├── Dockerfile
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── calculate_similarity.py
├── datasets
├── __init__.py
├── activity_net.pickle
├── cc_web_video.pickle
├── evve.pickle
└── fivr.pickle
├── evaluation.py
├── examples
├── video1.gif
└── video2.gif
├── model
├── __init__.py
├── layers.py
├── nets
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── i3d.py
│ ├── resnet_utils.py
│ ├── resnet_v1.py
│ └── vgg_preprocessing.py
├── similarity.py
└── visil.py
├── requirements.txt
└── video_similarity.png
/Dockerfile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | FROM tensorflow/tensorflow:1.15.0-gpu-py3
2 |
3 | WORKDIR /
4 |
5 | RUN apt-get update --fix-missing && \
6 | apt-get clean && \
7 | apt-get install -y libsm6 libxext6 libxrender-dev libgl1-mesa-glx git wget
8 |
9 | RUN git clone --depth 1 https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/visil /visil
10 |
11 | RUN wget http://ndd.iti.gr/visil/ckpt.zip
12 |
13 | RUN unzip ckpt.zip -d /visil
14 |
15 | RUN python -m pip install --upgrade pip
16 |
17 | RUN python -m pip install --upgrade numpy tqdm>=4.2 opencv-python>=3.1.0
18 |
19 | RUN python -m pip install --upgrade tensorflow-probability==0.7 dm-sonnet==1.25
20 |
21 | WORKDIR /visil
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Apache License
2 | Version 2.0, January 2004
3 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/
4 |
5 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
6 |
7 | 1. Definitions.
8 |
9 | "License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
10 | and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
11 |
12 | "Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
13 | the copyright owner that is granting the License.
14 |
15 | "Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
16 | other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
17 | control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
18 | "control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
19 | direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
20 | otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
21 | outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
22 |
23 | "You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
24 | exercising permissions granted by this License.
25 |
26 | "Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
27 | including but not limited to software source code, documentation
28 | source, and configuration files.
29 |
30 | "Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
31 | transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
32 | not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
33 | and conversions to other media types.
34 |
35 | "Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
36 | Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
37 | copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
38 | (an example is provided in the Appendix below).
39 |
40 | "Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
41 | form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
42 | editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
43 | represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
44 | of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
45 | separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
46 | the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
47 |
48 | "Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
49 | the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
50 | to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
51 | submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
52 | or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
53 | the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
54 | means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
55 | to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
56 | communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
57 | and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
58 | Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
59 | excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
60 | designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
61 |
62 | "Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
63 | on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
64 | subsequently incorporated within the Work.
65 |
66 | 2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
67 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
68 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
69 | copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
70 | publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
71 | Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
72 |
73 | 3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
74 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
75 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
76 | (except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
77 | use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
78 | where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
79 | by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
80 | Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
81 | with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
82 | institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
83 | cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
84 | or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
85 | or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
86 | granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
87 | as of the date such litigation is filed.
88 |
89 | 4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
90 | Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
91 | modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
92 | meet the following conditions:
93 |
94 | (a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
95 | Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
96 |
97 | (b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
98 | stating that You changed the files; and
99 |
100 | (c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
101 | that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
102 | attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
103 | excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
104 | the Derivative Works; and
105 |
106 | (d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
107 | distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
108 | include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
109 | within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
110 | pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
111 | of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
112 | as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
113 | documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
114 | within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
115 | wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
116 | of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
117 | do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
118 | notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
119 | or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
120 | that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
121 | as modifying the License.
122 |
123 | You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
124 | may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
125 | for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
126 | for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
127 | reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
128 | the conditions stated in this License.
129 |
130 | 5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
131 | any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
132 | by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
133 | this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
134 | Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
135 | the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
136 | with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
137 |
138 | 6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
139 | names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
140 | except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
141 | origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
142 |
143 | 7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
144 | agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
145 | Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
146 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
147 | implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
148 | of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
149 | PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
150 | appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
151 | risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
152 |
153 | 8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
154 | whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
155 | unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
156 | negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
157 | liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
158 | incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
159 | result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
160 | Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
161 | work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
162 | other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
163 | has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
164 |
165 | 9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
166 | the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
167 | and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
168 | or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
169 | License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
170 | on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
171 | of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
172 | defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
173 | incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
174 | of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
175 |
176 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
177 |
178 | APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
179 |
180 | To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
181 | boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
182 | replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
183 | the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
184 | comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
185 | file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
186 | same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
187 | identification within third-party archives.
188 |
189 | Copyright 2019 Giorgos Kordopatis-Zilos. All rights reserved.
190 |
191 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
192 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
193 | You may obtain a copy of the License at
194 |
195 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
196 |
197 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
198 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
199 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
200 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
201 | limitations under the License.
202 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # ViSiL: Fine-grained Spatio-Temporal Video Similarity Learning
2 | This repository contains the Tensorflow implementation of the paper
3 | [ViSiL: Fine-grained Spatio-Temporal Video Similarity Learning](http://openaccess.thecvf.com/content_ICCV_2019/papers/Kordopatis-Zilos_ViSiL_Fine-Grained_Spatio-Temporal_Video_Similarity_Learning_ICCV_2019_paper.pdf).
4 | It provides code for the calculation of similarities between the query and database videos given by the user.
5 | Also, it contains an evaluation script to reproduce the results of the paper. The video similarity calculation
6 | is achieved by applying a frame-to-frame function that respects the spatial within-frame structure of videos and
7 | a learned video-to-video similarity function that also considers the temporal structure of videos.
8 |
9 | The PyTorch implementation of ViSiL can be found [here](https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/tree/pytorch)
10 |
11 | 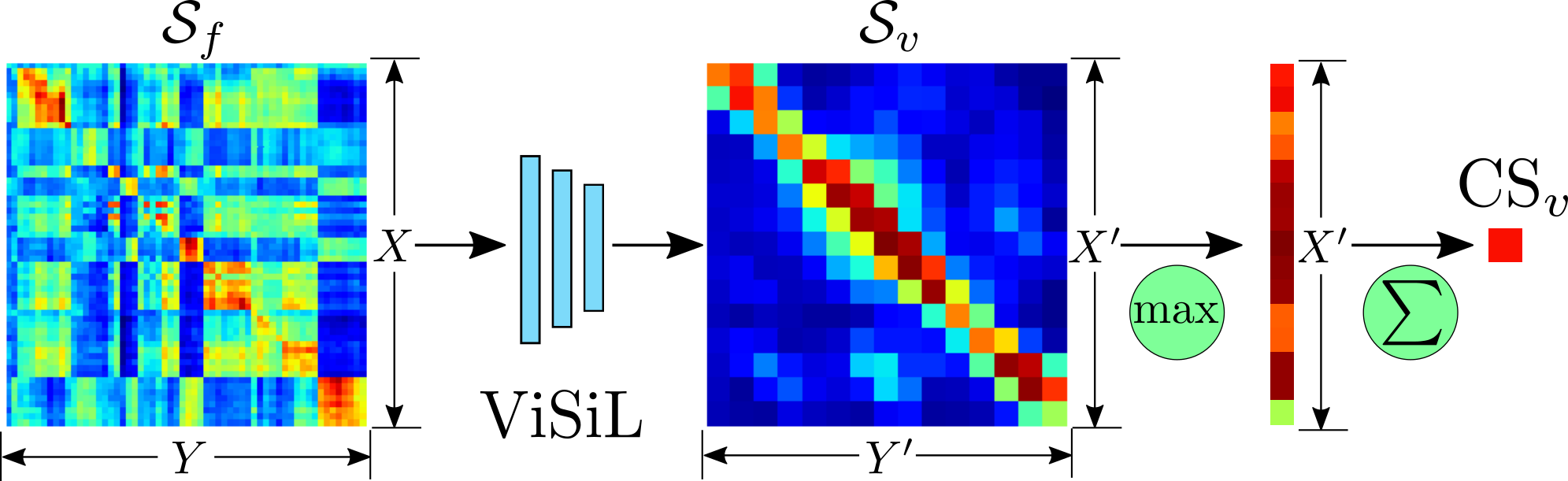 12 |
13 | ## Prerequisites
14 | * Python 3
15 | * Tensorflow 1.xx (tested with 1.8-1.15)
16 |
17 | ## Getting started
18 |
19 | ### Installation
20 |
21 | * Clone this repo:
22 | ```bash
23 | git clone https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/visil
24 | cd visil
25 | ```
26 | * You can install all the dependencies by
27 | ```bash
28 | pip install -r requirements.txt
29 | ```
30 |
31 | * Download and unzip the pretrained model:
32 | ```bash
33 | wget http://ndd.iti.gr/visil/ckpt.zip
34 | unzip ckpt.zip
35 | ```
36 |
37 | * If you want to use I3D as backbone network (used for AVR in the paper), then install the following packages:
38 | ```bash
39 | # For tensoflow version >= 1.14
40 | pip install tensorflow-probability==0.7 dm-sonnet==1.25
41 |
42 | # For tensoflow version < 1.14
43 | pip install tensorflow-probability==0.6 dm-sonnet==1.23
44 | ```
45 |
46 | ### Video similarity calculation
47 | * Create a file that contains the query videos.
48 | Each line of the file have to contain a video id and a path to the corresponding video file,
49 | separated by a tab character (\\t). Example:
50 |
51 | wrC_Uqk3juY queries/wrC_Uqk3juY.mp4
52 | k_NT43aJ_Jw queries/k_NT43aJ_Jw.mp4
53 | 2n30dbPBNKE queries/2n30dbPBNKE.mp4
54 | ...
55 |
56 |
57 | * Create a file with the same format for the database videos.
58 |
59 | * Run the following command to calculate the similarity between all the query and database videos
60 | ```bash
61 | python calculate_similarity.py --query_file queries.txt --database_file database.txt --model_dir model/
62 | ```
63 |
64 | * For faster processing, you can load the query videos to the GPU memory by adding the flag ```--load_queries```
65 | ```bash
66 | python calculate_similarity.py --query_file queries.txt --database_file database.txt --model_dir model/ --load_queries
67 | ```
68 |
69 | * The calculated similarities are stored to the file given to the ```--output_file```. The file is in JSON format and
70 | contains a dictionary with every query id as keys, and another dictionary that contains the similarities of the dataset
71 | videos to the corresponding queries as values. See the example below
72 | ```bash
73 | {
74 | "wrC_Uqk3juY": {
75 | "KQh6RCW_nAo": 0.716,
76 | "0q82oQa3upE": 0.300,
77 | ...},
78 | "k_NT43aJ_Jw": {
79 | "-KuR8y1gjJQ": 1.0,
80 | "Xb19O5Iur44": 0.417,
81 | ...},
82 | ....
83 | }
84 | ```
85 | ```
86 |
87 | * Add flag `--help` to display the detailed description for the arguments of the similarity calculation script
88 |
89 | ```
90 | -q, --query_file QUERY_FILE Path to file that contains the query videos
91 | -d, --database_file DATABASE_FILE Path to file that contains the database videos
92 | -o, --output_file OUTPUT_FILE Name of the output file. Default: "results.json"
93 | --network NETWORK Backbone network used for feature extraction.
94 | Options: "resnet" or "i3d". Default: "resnet"
95 | --model_dir MODEL_DIR Path to the directory of the pretrained model.
96 | Default: "ckpt/resnet"
97 | -s, --similarity_function SIMILARITY_FUNCTION Function that will be used to calculate the
98 | similarity between query-candidate frames and
99 | videos.Options: "chamfer" or "symmetric_chamfer".
100 | Default: "chamfer"
101 | --batch_sz BATCH_SZ Number of frames contained in each batch during
102 | feature extraction. Default: 128
103 | --gpu_id GPU_ID Id of the GPU used. Default: 0
104 | -l, --load_queries Flag that indicates that the queries will be loaded to
105 | the GPU memory.
106 | --threads THREADS Number of threads used for video loading. Default: 8
107 | ```
108 |
109 | ### Evaluation
110 | * We also provide code to reproduce the experiments in the paper.
111 |
112 | * First, download the videos of the dataset you want. The supported options are:
113 | * [CC_WEB_VIDEO](http://vireo.cs.cityu.edu.hk/webvideo/) - Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
114 | * [FIVR-5K, FIVR-200K](http://ndd.iti.gr/fivr/) - Fine-grained Incident Video Retrieval
115 | * [EVVE](http://pascal.inrialpes.fr/data/evve/) - Event-based Video Retrieval
116 | * [ActivityNet](http://activity-net.org/) - Action Video Retrieval
117 |
118 | * Determine the pattern based on the video id that the source videos are stored. For example,
119 | if all dataset videos are stored in a folder with filename the video id and the extension `.mp4`,
120 | then the pattern is `{id}.mp4`. If each dataset video is stored in a different folder based on their
121 | video id with filename `video.mp4`, then the pattern us `{id}/video.mp4`.
122 | * The code replaces the `{id}` string with the id of the videos in the dataset
123 | * Also, it support supports Unix style pathname pattern expansion. For example, if video files have
124 | various extension, then the pattern can be e.g. `{id}/video.*`
125 | * For FIVR-200K, EVVE, ActivityNet, the Youtube ids are considered as the video ids
126 | * For CC_WEB_VIDEO, video ids derives from the number of the query set that the video belongs to,
127 | and the basename of the file. In particular, the video ids are in form `/`, e.g. `1/1_1_Y`
128 |
129 | * Run the `evaluation.py` by providing the name of the evaluation dataset, the path to video files,
130 | the pattern that the videos are stored
131 | ```
132 | python evaluation.py --dataset FIVR-5K --video_dir /path/to/videos/ --pattern {id}/video.* --load_queries
133 | ```
134 |
135 | ### Use ViSiL in your Python code
136 |
137 | Here is a toy example to run ViSiL on any data.
138 |
139 | ```python
140 | from model.visil import ViSiL
141 | from datasets import load_video
142 |
143 | # Load the two videos from the video files
144 | query_video = load_video('/path/to/query/video')
145 | target_video = load_video('/path/to/target/video')
146 |
147 | # Initialize ViSiL model and load pre-trained weights
148 | model = ViSiL('ckpt/resnet/')
149 |
150 | # Extract features of the two videos
151 | query_features = model.extract_features(query_video, batch_sz=32)
152 | target_features = model.extract_features(target_video, batch_sz=32)
153 |
154 | # Calculate similarity between the two videos
155 | similarity = model.calculate_video_similarity(query_features, target_features)
156 | ```
157 |
158 | ## Docker
159 | Thanks to [@theycallmeloki](https://github.com/theycallmeloki) for providing a
160 | [Dockerfile](https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/blob/master/Dockerfile) to setup a docker container for the repo.
161 |
162 | * First build a docker image based on the Dockerfile
163 | ```bash
164 | docker build -t visil:latest .
165 | ```
166 |
167 | * Start a docker container based on the created docker image
168 | ```bash
169 | docker run -it --gpus all --name ViSiL visil:latest
170 | ```
171 |
172 | ## Visualization
173 | To visualize similarity matrices and the ViSiL outputs, you may use
174 | [this Colab notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1XwkQpXrpyr7jjq3xCL7anASBjNfNCnkn).
