├── Ant_Colony_Optimization
├── ACO_MatLab
│ ├── AC解决函数最优解
│ │ ├── F.m
│ │ └── SolveMax.m
│ ├── AC解决机器人路径规划
│ │ ├── DrawRoute.m
│ │ ├── G2D.m
│ │ ├── Magine.gif
│ │ ├── main.m
│ │ └── test.gif
│ └── AOC解决TSP问题
│ │ ├── DrawRoute.m
│ │ ├── TSP.gif
│ │ ├── mian.m
│ │ └── res.png
└── README.md
├── Genetic_Algorithm
├── GA_Java
│ ├── Chromosome.java
│ ├── GeneticAlgorithm.java
│ └── GeneticAlgorithmTest.java
├── GA_MatLab
│ ├── GA遗传算法工具箱
│ │ ├── Test.m
│ │ └── ga44.m
│ ├── GA遗传算法解决TSP问题
│ │ ├── cross.m
│ │ ├── exchange.m
│ │ ├── fit.m
│ │ ├── main.m
│ │ ├── mutation.m
│ │ ├── myLength.m
│ │ ├── plot_route.m
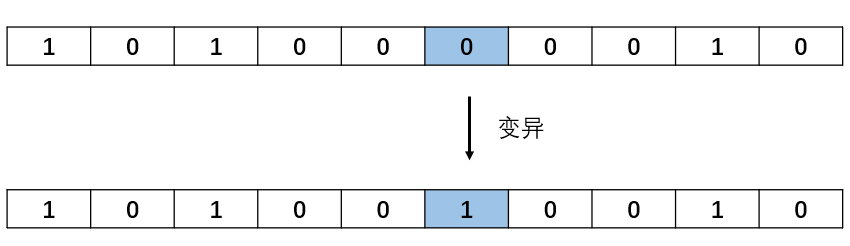
│ │ └── reverse.m
│ └── GA遗传算法解决非线性最优解
│ │ ├── README.md
│ │ ├── best.m
│ │ ├── binary2decimal.m
│ │ ├── cal_objvalue.m
│ │ ├── crossover.m
│ │ ├── initpop.m
│ │ ├── main.m
│ │ ├── mutation.m
│ │ └── selection.m
├── GA_Python
│ ├── GA_Test.py
│ └── Population.py
└── README.md
├── Immunity_Algorithm
├── IMA
│ ├── bamboo.bmp
│ ├── bird.bmp
│ ├── cross.m
│ ├── drawResult.m
│ ├── fit.m
│ ├── fitnessty.m
│ ├── isRgb.m
│ ├── main.asv
│ ├── main.m
│ ├── mutation.m
│ ├── select.m
│ ├── similarChromosome.m
│ └── similarPopulation.m
├── IMA解决TSP问题
│ ├── CharRecompose.m
│ ├── DisplaceInit.m
│ ├── DisplaceStr.m
│ ├── DrawRoute.m
│ ├── DrawRouteGif.m
│ ├── Mutation.m
│ ├── SelectAntigen.m
│ ├── main.m
│ └── test.gif
├── IMA解决非线性问题求解
│ ├── DecodeFun.m
│ ├── Hypermutation.m
│ ├── InitializeFun.m
│ ├── ReproduceFun.m
│ └── main.m
└── README.md
├── Particle_Swarm_Optimization
├── PSO-Toolbox
│ ├── main.m
│ └── pso_func.m
└── PSO-basic
│ ├── DrawGriewank.m
│ ├── DrawRastrigin.m
│ ├── Griewank.m
│ ├── PSO.m
│ ├── Rastrigin.m
│ ├── fitness.m
│ └── main.m
├── README.md
└── Smart-Algorithm.iml
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决函数最优解/F.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function z = F(x, y)
2 | z = -(x.^4 + 3 * y.^4 - 0.2 * cos(3 * pi * x) - 0.4 * cos(4 * pi * y) + 0.6);
3 |
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决函数最优解/SolveMax.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/LiYangSir/Smart-Algorithm/b0653c32aa1ed4ce0d97c8c138f93c9fde75ae6d/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决函数最优解/SolveMax.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决机器人路径规划/DrawRoute.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function DrawRoute(X, Y)
2 | for i = 2: length(X)
3 | plot([X(i - 1), X(i)], [Y(i - 1), Y(i)], 'b-')
4 | hold on
5 | pause(0.1)
6 | frame = getframe(gcf);
7 | imind = frame2im(frame);
8 | [imind, cm] = rgb2ind(imind, 256);
9 | if i == 2
10 | imwrite(imind, cm, 'test.gif', 'gif', 'Loopcount', inf, 'DelayTime', 1e-4);
11 | else
12 | imwrite(imind, cm, 'test.gif', 'gif', 'WriteMode', 'append', 'DelayTime', 1e-4);
13 | end
14 |
