67. Add Binary
Easy
Given two binary strings a and b, return their sum as a binary string.
4 |
Example 1:
5 |Input: a = "11", b = "1" 6 | Output: "100" 7 |
Example 2:
8 |Input: a = "1010", b = "1011" 9 | Output: "10101" 10 |11 |
12 |
Constraints:
13 | 14 |-
15 |
1 <= a.length, b.length <= 104
16 | aandbconsist only of'0'or'1'characters.
17 | - Each string does not contain leading zeros except for the zero itself. 18 |
Medium
Given an integer n, break it into the sum of k positive integers, where k >= 2, and maximize the product of those integers.
Return the maximum product you can get.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: n = 2 9 | Output: 1 10 | Explanation: 2 = 1 + 1, 1 × 1 = 1. 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: n = 10 16 | Output: 36 17 | Explanation: 10 = 3 + 3 + 4, 3 × 3 × 4 = 36. 18 |19 | 20 |
21 |
Constraints:
22 | 23 |-
24 |
2 <= n <= 58
25 |
976. Largest Perimeter Triangle
Easy
Given an integer array nums, return the largest perimeter of a triangle with a non-zero area, formed from three of these lengths. If it is impossible to form any triangle of a non-zero area, return 0.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: nums = [2,1,2] 7 | Output: 5 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: nums = [1,2,1] 13 | Output: 0 14 |15 | 16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
3 <= nums.length <= 104
21 | 1 <= nums[i] <= 106
22 |
1287. Element Appearing More Than 25% In Sorted Array
Easy
Given an integer array sorted in non-decreasing order, there is exactly one integer in the array that occurs more than 25% of the time, return that integer.
2 | 3 |4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: arr = [1,2,2,6,6,6,6,7,10] 7 | Output: 6 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: arr = [1,1] 13 | Output: 1 14 |15 | 16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
1 <= arr.length <= 104
21 | 0 <= arr[i] <= 105
22 |
131. Palindrome Partitioning
Medium
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome. Return all possible palindrome partitioning of s.
4 |
Example 1:
5 |Input: s = "aab" 6 | Output: [["a","a","b"],["aa","b"]] 7 |
Example 2:
8 |Input: s = "a" 9 | Output: [["a"]] 10 |11 |
12 |
Constraints:
13 | 14 |-
15 |
1 <= s.length <= 16
16 | scontains only lowercase English letters.
17 |
491. Non-decreasing Subsequences
Medium
Given an integer array nums, return all the different possible non-decreasing subsequences of the given array with at least two elements. You may return the answer in any order.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: nums = [4,6,7,7] 7 | Output: [[4,6],[4,6,7],[4,6,7,7],[4,7],[4,7,7],[6,7],[6,7,7],[7,7]] 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: nums = [4,4,3,2,1] 13 | Output: [[4,4]] 14 |15 | 16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
1 <= nums.length <= 15
21 | -100 <= nums[i] <= 100
22 |
5. Longest Palindromic Substring
Medium
Given a string s, return the longest palindromic substring in s.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: s = "babad" 7 | Output: "bab" 8 | Explanation: "aba" is also a valid answer. 9 |10 | 11 |
Example 2:
12 | 13 |Input: s = "cbbd" 14 | Output: "bb" 15 |16 | 17 |
18 |
Constraints:
19 | 20 |-
21 |
1 <= s.length <= 1000
22 | sconsist of only digits and English letters.
23 |
70. Climbing Stairs
Easy
You are climbing a staircase. It takes n steps to reach the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: n = 2 9 | Output: 2 10 | Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top. 11 | 1. 1 step + 1 step 12 | 2. 2 steps 13 |14 | 15 |
Example 2:
16 | 17 |Input: n = 3 18 | Output: 3 19 | Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top. 20 | 1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step 21 | 2. 1 step + 2 steps 22 | 3. 2 steps + 1 step 23 |24 | 25 |
26 |
Constraints:
27 | 28 |-
29 |
1 <= n <= 45
30 |
515. Find Largest Value in Each Tree Row
Medium
Given the root of a binary tree, return an array of the largest value in each row of the tree (0-indexed).
4 |
Example 1:
5 |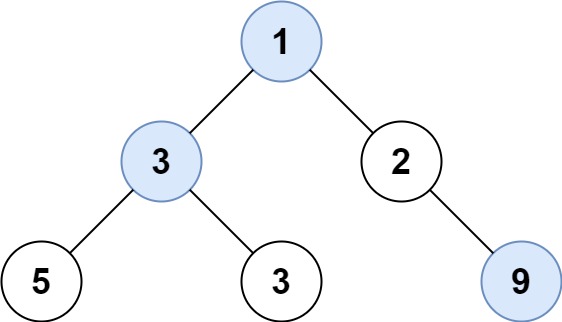 6 |
6 | Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9] 7 | Output: [1,3,9] 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: root = [1,2,3] 13 | Output: [1,3] 14 |15 | 16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
- The number of nodes in the tree will be in the range
[0, 104].
21 | -231 <= Node.val <= 231 - 1
22 |
342. Power of Four
Easy
Given an integer n, return true if it is a power of four. Otherwise, return false.
An integer n is a power of four, if there exists an integer x such that n == 4x.
6 |
Example 1:
7 |Input: n = 16 8 | Output: true 9 |
Example 2:
10 |Input: n = 5 11 | Output: false 12 |
Example 3:
13 |Input: n = 1 14 | Output: true 15 |16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
-231 <= n <= 231 - 1
21 |
24 | Follow up: Could you solve it without loops/recursion?
61. Rotate List
Medium
Given the head of a linked list, rotate the list to the right by k places.