175 |
176 | ## Citation
177 | If you use this code for your research, please consider citing our paper:
178 | ```bibtex
179 | @inproceedings{kordopatis2019visil,
180 | title={{ViSiL}: Fine-grained Spatio-Temporal Video Similarity Learning},
181 | author={Kordopatis-Zilos, Giorgos and Papadopoulos, Symeon and Patras, Ioannis and Kompatsiaris, Ioannis},
182 | booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
183 | year={2019}
184 | }
185 | ```
186 | ## Related Projects
187 |
188 | **[DnS](https://github.com/mever-team/distill-and-select)** - improved performance and better computational efficiency
189 |
190 | **[FIVR-200K](https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/FIVR-200K)** - download our FIVR-200K dataset
191 |
192 | ## License
193 | This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see the [LICENSE](LICENSE) file for details
194 |
195 | ## Contact for further details about the project
196 |
197 | Giorgos Kordopatis-Zilos (georgekordopatis@iti.gr)
12 |
13 | ## Prerequisites
14 | * Python 3
15 | * Tensorflow 1.xx (tested with 1.8-1.15)
16 |
17 | ## Getting started
18 |
19 | ### Installation
20 |
21 | * Clone this repo:
22 | ```bash
23 | git clone https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/visil
24 | cd visil
25 | ```
26 | * You can install all the dependencies by
27 | ```bash
28 | pip install -r requirements.txt
29 | ```
30 |
31 | * Download and unzip the pretrained model:
32 | ```bash
33 | wget http://ndd.iti.gr/visil/ckpt.zip
34 | unzip ckpt.zip
35 | ```
36 |
37 | * If you want to use I3D as backbone network (used for AVR in the paper), then install the following packages:
38 | ```bash
39 | # For tensoflow version >= 1.14
40 | pip install tensorflow-probability==0.7 dm-sonnet==1.25
41 |
42 | # For tensoflow version < 1.14
43 | pip install tensorflow-probability==0.6 dm-sonnet==1.23
44 | ```
45 |
46 | ### Video similarity calculation
47 | * Create a file that contains the query videos.
48 | Each line of the file have to contain a video id and a path to the corresponding video file,
49 | separated by a tab character (\\t). Example:
50 |
51 | wrC_Uqk3juY queries/wrC_Uqk3juY.mp4
52 | k_NT43aJ_Jw queries/k_NT43aJ_Jw.mp4
53 | 2n30dbPBNKE queries/2n30dbPBNKE.mp4
54 | ...
55 |
56 |
57 | * Create a file with the same format for the database videos.
58 |
59 | * Run the following command to calculate the similarity between all the query and database videos
60 | ```bash
61 | python calculate_similarity.py --query_file queries.txt --database_file database.txt --model_dir model/
62 | ```
63 |
64 | * For faster processing, you can load the query videos to the GPU memory by adding the flag ```--load_queries```
65 | ```bash
66 | python calculate_similarity.py --query_file queries.txt --database_file database.txt --model_dir model/ --load_queries
67 | ```
68 |
69 | * The calculated similarities are stored to the file given to the ```--output_file```. The file is in JSON format and
70 | contains a dictionary with every query id as keys, and another dictionary that contains the similarities of the dataset
71 | videos to the corresponding queries as values. See the example below
72 | ```bash
73 | {
74 | "wrC_Uqk3juY": {
75 | "KQh6RCW_nAo": 0.716,
76 | "0q82oQa3upE": 0.300,
77 | ...},
78 | "k_NT43aJ_Jw": {
79 | "-KuR8y1gjJQ": 1.0,
80 | "Xb19O5Iur44": 0.417,
81 | ...},
82 | ....
83 | }
84 | ```
85 | ```
86 |
87 | * Add flag `--help` to display the detailed description for the arguments of the similarity calculation script
88 |
89 | ```
90 | -q, --query_file QUERY_FILE Path to file that contains the query videos
91 | -d, --database_file DATABASE_FILE Path to file that contains the database videos
92 | -o, --output_file OUTPUT_FILE Name of the output file. Default: "results.json"
93 | --network NETWORK Backbone network used for feature extraction.
94 | Options: "resnet" or "i3d". Default: "resnet"
95 | --model_dir MODEL_DIR Path to the directory of the pretrained model.
96 | Default: "ckpt/resnet"
97 | -s, --similarity_function SIMILARITY_FUNCTION Function that will be used to calculate the
98 | similarity between query-candidate frames and
99 | videos.Options: "chamfer" or "symmetric_chamfer".
100 | Default: "chamfer"
101 | --batch_sz BATCH_SZ Number of frames contained in each batch during
102 | feature extraction. Default: 128
103 | --gpu_id GPU_ID Id of the GPU used. Default: 0
104 | -l, --load_queries Flag that indicates that the queries will be loaded to
105 | the GPU memory.
106 | --threads THREADS Number of threads used for video loading. Default: 8
107 | ```
108 |
109 | ### Evaluation
110 | * We also provide code to reproduce the experiments in the paper.
111 |
112 | * First, download the videos of the dataset you want. The supported options are:
113 | * [CC_WEB_VIDEO](http://vireo.cs.cityu.edu.hk/webvideo/) - Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
114 | * [FIVR-5K, FIVR-200K](http://ndd.iti.gr/fivr/) - Fine-grained Incident Video Retrieval
115 | * [EVVE](http://pascal.inrialpes.fr/data/evve/) - Event-based Video Retrieval
116 | * [ActivityNet](http://activity-net.org/) - Action Video Retrieval
117 |
118 | * Determine the pattern based on the video id that the source videos are stored. For example,
119 | if all dataset videos are stored in a folder with filename the video id and the extension `.mp4`,
120 | then the pattern is `{id}.mp4`. If each dataset video is stored in a different folder based on their
121 | video id with filename `video.mp4`, then the pattern us `{id}/video.mp4`.
122 | * The code replaces the `{id}` string with the id of the videos in the dataset
123 | * Also, it support supports Unix style pathname pattern expansion. For example, if video files have
124 | various extension, then the pattern can be e.g. `{id}/video.*`
125 | * For FIVR-200K, EVVE, ActivityNet, the Youtube ids are considered as the video ids
126 | * For CC_WEB_VIDEO, video ids derives from the number of the query set that the video belongs to,
127 | and the basename of the file. In particular, the video ids are in form `/`, e.g. `1/1_1_Y`
128 |
129 | * Run the `evaluation.py` by providing the name of the evaluation dataset, the path to video files,
130 | the pattern that the videos are stored
131 | ```
132 | python evaluation.py --dataset FIVR-5K --video_dir /path/to/videos/ --pattern {id}/video.* --load_queries
133 | ```
134 |
135 | ### Use ViSiL in your Python code
136 |
137 | Here is a toy example to run ViSiL on any data.
138 |
139 | ```python
140 | from model.visil import ViSiL
141 | from datasets import load_video
142 |
143 | # Load the two videos from the video files
144 | query_video = load_video('/path/to/query/video')
145 | target_video = load_video('/path/to/target/video')
146 |
147 | # Initialize ViSiL model and load pre-trained weights
148 | model = ViSiL('ckpt/resnet/')
149 |
150 | # Extract features of the two videos
151 | query_features = model.extract_features(query_video, batch_sz=32)
152 | target_features = model.extract_features(target_video, batch_sz=32)
153 |
154 | # Calculate similarity between the two videos
155 | similarity = model.calculate_video_similarity(query_features, target_features)
156 | ```
157 |
158 | ## Docker
159 | Thanks to [@theycallmeloki](https://github.com/theycallmeloki) for providing a
160 | [Dockerfile](https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/blob/master/Dockerfile) to setup a docker container for the repo.
161 |
162 | * First build a docker image based on the Dockerfile
163 | ```bash
164 | docker build -t visil:latest .
165 | ```
166 |
167 | * Start a docker container based on the created docker image
168 | ```bash
169 | docker run -it --gpus all --name ViSiL visil:latest
170 | ```
171 |
172 | ## Visualization
173 | To visualize similarity matrices and the ViSiL outputs, you may use
174 | [this Colab notebook](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1XwkQpXrpyr7jjq3xCL7anASBjNfNCnkn).
175 |
176 | ## Citation
177 | If you use this code for your research, please consider citing our paper:
178 | ```bibtex
179 | @inproceedings{kordopatis2019visil,
180 | title={{ViSiL}: Fine-grained Spatio-Temporal Video Similarity Learning},
181 | author={Kordopatis-Zilos, Giorgos and Papadopoulos, Symeon and Patras, Ioannis and Kompatsiaris, Ioannis},
182 | booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
183 | year={2019}
184 | }
185 | ```
186 | ## Related Projects
187 |
188 | **[DnS](https://github.com/mever-team/distill-and-select)** - improved performance and better computational efficiency
189 |
190 | **[FIVR-200K](https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/FIVR-200K)** - download our FIVR-200K dataset
191 |
192 | ## License
193 | This project is licensed under the Apache License 2.0 - see the [LICENSE](LICENSE) file for details
194 |
195 | ## Contact for further details about the project
196 |
197 | Giorgos Kordopatis-Zilos (georgekordopatis@iti.gr)
198 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/calculate_similarity.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import json
2 | import argparse
3 | import tensorflow as tf
4 |
5 | from tqdm import tqdm
6 | from model.visil import ViSiL
7 | from datasets import VideoGenerator
8 |
9 | if __name__ == '__main__':
10 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
11 | parser.add_argument('-q', '--query_file', type=str, required=True,
12 | help='Path to file that contains the query videos')
13 | parser.add_argument('-d', '--database_file', type=str, required=True,
14 | help='Path to file that contains the database videos')
15 | parser.add_argument('-o', '--output_file', type=str, default='results.json',
16 | help='Name of the output file. Default: \"results.json\"')
17 | parser.add_argument('-n', '--network', type=str, default='resnet',
18 | help='Backbone network used for feature extraction. '
19 | 'Options: \"resnet\" or \"i3d\". Default: \"resnet\"')
20 | parser.add_argument('-m', '--model_dir', type=str, default='ckpt/resnet',
21 | help='Path to the directory of the pretrained model. Default: \"ckpt/resnet\"')
22 | parser.add_argument('-s', '--similarity_function', type=str, default='chamfer',
23 | help='Function that will be used to calculate similarity '
24 | 'between query-target frames and videos.'
25 | 'Options: \"chamfer\" or \"symmetric_chamfer\". Default: \"chamfer\"')
26 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch_sz', type=int, default=128,
27 | help='Number of frames contained in each batch during feature extraction. Default: 128')
28 | parser.add_argument('-g', '--gpu_id', type=int, default=0,
29 | help='Id of the GPU used. Default: 0')
30 | parser.add_argument('-l', '--load_queries', action='store_true',
31 | help='Flag that indicates that the queries will be loaded to the GPU memory.')
32 | parser.add_argument('-t', '--threads', type=int, default=8,
33 | help='Number of threads used for video loading. Default: 8')
34 | args = parser.parse_args()
35 |
36 | # Create a video generator for the queries
37 | enqueuer = tf.keras.utils.OrderedEnqueuer(VideoGenerator(args.query_file, all_frames='i3d' in args.network),
38 | use_multiprocessing=True, shuffle=False)
39 | enqueuer.start(workers=args.threads, max_queue_size=args.threads*2)
40 | generator = enqueuer.get()
41 |
42 | # Initialize ViSiL model
43 | model = ViSiL(args.model_dir, net=args.network,
44 | load_queries=args.load_queries, gpu_id=args.gpu_id,
45 | similarity_function=args.similarity_function,
46 | queries_number=len(enqueuer.sequence) if args.load_queries else None)
47 |
48 | # Extract features of the queries
49 | queries, queries_ids = [], []
50 | pbar = tqdm(range(len(enqueuer.sequence)))
51 | for _ in pbar:
52 | frames, video_id = next(generator)
53 | features = model.extract_features(frames, args.batch_sz)
54 | queries.append(features)
55 | queries_ids.append(video_id)
56 | pbar.set_postfix(query_id=video_id)
57 | enqueuer.stop()
58 | model.set_queries(queries)
59 |
60 | # Create a video generator for the database video
61 | enqueuer = tf.keras.utils.OrderedEnqueuer(VideoGenerator(args.database_file, all_frames='i3d' in args.network),
62 | use_multiprocessing=True, shuffle=False)
63 | enqueuer.start(workers=args.threads, max_queue_size=args.threads*2)
64 | generator = enqueuer.get()
65 |
66 | # Calculate similarities between the queries and the database videos
67 | similarities = dict({query: dict() for query in queries_ids})
68 | pbar = tqdm(range(len(enqueuer.sequence)))
69 | for _ in pbar:
70 | frames, video_id = next(generator)
71 | if frames.shape[0] > 1:
72 | features = model.extract_features(frames, args.batch_sz)
73 | sims = model.calculate_similarities_to_queries(features)
74 | for i, s in enumerate(sims):
75 | similarities[queries_ids[i]][video_id] = float(s)
76 | pbar.set_postfix(video_id=video_id)
77 | enqueuer.stop()
78 |
79 | # Save similarities to a json file
80 | with open(args.output_file, 'w') as f:
81 | json.dump(similarities, f, indent=1)
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/datasets/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import cv2
3 | import glob
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import pickle as pk
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 |
8 |
9 | def resize_frame(frame, desired_size):
10 | min_size = np.min(frame.shape[:2])
11 | ratio = desired_size / float(min_size)
12 | frame = cv2.resize(frame, dsize=(0, 0), fx=ratio, fy=ratio, interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
13 | return frame
14 |
15 |
16 | def center_crop(frame, desired_size):
17 | old_size = frame.shape[:2]
18 | top = int(np.maximum(0, (old_size[0] - desired_size)/2))
19 | left = int(np.maximum(0, (old_size[1] - desired_size)/2))
20 | return frame[top: top+desired_size, left: left+desired_size, :]
21 |
22 |
23 | def load_video(video, all_frames=False):
24 | cv2.setNumThreads(3)
25 | cap = cv2.VideoCapture(video)
26 | fps = cap.get(cv2.CAP_PROP_FPS)
27 | if fps > 144 or fps is None:
28 | fps = 25
29 | frames = []
30 | count = 0
31 | while cap.isOpened():
32 | ret = cap.grab()
33 | if int(count % round(fps)) == 0 or all_frames:
34 | ret, frame = cap.retrieve()
35 | if isinstance(frame, np.ndarray):
36 | frame = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
37 | frames.append(center_crop(resize_frame(frame, 256), 256))
38 | else:
39 | break
40 | count += 1
41 | cap.release()
42 | return np.array(frames)
43 |
44 |
45 | class VideoGenerator(tf.keras.utils.Sequence):
46 | def __init__(self, video_file, all_frames=False):
47 | super(VideoGenerator, self).__init__()
48 | self.videos = np.loadtxt(video_file, dtype=str)
49 | self.videos = np.expand_dims(self.videos, axis=0) if self.videos.ndim == 1 else self.videos
50 | self.all_frames = all_frames
51 |
52 | def __len__(self):
53 | return len(self.videos)
54 |
55 | def __getitem__(self, index):
56 | return load_video(self.videos[index][1], all_frames=self.all_frames), self.videos[index][0]
57 |
58 |
59 | class DatasetGenerator(tf.keras.utils.Sequence):
60 | def __init__(self, rootDir, videos, pattern, all_frames=False):
61 | super(DatasetGenerator, self).__init__()