15 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决机器人路径规划/G2D.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | function D=G2D(G)
2 | l=size(G,1);
3 | D=zeros(l*l,l*l);
4 | for i=1:l
5 | for j=1:l
6 | if G(i,j)==0
7 | for m=1:l
8 | for n=1:l
9 | if G(m,n)==0
10 | im=abs(i-m);jn=abs(j-n);
11 | if im+jn==1||(im==1&&jn==1)
12 | D((i-1)*l+j,(m-1)*l+n)=(im+jn)^0.5;
13 | end
14 | end
15 | end
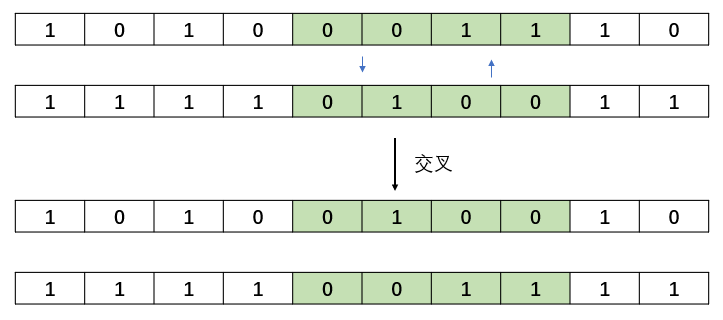
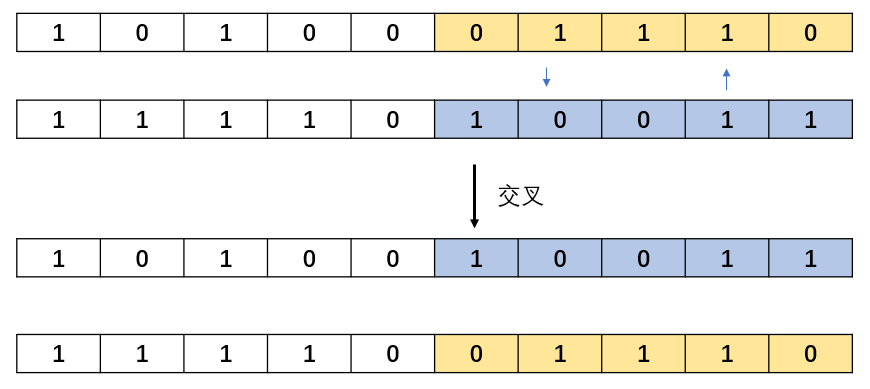
16 | end
17 | end
18 | end
19 | end
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决机器人路径规划/Magine.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/LiYangSir/Smart-Algorithm/b0653c32aa1ed4ce0d97c8c138f93c9fde75ae6d/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决机器人路径规划/Magine.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决机器人路径规划/main.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/LiYangSir/Smart-Algorithm/b0653c32aa1ed4ce0d97c8c138f93c9fde75ae6d/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决机器人路径规划/main.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决机器人路径规划/test.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/LiYangSir/Smart-Algorithm/b0653c32aa1ed4ce0d97c8c138f93c9fde75ae6d/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AC解决机器人路径规划/test.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AOC解决TSP问题/DrawRoute.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/LiYangSir/Smart-Algorithm/b0653c32aa1ed4ce0d97c8c138f93c9fde75ae6d/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AOC解决TSP问题/DrawRoute.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AOC解决TSP问题/TSP.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/LiYangSir/Smart-Algorithm/b0653c32aa1ed4ce0d97c8c138f93c9fde75ae6d/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AOC解决TSP问题/TSP.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AOC解决TSP问题/mian.m:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/LiYangSir/Smart-Algorithm/b0653c32aa1ed4ce0d97c8c138f93c9fde75ae6d/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AOC解决TSP问题/mian.m
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AOC解决TSP问题/res.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/LiYangSir/Smart-Algorithm/b0653c32aa1ed4ce0d97c8c138f93c9fde75ae6d/Ant_Colony_Optimization/ACO_MatLab/AOC解决TSP问题/res.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ant_Colony_Optimization/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | AntColonyOptimization蚁群算法
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | ------
10 |
11 | > 前言:本文主要围绕解决TSP旅行商问题展开,对于机器人的路线规划以及非线性方程求解的问题等解决方案大家可以直接参考[github源码地址](https://github.com/LiYangSir/SmartAlgorithm),
12 | > 对于一些其他优化算法例如遗传算法解决一些现实问题都有实现!! **欢迎小伙伴的star哦~~ 🤭**
13 |
14 | 先看一下效果图:
15 |
16 | **蚁群算法解决TSP问题:**
17 |
18 |
