├── paparazzi
└── README.md
├── README.md
├── ArduPilot
└── README.md
└── PX4
└── README.md
/paparazzi/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Robotic-vehicle-software-tutorial
2 |
3 | ## 1. Quickstart for Ubuntu users
4 | Ubuntu 16.04 or Ubuntu 18.04:
5 | ```
6 | sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:paparazzi-uav/ppa && sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:team-gcc-arm-embedded/ppa && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -f -y install paparazzi-dev paparazzi-jsbsim gcc-arm-embedded dfu-util && cd ~ && git clone --origin upstream https://github.com/paparazzi/paparazzi.git && cd ~/paparazzi && git remote update -p && git checkout -b v5.18 upstream/v5.18 && sudo cp conf/system/udev/rules/*.rules /etc/udev/rules.d/ && sudo udevadm control --reload-rules && make && ./paparazzi
7 | ```
8 |
9 | Ubuntu 20.04
10 | ```
11 | sudo add-apt-repository -y ppa:paparazzi-uav/ppa && sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get -f -y install paparazzi-dev paparazzi-jsbsim python-is-python3 python3-serial gcc-arm-none-eabi gdb-multiarch dfu-util && cd ~ && git clone --origin upstream https://github.com/paparazzi/paparazzi.git && cd ~/paparazzi && git remote update -p && git checkout -b v5.18 upstream/v5.18 && sudo cp conf/system/udev/rules/*.rules /etc/udev/rules.d/ && sudo udevadm control --reload-rules && make && ./paparazzi
12 | ```
13 |
14 | ## 2. Step by step
15 | ### 2-1. Download Paparazzi
16 | ```
17 | git clone https://github.com/paparazzi/paparazzi.git [folder name]
18 | cd [folder name]
19 | git checkout [commit hash]
20 | git submodule update --init --recursive
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ### 2-2. Compilation and demo simulation
24 | ```
25 | cd [paparazzi root folder]
26 | make
27 | ./paparazzi
28 | ```
29 | - Select the "Microjet" aircraft in the upper-left A/C combo box.
30 | - Select "sim" from upper-middle "target" combo box. Click "Build".
31 | - When the compilation is finished, select "Simulation" from the upper-right session combo box and click "Execute".
32 | - In the GCS, wait about 10s for the aircraft to be in the "Holding point" navigation block.
33 | - Switch to the "Takeoff" block (lower-left blue airway button in the strip). Takeoff with the green launch button.
34 |
35 | ## 3. Simulating sensor attacks
36 | ### 3-1. Adding gyro noise
37 | ```
38 | cd [paparazzi root folder]
39 | vim ./sw/simulator/nps/nps_sensor_gyro.c
40 | ```
41 | Changing 'bias_initial' and 'bias_random_walk_std_dev'
42 | For example, you can add 30 degrees of noise as follows.
43 | ```
44 | VECT3_ASSIGN(gyro->bias_initial,
45 | RadOfDeg(30), RadOfDeg(30), RadOfDeg(30));
46 | ...
47 | VECT3_ASSIGN(gyro->bias_random_walk_std_dev,
48 | RadOfDeg(30),
49 | RadOfDeg(30),
50 | RadOfDeg(30));
51 | ```
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Robotic-vehicle-software-tutorial
2 |
3 | Hello! It is not straightforward to precisely manipulate robotic vehicles (RVs) on simulators when you especially want to simulate cyber-physical attacks/defense.
4 | I will keep sharing how I run RV software on simulators. If you want to contribute to this tutorial, please create a pull request.
5 |
6 | ## 1. Download and Setup
7 | ### 1-1 ArduPilot (SITL, Gazebo)
8 |  9 |
10 |
11 | ### 1-2 PX4 (jMAVSim, Gazebo)
12 |
9 |
10 |
11 | ### 1-2 PX4 (jMAVSim, Gazebo)
12 |  13 |
14 |
15 | ### 1-3 Paparazzi (NPS)
16 |
13 |
14 |
15 | ### 1-3 Paparazzi (NPS)
16 |  17 |
18 |
19 | ## 2. Execute control software
20 | ArduPilot
21 |
17 |
18 |
19 | ## 2. Execute control software
20 | ArduPilot
21 |