62 | self.rootDir = rootDir
63 | self.videos = videos
64 | self.pattern = pattern
65 | self.all_frames = all_frames
66 |
67 | def __len__(self):
68 | return len(self.videos)
69 |
70 | def __getitem__(self, index):
71 | video = glob.glob(os.path.join(self.rootDir, self.pattern.replace('{id}', self.videos[index])))
72 | if not len(video):
73 | print('[WARNING] Video not found: ', self.videos[index])
74 | return np.array([]), None
75 | else:
76 | return load_video(video[0], all_frames=self.all_frames), self.videos[index]
77 |
78 |
79 | class CC_WEB_VIDEO(object):
80 |
81 | def __init__(self):
82 | with open('datasets/cc_web_video.pickle', 'rb') as f:
83 | dataset = pk.load(f)
84 | self.database = dataset['index']
85 | self.queries = dataset['queries']
86 | self.ground_truth = dataset['ground_truth']
87 | self.excluded = dataset['excluded']
88 |
89 | def get_queries(self):
90 | return self.queries
91 |
92 | def get_database(self):
93 | return list(map(str, self.database.keys()))
94 |
95 | def calculate_mAP(self, similarities, all_videos=False, clean=False, positive_labels='ESLMV'):
96 | mAP = 0.0
97 | for query_set, labels in enumerate(self.ground_truth):
98 | query_id = self.queries[query_set]
99 | i, ri, s = 0.0, 0.0, 0.0
100 | if query_id in similarities:
101 | res = similarities[query_id]
102 | for video_id in sorted(res.keys(), key=lambda x: res[x], reverse=True):
103 | video = self.database[video_id]
104 | if (all_videos or video in labels) and (not clean or video not in self.excluded[query_set]):
105 | ri += 1
106 | if video in labels and labels[video] in positive_labels:
107 | i += 1.0
108 | s += i / ri
109 | positives = np.sum([1.0 for k, v in labels.items() if
110 | v in positive_labels and (not clean or k not in self.excluded[query_set])])
111 | mAP += s / positives
112 | return mAP / len(set(self.queries).intersection(similarities.keys()))
113 |
114 | def evaluate(self, similarities, all_db=None):
115 | if all_db is None:
116 | all_db = self.database
117 |
118 | print('=' * 5, 'CC_WEB_VIDEO Dataset', '=' * 5)
119 | not_found = len(set(self.queries) - similarities.keys())
120 | if not_found > 0:
121 | print('[WARNING] {} queries are missing from the results and will be ignored'.format(not_found))
122 | print('Queries: {} videos'.format(len(similarities)))
123 | print('Database: {} videos'.format(len(all_db)))
124 |
125 | print('-' * 25)
126 | print('All dataset')
127 | print('CC_WEB mAP: {:.4f}\nCC_WEB* mAP: {:.4f}\n'.format(
128 | self.calculate_mAP(similarities, all_videos=False, clean=False),
129 | self.calculate_mAP(similarities, all_videos=True, clean=False)))
130 |
131 | print('Clean dataset')
132 | print('CC_WEB mAP: {:.4f}\nCC_WEB* mAP: {:.4f}'.format(
133 | self.calculate_mAP(similarities, all_videos=False, clean=True),
134 | self.calculate_mAP(similarities, all_videos=True, clean=True)))
135 |
136 |
137 | class FIVR(object):
138 |
139 | def __init__(self, version='200k'):
140 | self.version = version
141 | with open('datasets/fivr.pickle', 'rb') as f:
142 | dataset = pk.load(f)
143 | self.annotation = dataset['annotation']
144 | self.queries = dataset[self.version]['queries']
145 | self.database = dataset[self.version]['database']
146 |
147 | def get_queries(self):
148 | return self.queries
149 |
150 | def get_database(self):
151 | return list(self.database)
152 |
153 | def calculate_mAP(self, query, res, all_db, relevant_labels):
154 | gt_sets = self.annotation[query]
155 | query_gt = set(sum([gt_sets[label] for label in relevant_labels if label in gt_sets], []))
156 | query_gt = query_gt.intersection(all_db)
157 |
158 | i, ri, s = 0.0, 0, 0.0
159 | for video in sorted(res.keys(), key=lambda x: res[x], reverse=True):
160 | if video != query and video in all_db:
161 | ri += 1
162 | if video in query_gt:
163 | i += 1.0
164 | s += i / ri
165 | return s / len(query_gt)
166 |
167 | def evaluate(self, similarities, all_db=None):
168 | if all_db is None:
169 | all_db = self.database
170 |
171 | DSVR, CSVR, ISVR = [], [], []
172 | for query, res in similarities.items():
173 | if query in self.queries:
174 | DSVR.append(self.calculate_mAP(query, res, all_db, relevant_labels=['ND', 'DS']))
175 | CSVR.append(self.calculate_mAP(query, res, all_db, relevant_labels=['ND', 'DS', 'CS']))
176 | ISVR.append(self.calculate_mAP(query, res, all_db, relevant_labels=['ND', 'DS', 'CS', 'IS']))
177 |
178 | print('=' * 5, 'FIVR-{} Dataset'.format(self.version.upper()), '=' * 5)
179 | not_found = len(set(self.queries) - similarities.keys())
180 | if not_found > 0:
181 | print('[WARNING] {} queries are missing from the results and will be ignored'.format(not_found))
182 |
183 | print('Queries: {} videos'.format(len(similarities)))
184 | print('Database: {} videos'.format(len(all_db)))
185 |
186 | print('-' * 16)
187 | print('DSVR mAP: {:.4f}'.format(np.mean(DSVR)))
188 | print('CSVR mAP: {:.4f}'.format(np.mean(CSVR)))
189 | print('ISVR mAP: {:.4f}'.format(np.mean(ISVR)))
190 |
191 |
192 | class EVVE(object):
193 |
194 | def __init__(self):
195 | with open('datasets/evve.pickle', 'rb') as f:
196 | dataset = pk.load(f)
197 | self.events = dataset['annotation']
198 | self.queries = dataset['queries']
199 | self.database = dataset['database']
200 | self.query_to_event = {qname: evname
201 | for evname, (queries, _, _) in self.events.items()
202 | for qname in queries}
203 |
204 | def get_queries(self):
205 | return list(self.queries)
206 |
207 | def get_database(self):
208 | return list(self.database)
209 |
210 | def score_ap_from_ranks_1(self, ranks, nres):
211 | """ Compute the average precision of one search.
212 | ranks = ordered list of ranks of true positives (best rank = 0)
213 | nres = total number of positives in dataset
214 | """
215 | if nres == 0 or ranks == []:
216 | return 0.0
217 |
218 | ap = 0.0
219 |
220 | # accumulate trapezoids in PR-plot. All have an x-size of:
221 | recall_step = 1.0 / nres
222 |
223 | for ntp, rank in enumerate(ranks):
224 | # ntp = nb of true positives so far
225 | # rank = nb of retrieved items so far
226 |
227 | # y-size on left side of trapezoid:
228 | if rank == 0:
229 | precision_0 = 1.0
230 | else:
231 | precision_0 = ntp / float(rank)
232 | # y-size on right side of trapezoid:
233 | precision_1 = (ntp + 1) / float(rank + 1)
234 | ap += (precision_1 + precision_0) * recall_step / 2.0
235 | return ap
236 |
237 | def evaluate(self, similarities, all_db=None):
238 | results = {e: [] for e in self.events}
239 | if all_db is None:
240 | all_db = set(self.database).union(set(self.queries))
241 |
242 | not_found = 0
243 | for query in self.queries:
244 | if query not in similarities:
245 | not_found += 1
246 | else:
247 | res = similarities[query]
248 | evname = self.query_to_event[query]
249 | _, pos, null = self.events[evname]
250 | if all_db:
251 | pos = pos.intersection(all_db)
252 | pos_ranks = []
253 |
254 | ri, n_ext = 0.0, 0.0
255 | for ri, dbname in enumerate(sorted(res.keys(), key=lambda x: res[x], reverse=True)):
256 | if dbname in pos:
257 | pos_ranks.append(ri - n_ext)
258 | if dbname not in all_db:
259 | n_ext += 1
260 |
261 | ap = self.score_ap_from_ranks_1(pos_ranks, len(pos))
262 | results[evname].append(ap)
263 |
264 | print('=' * 18, 'EVVE Dataset', '=' * 18)
265 |
266 | if not_found > 0:
267 | print('[WARNING] {} queries are missing from the results and will be ignored'.format(not_found))
268 | print('Queries: {} videos'.format(len(similarities)))
269 | print('Database: {} videos\n'.format(len(all_db - set(self.queries))))
270 | print('-' * 50)
271 | ap = []
272 | for evname in sorted(self.events):
273 | queries, _, _ = self.events[evname]
274 | nq = len(queries.intersection(all_db))
275 | ap.extend(results[evname])
276 | print('{0: <36} '.format(evname), 'mAP = {:.4f}'.format(np.sum(results[evname]) / nq))
277 |
278 | print('=' * 50)
279 | print('overall mAP = {:.4f}'.format(np.mean(ap)))
280 |
281 |
282 | class ActivityNet(object):
283 |
284 | def __init__(self):
285 | with open('datasets/activity_net.pickle', 'rb') as f:
286 | self.dataset = pk.load(f)
287 |
288 | def get_queries(self):
289 | return list(map(str, self.dataset.keys()))
290 |
291 | def get_database(self):
292 | return list(map(str, self.dataset.keys()))
293 |
294 | def calculate_AP(self, res, pos):
295 | i, ri, s = 0.0, 0.0, 0.0
296 | for ri, video in enumerate(sorted(res.keys(), key=lambda x: res[x], reverse=True)):
297 | if video in pos:
298 | i += 1.0
299 | s += i / (ri + 1.)
300 | return s / len(pos)
301 |
302 | def evaluate(self, similarities, all_db=None):
303 | mAP, not_found = [], 0
304 | if all_db is None:
305 | all_db = set(self.get_database())
306 |
307 | for query in self.dataset.keys():
308 | if query not in similarities:
309 | not_found += 1
310 | else:
311 | pos = self.dataset[query].intersection(all_db)
312 | mAP += [self.calculate_AP(similarities[query], pos)]
313 |
314 | print('=' * 5, 'ActivityNet Dataset', '=' * 5)
315 | if not_found > 0:
316 | print('[WARNING] {} queries are missing from the results and will be ignored'.format(not_found))
317 | print('Database: {} videos'.format(len(all_db)))
318 |
319 | print('-' * 16)
320 | print('mAP: {:.4f}'.format(np.mean(mAP)))
321 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/datasets/activity_net.pickle:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/0971e54fb8325fceb1bc9748ecbfe4c66e5dabd2/datasets/activity_net.pickle
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/datasets/cc_web_video.pickle:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/0971e54fb8325fceb1bc9748ecbfe4c66e5dabd2/datasets/cc_web_video.pickle
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/datasets/evve.pickle:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/0971e54fb8325fceb1bc9748ecbfe4c66e5dabd2/datasets/evve.pickle
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/datasets/fivr.pickle:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/0971e54fb8325fceb1bc9748ecbfe4c66e5dabd2/datasets/fivr.pickle
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 |
4 | from tqdm import tqdm
5 | from model.visil import ViSiL
6 | from datasets import DatasetGenerator
7 |
8 |
9 | def query_vs_database(model, dataset, args):
10 | # Create a video generator for the queries
11 | enqueuer = tf.keras.utils.OrderedEnqueuer(
12 | DatasetGenerator(args.video_dir, dataset.get_queries(), args.pattern, all_frames='i3d' in args.network),
13 | use_multiprocessing=True, shuffle=False)
14 | enqueuer.start(workers=args.threads, max_queue_size=args.threads * 2)
15 |
16 | # Extract features of the queries
17 | all_db, queries, queries_ids = set(), [], []
18 | pbar = tqdm(range(len(enqueuer.sequence)))
19 | for _ in pbar:
20 | frames, query_id = next(enqueuer.get())
21 | if frames.shape[0] > 0:
22 | queries.append(model.extract_features(frames, batch_sz=25 if 'i3d' in args.network else args.batch_sz))
23 | queries_ids.append(query_id)
24 | all_db.add(query_id)
25 | pbar.set_postfix(query_id=query_id)
26 | enqueuer.stop()
27 | model.set_queries(queries)
28 |
29 | # Create a video generator for the database video
30 | enqueuer = tf.keras.utils.OrderedEnqueuer(
31 | DatasetGenerator(args.video_dir, dataset.get_database(), args.pattern, all_frames='i3d' in args.network),
32 | use_multiprocessing=True, shuffle=False)
33 | enqueuer.start(workers=args.threads, max_queue_size=args.threads * 2)
34 | generator = enqueuer.get()
35 |
36 | # Calculate similarities between the queries and the database videos
37 | similarities = dict({query: dict() for query in queries_ids})
38 | pbar = tqdm(range(len(enqueuer.sequence)))
39 | for _ in pbar:
40 | frames, video_id = next(generator)
41 | if frames.shape[0] > 1:
42 | features = model.extract_features(frames, batch_sz=25 if 'i3d' in args.network else args.batch_sz)
43 | sims = model.calculate_similarities_to_queries(features)
44 | all_db.add(video_id)
45 | for i, s in enumerate(sims):
46 | similarities[queries_ids[i]][video_id] = float(s)
47 | pbar.set_postfix(video_id=video_id)
48 | enqueuer.stop()
49 |
50 | dataset.evaluate(similarities, all_db)
51 |
52 |
53 | def all_vs_all(model, dataset, args):
54 | # Create a video generator for the dataset video
55 | enqueuer = tf.keras.utils.OrderedEnqueuer(
56 | DatasetGenerator(args.video_dir, dataset.get_queries(), args.pattern, all_frames='i3d' in args.network),
57 | use_multiprocessing=True, shuffle=False)
58 | enqueuer.start(workers=args.threads, max_queue_size=args.threads * 2)
59 |
60 | # Calculate similarities between all videos in the dataset
61 | all_db, similarities, features = set(), dict(), dict()
62 | pbar = tqdm(range(len(enqueuer.sequence)))
63 | for _ in pbar:
64 | frames, q = next(enqueuer.get())
65 | if frames.shape[0] > 0:
66 | all_db.add(q)
67 | similarities[q] = dict()
68 | feat = model.extract_features(frames, batch_sz=25 if 'i3d' in args.network else args.batch_sz)
69 | for k, v in features.items():
70 | if 'symmetric' in args.similarity_function:
71 | similarities[q][k] = similarities[k][q] = model.calculate_video_similarity(v, feat)
72 | else:
73 | similarities[k][q] = model.calculate_video_similarity(v, feat)
74 | similarities[q][k] = model.calculate_video_similarity(feat, v)
75 | features[q] = feat
76 | pbar.set_postfix(video_id=q, frames=frames.shape, features=feat.shape)
77 | enqueuer.stop()
78 |
79 | dataset.evaluate(similarities, all_db=all_db)
80 |
81 |
82 | if __name__ == '__main__':
83 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
84 | parser.add_argument('-d', '--dataset', type=str, required=True,
85 | help='Name of evaluation dataset. Options: CC_WEB_ VIDEO, '
86 | '\"FIVR-200K\", \"FIVR-5K\", \"EVVE\", \"ActivityNet\"')
87 | parser.add_argument('-v', '--video_dir', type=str, required=True,
88 | help='Path to file that contains the database videos')
89 | parser.add_argument('-p', '--pattern', type=str, required=True,
90 | help='Pattern that the videos are stored in the video directory, eg. \"{id}/video.*\" '
91 | 'where the \"{id}\" is replaced with the video Id. Also, it supports '
92 | 'Unix style pathname pattern expansion.')
93 | parser.add_argument('-n', '--network', type=str, default='resnet',
94 | help='Backbone network used for feature extraction. '
95 | 'Options: \"resnet\" or \"i3d\". Default: \"resnet\"')
96 | parser.add_argument('-m', '--model_dir', type=str, default='ckpt/resnet',
97 | help='Path to the directory of the pretrained model. Default: \"ckpt/resnet\"')
98 | parser.add_argument('-s', '--similarity_function', type=str, default='chamfer',
99 | help='Function that will be used to calculate similarity'
100 | 'between query-candidate frames and videos.'
101 | 'Options: \"chamfer\" or \"symmetric_chamfer\". Default: \"chamfer\"')
102 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch_sz', type=int, default=128,
103 | help='Number of frames contained in each batch during feature extraction. Default: 128')
104 | parser.add_argument('-g', '--gpu_id', type=int, default=0,
105 | help='Id of the GPU used. Default: 0')
106 | parser.add_argument('-l', '--load_queries', action='store_true',
107 | help='Flag that indicates that the queries will be loaded to the GPU memory.')
