370 | case NPP_HISTOGRAM_NUMBER_OF_LEVELS_ERROR:
371 | return "NPP_HISTOGRAM_NUMBER_OF_LEVELS_ERROR";
372 |
373 | case NPP_INVALID_HOST_POINTER_ERROR:
374 | return "NPP_INVALID_HOST_POINTER_ERROR";
375 |
376 | case NPP_INVALID_DEVICE_POINTER_ERROR:
377 | return "NPP_INVALID_DEVICE_POINTER_ERROR";
378 | #endif
379 |
380 | case NPP_LUT_NUMBER_OF_LEVELS_ERROR:
381 | return "NPP_LUT_NUMBER_OF_LEVELS_ERROR";
382 |
383 | case NPP_TEXTURE_BIND_ERROR:
384 | return "NPP_TEXTURE_BIND_ERROR";
385 |
386 | case NPP_WRONG_INTERSECTION_ROI_ERROR:
387 | return "NPP_WRONG_INTERSECTION_ROI_ERROR";
388 |
389 | case NPP_NOT_EVEN_STEP_ERROR:
390 | return "NPP_NOT_EVEN_STEP_ERROR";
391 |
392 | case NPP_INTERPOLATION_ERROR:
393 | return "NPP_INTERPOLATION_ERROR";
394 |
395 | case NPP_RESIZE_FACTOR_ERROR:
396 | return "NPP_RESIZE_FACTOR_ERROR";
397 |
398 | case NPP_HAAR_CLASSIFIER_PIXEL_MATCH_ERROR:
399 | return "NPP_HAAR_CLASSIFIER_PIXEL_MATCH_ERROR";
400 |
401 | #if ((NPP_VERSION_MAJOR << 12) + (NPP_VERSION_MINOR << 4)) <= 0x5000
402 |
403 | case NPP_MEMFREE_ERR:
404 | return "NPP_MEMFREE_ERR";
405 |
406 | case NPP_MEMSET_ERR:
407 | return "NPP_MEMSET_ERR";
408 |
409 | case NPP_MEMCPY_ERR:
410 | return "NPP_MEMCPY_ERROR";
411 |
412 | case NPP_MIRROR_FLIP_ERR:
413 | return "NPP_MIRROR_FLIP_ERR";
414 | #else
415 |
416 | case NPP_MEMFREE_ERROR:
417 | return "NPP_MEMFREE_ERROR";
418 |
419 | case NPP_MEMSET_ERROR:
420 | return "NPP_MEMSET_ERROR";
421 |
422 | case NPP_MEMCPY_ERROR:
423 | return "NPP_MEMCPY_ERROR";
424 |
425 | case NPP_MIRROR_FLIP_ERROR:
426 | return "NPP_MIRROR_FLIP_ERROR";
427 | #endif
428 |
429 | case NPP_ALIGNMENT_ERROR:
430 | return "NPP_ALIGNMENT_ERROR";
431 |
432 | case NPP_STEP_ERROR:
433 | return "NPP_STEP_ERROR";
434 |
435 | case NPP_SIZE_ERROR:
436 | return "NPP_SIZE_ERROR";
437 |
438 | case NPP_NULL_POINTER_ERROR:
439 | return "NPP_NULL_POINTER_ERROR";
440 |
441 | case NPP_CUDA_KERNEL_EXECUTION_ERROR:
442 | return "NPP_CUDA_KERNEL_EXECUTION_ERROR";
443 |
444 | case NPP_NOT_IMPLEMENTED_ERROR:
445 | return "NPP_NOT_IMPLEMENTED_ERROR";
446 |
447 | case NPP_ERROR:
448 | return "NPP_ERROR";
449 |
450 | case NPP_SUCCESS:
451 | return "NPP_SUCCESS";
452 |
453 | case NPP_WRONG_INTERSECTION_QUAD_WARNING:
454 | return "NPP_WRONG_INTERSECTION_QUAD_WARNING";
455 |
456 | case NPP_MISALIGNED_DST_ROI_WARNING:
457 | return "NPP_MISALIGNED_DST_ROI_WARNING";
458 |
459 | case NPP_AFFINE_QUAD_INCORRECT_WARNING:
460 | return "NPP_AFFINE_QUAD_INCORRECT_WARNING";
461 |
462 | case NPP_DOUBLE_SIZE_WARNING:
463 | return "NPP_DOUBLE_SIZE_WARNING";
464 |
465 | case NPP_WRONG_INTERSECTION_ROI_WARNING:
466 | return "NPP_WRONG_INTERSECTION_ROI_WARNING";
467 |
468 | #if ((NPP_VERSION_MAJOR << 12) + (NPP_VERSION_MINOR << 4)) >= 0x6000
469 | /* These are 6.0 or higher */
470 | case NPP_LUT_PALETTE_BITSIZE_ERROR:
471 | return "NPP_LUT_PALETTE_BITSIZE_ERROR";
472 |
473 | case NPP_ZC_MODE_NOT_SUPPORTED_ERROR:
474 | return "NPP_ZC_MODE_NOT_SUPPORTED_ERROR";
475 |
476 | case NPP_QUALITY_INDEX_ERROR:
477 | return "NPP_QUALITY_INDEX_ERROR";
478 |
479 | case NPP_CHANNEL_ORDER_ERROR:
480 | return "NPP_CHANNEL_ORDER_ERROR";
481 |
482 | case NPP_ZERO_MASK_VALUE_ERROR:
483 | return "NPP_ZERO_MASK_VALUE_ERROR";
484 |
485 | case NPP_NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS_ERROR:
486 | return "NPP_NUMBER_OF_CHANNELS_ERROR";
487 |
488 | case NPP_COI_ERROR:
489 | return "NPP_COI_ERROR";
490 |
491 | case NPP_DIVISOR_ERROR:
492 | return "NPP_DIVISOR_ERROR";
493 |
494 | case NPP_CHANNEL_ERROR:
495 | return "NPP_CHANNEL_ERROR";
496 |
497 | case NPP_STRIDE_ERROR:
498 | return "NPP_STRIDE_ERROR";
499 |
500 | case NPP_ANCHOR_ERROR:
501 | return "NPP_ANCHOR_ERROR";
502 |
503 | case NPP_MASK_SIZE_ERROR:
504 | return "NPP_MASK_SIZE_ERROR";
505 |
506 | case NPP_MOMENT_00_ZERO_ERROR:
507 | return "NPP_MOMENT_00_ZERO_ERROR";
508 |
509 | case NPP_THRESHOLD_NEGATIVE_LEVEL_ERROR:
510 | return "NPP_THRESHOLD_NEGATIVE_LEVEL_ERROR";
511 |
512 | case NPP_THRESHOLD_ERROR:
513 | return "NPP_THRESHOLD_ERROR";
514 |
515 | case NPP_CONTEXT_MATCH_ERROR:
516 | return "NPP_CONTEXT_MATCH_ERROR";
517 |
518 | case NPP_FFT_FLAG_ERROR:
519 | return "NPP_FFT_FLAG_ERROR";
520 |
521 | case NPP_FFT_ORDER_ERROR:
522 | return "NPP_FFT_ORDER_ERROR";
523 |
524 | case NPP_SCALE_RANGE_ERROR:
525 | return "NPP_SCALE_RANGE_ERROR";
526 |
527 | case NPP_DATA_TYPE_ERROR:
528 | return "NPP_DATA_TYPE_ERROR";
529 |
530 | case NPP_OUT_OFF_RANGE_ERROR:
531 | return "NPP_OUT_OFF_RANGE_ERROR";
532 |
533 | case NPP_DIVIDE_BY_ZERO_ERROR:
534 | return "NPP_DIVIDE_BY_ZERO_ERROR";
535 |
536 | case NPP_RANGE_ERROR:
537 | return "NPP_RANGE_ERROR";
538 |
539 | case NPP_NO_MEMORY_ERROR:
540 | return "NPP_NO_MEMORY_ERROR";
541 |
542 | case NPP_ERROR_RESERVED:
543 | return "NPP_ERROR_RESERVED";
544 |
545 | case NPP_NO_OPERATION_WARNING:
546 | return "NPP_NO_OPERATION_WARNING";
547 |
548 | case NPP_DIVIDE_BY_ZERO_WARNING:
549 | return "NPP_DIVIDE_BY_ZERO_WARNING";
550 | #endif
551 |
552 | #if ((NPP_VERSION_MAJOR << 12) + (NPP_VERSION_MINOR << 4)) >= 0x7000
553 | /* These are 7.0 or higher */
554 | case NPP_OVERFLOW_ERROR:
555 | return "NPP_OVERFLOW_ERROR";
556 |
557 | case NPP_CORRUPTED_DATA_ERROR:
558 | return "NPP_CORRUPTED_DATA_ERROR";
559 | #endif
560 | }
561 |
562 | return "";
563 | }
564 | #endif
565 |
566 | template
567 | void check(T result, char const *const func, const char *const file,
568 | int const line) {
569 | if (result) {
570 | fprintf(stderr, "CUDA error at %s:%d code=%d(%s) \"%s\" \n", file, line,
571 | static_cast(result), _cudaGetErrorEnum(result), func);
572 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
573 | }
574 | }
575 |
576 | #ifdef __DRIVER_TYPES_H__
577 | // This will output the proper CUDA error strings in the event
578 | // that a CUDA host call returns an error
579 | #define checkCudaErrors(val) check((val), #val, __FILE__, __LINE__)
580 |
581 | // This will output the proper error string when calling cudaGetLastError
582 | #define getLastCudaError(msg) __getLastCudaError(msg, __FILE__, __LINE__)
583 |
584 | inline void __getLastCudaError(const char *errorMessage, const char *file,
585 | const int line) {
586 | cudaError_t err = cudaGetLastError();
587 |
588 | if (cudaSuccess != err) {
589 | fprintf(stderr,
590 | "%s(%i) : getLastCudaError() CUDA error :"
591 | " %s : (%d) %s.\n",
592 | file, line, errorMessage, static_cast(err),
593 | cudaGetErrorString(err));
594 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
595 | }
596 | }
597 |
598 | // This will only print the proper error string when calling cudaGetLastError
599 | // but not exit program incase error detected.
