├── models
├── __init__.py
├── RigidityNet.py
└── PWCNet.py
├── external_packages
├── flow2pose
│ ├── .gitignore
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── flow2pose_lib
│ │ ├── flow2pose.h
│ │ ├── pyboostcvconverter.hpp
│ │ ├── py_flow2pose.cpp
│ │ ├── flow2pose.cpp
│ │ ├── pyboost_cv2_converter.cpp
│ │ └── pyboost_cv3_converter.cpp
│ ├── estimate_pose.cpp
│ ├── CMakeLists.txt
│ └── cmake
│ │ └── FindNumPy.cmake
└── correlation-pytorch-master
│ ├── correlation-pytorch
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── .eggs
│ │ └── .gitignore
│ ├── correlation_package
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── _ext
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ ├── .gitignore
│ │ │ └── corr
│ │ │ │ └── __init__.py
│ │ ├── functions
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ └── corr.py
│ │ ├── modules
│ │ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ │ └── corr.py
│ │ └── src
│ │ │ ├── .gitignore
│ │ │ ├── corr.h
│ │ │ ├── corr_cuda.h
│ │ │ ├── corr1d_cuda.h
│ │ │ ├── corr1d.h
│ │ │ ├── corr.c
│ │ │ ├── corr1d.c
│ │ │ ├── corr1d_cuda_kernel.h
│ │ │ ├── corr_cuda_kernel.h
│ │ │ ├── corr_cuda.c
│ │ │ ├── corr1d_cuda.c
│ │ │ ├── corr1d_cuda_kernel.cu
│ │ │ └── corr_cuda_kernel.cu
│ ├── dist
│ │ └── .gitignore
│ ├── .gitignore
│ ├── setup.py
│ └── build.py
│ ├── make_cuda.sh
│ └── readme.MD
├── .gitignore
├── data
├── rigidity-example.jpg
└── market_5
│ ├── clean
│ ├── frame_0011.png
│ └── frame_0012.png
│ ├── depth
│ ├── frame_0011.dpt
│ └── frame_0012.dpt
│ └── camdata_left
│ ├── frame_0010.cam
│ └── frame_0011.cam
├── setup
├── install_for_network.sh
├── install_for_refinement.sh
└── rigidity.yml
├── run_container.sh
├── dataset_description.md
├── SimpleLoader.py
├── Dockerfile
├── pose_refine.py
├── io_utils.py
├── geometry.py
├── README.md
└── run_inference.py
/models/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | build/*
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | weights/*
2 | tmp/*
3 | results/*
4 |
5 | *.pyc
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/.eggs/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *.txt
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/_ext/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/functions/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/modules/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/rigidity-example.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVlabs/learningrigidity/HEAD/data/rigidity-example.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/_ext/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *.pyc
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *.cu.o
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/dist/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *.1-py2.7-linux-x86_64.egg
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/market_5/clean/frame_0011.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVlabs/learningrigidity/HEAD/data/market_5/clean/frame_0011.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/market_5/clean/frame_0012.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVlabs/learningrigidity/HEAD/data/market_5/clean/frame_0012.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/market_5/depth/frame_0011.dpt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVlabs/learningrigidity/HEAD/data/market_5/depth/frame_0011.dpt
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/market_5/depth/frame_0012.dpt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVlabs/learningrigidity/HEAD/data/market_5/depth/frame_0012.dpt
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | build/*
2 | test/*
3 | correlation_package.egg-info/*
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/market_5/camdata_left/frame_0010.cam:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVlabs/learningrigidity/HEAD/data/market_5/camdata_left/frame_0010.cam
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data/market_5/camdata_left/frame_0011.cam:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NVlabs/learningrigidity/HEAD/data/market_5/camdata_left/frame_0011.cam
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup/install_for_network.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # install the flow modules
2 | cd external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master
3 | sh make_cuda.sh
4 | cd ..
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Flow2Pose Lib
2 |
3 | The flow2pose library is an algorithm that takes 3D ego-motion flow fields as input and estimate the pose transformation.
4 |
5 | ## Dependencies
6 |
7 | * gtsam
8 | * opencv3
9 |
10 | ## Install
11 |
12 | Use the following command manually
13 |
14 | ```
15 | mkdir build
16 | cd build
17 | cmake ..
18 | make -j8
19 | ```
20 |
21 | Or use '../../setup/install_for_refinement.sh' for an all-in-one install.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/make_cuda.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env bash
2 |
3 | #CUDA_PATH=/usr/local/cuda-8.0
4 |
5 | cd correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src
6 | echo "Compiling correlation layer kernels by nvcc..."
7 |
8 | # TODO (JEB): Check which arches we need
9 | nvcc -c -o corr_cuda_kernel.cu.o corr_cuda_kernel.cu -x cu -Xcompiler -fPIC -arch=sm_52
10 | nvcc -c -o corr1d_cuda_kernel.cu.o corr1d_cuda_kernel.cu -x cu -Xcompiler -fPIC -arch=sm_52
11 |
12 | cd ../../
13 | python setup.py build install
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/_ext/corr/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | from torch.utils.ffi import _wrap_function
3 | from ._corr import lib as _lib, ffi as _ffi
4 |
5 | __all__ = []
6 | def _import_symbols(locals):
7 | for symbol in dir(_lib):
8 | fn = getattr(_lib, symbol)
9 | if callable(fn):
10 | locals[symbol] = _wrap_function(fn, _ffi)
11 | else:
12 | locals[symbol] = fn
13 | __all__.append(symbol)
14 |
15 | _import_symbols(locals())
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup/install_for_refinement.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # system dependencies
2 | sudo apt-get install libboost-all-dev cmake libtbb-dev libopencv-dev
3 |
4 | # compile and install gtsam as dependency for the refinment module
5 | git clone --depth 1 -b develop git@bitbucket.org:gtborg/gtsam.git external_packages/gtsam
6 | cd external_packages/gtsam
7 | mkdir build
8 | cd build
9 | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=../../../tmp/
10 | make install -j8
11 |
12 | # compile the refinement module
13 | cd ../../external_packages/flow2pose
14 | mkdir build
15 | cd build
16 | cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=../../../tmp/
17 | make -j8
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 |
3 | import os
4 |
5 | from setuptools import setup, find_packages
6 |
7 | this_file = os.path.dirname(__file__)
8 |
9 | setup(
10 | name="correlation_package",
11 | version="0.1",
12 | description="Correlation layer from FlowNetC",
13 | url="https://github.com/jbarker-nvidia/pytorch-correlation",
14 | author="Jon Barker",
15 | author_email="jbarker@nvidia.com",
16 | # Require cffi
17 | install_requires=["cffi>=1.0.0"],
18 | setup_requires=["cffi>=1.0.0"],
19 | # Exclude the build files.
20 | packages=find_packages(exclude=["build"]),
21 | # Package where to put the extensions. Has to be a prefix of build.py
22 | ext_package="",
23 | # Extensions to compile
24 | cffi_modules=[
25 | os.path.join(this_file, "build.py:ffi")
26 | ],
27 | )
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/run_container.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env bash
2 | # Launch container and export DISPLAY
3 |
4 | IMAGE_NAME=rigidity:1.0
5 |
6 | # Make sure UID/GID are consistent inside the container with the current user
7 | TMP_DIR=/tmp
8 | CURR_DIR=$(pwd)
9 | UID_TO_USE=$(stat -c '%u' "${0}")
10 | GID_TO_USE=$(stat -c '%g' "${0}")
11 |
12 | FAUX_DIR=$(mktemp -d -p "${TMP_DIR}")
13 | FAUX_PASSWD="$FAUX_DIR/passwd"
14 | FAUX_GRP="$FAUX_DIR/group"
15 |
16 | echo "developer:x:$UID_TO_USE:$GID_TO_USE:developer:/:/bin/bash" > $FAUX_DIR/passwd
17 | echo "developer:x:$GID_TO_USE:developer" > $FAUX_DIR/group
18 |
19 | nvidia-docker run \
20 | --user=${UID_TO_USE}:${GID_TO_USE} \
21 | -v ${HOME}/.ssh:/.ssh \
22 | -v $FAUX_PASSWD:/etc/passwd:ro \
23 | -v $FAUX_GRP:/etc/group:ro \
24 | -v /tmp/.X11-unix:/tmp/.X11-unix \
25 | -v $HOME/.Xauthority:/.Xauthority \
26 | -v $CURR_DIR:/rigidity \
27 | -e DISPLAY=unix$DISPLAY \
28 | -it \
29 | --rm \
30 | "${IMAGE_NAME}"
31 |
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/readme.MD:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | This repository contains a custom pytorch package that adds a module and functional interface for the correlation layer described in "FlowNet: Learning Optical Flow with Convolutional Networks" (https://arxiv.org/abs/1504.06852)
2 |
3 | To install:
4 |
5 | 1. Run `pip install cffi`
6 |
7 | 2. Run `make_cuda.sh`
8 |
9 | 3. Run `python setup.py build install`
10 |
11 | 4. (optional) Run `python test/test.py`
12 |
13 |
14 | #### Acknowledgement
15 | - Thanks to Dr. Fitsum Reda for providing the wrapper to the correlation code
16 |
17 | If you find this implementation useful in your work, please acknowledge it appropriately and cite the paper:
18 | ```
19 | @misc{flownet2-pytorch,
20 | author = {Fitsum Reda and Robert Pottorff and Jon Barker and Bryan Catanzaro},
21 | title = {flownet2-pytorch: Pytorch implementation of FlowNet 2.0: Evolution of Optical Flow Estimation with Deep Networks},
22 | year = {2017},
23 | publisher = {GitHub},
24 | journal = {GitHub repository},
25 | howpublished = {\url{https://github.com/NVIDIA/flownet2-pytorch}}
26 | }
27 | ```
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | int corr_cpu_forward(THFloatTensor *input1,
2 | THFloatTensor *input2,
3 | THFloatTensor *rbot1,
4 | THFloatTensor *rbot2,
5 | THFloatTensor *output,
6 | int pad_size,
7 | int kernel_size,
8 | int max_displacement,
9 | int stride1,
10 | int stride2,
11 | int corr_type_multiply);
12 |
13 | int corr_cpu_backward(THFloatTensor *input1,
14 | THFloatTensor *input2,
15 | THFloatTensor *rbot1,
16 | THFloatTensor *rbot2,
17 | THFloatTensor *gradOutput,
18 | THFloatTensor *gradInput1,
19 | THFloatTensor *gradInput2,
20 | int pad_size,
21 | int kernel_size,
22 | int max_displacement,
23 | int stride1,
24 | int stride2,
25 | int corr_type_multiply);
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr_cuda.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | int corr_cuda_forward(THCudaTensor *input1,
2 | THCudaTensor *input2,
3 | THCudaTensor *rbot1,
4 | THCudaTensor *rbot2,
5 | THCudaTensor *output,
6 | int pad_size,
7 | int kernel_size,
8 | int max_displacement,
9 | int stride1,
10 | int stride2,
11 | int corr_type_multiply);
12 |
13 | int corr_cuda_backward(THCudaTensor *input1,
14 | THCudaTensor *input2,
