├── .gitignore
├── .travis.yml
├── CHANGELOG.md
├── LICENSE
├── Makefile
├── NOTICE
├── README.md
├── bfv
├── README.md
├── bfv_benchmark_test.go
├── bfv_test.go
├── ciphertext.go
├── decryptor.go
├── encoder.go
├── encryptor.go
├── evaluator.go
├── keygen.go
├── keys.go
├── marshaler.go
├── operand.go
├── params.go
└── plaintext.go
├── ckks
├── README.md
├── algorithms.go
├── bettersine
│ ├── arithmetic.go
│ └── bettersine.go
├── bootstrap.go
├── bootstrap_bench_test.go
├── bootstrap_params.go
├── bootstrap_test.go
├── bootstrapper.go
├── chebyshev_interpolation.go
├── ciphertext.go
├── ckks_benchmarks_test.go
├── ckks_test.go
├── decryptor.go
├── encoder.go
├── encryptor.go
├── evaluator.go
├── keygen.go
├── keys.go
├── linear_transform.go
├── marshaler.go
├── operand.go
├── params.go
├── plaintext.go
├── polynomial_evaluation.go
├── precision.go
└── utils.go
├── ckks_fv
├── RtF_bench_test.go
├── algorithms.go
├── bootstrap.go
├── bootstrap_params.go
├── bootstrapper.go
├── chebyshev_interpolation.go
├── ciphertext.go
├── ckks_decryptor.go
├── ckks_encoder.go
├── ckks_encryptor.go
├── ckks_evaluator.go
├── fv_hera.go
├── fv_rubato.go
├── halfboot.go
├── halfboot_params.go
├── halfbootstrapper.go
├── keygen.go
├── keys.go
├── linear_transform.go
├── mfv_decryptor.go
├── mfv_encoder.go
├── mfv_encryptor.go
├── mfv_evaluator.go
├── mfv_noise_estimator.go
├── operand.go
├── params.go
├── plaintext.go
├── polynomial_evaluation.go
├── precision.go
├── rtf_params.go
└── utils.go
├── dbfv
├── dbfv.go
├── dbfv_benchmark_test.go
├── dbfv_test.go
├── keyswitching.go
├── public_keyswitching.go
├── public_permute.go
├── public_refresh.go
├── publickey_gen.go
├── relinkey_gen.go
└── rotkey_gen.go
├── dckks
├── dckks.go
├── dckks_benchmark_test.go
├── dckks_test.go
├── keyswitching.go
├── public_keyswitching.go
├── public_permute.go
├── public_refresh.go
├── publickey_gen.go
├── relinkey_gen.go
├── rotkey_gen.go
└── utils.go
├── drlwe
├── public_key_gen.go
├── relin_key_gen.go
└── rot_key_gen.go
├── examples
├── bfv
│ └── main.go
├── ckks
│ ├── bootstrapping
│ │ ├── example
│ │ │ └── main.go
│ │ └── experiments
│ │ │ ├── boot_precision.go
│ │ │ ├── run_slotcount.sh
│ │ │ ├── run_slotdist.sh
│ │ │ ├── run_successive.sh
│ │ │ └── tpl
│ │ │ ├── slotcount.tex.tpl
│ │ │ ├── slotdist.tex.tpl
│ │ │ └── successive.tex.tpl
│ ├── euler
│ │ └── main.go
│ └── sigmoid
│ │ └── main.go
├── ckks_fv
│ └── main.go
└── dbfv
│ ├── pir
│ └── main.go
│ └── psi
│ └── main.go
├── go.mod
├── go.sum
├── lattigo.go
├── ring
├── complex128.go
├── int.go
├── int_test.go
├── modular_reduction.go
├── primes.go
├── ring.go
├── ring_automorphism.go
├── ring_basis_extension.go
├── ring_benchmark_test.go
├── ring_ntt.go
├── ring_ntt_test.go
├── ring_operations.go
├── ring_poly.go
├── ring_sampler.go
├── ring_sampler_gaussian.go
├── ring_sampler_ternary.go
├── ring_sampler_uniform.go
├── ring_scaling.go
├── ring_test.go
├── ring_test_params.go
└── utils.go
├── rlwe
└── keys.go
└── utils
├── buffer.go
├── buffer_test.go
├── prng.go
├── prng_test.go
├── utils.go
└── utils_test.go
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Created by .ignore support plugin (hsz.mobi)
2 | ### Go template
3 | # Binaries for programs and plugins
4 | *.exe
5 | *.exe~
6 | *.dll
7 | *.so
8 | *.dylib
9 |
10 | # Test binary, built with `go test -c`
11 | *.test
12 |
13 | # Output of the go coverage tool, specifically when used with LiteIDE
14 | *.out
15 |
16 | # Project-local glide cache, RE: https://github.com/Masterminds/glide/issues/736
17 | .glide/
18 |
19 | # Compiled Object files, Static and Dynamic libs (Shared Objects)
20 | *.o
21 | *.a
22 |
23 | # Folders
24 | _obj
25 | _test
26 |
27 | # Architecture specific extensions/prefixes
28 | *.[568vq]
29 | [568vq].out
30 |
31 | *.cgo1.go
32 | *.cgo2.c
33 | _cgo_defun.c
34 | _cgo_gotypes.go
35 | _cgo_export.*
36 |
37 | _testmain.go
38 |
39 | *.prof
40 | *.iml
41 | *.cov
42 | *.gob
43 |
44 | .DS_Store
45 |
46 | # Dependency directories (remove the comment below to include it)
47 | # vendor/
48 |
49 | .idea/
50 | .vscode/
51 |
52 |
53 | # generated
54 | /Coding
55 |
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.travis.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | language: go
2 |
3 | go:
4 | - 1.x
5 | - 1.14.x
6 | - 1.13.x
7 |
8 | script:
9 | - go build ./...
10 | - make ci_test
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .DEFAULT_GOAL := test
2 |
3 | Coding/bin/Makefile.base:
4 | git clone https://github.com/dedis/Coding
5 |
6 | .PHONY: test_examples
7 | test_examples:
8 | @echo Running the examples
9 | go run ./examples/bfv > /dev/null
10 | go run ./examples/ckks/euler > /dev/null
11 | go run ./examples/ckks/sigmoid > /dev/null
12 | go run ./examples/dbfv/pir &> /dev/null
13 | go run ./examples/dbfv/psi &> /dev/null
14 | @echo ok
15 | @echo Building resources-heavy examples
16 | go build -o /dev/null ./examples/ckks/bootstrapping
17 | @echo ok
18 |
19 | .PHONY: test_gotest
20 | test_gotest:
21 | go test -v -timeout=0 ./utils ./ring ./bfv ./dbfv ./dckks
22 | go test -v -timeout=0 ./ckks -test-bootstrapping
23 |
24 | .PHONY: test
25 | test: test_fmt test_gotest test_examples
26 |
27 | .PHONY: ci_test
28 | ci_test: test_fmt test_lint test_gotest test_examples
29 |
30 | %: force Coding/bin/Makefile.base
31 | @$(MAKE) -f Coding/bin/Makefile.base $@
32 | force: ;
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/NOTICE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Copyright 2020 EPFL
2 |
3 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 |
7 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 |
9 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | limitations under the License.
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # RtF Transciphering Framework
2 | This is an implementation of the RtF transciphering framework along with the HERA cipher (proposed in [Transciphering Framework for Approximate Homomorphic Encryption](https://eprint.iacr.org/2020/1335)) and the Rubato cipher (proposed in [Rubato: Noisy Ciphers for Approximate Homomorphic Encryption](https://eprint.iacr.org/2022/537)) using the `lattigo` library.
3 |
4 | ## New Package
5 | We implement the hybrid framework in [ckks_fv](./ckks_fv), which contains the following functionalities.
6 | - CKKS scheme (the same as [ckks](./ckks))
7 | - FV scheme supporting multi-level operations (named as `mfv`)
8 | - Halfboot operation
9 | - Evaluation of the HERA cipher in the FV scheme
10 |
11 | An example of finding modulus switching parameter in the RtF framework is given in [examples/ckks_fv](./examples/ckks_fv).
12 |
13 | ## Benchmark
14 | You can run the benchmark of RtF transciphering framework along with HERA or Rubato using [RtF_bench_test.go](./ckks_fv/RtF_bench_test.go).
15 | The benchmark parameters are given in [rtf_params.go](./ckks_fv/rtf_params.go).
16 | To benchmark all the parameters, run the following command in [ckks_fv](./ckks_fv) directory.
17 |
18 | ```go test -timeout=0s -bench=. ```
19 |
20 | You can also benchmark specific parameter.
21 | For example, to run benchmark with HERA, run the following command.
22 |
23 | ``` go test -timeout=0s -bench=BenchmarkRtFHera```
24 |
25 | To run the HERA parameter `80as` in the paper, run the following command.
26 |
27 | ```go test -timeout=0s -bench=BenchmarkRtFHera80as```
28 |
29 | Benchmark with Rubato is also possible in similar way.
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bfv/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # BFV
2 |
3 | The BFV package is an RNS-accelerated implementation of the Fan-Vercauteren version of Brakerski's scale-invariant homomorphic encryption scheme. It provides modular arithmetic over the integers.
4 |
5 | ## Brief description
6 |
7 | This scheme can be used to do arithmetic over 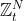.
8 |
9 | The plaintext space and the ciphertext space share the same domain
10 |
11 |
12 | 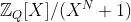 ,
13 |
,
13 |
14 | with 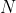 a power of 2.
15 |
16 | The batch encoding of this scheme
17 |
18 |
a power of 2.
15 |
16 | The batch encoding of this scheme
17 |
18 |
19 | 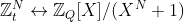 20 |
20 |
21 |
22 | maps an array of integers to a polynomial with the property:
23 |
24 |
25 | 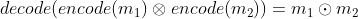 ,
26 |
,
26 |
27 | where represents  a component-wise product,and  represents a nega-cyclic convolution.
28 |
29 | ## Security parameters
30 |
31 | 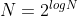: the ring dimension, which defines the degree of the cyclotomic polynomial, and the number of coefficients of the plaintext/ciphertext polynomials; it should always be a power of two. This parameter has an impact on both security and performance (security increases with N and performance decreases with N). It should be carefully chosen to suit the intended use of the scheme.
32 |
33 | 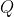: the ciphertext modulus. In Lattigo, it is chosen to be the product of small coprime moduli 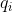 that verify 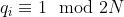 in order to enable both the RNS and NTT representation. The used moduli 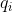 are chosen to be of size 50 to 60 bits for the best performance. This parameter has an impact on both security and performance (for a fixed 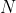, a larger 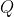 implies both lower security and lower performance). It is closely related to 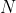 and should be chosen carefully to suit the intended use of the scheme.
34 |
35 | 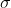: the variance used for the error polynomials. This parameter is closely tied to the security of the scheme (a larger 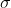 implies higher security).
36 |
37 | ## Other parameters
38 |
39 | 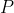: the extended ciphertext modulus. This modulus is used during the multiplication, and it has no impact on the security. It is also defined as the product of small coprime moduli 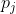 and should be chosen such that 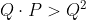 by a small margin (~20 bits). This can be done by using one more small coprime modulus than 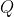.
40 |
41 | 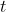: the plaintext modulus. This parameter defines the maximum value that a plaintext coefficient can take. If a computation leads to a higher value, this value will be reduced modulo the plaintext modulus. It can be initialized with any value, but in order to enable batching, it must be prime and verify 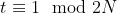. It has no impact on the security.
42 |
43 | ## Choosing security parameters
44 |
45 | The BFV scheme supports the standard recommended parameters chosen to offer a security of 128 bits for a secret key with uniform ternary distribution 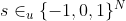, according to the Homomorphic Encryption Standards group (https://homomorphicencryption.org/standard/).
46 |
47 | Each set of parameters is defined by the tuple 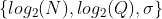:
48 |
49 | - **{12, 109, 3.2}**
50 | - **{13, 218, 3.2}**
51 | - **{14, 438, 3.2}**
52 | - **{15, 881, 3.2}**
53 |
54 | These parameter sets are hard-coded in the file [params.go](https://github.com/ldsec/lattigo/blob/master/bfv/params.go). By default the variance should always be set to 3.2 unless the user is perfectly aware of the security implications of changing this parameter.
55 |
56 | Finally, it is worth noting that these security parameters are computed for fully entropic ternary keys (with probability distribution {1/3,1/3,1/3} for values {-1,0,1}). Lattigo uses this fully-entropic key configuration by default. It is possible, though, to generate keys with lower entropy, by modifying their distribution to {(1-p)/2, p, (1-p)/2}, for any p between 0 and 1, which for p>>1/3 can result in low Hamming weight keys (*sparse* keys). *We recall that it has been shown that the security of sparse keys can be considerably lower than that of fully entropic keys, and the BFV security parameters should be re-evaluated if sparse keys are used*.
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bfv/ciphertext.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package bfv
2 |
3 | import "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
4 |
5 | // Ciphertext is a *ring.Poly array representing a polynomial of degree > 0 with coefficients in R_Q.
6 | type Ciphertext struct {
7 | *Element
8 | }
9 |
10 | // NewCiphertext creates a new ciphertext parameterized by degree, level and scale.
11 | func NewCiphertext(params *Parameters, degree int) (ciphertext *Ciphertext) {
12 | return &Ciphertext{newCiphertextElement(params, degree)}
13 | }
14 |
15 | // NewCiphertextRandom generates a new uniformly distributed ciphertext of degree, level and scale.
16 | func NewCiphertextRandom(prng utils.PRNG, params *Parameters, degree int) (ciphertext *Ciphertext) {
17 | ciphertext = &Ciphertext{newCiphertextElement(params, degree)}
18 | populateElementRandom(prng, params, ciphertext.Element)
19 | return
20 | }
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bfv/decryptor.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package bfv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | )
6 |
7 | // Decryptor is an interface for decryptors
8 | type Decryptor interface {
9 | // DecryptNew decrypts the input ciphertext and returns the result on a new
10 | // plaintext.
11 | DecryptNew(ciphertext *Ciphertext) *Plaintext
12 |
13 | // Decrypt decrypts the input ciphertext and returns the result on the
14 | // provided receiver plaintext.
15 | Decrypt(ciphertext *Ciphertext, plaintext *Plaintext)
16 | }
17 |
18 | // decryptor is a structure used to decrypt ciphertexts. It stores the secret-key.
19 | type decryptor struct {
20 | params *Parameters
21 | ringQ *ring.Ring
22 | sk *SecretKey
23 | polypool *ring.Poly
24 | }
25 |
26 | // NewDecryptor creates a new Decryptor from the parameters with the secret-key
27 | // given as input.
28 | func NewDecryptor(params *Parameters, sk *SecretKey) Decryptor {
29 |
30 | var ringQ *ring.Ring
31 | var err error
32 | if ringQ, err = ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.qi); err != nil {
33 | panic(err)
34 | }
35 |
36 | return &decryptor{
37 | params: params.Copy(),
38 | ringQ: ringQ,
39 | sk: sk,
40 | polypool: ringQ.NewPoly(),
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | func (decryptor *decryptor) DecryptNew(ciphertext *Ciphertext) *Plaintext {
45 | p := NewPlaintext(decryptor.params)
46 | decryptor.Decrypt(ciphertext, p)
47 | return p
48 | }
49 |
50 | func (decryptor *decryptor) Decrypt(ciphertext *Ciphertext, p *Plaintext) {
51 |
52 | ringQ := decryptor.ringQ
53 | tmp := decryptor.polypool
54 |
55 | ringQ.NTTLazy(ciphertext.value[ciphertext.Degree()], p.value)
56 |
57 | for i := ciphertext.Degree(); i > 0; i-- {
58 | ringQ.MulCoeffsMontgomery(p.value, decryptor.sk.Value, p.value)
59 | ringQ.NTTLazy(ciphertext.value[i-1], tmp)
60 | ringQ.Add(p.value, tmp, p.value)
61 |
62 | if i&3 == 3 {
63 | ringQ.Reduce(p.value, p.value)
64 | }
65 | }
66 |
67 | if (ciphertext.Degree())&3 != 3 {
68 | ringQ.Reduce(p.value, p.value)
69 | }
70 |
71 | ringQ.InvNTT(p.value, p.value)
72 | }
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bfv/keys.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package bfv
2 |
3 | import "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/rlwe"
4 |
5 | // SecretKey is a type for BFV secret keys.
6 | type SecretKey struct{ rlwe.SecretKey }
7 |
8 | // PublicKey is a type for BFV public keys.
9 | type PublicKey struct{ rlwe.PublicKey }
10 |
11 | // SwitchingKey is a type for BFV public switching keys.
12 | type SwitchingKey struct{ rlwe.SwitchingKey }
13 |
14 | // RelinearizationKey is a type for BFV public relinearization keys.
15 | type RelinearizationKey struct{ rlwe.RelinearizationKey }
16 |
17 | // RotationKeySet is a type for storing BFV public rotation keys.
18 | type RotationKeySet struct{ rlwe.RotationKeySet }
19 |
20 | // EvaluationKey is a type composing the relinearization and rotation keys into an evaluation
21 | // key that can be used to initialize bfv.Evaluator types.
22 | type EvaluationKey struct {
23 | Rlk *RelinearizationKey
24 | Rtks *RotationKeySet
25 | }
26 |
27 | // NewSecretKey returns an allocated BFV secret key with zero values.
28 | func NewSecretKey(params *Parameters) (sk *SecretKey) {
29 | return &SecretKey{*rlwe.NewSecretKey(params.N(), params.QPiCount())}
30 | }
31 |
32 | // NewPublicKey returns an allocated BFV public with zero values.
33 | func NewPublicKey(params *Parameters) (pk *PublicKey) {
34 | return &PublicKey{*rlwe.NewPublicKey(params.N(), params.QPiCount())}
35 | }
36 |
37 | // NewSwitchingKey returns an allocated BFV public switching key with zero values.
38 | func NewSwitchingKey(params *Parameters) *SwitchingKey {
39 | return &SwitchingKey{*rlwe.NewSwitchingKey(params.N(), params.QPiCount(), params.Beta())}
40 | }
41 |
42 | // NewRelinearizationKey returns an allocated BFV public relinearization key with zero value for each degree in [2 < maxRelinDegree].
43 | func NewRelinearizationKey(params *Parameters, maxRelinDegree int) *RelinearizationKey {
44 | return &RelinearizationKey{*rlwe.NewRelinKey(maxRelinDegree, params.N(), params.QPiCount(), params.Beta())}
45 | }
46 |
47 | // NewRotationKeySet return an allocated set of BFV public relineariation keys with zero values for each galois element
48 | // (i.e., for each supported rotation).
49 | func NewRotationKeySet(params *Parameters, galoisElements []uint64) *RotationKeySet {
50 | return &RotationKeySet{*rlwe.NewRotationKeySet(galoisElements, params.N(), params.QPiCount(), params.Beta())}
51 | }
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bfv/marshaler.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package bfv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | )
6 |
7 | // MarshalBinary encodes a Ciphertext in a byte slice.
8 | func (ciphertext *Ciphertext) MarshalBinary() (data []byte, err error) {
9 |
10 | data = make([]byte, ciphertext.GetDataLen(true))
11 |
12 | data[0] = uint8(len(ciphertext.value))
13 |
14 | var pointer, inc int
15 |
16 | pointer = 1
17 |
18 | for _, el := range ciphertext.value {
19 |
20 | if inc, err = el.WriteTo(data[pointer:]); err != nil {
21 | return nil, err
22 | }
23 |
24 | pointer += inc
25 | }
26 |
27 | return data, nil
28 | }
29 |
30 | // UnmarshalBinary decodes a previously marshaled Ciphertext in the target Ciphertext.
31 | func (ciphertext *Ciphertext) UnmarshalBinary(data []byte) (err error) {
32 |
33 | ciphertext.Element = new(Element)
34 |
35 | ciphertext.value = make([]*ring.Poly, uint8(data[0]))
36 |
37 | var pointer, inc int
38 | pointer = 1
39 |
40 | for i := range ciphertext.value {
41 |
42 | ciphertext.value[i] = new(ring.Poly)
43 |
44 | if inc, err = ciphertext.value[i].DecodePolyNew(data[pointer:]); err != nil {
45 | return err
46 | }
47 |
48 | pointer += inc
49 | }
50 |
51 | return nil
52 | }
53 |
54 | // GetDataLen returns the length in bytes of the target Ciphertext.
55 | func (ciphertext *Ciphertext) GetDataLen(WithMetaData bool) (dataLen int) {
56 | if WithMetaData {
57 | dataLen++
58 | }
59 |
60 | for _, el := range ciphertext.value {
61 | dataLen += el.GetDataLen(WithMetaData)
62 | }
63 |
64 | return dataLen
65 | }
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bfv/operand.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package bfv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
6 | )
7 |
8 | // Operand is a common interface for Ciphertext and Plaintext.
9 | type Operand interface {
10 | El() *Element
11 | Degree() int
12 | }
13 |
14 | // Element is a common struct for Plaintexts and Ciphertexts. It stores a value
15 | // as a slice of polynomials, and an isNTT flag that indicates if the element is in the NTT domain.
16 | type Element struct {
17 | value []*ring.Poly
18 | }
19 |
20 | func getSmallestLargest(el0, el1 *Element) (smallest, largest *Element, sameDegree bool) {
21 | switch {
22 | case el0.Degree() > el1.Degree():
23 | return el1, el0, false
24 | case el0.Degree() < el1.Degree():
25 | return el0, el1, false
26 | }
27 | return el0, el1, true
28 | }
29 |
30 | func newCiphertextElement(params *Parameters, degree int) *Element {
31 | el := new(Element)
32 | el.value = make([]*ring.Poly, degree+1)
33 | for i := 0; i < degree+1; i++ {
34 | el.value[i] = ring.NewPoly(params.N(), params.QiCount())
35 | }
36 | return el
37 | }
38 |
39 | func newPlaintextElement(params *Parameters) *Element {
40 | el := new(Element)
41 | el.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), params.QiCount())}
42 | return el
43 | }
44 |
45 | func newPlaintextRingTElement(params *Parameters) *Element {
46 | el := new(Element)
47 | el.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), 1)}
48 | return el
49 | }
50 |
51 | func newPlaintextMulElement(params *Parameters) *Element {
52 | el := new(Element)
53 | el.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), params.QiCount())}
54 | return el
55 | }
56 |
57 | // NewElementRandom creates a new Element with random coefficients
58 | func populateElementRandom(prng utils.PRNG, params *Parameters, el *Element) {
59 |
60 | ringQ, err := ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.qi)
61 | if err != nil {
62 | panic(err)
63 | }
64 | sampler := ring.NewUniformSampler(prng, ringQ)
65 | for i := range el.value {
66 | sampler.Read(el.value[i])
67 | }
68 | }
69 |
70 | // Value returns the value of the target Element (as a slice of polynomials in CRT form).
71 | func (el *Element) Value() []*ring.Poly {
72 | return el.value
73 | }
74 |
75 | // SetValue assigns the input slice of polynomials to the target Element value.
76 | func (el *Element) SetValue(value []*ring.Poly) {
77 | el.value = value
78 | }
79 |
80 | // Degree returns the degree of the target Element.
81 | func (el *Element) Degree() int {
82 | return len(el.value) - 1
83 | }
84 |
85 | // Level returns the level of the target element.
86 | func (el *Element) Level() int {
87 | return len(el.value[0].Coeffs) - 1
88 | }
89 |
90 | // Resize resizes the degree of the target element.
91 | func (el *Element) Resize(params *Parameters, degree int) {
92 | if el.Degree() > degree {
93 | el.value = el.value[:degree+1]
94 | } else if el.Degree() < degree {
95 | for el.Degree() < degree {
96 | el.value = append(el.value, []*ring.Poly{new(ring.Poly)}...)
97 | el.value[el.Degree()].Coeffs = make([][]uint64, el.Level()+1)
98 | for i := 0; i < el.Level()+1; i++ {
99 | el.value[el.Degree()].Coeffs[i] = make([]uint64, params.N())
100 | }
101 | }
102 | }
103 | }
104 |
105 | // CopyNew creates a new Element which is a copy of the target Element, and returns the value as
106 | // a Element.
107 | func (el *Element) CopyNew() *Element {
108 |
109 | ctxCopy := new(Element)
110 |
111 | ctxCopy.value = make([]*ring.Poly, el.Degree()+1)
112 | for i := range el.value {
113 | ctxCopy.value[i] = el.value[i].CopyNew()
114 | }
115 |
116 | return ctxCopy
117 | }
118 |
119 | // Copy copies the value and parameters of the input on the target Element.
120 | func (el *Element) Copy(ctxCopy *Element) {
121 | if el != ctxCopy {
122 | for i := range ctxCopy.Value() {
123 | el.Value()[i].Copy(ctxCopy.Value()[i])
124 | }
125 | }
126 | }
127 |
128 | // El sets the target Element type to Element.
129 | func (el *Element) El() *Element {
130 | return el
131 | }
132 |
133 | // Ciphertext sets the target Element type to Ciphertext.
134 | func (el *Element) Ciphertext() *Ciphertext {
135 | return &Ciphertext{el}
136 | }
137 |
138 | // Plaintext sets the target Element type to Plaintext.
139 | func (el *Element) Plaintext() *Plaintext {
140 | return &Plaintext{el, el.value[0]}
141 | }
142 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/bfv/plaintext.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package bfv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | )
6 |
7 | // Plaintext is a Element with only one Poly. It represents a Plaintext element in R_q that is the
8 | // result of scaling the corresponding element of R_t up by Q/t. This is a generic all-purpose type
9 | // of plaintext: it will work with for all operations. It is however less compact than PlaintextRingT
10 | // and will result in less efficient Ciphert-Plaintext multiplication than PlaintextMul. See bfv/encoder.go
11 | // for more information on plaintext types.
12 | type Plaintext struct {
13 | *Element
14 | value *ring.Poly
15 | }
16 |
17 | // PlaintextRingT represents a plaintext element in R_t.
18 | // This is the most compact representation of a plaintext, but performing operations have the extra-cost of performing
19 | // the scaling up by Q/t. See bfv/encoder.go for more information on plaintext types.
20 | type PlaintextRingT Plaintext
21 |
22 | // PlaintextMul represents a plaintext element in R_q, in NTT and Montgomery form, but without scale up by Q/t.
23 | // A PlaintextMul is a special-purpose plaintext for efficient Ciphertext-Plaintext multiplication. However,
24 | // other operations on plaintexts are not supported. See bfv/encoder.go for more information on plaintext types.
25 | type PlaintextMul Plaintext
26 |
27 | // NewPlaintext creates and allocates a new plaintext in RingQ (multiple moduli of Q).
28 | // The plaintext will be in RingQ and scaled by Q/t.
29 | // Slower encoding and larger plaintext size
30 | func NewPlaintext(params *Parameters) *Plaintext {
31 | plaintext := &Plaintext{newPlaintextElement(params), nil}
32 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
33 | return plaintext
34 | }
35 |
36 | // NewPlaintextRingT creates and allocates a new plaintext in RingT (single modulus T).
37 | // The plaintext will be in RingT.
38 | func NewPlaintextRingT(params *Parameters) *PlaintextRingT {
39 |
40 | plaintext := &PlaintextRingT{newPlaintextRingTElement(params), nil}
41 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
42 | return plaintext
43 | }
44 |
45 | // NewPlaintextMul creates and allocates a new plaintext optimized for ciphertext x plaintext multiplication.
46 | // The plaintext will be in the NTT and Montgomery domain of RingQ and not scaled by Q/t.
47 | func NewPlaintextMul(params *Parameters) *PlaintextMul {
48 | plaintext := &PlaintextMul{newPlaintextMulElement(params), nil}
49 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
50 | return plaintext
51 | }
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/algorithms.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "math/bits"
5 | )
6 |
7 | // PowerOf2 computes op^(2^logPow2), consuming logPow2 levels, and returns the result on opOut. Providing an evaluation
8 | // key is necessary when logPow2 > 1.
9 | func (eval *evaluator) PowerOf2(op *Ciphertext, logPow2 int, opOut *Ciphertext) {
10 |
11 | if logPow2 == 0 {
12 |
13 | if op != opOut {
14 | opOut.Copy(op.El())
15 | }
16 |
17 | } else {
18 |
19 | eval.MulRelin(op.El(), op.El(), opOut)
20 |
21 | if err := eval.Rescale(opOut, eval.scale, opOut); err != nil {
22 | panic(err)
23 | }
24 |
25 | for i := 1; i < logPow2; i++ {
26 |
27 | eval.MulRelin(opOut.El(), opOut.El(), opOut)
28 |
29 | if err := eval.Rescale(opOut, eval.scale, opOut); err != nil {
30 | panic(err)
31 | }
32 | }
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
36 | // PowerNew computes op^degree, consuming log(degree) levels, and returns the result on a new element. Providing an evaluation
37 | // key is necessary when degree > 2.
38 | func (eval *evaluator) PowerNew(op *Ciphertext, degree int) (opOut *Ciphertext) {
39 | opOut = NewCiphertext(eval.params, 1, op.Level(), op.Scale())
40 | eval.Power(op, degree, opOut)
41 | return
42 | }
43 |
44 | // Power computes op^degree, consuming log(degree) levels, and returns the result on opOut. Providing an evaluation
45 | // key is necessary when degree > 2.
46 | func (eval *evaluator) Power(op *Ciphertext, degree int, opOut *Ciphertext) {
47 |
48 | if degree < 1 {
49 | panic("eval.Power -> degree cannot be smaller than 1")
50 | }
51 |
52 | tmpct0 := op.CopyNew()
53 |
54 | var logDegree, po2Degree int
55 |
56 | logDegree = bits.Len64(uint64(degree)) - 1
57 | po2Degree = 1 << logDegree
58 |
59 | eval.PowerOf2(tmpct0.Ciphertext(), logDegree, opOut)
60 |
61 | degree -= po2Degree
62 |
63 | for degree > 0 {
64 |
65 | logDegree = bits.Len64(uint64(degree)) - 1
66 | po2Degree = 1 << logDegree
67 |
68 | tmp := NewCiphertext(eval.params, 1, tmpct0.Level(), tmpct0.Scale())
69 |
70 | eval.PowerOf2(tmpct0.Ciphertext(), logDegree, tmp)
71 |
72 | eval.MulRelin(opOut.El(), tmp.El(), opOut)
73 |
74 | if err := eval.Rescale(opOut, eval.scale, opOut); err != nil {
75 | panic(err)
76 | }
77 |
78 | degree -= po2Degree
79 | }
80 | }
81 |
82 | // InverseNew computes 1/op and returns the result on a new element, iterating for n steps and consuming n levels. The algorithm requires the encrypted values to be in the range
83 | // [-1.5 - 1.5i, 1.5 + 1.5i] or the result will be wrong. Each iteration increases the precision.
84 | func (eval *evaluator) InverseNew(op *Ciphertext, steps int) (opOut *Ciphertext) {
85 |
86 | cbar := eval.NegNew(op)
87 |
88 | eval.AddConst(cbar, 1, cbar)
89 |
90 | tmp := eval.AddConstNew(cbar, 1)
91 | opOut = tmp.CopyNew().Ciphertext()
92 |
93 | for i := 1; i < steps; i++ {
94 |
95 | eval.MulRelin(cbar.El(), cbar.El(), cbar.Ciphertext())
96 |
97 | if err := eval.Rescale(cbar, eval.scale, cbar); err != nil {
98 | panic(err)
99 | }
100 |
101 | tmp = eval.AddConstNew(cbar, 1)
102 |
103 | eval.MulRelin(tmp.El(), opOut.El(), tmp.Ciphertext())
104 |
105 | if err := eval.Rescale(tmp, eval.scale, tmp); err != nil {
106 | panic(err)
107 | }
108 |
109 | opOut = tmp.CopyNew().Ciphertext()
110 | }
111 |
112 | return opOut
113 | }
114 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/bettersine/arithmetic.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package bettersine
2 |
3 | import (
4 | //"fmt"
5 | "math"
6 | "math/big"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // NewFloat creates a new big.Float element with 1000 bits of precision
10 | func NewFloat(x float64) (y *big.Float) {
11 | y = new(big.Float)
12 | y.SetPrec(1000) // log2 precision
13 | y.SetFloat64(x)
14 | return
15 | }
16 |
17 | // Cos is an iterative arbitrary precision computation of Cos(x)
18 | // Iterative process with an error of ~10^{−0.60206*k} after k iterations.
19 | // ref : Johansson, B. Tomas, An elementary algorithm to evaluate trigonometric functions to high precision, 2018
20 | func Cos(x *big.Float) (cosx *big.Float) {
21 | tmp := new(big.Float)
22 |
23 | k := 1000 // number of iterations
24 | t := NewFloat(0.5)
25 | half := new(big.Float).Copy(t)
26 |
27 | for i := 1; i < k-1; i++ {
28 | t.Mul(t, half)
29 | }
30 |
31 | s := new(big.Float).Mul(x, t)
32 | s.Mul(s, x)
33 | s.Mul(s, t)
34 |
35 | four := NewFloat(4.0)
36 |
37 | for i := 1; i < k; i++ {
38 | tmp.Sub(four, s)
39 | s.Mul(s, tmp)
40 | }
41 |
42 | cosx = new(big.Float).Quo(s, NewFloat(2.0))
43 | cosx.Sub(NewFloat(1.0), cosx)
44 | return
45 |
46 | }
47 |
48 | // Sin is an iterative arbitrary precision computation of Sin(x)
49 | func Sin(x *big.Float) (sinx *big.Float) {
50 |
51 | sinx = NewFloat(1)
52 | tmp := Cos(x)
53 | tmp.Mul(tmp, tmp)
54 | sinx.Sub(sinx, tmp)
55 | sinx.Sqrt(sinx)
56 | return
57 | }
58 |
59 | func log2(x float64) float64 {
60 | return math.Log2(x)
61 | }
62 |
63 | func abs(x float64) float64 {
64 | return math.Abs(x)
65 | }
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/bootstrap_bench_test.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "math"
5 | "testing"
6 | "time"
7 | )
8 |
9 | func BenchmarkBootstrapp(b *testing.B) {
10 |
11 | if !*testBootstrapping {
12 | b.Skip("skipping bootstrapping test")
13 | }
14 |
15 | var err error
16 | var testContext = new(testParams)
17 | var btp *Bootstrapper
18 |
19 | paramSet := 2
20 |
21 | btpParams := DefaultBootstrapParams[paramSet]
22 |
23 | params, err := btpParams.Params()
24 | if err != nil {
25 | panic(err)
26 | }
27 | if testContext, err = genTestParams(params, btpParams.H); err != nil {
28 | panic(err)
29 | }
30 |
31 | rotations := testContext.kgen.GenRotationIndexesForBootstrapping(testContext.params.logSlots, btpParams)
32 |
33 | rotkeys := testContext.kgen.GenRotationKeysForRotations(rotations, true, testContext.sk)
34 |
35 | btpKey := BootstrappingKey{testContext.rlk, rotkeys}
36 |
37 | if btp, err = NewBootstrapper(testContext.params, btpParams, btpKey); err != nil {
38 | panic(err)
39 | }
40 |
41 | b.Run(testString(testContext, "Bootstrapp/"), func(b *testing.B) {
42 | for i := 0; i < b.N; i++ {
43 |
44 | b.StopTimer()
45 | ct := NewCiphertextRandom(testContext.prng, testContext.params, 1, 0, testContext.params.scale)
46 | b.StartTimer()
47 |
48 | var t time.Time
49 | var ct0, ct1 *Ciphertext
50 |
51 | // Brings the ciphertext scale to Q0/2^{10}
52 | btp.evaluator.ScaleUp(ct, math.Round(btp.prescale/ct.Scale()), ct)
53 |
54 | // ModUp ct_{Q_0} -> ct_{Q_L}
55 | t = time.Now()
56 | ct = btp.modUp(ct)
57 | b.Log("After ModUp :", time.Since(t), ct.Level(), ct.Scale())
58 |
59 | // Brings the ciphertext scale to sineQi/(Q0/scale) if its under
60 | btp.evaluator.ScaleUp(ct, math.Round(btp.postscale/ct.Scale()), ct)
61 |
62 | //SubSum X -> (N/dslots) * Y^dslots
63 | t = time.Now()
64 | ct = btp.subSum(ct)
65 | b.Log("After SubSum :", time.Since(t), ct.Level(), ct.Scale())
66 |
67 | // Part 1 : Coeffs to slots
68 | t = time.Now()
69 | ct0, ct1 = CoeffsToSlots(ct, btp.pDFTInv, btp.evaluator)
70 | b.Log("After CtS :", time.Since(t), ct0.Level(), ct0.Scale())
71 |
72 | // Part 2 : SineEval
73 | t = time.Now()
74 | ct0, ct1 = btp.evaluateSine(ct0, ct1)
75 | b.Log("After Sine :", time.Since(t), ct0.Level(), ct0.Scale())
76 |
77 | // Part 3 : Slots to coeffs
78 | t = time.Now()
79 | ct0 = SlotsToCoeffs(ct0, ct1, btp.pDFT, btp.evaluator)
80 | ct0.SetScale(math.Exp2(math.Round(math.Log2(ct0.Scale()))))
81 | b.Log("After StC :", time.Since(t), ct0.Level(), ct0.Scale())
82 | }
83 | })
84 | }
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/chebyshev_interpolation.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "math"
5 | )
6 |
7 | // ChebyshevInterpolation is a struct storing the coefficients, degree and range of a Chebyshev interpolation polynomial.
8 | type ChebyshevInterpolation struct {
9 | Poly
10 | a complex128
11 | b complex128
12 | }
13 |
14 | // A returns the start of the approximation interval.
15 | func (c *ChebyshevInterpolation) A() complex128 {
16 | return c.a
17 | }
18 |
19 | // B returns the end of the approximation interval.
20 | func (c *ChebyshevInterpolation) B() complex128 {
21 | return c.b
22 | }
23 |
24 | // Approximate computes a Chebyshev approximation of the input function, for the range [-a, b] of degree degree.
25 | // To be used in conjunction with the function EvaluateCheby.
26 | func Approximate(function func(complex128) complex128, a, b complex128, degree int) (cheby *ChebyshevInterpolation) {
27 |
28 | cheby = new(ChebyshevInterpolation)
29 | cheby.a = a
30 | cheby.b = b
31 | cheby.maxDeg = degree
32 | cheby.lead = true
33 |
34 | nodes := chebyshevNodes(degree+1, a, b)
35 |
36 | fi := make([]complex128, len(nodes))
37 | for i := range nodes {
38 | fi[i] = function(nodes[i])
39 | }
40 |
41 | cheby.coeffs = chebyCoeffs(nodes, fi, a, b)
42 |
43 | return
44 | }
45 |
46 | func chebyshevNodes(n int, a, b complex128) (u []complex128) {
47 | u = make([]complex128, n)
48 | var x, y complex128
49 | for k := 1; k < n+1; k++ {
50 | x = 0.5 * (a + b)
51 | y = 0.5 * (b - a)
52 | u[k-1] = x + y*complex(math.Cos((float64(k)-0.5)*(3.141592653589793/float64(n))), 0)
53 | }
54 | return
55 | }
56 |
57 | func chebyCoeffs(nodes, fi []complex128, a, b complex128) (coeffs []complex128) {
58 |
59 | var u, Tprev, T, Tnext complex128
60 |
61 | n := len(nodes)
62 |
63 | coeffs = make([]complex128, n)
64 |
65 | for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
66 |
67 | u = (2*nodes[i] - a - b) / (b - a)
68 | Tprev = 1
69 | T = u
70 |
71 | for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
72 | coeffs[j] += fi[i] * Tprev
73 | Tnext = 2*u*T - Tprev
74 | Tprev = T
75 | T = Tnext
76 | }
77 | }
78 |
79 | coeffs[0] /= complex(float64(n), 0)
80 | for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
81 | coeffs[i] *= (2.0 / complex(float64(n), 0))
82 | }
83 |
84 | return
85 | }
86 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/ciphertext.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
6 | )
7 |
8 | // Ciphertext is *ring.Poly array representing a polynomial of degree > 0 with coefficients in R_Q.
9 | type Ciphertext struct {
10 | *Element
11 | }
12 |
13 | // NewCiphertext creates a new Ciphertext parameterized by degree, level and scale.
14 | func NewCiphertext(params *Parameters, degree, level int, scale float64) (ciphertext *Ciphertext) {
15 |
16 | ciphertext = &Ciphertext{&Element{}}
17 |
18 | ciphertext.value = make([]*ring.Poly, degree+1)
19 | for i := 0; i < degree+1; i++ {
20 | ciphertext.value[i] = ring.NewPoly(params.N(), level+1)
21 | }
22 |
23 | ciphertext.scale = scale
24 | ciphertext.isNTT = true
25 |
26 | return ciphertext
27 | }
28 |
29 | // NewCiphertextRandom generates a new uniformly distributed Ciphertext of degree, level and scale.
30 | func NewCiphertextRandom(prng utils.PRNG, params *Parameters, degree, level int, scale float64) (ciphertext *Ciphertext) {
31 |
32 | ringQ, err := ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.qi[:level+1])
33 | if err != nil {
34 | panic(err)
35 | }
36 |
37 | sampler := ring.NewUniformSampler(prng, ringQ)
38 | ciphertext = NewCiphertext(params, degree, level, scale)
39 | for i := 0; i < degree+1; i++ {
40 | sampler.Read(ciphertext.value[i])
41 | }
42 |
43 | return ciphertext
44 | }
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/decryptor.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
6 | )
7 |
8 | // Decryptor is an interface for decrypting Ciphertexts. A Decryptor stores the secret-key.
9 | type Decryptor interface {
10 | // DecryptNew decrypts the ciphertext and returns a newly created
11 | // plaintext. A Horner method is used for evaluating the decryption.
12 | // The level of the output plaintext is ciphertext.Level().
13 | DecryptNew(ciphertext *Ciphertext) (plaintext *Plaintext)
14 |
15 | // Decrypt decrypts the ciphertext and returns the result on the provided
16 | // receiver plaintext. A Horner method is used for evaluating the
17 | // decryption.
18 | // The level of the output plaintext is min(ciphertext.Level(), plaintext.Level())
19 | Decrypt(ciphertext *Ciphertext, plaintext *Plaintext)
20 | }
21 |
22 | // decryptor is a structure used to decrypt ciphertext. It stores the secret-key.
23 | type decryptor struct {
24 | params *Parameters
25 | ringQ *ring.Ring
26 | sk *SecretKey
27 | }
28 |
29 | // NewDecryptor instantiates a new Decryptor that will be able to decrypt ciphertexts
30 | // encrypted under the provided secret-key.
31 | func NewDecryptor(params *Parameters, sk *SecretKey) Decryptor {
32 |
33 | if sk.Value.Degree() != params.N() {
34 | panic("secret_key is invalid for the provided parameters")
35 | }
36 |
37 | var q *ring.Ring
38 | var err error
39 | if q, err = ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.qi); err != nil {
40 | panic(err)
41 | }
42 |
43 | return &decryptor{
44 | params: params.Copy(),
45 | ringQ: q,
46 | sk: sk,
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
50 | func (decryptor *decryptor) DecryptNew(ciphertext *Ciphertext) (plaintext *Plaintext) {
51 |
52 | plaintext = NewPlaintext(decryptor.params, ciphertext.Level(), ciphertext.Scale())
53 |
54 | decryptor.Decrypt(ciphertext, plaintext)
55 |
56 | return plaintext
57 | }
58 |
59 | func (decryptor *decryptor) Decrypt(ciphertext *Ciphertext, plaintext *Plaintext) {
60 |
61 | level := utils.MinInt(ciphertext.Level(), plaintext.Level())
62 |
63 | plaintext.SetScale(ciphertext.Scale())
64 |
65 | decryptor.ringQ.CopyLvl(level, ciphertext.value[ciphertext.Degree()], plaintext.value)
66 |
67 | plaintext.value.Coeffs = plaintext.value.Coeffs[:ciphertext.Level()+1]
68 |
69 | for i := ciphertext.Degree(); i > 0; i-- {
70 |
71 | decryptor.ringQ.MulCoeffsMontgomeryLvl(level, plaintext.value, decryptor.sk.Value, plaintext.value)
72 | decryptor.ringQ.AddLvl(level, plaintext.value, ciphertext.value[i-1], plaintext.value)
73 |
74 | if i&7 == 7 {
75 | decryptor.ringQ.ReduceLvl(level, plaintext.value, plaintext.value)
76 | }
77 | }
78 |
79 | if (ciphertext.Degree())&7 != 7 {
80 | decryptor.ringQ.ReduceLvl(level, plaintext.value, plaintext.value)
81 | }
82 |
83 | plaintext.value.Coeffs = plaintext.value.Coeffs[:level+1]
84 | }
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/keys.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/rlwe"
4 |
5 | // SecretKey is a type for CKKS secret keys.
6 | type SecretKey struct{ rlwe.SecretKey }
7 |
8 | // PublicKey is a type for CKKS public keys.
9 | type PublicKey struct{ rlwe.PublicKey }
10 |
11 | // SwitchingKey is a type for CKKS public switching keys.
12 | type SwitchingKey struct{ rlwe.SwitchingKey }
13 |
14 | // RelinearizationKey is a type for CKKS public relinearization keys.
15 | type RelinearizationKey struct{ rlwe.RelinearizationKey }
16 |
17 | // RotationKeySet is a type for storing CKKS public rotation keys.
18 | type RotationKeySet struct{ rlwe.RotationKeySet }
19 |
20 | // EvaluationKey is a type composing the relinearization and rotation keys into an evaluation
21 | // key that can be used to initialize bfv.Evaluator types.
22 | type EvaluationKey struct {
23 | Rlk *RelinearizationKey
24 | Rtks *RotationKeySet
25 | }
26 |
27 | // BootstrappingKey is a type for a CKKS bootstrapping key, wich regroups the necessary public relinearization
28 | // and rotation keys (i.e., an EvaluationKey).
29 | type BootstrappingKey EvaluationKey
30 |
31 | // NewSecretKey returns an allocated CKKS secret key with zero values.
32 | func NewSecretKey(params *Parameters) (sk *SecretKey) {
33 | return &SecretKey{*rlwe.NewSecretKey(params.N(), params.QPiCount())}
34 | }
35 |
36 | // NewPublicKey returns an allocated CKKS public with zero values.
37 | func NewPublicKey(params *Parameters) (pk *PublicKey) {
38 | return &PublicKey{*rlwe.NewPublicKey(params.N(), params.QPiCount())}
39 | }
40 |
41 | // NewSwitchingKey returns an allocated CKKS public switching key with zero values.
42 | func NewSwitchingKey(params *Parameters) *SwitchingKey {
43 | return &SwitchingKey{*rlwe.NewSwitchingKey(params.N(), params.QPiCount(), params.Beta())}
44 | }
45 |
46 | // NewRelinearizationKey returns an allocated CKKS public relinearization key with zero value.
47 | func NewRelinearizationKey(params *Parameters) *RelinearizationKey {
48 | return &RelinearizationKey{*rlwe.NewRelinKey(2, params.N(), params.QPiCount(), params.Beta())}
49 | }
50 |
51 | // NewRotationKeySet return an allocated set of CKKS public relineariation keys with zero values for each galois element
52 | // (i.e., for each supported rotation).
53 | func NewRotationKeySet(params *Parameters, galoisElements []uint64) *RotationKeySet {
54 | return &RotationKeySet{*rlwe.NewRotationKeySet(galoisElements, params.N(), params.QPiCount(), params.Beta())}
55 | }
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/marshaler.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "encoding/binary"
5 | "errors"
6 | "math"
7 |
8 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
9 | )
10 |
11 | // GetDataLen returns the length in bytes of the target Ciphertext.
12 | func (ciphertext *Ciphertext) GetDataLen(WithMetaData bool) (dataLen int) {
13 | // MetaData is :
14 | // 1 byte : Degree
15 | // 9 byte : Scale
16 | // 1 byte : isNTT
17 | if WithMetaData {
18 | dataLen += 11
19 | }
20 |
21 | for _, el := range ciphertext.value {
22 | dataLen += el.GetDataLen(WithMetaData)
23 | }
24 |
25 | return dataLen
26 | }
27 |
28 | // MarshalBinary encodes a Ciphertext on a byte slice. The total size
29 | // in byte is 4 + 8* N * numberModuliQ * (degree + 1).
30 | func (ciphertext *Ciphertext) MarshalBinary() (data []byte, err error) {
31 |
32 | data = make([]byte, ciphertext.GetDataLen(true))
33 |
34 | data[0] = uint8(ciphertext.Degree() + 1)
35 |
36 | binary.LittleEndian.PutUint64(data[1:9], math.Float64bits(ciphertext.Scale()))
37 |
38 | if ciphertext.isNTT {
39 | data[10] = 1
40 | }
41 |
42 | var pointer, inc int
43 |
44 | pointer = 11
45 |
46 | for _, el := range ciphertext.value {
47 |
48 | if inc, err = el.WriteTo(data[pointer:]); err != nil {
49 | return nil, err
50 | }
51 |
52 | pointer += inc
53 | }
54 |
55 | return data, nil
56 | }
57 |
58 | // UnmarshalBinary decodes a previously marshaled Ciphertext on the target Ciphertext.
59 | func (ciphertext *Ciphertext) UnmarshalBinary(data []byte) (err error) {
60 | if len(data) < 11 { // cf. ciphertext.GetDataLen()
61 | return errors.New("too small bytearray")
62 | }
63 |
64 | ciphertext.Element = new(Element)
65 |
66 | ciphertext.value = make([]*ring.Poly, uint8(data[0]))
67 |
68 | ciphertext.scale = math.Float64frombits(binary.LittleEndian.Uint64(data[1:9]))
69 |
70 | if uint8(data[10]) == 1 {
71 | ciphertext.isNTT = true
72 | }
73 |
74 | var pointer, inc int
75 | pointer = 11
76 |
77 | for i := range ciphertext.value {
78 |
79 | ciphertext.value[i] = new(ring.Poly)
80 |
81 | if inc, err = ciphertext.value[i].DecodePolyNew(data[pointer:]); err != nil {
82 | return err
83 | }
84 |
85 | pointer += inc
86 | }
87 |
88 | if pointer != len(data) {
89 | return errors.New("remaining unparsed data")
90 | }
91 |
92 | return nil
93 | }
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/operand.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "fmt"
5 |
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // Operand is a common interface for Ciphertext and Plaintext types.
10 | type Operand interface {
11 | El() *Element
12 | Degree() int
13 | Level() int
14 | Scale() float64
15 | }
16 |
17 | // Element is a generic type for ciphertext and plaintexts
18 | type Element struct {
19 | value []*ring.Poly
20 | scale float64
21 | isNTT bool
22 | }
23 |
24 | // NewElement returns a new Element with zero values.
25 | func NewElement() *Element {
26 | return &Element{}
27 | }
28 |
29 | // Value returns the slice of polynomials of the target element.
30 | func (el *Element) Value() []*ring.Poly {
31 | return el.value
32 | }
33 |
34 | // SetValue sets the input slice of polynomials as the value of the target element.
35 | func (el *Element) SetValue(value []*ring.Poly) {
36 | el.value = value
37 | }
38 |
39 | // Degree returns the degree of the target element.
40 | func (el *Element) Degree() int {
41 | return len(el.value) - 1
42 | }
43 |
44 | // Level returns the level of the target element.
45 | func (el *Element) Level() int {
46 | return len(el.value[0].Coeffs) - 1
47 | }
48 |
49 | // Scale returns the scale of the target element.
50 | func (el *Element) Scale() float64 {
51 | return el.scale
52 | }
53 |
54 | // SetScale sets the scale of the the target element to the input scale.
55 | func (el *Element) SetScale(scale float64) {
56 | el.scale = scale
57 | }
58 |
59 | // MulScale multiplies the scale of the target element with the input scale.
60 | func (el *Element) MulScale(scale float64) {
61 | el.scale *= scale
62 | }
63 |
64 | // DivScale divides the scale of the target element by the input scale.
65 | func (el *Element) DivScale(scale float64) {
66 | el.scale /= scale
67 | }
68 |
69 | // Resize resizes the degree of the target element.
70 | func (el *Element) Resize(params *Parameters, degree int) {
71 | if el.Degree() > degree {
72 | el.value = el.value[:degree+1]
73 | } else if el.Degree() < degree {
74 | for el.Degree() < degree {
75 | el.value = append(el.value, []*ring.Poly{new(ring.Poly)}...)
76 | el.value[el.Degree()].Coeffs = make([][]uint64, el.Level()+1)
77 | for i := 0; i < el.Level()+1; i++ {
78 | el.value[el.Degree()].Coeffs[i] = make([]uint64, params.N())
79 | }
80 | }
81 | }
82 | }
83 |
84 | // IsNTT returns the value of the NTT flag of the target element.
85 | func (el *Element) IsNTT() bool {
86 | return el.isNTT
87 | }
88 |
89 | // SetIsNTT sets the value of the NTT flag of the target element with the input value.
90 | func (el *Element) SetIsNTT(value bool) {
91 | el.isNTT = value
92 | }
93 |
94 | // NTT puts the target element in the NTT domain and sets its isNTT flag to true. If it is already in the NTT domain, it does nothing.
95 | func (el *Element) NTT(ringQ *ring.Ring, c *Element) {
96 | if el.Degree() != c.Degree() {
97 | panic(fmt.Errorf("error: receiver element has invalid degree (it does not match)"))
98 | }
99 | if !el.IsNTT() {
100 | for i := range el.value {
101 | ringQ.NTTLvl(el.Level(), el.Value()[i], c.Value()[i])
102 | }
103 | c.SetIsNTT(true)
104 | }
105 | }
106 |
107 | // InvNTT puts the target element outside of the NTT domain, and sets its isNTT flag to false. If it is not in the NTT domain, it does nothing.
108 | func (el *Element) InvNTT(ringQ *ring.Ring, c *Element) {
109 | if el.Degree() != c.Degree() {
110 | panic(fmt.Errorf("error: receiver element invalid degree (it does not match)"))
111 | }
112 | if el.IsNTT() {
113 | for i := range el.value {
114 | ringQ.InvNTTLvl(el.Level(), el.Value()[i], c.Value()[i])
115 | }
116 | c.SetIsNTT(false)
117 | }
118 | }
119 |
120 | // CopyNew creates a new element as a copy of the target element.
121 | func (el *Element) CopyNew() *Element {
122 |
123 | ctxCopy := new(Element)
124 |
125 | ctxCopy.value = make([]*ring.Poly, el.Degree()+1)
126 | for i := range el.value {
127 | ctxCopy.value[i] = el.value[i].CopyNew()
128 | }
129 |
130 | ctxCopy.CopyParams(el)
131 |
132 | return ctxCopy
133 | }
134 |
135 | // Copy copies the input element and its parameters on the target element.
136 | func (el *Element) Copy(ctxCopy *Element) {
137 |
138 | if el != ctxCopy {
139 | for i := range ctxCopy.Value() {
140 | el.value[i].Copy(ctxCopy.Value()[i])
141 | }
142 |
143 | el.CopyParams(ctxCopy)
144 | }
145 | }
146 |
147 | // CopyParams copies the input element parameters on the target element
148 | func (el *Element) CopyParams(Element *Element) {
149 | el.SetScale(Element.Scale())
150 | el.SetIsNTT(Element.IsNTT())
151 | }
152 |
153 | // El sets the target element type to Element.
154 | func (el *Element) El() *Element {
155 | return el
156 | }
157 |
158 | // Ciphertext sets the target element type to Ciphertext.
159 | func (el *Element) Ciphertext() *Ciphertext {
160 | return &Ciphertext{el}
161 | }
162 |
163 | // Plaintext sets the target element type to Plaintext.
164 | func (el *Element) Plaintext() *Plaintext {
165 | return &Plaintext{el, el.value[0]}
166 | }
167 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/plaintext.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | )
6 |
7 | // Plaintext is is a Element with only one Poly.
8 | type Plaintext struct {
9 | *Element
10 | value *ring.Poly
11 | }
12 |
13 | // NewPlaintext creates a new Plaintext of level level and scale scale.
14 | func NewPlaintext(params *Parameters, level int, scale float64) *Plaintext {
15 |
16 | plaintext := &Plaintext{&Element{}, nil}
17 |
18 | plaintext.Element.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), level+1)}
19 |
20 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
21 |
22 | plaintext.scale = scale
23 | plaintext.isNTT = true
24 |
25 | return plaintext
26 | }
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/precision.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "fmt"
5 | "math"
6 | "sort"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // PrecisionStats is a struct storing statistic about the precision of a CKKS plaintext
10 | type PrecisionStats struct {
11 | MaxDelta complex128
12 | MinDelta complex128
13 | MaxPrecision complex128
14 | MinPrecision complex128
15 | MeanDelta complex128
16 | MeanPrecision complex128
17 | MedianDelta complex128
18 | MedianPrecision complex128
19 | STDFreq float64
20 | STDTime float64
21 |
22 | RealDist, ImagDist []struct {
23 | Prec float64
24 | Count int
25 | }
26 |
27 | cdfResol int
28 | }
29 |
30 | func (prec PrecisionStats) String() string {
31 | return fmt.Sprintf("\nMIN Prec : (%.2f, %.2f) Log2 \n", real(prec.MinPrecision), imag(prec.MinPrecision)) +
32 | fmt.Sprintf("MAX Prec : (%.2f, %.2f) Log2 \n", real(prec.MaxPrecision), imag(prec.MaxPrecision)) +
33 | fmt.Sprintf("AVG Prec : (%.2f, %.2f) Log2 \n", real(prec.MeanPrecision), imag(prec.MeanPrecision)) +
34 | fmt.Sprintf("MED Prec : (%.2f, %.2f) Log2 \n", real(prec.MedianPrecision), imag(prec.MedianPrecision)) +
35 | fmt.Sprintf("Err stdF : %5.2f Log2 \n", math.Log2(prec.STDFreq)) +
36 | fmt.Sprintf("Err stdT : %5.2f Log2 \n", math.Log2(prec.STDTime))
37 |
38 | }
39 |
40 | // GetPrecisionStats generates a PrecisionStats struct from the reference values and the decrypted values
41 | func GetPrecisionStats(params *Parameters, encoder Encoder, decryptor Decryptor, valuesWant []complex128, element interface{}, logSlots int, sigma float64) (prec PrecisionStats) {
42 |
43 | var valuesTest []complex128
44 |
45 | slots := uint64(1 << logSlots)
46 |
47 | switch element := element.(type) {
48 | case *Ciphertext:
49 | valuesTest = encoder.DecodePublic(decryptor.DecryptNew(element), logSlots, sigma)
50 | case *Plaintext:
51 | valuesTest = encoder.DecodePublic(element, logSlots, sigma)
52 | case []complex128:
53 | valuesTest = element
54 | }
55 |
56 | var deltaReal, deltaImag float64
57 |
58 | var delta complex128
59 |
60 | diff := make([]complex128, slots)
61 |
62 | prec.MaxDelta = complex(0, 0)
63 | prec.MinDelta = complex(1, 1)
64 |
65 | prec.MeanDelta = complex(0, 0)
66 |
67 | prec.cdfResol = 500
68 |
69 | prec.RealDist = make([]struct {
70 | Prec float64
71 | Count int
72 | }, prec.cdfResol)
73 | prec.ImagDist = make([]struct {
74 | Prec float64
75 | Count int
76 | }, prec.cdfResol)
77 |
78 | precReal := make([]float64, len(valuesWant))
79 | precImag := make([]float64, len(valuesWant))
80 |
81 | for i := range valuesWant {
82 |
83 | delta = valuesTest[i] - valuesWant[i]
84 | deltaReal = math.Abs(real(delta))
85 | deltaImag = math.Abs(imag(delta))
86 | precReal[i] = math.Log2(1 / deltaReal)
87 | precImag[i] = math.Log2(1 / deltaImag)
88 |
89 | diff[i] += complex(deltaReal, deltaImag)
90 |
91 | prec.MeanDelta += diff[i]
92 |
93 | if deltaReal > real(prec.MaxDelta) {
94 | prec.MaxDelta = complex(deltaReal, imag(prec.MaxDelta))
95 | }
96 |
97 | if deltaImag > imag(prec.MaxDelta) {
98 | prec.MaxDelta = complex(real(prec.MaxDelta), deltaImag)
99 | }
100 |
101 | if deltaReal < real(prec.MinDelta) {
102 | prec.MinDelta = complex(deltaReal, imag(prec.MinDelta))
103 | }
104 |
105 | if deltaImag < imag(prec.MinDelta) {
106 | prec.MinDelta = complex(real(prec.MinDelta), deltaImag)
107 | }
108 | }
109 |
110 | prec.calcCDF(precReal, prec.RealDist)
111 | prec.calcCDF(precImag, prec.ImagDist)
112 |
113 | prec.MinPrecision = deltaToPrecision(prec.MaxDelta)
114 | prec.MaxPrecision = deltaToPrecision(prec.MinDelta)
115 | prec.MeanDelta /= complex(float64(slots), 0)
116 | prec.MeanPrecision = deltaToPrecision(prec.MeanDelta)
117 | prec.MedianDelta = calcmedian(diff)
118 | prec.MedianPrecision = deltaToPrecision(prec.MedianDelta)
119 | prec.STDFreq = encoder.GetErrSTDFreqDom(valuesWant[:], valuesTest[:], params.Scale())
120 | prec.STDTime = encoder.GetErrSTDTimeDom(valuesWant, valuesTest, params.Scale())
121 | return prec
122 | }
123 |
124 | func deltaToPrecision(c complex128) complex128 {
125 | return complex(math.Log2(1/real(c)), math.Log2(1/imag(c)))
126 | }
127 |
128 | func (prec *PrecisionStats) calcCDF(precs []float64, res []struct {
129 | Prec float64
130 | Count int
131 | }) {
132 | sortedPrecs := make([]float64, len(precs))
133 | copy(sortedPrecs, precs)
134 | sort.Float64s(sortedPrecs)
135 | minPrec := sortedPrecs[0]
136 | maxPrec := sortedPrecs[len(sortedPrecs)-1]
137 | for i := 0; i < prec.cdfResol; i++ {
138 | curPrec := minPrec + float64(i)*(maxPrec-minPrec)/float64(prec.cdfResol)
139 | for countSmaller, p := range sortedPrecs {
140 | if p >= curPrec {
141 | res[i].Prec = curPrec
142 | res[i].Count = countSmaller
143 | break
144 | }
145 | }
146 | }
147 | }
148 |
149 | func calcmedian(values []complex128) (median complex128) {
150 |
151 | tmp := make([]float64, len(values))
152 |
153 | for i := range values {
154 | tmp[i] = real(values[i])
155 | }
156 |
157 | sort.Float64s(tmp)
158 |
159 | for i := range values {
160 | values[i] = complex(tmp[i], imag(values[i]))
161 | }
162 |
163 | for i := range values {
164 | tmp[i] = imag(values[i])
165 | }
166 |
167 | sort.Float64s(tmp)
168 |
169 | for i := range values {
170 | values[i] = complex(real(values[i]), tmp[i])
171 | }
172 |
173 | index := len(values) / 2
174 |
175 | if len(values)&1 == 1 {
176 | return values[index]
177 | }
178 |
179 | if index+1 == len(values) {
180 | return values[index]
181 | }
182 |
183 | return (values[index] + values[index+1]) / 2
184 | }
185 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks/utils.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | "math"
6 | "math/big"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // StandardDeviation computes the scaled standard deviation of the input vector.
10 | func StandardDeviation(vec []float64, scale float64) (std float64) {
11 | // We assume that the error is centered around zero
12 | var err, tmp, mean, n float64
13 |
14 | n = float64(len(vec))
15 |
16 | for _, c := range vec {
17 | mean += c
18 | }
19 |
20 | mean /= n
21 |
22 | for _, c := range vec {
23 | tmp = c - mean
24 | err += tmp * tmp
25 | }
26 |
27 | return math.Sqrt(err/n) * scale
28 | }
29 |
30 | func scaleUpExact(value float64, n float64, q uint64) (res uint64) {
31 |
32 | var isNegative bool
33 | var xFlo *big.Float
34 | var xInt *big.Int
35 |
36 | isNegative = false
37 | if value < 0 {
38 | isNegative = true
39 | xFlo = big.NewFloat(-n * value)
40 | } else {
41 | xFlo = big.NewFloat(n * value)
42 | }
43 |
44 | xFlo.Add(xFlo, big.NewFloat(0.5))
45 |
46 | xInt = new(big.Int)
47 | xFlo.Int(xInt)
48 | xInt.Mod(xInt, ring.NewUint(q))
49 |
50 | res = xInt.Uint64()
51 |
52 | if isNegative {
53 | res = q - res
54 | }
55 |
56 | return
57 | }
58 |
59 | func scaleUpVecExact(values []float64, n float64, moduli []uint64, coeffs [][]uint64) {
60 |
61 | var isNegative bool
62 | var xFlo *big.Float
63 | var xInt *big.Int
64 | tmp := new(big.Int)
65 |
66 | for i := range values {
67 |
68 | if n*math.Abs(values[i]) > 1.8446744073709552e+19 {
69 |
70 | isNegative = false
71 | if values[i] < 0 {
72 | isNegative = true
73 | xFlo = big.NewFloat(-n * values[i])
74 | } else {
75 | xFlo = big.NewFloat(n * values[i])
76 | }
77 |
78 | xFlo.Add(xFlo, big.NewFloat(0.5))
79 |
80 | xInt = new(big.Int)
81 | xFlo.Int(xInt)
82 |
83 | for j := range moduli {
84 | tmp.Mod(xInt, ring.NewUint(moduli[j]))
85 | if isNegative {
86 | coeffs[j][i] = moduli[j] - tmp.Uint64()
87 | } else {
88 | coeffs[j][i] = tmp.Uint64()
89 | }
90 | }
91 | } else {
92 |
93 | if values[i] < 0 {
94 | for j := range moduli {
95 | coeffs[j][i] = moduli[j] - (uint64(-n*values[i]+0.5) % moduli[j])
96 | }
97 | } else {
98 | for j := range moduli {
99 | coeffs[j][i] = uint64(n*values[i]+0.5) % moduli[j]
100 | }
101 | }
102 | }
103 | }
104 | }
105 |
106 | func scaleUpVecExactBigFloat(values []*big.Float, scale float64, moduli []uint64, coeffs [][]uint64) {
107 |
108 | prec := int(values[0].Prec())
109 |
110 | xFlo := ring.NewFloat(0, prec)
111 | xInt := new(big.Int)
112 | tmp := new(big.Int)
113 |
114 | zero := ring.NewFloat(0, prec)
115 |
116 | scaleFlo := ring.NewFloat(scale, prec)
117 | half := ring.NewFloat(0.5, prec)
118 |
119 | for i := range values {
120 |
121 | xFlo.Mul(scaleFlo, values[i])
122 |
123 | if values[i].Cmp(zero) < 0 {
124 | xFlo.Sub(xFlo, half)
125 | } else {
126 | xFlo.Add(xFlo, half)
127 | }
128 |
129 | xFlo.Int(xInt)
130 |
131 | for j := range moduli {
132 |
133 | Q := ring.NewUint(moduli[j])
134 |
135 | tmp.Mod(xInt, Q)
136 |
137 | if values[i].Cmp(zero) < 0 {
138 | tmp.Add(tmp, Q)
139 | }
140 |
141 | coeffs[j][i] = tmp.Uint64()
142 | }
143 | }
144 | }
145 |
146 | // Divides x by n^2, returns a float
147 | func scaleDown(coeff *big.Int, n float64) (x float64) {
148 |
149 | x, _ = new(big.Float).SetInt(coeff).Float64()
150 | x /= n
151 |
152 | return
153 | }
154 |
155 | func genBigIntChain(Q []uint64) (bigintChain []*big.Int) {
156 |
157 | bigintChain = make([]*big.Int, len(Q))
158 | bigintChain[0] = ring.NewUint(Q[0])
159 | for i := 1; i < len(Q); i++ {
160 | bigintChain[i] = ring.NewUint(Q[i])
161 | bigintChain[i].Mul(bigintChain[i], bigintChain[i-1])
162 | }
163 | return
164 | }
165 |
166 | // GenSwitchkeysRescalingParams generates the parameters for rescaling the switching keys
167 | func GenSwitchkeysRescalingParams(Q, P []uint64) (params []uint64) {
168 |
169 | params = make([]uint64, len(Q))
170 |
171 | PBig := ring.NewUint(1)
172 | for _, pj := range P {
173 | PBig.Mul(PBig, ring.NewUint(pj))
174 | }
175 |
176 | tmp := ring.NewUint(0)
177 |
178 | for i := 0; i < len(Q); i++ {
179 |
180 | params[i] = tmp.Mod(PBig, ring.NewUint(Q[i])).Uint64()
181 | params[i] = ring.ModExp(params[i], int(Q[i]-2), Q[i])
182 | params[i] = ring.MForm(params[i], Q[i], ring.BRedParams(Q[i]))
183 | }
184 |
185 | return
186 | }
187 |
188 | func sliceBitReverseInPlaceComplex128(slice []complex128, N int) {
189 |
190 | var bit, j int
191 |
192 | for i := 1; i < N; i++ {
193 |
194 | bit = N >> 1
195 |
196 | for j >= bit {
197 | j -= bit
198 | bit >>= 1
199 | }
200 |
201 | j += bit
202 |
203 | if i < j {
204 | slice[i], slice[j] = slice[j], slice[i]
205 | }
206 | }
207 | }
208 |
209 | func sliceBitReverseInPlaceRingComplex(slice []*ring.Complex, N int) {
210 |
211 | var bit, j int
212 |
213 | for i := 1; i < N; i++ {
214 |
215 | bit = N >> 1
216 |
217 | for j >= bit {
218 | j -= bit
219 | bit >>= 1
220 | }
221 |
222 | j += bit
223 |
224 | if i < j {
225 | slice[i], slice[j] = slice[j], slice[i]
226 | }
227 | }
228 | }
229 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/algorithms.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "math/bits"
5 | )
6 |
7 | // PowerOf2 computes op^(2^logPow2), consuming logPow2 levels, and returns the result on opOut. Providing an evaluation
8 | // key is necessary when logPow2 > 1.
9 | func (eval *ckksEvaluator) PowerOf2(op *Ciphertext, logPow2 int, opOut *Ciphertext) {
10 |
11 | if logPow2 == 0 {
12 |
13 | if op != opOut {
14 | opOut.Copy(op.El())
15 | }
16 |
17 | } else {
18 |
19 | eval.MulRelin(op.El(), op.El(), opOut)
20 |
21 | if err := eval.Rescale(opOut, eval.scale, opOut); err != nil {
22 | panic(err)
23 | }
24 |
25 | for i := 1; i < logPow2; i++ {
26 |
27 | eval.MulRelin(opOut.El(), opOut.El(), opOut)
28 |
29 | if err := eval.Rescale(opOut, eval.scale, opOut); err != nil {
30 | panic(err)
31 | }
32 | }
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
36 | // PowerNew computes op^degree, consuming log(degree) levels, and returns the result on a new element. Providing an evaluation
37 | // key is necessary when degree > 2.
38 | func (eval *ckksEvaluator) PowerNew(op *Ciphertext, degree int) (opOut *Ciphertext) {
39 | opOut = NewCiphertextCKKS(eval.params, 1, op.Level(), op.Scale())
40 | eval.Power(op, degree, opOut)
41 | return
42 | }
43 |
44 | // Power computes op^degree, consuming log(degree) levels, and returns the result on opOut. Providing an evaluation
45 | // key is necessary when degree > 2.
46 | func (eval *ckksEvaluator) Power(op *Ciphertext, degree int, opOut *Ciphertext) {
47 |
48 | if degree < 1 {
49 | panic("eval.Power -> degree cannot be smaller than 1")
50 | }
51 |
52 | tmpct0 := op.CopyNew()
53 |
54 | var logDegree, po2Degree int
55 |
56 | logDegree = bits.Len64(uint64(degree)) - 1
57 | po2Degree = 1 << logDegree
58 |
59 | eval.PowerOf2(tmpct0.Ciphertext(), logDegree, opOut)
60 |
61 | degree -= po2Degree
62 |
63 | for degree > 0 {
64 |
65 | logDegree = bits.Len64(uint64(degree)) - 1
66 | po2Degree = 1 << logDegree
67 |
68 | tmp := NewCiphertextCKKS(eval.params, 1, tmpct0.Level(), tmpct0.Scale())
69 |
70 | eval.PowerOf2(tmpct0.Ciphertext(), logDegree, tmp)
71 |
72 | eval.MulRelin(opOut.El(), tmp.El(), opOut)
73 |
74 | if err := eval.Rescale(opOut, eval.scale, opOut); err != nil {
75 | panic(err)
76 | }
77 |
78 | degree -= po2Degree
79 | }
80 | }
81 |
82 | // InverseNew computes 1/op and returns the result on a new element, iterating for n steps and consuming n levels. The algorithm requires the encrypted values to be in the range
83 | // [-1.5 - 1.5i, 1.5 + 1.5i] or the result will be wrong. Each iteration increases the precision.
84 | func (eval *ckksEvaluator) InverseNew(op *Ciphertext, steps int) (opOut *Ciphertext) {
85 |
86 | cbar := eval.NegNew(op)
87 |
88 | eval.AddConst(cbar, 1, cbar)
89 |
90 | tmp := eval.AddConstNew(cbar, 1)
91 | opOut = tmp.CopyNew().Ciphertext()
92 |
93 | for i := 1; i < steps; i++ {
94 |
95 | eval.MulRelin(cbar.El(), cbar.El(), cbar.Ciphertext())
96 |
97 | if err := eval.Rescale(cbar, eval.scale, cbar); err != nil {
98 | panic(err)
99 | }
100 |
101 | tmp = eval.AddConstNew(cbar, 1)
102 |
103 | eval.MulRelin(tmp.El(), opOut.El(), tmp.Ciphertext())
104 |
105 | if err := eval.Rescale(tmp, eval.scale, tmp); err != nil {
106 | panic(err)
107 | }
108 |
109 | opOut = tmp.CopyNew().Ciphertext()
110 | }
111 |
112 | return opOut
113 | }
114 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/chebyshev_interpolation.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "math"
5 | )
6 |
7 | // ChebyshevInterpolation is a struct storing the coefficients, degree and range of a Chebyshev interpolation polynomial.
8 | type ChebyshevInterpolation struct {
9 | Poly
10 | a complex128
11 | b complex128
12 | }
13 |
14 | // A returns the start of the approximation interval.
15 | func (c *ChebyshevInterpolation) A() complex128 {
16 | return c.a
17 | }
18 |
19 | // B returns the end of the approximation interval.
20 | func (c *ChebyshevInterpolation) B() complex128 {
21 | return c.b
22 | }
23 |
24 | // Approximate computes a Chebyshev approximation of the input function, for the range [-a, b] of degree degree.
25 | // To be used in conjunction with the function EvaluateCheby.
26 | func Approximate(function func(complex128) complex128, a, b complex128, degree int) (cheby *ChebyshevInterpolation) {
27 |
28 | cheby = new(ChebyshevInterpolation)
29 | cheby.a = a
30 | cheby.b = b
31 | cheby.maxDeg = degree
32 | cheby.lead = true
33 |
34 | nodes := chebyshevNodes(degree+1, a, b)
35 |
36 | fi := make([]complex128, len(nodes))
37 | for i := range nodes {
38 | fi[i] = function(nodes[i])
39 | }
40 |
41 | cheby.coeffs = chebyCoeffs(nodes, fi, a, b)
42 |
43 | return
44 | }
45 |
46 | func chebyshevNodes(n int, a, b complex128) (u []complex128) {
47 | u = make([]complex128, n)
48 | var x, y complex128
49 | for k := 1; k < n+1; k++ {
50 | x = 0.5 * (a + b)
51 | y = 0.5 * (b - a)
52 | u[k-1] = x + y*complex(math.Cos((float64(k)-0.5)*(3.141592653589793/float64(n))), 0)
53 | }
54 | return
55 | }
56 |
57 | func chebyCoeffs(nodes, fi []complex128, a, b complex128) (coeffs []complex128) {
58 |
59 | var u, Tprev, T, Tnext complex128
60 |
61 | n := len(nodes)
62 |
63 | coeffs = make([]complex128, n)
64 |
65 | for i := 0; i < n; i++ {
66 |
67 | u = (2*nodes[i] - a - b) / (b - a)
68 | Tprev = 1
69 | T = u
70 |
71 | for j := 0; j < n; j++ {
72 | coeffs[j] += fi[i] * Tprev
73 | Tnext = 2*u*T - Tprev
74 | Tprev = T
75 | T = Tnext
76 | }
77 | }
78 |
79 | coeffs[0] /= complex(float64(n), 0)
80 | for i := 1; i < n; i++ {
81 | coeffs[i] *= (2.0 / complex(float64(n), 0))
82 | }
83 |
84 | return
85 | }
86 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/ciphertext.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
6 | )
7 |
8 | // Ciphertext is *ring.Poly array representing a polynomial of degree > 0 with coefficients in R_Q.
9 | type Ciphertext struct {
10 | *Element
11 | }
12 |
13 | // NewCiphertextFV creates a new FV ciphertext parameterized by degree, level and scale.
14 | func NewCiphertextFV(params *Parameters, degree int) (ciphertext *Ciphertext) {
15 | return &Ciphertext{newCiphertextElement(params, degree)}
16 | }
17 |
18 | func NewCiphertextFVLvl(params *Parameters, degree int, level int) (ciphertext *Ciphertext) {
19 | ciphertext = &Ciphertext{&Element{}}
20 | ciphertext.value = make([]*ring.Poly, degree+1)
21 | for i := 0; i < degree+1; i++ {
22 | ciphertext.value[i] = ring.NewPoly(params.N(), level+1)
23 | }
24 |
25 | return ciphertext
26 | }
27 |
28 | // NewCiphertextFVRandom generates a new uniformly distributed FV ciphertext of degree, level and scale.
29 | func NewCiphertextFVRandom(prng utils.PRNG, params *Parameters, degree int) (ciphertext *Ciphertext) {
30 | ciphertext = &Ciphertext{newCiphertextElement(params, degree)}
31 | populateElementRandom(prng, params, ciphertext.Element)
32 | return
33 | }
34 |
35 | // NewCiphertextCKKS creates a new CKKS Ciphertext parameterized by degree, level and scale.
36 | func NewCiphertextCKKS(params *Parameters, degree, level int, scale float64) (ciphertext *Ciphertext) {
37 |
38 | ciphertext = &Ciphertext{&Element{}}
39 |
40 | ciphertext.value = make([]*ring.Poly, degree+1)
41 | for i := 0; i < degree+1; i++ {
42 | ciphertext.value[i] = ring.NewPoly(params.N(), level+1)
43 | }
44 |
45 | ciphertext.scale = scale
46 | ciphertext.isNTT = true
47 |
48 | return ciphertext
49 | }
50 |
51 | // NewCiphertextCKKSRandom generates a new uniformly distributed Ciphertext of degree, level and scale.
52 | func NewCiphertextCKKSRandom(prng utils.PRNG, params *Parameters, degree, level int, scale float64) (ciphertext *Ciphertext) {
53 |
54 | ringQ, err := ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.qi[:level+1])
55 | if err != nil {
56 | panic(err)
57 | }
58 |
59 | sampler := ring.NewUniformSampler(prng, ringQ)
60 | ciphertext = NewCiphertextCKKS(params, degree, level, scale)
61 | for i := 0; i < degree+1; i++ {
62 | sampler.Read(ciphertext.value[i])
63 | }
64 |
65 | return ciphertext
66 | }
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/ckks_decryptor.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
6 | )
7 |
8 | // CKKSDecryptor is an interface for decrypting Ciphertexts. A Decryptor stores the secret-key.
9 | type CKKSDecryptor interface {
10 | // DecryptNew decrypts the ciphertext and returns a newly created
11 | // plaintext. A Horner method is used for evaluating the decryption.
12 | // The level of the output plaintext is ciphertext.Level().
13 | DecryptNew(ciphertext *Ciphertext) (plaintext *Plaintext)
14 |
15 | // Decrypt decrypts the ciphertext and returns the result on the provided
16 | // receiver plaintext. A Horner method is used for evaluating the
17 | // decryption.
18 | // The level of the output plaintext is min(ciphertext.Level(), plaintext.Level())
19 | Decrypt(ciphertext *Ciphertext, plaintext *Plaintext)
20 | }
21 |
22 | // ckksDecryptor is a structure used to decrypt ciphertext. It stores the secret-key.
23 | type ckksDecryptor struct {
24 | params *Parameters
25 | ringQ *ring.Ring
26 | sk *SecretKey
27 | }
28 |
29 | // NewCKKSDecryptor instantiates a new Decryptor that will be able to decrypt ciphertexts
30 | // encrypted under the provided secret-key.
31 | func NewCKKSDecryptor(params *Parameters, sk *SecretKey) CKKSDecryptor {
32 |
33 | if sk.Value.Degree() != params.N() {
34 | panic("secret_key is invalid for the provided parameters")
35 | }
36 |
37 | var q *ring.Ring
38 | var err error
39 | if q, err = ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.qi); err != nil {
40 | panic(err)
41 | }
42 |
43 | return &ckksDecryptor{
44 | params: params.Copy(),
45 | ringQ: q,
46 | sk: sk,
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
50 | func (decryptor *ckksDecryptor) DecryptNew(ciphertext *Ciphertext) (plaintext *Plaintext) {
51 |
52 | plaintext = NewPlaintextCKKS(decryptor.params, ciphertext.Level(), ciphertext.Scale())
53 |
54 | decryptor.Decrypt(ciphertext, plaintext)
55 |
56 | return plaintext
57 | }
58 |
59 | func (decryptor *ckksDecryptor) Decrypt(ciphertext *Ciphertext, plaintext *Plaintext) {
60 |
61 | level := utils.MinInt(ciphertext.Level(), plaintext.Level())
62 |
63 | plaintext.SetScale(ciphertext.Scale())
64 |
65 | decryptor.ringQ.CopyLvl(level, ciphertext.value[ciphertext.Degree()], plaintext.value)
66 |
67 | plaintext.value.Coeffs = plaintext.value.Coeffs[:ciphertext.Level()+1]
68 |
69 | for i := ciphertext.Degree(); i > 0; i-- {
70 |
71 | decryptor.ringQ.MulCoeffsMontgomeryLvl(level, plaintext.value, decryptor.sk.Value, plaintext.value)
72 | decryptor.ringQ.AddLvl(level, plaintext.value, ciphertext.value[i-1], plaintext.value)
73 |
74 | if i&7 == 7 {
75 | decryptor.ringQ.ReduceLvl(level, plaintext.value, plaintext.value)
76 | }
77 | }
78 |
79 | if (ciphertext.Degree())&7 != 7 {
80 | decryptor.ringQ.ReduceLvl(level, plaintext.value, plaintext.value)
81 | }
82 |
83 | plaintext.value.Coeffs = plaintext.value.Coeffs[:level+1]
84 | }
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/halfbootstrapper.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "fmt"
5 | "math"
6 |
7 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ckks/bettersine"
8 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
9 | )
10 |
11 | // HalfBootstrapper is a struct to stores a memory pool the plaintext matrices
12 | // the polynomial approximation and the keys for the half-bootstrapping.
13 | type HalfBootstrapper struct {
14 | *ckksEvaluator
15 | HalfBootParameters
16 | *BootstrappingKey
17 | params *Parameters
18 |
19 | dslots int // Number of plaintext slots after the re-encoding
20 | logdslots int
21 |
22 | encoder CKKSEncoder // Encoder
23 |
24 | prescale float64 // Q[0]/(Q[0]/|m|)
25 | postscale float64 // Qi sineeval/(Q[0]/|m|)
26 | sinescale float64 // Qi sineeval
27 | sqrt2pi float64 // (1/2pi)^{-2^r}
28 | scFac float64 // 2^{r}
29 | sineEvalPoly *ChebyshevInterpolation // Coefficients of the Chebyshev Interpolation of sin(2*pi*x) or cos(2*pi*x/r)
30 | arcSinePoly *Poly // Coefficients of the Taylor series of arcsine(x)
31 |
32 | coeffsToSlotsDiffScale complex128 // Matrice rescaling
33 | diffScaleAfterSineEval float64 // Matrice rescaling
34 | pDFTInvWithoutRepack []*PtDiagMatrix // Matrice vectors
35 |
36 | rotKeyIndex []int // a list of the required rotation keys
37 | }
38 |
39 | // NewHalfBootstrapper creates a new HalfBootstrapper.
40 | func NewHalfBootstrapper(params *Parameters, hbtpParams *HalfBootParameters, btpKey BootstrappingKey) (hbtp *HalfBootstrapper, err error) {
41 |
42 | if hbtpParams.SinType == SinType(Sin) && hbtpParams.SinRescal != 0 {
43 | return nil, fmt.Errorf("cannot use double angle formul for SinType = Sin -> must use SinType = Cos")
44 | }
45 |
46 | hbtp = newHalfBootstrapper(params, hbtpParams)
47 |
48 | hbtp.BootstrappingKey = &BootstrappingKey{btpKey.Rlk, btpKey.Rtks}
49 | if err = hbtp.CheckKeys(); err != nil {
50 | return nil, fmt.Errorf("invalid bootstrapping key: %w", err)
51 | }
52 | hbtp.ckksEvaluator = hbtp.ckksEvaluator.WithKey(EvaluationKey{btpKey.Rlk, btpKey.Rtks}).(*ckksEvaluator)
53 |
54 | return hbtp, nil
55 | }
56 |
57 | // newHalfBootstrapper is a constructor of "dummy" half-bootstrapper to enable the generation of bootstrapping-related constants
58 | // without providing a bootstrapping key. To be replaced by a propper factorization of the bootstrapping pre-computations.
59 | func newHalfBootstrapper(params *Parameters, hbtpParams *HalfBootParameters) (hbtp *HalfBootstrapper) {
60 | hbtp = new(HalfBootstrapper)
61 |
62 | hbtp.params = params.Copy()
63 | hbtp.HalfBootParameters = *hbtpParams.Copy()
64 |
65 | hbtp.dslots = params.Slots()
66 | hbtp.logdslots = params.LogSlots()
67 | if params.logSlots < params.MaxLogSlots() {
68 | hbtp.dslots <<= 1
69 | hbtp.logdslots++
70 | }
71 |
72 | hbtp.prescale = math.Exp2(math.Round(math.Log2(float64(params.qi[0]) / hbtp.MessageRatio)))
73 | hbtp.sinescale = math.Exp2(math.Round(math.Log2(hbtp.SineEvalModuli.ScalingFactor)))
74 | hbtp.postscale = hbtp.sinescale / hbtp.MessageRatio
75 |
76 | hbtp.encoder = NewCKKSEncoder(params)
77 | hbtp.ckksEvaluator = NewCKKSEvaluator(params, EvaluationKey{}).(*ckksEvaluator) // creates an evaluator without keys for genDFTMatrices
78 |
79 | hbtp.genSinePoly()
80 | hbtp.genDFTMatrices()
81 |
82 | hbtp.ctxpool = NewCiphertextCKKS(params, 1, params.MaxLevel(), 0)
83 |
84 | return hbtp
85 | }
86 |
87 | // CheckKeys checks if all the necessary keys are present
88 | func (hbtp *HalfBootstrapper) CheckKeys() (err error) {
89 |
90 | if hbtp.Rlk == nil {
91 | return fmt.Errorf("relinearization key is nil")
92 | }
93 |
94 | if hbtp.Rtks == nil {
95 | return fmt.Errorf("rotation key is nil")
96 | }
97 |
98 | rotMissing := []int{}
99 | for _, i := range hbtp.rotKeyIndex {
100 | galEl := hbtp.params.GaloisElementForColumnRotationBy(int(i))
101 | if _, generated := hbtp.Rtks.Keys[galEl]; !generated {
102 | rotMissing = append(rotMissing, i)
103 | }
104 | }
105 |
106 | if len(rotMissing) != 0 {
107 | return fmt.Errorf("rotation key(s) missing: %d", rotMissing)
108 | }
109 |
110 | return nil
111 | }
112 |
113 | func (hbtp *HalfBootstrapper) genDFTMatrices() {
114 |
115 | a := real(hbtp.sineEvalPoly.a)
116 | b := real(hbtp.sineEvalPoly.b)
117 | n := float64(hbtp.params.N())
118 | qDiff := float64(hbtp.params.qi[0]) / math.Exp2(math.Round(math.Log2(float64(hbtp.params.qi[0]))))
119 |
120 | // Change of variable for the evaluation of the Chebyshev polynomial + cancelling factor for the DFT and SubSum + evantual scaling factor for the double angle formula
121 | hbtp.coeffsToSlotsDiffScale = complex(math.Pow(2.0/((b-a)*n*hbtp.scFac*qDiff), 1.0/float64(hbtp.CtSDepth(false))), 0)
122 |
123 | // Rescaling factor to set the final ciphertext to the desired scale
124 | hbtp.diffScaleAfterSineEval = (qDiff * hbtp.params.scale) / hbtp.postscale
125 |
126 | // CoeffsToSlotsWithoutRepack vectors
127 | hbtp.pDFTInvWithoutRepack = hbtp.HalfBootParameters.GenCoeffsToSlotsMatrixWithoutRepack(hbtp.coeffsToSlotsDiffScale, hbtp.encoder)
128 |
129 | // List of the rotation key values to needed for the bootstrapp
130 | hbtp.rotKeyIndex = []int{}
131 |
132 | //SubSum rotation needed X -> Y^slots rotations
133 | for i := hbtp.params.logSlots; i < hbtp.params.MaxLogSlots(); i++ {
134 | if !utils.IsInSliceInt(1< 0 {
152 | hbtp.sqrt2pi = 1.0
153 |
154 | coeffs := make([]complex128, hbtp.ArcSineDeg+1)
155 |
156 | coeffs[1] = 0.15915494309189535
157 |
158 | for i := 3; i < hbtp.ArcSineDeg+1; i += 2 {
159 |
160 | coeffs[i] = coeffs[i-2] * complex(float64(i*i-4*i+4)/float64(i*i-i), 0)
161 |
162 | }
163 |
164 | hbtp.arcSinePoly = NewPoly(coeffs)
165 |
166 | } else {
167 | hbtp.sqrt2pi = math.Pow(0.15915494309189535, 1.0/hbtp.scFac)
168 | }
169 |
170 | if hbtp.SinType == Sin {
171 |
172 | hbtp.sineEvalPoly = Approximate(sin2pi2pi, -complex(float64(K)/hbtp.scFac, 0), complex(float64(K)/hbtp.scFac, 0), deg)
173 |
174 | } else if hbtp.SinType == Cos1 {
175 |
176 | hbtp.sineEvalPoly = new(ChebyshevInterpolation)
177 |
178 | hbtp.sineEvalPoly.coeffs = bettersine.Approximate(K, deg, hbtp.MessageRatio, int(hbtp.SinRescal))
179 |
180 | hbtp.sineEvalPoly.maxDeg = hbtp.sineEvalPoly.Degree()
181 | hbtp.sineEvalPoly.a = complex(float64(-K)/hbtp.scFac, 0)
182 | hbtp.sineEvalPoly.b = complex(float64(K)/hbtp.scFac, 0)
183 | hbtp.sineEvalPoly.lead = true
184 |
185 | } else if hbtp.SinType == Cos2 {
186 |
187 | hbtp.sineEvalPoly = Approximate(cos2pi, -complex(float64(K)/hbtp.scFac, 0), complex(float64(K)/hbtp.scFac, 0), deg)
188 |
189 | } else {
190 | panic("Bootstrapper -> invalid sineType")
191 | }
192 |
193 | for i := range hbtp.sineEvalPoly.coeffs {
194 | hbtp.sineEvalPoly.coeffs[i] *= complex(hbtp.sqrt2pi, 0)
195 | }
196 | }
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/keys.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/rlwe"
4 |
5 | // SecretKey is a type for CKKS secret keys.
6 | type SecretKey struct{ rlwe.SecretKey }
7 |
8 | // PublicKey is a type for CKKS public keys.
9 | type PublicKey struct{ rlwe.PublicKey }
10 |
11 | // SwitchingKey is a type for CKKS public switching keys.
12 | type SwitchingKey struct{ rlwe.SwitchingKey }
13 |
14 | // RelinearizationKey is a type for CKKS public relinearization keys.
15 | type RelinearizationKey struct{ rlwe.RelinearizationKey }
16 |
17 | // RotationKeySet is a type for storing CKKS public rotation keys.
18 | type RotationKeySet struct{ rlwe.RotationKeySet }
19 |
20 | // EvaluationKey is a type composing the relinearization and rotation keys into an evaluation
21 | // key that can be used to initialize bfv.Evaluator types.
22 | type EvaluationKey struct {
23 | Rlk *RelinearizationKey
24 | Rtks *RotationKeySet
25 | }
26 |
27 | // BootstrappingKey is a type for a CKKS bootstrapping key, wich regroups the necessary public relinearization
28 | // and rotation keys (i.e., an EvaluationKey).
29 | type BootstrappingKey EvaluationKey
30 |
31 | // NewSecretKey returns an allocated CKKS secret key with zero values.
32 | func NewSecretKey(params *Parameters) (sk *SecretKey) {
33 | return &SecretKey{*rlwe.NewSecretKey(params.N(), params.QPiCount())}
34 | }
35 |
36 | // NewPublicKey returns an allocated CKKS public with zero values.
37 | func NewPublicKey(params *Parameters) (pk *PublicKey) {
38 | return &PublicKey{*rlwe.NewPublicKey(params.N(), params.QPiCount())}
39 | }
40 |
41 | // NewSwitchingKey returns an allocated CKKS public switching key with zero values.
42 | func NewSwitchingKey(params *Parameters) *SwitchingKey {
43 | return &SwitchingKey{*rlwe.NewSwitchingKey(params.N(), params.QPiCount(), params.Beta())}
44 | }
45 |
46 | // NewRelinearizationKey returns an allocated CKKS public relinearization key with zero value.
47 | func NewRelinearizationKey(params *Parameters) *RelinearizationKey {
48 | return &RelinearizationKey{*rlwe.NewRelinKey(2, params.N(), params.QPiCount(), params.Beta())}
49 | }
50 |
51 | // NewRotationKeySet return an allocated set of CKKS public relineariation keys with zero values for each galois element
52 | // (i.e., for each supported rotation).
53 | func NewRotationKeySet(params *Parameters, galoisElements []uint64) *RotationKeySet {
54 | return &RotationKeySet{*rlwe.NewRotationKeySet(galoisElements, params.N(), params.QPiCount(), params.Beta())}
55 | }
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/mfv_decryptor.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | )
6 |
7 | // MFVDecryptor is an interface for decryptors
8 | type MFVDecryptor interface {
9 | // DecryptNew decrypts the input ciphertext and returns the result on a new
10 | // plaintext.
11 | DecryptNew(ciphertext *Ciphertext) *Plaintext
12 |
13 | // Decrypt decrypts the input ciphertext and returns the result on the
14 | // provided receiver plaintext.
15 | Decrypt(ciphertext *Ciphertext, plaintext *Plaintext)
16 | }
17 |
18 | // mfvDecryptor is a structure used to decrypt ciphertexts. It stores the secret-key.
19 | type mfvDecryptor struct {
20 | params *Parameters
21 | ringQ *ring.Ring
22 | sk *SecretKey
23 | polypool *ring.Poly
24 | }
25 |
26 | // NewMFVDecryptor creates a new Decryptor from the parameters with the secret-key
27 | // given as input.
28 | func NewMFVDecryptor(params *Parameters, sk *SecretKey) MFVDecryptor {
29 |
30 | var ringQ *ring.Ring
31 | var err error
32 | if ringQ, err = ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.qi); err != nil {
33 | panic(err)
34 | }
35 |
36 | return &mfvDecryptor{
37 | params: params.Copy(),
38 | ringQ: ringQ,
39 | sk: sk,
40 | polypool: ringQ.NewPoly(),
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | func (decryptor *mfvDecryptor) DecryptNew(ciphertext *Ciphertext) *Plaintext {
45 | level := ciphertext.Level()
46 | p := NewPlaintextFVLvl(decryptor.params, level)
47 | decryptor.Decrypt(ciphertext, p)
48 | return p
49 | }
50 |
51 | func (decryptor *mfvDecryptor) Decrypt(ciphertext *Ciphertext, p *Plaintext) {
52 |
53 | if ciphertext.Level() != p.Level() {
54 | panic("ciphertext and p should have the same level")
55 | }
56 |
57 | ringQ := decryptor.ringQ
58 | tmp := decryptor.polypool
59 |
60 | level := p.Level()
61 | ringQ.NTTLazyLvl(level, ciphertext.value[ciphertext.Degree()], p.value)
62 |
63 | for i := ciphertext.Degree(); i > 0; i-- {
64 | ringQ.MulCoeffsMontgomeryLvl(level, p.value, decryptor.sk.Value, p.value)
65 | ringQ.NTTLazyLvl(level, ciphertext.value[i-1], tmp)
66 | ringQ.AddLvl(level, p.value, tmp, p.value)
67 |
68 | if i&3 == 3 {
69 | ringQ.ReduceLvl(level, p.value, p.value)
70 | }
71 | }
72 |
73 | if (ciphertext.Degree())&3 != 3 {
74 | ringQ.ReduceLvl(level, p.value, p.value)
75 | }
76 |
77 | ringQ.InvNTTLvl(level, p.value, p.value)
78 | }
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/mfv_noise_estimator.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "math"
5 | "math/big"
6 |
7 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
8 | )
9 |
10 | type MFVNoiseEstimator interface {
11 | InvariantNoiseBudget(ciphertext *Ciphertext) int
12 | }
13 |
14 | type mfvNoiseEstimator struct {
15 | params *Parameters
16 | sk *SecretKey
17 | ringQs []*ring.Ring
18 | plainModulus uint64
19 | qHalfs []*big.Int // (q+1)/2
20 |
21 | qib [][]uint64 // (Q/Qi)^-1 (mod each Qi)
22 | qispj [][]*big.Int // Q/Qi (mod Q)
23 |
24 | polypool1 *ring.Poly
25 | polypool2 *ring.Poly
26 | coeffspool []*big.Int
27 | bigintpool [4]*big.Int
28 | }
29 |
30 | func NewMFVNoiseEstimator(params *Parameters, sk *SecretKey) MFVNoiseEstimator {
31 |
32 | var err error
33 |
34 | Q := params.qi
35 | modCount := len(Q)
36 | ringQs := make([]*ring.Ring, modCount)
37 | for i := range ringQs {
38 | if ringQs[i], err = ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.qi[:i+1]); err != nil {
39 | panic(err)
40 | }
41 | }
42 |
43 | QjB := new(big.Int)
44 | QjStar := new(big.Int)
45 | QjBarre := new(big.Int)
46 |
47 | qHalfs := make([]*big.Int, modCount)
48 | qib := make([][]uint64, modCount)
49 | qispj := make([][]*big.Int, modCount)
50 |
51 | for i := 0; i < modCount; i++ {
52 | qHalfs[i] = new(big.Int)
53 | qHalfs[i].Set(ringQs[i].ModulusBigint)
54 | qHalfs[i].Add(qHalfs[i], new(big.Int).SetUint64(1))
55 | qHalfs[i].Rsh(qHalfs[i], 1)
56 |
57 | qib[i] = make([]uint64, i+1)
58 | qispj[i] = make([]*big.Int, i+1)
59 | for j := 0; j <= i; j++ {
60 | qj := Q[j]
61 | QjB.SetUint64(qj)
62 | QjStar.Quo(ringQs[i].ModulusBigint, QjB)
63 | QjBarre.ModInverse(QjStar, QjB)
64 | QjBarre.Mod(QjBarre, QjB)
65 |
66 | qib[i][j] = QjBarre.Uint64()
67 | qispj[i][j] = new(big.Int).Set(QjStar)
68 | }
69 | }
70 |
71 | polypool1 := ringQs[modCount-1].NewPoly()
72 | polypool2 := ringQs[modCount-1].NewPoly()
73 |
74 | coeffspool := make([]*big.Int, params.N())
75 | for i := range coeffspool {
76 | coeffspool[i] = new(big.Int).SetUint64(0)
77 | }
78 | bigintpool := [4]*big.Int{new(big.Int), new(big.Int), new(big.Int), new(big.Int)}
79 |
80 | return &mfvNoiseEstimator{
81 | params: params.Copy(),
82 | sk: sk,
83 | ringQs: ringQs,
84 | plainModulus: params.PlainModulus(),
85 | qHalfs: qHalfs,
86 |
87 | qib: qib,
88 | qispj: qispj,
89 |
90 | polypool1: polypool1,
91 | polypool2: polypool2,
92 | coeffspool: coeffspool,
93 | bigintpool: bigintpool,
94 | }
95 | }
96 |
97 | func (mfvNoiseEstimator *mfvNoiseEstimator) InvariantNoiseBudget(ciphertext *Ciphertext) int {
98 |
99 | if ciphertext.Degree() != 1 {
100 | panic("Ciphertext degree should be 1")
101 | }
102 |
103 | N := mfvNoiseEstimator.params.N()
104 | level := ciphertext.Level()
105 | ringQ := mfvNoiseEstimator.ringQs[level]
106 | Q := ringQ.Modulus
107 | modulusbigint := ringQ.ModulusBigint
108 |
109 | tmp := mfvNoiseEstimator.polypool1
110 | pool0Q := mfvNoiseEstimator.polypool2
111 | coeffspool := mfvNoiseEstimator.coeffspool
112 |
113 | tmpInt0 := mfvNoiseEstimator.bigintpool[0]
114 | tmpInt1 := mfvNoiseEstimator.bigintpool[1]
115 | tmpIntQi := mfvNoiseEstimator.bigintpool[2]
116 | norm := mfvNoiseEstimator.bigintpool[3]
117 |
118 | // Step 1. Dot product with the secret key
119 | ringQ.NTTLazy(ciphertext.value[1], pool0Q)
120 | ringQ.MulCoeffsMontgomery(pool0Q, mfvNoiseEstimator.sk.Value, pool0Q)
121 | ringQ.NTTLazy(ciphertext.value[0], tmp)
122 | ringQ.Add(pool0Q, tmp, pool0Q)
123 |
124 | ringQ.Reduce(pool0Q, pool0Q)
125 | ringQ.InvNTT(pool0Q, pool0Q)
126 |
127 | // Step 2. Multiply by t
128 | ringQ.MulScalar(pool0Q, mfvNoiseEstimator.plainModulus, pool0Q)
129 |
130 | // Step 3. CRT compose
131 | for i := 0; i < N; i++ {
132 | coeffspool[i].SetUint64(0)
133 | for j := 0; j <= level; j++ {
134 | tmpIntQi.SetUint64(Q[j])
135 | tmpInt0.SetUint64(pool0Q.Coeffs[j][i])
136 | tmpInt1.SetUint64(mfvNoiseEstimator.qib[level][j])
137 | tmpInt0.Mul(tmpInt0, tmpInt1)
138 | tmpInt0.Mod(tmpInt0, tmpIntQi)
139 |
140 | tmpInt0.Mul(tmpInt0, mfvNoiseEstimator.qispj[level][j])
141 | coeffspool[i].Add(coeffspool[i], tmpInt0)
142 | coeffspool[i].Mod(coeffspool[i], modulusbigint)
143 | }
144 | }
145 |
146 | // Step 4. Compute the infinity norm
147 | norm.SetUint64(0)
148 | qHalf := mfvNoiseEstimator.qHalfs[level]
149 | for i := 0; i < N; i++ {
150 | if coeffspool[i].Cmp(qHalf) >= 0 {
151 | coeffspool[i].Sub(modulusbigint, coeffspool[i])
152 | }
153 |
154 | if norm.Cmp(coeffspool[i]) < 0 {
155 | norm.Set(coeffspool[i])
156 | }
157 | }
158 |
159 | // Step 5. Compute noise budget
160 | bitCountDiff := getSignificantBitsCount(modulusbigint) - getSignificantBitsCount(norm) - 1
161 | if bitCountDiff < 0 {
162 | bitCountDiff = 0
163 | }
164 |
165 | return bitCountDiff
166 | }
167 |
168 | func getSignificantBitsCount(x *big.Int) int {
169 |
170 | bitCount := x.BitLen()
171 |
172 | if bitCount == 0 {
173 | return 0
174 | }
175 |
176 | if bitCount <= 32 {
177 | return int(math.Round(math.Log2(float64(x.Uint64()))))
178 | }
179 |
180 | numOne := 0
181 | for i := 1; i <= 12; i++ {
182 | if x.Bit(bitCount-1-i) == 1 {
183 | numOne++
184 | }
185 | if numOne < 6 {
186 | bitCount--
187 | }
188 | }
189 |
190 | return bitCount
191 | }
192 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/operand.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "fmt"
5 |
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
7 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
8 | )
9 |
10 | // Operand is a common interface for Ciphertext and Plaintext types.
11 | type Operand interface {
12 | El() *Element
13 | Degree() int
14 | Level() int
15 | Scale() float64
16 | }
17 |
18 | // Element is a generic type for ciphertext and plaintexts
19 | type Element struct {
20 | value []*ring.Poly
21 | scale float64
22 | isNTT bool
23 | }
24 |
25 | // NewElement returns a new Element with zero values.
26 | func NewElement() *Element {
27 | return &Element{}
28 | }
29 |
30 | // Value returns the slice of polynomials of the target element.
31 | func (el *Element) Value() []*ring.Poly {
32 | return el.value
33 | }
34 |
35 | // SetValue sets the input slice of polynomials as the value of the target element.
36 | func (el *Element) SetValue(value []*ring.Poly) {
37 | el.value = value
38 | }
39 |
40 | // Degree returns the degree of the target element.
41 | func (el *Element) Degree() int {
42 | return len(el.value) - 1
43 | }
44 |
45 | // Level returns the level of the target element.
46 | func (el *Element) Level() int {
47 | return len(el.value[0].Coeffs) - 1
48 | }
49 |
50 | // Scale returns the scale of the target element.
51 | func (el *Element) Scale() float64 {
52 | return el.scale
53 | }
54 |
55 | // SetScale sets the scale of the the target element to the input scale.
56 | func (el *Element) SetScale(scale float64) {
57 | el.scale = scale
58 | }
59 |
60 | // MulScale multiplies the scale of the target element with the input scale.
61 | func (el *Element) MulScale(scale float64) {
62 | el.scale *= scale
63 | }
64 |
65 | // DivScale divides the scale of the target element by the input scale.
66 | func (el *Element) DivScale(scale float64) {
67 | el.scale /= scale
68 | }
69 |
70 | // Resize resizes the degree of the target element.
71 | func (el *Element) Resize(params *Parameters, degree int) {
72 | if el.Degree() > degree {
73 | el.value = el.value[:degree+1]
74 | } else if el.Degree() < degree {
75 | for el.Degree() < degree {
76 | el.value = append(el.value, []*ring.Poly{new(ring.Poly)}...)
77 | el.value[el.Degree()].Coeffs = make([][]uint64, el.Level()+1)
78 | for i := 0; i < el.Level()+1; i++ {
79 | el.value[el.Degree()].Coeffs[i] = make([]uint64, params.N())
80 | }
81 | }
82 | }
83 | }
84 |
85 | // IsNTT returns the value of the NTT flag of the target element.
86 | func (el *Element) IsNTT() bool {
87 | return el.isNTT
88 | }
89 |
90 | // SetIsNTT sets the value of the NTT flag of the target element with the input value.
91 | func (el *Element) SetIsNTT(value bool) {
92 | el.isNTT = value
93 | }
94 |
95 | // NTT puts the target element in the NTT domain and sets its isNTT flag to true. If it is already in the NTT domain, it does nothing.
96 | func (el *Element) NTT(ringQ *ring.Ring, c *Element) {
97 | if el.Degree() != c.Degree() {
98 | panic(fmt.Errorf("error: receiver element has invalid degree (it does not match)"))
99 | }
100 | if !el.IsNTT() {
101 | for i := range el.value {
102 | ringQ.NTTLvl(el.Level(), el.Value()[i], c.Value()[i])
103 | }
104 | c.SetIsNTT(true)
105 | }
106 | }
107 |
108 | // InvNTT puts the target element outside of the NTT domain, and sets its isNTT flag to false. If it is not in the NTT domain, it does nothing.
109 | func (el *Element) InvNTT(ringQ *ring.Ring, c *Element) {
110 | if el.Degree() != c.Degree() {
111 | panic(fmt.Errorf("error: receiver element invalid degree (it does not match)"))
112 | }
113 | if el.IsNTT() {
114 | for i := range el.value {
115 | ringQ.InvNTTLvl(el.Level(), el.Value()[i], c.Value()[i])
116 | }
117 | c.SetIsNTT(false)
118 | }
119 | }
120 |
121 | // CopyNew creates a new element as a copy of the target element.
122 | func (el *Element) CopyNew() *Element {
123 |
124 | ctxCopy := new(Element)
125 |
126 | ctxCopy.value = make([]*ring.Poly, el.Degree()+1)
127 | for i := range el.value {
128 | ctxCopy.value[i] = el.value[i].CopyNew()
129 | }
130 |
131 | ctxCopy.CopyParams(el)
132 |
133 | return ctxCopy
134 | }
135 |
136 | // Copy copies the input element and its parameters on the target element.
137 | func (el *Element) Copy(ctxCopy *Element) {
138 |
139 | if el != ctxCopy {
140 | for i := range ctxCopy.Value() {
141 | el.value[i].Copy(ctxCopy.Value()[i])
142 | }
143 |
144 | el.CopyParams(ctxCopy)
145 | }
146 | }
147 |
148 | // CopyParams copies the input element parameters on the target element
149 | func (el *Element) CopyParams(Element *Element) {
150 | el.SetScale(Element.Scale())
151 | el.SetIsNTT(Element.IsNTT())
152 | }
153 |
154 | // El sets the target element type to Element.
155 | func (el *Element) El() *Element {
156 | return el
157 | }
158 |
159 | // Ciphertext sets the target element type to Ciphertext.
160 | func (el *Element) Ciphertext() *Ciphertext {
161 | return &Ciphertext{el}
162 | }
163 |
164 | // Plaintext sets the target element type to Plaintext.
165 | func (el *Element) Plaintext() *Plaintext {
166 | return &Plaintext{el, el.value[0]}
167 | }
168 |
169 | func getSmallestLargest(el0, el1 *Element) (smallest, largest *Element, sameDegree bool) {
170 | switch {
171 | case el0.Degree() > el1.Degree():
172 | return el1, el0, false
173 | case el0.Degree() < el1.Degree():
174 | return el0, el1, false
175 | }
176 | return el0, el1, true
177 | }
178 |
179 | func newCiphertextElement(params *Parameters, degree int) *Element {
180 | el := new(Element)
181 | el.value = make([]*ring.Poly, degree+1)
182 | for i := 0; i < degree+1; i++ {
183 | el.value[i] = ring.NewPoly(params.N(), params.QiCount())
184 | }
185 | return el
186 | }
187 |
188 | func newPlaintextElement(params *Parameters) *Element {
189 | el := new(Element)
190 | el.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), params.QiCount())}
191 | return el
192 | }
193 |
194 | func newPlaintextRingTElement(params *Parameters) *Element {
195 | el := new(Element)
196 | el.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), 1)}
197 | return el
198 | }
199 |
200 | func newPlaintextMulElement(params *Parameters) *Element {
201 | el := new(Element)
202 | el.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), params.QiCount())}
203 | return el
204 | }
205 |
206 | // NewElementRandom creates a new Element with random coefficients
207 | func populateElementRandom(prng utils.PRNG, params *Parameters, el *Element) {
208 |
209 | ringQ, err := ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.qi)
210 | if err != nil {
211 | panic(err)
212 | }
213 | sampler := ring.NewUniformSampler(prng, ringQ)
214 | for i := range el.value {
215 | sampler.Read(el.value[i])
216 | }
217 | }
218 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/plaintext.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
4 |
5 | // PlaintextCKKS is is a Element with only one Poly.
6 | type Plaintext struct {
7 | *Element
8 | value *ring.Poly
9 | }
10 |
11 | // PlaintextRingT represents a plaintext element in R_t.
12 | // This is the most compact representation of a plaintext, but performing operations have the extra-cost of performing
13 | // the scaling up by Q/t. See bfv/encoder.go for more information on plaintext types.
14 | type PlaintextRingT Plaintext
15 |
16 | // PlaintextMul represents a plaintext element in R_q, in NTT and Montgomery form, but without scale up by Q/t.
17 | // A PlaintextMul is a special-purpose plaintext for efficient Ciphertext-Plaintext multiplication. However,
18 | // other operations on plaintexts are not supported. See bfv/encoder.go for more information on plaintext types.
19 | type PlaintextMul Plaintext
20 |
21 | // NewPlaintext creates a new Plaintext of level level and scale scale.
22 | func NewPlaintextCKKS(params *Parameters, level int, scale float64) *Plaintext {
23 |
24 | plaintext := &Plaintext{&Element{}, nil}
25 |
26 | plaintext.Element.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), level+1)}
27 |
28 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
29 |
30 | plaintext.scale = scale
31 | plaintext.isNTT = true
32 |
33 | return plaintext
34 | }
35 |
36 | // NewPlaintext creates and allocates a new plaintext in RingQ (multiple moduli of Q).
37 | // The plaintext will be in RingQ and scaled by Q/t.
38 | // Slower encoding and larger plaintext size
39 | func NewPlaintextFV(params *Parameters) *Plaintext {
40 | plaintext := &Plaintext{newPlaintextElement(params), nil}
41 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
42 | return plaintext
43 | }
44 |
45 | // NewPlaintextLvl creates and allocates a new plaintext in RingQ (multiple moduli of Q)
46 | // of given level.
47 | // The plaintext will be in RingQ and scaled by Q/t.
48 | // Slower encoding and larger plaintext size
49 | func NewPlaintextFVLvl(params *Parameters, level int) *Plaintext {
50 | plaintext := &Plaintext{&Element{}, nil}
51 |
52 | plaintext.Element.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), level+1)}
53 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
54 |
55 | return plaintext
56 | }
57 |
58 | // NewPlaintextRingT creates and allocates a new plaintext in RingT (single modulus T).
59 | // The plaintext will be in RingT.
60 | func NewPlaintextRingT(params *Parameters) *PlaintextRingT {
61 |
62 | plaintext := &PlaintextRingT{newPlaintextRingTElement(params), nil}
63 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
64 | return plaintext
65 | }
66 |
67 | // NewPlaintextMul creates and allocates a new plaintext optimized for ciphertext x plaintext multiplication.
68 | // The plaintext will be in the NTT and Montgomery domain of RingQ and not scaled by Q/t.
69 | func NewPlaintextMul(params *Parameters) *PlaintextMul {
70 | plaintext := &PlaintextMul{newPlaintextMulElement(params), nil}
71 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
72 | return plaintext
73 | }
74 |
75 | // NewPlaintextMulLvl creates and allocates a new plaintext optimized for ciphertext x plaintext multiplication.
76 | // The plaintext will be in the NTT and Montgomery domain of RingQ of given level and not scaled by Q/t.
