├── src
├── figures
│ ├── Loss_Franke.png
│ └── PredictionOverTestPoints_Franke.png
└── multi_derivative_Sobolev.py
├── LICENSE
└── README.md
/src/figures/Loss_Franke.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FuhgJan/SobolevPytorch/HEAD/src/figures/Loss_Franke.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/figures/PredictionOverTestPoints_Franke.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/FuhgJan/SobolevPytorch/HEAD/src/figures/PredictionOverTestPoints_Franke.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2020 FuhgJan
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # SobolevPytorch
2 | An implementation of a neural network training routine using available derivative information in Pytorch.
3 |
4 | Original paper:
5 |
6 | Czarnecki, W. M., Osindero, S., Jaderberg, M., Swirszcz, G., & Pascanu, R. (2017). Sobolev training for neural networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (pp. 4278-4287).
7 |
8 | Using Sobolev training we can efficiently reduce the overall loss and are able to get better approximations of the derivatives of the inputs.
9 |
10 | ## Tested on
11 |
12 | - Python 3.8
13 | - Numpy 1.19.4
14 | - Pytorch 1.7.0
15 | - Matplotlib 3.1.2
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 | ## Example
21 | Test on Franke's function
22 |
23 | 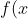&space;=&space;0.75&space;\exp{\left(-\frac{(9x-2)^2)}{4}&space;-&space;\frac{(9y-2)^2}{4}\right)}&space;+&space;0.75&space;\exp{\left(-\frac{(9x+1)^2)}{49}&space;-&space;\frac{(9y+1)}{10}\right)}&space;+&space;0.5&space;\exp{\left(-\frac{(9x-7)^2)}{4}&space;-&space;\frac{(9y-3)}{4}\right)}&space;-&space;0.2&space;\exp{\left(-(&space;9&space;x&space;-4)^2&space;-&space;(9y-7)^2&space;\right&space;)}) 24 |
25 | Training on 100 equidistant points between 0 and 1 yields the following convergence behavior:
26 |
27 |
24 |
25 | Training on 100 equidistant points between 0 and 1 yields the following convergence behavior:
26 |
27 |
28 |  29 |
29 |
30 |
31 | Testing on 1600 test points in the parametric space yields the following visualized results which are in good accordance with the target.
32 |
33 |
34 |  35 |
35 |
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/multi_derivative_Sobolev.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch.autograd import Variable
3 | import torch.utils.data as Data
4 | import torch.nn as nn
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
6 | import torch.optim as optim
7 |
8 | from matplotlib import cm
9 | import numpy as np
10 | import copy
11 |
12 |
13 | torch.manual_seed(1) # reproducible
14 |
15 | def franke(X, Y):
16 | term1 = .75*torch.exp(-((9*X - 2).pow(2) + (9*Y - 2).pow(2))/4)
17 | term2 = .75*torch.exp(-((9*X + 1).pow(2))/49 - (9*Y + 1)/10)
18 | term3 = .5*torch.exp(-((9*X - 7).pow(2) + (9*Y - 3).pow(2))/4)
19 | term4 = .2*torch.exp(-(9*X - 4).pow(2) - (9*Y - 7).pow(2))
20 |
21 | f = term1 + term2 + term3 - term4
22 | dfx = -2*(9*X - 2)*9/4 * term1 - 2*(9*X + 1)*9/49 * term2 + \
23 | -2*(9*X - 7)*9/4 * term3 + 2*(9*X - 4)*9 * term4
24 | dfy = -2*(9*Y - 2)*9/4 * term1 - 9/10 * term2 + \
25 | -2*(9*Y - 3)*9/4 * term3 + 2*(9*Y - 7)*9 * term4
26 |
27 | return f, dfx, dfy
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 | class Net(nn.Module):
33 | def __init__(self,inp,out, activation, num_hidden_units=100, num_layers=1):
34 | super(Net, self).__init__()
35 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(inp, num_hidden_units, bias=True)
36 | self.fc2 = nn.ModuleList()
37 | for i in range(num_layers):
38 | self.fc2.append(nn.Linear(num_hidden_units, num_hidden_units, bias=True))
39 | self.fc3 = nn.Linear(num_hidden_units, out, bias=True)
40 | self.activation = activation
41 |
42 | def forward(self, x):
43 | x = self.fc1(x)
44 | x = self.activation(x)
45 | for fc in self.fc2:
46 | x = fc(x)
47 | x = self.activation(x)
48 | x = self.fc3(x)
49 | return x
50 |
51 | def predict(self, x):
52 | self.eval()
53 | y = self(x)
54 | x = x.cpu().numpy().flatten()
55 | y = y.cpu().detach().numpy().flatten()
56 | return [x, y]
57 |
58 | def init_weights(m):
59 | classname = m.__class__.__name__
60 | # for every Linear layer in a model..
