├── BOM.md
├── Firmware-1.24
├── .gitignore
├── .travis.yml
├── BOM.md
├── CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md
├── Documentation
│ ├── Download Firmware.jpg
│ ├── Download IDE.jpg
│ ├── How To Contribute Pictures
│ │ ├── Clone.png
│ │ ├── Clone2.png
│ │ ├── Clone3.png
│ │ ├── Commit.png
│ │ ├── EditingFile.png
│ │ ├── Fork.jpg
│ │ ├── GithubHome.jpg
│ │ ├── GithubWelcome.jpg
│ │ ├── PR0.png
│ │ ├── PR1.png
│ │ ├── PR2.png
│ │ ├── PR3.png
│ │ └── Push Origin.png
│ ├── Open Firmware.jpg
│ ├── Select Board.jpg
│ ├── Select COM Port.jpg
│ ├── Upload.jpg
│ └── posErrorAlarm
│ │ ├── alarm.PNG
│ │ └── alarmSetting.PNG
├── INSTRUCTIONS.md
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── ROBOT.md
├── cnc_ctrl_v1
│ ├── Axis.cpp
│ ├── Axis.h
│ ├── Config.h
│ ├── Encoder.cpp
│ ├── Encoder.h
│ ├── GCode.cpp
│ ├── GCode.h
│ ├── Kinematics.cpp
│ ├── Kinematics.h
│ ├── Maslow.h
│ ├── Motion.cpp
│ ├── Motion.h
│ ├── Motor.cpp
│ ├── Motor.h
│ ├── MotorGearboxEncoder.cpp
│ ├── MotorGearboxEncoder.h
│ ├── NutsAndBolts.cpp
│ ├── NutsAndBolts.h
│ ├── PID_v1.cpp
│ ├── PID_v1.h
│ ├── Probe.cpp
│ ├── Probe.h
│ ├── Report.cpp
│ ├── Report.h
│ ├── RingBuffer.cpp
│ ├── RingBuffer.h
│ ├── Settings.cpp
│ ├── Settings.h
│ ├── SimavrSerial.cpp
│ ├── SimavrSerial.h
│ ├── Spindle.cpp
│ ├── Spindle.h
│ ├── System.cpp
│ ├── System.h
│ ├── Testing.cpp
│ ├── Testing.h
│ ├── TimerOne.cpp
│ ├── TimerOne.h
│ ├── cnc_ctrl_v1.ino
│ └── utility
│ │ ├── direct_pin_read.h
│ │ ├── interrupt_config.h
│ │ └── interrupt_pins.h
├── guestBook.txt
├── mainpicture.jpg
├── platformio.ini
└── platformio
│ ├── simavr_env.py
│ └── teensy_env.py
├── INSTRUCTIONS.md
├── README.md
├── ROBOT.md
├── Ring_Kit.jpg
├── mainpicture.jpg
└── usrinput.txt
/BOM.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Head over to [MakerMade](http://www.makermade.com/shop) to order.
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .pioenvs
2 | .piolibdeps
3 | .clang_complete
4 | .gcc-flags.json
5 | lib/readme.txt
6 | cnc_ctrl_v1/.DS_Store
7 | cnc_ctrl_v1/.DS_Store
8 | cnc_ctrl_v1/.DS_Store
9 | .DS_Store
10 | **/.DS_Store
11 | .vscode/
12 | .vscode/c_cpp_properties.json
13 | .vscode/launch.json
14 | simduino_atmega2560_flash.bin
15 | simduino
16 | .vscode/*.db
17 | obj-x86_64-apple-darwin17.4.0
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/.travis.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Continuous Integration (CI) is the practice, in software
2 | # engineering, of merging all developer working copies with a shared mainline
3 | # several times a day < http://docs.platformio.org/page/ci/index.html >
4 | #
5 | # Documentation:
6 | #
7 | # * Travis CI Embedded Builds with PlatformIO
8 | # < https://docs.travis-ci.com/user/integration/platformio/ >
9 | #
10 | # * PlatformIO integration with Travis CI
11 | # < http://docs.platformio.org/page/ci/travis.html >
12 | #
13 | # * User Guide for `platformio ci` command
14 | # < http://docs.platformio.org/page/userguide/cmd_ci.html >
15 | #
16 | #
17 | # Please choice one of the following templates (proposed below) and uncomment
18 | # it (remove "# " before each line) or use own configuration according to the
19 | # Travis CI documentation (see above).
20 | #
21 |
22 |
23 | #
24 | # Template #1: General project. Test it using existing `platformio.ini`.
25 | #
26 |
27 | language: python
28 | python:
29 | - "2.7"
30 |
31 | install:
32 | - pip install -U platformio
33 |
34 | script:
35 | - platformio run
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/BOM.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | The firmware is and always will be free!
2 |
3 | You can download the latest version [here](https://github.com/MaslowCNC/Firmware/releases)
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributor Covenant Code of Conduct
2 |
3 | ## Our Pledge
4 |
5 | In the interest of fostering an open and welcoming environment, we as contributors and maintainers pledge to making participation in our project and our community a harassment-free experience for everyone, regardless of age, body size, disability, ethnicity, gender identity and expression, level of experience, nationality, personal appearance, race, religion, or sexual identity and orientation.
6 |
7 | ## Our Standards
8 |
9 | Examples of behavior that contributes to creating a positive environment include:
10 |
11 | * Using welcoming and inclusive language
12 | * Being respectful of differing viewpoints and experiences
13 | * Gracefully accepting constructive criticism
14 | * Focusing on what is best for the community
15 | * Showing empathy towards other community members
16 |
17 | Examples of unacceptable behavior by participants include:
18 |
19 | * The use of sexualized language or imagery and unwelcome sexual attention or advances
20 | * Trolling, insulting/derogatory comments, and personal or political attacks
21 | * Public or private harassment
22 | * Publishing others' private information, such as a physical or electronic address, without explicit permission
23 | * Other conduct which could reasonably be considered inappropriate in a professional setting
24 |
25 | ## Our Responsibilities
26 |
27 | Project maintainers are responsible for clarifying the standards of acceptable behavior and are expected to take appropriate and fair corrective action in response to any instances of unacceptable behavior.
28 |
29 | Project maintainers have the right and responsibility to remove, edit, or reject comments, commits, code, wiki edits, issues, and other contributions that are not aligned to this Code of Conduct, or to ban temporarily or permanently any contributor for other behaviors that they deem inappropriate, threatening, offensive, or harmful.
30 |
31 | ## Scope
32 |
33 | This Code of Conduct applies both within project spaces and in public spaces when an individual is representing the project or its community. Examples of representing a project or community include using an official project e-mail address, posting via an official social media account, or acting as an appointed representative at an online or offline event. Representation of a project may be further defined and clarified by project maintainers.
34 |
35 | ## Enforcement
36 |
37 | Instances of abusive, harassing, or otherwise unacceptable behavior may be reported by contacting the project team at info@maslowcnc.com. The project team will review and investigate all complaints, and will respond in a way that it deems appropriate to the circumstances. The project team is obligated to maintain confidentiality with regard to the reporter of an incident. Further details of specific enforcement policies may be posted separately.
38 |
39 | Project maintainers who do not follow or enforce the Code of Conduct in good faith may face temporary or permanent repercussions as determined by other members of the project's leadership.
40 |
41 | ## Attribution
42 |
43 | This Code of Conduct is adapted from the [Contributor Covenant][homepage], version 1.4, available at [http://contributor-covenant.org/version/1/4][version]
44 |
45 | [homepage]: http://contributor-covenant.org
46 | [version]: http://contributor-covenant.org/version/1/4/
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Download Firmware.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Download Firmware.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Download IDE.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Download IDE.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Clone.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Clone.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Clone2.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Clone2.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Clone3.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Clone3.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Commit.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Commit.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/EditingFile.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/EditingFile.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Fork.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Fork.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/GithubHome.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/GithubHome.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/GithubWelcome.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/GithubWelcome.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/PR0.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/PR0.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/PR1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/PR1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/PR2.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/PR2.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/PR3.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/PR3.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Push Origin.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/How To Contribute Pictures/Push Origin.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Open Firmware.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Open Firmware.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Select Board.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Select Board.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Select COM Port.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Select COM Port.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Upload.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/Upload.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/posErrorAlarm/alarm.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/posErrorAlarm/alarm.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/posErrorAlarm/alarmSetting.PNG:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/Documentation/posErrorAlarm/alarmSetting.PNG
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/INSTRUCTIONS.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | # Maslow Firmware Setup
4 |
5 | Installing new firmware on your machine is important. We come out with a new firmware version every other week so be prepared to do this regularly. This process will also install the proper drivers to connect to your Arduino on some older computers so if you have trouble connecting it can be helpful to do this process on the same computer you will control the machine with.
6 |
7 | ### Step 1: Connect Your Arduino
8 | Connect your Arduino to your computer using the provided USB cable.
9 |
10 | ### Step 2: Download The Arduino IDE
11 | Download and install the last Arduino IDE from [https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software](https://www.arduino.cc/en/Main/Software). Older versions of Arduino IDE have problems with libraries when compiling the firmware, so make sure you have the latest version.
12 |
13 | Note - For Windows there are three options: "Windows Installer", "Windows Zip", and "Windows App".
14 | Some users have reported problems with the "Windows App" version.
15 | 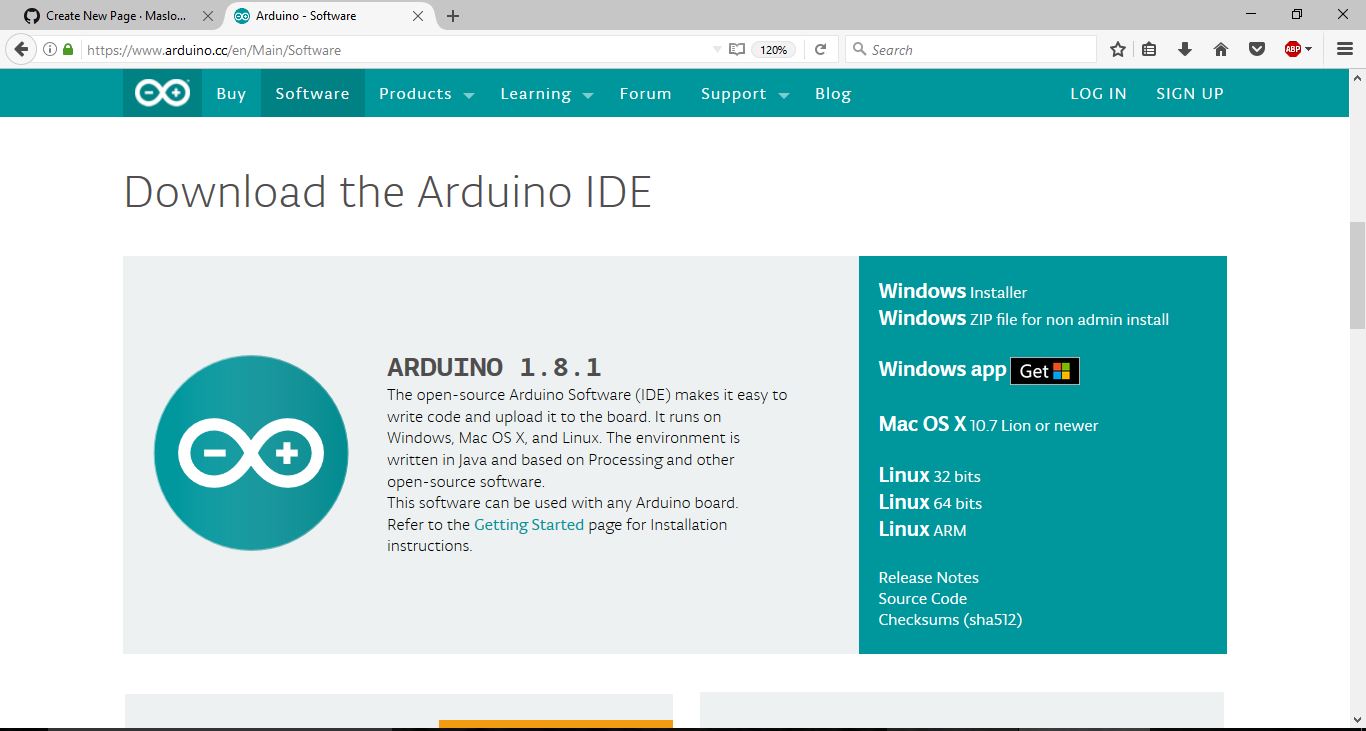
16 |
17 | ### Step 3: Download The Latest Maslow Firmware
18 | You can do this at http://github.com/MaslowCNC/Firmware/releases/ Click the zip file for the most recent release to download it. Extract the files from the zip folder.
19 | 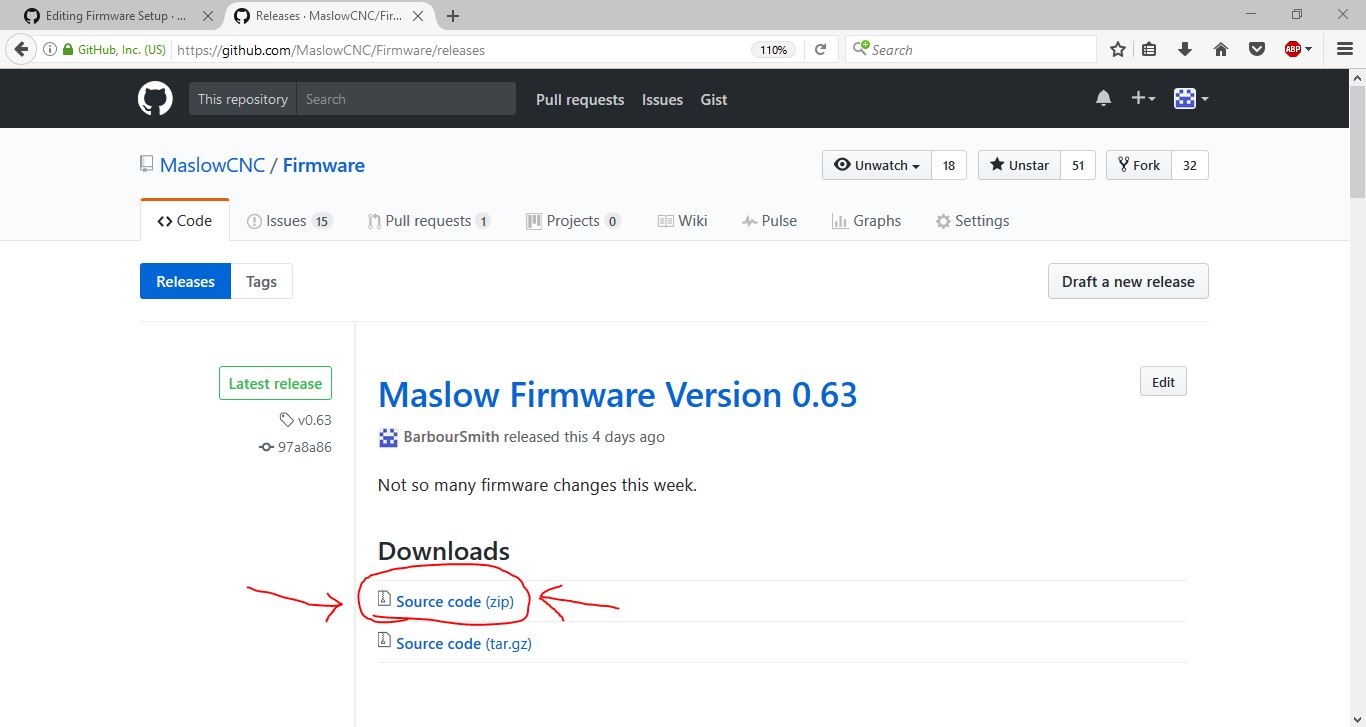
20 |
21 | ### Step 4: Open Firmware
22 | Click **File -> Open** and then open the firmware by selecting cnc_ctrl_v1.ino
23 | 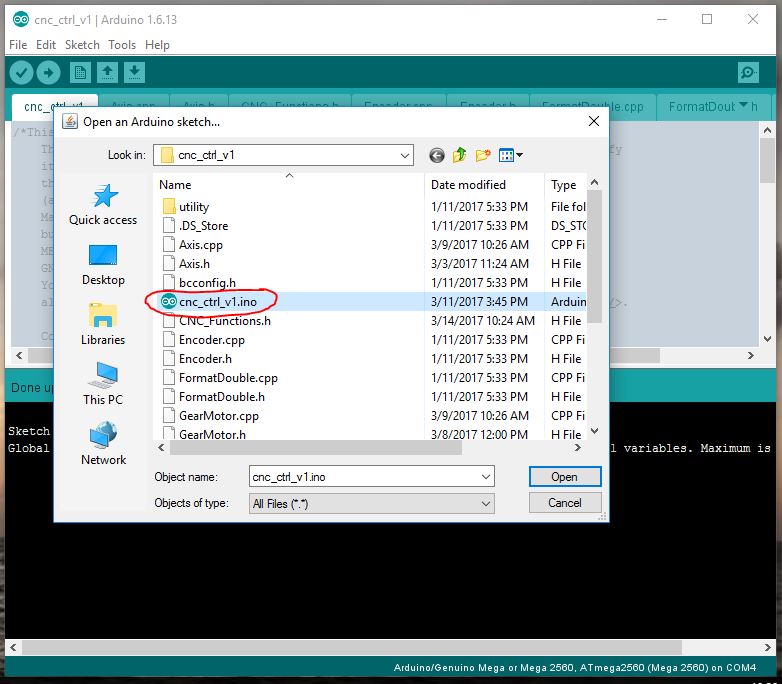
24 |
25 | ### Step 5: Select The Board Type
26 | Select the board type by clicking **Tools -> Board -> Arduino/Genuino Mega or Mega 2560**
27 | 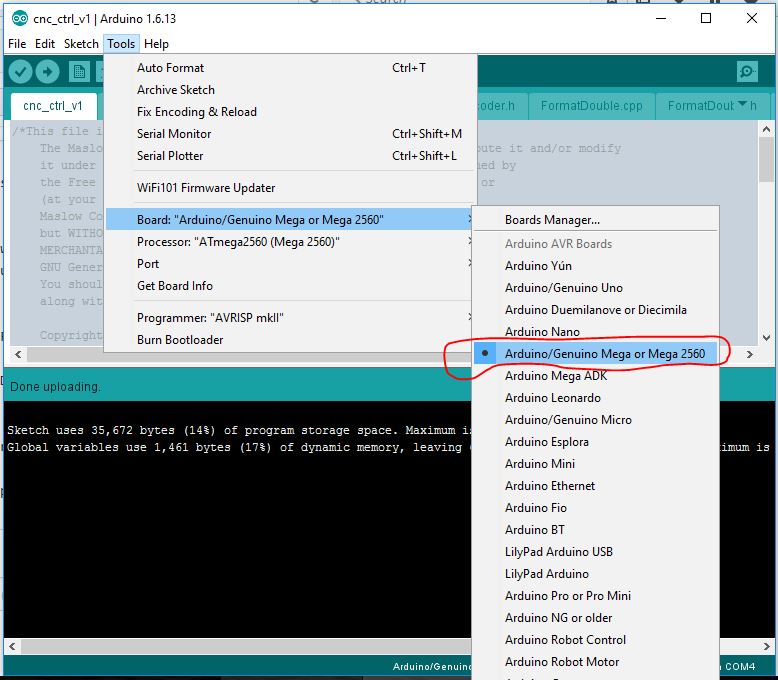
28 |
29 | ### Step 6: Select The Serial Port
30 | Select the correct port to connect to by clicking **Tools -> Port -> Your Port**. On Windows this will be something like COM3, on Mac and Linux computers it will be something like dev/tty/. You can find the right one by plugging and unplugging your Arduino compatible board and checking which option disappears.
31 | 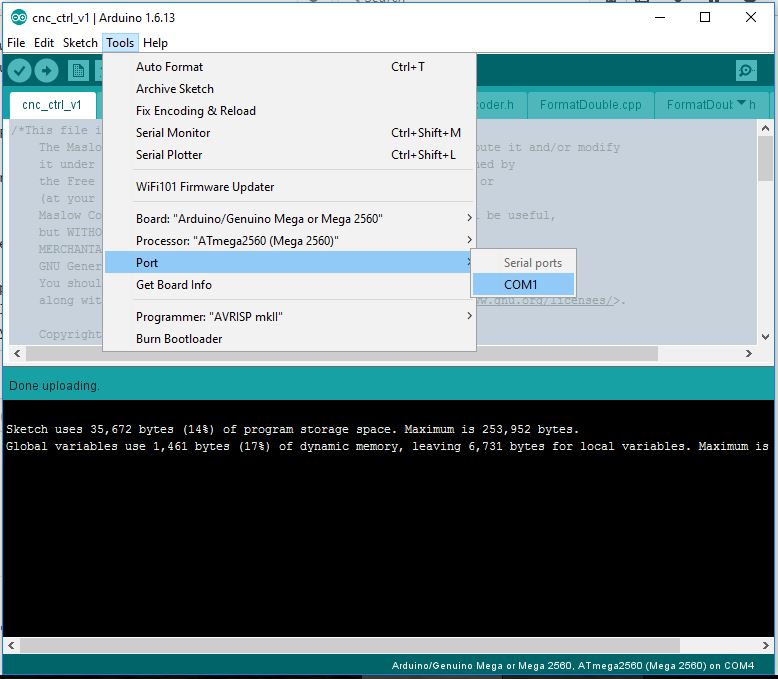
32 |
33 | ### Step 7: Upload The Firmware
34 | Upload the newest firmware to your machine by clicking the upload button in the top left corner. The arrow looks disabled until you hover over it! _Linux users_: if you are getting timeout or permissions errors, you may need to add your username to the `dialout` group and then logout and back in. [Instructions here.](https://askubuntu.com/questions/112568/how-do-i-allow-a-non-default-user-to-use-serial-device-ttyusb0)
35 | 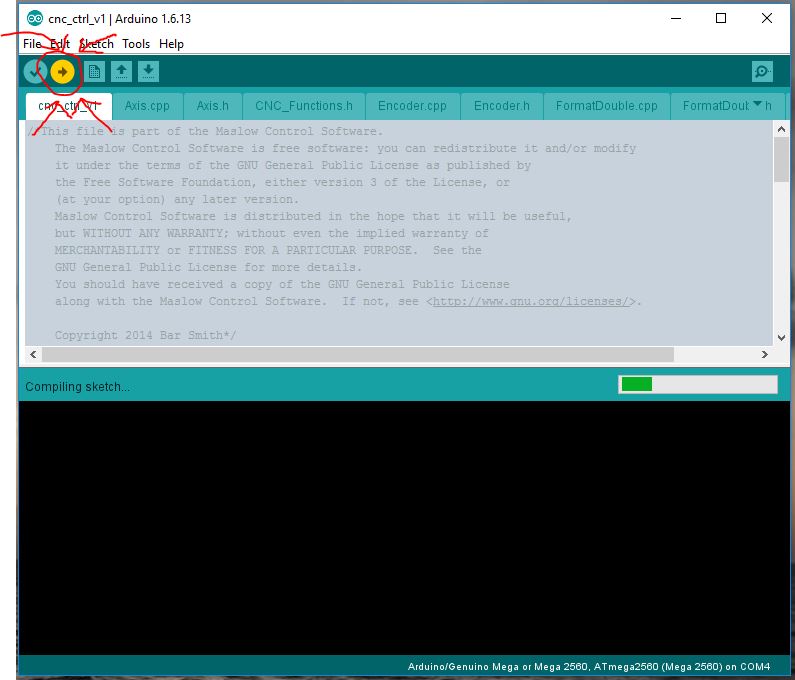
36 |
37 | ### Step 8: Finish
38 | You are now running the latest firmware. *Great Job!* Make sure you close the Arduino IDE before proceeding.
39 |
40 | ### Step 9: Proceed
41 | You have finished setting up the Maslow firmware. Proceed to the [next step](http://maslowcommunitygarden.org/GroundControl.html?instructions=true) to install Ground Control on your OS.
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/LICENSE
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Maslow Firmware
2 |
3 | This is the firmware which controls the Maslow CNC machine
4 |
5 | [](https://travis-ci.org/MaslowCNC/Firmware)
6 |
7 | This is the firmware for the Maslow CNC Router
8 |
9 |
10 | ## Steps to setup the Firmware development environment
11 |
12 | First clone the Firmware repository, then install and setup the IDE of your choice.
13 |
14 | ### Using Arduino IDE
15 | 1. Download [Arduino IDE](https://www.arduino.cc/en/main/software) 1.8.1 or higher
16 | 2. Install Arduino IDE and run Arduino IDE
17 | 3. Navigate menus: File, Open
18 | 4. In the file chooser navigate to the cloned repository and choose the "cnc_ctrl_v1.ino" file to open
19 | 5. Navigate menu: Tools, Board, change to "Arduino/Genuino Mega or Mega 2560"
20 | 6. Navigate menu: Sketch -> Upload
21 |
22 | This should compile the project without errors, and possibly some warnings.
23 |
24 | ### Using PlatformIO
25 | 1. Download package for [Atom](https://atom.io/)
26 | 2. Follow directions for [installing PlatformIO within Atom](http://docs.platformio.org/en/latest/ide/atom.html#ide-installation)
27 | 3. Within Atom navigate menus: PlatformIO, Open Project
28 | 4. Select "Firmware" directory
29 | 5. Click "Open Firmware"
30 |
31 | ### Using Eclipse Neon C/C++ with Sloeber plugin
32 |
33 | 1. Download [Eclipse C/C++](https://eclipse.org/downloads/) Neon or higher
34 | 2. Install Eclipse C/C++ and run Eclipse
35 | 3. Install Sloeber Arduino plugin
36 | * Navigate menus: Help, Install New Software...