22 | PX4
23 |
24 | Paparazzi
25 |
26 | ## 3. Tutorials
27 | ### 3-1. ArduPilot
28 | Injecting sensor noise
29 |
30 | Turning off filters
31 |
32 | Leveraging an optical flow sensor
33 |
34 | Testing object avoidance algorithms
35 |
36 | Changing the start time clock (timestamp)
37 |
38 | Troubleshooting
39 |
40 | ### 3-2. PX4
41 | Injecting sensor noise in Gazebo simulation
42 |
43 | Leveraging an optical flow sensor
44 |
45 | Deploying PX4 v.1.13.0 into Crazyflie 2.1
46 |
47 | Simulating mmWave radar with ROS2 and PX4
48 |
49 | Troubleshooting
50 |
51 | ### 3-3. Paparazzi
52 | Simulating sensor attacks
53 |
54 |
55 | ### 3-4 Installing Pymavlink to manipulate vehicles by using Python
56 |
57 | #### Ubuntu 20.04
58 | ```
59 | sudo apt-get install gcc python-dev libxml2-dev libxslt-dev
60 | sudo apt-get install python-numpy python-pytest
61 | sudo apt install curl
62 | sudo apt install python2
63 | curl https://bootstrap.pypa.io/pip/2.7/get-pip.py --output get-pip.py
64 | sudo python2 get-pip.py
65 | sudo python2 -m pip install --upgrade future lxml
66 |
67 | git clone https://github.com/ArduPilot/mavlink.git
68 | cd mavlink
69 | git submodule update --init --recursive
70 | cd pymavlink
71 | sudo MDEF=`pwd`/../message_definitions python2 -m pip install . -v
72 | ```
73 |
74 | #### Ubuntu 22.04
75 | ```
76 | # Update list of available packages
77 | sudo apt update
78 | sudo apt -y upgrade
79 |
80 | # Install some dependencies
81 | sudo apt install -y python3-pip
82 |
83 | # Install mavproxy module and everything else needed
84 | pip3 install mavproxy
85 | ```
86 |
87 | ### 3-5. Ground Control Station (GCS) Software
88 |
89 | #### 3-5-1. Installing QGroundControl
90 | 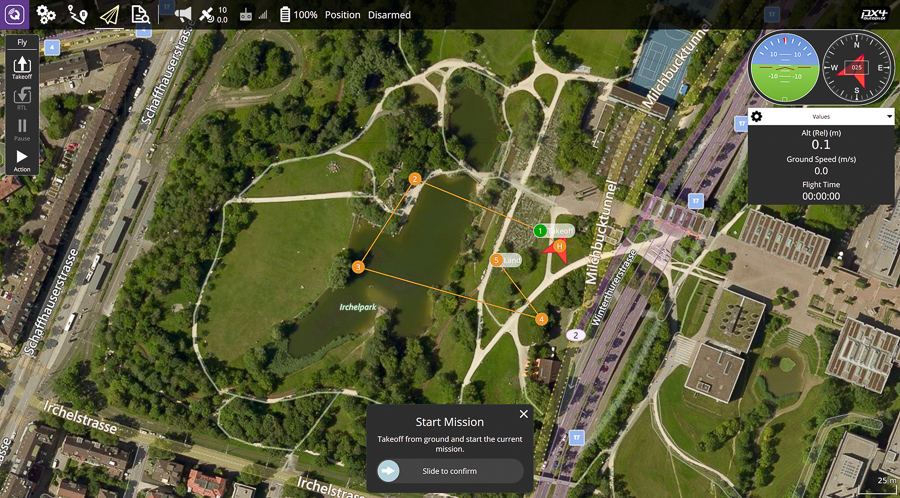 91 | When your operating system is Ubuntu 20.04 (or later version),
91 | When your operating system is Ubuntu 20.04 (or later version),
92 | ```
93 | sudo usermod -a -G dialout $USER
94 | sudo apt-get remove modemmanager -y
95 | sudo apt install gstreamer1.0-plugins-bad gstreamer1.0-libav gstreamer1.0-gl -y
96 | sudo apt install libqt5gui5 -y
97 | ```
98 | Logout and login again to enable the change to user permissions.
99 |
100 | Download QGroundControl
101 |
102 | When your operating system is Ubuntu 16.04,
103 | Download QGroundControl v3.5.6
104 |
105 | ```
106 | chmod +x ./QGroundControl.AppImage
107 | ./QGroundControl.AppImage (or double click)
108 | ```
109 | #### 3-5-2. Installing Mission Planner on Ubuntu 20.04
110 | 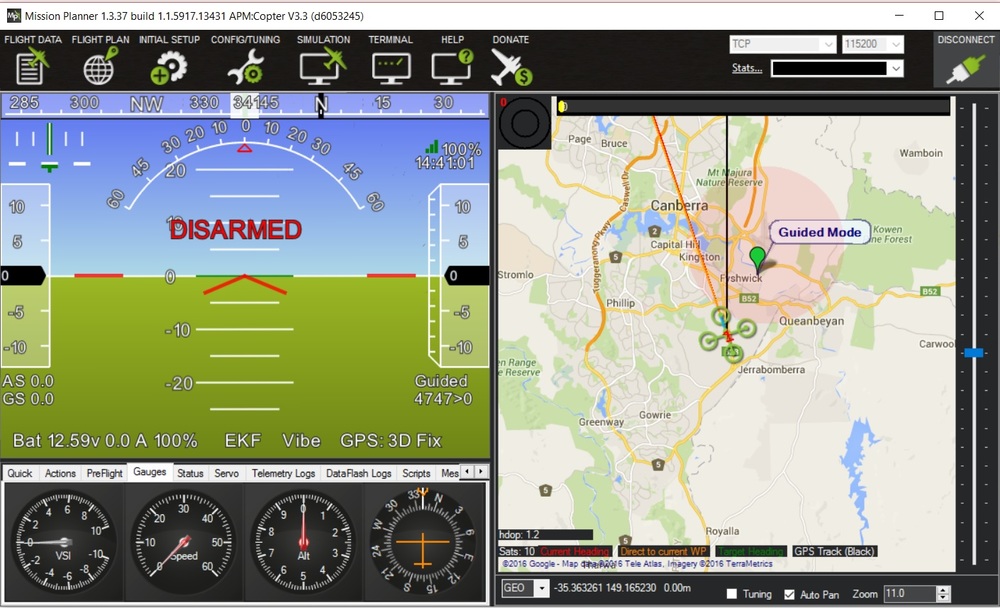 111 | Install dependecies
111 | Install dependecies
112 | ```
113 | sudo apt install mono-runtime libmono-system-windows-forms4.0-cil libmono-system-core4.0-cil libmono-system-management4.0-cil libmono-system-xml-linq4.0-cil
114 | ```
115 |
116 | Install mono
117 | ```
118 | sudo apt install mono-complete
119 | ```
120 | Get the lastest zipped version of Mission Planner (e.g., link)
121 |
122 | Unzip in the directory you want
123 |
124 | Go into the directory
125 |
126 | Run Mission Planner with mono
127 | ```
128 | mono MissionPlanner.exe
129 | ```
130 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ArduPilot/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Robotic-vehicle-software-tutorial
2 |
3 | ## 1. Download and Setup
4 | ```
5 | sudo apt-get update
6 | sudo apt-get install git
7 | sudo apt-get install gitk git-gui
8 |
9 | git clone https://github.com/ArduPilot/ardupilot.git ArduPilot
10 | cd ArduPilot
11 | git checkout [commit hash]
12 | git submodule update --init --recursive
13 |
14 | # If the command above fails to load submodule, you can try to use *https* instead of *git*.