61 | if classname.find('Linear') != -1:
62 | # apply a uniform distribution to the weights and a bias=0
63 | n = m.in_features
64 | y = 1.0 / np.sqrt(n)
65 | m.weight.data.uniform_(-y, y)
66 | m.bias.data.fill_(0)
67 |
68 |
69 |
70 |
71 | def train(lam1, loader, EPOCH, BATCH_SIZE):
72 | state = copy.deepcopy(net.state_dict())
73 | best_loss = np.inf
74 |
75 | lossTotal = np.zeros((EPOCH, 1))
76 | lossRegular = np.zeros((EPOCH, 1))
77 | lossDerivatives = np.zeros((EPOCH, 1))
78 | # start training
79 | for epoch in range(EPOCH):
80 | scheduler.step()
81 | epoch_mse0 = 0.0
82 | epoch_mse1 = 0.0
83 |
84 |
85 | for step, (batch_x, batch_y) in enumerate(loader): # for each training step
86 |
87 | b_x = Variable(batch_x)
88 | b_y = Variable(batch_y)
89 |
90 |
91 | net.eval()
92 | b_x.requires_grad = True
93 |
94 | output0 = net(b_x)
95 | output0.sum().backward(retain_graph=True, create_graph=True)
96 | output1 = b_x.grad
97 | b_x.requires_grad = False
98 |
99 | net.train()
100 |
101 | mse0 = loss_func(output0, b_y[:,0:1])
102 | mse1 = loss_func(output1, b_y[:,1:3])
103 | epoch_mse0 += mse0.item() * BATCH_SIZE
104 | epoch_mse1 += mse1.item() * BATCH_SIZE
105 |
106 | loss = mse0 + lam1 * mse1
107 |
108 |
109 | optimizer.zero_grad() # clear gradients for next train
110 | loss.backward() # backpropagation, compute gradients
111 | optimizer.step() # apply gradients
112 |
113 |
114 | epoch_mse0 /= num_data
115 | epoch_mse1 /= num_data
116 | epoch_loss = epoch_mse0+lam1*epoch_mse1
117 |
118 | lossTotal[epoch] = epoch_loss
119 | lossRegular[epoch] = epoch_mse0
120 | lossDerivatives[epoch] = epoch_mse1
121 | if epoch%50==0:
122 | print('epoch', epoch,
123 | 'lr', '{:.7f}'.format(optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']),
124 | 'mse0', '{:.5f}'.format(epoch_mse0),
125 | 'mse1', '{:.5f}'.format(epoch_mse1),
126 | 'loss', '{:.5f}'.format(epoch_loss))
127 | if epoch_loss < best_loss:
128 | best_loss = epoch_loss
129 | state = copy.deepcopy(net.state_dict())
130 | #state = copy.deepcopy(net.state_dict())
131 | print('Best score:', best_loss)
132 | return state, lossTotal, lossRegular, lossDerivatives
133 |
134 |
135 |
136 |
137 |
138 | def getDerivatives(x):
139 | x1 = x.requires_grad_(True)
140 | output = net.eval()(x1)
141 | nn = output.shape[0]
142 | gradx = np.zeros((nn,2))
143 | for ii in range(output.shape[0]):
144 | y_def =output[ii].backward(retain_graph=True)
145 | gradx[ii,:] = x1.grad[ii]
146 | return gradx
147 |
148 |
149 |
150 | def plotLoss(lossTotal, lossRegular, lossDerivatives):
151 |
152 | fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, dpi=120)
153 | plt.semilogy(lossTotal / lossTotal[0], label='Total loss')
154 | plt.semilogy(lossRegular[:, 0] / lossRegular[0], label='Regular loss')
155 | plt.semilogy(lossDerivatives[:, 0] / lossDerivatives[0], label='Derivatives loss')
156 | ax.set_xlabel("epochs")
157 | ax.set_ylabel("L/L0")
158 | ax.legend()
159 | fig.subplots_adjust(left=0.1, right=0.9, bottom=0.15, top=0.9, wspace=0.3, hspace=0.2)
160 | plt.savefig("figures/Loss.png")
161 | plt.show()
162 |
163 |
164 |
165 | def plotPredictions(prediction,gradx, f,dfx,dfy, extent):
166 |
167 | # Initialize plots
168 | fig, ax = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(14, 10))
169 | ax[0, 0].imshow(f, extent=extent)
170 | ax[0, 0].set_title('True values')
171 | psm_f = ax[0, 0].pcolormesh(f, cmap=cm.jet, vmin=np.amin(f.detach().numpy()), vmax=np.amax(f.detach().numpy()))
172 | fig.colorbar(psm_f, ax=ax[0, 0])
173 | ax[0, 0].set_aspect('auto')
174 | ax[0, 1].imshow(dfx, extent=extent, cmap=cm.jet)
175 | ax[0, 1].set_title('True x-derivatives')
176 | psm_dfx = ax[0, 1].pcolormesh(dfx, cmap=cm.jet, vmin=np.amin(dfx.detach().numpy()), vmax=np.amax(dfx.detach().numpy()))
177 | fig.colorbar(psm_dfx, ax=ax[0, 1])
178 | ax[0, 1].set_aspect('auto')
179 | ax[0, 2].imshow(dfy, extent=extent, cmap=cm.jet)
180 | ax[0, 2].set_title('True y-derivatives')
181 | psm_dfy = ax[0, 2].pcolormesh(dfy, cmap=cm.jet, vmin=np.amin(dfy.detach().numpy()), vmax=np.amax(dfy.detach().numpy()))
182 | fig.colorbar(psm_dfy, ax=ax[0, 2])
183 | ax[0, 2].set_aspect('auto')
184 |
185 |
186 |
187 | ax[1, 0].imshow(prediction[:, 0].detach().numpy().reshape(nx_test, ny_test), extent=extent, cmap=cm.jet)
188 | ax[1, 0].set_title('Predicted values')
189 | fig.colorbar(psm_f, ax=ax[1, 0])
190 | ax[1, 0].set_aspect('auto')
191 | ax[1, 1].imshow(gradx[:, 0].reshape(nx_test, ny_test), extent=extent, cmap=cm.jet)
192 | ax[1, 1].set_title('Predicted x-derivatives')
193 | fig.colorbar(psm_dfx, ax=ax[1, 1])
194 | ax[1, 1].set_aspect('auto')
195 | ax[1, 2].imshow(gradx[:, 1].reshape(nx_test, ny_test), extent=extent, cmap=cm.jet)
196 | ax[1, 2].set_title('Predicted y-derivatives')
197 | fig.colorbar(psm_dfy, ax=ax[1, 2])
198 | ax[1, 2].set_aspect('auto')
199 | plt.savefig("figures/PredictionOverTestPoints.png")
200 | plt.show()
201 |
202 |
203 | if __name__ == "__main__":
204 | nx_train = 10
205 | ny_train = 10
206 | xv, yv = torch.meshgrid([torch.linspace(0, 1, nx_train), torch.linspace(0, 1, ny_train)])
207 | train_x = torch.cat((
208 | xv.contiguous().view(xv.numel(), 1),
209 | yv.contiguous().view(yv.numel(), 1)),
210 | dim=1
211 | )
212 |
213 | f, dfx, dfy = franke(train_x[:, 0], train_x[:, 1])
214 | train_y = torch.stack([f, dfx, dfy], -1).squeeze(1)
215 |
216 |
217 | x, y = Variable(train_x), Variable(train_y)
218 |
219 | net = Net(inp=2, out=1, activation=nn.Tanh(), num_hidden_units=256, num_layers=2)
220 |
221 | optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(net.parameters(), lr=3e-4, weight_decay=1e-6)
222 | scheduler = optim.lr_scheduler.StepLR(optimizer, step_size=1000, gamma=0.5)
223 | loss_func = torch.nn.MSELoss() # this is for regression mean squared loss
224 |
225 | import torch.multiprocessing
226 | torch.multiprocessing.set_sharing_strategy('file_system')
227 |
228 | BATCH_SIZE = 100
229 | EPOCH = 10000
230 | num_data = train_x.shape[0]
231 | torch_dataset = Data.TensorDataset(x, y)
232 |
233 | loader = Data.DataLoader(
234 | dataset=torch_dataset,
235 | batch_size=BATCH_SIZE,
236 | shuffle=False, num_workers=2, )
237 |
238 | # Define derivative loss component to total loss
239 | lam1 = .5
240 | state, lossTotal, lossRegular, lossDerivatives = train(lam1, loader, EPOCH, BATCH_SIZE)
241 | net.load_state_dict(state)
242 |
243 | # Test points
244 | nx_test, ny_test = 40, 40
245 | xv, yv = torch.meshgrid([torch.linspace(0, 1, nx_test), torch.linspace(0, 1, ny_test)])
246 | f, dfx, dfy = franke(xv, yv)
247 |
248 | test_x = torch.stack([xv.reshape(nx_test * ny_test, 1), yv.reshape(nx_test * ny_test, 1)], -1).squeeze(1)
249 |
250 | gradx = getDerivatives(test_x)
251 | plotLoss(lossTotal, lossRegular, lossDerivatives)
252 |
253 | prediction = net(test_x)
254 | extent = (xv.min(), xv.max(), yv.max(), yv.min())
255 |
256 | plotPredictions(prediction, gradx, f, dfx, dfy, extent)
257 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 29 |
29 |  29 |
29 |  35 |
35 |