4 |
Example 1:
5 |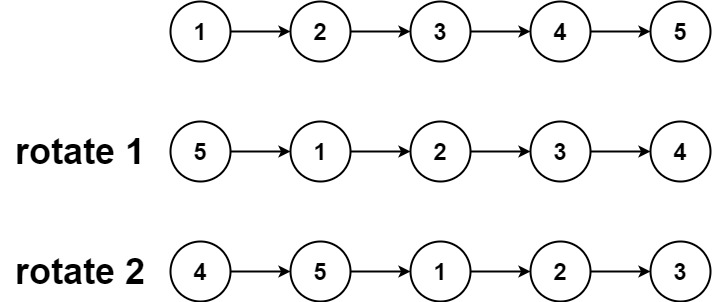 6 |
6 | Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2 7 | Output: [4,5,1,2,3] 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 |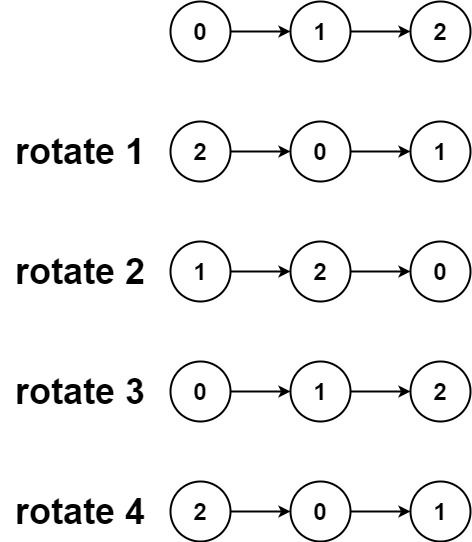 12 |
12 | Input: head = [0,1,2], k = 4 13 | Output: [2,0,1] 14 |15 | 16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[0, 500].
21 | -100 <= Node.val <= 100
22 | 0 <= k <= 2 * 109
23 |
169. Majority Element
Easy
Given an array nums of size n, return the majority element.
The majority element is the element that appears more than ⌊n / 2⌋ times. You may assume that the majority element always exists in the array.
6 |
Example 1:
7 |Input: nums = [3,2,3] 8 | Output: 3 9 |
Example 2:
10 |Input: nums = [2,2,1,1,1,2,2] 11 | Output: 2 12 |13 |
14 |
Constraints:
15 | 16 |-
17 |
n == nums.length
18 | 1 <= n <= 5 * 104
19 | -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
20 |
23 | Follow-up: Could you solve the problem in linear time and in
O(1) space?128. Longest Consecutive Sequence
Medium
Given an unsorted array of integers nums, return the length of the longest consecutive elements sequence.
You must write an algorithm that runs in O(n) time.
6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: nums = [100,4,200,1,3,2]
9 | Output: 4
10 | Explanation: The longest consecutive elements sequence is [1, 2, 3, 4]. Therefore its length is 4.
11 |
12 |
13 | Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: nums = [0,3,7,2,5,8,4,6,0,1] 16 | Output: 9 17 |18 | 19 |
20 |
Constraints:
21 | 22 |-
23 |
0 <= nums.length <= 105
24 | -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
25 |
389. Find the Difference
Easy
You are given two strings s and t.
String t is generated by random shuffling string s and then add one more letter at a random position.
Return the letter that was added to t.
8 |
Example 1:
9 | 10 |Input: s = "abcd", t = "abcde" 11 | Output: "e" 12 | Explanation: 'e' is the letter that was added. 13 |14 | 15 |
Example 2:
16 | 17 |Input: s = "", t = "y" 18 | Output: "y" 19 |20 | 21 |
22 |
Constraints:
23 | 24 |-
25 |
0 <= s.length <= 1000
26 | t.length == s.length + 1
27 | sandtconsist of lowercase English letters.
28 |
229. Majority Element II
Medium
Given an integer array of size n, find all elements that appear more than ⌊ n/3 ⌋ times.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: nums = [3,2,3] 7 | Output: [3] 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: nums = [1] 13 | Output: [1] 14 |15 | 16 |
Example 3:
17 | 18 |Input: nums = [1,2] 19 | Output: [1,2] 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
1 <= nums.length <= 5 * 104
27 | -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
28 |
31 |
Follow up: Could you solve the problem in linear time and in O(1) space?
Medium
Given a string s, return the number of palindromic substrings in it.
A string is a palindrome when it reads the same backward as forward.
4 | 5 |A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within the string.
6 | 7 |8 |
Example 1:
9 | 10 |Input: s = "abc" 11 | Output: 3 12 | Explanation: Three palindromic strings: "a", "b", "c". 13 |14 | 15 |
Example 2:
16 | 17 |Input: s = "aaa" 18 | Output: 6 19 | Explanation: Six palindromic strings: "a", "a", "a", "aa", "aa", "aaa". 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
1 <= s.length <= 1000
27 | sconsists of lowercase English letters.
28 |
Hard
Given a string containing just the characters '(' and ')', find the length of the longest valid (well-formed) parentheses substring.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: s = "(()" 7 | Output: 2 8 | Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()". 9 |10 | 11 |
Example 2:
12 | 13 |Input: s = ")()())" 14 | Output: 4 15 | Explanation: The longest valid parentheses substring is "()()". 16 |17 | 18 |
Example 3:
19 | 20 |Input: s = "" 21 | Output: 0 22 |23 | 24 |
25 |
Constraints:
26 | 27 |-
28 |
0 <= s.length <= 3 * 104
29 | s[i]is'(', or')'.
30 |
520. Detect Capital
Easy
We define the usage of capitals in a word to be right when one of the following cases holds:
2 | 3 |-
4 |
- All letters in this word are capitals, like
"USA".
5 | - All letters in this word are not capitals, like
"leetcode".
6 | - Only the first letter in this word is capital, like
"Google".
7 |
Given a string word, return true if the usage of capitals in it is right.
12 |
Example 1:
13 |Input: word = "USA" 14 | Output: true 15 |
Example 2:
16 |Input: word = "FlaG" 17 | Output: false 18 |19 |
20 |
Constraints:
21 | 22 |-
23 |
1 <= word.length <= 100
24 | wordconsists of lowercase and uppercase English letters.
25 |
557. Reverse Words in a String III
Easy
Given a string s, reverse the order of characters in each word within a sentence while still preserving whitespace and initial word order.
4 |
Example 1:
5 |Input: s = "Let's take LeetCode contest" 6 | Output: "s'teL ekat edoCteeL tsetnoc" 7 |
Example 2:
8 |Input: s = "God Ding" 9 | Output: "doG gniD" 10 |11 |
12 |
Constraints:
13 | 14 |-
15 |
1 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
16 | scontains printable ASCII characters.
17 | sdoes not contain any leading or trailing spaces.
18 | - There is at least one word in
s.
19 | - All the words in
sare separated by a single space.
20 |
647. Palindromic Substrings
Medium
Given a string s, return the number of palindromic substrings in it.