15 | git config --global url."https://".insteadOf git://
16 |
17 | Tools/environment_install/install-prereqs-ubuntu.sh -y
18 | . ~/.profile
19 | ```
20 |
21 | When you meet "No such file or directory: mavproxy.py" error. Please install MAVProxy.
22 | ```
23 | sudo apt-get install python3-dev python3-opencv python3-wxgtk4.0 python3-pip python3-matplotlib python3-lxml python3-pygame
24 | pip3 install PyYAML mavproxy --user
25 | echo 'export PATH="$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin"' >> ~/.bashrc
26 | ```
27 |
28 | ## 2. Execute ArduPilot
29 | ### 2-1. SITL
30 | Copter
31 | ```
32 | ./Tools/autotest/sim_vehicle.py -v ArduCopter --console
33 | ```
34 |
35 | Plane
36 | ```
37 | ./Tools/autotest/sim_vehicle.py -v ArduPlane --console
38 | ```
39 |
40 | Rover
41 | ```
42 | ./Tools/autotest/sim_vehicle.py -v Rover --console
43 | ```
44 |
45 | Submarine
46 | ```
47 | ./Tools/autotest/sim_vehicle.py -v ArduSub --console
48 | ```
49 |
50 | Key build options
51 | 1) -c: do a make clean before building
52 | 2) -G: use gdb for debugging ardupilot
53 | 3) -w: wipe EEPROM and reload parameters
54 |
55 |
56 | ### 2-2. Gazebo
57 | #### Install Gazebo simulator
58 | gz-garden
59 | ```
60 | sudo apt-get update
61 | sudo apt-get install lsb-release wget gnupg
62 |
63 | sudo wget https://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo.gpg -O /usr/share/keyrings/pkgs-osrf-archive-keyring.gpg
64 | echo "deb [arch=$(dpkg --print-architecture) signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/pkgs-osrf-archive-keyring.gpg] http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo/ubuntu-stable $(lsb_release -cs) main" | sudo tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gazebo-stable.list > /dev/null
65 | sudo apt-get update
66 | sudo apt-get install gz-garden
67 | ```
68 |
69 | gazebo-classic
70 | ```
71 | sudo sh -c 'echo "deb http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo/ubuntu-stable `lsb_release -cs` main" > /etc/apt/sources.list.d/gazebo-stable.list'
72 | wget http://packages.osrfoundation.org/gazebo.key -O - | sudo apt-key add -
73 | sudo apt update
74 | sudo apt-get install gazebo11 libgazebo11-dev
75 | ```
76 |
77 | #### Install the ArduPilot Gazebo Plugin
78 | ```
79 | cd ~
80 | git clone https://github.com/khancyr/ardupilot_gazebo.git
81 |
82 | cd ardupilot_gazebo
83 | mkdir build
84 | cd build
85 | cmake ..
86 | make -j4
87 | sudo make install
88 | echo 'source /usr/share/gazebo/setup.sh' >> ~/.bashrc
89 | echo 'export GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH=~/ardupilot_gazebo/models' >> ~/.bashrc
90 | . ~/.bashrc
91 | ```
92 |
93 | #### Configure the Gazebo environment
94 | In a terminal
95 | ```
96 | export GZ_SIM_SYSTEM_PLUGIN_PATH=$HOME/gz_ws/src/ardupilot_gazebo/build:$GZ_SIM_SYSTEM_PLUGIN_PATH
97 | export GZ_SIM_RESOURCE_PATH=$HOME/gz_ws/src/ardupilot_gazebo/models:$HOME/gz_ws/src/ardupilot_gazebo/worlds:$GZ_SIM_RESOURCE_PATH
98 | ```
99 |
100 | In .bashrc or .zshrc
101 | ```
102 | echo 'export GZ_SIM_SYSTEM_PLUGIN_PATH=$HOME/gz_ws/src/ardupilot_gazebo/build:${GZ_SIM_SYSTEM_PLUGIN_PATH}' >> ~/.bashrc
103 | echo 'export GZ_SIM_RESOURCE_PATH=$HOME/gz_ws/src/ardupilot_gazebo/models:$HOME/gz_ws/src/ardupilot_gazebo/worlds:${GZ_SIM_RESOURCE_PATH}' >> ~/.bashrc
104 | ```
105 |
106 | #### Run Gazebo simulator
107 | ##### gz-garden
108 | Terminal 1
109 | ```
110 | gz sim -v4 -r iris_runway.sdf
111 | ```
112 |
113 | Terminal 2
114 | ```
115 | ./Tools/autotest/sim_vehicle.py -v ArduCopter -f gazebo-iris --model JSON --map --console
116 | ```
117 |
118 | ##### gazebo-classic
119 | Terminal 1
120 | ```
121 | gazebo --verbose ~/ardupilot_gazebo/worlds/iris_arducopter_runway.world
122 | ```
123 |
124 | Terminal 2
125 | ```
126 | ./Tools/autotest/sim_vehicle.py -v ArduCopter -f gazebo-iris --console
127 | ```
128 |
129 | ## 3. Injecting sensor noise
130 | ### 3-1. Gyro sensor
131 | Source code
132 | ```
133 | param set SIM_GYR1_RND 3
134 | param set SIM_GYR2_RND 3
135 | param set SIM_GYR3_RND 3
136 | ```
137 |
138 | ### 3-2. Accelerometer sensor
139 | ```
140 | param set SIM_ACC1_RND 3
141 | param set SIM_ACC2_RND 3
142 | param set SIM_ACC3_RND 3
143 | ```
144 |
145 | ### 3-3. Air speed sensor
146 | ```
147 | param set SIM_ARSPD1_RND 3
148 | param set SIM_ARSPD2_RND 3
149 | param set SIM_ARSPD3_RND 3
150 | ```
151 |
152 | ### 3-4. Barometer sensor
153 | ```
154 | param set SIM_BARO1_RND 3
155 | param set SIM_BARO2_RND 3
156 | param set SIM_BARO3_RND 3
157 | ```
158 |
159 | ### 3-5. Optical flow sensor
160 | ```
161 | param set SIM_FLOW_RND 3
162 | param set SIM_FLOW_DELAY 3
163 | ```
164 |
165 | ### 3-6. Magnetometer sensor
166 | ```
167 | param set SIM_MAG2_FAIL 1
168 | param set SIM_MAG3_FAIL 1
169 | param set SIM_MAG_RND 3
170 | ```
171 |
172 | ### 3-7. Sonar sensor
173 | ```
174 | param set SIM_SONAR_RND 3
175 | ```
176 |
177 | ### 3-8. GPS
178 | You need to set 'SIM_GPS_TYPE' parameter (controling how GPS is used) before adding GPS noise.
179 |
180 | SIM_GPS_TYPE:
181 | - 0: Use 3D velocity & 2D position from GPS
182 | - 1: Use 2D velocity & 2D position (GPS velocity does not contribute to altitude estimate)
183 | - 2: Use 2D position
184 | - 3: No GPS (will use optical flow only if available)
185 |
186 | Changing parameters below triggers GPS glitch fail-safe logic on a software version (d0210f7b8930dc336e7de2c09dfe2029290f596b).
187 | ```
188 | param set SIM_GPS_NOISE 3 # Add noise
189 | param set SIM_GPS2_NOISE 3
190 |
191 | param set SIM_GPS_VERR_X 3 # Add velocity errors
192 | param set SIM_GPS_VERR_Y 3
193 | param set SIM_GPS_VERR_Z 3
194 |
195 | param set SIM_GPS2_VERR_X 3
196 | param set SIM_GPS2_VERR_Y 3
197 | param set SIM_GPS2_VERR_Z 3
198 |
199 | param set SIM_GPS_GLITCH_X 0.0002
200 | param set SIM_GPS_GLITCH_Y 0.0002
201 | param set SIM_GPS_GLITCH_Z 0.0002
202 | ```
203 |
204 | Changing parameters below does not trigger GPS glitch fail-safe logic on a software version (d0210f7b8930dc336e7de2c09dfe2029290f596b).
205 | ```
206 | param set SIM_GPS_NOISE 1 # Add noise
207 | param set SIM_GPS2_NOISE 1
208 |
209 | param set SIM_GPS_VERR_X 1 # Add velocity errors
210 | param set SIM_GPS_VERR_Y 1
211 | param set SIM_GPS_VERR_Z 1
212 |
213 | param set SIM_GPS2_VERR_X 1
214 | param set SIM_GPS2_VERR_Y 1
215 | param set SIM_GPS2_VERR_Z 1
216 |
217 | param set SIM_GPS_GLITCH_X 0.00001
218 | param set SIM_GPS_GLITCH_Y 0.00001
219 | param set SIM_GPS_GLITCH_Z 0.00001
220 | ```
221 | ### 3-9. EMI Signal Injection Attack
222 | Reference: Paralyzing Drones via EMI Signal Injection on Sensory Communication Channels, NDSS'23
223 |
224 | (Option 1) Turning off all sensors except for GNSS
225 | ```
226 | param set SIM_GYR_FAIL_MSK 1
227 | param set SIM_ACCEL1_FAIL 1
228 | param set SIM_ACCEL2_FAIL 1
229 | param set SIM_ACCEL3_FAIL 1
230 | param set SIM_BARO_DISABLE 1
231 | param set SIM_MAG1_FAIL 1
232 | param set SIM_MAG2_FAIL 1
233 | param set SIM_MAG3_FAIL 1
234 | ```
235 |
236 | (Option 2) Add noises into all sensors except for GNSS
237 | ```
238 | param set SIM_GYR1_RND 700
239 | param set SIM_GYR2_RND 700
240 | param set SIM_GYR3_RND 700
241 | param set SIM_ACC1_RND 700
242 | param set SIM_ACC2_RND 700
243 | param set SIM_ACC3_RND 700
244 | param set SIM_BARO_RND 700
245 | param set SIM_BAR2_RND 700
246 | param set SIM_BAR3_RND 700
247 | param set SIM_MAG_RND 700
248 | param set SIM_MAG2_FAIL 1
249 | param set SIM_MAG3_FAIL 1
250 | ```
251 |
252 | ## 4. Turning off filters
253 | This is useful when you want to measure each filter's effect and performance.