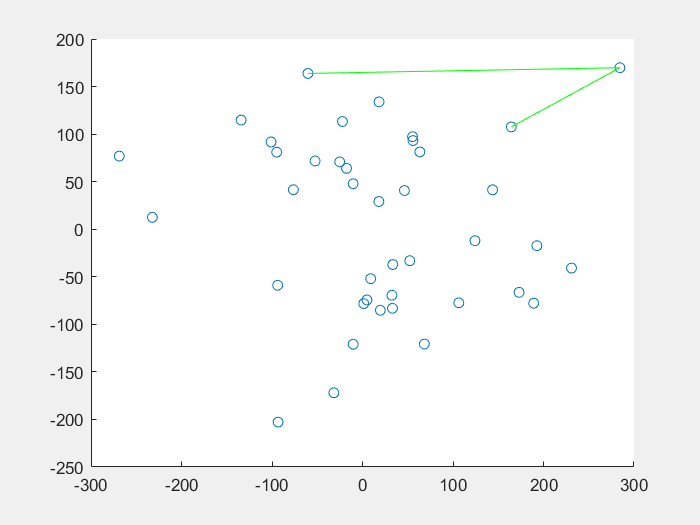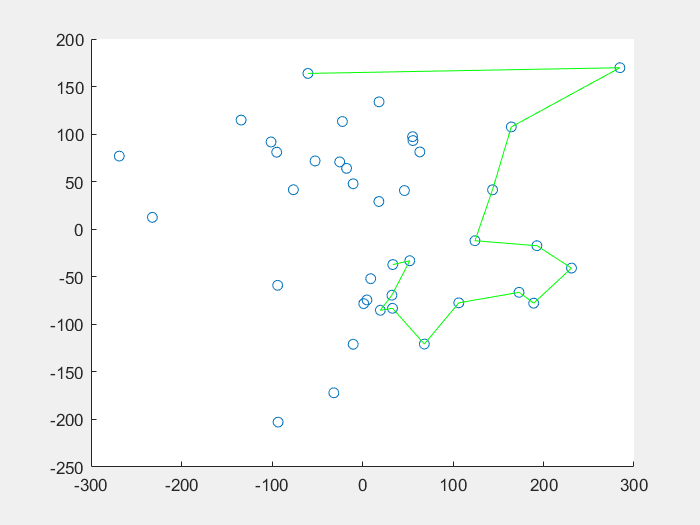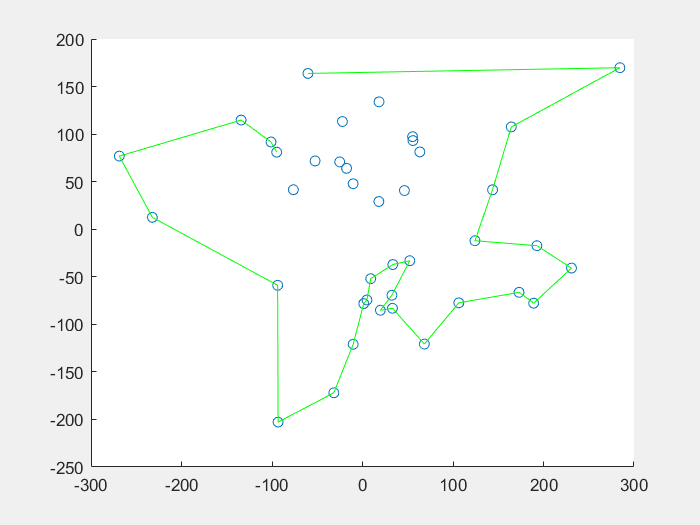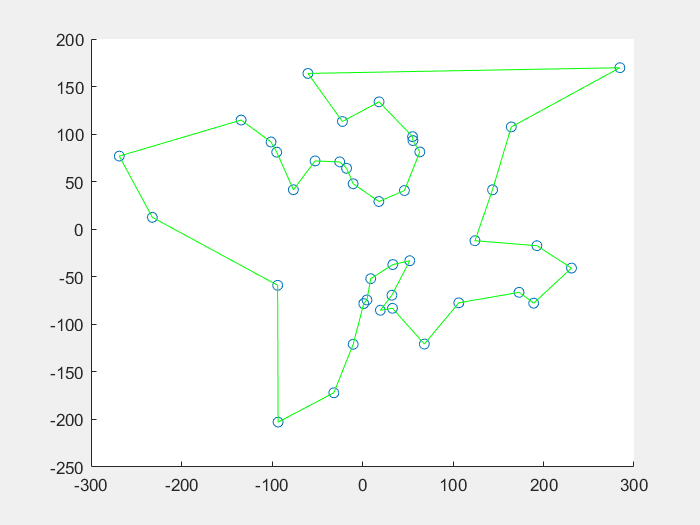
19 |
23 |
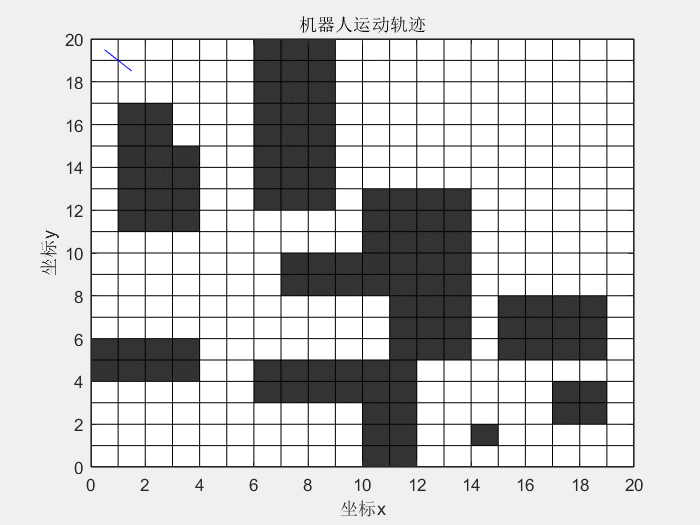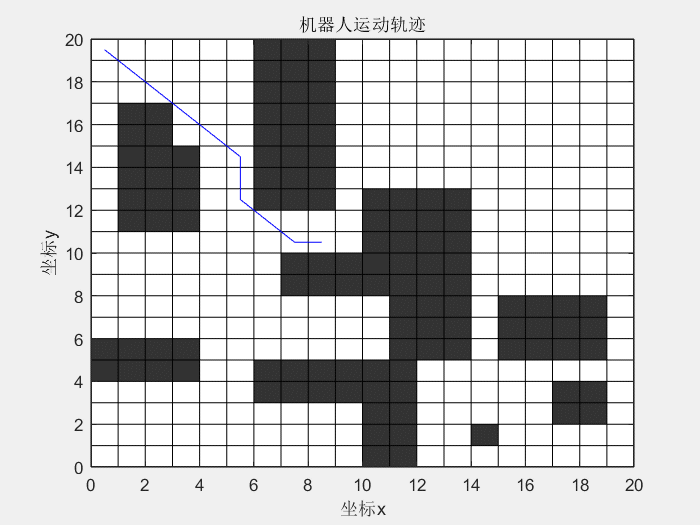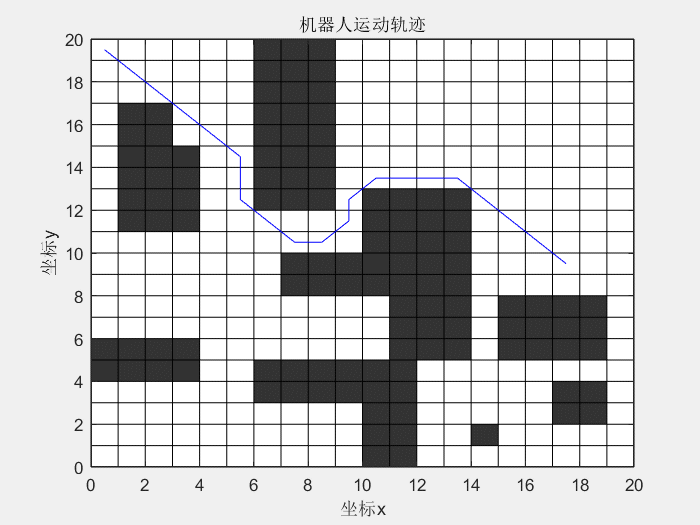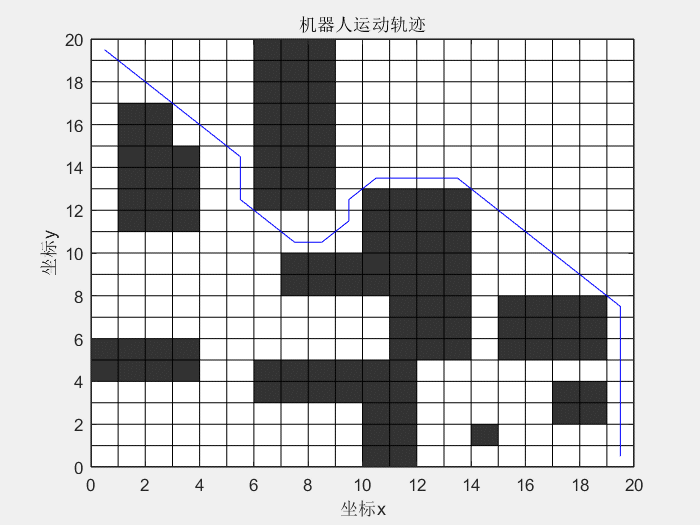
24 |
259 |
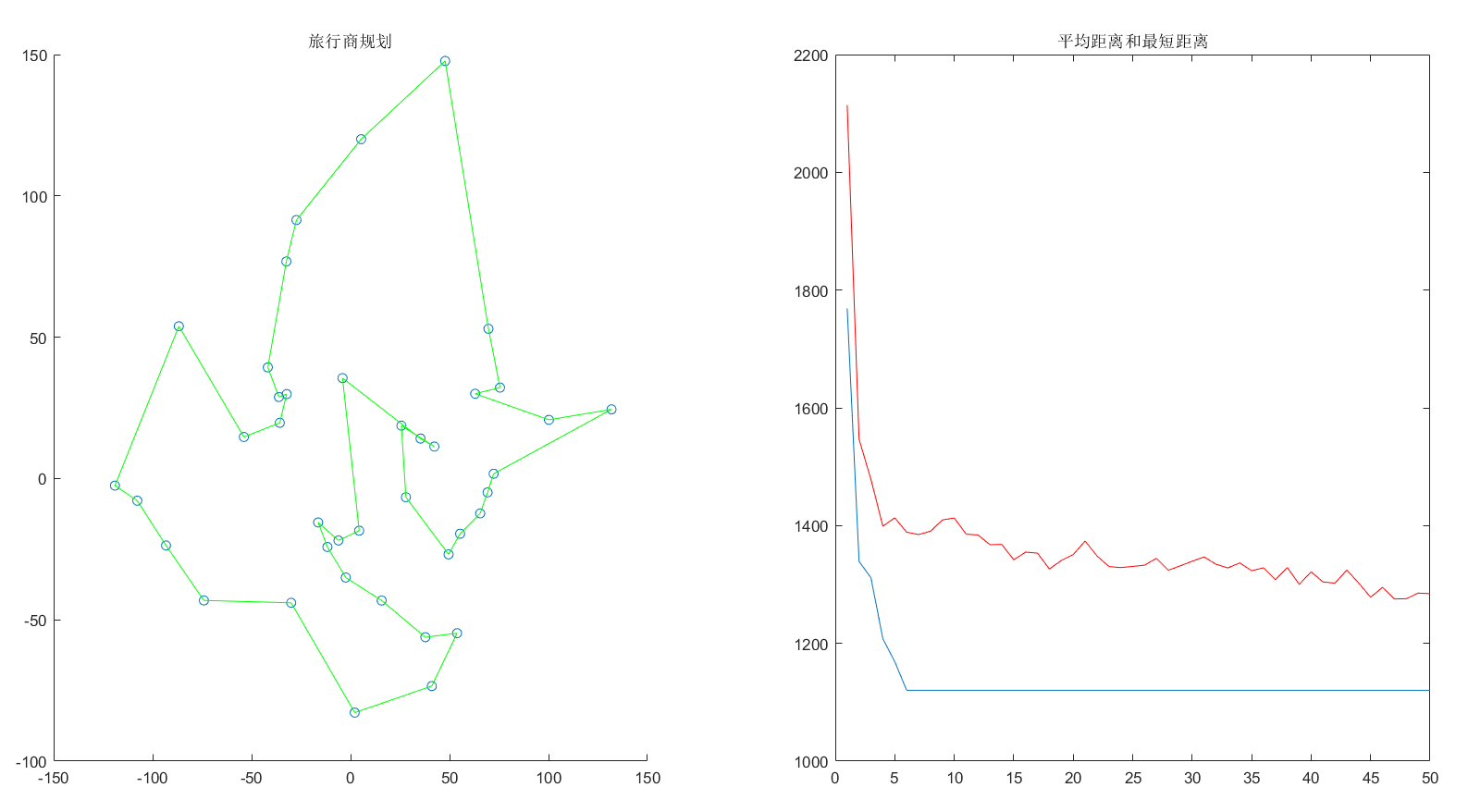
260 |
优化算法之遗传算法
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | -----
10 |
11 | [TOC]
12 |
13 | ## 1、什么是遗传算法
14 |
15 | 我们了解过深度学习的都知道,我们在进行网络优化的过程都是通过反向传播求导进行参数的不断优化,而这种类型的优化参数采用前向传播的方式继续优化网络,不断找出最优解,或者最优的参数。很多的优化算法都来自于大自然的启发,来一种算法叫做蚁群算法,灵感就是来自于蚂蚁,所以观察大自然有时也是灵感的来源。
16 |
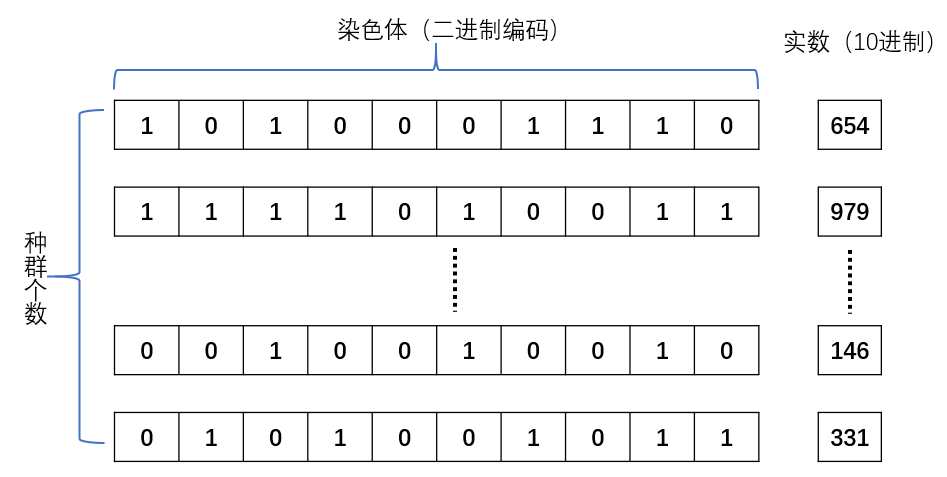
17 | 遗传算法,也叫Genetic Algorithm,简称 GA 算法他既然叫遗传算法,那么遗传之中必然有基因,那么基因染色体(Chromosome)就是它的需要调节的参数。我们在生物中了解到,大自然的法则是“物竞天择,适者生存”,我觉得遗传算法更适用于“**优胜劣汰**”。
18 | + 优:最优解,
19 | + 劣:非最优解。
20 |
21 | ## 2、遗传算法名词解释
22 |
23 | 下面主要通过疑问提问题的方式进行解释遗传算法当中的适应度函数、选择、交叉、变异这几个名词。
24 |
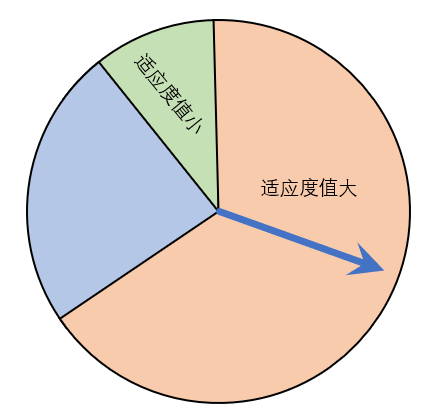
25 | **1. 都知道优胜劣汰,那怎么实现优胜劣汰呢?**
26 | 很重要的一个环节就是**选择**,也称之为“大自然的选择”,大自然怎么选择呢,大自然会抛弃掉一些适应能力差的,在程序当中就是离最优解较远的解,会被抛弃掉。
27 |
28 | **2. 如何实现大自然的选择呢?**
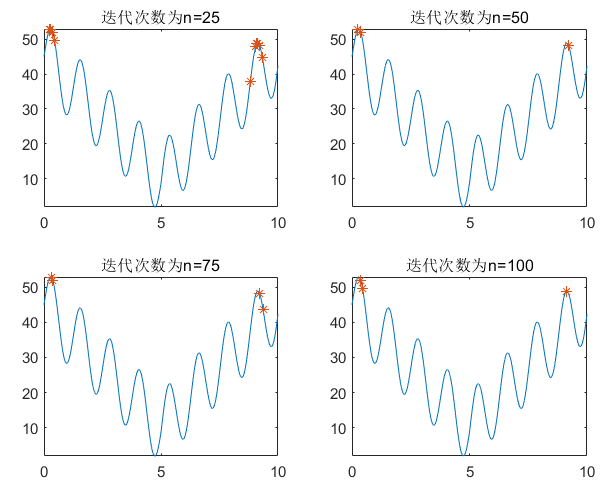
29 | 这里我们会引入轮盘赌法,进行大自然的选择。选择一些离最优解较近的个体。还有一些其他的经典的选择办法,例如锦标赛法进行选择。
30 |
31 | **3. 只靠选择就可以实现吗?那样会不会陷入局部最优解?**
32 | 如果只靠选择进行调优,那么最终的结果会受到初始种群的影响,只是在初始种群的群体中进行选择,得出的最优解也是在初始群体中的最优解。所以就需要引入大自然当中的“啪啪啪”,也叫**交叉**。正所谓“龙生龙,凤生风,老鼠生下来就会打洞”,所以说两个优秀的基因进行交叉可以将两者优秀的基因遗传给一代,也增加了群体的基因多样性,但这种不一定就是最好的,也可能发生“夭折”。
33 |
34 | **4. 大自然的选择好像不仅如此,还有变异吧?**
35 | 为了更好的模拟大自然的选择规律,来需要进入**变异**,变异发生的概率很低,但也是增加群体多样性的条件,和交叉相同,变异求解出来的不一定是最好的解,也会出现“夭折”。
36 |
37 | **5. 上面只是大自然的规则,那么大自然的环境又是什么呢?**
38 | 优秀的基因并不是独立的,就像北极熊不会存活在热带雨林一样。只有适合环境的基因才是优秀的,所以说基因具有相对性,环境是挑选基因的先决条件,这里的环境就是**适应度函数**。个体用过适应度函数后得到的结果越大,表明更加适合这里的环境,那么保留下来的概率越大。反之则越小。
39 |
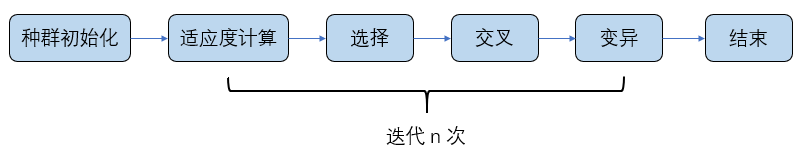
40 | ## 3、遗传算法的程序实现
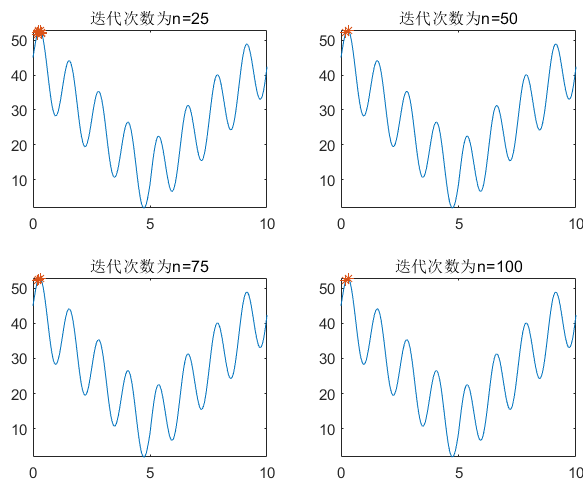
41 |
42 | 正所谓 “不结合代码的解释都是** ” 。下面结合代码来梳理遗传算法的实现。
43 |
44 |
45 |
73 |
74 |
105 |
106 |
 139 |
140 |
141 | **随机距离交叉(本例实现):**
142 |
139 |
140 |
141 | **随机距离交叉(本例实现):**
142 |
143 |
144 |
 170 |
171 |
172 | **程序实现:**
173 | ```matlab
174 | % pop: 总种群
175 | % pm: 变异概率
176 | function [newpop] = mutation(pop,pm)
177 | [px,py] = size(pop);
178 | newpop = ones(size(pop));
179 | for i = 1:px
180 | if(rand
198 |
170 |
171 |
172 | **程序实现:**
173 | ```matlab
174 | % pop: 总种群
175 | % pm: 变异概率
176 | function [newpop] = mutation(pop,pm)
177 | [px,py] = size(pop);
178 | newpop = ones(size(pop));
179 | for i = 1:px
180 | if(rand
198 |  199 |
200 |
201 | **程序实现:**
202 | ```matlab
203 | clear;
204 | clc;
205 | % 总种群数量
206 | popsize=100;
207 | % 染色体长度
208 | chromlength=10;
209 | % 交叉概率
210 | pc = 0.6;
211 | % 变异概率
212 | pm = 0.001;
213 | %初始化种群
214 | pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength); % 100 * 10
215 |
216 | for i = 1:100
217 | objvalue = cal_objvalue(pop);