15 | THCudaTensor *rbot1,
16 | THCudaTensor *rbot2,
17 | THCudaTensor *grad_output,
18 | THCudaTensor *grad_input1,
19 | THCudaTensor *grad_input2,
20 | int pad_size,
21 | int kernel_size,
22 | int max_displacement,
23 | int stride1,
24 | int stride2,
25 | int corr_type_multiply);
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr1d_cuda.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | int corr1d_cuda_forward(THCudaTensor *input1,
2 | THCudaTensor *input2,
3 | THCudaTensor *rbot1,
4 | THCudaTensor *rbot2,
5 | THCudaTensor *output,
6 | int pad_size,
7 | int kernel_size,
8 | int max_displacement,
9 | int stride1,
10 | int stride2,
11 | int corr_type_multiply);
12 |
13 | int corr1d_cuda_backward(THCudaTensor *input1,
14 | THCudaTensor *input2,
15 | THCudaTensor *rbot1,
16 | THCudaTensor *rbot2,
17 | THCudaTensor *grad_output,
18 | THCudaTensor *grad_input1,
19 | THCudaTensor *grad_input2,
20 | int pad_size,
21 | int kernel_size,
22 | int max_displacement,
23 | int stride1,
24 | int stride2,
25 | int corr_type_multiply);
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr1d.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | int corr1d_cpu_forward(THFloatTensor *input1,
2 | THFloatTensor *input2,
3 | THFloatTensor *rbot1,
4 | THFloatTensor *rbot2,
5 | THFloatTensor *output,
6 | int pad_size,
7 | int kernel_size,
8 | int max_displacement,
9 | int stride1,
10 | int stride2,
11 | int corr_type_multiply);
12 |
13 | int corr1d_cpu_backward(THFloatTensor *input1,
14 | THFloatTensor *input2,
15 | THFloatTensor *rbot1,
16 | THFloatTensor *rbot2,
17 | THFloatTensor *gradOutput,
18 | THFloatTensor *gradInput1,
19 | THFloatTensor *gradInput2,
20 | int pad_size,
21 | int kernel_size,
22 | int max_displacement,
23 | int stride1,
24 | int stride2,
25 | int corr_type_multiply);
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr.c:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include |
2 |
3 | int corr_cpu_forward(THFloatTensor *input1,
4 | THFloatTensor *input2,
5 | THFloatTensor *rbot1,
6 | THFloatTensor *rbot2,
7 | THFloatTensor *output,
8 | int pad_size,
9 | int kernel_size,
10 | int max_displacement,
11 | int stride1,
12 | int stride2,
13 | int corr_type_multiply)
14 | {
15 | return 1;
16 | }
17 |
18 | int corr_cpu_backward(THFloatTensor *input1,
19 | THFloatTensor *input2,
20 | THFloatTensor *rbot1,
21 | THFloatTensor *rbot2,
22 | THFloatTensor *gradOutput,
23 | THFloatTensor *gradInput1,
24 | THFloatTensor *gradInput2,
25 | int pad_size,
26 | int kernel_size,
27 | int max_displacement,
28 | int stride1,
29 | int stride2,
30 | int corr_type_multiply)
31 | {
32 | return 1;
33 | }
34 |
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr1d.c:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include |
2 |
3 | int corr1d_cpu_forward(THFloatTensor *input1,
4 | THFloatTensor *input2,
5 | THFloatTensor *rbot1,
6 | THFloatTensor *rbot2,
7 | THFloatTensor *output,
8 | int pad_size,
9 | int kernel_size,
10 | int max_displacement,
11 | int stride1,
12 | int stride2,
13 | int corr_type_multiply)
14 | {
15 | return 1;
16 | }
17 |
18 | int corr1d_cpu_backward(THFloatTensor *input1,
19 | THFloatTensor *input2,
20 | THFloatTensor *rbot1,
21 | THFloatTensor *rbot2,
22 | THFloatTensor *gradOutput,
23 | THFloatTensor *gradInput1,
24 | THFloatTensor *gradInput2,
25 | int pad_size,
26 | int kernel_size,
27 | int max_displacement,
28 | int stride1,
29 | int stride2,
30 | int corr_type_multiply)
31 | {
32 | return 1;
33 | }
34 |
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr1d_cuda_kernel.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef _CORR_CUDA_KERNEL
2 | #define _CORR_CUDA_KERNEL
3 |
4 | #ifdef __cplusplus
5 | extern "C" {
6 | #endif
7 |
8 | void blob_rearrange_ongpu_1d(const float *in, float *out, int num, int channels, int width, int height, int widthheight, int padding, int pwidthheight, cudaStream_t stream);
9 |
10 | void CorrelateData_ongpu_1d(const float *rbot1, const float *rbot2, float *output, int batchSize, int nOutputCols, int nOutputRows, int nOutputPlane, int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width_, int kernel_radius_, int kernel_size, int stride1, int stride2, int paddedbottomwidth, int paddedbottomheight, int nInputPlane, int corr_type_multiply, cudaStream_t stream);
11 |
12 | void CorrelateDataBackward_ongpu_1d(const float *rbot1, const float *rbot2, const float *gradOutput, float *gradInput1, float *gradInput2, int batchSize, int nOutputCols, int nOutputRows, int nOutputPlane, int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width_, int kernel_radius_, int stride1, int stride2, int nInputCols, int nInputRows, int paddedbottomwidth, int paddedbottomheight, int nInputPlane, int pad_size, int corr_type_multiply, cudaStream_t stream);
13 |
14 | #ifdef __cplusplus
15 | }
16 | #endif
17 |
18 | #endif
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/build.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import torch
3 | from torch.utils.ffi import create_extension
4 |
5 |
6 | sources = ['correlation_package/src/corr.c']
7 | headers = ['correlation_package/src/corr.h']
8 |
9 | sources += ['correlation_package/src/corr1d.c']
10 | headers += ['correlation_package/src/corr1d.h']
11 |
12 | defines = []
13 |
14 | # Add CUDA sources
15 | sources += ['correlation_package/src/corr_cuda.c']
16 | headers += ['correlation_package/src/corr_cuda.h']
17 |
18 | sources += ['correlation_package/src/corr1d_cuda.c']
19 | headers += ['correlation_package/src/corr1d_cuda.h']
20 |
21 | defines += [('WITH_CUDA', None)]
22 | with_cuda = True
23 |
24 | this_file = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
25 | extra_objects = ['correlation_package/src/corr_cuda_kernel.cu.o']
26 | extra_objects += ['correlation_package/src/corr1d_cuda_kernel.cu.o']
27 | extra_objects = [os.path.join(this_file, fname) for fname in extra_objects]
28 |
29 | ffi = create_extension(
30 | 'correlation_package._ext.corr',
31 | package=True,
32 | headers=headers,
33 | sources=sources,
34 | define_macros=defines,
35 | relative_to=__file__,
36 | with_cuda=with_cuda,
37 | extra_objects=extra_objects,
38 | )
39 |
40 | if __name__ == '__main__':
41 | ffi.build()
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr_cuda_kernel.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #ifndef _CORR_CUDA_KERNEL
2 | #define _CORR_CUDA_KERNEL
3 |
4 | #ifdef __cplusplus
5 | extern "C" {
6 | #endif
7 |
8 | void blob_rearrange_ongpu(const float *in, float *out, int num, int channels, int width, int height, int widthheight, int padding, int pwidthheight, cudaStream_t stream);
9 |
10 | void CorrelateData_ongpu(const float *rbot1, const float *rbot2, float *output, int batchSize, int nOutputCols, int nOutputRows, int nOutputPlane, int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius_, int neighborhood_grid_width_, int kernel_radius_, int kernel_size, int stride1, int stride2, int paddedbottomwidth, int paddedbottomheight, int nInputPlane, int corr_type_multiply, cudaStream_t stream);
11 |
12 | void CorrelateDataBackward_ongpu(const float *rbot1, const float *rbot2, const float *gradOutput, float *gradInput1, float *gradInput2, int batchSize, int nOutputCols, int nOutputRows, int nOutputPlane, int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius_, int neighborhood_grid_width_, int kernel_radius_, int stride1, int stride2, int nInputCols, int nInputRows, int paddedbottomwidth, int paddedbottomheight, int nInputPlane, int pad_size, int corr_type_multiply, cudaStream_t stream);
13 |
14 | #ifdef __cplusplus
15 | }
16 | #endif
17 |
18 | #endif
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/flow2pose_lib/flow2pose.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /**
2 | * Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | * Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | * (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 | *
6 | * Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 | */
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include
11 |
12 | #include
13 | #include
14 | #include
15 | #include
16 | #include
17 | #include
18 |
19 | #include
20 |
21 | struct Putative {
22 | gtsam::Point3 pt1;
23 | gtsam::Point3 pt2;
24 |
25 | Putative(const gtsam::Point3 p1, const gtsam::Point3 p2)
26 | : pt1(p1), pt2(p2) {
27 | }
28 | };
29 |
30 | struct Flow2Pose {
31 |
32 | enum {
33 | Gauss_Newton,
34 | Levenberg_Marquardt
35 | };
36 |
37 | double huber_threshold = 1;
38 | double ransacConfidence =0.999;
39 | double ransacIteration = 1000;
40 | int solver_type = Gauss_Newton;
41 |
42 | gtsam::SharedNoiseModel huber_measurement_model;
43 | gtsam::SharedNoiseModel measurement_noise_model;
44 |
45 | Flow2Pose();
46 |
47 | /* Solve Camera pose */
48 | gtsam::Pose3 solve(const std::vector& pts1,
49 | const std::vector& pts2, const gtsam::Pose3& initial_pose, const std::vector& inliers = std::vector());
50 |
51 | gtsam::Pose3 calculate_transform(const cv::Mat& v_map0, const cv::Mat& v_map1,
52 | const cv::Mat& flow, const cv::Mat& foreground_S0, const cv::Mat& foreground_S1, const cv::Mat& occlusion, const gtsam::Pose3& initial_pose);
53 |
54 | };
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataset_description.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # About the Generated Refresh Dataset
2 |
3 | The data is generated using the [RefRESH Toolkit][1]. If you want to generate your own data for training, please check the RefRESH repository.
4 |
5 | If you want to download the pre-generated data used in the paper at:
6 | [RefRESH data using BundleFusion][2].
7 |
8 | The calibration and camera pose ground truth are in the info.pkl for each trajectory: e.g. ‘office3/keyframe_1/0000_0100’. The .pkl file was generated by python 2 pickle module. If you load it using python3 please be aware of using python2 pickle module to read :
9 |
10 | ``` python
11 | with open('info.pkl', 'rb') as p:
12 | # the original pickle is in python2
13 | files = pickle.load(p, encoding='latin1')
14 | ```
15 |
16 | To read the calibration file from the pickle:
17 | ``` python
18 | calib = files['calib']
19 | # note that the color and depth calibration has very small shift
20 | # (< 0.2 (582.vs 583)). We will only use depth intrinsic since
21 | # it gives very good approximation
22 | Ks = calib['depth_intrinsic']
23 | ```
24 |
25 | To read the camera pose from the pickle:
26 | ``` python
27 | poses = files['pose']
28 | ```
29 |
30 | ## Several Notes:
31 | * The keyframe indicates the number of frame intervals we used at rendering. In each keyframe sequence, the length of the sequence are 100 at most.
32 |
33 | * The provided optical flow model is **backward optical flow**, Please be aware of it if you use it to train your dataset. The current toolkit in [RefRESH][1] has been updated to support rendering bidirection optical flow. If you need this feature, you can render the data using that tool.
34 |
35 | [1]: https://github.com/lvzhaoyang/RefRESH
36 | [2]: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/1DMb3qpoYoowa00EfzGzTKySbT_WIbhD7?usp=sharing
37 |
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/modules/corr.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from torch.nn.modules.module import Module
2 | from ..functions.corr import correlation, correlation1d
3 |
4 | class Correlation(Module):
5 |
6 | def __init__(self, pad_size=None, kernel_size=None, max_displacement=None,
7 | stride1=None, stride2=None, corr_multiply=None):
8 | super(Correlation, self).__init__()
9 | self.pad_size = pad_size
10 | self.kernel_size = kernel_size
11 | self.max_displacement = max_displacement
12 | self.stride1 = stride1
13 | self.stride2 = stride2
14 | self.corr_multiply = corr_multiply
15 |
16 | def reset_params(self):
17 | return
18 |
19 | def forward(self, input1, input2):
20 | return correlation(self.pad_size, self.kernel_size, self.max_displacement, self.stride1, self.stride2, self.corr_multiply)(input1, input2)
21 |
22 | def __repr__(self):
23 | return self.__class__.__name__
24 |
25 |
26 | #----- correlation in 1D (for disparity) Jinwei Gu -----
27 |
28 | class Correlation1d(Module):
29 |
30 | def __init__(self, pad_size=None, kernel_size=None, max_displacement=None,
31 | stride1=None, stride2=None, corr_multiply=None):
32 | super(Correlation1d, self).__init__()
33 | self.pad_size = pad_size
34 | self.kernel_size = kernel_size
35 | self.max_displacement = max_displacement
36 | self.stride1 = stride1
37 | self.stride2 = stride2
38 | self.corr_multiply = corr_multiply
39 |
40 | def reset_params(self):
41 | return
42 |
43 | def forward(self, input1, input2):
44 | return correlation1d(self.pad_size, self.kernel_size, self.max_displacement, self.stride1, self.stride2, self.corr_multiply)(input1, input2)
45 |
46 | def __repr__(self):
47 | return self.__class__.__name__
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/estimate_pose.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /**
2 | * Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | * Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | * (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 | *
6 | * Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 | */
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include
11 | #include
12 | #include
13 |
14 | #include
15 | #include
16 | #include
17 |
18 | #include
19 | #include
20 |
21 | using namespace std;
22 | using namespace gtsam;
23 |
24 | namespace po = boost::program_options;
25 | namespace fs = boost::filesystem;
26 |
27 | string parse_argument(int argc, char* argv[]) {
28 | po::options_description desc("Allowed options");
29 |
30 | string correspondence_path;
31 |
32 | desc.add_options()
33 | ("help", "produce help message")
34 | ("c", po::value(&correspondence_path)->default_value(""),
35 | "correspondence fields");
36 |
37 | po::variables_map vm;
38 | po::store(po::parse_command_line(argc, argv, desc), vm);
39 | po::notify(vm);
40 |
41 | return correspondence_path;
42 | }
43 |
44 | void parse_file(const string& file, vector& pts1, vector& pts2) {
45 |
46 | cout << "parse file" << file << endl;
47 |
48 | ifstream infile(file);
49 | string line;
50 | while( getline(infile, line) ) {
51 | double x0, y0, z0, x1, y1, z1;
52 | istringstream(line) >> x0 >> y0 >> z0 >> x1 >> y1 >> z1;
53 |
54 | pts1.push_back(Point3(x0, y0, z0));
55 | pts2.push_back(Point3(x1, y1, z1));
56 | }
57 | }
58 |
59 | int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
60 | auto string = parse_argument(argc, argv);
61 |
62 | vector pts1;
63 | vector pts2;
64 | parse_file(string, pts1, pts2);
65 |
66 | cout << "estimate pose with " << pts1.size() << " points pairs" << endl;
67 |
68 | Flow2Pose flow2pose;
69 | Pose3 raw_pose = Pose3::Create(Rot3::Rodrigues(0,0,0), Point3(0, 0, 0));
70 | Pose3 est_pose = flow2pose.solve(pts1, pts2, raw_pose);
71 |
72 | est_pose.print("estimated pose matrix is: ");
73 | }
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/SimpleLoader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 |
6 | Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 | """
8 |
9 | import os, io_utils
10 | import torch.utils.data as data
11 | import os.path as osp
12 | import numpy as np
13 |
14 | from scipy.misc import imread
15 |
16 | class SimpleLoader(data.Dataset):
17 |
18 | def __init__(self, color_dir, depth_dir):
19 | """
20 | :param the directory of color images
21 | :param the directory of depth images
22 | """
23 |
24 | color_files = sorted(os.listdir(color_dir))
25 | depth_files = sorted(os.listdir(depth_dir))
26 |
27 | # please ensure the two folders use the same number of synchronized files
28 | assert(len(color_files) == len(depth_files))
29 |
30 | self.color_pairs = []
31 | self.depth_pairs = []
32 | self.ids = len(color_files) - 1
33 | for idx in range(self.ids):
34 | self.color_pairs.append([
35 | osp.join(color_dir, color_files[idx]),
36 | osp.join(color_dir, color_files[idx+1])
37 | ] )
38 | self.depth_pairs.append([
39 | osp.join(depth_dir, depth_files[idx]),
40 | osp.join(depth_dir, depth_files[idx+1])
41 | ] )
42 |
43 | def __getitem__(self, index):
44 |
45 | image0_path, image1_path = self.color_pairs[index]
46 | depth0_path, depth1_path = self.depth_pairs[index]
47 |
48 | image0 = self.__load_rgb_tensor(image0_path)
49 | image1 = self.__load_rgb_tensor(image1_path)
50 |
51 | depth0 = self.__load_depth_tensor(depth0_path)
52 | depth1 = self.__load_depth_tensor(depth1_path)
53 |
54 | return image0, image1, depth0, depth1
55 |
56 | def __len__(self):
57 | return self.ids
58 |
59 | def __load_rgb_tensor(self, path):
60 | image = imread(path)
61 | image = image.astype(np.float32) / 255.0
62 | image = np.transpose(image, (2,0,1))
63 | return image
64 |
65 | def __load_depth_tensor(self, path):
66 | if path.endswith('.dpt'):
67 | depth = io_utils.depth_read(path)
68 | elif path.endswith('.png'):
69 | depth = imread(path) / 1000.0
70 | else:
71 | raise NotImplementedError
72 | return depth[np.newaxis, :]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/CMakeLists.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
2 |
3 | project(Flow2pose)
4 |
5 | set(CMAKE_MACOSX_RPATH 1)
6 |
7 | set( CMAKE_MODULE_PATH ${CMAKE_MODULE_PATH} ${CMAKE_CURRENT_LIST_DIR}/cmake )
8 |
9 | include(CheckCXXCompilerFlag)
10 | CHECK_CXX_COMPILER_FLAG("-std=c++11" COMPILER_SUPPORTS_CXX11)
11 | CHECK_CXX_COMPILER_FLAG("-std=c++0x" COMPILER_SUPPORTS_CXX0X)
12 | if(COMPILER_SUPPORTS_CXX11)
13 | set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++11")
14 | elseif(COMPILER_SUPPORTS_CXX0X)
15 | set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++0x")
16 | else()
17 | message(STATUS "The compiler ${CMAKE_CXX_COMPILER} has no C++11 support. Please use a different C++ compiler.")
18 | endif()
19 |
20 | find_package(Boost 1.54 COMPONENTS program_options filesystem python REQUIRED)
21 |
22 | find_package(OpenCV COMPONENTS core imgproc REQUIRED)
23 | message(STATUS "OpenCV include: " ${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
24 |
25 | find_package(GTSAM REQUIRED)
26 | message(STATUS "gtsam include: " ${GTSAM_INCLUDE_DIR})
27 |
28 | find_package(PythonLibs 2.7 REQUIRED)
29 | include_directories(${PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIRS})
30 |
31 | find_package(NumPy REQUIRED)
32 | include_directories(${NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS})
33 |
34 | if(NOT WIN32)
35 | FIND_PACKAGE(X11)
36 | FIND_PACKAGE(Threads REQUIRED)
37 | endif()
38 |
39 | if(X11_FOUND)
40 | link_directories(${X11_LIB_DIRS})
41 | include_directories(${X11_INCLUDE_DIR})
42 | SET( SYSTEM_LIBS ${SYSTEM_LIBS} ${X11_LIBRARIES} )
43 | endif()
44 |
45 | include_directories(BEFORE ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR})
46 | include_directories(${BOOST_INCLUDE_DIRS})
47 | include_directories(${OpenCV_INCLUDE_DIRS})
48 | include_directories(${GTSAM_INCLUDE_DIR})
49 |
50 | link_directories(${OpenCV_LIBRARY_DIRS})
51 | link_directories(${BOOST_LIBRARY_DIRS})
52 |
53 | file(GLOB srcs flow2pose_lib/flow2pose*)
54 | add_library(${PROJECT_NAME} SHARED ${srcs})
55 | target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME} gtsam opencv_core opencv_imgproc)
56 |
57 | file(GLOB pyboostcv_srcs flow2pose_lib/pyboost_*)
58 | add_library(pyboostcv_bridge SHARED ${pyboostcv_srcs})
59 | target_link_libraries(pyboostcv_bridge opencv_core ${PYTHON_LIBRARIES} ${BOOST_LIBRARIES})
60 |
61 | PYTHON_ADD_MODULE(pyFlow2Pose "flow2pose_lib/py_flow2pose.cpp")
62 | target_link_libraries(pyFlow2Pose pyboostcv_bridge Boost::python ${PYTHON_LIBRARIES} gtsam ${PROJECT_NAME} opencv_core opencv_highgui)
63 |
64 | add_executable(estimate_pose "estimate_pose.cpp")
65 | target_link_libraries(estimate_pose
66 | opencv_core opencv_imgproc
67 | Boost::program_options
68 | Boost::filesystem
69 | ${PROJECT_NAME}
70 | ${SYSTEM_LIBS})
71 |
72 | install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME} DESTINATION lib)
73 | install(TARGETS estimate_pose DESTINATION bin)
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Dockerfile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | FROM nvidia/cuda:8.0-devel-ubuntu16.04
2 |
3 | # Install some basic utilities
4 | RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y \
5 | curl \
6 | ca-certificates \
7 | sudo \
8 | git \
9 | bzip2 \
10 | libx11-6 \
11 | cmake \
12 | libboost-all-dev \
13 | libtbb-dev \
14 | libopencv-dev \
15 | && sudo rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
16 |
17 | # Create a working directory
18 | RUN mkdir /rigidity
19 | WORKDIR /rigidity
20 |
21 | # All users can use /home/user as their home directory
22 | ENV HOME=/home/user
23 | RUN mkdir /home/user
24 | RUN chmod 777 /home/user
25 |
26 | COPY ./setup /rigidity/setup
27 |
28 | # Install Miniconda
29 | ENV CONDA_AUTO_UPDATE_CONDA=false
30 |
31 | RUN curl https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda2-4.5.4-Linux-x86_64.sh -o ~/miniconda.sh && \
32 | /bin/bash ~/miniconda.sh -b -p /opt/conda && \
33 | rm ~/miniconda.sh && \
34 | ln -s /opt/conda/etc/profile.d/conda.sh /etc/profile.d/conda.sh && \
35 | echo ". /opt/conda/etc/profile.d/conda.sh" >> ~/.bashrc
36 |
37 |
38 | # Create a Python 2.7 environment with all the required packages
39 | RUN . /opt/conda/etc/profile.d/conda.sh \
40 | && conda env create -f ./setup/rigidity.yml \
41 | && echo "conda activate rigidity" >> ~/.bashrc \
42 | && conda activate rigidity
43 |
44 | # COPY External Packages
45 | COPY ./external_packages /rigidity/external_packages
46 |
47 | # Build GTSAM
48 | RUN cd /rigidity/external_packages/gtsam \
49 | && mkdir build \
50 | && cd build \
51 | && cmake .. \
52 | && make install -j8 \
53 | && cd ../..
54 |
55 | # Build correlation layer
56 | RUN . /opt/conda/etc/profile.d/conda.sh \
57 | && conda activate rigidity \
58 | && cd /rigidity/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src \
59 | && nvcc -c -o corr_cuda_kernel.cu.o corr_cuda_kernel.cu -x cu -Xcompiler -fPIC -arch=sm_52 \
60 | && nvcc -c -o corr1d_cuda_kernel.cu.o corr1d_cuda_kernel.cu -x cu -Xcompiler -fPIC -arch=sm_52 \
61 | && cd ../../ \
62 | && python setup.py build install
63 |
64 | # compile the refinement module
65 | RUN cd /rigidity/external_packages/flow2pose \
66 | && mkdir build \
67 | && cd build \
68 | && cmake .. \
69 | -DPYTHON_INCLUDE_DIR:PATH=/opt/conda/envs/rigidity/include/python2.7 \
70 | -DPYTHON_LIBRARY:PATH=/opt/conda/envs/rigidity/lib/python2.7 \
71 | -DPYTHON_EXECUTABLE:FILEPATH=/opt/conda/envs/rigidity/bin/python \
72 | && make install -j8 \
73 | && cp pyFlow2Pose.so /opt/conda/envs/rigidity/lib/python2.7/site-packages \
74 | && cp libpyboostcv_bridge.so /usr/local/lib
75 |
76 | RUN rm -rf /rigidity
77 |
78 | # Set the default cmd`
79 | CMD ["/bin/bash"]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup/rigidity.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: rigidity
2 | channels:
3 | - conda-forge
4 | - pytorch
5 | - defaults
6 | dependencies:
7 | - pip=18.0=py27_1
8 | - backports=1.0=py27_1
9 | - backports.functools_lru_cache=1.5=py27_1
10 | - backports_abc=0.5=py27h7b3c97b_0
11 | - blas=1.0=mkl
12 | - ca-certificates=2018.03.07=0
13 | - certifi=2018.8.24=py27_1
14 | - cffi=1.11.5=py27h9745a5d_0
15 | - cloudpickle=0.5.5=py27_0
16 | - cudatoolkit=8.0=3
17 | - cycler=0.10.0=py27_0
18 | - dask-core=0.18.2=py27_0
19 | - dbus=1.13.2=h714fa37_1
20 | - decorator=4.3.0=py27_0
21 | - expat=2.2.5=he0dffb1_0
22 | - fontconfig=2.13.0=h9420a91_0
23 | - freetype=2.9.1=h8a8886c_0
24 | - functools32=3.2.3.2=py27_1
25 | - futures=3.2.0=py27_0
26 | - glib=2.56.1=h000015b_0
27 | - gst-plugins-base=1.14.0=hbbd80ab_1
28 | - gstreamer=1.14.0=hb453b48_1
29 | - icu=58.2=h9c2bf20_1
30 | - imageio=2.3.0=py27_0
31 | - intel-openmp=2018.0.3=0
32 | - jpeg=9b=h024ee3a_2
33 | - kiwisolver=1.0.1=py27hf484d3e_0
34 | - libedit=3.1.20170329=h6b74fdf_2
35 | - libffi=3.2.1=hd88cf55_4
36 | - libgcc-ng=8.2.0=hdf63c60_1
37 | - libgfortran-ng=7.3.0=hdf63c60_0
38 | - libpng=1.6.34=hb9fc6fc_0
39 | - libstdcxx-ng=8.2.0=hdf63c60_1
40 | - libtiff=4.0.9=he85c1e1_2
41 | - libuuid=1.0.3=h1bed415_2
42 | - libxcb=1.13=h1bed415_1
43 | - libxml2=2.9.8=h26e45fe_1
44 | - matplotlib=2.2.3=py27hb69df0a_0
45 | - mkl=2018.0.3=1
46 | - mkl_fft=1.0.4=py27h4414c95_1
47 | - mkl_random=1.0.1=py27h4414c95_1
48 | - ncurses=6.1=hf484d3e_0
49 | - networkx=2.1=py27_0
50 | - ninja=1.8.2=py27h6bb024c_1
51 | - numpy=1.15.0=py27h1b885b7_0
52 | - numpy-base=1.15.0=py27h3dfced4_0
53 | - olefile=0.45.1=py27_0
54 | - openssl=1.0.2p=h14c3975_0
55 | - pcre=8.42=h439df22_0
56 | - pillow=5.2.0=py27heded4f4_0
57 | - pycparser=2.18=py27_1
58 | - pyparsing=2.2.0=py27_1
59 | - pyqt=5.9.2=py27h22d08a2_0
60 | - python=2.7.15=h1571d57_0
61 | - python-dateutil=2.7.3=py27_0
62 | - pytz=2018.5=py27_0
63 | - pywavelets=0.5.2=py27h035aef0_2
64 | - qt=5.9.6=h52aff34_0
65 | - readline=7.0=ha6073c6_4
66 | - scikit-image=0.14.0=py27hf484d3e_1
67 | - scipy=1.1.0=py27hc49cb51_0
68 | - setuptools=40.0.0=py27_0
69 | - singledispatch=3.4.0.3=py27h9bcb476_0
70 | - sip=4.19.8=py27hf484d3e_0
71 | - six=1.11.0=py27_1
72 | - sqlite=3.24.0=h84994c4_0
73 | - subprocess32=3.5.2=py27h14c3975_0
74 | - tk=8.6.7=hc745277_3
75 | - toolz=0.9.0=py27_0
76 | - tornado=5.1=py27h14c3975_0
77 | - wheel=0.31.1=py27_0
78 | - xz=5.2.4=h14c3975_4
79 | - zlib=1.2.11=ha838bed_2
80 | - cuda80=1.0=h205658b_0
81 | - pytorch=0.3.1=py27_cuda8.0.61_cudnn7.1.2_3
82 | - torchvision=0.2.0=py27hfb27419_1
83 | - pip:
84 | - cython==0.28.3
85 | - dask==0.18.2
86 | - torch==0.3.1.post3
87 | prefix: ~/anaconda2/envs/rigidity
88 |
89 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/flow2pose_lib/pyboostcvconverter.hpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * CVBoostConverter.hpp
3 | *
4 | * Created on: Mar 20, 2014
5 | * Author: Gregory Kramida
6 | * Copyright: (c) 2014 Gregory Kramida
7 | * License: MIT
8 | */
9 |
10 | #ifndef CVBOOSTCONVERTER_HPP_
11 | #define CVBOOSTCONVERTER_HPP_
12 |
13 | #define NPY_NO_DEPRECATED_API NPY_1_7_API_VERSION
14 | #include
15 | #include
16 | #include
17 | #include
18 | #include
19 |
20 | namespace pbcvt{
21 |
22 | using namespace cv;
23 |
24 |
25 | static PyObject* opencv_error = 0;
26 |
27 |
28 | //=================== MACROS =================================================================
29 | #define ERRWRAP2(expr) \
30 | try \
31 | { \
32 | PyAllowThreads allowThreads; \
33 | expr; \
34 | } \
35 | catch (const cv::Exception &e) \
36 | { \
37 | PyErr_SetString(opencv_error, e.what()); \
38 | return 0; \
39 | }
40 |
41 | //=================== ERROR HANDLING =========================================================
42 |
43 | static int failmsg(const char *fmt, ...);
44 | static PyObject* failmsgp(const char *fmt, ...);
45 |
46 | //=================== THREADING ==============================================================
47 | class PyAllowThreads;
48 | class PyEnsureGIL;
49 |
50 | static size_t REFCOUNT_OFFSET = (size_t)&(((PyObject*)0)->ob_refcnt) +
51 | (0x12345678 != *(const size_t*)"\x78\x56\x34\x12\0\0\0\0\0")*sizeof(int);
52 |
53 | static inline PyObject* pyObjectFromRefcount(const int* refcount)
54 | {
55 | return (PyObject*)((size_t)refcount - REFCOUNT_OFFSET);
56 | }
57 |
58 | static inline int* refcountFromPyObject(const PyObject* obj)
59 | {
60 | return (int*)((size_t)obj + REFCOUNT_OFFSET);
61 | }
62 |
63 | //=================== NUMPY ALLOCATOR FOR OPENCV =============================================
64 |
65 | class NumpyAllocator;
66 |
67 | //=================== STANDALONE CONVERTER FUNCTIONS =========================================
68 |
69 | PyObject* fromMatToNDArray(const Mat& m);
70 | Mat fromNDArrayToMat(PyObject* o);
71 |
72 | //=================== BOOST CONVERTERS =======================================================
73 |
74 | struct matToNDArrayBoostConverter {
75 | static PyObject* convert(Mat const& m);
76 | };
77 |
78 |
79 | struct matFromNDArrayBoostConverter {
80 |
81 | matFromNDArrayBoostConverter();
82 |
83 | /// @brief Check if PyObject is an array and can be converted to OpenCV matrix.
84 | static void* convertible(PyObject* object);
85 |
86 | /// @brief Construct a Mat from an NDArray object.
87 | static void construct(PyObject* object,
88 | boost::python::converter::rvalue_from_python_stage1_data* data);
89 | };
90 | } // end namespace pbcvt
91 | #endif /* CVBOOSTCONVERTER_HPP_ */
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/cmake/FindNumPy.cmake:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # - Find the NumPy libraries
2 | # This module finds if NumPy is installed, and sets the following variables
3 | # indicating where it is.
4 | #
5 | # TODO: Update to provide the libraries and paths for linking npymath lib.
6 | #
7 | # NUMPY_FOUND - was NumPy found
8 | # NUMPY_VERSION - the version of NumPy found as a string
9 | # NUMPY_VERSION_MAJOR - the major version number of NumPy
10 | # NUMPY_VERSION_MINOR - the minor version number of NumPy
11 | # NUMPY_VERSION_PATCH - the patch version number of NumPy
12 | # NUMPY_VERSION_DECIMAL - e.g. version 1.6.1 is 10601
13 | # NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS - path to the NumPy include files
14 |
15 | #============================================================================
16 | # Copyright 2012 Continuum Analytics, Inc.
17 | #
18 | # MIT License
19 | #
20 | # Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining
21 | # a copy of this software and associated documentation files
22 | # (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
23 | # without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish,
24 | # distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit
25 | # persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to
26 | # the following conditions:
27 | #
28 | # The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included
29 | # in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
30 | #
31 | # THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS
32 | # OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
33 | # FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL
34 | # THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR
35 | # OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE,
36 | # ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR
37 | # OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
38 | #
39 | #============================================================================
40 |
41 | # Finding NumPy involves calling the Python interpreter
42 | if(NumPy_FIND_REQUIRED)
43 | find_package(PythonInterp REQUIRED)
44 | else()
45 | find_package(PythonInterp)
46 | endif()
47 |
48 | if(NOT PYTHONINTERP_FOUND)
49 | set(NUMPY_FOUND FALSE)
50 | endif()
51 |
52 | execute_process(COMMAND "${PYTHON_EXECUTABLE}" "-c"
53 | "import numpy as n; print(n.__version__); print(n.get_include());"
54 | RESULT_VARIABLE _NUMPY_SEARCH_SUCCESS
55 | OUTPUT_VARIABLE _NUMPY_VALUES
56 | ERROR_VARIABLE _NUMPY_ERROR_VALUE
57 | OUTPUT_STRIP_TRAILING_WHITESPACE)
58 |
59 | if(NOT _NUMPY_SEARCH_SUCCESS MATCHES 0)
60 | if(NumPy_FIND_REQUIRED)
61 | message(FATAL_ERROR
62 | "NumPy import failure:\n${_NUMPY_ERROR_VALUE}")
63 | endif()
64 | set(NUMPY_FOUND FALSE)
65 | endif()
66 |
67 | # Convert the process output into a list
68 | string(REGEX REPLACE ";" "\\\\;" _NUMPY_VALUES ${_NUMPY_VALUES})
69 | string(REGEX REPLACE "\n" ";" _NUMPY_VALUES ${_NUMPY_VALUES})
70 | list(GET _NUMPY_VALUES 0 NUMPY_VERSION)
71 | list(GET _NUMPY_VALUES 1 NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS)
72 |
73 | # Make sure all directory separators are '/'
74 | string(REGEX REPLACE "\\\\" "/" NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS ${NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS})
75 |
76 | # Get the major and minor version numbers
77 | string(REGEX REPLACE "\\." ";" _NUMPY_VERSION_LIST ${NUMPY_VERSION})
78 | list(GET _NUMPY_VERSION_LIST 0 NUMPY_VERSION_MAJOR)
79 | list(GET _NUMPY_VERSION_LIST 1 NUMPY_VERSION_MINOR)
80 | list(GET _NUMPY_VERSION_LIST 2 NUMPY_VERSION_PATCH)
81 | string(REGEX MATCH "[0-9]*" NUMPY_VERSION_PATCH ${NUMPY_VERSION_PATCH})
82 | math(EXPR NUMPY_VERSION_DECIMAL
83 | "(${NUMPY_VERSION_MAJOR} * 10000) + (${NUMPY_VERSION_MINOR} * 100) + ${NUMPY_VERSION_PATCH}")
84 |
85 | find_package_message(NUMPY
86 | "Found NumPy: version \"${NUMPY_VERSION}\" ${NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS}"
87 | "${NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIRS}${NUMPY_VERSION}")
88 |
89 | set(NUMPY_FOUND TRUE)
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/functions/corr.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch.autograd import Function
3 | from .._ext import corr
4 |
5 | class correlation(Function):
6 |
7 | def __init__(self, pad_size=3, kernel_size=3, max_displacement=20, stride1=1, stride2=1, corr_multiply=1):
8 | super(correlation, self).__init__()
9 | self.pad_size = pad_size
10 | self.kernel_size = kernel_size
11 | self.max_displacement = max_displacement
12 | self.stride1 = stride1
13 | self.stride2 = stride2
14 | self.corr_multiply = corr_multiply
15 |
16 | def forward(self, input1, input2):
17 |
18 | self.save_for_backward(input1, input2)
19 |
20 | rbot1 = input1.new()
21 | rbot2 = input2.new()
22 | output = input1.new()
23 |
24 | corr.corr_cuda_forward(input1, input2,
25 | rbot1, rbot2,
26 | output,
27 | self.pad_size,
28 | self.kernel_size,
29 | self.max_displacement,
30 | self.stride1,
31 | self.stride2,
32 | self.corr_multiply)
33 |
34 | return output
35 |
36 | def backward(self, grad_output):
37 |
38 | input1, input2 = self.saved_tensors
39 |
40 | rbot1 = input1.new()
41 | rbot2 = input2.new()
42 |
43 | grad_input1 = torch.zeros(input1.size()).cuda()
44 | grad_input2 = torch.zeros(input2.size()).cuda()
45 |
46 | corr.corr_cuda_backward(input1, input2,
47 | rbot1, rbot2,
48 | grad_output,
49 | grad_input1,
50 | grad_input2,
51 | self.pad_size,
52 | self.kernel_size,
53 | self.max_displacement,
54 | self.stride1,
55 | self.stride2,
56 | self.corr_multiply)
57 |
58 | return grad_input1, grad_input2
59 |
60 |
61 | #----- 1D correlation (for disparity) Jinwei Gu -----
62 |
63 | class correlation1d(Function):
64 |
65 | def __init__(self, pad_size=3, kernel_size=3, max_displacement=20, stride1=1, stride2=1, corr_multiply=1):
66 | super(correlation1d, self).__init__()
67 | self.pad_size = pad_size
68 | self.kernel_size = kernel_size
69 | self.max_displacement = max_displacement
70 | self.stride1 = stride1
71 | self.stride2 = stride2
72 | self.corr_multiply = corr_multiply
73 |
74 | def forward(self, input1, input2):
75 |
76 | self.save_for_backward(input1, input2)
77 |
78 | rbot1 = input1.new()
79 | rbot2 = input2.new()
80 | output = input1.new()
81 |
82 | corr.corr1d_cuda_forward(input1, input2,
83 | rbot1, rbot2,
84 | output,
85 | self.pad_size,
86 | self.kernel_size,
87 | self.max_displacement,
88 | self.stride1,
89 | self.stride2,
90 | self.corr_multiply)
91 |
92 | return output
93 |
94 | def backward(self, grad_output):
95 |
96 | input1, input2 = self.saved_tensors
97 |
98 | rbot1 = input1.new()
99 | rbot2 = input2.new()
100 |
101 | grad_input1 = torch.zeros(input1.size()).cuda()
102 | grad_input2 = torch.zeros(input2.size()).cuda()
103 |
104 | #grad_input1 = grad_output.new()
105 | #grad_input2 = grad_output.new()
106 |
107 | corr.corr1d_cuda_backward(input1, input2,
108 | rbot1, rbot2,
109 | grad_output,
110 | grad_input1,
111 | grad_input2,
112 | self.pad_size,
113 | self.kernel_size,
114 | self.max_displacement,
115 | self.stride1,
116 | self.stride2,
117 | self.corr_multiply)
118 |
119 | return grad_input1, grad_input2
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pose_refine.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 |
6 | Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 | """
8 |
9 | import os, sys, time
10 | import numpy as np
11 |
12 | sys.path.append('external_packages/flow2pose/build')
13 | from pyFlow2Pose import pyFlow2Pose
14 |
15 | from scipy.misc import imsave
16 | from scipy import ndimage
17 | from skimage.morphology import dilation, square, erosion
18 |
19 | def forward_backward_consistency(F_f, F_b, threshold):
20 | """ get the mask that is foreward-backward consistent
21 | """
22 | u_b = F_b[0]
23 | v_b = F_b[1]
24 | u_f = F_f[0]
25 | v_f = F_f[1]
26 | [H,W] = np.shape(u_b)
27 | [x,y] = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0,W),np.arange(0,H))
28 | x2 = x + u_b
29 | y2 = y + v_b
30 | # Out of boundary
31 | B = (x2 > W-1) | (y2 > H-1) | (x2 < 0) | (y2 <0)
32 | u = ndimage.map_coordinates(u_f, [y2, x2])
33 | v = ndimage.map_coordinates(v_f, [y2, x2])
34 | u_inv = u
35 | v_inv = v
36 | dif = np.zeros((H, W), dtype=np.float64)
37 | dif = ((u_b + u_inv)**2 + (v_b + v_inv)**2)**0.5
38 | mask = (dif < threshold)
39 | mask = mask | B
40 |
41 | return mask
42 |
43 | def depth2pointcloud_batch(K0, depth0):
44 | """ Transfer a pair of depth images into point cloud
45 | """
46 | B, _, H, W = depth0.shape
47 |
48 | inv_K0 = np.linalg.inv(K0)
49 |
50 | u_mat = np.repeat(np.array(range(0, W)).reshape(1, W), H, axis=0)
51 | v_mat = np.repeat(np.array(range(0, H)).reshape(H, 1), W, axis=1)
52 |
53 | uvd_map_0 = np.concatenate((depth0 * u_mat, depth0 * v_mat, depth0), axis=1)
54 |
55 | vertex_map_0 = uvd_map_0.copy()
56 |
57 | for idx in range(B):
58 | vertex_map_0[idx] = np.tensordot(inv_K0[idx], uvd_map_0[idx], axes=1)
59 |
60 | return vertex_map_0
61 |
62 | class PoseRefine():
63 |
64 | def __init__(self):
65 |
66 | self.f2p = pyFlow2Pose()
67 |
68 | def run(self, f_flow, b_flow, V0, V1, bg0, bg1,
69 | pose_init=None, max_depth=None):
70 | """
71 | :param f_flow: forward flow vector
72 | :param b_flow: backward flow vector
73 | :param V0: vertex map for frame0
74 | :param V1: vertex map for frame1
75 | :param bg0: background for frame0
76 | :param bg1: background for frame1
77 | :param pose_init: initial pose
78 | """
79 | # the threshold is hard-coded
80 | m = forward_backward_consistency(f_flow, b_flow, 0.75)
81 |
82 | flow = f_flow.transpose((1,2,0))
83 |
84 | bg0 = dilation(bg0, square(5))
85 | bg1 = dilation(bg1, square(5))
86 | occlusion = erosion(m.astype(int), square(10))
87 |
88 | if max_depth is not None:
89 | invalid = (V0[:,:,2] < max_depth) & (V0[:,:,2] > 1e-4)
90 | occlusion *= invalid.astype(int)
91 |
92 | if pose_init is None:
93 | pose_init = np.zeros((3,4)).astype(np.float32)
94 | pose_init[:, :3] = np.eye(3)
95 |
96 | ## Becareful about the type of input:
97 | # V0: double
98 | # V1: double
99 | # flow: float32
100 | # bg0: int
101 | # bg1: int
102 | # occlusion: int
103 | # pose_init: float32
104 | pose_refined = self.f2p.calculate_transform(
105 | V0.astype(np.float64), V1.astype(np.float64), flow.astype(np.float32),
106 | bg0.astype(int), bg1.astype(int), occlusion.astype(int),
107 | pose_init.astype(np.float32))
108 |
109 | return pose_refined
110 |
111 | def run_batch(self, vertices0, vertices1, rigidity0, rigidity1,
112 | forward_flow, backward_flow, max_depth=None):
113 | """ Run the pose refine algorithm in batches
114 | :param the first image point cloud (x0, y0, z0)
115 | :param the second image point cloud (x1, y1, z1)
116 | :param the first frame rigidity mask
117 | :param the second frame rigidity mask
118 | :param forward optical flow
119 | :param backward optical flow
120 | :param maximum depth range
121 | """
122 | # V0_batch = depth2pointcloud_batch(K0, D0)
123 | # V1_batch = depth2pointcloud_batch(K1, D1)
124 |
125 | B = vertices0.shape[0]
126 | est_Rt44 = np.zeros((B, 4, 4))
127 | for idx in range(B):
128 | V0 = vertices0[idx].transpose((1,2,0))
129 | V1 = vertices1[idx].transpose((1,2,0))
130 |
131 | est_Rt44[idx] = self.run(forward_flow[idx],
132 | backward_flow[idx], V0, V1,
133 | rigidity0[idx], rigidity1[idx], max_depth=None)
134 |
135 | return est_Rt44
136 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/RigidityNet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 |
6 | Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 | """
8 |
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import torchvision.models as models
12 |
13 | from torch.autograd import Variable
14 | from torch.nn import init
15 |
16 | def conv(inplanes, outplanes, ks=3, st=1):
17 | return nn.Sequential(
18 | nn.Conv2d( inplanes, outplanes, kernel_size=ks, stride=st, padding=(ks-1)//2, bias=True),
19 | nn.BatchNorm2d(outplanes),
20 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
21 | )
22 |
23 | def transpose_conv(inplanes, outplanes, ks=4, st=2):
24 | return nn.Sequential(
25 | nn.ConvTranspose2d(inplanes, outplanes, kernel_size=ks, stride=st, padding=(ks-1)//2, bias=True),
26 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
27 | )
28 |
29 | class RigidityNet(nn.Module):
30 | """ The Rigidity Transform network
31 | """
32 | def __init__(self):
33 | super(RigidityNet, self).__init__()
34 |
35 | self.conv_ch = [12, 32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024]
36 |
37 | self.conv1 = conv(self.conv_ch[0], self.conv_ch[1], 7, 2)
38 | self.conv2 = conv(self.conv_ch[1], self.conv_ch[2], 7, 2)
39 | self.conv3 = conv(self.conv_ch[2], self.conv_ch[3], 5, 2)
40 | self.conv4 = conv(self.conv_ch[3], self.conv_ch[4], 3, 2)
41 | self.conv5 = conv(self.conv_ch[4], self.conv_ch[5], 3, 2)
42 | self.conv6 = conv(self.conv_ch[5], self.conv_ch[6], 3, 1)
43 |
44 | self.predict_translate = nn.Conv2d(1024, 3, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
45 | self.predict_rotate = nn.Conv2d(1024, 3, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
46 |
47 | self.transpose_conv_ch = [32, 64, 128, 256, 512, 1024]
48 |
49 | self.transpose_conv5 = transpose_conv(self.transpose_conv_ch[5], self.transpose_conv_ch[4])
50 | self.transpose_conv4 = transpose_conv(self.transpose_conv_ch[4], self.transpose_conv_ch[3])
51 | self.transpose_conv3 = transpose_conv(self.transpose_conv_ch[3], self.transpose_conv_ch[2])
52 | self.transpose_conv2 = transpose_conv(self.transpose_conv_ch[2], self.transpose_conv_ch[1])
53 | self.transpose_conv1 = transpose_conv(self.transpose_conv_ch[1], self.transpose_conv_ch[0])
54 |
55 | # Use 1x1 convolution to predict the final mask
56 | self.predict_fg5 = nn.Conv2d(self.transpose_conv_ch[4], 2, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
57 | self.predict_fg4 = nn.Conv2d(self.transpose_conv_ch[3], 2, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
58 | self.predict_fg3 = nn.Conv2d(self.transpose_conv_ch[2], 2, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
59 | self.predict_fg2 = nn.Conv2d(self.transpose_conv_ch[1], 2, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
60 | self.predict_fg1 = nn.Conv2d(self.transpose_conv_ch[0], 2, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
61 |
62 | self._initialize_weights()
63 |
64 | def forward(self, x):
65 | out_conv1 = self.conv1(x)
66 | out_conv2 = self.conv2(out_conv1)
67 | out_conv3 = self.conv3(out_conv2)
68 | out_conv4 = self.conv4(out_conv3)
69 | out_conv5 = self.conv5(out_conv4)
70 | bottleneck = self.conv6(out_conv5)
71 |
72 | t = self.predict_translate(bottleneck)
73 | R = self.predict_rotate(bottleneck)
74 |
75 | out_transpose_conv5 = self.transpose_conv5(bottleneck)
76 | out_transpose_conv4 = self.transpose_conv4(out_transpose_conv5)
77 | out_transpose_conv3 = self.transpose_conv3(out_transpose_conv4)
78 | out_transpose_conv2 = self.transpose_conv2(out_transpose_conv3)
79 | out_transpose_conv1 = self.transpose_conv1(out_transpose_conv2)
80 |
81 | rg5 = self.predict_fg5(out_transpose_conv5)
82 | rg4 = self.predict_fg4(out_transpose_conv4)
83 | rg3 = self.predict_fg3(out_transpose_conv3)
84 | rg2 = self.predict_fg2(out_transpose_conv2)
85 | rg1 = self.predict_fg1(out_transpose_conv1)
86 |
87 | if self.training:
88 | return torch.cat([t,R], dim=1), rg1, rg2, rg3, rg4, rg5
89 | else:
90 | return torch.cat([t,R], dim=1), rg1
91 |
92 | def _initialize_weights(self):
93 |
94 | for idx, m in enumerate(self.modules()):
95 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
96 | init.kaiming_uniform(m.weight.data) # the MSRA initialization
97 | m.bias.data.zero_()
98 | elif isinstance(m, nn.ConvTranspose2d):
99 | init.kaiming_uniform(m.weight.data) # the MSRA initialization
100 | m.bias.data.zero_()
101 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
102 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
103 | m.bias.data.zero_()
104 |
105 | def rigidity_transform_net(checkpoint_path=None):
106 | """ Load the rigidity attention network
107 | """
108 | model = RigidityNet()
109 | if checkpoint_path is not None:
110 | data = torch.load(checkpoint_path)
111 | if 'state_dict' in data.keys():
112 | model.load_state_dict(data['state_dict'])
113 | else:
114 | model.load_state_dict(data)
115 | return model
116 |
117 | if __name__ == '__main__':
118 |
119 | net = rigidity_transform_net()
120 | print(net)
121 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/flow2pose_lib/py_flow2pose.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /**
2 | * Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | * Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | * (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 | *
6 | * Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 | */
8 |
9 | #define PY_ARRAY_UNIQUE_SYMBOL pbcvt_ARRAY_API
10 |
11 | #include "flow2pose.h"
12 |
13 | #include "Python.h"
14 | #include "pyboostcvconverter.hpp"
15 |
16 | #include
17 | #include
18 |
19 | #include
20 | #include
21 | #include
22 |
23 | #include
24 |
25 | #include
26 |
27 | using namespace boost::python;
28 | using namespace gtsam;
29 |
30 | // transform the vector to a numpy array
31 | static object array_to_nparray(double* data, npy_intp size) {
32 | npy_intp shape[1] = { size }; // array size
33 | PyObject* obj = PyArray_New(&PyArray_Type, 1, shape, NPY_DOUBLE, // data type
34 | NULL, data, // data pointer
35 | 0, NPY_ARRAY_CARRAY, // NPY_ARRAY_CARRAY_RO for readonly
36 | NULL);
37 | handle<> array( obj );
38 | return object(array);
39 | }
40 |
41 | // transform the numpy array to a vector
42 | static std::vector nparray_to_vector(PyArrayObject* np_array) {
43 | // get the size
44 | npy_intp length = PyArray_SIZE(np_array);
45 | int size = length / 6;
46 | // get the pointer to the array
47 | double* c_array = (double*) PyArray_GETPTR1( np_array, 0 );
48 |
49 | std::vector points;
50 | for (int idx = 0; idx < size; idx ++) {
51 | Point3 pt (c_array[idx*6], c_array[idx*6 + 1], c_array[idx*6 + 2]);
52 | points.push_back(pt);
53 | }
54 | return points;
55 | }
56 |
57 | static Pose3 nparray_to_pose(PyArrayObject* np_array) {
58 | float* c_array = (float*) PyArray_GETPTR1( np_array, 0 );
59 |
60 | Matrix4 pose_matrix;
61 | pose_matrix << c_array[0], c_array[1], c_array[2], c_array[3],
62 | c_array[4], c_array[5], c_array[6], c_array[7],
63 | c_array[8], c_array[9], c_array[10], c_array[11],
64 | 0, 0, 0, 1;
65 |
66 | return Pose3(pose_matrix);
67 | }
68 |
69 | struct pyFlow2Pose : Flow2Pose {
70 |
71 | // calculate the transform given the raw vertices map
72 | PyObject* calculate_transform(PyObject *vertices0, PyObject *vertices1, PyObject *flow, PyObject *foreground0, PyObject *foreground1, PyObject *occlusion, PyObject* initial_pose) {
73 | cv::Mat vMat0, vMat1, flowMat, segMat0, segMat1, occMat;
74 | vMat0 = pbcvt::fromNDArrayToMat(vertices0);
75 | vMat1 = pbcvt::fromNDArrayToMat(vertices1);
76 | flowMat= pbcvt::fromNDArrayToMat(flow);
77 | segMat0 = pbcvt::fromNDArrayToMat(foreground0);
78 | segMat1 = pbcvt::fromNDArrayToMat(foreground1);
79 | occMat = pbcvt::fromNDArrayToMat(occlusion);
80 |
81 | Pose3 pose_init = nparray_to_pose((PyArrayObject*) initial_pose);
82 |
83 | Pose3 result = Flow2Pose::calculate_transform(vMat0, vMat1, flowMat, segMat0, segMat1, occMat, pose_init);
84 |
85 | return gtsam_pose3_to_pyobject(result);
86 | }
87 |
88 | // calculate the transform given the matched correspondences
89 | PyObject* solve_pose(PyObject* py_pts1, PyObject* py_pts2, PyObject* py_pose) {
90 | PyArrayObject* np_pts1 = (PyArrayObject*) py_pts1;
91 | PyArrayObject* np_pts2 = (PyArrayObject*) py_pts2;
92 | PyArrayObject* np_pose = (PyArrayObject*) py_pose;
93 | double* pose_ptr = (double*) PyArray_GETPTR1( np_pose, 0 );
94 |
95 | const std::vector pts1 = nparray_to_vector(np_pts1);
96 | const std::vector pts2 = nparray_to_vector(np_pts2);
97 |
98 | Pose3 initial_pose(Rot3::Rodrigues(pose_ptr[0], pose_ptr[1], pose_ptr[2]), Point3(pose_ptr[3], pose_ptr[4], pose_ptr[5]));
99 |
100 | Pose3 result = Flow2Pose::solve(pts1, pts2, initial_pose);
101 |
102 | return gtsam_pose3_to_pyobject(result);
103 | }
104 |
105 | PyObject* gtsam_pose3_to_pyobject(const gtsam::Pose3& pose) {
106 | Matrix4 pose_out = pose.matrix();
107 | // transform the estimated pose into an numpy object
108 |
109 | double pose_array[16];
110 | for (auto u = 0; u < 4; u++) {
111 | for (auto v = 0; v < 4; v++) {
112 | pose_array[u*4 +v] = pose_out(u, v);
113 | }
114 | }
115 |
116 | npy_intp dims[2]{4,4};
117 | PyObject* np_pose_out = PyArray_SimpleNew(2, dims, NPY_DOUBLE);
118 | memcpy(PyArray_DATA((PyArrayObject*)np_pose_out), pose_array, sizeof(pose_array));
119 | return np_pose_out;
120 | }
121 |
122 | };
123 |
124 | void test(PyObject* obj) {
125 |
126 | PyArrayObject* np_obj = (PyArrayObject*) obj;
127 |
128 | npy_intp s = PyArray_SIZE(np_obj);
129 | // get the pointer to the array
130 | double* c_array = (double*) PyArray_GETPTR1( np_obj, 0 );
131 |
132 | std::cout << "the size of the array is :" << s << std::endl;
133 |
134 | for (int idx=0; idx < s; idx++) {
135 | std::cout << c_array[idx] << std::endl;
136 | }
137 |
138 | std::cout << "Just to show it passed test" << std::endl;
139 | }
140 |
141 | BOOST_PYTHON_MODULE(pyFlow2Pose) {
142 |
143 | // numpy requires this
144 | import_array();
145 |
146 | def("test", &test);
147 |
148 | class_("pyFlow2Pose")
149 | .def( "calculate_transform", &pyFlow2Pose::calculate_transform )
150 | .def( "solve_pose", &pyFlow2Pose::solve_pose )
151 | .def_readwrite("solver_type", &pyFlow2Pose::solver_type)
152 | .def_readwrite("huber_threshold", &pyFlow2Pose::huber_threshold);
153 | }
154 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/io_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 |
6 | Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 |
8 | Partially refer to:
9 | =============================================================================
10 |
11 | The I/O script to save and load the data coming with the MPI-Sintel low-level
12 | computer vision benchmark.
13 |
14 | CHANGELOG:
15 | v1.0 (2015/02/03): First release
16 |
17 | Copyright (c) 2015 Jonas Wulff
18 | Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Tuebingen, Germany
19 | """
20 |
21 | # Requirements: Numpy as PIL/Pillow
22 | import os
23 | import numpy as np
24 | from PIL import Image, ImageDraw, ImageFont
25 |
26 | import matplotlib.colors as color
27 |
28 | # Check for endianness, based on Daniel Scharstein's optical flow code.
29 | # Using little-endian architecture, these two should be equal.
30 | TAG_FLOAT = 202021.25
31 | TAG_CHAR = 'PIEH'
32 |
33 | def flow_visualize(flow, max_range = 1e3):
34 | du = flow[0]
35 | dv = flow[1]
36 | [h,w] = du.shape
37 | max_flow = min(max_range, np.max(np.sqrt(du * du + dv * dv)))
38 | img = np.ones((h, w, 3), dtype=np.float64)
39 | # angle layer
40 | img[:, :, 0] = (np.arctan2(dv, du) / (2 * np.pi) + 1) % 1.0
41 | # magnitude layer, normalized to 1
42 | img[:, :, 1] = np.sqrt(du * du + dv * dv) / (max_flow + 1e-8)
43 | # phase layer
44 | #img[:, :, 2] = valid
45 | # convert to rgb
46 | img = color.hsv_to_rgb(img)
47 | # remove invalid point
48 | img[:, :, 0] = img[:, :, 0]
49 | img[:, :, 1] = img[:, :, 1]
50 | img[:, :, 2] = img[:, :, 2]
51 | return img
52 |
53 | def flow_read_from_flo(filename):
54 | """ Read optical flow from file, return (U,V) tuple.
55 |
56 | Original code by Deqing Sun, adapted from Daniel Scharstein.
57 | """
58 | f = open(filename,'rb')
59 | check = np.fromfile(f,dtype=np.float32,count=1)[0]
60 | assert check == TAG_FLOAT, ' flow_read:: Wrong tag in flow file (should be: {0}, is: {1}). Big-endian machine? '.format(TAG_FLOAT,check)
61 | width = np.fromfile(f,dtype=np.int32,count=1)[0]
62 | height = np.fromfile(f,dtype=np.int32,count=1)[0]
63 | size = width*height
64 | assert width > 0 and height > 0 and size > 1 and size < 100000000, ' flow_read:: Wrong input size (width = {0}, height = {1}).'.format(width,height)
65 | tmp = np.fromfile(f,dtype=np.float32,count=-1).reshape((height,width*2))
66 | u = tmp[:,np.arange(width)*2]
67 | v = tmp[:,np.arange(width)*2 + 1]
68 | return u,v
69 |
70 | def flow_write(filename,uv,v=None):
71 | """ Write optical flow to file.
72 |
73 | If v is None, uv is assumed to contain both u and v channels,
74 | stacked in depth.
75 |
76 | Original code by Deqing Sun, adapted from Daniel Scharstein.
77 | """
78 | nBands = 2
79 |
80 | if v is None:
81 | assert(uv.ndim == 3)
82 | assert(uv.shape[2] == 2)
83 | u = uv[:,:,0]
84 | v = uv[:,:,1]
85 | else:
86 | u = uv
87 |
88 | assert(u.shape == v.shape)
89 | height,width = u.shape
90 | f = open(filename,'wb')
91 | # write the header
92 | f.write(TAG_CHAR)
93 | np.array(width).astype(np.int32).tofile(f)
94 | np.array(height).astype(np.int32).tofile(f)
95 | # arrange into matrix form
96 | tmp = np.zeros((height, width*nBands))
97 | tmp[:,np.arange(width)*2] = u
98 | tmp[:,np.arange(width)*2 + 1] = v
99 | tmp.astype(np.float32).tofile(f)
100 | f.close()
101 |
102 |
103 | def depth_read(filename):
104 | """ Read depth data from file, return as numpy array. """
105 | f = open(filename,'rb')
106 | check = np.fromfile(f,dtype=np.float32,count=1)[0]
107 | assert check == TAG_FLOAT, ' depth_read:: Wrong tag in flow file (should be: {0}, is: {1}). Big-endian machine? '.format(TAG_FLOAT,check)
108 | width = np.fromfile(f,dtype=np.int32,count=1)[0]
109 | height = np.fromfile(f,dtype=np.int32,count=1)[0]
110 | size = width*height
111 | assert width > 0 and height > 0 and size > 1 and size < 100000000, ' depth_read:: Wrong input size (width = {0}, height = {1}).'.format(width,height)
112 | depth = np.fromfile(f,dtype=np.float32,count=-1).reshape((height,width))
113 | return depth
114 |
115 | def depth_write(filename, depth):
116 | """ Write depth to file. """
117 | height,width = depth.shape[:2]
118 | f = open(filename,'wb')
119 | # write the header
120 | f.write(TAG_CHAR)
121 | np.array(width).astype(np.int32).tofile(f)
122 | np.array(height).astype(np.int32).tofile(f)
123 |
124 | depth.astype(np.float32).tofile(f)
125 | f.close()
126 |
127 | def cam_read(filename):
128 | """ Read camera data, return (M,N) tuple.
129 |
130 | M is the intrinsic matrix, N is the extrinsic matrix, so that
131 |
132 | x = M*N*X,
133 | with x being a point in homogeneous image pixel coordinates, X being a
134 | point in homogeneous world coordinates.
135 | """
136 | f = open(filename,'rb')
137 | check = np.fromfile(f,dtype=np.float32,count=1)[0]
138 | assert check == TAG_FLOAT, ' cam_read:: Wrong tag in flow file (should be: {0}, is: {1}). Big-endian machine? '.format(TAG_FLOAT,check)
139 | M = np.fromfile(f,dtype='float64',count=9).reshape((3,3))
140 | N = np.fromfile(f,dtype='float64',count=12).reshape((3,4))
141 | return M,N
142 |
143 | def cam_write(filename, M, N):
144 | """ Write intrinsic matrix M and extrinsic matrix N to file. """
145 | f = open(filename,'wb')
146 | # write the header
147 | f.write(TAG_CHAR)
148 | M.astype('float64').tofile(f)
149 | N.astype('float64').tofile(f)
150 | f.close()
151 |
152 | def image_with_mask(image, mask):
153 | """ return the masked image visualization
154 | """
155 | H, W = mask.shape
156 | color_mask = image.copy()
157 | color_mask[mask>0] = [125, 0, 0]
158 | hsv_mask = color.rgb_to_hsv(color_mask)
159 | I_hsv = color.rgb_to_hsv(image)
160 | I_hsv[..., 0] = hsv_mask[..., 0]
161 | I_hsv[..., 1] = hsv_mask[..., 1] * 0.6
162 | return color.hsv_to_rgb(I_hsv)
163 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/geometry.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 |
6 | Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 | """
8 |
9 | import torch
10 | import numpy as np
11 |
12 | def generate_index_grid(h, w):
13 | """ Generate a meshgrid
14 | :param height of the image
15 | :param H of the image
16 | """
17 | u = torch.arange(0, w).cuda()
18 | v = torch.arange(0, h).cuda()
19 |
20 | return u.repeat(h, 1), v.repeat(w, 1).t()
21 |
22 | def torch_rgbd2uvd(color, depth, fx, fy, cx, cy):
23 | """ Generate the u, v, inverse depth point cloud,
24 | given color, depth and intrinsic parameters
25 |
26 | The input image dimension is as following:
27 |
28 | :param Color dim B * 3 * H * W
29 | :param Depth dim B * H * W
30 | :param fx dim B
31 | :param fy dim B
32 | :param cx dim B
33 | :param cy dim B
34 | """
35 | B, C, H, W = color.size()
36 |
37 | u_, v_ = generate_index_grid(H, W)
38 |
39 | x_ = (u_ - cx) / fx
40 | y_ = (v_ - cy) / fy
41 |
42 | inv_z_ = 1.0 / depth
43 |
44 | uvdrgb = torch.cat(( x_.view(B,1,H,W), y_.view(B,1,H,W),
45 | inv_z_.view(B,1,H,W), color ), 1)
46 |
47 | return uvdrgb
48 |
49 | def torch_depth2xyz(depth, fx, fy, cx, cy):
50 | """ Generate the xyz point cloud
51 | :param Depth dim B * H * W
52 | :param fx dim B
53 | :param fy dim B
54 | :param cx dim B
55 | :param cy dim B
56 | """
57 | B, C, H, W = depth.size()
58 |
59 | u_, v_ = generate_index_grid(H, W)
60 |
61 | x_ = depth * (u_ - cx) / fx
62 | y_ = depth * (v_ - cy) / fy
63 |
64 | xyz = torch.cat((x_.view(B,1,H,W), y_.view(B,1,H,W), depth.view(B,1,H,W)), 1)
65 |
66 | return xyz
67 |
68 | _NEXT_AXIS = [1, 2, 0, 1]
69 |
70 | # map axes strings to/from tuples of inner axis, parity, repetition, frame
71 | _AXES2TUPLE = {
72 | 'sxyz': (0, 0, 0, 0), 'sxyx': (0, 0, 1, 0), 'sxzy': (0, 1, 0, 0),
73 | 'sxzx': (0, 1, 1, 0), 'syzx': (1, 0, 0, 0), 'syzy': (1, 0, 1, 0),
74 | 'syxz': (1, 1, 0, 0), 'syxy': (1, 1, 1, 0), 'szxy': (2, 0, 0, 0),
75 | 'szxz': (2, 0, 1, 0), 'szyx': (2, 1, 0, 0), 'szyz': (2, 1, 1, 0),
76 | 'rzyx': (0, 0, 0, 1), 'rxyx': (0, 0, 1, 1), 'ryzx': (0, 1, 0, 1),
77 | 'rxzx': (0, 1, 1, 1), 'rxzy': (1, 0, 0, 1), 'ryzy': (1, 0, 1, 1),
78 | 'rzxy': (1, 1, 0, 1), 'ryxy': (1, 1, 1, 1), 'ryxz': (2, 0, 0, 1),
79 | 'rzxz': (2, 0, 1, 1), 'rxyz': (2, 1, 0, 1), 'rzyz': (2, 1, 1, 1)}
80 |
81 | _TUPLE2AXES = dict((v, k) for k, v in _AXES2TUPLE.items())
82 |
83 | def torch_euler2mat(ai, aj, ak, axes='sxyz'):
84 | """ A gpu version euler2mat from transform3d:
85 | https://github.com/matthew-brett/transforms3d/blob/master/transforms3d/euler.py
86 | :param ai : First rotation angle (according to `axes`).
87 | :param aj : Second rotation angle (according to `axes`).
88 | :param ak : Third rotation angle (according to `axes`).
89 | :param axes : Axis specification; one of 24 axis sequences as string or encoded tuple - e.g. ``sxyz`` (the default).
90 | Returns
91 | -------
92 | mat : array-like shape (B, 3, 3)
93 |
94 | Tested w.r.t. transforms3d.euler module
95 | """
96 |
97 | B = ai.size()[0]
98 |
99 | cos = torch.cos
100 | sin = torch.sin
101 |
102 | try:
103 | firstaxis, parity, repetition, frame = _AXES2TUPLE[axes]
104 | except (AttributeError, KeyError):
105 | _TUPLE2AXES[axes] # validation
106 | firstaxis, parity, repetition, frame = axes
107 |
108 | i = firstaxis
109 | j = _NEXT_AXIS[i+parity]
110 | k = _NEXT_AXIS[i-parity+1]
111 | order = [i, j, k]
112 |
113 | if frame:
114 | ai, ak = ak, ai
115 | if parity:
116 | ai, aj, ak = -ai, -aj, -ak
117 |
118 | si, sj, sk = sin(ai), sin(aj), sin(ak)
119 | ci, cj, ck = cos(ai), cos(aj), cos(ak)
120 | cc, cs = ci*ck, ci*sk
121 | sc, ss = si*ck, si*sk
122 |
123 | # M = torch.zeros(B, 3, 3).cuda()
124 | if repetition:
125 | c_i = [cj, sj*si, sj*ci]
126 | c_j = [sj*sk, -cj*ss+cc, -cj*cs-sc]
127 | c_k = [-sj*ck, cj*sc+cs, cj*cc-ss]
128 | else:
129 | c_i = [cj*ck, sj*sc-cs, sj*cc+ss]
130 | c_j = [cj*sk, sj*ss+cc, sj*cs-sc]
131 | c_k = [-sj, cj*si, cj*ci]
132 |
133 | def permute(X): # sort X w.r.t. the axis indices
134 | return [ x for (y, x) in sorted(zip(order, X)) ]
135 |
136 | c_i = permute(c_i)
137 | c_j = permute(c_j)
138 | c_k = permute(c_k)
139 |
140 | r =[torch.stack(c_i, 1),
141 | torch.stack(c_j, 1),
142 | torch.stack(c_k, 1)]
143 | r = permute(r)
144 |
145 | return torch.stack(r, 1)
146 |
147 |
148 | def np_depth2flow(depth, K0, T0, K1, T1):
149 | """ Numpy implementation.
150 | Estimate the ego-motion flow given two frames depths and transformation matrices.
151 | The output is an ego-motion flow in 2D (2*H*W).
