├── README.md
├── eval
├── eval_img_process_tf.py
├── eval_ssd
├── np_methods.py
├── show_ssd_network.py
└── timg.jpeg
├── preprocess_img_tf.py
├── ssd_vgg300_tf.py
├── tfr_data_process.py
├── tfr_generate.ipynb
├── train_ssd_network.py
└── util_tf.py
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # SSD_Realization_TensorFlow
2 | [『TensorFlow × MXNet』SSD项目复现经验](https://www.cnblogs.com/hellcat/p/9540591.html)
3 | ## 使用
4 | #### 数据准备
5 | 将VOC2012数据解压到文件夹VOC2012中,注意检查下一级目录包含Annotations文件夹和JPEGImages文件夹。
6 | #### 生成TFR压缩数据
7 | 使用jupyter运行`tfr_generate.ipynb`脚本,使用TFR格式压缩图片对于提升训练速度大有裨益
8 | #### 训练模型
9 | 调用脚本即可
10 | ```bash
11 | python train_ssd_network.py
12 | ```
13 | #### 测试运行
14 | 进入eval目录,运行:
15 | ```bash
16 | python show_ssd_network.py
17 | ```
18 | 在该脚本中有设置图片路径的位置,替换为想要检测的图片即可。
19 | ## 实验说明
20 | 本工程17w steps后结果(框体过多的可以将NMS阈值减小):
21 | 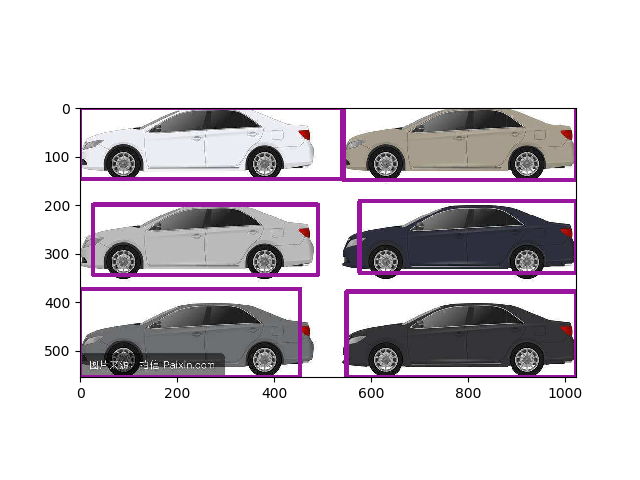
22 | 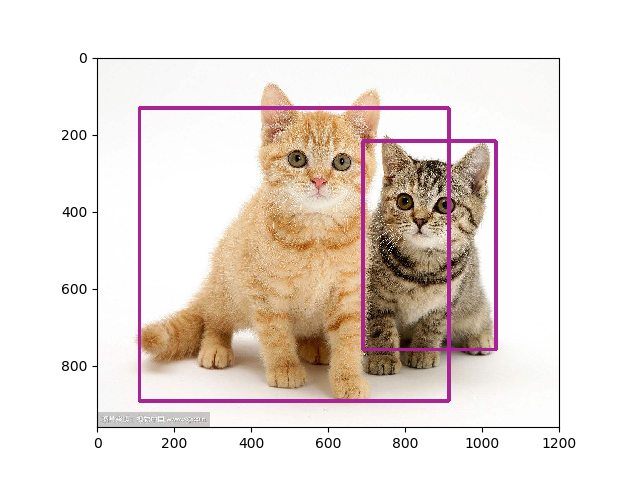
23 | 损失函数变化情况如图:
24 | 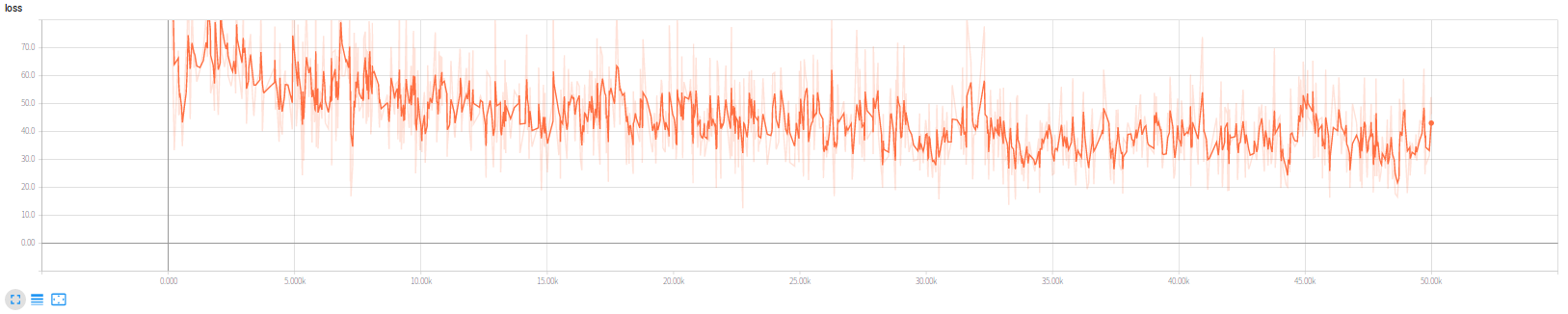
25 | ## 简要说明
26 | SSD架构主要有四个部分,网络设计、搜索框设计、学习目标处理、损失函数实现。
27 | ###### 网络设计
28 | 重点在于正常前向网络中挑选出的特征层分别添加两个卷积出口:分类和回归出口,用于对应后面的每个搜索框的各个类别得分、以及4个坐标值。
29 | ###### 搜索框设计
30 | 对应网络的特征层:每个层有若干搜索框,我们需要搜索框位置形状信息。对于tf版本我们保存了每个框的中心点以及HW信息,而mx版本我们保存的是左上右下两个的4个坐标数值,mx更为直观,但是tf版本节省空间:一组框对应同一个中心点,不过搜索框信息量不大,b无伤大雅。
31 | ###### 学习目标处理
32 | 个人感觉最为繁琐,我们需要的的信息包含(此时已经获得了):一组搜索框(实际上指的是全部搜索框的n*4个坐标值),图片的label、图片的真实框坐标(对应label数目*4),我们需要的就是找到搜索框和真是图片的标签联系,
33 | 获取:
34 | 每个搜索框对应的分类(和哪个真实框的IOU最大就选真实框的类别标注给该搜索,也就是说会出现大量的0 class搜索框)
35 | 每个搜索框的坐标的回归目标(同上的寻找方法,空位也为0)
36 | 负类掩码,虽然每张图片里面通常只有几个标注的边框,但SSD会生成大量的锚框。可以想象很多锚框都不会框住感兴趣的物体,就是说跟任何对应感兴趣物体的表框的IoU都小于某个阈值。这样就会产生大量的负类锚框,或者说对应标号为0的锚框。对于这类锚框有两点要考虑的:
37 | 1、边框预测的损失函数不应该包括负类锚框,因为它们并没有对应的真实边框
38 | 2、因为负类锚框数目可能远多于其他,我们可以只保留其中的一些。而且是保留那些目前预测最不确信它是负类的,就是对类0预测值排序,选取数值最小的哪一些困难的负类锚框
39 | 所以需要使用掩码,抑制一部分计算出来的loss。
40 | 损失函数可讲的不多,按照公式实现即可,重点也在上一步计算出来的掩码处理损失函数值一步。
41 | ## 日志
42 | #### 18.8.27
43 | 截止目前,本改版网络已经可以正常运行稳定收敛,之前的问题及解决思路如下:
44 | ###### 1.解决了之前版本Loss值过大且不收敛的问题
45 | 这个问题实际上是因为我个人的疏忽,将未预处理的图片送入ssd.bboxes_encode函数中,修正后如下,
46 | ```python
47 | image, glabels, gbboxes = \
48 | tfr_data_process.tfr_read(dataset)
49 |
50 | image, glabels, gbboxes = \
51 | preprocess_img_tf.preprocess_image(image, glabels, gbboxes, out_shape=(300, 300))
52 |
53 | gclasses, glocalisations, gscores = \
54 | ssd.bboxes_encode(glabels, gbboxes, ssd_anchors)
55 | ```
56 | 这个疏忽导致Loss值维持在200~400之间且不收敛,修改后经过300左右steps损失函数会稳定到60左右,和原SSD网络一致(示意如下)。
57 | 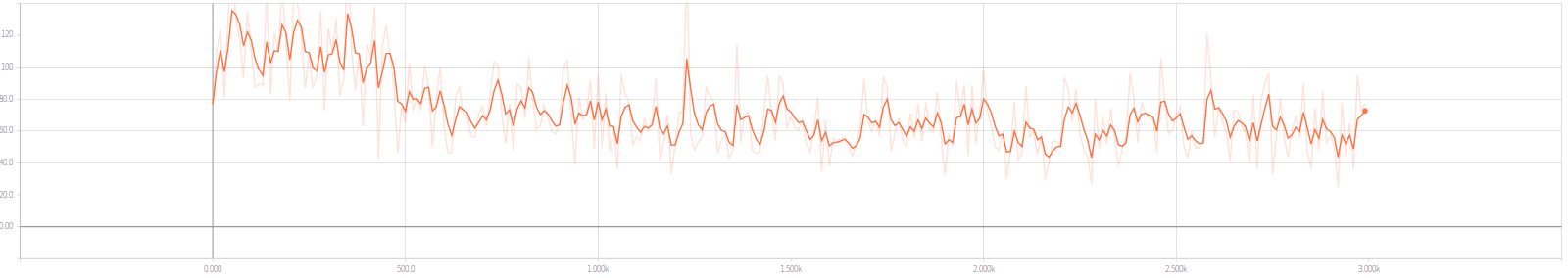
58 | ###### 2.解决了训练速度过慢的问题
59 | 原SSD模型训练速度(CPU:E5-2690,GPU:1080Ti)大概50 samples/sec(实际上略高与此),我的训练速度仅仅22-24 samples/sec,经对比查验,应该是节点分配硬件设备的配置优化问题,涉及队列(主要是数据输入)、优化器设定的节点分派给CPU后(其他节点会默认优先分配给GPU),速度明显提升,大概到达44-46 samples/sec。
60 | 另外,tfr数据解析过程放在GPU下,生成队列过程放在CPU下有不明显加速,理想情况下能提升0-1 samples/sec。
61 | 综上,现阶段的程序比原程序训练阶段还是要慢5 samples/sec左右,原因还在排查中。
62 | #### 18.8.31
63 | ###### 添加了测试脚本
64 | 参考资料见博客,由于该作者写的很好,稍作调整即可使用。
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/eval/eval_img_process_tf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author : hellcat
2 | # Time : 18-8-30
3 |
4 | """
5 | import os
6 | os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"]="-1"
7 |
8 | import numpy as np
9 | np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
10 |
11 | import tensorflow as tf
12 | config = tf.ConfigProto()
13 | config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
14 | sess = tf.Session(config=config)
15 | """
16 | import tensorflow as tf
17 | from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
18 | from tensorflow.python.ops import variables
19 | from tensorflow.python.ops import control_flow_ops
20 | from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
21 | from tensorflow.python.ops import check_ops
22 | from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
23 | import util_tf
24 |
25 |
26 | from enum import Enum, IntEnum
27 | # Resizing strategies.
28 | Resize = IntEnum('Resize', ('NONE', # Nothing!
29 | 'CENTRAL_CROP', # Crop (and pad if necessary).
30 | 'PAD_AND_RESIZE', # Pad, and resize to output shape.
31 | 'WARP_RESIZE')) # Warp resize.
32 | # VGG mean parameters.
33 | _R_MEAN = 123.
34 | _G_MEAN = 117.
35 | _B_MEAN = 104.
36 | EVAL_SIZE = (300, 300)
37 |
38 |
39 | def _is_tensor(x):
40 | """Returns `True` if `x` is a symbolic tensor-like object.
41 | Args:
42 | x: A python object to check.
43 | Returns:
44 | `True` if `x` is a `tf.Tensor` or `tf.Variable`, otherwise `False`.
45 | """
46 | return isinstance(x, (ops.Tensor, variables.Variable))
47 |
48 |
49 | def _assert(cond, ex_type, msg):
50 | """A polymorphic assert, works with tensors and boolean expressions.
51 | If `cond` is not a tensor, behave like an ordinary assert statement, except
52 | that a empty list is returned. If `cond` is a tensor, return a list
53 | containing a single TensorFlow assert op.
54 | Args:
55 | cond: Something evaluates to a boolean value. May be a tensor.
56 | ex_type: The exception class to use.
57 | msg: The error message.
58 | Returns:
59 | A list, containing at most one assert op.
60 | """
61 | if _is_tensor(cond):
62 | return [control_flow_ops.Assert(cond, [msg])]
63 | else:
64 | if not cond:
65 | raise ex_type(msg)
66 | else:
67 | return []
68 |
69 |
70 | def _Check3DImage(image, require_static=True):
71 | """Assert that we are working with properly shaped image.
72 | Args:
73 | image: 3-D Tensor of shape [height, width, channels]
74 | require_static: If `True`, requires that all dimensions of `image` are
75 | known and non-zero.
76 | Raises:
77 | ValueError: if `image.shape` is not a 3-vector.
78 | Returns:
79 | An empty list, if `image` has fully defined dimensions. Otherwise, a list
80 | containing an assert op is returned.
81 | """
82 | try:
83 | image_shape = image.get_shape().with_rank(3)
84 | except ValueError:
85 | raise ValueError("'image' must be three-dimensional.")
86 | if require_static and not image_shape.is_fully_defined():
87 | raise ValueError("'image' must be fully defined.")
88 | if any(x == 0 for x in image_shape):
89 | raise ValueError("all dims of 'image.shape' must be > 0: %s" %
90 | image_shape)
91 | if not image_shape.is_fully_defined():
92 | return [check_ops.assert_positive(array_ops.shape(image),
93 | ["all dims of 'image.shape' "
94 | "must be > 0."])]
95 | else:
96 | return []
97 |
98 |
99 | def bboxes_crop_or_pad(bboxes,
100 | height, width,
101 | offset_y, offset_x,
102 | target_height, target_width):
103 | """Adapt bounding boxes to crop or pad operations.
104 | Coordinates are always supposed to be relative to the image.
105 |
106 | Arguments:
107 | bboxes: Tensor Nx4 with bboxes coordinates [y_min, x_min, y_max, x_max];
108 | height, width: Original image dimension;
109 | offset_y, offset_x: Offset to apply,
110 | negative if cropping, positive if padding;
111 | target_height, target_width: Target dimension after cropping / padding.
112 | """
113 | with tf.name_scope('bboxes_crop_or_pad'):
114 | # Rescale bounding boxes in pixels.
115 | scale = tf.cast(tf.stack([height, width, height, width]), bboxes.dtype)
116 | bboxes = bboxes * scale
117 | # Add offset.
118 | offset = tf.cast(tf.stack([offset_y, offset_x, offset_y, offset_x]), bboxes.dtype)
119 | bboxes = bboxes + offset
120 | # Rescale to target dimension.
121 | scale = tf.cast(tf.stack([target_height, target_width,
122 | target_height, target_width]), bboxes.dtype)
123 | bboxes = bboxes / scale
124 | return bboxes
125 |
126 |
127 | def _ImageDimensions(image):
128 | """Returns the dimensions of an image tensor.
129 | Args:
130 | image: A 3-D Tensor of shape `[height, width, channels]`.
131 | Returns:
132 | A list of `[height, width, channels]` corresponding to the dimensions of the
133 | input image. Dimensions that are statically known are python integers,
134 | otherwise they are integer scalar tensors.
135 | """
136 | if image.get_shape().is_fully_defined():
137 | return image.get_shape().as_list()
138 | else:
139 | static_shape = image.get_shape().with_rank(3).as_list()
140 | dynamic_shape = array_ops.unstack(array_ops.shape(image), 3)
141 | return [s if s is not None else d
142 | for s, d in zip(static_shape, dynamic_shape)]
143 |
144 |
145 | def resize_image_bboxes_with_crop_or_pad(image, bboxes,
146 | target_height, target_width):
147 | """Crops and/or pads an image to a target width and height.
148 | Resizes an image to a target width and height by either centrally
149 | cropping the image or padding it evenly with zeros.
150 |
151 | If `width` or `height` is greater than the specified `target_width` or
152 | `target_height` respectively, this op centrally crops along that dimension.
153 | If `width` or `height` is smaller than the specified `target_width` or
154 | `target_height` respectively, this op centrally pads with 0 along that
155 | dimension.
156 | Args:
157 | image: 3-D tensor of shape `[height, width, channels]`
158 | target_height: Target height.
159 | target_width: Target width.
160 | Raises:
161 | ValueError: if `target_height` or `target_width` are zero or negative.
162 | Returns:
163 | Cropped and/or padded image of shape
164 | `[target_height, target_width, channels]`
165 | """
166 | with tf.name_scope('resize_with_crop_or_pad'):
167 | image = ops.convert_to_tensor(image, name='image')
168 |
169 | assert_ops = []
170 | assert_ops += _Check3DImage(image, require_static=False)
171 | assert_ops += _assert(target_width > 0, ValueError,
172 | 'target_width must be > 0.')
173 | assert_ops += _assert(target_height > 0, ValueError,
174 | 'target_height must be > 0.')
175 |
176 | image = control_flow_ops.with_dependencies(assert_ops, image)
177 | # `crop_to_bounding_box` and `pad_to_bounding_box` have their own checks.
178 | # Make sure our checks come first, so that error messages are clearer.
179 | if _is_tensor(target_height):
180 | target_height = control_flow_ops.with_dependencies(
181 | assert_ops, target_height)
182 | if _is_tensor(target_width):
183 | target_width = control_flow_ops.with_dependencies(assert_ops, target_width)
184 |
185 | def max_(x, y):
186 | if _is_tensor(x) or _is_tensor(y):
187 | return math_ops.maximum(x, y)
188 | else:
189 | return max(x, y)
190 |
191 | def min_(x, y):
192 | if _is_tensor(x) or _is_tensor(y):
193 | return math_ops.minimum(x, y)
194 | else:
195 | return min(x, y)
196 |
197 | def equal_(x, y):
198 | if _is_tensor(x) or _is_tensor(y):
199 | return math_ops.equal(x, y)
200 | else:
201 | return x == y
202 |
203 | height, width, _ = _ImageDimensions(image)
204 | width_diff = target_width - width
205 | offset_crop_width = max_(-width_diff // 2, 0)
206 | offset_pad_width = max_(width_diff // 2, 0)
207 |
208 | height_diff = target_height - height
209 | offset_crop_height = max_(-height_diff // 2, 0)
210 | offset_pad_height = max_(height_diff // 2, 0)
211 |
212 | # Maybe crop if needed.
213 | height_crop = min_(target_height, height)
214 | width_crop = min_(target_width, width)
215 | cropped = tf.image.crop_to_bounding_box(image, offset_crop_height, offset_crop_width,
216 | height_crop, width_crop)
217 | bboxes = bboxes_crop_or_pad(bboxes,
218 | height, width,
219 | -offset_crop_height, -offset_crop_width,
220 | height_crop, width_crop)
221 | # Maybe pad if needed.
222 | resized = tf.image.pad_to_bounding_box(cropped, offset_pad_height, offset_pad_width,
223 | target_height, target_width)
224 | bboxes = bboxes_crop_or_pad(bboxes,
225 | height_crop, width_crop,
226 | offset_pad_height, offset_pad_width,
227 | target_height, target_width)
228 |
229 | # In theory all the checks below are redundant.
230 | if resized.get_shape().ndims is None:
231 | raise ValueError('resized contains no shape.')
232 |
233 | resized_height, resized_width, _ = _ImageDimensions(resized)
234 |
235 | assert_ops = []
236 | assert_ops += _assert(equal_(resized_height, target_height), ValueError,
237 | 'resized height is not correct.')
238 | assert_ops += _assert(equal_(resized_width, target_width), ValueError,
239 | 'resized width is not correct.')
240 |
241 | resized = control_flow_ops.with_dependencies(assert_ops, resized)
242 | return resized, bboxes
243 |
244 |
245 | def tf_image_whitened(image, means=(_R_MEAN, _G_MEAN, _B_MEAN)):
246 | """Subtracts the given means from each image channel.
247 |
248 | Returns:
249 | the centered image.
250 | """
251 | if image.get_shape().ndims != 3:
252 | raise ValueError('Input must be of size [height, width, C>0]')
253 | num_channels = image.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
254 | if len(means) != num_channels:
255 | raise ValueError('len(means) must match the number of channels')
256 |
257 | mean = tf.constant(means, dtype=image.dtype)
258 | image = image - mean
259 | return image
260 |
261 |
262 | def preprocess_for_eval(image, labels, bboxes,
263 | out_shape=EVAL_SIZE, data_format='NHWC',
264 | difficults=None, resize=Resize.WARP_RESIZE,
265 | scope='ssd_preprocessing_train'):
266 | """Preprocess an image for evaluation.
267 | Returns:
268 | A preprocessed image.
269 | """
270 | with tf.name_scope(scope):
271 | if image.get_shape().ndims != 3:
272 | raise ValueError('Input must be of size [height, width, C>0]')
273 |
274 | image = tf.to_float(image)
275 | image = tf_image_whitened(image, [_R_MEAN, _G_MEAN, _B_MEAN])
276 |
277 | # Add image rectangle to bboxes.
278 | bbox_img = tf.constant([[0., 0., 1., 1.]])
279 | if bboxes is None:
280 | bboxes = bbox_img
281 | else:
282 | bboxes = tf.concat([bbox_img, bboxes], axis=0)
283 |
284 | if resize == Resize.NONE:
285 | # No resizing...
286 | pass
287 | elif resize == Resize.CENTRAL_CROP:
288 | # Central cropping of the image.
289 | image, bboxes = resize_image_bboxes_with_crop_or_pad(
290 | image, bboxes, out_shape[0], out_shape[1])
291 | elif resize == Resize.PAD_AND_RESIZE:
292 | # Resize image first: find the correct factor...
293 | shape = tf.shape(image)
294 | factor = tf.minimum(tf.to_double(1.0),
295 | tf.minimum(tf.to_double(out_shape[0] / shape[0]),
296 | tf.to_double(out_shape[1] / shape[1])))
297 | resize_shape = factor * tf.to_double(shape[0:2])
298 | resize_shape = tf.cast(tf.floor(resize_shape), tf.int32)
299 |
300 | image = util_tf.resize_image(image, resize_shape,
301 | method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.BILINEAR,
302 | align_corners=False)
303 | # Pad to expected size.
304 | image, bboxes = resize_image_bboxes_with_crop_or_pad(
305 | image, bboxes, out_shape[0], out_shape[1])
306 | elif resize == Resize.WARP_RESIZE:
307 | # Warp resize of the image.
308 | image = util_tf.resize_image(image, out_shape,
309 | method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.BILINEAR,
310 | align_corners=False)
311 |
312 | # Split back bounding boxes.
313 | bbox_img = bboxes[0]
314 | bboxes = bboxes[1:]
315 | # Remove difficult boxes.
316 | if difficults is not None:
317 | mask = tf.logical_not(tf.cast(difficults, tf.bool))
318 | labels = tf.boolean_mask(labels, mask)
319 | bboxes = tf.boolean_mask(bboxes, mask)
320 | # Image data format.
321 | if data_format == 'NCHW':
322 | image = tf.transpose(image, perm=(2, 0, 1))
323 | return image, labels, bboxes, bbox_img
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/eval/eval_ssd:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | eval
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/eval/np_methods.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2017 Paul Balanca. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """Additional Numpy methods. Big mess of many things!
16 | """
17 | import numpy as np
18 |
19 |
20 | # =========================================================================== #
21 | # Numpy implementations of SSD boxes functions.
22 | # =========================================================================== #
23 | def ssd_bboxes_decode(feat_localizations,
24 | anchor_bboxes,
25 | prior_scaling=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]):
26 | """Compute the relative bounding boxes from the layer features and
27 | reference anchor bounding boxes.
28 |
29 | Return:
30 | numpy array Nx4: ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax
31 | """
32 | # Reshape for easier broadcasting.
33 | l_shape = feat_localizations.shape
34 | feat_localizations = np.reshape(feat_localizations,
35 | (-1, l_shape[-2], l_shape[-1]))
36 | yref, xref, href, wref = anchor_bboxes
37 | xref = np.reshape(xref, [-1, 1])
38 | yref = np.reshape(yref, [-1, 1])
39 |
40 | # Compute center, height and width
41 | cx = feat_localizations[:, :, 0] * wref * prior_scaling[0] + xref
42 | cy = feat_localizations[:, :, 1] * href * prior_scaling[1] + yref
43 | w = wref * np.exp(feat_localizations[:, :, 2] * prior_scaling[2])
44 | h = href * np.exp(feat_localizations[:, :, 3] * prior_scaling[3])
45 | # bboxes: ymin, xmin, xmax, ymax.
46 | bboxes = np.zeros_like(feat_localizations)
47 | bboxes[:, :, 0] = cy - h / 2.
48 | bboxes[:, :, 1] = cx - w / 2.
49 | bboxes[:, :, 2] = cy + h / 2.
50 | bboxes[:, :, 3] = cx + w / 2.
51 | # Back to original shape.
52 | bboxes = np.reshape(bboxes, l_shape)
53 | return bboxes
54 |
55 |
56 | def ssd_bboxes_select_layer(predictions_layer,
57 | localizations_layer,
58 | anchors_layer,
59 | select_threshold=0.5,
60 | img_shape=(300, 300),
61 | num_classes=21,
62 | decode=True):
63 | """Extract classes, scores and bounding boxes from features in one layer.
64 |
65 | Return:
66 | classes, scores, bboxes: Numpy arrays...
67 | """
68 | # First decode localizations features if necessary.
69 | if decode:
70 | localizations_layer = ssd_bboxes_decode(localizations_layer, anchors_layer)
71 |
72 | # Reshape features to: Batches x N x N_labels | 4.
73 | p_shape = predictions_layer.shape
74 | batch_size = p_shape[0] if len(p_shape) == 5 else 1
75 | predictions_layer = np.reshape(predictions_layer,
76 | (batch_size, -1, p_shape[-1]))
77 | l_shape = localizations_layer.shape
78 | localizations_layer = np.reshape(localizations_layer,
79 | (batch_size, -1, l_shape[-1]))
80 |
81 | # Boxes selection: use threshold or score > no-label criteria.
82 | if select_threshold is None or select_threshold == 0:
83 | # Class prediction and scores: assign 0. to 0-class
84 | classes = np.argmax(predictions_layer, axis=2)
85 | scores = np.amax(predictions_layer, axis=2)
86 | mask = (classes > 0)
87 | classes = classes[mask]
88 | scores = scores[mask]
89 | bboxes = localizations_layer[mask]
90 | else:
91 | sub_predictions = predictions_layer[:, :, 1:]
92 | idxes = np.where(sub_predictions > select_threshold)
93 | classes = idxes[-1]+1
94 | scores = sub_predictions[idxes]
95 | bboxes = localizations_layer[idxes[:-1]]
96 |
97 | return classes, scores, bboxes
98 |
99 |
100 | def ssd_bboxes_select(predictions_net,
101 | localizations_net,
102 | anchors_net,
103 | select_threshold=0.5,
104 | img_shape=(300, 300),
105 | num_classes=21,
106 | decode=True):
107 | """Extract classes, scores and bounding boxes from network output layers.
108 |
109 | Return:
110 | classes, scores, bboxes: Numpy arrays...