218 | fitvalue = objvalue;
219 | newpop = selection(pop,fitvalue);
220 | newpop = crossover(newpop,pc);
221 | newpop = mutation(newpop,pm);
222 | pop = newpop;
223 | [bestindividual,bestfit] = best(pop,fitvalue);
224 | x2 = binary2decimal(bestindividual); % 最优解 x 值
225 | x1 = binary2decimal(newpop);
226 | y1 = cal_objvalue(newpop);
227 | if mod(i,20) == 0
228 | figure;
229 | fplot(@(x)10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10,[0 10]);
230 | hold on;
231 | plot(x1,y1,'*');
232 | title(['迭代次数:%d' num2str(i)]);
233 | end
234 | end
235 | fprintf('The best X is --->>%5.2f\n',x2);
236 | fprintf('The best Y is --->>%5.2f\n',bestfit);
237 | ```
238 |
239 | ## 4、运行结果展示
240 |
199 |
200 |
201 | **程序实现:**
202 | ```matlab
203 | clear;
204 | clc;
205 | % 总种群数量
206 | popsize=100;
207 | % 染色体长度
208 | chromlength=10;
209 | % 交叉概率
210 | pc = 0.6;
211 | % 变异概率
212 | pm = 0.001;
213 | %初始化种群
214 | pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength); % 100 * 10
215 |
216 | for i = 1:100
217 | objvalue = cal_objvalue(pop);
218 | fitvalue = objvalue;
219 | newpop = selection(pop,fitvalue);
220 | newpop = crossover(newpop,pc);
221 | newpop = mutation(newpop,pm);
222 | pop = newpop;
223 | [bestindividual,bestfit] = best(pop,fitvalue);
224 | x2 = binary2decimal(bestindividual); % 最优解 x 值
225 | x1 = binary2decimal(newpop);
226 | y1 = cal_objvalue(newpop);
227 | if mod(i,20) == 0
228 | figure;
229 | fplot(@(x)10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10,[0 10]);
230 | hold on;
231 | plot(x1,y1,'*');
232 | title(['迭代次数:%d' num2str(i)]);
233 | end
234 | end
235 | fprintf('The best X is --->>%5.2f\n',x2);
236 | fprintf('The best Y is --->>%5.2f\n',bestfit);
237 | ```
238 |
239 | ## 4、运行结果展示
240 |
241 |
242 |
248 |
249 |
智能算法之Genetic Algorithm遗传算法
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | -----
11 | > 前言:本文主要围绕 Matlab 的实现展开,Java版本以及Python版本参考文章最后的源码地址,MatLab和python实现大致相同,Java较为不同。
12 |
13 |
14 | ## 1、什么是遗传算法
15 |
16 | 我们了解过深度学习的都知道,我们在进行网络优化的过程都是通过反向传播求导进行参数的不断优化,而这种类型的优化参数采用前向传播的方式继续优化网络,不断找出最优解,或者最优的参数。很多的优化算法都来自于大自然的启发,来一种算法叫做蚁群算法,灵感就是来自于蚂蚁,所以观察大自然有时也是灵感的来源。
17 |
18 | 遗传算法,也叫Genetic Algorithm,简称 GA 算法他既然叫遗传算法,那么遗传之中必然有基因,那么基因染色体(Chromosome)就是它的需要调节的参数。我们在生物中了解到,大自然的法则是“物竞天择,适者生存”,我觉得遗传算法更适用于“**优胜劣汰**”。
19 | + 优:最优解,
20 | + 劣:非最优解。
21 |
22 | ## 2、遗传算法名词解释
23 |
24 | 下面主要通过疑问提问题的方式进行解释遗传算法当中的适应度函数、选择、交叉、变异这几个名词。
25 |
26 | **1. 都知道优胜劣汰,那怎么实现优胜劣汰呢?**
27 | 很重要的一个环节就是**选择**,也称之为“大自然的选择”,大自然怎么选择呢,大自然会抛弃掉一些适应能力差的,在程序当中就是离最优解较远的解,会被抛弃掉。
28 |
29 | **2. 如何实现大自然的选择呢?**
30 | 这里我们会引入轮盘赌法,进行大自然的选择。选择一些离最优解较近的个体。还有一些其他的经典的选择办法,例如锦标赛法进行选择。
31 |
32 | **3. 只靠选择就可以实现吗?那样会不会陷入局部最优解?**
33 | 如果只靠选择进行调优,那么最终的结果会受到初始种群的影响,只是在初始种群的群体中进行选择,得出的最优解也是在初始群体中的最优解。所以就需要引入大自然当中的“啪啪啪”,也叫**交叉**。正所谓“龙生龙,凤生风,老鼠生下来就会打洞”,所以说两个优秀的基因进行交叉可以将两者优秀的基因遗传给一代,也增加了群体的基因多样性,但这种不一定就是最好的,也可能发生“夭折”。
