 9 |
9 | 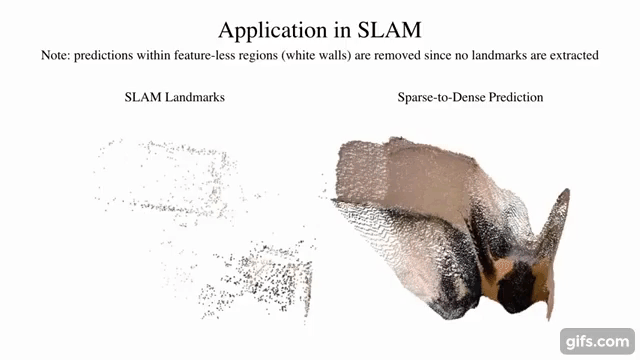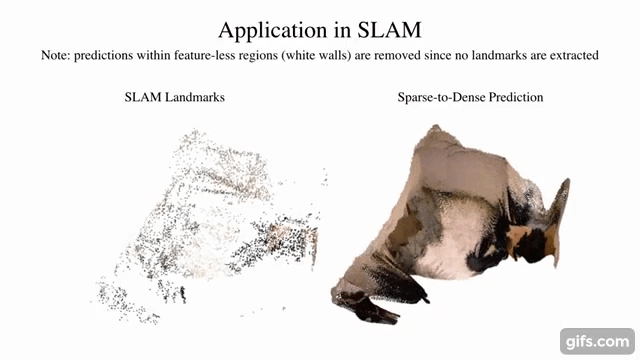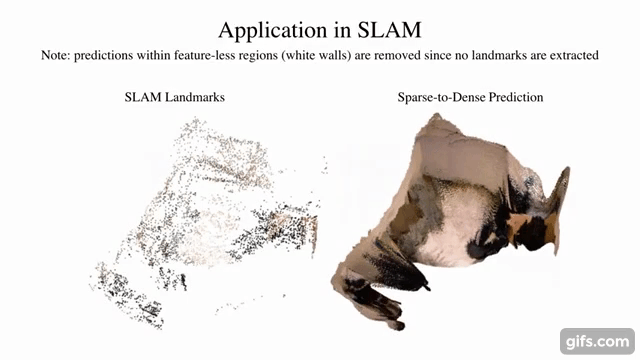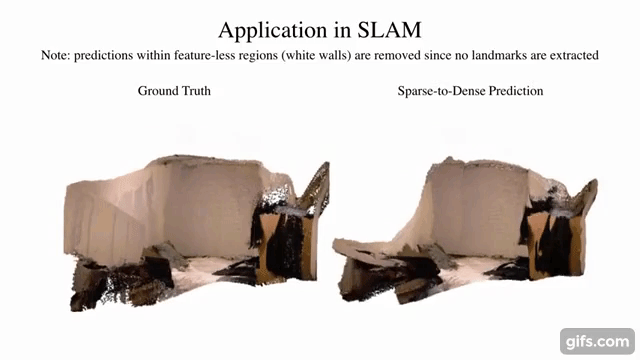 10 |
10 |
8 |  9 |
9 |  10 |
10 |
 85 |
86 | - Error metrics on KITTI dataset:
87 |
88 | | RGB | rms | rel | delta1 | delta2 | delta3 |
89 | |-----------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|
90 | | [Make3D](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5539-depth-map-prediction-from-a-single-image-using-a-multi-scale-deep-network.pdf) | 8.734 | 0.280 | 60.1 | 82.0 | 92.6 |
91 | | [Mancini et al](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.06349.pdf) (_IROS 2016_) | 7.508 | - | 31.8 | 61.7 | 81.3 |
92 | | [Eigen et al](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5539-depth-map-prediction-from-a-single-image-using-a-multi-scale-deep-network.pdf) (_NIPS 2014_) | 7.156 | **0.190** | **69.2** | 89.9 | **96.7** |
93 | | Ours-RGB | **6.266** | 0.208 | 59.1 | **90.0** | 96.2 |
94 |
95 | | RGBd-#samples | rms | rel | delta1 | delta2 | delta3 |
96 | |-----------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|
97 | | [Cadena et al](https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/18d5/f0747a23706a344f1d15b032ea22795324fa.pdf) (_RSS 2016_)-650 | 7.14 | 0.179 | 70.9 | 88.8 | 95.6 |
98 | | Ours-50 | 4.884 | 0.109 | 87.1 | 95.2 | 97.9 |
99 | | [Liao et al](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.02174) (_ICRA 2017_)-225 | 4.50 | 0.113 | 87.4 | 96.0 | 98.4 |
100 | | Ours-100 | 4.303 | 0.095 | 90.0 | 96.3 | 98.3 |
101 | | Ours-200 | 3.851 | 0.083 | 91.9 | 97.0 | 98.6 |
102 | | Ours-500| **3.378** | **0.073** | **93.5** | **97.6** | **98.9** |
103 |
104 |
85 |
86 | - Error metrics on KITTI dataset:
87 |
88 | | RGB | rms | rel | delta1 | delta2 | delta3 |
89 | |-----------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|
90 | | [Make3D](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5539-depth-map-prediction-from-a-single-image-using-a-multi-scale-deep-network.pdf) | 8.734 | 0.280 | 60.1 | 82.0 | 92.6 |
91 | | [Mancini et al](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.06349.pdf) (_IROS 2016_) | 7.508 | - | 31.8 | 61.7 | 81.3 |
92 | | [Eigen et al](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5539-depth-map-prediction-from-a-single-image-using-a-multi-scale-deep-network.pdf) (_NIPS 2014_) | 7.156 | **0.190** | **69.2** | 89.9 | **96.7** |
93 | | Ours-RGB | **6.266** | 0.208 | 59.1 | **90.0** | 96.2 |
94 |
95 | | RGBd-#samples | rms | rel | delta1 | delta2 | delta3 |
96 | |-----------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|
97 | | [Cadena et al](https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/18d5/f0747a23706a344f1d15b032ea22795324fa.pdf) (_RSS 2016_)-650 | 7.14 | 0.179 | 70.9 | 88.8 | 95.6 |
98 | | Ours-50 | 4.884 | 0.109 | 87.1 | 95.2 | 97.9 |
99 | | [Liao et al](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.02174) (_ICRA 2017_)-225 | 4.50 | 0.113 | 87.4 | 96.0 | 98.4 |
100 | | Ours-100 | 4.303 | 0.095 | 90.0 | 96.3 | 98.3 |
101 | | Ours-200 | 3.851 | 0.083 | 91.9 | 97.0 | 98.6 |
102 | | Ours-500| **3.378** | **0.073** | **93.5** | **97.6** | **98.9** |
103 |
104 |  105 |
106 | Note: our networks are trained on the KITTI odometry dataset, using only sparse labels from laser measurements.
107 |
108 | ## Citation
109 | If you use our code or method in your work, please cite:
110 |
111 | @article{Ma2017SparseToDense,
112 | title={Sparse-to-Dense: Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth Samples and a Single Image},
113 | author={Ma, Fangchang and Karaman, Sertac},
114 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.07492},
115 | year={2017}
116 | }
117 |
118 | Please direct any questions to [Fangchang Ma](http://www.mit.edu/~fcma) at fcma@mit.edu.
119 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/nyu_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import os.path
3 | import cv2 # opencv的python版本
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import torch.utils.data as data
6 | import h5py # HDF5的python版本
7 | import transforms
8 | from PIL import Image
9 |
10 | IMG_EXTENSIONS = [
11 | '.h5',
12 | ]
13 |
14 | def is_image_file(filename):
15 | # return any(): 只要迭代器中有一个元素为真就返回为真。
16 | # 详见https://blog.csdn.net/heatdeath/article/details/70178511
17 | # 详见https://blog.csdn.net/u013630349/article/details/47374333
18 | # 其中,...for...in...是迭代器(iterable)
19 | return any(filename.endswith(extension) for extension in IMG_EXTENSIONS)
20 |
21 | def find_classes(dir):
22 | # ...for...in...if... 挑选出in后面的内容中符合if条件的元素,组成一个新的list
23 | # 详见http://www.jb51.net/article/86987.htm
24 | classes = [d for d in os.listdir(dir) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(dir, d))]
25 | classes.sort() # 升序排列
26 | # Python中[],(),{}的区别:
27 | # {}表示字典,[]表示数组,()表示元组
28 | # 数组的值可以改变,可以使用切片获取部分数据
29 | # 元组的值一旦设置,不可更改,不可使用切片
30 | # 详见https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/484920124.html
31 | class_to_idx = {classes[i]: i for i in range(len(classes))}
32 | return classes, class_to_idx
33 |
34 | # 这个函数可以用于生成自己的数据集
35 | def make_dataset(dir, class_to_idx):
36 | images = [] # 存放图片序号的数组
37 | # dir是路径
38 | dir = os.path.expanduser(dir)
39 | for target in sorted(os.listdir(dir)): # sorted(): 输出排序后的列表 升序排列
40 | # print(target)
41 | # target只是文件名,不含路径。为了获得文件的完整路径,用os.path.join(dirpath, name)
42 | d = os.path.join(dir, target)
43 | if not os.path.isdir(d):
44 | continue
45 |
46 | for root, _, fnames in sorted(os.walk(d)): # tuple: 元组,数组
47 | for fname in sorted(fnames):
48 | if is_image_file(fname):
49 | path = os.path.join(root, fname)
50 | item = (path, class_to_idx[target])
51 | images.append(item) # append()用于在列表末尾添加新的对象,和C++中的push_back()一样
52 |
53 | return images
54 |
55 |
56 | def h5_loader(path):
57 | # 关于HDF5的文件操作,详见https://blog.csdn.net/yudf2010/article/details/50353292
58 | h5f = h5py.File(path, "r") # r是读的意思
59 | rgb = np.array(h5f['rgb']) # 使用array()函数可以将python的array_like数据转变成数组形式,使用matrix()函数转变成矩阵形式。
60 | # 基于习惯,在实际使用中较常用array而少用matrix来表示矩阵。
61 | rgb = np.transpose(rgb, (1, 2, 0)) # 关于np.transpose()对高维数组的转置,详见https://www.cnblogs.com/sunshinewang/p/6893503.html
62 | depth = np.array(h5f['depth'])
63 |
64 | return rgb, depth
65 |
66 | iheight, iwidth = 480, 640 # raw image size
67 | oheight, owidth = 228, 304 # image size after pre-processing
68 | color_jitter = transforms.ColorJitter(0.4, 0.4, 0.4)
69 |
70 | # 数据增强(论文中的方法)
71 | def train_transform(rgb, depth):
72 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
73 | # print("scale factor s={}".format(s))
74 | depth_np = depth / s
75 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
76 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
77 |
78 | # perform 1st part of data augmentation
79 | transform = transforms.Compose([
80 | transforms.Resize(250.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation is very slow
81 | transforms.Rotate(angle),
82 | transforms.Resize(s),
83 | transforms.CenterCrop((oheight, owidth)),
84 | transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
85 | ])
86 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
87 |
88 | # random color jittering
89 | rgb_np = color_jitter(rgb_np)
90 |
91 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
92 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
93 |
94 | return rgb_np, depth_np
95 |
96 | # 数据增强(论文中的方法)
97 | def val_transform(rgb, depth):
98 | depth_np = depth
99 |
100 | # perform 1st part of data augmentation
101 | transform = transforms.Compose([
102 | transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight),
103 | transforms.CenterCrop((oheight, owidth)),
104 | ])
105 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
106 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
107 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
108 |
109 | return rgb_np, depth_np
110 |
111 | def rgb2grayscale(rgb):
112 | return rgb[:,:,0] * 0.2989 + rgb[:,:,1] * 0.587 + rgb[:,:,2] * 0.114
113 |
114 | # 仅限RGB图像
115 | def MatrixTocvMat(data):
116 | data = data*255
117 | im = Image.fromarray(data.astype(np.uint8))
118 | new_im = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(im),cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
119 | return new_im
120 |
121 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
122 |
123 | class NYUDataset(data.Dataset):
124 | modality_names = ['rgb', 'rgbd', 'd']
125 |
126 | def __init__(self, root, type, modality='rgb', num_samples=0, loader=h5_loader):
127 | classes, class_to_idx = find_classes(root)
128 | imgs = make_dataset(root, class_to_idx)
129 | if len(imgs) == 0:
130 | raise(RuntimeError("Found 0 images in subfolders of: " + root + "\n"
131 | "Supported image extensions are: " + ",".join(IMG_EXTENSIONS)))
132 |
133 | self.root = root
134 | self.imgs = imgs
135 | self.classes = classes
136 | self.class_to_idx = class_to_idx
137 | if type == 'train':
138 | self.transform = train_transform
139 | elif type == 'val':
140 | self.transform = val_transform
141 | else:
142 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
143 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
144 | self.loader = loader
145 |
146 | if modality in self.modality_names: # 如果在...中有...
147 | self.modality = modality
148 | if modality in ['rgbd', 'd', 'gd']:
149 | if num_samples <= 0:
150 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid number of samples: {}\n".format(num_samples)))
151 | self.num_samples = num_samples
152 | else:
153 | self.num_samples = 0
154 | else:
155 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid modality type: " + modality + "\n"
156 | "Supported dataset types are: " + ''.join(self.modality_names)))
157 |
158 | # 生成稀疏深度图 原版
159 | def create_sparse_depth(self, depth, num_samples):
160 | prob = float(num_samples) / depth.size # 概率
161 | mask_keep = np.random.uniform(0, 1, depth.shape) < prob # 生成一个0-1的mask,0-1是随机产生的,0-1产生的概率小于预设的概率
162 | sparse_depth = np.zeros(depth.shape)
163 | sparse_depth[mask_keep] = depth[mask_keep] # 把深度图中和mask_keep对应的元素赋值给sparse_depth中的对应元素
164 | return sparse_depth
165 |
166 | # 生成稀疏深度图 ORB特征提取
167 | def create_sparse_depth_ORB(self, rgb_np, depth, num_samples):
168 | # num_samples = int(prob * depth.size)
169 | rgb = MatrixTocvMat(rgb_np)
170 | gray = cv2.cvtColor(rgb, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
171 | orb = cv2.ORB_create(num_samples, 1.2, 4, 10, 0, 2, cv2.ORB_HARRIS_SCORE, 10) # 需要进行网格化
172 | kp = orb.detect(gray, None)
173 | # print("number of ORB KeyPoints:", len(kp))
174 | # cv2.namedWindow("ORB")
175 | # rgb_orb = cv2.drawKeypoints(rgb,kp,(255,0,0),-1)
176 | # cv2.imshow("ORB",rgb_orb)
177 | # cv2.waitKey(0)
178 |
179 | # print(len(kp)) # keypoint的个数
180 | # print(kp[0]) # 多少个角点,就有多少个下标
181 | # tu = kp[0].pt #(提取坐标) pt指的是元组 tuple(x,y)
182 | # print(tu[0],tu[1]) # 输出第一个keypoint的x,y坐标
183 |
184 | sparse_depth = np.zeros(depth.shape)
185 | for i in range(len(kp)):
186 | tu = kp[i].pt
187 | x = int(tu[0])
188 | y = int(tu[1])
189 | sparse_depth[y,x] = depth[y,x] # x,y和行,列的顺序不一样
190 |
191 | return sparse_depth
192 |
193 | def create_rgbd(self, rgb, depth, num_samples):
194 | sparse_depth = self.create_sparse_depth_ORB(rgb, depth, num_samples)
195 | # sparse_depth = self.create_sparse_depth(depth, num_samples)
196 |
197 | # rgbd = np.dstack((rgb[:,:,0], rgb[:,:,1], rgb[:,:,2], sparse_depth))
198 | rgbd = np.append(rgb, np.expand_dims(sparse_depth, axis=2), axis=2) # append()相当于push_back()
199 | return rgbd
200 |
201 | # 获取原始图像
202 | def __getraw__(self, index):
203 | """
204 | Args:
205 | index (int): Index
206 |
207 | Returns:
208 | tuple: (rgb, depth) the raw data.
209 | """
210 | path, target = self.imgs[index]
211 | rgb, depth = self.loader(path) # 这个loader就是h5_loader
212 | return rgb, depth
213 |
214 | def __get_all_item__(self, index):
215 | """
216 | Args:
217 | index (int): Index
218 |
219 | Returns:
220 | tuple: (input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np)
221 | """
222 | rgb, depth = self.__getraw__(index)
223 | if self.transform is not None:
224 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth) # 经过数据增强步骤后的结果
225 | else:
226 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
227 |
228 | # color normalization
229 | # rgb_tensor = normalize_rgb(rgb_tensor)
230 | # rgb_np = normalize_np(rgb_np)
231 |
232 | if self.modality == 'rgb':
233 | input_np = rgb_np
234 | elif self.modality == 'rgbd':
235 | input_np = self.create_rgbd(rgb_np, depth_np, self.num_samples)
236 | elif self.modality == 'd':
237 | input_np = self.create_sparse_depth_ORB(rgb_np, depth_np, self.num_samples)
238 | # input_np = self.create_sparse_depth(depth_np, self.num_samples)
239 |
240 | input_tensor = to_tensor(input_np)
241 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
242 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
243 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
244 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
245 |
246 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np
247 |
248 | def __getitem__(self, index):
249 | """
250 | Args:
251 | index (int): Index
252 |
253 | Returns:
254 | tuple: (input_tensor, depth_tensor)
255 | """
256 | input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np = self.__get_all_item__(index)
257 |
258 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
259 |
260 | def __len__(self):
261 | return len(self.imgs)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/transforms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 对图片做各种变换的函数
2 |
3 | from __future__ import division # 导入未来支持的语言 division是精确除法 相见https://blog.csdn.net/feixingfei/article/details/7081446
4 | import torch
5 | import math
6 | import random
7 |
8 | from PIL import Image, ImageOps, ImageEnhance
9 | try: # 尝试做...如果不行则... python中所有含条件的语句都要加冒号
10 | import accimage
11 | except ImportError:
12 | accimage = None
13 |
14 | import numpy as np
15 | import numbers
16 | import types
17 | import collections
18 | import warnings
19 |
20 | import scipy.ndimage.interpolation as itpl
21 | import scipy.misc as misc
22 |
23 |
24 | def _is_numpy_image(img): # numpy格式的图像
25 | return isinstance(img, np.ndarray) and (img.ndim in {2, 3})
26 | # return ... and ... 和 return ... or ...
27 | # 详见https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/1642792031752755300.html
28 | # 详见http://www.mamicode.com/info-detail-1765166.html
29 |
30 | def _is_pil_image(img): # PIL格式的图像
31 | if accimage is not None:
32 | return isinstance(img, (Image.Image, accimage.Image))
33 | else:
34 | return isinstance(img, Image.Image)
35 |
36 | def _is_tensor_image(img): # tensor格式的图像
37 | return torch.is_tensor(img) and img.ndimension() == 3
38 |
39 | def adjust_brightness(img, brightness_factor):
40 | """Adjust brightness of an Image.
41 |
42 | Args:
43 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
44 | brightness_factor (float): How much to adjust the brightness. Can be
45 | any non negative number. 0 gives a black image, 1 gives the
46 | original image while 2 increases the brightness by a factor of 2.
47 |
48 | Returns:
49 | PIL Image: Brightness adjusted image.
50 | """
51 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
52 | # 当程序出现错误时,python会自动引发异常,也可以通过raise显示地引发异常。
53 | # 一旦执行了raise语句,raise后面的语句将不能执行。
54 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
55 |
56 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Brightness(img)
57 | img = enhancer.enhance(brightness_factor)
58 | return img
59 |
60 |
61 | def adjust_contrast(img, contrast_factor):
62 | """Adjust contrast of an Image.
63 |
64 | Args:
65 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
66 | contrast_factor (float): How much to adjust the contrast. Can be any
67 | non negative number. 0 gives a solid gray image, 1 gives the
68 | original image while 2 increases the contrast by a factor of 2.
69 |
70 | Returns:
71 | PIL Image: Contrast adjusted image.
72 | """
73 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
74 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
75 |
76 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Contrast(img)
77 | img = enhancer.enhance(contrast_factor)
78 | return img
79 |
80 |
81 | def adjust_saturation(img, saturation_factor):
82 | """Adjust color saturation of an image.
83 |
84 | Args:
85 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
86 | saturation_factor (float): How much to adjust the saturation. 0 will
87 | give a black and white image, 1 will give the original image while
88 | 2 will enhance the saturation by a factor of 2.
89 |
90 | Returns:
91 | PIL Image: Saturation adjusted image.
92 | """
93 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
94 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
95 |
96 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Color(img)
97 | img = enhancer.enhance(saturation_factor)
98 | return img
99 |
100 |
101 | def adjust_hue(img, hue_factor): # hue: 色调
102 | """Adjust hue of an image.
103 |
104 | The image hue is adjusted by converting the image to HSV and
105 | cyclically shifting the intensities in the hue channel (H).
106 | The image is then converted back to original image mode.
107 |
108 | `hue_factor` is the amount of shift in H channel and must be in the
109 | interval `[-0.5, 0.5]`.
110 |
111 | See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hue for more details on Hue.
112 |
113 | Args:
114 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
115 | hue_factor (float): How much to shift the hue channel. Should be in
116 | [-0.5, 0.5]. 0.5 and -0.5 give complete reversal of hue channel in
117 | HSV space in positive and negative direction respectively.
118 | 0 means no shift. Therefore, both -0.5 and 0.5 will give an image
119 | with complementary colors while 0 gives the original image.
120 |
121 | Returns:
122 | PIL Image: Hue adjusted image.
123 | """
124 | if not(-0.5 <= hue_factor <= 0.5):
125 | raise ValueError('hue_factor is not in [-0.5, 0.5].'.format(hue_factor))
126 |
127 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
128 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
129 |
130 | input_mode = img.mode
131 | if input_mode in {'L', '1', 'I', 'F'}:
132 | return img
133 |
134 | h, s, v = img.convert('HSV').split()
135 |
136 | np_h = np.array(h, dtype=np.uint8)
137 | # uint8 addition take cares of rotation across boundaries
138 | with np.errstate(over='ignore'):
139 | np_h += np.uint8(hue_factor * 255)
140 | h = Image.fromarray(np_h, 'L')
141 |
142 | img = Image.merge('HSV', (h, s, v)).convert(input_mode)
143 | return img
144 |
145 |
146 | def adjust_gamma(img, gamma, gain=1):
147 | """Perform gamma correction on an image.
148 |
149 | Also known as Power Law Transform. Intensities in RGB mode are adjusted
150 | based on the following equation:
151 |
152 | I_out = 255 * gain * ((I_in / 255) ** gamma)
153 |
154 | See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction for more details.
155 |
156 | Args:
157 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
158 | gamma (float): Non negative real number. gamma larger than 1 make the
159 | shadows darker, while gamma smaller than 1 make dark regions
160 | lighter.
161 | gain (float): The constant multiplier.
162 | """
163 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
164 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
165 |
166 | if gamma < 0:
167 | raise ValueError('Gamma should be a non-negative real number')
168 |
169 | input_mode = img.mode
170 | img = img.convert('RGB')
171 |
172 | np_img = np.array(img, dtype=np.float32)
173 | np_img = 255 * gain * ((np_img / 255) ** gamma)
174 | np_img = np.uint8(np.clip(np_img, 0, 255))
175 |
176 | img = Image.fromarray(np_img, 'RGB').convert(input_mode)
177 | return img
178 |
179 |
180 | class Compose(object):
181 | """Composes several transforms together.
182 |
183 | Args:
184 | transforms (list of ``Transform`` objects): list of transforms to compose.
185 |
186 | Example:
187 | >>> transforms.Compose([
188 | >>> transforms.CenterCrop(10),
189 | >>> transforms.ToTensor(),
190 | >>> ])
191 | """
192 |
193 | def __init__(self, transforms):
194 | self.transforms = transforms
195 |
196 | # __call__:把类的实例当成函数来用,详见https://blog.csdn.net/yaokai_assultmaster/article/details/70256621
197 | def __call__(self, img):
198 | for t in self.transforms:
199 | img = t(img)
200 | return img
201 |
202 |
203 | class ToTensor(object):
204 | """Convert a ``numpy.ndarray`` to tensor.
205 |
206 | Converts a numpy.ndarray (H x W x C) to a torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W).
207 | """
208 |
209 | def __call__(self, img):
210 | """Convert a ``numpy.ndarray`` to tensor.
211 |
212 | Args:
213 | img (numpy.ndarray): Image to be converted to tensor.
214 |
215 | Returns:
216 | Tensor: Converted image.
217 | """
218 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
219 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
220 |
221 | if isinstance(img, np.ndarray):
222 | # handle numpy array
223 | if img.ndim == 3:
224 | img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose((2, 0, 1)).copy())
225 | elif img.ndim == 2:
226 | img = torch.from_numpy(img.copy())
227 | else:
228 | raise RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
229 |
230 | # backward compatibility
231 | # return img.float().div(255)
232 | return img.float()
233 |
234 |
235 | class NormalizeNumpyArray(object):
236 | """Normalize a ``numpy.ndarray`` with mean and standard deviation.
237 | Given mean: ``(M1,...,Mn)`` and std: ``(M1,..,Mn)`` for ``n`` channels, this transform
238 | will normalize each channel of the input ``numpy.ndarray`` i.e.
239 | ``input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
240 |
241 | Args:
242 | mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
243 | std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
244 | """
245 |
246 | def __init__(self, mean, std):
247 | self.mean = mean
248 | self.std = std
249 |
250 | def __call__(self, img):
251 | """
252 | Args:
253 | img (numpy.ndarray): Image of size (H, W, C) to be normalized.
254 |
255 | Returns:
256 | Tensor: Normalized image.
257 | """
258 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
259 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
260 | # TODO: make efficient
261 | # TODO在python中是一种助记符(Mnemonics),用来解释将要做什么。
262 | print(img.shape)
263 | for i in range(3): # 对RGB图像的每个通道进行同样的操作
264 | img[:,:,i] = (img[:,:,i] - self.mean[i]) / self.std[i]
265 | return img
266 |
267 | class NormalizeTensor(object):
268 | """Normalize an tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
269 | Given mean: ``(M1,...,Mn)`` and std: ``(M1,..,Mn)`` for ``n`` channels, this transform
270 | will normalize each channel of the input ``torch.*Tensor`` i.e.
271 | ``input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
272 |
273 | Args:
274 | mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
275 | std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
276 | """
277 |
278 | def __init__(self, mean, std):
279 | self.mean = mean
280 | self.std = std
281 |
282 | def __call__(self, tensor):
283 | """
284 | Args:
285 | tensor (Tensor): Tensor image of size (C, H, W) to be normalized.
286 |
287 | Returns:
288 | Tensor: Normalized Tensor image.
289 | """
290 | if not _is_tensor_image(tensor):
291 | raise TypeError('tensor is not a torch image.')
292 | # TODO: make efficient
293 | # zip()函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。
294 | # 详见http://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-zip.html
295 | for t, m, s in zip(tensor, self.mean, self.std):
296 | t.sub_(m).div_(s)
297 | return tensor
298 |
299 | class Rotate(object):
300 | """Rotates the given ``numpy.ndarray``.
301 |
302 | Args:
303 | angle (float): The rotation angle in degrees.
304 | """
305 |
306 | def __init__(self, angle):
307 | self.angle = angle
308 |
309 | def __call__(self, img):
310 | """
311 | Args:
312 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be rotated.
313 |
314 | Returns:
315 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Rotated image.
316 | """
317 |
318 | return itpl.rotate(img, self.angle, reshape=False, prefilter=False)
319 |
320 | class Resize(object):
321 | """Resize the the given ``numpy.ndarray`` to the given size.
322 | Args:
323 | size (sequence or int): Desired output size. If size is a sequence like
324 | (h, w), output size will be matched to this. If size is an int,
325 | smaller edge of the image will be matched to this number.
326 | i.e, if height > width, then image will be rescaled to
327 | (size * height / width, size)
328 | interpolation (int, optional): Desired interpolation. Default is
329 | ``PIL.Image.BILINEAR``
330 | """
331 |
332 | def __init__(self, size, interpolation='nearest'):
333 | assert isinstance(size, int) or isinstance(size, float) or \
334 | (isinstance(size, collections.Iterable) and len(size) == 2)
335 | self.size = size
336 | self.interpolation = interpolation
337 |
338 | def __call__(self, img):
339 | """
340 | Args:
341 | img (PIL Image): Image to be scaled.
342 | Returns:
343 | PIL Image: Rescaled image.
344 | """
345 | if img.ndim == 3:
346 | return misc.imresize(img, self.size, self.interpolation)
347 | elif img.ndim == 2:
348 | return misc.imresize(img, self.size, self.interpolation, 'F')
349 | else:
350 | RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
351 |
352 |
353 | class CenterCrop(object):
354 | """Crops the given ``numpy.ndarray`` at the center.
355 |
356 | Args:
357 | size (sequence or int): Desired output size of the crop. If size is an
358 | int instead of sequence like (h, w), a square crop (size, size) is
359 | made.
360 | """
361 |
362 | def __init__(self, size):
363 | if isinstance(size, numbers.Number):
364 | self.size = (int(size), int(size))
365 | else:
366 | self.size = size
367 |
368 | # @staticmethod详见https://www.zhihu.com/question/20021164
369 | @staticmethod
370 | def get_params(img, output_size):
371 | """Get parameters for ``crop`` for center crop.
372 |
373 | Args:
374 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
375 | output_size (tuple): Expected output size of the crop.
376 |
377 | Returns:
378 | tuple: params (i, j, h, w) to be passed to ``crop`` for center crop.
379 | """
380 | h = img.shape[0]
381 | w = img.shape[1]
382 | th, tw = output_size
383 | i = int(round((h - th) / 2.))
384 | j = int(round((w - tw) / 2.))
385 |
386 | # # randomized cropping
387 | # i = np.random.randint(i-3, i+4)
388 | # j = np.random.randint(j-3, j+4)
389 |
390 | return i, j, th, tw
391 |
392 | def __call__(self, img):
393 | """
394 | Args:
395 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
396 |
397 | Returns:
398 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Cropped image.
399 | """
400 | i, j, h, w = self.get_params(img, self.size)
401 |
402 | """
403 | i: Upper pixel coordinate.
404 | j: Left pixel coordinate.
405 | h: Height of the cropped image.
406 | w: Width of the cropped image.
407 | """
408 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
409 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
410 | if img.ndim == 3:
411 | return img[i:i+h, j:j+w, :]
412 | elif img.ndim == 2:
413 | return img[i:i + h, j:j + w]
414 | else:
415 | raise RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
416 |
417 |
418 | class Lambda(object):
419 | """Apply a user-defined lambda as a transform.
420 |
421 | Args:
422 | lambd (function): Lambda/function to be used for transform.
423 | """
424 |
425 | def __init__(self, lambd):
426 | assert isinstance(lambd, types.LambdaType)
427 | self.lambd = lambd
428 |
429 | def __call__(self, img):
430 | return self.lambd(img)
431 |
432 |
433 | class HorizontalFlip(object):
434 | """Horizontally flip the given ``numpy.ndarray``.
435 |
436 | Args:
437 | do_flip (boolean): whether or not do horizontal flip.
438 |
439 | """
440 |
441 | def __init__(self, do_flip):
442 | self.do_flip = do_flip
443 |
444 | def __call__(self, img):
445 | """
446 | Args:
447 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be flipped.
448 |
449 | Returns:
450 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): flipped image.
451 | """
452 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
453 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
454 |
455 | if self.do_flip:
456 | return np.fliplr(img)
457 | else:
458 | return img
459 |
460 |
461 | class ColorJitter(object): # jitter:抖动
462 | """Randomly change the brightness, contrast and saturation of an image.
463 |
464 | Args:
465 | brightness (float): How much to jitter brightness. brightness_factor
466 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - brightness), 1 + brightness].
467 | contrast (float): How much to jitter contrast. contrast_factor
468 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - contrast), 1 + contrast].
469 | saturation (float): How much to jitter saturation. saturation_factor
470 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - saturation), 1 + saturation].
471 | hue(float): How much to jitter hue. hue_factor is chosen uniformly from
472 | [-hue, hue]. Should be >=0 and <= 0.5.
473 | """
474 | def __init__(self, brightness=0, contrast=0, saturation=0, hue=0):
475 | self.brightness = brightness
476 | self.contrast = contrast
477 | self.saturation = saturation
478 | self.hue = hue
479 |
480 | @staticmethod
481 | def get_params(brightness, contrast, saturation, hue):
482 | """Get a randomized transform to be applied on image.
483 |
484 | Arguments are same as that of __init__.
485 |
486 | Returns:
487 | Transform which randomly adjusts brightness, contrast and
488 | saturation in a random order.
489 | """
490 | transforms = []
491 | if brightness > 0:
492 | brightness_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - brightness), 1 + brightness)
493 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_brightness(img, brightness_factor)))
494 |
495 | if contrast > 0:
496 | contrast_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - contrast), 1 + contrast)
497 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_contrast(img, contrast_factor)))
498 |
499 | if saturation > 0:
500 | saturation_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - saturation), 1 + saturation)
501 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_saturation(img, saturation_factor)))
502 |
503 | if hue > 0:
504 | hue_factor = np.random.uniform(-hue, hue)
505 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_hue(img, hue_factor)))
506 |
507 | np.random.shuffle(transforms)
508 | transform = Compose(transforms)
509 |
510 | return transform
511 |
512 | def __call__(self, img):
513 | """
514 | Args:
515 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Input image.
516 |
517 | Returns:
518 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Color jittered image.
519 | """
520 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
521 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
522 |
523 | pil = Image.fromarray(img)
524 | transform = self.get_params(self.brightness, self.contrast,
525 | self.saturation, self.hue)
526 | return np.array(transform(pil))
527 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 导入一般的文件操作模块
2 | import argparse # 导入自动命令解析器 详见https://blog.csdn.net/ali197294332/article/details/51180628
3 | import os # 导入Python的系统基础操作模块
4 | import shutil # 导入高级的文件操作模块 详见https://www.cnblogs.com/MnCu8261/p/5494807.html
5 | import time # 导入对时间操作的函数 详见http://www.jb51.net/article/87721.htm
6 | import sys # 导入系统相关的信息模块
7 | import csv # 导入处理csv格式文件的相关模块 详见https://www.cnblogs.com/yanglang/p/7126660.html
8 |
9 | # 导入pytorch相关的模块
10 | import torch
11 | import torch.nn as nn
12 | import torch.nn.parallel # 可以实现模块级别的并行计算。可以将一个模块forward部分分到各个gpu中,然后backward时合并gradient到original module。
13 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn # cudnn: CUDA Deep Neural Network 相比标准的cuda,它在一些常用的神经网络操作上进行了性能的优化,比如卷积,pooling,归一化,以及激活层等等。
14 | import torch.optim
15 | import torch.utils.data
16 |
17 | # 导入自定义的模块
18 | from nyu_dataloader import NYUDataset
19 | from models import Decoder, ResNet
20 | from metrics import AverageMeter, Result
21 | import criteria
22 | import utils
23 |
24 | model_names = ['resnet18', 'resnet50']
25 | loss_names = ['l1', 'l2']
26 | data_names = ['NYUDataset']
27 | decoder_names = Decoder.names
28 | modality_names = NYUDataset.modality_names
29 |
30 | cudnn.benchmark = True
31 |
32 | # 创建一个解析处理器
33 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Sparse-to-Dense Training')
34 | # parser.add_argument('--data', metavar='DIR', help='path to dataset',
35 | # default="data/NYUDataset")
36 |
37 | # 设置多个参数
38 | parser.add_argument('--arch', '-a', metavar='ARCH', default='resnet18',
39 | choices=model_names,
40 | help='model architecture: ' +
41 | ' | '.join(model_names) +
42 | ' (default: resnet18)')
43 | # metavar:占位字符串,用于在输出帮助信息时,代替当前命令行选项的附加参数的值进行输出
44 | # join:连接字符串数组。将字符串、元组、列表中的元素以指定的字符(分隔符)连接生成一个新的字符串。详见https://blog.csdn.net/zmdzbzbhss123/article/details/52279008
45 | parser.add_argument('--data', metavar='DATA', default='nyudepthv2',
46 | choices=data_names,
47 | help='dataset: ' +
48 | ' | '.join(data_names) +
49 | ' (default: nyudepthv2)')
50 | parser.add_argument('--modality', '-m', metavar='MODALITY', default='rgb',
51 | choices=modality_names,
52 | help='modality: ' +
53 | ' | '.join(modality_names) +
54 | ' (default: rgb)')
55 | parser.add_argument('-s', '--num-samples', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
56 | help='number of sparse depth samples (default: 0)')
57 | parser.add_argument('--decoder', '-d', metavar='DECODER', default='deconv2',
58 | choices=decoder_names,
59 | help='decoder: ' +
60 | ' | '.join(decoder_names) +
61 | ' (default: deconv2)')
62 | parser.add_argument('-j', '--workers', default=10, type=int, metavar='N',
63 | help='number of data loading workers (default: 10)')
64 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=30, type=int, metavar='N',
65 | help='number of total epochs to run (default: 30)')
66 | parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
67 | help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
68 | parser.add_argument('-c', '--criterion', metavar='LOSS', default='l1',
69 | choices=loss_names,
70 | help='loss function: ' +
71 | ' | '.join(loss_names) +
72 | ' (default: l1)')
73 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=8, type=int,
74 | help='mini-batch size (default: 8)')
75 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.01, type=float,
76 | metavar='LR', help='initial learning rate (default 0.01)')
77 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, metavar='M',
78 | help='momentum')
79 | parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', '--wd', default=1e-4, type=float,
80 | metavar='W', help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)')
81 | parser.add_argument('--print-freq', '-p', default=10, type=int,
82 | metavar='N', help='print frequency (default: 10)')
83 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
84 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
85 | parser.add_argument('-e', '--evaluate', dest='evaluate', action='store_true',
86 | help='evaluate model on validation set')
87 | parser.add_argument('--pretrained', dest='pretrained', action='store_true',
88 | default=True, help='use ImageNet pre-trained weights (default: True)')
89 |
90 | fieldnames = ['mse', 'rmse', 'absrel', 'lg10', 'mae',
91 | 'delta1', 'delta2', 'delta3',
92 | 'data_time', 'gpu_time']
93 |
94 | # Result()是criteria.py中的类
95 | best_result = Result()
96 | best_result.set_to_worst()
97 |
98 | # 定义函数
99 | # 基本格式:
100 | # def function_name(parameters):
101 | # expressions
102 | # Python使用缩进来规定代码的作用域
103 | def main():
104 | global args, best_result, output_directory, train_csv, test_csv # 全局变量
105 | args = parser.parse_args() # 获取参数值
106 | args.data = os.path.join('data', args.data)
107 | # os.path.join()函数:将多个路径组合后返回
108 | # 语法:os.path.join(path1[,path2[,......]])
109 | # 注:第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
110 | # 注意if的语句后面有冒号
111 | # args中modality的参数值。modality之前定义过
112 | if args.modality == 'rgb' and args.num_samples != 0:
113 | print("number of samples is forced to be 0 when input modality is rgb")
114 | args.num_samples = 0
115 | # 若是RGB的sparse-to-dense,则在生成训练数据时将稀疏深度点设为0
116 |
117 | # create results folder, if not already exists
118 | output_directory = os.path.join('results',
119 | 'NYUDataset.modality={}.nsample={}.arch={}.decoder={}.criterion={}.lr={}.bs={}'.
120 | format(args.modality, args.num_samples, args.arch, args.decoder, args.criterion, args.lr, args.batch_size)) # 输出文件名的格式
121 |
122 | # 如果路径不存在
123 | if not os.path.exists(output_directory):
124 | os.makedirs(output_directory)
125 |
126 | train_csv = os.path.join(output_directory, 'train.csv')
127 | test_csv = os.path.join(output_directory, 'test.csv')
128 | best_txt = os.path.join(output_directory, 'best.txt')
129 |
130 | # define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
131 | if args.criterion == 'l2':
132 | criterion = criteria.MaskedMSELoss().cuda() # 调用别的py文件中的内容时,若被调用的是函数,则直接写函数名即可;若被调用的是类,则要按这句话的格式写
133 | out_channels = 1
134 | # elif: else if
135 | elif args.criterion == 'l1':
136 | criterion = criteria.MaskedL1Loss().cuda()
137 | out_channels = 1
138 |
139 | # Data loading code
140 | print("=> creating data loaders ...")
141 | traindir = os.path.join(args.data, 'train')
142 | valdir = os.path.join(args.data, 'val')
143 |
144 | train_dataset = NYUDataset(traindir, type='train',
145 | modality=args.modality, num_samples=args.num_samples)
146 | # DataLoader是导入数据的函数
147 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
148 | train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True,
149 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True, sampler=None)
150 |
151 | # set batch size to be 1 for validation
152 | val_dataset = NYUDataset(valdir, type='val',
153 | modality=args.modality, num_samples=args.num_samples)
154 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
155 | batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True)
156 |
157 | print("=> data loaders created.")
158 |
159 | # evaluation mode
160 | if args.evaluate:
161 | best_model_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'model_best.pth.tar')
162 | if os.path.isfile(best_model_filename):
163 | print("=> loading best model '{}'".format(best_model_filename))
164 | checkpoint = torch.load(best_model_filename)
165 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
166 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
167 | model = checkpoint['model']
168 | print("=> loaded best model (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
169 | else: # else也要加:
170 | print("=> no best model found at '{}'".format(best_model_filename))
171 | validate(val_loader, model, checkpoint['epoch'], write_to_file=False)
172 | return
173 |
174 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
175 | elif args.resume:
176 | if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
177 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
178 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
179 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']+1
180 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
181 | model = checkpoint['model']
182 | optimizer = checkpoint['optimizer']
183 | print("=> loaded checkpoint (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
184 | else:
185 | print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
186 |
187 | # create new model
188 | else:
189 | # define model
190 | print("=> creating Model ({}-{}) ...".format(args.arch, args.decoder))
191 | in_channels = len(args.modality) # len()返回对象的长度或项目个数
192 | if args.arch == 'resnet50':
193 | model = ResNet(layers=50, decoder=args.decoder, in_channels=in_channels,
194 | out_channels=out_channels, pretrained=args.pretrained)
195 | elif args.arch == 'resnet18':
196 | model = ResNet(layers=18, decoder=args.decoder, in_channels=in_channels,
197 | out_channels=out_channels, pretrained=args.pretrained)
198 | print("=> model created.")
199 |
200 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr, momentum=args.momentum, weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
201 |
202 | # create new csv files with only header
203 | # with open() as xxx: 的用法详见https://www.cnblogs.com/ymjyqsx/p/6554817.html
204 | with open(train_csv, 'w') as csvfile:
205 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
206 | writer.writeheader()
207 | with open(test_csv, 'w') as csvfile:
208 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
209 | writer.writeheader()
210 |
211 | # model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
212 | model = model.cuda()
213 | print(model)
214 | print("=> model transferred to GPU.")
215 |
216 | # for循环也要有:
217 | # 一般情况下,循环次数未知采用while循环,循环次数已知采用for
218 | for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
219 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch)
220 |
221 | # train for one epoch
222 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
223 |
224 | # evaluate on validation set
225 | result, img_merge = validate(val_loader, model, epoch)
226 | # Python的return可以返回多个值
227 |
228 | # remember best rmse and save checkpoint
229 | is_best = result.rmse < best_result.rmse
230 | if is_best:
231 | best_result = result
232 | with open(best_txt, 'w') as txtfile:
233 | # 字符串格式化输出
234 | # :3f中,3表示输出宽度,f表示浮点型。若输出位数小于此宽度,则默认右对齐,左边补空格。
235 | # 若输出位数大于宽度,则按实际位数输出。
236 | # :.3f中,.3表示指定除小数点外的输出位数,f表示浮点型。
237 | txtfile.write("epoch={}\nmse={:.3f}\nrmse={:.3f}\nabsrel={:.3f}\nlg10={:.3f}\nmae={:.3f}\ndelta1={:.3f}\nt_gpu={:.4f}\n".
238 | format(epoch, result.mse, result.rmse, result.absrel, result.lg10, result.mae, result.delta1, result.gpu_time))
239 | # None表示该值是一个空对象,空值是Python里一个特殊的值,用None表示。None不能理解为0,因为0是有意义的,而None是一个特殊的空值。
240 | # 你可以将None赋值给任何变量,也可以将任何变量赋值给一个None值的对象
241 | # None在判断的时候是False
242 | # NULL是空字符,和None不一样
243 | if img_merge is not None:
244 | img_filename = output_directory + '/comparison_best.png'
245 | utils.save_image(img_merge, img_filename)
246 |
247 | # Python中,万物皆对象,所有的操作都是针对对象的。一个对象包括两方面的特征:
248 | # 属性:去描述它的特征
249 | # 方法:它所具有的行为
250 | # 所以,对象=属性+方法 (其实方法也是一种属性,一种区别于数据属性的可调用属性)
251 |
252 | save_checkpoint({
253 | 'epoch': epoch,
254 | 'arch': args.arch,
255 | 'model': model,
256 | 'best_result': best_result,
257 | 'optimizer' : optimizer,
258 | }, is_best, epoch)
259 |
260 |
261 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
262 | average_meter = AverageMeter()
263 |
264 | # switch to train mode
265 | model.train()
266 |
267 | end = time.time() # 计时开始
268 | # enumerate()用于将一个可遍历的数据对象(如列表、元组或字符串)组合为一个索引序列,同时列出数据和数据下标,一般用在for循环当中。
269 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
270 |
271 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda()
272 | # torch.autograd提供实现任意标量值功能的自动区分的类和功能。它将所有张量包装在Variable对象中。
273 | # Variable可以看作是对Tensor对象周围的一个薄包装,也包含了和张量相关的梯度,以及对创建它的函数的引用。
274 | # 此引用允许对创建数据的整个操作链进行回溯。需要BP的网络都是通过Variable来计算的。
275 | # pytorch中的所有运算都是基于Tensor的,Variable只是一个Wrapper,Variable的计算的实质就是里面的Tensor在计算。
276 | # 详见https://blog.csdn.net/KGzhang/article/details/77483383
277 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
278 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
279 | torch.cuda.synchronize() # 等待当前设备上所有流中的所有内核完成
280 | data_time = time.time() - end # 计算用时
281 |
282 | # compute depth_pred
283 | end = time.time()
284 | depth_pred = model(input_var)
285 | loss = criterion(depth_pred, target_var)
286 | # optimizer包提供训练时更新参数的功能
287 | optimizer.zero_grad() # zero the gradient buffers,必须要置零
288 | # 在BP的时候,pytorch将Variable的梯度放在Variable对象中,我们随时可以用Variable.grad得到grad。
289 | # 刚创建Variable的时候,它的grad属性初始化为0.0
290 | loss.backward() # compute gradient and do SGD step
291 | optimizer.step() # 更新
292 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
293 | gpu_time = time.time() - end
294 |
295 | # measure accuracy and record loss
296 | result = Result()
297 | output1 = torch.index_select(depth_pred.data, 1, torch.cuda.LongTensor([0]))
298 | result.evaluate(output1, target)
299 | average_meter.update(result, gpu_time, data_time, input.size(0))
300 | end = time.time()
301 |
302 | if (i + 1) % args.print_freq == 0:
303 | print('=> output: {}'.format(output_directory))
304 | print('Train Epoch: {0} [{1}/{2}]\t'
305 | 't_Data={data_time:.3f}({average.data_time:.3f}) '
306 | 't_GPU={gpu_time:.3f}({average.gpu_time:.3f}) '
307 | 'RMSE={result.rmse:.2f}({average.rmse:.2f}) '
308 | 'MAE={result.mae:.2f}({average.mae:.2f}) '
309 | 'Delta1={result.delta1:.3f}({average.delta1:.3f}) '
310 | 'REL={result.absrel:.3f}({average.absrel:.3f}) '
311 | 'Lg10={result.lg10:.3f}({average.lg10:.3f}) '.format(
312 | epoch, i+1, len(train_loader), data_time=data_time,
313 | gpu_time=gpu_time, result=result, average=average_meter.average()))
314 |
315 | avg = average_meter.average()
316 | with open(train_csv, 'a') as csvfile:
317 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
318 | writer.writerow({'mse': avg.mse, 'rmse': avg.rmse, 'absrel': avg.absrel, 'lg10': avg.lg10,
319 | 'mae': avg.mae, 'delta1': avg.delta1, 'delta2': avg.delta2, 'delta3': avg.delta3,
320 | 'gpu_time': avg.gpu_time, 'data_time': avg.data_time})
321 |
322 |
323 | def validate(val_loader, model, epoch, write_to_file=True):
324 | average_meter = AverageMeter()
325 |
326 | # switch to evaluate mode
327 | model.eval()
328 |
329 | end = time.time()
330 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
331 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda() # 从后面看,这里的target应该是深度图的ground truth
332 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
333 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
334 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
335 | data_time = time.time() - end
336 |
337 | # compute output
338 | end = time.time()
339 | depth_pred = model(input_var)
340 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
341 | gpu_time = time.time() - end
342 |
343 | # measure accuracy and record loss
344 | result = Result()
345 | output1 = torch.index_select(depth_pred.data, 1, torch.cuda.LongTensor([0]))
346 | result.evaluate(output1, target)
347 | average_meter.update(result, gpu_time, data_time, input.size(0))
348 | end = time.time()
349 |
350 | # save 8 images for visualization
351 | skip = 50
352 | if args.modality == 'd':
353 | img_merge = None
354 | else:
355 | if args.modality == 'rgb':
356 | rgb = input
357 | elif args.modality == 'rgbd':
358 | rgb = input[:,:3,:,:]
359 |
360 | if i == 0:
361 | img_merge = utils.merge_into_row(rgb, target, depth_pred)
362 | # 隔50个图片抽一张作为可视化结果
363 | elif (i < 8*skip) and (i % skip == 0): # and等同于C++中的&&
364 | row = utils.merge_into_row(rgb, target, depth_pred)
365 | img_merge = utils.add_row(img_merge, row) # 添加一行
366 | elif i == 8*skip: # 只保存8张图片,保存够8张后输出
367 | filename = output_directory + '/comparison_' + str(epoch) + '.png' # str():将()中的对象转换为字符串
368 | utils.save_image(img_merge, filename) # 建议:把这种常用的功能写到特定的脚本文件中,再像这样调用
369 |
370 | if (i+1) % args.print_freq == 0:
371 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
372 | 't_GPU={gpu_time:.3f}({average.gpu_time:.3f})\t'
373 | 'RMSE={result.rmse:.2f}({average.rmse:.2f}) '
374 | 'MAE={result.mae:.2f}({average.mae:.2f}) '
375 | 'Delta1={result.delta1:.3f}({average.delta1:.3f}) '
376 | 'REL={result.absrel:.3f}({average.absrel:.3f}) '
377 | 'Lg10={result.lg10:.3f}({average.lg10:.3f}) '.format(
378 | i+1, len(val_loader), gpu_time=gpu_time, result=result, average=average_meter.average()))
379 |
380 | avg = average_meter.average()
381 |
382 | print('\n*\n'
383 | 'RMSE={average.rmse:.3f}\n'
384 | 'MAE={average.mae:.3f}\n'
385 | 'Delta1={average.delta1:.3f}\n'
386 | 'REL={average.absrel:.3f}\n'
387 | 'Lg10={average.lg10:.3f}\n'
388 | 't_GPU={time:.3f}\n'.format(
389 | average=avg, time=avg.gpu_time))
390 |
391 | if write_to_file:
392 | with open(test_csv, 'a') as csvfile:
393 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
394 | writer.writerow({'mse': avg.mse, 'rmse': avg.rmse, 'absrel': avg.absrel, 'lg10': avg.lg10,
395 | 'mae': avg.mae, 'delta1': avg.delta1, 'delta2': avg.delta2, 'delta3': avg.delta3,
396 | 'data_time': avg.data_time, 'gpu_time': avg.gpu_time})
397 |
398 | return avg, img_merge
399 |
400 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, epoch):
401 | checkpoint_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'checkpoint-' + str(epoch) + '.pth.tar')
402 | torch.save(state, checkpoint_filename)
403 | if is_best:
404 | best_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'model_best.pth.tar')
405 | shutil.copyfile(checkpoint_filename, best_filename)
406 | if epoch > 0:
407 | prev_checkpoint_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'checkpoint-' + str(epoch-1) + '.pth.tar')
408 | if os.path.exists(prev_checkpoint_filename):
409 | os.remove(prev_checkpoint_filename)
410 |
411 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch):
412 | # """ """中的内容为函数的说明,在鼠标放在此函数上时会自动显示该说明
413 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 every 10 epochs"""
414 | # //:整数除法,返回不大于结果的一个最大的整数
415 | # /:浮点数除法。在符号前后的数字都为整型时,输出的也是整型,和c++一样
416 | # 在Python数学运算中*代表乘法,**为指数运算
417 | lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 10))
418 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
419 | param_group['lr'] = lr
420 |
421 | # 这句话是程序的入口
422 | # 意思是:当.py文件被直接运行时,if __name__ == '__main__'之下的代码块将被运行;当.py文件以模块形式被导入时,if __name__ == '__main__'之下的代码块不被运行。
423 | # 详见https://blog.csdn.net/yjk13703623757/article/details/77918633
424 | if __name__ == '__main__':
425 | main()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
105 |
106 | Note: our networks are trained on the KITTI odometry dataset, using only sparse labels from laser measurements.
107 |
108 | ## Citation
109 | If you use our code or method in your work, please cite:
110 |
111 | @article{Ma2017SparseToDense,
112 | title={Sparse-to-Dense: Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth Samples and a Single Image},
113 | author={Ma, Fangchang and Karaman, Sertac},
114 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1709.07492},
115 | year={2017}
116 | }
117 |
118 | Please direct any questions to [Fangchang Ma](http://www.mit.edu/~fcma) at fcma@mit.edu.
119 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/nyu_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import os.path
3 | import cv2 # opencv的python版本
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import torch.utils.data as data
6 | import h5py # HDF5的python版本
7 | import transforms
8 | from PIL import Image
9 |
10 | IMG_EXTENSIONS = [
11 | '.h5',
12 | ]
13 |
14 | def is_image_file(filename):
15 | # return any(): 只要迭代器中有一个元素为真就返回为真。
16 | # 详见https://blog.csdn.net/heatdeath/article/details/70178511
17 | # 详见https://blog.csdn.net/u013630349/article/details/47374333
18 | # 其中,...for...in...是迭代器(iterable)
19 | return any(filename.endswith(extension) for extension in IMG_EXTENSIONS)
20 |
21 | def find_classes(dir):
22 | # ...for...in...if... 挑选出in后面的内容中符合if条件的元素,组成一个新的list
23 | # 详见http://www.jb51.net/article/86987.htm
24 | classes = [d for d in os.listdir(dir) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(dir, d))]
25 | classes.sort() # 升序排列
26 | # Python中[],(),{}的区别:
27 | # {}表示字典,[]表示数组,()表示元组
28 | # 数组的值可以改变,可以使用切片获取部分数据
29 | # 元组的值一旦设置,不可更改,不可使用切片
30 | # 详见https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/484920124.html
31 | class_to_idx = {classes[i]: i for i in range(len(classes))}
32 | return classes, class_to_idx
33 |
34 | # 这个函数可以用于生成自己的数据集
35 | def make_dataset(dir, class_to_idx):
36 | images = [] # 存放图片序号的数组
37 | # dir是路径
38 | dir = os.path.expanduser(dir)
39 | for target in sorted(os.listdir(dir)): # sorted(): 输出排序后的列表 升序排列
40 | # print(target)
41 | # target只是文件名,不含路径。为了获得文件的完整路径,用os.path.join(dirpath, name)
42 | d = os.path.join(dir, target)
43 | if not os.path.isdir(d):
44 | continue
45 |
46 | for root, _, fnames in sorted(os.walk(d)): # tuple: 元组,数组
47 | for fname in sorted(fnames):
48 | if is_image_file(fname):
49 | path = os.path.join(root, fname)
50 | item = (path, class_to_idx[target])
51 | images.append(item) # append()用于在列表末尾添加新的对象,和C++中的push_back()一样
52 |
53 | return images
54 |
55 |
56 | def h5_loader(path):
57 | # 关于HDF5的文件操作,详见https://blog.csdn.net/yudf2010/article/details/50353292
58 | h5f = h5py.File(path, "r") # r是读的意思
59 | rgb = np.array(h5f['rgb']) # 使用array()函数可以将python的array_like数据转变成数组形式,使用matrix()函数转变成矩阵形式。
60 | # 基于习惯,在实际使用中较常用array而少用matrix来表示矩阵。
61 | rgb = np.transpose(rgb, (1, 2, 0)) # 关于np.transpose()对高维数组的转置,详见https://www.cnblogs.com/sunshinewang/p/6893503.html
62 | depth = np.array(h5f['depth'])
63 |
64 | return rgb, depth
65 |
66 | iheight, iwidth = 480, 640 # raw image size
67 | oheight, owidth = 228, 304 # image size after pre-processing
68 | color_jitter = transforms.ColorJitter(0.4, 0.4, 0.4)
69 |
70 | # 数据增强(论文中的方法)
71 | def train_transform(rgb, depth):
72 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
73 | # print("scale factor s={}".format(s))
74 | depth_np = depth / s
75 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
76 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
77 |
78 | # perform 1st part of data augmentation
79 | transform = transforms.Compose([
80 | transforms.Resize(250.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation is very slow
81 | transforms.Rotate(angle),
82 | transforms.Resize(s),
83 | transforms.CenterCrop((oheight, owidth)),
84 | transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
85 | ])
86 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
87 |
88 | # random color jittering
89 | rgb_np = color_jitter(rgb_np)
90 |
91 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
92 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
93 |
94 | return rgb_np, depth_np
95 |
96 | # 数据增强(论文中的方法)
97 | def val_transform(rgb, depth):
98 | depth_np = depth
99 |
100 | # perform 1st part of data augmentation
101 | transform = transforms.Compose([
102 | transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight),
103 | transforms.CenterCrop((oheight, owidth)),
104 | ])
105 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
106 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
107 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
108 |
109 | return rgb_np, depth_np
110 |
111 | def rgb2grayscale(rgb):
112 | return rgb[:,:,0] * 0.2989 + rgb[:,:,1] * 0.587 + rgb[:,:,2] * 0.114
113 |
114 | # 仅限RGB图像
115 | def MatrixTocvMat(data):
116 | data = data*255
117 | im = Image.fromarray(data.astype(np.uint8))
118 | new_im = cv2.cvtColor(np.asarray(im),cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
119 | return new_im
120 |
121 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
122 |
123 | class NYUDataset(data.Dataset):
124 | modality_names = ['rgb', 'rgbd', 'd']
125 |
126 | def __init__(self, root, type, modality='rgb', num_samples=0, loader=h5_loader):
127 | classes, class_to_idx = find_classes(root)
128 | imgs = make_dataset(root, class_to_idx)
129 | if len(imgs) == 0:
130 | raise(RuntimeError("Found 0 images in subfolders of: " + root + "\n"
131 | "Supported image extensions are: " + ",".join(IMG_EXTENSIONS)))
132 |
133 | self.root = root
134 | self.imgs = imgs
135 | self.classes = classes
136 | self.class_to_idx = class_to_idx
137 | if type == 'train':
138 | self.transform = train_transform
139 | elif type == 'val':
140 | self.transform = val_transform
141 | else:
142 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
143 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
144 | self.loader = loader
145 |
146 | if modality in self.modality_names: # 如果在...中有...
147 | self.modality = modality
148 | if modality in ['rgbd', 'd', 'gd']:
149 | if num_samples <= 0:
150 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid number of samples: {}\n".format(num_samples)))
151 | self.num_samples = num_samples
152 | else:
153 | self.num_samples = 0
154 | else:
155 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid modality type: " + modality + "\n"
156 | "Supported dataset types are: " + ''.join(self.modality_names)))
157 |
158 | # 生成稀疏深度图 原版
159 | def create_sparse_depth(self, depth, num_samples):
160 | prob = float(num_samples) / depth.size # 概率
161 | mask_keep = np.random.uniform(0, 1, depth.shape) < prob # 生成一个0-1的mask,0-1是随机产生的,0-1产生的概率小于预设的概率
162 | sparse_depth = np.zeros(depth.shape)
163 | sparse_depth[mask_keep] = depth[mask_keep] # 把深度图中和mask_keep对应的元素赋值给sparse_depth中的对应元素
164 | return sparse_depth
165 |
166 | # 生成稀疏深度图 ORB特征提取
167 | def create_sparse_depth_ORB(self, rgb_np, depth, num_samples):
168 | # num_samples = int(prob * depth.size)
169 | rgb = MatrixTocvMat(rgb_np)
170 | gray = cv2.cvtColor(rgb, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
171 | orb = cv2.ORB_create(num_samples, 1.2, 4, 10, 0, 2, cv2.ORB_HARRIS_SCORE, 10) # 需要进行网格化
172 | kp = orb.detect(gray, None)
173 | # print("number of ORB KeyPoints:", len(kp))
174 | # cv2.namedWindow("ORB")
175 | # rgb_orb = cv2.drawKeypoints(rgb,kp,(255,0,0),-1)
176 | # cv2.imshow("ORB",rgb_orb)
177 | # cv2.waitKey(0)
178 |
179 | # print(len(kp)) # keypoint的个数
180 | # print(kp[0]) # 多少个角点,就有多少个下标
181 | # tu = kp[0].pt #(提取坐标) pt指的是元组 tuple(x,y)
182 | # print(tu[0],tu[1]) # 输出第一个keypoint的x,y坐标
183 |
184 | sparse_depth = np.zeros(depth.shape)
185 | for i in range(len(kp)):
186 | tu = kp[i].pt
187 | x = int(tu[0])
188 | y = int(tu[1])
189 | sparse_depth[y,x] = depth[y,x] # x,y和行,列的顺序不一样
190 |
191 | return sparse_depth
192 |
193 | def create_rgbd(self, rgb, depth, num_samples):
194 | sparse_depth = self.create_sparse_depth_ORB(rgb, depth, num_samples)
195 | # sparse_depth = self.create_sparse_depth(depth, num_samples)
196 |
197 | # rgbd = np.dstack((rgb[:,:,0], rgb[:,:,1], rgb[:,:,2], sparse_depth))
198 | rgbd = np.append(rgb, np.expand_dims(sparse_depth, axis=2), axis=2) # append()相当于push_back()
199 | return rgbd
200 |
201 | # 获取原始图像
202 | def __getraw__(self, index):
203 | """
204 | Args:
205 | index (int): Index
206 |
207 | Returns:
208 | tuple: (rgb, depth) the raw data.
209 | """
210 | path, target = self.imgs[index]
211 | rgb, depth = self.loader(path) # 这个loader就是h5_loader
212 | return rgb, depth
213 |
214 | def __get_all_item__(self, index):
215 | """
216 | Args:
217 | index (int): Index
218 |
219 | Returns:
220 | tuple: (input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np)
221 | """
222 | rgb, depth = self.__getraw__(index)
223 | if self.transform is not None:
224 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth) # 经过数据增强步骤后的结果
225 | else:
226 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
227 |
228 | # color normalization
229 | # rgb_tensor = normalize_rgb(rgb_tensor)
230 | # rgb_np = normalize_np(rgb_np)
231 |
232 | if self.modality == 'rgb':
233 | input_np = rgb_np
234 | elif self.modality == 'rgbd':
235 | input_np = self.create_rgbd(rgb_np, depth_np, self.num_samples)
236 | elif self.modality == 'd':
237 | input_np = self.create_sparse_depth_ORB(rgb_np, depth_np, self.num_samples)
238 | # input_np = self.create_sparse_depth(depth_np, self.num_samples)
239 |
240 | input_tensor = to_tensor(input_np)
241 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
242 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
243 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
244 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
245 |
246 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np
247 |
248 | def __getitem__(self, index):
249 | """
250 | Args:
251 | index (int): Index
252 |
253 | Returns:
254 | tuple: (input_tensor, depth_tensor)
255 | """
256 | input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np = self.__get_all_item__(index)
257 |
258 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
259 |
260 | def __len__(self):
261 | return len(self.imgs)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/transforms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 对图片做各种变换的函数
2 |
3 | from __future__ import division # 导入未来支持的语言 division是精确除法 相见https://blog.csdn.net/feixingfei/article/details/7081446
4 | import torch
5 | import math
6 | import random
7 |
8 | from PIL import Image, ImageOps, ImageEnhance
9 | try: # 尝试做...如果不行则... python中所有含条件的语句都要加冒号
10 | import accimage
11 | except ImportError:
12 | accimage = None
13 |
14 | import numpy as np
15 | import numbers
16 | import types
17 | import collections
18 | import warnings
19 |
20 | import scipy.ndimage.interpolation as itpl
21 | import scipy.misc as misc
22 |
23 |
24 | def _is_numpy_image(img): # numpy格式的图像
25 | return isinstance(img, np.ndarray) and (img.ndim in {2, 3})
26 | # return ... and ... 和 return ... or ...
27 | # 详见https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/1642792031752755300.html
28 | # 详见http://www.mamicode.com/info-detail-1765166.html
29 |
30 | def _is_pil_image(img): # PIL格式的图像
31 | if accimage is not None:
32 | return isinstance(img, (Image.Image, accimage.Image))
33 | else:
34 | return isinstance(img, Image.Image)
35 |
36 | def _is_tensor_image(img): # tensor格式的图像
37 | return torch.is_tensor(img) and img.ndimension() == 3
38 |
39 | def adjust_brightness(img, brightness_factor):
40 | """Adjust brightness of an Image.
41 |
42 | Args:
43 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
44 | brightness_factor (float): How much to adjust the brightness. Can be
45 | any non negative number. 0 gives a black image, 1 gives the
46 | original image while 2 increases the brightness by a factor of 2.
47 |
48 | Returns:
49 | PIL Image: Brightness adjusted image.
50 | """
51 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
52 | # 当程序出现错误时,python会自动引发异常,也可以通过raise显示地引发异常。
53 | # 一旦执行了raise语句,raise后面的语句将不能执行。
54 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
55 |
56 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Brightness(img)
57 | img = enhancer.enhance(brightness_factor)
58 | return img
59 |
60 |
61 | def adjust_contrast(img, contrast_factor):
62 | """Adjust contrast of an Image.
63 |
64 | Args:
65 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
66 | contrast_factor (float): How much to adjust the contrast. Can be any
67 | non negative number. 0 gives a solid gray image, 1 gives the
68 | original image while 2 increases the contrast by a factor of 2.
69 |
70 | Returns:
71 | PIL Image: Contrast adjusted image.
72 | """
73 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
74 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
75 |
76 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Contrast(img)
77 | img = enhancer.enhance(contrast_factor)
78 | return img
79 |
80 |
81 | def adjust_saturation(img, saturation_factor):
82 | """Adjust color saturation of an image.
83 |
84 | Args:
85 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
86 | saturation_factor (float): How much to adjust the saturation. 0 will
87 | give a black and white image, 1 will give the original image while
88 | 2 will enhance the saturation by a factor of 2.
89 |
90 | Returns:
91 | PIL Image: Saturation adjusted image.
92 | """
93 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
94 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
95 |
96 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Color(img)
97 | img = enhancer.enhance(saturation_factor)
98 | return img
99 |
100 |
101 | def adjust_hue(img, hue_factor): # hue: 色调
102 | """Adjust hue of an image.
103 |
104 | The image hue is adjusted by converting the image to HSV and
105 | cyclically shifting the intensities in the hue channel (H).
106 | The image is then converted back to original image mode.
107 |
108 | `hue_factor` is the amount of shift in H channel and must be in the
109 | interval `[-0.5, 0.5]`.
110 |
111 | See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hue for more details on Hue.
112 |
113 | Args:
114 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
115 | hue_factor (float): How much to shift the hue channel. Should be in
116 | [-0.5, 0.5]. 0.5 and -0.5 give complete reversal of hue channel in
117 | HSV space in positive and negative direction respectively.
118 | 0 means no shift. Therefore, both -0.5 and 0.5 will give an image
119 | with complementary colors while 0 gives the original image.
120 |
121 | Returns:
122 | PIL Image: Hue adjusted image.
123 | """
124 | if not(-0.5 <= hue_factor <= 0.5):
125 | raise ValueError('hue_factor is not in [-0.5, 0.5].'.format(hue_factor))
126 |
127 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
128 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
129 |
130 | input_mode = img.mode
131 | if input_mode in {'L', '1', 'I', 'F'}:
132 | return img
133 |
134 | h, s, v = img.convert('HSV').split()
135 |
136 | np_h = np.array(h, dtype=np.uint8)
137 | # uint8 addition take cares of rotation across boundaries
138 | with np.errstate(over='ignore'):
139 | np_h += np.uint8(hue_factor * 255)
140 | h = Image.fromarray(np_h, 'L')
141 |
142 | img = Image.merge('HSV', (h, s, v)).convert(input_mode)
143 | return img
144 |
145 |
146 | def adjust_gamma(img, gamma, gain=1):
147 | """Perform gamma correction on an image.
148 |
149 | Also known as Power Law Transform. Intensities in RGB mode are adjusted
150 | based on the following equation:
151 |
152 | I_out = 255 * gain * ((I_in / 255) ** gamma)
153 |
154 | See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction for more details.
155 |
156 | Args:
157 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
158 | gamma (float): Non negative real number. gamma larger than 1 make the
159 | shadows darker, while gamma smaller than 1 make dark regions
160 | lighter.
161 | gain (float): The constant multiplier.
162 | """
163 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
164 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
165 |
166 | if gamma < 0:
167 | raise ValueError('Gamma should be a non-negative real number')
168 |
169 | input_mode = img.mode
170 | img = img.convert('RGB')
171 |
172 | np_img = np.array(img, dtype=np.float32)
173 | np_img = 255 * gain * ((np_img / 255) ** gamma)
174 | np_img = np.uint8(np.clip(np_img, 0, 255))
175 |
176 | img = Image.fromarray(np_img, 'RGB').convert(input_mode)
177 | return img
178 |
179 |
180 | class Compose(object):
181 | """Composes several transforms together.
182 |
183 | Args:
184 | transforms (list of ``Transform`` objects): list of transforms to compose.
185 |
186 | Example:
187 | >>> transforms.Compose([
188 | >>> transforms.CenterCrop(10),
189 | >>> transforms.ToTensor(),
190 | >>> ])
191 | """
192 |
193 | def __init__(self, transforms):
194 | self.transforms = transforms
195 |
196 | # __call__:把类的实例当成函数来用,详见https://blog.csdn.net/yaokai_assultmaster/article/details/70256621
197 | def __call__(self, img):
198 | for t in self.transforms:
199 | img = t(img)
200 | return img
201 |
202 |
203 | class ToTensor(object):
204 | """Convert a ``numpy.ndarray`` to tensor.
205 |
206 | Converts a numpy.ndarray (H x W x C) to a torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W).
207 | """
208 |
209 | def __call__(self, img):
210 | """Convert a ``numpy.ndarray`` to tensor.
211 |
212 | Args:
213 | img (numpy.ndarray): Image to be converted to tensor.
214 |
215 | Returns:
216 | Tensor: Converted image.
217 | """
218 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
219 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
220 |
221 | if isinstance(img, np.ndarray):
222 | # handle numpy array
223 | if img.ndim == 3:
224 | img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose((2, 0, 1)).copy())
225 | elif img.ndim == 2:
226 | img = torch.from_numpy(img.copy())
227 | else:
228 | raise RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
229 |
230 | # backward compatibility
231 | # return img.float().div(255)
232 | return img.float()
233 |
234 |
235 | class NormalizeNumpyArray(object):
236 | """Normalize a ``numpy.ndarray`` with mean and standard deviation.
237 | Given mean: ``(M1,...,Mn)`` and std: ``(M1,..,Mn)`` for ``n`` channels, this transform
238 | will normalize each channel of the input ``numpy.ndarray`` i.e.
239 | ``input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
240 |
241 | Args:
242 | mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
243 | std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
244 | """
245 |
246 | def __init__(self, mean, std):
247 | self.mean = mean
248 | self.std = std
249 |
250 | def __call__(self, img):
251 | """
252 | Args:
253 | img (numpy.ndarray): Image of size (H, W, C) to be normalized.
254 |
255 | Returns:
256 | Tensor: Normalized image.
257 | """
258 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
259 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
260 | # TODO: make efficient
261 | # TODO在python中是一种助记符(Mnemonics),用来解释将要做什么。
262 | print(img.shape)
263 | for i in range(3): # 对RGB图像的每个通道进行同样的操作
264 | img[:,:,i] = (img[:,:,i] - self.mean[i]) / self.std[i]
265 | return img
266 |
267 | class NormalizeTensor(object):
268 | """Normalize an tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
269 | Given mean: ``(M1,...,Mn)`` and std: ``(M1,..,Mn)`` for ``n`` channels, this transform
270 | will normalize each channel of the input ``torch.*Tensor`` i.e.
271 | ``input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
272 |
273 | Args:
274 | mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
275 | std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
276 | """
277 |
278 | def __init__(self, mean, std):
279 | self.mean = mean
280 | self.std = std
281 |
282 | def __call__(self, tensor):
283 | """
284 | Args:
285 | tensor (Tensor): Tensor image of size (C, H, W) to be normalized.
286 |
287 | Returns:
288 | Tensor: Normalized Tensor image.
289 | """
290 | if not _is_tensor_image(tensor):
291 | raise TypeError('tensor is not a torch image.')
292 | # TODO: make efficient
293 | # zip()函数用于将可迭代的对象作为参数,将对象中对应的元素打包成一个个元组,然后返回由这些元组组成的列表。
294 | # 详见http://www.runoob.com/python/python-func-zip.html
295 | for t, m, s in zip(tensor, self.mean, self.std):
296 | t.sub_(m).div_(s)
297 | return tensor
298 |
299 | class Rotate(object):
300 | """Rotates the given ``numpy.ndarray``.
301 |
302 | Args:
303 | angle (float): The rotation angle in degrees.
304 | """
305 |
306 | def __init__(self, angle):
307 | self.angle = angle
308 |
309 | def __call__(self, img):
310 | """
311 | Args:
312 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be rotated.
313 |
314 | Returns:
315 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Rotated image.
316 | """
317 |
318 | return itpl.rotate(img, self.angle, reshape=False, prefilter=False)
319 |
320 | class Resize(object):
321 | """Resize the the given ``numpy.ndarray`` to the given size.
322 | Args:
323 | size (sequence or int): Desired output size. If size is a sequence like
324 | (h, w), output size will be matched to this. If size is an int,
325 | smaller edge of the image will be matched to this number.
326 | i.e, if height > width, then image will be rescaled to
327 | (size * height / width, size)
328 | interpolation (int, optional): Desired interpolation. Default is
329 | ``PIL.Image.BILINEAR``
330 | """
331 |
332 | def __init__(self, size, interpolation='nearest'):
333 | assert isinstance(size, int) or isinstance(size, float) or \
334 | (isinstance(size, collections.Iterable) and len(size) == 2)
335 | self.size = size
336 | self.interpolation = interpolation
337 |
338 | def __call__(self, img):
339 | """
340 | Args:
341 | img (PIL Image): Image to be scaled.
342 | Returns:
343 | PIL Image: Rescaled image.
344 | """
345 | if img.ndim == 3:
346 | return misc.imresize(img, self.size, self.interpolation)
347 | elif img.ndim == 2:
348 | return misc.imresize(img, self.size, self.interpolation, 'F')
349 | else:
350 | RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
351 |
352 |
353 | class CenterCrop(object):
354 | """Crops the given ``numpy.ndarray`` at the center.
355 |
356 | Args:
357 | size (sequence or int): Desired output size of the crop. If size is an
358 | int instead of sequence like (h, w), a square crop (size, size) is
359 | made.
360 | """
361 |
362 | def __init__(self, size):
363 | if isinstance(size, numbers.Number):
364 | self.size = (int(size), int(size))
365 | else:
366 | self.size = size
367 |
368 | # @staticmethod详见https://www.zhihu.com/question/20021164
369 | @staticmethod
370 | def get_params(img, output_size):
371 | """Get parameters for ``crop`` for center crop.
372 |
373 | Args:
374 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
375 | output_size (tuple): Expected output size of the crop.
376 |
377 | Returns:
378 | tuple: params (i, j, h, w) to be passed to ``crop`` for center crop.
379 | """
380 | h = img.shape[0]
381 | w = img.shape[1]
382 | th, tw = output_size
383 | i = int(round((h - th) / 2.))
384 | j = int(round((w - tw) / 2.))
385 |
386 | # # randomized cropping
387 | # i = np.random.randint(i-3, i+4)
388 | # j = np.random.randint(j-3, j+4)
389 |
390 | return i, j, th, tw
391 |
392 | def __call__(self, img):
393 | """
394 | Args:
395 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
396 |
397 | Returns:
398 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Cropped image.
399 | """
400 | i, j, h, w = self.get_params(img, self.size)
401 |
402 | """
403 | i: Upper pixel coordinate.
404 | j: Left pixel coordinate.
405 | h: Height of the cropped image.
406 | w: Width of the cropped image.
407 | """
408 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
409 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
410 | if img.ndim == 3:
411 | return img[i:i+h, j:j+w, :]
412 | elif img.ndim == 2:
413 | return img[i:i + h, j:j + w]
414 | else:
415 | raise RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
416 |
417 |
418 | class Lambda(object):
419 | """Apply a user-defined lambda as a transform.
420 |
421 | Args:
422 | lambd (function): Lambda/function to be used for transform.
423 | """
424 |
425 | def __init__(self, lambd):
426 | assert isinstance(lambd, types.LambdaType)
427 | self.lambd = lambd
428 |
429 | def __call__(self, img):
430 | return self.lambd(img)
431 |
432 |
433 | class HorizontalFlip(object):
434 | """Horizontally flip the given ``numpy.ndarray``.
435 |
436 | Args:
437 | do_flip (boolean): whether or not do horizontal flip.
438 |
439 | """
440 |
441 | def __init__(self, do_flip):
442 | self.do_flip = do_flip
443 |
444 | def __call__(self, img):
445 | """
446 | Args:
447 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be flipped.
448 |
449 | Returns:
450 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): flipped image.
451 | """
452 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
453 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
454 |
455 | if self.do_flip:
456 | return np.fliplr(img)
457 | else:
458 | return img
459 |
460 |
461 | class ColorJitter(object): # jitter:抖动
462 | """Randomly change the brightness, contrast and saturation of an image.
463 |
464 | Args:
465 | brightness (float): How much to jitter brightness. brightness_factor
466 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - brightness), 1 + brightness].
467 | contrast (float): How much to jitter contrast. contrast_factor
468 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - contrast), 1 + contrast].
469 | saturation (float): How much to jitter saturation. saturation_factor
470 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - saturation), 1 + saturation].
471 | hue(float): How much to jitter hue. hue_factor is chosen uniformly from
472 | [-hue, hue]. Should be >=0 and <= 0.5.
473 | """
474 | def __init__(self, brightness=0, contrast=0, saturation=0, hue=0):
475 | self.brightness = brightness
476 | self.contrast = contrast
477 | self.saturation = saturation
478 | self.hue = hue
479 |
480 | @staticmethod
481 | def get_params(brightness, contrast, saturation, hue):
482 | """Get a randomized transform to be applied on image.
483 |
484 | Arguments are same as that of __init__.
485 |
486 | Returns:
487 | Transform which randomly adjusts brightness, contrast and
488 | saturation in a random order.
489 | """
490 | transforms = []
491 | if brightness > 0:
492 | brightness_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - brightness), 1 + brightness)
493 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_brightness(img, brightness_factor)))
494 |
495 | if contrast > 0:
496 | contrast_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - contrast), 1 + contrast)
497 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_contrast(img, contrast_factor)))
498 |
499 | if saturation > 0:
500 | saturation_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - saturation), 1 + saturation)
501 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_saturation(img, saturation_factor)))
502 |
503 | if hue > 0:
504 | hue_factor = np.random.uniform(-hue, hue)
505 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_hue(img, hue_factor)))
506 |
507 | np.random.shuffle(transforms)
508 | transform = Compose(transforms)
509 |
510 | return transform
511 |
512 | def __call__(self, img):
513 | """
514 | Args:
515 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Input image.
516 |
517 | Returns:
518 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Color jittered image.
519 | """
520 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
521 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
522 |
523 | pil = Image.fromarray(img)
524 | transform = self.get_params(self.brightness, self.contrast,
525 | self.saturation, self.hue)
526 | return np.array(transform(pil))
527 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 导入一般的文件操作模块
2 | import argparse # 导入自动命令解析器 详见https://blog.csdn.net/ali197294332/article/details/51180628
3 | import os # 导入Python的系统基础操作模块
4 | import shutil # 导入高级的文件操作模块 详见https://www.cnblogs.com/MnCu8261/p/5494807.html
5 | import time # 导入对时间操作的函数 详见http://www.jb51.net/article/87721.htm
6 | import sys # 导入系统相关的信息模块
7 | import csv # 导入处理csv格式文件的相关模块 详见https://www.cnblogs.com/yanglang/p/7126660.html
8 |
9 | # 导入pytorch相关的模块
10 | import torch
11 | import torch.nn as nn
12 | import torch.nn.parallel # 可以实现模块级别的并行计算。可以将一个模块forward部分分到各个gpu中,然后backward时合并gradient到original module。
13 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn # cudnn: CUDA Deep Neural Network 相比标准的cuda,它在一些常用的神经网络操作上进行了性能的优化,比如卷积,pooling,归一化,以及激活层等等。
14 | import torch.optim
15 | import torch.utils.data
16 |
17 | # 导入自定义的模块
18 | from nyu_dataloader import NYUDataset
19 | from models import Decoder, ResNet
20 | from metrics import AverageMeter, Result
21 | import criteria
22 | import utils
23 |
24 | model_names = ['resnet18', 'resnet50']
25 | loss_names = ['l1', 'l2']
26 | data_names = ['NYUDataset']
27 | decoder_names = Decoder.names
28 | modality_names = NYUDataset.modality_names
29 |
30 | cudnn.benchmark = True
31 |
32 | # 创建一个解析处理器
33 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Sparse-to-Dense Training')
34 | # parser.add_argument('--data', metavar='DIR', help='path to dataset',
35 | # default="data/NYUDataset")
36 |
37 | # 设置多个参数
38 | parser.add_argument('--arch', '-a', metavar='ARCH', default='resnet18',
39 | choices=model_names,
40 | help='model architecture: ' +
41 | ' | '.join(model_names) +
42 | ' (default: resnet18)')
43 | # metavar:占位字符串,用于在输出帮助信息时,代替当前命令行选项的附加参数的值进行输出
44 | # join:连接字符串数组。将字符串、元组、列表中的元素以指定的字符(分隔符)连接生成一个新的字符串。详见https://blog.csdn.net/zmdzbzbhss123/article/details/52279008
45 | parser.add_argument('--data', metavar='DATA', default='nyudepthv2',
46 | choices=data_names,
47 | help='dataset: ' +
48 | ' | '.join(data_names) +
49 | ' (default: nyudepthv2)')
50 | parser.add_argument('--modality', '-m', metavar='MODALITY', default='rgb',
51 | choices=modality_names,
52 | help='modality: ' +
53 | ' | '.join(modality_names) +
54 | ' (default: rgb)')
55 | parser.add_argument('-s', '--num-samples', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
56 | help='number of sparse depth samples (default: 0)')
57 | parser.add_argument('--decoder', '-d', metavar='DECODER', default='deconv2',
58 | choices=decoder_names,
59 | help='decoder: ' +
60 | ' | '.join(decoder_names) +
61 | ' (default: deconv2)')
62 | parser.add_argument('-j', '--workers', default=10, type=int, metavar='N',
63 | help='number of data loading workers (default: 10)')
64 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=30, type=int, metavar='N',
65 | help='number of total epochs to run (default: 30)')
66 | parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
67 | help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
68 | parser.add_argument('-c', '--criterion', metavar='LOSS', default='l1',
69 | choices=loss_names,
70 | help='loss function: ' +
71 | ' | '.join(loss_names) +
72 | ' (default: l1)')
73 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=8, type=int,
74 | help='mini-batch size (default: 8)')
75 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.01, type=float,
76 | metavar='LR', help='initial learning rate (default 0.01)')
77 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, metavar='M',
78 | help='momentum')
79 | parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', '--wd', default=1e-4, type=float,
80 | metavar='W', help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)')
81 | parser.add_argument('--print-freq', '-p', default=10, type=int,
82 | metavar='N', help='print frequency (default: 10)')
83 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
84 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
85 | parser.add_argument('-e', '--evaluate', dest='evaluate', action='store_true',
86 | help='evaluate model on validation set')
87 | parser.add_argument('--pretrained', dest='pretrained', action='store_true',
88 | default=True, help='use ImageNet pre-trained weights (default: True)')
89 |
90 | fieldnames = ['mse', 'rmse', 'absrel', 'lg10', 'mae',
91 | 'delta1', 'delta2', 'delta3',
92 | 'data_time', 'gpu_time']
93 |
94 | # Result()是criteria.py中的类
95 | best_result = Result()
96 | best_result.set_to_worst()
97 |
98 | # 定义函数
99 | # 基本格式:
100 | # def function_name(parameters):
101 | # expressions
102 | # Python使用缩进来规定代码的作用域
103 | def main():
104 | global args, best_result, output_directory, train_csv, test_csv # 全局变量
105 | args = parser.parse_args() # 获取参数值
106 | args.data = os.path.join('data', args.data)
107 | # os.path.join()函数:将多个路径组合后返回
108 | # 语法:os.path.join(path1[,path2[,......]])
109 | # 注:第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
110 | # 注意if的语句后面有冒号
111 | # args中modality的参数值。modality之前定义过
112 | if args.modality == 'rgb' and args.num_samples != 0:
113 | print("number of samples is forced to be 0 when input modality is rgb")
114 | args.num_samples = 0
115 | # 若是RGB的sparse-to-dense,则在生成训练数据时将稀疏深度点设为0
116 |
117 | # create results folder, if not already exists
118 | output_directory = os.path.join('results',
119 | 'NYUDataset.modality={}.nsample={}.arch={}.decoder={}.criterion={}.lr={}.bs={}'.
120 | format(args.modality, args.num_samples, args.arch, args.decoder, args.criterion, args.lr, args.batch_size)) # 输出文件名的格式
121 |
122 | # 如果路径不存在
123 | if not os.path.exists(output_directory):
124 | os.makedirs(output_directory)
125 |
126 | train_csv = os.path.join(output_directory, 'train.csv')
127 | test_csv = os.path.join(output_directory, 'test.csv')
128 | best_txt = os.path.join(output_directory, 'best.txt')
129 |
130 | # define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
131 | if args.criterion == 'l2':
132 | criterion = criteria.MaskedMSELoss().cuda() # 调用别的py文件中的内容时,若被调用的是函数,则直接写函数名即可;若被调用的是类,则要按这句话的格式写
133 | out_channels = 1
134 | # elif: else if
135 | elif args.criterion == 'l1':
136 | criterion = criteria.MaskedL1Loss().cuda()
137 | out_channels = 1
138 |
139 | # Data loading code
140 | print("=> creating data loaders ...")
141 | traindir = os.path.join(args.data, 'train')
142 | valdir = os.path.join(args.data, 'val')
143 |
144 | train_dataset = NYUDataset(traindir, type='train',
145 | modality=args.modality, num_samples=args.num_samples)
146 | # DataLoader是导入数据的函数
147 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
148 | train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True,
149 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True, sampler=None)
150 |
151 | # set batch size to be 1 for validation
152 | val_dataset = NYUDataset(valdir, type='val',
153 | modality=args.modality, num_samples=args.num_samples)
154 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
155 | batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True)
156 |
157 | print("=> data loaders created.")
158 |
159 | # evaluation mode
160 | if args.evaluate:
161 | best_model_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'model_best.pth.tar')
162 | if os.path.isfile(best_model_filename):
163 | print("=> loading best model '{}'".format(best_model_filename))
164 | checkpoint = torch.load(best_model_filename)
165 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
166 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
167 | model = checkpoint['model']
168 | print("=> loaded best model (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
169 | else: # else也要加:
170 | print("=> no best model found at '{}'".format(best_model_filename))
171 | validate(val_loader, model, checkpoint['epoch'], write_to_file=False)
172 | return
173 |
174 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
175 | elif args.resume:
176 | if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
177 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
178 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
179 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']+1
180 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
181 | model = checkpoint['model']
182 | optimizer = checkpoint['optimizer']
183 | print("=> loaded checkpoint (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
184 | else:
185 | print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
186 |
187 | # create new model
188 | else:
189 | # define model
190 | print("=> creating Model ({}-{}) ...".format(args.arch, args.decoder))
191 | in_channels = len(args.modality) # len()返回对象的长度或项目个数
192 | if args.arch == 'resnet50':
193 | model = ResNet(layers=50, decoder=args.decoder, in_channels=in_channels,
194 | out_channels=out_channels, pretrained=args.pretrained)
195 | elif args.arch == 'resnet18':
196 | model = ResNet(layers=18, decoder=args.decoder, in_channels=in_channels,
197 | out_channels=out_channels, pretrained=args.pretrained)
198 | print("=> model created.")
199 |
200 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr, momentum=args.momentum, weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
201 |
202 | # create new csv files with only header
203 | # with open() as xxx: 的用法详见https://www.cnblogs.com/ymjyqsx/p/6554817.html
204 | with open(train_csv, 'w') as csvfile:
205 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
206 | writer.writeheader()
207 | with open(test_csv, 'w') as csvfile:
208 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
209 | writer.writeheader()
210 |
211 | # model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
212 | model = model.cuda()
213 | print(model)
214 | print("=> model transferred to GPU.")
215 |
216 | # for循环也要有:
217 | # 一般情况下,循环次数未知采用while循环,循环次数已知采用for
218 | for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
219 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch)
220 |
221 | # train for one epoch
222 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
223 |
224 | # evaluate on validation set
225 | result, img_merge = validate(val_loader, model, epoch)
226 | # Python的return可以返回多个值
227 |
228 | # remember best rmse and save checkpoint
229 | is_best = result.rmse < best_result.rmse
230 | if is_best:
231 | best_result = result
232 | with open(best_txt, 'w') as txtfile:
233 | # 字符串格式化输出
234 | # :3f中,3表示输出宽度,f表示浮点型。若输出位数小于此宽度,则默认右对齐,左边补空格。
235 | # 若输出位数大于宽度,则按实际位数输出。
236 | # :.3f中,.3表示指定除小数点外的输出位数,f表示浮点型。
237 | txtfile.write("epoch={}\nmse={:.3f}\nrmse={:.3f}\nabsrel={:.3f}\nlg10={:.3f}\nmae={:.3f}\ndelta1={:.3f}\nt_gpu={:.4f}\n".
238 | format(epoch, result.mse, result.rmse, result.absrel, result.lg10, result.mae, result.delta1, result.gpu_time))
239 | # None表示该值是一个空对象,空值是Python里一个特殊的值,用None表示。None不能理解为0,因为0是有意义的,而None是一个特殊的空值。
240 | # 你可以将None赋值给任何变量,也可以将任何变量赋值给一个None值的对象
241 | # None在判断的时候是False
242 | # NULL是空字符,和None不一样
243 | if img_merge is not None:
244 | img_filename = output_directory + '/comparison_best.png'
245 | utils.save_image(img_merge, img_filename)
246 |
247 | # Python中,万物皆对象,所有的操作都是针对对象的。一个对象包括两方面的特征:
248 | # 属性:去描述它的特征
249 | # 方法:它所具有的行为
250 | # 所以,对象=属性+方法 (其实方法也是一种属性,一种区别于数据属性的可调用属性)
251 |
252 | save_checkpoint({
253 | 'epoch': epoch,
254 | 'arch': args.arch,
255 | 'model': model,
256 | 'best_result': best_result,
257 | 'optimizer' : optimizer,
258 | }, is_best, epoch)
259 |
260 |
261 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
262 | average_meter = AverageMeter()
263 |
264 | # switch to train mode
265 | model.train()
266 |
267 | end = time.time() # 计时开始
268 | # enumerate()用于将一个可遍历的数据对象(如列表、元组或字符串)组合为一个索引序列,同时列出数据和数据下标,一般用在for循环当中。
269 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
270 |
271 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda()
272 | # torch.autograd提供实现任意标量值功能的自动区分的类和功能。它将所有张量包装在Variable对象中。
273 | # Variable可以看作是对Tensor对象周围的一个薄包装,也包含了和张量相关的梯度,以及对创建它的函数的引用。
274 | # 此引用允许对创建数据的整个操作链进行回溯。需要BP的网络都是通过Variable来计算的。
275 | # pytorch中的所有运算都是基于Tensor的,Variable只是一个Wrapper,Variable的计算的实质就是里面的Tensor在计算。
276 | # 详见https://blog.csdn.net/KGzhang/article/details/77483383
277 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
278 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
279 | torch.cuda.synchronize() # 等待当前设备上所有流中的所有内核完成
280 | data_time = time.time() - end # 计算用时
281 |
282 | # compute depth_pred
283 | end = time.time()
284 | depth_pred = model(input_var)
285 | loss = criterion(depth_pred, target_var)
286 | # optimizer包提供训练时更新参数的功能
287 | optimizer.zero_grad() # zero the gradient buffers,必须要置零
288 | # 在BP的时候,pytorch将Variable的梯度放在Variable对象中,我们随时可以用Variable.grad得到grad。
289 | # 刚创建Variable的时候,它的grad属性初始化为0.0
290 | loss.backward() # compute gradient and do SGD step
291 | optimizer.step() # 更新
292 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
293 | gpu_time = time.time() - end
294 |
295 | # measure accuracy and record loss
296 | result = Result()
297 | output1 = torch.index_select(depth_pred.data, 1, torch.cuda.LongTensor([0]))
298 | result.evaluate(output1, target)
299 | average_meter.update(result, gpu_time, data_time, input.size(0))
300 | end = time.time()
301 |
302 | if (i + 1) % args.print_freq == 0:
303 | print('=> output: {}'.format(output_directory))
304 | print('Train Epoch: {0} [{1}/{2}]\t'
305 | 't_Data={data_time:.3f}({average.data_time:.3f}) '
306 | 't_GPU={gpu_time:.3f}({average.gpu_time:.3f}) '
307 | 'RMSE={result.rmse:.2f}({average.rmse:.2f}) '
308 | 'MAE={result.mae:.2f}({average.mae:.2f}) '
309 | 'Delta1={result.delta1:.3f}({average.delta1:.3f}) '
310 | 'REL={result.absrel:.3f}({average.absrel:.3f}) '
311 | 'Lg10={result.lg10:.3f}({average.lg10:.3f}) '.format(
312 | epoch, i+1, len(train_loader), data_time=data_time,
313 | gpu_time=gpu_time, result=result, average=average_meter.average()))
314 |
315 | avg = average_meter.average()
316 | with open(train_csv, 'a') as csvfile:
317 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
318 | writer.writerow({'mse': avg.mse, 'rmse': avg.rmse, 'absrel': avg.absrel, 'lg10': avg.lg10,
319 | 'mae': avg.mae, 'delta1': avg.delta1, 'delta2': avg.delta2, 'delta3': avg.delta3,
320 | 'gpu_time': avg.gpu_time, 'data_time': avg.data_time})
321 |
322 |
323 | def validate(val_loader, model, epoch, write_to_file=True):
324 | average_meter = AverageMeter()
325 |
326 | # switch to evaluate mode
327 | model.eval()
328 |
329 | end = time.time()
330 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
331 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda() # 从后面看,这里的target应该是深度图的ground truth
332 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
333 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
334 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
335 | data_time = time.time() - end
336 |
337 | # compute output
338 | end = time.time()
339 | depth_pred = model(input_var)
340 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
341 | gpu_time = time.time() - end
342 |
343 | # measure accuracy and record loss
344 | result = Result()
345 | output1 = torch.index_select(depth_pred.data, 1, torch.cuda.LongTensor([0]))
346 | result.evaluate(output1, target)
347 | average_meter.update(result, gpu_time, data_time, input.size(0))
348 | end = time.time()
349 |
350 | # save 8 images for visualization
351 | skip = 50
352 | if args.modality == 'd':
353 | img_merge = None
354 | else:
355 | if args.modality == 'rgb':
356 | rgb = input
357 | elif args.modality == 'rgbd':
358 | rgb = input[:,:3,:,:]
359 |
360 | if i == 0:
361 | img_merge = utils.merge_into_row(rgb, target, depth_pred)
362 | # 隔50个图片抽一张作为可视化结果
363 | elif (i < 8*skip) and (i % skip == 0): # and等同于C++中的&&
364 | row = utils.merge_into_row(rgb, target, depth_pred)
365 | img_merge = utils.add_row(img_merge, row) # 添加一行
366 | elif i == 8*skip: # 只保存8张图片,保存够8张后输出
367 | filename = output_directory + '/comparison_' + str(epoch) + '.png' # str():将()中的对象转换为字符串
368 | utils.save_image(img_merge, filename) # 建议:把这种常用的功能写到特定的脚本文件中,再像这样调用
369 |
370 | if (i+1) % args.print_freq == 0:
371 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
372 | 't_GPU={gpu_time:.3f}({average.gpu_time:.3f})\t'
373 | 'RMSE={result.rmse:.2f}({average.rmse:.2f}) '
374 | 'MAE={result.mae:.2f}({average.mae:.2f}) '
375 | 'Delta1={result.delta1:.3f}({average.delta1:.3f}) '
376 | 'REL={result.absrel:.3f}({average.absrel:.3f}) '
377 | 'Lg10={result.lg10:.3f}({average.lg10:.3f}) '.format(
378 | i+1, len(val_loader), gpu_time=gpu_time, result=result, average=average_meter.average()))
379 |
380 | avg = average_meter.average()
381 |
382 | print('\n*\n'
383 | 'RMSE={average.rmse:.3f}\n'
384 | 'MAE={average.mae:.3f}\n'
385 | 'Delta1={average.delta1:.3f}\n'
386 | 'REL={average.absrel:.3f}\n'
387 | 'Lg10={average.lg10:.3f}\n'
388 | 't_GPU={time:.3f}\n'.format(
389 | average=avg, time=avg.gpu_time))
390 |
391 | if write_to_file:
392 | with open(test_csv, 'a') as csvfile:
393 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
394 | writer.writerow({'mse': avg.mse, 'rmse': avg.rmse, 'absrel': avg.absrel, 'lg10': avg.lg10,
395 | 'mae': avg.mae, 'delta1': avg.delta1, 'delta2': avg.delta2, 'delta3': avg.delta3,
396 | 'data_time': avg.data_time, 'gpu_time': avg.gpu_time})
397 |
398 | return avg, img_merge
399 |
400 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, epoch):
401 | checkpoint_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'checkpoint-' + str(epoch) + '.pth.tar')
402 | torch.save(state, checkpoint_filename)
403 | if is_best:
404 | best_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'model_best.pth.tar')
405 | shutil.copyfile(checkpoint_filename, best_filename)
406 | if epoch > 0:
407 | prev_checkpoint_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'checkpoint-' + str(epoch-1) + '.pth.tar')
408 | if os.path.exists(prev_checkpoint_filename):
409 | os.remove(prev_checkpoint_filename)
410 |
411 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch):
412 | # """ """中的内容为函数的说明,在鼠标放在此函数上时会自动显示该说明
413 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 every 10 epochs"""
414 | # //:整数除法,返回不大于结果的一个最大的整数
415 | # /:浮点数除法。在符号前后的数字都为整型时,输出的也是整型,和c++一样
416 | # 在Python数学运算中*代表乘法,**为指数运算
417 | lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 10))
418 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
419 | param_group['lr'] = lr
420 |
421 | # 这句话是程序的入口
422 | # 意思是:当.py文件被直接运行时,if __name__ == '__main__'之下的代码块将被运行;当.py文件以模块形式被导入时,if __name__ == '__main__'之下的代码块不被运行。
423 | # 详见https://blog.csdn.net/yjk13703623757/article/details/77918633
424 | if __name__ == '__main__':
425 | main()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------