37 | * Copy this URL in the "Work With" field: http://eclipse.baeyens.it/update/V4/stable
38 | * Select "Add" button
39 | * Select "Sloeber Arduino IDE" check box
40 | * Select "Finish" button
41 | * Accept defaults and accept licenses, the plugin will restart Eclipse, and configure the plugin
42 | 4. Change to Arduino perspective, navigate menus: Window, Perspective, Open Perspective, Other...
43 | * Choose the "Arduino" perspective and select "Ok" button
44 | 5. Create an Arduino project
45 | * Navigate menus: File, New, New Arduino Sketch
46 | * Project Name: cnc_ctrl_v1
47 | * Select "Next" button
48 | * Select appropriate item from "Platform folder" drop down listing
49 | * Select Board: Arduino/Genuino Mega or Mega 2560
50 | * Select Upload Protocol: Default
51 | * Select Processor: ATmega2560 (Mega 2560)
52 | * Select "Finish" button
53 | 6. Import project source code
54 | * Select project folder, navigate menus: File, Import...
55 | * Expand "General" and select "File system"
56 | * Select "Next" button
57 | * Select the "Browse" button to select the source location (location of the cloned repository cnc_ctrl_v1 directory)
58 | * Select whole source directory in the left pane
59 | * Open Advanced Settings by klicking on "Advanced>>" button
60 | * Select 'Create Links in Workspace' and 'Create virtual folders' leave other settings untouched
61 | * Select 'Finish' button
62 | * Eclipse asks if overwriting the original cnc_ctrl_v1.ino file is ok. Confirm with 'yes'.
63 | 7. Update eclipse project include paths
64 | * Select the project folder in the project explorer and click Project->Properties in the menu.
65 | * In the Project properties left Pane select C/C++ Build->Settings
66 | * In the right Pane select the 'Tool Settings' Tab and add the path to the source location to the include paths of all compilers/linkers of the toolchain.
67 | * The last two steps may differ between toolchains.
68 |
69 |
70 | ### Using NotePad++ in Conjunction with the Arduino IDE
71 | 1. Download NotePad++ (Windows only) [link](https://notepad-plus-plus.org/)
72 | 2. Download the Arduino IDE [link](https://www.arduino.cc/en/main/software)
73 | 3. Set that you would like use an external editor from within the Arduino IDE by clicking File -> Preferences -> Use External Editor
74 | *The Arduino editor will no longer allow you to edit the files, but instead will only work to compile and upload your code.
75 | *The code can be edited from within NotePad++
76 | *This method can be used on other platforms with editing programs other than NP++
77 |
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/ROBOT.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "ModerationLevel": "communityManaged",
3 | "Facilitator": "barboursmith",
4 | "DownloadTarget": "/releases",
5 | "Category": "maslow"
6 | }
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Axis.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 |
19 | #include "Maslow.h"
20 |
21 | void Axis::setup(const int& pwmPin, const int& directionPin1, const int& directionPin2, const int& encoderPin1, const int& encoderPin2, const char& axisName, const unsigned long& loopInterval)
22 | {
23 | // I don't really like this, but I don't know how else to initialize a pointer to a value
24 | float zero = 0.0;
25 | float one = 1.0;
26 | _Kp = _Ki = _Kd = &zero;
27 |
28 | motorGearboxEncoder.setup(pwmPin, directionPin1, directionPin2, encoderPin1, encoderPin2, loopInterval);
29 | _pidController.setup(&_pidInput, &_pidOutput, &_pidSetpoint, _Kp, _Ki, _Kd, &one, REVERSE);
30 |
31 | //initialize variables
32 | _axisName = axisName;
33 |
34 | initializePID(loopInterval);
35 |
36 | motorGearboxEncoder.setName(&_axisName);
37 | }
38 |
39 | void Axis::initializePID(const unsigned long& loopInterval){
40 | _pidController.SetMode(AUTOMATIC);
41 | _pidController.SetOutputLimits(-20, 20);
42 | _pidController.SetSampleTime( loopInterval / 1000);
43 | }
44 |
45 | void Axis::write(const float& targetPosition){
46 | _timeLastMoved = millis();
47 | _pidSetpoint = targetPosition/ *_mmPerRotation;
48 | return;
49 | }
50 |
51 | float Axis::read(){
52 | //returns the true axis position
53 |
54 | return (motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.read()/ *_encoderSteps) * *_mmPerRotation;
55 |
56 | }
57 |
58 | float Axis::setpoint(){
59 | return _pidSetpoint * *_mmPerRotation;
60 | }
61 |
62 | void Axis::set(const float& newAxisPosition){
63 |
64 | //reset everything to the new value
65 | _pidSetpoint = newAxisPosition/ *_mmPerRotation;
66 | motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.write((newAxisPosition * *_encoderSteps)/ *_mmPerRotation);
67 |
68 | }
69 |
70 | long Axis::steps(){
71 | /*
72 | Returns the number of steps reported by the encoder
73 | */
74 | return motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.read();
75 | }
76 |
77 | void Axis::setSteps(const long& steps){
78 |
79 | //reset everything to the new value
80 | _pidSetpoint = steps/ *_encoderSteps;
81 | motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.write(steps);
82 |
83 | }
84 |
85 | void Axis::computePID(){
86 |
87 | #ifdef FAKE_SERVO
88 | if (motorGearboxEncoder.motor.attached()){
89 | // Adds up to 10% error just to simulate servo noise
90 | double rpm = (-1 * _pidOutput) * random(90, 110) / 100;
91 | unsigned long steps = motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.read() + round( rpm * *_encoderSteps * LOOPINTERVAL)/(60 * 1000000);
92 | motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.write(steps);
93 | }
94 | #endif
95 |
96 | if (_disableAxisForTesting || !motorGearboxEncoder.motor.attached()){
97 | return;
98 | }
99 |
100 | _pidInput = motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.read()/ *_encoderSteps;
101 |
102 | if (_pidController.Compute()){
103 | // Only write output if the PID calculation was performed
104 | motorGearboxEncoder.write(_pidOutput);
105 | }
106 |
107 | motorGearboxEncoder.computePID();
108 |
109 | }
110 |
111 | void Axis::disablePositionPID(){
112 |
113 | _pidController.SetMode(MANUAL);
114 |
115 | }
116 |
117 | void Axis::enablePositionPID(){
118 |
119 | _pidController.SetMode(AUTOMATIC);
120 |
121 | }
122 |
123 | void Axis::setPIDValues(float* KpPos, float* KiPos, float* KdPos, float* propWeight, float* KpV, float* KiV, float* KdV, float* propWeightV){
124 | /*
125 |
126 | Sets the positional PID values for the axis
127 |
128 | */
129 | _Kp = KpPos;
130 | _Ki = KiPos;
131 | _Kd = KdPos;
132 |
133 | _pidController.SetTunings(_Kp, _Ki, _Kd, propWeight);
134 |
135 | motorGearboxEncoder.setPIDValues(KpV, KiV, KdV, propWeightV);
136 | }
137 |
138 | String Axis::getPIDString(){
139 | /*
140 |
141 | Get PID tuning values
142 |
143 | */
144 | String PIDString = "Kp=";
145 | return PIDString + *_Kp + ",Ki=" + *_Ki + ",Kd=" + *_Kd;
146 | }
147 |
148 | void Axis::setPIDAggressiveness(float aggressiveness){
149 | /*
150 |
151 | The setPIDAggressiveness() function sets the aggressiveness of the PID controller to
152 | compensate for a change in the load on the motor.
153 |
154 | */
155 |
156 | motorGearboxEncoder.setPIDAggressiveness(aggressiveness);
157 | }
158 |
159 | float Axis::error(){
160 |
161 | float encoderErr = (motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.read()/ *_encoderSteps) - _pidSetpoint;
162 |
163 | return encoderErr * *_mmPerRotation;
164 | }
165 |
166 | void Axis::changePitch(float *newPitch){
167 | /*
168 | Reassign the distance moved per-rotation for the axis.
169 | */
170 | _mmPerRotation = newPitch;
171 | }
172 |
173 | float Axis::getPitch(){
174 | /*
175 | Returns the distance moved per-rotation for the axis.
176 | */
177 | return *_mmPerRotation;
178 | }
179 |
180 | void Axis::changeEncoderResolution(float *newResolution){
181 | /*
182 | Reassign the encoder resolution for the axis.
183 | */
184 | _encoderSteps = newResolution;
185 |
186 | //push to the gearbox for calculating RPM
187 | motorGearboxEncoder.setEncoderResolution(*newResolution);
188 |
189 | }
190 |
191 | int Axis::detach(){
192 |
193 | motorGearboxEncoder.motor.detach();
194 |
195 | return 1;
196 | }
197 |
198 | int Axis::attach(){
199 | motorGearboxEncoder.motor.attach();
200 | return 1;
201 | }
202 |
203 | bool Axis::attached(){
204 | /*
205 |
206 | Returns true if the axis is attached, false if it is not.
207 |
208 | */
209 |
210 | return motorGearboxEncoder.motor.attached();
211 | }
212 |
213 | void Axis::detachIfIdle(){
214 | /*
215 | Detaches the axis, turning off the motor and PID control, if it has been
216 | stationary for more than axisDetachTime
217 | */
218 | if (millis() - _timeLastMoved > sysSettings.axisDetachTime){
219 | detach();
220 | }
221 |
222 | }
223 |
224 | void Axis::endMove(const float& finalTarget){
225 |
226 | _timeLastMoved = millis();
227 | _pidSetpoint = finalTarget/ *_mmPerRotation;
228 |
229 | }
230 |
231 | void Axis::stop(){
232 | /*
233 |
234 | Immediately stop the axis where it is, not where it should be
235 |
236 | */
237 |
238 | _timeLastMoved = millis();
239 | _pidSetpoint = read()/ *_mmPerRotation;
240 |
241 | }
242 |
243 | void Axis::test(){
244 | /*
245 | Test the axis by directly commanding the motor and observing if the encoder moves
246 | */
247 |
248 | Serial.print(F("Testing "));
249 | Serial.print(_axisName);
250 | Serial.println(F(" motor:"));
251 |
252 | //print something to prevent the connection from timing out
253 | Serial.print(F(""));
254 |
255 | int i = 0;
256 | double encoderPos = motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.read(); //record the position now
257 |
258 | //move the motor
259 | while (i < 1000){
260 | motorGearboxEncoder.motor.directWrite(255);
261 | i++;
262 | maslowDelay(1);
263 | if (sys.stop){return;}
264 | }
265 |
266 | //check to see if it moved
267 | if(encoderPos - motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.read() > 500){
268 | Serial.println(F("Direction 1 - Pass"));
269 | }
270 | else{
271 | Serial.println(F("Direction 1 - Fail"));
272 | }
273 |
274 | //record the position again
275 | encoderPos = motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.read();
276 | Serial.print(F(""));
277 |
278 | //move the motor in the other direction
279 | i = 0;
280 | while (i < 1000){
281 | motorGearboxEncoder.motor.directWrite(-255);
282 | i++;
283 | maslowDelay(1);
284 | if (sys.stop){return;}
285 | }
286 |
287 | //check to see if it moved
288 | if(encoderPos - motorGearboxEncoder.encoder.read() < -500){
289 | Serial.println(F("Direction 2 - Pass"));
290 | }
291 | else{
292 | Serial.println(F("Direction 2 - Fail"));
293 | }
294 |
295 | //stop the motor
296 | motorGearboxEncoder.motor.directWrite(0);
297 | Serial.print(F(""));
298 | }
299 |
300 | double Axis::pidInput(){ return _pidInput * *_mmPerRotation;}
301 | double Axis::pidOutput(){ return _pidOutput;}
302 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Axis.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | #ifndef Axis_h
19 | #define Axis_h
20 |
21 | class Axis{
22 | public:
23 | void setup(const int& pwmPin, const int& directionPin1, const int& directionPin2, const int& encoderPin1, const int& encoderPin2, const char& axisName, const unsigned long& loopInterval);
24 | void write(const float& targetPosition);
25 | float read();
26 | void set(const float& newAxisPosition);
27 | void setSteps(const long& steps);
28 | int updatePositionFromEncoder();
29 | void initializePID(const unsigned long& loopInterval);
30 | int detach();
31 | int attach();
32 | void detachIfIdle();
33 | void endMove(const float& finalTarget);
34 | void stop();
35 | float target();
36 | float error();
37 | float setpoint();
38 | void computePID();
39 | void disablePositionPID();
40 | void enablePositionPID();
41 | void setPIDAggressiveness(float aggressiveness);
42 | void test();
43 | void changePitch(float* newPitch);
44 | float getPitch();
45 | void changeEncoderResolution(float* newResolution);
46 | bool attached();
47 | MotorGearboxEncoder motorGearboxEncoder;
48 | void setPIDValues(float* Kp, float* Ki, float* Kd, float* propWeight, float* KpV, float* KiV, float* KdV, float* propWeightV);
49 | String getPIDString();
50 | double pidInput();
51 | double pidOutput();
52 | long steps();
53 |
54 | private:
55 | int _PWMread(int pin);
56 | void _writeFloat(const unsigned int& addr, const float& x);
57 | float _readFloat(const unsigned int& addr);
58 | unsigned long _timeLastMoved;
59 | volatile double _pidSetpoint;
60 | volatile double _pidInput;
61 | volatile double _pidOutput;
62 | float *_Kp, *_Ki, *_Kd;
63 | PID _pidController;
64 | float *_mmPerRotation;
65 | float *_encoderSteps;
66 | bool _disableAxisForTesting = false;
67 | char _axisName;
68 | };
69 |
70 | #endif
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Config.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
3 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
4 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
5 | (at your option) any later version.
6 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
7 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
8 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
9 | GNU General Public License for more details.
10 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
11 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
12 |
13 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
14 |
15 | // This file contains precompile configuration settings that apply to the
16 | // whole system
17 |
18 | #ifndef config_h
19 | #define config_h
20 |
21 | // Debugging Options
22 | #define verboseDebug 0 // set to 0 for no debug messages, 1 for single-line messages, 2 to also output ring buffer contents
23 | #define misloopDebug 0 // set to 1 for a warning every time the movement loop fails
24 | // to complete before being interrupted, helpful for loop
25 | // LOOPINTERVAL tuning
26 | #define KINEMATICSDBG 0 // set to 1 for additional kinematics debug messaging
27 |
28 | // #define FAKE_SERVO // Uncomment this line to cause the Firmware to mimic
29 | // a servo updating the encoder steps even if no servo
30 | // is connected. Useful for testing on an arduino only
31 |
32 | // #define SIMAVR // Uncomment this if you plan to run the Firmware in the simavr
33 | // simulator. Normally, you would not define this directly, but
34 | // use PlatformIO to build the simavr environment.
35 |
36 | #define LOOPINTERVAL 10000 // What is the frequency of the PID loop in microseconds
37 |
38 | // Define version detect pins
39 | #define VERS1 22
40 | #define VERS2 23
41 | #define VERS3 24
42 | #define VERS4 25
43 | #define VERS5 26
44 | #define VERS6 27
45 |
46 | // Serial variables
47 | #define INCBUFFERLENGTH 128 // The number of bytes(characters) allocated to the
48 | // incoming buffer.
49 | #define EXPGCODELINE 60 // Maximum expected Gcode line length in characters
50 | // including line ending character(s). Assumes
51 | // client will not send more than this. Ground
52 | // Control is currently set to 60. NIST spec allows
53 | // 256. This value must be <= INCBUFFERLENGTH
54 | #define MAXBUFFERLINES 4 // The maximum number of lines allowed in the buffer
55 | #define POSITIONTIMEOUT 200 // The minimum number of milliseconds between
56 | // position reports sent to Ground Control. This
57 | // cannot be larger than the connection timout in
58 | // Ground Control which is 2000, a smaller number
59 | // takes more processing time for sending data
60 | // a larger number make position updates in GC less
61 | // smooth. This is only a minimum, and the actual
62 | // timeout could be significantly larger.
63 |
64 | #endif
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Encoder.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | #include "Maslow.h"
3 |
4 | // Yes, all the code is in the header file, to provide the user
5 | // configure options with #define (before they include it), and
6 | // to facilitate some crafty optimizations!
7 |
8 | Encoder_internal_state_t * Encoder::interruptArgs[];
9 |
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/GCode.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | #ifndef gcode_h
19 | #define gcode_h
20 |
21 | // Define line flags. Includes comment type tracking and line overflow detection.
22 | #define LINE_FLAG_COMMENT_PARENTHESES bit(0)
23 | #define LINE_FLAG_COMMENT_SEMICOLON bit(1)
24 |
25 | extern String readyCommandString; //next command queued up and ready to send
26 | extern String gcodeLine; //The next individual line of gcode (for example G91 G01 X19 would be run as two lines)
27 |
28 | void initGCode();
29 | void gcodeExecuteLoop();
30 | void readSerialCommands();
31 | String gcodeBufferReadline();
32 | int findEndOfNumber(const String&, const int&);
33 | float extractGcodeValue(const String&, char, const float&);
34 | byte executeBcodeLine(const String&);
35 | void executeGcodeLine(const String&);
36 | void executeMcodeLine(const String&);
37 | void executeOtherCodeLine(const String&);
38 | int findNextGM(const String&, const int&);
39 | void sanitizeCommandString(String&);
40 | byte interpretCommandString(String&);
41 | void G1(const String&, int);
42 | void G2(const String&, int);
43 | void G4(const String&);
44 | void G10(const String&);
45 | void G38(const String&);
46 | void setInchesToMillimetersConversion(float);
47 | extern int SpindlePowerControlPin;
48 | extern int ProbePin;
49 |
50 | #endif
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Kinematics.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | /*
19 | The Kinematics module relates the lengths of the chains to the position of the cutting head
20 | in X-Y space.
21 | */
22 |
23 | #include "Maslow.h"
24 |
25 |
26 | Kinematics::Kinematics(){
27 | recomputeGeometry();
28 | }
29 |
30 | void Kinematics::init(){
31 | recomputeGeometry();
32 | if (sys.state != STATE_OLD_SETTINGS){
33 | forward(leftAxis.read(), rightAxis.read(), &sys.xPosition, &sys.yPosition, sys.xPosition, sys.yPosition);
34 | }
35 | }
36 |
37 | void Kinematics::_verifyValidTarget(float* xTarget,float* yTarget){
38 | //If the target point is beyond one of the edges of the board, the machine stops at the edge
39 |
40 | *xTarget = (*xTarget < -halfWidth) ? -halfWidth : (*xTarget > halfWidth) ? halfWidth : *xTarget;
41 | *yTarget = (*yTarget < -halfHeight) ? -halfHeight : (*yTarget > halfHeight) ? halfHeight : *yTarget;
42 |
43 | }
44 |
45 | void Kinematics::recomputeGeometry(){
46 | /*
47 | Some variables are computed on class creation for the geometry of the machine to reduce overhead,
48 | calling this function regenerates those values. These are all floats so they take up
49 | ~32bytes of RAM to keep them in memory.
50 | */
51 | Phi = -0.2;
52 | h = sqrt((sysSettings.sledWidth/2)*(sysSettings.sledWidth/2) + sysSettings.sledHeight * sysSettings.sledHeight);
53 | Theta = atan(2*sysSettings.sledHeight/sysSettings.sledWidth);
54 | Psi1 = Theta - Phi;
55 | Psi2 = Theta + Phi;
56 |
57 | halfWidth = sysSettings.machineWidth / 2.0;
58 | halfHeight = sysSettings.machineHeight / 2.0;
59 | _xCordOfMotor = sysSettings.distBetweenMotors/2;
60 | _yCordOfMotor = halfHeight + sysSettings.motorOffsetY;
61 |
62 | }
63 |
64 | void Kinematics::inverse(float xTarget,float yTarget, float* aChainLength, float* bChainLength){
65 | /*
66 |
67 | This function works as a switch to call either the quadrilateralInverse kinematic function
68 | or the triangularInverse kinematic function
69 |
70 | */
71 |
72 | if(sysSettings.kinematicsType == 1){
73 | quadrilateralInverse(xTarget, yTarget, aChainLength, bChainLength);
74 | }
75 | else{
76 | triangularInverse(xTarget, yTarget, aChainLength, bChainLength);
77 | }
78 |
79 | }
80 |
81 | void Kinematics::quadrilateralInverse(float xTarget,float yTarget, float* aChainLength, float* bChainLength){
82 |
83 | //Confirm that the coordinates are on the wood
84 | _verifyValidTarget(&xTarget, &yTarget);
85 |
86 | //coordinate shift to put (0,0) in the center of the plywood from the left sprocket
87 | y = (halfHeight) + sysSettings.motorOffsetY - yTarget;
88 | x = (sysSettings.distBetweenMotors/2.0) + xTarget;
89 |
90 | //Coordinates definition:
91 | // x -->, y |
92 | // v
93 | // (0,0) at center of left sprocket
94 | // upper left corner of plywood (270, 270)
95 |
96 | byte Tries = 0; //initialize
97 | if(x > sysSettings.distBetweenMotors/2.0){ //the right half of the board mirrors the left half so all computations are done using left half coordinates.
98 | x = sysSettings.distBetweenMotors-x; //Chain lengths are swapped at exit if the x,y is on the right half
99 | Mirror = true;
100 | }
101 | else{
102 | Mirror = false;
103 | }
104 |
105 | TanGamma = y/x;
106 | TanLambda = y/(sysSettings.distBetweenMotors-x);
107 | Y1Plus = R * sqrt(1 + TanGamma * TanGamma);
108 | Y2Plus = R * sqrt(1 + TanLambda * TanLambda);
109 |
110 |
111 | while (Tries <= KINEMATICSMAXINVERSE) {
112 |
113 | _MyTrig();
114 | //These criteria will be zero when the correct values are reached
115 | //They are negated here as a numerical efficiency expedient
116 |
117 | Crit[0]= - _moment(Y1Plus, Y2Plus, MySinPhi, SinPsi1, CosPsi1, SinPsi2, CosPsi2);
118 | Crit[1] = - _YOffsetEqn(Y1Plus, x - h * CosPsi1, SinPsi1);
119 | Crit[2] = - _YOffsetEqn(Y2Plus, sysSettings.distBetweenMotors - (x + h * CosPsi2), SinPsi2);
120 |
121 | if (abs(Crit[0]) < KINEMATICSMAXERROR) {
122 | if (abs(Crit[1]) < KINEMATICSMAXERROR) {
123 | if (abs(Crit[2]) < KINEMATICSMAXERROR){
124 | break;
125 | }
126 | }
127 | }
128 |
129 | //estimate the tilt angle that results in zero net _moment about the pen
130 | //and refine the estimate until the error is acceptable or time runs out
131 |
132 | //Estimate the Jacobian components
133 |
134 | Jac[0] = (_moment( Y1Plus, Y2Plus, MySinPhiDelta, SinPsi1D, CosPsi1D, SinPsi2D, CosPsi2D) + Crit[0])/DELTAPHI;
135 | Jac[1] = (_moment( Y1Plus + DELTAY, Y2Plus, MySinPhi, SinPsi1, CosPsi1, SinPsi2, CosPsi2) + Crit[0])/DELTAY;
136 | Jac[2] = (_moment(Y1Plus, Y2Plus + DELTAY, MySinPhi, SinPsi1, CosPsi1, SinPsi2, CosPsi2) + Crit[0])/DELTAY;
137 | Jac[3] = (_YOffsetEqn(Y1Plus, x - h * CosPsi1D, SinPsi1D) + Crit[1])/DELTAPHI;
138 | Jac[4] = (_YOffsetEqn(Y1Plus + DELTAY, x - h * CosPsi1,SinPsi1) + Crit[1])/DELTAY;
139 | Jac[5] = 0.0;
140 | Jac[6] = (_YOffsetEqn(Y2Plus, sysSettings.distBetweenMotors - (x + h * CosPsi2D), SinPsi2D) + Crit[2])/DELTAPHI;
141 | Jac[7] = 0.0;
142 | Jac[8] = (_YOffsetEqn(Y2Plus + DELTAY, sysSettings.distBetweenMotors - (x + h * CosPsi2D), SinPsi2) + Crit[2])/DELTAY;
143 |
144 |
145 | //solve for the next guess
146 | _MatSolv(); // solves the matrix equation Jx=-Criterion
147 |
148 | // update the variables with the new estimate
149 |
150 | Phi = Phi + Solution[0];
151 | Y1Plus = Y1Plus + Solution[1]; //don't allow the anchor points to be inside a sprocket
152 | Y1Plus = (Y1Plus < R) ? R : Y1Plus;
153 |
154 | Y2Plus = Y2Plus + Solution[2]; //don't allow the anchor points to be inside a sprocke
155 | Y2Plus = (Y2Plus < R) ? R : Y2Plus;
156 |
157 | Psi1 = Theta - Phi;
158 | Psi2 = Theta + Phi;
159 |
160 | Tries++; // increment itteration count
161 |
162 | }
163 |
164 | //Variables are within accuracy limits
165 | // perform output computation
166 |
167 | Offsetx1 = h * CosPsi1;
168 | Offsetx2 = h * CosPsi2;
169 | Offsety1 = h * SinPsi1;
170 | Offsety2 = h * SinPsi2;
171 | TanGamma = (y - Offsety1 + Y1Plus)/(x - Offsetx1);
172 | TanLambda = (y - Offsety2 + Y2Plus)/(sysSettings.distBetweenMotors -(x + Offsetx2));
173 | Gamma = atan(TanGamma);
174 | Lambda =atan(TanLambda);
175 |
176 | //compute the chain lengths
177 |
178 | if(Mirror){
179 | Chain2 = sqrt((x - Offsetx1)*(x - Offsetx1) + (y + Y1Plus - Offsety1)*(y + Y1Plus - Offsety1)) - R * TanGamma + R * Gamma; //right chain length
180 | Chain1 = sqrt((sysSettings.distBetweenMotors - (x + Offsetx2))*(sysSettings.distBetweenMotors - (x + Offsetx2))+(y + Y2Plus - Offsety2)*(y + Y2Plus - Offsety2)) - R * TanLambda + R * Lambda; //left chain length
181 | }
182 | else{
183 | Chain1 = sqrt((x - Offsetx1)*(x - Offsetx1) + (y + Y1Plus - Offsety1)*(y + Y1Plus - Offsety1)) - R * TanGamma + R * Gamma; //left chain length
184 | Chain2 = sqrt((sysSettings.distBetweenMotors - (x + Offsetx2))*(sysSettings.distBetweenMotors - (x + Offsetx2))+(y + Y2Plus - Offsety2)*(y + Y2Plus - Offsety2)) - R * TanLambda + R * Lambda; //right chain length
185 | }
186 |
187 | *aChainLength = Chain1;
188 | *bChainLength = Chain2;
189 |
190 | }
191 |
192 | void Kinematics::triangularInverse(float xTarget,float yTarget, float* aChainLength, float* bChainLength){
193 | /*
194 |
195 | The inverse kinematics (relating an xy coordinate pair to the required chain lengths to hit that point)
196 | function for a triangular set up where the chains meet at a point, or are arranged so that they simulate
197 | meeting at a point.