34 |
35 | **4. 大自然的选择好像不仅如此,还有变异吧?**
36 | 为了更好的模拟大自然的选择规律,来需要进入**变异**,变异发生的概率很低,但也是增加群体多样性的条件,和交叉相同,变异求解出来的不一定是最好的解,也会出现“夭折”。
37 |
38 | **5. 上面只是大自然的规则,那么大自然的环境又是什么呢?**
39 | 优秀的基因并不是独立的,就像北极熊不会存活在热带雨林一样。只有适合环境的基因才是优秀的,所以说基因具有相对性,环境是挑选基因的先决条件,这里的环境就是**适应度函数**。个体用过适应度函数后得到的结果越大,表明更加适合这里的环境,那么保留下来的概率越大。反之则越小。
40 |
41 | ## 3、遗传算法的程序实现
42 |
43 | 正所谓 “不结合代码的解释都是** ” 。下面结合代码来梳理遗传算法的实现。
44 |
45 |

46 |
74 |

75 |
106 |

107 |
 140 |
141 |
142 | **随机距离交叉(本例实现):**
143 |
140 |
141 |
142 | **随机距离交叉(本例实现):**
143 |
144 |

145 |
 171 |
172 |
173 | **程序实现:**
174 | ```matlab
175 | % pop: 总种群
176 | % pm: 变异概率
177 | function [newpop] = mutation(pop,pm)
178 | [px,py] = size(pop);
179 | newpop = ones(size(pop));
180 | for i = 1:px
181 | if(rand
199 |
171 |
172 |
173 | **程序实现:**
174 | ```matlab
175 | % pop: 总种群
176 | % pm: 变异概率
177 | function [newpop] = mutation(pop,pm)
178 | [px,py] = size(pop);
179 | newpop = ones(size(pop));
180 | for i = 1:px
181 | if(rand
199 |  200 |
201 |
202 | **程序实现:**
203 | ```matlab
204 | clear;
205 | clc;
206 | % 总种群数量
207 | popsize=100;
208 | % 染色体长度
209 | chromlength=10;
210 | % 交叉概率
211 | pc = 0.6;
212 | % 变异概率
213 | pm = 0.001;
214 | %初始化种群
215 | pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength); % 100 * 10
216 |
217 | for i = 1:100
218 | objvalue = cal_objvalue(pop);
219 | fitvalue = objvalue;
220 | newpop = selection(pop,fitvalue);
221 | newpop = crossover(newpop,pc);
222 | newpop = mutation(newpop,pm);
223 | pop = newpop;
224 | [bestindividual,bestfit] = best(pop,fitvalue);
225 | x2 = binary2decimal(bestindividual); % 最优解 x 值
226 | x1 = binary2decimal(newpop);
227 | y1 = cal_objvalue(newpop);
228 | if mod(i,20) == 0
229 | figure;
230 | fplot(@(x)10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10,[0 10]);
231 | hold on;
232 | plot(x1,y1,'*');
233 | title(['迭代次数:%d' num2str(i)]);
234 | end
235 | end
236 | fprintf('The best X is --->>%5.2f\n',x2);
237 | fprintf('The best Y is --->>%5.2f\n',bestfit);
238 | ```
239 |
240 | ## 4、运行结果展示
241 |
200 |
201 |
202 | **程序实现:**
203 | ```matlab
204 | clear;
205 | clc;
206 | % 总种群数量
207 | popsize=100;
208 | % 染色体长度
209 | chromlength=10;
210 | % 交叉概率
211 | pc = 0.6;
212 | % 变异概率
213 | pm = 0.001;
214 | %初始化种群
215 | pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength); % 100 * 10
216 |
217 | for i = 1:100
218 | objvalue = cal_objvalue(pop);
219 | fitvalue = objvalue;
220 | newpop = selection(pop,fitvalue);
221 | newpop = crossover(newpop,pc);
222 | newpop = mutation(newpop,pm);
223 | pop = newpop;
224 | [bestindividual,bestfit] = best(pop,fitvalue);
225 | x2 = binary2decimal(bestindividual); % 最优解 x 值
226 | x1 = binary2decimal(newpop);
227 | y1 = cal_objvalue(newpop);
228 | if mod(i,20) == 0
229 | figure;
230 | fplot(@(x)10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10,[0 10]);