A string is a palindrome when it reads the same backward as forward.
4 | 5 |A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within the string.
6 | 7 |8 |
Example 1:
9 | 10 |Input: s = "abc" 11 | Output: 3 12 | Explanation: Three palindromic strings: "a", "b", "c". 13 |14 | 15 |
Example 2:
16 | 17 |Input: s = "aaa" 18 | Output: 6 19 | Explanation: Six palindromic strings: "a", "a", "a", "aa", "aa", "aaa". 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
1 <= s.length <= 1000
27 | sconsists of lowercase English letters.
28 |
907. Sum of Subarray Minimums
Medium
Given an array of integers arr, find the sum of min(b), where b ranges over every (contiguous) subarray of arr. Since the answer may be large, return the answer modulo 109 + 7.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: arr = [3,1,2,4] 7 | Output: 17 8 | Explanation: 9 | Subarrays are [3], [1], [2], [4], [3,1], [1,2], [2,4], [3,1,2], [1,2,4], [3,1,2,4]. 10 | Minimums are 3, 1, 2, 4, 1, 1, 2, 1, 1, 1. 11 | Sum is 17. 12 |13 | 14 |
Example 2:
15 | 16 |Input: arr = [11,81,94,43,3] 17 | Output: 444 18 |19 | 20 |
21 |
Constraints:
22 | 23 |-
24 |
1 <= arr.length <= 3 * 104
25 | 1 <= arr[i] <= 3 * 104
26 |
94. Binary Tree Inorder Traversal
Easy
Given the root of a binary tree, return the inorder traversal of its nodes' values.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |
6 | Input: root = [1,null,2,3] 7 | Output: [1,3,2] 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: root = [] 13 | Output: [] 14 |15 | 16 |
Example 3:
17 | 18 |Input: root = [1] 19 | Output: [1] 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100].
27 | -100 <= Node.val <= 100
28 |
31 | Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
1207. Unique Number of Occurrences
Easy
Given an array of integers arr, return true if the number of occurrences of each value in the array is unique or false otherwise.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: arr = [1,2,2,1,1,3] 7 | Output: true 8 | Explanation: The value 1 has 3 occurrences, 2 has 2 and 3 has 1. No two values have the same number of occurrences.9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: arr = [1,2] 13 | Output: false 14 |15 | 16 |
Example 3:
17 | 18 |Input: arr = [-3,0,1,-3,1,1,1,-3,10,0] 19 | Output: true 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
1 <= arr.length <= 1000
27 | -1000 <= arr[i] <= 1000
28 |
219. Contains Duplicate II
Easy
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return true if there are two distinct indices i and j in the array such that nums[i] == nums[j] and abs(i - j) <= k.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: nums = [1,2,3,1], k = 3 7 | Output: true 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: nums = [1,0,1,1], k = 1 13 | Output: true 14 |15 | 16 |
Example 3:
17 | 18 |Input: nums = [1,2,3,1,2,3], k = 2 19 | Output: false 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
1 <= nums.length <= 105
27 | -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
28 | 0 <= k <= 105
29 |
1832. Check if the Sentence Is Pangram
Easy
A pangram is a sentence where every letter of the English alphabet appears at least once.
2 | 3 |Given a string sentence containing only lowercase English letters, return true if sentence is a pangram, or false otherwise.
6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: sentence = "thequickbrownfoxjumpsoverthelazydog" 9 | Output: true 10 | Explanation: sentence contains at least one of every letter of the English alphabet. 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: sentence = "leetcode" 16 | Output: false 17 |18 | 19 |
20 |
Constraints:
21 | 22 |-
23 |
1 <= sentence.length <= 1000
24 | sentenceconsists of lowercase English letters.
25 |
144. Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
Easy
Given the root of a binary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes' values.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |
6 | Input: root = [1,null,2,3] 7 | Output: [1,2,3] 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: root = [] 13 | Output: [] 14 |15 | 16 |
Example 3:
17 | 18 |Input: root = [1] 19 | Output: [1] 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[0, 100].
27 | -100 <= Node.val <= 100
28 |
31 |
Follow up: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
32 |242. Valid Anagram
Easy
Given two strings s and t, return true if t is an anagram of s, and false otherwise.
An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 |Input: s = "anagram", t = "nagaram" 8 | Output: true 9 |
Example 2:
10 |Input: s = "rat", t = "car" 11 | Output: false 12 |13 |
14 |
Constraints:
15 | 16 |-
17 |
1 <= s.length, t.length <= 5 * 104
18 | sandtconsist of lowercase English letters.
19 |
22 |
Follow up: What if the inputs contain Unicode characters? How would you adapt your solution to such a case?
23 |645. Set Mismatch
Easy
You have a set of integers s, which originally contains all the numbers from 1 to n. Unfortunately, due to some error, one of the numbers in s got duplicated to another number in the set, which results in repetition of one number and loss of another number.
You are given an integer array nums representing the data status of this set after the error.
Find the number that occurs twice and the number that is missing and return them in the form of an array.
6 | 7 |8 |
Example 1:
9 |Input: nums = [1,2,2,4] 10 | Output: [2,3] 11 |
Example 2:
12 |Input: nums = [1,1] 13 | Output: [1,2] 14 |15 |
16 |
Constraints:
17 | 18 |-
19 |
2 <= nums.length <= 104
20 | 1 <= nums[i] <= 104
21 |
974. Subarray Sums Divisible by K
Medium
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the number of non-empty subarrays that have a sum divisible by k.
A subarray is a contiguous part of an array.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: nums = [4,5,0,-2,-3,1], k = 5 9 | Output: 7 10 | Explanation: There are 7 subarrays with a sum divisible by k = 5: 11 | [4, 5, 0, -2, -3, 1], [5], [5, 0], [5, 0, -2, -3], [0], [0, -2, -3], [-2, -3] 12 |13 | 14 |
Example 2:
15 | 16 |Input: nums = [5], k = 9 17 | Output: 0 18 |19 | 20 |
21 |
Constraints:
22 | 23 |-
24 |
1 <= nums.length <= 3 * 104
25 | -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
26 | 2 <= k <= 104
27 |
1512. Number of Good Pairs
Easy
Given an array of integers nums, return the number of good pairs.
A pair (i, j) is called good if nums[i] == nums[j] and i < j.
6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: nums = [1,2,3,1,1,3] 9 | Output: 4 10 | Explanation: There are 4 good pairs (0,3), (0,4), (3,4), (2,5) 0-indexed. 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: nums = [1,1,1,1] 16 | Output: 6 17 | Explanation: Each pair in the array are good. 18 |19 | 20 |
Example 3:
21 | 22 |Input: nums = [1,2,3] 23 | Output: 0 24 |25 | 26 |
27 |
Constraints:
28 | 29 |-
30 |
1 <= nums.length <= 100
31 | 1 <= nums[i] <= 100
32 |
Medium
Given an array of strings strs, group the anagrams together. You can return the answer in any order.
An Anagram is a word or phrase formed by rearranging the letters of a different word or phrase, typically using all the original letters exactly once.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 |Input: strs = ["eat","tea","tan","ate","nat","bat"] 8 | Output: [["bat"],["nat","tan"],["ate","eat","tea"]] 9 |
Example 2:
10 |Input: strs = [""] 11 | Output: [[""]] 12 |
Example 3:
13 |Input: strs = ["a"] 14 | Output: [["a"]] 15 |16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
1 <= strs.length <= 104
21 | 0 <= strs[i].length <= 100
22 | strs[i]consists of lowercase English letters.
23 |
55. Jump Game
Medium
You are given an integer array nums. You are initially positioned at the array's first index, and each element in the array represents your maximum jump length at that position.
Return true if you can reach the last index, or false otherwise.
6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: nums = [2,3,1,1,4] 9 | Output: true 10 | Explanation: Jump 1 step from index 0 to 1, then 3 steps to the last index. 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: nums = [3,2,1,0,4] 16 | Output: false 17 | Explanation: You will always arrive at index 3 no matter what. Its maximum jump length is 0, which makes it impossible to reach the last index. 18 |19 | 20 |
21 |
Constraints:
22 | 23 |-
24 |
1 <= nums.length <= 104
25 | 0 <= nums[i] <= 105
26 |
347. Top K Frequent Elements
Medium
Given an integer array nums and an integer k, return the k most frequent elements. You may return the answer in any order.
4 |
Example 1:
5 |Input: nums = [1,1,1,2,2,3], k = 2 6 | Output: [1,2] 7 |
Example 2:
8 |Input: nums = [1], k = 1 9 | Output: [1] 10 |11 |
12 |
Constraints:
13 | 14 |-
15 |
1 <= nums.length <= 105
16 | -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
17 | kis in the range[1, the number of unique elements in the array].
18 | - It is guaranteed that the answer is unique. 19 |
22 |
Follow up: Your algorithm's time complexity must be better than O(n log n), where n is the array's size.
16. 3Sum Closest
Medium
Given an integer array nums of length n and an integer target, find three integers in nums such that the sum is closest to target.
Return the sum of the three integers.
4 | 5 |You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution.
6 | 7 |8 |
Example 1:
9 | 10 |Input: nums = [-1,2,1,-4], target = 1 11 | Output: 2 12 | Explanation: The sum that is closest to the target is 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2). 13 |14 | 15 |
Example 2:
16 | 17 |Input: nums = [0,0,0], target = 1 18 | Output: 0 19 | Explanation: The sum that is closest to the target is 0. (0 + 0 + 0 = 0). 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
3 <= nums.length <= 1000
27 | -1000 <= nums[i] <= 1000
28 | -104 <= target <= 104
29 |
739. Daily Temperatures
Medium
Given an array of integers temperatures represents the daily temperatures, return an array answer such that answer[i] is the number of days you have to wait after the ith day to get a warmer temperature. If there is no future day for which this is possible, keep answer[i] == 0 instead.
4 |
Example 1:
5 |Input: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73] 6 | Output: [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0] 7 |
Example 2:
8 |Input: temperatures = [30,40,50,60] 9 | Output: [1,1,1,0] 10 |
Example 3:
11 |Input: temperatures = [30,60,90] 12 | Output: [1,1,0] 13 |14 |
15 |
Constraints:
16 | 17 |-
18 |
1 <= temperatures.length <= 105
19 | 30 <= temperatures[i] <= 100
20 |
119. Pascal's Triangle II
Easy
Given an integer rowIndex, return the rowIndexth (0-indexed) row of the Pascal's triangle.
In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it as shown:
4 | 5 |
5 | 6 |
Example 1:
7 |Input: rowIndex = 3 8 | Output: [1,3,3,1] 9 |
Example 2:
10 |Input: rowIndex = 0 11 | Output: [1] 12 |
Example 3:
13 |Input: rowIndex = 1 14 | Output: [1,1] 15 |16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
0 <= rowIndex <= 33
21 |
24 |
Follow up: Could you optimize your algorithm to use only O(rowIndex) extra space?
867. Transpose Matrix
Easy
Given a 2D integer array matrix, return the transpose of matrix.
The transpose of a matrix is the matrix flipped over its main diagonal, switching the matrix's row and column indices.