254 |
255 | ### 4-1. Turning off Harmonic Notch filter
256 | ```
257 | param set INS_HNTCH_ENABLE 0
258 | ```
259 |
260 | ### 4-2. Turning off Low Pass filter
261 | Comment out the code line below (here)
262 | ```
263 | // apply the low pass filter last to attentuate any notch induced noise
264 | gyro_filtered = _imu._gyro_filter[instance].apply(gyro_filtered);
265 | ```
266 |
267 | ## 5. Leveraging an optical flow sensor
268 | ### 5-1. Adding a rangefinder sensor
269 | ```
270 | param set SIM_SONAR_SCALE 10
271 | param set RNGFND1_TYPE 1
272 | param set RNGFND1_SCALING 10
273 | param set RNGFND1_PIN 0
274 | param set RNGFND1_MAX_CM 5000
275 | param set RNGFND1_MIN_CM 0
276 |
277 | module load graph
278 | graph RANGEFINDER.distance # You can check measured distances.
279 | ```
280 |
281 | ### 5-2. Adding an optical flow sensor
282 | ```
283 | param set SIM_FLOW_ENABLE 1
284 | param set FLOW_TYPE 10
285 |
286 | module load graph
287 | graph OPTICAL_FLOW.flow_comp_m_x OPTICAL_FLOW.flow_comp_m_y # You can check measured (x, y) positions.
288 | ```
289 |
290 | ### 5-3. Parameter setting for fusing optical flow sensor data
291 | If you use EKF version 3,
292 | ```
293 | param set EK3_SRC1_VELXY 5 # Velocity Horizontal Source
294 | param set EK3_SRC1_POSXY 0 # Position Horizontal Source
295 | param set EK3_SRC_OPTIONS 0
296 | param set EK3_SRC1_POSZ 1
297 | param set EK3_SRC1_VELZ 0
298 | param set EK3_SRC1_YAW 1
299 | ```
300 |
301 | If you use EKF version 2,
302 | ```
303 | param set EK2_SRC1_VELXY 5
304 | param set EK2_SRC1_POSXY 0
305 | param set EK2_SRC_OPTIONS 0
306 | param set EK2_SRC1_POSZ 1
307 | param set EK2_SRC1_VELZ 0
308 | param set EK2_SRC1_YAW 1
309 | ```
310 |
311 | ### 5-4. Controling sensor fusion source
312 | By setting EK2_GPS_TYPE/SIM_GPS_TYPE parameters, you can decide whether ArduPilot uses (i) GPS and optical flow data or (ii) just optical flow.
313 | - 0: GPS 3D Vel and 2D Pos
314 | - 1: GPS 2D vel and 2D pos
315 | - 2: GPS 2D pos
316 | - 3: No GPS
317 | ```
318 | # Stop to use GPS data when you fly a real drone
319 | param set EK2_GPS_TYPE 3
320 |
321 | # Stop to use GPS data when you fly a drone on a simulator
322 | param set SIM_GPS_TYPE 3
323 | ```
324 |
325 | ### 5-5. Running Gazebo simulator to test the optical flow sensor
326 | Open Terminal 1
327 | ```
328 | gazebo --verbose ~/ardupilot_gazebo/worlds/iris_arducopter_runway.world
329 | ```
330 |
331 | Open Terminal 2
332 | ```
333 | ./Tools/autotest/sim_vehicle.py -v ArduCopter -f gazebo-iris
334 | ```
335 |
336 | ## 6. Testing object avoidance algorithms
337 | ```
338 | param set AVOID_ENABLE 7
339 | param set FENCE_ENABLE 1
340 | param set FENCE_RADIUS 10000
341 | param set OA_TYPE 2
342 | param set OA_MARGIN_MAX 10
343 | ```
344 | By setting OA_TYPE parameter, you can choose the object avoidance algorithm.
345 | - 0: Disabled
346 | - 1: BendyRuler
347 | - 2: Dijkstra
348 | - 3: Dijkstra with BendyRuler
349 |
350 | ## 7. How to change the start time clock (timestamp)?
351 | You need to change a code line (here).
352 |
353 | ```
354 | # Original code line
355 | time_now_us(0),
356 |
357 | # Modify the code line as follows, which leads to system time wrap after 60 seconds
358 | time_now_us(4294900000ULL * 1000ULL),
359 | ```
360 | Q. What is the purpose of the changed time clock?
361 | A. In case of me, it was useful to test MAVLink 2.0 Packet Signing.
362 |
363 | ## 8. Troubleshooting
364 | ### 8-1. "No module named console" or "No module named map"
365 | İf you using anaconda, you can download Mavproxy requirements with conda.
366 | ```
367 | conda install -c anaconda wxpython
368 | ```
369 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PX4/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Robotic-vehicle-software-tutorial
2 |
3 | ## 1. Download and Setup
4 | ```
5 | git clone https://github.com/PX4/PX4-Autopilot.git PX4
6 | CD PX4
7 | git checkout [commit hash] // e.g., 6823cbc (v.1.13)
8 | git submodule update --init --recursive
9 | ./Tools/setup/ubuntu.sh -y
10 | ```
11 | Running jMAVSim with SITL to ensure that the simulation prerequisites are installed on the system
12 | ```
13 | make px4_sitl_default jmavsim
14 | ```
15 |
16 | If you use Java 11 version, you need to fall back to Java 8.
17 | ```
18 | sudo apt install openjdk-8-jdk
19 | sudo update-alternatives --config java # choose 8
20 | rm -rf Tools/jMAVSim/out
21 | ```
22 | ```
23 | sudo gedit /etc/java-8-openjdk/accessibility.properties
24 | ```
25 | and comment out the following line like this:
26 | ```
27 | #assistive_technologies=org.GNOME.Acessibility.AtkWrapper
28 | ```
29 |
30 |
31 | ## 2. Execute PX4 with Gazebo simulator
32 | ### Takeoff position in the simulator
33 | In the case of **ground** and **aerial vehicles**, the default starting position is Zurich Irchel Park (lat: 47.397742, lon: 8.545594, alt: 488.0).
34 | If the vehicle type is **underwater**, the default starting position is (lat: 47.3334475, lon: 8.5471141).
35 | The takeoff location in SITL Gazebo can be set using environment variables.
36 | ```
37 | export PX4_HOME_LAT=28.452386
38 | export PX4_HOME_LON=-13.867138
39 | export PX4_HOME_ALT=28.5
40 | ```
41 |
42 | ### 2-1. Quadrotor
43 | ```
44 | make clean
45 | make distclean
46 | make px4_sitl gazebo
47 | ```
48 |
49 | ### 2-2. Quadrotor with Optical Flow
50 | ```
51 | make px4_sitl gazebo_iris_opt_flow
52 | ```
53 |
54 |
55 | Gazebo can be run in a headless mode in which the Gazebo UI is not launched. This starts up more quickly and uses less system resources (i.e. it is a more "lightweight" way to run the simulation).
56 |
57 | Simply prefix the normal make command with HEADLESS=1 as shown:
58 | ```
59 | HEADLESS=1 make px4_sitl gazebo_iris_opt_flow
60 | ```
61 |
62 | ### 2-3. 3DR Solo (Quadrotor)
63 | ```
64 | make px4_sitl gazebo_solo
65 | ```
66 |
67 | ### 2-4. Typhoon H480 (Hexrotor) (supports video streaming)
68 | ```
69 | make px4_sitl gazebo_typhoon_h480
70 | ```
71 |
72 | ### 2-5. Standard Plane
73 | ```
74 | make px4_sitl gazebo_plane
75 | ```
76 |
77 | ### 2-6. Standard Plane (with catapult launch)
78 | ```
79 | make px4_sitl gazebo_plane_catapult
80 | ```
81 |
82 | ### 2-7. Standard VTOL
83 | ```
84 | make px4_sitl gazebo_standard_vtol
85 | ```
86 |
87 | ### 2-8. Tailsitter VTOL
88 | ```
89 | make px4_sitl gazebo_tailsitter
90 | ```
91 |
92 | ### 2-9. Ackerman UGV (Rover)
93 | ```
94 | make px4_sitl gazebo_rover
95 | ```
96 |
97 | ### 2-10. Differential UGV (Rover)
98 | ```
99 | make px4_sitl gazebo_r1_rover
100 | ```
101 |
102 | ### 2-11. HippoCampus TUHH (UUV: Unmanned Underwater Vehicle)
103 | ```
104 | make px4_sitl gazebo_uuv_hippocampus
105 | ```
106 |
107 | ### 2-12. Boat (USV: Unmanned Surface Vehicle)
108 | ```
109 | make px4_sitl gazebo_boat
110 | ```
111 |
112 | ### 2-13. Cloudship (Airship)
113 | ```
114 | make px4_sitl gazebo_cloudship
115 | ```
116 |
117 | ## 3. Injecting sensor noise in Gazebo simulation
118 |
119 | ### Disable preflight checks for 'forced arming'
120 | This is an original code snippet in /src/modules/commander/Commander.cpp.
121 | ```
122 | transition_result_t Commander::arm(arm_disarm_reason_t calling_reason, bool run_preflight_checks)
123 | {
124 | // allow a grace period for re-arming: preflight checks don't need to pass during that time, for example for accidential in-air disarming
125 | if (calling_reason == arm_disarm_reason_t::rc_switch
126 | && (hrt_elapsed_time(&_last_disarmed_timestamp) < 5_s)) {
127 | run_preflight_checks = false;
128 | }
129 |
130 | ```
131 |
132 | This example code line disables preflight checks for 'forced arming'.
133 | ```
134 | transition_result_t Commander::arm(arm_disarm_reason_t calling_reason, bool run_preflight_checks)
135 | {
136 | run_preflight_checks = false;
137 |
138 | // allow a grace period for re-arming: preflight checks don't need to pass during that time, for example for accidential in-air disarming
139 | if (calling_reason == arm_disarm_reason_t::rc_switch
140 | && (hrt_elapsed_time(&_last_disarmed_timestamp) < 5_s)) {
141 | run_preflight_checks = false;
142 | }
143 |
144 | ```
145 |
146 | This is an original code snippet in /src/modules/commander/Commander.cpp.
