├── .gitignore
├── LICENSE_Occupancy_Network.md
├── LICENSE_Ours.md
├── ObjectWakeup.mp4
├── Object_Wakeup_Poster_Final.pdf
├── README.md
├── checkpoint
└── .gitkeep
├── demo.py
├── demo.yaml
├── demo_chair
└── .gitkeep
├── environment.yaml
├── main
├── __init__.py
├── common.py
├── config.py
├── data
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── core.py
│ └── fields.py
├── network
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── config.py
│ ├── encoder
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ └── conv.py
│ ├── generation.py
│ └── models
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── decoder.py
│ │ ├── encoder_latent.py
│ │ ├── layers.py
│ │ └── voxel_decoder.py
└── utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── binvox_rw.py
│ ├── icp.py
│ ├── io.py
│ ├── libkdtree
│ ├── .gitignore
│ ├── LICENSE.txt
│ ├── MANIFEST.in
│ ├── README
│ ├── README.rst
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── pykdtree
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── _kdtree_core.c
│ │ ├── _kdtree_core.c.mako
│ │ ├── kdtree.c
│ │ ├── kdtree.pyx
│ │ ├── render_template.py
│ │ └── test_tree.py
│ └── setup.cfg
│ ├── libmcubes
│ ├── .gitignore
│ ├── LICENSE
│ ├── README.rst
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── exporter.py
│ ├── marchingcubes.cpp
│ ├── marchingcubes.h
│ ├── mcubes.pyx
│ ├── pyarray_symbol.h
│ ├── pyarraymodule.h
│ ├── pywrapper.cpp
│ └── pywrapper.h
│ ├── libmesh
│ ├── .gitignore
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── inside_mesh.py
│ ├── inside_mesh_2.py
│ └── triangle_hash.pyx
│ ├── libmise
│ ├── .gitignore
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── mise.pyx
│ └── test.py
│ ├── libsimplify
│ ├── Simplify.h
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── simplify_mesh.pyx
│ └── test.py
│ ├── libvoxelize
│ ├── .gitignore
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── tribox2.h
│ └── voxelize.pyx
│ ├── mesh.py
│ ├── visualize.py
│ └── voxels.py
├── setup.py
└── utils.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /output
2 | /out
3 | /data
4 | build
5 | .vscode
6 | .pytest_cache
7 | .cache
8 | *.pyc
9 | *.pt
10 | *.so
11 | *.o
12 | *.prof
13 | .nfs*
14 | /main/utils/libmcubes/mcubes.cpp
15 | /main/utils/libsimplify/simplify_mesh.cpp
16 | /main/utils/libsimplify/build
17 |
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE_Occupancy_Network.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Copyright 2019 Lars Mescheder, Michael Oechsle, Michael Niemeyer, Andreas Geiger, Sebastian Nowozin
2 |
3 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
4 |
5 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
6 |
7 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE_Ours.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Copyright 2021 Paper Authors
2 |
3 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
4 |
5 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
6 |
7 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ObjectWakeup.mp4:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kulbear/object-wakeup/62cfb70aa6369aadbca24fd1d51241f2db86e494/ObjectWakeup.mp4
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Object_Wakeup_Poster_Final.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kulbear/object-wakeup/62cfb70aa6369aadbca24fd1d51241f2db86e494/Object_Wakeup_Poster_Final.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## NOTE: This page is still under construction.
2 | ## Now we provide a minimal demo only. More to come.
3 |
4 | # Object Wake-up: 3D Object Rigging from a Single Image (ECCV 2022)
5 |
6 | ## | [[Project Page]](https://kulbear.github.io/object-wakeup/) | [[Arxiv]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.02708v3.pdf) | [[Supplementary]](#) | [[Data]](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1y360MpyGendcp7gFsjD1Gr8L0wpzFVLg?usp=sharing) |
7 |
8 | 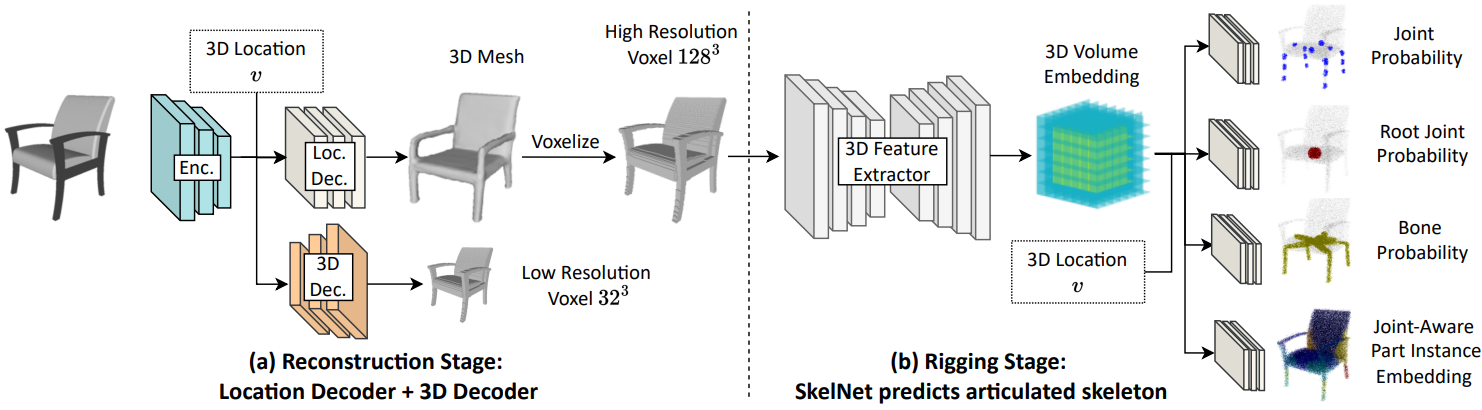
9 | 
10 |
11 | >> Given a single chair image, could we wake it up by reconstructing its 3D shape and skeleton, as well as animating its plausible articulations and motions, similar to that of human modeling?
12 |
13 | >> It is a new problem that not only goes beyond image-based object reconstruction but also involves articulated animation of generic objects in 3D, which could give rise to numerous downstream augmented and virtual reality applications.
14 |
15 | ## Environment Setup
16 |
17 | ```
18 | conda env create -f environment.yaml
19 | conda activate object-wakeup
20 | python setup.py build_ext --inplace
21 | ```
22 |
23 |
24 | ## Dataset
25 |
26 | **(Work in Progress)**
27 |
28 | Now we have a release contains sample dataset as well as the source code of the tool we developed in UNREAL 4. It is not yet finished but it is ready to play with if you are interested in.
29 |
30 | [[Data Download]](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1y360MpyGendcp7gFsjD1Gr8L0wpzFVLg?usp=sharing)
31 |
32 | - `ShapeRR_Generation` contains the plug-in we developed in UE4.
33 | - `Chair_Out` provides sample high-resolution rendering data for the Chairs category in ShapeNet.
34 | - Other 3 categories presented in paper is still being processed and a full release is expected in the future.
35 |
36 |
37 | ## Demo
38 |
39 | To run a demo on our method for 3D reconstruction, please download the sample demo image from [here](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1gQbQZcewn0PsTe80BZp3u1Xuw7iq1MYP?usp=sharing).
40 |
41 |
42 | Put the sample image in folder `./demo_chair`.
43 |
44 |
45 | Then you may want to download the pretrained model weights from [here](https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1XPdBjsV21Vmc4s1GLpHW9Yhvaym20j9T?usp=sharing).
46 |
47 | Put the checkpoint file in folder `./checkpoint`.
48 |
49 | To generate sample meshes using a trained model, use
50 |
51 | ```
52 | python demo.py demo.yaml
53 | ```
54 |
55 | ## Misc
56 |
57 | Contact Ji Yang at jyang7@ualberta.ca for any questions or comments.
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/checkpoint/.gitkeep:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kulbear/object-wakeup/62cfb70aa6369aadbca24fd1d51241f2db86e494/checkpoint/.gitkeep
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | os.environ["CUDA_DEVICE_ORDER"] = "PCI_BUS_ID"
3 | os.environ["CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES"] = "0"
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | import os
7 | import argparse
8 | from tqdm import tqdm
9 | from pathlib import Path
10 | from main import config
11 | from utils import CheckpointIO
12 | from main.utils.visualize import visualize_data
13 |
14 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
15 | parser.add_argument('config', type=str, help='Path to config file.')
16 |
17 | args = parser.parse_args()
18 | cfg = config.load_config(args.config, 'demo.yaml')
19 | device = torch.device("cuda")
20 |
21 | out_dir = './demo_chair/'
22 | generation_dir = './demo_chair/generation'
23 | mesh_dir = os.path.join(generation_dir, 'meshes')
24 | in_dir = os.path.join(generation_dir, 'input')
25 | generation_vis_dir = os.path.join(generation_dir, 'vis')
26 |
27 | Path(generation_dir).mkdir(exist_ok=True)
28 | Path(mesh_dir).mkdir(exist_ok=True)
29 | Path(in_dir).mkdir(exist_ok=True)
30 | Path(generation_vis_dir).mkdir(exist_ok=True)
31 | vis_n_outputs = 30
32 |
33 | dataset = config.get_dataset('test', cfg, return_idx=True)
34 | model = config.get_model(cfg, device=device, dataset=dataset)
35 | model.eval()
36 | generator = config.get_generator(model, cfg, device=device)
37 | checkpoint_io = CheckpointIO('checkpoint', model=model)
38 | checkpoint_io.load('model.pt')
39 |
40 | generate_mesh = True
41 |
42 | test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
43 | dataset, batch_size=1, num_workers=0, shuffle=False)
44 |
45 |
46 | for it, data in enumerate(tqdm(test_loader)):
47 | # Get index etc.
48 | idx = data['idx'].item()
49 | model_dict = {'model': str(idx), 'category': 'n/a'}
50 |
51 | # Generate outputs
52 | out_file_dict = {}
53 | modelpath = os.path.join(
54 | './demo_chair/', model_dict['model'],
55 | cfg['data']['watertight_file'])
56 | out_file_dict['gt'] = modelpath
57 |
58 | if generate_mesh:
59 | out = generator.generate_mesh(data)
60 | try:
61 | mesh, stats_dict = out
62 | except TypeError:
63 | mesh, stats_dict = out, {}
64 |
65 | # Write output
66 | mesh_out_file = os.path.join(mesh_dir, '%s.off' % model_dict['model'])
67 | mesh.export(mesh_out_file)
68 | out_file_dict['mesh'] = mesh_out_file
69 |
70 |
71 | inputs_path = os.path.join(in_dir, '%s.jpg' % model_dict['model'])
72 | inputs = data['inputs'].squeeze(0).cpu()
73 | visualize_data(inputs, 'img', inputs_path)
74 | out_file_dict['in'] = inputs_path
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | method: network
3 | data:
4 | dataset: images
5 | classes: ['03001627']
6 | path: ./demo_chair/
7 | img_folder: img_choy2016
8 | img_size: 224
9 | points_subsample: 2048
10 | dim: 3
11 | points_file: points.npz
12 | points_iou_file: points.npz
13 | points_unpackbits: true
14 | model_file: model.off
15 | watertight_file: model_watertight.off
16 | img_with_camera: false
17 | img_augment: false
18 |
19 | model:
20 | encoder_latent: null
21 | decoder: cbatchnorm
22 | encoder: vit_light
23 | c_dim: 256
24 | z_dim: 0
25 | decoder_kwargs: { }
26 | encoder_kwargs: { }
27 | encoder_latent_kwargs: { }
28 | multi_gpu: false
29 | use_camera: false
30 | dmc_weight_prior: 10.
31 | training:
32 | out_dir: ./demo_chair/
33 | batch_size: 64
34 | model_selection_metric: iou
35 | model_selection_mode: maximize
36 | visualize_every: 2000
37 | validate_every: 2500
38 | test:
39 | threshold: 0.2
40 | eval_mesh: true
41 | eval_pointcloud: false
42 | model_file: ./checkpoint/model_best.pt
43 | generation:
44 | batch_size: 100000
45 | refine: false
46 | n_x: 128
47 | n_z: 1
48 | resolution_0: 32
49 | upsampling_steps: 2
50 | generation_dir: generation
51 | refinement_step: 30
52 | simplify_nfaces: 5000
53 | vis_n_outputs: 30
54 | generate_mesh: true
55 | generate_pointcloud: false
56 | use_sampling: false
57 | copy_groundtruth: false
58 | copy_input: true
59 | latent_number: 4
60 | latent_H: 8
61 | latent_W: 8
62 | latent_ny: 2
63 | latent_nx: 2
64 | latent_repeat: true
65 |
66 | preprocessor:
67 | type: null
68 | config: ""
69 | model_file: null
70 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo_chair/.gitkeep:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kulbear/object-wakeup/62cfb70aa6369aadbca24fd1d51241f2db86e494/demo_chair/.gitkeep
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/environment.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: object-wakeup
2 | channels:
3 | - conda-forge
4 | - pytorch
5 | - defaults
6 | dependencies:
7 | - cython=0.29.2
8 | - imageio=2.4.1
9 | - numpy=1.15.4
10 | - numpy-base=1.15.4
11 | - matplotlib=3.0.3
12 | - matplotlib-base=3.0.3
13 | - pandas=0.23.4
14 | - pillow=5.3.0
15 | - pyembree=0.1.4
16 | - pytest=4.0.2
17 | - python=3.6.7
18 | - pytorch=1.0.0
19 | - pyyaml=3.13
20 | - scikit-image=0.14.1
21 | - scipy=1.1.0
22 | - tensorboardx=1.4
23 | - torchvision=0.2.1
24 | - tqdm=4.28.1
25 | - trimesh=2.37.7
26 | - pip:
27 | - h5py==2.9.0
28 | - plyfile==0.7
29 | - transformers
30 |
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kulbear/object-wakeup/62cfb70aa6369aadbca24fd1d51241f2db86e494/main/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/common.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # import multiprocessing
2 | import torch
3 | from main.utils.libkdtree import KDTree
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 |
7 | def compute_iou(occ1, occ2):
8 | ''' Computes the Intersection over Union (IoU) value for two sets of
9 | occupancy values.
10 |
11 | Args:
12 | occ1 (tensor): first set of occupancy values
13 | occ2 (tensor): second set of occupancy values
14 | '''
15 | occ1 = np.asarray(occ1)
16 | occ2 = np.asarray(occ2)
17 |
18 | # Put all data in second dimension
19 | # Also works for 1-dimensional data
20 | if occ1.ndim >= 2:
21 | occ1 = occ1.reshape(occ1.shape[0], -1)
22 | if occ2.ndim >= 2:
23 | occ2 = occ2.reshape(occ2.shape[0], -1)
24 |
25 | # Convert to boolean values
26 | occ1 = (occ1 >= 0.5)
27 | occ2 = (occ2 >= 0.5)
28 |
29 | # Compute IOU
30 | area_union = (occ1 | occ2).astype(np.float32).sum(axis=-1)
31 | area_intersect = (occ1 & occ2).astype(np.float32).sum(axis=-1)
32 |
33 | iou = (area_intersect / area_union)
34 |
35 | return iou
36 |
37 |
38 | def chamfer_distance(points1, points2, use_kdtree=True, give_id=False):
39 | ''' Returns the chamfer distance for the sets of points.
40 |
41 | Args:
42 | points1 (numpy array): first point set
43 | points2 (numpy array): second point set
44 | use_kdtree (bool): whether to use a kdtree
45 | give_id (bool): whether to return the IDs of nearest points
46 | '''
47 | if use_kdtree:
48 | return chamfer_distance_kdtree(points1, points2, give_id=give_id)
49 | else:
50 | return chamfer_distance_naive(points1, points2)
51 |
52 |
53 | def chamfer_distance_naive(points1, points2):
54 | ''' Naive implementation of the Chamfer distance.
55 |
56 | Args:
57 | points1 (numpy array): first point set
58 | points2 (numpy array): second point set
59 | '''
60 | assert(points1.size() == points2.size())
61 | batch_size, T, _ = points1.size()
62 |
63 | points1 = points1.view(batch_size, T, 1, 3)
64 | points2 = points2.view(batch_size, 1, T, 3)
65 |
66 | distances = (points1 - points2).pow(2).sum(-1)
67 |
68 | chamfer1 = distances.min(dim=1)[0].mean(dim=1)
69 | chamfer2 = distances.min(dim=2)[0].mean(dim=1)
70 |
71 | chamfer = chamfer1 + chamfer2
72 | return chamfer
73 |
74 |
75 | def chamfer_distance_kdtree(points1, points2, give_id=False):
76 | ''' KD-tree based implementation of the Chamfer distance.
77 |
78 | Args:
79 | points1 (numpy array): first point set
80 | points2 (numpy array): second point set
81 | give_id (bool): whether to return the IDs of the nearest points
82 | '''
83 | # Points have size batch_size x T x 3
84 | batch_size = points1.size(0)
85 |
86 | # First convert points to numpy
87 | points1_np = points1.detach().cpu().numpy()
88 | points2_np = points2.detach().cpu().numpy()
89 |
90 | # Get list of nearest neighbors indieces
91 | idx_nn_12, _ = get_nearest_neighbors_indices_batch(points1_np, points2_np)
92 | idx_nn_12 = torch.LongTensor(idx_nn_12).to(points1.device)
93 | # Expands it as batch_size x 1 x 3
94 | idx_nn_12_expand = idx_nn_12.view(batch_size, -1, 1).expand_as(points1)
95 |
96 | # Get list of nearest neighbors indieces
97 | idx_nn_21, _ = get_nearest_neighbors_indices_batch(points2_np, points1_np)
98 | idx_nn_21 = torch.LongTensor(idx_nn_21).to(points1.device)
99 | # Expands it as batch_size x T x 3
100 | idx_nn_21_expand = idx_nn_21.view(batch_size, -1, 1).expand_as(points2)
101 |
102 | # Compute nearest neighbors in points2 to points in points1
103 | # points_12[i, j, k] = points2[i, idx_nn_12_expand[i, j, k], k]
104 | points_12 = torch.gather(points2, dim=1, index=idx_nn_12_expand)
105 |
106 | # Compute nearest neighbors in points1 to points in points2
107 | # points_21[i, j, k] = points2[i, idx_nn_21_expand[i, j, k], k]
108 | points_21 = torch.gather(points1, dim=1, index=idx_nn_21_expand)
109 |
110 | # Compute chamfer distance
111 | chamfer1 = (points1 - points_12).pow(2).sum(2).mean(1)
112 | chamfer2 = (points2 - points_21).pow(2).sum(2).mean(1)
113 |
114 | # Take sum
115 | chamfer = chamfer1 + chamfer2
116 |
117 | # If required, also return nearest neighbors
118 | if give_id:
119 | return chamfer1, chamfer2, idx_nn_12, idx_nn_21
120 |
121 | return chamfer
122 |
123 |
124 | def get_nearest_neighbors_indices_batch(points_src, points_tgt, k=1):
125 | ''' Returns the nearest neighbors for point sets batchwise.
126 |
127 | Args:
128 | points_src (numpy array): source points
129 | points_tgt (numpy array): target points
130 | k (int): number of nearest neighbors to return
131 | '''
132 | indices = []
133 | distances = []
134 |
135 | for (p1, p2) in zip(points_src, points_tgt):
136 | kdtree = KDTree(p2)
137 | dist, idx = kdtree.query(p1, k=k)
138 | indices.append(idx)
139 | distances.append(dist)
140 |
141 | return indices, distances
142 |
143 |
144 | def normalize_imagenet(x):
145 | ''' Normalize input images according to ImageNet standards.
146 |
147 | Args:
148 | x (tensor): input images
149 | '''
150 | x = x.clone()
151 | x[:, 0] = (x[:, 0] - 0.485) / 0.229
152 | x[:, 1] = (x[:, 1] - 0.456) / 0.224
153 | x[:, 2] = (x[:, 2] - 0.406) / 0.225
154 | return x
155 |
156 |
157 | def make_3d_grid(bb_min, bb_max, shape):
158 | ''' Makes a 3D grid.
159 |
160 | Args:
161 | bb_min (tuple): bounding box minimum
162 | bb_max (tuple): bounding box maximum
163 | shape (tuple): output shape
164 | '''
165 | size = shape[0] * shape[1] * shape[2]
166 |
167 | pxs = torch.linspace(bb_min[0], bb_max[0], shape[0])
168 | pys = torch.linspace(bb_min[1], bb_max[1], shape[1])
169 | pzs = torch.linspace(bb_min[2], bb_max[2], shape[2])
170 |
171 | pxs = pxs.view(-1, 1, 1).expand(*shape).contiguous().view(size)
172 | pys = pys.view(1, -1, 1).expand(*shape).contiguous().view(size)
173 | pzs = pzs.view(1, 1, -1).expand(*shape).contiguous().view(size)
174 | p = torch.stack([pxs, pys, pzs], dim=1)
175 |
176 | return p
177 |
178 |
179 | def transform_points(points, transform):
180 | ''' Transforms points with regard to passed camera information.
181 |
182 | Args:
183 | points (tensor): points tensor
184 | transform (tensor): transformation matrices
185 | '''
186 | assert(points.size(2) == 3)
187 | assert(transform.size(1) == 3)
188 | assert(points.size(0) == transform.size(0))
189 |
190 | if transform.size(2) == 4:
191 | R = transform[:, :, :3]
192 | t = transform[:, :, 3:]
193 | points_out = points @ R.transpose(1, 2) + t.transpose(1, 2)
194 | elif transform.size(2) == 3:
195 | K = transform
196 | points_out = points @ K.transpose(1, 2)
197 |
198 | return points_out
199 |
200 |
201 | def b_inv(b_mat):
202 | ''' Performs batch matrix inversion.
203 |
204 | Arguments:
205 | b_mat: the batch of matrices that should be inverted
206 | '''
207 |
208 | eye = b_mat.new_ones(b_mat.size(-1)).diag().expand_as(b_mat)
209 | b_inv, _ = torch.gesv(eye, b_mat)
210 | return b_inv
211 |
212 |
213 | def transform_points_back(points, transform):
214 | ''' Inverts the transformation.
215 |
216 | Args:
217 | points (tensor): points tensor
218 | transform (tensor): transformation matrices
219 | '''
220 | assert(points.size(2) == 3)
221 | assert(transform.size(1) == 3)
222 | assert(points.size(0) == transform.size(0))
223 |
224 | if transform.size(2) == 4:
225 | R = transform[:, :, :3]
226 | t = transform[:, :, 3:]
227 | points_out = points - t.transpose(1, 2)
228 | points_out = points_out @ b_inv(R.transpose(1, 2))
229 | elif transform.size(2) == 3:
230 | K = transform
231 | points_out = points @ b_inv(K.transpose(1, 2))
232 |
233 | return points_out
234 |
235 |
236 | def project_to_camera(points, transform):
237 | ''' Projects points to the camera plane.
238 |
239 | Args:
240 | points (tensor): points tensor
241 | transform (tensor): transformation matrices
242 | '''
243 | p_camera = transform_points(points, transform)
244 | p_camera = p_camera[..., :2] / p_camera[..., 2:]
245 | return p_camera
246 |
247 |
248 | def get_camera_args(data, loc_field=None, scale_field=None, device=None):
249 | ''' Returns dictionary of camera arguments.
250 |
251 | Args:
252 | data (dict): data dictionary
253 | loc_field (str): name of location field
254 | scale_field (str): name of scale field
255 | device (device): pytorch device
256 | '''
257 | Rt = data['inputs.world_mat'].to(device)
258 | K = data['inputs.camera_mat'].to(device)
259 |
260 | if loc_field is not None:
261 | loc = data[loc_field].to(device)
262 | else:
263 | loc = torch.zeros(K.size(0), 3, device=K.device, dtype=K.dtype)
264 |
265 | if scale_field is not None:
266 | scale = data[scale_field].to(device)
267 | else:
268 | scale = torch.zeros(K.size(0), device=K.device, dtype=K.dtype)
269 |
270 | Rt = fix_Rt_camera(Rt, loc, scale)
271 | K = fix_K_camera(K, img_size=137.)
272 | kwargs = {'Rt': Rt, 'K': K}
273 | return kwargs
274 |
275 |
276 | def fix_Rt_camera(Rt, loc, scale):
277 | ''' Fixes Rt camera matrix.
278 |
279 | Args:
280 | Rt (tensor): Rt camera matrix
281 | loc (tensor): location
282 | scale (float): scale
283 | '''
284 | # Rt is B x 3 x 4
285 | # loc is B x 3 and scale is B
286 | batch_size = Rt.size(0)
287 | R = Rt[:, :, :3]
288 | t = Rt[:, :, 3:]
289 |
290 | scale = scale.view(batch_size, 1, 1)
291 | R_new = R * scale
292 | t_new = t + R @ loc.unsqueeze(2)
293 |
294 | Rt_new = torch.cat([R_new, t_new], dim=2)
295 |
296 | assert(Rt_new.size() == (batch_size, 3, 4))
297 | return Rt_new
298 |
299 |
300 | def fix_K_camera(K, img_size=137):
301 | """Fix camera projection matrix.
302 |
303 | This changes a camera projection matrix that maps to
304 | [0, img_size] x [0, img_size] to one that maps to [-1, 1] x [-1, 1].
305 |
306 | Args:
307 | K (np.ndarray): Camera projection matrix.
308 | img_size (float): Size of image plane K projects to.
309 | """
310 | # Unscale and recenter
311 | scale_mat = torch.tensor([
312 | [2./img_size, 0, -1],
313 | [0, 2./img_size, -1],
314 | [0, 0, 1.],
315 | ], device=K.device, dtype=K.dtype)
316 | K_new = scale_mat.view(1, 3, 3) @ K
317 | return K_new
318 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import yaml
2 | from torchvision import transforms
3 | from main import data
4 | from main import network
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 | method_dict = {
9 | 'network': network
10 | }
11 |
12 |
13 | # General config
14 | def load_config(path, default_path=None):
15 | ''' Loads config file.
16 |
17 | Args:
18 | path (str): path to config file
19 | default_path (bool): whether to use default path
20 | '''
21 | # Load configuration from file itself
22 | with open(path, 'r') as f:
23 | cfg_special = yaml.load(f)
24 |
25 | # Check if we should inherit from a config
26 | inherit_from = cfg_special.get('inherit_from')
27 |
28 | # If yes, load this config first as default
29 | # If no, use the default_path
30 | if inherit_from is not None:
31 | cfg = load_config(inherit_from, default_path)
32 | elif default_path is not None:
33 | with open(default_path, 'r') as f:
34 | cfg = yaml.load(f)
35 | else:
36 | cfg = dict()
37 |
38 | # Include main configuration
39 | update_recursive(cfg, cfg_special)
40 |
41 | return cfg
42 |
43 |
44 | def update_recursive(dict1, dict2):
45 | ''' Update two config dictionaries recursively.
46 |
47 | Args:
48 | dict1 (dict): first dictionary to be updated
49 | dict2 (dict): second dictionary which entries should be used
50 |
51 | '''
52 | for k, v in dict2.items():
53 | if k not in dict1:
54 | dict1[k] = dict()
55 | if isinstance(v, dict):
56 | update_recursive(dict1[k], v)
57 | else:
58 | dict1[k] = v
59 |
60 |
61 | # Models
62 | def get_model(cfg, device=None, dataset=None):
63 | ''' Returns the model instance.
64 |
65 | Args:
66 | cfg (dict): config dictionary
67 | device (device): pytorch device
68 | dataset (dataset): dataset
69 | '''
70 | method = cfg['method']
71 | model = method_dict[method].config.get_model(
72 | cfg, device=device, dataset=dataset)
73 | return model
74 |
75 |
76 | # Trainer
77 | def get_trainer(model, optimizer, cfg, device):
78 | ''' Returns a trainer instance.
79 |
80 | Args:
81 | model (nn.Module): the model which is used
82 | optimizer (optimizer): pytorch optimizer
83 | cfg (dict): config dictionary
84 | device (device): pytorch device
85 | '''
86 | method = cfg['method']
87 | trainer = method_dict[method].config.get_trainer(
88 | model, optimizer, cfg, device)
89 | return trainer
90 |
91 |
92 | # Generator for final mesh extraction
93 | def get_generator(model, cfg, device):
94 | ''' Returns a generator instance.
95 |
96 | Args:
97 | model (nn.Module): the model which is used
98 | cfg (dict): config dictionary
99 | device (device): pytorch device
100 | '''
101 | method = cfg['method']
102 | generator = method_dict[method].config.get_generator(model, cfg, device)
103 | return generator
104 |
105 |
106 | # Datasets
107 | def get_dataset(mode, cfg, return_idx=False, return_category=False):
108 | ''' Returns the dataset.
109 |
110 | Args:
111 | model (nn.Module): the model which is used
112 | cfg (dict): config dictionary
113 | return_idx (bool): whether to include an ID field
114 | '''
115 | method = cfg['method']
116 | dataset_type = cfg['data']['dataset']
117 | dataset_folder = cfg['data']['path']
118 | categories = cfg['data']['classes']
119 |
120 | if dataset_type == 'images':
121 | dataset = data.ImageDataset(
122 | dataset_folder, img_size=cfg['data']['img_size'],
123 | return_idx=return_idx,
124 | )
125 | else:
126 | raise ValueError('Invalid dataset "%s"' % cfg['data']['dataset'])
127 |
128 | return dataset
129 |
130 |
131 | def get_inputs_field(mode, cfg):
132 | ''' Returns the inputs fields.
133 |
134 | Args:
135 | mode (str): the mode which is used
136 | cfg (dict): config dictionary
137 | '''
138 | input_type = cfg['data']['input_type']
139 |
140 | if input_type is None:
141 | inputs_field = None
142 | elif input_type == 'img':
143 | if mode == 'train' and cfg['data']['img_augment']:
144 | resize_op = transforms.RandomResizedCrop(
145 | cfg['data']['img_size'], (0.75, 1.), (1., 1.))
146 | else:
147 | resize_op = transforms.Resize((cfg['data']['img_size']))
148 |
149 | transform = transforms.Compose([
150 | resize_op, transforms.ToTensor(),
151 | ])
152 |
153 | with_camera = cfg['data']['img_with_camera']
154 |
155 | if mode == 'train':
156 | random_view = True
157 | else:
158 | random_view = False
159 |
160 | inputs_field = data.ImagesField(
161 | cfg['data']['img_folder'], transform,
162 | with_camera=with_camera, random_view=random_view
163 | )
164 | return inputs_field
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/data/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from main.data.core import (
3 | Shapes3dDataset, collate_remove_none, worker_init_fn
4 | )
5 | from main.data.fields import (
6 | IndexField, CategoryField, ImagesField, PointsField,
7 | VoxelsField, PointCloudField, MeshField,
8 | )
9 |
10 | import os
11 | from PIL import Image
12 | import torch
13 | from torch.utils import data
14 | from torchvision import transforms
15 |
16 | IMAGE_EXTENSIONS = (
17 | '.jpg', '.jpeg', '.JPG', '.JPEG', '.png', '.PNG'
18 | )
19 |
20 |
21 | class ImageDataset(data.Dataset):
22 | r""" Cars Dataset.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | dataset_folder (str): path to the dataset dataset
26 | img_size (int): size of the cropped images
27 | transform (list): list of transformations applied to the data points
28 | """
29 |
30 | def __init__(self, dataset_folder, img_size=224, transform=None, return_idx=False):
31 | """
32 |
33 | Arguments:
34 | dataset_folder (path): path to the KITTI dataset
35 | img_size (int): required size of the cropped images
36 | return_idx (bool): wether to return index
37 | """
38 |
39 | self.img_size = img_size
40 | self.img_path = dataset_folder
41 | self.file_list = os.listdir(self.img_path)
42 | self.file_list = [
43 | f for f in self.file_list
44 | if os.path.splitext(f)[1] in IMAGE_EXTENSIONS
45 | ]
46 | self.len = len(self.file_list)
47 | self.transform = transforms.Compose([
48 | transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
49 | transforms.ToTensor()
50 | ])
51 | self.return_idx = return_idx
52 |
53 | def get_model(self, idx):
54 | ''' Returns the model.
55 |
56 | Args:
57 | idx (int): ID of data point
58 | '''
59 | f_name = os.path.basename(self.file_list[idx])
60 | f_name = os.path.splitext(f_name)[0]
61 | return f_name
62 |
63 | def get_model_dict(self, idx):
64 | f_name = os.path.basename(self.file_list[idx])
65 | model_dict = {
66 | 'model': f_name
67 | }
68 | return model_dict
69 |
70 | def __len__(self):
71 | ''' Returns the length of the dataset.'''
72 | return self.len
73 |
74 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
75 | ''' Returns the data point.
76 |
77 | Args:
78 | idx (int): ID of data point
79 | '''
80 | f = os.path.join(self.img_path, self.file_list[idx])
81 | img_in = Image.open(f)
82 | img = Image.new("RGB", img_in.size)
83 | img.paste(img_in)
84 | if self.transform:
85 | img = self.transform(img)
86 |
87 | idx = torch.tensor(idx)
88 |
89 | data = {
90 | 'inputs': img,
91 | }
92 |
93 | if self.return_idx:
94 | data['idx'] = idx
95 |
96 | return data
97 |
98 | __all__ = [
99 | # Core
100 | Shapes3dDataset,
101 | collate_remove_none,
102 | worker_init_fn,
103 | # Fields
104 | IndexField,
105 | CategoryField,
106 | ImagesField,
107 | PointsField,
108 | VoxelsField,
109 | PointCloudField,
110 | MeshField,
111 | ImageDataset,
112 | ]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/data/core.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import logging
3 | from torch.utils import data
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import yaml
6 |
7 |
8 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
9 |
10 |
11 | # Fields
12 | class Field(object):
13 | ''' Data fields class.
14 | '''
15 |
16 | def load(self, data_path, idx, category):
17 | ''' Loads a data point.
18 |
19 | Args:
20 | data_path (str): path to data file
21 | idx (int): index of data point
22 | category (int): index of category
23 | '''
24 | raise NotImplementedError
25 |
26 | def check_complete(self, files):
27 | ''' Checks if set is complete.
28 |
29 | Args:
30 | files: files
31 | '''
32 | raise NotImplementedError
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | class Pix3dDataset(data.Dataset):
37 | ''' Pix3D dataset class.
38 | '''
39 |
40 | def __init__(self, dataset_folder, fields, split=None,
41 | categories=None, no_except=True, transform=None):
42 | ''' Initialization of the the 3D shape dataset.
43 |
44 | Args:
45 | dataset_folder (str): dataset folder
46 | fields (dict): dictionary of fields
47 | split (str): which split is used
48 | categories (list): list of categories to use
49 | no_except (bool): no exception
50 | transform (callable): transformation applied to data points
51 | '''
52 | # Attributes
53 | self.dataset_folder = dataset_folder
54 | self.fields = fields
55 | self.no_except = no_except
56 | self.transform = transform
57 |
58 | # If categories is None, use all subfolders
59 | if categories is None:
60 | categories = os.listdir(dataset_folder)
61 | categories = [c for c in categories
62 | if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(dataset_folder, c))]
63 |
64 | # Read metadata file
65 | metadata_file = os.path.join(dataset_folder, 'metadata.yaml')
66 |
67 | if os.path.exists(metadata_file):
68 | with open(metadata_file, 'r') as f:
69 | self.metadata = yaml.load(f)
70 | else:
71 | self.metadata = {
72 | c: {'id': c, 'name': 'n/a'} for c in categories
73 | }
74 |
75 | # Set index
76 | for c_idx, c in enumerate(categories):
77 | self.metadata[c]['idx'] = c_idx
78 |
79 | # Get all models
80 | self.models = []
81 | for c_idx, c in enumerate(categories):
82 | subpath = os.path.join(dataset_folder, c)
83 | if not os.path.isdir(subpath):
84 | logger.warning('Category %s does not exist in dataset.' % c)
85 |
86 | split_file = os.path.join(subpath, split + '.lst')
87 | with open(split_file, 'r') as f:
88 | models_c = f.read().split('\n')
89 |
90 | self.models += [
91 | {'category': c, 'model': m}
92 | for m in models_c
93 | ]
94 |
95 | def __len__(self):
96 | ''' Returns the length of the dataset.
97 | '''
98 | return len(self.models)
99 |
100 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
101 | ''' Returns an item of the dataset.
102 |
103 | Args:
104 | idx (int): ID of data point
105 | '''
106 | category = self.models[idx]['category']
107 | model = self.models[idx]['model']
108 | c_idx = self.metadata[category]['idx']
109 |
110 | model_path = os.path.join(self.dataset_folder, category, model)
111 | data = {}
112 |
113 | for field_name, field in self.fields.items():
114 | try:
115 | field_data = field.load(model_path, idx, c_idx)
116 | except Exception:
117 | if self.no_except:
118 | logger.warn(
119 | 'Error occured when loading field %s of model %s'
120 | % (field_name, model)
121 | )
122 | return None
123 | else:
124 | raise
125 |
126 | if isinstance(field_data, dict):
127 | for k, v in field_data.items():
128 | if k is None:
129 | data[field_name] = v
130 | else:
131 | data['%s.%s' % (field_name, k)] = v
132 | else:
133 | data[field_name] = field_data
134 |
135 | if self.transform is not None:
136 | data = self.transform(data)
137 |
138 | return data
139 |
140 | def get_model_dict(self, idx):
141 | return self.models[idx]
142 |
143 | def test_model_complete(self, category, model):
144 | ''' Tests if model is complete.
145 |
146 | Args:
147 | model (str): modelname
148 | '''
149 | model_path = os.path.join(self.dataset_folder, category, model)
150 | files = os.listdir(model_path)
151 | for field_name, field in self.fields.items():
152 | if not field.check_complete(files):
153 | logger.warn('Field "%s" is incomplete: %s'
154 | % (field_name, model_path))
155 | return False
156 |
157 | return True
158 |
159 |
160 | class Shapes3dDataset(data.Dataset):
161 | ''' 3D Shapes dataset class.
162 | '''
163 |
164 | def __init__(self, dataset_folder, fields, split=None,
165 | categories=None, no_except=True, transform=None):
166 | ''' Initialization of the the 3D shape dataset.
167 |
168 | Args:
169 | dataset_folder (str): dataset folder
170 | fields (dict): dictionary of fields
171 | split (str): which split is used
172 | categories (list): list of categories to use
173 | no_except (bool): no exception
174 | transform (callable): transformation applied to data points
175 | '''
176 | # Attributes
177 | self.dataset_folder = dataset_folder
178 | self.fields = fields
179 | self.no_except = no_except
180 | self.transform = transform
181 |
182 | # If categories is None, use all subfolders
183 | if categories is None:
184 | categories = os.listdir(dataset_folder)
185 | categories = [c for c in categories
186 | if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(dataset_folder, c))]
187 |
188 | # Read metadata file
189 | metadata_file = os.path.join(dataset_folder, 'metadata.yaml')
190 |
191 | if os.path.exists(metadata_file):
192 | with open(metadata_file, 'r') as f:
193 | self.metadata = yaml.load(f)
194 | else:
195 | self.metadata = {
196 | c: {'id': c, 'name': 'n/a'} for c in categories
197 | }
198 |
199 | # Set index
200 | for c_idx, c in enumerate(categories):
201 | self.metadata[c]['idx'] = c_idx
202 |
203 | # Get all models
204 | self.models = []
205 | for c_idx, c in enumerate(categories):
206 | subpath = os.path.join(dataset_folder, c)
207 | if not os.path.isdir(subpath):
208 | logger.warning('Category %s does not exist in dataset.' % c)
209 |
210 | split_file = os.path.join(subpath, split + '.lst')
211 | with open(split_file, 'r') as f:
212 | models_c = f.read().split('\n')
213 |
214 | self.models += [
215 | {'category': c, 'model': m}
216 | for m in models_c
217 | ]
218 |
219 | def __len__(self):
220 | ''' Returns the length of the dataset.
221 | '''
222 | return len(self.models)
223 |
224 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
225 | ''' Returns an item of the dataset.
226 |
227 | Args:
228 | idx (int): ID of data point
229 | '''
230 | category = self.models[idx]['category']
231 | model = self.models[idx]['model']
232 | c_idx = self.metadata[category]['idx']
233 |
234 | model_path = os.path.join(self.dataset_folder, category, model)
235 | data = {}
236 |
237 | for field_name, field in self.fields.items():
238 | try:
239 | field_data = field.load(model_path, idx, c_idx)
240 | except Exception:
241 | if self.no_except:
242 | logger.warn(
243 | 'Error occured when loading field %s of model %s'
244 | % (field_name, model)
245 | )
246 | return None
247 | else:
248 | raise
249 |
250 | if isinstance(field_data, dict):
251 | for k, v in field_data.items():
252 | if k is None:
253 | data[field_name] = v
254 | else:
255 | data['%s.%s' % (field_name, k)] = v
256 | else:
257 | data[field_name] = field_data
258 |
259 | if self.transform is not None:
260 | data = self.transform(data)
261 |
262 | return data
263 |
264 | def get_model_dict(self, idx):
265 | return self.models[idx]
266 |
267 | def test_model_complete(self, category, model):
268 | ''' Tests if model is complete.
269 |
270 | Args:
271 | model (str): modelname
272 | '''
273 | model_path = os.path.join(self.dataset_folder, category, model)
274 | files = os.listdir(model_path)
275 | for field_name, field in self.fields.items():
276 | if not field.check_complete(files):
277 | logger.warn('Field "%s" is incomplete: %s'
278 | % (field_name, model_path))
279 | return False
280 |
281 | return True
282 |
283 |
284 | def collate_remove_none(batch):
285 | ''' Collater that puts each data field into a tensor with outer dimension
286 | batch size.
287 |
288 | Args:
289 | batch: batch
290 | '''
291 |
292 | batch = list(filter(lambda x: x is not None, batch))
293 | return data.dataloader.default_collate(batch)
294 |
295 |
296 | def worker_init_fn(worker_id):
297 | ''' Worker init function to ensure true randomness.
298 | '''
299 | random_data = os.urandom(4)
300 | base_seed = int.from_bytes(random_data, byteorder="big")
301 | np.random.seed(base_seed + worker_id)
302 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/data/fields.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import glob
3 | import random
4 | from PIL import Image
5 | import numpy as np
6 | import trimesh
7 | from main.data.core import Field
8 | from main.utils import binvox_rw
9 |
10 |
11 | class IndexField(Field):
12 | ''' Basic index field.'''
13 | def load(self, model_path, idx, category):
14 | ''' Loads the index field.
15 |
16 | Args:
17 | model_path (str): path to model
18 | idx (int): ID of data point
19 | category (int): index of category
20 | '''
21 | return idx
22 |
23 | def check_complete(self, files):
24 | ''' Check if field is complete.
25 |
26 | Args:
27 | files: files
28 | '''
29 | return True
30 |
31 |
32 | class CategoryField(Field):
33 | ''' Basic category field.'''
34 | def load(self, model_path, idx, category):
35 | ''' Loads the category field.
36 |
37 | Args:
38 | model_path (str): path to model
39 | idx (int): ID of data point
40 | category (int): index of category
41 | '''
42 | return category
43 |
44 | def check_complete(self, files):
45 | ''' Check if field is complete.
46 |
47 | Args:
48 | files: files
49 | '''
50 | return True
51 |
52 |
53 | class ImagesField(Field):
54 | ''' Image Field.
55 |
56 | It is the field used for loading images.
57 |
58 | Args:
59 | folder_name (str): folder name
60 | transform (list): list of transformations applied to loaded images
61 | extension (str): image extension
62 | random_view (bool): whether a random view should be used
63 | with_camera (bool): whether camera data should be provided
64 | '''
65 | def __init__(self, folder_name, transform=None,
66 | extension='jpg', random_view=True, with_camera=False):
67 | self.folder_name = folder_name
68 | self.transform = transform
69 | self.extension = extension
70 | self.random_view = random_view
71 | self.with_camera = with_camera
72 |
73 | def load(self, model_path, idx, category):
74 | ''' Loads the data point.
75 |
76 | Args:
77 | model_path (str): path to model
78 | idx (int): ID of data point
79 | category (int): index of category
80 | '''
81 | folder = os.path.join(model_path, self.folder_name)
82 | files = glob.glob(os.path.join(folder, '*.%s' % self.extension))
83 | files.sort()
84 |
85 | if self.random_view:
86 | idx_img = random.randint(0, len(files)-1)
87 | else:
88 | idx_img = 0
89 | filename = files[idx_img]
90 | print(filename)
91 | image = Image.open(filename).convert('RGB')
92 | if self.transform is not None:
93 | image = self.transform(image)
94 |
95 | data = {
96 | None: image
97 | }
98 |
99 | if self.with_camera:
100 | camera_file = os.path.join(folder, 'cameras.npz')
101 | camera_dict = np.load(camera_file)
102 | Rt = camera_dict['world_mat_%d' % idx_img].astype(np.float32)
103 | K = camera_dict['camera_mat_%d' % idx_img].astype(np.float32)
104 | data['world_mat'] = Rt
105 | data['camera_mat'] = K
106 |
107 | return data
108 |
109 | def check_complete(self, files):
110 | ''' Check if field is complete.
111 |
112 | Args:
113 | files: files
114 | '''
115 | complete = (self.folder_name in files)
116 | # TODO: check camera
117 | return complete
118 |
119 |
120 | # 3D Fields
121 | class PointsField(Field):
122 | ''' Point Field.
123 |
124 | It provides the field to load point data. This is used for the points
125 | randomly sampled in the bounding volume of the 3D shape.
126 |
127 | Args:
128 | file_name (str): file name
129 | transform (list): list of transformations which will be applied to the
130 | points tensor
131 | with_transforms (bool): whether scaling and rotation data should be
132 | provided
133 |
134 | '''
135 | def __init__(self, file_name, transform=None, with_transforms=False, unpackbits=False):
136 | self.file_name = file_name
137 | self.transform = transform
138 | self.with_transforms = with_transforms
139 | self.unpackbits = unpackbits
140 |
141 | def load(self, model_path, idx, category):
142 | ''' Loads the data point.
143 |
144 | Args:
145 | model_path (str): path to model
146 | idx (int): ID of data point
147 | category (int): index of category
148 | '''
149 | file_path = os.path.join(model_path, self.file_name)
150 |
151 | points_dict = np.load(file_path)
152 | points = points_dict['points']
153 | # Break symmetry if given in float16:
154 | if points.dtype == np.float16:
155 | points = points.astype(np.float32)
156 | points += 1e-4 * np.random.randn(*points.shape)
157 | else:
158 | points = points.astype(np.float32)
159 |
160 | occupancies = points_dict['occupancies']
161 | if self.unpackbits:
162 | occupancies = np.unpackbits(occupancies)[:points.shape[0]]
163 | occupancies = occupancies.astype(np.float32)
164 |
165 | data = {
166 | None: points,
167 | 'occ': occupancies,
168 | }
169 |
170 | if self.with_transforms:
171 | data['loc'] = points_dict['loc'].astype(np.float32)
172 | data['scale'] = points_dict['scale'].astype(np.float32)
173 |
174 | if self.transform is not None:
175 | data = self.transform(data)
176 |
177 | return data
178 |
179 |
180 | class VoxelsField(Field):
181 | ''' Voxel field class.
182 |
183 | It provides the class used for voxel-based data.
184 |
185 | Args:
186 | file_name (str): file name
187 | transform (list): list of transformations applied to data points
188 | '''
189 | def __init__(self, file_name, transform=None):
190 | self.file_name = file_name
191 | self.transform = transform
192 |
193 | def load(self, model_path, idx, category):
194 | ''' Loads the data point.
195 |
196 | Args:
197 | model_path (str): path to model
198 | idx (int): ID of data point
199 | category (int): index of category
200 | '''
201 | file_path = os.path.join(model_path, self.file_name)
202 | if file_path.endswith('vox'):
203 | with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
204 | voxels = binvox_rw.read_as_3d_array(f)
205 | else:
206 | with open(file_path, 'rb') as f:
207 | voxels = binvox_rw.read_as_3d_array_np(f)
208 | voxels = voxels.data.astype(np.float32)
209 |
210 | if self.transform is not None:
211 | voxels = self.transform(voxels)
212 |
213 | return voxels
214 |
215 | def check_complete(self, files):
216 | ''' Check if field is complete.
217 |
218 | Args:
219 | files: files
220 | '''
221 | complete = (self.file_name in files)
222 | return complete
223 |
224 |
225 | class PointCloudField(Field):
226 | ''' Point cloud field.
227 |
228 | It provides the field used for point cloud data. These are the points
229 | randomly sampled on the mesh.
230 |
231 | Args:
232 | file_name (str): file name
233 | transform (list): list of transformations applied to data points
234 | with_transforms (bool): whether scaling and rotation dat should be
235 | provided
236 | '''
237 | def __init__(self, file_name, transform=None, with_transforms=False):
238 | self.file_name = file_name
239 | self.transform = transform
240 | self.with_transforms = with_transforms
241 |
242 | def load(self, model_path, idx, category):
243 | ''' Loads the data point.
244 |
245 | Args:
246 | model_path (str): path to model
247 | idx (int): ID of data point
248 | category (int): index of category
249 | '''
250 | file_path = os.path.join(model_path, self.file_name)
251 |
252 | pointcloud_dict = np.load(file_path)
253 |
254 | points = pointcloud_dict['points'].astype(np.float32)
255 | normals = pointcloud_dict['normals'].astype(np.float32)
256 |
257 | data = {
258 | None: points,
259 | 'normals': normals,
260 | }
261 |
262 | if self.with_transforms:
263 | data['loc'] = pointcloud_dict['loc'].astype(np.float32)
264 | data['scale'] = pointcloud_dict['scale'].astype(np.float32)
265 |
266 | if self.transform is not None:
267 | data = self.transform(data)
268 |
269 | return data
270 |
271 | def check_complete(self, files):
272 | ''' Check if field is complete.
273 |
274 | Args:
275 | files: files
276 | '''
277 | complete = (self.file_name in files)
278 | return complete
279 |
280 |
281 | # NOTE: this will produce variable length output.
282 | # You need to specify collate_fn to make it work with a data laoder
283 | class MeshField(Field):
284 | ''' Mesh field.
285 |
286 | It provides the field used for mesh data. Note that, depending on the
287 | dataset, it produces variable length output, so that you need to specify
288 | collate_fn to make it work with a data loader.
289 |
290 | Args:
291 | file_name (str): file name
292 | transform (list): list of transforms applied to data points
293 | '''
294 | def __init__(self, file_name, transform=None):
295 | self.file_name = file_name
296 | self.transform = transform
297 |
298 | def load(self, model_path, idx, category):
299 | ''' Loads the data point.
300 |
301 | Args:
302 | model_path (str): path to model
303 | idx (int): ID of data point
304 | category (int): index of category
305 | '''
306 | file_path = os.path.join(model_path, self.file_name)
307 |
308 | mesh = trimesh.load(file_path, process=False)
309 | if self.transform is not None:
310 | mesh = self.transform(mesh)
311 |
312 | data = {
313 | 'verts': mesh.vertices,
314 | 'faces': mesh.faces,
315 | }
316 |
317 | return data
318 |
319 | def check_complete(self, files):
320 | ''' Check if field is complete.
321 |
322 | Args:
323 | files: files
324 | '''
325 | complete = (self.file_name in files)
326 | return complete
327 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/network/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from main.network import (
2 | config, generation, models
3 | )
4 |
5 | __all__ = [
6 | config, generation, models
7 | ]
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/network/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.distributions as dist
3 | from torch import nn
4 | import os
5 | from main.network.encoder import encoder_dict
6 | from main.network import models, generation
7 | from main import data
8 |
9 |
10 | def get_model(cfg, device=None, dataset=None, **kwargs):
11 | ''' Return the Occupancy Network model.
12 |
13 | Args:
14 | cfg (dict): imported yaml config
15 | device (device): pytorch device
16 | dataset (dataset): dataset
17 | '''
18 | decoder = cfg['model']['decoder']
19 | encoder = cfg['model']['encoder']
20 | encoder_latent = cfg['model']['encoder_latent']
21 | dim = cfg['data']['dim']
22 | z_dim = cfg['model']['z_dim']
23 | c_dim = cfg['model']['c_dim']
24 | decoder_kwargs = cfg['model']['decoder_kwargs']
25 | encoder_kwargs = cfg['model']['encoder_kwargs']
26 | encoder_latent_kwargs = cfg['model']['encoder_latent_kwargs']
27 |
28 | decoder = models.decoder_dict[decoder](
29 | dim=dim, z_dim=z_dim, c_dim=c_dim,
30 | **decoder_kwargs
31 | )
32 |
33 | if z_dim != 0:
34 | encoder_latent = models.encoder_latent_dict[encoder_latent](
35 | dim=dim, z_dim=z_dim, c_dim=c_dim,
36 | **encoder_latent_kwargs
37 | )
38 | else:
39 | encoder_latent = None
40 |
41 | if encoder == 'idx':
42 | encoder = nn.Embedding(len(dataset), c_dim)
43 | elif encoder is not None:
44 | encoder = encoder_dict[encoder](
45 | c_dim=c_dim,
46 | **encoder_kwargs
47 | )
48 | else:
49 | encoder = None
50 |
51 | p0_z = get_prior_z(cfg, device)
52 | model = models.OccupancyNetwork(
53 | decoder, encoder, encoder_latent, p0_z, device=device
54 | )
55 |
56 | return model
57 |
58 |
59 | def get_trainer(model, optimizer, cfg, device, **kwargs):
60 | ''' Returns the trainer object.
61 |
62 | Args:
63 | model (nn.Module): the Occupancy Network model
64 | optimizer (optimizer): pytorch optimizer object
65 | cfg (dict): imported yaml config
66 | device (device): pytorch device
67 | '''
68 | threshold = cfg['test']['threshold']
69 | out_dir = cfg['training']['out_dir']
70 | vis_dir = os.path.join(out_dir, 'vis')
71 | input_type = cfg['data']['input_type']
72 |
73 | trainer = training.Trainer(
74 | model, optimizer,
75 | device=device, input_type=input_type,
76 | vis_dir=vis_dir, threshold=threshold,
77 | eval_sample=cfg['training']['eval_sample'],
78 | )
79 |
80 | return trainer
81 |
82 |
83 | def get_generator(model, cfg, device, **kwargs):
84 | ''' Returns the generator object.
85 |
86 | Args:
87 | model (nn.Module): Occupancy Network model
88 | cfg (dict): imported yaml config
89 | device (device): pytorch device
90 | '''
91 |
92 | generator = generation.Generator3D(
93 | model,
94 | device=device,
95 | threshold=cfg['test']['threshold'],
96 | resolution0=cfg['generation']['resolution_0'],
97 | upsampling_steps=cfg['generation']['upsampling_steps'],
98 | sample=cfg['generation']['use_sampling'],
99 | refinement_step=cfg['generation']['refinement_step'],
100 | simplify_nfaces=cfg['generation']['simplify_nfaces'],
101 | preprocessor=None,
102 | )
103 | return generator
104 |
105 |
106 | def get_prior_z(cfg, device, **kwargs):
107 | ''' Returns prior distribution for latent code z.
108 |
109 | Args:
110 | cfg (dict): imported yaml config
111 | device (device): pytorch device
112 | '''
113 | z_dim = cfg['model']['z_dim']
114 | p0_z = dist.Normal(
115 | torch.zeros(z_dim, device=device),
116 | torch.ones(z_dim, device=device)
117 | )
118 |
119 | return p0_z
120 |
121 |
122 | def get_data_fields(mode, cfg):
123 | ''' Returns the data fields.
124 |
125 | Args:
126 | mode (str): the mode which is used
127 | cfg (dict): imported yaml config
128 | '''
129 | points_transform = data.SubsamplePoints(cfg['data']['points_subsample'])
130 | with_transforms = cfg['model']['use_camera']
131 |
132 | fields = {}
133 | fields['points'] = data.PointsField(
134 | cfg['data']['points_file'], points_transform,
135 | with_transforms=with_transforms,
136 | unpackbits=cfg['data']['points_unpackbits'],
137 | )
138 |
139 | if mode in ('val', 'test'):
140 | points_iou_file = cfg['data']['points_iou_file']
141 | voxels_file = cfg['data']['voxels_file']
142 | if points_iou_file is not None:
143 | fields['points_iou'] = data.PointsField(
144 | points_iou_file,
145 | with_transforms=with_transforms,
146 | unpackbits=cfg['data']['points_unpackbits'],
147 | )
148 | if voxels_file is not None:
149 | fields['voxels'] = data.VoxelsField(voxels_file)
150 |
151 | return fields
152 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/network/encoder/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from main.network.encoder import conv
2 |
3 | encoder_dict = {
4 | 'simple_conv': conv.ConvEncoder,
5 | 'resnet18': conv.Resnet18,
6 | 'vit_light': conv.ViTLight,
7 | 'vit_large': conv.ViTLarge,
8 | }
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/network/encoder/conv.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | from torchvision import models
3 | from main.common import normalize_imagenet
4 | from transformers import ViTModel
5 |
6 | class ViTLarge(nn.Module):
7 | def __init__(self, c_dim=128, normalize=True, use_linear=True):
8 | super(ViTLarge, self).__init__()
9 | self.model = ViTModel.from_pretrained('google/vit-large-patch16-224-in21k', return_dict=True,
10 | output_hidden_states=True)
11 | self.c_dim = c_dim
12 | if use_linear:
13 | self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, c_dim)
14 | elif c_dim == 512:
15 | self.fc = nn.Sequential()
16 | else:
17 | raise ValueError('c_dim must be 512 if use_linear is False')
18 |
19 | self.actvn = nn.ReLU()
20 |
21 | def forward(self, x):
22 | outputs = self.model(x)
23 | sequence_output = outputs[0]
24 | h = sequence_output[:, 0, :]
25 | h = self.fc(h)
26 | return h
27 |
28 | class ViTLight(nn.Module):
29 | def __init__(self, c_dim=128, normalize=True, use_linear=True):
30 | super(ViTLight, self).__init__()
31 | self.model = ViTModel.from_pretrained('google/vit-base-patch16-224-in21k', return_dict=True,
32 | output_hidden_states=True)
33 | self.c_dim = c_dim
34 | if use_linear:
35 | self.fc = nn.Linear(768, c_dim)
36 | elif c_dim == 512:
37 | self.fc = nn.Sequential()
38 | else:
39 | raise ValueError('c_dim must be 512 if use_linear is False')
40 |
41 | self.actvn = nn.ReLU()
42 |
43 | def forward(self, x):
44 | outputs = self.model(x)
45 | sequence_output = outputs[0]
46 | h = sequence_output[:, 0, :]
47 | h = self.fc(h)
48 | return h
49 |
50 | class ConvEncoder(nn.Module):
51 | r''' Simple convolutional encoder network.
52 |
53 | It consists of 5 convolutional layers, each downsampling the input by a
54 | factor of 2, and a final fully-connected layer projecting the output to
55 | c_dim dimenions.
56 |
57 | Args:
58 | c_dim (int): output dimension of latent embedding
59 | '''
60 |
61 | def __init__(self, c_dim=128):
62 | super().__init__()
63 | self.conv0 = nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3, stride=2)
64 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, stride=2)
65 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, 3, stride=2)
66 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, 3, stride=2)
67 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, 3, stride=2)
68 | self.fc_out = nn.Linear(512, c_dim)
69 | self.actvn = nn.ReLU()
70 |
71 | def forward(self, x):
72 | batch_size = x.size(0)
73 |
74 | net = self.conv0(x)
75 | net = self.conv1(self.actvn(net))
76 | net = self.conv2(self.actvn(net))
77 | net = self.conv3(self.actvn(net))
78 | net = self.conv4(self.actvn(net))
79 | net = net.view(batch_size, 512, -1).mean(2)
80 | out = self.fc_out(self.actvn(net))
81 |
82 | return out
83 |
84 |
85 | class Resnet18(nn.Module):
86 | r''' ResNet-18 encoder network for image input.
87 | Args:
88 | c_dim (int): output dimension of the latent embedding
89 | normalize (bool): whether the input images should be normalized
90 | use_linear (bool): whether a final linear layer should be used
91 | '''
92 |
93 | def __init__(self, c_dim, normalize=True, use_linear=True):
94 | super().__init__()
95 | self.normalize = normalize
96 | self.use_linear = use_linear
97 | self.features = models.resnet18(pretrained=True)
98 | self.features.fc = nn.Sequential()
99 | if use_linear:
100 | self.fc = nn.Linear(512, c_dim)
101 | elif c_dim == 512:
102 | self.fc = nn.Sequential()
103 | else:
104 | raise ValueError('c_dim must be 512 if use_linear is False')
105 |
106 | def forward(self, x):
107 | if self.normalize:
108 | x = normalize_imagenet(x)
109 | net = self.features(x)
110 | out = self.fc(net)
111 | return out
112 |
113 |
114 | class Resnet34(nn.Module):
115 | r''' ResNet-34 encoder network.
116 |
117 | Args:
118 | c_dim (int): output dimension of the latent embedding
119 | normalize (bool): whether the input images should be normalized
120 | use_linear (bool): whether a final linear layer should be used
121 | '''
122 |
123 | def __init__(self, c_dim, normalize=True, use_linear=True):
124 | super().__init__()
125 | self.normalize = normalize
126 | self.use_linear = use_linear
127 | self.features = models.resnet34(pretrained=True)
128 | self.features.fc = nn.Sequential()
129 | if use_linear:
130 | self.fc = nn.Linear(512, c_dim)
131 | elif c_dim == 512:
132 | self.fc = nn.Sequential()
133 | else:
134 | raise ValueError('c_dim must be 512 if use_linear is False')
135 |
136 | def forward(self, x):
137 | if self.normalize:
138 | x = normalize_imagenet(x)
139 | net = self.features(x)
140 | out = self.fc(net)
141 | return out
142 |
143 |
144 | class Resnet50(nn.Module):
145 | r''' ResNet-50 encoder network.
146 |
147 | Args:
148 | c_dim (int): output dimension of the latent embedding
149 | normalize (bool): whether the input images should be normalized
150 | use_linear (bool): whether a final linear layer should be used
151 | '''
152 |
153 | def __init__(self, c_dim, normalize=True, use_linear=True):
154 | super().__init__()
155 | self.normalize = normalize
156 | self.use_linear = use_linear
157 | self.features = models.resnet50(pretrained=True)
158 | self.features.fc = nn.Sequential()
159 | if use_linear:
160 | self.fc = nn.Linear(2048, c_dim)
161 | elif c_dim == 2048:
162 | self.fc = nn.Sequential()
163 | else:
164 | raise ValueError('c_dim must be 2048 if use_linear is False')
165 |
166 | def forward(self, x):
167 | if self.normalize:
168 | x = normalize_imagenet(x)
169 | net = self.features(x)
170 | out = self.fc(net)
171 | return out
172 |
173 |
174 | class Resnet101(nn.Module):
175 | r''' ResNet-101 encoder network.
176 | Args:
177 | c_dim (int): output dimension of the latent embedding
178 | normalize (bool): whether the input images should be normalized
179 | use_linear (bool): whether a final linear layer should be used
180 | '''
181 |
182 | def __init__(self, c_dim, normalize=True, use_linear=True):
183 | super().__init__()
184 | self.normalize = normalize
185 | self.use_linear = use_linear
186 | self.features = models.resnet50(pretrained=True)
187 | self.features.fc = nn.Sequential()
188 | if use_linear:
189 | self.fc = nn.Linear(2048, c_dim)
190 | elif c_dim == 2048:
191 | self.fc = nn.Sequential()
192 | else:
193 | raise ValueError('c_dim must be 2048 if use_linear is False')
194 |
195 | def forward(self, x):
196 | if self.normalize:
197 | x = normalize_imagenet(x)
198 | net = self.features(x)
199 | out = self.fc(net)
200 | return out
201 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/network/models/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from torch import distributions as dist
4 | from main.network.models import encoder_latent, decoder
5 |
6 | # Encoder latent dictionary
7 | encoder_latent_dict = {
8 | 'simple': encoder_latent.Encoder,
9 | }
10 |
11 | # Decoder dictionary
12 | decoder_dict = {
13 | 'simple': decoder.Decoder,
14 | 'cbatchnorm': decoder.DecoderCBatchNorm,
15 | 'cbatchnorm2': decoder.DecoderCBatchNorm2,
16 | 'batchnorm': decoder.DecoderBatchNorm,
17 | 'cbatchnorm_noresnet': decoder.DecoderCBatchNormNoResnet,
18 | }
19 |
20 |
21 | class OccupancyNetwork(nn.Module):
22 | ''' Occupancy Network class.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | decoder (nn.Module): decoder network
26 | encoder (nn.Module): encoder network
27 | encoder_latent (nn.Module): latent encoder network
28 | p0_z (dist): prior distribution for latent code z
29 | device (device): torch device
30 | '''
31 |
32 | def __init__(self, decoder, encoder=None, encoder_latent=None, p0_z=None, voxel_decoder=None,
33 | device=None):
34 | super().__init__()
35 | if p0_z is None:
36 | p0_z = dist.Normal(torch.tensor([]), torch.tensor([]))
37 |
38 | self.decoder = decoder.to(device)
39 |
40 | if encoder_latent is not None:
41 | self.encoder_latent = encoder_latent.to(device)
42 | else:
43 | self.encoder_latent = None
44 |
45 | if encoder is not None:
46 | self.encoder = encoder.to(device)
47 | else:
48 | self.encoder = None
49 |
50 | if voxel_decoder is not None:
51 | self.voxel_decoder = voxel_decoder.to(device)
52 | else:
53 | self.voxel_decoder = None
54 |
55 | self._device = device
56 | self.p0_z = p0_z
57 |
58 | def forward(self, p, inputs, sample=True, **kwargs):
59 | ''' Performs a forward pass through the network.
60 |
61 | Args:
62 | p (tensor): sampled points
63 | inputs (tensor): conditioning input
64 | sample (bool): whether to sample for z
65 | '''
66 | batch_size = p.size(0)
67 | # print(inputs.size())
68 | c = self.encode_inputs(inputs)
69 | # print(c.size())
70 | z = self.get_z_from_prior((batch_size,), sample=sample)
71 | # print(z.size())
72 | p_r = self.decode(p, z, c, **kwargs)
73 | # print(p_r.size())
74 | return p_r
75 |
76 | def compute_elbo(self, p, occ, inputs, **kwargs):
77 | ''' Computes the expectation lower bound.
78 |
79 | Args:
80 | p (tensor): sampled points
81 | occ (tensor): occupancy values for p
82 | inputs (tensor): conditioning input
83 | '''
84 | c = self.encode_inputs(inputs)
85 | q_z = self.infer_z(p, occ, c, **kwargs)
86 | z = q_z.rsample()
87 | p_r = self.decode(p, z, c, **kwargs)
88 |
89 | rec_error = -p_r.log_prob(occ).sum(dim=-1)
90 | kl = dist.kl_divergence(q_z, self.p0_z).sum(dim=-1)
91 | elbo = -rec_error - kl
92 |
93 | return elbo, rec_error, kl
94 |
95 | def encode_inputs(self, inputs):
96 | ''' Encodes the input.
97 |
98 | Args:
99 | input (tensor): the input
100 | '''
101 |
102 | if self.encoder is not None:
103 | c = self.encoder(inputs)
104 | else:
105 | # Return inputs?
106 | c = torch.empty(inputs.size(0), 0)
107 |
108 | return c
109 |
110 | def decode(self, p, z, c, **kwargs):
111 | ''' Returns occupancy probabilities for the sampled points.
112 |
113 | Args:
114 | p (tensor): points
115 | z (tensor): latent code z
116 | c (tensor): latent conditioned code c
117 | '''
118 | logits = self.decoder(p, z, c, **kwargs)
119 | p_r = dist.Bernoulli(logits=logits)
120 | if self.voxel_decoder is not None:
121 | voxel = self.voxel_decoder(z, c)
122 | return p_r, voxel
123 | return p_r
124 |
125 | def infer_z(self, p, occ, c, **kwargs):
126 | ''' Infers z.
127 |
128 | Args:
129 | p (tensor): points tensor
130 | occ (tensor): occupancy values for occ
131 | c (tensor): latent conditioned code c
132 | '''
133 | if self.encoder_latent is not None:
134 | mean_z, logstd_z = self.encoder_latent(p, occ, c, **kwargs)
135 | else:
136 | batch_size = p.size(0)
137 | mean_z = torch.empty(batch_size, 0).to(self._device)
138 | logstd_z = torch.empty(batch_size, 0).to(self._device)
139 |
140 | q_z = dist.Normal(mean_z, torch.exp(logstd_z))
141 | return q_z
142 |
143 | def get_z_from_prior(self, size=torch.Size([]), sample=True):
144 | ''' Returns z from prior distribution.
145 |
146 | Args:
147 | size (Size): size of z
148 | sample (bool): whether to sample
149 | '''
150 | if sample:
151 | z = self.p0_z.sample(size).to(self._device)
152 | else:
153 | z = self.p0_z.mean.to(self._device)
154 | z = z.expand(*size, *z.size())
155 |
156 | return z
157 |
158 | def to(self, device):
159 | ''' Puts the model to the device.
160 |
161 | Args:
162 | device (device): pytorch device
163 | '''
164 | model = super().to(device)
165 | model._device = device
166 | return model
167 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/network/models/decoder.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | from main.network.models.layers import (
5 | ResnetBlockFC, CResnetBlockConv1d,
6 | CBatchNorm1d, CBatchNorm1d_legacy,
7 | ResnetBlockConv1d
8 | )
9 |
10 |
11 | class Decoder(nn.Module):
12 | ''' Decoder class.
13 |
14 | It does not perform any form of normalization.
15 |
16 | Args:
17 | dim (int): input dimension
18 | z_dim (int): dimension of latent code z
19 | c_dim (int): dimension of latent conditioned code c
20 | hidden_size (int): hidden size of Decoder network
21 | leaky (bool): whether to use leaky ReLUs
22 | '''
23 |
24 | def __init__(self, dim=3, z_dim=128, c_dim=128,
25 | hidden_size=128, leaky=False):
26 | super().__init__()
27 | self.z_dim = z_dim
28 | self.c_dim = c_dim
29 |
30 | # Submodules
31 | self.fc_p = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_size)
32 |
33 | if not z_dim == 0:
34 | self.fc_z = nn.Linear(z_dim, hidden_size)
35 |
36 | if not c_dim == 0:
37 | self.fc_c = nn.Linear(c_dim, hidden_size)
38 |
39 | self.block0 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size)
40 | self.block1 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size)
41 | self.block2 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size)
42 | self.block3 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size)
43 | self.block4 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size)
44 |
45 | self.fc_out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 1)
46 |
47 | if not leaky:
48 | self.actvn = F.relu
49 | else:
50 | self.actvn = lambda x: F.leaky_relu(x, 0.2)
51 |
52 | def forward(self, p, z, c=None, **kwargs):
53 | batch_size, T, D = p.size()
54 |
55 | net = self.fc_p(p)
56 |
57 | if self.z_dim != 0:
58 | net_z = self.fc_z(z).unsqueeze(1)
59 | net = net + net_z
60 |
61 | if self.c_dim != 0:
62 | net_c = self.fc_c(c).unsqueeze(1)
63 | net = net + net_c
64 |
65 | net = self.block0(net)
66 | net = self.block1(net)
67 | net = self.block2(net)
68 | net = self.block3(net)
69 | net = self.block4(net)
70 |
71 | out = self.fc_out(self.actvn(net))
72 | out = out.squeeze(-1)
73 |
74 | return out
75 |
76 |
77 | class DecoderCBatchNorm(nn.Module):
78 | ''' Decoder with conditional batch normalization (CBN) class.
79 |
80 | Args:
81 | dim (int): input dimension
82 | z_dim (int): dimension of latent code z
83 | c_dim (int): dimension of latent conditioned code c
84 | hidden_size (int): hidden size of Decoder network
85 | leaky (bool): whether to use leaky ReLUs
86 | legacy (bool): whether to use the legacy structure
87 | '''
88 |
89 | def __init__(self, dim=3, z_dim=128, c_dim=128,
90 | hidden_size=256, leaky=False, legacy=False):
91 | super().__init__()
92 | self.z_dim = z_dim
93 | if not z_dim == 0:
94 | self.fc_z = nn.Linear(z_dim, hidden_size)
95 |
96 | self.fc_p = nn.Conv1d(dim, hidden_size, 1)
97 | self.block0 = CResnetBlockConv1d(c_dim, hidden_size, legacy=legacy)
98 | self.block1 = CResnetBlockConv1d(c_dim, hidden_size, legacy=legacy)
99 | self.block2 = CResnetBlockConv1d(c_dim, hidden_size, legacy=legacy)
100 | self.block3 = CResnetBlockConv1d(c_dim, hidden_size, legacy=legacy)
101 | self.block4 = CResnetBlockConv1d(c_dim, hidden_size, legacy=legacy)
102 |
103 | if not legacy:
104 | self.bn = CBatchNorm1d(c_dim, hidden_size)
105 | else:
106 | self.bn = CBatchNorm1d_legacy(c_dim, hidden_size)
107 |
108 | self.fc_out = nn.Conv1d(hidden_size, 1, 1)
109 |
110 | if not leaky:
111 | self.actvn = F.relu
112 | else:
113 | self.actvn = lambda x: F.leaky_relu(x, 0.2)
114 |
115 | def forward(self, p, z, c, **kwargs):
116 | p = p.transpose(1, 2)
117 | batch_size, D, T = p.size()
118 | net = self.fc_p(p)
119 |
120 | if self.z_dim != 0:
121 | net_z = self.fc_z(z).unsqueeze(2)
122 | net = net + net_z
123 |
124 | net = self.block0(net, c)
125 | net = self.block1(net, c)
126 | net = self.block2(net, c)
127 | net = self.block3(net, c)
128 | net = self.block4(net, c)
129 |
130 | out = self.fc_out(self.actvn(self.bn(net, c)))
131 | out = out.squeeze(1)
132 |
133 | return out
134 |
135 |
136 | class DecoderCBatchNorm2(nn.Module):
137 | ''' Decoder with CBN class 2.
138 |
139 | It differs from the previous one in that the number of blocks can be
140 | chosen.
141 |
142 | Args:
143 | dim (int): input dimension
144 | z_dim (int): dimension of latent code z
145 | c_dim (int): dimension of latent conditioned code c
146 | hidden_size (int): hidden size of Decoder network
147 | leaky (bool): whether to use leaky ReLUs
148 | n_blocks (int): number of ResNet blocks
149 | '''
150 |
151 | def __init__(self, dim=3, z_dim=0, c_dim=128,
152 | hidden_size=256, n_blocks=5):
153 | super().__init__()
154 | self.z_dim = z_dim
155 | if z_dim != 0:
156 | self.fc_z = nn.Linear(z_dim, c_dim)
157 |
158 | self.conv_p = nn.Conv1d(dim, hidden_size, 1)
159 | self.blocks = nn.ModuleList([
160 | CResnetBlockConv1d(c_dim, hidden_size) for i in range(n_blocks)
161 | ])
162 |
163 | self.bn = CBatchNorm1d(c_dim, hidden_size)
164 | self.conv_out = nn.Conv1d(hidden_size, 1, 1)
165 | self.actvn = nn.ReLU()
166 |
167 | def forward(self, p, z, c, **kwargs):
168 | p = p.transpose(1, 2)
169 | batch_size, D, T = p.size()
170 | net = self.conv_p(p)
171 |
172 | if self.z_dim != 0:
173 | c = c + self.fc_z(z)
174 |
175 | for block in self.blocks:
176 | net = block(net, c)
177 |
178 | out = self.conv_out(self.actvn(self.bn(net, c)))
179 | out = out.squeeze(1)
180 |
181 | return out
182 |
183 |
184 | class DecoderCBatchNormNoResnet(nn.Module):
185 | ''' Decoder CBN with no ResNet blocks class.
186 |
187 | Args:
188 | dim (int): input dimension
189 | z_dim (int): dimension of latent code z
190 | c_dim (int): dimension of latent conditioned code c
191 | hidden_size (int): hidden size of Decoder network
192 | leaky (bool): whether to use leaky ReLUs
193 | '''
194 |
195 | def __init__(self, dim=3, z_dim=128, c_dim=128,
196 | hidden_size=256, leaky=False):
197 | super().__init__()
198 | self.z_dim = z_dim
199 | if not z_dim == 0:
200 | self.fc_z = nn.Linear(z_dim, hidden_size)
201 |
202 | self.fc_p = nn.Conv1d(dim, hidden_size, 1)
203 | self.fc_0 = nn.Conv1d(hidden_size, hidden_size, 1)
204 | self.fc_1 = nn.Conv1d(hidden_size, hidden_size, 1)
205 | self.fc_2 = nn.Conv1d(hidden_size, hidden_size, 1)
206 | self.fc_3 = nn.Conv1d(hidden_size, hidden_size, 1)
207 | self.fc_4 = nn.Conv1d(hidden_size, hidden_size, 1)
208 |
209 | self.bn_0 = CBatchNorm1d(c_dim, hidden_size)
210 | self.bn_1 = CBatchNorm1d(c_dim, hidden_size)
211 | self.bn_2 = CBatchNorm1d(c_dim, hidden_size)
212 | self.bn_3 = CBatchNorm1d(c_dim, hidden_size)
213 | self.bn_4 = CBatchNorm1d(c_dim, hidden_size)
214 | self.bn_5 = CBatchNorm1d(c_dim, hidden_size)
215 |
216 | self.fc_out = nn.Conv1d(hidden_size, 1, 1)
217 |
218 | if not leaky:
219 | self.actvn = F.relu
220 | else:
221 | self.actvn = lambda x: F.leaky_relu(x, 0.2)
222 |
223 | def forward(self, p, z, c, **kwargs):
224 | p = p.transpose(1, 2)
225 | batch_size, D, T = p.size()
226 | net = self.fc_p(p)
227 |
228 | if self.z_dim != 0:
229 | net_z = self.fc_z(z).unsqueeze(2)
230 | net = net + net_z
231 |
232 | net = self.actvn(self.bn_0(net, c))
233 | net = self.fc_0(net)
234 | net = self.actvn(self.bn_1(net, c))
235 | net = self.fc_1(net)
236 | net = self.actvn(self.bn_2(net, c))
237 | net = self.fc_2(net)
238 | net = self.actvn(self.bn_3(net, c))
239 | net = self.fc_3(net)
240 | net = self.actvn(self.bn_4(net, c))
241 | net = self.fc_4(net)
242 | net = self.actvn(self.bn_5(net, c))
243 | out = self.fc_out(net)
244 | out = out.squeeze(1)
245 |
246 | return out
247 |
248 |
249 | class DecoderBatchNorm(nn.Module):
250 | ''' Decoder with batch normalization class.
251 |
252 | Args:
253 | dim (int): input dimension
254 | z_dim (int): dimension of latent code z
255 | c_dim (int): dimension of latent conditioned code c
256 | hidden_size (int): hidden size of Decoder network
257 | leaky (bool): whether to use leaky ReLUs
258 | '''
259 |
260 | def __init__(self, dim=3, z_dim=128, c_dim=128,
261 | hidden_size=256, leaky=False):
262 | super().__init__()
263 | self.z_dim = z_dim
264 | self.c_dim = c_dim
265 |
266 | # Submodules
267 | if not z_dim == 0:
268 | self.fc_z = nn.Linear(z_dim, hidden_size)
269 |
270 | if self.c_dim != 0:
271 | self.fc_c = nn.Linear(c_dim, hidden_size)
272 | self.fc_p = nn.Conv1d(dim, hidden_size, 1)
273 | self.block0 = ResnetBlockConv1d(hidden_size)
274 | self.block1 = ResnetBlockConv1d(hidden_size)
275 | self.block2 = ResnetBlockConv1d(hidden_size)
276 | self.block3 = ResnetBlockConv1d(hidden_size)
277 | self.block4 = ResnetBlockConv1d(hidden_size)
278 |
279 | self.bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(hidden_size)
280 |
281 | self.fc_out = nn.Conv1d(hidden_size, 1, 1)
282 |
283 | if not leaky:
284 | self.actvn = F.relu
285 | else:
286 | self.actvn = lambda x: F.leaky_relu(x, 0.2)
287 |
288 | def forward(self, p, z, c, **kwargs):
289 | p = p.transpose(1, 2)
290 | batch_size, D, T = p.size()
291 | net = self.fc_p(p)
292 |
293 | if self.z_dim != 0:
294 | net_z = self.fc_z(z).unsqueeze(2)
295 | net = net + net_z
296 |
297 | if self.c_dim != 0:
298 | net_c = self.fc_c(c).unsqueeze(2)
299 | net = net + net_c
300 |
301 | net = self.block0(net)
302 | net = self.block1(net)
303 | net = self.block2(net)
304 | net = self.block3(net)
305 | net = self.block4(net)
306 |
307 | out = self.fc_out(self.actvn(self.bn(net)))
308 | out = out.squeeze(1)
309 |
310 | return out
311 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/network/models/encoder_latent.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 |
5 |
6 | # Max Pooling operation
7 | def maxpool(x, dim=-1, keepdim=False):
8 | out, _ = x.max(dim=dim, keepdim=keepdim)
9 | return out
10 |
11 |
12 | class Encoder(nn.Module):
13 | ''' Latent encoder class.
14 |
15 | It encodes the input points and returns mean and standard deviation for the
16 | posterior Gaussian distribution.
17 |
18 | Args:
19 | z_dim (int): dimension if output code z
20 | c_dim (int): dimension of latent conditioned code c
21 | dim (int): input dimension
22 | leaky (bool): whether to use leaky ReLUs
23 | '''
24 | def __init__(self, z_dim=128, c_dim=128, dim=3, leaky=False):
25 | super().__init__()
26 | self.z_dim = z_dim
27 | self.c_dim = c_dim
28 |
29 | # Submodules
30 | self.fc_pos = nn.Linear(dim, 128)
31 |
32 | if c_dim != 0:
33 | self.fc_c = nn.Linear(c_dim, 128)
34 |
35 | self.fc_0 = nn.Linear(1, 128)
36 | self.fc_1 = nn.Linear(128, 128)
37 | self.fc_2 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
38 | self.fc_3 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
39 | self.fc_mean = nn.Linear(128, z_dim)
40 | self.fc_logstd = nn.Linear(128, z_dim)
41 |
42 | if not leaky:
43 | self.actvn = F.relu
44 | self.pool = maxpool
45 | else:
46 | self.actvn = lambda x: F.leaky_relu(x, 0.2)
47 | self.pool = torch.mean
48 |
49 | def forward(self, p, x, c=None, **kwargs):
50 | batch_size, T, D = p.size()
51 |
52 | # output size: B x T X F
53 | net = self.fc_0(x.unsqueeze(-1))
54 | net = net + self.fc_pos(p)
55 |
56 | if self.c_dim != 0:
57 | net = net + self.fc_c(c).unsqueeze(1)
58 |
59 | net = self.fc_1(self.actvn(net))
60 | pooled = self.pool(net, dim=1, keepdim=True).expand(net.size())
61 | net = torch.cat([net, pooled], dim=2)
62 |
63 | net = self.fc_2(self.actvn(net))
64 | pooled = self.pool(net, dim=1, keepdim=True).expand(net.size())
65 | net = torch.cat([net, pooled], dim=2)
66 |
67 | net = self.fc_3(self.actvn(net))
68 | # Reduce
69 | # to B x F
70 | net = self.pool(net, dim=1)
71 |
72 | mean = self.fc_mean(net)
73 | logstd = self.fc_logstd(net)
74 |
75 | return mean, logstd
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/network/models/layers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 |
4 |
5 | # Resnet Blocks
6 | class ResnetBlockFC(nn.Module):
7 | ''' Fully connected ResNet Block class.
8 |
9 | Args:
10 | size_in (int): input dimension
11 | size_out (int): output dimension
12 | size_h (int): hidden dimension
13 | '''
14 |
15 | def __init__(self, size_in, size_out=None, size_h=None):
16 | super().__init__()
17 | # Attributes
18 | if size_out is None:
19 | size_out = size_in
20 |
21 | if size_h is None:
22 | size_h = min(size_in, size_out)
23 |
24 | self.size_in = size_in
25 | self.size_h = size_h
26 | self.size_out = size_out
27 | # Submodules
28 | self.fc_0 = nn.Linear(size_in, size_h)
29 | self.fc_1 = nn.Linear(size_h, size_out)
30 | self.actvn = nn.ReLU()
31 |
32 | if size_in == size_out:
33 | self.shortcut = None
34 | else:
35 | self.shortcut = nn.Linear(size_in, size_out, bias=False)
36 | # Initialization
37 | nn.init.zeros_(self.fc_1.weight)
38 |
39 | def forward(self, x):
40 | net = self.fc_0(self.actvn(x))
41 | dx = self.fc_1(self.actvn(net))
42 |
43 | if self.shortcut is not None:
44 | x_s = self.shortcut(x)
45 | else:
46 | x_s = x
47 |
48 | return x_s + dx
49 |
50 |
51 | class CResnetBlockConv1d(nn.Module):
52 | ''' Conditional batch normalization-based Resnet block class.
53 |
54 | Args:
55 | c_dim (int): dimension of latend conditioned code c
56 | size_in (int): input dimension
57 | size_out (int): output dimension
58 | size_h (int): hidden dimension
59 | norm_method (str): normalization method
60 | legacy (bool): whether to use legacy blocks
61 | '''
62 |
63 | def __init__(self, c_dim, size_in, size_h=None, size_out=None,
64 | norm_method='batch_norm', legacy=False):
65 | super().__init__()
66 | # Attributes
67 | if size_h is None:
68 | size_h = size_in
69 | if size_out is None:
70 | size_out = size_in
71 |
72 | self.size_in = size_in
73 | self.size_h = size_h
74 | self.size_out = size_out
75 | # Submodules
76 | if not legacy:
77 | self.bn_0 = CBatchNorm1d(
78 | c_dim, size_in, norm_method=norm_method)
79 | self.bn_1 = CBatchNorm1d(
80 | c_dim, size_h, norm_method=norm_method)
81 | else:
82 | self.bn_0 = CBatchNorm1d_legacy(
83 | c_dim, size_in, norm_method=norm_method)
84 | self.bn_1 = CBatchNorm1d_legacy(
85 | c_dim, size_h, norm_method=norm_method)
86 |
87 | self.fc_0 = nn.Conv1d(size_in, size_h, 1)
88 | self.fc_1 = nn.Conv1d(size_h, size_out, 1)
89 | self.actvn = nn.ReLU()
90 |
91 | if size_in == size_out:
92 | self.shortcut = None
93 | else:
94 | self.shortcut = nn.Conv1d(size_in, size_out, 1, bias=False)
95 | # Initialization
96 | nn.init.zeros_(self.fc_1.weight)
97 |
98 | def forward(self, x, c):
99 | net = self.fc_0(self.actvn(self.bn_0(x, c)))
100 | dx = self.fc_1(self.actvn(self.bn_1(net, c)))
101 |
102 | if self.shortcut is not None:
103 | x_s = self.shortcut(x)
104 | else:
105 | x_s = x
106 |
107 | return x_s + dx
108 |
109 |
110 | class ResnetBlockConv1d(nn.Module):
111 | ''' 1D-Convolutional ResNet block class.
112 |
113 | Args:
114 | size_in (int): input dimension
115 | size_out (int): output dimension
116 | size_h (int): hidden dimension
117 | '''
118 |
119 | def __init__(self, size_in, size_h=None, size_out=None):
120 | super().__init__()
121 | # Attributes
122 | if size_h is None:
123 | size_h = size_in
124 | if size_out is None:
125 | size_out = size_in
126 |
127 | self.size_in = size_in
128 | self.size_h = size_h
129 | self.size_out = size_out
130 | # Submodules
131 | self.bn_0 = nn.BatchNorm1d(size_in)
132 | self.bn_1 = nn.BatchNorm1d(size_h)
133 |
134 | self.fc_0 = nn.Conv1d(size_in, size_h, 1)
135 | self.fc_1 = nn.Conv1d(size_h, size_out, 1)
136 | self.actvn = nn.ReLU()
137 |
138 | if size_in == size_out:
139 | self.shortcut = None
140 | else:
141 | self.shortcut = nn.Conv1d(size_in, size_out, 1, bias=False)
142 |
143 | # Initialization
144 | nn.init.zeros_(self.fc_1.weight)
145 |
146 | def forward(self, x):
147 | net = self.fc_0(self.actvn(self.bn_0(x)))
148 | dx = self.fc_1(self.actvn(self.bn_1(net)))
149 |
150 | if self.shortcut is not None:
151 | x_s = self.shortcut(x)
152 | else:
153 | x_s = x
154 |
155 | return x_s + dx
156 |
157 |
158 | # Utility modules
159 | class AffineLayer(nn.Module):
160 | ''' Affine layer class.
161 |
162 | Args:
163 | c_dim (tensor): dimension of latent conditioned code c
164 | dim (int): input dimension
165 | '''
166 |
167 | def __init__(self, c_dim, dim=3):
168 | super().__init__()
169 | self.c_dim = c_dim
170 | self.dim = dim
171 | # Submodules
172 | self.fc_A = nn.Linear(c_dim, dim * dim)
173 | self.fc_b = nn.Linear(c_dim, dim)
174 | self.reset_parameters()
175 |
176 | def reset_parameters(self):
177 | nn.init.zeros_(self.fc_A.weight)
178 | nn.init.zeros_(self.fc_b.weight)
179 | with torch.no_grad():
180 | self.fc_A.bias.copy_(torch.eye(3).view(-1))
181 | self.fc_b.bias.copy_(torch.tensor([0., 0., 2.]))
182 |
183 | def forward(self, x, p):
184 | assert(x.size(0) == p.size(0))
185 | assert(p.size(2) == self.dim)
186 | batch_size = x.size(0)
187 | A = self.fc_A(x).view(batch_size, 3, 3)
188 | b = self.fc_b(x).view(batch_size, 1, 3)
189 | out = p @ A + b
190 | return out
191 |
192 |
193 | class CBatchNorm1d(nn.Module):
194 | ''' Conditional batch normalization layer class.
195 |
196 | Args:
197 | c_dim (int): dimension of latent conditioned code c
198 | f_dim (int): feature dimension
199 | norm_method (str): normalization method
200 | '''
201 |
202 | def __init__(self, c_dim, f_dim, norm_method='batch_norm'):
203 | super().__init__()
204 | self.c_dim = c_dim
205 | self.f_dim = f_dim
206 | self.norm_method = norm_method
207 | # Submodules
208 | self.conv_gamma = nn.Conv1d(c_dim, f_dim, 1)
209 | self.conv_beta = nn.Conv1d(c_dim, f_dim, 1)
210 | if norm_method == 'batch_norm':
211 | self.bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(f_dim, affine=False)
212 | elif norm_method == 'instance_norm':
213 | self.bn = nn.InstanceNorm1d(f_dim, affine=False)
214 | elif norm_method == 'group_norm':
215 | self.bn = nn.GroupNorm1d(f_dim, affine=False)
216 | else:
217 | raise ValueError('Invalid normalization method!')
218 | self.reset_parameters()
219 |
220 | def reset_parameters(self):
221 | nn.init.zeros_(self.conv_gamma.weight)
222 | nn.init.zeros_(self.conv_beta.weight)
223 | nn.init.ones_(self.conv_gamma.bias)
224 | nn.init.zeros_(self.conv_beta.bias)
225 |
226 | def forward(self, x, c):
227 | assert(x.size(0) == c.size(0))
228 | assert(c.size(1) == self.c_dim)
229 |
230 | # c is assumed to be of size batch_size x c_dim x T
231 | if len(c.size()) == 2:
232 | c = c.unsqueeze(2)
233 |
234 | # Affine mapping
235 | gamma = self.conv_gamma(c)
236 | beta = self.conv_beta(c)
237 |
238 | # Batchnorm
239 | net = self.bn(x)
240 | out = gamma * net + beta
241 |
242 | return out
243 |
244 |
245 | class CBatchNorm1d_legacy(nn.Module):
246 | ''' Conditional batch normalization legacy layer class.
247 |
248 | Args:
249 | c_dim (int): dimension of latent conditioned code c
250 | f_dim (int): feature dimension
251 | norm_method (str): normalization method
252 | '''
253 |
254 | def __init__(self, c_dim, f_dim, norm_method='batch_norm'):
255 | super().__init__()
256 | self.c_dim = c_dim
257 | self.f_dim = f_dim
258 | self.norm_method = norm_method
259 | # Submodules
260 | self.fc_gamma = nn.Linear(c_dim, f_dim)
261 | self.fc_beta = nn.Linear(c_dim, f_dim)
262 | if norm_method == 'batch_norm':
263 | self.bn = nn.BatchNorm1d(f_dim, affine=False)
264 | elif norm_method == 'instance_norm':
265 | self.bn = nn.InstanceNorm1d(f_dim, affine=False)
266 | elif norm_method == 'group_norm':
267 | self.bn = nn.GroupNorm1d(f_dim, affine=False)
268 | else:
269 | raise ValueError('Invalid normalization method!')
270 | self.reset_parameters()
271 |
272 | def reset_parameters(self):
273 | nn.init.zeros_(self.fc_gamma.weight)
274 | nn.init.zeros_(self.fc_beta.weight)
275 | nn.init.ones_(self.fc_gamma.bias)
276 | nn.init.zeros_(self.fc_beta.bias)
277 |
278 | def forward(self, x, c):
279 | batch_size = x.size(0)
280 | # Affine mapping
281 | gamma = self.fc_gamma(c)
282 | beta = self.fc_beta(c)
283 | gamma = gamma.view(batch_size, self.f_dim, 1)
284 | beta = beta.view(batch_size, self.f_dim, 1)
285 | # Batchnorm
286 | net = self.bn(x)
287 | out = gamma * net + beta
288 |
289 | return out
290 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/network/models/voxel_decoder.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | from main.network.models.layers import ResnetBlockFC, AffineLayer
5 |
6 |
7 | class VoxelDecoder(nn.Module):
8 | def __init__(self, dim=3, z_dim=128, c_dim=128, hidden_size=128):
9 | super().__init__()
10 | self.c_dim = c_dim
11 | self.z_dim = z_dim
12 | # Submodules
13 | self.actvn = F.relu
14 | # 3D decoder
15 | self.fc_in = nn.Linear(c_dim + z_dim, 256*4*4*4)
16 | self.convtrp_0 = nn.ConvTranspose3d(256, 128, 3, stride=2,
17 | padding=1, output_padding=1)
18 | self.convtrp_1 = nn.ConvTranspose3d(128, 64, 3, stride=2,
19 | padding=1, output_padding=1)
20 | self.convtrp_2 = nn.ConvTranspose3d(64, 32, 3, stride=2,
21 | padding=1, output_padding=1)
22 | # Fully connected decoder
23 | self.z_dim = z_dim
24 | if not z_dim == 0:
25 | self.fc_z = nn.Linear(z_dim, hidden_size)
26 | self.fc_f = nn.Linear(32, hidden_size)
27 | self.fc_c = nn.Linear(c_dim, hidden_size)
28 | self.fc_p = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_size)
29 |
30 | self.block0 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size, hidden_size)
31 | self.block1 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size, hidden_size)
32 | self.fc_out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 1)
33 |
34 | def forward(self, p, z, c, **kwargs):
35 | batch_size = c.size(0)
36 |
37 | if self.z_dim != 0:
38 | net = torch.cat([z, c], dim=1)
39 | else:
40 | net = c
41 |
42 | net = self.fc_in(net)
43 | net = net.view(batch_size, 256, 4, 4, 4)
44 | net = self.convtrp_0(self.actvn(net))
45 | net = self.convtrp_1(self.actvn(net))
46 | net = self.convtrp_2(self.actvn(net))
47 |
48 | net = F.grid_sample(
49 | net, 2*p.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(1), padding_mode='border')
50 | net = net.squeeze(2).squeeze(2).transpose(1, 2)
51 | net = self.fc_f(self.actvn(net))
52 |
53 | net_p = self.fc_p(p)
54 | net = net + net_p
55 |
56 | if self.z_dim != 0:
57 | net_z = self.fc_z(z).unsqueeze(1)
58 | net = net + net_z
59 |
60 | if self.c_dim != 0:
61 | net_c = self.fc_c(c).unsqueeze(1)
62 | net = net + net_c
63 |
64 | net = self.block0(net)
65 | net = self.block1(net)
66 |
67 | out = self.fc_out(self.actvn(net))
68 | out = out.squeeze(-1)
69 |
70 | return out
71 |
72 |
73 | class FeatureDecoder(nn.Module):
74 | def __init__(self, dim=3, z_dim=128, c_dim=128, hidden_size=256):
75 | super().__init__()
76 | self.z_dim = z_dim
77 | self.c_dim = c_dim
78 | self.dim = dim
79 |
80 | self.actvn = nn.ReLU()
81 |
82 | self.affine = AffineLayer(c_dim, dim)
83 | if not z_dim == 0:
84 | self.fc_z = nn.Linear(z_dim, hidden_size)
85 | self.fc_p1 = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_size)
86 | self.fc_p2 = nn.Linear(dim, hidden_size)
87 |
88 | self.fc_c1 = nn.Linear(c_dim, hidden_size)
89 | self.fc_c2 = nn.Linear(c_dim, hidden_size)
90 |
91 | self.block0 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size, hidden_size)
92 | self.block1 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size, hidden_size)
93 | self.block2 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size, hidden_size)
94 | self.block3 = ResnetBlockFC(hidden_size, hidden_size)
95 |
96 | self.fc_out = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 1)
97 |
98 | def forward(self, p, z, c, **kwargs):
99 | batch_size, T, D = p.size()
100 |
101 | c1 = c.view(batch_size, self.c_dim, -1).max(dim=2)[0]
102 | Ap = self.affine(c1, p)
103 | Ap2 = Ap[:, :, :2] / (Ap[:, :, 2:].abs() + 1e-5)
104 |
105 | c2 = F.grid_sample(c, 2*Ap2.unsqueeze(1), padding_mode='border')
106 | c2 = c2.squeeze(2).transpose(1, 2)
107 |
108 | net = self.fc_p1(p) + self.fc_p2(Ap)
109 |
110 | if self.z_dim != 0:
111 | net_z = self.fc_z(z).unsqueeze(1)
112 | net = net + net_z
113 |
114 | net_c = self.fc_c2(c2) + self.fc_c1(c1).unsqueeze(1)
115 | net = net + net_c
116 |
117 | net = self.block0(net)
118 | net = self.block1(net)
119 | net = self.block2(net)
120 | net = self.block3(net)
121 |
122 | out = self.fc_out(self.actvn(net))
123 | out = out.squeeze(-1)
124 |
125 | return out
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kulbear/object-wakeup/62cfb70aa6369aadbca24fd1d51241f2db86e494/main/utils/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/binvox_rw.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (C) 2012 Daniel Maturana
2 | # This file is part of binvox-rw-py.
3 | #
4 | # binvox-rw-py is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
5 | # it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
6 | # the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
7 | # (at your option) any later version.
8 | #
9 | # binvox-rw-py is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
10 | # but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
11 | # MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
12 | # GNU General Public License for more details.
13 | #
14 | # You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
15 | # along with binvox-rw-py. If not, see .
16 | #
17 | # Modified by Christopher B. Choy
18 | # for python 3 support
19 |
20 | """
21 | Binvox to Numpy and back.
22 |
23 |
24 | >>> import numpy as np
25 | >>> import binvox_rw
26 | >>> with open('chair.binvox', 'rb') as f:
27 | ... m1 = binvox_rw.read_as_3d_array(f)
28 | ...
29 | >>> m1.dims
30 | [32, 32, 32]
31 | >>> m1.scale
32 | 41.133000000000003
33 | >>> m1.translate
34 | [0.0, 0.0, 0.0]
35 | >>> with open('chair_out.binvox', 'wb') as f:
36 | ... m1.write(f)
37 | ...
38 | >>> with open('chair_out.binvox', 'rb') as f:
39 | ... m2 = binvox_rw.read_as_3d_array(f)
40 | ...
41 | >>> m1.dims==m2.dims
42 | True
43 | >>> m1.scale==m2.scale
44 | True
45 | >>> m1.translate==m2.translate
46 | True
47 | >>> np.all(m1.data==m2.data)
48 | True
49 |
50 | >>> with open('chair.binvox', 'rb') as f:
51 | ... md = binvox_rw.read_as_3d_array(f)
52 | ...
53 | >>> with open('chair.binvox', 'rb') as f:
54 | ... ms = binvox_rw.read_as_coord_array(f)
55 | ...
56 | >>> data_ds = binvox_rw.dense_to_sparse(md.data)
57 | >>> data_sd = binvox_rw.sparse_to_dense(ms.data, 32)
58 | >>> np.all(data_sd==md.data)
59 | True
60 | >>> # the ordering of elements returned by numpy.nonzero changes with axis
61 | >>> # ordering, so to compare for equality we first lexically sort the voxels.
62 | >>> np.all(ms.data[:, np.lexsort(ms.data)] == data_ds[:, np.lexsort(data_ds)])
63 | True
64 | """
65 |
66 | import numpy as np
67 |
68 | class Voxels(object):
69 | """ Holds a binvox model.
70 | data is either a three-dimensional numpy boolean array (dense representation)
71 | or a two-dimensional numpy float array (coordinate representation).
72 |
73 | dims, translate and scale are the model metadata.
74 |
75 | dims are the voxel dimensions, e.g. [32, 32, 32] for a 32x32x32 model.
76 |
77 | scale and translate relate the voxels to the original model coordinates.
78 |
79 | To translate voxel coordinates i, j, k to original coordinates x, y, z:
80 |
81 | x_n = (i+.5)/dims[0]
82 | y_n = (j+.5)/dims[1]
83 | z_n = (k+.5)/dims[2]
84 | x = scale*x_n + translate[0]
85 | y = scale*y_n + translate[1]
86 | z = scale*z_n + translate[2]
87 |
88 | """
89 |
90 | def __init__(self, data, dims, translate, scale, axis_order):
91 | self.data = data
92 | self.dims = dims
93 | self.translate = translate
94 | self.scale = scale
95 | assert (axis_order in ('xzy', 'xyz'))
96 | self.axis_order = axis_order
97 |
98 | def clone(self):
99 | data = self.data.copy()
100 | dims = self.dims[:]
101 | translate = self.translate[:]
102 | return Voxels(data, dims, translate, self.scale, self.axis_order)
103 |
104 | def write(self, fp):
105 | write(self, fp)
106 |
107 | def read_header(fp):
108 | """ Read binvox header. Mostly meant for internal use.
109 | """
110 | line = fp.readline().strip()
111 | if not line.startswith(b'#binvox'):
112 | raise IOError('Not a binvox file')
113 | dims = [int(i) for i in fp.readline().strip().split(b' ')[1:]]
114 | translate = [float(i) for i in fp.readline().strip().split(b' ')[1:]]
115 | scale = [float(i) for i in fp.readline().strip().split(b' ')[1:]][0]
116 | line = fp.readline()
117 | return dims, translate, scale
118 |
119 | def read_as_3d_array_np(fp, fix_coords=False):
120 | """ Read binary binvox format as array.
121 |
122 | Returns the model with accompanying metadata.
123 |
124 | Voxels are stored in a three-dimensional numpy array, which is simple and
125 | direct, but may use a lot of memory for large models. (Storage requirements
126 | are 8*(d^3) bytes, where d is the dimensions of the binvox model. Numpy
127 | boolean arrays use a byte per element).
128 |
129 | Doesn't do any checks on input except for the '#binvox' line.
130 | """
131 | # dims, translate, scale = read_header(fp)
132 | dim = 32
133 | dims = [dim] * 3
134 | translate = []
135 | scale = []
136 | occ = np.unpackbits(np.load(fp))
137 | voxels = np.reshape(occ, (dim,) * 3)
138 | # raw_data = voxels
139 | # if just using reshape() on the raw data:
140 | # indexing the array as array[i,j,k], the indices map into the
141 | # coords as:
142 | # i -> x
143 | # j -> z
144 | # k -> y
145 | # if fix_coords is true, then data is rearranged so that
146 | # mapping is
147 | # i -> x
148 | # j -> y
149 | # k -> z
150 | # values, counts = raw_data[::2], raw_data[1::2]
151 | # data = np.repeat(values, counts).astype(np.bool)
152 | data = voxels
153 | if fix_coords:
154 | # xzy to xyz TODO the right thing
155 | data = np.transpose(data, (0, 2, 1))
156 | axis_order = 'xzy'
157 | else:
158 | axis_order = 'xyz'
159 | return Voxels(data, dims, translate, scale, axis_order)
160 |
161 | def read_as_3d_array(fp, fix_coords=True):
162 | """ Read binary binvox format as array.
163 |
164 | Returns the model with accompanying metadata.
165 |
166 | Voxels are stored in a three-dimensional numpy array, which is simple and
167 | direct, but may use a lot of memory for large models. (Storage requirements
168 | are 8*(d^3) bytes, where d is the dimensions of the binvox model. Numpy
169 | boolean arrays use a byte per element).
170 |
171 | Doesn't do any checks on input except for the '#binvox' line.
172 | """
173 | dims, translate, scale = read_header(fp)
174 | raw_data = np.frombuffer(fp.read(), dtype=np.uint8)
175 | # if just using reshape() on the raw data:
176 | # indexing the array as array[i,j,k], the indices map into the
177 | # coords as:
178 | # i -> x
179 | # j -> z
180 | # k -> y
181 | # if fix_coords is true, then data is rearranged so that
182 | # mapping is
183 | # i -> x
184 | # j -> y
185 | # k -> z
186 | values, counts = raw_data[::2], raw_data[1::2]
187 | data = np.repeat(values, counts).astype(np.bool)
188 | data = data.reshape(dims)
189 | if fix_coords:
190 | # xzy to xyz TODO the right thing
191 | data = np.transpose(data, (0, 2, 1))
192 | axis_order = 'xyz'
193 | else:
194 | axis_order = 'xzy'
195 | return Voxels(data, dims, translate, scale, axis_order)
196 |
197 |
198 | def read_as_coord_array(fp, fix_coords=True):
199 | """ Read binary binvox format as coordinates.
200 |
201 | Returns binvox model with voxels in a "coordinate" representation, i.e. an
202 | 3 x N array where N is the number of nonzero voxels. Each column
203 | corresponds to a nonzero voxel and the 3 rows are the (x, z, y) coordinates
204 | of the voxel. (The odd ordering is due to the way binvox format lays out
205 | data). Note that coordinates refer to the binvox voxels, without any
206 | scaling or translation.
207 |
208 | Use this to save memory if your model is very sparse (mostly empty).
209 |
210 | Doesn't do any checks on input except for the '#binvox' line.
211 | """
212 | dims, translate, scale = read_header(fp)
213 | raw_data = np.frombuffer(fp.read(), dtype=np.uint8)
214 |
215 | values, counts = raw_data[::2], raw_data[1::2]
216 |
217 | sz = np.prod(dims)
218 | index, end_index = 0, 0
219 | end_indices = np.cumsum(counts)
220 | indices = np.concatenate(([0], end_indices[:-1])).astype(end_indices.dtype)
221 |
222 | values = values.astype(np.bool)
223 | indices = indices[values]
224 | end_indices = end_indices[values]
225 |
226 | nz_voxels = []
227 | for index, end_index in zip(indices, end_indices):
228 | nz_voxels.extend(range(index, end_index))
229 | nz_voxels = np.array(nz_voxels)
230 | # TODO are these dims correct?
231 | # according to docs,
232 | # index = x * wxh + z * width + y; // wxh = width * height = d * d
233 |
234 | x = nz_voxels / (dims[0]*dims[1])
235 | zwpy = nz_voxels % (dims[0]*dims[1]) # z*w + y
236 | z = zwpy / dims[0]
237 | y = zwpy % dims[0]
238 | if fix_coords:
239 | data = np.vstack((x, y, z))
240 | axis_order = 'xyz'
241 | else:
242 | data = np.vstack((x, z, y))
243 | axis_order = 'xzy'
244 |
245 | #return Voxels(data, dims, translate, scale, axis_order)
246 | return Voxels(np.ascontiguousarray(data), dims, translate, scale, axis_order)
247 |
248 | def dense_to_sparse(voxel_data, dtype=np.int):
249 | """ From dense representation to sparse (coordinate) representation.
250 | No coordinate reordering.
251 | """
252 | if voxel_data.ndim!=3:
253 | raise ValueError('voxel_data is wrong shape; should be 3D array.')
254 | return np.asarray(np.nonzero(voxel_data), dtype)
255 |
256 | def sparse_to_dense(voxel_data, dims, dtype=np.bool):
257 | if voxel_data.ndim!=2 or voxel_data.shape[0]!=3:
258 | raise ValueError('voxel_data is wrong shape; should be 3xN array.')
259 | if np.isscalar(dims):
260 | dims = [dims]*3
261 | dims = np.atleast_2d(dims).T
262 | # truncate to integers
263 | xyz = voxel_data.astype(np.int)
264 | # discard voxels that fall outside dims
265 | valid_ix = ~np.any((xyz < 0) | (xyz >= dims), 0)
266 | xyz = xyz[:,valid_ix]
267 | out = np.zeros(dims.flatten(), dtype=dtype)
268 | out[tuple(xyz)] = True
269 | return out
270 |
271 | #def get_linear_index(x, y, z, dims):
272 | #""" Assuming xzy order. (y increasing fastest.
273 | #TODO ensure this is right when dims are not all same
274 | #"""
275 | #return x*(dims[1]*dims[2]) + z*dims[1] + y
276 |
277 | def write(voxel_model, fp):
278 | """ Write binary binvox format.
279 |
280 | Note that when saving a model in sparse (coordinate) format, it is first
281 | converted to dense format.
282 |
283 | Doesn't check if the model is 'sane'.
284 |
285 | """
286 | if voxel_model.data.ndim==2:
287 | # TODO avoid conversion to dense
288 | dense_voxel_data = sparse_to_dense(voxel_model.data, voxel_model.dims)
289 | else:
290 | dense_voxel_data = voxel_model.data
291 |
292 | fp.write('#binvox 1\n')
293 | fp.write('dim '+' '.join(map(str, voxel_model.dims))+'\n')
294 | fp.write('translate '+' '.join(map(str, voxel_model.translate))+'\n')
295 | fp.write('scale '+str(voxel_model.scale)+'\n')
296 | fp.write('data\n')
297 | if not voxel_model.axis_order in ('xzy', 'xyz'):
298 | raise ValueError('Unsupported voxel model axis order')
299 |
300 | if voxel_model.axis_order=='xzy':
301 | voxels_flat = dense_voxel_data.flatten()
302 | elif voxel_model.axis_order=='xyz':
303 | voxels_flat = np.transpose(dense_voxel_data, (0, 2, 1)).flatten()
304 |
305 | # keep a sort of state machine for writing run length encoding
306 | state = voxels_flat[0]
307 | ctr = 0
308 | for c in voxels_flat:
309 | if c==state:
310 | ctr += 1
311 | # if ctr hits max, dump
312 | if ctr==255:
313 | fp.write(chr(state))
314 | fp.write(chr(ctr))
315 | ctr = 0
316 | else:
317 | # if switch state, dump
318 | fp.write(chr(state))
319 | fp.write(chr(ctr))
320 | state = c
321 | ctr = 1
322 | # flush out remainders
323 | if ctr > 0:
324 | fp.write(chr(state))
325 | fp.write(chr(ctr))
326 |
327 | if __name__ == '__main__':
328 | import doctest
329 | doctest.testmod()
330 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/icp.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from sklearn.neighbors import NearestNeighbors
3 |
4 |
5 | def best_fit_transform(A, B):
6 | '''
7 | Calculates the least-squares best-fit transform that maps corresponding
8 | points A to B in m spatial dimensions
9 | Input:
10 | A: Nxm numpy array of corresponding points
11 | B: Nxm numpy array of corresponding points
12 | Returns:
13 | T: (m+1)x(m+1) homogeneous transformation matrix that maps A on to B
14 | R: mxm rotation matrix
15 | t: mx1 translation vector
16 | '''
17 |
18 | assert A.shape == B.shape
19 |
20 | # get number of dimensions
21 | m = A.shape[1]
22 |
23 | # translate points to their centroids
24 | centroid_A = np.mean(A, axis=0)
25 | centroid_B = np.mean(B, axis=0)
26 | AA = A - centroid_A
27 | BB = B - centroid_B
28 |
29 | # rotation matrix
30 | H = np.dot(AA.T, BB)
31 | U, S, Vt = np.linalg.svd(H)
32 | R = np.dot(Vt.T, U.T)
33 |
34 | # special reflection case
35 | if np.linalg.det(R) < 0:
36 | Vt[m-1,:] *= -1
37 | R = np.dot(Vt.T, U.T)
38 |
39 | # translation
40 | t = centroid_B.T - np.dot(R,centroid_A.T)
41 |
42 | # homogeneous transformation
43 | T = np.identity(m+1)
44 | T[:m, :m] = R
45 | T[:m, m] = t
46 |
47 | return T, R, t
48 |
49 |
50 | def nearest_neighbor(src, dst):
51 | '''
52 | Find the nearest (Euclidean) neighbor in dst for each point in src
53 | Input:
54 | src: Nxm array of points
55 | dst: Nxm array of points
56 | Output:
57 | distances: Euclidean distances of the nearest neighbor
58 | indices: dst indices of the nearest neighbor
59 | '''
60 |
61 | assert src.shape == dst.shape
62 |
63 | neigh = NearestNeighbors(n_neighbors=1)
64 | neigh.fit(dst)
65 | distances, indices = neigh.kneighbors(src, return_distance=True)
66 | return distances.ravel(), indices.ravel()
67 |
68 |
69 | def icp(A, B, init_pose=None, max_iterations=20, tolerance=0.001):
70 | '''
71 | The Iterative Closest Point method: finds best-fit transform that maps
72 | points A on to points B
73 | Input:
74 | A: Nxm numpy array of source mD points
75 | B: Nxm numpy array of destination mD point
76 | init_pose: (m+1)x(m+1) homogeneous transformation
77 | max_iterations: exit algorithm after max_iterations
78 | tolerance: convergence criteria
79 | Output:
80 | T: final homogeneous transformation that maps A on to B
81 | distances: Euclidean distances (errors) of the nearest neighbor
82 | i: number of iterations to converge
83 | '''
84 |
85 | assert A.shape == B.shape
86 |
87 | # get number of dimensions
88 | m = A.shape[1]
89 |
90 | # make points homogeneous, copy them to maintain the originals
91 | src = np.ones((m+1,A.shape[0]))
92 | dst = np.ones((m+1,B.shape[0]))
93 | src[:m,:] = np.copy(A.T)
94 | dst[:m,:] = np.copy(B.T)
95 |
96 | # apply the initial pose estimation
97 | if init_pose is not None:
98 | src = np.dot(init_pose, src)
99 |
100 | prev_error = 0
101 |
102 | for i in range(max_iterations):
103 | # find the nearest neighbors between the current source and destination points
104 | distances, indices = nearest_neighbor(src[:m,:].T, dst[:m,:].T)
105 |
106 | # compute the transformation between the current source and nearest destination points
107 | T,_,_ = best_fit_transform(src[:m,:].T, dst[:m,indices].T)
108 |
109 | # update the current source
110 | src = np.dot(T, src)
111 |
112 | # check error
113 | mean_error = np.mean(distances)
114 | if np.abs(prev_error - mean_error) < tolerance:
115 | break
116 | prev_error = mean_error
117 |
118 | # calculate final transformation
119 | T,_,_ = best_fit_transform(A, src[:m,:].T)
120 |
121 | return T, distances, i
122 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/io.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | from plyfile import PlyElement, PlyData
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 |
6 | def export_pointcloud(vertices, out_file, as_text=True):
7 | assert(vertices.shape[1] == 3)
8 | vertices = vertices.astype(np.float32)
9 | vertices = np.ascontiguousarray(vertices)
10 | vector_dtype = [('x', 'f4'), ('y', 'f4'), ('z', 'f4')]
11 | vertices = vertices.view(dtype=vector_dtype).flatten()
12 | plyel = PlyElement.describe(vertices, 'vertex')
13 | plydata = PlyData([plyel], text=as_text)
14 | plydata.write(out_file)
15 |
16 |
17 | def load_pointcloud(in_file):
18 | plydata = PlyData.read(in_file)
19 | vertices = np.stack([
20 | plydata['vertex']['x'],
21 | plydata['vertex']['y'],
22 | plydata['vertex']['z']
23 | ], axis=1)
24 | return vertices
25 |
26 |
27 | def read_off(file):
28 | """
29 | Reads vertices and faces from an off file.
30 |
31 | :param file: path to file to read
32 | :type file: str
33 | :return: vertices and faces as lists of tuples
34 | :rtype: [(float)], [(int)]
35 | """
36 |
37 | assert os.path.exists(file), 'file %s not found' % file
38 |
39 | with open(file, 'r') as fp:
40 | lines = fp.readlines()
41 | lines = [line.strip() for line in lines]
42 |
43 | # Fix for ModelNet bug were 'OFF' and the number of vertices and faces
44 | # are all in the first line.
45 | if len(lines[0]) > 3:
46 | assert lines[0][:3] == 'OFF' or lines[0][:3] == 'off', \
47 | 'invalid OFF file %s' % file
48 |
49 | parts = lines[0][3:].split(' ')
50 | assert len(parts) == 3
51 |
52 | num_vertices = int(parts[0])
53 | assert num_vertices > 0
54 |
55 | num_faces = int(parts[1])
56 | assert num_faces > 0
57 |
58 | start_index = 1
59 | # This is the regular case!
60 | else:
61 | assert lines[0] == 'OFF' or lines[0] == 'off', \
62 | 'invalid OFF file %s' % file
63 |
64 | parts = lines[1].split(' ')
65 | assert len(parts) == 3
66 |
67 | num_vertices = int(parts[0])
68 | assert num_vertices > 0
69 |
70 | num_faces = int(parts[1])
71 | assert num_faces > 0
72 |
73 | start_index = 2
74 |
75 | vertices = []
76 | for i in range(num_vertices):
77 | vertex = lines[start_index + i].split(' ')
78 | vertex = [float(point.strip()) for point in vertex if point != '']
79 | assert len(vertex) == 3
80 |
81 | vertices.append(vertex)
82 |
83 | faces = []
84 | for i in range(num_faces):
85 | face = lines[start_index + num_vertices + i].split(' ')
86 | face = [index.strip() for index in face if index != '']
87 |
88 | # check to be sure
89 | for index in face:
90 | assert index != '', \
91 | 'found empty vertex index: %s (%s)' \
92 | % (lines[start_index + num_vertices + i], file)
93 |
94 | face = [int(index) for index in face]
95 |
96 | assert face[0] == len(face) - 1, \
97 | 'face should have %d vertices but as %d (%s)' \
98 | % (face[0], len(face) - 1, file)
99 | assert face[0] == 3, \
100 | 'only triangular meshes supported (%s)' % file
101 | for index in face:
102 | assert index >= 0 and index < num_vertices, \
103 | 'vertex %d (of %d vertices) does not exist (%s)' \
104 | % (index, num_vertices, file)
105 |
106 | assert len(face) > 1
107 |
108 | faces.append(face)
109 |
110 | return vertices, faces
111 |
112 | assert False, 'could not open %s' % file
113 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libkdtree/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | build
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libkdtree/LICENSE.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
2 | Version 3, 29 June 2007
3 |
4 | Copyright (C) 2007, 2015 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
5 | Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
6 | of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
7 |
8 |
9 | This version of the GNU Lesser General Public License incorporates
10 | the terms and conditions of version 3 of the GNU General Public
11 | License, supplemented by the additional permissions listed below.
12 |
13 | 0. Additional Definitions.
14 |
15 | As used herein, "this License" refers to version 3 of the GNU Lesser
16 | General Public License, and the "GNU GPL" refers to version 3 of the GNU
17 | General Public License.
18 |
19 | "The Library" refers to a covered work governed by this License,
20 | other than an Application or a Combined Work as defined below.
21 |
22 | An "Application" is any work that makes use of an interface provided
23 | by the Library, but which is not otherwise based on the Library.
24 | Defining a subclass of a class defined by the Library is deemed a mode
25 | of using an interface provided by the Library.
26 |
27 | A "Combined Work" is a work produced by combining or linking an
28 | Application with the Library. The particular version of the Library
29 | with which the Combined Work was made is also called the "Linked
30 | Version".
31 |
32 | The "Minimal Corresponding Source" for a Combined Work means the
33 | Corresponding Source for the Combined Work, excluding any source code
34 | for portions of the Combined Work that, considered in isolation, are
35 | based on the Application, and not on the Linked Version.
36 |
37 | The "Corresponding Application Code" for a Combined Work means the
38 | object code and/or source code for the Application, including any data
39 | and utility programs needed for reproducing the Combined Work from the
40 | Application, but excluding the System Libraries of the Combined Work.
41 |
42 | 1. Exception to Section 3 of the GNU GPL.
43 |
44 | You may convey a covered work under sections 3 and 4 of this License
45 | without being bound by section 3 of the GNU GPL.
46 |
47 | 2. Conveying Modified Versions.
48 |
49 | If you modify a copy of the Library, and, in your modifications, a
50 | facility refers to a function or data to be supplied by an Application
51 | that uses the facility (other than as an argument passed when the
52 | facility is invoked), then you may convey a copy of the modified
53 | version:
54 |
55 | a) under this License, provided that you make a good faith effort to
56 | ensure that, in the event an Application does not supply the
57 | function or data, the facility still operates, and performs
58 | whatever part of its purpose remains meaningful, or
59 |
60 | b) under the GNU GPL, with none of the additional permissions of
61 | this License applicable to that copy.
62 |
63 | 3. Object Code Incorporating Material from Library Header Files.
64 |
65 | The object code form of an Application may incorporate material from
66 | a header file that is part of the Library. You may convey such object
67 | code under terms of your choice, provided that, if the incorporated
68 | material is not limited to numerical parameters, data structure
69 | layouts and accessors, or small macros, inline functions and templates
70 | (ten or fewer lines in length), you do both of the following:
71 |
72 | a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the object code that the
73 | Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are
74 | covered by this License.
75 |
76 | b) Accompany the object code with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license
77 | document.
78 |
79 | 4. Combined Works.
80 |
81 | You may convey a Combined Work under terms of your choice that,
82 | taken together, effectively do not restrict modification of the
83 | portions of the Library contained in the Combined Work and reverse
84 | engineering for debugging such modifications, if you also do each of
85 | the following:
86 |
87 | a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the Combined Work that
88 | the Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are
89 | covered by this License.
90 |
91 | b) Accompany the Combined Work with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license
92 | document.
93 |
94 | c) For a Combined Work that displays copyright notices during
95 | execution, include the copyright notice for the Library among
96 | these notices, as well as a reference directing the user to the
97 | copies of the GNU GPL and this license document.
98 |
99 | d) Do one of the following:
100 |
101 | 0) Convey the Minimal Corresponding Source under the terms of this
102 | License, and the Corresponding Application Code in a form
103 | suitable for, and under terms that permit, the user to
104 | recombine or relink the Application with a modified version of
105 | the Linked Version to produce a modified Combined Work, in the
106 | manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL for conveying
107 | Corresponding Source.
108 |
109 | 1) Use a suitable shared library mechanism for linking with the
110 | Library. A suitable mechanism is one that (a) uses at run time
111 | a copy of the Library already present on the user's computer
112 | system, and (b) will operate properly with a modified version
113 | of the Library that is interface-compatible with the Linked
114 | Version.
115 |
116 | e) Provide Installation Information, but only if you would otherwise
117 | be required to provide such information under section 6 of the
118 | GNU GPL, and only to the extent that such information is
119 | necessary to install and execute a modified version of the
120 | Combined Work produced by recombining or relinking the
121 | Application with a modified version of the Linked Version. (If
122 | you use option 4d0, the Installation Information must accompany
123 | the Minimal Corresponding Source and Corresponding Application
124 | Code. If you use option 4d1, you must provide the Installation
125 | Information in the manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL
126 | for conveying Corresponding Source.)
127 |
128 | 5. Combined Libraries.
129 |
130 | You may place library facilities that are a work based on the
131 | Library side by side in a single library together with other library
132 | facilities that are not Applications and are not covered by this
133 | License, and convey such a combined library under terms of your
134 | choice, if you do both of the following:
135 |
136 | a) Accompany the combined library with a copy of the same work based
137 | on the Library, uncombined with any other library facilities,
138 | conveyed under the terms of this License.
139 |
140 | b) Give prominent notice with the combined library that part of it
141 | is a work based on the Library, and explaining where to find the
142 | accompanying uncombined form of the same work.
143 |
144 | 6. Revised Versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License.
145 |
146 | The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions
147 | of the GNU Lesser General Public License from time to time. Such new
148 | versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may
149 | differ in detail to address new problems or concerns.
150 |
151 | Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
152 | Library as you received it specifies that a certain numbered version
153 | of the GNU Lesser General Public License "or any later version"
154 | applies to it, you have the option of following the terms and
155 | conditions either of that published version or of any later version
156 | published by the Free Software Foundation. If the Library as you
157 | received it does not specify a version number of the GNU Lesser
158 | General Public License, you may choose any version of the GNU Lesser
159 | General Public License ever published by the Free Software Foundation.
160 |
161 | If the Library as you received it specifies that a proxy can decide
162 | whether future versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License shall
163 | apply, that proxy's public statement of acceptance of any version is
164 | permanent authorization for you to choose that version for the
165 | Library.
166 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libkdtree/MANIFEST.in:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | exclude pykdtree/render_template.py
2 | include LICENSE.txt
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libkdtree/README:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. image:: https://travis-ci.org/storpipfugl/pykdtree.svg?branch=master
2 | :target: https://travis-ci.org/storpipfugl/pykdtree
3 | .. image:: https://ci.appveyor.com/api/projects/status/ubo92368ktt2d25g/branch/master
4 | :target: https://ci.appveyor.com/project/storpipfugl/pykdtree
5 |
6 | ========
7 | pykdtree
8 | ========
9 |
10 | Objective
11 | ---------
12 | pykdtree is a kd-tree implementation for fast nearest neighbour search in Python.
13 | The aim is to be the fastest implementation around for common use cases (low dimensions and low number of neighbours) for both tree construction and queries.
14 |
15 | The implementation is based on scipy.spatial.cKDTree and libANN by combining the best features from both and focus on implementation efficiency.
16 |
17 | The interface is similar to that of scipy.spatial.cKDTree except only Euclidean distance measure is supported.
18 |
19 | Queries are optionally multithreaded using OpenMP.
20 |
21 | Installation
22 | ------------
23 | Default build of pykdtree with OpenMP enabled queries using libgomp
24 |
25 | .. code-block:: bash
26 |
27 | $ cd
28 | $ python setup.py install
29 |
30 | If it fails with undefined compiler flags or you want to use another OpenMP implementation please modify setup.py at the indicated point to match your system.
31 |
32 | Building without OpenMP support is controlled by the USE_OMP environment variable
33 |
34 | .. code-block:: bash
35 |
36 | $ cd
37 | $ export USE_OMP=0
38 | $ python setup.py install
39 |
40 | Note evironment variables are by default not exported when using sudo so in this case do
41 |
42 | .. code-block:: bash
43 |
44 | $ USE_OMP=0 sudo -E python setup.py install
45 |
46 | Usage
47 | -----
48 | The usage of pykdtree is similar to scipy.spatial.cKDTree so for now refer to its documentation
49 |
50 | >>> from pykdtree.kdtree import KDTree
51 | >>> kd_tree = KDTree(data_pts)
52 | >>> dist, idx = kd_tree.query(query_pts, k=8)
53 |
54 | The number of threads to be used in OpenMP enabled queries can be controlled with the standard OpenMP environment variable OMP_NUM_THREADS.
55 |
56 | The **leafsize** argument (number of data points per leaf) for the tree creation can be used to control the memory overhead of the kd-tree. pykdtree uses a default **leafsize=16**.
57 | Increasing **leafsize** will reduce the memory overhead and construction time but increase query time.
58 |
59 | pykdtree accepts data in double precision (numpy.float64) or single precision (numpy.float32) floating point. If data of another type is used an internal copy in double precision is made resulting in a memory overhead. If the kd-tree is constructed on single precision data the query points must be single precision as well.
60 |
61 | Benchmarks
62 | ----------
63 | Comparison with scipy.spatial.cKDTree and libANN. This benchmark is on geospatial 3D data with 10053632 data points and 4276224 query points. The results are indexed relative to the construction time of scipy.spatial.cKDTree. A leafsize of 10 (scipy.spatial.cKDTree default) is used.
64 |
65 | Note: libANN is *not* thread safe. In this benchmark libANN is compiled with "-O3 -funroll-loops -ffast-math -fprefetch-loop-arrays" in order to achieve optimum performance.
66 |
67 | ================== ===================== ====== ======== ==================
68 | Operation scipy.spatial.cKDTree libANN pykdtree pykdtree 4 threads
69 | ------------------ --------------------- ------ -------- ------------------
70 |
71 | Construction 100 304 96 96
72 |
73 | query 1 neighbour 1267 294 223 70
74 |
75 | Total 1 neighbour 1367 598 319 166
76 |
77 | query 8 neighbours 2193 625 449 143
78 |
79 | Total 8 neighbours 2293 929 545 293
80 | ================== ===================== ====== ======== ==================
81 |
82 | Looking at the combined construction and query this gives the following performance improvement relative to scipy.spatial.cKDTree
83 |
84 | ========== ====== ======== ==================
85 | Neighbours libANN pykdtree pykdtree 4 threads
86 | ---------- ------ -------- ------------------
87 | 1 129% 329% 723%
88 |
89 | 8 147% 320% 682%
90 | ========== ====== ======== ==================
91 |
92 | Note: mileage will vary with the dataset at hand and computer architecture.
93 |
94 | Test
95 | ----
96 | Run the unit tests using nosetest
97 |
98 | .. code-block:: bash
99 |
100 | $ cd
101 | $ python setup.py nosetests
102 |
103 | Installing on AppVeyor
104 | ----------------------
105 |
106 | Pykdtree requires the "stdint.h" header file which is not available on certain
107 | versions of Windows or certain Windows compilers including those on the
108 | continuous integration platform AppVeyor. To get around this the header file(s)
109 | can be downloaded and placed in the correct "include" directory. This can
110 | be done by adding the `anaconda/missing-headers.ps1` script to your repository
111 | and running it the install step of `appveyor.yml`:
112 |
113 | # install missing headers that aren't included with MSVC 2008
114 | # https://github.com/omnia-md/conda-recipes/pull/524
115 | - "powershell ./appveyor/missing-headers.ps1"
116 |
117 | In addition to this, AppVeyor does not support OpenMP so this feature must be
118 | turned off by adding the following to `appveyor.yml` in the
119 | `environment` section:
120 |
121 | environment:
122 | global:
123 | # Don't build with openmp because it isn't supported in appveyor's compilers
124 | USE_OMP: "0"
125 |
126 | Changelog
127 | ---------
128 | v1.3.1 : Fix masking in the "query" method introduced in 1.3.0
129 |
130 | v1.3.0 : Keyword argument "mask" added to "query" method. OpenMP compilation now works for MS Visual Studio compiler
131 |
132 | v1.2.2 : Build process fixes
133 |
134 | v1.2.1 : Fixed OpenMP thread safety issue introduced in v1.2.0
135 |
136 | v1.2.0 : 64 and 32 bit MSVC Windows support added
137 |
138 | v1.1.1 : Same as v1.1 release due to incorrect pypi release
139 |
140 | v1.1 : Build process improvements. Add data attribute to kdtree class for scipy interface compatibility
141 |
142 | v1.0 : Switched license from GPLv3 to LGPLv3
143 |
144 | v0.3 : Avoid zipping of installed egg
145 |
146 | v0.2 : Reduced memory footprint. Can now handle single precision data internally avoiding copy conversion to double precision. Default leafsize changed from 10 to 16 as this reduces the memory footprint and makes it a cache line multiplum (negligible if any query performance observed in benchmarks). Reduced memory allocation for leaf nodes. Applied patch for building on OS X.
147 |
148 | v0.1 : Initial version.
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libkdtree/README.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .. image:: https://travis-ci.org/storpipfugl/pykdtree.svg?branch=master
2 | :target: https://travis-ci.org/storpipfugl/pykdtree
3 | .. image:: https://ci.appveyor.com/api/projects/status/ubo92368ktt2d25g/branch/master
4 | :target: https://ci.appveyor.com/project/storpipfugl/pykdtree
5 |
6 | ========
7 | pykdtree
8 | ========
9 |
10 | Objective
11 | ---------
12 | pykdtree is a kd-tree implementation for fast nearest neighbour search in Python.
13 | The aim is to be the fastest implementation around for common use cases (low dimensions and low number of neighbours) for both tree construction and queries.
14 |
15 | The implementation is based on scipy.spatial.cKDTree and libANN by combining the best features from both and focus on implementation efficiency.
16 |
17 | The interface is similar to that of scipy.spatial.cKDTree except only Euclidean distance measure is supported.
18 |
19 | Queries are optionally multithreaded using OpenMP.
20 |
21 | Installation
22 | ------------
23 | Default build of pykdtree with OpenMP enabled queries using libgomp
24 |
25 | .. code-block:: bash
26 |
27 | $ cd
28 | $ python setup.py install
29 |
30 | If it fails with undefined compiler flags or you want to use another OpenMP implementation please modify setup.py at the indicated point to match your system.
31 |
32 | Building without OpenMP support is controlled by the USE_OMP environment variable
33 |
34 | .. code-block:: bash
35 |
36 | $ cd
37 | $ export USE_OMP=0
38 | $ python setup.py install
39 |
40 | Note evironment variables are by default not exported when using sudo so in this case do
41 |
42 | .. code-block:: bash
43 |
44 | $ USE_OMP=0 sudo -E python setup.py install
45 |
46 | Usage
47 | -----
48 | The usage of pykdtree is similar to scipy.spatial.cKDTree so for now refer to its documentation
49 |
50 | >>> from pykdtree.kdtree import KDTree
51 | >>> kd_tree = KDTree(data_pts)
52 | >>> dist, idx = kd_tree.query(query_pts, k=8)
53 |
54 | The number of threads to be used in OpenMP enabled queries can be controlled with the standard OpenMP environment variable OMP_NUM_THREADS.
55 |
56 | The **leafsize** argument (number of data points per leaf) for the tree creation can be used to control the memory overhead of the kd-tree. pykdtree uses a default **leafsize=16**.
57 | Increasing **leafsize** will reduce the memory overhead and construction time but increase query time.
58 |
59 | pykdtree accepts data in double precision (numpy.float64) or single precision (numpy.float32) floating point. If data of another type is used an internal copy in double precision is made resulting in a memory overhead. If the kd-tree is constructed on single precision data the query points must be single precision as well.
60 |
61 | Benchmarks
62 | ----------
63 | Comparison with scipy.spatial.cKDTree and libANN. This benchmark is on geospatial 3D data with 10053632 data points and 4276224 query points. The results are indexed relative to the construction time of scipy.spatial.cKDTree. A leafsize of 10 (scipy.spatial.cKDTree default) is used.
64 |
65 | Note: libANN is *not* thread safe. In this benchmark libANN is compiled with "-O3 -funroll-loops -ffast-math -fprefetch-loop-arrays" in order to achieve optimum performance.
66 |
67 | ================== ===================== ====== ======== ==================
68 | Operation scipy.spatial.cKDTree libANN pykdtree pykdtree 4 threads
69 | ------------------ --------------------- ------ -------- ------------------
70 |
71 | Construction 100 304 96 96
72 |
73 | query 1 neighbour 1267 294 223 70
74 |
75 | Total 1 neighbour 1367 598 319 166
76 |
77 | query 8 neighbours 2193 625 449 143
78 |
79 | Total 8 neighbours 2293 929 545 293
80 | ================== ===================== ====== ======== ==================
81 |
82 | Looking at the combined construction and query this gives the following performance improvement relative to scipy.spatial.cKDTree
83 |
84 | ========== ====== ======== ==================
85 | Neighbours libANN pykdtree pykdtree 4 threads
86 | ---------- ------ -------- ------------------
87 | 1 129% 329% 723%
88 |
89 | 8 147% 320% 682%
90 | ========== ====== ======== ==================
91 |
92 | Note: mileage will vary with the dataset at hand and computer architecture.
93 |
94 | Test
95 | ----
96 | Run the unit tests using nosetest
97 |
98 | .. code-block:: bash
99 |
100 | $ cd
101 | $ python setup.py nosetests
102 |
103 | Installing on AppVeyor
104 | ----------------------
105 |
106 | Pykdtree requires the "stdint.h" header file which is not available on certain
107 | versions of Windows or certain Windows compilers including those on the
108 | continuous integration platform AppVeyor. To get around this the header file(s)
109 | can be downloaded and placed in the correct "include" directory. This can
110 | be done by adding the `anaconda/missing-headers.ps1` script to your repository
111 | and running it the install step of `appveyor.yml`:
112 |
113 | # install missing headers that aren't included with MSVC 2008
114 | # https://github.com/omnia-md/conda-recipes/pull/524
115 | - "powershell ./appveyor/missing-headers.ps1"
116 |
117 | In addition to this, AppVeyor does not support OpenMP so this feature must be
118 | turned off by adding the following to `appveyor.yml` in the
119 | `environment` section:
120 |
121 | environment:
122 | global:
123 | # Don't build with openmp because it isn't supported in appveyor's compilers
124 | USE_OMP: "0"
125 |
126 | Changelog
127 | ---------
128 | v1.3.1 : Fix masking in the "query" method introduced in 1.3.0
129 |
130 | v1.3.0 : Keyword argument "mask" added to "query" method. OpenMP compilation now works for MS Visual Studio compiler
131 |
132 | v1.2.2 : Build process fixes
133 |
134 | v1.2.1 : Fixed OpenMP thread safety issue introduced in v1.2.0
135 |
136 | v1.2.0 : 64 and 32 bit MSVC Windows support added
137 |
138 | v1.1.1 : Same as v1.1 release due to incorrect pypi release
139 |
140 | v1.1 : Build process improvements. Add data attribute to kdtree class for scipy interface compatibility
141 |
142 | v1.0 : Switched license from GPLv3 to LGPLv3
143 |
144 | v0.3 : Avoid zipping of installed egg
145 |
146 | v0.2 : Reduced memory footprint. Can now handle single precision data internally avoiding copy conversion to double precision. Default leafsize changed from 10 to 16 as this reduces the memory footprint and makes it a cache line multiplum (negligible if any query performance observed in benchmarks). Reduced memory allocation for leaf nodes. Applied patch for building on OS X.
147 |
148 | v0.1 : Initial version.
149 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libkdtree/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .pykdtree.kdtree import KDTree
2 |
3 |
4 | __all__ = [
5 | KDTree
6 | ]
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libkdtree/pykdtree/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kulbear/object-wakeup/62cfb70aa6369aadbca24fd1d51241f2db86e494/main/utils/libkdtree/pykdtree/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libkdtree/pykdtree/render_template.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 |
3 | from mako.template import Template
4 |
5 | mytemplate = Template(filename='_kdtree_core.c.mako')
6 | with open('_kdtree_core.c', 'w') as fp:
7 | fp.write(mytemplate.render())
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libkdtree/setup.cfg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [bdist_rpm]
2 | requires=numpy
3 | release=1
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | PyMCubes.egg-info
2 | build
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Copyright (c) 2012-2015, P. M. Neila
2 | All rights reserved.
3 |
4 | Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
5 | modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
6 |
7 | * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
8 | list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
9 |
10 | * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
11 | this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
12 | and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
13 |
14 | * Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its
15 | contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
16 | this software without specific prior written permission.
17 |
18 | THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
19 | AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
20 | IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
21 | DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
22 | FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
23 | DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
24 | SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
25 | CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
26 | OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
27 | OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/README.rst:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ========
2 | PyMCubes
3 | ========
4 |
5 | PyMCubes is an implementation of the marching cubes algorithm to extract
6 | isosurfaces from volumetric data. The volumetric data can be given as a
7 | three-dimensional NumPy array or as a Python function ``f(x, y, z)``. The first
8 | option is much faster, but it requires more memory and becomes unfeasible for
9 | very large volumes.
10 |
11 | PyMCubes also provides a function to export the results of the marching cubes as
12 | COLLADA ``(.dae)`` files. This requires the
13 | `PyCollada `_ library.
14 |
15 | Installation
16 | ============
17 |
18 | Just as any standard Python package, clone or download the project
19 | and run::
20 |
21 | $ cd path/to/PyMCubes
22 | $ python setup.py build
23 | $ python setup.py install
24 |
25 | If you do not have write permission on the directory of Python packages,
26 | install with the ``--user`` option::
27 |
28 | $ python setup.py install --user
29 |
30 | Example
31 | =======
32 |
33 | The following example creates a data volume with spherical isosurfaces and
34 | extracts one of them (i.e., a sphere) with PyMCubes. The result is exported as
35 | ``sphere.dae``::
36 |
37 | >>> import numpy as np
38 | >>> import mcubes
39 |
40 | # Create a data volume (30 x 30 x 30)
41 | >>> X, Y, Z = np.mgrid[:30, :30, :30]
42 | >>> u = (X-15)**2 + (Y-15)**2 + (Z-15)**2 - 8**2
43 |
44 | # Extract the 0-isosurface
45 | >>> vertices, triangles = mcubes.marching_cubes(u, 0)
46 |
47 | # Export the result to sphere.dae
48 | >>> mcubes.export_mesh(vertices, triangles, "sphere.dae", "MySphere")
49 |
50 | The second example is very similar to the first one, but it uses a function
51 | to represent the volume instead of a NumPy array::
52 |
53 | >>> import numpy as np
54 | >>> import mcubes
55 |
56 | # Create the volume
57 | >>> f = lambda x, y, z: x**2 + y**2 + z**2
58 |
59 | # Extract the 16-isosurface
60 | >>> vertices, triangles = mcubes.marching_cubes_func((-10,-10,-10), (10,10,10),
61 | ... 100, 100, 100, f, 16)
62 |
63 | # Export the result to sphere2.dae
64 | >>> mcubes.export_mesh(vertices, triangles, "sphere2.dae", "MySphere")
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from main.utils.libmcubes.mcubes import (
2 | marching_cubes, marching_cubes_func
3 | )
4 | from main.utils.libmcubes.exporter import (
5 | export_mesh, export_obj, export_off
6 | )
7 |
8 |
9 | __all__ = [
10 | marching_cubes, marching_cubes_func,
11 | export_mesh, export_obj, export_off
12 | ]
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/exporter.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | import numpy as np
3 |
4 |
5 | def export_obj(vertices, triangles, filename):
6 | """
7 | Exports a mesh in the (.obj) format.
8 | """
9 |
10 | with open(filename, 'w') as fh:
11 |
12 | for v in vertices:
13 | fh.write("v {} {} {}\n".format(*v))
14 |
15 | for f in triangles:
16 | fh.write("f {} {} {}\n".format(*(f + 1)))
17 |
18 |
19 | def export_off(vertices, triangles, filename):
20 | """
21 | Exports a mesh in the (.off) format.
22 | """
23 |
24 | with open(filename, 'w') as fh:
25 | fh.write('OFF\n')
26 | fh.write('{} {} 0\n'.format(len(vertices), len(triangles)))
27 |
28 | for v in vertices:
29 | fh.write("{} {} {}\n".format(*v))
30 |
31 | for f in triangles:
32 | fh.write("3 {} {} {}\n".format(*f))
33 |
34 |
35 | def export_mesh(vertices, triangles, filename, mesh_name="mcubes_mesh"):
36 | """
37 | Exports a mesh in the COLLADA (.dae) format.
38 |
39 | Needs PyCollada (https://github.com/pycollada/pycollada).
40 | """
41 |
42 | import collada
43 |
44 | mesh = collada.Collada()
45 |
46 | vert_src = collada.source.FloatSource("verts-array", vertices, ('X','Y','Z'))
47 | geom = collada.geometry.Geometry(mesh, "geometry0", mesh_name, [vert_src])
48 |
49 | input_list = collada.source.InputList()
50 | input_list.addInput(0, 'VERTEX', "#verts-array")
51 |
52 | triset = geom.createTriangleSet(np.copy(triangles), input_list, "")
53 | geom.primitives.append(triset)
54 | mesh.geometries.append(geom)
55 |
56 | geomnode = collada.scene.GeometryNode(geom, [])
57 | node = collada.scene.Node(mesh_name, children=[geomnode])
58 |
59 | myscene = collada.scene.Scene("mcubes_scene", [node])
60 | mesh.scenes.append(myscene)
61 | mesh.scene = myscene
62 |
63 | mesh.write(filename)
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/mcubes.pyx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # distutils: language = c++
3 | # cython: embedsignature = True
4 |
5 | # from libcpp.vector cimport vector
6 | import numpy as np
7 |
8 | # Define PY_ARRAY_UNIQUE_SYMBOL
9 | cdef extern from "pyarray_symbol.h":
10 | pass
11 |
12 | cimport numpy as np
13 |
14 | np.import_array()
15 |
16 | cdef extern from "pywrapper.h":
17 | cdef object c_marching_cubes "marching_cubes"(np.ndarray, double) except +
18 | cdef object c_marching_cubes2 "marching_cubes2"(np.ndarray, double) except +
19 | cdef object c_marching_cubes3 "marching_cubes3"(np.ndarray, double) except +
20 | cdef object c_marching_cubes_func "marching_cubes_func"(tuple, tuple, int, int, int, object, double) except +
21 |
22 | def marching_cubes(np.ndarray volume, float isovalue):
23 |
24 | verts, faces = c_marching_cubes(volume, isovalue)
25 | verts.shape = (-1, 3)
26 | faces.shape = (-1, 3)
27 | return verts, faces
28 |
29 | def marching_cubes2(np.ndarray volume, float isovalue):
30 |
31 | verts, faces = c_marching_cubes2(volume, isovalue)
32 | verts.shape = (-1, 3)
33 | faces.shape = (-1, 3)
34 | return verts, faces
35 |
36 | def marching_cubes3(np.ndarray volume, float isovalue):
37 |
38 | verts, faces = c_marching_cubes3(volume, isovalue)
39 | verts.shape = (-1, 3)
40 | faces.shape = (-1, 3)
41 | return verts, faces
42 |
43 | def marching_cubes_func(tuple lower, tuple upper, int numx, int numy, int numz, object f, double isovalue):
44 |
45 | verts, faces = c_marching_cubes_func(lower, upper, numx, numy, numz, f, isovalue)
46 | verts.shape = (-1, 3)
47 | faces.shape = (-1, 3)
48 | return verts, faces
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/pyarray_symbol.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | #define PY_ARRAY_UNIQUE_SYMBOL mcubes_PyArray_API
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/pyarraymodule.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | #ifndef _EXTMODULE_H
3 | #define _EXTMODULE_H
4 |
5 | #include
6 | #include
7 |
8 | // #define NPY_NO_DEPRECATED_API NPY_1_7_API_VERSION
9 | #define PY_ARRAY_UNIQUE_SYMBOL mcubes_PyArray_API
10 | #define NO_IMPORT_ARRAY
11 | #include "numpy/arrayobject.h"
12 |
13 | #include
14 |
15 | template
16 | struct numpy_typemap;
17 |
18 | #define define_numpy_type(ctype, dtype) \
19 | template<> \
20 | struct numpy_typemap \
21 | {static const int type = dtype;};
22 |
23 | define_numpy_type(bool, NPY_BOOL);
24 | define_numpy_type(char, NPY_BYTE);
25 | define_numpy_type(short, NPY_SHORT);
26 | define_numpy_type(int, NPY_INT);
27 | define_numpy_type(long, NPY_LONG);
28 | define_numpy_type(long long, NPY_LONGLONG);
29 | define_numpy_type(unsigned char, NPY_UBYTE);
30 | define_numpy_type(unsigned short, NPY_USHORT);
31 | define_numpy_type(unsigned int, NPY_UINT);
32 | define_numpy_type(unsigned long, NPY_ULONG);
33 | define_numpy_type(unsigned long long, NPY_ULONGLONG);
34 | define_numpy_type(float, NPY_FLOAT);
35 | define_numpy_type(double, NPY_DOUBLE);
36 | define_numpy_type(long double, NPY_LONGDOUBLE);
37 | define_numpy_type(std::complex, NPY_CFLOAT);
38 | define_numpy_type(std::complex, NPY_CDOUBLE);
39 | define_numpy_type(std::complex, NPY_CLONGDOUBLE);
40 |
41 | template
42 | T PyArray_SafeGet(const PyArrayObject* aobj, const npy_intp* indaux)
43 | {
44 | // HORROR.
45 | npy_intp* ind = const_cast(indaux);
46 | void* ptr = PyArray_GetPtr(const_cast(aobj), ind);
47 | switch(PyArray_TYPE(aobj))
48 | {
49 | case NPY_BOOL:
50 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
51 | case NPY_BYTE:
52 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
53 | case NPY_SHORT:
54 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
55 | case NPY_INT:
56 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
57 | case NPY_LONG:
58 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
59 | case NPY_LONGLONG:
60 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
61 | case NPY_UBYTE:
62 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
63 | case NPY_USHORT:
64 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
65 | case NPY_UINT:
66 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
67 | case NPY_ULONG:
68 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
69 | case NPY_ULONGLONG:
70 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
71 | case NPY_FLOAT:
72 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
73 | case NPY_DOUBLE:
74 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
75 | case NPY_LONGDOUBLE:
76 | return static_cast(*reinterpret_cast(ptr));
77 | default:
78 | throw std::runtime_error("data type not supported");
79 | }
80 | }
81 |
82 | template
83 | T PyArray_SafeSet(PyArrayObject* aobj, const npy_intp* indaux, const T& value)
84 | {
85 | // HORROR.
86 | npy_intp* ind = const_cast(indaux);
87 | void* ptr = PyArray_GetPtr(aobj, ind);
88 | switch(PyArray_TYPE(aobj))
89 | {
90 | case NPY_BOOL:
91 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
92 | break;
93 | case NPY_BYTE:
94 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
95 | break;
96 | case NPY_SHORT:
97 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
98 | break;
99 | case NPY_INT:
100 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
101 | break;
102 | case NPY_LONG:
103 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
104 | break;
105 | case NPY_LONGLONG:
106 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
107 | break;
108 | case NPY_UBYTE:
109 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
110 | break;
111 | case NPY_USHORT:
112 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
113 | break;
114 | case NPY_UINT:
115 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
116 | break;
117 | case NPY_ULONG:
118 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
119 | break;
120 | case NPY_ULONGLONG:
121 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
122 | break;
123 | case NPY_FLOAT:
124 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
125 | break;
126 | case NPY_DOUBLE:
127 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
128 | break;
129 | case NPY_LONGDOUBLE:
130 | *reinterpret_cast(ptr) = static_cast(value);
131 | break;
132 | default:
133 | throw std::runtime_error("data type not supported");
134 | }
135 | }
136 |
137 | #endif
138 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/pywrapper.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | #include "pywrapper.h"
3 |
4 | #include "marchingcubes.h"
5 |
6 | #include
7 |
8 | struct PythonToCFunc
9 | {
10 | PyObject* func;
11 | PythonToCFunc(PyObject* func) {this->func = func;}
12 | double operator()(double x, double y, double z)
13 | {
14 | PyObject* res = PyObject_CallFunction(func, "(d,d,d)", x, y, z); // py::extract(func(x,y,z));
15 | if(res == NULL)
16 | return 0.0;
17 |
18 | double result = PyFloat_AsDouble(res);
19 | Py_DECREF(res);
20 | return result;
21 | }
22 | };
23 |
24 | PyObject* marching_cubes_func(PyObject* lower, PyObject* upper,
25 | int numx, int numy, int numz, PyObject* f, double isovalue)
26 | {
27 | std::vector vertices;
28 | std::vector polygons;
29 |
30 | // Copy the lower and upper coordinates to a C array.
31 | double lower_[3];
32 | double upper_[3];
33 | for(int i=0; i<3; ++i)
34 | {
35 | PyObject* l = PySequence_GetItem(lower, i);
36 | if(l == NULL)
37 | throw std::runtime_error("error");
38 | PyObject* u = PySequence_GetItem(upper, i);
39 | if(u == NULL)
40 | {
41 | Py_DECREF(l);
42 | throw std::runtime_error("error");
43 | }
44 |
45 | lower_[i] = PyFloat_AsDouble(l);
46 | upper_[i] = PyFloat_AsDouble(u);
47 |
48 | Py_DECREF(l);
49 | Py_DECREF(u);
50 | if(lower_[i]==-1.0 || upper_[i]==-1.0)
51 | {
52 | if(PyErr_Occurred())
53 | throw std::runtime_error("error");
54 | }
55 | }
56 |
57 | // Marching cubes.
58 | mc::marching_cubes(lower_, upper_, numx, numy, numz, PythonToCFunc(f), isovalue, vertices, polygons);
59 |
60 | // Copy the result to two Python ndarrays.
61 | npy_intp size_vertices = vertices.size();
62 | npy_intp size_polygons = polygons.size();
63 | PyArrayObject* verticesarr = reinterpret_cast(PyArray_SimpleNew(1, &size_vertices, PyArray_DOUBLE));
64 | PyArrayObject* polygonsarr = reinterpret_cast(PyArray_SimpleNew(1, &size_polygons, PyArray_ULONG));
65 |
66 | std::vector::const_iterator it = vertices.begin();
67 | for(int i=0; it!=vertices.end(); ++i, ++it)
68 | *reinterpret_cast(PyArray_GETPTR1(verticesarr, i)) = *it;
69 | std::vector::const_iterator it2 = polygons.begin();
70 | for(int i=0; it2!=polygons.end(); ++i, ++it2)
71 | *reinterpret_cast(PyArray_GETPTR1(polygonsarr, i)) = *it2;
72 |
73 | PyObject* res = Py_BuildValue("(O,O)", verticesarr, polygonsarr);
74 | Py_XDECREF(verticesarr);
75 | Py_XDECREF(polygonsarr);
76 | return res;
77 | }
78 |
79 | struct PyArrayToCFunc
80 | {
81 | PyArrayObject* arr;
82 | PyArrayToCFunc(PyArrayObject* arr) {this->arr = arr;}
83 | double operator()(int x, int y, int z)
84 | {
85 | npy_intp c[3] = {x,y,z};
86 | return PyArray_SafeGet(arr, c);
87 | }
88 | };
89 |
90 | PyObject* marching_cubes(PyArrayObject* arr, double isovalue)
91 | {
92 | if(PyArray_NDIM(arr) != 3)
93 | throw std::runtime_error("Only three-dimensional arrays are supported.");
94 |
95 | // Prepare data.
96 | npy_intp* shape = PyArray_DIMS(arr);
97 | double lower[3] = {0,0,0};
98 | double upper[3] = {shape[0]-1, shape[1]-1, shape[2]-1};
99 | long numx = upper[0] - lower[0] + 1;
100 | long numy = upper[1] - lower[1] + 1;
101 | long numz = upper[2] - lower[2] + 1;
102 | std::vector vertices;
103 | std::vector polygons;
104 |
105 | // Marching cubes.
106 | mc::marching_cubes(lower, upper, numx, numy, numz, PyArrayToCFunc(arr), isovalue,
107 | vertices, polygons);
108 |
109 | // Copy the result to two Python ndarrays.
110 | npy_intp size_vertices = vertices.size();
111 | npy_intp size_polygons = polygons.size();
112 | PyArrayObject* verticesarr = reinterpret_cast(PyArray_SimpleNew(1, &size_vertices, PyArray_DOUBLE));
113 | PyArrayObject* polygonsarr = reinterpret_cast(PyArray_SimpleNew(1, &size_polygons, PyArray_ULONG));
114 |
115 | std::vector::const_iterator it = vertices.begin();
116 | for(int i=0; it!=vertices.end(); ++i, ++it)
117 | *reinterpret_cast(PyArray_GETPTR1(verticesarr, i)) = *it;
118 | std::vector::const_iterator it2 = polygons.begin();
119 | for(int i=0; it2!=polygons.end(); ++i, ++it2)
120 | *reinterpret_cast(PyArray_GETPTR1(polygonsarr, i)) = *it2;
121 |
122 | PyObject* res = Py_BuildValue("(O,O)", verticesarr, polygonsarr);
123 | Py_XDECREF(verticesarr);
124 | Py_XDECREF(polygonsarr);
125 |
126 | return res;
127 | }
128 |
129 | PyObject* marching_cubes2(PyArrayObject* arr, double isovalue)
130 | {
131 | if(PyArray_NDIM(arr) != 3)
132 | throw std::runtime_error("Only three-dimensional arrays are supported.");
133 |
134 | // Prepare data.
135 | npy_intp* shape = PyArray_DIMS(arr);
136 | double lower[3] = {0,0,0};
137 | double upper[3] = {shape[0]-1, shape[1]-1, shape[2]-1};
138 | long numx = upper[0] - lower[0] + 1;
139 | long numy = upper[1] - lower[1] + 1;
140 | long numz = upper[2] - lower[2] + 1;
141 | std::vector vertices;
142 | std::vector polygons;
143 |
144 | // Marching cubes.
145 | mc::marching_cubes2(lower, upper, numx, numy, numz, PyArrayToCFunc(arr), isovalue,
146 | vertices, polygons);
147 |
148 | // Copy the result to two Python ndarrays.
149 | npy_intp size_vertices = vertices.size();
150 | npy_intp size_polygons = polygons.size();
151 | PyArrayObject* verticesarr = reinterpret_cast(PyArray_SimpleNew(1, &size_vertices, PyArray_DOUBLE));
152 | PyArrayObject* polygonsarr = reinterpret_cast(PyArray_SimpleNew(1, &size_polygons, PyArray_ULONG));
153 |
154 | std::vector::const_iterator it = vertices.begin();
155 | for(int i=0; it!=vertices.end(); ++i, ++it)
156 | *reinterpret_cast(PyArray_GETPTR1(verticesarr, i)) = *it;
157 | std::vector::const_iterator it2 = polygons.begin();
158 | for(int i=0; it2!=polygons.end(); ++i, ++it2)
159 | *reinterpret_cast(PyArray_GETPTR1(polygonsarr, i)) = *it2;
160 |
161 | PyObject* res = Py_BuildValue("(O,O)", verticesarr, polygonsarr);
162 | Py_XDECREF(verticesarr);
163 | Py_XDECREF(polygonsarr);
164 |
165 | return res;
166 | }
167 |
168 | PyObject* marching_cubes3(PyArrayObject* arr, double isovalue)
169 | {
170 | if(PyArray_NDIM(arr) != 3)
171 | throw std::runtime_error("Only three-dimensional arrays are supported.");
172 |
173 | // Prepare data.
174 | npy_intp* shape = PyArray_DIMS(arr);
175 | double lower[3] = {0,0,0};
176 | double upper[3] = {shape[0]-1, shape[1]-1, shape[2]-1};
177 | long numx = upper[0] - lower[0] + 1;
178 | long numy = upper[1] - lower[1] + 1;
179 | long numz = upper[2] - lower[2] + 1;
180 | std::vector vertices;
181 | std::vector polygons;
182 |
183 | // Marching cubes.
184 | mc::marching_cubes3(lower, upper, numx, numy, numz, PyArrayToCFunc(arr), isovalue,
185 | vertices, polygons);
186 |
187 | // Copy the result to two Python ndarrays.
188 | npy_intp size_vertices = vertices.size();
189 | npy_intp size_polygons = polygons.size();
190 | PyArrayObject* verticesarr = reinterpret_cast(PyArray_SimpleNew(1, &size_vertices, PyArray_DOUBLE));
191 | PyArrayObject* polygonsarr = reinterpret_cast(PyArray_SimpleNew(1, &size_polygons, PyArray_ULONG));
192 |
193 | std::vector::const_iterator it = vertices.begin();
194 | for(int i=0; it!=vertices.end(); ++i, ++it)
195 | *reinterpret_cast(PyArray_GETPTR1(verticesarr, i)) = *it;
196 | std::vector::const_iterator it2 = polygons.begin();
197 | for(int i=0; it2!=polygons.end(); ++i, ++it2)
198 | *reinterpret_cast(PyArray_GETPTR1(polygonsarr, i)) = *it2;
199 |
200 | PyObject* res = Py_BuildValue("(O,O)", verticesarr, polygonsarr);
201 | Py_XDECREF(verticesarr);
202 | Py_XDECREF(polygonsarr);
203 |
204 | return res;
205 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmcubes/pywrapper.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | #ifndef _PYWRAPPER_H
3 | #define _PYWRAPPER_H
4 |
5 | #include
6 | #include "pyarraymodule.h"
7 |
8 | #include
9 |
10 | PyObject* marching_cubes(PyArrayObject* arr, double isovalue);
11 | PyObject* marching_cubes2(PyArrayObject* arr, double isovalue);
12 | PyObject* marching_cubes3(PyArrayObject* arr, double isovalue);
13 | PyObject* marching_cubes_func(PyObject* lower, PyObject* upper,
14 | int numx, int numy, int numz, PyObject* f, double isovalue);
15 |
16 | #endif // _PYWRAPPER_H
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmesh/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | triangle_hash.cpp
2 | build
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmesh/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .inside_mesh import (
2 | check_mesh_contains, MeshIntersector
3 | )
4 |
5 |
6 | __all__ = [
7 | check_mesh_contains, MeshIntersector
8 | ]
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmesh/inside_mesh.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from .triangle_hash import TriangleHash as _TriangleHash
3 |
4 | def check_mesh_contains(mesh, points, hash_resolution=512):
5 | intersector = MeshIntersector(mesh, hash_resolution)
6 | contains = intersector.query(points)
7 | return contains
8 |
9 |
10 | class MeshIntersector:
11 | def __init__(self, mesh, resolution=512):
12 | triangles = mesh.vertices[mesh.faces].astype(np.float64)
13 | n_tri = triangles.shape[0]
14 |
15 | self.resolution = resolution
16 | self.bbox_min = triangles.reshape(3 * n_tri, 3).min(axis=0)
17 | self.bbox_max = triangles.reshape(3 * n_tri, 3).max(axis=0)
18 | # Tranlate and scale it to [0.5, self.resolution - 0.5]^3
19 | self.scale = (resolution - 1) / (self.bbox_max - self.bbox_min)
20 | self.translate = 0.5 - self.scale * self.bbox_min
21 |
22 | self._triangles = triangles = self.rescale(triangles)
23 | # assert(np.allclose(triangles.reshape(-1, 3).min(0), 0.5))
24 | # assert(np.allclose(triangles.reshape(-1, 3).max(0), resolution - 0.5))
25 |
26 | triangles2d = triangles[:, :, :2]
27 | self._tri_intersector2d = TriangleIntersector2d(
28 | triangles2d, resolution)
29 |
30 | def query(self, points):
31 | # Rescale points
32 | points = self.rescale(points)
33 |
34 | # placeholder result with no hits we'll fill in later
35 | contains = np.zeros(len(points), dtype=np.bool)
36 |
37 | # cull points outside of the axis aligned bounding box
38 | # this avoids running ray tests unless points are close
39 | inside_aabb = np.all(
40 | (0 <= points) & (points <= self.resolution), axis=1)
41 | if not inside_aabb.any():
42 | return contains
43 |
44 | # Only consider points inside bounding box
45 | mask = inside_aabb
46 | points = points[mask]
47 |
48 | # Compute intersection depth and check order
49 | points_indices, tri_indices = self._tri_intersector2d.query(points[:, :2])
50 |
51 | triangles_intersect = self._triangles[tri_indices]
52 | points_intersect = points[points_indices]
53 |
54 | depth_intersect, abs_n_2 = self.compute_intersection_depth(
55 | points_intersect, triangles_intersect)
56 |
57 | # Count number of intersections in both directions
58 | smaller_depth = depth_intersect >= points_intersect[:, 2] * abs_n_2
59 | bigger_depth = depth_intersect < points_intersect[:, 2] * abs_n_2
60 | points_indices_0 = points_indices[smaller_depth]
61 | points_indices_1 = points_indices[bigger_depth]
62 |
63 | nintersect0 = np.bincount(points_indices_0, minlength=points.shape[0])
64 | nintersect1 = np.bincount(points_indices_1, minlength=points.shape[0])
65 |
66 | # Check if point contained in mesh
67 | contains1 = (np.mod(nintersect0, 2) == 1)
68 | contains2 = (np.mod(nintersect1, 2) == 1)
69 | if (contains1 != contains2).any():
70 | print('Warning: contains1 != contains2 for some points.')
71 | contains[mask] = (contains1 & contains2)
72 | return contains
73 |
74 | def compute_intersection_depth(self, points, triangles):
75 | t1 = triangles[:, 0, :]
76 | t2 = triangles[:, 1, :]
77 | t3 = triangles[:, 2, :]
78 |
79 | v1 = t3 - t1
80 | v2 = t2 - t1
81 | # v1 = v1 / np.linalg.norm(v1, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
82 | # v2 = v2 / np.linalg.norm(v2, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
83 |
84 | normals = np.cross(v1, v2)
85 | alpha = np.sum(normals[:, :2] * (t1[:, :2] - points[:, :2]), axis=1)
86 |
87 | n_2 = normals[:, 2]
88 | t1_2 = t1[:, 2]
89 | s_n_2 = np.sign(n_2)
90 | abs_n_2 = np.abs(n_2)
91 |
92 | mask = (abs_n_2 != 0)
93 |
94 | depth_intersect = np.full(points.shape[0], np.nan)
95 | depth_intersect[mask] = \
96 | t1_2[mask] * abs_n_2[mask] + alpha[mask] * s_n_2[mask]
97 |
98 | # Test the depth:
99 | # TODO: remove and put into tests
100 | # points_new = np.concatenate([points[:, :2], depth_intersect[:, None]], axis=1)
101 | # alpha = (normals * t1).sum(-1)
102 | # mask = (depth_intersect == depth_intersect)
103 | # assert(np.allclose((points_new[mask] * normals[mask]).sum(-1),
104 | # alpha[mask]))
105 | return depth_intersect, abs_n_2
106 |
107 | def rescale(self, array):
108 | array = self.scale * array + self.translate
109 | return array
110 |
111 | class TriangleIntersector2d:
112 | def __init__(self, triangles, resolution=128):
113 | self.triangles = triangles
114 | self.tri_hash = _TriangleHash(triangles, resolution)
115 |
116 | def query(self, points):
117 | point_indices, tri_indices = self.tri_hash.query(points)
118 | point_indices = np.array(point_indices, dtype=np.int64)
119 | tri_indices = np.array(tri_indices, dtype=np.int64)
120 | points = points[point_indices]
121 | triangles = self.triangles[tri_indices]
122 | mask = self.check_triangles(points, triangles)
123 | point_indices = point_indices[mask]
124 | tri_indices = tri_indices[mask]
125 | return point_indices, tri_indices
126 |
127 | def check_triangles(self, points, triangles):
128 | contains = np.zeros(points.shape[0], dtype=np.bool)
129 | A = triangles[:, :2] - triangles[:, 2:]
130 | A = A.transpose([0, 2, 1])
131 | y = points - triangles[:, 2]
132 |
133 | detA = A[:, 0, 0] * A[:, 1, 1] - A[:, 0, 1] * A[:, 1, 0]
134 |
135 | mask = (np.abs(detA) != 0.)
136 | A = A[mask]
137 | y = y[mask]
138 | detA = detA[mask]
139 |
140 | s_detA = np.sign(detA)
141 | abs_detA = np.abs(detA)
142 |
143 | u = (A[:, 1, 1] * y[:, 0] - A[:, 0, 1] * y[:, 1]) * s_detA
144 | v = (-A[:, 1, 0] * y[:, 0] + A[:, 0, 0] * y[:, 1]) * s_detA
145 |
146 | sum_uv = u + v
147 | contains[mask] = (
148 | (0 < u) & (u < abs_detA) & (0 < v) & (v < abs_detA)
149 | & (0 < sum_uv) & (sum_uv < abs_detA)
150 | )
151 | return contains
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmesh/inside_mesh_2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from .triangle_hash import TriangleHash as _TriangleHash
3 |
4 |
5 | def check_mesh_contains(mesh, points, hash_resolution=512):
6 | intersector = MeshIntersector(mesh, hash_resolution)
7 | contains = intersector.query(points)
8 | return contains
9 |
10 |
11 | class MeshIntersector:
12 | def __init__(self, mesh, resolution=512):
13 | triangles = mesh.vertices[mesh.faces].astype(np.float64)
14 | n_tri = triangles.shape[0]
15 |
16 | self.resolution = resolution
17 | self.bbox_min = triangles.reshape(3 * n_tri, 3).min(axis=0)
18 | self.bbox_max = triangles.reshape(3 * n_tri, 3).max(axis=0)
19 | # Tranlate and scale it to [0.5, self.resolution - 0.5]^3
20 | self.scale = (resolution - 1) / (self.bbox_max - self.bbox_min)
21 | self.translate = 0.5 - self.scale * self.bbox_min
22 |
23 | self._triangles = triangles = self.rescale(triangles)
24 | # assert(np.allclose(triangles.reshape(-1, 3).min(0), 0.5))
25 | # assert(np.allclose(triangles.reshape(-1, 3).max(0), resolution - 0.5))
26 |
27 | triangles2d = triangles[:, :, :2]
28 | self._tri_intersector2d = TriangleIntersector2d(
29 | triangles2d, resolution)
30 |
31 | def query(self, points):
32 | # Rescale points
33 | points = self.rescale(points)
34 |
35 | # placeholder result with no hits we'll fill in later
36 | contains = np.zeros(len(points), dtype=np.bool)
37 |
38 | # cull points outside of the axis aligned bounding box
39 | # this avoids running ray tests unless points are close
40 | inside_aabb = np.all(
41 | (0 <= points) & (points <= self.resolution), axis=1)
42 | if not inside_aabb.any():
43 | return contains
44 |
45 | # Only consider points inside bounding box
46 | mask = inside_aabb
47 | points = points[mask]
48 |
49 | # Compute intersection depth and check order
50 | points_indices, tri_indices = self._tri_intersector2d.query(points[:, :2])
51 |
52 | triangles_intersect = self._triangles[tri_indices]
53 | points_intersect = points[points_indices]
54 |
55 | depth_intersect, abs_n_2 = self.compute_intersection_depth(
56 | points_intersect, triangles_intersect)
57 |
58 | # Count number of intersections in both directions
59 | smaller_depth = depth_intersect >= points_intersect[:, 2] * abs_n_2
60 | bigger_depth = depth_intersect < points_intersect[:, 2] * abs_n_2
61 | points_indices_0 = points_indices[smaller_depth]
62 | points_indices_1 = points_indices[bigger_depth]
63 |
64 | nintersect0 = np.bincount(points_indices_0, minlength=points.shape[0])
65 | nintersect1 = np.bincount(points_indices_1, minlength=points.shape[0])
66 |
67 | # Check if point contained in mesh
68 | contains1 = (np.mod(nintersect0, 2) == 1)
69 | contains2 = (np.mod(nintersect1, 2) == 1)
70 | if (contains1 != contains2).any():
71 | print('Warning: contains1 != contains2 for some points.')
72 | contains[mask] = (contains1 & contains2)
73 | return contains
74 |
75 | def compute_intersection_depth(self, points, triangles):
76 | t1 = triangles[:, 0, :]
77 | t2 = triangles[:, 1, :]
78 | t3 = triangles[:, 2, :]
79 |
80 | v1 = t3 - t1
81 | v2 = t2 - t1
82 | # v1 = v1 / np.linalg.norm(v1, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
83 | # v2 = v2 / np.linalg.norm(v2, axis=-1, keepdims=True)
84 |
85 | normals = np.cross(v1, v2)
86 | alpha = np.sum(normals[:, :2] * (t1[:, :2] - points[:, :2]), axis=1)
87 |
88 | n_2 = normals[:, 2]
89 | t1_2 = t1[:, 2]
90 | s_n_2 = np.sign(n_2)
91 | abs_n_2 = np.abs(n_2)
92 |
93 | mask = (abs_n_2 != 0)
94 |
95 | depth_intersect = np.full(points.shape[0], np.nan)
96 | depth_intersect[mask] = \
97 | t1_2[mask] * abs_n_2[mask] + alpha[mask] * s_n_2[mask]
98 |
99 | # Test the depth:
100 | # TODO: remove and put into tests
101 | # points_new = np.concatenate([points[:, :2], depth_intersect[:, None]], axis=1)
102 | # alpha = (normals * t1).sum(-1)
103 | # mask = (depth_intersect == depth_intersect)
104 | # assert(np.allclose((points_new[mask] * normals[mask]).sum(-1),
105 | # alpha[mask]))
106 | return depth_intersect, abs_n_2
107 |
108 | def rescale(self, array):
109 | array = self.scale * array + self.translate
110 | return array
111 |
112 |
113 | class TriangleIntersector2d:
114 | def __init__(self, triangles, resolution=128):
115 | self.triangles = triangles
116 | self.tri_hash = _TriangleHash(triangles, resolution)
117 |
118 | def query(self, points):
119 | point_indices, tri_indices = self.tri_hash.query(points)
120 | point_indices = np.array(point_indices, dtype=np.int64)
121 | tri_indices = np.array(tri_indices, dtype=np.int64)
122 | points = points[point_indices]
123 | triangles = self.triangles[tri_indices]
124 | mask = self.check_triangles(points, triangles)
125 | point_indices = point_indices[mask]
126 | tri_indices = tri_indices[mask]
127 | return point_indices, tri_indices
128 |
129 | def check_triangles(self, points, triangles):
130 | contains = np.zeros(points.shape[0], dtype=np.bool)
131 | A = triangles[:, :2] - triangles[:, 2:]
132 | A = A.transpose([0, 2, 1])
133 | y = points - triangles[:, 2]
134 |
135 | detA = A[:, 0, 0] * A[:, 1, 1] - A[:, 0, 1] * A[:, 1, 0]
136 |
137 | mask = (np.abs(detA) != 0.)
138 | A = A[mask]
139 | y = y[mask]
140 | detA = detA[mask]
141 |
142 | s_detA = np.sign(detA)
143 | abs_detA = np.abs(detA)
144 |
145 | u = (A[:, 1, 1] * y[:, 0] - A[:, 0, 1] * y[:, 1]) * s_detA
146 | v = (-A[:, 1, 0] * y[:, 0] + A[:, 0, 0] * y[:, 1]) * s_detA
147 |
148 | sum_uv = u + v
149 | contains[mask] = (
150 | (0 < u) & (u < abs_detA) & (0 < v) & (v < abs_detA)
151 | & (0 < sum_uv) & (sum_uv < abs_detA)
152 | )
153 | return contains
154 |
155 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmesh/triangle_hash.pyx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # distutils: language=c++
3 | import numpy as np
4 | cimport numpy as np
5 | cimport cython
6 | from libcpp.vector cimport vector
7 | from libc.math cimport floor, ceil
8 |
9 | cdef class TriangleHash:
10 | cdef vector[vector[int]] spatial_hash
11 | cdef int resolution
12 |
13 | def __cinit__(self, double[:, :, :] triangles, int resolution):
14 | self.spatial_hash.resize(resolution * resolution)
15 | self.resolution = resolution
16 | self._build_hash(triangles)
17 |
18 | @cython.boundscheck(False) # Deactivate bounds checking
19 | @cython.wraparound(False) # Deactivate negative indexing.
20 | cdef int _build_hash(self, double[:, :, :] triangles):
21 | assert(triangles.shape[1] == 3)
22 | assert(triangles.shape[2] == 2)
23 |
24 | cdef int n_tri = triangles.shape[0]
25 | cdef int bbox_min[2]
26 | cdef int bbox_max[2]
27 |
28 | cdef int i_tri, j, x, y
29 | cdef int spatial_idx
30 |
31 | for i_tri in range(n_tri):
32 | # Compute bounding box
33 | for j in range(2):
34 | bbox_min[j] = min(
35 | triangles[i_tri, 0, j], triangles[i_tri, 1, j], triangles[i_tri, 2, j]
36 | )
37 | bbox_max[j] = max(
38 | triangles[i_tri, 0, j], triangles[i_tri, 1, j], triangles[i_tri, 2, j]
39 | )
40 | bbox_min[j] = min(max(bbox_min[j], 0), self.resolution - 1)
41 | bbox_max[j] = min(max(bbox_max[j], 0), self.resolution - 1)
42 |
43 | # Find all voxels where bounding box intersects
44 | for x in range(bbox_min[0], bbox_max[0] + 1):
45 | for y in range(bbox_min[1], bbox_max[1] + 1):
46 | spatial_idx = self.resolution * x + y
47 | self.spatial_hash[spatial_idx].push_back(i_tri)
48 |
49 | @cython.boundscheck(False) # Deactivate bounds checking
50 | @cython.wraparound(False) # Deactivate negative indexing.
51 | cpdef query(self, double[:, :] points):
52 | assert(points.shape[1] == 2)
53 | cdef int n_points = points.shape[0]
54 |
55 | cdef vector[int] points_indices
56 | cdef vector[int] tri_indices
57 | # cdef int[:] points_indices_np
58 | # cdef int[:] tri_indices_np
59 |
60 | cdef int i_point, k, x, y
61 | cdef int spatial_idx
62 |
63 | for i_point in range(n_points):
64 | x = int(points[i_point, 0])
65 | y = int(points[i_point, 1])
66 | if not (0 <= x < self.resolution and 0 <= y < self.resolution):
67 | continue
68 |
69 | spatial_idx = self.resolution * x + y
70 | for i_tri in self.spatial_hash[spatial_idx]:
71 | points_indices.push_back(i_point)
72 | tri_indices.push_back(i_tri)
73 |
74 | points_indices_np = np.zeros(points_indices.size(), dtype=np.int32)
75 | tri_indices_np = np.zeros(tri_indices.size(), dtype=np.int32)
76 |
77 | cdef int[:] points_indices_view = points_indices_np
78 | cdef int[:] tri_indices_view = tri_indices_np
79 |
80 | for k in range(points_indices.size()):
81 | points_indices_view[k] = points_indices[k]
82 |
83 | for k in range(tri_indices.size()):
84 | tri_indices_view[k] = tri_indices[k]
85 |
86 | return points_indices_np, tri_indices_np
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmise/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | mise.c
2 | mise.cpp
3 | mise.html
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmise/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .mise import MISE
2 |
3 |
4 | __all__ = [
5 | MISE
6 | ]
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libmise/test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from mise import MISE
3 | import time
4 |
5 | t0 = time.time()
6 | extractor = MISE(1, 2, 0.)
7 |
8 | p = extractor.query()
9 | i = 0
10 |
11 | while p.shape[0] != 0:
12 | print(i)
13 | print(p)
14 | v = 2 * (p.sum(axis=-1) > 2).astype(np.float64) - 1
15 | extractor.update(p, v)
16 | p = extractor.query()
17 | i += 1
18 | if (i >= 8):
19 | break
20 |
21 | print(extractor.to_dense())
22 | # p, v = extractor.get_points()
23 | # print(p)
24 | # print(v)
25 | print('Total time: %f' % (time.time() - t0))
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libsimplify/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .simplify_mesh import (
2 | mesh_simplify
3 | )
4 | import trimesh
5 |
6 |
7 | def simplify_mesh(mesh, f_target=10000, agressiveness=7.):
8 | vertices = mesh.vertices
9 | faces = mesh.faces
10 |
11 | vertices, faces = mesh_simplify(vertices, faces, f_target, agressiveness)
12 |
13 | mesh_simplified = trimesh.Trimesh(vertices, faces, process=False)
14 |
15 | return mesh_simplified
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libsimplify/simplify_mesh.pyx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # distutils: language = c++
2 | from libcpp.vector cimport vector
3 | import numpy as np
4 | cimport numpy as np
5 |
6 |
7 | cdef extern from "Simplify.h":
8 | cdef struct vec3f:
9 | double x, y, z
10 |
11 | cdef cppclass SymetricMatrix:
12 | SymetricMatrix() except +
13 |
14 |
15 | cdef extern from "Simplify.h" namespace "Simplify":
16 | cdef struct Triangle:
17 | int v[3]
18 | double err[4]
19 | int deleted, dirty, attr
20 | vec3f uvs[3]
21 | int material
22 |
23 | cdef struct Vertex:
24 | vec3f p
25 | int tstart, tcount
26 | SymetricMatrix q
27 | int border
28 |
29 | cdef vector[Triangle] triangles
30 | cdef vector[Vertex] vertices
31 | cdef void simplify_mesh(int, double)
32 |
33 |
34 | cpdef mesh_simplify(double[:, ::1] vertices_in, long[:, ::1] triangles_in,
35 | int f_target, double agressiveness=7.) except +:
36 | vertices.clear()
37 | triangles.clear()
38 |
39 | # Read in vertices and triangles
40 | cdef Vertex v
41 | for iv in range(vertices_in.shape[0]):
42 | v = Vertex()
43 | v.p.x = vertices_in[iv, 0]
44 | v.p.y = vertices_in[iv, 1]
45 | v.p.z = vertices_in[iv, 2]
46 | vertices.push_back(v)
47 |
48 | cdef Triangle t
49 | for it in range(triangles_in.shape[0]):
50 | t = Triangle()
51 | t.v[0] = triangles_in[it, 0]
52 | t.v[1] = triangles_in[it, 1]
53 | t.v[2] = triangles_in[it, 2]
54 | triangles.push_back(t)
55 |
56 | # Simplify
57 | # print('Simplify...')
58 | simplify_mesh(f_target, agressiveness)
59 |
60 | # Only use triangles that are not deleted
61 | cdef vector[Triangle] triangles_notdel
62 | triangles_notdel.reserve(triangles.size())
63 |
64 | for t in triangles:
65 | if not t.deleted:
66 | triangles_notdel.push_back(t)
67 |
68 | # Read out triangles
69 | vertices_out = np.empty((vertices.size(), 3), dtype=np.float64)
70 | triangles_out = np.empty((triangles_notdel.size(), 3), dtype=np.int64)
71 |
72 | cdef double[:, :] vertices_out_view = vertices_out
73 | cdef long[:, :] triangles_out_view = triangles_out
74 |
75 | for iv in range(vertices.size()):
76 | vertices_out_view[iv, 0] = vertices[iv].p.x
77 | vertices_out_view[iv, 1] = vertices[iv].p.y
78 | vertices_out_view[iv, 2] = vertices[iv].p.z
79 |
80 | for it in range(triangles_notdel.size()):
81 | triangles_out_view[it, 0] = triangles_notdel[it].v[0]
82 | triangles_out_view[it, 1] = triangles_notdel[it].v[1]
83 | triangles_out_view[it, 2] = triangles_notdel[it].v[2]
84 |
85 | # Clear vertices and triangles
86 | vertices.clear()
87 | triangles.clear()
88 |
89 | return vertices_out, triangles_out
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libsimplify/test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from simplify_mesh import mesh_simplify
2 | import numpy as np
3 |
4 | v = np.random.rand(100, 3)
5 | f = np.random.choice(range(100), (50, 3))
6 |
7 | mesh_simplify(v, f, 50)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libvoxelize/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | voxelize.c
2 | voxelize.html
3 | build
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libvoxelize/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Kulbear/object-wakeup/62cfb70aa6369aadbca24fd1d51241f2db86e494/main/utils/libvoxelize/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libvoxelize/tribox2.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /********************************************************/
2 | /* AABB-triangle overlap test code */
3 | /* by Tomas Akenine-M�ller */
4 | /* Function: int triBoxOverlap(float boxcenter[3], */
5 | /* float boxhalfsize[3],float triverts[3][3]); */
6 | /* History: */
7 | /* 2001-03-05: released the code in its first version */
8 | /* 2001-06-18: changed the order of the tests, faster */
9 | /* */
10 | /* Acknowledgement: Many thanks to Pierre Terdiman for */
11 | /* suggestions and discussions on how to optimize code. */
12 | /* Thanks to David Hunt for finding a ">="-bug! */
13 | /********************************************************/
14 | #include
15 | #include
16 |
17 | #define X 0
18 | #define Y 1
19 | #define Z 2
20 |
21 | #define CROSS(dest,v1,v2) \
22 | dest[0]=v1[1]*v2[2]-v1[2]*v2[1]; \
23 | dest[1]=v1[2]*v2[0]-v1[0]*v2[2]; \
24 | dest[2]=v1[0]*v2[1]-v1[1]*v2[0];
25 |
26 | #define DOT(v1,v2) (v1[0]*v2[0]+v1[1]*v2[1]+v1[2]*v2[2])
27 |
28 | #define SUB(dest,v1,v2) \
29 | dest[0]=v1[0]-v2[0]; \
30 | dest[1]=v1[1]-v2[1]; \
31 | dest[2]=v1[2]-v2[2];
32 |
33 | #define FINDMINMAX(x0,x1,x2,min,max) \
34 | min = max = x0; \
35 | if(x1max) max=x1;\
37 | if(x2max) max=x2;
39 |
40 | int planeBoxOverlap(float normal[3],float d, float maxbox[3])
41 | {
42 | int q;
43 | float vmin[3],vmax[3];
44 | for(q=X;q<=Z;q++)
45 | {
46 | if(normal[q]>0.0f)
47 | {
48 | vmin[q]=-maxbox[q];
49 | vmax[q]=maxbox[q];
50 | }
51 | else
52 | {
53 | vmin[q]=maxbox[q];
54 | vmax[q]=-maxbox[q];
55 | }
56 | }
57 | if(DOT(normal,vmin)+d>0.0f) return 0;
58 | if(DOT(normal,vmax)+d>=0.0f) return 1;
59 |
60 | return 0;
61 | }
62 |
63 |
64 | /*======================== X-tests ========================*/
65 | #define AXISTEST_X01(a, b, fa, fb) \
66 | p0 = a*v0[Y] - b*v0[Z]; \
67 | p2 = a*v2[Y] - b*v2[Z]; \
68 | if(p0rad || max<-rad) return 0;
71 |
72 | #define AXISTEST_X2(a, b, fa, fb) \
73 | p0 = a*v0[Y] - b*v0[Z]; \
74 | p1 = a*v1[Y] - b*v1[Z]; \
75 | if(p0rad || max<-rad) return 0;
78 |
79 | /*======================== Y-tests ========================*/
80 | #define AXISTEST_Y02(a, b, fa, fb) \
81 | p0 = -a*v0[X] + b*v0[Z]; \
82 | p2 = -a*v2[X] + b*v2[Z]; \
83 | if(p0rad || max<-rad) return 0;
86 |
87 | #define AXISTEST_Y1(a, b, fa, fb) \
88 | p0 = -a*v0[X] + b*v0[Z]; \
89 | p1 = -a*v1[X] + b*v1[Z]; \
90 | if(p0rad || max<-rad) return 0;
93 |
94 | /*======================== Z-tests ========================*/
95 |
96 | #define AXISTEST_Z12(a, b, fa, fb) \
97 | p1 = a*v1[X] - b*v1[Y]; \
98 | p2 = a*v2[X] - b*v2[Y]; \
99 | if(p2rad || max<-rad) return 0;
102 |
103 | #define AXISTEST_Z0(a, b, fa, fb) \
104 | p0 = a*v0[X] - b*v0[Y]; \
105 | p1 = a*v1[X] - b*v1[Y]; \
106 | if(p0rad || max<-rad) return 0;
109 |
110 | int triBoxOverlap(float boxcenter[3],float boxhalfsize[3],float tri0[3], float tri1[3], float tri2[3])
111 | {
112 |
113 | /* use separating axis theorem to test overlap between triangle and box */
114 | /* need to test for overlap in these directions: */
115 | /* 1) the {x,y,z}-directions (actually, since we use the AABB of the triangle */
116 | /* we do not even need to test these) */
117 | /* 2) normal of the triangle */
118 | /* 3) crossproduct(edge from tri, {x,y,z}-directin) */
119 | /* this gives 3x3=9 more tests */
120 | float v0[3],v1[3],v2[3];
121 | float min,max,d,p0,p1,p2,rad,fex,fey,fez;
122 | float normal[3],e0[3],e1[3],e2[3];
123 |
124 | /* This is the fastest branch on Sun */
125 | /* move everything so that the boxcenter is in (0,0,0) */
126 | SUB(v0, tri0, boxcenter);
127 | SUB(v1, tri1, boxcenter);
128 | SUB(v2, tri2, boxcenter);
129 |
130 | /* compute triangle edges */
131 | SUB(e0,v1,v0); /* tri edge 0 */
132 | SUB(e1,v2,v1); /* tri edge 1 */
133 | SUB(e2,v0,v2); /* tri edge 2 */
134 |
135 | /* Bullet 3: */
136 | /* test the 9 tests first (this was faster) */
137 | fex = fabs(e0[X]);
138 | fey = fabs(e0[Y]);
139 | fez = fabs(e0[Z]);
140 | AXISTEST_X01(e0[Z], e0[Y], fez, fey);
141 | AXISTEST_Y02(e0[Z], e0[X], fez, fex);
142 | AXISTEST_Z12(e0[Y], e0[X], fey, fex);
143 |
144 | fex = fabs(e1[X]);
145 | fey = fabs(e1[Y]);
146 | fez = fabs(e1[Z]);
147 | AXISTEST_X01(e1[Z], e1[Y], fez, fey);
148 | AXISTEST_Y02(e1[Z], e1[X], fez, fex);
149 | AXISTEST_Z0(e1[Y], e1[X], fey, fex);
150 |
151 | fex = fabs(e2[X]);
152 | fey = fabs(e2[Y]);
153 | fez = fabs(e2[Z]);
154 | AXISTEST_X2(e2[Z], e2[Y], fez, fey);
155 | AXISTEST_Y1(e2[Z], e2[X], fez, fex);
156 | AXISTEST_Z12(e2[Y], e2[X], fey, fex);
157 |
158 | /* Bullet 1: */
159 | /* first test overlap in the {x,y,z}-directions */
160 | /* find min, max of the triangle each direction, and test for overlap in */
161 | /* that direction -- this is equivalent to testing a minimal AABB around */
162 | /* the triangle against the AABB */
163 |
164 | /* test in X-direction */
165 | FINDMINMAX(v0[X],v1[X],v2[X],min,max);
166 | if(min>boxhalfsize[X] || max<-boxhalfsize[X]) return 0;
167 |
168 | /* test in Y-direction */
169 | FINDMINMAX(v0[Y],v1[Y],v2[Y],min,max);
170 | if(min>boxhalfsize[Y] || max<-boxhalfsize[Y]) return 0;
171 |
172 | /* test in Z-direction */
173 | FINDMINMAX(v0[Z],v1[Z],v2[Z],min,max);
174 | if(min>boxhalfsize[Z] || max<-boxhalfsize[Z]) return 0;
175 |
176 | /* Bullet 2: */
177 | /* test if the box intersects the plane of the triangle */
178 | /* compute plane equation of triangle: normal*x+d=0 */
179 | CROSS(normal,e0,e1);
180 | d=-DOT(normal,v0); /* plane eq: normal.x+d=0 */
181 | if(!planeBoxOverlap(normal,d,boxhalfsize)) return 0;
182 |
183 | return 1; /* box and triangle overlaps */
184 | }
185 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/libvoxelize/voxelize.pyx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | cimport cython
2 | from libc.math cimport floor, ceil
3 | from cython.view cimport array as cvarray
4 |
5 | cdef extern from "tribox2.h":
6 | int triBoxOverlap(float boxcenter[3], float boxhalfsize[3],
7 | float tri0[3], float tri1[3], float tri2[3])
8 |
9 |
10 | @cython.boundscheck(False) # Deactivate bounds checking
11 | @cython.wraparound(False) # Deactivate negative indexing.
12 | cpdef int voxelize_mesh_(bint[:, :, :] occ, float[:, :, ::1] faces):
13 | assert(faces.shape[1] == 3)
14 | assert(faces.shape[2] == 3)
15 |
16 | n_faces = faces.shape[0]
17 | cdef int i
18 | for i in range(n_faces):
19 | voxelize_triangle_(occ, faces[i])
20 |
21 |
22 | @cython.boundscheck(False) # Deactivate bounds checking
23 | @cython.wraparound(False) # Deactivate negative indexing.
24 | cpdef int voxelize_triangle_(bint[:, :, :] occupancies, float[:, ::1] triverts):
25 | cdef int bbox_min[3]
26 | cdef int bbox_max[3]
27 | cdef int i, j, k
28 | cdef float boxhalfsize[3]
29 | cdef float boxcenter[3]
30 | cdef bint intersection
31 |
32 | boxhalfsize[:] = (0.5, 0.5, 0.5)
33 |
34 | for i in range(3):
35 | bbox_min[i] = (
36 | min(triverts[0, i], triverts[1, i], triverts[2, i])
37 | )
38 | bbox_min[i] = min(max(bbox_min[i], 0), occupancies.shape[i] - 1)
39 |
40 | for i in range(3):
41 | bbox_max[i] = (
42 | max(triverts[0, i], triverts[1, i], triverts[2, i])
43 | )
44 | bbox_max[i] = min(max(bbox_max[i], 0), occupancies.shape[i] - 1)
45 |
46 | for i in range(bbox_min[0], bbox_max[0] + 1):
47 | for j in range(bbox_min[1], bbox_max[1] + 1):
48 | for k in range(bbox_min[2], bbox_max[2] + 1):
49 | boxcenter[:] = (i + 0.5, j + 0.5, k + 0.5)
50 | intersection = triBoxOverlap(&boxcenter[0], &boxhalfsize[0],
51 | &triverts[0, 0], &triverts[1, 0], &triverts[2, 0])
52 | occupancies[i, j, k] |= intersection
53 |
54 |
55 | @cython.boundscheck(False) # Deactivate bounds checking
56 | @cython.wraparound(False) # Deactivate negative indexing.
57 | cdef int test_triangle_aabb(float[::1] boxcenter, float[::1] boxhalfsize, float[:, ::1] triverts):
58 | assert(boxcenter.shape[0] == 3)
59 | assert(boxhalfsize.shape[0] == 3)
60 | assert(triverts.shape[0] == triverts.shape[1] == 3)
61 |
62 | # print(triverts)
63 | # Call functions
64 | cdef int result = triBoxOverlap(&boxcenter[0], &boxhalfsize[0],
65 | &triverts[0, 0], &triverts[1, 0], &triverts[2, 0])
66 | return result
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/mesh.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from scipy.spatial import Delaunay
2 | from itertools import combinations
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from main.utils import voxels
5 |
6 |
7 | class MultiGridExtractor(object):
8 | def __init__(self, resolution0, threshold):
9 | # Attributes
10 | self.resolution = resolution0
11 | self.threshold = threshold
12 |
13 | # Voxels are active or inactive,
14 | # values live on the space between voxels and are either
15 | # known exactly or guessed by interpolation (unknown)
16 | shape_voxels = (resolution0,) * 3
17 | shape_values = (resolution0 + 1,) * 3
18 | self.values = np.empty(shape_values)
19 | self.value_known = np.full(shape_values, False)
20 | self.voxel_active = np.full(shape_voxels, True)
21 |
22 | def query(self):
23 | # Query locations in grid that are active but unkown
24 | idx1, idx2, idx3 = np.where(
25 | ~self.value_known & self.value_active
26 | )
27 | points = np.stack([idx1, idx2, idx3], axis=-1)
28 | return points
29 |
30 | def update(self, points, values):
31 | # Update locations and set known status to true
32 | idx0, idx1, idx2 = points.transpose()
33 | self.values[idx0, idx1, idx2] = values
34 | self.value_known[idx0, idx1, idx2] = True
35 |
36 | # Update activity status of voxels accordings to new values
37 | self.voxel_active = ~self.voxel_empty
38 | # (
39 | # # self.voxel_active &
40 | # self.voxel_known & ~self.voxel_empty
41 | # )
42 |
43 | def increase_resolution(self):
44 | self.resolution = 2 * self.resolution
45 | shape_values = (self.resolution + 1,) * 3
46 |
47 | value_known = np.full(shape_values, False)
48 | value_known[::2, ::2, ::2] = self.value_known
49 | values = upsample3d_nn(self.values)
50 | values = values[:-1, :-1, :-1]
51 |
52 | self.values = values
53 | self.value_known = value_known
54 | self.voxel_active = upsample3d_nn(self.voxel_active)
55 |
56 | @property
57 | def occupancies(self):
58 | return (self.values < self.threshold)
59 |
60 | @property
61 | def value_active(self):
62 | value_active = np.full(self.values.shape, False)
63 | # Active if adjacent to active voxel
64 | value_active[:-1, :-1, :-1] |= self.voxel_active
65 | value_active[:-1, :-1, 1:] |= self.voxel_active
66 | value_active[:-1, 1:, :-1] |= self.voxel_active
67 | value_active[:-1, 1:, 1:] |= self.voxel_active
68 | value_active[1:, :-1, :-1] |= self.voxel_active
69 | value_active[1:, :-1, 1:] |= self.voxel_active
70 | value_active[1:, 1:, :-1] |= self.voxel_active
71 | value_active[1:, 1:, 1:] |= self.voxel_active
72 |
73 | return value_active
74 |
75 | @property
76 | def voxel_known(self):
77 | value_known = self.value_known
78 | voxel_known = voxels.check_voxel_occupied(value_known)
79 | return voxel_known
80 |
81 | @property
82 | def voxel_empty(self):
83 | occ = self.occupancies
84 | return ~voxels.check_voxel_boundary(occ)
85 |
86 |
87 | def upsample3d_nn(x):
88 | xshape = x.shape
89 | yshape = (2*xshape[0], 2*xshape[1], 2*xshape[2])
90 |
91 | y = np.zeros(yshape, dtype=x.dtype)
92 | y[::2, ::2, ::2] = x
93 | y[::2, ::2, 1::2] = x
94 | y[::2, 1::2, ::2] = x
95 | y[::2, 1::2, 1::2] = x
96 | y[1::2, ::2, ::2] = x
97 | y[1::2, ::2, 1::2] = x
98 | y[1::2, 1::2, ::2] = x
99 | y[1::2, 1::2, 1::2] = x
100 |
101 | return y
102 |
103 |
104 | class DelauneyMeshExtractor(object):
105 | """Algorithm for extacting meshes from implicit function using
106 | delauney triangulation and random sampling."""
107 | def __init__(self, points, values, threshold=0.):
108 | self.points = points
109 | self.values = values
110 | self.delaunay = Delaunay(self.points)
111 | self.threshold = threshold
112 |
113 | def update(self, points, values, reduce_to_active=True):
114 | # Find all active points
115 | if reduce_to_active:
116 | active_simplices = self.active_simplices()
117 | active_point_idx = np.unique(active_simplices.flatten())
118 | self.points = self.points[active_point_idx]
119 | self.values = self.values[active_point_idx]
120 |
121 | self.points = np.concatenate([self.points, points], axis=0)
122 | self.values = np.concatenate([self.values, values], axis=0)
123 | self.delaunay = Delaunay(self.points)
124 |
125 | def extract_mesh(self):
126 | threshold = self.threshold
127 | vertices = []
128 | triangles = []
129 | vertex_dict = dict()
130 |
131 | active_simplices = self.active_simplices()
132 | active_simplices.sort(axis=1)
133 | for simplex in active_simplices:
134 | new_vertices = []
135 | for i1, i2 in combinations(simplex, 2):
136 | assert(i1 < i2)
137 | v1 = self.values[i1]
138 | v2 = self.values[i2]
139 | if (v1 < threshold) ^ (v2 < threshold):
140 | # Subdivide edge
141 | vertex_idx = vertex_dict.get((i1, i2), len(vertices))
142 | vertex_idx = len(vertices)
143 | if vertex_idx == len(vertices):
144 | tau = (threshold - v1) / (v2 - v1)
145 | assert(0 <= tau <= 1)
146 | p = (1 - tau) * self.points[i1] + tau * self.points[i2]
147 | vertices.append(p)
148 | vertex_dict[i1, i2] = vertex_idx
149 | new_vertices.append(vertex_idx)
150 |
151 | assert(len(new_vertices) in (3, 4))
152 | p0 = self.points[simplex[0]]
153 | v0 = self.values[simplex[0]]
154 | if len(new_vertices) == 3:
155 | i1, i2, i3 = new_vertices
156 | p1, p2, p3 = vertices[i1], vertices[i2], vertices[i3]
157 | vol = get_tetrahedon_volume(np.asarray([p0, p1, p2, p3]))
158 | if vol * (v0 - threshold) <= 0:
159 | triangles.append((i1, i2, i3))
160 | else:
161 | triangles.append((i1, i3, i2))
162 | elif len(new_vertices) == 4:
163 | i1, i2, i3, i4 = new_vertices
164 | p1, p2, p3, p4 = \
165 | vertices[i1], vertices[i2], vertices[i3], vertices[i4]
166 | vol = get_tetrahedon_volume(np.asarray([p0, p1, p2, p3]))
167 | if vol * (v0 - threshold) <= 0:
168 | triangles.append((i1, i2, i3))
169 | else:
170 | triangles.append((i1, i3, i2))
171 |
172 | vol = get_tetrahedon_volume(np.asarray([p0, p2, p3, p4]))
173 | if vol * (v0 - threshold) <= 0:
174 | triangles.append((i2, i3, i4))
175 | else:
176 | triangles.append((i2, i4, i3))
177 |
178 | vertices = np.asarray(vertices, dtype=np.float32)
179 | triangles = np.asarray(triangles, dtype=np.int32)
180 |
181 | return vertices, triangles
182 |
183 | def query(self, size):
184 | active_simplices = self.active_simplices()
185 | active_simplices_points = self.points[active_simplices]
186 | new_points = sample_tetraheda(active_simplices_points, size=size)
187 | return new_points
188 |
189 | def active_simplices(self):
190 | occ = (self.values >= self.threshold)
191 | simplices = self.delaunay.simplices
192 | simplices_occ = occ[simplices]
193 |
194 | active = (
195 | np.any(simplices_occ, axis=1) & np.any(~simplices_occ, axis=1)
196 | )
197 |
198 | simplices = self.delaunay.simplices[active]
199 | return simplices
200 |
201 |
202 | def sample_tetraheda(tetraheda_points, size):
203 | N_tetraheda = tetraheda_points.shape[0]
204 | volume = np.abs(get_tetrahedon_volume(tetraheda_points))
205 | probs = volume / volume.sum()
206 |
207 | tetraheda_rnd = np.random.choice(range(N_tetraheda), p=probs, size=size)
208 | tetraheda_rnd_points = tetraheda_points[tetraheda_rnd]
209 | weights_rnd = np.random.dirichlet([1, 1, 1, 1], size=size)
210 | weights_rnd = weights_rnd.reshape(size, 4, 1)
211 | points_rnd = (weights_rnd * tetraheda_rnd_points).sum(axis=1)
212 | # points_rnd = tetraheda_rnd_points.mean(1)
213 |
214 | return points_rnd
215 |
216 |
217 | def get_tetrahedon_volume(points):
218 | vectors = points[..., :3, :] - points[..., 3:, :]
219 | volume = 1/6 * np.linalg.det(vectors)
220 | return volume
221 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/visualize.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
3 | from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
4 | from torchvision.utils import save_image
5 | import main.common as common
6 |
7 |
8 | def visualize_data(data, data_type, out_file):
9 | r''' Visualizes the data with regard to its type.
10 |
11 | Args:
12 | data (tensor): batch of data
13 | data_type (string): data type (img, voxels or pointcloud)
14 | out_file (string): output file
15 | '''
16 | if data_type == 'img':
17 | if data.dim() == 3:
18 | data = data.unsqueeze(0)
19 | save_image(data, out_file, nrow=4)
20 | elif data_type == 'voxels':
21 | visualize_voxels(data, out_file=out_file)
22 | elif data_type == 'pointcloud':
23 | visualize_pointcloud(data, out_file=out_file)
24 | elif data_type is None or data_type == 'idx':
25 | pass
26 | else:
27 | raise ValueError('Invalid data_type "%s"' % data_type)
28 |
29 |
30 | def visualize_voxels(voxels, out_file=None, show=False):
31 | r''' Visualizes voxel data.
32 |
33 | Args:
34 | voxels (tensor): voxel data
35 | out_file (string): output file
36 | show (bool): whether the plot should be shown
37 | '''
38 | # Use numpy
39 | voxels = np.asarray(voxels)
40 | # Create plot
41 | fig = plt.figure()
42 | ax = fig.gca(projection=Axes3D.name)
43 | voxels = voxels.transpose(2, 0, 1)
44 | ax.voxels(voxels, edgecolor='k')
45 | ax.set_xlabel('Z')
46 | ax.set_ylabel('X')
47 | ax.set_zlabel('Y')
48 | ax.view_init(elev=30, azim=45)
49 | if out_file is not None:
50 | plt.savefig(out_file)
51 | if show:
52 | plt.show()
53 | plt.close(fig)
54 |
55 |
56 | def visualize_pointcloud(points, normals=None,
57 | out_file=None, show=False):
58 | r''' Visualizes point cloud data.
59 |
60 | Args:
61 | points (tensor): point data
62 | normals (tensor): normal data (if existing)
63 | out_file (string): output file
64 | show (bool): whether the plot should be shown
65 | '''
66 | # Use numpy
67 | points = np.asarray(points)
68 | # Create plot
69 | fig = plt.figure()
70 | ax = fig.gca(projection=Axes3D.name)
71 | ax.scatter(points[:, 2], points[:, 0], points[:, 1])
72 | if normals is not None:
73 | ax.quiver(
74 | points[:, 2], points[:, 0], points[:, 1],
75 | normals[:, 2], normals[:, 0], normals[:, 1],
76 | length=0.1, color='k'
77 | )
78 | ax.set_xlabel('Z')
79 | ax.set_ylabel('X')
80 | ax.set_zlabel('Y')
81 | ax.set_xlim(-0.5, 0.5)
82 | ax.set_ylim(-0.5, 0.5)
83 | ax.set_zlim(-0.5, 0.5)
84 | ax.view_init(elev=30, azim=45)
85 | if out_file is not None:
86 | plt.savefig(out_file)
87 | if show:
88 | plt.show()
89 | plt.close(fig)
90 |
91 |
92 | def visualise_projection(
93 | self, points, world_mat, camera_mat, img, output_file='out.png'):
94 | r''' Visualizes the transformation and projection to image plane.
95 |
96 | The first points of the batch are transformed and projected to the
97 | respective image. After performing the relevant transformations, the
98 | visualization is saved in the provided output_file path.
99 |
100 | Arguments:
101 | points (tensor): batch of point cloud points
102 | world_mat (tensor): batch of matrices to rotate pc to camera-based
103 | coordinates
104 | camera_mat (tensor): batch of camera matrices to project to 2D image
105 | plane
106 | img (tensor): tensor of batch GT image files
107 | output_file (string): where the output should be saved
108 | '''
109 | points_transformed = common.transform_points(points, world_mat)
110 | points_img = common.project_to_camera(points_transformed, camera_mat)
111 | pimg2 = points_img[0].detach().cpu().numpy()
112 | image = img[0].cpu().numpy()
113 | plt.imshow(image.transpose(1, 2, 0))
114 | plt.plot(
115 | (pimg2[:, 0] + 1)*image.shape[1]/2,
116 | (pimg2[:, 1] + 1) * image.shape[2]/2, 'x')
117 | plt.savefig(output_file)
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main/utils/voxels.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import trimesh
4 | from scipy import ndimage
5 | from skimage.measure import block_reduce
6 | from main.utils.libvoxelize.voxelize import voxelize_mesh_
7 | from main.utils.libmesh import check_mesh_contains
8 | from main.common import make_3d_grid
9 |
10 |
11 | class VoxelGrid:
12 | def __init__(self, data, loc=(0., 0., 0.), scale=1):
13 | assert(data.shape[0] == data.shape[1] == data.shape[2])
14 | data = np.asarray(data, dtype=np.bool)
15 | loc = np.asarray(loc)
16 | self.data = data
17 | self.loc = loc
18 | self.scale = scale
19 |
20 | @classmethod
21 | def from_mesh(cls, mesh, resolution, loc=None, scale=None, method='ray'):
22 | bounds = mesh.bounds
23 | # Default location is center
24 | if loc is None:
25 | loc = (bounds[0] + bounds[1]) / 2
26 |
27 | # Default scale, scales the mesh to [-0.45, 0.45]^3
28 | if scale is None:
29 | scale = (bounds[1] - bounds[0]).max()/0.9
30 |
31 | loc = np.asarray(loc)
32 | scale = float(scale)
33 |
34 | # Transform mesh
35 | mesh = mesh.copy()
36 | mesh.apply_translation(-loc)
37 | mesh.apply_scale(1/scale)
38 |
39 | # Apply method
40 | if method == 'ray':
41 | voxel_data = voxelize_ray(mesh, resolution)
42 | elif method == 'fill':
43 | voxel_data = voxelize_fill(mesh, resolution)
44 |
45 | voxels = cls(voxel_data, loc, scale)
46 | return voxels
47 |
48 | def down_sample(self, factor=2):
49 | if not (self.resolution % factor) == 0:
50 | raise ValueError('Resolution must be divisible by factor.')
51 | new_data = block_reduce(self.data, (factor,) * 3, np.max)
52 | return VoxelGrid(new_data, self.loc, self.scale)
53 |
54 | def to_mesh(self):
55 | # Shorthand
56 | occ = self.data
57 |
58 | # Shape of voxel grid
59 | nx, ny, nz = occ.shape
60 | # Shape of corresponding occupancy grid
61 | grid_shape = (nx + 1, ny + 1, nz + 1)
62 |
63 | # Convert values to occupancies
64 | occ = np.pad(occ, 1, 'constant')
65 |
66 | # Determine if face present
67 | f1_r = (occ[:-1, 1:-1, 1:-1] & ~occ[1:, 1:-1, 1:-1])
68 | f2_r = (occ[1:-1, :-1, 1:-1] & ~occ[1:-1, 1:, 1:-1])
69 | f3_r = (occ[1:-1, 1:-1, :-1] & ~occ[1:-1, 1:-1, 1:])
70 |
71 | f1_l = (~occ[:-1, 1:-1, 1:-1] & occ[1:, 1:-1, 1:-1])
72 | f2_l = (~occ[1:-1, :-1, 1:-1] & occ[1:-1, 1:, 1:-1])
73 | f3_l = (~occ[1:-1, 1:-1, :-1] & occ[1:-1, 1:-1, 1:])
74 |
75 | f1 = f1_r | f1_l
76 | f2 = f2_r | f2_l
77 | f3 = f3_r | f3_l
78 |
79 | assert(f1.shape == (nx + 1, ny, nz))
80 | assert(f2.shape == (nx, ny + 1, nz))
81 | assert(f3.shape == (nx, ny, nz + 1))
82 |
83 | # Determine if vertex present
84 | v = np.full(grid_shape, False)
85 |
86 | v[:, :-1, :-1] |= f1
87 | v[:, :-1, 1:] |= f1
88 | v[:, 1:, :-1] |= f1
89 | v[:, 1:, 1:] |= f1
90 |
91 | v[:-1, :, :-1] |= f2
92 | v[:-1, :, 1:] |= f2
93 | v[1:, :, :-1] |= f2
94 | v[1:, :, 1:] |= f2
95 |
96 | v[:-1, :-1, :] |= f3
97 | v[:-1, 1:, :] |= f3
98 | v[1:, :-1, :] |= f3
99 | v[1:, 1:, :] |= f3
100 |
101 | # Calculate indices for vertices
102 | n_vertices = v.sum()
103 | v_idx = np.full(grid_shape, -1)
104 | v_idx[v] = np.arange(n_vertices)
105 |
106 | # Vertices
107 | v_x, v_y, v_z = np.where(v)
108 | v_x = v_x / nx - 0.5
109 | v_y = v_y / ny - 0.5
110 | v_z = v_z / nz - 0.5
111 | vertices = np.stack([v_x, v_y, v_z], axis=1)
112 |
113 | # Face indices
114 | f1_l_x, f1_l_y, f1_l_z = np.where(f1_l)
115 | f2_l_x, f2_l_y, f2_l_z = np.where(f2_l)
116 | f3_l_x, f3_l_y, f3_l_z = np.where(f3_l)
117 |
118 | f1_r_x, f1_r_y, f1_r_z = np.where(f1_r)
119 | f2_r_x, f2_r_y, f2_r_z = np.where(f2_r)
120 | f3_r_x, f3_r_y, f3_r_z = np.where(f3_r)
121 |
122 | faces_1_l = np.stack([
123 | v_idx[f1_l_x, f1_l_y, f1_l_z],
124 | v_idx[f1_l_x, f1_l_y, f1_l_z + 1],
125 | v_idx[f1_l_x, f1_l_y + 1, f1_l_z + 1],
126 | v_idx[f1_l_x, f1_l_y + 1, f1_l_z],
127 | ], axis=1)
128 |
129 | faces_1_r = np.stack([
130 | v_idx[f1_r_x, f1_r_y, f1_r_z],
131 | v_idx[f1_r_x, f1_r_y + 1, f1_r_z],
132 | v_idx[f1_r_x, f1_r_y + 1, f1_r_z + 1],
133 | v_idx[f1_r_x, f1_r_y, f1_r_z + 1],
134 | ], axis=1)
135 |
136 | faces_2_l = np.stack([
137 | v_idx[f2_l_x, f2_l_y, f2_l_z],
138 | v_idx[f2_l_x + 1, f2_l_y, f2_l_z],
139 | v_idx[f2_l_x + 1, f2_l_y, f2_l_z + 1],
140 | v_idx[f2_l_x, f2_l_y, f2_l_z + 1],
141 | ], axis=1)
142 |
143 | faces_2_r = np.stack([
144 | v_idx[f2_r_x, f2_r_y, f2_r_z],
145 | v_idx[f2_r_x, f2_r_y, f2_r_z + 1],
146 | v_idx[f2_r_x + 1, f2_r_y, f2_r_z + 1],
147 | v_idx[f2_r_x + 1, f2_r_y, f2_r_z],
148 | ], axis=1)
149 |
150 | faces_3_l = np.stack([
151 | v_idx[f3_l_x, f3_l_y, f3_l_z],
152 | v_idx[f3_l_x, f3_l_y + 1, f3_l_z],
153 | v_idx[f3_l_x + 1, f3_l_y + 1, f3_l_z],
154 | v_idx[f3_l_x + 1, f3_l_y, f3_l_z],
155 | ], axis=1)
156 |
157 | faces_3_r = np.stack([
158 | v_idx[f3_r_x, f3_r_y, f3_r_z],
159 | v_idx[f3_r_x + 1, f3_r_y, f3_r_z],
160 | v_idx[f3_r_x + 1, f3_r_y + 1, f3_r_z],
161 | v_idx[f3_r_x, f3_r_y + 1, f3_r_z],
162 | ], axis=1)
163 |
164 | faces = np.concatenate([
165 | faces_1_l, faces_1_r,
166 | faces_2_l, faces_2_r,
167 | faces_3_l, faces_3_r,
168 | ], axis=0)
169 |
170 | vertices = self.loc + self.scale * vertices
171 | mesh = trimesh.Trimesh(vertices, faces, process=False)
172 | return mesh
173 |
174 | @property
175 | def resolution(self):
176 | assert(self.data.shape[0] == self.data.shape[1] == self.data.shape[2])
177 | return self.data.shape[0]
178 |
179 | def contains(self, points):
180 | nx = self.resolution
181 |
182 | # Rescale bounding box to [-0.5, 0.5]^3
183 | points = (points - self.loc) / self.scale
184 | # Discretize points to [0, nx-1]^3
185 | points_i = ((points + 0.5) * nx).astype(np.int32)
186 | # i1, i2, i3 have sizes (batch_size, T)
187 | i1, i2, i3 = points_i[..., 0], points_i[..., 1], points_i[..., 2]
188 | # Only use indices inside bounding box
189 | mask = (
190 | (i1 >= 0) & (i2 >= 0) & (i3 >= 0)
191 | & (nx > i1) & (nx > i2) & (nx > i3)
192 | )
193 | # Prevent out of bounds error
194 | i1 = i1[mask]
195 | i2 = i2[mask]
196 | i3 = i3[mask]
197 |
198 | # Compute values, default value outside box is 0
199 | occ = np.zeros(points.shape[:-1], dtype=np.bool)
200 | occ[mask] = self.data[i1, i2, i3]
201 |
202 | return occ
203 |
204 |
205 | def voxelize_ray(mesh, resolution):
206 | occ_surface = voxelize_surface(mesh, resolution)
207 | # TODO: use surface voxels here?
208 | occ_interior = voxelize_interior(mesh, resolution)
209 | occ = (occ_interior | occ_surface)
210 | return occ
211 |
212 |
213 | def voxelize_fill(mesh, resolution):
214 | bounds = mesh.bounds
215 | if (np.abs(bounds) >= 0.5).any():
216 | raise ValueError('voxelize fill is only supported if mesh is inside [-0.5, 0.5]^3/')
217 |
218 | occ = voxelize_surface(mesh, resolution)
219 | occ = ndimage.morphology.binary_fill_holes(occ)
220 | return occ
221 |
222 |
223 | def voxelize_surface(mesh, resolution):
224 | vertices = mesh.vertices
225 | faces = mesh.faces
226 |
227 | vertices = (vertices + 0.5) * resolution
228 |
229 | face_loc = vertices[faces]
230 | occ = np.full((resolution,) * 3, 0, dtype=np.int32)
231 | face_loc = face_loc.astype(np.float32)
232 |
233 | voxelize_mesh_(occ, face_loc)
234 | occ = (occ != 0)
235 |
236 | return occ
237 |
238 |
239 | def voxelize_interior(mesh, resolution):
240 | shape = (resolution,) * 3
241 | bb_min = (0.5,) * 3
242 | bb_max = (resolution - 0.5,) * 3
243 | # Create points. Add noise to break symmetry
244 | points = make_3d_grid(bb_min, bb_max, shape=shape).numpy()
245 | points = points + 0.1 * (np.random.rand(*points.shape) - 0.5)
246 | points = (points / resolution - 0.5)
247 | occ = check_mesh_contains(mesh, points)
248 | occ = occ.reshape(shape)
249 | return occ
250 |
251 |
252 | def check_voxel_occupied(occupancy_grid):
253 | occ = occupancy_grid
254 |
255 | occupied = (
256 | occ[..., :-1, :-1, :-1]
257 | & occ[..., :-1, :-1, 1:]
258 | & occ[..., :-1, 1:, :-1]
259 | & occ[..., :-1, 1:, 1:]
260 | & occ[..., 1:, :-1, :-1]
261 | & occ[..., 1:, :-1, 1:]
262 | & occ[..., 1:, 1:, :-1]
263 | & occ[..., 1:, 1:, 1:]
264 | )
265 | return occupied
266 |
267 |
268 | def check_voxel_unoccupied(occupancy_grid):
269 | occ = occupancy_grid
270 |
271 | unoccupied = ~(
272 | occ[..., :-1, :-1, :-1]
273 | | occ[..., :-1, :-1, 1:]
274 | | occ[..., :-1, 1:, :-1]
275 | | occ[..., :-1, 1:, 1:]
276 | | occ[..., 1:, :-1, :-1]
277 | | occ[..., 1:, :-1, 1:]
278 | | occ[..., 1:, 1:, :-1]
279 | | occ[..., 1:, 1:, 1:]
280 | )
281 | return unoccupied
282 |
283 |
284 | def check_voxel_boundary(occupancy_grid):
285 | occupied = check_voxel_occupied(occupancy_grid)
286 | unoccupied = check_voxel_unoccupied(occupancy_grid)
287 | return ~occupied & ~unoccupied
288 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | try:
2 | from setuptools import setup
3 | except ImportError:
4 | from distutils.core import setup
5 | from distutils.extension import Extension
6 | from Cython.Build import cythonize
7 | from torch.utils.cpp_extension import BuildExtension, CppExtension, CUDAExtension
8 | import numpy
9 |
10 |
11 | # Get the numpy include directory.
12 | numpy_include_dir = numpy.get_include()
13 |
14 | # Extensions
15 | # pykdtree (kd tree)
16 | pykdtree = Extension(
17 | 'main.utils.libkdtree.pykdtree.kdtree',
18 | sources=[
19 | 'main/utils/libkdtree/pykdtree/kdtree.c',
20 | 'main/utils/libkdtree/pykdtree/_kdtree_core.c'
21 | ],
22 | language='c',
23 | extra_compile_args=['-std=c99', '-O3', '-fopenmp'],
24 | extra_link_args=['-lgomp'],
25 | )
26 |
27 | # mcubes (marching cubes algorithm)
28 | mcubes_module = Extension(
29 | 'main.utils.libmcubes.mcubes',
30 | sources=[
31 | 'main/utils/libmcubes/mcubes.pyx',
32 | 'main/utils/libmcubes/pywrapper.cpp',
33 | 'main/utils/libmcubes/marchingcubes.cpp'
34 | ],
35 | language='c++',
36 | extra_compile_args=['-std=c++11'],
37 | include_dirs=[numpy_include_dir]
38 | )
39 |
40 | # triangle hash (efficient mesh intersection)
41 | triangle_hash_module = Extension(
42 | 'main.utils.libmesh.triangle_hash',
43 | sources=[
44 | 'main/utils/libmesh/triangle_hash.pyx'
45 | ],
46 | libraries=['m'] # Unix-like specific
47 | )
48 |
49 | # mise (efficient mesh extraction)
50 | mise_module = Extension(
51 | 'main.utils.libmise.mise',
52 | sources=[
53 | 'main/utils/libmise/mise.pyx'
54 | ],
55 | )
56 |
57 | # simplify (efficient mesh simplification)
58 | simplify_mesh_module = Extension(
59 | 'main.utils.libsimplify.simplify_mesh',
60 | sources=[
61 | 'main/utils/libsimplify/simplify_mesh.pyx'
62 | ]
63 | )
64 |
65 | # voxelization (efficient mesh voxelization)
66 | voxelize_module = Extension(
67 | 'main.utils.libvoxelize.voxelize',
68 | sources=[
69 | 'main/utils/libvoxelize/voxelize.pyx'
70 | ],
71 | libraries=['m'] # Unix-like specific
72 | )
73 |
74 | # DMC extensions
75 | dmc_pred2mesh_module = CppExtension(
76 | 'main.dmc.ops.cpp_modules.pred2mesh',
77 | sources=[
78 | 'main/dmc/ops/cpp_modules/pred_to_mesh_.cpp',
79 | ]
80 | )
81 |
82 | dmc_cuda_module = CUDAExtension(
83 | 'main.dmc.ops._cuda_ext',
84 | sources=[
85 | 'main/dmc/ops/src/extension.cpp',
86 | 'main/dmc/ops/src/curvature_constraint_kernel.cu',
87 | 'main/dmc/ops/src/grid_pooling_kernel.cu',
88 | 'main/dmc/ops/src/occupancy_to_topology_kernel.cu',
89 | 'main/dmc/ops/src/occupancy_connectivity_kernel.cu',
90 | 'main/dmc/ops/src/point_triangle_distance_kernel.cu',
91 | ]
92 | )
93 |
94 | # Gather all extension modules
95 | ext_modules = [
96 | pykdtree,
97 | mcubes_module,
98 | triangle_hash_module,
99 | mise_module,
100 | simplify_mesh_module,
101 | voxelize_module,
102 | dmc_pred2mesh_module,
103 | dmc_cuda_module,
104 | ]
105 |
106 | setup(
107 | ext_modules=cythonize(ext_modules),
108 | cmdclass={
109 | 'build_ext': BuildExtension
110 | }
111 | )
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import urllib
3 | import torch
4 | from torch.utils import model_zoo
5 |
6 | import os
7 |
8 |
9 | class CheckpointIO(object):
10 | ''' CheckpointIO class.
11 |
12 | It handles saving and loading checkpoints.
13 |
14 | Args:
15 | checkpoint_dir (str): path where checkpoints are saved
16 | '''
17 |
18 | def __init__(self, checkpoint_dir='./chkpts', **kwargs):
19 | self.module_dict = kwargs
20 | self.checkpoint_dir = checkpoint_dir
21 | if not os.path.exists(checkpoint_dir):
22 | os.makedirs(checkpoint_dir)
23 |
24 | def register_modules(self, **kwargs):
25 | ''' Registers modules in current module dictionary.
26 | '''
27 | self.module_dict.update(kwargs)
28 |
29 | def save(self, filename, **kwargs):
30 | ''' Saves the current module dictionary.
31 |
32 | Args:
33 | filename (str): name of output file
34 | '''
35 | if not os.path.isabs(filename):
36 | filename = os.path.join(self.checkpoint_dir, filename)
37 |
38 | outdict = kwargs
39 | for k, v in self.module_dict.items():
40 | outdict[k] = v.state_dict()
41 | torch.save(outdict, filename)
42 |
43 | def load(self, filename):
44 | '''Loads a module dictionary from local file or url.
45 |
46 | Args:
47 | filename (str): name of saved module dictionary
48 | '''
49 | if is_url(filename):
50 | return self.load_url(filename)
51 | else:
52 | print(filename)
53 | return self.load_file(filename)
54 |
55 | def load_file(self, filename):
56 | '''Loads a module dictionary from file.
57 |
58 | Args:
59 | filename (str): name of saved module dictionary
60 | '''
61 |
62 | if not os.path.isabs(filename):
63 | filename = os.path.join(self.checkpoint_dir, filename)
64 | print(filename)
65 | if os.path.exists(filename):
66 | print(filename)
67 | print('=> Loading checkpoint from local file...')
68 | state_dict = torch.load(filename)
69 | scalars = self.parse_state_dict(state_dict)
70 | return scalars
71 | else:
72 | raise FileExistsError
73 |
74 | def load_url(self, url):
75 | '''Load a module dictionary from url.
76 |
77 | Args:
78 | url (str): url to saved model
79 | '''
80 | print(url)
81 | print('=> Loading checkpoint from url...')
82 | state_dict = model_zoo.load_url(url, progress=True)
83 | scalars = self.parse_state_dict(state_dict)
84 | return scalars
85 |
86 | def parse_state_dict(self, state_dict):
87 | '''Parse state_dict of model and return scalars.
88 |
89 | Args:
90 | state_dict (dict): State dict of model
91 | '''
92 |
93 | for k, v in self.module_dict.items():
94 | if k in state_dict:
95 | print(k, v)
96 | v.load_state_dict(state_dict[k])
97 | else:
98 | print('Warning: Could not find %s in checkpoint!' % k)
99 | scalars = {k: v for k, v in state_dict.items()
100 | if k not in self.module_dict}
101 | return scalars
102 |
103 |
104 | def is_url(url):
105 | scheme = urllib.parse.urlparse(url).scheme
106 | return scheme in ('http', 'https')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------