231 | hold on;
232 | plot(x1,y1,'*');
233 | title(['迭代次数:%d' num2str(i)]);
234 | end
235 | end
236 | fprintf('The best X is --->>%5.2f\n',x2);
237 | fprintf('The best Y is --->>%5.2f\n',bestfit);
238 | ```
239 |
240 | ## 4、运行结果展示
241 |
242 |

243 |
249 |

250 |
Immunity Algorithm免疫算法
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | ------
11 | > 前言:本文主要围绕解决TSP旅行商问题展开,对于机器人的路线规划以及非线性方程求解的问题等解决方案大家可以直接参考[github源码地址](https://github.com/LiYangSir/SmartAlgorithm),
12 | > 对于一些其他智能算法例如遗传算法解决一些现实问题都有实现!! **欢迎小伙伴的star哦~~ 🤭**
13 |
14 |
15 | **效果图:**
16 |
17 |
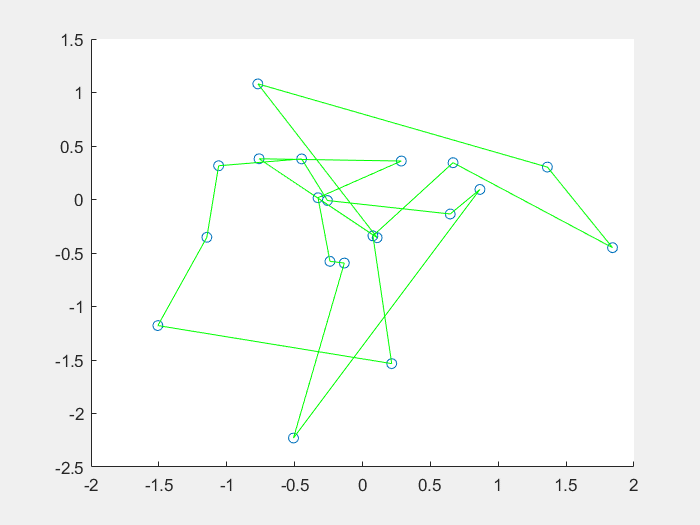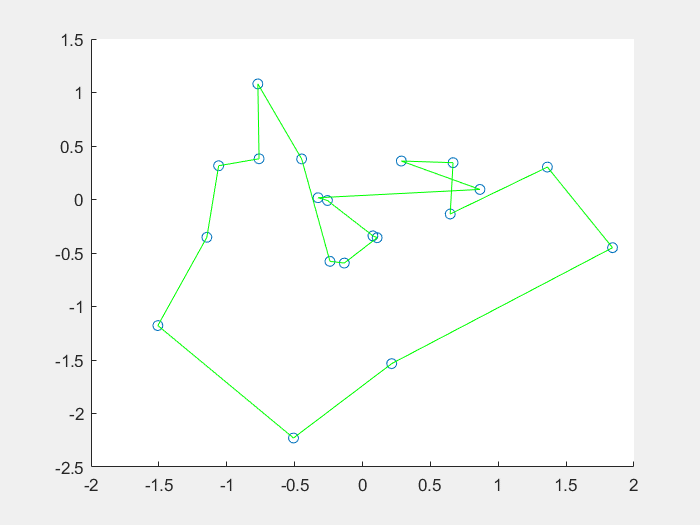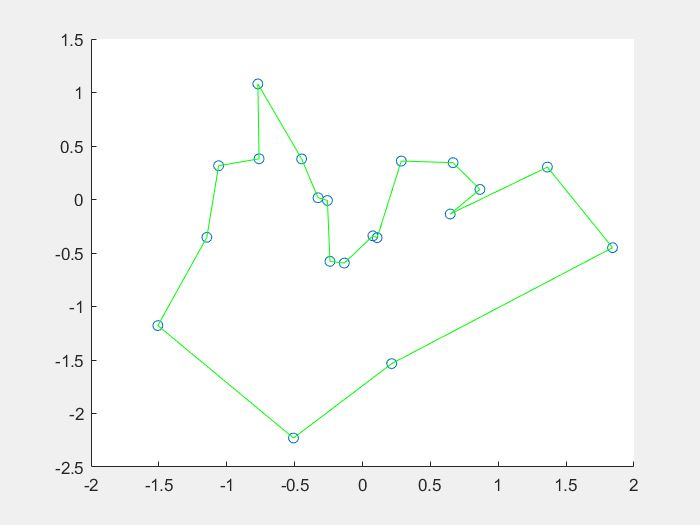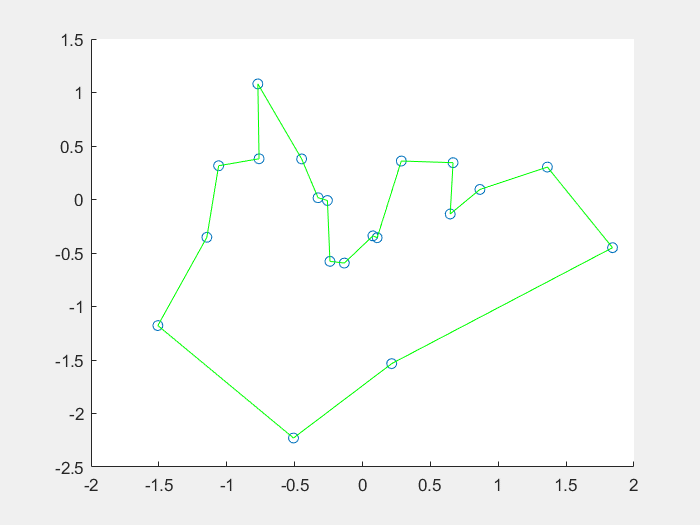
18 |
摘自百度百科
23 |
24 | 也就是说,免疫算法的思想来自于生物体的免疫机制,构造具有动态性和自适应性的信息防御机制,用来抵抗外部无用的有害信息的侵入(*退化解*),从而保证信息的有效性和无害性(*最优解*)。
25 | **注**:退化解的来自于变异等操作过后的适应度值低于父类的解。
26 |
27 | ### 1.1 生物免疫系统
28 |
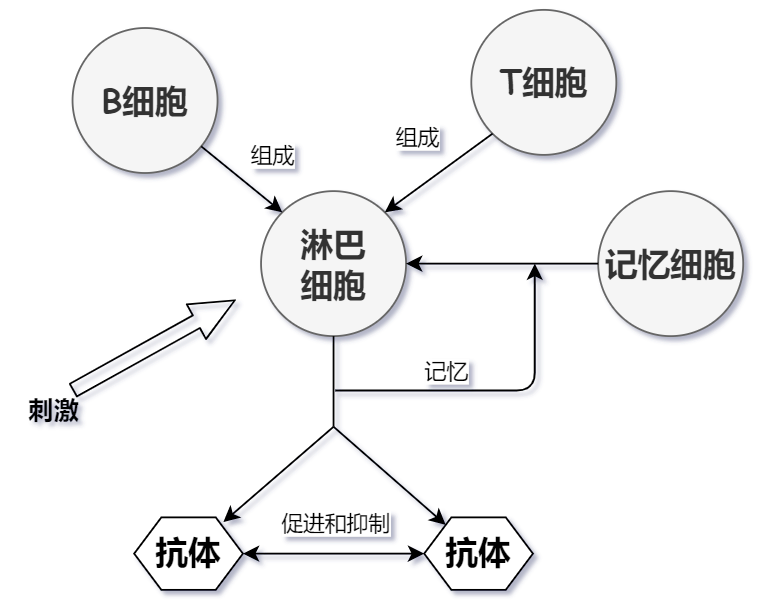
29 | 在生物课上学过,免疫系统的构成元素主要是淋巴细胞,淋巴细胞包括B细胞和T细胞。
30 | + T细胞主要在收到抗原刺激后可以分化成淋巴母细胞,产生多种淋巴因子,引起细胞免疫反应。
31 | + B细胞又称为抗体形成细胞,可以产生抗体,抗体会同抗原产生一系列的反应,最后通过吞噬细胞的作用来消灭抗原。并且抗体具有专一性,而且免疫系统具备识别能力和记忆能力,可以对旧抗原做出更快的反应。
32 |
33 |
34 |
61 |

62 |
72 |
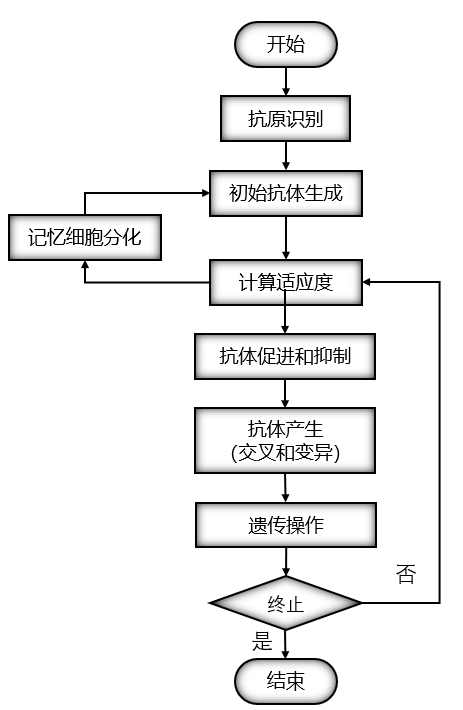
73 |
88 |
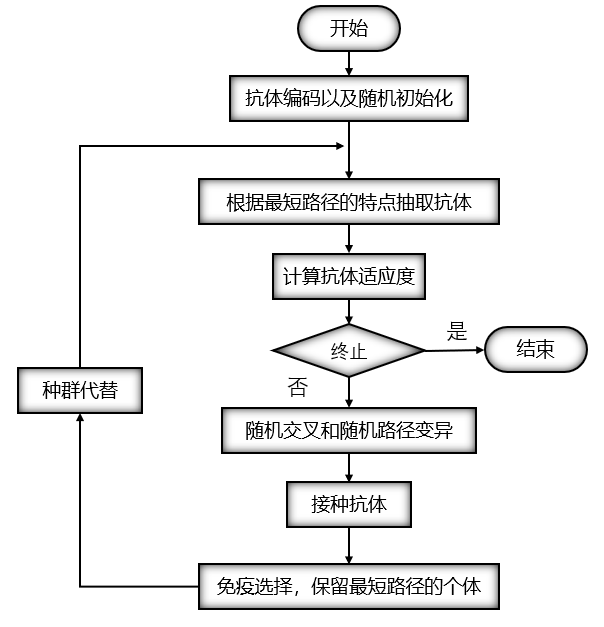
89 |
282 |
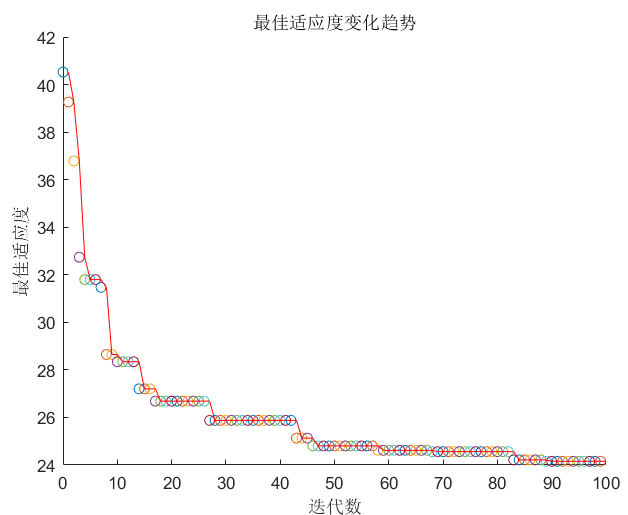
283 |
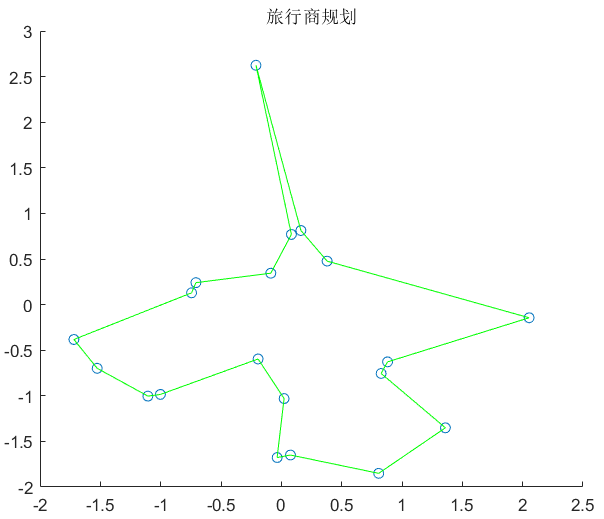
284 |
Smart Algorithm
2 |
3 | >智能算法是路线规划、深度学习等等一系列领域所使用的优化算法,是算法进阶之路的必备之路。
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | ------
13 |
14 | ### 简介
15 |
16 | 主要针对目前主流的算法进行实现,例如遗传算法、粒子群算法、模拟退火算法、免疫算法、蚁群算法等等一系列的算法。
17 |
18 | > [个人主页](http://quguai.cn) | [CSDN](https://me.csdn.net/qq_41503660) | 微信公众号: TeaUrn
19 |
20 | ### 开始使用
21 |
22 | 智能算法-遗传算法、蚁群算法、粒子群算法实现。实现版本Java,Python,MatLab多版本实现。具体详细说明点击下面连接针对每个算法有着详细的说明。
23 |
24 | [蚁群算法:Ant_Colony_Optimization](/Ant_Colony_Optimization)
25 |
26 | [遗传算法:Genetic_Algorithm](/Genetic_Algorithm)
27 |
28 | [免疫算法:Immunity_Algorithm](/Immunity_Algorithm)
29 |
30 | [粒子群:Particle Swarm Optimization](/Particle_Swarm_Optimization)
31 |
32 |
33 | ### 联系方式:
34 | 微信公众号:**TeaUrn**
35 | 或者扫描下方二维码进行关注。里面有惊喜等你哦~~
36 |
37 |  38 |
39 | ### 捐赠
40 | 如果您觉得文章对您有所帮助,可以请作者喝☕。
41 |
42 | |支付宝/微信/QQ|
43 | |-------------|
44 | ||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Smart-Algorithm.iml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
38 |
39 | ### 捐赠
40 | 如果您觉得文章对您有所帮助,可以请作者喝☕。
41 |
42 | |支付宝/微信/QQ|
43 | |-------------|
44 | ||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Smart-Algorithm.iml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 19 |
19 |  19 |
19 |  24 |
24 |  260 |
260 |  45 |
45 |  74 |
74 |  106 |
106 |  139 |
140 |
141 | **随机距离交叉(本例实现):**
142 |
139 |
140 |
141 | **随机距离交叉(本例实现):**
142 |  144 |
144 |  170 |
171 |
172 | **程序实现:**
173 | ```matlab
174 | % pop: 总种群