77 | func NewPlaintextMulLvl(params *Parameters, level int) *PlaintextMul {
78 | plaintext := &PlaintextMul{&Element{}, nil}
79 |
80 | plaintext.Element.value = []*ring.Poly{ring.NewPoly(params.N(), level+1)}
81 | plaintext.value = plaintext.Element.value[0]
82 |
83 | return plaintext
84 | }
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/precision.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "fmt"
5 | "math"
6 | "sort"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // PrecisionStats is a struct storing statistic about the precision of a CKKS plaintext
10 | type PrecisionStats struct {
11 | MaxDelta complex128
12 | MinDelta complex128
13 | MaxPrecision complex128
14 | MinPrecision complex128
15 | MeanDelta complex128
16 | MeanPrecision complex128
17 | MedianDelta complex128
18 | MedianPrecision complex128
19 | STDFreq float64
20 | STDTime float64
21 |
22 | RealDist, ImagDist []struct {
23 | Prec float64
24 | Count int
25 | }
26 |
27 | cdfResol int
28 | }
29 |
30 | func (prec PrecisionStats) String() string {
31 | return fmt.Sprintf("\nMIN Prec : (%.2f, %.2f) Log2 \n", real(prec.MinPrecision), imag(prec.MinPrecision)) +
32 | fmt.Sprintf("MAX Prec : (%.2f, %.2f) Log2 \n", real(prec.MaxPrecision), imag(prec.MaxPrecision)) +
33 | fmt.Sprintf("AVG Prec : (%.2f, %.2f) Log2 \n", real(prec.MeanPrecision), imag(prec.MeanPrecision)) +
34 | fmt.Sprintf("MED Prec : (%.2f, %.2f) Log2 \n", real(prec.MedianPrecision), imag(prec.MedianPrecision)) +
35 | fmt.Sprintf("Err stdF : %5.2f Log2 \n", math.Log2(prec.STDFreq)) +
36 | fmt.Sprintf("Err stdT : %5.2f Log2 \n", math.Log2(prec.STDTime))
37 |
38 | }
39 |
40 | // GetPrecisionStats generates a PrecisionStats struct from the reference values and the decrypted values
41 | func GetPrecisionStats(params *Parameters, encoder CKKSEncoder, decryptor CKKSDecryptor, valuesWant []complex128, element interface{}, logSlots int, sigma float64) (prec PrecisionStats) {
42 |
43 | var valuesTest []complex128
44 |
45 | slots := uint64(1 << logSlots)
46 |
47 | switch element := element.(type) {
48 | case *Ciphertext:
49 | valuesTest = encoder.DecodeComplexPublic(decryptor.DecryptNew(element), logSlots, sigma)
50 | case *Plaintext:
51 | valuesTest = encoder.DecodeComplexPublic(element, logSlots, sigma)
52 | case []complex128:
53 | valuesTest = element
54 | }
55 |
56 | var deltaReal, deltaImag float64
57 |
58 | var delta complex128
59 |
60 | diff := make([]complex128, slots)
61 |
62 | prec.MaxDelta = complex(0, 0)
63 | prec.MinDelta = complex(1, 1)
64 |
65 | prec.MeanDelta = complex(0, 0)
66 |
67 | prec.cdfResol = 500
68 |
69 | prec.RealDist = make([]struct {
70 | Prec float64
71 | Count int
72 | }, prec.cdfResol)
73 | prec.ImagDist = make([]struct {
74 | Prec float64
75 | Count int
76 | }, prec.cdfResol)
77 |
78 | precReal := make([]float64, len(valuesWant))
79 | precImag := make([]float64, len(valuesWant))
80 |
81 | for i := range valuesWant {
82 |
83 | delta = valuesTest[i] - valuesWant[i]
84 | deltaReal = math.Abs(real(delta))
85 | deltaImag = math.Abs(imag(delta))
86 | precReal[i] = math.Log2(1 / deltaReal)
87 | precImag[i] = math.Log2(1 / deltaImag)
88 |
89 | diff[i] += complex(deltaReal, deltaImag)
90 |
91 | prec.MeanDelta += diff[i]
92 |
93 | if deltaReal > real(prec.MaxDelta) {
94 | prec.MaxDelta = complex(deltaReal, imag(prec.MaxDelta))
95 | }
96 |
97 | if deltaImag > imag(prec.MaxDelta) {
98 | prec.MaxDelta = complex(real(prec.MaxDelta), deltaImag)
99 | }
100 |
101 | if deltaReal < real(prec.MinDelta) {
102 | prec.MinDelta = complex(deltaReal, imag(prec.MinDelta))
103 | }
104 |
105 | if deltaImag < imag(prec.MinDelta) {
106 | prec.MinDelta = complex(real(prec.MinDelta), deltaImag)
107 | }
108 | }
109 |
110 | prec.calcCDF(precReal, prec.RealDist)
111 | prec.calcCDF(precImag, prec.ImagDist)
112 |
113 | prec.MinPrecision = deltaToPrecision(prec.MaxDelta)
114 | prec.MaxPrecision = deltaToPrecision(prec.MinDelta)
115 | prec.MeanDelta /= complex(float64(slots), 0)
116 | prec.MeanPrecision = deltaToPrecision(prec.MeanDelta)
117 | prec.MedianDelta = calcmedian(diff)
118 | prec.MedianPrecision = deltaToPrecision(prec.MedianDelta)
119 | prec.STDFreq = encoder.GetErrSTDFreqDom(valuesWant[:], valuesTest[:], params.Scale())
120 | prec.STDTime = encoder.GetErrSTDTimeDom(valuesWant, valuesTest, params.Scale())
121 | return prec
122 | }
123 |
124 | func deltaToPrecision(c complex128) complex128 {
125 | return complex(math.Log2(1/real(c)), math.Log2(1/imag(c)))
126 | }
127 |
128 | func (prec *PrecisionStats) calcCDF(precs []float64, res []struct {
129 | Prec float64
130 | Count int
131 | }) {
132 | sortedPrecs := make([]float64, len(precs))
133 | copy(sortedPrecs, precs)
134 | sort.Float64s(sortedPrecs)
135 | minPrec := sortedPrecs[0]
136 | maxPrec := sortedPrecs[len(sortedPrecs)-1]
137 | for i := 0; i < prec.cdfResol; i++ {
138 | curPrec := minPrec + float64(i)*(maxPrec-minPrec)/float64(prec.cdfResol)
139 | for countSmaller, p := range sortedPrecs {
140 | if p >= curPrec {
141 | res[i].Prec = curPrec
142 | res[i].Count = countSmaller
143 | break
144 | }
145 | }
146 | }
147 | }
148 |
149 | func calcmedian(values []complex128) (median complex128) {
150 |
151 | tmp := make([]float64, len(values))
152 |
153 | for i := range values {
154 | tmp[i] = real(values[i])
155 | }
156 |
157 | sort.Float64s(tmp)
158 |
159 | for i := range values {
160 | values[i] = complex(tmp[i], imag(values[i]))
161 | }
162 |
163 | for i := range values {
164 | tmp[i] = imag(values[i])
165 | }
166 |
167 | sort.Float64s(tmp)
168 |
169 | for i := range values {
170 | values[i] = complex(real(values[i]), tmp[i])
171 | }
172 |
173 | index := len(values) / 2
174 |
175 | if len(values)&1 == 1 {
176 | return values[index]
177 | }
178 |
179 | if index+1 == len(values) {
180 | return values[index]
181 | }
182 |
183 | return (values[index] + values[index+1]) / 2
184 | }
185 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ckks_fv/utils.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ckks_fv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "io"
5 | "math"
6 | "math/big"
7 | "math/bits"
8 |
9 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
10 | )
11 |
12 | // Returns uniform random value in (0,q) by rejection sampling
13 | func SampleZqx(rand io.Reader, q uint64) (res uint64) {
14 | bitLen := bits.Len64(q - 2)
15 | byteLen := (bitLen + 7) / 8
16 | b := bitLen % 8
17 | if b == 0 {
18 | b = 8
19 | }
20 |
21 | bytes := make([]byte, byteLen)
22 | for {
23 | _, err := io.ReadFull(rand, bytes)
24 | if err != nil {
25 | panic(err)
26 | }
27 | bytes[byteLen-1] &= uint8((1 << b) - 1)
28 |
29 | res = 0
30 | for i := 0; i < byteLen; i++ {
31 | res += uint64(bytes[i]) << (8 * i)
32 | }
33 |
34 | if res < q {
35 | return
36 | }
37 | }
38 | }
39 |
40 | // StandardDeviation computes the scaled standard deviation of the input vector.
41 | func StandardDeviation(vec []float64, scale float64) (std float64) {
42 | // We assume that the error is centered around zero
43 | var err, tmp, mean, n float64
44 |
45 | n = float64(len(vec))
46 |
47 | for _, c := range vec {
48 | mean += c
49 | }
50 |
51 | mean /= n
52 |
53 | for _, c := range vec {
54 | tmp = c - mean
55 | err += tmp * tmp
56 | }
57 |
58 | return math.Sqrt(err/n) * scale
59 | }
60 |
61 | func scaleUpExact(value float64, n float64, q uint64) (res uint64) {
62 |
63 | var isNegative bool
64 | var xFlo *big.Float
65 | var xInt *big.Int
66 |
67 | isNegative = false
68 | if value < 0 {
69 | isNegative = true
70 | xFlo = big.NewFloat(-n * value)
71 | } else {
72 | xFlo = big.NewFloat(n * value)
73 | }
74 |
75 | xFlo.Add(xFlo, big.NewFloat(0.5))
76 |
77 | xInt = new(big.Int)
78 | xFlo.Int(xInt)
79 | xInt.Mod(xInt, ring.NewUint(q))
80 |
81 | res = xInt.Uint64()
82 |
83 | if isNegative {
84 | res = q - res
85 | }
86 |
87 | return
88 | }
89 |
90 | func scaleUpVecExact(values []float64, n float64, moduli []uint64, coeffs [][]uint64) {
91 |
92 | var isNegative bool
93 | var xFlo *big.Float
94 | var xInt *big.Int
95 | tmp := new(big.Int)
96 |
97 | for i := range values {
98 |
99 | if n*math.Abs(values[i]) > 1.8446744073709552e+19 {
100 |
101 | isNegative = false
102 | if values[i] < 0 {
103 | isNegative = true
104 | xFlo = big.NewFloat(-n * values[i])
105 | } else {
106 | xFlo = big.NewFloat(n * values[i])
107 | }
108 |
109 | xFlo.Add(xFlo, big.NewFloat(0.5))
110 |
111 | xInt = new(big.Int)
112 | xFlo.Int(xInt)
113 |
114 | for j := range moduli {
115 | tmp.Mod(xInt, ring.NewUint(moduli[j]))
116 | if isNegative {
117 | coeffs[j][i] = moduli[j] - tmp.Uint64()
118 | } else {
119 | coeffs[j][i] = tmp.Uint64()
120 | }
121 | }
122 | } else {
123 |
124 | if values[i] < 0 {
125 | for j := range moduli {
126 | coeffs[j][i] = moduli[j] - (uint64(-n*values[i]+0.5) % moduli[j])
127 | }
128 | } else {
129 | for j := range moduli {
130 | coeffs[j][i] = uint64(n*values[i]+0.5) % moduli[j]
131 | }
132 | }
133 | }
134 | }
135 | }
136 |
137 | func scaleUpVecExactBigFloat(values []*big.Float, scale float64, moduli []uint64, coeffs [][]uint64) {
138 |
139 | prec := int(values[0].Prec())
140 |
141 | xFlo := ring.NewFloat(0, prec)
142 | xInt := new(big.Int)
143 | tmp := new(big.Int)
144 |
145 | zero := ring.NewFloat(0, prec)
146 |
147 | scaleFlo := ring.NewFloat(scale, prec)
148 | half := ring.NewFloat(0.5, prec)
149 |
150 | for i := range values {
151 |
152 | xFlo.Mul(scaleFlo, values[i])
153 |
154 | if values[i].Cmp(zero) < 0 {
155 | xFlo.Sub(xFlo, half)
156 | } else {
157 | xFlo.Add(xFlo, half)
158 | }
159 |
160 | xFlo.Int(xInt)
161 |
162 | for j := range moduli {
163 |
164 | Q := ring.NewUint(moduli[j])
165 |
166 | tmp.Mod(xInt, Q)
167 |
168 | if values[i].Cmp(zero) < 0 {
169 | tmp.Add(tmp, Q)
170 | }
171 |
172 | coeffs[j][i] = tmp.Uint64()
173 | }
174 | }
175 | }
176 |
177 | // Divides x by n^2, returns a float
178 | func scaleDown(coeff *big.Int, n float64) (x float64) {
179 |
180 | x, _ = new(big.Float).SetInt(coeff).Float64()
181 | x /= n
182 |
183 | return
184 | }
185 |
186 | func genBigIntChain(Q []uint64) (bigintChain []*big.Int) {
187 |
188 | bigintChain = make([]*big.Int, len(Q))
189 | bigintChain[0] = ring.NewUint(Q[0])
190 | for i := 1; i < len(Q); i++ {
191 | bigintChain[i] = ring.NewUint(Q[i])
192 | bigintChain[i].Mul(bigintChain[i], bigintChain[i-1])
193 | }
194 | return
195 | }
196 |
197 | // GenSwitchkeysRescalingParams generates the parameters for rescaling the switching keys
198 | func GenSwitchkeysRescalingParams(Q, P []uint64) (params []uint64) {
199 |
200 | params = make([]uint64, len(Q))
201 |
202 | PBig := ring.NewUint(1)
203 | for _, pj := range P {
204 | PBig.Mul(PBig, ring.NewUint(pj))
205 | }
206 |
207 | tmp := ring.NewUint(0)
208 |
209 | for i := 0; i < len(Q); i++ {
210 |
211 | params[i] = tmp.Mod(PBig, ring.NewUint(Q[i])).Uint64()
212 | params[i] = ring.ModExp(params[i], int(Q[i]-2), Q[i])
213 | params[i] = ring.MForm(params[i], Q[i], ring.BRedParams(Q[i]))
214 | }
215 |
216 | return
217 | }
218 |
219 | func sliceBitReverseInPlaceComplex128(slice []complex128, N int) {
220 |
221 | var bit, j int
222 |
223 | for i := 1; i < N; i++ {
224 |
225 | bit = N >> 1
226 |
227 | for j >= bit {
228 | j -= bit
229 | bit >>= 1
230 | }
231 |
232 | j += bit
233 |
234 | if i < j {
235 | slice[i], slice[j] = slice[j], slice[i]
236 | }
237 | }
238 | }
239 |
240 | func sliceBitReverseInPlaceRingComplex(slice []*ring.Complex, N int) {
241 |
242 | var bit, j int
243 |
244 | for i := 1; i < N; i++ {
245 |
246 | bit = N >> 1
247 |
248 | for j >= bit {
249 | j -= bit
250 | bit >>= 1
251 | }
252 |
253 | j += bit
254 |
255 | if i < j {
256 | slice[i], slice[j] = slice[j], slice[i]
257 | }
258 | }
259 | }
260 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dbfv/dbfv.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dbfv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/bfv"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
6 | )
7 |
8 | type dbfvContext struct {
9 | params *bfv.Parameters
10 |
11 | // Polynomial degree
12 | n int
13 |
14 | // floor(Q/T) mod each Qi in Montgomery form
15 | deltaMont []uint64
16 |
17 | // Polynomial contexts
18 | ringT *ring.Ring
19 | ringQ *ring.Ring
20 | ringP *ring.Ring
21 | ringQP *ring.Ring
22 | }
23 |
24 | func newDbfvContext(params *bfv.Parameters) *dbfvContext {
25 |
26 | n := params.N()
27 |
28 | ringT, err := ring.NewRing(n, []uint64{params.T()})
29 | if err != nil {
30 | panic(err)
31 | }
32 |
33 | ringQ, err := ring.NewRing(n, params.Qi())
34 | if err != nil {
35 | panic(err)
36 | }
37 |
38 | ringP, err := ring.NewRing(n, params.Pi())
39 | if err != nil {
40 | panic(err)
41 | }
42 |
43 | ringQP, err := ring.NewRing(n, append(params.Qi(), params.Pi()...))
44 | if err != nil {
45 | panic(err)
46 | }
47 |
48 | deltaMont := bfv.GenLiftParams(ringQ, params.T())
49 |
50 | return &dbfvContext{
51 | params: params.Copy(),
52 | n: n,
53 | deltaMont: deltaMont,
54 | ringT: ringT,
55 | ringQ: ringQ,
56 | ringP: ringP,
57 | ringQP: ringQP,
58 | }
59 | }
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dbfv/keyswitching.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dbfv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/bfv"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // CKSProtocol is a structure storing the parameters for the collective key-switching protocol.
10 | type CKSProtocol struct {
11 | context *dbfvContext
12 |
13 | sigmaSmudging float64
14 |
15 | tmpNtt *ring.Poly
16 | tmpDelta *ring.Poly
17 | hP *ring.Poly
18 |
19 | baseconverter *ring.FastBasisExtender
20 | gaussianSampler *ring.GaussianSampler
21 | }
22 |
23 | // CKSShare is a type for the CKS protocol shares.
24 | type CKSShare struct {
25 | *ring.Poly
26 | }
27 |
28 | // UnmarshalBinary decodes a previouls marshaled share on the target share.
29 | func (share *CKSShare) UnmarshalBinary(data []byte) error {
30 | share.Poly = new(ring.Poly)
31 | err := share.Poly.UnmarshalBinary(data)
32 | return err
33 |
34 | }
35 |
36 | // NewCKSProtocol creates a new CKSProtocol that will be used to operate a collective key-switching on a ciphertext encrypted under a collective public-key, whose
37 | // secret-shares are distributed among j parties, re-encrypting the ciphertext under another public-key, whose secret-shares are also known to the
38 | // parties.
39 | func NewCKSProtocol(params *bfv.Parameters, sigmaSmudging float64) *CKSProtocol {
40 |
41 | context := newDbfvContext(params)
42 |
43 | cks := new(CKSProtocol)
44 |
45 | cks.context = context
46 |
47 | cks.sigmaSmudging = sigmaSmudging
48 |
49 | cks.tmpNtt = cks.context.ringQP.NewPoly()
50 | cks.tmpDelta = cks.context.ringQ.NewPoly()
51 | cks.hP = cks.context.ringP.NewPoly()
52 |
53 | cks.baseconverter = ring.NewFastBasisExtender(cks.context.ringQ, cks.context.ringP)
54 | prng, err := utils.NewPRNG()
55 | if err != nil {
56 | panic(err)
57 | }
58 | cks.gaussianSampler = ring.NewGaussianSampler(prng)
59 |
60 | return cks
61 | }
62 |
63 | // AllocateShare allocates the shares of the CKSProtocol
64 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) AllocateShare() CKSShare {
65 |
66 | return CKSShare{cks.context.ringQ.NewPoly()}
67 |
68 | }
69 |
70 | // GenShare is the first and unique round of the CKSProtocol protocol. Each party holding a ciphertext ctx encrypted under a collective publick-key musth
71 | // compute the following :
72 | //
73 | // [(skInput_i - skOutput_i) * ctx[0] + e_i]
74 | //
75 | // Each party then broadcast the result of this computation to the other j-1 parties.
76 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) GenShare(skInput, skOutput *ring.Poly, ct *bfv.Ciphertext, shareOut CKSShare) {
77 |
78 | cks.context.ringQ.Sub(skInput, skOutput, cks.tmpDelta)
79 |
80 | cks.genShareDelta(cks.tmpDelta, ct, shareOut)
81 | }
82 |
83 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) genShareDelta(skDelta *ring.Poly, ct *bfv.Ciphertext, shareOut CKSShare) {
84 |
85 | level := len(ct.Value()[1].Coeffs) - 1
86 |
87 | ringQ := cks.context.ringQ
88 | ringQP := cks.context.ringQP
89 |
90 | ringQ.NTTLazy(ct.Value()[1], cks.tmpNtt)
91 | ringQ.MulCoeffsMontgomeryConstant(cks.tmpNtt, skDelta, shareOut.Poly)
92 | ringQ.MulScalarBigint(shareOut.Poly, cks.context.ringP.ModulusBigint, shareOut.Poly)
93 |
94 | ringQ.InvNTTLazy(shareOut.Poly, shareOut.Poly)
95 |
96 | cks.gaussianSampler.ReadLvl(len(ringQP.Modulus)-1, cks.tmpNtt, ringQP, cks.sigmaSmudging, int(6*cks.sigmaSmudging))
97 | ringQ.AddNoMod(shareOut.Poly, cks.tmpNtt, shareOut.Poly)
98 |
99 | for x, i := 0, len(ringQ.Modulus); i < len(cks.context.ringQP.Modulus); x, i = x+1, i+1 {
100 | tmphP := cks.hP.Coeffs[x]
101 | tmpNTT := cks.tmpNtt.Coeffs[i]
102 | for j := 0; j < ringQ.N; j++ {
103 | tmphP[j] += tmpNTT[j]
104 | }
105 | }
106 |
107 | cks.baseconverter.ModDownSplitPQ(level, shareOut.Poly, cks.hP, shareOut.Poly)
108 |
109 | cks.tmpNtt.Zero()
110 | cks.hP.Zero()
111 | }
112 |
113 | // AggregateShares is the second part of the unique round of the CKSProtocol protocol. Upon receiving the j-1 elements each party computes :
114 | //
115 | // [ctx[0] + sum((skInput_i - skOutput_i) * ctx[0] + e_i), ctx[1]]
116 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) AggregateShares(share1, share2, shareOut CKSShare) {
117 | cks.context.ringQ.Add(share1.Poly, share2.Poly, shareOut.Poly)
118 | }
119 |
120 | // KeySwitch performs the actual keyswitching operation on a ciphertext ct and put the result in ctOut
121 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) KeySwitch(combined CKSShare, ct *bfv.Ciphertext, ctOut *bfv.Ciphertext) {
122 | cks.context.ringQ.Add(ct.Value()[0], combined.Poly, ctOut.Value()[0])
123 | cks.context.ringQ.Copy(ct.Value()[1], ctOut.Value()[1])
124 | }
125 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dbfv/public_keyswitching.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dbfv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/bfv"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // PCKSProtocol is the structure storing the parameters for the collective public key-switching.
10 | type PCKSProtocol struct {
11 | context *dbfvContext
12 |
13 | sigmaSmudging float64
14 |
15 | tmp *ring.Poly
16 | share0tmp *ring.Poly
17 | share1tmp *ring.Poly
18 |
19 | baseconverter *ring.FastBasisExtender
20 | gaussianSampler *ring.GaussianSampler
21 | ternarySamplerMontgomery *ring.TernarySampler
22 | }
23 |
24 | // PCKSShare is a type for the PCKS protocol shares.
25 | type PCKSShare [2]*ring.Poly
26 |
27 | //type PCKSShare struct {
28 | // share [2]*ring.Poly
29 | //}
30 |
31 | // MarshalBinary encodes a PCKS share on a slice of bytes.
32 | func (share *PCKSShare) MarshalBinary() ([]byte, error) {
33 | //Discuss choice here.
34 | //Maybe not worth it to have the metadata separated. we "lose" two bytes but complexity of the code would be higher in Unmarshalling.
35 | lenR1 := share[0].GetDataLen(true)
36 | lenR2 := share[1].GetDataLen(true)
37 |
38 | data := make([]byte, lenR1+lenR2)
39 | _, err := share[0].WriteTo(data[0:lenR1])
40 | if err != nil {
41 | return []byte{}, err
42 | }
43 |
44 | _, err = share[1].WriteTo(data[lenR1 : lenR1+lenR2])
45 | if err != nil {
46 | return []byte{}, err
47 | }
48 |
49 | return data, nil
50 | }
51 |
52 | // UnmarshalBinary decodes marshaled PCKS share on the target PCKS share.
53 | func (share *PCKSShare) UnmarshalBinary(data []byte) error {
54 |
55 | if share[0] == nil {
56 | share[0] = new(ring.Poly)
57 | }
58 |
59 | if share[1] == nil {
60 | share[1] = new(ring.Poly)
61 | }
62 |
63 | err := share[0].UnmarshalBinary(data[0 : len(data)/2])
64 | if err != nil {
65 | return err
66 | }
67 |
68 | err = share[1].UnmarshalBinary(data[len(data)/2:])
69 | if err != nil {
70 | return err
71 | }
72 |
73 | return nil
74 | }
75 |
76 | // NewPCKSProtocol creates a new PCKSProtocol object and will be used to re-encrypt a ciphertext ctx encrypted under a secret-shared key among j parties under a new
77 | // collective public-key.
78 | func NewPCKSProtocol(params *bfv.Parameters, sigmaSmudging float64) *PCKSProtocol {
79 |
80 | context := newDbfvContext(params)
81 |
82 | pcks := new(PCKSProtocol)
83 |
84 | pcks.context = context
85 |
86 | pcks.sigmaSmudging = sigmaSmudging
87 |
88 | pcks.tmp = context.ringQP.NewPoly()
89 | pcks.share0tmp = context.ringQP.NewPoly()
90 | pcks.share1tmp = context.ringQP.NewPoly()
91 |
92 | pcks.baseconverter = ring.NewFastBasisExtender(context.ringQ, context.ringP)
93 | prng, err := utils.NewPRNG()
94 | if err != nil {
95 | panic(err)
96 | }
97 | pcks.gaussianSampler = ring.NewGaussianSampler(prng)
98 | pcks.ternarySamplerMontgomery = ring.NewTernarySampler(prng, context.ringQP, 0.5, true)
99 |
100 | return pcks
101 | }
102 |
103 | // AllocateShares allocates the shares of the PCKS protocol
104 | func (pcks *PCKSProtocol) AllocateShares() (s PCKSShare) {
105 | s[0] = pcks.context.ringQ.NewPoly()
106 | s[1] = pcks.context.ringQ.NewPoly()
107 | return
108 | }
109 |
110 | // GenShare is the first part of the unique round of the PCKSProtocol protocol. Each party computes the following :
111 | //
112 | // [s_i * ctx[0] + (u_i * pk[0] + e_0i)/P, (u_i * pk[1] + e_1i)/P]
113 | //
114 | // and broadcasts the result to the other j-1 parties.
115 | func (pcks *PCKSProtocol) GenShare(sk *ring.Poly, pk *bfv.PublicKey, ct *bfv.Ciphertext, shareOut PCKSShare) {
116 |
117 | ringQ := pcks.context.ringQ
118 | ringQP := pcks.context.ringQP
119 |
120 | pcks.ternarySamplerMontgomery.Read(pcks.tmp)
121 | ringQP.NTTLazy(pcks.tmp, pcks.tmp)
122 |
123 | // h_0 = u_i * pk_0
124 | ringQP.MulCoeffsMontgomeryConstant(pcks.tmp, pk.Value[0], pcks.share0tmp)
125 | // h_1 = u_i * pk_1
126 | ringQP.MulCoeffsMontgomeryConstant(pcks.tmp, pk.Value[1], pcks.share1tmp)
127 |
128 | ringQP.InvNTTLazy(pcks.share0tmp, pcks.share0tmp)
129 | ringQP.InvNTTLazy(pcks.share1tmp, pcks.share1tmp)
130 |
131 | // h_0 = u_i * pk_0 + e0
132 | pcks.gaussianSampler.ReadAndAdd(pcks.share0tmp, ringQP, pcks.sigmaSmudging, int(6*pcks.sigmaSmudging))
133 |
134 | // h_1 = u_i * pk_1 + e1
135 | pcks.gaussianSampler.ReadAndAdd(pcks.share1tmp, ringQP, pcks.sigmaSmudging, int(6*pcks.sigmaSmudging))
136 |
137 | // h_0 = (u_i * pk_0 + e0)/P
138 | pcks.baseconverter.ModDownPQ(len(ringQ.Modulus)-1, pcks.share0tmp, shareOut[0])
139 |
140 | // h_0 = (u_i * pk_0 + e0)/P
141 | // Could be moved to the keyswitch phase, but the second element of the shares will be larger
142 | pcks.baseconverter.ModDownPQ(len(ringQ.Modulus)-1, pcks.share1tmp, shareOut[1])
143 |
144 | // tmp = s_i*c_1
145 | ringQ.NTTLazy(ct.Value()[1], pcks.tmp)
146 | ringQ.MulCoeffsMontgomeryConstant(pcks.tmp, sk, pcks.tmp)
147 | ringQ.InvNTT(pcks.tmp, pcks.tmp)
148 |
149 | // h_0 = s_i*c_1 + (u_i * pk_0 + e0)/P
150 | ringQ.Add(shareOut[0], pcks.tmp, shareOut[0])
151 |
152 | pcks.tmp.Zero()
153 |
154 | }
155 |
156 | // AggregateShares is the second part of the first and unique round of the PCKSProtocol protocol. Each party uppon receiving the j-1 elements from the
157 | // other parties computes :
158 | //
159 | // [ctx[0] + sum(s_i * ctx[0] + u_i * pk[0] + e_0i), sum(u_i * pk[1] + e_1i)]
160 | func (pcks *PCKSProtocol) AggregateShares(share1, share2, shareOut PCKSShare) {
161 |
162 | pcks.context.ringQ.Add(share1[0], share2[0], shareOut[0])
163 | pcks.context.ringQ.Add(share1[1], share2[1], shareOut[1])
164 | }
165 |
166 | // KeySwitch performs the actual keyswitching operation on a ciphertext ct and put the result in ctOut
167 | func (pcks *PCKSProtocol) KeySwitch(combined PCKSShare, ct, ctOut *bfv.Ciphertext) {
168 |
169 | pcks.context.ringQ.Add(ct.Value()[0], combined[0], ctOut.Value()[0])
170 | pcks.context.ringQ.Copy(combined[1], ctOut.Value()[1])
171 | }
172 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dbfv/publickey_gen.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //Package dbfv implements a distributed (or threshold) version of the BFV scheme that enables secure multiparty computation solutions with secret-shared secret keys.
2 | package dbfv
3 |
4 | import (
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/bfv"
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/drlwe"
7 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
8 | )
9 |
10 | // CKGProtocol is the structure storing the parameters and state for a party in the collective key generation protocol.
11 | type CKGProtocol struct {
12 | drlwe.CKGProtocol
13 | }
14 |
15 | // NewCKGProtocol creates a new CKGProtocol instance
16 | func NewCKGProtocol(params *bfv.Parameters) *CKGProtocol {
17 | ckg := new(CKGProtocol)
18 | ckg.CKGProtocol = *drlwe.NewCKGProtocol(params.N(), params.Qi(), params.Pi(), params.Sigma())
19 | return ckg
20 | }
21 |
22 | // GenBFVPublicKey return the current aggregation of the received shares as a bfv.PublicKey.
23 | func (ckg *CKGProtocol) GenBFVPublicKey(roundShare *drlwe.CKGShare, crs *ring.Poly, pubkey *bfv.PublicKey) {
24 | ckg.CKGProtocol.GenPublicKey(roundShare, crs, &pubkey.PublicKey)
25 | }
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dbfv/relinkey_gen.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dbfv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/bfv"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/drlwe"
6 | )
7 |
8 | // RKGProtocol is the structure storing the parameters and state for a party in the collective relinearization key
9 | // generation protocol.
10 | type RKGProtocol struct {
11 | drlwe.RKGProtocol
12 | }
13 |
14 | // NewRKGProtocol creates a new RKGProtocol object that will be used to generate a collective evaluation-key
15 | // among j parties in the given context with the given bit-decomposition.
16 | func NewRKGProtocol(params *bfv.Parameters) *RKGProtocol {
17 | return &RKGProtocol{*drlwe.NewRKGProtocol(params.N(), params.Qi(), params.Pi(), 0.5, params.Sigma())}
18 | }
19 |
20 | // GenBFVRelinearizationKey finalizes the protocol and returns the common EvaluationKey.
21 | func (ekg *RKGProtocol) GenBFVRelinearizationKey(round1 *drlwe.RKGShare, round2 *drlwe.RKGShare, evalKeyOut *bfv.RelinearizationKey) {
22 | ekg.GenRelinearizationKey(round1, round2, &evalKeyOut.RelinearizationKey)
23 | }
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dbfv/rotkey_gen.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dbfv
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/bfv"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/drlwe"
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // RTGProtocol is the structure storing the parameters for the collective rotation-keys generation.
10 | type RTGProtocol struct {
11 | drlwe.RTGProtocol
12 | }
13 |
14 | // NewRotKGProtocol creates a new rotkg object and will be used to generate collective rotation-keys from a shared secret-key among j parties.
15 | func NewRotKGProtocol(params *bfv.Parameters) (rtg *RTGProtocol) {
16 | return &RTGProtocol{*drlwe.NewRTGProtocol(params.N(), params.Qi(), params.Pi(), params.Sigma())}
17 | }
18 |
19 | // GenBFVRotationKey populates the input RotationKeys struture with the Switching key computed from the protocol.
20 | func (rtg *RTGProtocol) GenBFVRotationKey(share *drlwe.RTGShare, crp []*ring.Poly, rotKey *bfv.SwitchingKey) {
21 | rtg.GenRotationKey(share, crp, &rotKey.SwitchingKey)
22 | }
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dckks/dckks.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ckks"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
6 | )
7 |
8 | type dckksContext struct {
9 | params *ckks.Parameters
10 |
11 | n int
12 |
13 | ringQ *ring.Ring
14 | ringP *ring.Ring
15 | ringQP *ring.Ring
16 |
17 | alpha int
18 | beta int
19 | }
20 |
21 | func newDckksContext(params *ckks.Parameters) (context *dckksContext) {
22 |
23 | context = new(dckksContext)
24 |
25 | context.params = params.Copy()
26 |
27 | context.n = params.N()
28 |
29 | context.alpha = params.Alpha()
30 | context.beta = params.Beta()
31 |
32 | var err error
33 | if context.ringQ, err = ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.Qi()); err != nil {
34 | panic(err)
35 | }
36 |
37 | if context.ringP, err = ring.NewRing(params.N(), params.Pi()); err != nil {
38 | panic(err)
39 | }
40 |
41 | if context.ringQP, err = ring.NewRing(params.N(), append(params.Qi(), params.Pi()...)); err != nil {
42 | panic(err)
43 | }
44 |
45 | return
46 | }
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dckks/keyswitching.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ckks"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // CKSProtocol is a structure storing the parameters for the collective key-switching protocol.
10 | type CKSProtocol struct {
11 | dckksContext *dckksContext
12 |
13 | sigmaSmudging float64
14 |
15 | tmpQ *ring.Poly
16 | tmpP *ring.Poly
17 | tmpDelta *ring.Poly
18 | hP *ring.Poly
19 |
20 | baseconverter *ring.FastBasisExtender
21 | gaussianSampler *ring.GaussianSampler
22 | }
23 |
24 | // CKSShare is a struct holding a share of the CKS protocol.
25 | type CKSShare *ring.Poly
26 |
27 | // NewCKSProtocol creates a new CKSProtocol that will be used to operate a collective key-switching on a ciphertext encrypted under a collective public-key, whose
28 | // secret-shares are distributed among j parties, re-encrypting the ciphertext under another public-key, whose secret-shares are also known to the
29 | // parties.
30 | func NewCKSProtocol(params *ckks.Parameters, sigmaSmudging float64) (cks *CKSProtocol) {
31 |
32 | cks = new(CKSProtocol)
33 |
34 | dckksContext := newDckksContext(params)
35 |
36 | cks.dckksContext = dckksContext
37 |
38 | cks.tmpQ = dckksContext.ringQ.NewPoly()
39 | cks.tmpP = dckksContext.ringP.NewPoly()
40 | cks.tmpDelta = dckksContext.ringQ.NewPoly()
41 | cks.hP = dckksContext.ringP.NewPoly()
42 |
43 | cks.sigmaSmudging = sigmaSmudging
44 |
45 | cks.baseconverter = ring.NewFastBasisExtender(dckksContext.ringQ, dckksContext.ringP)
46 | prng, err := utils.NewPRNG()
47 | if err != nil {
48 | panic(err)
49 | }
50 | cks.gaussianSampler = ring.NewGaussianSampler(prng)
51 |
52 | return cks
53 | }
54 |
55 | // AllocateShare allocates the share of the CKS protocol.
56 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) AllocateShare() CKSShare {
57 | return cks.dckksContext.ringQ.NewPoly()
58 | }
59 |
60 | // GenShare is the first and unique round of the CKSProtocol protocol. Each party holding a ciphertext ctx encrypted under a collective publick-key must
61 | // compute the following :
62 | //
63 | // [(skInput_i - skOutput_i) * ctx[0] + e_i]
64 | //
65 | // Each party then broadcasts the result of this computation to the other j-1 parties.
66 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) GenShare(skInput, skOutput *ring.Poly, ct *ckks.Ciphertext, shareOut CKSShare) {
67 |
68 | cks.dckksContext.ringQ.SubNoMod(skInput, skOutput, cks.tmpDelta)
69 |
70 | cks.genShareDelta(cks.tmpDelta, ct, shareOut)
71 | }
72 |
73 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) genShareDelta(skDelta *ring.Poly, ct *ckks.Ciphertext, shareOut CKSShare) {
74 |
75 | ringQ := cks.dckksContext.ringQ
76 | ringP := cks.dckksContext.ringP
77 | sigma := cks.dckksContext.params.Sigma()
78 |
79 | ringQ.MulCoeffsMontgomeryConstantLvl(ct.Level(), ct.Value()[1], skDelta, shareOut)
80 |
81 | ringQ.MulScalarBigintLvl(ct.Level(), shareOut, ringP.ModulusBigint, shareOut)
82 |
83 | cks.gaussianSampler.ReadLvl(ct.Level(), cks.tmpQ, ringQ, sigma, int(6*sigma))
84 | extendBasisSmallNormAndCenter(ringQ, ringP, cks.tmpQ, cks.tmpP)
85 |
86 | ringQ.NTTLvl(ct.Level(), cks.tmpQ, cks.tmpQ)
87 | ringP.NTT(cks.tmpP, cks.tmpP)
88 |
89 | ringQ.AddLvl(ct.Level(), shareOut, cks.tmpQ, shareOut)
90 |
91 | cks.baseconverter.ModDownSplitNTTPQ(ct.Level(), shareOut, cks.tmpP, shareOut)
92 |
93 | cks.tmpQ.Zero()
94 | cks.tmpP.Zero()
95 | }
96 |
97 | // AggregateShares is the second part of the unique round of the CKSProtocol protocol. Upon receiving the j-1 elements each party computes :
98 | //
99 | // [ctx[0] + sum((skInput_i - skOutput_i) * ctx[0] + e_i), ctx[1]]
100 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) AggregateShares(share1, share2, shareOut CKSShare) {
101 | cks.dckksContext.ringQ.AddLvl(len(share1.Coeffs)-1, share1, share2, shareOut)
102 | }
103 |
104 | // KeySwitch performs the actual keyswitching operation on a ciphertext ct and put the result in ctOut
105 | func (cks *CKSProtocol) KeySwitch(combined CKSShare, ct *ckks.Ciphertext, ctOut *ckks.Ciphertext) {
106 | ctOut.SetScale(ct.Scale())
107 | cks.dckksContext.ringQ.AddLvl(ct.Level(), ct.Value()[0], combined, ctOut.Value()[0])
108 | cks.dckksContext.ringQ.CopyLvl(ct.Level(), ct.Value()[1], ctOut.Value()[1])
109 | }
110 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dckks/public_keyswitching.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ckks"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // PCKSProtocol is the structure storing the parameters for the collective public key-switching.
10 | type PCKSProtocol struct {
11 | dckksContext *dckksContext
12 |
13 | sigmaSmudging float64
14 |
15 | tmp *ring.Poly
16 |
17 | share0tmp *ring.Poly
18 | share1tmp *ring.Poly
19 |
20 | baseconverter *ring.FastBasisExtender
21 | gaussianSampler *ring.GaussianSampler
22 | ternarySamplerMontgomery *ring.TernarySampler
23 | }
24 |
25 | // PCKSShare is a struct storing the share of the PCKS protocol.
26 | type PCKSShare [2]*ring.Poly
27 |
28 | // NewPCKSProtocol creates a new PCKSProtocol object and will be used to re-encrypt a ciphertext ctx encrypted under a secret-shared key mong j parties under a new
29 | // collective public-key.
30 | func NewPCKSProtocol(params *ckks.Parameters, sigmaSmudging float64) *PCKSProtocol {
31 |
32 | pcks := new(PCKSProtocol)
33 |
34 | dckksContext := newDckksContext(params)
35 |
36 | pcks.dckksContext = dckksContext
37 |
38 | pcks.tmp = dckksContext.ringQP.NewPoly()
39 | pcks.share0tmp = dckksContext.ringQP.NewPoly()
40 | pcks.share1tmp = dckksContext.ringQP.NewPoly()
41 |
42 | pcks.sigmaSmudging = sigmaSmudging
43 |
44 | pcks.baseconverter = ring.NewFastBasisExtender(dckksContext.ringQ, dckksContext.ringP)
45 | prng, err := utils.NewPRNG()
46 | if err != nil {
47 | panic(err)
48 | }
49 | pcks.gaussianSampler = ring.NewGaussianSampler(prng)
50 | pcks.ternarySamplerMontgomery = ring.NewTernarySampler(prng, dckksContext.ringQP, 0.5, true)
51 |
52 | return pcks
53 | }
54 |
55 | // AllocateShares allocates the share of the PCKS protocol.
56 | func (pcks *PCKSProtocol) AllocateShares(level int) (s PCKSShare) {
57 | s[0] = pcks.dckksContext.ringQ.NewPolyLvl(level)
58 | s[1] = pcks.dckksContext.ringQ.NewPolyLvl(level)
59 | return
60 | }
61 |
62 | // GenShare is the first part of the unique round of the PCKSProtocol protocol. Each party computes the following :
63 | //
64 | // [s_i * ctx[0] + u_i * pk[0] + e_0i, u_i * pk[1] + e_1i]
65 | //
66 | // and broadcasts the result to the other j-1 parties.
67 | func (pcks *PCKSProtocol) GenShare(sk *ring.Poly, pk *ckks.PublicKey, ct *ckks.Ciphertext, shareOut PCKSShare) {
68 |
69 | // Planned improvement : adapt share size to ct.Level() to improve efficiency.
70 |
71 | ringQ := pcks.dckksContext.ringQ
72 | ringQP := pcks.dckksContext.ringQP
73 | sigma := pcks.dckksContext.params.Sigma()
74 |
75 | pcks.ternarySamplerMontgomery.Read(pcks.tmp)
76 | ringQP.NTTLazy(pcks.tmp, pcks.tmp)
77 |
78 | // h_0 = u_i * pk_0
79 | ringQP.MulCoeffsMontgomeryConstant(pcks.tmp, pk.Value[0], pcks.share0tmp)
80 | // h_1 = u_i * pk_1
81 | ringQP.MulCoeffsMontgomeryConstant(pcks.tmp, pk.Value[1], pcks.share1tmp)
82 |
83 | // h_0 = u_i * pk_0 + e0
84 | pcks.gaussianSampler.Read(pcks.tmp, ringQP, sigma, int(sigma))
85 | ringQP.NTT(pcks.tmp, pcks.tmp)
86 | ringQP.Add(pcks.share0tmp, pcks.tmp, pcks.share0tmp)
87 | // h_1 = u_i * pk_1 + e1
88 | pcks.gaussianSampler.Read(pcks.tmp, ringQP, sigma, int(sigma))
89 | ringQP.NTT(pcks.tmp, pcks.tmp)
90 | ringQP.Add(pcks.share1tmp, pcks.tmp, pcks.share1tmp)
91 |
92 | // h_0 = (u_i * pk_0 + e0)/P
93 | pcks.baseconverter.ModDownNTTPQ(ct.Level(), pcks.share0tmp, shareOut[0])
94 |
95 | // h_1 = (u_i * pk_1 + e1)/P
96 | // Cound be moved to the keyswitch part of the protocol, but the second element of the shares will be larger.
97 | pcks.baseconverter.ModDownNTTPQ(ct.Level(), pcks.share1tmp, shareOut[1])
98 |
99 | // h_0 = s_i*c_1 + (u_i * pk_0 + e0)/P
100 | ringQ.MulCoeffsMontgomeryAndAddLvl(ct.Level(), ct.Value()[1], sk, shareOut[0])
101 |
102 | pcks.tmp.Zero()
103 | }
104 |
105 | // AggregateShares is the second part of the first and unique round of the PCKSProtocol protocol. Each party uppon receiving the j-1 elements from the
106 | // other parties computes :
107 | //
108 | // [ctx[0] + sum(s_i * ctx[0] + u_i * pk[0] + e_0i), sum(u_i * pk[1] + e_1i)]
109 | func (pcks *PCKSProtocol) AggregateShares(share1, share2, shareOut PCKSShare) {
110 |
111 | level := len(share1[0].Coeffs) - 1
112 | pcks.dckksContext.ringQ.AddLvl(level, share1[0], share2[0], shareOut[0])
113 | pcks.dckksContext.ringQ.AddLvl(level, share1[1], share2[1], shareOut[1])
114 | }
115 |
116 | // KeySwitch performs the actual keyswitching operation on a ciphertext ct and put the result in ctOut
117 | func (pcks *PCKSProtocol) KeySwitch(combined PCKSShare, ct, ctOut *ckks.Ciphertext) {
118 |
119 | ctOut.SetScale(ct.Scale())
120 |
121 | pcks.dckksContext.ringQ.AddLvl(ct.Level(), ct.Value()[0], combined[0], ctOut.Value()[0])
122 | pcks.dckksContext.ringQ.CopyLvl(ct.Level(), combined[1], ctOut.Value()[1])
123 | }
124 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dckks/publickey_gen.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //Package dckks implements a distributed (or threshold) version of the CKKS scheme that enables secure multiparty computation solutions with secret-shared secret keys.
2 | package dckks
3 |
4 | import (
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ckks"
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/drlwe"
7 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
8 | )
9 |
10 | // CKGProtocol is the structure storing the parameters and state for a party in the collective key generation protocol.
11 | type CKGProtocol struct {
12 | drlwe.CKGProtocol
13 | }
14 |
15 | // NewCKGProtocol creates a new CKGProtocol instance
16 | func NewCKGProtocol(params *ckks.Parameters) *CKGProtocol {
17 |
18 | ckg := new(CKGProtocol)
19 | ckg.CKGProtocol = *drlwe.NewCKGProtocol(params.N(), params.Qi(), params.Pi(), params.Sigma())
20 | return ckg
21 | }
22 |
23 | // GenCKKSPublicKey return the current aggregation of the received shares as a ckks.PublicKey.
24 | func (ckg *CKGProtocol) GenCKKSPublicKey(roundShare *drlwe.CKGShare, crs *ring.Poly, pubkey *ckks.PublicKey) {
25 | ckg.CKGProtocol.GenPublicKey(roundShare, crs, &pubkey.PublicKey)
26 | }
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dckks/relinkey_gen.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ckks"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/drlwe"
6 | )
7 |
8 | // RKGProtocol is the structure storing the parameters and state for a party in the collective relinearization key
9 | // generation protocol.
10 | type RKGProtocol struct {
11 | drlwe.RKGProtocol
12 | }
13 |
14 | // NewRKGProtocol creates a new RKGProtocol object that will be used to generate a collective evaluation-key
15 | // among j parties in the given context with the given bit-decomposition.
16 | func NewRKGProtocol(params *ckks.Parameters) *RKGProtocol {
17 | return &RKGProtocol{*drlwe.NewRKGProtocol(params.N(), params.Qi(), params.Pi(), 0.5, params.Sigma())}
18 | }
19 |
20 | // GenCKKSRelinearizationKey finalizes the protocol and returns the common EvaluationKey.
21 | func (ekg *RKGProtocol) GenCKKSRelinearizationKey(round1 *drlwe.RKGShare, round2 *drlwe.RKGShare, evalKeyOut *ckks.RelinearizationKey) {
22 | ekg.GenRelinearizationKey(round1, round2, &evalKeyOut.RelinearizationKey)
23 | }
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dckks/rotkey_gen.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ckks"
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/drlwe"
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // RTGProtocol is the structure storing the parameters for the collective rotation-keys generation.
10 | type RTGProtocol struct {
11 | drlwe.RTGProtocol
12 | }
13 |
14 | // NewRotKGProtocol creates a new rotkg object and will be used to generate collective rotation-keys from a shared secret-key among j parties.
15 | func NewRotKGProtocol(params *ckks.Parameters) (rtg *RTGProtocol) {
16 | return &RTGProtocol{*drlwe.NewRTGProtocol(params.N(), params.Qi(), params.Pi(), params.Sigma())}
17 | }
18 |
19 | // GenCKKSRotationKey populates the input RotationKeys struture with the Switching key computed from the protocol.
20 | func (rtg *RTGProtocol) GenCKKSRotationKey(share *drlwe.RTGShare, crp []*ring.Poly, rotKey *ckks.SwitchingKey) {
21 | rtg.GenRotationKey(share, crp, &rotKey.SwitchingKey)
22 | }
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dckks/utils.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package dckks
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
5 | )
6 |
7 | func extendBasisSmallNormAndCenter(ringQ, ringP *ring.Ring, polQ, polP *ring.Poly) {
8 | var coeff, Q, QHalf, sign uint64
9 | Q = ringQ.Modulus[0]
10 | QHalf = Q >> 1
11 |
12 | for j := 0; j < ringQ.N; j++ {
13 |
14 | coeff = polQ.Coeffs[0][j]
15 |
16 | sign = 1
17 | if coeff > QHalf {
18 | coeff = Q - coeff
19 | sign = 0
20 | }
21 |
22 | for i, pi := range ringP.Modulus {
23 | polP.Coeffs[i][j] = (coeff * sign) | (pi-coeff)*(sign^1)
24 | }
25 | }
26 | }
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/drlwe/public_key_gen.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | //Package drlwe implements a distributed (or threshold) version of the CKKS scheme that enables secure multiparty computation solutions with secret-shared secret keys.
2 | package drlwe
3 |
4 | import (
5 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/rlwe"
7 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
8 | )
9 |
10 | // CollectivePublicKeyGenerator is an interface describing the local steps of a generic RLWE CKG protocol
11 | type CollectivePublicKeyGenerator interface {
12 | AllocateShares() *CKGShare
13 | GenShare(sk *rlwe.SecretKey, crs *ring.Poly, shareOut *CKGShare)
14 | AggregateShares(share1, share2, shareOut *CKGShare)
15 | GenPublicKey(aggregatedShare *CKGShare, crs *ring.Poly, pubkey *rlwe.PublicKey)
16 | }
17 |
18 | // CKGProtocol is the structure storing the parameters and and precomputations for the collective key generation protocol.
19 | type CKGProtocol struct {
20 | n int
21 |
22 | ringQ *ring.Ring
23 | ringP *ring.Ring
24 | ringQP *ring.Ring
25 | gaussianSampler *ring.GaussianSampler
26 | sigma float64
27 | }
28 |
29 | // CKGShare is a struct storing the CKG protocol's share.
30 | type CKGShare struct {
31 | *ring.Poly
32 | }
33 |
34 | // UnmarshalBinary decode a marshaled CKG share on the target CKG share.
35 | func (share *CKGShare) UnmarshalBinary(data []byte) error {
36 | if share.Poly == nil {
37 | share.Poly = new(ring.Poly)
38 | }
39 | err := share.Poly.UnmarshalBinary(data)
40 | return err
41 | }
42 |
43 | // NewCKGProtocol creates a new CKGProtocol instance
44 | func NewCKGProtocol(n int, q, p []uint64, sigma float64) *CKGProtocol { // TODO drlwe.Params
45 |
46 | ckg := new(CKGProtocol)
47 | var err error
48 | if ckg.ringQ, err = ring.NewRing(n, q); err != nil {
49 | panic(err) // TODO error
50 | }
51 |
52 | if ckg.ringP, err = ring.NewRing(n, p); err != nil {
53 | panic(err)
54 | }
55 |
56 | if ckg.ringQP, err = ring.NewRing(n, append(q, p...)); err != nil {
57 | panic(err)
58 | }
59 |
60 | prng, err := utils.NewPRNG()
61 | if err != nil {
62 | panic(err)
63 | }
64 | ckg.gaussianSampler = ring.NewGaussianSampler(prng)
65 | ckg.sigma = sigma
66 | return ckg
67 | }
68 |
69 | // AllocateShares allocates the share of the CKG protocol.
70 | func (ckg *CKGProtocol) AllocateShares() *CKGShare {
71 | return &CKGShare{ckg.ringQP.NewPoly()}
72 | }
73 |
74 | // GenShare generates the party's public key share from its secret key as:
75 | //
76 | // crs*s_i + e_i
77 | //
78 | // for the receiver protocol. Has no effect is the share was already generated.
79 | func (ckg *CKGProtocol) GenShare(sk *rlwe.SecretKey, crs *ring.Poly, shareOut *CKGShare) {
80 | ringQP := ckg.ringQP
81 | ckg.gaussianSampler.Read(shareOut.Poly, ckg.ringQP, ckg.sigma, int(6*ckg.sigma))
82 | ringQP.NTT(shareOut.Poly, shareOut.Poly)
83 | ringQP.MulCoeffsMontgomeryAndSub(sk.Value, crs, shareOut.Poly)
84 | }
85 |
86 | // AggregateShares aggregates a new share to the aggregate key
87 | func (ckg *CKGProtocol) AggregateShares(share1, share2, shareOut *CKGShare) {
88 | ckg.ringQP.Add(share1.Poly, share2.Poly, shareOut.Poly)
89 | }
90 |
91 | // GenPublicKey return the current aggregation of the received shares as a bfv.PublicKey.
92 | func (ckg *CKGProtocol) GenPublicKey(roundShare *CKGShare, crs *ring.Poly, pubkey *rlwe.PublicKey) {
93 | pubkey.Value[0].Copy(roundShare.Poly)
94 | pubkey.Value[1].Copy(crs)
95 | }
96 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/drlwe/rot_key_gen.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package drlwe
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "encoding/binary"
5 | "errors"
6 | "math"
7 | "math/big"
8 |
9 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
10 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/rlwe"
11 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
12 | )
13 |
14 | // RotationKeyGenerator is an interface for the local operation in the generation of rotation keys
15 | type RotationKeyGenerator interface {
16 | AllocateShares() (rtgShare *RTGShare)
17 | GenShare(sk *rlwe.SecretKey, galEl uint64, crp []*ring.Poly, shareOut *RTGShare)
18 | Aggregate(share1, share2, shareOut *RTGShare)
19 | GenRotationKey(share *RTGShare, crp []*ring.Poly, rotKey *rlwe.SwitchingKey)
20 | }
21 |
22 | // RTGShare is represent a Party's share in the RTG protocol
23 | type RTGShare struct {
24 | Value []*ring.Poly
25 | }
26 |
27 | // RTGProtocol is the structure storing the parameters for the collective rotation-keys generation.
28 | type RTGProtocol struct { // TODO rename GaloisKeyGen ?
29 | ringQP *ring.Ring
30 | ringPModulusBigint *big.Int
31 | ringQModCount int
32 | alpha int
33 | beta int
34 |
35 | tmpPoly [2]*ring.Poly
36 | gaussianSampler *ring.GaussianSampler
37 | sigma float64
38 | }
39 |
40 | // NewRTGProtocol creates a RTGProtocol instance
41 | func NewRTGProtocol(n int, q, p []uint64, sigma float64) *RTGProtocol {
42 | rtg := new(RTGProtocol)
43 | rtg.ringQModCount = len(q)
44 | rtg.ringPModulusBigint = big.NewInt(1)
45 | for _, pi := range p {
46 | rtg.ringPModulusBigint.Mul(rtg.ringPModulusBigint, new(big.Int).SetUint64(pi))
47 | }
48 | rtg.alpha = len(p)
49 | if rtg.alpha != 0 {
50 | rtg.beta = int(math.Ceil(float64(len(q)) / float64(len(p))))
51 | } else {
52 | rtg.beta = 1
53 | }
54 | var err error
55 | rtg.ringQP, err = ring.NewRing(n, append(q, p...))
56 | if err != nil {
57 | panic(err) // TODO error
58 | }
59 |
60 | prng, err := utils.NewPRNG()
61 | if err != nil {
62 | panic(err)
63 | }
64 | rtg.gaussianSampler = ring.NewGaussianSampler(prng)
65 | rtg.sigma = sigma
66 |
67 | rtg.tmpPoly = [2]*ring.Poly{rtg.ringQP.NewPoly(), rtg.ringQP.NewPoly()}
68 |
69 | return rtg
70 | }
71 |
72 | // AllocateShares allocates a party's share in the RTG protocol
73 | func (rtg *RTGProtocol) AllocateShares() (rtgShare *RTGShare) {
74 | rtgShare = new(RTGShare)
75 | rtgShare.Value = make([]*ring.Poly, rtg.beta)
76 | for i := range rtgShare.Value {
77 | rtgShare.Value[i] = rtg.ringQP.NewPoly()
78 | }
79 | return
80 | }
81 |
82 | // GenShare generates a party's share in the RTG protocol
83 | func (rtg *RTGProtocol) GenShare(sk *rlwe.SecretKey, galEl uint64, crp []*ring.Poly, shareOut *RTGShare) {
84 |
85 | twoN := rtg.ringQP.N << 2
86 | galElInv := ring.ModExp(galEl, int(twoN-1), uint64(twoN))
87 |
88 | ring.PermuteNTT(sk.Value, galElInv, rtg.tmpPoly[1])
89 |
90 | rtg.ringQP.MulScalarBigint(sk.Value, rtg.ringPModulusBigint, rtg.tmpPoly[0])
91 |
92 | var index int
93 |
94 | for i := 0; i < rtg.beta; i++ {
95 |
96 | // e
97 | rtg.gaussianSampler.Read(shareOut.Value[i], rtg.ringQP, rtg.sigma, int(6*rtg.sigma))
98 | rtg.ringQP.NTTLazy(shareOut.Value[i], shareOut.Value[i])
99 | rtg.ringQP.MForm(shareOut.Value[i], shareOut.Value[i])
100 |
101 | // a is the CRP
102 |
103 | // e + sk_in * (qiBarre*qiStar) * 2^w
104 | // (qiBarre*qiStar)%qi = 1, else 0
105 | for j := 0; j < rtg.alpha; j++ {
106 |
107 | index = i*rtg.alpha + j
108 |
109 | qi := rtg.ringQP.Modulus[index]
110 | tmp0 := rtg.tmpPoly[0].Coeffs[index]
111 | tmp1 := shareOut.Value[i].Coeffs[index]
112 |
113 | for w := 0; w < rtg.ringQP.N; w++ {
114 | tmp1[w] = ring.CRed(tmp1[w]+tmp0[w], qi)
115 | }
116 |
117 | // Handles the case where nb pj does not divides nb qi
118 | if index >= rtg.ringQModCount {
119 | break
120 | }
121 | }
122 |
123 | // sk_in * (qiBarre*qiStar) * 2^w - a*sk + e
124 | rtg.ringQP.MulCoeffsMontgomeryAndSub(crp[i], rtg.tmpPoly[1], shareOut.Value[i])
125 | }
126 |
127 | rtg.tmpPoly[0].Zero()
128 | rtg.tmpPoly[1].Zero()
129 |
130 | return
131 | }
132 |
133 | // Aggregate aggregates two shares in the Rotation Key Generation protocol
134 | func (rtg *RTGProtocol) Aggregate(share1, share2, shareOut *RTGShare) {
135 | for i := 0; i < rtg.beta; i++ {
136 | rtg.ringQP.Add(share1.Value[i], share2.Value[i], shareOut.Value[i])
137 | }
138 | }
139 |
140 | // GenRotationKey finalizes the RTG protocol and populates the input RotationKey with the computed collective SwitchingKey.
141 | func (rtg *RTGProtocol) GenRotationKey(share *RTGShare, crp []*ring.Poly, rotKey *rlwe.SwitchingKey) {
142 | for i := 0; i < rtg.beta; i++ {
143 | rtg.ringQP.Copy(share.Value[i], rotKey.Value[i][0])
144 | rtg.ringQP.Copy(crp[i], rotKey.Value[i][1])
145 | }
146 | }
147 |
148 | // MarshalBinary encode the target element on a slice of byte.
149 | func (share *RTGShare) MarshalBinary() ([]byte, error) {
150 | lenRing := share.Value[0].GetDataLen(true)
151 | data := make([]byte, 8+lenRing*len(share.Value))
152 | binary.BigEndian.PutUint64(data[:8], uint64(lenRing))
153 | ptr := 8
154 | for _, val := range share.Value {
155 | cnt, err := val.WriteTo(data[ptr : ptr+lenRing])
156 | if err != nil {
157 | return []byte{}, err
158 | }
159 | ptr += cnt
160 | }
161 |
162 | return data, nil
163 | }
164 |
165 | // UnmarshalBinary decodes a slice of bytes on the target element.
166 | func (share *RTGShare) UnmarshalBinary(data []byte) error {
167 | if len(data) <= 8 {
168 | return errors.New("Unsufficient data length")
169 | }
170 |
171 | lenRing := binary.BigEndian.Uint64(data[:8])
172 | valLength := uint64(len(data)-8) / lenRing
173 | share.Value = make([]*ring.Poly, valLength)
174 | ptr := uint64(8)
175 | for i := range share.Value {
176 | share.Value[i] = new(ring.Poly)
177 | err := share.Value[i].UnmarshalBinary(data[ptr : ptr+lenRing])
178 | if err != nil {
179 | return err
180 | }
181 | ptr += lenRing
182 | }
183 |
184 | return nil
185 | }
186 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/bfv/main.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package main
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "fmt"
5 | "math"
6 | "math/bits"
7 |
8 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
9 |
10 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/bfv"
11 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ring"
12 | )
13 |
14 | func obliviousRiding() {
15 |
16 | // This example simulates a situation where an anonymous rider
17 | // wants to find the closest available rider within a given area.
18 | // The application is inspired by the paper https://oride.epfl.ch/
19 | //
20 | // A. Pham, I. Dacosta, G. Endignoux, J. Troncoso-Pastoriza,
21 | // K. Huguenin, and J.-P. Hubaux. ORide: A Privacy-Preserving
22 | // yet Accountable Ride-Hailing Service. In Proceedings of the
23 | // 26th USENIX Security Symposium, Vancouver, BC, Canada, August 2017.
24 | //
25 | // Each area is represented as a rectangular grid where each driver
26 | // anyonymously signs in (i.e. the server only knows the driver is located
27 | // in the area).
28 | //
29 | // First, the rider generates an ephemeral key pair (riderSk, riderPk), which she
30 | // uses to encrypt her coordinates. She then sends the tuple (riderPk, enc(coordinates))
31 | // to the server handling the area she is in.
32 | //
33 | // Once the public key and the encrypted rider coordinates of the rider
34 | // have been received by the server, the rider's public key is transferred
35 | // to all the drivers within the area, with a randomized different index
36 | // for each of them, that indicates in which coefficient each driver must
37 | // encode her coordinates.
38 | //
39 | // Each driver encodes her coordinates in the designated coefficient and
40 | // uses the received public key to encrypt her encoded coordinates.
41 | // She then sends back the encrypted coordinates to the server.
42 | //
43 | // Once the encrypted coordinates of the drivers have been received, the server
44 | // homomorphically computes the squared distance: (x0 - x1)^2 + (y0 - y1)^2 between
45 | // the rider and each of the drivers, and sends back the encrypted result to the rider.
46 | //
47 | // The rider decrypts the result and chooses the closest driver.
48 |
49 | // Number of drivers in the area
50 | nbDrivers := 2048 //max is N
51 |
52 | // BFV parameters (128 bit security) with plaintext modulus 65929217
53 | params := bfv.DefaultParams[bfv.PN13QP218].WithT(0x3ee0001)
54 |
55 | encoder := bfv.NewEncoder(params)
56 |
57 | // Rider's keygen
58 | kgen := bfv.NewKeyGenerator(params)
59 |
60 | riderSk, riderPk := kgen.GenKeyPair()
61 |
62 | decryptor := bfv.NewDecryptor(params, riderSk)
63 |
64 | encryptorRiderPk := bfv.NewEncryptorFromPk(params, riderPk)
65 |
66 | encryptorRiderSk := bfv.NewEncryptorFromSk(params, riderSk)
67 |
68 | evaluator := bfv.NewEvaluator(params, bfv.EvaluationKey{})
69 |
70 | fmt.Println("============================================")
71 | fmt.Println("Homomorphic computations on batched integers")
72 | fmt.Println("============================================")
73 | fmt.Println()
74 | fmt.Printf("Parameters : N=%d, T=%d, Q = %d bits, sigma = %f \n",
75 | 1< nbDrivers-5 {
156 | fmt.Printf("Distance with Driver %d : %8d = (%4d - %4d)^2 + (%4d - %4d)^2 --> correct: %t\n",
157 | i, computedDist, driverPosX, riderPosX, driverPosY, riderPosY, computedDist == expectedDist)
158 | }
159 |
160 | if i == nbDrivers>>1 {
161 | fmt.Println("...")
162 | }
163 | }
164 |
165 | fmt.Printf("\nFinished with %.2f%% errors\n\n", 100*float64(errors)/float64(nbDrivers))
166 | fmt.Printf("Closest Driver to Rider is n°%d (%d, %d) with a distance of %d units\n",
167 | minIndex, minPosX, minPosY, int(math.Sqrt(float64(minDist))))
168 | }
169 |
170 | func distance(a, b, c, d uint64) uint64 {
171 | if a > c {
172 | a, c = c, a
173 | }
174 | if b > d {
175 | b, d = d, b
176 | }
177 | x, y := a-c, b-d
178 | return x*x + y*y
179 | }
180 |
181 | func main() {
182 | obliviousRiding()
183 | }
184 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/ckks/bootstrapping/example/main.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package main
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "fmt"
5 | "math"
6 |
7 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ckks"
8 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
9 | )
10 |
11 | func main() {
12 |
13 | var err error
14 |
15 | var btp *ckks.Bootstrapper
16 | var kgen ckks.KeyGenerator
17 | var encoder ckks.Encoder
18 | var sk *ckks.SecretKey
19 | var pk *ckks.PublicKey
20 | var encryptor ckks.Encryptor
21 | var decryptor ckks.Decryptor
22 | var plaintext *ckks.Plaintext
23 |
24 | // Bootstrapping parameters
25 | // Four sets of parameters (index 0 to 3) ensuring 128 bit of security
26 | // are available in github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/ckks/bootstrap_params
27 | // LogSlots is hardcoded to 15 in the parameters, but can be changed from 1 to 15.
28 | // When changing logSlots make sure that the number of levels allocated to CtS and StC is
29 | // smaller or equal to logSlots.
30 |
31 | btpParams := ckks.DefaultBootstrapParams[0]
32 | params, err := btpParams.Params()
33 | if err != nil {
34 | panic(err)
35 | }
36 |
37 | fmt.Println()
38 | fmt.Printf("CKKS parameters: logN = %d, logSlots = %d, h = %d, logQP = %d, levels = %d, scale= 2^%f, sigma = %f \n", params.LogN(), params.LogSlots(), btpParams.H, params.LogQP(), params.Levels(), math.Log2(params.Scale()), params.Sigma())
39 |
40 | // Scheme context and keys
41 | kgen = ckks.NewKeyGenerator(params)
42 |
43 | sk, pk = kgen.GenKeyPairSparse(btpParams.H)
44 |
45 | encoder = ckks.NewEncoder(params)
46 | decryptor = ckks.NewDecryptor(params, sk)
47 | encryptor = ckks.NewEncryptorFromPk(params, pk)
48 |
49 | fmt.Println()
50 | fmt.Println("Generating bootstrapping keys...")
51 | rotations := kgen.GenRotationIndexesForBootstrapping(params.LogSlots(), btpParams)
52 | rotkeys := kgen.GenRotationKeysForRotations(rotations, true, sk)
53 | rlk := kgen.GenRelinearizationKey(sk)
54 | btpKey := ckks.BootstrappingKey{Rlk: rlk, Rtks: rotkeys}
55 | if btp, err = ckks.NewBootstrapper(params, btpParams, btpKey); err != nil {
56 | panic(err)
57 | }
58 | fmt.Println("Done")
59 |
60 | // Generate a random plaintext
61 | valuesWant := make([]complex128, params.Slots())
62 | for i := range valuesWant {
63 | valuesWant[i] = utils.RandComplex128(-1, 1)
64 | }
65 |
66 | plaintext = encoder.EncodeNew(valuesWant, params.LogSlots())
67 |
68 | // Encrypt
69 | ciphertext1 := encryptor.EncryptNew(plaintext)
70 |
71 | // Decrypt, print and compare with the plaintext values
72 | fmt.Println()
73 | fmt.Println("Precision of values vs. ciphertext")
74 | valuesTest1 := printDebug(params, ciphertext1, valuesWant, decryptor, encoder)
75 |
76 | // Bootstrap the ciphertext (homomorphic re-encryption)
77 | // It takes a ciphertext at level 0 (if not at level 0, then it will reduce it to level 0)
78 | // and returns a ciphertext at level MaxLevel - k, where k is the depth of the bootstrapping circuit.
79 | // CAUTION: the scale of the ciphertext MUST be equal (or very close) to params.Scale
80 | // To equalize the scale, the function evaluator.SetScale(ciphertext, parameters.Scale) can be used at the expense of one level.
81 | fmt.Println()
82 | fmt.Println("Bootstrapping...")
83 | ciphertext2 := btp.Bootstrapp(ciphertext1)
84 | fmt.Println("Done")
85 |
86 | // Decrypt, print and compare with the plaintext values
87 | fmt.Println()
88 | fmt.Println("Precision of ciphertext vs. Bootstrapp(ciphertext)")
89 | printDebug(params, ciphertext2, valuesTest1, decryptor, encoder)
90 | }
91 |
92 | func printDebug(params *ckks.Parameters, ciphertext *ckks.Ciphertext, valuesWant []complex128, decryptor ckks.Decryptor, encoder ckks.Encoder) (valuesTest []complex128) {
93 |
94 | valuesTest = encoder.Decode(decryptor.DecryptNew(ciphertext), params.LogSlots())
95 |
96 | fmt.Println()
97 | fmt.Printf("Level: %d (logQ = %d)\n", ciphertext.Level(), params.LogQLvl(ciphertext.Level()))
98 | fmt.Printf("Scale: 2^%f\n", math.Log2(ciphertext.Scale()))
99 | fmt.Printf("ValuesTest: %6.10f %6.10f %6.10f %6.10f...\n", valuesTest[0], valuesTest[1], valuesTest[2], valuesTest[3])
100 | fmt.Printf("ValuesWant: %6.10f %6.10f %6.10f %6.10f...\n", valuesWant[0], valuesWant[1], valuesWant[2], valuesWant[3])
101 |
102 | precStats := ckks.GetPrecisionStats(params, encoder, nil, valuesWant, valuesTest, params.LogSlots(), 0)
103 |
104 | fmt.Println(precStats.String())
105 | fmt.Println()
106 |
107 | return
108 | }
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/ckks/bootstrapping/experiments/run_slotcount.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #/bin/sh
2 |
3 | go build boot_precision.go
4 |
5 | mkdir -p out
6 |
7 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -paramSet 0 slotcount | tee out/slotcount_p0.tex
8 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -paramSet 1 slotcount | tee out/slotcount_p1.tex
9 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -paramSet 2 slotcount | tee out/slotcount_p2.tex
10 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -paramSet 3 slotcount | tee out/slotcount_p4.tex
11 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -paramSet 4 slotcount | tee out/slotcount_p5.tex
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/ckks/bootstrapping/experiments/run_slotdist.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #/bin/sh
2 |
3 | go build boot_precision.go
4 |
5 | mkdir -p out
6 |
7 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 14 -paramSet 0 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p0_14.tex
8 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 15 -paramSet 0 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p0_15.tex
9 |
10 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 14 -paramSet 1 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p1_14.tex
11 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 15 -paramSet 1 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p1_15.tex
12 |
13 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 14 -paramSet 2 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p2_14.tex
14 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 15 -paramSet 2 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p2_15.tex
15 |
16 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 14 -paramSet 3 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p3_14.tex
17 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 15 -paramSet 3 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p3_15.tex
18 |
19 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 13 -paramSet 4 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p4_13.tex
20 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 14 -paramSet 4 slotdist | tee out/slotdist_p4_14.tex
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/ckks/bootstrapping/experiments/run_successive.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #/bin/sh
2 |
3 | go build boot_precision.go
4 |
5 | mkdir -p out
6 |
7 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 15 -nboot 50 -paramSet 0 successive | tee out/successive_p0.tex
8 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 15 -nboot 50 -paramSet 1 successive | tee out/successive_p1.tex
9 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 15 -nboot 50 -paramSet 2 successive | tee out/successive_p2.tex
10 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 15 -nboot 50 -paramSet 3 successive | tee out/successive_p3.tex
11 | ./boot_precision -makeplot -logslot 14 -nboot 50 -paramSet 4 successive | tee out/successive_p4.tex
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/ckks/bootstrapping/experiments/tpl/slotcount.tex.tpl:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | \begin{tikzpicture}
2 | \begin{axis}[
3 | title={},
4 | width=0.50\textwidth,
5 | height=0.50\textwidth,
6 | xlabel={$\log(\text{slots})$},
7 | ylabel={$\log(1/\epsilon)$},
8 | xmin=3, xmax=16,
9 | ymin=8, ymax=40,
10 | xtick distance = 2,
11 | ytick distance = 2,
12 | legend pos=north west,
13 | ymajorgrids=true,
14 | grid style=dashed],
15 | ]
16 | \addplot+[color=red, mark=triangle*, error bars/.cd, y dir=both, y explicit]
17 | coordinates{
18 | {{.DataReal}}};
19 | \addplot+[color=blue, mark=square*, error bars/.cd, y dir=both, y explicit]
20 | coordinates{
21 | {{.DataImag}}
22 | };
23 | \legend{Real, Imag}
24 |
25 | \end{axis}
26 | \end{tikzpicture}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/ckks/bootstrapping/experiments/tpl/slotdist.tex.tpl:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | \begin{tikzpicture}
2 | \begin{axis}[
3 | title={},
4 | width=0.5\textwidth,
5 | height=0.5\textwidth,
6 | xlabel={$\log(1/\epsilon)$},
7 | ylabel={$\Pr[\log(1/\epsilon_{i})= q {
14 | r -= q
15 | }
16 | return
17 | }
18 |
19 | // MFormConstant switches a to the Montgomery domain by computing
20 | // a*2^64 mod q in constant time.
21 | // The result is between 0 and 2*q-1.
22 | func MFormConstant(a, q uint64, u []uint64) (r uint64) {
23 | mhi, _ := bits.Mul64(a, u[1])
24 | r = -(a*u[0] + mhi) * q
25 | return
26 | }
27 |
28 | // InvMForm switches a from the Montgomery domain back to the
29 | // standard domain by computing a*(1/2^64) mod q.
30 | func InvMForm(a, q, qInv uint64) (r uint64) {
31 | r, _ = bits.Mul64(a*qInv, q)
32 | r = q - r
33 | if r >= q {
34 | r -= q
35 | }
36 | return
37 | }
38 |
39 | // InvMFormConstant switches a from the Montgomery domain back to the
40 | // standard domain by computing a*(1/2^64) mod q in constant time.
41 | // The result is between 0 and 2*q-1.
42 | func InvMFormConstant(a, q, qInv uint64) (r uint64) {
43 | r, _ = bits.Mul64(a*qInv, q)
44 | r = q - r
45 | return
46 | }
47 |
48 | // MRedParams computes the parameter qInv = (q^-1) mod 2^64,
49 | // required for MRed.
50 | func MRedParams(q uint64) (qInv uint64) {
51 | qInv = 1
52 | for i := 0; i < 63; i++ {
53 | qInv *= q
54 | q *= q
55 | }
56 | return
57 | }
58 |
59 | // MRed computes x * y * (1/2^64) mod q.
60 | func MRed(x, y, q, qInv uint64) (r uint64) {
61 | mhi, mlo := bits.Mul64(x, y)
62 | hhi, _ := bits.Mul64(mlo*qInv, q)
63 | r = mhi - hhi + q
64 | if r >= q {
65 | r -= q
66 | }
67 | return
68 | }
69 |
70 | // MRedConstant computes x * y * (1/2^64) mod q in constant time.
71 | // The result is between 0 and 2*q-1.
72 | func MRedConstant(x, y, q, qInv uint64) (r uint64) {
73 | ahi, alo := bits.Mul64(x, y)
74 | H, _ := bits.Mul64(alo*qInv, q)
75 | r = ahi - H + q
76 | return
77 | }
78 |
79 | // BRedParams computes the parameters for the BRed algorithm.
80 | // Returns ((2^128)/q)/(2^64) and (2^128)/q mod 2^64.
81 | func BRedParams(q uint64) (params []uint64) {
82 | bigR := new(big.Int).Lsh(NewUint(1), 128)
83 | bigR.Quo(bigR, NewUint(q))
84 |
85 | mhi := new(big.Int).Rsh(bigR, 64).Uint64()
86 | mlo := bigR.Uint64()
87 |
88 | return []uint64{mhi, mlo}
89 | }
90 |
91 | // BRedAdd computes a mod q.
92 | func BRedAdd(a, q uint64, u []uint64) (r uint64) {
93 | mhi, _ := bits.Mul64(a, u[0])
94 | r = a - mhi*q
95 | if r >= q {
96 | r -= q
97 | }
98 | return
99 | }
100 |
101 | // BRedAddConstant computes a mod q in constant time.
102 | // The result is between 0 and 2*q-1.
103 | func BRedAddConstant(x, q uint64, u []uint64) uint64 {
104 | s0, _ := bits.Mul64(x, u[0])
105 | return x - s0*q
106 | }
107 |
108 | // BRed computes x*y mod q.
109 | func BRed(x, y, q uint64, u []uint64) (r uint64) {
110 |
111 | var mhi, mlo, lhi, hhi, hlo, s0, carry uint64
112 |
113 | mhi, mlo = bits.Mul64(x, y)
114 |
115 | // computes r = mhi * uhi + (mlo * uhi + mhi * ulo)<<64 + (mlo * ulo)) >> 128
116 |
117 | r = mhi * u[0] // r = mhi * uhi
118 |
119 | hhi, hlo = bits.Mul64(mlo, u[0]) // mlo * uhi
120 |
121 | r += hhi
122 |
123 | lhi, _ = bits.Mul64(mlo, u[1]) // mlo * ulo
124 |
125 | s0, carry = bits.Add64(hlo, lhi, 0)
126 |
127 | r += carry
128 |
129 | hhi, hlo = bits.Mul64(mhi, u[1]) // mhi * ulo
130 |
131 | r += hhi
132 |
133 | _, carry = bits.Add64(hlo, s0, 0)
134 |
135 | r += carry
136 |
137 | r = mlo - r*q
138 |
139 | if r >= q {
140 | r -= q
141 | }
142 |
143 | return
144 | }
145 |
146 | // BRedConstant computes x*y mod q in constant time.
147 | // The result is between 0 and 2*q-1.
148 | func BRedConstant(x, y, q uint64, u []uint64) (r uint64) {
149 |
150 | var mhi, mlo, lhi, hhi, hlo, s0, carry uint64
151 |
152 | mhi, mlo = bits.Mul64(x, y)
153 |
154 | // computes r = mhi * uhi + (mlo * uhi + mhi * ulo)<<64 + (mlo * ulo)) >> 128
155 |
156 | r = mhi * u[0] // r = mhi * uhi
157 |
158 | hhi, hlo = bits.Mul64(mlo, u[0]) // mlo * uhi
159 |
160 | r += hhi
161 |
162 | lhi, _ = bits.Mul64(mlo, u[1]) // mlo * ulo
163 |
164 | s0, carry = bits.Add64(hlo, lhi, 0)
165 |
166 | r += carry
167 |
168 | hhi, hlo = bits.Mul64(mhi, u[1]) // mhi * ulo
169 |
170 | r += hhi
171 |
172 | _, carry = bits.Add64(hlo, s0, 0)
173 |
174 | r += carry
175 |
176 | r = mlo - r*q
177 |
178 | return
179 | }
180 |
181 | // CRed reduce returns a mod q where a is between 0 and 2*q-1.
182 | func CRed(a, q uint64) uint64 {
183 | if a >= q {
184 | return a - q
185 | }
186 | return a
187 | }
188 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ring/primes.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ring
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "fmt"
5 | "math/bits"
6 | )
7 |
8 | // IsPrime applies the Baillie-PSW, which is 100% accurate for numbers bellow 2^64.
9 | func IsPrime(x uint64) bool {
10 | return NewUint(x).ProbablyPrime(0)
11 | }
12 |
13 | // GenerateNTTPrimes generates n NthRoot NTT friendly primes given logQ = size of the primes.
14 | // It will return all the appropriate primes, up to the number of n, with the
15 | // best available deviation from the base power of 2 for the given n.
16 | func GenerateNTTPrimes(logQ, NthRoot, n int) (primes []uint64) {
17 |
18 | if logQ > 61 {
19 | panic("logQ must be between 1 and 61")
20 | }
21 |
22 | if logQ == 61 {
23 | return GenerateNTTPrimesP(logQ, NthRoot, n)
24 | }
25 |
26 | return GenerateNTTPrimesQ(logQ, NthRoot, n)
27 | }
28 |
29 | // NextNTTPrime returns the next NthRoot NTT prime after q.
30 | // The input q must be itself an NTT prime for the given NthRoot.
31 | func NextNTTPrime(q uint64, NthRoot int) (qNext uint64, err error) {
32 |
33 | qNext = q + uint64(NthRoot)
34 |
35 | for !IsPrime(qNext) {
36 |
37 | qNext += uint64(NthRoot)
38 |
39 | if bits.Len64(qNext) > 61 {
40 | return 0, fmt.Errorf("next NTT prime exceeds the maximum bit-size of 61 bits")
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | return qNext, nil
45 | }
46 |
47 | // PreviousNTTPrime returns the previous NthRoot NTT prime after q.
48 | // The input q must be itself an NTT prime for the given NthRoot.
49 | func PreviousNTTPrime(q uint64, NthRoot int) (qPrev uint64, err error) {
50 |
51 | if q < uint64(NthRoot) {
52 | return 0, fmt.Errorf("previous NTT prime is smaller than NthRoot")
53 | }
54 |
55 | qPrev = q - uint64(NthRoot)
56 |
57 | for !IsPrime(qPrev) {
58 |
59 | if q < uint64(NthRoot) {
60 | return 0, fmt.Errorf("previous NTT prime is smaller than NthRoot")
61 | }
62 |
63 | qPrev -= uint64(NthRoot)
64 | }
65 |
66 | return qPrev, nil
67 | }
68 |
69 | // GenerateNTTPrimesQ generates "levels" different NthRoot NTT-friendly
70 | // primes starting from 2**LogQ and alternating between upward and downward.
71 | func GenerateNTTPrimesQ(logQ, NthRoot, levels int) (primes []uint64) {
72 |
73 | var nextPrime, previousPrime, Qpow2 uint64
74 | var checkfornextprime, checkforpreviousprime bool
75 |
76 | primes = []uint64{}
77 |
78 | Qpow2 = uint64(1 << logQ)
79 |
80 | nextPrime = Qpow2 + 1
81 | previousPrime = Qpow2 + 1
82 |
83 | checkfornextprime = true
84 | checkforpreviousprime = true
85 |
86 | for {
87 |
88 | if !(checkfornextprime || checkforpreviousprime) {
89 | panic("generateNTTPrimesQ error: cannot generate enough primes for the given parameters")
90 | }
91 |
92 | if checkfornextprime {
93 |
94 | if nextPrime > 0xffffffffffffffff-uint64(NthRoot) {
95 |
96 | checkfornextprime = false
97 |
98 | } else {
99 |
100 | nextPrime += uint64(NthRoot)
101 |
102 | if IsPrime(nextPrime) {
103 |
104 | primes = append(primes, nextPrime)
105 |
106 | if len(primes) == levels {
107 | return
108 | }
109 | }
110 | }
111 | }
112 |
113 | if checkforpreviousprime {
114 |
115 | if previousPrime < uint64(NthRoot) {
116 |
117 | checkforpreviousprime = false
118 |
119 | } else {
120 |
121 | previousPrime -= uint64(NthRoot)
122 |
123 | if IsPrime(previousPrime) {
124 |
125 | primes = append(primes, previousPrime)
126 |
127 | if len(primes) == levels {
128 | return
129 | }
130 | }
131 | }
132 |
133 | }
134 | }
135 | }
136 |
137 | // GenerateNTTPrimesP generates "levels" different NthRoot NTT-friendly
138 | // primes starting from 2**LogP and downward.
139 | // Special case were primes close to 2^{LogP} but with a smaller bit-size than LogP are sought.
140 | func GenerateNTTPrimesP(logP, NthRoot, n int) (primes []uint64) {
141 |
142 | var x, Ppow2 uint64
143 |
144 | primes = []uint64{}
145 |
146 | Ppow2 = uint64(1 << logP)
147 |
148 | x = Ppow2 + 1
149 |
150 | for {
151 |
152 | // We start by subtracting 2N to ensure that the prime bit-length is smaller than LogP
153 |
154 | if x > uint64(NthRoot) {
155 |
156 | x -= uint64(NthRoot)
157 |
158 | if IsPrime(x) {
159 |
160 | primes = append(primes, x)
161 |
162 | if len(primes) == n {
163 | return primes
164 | }
165 | }
166 |
167 | } else {
168 | panic("generateNTTPrimesP error: cannot generate enough primes for the given parameters")
169 | }
170 | }
171 | }
172 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ring/ring_automorphism.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ring
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "math/bits"
5 | "unsafe"
6 |
7 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
8 | )
9 |
10 | // GenGaloisParams generates the generators for the Galois endomorphisms.
11 | func GenGaloisParams(n, gen uint64) (galElRotCol []uint64) {
12 |
13 | var m, mask uint64
14 |
15 | m = n << 1
16 |
17 | mask = m - 1
18 |
19 | galElRotCol = make([]uint64, n>>1)
20 |
21 | galElRotCol[0] = 1
22 |
23 | for i := uint64(1); i < n>>1; i++ {
24 | galElRotCol[i] = (galElRotCol[i-1] * gen) & mask
25 | }
26 |
27 | return
28 | }
29 |
30 | // PermuteNTTIndex computes the index table for PermuteNTT.
31 | func PermuteNTTIndex(galEl, N uint64) (index []uint64) {
32 |
33 | var mask, logN, tmp1, tmp2 uint64
34 |
35 | logN = uint64(bits.Len64(N) - 1)
36 |
37 | mask = (N << 1) - 1
38 |
39 | index = make([]uint64, N)
40 |
41 | for i := uint64(0); i < N; i++ {
42 | tmp1 = 2*utils.BitReverse64(i, logN) + 1
43 |
44 | tmp2 = ((galEl * tmp1 & mask) - 1) >> 1
45 |
46 | index[i] = utils.BitReverse64(tmp2, logN)
47 | }
48 |
49 | return
50 | }
51 |
52 | // PermuteNTT applies the Galois transform on a polynomial in the NTT domain.
53 | // It maps the coefficients x^i to x^(gen*i)
54 | // It must be noted that the result cannot be in-place.
55 | func PermuteNTT(polIn *Poly, gen uint64, polOut *Poly) {
56 |
57 | var N, tmp, mask, logN, tmp1, tmp2 uint64
58 |
59 | N = uint64(len(polIn.Coeffs[0]))
60 |
61 | logN = uint64(bits.Len64(N) - 1)
62 |
63 | mask = (N << 1) - 1
64 |
65 | index := make([]uint64, N)
66 |
67 | for i := uint64(0); i < N; i++ {
68 | tmp1 = 2*utils.BitReverse64(i, logN) + 1
69 |
70 | tmp2 = ((gen * tmp1 & mask) - 1) >> 1
71 |
72 | index[i] = utils.BitReverse64(tmp2, logN)
73 | }
74 |
75 | for j := uint64(0); j < N; j++ {
76 |
77 | tmp = index[j]
78 |
79 | for i := 0; i < len(polIn.Coeffs); i++ {
80 |
81 | polOut.Coeffs[i][j] = polIn.Coeffs[i][tmp]
82 | }
83 | }
84 | }
85 |
86 | // PermuteNTTLvl applies the Galois transform on a polynomial in the NTT domain, up to a given level.
87 | // It maps the coefficients x^i to x^(gen*i)
88 | // It must be noted that the result cannot be in-place.
89 | func PermuteNTTLvl(level int, polIn *Poly, gen uint64, polOut *Poly) {
90 |
91 | var tmp, tmp1, tmp2 uint64
92 |
93 | N := len(polIn.Coeffs[0])
94 |
95 | logN := uint64(bits.Len64(uint64(N)) - 1)
96 |
97 | mask := uint64((N << 1) - 1)
98 |
99 | index := make([]uint64, N)
100 |
101 | for i := 0; i < N; i++ {
102 | tmp1 = 2*utils.BitReverse64(uint64(i), logN) + 1
103 |
104 | tmp2 = ((gen * tmp1 & mask) - 1) >> 1
105 |
106 | index[i] = utils.BitReverse64(tmp2, logN)
107 | }
108 |
109 | for j := 0; j < N; j++ {
110 |
111 | tmp = index[j]
112 |
113 | for i := 0; i < level+1; i++ {
114 |
115 | polOut.Coeffs[i][j] = polIn.Coeffs[i][tmp]
116 | }
117 | }
118 | }
119 |
120 | // PermuteNTTWithIndexLvl applies the Galois transform on a polynomial in the NTT domain, up to a given level.
121 | // It maps the coefficients x^i to x^(gen*i) using the PermuteNTTIndex table.
122 | // It must be noted that the result cannot be in-place.
123 | func PermuteNTTWithIndexLvl(level int, polIn *Poly, index []uint64, polOut *Poly) {
124 |
125 | for j := 0; j < len(polIn.Coeffs[0]); j = j + 8 {
126 |
127 | x := (*[8]uint64)(unsafe.Pointer(&index[j]))
128 |
129 | for i := 0; i < level+1; i++ {
130 |
131 | z := (*[8]uint64)(unsafe.Pointer(&polOut.Coeffs[i][j]))
132 | y := polIn.Coeffs[i]
133 |
134 | z[0] = y[x[0]]
135 | z[1] = y[x[1]]
136 | z[2] = y[x[2]]
137 | z[3] = y[x[3]]
138 | z[4] = y[x[4]]
139 | z[5] = y[x[5]]
140 | z[6] = y[x[6]]
141 | z[7] = y[x[7]]
142 | }
143 | }
144 | }
145 |
146 | // PermuteNTTWithIndexAndAddNoModLvl applies the Galois transform on a polynomial in the NTT domain, up to a given level,
147 | // and adds the result to the output polynomial without modular reduction.
148 | // It maps the coefficients x^i to x^(gen*i) using the PermuteNTTIndex table.
149 | // It must be noted that the result cannot be in-place.
150 | func PermuteNTTWithIndexAndAddNoModLvl(level int, polIn *Poly, index []uint64, polOut *Poly) {
151 |
152 | for j := 0; j < len(polIn.Coeffs[0]); j = j + 8 {
153 |
154 | x := (*[8]uint64)(unsafe.Pointer(&index[j]))
155 |
156 | for i := 0; i < level+1; i++ {
157 |
158 | z := (*[8]uint64)(unsafe.Pointer(&polOut.Coeffs[i][j]))
159 | y := polIn.Coeffs[i]
160 |
161 | z[0] += y[x[0]]
162 | z[1] += y[x[1]]
163 | z[2] += y[x[2]]
164 | z[3] += y[x[3]]
165 | z[4] += y[x[4]]
166 | z[5] += y[x[5]]
167 | z[6] += y[x[6]]
168 | z[7] += y[x[7]]
169 | }
170 | }
171 | }
172 |
173 | // Permute applies the Galois transform on a polynomial outside of the NTT domain.
174 | // It maps the coefficients x^i to x^(gen*i)
175 | // It must be noted that the result cannot be in-place.
176 | func (r *Ring) Permute(polIn *Poly, gen uint64, polOut *Poly) {
177 |
178 | var mask, index, indexRaw, logN, tmp uint64
179 |
180 | mask = uint64(r.N - 1)
181 |
182 | logN = uint64(bits.Len64(mask))
183 |
184 | for i := uint64(0); i < uint64(r.N); i++ {
185 |
186 | indexRaw = i * gen
187 |
188 | index = indexRaw & mask
189 |
190 | tmp = (indexRaw >> logN) & 1
191 |
192 | for j, qi := range r.Modulus {
193 |
194 | polOut.Coeffs[j][index] = polIn.Coeffs[j][i]*(tmp^1) | (qi-polIn.Coeffs[j][i])*tmp
195 | }
196 | }
197 | }
198 |
199 | // PermuteLvl applies the Galois transform on a polynomial outside of the NTT domain.
200 | // It maps the coefficients x^i to x^(gen*i)
201 | // It must be noted that the result cannot be in-place.
202 | func (r *Ring) PermuteLvl(level int, polIn *Poly, gen uint64, polOut *Poly) {
203 |
204 | var mask, index, indexRaw, logN, tmp uint64
205 |
206 | mask = uint64(r.N - 1)
207 |
208 | logN = uint64(bits.Len64(mask))
209 |
210 | for i := uint64(0); i < uint64(r.N); i++ {
211 |
212 | indexRaw = i * gen
213 |
214 | index = indexRaw & mask
215 |
216 | tmp = (indexRaw >> logN) & 1
217 |
218 | // for j, qi := range r.Modulus {
219 | for j := 0; j < level+1; j++ {
220 |
221 | qi := r.Modulus[j]
222 | polOut.Coeffs[j][index] = polIn.Coeffs[j][i]*(tmp^1) | (qi-polIn.Coeffs[j][i])*tmp
223 | }
224 | }
225 | }
226 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ring/ring_sampler.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ring
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
5 | )
6 |
7 | const precision = uint64(56)
8 |
9 | type baseSampler struct {
10 | prng utils.PRNG
11 | baseRing *Ring
12 | }
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ring/ring_sampler_uniform.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ring
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "encoding/binary"
5 |
6 | "github.com/ldsec/lattigo/v2/utils"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // UniformSampler wraps a util.PRNG and represents the state of a sampler of uniform polynomials.
10 | type UniformSampler struct {
11 | baseSampler
12 | randomBufferN []byte
13 | }
14 |
15 | // NewUniformSampler creates a new instance of UniformSampler from a PRNG and ring definition.
16 | func NewUniformSampler(prng utils.PRNG, baseRing *Ring) *UniformSampler {
17 | uniformSampler := new(UniformSampler)
18 | uniformSampler.baseRing = baseRing
19 | uniformSampler.prng = prng
20 | uniformSampler.randomBufferN = make([]byte, baseRing.N)
21 | return uniformSampler
22 | }
23 |
24 | // Read generates a new polynomial with coefficients following a uniform distribution over [0, Qi-1].
25 | func (uniformSampler *UniformSampler) Read(Pol *Poly) {
26 |
27 | var randomUint, mask, qi uint64
28 | var ptr int
29 |
30 | uniformSampler.prng.Clock(uniformSampler.randomBufferN)
31 |
32 | for j := range uniformSampler.baseRing.Modulus {
33 |
34 | qi = uniformSampler.baseRing.Modulus[j]
35 |
36 | // Start by computing the mask
37 | mask = uniformSampler.baseRing.Mask[j]
38 |
39 | ptmp := Pol.Coeffs[j]
40 |
41 | // Iterate for each modulus over each coefficient
42 | for i := 0; i < uniformSampler.baseRing.N; i++ {
43 |
44 | // Sample an integer between [0, qi-1]
45 | for {
46 |
47 | // Refill the pool if it runs empty
48 | if ptr == uniformSampler.baseRing.N {
49 | uniformSampler.prng.Clock(uniformSampler.randomBufferN)
50 | ptr = 0
51 | }
52 |
53 | // Read bytes from the pool
54 | randomUint = binary.BigEndian.Uint64(uniformSampler.randomBufferN[ptr:ptr+8]) & mask
55 | ptr += 8
56 |
57 | // If the integer is between [0, qi-1], break the loop
58 | if randomUint < qi {
59 | break
60 | }
61 | }
62 |
63 | ptmp[i] = randomUint
64 | }
65 | }
66 | }
67 |
68 | // Readlvl generates a new polynomial with coefficients following a uniform distribution over [0, Qi-1].
69 | func (uniformSampler *UniformSampler) Readlvl(level int, Pol *Poly) {
70 |
71 | var randomUint, mask, qi uint64
72 | var ptr int
73 |
74 | uniformSampler.prng.Clock(uniformSampler.randomBufferN)
75 |
76 | for j := 0; j < level+1; j++ {
77 |
78 | qi = uniformSampler.baseRing.Modulus[j]
79 |
80 | // Start by computing the mask
81 | mask = uniformSampler.baseRing.Mask[j]
82 |
83 | ptmp := Pol.Coeffs[j]
84 |
85 | // Iterate for each modulus over each coefficient
86 | for i := 0; i < uniformSampler.baseRing.N; i++ {
87 |
88 | // Sample an integer between [0, qi-1]
89 | for {
90 |
91 | // Refill the pool if it runs empty
92 | if ptr == uniformSampler.baseRing.N {
93 | uniformSampler.prng.Clock(uniformSampler.randomBufferN)
94 | ptr = 0
95 | }
96 |
97 | // Read bytes from the pool
98 | randomUint = binary.BigEndian.Uint64(uniformSampler.randomBufferN[ptr:ptr+8]) & mask
99 | ptr += 8
100 |
101 | // If the integer is between [0, qi-1], break the loop
102 | if randomUint < qi {
103 | break
104 | }
105 | }
106 |
107 | ptmp[i] = randomUint
108 | }
109 | }
110 | }
111 |
112 | // ReadNew generates a new polynomial with coefficients following a uniform distribution over [0, Qi-1].
113 | // Polynomial is created at the max level.
114 | func (uniformSampler *UniformSampler) ReadNew() (Pol *Poly) {
115 | Pol = uniformSampler.baseRing.NewPoly()
116 | uniformSampler.Read(Pol)
117 | return
118 | }
119 |
120 | // ReadLvlNew generates a new polynomial with coefficients following a uniform distribution over [0, Qi-1].
121 | // Polynomial is created at the specified level.
122 | func (uniformSampler *UniformSampler) ReadLvlNew(level int) (Pol *Poly) {
123 | Pol = uniformSampler.baseRing.NewPolyLvl(level)
124 | uniformSampler.Read(Pol)
125 | return
126 | }
127 |
128 | // RandUniform samples a uniform randomInt variable in the range [0, mask] until randomInt is in the range [0, v-1].
129 | // mask needs to be of the form 2^n -1.
130 | func RandUniform(prng utils.PRNG, v uint64, mask uint64) (randomInt uint64) {
131 | for {
132 | randomInt = randInt64(prng, mask)
133 | if randomInt < v {
134 | return randomInt
135 | }
136 | }
137 | }
138 |
139 | // randInt32 samples a uniform variable in the range [0, mask], where mask is of the form 2^n-1, with n in [0, 32].
140 | func randInt32(prng utils.PRNG, mask uint64) uint64 {
141 |
142 | // generate random 4 bytes
143 | randomBytes := make([]byte, 4)
144 | prng.Clock(randomBytes)
145 |
146 | // convert 4 bytes to a uint32
147 | randomUint32 := uint64(binary.BigEndian.Uint32(randomBytes))
148 |
149 | // return required bits
150 | return mask & randomUint32
151 | }
152 |
153 | // randInt64 samples a uniform variable in the range [0, mask], where mask is of the form 2^n-1, with n in [0, 64].
154 | func randInt64(prng utils.PRNG, mask uint64) uint64 {
155 |
156 | // generate random 8 bytes
157 | randomBytes := make([]byte, 8)
158 | prng.Clock(randomBytes)
159 |
160 | // convert 8 bytes to a uint64
161 | randomUint64 := binary.BigEndian.Uint64(randomBytes)
162 |
163 | // return required bits
164 | return mask & randomUint64
165 | }
166 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ring/ring_test_params.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package ring
2 |
3 | // Parameters is a struct storing test parameters for the package Ring.
4 | type Parameters struct {
5 | logN uint64
6 | qi []uint64
7 | pi []uint64
8 | }
9 |
10 | // DefaultParams is a struct storing default test parameters of the Qi and Pi moduli for the package Ring.
11 | var DefaultParams = []*Parameters{
12 | {12, Qi60[len(Qi60)-2:], Pi60[len(Pi60)-2:]},
13 | {13, Qi60[len(Qi60)-4:], Pi60[len(Pi60)-4:]},
14 | {14, Qi60[len(Qi60)-7:], Pi60[len(Pi60)-7:]},
15 | {15, Qi60[len(Qi60)-14:], Pi60[len(Pi60)-14:]},
16 | {16, Qi60[len(Qi60)-29:], Pi60[len(Pi60)-29:]},
17 | }
18 |
19 | // Qi60 are the first [0:32] 61-bit close to 2^{62} NTT-friendly primes for N up to 2^{17}
20 | var Qi60 = []uint64{0x1fffffffffe00001, 0x1fffffffffc80001, 0x1fffffffffb40001, 0x1fffffffff500001,
21 | 0x1fffffffff380001, 0x1fffffffff000001, 0x1ffffffffef00001, 0x1ffffffffee80001,
22 | 0x1ffffffffeb40001, 0x1ffffffffe780001, 0x1ffffffffe600001, 0x1ffffffffe4c0001,
23 | 0x1ffffffffdf40001, 0x1ffffffffdac0001, 0x1ffffffffda40001, 0x1ffffffffc680001,
24 | 0x1ffffffffc000001, 0x1ffffffffb880001, 0x1ffffffffb7c0001, 0x1ffffffffb300001,
25 | 0x1ffffffffb1c0001, 0x1ffffffffadc0001, 0x1ffffffffa400001, 0x1ffffffffa140001,
26 | 0x1ffffffff9d80001, 0x1ffffffff9140001, 0x1ffffffff8ac0001, 0x1ffffffff8a80001,
27 | 0x1ffffffff81c0001, 0x1ffffffff7800001, 0x1ffffffff7680001, 0x1ffffffff7080001}
28 |
29 | // Pi60 are the next [32:64] 61-bit close to 2^{62} NTT-friendly primes for N up to 2^{17}
30 | var Pi60 = []uint64{0x1ffffffff6c80001, 0x1ffffffff6140001, 0x1ffffffff5f40001, 0x1ffffffff5700001,
31 | 0x1ffffffff4bc0001, 0x1ffffffff4380001, 0x1ffffffff3240001, 0x1ffffffff2dc0001,
32 | 0x1ffffffff1a40001, 0x1ffffffff11c0001, 0x1ffffffff0fc0001, 0x1ffffffff0d80001,
33 | 0x1ffffffff0c80001, 0x1ffffffff08c0001, 0x1fffffffefd00001, 0x1fffffffef9c0001,
34 | 0x1fffffffef600001, 0x1fffffffeef40001, 0x1fffffffeed40001, 0x1fffffffeed00001,
35 | 0x1fffffffeebc0001, 0x1fffffffed540001, 0x1fffffffed440001, 0x1fffffffed2c0001,
36 | 0x1fffffffed200001, 0x1fffffffec940001, 0x1fffffffec6c0001, 0x1fffffffebe80001,
37 | 0x1fffffffebac0001, 0x1fffffffeba40001, 0x1fffffffeb4c0001, 0x1fffffffeb280001}
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils/buffer.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // Package utils contains helper structures and function
2 | package utils
3 |
4 | // Buffer is a simple wrapper around a []byte to facilitate efficient marshaling of lattigo's objects
5 | type Buffer struct {
6 | buf []byte
7 | }
8 |
9 | // NewBuffer creates a new buffer from the provided backing slice
10 | func NewBuffer(s []byte) *Buffer {
11 | return &Buffer{s}
12 | }
13 |
14 | // WriteUint8 writes an uint8 on the target byte buffer.
15 | func (b *Buffer) WriteUint8(c byte) {
16 | b.buf = append(b.buf, c)
17 | }
18 |
19 | // WriteUint64 writes an uint64 on the target byte buffer.
20 | func (b *Buffer) WriteUint64(v uint64) {
21 | b.buf = append(b.buf, byte(v>>56),
22 | byte(v>>48),
23 | byte(v>>40),
24 | byte(v>>32),
25 | byte(v>>24),
26 | byte(v>>16),
27 | byte(v>>8),
28 | byte(v))
29 | }
30 |
31 | // WriteUint64Slice writes an uint64 slice on the target byte buffer.
32 | func (b *Buffer) WriteUint64Slice(s []uint64) {
33 | for _, v := range s {
34 | b.WriteUint64(v)
35 | }
36 | }
37 |
38 | // WriteUint8Slice writes an uint8 slice on the target byte buffer.
39 | func (b *Buffer) WriteUint8Slice(s []uint8) {
40 | for _, v := range s {
41 | b.WriteUint8(v)
42 | }
43 | }
44 |
45 | // ReadUint8 reads an uint8 from the target byte buffer.
46 | func (b *Buffer) ReadUint8() byte {
47 | v := b.buf[0]
48 | b.buf = b.buf[1:]
49 | return v
50 | }
51 |
52 | // ReadUint64 reads an uint64 from the target byte buffer.
53 | func (b *Buffer) ReadUint64() uint64 {
54 | v := b.buf[:8]
55 | b.buf = b.buf[8:]
56 | return uint64(v[7]) | uint64(v[6])<<8 | uint64(v[5])<<16 | uint64(v[4])<<24 |
57 | uint64(v[3])<<32 | uint64(v[2])<<40 | uint64(v[1])<<48 | uint64(v[0])<<56
58 | }
59 |
60 | // ReadUint64Slice reads an uint64 slice from the target byte buffer.
61 | func (b *Buffer) ReadUint64Slice(rec []uint64) {
62 | for i := range rec {
63 | rec[i] = b.ReadUint64()
64 | }
65 | }
66 |
67 | // ReadUint8Slice reads an uint8 slice from the target byte buffer.
68 | func (b *Buffer) ReadUint8Slice(rec []uint8) {
69 | for i := range rec {
70 | rec[i] = b.ReadUint8()
71 | }
72 | }
73 |
74 | // Bytes creates a new byte buffer
75 | func (b *Buffer) Bytes() []byte {
76 | return b.buf
77 | }
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils/buffer_test.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // Package containing helper structures and function
2 | package utils
3 |
4 | import (
5 | "github.com/stretchr/testify/assert"
6 | "testing"
7 | )
8 |
9 | func TestNewBuffer(t *testing.T) {
10 | assert.Equal(t, []byte(nil), NewBuffer(nil).Bytes())
11 | assert.Equal(t, []byte{}, NewBuffer([]byte{}).Bytes())
12 | assert.Equal(t, []byte{1, 2, 3}, NewBuffer([]byte{1, 2, 3}).Bytes())
13 | }
14 |
15 | func TestBuffer_WriteReadUint8(t *testing.T) {
16 | b := NewBuffer(make([]byte, 0, 1))
17 | b.WriteUint8(0xff)
18 | assert.Equal(t, []byte{0xff}, b.Bytes())
19 | assert.Equal(t, byte(0xff), b.ReadUint8())
20 | assert.Equal(t, []byte{}, b.Bytes())
21 | }
22 |
23 | func TestBuffer_WriteReadUint64(t *testing.T) {
24 | b := NewBuffer(make([]byte, 0, 8))
25 | b.WriteUint64(0x1122334455667788)
26 | assert.Equal(t, []byte{0x11, 0x22, 0x33, 0x44, 0x55, 0x66, 0x77, 0x88}, b.Bytes())
27 | assert.Equal(t, uint64(0x1122334455667788), b.ReadUint64())
28 | assert.Equal(t, []byte{}, b.Bytes())
29 | }
30 |
31 | func TestBuffer_WriteReadUint64Slice(t *testing.T) {
32 | b := NewBuffer(make([]byte, 0, 8))
33 | b.WriteUint64Slice([]uint64{0x1122334455667788})
34 | assert.Equal(t, []byte{0x11, 0x22, 0x33, 0x44, 0x55, 0x66, 0x77, 0x88}, b.Bytes())
35 | s := make([]uint64, 1)
36 | b.ReadUint64Slice(s)
37 | assert.Equal(t, []uint64{0x1122334455667788}, s)
38 | assert.Equal(t, []byte{}, b.Bytes())
39 | }
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils/prng.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package utils
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "crypto/rand"
5 | "errors"
6 |
7 | "golang.org/x/crypto/blake2b"
8 | )
9 |
10 | // PRNG is an interface for secure (keyed) deterministic generation of random bytes
11 | type PRNG interface {
12 | Clock(sum []byte)
13 | GetClock() uint64
14 | SetClock(sum []byte, n uint64) error
15 | }
16 |
17 | // KeyedPRNG is a structure storing the parameters used to securely and deterministically generate shared
18 | // sequences of random bytes among different parties using the hash function blake2b. Backward sequence
19 | // security (given the digest i, compute the digest i-1) is ensured by default, however forward sequence
20 | // security (given the digest i, compute the digest i+1) is only ensured if the KeyedPRNG is keyed.
21 | type KeyedPRNG struct {
22 | clock uint64
23 | xof blake2b.XOF
24 | }
25 |
26 | // NewKeyedPRNG creates a new instance of KeyedPRNG.
27 | // Accepts an optional key, else set key=nil which is treated as key=[]byte{}
28 | // WARNING: A PRNG INITIALISED WITH key=nil IS INSECURE!
29 | func NewKeyedPRNG(key []byte) (*KeyedPRNG, error) {
30 | var err error
31 | prng := new(KeyedPRNG)
32 | prng.clock = 0
33 | prng.xof, err = blake2b.NewXOF(blake2b.OutputLengthUnknown, key)
34 | return prng, err
35 | }
36 |
37 | // NewPRNG creates KeyedPRNG keyed from rand.Read for instances were no key should be provided by the user
38 | func NewPRNG() (*KeyedPRNG, error) {
39 | var err error
40 | prng := new(KeyedPRNG)
41 | prng.clock = 0
42 | randomBytes := make([]byte, 64)
43 | if _, err := rand.Read(randomBytes); err != nil {
44 | panic("crypto rand error")
45 | }
46 | prng.xof, err = blake2b.NewXOF(blake2b.OutputLengthUnknown, randomBytes)
47 | return prng, err
48 | }
49 |
50 | // GetClock returns the value of the clock cycle of the KeyedPRNG.
51 | func (prng *KeyedPRNG) GetClock() uint64 {
52 | return prng.clock
53 | }
54 |
55 | // Clock reads bytes from the KeyedPRNG on sum.
56 | func (prng *KeyedPRNG) Clock(sum []byte) {
57 | if _, err := prng.xof.Read(sum); err != nil {
58 | panic(err)
59 | }
60 | prng.clock++
61 | }
62 |
63 | // SetClock sets the clock cycle of the KeyedPRNG to a given number by calling Clock until
64 | // the clock cycle reaches the desired number. Returns an error if the target clock
65 | // cycle is smaller than the current clock cycle.
66 | func (prng *KeyedPRNG) SetClock(sum []byte, n uint64) error {
67 | if prng.clock > n {
68 | return errors.New("error: cannot set KeyedPRNG clock to a previous state")
69 | }
70 | for prng.clock != n {
71 | if _, err := prng.xof.Read(sum); err != nil {
72 | panic(err)
73 | }
74 | prng.clock++
75 | }
76 | return nil
77 | }
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils/prng_test.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package utils
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "testing"
5 |
6 | "github.com/stretchr/testify/require"
7 | )
8 |
9 | func Test_PRNG(t *testing.T) {
10 |
11 | t.Run("PRNG", func(t *testing.T) {
12 |
13 | key := []byte{0x49, 0x0a, 0x42, 0x3d, 0x97, 0x9d, 0xc1, 0x07, 0xa1, 0xd7, 0xe9, 0x7b, 0x3b, 0xce, 0xa1, 0xdb,
14 | 0x42, 0xf3, 0xa6, 0xd5, 0x75, 0xd2, 0x0c, 0x92, 0xb7, 0x35, 0xce, 0x0c, 0xee, 0x09, 0x7c, 0x98}
15 |
16 | Ha, _ := NewKeyedPRNG(key)
17 | Hb, _ := NewKeyedPRNG(key)
18 |
19 | sum0 := make([]byte, 512)
20 | sum1 := make([]byte, 512)
21 |
22 | Ha.SetClock(sum0, 256)
23 | Hb.SetClock(sum1, 128)
24 |
25 | for i := 0; i < 128; i++ {
26 | Hb.Clock(sum1)
27 | }
28 |
29 | Ha.Clock(sum0)
30 | Hb.Clock(sum1)
31 |
32 | require.Equal(t, sum0, sum1)
33 | })
34 |
35 | }
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils/utils.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package utils
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "crypto/rand"
5 | "encoding/binary"
6 | "math/bits"
7 | )
8 |
9 | // RandUint64 return a random value between 0 and 0xFFFFFFFFFFFFFFFF
10 | func RandUint64() uint64 {
11 | b := []byte{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
12 | if _, err := rand.Read(b); err != nil {
13 | panic(err)
14 | }
15 | return binary.BigEndian.Uint64(b)
16 | }
17 |
18 | // RandFloat64 returns a random float between min and max
19 | func RandFloat64(min, max float64) float64 {
20 | b := []byte{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}
21 | if _, err := rand.Read(b); err != nil {
22 | panic(err)
23 | }
24 | f := float64(binary.BigEndian.Uint64(b)) / 1.8446744073709552e+19
25 | return min + f*(max-min)
26 | }
27 |
28 | // RandComplex128 returns a random complex with the real and imaginary part between min and max
29 | func RandComplex128(min, max float64) complex128 {
30 | return complex(RandFloat64(min, max), RandFloat64(min, max))
31 | }
32 |
33 | // EqualSliceUint64 checks the equality between two uint64 slices.
34 | func EqualSliceUint64(a, b []uint64) (v bool) {
35 | v = true
36 | for i := range a {
37 | v = v && (a[i] == b[i])
38 | }
39 | return
40 | }
41 |
42 | // EqualSliceInt64 checks the equality between two int64 slices.
43 | func EqualSliceInt64(a, b []int64) (v bool) {
44 | v = true
45 | for i := range a {
46 | v = v && (a[i] == b[i])
47 | }
48 | return
49 | }
50 |
51 | // EqualSliceUint8 checks the equality between two uint8 slices.
52 | func EqualSliceUint8(a, b []uint8) (v bool) {
53 | v = true
54 | for i := range a {
55 | v = v && (a[i] == b[i])
56 | }
57 | return
58 | }
59 |
60 | // IsInSliceUint64 checks if x is in slice.
61 | func IsInSliceUint64(x uint64, slice []uint64) (v bool) {
62 | for i := range slice {
63 | v = v || (slice[i] == x)
64 | }
65 | return
66 | }
67 |
68 | // IsInSliceInt checks if x is in slice.
69 | func IsInSliceInt(x int, slice []int) (v bool) {
70 | for i := range slice {
71 | v = v || (slice[i] == x)
72 | }
73 | return
74 | }
75 |
76 | // MinUint64 returns the minimum value of the input of uint64 values.
77 | func MinUint64(a, b uint64) (r uint64) {
78 | if a <= b {
79 | return a
80 | }
81 | return b
82 | }
83 |
84 | // MinInt returns the minimum value of the input of int values.
85 | func MinInt(a, b int) (r int) {
86 | if a <= b {
87 | return a
88 | }
89 | return b
90 | }
91 |
92 | // MaxUint64 returns the maximum value of the input of uint64 values.
93 | func MaxUint64(a, b uint64) (r uint64) {
94 | if a >= b {
95 | return a
96 | }
97 | return b
98 | }
99 |
100 | // MaxInt returns the maximum value of the input of int values.
101 | func MaxInt(a, b int) (r int) {
102 | if a >= b {
103 | return a
104 | }
105 | return b
106 | }
107 |
108 | // MaxFloat64 returns the maximum value of the input slice of float64 values.
109 | func MaxFloat64(a, b float64) (r float64) {
110 | if a >= b {
111 | return a
112 | }
113 | return b
114 | }
115 |
116 | // MaxSliceUint64 returns the maximum value of the input slice of uint64 values.
117 | func MaxSliceUint64(slice []uint64) (max uint64) {
118 | for i := range slice {
119 | max = MaxUint64(max, slice[i])
120 | }
121 | return
122 | }
123 |
124 | // BitReverse64 returns the bit-reverse value of the input value, within a context of 2^bitLen.
125 | func BitReverse64(index, bitLen uint64) uint64 {
126 | return bits.Reverse64(index) >> (64 - bitLen)
127 | }
128 |
129 | // HammingWeight64 returns the hammingweight if the input value.
130 | func HammingWeight64(x uint64) uint64 {
131 | x -= (x >> 1) & 0x5555555555555555
132 | x = (x & 0x3333333333333333) + ((x >> 2) & 0x3333333333333333)
133 | x = (x + (x >> 4)) & 0x0f0f0f0f0f0f0f0f
134 | return ((x * 0x0101010101010101) & 0xffffffffffffffff) >> 56
135 | }
136 |
137 | // AllDistinct returns true if all elements in s are distinct, and false otherwise.
138 | func AllDistinct(s []uint64) bool {
139 | m := make(map[uint64]struct{}, len(s))
140 | for _, si := range s {
141 | if _, exists := m[si]; exists {
142 | return false
143 | }
144 | m[si] = struct{}{}
145 | }
146 | return true
147 | }
148 |
149 | // RotateUint64Slice returns a new slice corresponding to s rotated by k positions to the left.
150 | func RotateUint64Slice(s []uint64, k int) []uint64 {
151 | if k == 0 || len(s) == 0 {
152 | return s
153 | }
154 | r := k % len(s)
155 | if r < 0 {
156 | r = r + len(s)
157 | }
158 | ret := make([]uint64, len(s), len(s))
159 | copy(ret[:len(s)-r], s[r:])
160 | copy(ret[len(s)-r:], s[:r])
161 | return ret
162 | }
163 |
164 | // RotateUint64Slots returns a new slice corresponding to s where each half of the slice
165 | // have been rotated by k positions to the left.
166 | func RotateUint64Slots(s []uint64, k int) []uint64 {
167 | ret := make([]uint64, len(s), len(s))
168 | slots := len(s) >> 1
169 | copy(ret[:slots], RotateUint64Slice(s[:slots], k))
170 | copy(ret[slots:], RotateUint64Slice(s[slots:], k))
171 | return ret
172 | }
173 |
174 | // RotateComplex128Slice returns a new slice corresponding to s rotated by k positions to the left.
175 | func RotateComplex128Slice(s []complex128, k int) []complex128 {
176 | if k == 0 || len(s) == 0 {
177 | return s
178 | }
179 | r := k % len(s)
180 | if r < 0 {
181 | r = r + len(s)
182 | }
183 | ret := make([]complex128, len(s), len(s))
184 | copy(ret[:len(s)-r], s[r:])
185 | copy(ret[len(s)-r:], s[:r])
186 | return ret
187 | }
188 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils/utils_test.go:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package utils
2 |
3 | import (
4 | "testing"
5 |
6 | "github.com/stretchr/testify/require"
7 | )
8 |
9 | func TestAllDistinct(t *testing.T) {
10 | require.True(t, AllDistinct([]uint64{}))
11 | require.True(t, AllDistinct([]uint64{1}))
12 | require.True(t, AllDistinct([]uint64{1, 2, 3}))
13 | require.False(t, AllDistinct([]uint64{1, 1}))
14 | require.False(t, AllDistinct([]uint64{1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5}))
15 | }
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
,
13 |
20 |
,
26 |