600 | #define printLastCudaError(msg) __printLastCudaError(msg, __FILE__, __LINE__)
601 |
602 | inline void __printLastCudaError(const char *errorMessage, const char *file,
603 | const int line) {
604 | cudaError_t err = cudaGetLastError();
605 |
606 | if (cudaSuccess != err) {
607 | fprintf(stderr,
608 | "%s(%i) : getLastCudaError() CUDA error :"
609 | " %s : (%d) %s.\n",
610 | file, line, errorMessage, static_cast(err),
611 | cudaGetErrorString(err));
612 | }
613 | }
614 | #endif
615 |
616 | #ifndef MAX
617 | #define MAX(a, b) (a > b ? a : b)
618 | #endif
619 |
620 | // Float To Int conversion
621 | inline int ftoi(float value) {
622 | return (value >= 0 ? static_cast(value + 0.5)
623 | : static_cast(value - 0.5));
624 | }
625 |
626 | // Beginning of GPU Architecture definitions
627 | inline int _ConvertSMVer2Cores(int major, int minor) {
628 | // Defines for GPU Architecture types (using the SM version to determine
629 | // the # of cores per SM
630 | typedef struct {
631 | int SM; // 0xMm (hexidecimal notation), M = SM Major version,
632 | // and m = SM minor version
633 | int Cores;
634 | } sSMtoCores;
635 |
636 | sSMtoCores nGpuArchCoresPerSM[] = {
637 | {0x30, 192},
638 | {0x32, 192},
639 | {0x35, 192},
640 | {0x37, 192},
641 | {0x50, 128},
642 | {0x52, 128},
643 | {0x53, 128},
644 | {0x60, 64},
645 | {0x61, 128},
646 | {0x62, 128},
647 | {0x70, 64},
648 | {0x72, 64},
649 | {0x75, 64},
650 | {0x80, 64},
651 | {0x86, 128},
652 | {-1, -1}};
653 |
654 | int index = 0;
655 |
656 | while (nGpuArchCoresPerSM[index].SM != -1) {
657 | if (nGpuArchCoresPerSM[index].SM == ((major << 4) + minor)) {
658 | return nGpuArchCoresPerSM[index].Cores;
659 | }
660 |
661 | index++;
662 | }
663 |
664 | // If we don't find the values, we default use the previous one
665 | // to run properly
666 | printf(
667 | "MapSMtoCores for SM %d.%d is undefined."
668 | " Default to use %d Cores/SM\n",
669 | major, minor, nGpuArchCoresPerSM[index - 1].Cores);
670 | return nGpuArchCoresPerSM[index - 1].Cores;
671 | }
672 |
673 | inline const char* _ConvertSMVer2ArchName(int major, int minor) {
674 | // Defines for GPU Architecture types (using the SM version to determine
675 | // the GPU Arch name)
676 | typedef struct {
677 | int SM; // 0xMm (hexidecimal notation), M = SM Major version,
678 | // and m = SM minor version
679 | const char* name;
680 | } sSMtoArchName;
681 |
682 | sSMtoArchName nGpuArchNameSM[] = {
683 | {0x30, "Kepler"},
684 | {0x32, "Kepler"},
685 | {0x35, "Kepler"},
686 | {0x37, "Kepler"},
687 | {0x50, "Maxwell"},
688 | {0x52, "Maxwell"},
689 | {0x53, "Maxwell"},
690 | {0x60, "Pascal"},
691 | {0x61, "Pascal"},
692 | {0x62, "Pascal"},
693 | {0x70, "Volta"},
694 | {0x72, "Xavier"},
695 | {0x75, "Turing"},
696 | {0x80, "Ampere"},
697 | {0x86, "Ampere"},
698 | {-1, "Graphics Device"}};
699 |
700 | int index = 0;
701 |
702 | while (nGpuArchNameSM[index].SM != -1) {
703 | if (nGpuArchNameSM[index].SM == ((major << 4) + minor)) {
704 | return nGpuArchNameSM[index].name;
705 | }
706 |
707 | index++;
708 | }
709 |
710 | // If we don't find the values, we default use the previous one
711 | // to run properly
712 | printf(
713 | "MapSMtoArchName for SM %d.%d is undefined."
714 | " Default to use %s\n",
715 | major, minor, nGpuArchNameSM[index - 1].name);
716 | return nGpuArchNameSM[index - 1].name;
717 | }
718 | // end of GPU Architecture definitions
719 |
720 | #ifdef __CUDA_RUNTIME_H__
721 | // General GPU Device CUDA Initialization
722 | inline int gpuDeviceInit(int devID) {
723 | int device_count;
724 | checkCudaErrors(cudaGetDeviceCount(&device_count));
725 |
726 | if (device_count == 0) {
727 | fprintf(stderr,
728 | "gpuDeviceInit() CUDA error: "
729 | "no devices supporting CUDA.\n");
730 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
731 | }
732 |
733 | if (devID < 0) {
734 | devID = 0;
735 | }
736 |
737 | if (devID > device_count - 1) {
738 | fprintf(stderr, "\n");
739 | fprintf(stderr, ">> %d CUDA capable GPU device(s) detected. <<\n",
740 | device_count);
741 | fprintf(stderr,
742 | ">> gpuDeviceInit (-device=%d) is not a valid"
743 | " GPU device. <<\n",
744 | devID);
745 | fprintf(stderr, "\n");
746 | return -devID;
747 | }
748 |
749 | int computeMode = -1, major = 0, minor = 0;
750 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&computeMode, cudaDevAttrComputeMode, devID));
751 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&major, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMajor, devID));
752 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&minor, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMinor, devID));
753 | if (computeMode == cudaComputeModeProhibited) {
754 | fprintf(stderr,
755 | "Error: device is running in , no threads can use cudaSetDevice().\n");
757 | return -1;
758 | }
759 |
760 | if (major < 1) {
761 | fprintf(stderr, "gpuDeviceInit(): GPU device does not support CUDA.\n");