108 | parser.add_argument('-t', '--threads', type=int, default=8,
109 | help='Number of threads used for video loading. Default: 8')
110 | args = parser.parse_args()
111 |
112 | if 'CC_WEB' in args.dataset:
113 | from datasets import CC_WEB_VIDEO
114 | dataset = CC_WEB_VIDEO()
115 | eval_function = query_vs_database
116 | elif 'FIVR' in args.dataset:
117 | from datasets import FIVR
118 | dataset = FIVR(version=args.dataset.split('-')[1].lower())
119 | eval_function = query_vs_database
120 | elif 'EVVE' in args.dataset:
121 | from datasets import EVVE
122 | dataset = EVVE()
123 | eval_function = query_vs_database
124 | elif 'ActivityNet' in args.dataset:
125 | from datasets import ActivityNet
126 | dataset = ActivityNet()
127 | eval_function = all_vs_all
128 | else:
129 | raise Exception('[ERROR] Not supported evaluation dataset. '
130 | 'Supported options: \"CC_WEB_ VIDEO\", \"FIVR-200K\", \"FIVR-5K\", \"EVVE\", \"ActivityNet\"')
131 |
132 | model = ViSiL(args.model_dir, net=args.network,
133 | load_queries=args.load_queries, gpu_id=args.gpu_id,
134 | similarity_function=args.similarity_function,
135 | queries_number=len(dataset.get_queries()) if args.load_queries else None)
136 |
137 | eval_function(model, dataset, args)
138 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/video1.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/0971e54fb8325fceb1bc9748ecbfe4c66e5dabd2/examples/video1.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/video2.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/0971e54fb8325fceb1bc9748ecbfe4c66e5dabd2/examples/video2.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/0971e54fb8325fceb1bc9748ecbfe4c66e5dabd2/model/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model/layers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 |
4 |
5 | class PCA_layer(object):
6 |
7 | def __init__(self, whitening=True, dims=None, net='resnet'):
8 | pca = np.load('ckpt/{}/pca.npz'.format(net))
9 | with tf.variable_scope('PCA'):
10 | self.mean = tf.get_variable('mean_sift',
11 | initializer=pca['mean'],
12 | dtype=tf.float32,
13 | trainable=False)
14 |
15 | weights = pca['V'][:, :dims]
16 | if whitening:
17 | d = pca['d'][:dims]
18 | D = np.diag(1. / np.sqrt(d))
19 | weights = np.dot(D, weights.T).T
20 |
21 | self.weights = tf.get_variable('weights',
22 | initializer=weights,
23 | dtype=tf.float32,
24 | trainable=False)
25 |
26 | def __call__(self, logits):
27 | logits = logits - self.mean
28 | logits = tf.tensordot(logits, self.weights, axes=1)
29 | return logits
30 |
31 |
32 | class Attention_layer(object):
33 |
34 | def __init__(self, shape=3840):
35 | with tf.variable_scope('attention_layer'):
36 | self.context_vector = tf.get_variable('context_vector', shape=(shape, 1),
37 | dtype=tf.float32, trainable=False)
38 |
39 | def __call__(self, logits):
40 | weights = tf.tensordot(logits, self.context_vector, axes=1) / 2.0 + 0.5
41 | return tf.multiply(logits, weights), weights
42 |
43 |
44 | class Video_Comparator(object):
45 |
46 | def __init__(self):
47 | self.conv1 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(32, [3, 3], activation='relu')
48 | self.mpool1 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D([2, 2], 2)
49 | self.conv2 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(64, [3, 3], activation='relu')
50 | self.mpool2 = tf.keras.layers.MaxPool2D([2, 2], 2)
51 | self.conv3 = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(128, [3, 3], activation='relu')
52 | self.fconv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(1, [1, 1])
53 |
54 | def __call__(self, sim_matrix):
55 | with tf.variable_scope('video_comparator'):
56 | sim = tf.reshape(sim_matrix, (1, tf.shape(sim_matrix)[0], tf.shape(sim_matrix)[1], 1))
57 | sim = tf.pad(sim, [[0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 1], [0, 0]], 'SYMMETRIC')
58 | sim = self.conv1(sim)
59 | sim = self.mpool1(sim)
60 | sim = tf.pad(sim, [[0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 1], [0, 0]], 'SYMMETRIC')
61 | sim = self.conv2(sim)
62 | sim = self.mpool2(sim)
63 | sim = tf.pad(sim, [[0, 0], [1, 1], [1, 1], [0, 0]], 'SYMMETRIC')
64 | sim = self.conv3(sim)
65 | sim = self.fconv(sim)
66 | sim = tf.clip_by_value(sim, -1.0, 1.0)
67 | sim = tf.squeeze(sim, [0, 3])
68 | return sim
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model/nets/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/0971e54fb8325fceb1bc9748ecbfe4c66e5dabd2/model/nets/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model/nets/i3d.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2017 Google Inc.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ============================================================================
15 | """Inception-v1 Inflated 3D ConvNet used for Kinetics CVPR paper.
16 |
17 | The model is introduced in:
18 |
19 | Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset
20 | Joao Carreira, Andrew Zisserman
21 | https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.07750v1.pdf.
22 | """
23 |
24 | from __future__ import absolute_import
25 | from __future__ import division
26 | from __future__ import print_function
27 |
28 | import sonnet as snt
29 | import tensorflow as tf
30 |
31 |
32 | class Unit3D(snt.AbstractModule):
33 | """Basic unit containing Conv3D + BatchNorm + non-linearity."""
34 |
35 | def __init__(self, output_channels,
36 | kernel_shape=(1, 1, 1),
37 | stride=(1, 1, 1),
38 | activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
39 | use_batch_norm=True,
40 | use_bias=False,
41 | name='unit_3d'):
42 | """Initializes Unit3D module."""
43 | super(Unit3D, self).__init__(name=name)
44 | self._output_channels = output_channels
45 | self._kernel_shape = kernel_shape
46 | self._stride = stride
47 | self._use_batch_norm = use_batch_norm
48 | self._activation_fn = activation_fn
49 | self._use_bias = use_bias
50 |
51 | def _build(self, inputs, is_training):
52 | """Connects the module to inputs.
53 |
54 | Args:
55 | inputs: Inputs to the Unit3D component.
56 | is_training: whether to use training mode for snt.BatchNorm (boolean).
57 |
58 | Returns:
59 | Outputs from the module.
60 | """
61 | net = snt.Conv3D(output_channels=self._output_channels,
62 | kernel_shape=self._kernel_shape,
63 | stride=self._stride,
64 | padding=snt.SAME,
65 | use_bias=self._use_bias)(inputs)
66 | if self._use_batch_norm:
67 | bn = snt.BatchNorm()
68 | net = bn(net, is_training=is_training, test_local_stats=False)
69 | if self._activation_fn is not None:
70 | net = self._activation_fn(net)
71 | return net
72 |
73 |
74 | class InceptionI3d(snt.AbstractModule):
75 | """Inception-v1 I3D architecture.
76 |
77 | The model is introduced in:
78 |
79 | Quo Vadis, Action Recognition? A New Model and the Kinetics Dataset
80 | Joao Carreira, Andrew Zisserman
81 | https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.07750v1.pdf.
82 |
83 | See also the Inception architecture, introduced in:
84 |
85 | Going deeper with convolutions
86 | Christian Szegedy, Wei Liu, Yangqing Jia, Pierre Sermanet, Scott Reed,
87 | Dragomir Anguelov, Dumitru Erhan, Vincent Vanhoucke, Andrew Rabinovich.
88 | http://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.4842v1.pdf.
89 | """
90 |
91 | # Endpoints of the model in order. During construction, all the endpoints up
92 | # to a designated `final_endpoint` are returned in a dictionary as the
93 | # second return value.
94 | VALID_ENDPOINTS = (
95 | 'Conv3d_1a_7x7',
96 | 'MaxPool3d_2a_3x3',
97 | 'Conv3d_2b_1x1',
98 | 'Conv3d_2c_3x3',
99 | 'MaxPool3d_3a_3x3',
100 | 'Mixed_3b',
101 | 'Mixed_3c',
102 | 'MaxPool3d_4a_3x3',
103 | 'Mixed_4b',
104 | 'Mixed_4c',
105 | 'Mixed_4d',
106 | 'Mixed_4e',
107 | 'Mixed_4f',
108 | 'MaxPool3d_5a_2x2',
109 | 'Mixed_5b',
110 | 'Mixed_5c',
111 | 'Logits',
112 | 'Predictions',
113 | )
114 |
115 | def __init__(self, num_classes=400, spatial_squeeze=True,
116 | final_endpoint='Logits', name='inception_i3d'):
117 | """Initializes I3D model instance.
118 |
119 | Args:
120 | num_classes: The number of outputs in the logit layer (default 400, which
121 | matches the Kinetics dataset).
122 | spatial_squeeze: Whether to squeeze the spatial dimensions for the logits
123 | before returning (default True).
124 | final_endpoint: The model contains many possible endpoints.
125 | `final_endpoint` specifies the last endpoint for the model to be built
126 | up to. In addition to the output at `final_endpoint`, all the outputs
127 | at endpoints up to `final_endpoint` will also be returned, in a
128 | dictionary. `final_endpoint` must be one of
129 | InceptionI3d.VALID_ENDPOINTS (default 'Logits').
130 | name: A string (optional). The name of this module.
131 |
132 | Raises:
133 | ValueError: if `final_endpoint` is not recognized.
134 | """
135 |
136 | if final_endpoint not in self.VALID_ENDPOINTS:
137 | raise ValueError('Unknown final endpoint %s' % final_endpoint)
138 |
139 | super(InceptionI3d, self).__init__(name=name)
140 | self._num_classes = num_classes
141 | self._spatial_squeeze = spatial_squeeze
142 | self._final_endpoint = final_endpoint
143 |
144 | def _build(self, inputs, is_training, dropout_keep_prob=1.0):
145 | """Connects the model to inputs.
146 |
147 | Args:
148 | inputs: Inputs to the model, which should have dimensions
149 | `batch_size` x `num_frames` x 224 x 224 x `num_channels`.
150 | is_training: whether to use training mode for snt.BatchNorm (boolean).
151 | dropout_keep_prob: Probability for the tf.nn.dropout layer (float in
152 | [0, 1)).
153 |
154 | Returns:
155 | A tuple consisting of:
156 | 1. Network output at location `self._final_endpoint`.
157 | 2. Dictionary containing all endpoints up to `self._final_endpoint`,
158 | indexed by endpoint name.
159 |
160 | Raises:
161 | ValueError: if `self._final_endpoint` is not recognized.
162 | """
163 | if self._final_endpoint not in self.VALID_ENDPOINTS:
164 | raise ValueError('Unknown final endpoint %s' % self._final_endpoint)
165 |
166 | net = inputs
167 | end_points = {}
168 | end_point = 'Conv3d_1a_7x7'
169 | net = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[7, 7, 7],
170 | stride=[2, 2, 2], name=end_point)(net, is_training=is_training)
171 | end_points[end_point] = net
172 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
173 | end_point = 'MaxPool3d_2a_3x3'
174 | net = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 1, 2, 2, 1],
175 | padding=snt.SAME, name=end_point)
176 | end_points[end_point] = net
177 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
178 | end_point = 'Conv3d_2b_1x1'
179 | net = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
180 | name=end_point)(net, is_training=is_training)
181 | end_points[end_point] = net
182 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
183 | end_point = 'Conv3d_2c_3x3'
184 | net = Unit3D(output_channels=192, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
185 | name=end_point)(net, is_training=is_training)
186 | end_points[end_point] = net
187 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
188 | end_point = 'MaxPool3d_3a_3x3'
189 | net = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 1, 2, 2, 1],
190 | padding=snt.SAME, name=end_point)
191 | end_points[end_point] = net
192 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
193 |
194 | end_point = 'Mixed_3b'
195 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
196 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
197 | branch_0 = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
198 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
199 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
200 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=96, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
201 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
202 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
203 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_1,
204 | is_training=is_training)
205 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
206 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=16, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
207 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
208 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=32, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
209 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_2,
210 | is_training=is_training)
211 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
212 | branch_3 = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1],
213 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.SAME,
214 | name='MaxPool3d_0a_3x3')
215 | branch_3 = Unit3D(output_channels=32, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
216 | name='Conv3d_0b_1x1')(branch_3,
217 | is_training=is_training)
218 |
219 | net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 4)
220 | end_points[end_point] = net
221 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
222 |
223 | end_point = 'Mixed_3c'
224 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
225 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
226 | branch_0 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
227 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
228 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
229 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
230 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
231 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=192, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
232 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_1,
233 | is_training=is_training)
234 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
235 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=32, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
236 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
237 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=96, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
238 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_2,
239 | is_training=is_training)
240 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
241 | branch_3 = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1],
242 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.SAME,
243 | name='MaxPool3d_0a_3x3')
244 | branch_3 = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
245 | name='Conv3d_0b_1x1')(branch_3,
246 | is_training=is_training)
247 | net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 4)
248 | end_points[end_point] = net
249 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
250 |
251 | end_point = 'MaxPool3d_4a_3x3'
252 | net = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 2, 1],
253 | padding=snt.SAME, name=end_point)
254 | end_points[end_point] = net
255 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
256 |
257 | end_point = 'Mixed_4b'
258 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
259 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
260 | branch_0 = Unit3D(output_channels=192, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
261 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
262 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
263 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=96, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
264 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
265 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=208, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
266 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_1,
267 | is_training=is_training)
268 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
269 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=16, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
270 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
271 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=48, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
272 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_2,
273 | is_training=is_training)
274 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
275 | branch_3 = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1],
276 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.SAME,
277 | name='MaxPool3d_0a_3x3')
278 | branch_3 = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
279 | name='Conv3d_0b_1x1')(branch_3,
280 | is_training=is_training)
281 | net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 4)
282 | end_points[end_point] = net
283 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
284 |
285 | end_point = 'Mixed_4c'
286 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
287 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
288 | branch_0 = Unit3D(output_channels=160, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
289 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
290 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
291 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=112, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
292 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
293 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=224, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
294 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_1,
295 | is_training=is_training)
296 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
297 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=24, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
298 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
299 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
300 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_2,
301 | is_training=is_training)
302 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
303 | branch_3 = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1],
304 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.SAME,
305 | name='MaxPool3d_0a_3x3')
306 | branch_3 = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
307 | name='Conv3d_0b_1x1')(branch_3,
308 | is_training=is_training)
309 | net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 4)
310 | end_points[end_point] = net
311 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
312 |
313 | end_point = 'Mixed_4d'
314 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
315 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
316 | branch_0 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
317 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
318 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
319 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
320 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
321 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=256, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
322 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_1,
323 | is_training=is_training)
324 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
325 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=24, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
326 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
327 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
328 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_2,
329 | is_training=is_training)
330 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
331 | branch_3 = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1],
332 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.SAME,
333 | name='MaxPool3d_0a_3x3')
334 | branch_3 = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
335 | name='Conv3d_0b_1x1')(branch_3,
336 | is_training=is_training)
337 | net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 4)
338 | end_points[end_point] = net
339 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
340 |
341 | end_point = 'Mixed_4e'
342 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
343 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
344 | branch_0 = Unit3D(output_channels=112, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
345 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
346 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
347 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=144, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
348 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
349 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=288, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
350 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_1,
351 | is_training=is_training)
352 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
353 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=32, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
354 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
355 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
356 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_2,
357 | is_training=is_training)
358 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
359 | branch_3 = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1],
360 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.SAME,
361 | name='MaxPool3d_0a_3x3')
362 | branch_3 = Unit3D(output_channels=64, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
363 | name='Conv3d_0b_1x1')(branch_3,
364 | is_training=is_training)
365 | net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 4)
366 | end_points[end_point] = net
367 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
368 |
369 | end_point = 'Mixed_4f'
370 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
371 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
372 | branch_0 = Unit3D(output_channels=256, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
373 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
374 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
375 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=160, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
376 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
377 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=320, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
378 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_1,
379 | is_training=is_training)
380 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
381 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=32, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
382 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
383 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
384 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_2,
385 | is_training=is_training)
386 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
387 | branch_3 = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1],
388 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.SAME,
389 | name='MaxPool3d_0a_3x3')
390 | branch_3 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
391 | name='Conv3d_0b_1x1')(branch_3,
392 | is_training=is_training)
393 | net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 4)
394 | end_points[end_point] = net
395 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
396 |
397 | end_point = 'MaxPool3d_5a_2x2'
398 | net = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 2, 1],
399 | padding=snt.SAME, name=end_point)
400 | end_points[end_point] = net
401 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
402 |
403 | end_point = 'Mixed_5b'
404 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
405 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
406 | branch_0 = Unit3D(output_channels=256, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
407 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
408 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
409 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=160, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
410 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
411 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=320, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
412 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_1,
413 | is_training=is_training)
414 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
415 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=32, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
416 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
417 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
418 | name='Conv3d_0a_3x3')(branch_2,
419 | is_training=is_training)
420 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
421 | branch_3 = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1],
422 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.SAME,
423 | name='MaxPool3d_0a_3x3')
424 | branch_3 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
425 | name='Conv3d_0b_1x1')(branch_3,
426 | is_training=is_training)
427 | net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 4)
428 | end_points[end_point] = net
429 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
430 |
431 | end_point = 'Mixed_5c'
432 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
433 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_0'):
434 | branch_0 = Unit3D(output_channels=384, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
435 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
436 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_1'):
437 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=192, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
438 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
439 | branch_1 = Unit3D(output_channels=384, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
440 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_1,
441 | is_training=is_training)
442 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_2'):
443 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=48, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
444 | name='Conv3d_0a_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
445 | branch_2 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[3, 3, 3],
446 | name='Conv3d_0b_3x3')(branch_2,
447 | is_training=is_training)
448 | with tf.variable_scope('Branch_3'):
449 | branch_3 = tf.nn.max_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 3, 1],
450 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.SAME,
451 | name='MaxPool3d_0a_3x3')
452 | branch_3 = Unit3D(output_channels=128, kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
453 | name='Conv3d_0b_1x1')(branch_3,
454 | is_training=is_training)
455 | net = tf.concat([branch_0, branch_1, branch_2, branch_3], 4)
456 | end_points[end_point] = net
457 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return net, end_points
458 |
459 | end_point = 'Logits'
460 | with tf.variable_scope(end_point):
461 | net = tf.nn.avg_pool3d(net, ksize=[1, 2, 7, 7, 1],
462 | strides=[1, 1, 1, 1, 1], padding=snt.VALID)
463 | net = tf.nn.dropout(net, dropout_keep_prob)
464 | logits = Unit3D(output_channels=self._num_classes,
465 | kernel_shape=[1, 1, 1],
466 | activation_fn=None,
467 | use_batch_norm=False,
468 | use_bias=True,
469 | name='Conv3d_0c_1x1')(net, is_training=is_training)
470 | if self._spatial_squeeze:
471 | logits = tf.squeeze(logits, [2, 3], name='SpatialSqueeze')
472 |
473 | if self._final_endpoint == end_point: return logits, end_points
474 | averaged_logits = tf.reduce_mean(logits, axis=1)
475 | end_points[end_point] = averaged_logits
476 |
477 | end_point = 'Predictions'
478 | predictions = tf.nn.softmax(averaged_logits)
479 | end_points[end_point] = predictions
480 | return predictions, end_points
481 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model/nets/resnet_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """Contains building blocks for various versions of Residual Networks.