175 | % pm: 变异概率
176 | function [newpop] = mutation(pop,pm)
177 | [px,py] = size(pop);
178 | newpop = ones(size(pop));
179 | for i = 1:px
180 | if(rand
170 |
171 |
172 | **程序实现:**
173 | ```matlab
174 | % pop: 总种群
175 | % pm: 变异概率
176 | function [newpop] = mutation(pop,pm)
177 | [px,py] = size(pop);
178 | newpop = ones(size(pop));
179 | for i = 1:px
180 | if(rand 199 |
200 |
201 | **程序实现:**
202 | ```matlab
203 | clear;
204 | clc;
205 | % 总种群数量
206 | popsize=100;
207 | % 染色体长度
208 | chromlength=10;
209 | % 交叉概率
210 | pc = 0.6;
211 | % 变异概率
212 | pm = 0.001;
213 | %初始化种群
214 | pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength); % 100 * 10
215 |
216 | for i = 1:100
217 | objvalue = cal_objvalue(pop);
218 | fitvalue = objvalue;
219 | newpop = selection(pop,fitvalue);
220 | newpop = crossover(newpop,pc);
221 | newpop = mutation(newpop,pm);
222 | pop = newpop;
223 | [bestindividual,bestfit] = best(pop,fitvalue);
224 | x2 = binary2decimal(bestindividual); % 最优解 x 值
225 | x1 = binary2decimal(newpop);
226 | y1 = cal_objvalue(newpop);
227 | if mod(i,20) == 0
228 | figure;
229 | fplot(@(x)10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10,[0 10]);
230 | hold on;
231 | plot(x1,y1,'*');
232 | title(['迭代次数:%d' num2str(i)]);
233 | end
234 | end
235 | fprintf('The best X is --->>%5.2f\n',x2);
236 | fprintf('The best Y is --->>%5.2f\n',bestfit);
237 | ```
238 |
239 | ## 4、运行结果展示
240 |
199 |
200 |
201 | **程序实现:**
202 | ```matlab
203 | clear;
204 | clc;
205 | % 总种群数量
206 | popsize=100;
207 | % 染色体长度
208 | chromlength=10;
209 | % 交叉概率
210 | pc = 0.6;
211 | % 变异概率
212 | pm = 0.001;
213 | %初始化种群
214 | pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength); % 100 * 10
215 |
216 | for i = 1:100
217 | objvalue = cal_objvalue(pop);
218 | fitvalue = objvalue;
219 | newpop = selection(pop,fitvalue);
220 | newpop = crossover(newpop,pc);
221 | newpop = mutation(newpop,pm);
222 | pop = newpop;
223 | [bestindividual,bestfit] = best(pop,fitvalue);
224 | x2 = binary2decimal(bestindividual); % 最优解 x 值
225 | x1 = binary2decimal(newpop);
226 | y1 = cal_objvalue(newpop);
227 | if mod(i,20) == 0
228 | figure;
229 | fplot(@(x)10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10,[0 10]);
230 | hold on;
231 | plot(x1,y1,'*');
232 | title(['迭代次数:%d' num2str(i)]);
233 | end
234 | end
235 | fprintf('The best X is --->>%5.2f\n',x2);
236 | fprintf('The best Y is --->>%5.2f\n',bestfit);
237 | ```
238 |
239 | ## 4、运行结果展示
240 |  242 |
242 |  249 |
249 |  46 |
46 |  75 |
75 |  107 |
107 |  140 |
141 |
142 | **随机距离交叉(本例实现):**
143 |
140 |
141 |
142 | **随机距离交叉(本例实现):**
143 |  145 |
145 |  171 |
172 |
173 | **程序实现:**
174 | ```matlab
175 | % pop: 总种群
176 | % pm: 变异概率
177 | function [newpop] = mutation(pop,pm)
178 | [px,py] = size(pop);
179 | newpop = ones(size(pop));
180 | for i = 1:px
