├── Animations
├── Demo.gif
├── FreeMotion.gif
├── ObstacleAvoidance.gif
├── StraightTrajectory.gif
└── tangentbug.gif
├── Coursework Report-JinhangZ-WenxingP.pdf
├── MATLAB Codes
├── Part 1 - Lynxmotion
│ ├── ComputeFramePosition.m
│ ├── FK.m
│ ├── FindqSet.m
│ ├── FreeMotion.m
│ ├── GenerateLinearPath.m
│ ├── GenerateSphereObstacle.m
│ ├── IK.m
│ ├── InsertPoint.m
│ ├── ObstacleAvoidance.m
│ ├── StraightTrajectory.m
│ ├── atan2d_05pi.m
│ ├── atand_0pi.m
│ ├── del_nega_zeros.m
│ ├── drawAnimation.m
│ ├── ik_func.m
│ ├── modified_DH_single.m
│ ├── modified_DH_whole.m
│ ├── specifications.m
│ └── specifications.mat
├── Part 2 - Planar parallel robot
│ ├── 2position.m
│ └── workspace.m
└── Part 3 - Tangent Bug
│ ├── boundaryfollow2next.m
│ ├── checkIntersect.m
│ ├── checkalong.m
│ ├── checkoff.m
│ ├── createobstacles.m
│ ├── decideOi.m
│ ├── drawcircle.m
│ ├── getcurve.m
│ ├── inputstartend.m
│ ├── lineEquation.m
│ ├── readshortest.m
│ ├── straight2next.m
│ └── tangentbug.m
└── README.md
/Animations/Demo.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JinhangZhu/robotics-fundamentals/d94bf3a3e0a16e3428918e98bda65cef877a0dc0/Animations/Demo.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Animations/FreeMotion.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JinhangZhu/robotics-fundamentals/d94bf3a3e0a16e3428918e98bda65cef877a0dc0/Animations/FreeMotion.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Animations/ObstacleAvoidance.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JinhangZhu/robotics-fundamentals/d94bf3a3e0a16e3428918e98bda65cef877a0dc0/Animations/ObstacleAvoidance.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Animations/StraightTrajectory.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JinhangZhu/robotics-fundamentals/d94bf3a3e0a16e3428918e98bda65cef877a0dc0/Animations/StraightTrajectory.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Animations/tangentbug.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JinhangZhu/robotics-fundamentals/d94bf3a3e0a16e3428918e98bda65cef877a0dc0/Animations/tangentbug.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Coursework Report-JinhangZ-WenxingP.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JinhangZhu/robotics-fundamentals/d94bf3a3e0a16e3428918e98bda65cef877a0dc0/Coursework Report-JinhangZ-WenxingP.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/ComputeFramePosition.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [frames_pos,HT] = ComputeFramePosition(DH_param_whole)
2 | % Compute frames positions at under certain DH parameters
3 | % draw one robot at a call
4 | n_frames = size(DH_param_whole,1); % get row count, number of frames
5 | % frames position matrix; 3*n_frames
6 | % e.g. frames_pos(:,1)=[x,y,z]' of frame 1
7 | frames_pos = zeros(3,n_frames);
8 | frames_pos0 = [0,0,0]';
9 |
10 | for i = 1:n_frames
11 | T_till_now = modified_DH_whole(DH_param_whole(1:i,:)); % single transformation matrix
12 | frames_pos(:,i) = T_till_now(1:3,4);
13 | end
14 |
15 | HT = T_till_now;
16 | frames_pos = [frames_pos0 frames_pos];
17 |
18 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/FK.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | %%%%%%%%%%%%% Jinhang Zhu %%%%%%%%%%%
2 | %%%%%%%%%%% Robotics Fundamentals %%%%%%%%%
3 | %%%%%%%%%%%%%% October 2019 %%%%%%%%%%%%%
4 | % The following code simulates the forward kinematics of a 4DOF Lynxmotion
5 | % robot. Figure 2 shows its movement from start to end
6 | % position, Figure 1 shows the location of its end effector at points of
7 | % its trajectory and Figure 2,3 shows the maximum potential workspace of the
8 | % arm's end effector.
9 |
10 | close all
11 | clc
12 | disp('The following code simulates the forward kinematics of a 4DOF Lynxmotion')
13 | disp('robot. Figure 2 shows its movement from start to end position,')
14 | disp('Figure 1 shows the location of its end effector at points of its trajectory')
15 | disp('and Figure 2,3 shows the maximum potential workspace of its end effector')
16 |
17 | %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
18 | %% Specifications
19 | % A series of joint angles
20 | % The following variables are defined in the form of column-vectors with
21 | % 4 rows each. Each row represents a different position (angle) of the joint.
22 | q1 = [60 70 80 90]';
23 | q2 = [-30 -35 -40 -45]';
24 | q3 = [45 55 60 65]';
25 | q4 = [-60 -55 -50 -45]';
26 |
27 | load('specifications.mat');
28 |
29 | %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
30 | %% Trajectory and the arm based on 4 statuses
31 | % Prepare end-effector positions coordinates matrix
32 | % columns: x, y, z
33 | % rows: 4 statuses
34 | pt_ee = zeros(3,4);
35 |
36 | % Relative position of end-effector in frame 4
37 | p_rel_in_4 = [0 d5 0 1]';
38 |
39 | % Prepare coordinates matrices of all frames
40 | % columns: frame 0-5
41 | % rows: 4 statuses
42 | frames_x = zeros(6,4);
43 | frames_y = zeros(6,4);
44 | frames_z = zeros(6,4);
45 |
46 | for i = 1:4
47 | % Transformations between frames
48 | T01 = modified_DH_single([alpha(1),a(1),q1(i),d(1)]); % reveal frame 1 position
49 | T12 = modified_DH_single([alpha(2),a(2),q2(i),d(2)]); % reveal frame 2 position
50 | T23 = modified_DH_single([alpha(3),a(3),q3(i),d(3)]); % reveal frame 3 position
51 | T34 = modified_DH_single([alpha(4),a(4),q4(i),d(4)]); % reveal frame 4 position
52 | % Get forward kinemtics transformation matrices
53 | T02 = T01*T12;
54 | T03 = T02*T23;
55 | T04 = T03*T34;
56 | P5_ee = T04*p_rel_in_4;
57 | % Fill ee position matrix
58 | pt_ee(:,i) = P5_ee(1:3,:);
59 | % Fill frames position matrices
60 | frames_x(:,i) = [0, T01(1,4), T02(1,4), T03(1,4), T04(1,4), pt_ee(1,i)]'; % x coordinate of frames
61 | frames_y(:,i) = [0, T01(2,4), T02(2,4), T03(2,4), T04(2,4), pt_ee(2,i)]'; % y coordinate of frames
62 | frames_z(:,i) = [0, T01(3,4), T02(3,4), T03(3,4), T04(3,4), pt_ee(3,i)]'; % z coordinate of frames
63 | end
64 |
65 | % Plot the trajectory
66 | figure(1);
67 | plot3(pt_ee(1,1),pt_ee(2,1),pt_ee(3,1),'rx') % plot the first position of the robot's end effector
68 | hold on
69 | plot3(pt_ee(1,2:4),pt_ee(2,2:4),pt_ee(3,2:4),'x') % plot the 3 following positions of the robot's end effector
70 | title('Tip Trajectory'); xlabel('x (m)'); ylabel('y (m)'); zlabel('z (m)');
71 |
72 | % Plot the robot arm
73 | figure (2)
74 | for i = 1:4
75 | plot3(frames_x(:,i),frames_y(:,i),frames_z(:,i),'o-','Linewidth',2)
76 | axis equal
77 | hold on
78 | xlabel('x (m)'); ylabel('y (m)'); zlabel('z (m)');
79 | % Mark start and end positions
80 | text(pt_ee(1,1),pt_ee(2,1),pt_ee(3,1),'x');
81 | text(pt_ee(1,1) + 0.002,pt_ee(2,1) + 0.002,pt_ee(3,1) + 0.002,'ptStart');
82 | text(pt_ee(1,4),pt_ee(2,4),pt_ee(3,4),'x');
83 | text(pt_ee(1,4) + 0.002,pt_ee(2,4) + 0.002,pt_ee(3,4) + 0.002,'ptEnd');
84 | pause(0.05)
85 | % hold off
86 | pause(0.1)
87 | end
88 |
89 | %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
90 | %% Workspace
91 | % Similarly, we extend the test sample to many points over the whole [0,360]
92 | numStatus = 18;
93 | q1_axis = linspace(q1_range(1),q1_range(2),numStatus);
94 | q2_axis = linspace(q2_range(1),q2_range(2),numStatus);
95 | q3_axis = linspace(q3_range(1),q3_range(2),numStatus);
96 | q4_axis = linspace(q4_range(1),q4_range(2),numStatus);
97 |
98 | % Prepare end-effector positions coordinates matrix
99 | % columns: x, y, z
100 | % rows: numStatus^4 statuses
101 | pt_ee = zeros(3,numStatus^4);
102 | % Count of end-effector position indices
103 | count = 0;
104 |
105 | tic
106 | % Loop: Fill the coordinates matrix of the robot
107 | for i_link1 = 1:numStatus % for q1
108 | for i_link2 = 1:numStatus % for q2
109 | for i_link3 = 1:numStatus % for q3
110 | for i_link4 = 1:numStatus % for q4
111 | count = count + 1;
112 | q = [q1_axis(i_link1),q2_axis(i_link2),q3_axis(i_link3),q4_axis(i_link4)]';
113 | T04 = modified_DH_whole([alpha(1:4,:),a(1:4,:),q,d(1:4,:)]);
114 | P5_ee = T04*p_rel_in_4;
115 | pt_ee(:,count) = P5_ee(1:3,:);
116 | end
117 | end
118 | end
119 | end
120 |
121 | % Plot the workspace
122 | % 2D view
123 | figure(3)
124 | plot(pt_ee(1,:),pt_ee(2,:),'.');
125 | xlabel('x (m)'); ylabel('y (m)');
126 | axis equal
127 | % 3D view
128 | figure(4)
129 | plot3(pt_ee(1,:),pt_ee(2,:),pt_ee(3,:),'.');
130 | xlabel('x (m)'); ylabel('y (m)'); zlabel('z (m)');
131 | axis equal
132 | disp('Rendering time:');
133 | toc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/FindqSet.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,lastq)
2 | % Find the best q set for the specific position
3 | % The q variables are deduced from inverse kinematics
4 | if isnan(lastq) % No last q: start position
5 | if size(q2,2) == 1
6 | q = [q1,q2,q3,q4,q5]';
7 | else
8 | temp = [q1,q2(1),q3(1),q4(1),q5;q1,q2(2),q3(2),q4(2),q5]';
9 | % column 1 closer to previous
10 | if rand > 0.5
11 | q = temp(:,1);
12 | else
13 | q = temp(:,2);
14 | end
15 | end
16 | else % Last q exists: sampled points or end point
17 | if size(q2,2) == 1
18 | q = [q1,q2,q3,q4,q5]';
19 | else
20 | temp = [q1,q2(1),q3(1),q4(1),q5;q1,q2(2),q3(2),q4(2),q5]';
21 | % column 1 closer to previous
22 | if norm(lastq-temp(:,1)) <= norm(lastq-temp(:,2))
23 | q = temp(:,1);
24 | else
25 | q = temp(:,2);
26 | end
27 | end
28 | end
29 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/FreeMotion.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | %
2 | % Author: Jinhang
3 | % Description: Implement a free motion along the viapoints
4 | % The trajectory is generated through polynomial curve
5 | % fitting.
6 | %
7 |
8 |
9 | %% Load specifications & Global variables
10 | close all
11 | clc
12 | load('specifications.mat');
13 | psi = -90; % Angle of elevation
14 | t_interval = 0.01; % Time interval
15 | M = 60; % Number of samples
16 | motionFlag = 0; % Flag to specify varying-speed motion
17 | n_frames = size(alpha,1); % Number of frames
18 | n_viapoints = size(viapoints,2); % Number of viapoints
19 |
20 | %% Polynomial curve fitting of viapoints
21 | pts = zeros(3,(n_viapoints-1)*M+n_viapoints);
22 | poly_coeff_ZofY = polyfit(viapoints(2,:),viapoints(3,:),5);
23 | y_axis = linspace(viapoints(2,1),viapoints(2,n_viapoints),size(pts,2));
24 | poly_model_ZofY = polyval(poly_coeff_ZofY,y_axis);
25 | pts(1,:) = viapoints(1,1);
26 | pts(2,:) = y_axis;
27 | pts(3,:) = poly_model_ZofY;
28 | n_pts = size(pts,2);
29 |
30 | %% Plot all viapoints
31 | h = figure('units','normalized','outerposition',[0 0 1 1]);
32 | plot3(viapoints(1,:),viapoints(2,:),viapoints(3,:),...
33 | 'g*',...
34 | 'MarkerSize',5,...
35 | 'LineWidth',2); hold on
36 |
37 | %% Specify the very first position
38 | pt_start = viapoints(:,1);
39 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pt_start,psi,a,d);
40 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,NaN);
41 |
42 | %% Compute inverse kinematics
43 | frames_pos_pts = zeros(3,n_frames+1,n_pts);
44 | HT_pts = zeros(4,4,n_pts);
45 | q_pts = zeros(n_frames,n_pts);
46 | for i = 1:n_pts
47 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pts(:,i),psi,a,d);
48 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q);
49 | q_pts(:,i) = q;
50 | [frames_pos,HT] = ComputeFramePosition([alpha,a,q,d]);
51 | frames_pos(:,n_frames+1) = pts(:,i); % adjust end-effector position
52 | frames_pos_pts(:,:,i) = frames_pos;
53 | HT_pts(:,:,i) = HT;
54 | end
55 |
56 | %% Animation: Trajectory
57 | for i = 1:n_pts
58 | [frame_plot,ee_points,ee_info] = drawAnimation(frames_pos_pts(:,:,i),HT_pts(:,:,i),'Obstacle Avoidance',1);
59 | xlim(xlim_range);
60 | ylim(ylim_range);
61 | zlim(zlim_range);
62 | pause(t_interval);
63 | if i ~= n_pts
64 | delete(frame_plot);
65 | delete(ee_info);
66 | end
67 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/GenerateLinearPath.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [pts,t_interval,vee] = GenerateLinearPath(pt_start,pt_end,u,M,motionFlag)
2 | % Generate linear path between start point and end point.
3 | % IMPORTANT: The path excludes start point and end point.
4 | % MotionFlag: 1 constant | 0 varying speed
5 | if nargin == 4
6 | motionFlag = 0;
7 | end
8 |
9 | vee = ones(1,M+2);
10 | delta_dist = pt_end-pt_start;
11 | dist = norm(delta_dist);
12 | % Constant speed
13 | if motionFlag
14 | pts = [linspace(pt_start(1),pt_end(1),M+2);...
15 | linspace(pt_start(2),pt_end(2),M+2);...
16 | linspace(pt_start(3),pt_end(3),M+2)];
17 | t_total = dist/u;
18 | t_interval = t_total/(M+1);
19 | vee = vee*u;
20 |
21 | % Varying accelerated motion
22 | else
23 | % motion parameters
24 | t2_t1_ratio = 2;
25 | t2 = dist/u;
26 | t1 = t2/t2_t1_ratio;
27 | t_total = (1 + t2_t1_ratio)*t1; % positive acceleration duration time = 1/3*
28 | t_interval = t_total/(M+1); % constant motion duration time
29 | a = t2_t1_ratio*(u^2)/dist; % acceleration rate
30 | % ratio on three axes
31 | delta_ratio = [delta_dist(1);...
32 | delta_dist(2);...
33 | delta_dist(3)]/dist;
34 | pts = zeros(3,M+2);
35 | for i = 0:M+1 % M sample points -> M+1 intervals
36 | t = i*t_interval;
37 | if t <= t1
38 | pts(:,i+1) = pt_start + 1/2*a*(t^2)*delta_ratio;
39 | vee(:,i+1) = a*t;
40 | elseif t > t1 && t <= t2
41 | pts(:,i+1) = pt_start + (1/2*a*(t1^2) + u*(t-t1))*delta_ratio;
42 | vee(:,i+1) = u;
43 | else
44 | pts(:,i+1) = pt_start + (dist - 1/2*a*((t_total-t)^2))*delta_ratio;
45 | vee(:,i+1) = u - a*(t-t2);
46 | end
47 | end
48 | end
49 |
50 | % Exclude start point and end point
51 | pts = pts(:,2:M+1);
52 | vee = vee(:,2:M+1);
53 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/GenerateSphereObstacle.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function GenerateSphereObstacle(pt_start,pt_end,radius)
2 | % Generate a sphere-shape obstacle
3 | pt_centre = (pt_start+pt_end)/2;
4 |
5 | [x,y,z] = sphere; % Generate a sphere
6 | x = x*radius; % Rescaled to specified radius
7 | y = y*radius;
8 | z = z*radius;
9 |
10 | surf(x+pt_centre(1),y+pt_centre(2),z+pt_centre(3)); % Draw the sphere at centre
11 | hold on
12 |
13 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/IK.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | %%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
2 | % Author: Jinhang Zhu
3 | % Description:
4 | % Input: psi(theta2+3+4), px, py, pz
5 | % Output: theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4
6 | % Verification: Transform matrix
7 |
8 | %% Load specifications
9 | load('specifications.mat');
10 |
11 | %% Inverse kinematics
12 | while true
13 | disp('========================================')
14 | disp('Input position');
15 | px = input('Px: ');
16 | py = input('Py: ');
17 | pz = input('Pz: ');
18 | disp('========================================')
19 | disp('Input orientation');
20 | disp('orientation: angle of elevation of');
21 | disp('end-effector or q2 + q3 + q4')
22 | psi = input('Psi: ');
23 |
24 | % Call ik_func module to calculate joint values q1,q2,q3,q4
25 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func([px,py,pz],psi,a,d);
26 | if isnan(flag)
27 | disp('========================================')
28 | disp('Point NOT in workspace! Re-input now!')
29 | continue
30 | end
31 |
32 | % Solution discussion
33 | if size(q2,2) == 1
34 | isWorkspace = q1 >= q1_range(1) && q1 <= q1_range(2) &&...
35 | q2 >= q2_range(1) && q2 <= q2_range(2) &&...
36 | q3 >= q3_range(1) && q3 <= q3_range(2) &&...
37 | q4 >= q4_range(1) && q4 <= q4_range(2);
38 | if ~isWorkspace
39 | disp('========================================')
40 | disp('Point NOT in workspace! Re-input now!')
41 | continue
42 | else
43 | q = [q1,q2,q3,q4,q5]';
44 | break
45 | end
46 | else % 2 theta 2 values
47 | % check 1st set
48 | isWorkspace_1 = q1 >= q1_range(1) && q1 <= q1_range(2) &&...
49 | q2(1) >= q2_range(1) && q2(2) <= q2_range(2) &&...
50 | q3(1) >= q3_range(1) && q3(2) <= q3_range(2) &&...
51 | q4(1) >= q4_range(1) && q4(2) <= q4_range(2);
52 | if isWorkspace_1
53 | % 1st solution set effective
54 | % check 2nd set
55 | isWorkspace_2 = q1 >= q1_range(1) && q1 <= q1_range(2) &&...
56 | q2(2) >= q2_range(1) && q2(2) <= q2_range(2) &&...
57 | q3(2) >= q3_range(1) && q3(2) <= q3_range(2) &&...
58 | q4(2) >= q4_range(1) && q4(2) <= q4_range(2);
59 | if isWorkspace_2
60 | % both solution sets effective
61 | q = [q1,q2(1),q3(1),q4(1),q5;q1,q2(2),q3(2),q4(2),q5]';
62 | break
63 | else
64 | % 1st set effective, but 2nd set not
65 | q = [q1,q2(1),q3(1),q4(1),q5]';
66 | break
67 | end
68 | else
69 | % 1st solution set not effective
70 | % check 2nd set
71 | isWorkspace_2 = q1 >= q1_range(1) && q1 <= q1_range(2) &&...
72 | q2(2) >= q2_range(1) && q2(2) <= q2_range(2) &&...
73 | q3(2) >= q3_range(1) && q3(2) <= q3_range(2) &&...
74 | q4(2) >= q4_range(1) && q4(2) <= q4_range(2);
75 | if isWorkspace_2
76 | % 2nd set effective, but 1st set not
77 | q = [q1,q2(2),q3(2),q4(2),q5]';
78 | break
79 | else
80 | % either of two sets effective
81 | disp('========================================')
82 | disp('Point NOT in workspace! Re-input now!')
83 | continue
84 | end
85 | end
86 | end
87 | end
88 |
89 | disp('========================================')
90 | disp('Joint values')
91 | q = round(q);
92 | disp(q');
93 |
94 | %% Forward kinematics: Verification
95 | if size(q,2)==1 % 1 set
96 | DH_param_whole = [alpha,a,q,d];
97 | figure(1);
98 | [frames_pos,HT] = ComputeFramePosition(DH_param_whole);
99 | drawAnimation(frames_pos,HT,'Result',1);
100 | xlim(xlim_range);
101 | ylim(ylim_range);
102 | zlim(zlim_range);
103 | T05 = del_nega_zeros(modified_DH_whole(DH_param_whole));
104 | disp('========================================')
105 | disp('Final matrix');
106 | disp(T05);
107 | if round(P,2) == round(T05,2)
108 | disp('Correct!')
109 | end
110 | else % 2 sets
111 | DH_param_whole_1 = [alpha,a,q(:,1),d];
112 | DH_param_whole_2 = [alpha,a,q(:,2),d];
113 | figure(1);
114 | [frames_pos,HT] = ComputeFramePosition(DH_param_whole_1);
115 | drawAnimation(frames_pos,HT,'Result',1);
116 | [frames_pos,HT] = ComputeFramePosition(DH_param_whole_2);
117 | drawAnimation(frames_pos,HT,'Result',1);
118 | xlim(xlim_range);
119 | ylim(ylim_range);
120 | zlim(zlim_range);
121 | T05_1 = del_nega_zeros(modified_DH_whole(DH_param_whole_1));
122 | T05_2 = del_nega_zeros(modified_DH_whole(DH_param_whole_2));
123 | disp('========================================')
124 | disp('Final matrix');
125 | disp(T05_1);
126 | disp('or')
127 | disp(T05_2);
128 | if all(all(round(P,2) == round(T05_1,2))) && all(all(round(P,2) == round(T05_2,2)))
129 | disp('Both Correct!')
130 | end
131 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/InsertPoint.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function pt_insert = InsertPoint(pt_start,pt_end,radius,offset)
2 | % Find a new point to pass through to avoid the obstacle
3 |
4 | half_dist = norm(pt_end-pt_start)/2;
5 | pt_centre = (pt_start+pt_end)/2;
6 | dist2centre = sqrt((half_dist^2*radius^2)/(half_dist^2-radius^2))+offset;
7 |
8 | % Normal vector from sphere centre
9 | temp = (pt_centre - pt_start)/norm(pt_centre - pt_start);
10 | normal_vector = null(temp');
11 |
12 | pt_insert = pt_centre + dist2centre*normal_vector(:,1);
13 |
14 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/ObstacleAvoidance.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | %
2 | % Author: Jinhang
3 | % Description: Avoid obstacles in line trajectory.
4 | %
5 |
6 | %% Load specifications & Global variables
7 | close all
8 | clc
9 | load('specifications.mat');
10 | psi = -90; % Angle of elevation
11 | u = 0.1; % Speed of end effector in eCartesian space
12 | M = 60; % Number of samples
13 | motionFlag = 0; % Flag to specify varying-speed motion
14 | n_frames = size(alpha,1); % Number of frames
15 | n_viapoints = size(viapoints,2); % Number of viapoints
16 |
17 | %% Interpolate viapoints
18 | temp = zeros(3,2*n_viapoints-1);
19 | for i_loop = 1:n_viapoints-1
20 | %% Get inserted point position
21 | pt_start = viapoints(:,i_loop);
22 | pt_end = viapoints(:,i_loop+1);
23 | dist = norm(pt_end-pt_start);
24 | radius = dist/5;
25 | offset = radius;
26 | pt_insert = InsertPoint(pt_start,pt_end,radius,offset);
27 | temp(:,i_loop*2-1:(i_loop+1)*2-1) = [pt_start pt_insert pt_end];
28 | end
29 | viapoints = temp;
30 | n_viapoints = size(viapoints,2); % Number of viapoints
31 |
32 | %% Main loop: Get positions and plot trajectory
33 | h = figure('units','normalized','outerposition',[0 0 1 1]);
34 |
35 | %% Specify the very first position
36 | pt_start = viapoints(:,1);
37 | plot3(pt_start(1),pt_start(2),pt_start(3),...
38 | 'g*',...
39 | 'MarkerSize',5,...
40 | 'LineWidth',2); hold on
41 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pt_start,psi,a,d);
42 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,NaN);
43 | for i_loop = 1:n_viapoints-1
44 | %% Get 2 ajoint points from the set;
45 | % Assign them to start position and end position separately
46 | pt_start = viapoints(:,i_loop);
47 | pt_end = viapoints(:,i_loop+1);
48 | dist = norm(pt_end-pt_start);
49 | radius = dist/5;
50 | offset = radius;
51 |
52 | %% Generate sphere obstacle
53 | if mod(i_loop,2)
54 | GenerateSphereObstacle(viapoints(:,i_loop),viapoints(:,i_loop+2),radius);
55 | plot3(viapoints(1,i_loop+2),viapoints(2,i_loop+2),viapoints(3,i_loop+2),...
56 | 'g*',...
57 | 'MarkerSize',5,...
58 | 'LineWidth',2); hold on
59 | end
60 |
61 | %% Generate trajectory consisted of M sampled points between the 2 positions
62 | [pts,t_interval,vee] = GenerateLinearPath(pt_start,pt_end,u,M,motionFlag);
63 |
64 | frames_pos_samples = zeros(3,n_frames+1,M);
65 | HT_samples = zeros(4,4,M);
66 | q_samples = zeros(n_frames,M);
67 |
68 | %% Compute inverse kinematics
69 | % Start position
70 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pt_start,psi,a,d);
71 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q);
72 | q_start = q;
73 | DH_param_whole_start = [alpha,a,q,d];
74 | [frames_pos_start,HT_start] = ComputeFramePosition(DH_param_whole_start);
75 | frames_pos_start(:,n_frames+1) = pt_start; % Adjust end-effector position
76 | % samples positions
77 | for i_sample = 1:M
78 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pts(:,i_sample),psi,a,d);
79 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q);
80 | q_samples(:,i_sample) = q;
81 | [frames_pos,HT] = ComputeFramePosition([alpha,a,q,d]);
82 | frames_pos(:,n_frames+1) = pts(:,i_sample); % adjust end-effector position
83 | frames_pos_samples(:,:,i_sample) = frames_pos;
84 | HT_samples(:,:,i_sample) = HT;
85 | end
86 | % end position
87 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pt_end,psi,a,d);% Ensured to be effective
88 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q);
89 | q_end = q;
90 | DH_param_whole_end = [alpha,a,q,d];
91 | [frames_pos_end,HT_end] = ComputeFramePosition(DH_param_whole_end);
92 | frames_pos_end(:,n_frames+1) = pt_end; % adjust end-effector position
93 |
94 | %% Animation: Trajectory
95 | [frame_plot,ee_points,ee_info] = drawAnimation(frames_pos_start,HT_start,'Obstacle Avoidance',1);
96 | xlim(xlim_range);
97 | ylim(ylim_range);
98 | zlim(zlim_range);
99 | pause(t_interval);
100 | delete(frame_plot);
101 | delete(ee_info);
102 |
103 | for i_sample = 1:M
104 | [frame_plot,ee_points,ee_info] = drawAnimation(frames_pos_samples(:,:,i_sample),HT_samples(:,:,i_sample),'Obstacle Avoidance',1);
105 | xlim(xlim_range);
106 | ylim(ylim_range);
107 | zlim(zlim_range);
108 | pause(t_interval);
109 | delete(frame_plot);
110 | delete(ee_info);
111 | end
112 |
113 | [frame_plot,ee_points,ee_info] = drawAnimation(frames_pos_end,HT_end,'Obstacle Avoidance',1);
114 | xlim(xlim_range);
115 | ylim(ylim_range);
116 | zlim(zlim_range);
117 | if i_loop ~= n_viapoints-1
118 | delete(frame_plot);
119 | delete(ee_info);
120 | end
121 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/StraightTrajectory.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | %
2 | % Author: Jinhang
3 | % Description: Implement a straight line trajectory between the points
4 | %
5 |
6 | %% Load specifications & Global variables
7 | close all
8 | clc
9 | load('specifications.mat');
10 | psi = -90; % Angle of elevation
11 | u = 0.1; % Speed of end effector in Cartesian space
12 | M = 60; % Number of samples
13 | motionFlag = 0; % Flag to specify varying-speed motion
14 | n_frames = size(alpha,1); % Number of frames
15 | n_viapoints = size(viapoints,2); % Number of viapoints
16 | t_axis = zeros(1,M*(n_viapoints-1)+n_viapoints); % Time axis
17 | qset = zeros(n_frames,M*(n_viapoints-1)+n_viapoints); % q set
18 | vset = zeros(1,M*(n_viapoints-1)+n_viapoints); % velocity set
19 |
20 | %% Main loop: Get positions and plot trajectory
21 | h = figure('units','normalized','outerposition',[0 0 1 1]);
22 |
23 | %% Specify the very first position
24 | pt_start = viapoints(:,1);
25 | plot3(pt_start(1),pt_start(2),pt_start(3),...
26 | 'g*',...
27 | 'MarkerSize',5,...
28 | 'LineWidth',2); hold on
29 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pt_start,psi,a,d);
30 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,NaN);
31 | for i_loop = 1:n_viapoints-1
32 | %% Get 2 ajoint points from the set;
33 | % Assign them to start position and end position separately
34 | pt_start = viapoints(:,i_loop);
35 | pt_end = viapoints(:,i_loop+1);
36 | plot3(pt_end(1),pt_end(2),pt_end(3),...
37 | 'g*',...
38 | 'MarkerSize',5,...
39 | 'LineWidth',2);
40 | hold on
41 |
42 | %% Generate trajectory consisted of M sampled points between the 2 positions
43 | [pts,t_interval,vee] = GenerateLinearPath(pt_start,pt_end,u,M,motionFlag);
44 | for j = (i_loop-1)*(M+1)+1:i_loop*(M+1)+1
45 | if j == 1
46 | t_axis(j) = 0;
47 | else
48 | t_axis(j) = t_axis(j-1)+t_interval;
49 | end
50 | end
51 | vset(:,(i_loop-1)*(M+1)+2:i_loop*(M+1)) = vee;
52 |
53 | frames_pos_samples = zeros(3,n_frames+1,M);
54 | HT_samples = zeros(4,4,M);
55 | q_samples = zeros(n_frames,M);
56 |
57 | %% Compute inverse kinematics
58 | % Start position
59 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pt_start,psi,a,d);
60 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q);
61 | q_start = q;
62 | DH_param_whole_start = [alpha,a,q,d];
63 | [frames_pos_start,HT_start] = ComputeFramePosition(DH_param_whole_start);
64 | frames_pos_start(:,n_frames+1) = pt_start; % Adjust end-effector position
65 | % samples positions
66 | for i_sample = 1:M
67 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pts(:,i_sample),psi,a,d);
68 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q);
69 | q_samples(:,i_sample) = q;
70 | [frames_pos,HT] = ComputeFramePosition([alpha,a,q,d]);
71 | frames_pos(:,n_frames+1) = pts(:,i_sample); % adjust end-effector position
72 | frames_pos_samples(:,:,i_sample) = frames_pos;
73 | HT_samples(:,:,i_sample) = HT;
74 | end
75 | % end position
76 | [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pt_end,psi,a,d);% Ensured to be effective
77 | q = FindqSet(q1,q2,q3,q4,q5,q);
78 | q_end = q;
79 | DH_param_whole_end = [alpha,a,q,d];
80 | [frames_pos_end,HT_end] = ComputeFramePosition(DH_param_whole_end);
81 | frames_pos_end(:,n_frames+1) = pt_end; % adjust end-effector position
82 | qset(:,(i_loop-1)*(M+1)+1:i_loop*(M+1)+1) = [q_start q_samples q_end]; % save q
83 |
84 | %% Animation: Trajectory
85 | [frame_plot,ee_points,ee_info] = drawAnimation(frames_pos_start,HT_start,'Linear Trajectory with Varying Speed',1);
86 | xlim(xlim_range);
87 | ylim(ylim_range);
88 | zlim(zlim_range);
89 | pause(t_interval);
90 | delete(frame_plot);
91 | delete(ee_info);
92 | % hold off
93 | for i_sample = 1:M
94 | [frame_plot,ee_points,ee_info] = drawAnimation(frames_pos_samples(:,:,i_sample),HT_samples(:,:,i_sample),'Linear Trajectory with Varying Speed',1);
95 | xlim(xlim_range);
96 | ylim(ylim_range);
97 | zlim(zlim_range);
98 | pause(t_interval);
99 | delete(frame_plot);
100 | delete(ee_info);
101 | end
102 | [frame_plot,ee_points,ee_info] = drawAnimation(frames_pos_end,HT_end,'Linear Trajectory with Varying Speed',1);
103 | xlim(xlim_range);
104 | ylim(ylim_range);
105 | zlim(zlim_range);
106 | if i_loop ~= n_viapoints-1
107 | delete(frame_plot);
108 | delete(ee_info);
109 | end
110 | end
111 |
112 | %% Plot joins positions & velocity of end-effector
113 | figure(2);
114 | subplot(1,2,1);
115 | for i = 1:n_frames
116 | plot(t_axis,qset(i,:),'.'); hold on
117 | end
118 | xlabel('Time');
119 | ylabel('Joint positions');
120 | legend('q1','q2','q3','q4','q5');
121 | axis square
122 | subplot(1,2,2);
123 | plot(t_axis,vset,'--.',...
124 | 'MarkerEdgeColor','r',...
125 | 'MarkerFaceColor','r')
126 | xlabel('Time');
127 | ylabel('Velocity of end-effector');
128 | axis square
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/atan2d_05pi.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function result = atan2d_05pi(up,down)
2 | %Return value of atand in the range of [-90,90]
3 | if up || down
4 | result = atand(up/down);
5 | else
6 | result = atan2d(up,down);
7 | end
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/atand_0pi.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function result = atand_0pi(fraction)
2 | %Return value of atand in the range of [0,180]
3 | if atand(fraction) >= 0
4 | result = atand(fraction);
5 | else
6 | result = atand(fraction) + 180;
7 | end
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/del_nega_zeros.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function dstMat = del_nega_zeros(srcMat)
2 | % Convert negative zeros to zeros
3 | thres_nega_zero = -1e-10;
4 | srcMat(srcMat<0 & srcMat>thres_nega_zero)=0;
5 | dstMat = srcMat;
6 |
7 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/drawAnimation.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [frame_plot,ee_points,ee_info] = drawAnimation(frames_pos,HT,title_animation,streeFlag)
2 | % draw one robot at a call
3 |
4 | n_frames = size(frames_pos,2) - 1;
5 |
6 | % Convert negative zeros to zeros
7 | HT = del_nega_zeros(HT);
8 | pt_ee = [frames_pos(1,n_frames+1),frames_pos(2,n_frames+1),frames_pos(3,n_frames+1)];
9 | angle_elevation = round(atand(HT(3,1)/HT(3,3))+90);
10 |
11 | % Plot
12 | frame_plot = plot3(frames_pos(1,:),frames_pos(2,:),frames_pos(3,:),'bo-','Linewidth',2);
13 | hold on
14 | ee_points = plot3(pt_ee(1),pt_ee(2),pt_ee(3),'r.');
15 | hold on
16 |
17 | if streeFlag
18 | str_ee_position = sprintf('(%0.4f, %0.4f, %0.4f, %d degrees)',pt_ee(1),pt_ee(2),pt_ee(3),angle_elevation);
19 | ee_info = text(pt_ee(1) + 0.002,pt_ee(2) + 0.002,pt_ee(3) + 0.002,str_ee_position);
20 | end
21 |
22 | title(title_animation);
23 |
24 | axis equal
25 | hold on
26 | xlabel('x (m)'); ylabel('y (m)'); zlabel('z (m)');
27 | grid on
28 | % pause(time_pause);
29 | % delete(frame_plot);
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/ik_func.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [P,flag,q1,q2,q3,q4] = ik_func(pos,psi,a,d)
2 | % Inverse kinematics function module
3 | % specifications
4 | a3 = a(3);
5 | a4 = a(4);
6 | d1 = d(1);
7 | d5 = d(5);
8 | px = pos(1);
9 | py = pos(2);
10 | pz = pos(3);
11 |
12 | % theta 1
13 | q1 = atan2d_05pi(py,px); % q1 = atand(py/px)
14 | % fill T05: 4 by 4 matrix elements
15 | nx = cosd(q1)*cosd(psi);
16 | ny = sind(q1)*cosd(psi);
17 | nz = sind(psi);
18 | ax = -cosd(q1)*sind(psi);
19 | ay = -sind(q1)*sind(psi);
20 | az = -cosd(psi);
21 | ox = -sind(q1);
22 | oy = cosd(q1);
23 | oz = 0;
24 | P = [nx ox ax px;ny oy ay py;nz oz az pz;0 0 0 1];
25 | P = del_nega_zeros(P);
26 | % disp('========================================')
27 | % disp('Given condition')
28 | % disp(P)
29 |
30 | % theta 2
31 | m = (px-ax*d5)/cosd(q1);
32 | n = pz - az*d5-d1;
33 | e = (m^2+n^2+a3^2-a4^2)/2/a3;
34 | isOutofWorkspace = n^2+m^2-e^2 < 0;
35 | if isOutofWorkspace
36 | flag = NaN;
37 | return
38 | end
39 | q2 = [atand_0pi(e/sqrt(n^2+m^2-e^2))-atand_0pi(m/n),...
40 | atand_0pi(-e/sqrt(n^2+m^2-e^2))-atand_0pi(m/n)];
41 |
42 | k1 = (m-a3*cosd(q2))/a4;
43 | k2 = (n-a3*sind(q2))/a4;
44 | % theta 3
45 | q3 = atan2d(k2,k1) - q2;
46 | % theta 4
47 | q4 = psi - q2 - q3;
48 | flag = 1;
49 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/modified_DH_single.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | % File: modified_DH_single.m
2 | % Author: Jinhang Zhu
3 | % Date: 25 Oct. 2019
4 | % Email: lm19073@bristol.ac.uk
5 |
6 | function FK_mat_single = modified_DH_single(DH_param_single)
7 | % This function calculate the homogeneous transformation from frame i-1 to the ajoint frame i.
8 | % DH parameters in single transformation.
9 | alpha_im1 = DH_param_single(1,1); % alpha i-1 m for minus
10 | a_im1 = DH_param_single(1,2); % a i-1
11 | theta_i = DH_param_single(1,3); % theta i
12 | d_i = DH_param_single(1,4); % d i
13 |
14 | % Single homogeneous transformation from frame i-1 to the ajoint frame i.
15 | T_im1_i = zeros(4,4);
16 | T_im1_i(1,:) = [cosd(theta_i), -sind(theta_i), 0, a_im1];
17 | T_im1_i(2,:) = [sind(theta_i)*cosd(alpha_im1), cosd(theta_i)*cosd(alpha_im1), -sind(alpha_im1), -d_i*sind(alpha_im1)];
18 | T_im1_i(3,:) = [sind(theta_i)*sind(alpha_im1), cosd(theta_i)*sind(alpha_im1), cosd(alpha_im1), d_i*cosd(alpha_im1)];
19 | T_im1_i(4,:) = [0, 0, 0, 1];
20 | FK_mat_single = T_im1_i;
21 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/modified_DH_whole.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | % File: modified_DH_whole.m
2 | % Author: Jinhang Zhu
3 | % Date: 25 Oct. 2019
4 | % Email: lm19073@bristol.ac.uk
5 |
6 | function FK_mat_whole = modified_DH_whole(DH_param_whole)
7 | % This function calculate the homogeneous transformation from base to the end-effector.
8 | % Get the number of transformations, i.e. frames
9 | DH_param_size = size(DH_param_whole);
10 | n_trans = DH_param_size(1,1);
11 | % Calculate the whole homogeneous transformation matrix via a loop.
12 | T_0_n = eye(4);
13 |
14 | for i = 1:n_trans
15 | T_im1_i = modified_DH_single(DH_param_whole(i,:)); % Single homogeneous matrix from i-1 to i
16 | T_0_n = T_0_n *T_im1_i;
17 | end
18 | FK_mat_whole = T_0_n;
19 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/specifications.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | %% DH convention specifications
2 | d1 = 0.1;
3 | a3 = 0.1;
4 | a4 = 0.1;
5 | d5 = 0.1;
6 | alpha = [0 90 0 0 -90]';
7 | a = [0 0 a3 a4 0]';
8 | d = [d1 0 0 0 d5]';
9 | q5 =0;
10 |
11 | %% Range of motions per axis
12 | q1_range = [-90,90];
13 | q2_range = [0,180];
14 | q3_range = [-135,45];
15 | q4_range = [-180,0];
16 |
17 | %% Animation specifications
18 | xlim_range = [0 0.3];
19 | ylim_range = [-0.2 0.2];
20 | zlim_range = [0 0.2];
21 | axes_limit = [xlim_range;ylim_range;zlim_range];
22 |
23 | %% Trajectory: 5 viapoints
24 | viapoints = [0.2 0.1 0.1;0.2 0.05 0.15;0.2 0 0.1;0.2 -0.05 0.15;0.2 -0.1 0.1]';
25 |
26 | save('specifications');
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/specifications.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/JinhangZhu/robotics-fundamentals/d94bf3a3e0a16e3428918e98bda65cef877a0dc0/MATLAB Codes/Part 1 - Lynxmotion/specifications.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 2 - Planar parallel robot/2position.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | %% base coordinate
2 | R=290*sqrt(3); % side lenth of the triangle base.(mm)
3 | r=130;%the distance from the vertex to the center of the platform
4 | %coordinate of three vertex of the base
5 | PB1=[0,0];
6 | PB2=[R,0];
7 | PB3=[R/2,sqrt(3)*R/2];
8 |
9 | %% link lenth (mm)
10 | %lenth of first arm
11 | SA=170;
12 | SB=170;
13 | SC=170;
14 | %length of second arm
15 | L=130;
16 |
17 | %%
18 | %input the cartesian coordinate
19 | xc=input('please input the x coordinate of the center:');
20 | yc=input('please input the y coordinate of the center:');
21 | a=input('please input the orientation of the center:');
22 |
23 | phi_1=a+pi/6;
24 | phi_2=a+5*pi/6;
25 | phi_3=a+3*pi/2;
26 |
27 | %coordinate of three vertexs of the platform
28 | pp1=[xc-r*cos(phi_1),yc-r*sin(phi_1)];
29 | pp2=[xc+r*cos(phi_2-pi),yc+r*sin(phi_2-pi)];
30 | pp3=[(xc-r*cos(2*pi-phi_3)),yc+r*sin(2*pi-phi_3)];
31 |
32 | %parameter for theta1
33 | c1=atan((yc-r*sin(phi_1))/(xc-r*cos(phi_1)));
34 | d1=acos((SA^2-L^2+norm(pp1-PB1)*norm(pp1-PB1))/(2*SA*norm(pp1-PB1)));
35 | theta1=c1+d1;
36 |
37 | %parameter for theta2
38 | c2=atan2(pp2(2)-PB2(2),pp2(1)-PB2(1));
39 | d2=acos((SB^2-L^2+norm(pp2-PB2)*norm(pp2-PB2))/(2*SB*norm(pp2-PB2)));
40 | theta2=c2+d2;
41 |
42 | %parameter for theta3
43 | c3=atan2(pp3(2)-PB3(2),pp3(1)-PB3(1));
44 | d3=acos((SC^2-L^2+norm(pp3-PB3)*norm(pp3-PB3))/(2*SC*norm(pp3-PB3)));
45 | theta3=c3+d3;
46 |
47 | %two position of M
48 | M1=[SA*cos(theta1),SA*sin(theta1)];
49 | M2=[R+SB*cos(theta2),SB*sin(theta2)];
50 | M3=[R/2+SC*cos(theta3),sqrt(3)*R/2+SC*sin(theta3)];
51 |
52 | %computed length for the second arm
53 | L1=norm(M1-pp1);
54 | L2=norm(M2-pp2);
55 | L3=norm(M3-pp3);
56 |
57 | if(L1-130<1e-5&&L2-130<1e-5&&L3-130<1e-5)
58 | %plot the base
59 | Base=[PB1;PB2;PB3;PB1];
60 | plot(Base(:,1),Base(:,2),'linewidth',3);
61 | axis([-100 550 -100 500]);
62 | hold on
63 |
64 | %plot the platform
65 | Platform=[pp1;pp2;pp3;pp1];
66 | plot(Platform(:,1),Platform(:,2),'g-','linewidth',3);
67 |
68 | %plot three arms
69 | arm1=[PB1;M1;pp1];
70 | arm2=[PB2;M2;pp2];
71 | arm3=[PB3;M3;pp3];
72 | plot(arm1(:,1),arm1(:,2),'k-^','linewidth',3);
73 | plot(arm2(:,1),arm2(:,2),'r-^','linewidth',3);
74 | plot(arm3(:,1),arm3(:,2),'y-^','linewidth',3);
75 | else
76 | disp("the center and orientation is out of the workspace of the robot");
77 | end
78 | hold off
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 2 - Planar parallel robot/workspace.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | %% this is to generate the workspace of the parallel robots
2 | R=290*sqrt(3); % side lenth of the triangle base.(mm)
3 | r=130;
4 | PB1=[0,0];
5 | PB2=[R,0];
6 | PB3=[R/2,sqrt(3)*R/2];
7 |
8 | base=[PB1;PB2;PB3;PB1];
9 | plot(base(:,1),base(:,2));
10 | axis([-20,inf,-20,inf])
11 | hold on
12 |
13 | %% link lenth (mm)
14 | S=170;
15 | L=130;
16 |
17 | a=input("please input an angle: ");
18 | phi_1=a+pi/6;
19 | phi_2=a+5*pi/6;
20 | phi_3=a+3*pi/2;
21 | %% traversal of xc,yc
22 | xc = 0:2:506;
23 | yc = 0:2:449;
24 | for i=1:size(xc,2)
25 | for j=1:size(yc,2)
26 | pp1=[xc(i)-r*cos(phi_1),yc(j)-r*sin(phi_1)];%note:
27 | pp2=[xc(i)+r*cos(a-pi/6),yc(j)+r*sin(a-pi/6)];
28 | pp3=[(xc(i)-r*cos(pi/2-a)),yc(j)+r*sin(pi/2-a)];
29 |
30 | d1=norm(pp1-PB1);
31 | d2=norm(pp2-PB2);
32 | d3=norm(pp3-PB3);
33 | if (d1<(S+L)&&d1>(S-L)&&d2<(S+L)&&d2>(S-L)&&d3<(S+L)&&d3>(S-L))
34 | plot(xc(i),yc(j),'r.')
35 | end
36 | end
37 | end
38 | hold off
39 |
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/boundaryfollow2next.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [pt_next,angle_next] = boundaryfollow2next(angle_previous,pt_current,pt_dest,LEN_STEP,obstacles)
2 | %boundaryfollow2next Find next point on normal direction while following boudary
3 | % input: pt_currrent, pt_dest (the most recent destination), curve
4 | % output: pt_next
5 | pt_next = zeros(2,1);
6 |
7 | %
8 | % angle_most_current = atan2(pt_dest(2)-pt_current(2),pt_dest(1)-pt_current(1));
9 | angle_most_current = angle_previous;
10 |
11 | % Find the closest point on the curve to the current point
12 | n_curve = size(obstacles,2);
13 | min_dist = norm(pt_current-obstacles(:,1));
14 | pt_closest = obstacles(:,1);
15 | for i = 2:n_curve
16 | if norm(pt_current-obstacles(:,i)) < min_dist
17 | min_dist = norm(pt_current-obstacles(:,i));
18 | pt_closest = obstacles(:,i);
19 | else
20 | continue
21 | end
22 | end
23 |
24 | angle_closest = atan2(pt_closest(2)-pt_current(2),pt_closest(1)-pt_current(1));
25 | if angle_closest > angle_most_current
26 | angle_next = angle_closest - pi/2;
27 | else
28 | angle_next = angle_closest + pi/2;
29 | end
30 |
31 | pt_next(1) = pt_current(1)+cos(angle_next)*LEN_STEP;
32 | pt_next(2) = pt_current(2)+sin(angle_next)*LEN_STEP;
33 |
34 | end
35 |
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/checkIntersect.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function isIntersect = checkIntersect(pt_current,PT_GOAL,endpoints)
2 | %CHECKINTERSECT Check if the obstacle is blocking.
3 | % Check if current-goal line intersects
4 | O1 = endpoints(:,1);
5 | O2 = endpoints(:,2);
6 | if pt_current(1) ~= PT_GOAL(1)
7 | multi = (O1(2)-lineEquation(pt_current,PT_GOAL,O1(1)))*...
8 | (O2(2)-lineEquation(pt_current,PT_GOAL,O2(1)));
9 | else
10 | multi = (O1(1)-pt_current(1))*(O2(1)-PT_GOAL(1));
11 | end
12 |
13 | if multi > 0
14 | isIntersect = false;
15 | else
16 | isIntersect = true;
17 | end
18 |
19 | end
20 |
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/checkalong.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function mode = checkalong(pt_previous,pt_current,PT_GOAL,obstacles,LEN_STEP)
2 | %checkalong Check the condition to start boundary following
3 | % Happens in motion-to-goal mode and turns the mode into
4 | % boundary-following mode if true.
5 |
6 | min_dist = readshortest(pt_current,obstacles);
7 |
8 | if norm(pt_current-PT_GOAL) > norm(pt_previous-PT_GOAL)...
9 | || min_dist < LEN_STEP*20
10 | mode = 1;
11 | else
12 | mode = 0;
13 | end
14 |
15 | end
16 |
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/checkoff.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function mode = checkoff(pt_current,curve,PT_GOAL,SENSOR_RANGE,obstacles,LEN_STEP,endpoints)
2 | %checkoff Check the condition to terminate boundary following
3 | % Happens in boundary-following mode and turns the mode into
4 | % motion-to-goal mode if true.
5 | min_dist = readshortest(pt_current,curve);
6 |
7 | d_reach = norm(pt_current-PT_GOAL)-SENSOR_RANGE;
8 | d_followed = norm(curve(:,1)-PT_GOAL);
9 | n_curve = size(curve,2);
10 | for i = 1:n_curve
11 | if norm(curve(:,i)-PT_GOAL) < d_followed
12 | d_followed = norm(curve(:,i)-PT_GOAL);
13 | else
14 | continue
15 | end
16 | end
17 |
18 | if ~isnan(endpoints)
19 | if checkIntersect(pt_current,PT_GOAL,endpoints)
20 | mode = 1;
21 | else
22 | mode = 0;
23 | return;
24 | end
25 | end
26 |
27 | if d_reach < d_followed && min_dist >= LEN_STEP*20
28 | mode = 0;
29 | else
30 | mode = 1;
31 | end
32 |
33 | end
34 |
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/createobstacles.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [obstacles,obs_1,obs_2,obs_3] = createobstacles(PT_START,PT_GOAL)
2 | %createobstacles Create obstacles in the plane
3 | % Scale the 10*10 plane to given-points-formed rectangle
4 | n = 100;
5 | obstacles = zeros(2,15*n-15);
6 |
7 | %
8 | width = abs(PT_GOAL(1)-PT_START(1));
9 | height = abs(PT_GOAL(2)-PT_START(2));
10 | left_bottom = [min(PT_START(1),PT_GOAL(1));min(PT_START(2),PT_GOAL(2))];
11 |
12 | % Obstacle 1: blocking triangle
13 | side_1 = [linspace(0.7,2.5,n);linspace(2.1,1.3,n)];
14 | side_2 = [linspace(2.5,1.8,n);linspace(1.3,3.2,n)];
15 | side_3 = [linspace(1.8,0.7,n);linspace(3.2,2.1,n)];
16 | obs_1 = [side_1(:,1:n-1) ...
17 | side_2(:,1:n-1) ...
18 | side_3(:,1:n-1)];
19 |
20 | % Obstacle 2: passed pentagon
21 | side_4 = [linspace(5.0,5.2,n);linspace(3.0,1.9,n)];
22 | side_5 = [linspace(5.2,6.9,n);linspace(1.9,1.8,n)];
23 | side_6 = [linspace(6.9,7.1,n);linspace(1.8,3.1,n)];
24 | side_7 = [linspace(7.1,6.3,n);linspace(3.1,4.1,n)];
25 | side_8 = [linspace(6.3,5.0,n);linspace(4.1,3.0,n)];
26 | obs_2 = [side_4(:,1:n-1) ...
27 | side_5(:,1:n-1) ...
28 | side_6(:,1:n-1)...
29 | side_7(:,1:n-1) ...
30 | side_8(:,1:n-1)];
31 |
32 | % Obstacle 3: blocking polygon
33 | side_9 = [linspace(5.0,6.3,n);linspace(7.2,7.4,n)];
34 | side_10 = [linspace(6.3,7.9,n);linspace(7.4,6.0,n)];
35 | side_11 = [linspace(7.9,9.0,n);linspace(6.0,6.5,n)];
36 | side_12 = [linspace(9.0,9.0,n);linspace(6.5,7.6,n)];
37 | side_13 = [linspace(9.0,6.8,n);linspace(7.6,9.3,n)];
38 | side_14 = [linspace(6.8,4.5,n);linspace(9.3,9.1,n)];
39 | side_15 = [linspace(4.5,5.0,n);linspace(9.1,7.2,n)];
40 | obs_3 = [side_9(:,1:n-1) ...
41 | side_10(:,1:n-1) ...
42 | side_11(:,1:n-1)...
43 | side_12(:,1:n-1)...
44 | side_13(:,1:n-1)...
45 | side_14(:,1:n-1)...
46 | side_15(:,1:n-1)];
47 |
48 | obs_1(1,:) = obs_1(1,:)/10*width+left_bottom(1);
49 | obs_1(2,:) = obs_1(2,:)/10*height+left_bottom(2);
50 | obs_2(1,:) = obs_2(1,:)/10*width+left_bottom(1);
51 | obs_2(2,:) = obs_2(2,:)/10*height+left_bottom(2);
52 | obs_3(1,:) = obs_3(1,:)/10*width+left_bottom(1);
53 | obs_3(2,:) = obs_3(2,:)/10*height+left_bottom(2);
54 | obstacles = [obs_1 obs_2 obs_3];
55 |
56 |
57 | end
58 |
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/decideOi.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function Oi = decideOi(pt_current,PT_GOAL,endpoints)
2 | %DECIDEOI Determine which endpoint to go towards
3 | % Detailed explanation goes here
4 | heuristic_distance_1 = norm(pt_current-endpoints(:,1))+...
5 | norm(endpoints(:,1)-PT_GOAL);
6 | heuristic_distance_2 = norm(pt_current-endpoints(:,2))+...
7 | norm(endpoints(:,2)-PT_GOAL);
8 |
9 | if heuristic_distance_1 < heuristic_distance_2
10 | Oi = endpoints(:,1);
11 | else
12 | Oi = endpoints(:,2);
13 | end
14 |
15 | end
16 |
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/drawcircle.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function circle_plot = drawcircle(centre,radius)
2 | %drawcircle Draw a circle around centre with radius
3 |
4 | theta = linspace(0,2*pi);
5 | x = radius*cos(theta) + centre(1);
6 | y = radius*sin(theta) + centre(2);
7 | circle_plot = plot(x,y,'m');
8 |
9 | end
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/getcurve.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [isExist,curve,endpoints] = getcurve(obstacles,pt_current,PT_GOAL,SENSOR_RANGE)
2 | %getcurve Get sensing curve and indicate endpoints
3 | % There may be multiple curves and we only care about the curve that
4 | % intersects with current-goal line (initially as m-line).
5 |
6 | n_iter = 720;
7 | angle_axis = linspace(0,2*pi,n_iter);
8 | angle_step = angle_axis(2)-angle_axis(1);
9 |
10 | circ_scanned = Inf(2,n_iter); % Circumference points coordinates
11 | circ_occupied = zeros(1,n_iter); % Check the occupancy of circ_scanned
12 |
13 | n_obs = size(obstacles,2);
14 |
15 | for i_angle = 1:n_iter
16 | len_closest = SENSOR_RANGE;
17 | for i_obs = 1:n_obs
18 | pt_obs = obstacles(:,i_obs);
19 | angle_obs = atan2(pt_obs(2)-pt_current(2),...
20 | pt_obs(1)-pt_current(1));
21 |
22 | % Find obstacle points at the same angle
23 | if abs(angle_obs - angle_axis(i_angle)) < angle_step
24 | % Assumed as the same if angles are very close
25 | len_temp = norm(pt_current-pt_obs);
26 | if len_temp < len_closest
27 | circ_scanned(:,i_angle) = pt_obs;
28 | len_closest = len_temp;
29 | if ~circ_occupied(i_angle) % First-time scanned
30 | circ_occupied(i_angle) = true;
31 | end
32 | end
33 | end
34 | end
35 | end
36 |
37 | % Split the circumference points into curves
38 | % and chooose the intersecting curve.
39 | diff_occupied = [diff(circ_occupied) ...
40 | circ_occupied(1)-circ_occupied(n_iter)];
41 |
42 | % Means filter to eliminate odd ajoint -1 and 1, core: 3
43 | temp = zeros(1,n_iter);
44 | for i_filter = 1:n_iter
45 | if i_filter == 1
46 | temp(i_filter) = diff_occupied(1)+...
47 | diff_occupied(n_iter)+diff_occupied(2);
48 | elseif i_filter == n_iter
49 | temp(i_filter) = diff_occupied(n_iter)+...
50 | diff_occupied(n_iter-1)+ diff_occupied(1);
51 | else
52 | temp(i_filter) = diff_occupied(i_filter)+...
53 | diff_occupied(i_filter-1)+diff_occupied(i_filter+1);
54 | end
55 | end
56 | diff_occupied = temp;
57 |
58 | id_end_pos = find(diff_occupied == 1) + 1;
59 | id_end_neg = find(diff_occupied == -1);
60 | if ~circ_occupied(n_iter)
61 | id_end_pos(id_end_pos > n_iter) = 1;
62 | end
63 | id_end_pos = sort(id_end_pos);
64 | id_end_neg = sort(id_end_neg);
65 |
66 | if isempty(id_end_pos) || isempty(id_end_neg)
67 | curve = NaN;
68 | endpoints = NaN;
69 | isExist = false;
70 | return
71 | end
72 |
73 |
74 | % Use min and max
75 | id_pos = min(id_end_pos);
76 | id_neg = max(id_end_neg);
77 |
78 | if id_pos == id_neg % only one scanned point
79 | curve = NaN;
80 | endpoints = NaN;
81 | isExist = false;
82 | return
83 | end
84 | curve = circ_scanned(:,id_pos:id_neg);
85 | curve = curve(:,~isinf(curve(1,:)));
86 | % endpoints = [circ_scanned(:,id_pos) circ_scanned(:,id_neg)];
87 | endpoints = [curve(:,1) curve(:,size(curve,2))];
88 | if checkIntersect(pt_current,PT_GOAL,endpoints)
89 | % curve = circ_scanned(:,(min(id_pos,id_neg):max(id_pos,id_neg)));
90 | isExist = true;
91 | else
92 | curve = NaN;
93 | endpoints = NaN;
94 | isExist = false;
95 | end
96 | %
97 | % % Curve: from id_end_pos to id_end_neg
98 | % for i = 1:size(id_end_pos,2)
99 | % id_pos = id_end_pos(i);
100 | % id_temp = id_pos;
101 | % while true
102 | % if any(id_end_neg(:) == id_temp)
103 | % break;
104 | % else
105 | % id_temp = id_temp + 1;
106 | % if id_temp > n_iter
107 | % id_temp = 1;
108 | % end
109 | % end
110 | % end
111 | % id_neg = id_temp;
112 | % if id_pos == id_neg % only one scanned point
113 | % continue
114 | % end
115 | % curve = circ_scanned(:,(min(id_pos,id_neg):max(id_pos,id_neg)));
116 | % curve = curve(:,~isinf(curve(1,:)));
117 | % % endpoints = [circ_scanned(:,id_pos) circ_scanned(:,id_neg)];
118 | % endpoints = [curve(:,1) curve(:,size(curve,2))];
119 | % if checkIntersect(pt_current,PT_GOAL,endpoints)
120 | % % curve = circ_scanned(:,(min(id_pos,id_neg):max(id_pos,id_neg)));
121 | % isExist = true;
122 | % break; % Find intersecting curve, end loop.
123 | % else
124 | % curve = NaN;
125 | % endpoints = NaN;
126 | % isExist = false;
127 | % end
128 | % end
129 |
130 | end
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/inputstartend.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function [pt_start,pt_goal] = inputstartend()
2 | %INPUTSTARTEND Call this function to get the two endpoints
3 | % Tell the user to input start x, start y, end x and end y separately.
4 | % And the function combines them to make two point vectors.
5 | pt_start = zeros(2,1);
6 | pt_goal = zeros(2,1);
7 |
8 | %
9 | disp('Input coordinates of start point and goal point...')
10 |
11 | while true
12 | start_x = input('Input x of start point: ');
13 | if isempty(start_x)
14 | continue
15 | else
16 | break
17 | end
18 | end
19 | while true
20 | start_y = input('Input y of start point: ');
21 | if isempty(start_y)
22 | continue
23 | else
24 | break
25 | end
26 | end
27 | while true
28 | goal_x = input('Input x of start point: ');
29 | if isempty(goal_x)
30 | continue
31 | else
32 | break
33 | end
34 | end
35 | while true
36 | goal_y = input('Input y of start point: ');
37 | if isempty(goal_y)
38 | continue
39 | else
40 | break
41 | end
42 | end
43 |
44 | pt_start = [start_x;start_y];
45 | pt_goal = [goal_x;goal_y];
46 | clc
47 |
48 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/lineEquation.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function y = lineEquation(pt1,pt2,x)
2 | %LINEEQUATION Calculate y w.r.t x on line from pt1 to pt2.
3 | y = (pt2(2)-pt1(2))/(pt2(2)-pt1(1))*(x-pt1(1))+pt1(2);
4 | end
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/readshortest.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function min_dist = readshortest(pt_current,obstacles)
2 | %readshortest Get the shortest distance between current point and the curve
3 |
4 | n_curve = size(obstacles,2);
5 | min_dist = Inf;
6 | for i_obs = 1:n_curve
7 | temp_dist = norm(pt_current-obstacles(:,i_obs));
8 | if temp_dist < min_dist
9 | min_dist = temp_dist;
10 | end
11 | end
12 |
13 | end
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/straight2next.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function pt_next = straight2next(pt_current,pt_dest,LEN_STEP)
2 | %STRAIGHT2NEXT Find the next point to move to in a straight line.
3 | % Find the next point based on the step size and angle of gradients. If
4 | % the distance between the current spot and destination is less than step
5 | % size, let pt_next be pt_dest.
6 | pt_next = zeros(2,1);
7 |
8 | %
9 | angle = atan2(pt_dest(2)-pt_current(2),pt_dest(1)-pt_current(1));
10 |
11 | if norm(pt_dest-pt_current) > LEN_STEP
12 | pt_next(1) = pt_current(1)+cos(angle)*LEN_STEP;
13 | pt_next(2) = pt_current(2)+sin(angle)*LEN_STEP;
14 | else
15 | pt_next = pt_dest;
16 | end
17 |
18 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/MATLAB Codes/Part 3 - Tangent Bug/tangentbug.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | %% TANGENTBUG.M
2 | % Author: Jinhang Zhu
3 | % Date: 8 Dec 2019
4 | % Description: Implement TangentBug path planning algorithm.
5 | %
6 |
7 | %% Global variables
8 | global SENSOR_RANGE % Sensing range of the range sensor
9 | global LEN_STEP % Step length of a movement of the robot
10 | global PT_START % Start point coordinates
11 | global PT_GOAL % Goal point coordinates
12 |
13 | SENSOR_RANGE = 0.5;
14 | LEN_STEP = 0.01;
15 | [PT_START,PT_GOAL] = inputstartend();
16 | left_bottom = [min(PT_START(1),PT_GOAL(1));min(PT_START(2),PT_GOAL(2))];
17 | right_top = [max(PT_START(1),PT_GOAL(1));max(PT_START(2),PT_GOAL(2))];
18 |
19 | disp(['Start from: (',num2str(PT_START(1)),',',num2str(PT_START(2)),')']);
20 | disp(['Go to: (',num2str(PT_GOAL(1)),',',num2str(PT_GOAL(2)),')']);
21 | close
22 | h = figure('units','normalized','outerposition',[0 0 1 1]);
23 | plot(PT_START(1),PT_START(2),'r+',"LineWidth",2,"MarkerSize",5); hold on
24 | plot(PT_GOAL(1),PT_GOAL(2),'r*',"LineWidth",2,"MarkerSize",5); hold on
25 | title(['Step length: ',num2str(LEN_STEP),...
26 | '; Sensor range: ',num2str(SENSOR_RANGE)]);
27 |
28 | %% Create obstacles in the plane
29 | [obstacles,obs_1,obs_2,obs_3] = createobstacles(PT_START,PT_GOAL);
30 | plot(PT_START(1),PT_START(2),'r+',"LineWidth",2,"MarkerSize",5); hold on
31 | plot(PT_GOAL(1),PT_GOAL(2),'r*',"LineWidth",2,"MarkerSize",5); hold on
32 | plot(obs_1(1,:),obs_1(2,:),'k'); hold on
33 | plot(obs_2(1,:),obs_2(2,:),'k'); hold on
34 | plot(obs_3(1,:),obs_3(2,:),'k'); hold on
35 |
36 | tic
37 | %% Main loop
38 | % motion-to-goal & boundary-following
39 | x_path = []; % Record of path's x
40 | y_path = []; % Record of path's y
41 | x_path = [x_path PT_START(1)]; % Start point stored
42 | y_path = [y_path PT_START(2)]; %
43 |
44 | pt_current = PT_START;
45 | pt_previous = pt_current;
46 |
47 | mode = 0; % mode = 0, do motion-to-goal
48 | % mode = 1, do boundary-following
49 |
50 | while true
51 | robot_plot = plot(pt_current(1),pt_current(2),... % Current location
52 | 'bo',... % Blue o
53 | "LineWidth",2,... %
54 | "MarkerSize",5); hold on %
55 | path_plot = plot(x_path,y_path,'b'); hold on % Path experienced
56 | current_goal_plot = line([pt_current(1) PT_GOAL(1)],...
57 | [pt_current(2) PT_GOAL(2)],... % Current-goal line
58 | 'Color','green','LineStyle','--'); %
59 | circle_plot = drawcircle(pt_current,... % Sensor range
60 | SENSOR_RANGE); hold on
61 |
62 | [isExist,curve,endpoints] = getcurve(obstacles,... % Scan with sensor to get
63 | pt_current,... % the intersecting curve
64 | PT_GOAL,SENSOR_RANGE); % and indicate endpoints
65 |
66 | if ~isExist % No blocking obstacle
67 | pt_dest = PT_GOAL; % Drive towards goal point
68 | else % Existing blocking obstacle
69 | if checkIntersect(pt_current,PT_GOAL,endpoints)
70 | curve_plot = plot(curve(1,:),curve(2,:),'r.'); hold on
71 | endpt_plot = plot(endpoints(1,:),endpoints(2,:),'ro'); hold on
72 | end
73 | pt_dest = decideOi(pt_current,... % Drive towards Oi
74 | PT_GOAL,endpoints); %
75 | end
76 | axis([left_bottom(1) right_top(1) left_bottom(2) right_top(2)]);
77 | axis equal
78 |
79 | % disp(['Go to endpoint: (',...
80 | % num2str(pt_dest(1)),',',num2str(pt_dest(2)),')']);
81 | if ~mode
82 | %% motion-to-goal
83 | pt_current = straight2next(pt_current,pt_dest,LEN_STEP);
84 |
85 | mode = checkalong(pt_previous,... % Check the condition
86 | pt_current,PT_GOAL,... % to start boundary following.
87 | curve,LEN_STEP); %
88 | if mode % mode from 0 to 1.
89 | disp('End motion-to-goal, start boundary-following...');
90 | angle_previous = atan2(pt_dest(2)-pt_current(2),...
91 | pt_dest(1)-pt_current(1));
92 | end
93 | else
94 | %% boundary-following
95 | [pt_current,angle_next] = boundaryfollow2next(...
96 | angle_previous,... % Follow the most recent
97 | pt_current,pt_dest,LEN_STEP,obstacles); % direction. Initially
98 | % from motion-to-goal
99 | angle_previous = angle_next; %
100 | %
101 | mode = checkoff(pt_current,... % Check the condition
102 | curve,PT_GOAL,SENSOR_RANGE,... %
103 | obstacles,LEN_STEP,endpoints); % to terminate boundary
104 | % following.
105 | if ~mode % mode from 1 to 0.
106 | disp('End boundary-following, start motion-to-goal...');
107 | end
108 | end
109 |
110 | x_path = [x_path pt_current(1)];
111 | y_path = [y_path pt_current(2)];
112 |
113 | pause(0.01);
114 | if pt_current ~= PT_GOAL
115 | delete(path_plot);
116 | delete(robot_plot);
117 | delete(circle_plot);
118 | delete(current_goal_plot);