16 |
17 | Residual networks (ResNets) were proposed in:
18 | Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun
19 | Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv:1512.03385, 2015
20 |
21 | More variants were introduced in:
22 | Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun
23 | Identity Mappings in Deep Residual Networks. arXiv: 1603.05027, 2016
24 |
25 | We can obtain different ResNet variants by changing the network depth, width,
26 | and form of residual unit. This module implements the infrastructure for
27 | building them. Concrete ResNet units and full ResNet networks are implemented in
28 | the accompanying resnet_v1.py and resnet_v2.py modules.
29 |
30 | Compared to https://github.com/KaimingHe/deep-residual-networks, in the current
31 | implementation we subsample the output activations in the last residual unit of
32 | each block, instead of subsampling the input activations in the first residual
33 | unit of each block. The two implementations give identical results but our
34 | implementation is more memory efficient.
35 | """
36 | from __future__ import absolute_import
37 | from __future__ import division
38 | from __future__ import print_function
39 |
40 | import collections
41 | import tensorflow as tf
42 |
43 | slim = tf.contrib.slim
44 |
45 |
46 | class Block(collections.namedtuple('Block', ['scope', 'unit_fn', 'args'])):
47 | """A named tuple describing a ResNet block.
48 |
49 | Its parts are:
50 | scope: The scope of the `Block`.
51 | unit_fn: The ResNet unit function which takes as input a `Tensor` and
52 | returns another `Tensor` with the output of the ResNet unit.
53 | args: A list of length equal to the number of units in the `Block`. The list
54 | contains one (depth, depth_bottleneck, stride) tuple for each unit in the
55 | block to serve as argument to unit_fn.
56 | """
57 |
58 |
59 | def subsample(inputs, factor, scope=None):
60 | """Subsamples the input along the spatial dimensions.
61 |
62 | Args:
63 | inputs: A `Tensor` of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels].
64 | factor: The subsampling factor.
65 | scope: Optional variable_scope.
66 |
67 | Returns:
68 | output: A `Tensor` of size [batch, height_out, width_out, channels] with the
69 | input, either intact (if factor == 1) or subsampled (if factor > 1).
70 | """
71 | if factor == 1:
72 | return inputs
73 | else:
74 | return slim.max_pool2d(inputs, [1, 1], stride=factor, scope=scope)
75 |
76 |
77 | def conv2d_same(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride, rate=1, scope=None):
78 | """Strided 2-D convolution with 'SAME' padding.
79 |
80 | When stride > 1, then we do explicit zero-padding, followed by conv2d with
81 | 'VALID' padding.
82 |
83 | Note that
84 |
85 | net = conv2d_same(inputs, num_outputs, 3, stride=stride)
86 |
87 | is equivalent to
88 |
89 | net = slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, 3, stride=1, padding='SAME')
90 | net = subsample(net, factor=stride)
91 |
92 | whereas
93 |
94 | net = slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, 3, stride=stride, padding='SAME')
95 |
96 | is different when the input's height or width is even, which is why we add the
97 | current function. For more details, see ResnetUtilsTest.testConv2DSameEven().
98 |
99 | Args:
100 | inputs: A 4-D tensor of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels].
101 | num_outputs: An integer, the number of output filters.
102 | kernel_size: An int with the kernel_size of the filters.
103 | stride: An integer, the output stride.
104 | rate: An integer, rate for atrous convolution.
105 | scope: Scope.
106 |
107 | Returns:
108 | output: A 4-D tensor of size [batch, height_out, width_out, channels] with
109 | the convolution output.
110 | """
111 | if stride == 1:
112 | return slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride=1, rate=rate,
113 | padding='SAME', scope=scope)
114 | else:
115 | kernel_size_effective = kernel_size + (kernel_size - 1) * (rate - 1)
116 | pad_total = kernel_size_effective - 1
117 | pad_beg = pad_total // 2
118 | pad_end = pad_total - pad_beg
119 | inputs = tf.pad(inputs,
120 | [[0, 0], [pad_beg, pad_end], [pad_beg, pad_end], [0, 0]])
121 | return slim.conv2d(inputs, num_outputs, kernel_size, stride=stride,
122 | rate=rate, padding='VALID', scope=scope)
123 |
124 |
125 | @slim.add_arg_scope
126 | def stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks, output_stride=None,
127 | outputs_collections=None):
128 | """Stacks ResNet `Blocks` and controls output feature density.
129 |
130 | First, this function creates scopes for the ResNet in the form of
131 | 'block_name/unit_1', 'block_name/unit_2', etc.
132 |
133 | Second, this function allows the user to explicitly control the ResNet
134 | output_stride, which is the ratio of the input to output spatial resolution.
135 | This is useful for dense prediction tasks such as semantic segmentation or
136 | object detection.
137 |
138 | Most ResNets consist of 4 ResNet blocks and subsample the activations by a
139 | factor of 2 when transitioning between consecutive ResNet blocks. This results
140 | to a nominal ResNet output_stride equal to 8. If we set the output_stride to
141 | half the nominal network stride (e.g., output_stride=4), then we compute
142 | responses twice.
143 |
144 | Control of the output feature density is implemented by atrous convolution.
145 |
146 | Args:
147 | net: A `Tensor` of size [batch, height, width, channels].
148 | blocks: A list of length equal to the number of ResNet `Blocks`. Each
149 | element is a ResNet `Block` object describing the units in the `Block`.
150 | output_stride: If `None`, then the output will be computed at the nominal
151 | network stride. If output_stride is not `None`, it specifies the requested
152 | ratio of input to output spatial resolution, which needs to be equal to
153 | the product of unit strides from the start up to some level of the ResNet.
154 | For example, if the ResNet employs units with strides 1, 2, 1, 3, 4, 1,
155 | then valid values for the output_stride are 1, 2, 6, 24 or None (which
156 | is equivalent to output_stride=24).
157 | outputs_collections: Collection to add the ResNet block outputs.
158 |
159 | Returns:
160 | net: Output tensor with stride equal to the specified output_stride.
161 |
162 | Raises:
163 | ValueError: If the target output_stride is not valid.
164 | """
165 | # The current_stride variable keeps track of the effective stride of the
166 | # activations. This allows us to invoke atrous convolution whenever applying
167 | # the next residual unit would result in the activations having stride larger
168 | # than the target output_stride.
169 | current_stride = 1
170 |
171 | # The atrous convolution rate parameter.
172 | rate = 1
173 |
174 | for block in blocks:
175 | with tf.variable_scope(block.scope, 'block', [net]) as sc:
176 | for i, unit in enumerate(block.args):
177 | if output_stride is not None and current_stride > output_stride:
178 | raise ValueError('The target output_stride cannot be reached.')
179 |
180 | with tf.variable_scope('unit_%d' % (i + 1), values=[net]):
181 | # If we have reached the target output_stride, then we need to employ
182 | # atrous convolution with stride=1 and multiply the atrous rate by the
183 | # current unit's stride for use in subsequent layers.
184 | if output_stride is not None and current_stride == output_stride:
185 | net = block.unit_fn(net, rate=rate, **dict(unit, stride=1))
186 | rate *= unit.get('stride', 1)
187 |
188 | else:
189 | net = block.unit_fn(net, rate=1, **unit)
190 | current_stride *= unit.get('stride', 1)
191 | net = slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections, sc.name, net)
192 |
193 | if output_stride is not None and current_stride != output_stride:
194 | raise ValueError('The target output_stride cannot be reached.')
195 |
196 | return net
197 |
198 |
199 | def resnet_arg_scope(weight_decay=0.0001,
200 | batch_norm_decay=0.997,
201 | batch_norm_epsilon=1e-5,
202 | batch_norm_scale=True,
203 | activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
204 | use_batch_norm=True):
205 | """Defines the default ResNet arg scope.
206 |
207 | TODO(gpapan): The batch-normalization related default values above are
208 | appropriate for use in conjunction with the reference ResNet models
209 | released at https://github.com/KaimingHe/deep-residual-networks. When
210 | training ResNets from scratch, they might need to be tuned.
211 |
212 | Args:
213 | weight_decay: The weight decay to use for regularizing the model.
214 | batch_norm_decay: The moving average decay when estimating layer activation
215 | statistics in batch normalization.
216 | batch_norm_epsilon: Small constant to prevent division by zero when
217 | normalizing activations by their variance in batch normalization.
218 | batch_norm_scale: If True, uses an explicit `gamma` multiplier to scale the
219 | activations in the batch normalization layer.
220 | activation_fn: The activation function which is used in ResNet.
221 | use_batch_norm: Whether or not to use batch normalization.
222 |
223 | Returns:
224 | An `arg_scope` to use for the resnet models.
225 | """
226 | batch_norm_params = {
227 | 'decay': batch_norm_decay,
228 | 'epsilon': batch_norm_epsilon,
229 | 'scale': batch_norm_scale,
230 | 'updates_collections': tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
231 | 'fused': None, # Use fused batch norm if possible.
232 | }
233 |
234 | with slim.arg_scope(
235 | [slim.conv2d],
236 | weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(weight_decay),
237 | weights_initializer=slim.variance_scaling_initializer(),
238 | activation_fn=activation_fn,
239 | normalizer_fn=slim.batch_norm if use_batch_norm else None,
240 | normalizer_params=batch_norm_params):
241 | with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm], **batch_norm_params):
242 | # The following implies padding='SAME' for pool1, which makes feature
243 | # alignment easier for dense prediction tasks. This is also used in
244 | # https://github.com/facebook/fb.resnet.torch. However the accompanying
245 | # code of 'Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition' uses
246 | # padding='VALID' for pool1. You can switch to that choice by setting
247 | # slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d], padding='VALID').
248 | with slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d], padding='SAME') as arg_sc:
249 | return arg_sc
250 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model/nets/resnet_v1.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """Contains definitions for the original form of Residual Networks.
16 |
17 | The 'v1' residual networks (ResNets) implemented in this module were proposed
18 | by:
19 | [1] Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun
20 | Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition. arXiv:1512.03385
21 |
22 | Other variants were introduced in:
23 | [2] Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun
24 | Identity Mappings in Deep Residual Networks. arXiv: 1603.05027
25 |
26 | The networks defined in this module utilize the bottleneck building block of
27 | [1] with projection shortcuts only for increasing depths. They employ batch
28 | normalization *after* every weight layer. This is the architecture used by
29 | MSRA in the Imagenet and MSCOCO 2016 competition models ResNet-101 and
30 | ResNet-152. See [2; Fig. 1a] for a comparison between the current 'v1'
31 | architecture and the alternative 'v2' architecture of [2] which uses batch
32 | normalization *before* every weight layer in the so-called full pre-activation
33 | units.
34 |
35 | Typical use:
36 |
37 | from tensorflow.contrib.slim.nets import resnet_v1
38 |
39 | ResNet-101 for image classification into 1000 classes:
40 |
41 | # inputs has shape [batch, 224, 224, 3]
42 | with slim.arg_scope(resnet_v1.resnet_arg_scope()):
43 | net, end_points = resnet_v1.resnet_v1_101(inputs, 1000, is_training=False)
44 |
45 | ResNet-101 for semantic segmentation into 21 classes:
46 |
47 | # inputs has shape [batch, 513, 513, 3]
48 | with slim.arg_scope(resnet_v1.resnet_arg_scope()):
49 | net, end_points = resnet_v1.resnet_v1_101(inputs,
50 | 21,
51 | is_training=False,
52 | global_pool=False,
53 | output_stride=16)
54 | """
55 | from __future__ import absolute_import
56 | from __future__ import division
57 | from __future__ import print_function
58 |
59 | import tensorflow as tf
60 |
61 | from . import resnet_utils
62 |
63 |
64 | resnet_arg_scope = resnet_utils.resnet_arg_scope
65 | slim = tf.contrib.slim
66 |
67 |
68 | @slim.add_arg_scope
69 | def bottleneck(inputs,
70 | depth,
71 | depth_bottleneck,
72 | stride,
73 | rate=1,
74 | outputs_collections=None,
75 | scope=None,
76 | use_bounded_activations=False):
77 | """Bottleneck residual unit variant with BN after convolutions.
78 |
79 | This is the original residual unit proposed in [1]. See Fig. 1(a) of [2] for
80 | its definition. Note that we use here the bottleneck variant which has an
81 | extra bottleneck layer.
82 |
83 | When putting together two consecutive ResNet blocks that use this unit, one
84 | should use stride = 2 in the last unit of the first block.
85 |
86 | Args:
87 | inputs: A tensor of size [batch, height, width, channels].
88 | depth: The depth of the ResNet unit output.
89 | depth_bottleneck: The depth of the bottleneck layers.
90 | stride: The ResNet unit's stride. Determines the amount of downsampling of
91 | the units output compared to its input.
92 | rate: An integer, rate for atrous convolution.
93 | outputs_collections: Collection to add the ResNet unit output.
94 | scope: Optional variable_scope.
95 | use_bounded_activations: Whether or not to use bounded activations. Bounded
96 | activations better lend themselves to quantized inference.
97 |
98 | Returns:
99 | The ResNet unit's output.
100 | """
101 | with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'bottleneck_v1', [inputs]) as sc:
102 | depth_in = slim.utils.last_dimension(inputs.get_shape(), min_rank=4)
103 | if depth == depth_in:
104 | shortcut = resnet_utils.subsample(inputs, stride, 'shortcut')
105 | else:
106 | shortcut = slim.conv2d(
107 | inputs,
108 | depth, [1, 1],
109 | stride=stride,
110 | activation_fn=tf.nn.relu6 if use_bounded_activations else None,
111 | scope='shortcut')
112 |
113 | residual = slim.conv2d(inputs, depth_bottleneck, [1, 1], stride=1,
114 | scope='conv1')
115 | residual = resnet_utils.conv2d_same(residual, depth_bottleneck, 3, stride,
116 | rate=rate, scope='conv2')
117 | residual = slim.conv2d(residual, depth, [1, 1], stride=1,
118 | activation_fn=None, scope='conv3')
119 |
120 | if use_bounded_activations:
121 | # Use clip_by_value to simulate bandpass activation.
122 | residual = tf.clip_by_value(residual, -6.0, 6.0)
123 | output = tf.nn.relu6(shortcut + residual)
124 | else:
125 | output = tf.nn.relu(shortcut + residual)
126 |
127 | return slim.utils.collect_named_outputs(outputs_collections,
128 | sc.name,
129 | output)
130 |
131 |
132 | def resnet_v1(inputs,
133 | blocks,
134 | num_classes=None,
135 | is_training=True,
136 | global_pool=True,
137 | output_stride=None,
138 | include_root_block=True,
139 | spatial_squeeze=True,
140 | reuse=None,
141 | scope=None):
142 | """Generator for v1 ResNet models.
143 |
144 | This function generates a family of ResNet v1 models. See the resnet_v1_*()
145 | methods for specific model instantiations, obtained by selecting different
146 | block instantiations that produce ResNets of various depths.
147 |
148 | Training for image classification on Imagenet is usually done with [224, 224]
149 | inputs, resulting in [7, 7] feature maps at the output of the last ResNet
150 | block for the ResNets defined in [1] that have nominal stride equal to 32.
151 | However, for dense prediction tasks we advise that one uses inputs with
152 | spatial dimensions that are multiples of 32 plus 1, e.g., [321, 321]. In
153 | this case the feature maps at the ResNet output will have spatial shape
154 | [(height - 1) / output_stride + 1, (width - 1) / output_stride + 1]
155 | and corners exactly aligned with the input image corners, which greatly
156 | facilitates alignment of the features to the image. Using as input [225, 225]
157 | images results in [8, 8] feature maps at the output of the last ResNet block.
158 |
159 | For dense prediction tasks, the ResNet needs to run in fully-convolutional
160 | (FCN) mode and global_pool needs to be set to False. The ResNets in [1, 2] all
161 | have nominal stride equal to 32 and a good choice in FCN mode is to use
162 | output_stride=16 in order to increase the density of the computed features at
163 | small computational and memory overhead, cf. http://arxiv.org/abs/1606.00915.
164 |
165 | Args:
166 | inputs: A tensor of size [batch, height_in, width_in, channels].
167 | blocks: A list of length equal to the number of ResNet blocks. Each element
168 | is a resnet_utils.Block object describing the units in the block.
169 | num_classes: Number of predicted classes for classification tasks.
170 | If 0 or None, we return the features before the logit layer.
171 | is_training: whether batch_norm layers are in training mode.
172 | global_pool: If True, we perform global average pooling before computing the
173 | logits. Set to True for image classification, False for dense prediction.
174 | output_stride: If None, then the output will be computed at the nominal
175 | network stride. If output_stride is not None, it specifies the requested
176 | ratio of input to output spatial resolution.
177 | include_root_block: If True, include the initial convolution followed by
178 | max-pooling, if False excludes it.
179 | spatial_squeeze: if True, logits is of shape [B, C], if false logits is
180 | of shape [B, 1, 1, C], where B is batch_size and C is number of classes.
181 | To use this parameter, the input images must be smaller than 300x300
182 | pixels, in which case the output logit layer does not contain spatial
183 | information and can be removed.
184 | reuse: whether or not the network and its variables should be reused. To be
185 | able to reuse 'scope' must be given.
186 | scope: Optional variable_scope.
187 |
188 | Returns:
189 | net: A rank-4 tensor of size [batch, height_out, width_out, channels_out].
190 | If global_pool is False, then height_out and width_out are reduced by a
191 | factor of output_stride compared to the respective height_in and width_in,
192 | else both height_out and width_out equal one. If num_classes is 0 or None,
193 | then net is the output of the last ResNet block, potentially after global
194 | average pooling. If num_classes a non-zero integer, net contains the
195 | pre-softmax activations.
196 | end_points: A dictionary from components of the network to the corresponding
197 | activation.
198 |
199 | Raises:
200 | ValueError: If the target output_stride is not valid.
201 | """
202 | with tf.variable_scope(scope, 'resnet_v1', [inputs], reuse=reuse) as sc:
203 | end_points_collection = sc.original_name_scope + '_end_points'
204 | with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, bottleneck,
205 | resnet_utils.stack_blocks_dense],
206 | outputs_collections=end_points_collection):
207 | with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm], is_training=is_training):
208 | net = inputs
209 | if include_root_block:
210 | if output_stride is not None:
211 | if output_stride % 4 != 0:
212 | raise ValueError('The output_stride needs to be a multiple of 4.')
213 | output_stride /= 4
214 | net = resnet_utils.conv2d_same(net, 64, 7, stride=2, scope='conv1')
215 | net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='pool1')
216 | net = resnet_utils.stack_blocks_dense(net, blocks, output_stride)
217 | # Convert end_points_collection into a dictionary of end_points.
218 | end_points = slim.utils.convert_collection_to_dict(
219 | end_points_collection)
220 |
221 | if global_pool:
222 | # Global average pooling.
223 | net = tf.reduce_mean(net, [1, 2], name='pool5', keep_dims=True)
224 | end_points['global_pool'] = net
225 | if num_classes:
226 | net = slim.conv2d(net, num_classes, [1, 1], activation_fn=None,
227 | normalizer_fn=None, scope='logits')
228 | end_points[sc.name + '/logits'] = net
229 | if spatial_squeeze:
230 | net = tf.squeeze(net, [1, 2], name='SpatialSqueeze')
231 | end_points[sc.name + '/spatial_squeeze'] = net
232 | end_points['predictions'] = slim.softmax(net, scope='predictions')
233 | return net, end_points
234 | resnet_v1.default_image_size = 224
235 |
236 |
237 | def resnet_v1_block(scope, base_depth, num_units, stride):
238 | """Helper function for creating a resnet_v1 bottleneck block.
239 |
240 | Args:
241 | scope: The scope of the block.
242 | base_depth: The depth of the bottleneck layer for each unit.
243 | num_units: The number of units in the block.
244 | stride: The stride of the block, implemented as a stride in the last unit.
245 | All other units have stride=1.
246 |
247 | Returns:
248 | A resnet_v1 bottleneck block.
249 | """
250 | return resnet_utils.Block(scope, bottleneck, [{
251 | 'depth': base_depth * 4,
252 | 'depth_bottleneck': base_depth,
253 | 'stride': 1
254 | }] * (num_units - 1) + [{
255 | 'depth': base_depth * 4,
256 | 'depth_bottleneck': base_depth,
257 | 'stride': stride
258 | }])
259 |
260 |
261 | def resnet_v1_50(inputs,
262 | num_classes=None,
263 | is_training=True,
264 | global_pool=True,
265 | output_stride=None,
266 | spatial_squeeze=True,
267 | reuse=None,
268 | scope='resnet_v1_50'):
269 | """ResNet-50 model of [1]. See resnet_v1() for arg and return description."""
270 | blocks = [
271 | resnet_v1_block('block1', base_depth=64, num_units=3, stride=2),
272 | resnet_v1_block('block2', base_depth=128, num_units=4, stride=2),
273 | resnet_v1_block('block3', base_depth=256, num_units=6, stride=2),
274 | resnet_v1_block('block4', base_depth=512, num_units=3, stride=1),
275 | ]
276 | return resnet_v1(inputs, blocks, num_classes, is_training,
277 | global_pool=global_pool, output_stride=output_stride,
278 | include_root_block=True, spatial_squeeze=spatial_squeeze,
279 | reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
280 | resnet_v1_50.default_image_size = resnet_v1.default_image_size
281 |
282 |
283 | def resnet_v1_101(inputs,
284 | num_classes=None,
285 | is_training=True,
286 | global_pool=True,
287 | output_stride=None,
288 | spatial_squeeze=True,
289 | reuse=None,
290 | scope='resnet_v1_101'):
291 | """ResNet-101 model of [1]. See resnet_v1() for arg and return description."""
292 | blocks = [
293 | resnet_v1_block('block1', base_depth=64, num_units=3, stride=2),
294 | resnet_v1_block('block2', base_depth=128, num_units=4, stride=2),
295 | resnet_v1_block('block3', base_depth=256, num_units=23, stride=2),
296 | resnet_v1_block('block4', base_depth=512, num_units=3, stride=1),
297 | ]
298 | return resnet_v1(inputs, blocks, num_classes, is_training,
299 | global_pool=global_pool, output_stride=output_stride,
300 | include_root_block=True, spatial_squeeze=spatial_squeeze,
301 | reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
302 | resnet_v1_101.default_image_size = resnet_v1.default_image_size
303 |
304 |
305 | def resnet_v1_152(inputs,
306 | num_classes=None,
307 | is_training=True,
308 | global_pool=True,
309 | output_stride=None,
310 | spatial_squeeze=True,
311 | reuse=None,
312 | scope='resnet_v1_152'):
313 | """ResNet-152 model of [1]. See resnet_v1() for arg and return description."""
314 | blocks = [
315 | resnet_v1_block('block1', base_depth=64, num_units=3, stride=2),
316 | resnet_v1_block('block2', base_depth=128, num_units=8, stride=2),
317 | resnet_v1_block('block3', base_depth=256, num_units=36, stride=2),
318 | resnet_v1_block('block4', base_depth=512, num_units=3, stride=1),
319 | ]
320 | return resnet_v1(inputs, blocks, num_classes, is_training,
321 | global_pool=global_pool, output_stride=output_stride,
322 | include_root_block=True, spatial_squeeze=spatial_squeeze,
323 | reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
324 | resnet_v1_152.default_image_size = resnet_v1.default_image_size
325 |
326 |
327 | def resnet_v1_200(inputs,
328 | num_classes=None,
329 | is_training=True,
330 | global_pool=True,
331 | output_stride=None,
332 | spatial_squeeze=True,
333 | reuse=None,
334 | scope='resnet_v1_200'):
335 | """ResNet-200 model of [2]. See resnet_v1() for arg and return description."""
336 | blocks = [
337 | resnet_v1_block('block1', base_depth=64, num_units=3, stride=2),
338 | resnet_v1_block('block2', base_depth=128, num_units=24, stride=2),
339 | resnet_v1_block('block3', base_depth=256, num_units=36, stride=2),
340 | resnet_v1_block('block4', base_depth=512, num_units=3, stride=1),
341 | ]
342 | return resnet_v1(inputs, blocks, num_classes, is_training,
343 | global_pool=global_pool, output_stride=output_stride,
344 | include_root_block=True, spatial_squeeze=spatial_squeeze,
345 | reuse=reuse, scope=scope)
346 | resnet_v1_200.default_image_size = resnet_v1.default_image_size
347 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model/nets/vgg_preprocessing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 | """Provides utilities to preprocess images.
16 |
17 | The preprocessing steps for VGG were introduced in the following technical
18 | report:
19 |
20 | Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition
21 | Karen Simonyan and Andrew Zisserman
22 | arXiv technical report, 2015
23 | PDF: http://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf
24 | ILSVRC 2014 Slides: http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~karen/pdf/ILSVRC_2014.pdf
25 | CC-BY-4.0
26 |
27 | More information can be obtained from the VGG website:
28 | www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/research/very_deep/
29 | """
30 |
31 | from __future__ import absolute_import
32 | from __future__ import division
33 | from __future__ import print_function
34 |
35 | import tensorflow as tf
36 |
37 | slim = tf.contrib.slim
38 |
39 | _R_MEAN = 123.68
40 | _G_MEAN = 116.78
41 | _B_MEAN = 103.94
42 |
43 | _RESIZE_SIDE_MIN = 256
44 | _RESIZE_SIDE_MAX = 512
45 |
46 |
47 | def _crop(image, offset_height, offset_width, crop_height, crop_width):
48 | """Crops the given image using the provided offsets and sizes.
49 |
50 | Note that the method doesn't assume we know the input image size but it does
51 | assume we know the input image rank.
52 |
53 | Args:
54 | image: an image of shape [height, width, channels].
55 | offset_height: a scalar tensor indicating the height offset.
56 | offset_width: a scalar tensor indicating the width offset.
57 | crop_height: the height of the cropped image.
58 | crop_width: the width of the cropped image.
59 |
60 | Returns:
61 | the cropped (and resized) image.
62 |
63 | Raises:
64 | InvalidArgumentError: if the rank is not 3 or if the image dimensions are
65 | less than the crop size.
66 | """
67 | original_shape = tf.shape(image)
68 |
69 | rank_assertion = tf.Assert(
70 | tf.equal(tf.rank(image), 3),
71 | ['Rank of image must be equal to 3.'])
72 | with tf.control_dependencies([rank_assertion]):
73 | cropped_shape = tf.stack([crop_height, crop_width, original_shape[2]])
74 |
75 | size_assertion = tf.Assert(
76 | tf.logical_and(
77 | tf.greater_equal(original_shape[0], crop_height),
78 | tf.greater_equal(original_shape[1], crop_width)),
79 | ['Crop size greater than the image size.'])
80 |
81 | offsets = tf.to_int32(tf.stack([offset_height, offset_width, 0]))
82 |
83 | # Use tf.slice instead of crop_to_bounding box as it accepts tensors to
84 | # define the crop size.
85 | with tf.control_dependencies([size_assertion]):
86 | image = tf.slice(image, offsets, cropped_shape)
87 | return tf.reshape(image, cropped_shape)
88 |
89 |
90 | def _random_crop(image_list, crop_height, crop_width):
91 | """Crops the given list of images.
92 |
93 | The function applies the same crop to each image in the list. This can be
94 | effectively applied when there are multiple image inputs of the same
95 | dimension such as:
96 |
97 | image, depths, normals = _random_crop([image, depths, normals], 120, 150)
98 |
99 | Args:
100 | image_list: a list of image tensors of the same dimension but possibly
101 | varying channel.
102 | crop_height: the new height.
103 | crop_width: the new width.
104 |
105 | Returns:
106 | the image_list with cropped images.