181 | if(rand
171 |
172 |
173 | **程序实现:**
174 | ```matlab
175 | % pop: 总种群
176 | % pm: 变异概率
177 | function [newpop] = mutation(pop,pm)
178 | [px,py] = size(pop);
179 | newpop = ones(size(pop));
180 | for i = 1:px
181 | if(rand 200 |
201 |
202 | **程序实现:**
203 | ```matlab
204 | clear;
205 | clc;
206 | % 总种群数量
207 | popsize=100;
208 | % 染色体长度
209 | chromlength=10;
210 | % 交叉概率
211 | pc = 0.6;
212 | % 变异概率
213 | pm = 0.001;
214 | %初始化种群
215 | pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength); % 100 * 10
216 |
217 | for i = 1:100
218 | objvalue = cal_objvalue(pop);
219 | fitvalue = objvalue;
220 | newpop = selection(pop,fitvalue);
221 | newpop = crossover(newpop,pc);
222 | newpop = mutation(newpop,pm);
223 | pop = newpop;
224 | [bestindividual,bestfit] = best(pop,fitvalue);
225 | x2 = binary2decimal(bestindividual); % 最优解 x 值
226 | x1 = binary2decimal(newpop);
227 | y1 = cal_objvalue(newpop);
228 | if mod(i,20) == 0
229 | figure;
230 | fplot(@(x)10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10,[0 10]);
231 | hold on;
232 | plot(x1,y1,'*');
233 | title(['迭代次数:%d' num2str(i)]);
234 | end
235 | end
236 | fprintf('The best X is --->>%5.2f\n',x2);
237 | fprintf('The best Y is --->>%5.2f\n',bestfit);
238 | ```
239 |
240 | ## 4、运行结果展示
241 |
200 |
201 |
202 | **程序实现:**
203 | ```matlab
204 | clear;
205 | clc;
206 | % 总种群数量
207 | popsize=100;
208 | % 染色体长度
209 | chromlength=10;
210 | % 交叉概率
211 | pc = 0.6;
212 | % 变异概率
213 | pm = 0.001;
214 | %初始化种群
215 | pop = initpop(popsize,chromlength); % 100 * 10
216 |
217 | for i = 1:100
218 | objvalue = cal_objvalue(pop);
219 | fitvalue = objvalue;
220 | newpop = selection(pop,fitvalue);
221 | newpop = crossover(newpop,pc);
222 | newpop = mutation(newpop,pm);
223 | pop = newpop;
224 | [bestindividual,bestfit] = best(pop,fitvalue);
225 | x2 = binary2decimal(bestindividual); % 最优解 x 值
226 | x1 = binary2decimal(newpop);
227 | y1 = cal_objvalue(newpop);
228 | if mod(i,20) == 0
229 | figure;
230 | fplot(@(x)10*sin(5*x)+7*abs(x-5)+10,[0 10]);
231 | hold on;
232 | plot(x1,y1,'*');
233 | title(['迭代次数:%d' num2str(i)]);
234 | end
235 | end
236 | fprintf('The best X is --->>%5.2f\n',x2);
237 | fprintf('The best Y is --->>%5.2f\n',bestfit);
238 | ```
239 |
240 | ## 4、运行结果展示
241 |  243 |
243 |  250 |
250 |  18 |
18 |  34 |
34 |  62 |
62 |  73 |
73 |  89 |
89 |  283 |
283 |  284 |
284 |  38 |
39 | ### 捐赠
40 | 如果您觉得文章对您有所帮助,可以请作者喝☕。
41 |
42 | |支付宝/微信/QQ|
43 | |-------------|
44 | ||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Smart-Algorithm.iml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
38 |
39 | ### 捐赠
40 | 如果您觉得文章对您有所帮助,可以请作者喝☕。
41 |
42 | |支付宝/微信/QQ|
43 | |-------------|
44 | ||
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Smart-Algorithm.iml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |