├── .gitignore
├── EA.jpg
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── demo
├── es.gif
├── es_rl.gif
├── find path.gif
├── ga.gif
├── mga.gif
├── nes.gif
├── phrase.gif
└── tsp.gif
└── tutorial-contents
├── Evolution Strategy
├── (1+1)-ES.py
├── Evolution Strategy Basic.py
└── Natural Evolution Strategy (NES).py
├── Genetic Algorithm
├── Find Path.py
├── Genetic Algorithm Basic.py
├── Match Phrase.py
├── Microbial Genetic Algorithm.py
└── Travel Sales Person.py
└── Using Neural Nets
├── Evolution Strategy with Neural Nets.py
├── NEAT
├── config-feedforward
├── run_xor.py
└── visualize.py
└── NEAT_gym
├── config
├── run_cartpole.py
└── visualize.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | .idea
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/EA.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/EA.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2017 Andrew Gambardella
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |  4 |
5 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | In these tutorials, we will demonstrate and visualize algorithms like Genetic Algorithm,
8 | Evolution Strategy, NEAT etc.
9 |
10 | All methods mentioned below have their video and text tutorial in Chinese. Visit [莫烦 Python](https://mofanpy.com/) for more.
11 |
12 | A python package for Evolution algorithm is now available. Details are found at [MEvo](https://github.com/MorvanZhou/mevo).
13 |
14 | * [Genetic Algorithm](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm)
15 | * [Basic GA](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Genetic%20Algorithm%20Basic.py)
16 | * [Match Phrase Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Match%20Phrase.py)
17 | * [Travel Sales Problem](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Travel%20Sales%20Person.py)
18 | * [Find Path Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Find%20Path.py)
19 | * [Microbial GA](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Microbial%20Genetic%20Algorithm.py)
20 | * [Evolution Strategy](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy)
21 | * [Basic ES](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Evolution%20Strategy%20Basic.py)
22 | * [(1+1)-ES](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/(1%2B1)-ES.py)
23 | * [Natural Evolution Strategy (NES)](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Natural%20Evolution%20Strategy%20(NES).py)
24 | * [Using Neural Nets](tutorial-contents/Using%20Neural%20Nets)
25 | * [NEAT for Supervised-Learning](tutorial-contents/Using%20Neural%20Nets/NEAT)
26 | * [NEAT for Reinforcement-Learning](tutorial-contents/Using%20Neural%20Nets/NEAT_gym)
27 | * [Distributed ES with Neural Nets (OpenAI)](tutorial-contents/Using%20Neural%20Nets/Evolution%20Strategy%20with%20Neural%20Nets.py)
28 |
29 |
30 | ### [Basic GA](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Genetic%20Algorithm%20Basic.py)
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 |  35 |
36 |
37 | ### [Match Phrase Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Match%20Phrase.py)
38 |
39 |
40 |
35 |
36 |
37 | ### [Match Phrase Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Match%20Phrase.py)
38 |
39 |
40 |  41 |
42 |
43 | ### [Travel Sales Problem](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Travel%20Sales%20Person.py)
44 |
45 |
46 |
41 |
42 |
43 | ### [Travel Sales Problem](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Travel%20Sales%20Person.py)
44 |
45 |
46 | 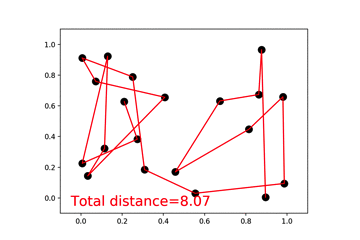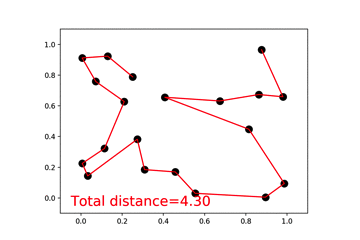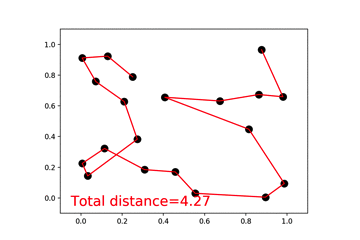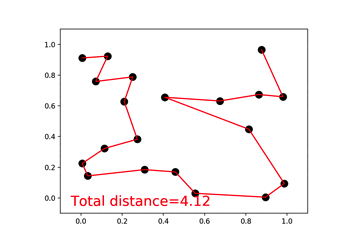 47 |
48 |
49 | ### [Find Path Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Find%20Path.py)
50 |
51 |
47 |
48 |
49 | ### [Find Path Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Find%20Path.py)
50 |
51 |  52 |
53 |
54 | ### [Basic ES](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Evolution%20Strategy%20Basic.py)
55 |
56 |
57 |
52 |
53 |
54 | ### [Basic ES](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Evolution%20Strategy%20Basic.py)
55 |
56 |
57 |  58 |
59 |
60 | ### [Natural Evolution Strategy (NES)](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Natural%20Evolution%20Strategy%20(NES).py)
61 |
62 |
63 |
58 |
59 |
60 | ### [Natural Evolution Strategy (NES)](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Natural%20Evolution%20Strategy%20(NES).py)
61 |
62 |
63 |  64 |
65 |
66 | ### [Distributed ES with Neural Nets (OpenAI)](tutorial-contents/Using%20Neural%20Nets/Evolution%20Strategy%20with%20Neural%20Nets.py)
67 |
68 |
69 |
64 |
65 |
66 | ### [Distributed ES with Neural Nets (OpenAI)](tutorial-contents/Using%20Neural%20Nets/Evolution%20Strategy%20with%20Neural%20Nets.py)
67 |
68 |
69 |  70 |
71 |
72 | # Donation
73 |
74 | *If this does help you, please consider donating to support me for better tutorials! Any contribution is greatly appreciated!*
75 |
76 |
83 |
84 |
91 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/es.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/es.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/es_rl.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/es_rl.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/find path.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/find path.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/ga.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/ga.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/mga.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/mga.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/nes.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/nes.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/phrase.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/phrase.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/tsp.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/tsp.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Evolution Strategy/(1+1)-ES.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | (1+1)-ES with 1/5th success rule with visualization.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | DNA_SIZE = 1 # DNA (real number)
10 | DNA_BOUND = [0, 5] # solution upper and lower bounds
11 | N_GENERATIONS = 200
12 | MUT_STRENGTH = 5. # initial step size (dynamic mutation strength)
13 |
14 |
15 | def F(x): return np.sin(10*x)*x + np.cos(2*x)*x # to find the maximum of this function
16 |
17 |
18 | # find non-zero fitness for selection
19 | def get_fitness(pred): return pred.flatten()
20 |
21 |
22 | def make_kid(parent):
23 | # no crossover, only mutation
24 | k = parent + MUT_STRENGTH * np.random.randn(DNA_SIZE)
25 | k = np.clip(k, *DNA_BOUND)
26 | return k
27 |
28 |
29 | def kill_bad(parent, kid):
30 | global MUT_STRENGTH
31 | fp = get_fitness(F(parent))[0]
32 | fk = get_fitness(F(kid))[0]
33 | p_target = 1/5
34 | if fp < fk: # kid better than parent
35 | parent = kid
36 | ps = 1. # kid win -> ps = 1 (successful offspring)
37 | else:
38 | ps = 0.
39 | # adjust global mutation strength
40 | MUT_STRENGTH *= np.exp(1/np.sqrt(DNA_SIZE+1) * (ps - p_target)/(1 - p_target))
41 | return parent
42 |
43 |
44 | parent = 5 * np.random.rand(DNA_SIZE) # parent DNA
45 |
46 | plt.ion() # something about plotting
47 | x = np.linspace(*DNA_BOUND, 200)
48 |
49 | for _ in range(N_GENERATIONS):
50 | # ES part
51 | kid = make_kid(parent)
52 | py, ky = F(parent), F(kid) # for later plot
53 | parent = kill_bad(parent, kid)
54 |
55 | # something about plotting
56 | plt.cla()
57 | plt.scatter(parent, py, s=200, lw=0, c='red', alpha=0.5,)
58 | plt.scatter(kid, ky, s=200, lw=0, c='blue', alpha=0.5)
59 | plt.text(0, -7, 'Mutation strength=%.2f' % MUT_STRENGTH)
60 | plt.plot(x, F(x)); plt.pause(0.05)
61 |
62 | plt.ioff(); plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Evolution Strategy/Evolution Strategy Basic.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The Evolution Strategy can be summarized as the following term:
3 | {mu/rho +, lambda}-ES
4 |
5 | Here we use following term to find a maximum point.
6 | {n_pop/n_pop + n_kid}-ES
7 |
8 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
9 | """
10 | import numpy as np
11 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
12 |
13 | DNA_SIZE = 1 # DNA (real number)
14 | DNA_BOUND = [0, 5] # solution upper and lower bounds
15 | N_GENERATIONS = 200
16 | POP_SIZE = 100 # population size
17 | N_KID = 50 # n kids per generation
18 |
19 |
20 | def F(x): return np.sin(10*x)*x + np.cos(2*x)*x # to find the maximum of this function
21 |
22 |
23 | # find non-zero fitness for selection
24 | def get_fitness(pred): return pred.flatten()
25 |
26 |
27 | def make_kid(pop, n_kid):
28 | # generate empty kid holder
29 | kids = {'DNA': np.empty((n_kid, DNA_SIZE))}
30 | kids['mut_strength'] = np.empty_like(kids['DNA'])
31 | for kv, ks in zip(kids['DNA'], kids['mut_strength']):
32 | # crossover (roughly half p1 and half p2)
33 | p1, p2 = np.random.choice(np.arange(POP_SIZE), size=2, replace=False)
34 | cp = np.random.randint(0, 2, DNA_SIZE, dtype=np.bool) # crossover points
35 | kv[cp] = pop['DNA'][p1, cp]
36 | kv[~cp] = pop['DNA'][p2, ~cp]
37 | ks[cp] = pop['mut_strength'][p1, cp]
38 | ks[~cp] = pop['mut_strength'][p2, ~cp]
39 |
40 | # mutate (change DNA based on normal distribution)
41 | ks[:] = np.maximum(ks + (np.random.rand(*ks.shape)-0.5), 0.) # must > 0
42 | kv += ks * np.random.randn(*kv.shape)
43 | kv[:] = np.clip(kv, *DNA_BOUND) # clip the mutated value
44 | return kids
45 |
46 |
47 | def kill_bad(pop, kids):
48 | # put pop and kids together
49 | for key in ['DNA', 'mut_strength']:
50 | pop[key] = np.vstack((pop[key], kids[key]))
51 |
52 | fitness = get_fitness(F(pop['DNA'])) # calculate global fitness
53 | idx = np.arange(pop['DNA'].shape[0])
54 | good_idx = idx[fitness.argsort()][-POP_SIZE:] # selected by fitness ranking (not value)
55 | for key in ['DNA', 'mut_strength']:
56 | pop[key] = pop[key][good_idx]
57 | return pop
58 |
59 |
60 | pop = dict(DNA=5 * np.random.rand(1, DNA_SIZE).repeat(POP_SIZE, axis=0), # initialize the pop DNA values
61 | mut_strength=np.random.rand(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE)) # initialize the pop mutation strength values
62 |
63 | plt.ion() # something about plotting
64 | x = np.linspace(*DNA_BOUND, 200)
65 | plt.plot(x, F(x))
66 |
67 | for _ in range(N_GENERATIONS):
68 | # something about plotting
69 | if 'sca' in globals(): sca.remove()
70 | sca = plt.scatter(pop['DNA'], F(pop['DNA']), s=200, lw=0, c='red', alpha=0.5); plt.pause(0.05)
71 |
72 | # ES part
73 | kids = make_kid(pop, N_KID)
74 | pop = kill_bad(pop, kids) # keep some good parent for elitism
75 |
76 | plt.ioff(); plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Evolution Strategy/Natural Evolution Strategy (NES).py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The basic idea about Nature Evolution Strategy with visualation.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 |
6 | Dependencies:
7 | Tensorflow >= r1.2
8 | numpy
9 | matplotlib
10 | """
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
13 | import tensorflow as tf
14 | from tensorflow.contrib.distributions import MultivariateNormalFullCovariance
15 |
16 | DNA_SIZE = 2 # parameter (solution) number
17 | N_POP = 20 # population size
18 | N_GENERATION = 100 # training step
19 | LR = 0.02 # learning rate
20 |
21 |
22 | # fitness function
23 | def get_fitness(pred): return -((pred[:, 0])**2 + pred[:, 1]**2)
24 |
25 | # build multivariate distribution
26 | mean = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, ], 13., 1.), dtype=tf.float32)
27 | cov = tf.Variable(5. * tf.eye(DNA_SIZE), dtype=tf.float32)
28 | mvn = MultivariateNormalFullCovariance(loc=mean, covariance_matrix=cov)
29 | make_kid = mvn.sample(N_POP) # sampling operation
30 |
31 | # compute gradient and update mean and covariance matrix from sample and fitness
32 | tfkids_fit = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [N_POP, ])
33 | tfkids = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [N_POP, DNA_SIZE])
34 | loss = -tf.reduce_mean(mvn.log_prob(tfkids)*tfkids_fit) # log prob * fitness
35 | train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(LR).minimize(loss) # compute and apply gradients for mean and cov
36 |
37 | sess = tf.Session()
38 | sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # initialize tf variables
39 |
40 | # something about plotting (can be ignored)
41 | n = 300
42 | x = np.linspace(-20, 20, n)
43 | X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, x)
44 | Z = np.zeros_like(X)
45 | for i in range(n):
46 | for j in range(n):
47 | Z[i, j] = get_fitness(np.array([[x[i], x[j]]]))
48 | plt.contourf(X, Y, -Z, 100, cmap=plt.cm.rainbow); plt.ylim(-20, 20); plt.xlim(-20, 20); plt.ion()
49 |
50 | # training
51 | for g in range(N_GENERATION):
52 | kids = sess.run(make_kid)
53 | kids_fit = get_fitness(kids)
54 | sess.run(train_op, {tfkids_fit: kids_fit, tfkids: kids}) # update distribution parameters
55 |
56 | # plotting update
57 | if 'sca' in globals(): sca.remove()
58 | sca = plt.scatter(kids[:, 0], kids[:, 1], s=30, c='k');plt.pause(0.01)
59 |
60 | print('Finished'); plt.ioff(); plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Find Path.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Genetic Algorithm to find a path to the target.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 |
9 | N_MOVES = 150
10 | DNA_SIZE = N_MOVES*2 # 40 x moves, 40 y moves
11 | DIRECTION_BOUND = [0, 1]
12 | CROSS_RATE = 0.8
13 | MUTATE_RATE = 0.0001
14 | POP_SIZE = 100
15 | N_GENERATIONS = 100
16 | GOAL_POINT = [10, 5]
17 | START_POINT = [0, 5]
18 | OBSTACLE_LINE = np.array([[5, 2], [5, 8]])
19 |
20 |
21 | class GA(object):
22 | def __init__(self, DNA_size, DNA_bound, cross_rate, mutation_rate, pop_size, ):
23 | self.DNA_size = DNA_size
24 | DNA_bound[1] += 1
25 | self.DNA_bound = DNA_bound
26 | self.cross_rate = cross_rate
27 | self.mutate_rate = mutation_rate
28 | self.pop_size = pop_size
29 |
30 | self.pop = np.random.randint(*DNA_bound, size=(pop_size, DNA_size))
31 |
32 | def DNA2product(self, DNA, n_moves, start_point): # convert to readable string
33 | pop = (DNA - 0.5) / 2
34 | pop[:, 0], pop[:, n_moves] = start_point[0], start_point[1]
35 | lines_x = np.cumsum(pop[:, :n_moves], axis=1)
36 | lines_y = np.cumsum(pop[:, n_moves:], axis=1)
37 | return lines_x, lines_y
38 |
39 | def get_fitness(self, lines_x, lines_y, goal_point, obstacle_line):
40 | dist2goal = np.sqrt((goal_point[0] - lines_x[:, -1]) ** 2 + (goal_point[1] - lines_y[:, -1]) ** 2)
41 | fitness = np.power(1 / (dist2goal + 1), 2)
42 | points = (lines_x > obstacle_line[0, 0] - 0.5) & (lines_x < obstacle_line[1, 0] + 0.5)
43 | y_values = np.where(points, lines_y, np.zeros_like(lines_y) - 100)
44 | bad_lines = ((y_values > obstacle_line[0, 1]) & (y_values < obstacle_line[1, 1])).max(axis=1)
45 | fitness[bad_lines] = 1e-6
46 | return fitness
47 |
48 | def select(self, fitness):
49 | idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.pop_size), size=self.pop_size, replace=True, p=fitness/fitness.sum())
50 | return self.pop[idx]
51 |
52 | def crossover(self, parent, pop):
53 | if np.random.rand() < self.cross_rate:
54 | i_ = np.random.randint(0, self.pop_size, size=1) # select another individual from pop
55 | cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, self.DNA_size).astype(np.bool) # choose crossover points
56 | parent[cross_points] = pop[i_, cross_points] # mating and produce one child
57 | return parent
58 |
59 | def mutate(self, child):
60 | for point in range(self.DNA_size):
61 | if np.random.rand() < self.mutate_rate:
62 | child[point] = np.random.randint(*self.DNA_bound)
63 | return child
64 |
65 | def evolve(self, fitness):
66 | pop = self.select(fitness)
67 | pop_copy = pop.copy()
68 | for parent in pop: # for every parent
69 | child = self.crossover(parent, pop_copy)
70 | child = self.mutate(child)
71 | parent[:] = child
72 | self.pop = pop
73 |
74 |
75 | class Line(object):
76 | def __init__(self, n_moves, goal_point, start_point, obstacle_line):
77 | self.n_moves = n_moves
78 | self.goal_point = goal_point
79 | self.start_point = start_point
80 | self.obstacle_line = obstacle_line
81 |
82 | plt.ion()
83 |
84 | def plotting(self, lines_x, lines_y):
85 | plt.cla()
86 | plt.scatter(*self.goal_point, s=200, c='r')
87 | plt.scatter(*self.start_point, s=100, c='b')
88 | plt.plot(self.obstacle_line[:, 0], self.obstacle_line[:, 1], lw=3, c='k')
89 | plt.plot(lines_x.T, lines_y.T, c='k')
90 | plt.xlim((-5, 15))
91 | plt.ylim((-5, 15))
92 | plt.pause(0.01)
93 |
94 |
95 | ga = GA(DNA_size=DNA_SIZE, DNA_bound=DIRECTION_BOUND,
96 | cross_rate=CROSS_RATE, mutation_rate=MUTATE_RATE, pop_size=POP_SIZE)
97 |
98 | env = Line(N_MOVES, GOAL_POINT, START_POINT, OBSTACLE_LINE)
99 |
100 | for generation in range(N_GENERATIONS):
101 | lx, ly = ga.DNA2product(ga.pop, N_MOVES, START_POINT)
102 | fitness = ga.get_fitness(lx, ly, GOAL_POINT, OBSTACLE_LINE)
103 | ga.evolve(fitness)
104 | print('Gen:', generation, '| best fit:', fitness.max())
105 | env.plotting(lx, ly)
106 |
107 | plt.ioff()
108 | plt.show()
109 |
110 |
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Genetic Algorithm Basic.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Genetic Algorithm to find a maximum point in a function.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | DNA_SIZE = 10 # DNA length
10 | POP_SIZE = 100 # population size
11 | CROSS_RATE = 0.8 # mating probability (DNA crossover)
12 | MUTATION_RATE = 0.003 # mutation probability
13 | N_GENERATIONS = 200
14 | X_BOUND = [0, 5] # x upper and lower bounds
15 |
16 |
17 | def F(x): return np.sin(10*x)*x + np.cos(2*x)*x # to find the maximum of this function
18 |
19 |
20 | # find non-zero fitness for selection
21 | def get_fitness(pred): return pred + 1e-3 - np.min(pred)
22 |
23 |
24 | # convert binary DNA to decimal and normalize it to a range(0, 5)
25 | def translateDNA(pop): return pop.dot(2 ** np.arange(DNA_SIZE)[::-1]) / float(2**DNA_SIZE-1) * X_BOUND[1]
26 |
27 |
28 | def select(pop, fitness): # nature selection wrt pop's fitness
29 | idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(POP_SIZE), size=POP_SIZE, replace=True,
30 | p=fitness/fitness.sum())
31 | return pop[idx]
32 |
33 |
34 | def crossover(parent, pop): # mating process (genes crossover)
35 | if np.random.rand() < CROSS_RATE:
36 | i_ = np.random.randint(0, POP_SIZE, size=1) # select another individual from pop
37 | cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=DNA_SIZE).astype(np.bool_) # choose crossover points
38 | parent[cross_points] = pop[i_, cross_points] # mating and produce one child
39 | return parent
40 |
41 |
42 | def mutate(child):
43 | for point in range(DNA_SIZE):
44 | if np.random.rand() < MUTATION_RATE:
45 | child[point] = 1 if child[point] == 0 else 0
46 | return child
47 |
48 |
49 | pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE)) # initialize the pop DNA
50 |
51 | plt.ion() # something about plotting
52 | x = np.linspace(*X_BOUND, 200)
53 | plt.plot(x, F(x))
54 |
55 | for _ in range(N_GENERATIONS):
56 | F_values = F(translateDNA(pop)) # compute function value by extracting DNA
57 |
58 | # something about plotting
59 | if 'sca' in globals(): sca.remove()
60 | sca = plt.scatter(translateDNA(pop), F_values, s=200, lw=0, c='red', alpha=0.5); plt.pause(0.05)
61 |
62 | # GA part (evolution)
63 | fitness = get_fitness(F_values)
64 | print("Most fitted DNA: ", pop[np.argmax(fitness), :])
65 | pop = select(pop, fitness)
66 | pop_copy = pop.copy()
67 | for parent in pop:
68 | child = crossover(parent, pop_copy)
69 | child = mutate(child)
70 | parent[:] = child # parent is replaced by its child
71 |
72 | plt.ioff(); plt.show()
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Match Phrase.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Genetic Algorithm to match the target phrase.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import numpy as np
7 |
8 | TARGET_PHRASE = 'You get it!' # target DNA
9 | POP_SIZE = 300 # population size
10 | CROSS_RATE = 0.4 # mating probability (DNA crossover)
11 | MUTATION_RATE = 0.01 # mutation probability
12 | N_GENERATIONS = 1000
13 |
14 | DNA_SIZE = len(TARGET_PHRASE)
15 | TARGET_ASCII = np.fromstring(TARGET_PHRASE, dtype=np.uint8) # convert string to number
16 | ASCII_BOUND = [32, 126]
17 |
18 |
19 | class GA(object):
20 | def __init__(self, DNA_size, DNA_bound, cross_rate, mutation_rate, pop_size):
21 | self.DNA_size = DNA_size
22 | DNA_bound[1] += 1
23 | self.DNA_bound = DNA_bound
24 | self.cross_rate = cross_rate
25 | self.mutate_rate = mutation_rate
26 | self.pop_size = pop_size
27 |
28 | self.pop = np.random.randint(*DNA_bound, size=(pop_size, DNA_size)).astype(np.int8) # int8 for convert to ASCII
29 |
30 | def translateDNA(self, DNA): # convert to readable string
31 | return DNA.tostring().decode('ascii')
32 |
33 | def get_fitness(self): # count how many character matches
34 | match_count = (self.pop == TARGET_ASCII).sum(axis=1)
35 | return match_count
36 |
37 | def select(self):
38 | fitness = self.get_fitness() + 1e-4 # add a small amount to avoid all zero fitness
39 | idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.pop_size), size=self.pop_size, replace=True, p=fitness/fitness.sum())
40 | return self.pop[idx]
41 |
42 | def crossover(self, parent, pop):
43 | if np.random.rand() < self.cross_rate:
44 | i_ = np.random.randint(0, self.pop_size, size=1) # select another individual from pop
45 | cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, self.DNA_size).astype(np.bool) # choose crossover points
46 | parent[cross_points] = pop[i_, cross_points] # mating and produce one child
47 | return parent
48 |
49 | def mutate(self, child):
50 | for point in range(self.DNA_size):
51 | if np.random.rand() < self.mutate_rate:
52 | child[point] = np.random.randint(*self.DNA_bound) # choose a random ASCII index
53 | return child
54 |
55 | def evolve(self):
56 | pop = self.select()
57 | pop_copy = pop.copy()
58 | for parent in pop: # for every parent
59 | child = self.crossover(parent, pop_copy)
60 | child = self.mutate(child)
61 | parent[:] = child
62 | self.pop = pop
63 |
64 | if __name__ == '__main__':
65 | ga = GA(DNA_size=DNA_SIZE, DNA_bound=ASCII_BOUND, cross_rate=CROSS_RATE,
66 | mutation_rate=MUTATION_RATE, pop_size=POP_SIZE)
67 |
68 | for generation in range(N_GENERATIONS):
69 | fitness = ga.get_fitness()
70 | best_DNA = ga.pop[np.argmax(fitness)]
71 | best_phrase = ga.translateDNA(best_DNA)
72 | print('Gen', generation, ': ', best_phrase)
73 | if best_phrase == TARGET_PHRASE:
74 | break
75 | ga.evolve()
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Microbial Genetic Algorithm.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Microbial Genetic Algorithm to find the maximum point in a graph.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | DNA_SIZE = 10 # DNA length
10 | POP_SIZE = 20 # population size
11 | CROSS_RATE = 0.6 # mating probability (DNA crossover)
12 | MUTATION_RATE = 0.01 # mutation probability
13 | N_GENERATIONS = 200
14 | X_BOUND = [0, 5] # x upper and lower bounds
15 |
16 |
17 | def F(x): return np.sin(10*x)*x + np.cos(2*x)*x # to find the maximum of this function
18 |
19 |
20 | class MGA(object):
21 | def __init__(self, DNA_size, DNA_bound, cross_rate, mutation_rate, pop_size):
22 | self.DNA_size = DNA_size
23 | DNA_bound[1] += 1
24 | self.DNA_bound = DNA_bound
25 | self.cross_rate = cross_rate
26 | self.mutate_rate = mutation_rate
27 | self.pop_size = pop_size
28 |
29 | # initial DNAs for winner and loser
30 | self.pop = np.random.randint(*DNA_bound, size=(1, self.DNA_size)).repeat(pop_size, axis=0)
31 |
32 | def translateDNA(self, pop):
33 | # convert binary DNA to decimal and normalize it to a range(0, 5)
34 | return pop.dot(2 ** np.arange(self.DNA_size)[::-1]) / float(2 ** self.DNA_size - 1) * X_BOUND[1]
35 |
36 | def get_fitness(self, product):
37 | return product # it is OK to use product value as fitness in here
38 |
39 | def crossover(self, loser_winner): # crossover for loser
40 | cross_idx = np.empty((self.DNA_size,)).astype(np.bool)
41 | for i in range(self.DNA_size):
42 | cross_idx[i] = True if np.random.rand() < self.cross_rate else False # crossover index
43 | loser_winner[0, cross_idx] = loser_winner[1, cross_idx] # assign winners genes to loser
44 | return loser_winner
45 |
46 | def mutate(self, loser_winner): # mutation for loser
47 | mutation_idx = np.empty((self.DNA_size,)).astype(np.bool)
48 | for i in range(self.DNA_size):
49 | mutation_idx[i] = True if np.random.rand() < self.mutate_rate else False # mutation index
50 | # flip values in mutation points
51 | loser_winner[0, mutation_idx] = ~loser_winner[0, mutation_idx].astype(np.bool)
52 | return loser_winner
53 |
54 | def evolve(self, n): # nature selection wrt pop's fitness
55 | for _ in range(n): # random pick and compare n times
56 | sub_pop_idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(0, self.pop_size), size=2, replace=False)
57 | sub_pop = self.pop[sub_pop_idx] # pick 2 from pop
58 | product = F(self.translateDNA(sub_pop))
59 | fitness = self.get_fitness(product)
60 | loser_winner_idx = np.argsort(fitness)
61 | loser_winner = sub_pop[loser_winner_idx] # the first is loser and second is winner
62 | loser_winner = self.crossover(loser_winner)
63 | loser_winner = self.mutate(loser_winner)
64 | self.pop[sub_pop_idx] = loser_winner
65 |
66 | DNA_prod = self.translateDNA(self.pop)
67 | pred = F(DNA_prod)
68 | return DNA_prod, pred
69 |
70 |
71 | plt.ion() # something about plotting
72 | x = np.linspace(*X_BOUND, 200)
73 | plt.plot(x, F(x))
74 |
75 | ga = MGA(DNA_size=DNA_SIZE, DNA_bound=[0, 1], cross_rate=CROSS_RATE, mutation_rate=MUTATION_RATE, pop_size=POP_SIZE)
76 |
77 | for _ in range(N_GENERATIONS): # 100 generations
78 | DNA_prod, pred = ga.evolve(5) # natural selection, crossover and mutation
79 |
80 | # something about plotting
81 | if 'sca' in globals(): sca.remove()
82 | sca = plt.scatter(DNA_prod, pred, s=200, lw=0, c='red', alpha=0.5); plt.pause(0.05)
83 |
84 | plt.ioff();plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Travel Sales Person.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Genetic Algorithm to find the shortest path for travel sales problem.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 |
9 | N_CITIES = 20 # DNA size
10 | CROSS_RATE = 0.1
11 | MUTATE_RATE = 0.02
12 | POP_SIZE = 500
13 | N_GENERATIONS = 500
14 |
15 |
16 | class GA(object):
17 | def __init__(self, DNA_size, cross_rate, mutation_rate, pop_size, ):
18 | self.DNA_size = DNA_size
19 | self.cross_rate = cross_rate
20 | self.mutate_rate = mutation_rate
21 | self.pop_size = pop_size
22 |
23 | self.pop = np.vstack([np.random.permutation(DNA_size) for _ in range(pop_size)])
24 |
25 | def translateDNA(self, DNA, city_position): # get cities' coord in order
26 | line_x = np.empty_like(DNA, dtype=np.float64)
27 | line_y = np.empty_like(DNA, dtype=np.float64)
28 | for i, d in enumerate(DNA):
29 | city_coord = city_position[d]
30 | line_x[i, :] = city_coord[:, 0]
31 | line_y[i, :] = city_coord[:, 1]
32 | return line_x, line_y
33 |
34 | def get_fitness(self, line_x, line_y):
35 | total_distance = np.empty((line_x.shape[0],), dtype=np.float64)
36 | for i, (xs, ys) in enumerate(zip(line_x, line_y)):
37 | total_distance[i] = np.sum(np.sqrt(np.square(np.diff(xs)) + np.square(np.diff(ys))))
38 | fitness = np.exp(self.DNA_size * 2 / total_distance)
39 | return fitness, total_distance
40 |
41 | def select(self, fitness):
42 | idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.pop_size), size=self.pop_size, replace=True, p=fitness / fitness.sum())
43 | return self.pop[idx]
44 |
45 | def crossover(self, parent, pop):
46 | if np.random.rand() < self.cross_rate:
47 | i_ = np.random.randint(0, self.pop_size, size=1) # select another individual from pop
48 | cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, self.DNA_size).astype(np.bool) # choose crossover points
49 | keep_city = parent[~cross_points] # find the city number
50 | swap_city = pop[i_, np.isin(pop[i_].ravel(), keep_city, invert=True)]
51 | parent[:] = np.concatenate((keep_city, swap_city))
52 | return parent
53 |
54 | def mutate(self, child):
55 | for point in range(self.DNA_size):
56 | if np.random.rand() < self.mutate_rate:
57 | swap_point = np.random.randint(0, self.DNA_size)
58 | swapA, swapB = child[point], child[swap_point]
59 | child[point], child[swap_point] = swapB, swapA
60 | return child
61 |
62 | def evolve(self, fitness):
63 | pop = self.select(fitness)
64 | pop_copy = pop.copy()
65 | for parent in pop: # for every parent
66 | child = self.crossover(parent, pop_copy)
67 | child = self.mutate(child)
68 | parent[:] = child
69 | self.pop = pop
70 |
71 |
72 | class TravelSalesPerson(object):
73 | def __init__(self, n_cities):
74 | self.city_position = np.random.rand(n_cities, 2)
75 | plt.ion()
76 |
77 | def plotting(self, lx, ly, total_d):
78 | plt.cla()
79 | plt.scatter(self.city_position[:, 0].T, self.city_position[:, 1].T, s=100, c='k')
80 | plt.plot(lx.T, ly.T, 'r-')
81 | plt.text(-0.05, -0.05, "Total distance=%.2f" % total_d, fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
82 | plt.xlim((-0.1, 1.1))
83 | plt.ylim((-0.1, 1.1))
84 | plt.pause(0.01)
85 |
86 |
87 | ga = GA(DNA_size=N_CITIES, cross_rate=CROSS_RATE, mutation_rate=MUTATE_RATE, pop_size=POP_SIZE)
88 |
89 | env = TravelSalesPerson(N_CITIES)
90 | for generation in range(N_GENERATIONS):
91 | lx, ly = ga.translateDNA(ga.pop, env.city_position)
92 | fitness, total_distance = ga.get_fitness(lx, ly)
93 | ga.evolve(fitness)
94 | best_idx = np.argmax(fitness)
95 | print('Gen:', generation, '| best fit: %.2f' % fitness[best_idx],)
96 |
97 | env.plotting(lx[best_idx], ly[best_idx], total_distance[best_idx])
98 |
99 | plt.ioff()
100 | plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/Evolution Strategy with Neural Nets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Simple code for Distributed ES proposed by OpenAI.
3 | Based on this paper: Evolution Strategies as a Scalable Alternative to Reinforcement Learning
4 | Details can be found in : https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.03864
5 |
6 | Visit more on my tutorial site: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
7 | """
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import gym
10 | import multiprocessing as mp
11 | import time
12 |
13 | N_KID = 10 # half of the training population
14 | N_GENERATION = 5000 # training step
15 | LR = .05 # learning rate
16 | SIGMA = .05 # mutation strength or step size
17 | N_CORE = mp.cpu_count()-1
18 | CONFIG = [
19 | dict(game="CartPole-v0",
20 | n_feature=4, n_action=2, continuous_a=[False], ep_max_step=700, eval_threshold=500),
21 | dict(game="MountainCar-v0",
22 | n_feature=2, n_action=3, continuous_a=[False], ep_max_step=200, eval_threshold=-120),
23 | dict(game="Pendulum-v0",
24 | n_feature=3, n_action=1, continuous_a=[True, 2.], ep_max_step=200, eval_threshold=-180)
25 | ][2] # choose your game
26 |
27 |
28 | def sign(k_id): return -1. if k_id % 2 == 0 else 1. # mirrored sampling
29 |
30 |
31 | class SGD(object): # optimizer with momentum
32 | def __init__(self, params, learning_rate, momentum=0.9):
33 | self.v = np.zeros_like(params).astype(np.float32)
34 | self.lr, self.momentum = learning_rate, momentum
35 |
36 | def get_gradients(self, gradients):
37 | self.v = self.momentum * self.v + (1. - self.momentum) * gradients
38 | return self.lr * self.v
39 |
40 |
41 | def params_reshape(shapes, params): # reshape to be a matrix
42 | p, start = [], 0
43 | for i, shape in enumerate(shapes): # flat params to matrix
44 | n_w, n_b = shape[0] * shape[1], shape[1]
45 | p = p + [params[start: start + n_w].reshape(shape),
46 | params[start + n_w: start + n_w + n_b].reshape((1, shape[1]))]
47 | start += n_w + n_b
48 | return p
49 |
50 |
51 | def get_reward(shapes, params, env, ep_max_step, continuous_a, seed_and_id=None,):
52 | # perturb parameters using seed
53 | if seed_and_id is not None:
54 | seed, k_id = seed_and_id
55 | np.random.seed(seed)
56 | params += sign(k_id) * SIGMA * np.random.randn(params.size)
57 | p = params_reshape(shapes, params)
58 | # run episode
59 | s = env.reset()
60 | ep_r = 0.
61 | for step in range(ep_max_step):
62 | a = get_action(p, s, continuous_a)
63 | s, r, done, _ = env.step(a)
64 | # mountain car's reward can be tricky
65 | if env.spec._env_name == 'MountainCar' and s[0] > -0.1: r = 0.
66 | ep_r += r
67 | if done: break
68 | return ep_r
69 |
70 |
71 | def get_action(params, x, continuous_a):
72 | x = x[np.newaxis, :]
73 | x = np.tanh(x.dot(params[0]) + params[1])
74 | x = np.tanh(x.dot(params[2]) + params[3])
75 | x = x.dot(params[4]) + params[5]
76 | if not continuous_a[0]: return np.argmax(x, axis=1)[0] # for discrete action
77 | else: return continuous_a[1] * np.tanh(x)[0] # for continuous action
78 |
79 |
80 | def build_net():
81 | def linear(n_in, n_out): # network linear layer
82 | w = np.random.randn(n_in * n_out).astype(np.float32) * .1
83 | b = np.random.randn(n_out).astype(np.float32) * .1
84 | return (n_in, n_out), np.concatenate((w, b))
85 | s0, p0 = linear(CONFIG['n_feature'], 30)
86 | s1, p1 = linear(30, 20)
87 | s2, p2 = linear(20, CONFIG['n_action'])
88 | return [s0, s1, s2], np.concatenate((p0, p1, p2))
89 |
90 |
91 | def train(net_shapes, net_params, optimizer, utility, pool):
92 | # pass seed instead whole noise matrix to parallel will save your time
93 | noise_seed = np.random.randint(0, 2 ** 32 - 1, size=N_KID, dtype=np.uint32).repeat(2) # mirrored sampling
94 |
95 | # distribute training in parallel
96 | jobs = [pool.apply_async(get_reward, (net_shapes, net_params, env, CONFIG['ep_max_step'], CONFIG['continuous_a'],
97 | [noise_seed[k_id], k_id], )) for k_id in range(N_KID*2)]
98 | rewards = np.array([j.get() for j in jobs])
99 | kids_rank = np.argsort(rewards)[::-1] # rank kid id by reward
100 |
101 | cumulative_update = np.zeros_like(net_params) # initialize update values
102 | for ui, k_id in enumerate(kids_rank):
103 | np.random.seed(noise_seed[k_id]) # reconstruct noise using seed
104 | cumulative_update += utility[ui] * sign(k_id) * np.random.randn(net_params.size)
105 |
106 | gradients = optimizer.get_gradients(cumulative_update/(2*N_KID*SIGMA))
107 | return net_params + gradients, rewards
108 |
109 |
110 | if __name__ == "__main__":
111 | # utility instead reward for update parameters (rank transformation)
112 | base = N_KID * 2 # *2 for mirrored sampling
113 | rank = np.arange(1, base + 1)
114 | util_ = np.maximum(0, np.log(base / 2 + 1) - np.log(rank))
115 | utility = util_ / util_.sum() - 1 / base
116 |
117 | # training
118 | net_shapes, net_params = build_net()
119 | env = gym.make(CONFIG['game']).unwrapped
120 | optimizer = SGD(net_params, LR)
121 | pool = mp.Pool(processes=N_CORE)
122 | mar = None # moving average reward
123 | for g in range(N_GENERATION):
124 | t0 = time.time()
125 | net_params, kid_rewards = train(net_shapes, net_params, optimizer, utility, pool)
126 |
127 | # test trained net without noise
128 | net_r = get_reward(net_shapes, net_params, env, CONFIG['ep_max_step'], CONFIG['continuous_a'], None,)
129 | mar = net_r if mar is None else 0.9 * mar + 0.1 * net_r # moving average reward
130 | print(
131 | 'Gen: ', g,
132 | '| Net_R: %.1f' % mar,
133 | '| Kid_avg_R: %.1f' % kid_rewards.mean(),
134 | '| Gen_T: %.2f' % (time.time() - t0),)
135 | if mar >= CONFIG['eval_threshold']: break
136 |
137 | # test
138 | print("\nTESTING....")
139 | p = params_reshape(net_shapes, net_params)
140 | while True:
141 | s = env.reset()
142 | for _ in range(CONFIG['ep_max_step']):
143 | env.render()
144 | a = get_action(p, s, CONFIG['continuous_a'])
145 | s, _, done, _ = env.step(a)
146 | if done: break
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT/config-feedforward:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #--- parameters for the XOR-2 experiment ---#
2 |
3 | [NEAT]
4 | fitness_criterion = max
5 | fitness_threshold = 3.9
6 | pop_size = 150
7 | reset_on_extinction = False
8 |
9 | [DefaultGenome]
10 | # node activation options
11 | activation_default = sigmoid
12 | activation_mutate_rate = 0.0
13 | activation_options = sigmoid
14 |
15 | # node aggregation options
16 | aggregation_default = sum
17 | aggregation_mutate_rate = 0.0
18 | aggregation_options = sum
19 |
20 | # node bias options
21 | bias_init_mean = 0.0
22 | bias_init_stdev = 1.0
23 | bias_max_value = 30.0
24 | bias_min_value = -30.0
25 | bias_mutate_power = 0.5
26 | bias_mutate_rate = 0.7
27 | bias_replace_rate = 0.1
28 |
29 | # genome compatibility options
30 | compatibility_disjoint_coefficient = 1.0
31 | compatibility_weight_coefficient = 0.5
32 |
33 | # connection add/remove rates
34 | conn_add_prob = 0.5
35 | conn_delete_prob = 0.5
36 |
37 | # connection enable options
38 | enabled_default = True
39 | enabled_mutate_rate = 0.01
40 |
41 | feed_forward = True
42 | initial_connection = full
43 |
44 | # node add/remove rates
45 | node_add_prob = 0.2
46 | node_delete_prob = 0.2
47 |
48 | # network parameters
49 | num_hidden = 0
50 | num_inputs = 2
51 | num_outputs = 1
52 |
53 | # node response options
54 | response_init_mean = 1.0
55 | response_init_stdev = 0.0
56 | response_max_value = 30.0
57 | response_min_value = -30.0
58 | response_mutate_power = 0.0
59 | response_mutate_rate = 0.0
60 | response_replace_rate = 0.0
61 |
62 | # connection weight options
63 | weight_init_mean = 0.0
64 | weight_init_stdev = 1.0
65 | weight_max_value = 30
66 | weight_min_value = -30
67 | weight_mutate_power = 0.5
68 | weight_mutate_rate = 0.8
69 | weight_replace_rate = 0.1
70 |
71 | [DefaultSpeciesSet]
72 | compatibility_threshold = 3.0
73 |
74 | [DefaultStagnation]
75 | species_fitness_func = max
76 | max_stagnation = 20
77 | species_elitism = 2
78 |
79 | [DefaultReproduction]
80 | elitism = 2
81 | survival_threshold = 0.2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT/run_xor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Using NEAT for supervised learning. This example comes from http://neat-python.readthedocs.io/en/latest/xor_example.html
3 |
4 | The detail for NEAT can be find in : http://nn.cs.utexas.edu/downloads/papers/stanley.cec02.pdf
5 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
6 | """
7 |
8 | import os
9 | import neat
10 | import visualize
11 |
12 | # 2-input XOR inputs and expected outputs.
13 | xor_inputs = [(0.0, 0.0), (0.0, 1.0), (1.0, 0.0), (1.0, 1.0)]
14 | xor_outputs = [ (0.0,), (1.0,), (1.0,), (0.0,)]
15 |
16 |
17 | def eval_genomes(genomes, config):
18 | for genome_id, genome in genomes: # for each individual
19 | genome.fitness = 4.0 # 4 xor evaluations
20 | net = neat.nn.FeedForwardNetwork.create(genome, config)
21 | for xi, xo in zip(xor_inputs, xor_outputs):
22 | output = net.activate(xi)
23 | genome.fitness -= (output[0] - xo[0]) ** 2
24 |
25 |
26 | def run(config_file):
27 | # Load configuration.
28 | config = neat.Config(neat.DefaultGenome, neat.DefaultReproduction,
29 | neat.DefaultSpeciesSet, neat.DefaultStagnation,
30 | config_file)
31 |
32 | # Create the population, which is the top-level object for a NEAT run.
33 | p = neat.Population(config)
34 |
35 | # Add a stdout reporter to show progress in the terminal.
36 | p.add_reporter(neat.StdOutReporter(True))
37 | stats = neat.StatisticsReporter()
38 | p.add_reporter(stats)
39 | p.add_reporter(neat.Checkpointer(50))
40 |
41 | # Run for up to 300 generations.
42 | winner = p.run(eval_genomes, 300)
43 |
44 | # Display the winning genome.
45 | print('\nBest genome:\n{!s}'.format(winner))
46 |
47 | # Show output of the most fit genome against training data.
48 | print('\nOutput:')
49 | winner_net = neat.nn.FeedForwardNetwork.create(winner, config)
50 | for xi, xo in zip(xor_inputs, xor_outputs):
51 | output = winner_net.activate(xi)
52 | print("input {!r}, expected output {!r}, got {!r}".format(xi, xo, output))
53 |
54 | node_names = {-1:'A', -2: 'B', 0:'A XOR B'}
55 | visualize.draw_net(config, winner, True, node_names=node_names)
56 | visualize.plot_stats(stats, ylog=False, view=True)
57 | visualize.plot_species(stats, view=True)
58 |
59 | p = neat.Checkpointer.restore_checkpoint('neat-checkpoint-49')
60 | p.run(eval_genomes, 10)
61 |
62 |
63 | if __name__ == '__main__':
64 | # Determine path to configuration file. This path manipulation is
65 | # here so that the script will run successfully regardless of the
66 | # current working directory.