107 |
108 | Raises:
109 | ValueError: if there are multiple image inputs provided with different size
110 | or the images are smaller than the crop dimensions.
111 | """
112 | if not image_list:
113 | raise ValueError('Empty image_list.')
114 |
115 | # Compute the rank assertions.
116 | rank_assertions = []
117 | for i in range(len(image_list)):
118 | image_rank = tf.rank(image_list[i])
119 | rank_assert = tf.Assert(
120 | tf.equal(image_rank, 3),
121 | ['Wrong rank for tensor %s [expected] [actual]',
122 | image_list[i].name, 3, image_rank])
123 | rank_assertions.append(rank_assert)
124 |
125 | with tf.control_dependencies([rank_assertions[0]]):
126 | image_shape = tf.shape(image_list[0])
127 | image_height = image_shape[0]
128 | image_width = image_shape[1]
129 | crop_size_assert = tf.Assert(
130 | tf.logical_and(
131 | tf.greater_equal(image_height, crop_height),
132 | tf.greater_equal(image_width, crop_width)),
133 | ['Crop size greater than the image size.'])
134 |
135 | asserts = [rank_assertions[0], crop_size_assert]
136 |
137 | for i in range(1, len(image_list)):
138 | image = image_list[i]
139 | asserts.append(rank_assertions[i])
140 | with tf.control_dependencies([rank_assertions[i]]):
141 | shape = tf.shape(image)
142 | height = shape[0]
143 | width = shape[1]
144 |
145 | height_assert = tf.Assert(
146 | tf.equal(height, image_height),
147 | ['Wrong height for tensor %s [expected][actual]',
148 | image.name, height, image_height])
149 | width_assert = tf.Assert(
150 | tf.equal(width, image_width),
151 | ['Wrong width for tensor %s [expected][actual]',
152 | image.name, width, image_width])
153 | asserts.extend([height_assert, width_assert])
154 |
155 | # Create a random bounding box.
156 | #
157 | # Use tf.random_uniform and not numpy.random.rand as doing the former would
158 | # generate random numbers at graph eval time, unlike the latter which
159 | # generates random numbers at graph definition time.
160 | with tf.control_dependencies(asserts):
161 | max_offset_height = tf.reshape(image_height - crop_height + 1, [])
162 | with tf.control_dependencies(asserts):
163 | max_offset_width = tf.reshape(image_width - crop_width + 1, [])
164 | offset_height = tf.random_uniform(
165 | [], maxval=max_offset_height, dtype=tf.int32)
166 | offset_width = tf.random_uniform(
167 | [], maxval=max_offset_width, dtype=tf.int32)
168 |
169 | return [_crop(image, offset_height, offset_width,
170 | crop_height, crop_width) for image in image_list]
171 |
172 |
173 | def _central_crop(image_list, crop_height, crop_width):
174 | """Performs central crops of the given image list.
175 |
176 | Args:
177 | image_list: a list of image tensors of the same dimension but possibly
178 | varying channel.
179 | crop_height: the height of the image following the crop.
180 | crop_width: the width of the image following the crop.
181 |
182 | Returns:
183 | the list of cropped images.
184 | """
185 | outputs = []
186 | for image in image_list:
187 | image_height = tf.shape(image)[0]
188 | image_width = tf.shape(image)[1]
189 |
190 | offset_height = (image_height - crop_height) / 2
191 | offset_width = (image_width - crop_width) / 2
192 |
193 | outputs.append(_crop(image, offset_height, offset_width,
194 | crop_height, crop_width))
195 | return outputs
196 |
197 |
198 | def _mean_image_subtraction(image, means):
199 | """Subtracts the given means from each image channel.
200 |
201 | For example:
202 | means = [123.68, 116.779, 103.939]
203 | image = _mean_image_subtraction(image, means)
204 |
205 | Note that the rank of `image` must be known.
206 |
207 | Args:
208 | image: a tensor of size [height, width, C].
209 | means: a C-vector of values to subtract from each channel.
210 |
211 | Returns:
212 | the centered image.
213 |
214 | Raises:
215 | ValueError: If the rank of `image` is unknown, if `image` has a rank other
216 | than three or if the number of channels in `image` doesn't match the
217 | number of values in `means`.
218 | """
219 | if image.get_shape().ndims != 3:
220 | raise ValueError('Input must be of size [height, width, C>0]')
221 | num_channels = image.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
222 | if len(means) != num_channels:
223 | raise ValueError('len(means) must match the number of channels')
224 |
225 | channels = tf.split(axis=2, num_or_size_splits=num_channels, value=image)
226 | for i in range(num_channels):
227 | channels[i] -= means[i]
228 | return tf.concat(axis=2, values=channels)
229 |
230 |
231 | def _smallest_size_at_least(height, width, smallest_side):
232 | """Computes new shape with the smallest side equal to `smallest_side`.
233 |
234 | Computes new shape with the smallest side equal to `smallest_side` while
235 | preserving the original aspect ratio.
236 |
237 | Args:
238 | height: an int32 scalar tensor indicating the current height.
239 | width: an int32 scalar tensor indicating the current width.
240 | smallest_side: A python integer or scalar `Tensor` indicating the size of
241 | the smallest side after resize.
242 |
243 | Returns:
244 | new_height: an int32 scalar tensor indicating the new height.
245 | new_width: and int32 scalar tensor indicating the new width.
246 | """
247 | smallest_side = tf.convert_to_tensor(smallest_side, dtype=tf.int32)
248 |
249 | height = tf.to_float(height)
250 | width = tf.to_float(width)
251 | smallest_side = tf.to_float(smallest_side)
252 |
253 | scale = tf.cond(tf.greater(height, width),
254 | lambda: smallest_side / width,
255 | lambda: smallest_side / height)
256 | new_height = tf.to_int32(tf.rint(height * scale))
257 | new_width = tf.to_int32(tf.rint(width * scale))
258 | return new_height, new_width
259 |
260 |
261 | def _aspect_preserving_resize(image, smallest_side):
262 | """Resize images preserving the original aspect ratio.
263 |
264 | Args:
265 | image: A 3-D image `Tensor`.
266 | smallest_side: A python integer or scalar `Tensor` indicating the size of
267 | the smallest side after resize.
268 |
269 | Returns:
270 | resized_image: A 3-D tensor containing the resized image.
271 | """
272 | smallest_side = tf.convert_to_tensor(smallest_side, dtype=tf.int32)
273 |
274 | shape = tf.shape(image)
275 | height = shape[0]
276 | width = shape[1]
277 | new_height, new_width = _smallest_size_at_least(height, width, smallest_side)
278 | image = tf.expand_dims(image, 0)
279 | resized_image = tf.image.resize_bilinear(image, [new_height, new_width],
280 | align_corners=False)
281 | resized_image = tf.squeeze(resized_image)
282 | resized_image.set_shape([None, None, 3])
283 | return resized_image
284 |
285 |
286 | def preprocess_for_train(image,
287 | output_height,
288 | output_width,
289 | resize_side_min=_RESIZE_SIDE_MIN,
290 | resize_side_max=_RESIZE_SIDE_MAX):
291 | """Preprocesses the given image for training.
292 |
293 | Note that the actual resizing scale is sampled from
294 | [`resize_size_min`, `resize_size_max`].
295 |
296 | Args:
297 | image: A `Tensor` representing an image of arbitrary size.
298 | output_height: The height of the image after preprocessing.
299 | output_width: The width of the image after preprocessing.
300 | resize_side_min: The lower bound for the smallest side of the image for
301 | aspect-preserving resizing.
302 | resize_side_max: The upper bound for the smallest side of the image for
303 | aspect-preserving resizing.
304 |
305 | Returns:
306 | A preprocessed image.
307 | """
308 | resize_side = tf.random_uniform(
309 | [], minval=resize_side_min, maxval=resize_side_max+1, dtype=tf.int32)
310 |
311 | image = _aspect_preserving_resize(image, resize_side)
312 | image = _random_crop([image], output_height, output_width)[0]
313 | image.set_shape([output_height, output_width, 3])
314 | image = tf.to_float(image)
315 | image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image)
316 | return _mean_image_subtraction(image, [_R_MEAN, _G_MEAN, _B_MEAN])
317 |
318 |
319 | def preprocess_for_eval(image, output_height, output_width, resize_side):
320 | """Preprocesses the given image for evaluation.
321 |
322 | Args:
323 | image: A `Tensor` representing an image of arbitrary size.
324 | output_height: The height of the image after preprocessing.
325 | output_width: The width of the image after preprocessing.
326 | resize_side: The smallest side of the image for aspect-preserving resizing.
327 |
328 | Returns:
329 | A preprocessed image.
330 | """
331 | image = _aspect_preserving_resize(image, resize_side)
332 | image = _central_crop([image], output_height, output_width)[0]
333 | image.set_shape([output_height, output_width, 3])
334 | image = tf.to_float(image)
335 | return _mean_image_subtraction(image, [_R_MEAN, _G_MEAN, _B_MEAN])
336 |
337 |
338 | def preprocess_image(image, output_height, output_width, is_training=False,
339 | resize_side_min=_RESIZE_SIDE_MIN,
340 | resize_side_max=_RESIZE_SIDE_MAX):
341 | """Preprocesses the given image.
342 |
343 | Args:
344 | image: A `Tensor` representing an image of arbitrary size.
345 | output_height: The height of the image after preprocessing.
346 | output_width: The width of the image after preprocessing.
347 | is_training: `True` if we're preprocessing the image for training and
348 | `False` otherwise.
349 | resize_side_min: The lower bound for the smallest side of the image for
350 | aspect-preserving resizing. If `is_training` is `False`, then this value
351 | is used for rescaling.
352 | resize_side_max: The upper bound for the smallest side of the image for
353 | aspect-preserving resizing. If `is_training` is `False`, this value is
354 | ignored. Otherwise, the resize side is sampled from
355 | [resize_size_min, resize_size_max].
356 |
357 | Returns:
358 | A preprocessed image.
359 | """
360 | if is_training:
361 | return preprocess_for_train(image, output_height, output_width,
362 | resize_side_min, resize_side_max)
363 | else:
364 | return preprocess_for_eval(image, output_height, output_width,
365 | resize_side_min)
366 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model/similarity.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import tensorflow as tf
2 |
3 |
4 | def chamfer_similarity(sim, max_axis=1, mean_axis=0):
5 | sim = tf.reduce_max(sim, axis=max_axis, keepdims=True)
6 | sim = tf.reduce_mean(sim, axis=mean_axis, keepdims=True)
7 | return tf.squeeze(sim, [max_axis, mean_axis])
8 |
9 |
10 | def symmetric_chamfer_similarity(sim, axes=[0, 1]):
11 | return (chamfer_similarity(sim, axes[0], axes[1]) +
12 | chamfer_similarity(sim, axes[1], axes[0])) / 2
13 |
14 |
15 | def triplet_loss(sim_pos, sim_neg, gamma=0.5):
16 | with tf.variable_scope('triplet_loss'):
17 | return tf.maximum(0., sim_neg - sim_pos + gamma)
18 |
19 |
20 | def similarity_regularization_loss(sim, lower_limit=-1., upper_limit=1.):
21 | with tf.variable_scope('similarity_regularization_loss'):
22 | return tf.reduce_sum(tf.abs(tf.minimum(.0, sim - lower_limit))) + \
23 | tf.reduce_sum(tf.abs(tf.maximum(.0, sim - upper_limit)))
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/model/visil.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 |
4 | from .layers import PCA_layer, Attention_layer, Video_Comparator
5 | from .similarity import chamfer_similarity, symmetric_chamfer_similarity
6 |
7 |
8 | class ViSiL(object):
9 |
10 | def __init__(self, model_dir, net='resnet', load_queries=False,
11 | dims=None, whitening=True, attention=True, video_comparator=True,
12 | queries_number=None, gpu_id=0, similarity_function='chamfer'):
13 |
14 | self.net = net
15 | if self.net not in ['resnet', 'i3d']:
16 | raise Exception('[ERROR] Not supported backbone network: {}. '
17 | 'Supported options: resnet or i3d'.format(self.net))
18 |
19 | self.load_queries = load_queries
20 | if whitening or dims is not None:
21 | self.PCA = PCA_layer(dims=dims, whitening=whitening, net=self.net)
22 | if attention:
23 | if whitening and dims is None:
24 | self.att = Attention_layer(shape=400 if self.net == 'i3d' else 3840)
25 | else:
26 | print('[WARNING] Attention layer has been deactivated. '
27 | 'It works only with Whitening layer of {} dimensions. '.