4 | 5 |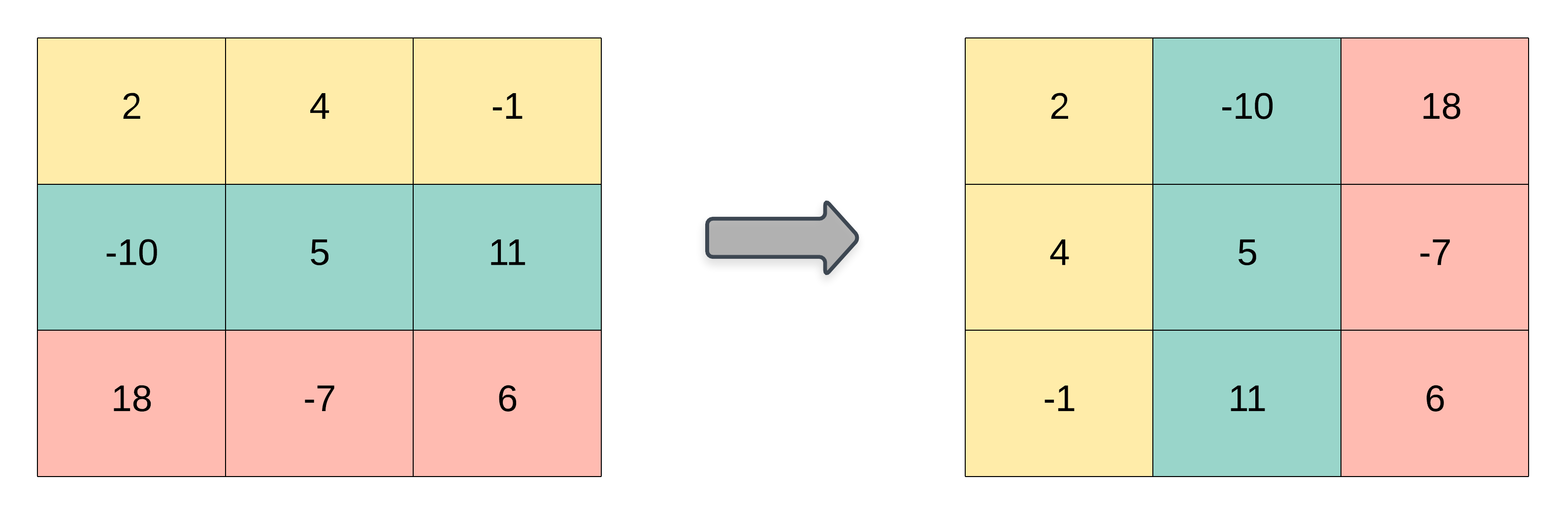
8 |
Example 1:
9 | 10 |Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 11 | Output: [[1,4,7],[2,5,8],[3,6,9]] 12 |13 | 14 |
Example 2:
15 | 16 |Input: matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6]] 17 | Output: [[1,4],[2,5],[3,6]] 18 |19 | 20 |
21 |
Constraints:
22 | 23 |-
24 |
m == matrix.length
25 | n == matrix[i].length
26 | 1 <= m, n <= 1000
27 | 1 <= m * n <= 105
28 | -109 <= matrix[i][j] <= 109
29 |
50. Pow(x, n)
Medium
Implement pow(x, n), which calculates x raised to the power n (i.e., xn).
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: x = 2.00000, n = 10 7 | Output: 1024.00000 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |Input: x = 2.10000, n = 3 13 | Output: 9.26100 14 |15 | 16 |
Example 3:
17 | 18 |Input: x = 2.00000, n = -2 19 | Output: 0.25000 20 | Explanation: 2-2 = 1/22 = 1/4 = 0.25 21 |22 | 23 |
24 |
Constraints:
25 | 26 |-
27 |
-100.0 < x < 100.0
28 | -231 <= n <= 231-1
29 | nis an integer.
30 | - Either
xis not zero orn > 0.
31 | -104 <= xn <= 104
32 |
149. Max Points on a Line
Hard
Given an array of points where points[i] = [xi, yi] represents a point on the X-Y plane, return the maximum number of points that lie on the same straight line.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |
6 | Input: points = [[1,1],[2,2],[3,3]] 7 | Output: 3 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |
12 | Input: points = [[1,1],[3,2],[5,3],[4,1],[2,3],[1,4]] 13 | Output: 4 14 |15 | 16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
1 <= points.length <= 300
21 | points[i].length == 2
22 | -104 <= xi, yi <= 104
23 | - All the
pointsare unique.
24 |
876. Middle of the Linked List
Easy
Given the head of a singly linked list, return the middle node of the linked list.
If there are two middle nodes, return the second middle node.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |
8 | Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5] 9 | Output: [3,4,5] 10 | Explanation: The middle node of the list is node 3. 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |
15 | Input: head = [1,2,3,4,5,6] 16 | Output: [4,5,6] 17 | Explanation: Since the list has two middle nodes with values 3 and 4, we return the second one. 18 |19 | 20 |
21 |
Constraints:
22 | 23 |-
24 |
- The number of nodes in the list is in the range
[1, 100].
25 | 1 <= Node.val <= 100
26 |
4. Median of Two Sorted Arrays
Hard
Given two sorted arrays nums1 and nums2 of size m and n respectively, return the median of the two sorted arrays.
The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: nums1 = [1,3], nums2 = [2] 9 | Output: 2.00000 10 | Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3] and median is 2. 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: nums1 = [1,2], nums2 = [3,4] 16 | Output: 2.50000 17 | Explanation: merged array = [1,2,3,4] and median is (2 + 3) / 2 = 2.5. 18 |19 | 20 |
21 |
Constraints:
22 | 23 |-
24 |
nums1.length == m
25 | nums2.length == n
26 | 0 <= m <= 1000
27 | 0 <= n <= 1000
28 | 1 <= m + n <= 2000
29 | -106 <= nums1[i], nums2[i] <= 106
30 |
300. Longest Increasing Subsequence
Medium
Given an integer array nums, return the length of the longest strictly increasing subsequence.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: nums = [10,9,2,5,3,7,101,18] 7 | Output: 4 8 | Explanation: The longest increasing subsequence is [2,3,7,101], therefore the length is 4. 9 |10 | 11 |
Example 2:
12 | 13 |Input: nums = [0,1,0,3,2,3] 14 | Output: 4 15 |16 | 17 |
Example 3:
18 | 19 |Input: nums = [7,7,7,7,7,7,7] 20 | Output: 1 21 |22 | 23 |
24 |
Constraints:
25 | 26 |-
27 |
1 <= nums.length <= 2500
28 | -104 <= nums[i] <= 104
29 |
32 |
Follow up: Can you come up with an algorithm that runs in O(n log(n)) time complexity?
653. Two Sum IV - Input is a BST
Easy
Given the root of a Binary Search Tree and a target number k, return true if there exist two elements in the BST such that their sum is equal to the given target.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |
6 | Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 9 7 | Output: true 8 |9 | 10 |
Example 2:
11 | 12 |
12 | Input: root = [5,3,6,2,4,null,7], k = 28 13 | Output: false 14 |15 | 16 |
17 |
Constraints:
18 | 19 |-
20 |
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 104].
21 | -104 <= Node.val <= 104
22 | rootis guaranteed to be a valid binary search tree.
23 | -105 <= k <= 105
24 |
629. K Inverse Pairs Array
Hard
For an integer array nums, an inverse pair is a pair of integers [i, j] where 0 <= i < j < nums.length and nums[i] > nums[j].