147 | ```
148 | }
149 | break;
150 |
151 | case vehicle_command_s::VEHICLE_CMD_DO_FLIGHTTERMINATION: {
152 | ```
153 |
154 | This example code line disables preflight checks for 'forced arming'.
155 | ```
156 | }
157 |
158 | cmd_result = 1;
159 |
160 | break;
161 |
162 | case vehicle_command_s::VEHICLE_CMD_DO_FLIGHTTERMINATION: {
163 | ```
164 |
165 | ### 3-1. Add noises to gyroscopes
166 |
167 | Manually add noise into each sensor in this file
168 |
169 | This is an original code snippet.
170 | ```
171 | gyroscope_bias_[i] = phi_g_d * gyroscope_bias_[i] +
172 | sigma_b_g_d * standard_normal_distribution_(random_generator_);
173 | ```
174 | This example code lines add noise into gyroscope sensors.
175 | ```
176 | gyroscope_bias_[i] = phi_g_d * gyroscope_bias_[i] +
177 | sigma_b_g_d * standard_normal_distribution_(random_generator_) * 20;
178 | ```
179 |
180 | Q. Why should we modify PX4 source code to add noise? Is there any more easy way (e.g., changing configuration parameters)?
181 | A. Unfortunately, PX4's failure injection is broken.
182 |
183 | ### 3-2. Add noises to accelerometers
184 |
185 | Manually add noise into each sensor in this file
186 |
187 | This is an original code snippet.
188 | ```
189 | accelerometer_bias_[i] = phi_a_d * accelerometer_bias_[i] +
190 | sigma_b_a_d * standard_normal_distribution_(random_generator_);
191 | ```
192 | This example code lines add noise into accelerometer sensors.
193 | ```
194 | accelerometer_bias_[i] = phi_a_d * accelerometer_bias_[i] +
195 | sigma_b_a_d * standard_normal_distribution_(random_generator_) * 20;
196 | ```
197 |
198 | ### 3-3. Add noises to magnetometers
199 |
200 | Manually add noise into each sensor in this file
201 |
202 | This is an original code snippet.
203 | ```
204 | bias_[i] = phi_d * bias_[i] + sigma_b_d * standard_normal_distribution_(random_generator_);
205 | ```
206 | This example code lines add noise into magnetometer sensors.
207 | ```
208 | bias_[i] = phi_d * bias_[i] + sigma_b_d * standard_normal_distribution_(random_generator_) * 20;
209 | ```
210 |
211 | ### 3-4. Add noises to a barometer
212 |
213 | Manually add noise into each sensor in this file
214 |
215 | This is an original code snippet.
216 | ```
217 | // Apply noise and drift
218 | const float abs_pressure_noise = 1.0f * (float)y1; // 1 Pa RMS noise
219 | ```
220 | This example code lines add noise into magnetometer sensors.
221 | ```
222 | // Apply noise and drift
223 | const float abs_pressure_noise = 1.0f * (float)y1 * 20; // 1 Pa RMS noise
224 | ```
225 |
226 | ### 3-5. Add noises to GNSS
227 | Manually add noise into each sensor in this file
228 |
229 | This is an original code snippet.
230 | ```
231 | noise_gps_pos_.X() = gps_xy_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_);
232 | noise_gps_pos_.Y() = gps_xy_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_);
233 | noise_gps_pos_.Z() = gps_z_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_);
234 | noise_gps_vel_.X() = gps_vxy_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_);
235 | noise_gps_vel_.Y() = gps_vxy_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_);
236 | noise_gps_vel_.Z() = gps_vz_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_);
237 | random_walk_gps_.X() = gps_xy_random_walk_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_);
238 | random_walk_gps_.Y() = gps_xy_random_walk_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_);
239 | random_walk_gps_.Z() = gps_z_random_walk_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_);
240 | ```
241 | This example code lines add noise into magnetometer sensors.
242 | ```
243 | noise_gps_pos_.X() = gps_xy_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_) * 60;
244 | noise_gps_pos_.Y() = gps_xy_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_) * 60;
245 | noise_gps_pos_.Z() = gps_z_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_) * 60;
246 | noise_gps_vel_.X() = gps_vxy_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_) * 60;
247 | noise_gps_vel_.Y() = gps_vxy_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_) * 60;
248 | noise_gps_vel_.Z() = gps_vz_noise_density_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_) * 60;
249 | random_walk_gps_.X() = gps_xy_random_walk_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_) * 60;
250 | random_walk_gps_.Y() = gps_xy_random_walk_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_) * 60;
251 | random_walk_gps_.Z() = gps_z_random_walk_ * sqrt(dt) * randn_(rand_) * 60;
252 | ```
253 |
254 | ### 3-6. Add noises to an optical flow sensor
255 | Manually add noise into each sensor in this file
256 |
257 | This is an original code snippet.
258 | ```
259 | opticalFlow_message.set_integrated_x(quality ? flow_x_ang : 0.0f);
260 | opticalFlow_message.set_integrated_y(quality ? flow_y_ang : 0.0f);
261 | ```
262 | This example code lines add noise into an optical flow.
263 | ```
264 | opticalFlow_message.set_integrated_x(quality ? flow_x_ang * 20 : 0.0f);
265 | opticalFlow_message.set_integrated_y(quality ? flow_y_ang * 20 : 0.0f);
266 | ```
267 |
268 | ## 4. Leveraging an optical flow sensor
269 | ```
270 | cd [PX4 source folder]
271 | make px4_sitl gazebo_iris_opt_flow
272 | ```
273 | You can configure EKF2_AID_MASK parameter to control sensor fusion sources.