119 | if isExist && ~isempty(curve_plot)
120 | delete(curve_plot);
121 | delete(endpt_plot);
122 | end
123 | else
124 | break;
125 | end
126 | end
127 |
128 | disp('Reach goal point!');
129 | toc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Serial and Parallel Robot Kinematics and Mobile Robot Motion Planning
2 | Robotics fundamentals coursework at the University of Bristol and UWE Bristol
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 | This repo has been saved in Arctic by means of [2020 GitHub Archive Program](https://archiveprogram.github.com/)! Thank you GitHub!
7 |
8 |  9 |
10 |
11 |
9 |
10 |
11 | Table of Contents
12 |
13 |
14 | - [Abstract](#abstract)
15 | - [Animations](#animations)
16 | - [Contributors](#contributors)
17 | - [License](#license)
18 |
19 |
20 |
21 |
22 | ## Abstract
23 |
24 | Kinematics concept has been the essential part of robots controlling. This report of the coursework demonstrates our understanding on robots fundamentals. Denavit-Hartenberg convention is highlighted in kinematics and is further used in the analytical approach to derive the inverse kinematics on both serial and parallel robots. Additionally, an algorithm in motion planning is implemented in simulation. Detailed discussion is given in the following parts.
25 |
26 | ## Animations
27 |
28 | - Free motion
29 |
30 | 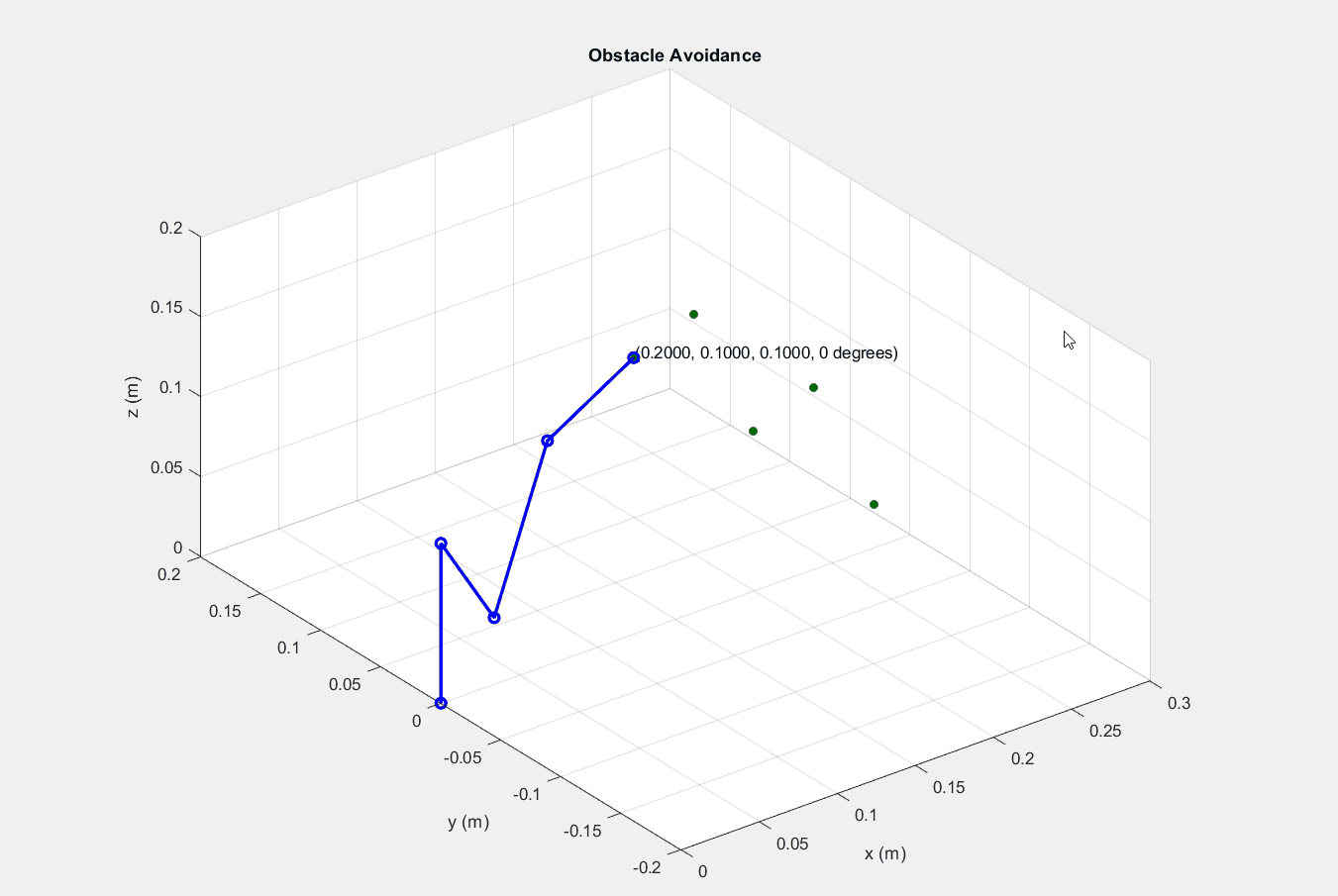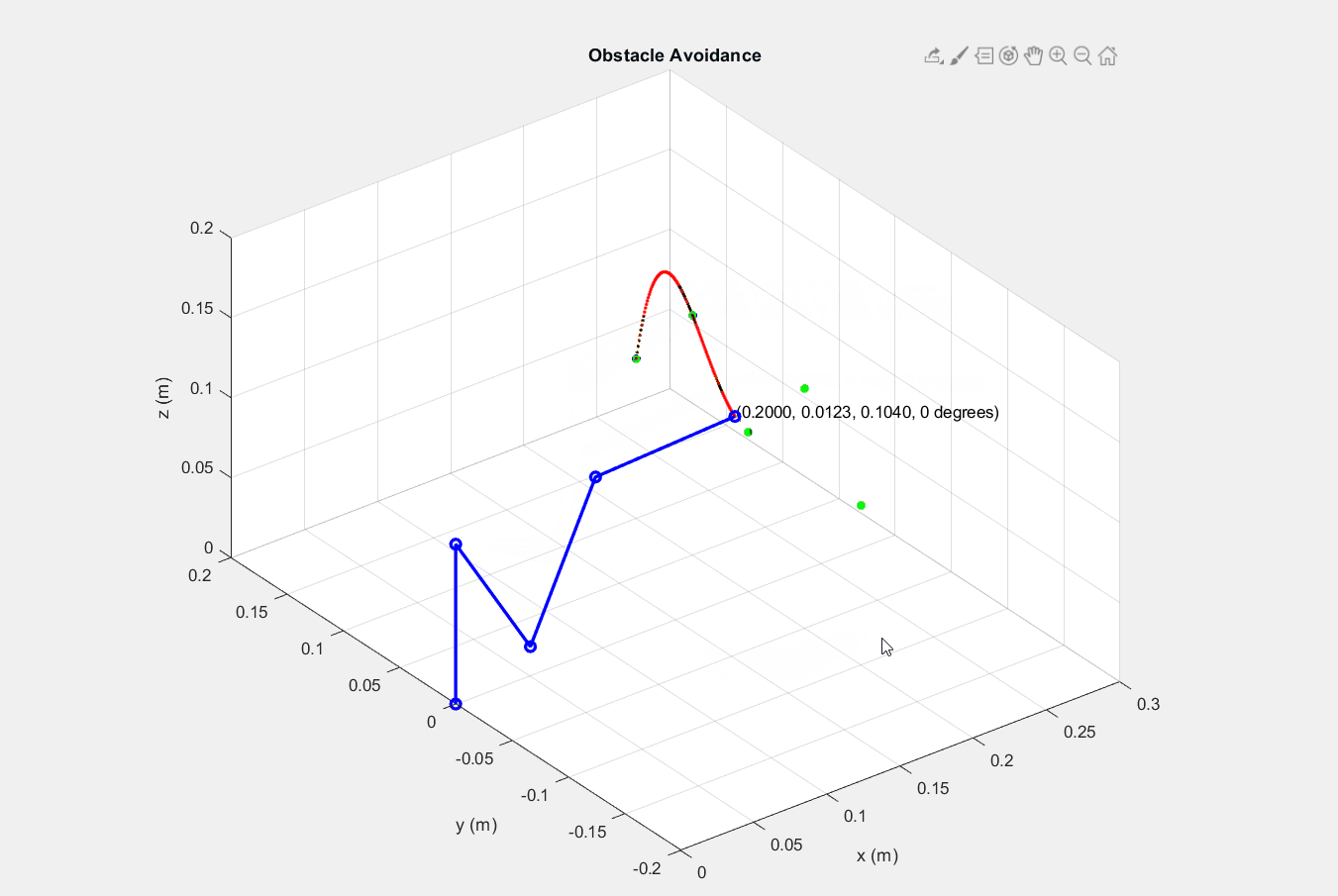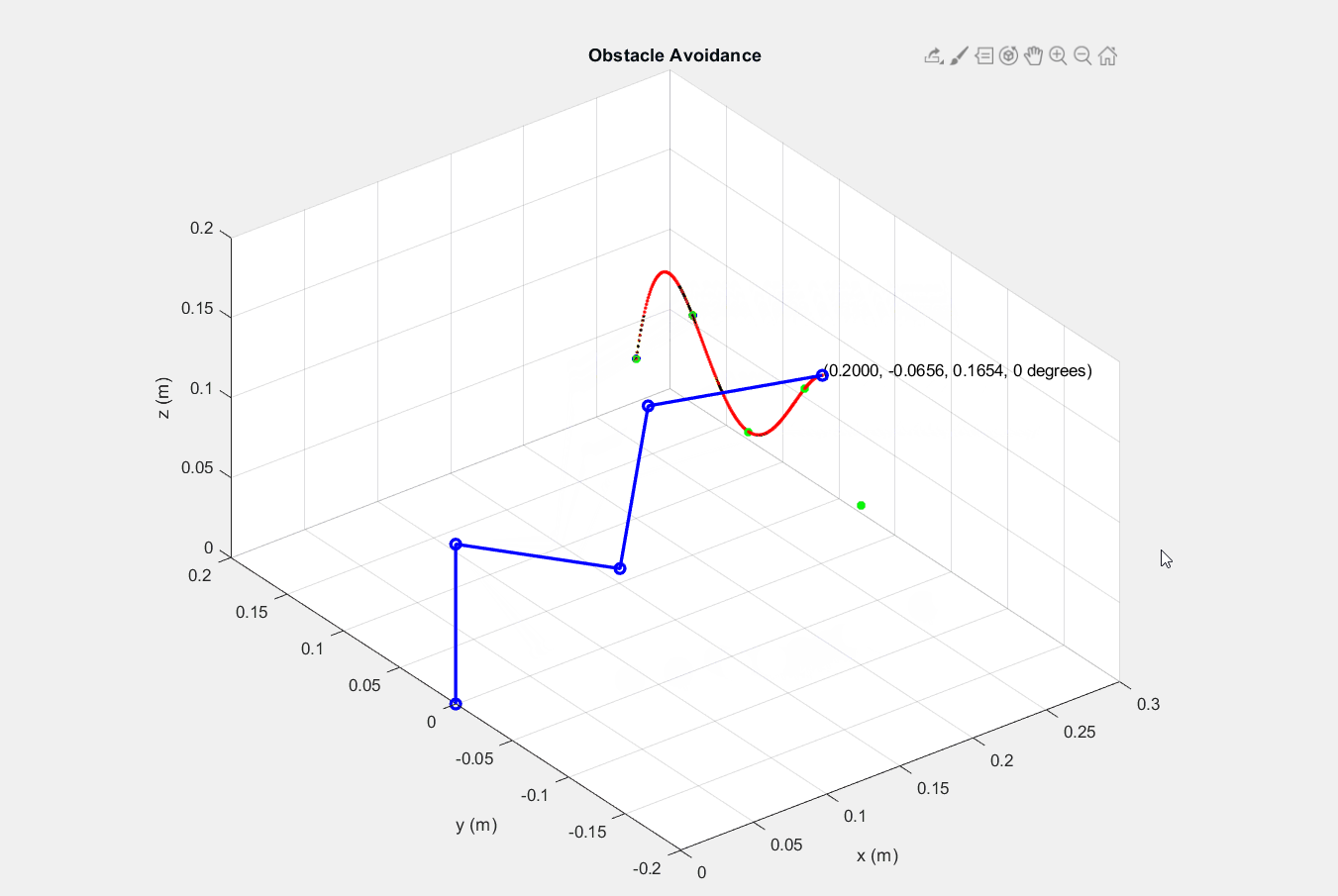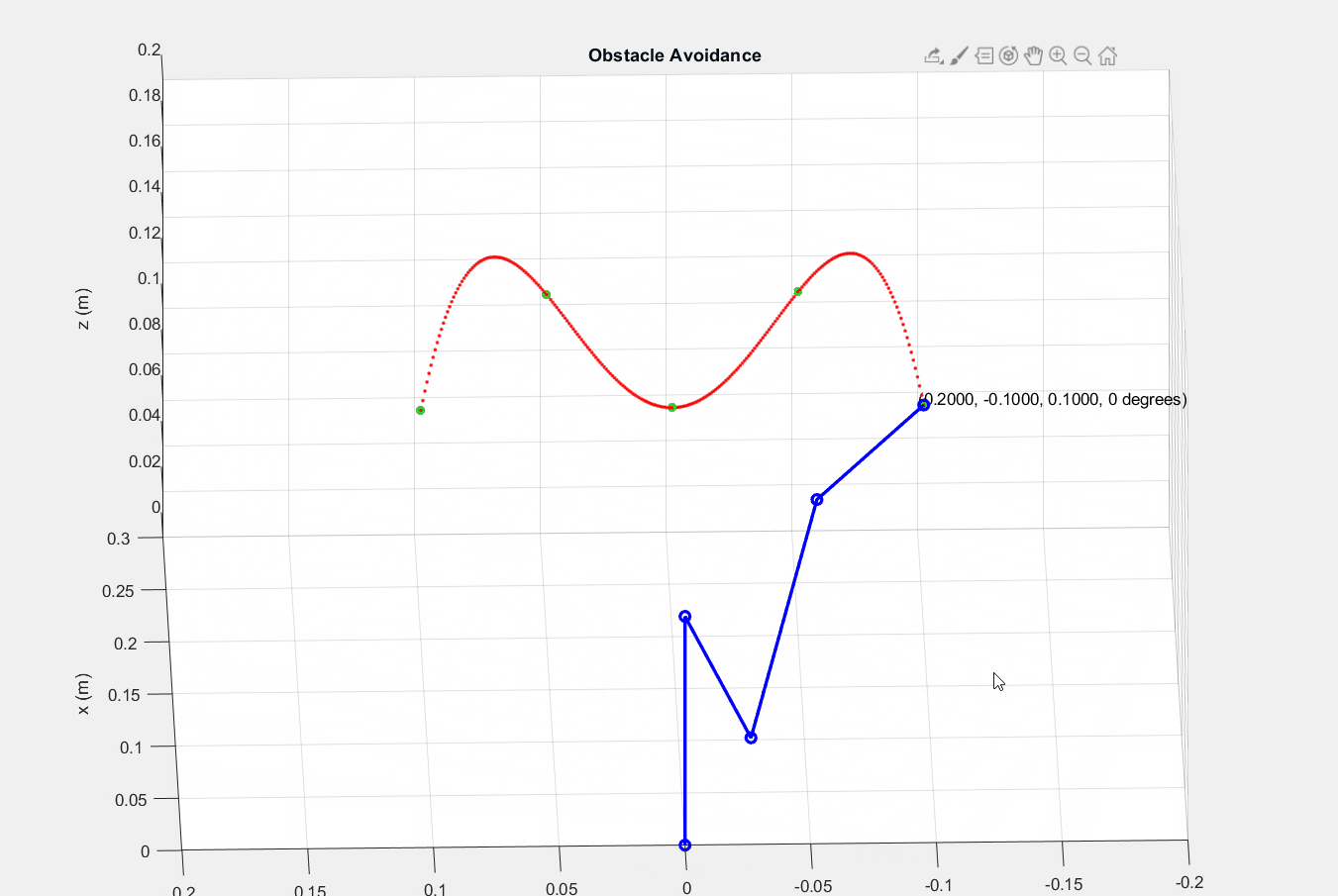
31 |
32 | - Demo of straight line trajectory
33 |
34 | 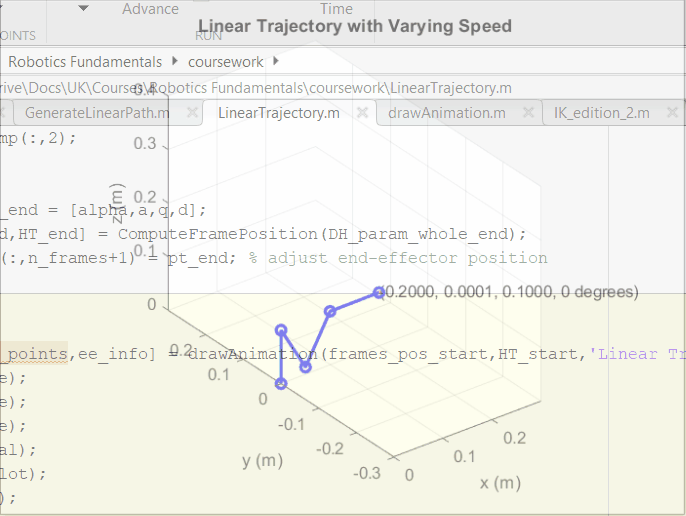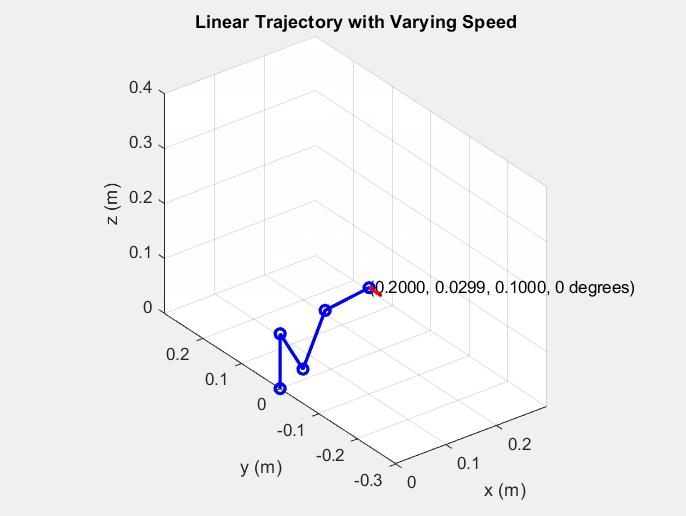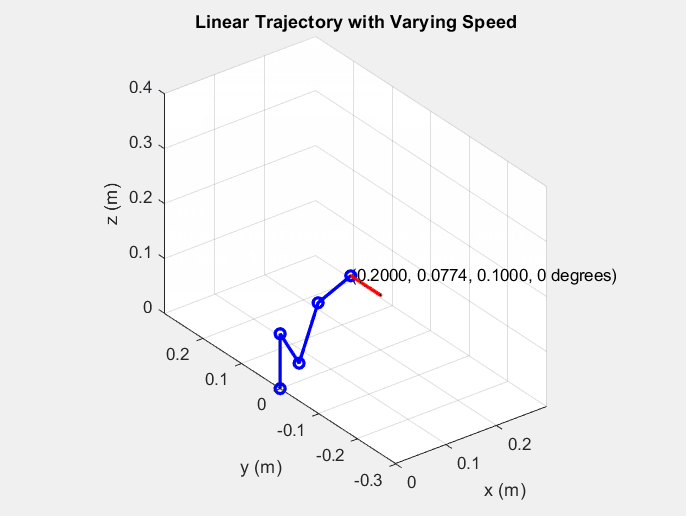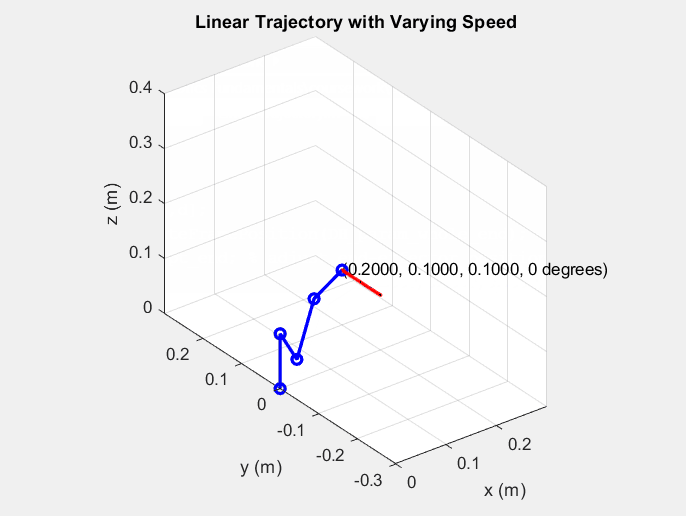
35 |
36 | - Straight line trajectory
37 |
38 | 
39 |
40 | - Obstacle avoidance
41 |
42 | 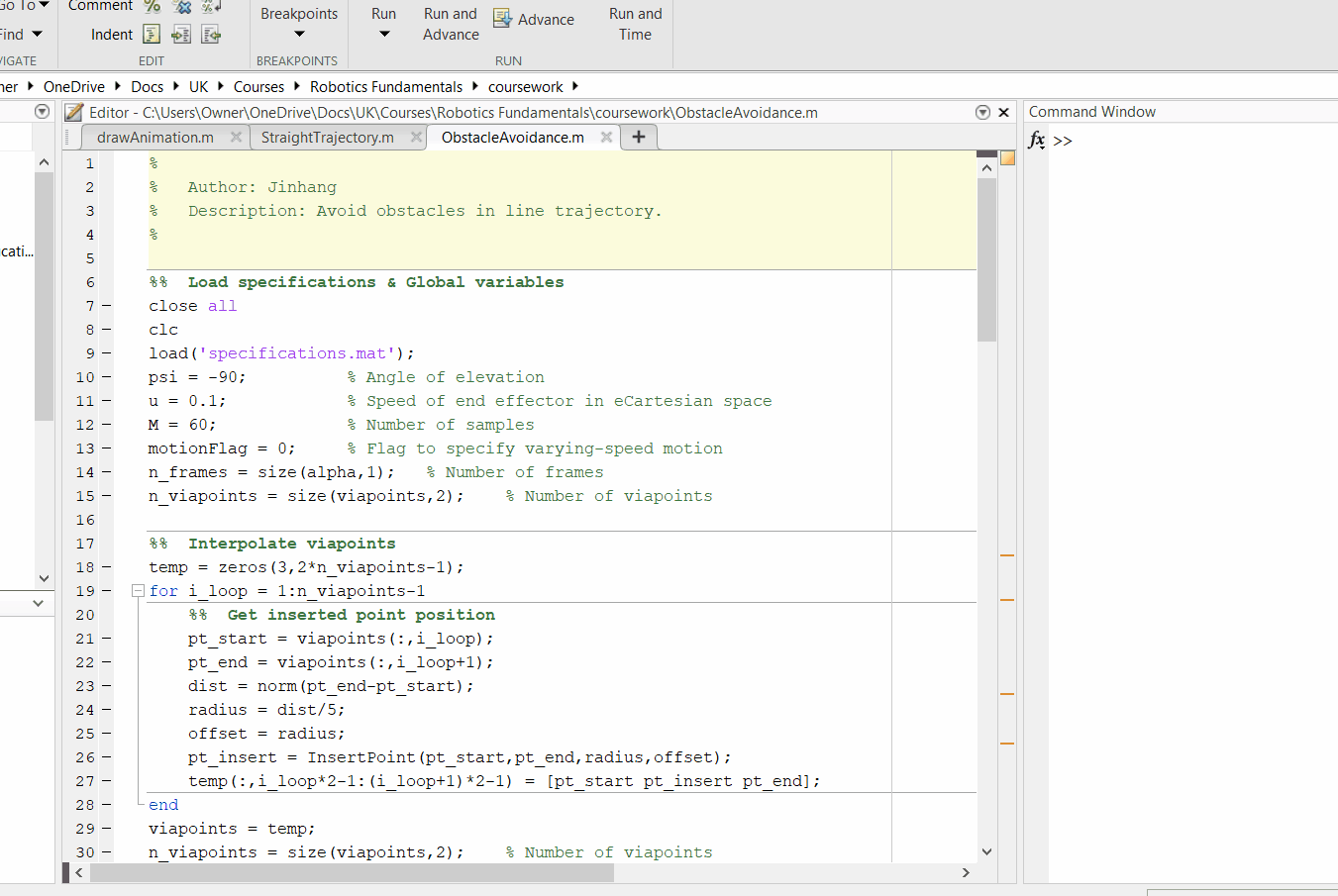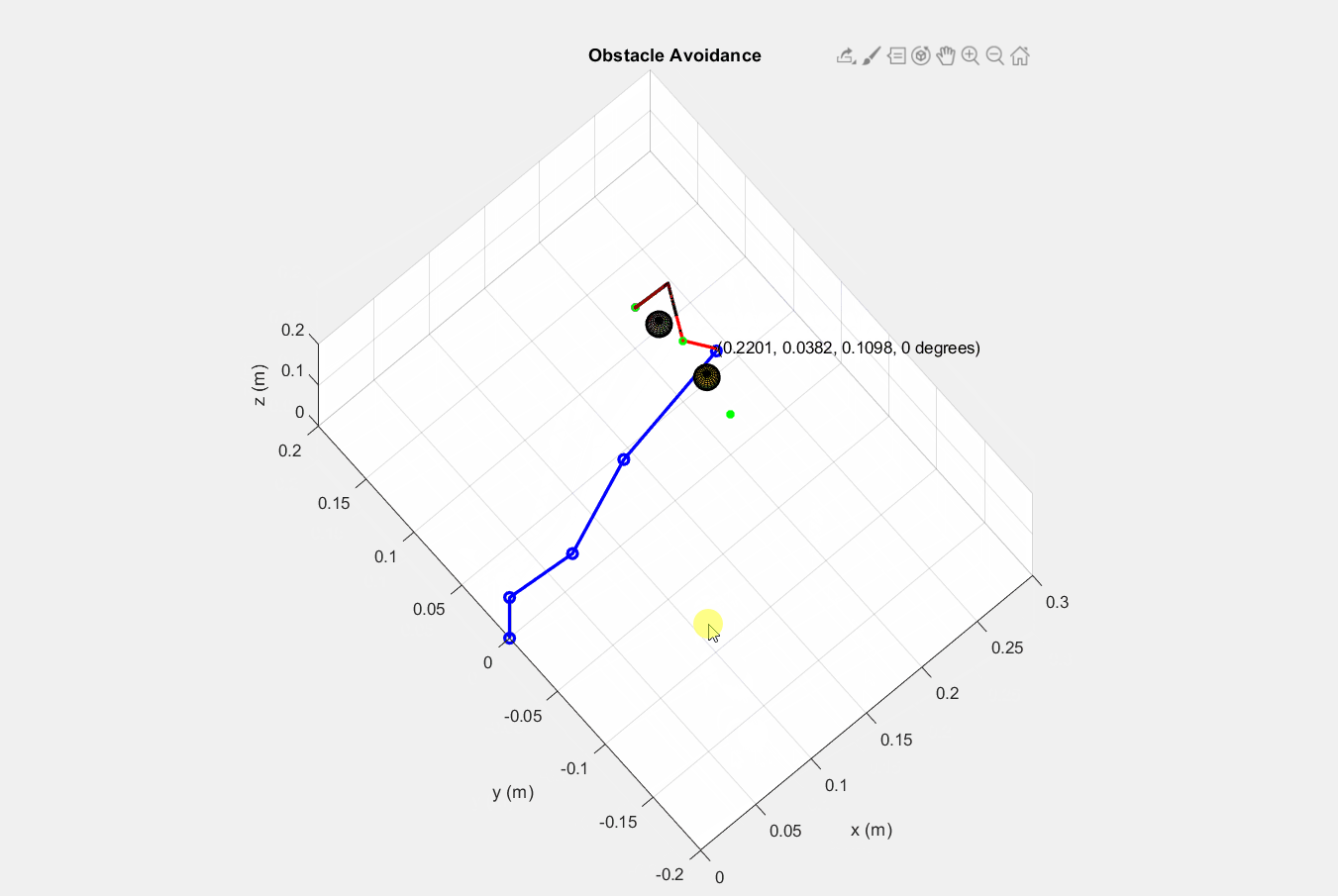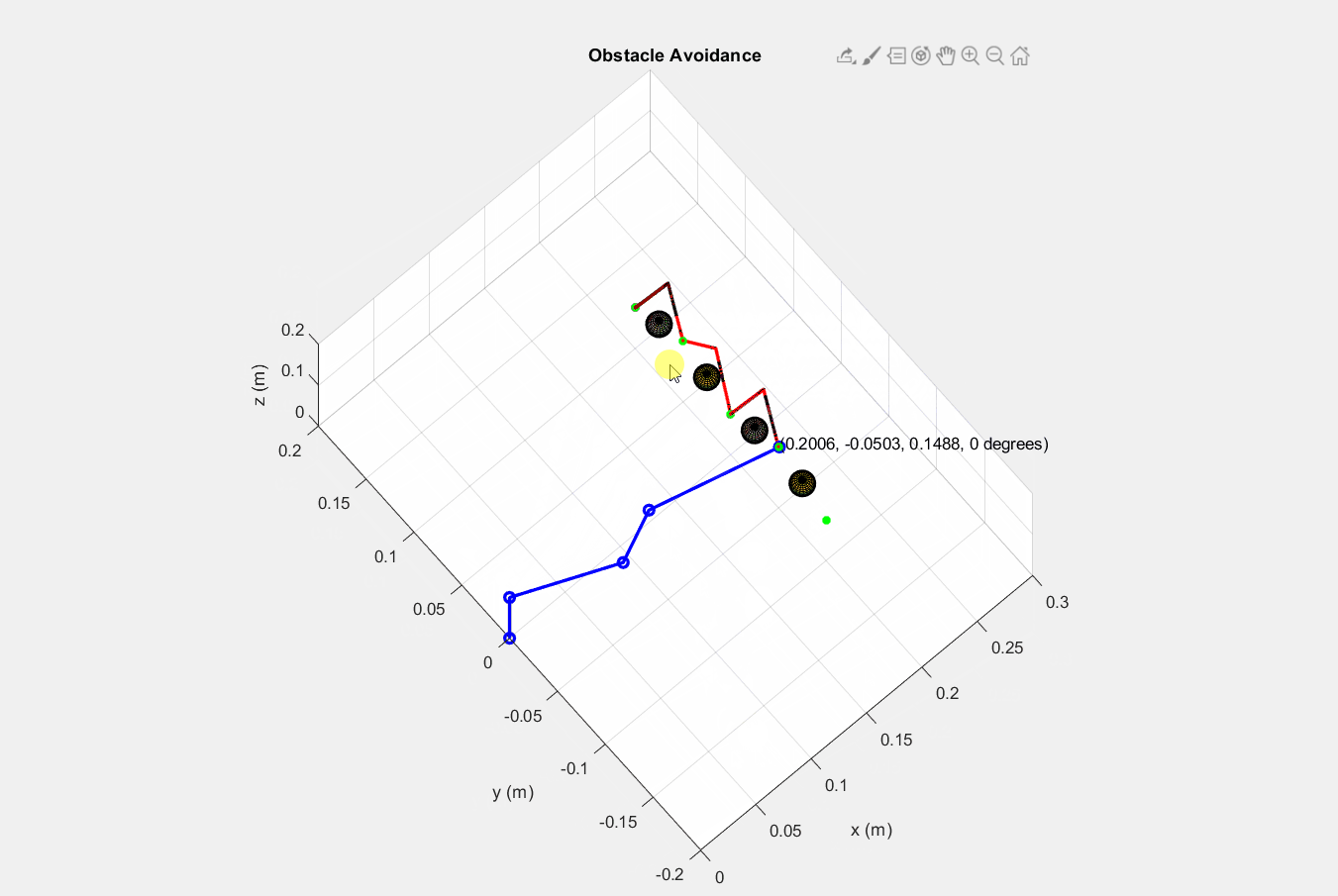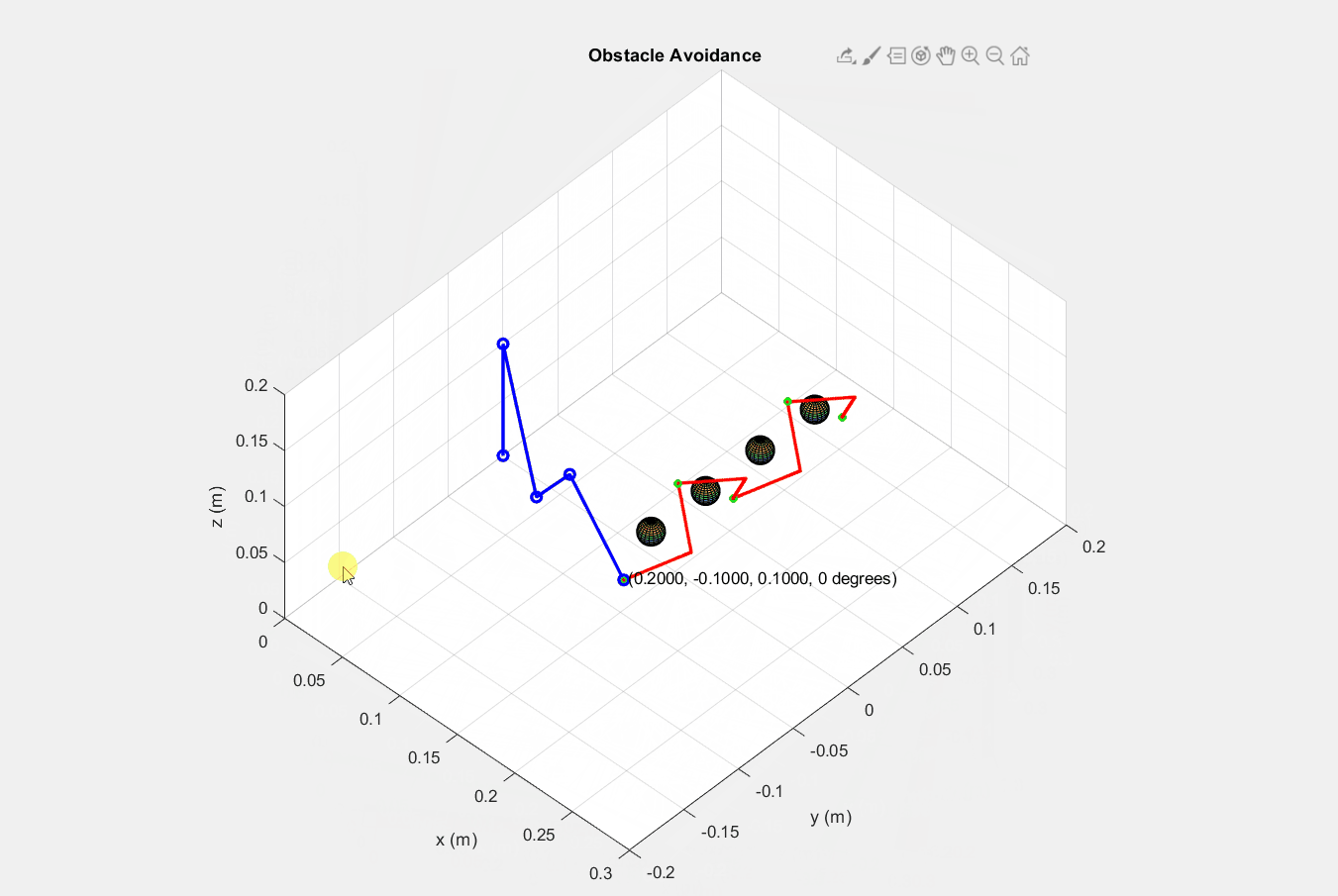
43 |
44 | - Tangent Bug motion planning
45 |
46 | 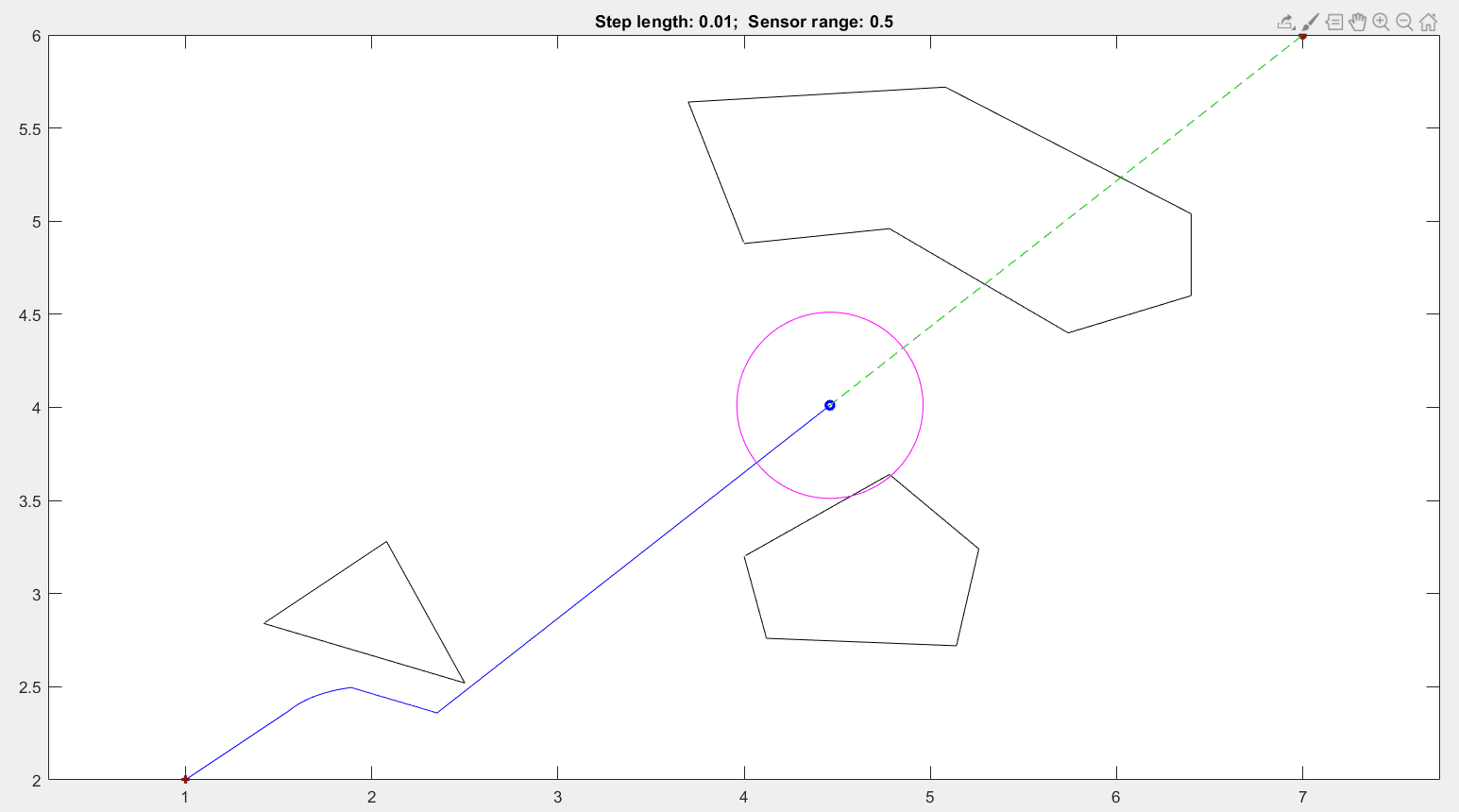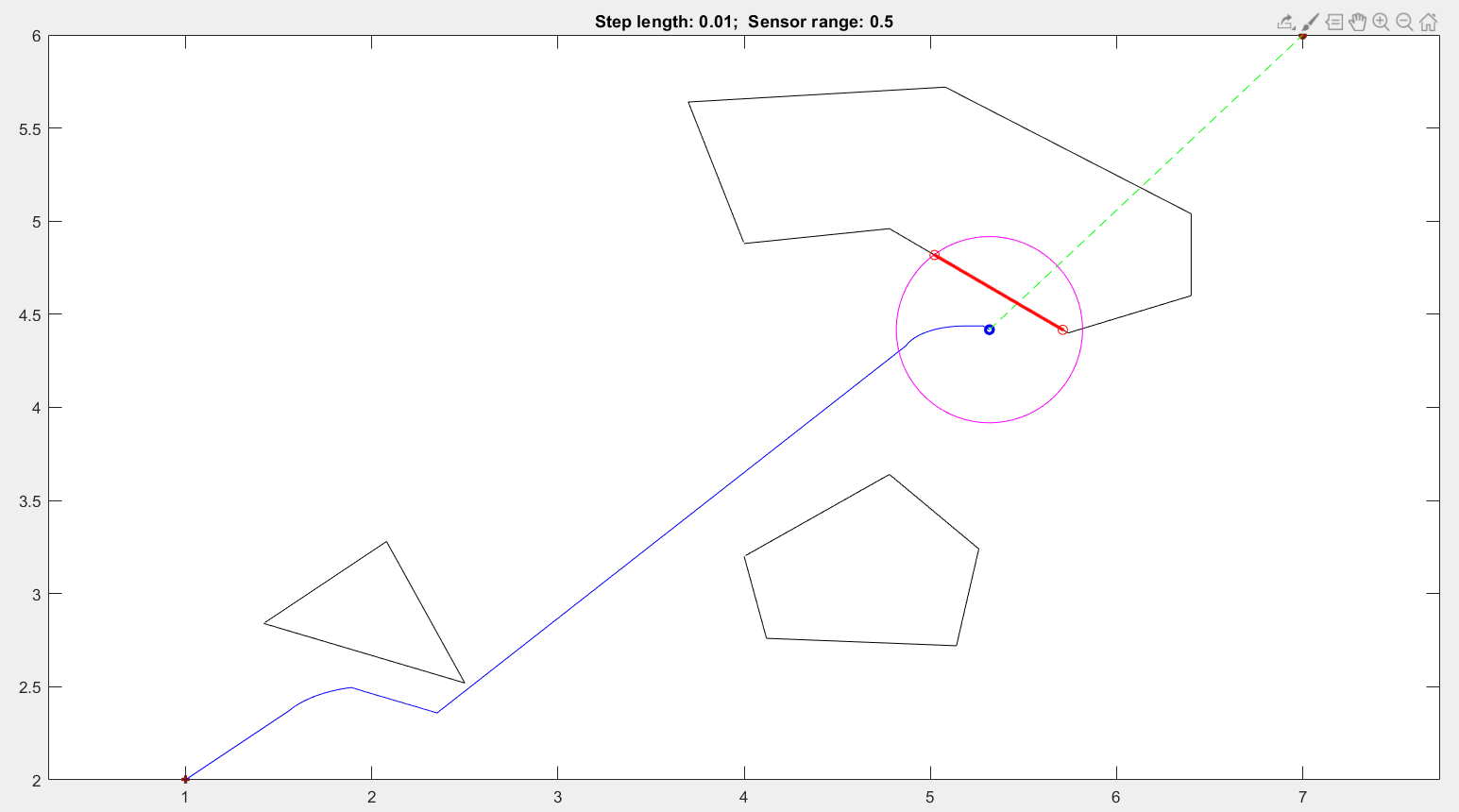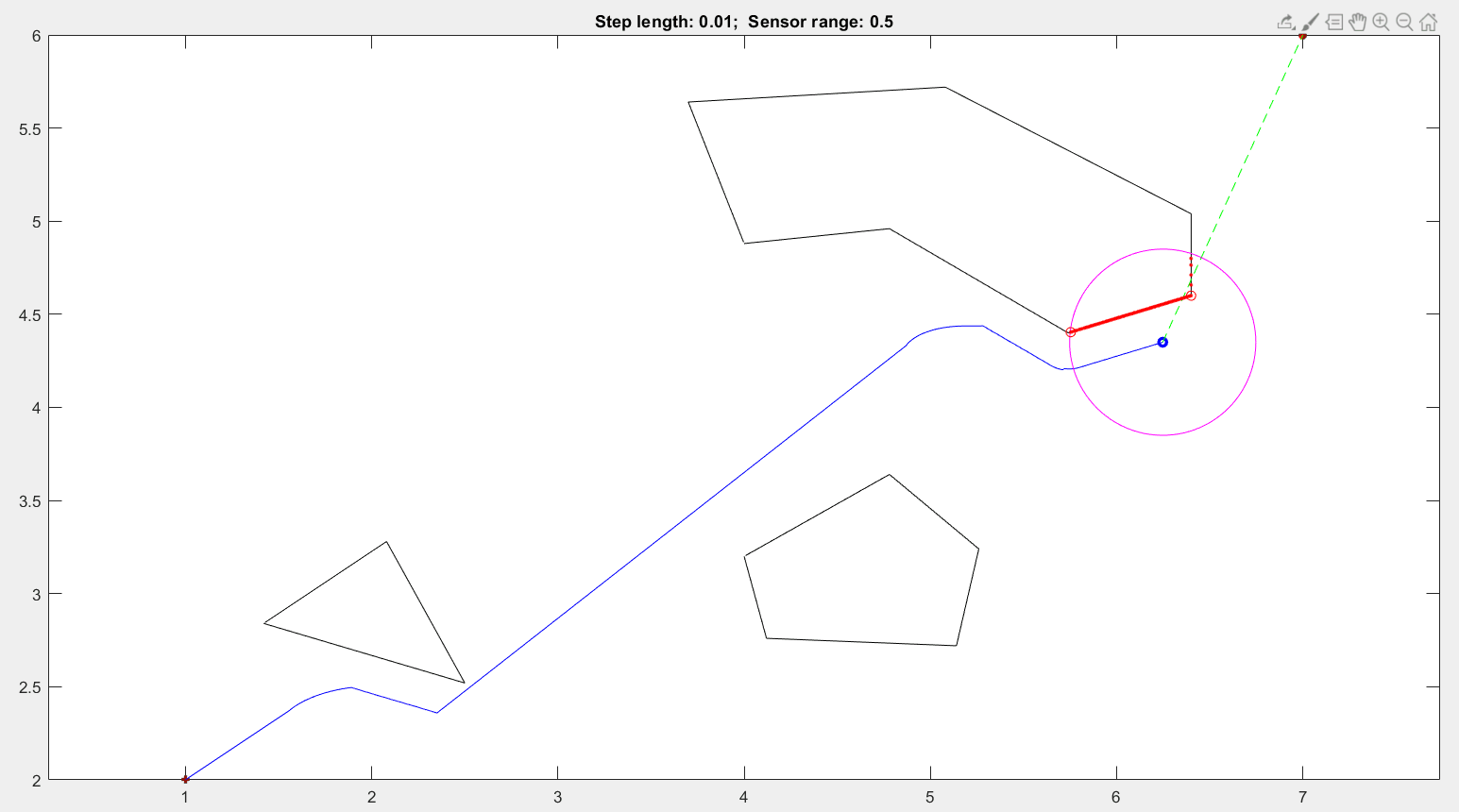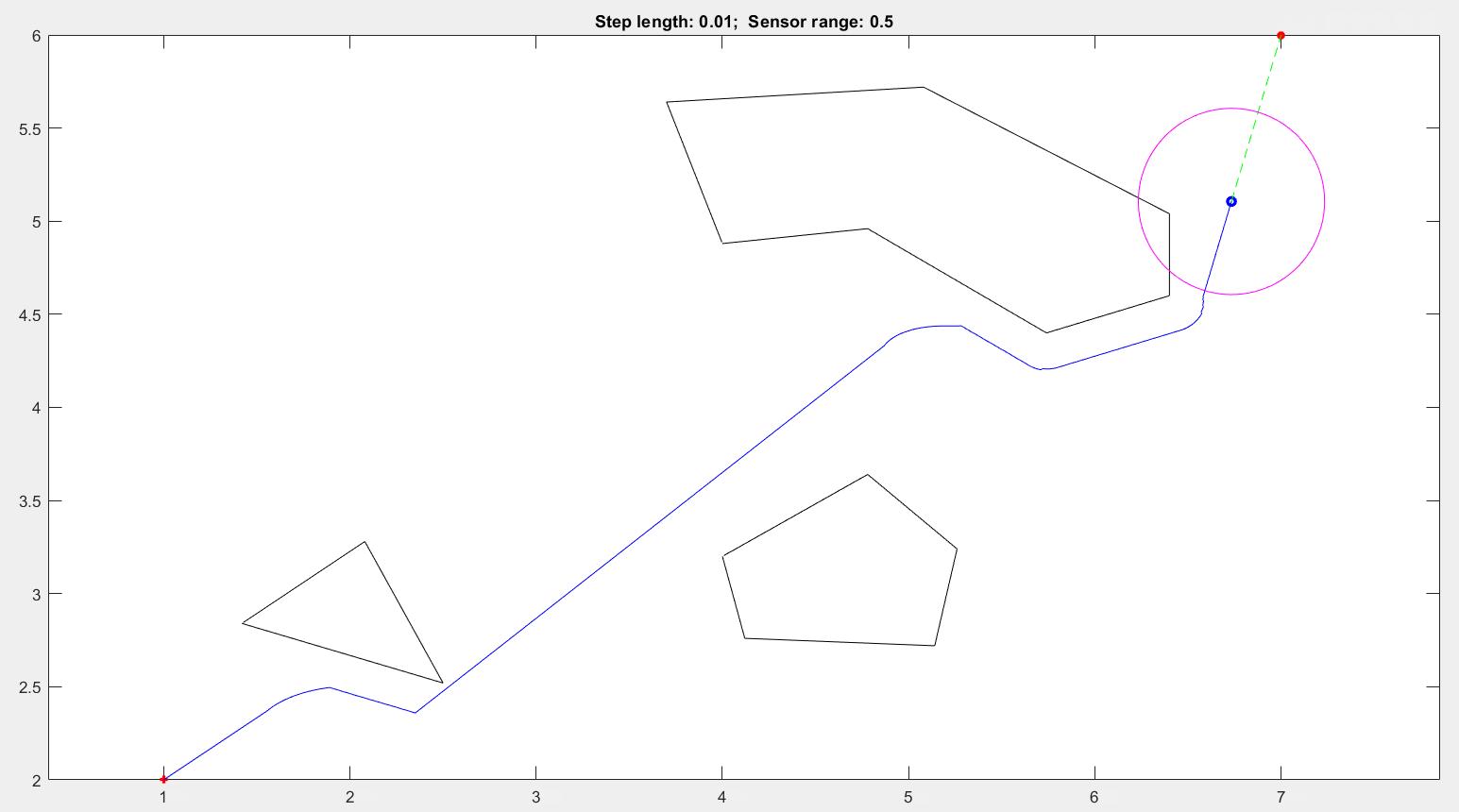
47 |
48 | ## Contributors
49 |
50 | [Jinhang Zhu](https://github.com/JinhangZhu)
51 |
52 | [Wengxing Peng](https://github.com/WenxingPeng)
53 |
54 | ## License
55 |
56 | - [MIT](https://opensource.org/licenses/MIT)
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 9 |
10 |
11 |
9 |
10 |
11 |