Given two integers n and k, return the number of different arrays consist of numbers from 1 to n such that there are exactly k inverse pairs. Since the answer can be huge, return it modulo 109 + 7.
6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: n = 3, k = 0 9 | Output: 1 10 | Explanation: Only the array [1,2,3] which consists of numbers from 1 to 3 has exactly 0 inverse pairs. 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: n = 3, k = 1 16 | Output: 2 17 | Explanation: The array [1,3,2] and [2,1,3] have exactly 1 inverse pair. 18 |19 | 20 |
21 |
Constraints:
22 | 23 |-
24 |
1 <= n <= 1000
25 | 0 <= k <= 1000
26 |
322. Coin Change
Medium
You are given an integer array coins representing coins of different denominations and an integer amount representing a total amount of money.
Return the fewest number of coins that you need to make up that amount. If that amount of money cannot be made up by any combination of the coins, return -1.
You may assume that you have an infinite number of each kind of coin.
6 | 7 |8 |
Example 1:
9 | 10 |Input: coins = [1,2,5], amount = 11 11 | Output: 3 12 | Explanation: 11 = 5 + 5 + 1 13 |14 | 15 |
Example 2:
16 | 17 |Input: coins = [2], amount = 3 18 | Output: -1 19 |20 | 21 |
Example 3:
22 | 23 |Input: coins = [1], amount = 0 24 | Output: 0 25 |26 | 27 |
28 |
Constraints:
29 | 30 |-
31 |
1 <= coins.length <= 12
32 | 1 <= coins[i] <= 231 - 1
33 | 0 <= amount <= 104
34 |
3. Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters
Medium
Given a string s, find the length of the longest substring without repeating characters.
4 |
Example 1:
5 | 6 |Input: s = "abcabcbb" 7 | Output: 3 8 | Explanation: The answer is "abc", with the length of 3. 9 |10 | 11 |
Example 2:
12 | 13 |Input: s = "bbbbb" 14 | Output: 1 15 | Explanation: The answer is "b", with the length of 1. 16 |17 | 18 |
Example 3:
19 | 20 |Input: s = "pwwkew" 21 | Output: 3 22 | Explanation: The answer is "wke", with the length of 3. 23 | Notice that the answer must be a substring, "pwke" is a subsequence and not a substring. 24 |25 | 26 |
27 |
Constraints:
28 | 29 |-
30 |
0 <= s.length <= 5 * 104
31 | sconsists of English letters, digits, symbols and spaces.
32 |
1624. Largest Substring Between Two Equal Characters
Easy
Given a string s, return the length of the longest substring between two equal characters, excluding the two characters. If there is no such substring return -1.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: s = "aa"
9 | Output: 0
10 | Explanation: The optimal substring here is an empty substring between the two 'a's.
11 |
12 | Example 2:
13 | 14 |Input: s = "abca" 15 | Output: 2 16 | Explanation: The optimal substring here is "bc". 17 |18 | 19 |
Example 3:
20 | 21 |Input: s = "cbzxy" 22 | Output: -1 23 | Explanation: There are no characters that appear twice in s. 24 |25 | 26 |
27 |
Constraints:
28 | 29 |-
30 |
1 <= s.length <= 300
31 | scontains only lowercase English letters.
32 |
100. Same Tree
Easy
Given the roots of two binary trees p and q, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 |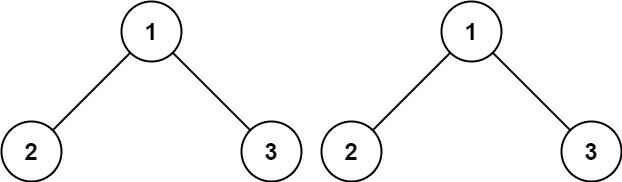 8 |
8 | Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3] 9 | Output: true 10 |11 | 12 |
Example 2:
13 |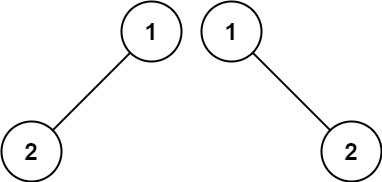 14 |
14 | Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2] 15 | Output: false 16 |17 | 18 |
Example 3:
19 |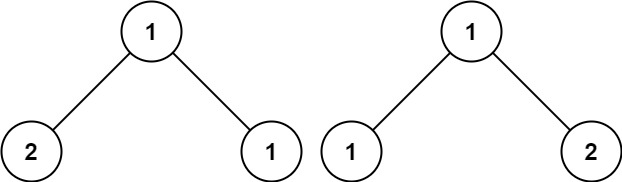 20 |
20 | Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2] 21 | Output: false 22 |23 | 24 |
25 |
Constraints:
26 | 27 |-
28 |
- The number of nodes in both trees is in the range
[0, 100].
29 | -104 <= Node.val <= 104
30 |
790. Domino and Tromino Tiling
Medium
You have two types of tiles: a 2 x 1 domino shape and a tromino shape. You may rotate these shapes.
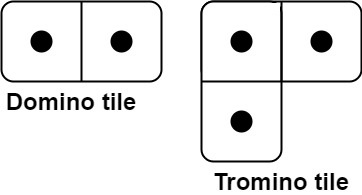 3 |
3 | Given an integer n, return the number of ways to tile an 2 x n board. Since the answer may be very large, return it modulo 109 + 7.
In a tiling, every square must be covered by a tile. Two tilings are different if and only if there are two 4-directionally adjacent cells on the board such that exactly one of the tilings has both squares occupied by a tile.
6 | 7 |8 |
Example 1:
9 |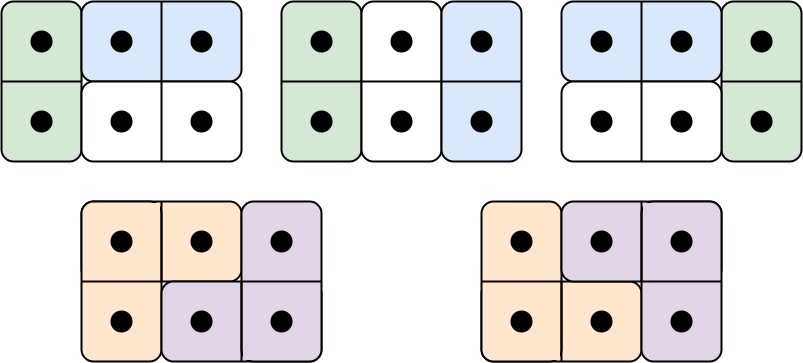 10 |
10 | Input: n = 3 11 | Output: 5 12 | Explanation: The five different ways are show above. 13 |14 | 15 |
Example 2:
16 | 17 |Input: n = 1 18 | Output: 1 19 |20 | 21 |
22 |
Constraints:
23 | 24 |-
25 |
1 <= n <= 1000
26 |
34. Find First and Last Position of Element in Sorted Array
Medium
Given an array of integers nums sorted in non-decreasing order, find the starting and ending position of a given target value.
If target is not found in the array, return [-1, -1].
You must write an algorithm with O(log n) runtime complexity.
8 |
Example 1:
9 |Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 8 10 | Output: [3,4] 11 |
Example 2:
12 |Input: nums = [5,7,7,8,8,10], target = 6 13 | Output: [-1,-1] 14 |
Example 3:
15 |Input: nums = [], target = 0 16 | Output: [-1,-1] 17 |18 |
19 |
Constraints:
20 | 21 |-
22 |
0 <= nums.length <= 105
23 | -109 <= nums[i] <= 109
24 | numsis a non-decreasing array.
25 | -109 <= target <= 109
26 |
823. Binary Trees With Factors
Medium
Given an array of unique integers, arr, where each integer arr[i] is strictly greater than 1.
We make a binary tree using these integers, and each number may be used for any number of times. Each non-leaf node's value should be equal to the product of the values of its children.
4 | 5 |Return the number of binary trees we can make. The answer may be too large so return the answer modulo 109 + 7.
8 |
Example 1:
9 | 10 |Input: arr = [2,4]
11 | Output: 3
12 | Explanation: We can make these trees: [2], [4], [4, 2, 2]
13 |
14 | Example 2:
15 | 16 |Input: arr = [2,4,5,10]
17 | Output: 7
18 | Explanation: We can make these trees: [2], [4], [5], [10], [4, 2, 2], [10, 2, 5], [10, 5, 2].
19 |
20 | 21 |
Constraints:
22 | 23 |-
24 |
1 <= arr.length <= 1000
25 | 2 <= arr[i] <= 109
26 | - All the values of
arrare unique.
27 |
1356. Sort Integers by The Number of 1 Bits
Easy
You are given an integer array arr. Sort the integers in the array in ascending order by the number of 1's in their binary representation and in case of two or more integers have the same number of 1's you have to sort them in ascending order.
Return the array after sorting it.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: arr = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8] 9 | Output: [0,1,2,4,8,3,5,6,7] 10 | Explantion: [0] is the only integer with 0 bits. 11 | [1,2,4,8] all have 1 bit. 12 | [3,5,6] have 2 bits. 13 | [7] has 3 bits. 14 | The sorted array by bits is [0,1,2,4,8,3,5,6,7] 15 |16 | 17 |
Example 2:
18 | 19 |Input: arr = [1024,512,256,128,64,32,16,8,4,2,1] 20 | Output: [1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128,256,512,1024] 21 | Explantion: All integers have 1 bit in the binary representation, you should just sort them in ascending order. 22 |23 | 24 |
25 |
Constraints:
26 | 27 |-
28 |
1 <= arr.length <= 500
29 | 0 <= arr[i] <= 104
30 |
617. Merge Two Binary Trees
Easy
You are given two binary trees root1 and root2.
Imagine that when you put one of them to cover the other, some nodes of the two trees are overlapped while the others are not. You need to merge the two trees into a new binary tree. The merge rule is that if two nodes overlap, then sum node values up as the new value of the merged node. Otherwise, the NOT null node will be used as the node of the new tree.
4 | 5 |Return the merged tree.
6 | 7 |Note: The merging process must start from the root nodes of both trees.
8 | 9 |10 |
Example 1:
11 | 12 |
12 | Input: root1 = [1,3,2,5], root2 = [2,1,3,null,4,null,7] 13 | Output: [3,4,5,5,4,null,7] 14 |15 | 16 |
Example 2:
17 | 18 |Input: root1 = [1], root2 = [1,2] 19 | Output: [2,2] 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
- The number of nodes in both trees is in the range
[0, 2000].
27 | -104 <= Node.val <= 104
28 |
1793. Maximum Score of a Good Subarray
Hard
You are given an array of integers nums (0-indexed) and an integer k.
The score of a subarray (i, j) is defined as min(nums[i], nums[i+1], ..., nums[j]) * (j - i + 1). A good subarray is a subarray where i <= k <= j.
Return the maximum possible score of a good subarray.
6 | 7 |8 |
Example 1:
9 | 10 |Input: nums = [1,4,3,7,4,5], k = 3 11 | Output: 15 12 | Explanation: The optimal subarray is (1, 5) with a score of min(4,3,7,4,5) * (5-1+1) = 3 * 5 = 15. 13 |14 | 15 |
Example 2:
16 | 17 |Input: nums = [5,5,4,5,4,1,1,1], k = 0 18 | Output: 20 19 | Explanation: The optimal subarray is (0, 4) with a score of min(5,5,4,5,4) * (4-0+1) = 4 * 5 = 20. 20 |21 | 22 |
23 |
Constraints:
24 | 25 |-
26 |
1 <= nums.length <= 105
27 | 1 <= nums[i] <= 2 * 104
28 | 0 <= k < nums.length
29 |
2433. Find The Original Array of Prefix Xor
Medium
You are given an integer array pref of size n. Find and return the array arr of size n that satisfies:
-
4 |
pref[i] = arr[0] ^ arr[1] ^ ... ^ arr[i].
5 |
Note that ^ denotes the bitwise-xor operation.
It can be proven that the answer is unique.
10 | 11 |12 |
Example 1:
13 | 14 |Input: pref = [5,2,0,3,1] 15 | Output: [5,7,2,3,2] 16 | Explanation: From the array [5,7,2,3,2] we have the following: 17 | - pref[0] = 5. 18 | - pref[1] = 5 ^ 7 = 2. 19 | - pref[2] = 5 ^ 7 ^ 2 = 0. 20 | - pref[3] = 5 ^ 7 ^ 2 ^ 3 = 3. 21 | - pref[4] = 5 ^ 7 ^ 2 ^ 3 ^ 2 = 1. 22 |23 | 24 |
Example 2:
25 | 26 |Input: pref = [13] 27 | Output: [13] 28 | Explanation: We have pref[0] = arr[0] = 13. 29 |30 | 31 |
32 |
Constraints:
33 | 34 |-
35 |
1 <= pref.length <= 105
36 | 0 <= pref[i] <= 106
37 |
290. Word Pattern
Easy
Given a pattern and a string s, find if s follows the same pattern.
Here follow means a full match, such that there is a bijection between a letter in pattern and a non-empty word in s.
6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: pattern = "abba", s = "dog cat cat dog" 9 | Output: true 10 |11 | 12 |
Example 2:
13 | 14 |Input: pattern = "abba", s = "dog cat cat fish" 15 | Output: false 16 |17 | 18 |
Example 3:
19 | 20 |Input: pattern = "aaaa", s = "dog cat cat dog" 21 | Output: false 22 |23 | 24 |
25 |
Constraints:
26 | 27 |-
28 |
1 <= pattern.length <= 300
29 | patterncontains only lower-case English letters.
30 | 1 <= s.length <= 3000
31 | scontains only lowercase English letters and spaces' '.
32 | sdoes not contain any leading or trailing spaces.
33 | - All the words in
sare separated by a single space.
34 |
1903. Largest Odd Number in String
Easy
You are given a string num, representing a large integer. Return the largest-valued odd integer (as a string) that is a non-empty substring of num, or an empty string "" if no odd integer exists.
A substring is a contiguous sequence of characters within a string.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: num = "52" 9 | Output: "5" 10 | Explanation: The only non-empty substrings are "5", "2", and "52". "5" is the only odd number. 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: num = "4206" 16 | Output: "" 17 | Explanation: There are no odd numbers in "4206". 18 |19 | 20 |
Example 3:
21 | 22 |Input: num = "35427" 23 | Output: "35427" 24 | Explanation: "35427" is already an odd number. 25 |26 | 27 |
28 |
Constraints:
29 | 30 |-
31 |
1 <= num.length <= 105
32 | numonly consists of digits and does not contain any leading zeros.
33 |
844. Backspace String Compare
Easy
Given two strings s and t, return true if they are equal when both are typed into empty text editors. '#' means a backspace character.
Note that after backspacing an empty text, the text will continue empty.
4 | 5 |6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: s = "ab#c", t = "ad#c" 9 | Output: true 10 | Explanation: Both s and t become "ac". 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: s = "ab##", t = "c#d#" 16 | Output: true 17 | Explanation: Both s and t become "". 18 |19 | 20 |
Example 3:
21 | 22 |Input: s = "a#c", t = "b" 23 | Output: false 24 | Explanation: s becomes "c" while t becomes "b". 25 |26 | 27 |
28 |
Constraints:
29 | 30 |-
31 |
1 <= s.length, t.length <= 200
32 | sandtonly contain lowercase letters and'#'characters.
33 |
36 |
Follow up: Can you solve it in O(n) time and O(1) space?
1493. Longest Subarray of 1's After Deleting One Element
Medium
Given a binary array nums, you should delete one element from it.
Return the size of the longest non-empty subarray containing only 1's in the resulting array. Return 0 if there is no such subarray.
6 |
Example 1:
7 | 8 |Input: nums = [1,1,0,1] 9 | Output: 3 10 | Explanation: After deleting the number in position 2, [1,1,1] contains 3 numbers with value of 1's. 11 |12 | 13 |
Example 2:
14 | 15 |Input: nums = [0,1,1,1,0,1,1,0,1] 16 | Output: 5 17 | Explanation: After deleting the number in position 4, [0,1,1,1,1,1,0,1] longest subarray with value of 1's is [1,1,1,1,1]. 18 |19 | 20 |
Example 3:
21 | 22 |Input: nums = [1,1,1] 23 | Output: 2 24 | Explanation: You must delete one element. 25 |26 | 27 |
28 |
Constraints:
29 | 30 |-
31 |
1 <= nums.length <= 105
32 | nums[i]is either0or1.
33 |
938. Range Sum of BST
Easy
Given the root node of a binary search tree and two integers low and high, return the sum of values of all nodes with a value in the inclusive range [low, high].
4 |
Example 1:
5 |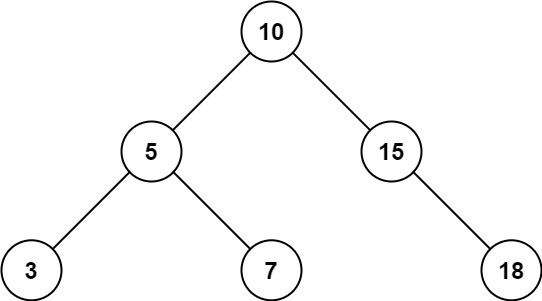 6 |
6 | Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,null,18], low = 7, high = 15 7 | Output: 32 8 | Explanation: Nodes 7, 10, and 15 are in the range [7, 15]. 7 + 10 + 15 = 32. 9 |10 | 11 |
Example 2:
12 |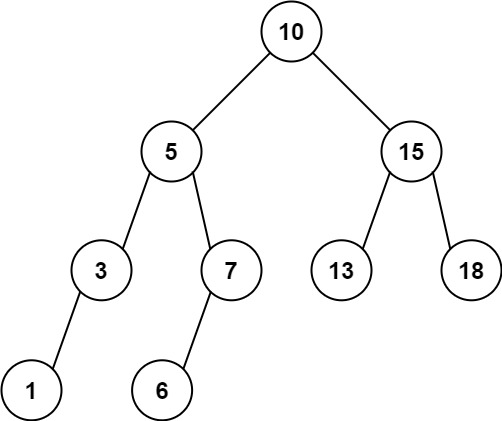 13 |
13 | Input: root = [10,5,15,3,7,13,18,1,null,6], low = 6, high = 10 14 | Output: 23 15 | Explanation: Nodes 6, 7, and 10 are in the range [6, 10]. 6 + 7 + 10 = 23. 16 |17 | 18 |
19 |
Constraints:
20 | 21 |-
22 |
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 2 * 104].
23 | 1 <= Node.val <= 105
24 | 1 <= low <= high <= 105
25 | - All
Node.valare unique.
26 |