274 | - 0: use GPS
275 | - 1: use optical flow
276 | - 2: inhibit IMU bias estimation
277 | - 3: vision position fusion
278 | - 4: vision yaw fusion
279 | - 5: multi-rotor drag fusion
280 | - 6: rotate external vision
281 | - 7: GPS yaw fusion
282 | - 8: vision velocity fusion
283 |
284 | ## 5. Deploying PX4 v.1.13.0 into Crazyflie 2.1
285 | ### 5-1. Build PX4
286 | ```
287 | git clone https://github.com/PX4/PX4-Autopilot.git PX4
288 | CD PX4
289 | git checkout 6823cbc4140e29568f00e1211ae60e057adb1a1f
290 | git submodule update --init --recursive
291 | ```
292 |
293 | ### 5-2. Upload firmware into Crazyflie 2.1
294 | ```
295 | make bitcraze_crazyflie21_default upload
296 | ```
297 |
298 | ### 5-3. Build cfbridge for Crazyradio PA
299 | ```
300 | git clone https://github.com/dennisss/cfbridge.git
301 | git submodule update --init
302 | make build
303 | sudo make run
304 | ```
305 |
306 | ### 5-4. Open QGC and enjoy!
307 |
308 | ### 5-5. Flying Crazyflie 2.1
309 | Altitude mode works well and is supported by the current setup.
310 |
311 | ## 6. Troubleshooting
312 | ### 6-1. No package 'eigen3' found
313 | ```
314 | sudo apt-add-repository universe
315 | sudo apt-get install libeigen3-dev
316 | ```
317 |
318 | ### 6-2. Could not find a package configuration file provided by "OpenCV"
319 | #### Installing required build dependencies
320 | ```
321 | sudo apt-get install cmake
322 | sudo apt-get install gcc g++
323 |
324 | sudo apt-get install python-dev python-numpy
325 | sudo apt-get install python3-dev python3-numpy
326 |
327 | sudo apt-get install libavcodec-dev libavformat-dev libswscale-dev
328 | sudo apt-get install libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev libgstreamer1.0-dev
329 |
330 | sudo apt-get install libgtk2.0-dev
331 | sudo apt-get install libgtk-3-dev
332 |
333 | sudo apt-get install libpng-dev
334 | sudo apt-get install libjpeg-dev
335 | sudo apt-get install libopenexr-dev
336 | sudo apt-get install libtiff-dev
337 | sudo apt-get install libwebp-dev
338 | ```
339 |
340 | #### Downloading and installing OpenCV
341 | ```
342 | sudo apt-get install git
343 | git clone https://github.com/opencv/opencv.git
344 |
345 | mkdir build
346 | cd build
347 |
348 | cmake ../
349 | make
350 | sudo make install
351 | ```
352 |
353 | #### Verifying the installation
354 | ```
355 | python -c "import cv2; print(cv2.__version__)"
356 | python3 -c "import cv2; print(cv2.__version__)"
357 | ```
358 | ```
359 | Output
360 | 4.6.0-dev
361 | 3.2.0
362 | ```
363 | ### 6-3. Failed to import jinja2: No module named 'jinja2'
364 | ```
365 | sudo apt remove python-jinja2
366 | sudo apt remove python3-jinja2
367 |
368 | pip3 install --user jinja2
369 | ```
370 |
371 | ### 6-4. CMake Error: The following variables are used in this project, but they are set to NOTFOUND
372 | ```
373 | sudo apt-get install libgstreamer-plugins-base1.0-dev
374 | ```
375 |
376 | ### 6-5. CMake Error: Could not find a package configuration file provided by "MAVSDK" (requested version 1.3.1) with any of the following names
377 | ```
378 | wget https://github.com/mavlink/MAVSDK/releases/download/v1.4.16/libmavsdk-dev_1.4.16_ubuntu20.04_amd64.deb
379 | sudo chmod 777 libmavsdk-dev_1.4.16_ubuntu20.04_amd64.deb
380 | sudo dpkg -i libmavsdk-dev_1.4.16_ubuntu20.04_amd64.deb
381 | ```
382 |
383 | ### 6-6. Waiting for simulator to accept connection on TCP port 4560
384 | Installing ant package
385 | ```
386 | sudo apt install ant
387 | ```
388 |
389 | ### 6-7. Exception in thread "main" java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException
390 | ```
391 | sudo vim /etc/java-8-openjdk/accessibility.properties
392 | ```
393 |
394 | Commented out the following line:
395 | ```
396 | #assistive_technologies=org.GNOME.Accessibility.AtkWrapper
397 | ```
398 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 9 |
10 |
11 | ### 1-2 PX4 (jMAVSim, Gazebo)
12 |
9 |
10 |
11 | ### 1-2 PX4 (jMAVSim, Gazebo)
12 |  13 |
14 |
15 | ### 1-3 Paparazzi (NPS)
16 |
13 |
14 |
15 | ### 1-3 Paparazzi (NPS)
16 |  17 |
18 |
19 | ## 2. Execute control software
20 | ArduPilot
21 |
17 |
18 |
19 | ## 2. Execute control software
20 | ArduPilot
21 |  91 | When your operating system is Ubuntu 20.04 (or later version),
91 | When your operating system is Ubuntu 20.04 (or later version),  111 | Install dependecies
111 | Install dependecies