198 |
199 | */
200 |
201 | //Confirm that the coordinates are on the wood
202 | _verifyValidTarget(&xTarget, &yTarget);
203 |
204 | //Set up variables
205 | float Chain1Angle = 0;
206 | float Chain2Angle = 0;
207 | float Chain1AroundSprocket = 0;
208 | float Chain2AroundSprocket = 0;
209 |
210 | //Calculate motor axes length to the bit
211 | float Motor1Distance = sqrt(pow((-1*_xCordOfMotor - xTarget),2)+pow((_yCordOfMotor - yTarget),2));
212 | float Motor2Distance = sqrt(pow((_xCordOfMotor - xTarget),2)+pow((_yCordOfMotor - yTarget),2));
213 |
214 | //Calculate the chain angles from horizontal, based on if the chain connects to the sled from the top or bottom of the sprocket
215 | if(sysSettings.chainOverSprocket == 1){
216 | Chain1Angle = asin((_yCordOfMotor - yTarget)/Motor1Distance) + asin(R/Motor1Distance);
217 | Chain2Angle = asin((_yCordOfMotor - yTarget)/Motor2Distance) + asin(R/Motor2Distance);
218 |
219 | Chain1AroundSprocket = R * Chain1Angle;
220 | Chain2AroundSprocket = R * Chain2Angle;
221 | }
222 | else{
223 | Chain1Angle = asin((_yCordOfMotor - yTarget)/Motor1Distance) - asin(R/Motor1Distance);
224 | Chain2Angle = asin((_yCordOfMotor - yTarget)/Motor2Distance) - asin(R/Motor2Distance);
225 |
226 | Chain1AroundSprocket = R * (3.14159 - Chain1Angle);
227 | Chain2AroundSprocket = R * (3.14159 - Chain2Angle);
228 | }
229 |
230 | //Calculate the straight chain length from the sprocket to the bit
231 | float Chain1Straight = sqrt(pow(Motor1Distance,2)-pow(R,2));
232 | float Chain2Straight = sqrt(pow(Motor2Distance,2)-pow(R,2));
233 |
234 | //Correct the straight chain lengths to account for chain sag
235 | Chain1Straight *= (1 + ((sysSettings.chainSagCorrection / 1000000000000) * pow(cos(Chain1Angle),2) * pow(Chain1Straight,2) * pow((tan(Chain2Angle) * cos(Chain1Angle)) + sin(Chain1Angle),2)));
236 | Chain2Straight *= (1 + ((sysSettings.chainSagCorrection / 1000000000000) * pow(cos(Chain2Angle),2) * pow(Chain2Straight,2) * pow((tan(Chain1Angle) * cos(Chain2Angle)) + sin(Chain2Angle),2)));
237 |
238 | //Calculate total chain lengths accounting for sprocket geometry and chain sag
239 | float Chain1 = Chain1AroundSprocket + Chain1Straight * (1.0f + sysSettings.leftChainTolerance / 100.0f);
240 | float Chain2 = Chain2AroundSprocket + Chain2Straight * (1.0f + sysSettings.rightChainTolerance / 100.0f);
241 |
242 | //Subtract of the virtual length which is added to the chain by the rotation mechanism
243 | Chain1 = Chain1 - sysSettings.rotationDiskRadius;
244 | Chain2 = Chain2 - sysSettings.rotationDiskRadius;
245 |
246 | *aChainLength = Chain1;
247 | *bChainLength = Chain2;
248 | }
249 |
250 | void Kinematics::forward(const float& chainALength, const float& chainBLength, float* xPos, float* yPos, float xGuess, float yGuess){
251 |
252 | Serial.println(F("[Forward Calculating Position]"));
253 |
254 |
255 | float guessLengthA;
256 | float guessLengthB;
257 |
258 | int guessCount = 0;
259 |
260 | while(1){
261 |
262 |
263 | //check our guess
264 | inverse(xGuess, yGuess, &guessLengthA, &guessLengthB);
265 |
266 | float aChainError = chainALength - guessLengthA;
267 | float bChainError = chainBLength - guessLengthB;
268 |
269 |
270 | //adjust the guess based on the result
271 | xGuess = xGuess + .1*aChainError - .1*bChainError;
272 | yGuess = yGuess - .1*aChainError - .1*bChainError;
273 |
274 | guessCount++;
275 |
276 | #if defined (KINEMATICSDBG) && KINEMATICSDBG > 0
277 | Serial.print(F("[PEk:"));
278 | Serial.print(aChainError);
279 | Serial.print(',');
280 | Serial.print(bChainError);
281 | Serial.print(',');
282 | Serial.print('0');
283 | Serial.println(F("]"));
284 | #endif
285 |
286 | execSystemRealtime();
287 | // No need for sys.stop check here
288 |
289 | //if we've converged on the point...or it's time to give up, exit the loop
290 | if((abs(aChainError) < .1 && abs(bChainError) < .1) or guessCount > KINEMATICSMAXGUESS or guessLengthA > sysSettings.chainLength or guessLengthB > sysSettings.chainLength){
291 | if((guessCount > KINEMATICSMAXGUESS) or guessLengthA > sysSettings.chainLength or guessLengthB > sysSettings.chainLength){
292 | Serial.print(F("Message: Unable to find valid machine position for chain lengths "));
293 | Serial.print(chainALength);
294 | Serial.print(", ");
295 | Serial.print(chainBLength);
296 | Serial.println(F(" . Please set the chains to a known length (Actions -> Set Chain Lengths)"));
297 | *xPos = 0;
298 | *yPos = 0;
299 | }
300 | else{
301 | Serial.println("position loaded at:");
302 | Serial.println(xGuess);
303 | Serial.println(yGuess);
304 | *xPos = xGuess;
305 | *yPos = yGuess;
306 | }
307 | break;
308 | }
309 | }
310 | }
311 |
312 | void Kinematics::_MatSolv(){
313 | float Sum;
314 | int NN;
315 | int i;
316 | int ii;
317 | int J;
318 | int JJ;
319 | int K;
320 | int KK;
321 | int L;
322 | int M;
323 | int N;
324 |
325 | float fact;
326 |
327 | // gaus elimination, no pivot
328 |
329 | N = 3;
330 | NN = N-1;
331 | for (i=1;i<=NN;i++){
332 | J = (N+1-i);
333 | JJ = (J-1) * N-1;
334 | L = J-1;
335 | KK = -1;
336 | for (K=0;K.
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | #ifndef Kinematics_h
19 | #define Kinematics_h
20 |
21 |
22 | //Calculation tolerances
23 | #define DELTAPHI 0.001
24 | #define DELTAY 0.01
25 | #define KINEMATICSMAXERROR 0.001
26 | #define KINEMATICSMAXINVERSE 10
27 | #define KINEMATICSMAXGUESS 200
28 |
29 | class Kinematics{
30 | public:
31 | Kinematics();
32 | void init ();
33 | void inverse (float xTarget,float yTarget, float* aChainLength, float* bChainLength);
34 | void quadrilateralInverse (float xTarget,float yTarget, float* aChainLength, float* bChainLength);
35 | void triangularInverse (float xTarget,float yTarget, float* aChainLength, float* bChainLength);
36 | void recomputeGeometry();
37 | void forward(const float& chainALength, const float& chainBLength, float* xPos, float* yPos, float xGuess, float yGuess);
38 | //geometry
39 | float h; //distance between sled attach point and bit
40 | float R = 10.1; //sprocket radius
41 |
42 | float halfWidth; //Half the machine width
43 | float halfHeight; //Half the machine height
44 | private:
45 | float _moment(const float& Y1Plus, const float& Y2Plus, const float& MSinPhi, const float& MSinPsi1, const float& MCosPsi1, const float& MSinPsi2, const float& MCosPsi2);
46 | float _YOffsetEqn(const float& YPlus, const float& Denominator, const float& Psi);
47 | void _MatSolv();
48 | void _MyTrig();
49 | void _verifyValidTarget(float* xTarget,float* yTarget);
50 | //target router bit coordinates.
51 | float x = 0;
52 | float y = 0;
53 | float _xCordOfMotor;
54 | float _yCordOfMotor;
55 |
56 | //utility variables
57 | boolean Mirror;
58 |
59 | //Criterion Computation Variables
60 | float Phi = -0.2;
61 | float TanGamma;
62 | float TanLambda;
63 | float Y1Plus ;
64 | float Y2Plus;
65 | float Theta;
66 | float Psi1 = Theta - Phi;
67 | float Psi2 = Theta + Phi;
68 | float Jac[9];
69 | float Solution[3];
70 | float Crit[3];
71 | float Offsetx1;
72 | float Offsetx2;
73 | float Offsety1;
74 | float Offsety2;
75 | float SinPsi1;
76 | float CosPsi1;
77 | float SinPsi2;
78 | float CosPsi2;
79 | float SinPsi1D;
80 | float CosPsi1D;
81 | float SinPsi2D;
82 | float CosPsi2D;
83 | float MySinPhi;
84 | float MySinPhiDelta;
85 |
86 | //intermediate output
87 | float Lambda;
88 | float Gamma;
89 |
90 | // Motor axes length to the bit for triangular kinematics
91 | float Motor1Distance; //left motor axis distance to sled
92 | float Motor2Distance; //right motor axis distance to sled
93 |
94 | // output = chain lengths measured from 12 o'clock
95 | float Chain1; //left chain length
96 | float Chain2; //right chain length
97 | };
98 |
99 | #endif
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Maslow.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
3 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
4 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
5 | (at your option) any later version.
6 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
7 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
8 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
9 | GNU General Public License for more details.
10 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
11 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
12 |
13 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
14 |
15 | // This is the main maslow include file
16 |
17 | #ifndef maslow_h
18 | #define maslow_h
19 |
20 | // Maslow Firmware Version tracking
21 | #define VERSIONNUMBER 1.24
22 |
23 | // Define standard libraries used by maslow.
24 | #include
25 | #include
26 | #include
27 | #include
28 |
29 | // Define the maslow system include files. This ensures that dependencies are
30 | // loaded in the proper order. Be careful moving these around.
31 | #include "Config.h"
32 | #include "TimerOne.h"
33 | #include "Motor.h"
34 | #include "PID_v1.h"
35 | #include "utility/direct_pin_read.h"
36 | #include "Encoder.h"
37 | #include "MotorGearboxEncoder.h"
38 | #include "Axis.h"
39 | #include "Kinematics.h"
40 | #include "RingBuffer.h"
41 | #include "GCode.h"
42 | #include "Testing.h"
43 | #include "Motion.h"
44 | #include "Report.h"
45 | #include "Spindle.h"
46 | #include "Probe.h"
47 | #include "Settings.h"
48 | #include "NutsAndBolts.h"
49 | #include "System.h"
50 | #include "SimavrSerial.h"
51 |
52 | #endif
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Motion.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
3 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
4 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
5 | (at your option) any later version.
6 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
7 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
8 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
9 | GNU General Public License for more details.
10 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
11 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
12 |
13 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
14 |
15 | // This contains all of the Motion commands
16 |
17 | #include "Maslow.h"
18 |
19 | // Flag for when to send movement commands
20 | volatile bool movementUpdated = false;
21 | // Global variables for misloop tracking
22 | #if misloopDebug > 0
23 | volatile bool inMovementLoop = false;
24 | volatile bool movementFail = false;
25 | #endif
26 |
27 | void initMotion(){
28 | // Called on startup or after a stop command
29 | leftAxis.stop();
30 | rightAxis.stop();
31 | if(sysSettings.zAxisAttached){
32 | zAxis.stop();
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
36 |
37 | float calculateFeedrate(const float& stepSizeMM, const float& usPerStep){
38 | /*
39 | Calculate the time delay between each step for a given feedrate
40 | */
41 |
42 | #define MINUTEINUS 60000000.0
43 |
44 | // derivation: ms / step = 1 min in ms / dist in one min
45 |
46 | float tempFeedrate = (stepSizeMM*MINUTEINUS)/usPerStep;
47 |
48 | return tempFeedrate;
49 | }
50 |
51 | float computeStepSize(const float& MMPerMin){
52 | /*
53 |
54 | Determines the minimum step size which can be taken for the given feed-rate
55 | based on the loop interval frequency. Converts to MM per microsecond first,
56 | then mutiplies by the number of microseconds in each loop interval
57 |
58 | */
59 | return LOOPINTERVAL*(MMPerMin/(60 * 1000000));
60 | }
61 |
62 | void movementUpdate(){
63 | #if misloopDebug > 0
64 | if (movementFail){
65 | Serial.println("Movement loop failed to complete before interrupt.");
66 | movementFail = false;
67 | }
68 | #endif
69 | movementUpdated = true;
70 | }
71 |
72 |
73 | // why does this return anything
74 | int coordinatedMove(const float& xEnd, const float& yEnd, const float& zEnd, float MMPerMin){
75 |
76 | /*The move() function moves the tool in a straight line to the position (xEnd, yEnd) at
77 | the speed moveSpeed. Movements are correlated so that regardless of the distances moved in each
78 | direction, the tool moves to the target in a straight line. This function is used by the G00
79 | and G01 commands. The units at this point should all be in mm or mm per minute*/
80 |
81 | float xStartingLocation = sys.xPosition;
82 | float yStartingLocation = sys.yPosition;
83 | float zStartingLocation = zAxis.read(); // I don't know why we treat the zaxis differently
84 | float zMaxFeed = sysSettings.maxZRPM * abs(zAxis.getPitch());
85 |
86 | //find the total distances to move
87 | float distanceToMoveInMM = sqrt( sq(xEnd - xStartingLocation) + sq(yEnd - yStartingLocation) + sq(zEnd - zStartingLocation));
88 | float xDistanceToMoveInMM = xEnd - xStartingLocation;
89 | float yDistanceToMoveInMM = yEnd - yStartingLocation;
90 | float zDistanceToMoveInMM = zEnd - zStartingLocation;
91 |
92 | //compute feed details
93 | MMPerMin = constrain(MMPerMin, 1, sysSettings.maxFeed); //constrain the maximum feedrate, 35ipm = 900 mmpm
94 | float stepSizeMM = computeStepSize(MMPerMin);
95 | float finalNumberOfSteps = abs(distanceToMoveInMM/stepSizeMM);
96 | float delayTime = LOOPINTERVAL;
97 | float zFeedrate = calculateFeedrate(fabs(zDistanceToMoveInMM/finalNumberOfSteps), delayTime);
98 |
99 | //throttle back federate if it exceeds zaxis max
100 | if (zFeedrate > zMaxFeed){
101 | float zStepSizeMM = computeStepSize(zMaxFeed);
102 | finalNumberOfSteps = abs(zDistanceToMoveInMM/zStepSizeMM);
103 | stepSizeMM = (distanceToMoveInMM/finalNumberOfSteps);
104 | MMPerMin = calculateFeedrate(stepSizeMM, delayTime);
105 | }
106 |
107 | // (fraction of distance in x direction)* size of step toward target
108 | float xStepSize = (xDistanceToMoveInMM/finalNumberOfSteps);
109 | float yStepSize = (yDistanceToMoveInMM/finalNumberOfSteps);
110 | float zStepSize = (zDistanceToMoveInMM/finalNumberOfSteps);
111 |
112 | //attach the axes
113 | leftAxis.attach();
114 | rightAxis.attach();
115 | if(sysSettings.zAxisAttached){
116 | zAxis.attach();
117 | }
118 |
119 | float aChainLength;
120 | float bChainLength;
121 | float zPosition = zStartingLocation;
122 | long numberOfStepsTaken = 0;
123 |
124 | while(numberOfStepsTaken < finalNumberOfSteps){
125 |
126 | #if misloopDebug > 0
127 | inMovementLoop = true;
128 | #endif
129 | //if last movment was performed start the next
130 | if (!movementUpdated) {
131 | //find the target point for this step
132 | // This section ~20us
133 | sys.xPosition += xStepSize;
134 | sys.yPosition += yStepSize;
135 | zPosition += zStepSize;
136 |
137 | //find the chain lengths for this step
138 | // This section ~180us
139 | kinematics.inverse(sys.xPosition,sys.yPosition,&aChainLength,&bChainLength);
140 |
141 | //write to each axis
142 | // This section ~180us
143 | leftAxis.write(aChainLength);
144 | rightAxis.write(bChainLength);
145 | if(sysSettings.zAxisAttached){
146 | zAxis.write(zPosition);
147 | }
148 |
149 | movementUpdate();
150 |
151 | //increment the number of steps taken
152 | numberOfStepsTaken++;
153 |
154 | // Run realtime commands
155 | execSystemRealtime();
156 | if (sys.stop){return 1;}
157 | }
158 | }
159 | #if misloopDebug > 0
160 | inMovementLoop = false;
161 | #endif
162 |
163 | kinematics.inverse(xEnd,yEnd,&aChainLength,&bChainLength);
164 | leftAxis.endMove(aChainLength);
165 | rightAxis.endMove(bChainLength);
166 | if(sysSettings.zAxisAttached){
167 | zAxis.endMove(zPosition);
168 | }
169 |
170 | sys.xPosition = xEnd;
171 | sys.yPosition = yEnd;
172 |
173 | return 1;
174 |
175 | }
176 |
177 | void singleAxisMove(Axis* axis, const float& endPos, const float& MMPerMin){
178 | /*
179 | Takes a pointer to an axis object and moves that axis to endPos at speed MMPerMin
180 | */
181 |
182 | float startingPos = axis->read();
183 | float moveDist = endPos - startingPos; //total distance to move
184 |
185 | float direction = moveDist/abs(moveDist); //determine the direction of the move
186 |
187 | float stepSizeMM = computeStepSize(MMPerMin); //step size in mm
188 |
189 | //the argument to abs should only be a variable -- splitting calc into 2 lines
190 | long finalNumberOfSteps = abs(moveDist/stepSizeMM); //number of steps taken in move
191 | finalNumberOfSteps = abs(finalNumberOfSteps);
192 | stepSizeMM = stepSizeMM*direction;
193 |
194 | long numberOfStepsTaken = 0;
195 |
196 | //attach the axis we want to move
197 | axis->attach();
198 |
199 | float whereAxisShouldBeAtThisStep = startingPos;
200 | #if misloopDebug > 0
201 | inMovementLoop = true;
202 | #endif
203 | while(numberOfStepsTaken < finalNumberOfSteps){
204 | if (!movementUpdated) {
205 | //find the target point for this step
206 | whereAxisShouldBeAtThisStep += stepSizeMM;
207 |
208 | //write to axis
209 | axis->write(whereAxisShouldBeAtThisStep);
210 | movementUpdate();
211 |
212 | // Run realtime commands
213 | execSystemRealtime();
214 | if (sys.stop){return;}
215 |
216 | //increment the number of steps taken
217 | numberOfStepsTaken++;
218 | }
219 | }
220 | #if misloopDebug > 0
221 | inMovementLoop = false;
222 | #endif
223 |
224 | axis->endMove(endPos);
225 |
226 | }
227 |
228 | // return the sign of the parameter
229 | int sign(double x) { return x<0 ? -1 : 1; }
230 |
231 | // why does this return anything
232 | int arc(const float& X1, const float& Y1, const float& Z1, const float& X2, const float& Y2, const float& Z2, const float& centerX, const float& centerY, const float& MMPerMin, const float& direction){
233 | /*
234 |
235 | Move the machine through an arc from point (X1, Y1) to point (X2, Y2) along the
236 | arc defined by center (centerX, centerY) at speed MMPerMin
237 |
238 | */
239 |
240 | //compute geometry
241 | float pi = 3.1415;
242 | float radius = sqrt( sq(centerX - X1) + sq(centerY - Y1) );
243 | float circumference = 2.0*pi*radius;
244 |
245 | float startingAngle = atan2(Y1 - centerY, X1 - centerX);
246 | float endingAngle = atan2(Y2 - centerY, X2 - centerX);
247 |
248 | // compute chord height of arc
249 | float chordSquared = sqrt(sq(X2 - X1) + sq(Y2 - Y1));
250 | float tau = sqrt( sq(radius) - (chordSquared/4.0));
251 | float chordHeight = radius - tau;
252 |
253 | //compute angle between lines
254 | float theta = endingAngle - startingAngle;
255 | if (direction == COUNTERCLOCKWISE){
256 | if (theta <= 0){
257 | theta += 2*pi;
258 | }
259 | }
260 | else {
261 | //CLOCKWISE
262 | if (theta >= 0){
263 | theta -= 2*pi;
264 | }
265 | }
266 | if ((sign(theta) != sign(direction)) || ((abs(chordHeight) < .01) && (abs(theta) < 0.5)) || (radius > 25400)) {
267 | // There is a parameter error in this line of gcode, either in the size of the angle calculated
268 | // or the chord height of the arc between the starting and ending points
269 | // In either case, the gcode cut was essentially a straight line, so
270 | // Replace it with a G1 cut to the endpoint
271 | String gcodeSubstitution = "G1 X";
272 | gcodeSubstitution = gcodeSubstitution + String(X2 / sys.inchesToMMConversion, 3) + " Y" + String(Y2 / sys.inchesToMMConversion, 3) + " Z" + String(Z2 / sys.inchesToMMConversion, 3) + " ";
273 | Serial.println("Large-radius arc replaced by straight line to improve accuracy: " + gcodeSubstitution);
274 | G1(gcodeSubstitution, 1);
275 | return 1;
276 | }
277 |
278 | float arcLengthMM = fabs(circumference * (theta / (2*pi) ));
279 | float zDistanceToMoveInMM = Z2 - Z1;
280 |
281 | //set up variables for movement
282 | long numberOfStepsTaken = 0;
283 |
284 | float feedMMPerMin = constrain(MMPerMin, 1, sysSettings.maxFeed);
285 | float stepSizeMM = computeStepSize(feedMMPerMin);
286 |
287 | long finalNumberOfSteps = arcLengthMM/stepSizeMM;
288 | float delayTime = LOOPINTERVAL;
289 |
290 | float zFeedRate = calculateFeedrate(fabs(zDistanceToMoveInMM/finalNumberOfSteps), delayTime);
291 | float zMaxFeed = sysSettings.maxZRPM * abs(zAxis.getPitch());
292 | // float zStepSizeMM = computeStepSize(zMaxFeed);
293 | float zStepSizeMM = zDistanceToMoveInMM/finalNumberOfSteps;
294 |
295 | if (zFeedRate > zMaxFeed){
296 | zStepSizeMM = computeStepSize(zMaxFeed);
297 | finalNumberOfSteps = fabs(zDistanceToMoveInMM/zStepSizeMM);
298 | stepSizeMM = arcLengthMM/finalNumberOfSteps;
299 | feedMMPerMin = calculateFeedrate(stepSizeMM, delayTime);
300 | }
301 |
302 | zStepSizeMM = zDistanceToMoveInMM/finalNumberOfSteps;
303 |
304 | //Compute the starting position
305 | float angleNow = startingAngle;
306 | float degreeComplete = 0.0;
307 |
308 | float aChainLength;
309 | float bChainLength;
310 | float zPosition = Z1 + zStepSizeMM;
311 |
312 | //attach the axes
313 | leftAxis.attach();
314 | rightAxis.attach();
315 | if (sysSettings.zAxisAttached) {
316 | zAxis.attach();
317 | }
318 |
319 | while(numberOfStepsTaken < abs(finalNumberOfSteps)){
320 | #if misloopDebug > 0
321 | inMovementLoop = true;
322 | #endif
323 |
324 | //if last movement was performed start the next one
325 | if (!movementUpdated){
326 |
327 | degreeComplete = float(numberOfStepsTaken)/float(finalNumberOfSteps);
328 |
329 | angleNow = startingAngle + theta*direction*degreeComplete;
330 |
331 | sys.xPosition = radius * cos(angleNow) + centerX;
332 | sys.yPosition = radius * sin(angleNow) + centerY;
333 |
334 | kinematics.inverse(sys.xPosition,sys.yPosition,&aChainLength,&bChainLength);
335 |
336 | leftAxis.write(aChainLength);
337 | rightAxis.write(bChainLength);
338 | if(sysSettings.zAxisAttached){
339 | zAxis.write(zPosition);
340 | }
341 | movementUpdate();
342 |
343 | // Run realtime commands
344 | execSystemRealtime();
345 | if (sys.stop){return 1;}
346 |
347 | numberOfStepsTaken++;
348 | zPosition += zStepSizeMM;
349 | }
350 | }
351 | #if misloopDebug > 0
352 | inMovementLoop = false;
353 | #endif
354 |
355 | kinematics.inverse(X2,Y2,&aChainLength,&bChainLength);
356 | leftAxis.endMove(aChainLength);
357 | rightAxis.endMove(bChainLength);
358 |
359 | sys.xPosition = X2;
360 | sys.yPosition = Y2;
361 |
362 | return 1;
363 | }
364 |
365 | void motionDetachIfIdle(){
366 | /*
367 |
368 | This function is called every time the main loop runs. When the machine is executing a move it is not called, but when the machine is
369 | not executing a line it is called regularly and causes the motors to hold their positions.
370 |
371 | */
372 |
373 | leftAxis.detachIfIdle();
374 | rightAxis.detachIfIdle();
375 | zAxis.detachIfIdle();
376 | }
377 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Motion.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
3 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
4 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
5 | (at your option) any later version.
6 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
7 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
8 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
9 | GNU General Public License for more details.
10 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
11 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
12 |
13 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
14 |
15 | // This contains all of the Motion commands
16 |
17 | #ifndef motion_h
18 | #define motion_h
19 |
20 | // These are used for movement tracking and need to be available to the ISR
21 | extern volatile bool movementUpdated;
22 | #if misloopDebug > 0
23 | extern volatile bool inMovementLoop;
24 | extern volatile bool movementFail;
25 | #endif
26 |
27 | void initMotion();
28 | int coordinatedMove(const float&, const float&, const float&, float);
29 | void singleAxisMove(Axis*, const float&, const float&);
30 | int arc(const float&, const float&, const float&, const float&, const float&, const float&, const float&, const float&, const float&, const float&);
31 | float calculateFeedrate(const float&, const float&);
32 | float computeStepSize(const float&);
33 | void movementUpdate();
34 | void motionDetachIfIdle();
35 |
36 | #endif
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Motor.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | /*
19 | The Motor module imitates the behavior of the Arduino servo module. It allows a gear motor (or any electric motor)
20 | to be a drop in replacement for a continuous rotation servo.
21 |
22 | */
23 |
24 | #include "Maslow.h"
25 |
26 | Motor::Motor(){
27 |
28 | _attachedState = 0;
29 |
30 |
31 | }
32 |
33 | int Motor::setupMotor(const int& pwmPin, const int& pin1, const int& pin2){
34 |
35 | //store pin numbers as private variables
36 | _pwmPin = pwmPin;
37 | _pin1 = pin1;
38 | _pin2 = pin2;
39 | _attachedState = 0;
40 |
41 | if (TLE5206 == false) {
42 | //set pinmodes
43 | pinMode(_pwmPin, OUTPUT);
44 | pinMode(_pin1, OUTPUT);
45 | pinMode(_pin2, OUTPUT);
46 |
47 | //stop the motor
48 | digitalWrite(_pin1, HIGH);
49 | digitalWrite(_pin2, LOW) ;
50 | digitalWrite(_pwmPin, LOW);
51 | } else {
52 | pinMode(_pwmPin, INPUT);
53 | pinMode(_pin1, OUTPUT);
54 | pinMode(_pin2, OUTPUT);
55 |
56 | //stop the motor
57 | digitalWrite(_pin1, LOW);
58 | digitalWrite(_pin2, LOW) ;
59 | }
60 | return 1;
61 | }
62 |
63 | void Motor::attach(){
64 | _attachedState = 1;
65 | }
66 |
67 | void Motor::detach(){
68 | _attachedState = 0;
69 |
70 | if (TLE5206 == false) {
71 | //stop the motor
72 | digitalWrite(_pin1, HIGH);
73 | digitalWrite(_pin2, LOW) ;
74 | digitalWrite(_pwmPin, LOW);
75 | } else {
76 | //stop the motor
77 | digitalWrite(_pin1, LOW);
78 | digitalWrite(_pin2, LOW) ;
79 | }
80 | }
81 |
82 | int Motor::lastSpeed(){
83 | /*
84 | Returns the last speed(voltage) value sent to the pwm
85 | */
86 | return _lastSpeed;
87 | }
88 |
89 | void Motor::additiveWrite(int speed){
90 | /*
91 | Increases/decreases the motor speed by the passed speed amount
92 | */
93 | write(_lastSpeed + speed);
94 | }
95 |
96 | void Motor::write(int speed, bool force){
97 | /*
98 | Sets motor speed from input. Speed = 0 is stopped, -255 is full reverse, 255 is full ahead. If force is true the motor attached state will be ignored
99 | */
100 | if (_attachedState == 1 or force){
101 | speed = constrain(speed, -255, 255);
102 | _lastSpeed = speed; //saves speed for use in additive write
103 | bool forward = (speed > 0);
104 | speed = abs(speed); //remove sign from input because direction is set by control pins on H-bridge
105 |
106 | bool usePin1 = ((_pin1 != 4) && (_pin1 != 13) && (_pin1 != 11) && (_pin1 != 12)); // avoid PWM using timer0 or timer1
107 | bool usePin2 = ((_pin2 != 4) && (_pin2 != 13) && (_pin2 != 11) && (_pin2 != 12)); // avoid PWM using timer0 or timer1
108 | bool usepwmPin = ((TLE5206 == false) && (_pwmPin != 4) && (_pwmPin != 13) && (_pwmPin != 11) && (_pwmPin != 12)); // avoid PWM using timer0 or timer1
109 | if (!TLE5206) {
110 | if (forward){
111 | if (usepwmPin){
112 | digitalWrite(_pin1 , HIGH );
113 | digitalWrite(_pin2 , LOW );
114 | analogWrite(_pwmPin, speed);
115 | }
116 | else if (usePin2) {
117 | digitalWrite(_pin1 , HIGH );
118 | analogWrite(_pin2 , 255 - speed); // invert drive signals - don't alter speed
119 | digitalWrite(_pwmPin, HIGH);
120 | }
121 | else{
122 | analogWrite(_pin1 , speed);
123 | digitalWrite(_pin2 , LOW );
124 | digitalWrite(_pwmPin, HIGH);
125 | }
126 | }
127 | else { // reverse or zero speed
128 | if (usepwmPin){
129 | digitalWrite(_pin2 , HIGH);
130 | digitalWrite(_pin1 , LOW );
131 | analogWrite(_pwmPin, speed);
132 | }
133 | else if (usePin1) {
134 | analogWrite(_pin1 , 255 - speed); // invert drive signals - don't alter speed
135 | digitalWrite(_pin2 , HIGH );
136 | digitalWrite(_pwmPin, HIGH);
137 | }
138 | else {
139 | analogWrite(_pin2 , speed);
140 | digitalWrite(_pin1 , LOW );
141 | digitalWrite(_pwmPin, HIGH);
142 | }
143 | }
144 | }
145 | else { // TLE5206
146 | if (forward) {
147 | if (speed > 0) {
148 | if (usePin2) {
149 | digitalWrite(_pin1 , HIGH );
150 | analogWrite(_pin2 , 255 - speed); // invert drive signals - don't alter speed
151 | }
152 | else {
153 | analogWrite(_pin1 , speed);
154 | digitalWrite(_pin2 , LOW );
155 | }
156 | }
157 | else { // speed = 0 so put on the brakes
158 | digitalWrite(_pin1 , LOW );
159 | digitalWrite(_pin2 , LOW );
160 | }
161 | }
162 | else { // reverse
163 | if (usePin1) {
164 | analogWrite(_pin1 , 255 - speed); // invert drive signals - don't alter speed
165 | digitalWrite(_pin2 , HIGH );
166 | } else {
167 | analogWrite(_pin2 , speed);
168 | digitalWrite(_pin1 , LOW );
169 | }
170 | }
171 | }
172 | }
173 | }
174 |
175 | void Motor::directWrite(int voltage){
176 | /*
177 | Write directly to the motor, ignoring if the axis is attached or any applied calibration.
178 | */
179 | write(voltage, true);
180 | }
181 |
182 | int Motor::attached(){
183 |
184 | return _attachedState;
185 | }
186 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Motor.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Makesmith Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Makesmith Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Makesmith Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Makesmith Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | #ifndef Motor_h
19 | #define Motor_h
20 |
21 | struct LinSegment{
22 | float slope = 1;
23 | float intercept = 0;
24 | //The bounds are strict, so if the bounds are 0,1 .9 would work
25 | //but 1 and 0 will not
26 | int positiveBound = 0;
27 | int negativeBound = 0;
28 | };
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 | class Motor{
33 | public:
34 | Motor();
35 | void attach();
36 | int setupMotor(const int& pwmPin, const int& pin1, const int& pin2);
37 | void detach();
38 | void write(int speed, bool force = false);
39 | int lastSpeed();
40 | void additiveWrite(int speed);
41 | int attached();
42 | void directWrite(int voltage);
43 | private:
44 | int _pwmPin;
45 | int _pin1;
46 | int _pin2;
47 | bool _attachedState = false;
48 | LinSegment _linSegments[4];
49 | int _lastSpeed = 0;
50 |
51 | };
52 | extern bool TLE5206;
53 | #endif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/MotorGearboxEncoder.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | /*
19 | The Motor module imitates the behavior of the Arduino servo module. It allows a gear motor (or any electric motor)
20 | to be a drop in replacement for a continuous rotation servo.
21 |
22 | */
23 |
24 | #include "Maslow.h"
25 |
26 | void MotorGearboxEncoder::setup(const int& pwmPin, const int& directionPin1, const int& directionPin2, const int& encoderPin1, const int& encoderPin2, const unsigned long& loopInterval)
27 | {
28 | //initialize encoder
29 | encoder.setup(encoderPin1,encoderPin2);
30 | // I don't like this, but I don't know how else to initialize a pointer to a value
31 | float zero = 0.0;
32 | float one = 1.0;
33 | _Kp = _Ki = _Kd = &zero;
34 |
35 | //initialize motor
36 | motor.setupMotor(pwmPin, directionPin1, directionPin2);
37 | motor.write(0);
38 |
39 | //initialize the PID
40 | _PIDController.setup(&_currentSpeed, &_pidOutput, &_targetSpeed, _Kp, _Ki, _Kd, &one, DIRECT);
41 | initializePID(loopInterval);
42 |
43 |
44 | }
45 |
46 | void MotorGearboxEncoder::write(const float& speed){
47 | /*
48 | Command the motor to turn at the given speed. Should be RPM is PWM right now.
49 | */
50 |
51 | _targetSpeed = speed;
52 |
53 | }
54 |
55 | void MotorGearboxEncoder::initializePID(const unsigned long& loopInterval){
56 | //setup positive PID controller
57 | _PIDController.SetMode(AUTOMATIC);
58 | _PIDController.SetOutputLimits(-255, 255);
59 | _PIDController.SetSampleTime(loopInterval / 1000);
60 | }
61 |
62 | void MotorGearboxEncoder::computePID(){
63 | /*
64 | Recompute the speed control PID loop and command the motor to move.
65 | */
66 | _currentSpeed = computeSpeed();
67 |
68 | _PIDController.Compute();
69 |
70 | motor.additiveWrite(_pidOutput);
71 | }
72 |
73 | void MotorGearboxEncoder::setPIDValues(float* KpV, float* KiV, float* KdV, float* propWeightV){
74 | /*
75 |
76 | Set PID tuning values
77 |
78 | */
79 |
80 | _Kp = KpV;
81 | _Ki = KiV;
82 | _Kd = KdV;
83 |
84 | _PIDController.SetTunings(_Kp, _Ki, _Kd, propWeightV);
85 | }
86 |
87 | String MotorGearboxEncoder::getPIDString(){
88 | /*
89 |
90 | Get PID tuning values
91 |
92 | */
93 | String PIDString = "Kp=";
94 | return PIDString + *_Kp + ",Ki=" + *_Ki + ",Kd=" + *_Kd;
95 | }
96 |
97 | String MotorGearboxEncoder::pidState(){
98 | /*
99 |
100 | Get current value of PID variables, setpoint, input, output
101 |
102 | */
103 | return _PIDController.pidState();
104 | }
105 |
106 | void MotorGearboxEncoder::setPIDAggressiveness(float aggressiveness){
107 | /*
108 |
109 | The setPIDAggressiveness() function sets the aggressiveness of the PID controller to
110 | compensate for a change in the load on the motor.
111 |
112 | */
113 |
114 | float adjustedKp = aggressiveness * *_Kp;
115 | float one = 1.0;
116 |
117 | _PIDController.SetTunings(&adjustedKp, _Ki, _Kd, &one);
118 |
119 | }
120 |
121 | void MotorGearboxEncoder::setEncoderResolution(float resolution){
122 | /*
123 |
124 | Change the encoder resolution
125 |
126 | */
127 |
128 | _encoderStepsToRPMScaleFactor = 60000000.0/resolution; //6*10^7 us per minute divided by 8113.73 steps per revolution
129 |
130 | }
131 |
132 | float MotorGearboxEncoder::computeSpeed(){
133 | /*
134 |
135 | Returns the motors speed in RPM since the last time this function was called
136 | should only be called by the PID process otherwise we are calculating the
137 | distance moved over a varying amount of time.
138 |
139 | */
140 |
141 | float currentPosition = encoder.read();
142 | float currentMicros = micros();
143 |
144 | float distMoved = currentPosition - _lastPosition;
145 | if (distMoved > 3 || distMoved < -3){
146 |
147 | // This dampens some of the effects of quantization without having
148 | // a big effect on other changes
149 | float saveDistMoved = distMoved;
150 | if (distMoved - _lastDistMoved <= -1){ distMoved += .5;}
151 | else if (distMoved - _lastDistMoved >= 1){distMoved -= .5;}
152 | _lastDistMoved = saveDistMoved;
153 |
154 | unsigned long timeElapsed = currentMicros - _lastTimeStamp;
155 | //Compute the speed in RPM
156 | _RPM = (_encoderStepsToRPMScaleFactor*distMoved)/float(timeElapsed);
157 |
158 | }
159 | else {
160 | float elapsedTime = encoder.elapsedTime();
161 | float lastTime = micros() - encoder.lastStepTime(); // no direction associated with this
162 | if (lastTime > abs(elapsedTime)) {
163 | // This allows the RPM to approach 0
164 | if (elapsedTime < 0){
165 | elapsedTime = -lastTime;
166 | }
167 | else {
168 | elapsedTime = lastTime;
169 | }
170 | };
171 |
172 | _RPM = 0 ;
173 | if (elapsedTime != 0){
174 | _RPM = _encoderStepsToRPMScaleFactor / elapsedTime;
175 | }
176 | }
177 | _RPM = _RPM * -1.0;
178 |
179 | //Store values for next time
180 | _lastTimeStamp = currentMicros;
181 | _lastPosition = currentPosition;
182 |
183 | return _RPM;
184 | }
185 |
186 | float MotorGearboxEncoder::cachedSpeed(){
187 | /*
188 | Returns the last result of computeSpeed
189 | */
190 | return _RPM;
191 | }
192 |
193 | void MotorGearboxEncoder::setName(char *newName){
194 | /*
195 | Set the name for the object
196 | */
197 | _motorName = newName;
198 | }
199 |
200 | char MotorGearboxEncoder::name(){
201 | /*
202 | Get the name for the object
203 | */
204 | return *_motorName;
205 | }
206 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/MotorGearboxEncoder.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Makesmith Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Makesmith Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Makesmith Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Makesmith Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | #ifndef MotorGearboxEncoder_h
19 | #define MotorGearboxEncoder_h
20 |
21 | class MotorGearboxEncoder{
22 | public:
23 | void setup(const int& pwmPin, const int& directionPin1, const int& directionPin2, const int& encoderPin1, const int& encoderPin2, const unsigned long& loopInterval);
24 | Encoder encoder;
25 | Motor motor;
26 | float cachedSpeed();
27 | void write(const float& speed);
28 | void computePID();
29 | void setName(char *newName);
30 | char name();
31 | void initializePID(const unsigned long& loopInterval);
32 | void setPIDAggressiveness(float aggressiveness);
33 | void setPIDValues(float* KpV, float* KiV, float* KdV, float* propWeight);
34 | void setEncoderResolution(float resolution);
35 | float computeSpeed();
36 | String getPIDString();
37 | String pidState();
38 | private:
39 | double _targetSpeed;
40 | double _currentSpeed;
41 | volatile double _lastPosition;
42 | volatile double _lastTimeStamp;
43 | float _lastDistMoved;
44 | float _RPM;
45 | char *_motorName;
46 | double _pidOutput;
47 | PID _PIDController;
48 | float *_Kp, *_Ki, *_Kd;
49 | // This could be converted to a pointer to save 4 bytes, but the
50 | // calculation would have to be done at a much higher level and
51 | // passed through each axis for it to have a single pointer to
52 | // both main motors
53 | float _encoderStepsToRPMScaleFactor = 7394.87; //6*10^7 us per minute divided by 8113.73 steps per revolution
54 | };
55 |
56 | #endif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/NutsAndBolts.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | // This file contains helper functions that are used throughout
19 |
20 | #include "Maslow.h"
21 |
22 | float readFloat(const String& str, byte& index, float& retVal){
23 | /*
24 | Takes a string and a starting character index and returns a float if it can
25 | be parsed from the string, it will skip leading spaces. Does not support
26 | scientific notation as this is officially not supported by GCode.
27 | Code was adopted from arduino Stream::parseFloat and some from Grbl's
28 | read_float. It is a custom function because all arduino and c++ functions
29 | appear to handle scientific notation or hexadecimal notation, or some other
30 | type of numerical representation that we don't want supported.
31 | */
32 | bool isNegative = false;
33 | bool isFraction = false;
34 | long value = 0;
35 | float fraction = 1.0;
36 | byte ndigit = 0;
37 | while (str[index] == ' ' && index < str.length()){
38 | index++;
39 | }
40 | do{
41 | if (index < str.length()){
42 | if(str[index] == '-')
43 | isNegative = true;
44 | else if (str[index] == '.')
45 | isFraction = true;
46 | else if(str[index] >= '0' && str[index] <= '9') {// is a digit?
47 | ndigit++;
48 | value = value * 10 + str[index] - '0';
49 | if(isFraction)
50 | fraction *= 0.1;
51 | }
52 | index++;
53 | }
54 | }
55 | while(((str[index] >= '0' && str[index] <= '9') || (str[index] == '.' && !isFraction)) && index < str.length());
56 |
57 | if (!ndigit) { return false; };
58 |
59 | if(isNegative)
60 | value = -value;
61 | if(isFraction)
62 | retVal = value * fraction;
63 | else
64 | retVal = value;
65 |
66 | return true;
67 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/NutsAndBolts.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | // This file contains helper functions that are used throughout
19 |
20 | #ifndef nutsandbolts_h
21 | #define nutsandbolts_h
22 |
23 | // These are nifty functions from Grbl
24 | #define bit_true(x,mask) (x) |= (mask)
25 | #define bit_false(x,mask) (x) &= ~(mask)
26 | #define bit_istrue(x,mask) ((x & mask) != 0)
27 | #define bit_isfalse(x,mask) ((x & mask) == 0)
28 |
29 | float readFloat(const String&, byte&, float&);
30 |
31 | #endif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/PID_v1.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /**********************************************************************************************
2 | * Arduino PID Library - Version 1.2.1
3 | * by Brett Beauregard brettbeauregard.com
4 | *
5 | * This Library is licensed under the MIT License
6 | **********************************************************************************************/
7 |
8 | #if ARDUINO >= 100
9 | #include "Arduino.h"
10 | #else
11 | #include "WProgram.h"
12 | #endif
13 |
14 | #include "Maslow.h"
15 |
16 | /*Constructor (...)*********************************************************
17 | * The parameters specified here are those for for which we can't set up
18 | * reliable defaults, so we need to have the user set them.
19 | ***************************************************************************/
20 | PID::PID()
21 | {
22 | inAuto = false;
23 | }
24 |
25 | void PID::setup(volatile double* Input, volatile double* Output, volatile double* Setpoint,
26 | float* Kp, float* Ki, float* Kd, float* POn, const int& ControllerDirection)
27 | {
28 |
29 | myOutput = Output;
30 | myInput = Input;
31 | mySetpoint = Setpoint;
32 | inAuto = false;
33 |
34 | PID::SetOutputLimits(0, 255); //default output limit corresponds to
35 | //the arduino pwm limits
36 |
37 | SampleTime = 100; //default Controller Sample Time is 0.1 seconds
38 |
39 | PID::SetControllerDirection(ControllerDirection);
40 | PID::SetTunings(Kp, Ki, Kd, POn);
41 |
42 | lastTime = millis()-SampleTime;
43 | }
44 |
45 | /* Compute() **********************************************************************
46 | * This, as they say, is where the magic happens. this function should be called
47 | * every time "void loop()" executes. the function will decide for itself whether a new
48 | * pid Output needs to be computed. returns true when the output is computed,
49 | * false when nothing has been done.
50 | **********************************************************************************/
51 | bool PID::Compute()
52 | {
53 | if(!inAuto) return false;
54 | //unsigned long now = millis();
55 | //unsigned long timeChange = (now - lastTime);
56 | //if(timeChange>=SampleTime)
57 | //{ <--- This if statement has been removed to reduce timing jitter on the interrupt.
58 | //because we are calling the function from within an interrupt timer it will be called
59 | //with a consistent sample period
60 |
61 | /*Compute all the working error variables*/
62 | double input = *myInput;
63 | double error = *mySetpoint - input;
64 | double dInput = (input - lastInput);
65 | outputSum+= (ki * error);
66 |
67 | /*Add Proportional on Measurement, if P_ON_M is specified*/
68 | if(pOnM) outputSum-= pOnMKp * dInput;
69 |
70 | if(outputSum > outMax) outputSum= outMax;
71 | else if(outputSum < outMin) outputSum= outMin;
72 |
73 | /*Add Proportional on Error, if P_ON_E is specified*/
74 | double output;
75 | if(pOnE) output = pOnEKp * error;
76 | else output = 0;
77 |
78 | /*Compute Rest of PID Output*/
79 | output += outputSum - kd * dInput;
80 |
81 | if(output > outMax) output = outMax;
82 | else if(output < outMin) output = outMin;
83 | *myOutput = output;
84 |
85 | /*Remember some variables for next time*/
86 | lastInput = input;
87 | //lastTime = now;
88 | return true;
89 | //}
90 | //else return false;
91 | }
92 |
93 |
94 | /* SetTunings(...)*************************************************************
95 | * This function allows the controller's dynamic performance to be adjusted.
96 | * it's called automatically from the constructor, but tunings can also
97 | * be adjusted on the fly during normal operation
98 | ******************************************************************************/
99 | void PID::SetTunings(float* Kp, float* Ki, float* Kd, float* pOn)
100 | {
101 | if (*Kp<0 || *Ki<0 || *Kd<0 || *pOn<0 || *pOn>1) return;
102 |
103 | pOnE = *pOn>0; //some p on error is desired;
104 | pOnM = *pOn<1; //some p on measurement is desired;
105 |
106 | dispKp = Kp; dispKi = Ki; dispKd = Kd;
107 |
108 | double SampleTimeInSec = ((double)SampleTime)/1000;
109 | kp = *Kp;
110 | ki = *Ki * SampleTimeInSec;
111 | kd = *Kd / SampleTimeInSec;
112 |
113 | if(controllerDirection ==REVERSE)
114 | {
115 | kp = (0 - kp);
116 | ki = (0 - ki);
117 | kd = (0 - kd);
118 | }
119 | pOnEKp = *pOn * kp;
120 | pOnMKp = (1 - *pOn) * kp;
121 | }
122 |
123 | /* SetSampleTime(...) *********************************************************
124 | * sets the period, in Milliseconds, at which the calculation is performed
125 | ******************************************************************************/
126 | void PID::SetSampleTime(const int& NewSampleTime)
127 | {
128 | if (NewSampleTime > 0)
129 | {
130 | double ratio = (double)NewSampleTime
131 | / (double)SampleTime;
132 | ki *= ratio;
133 | kd /= ratio;
134 | SampleTime = (unsigned long)NewSampleTime;
135 | }
136 | }
137 |
138 | /* SetOutputLimits(...)****************************************************
139 | * This function will be used far more often than SetInputLimits. while
140 | * the input to the controller will generally be in the 0-1023 range (which is
141 | * the default already,) the output will be a little different. maybe they'll
142 | * be doing a time window and will need 0-8000 or something. or maybe they'll
143 | * want to clamp it from 0-125. who knows. at any rate, that can all be done
144 | * here.
145 | **************************************************************************/
146 | void PID::SetOutputLimits(const double& Min, const double& Max)
147 | {
148 | if(Min >= Max) return;
149 | outMin = Min;
150 | outMax = Max;
151 |
152 | if(inAuto)
153 | {
154 |
155 | //clamp myOutput and ITerm
156 | *myOutput =
157 | (*myOutput > outMax) ? outMax : (*myOutput < outMin) ? outMin : *myOutput;
158 |
159 | if(outputSum > outMax) outputSum= outMax;
160 | else if(outputSum < outMin) outputSum= outMin;
161 |
162 | }
163 | }
164 |
165 | /* SetMode(...)****************************************************************
166 | * Allows the controller Mode to be set to manual (0) or Automatic (non-zero)
167 | * when the transition from manual to auto occurs, the controller is
168 | * automatically initialized
169 | ******************************************************************************/
170 | void PID::SetMode(const int& Mode)
171 | {
172 | bool newAuto = (Mode == AUTOMATIC);
173 | if(newAuto && !inAuto)
174 | { /*we just went from manual to auto*/
175 | PID::Initialize();
176 | }
177 | inAuto = newAuto;
178 | }
179 |
180 | /* Initialize()****************************************************************
181 | * does all the things that need to happen to ensure a bumpless transfer
182 | * from manual to automatic mode.