762 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
763 | }
764 |
765 | checkCudaErrors(cudaSetDevice(devID));
766 | printf("gpuDeviceInit() CUDA Device [%d]: \"%s\n", devID, _ConvertSMVer2ArchName(major, minor));
767 |
768 | return devID;
769 | }
770 |
771 | // This function returns the best GPU (with maximum GFLOPS)
772 | inline int gpuGetMaxGflopsDeviceId() {
773 | int current_device = 0, sm_per_multiproc = 0;
774 | int max_perf_device = 0;
775 | int device_count = 0;
776 | int devices_prohibited = 0;
777 |
778 | uint64_t max_compute_perf = 0;
779 | checkCudaErrors(cudaGetDeviceCount(&device_count));
780 |
781 | if (device_count == 0) {
782 | fprintf(stderr,
783 | "gpuGetMaxGflopsDeviceId() CUDA error:"
784 | " no devices supporting CUDA.\n");
785 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
786 | }
787 |
788 | // Find the best CUDA capable GPU device
789 | current_device = 0;
790 |
791 | while (current_device < device_count) {
792 | int computeMode = -1, major = 0, minor = 0;
793 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&computeMode, cudaDevAttrComputeMode, current_device));
794 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&major, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMajor, current_device));
795 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&minor, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMinor, current_device));
796 |
797 | // If this GPU is not running on Compute Mode prohibited,
798 | // then we can add it to the list
799 | if (computeMode != cudaComputeModeProhibited) {
800 | if (major == 9999 && minor == 9999) {
801 | sm_per_multiproc = 1;
802 | } else {
803 | sm_per_multiproc =
804 | _ConvertSMVer2Cores(major, minor);
805 | }
806 | int multiProcessorCount = 0, clockRate = 0;
807 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&multiProcessorCount, cudaDevAttrMultiProcessorCount, current_device));
808 | cudaError_t result = cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&clockRate, cudaDevAttrClockRate, current_device);
809 | if (result != cudaSuccess) {
810 | // If cudaDevAttrClockRate attribute is not supported we
811 | // set clockRate as 1, to consider GPU with most SMs and CUDA Cores.
812 | if(result == cudaErrorInvalidValue) {
813 | clockRate = 1;
814 | }
815 | else {
816 | fprintf(stderr, "CUDA error at %s:%d code=%d(%s) \n", __FILE__, __LINE__,
817 | static_cast(result), _cudaGetErrorEnum(result));
818 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
819 | }
820 | }
821 | uint64_t compute_perf = (uint64_t)multiProcessorCount * sm_per_multiproc * clockRate;
822 |
823 | if (compute_perf > max_compute_perf) {
824 | max_compute_perf = compute_perf;
825 | max_perf_device = current_device;
826 | }
827 | } else {
828 | devices_prohibited++;
829 | }
830 |
831 | ++current_device;
832 | }
833 |
834 | if (devices_prohibited == device_count) {
835 | fprintf(stderr,
836 | "gpuGetMaxGflopsDeviceId() CUDA error:"
837 | " all devices have compute mode prohibited.\n");
838 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
839 | }
840 |
841 | return max_perf_device;
842 | }
843 |
844 | // Initialization code to find the best CUDA Device
845 | inline int findCudaDevice(int argc, const char **argv) {
846 | int devID = 0;
847 |
848 | // If the command-line has a device number specified, use it
849 | if (checkCmdLineFlag(argc, argv, "device")) {
850 | devID = getCmdLineArgumentInt(argc, argv, "device=");
851 |
852 | if (devID < 0) {
853 | printf("Invalid command line parameter\n ");
854 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
855 | } else {
856 | devID = gpuDeviceInit(devID);
857 |
858 | if (devID < 0) {
859 | printf("exiting...\n");
860 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
861 | }
862 | }
863 | } else {
864 | // Otherwise pick the device with highest Gflops/s
865 | devID = gpuGetMaxGflopsDeviceId();
866 | checkCudaErrors(cudaSetDevice(devID));
867 | int major = 0, minor = 0;
868 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&major, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMajor, devID));
869 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&minor, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMinor, devID));
870 | printf("GPU Device %d: \"%s\" with compute capability %d.%d\n\n",
871 | devID, _ConvertSMVer2ArchName(major, minor), major, minor);
872 |
873 | }
874 |
875 | return devID;
876 | }
877 |
878 | inline int findIntegratedGPU() {
879 | int current_device = 0;
880 | int device_count = 0;
881 | int devices_prohibited = 0;
882 |
883 | checkCudaErrors(cudaGetDeviceCount(&device_count));
884 |
885 | if (device_count == 0) {
886 | fprintf(stderr, "CUDA error: no devices supporting CUDA.\n");
887 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
888 | }
889 |
890 | // Find the integrated GPU which is compute capable
891 | while (current_device < device_count) {
892 | int computeMode = -1, integrated = -1;
893 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&computeMode, cudaDevAttrComputeMode, current_device));
894 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&integrated, cudaDevAttrIntegrated, current_device));
895 | // If GPU is integrated and is not running on Compute Mode prohibited,
896 | // then cuda can map to GLES resource
897 | if (integrated && (computeMode != cudaComputeModeProhibited)) {
898 | checkCudaErrors(cudaSetDevice(current_device));
899 |
900 | int major = 0, minor = 0;
901 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&major, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMajor, current_device));
902 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&minor, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMinor, current_device));
903 | printf("GPU Device %d: \"%s\" with compute capability %d.%d\n\n",
904 | current_device, _ConvertSMVer2ArchName(major, minor), major, minor);
905 |
906 | return current_device;
907 | } else {
908 | devices_prohibited++;
909 | }
910 |
911 | current_device++;
912 | }
913 |
914 | if (devices_prohibited == device_count) {
915 | fprintf(stderr,
916 | "CUDA error:"
917 | " No GLES-CUDA Interop capable GPU found.\n");
918 | exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
919 | }
920 |
921 | return -1;
922 | }
923 |
924 | // General check for CUDA GPU SM Capabilities
925 | inline bool checkCudaCapabilities(int major_version, int minor_version) {
926 | int dev;
927 | int major = 0, minor = 0;
928 |
929 | checkCudaErrors(cudaGetDevice(&dev));
930 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&major, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMajor, dev));
931 | checkCudaErrors(cudaDeviceGetAttribute(&minor, cudaDevAttrComputeCapabilityMinor, dev));
932 |
933 | if ((major > major_version) ||
934 | (major == major_version &&
935 | minor >= minor_version)) {
936 | printf(" Device %d: <%16s >, Compute SM %d.%d detected\n", dev,
937 | _ConvertSMVer2ArchName(major, minor), major, minor);
938 | return true;
939 | } else {
940 | printf(
941 | " No GPU device was found that can support "
942 | "CUDA compute capability %d.%d.\n",
943 | major_version, minor_version);
944 | return false;
945 | }
946 | }
947 | #endif
948 |
949 | // end of CUDA Helper Functions
950 |
951 | #endif // COMMON_HELPER_CUDA_H_
952 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/libs/helper_string.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /**
2 | * Copyright 1993-2013 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | *
4 | * Please refer to the NVIDIA end user license agreement (EULA) associated
5 | * with this source code for terms and conditions that govern your use of
6 | * this software. Any use, reproduction, disclosure, or distribution of
7 | * this software and related documentation outside the terms of the EULA
8 | * is strictly prohibited.
9 | *
10 | */
11 |
12 | // These are helper functions for the SDK samples (string parsing, timers, etc)
13 | #ifndef COMMON_HELPER_STRING_H_
14 | #define COMMON_HELPER_STRING_H_
15 |
16 | #include
17 | #include
18 | #include
19 | #include
20 |
21 | #if defined(WIN32) || defined(_WIN32) || defined(WIN64) || defined(_WIN64)
22 | #ifndef _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE
23 | #define _CRT_SECURE_NO_DEPRECATE
24 | #endif
25 | #ifndef STRCASECMP
26 | #define STRCASECMP _stricmp
27 | #endif
28 | #ifndef STRNCASECMP
29 | #define STRNCASECMP _strnicmp
30 | #endif
31 | #ifndef STRCPY
32 | #define STRCPY(sFilePath, nLength, sPath) strcpy_s(sFilePath, nLength, sPath)
33 | #endif
34 |
35 | #ifndef FOPEN
36 | #define FOPEN(fHandle, filename, mode) fopen_s(&fHandle, filename, mode)
37 | #endif
38 | #ifndef FOPEN_FAIL
39 | #define FOPEN_FAIL(result) (result != 0)
40 | #endif
41 | #ifndef SSCANF
42 | #define SSCANF sscanf_s
43 | #endif
44 | #ifndef SPRINTF
45 | #define SPRINTF sprintf_s
46 | #endif
47 | #else // Linux Includes
48 | #include
49 | #include
50 |
51 | #ifndef STRCASECMP
52 | #define STRCASECMP strcasecmp
53 | #endif
54 | #ifndef STRNCASECMP
55 | #define STRNCASECMP strncasecmp
56 | #endif
57 | #ifndef STRCPY
58 | #define STRCPY(sFilePath, nLength, sPath) strcpy(sFilePath, sPath)
59 | #endif
60 |
61 | #ifndef FOPEN
62 | #define FOPEN(fHandle, filename, mode) (fHandle = fopen(filename, mode))
63 | #endif
64 | #ifndef FOPEN_FAIL
65 | #define FOPEN_FAIL(result) (result == NULL)
66 | #endif
67 | #ifndef SSCANF
68 | #define SSCANF sscanf
69 | #endif
70 | #ifndef SPRINTF
71 | #define SPRINTF sprintf
72 | #endif
73 | #endif
74 |
75 | #ifndef EXIT_WAIVED
76 | #define EXIT_WAIVED 2
77 | #endif
78 |
79 | // CUDA Utility Helper Functions
80 | inline int stringRemoveDelimiter(char delimiter, const char *string) {
81 | int string_start = 0;
82 |
83 | while (string[string_start] == delimiter) {
84 | string_start++;
85 | }
86 |
87 | if (string_start >= static_cast(strlen(string) - 1)) {
88 | return 0;
89 | }
90 |
91 | return string_start;
92 | }
93 |
94 | inline int getFileExtension(char *filename, char **extension) {
95 | int string_length = static_cast(strlen(filename));
96 |
97 | while (filename[string_length--] != '.') {
98 | if (string_length == 0) break;
99 | }
100 |
101 | if (string_length > 0) string_length += 2;
102 |
103 | if (string_length == 0)
104 | *extension = NULL;
105 | else
106 | *extension = &filename[string_length];
107 |
108 | return string_length;
109 | }
110 |
111 | inline bool checkCmdLineFlag(const int argc, const char **argv,
112 | const char *string_ref) {
113 | bool bFound = false;
114 |
115 | if (argc >= 1) {
116 | for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
117 | int string_start = stringRemoveDelimiter('-', argv[i]);
118 | const char *string_argv = &argv[i][string_start];
119 |
120 | const char *equal_pos = strchr(string_argv, '=');
121 | int argv_length = static_cast(
122 | equal_pos == 0 ? strlen(string_argv) : equal_pos - string_argv);
123 |
124 | int length = static_cast(strlen(string_ref));
125 |
126 | if (length == argv_length &&
127 | !STRNCASECMP(string_argv, string_ref, length)) {
128 | bFound = true;
129 | continue;
130 | }
131 | }
132 | }
133 |
134 | return bFound;
135 | }
136 |
137 | // This function wraps the CUDA Driver API into a template function
138 | template
139 | inline bool getCmdLineArgumentValue(const int argc, const char **argv,
140 | const char *string_ref, T *value) {
141 | bool bFound = false;
142 |
143 | if (argc >= 1) {
144 | for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
145 | int string_start = stringRemoveDelimiter('-', argv[i]);
146 | const char *string_argv = &argv[i][string_start];
147 | int length = static_cast(strlen(string_ref));
148 |
149 | if (!STRNCASECMP(string_argv, string_ref, length)) {
150 | if (length + 1 <= static_cast(strlen(string_argv))) {
151 | int auto_inc = (string_argv[length] == '=') ? 1 : 0;
152 | *value = (T)atoi(&string_argv[length + auto_inc]);
153 | }
154 |
155 | bFound = true;
156 | i = argc;
157 | }
158 | }
159 | }
160 |
161 | return bFound;
162 | }
163 |
164 | inline int getCmdLineArgumentInt(const int argc, const char **argv,
165 | const char *string_ref) {
166 | bool bFound = false;
167 | int value = -1;
168 |
169 | if (argc >= 1) {
170 | for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
171 | int string_start = stringRemoveDelimiter('-', argv[i]);
172 | const char *string_argv = &argv[i][string_start];
173 | int length = static_cast(strlen(string_ref));
174 |
175 | if (!STRNCASECMP(string_argv, string_ref, length)) {
176 | if (length + 1 <= static_cast(strlen(string_argv))) {
177 | int auto_inc = (string_argv[length] == '=') ? 1 : 0;
178 | value = atoi(&string_argv[length + auto_inc]);
179 | } else {
180 | value = 0;
181 | }
182 |
183 | bFound = true;
184 | continue;
185 | }
186 | }
187 | }
188 |
189 | if (bFound) {
190 | return value;
191 | } else {
192 | return 0;
193 | }
194 | }
195 |
196 | inline float getCmdLineArgumentFloat(const int argc, const char **argv,
197 | const char *string_ref) {
198 | bool bFound = false;
199 | float value = -1;
200 |
201 | if (argc >= 1) {
202 | for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
203 | int string_start = stringRemoveDelimiter('-', argv[i]);
204 | const char *string_argv = &argv[i][string_start];
205 | int length = static_cast(strlen(string_ref));
206 |
207 | if (!STRNCASECMP(string_argv, string_ref, length)) {
208 | if (length + 1 <= static_cast(strlen(string_argv))) {
209 | int auto_inc = (string_argv[length] == '=') ? 1 : 0;
210 | value = static_cast(atof(&string_argv[length + auto_inc]));
211 | } else {
212 | value = 0.f;
213 | }
214 |
215 | bFound = true;
216 | continue;
217 | }
218 | }
219 | }
220 |
221 | if (bFound) {
222 | return value;
223 | } else {
224 | return 0;
225 | }
226 | }
227 |
228 | inline bool getCmdLineArgumentString(const int argc, const char **argv,
229 | const char *string_ref,
230 | char **string_retval) {
231 | bool bFound = false;
232 |
233 | if (argc >= 1) {
234 | for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
235 | int string_start = stringRemoveDelimiter('-', argv[i]);
236 | char *string_argv = const_cast(&argv[i][string_start]);
237 | int length = static_cast(strlen(string_ref));
238 |
239 | if (!STRNCASECMP(string_argv, string_ref, length)) {
240 | *string_retval = &string_argv[length + 1];
241 | bFound = true;
242 | continue;
243 | }
244 | }
245 | }
246 |
247 | if (!bFound) {
248 | *string_retval = NULL;
249 | }
250 |
251 | return bFound;
252 | }
253 |
254 | //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
255 | //! Find the path for a file assuming that
256 | //! files are found in the searchPath.
257 | //!
258 | //! @return the path if succeeded, otherwise 0
259 | //! @param filename name of the file
260 | //! @param executable_path optional absolute path of the executable
261 | //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////
262 | inline char *sdkFindFilePath(const char *filename,
263 | const char *executable_path) {
264 | // defines a variable that is replaced with the name of the
265 | // executable
266 |
267 | // Typical relative search paths to locate needed companion files (e.g. sample
268 | // input data, or JIT source files) The origin for the relative search may be
269 | // the .exe file, a .bat file launching an .exe, a browser .exe launching the
270 | // .exe or .bat, etc
271 | const char *searchPath[] = {
272 | "./", // same dir
273 | "./_data_files/",
274 | "./common/", // "/common/" subdir
275 | "./common/data/", // "/common/data/" subdir
276 | "./data/", // "/data/" subdir
277 | "./src/", // "/src/" subdir
278 | "./src//data/", // "/src//data/" subdir
279 | "./inc/", // "/inc/" subdir
280 | "./0_Simple/", // "/0_Simple/" subdir
281 | "./1_Utilities/", // "/1_Utilities/" subdir
282 | "./2_Graphics/", // "/2_Graphics/" subdir
283 | "./3_Imaging/", // "/3_Imaging/" subdir
284 | "./4_Finance/", // "/4_Finance/" subdir
285 | "./5_Simulations/", // "/5_Simulations/" subdir
286 | "./6_Advanced/", // "/6_Advanced/" subdir
287 | "./7_CUDALibraries/", // "/7_CUDALibraries/" subdir
288 | "./8_Android/", // "/8_Android/" subdir
289 | "./samples/", // "/samples/" subdir
290 |
291 | "./0_Simple//data/", // "/0_Simple//data/"
292 | // subdir
293 | "./1_Utilities//data/", // "/1_Utilities//data/"
294 | // subdir
295 | "./2_Graphics//data/", // "/2_Graphics//data/"
296 | // subdir
297 | "./3_Imaging//data/", // "/3_Imaging//data/"
298 | // subdir
299 | "./4_Finance//data/", // "/4_Finance//data/"
300 | // subdir
301 | "./5_Simulations//data/", // "/5_Simulations//data/"
302 | // subdir
303 | "./6_Advanced//data/", // "/6_Advanced//data/"
304 | // subdir
305 | "./7_CUDALibraries//", // "/7_CUDALibraries//"
306 | // subdir
307 | "./7_CUDALibraries//data/", // "/7_CUDALibraries//data/"
308 | // subdir
309 |
310 | "../", // up 1 in tree
311 | "../common/", // up 1 in tree, "/common/" subdir
312 | "../common/data/", // up 1 in tree, "/common/data/" subdir
313 | "../data/", // up 1 in tree, "/data/" subdir
314 | "../src/", // up 1 in tree, "/src/" subdir
315 | "../inc/", // up 1 in tree, "/inc/" subdir
316 |
317 | "../0_Simple//data/", // up 1 in tree,
318 | // "/0_Simple//"
319 | // subdir
320 | "../1_Utilities//data/", // up 1 in tree,
321 | // "/1_Utilities//"
322 | // subdir
323 | "../2_Graphics//data/", // up 1 in tree,
324 | // "/2_Graphics//"
325 | // subdir
326 | "../3_Imaging//data/", // up 1 in tree,
327 | // "/3_Imaging//"
328 | // subdir
329 | "../4_Finance//data/", // up 1 in tree,
330 | // "/4_Finance//"
331 | // subdir
332 | "../5_Simulations//data/", // up 1 in tree,
333 | // "/5_Simulations//"
334 | // subdir
335 | "../6_Advanced//data/", // up 1 in tree,
336 | // "/6_Advanced//"
337 | // subdir
338 | "../7_CUDALibraries//data/", // up 1 in tree,
339 | // "/7_CUDALibraries//"
340 | // subdir
341 | "../8_Android//data/", // up 1 in tree,
342 | // "/8_Android//"
343 | // subdir
344 | "../samples//data/", // up 1 in tree,
345 | // "/samples//"
346 | // subdir
347 | "../../", // up 2 in tree
348 | "../../common/", // up 2 in tree, "/common/" subdir
349 | "../../common/data/", // up 2 in tree, "/common/data/" subdir
350 | "../../data/", // up 2 in tree, "/data/" subdir
351 | "../../src/", // up 2 in tree, "/src/" subdir
352 | "../../inc/", // up 2 in tree, "/inc/" subdir
353 | "../../sandbox//data/", // up 2 in tree,
354 | // "/sandbox//"
355 | // subdir
356 | "../../0_Simple//data/", // up 2 in tree,
357 | // "/0_Simple//"
358 | // subdir
359 | "../../1_Utilities//data/", // up 2 in tree,
360 | // "/1_Utilities//"
361 | // subdir
362 | "../../2_Graphics//data/", // up 2 in tree,
363 | // "/2_Graphics//"
364 | // subdir
365 | "../../3_Imaging//data/", // up 2 in tree,
366 | // "/3_Imaging//"
367 | // subdir
368 | "../../4_Finance//data/", // up 2 in tree,
369 | // "/4_Finance//"
370 | // subdir
371 | "../../5_Simulations//data/", // up 2 in tree,
372 | // "/5_Simulations//"
373 | // subdir
374 | "../../6_Advanced//data/", // up 2 in tree,
375 | // "/6_Advanced//"
376 | // subdir
377 | "../../7_CUDALibraries//data/", // up 2 in tree,
378 | // "/7_CUDALibraries//"
379 | // subdir
380 | "../../8_Android//data/", // up 2 in tree,
381 | // "/8_Android//"
382 | // subdir
383 | "../../samples//data/", // up 2 in tree,
384 | // "/samples//"
385 | // subdir
386 | "../../../", // up 3 in tree
387 | "../../../src//", // up 3 in tree,
388 | // "/src//" subdir
389 | "../../../src//data/", // up 3 in tree,
390 | // "/src//data/"
391 | // subdir
392 | "../../../src//src/", // up 3 in tree,
393 | // "/src//src/"
394 | // subdir
395 | "../../../src//inc/", // up 3 in tree,
396 | // "/src//inc/"
397 | // subdir
398 | "../../../sandbox//", // up 3 in tree,
399 | // "/sandbox//"
400 | // subdir
401 | "../../../sandbox//data/", // up 3 in tree,
402 | // "/sandbox//data/"
403 | // subdir
404 | "../../../sandbox//src/", // up 3 in tree,
405 | // "/sandbox//src/"
406 | // subdir
407 | "../../../sandbox//inc/", // up 3 in tree,
408 | // "/sandbox//inc/"
409 | // subdir
410 | "../../../0_Simple//data/", // up 3 in tree,
411 | // "/0_Simple//"
412 | // subdir
413 | "../../../1_Utilities//data/", // up 3 in tree,
414 | // "/1_Utilities//"
415 | // subdir
416 | "../../../2_Graphics//data/", // up 3 in tree,
417 | // "/2_Graphics//"
418 | // subdir
419 | "../../../3_Imaging//data/", // up 3 in tree,
420 | // "/3_Imaging//"
421 | // subdir
422 | "../../../4_Finance//data/", // up 3 in tree,
423 | // "/4_Finance//"
424 | // subdir
425 | "../../../5_Simulations//data/", // up 3 in tree,
426 | // "/5_Simulations//"
427 | // subdir
428 | "../../../6_Advanced//data/", // up 3 in tree,
429 | // "/6_Advanced//"
430 | // subdir
431 | "../../../7_CUDALibraries//data/", // up 3 in tree,
432 | // "/7_CUDALibraries//"
433 | // subdir
434 | "../../../8_Android//data/", // up 3 in tree,
435 | // "/8_Android//"
436 | // subdir
437 | "../../../0_Simple//", // up 3 in tree,
438 | // "/0_Simple//"
439 | // subdir
440 | "../../../1_Utilities//", // up 3 in tree,
441 | // "/1_Utilities//"
442 | // subdir
443 | "../../../2_Graphics//", // up 3 in tree,
444 | // "/2_Graphics//"
445 | // subdir
446 | "../../../3_Imaging//", // up 3 in tree,
447 | // "/3_Imaging//"
448 | // subdir
449 | "../../../4_Finance//", // up 3 in tree,
450 | // "/4_Finance//"
451 | // subdir
452 | "../../../5_Simulations//", // up 3 in tree,
453 | // "/5_Simulations//"
454 | // subdir
455 | "../../../6_Advanced//", // up 3 in tree,
456 | // "/6_Advanced//"
457 | // subdir
458 | "../../../7_CUDALibraries//", // up 3 in tree,
459 | // "/7_CUDALibraries//"
460 | // subdir
461 | "../../../8_Android//", // up 3 in tree,
462 | // "/8_Android//"
463 | // subdir
464 | "../../../samples//data/", // up 3 in tree,
465 | // "/samples//"
466 | // subdir
467 | "../../../common/", // up 3 in tree, "../../../common/" subdir
468 | "../../../common/data/", // up 3 in tree, "../../../common/data/" subdir
469 | "../../../data/", // up 3 in tree, "../../../data/" subdir
470 | "../../../../", // up 4 in tree
471 | "../../../../src//", // up 4 in tree,
472 | // "/src//" subdir
473 | "../../../../src//data/", // up 4 in tree,
474 | // "/src//data/"
475 | // subdir
476 | "../../../../src//src/", // up 4 in tree,
477 | // "/src//src/"
478 | // subdir
479 | "../../../../src//inc/", // up 4 in tree,
480 | // "/src//inc/"
481 | // subdir
482 | "../../../../sandbox//", // up 4 in tree,
483 | // "/sandbox//"
484 | // subdir
485 | "../../../../sandbox//data/", // up 4 in tree,
486 | // "/sandbox//data/"
487 | // subdir
488 | "../../../../sandbox//src/", // up 4 in tree,
489 | // "/sandbox//src/"
490 | // subdir
491 | "../../../../sandbox//inc/", // up 4 in tree,
492 | // "/sandbox//inc/"
493 | // subdir
494 | "../../../../0_Simple//data/", // up 4 in tree,
495 | // "/0_Simple//"
496 | // subdir
497 | "../../../../1_Utilities//data/", // up 4 in tree,
498 | // "/1_Utilities//"
499 | // subdir
500 | "../../../../2_Graphics//data/", // up 4 in tree,
501 | // "/2_Graphics//"
502 | // subdir
503 | "../../../../3_Imaging//data/", // up 4 in tree,
504 | // "/3_Imaging//"
505 | // subdir
506 | "../../../../4_Finance//data/", // up 4 in tree,
507 | // "/4_Finance//"
508 | // subdir
509 | "../../../../5_Simulations//data/", // up 4 in tree,
510 | // "/5_Simulations//"
511 | // subdir
512 | "../../../../6_Advanced//data/", // up 4 in tree,
513 | // "/6_Advanced//"
514 | // subdir
515 | "../../../../7_CUDALibraries//data/", // up 4 in tree,
516 | // "/7_CUDALibraries//"
517 | // subdir
518 | "../../../../8_Android//data/", // up 4 in tree,
519 | // "/8_Android//"
520 | // subdir
521 | "../../../../0_Simple//", // up 4 in tree,
522 | // "/0_Simple//"
523 | // subdir
524 | "../../../../1_Utilities//", // up 4 in tree,
525 | // "/1_Utilities//"
526 | // subdir
527 | "../../../../2_Graphics//", // up 4 in tree,
528 | // "/2_Graphics//"
529 | // subdir
530 | "../../../../3_Imaging//", // up 4 in tree,
531 | // "/3_Imaging//"
532 | // subdir
533 | "../../../../4_Finance//", // up 4 in tree,
534 | // "/4_Finance//"
535 | // subdir
536 | "../../../../5_Simulations//", // up 4 in tree,
537 | // "/5_Simulations//"
538 | // subdir
539 | "../../../../6_Advanced/