111 | """
112 | l_classes = []
113 | l_scores = []
114 | l_bboxes = []
115 | # l_layers = []
116 | # l_idxes = []
117 | for i in range(len(predictions_net)):
118 | classes, scores, bboxes = ssd_bboxes_select_layer(
119 | predictions_net[i], localizations_net[i], anchors_net[i],
120 | select_threshold, img_shape, num_classes, decode)
121 | l_classes.append(classes)
122 | l_scores.append(scores)
123 | l_bboxes.append(bboxes)
124 | # Debug information.
125 | # l_layers.append(i)
126 | # l_idxes.append((i, idxes))
127 |
128 | classes = np.concatenate(l_classes, 0)
129 | scores = np.concatenate(l_scores, 0)
130 | bboxes = np.concatenate(l_bboxes, 0)
131 | return classes, scores, bboxes
132 |
133 |
134 | # =========================================================================== #
135 | # Common functions for bboxes handling and selection.
136 | # =========================================================================== #
137 | def bboxes_sort(classes, scores, bboxes, top_k=400):
138 | """Sort bounding boxes by decreasing order and keep only the top_k
139 | """
140 | # if priority_inside:
141 | # inside = (bboxes[:, 0] > margin) & (bboxes[:, 1] > margin) & \
142 | # (bboxes[:, 2] < 1-margin) & (bboxes[:, 3] < 1-margin)
143 | # idxes = np.argsort(-scores)
144 | # inside = inside[idxes]
145 | # idxes = np.concatenate([idxes[inside], idxes[~inside]])
146 | idxes = np.argsort(-scores)
147 | classes = classes[idxes][:top_k]
148 | scores = scores[idxes][:top_k]
149 | bboxes = bboxes[idxes][:top_k]
150 | return classes, scores, bboxes
151 |
152 |
153 | def bboxes_clip(bbox_ref, bboxes):
154 | """Clip bounding boxes with respect to reference bbox.
155 | """
156 | bboxes = np.copy(bboxes)
157 | bboxes = np.transpose(bboxes)
158 | bbox_ref = np.transpose(bbox_ref)
159 | bboxes[0] = np.maximum(bboxes[0], bbox_ref[0])
160 | bboxes[1] = np.maximum(bboxes[1], bbox_ref[1])
161 | bboxes[2] = np.minimum(bboxes[2], bbox_ref[2])
162 | bboxes[3] = np.minimum(bboxes[3], bbox_ref[3])
163 | bboxes = np.transpose(bboxes)
164 | return bboxes
165 |
166 |
167 | def bboxes_resize(bbox_ref, bboxes):
168 | """Resize bounding boxes based on a reference bounding box,
169 | assuming that the latter is [0, 0, 1, 1] after transform.
170 | """
171 | bboxes = np.copy(bboxes)
172 | # Translate.
173 | bboxes[:, 0] -= bbox_ref[0]
174 | bboxes[:, 1] -= bbox_ref[1]
175 | bboxes[:, 2] -= bbox_ref[0]
176 | bboxes[:, 3] -= bbox_ref[1]
177 | # Resize.
178 | resize = [bbox_ref[2] - bbox_ref[0], bbox_ref[3] - bbox_ref[1]]
179 | bboxes[:, 0] /= resize[0]
180 | bboxes[:, 1] /= resize[1]
181 | bboxes[:, 2] /= resize[0]
182 | bboxes[:, 3] /= resize[1]
183 | return bboxes
184 |
185 |
186 | def bboxes_jaccard(bboxes1, bboxes2):
187 | """Computing jaccard index between bboxes1 and bboxes2.
188 | Note: bboxes1 and bboxes2 can be multi-dimensional, but should broacastable.
189 | """
190 | bboxes1 = np.transpose(bboxes1)
191 | bboxes2 = np.transpose(bboxes2)
192 | # Intersection bbox and volume.
193 | int_ymin = np.maximum(bboxes1[0], bboxes2[0])
194 | int_xmin = np.maximum(bboxes1[1], bboxes2[1])
195 | int_ymax = np.minimum(bboxes1[2], bboxes2[2])
196 | int_xmax = np.minimum(bboxes1[3], bboxes2[3])
197 |
198 | int_h = np.maximum(int_ymax - int_ymin, 0.)
199 | int_w = np.maximum(int_xmax - int_xmin, 0.)
200 | int_vol = int_h * int_w
201 | # Union volume.
202 | vol1 = (bboxes1[2] - bboxes1[0]) * (bboxes1[3] - bboxes1[1])
203 | vol2 = (bboxes2[2] - bboxes2[0]) * (bboxes2[3] - bboxes2[1])
204 | jaccard = int_vol / (vol1 + vol2 - int_vol)
205 | return jaccard
206 |
207 |
208 | def bboxes_intersection(bboxes_ref, bboxes2):
209 | """Computing jaccard index between bboxes1 and bboxes2.
210 | Note: bboxes1 and bboxes2 can be multi-dimensional, but should broacastable.
211 | """
212 | bboxes_ref = np.transpose(bboxes_ref)
213 | bboxes2 = np.transpose(bboxes2)
214 | # Intersection bbox and volume.
215 | int_ymin = np.maximum(bboxes_ref[0], bboxes2[0])
216 | int_xmin = np.maximum(bboxes_ref[1], bboxes2[1])
217 | int_ymax = np.minimum(bboxes_ref[2], bboxes2[2])
218 | int_xmax = np.minimum(bboxes_ref[3], bboxes2[3])
219 |
220 | int_h = np.maximum(int_ymax - int_ymin, 0.)
221 | int_w = np.maximum(int_xmax - int_xmin, 0.)
222 | int_vol = int_h * int_w
223 | # Union volume.
224 | vol = (bboxes_ref[2] - bboxes_ref[0]) * (bboxes_ref[3] - bboxes_ref[1])
225 | score = int_vol / vol
226 | return score
227 |
228 |
229 | def bboxes_nms(classes, scores, bboxes, nms_threshold=0.45):
230 | """Apply non-maximum selection to bounding boxes.
231 | """
232 | keep_bboxes = np.ones(scores.shape, dtype=np.bool)
233 | for i in range(scores.size-1):
234 | if keep_bboxes[i]:
235 | # Computer overlap with bboxes which are following.
236 | overlap = bboxes_jaccard(bboxes[i], bboxes[(i+1):])
237 | # Overlap threshold for keeping + checking part of the same class
238 | keep_overlap = np.logical_or(overlap < nms_threshold, classes[(i+1):] != classes[i])
239 | keep_bboxes[(i+1):] = np.logical_and(keep_bboxes[(i+1):], keep_overlap)
240 |
241 | idxes = np.where(keep_bboxes)
242 | return classes[idxes], scores[idxes], bboxes[idxes]
243 |
244 |
245 | def bboxes_nms_fast(classes, scores, bboxes, threshold=0.45):
246 | """Apply non-maximum selection to bounding boxes.
247 | """
248 | pass
249 |
250 |
251 |
252 |
253 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/eval/show_ssd_network.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author : hellcat
2 | # Time : 18-8-30
3 |
4 | """
5 | import os
6 | os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"]="-1"
7 |
8 | import numpy as np
9 | np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
10 |
11 | import tensorflow as tf
12 | config = tf.ConfigProto()
13 | config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
14 | sess = tf.Session(config=config)
15 | """
16 |
17 | import tensorflow as tf
18 |
19 | from eval.eval_img_process_tf import preprocess_for_eval, Resize
20 | from ssd_vgg300_tf import SSDNet
21 |
22 | tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.INFO)
23 | slim = tf.contrib.slim
24 |
25 | gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(allow_growth=True)
26 | config = tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=False, gpu_options=gpu_options)
27 | isess = tf.InteractiveSession(config=config)
28 |
29 |
30 | img_input = tf.placeholder(tf.uint8, shape=(None, None, 3))
31 | image_pre, labels_pre, bboxes_pre, bbox_img = preprocess_for_eval(
32 | img_input,
33 | None,
34 | None,
35 | (300, 300),
36 | 'NHWC',
37 | resize=Resize.WARP_RESIZE
38 | )
39 | image_4d = tf.expand_dims(image_pre, 0)
40 |
41 | ssd = SSDNet()
42 | predictions, localisations, _, _ =\
43 | ssd.net(image_4d, is_training=False)
44 |
45 | isess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
46 |
47 | ckpt = tf.train.get_checkpoint_state('./logs/model/')
48 | # saver = tf.train.import_meta_graph(ckpt.model_checkpoint_path + '.meta')
49 | saver = tf.train.Saver()
50 | saver.restore(isess, ckpt.model_checkpoint_path)
51 |
52 |
53 | # 在网络模型结构中,提取搜索网格的位置
54 | ssd_anchors = ssd.anchors
55 |
56 |
57 | import cv2
58 | from eval import np_methods
59 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
60 | import matplotlib.cm as mpcm
61 | l_VOC_CLASS = [
62 | 'aeroplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat', 'bottle',
63 | 'bus', 'car', 'cat', 'chair', 'cow',
64 | 'diningTable', 'dog', 'horse', 'motorbike', 'person',
65 | 'pottedPlant', 'sheep', 'sofa', 'train', 'TV'
66 | ]
67 |
68 |
69 | def colors_subselect(colors, num_classes=21):
70 | dt = len(colors) // num_classes
71 | sub_colors = []
72 | for i in range(num_classes):
73 | color = colors[i*dt]
74 | if isinstance(color[0], float):
75 | sub_colors.append([int(c * 255) for c in color])
76 | else:
77 | sub_colors.append([c for c in color])
78 | return sub_colors
79 |
80 |
81 | def bboxes_draw_on_img(img, classes, scores, bboxes, colors, thickness=2):
82 | shape = img.shape
83 | for i in range(bboxes.shape[0]):
84 | bbox = bboxes[i]
85 | color = colors[classes[i]]
86 | # Draw bounding box...
87 | p1 = (int(bbox[0] * shape[0]), int(bbox[1] * shape[1]))
88 | p2 = (int(bbox[2] * shape[0]), int(bbox[3] * shape[1]))
89 | cv2.rectangle(img, p1[::-1], p2[::-1], color, thickness)
90 | # Draw text...
91 | s = '%s/%.3f' % ( l_VOC_CLASS[int(classes[i])-1], scores[i])
92 | p1 = (p1[0]-5, p1[1])
93 | #cv2.putText(img, s, p1[::-1], cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_DUPLEX, 1.5, color, 3)
94 |
95 | colors_plasma = colors_subselect(mpcm.plasma.colors, num_classes=21)
96 |
97 |
98 | # Main image processing routine.
99 | def process_image(img, select_threshold=0.3, nms_threshold=.8, net_shape=(300, 300)):
100 | # Run SSD network.
101 | rimg, rpredictions, rlocalisations, rbbox_img = isess.run([image_4d, predictions, localisations, bbox_img],
102 | feed_dict={img_input: img})
103 |
104 | # Get classes and bboxes from the net outputs.
105 | rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = np_methods.ssd_bboxes_select(
106 | rpredictions, rlocalisations, ssd_anchors,
107 | select_threshold=select_threshold, img_shape=net_shape, num_classes=21, decode=True)
108 |
109 | rbboxes = np_methods.bboxes_clip(rbbox_img, rbboxes)
110 | rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = np_methods.bboxes_sort(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes, top_k=400)
111 | rclasses, rscores, rbboxes = np_methods.bboxes_nms(rclasses, rscores, rbboxes, nms_threshold=nms_threshold)
112 | # Resize bboxes to original image shape. Note: useless for Resize.WARP!
113 | rbboxes = np_methods.bboxes_resize(rbbox_img, rbboxes)
114 | bboxes_draw_on_img(img, rclasses, rscores, rbboxes, colors_plasma, thickness=8)
115 | return img
116 |
117 | img = cv2.imread("./eval/timg.jpeg")
118 | img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
119 | plt.imshow(process_image(img))
120 | plt.show()
121 |
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/eval/timg.jpeg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Hellcatzm/SSD_Realization_TensorFlow/628924987fd4ff1d5bc50db5238257bba9357dac/eval/timg.jpeg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/preprocess_img_tf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import tensorflow as tf
2 | import util_tf
3 |
4 |
5 | def bboxes_intersection(bbox_ref, bboxes, name=None):
6 | """Compute relative intersection between a reference box and a
7 | collection of bounding boxes. Namely, compute the quotient between
8 | intersection area and box area.
9 |
10 | Args:
11 | bbox_ref: (N, 4) or (4,) Tensor with reference bounding box(es).
12 | bboxes: (N, 4) Tensor, collection of bounding boxes.
13 | Return:
14 | (N,) Tensor with relative intersection.
15 | """
16 | with tf.name_scope(name, 'bboxes_intersection'):
17 | # Should be more efficient to first transpose.
18 | bboxes = tf.transpose(bboxes)
19 | bbox_ref = tf.transpose(bbox_ref)
20 | # Intersection bbox and volume.
21 | int_ymin = tf.maximum(bboxes[0], bbox_ref[0])
22 | int_xmin = tf.maximum(bboxes[1], bbox_ref[1])
23 | int_ymax = tf.minimum(bboxes[2], bbox_ref[2])
24 | int_xmax = tf.minimum(bboxes[3], bbox_ref[3])
25 | h = tf.maximum(int_ymax - int_ymin, 0.)
26 | w = tf.maximum(int_xmax - int_xmin, 0.)
27 | # Volumes.
28 | inter_vol = h * w # 各个框在[0,0,1,1]内的面积
29 | bboxes_vol = (bboxes[2] - bboxes[0]) * (bboxes[3] - bboxes[1]) # 各个框面积
30 | scores = tf.where(
31 | tf.greater(bboxes_vol, 0),
32 | tf.divide(inter_vol, bboxes_vol),
33 | tf.zeros_like(inter_vol),
34 | name='intersection')
35 | return scores
36 |
37 |
38 | def bboxes_filter_overlap(labels, bboxes,
39 | threshold=0.5, assign_negative=False,
40 | scope=None):
41 | """Filter out bounding boxes based on (relative )overlap with reference
42 | box [0, 0, 1, 1]. Remove completely bounding boxes, or assign negative
43 | labels to the one outside (useful for latter processing...).
44 |
45 | Return:
46 | labels, bboxes: Filtered (or newly assigned) elements.
47 | """
48 | with tf.name_scope(scope, 'bboxes_filter', [labels, bboxes]):
49 | # (N,) Tensor:和[0,0,1,1]相交面积大于0的位置返回面积比(相交/原本),小于0的位置返回0
50 | scores = bboxes_intersection(tf.constant([0, 0, 1, 1], bboxes.dtype),
51 | bboxes)
52 | mask = scores > threshold
53 | if assign_negative: # 保留所有的label和框,重叠区不够的label置负
54 | labels = tf.where(mask, labels, -labels) # 交叉满足的标记为正,否则为负
55 | else: # 删除重叠区不够的label和框
56 | labels = tf.boolean_mask(labels, mask) # bool掩码,类似于array的bool切片
57 | bboxes = tf.boolean_mask(bboxes, mask)
58 | return labels, bboxes
59 |
60 |
61 | def bboxes_resize(bbox_ref, bboxes, name=None):
62 | """
63 | 使用新的参考点和基底长度(bbox_ref)重置bboxes的表示
64 | :param bbox_ref: 参考框,左上角点为新的参考点,hw为新的参考基
65 | :param bboxes: 目标框
66 | :param name: 域名
67 | :return: 目标框重新表示后的写法
68 | """
69 | # Tensors inputs.
70 | with tf.name_scope(name, 'bboxes_resize'):
71 | # Translate.
72 | # bbox_ref:['ymin', 'xmin', 'ymax', 'xmax']
73 | v = tf.stack([bbox_ref[0], bbox_ref[1], bbox_ref[0], bbox_ref[1]])
74 | bboxes = bboxes - v
75 | # Scale.
76 | s = tf.stack([bbox_ref[2] - bbox_ref[0], # h
77 | bbox_ref[3] - bbox_ref[1], # w
78 | bbox_ref[2] - bbox_ref[0],
79 | bbox_ref[3] - bbox_ref[1]])
80 | bboxes = bboxes / s
81 | return bboxes
82 |
83 |
84 | def distorted_bounding_box_crop(image,
85 | labels,
86 | bboxes,
87 | min_object_covered=0.3,
88 | aspect_ratio_range=(0.9, 1.1),
89 | area_range=(0.1, 1.0),
90 | max_attempts=200,
91 | scope=None):
92 | """Generates cropped_image using a one of the bboxes randomly distorted.
93 |
94 | See `tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box` for more documentation.
95 |
96 | Args:
97 | image: 3-D Tensor of image (it will be converted to floats in [0, 1]).
98 | bbox: 3-D float Tensor of bounding boxes arranged [1, num_boxes, coords]
99 | where each coordinate is [0, 1) and the coordinates are arranged
100 | as [ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax]. If num_boxes is 0 then it would use the whole
101 | image.
102 | min_object_covered: An optional `float`. Defaults to `0.1`. The cropped
103 | area of the image must contain at least this fraction of any bounding box
104 | supplied.
105 | aspect_ratio_range: An optional list of `floats`. The cropped area of the
106 | image must have an aspect ratio = width / height within this range.
107 | area_range: An optional list of `floats`. The cropped area of the image
108 | must contain a fraction of the supplied image within in this range.
109 | max_attempts: An optional `int`. Number of attempts at generating a cropped
110 | region of the image of the specified constraints. After `max_attempts`
111 | failures, return the entire image.
112 | scope: Optional scope for name_scope.
113 | Returns:
114 | A tuple, a 3-D Tensor cropped_image and the distorted bbox
115 | """
116 | with tf.name_scope(scope, 'distorted_bounding_box_crop', [image, bboxes]):
117 | # 高级的随机裁剪
118 | # The bounding box coordinates are floats in `[0.0, 1.0]` relative to the width
119 | # and height of the underlying image.
120 | # 1-D, 1-D, [1, 1, 4]
121 | bbox_begin, bbox_size, distort_bbox = tf.image.sample_distorted_bounding_box(
122 | tf.shape(image),
123 | bounding_boxes=tf.expand_dims(bboxes, 0), # [1, n, 4]
124 | min_object_covered=min_object_covered,
125 | aspect_ratio_range=aspect_ratio_range,
126 | area_range=area_range,
127 | max_attempts=max_attempts, # 最大尝试裁剪次数,失败则返回原图
128 | use_image_if_no_bounding_boxes=True)
129 | '''
130 | Returns:
131 | A tuple of `Tensor` objects (begin, size, bboxes).
132 |
133 | begin: A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `image_size`. 1-D, containing `[offset_height, offset_width, 0]`.
134 | Provide as input to `tf.slice`.
135 | size: A `Tensor`. Has the same type as `image_size`. 1-D, containing `[target_height, target_width, -1]`.
136 | Provide as input to `tf.slice`.
137 | bboxes: A `Tensor` of type `float32`. 3-D with shape `[1, 1, 4]` containing the distorted bounding box.
138 | Provide as input to `tf.image.draw_bounding_boxes`.
139 | '''
140 | # [4],裁剪结果相对原图的(y, x, h, w)
141 | distort_bbox = distort_bbox[0, 0]
142 |
143 | # Crop the image to the specified bounding box.
144 | cropped_image = tf.slice(image, bbox_begin, bbox_size)
145 | # Restore the shape since the dynamic slice loses 3rd dimension.
146 | cropped_image.set_shape([None, None, 3]) # <-----设置了尺寸了哈
147 |
148 | # Update bounding boxes: resize and filter out.
149 | # 以裁剪子图为参考,将bboxes更换参考点和基长度
150 | bboxes = bboxes_resize(distort_bbox, bboxes) # [4], [n, 4]
151 | # 筛选变换后的bboxes和裁剪子图交集大于阈值的图bboxes
152 | labels, bboxes = bboxes_filter_overlap(labels, bboxes,
153 | threshold=0.5,
154 | assign_negative=False)
155 | # 返回随机裁剪的图片,筛选调整后的labels(n,)、bboxes(n, 4),裁剪图片对应原图坐标(4,)
156 | return cropped_image, labels, bboxes, distort_bbox
157 |
158 |
159 | def preprocess_image(image, labels, bboxes, out_shape,
160 | scope='ssd_preprocessing_train'):
161 |
162 | with tf.name_scope(scope, 'ssd_preprocessing_train', [image, labels, bboxes]):
163 | if image.get_shape().ndims != 3:
164 | raise ValueError('Input must be of size [height, width, C>0]')
165 | # Convert to float scaled [0, 1].
166 | # 并不单单是float化,而是将255像素表示放缩为01表示
167 | if image.dtype != tf.float32:
168 | image = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(image, dtype=tf.float32)
169 |
170 | # (有条件的)随机裁剪,筛选调整后的labels(n,)、bboxes(n, 4),裁剪图片对应原图坐标(4,)
171 | dst_image, labels, bboxes, distort_bbox = \
172 | distorted_bounding_box_crop(image, labels, bboxes,
173 | min_object_covered=0.25,
174 | aspect_ratio_range=(0.6, 1.67))
175 | # Resize image to output size.
176 | dst_image = util_tf.resize_image(dst_image, out_shape,
177 | method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.BILINEAR,
178 | align_corners=False)
179 |
180 | # Randomly flip the image horizontally.
181 | dst_image, bboxes = util_tf.random_flip_left_right(dst_image, bboxes)
182 |
183 | # Randomly distort the colors. There are 4 ways to do it.
184 | dst_image = util_tf.apply_with_random_selector(
185 | dst_image,
186 | lambda x, ordering: util_tf.distort_color(x, ordering, False),
187 | num_cases=4)
188 |
189 | # Rescale to VGG input scale.
190 | image = dst_image * 255.
191 | image = util_tf.tf_image_whitened(image)
192 | # mean = tf.constant(means, dtype=image.dtype)
193 | # image = image - mean
194 |
195 | # 'NHWC' (n,) (n, 4)
196 | return image, labels, bboxes
197 |
198 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ssd_vgg300_tf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import sys
2 | import math
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import tensorflow as tf
5 | from collections import namedtuple
6 |
7 | from util_tf import *
8 |
9 | slim = tf.contrib.slim
10 |
11 | SSDParams = namedtuple('SSDParameters', ['img_shape',
12 | 'num_classes',
13 | 'no_annotation_label',
14 | 'feat_layers',
15 | 'feat_shapes',
16 | 'anchor_size_bounds',
17 | 'anchor_sizes',
18 | 'anchor_ratios',
19 | 'anchor_steps',
20 | 'anchor_offset',
21 | 'normalizations',
22 | 'prior_scaling'
23 | ])
24 |
25 |
26 | class SSDNet(object):
27 | default_params = SSDParams(
28 | img_shape=(300, 300),
29 | num_classes=21,
30 | no_annotation_label=21,
31 | feat_layers=['block4', 'block7', 'block8', 'block9', 'block10', 'block11'],
32 | feat_shapes=[(38, 38), (19, 19), (10, 10), (5, 5), (3, 3), (1, 1)],
33 | anchor_size_bounds=[0.15, 0.90],
34 | anchor_sizes=[(21., 45.),
35 | (45., 99.),
36 | (99., 153.),
37 | (153., 207.),
38 | (207., 261.),
39 | (261., 315.)],
40 | anchor_ratios=[[2, .5],
41 | [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3],
42 | [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3],
43 | [2, .5, 3, 1. / 3],
44 | [2, .5],
45 | [2, .5]],
46 | anchor_steps=[8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300],
47 | anchor_offset=0.5,
48 | normalizations=[1, -1, -1, -1, -1, -1], # 控制SSD层处理时是否预先沿着HW正则化
49 | prior_scaling=[0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2]
50 | )
51 |
52 | def __init__(self, params=None):
53 | if isinstance(params, SSDParams):
54 | self.params = params
55 | else:
56 | self.params = SSDNet.default_params
57 |
58 | def net(self, input_data, weight_decay, update_feat_shapes=True, is_training=True):
59 | with slim.arg_scope(self._ssd_arg_scope(weight_decay)):
60 | output = self._ssd_net(input_data, is_training=is_training)
61 | # Update feature shapes (try at least!)
62 | if update_feat_shapes:
63 | feat_shapes = []
64 | # 获取各个中间层shape(不含0维),如果含有None则返回默认的feat_shapes
65 | for l in output[0]:
66 | if isinstance(l, np.ndarray):
67 | shape = l.shape
68 | else:
69 | shape = l.get_shape().as_list()
70 | shape = shape[1:4]
71 | if None in shape:
72 | feat_shapes = self.params.feat_shapes
73 | break
74 | else:
75 | feat_shapes.append(shape)
76 | self.params = self.params._replace(feat_shapes=feat_shapes)
77 | sys.stdout.write('[*] Report: variable feat_shapes is {}\n'.format(self.params.feat_shapes))
78 | return output
79 |
80 | @property
81 | def anchors(self):
82 | return self._ssd_anchors_all_layers(self.params.img_shape,
83 | self.params.feat_shapes,
84 | self.params.anchor_sizes,
85 | self.params.anchor_ratios,
86 | self.params.anchor_steps, # [8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300]
87 | self.params.anchor_offset # 0.5
88 | )
89 |
90 | def _ssd_net(self, inputs,
91 | scope='ssd_net',
92 | reuse=False,
93 | is_training=True,
94 | dropout_keep_prob=0.5):
95 | with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'ssd_net', [inputs], reuse=reuse) as sc:
96 | end_points_collection = sc.original_name_scope + '_end_points'
97 | # Collect outputs for conv2d, fully_connected and max_pool2d.
98 | with slim.arg_scope(
99 | [slim.conv2d, slim.max_pool2d],
100 | outputs_collections=end_points_collection):
101 | end_points = {}
102 | # ——————————————————Original VGG-16 blocks.———————————————————
103 | # Block 1.
104 | net = slim.repeat(inputs, 2, slim.conv2d, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv1')
105 | end_points['block1'] = net
106 | net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool1')
107 | # Block 2.
108 | net = slim.repeat(net, 2, slim.conv2d, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv2')
109 | end_points['block2'] = net
110 | net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool2')
111 | # Block 3.
112 | net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3')
113 | end_points['block3'] = net
114 | net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool3')
115 | # Block 4.
116 | net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv4')
117 | end_points['block4'] = net
118 | net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [2, 2], scope='pool4')
119 | # Block 5.
120 | net = slim.repeat(net, 3, slim.conv2d, 512, [3, 3], scope='conv5')
121 | end_points['block5'] = net
122 | net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=1, scope='pool5')
123 | # ————————————Additional SSD blocks.——————————————————————
124 | # Block 6
125 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [3, 3], rate=6, scope='conv6')
126 | end_points['block6'] = net
127 | net = tf.layers.dropout(net, rate=dropout_keep_prob, training=is_training)
128 | # Block 7
129 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 1024, [1, 1], scope='conv7')
130 | end_points['block7'] = net
131 | net = tf.layers.dropout(net, rate=dropout_keep_prob, training=is_training)
132 | # Block 8/9/10/11: 1x1 and 3x3 convolutions stride 2 (except lasts).