183 | ******************************************************************************/
184 | void PID::Initialize()
185 | {
186 | outputSum = *myOutput;
187 | lastInput = *myInput;
188 | if(outputSum > outMax) outputSum = outMax;
189 | else if(outputSum < outMin) outputSum = outMin;
190 | }
191 |
192 | /* SetControllerDirection(...)*************************************************
193 | * The PID will either be connected to a DIRECT acting process (+Output leads
194 | * to +Input) or a REVERSE acting process(+Output leads to -Input.) we need to
195 | * know which one, because otherwise we may increase the output when we should
196 | * be decreasing. This is called from the constructor.
197 | ******************************************************************************/
198 | void PID::SetControllerDirection(const int& Direction)
199 | {
200 | if(inAuto && Direction !=controllerDirection)
201 | {
202 | kp = (0 - kp);
203 | ki = (0 - ki);
204 | kd = (0 - kd);
205 | }
206 | controllerDirection = Direction;
207 | }
208 |
209 | /* Status Funcions*************************************************************
210 | * Just because you set the Kp=-1 doesn't mean it actually happened. these
211 | * functions query the internal state of the PID. they're here for display
212 | * purposes. this are the functions the PID Front-end uses for example
213 | ******************************************************************************/
214 | double PID::GetKp(){ return *dispKp;}
215 | double PID::GetKi(){ return *dispKi;}
216 | double PID::GetKd(){ return *dispKd;}
217 | int PID::GetMode(){ return inAuto ? AUTOMATIC : MANUAL;}
218 | int PID::GetDirection(){ return controllerDirection;}
219 | double PID::GetIterm(){ return outputSum; }
220 | String PID::pidState() {
221 | /*
222 | Returns a comma seperated string of the PID setpoint, input, & output
223 | useful for debugging
224 | */
225 | double input = *myInput;
226 | double setpoint = *mySetpoint;
227 | double output = *myOutput;
228 | String ret = "";
229 | ret.concat((double)setpoint);
230 | ret.concat(",");
231 | ret.concat((double)input);
232 | ret.concat(",");
233 | ret.concat((double)output);
234 | return ret;
235 | }
236 |
237 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/PID_v1.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef PID_v1_h
2 | #define PID_v1_h
3 | #define LIBRARY_VERSION 1.2.1
4 |
5 | class PID
6 | {
7 |
8 |
9 | public:
10 |
11 | //Constants used in some of the functions below
12 | #define AUTOMATIC 1
13 | #define MANUAL 0
14 | #define DIRECT 0
15 | #define REVERSE 1
16 | #define P_ON_M 0.0
17 | #define P_ON_E 1.0
18 | bool pOnE = true, pOnM = false;
19 | double pOnEKp, pOnMKp;
20 |
21 | //commonly used functions **************************************************************************
22 |
23 | PID();
24 |
25 | void setup(volatile double*, volatile double*, volatile double*, // * constructor. links the PID to the Input, Output, and
26 | float*, float*, float*, float*, const int&);// Setpoint. Initial tuning parameters are also set here.
27 | // (overload for specifying proportional mode)
28 |
29 | PID(double*, double*, double*, // * constructor. links the PID to the Input, Output, and
30 | double, double, double, int); // Setpoint. Initial tuning parameters are also set here
31 |
32 | void SetMode(const int& Mode); // * sets PID to either Manual (0) or Auto (non-0)
33 |
34 | bool Compute(); // * performs the PID calculation. it should be
35 | // called every time loop() cycles. ON/OFF and
36 | // calculation frequency can be set using SetMode
37 | // SetSampleTime respectively
38 |
39 | void SetOutputLimits(const double&, const double&); //clamps the output to a specific range. 0-255 by default, but
40 | //it's likely the user will want to change this depending on
41 | //the application
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 | //available but not commonly used functions ********************************************************
46 | void SetTunings(float*, float*, // * While most users will set the tunings once in the
47 | float*); // constructor, this function gives the user the option
48 | // of changing tunings during runtime for Adaptive control
49 | void SetTunings(float*, float*, // * overload for specifying proportional mode
50 | float*, float*);
51 |
52 | void SetControllerDirection(const int&); // * Sets the Direction, or "Action" of the controller. DIRECT
53 | // means the output will increase when error is positive. REVERSE
54 | // means the opposite. it's very unlikely that this will be needed
55 | // once it is set in the constructor.
56 | void SetSampleTime(const int&); // * sets the frequency, in Milliseconds, with which
57 | // the PID calculation is performed. default is 100
58 |
59 |
60 | //Display functions ****************************************************************
61 | double GetKp(); // These functions query the pid for interal values.
62 | double GetKi(); // they were created mainly for the pid front-end,
63 | double GetKd(); // where it's important to know what is actually
64 | int GetMode(); // inside the PID.
65 | int GetDirection(); //
66 | double GetIterm();
67 | String pidState();
68 |
69 | private:
70 | void Initialize();
71 |
72 | float *dispKp; // * we'll hold on to the tuning parameters in user-entered
73 | float *dispKi; // format for display purposes
74 | float *dispKd; //
75 |
76 | // While shared by both main motors, these are not pointers because they are
77 | // calculated using sample time in this file.
78 | double kp; // * (P)roportional Tuning Parameter
79 | double ki; // * (I)ntegral Tuning Parameter
80 | double kd; // * (D)erivative Tuning Parameter
81 |
82 | int controllerDirection;
83 | int pOn;
84 |
85 | volatile double *myInput; // * Pointers to the Input, Output, and Setpoint variables
86 | volatile double *myOutput; // This creates a hard link between the variables and the
87 | volatile double *mySetpoint; // PID, freeing the user from having to constantly tell us
88 | // what these values are. with pointers we'll just know.
89 |
90 | unsigned long lastTime;
91 | double outputSum, lastInput;
92 |
93 | unsigned long SampleTime;
94 | double outMin, outMax;
95 | bool inAuto;
96 | };
97 | #endif
98 |
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Probe.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | // This file contains functions related to the probe
19 |
20 | #include "Maslow.h"
21 |
22 | // the variable probePin is assigned in configAuxLow() in System.cpp
23 |
24 | bool checkForProbeTouch(const int& probePin) {
25 | /*
26 | Check to see if ProbePin has gone LOW
27 | */
28 | if (digitalRead(probePin) == LOW) {
29 | readyCommandString = "";
30 | return 1;
31 | }
32 | return 0;
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Probe.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | // This file contains functions related to the probe
19 |
20 | #ifndef probe_h
21 | #define probe_h
22 |
23 | bool checkForProbeTouch(const int&);
24 |
25 | #endif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Report.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | // This file contains the functions for outgoing Serial responses
19 |
20 | #include "Maslow.h"
21 |
22 | void reportStatusMessage(byte status_code){
23 | /*
24 |
25 | Sends confirmation protocol response for commands. For every incoming line,
26 | this method responds with an 'ok' for a successful command or an 'error:'
27 | to indicate some error event with the line or some critical system error during
28 | operation.
29 |
30 | Taken from Grbl http://github.com/grbl/grbl
31 | */
32 | if (status_code == 0) { // STATUS_OK
33 | Serial.println(F("ok"));
34 | } else {
35 | Serial.print(F("error: "));
36 | #ifdef REPORT_GUI_MODE
37 | Serial.println(status_code);
38 | #else
39 | switch(status_code) {
40 | // case STATUS_EXPECTED_COMMAND_LETTER=")); Serial.println( // Serial.println(F("Expected command letter")); break;
41 | case STATUS_BAD_NUMBER_FORMAT:
42 | Serial.println(F("Bad number format")); break;
43 | case STATUS_INVALID_STATEMENT:
44 | Serial.println(F("Invalid statement")); break;
45 | case STATUS_OLD_SETTINGS:
46 | Serial.println(F("Please set $12, $13, $19, and $20 to load old position data.")); break;
47 | // case STATUS_NEGATIVE_VALUE:
48 | // Serial.println(F("Value < 0")); break;
49 | // case STATUS_SETTING_DISABLED:
50 | // Serial.println(F("Setting disabled")); break;
51 | // case STATUS_SETTING_STEP_PULSE_MIN:
52 | // Serial.println(F("Value < 3 usec")); break;
53 | case STATUS_SETTING_READ_FAIL:
54 | Serial.println(F("EEPROM read fail. Using default settings.")); break;
55 | // case STATUS_IDLE_ERROR:
56 | // Serial.println(F("Not idle")); break;
57 | // case STATUS_ALARM_LOCK:
58 | // Serial.println(F("Alarm lock")); break;
59 | // case STATUS_SOFT_LIMIT_ERROR:
60 | // Serial.println(F("Homing not enabled")); break;
61 | // case STATUS_OVERFLOW:
62 | // Serial.println(F("Line overflow")); break;
63 | // #ifdef MAX_STEP_RATE_HZ
64 | // case STATUS_MAX_STEP_RATE_EXCEEDED:
65 | // Serial.println(F("Step rate > 30kHz")); break;
66 | // #endif
67 | // Common g-code parser errors.
68 | // case STATUS_GCODE_MODAL_GROUP_VIOLATION:
69 | // Serial.println(F("Modal group violation")); break;
70 | // case STATUS_GCODE_UNSUPPORTED_COMMAND:
71 | // Serial.println(F("Unsupported command")); break;
72 | // case STATUS_GCODE_UNDEFINED_FEED_RATE:
73 | // Serial.println(F("Undefined feed rate")); break;
74 | default:
75 | // Remaining g-code parser errors with error codes
76 | Serial.print(F("Invalid gcode ID:"));
77 | Serial.println(status_code); // Print error code for user reference
78 | }
79 | #endif
80 | }
81 | }
82 |
83 | void reportFeedbackMessage(byte message_code){
84 | Serial.print(F("Message: "));
85 | switch(message_code) {
86 | // case MESSAGE_CRITICAL_EVENT:
87 | // Serial.print(F("Reset to continue")); break;
88 | // case MESSAGE_ALARM_LOCK:
89 | // Serial.print(F("'$H'|'$X' to unlock")); break;
90 | // case MESSAGE_ALARM_UNLOCK:
91 | // Serial.print(F("Caution: Unlocked")); break;
92 | // case MESSAGE_ENABLED:
93 | // Serial.print(F("Enabled")); break;
94 | // case MESSAGE_DISABLED:
95 | // Serial.print(F("Disabled")); break;
96 | // case MESSAGE_SAFETY_DOOR_AJAR:
97 | // Serial.print(F("Check Door")); break;
98 | // case MESSAGE_CHECK_LIMITS:
99 | // Serial.print(F("Check Limits")); break;
100 | // case MESSAGE_PROGRAM_END:
101 | // Serial.print(F("Pgm End")); break;
102 | case MESSAGE_RESTORE_DEFAULTS:
103 | Serial.print(F("Restoring defaults")); break;
104 | // case MESSAGE_SPINDLE_RESTORE:
105 | // Serial.print(F("Restoring spindle")); break;
106 | // case MESSAGE_SLEEP_MODE:
107 | // Serial.print(F("Sleeping")); break;
108 | }
109 | Serial.println(F(" "));
110 | }
111 |
112 | // Prints alarm messages.
113 | void reportAlarmMessage(byte alarm_code) {
114 | Serial.print(F("ALARM: "));
115 | #ifdef REPORT_GUI_MODE
116 | Serial.println(alarm_code);
117 | #else
118 | switch (alarm_code) {
119 | case ALARM_POSITION_LOST: {
120 | Serial.println(F("Position Lost")); break;
121 | }
122 | case ALARM_GCODE_PARAM_ERROR: {
123 | Serial.println(F("There is a parameter error in this line of Gcode - make a note of the line number. Cutting will be put on hold until you choose whether to 'Resume Cut' (skipping this line) or 'Stop'. "));
124 | pause(); //This pause() waits for user acknowledgement of message
125 | pause(); //Now wait for user decision about 'Stop' or 'Resume'
126 | break;
127 | }
128 | case ALARM_POSITION_LIMIT_ERROR: {
129 | Serial.println(F("The sled is not keeping up with its expected position and has halted. Click the 'Stop' button to clear the alarm. More information at: https://github.com/MaslowCNC/Firmware/wiki/Keeping-Up "));
130 | sys.stop = true;
131 | break;
132 | }
133 | }
134 | #endif
135 | }
136 |
137 | // Maslow global settings print out.
138 | // NOTE: The numbering scheme here must correlate to storing in settings.c
139 | void reportMaslowSettings() {
140 | // Print Maslow settings.
141 | // Taken from Grbl. http://github.com/grbl/grbl
142 | #ifdef REPORT_GUI_MODE
143 | Serial.print(F("$0=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.machineWidth, 8);
144 | Serial.print(F("$1=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.machineHeight, 8);
145 | Serial.print(F("$2=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.distBetweenMotors, 8);
146 | Serial.print(F("$3=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.motorOffsetY, 8);
147 | Serial.print(F("$4=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.sledWidth, 8);
148 | Serial.print(F("$5=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.sledHeight, 8);
149 | Serial.print(F("$6=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.sledCG, 8);
150 | Serial.print(F("$7=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.kinematicsType);
151 | Serial.print(F("$8=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.rotationDiskRadius, 8);
152 | Serial.print(F("$9=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.axisDetachTime);
153 | Serial.print(F("$10=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.chainLength);
154 | Serial.print(F("$11=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.originalChainLength);
155 | Serial.print(F("$12=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.encoderSteps, 8);
156 | Serial.print(F("$13=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.distPerRot, 8);
157 | Serial.print(F("$15=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.maxFeed);
158 | Serial.print(F("$16=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zAxisAttached);
159 | Serial.print(F("$17=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.spindleAutomate);
160 | Serial.print(F("$18=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.maxZRPM, 8);
161 | Serial.print(F("$19=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zDistPerRot, 8);
162 | Serial.print(F("$20=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zEncoderSteps, 8);
163 | Serial.print(F("$21=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.KpPos, 8);
164 | Serial.print(F("$22=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.KiPos, 8);
165 | Serial.print(F("$23=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.KdPos, 8);
166 | Serial.print(F("$24=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.propWeightPos, 8);
167 | Serial.print(F("$25=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.KpV, 8);
168 | Serial.print(F("$26=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.KiV, 8);
169 | Serial.print(F("$27=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.KdV, 8);
170 | Serial.print(F("$28=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.propWeightV, 8);
171 | Serial.print(F("$29=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zKpPos, 8);
172 | Serial.print(F("$30=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zKiPos, 8);
173 | Serial.print(F("$31=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zKdPos, 8);
174 | Serial.print(F("$32=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zPropWeightPos, 8);
175 | Serial.print(F("$33=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zKpV, 8);
176 | Serial.print(F("$34=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zKiV, 8);
177 | Serial.print(F("$35=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zKdV, 8);
178 | Serial.print(F("$36=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.zPropWeightV, 8);
179 | Serial.print(F("$37=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.chainSagCorrection, 8);
180 | Serial.print(F("$38=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.chainOverSprocket);
181 | Serial.print(F("$39=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.fPWM);
182 | Serial.print(F("$40=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.leftChainTolerance, 8);
183 | Serial.print(F("$41=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.rightChainTolerance, 8);
184 | Serial.print(F("$42=")); Serial.println(sysSettings.positionErrorLimit, 8);
185 |
186 | #else
187 | Serial.print(F("$0=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.machineWidth);
188 | Serial.print(F(" (machine width, mm)\r\n$1=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.machineHeight, 8);
189 | Serial.print(F(" (machine height, mm)\r\n$2=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.distBetweenMotors, 8);
190 | Serial.print(F(" (motor distance, mm)\r\n$3=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.motorOffsetY, 8);
191 | Serial.print(F(" (motor height, mm)\r\n$4=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.sledWidth, 8);
192 | Serial.print(F(" (sled width, mm)\r\n$5=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.sledHeight, 8);
193 | Serial.print(F(" (sled height, mm)\r\n$6=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.sledCG, 8);
194 | Serial.print(F(" (sled cg, mm)\r\n$7=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.kinematicsType);
195 | Serial.print(F(" (Kinematics Type 1=Quadrilateral, 2=Triangular)\r\n$8=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.rotationDiskRadius, 8);
196 | Serial.print(F(" (rotation radius, mm)\r\n$9=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.axisDetachTime);
197 | Serial.print(F(" (axis idle before detach, ms)\r\n$10=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.chainLength);
198 | Serial.print(F(" (full length of chain, mm)\r\n$11=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.originalChainLength);
199 | Serial.print(F(" (calibration chain length, mm)\r\n$12=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.encoderSteps, 8);
200 | Serial.print(F(" (main steps per revolution)\r\n$13=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.distPerRot, 8);
201 | Serial.print(F(" (distance / rotation, mm)\r\n$15=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.maxFeed);
202 | Serial.print(F(" (max feed, mm/min)\r\n$16=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zAxisAttached);
203 | Serial.print(F(" (Auto Z Axis, 1 = Yes)\r\n$17=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.spindleAutomateType);
204 | Serial.print(F(" (auto spindle enable 1=servo, 2=relay_h, 3=relay_l)\r\n$18=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.maxZRPM, 8);
205 | Serial.print(F(" (max z axis RPM)\r\n$19=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zDistPerRot, 8);
206 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis distance / rotation)\r\n$20=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zEncoderSteps, 8);
207 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis steps per revolution)\r\n$21=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.KpPos, 8);
208 | Serial.print(F(" (main Kp Pos)\r\n$22=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.KiPos, 8);
209 | Serial.print(F(" (main Ki Pos)\r\n$23=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.KdPos, 8);
210 | Serial.print(F(" (main Kd Pos)\r\n$24=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.propWeightPos, 8);
211 | Serial.print(F(" (main Pos proportional weight)\r\n$25=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.KpV, 8);
212 | Serial.print(F(" (main Kp Velocity)\r\n$26=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.KiV, 8);
213 | Serial.print(F(" (main Ki Velocity)\r\n$27=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.KdV, 8);
214 | Serial.print(F(" (main Kd Velocity)\r\n$28=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.propWeightV, 8);
215 | Serial.print(F(" (main Velocity proportional weight)\r\n$29=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zKpPos, 8);
216 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis Kp Pos)\r\n$30=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zKiPos, 8);
217 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis Ki Pos)\r\n$31=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zKdPos, 8);
218 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis Kd Pos)\r\n$32=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zPropWeightPos, 8);
219 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis Pos proportional weight)\r\n$33=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zKpV, 8);
220 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis Kp Velocity)\r\n$34=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zKiV, 8);
221 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis Ki Velocity)\r\n$35=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zKdV, 8);
222 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis Kd Velocity)\r\n$36=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.zPropWeightV, 8);
223 | Serial.print(F(" (z axis Velocity proportional weight)\r\n$37=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.chainSagCorrection, 8);
224 | Serial.print(F(" (chain sag correction value)\r\n$38=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.chainOverSprocket);
225 | Serial.print(F(" (chain over sprocket)\r\n$39=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.fPWM);
226 | Serial.print(F(" (PWM frequency value 1=39,000Hz, 2=4,100Hz, 3=490Hz)\r\n$40=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.leftChainTolerance, 8);
227 | Serial.print(F(" (chain tolerance, left chain, mm)\r\n$41=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.rightChainTolerance, 8);
228 | Serial.print(F(" (chain tolerance, right chain, mm)\r\n$42=")); Serial.print(sysSettings.positionErrorLimit, 8);
229 | Serial.print(F(" (position error alarm limit, mm)"));
230 | Serial.println();
231 | #endif
232 | }
233 |
234 | void returnError(){
235 | /*
236 | Prints the machine's positional error and the amount of space available in the
237 | gcode buffer
238 | */
239 | Serial.print(F("[PE:"));
240 | Serial.print(leftAxis.error());
241 | Serial.print(',');
242 | Serial.print(rightAxis.error());
243 | Serial.print(',');
244 | Serial.print(incSerialBuffer.spaceAvailable());
245 | Serial.println(F("]"));
246 | if (!sys.stop) {
247 | if (!(sys.state & STATE_POS_ERR_IGNORE)) {
248 | if ((abs(leftAxis.error()) >= sysSettings.positionErrorLimit) || (abs(rightAxis.error()) >= sysSettings.positionErrorLimit)) {
249 | reportAlarmMessage(ALARM_POSITION_LIMIT_ERROR);
250 | }
251 | }
252 | }
253 | }
254 |
255 | void returnPoz(){
256 | /*
257 | Causes the machine's position (x,y) to be sent over the serial connection updated on the UI
258 | in Ground Control. Also causes the error report to be sent. Only executes
259 | if hasn't been called in at least POSITIONTIMEOUT ms.
260 | */
261 |
262 | static unsigned long lastRan = millis();
263 |
264 | if (millis() - lastRan > POSITIONTIMEOUT){
265 |
266 |
267 | Serial.print(F("<"));
268 | if (sys.stop){
269 | Serial.print(F("Stop,MPos:"));
270 | }
271 | else if (sys.pause){
272 | Serial.print(F("Pause,MPos:"));
273 | }
274 | else{
275 | Serial.print(F("Idle,MPos:"));
276 | }
277 | Serial.print(sys.xPosition/sys.inchesToMMConversion);
278 | Serial.print(F(","));
279 | Serial.print(sys.yPosition/sys.inchesToMMConversion);
280 | Serial.print(F(","));
281 | Serial.print(zAxis.read()/sys.inchesToMMConversion);
282 | Serial.println(F(",WPos:0.000,0.000,0.000>"));
283 |
284 |
285 | returnError();
286 |
287 | lastRan = millis();
288 | }
289 |
290 | }
291 |
292 | void reportMaslowHelp(){
293 | /*
294 | This function outputs a brief summary of the $ system commands available.
295 | The list is somewhat aspirational based on what Grbl offers. Maslow
296 | does not currently support all of these features.
297 |
298 | This is taken heavily from grbl. https://github.com/grbl/grbl
299 | */
300 | #ifndef REPORT_GUI_MODE
301 | Serial.println(F("$$ (view Maslow settings)"));
302 | // Serial.println(F("$# (view # parameters)"));
303 | // Serial.println(F("$G (view parser state)"));
304 | // Serial.println(F("$I (view build info)"));
305 | // Serial.println(F("$N (view startup blocks)"));
306 | Serial.println(F("$x=value (save Maslow setting)"));
307 | // Serial.println(F("$Nx=line (save startup block)"));
308 | // Serial.println(F("$C (check gcode mode)"));
309 | // Serial.println(F("$X (kill alarm lock)"));
310 | // Serial.println(F("$H (run homing cycle)"));
311 | Serial.println(F("~ (cycle start)")); // Maslow treats this as resume or un-pause currently
312 | Serial.println(F("! (feed hold)")); // Maslow treats this as a cycle stop.
313 | // Serial.println(F("? (current status)"));
314 | // Serial.println(F("ctrl-x (reset Maslow)"));
315 | #endif
316 | }
317 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Report.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | // This file contains the functions for outgoing Serial responses
19 |
20 | #ifndef report_h
21 | #define report_h
22 |
23 | // Define Maslow status codes.
24 | // Taken from Grbl http://github.com/grbl/grbl
25 | #define STATUS_OK 0
26 | #define STATUS_EXPECTED_COMMAND_LETTER 1
27 | #define STATUS_BAD_NUMBER_FORMAT 2
28 | #define STATUS_INVALID_STATEMENT 3
29 | #define STATUS_NEGATIVE_VALUE 4
30 | #define STATUS_SETTING_DISABLED 5
31 | #define STATUS_SETTING_STEP_PULSE_MIN 6
32 | #define STATUS_SETTING_READ_FAIL 7
33 | #define STATUS_IDLE_ERROR 8
34 | #define STATUS_ALARM_LOCK 9
35 | #define STATUS_SOFT_LIMIT_ERROR 10
36 | #define STATUS_OVERFLOW 11
37 | #define STATUS_MAX_STEP_RATE_EXCEEDED 12
38 | #define STATUS_OLD_SETTINGS 13
39 |
40 | #define STATUS_GCODE_UNSUPPORTED_COMMAND 20
41 | #define STATUS_GCODE_MODAL_GROUP_VIOLATION 21
42 | #define STATUS_GCODE_UNDEFINED_FEED_RATE 22
43 | #define STATUS_GCODE_COMMAND_VALUE_NOT_INTEGER 23
44 | #define STATUS_GCODE_AXIS_COMMAND_CONFLICT 24
45 | #define STATUS_GCODE_WORD_REPEATED 25
46 | #define STATUS_GCODE_NO_AXIS_WORDS 26
47 | #define STATUS_GCODE_INVALID_LINE_NUMBER 27
48 | #define STATUS_GCODE_VALUE_WORD_MISSING 28
49 | #define STATUS_GCODE_UNSUPPORTED_COORD_SYS 29
50 | #define STATUS_GCODE_G53_INVALID_MOTION_MODE 30
51 | #define STATUS_GCODE_AXIS_WORDS_EXIST 31
52 | #define STATUS_GCODE_NO_AXIS_WORDS_IN_PLANE 32
53 | #define STATUS_GCODE_INVALID_TARGET 33
54 | #define STATUS_GCODE_ARC_RADIUS_ERROR 34
55 | #define STATUS_GCODE_NO_OFFSETS_IN_PLANE 35
56 | #define STATUS_GCODE_UNUSED_WORDS 36
57 | #define STATUS_GCODE_G43_DYNAMIC_AXIS_ERROR 37
58 |
59 | // Define Maslow alarm codes.
60 | #define ALARM_POSITION_LOST bit(0)
61 | #define ALARM_GCODE_PARAM_ERROR bit(1)
62 | #define ALARM_POSITION_LIMIT_ERROR bit(2)
63 |
64 | // Define Maslow feedback message codes. Valid values (0-255).