67 | local_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__)
68 | config_path = os.path.join(local_dir, 'config-feedforward')
69 | run(config_path)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT/visualize.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import print_function
2 |
3 | import copy
4 | import warnings
5 |
6 | import graphviz
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 | import numpy as np
9 |
10 |
11 | def plot_stats(statistics, ylog=False, view=False, filename='avg_fitness.svg'):
12 | """ Plots the population's average and best fitness. """
13 | if plt is None:
14 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (matplotlib)")
15 | return
16 |
17 | generation = range(len(statistics.most_fit_genomes))
18 | best_fitness = [c.fitness for c in statistics.most_fit_genomes]
19 | avg_fitness = np.array(statistics.get_fitness_mean())
20 | stdev_fitness = np.array(statistics.get_fitness_stdev())
21 |
22 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness, 'b-', label="average")
23 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness - stdev_fitness, 'g-.', label="-1 sd")
24 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness + stdev_fitness, 'g-.', label="+1 sd")
25 | plt.plot(generation, best_fitness, 'r-', label="best")
26 |
27 | plt.title("Population's average and best fitness")
28 | plt.xlabel("Generations")
29 | plt.ylabel("Fitness")
30 | plt.grid()
31 | plt.legend(loc="best")
32 | if ylog:
33 | plt.gca().set_yscale('symlog')
34 |
35 | plt.savefig(filename)
36 | if view:
37 | plt.show()
38 |
39 | plt.close()
40 |
41 |
42 | def plot_spikes(spikes, view=False, filename=None, title=None):
43 | """ Plots the trains for a single spiking neuron. """
44 | t_values = [t for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
45 | v_values = [v for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
46 | u_values = [u for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
47 | I_values = [I for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
48 | f_values = [f for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
49 |
50 | fig = plt.figure()
51 | plt.subplot(4, 1, 1)
52 | plt.ylabel("Potential (mv)")
53 | plt.xlabel("Time (in ms)")
54 | plt.grid()
55 | plt.plot(t_values, v_values, "g-")
56 |
57 | if title is None:
58 | plt.title("Izhikevich's spiking neuron model")
59 | else:
60 | plt.title("Izhikevich's spiking neuron model ({0!s})".format(title))
61 |
62 | plt.subplot(4, 1, 2)
63 | plt.ylabel("Fired")
64 | plt.xlabel("Time (in ms)")
65 | plt.grid()
66 | plt.plot(t_values, f_values, "r-")
67 |
68 | plt.subplot(4, 1, 3)
69 | plt.ylabel("Recovery (u)")
70 | plt.xlabel("Time (in ms)")
71 | plt.grid()
72 | plt.plot(t_values, u_values, "r-")
73 |
74 | plt.subplot(4, 1, 4)
75 | plt.ylabel("Current (I)")
76 | plt.xlabel("Time (in ms)")
77 | plt.grid()
78 | plt.plot(t_values, I_values, "r-o")
79 |
80 | if filename is not None:
81 | plt.savefig(filename)
82 |
83 | if view:
84 | plt.show()
85 | plt.close()
86 | fig = None
87 |
88 | return fig
89 |
90 |
91 | def plot_species(statistics, view=False, filename='speciation.svg'):
92 | """ Visualizes speciation throughout evolution. """
93 | if plt is None:
94 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (matplotlib)")
95 | return
96 |
97 | species_sizes = statistics.get_species_sizes()
98 | num_generations = len(species_sizes)
99 | curves = np.array(species_sizes).T
100 |
101 | fig, ax = plt.subplots()
102 | ax.stackplot(range(num_generations), *curves)
103 |
104 | plt.title("Speciation")
105 | plt.ylabel("Size per Species")
106 | plt.xlabel("Generations")
107 |
108 | plt.savefig(filename)
109 |
110 | if view:
111 | plt.show()
112 |
113 | plt.close()
114 |
115 |
116 | def draw_net(config, genome, view=False, filename=None, node_names=None, show_disabled=True, prune_unused=False,
117 | node_colors=None, fmt='svg'):
118 | """ Receives a genome and draws a neural network with arbitrary topology. """
119 | # Attributes for network nodes.
120 | if graphviz is None:
121 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (graphviz)")
122 | return
123 |
124 | if node_names is None:
125 | node_names = {}
126 |
127 | assert type(node_names) is dict
128 |
129 | if node_colors is None:
130 | node_colors = {}
131 |
132 | assert type(node_colors) is dict
133 |
134 | node_attrs = {
135 | 'shape': 'circle',
136 | 'fontsize': '9',
137 | 'height': '0.2',
138 | 'width': '0.2'}
139 |
140 | dot = graphviz.Digraph(format=fmt, node_attr=node_attrs)
141 |
142 | inputs = set()
143 | for k in config.genome_config.input_keys:
144 | inputs.add(k)
145 | name = node_names.get(k, str(k))
146 | input_attrs = {'style': 'filled',
147 | 'shape': 'box'}
148 | input_attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(k, 'lightgray')
149 | dot.node(name, _attributes=input_attrs)
150 |
151 | outputs = set()
152 | for k in config.genome_config.output_keys:
153 | outputs.add(k)
154 | name = node_names.get(k, str(k))
155 | node_attrs = {'style': 'filled'}
156 | node_attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(k, 'lightblue')
157 |
158 | dot.node(name, _attributes=node_attrs)
159 |
160 | if prune_unused:
161 | connections = set()
162 | for cg in genome.connections.values():
163 | if cg.enabled or show_disabled:
164 | connections.add((cg.in_node_id, cg.out_node_id))
165 |
166 | used_nodes = copy.copy(outputs)
167 | pending = copy.copy(outputs)
168 | while pending:
169 | new_pending = set()
170 | for a, b in connections:
171 | if b in pending and a not in used_nodes:
172 | new_pending.add(a)
173 | used_nodes.add(a)
174 | pending = new_pending
175 | else:
176 | used_nodes = set(genome.nodes.keys())
177 |
178 | for n in used_nodes:
179 | if n in inputs or n in outputs:
180 | continue
181 |
182 | attrs = {'style': 'filled',
183 | 'fillcolor': node_colors.get(n, 'white')}
184 | dot.node(str(n), _attributes=attrs)
185 |
186 | for cg in genome.connections.values():
187 | if cg.enabled or show_disabled:
188 | #if cg.input not in used_nodes or cg.output not in used_nodes:
189 | # continue
190 | input, output = cg.key
191 | a = node_names.get(input, str(input))
192 | b = node_names.get(output, str(output))
193 | style = 'solid' if cg.enabled else 'dotted'
194 | color = 'green' if cg.weight > 0 else 'red'
195 | width = str(0.1 + abs(cg.weight / 5.0))
196 | dot.edge(a, b, _attributes={'style': style, 'color': color, 'penwidth': width})
197 |
198 | dot.render(filename, view=view)
199 |
200 | return dot
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT_gym/config:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # neat-python configuration for the LunarLander-v2 environment on OpenAI Gym
2 |
3 | [NEAT]
4 | pop_size = 100
5 | # Note: the fitness threshold will never be reached because
6 | # we are controlling the termination ourselves based on simulation performance.
7 | fitness_criterion = max
8 | fitness_threshold = 2.
9 | reset_on_extinction = 0
10 |
11 | [DefaultGenome]
12 | # node activation options
13 | activation_default = relu
14 | activation_mutate_rate = 0.0
15 | activation_options = relu
16 |
17 | # node aggregation options
18 | aggregation_default = sum
19 | aggregation_mutate_rate = 0.0
20 | aggregation_options = sum
21 |
22 | # node bias options
23 | bias_init_mean = 0.0
24 | bias_init_stdev = 1.0
25 | bias_max_value = 30.0
26 | bias_min_value = -30.0
27 | bias_mutate_power = 0.5
28 | bias_mutate_rate = 0.7
29 | bias_replace_rate = 0.1
30 |
31 | # genome compatibility options
32 | compatibility_disjoint_coefficient = 1.0
33 | compatibility_weight_coefficient = 1.0
34 |
35 | # connection add/remove rates
36 | conn_add_prob = 0.9
37 | conn_delete_prob = 0.2
38 |
39 | # connection enable options
40 | enabled_default = True
41 | enabled_mutate_rate = 0.01
42 |
43 | feed_forward = True
44 | initial_connection = full
45 | # options (unconnected, fs_neat, full)
46 |
47 | # node add/remove rates
48 | node_add_prob = 0.9
49 | node_delete_prob = 0.2
50 |
51 | # network parameters
52 | num_hidden = 0
53 | num_inputs = 4
54 | num_outputs = 2
55 |
56 | # node response options
57 | response_init_mean = 1.0
58 | response_init_stdev = 0.0
59 | response_max_value = 30.0
60 | response_min_value = -30.0
61 | response_mutate_power = 0.0
62 | response_mutate_rate = 0.0
63 | response_replace_rate = 0.0
64 |
65 | # connection weight options
66 | weight_init_mean = 0.0
67 | weight_init_stdev = 1.0
68 | weight_max_value = 30.
69 | weight_min_value = -30.
70 | weight_mutate_power = 0.5
71 | weight_mutate_rate = 0.8
72 | weight_replace_rate = 0.1
73 |
74 | [DefaultSpeciesSet]
75 | compatibility_threshold = 3.0
76 |
77 | [DefaultStagnation]
78 | species_fitness_func = max
79 | max_stagnation = 20
80 | species_elitism = 4
81 |
82 | [DefaultReproduction]
83 | elitism = 2
84 | survival_threshold = 0.2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT_gym/run_cartpole.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Using NEAT for reinforcement learning.
3 |
4 | The detail for NEAT can be find in : http://nn.cs.utexas.edu/downloads/papers/stanley.cec02.pdf
5 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
6 | """
7 | import neat
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import gym
10 | import visualize
11 |
12 | GAME = 'CartPole-v0'
13 | env = gym.make(GAME).unwrapped
14 |
15 | CONFIG = "./config"
16 | EP_STEP = 300 # maximum episode steps
17 | GENERATION_EP = 10 # evaluate by the minimum of 10-episode rewards
18 | TRAINING = False # training or testing
19 | CHECKPOINT = 9 # test on this checkpoint
20 |
21 |
22 | def eval_genomes(genomes, config):
23 | for genome_id, genome in genomes:
24 | net = neat.nn.FeedForwardNetwork.create(genome, config)
25 | ep_r = []
26 | for ep in range(GENERATION_EP): # run many episodes for the genome in case it's lucky
27 | accumulative_r = 0. # stage longer to get a greater episode reward
28 | observation = env.reset()
29 | for t in range(EP_STEP):
30 | action_values = net.activate(observation)
31 | action = np.argmax(action_values)
32 | observation_, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
33 | accumulative_r += reward
34 | if done:
35 | break
36 | observation = observation_
37 | ep_r.append(accumulative_r)
38 | genome.fitness = np.min(ep_r)/float(EP_STEP) # depends on the minimum episode reward
39 |
40 |
41 | def run():
42 | config = neat.Config(neat.DefaultGenome, neat.DefaultReproduction,
43 | neat.DefaultSpeciesSet, neat.DefaultStagnation, CONFIG)
44 | pop = neat.Population(config)
45 |
46 | # recode history
47 | stats = neat.StatisticsReporter()
48 | pop.add_reporter(stats)
49 | pop.add_reporter(neat.StdOutReporter(True))
50 | pop.add_reporter(neat.Checkpointer(5))
51 |
52 | pop.run(eval_genomes, 10) # train 10 generations
53 |
54 | # visualize training
55 | visualize.plot_stats(stats, ylog=False, view=True)
56 | visualize.plot_species(stats, view=True)
57 |
58 |
59 | def evaluation():
60 | p = neat.Checkpointer.restore_checkpoint('neat-checkpoint-%i' % CHECKPOINT)
61 | winner = p.run(eval_genomes, 1) # find the winner in restored population
62 |
63 | # show winner net
64 | node_names = {-1: 'In0', -2: 'In1', -3: 'In3', -4: 'In4', 0: 'act1', 1: 'act2'}
65 | visualize.draw_net(p.config, winner, True, node_names=node_names)
66 |
67 | net = neat.nn.FeedForwardNetwork.create(winner, p.config)
68 | while True:
69 | s = env.reset()
70 | while True:
71 | env.render()
72 | a = np.argmax(net.activate(s))
73 | s, r, done, _ = env.step(a)
74 | if done: break
75 |
76 |
77 | if __name__ == '__main__':
78 | if TRAINING:
79 | run()
80 | else:
81 | evaluation()
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT_gym/visualize.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import print_function
2 |
3 | import copy
4 | import warnings
5 |
6 | import graphviz
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 | import numpy as np
9 |
10 |
11 | def plot_stats(statistics, ylog=False, view=False, filename='avg_fitness.svg'):
12 | """ Plots the population's average and best fitness. """
13 | if plt is None:
14 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (matplotlib)")
15 | return
16 |
17 | generation = range(len(statistics.most_fit_genomes))
18 | best_fitness = [c.fitness for c in statistics.most_fit_genomes]
19 | avg_fitness = np.array(statistics.get_fitness_mean())
20 | stdev_fitness = np.array(statistics.get_fitness_stdev())
21 |
22 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness, 'b-', label="average")
23 | #plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness - stdev_fitness, 'g-.', label="-1 sd")
24 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness + stdev_fitness, 'g-.', label="+1 sd")
25 | plt.plot(generation, best_fitness, 'r-', label="best")
26 |
27 | plt.title("Population's average and best fitness")
28 | plt.xlabel("Generations")
29 | plt.ylabel("Fitness")
30 | plt.grid()
31 | plt.legend(loc="best")
32 | if ylog:
33 | plt.gca().set_yscale('symlog')
34 |
35 | plt.savefig(filename)
36 | if view:
37 | plt.show()
38 |
39 | plt.close()
40 |
41 |
42 | def plot_species(statistics, view=False, filename='speciation.svg'):
43 | """ Visualizes speciation throughout evolution. """
44 | if plt is None:
45 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (matplotlib)")
46 | return
47 |
48 | species_sizes = statistics.get_species_sizes()
49 | num_generations = len(species_sizes)
50 | curves = np.array(species_sizes).T
51 |
52 | fig, ax = plt.subplots()
53 | ax.stackplot(range(num_generations), *curves)
54 |
55 | plt.title("Speciation")
56 | plt.ylabel("Size per Species")
57 | plt.xlabel("Generations")
58 |
59 | plt.savefig(filename)
60 |
61 | if view:
62 | plt.show()
63 |
64 | plt.close()
65 |
66 |
67 | def draw_net(config, genome, view=False, filename=None, node_names=None, show_disabled=True, prune_unused=False,
68 | node_colors=None, fmt='svg'):
69 | """ Receives a genome and draws a neural network with arbitrary topology. """
70 | # Attributes for network nodes.
71 | if graphviz is None:
72 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (graphviz)")
73 | return
74 |
75 | if node_names is None:
76 | node_names = {}
77 |
78 | assert type(node_names) is dict
79 |
80 | if node_colors is None:
81 | node_colors = {}
82 |
83 | assert type(node_colors) is dict
84 |
85 | node_attrs = {
86 | 'shape': 'circle',
87 | 'fontsize': '9',
88 | 'height': '0.2',
89 | 'width': '0.2'}
90 |
91 | dot = graphviz.Digraph(format=fmt, node_attr=node_attrs)
92 |
93 | inputs = set()
94 | for k in config.genome_config.input_keys:
95 | inputs.add(k)
96 | name = node_names.get(k, str(k))
97 | input_attrs = {'style': 'filled',
98 | 'shape': 'box'}
99 | input_attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(k, 'lightgray')
100 | dot.node(name, _attributes=input_attrs)
101 |
102 | outputs = set()
103 | for k in config.genome_config.output_keys:
104 | outputs.add(k)
105 | name = node_names.get(k, str(k))
106 | node_attrs = {'style': 'filled'}
107 | node_attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(k, 'lightblue')
108 |
109 | dot.node(name, _attributes=node_attrs)
110 |
111 | if prune_unused:
112 | connections = set()
113 | for cg in genome.connections.values():
114 | if cg.enabled or show_disabled:
115 | connections.add(cg.key)
116 |
117 | used_nodes = copy.copy(outputs)
118 | pending = copy.copy(outputs)
119 | while pending:
120 | #print(pending, used_nodes)
121 | new_pending = set()
122 | for a, b in connections:
123 | if b in pending and a not in used_nodes:
124 | new_pending.add(a)
125 | used_nodes.add(a)
126 | pending = new_pending
127 | else:
128 | used_nodes = set(genome.nodes.keys())
129 |
130 | for n in used_nodes:
131 | if n in inputs or n in outputs:
132 | continue
133 |
134 | attrs = {'style': 'filled'}
135 | attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(n, 'white')
136 | dot.node(str(n), _attributes=attrs)
137 |
138 | for cg in genome.connections.values():
139 | if cg.enabled or show_disabled:
140 | #if cg.input not in used_nodes or cg.output not in used_nodes:
141 | # continue
142 | input, output = cg.key
143 | a = node_names.get(input, str(input))
144 | b = node_names.get(output, str(output))
145 | style = 'solid' if cg.enabled else 'dotted'
146 | color = 'green' if cg.weight > 0 else 'red'
147 | width = str(0.1 + abs(cg.weight / 5.0))
148 | dot.edge(a, b, _attributes={'style': style, 'color': color, 'penwidth': width})
149 |
150 | dot.render(filename, view=view)
151 |
152 | return dot
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
70 |
71 |
72 | # Donation
73 |
74 | *If this does help you, please consider donating to support me for better tutorials! Any contribution is greatly appreciated!*
75 |
76 |
83 |
84 |
91 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/es.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/es.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/es_rl.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/es_rl.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/find path.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/find path.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/ga.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/ga.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/mga.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/mga.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/nes.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/nes.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/phrase.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/phrase.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/demo/tsp.gif:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/MorvanZhou/Evolutionary-Algorithm/9a9c703580553c84ba3d9ef5aba788e320afe301/demo/tsp.gif
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Evolution Strategy/(1+1)-ES.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | (1+1)-ES with 1/5th success rule with visualization.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | DNA_SIZE = 1 # DNA (real number)
10 | DNA_BOUND = [0, 5] # solution upper and lower bounds
11 | N_GENERATIONS = 200
12 | MUT_STRENGTH = 5. # initial step size (dynamic mutation strength)
13 |
14 |
15 | def F(x): return np.sin(10*x)*x + np.cos(2*x)*x # to find the maximum of this function
16 |
17 |
18 | # find non-zero fitness for selection
19 | def get_fitness(pred): return pred.flatten()
20 |
21 |
22 | def make_kid(parent):
23 | # no crossover, only mutation
24 | k = parent + MUT_STRENGTH * np.random.randn(DNA_SIZE)
25 | k = np.clip(k, *DNA_BOUND)
26 | return k
27 |
28 |
29 | def kill_bad(parent, kid):
30 | global MUT_STRENGTH
31 | fp = get_fitness(F(parent))[0]
32 | fk = get_fitness(F(kid))[0]
33 | p_target = 1/5
34 | if fp < fk: # kid better than parent
35 | parent = kid
36 | ps = 1. # kid win -> ps = 1 (successful offspring)
37 | else:
38 | ps = 0.
39 | # adjust global mutation strength
40 | MUT_STRENGTH *= np.exp(1/np.sqrt(DNA_SIZE+1) * (ps - p_target)/(1 - p_target))
41 | return parent
42 |
43 |
44 | parent = 5 * np.random.rand(DNA_SIZE) # parent DNA
45 |
46 | plt.ion() # something about plotting
47 | x = np.linspace(*DNA_BOUND, 200)
48 |
49 | for _ in range(N_GENERATIONS):
50 | # ES part
51 | kid = make_kid(parent)
52 | py, ky = F(parent), F(kid) # for later plot
53 | parent = kill_bad(parent, kid)
54 |
55 | # something about plotting
56 | plt.cla()
57 | plt.scatter(parent, py, s=200, lw=0, c='red', alpha=0.5,)
58 | plt.scatter(kid, ky, s=200, lw=0, c='blue', alpha=0.5)
59 | plt.text(0, -7, 'Mutation strength=%.2f' % MUT_STRENGTH)
60 | plt.plot(x, F(x)); plt.pause(0.05)
61 |
62 | plt.ioff(); plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Evolution Strategy/Evolution Strategy Basic.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The Evolution Strategy can be summarized as the following term:
3 | {mu/rho +, lambda}-ES
4 |
5 | Here we use following term to find a maximum point.
6 | {n_pop/n_pop + n_kid}-ES
7 |
8 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
9 | """
10 | import numpy as np
11 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
12 |
13 | DNA_SIZE = 1 # DNA (real number)
14 | DNA_BOUND = [0, 5] # solution upper and lower bounds
15 | N_GENERATIONS = 200
16 | POP_SIZE = 100 # population size
17 | N_KID = 50 # n kids per generation
18 |
19 |
20 | def F(x): return np.sin(10*x)*x + np.cos(2*x)*x # to find the maximum of this function
21 |
22 |
23 | # find non-zero fitness for selection
24 | def get_fitness(pred): return pred.flatten()
25 |
26 |
27 | def make_kid(pop, n_kid):
28 | # generate empty kid holder
29 | kids = {'DNA': np.empty((n_kid, DNA_SIZE))}
30 | kids['mut_strength'] = np.empty_like(kids['DNA'])
31 | for kv, ks in zip(kids['DNA'], kids['mut_strength']):
32 | # crossover (roughly half p1 and half p2)
33 | p1, p2 = np.random.choice(np.arange(POP_SIZE), size=2, replace=False)
34 | cp = np.random.randint(0, 2, DNA_SIZE, dtype=np.bool) # crossover points
35 | kv[cp] = pop['DNA'][p1, cp]
36 | kv[~cp] = pop['DNA'][p2, ~cp]
37 | ks[cp] = pop['mut_strength'][p1, cp]
38 | ks[~cp] = pop['mut_strength'][p2, ~cp]
39 |
40 | # mutate (change DNA based on normal distribution)
41 | ks[:] = np.maximum(ks + (np.random.rand(*ks.shape)-0.5), 0.) # must > 0
42 | kv += ks * np.random.randn(*kv.shape)
43 | kv[:] = np.clip(kv, *DNA_BOUND) # clip the mutated value
44 | return kids
45 |
46 |
47 | def kill_bad(pop, kids):
48 | # put pop and kids together
49 | for key in ['DNA', 'mut_strength']:
50 | pop[key] = np.vstack((pop[key], kids[key]))
51 |
52 | fitness = get_fitness(F(pop['DNA'])) # calculate global fitness
53 | idx = np.arange(pop['DNA'].shape[0])
54 | good_idx = idx[fitness.argsort()][-POP_SIZE:] # selected by fitness ranking (not value)
55 | for key in ['DNA', 'mut_strength']:
56 | pop[key] = pop[key][good_idx]
57 | return pop
58 |
59 |
60 | pop = dict(DNA=5 * np.random.rand(1, DNA_SIZE).repeat(POP_SIZE, axis=0), # initialize the pop DNA values
61 | mut_strength=np.random.rand(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE)) # initialize the pop mutation strength values
62 |
63 | plt.ion() # something about plotting
64 | x = np.linspace(*DNA_BOUND, 200)
65 | plt.plot(x, F(x))
66 |
67 | for _ in range(N_GENERATIONS):
68 | # something about plotting
69 | if 'sca' in globals(): sca.remove()
70 | sca = plt.scatter(pop['DNA'], F(pop['DNA']), s=200, lw=0, c='red', alpha=0.5); plt.pause(0.05)
71 |
72 | # ES part
73 | kids = make_kid(pop, N_KID)
74 | pop = kill_bad(pop, kids) # keep some good parent for elitism
75 |
76 | plt.ioff(); plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Evolution Strategy/Natural Evolution Strategy (NES).py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The basic idea about Nature Evolution Strategy with visualation.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 |
6 | Dependencies:
7 | Tensorflow >= r1.2
8 | numpy
9 | matplotlib
10 | """
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
13 | import tensorflow as tf
14 | from tensorflow.contrib.distributions import MultivariateNormalFullCovariance
15 |
16 | DNA_SIZE = 2 # parameter (solution) number
17 | N_POP = 20 # population size
18 | N_GENERATION = 100 # training step
19 | LR = 0.02 # learning rate
20 |
21 |
22 | # fitness function
23 | def get_fitness(pred): return -((pred[:, 0])**2 + pred[:, 1]**2)
24 |
25 | # build multivariate distribution
26 | mean = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([2, ], 13., 1.), dtype=tf.float32)
27 | cov = tf.Variable(5. * tf.eye(DNA_SIZE), dtype=tf.float32)
28 | mvn = MultivariateNormalFullCovariance(loc=mean, covariance_matrix=cov)
29 | make_kid = mvn.sample(N_POP) # sampling operation
30 |
31 | # compute gradient and update mean and covariance matrix from sample and fitness
32 | tfkids_fit = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [N_POP, ])
33 | tfkids = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [N_POP, DNA_SIZE])
34 | loss = -tf.reduce_mean(mvn.log_prob(tfkids)*tfkids_fit) # log prob * fitness
35 | train_op = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(LR).minimize(loss) # compute and apply gradients for mean and cov
36 |
37 | sess = tf.Session()
38 | sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()) # initialize tf variables
39 |
40 | # something about plotting (can be ignored)
41 | n = 300
42 | x = np.linspace(-20, 20, n)
43 | X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, x)
44 | Z = np.zeros_like(X)
45 | for i in range(n):
46 | for j in range(n):
47 | Z[i, j] = get_fitness(np.array([[x[i], x[j]]]))
48 | plt.contourf(X, Y, -Z, 100, cmap=plt.cm.rainbow); plt.ylim(-20, 20); plt.xlim(-20, 20); plt.ion()
49 |
50 | # training
51 | for g in range(N_GENERATION):
52 | kids = sess.run(make_kid)
53 | kids_fit = get_fitness(kids)
54 | sess.run(train_op, {tfkids_fit: kids_fit, tfkids: kids}) # update distribution parameters
55 |
56 | # plotting update
57 | if 'sca' in globals(): sca.remove()
58 | sca = plt.scatter(kids[:, 0], kids[:, 1], s=30, c='k');plt.pause(0.01)
59 |
60 | print('Finished'); plt.ioff(); plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Find Path.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Genetic Algorithm to find a path to the target.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 |
9 | N_MOVES = 150
10 | DNA_SIZE = N_MOVES*2 # 40 x moves, 40 y moves
11 | DIRECTION_BOUND = [0, 1]
12 | CROSS_RATE = 0.8
13 | MUTATE_RATE = 0.0001
14 | POP_SIZE = 100
15 | N_GENERATIONS = 100
16 | GOAL_POINT = [10, 5]
17 | START_POINT = [0, 5]
18 | OBSTACLE_LINE = np.array([[5, 2], [5, 8]])
19 |
20 |
21 | class GA(object):
22 | def __init__(self, DNA_size, DNA_bound, cross_rate, mutation_rate, pop_size, ):
23 | self.DNA_size = DNA_size
24 | DNA_bound[1] += 1
25 | self.DNA_bound = DNA_bound
26 | self.cross_rate = cross_rate
27 | self.mutate_rate = mutation_rate
28 | self.pop_size = pop_size
29 |
30 | self.pop = np.random.randint(*DNA_bound, size=(pop_size, DNA_size))
31 |
32 | def DNA2product(self, DNA, n_moves, start_point): # convert to readable string
33 | pop = (DNA - 0.5) / 2
34 | pop[:, 0], pop[:, n_moves] = start_point[0], start_point[1]
35 | lines_x = np.cumsum(pop[:, :n_moves], axis=1)
36 | lines_y = np.cumsum(pop[:, n_moves:], axis=1)
37 | return lines_x, lines_y
38 |
39 | def get_fitness(self, lines_x, lines_y, goal_point, obstacle_line):
40 | dist2goal = np.sqrt((goal_point[0] - lines_x[:, -1]) ** 2 + (goal_point[1] - lines_y[:, -1]) ** 2)
41 | fitness = np.power(1 / (dist2goal + 1), 2)
42 | points = (lines_x > obstacle_line[0, 0] - 0.5) & (lines_x < obstacle_line[1, 0] + 0.5)
43 | y_values = np.where(points, lines_y, np.zeros_like(lines_y) - 100)
44 | bad_lines = ((y_values > obstacle_line[0, 1]) & (y_values < obstacle_line[1, 1])).max(axis=1)
45 | fitness[bad_lines] = 1e-6
46 | return fitness
47 |
48 | def select(self, fitness):
49 | idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.pop_size), size=self.pop_size, replace=True, p=fitness/fitness.sum())
50 | return self.pop[idx]
51 |
52 | def crossover(self, parent, pop):
53 | if np.random.rand() < self.cross_rate:
54 | i_ = np.random.randint(0, self.pop_size, size=1) # select another individual from pop
55 | cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, self.DNA_size).astype(np.bool) # choose crossover points
56 | parent[cross_points] = pop[i_, cross_points] # mating and produce one child
57 | return parent
58 |
59 | def mutate(self, child):
60 | for point in range(self.DNA_size):
61 | if np.random.rand() < self.mutate_rate:
62 | child[point] = np.random.randint(*self.DNA_bound)
63 | return child
64 |
65 | def evolve(self, fitness):
66 | pop = self.select(fitness)
67 | pop_copy = pop.copy()
68 | for parent in pop: # for every parent
69 | child = self.crossover(parent, pop_copy)
70 | child = self.mutate(child)
71 | parent[:] = child
72 | self.pop = pop
73 |
74 |
75 | class Line(object):
76 | def __init__(self, n_moves, goal_point, start_point, obstacle_line):
77 | self.n_moves = n_moves
78 | self.goal_point = goal_point
79 | self.start_point = start_point
80 | self.obstacle_line = obstacle_line
81 |
82 | plt.ion()
83 |
84 | def plotting(self, lines_x, lines_y):
85 | plt.cla()
86 | plt.scatter(*self.goal_point, s=200, c='r')
87 | plt.scatter(*self.start_point, s=100, c='b')
88 | plt.plot(self.obstacle_line[:, 0], self.obstacle_line[:, 1], lw=3, c='k')
89 | plt.plot(lines_x.T, lines_y.T, c='k')
90 | plt.xlim((-5, 15))
91 | plt.ylim((-5, 15))
92 | plt.pause(0.01)
93 |
94 |
95 | ga = GA(DNA_size=DNA_SIZE, DNA_bound=DIRECTION_BOUND,
96 | cross_rate=CROSS_RATE, mutation_rate=MUTATE_RATE, pop_size=POP_SIZE)
97 |
98 | env = Line(N_MOVES, GOAL_POINT, START_POINT, OBSTACLE_LINE)
99 |
100 | for generation in range(N_GENERATIONS):
101 | lx, ly = ga.DNA2product(ga.pop, N_MOVES, START_POINT)
102 | fitness = ga.get_fitness(lx, ly, GOAL_POINT, OBSTACLE_LINE)
103 | ga.evolve(fitness)
104 | print('Gen:', generation, '| best fit:', fitness.max())
105 | env.plotting(lx, ly)
106 |
107 | plt.ioff()
108 | plt.show()
109 |
110 |
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Genetic Algorithm Basic.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Genetic Algorithm to find a maximum point in a function.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | DNA_SIZE = 10 # DNA length
10 | POP_SIZE = 100 # population size
11 | CROSS_RATE = 0.8 # mating probability (DNA crossover)
12 | MUTATION_RATE = 0.003 # mutation probability
13 | N_GENERATIONS = 200
14 | X_BOUND = [0, 5] # x upper and lower bounds
15 |
16 |
17 | def F(x): return np.sin(10*x)*x + np.cos(2*x)*x # to find the maximum of this function
18 |
19 |
20 | # find non-zero fitness for selection
21 | def get_fitness(pred): return pred + 1e-3 - np.min(pred)
22 |
23 |
24 | # convert binary DNA to decimal and normalize it to a range(0, 5)
25 | def translateDNA(pop): return pop.dot(2 ** np.arange(DNA_SIZE)[::-1]) / float(2**DNA_SIZE-1) * X_BOUND[1]
26 |
27 |
28 | def select(pop, fitness): # nature selection wrt pop's fitness
29 | idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(POP_SIZE), size=POP_SIZE, replace=True,
30 | p=fitness/fitness.sum())
31 | return pop[idx]
32 |
33 |
34 | def crossover(parent, pop): # mating process (genes crossover)
35 | if np.random.rand() < CROSS_RATE:
36 | i_ = np.random.randint(0, POP_SIZE, size=1) # select another individual from pop
37 | cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, size=DNA_SIZE).astype(np.bool_) # choose crossover points
38 | parent[cross_points] = pop[i_, cross_points] # mating and produce one child
39 | return parent
40 |
41 |
42 | def mutate(child):
43 | for point in range(DNA_SIZE):
44 | if np.random.rand() < MUTATION_RATE:
45 | child[point] = 1 if child[point] == 0 else 0
46 | return child
47 |
48 |
49 | pop = np.random.randint(2, size=(POP_SIZE, DNA_SIZE)) # initialize the pop DNA
50 |
51 | plt.ion() # something about plotting
52 | x = np.linspace(*X_BOUND, 200)
53 | plt.plot(x, F(x))
54 |
55 | for _ in range(N_GENERATIONS):
56 | F_values = F(translateDNA(pop)) # compute function value by extracting DNA
57 |
58 | # something about plotting
59 | if 'sca' in globals(): sca.remove()
60 | sca = plt.scatter(translateDNA(pop), F_values, s=200, lw=0, c='red', alpha=0.5); plt.pause(0.05)
61 |
62 | # GA part (evolution)
63 | fitness = get_fitness(F_values)
64 | print("Most fitted DNA: ", pop[np.argmax(fitness), :])
65 | pop = select(pop, fitness)
66 | pop_copy = pop.copy()
67 | for parent in pop:
68 | child = crossover(parent, pop_copy)
69 | child = mutate(child)
70 | parent[:] = child # parent is replaced by its child
71 |
72 | plt.ioff(); plt.show()
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Match Phrase.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Genetic Algorithm to match the target phrase.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import numpy as np
7 |
8 | TARGET_PHRASE = 'You get it!' # target DNA
9 | POP_SIZE = 300 # population size
10 | CROSS_RATE = 0.4 # mating probability (DNA crossover)
11 | MUTATION_RATE = 0.01 # mutation probability
12 | N_GENERATIONS = 1000
13 |
14 | DNA_SIZE = len(TARGET_PHRASE)
15 | TARGET_ASCII = np.fromstring(TARGET_PHRASE, dtype=np.uint8) # convert string to number
16 | ASCII_BOUND = [32, 126]
17 |
18 |
19 | class GA(object):
20 | def __init__(self, DNA_size, DNA_bound, cross_rate, mutation_rate, pop_size):
21 | self.DNA_size = DNA_size
22 | DNA_bound[1] += 1
23 | self.DNA_bound = DNA_bound
24 | self.cross_rate = cross_rate
25 | self.mutate_rate = mutation_rate
26 | self.pop_size = pop_size
27 |
28 | self.pop = np.random.randint(*DNA_bound, size=(pop_size, DNA_size)).astype(np.int8) # int8 for convert to ASCII
29 |
30 | def translateDNA(self, DNA): # convert to readable string
31 | return DNA.tostring().decode('ascii')
32 |
33 | def get_fitness(self): # count how many character matches
34 | match_count = (self.pop == TARGET_ASCII).sum(axis=1)
35 | return match_count
36 |
37 | def select(self):
38 | fitness = self.get_fitness() + 1e-4 # add a small amount to avoid all zero fitness
39 | idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.pop_size), size=self.pop_size, replace=True, p=fitness/fitness.sum())
40 | return self.pop[idx]
41 |
42 | def crossover(self, parent, pop):
43 | if np.random.rand() < self.cross_rate:
44 | i_ = np.random.randint(0, self.pop_size, size=1) # select another individual from pop
45 | cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, self.DNA_size).astype(np.bool) # choose crossover points
46 | parent[cross_points] = pop[i_, cross_points] # mating and produce one child
47 | return parent
48 |
49 | def mutate(self, child):
50 | for point in range(self.DNA_size):
51 | if np.random.rand() < self.mutate_rate:
52 | child[point] = np.random.randint(*self.DNA_bound) # choose a random ASCII index
53 | return child
54 |
55 | def evolve(self):
56 | pop = self.select()
57 | pop_copy = pop.copy()
58 | for parent in pop: # for every parent
59 | child = self.crossover(parent, pop_copy)
60 | child = self.mutate(child)
61 | parent[:] = child
62 | self.pop = pop
63 |
64 | if __name__ == '__main__':
65 | ga = GA(DNA_size=DNA_SIZE, DNA_bound=ASCII_BOUND, cross_rate=CROSS_RATE,
66 | mutation_rate=MUTATION_RATE, pop_size=POP_SIZE)
67 |
68 | for generation in range(N_GENERATIONS):
69 | fitness = ga.get_fitness()
70 | best_DNA = ga.pop[np.argmax(fitness)]
71 | best_phrase = ga.translateDNA(best_DNA)
72 | print('Gen', generation, ': ', best_phrase)
73 | if best_phrase == TARGET_PHRASE:
74 | break
75 | ga.evolve()
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Microbial Genetic Algorithm.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Microbial Genetic Algorithm to find the maximum point in a graph.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 |
9 | DNA_SIZE = 10 # DNA length
10 | POP_SIZE = 20 # population size
11 | CROSS_RATE = 0.6 # mating probability (DNA crossover)
12 | MUTATION_RATE = 0.01 # mutation probability
13 | N_GENERATIONS = 200
14 | X_BOUND = [0, 5] # x upper and lower bounds
15 |
16 |
17 | def F(x): return np.sin(10*x)*x + np.cos(2*x)*x # to find the maximum of this function
18 |
19 |
20 | class MGA(object):
21 | def __init__(self, DNA_size, DNA_bound, cross_rate, mutation_rate, pop_size):
22 | self.DNA_size = DNA_size
23 | DNA_bound[1] += 1
24 | self.DNA_bound = DNA_bound
25 | self.cross_rate = cross_rate
26 | self.mutate_rate = mutation_rate
27 | self.pop_size = pop_size
28 |
29 | # initial DNAs for winner and loser
30 | self.pop = np.random.randint(*DNA_bound, size=(1, self.DNA_size)).repeat(pop_size, axis=0)
31 |
32 | def translateDNA(self, pop):
33 | # convert binary DNA to decimal and normalize it to a range(0, 5)
34 | return pop.dot(2 ** np.arange(self.DNA_size)[::-1]) / float(2 ** self.DNA_size - 1) * X_BOUND[1]
35 |
36 | def get_fitness(self, product):
37 | return product # it is OK to use product value as fitness in here
38 |
39 | def crossover(self, loser_winner): # crossover for loser
40 | cross_idx = np.empty((self.DNA_size,)).astype(np.bool)
41 | for i in range(self.DNA_size):
42 | cross_idx[i] = True if np.random.rand() < self.cross_rate else False # crossover index
43 | loser_winner[0, cross_idx] = loser_winner[1, cross_idx] # assign winners genes to loser
44 | return loser_winner
45 |
46 | def mutate(self, loser_winner): # mutation for loser
47 | mutation_idx = np.empty((self.DNA_size,)).astype(np.bool)
48 | for i in range(self.DNA_size):
49 | mutation_idx[i] = True if np.random.rand() < self.mutate_rate else False # mutation index
50 | # flip values in mutation points
51 | loser_winner[0, mutation_idx] = ~loser_winner[0, mutation_idx].astype(np.bool)
52 | return loser_winner
53 |
54 | def evolve(self, n): # nature selection wrt pop's fitness
55 | for _ in range(n): # random pick and compare n times
56 | sub_pop_idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(0, self.pop_size), size=2, replace=False)
57 | sub_pop = self.pop[sub_pop_idx] # pick 2 from pop
58 | product = F(self.translateDNA(sub_pop))
59 | fitness = self.get_fitness(product)
60 | loser_winner_idx = np.argsort(fitness)
61 | loser_winner = sub_pop[loser_winner_idx] # the first is loser and second is winner
62 | loser_winner = self.crossover(loser_winner)
63 | loser_winner = self.mutate(loser_winner)
64 | self.pop[sub_pop_idx] = loser_winner
65 |
66 | DNA_prod = self.translateDNA(self.pop)
67 | pred = F(DNA_prod)
68 | return DNA_prod, pred
69 |
70 |
71 | plt.ion() # something about plotting
72 | x = np.linspace(*X_BOUND, 200)
73 | plt.plot(x, F(x))
74 |
75 | ga = MGA(DNA_size=DNA_SIZE, DNA_bound=[0, 1], cross_rate=CROSS_RATE, mutation_rate=MUTATION_RATE, pop_size=POP_SIZE)
76 |
77 | for _ in range(N_GENERATIONS): # 100 generations
78 | DNA_prod, pred = ga.evolve(5) # natural selection, crossover and mutation
79 |
80 | # something about plotting
81 | if 'sca' in globals(): sca.remove()
82 | sca = plt.scatter(DNA_prod, pred, s=200, lw=0, c='red', alpha=0.5); plt.pause(0.05)
83 |
84 | plt.ioff();plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Genetic Algorithm/Travel Sales Person.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Visualize Genetic Algorithm to find the shortest path for travel sales problem.
3 |
4 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
5 | """
6 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
7 | import numpy as np
8 |
9 | N_CITIES = 20 # DNA size
10 | CROSS_RATE = 0.1
11 | MUTATE_RATE = 0.02
12 | POP_SIZE = 500
13 | N_GENERATIONS = 500
14 |
15 |
16 | class GA(object):
17 | def __init__(self, DNA_size, cross_rate, mutation_rate, pop_size, ):
18 | self.DNA_size = DNA_size
19 | self.cross_rate = cross_rate
20 | self.mutate_rate = mutation_rate
21 | self.pop_size = pop_size
22 |
23 | self.pop = np.vstack([np.random.permutation(DNA_size) for _ in range(pop_size)])
24 |
25 | def translateDNA(self, DNA, city_position): # get cities' coord in order
26 | line_x = np.empty_like(DNA, dtype=np.float64)
27 | line_y = np.empty_like(DNA, dtype=np.float64)
28 | for i, d in enumerate(DNA):
29 | city_coord = city_position[d]
30 | line_x[i, :] = city_coord[:, 0]
31 | line_y[i, :] = city_coord[:, 1]
32 | return line_x, line_y
33 |
34 | def get_fitness(self, line_x, line_y):
35 | total_distance = np.empty((line_x.shape[0],), dtype=np.float64)
36 | for i, (xs, ys) in enumerate(zip(line_x, line_y)):
37 | total_distance[i] = np.sum(np.sqrt(np.square(np.diff(xs)) + np.square(np.diff(ys))))
38 | fitness = np.exp(self.DNA_size * 2 / total_distance)
39 | return fitness, total_distance
40 |
41 | def select(self, fitness):
42 | idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(self.pop_size), size=self.pop_size, replace=True, p=fitness / fitness.sum())
43 | return self.pop[idx]
44 |
45 | def crossover(self, parent, pop):
46 | if np.random.rand() < self.cross_rate:
47 | i_ = np.random.randint(0, self.pop_size, size=1) # select another individual from pop
48 | cross_points = np.random.randint(0, 2, self.DNA_size).astype(np.bool) # choose crossover points
49 | keep_city = parent[~cross_points] # find the city number
50 | swap_city = pop[i_, np.isin(pop[i_].ravel(), keep_city, invert=True)]
51 | parent[:] = np.concatenate((keep_city, swap_city))
52 | return parent
53 |
54 | def mutate(self, child):
55 | for point in range(self.DNA_size):
56 | if np.random.rand() < self.mutate_rate:
57 | swap_point = np.random.randint(0, self.DNA_size)
58 | swapA, swapB = child[point], child[swap_point]
59 | child[point], child[swap_point] = swapB, swapA
60 | return child
61 |
62 | def evolve(self, fitness):
63 | pop = self.select(fitness)
64 | pop_copy = pop.copy()
65 | for parent in pop: # for every parent
66 | child = self.crossover(parent, pop_copy)
67 | child = self.mutate(child)
68 | parent[:] = child
69 | self.pop = pop
70 |
71 |
72 | class TravelSalesPerson(object):
73 | def __init__(self, n_cities):
74 | self.city_position = np.random.rand(n_cities, 2)
75 | plt.ion()
76 |
77 | def plotting(self, lx, ly, total_d):
78 | plt.cla()
79 | plt.scatter(self.city_position[:, 0].T, self.city_position[:, 1].T, s=100, c='k')
80 | plt.plot(lx.T, ly.T, 'r-')
81 | plt.text(-0.05, -0.05, "Total distance=%.2f" % total_d, fontdict={'size': 20, 'color': 'red'})
82 | plt.xlim((-0.1, 1.1))
83 | plt.ylim((-0.1, 1.1))
84 | plt.pause(0.01)
85 |
86 |
87 | ga = GA(DNA_size=N_CITIES, cross_rate=CROSS_RATE, mutation_rate=MUTATE_RATE, pop_size=POP_SIZE)
88 |
89 | env = TravelSalesPerson(N_CITIES)
90 | for generation in range(N_GENERATIONS):
91 | lx, ly = ga.translateDNA(ga.pop, env.city_position)
92 | fitness, total_distance = ga.get_fitness(lx, ly)
93 | ga.evolve(fitness)
94 | best_idx = np.argmax(fitness)
95 | print('Gen:', generation, '| best fit: %.2f' % fitness[best_idx],)
96 |
97 | env.plotting(lx[best_idx], ly[best_idx], total_distance[best_idx])
98 |
99 | plt.ioff()
100 | plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/Evolution Strategy with Neural Nets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Simple code for Distributed ES proposed by OpenAI.