133 | end_point = 'block8'
134 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
135 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
136 | net = tf.pad(net, ([0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 1], [0, 0]), mode='CONSTANT')
137 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 512, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
138 | end_points[end_point] = net
139 | end_point = 'block9'
140 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
141 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
142 | net = tf.pad(net, ([0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 1], [0, 0]), mode='CONSTANT')
143 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
144 | end_points[end_point] = net
145 | end_point = 'block10'
146 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
147 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
148 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
149 | end_points[end_point] = net
150 | end_point = 'block11'
151 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
152 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [1, 1], scope='conv1x1')
153 | net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv3x3', padding='VALID')
154 | end_points[end_point] = net
155 |
156 | predictions = []
157 | logits = []
158 | localisations = []
159 | # 对于每一feat层进行特征输出
160 | for i, layer in enumerate(self.default_params.feat_layers):
161 | with tf.variable_scope(layer + '_box'):
162 | p, l = self._ssd_multibox_layer(end_points[layer], # <-----SSD处理
163 | self.params.num_classes,
164 | self.params.anchor_sizes[i],
165 | self.params.anchor_ratios[i],
166 | self.params.normalizations[i])
167 | predictions.append(slim.softmax(p)) # prediction_fn=slim.softmax
168 | logits.append(p)
169 | localisations.append(l)
170 |
171 | # import pprint as pp
172 | # from tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.layers import utils
173 | # pp.pprint(end_points)
174 | end_points_total = slim.utils.convert_collection_to_dict(end_points_collection)
175 | return predictions, localisations, logits, end_points
176 |
177 | @staticmethod
178 | def _ssd_arg_scope(weight_decay=0.0005):
179 | with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.fully_connected],
180 | activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
181 | weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay),
182 | weights_initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer(),
183 | biases_initializer=tf.zeros_initializer()):
184 | with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.max_pool2d],
185 | padding='SAME') as sc:
186 | return sc
187 |
188 | @staticmethod
189 | def _ssd_multibox_layer(net,
190 | num_classes,
191 | sizes,
192 | ratios=(1,),
193 | normalization=-1):
194 | # l2 normalize layer
195 | if normalization > 0:
196 | scale = tf.Variable(dtype=tf.float32, initial_value=tf.ones(shape=(net.get_shape()[-1],)), trainable=True)
197 | net = tf.multiply(tf.nn.l2_normalize(net, net.get_shape().ndims-1, epsilon=1e-12), scale)
198 |
199 | # Number of anchors.
200 | num_anchors = len(sizes) + len(ratios)
201 |
202 | # Location.
203 | num_loc_pred = num_anchors * 4 # 每一个框有四个坐标
204 | loc_pred = slim.conv2d(net, num_loc_pred, [3, 3], activation_fn=None,
205 | scope='conv_loc') # 输出C表示不同框的某个坐标
206 | loc_shape = tensor_shape(loc_pred, rank=4)
207 | loc_pred = tf.reshape(loc_pred, loc_shape[0:-1]+[loc_shape[-1]//4, 4])
208 |
209 | # Class prediction.
210 | num_cls_pred = num_anchors * num_classes # 每一个框都要计算所有的类别
211 | cls_pred = slim.conv2d(net, num_cls_pred, [3, 3], activation_fn=None,
212 | scope='conv_cls') # 输出C表示不同框的对某个类的预测
213 | cls_shape = tensor_shape(cls_pred, rank=4)
214 | cls_pred = tf.reshape(cls_pred, cls_shape[0:-1] + [cls_shape[-1] // num_classes, num_classes])
215 | return cls_pred, loc_pred
216 |
217 | @staticmethod
218 | def _ssd_anchors_all_layers(img_shape,
219 | layers_shape,
220 | anchor_sizes,
221 | anchor_ratios,
222 | anchor_steps, # [8, 16, 32, 64, 100, 300]
223 | offset=0.5,
224 | dtype=np.float32):
225 | layers_anchors = []
226 | for i, feat_shape in enumerate(layers_shape):
227 | # anchor_bboxes = ssd_anchor_one_layer(img_shape,
228 | # feat_shape,
229 | # anchor_sizes[i],
230 | # anchor_ratios[i],
231 | # anchor_steps[i],
232 | # offset=offset, dtype=dtype)
233 | # layers_anchors.append(anchor_bboxes)
234 | # 生成feat_shape中HW对应的网格坐标
235 | y, x = np.mgrid[0:feat_shape[0], 0:feat_shape[1]]
236 | # step*feat_shape 约等于img_shape,这使得网格点坐标介于0~1,放缩一下即可到图像大小
237 | y = (y.astype(dtype) + offset) * anchor_steps[i] / img_shape[0]
238 | x = (x.astype(dtype) + offset) * anchor_steps[i] / img_shape[1]
239 |
240 | # Expand dims to support easy broadcasting.
241 | y = np.expand_dims(y, axis=-1)
242 | x = np.expand_dims(x, axis=-1)
243 |
244 | # Compute relative height and width.
245 | # Tries to follow the original implementation of SSD for the order.
246 | num_anchors = len(anchor_sizes[i]) + len(anchor_ratios[i])
247 | h = np.zeros((num_anchors,), dtype=dtype)
248 | w = np.zeros((num_anchors,), dtype=dtype)
249 | # Add first anchor boxes with ratio=1.
250 | h[0] = anchor_sizes[i][0] / img_shape[0]
251 | w[0] = anchor_sizes[i][0] / img_shape[1]
252 | di = 1
253 | if len(anchor_sizes[i]) > 1:
254 | h[1] = math.sqrt(anchor_sizes[i][0] * anchor_sizes[i][1]) / img_shape[0]
255 | w[1] = math.sqrt(anchor_sizes[i][0] * anchor_sizes[i][1]) / img_shape[1]
256 | di += 1
257 | for l, r in enumerate(anchor_ratios[i]):
258 | h[l + di] = anchor_sizes[l][0] / img_shape[0] / math.sqrt(r)
259 | w[l + di] = anchor_sizes[l][0] / img_shape[1] * math.sqrt(r)
260 | layers_anchors.append((y, x, h, w))
261 | return layers_anchors
262 |
263 | # 绘制各层中心点示意
264 | # import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
265 | # plt.scatter(y, x, c='r', marker='.')
266 | # plt.grid(True)
267 | # plt.show()
268 | # print(h, w)
269 |
270 | def bboxes_encode(self, labels, bboxes, anchors, scope=None):
271 | return tf_ssd_bboxes_encode(
272 | labels, bboxes, anchors,
273 | self.params.num_classes,
274 | self.params.no_annotation_label, # 21
275 | ignore_threshold=0.5,
276 | prior_scaling=self.params.prior_scaling,
277 | scope=scope)
278 |
279 | @staticmethod
280 | def losses(logits, localisations,
281 | gclasses, glocalisations, gscores,
282 | match_threshold=0.5,
283 | negative_ratio=3.,
284 | alpha=1.,
285 | label_smoothing=0.,
286 | scope='ssd_losses'):
287 | """Define the SSD network losses.
288 | """
289 | return ssd_losses(logits, localisations,
290 | gclasses, glocalisations, gscores,
291 | match_threshold=match_threshold,
292 | negative_ratio=negative_ratio,
293 | alpha=alpha,
294 | label_smoothing=label_smoothing,
295 | scope=scope)
296 |
297 |
298 | def tf_ssd_bboxes_encode(labels,
299 | bboxes,
300 | anchors,
301 | num_classes,
302 | no_annotation_label,
303 | ignore_threshold=0.5,
304 | prior_scaling=(0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2),
305 | dtype=tf.float32,
306 | scope='ssd_bboxes_encode'):
307 | with tf.name_scope(scope):
308 | target_labels = []
309 | target_localizations = []
310 | target_scores = []
311 | # anchors_layer: (y, x, h, w)
312 | for i, anchors_layer in enumerate(anchors):
313 | with tf.name_scope('bboxes_encode_block_%i' % i):
314 | # (m,m,k),xywh(m,m,4k),(m,m,k)
315 | t_labels, t_loc, t_scores = \
316 | tf_ssd_bboxes_encode_layer(labels, bboxes, anchors_layer,
317 | num_classes, no_annotation_label,
318 | ignore_threshold,
319 | prior_scaling, dtype)
320 | target_labels.append(t_labels)
321 | target_localizations.append(t_loc)
322 | target_scores.append(t_scores)
323 | return target_labels, target_localizations, target_scores
324 |
325 |
326 | # 为了有助理解,m表示该层中心点行列数,k为每个中心点对应的框数,n为图像上的目标数
327 | def tf_ssd_bboxes_encode_layer(labels, # (n,)
328 | bboxes, # (n, 4)
329 | anchors_layer, # y(m, m, 1), x(m, m, 1), h(k,), w(k,)
330 | num_classes,
331 | no_annotation_label,
332 | ignore_threshold=0.5,
333 | prior_scaling=(0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2),
334 | dtype=tf.float32):
335 | """Encode groundtruth labels and bounding boxes using SSD anchors from
336 | one layer.
337 |
338 | Arguments:
339 | labels: 1D Tensor(int64) containing groundtruth labels;
340 | bboxes: Nx4 Tensor(float) with bboxes relative coordinates;
341 | anchors_layer: Numpy array with layer anchors;
342 | matching_threshold: Threshold for positive match with groundtruth bboxes;
343 | prior_scaling: Scaling of encoded coordinates.
344 |
345 | Return:
346 | (target_labels, target_localizations, target_scores): Target Tensors.
347 | """
348 | # Anchors coordinates and volume.
349 | yref, xref, href, wref = anchors_layer # y(m, m, 1), x(m, m, 1), h(k,), w(k,)
350 | ymin = yref - href / 2. # (m, m, k)
351 | xmin = xref - wref / 2.
352 | ymax = yref + href / 2.
353 | xmax = xref + wref / 2.
354 | vol_anchors = (xmax - xmin) * (ymax - ymin) # 搜索框面积(m, m, k)
355 |
356 | # Initialize tensors...
357 | # 下面各个Tensor矩阵的shape等于中心点坐标矩阵的shape
358 | shape = (yref.shape[0], yref.shape[1], href.size) # (m, m, k)
359 | feat_labels = tf.zeros(shape, dtype=tf.int64) # (m, m, k)
360 | feat_scores = tf.zeros(shape, dtype=dtype)
361 |
362 | feat_ymin = tf.zeros(shape, dtype=dtype)
363 | feat_xmin = tf.zeros(shape, dtype=dtype)
364 | feat_ymax = tf.ones(shape, dtype=dtype)
365 | feat_xmax = tf.ones(shape, dtype=dtype)
366 |
367 | def jaccard_with_anchors(bbox):
368 | """Compute jaccard score between a box and the anchors.
369 | """
370 | int_ymin = tf.maximum(ymin, bbox[0]) # (m, m, k)
371 | int_xmin = tf.maximum(xmin, bbox[1])
372 | int_ymax = tf.minimum(ymax, bbox[2])
373 | int_xmax = tf.minimum(xmax, bbox[3])
374 | h = tf.maximum(int_ymax - int_ymin, 0.)
375 | w = tf.maximum(int_xmax - int_xmin, 0.)
376 | # Volumes.
377 | # 处理搜索框和bbox之间的联系
378 | inter_vol = h * w # 交集面积
379 | union_vol = vol_anchors - inter_vol \
380 | + (bbox[2] - bbox[0]) * (bbox[3] - bbox[1]) # 并集面积
381 | jaccard = tf.div(inter_vol, union_vol) # 交集/并集,即IOU
382 | return jaccard # (m, m, k)
383 |
384 | def condition(i, feat_labels, feat_scores,
385 | feat_ymin, feat_xmin, feat_ymax, feat_xmax):
386 | """Condition: check label index.
387 | """
388 | r = tf.less(i, tf.shape(labels))
389 | return r[0] # tf.shape(labels)有维度,所以r有维度
390 |
391 | def body(i, feat_labels, feat_scores,
392 | feat_ymin, feat_xmin, feat_ymax, feat_xmax):
393 | """Body: update feature labels, scores and bboxes.
394 | Follow the original SSD paper for that purpose:
395 | - assign values when jaccard > 0.5;
396 | - only update if beat the score of other bboxes.
397 | """
398 | # Jaccard score.
399 | label = labels[i] # 当前图片上第i个对象的标签
400 | bbox = bboxes[i] # 当前图片上第i个对象的真实框bbox
401 | jaccard = jaccard_with_anchors(bbox) # 当前对象的bbox和当前层的搜索网格IOU,(m, m, k)
402 | # Mask: check threshold + scores + no annotations + num_classes.
403 | mask = tf.greater(jaccard, feat_scores) # 掩码矩阵,IOU大于历史得分的为True,(m, m, k)
404 | # mask = tf.logical_and(mask, tf.greater(jaccard, matching_threshold))
405 | mask = tf.logical_and(mask, feat_scores > -0.5)
406 | mask = tf.logical_and(mask, label < num_classes) # 不太懂,label应该必定小于类别数
407 | imask = tf.cast(mask, tf.int64) # 整形mask
408 | fmask = tf.cast(mask, dtype) # 浮点型mask
409 |
410 | # Update values using mask.
411 | # 保证feat_labels存储对应位置得分最大对象标签,feat_scores存储那个得分
412 | # (m, m, k) × 当前类别scalar + (1 - (m, m, k)) × (m, m, k)
413 | # 更新label记录,此时的imask已经保证了True位置当前对像得分高于之前的对象得分,其他位置值不变
414 | feat_labels = imask * label + (1 - imask) * feat_labels
415 | # 更新score记录,mask为True使用本类别IOU,否则不变
416 | feat_scores = tf.where(mask, jaccard, feat_scores)
417 |
418 | # 下面四个矩阵存储对应label的真实框坐标
419 | # (m, m, k) × 当前框坐标scalar + (1 - (m, m, k)) × (m, m, k)
420 | feat_ymin = fmask * bbox[0] + (1 - fmask) * feat_ymin
421 | feat_xmin = fmask * bbox[1] + (1 - fmask) * feat_xmin
422 | feat_ymax = fmask * bbox[2] + (1 - fmask) * feat_ymax
423 | feat_xmax = fmask * bbox[3] + (1 - fmask) * feat_xmax
424 |
425 | return [i + 1, feat_labels, feat_scores,
426 | feat_ymin, feat_xmin, feat_ymax, feat_xmax]
427 |
428 | # Main loop definition.
429 | # 对当前图像上每一个目标进行循环
430 | i = 0
431 | (i,
432 | feat_labels, feat_scores,
433 | feat_ymin, feat_xmin,
434 | feat_ymax, feat_xmax) = tf.while_loop(condition, body,
435 | [i,
436 | feat_labels, feat_scores,
437 | feat_ymin, feat_xmin,
438 | feat_ymax, feat_xmax])
439 | # Transform to center / size.
440 | # 这里的y、x、h、w指的是对应位置所属真实框的相关属性
441 | feat_cy = (feat_ymax + feat_ymin) / 2.
442 | feat_cx = (feat_xmax + feat_xmin) / 2.
443 | feat_h = feat_ymax - feat_ymin
444 | feat_w = feat_xmax - feat_xmin
445 |
446 | # Encode features.
447 | # prior_scaling: [0.1, 0.1, 0.2, 0.2],放缩意义不明
448 | # ((m, m, k) - (m, m, 1)) / (k,) * 10
449 | # 以搜索网格中心点为参考,真实框中心的偏移,单位长度为网格hw
450 | feat_cy = (feat_cy - yref) / href / prior_scaling[0]
451 | feat_cx = (feat_cx - xref) / wref / prior_scaling[1]
452 | # log((m, m, k) / (m, m, 1)) * 5
453 | # 真实框宽高/搜索网格宽高,取对
454 | feat_h = tf.log(feat_h / href) / prior_scaling[2]
455 | feat_w = tf.log(feat_w / wref) / prior_scaling[3]
456 | # Use SSD ordering: x / y / w / h instead of ours.(m, m, k, 4)
457 | feat_localizations = tf.stack([feat_cx, feat_cy, feat_w, feat_h], axis=-1) # -1会扩维,故有4
458 |
459 | return feat_labels, feat_localizations, feat_scores
460 |
461 |
462 | def ssd_losses(logits, localisations, # 预测类别,位置
463 | gclasses, glocalisations, gscores, # ground truth类别,位置,得分
464 | match_threshold=0.5,
465 | negative_ratio=3.,
466 | alpha=1.,
467 | label_smoothing=0.,
468 | scope=None):
469 | with tf.name_scope(scope, 'ssd_losses'):
470 | # 提取类别数和batch_size
471 | lshape = tensor_shape(logits[0], 5) # tensor_shape函数可以取代
472 | num_classes = lshape[-1]
473 | batch_size = lshape[0]
474 |
475 | # Flatten out all vectors!
476 | flogits = []
477 | fgclasses = []
478 | fgscores = []
479 | flocalisations = []
480 | fglocalisations = []
481 | for i in range(len(logits)): # 按照图片循环
482 | flogits.append(tf.reshape(logits[i], [-1, num_classes]))
483 | fgclasses.append(tf.reshape(gclasses[i], [-1]))
484 | fgscores.append(tf.reshape(gscores[i], [-1]))
485 | flocalisations.append(tf.reshape(localisations[i], [-1, 4]))
486 | fglocalisations.append(tf.reshape(glocalisations[i], [-1, 4]))
487 | # And concat the crap!
488 | logits = tf.concat(flogits, axis=0) # 全部的搜索框,对应的21类别的输出
489 | gclasses = tf.concat(fgclasses, axis=0) # 全部的搜索框,真实的类别数字
490 | gscores = tf.concat(fgscores, axis=0) # 全部的搜索框,和真实框的IOU
491 | localisations = tf.concat(flocalisations, axis=0)
492 | glocalisations = tf.concat(fglocalisations, axis=0)
493 |
494 | dtype = logits.dtype
495 | pmask = gscores > match_threshold # (全部搜索框数目, 21),类别搜索框和真实框IOU大于阈值
496 | fpmask = tf.cast(pmask, dtype) # 浮点型前景掩码(前景假定为含有对象的IOU足够的搜索框标号)
497 | n_positives = tf.reduce_sum(fpmask) # 前景总数
498 |
499 | # Hard negative mining...
500 | no_classes = tf.cast(pmask, tf.int32)
501 | predictions = slim.softmax(logits) # 此时每一行的21个数转化为概率
502 | nmask = tf.logical_and(tf.logical_not(pmask),
503 | gscores > -0.5) # IOU达不到阈值的类别搜索框位置记1
504 | fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype)
505 | nvalues = tf.where(nmask,
506 | predictions[:, 0], # 框内无物体标记为背景预测概率
507 | 1. - fnmask) # 框内有物体位置标记为1
508 | nvalues_flat = tf.reshape(nvalues, [-1])
509 |
510 | # Number of negative entries to select.
511 | # 在nmask中剔除n_neg个最不可能背景点(对应的class0概率最低)
512 | max_neg_entries = tf.cast(tf.reduce_sum(fnmask), tf.int32)
513 | # 3 × 前景掩码数量 + batch_size
514 | n_neg = tf.cast(negative_ratio * n_positives, tf.int32) + batch_size
515 | n_neg = tf.minimum(n_neg, max_neg_entries)
516 | val, idxes = tf.nn.top_k(-nvalues_flat, k=n_neg) # 最不可能为背景的n_neg个点
517 | max_hard_pred = -val[-1]
518 | # Final negative mask.
519 | nmask = tf.logical_and(nmask, nvalues < max_hard_pred) # 不是前景,又最不像背景的n_neg个点
520 | fnmask = tf.cast(nmask, dtype)
521 |
522 | # Add cross-entropy loss.
523 | with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_pos'):
524 | loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
525 | labels=gclasses) # 0-20
526 | loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fpmask), batch_size, name='value')
527 | tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
528 |
529 | with tf.name_scope('cross_entropy_neg'):
530 | loss = tf.nn.sparse_softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(logits=logits,
531 | labels=no_classes) # {0,1}
532 | loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * fnmask), batch_size, name='value')
533 | tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
534 |
535 | # Add localization loss: smooth L1, L2, ...
536 | with tf.name_scope('localization'):
537 | # Weights Tensor: positive mask + random negative.
538 | weights = tf.expand_dims(alpha * fpmask, axis=-1)
539 | loss = abs_smooth(localisations - glocalisations)
540 | loss = tf.div(tf.reduce_sum(loss * weights), batch_size, name='value')
541 | tf.losses.add_loss(loss)
542 |
543 |
544 | if __name__ == '__main__':
545 | ssd = SSDNet()
546 | ssd.net(tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[5, 304, 304, 3]))
547 |
548 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tfr_data_process.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 |
4 | slim = tf.contrib.slim
5 |
6 |
7 | def get_split(tfr_path, tfr_pattren, num_classes=21, num_samples=17125):
8 | # ===============TFR文件名匹配模板===============
9 | tfr_pattren = os.path.join(tfr_path, tfr_pattren)
10 |
11 | # =========阅读器=========
12 | reader = tf.TFRecordReader
13 |
14 | # ===================解码器===================
15 | keys_to_features = { # 解码TFR文件方式
16 | 'image/encoded': tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, default_value=''),
17 | 'image/format': tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, default_value='jpeg'),
18 | 'image/object/bbox/xmin': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.float32),
19 | 'image/object/bbox/ymin': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.float32),
20 | 'image/object/bbox/xmax': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.float32),
21 | 'image/object/bbox/ymax': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.float32),
22 | 'image/object/bbox/label': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.int64),
23 | }
24 | items_to_handlers = { # 解码二进制数据
25 | # 图像解码设置蛮有意思的
26 | 'image': slim.tfexample_decoder.Image('image/encoded', 'image/format'),
27 | 'object/bbox': slim.tfexample_decoder.BoundingBox(
28 | ['ymin', 'xmin', 'ymax', 'xmax'], 'image/object/bbox/'),
29 | 'object/label': slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor('image/object/bbox/label'),
30 | }
31 | decoder = slim.tfexample_decoder.TFExampleDecoder(keys_to_features, items_to_handlers)
32 |
33 | # =======描述字段=======
34 | items_to_descriptions = {
35 | 'image': 'A color image of varying height and width.',
36 | 'shape': 'Shape of the image',
37 | 'object/bbox': 'A list of bounding boxes, one per each object.',
38 | 'object/label': 'A list of labels, one per each object.',
39 | }
40 |
41 | return slim.dataset.Dataset(
42 | data_sources=tfr_pattren, # TFR文件名
43 | reader=reader, # 阅读器
44 | decoder=decoder, # 解码器
45 | num_samples=num_samples, # 数目
46 | items_to_descriptions=items_to_descriptions, # decoder条目描述字段
47 | num_classes=num_classes, # 类别数
48 | labels_to_names=None # 字典{图片:类别,……}
49 | )
50 |
51 |
52 | def tfr_read(dataset):
53 | # 涉及队列操作,本部使用CPU设备
54 | provider = slim.dataset_data_provider.DatasetDataProvider(
55 | dataset, # DatasetDataProvider 需要 slim.dataset.Dataset 做参数
56 | num_readers=2,
57 | common_queue_capacity=20 * 5,
58 | common_queue_min=10 * 5,
59 | shuffle=True)
60 | image, glabels, gbboxes = provider.get(['image',
61 | 'object/label',
62 | 'object/bbox'])
63 | return image, glabels, gbboxes
64 |
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tfr_generate.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "## 数据格式转化脚本\n",
8 | "\n",
9 | "#### 将voc目标检测数据转换为TFRecord格式,方便TensorFlow读取"
10 | ]
11 | },
12 | {
13 | "cell_type": "code",
14 | "execution_count": 1,
15 | "metadata": {
16 | "collapsed": false,
17 | "scrolled": true
18 | },
19 | "outputs": [
20 | {
21 | "name": "stderr",
22 | "output_type": "stream",
23 | "text": [
24 | "/home/hellcat/anaconda3/lib/python3.6/importlib/_bootstrap.py:219: RuntimeWarning: compiletime version 3.5 of module 'tensorflow.python.framework.fast_tensor_util' does not match runtime version 3.6\n",
25 | " return f(*args, **kwds)\n"
26 | ]
27 | },
28 | {
29 | "name": "stdout",
30 | "output_type": "stream",
31 | "text": [
32 | "Number of images is 17125"
33 | ]
34 | }
35 | ],
36 | "source": [
37 | "import os\n",
38 | "import sys\n",
39 | "import random\n",
40 | "from math import ceil\n",
41 | "import tensorflow as tf\n",
42 | "import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET\n",
43 | "\n",
44 | "TFR_NAME = './TFR_Data/voc2012'\n",
45 | "IMAGE_PATH = './VOC2012/JPEGImages'\n",
46 | "ANNOTATION_PATH = './VOC2012/Annotations'\n",
47 | "SAMPLES_PER_FILES = 2000\n",
48 | "VOC_LABELS = {\n",
49 | " 'none': (0, 'Background'),\n",
50 | " 'aeroplane': (1, 'Vehicle'),\n",
51 | " 'bicycle': (2, 'Vehicle'),\n",
52 | " 'bird': (3, 'Animal'),\n",
53 | " 'boat': (4, 'Vehicle'),\n",
54 | " 'bottle': (5, 'Indoor'),\n",
55 | " 'bus': (6, 'Vehicle'),\n",
56 | " 'car': (7, 'Vehicle'),\n",
57 | " 'cat': (8, 'Animal'),\n",
58 | " 'chair': (9, 'Indoor'),\n",
59 | " 'cow': (10, 'Animal'),\n",
60 | " 'diningtable': (11, 'Indoor'),\n",
61 | " 'dog': (12, 'Animal'),\n",
62 | " 'horse': (13, 'Animal'),\n",
63 | " 'motorbike': (14, 'Vehicle'),\n",
64 | " 'person': (15, 'Person'),\n",
65 | " 'pottedplant': (16, 'Indoor'),\n",
66 | " 'sheep': (17, 'Animal'),\n",
67 | " 'sofa': (18, 'Indoor'),\n",
68 | " 'train': (19, 'Vehicle'),\n",
69 | " 'tvmonitor': (20, 'Indoor'),\n",
70 | "}\n",
71 | "tfr_dir = os.path.split(TFR_NAME)[0]\n",
72 | "if not os.path.exists(tfr_dir):\n",
73 | " os.makedirs(tfr_dir)\n",
74 | "if not os.path.exists(IMAGE_PATH):\n",
75 | " raise BaseException('file {} is not exists'.format(IMAGE_PATH))\n",
76 | "file_names = sorted(os.listdir(IMAGE_PATH))\n",
77 | "random.seed = 10\n",
78 | "random.shuffle(file_names)\n",
79 | "sys.stdout.write('Number of images is {}'.format(len(file_names)))"
80 | ]
81 | },
82 | {
83 | "cell_type": "code",
84 | "execution_count": 2,
85 | "metadata": {
86 | "collapsed": true
87 | },
88 | "outputs": [],
89 | "source": [
90 | "def int64_feature(value):\n",
91 | " \"\"\"Wrapper for inserting int64 features into Example proto.\n",
92 | " \"\"\"\n",
93 | " if not isinstance(value, list):\n",
94 | " value = [value]\n",
95 | " return tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=value))\n",
96 | " \n",
97 | "def float_feature(value):\n",
98 | " \"\"\"Wrapper for inserting float features into Example proto.\n",
99 | " \"\"\"\n",
100 | " if not isinstance(value, list):\n",
101 | " value = [value]\n",
102 | " return tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=value))\n",
103 | " \n",
104 | "def bytes_feature(value):\n",
105 | " \"\"\"Wrapper for inserting bytes features into Example proto.\n",
106 | " \"\"\"\n",
107 | " if not isinstance(value, list):\n",
108 | " value = [value]\n",
109 | " return tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=value))\n",
110 | "\n",
111 | "def xml_parse(xml_path):\n",
112 | " tree = ET.parse(xml_path)\n",
113 | " root = tree.getroot()\n",
114 | " # Image shape.\n",
115 | " size = root.find('size')\n",
116 | " shape = [int(size.find('height').text),\n",
117 | " int(size.find('width').text),\n",
118 | " int(size.find('depth').text)]\n",
119 | " # Find annotations.\n",
120 | " bboxes = []\n",
121 | " labels = []\n",
122 | " labels_text = []\n",
123 | " difficult = []\n",
124 | " truncated = []\n",
125 | " for obj in root.findall('object'):\n",
126 | " label = obj.find('name').text\n",
127 | " labels.append(VOC_LABELS[label][0])\n",
128 | " \n",
129 | " if obj.find('difficult'):\n",
130 | " difficult.append(int(obj.find('difficult').text))\n",
131 | " else:\n",
132 | " difficult.append(0)\n",
133 | " if obj.find('truncated'):\n",
134 | " truncated.append(int(obj.find('truncated').text))\n",
135 | " else:\n",
136 | " truncated.append(0)\n",
137 | " bbox = obj.find('bndbox')\n",
138 | " bboxes.append((float(bbox.find('ymin').text) / shape[0],\n",
139 | " float(bbox.find('xmin').text) / shape[1],\n",
140 | " float(bbox.find('ymax').text) / shape[0],\n",
141 | " float(bbox.find('xmax').text) / shape[1]\n",
142 | " ))\n",
143 | " return shape, bboxes, labels, labels_text, difficult, truncated"
144 | ]
145 | },
146 | {
147 | "cell_type": "code",
148 | "execution_count": 3,
149 | "metadata": {
150 | "collapsed": false
151 | },
152 | "outputs": [
153 | {
154 | "name": "stdout",
155 | "output_type": "stream",
156 | "text": [
157 | "Writing file './TFR_Data/voc2012_000.tfrecord'......\n",
158 | "Writing file './TFR_Data/voc2012_001.tfrecord'......\n",
159 | "Writing file './TFR_Data/voc2012_002.tfrecord'......\n",
160 | "Writing file './TFR_Data/voc2012_003.tfrecord'......\n",
161 | "Writing file './TFR_Data/voc2012_004.tfrecord'......\n",
162 | "Writing file './TFR_Data/voc2012_005.tfrecord'......\n",
163 | "Writing file './TFR_Data/voc2012_006.tfrecord'......\n",
164 | "Writing file './TFR_Data/voc2012_007.tfrecord'......\n",
165 | "Writing file './TFR_Data/voc2012_008.tfrecord'......\n"
166 | ]
167 | }
168 | ],
169 | "source": [
170 | "num_tfr = ceil(len(file_names)/SAMPLES_PER_FILES)\n",
171 | "i = 0\n",
172 | "for idx in range(num_tfr):\n",
173 | " tfr_file = '{}_{:03d}.tfrecord'.format(TFR_NAME, idx)\n",
174 | " sys.stdout.write(\"Writing file '{}'......\\n\".format(tfr_file))\n",
175 | " # 建立书写器\n",
176 | " with tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tfr_file) as writer:\n",
177 | " while i < SAMPLES_PER_FILES * (idx + 1) and i < len(file_names):\n",
178 | " xml_file = os.path.join(ANNOTATION_PATH, \n",
179 | " file_names[i].strip('.jpg') + '.xml')\n",
180 | " image_file = os.path.join(IMAGE_PATH, file_names[i])\n",
181 | " _, box, label, _, _, _ = xml_parse(xml_file)\n",
182 | " image_data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(image_file, 'rb').read()\n",
183 | " i += 1\n",
184 | " \n",
185 | " xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = ([] for _ in range(4))\n",
186 | " for b in box:\n",
187 | " assert len(b) == 4\n",
188 | " [coord.append(point) for coord, point in zip([ymin, xmin, ymax, xmax], b)]\n",
189 | " image_format = b'JPEG'\n",
190 | " # 建立example\n",
191 | " example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={\n",
192 | " 'image/object/bbox/xmin': float_feature(xmin),\n",
193 | " 'image/object/bbox/xmax': float_feature(xmax),\n",
194 | " 'image/object/bbox/ymin': float_feature(ymin),\n",
195 | " 'image/object/bbox/ymax': float_feature(ymax),\n",
196 | " 'image/object/bbox/label': int64_feature(label),\n",
197 | " 'image/format': bytes_feature(image_format), # 图像编码格式\n",
198 | " 'image/encoded': bytes_feature(image_data)})) # 二进制图像数据\n",
199 | " # 书写入文件\n",
200 | " writer.write(example.SerializeToString())"
201 | ]
202 | },
203 | {
204 | "cell_type": "code",
205 | "execution_count": 6,
206 | "metadata": {
207 | "collapsed": false
208 | },
209 | "outputs": [
210 | {
211 | "data": {
212 | "text/plain": [
213 | "(,\n",
214 | " ,\n",
215 | " )"
216 | ]
217 | },
218 | "execution_count": 6,
219 | "metadata": {},
220 | "output_type": "execute_result"
221 | }
222 | ],
223 | "source": [
224 | "import tensorflow.contrib.slim as slim\n",
225 | "\n",
226 | "def get_split(tfr_path, tfr_pattren, num_classes=21):\n",
227 | " \n",
228 | " # ===============TFR文件名匹配模板===============\n",
229 | " tfr_pattren = os.path.join(tfr_path, tfr_pattren)\n",
230 | " \n",
231 | " # =========阅读器=========\n",
232 | " reader = tf.TFRecordReader\n",
233 | " \n",
234 | " # ===================解码器===================\n",
235 | " keys_to_features = { # 解码TFR文件方式\n",
236 | " 'image/encoded': tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, default_value=''),\n",
237 | " 'image/format': tf.FixedLenFeature((), tf.string, default_value='jpeg'),\n",
238 | " 'image/object/bbox/xmin': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.float32),\n",
239 | " 'image/object/bbox/ymin': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.float32),\n",
240 | " 'image/object/bbox/xmax': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.float32),\n",
241 | " 'image/object/bbox/ymax': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.float32),\n",
242 | " 'image/object/bbox/label': tf.VarLenFeature(dtype=tf.int64),\n",
243 | " }\n",
244 | " items_to_handlers = { # 解码二进制数据\n",
245 | " # 图像解码设置蛮有意思的\n",
246 | " 'image': slim.tfexample_decoder.Image('image/encoded', 'image/format'),\n",
247 | " 'object/bbox': slim.tfexample_decoder.BoundingBox(\n",
248 | " ['ymin', 'xmin', 'ymax', 'xmax'], 'image/object/bbox/'),\n",
249 | " 'object/label': slim.tfexample_decoder.Tensor('image/object/bbox/label'),\n",
250 | " }\n",
251 | " decoder = slim.tfexample_decoder.TFExampleDecoder(keys_to_features, items_to_handlers)\n",
252 | " \n",
253 | " # =======描述字段=======\n",
254 | " items_to_descriptions={\n",
255 | " 'image': 'A color image of varying height and width.',\n",
256 | " 'shape': 'Shape of the image',\n",
257 | " 'object/bbox': 'A list of bounding boxes, one per each object.',\n",
258 | " 'object/label': 'A list of labels, one per each object.',\n",
259 | " }\n",
260 | " \n",
261 | " return slim.dataset.Dataset(\n",
262 | " data_sources=tfr_pattren, # TFR文件名\n",
263 | " reader=reader, # 阅读器\n",
264 | " decoder=decoder, # 解码器\n",
265 | " num_samples=len(file_names), # 数目\n",
266 | " items_to_descriptions=items_to_descriptions, # decoder条目描述字段\n",
267 | " num_classes=num_classes, # 类别数\n",
268 | " labels_to_names=None # 字典{图片:类别,……}\n",
269 | " )\n",
270 | "\n",
271 | "pattren = 'voc2012_*.tfrecord'\n",
272 | "dataset = get_split(tfr_dir, pattren, num_classes=21)\n",
273 | "provider = slim.dataset_data_provider.DatasetDataProvider(\n",
274 | " dataset, # DatasetDataProvider 需要 slim.dataset.Dataset 做参数\n",
275 | " num_readers=2,\n",
276 | " common_queue_capacity=20 * 5,\n",
277 | " common_queue_min=10 * 5,\n",
278 | " shuffle=True)\n",
279 | "image, glabels, gbboxes = provider.get(['image',\n",
280 | " 'object/label',\n",
281 | " 'object/bbox'])\n",
282 | "image, glabels, gbboxes"
283 | ]
284 | },
285 | {
286 | "cell_type": "code",
287 | "execution_count": 5,
288 | "metadata": {
289 | "collapsed": false
290 | },
291 | "outputs": [
292 | {
293 | "name": "stdout",
294 | "output_type": "stream",
295 | "text": [
296 | "[array([15]), array([[ 0.40266666, 0.252 , 1. , 0.76999998]], dtype=float32)]\n"
297 | ]
298 | }
299 | ],
300 | "source": [
301 | "with tf.Session() as sess:\n",
302 | " init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),\n",
303 | " tf.local_variables_initializer())\n",
304 | " sess.run(init_op)\n",
305 | " coord = tf.train.Coordinator()\n",
306 | " threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)\n",
307 | " print(sess.run([glabels, gbboxes]))\n",
308 | " coord.request_stop()\n",
309 | " coord.join(threads)"
310 | ]
311 | },
312 | {
313 | "cell_type": "code",
314 | "execution_count": null,
315 | "metadata": {
316 | "collapsed": true
317 | },
318 | "outputs": [],
319 | "source": [
320 | "class SSD:\n",
321 | " def __init__(self):\n",
322 | " pass\n",
323 | " def inference(self):\n",
324 | " pass"
325 | ]
326 | }
327 | ],
328 | "metadata": {
329 | "kernelspec": {
330 | "display_name": "Python 3",
331 | "language": "python",
332 | "name": "python3"
333 | },
334 | "language_info": {
335 | "codemirror_mode": {
336 | "name": "ipython",
337 | "version": 3
338 | },
339 | "file_extension": ".py",
340 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
341 | "name": "python",
342 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
343 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
344 | "version": "3.6.3"
345 | }
346 | },
347 | "nbformat": 4,
348 | "nbformat_minor": 2
349 | }
350 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/train_ssd_network.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Author : hellcat
2 | # Time : 18-8-24
3 |
4 | """
5 | import os
6 | os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"]="-1"
7 |
8 | import numpy as np
9 | np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
10 |
11 | import tensorflow as tf
12 | config = tf.ConfigProto()
13 | config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
14 | sess = tf.Session(config=config)
15 | """
16 | import tensorflow as tf
17 |
18 |
19 | import util_tf
20 | import tfr_data_process
21 | import preprocess_img_tf
22 | from ssd_vgg300_tf import SSDNet
23 |
24 |
25 | slim = tf.contrib.slim
26 |
27 |
28 | # =========================================================================== #
29 | # Main training routine.
30 | # =========================================================================== #
31 | def main():
32 |
33 | max_steps = 1500
34 | batch_size = 32
35 | adam_beta1 = 0.9
36 | adam_beta2 = 0.999
37 | opt_epsilon = 1.0
38 | num_epochs_per_decay = 2.0
39 | num_samples_per_epoch = 17125
40 | moving_average_decay = None
41 |
42 | tf.logging.set_verbosity(tf.logging.DEBUG)
43 | with tf.Graph().as_default():
44 |
45 | # Create global_step.
46 | with tf.device("/device:CPU:0"):
47 | global_step = tf.train.create_global_step()
48 |
49 | ssd = SSDNet()
50 | ssd_anchors = ssd.anchors
51 |
52 | # tfr解析操作放在GPU下有加速,效果不稳定
53 | dataset = \
54 | tfr_data_process.get_split('./TFR_Data',
55 | 'voc2012_*.tfrecord',
56 | num_classes=21,
57 | num_samples=num_samples_per_epoch)
58 |
59 | with tf.device("/device:CPU:0"): # 仅CPU支持队列操作
60 | image, glabels, gbboxes = \
61 | tfr_data_process.tfr_read(dataset)
62 |
63 | image, glabels, gbboxes = \
64 | preprocess_img_tf.preprocess_image(image, glabels, gbboxes, out_shape=(300, 300))
65 |
66 | gclasses, glocalisations, gscores = \
67 | ssd.bboxes_encode(glabels, gbboxes, ssd_anchors)
68 |
69 | batch_shape = [1] + [len(ssd_anchors)] * 3 # (1,f层,f层,f层)
70 | # Training batches and queue.
71 | r = tf.train.batch( # 图片,中心点类别,真实框坐标,得分
72 | util_tf.reshape_list([image, gclasses, glocalisations, gscores]),
73 | batch_size=batch_size,
74 | num_threads=4,
75 | capacity=5 * batch_size)
76 | batch_queue = slim.prefetch_queue.prefetch_queue(
77 | r, # <-----输入格式实际上并不需要调整
78 | capacity=2 * 1)
79 |
80 | # Dequeue batch.
81 | b_image, b_gclasses, b_glocalisations, b_gscores = \
82 | util_tf.reshape_list(batch_queue.dequeue(), batch_shape) # 重整list
83 |
84 | predictions, localisations, logits, end_points = \
85 | ssd.net(b_image, is_training=True, weight_decay=0.00004)
86 |
87 | ssd.losses(logits, localisations,
88 | b_gclasses, b_glocalisations, b_gscores,
89 | match_threshold=.5,
90 | negative_ratio=3,
91 | alpha=1,
92 | label_smoothing=.0)
93 |
94 | update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS)
95 | # =================================================================== #
96 | # Configure the moving averages.
97 | # =================================================================== #
98 | if moving_average_decay:
99 | moving_average_variables = slim.get_model_variables()
100 | variable_averages = tf.train.ExponentialMovingAverage(
101 | moving_average_decay, global_step)
102 | else:
103 | moving_average_variables, variable_averages = None, None
104 |
105 | # =================================================================== #
106 | # Configure the optimization procedure.
107 | # =================================================================== #
108 | with tf.device("/device:CPU:0"): # learning_rate节点使用CPU(不明)
109 | decay_steps = int(num_samples_per_epoch / batch_size * num_epochs_per_decay)
110 | learning_rate = tf.train.exponential_decay(0.01,
111 | global_step,
112 | decay_steps,
113 | 0.94, # learning_rate_decay_factor,
114 | staircase=True,
115 | name='exponential_decay_learning_rate')
116 | optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(
117 | learning_rate,
118 | beta1=adam_beta1,
119 | beta2=adam_beta2,
120 | epsilon=opt_epsilon)
121 | tf.summary.scalar('learning_rate', learning_rate)
122 |
123 | if moving_average_decay:
124 | # Update ops executed locally by trainer.