65 | #define MESSAGE_CRITICAL_EVENT 1
66 | #define MESSAGE_ALARM_LOCK 2
67 | #define MESSAGE_ALARM_UNLOCK 3
68 | #define MESSAGE_ENABLED 4
69 | #define MESSAGE_DISABLED 5
70 | #define MESSAGE_SAFETY_DOOR_AJAR 6
71 | #define MESSAGE_CHECK_LIMITS 7
72 | #define MESSAGE_PROGRAM_END 8
73 | #define MESSAGE_RESTORE_DEFAULTS 9
74 | #define MESSAGE_SPINDLE_RESTORE 10
75 | #define MESSAGE_SLEEP_MODE 11
76 |
77 | void reportStatusMessage(byte);
78 | void reportFeedbackMessage(byte);
79 | void reportMaslowSettings();
80 | void reportAlarmMessage(byte);
81 | void returnError();
82 | void returnPoz();
83 | void reportMaslowHelp();
84 |
85 | #endif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/RingBuffer.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | /*
19 | The RingBuffer module creates a circular character buffer used for storing incoming
20 | serial data.
21 | */
22 |
23 | #include "Maslow.h"
24 |
25 | RingBuffer::RingBuffer(){
26 |
27 | }
28 | int RingBuffer::write(char letter){
29 | /*
30 |
31 | Write one character into the ring buffer.
32 | Return 0 on success
33 | Return 1 on buffer overflow
34 |
35 | */
36 | if (letter != '?'){ //ignore question marks because grbl sends them all the time
37 | _buffer[_endOfString] = letter;
38 | int bufferOverflow = _incrementEnd();
39 | return bufferOverflow;
40 | }
41 | return 0;
42 | }
43 |
44 | char RingBuffer::read(){
45 | /*
46 |
47 | Read one character from the ring buffer.
48 |
49 | */
50 |
51 | char letter;
52 | if (_beginningOfString == _endOfString){
53 | letter = '\0'; //if the buffer is empty return null
54 | }
55 | else{
56 | letter = _buffer[_beginningOfString]; //else return first character
57 | _buffer[_beginningOfString] = '\0'; //set the read character to null so it cannot be read again
58 | _incrementBeginning(); //and increment the pointer
59 | }
60 |
61 | return letter;
62 | }
63 |
64 | int RingBuffer::numberOfLines() {
65 | /*
66 |
67 | Return the number of full lines (as determined by \n terminations) in the buffer
68 |
69 | */
70 |
71 | int lineCount = 0;
72 |
73 | int i = _beginningOfString;
74 | while (i != _endOfString) { // if we haven't gotten to the end of the buffer yet
75 | if(_buffer[i] == '\n'){ // check to see if the buffer contains a complete line terminated with \n
76 | lineCount++; // yes, so increment lineCount
77 | }
78 | _incrementVariable(&i); // go to the next character in the buffer
79 | }
80 |
81 | return lineCount;
82 | }
83 |
84 | void RingBuffer::readLine(String &lineToReturn){
85 | /*
86 |
87 | Return one line (terminated with \n) from the buffer
88 | if there are no full lines in the buffer, passed string will be empty
89 |
90 | */
91 | lineToReturn = ""; // begin with an empty string
92 |
93 | if (numberOfLines() > 0) { // there is at least one full line in the buffer
94 | char lastReadValue = '\0';
95 | while(lastReadValue != '\n'){ //read until the end of the line is found, building the string
96 | lastReadValue = read();
97 | lineToReturn += lastReadValue;
98 | }
99 | }
100 | }
101 |
102 | void RingBuffer::prettyReadLine(String &lineToReturn){
103 | /*
104 |
105 | Return one line (terminated with \n) from the buffer, but in all uppercase
106 | with no leading or trailing whitespaces
107 |
108 | */
109 | readLine(lineToReturn);
110 | lineToReturn.trim(); // remove leading and trailing white space
111 | lineToReturn.toUpperCase();
112 | }
113 |
114 | void RingBuffer::print(){
115 | Serial.print(F("Buffer Used: "));
116 | Serial.println(length());
117 | Serial.print(F("Buffer Number of Lines: "));
118 | Serial.println(numberOfLines());
119 | Serial.print(F("Buffer Begin: "));
120 | Serial.println(_beginningOfString);
121 | Serial.print(F("Buffer End: "));
122 | Serial.println(_endOfString);
123 |
124 | Serial.print(F("Buffer Contents: "));
125 | int i = _beginningOfString;
126 | while(i != _endOfString){
127 | if (_buffer[i] == '\n') {
128 | Serial.print(F("\\n"));
129 | }
130 | else if (_buffer[i] == '\r') {
131 | Serial.print(F("\\r"));
132 | }
133 | else if (_buffer[i] == '\t') {
134 | Serial.print(F("\\t"));
135 | }
136 | else {
137 | Serial.print(_buffer[i]);
138 | }
139 | _incrementVariable(&i);
140 | }
141 |
142 | Serial.println(F("(End of Buffer)"));
143 |
144 | }
145 |
146 | void RingBuffer::_incrementBeginning(){
147 | /*
148 |
149 | Increment the pointer to the beginning of the ring buffer by one.
150 |
151 | */
152 |
153 | if (_beginningOfString == _endOfString)
154 | return; //don't allow the beginning to pass the end
155 | else
156 | _beginningOfString = (_beginningOfString + 1) % INCBUFFERLENGTH; //move the beginning up one and wrap to zero based upon INCBUFFERLENGTH
157 | }
158 |
159 | int RingBuffer::_incrementEnd(){
160 | /*
161 |
162 | Increment the pointer to the end of the ring buffer by one.
163 |
164 | */
165 | if ( spaceAvailable() == 0 ) {
166 | Serial.println(F("Buffer overflow!"));
167 | print(); // print buffer info and contents
168 | return 1;
169 | }
170 | else
171 | _endOfString = (_endOfString+1) % INCBUFFERLENGTH;
172 | return 0;
173 | }
174 |
175 | void RingBuffer::_incrementVariable(int* variable){
176 | /*
177 | Increment the target variable.
178 | */
179 | *variable = (*variable + 1 ) % INCBUFFERLENGTH;
180 | }
181 |
182 | int RingBuffer::spaceAvailable(){
183 | /*
184 | Returns the number of characters available in the buffer
185 | */
186 | return INCBUFFERLENGTH - length() - 1;
187 | }
188 |
189 | int RingBuffer::length(void)
190 | /*
191 | Returns the number of characters held in the buffer
192 | */
193 | {
194 | if ( _endOfString >= _beginningOfString ) // Linear
195 | return _endOfString - _beginningOfString ;
196 | else // must have rolled
197 | return ( INCBUFFERLENGTH - _beginningOfString + _endOfString);
198 | }
199 |
200 |
201 | void RingBuffer::empty(){
202 | /*
203 | Empty the contents of the ring buffer
204 | */
205 |
206 | _beginningOfString = 0;
207 | _endOfString = 0;
208 | }
209 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/RingBuffer.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | #ifndef RingBuffer_h
19 | #define RingBuffer_h
20 |
21 | class RingBuffer{
22 | public:
23 | RingBuffer();
24 | int write(char letter);
25 | void print();
26 | char read();
27 | int length();
28 | int numberOfLines();
29 | int spaceAvailable();
30 | void empty();
31 | void readLine(String&);
32 | void prettyReadLine(String&);
33 | private:
34 | void _incrementBeginning();
35 | int _incrementEnd();
36 | void _incrementVariable(int* variable);
37 | int _beginningOfString = 0; //points to the first valid character which can be read
38 | int _endOfString = 0; //points to the first open space which can be written
39 | char _buffer[INCBUFFERLENGTH];
40 | };
41 |
42 | #endif
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Settings.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | // This file contains the machine settings that are saved to eeprom
19 |
20 | // EEPROM addresses 300 and up can be used by Maslow. Under 300 was used
21 | // previously by pre v1.00 Firmware.
22 |
23 | #include "Maslow.h"
24 | #include
25 |
26 | void settingsLoadFromEEprom(){
27 | /*
28 | Loads data from EEPROM if EEPROM data is valid, only called on startup
29 |
30 | Settings are stored starting at address 340 all the way up.
31 | */
32 | settingsVersion_t settingsVersionStruct;
33 | settings_t tempSettings;
34 |
35 | settingsReset(); // Load default values first
36 | EEPROM.get(300, settingsVersionStruct);
37 | EEPROM.get(340, tempSettings);
38 | if (settingsVersionStruct.settingsVersion == SETTINGSVERSION &&
39 | settingsVersionStruct.eepromValidData == EEPROMVALIDDATA &&
40 | tempSettings.eepromValidData == EEPROMVALIDDATA){
41 | sysSettings = tempSettings;
42 | }
43 | else {
44 | reportStatusMessage(STATUS_SETTING_READ_FAIL);
45 | }
46 |
47 | // Apply settings
48 | setPWMPrescalers(int(sysSettings.fPWM));
49 | kinematics.recomputeGeometry();
50 | leftAxis.changeEncoderResolution(&sysSettings.encoderSteps);
51 | rightAxis.changeEncoderResolution(&sysSettings.encoderSteps);
52 | leftAxis.changePitch(&sysSettings.distPerRot);
53 | rightAxis.changePitch(&sysSettings.distPerRot);
54 | zAxis.changePitch(&sysSettings.zDistPerRot);
55 | zAxis.changeEncoderResolution(&sysSettings.zEncoderSteps);
56 | }
57 |
58 | void settingsReset() {
59 | /*
60 | Loads default data into settings, many of these values are approximations
61 | from the an ideal stock frame. Other values are just the recommended
62 | value. Ideally we want these defaults to match the defaults in GroundControl
63 | so that if a value is not changed by a user or is not used, it doesn't
64 | need to be updated here.
65 | */
66 | sysSettings.machineWidth = 2438.4; // float machineWidth;
67 | sysSettings.machineHeight = 1219.2; // float machineHeight;
68 | sysSettings.distBetweenMotors = 2978.4; // float distBetweenMotors;
69 | sysSettings.motorOffsetY = 463.0; // float motorOffsetY;
70 | sysSettings.sledWidth = 310.0; // float sledWidth;
71 | sysSettings.sledHeight = 139.0; // float sledHeight;
72 | sysSettings.sledCG = 79.0; // float sledCG;
73 | sysSettings.kinematicsType = 1; // byte kinematicsType;
74 | sysSettings.rotationDiskRadius = 250.0; // float rotationDiskRadius;
75 | sysSettings.axisDetachTime = 2000; // int axisDetachTime;
76 | sysSettings.chainLength = 3360; // int maximum length of chain;
77 | sysSettings.originalChainLength = 1650; // int originalChainLength;
78 | sysSettings.encoderSteps = 8113.73; // float encoderSteps;
79 | sysSettings.distPerRot = 63.5; // float distPerRot;
80 | sysSettings.maxFeed = 700; // int maxFeed;
81 | sysSettings.zAxisAttached = true; // zAxisAttached;
82 | sysSettings.spindleAutomateType = NONE; // bool spindleAutomate;
83 | sysSettings.maxZRPM = 12.60; // float maxZRPM;
84 | sysSettings.zDistPerRot = 3.17; // float zDistPerRot;
85 | sysSettings.zEncoderSteps = 7560.0; // float zEncoderSteps;
86 | sysSettings.KpPos = 1300.0; // float KpPos;
87 | sysSettings.KiPos = 0.0; // float KiPos;
88 | sysSettings.KdPos = 34.0; // float KdPos;
89 | sysSettings.propWeightPos = 1.0; // float propWeightPos;
90 | sysSettings.KpV = 5.0; // float KpV;
91 | sysSettings.KiV = 0.0; // float KiV;
92 | sysSettings.KdV = 0.28; // float KdV;
93 | sysSettings.propWeightV = 1.0; // float propWeightV;
94 | sysSettings.zKdPos = 1300.0; // float zKpPos;
95 | sysSettings.zKiPos = 0.0; // float zKiPos;
96 | sysSettings.zKdPos = 34.0; // float zKdPos;
97 | sysSettings.zPropWeightPos = 1.0; // float zPropWeightPos;
98 | sysSettings.zKpV = 5.0; // float zKpV;
99 | sysSettings.zKiV = 0.0; // float zKiV;
100 | sysSettings.zKdV = 0.28; // float zKdV;
101 | sysSettings.zPropWeightV = 1.0; // float zPropWeightV;
102 | sysSettings.chainSagCorrection = 0.0; // float chainSagCorrection;
103 | sysSettings.chainOverSprocket = 1; // byte chainOverSprocket;
104 | sysSettings.fPWM = 3; // byte fPWM;
105 | sysSettings.leftChainTolerance = 0.0; // float leftChainTolerance;
106 | sysSettings.rightChainTolerance = 0.0; // float rightChainTolerance;
107 | sysSettings.positionErrorLimit = 2.0; // float positionErrorLimit;
108 | sysSettings.eepromValidData = EEPROMVALIDDATA; // byte eepromValidData;
109 | }
110 |
111 | void settingsWipe(byte resetType){
112 | /*
113 | Wipes certain bytes in the EEPROM, you probably want to reset after calling
114 | this
115 | */
116 | if (bit_istrue(resetType, SETTINGS_RESTORE_SETTINGS)){
117 | for (size_t i = 340 ; i < sizeof(sysSettings) + 340 ; i++) {
118 | EEPROM.write(i, 0);
119 | }
120 | }
121 | else if (bit_istrue(resetType, SETTINGS_RESTORE_MASLOW)){
122 | for (size_t i = 300 ; i < sizeof(sysSettings) + 340; i++) {
123 | EEPROM.write(i, 0);
124 | }
125 | }
126 | else if (bit_istrue(resetType, SETTINGS_RESTORE_ALL)){
127 | for (size_t i = 0 ; i < EEPROM.length() ; i++) {
128 | EEPROM.write(i, 0);
129 | }
130 | }
131 | }
132 |
133 | void settingsSaveToEEprom(){
134 | /*
135 | Saves settings to EEPROM, only called when settings change
136 |
137 | Settings are stored starting at address 340 all the way up.
138 | */
139 | settingsVersion_t settingsVersionStruct = {SETTINGSVERSION, EEPROMVALIDDATA};
140 | EEPROM.put(300, settingsVersionStruct);
141 | EEPROM.put(340, sysSettings);
142 | }
143 |
144 | void settingsSaveStepstoEEprom(){
145 | /*
146 | Saves position to EEPROM, is called frequently by execSystemRealtime
147 |
148 | Steps are saved in address 310 -> 339. Room for expansion for additional
149 | axes in the future.
150 | */
151 | // don't run if old position data has not been incorporated yet
152 | if (!sys.oldSettingsFlag){
153 | settingsStepsV1_t sysSteps = {
154 | leftAxis.steps(),
155 | rightAxis.steps(),
156 | zAxis.steps(),
157 | EEPROMVALIDDATA
158 | };
159 | EEPROM.put(310, sysSteps);
160 | }
161 | }
162 |
163 | void settingsLoadStepsFromEEprom(){
164 | /*
165 | Loads position to EEPROM, is called on startup.
166 |
167 | Steps are saved in address 310 -> 339. Room for expansion for additional
168 | axes in the future.
169 | */
170 | settingsStepsV1_t tempStepsV1;
171 |
172 | EEPROM.get(310, tempStepsV1);
173 | if (tempStepsV1.eepromValidData == EEPROMVALIDDATA){
174 | leftAxis.setSteps(tempStepsV1.lSteps);
175 | rightAxis.setSteps(tempStepsV1.rSteps);
176 | zAxis.setSteps(tempStepsV1.zSteps);
177 | }
178 | else if (EEPROM.read(5) == EEPROMVALIDDATA &&
179 | EEPROM.read(105) == EEPROMVALIDDATA &&
180 | EEPROM.read(205) == EEPROMVALIDDATA){
181 | bit_true(sys.oldSettingsFlag, NEED_ENCODER_STEPS);
182 | bit_true(sys.oldSettingsFlag, NEED_DIST_PER_ROT);
183 | bit_true(sys.oldSettingsFlag, NEED_Z_ENCODER_STEPS);
184 | bit_true(sys.oldSettingsFlag, NEED_Z_DIST_PER_ROT);
185 | sys.state = STATE_OLD_SETTINGS;
186 | Serial.println(F("Old position data detected."));
187 | Serial.println(F("Please set $12, $13, $19, and $20 to load position."));
188 | }
189 | else {
190 | systemRtExecAlarm |= ALARM_POSITION_LOST; // if this same global is touched by ISR then need to make atomic somehow
191 | // also need to consider if need difference between flag with bits and
192 | // error message as a byte.
193 | }
194 | }
195 |
196 | void settingsLoadOldSteps(){
197 | /*
198 | Loads the old version of step settings, only called once encoder steps
199 | and distance per rotation have been loaded. Wipes the old data once
200 | incorporated to prevent oddities in the future
201 | */
202 | if (sys.state == STATE_OLD_SETTINGS){
203 | float l, r , z;
204 | EEPROM.get(9, l);
205 | EEPROM.get(109, r);
206 | EEPROM.get(209, z);
207 | leftAxis.set(l);
208 | rightAxis.set(r);
209 | zAxis.set(z);
210 | for (int i = 0; i <= 200; i = i +100){
211 | for (int j = 5; j <= 13; j++){
212 | EEPROM.write(i + j, 0);
213 | }
214 | }
215 | sys.state = STATE_IDLE;
216 | }
217 | }
218 |
219 | byte settingsStoreGlobalSetting(const byte& parameter,const float& value){
220 | /*
221 | Alters individual settings which are then stored to EEPROM. Returns a
222 | status message byte value
223 | */
224 |
225 | // We can add whatever sanity checks we want here and error out if we like
226 | switch(parameter) {
227 | case 0: case 1: case 2: case 3: case 4: case 5: case 6: case 7: case 8:
228 | switch(parameter) {
229 | case 0:
230 | sysSettings.machineWidth = value;
231 | break;
232 | case 1:
233 | sysSettings.machineHeight = value;
234 | break;
235 | case 2:
236 | sysSettings.distBetweenMotors = value;
237 | break;
238 | case 3:
239 | sysSettings.motorOffsetY = value;
240 | break;
241 | case 4:
242 | sysSettings.sledWidth = value;
243 | break;
244 | case 5:
245 | sysSettings.sledHeight = value;
246 | break;
247 | case 6:
248 | sysSettings.sledCG = value;
249 | break;
250 | case 7:
251 | sysSettings.kinematicsType = value;
252 | break;
253 | case 8:
254 | sysSettings.rotationDiskRadius = value;
255 | break;
256 | }
257 | kinematics.init();
258 | break;
259 | case 9:
260 | sysSettings.axisDetachTime = value;
261 | break;
262 | case 10:
263 | sysSettings.chainLength = value;
264 | break;
265 | case 11:
266 | sysSettings.originalChainLength = value;
267 | break;
268 | case 12:
269 | sysSettings.encoderSteps = value;
270 | leftAxis.changeEncoderResolution(&sysSettings.encoderSteps);
271 | rightAxis.changeEncoderResolution(&sysSettings.encoderSteps);
272 | if (sys.oldSettingsFlag){
273 | bit_false(sys.oldSettingsFlag, NEED_ENCODER_STEPS);
274 | if (!sys.oldSettingsFlag){
275 | settingsLoadOldSteps();
276 | }
277 | }
278 | kinematics.init();
279 | break;
280 | case 13:
281 | sysSettings.distPerRot = value;
282 | kinematics.R = (sysSettings.distPerRot)/(2.0 * 3.14159);
283 | if (sys.oldSettingsFlag){
284 | bit_false(sys.oldSettingsFlag, NEED_DIST_PER_ROT);
285 | if (!sys.oldSettingsFlag){
286 | settingsLoadOldSteps();
287 | }
288 | }
289 | kinematics.init();
290 | break;
291 | case 15:
292 | sysSettings.maxFeed = value;
293 | break;
294 | case 16:
295 | sysSettings.zAxisAttached = value;
296 | break;
297 | case 17:
298 | sysSettings.spindleAutomateType = static_cast(value);
299 | break;
300 | case 18:
301 | sysSettings.maxZRPM = value;
302 | break;
303 | case 19:
304 | sysSettings.zDistPerRot = value;
305 | zAxis.changePitch(&sysSettings.zDistPerRot);
306 | if (sys.oldSettingsFlag){
307 | bit_false(sys.oldSettingsFlag, NEED_Z_DIST_PER_ROT);
308 | if (!sys.oldSettingsFlag){
309 | settingsLoadOldSteps();
310 | }
311 | }
312 | break;
313 | case 20:
314 | sysSettings.zEncoderSteps = value;
315 | zAxis.changeEncoderResolution(&sysSettings.zEncoderSteps);
316 | if (sys.oldSettingsFlag){
317 | bit_false(sys.oldSettingsFlag, NEED_Z_ENCODER_STEPS);
318 | if (!sys.oldSettingsFlag){
319 | settingsLoadOldSteps();
320 | }
321 | }
322 | break;
323 | case 21: case 22: case 23: case 24: case 25: case 26: case 27: case 28:
324 | switch(parameter) {
325 | case 21:
326 | sysSettings.KpPos = value;
327 | break;
328 | case 22:
329 | sysSettings.KiPos = value;
330 | break;
331 | case 23:
332 | sysSettings.KdPos = value;
333 | break;
334 | case 24:
335 | sysSettings.propWeightPos = value;
336 | break;
337 | case 25:
338 | sysSettings.KpV = value;
339 | break;
340 | case 26:
341 | sysSettings.KiV = value;
342 | break;
343 | case 27:
344 | sysSettings.KdV = value;
345 | break;
346 | case 28:
347 | sysSettings.propWeightV = value;
348 | break;
349 | }
350 | leftAxis.setPIDValues(&sysSettings.KpPos, &sysSettings.KiPos, &sysSettings.KdPos, &sysSettings.propWeightPos, &sysSettings.KpV, &sysSettings.KiV, &sysSettings.KdV, &sysSettings.propWeightV);
351 | rightAxis.setPIDValues(&sysSettings.KpPos, &sysSettings.KiPos, &sysSettings.KdPos, &sysSettings.propWeightPos, &sysSettings.KpV, &sysSettings.KiV, &sysSettings.KdV, &sysSettings.propWeightV);
352 | break;
353 | case 29: case 30: case 31: case 32: case 33: case 34: case 35: case 36:
354 | switch(parameter) {
355 | case 29:
356 | sysSettings.zKpPos = value;
357 | break;
358 | case 30:
359 | sysSettings.zKiPos = value;
360 | break;
361 | case 31:
362 | sysSettings.zKdPos = value;
363 | break;
364 | case 32:
365 | sysSettings.zPropWeightPos = value;
366 | break;
367 | case 33:
368 | sysSettings.zKpV = value;
369 | break;
370 | case 34:
371 | sysSettings.zKiV = value;
372 | break;
373 | case 35:
374 | sysSettings.zKdV = value;
375 | break;
376 | case 36:
377 | sysSettings.zPropWeightV = value;
378 | break;
379 | }
380 | zAxis.setPIDValues(&sysSettings.zKpPos, &sysSettings.zKiPos, &sysSettings.zKdPos, &sysSettings.zPropWeightPos, &sysSettings.zKpV, &sysSettings.zKiV, &sysSettings.zKdV, &sysSettings.zPropWeightV);
381 | break;
382 | case 37:
383 | sysSettings.chainSagCorrection = value;
384 | break;
385 | case 38:
386 | settingsSaveStepstoEEprom();
387 | sysSettings.chainOverSprocket = value;
388 | setupAxes();
389 | settingsLoadStepsFromEEprom();
390 | // Set initial desired position of the machine to its current position
391 | leftAxis.write(leftAxis.read());
392 | rightAxis.write(rightAxis.read());
393 | zAxis.write(zAxis.read());
394 | kinematics.init();
395 | break;
396 | case 39:
397 | sysSettings.fPWM = value;
398 | setPWMPrescalers(value);
399 | break;
400 | case 40:
401 | sysSettings.leftChainTolerance = value;
402 | break;
403 | case 41:
404 | sysSettings.rightChainTolerance = value;
405 | break;
406 | case 42:
407 | sysSettings.positionErrorLimit = value;
408 | break;
409 | default:
410 | return(STATUS_INVALID_STATEMENT);
411 | }
412 | settingsSaveToEEprom();
413 | return(STATUS_OK);
414 | }
415 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Settings.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | // This file contains the machine settings that are saved to eeprom
19 |
20 | #ifndef settings_h
21 | #define settings_h
22 |
23 | #define SETTINGSVERSION 5 // The current version of settings, if this doesn't
24 | // match what is in EEPROM then settings on
25 | // machine are reset to defaults
26 | #define EEPROMVALIDDATA 56 // This is just a random byte value that is used
27 | // to determine if the data in the EEPROM was
28 | // saved by maslow, or something else.