3 | Based on this paper: Evolution Strategies as a Scalable Alternative to Reinforcement Learning
4 | Details can be found in : https://arxiv.org/abs/1703.03864
5 |
6 | Visit more on my tutorial site: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
7 | """
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import gym
10 | import multiprocessing as mp
11 | import time
12 |
13 | N_KID = 10 # half of the training population
14 | N_GENERATION = 5000 # training step
15 | LR = .05 # learning rate
16 | SIGMA = .05 # mutation strength or step size
17 | N_CORE = mp.cpu_count()-1
18 | CONFIG = [
19 | dict(game="CartPole-v0",
20 | n_feature=4, n_action=2, continuous_a=[False], ep_max_step=700, eval_threshold=500),
21 | dict(game="MountainCar-v0",
22 | n_feature=2, n_action=3, continuous_a=[False], ep_max_step=200, eval_threshold=-120),
23 | dict(game="Pendulum-v0",
24 | n_feature=3, n_action=1, continuous_a=[True, 2.], ep_max_step=200, eval_threshold=-180)
25 | ][2] # choose your game
26 |
27 |
28 | def sign(k_id): return -1. if k_id % 2 == 0 else 1. # mirrored sampling
29 |
30 |
31 | class SGD(object): # optimizer with momentum
32 | def __init__(self, params, learning_rate, momentum=0.9):
33 | self.v = np.zeros_like(params).astype(np.float32)
34 | self.lr, self.momentum = learning_rate, momentum
35 |
36 | def get_gradients(self, gradients):
37 | self.v = self.momentum * self.v + (1. - self.momentum) * gradients
38 | return self.lr * self.v
39 |
40 |
41 | def params_reshape(shapes, params): # reshape to be a matrix
42 | p, start = [], 0
43 | for i, shape in enumerate(shapes): # flat params to matrix
44 | n_w, n_b = shape[0] * shape[1], shape[1]
45 | p = p + [params[start: start + n_w].reshape(shape),
46 | params[start + n_w: start + n_w + n_b].reshape((1, shape[1]))]
47 | start += n_w + n_b
48 | return p
49 |
50 |
51 | def get_reward(shapes, params, env, ep_max_step, continuous_a, seed_and_id=None,):
52 | # perturb parameters using seed
53 | if seed_and_id is not None:
54 | seed, k_id = seed_and_id
55 | np.random.seed(seed)
56 | params += sign(k_id) * SIGMA * np.random.randn(params.size)
57 | p = params_reshape(shapes, params)
58 | # run episode
59 | s = env.reset()
60 | ep_r = 0.
61 | for step in range(ep_max_step):
62 | a = get_action(p, s, continuous_a)
63 | s, r, done, _ = env.step(a)
64 | # mountain car's reward can be tricky
65 | if env.spec._env_name == 'MountainCar' and s[0] > -0.1: r = 0.
66 | ep_r += r
67 | if done: break
68 | return ep_r
69 |
70 |
71 | def get_action(params, x, continuous_a):
72 | x = x[np.newaxis, :]
73 | x = np.tanh(x.dot(params[0]) + params[1])
74 | x = np.tanh(x.dot(params[2]) + params[3])
75 | x = x.dot(params[4]) + params[5]
76 | if not continuous_a[0]: return np.argmax(x, axis=1)[0] # for discrete action
77 | else: return continuous_a[1] * np.tanh(x)[0] # for continuous action
78 |
79 |
80 | def build_net():
81 | def linear(n_in, n_out): # network linear layer
82 | w = np.random.randn(n_in * n_out).astype(np.float32) * .1
83 | b = np.random.randn(n_out).astype(np.float32) * .1
84 | return (n_in, n_out), np.concatenate((w, b))
85 | s0, p0 = linear(CONFIG['n_feature'], 30)
86 | s1, p1 = linear(30, 20)
87 | s2, p2 = linear(20, CONFIG['n_action'])
88 | return [s0, s1, s2], np.concatenate((p0, p1, p2))
89 |
90 |
91 | def train(net_shapes, net_params, optimizer, utility, pool):
92 | # pass seed instead whole noise matrix to parallel will save your time
93 | noise_seed = np.random.randint(0, 2 ** 32 - 1, size=N_KID, dtype=np.uint32).repeat(2) # mirrored sampling
94 |
95 | # distribute training in parallel
96 | jobs = [pool.apply_async(get_reward, (net_shapes, net_params, env, CONFIG['ep_max_step'], CONFIG['continuous_a'],
97 | [noise_seed[k_id], k_id], )) for k_id in range(N_KID*2)]
98 | rewards = np.array([j.get() for j in jobs])
99 | kids_rank = np.argsort(rewards)[::-1] # rank kid id by reward
100 |
101 | cumulative_update = np.zeros_like(net_params) # initialize update values
102 | for ui, k_id in enumerate(kids_rank):
103 | np.random.seed(noise_seed[k_id]) # reconstruct noise using seed
104 | cumulative_update += utility[ui] * sign(k_id) * np.random.randn(net_params.size)
105 |
106 | gradients = optimizer.get_gradients(cumulative_update/(2*N_KID*SIGMA))
107 | return net_params + gradients, rewards
108 |
109 |
110 | if __name__ == "__main__":
111 | # utility instead reward for update parameters (rank transformation)
112 | base = N_KID * 2 # *2 for mirrored sampling
113 | rank = np.arange(1, base + 1)
114 | util_ = np.maximum(0, np.log(base / 2 + 1) - np.log(rank))
115 | utility = util_ / util_.sum() - 1 / base
116 |
117 | # training
118 | net_shapes, net_params = build_net()
119 | env = gym.make(CONFIG['game']).unwrapped
120 | optimizer = SGD(net_params, LR)
121 | pool = mp.Pool(processes=N_CORE)
122 | mar = None # moving average reward
123 | for g in range(N_GENERATION):
124 | t0 = time.time()
125 | net_params, kid_rewards = train(net_shapes, net_params, optimizer, utility, pool)
126 |
127 | # test trained net without noise
128 | net_r = get_reward(net_shapes, net_params, env, CONFIG['ep_max_step'], CONFIG['continuous_a'], None,)
129 | mar = net_r if mar is None else 0.9 * mar + 0.1 * net_r # moving average reward
130 | print(
131 | 'Gen: ', g,
132 | '| Net_R: %.1f' % mar,
133 | '| Kid_avg_R: %.1f' % kid_rewards.mean(),
134 | '| Gen_T: %.2f' % (time.time() - t0),)
135 | if mar >= CONFIG['eval_threshold']: break
136 |
137 | # test
138 | print("\nTESTING....")
139 | p = params_reshape(net_shapes, net_params)
140 | while True:
141 | s = env.reset()
142 | for _ in range(CONFIG['ep_max_step']):
143 | env.render()
144 | a = get_action(p, s, CONFIG['continuous_a'])
145 | s, _, done, _ = env.step(a)
146 | if done: break
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT/config-feedforward:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #--- parameters for the XOR-2 experiment ---#
2 |
3 | [NEAT]
4 | fitness_criterion = max
5 | fitness_threshold = 3.9
6 | pop_size = 150
7 | reset_on_extinction = False
8 |
9 | [DefaultGenome]
10 | # node activation options
11 | activation_default = sigmoid
12 | activation_mutate_rate = 0.0
13 | activation_options = sigmoid
14 |
15 | # node aggregation options
16 | aggregation_default = sum
17 | aggregation_mutate_rate = 0.0
18 | aggregation_options = sum
19 |
20 | # node bias options
21 | bias_init_mean = 0.0
22 | bias_init_stdev = 1.0
23 | bias_max_value = 30.0
24 | bias_min_value = -30.0
25 | bias_mutate_power = 0.5
26 | bias_mutate_rate = 0.7
27 | bias_replace_rate = 0.1
28 |
29 | # genome compatibility options
30 | compatibility_disjoint_coefficient = 1.0
31 | compatibility_weight_coefficient = 0.5
32 |
33 | # connection add/remove rates
34 | conn_add_prob = 0.5
35 | conn_delete_prob = 0.5
36 |
37 | # connection enable options
38 | enabled_default = True
39 | enabled_mutate_rate = 0.01
40 |
41 | feed_forward = True
42 | initial_connection = full
43 |
44 | # node add/remove rates
45 | node_add_prob = 0.2
46 | node_delete_prob = 0.2
47 |
48 | # network parameters
49 | num_hidden = 0
50 | num_inputs = 2
51 | num_outputs = 1
52 |
53 | # node response options
54 | response_init_mean = 1.0
55 | response_init_stdev = 0.0
56 | response_max_value = 30.0
57 | response_min_value = -30.0
58 | response_mutate_power = 0.0
59 | response_mutate_rate = 0.0
60 | response_replace_rate = 0.0
61 |
62 | # connection weight options
63 | weight_init_mean = 0.0
64 | weight_init_stdev = 1.0
65 | weight_max_value = 30
66 | weight_min_value = -30
67 | weight_mutate_power = 0.5
68 | weight_mutate_rate = 0.8
69 | weight_replace_rate = 0.1
70 |
71 | [DefaultSpeciesSet]
72 | compatibility_threshold = 3.0
73 |
74 | [DefaultStagnation]
75 | species_fitness_func = max
76 | max_stagnation = 20
77 | species_elitism = 2
78 |
79 | [DefaultReproduction]
80 | elitism = 2
81 | survival_threshold = 0.2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT/run_xor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Using NEAT for supervised learning. This example comes from http://neat-python.readthedocs.io/en/latest/xor_example.html
3 |
4 | The detail for NEAT can be find in : http://nn.cs.utexas.edu/downloads/papers/stanley.cec02.pdf
5 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
6 | """
7 |
8 | import os
9 | import neat
10 | import visualize
11 |
12 | # 2-input XOR inputs and expected outputs.
13 | xor_inputs = [(0.0, 0.0), (0.0, 1.0), (1.0, 0.0), (1.0, 1.0)]
14 | xor_outputs = [ (0.0,), (1.0,), (1.0,), (0.0,)]
15 |
16 |
17 | def eval_genomes(genomes, config):
18 | for genome_id, genome in genomes: # for each individual
19 | genome.fitness = 4.0 # 4 xor evaluations
20 | net = neat.nn.FeedForwardNetwork.create(genome, config)
21 | for xi, xo in zip(xor_inputs, xor_outputs):
22 | output = net.activate(xi)
23 | genome.fitness -= (output[0] - xo[0]) ** 2
24 |
25 |
26 | def run(config_file):
27 | # Load configuration.
28 | config = neat.Config(neat.DefaultGenome, neat.DefaultReproduction,
29 | neat.DefaultSpeciesSet, neat.DefaultStagnation,
30 | config_file)
31 |
32 | # Create the population, which is the top-level object for a NEAT run.
33 | p = neat.Population(config)
34 |
35 | # Add a stdout reporter to show progress in the terminal.
36 | p.add_reporter(neat.StdOutReporter(True))
37 | stats = neat.StatisticsReporter()
38 | p.add_reporter(stats)
39 | p.add_reporter(neat.Checkpointer(50))
40 |
41 | # Run for up to 300 generations.
42 | winner = p.run(eval_genomes, 300)
43 |
44 | # Display the winning genome.
45 | print('\nBest genome:\n{!s}'.format(winner))
46 |
47 | # Show output of the most fit genome against training data.
48 | print('\nOutput:')
49 | winner_net = neat.nn.FeedForwardNetwork.create(winner, config)
50 | for xi, xo in zip(xor_inputs, xor_outputs):
51 | output = winner_net.activate(xi)
52 | print("input {!r}, expected output {!r}, got {!r}".format(xi, xo, output))
53 |
54 | node_names = {-1:'A', -2: 'B', 0:'A XOR B'}
55 | visualize.draw_net(config, winner, True, node_names=node_names)
56 | visualize.plot_stats(stats, ylog=False, view=True)
57 | visualize.plot_species(stats, view=True)
58 |
59 | p = neat.Checkpointer.restore_checkpoint('neat-checkpoint-49')
60 | p.run(eval_genomes, 10)
61 |
62 |
63 | if __name__ == '__main__':
64 | # Determine path to configuration file. This path manipulation is
65 | # here so that the script will run successfully regardless of the
66 | # current working directory.
67 | local_dir = os.path.dirname(__file__)
68 | config_path = os.path.join(local_dir, 'config-feedforward')
69 | run(config_path)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT/visualize.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import print_function
2 |
3 | import copy
4 | import warnings
5 |
6 | import graphviz
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 | import numpy as np
9 |
10 |
11 | def plot_stats(statistics, ylog=False, view=False, filename='avg_fitness.svg'):
12 | """ Plots the population's average and best fitness. """
13 | if plt is None:
14 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (matplotlib)")
15 | return
16 |
17 | generation = range(len(statistics.most_fit_genomes))
18 | best_fitness = [c.fitness for c in statistics.most_fit_genomes]
19 | avg_fitness = np.array(statistics.get_fitness_mean())
20 | stdev_fitness = np.array(statistics.get_fitness_stdev())
21 |
22 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness, 'b-', label="average")
23 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness - stdev_fitness, 'g-.', label="-1 sd")
24 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness + stdev_fitness, 'g-.', label="+1 sd")
25 | plt.plot(generation, best_fitness, 'r-', label="best")
26 |
27 | plt.title("Population's average and best fitness")
28 | plt.xlabel("Generations")
29 | plt.ylabel("Fitness")
30 | plt.grid()
31 | plt.legend(loc="best")
32 | if ylog:
33 | plt.gca().set_yscale('symlog')
34 |
35 | plt.savefig(filename)
36 | if view:
37 | plt.show()
38 |
39 | plt.close()
40 |
41 |
42 | def plot_spikes(spikes, view=False, filename=None, title=None):
43 | """ Plots the trains for a single spiking neuron. """
44 | t_values = [t for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
45 | v_values = [v for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
46 | u_values = [u for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
47 | I_values = [I for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
48 | f_values = [f for t, I, v, u, f in spikes]
49 |
50 | fig = plt.figure()
51 | plt.subplot(4, 1, 1)
52 | plt.ylabel("Potential (mv)")
53 | plt.xlabel("Time (in ms)")
54 | plt.grid()
55 | plt.plot(t_values, v_values, "g-")
56 |
57 | if title is None:
58 | plt.title("Izhikevich's spiking neuron model")
59 | else:
60 | plt.title("Izhikevich's spiking neuron model ({0!s})".format(title))
61 |
62 | plt.subplot(4, 1, 2)
63 | plt.ylabel("Fired")
64 | plt.xlabel("Time (in ms)")
65 | plt.grid()
66 | plt.plot(t_values, f_values, "r-")
67 |
68 | plt.subplot(4, 1, 3)
69 | plt.ylabel("Recovery (u)")
70 | plt.xlabel("Time (in ms)")
71 | plt.grid()
72 | plt.plot(t_values, u_values, "r-")
73 |
74 | plt.subplot(4, 1, 4)
75 | plt.ylabel("Current (I)")
76 | plt.xlabel("Time (in ms)")
77 | plt.grid()
78 | plt.plot(t_values, I_values, "r-o")
79 |
80 | if filename is not None:
81 | plt.savefig(filename)
82 |
83 | if view:
84 | plt.show()
85 | plt.close()
86 | fig = None
87 |
88 | return fig
89 |
90 |
91 | def plot_species(statistics, view=False, filename='speciation.svg'):
92 | """ Visualizes speciation throughout evolution. """
93 | if plt is None:
94 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (matplotlib)")
95 | return
96 |
97 | species_sizes = statistics.get_species_sizes()
98 | num_generations = len(species_sizes)
99 | curves = np.array(species_sizes).T
100 |
101 | fig, ax = plt.subplots()
102 | ax.stackplot(range(num_generations), *curves)
103 |
104 | plt.title("Speciation")
105 | plt.ylabel("Size per Species")
106 | plt.xlabel("Generations")
107 |
108 | plt.savefig(filename)
109 |
110 | if view:
111 | plt.show()
112 |
113 | plt.close()
114 |
115 |
116 | def draw_net(config, genome, view=False, filename=None, node_names=None, show_disabled=True, prune_unused=False,
117 | node_colors=None, fmt='svg'):
118 | """ Receives a genome and draws a neural network with arbitrary topology. """
119 | # Attributes for network nodes.
120 | if graphviz is None:
121 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (graphviz)")
122 | return
123 |
124 | if node_names is None:
125 | node_names = {}
126 |
127 | assert type(node_names) is dict
128 |
129 | if node_colors is None:
130 | node_colors = {}
131 |
132 | assert type(node_colors) is dict
133 |
134 | node_attrs = {
135 | 'shape': 'circle',
136 | 'fontsize': '9',
137 | 'height': '0.2',
138 | 'width': '0.2'}
139 |
140 | dot = graphviz.Digraph(format=fmt, node_attr=node_attrs)
141 |
142 | inputs = set()
143 | for k in config.genome_config.input_keys:
144 | inputs.add(k)
145 | name = node_names.get(k, str(k))
146 | input_attrs = {'style': 'filled',
147 | 'shape': 'box'}
148 | input_attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(k, 'lightgray')
149 | dot.node(name, _attributes=input_attrs)
150 |
151 | outputs = set()
152 | for k in config.genome_config.output_keys:
153 | outputs.add(k)
154 | name = node_names.get(k, str(k))
155 | node_attrs = {'style': 'filled'}
156 | node_attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(k, 'lightblue')
157 |
158 | dot.node(name, _attributes=node_attrs)
159 |
160 | if prune_unused:
161 | connections = set()
162 | for cg in genome.connections.values():
163 | if cg.enabled or show_disabled:
164 | connections.add((cg.in_node_id, cg.out_node_id))
165 |
166 | used_nodes = copy.copy(outputs)
167 | pending = copy.copy(outputs)
168 | while pending:
169 | new_pending = set()
170 | for a, b in connections:
171 | if b in pending and a not in used_nodes:
172 | new_pending.add(a)
173 | used_nodes.add(a)
174 | pending = new_pending
175 | else:
176 | used_nodes = set(genome.nodes.keys())
177 |
178 | for n in used_nodes:
179 | if n in inputs or n in outputs:
180 | continue
181 |
182 | attrs = {'style': 'filled',
183 | 'fillcolor': node_colors.get(n, 'white')}
184 | dot.node(str(n), _attributes=attrs)
185 |
186 | for cg in genome.connections.values():
187 | if cg.enabled or show_disabled:
188 | #if cg.input not in used_nodes or cg.output not in used_nodes:
189 | # continue
190 | input, output = cg.key
191 | a = node_names.get(input, str(input))
192 | b = node_names.get(output, str(output))
193 | style = 'solid' if cg.enabled else 'dotted'
194 | color = 'green' if cg.weight > 0 else 'red'
195 | width = str(0.1 + abs(cg.weight / 5.0))
196 | dot.edge(a, b, _attributes={'style': style, 'color': color, 'penwidth': width})
197 |
198 | dot.render(filename, view=view)
199 |
200 | return dot
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT_gym/config:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # neat-python configuration for the LunarLander-v2 environment on OpenAI Gym
2 |
3 | [NEAT]
4 | pop_size = 100
5 | # Note: the fitness threshold will never be reached because
6 | # we are controlling the termination ourselves based on simulation performance.
7 | fitness_criterion = max
8 | fitness_threshold = 2.
9 | reset_on_extinction = 0
10 |
11 | [DefaultGenome]
12 | # node activation options
13 | activation_default = relu
14 | activation_mutate_rate = 0.0
15 | activation_options = relu
16 |
17 | # node aggregation options
18 | aggregation_default = sum
19 | aggregation_mutate_rate = 0.0
20 | aggregation_options = sum
21 |
22 | # node bias options
23 | bias_init_mean = 0.0
24 | bias_init_stdev = 1.0
25 | bias_max_value = 30.0
26 | bias_min_value = -30.0
27 | bias_mutate_power = 0.5
28 | bias_mutate_rate = 0.7
29 | bias_replace_rate = 0.1
30 |
31 | # genome compatibility options
32 | compatibility_disjoint_coefficient = 1.0
33 | compatibility_weight_coefficient = 1.0
34 |
35 | # connection add/remove rates
36 | conn_add_prob = 0.9
37 | conn_delete_prob = 0.2
38 |
39 | # connection enable options
40 | enabled_default = True
41 | enabled_mutate_rate = 0.01
42 |
43 | feed_forward = True
44 | initial_connection = full
45 | # options (unconnected, fs_neat, full)
46 |
47 | # node add/remove rates
48 | node_add_prob = 0.9
49 | node_delete_prob = 0.2
50 |
51 | # network parameters
52 | num_hidden = 0
53 | num_inputs = 4
54 | num_outputs = 2
55 |
56 | # node response options
57 | response_init_mean = 1.0
58 | response_init_stdev = 0.0
59 | response_max_value = 30.0
60 | response_min_value = -30.0
61 | response_mutate_power = 0.0
62 | response_mutate_rate = 0.0
63 | response_replace_rate = 0.0
64 |
65 | # connection weight options
66 | weight_init_mean = 0.0
67 | weight_init_stdev = 1.0
68 | weight_max_value = 30.
69 | weight_min_value = -30.
70 | weight_mutate_power = 0.5
71 | weight_mutate_rate = 0.8
72 | weight_replace_rate = 0.1
73 |
74 | [DefaultSpeciesSet]
75 | compatibility_threshold = 3.0
76 |
77 | [DefaultStagnation]
78 | species_fitness_func = max
79 | max_stagnation = 20
80 | species_elitism = 4
81 |
82 | [DefaultReproduction]
83 | elitism = 2
84 | survival_threshold = 0.2
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT_gym/run_cartpole.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Using NEAT for reinforcement learning.
3 |
4 | The detail for NEAT can be find in : http://nn.cs.utexas.edu/downloads/papers/stanley.cec02.pdf
5 | Visit my tutorial website for more: https://mofanpy.com/tutorials/
6 | """
7 | import neat
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import gym
10 | import visualize
11 |
12 | GAME = 'CartPole-v0'
13 | env = gym.make(GAME).unwrapped
14 |
15 | CONFIG = "./config"
16 | EP_STEP = 300 # maximum episode steps
17 | GENERATION_EP = 10 # evaluate by the minimum of 10-episode rewards
18 | TRAINING = False # training or testing
19 | CHECKPOINT = 9 # test on this checkpoint
20 |
21 |
22 | def eval_genomes(genomes, config):
23 | for genome_id, genome in genomes:
24 | net = neat.nn.FeedForwardNetwork.create(genome, config)
25 | ep_r = []
26 | for ep in range(GENERATION_EP): # run many episodes for the genome in case it's lucky
27 | accumulative_r = 0. # stage longer to get a greater episode reward
28 | observation = env.reset()
29 | for t in range(EP_STEP):
30 | action_values = net.activate(observation)
31 | action = np.argmax(action_values)
32 | observation_, reward, done, _ = env.step(action)
33 | accumulative_r += reward
34 | if done:
35 | break
36 | observation = observation_
37 | ep_r.append(accumulative_r)
38 | genome.fitness = np.min(ep_r)/float(EP_STEP) # depends on the minimum episode reward
39 |
40 |
41 | def run():
42 | config = neat.Config(neat.DefaultGenome, neat.DefaultReproduction,
43 | neat.DefaultSpeciesSet, neat.DefaultStagnation, CONFIG)
44 | pop = neat.Population(config)
45 |
46 | # recode history
47 | stats = neat.StatisticsReporter()
48 | pop.add_reporter(stats)
49 | pop.add_reporter(neat.StdOutReporter(True))
50 | pop.add_reporter(neat.Checkpointer(5))
51 |
52 | pop.run(eval_genomes, 10) # train 10 generations
53 |
54 | # visualize training
55 | visualize.plot_stats(stats, ylog=False, view=True)
56 | visualize.plot_species(stats, view=True)
57 |
58 |
59 | def evaluation():
60 | p = neat.Checkpointer.restore_checkpoint('neat-checkpoint-%i' % CHECKPOINT)
61 | winner = p.run(eval_genomes, 1) # find the winner in restored population
62 |
63 | # show winner net
64 | node_names = {-1: 'In0', -2: 'In1', -3: 'In3', -4: 'In4', 0: 'act1', 1: 'act2'}
65 | visualize.draw_net(p.config, winner, True, node_names=node_names)
66 |
67 | net = neat.nn.FeedForwardNetwork.create(winner, p.config)
68 | while True:
69 | s = env.reset()
70 | while True:
71 | env.render()
72 | a = np.argmax(net.activate(s))
73 | s, r, done, _ = env.step(a)
74 | if done: break
75 |
76 |
77 | if __name__ == '__main__':
78 | if TRAINING:
79 | run()
80 | else:
81 | evaluation()
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tutorial-contents/Using Neural Nets/NEAT_gym/visualize.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import print_function
2 |
3 | import copy
4 | import warnings
5 |
6 | import graphviz
7 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
8 | import numpy as np
9 |
10 |
11 | def plot_stats(statistics, ylog=False, view=False, filename='avg_fitness.svg'):
12 | """ Plots the population's average and best fitness. """
13 | if plt is None:
14 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (matplotlib)")
15 | return
16 |
17 | generation = range(len(statistics.most_fit_genomes))
18 | best_fitness = [c.fitness for c in statistics.most_fit_genomes]
19 | avg_fitness = np.array(statistics.get_fitness_mean())
20 | stdev_fitness = np.array(statistics.get_fitness_stdev())
21 |
22 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness, 'b-', label="average")
23 | #plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness - stdev_fitness, 'g-.', label="-1 sd")
24 | plt.plot(generation, avg_fitness + stdev_fitness, 'g-.', label="+1 sd")
25 | plt.plot(generation, best_fitness, 'r-', label="best")
26 |
27 | plt.title("Population's average and best fitness")
28 | plt.xlabel("Generations")
29 | plt.ylabel("Fitness")
30 | plt.grid()
31 | plt.legend(loc="best")
32 | if ylog:
33 | plt.gca().set_yscale('symlog')
34 |
35 | plt.savefig(filename)
36 | if view:
37 | plt.show()
38 |
39 | plt.close()
40 |
41 |
42 | def plot_species(statistics, view=False, filename='speciation.svg'):
43 | """ Visualizes speciation throughout evolution. """
44 | if plt is None:
45 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (matplotlib)")
46 | return
47 |
48 | species_sizes = statistics.get_species_sizes()
49 | num_generations = len(species_sizes)
50 | curves = np.array(species_sizes).T
51 |
52 | fig, ax = plt.subplots()
53 | ax.stackplot(range(num_generations), *curves)
54 |
55 | plt.title("Speciation")
56 | plt.ylabel("Size per Species")
57 | plt.xlabel("Generations")
58 |
59 | plt.savefig(filename)
60 |
61 | if view:
62 | plt.show()
63 |
64 | plt.close()
65 |
66 |
67 | def draw_net(config, genome, view=False, filename=None, node_names=None, show_disabled=True, prune_unused=False,
68 | node_colors=None, fmt='svg'):
69 | """ Receives a genome and draws a neural network with arbitrary topology. """
70 | # Attributes for network nodes.
71 | if graphviz is None:
72 | warnings.warn("This display is not available due to a missing optional dependency (graphviz)")
73 | return
74 |
75 | if node_names is None:
76 | node_names = {}
77 |
78 | assert type(node_names) is dict
79 |
80 | if node_colors is None:
81 | node_colors = {}
82 |
83 | assert type(node_colors) is dict
84 |
85 | node_attrs = {
86 | 'shape': 'circle',
87 | 'fontsize': '9',
88 | 'height': '0.2',
89 | 'width': '0.2'}
90 |
91 | dot = graphviz.Digraph(format=fmt, node_attr=node_attrs)
92 |
93 | inputs = set()
94 | for k in config.genome_config.input_keys:
95 | inputs.add(k)
96 | name = node_names.get(k, str(k))
97 | input_attrs = {'style': 'filled',
98 | 'shape': 'box'}
99 | input_attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(k, 'lightgray')
100 | dot.node(name, _attributes=input_attrs)
101 |
102 | outputs = set()
103 | for k in config.genome_config.output_keys:
104 | outputs.add(k)
105 | name = node_names.get(k, str(k))
106 | node_attrs = {'style': 'filled'}
107 | node_attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(k, 'lightblue')
108 |
109 | dot.node(name, _attributes=node_attrs)
110 |
111 | if prune_unused:
112 | connections = set()
113 | for cg in genome.connections.values():
114 | if cg.enabled or show_disabled:
115 | connections.add(cg.key)
116 |
117 | used_nodes = copy.copy(outputs)
118 | pending = copy.copy(outputs)
119 | while pending:
120 | #print(pending, used_nodes)
121 | new_pending = set()
122 | for a, b in connections:
123 | if b in pending and a not in used_nodes:
124 | new_pending.add(a)
125 | used_nodes.add(a)
126 | pending = new_pending
127 | else:
128 | used_nodes = set(genome.nodes.keys())
129 |
130 | for n in used_nodes:
131 | if n in inputs or n in outputs:
132 | continue
133 |
134 | attrs = {'style': 'filled'}
135 | attrs['fillcolor'] = node_colors.get(n, 'white')
136 | dot.node(str(n), _attributes=attrs)
137 |
138 | for cg in genome.connections.values():
139 | if cg.enabled or show_disabled:
140 | #if cg.input not in used_nodes or cg.output not in used_nodes:
141 | # continue
142 | input, output = cg.key
143 | a = node_names.get(input, str(input))
144 | b = node_names.get(output, str(output))
145 | style = 'solid' if cg.enabled else 'dotted'
146 | color = 'green' if cg.weight > 0 else 'red'
147 | width = str(0.1 + abs(cg.weight / 5.0))
148 | dot.edge(a, b, _attributes={'style': style, 'color': color, 'penwidth': width})
149 |
150 | dot.render(filename, view=view)
151 |
152 | return dot
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 4 |
5 |
4 |
5 |  4 |
5 |
4 |
5 |  35 |
36 |
37 | ### [Match Phrase Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Match%20Phrase.py)
38 |
39 |
40 |
35 |
36 |
37 | ### [Match Phrase Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Match%20Phrase.py)
38 |
39 |
40 |  41 |
42 |
43 | ### [Travel Sales Problem](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Travel%20Sales%20Person.py)
44 |
45 |
46 |
41 |
42 |
43 | ### [Travel Sales Problem](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Travel%20Sales%20Person.py)
44 |
45 |
46 |  47 |
48 |
49 | ### [Find Path Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Find%20Path.py)
50 |
51 |
47 |
48 |
49 | ### [Find Path Example](tutorial-contents/Genetic%20Algorithm/Find%20Path.py)
50 |
51 |  52 |
53 |
54 | ### [Basic ES](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Evolution%20Strategy%20Basic.py)
55 |
56 |
57 |
52 |
53 |
54 | ### [Basic ES](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Evolution%20Strategy%20Basic.py)
55 |
56 |
57 |  58 |
59 |
60 | ### [Natural Evolution Strategy (NES)](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Natural%20Evolution%20Strategy%20(NES).py)
61 |
62 |
63 |
58 |
59 |
60 | ### [Natural Evolution Strategy (NES)](tutorial-contents/Evolution%20Strategy/Natural%20Evolution%20Strategy%20(NES).py)
61 |
62 |
63 |  64 |
65 |
66 | ### [Distributed ES with Neural Nets (OpenAI)](tutorial-contents/Using%20Neural%20Nets/Evolution%20Strategy%20with%20Neural%20Nets.py)
67 |
68 |
69 |
64 |
65 |
66 | ### [Distributed ES with Neural Nets (OpenAI)](tutorial-contents/Using%20Neural%20Nets/Evolution%20Strategy%20with%20Neural%20Nets.py)
67 |
68 |
69 |  70 |
71 |
72 | # Donation
73 |
74 | *If this does help you, please consider donating to support me for better tutorials! Any contribution is greatly appreciated!*
75 |
76 |
70 |
71 |
72 | # Donation
73 |
74 | *If this does help you, please consider donating to support me for better tutorials! Any contribution is greatly appreciated!*
75 |
76 |  82 |
82 |  89 |
90 |
89 |
90 |