125 | update_ops.append(variable_averages.apply(moving_average_variables))
126 |
127 | # Variables to train.
128 | trainable_scopes = None
129 | if trainable_scopes is None:
130 | variables_to_train = tf.trainable_variables()
131 | else:
132 | scopes = [scope.strip() for scope in trainable_scopes.split(',')]
133 | variables_to_train = []
134 | for scope in scopes:
135 | variables = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope)
136 | variables_to_train.extend(variables)
137 |
138 | losses = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.LOSSES)
139 | regularization_losses = tf.get_collection(
140 | tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES)
141 | regularization_loss = tf.add_n(regularization_losses)
142 | loss = tf.add_n(losses)
143 | tf.summary.scalar("loss", loss)
144 | tf.summary.scalar("regularization_loss", regularization_loss)
145 |
146 | grad = optimizer.compute_gradients(loss, var_list=variables_to_train)
147 | grad_updates = optimizer.apply_gradients(grad,
148 | global_step=global_step)
149 | update_ops.append(grad_updates)
150 | # update_op = tf.group(*update_ops)
151 |
152 | with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops):
153 | total_loss = tf.add_n([loss, regularization_loss])
154 | tf.summary.scalar("total_loss", total_loss)
155 |
156 | # =================================================================== #
157 | # Kicks off the training.
158 | # =================================================================== #
159 | gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.8)
160 | config = tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=False,
161 | gpu_options=gpu_options)
162 | saver = tf.train.Saver(max_to_keep=5,
163 | keep_checkpoint_every_n_hours=1.0,
164 | write_version=2,
165 | pad_step_number=False)
166 |
167 | if True:
168 | import os
169 | import time
170 |
171 | print('start......')
172 | model_path = './logs'
173 | batch_size = batch_size
174 | with tf.Session(config=config) as sess:
175 | summary = tf.summary.merge_all()
176 | coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
177 | threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess, coord=coord)
178 | writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(model_path, sess.graph)
179 |
180 | init_op = tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),
181 | tf.local_variables_initializer())
182 | init_op.run()
183 | for step in range(max_steps):
184 | start_time = time.time()
185 | loss_value = sess.run(total_loss)
186 | # loss_value, summary_str = sess.run([train_tensor, summary_op])
187 | # writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
188 |
189 | duration = time.time() - start_time
190 | if step % 10 == 0:
191 | summary_str = sess.run(summary)
192 | writer.add_summary(summary_str, step)
193 |
194 | examples_per_sec = batch_size / duration
195 | sec_per_batch = float(duration)
196 | format_str = "[*] step %d, loss=%.2f (%.1f examples/sec; %.3f sec/batch)"
197 | print(format_str % (step, loss_value, examples_per_sec, sec_per_batch))
198 | # if step % 100 == 0:
199 | # accuracy_step = test_cifar10(sess, training=False)
200 | # acc.append('{:.3f}'.format(accuracy_step))
201 | # print(acc)
202 | if step % 500 == 0 and step != 0:
203 | saver.save(sess, os.path.join(model_path, "ssd_tf.model"), global_step=step)
204 |
205 | coord.request_stop()
206 | coord.join(threads)
207 |
208 |
209 | if __name__ == '__main__':
210 | main()
211 |
212 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/util_tf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import tensorflow as tf
2 | from tensorflow.python.ops import control_flow_ops
3 |
4 | slim = tf.contrib.slim
5 |
6 | _R_MEAN = 123.68
7 | _G_MEAN = 116.78
8 | _B_MEAN = 103.94
9 |
10 | _RESIZE_SIDE_MIN = 256
11 | _RESIZE_SIDE_MAX = 512
12 |
13 |
14 | def tensor_shape(x, rank=3):
15 | """Returns the dimensions of a tensor.
16 | """
17 | if x.get_shape().is_fully_defined():
18 | return x.get_shape().as_list()
19 | else:
20 | # get_shape返回值,with_rank相当于断言assert,是否rank为指定值
21 | static_shape = x.get_shape().with_rank(rank).as_list()
22 | # tf.shape返回张量,其中num解释为"The length of the dimension `axis`.",axis默认为0
23 | dynamic_shape = tf.unstack(tf.shape(x), num=rank)
24 | # list,有定义的给数字,没有的给tensor
25 | return [s if s is not None else d
26 | for s, d in zip(static_shape, dynamic_shape)]
27 |
28 |
29 | def abs_smooth(x):
30 | """Smoothed absolute function. Useful to compute an L1 smooth error.
31 |
32 | Define as:
33 | x^2 / 2 if abs(x) < 1
34 | abs(x) - 0.5 if abs(x) > 1
35 | We use here a differentiable definition using min(x) and abs(x). Clearly
36 | not optimal, but good enough for our purpose!
37 | """
38 | absx = tf.abs(x)
39 | minx = tf.minimum(absx, 1)
40 | r = 0.5 * ((absx - 1) * minx + absx)
41 | return r
42 |
43 |
44 | def reshape_list(l, shape=None):
45 | """Reshape list of (list): 1D to 2D or the other way around.
46 |
47 | Args:
48 | l: List or List of list.
49 | shape: 1D or 2D shape.
50 | Return
51 | Reshaped list.
52 | """
53 | r = []
54 | if shape is None:
55 | # Flatten everything.
56 | for a in l:
57 | if isinstance(a, (list, tuple)):
58 | r = r + list(a)
59 | else:
60 | r.append(a)
61 | else:
62 | # Reshape to list of list.
63 | i = 0
64 | for s in shape:
65 | if s == 1:
66 | r.append(l[i])
67 | else:
68 | r.append(l[i:i + s])
69 | i += s
70 | return r
71 |
72 |
73 | def resize_image(image, size,
74 | method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.BILINEAR,
75 | align_corners=False):
76 | """Resize an image and bounding boxes.
77 | """
78 | # Resize image.
79 | with tf.name_scope('resize_image'):
80 | height, width, channels = tensor_shape(image)
81 | image = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
82 | image = tf.image.resize_images(image, size,
83 | method, align_corners)
84 | image = tf.reshape(image, tf.stack([size[0], size[1], channels]))
85 | return image
86 |
87 |
88 | def _check3dimage(image, require_static=True):
89 | """Assert that we are working with properly shaped image.
90 | Args:
91 | image: 3-D Tensor of shape [height, width, channels]
92 | require_static: If `True`, requires that all dimensions of `image` are
93 | known and non-zero.
94 | Raises:
95 | ValueError: if `image.shape` is not a 3-vector.
96 | Returns:
97 | An empty list, if `image` has fully defined dimensions. Otherwise, a list
98 | containing an assert op is returned.
99 | """
100 | try:
101 | image_shape = image.get_shape().with_rank(3)
102 | except ValueError:
103 | raise ValueError("'image' must be three-dimensional.")
104 | if require_static and not image_shape.is_fully_defined():
105 | raise ValueError("'image' must be fully defined.")
106 | if any(x == 0 for x in image_shape):
107 | raise ValueError("all dims of 'image.shape' must be > 0: %s" %
108 | image_shape)
109 | if not image_shape.is_fully_defined():
110 | return [tf.assert_positive(tf.shape(image),
111 | ["all dims of 'image.shape' "
112 | "must be > 0."])]
113 | else:
114 | return []
115 |
116 |
117 | def random_flip_left_right(image, bboxes, seed=None):
118 | """Random flip left-right of an image and its bounding boxes.
119 | """
120 | def flip_bboxes(bboxes):
121 | """Flip bounding boxes coordinates.
122 | """
123 | bboxes = tf.stack([bboxes[:, 0], 1 - bboxes[:, 3],
124 | bboxes[:, 2], 1 - bboxes[:, 1]], axis=-1)
125 | return bboxes
126 |
127 | # Random flip. Tensorflow implementation.
128 | with tf.name_scope('random_flip_left_right'):
129 | image = tf.convert_to_tensor(image, name='image')
130 | _check3dimage(image, require_static=False)
131 | uniform_random = tf.random_uniform([], 0, 1.0, seed=seed)
132 | mirror_cond = tf.less(uniform_random, .5)
133 | # Flip image.
134 | result = tf.cond(mirror_cond,
135 | lambda: tf.reverse_v2(image, [1]),
136 | lambda: image)
137 | # Flip bboxes.
138 | bboxes = tf.cond(mirror_cond,
139 | lambda: flip_bboxes(bboxes),
140 | lambda: bboxes)
141 |
142 | image_shape = image.get_shape()
143 | result.set_shape(image_shape)
144 | return result, bboxes
145 |
146 |
147 | def tf_image_whitened(image, means=(_R_MEAN, _G_MEAN, _B_MEAN)):
148 | """Subtracts the given means from each image channel.
149 | Returns:
150 | the centered image.
151 | """
152 | if image.get_shape().ndims != 3:
153 | raise ValueError('Input must be of size [height, width, C>0]')
154 | num_channels = image.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
155 | if len(means) != num_channels:
156 | raise ValueError('len(means) must match the number of channels')
157 |
158 | mean = tf.constant(means, dtype=image.dtype)
159 | image = image - mean
160 | return image
161 |
162 |
163 | def distort_color(image, color_ordering=0, fast_mode=True, scope=None):
164 | """Distort the color of a Tensor image.
165 | Each color distortion is non-commutative and thus ordering of the color ops
166 | matters. Ideally we would randomly permute the ordering of the color ops.
167 | Rather then adding that level of complication, we select a distinct ordering
168 | of color ops for each preprocessing thread.
169 | Args:
170 | image: 3-D Tensor containing single image in [0, 1].
171 | color_ordering: Python int, a type of distortion (valid values: 0-3).
172 | fast_mode: Avoids slower ops (random_hue and random_contrast)
173 | scope: Optional scope for name_scope.
174 | Returns:
175 | 3-D Tensor color-distorted image on range [0, 1]
176 | Raises:
177 | ValueError: if color_ordering not in [0, 3]
178 | """
179 | with tf.name_scope(scope, 'distort_color', [image]):
180 | if fast_mode:
181 | if color_ordering == 0:
182 | image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255.)
183 | image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
184 | else:
185 | image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
186 | image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255.)
187 | else:
188 | if color_ordering == 0:
189 | image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255.)
190 | image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
191 | image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2)
192 | image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
193 | elif color_ordering == 1:
194 | image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
195 | image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255.)
196 | image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
197 | image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2)
198 | elif color_ordering == 2:
199 | image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
200 | image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2)
201 | image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255.)
202 | image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
203 | elif color_ordering == 3:
204 | image = tf.image.random_hue(image, max_delta=0.2)
205 | image = tf.image.random_saturation(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
206 | image = tf.image.random_contrast(image, lower=0.5, upper=1.5)
207 | image = tf.image.random_brightness(image, max_delta=32. / 255.)
208 | else:
209 | raise ValueError('color_ordering must be in [0, 3]')
210 | # The random_* ops do not necessarily clamp.
211 | return tf.clip_by_value(image, 0.0, 1.0)
212 |
213 |
214 | def apply_with_random_selector(x, func, num_cases):
215 | """Computes func(x, sel), with sel sampled from [0...num_cases-1].
216 | Args:
217 | x: input Tensor.
218 | func: Python function to apply.
219 | num_cases: Python int32, number of cases to sample sel from.
220 | Returns:
221 | The result of func(x, sel), where func receives the value of the
222 | selector as a python integer, but sel is sampled dynamically.
223 | """
224 | sel = tf.random_uniform([], maxval=num_cases, dtype=tf.int32)
225 | # Pass the real x only to one of the func calls.
226 | return control_flow_ops.merge([
227 | func(control_flow_ops.switch(x, tf.equal(sel, case))[1], case)
228 | for case in range(num_cases)])[0]
229 |
230 |
231 | def get_init_fn(checkpoint_path,
232 | train_dir,
233 | checkpoint_exclude_scopes,
234 | checkpoint_model_scope,
235 | model_name,
236 | ignore_missing_vars):
237 | """Returns a function run by the chief worker to warm-start the training.
238 | Note that the init_fn is only run when initializing the model during the very
239 | first global step.
240 |
241 | Returns:
242 | An init function run by the supervisor.
243 | """
244 | if checkpoint_path is None:
245 | return None
246 | # Warn the user if a checkpoint exists in the train_dir. Then ignore.
247 | if tf.train.latest_checkpoint(train_dir):
248 | tf.logging.info(
249 | 'Ignoring --checkpoint_path because a checkpoint already exists in %s'
250 | % train_dir)
251 | return None
252 |
253 | exclusions = []
254 | if checkpoint_exclude_scopes:
255 | exclusions = [scope.strip()
256 | for scope in checkpoint_exclude_scopes.split(',')]
257 | variables_to_restore = []
258 | for var in slim.get_model_variables():
259 | excluded = False
260 | for exclusion in exclusions:
261 | if var.op.name.startswith(exclusion):
262 | excluded = True
263 | break
264 | if not excluded:
265 | variables_to_restore.append(var)
266 | # Change model scope if necessary.
267 | if checkpoint_model_scope is not None:
268 | variables_to_restore = \
269 | {var.op.name.replace(model_name,
270 | checkpoint_model_scope): var
271 | for var in variables_to_restore}
272 |
273 | if tf.gfile.IsDirectory(checkpoint_path):
274 | checkpoint_path = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(checkpoint_path)
275 | tf.logging.info('Fine-tuning from %s. Ignoring missing vars: %s' % (checkpoint_path, ignore_missing_vars))
276 |
277 | return slim.assign_from_checkpoint_fn(
278 | checkpoint_path,
279 | variables_to_restore,
280 | ignore_missing_vars=ignore_missing_vars)
281 |
282 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------