29 |
30 | // Reset Types
31 | #define SETTINGS_RESTORE_SETTINGS bit(0)
32 | #define SETTINGS_RESTORE_MASLOW bit(1)
33 | #define SETTINGS_RESTORE_ALL bit(2)
34 |
35 | enum SpindleAutomationType {
36 | NONE,
37 | SERVO,
38 | RELAY_ACTIVE_HIGH,
39 | RELAY_ACTIVE_LOW };
40 |
41 | typedef struct { // I think this is about ~128 bytes in size if I counted correctly
42 | float machineWidth;
43 | float machineHeight;
44 | float distBetweenMotors;
45 | float motorOffsetY;
46 | float sledWidth;
47 | float sledHeight;
48 | float sledCG;
49 | byte kinematicsType;
50 | float rotationDiskRadius;
51 | unsigned int axisDetachTime;
52 | unsigned int chainLength;
53 | unsigned int originalChainLength;
54 | float encoderSteps;
55 | float distPerRot;
56 | unsigned int maxFeed;
57 | bool zAxisAttached;
58 | SpindleAutomationType spindleAutomateType;
59 | float maxZRPM;
60 | float zDistPerRot;
61 | float zEncoderSteps;
62 | float KpPos;
63 | float KiPos;
64 | float KdPos;
65 | float propWeightPos;
66 | float KpV;
67 | float KiV;
68 | float KdV;
69 | float propWeightV;
70 | float zKpPos;
71 | float zKiPos;
72 | float zKdPos;
73 | float zPropWeightPos;
74 | float zKpV;
75 | float zKiV;
76 | float zKdV;
77 | float zPropWeightV;
78 | float chainSagCorrection;
79 | byte chainOverSprocket;
80 | byte fPWM;
81 | float leftChainTolerance;
82 | float rightChainTolerance;
83 | float positionErrorLimit;
84 | byte eepromValidData; // This should always be last, that way if an error
85 | // happens in writing, it will not be written and we
86 | } settings_t; // will know to reset the settings
87 | extern settings_t sysSettings;
88 |
89 | typedef struct {
90 | byte settingsVersion;
91 | byte eepromValidData;
92 | } settingsVersion_t;
93 |
94 | typedef struct {
95 | long lSteps;
96 | long rSteps;
97 | long zSteps;
98 | byte eepromValidData;
99 | } settingsStepsV1_t;
100 |
101 | void settingsLoadFromEEprom();
102 | void settingsReset();
103 | void settingsWipe(byte);
104 | void settingsSaveToEEprom();
105 | void settingsSaveStepstoEEprom();
106 | void settingsLoadStepsFromEEprom();
107 | byte settingsStoreGlobalSetting(const byte&,const float&);
108 |
109 | #endif
110 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/SimavrSerial.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "SimavrSerial.h"
2 |
3 | #ifdef Serial
4 | #undef Serial
5 | #endif
6 |
7 | SimavrSerial_ SimavrSerial;
8 |
9 | size_t SimavrSerial_::write(uint8_t c)
10 | {
11 | size_t n = Serial.write(c);
12 | Serial.flush();
13 |
14 | return n;
15 | }
16 |
17 | void SimavrSerial_::begin(unsigned long baud) {
18 | Serial.begin(baud);
19 | }
20 |
21 | int SimavrSerial_::available() {
22 | return Serial.available();
23 | }
24 |
25 | int SimavrSerial_::read() {
26 | return Serial.read();
27 | }
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/SimavrSerial.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include "Maslow.h"
2 |
3 | #ifndef SimavrSerial_h_
4 | #define SimavrSerial_h_
5 |
6 | #ifdef SIMAVR
7 | #define Serial SimavrSerial
8 | #endif
9 |
10 | // This class is a wrapper around Serial, to be used when running in the simavr simulator
11 | // (https://github.com/buserror/simavr)
12 | //
13 | // Simavr's UART seems to lock up and crash when you write more than a few characters to it.
14 | // SimavrSerial works around this issue by flushing after every single character. On a real
15 | // controller, this might cause a performance issue, so this class is only used if SIMAVR is defined.
16 | // If SIMAVR is defined, though, any reference to Serial is replaces to a reference to SimavrSerial.
17 | // This means that every Serial method that is used in our code also needs a wrapper in SimavrSerial,
18 | // of the simavr environment will not compile.
19 | //
20 | // Not the cleanest thing ever, but it's the best I could come up with that
21 | // will have zero impact on the actual production code.
22 | class SimavrSerial_ : public Print
23 | {
24 | public:
25 | virtual size_t write(uint8_t);
26 | virtual int available();
27 | virtual int read();
28 | void begin(unsigned long baud);
29 | };
30 |
31 | extern SimavrSerial_ SimavrSerial;
32 | #endif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Spindle.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
3 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
4 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
5 | (at your option) any later version.
6 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
7 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
8 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
9 | GNU General Public License for more details.
10 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
11 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
12 |
13 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
14 |
15 | // This contains all of the Spindle commands
16 |
17 | #include "Maslow.h"
18 | #include "Settings.h"
19 |
20 | // the variables SpindlePowerControlPin and LaserPowerPin are assigned in configAuxLow() in System.cpp
21 |
22 | // Globals for Spindle control, both poorly named
23 | Servo myservo; // create servo object to control a servo
24 |
25 | void setSpindlePower(bool powerState) {
26 | /*
27 | * Turn spindle on or off depending on powerState
28 | */
29 | SpindleAutomationType spindleAutomateType = sysSettings.spindleAutomateType;
30 |
31 | int delayAfterChange = 1000; // milliseconds
32 | int servoIdle = 90; // degrees
33 | int servoOn = 180; // degrees
34 | int servoOff = 0; // degrees
35 | int servoDelay = 2000; // milliseconds
36 |
37 | // Now for the main code
38 | #if defined (verboseDebug) && verboseDebug > 1
39 | Serial.print(F("Spindle control uses pin "));
40 | Serial.print(SpindlePowerControlPin);
41 | Serial.print(F("Spindle automation type "));
42 | Serial.print(spindleAutomateType);
43 | #endif
44 | if (spindleAutomateType == SERVO) { // use a servo to control a standard wall switch
45 | #if defined (verboseDebug) && verboseDebug > 1
46 | Serial.print(F(" with servo (idle="));
47 | Serial.print(servoIdle);
48 | Serial.print(F(", on="));
49 | Serial.print(servoOn);
50 | Serial.print(F(", off="));
51 | Serial.print(servoOff);
52 | Serial.println(F(")"));
53 | #endif
54 | myservo.attach(SpindlePowerControlPin); // start servo control
55 | myservo.write(servoIdle); // move servo to idle position
56 | maslowDelay(servoDelay); // wait for move to complete
57 | if(sys.stop){return;}
58 | if (powerState) { // turn on spindle
59 | Serial.println(F("Turning Spindle On"));
60 | myservo.write(servoOn); // move servo to turn on switch
61 | }
62 | else { // turn off spindle
63 | Serial.println(F("Turning Spindle Off"));
64 | myservo.write(servoOff); // move servo to turn off switch
65 | }
66 | maslowDelay(servoDelay); // wait for move to complete
67 | if(sys.stop){return;}
68 | myservo.write(servoIdle); // return servo to idle position
69 | maslowDelay(servoDelay); // wait for move to complete
70 | if(sys.stop){return;}
71 | myservo.detach(); // stop servo control
72 | }
73 | else if (spindleAutomateType == RELAY_ACTIVE_HIGH) {
74 | #if defined (verboseDebug) && verboseDebug > 1
75 | Serial.print(F(" as digital output, active high"));
76 | #endif
77 | pinMode(SpindlePowerControlPin, OUTPUT);
78 | if (powerState) { // turn on spindle
79 | Serial.println(F("Turning Spindle On"));
80 | digitalWrite(SpindlePowerControlPin, HIGH);
81 | }
82 | else { // turn off spindle
83 | Serial.println(F("Turning Spindle Off"));
84 | digitalWrite(SpindlePowerControlPin, LOW);
85 | }
86 | }
87 | else if (spindleAutomateType == RELAY_ACTIVE_LOW) { // use a digital I/O pin to control a relay
88 | #if defined (verboseDebug) && verboseDebug > 1
89 | Serial.print(F(" as digital output, active low"));
90 | #endif
91 | pinMode(SpindlePowerControlPin, OUTPUT);
92 | if (powerState) { // turn on spindle
93 | Serial.println(F("Turning Spindle On"));
94 | digitalWrite(SpindlePowerControlPin, LOW);
95 | }
96 | else { // turn off spindle
97 | Serial.println(F("Turning Spindle Off"));
98 | digitalWrite(SpindlePowerControlPin, HIGH);
99 | }
100 | }
101 | if (spindleAutomateType != NONE) {
102 | maslowDelay(delayAfterChange);
103 | }
104 | }
105 |
106 | void laserOn() {
107 | Serial.println("Laser on");
108 | pinMode(LaserPowerPin, OUTPUT);
109 | digitalWrite(LaserPowerPin, HIGH);
110 | }
111 |
112 | void laserOff(){
113 | Serial.println("Laser off");
114 | pinMode(LaserPowerPin, OUTPUT);
115 | digitalWrite(LaserPowerPin, LOW);
116 | }
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Spindle.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
3 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
4 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
5 | (at your option) any later version.
6 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
7 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
8 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
9 | GNU General Public License for more details.
10 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
11 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
12 |
13 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
14 |
15 | // This contains all of the Spindle commands
16 |
17 | #ifndef spindle_h
18 | #define spindle_h
19 |
20 | void setSpindlePower(bool powerState);
21 | void laserOn();
22 | void laserOff();
23 |
24 | #endif
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/System.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 |
3 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
4 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
5 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
6 | (at your option) any later version.
7 |
8 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
9 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
10 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
11 | GNU General Public License for more details.
12 |
13 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
14 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
15 |
16 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
17 |
18 | #ifndef system_h
19 | #define system_h
20 |
21 | // Convenience Defines - Maybe move into a nuts and bolts file?
22 | #define FORWARD 1
23 | #define BACKWARD -1
24 | #define CLOCKWISE -1
25 | #define COUNTERCLOCKWISE 1
26 | #define MILLIMETERS 1
27 | #define INCHES 25.4
28 |
29 | // Define various pause bits
30 | #define PAUSE_FLAG_USER_PAUSE bit(0) // a pause triggered within the code that must be cleared by user using the ~ command
31 |
32 | // Define system state bit map. The state variable primarily tracks the individual functions
33 | // of Maslow to manage each without overlapping. It is also used as a messaging flag for
34 | // critical events.
35 | #define STATE_IDLE 0 // Must be zero. No flags.
36 | #define STATE_ALARM bit(0) // In alarm state. Locks out all g-code processes. Allows settings access.
37 | #define STATE_CHECK_MODE bit(1) // G-code check mode. Locks out planner and motion only.
38 | #define STATE_OLD_SETTINGS bit(2) // Locks out all g-code processes, allows settings access until old settings are loaded
39 | #define STATE_CYCLE bit(3) // Cycle is running or motions are being executed.
40 | #define STATE_HOLD bit(4) // Active feed hold
41 | #define STATE_SAFETY_DOOR bit(5) // Safety door is ajar. Feed holds and de-energizes system.
42 | #define STATE_MOTION_CANCEL bit(6) // Motion cancel by feed hold and return to idle.
43 | #define STATE_POS_ERR_IGNORE bit(7) // Motion not checked for position error
44 |
45 | // Define old settings flag details
46 | #define NEED_ENCODER_STEPS bit(0)
47 | #define NEED_DIST_PER_ROT bit(1)
48 | #define NEED_Z_ENCODER_STEPS bit(2)
49 | #define NEED_Z_DIST_PER_ROT bit(3)
50 |
51 | // Storage for global system states
52 | // Some of this could be more appropriately moved to the gcode parser
53 | typedef struct {
54 | bool stop; // Stop flag.
55 | byte state; // State tracking flag
56 | byte pause; // Pause flag.
57 | float xPosition; // Cartessian position of XY axes
58 | float yPosition; // Cached because calculating position is intensive
59 | float steps[3]; // Encoder position of axes
60 | bool useRelativeUnits; //
61 | unsigned long lastSerialRcvd; // The millis of the last rcvd serial command, used by watchdo
62 | int lastGCommand; //Stores the value of the last command run eg: G01 -> 1
63 | int lastTool; //Stores the value of the last tool number eg: T4 -> 4
64 | int nextTool; //Stores the value of the next tool number eg: T4 -> 4
65 | float inchesToMMConversion; //Used to track whether to convert from inches, can probably be done in a way that doesn't require RAM
66 | float feedrate; //The feedrate of the machine in mm/min
67 | // THE FOLLOWING IS USED FOR IMPORTING SETTINGS FROM FIRMWARE v1.00 AND EARLIER
68 | // It can be deleted at some point
69 | byte oldSettingsFlag;
70 | } system_t;
71 | extern system_t sys;
72 | extern Axis leftAxis;
73 | extern Axis rightAxis;
74 | extern Axis zAxis;
75 | extern RingBuffer incSerialBuffer;
76 | extern Kinematics kinematics;
77 | extern byte systemRtExecAlarm;
78 | extern int SpindlePowerControlPin;
79 | extern int LaserPowerPin;
80 | extern int ProbePin;
81 |
82 | void calibrateChainLengths(String);
83 | void setupAxes();
84 | int getPCBVersion();
85 | void pause();
86 | void maslowDelay(unsigned long);
87 | void execSystemRealtime();
88 | void systemSaveAxesPosition();
89 | void systemReset();
90 | byte systemExecuteCmdstring(String&);
91 | void setPWMPrescalers(int prescalerChoice);
92 | void configAuxLow(int A1, int A2, int A3, int A4, int A5, int A6);
93 | void configAuxHigh(int A7, int A8, int A9);
94 | #endif
95 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Testing.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
3 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
4 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
5 | (at your option) any later version.
6 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
7 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
8 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
9 | GNU General Public License for more details.
10 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
11 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
12 |
13 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
14 |
15 | // This file contains various testing provisions
16 |
17 | #include "Maslow.h"
18 |
19 | void PIDTestVelocity(Axis* axis, const float start, const float stop, const float steps, const float version){
20 | // Moves the defined Axis at series of speed steps for PID tuning
21 | // Start Log
22 | Serial.println(F("--PID Velocity Test Start--"));
23 | Serial.println(axis->motorGearboxEncoder.getPIDString());
24 | if (version == 2) {
25 | Serial.println(F("setpoint,input,output"));
26 | }
27 |
28 | double startTime;
29 | double print = micros();
30 | double current = micros();
31 | float error;
32 | float reportedSpeed;
33 | float span = stop - start;
34 | float speed;
35 |
36 | // Start the steps
37 | axis->disablePositionPID();
38 | axis->attach();
39 | for(int i = 0; i < steps; i++){
40 | // 1 step = start, 2 step = start & finish, 3 = start, start + 1/2 span...
41 | speed = start;
42 | if (i > 0){
43 | speed = start + (span * (i/(steps-1)));
44 | }
45 | startTime = micros();
46 | axis->motorGearboxEncoder.write(speed);
47 | while (startTime + 2000000 > current){
48 | if (current - print > LOOPINTERVAL){
49 | if (version == 2) {
50 | Serial.println(axis->motorGearboxEncoder.pidState());
51 | }
52 | else {
53 | reportedSpeed= axis->motorGearboxEncoder.cachedSpeed();
54 | error = reportedSpeed - speed;
55 | print = current;
56 | Serial.println(error);
57 | }
58 | }
59 | current = micros();
60 | }
61 | }
62 | axis->motorGearboxEncoder.write(0);
63 |
64 | // Print end of log, and update axis for use again
65 | Serial.println(F("--PID Velocity Test Stop--\n"));
66 | axis->write(axis->read());
67 | axis->detach();
68 | axis->enablePositionPID();
69 | kinematics.forward(leftAxis.read(), rightAxis.read(), &sys.xPosition, &sys.yPosition, 0.0, 0.0);
70 | }
71 |
72 | void positionPIDOutput (Axis* axis, float setpoint, float startingPoint){
73 | Serial.print((setpoint - startingPoint), 4);
74 | Serial.print(F(","));
75 | Serial.print((axis->pidInput() - startingPoint),4);
76 | Serial.print(F(","));
77 | Serial.print(axis->pidOutput(),4);
78 | Serial.print(F(","));
79 | Serial.print(axis->motorGearboxEncoder.cachedSpeed(), 4);
80 | Serial.print(F(","));
81 | Serial.println(axis->motorGearboxEncoder.motor.lastSpeed());
82 | }
83 |
84 | void PIDTestPosition(Axis* axis, float start, float stop, const float steps, const float stepTime, const float version){
85 | // Moves the defined Axis at series of chain distance steps for PID tuning
86 | // Start Log
87 | Serial.println(F("--PID Position Test Start--"));
88 | Serial.println(axis->getPIDString());
89 | if (version == 2) {
90 | Serial.println(F("setpoint,input,output,rpminput,voltage"));
91 | }
92 |
93 | unsigned long startTime;
94 | unsigned long print = micros();
95 | unsigned long current = micros();
96 | float error;
97 | float startingPoint = axis->read();
98 | start = startingPoint + start;
99 | stop = startingPoint + stop;
100 | float span = stop - start;
101 | float location;
102 |
103 | // Start the steps
104 | axis->attach();
105 | for(int i = 0; i < steps; i++){
106 | // 1 step = start, 2 step = start & finish, 3 = start, start + 1/2 span...
107 | location = start;
108 | if (i > 0){
109 | location = start + (span * (i/(steps-1)));
110 | }
111 | startTime = micros();
112 | current = micros();
113 | axis->write(location);
114 | while (startTime + (stepTime * 1000) > current){
115 | if (current - print > LOOPINTERVAL){
116 | if (version == 2) {
117 | positionPIDOutput(axis, location, startingPoint);
118 | }
119 | else {
120 | error = axis->read() - location;
121 | Serial.println(error);
122 | }
123 | print = current;
124 | }
125 | current = micros();
126 | }
127 | }
128 | startTime = micros();
129 | current = micros();
130 | //Allow 1 seccond to settle out
131 | while (startTime + 1000000 > current){
132 | if (current - print > LOOPINTERVAL){
133 | if (version == 2) {
134 | positionPIDOutput(axis, location, startingPoint);
135 | }
136 | else {
137 | error = axis->read() - location;
138 | Serial.println(error);
139 | }
140 | print = current;
141 | }
142 | current = micros();
143 | }
144 | // Print end of log, and update axis for use again
145 | Serial.println(F("--PID Position Test Stop--\n"));
146 | axis->write(axis->read());
147 | axis->detach();
148 | kinematics.forward(leftAxis.read(), rightAxis.read(), &sys.xPosition, &sys.yPosition, 0.0, 0.0);
149 | }
150 |
151 | void voltageTest(Axis* axis, int start, int stop){
152 | // Moves the defined Axis at a series of voltages and reports the resulting
153 | // RPM
154 | Serial.println(F("--Voltage Test Start--"));
155 | int direction = 1;
156 | if (stop < start){ direction = -1;}
157 | int steps = abs(start - stop);
158 | unsigned long startTime = millis() + 200;
159 | unsigned long currentTime = millis();
160 | unsigned long printTime = 0;
161 |
162 | for (int i = 0; i <= steps; i++){
163 | axis->motorGearboxEncoder.motor.directWrite((start + (i*direction)));
164 | while (startTime > currentTime - (i * 200)){
165 | currentTime = millis();
166 | if ((printTime + 50) <= currentTime){
167 | Serial.print((start + (i*direction)));
168 | Serial.print(F(","));
169 | Serial.print(axis->motorGearboxEncoder.computeSpeed(),4);
170 | Serial.print(F("\n"));
171 | printTime = millis();
172 | }
173 | }
174 | }
175 |
176 | // Print end of log, and update axis for use again
177 | axis->motorGearboxEncoder.motor.directWrite(0);
178 | Serial.println(F("--Voltage Test Stop--\n"));
179 | axis->write(axis->read());
180 | kinematics.forward(leftAxis.read(), rightAxis.read(), &sys.xPosition, &sys.yPosition, 0.0, 0.0);
181 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/Testing.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
3 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
4 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
5 | (at your option) any later version.
6 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
7 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
8 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
9 | GNU General Public License for more details.
10 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
11 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
12 |
13 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
14 |
15 | // This file contains various testing provisions
16 |
17 | #ifndef testing_h
18 | #define testing_h
19 |
20 | void PIDTestVelocity(Axis*, const float, const float, const float, const float);
21 | void positionPIDOutput (Axis*, float, float);
22 | void PIDTestPosition(Axis*, float, float, const float, const float, const float);
23 | void voltageTest(Axis*, int, int);
24 |
25 | #endif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/TimerOne.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * Interrupt and PWM utilities for 16 bit Timer1 on ATmega168/328
3 | * Original code by Jesse Tane for http://labs.ideo.com August 2008
4 | * Modified March 2009 by Jérôme Despatis and Jesse Tane for ATmega328 support
5 | * Modified June 2009 by Michael Polli and Jesse Tane to fix a bug in setPeriod() which caused the timer to stop
6 | * Modified June 2011 by Lex Talionis to add a function to read the timer
7 | * Modified Oct 2011 by Andrew Richards to avoid certain problems:
8 | * - Add (long) assignments and casts to TimerOne::read() to ensure calculations involving tmp, ICR1 and TCNT1 aren't truncated
9 | * - Ensure 16 bit registers accesses are atomic - run with interrupts disabled when accessing
10 | * - Remove global enable of interrupts (sei())- could be running within an interrupt routine)
11 | * - Disable interrupts whilst TCTN1 == 0. Datasheet vague on this, but experiment shows that overflow interrupt
12 | * flag gets set whilst TCNT1 == 0, resulting in a phantom interrupt. Could just set to 1, but gets inaccurate
13 | * at very short durations
14 | * - startBottom() added to start counter at 0 and handle all interrupt enabling.
15 | * - start() amended to enable interrupts
16 | * - restart() amended to point at startBottom()
17 | * Modiied 7:26 PM Sunday, October 09, 2011 by Lex Talionis
18 | * - renamed start() to resume() to reflect it's actual role
19 | * - renamed startBottom() to start(). This breaks some old code that expects start to continue counting where it left off
20 | *
21 | * This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
22 | * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
23 | * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
24 | * (at your option) any later version.
25 | *
26 | * This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
27 | * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
28 | * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
29 | * GNU General Public License for more details.
30 | *
31 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
32 | * along with this program. If not, see .
33 | *
34 | * See Google Code project http://code.google.com/p/arduino-timerone/ for latest
35 | */
36 | #ifndef TIMERONE_cpp
37 | #define TIMERONE_cpp
38 |
39 | #include "Maslow.h"
40 |
41 | TimerOne Timer1; // preinstatiate
42 |
43 | ISR(TIMER1_OVF_vect) // interrupt service routine that wraps a user defined function supplied by attachInterrupt
44 | {
45 | Timer1.isrCallback();
46 | }
47 |
48 |
49 | void TimerOne::initialize(long microseconds)
50 | {
51 | TCCR1A = 0; // clear control register A
52 | TCCR1B = _BV(WGM13); // set mode 8: phase and frequency correct pwm, stop the timer
53 | setPeriod(microseconds);
54 | }
55 |
56 |
57 | void TimerOne::setPeriod(long microseconds) // AR modified for atomic access
58 | {
59 |
60 | long cycles = (F_CPU / 2000000) * microseconds; // the counter runs backwards after TOP, interrupt is at BOTTOM so divide microseconds by 2
61 | if(cycles < RESOLUTION) clockSelectBits = _BV(CS10); // no prescale, full xtal
62 | else if((cycles >>= 3) < RESOLUTION) clockSelectBits = _BV(CS11); // prescale by /8
63 | else if((cycles >>= 3) < RESOLUTION) clockSelectBits = _BV(CS11) | _BV(CS10); // prescale by /64
64 | else if((cycles >>= 2) < RESOLUTION) clockSelectBits = _BV(CS12); // prescale by /256
65 | else if((cycles >>= 2) < RESOLUTION) clockSelectBits = _BV(CS12) | _BV(CS10); // prescale by /1024
66 | else cycles = RESOLUTION - 1, clockSelectBits = _BV(CS12) | _BV(CS10); // request was out of bounds, set as maximum
67 |
68 | oldSREG = SREG;
69 | cli(); // Disable interrupts for 16 bit register access
70 | ICR1 = pwmPeriod = cycles; // ICR1 is TOP in p & f correct pwm mode
71 | SREG = oldSREG;
72 |
73 | TCCR1B &= ~(_BV(CS10) | _BV(CS11) | _BV(CS12));
74 | TCCR1B |= clockSelectBits; // reset clock select register, and starts the clock
75 | }
76 |
77 | void TimerOne::setPwmDuty(char pin, int duty)
78 | {
79 | unsigned long dutyCycle = pwmPeriod;
80 |
81 | dutyCycle *= duty;
82 | dutyCycle >>= 10;
83 |
84 | oldSREG = SREG;
85 | cli();
86 | if(pin == 1 || pin == 9) OCR1A = dutyCycle;
87 | else if(pin == 2 || pin == 10) OCR1B = dutyCycle;
88 | SREG = oldSREG;
89 | }
90 |
91 | void TimerOne::pwm(char pin, int duty, long microseconds) // expects duty cycle to be 10 bit (1024)
92 | {
93 | if(microseconds > 0) setPeriod(microseconds);
94 | if(pin == 1 || pin == 9) {
95 | DDRB |= _BV(PORTB1); // sets data direction register for pwm output pin
96 | TCCR1A |= _BV(COM1A1); // activates the output pin
97 | }
98 | else if(pin == 2 || pin == 10) {
99 | DDRB |= _BV(PORTB2);
100 | TCCR1A |= _BV(COM1B1);
101 | }
102 | setPwmDuty(pin, duty);
103 | resume(); // Lex - make sure the clock is running. We don't want to restart the count, in case we are starting the second WGM
104 | // and the first one is in the middle of a cycle
105 | }
106 |
107 | void TimerOne::disablePwm(char pin)
108 | {
109 | if(pin == 1 || pin == 9) TCCR1A &= ~_BV(COM1A1); // clear the bit that enables pwm on PB1
110 | else if(pin == 2 || pin == 10) TCCR1A &= ~_BV(COM1B1); // clear the bit that enables pwm on PB2
111 | }
112 |
113 | void TimerOne::attachInterrupt(void (*isr)(), long microseconds)
114 | {
115 | if(microseconds > 0) setPeriod(microseconds);
116 | isrCallback = isr; // register the user's callback with the real ISR
117 | TIMSK1 = _BV(TOIE1); // sets the timer overflow interrupt enable bit
118 | // might be running with interrupts disabled (eg inside an ISR), so don't touch the global state
119 | // sei();
120 | resume();
121 | }
122 |
123 | void TimerOne::detachInterrupt()
124 | {
125 | TIMSK1 &= ~_BV(TOIE1); // clears the timer overflow interrupt enable bit
126 | // timer continues to count without calling the isr
127 | }
128 |
129 | void TimerOne::resume() // AR suggested
130 | {
131 | TCCR1B |= clockSelectBits;
132 | }
133 |
134 | void TimerOne::restart() // Depricated - Public interface to start at zero - Lex 10/9/2011
135 | {
136 | start();
137 | }
138 |
139 | void TimerOne::start() // AR addition, renamed by Lex to reflect it's actual role
140 | {
141 | unsigned int tcnt1;
142 |
143 | TIMSK1 &= ~_BV(TOIE1); // AR added
144 | GTCCR |= _BV(PSRSYNC); // AR added - reset prescaler (NB: shared with all 16 bit timers);
145 |
146 | oldSREG = SREG; // AR - save status register
147 | cli(); // AR - Disable interrupts
148 | TCNT1 = 0;
149 | SREG = oldSREG; // AR - Restore status register
150 | resume();
151 | do { // Nothing -- wait until timer moved on from zero - otherwise get a phantom interrupt
152 | oldSREG = SREG;
153 | cli();
154 | tcnt1 = TCNT1;
155 | SREG = oldSREG;
156 | } while (tcnt1==0);
157 |
158 | // TIFR1 = 0xff; // AR - Clear interrupt flags
159 | // TIMSK1 = _BV(TOIE1); // sets the timer overflow interrupt enable bit
160 | }
161 |
162 | void TimerOne::stop()
163 | {
164 | TCCR1B &= ~(_BV(CS10) | _BV(CS11) | _BV(CS12)); // clears all clock selects bits
165 | }
166 |
167 | unsigned long TimerOne::read() //returns the value of the timer in microseconds
168 | { //rember! phase and freq correct mode counts up to then down again
169 | unsigned long tmp; // AR amended to hold more than 65536 (could be nearly double this)
170 | unsigned int tcnt1; // AR added
171 |
172 | oldSREG= SREG;
173 | cli();
174 | tmp=TCNT1;
175 | SREG = oldSREG;
176 |
177 | char scale=0;
178 | switch (clockSelectBits)
179 | {
180 | case 1:// no prescalse
181 | scale=0;
182 | break;
183 | case 2:// x8 prescale
184 | scale=3;
185 | break;
186 | case 3:// x64
187 | scale=6;
188 | break;
189 | case 4:// x256
190 | scale=8;
191 | break;
192 | case 5:// x1024
193 | scale=10;
194 | break;
195 | }
196 |
197 | do { // Nothing -- max delay here is ~1023 cycles. AR modified
198 | oldSREG = SREG;
199 | cli();
200 | tcnt1 = TCNT1;
201 | SREG = oldSREG;
202 | } while (tcnt1==tmp); //if the timer has not ticked yet
203 |
204 | //if we are counting down add the top value to how far we have counted down
205 | tmp = ( (tcnt1>tmp) ? (tmp) : (long)(ICR1-tcnt1)+(long)ICR1 ); // AR amended to add casts and reuse previous TCNT1
206 | return ((tmp*1000L)/(F_CPU /1000L))<.