28 | format(400 if self.net == 'i3d' else 3840))
29 | if video_comparator:
30 | if whitening and attention and dims is None:
31 | self.vid_comp = Video_Comparator()
32 | else:
33 | print('[WARNING] Video comparator has been deactivated. '
34 | 'It works only with Whitening layer of {} dimensions '
35 | 'and Attention layer. '.format(400 if self.net == 'i3d' else 3840))
36 |
37 | if similarity_function == 'chamfer':
38 | self.f2f_sim = lambda x: chamfer_similarity(x, max_axis=2, mean_axis=1)
39 | self.v2v_sim = lambda x: chamfer_similarity(x, max_axis=1, mean_axis=0)
40 | elif similarity_function == 'symmetric_chamfer':
41 | self.f2f_sim = lambda x: symmetric_chamfer_similarity(x, axes=[1, 2])
42 | self.v2v_sim = lambda x: symmetric_chamfer_similarity(x, axes=[0, 1])
43 | else:
44 | raise Exception('[ERROR] Not implemented similarity function: {}. '
45 | 'Supported options: chamfer or symmetric_chamfer'.format(similarity_function))
46 |
47 | self.frames = tf.placeholder(tf.uint8, shape=(None, None, None, 3), name='input')
48 | with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
49 | if self.net == 'resnet':
50 | processed_frames = self.preprocess_resnet(self.frames)
51 | elif self.net == 'i3d':
52 | processed_frames = self.preprocess_i3d(self.frames)
53 |
54 | with tf.device('/gpu:%i' % gpu_id):
55 | self.region_vectors = self.extract_region_vectors(processed_frames)
56 | if self.load_queries:
57 | print('[INFO] Queries will be loaded to the gpu')
58 | self.queries = [tf.Variable(np.zeros((1, 9, 3840)), dtype=tf.float32,
59 | validate_shape=False) for _ in range(queries_number)]
60 | self.target = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, None, None], name='target')
61 | self.similarities = []
62 | for q in self.queries:
63 | sim_matrix = self.frame_to_frame_similarity(q, self.target)
64 | similarity = self.video_to_video_similarity(sim_matrix)
65 | self.similarities.append(similarity)
66 | else:
67 | print('[INFO] Queries will NOT be loaded to the gpu')
68 | self.query = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, None, None], name='query')
69 | self.target = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, None, None], name='target')
70 | self.sim_matrix = self.frame_to_frame_similarity(self.query, self.target)
71 | self.similarity = self.video_to_video_similarity(self.sim_matrix)
72 |
73 | init = self.load_model(model_dir)
74 | config = tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True)
75 | config.gpu_options.allow_growth = True
76 | self.sess = tf.Session(config=config)
77 | self.sess.run(init)
78 |
79 | def preprocess_resnet(self, video):
80 | from .nets import vgg_preprocessing
81 | video = tf.map_fn(lambda x: vgg_preprocessing.preprocess_for_eval(x, 224, 224, 256), video,
82 | parallel_iterations=100, dtype=tf.float32, swap_memory=True)
83 | return video
84 |
85 | def preprocess_i3d(self, video):
86 | video = tf.image.resize_with_crop_or_pad(video, 224, 224)
87 | video = tf.image.convert_image_dtype(video, dtype=tf.float32)
88 | video = tf.multiply(tf.subtract(video, 0.5), 2.0)
89 | video = tf.expand_dims(video, 0)
90 | return video
91 |
92 | def region_pooling(self, video):
93 | if self.net == 'resnet':
94 | from .nets import resnet_v1
95 | with tf.contrib.slim.arg_scope(resnet_v1.resnet_arg_scope()):
96 | _, network = resnet_v1.resnet_v1_50(video, num_classes=None, is_training=False)
97 |
98 | layers = [['resnet_v1_50/block1', 8], ['resnet_v1_50/block2', 4],
99 | ['resnet_v1_50/block3', 2], ['resnet_v1_50/block4', 2]]
100 |
101 | with tf.variable_scope('region_vectors'):
102 | features = []
103 | for l, p in layers:
104 | logits = tf.nn.relu(network[l])
105 | logits = tf.layers.max_pooling2d(logits, [np.floor(p+p/2), np.floor(p+p/2)], p, padding='VALID')
106 | logits = tf.nn.l2_normalize(logits, -1, epsilon=1e-15)
107 | features.append(logits)
108 | logits = tf.concat(features, axis=-1)
109 | logits = tf.nn.l2_normalize(logits, -1, epsilon=1e-15)
110 | logits = tf.reshape(logits, [tf.shape(logits)[0], -1, tf.shape(logits)[-1]])
111 | elif self.net == 'i3d':
112 | from .nets import i3d
113 | with tf.variable_scope('RGB'):
114 | model = i3d.InceptionI3d(400, spatial_squeeze=True, final_endpoint='Logits')
115 | logits, _ = model(video, is_training=False, dropout_keep_prob=1.0)
116 |
117 | with tf.variable_scope('region_vectors'):
118 | logits = tf.nn.l2_normalize(tf.nn.relu(logits), -1, epsilon=1e-15)
119 |
120 | return tf.expand_dims(logits, axis=1) if len(logits.shape) < 3 else logits
121 |
122 | def extract_region_vectors(self, video):
123 | logits = self.region_pooling(video)
124 | if hasattr(self, 'PCA'):
125 | logits = tf.nn.l2_normalize(self.PCA(logits), -1, epsilon=1e-15)
126 | if hasattr(self, 'att'):
127 | logits, weights = self.att(logits)
128 | return logits
129 |
130 | def frame_to_frame_similarity(self, query, target):
131 | tensor_dot = tf.tensordot(query, tf.transpose(target), axes=1)
132 | sim_matrix = self.f2f_sim(tensor_dot)
133 | return sim_matrix
134 |
135 | def video_to_video_similarity(self, sim):
136 | if hasattr(self, 'vid_comp'):
137 | sim = self.vid_comp(sim)
138 | self.visil_output = sim
139 | sim = self.v2v_sim(sim)
140 | return sim
141 |
142 | def load_model(self, model_path):
143 | previous_variables = [var_name for var_name, _ in tf.contrib.framework.list_variables(model_path)]
144 | restore_map = {variable.op.name: variable for variable in tf.global_variables()
145 | if variable.op.name in previous_variables and 'PCA' not in variable.op.name} #
146 | print('[INFO] {} layers loaded'.format(len(restore_map)))
147 | tf.contrib.framework.init_from_checkpoint(model_path, restore_map)
148 | tf_init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
149 | return tf_init
150 |
151 | def extract_features(self, frames, batch_sz):
152 | features = []
153 | for b in range(frames.shape[0] // batch_sz + 1):
154 | batch = frames[b * batch_sz: (b+1) * batch_sz]
155 | if batch.shape[0] > 0:
156 | if batch.shape[0] >= batch_sz or self.net == 'resnet':
157 | features.append(self.sess.run(self.region_vectors, feed_dict={self.frames: batch}))
158 | features = np.concatenate(features, axis=0)
159 | while features.shape[0] < 4:
160 | features = np.concatenate([features, features], axis=0)
161 | return features
162 |
163 | def set_queries(self, queries):
164 | if self.load_queries:
165 | self.sess.run([tf.assign(self.queries[i], queries[i], validate_shape=False) for i in range(len(queries))])
166 | else:
167 | self.queries = queries
168 |
169 | def add_query(self, query):
170 | if self.load_queries:
171 | raise Exception('[ERROR] Operation not permitted when queries are loaded to GPU.')
172 | else:
173 | self.queries.append(query)
174 |
175 | def calculate_similarities_to_queries(self, target):
176 | if self.load_queries:
177 | return self.sess.run(self.similarities, feed_dict={self.target: target})
178 | else:
179 | return [self.calculate_video_similarity(q, target) for q in self.queries]
180 |
181 | def calculate_video_similarity(self, query, target):
182 | return self.sess.run(self.similarity, feed_dict={self.query: query, self.target: target})
183 |
184 | def calculate_f2f_matrix(self, query, target):
185 | return self.sess.run(self.sim_matrix, feed_dict={self.query: query, self.target: target})
186 |
187 | def calculate_visil_output(self, query, target):
188 | return self.sess.run(self.visil_output, feed_dict={self.query: query, self.target: target})
189 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | numpy>=1.9
2 | tqdm>=4.2
3 | opencv-python>=3.1
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/video_similarity.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MKLab-ITI/visil/0971e54fb8325fceb1bc9748ecbfe4c66e5dabd2/video_similarity.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 12 |
13 | ## Prerequisites
14 | * Python 3
15 | * Tensorflow 1.xx (tested with 1.8-1.15)
16 |
17 | ## Getting started
18 |
19 | ### Installation
20 |
21 | * Clone this repo:
22 | ```bash
23 | git clone https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/visil
24 | cd visil
25 | ```
26 | * You can install all the dependencies by
27 | ```bash
28 | pip install -r requirements.txt
29 | ```
30 |
31 | * Download and unzip the pretrained model:
32 | ```bash
33 | wget http://ndd.iti.gr/visil/ckpt.zip
34 | unzip ckpt.zip
35 | ```
36 |
37 | * If you want to use I3D as backbone network (used for AVR in the paper), then install the following packages:
38 | ```bash
39 | # For tensoflow version >= 1.14
40 | pip install tensorflow-probability==0.7 dm-sonnet==1.25
41 |
42 | # For tensoflow version < 1.14
43 | pip install tensorflow-probability==0.6 dm-sonnet==1.23
44 | ```
45 |
46 | ### Video similarity calculation
47 | * Create a file that contains the query videos.
48 | Each line of the file have to contain a video id and a path to the corresponding video file,
49 | separated by a tab character (\\t). Example:
50 |
51 | wrC_Uqk3juY queries/wrC_Uqk3juY.mp4
52 | k_NT43aJ_Jw queries/k_NT43aJ_Jw.mp4
53 | 2n30dbPBNKE queries/2n30dbPBNKE.mp4
54 | ...
55 |
56 |
57 | * Create a file with the same format for the database videos.
58 |
59 | * Run the following command to calculate the similarity between all the query and database videos
60 | ```bash
61 | python calculate_similarity.py --query_file queries.txt --database_file database.txt --model_dir model/
62 | ```
63 |
64 | * For faster processing, you can load the query videos to the GPU memory by adding the flag ```--load_queries```
65 | ```bash
66 | python calculate_similarity.py --query_file queries.txt --database_file database.txt --model_dir model/ --load_queries
67 | ```
68 |
69 | * The calculated similarities are stored to the file given to the ```--output_file```. The file is in JSON format and
70 | contains a dictionary with every query id as keys, and another dictionary that contains the similarities of the dataset
71 | videos to the corresponding queries as values. See the example below
72 | ```bash
73 | {
74 | "wrC_Uqk3juY": {
75 | "KQh6RCW_nAo": 0.716,
76 | "0q82oQa3upE": 0.300,
77 | ...},
78 | "k_NT43aJ_Jw": {
79 | "-KuR8y1gjJQ": 1.0,
80 | "Xb19O5Iur44": 0.417,
81 | ...},
82 | ....
83 | }
84 | ```
85 | ```
86 |
87 | * Add flag `--help` to display the detailed description for the arguments of the similarity calculation script
88 |
89 | ```
90 | -q, --query_file QUERY_FILE Path to file that contains the query videos
91 | -d, --database_file DATABASE_FILE Path to file that contains the database videos
92 | -o, --output_file OUTPUT_FILE Name of the output file. Default: "results.json"
93 | --network NETWORK Backbone network used for feature extraction.
94 | Options: "resnet" or "i3d". Default: "resnet"
95 | --model_dir MODEL_DIR Path to the directory of the pretrained model.
96 | Default: "ckpt/resnet"
97 | -s, --similarity_function SIMILARITY_FUNCTION Function that will be used to calculate the
98 | similarity between query-candidate frames and
99 | videos.Options: "chamfer" or "symmetric_chamfer".
100 | Default: "chamfer"
101 | --batch_sz BATCH_SZ Number of frames contained in each batch during
102 | feature extraction. Default: 128
103 | --gpu_id GPU_ID Id of the GPU used. Default: 0
104 | -l, --load_queries Flag that indicates that the queries will be loaded to
105 | the GPU memory.
106 | --threads THREADS Number of threads used for video loading. Default: 8
107 | ```
108 |
109 | ### Evaluation
110 | * We also provide code to reproduce the experiments in the paper.
111 |
112 | * First, download the videos of the dataset you want. The supported options are:
113 | * [CC_WEB_VIDEO](http://vireo.cs.cityu.edu.hk/webvideo/) - Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
114 | * [FIVR-5K, FIVR-200K](http://ndd.iti.gr/fivr/) - Fine-grained Incident Video Retrieval
115 | * [EVVE](http://pascal.inrialpes.fr/data/evve/) - Event-based Video Retrieval
116 | * [ActivityNet](http://activity-net.org/) - Action Video Retrieval
117 |
118 | * Determine the pattern based on the video id that the source videos are stored. For example,
119 | if all dataset videos are stored in a folder with filename the video id and the extension `.mp4`,
120 | then the pattern is `{id}.mp4`. If each dataset video is stored in a different folder based on their
121 | video id with filename `video.mp4`, then the pattern us `{id}/video.mp4`.
122 | * The code replaces the `{id}` string with the id of the videos in the dataset
123 | * Also, it support supports Unix style pathname pattern expansion. For example, if video files have
124 | various extension, then the pattern can be e.g. `{id}/video.*`
125 | * For FIVR-200K, EVVE, ActivityNet, the Youtube ids are considered as the video ids
126 | * For CC_WEB_VIDEO, video ids derives from the number of the query set that the video belongs to,
127 | and the basename of the file. In particular, the video ids are in form `
12 |
13 | ## Prerequisites
14 | * Python 3
15 | * Tensorflow 1.xx (tested with 1.8-1.15)
16 |
17 | ## Getting started
18 |
19 | ### Installation
20 |
21 | * Clone this repo:
22 | ```bash
23 | git clone https://github.com/MKLab-ITI/visil
24 | cd visil
25 | ```
26 | * You can install all the dependencies by
27 | ```bash
28 | pip install -r requirements.txt
29 | ```
30 |
31 | * Download and unzip the pretrained model:
32 | ```bash
33 | wget http://ndd.iti.gr/visil/ckpt.zip
34 | unzip ckpt.zip
35 | ```
36 |
37 | * If you want to use I3D as backbone network (used for AVR in the paper), then install the following packages:
38 | ```bash
39 | # For tensoflow version >= 1.14
40 | pip install tensorflow-probability==0.7 dm-sonnet==1.25
41 |
42 | # For tensoflow version < 1.14
43 | pip install tensorflow-probability==0.6 dm-sonnet==1.23
44 | ```
45 |
46 | ### Video similarity calculation
47 | * Create a file that contains the query videos.
48 | Each line of the file have to contain a video id and a path to the corresponding video file,
49 | separated by a tab character (\\t). Example:
50 |
51 | wrC_Uqk3juY queries/wrC_Uqk3juY.mp4
52 | k_NT43aJ_Jw queries/k_NT43aJ_Jw.mp4
53 | 2n30dbPBNKE queries/2n30dbPBNKE.mp4
54 | ...
55 |
56 |
57 | * Create a file with the same format for the database videos.
58 |
59 | * Run the following command to calculate the similarity between all the query and database videos
60 | ```bash
61 | python calculate_similarity.py --query_file queries.txt --database_file database.txt --model_dir model/
62 | ```
63 |
64 | * For faster processing, you can load the query videos to the GPU memory by adding the flag ```--load_queries```
65 | ```bash
66 | python calculate_similarity.py --query_file queries.txt --database_file database.txt --model_dir model/ --load_queries
67 | ```
68 |
69 | * The calculated similarities are stored to the file given to the ```--output_file```. The file is in JSON format and
70 | contains a dictionary with every query id as keys, and another dictionary that contains the similarities of the dataset
71 | videos to the corresponding queries as values. See the example below
72 | ```bash
73 | {
74 | "wrC_Uqk3juY": {
75 | "KQh6RCW_nAo": 0.716,
76 | "0q82oQa3upE": 0.300,
77 | ...},
78 | "k_NT43aJ_Jw": {
79 | "-KuR8y1gjJQ": 1.0,
80 | "Xb19O5Iur44": 0.417,
81 | ...},
82 | ....
83 | }
84 | ```
85 | ```
86 |
87 | * Add flag `--help` to display the detailed description for the arguments of the similarity calculation script
88 |
89 | ```
90 | -q, --query_file QUERY_FILE Path to file that contains the query videos
91 | -d, --database_file DATABASE_FILE Path to file that contains the database videos
92 | -o, --output_file OUTPUT_FILE Name of the output file. Default: "results.json"
93 | --network NETWORK Backbone network used for feature extraction.
94 | Options: "resnet" or "i3d". Default: "resnet"
95 | --model_dir MODEL_DIR Path to the directory of the pretrained model.
96 | Default: "ckpt/resnet"
97 | -s, --similarity_function SIMILARITY_FUNCTION Function that will be used to calculate the
98 | similarity between query-candidate frames and
99 | videos.Options: "chamfer" or "symmetric_chamfer".
100 | Default: "chamfer"
101 | --batch_sz BATCH_SZ Number of frames contained in each batch during
102 | feature extraction. Default: 128
103 | --gpu_id GPU_ID Id of the GPU used. Default: 0
104 | -l, --load_queries Flag that indicates that the queries will be loaded to
105 | the GPU memory.
106 | --threads THREADS Number of threads used for video loading. Default: 8
107 | ```
108 |
109 | ### Evaluation
110 | * We also provide code to reproduce the experiments in the paper.
111 |
112 | * First, download the videos of the dataset you want. The supported options are:
113 | * [CC_WEB_VIDEO](http://vireo.cs.cityu.edu.hk/webvideo/) - Near-Duplicate Video Retrieval
114 | * [FIVR-5K, FIVR-200K](http://ndd.iti.gr/fivr/) - Fine-grained Incident Video Retrieval
115 | * [EVVE](http://pascal.inrialpes.fr/data/evve/) - Event-based Video Retrieval
116 | * [ActivityNet](http://activity-net.org/) - Action Video Retrieval
117 |
118 | * Determine the pattern based on the video id that the source videos are stored. For example,
119 | if all dataset videos are stored in a folder with filename the video id and the extension `.mp4`,
120 | then the pattern is `{id}.mp4`. If each dataset video is stored in a different folder based on their
121 | video id with filename `video.mp4`, then the pattern us `{id}/video.mp4`.
122 | * The code replaces the `{id}` string with the id of the videos in the dataset
123 | * Also, it support supports Unix style pathname pattern expansion. For example, if video files have
124 | various extension, then the pattern can be e.g. `{id}/video.*`
125 | * For FIVR-200K, EVVE, ActivityNet, the Youtube ids are considered as the video ids
126 | * For CC_WEB_VIDEO, video ids derives from the number of the query set that the video belongs to,
127 | and the basename of the file. In particular, the video ids are in form `