33 | *
34 | * See Google Code project http://code.google.com/p/arduino-timerone/ for latest
35 | */
36 | #ifndef TIMERONE_h
37 | #define TIMERONE_h
38 |
39 | #define RESOLUTION 65536 // Timer1 is 16 bit
40 |
41 | class TimerOne
42 | {
43 | public:
44 |
45 | // properties
46 | unsigned int pwmPeriod;
47 | unsigned char clockSelectBits;
48 | char oldSREG; // To hold Status Register while ints disabled
49 |
50 | // methods
51 | void initialize(long microseconds=1000000);
52 | void start();
53 | void stop();
54 | void restart();
55 | void resume();
56 | unsigned long read();
57 | void pwm(char pin, int duty, long microseconds=-1);
58 | void disablePwm(char pin);
59 | void attachInterrupt(void (*isr)(), long microseconds=-1);
60 | void detachInterrupt();
61 | void setPeriod(long microseconds);
62 | void setPwmDuty(char pin, int duty);
63 | void (*isrCallback)();
64 | };
65 |
66 | extern TimerOne Timer1;
67 | #endif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/cnc_ctrl_v1.ino:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*This file is part of the Maslow Control Software.
2 | The Maslow Control Software is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
3 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
4 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
5 | (at your option) any later version.
6 | Maslow Control Software is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
7 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
8 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
9 | GNU General Public License for more details.
10 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
11 | along with the Maslow Control Software. If not, see .
12 |
13 | Copyright 2014-2017 Bar Smith*/
14 |
15 |
16 | /* To the projects contributers:
17 | *
18 | * it is highly recommended to activate warning output of the arduino gcc compiler.
19 | * Compiler warnings are a great help to keep the codebase clean and can give clues
20 | * to potentally wrong code. Also, if a codebase produces too many warnings it gets
21 | * more likely that possibly important warnings could be overlooked.
22 | *
23 | * Since the Arduino IDE suppresses any compiler output by default we have to activate it.
24 | *
25 | * Therefore Arduino IDE users need to activate compiler output in the
26 | * preferences dialog. Additionally Arduino IDE needs to tell the compiler to generate
27 | * warning messages. This is done in the Arduino IDE's preferences.txt file - you can
28 | * get there via the Preferences Dialog - there is a link to the file at the bottom.
29 | * Edit the line "compiler.warning_level=none" to "compiler.warning_level=all"
30 | * and restart the IDE.
31 | */
32 |
33 |
34 | // TLE5206 version
35 |
36 | #include "Maslow.h"
37 |
38 | // Define system global state structure
39 | system_t sys;
40 |
41 | // Define the global settings storage - treat as readonly
42 | settings_t sysSettings;
43 |
44 | // Global realtime executor bitflag variable for setting various alarms.
45 | byte systemRtExecAlarm;
46 |
47 | // Define axes, it might be tighter to define these within the sys struct
48 | Axis leftAxis;
49 | Axis rightAxis;
50 | Axis zAxis;
51 |
52 | // Define kinematics, is it necessary for this to be a class? Is this really
53 | // going to be reused?
54 | Kinematics kinematics;
55 |
56 | void setup(){
57 | Serial.begin(57600);
58 | Serial.print(F("PCB v1."));
59 | Serial.print(getPCBVersion());
60 | if (TLE5206 == true) { Serial.print(F(" TLE5206 ")); }
61 | Serial.println(F(" Detected"));
62 | sys.inchesToMMConversion = 1;
63 | settingsLoadFromEEprom();
64 | setupAxes();
65 | settingsLoadStepsFromEEprom();
66 | // Set initial desired position of the machine to its current position
67 | leftAxis.write(leftAxis.read());
68 | rightAxis.write(rightAxis.read());
69 | zAxis.write(zAxis.read());
70 | readyCommandString.reserve(INCBUFFERLENGTH); //Allocate memory so that this string doesn't fragment the heap as it grows and shrinks
71 | gcodeLine.reserve(INCBUFFERLENGTH);
72 |
73 | #ifndef SIMAVR // Using the timer will crash simavr, so we disable it.
74 | // Instead, we'll run runsOnATimer periodically in loop().
75 | Timer1.initialize(LOOPINTERVAL);
76 | Timer1.attachInterrupt(runsOnATimer);
77 | #endif
78 |
79 | Serial.println(F("Grbl v1.00")); // Why GRBL? Apparently because some programs are silly and look for this as an initialization command
80 | Serial.println(F("ready"));
81 | reportStatusMessage(STATUS_OK);
82 |
83 | }
84 |
85 | void runsOnATimer(){
86 | #if misloopDebug > 0
87 | if (inMovementLoop && !movementUpdated){
88 | movementFail = true;
89 | }
90 | #endif
91 | movementUpdated = false;
92 | leftAxis.computePID();
93 | rightAxis.computePID();
94 | zAxis.computePID();
95 | }
96 |
97 | void loop(){
98 | // This section is called on startup and whenever a stop command is issued
99 | initGCode();
100 | if (sys.stop){ // only called on sys.stop to prevent stopping
101 | initMotion(); // on USB disconnect. Might consider removing
102 | setSpindlePower(false); // this restriction for safety if we are
103 | } // comfortable that USB disconnects are
104 | // not a common occurrence anymore
105 | kinematics.init();
106 |
107 | // Let's go!
108 | sys.stop = false; // We should consider an abort option which
109 | // is not reset automatically such as a software
110 | // limit
111 | while (!sys.stop){
112 | gcodeExecuteLoop();
113 | #ifdef SIMAVR // Normally, runsOnATimer() will, well, run on a timer. See also setup().
114 | runsOnATimer();
115 | #endif
116 | execSystemRealtime();
117 | }
118 | }
119 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/utility/direct_pin_read.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef direct_pin_read_h_
2 | #define direct_pin_read_h_
3 |
4 | #if defined(__AVR__) || defined(__MK20DX128__) || defined(__MK20DX256__)
5 |
6 | #define IO_REG_TYPE uint8_t
7 | #define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (portInputRegister(digitalPinToPort(pin)))
8 | #define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (digitalPinToBitMask(pin))
9 | #define DIRECT_PIN_READ(base, mask) (((*(base)) & (mask)) ? 1 : 0)
10 |
11 | #elif defined(__SAM3X8E__)
12 |
13 | #define IO_REG_TYPE uint32_t
14 | #define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (portInputRegister(digitalPinToPort(pin)))
15 | #define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (digitalPinToBitMask(pin))
16 | #define DIRECT_PIN_READ(base, mask) (((*(base)) & (mask)) ? 1 : 0)
17 |
18 | #elif defined(__PIC32MX__)
19 |
20 | #define IO_REG_TYPE uint32_t
21 | #define PIN_TO_BASEREG(pin) (portModeRegister(digitalPinToPort(pin)))
22 | #define PIN_TO_BITMASK(pin) (digitalPinToBitMask(pin))
23 | #define DIRECT_PIN_READ(base, mask) (((*(base+4)) & (mask)) ? 1 : 0)
24 |
25 | #endif
26 |
27 | #endif
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/utility/interrupt_config.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #if defined(__AVR__)
2 |
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 |
6 | #define attachInterrupt(num, func, mode) enableInterrupt(num)
7 | #if defined(__AVR_ATmega1280__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega2560__)
8 | #define SCRAMBLE_INT_ORDER(num) ((num < 4) ? num + 2 : ((num < 6) ? num - 4 : num))
9 | #define DESCRAMBLE_INT_ORDER(num) ((num < 2) ? num + 4 : ((num < 6) ? num - 2 : num))
10 | #else
11 | #define SCRAMBLE_INT_ORDER(num) (num)
12 | #define DESCRAMBLE_INT_ORDER(num) (num)
13 | #endif
14 |
15 | static void enableInterrupt(uint8_t num)
16 | {
17 | switch (DESCRAMBLE_INT_ORDER(num)) {
18 | #if defined(EICRA) && defined(EIMSK)
19 | case 0:
20 | EICRA = (EICRA & 0xFC) | 0x01;
21 | EIMSK |= 0x01;
22 | return;
23 | case 1:
24 | EICRA = (EICRA & 0xF3) | 0x04;
25 | EIMSK |= 0x02;
26 | return;
27 | case 2:
28 | EICRA = (EICRA & 0xCF) | 0x10;
29 | EIMSK |= 0x04;
30 | return;
31 | case 3:
32 | EICRA = (EICRA & 0x3F) | 0x40;
33 | EIMSK |= 0x08;
34 | return;
35 | #elif defined(MCUCR) && defined(GICR)
36 | case 0:
37 | MCUCR = (MCUCR & ~((1 << ISC00) | (1 << ISC01))) | (mode << ISC00);
38 | GICR |= (1 << INT0);
39 | return;
40 | case 1:
41 | MCUCR = (MCUCR & ~((1 << ISC10) | (1 << ISC11))) | (mode << ISC10);
42 | GICR |= (1 << INT1);
43 | return;
44 | #elif defined(MCUCR) && defined(GIMSK)
45 | case 0:
46 | MCUCR = (MCUCR & ~((1 << ISC00) | (1 << ISC01))) | (mode << ISC00);
47 | GIMSK |= (1 << INT0);
48 | return;
49 | case 1:
50 | MCUCR = (MCUCR & ~((1 << ISC10) | (1 << ISC11))) | (mode << ISC10);
51 | GIMSK |= (1 << INT1);
52 | return;
53 | #endif
54 | #if defined(EICRB) && defined(EIMSK)
55 | case 4:
56 | EICRB = (EICRB & 0xFC) | 0x01;
57 | EIMSK |= 0x10;
58 | return;
59 | case 5:
60 | EICRB = (EICRB & 0xF3) | 0x04;
61 | EIMSK |= 0x20;
62 | return;
63 | case 6:
64 | EICRB = (EICRB & 0xCF) | 0x10;
65 | EIMSK |= 0x40;
66 | return;
67 | case 7:
68 | EICRB = (EICRB & 0x3F) | 0x40;
69 | EIMSK |= 0x80;
70 | return;
71 | #endif
72 | }
73 | }
74 |
75 | #elif defined(__PIC32MX__)
76 |
77 | #ifdef ENCODER_OPTIMIZE_INTERRUPTS
78 | #undef ENCODER_OPTIMIZE_INTERRUPTS
79 | #endif
80 |
81 | #else
82 |
83 | #ifdef ENCODER_OPTIMIZE_INTERRUPTS
84 | #undef ENCODER_OPTIMIZE_INTERRUPTS
85 | #endif
86 |
87 | #endif
88 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/cnc_ctrl_v1/utility/interrupt_pins.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | // interrupt pins for known boards
2 |
3 | // Teensy (and maybe others) define these automatically
4 | #if !defined(CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT)
5 |
6 | // Wiring boards
7 | #if defined(WIRING)
8 | #define CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT NUM_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPTS
9 | #if NUM_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPTS > 0
10 | #define CORE_INT0_PIN EI0
11 | #endif
12 | #if NUM_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPTS > 1
13 | #define CORE_INT1_PIN EI1
14 | #endif
15 | #if NUM_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPTS > 2
16 | #define CORE_INT2_PIN EI2
17 | #endif
18 | #if NUM_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPTS > 3
19 | #define CORE_INT3_PIN EI3
20 | #endif
21 | #if NUM_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPTS > 4
22 | #define CORE_INT4_PIN EI4
23 | #endif
24 | #if NUM_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPTS > 5
25 | #define CORE_INT5_PIN EI5
26 | #endif
27 | #if NUM_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPTS > 6
28 | #define CORE_INT6_PIN EI6
29 | #endif
30 | #if NUM_EXTERNAL_INTERRUPTS > 7
31 | #define CORE_INT7_PIN EI7
32 | #endif
33 |
34 | // Arduino Uno, Duemilanove, Diecimila, LilyPad, Mini, Fio, etc...
35 | #elif defined(__AVR_ATmega328P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega168__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega8__)
36 | #define CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT 2
37 | #define CORE_INT0_PIN 2
38 | #define CORE_INT1_PIN 3
39 |
40 | // Arduino Mega
41 | #elif defined(__AVR_ATmega1280__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega2560__)
42 | #define CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT 6
43 | #define CORE_INT0_PIN 2
44 | #define CORE_INT1_PIN 3
45 | #define CORE_INT2_PIN 21
46 | #define CORE_INT3_PIN 20
47 | #define CORE_INT4_PIN 19
48 | #define CORE_INT5_PIN 18
49 |
50 | // Arduino Leonardo (untested)
51 | #elif defined(__AVR_ATmega32U4__) && !defined(CORE_TEENSY)
52 | #define CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT 4
53 | #define CORE_INT0_PIN 3
54 | #define CORE_INT1_PIN 2
55 | #define CORE_INT2_PIN 0
56 | #define CORE_INT3_PIN 1
57 |
58 | // Sanguino (untested)
59 | #elif defined(__AVR_ATmega644P__) || defined(__AVR_ATmega644__)
60 | #define CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT 3
61 | #define CORE_INT0_PIN 10
62 | #define CORE_INT1_PIN 11
63 | #define CORE_INT2_PIN 2
64 |
65 | // Chipkit Uno32 - attachInterrupt may not support CHANGE option
66 | #elif defined(__PIC32MX__) && defined(_BOARD_UNO_)
67 | #define CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT 5
68 | #define CORE_INT0_PIN 38
69 | #define CORE_INT1_PIN 2
70 | #define CORE_INT2_PIN 7
71 | #define CORE_INT3_PIN 8
72 | #define CORE_INT4_PIN 35
73 |
74 | // Chipkit Uno32 - attachInterrupt may not support CHANGE option
75 | #elif defined(__PIC32MX__) && defined(_BOARD_MEGA_)
76 | #define CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT 5
77 | #define CORE_INT0_PIN 3
78 | #define CORE_INT1_PIN 2
79 | #define CORE_INT2_PIN 7
80 | #define CORE_INT3_PIN 21
81 | #define CORE_INT4_PIN 20
82 |
83 | // http://hlt.media.mit.edu/?p=1229
84 | #elif defined(__AVR_ATtiny45__) || defined(__AVR_ATtiny85__)
85 | #define CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT 1
86 | #define CORE_INT0_PIN 2
87 |
88 | // Arduino Due (untested)
89 | #elif defined(__SAM3X8E__)
90 | #define CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT 54
91 | #define CORE_INT0_PIN 0
92 | #define CORE_INT1_PIN 1
93 | #define CORE_INT2_PIN 2
94 | #define CORE_INT3_PIN 3
95 | #define CORE_INT4_PIN 4
96 | #define CORE_INT5_PIN 5
97 | #define CORE_INT6_PIN 6
98 | #define CORE_INT7_PIN 7
99 | #define CORE_INT8_PIN 8
100 | #define CORE_INT9_PIN 9
101 | #define CORE_INT10_PIN 10
102 | #define CORE_INT11_PIN 11
103 | #define CORE_INT12_PIN 12
104 | #define CORE_INT13_PIN 13
105 | #define CORE_INT14_PIN 14
106 | #define CORE_INT15_PIN 15
107 | #define CORE_INT16_PIN 16
108 | #define CORE_INT17_PIN 17
109 | #define CORE_INT18_PIN 18
110 | #define CORE_INT19_PIN 19
111 | #define CORE_INT20_PIN 20
112 | #define CORE_INT21_PIN 21
113 | #define CORE_INT22_PIN 22
114 | #define CORE_INT23_PIN 23
115 | #define CORE_INT24_PIN 24
116 | #define CORE_INT25_PIN 25
117 | #define CORE_INT26_PIN 26
118 | #define CORE_INT27_PIN 27
119 | #define CORE_INT28_PIN 28
120 | #define CORE_INT29_PIN 29
121 | #define CORE_INT30_PIN 30
122 | #define CORE_INT31_PIN 31
123 | #define CORE_INT32_PIN 32
124 | #define CORE_INT33_PIN 33
125 | #define CORE_INT34_PIN 34
126 | #define CORE_INT35_PIN 35
127 | #define CORE_INT36_PIN 36
128 | #define CORE_INT37_PIN 37
129 | #define CORE_INT38_PIN 38
130 | #define CORE_INT39_PIN 39
131 | #define CORE_INT40_PIN 40
132 | #define CORE_INT41_PIN 41
133 | #define CORE_INT42_PIN 42
134 | #define CORE_INT43_PIN 43
135 | #define CORE_INT44_PIN 44
136 | #define CORE_INT45_PIN 45
137 | #define CORE_INT46_PIN 46
138 | #define CORE_INT47_PIN 47
139 | #define CORE_INT48_PIN 48
140 | #define CORE_INT49_PIN 49
141 | #define CORE_INT50_PIN 50
142 | #define CORE_INT51_PIN 51
143 | #define CORE_INT52_PIN 52
144 | #define CORE_INT53_PIN 53
145 |
146 | #endif
147 | #endif
148 |
149 | #if !defined(CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT)
150 | #error "Interrupts are unknown for this board, please add to this code"
151 | #endif
152 | #if CORE_NUM_INTERRUPT <= 0
153 | #error "Encoder requires interrupt pins, but this board does not have any :("
154 | #error "You could try defining ENCODER_DO_NOT_USE_INTERRUPTS as a kludge."
155 | #endif
156 |
157 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/guestBook.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | ****************************
3 | -=%* *%=-
4 | * MaslowCNC Guest Book *
5 | -=%* *%=-
6 | ****************************
7 |
8 | The guest book is a way to say hello, practice contributing to the project, and put your name in the project! Write your name! Put a message to prove you were here!
9 |
10 | Bar was here - 1/1/17
11 |
12 | Bar was back for the weekly Wednesday update!
13 |
14 | Kim was here too - 1/11/2017
15 |
16 | Thanks for all the great work! Thomas Kristensen (Denmark) - 12/1/2017
17 |
18 | Can't wait to get my Maslow. Keep going! Benedict (Germany) - 12/1/2017
19 |
20 | Andrew was here January 12, 2017
21 |
22 | jbnimble - January 14, 2017
23 |
24 | jbarchuk March 3 2017 New to git at this level. The more I see it the more I like.
25 |
26 | jwolter0 (Ohio, USA) - March 25, 2017 - Figuring out how to use git on my Linux machine. There's no GitHub Desktop for Linux, so I'm learning how to do it from the command line like the cavemen used to.
27 |
28 | TheRiflesSpiral - confusedly contributing correspondence concordently. 3/30/17
29 |
30 | seware74 - When 900 years old, you reach… Look as good, you will not. Hmm. - 5/26/2017
31 |
32 | ladams00 - Can't wait for Maslow to show up at my door! Jan 7th 2018
33 |
34 | Bar - Back to update the how to contribute page for the new look of GitHub :)
35 |
36 | I'm Batman.
37 |
38 | Tanju B - Hello! we finally making cuts down at the Maker Station makerspace in Marietta, GA. Finally! 18-Feb-2018
39 |
40 | Maslow Bahrain (GeroBH) made it into the guestBook ;-) 21 Feb 2018
41 |
42 | Morriz was here - 9/5/2018
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/mainpicture.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Firmware-1.24/mainpicture.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/platformio.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ; PlatformIO Project Configuration File
2 | ;
3 | ; Build options: build flags, source filter
4 | ; Upload options: custom upload port, speed and extra flags
5 | ; Library options: dependencies, extra library storages
6 | ; Advanced options: extra scripting
7 | ;
8 | ; Please visit documentation for the other options and examples
9 | ; http://docs.platformio.org/page/projectconf.html
10 |
11 | [platformio]
12 | src_dir = cnc_ctrl_v1
13 |
14 | [env:megaatmega2560]
15 | platform = atmelavr
16 | board = megaatmega2560
17 | framework = arduino
18 |
19 | [env:simavr]
20 | platform = atmelavr
21 | board = megaatmega2560
22 | framework = arduino
23 | extra_scripts = platformio/simavr_env.py
24 | build_unflags = -Os
25 | build_flags = -g -O0 -DSIMAVR -DFAKE_SERVO
26 | monitor_port = /tmp/simavr-uart0
27 |
28 | ;[env:teensy36]
29 | ;platform = teensy
30 | ;board = teensy36
31 | ;framework = arduino
32 | ;extra_scripts = platformio/teensy_env.py
33 |
34 | ;[env:teensy35]
35 | ;platform = teensy
36 | ;board = teensy35
37 | ;framework = arduino
38 | ;extra_scripts = platformio/teensy_env.py
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/platformio/simavr_env.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from SCons.Script import ARGUMENTS, AlwaysBuild
2 |
3 | Import('env')
4 |
5 | # Run the linker with "-g", to prevent stripping of debugging symbols
6 | env.Append(
7 | LINKFLAGS=[
8 | "-g"
9 | ]
10 | )
11 |
12 | # Don't try to upload the firmware
13 | env.Replace(UPLOADHEXCMD="echo Upload is not supported for ${PIOENV}. Skipping")
14 |
15 | pioenv = env.get("PIOENV")
16 | progname = env.get("PROGNAME")
17 |
18 | def simulate_callback(*args, **kwargs):
19 | env.Execute("./simduino/simduino .pioenvs/" + pioenv + "/" + progname + ".elf")
20 |
21 | AlwaysBuild(env.Alias("simulate", "", simulate_callback))
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Firmware-1.24/platformio/teensy_env.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 |
3 | Import('env')
4 |
5 | varname = env.get("PIOENV") + "_UPLOAD"
6 |
7 | if varname in os.environ:
8 | print "$"+ varname + " is set, enabling upload."
9 | else:
10 | # Don't try to upload the firmware
11 | env.Replace(UPLOADHEXCMD="echo Upload is disabled by default for ${PIOENV}. " +
12 | "To enable upload, set " + varname + "environment variable")
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/INSTRUCTIONS.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Head over to [Maker Made](http:www.makermade.com/shop) to order.
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Sled Ring Kit
2 |
3 |
4 | 
5 |
6 | # Sled Ring Kit
7 |
8 | ## Maslow/M2 CNC Universal Ring Kit Component by MakerMade
9 |
10 |
11 | Ring and bearing kit that ensures smooth and accurate cuts on your Maslow CNC.
12 |
13 | Includes:
14 | * Sled ring
15 | * 4 ring bearings
16 | * 3 L-brackets
17 | * 2 carriage brackets.
18 |
19 | *All MakerMade’s CNC Maslow kits come with a ring kit included.*
20 |
21 | ### ***Use promo code MASLOW10 for 10% off your order!***
22 |
23 | Head over to [MakerMade](https://makermade.com/collections/all/products/maslow-m2-cnc-universal-ring-kit-component) to order!
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ROBOT.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "ModerationLevel": "customManaged",
3 | "Facilitator": "skilescm",
4 | "Price":"$79",
5 | "Category": "market"
6 | }
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Ring_Kit.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/Ring_Kit.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mainpicture.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MaslowCommunityGarden/CNC-Compression-Bit/fcf2d4d49632e6302f3956f970cd157669506163/mainpicture.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/usrinput.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | CNC Compression Bit~1/4" CNC Compression Bit~customManaged~skilescm~Market
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------