152 |
153 | :param the depth map of the reference frame
154 | :param the intrinsics of the reference frame
155 | :param the camera coordinate of the reference frame
156 | :param the intrinsics of the target frame
157 | :param the camera coordinate of the target frame
158 | """
159 | rows, cols = depth.shape
160 | u_mat = np.repeat(np.array(range(0, cols)).reshape(1, cols), rows, axis=0)
161 | v_mat = np.repeat(np.array(range(0, rows)).reshape(rows, 1), cols, axis=1)
162 |
163 | # inv_k = [ 1/f_x, 0, -c_x/f_x, 0;
164 | # 0, 1/f_y, -c_y/f_y, 0;
165 | # 0, 0, 1, 0;
166 | # 0, 0, 0, 1]
167 | inv_K = np.eye(4)
168 | inv_K[0,0], inv_K[1,1] = 1.0 / K0[0], 1.0 / K0[1]
169 | inv_K[0,2], inv_K[1,2] = -K0[2] / K0[0], -K0[3] / K0[1]
170 |
171 | # the point cloud move w.r.t. the inverse of camera transform
172 | K = np.eye(4)
173 | K[0,0], K[1,1], K[0,2], K[1,2] = K1[0], K1[1], K1[2], K1[3]
174 |
175 | if T0.shape != (4,4):
176 | T0, T1 = to_homogenous(T0), to_homogenous(T1)
177 | T = reduce(np.dot, [K, T1, np.linalg.inv(T0), inv_K])
178 |
179 | # blender's coordinate is different from sintel
180 | ones = np.ones((rows, cols))
181 | z = depth
182 | x = depth * u_mat
183 | y = depth * v_mat
184 | p4d = np.dstack((x, y, z, ones)).transpose((2,0,1))
185 | p4d_t = np.tensordot(T, p4d, axes=1)
186 |
187 | x_t, y_t, z_t, w_t = np.split(p4d_t, 4)
188 | # homogenous to cartsian
189 | x_t, y_t, z_t = x_t[0] / w_t[0], y_t[0] / w_t[0], z_t[0] / w_t[0]
190 |
191 | u_t_mat = x_t / z_t
192 | v_t_mat = y_t / z_t
193 |
194 | # this is the final ego-motion flow
195 | d_u = u_t_mat - u_mat
196 | d_v = v_t_mat - v_mat
197 |
198 | return np.stack((d_u, d_v), axis=0), u_t_mat, v_t_mat, z_t
199 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr_cuda.c:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include
2 | #include "corr_cuda_kernel.h"
3 |
4 | extern THCState *state;
5 |
6 | // == Forward
7 | int corr_cuda_forward(THCudaTensor *input1,
8 | THCudaTensor *input2,
9 | THCudaTensor *rbot1,
10 | THCudaTensor *rbot2,
11 | THCudaTensor *output,
12 | int pad_size,
13 | int kernel_size,
14 | int max_displacement,
15 | int stride1,
16 | int stride2,
17 | int corr_type_multiply
18 | )
19 | {
20 |
21 | // TODO: Shapechecks
22 |
23 | int batchSize = input1->size[0];
24 |
25 | long nInputPlane = input1->size[1];
26 | long nInputRows = input1->size[2];
27 | long nInputCols = input1->size[3];
28 | long inputWidthHeight = nInputRows * nInputCols;
29 |
30 | long kernel_radius_ = (kernel_size - 1) / 2;
31 | long border_size_ = max_displacement + kernel_radius_; // size of unreachable border region (on each side)
32 |
33 | long paddedbottomheight = nInputRows + 2 * pad_size;
34 | long paddedbottomwidth = nInputCols + 2 * pad_size;
35 |
36 | long nOutputCols = ceil((float)(paddedbottomwidth - border_size_ * 2) / (float)stride1);
37 | long nOutputRows = ceil((float)(paddedbottomheight - border_size_ * 2) / (float)stride1);
38 |
39 | // Given a center position in image 1, how many displaced positions in -x / +x
40 | // direction do we consider in image2 (neighborhood_grid_width)
41 | long neighborhood_grid_radius_ = max_displacement / stride2;
42 | long neighborhood_grid_width_ = neighborhood_grid_radius_ * 2 + 1;
43 |
44 | // Number of output channels amounts to displacement combinations in X and Y direction
45 | int nOutputPlane = neighborhood_grid_width_ * neighborhood_grid_width_;
46 |
47 | // Inputs
48 | float * input1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, input1);
49 | float * input2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, input2);
50 |
51 | // Outputs
52 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, output, batchSize, nOutputPlane, nOutputRows, nOutputCols);
53 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, output); // added by Jinwei
54 | float * output_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, output);
55 |
56 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, rbot1, batchSize, nInputPlane, paddedbottomheight, paddedbottomwidth);
57 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, rbot2, batchSize, nInputPlane, paddedbottomheight, paddedbottomwidth);
58 |
59 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, rbot1); // added by Jinwei
60 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, rbot2); // added by Jinwei
61 |
62 | float * rbot1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, rbot1);
63 | float * rbot2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, rbot2);
64 |
65 | cudaStream_t stream = THCState_getCurrentStream(state);
66 |
67 | int pwidthheight = paddedbottomwidth * paddedbottomheight;
68 |
69 | blob_rearrange_ongpu(input1_data,rbot1_data,batchSize,nInputPlane,nInputCols,nInputRows,inputWidthHeight,pad_size,pwidthheight,stream);
70 |
71 | blob_rearrange_ongpu(input2_data,rbot2_data,batchSize,nInputPlane,nInputCols,nInputRows,inputWidthHeight,pad_size,pwidthheight,stream);
72 |
73 | CorrelateData_ongpu(rbot1_data,rbot2_data,output_data,batchSize,nOutputCols,nOutputRows,nOutputPlane,max_displacement,neighborhood_grid_radius_,neighborhood_grid_width_,kernel_radius_,kernel_size,stride1,stride2,paddedbottomwidth,paddedbottomheight,nInputPlane,corr_type_multiply,stream);
74 |
75 | // THCudaTensor_free(state, input1);
76 | // THCudaTensor_free(state, input2);
77 | THCudaTensor_free(state, rbot1);
78 | THCudaTensor_free(state, rbot2);
79 |
80 | return 1;
81 |
82 | }
83 |
84 | int corr_cuda_backward(THCudaTensor *input1,
85 | THCudaTensor *input2,
86 | THCudaTensor *rbot1,
87 | THCudaTensor *rbot2,
88 | THCudaTensor *gradOutput,
89 | THCudaTensor *gradInput1,
90 | THCudaTensor *gradInput2,
91 | int pad_size,
92 | int kernel_size,
93 | int max_displacement,
94 | int stride1,
95 | int stride2,
96 | int corr_type_multiply
97 | )
98 | {
99 |
100 | float * input1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, input1);
101 | float * input2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, input2);
102 |
103 | long nInputCols = input1->size[3];
104 | long nInputRows = input1->size[2];
105 | long nInputPlane = input1->size[1];
106 | long batchSize = input1->size[0];
107 |
108 | // THCudaTensor_resizeAs(state, gradInput1, input1);
109 | // THCudaTensor_resizeAs(state, gradInput2, input2);
110 | float * gradOutput_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, gradOutput);
111 | float * gradInput1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, gradInput1);
112 | float * gradInput2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, gradInput2);
113 |
114 | long inputWidthHeight = nInputRows * nInputCols;
115 |
116 | long kernel_radius_ = (kernel_size - 1) / 2;
117 | long border_size_ = max_displacement + kernel_radius_; // size of unreachable border region (on each side)
118 |
119 | long paddedbottomheight = nInputRows + 2 * pad_size;
120 | long paddedbottomwidth = nInputCols + 2 * pad_size;
121 |
122 | long nOutputCols = ceil((float)(paddedbottomwidth - border_size_ * 2) / (float)stride1);
123 | long nOutputRows = ceil((float)(paddedbottomheight - border_size_ * 2) / (float)stride1);
124 |
125 | // Given a center position in image 1, how many displaced positions in -x / +x
126 | // direction do we consider in image2 (neighborhood_grid_width)
127 | long neighborhood_grid_radius_ = max_displacement / stride2;
128 | long neighborhood_grid_width_ = neighborhood_grid_radius_ * 2 + 1;
129 |
130 | // Number of output channels amounts to displacement combinations in X and Y direction
131 | int nOutputPlane = neighborhood_grid_width_ * neighborhood_grid_width_;
132 |
133 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, rbot1, batchSize, nInputPlane, paddedbottomheight, paddedbottomwidth);
134 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, rbot2, batchSize, nInputPlane, paddedbottomheight, paddedbottomwidth);
135 |
136 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, rbot1); // added by Jinwei
137 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, rbot2); // added by Jinwei
138 |
139 | float * rbot1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, rbot1);
140 | float * rbot2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, rbot2);
141 |
142 | int pwidthheight = paddedbottomwidth * paddedbottomheight;
143 |
144 | cudaStream_t stream = THCState_getCurrentStream(state);
145 |
146 | blob_rearrange_ongpu(input1_data,rbot1_data,batchSize,nInputPlane,nInputCols,nInputRows,inputWidthHeight,pad_size,pwidthheight,stream);
147 |
148 | blob_rearrange_ongpu(input2_data,rbot2_data,batchSize,nInputPlane,nInputCols,nInputRows,inputWidthHeight,pad_size,pwidthheight,stream);
149 |
150 | // CorrelationLayerBackward
151 |
152 | CorrelateDataBackward_ongpu(rbot1_data,rbot2_data,gradOutput_data,gradInput1_data,gradInput2_data,batchSize,nOutputCols,nOutputRows,nOutputPlane,max_displacement,neighborhood_grid_radius_,neighborhood_grid_width_,kernel_radius_,stride1,stride2,nInputCols,nInputRows,paddedbottomwidth,paddedbottomheight,nInputPlane,pad_size,corr_type_multiply,stream);
153 |
154 | // THCudaTensor_free(state, input1);
155 | // THCudaTensor_free(state, input2);
156 | THCudaTensor_free(state, rbot1);
157 | THCudaTensor_free(state, rbot2);
158 |
159 | return 1;
160 | }
161 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr1d_cuda.c:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include
2 | #include "corr1d_cuda_kernel.h"
3 |
4 | extern THCState *state;
5 |
6 | // == Forward
7 | int corr1d_cuda_forward(THCudaTensor *input1,
8 | THCudaTensor *input2,
9 | THCudaTensor *rbot1,
10 | THCudaTensor *rbot2,
11 | THCudaTensor *output,
12 | int pad_size,
13 | int kernel_size,
14 | int max_displacement,
15 | int stride1,
16 | int stride2,
17 | int corr_type_multiply
18 | //single_direction=0
19 | )
20 | {
21 |
22 | // TODO: Shapechecks
23 |
24 | int batchSize = input1->size[0];
25 |
26 | long nInputPlane = input1->size[1];
27 | long nInputRows = input1->size[2];
28 | long nInputCols = input1->size[3];
29 | long inputWidthHeight = nInputRows * nInputCols;
30 |
31 | long kernel_radius_ = (kernel_size - 1) / 2;
32 | long border_size_ = max_displacement + kernel_radius_; // size of unreachable border region (on each side)
33 |
34 | long paddedbottomheight = nInputRows;
35 | long paddedbottomwidth = nInputCols + 2 * pad_size;
36 |
37 | long nOutputCols = ceil((float)(paddedbottomwidth - border_size_ * 2) / (float)stride1);
38 | long nOutputRows = ceil((float)(paddedbottomheight - kernel_radius_ * 2) / (float)stride1);
39 |
40 | // Given a center position in image 1, how many displaced positions in -x / +x
41 | // direction do we consider in image2 (neighborhood_grid_width)
42 | long neighborhood_grid_radius_ = max_displacement / stride2;
43 | long neighborhood_grid_width_ = neighborhood_grid_radius_ * 2 + 1;
44 | int x_shift = -neighborhood_grid_radius_;
45 |
46 | // Number of output channels amounts to displacement combinations in X direction only!!
47 | int nOutputPlane = neighborhood_grid_width_;//Same, because 1D X-correlation
48 |
49 | // Inputs
50 | float * input1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, input1);
51 | float * input2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, input2);
52 |
53 | // Outputs
54 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, output, batchSize, nOutputPlane, nOutputRows, nOutputCols);
55 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, output); // added by Jinwei
56 | float * output_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, output);
57 |
58 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, rbot1, batchSize, nInputPlane, paddedbottomheight, paddedbottomwidth);
59 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, rbot2, batchSize, nInputPlane, paddedbottomheight, paddedbottomwidth);
60 |
61 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, rbot1); // added by Jinwei
62 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, rbot2); // added by Jinwei
63 |
64 | float * rbot1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, rbot1);
65 | float * rbot2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, rbot2);
66 |
67 | cudaStream_t stream = THCState_getCurrentStream(state);
68 |
69 | int pwidthheight = paddedbottomwidth * paddedbottomheight;
70 |
71 | blob_rearrange_ongpu_1d(input1_data,rbot1_data,batchSize,nInputPlane,nInputCols,nInputRows,inputWidthHeight,pad_size,pwidthheight,stream);
72 |
73 | blob_rearrange_ongpu_1d(input2_data,rbot2_data,batchSize,nInputPlane,nInputCols,nInputRows,inputWidthHeight,pad_size,pwidthheight,stream);
74 |
75 | CorrelateData_ongpu_1d(rbot1_data,rbot2_data,output_data,batchSize,nOutputCols,nOutputRows,nOutputPlane,max_displacement,x_shift,neighborhood_grid_width_,kernel_radius_,kernel_size,stride1,stride2,paddedbottomwidth,paddedbottomheight,nInputPlane,corr_type_multiply,stream);
76 |
77 | // THCudaTensor_free(state, input1);
78 | // THCudaTensor_free(state, input2);
79 | THCudaTensor_free(state, rbot1);
80 | THCudaTensor_free(state, rbot2);
81 |
82 | return 1;
83 |
84 | }
85 |
86 | int corr1d_cuda_backward(THCudaTensor *input1,
87 | THCudaTensor *input2,
88 | THCudaTensor *rbot1,
89 | THCudaTensor *rbot2,
90 | THCudaTensor *gradOutput,
91 | THCudaTensor *gradInput1,
92 | THCudaTensor *gradInput2,
93 | int pad_size,
94 | int kernel_size,
95 | int max_displacement,
96 | int stride1,
97 | int stride2,
98 | int corr_type_multiply
99 | // single_direction=0
100 | )
101 | {
102 |
103 | float * input1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, input1);
104 | float * input2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, input2);
105 |
106 | long nInputCols = input1->size[3];
107 | long nInputRows = input1->size[2];
108 | long nInputPlane = input1->size[1];
109 | long batchSize = input1->size[0];
110 |
111 | // THCudaTensor_resizeAs(state, gradInput1, input1);
112 | // THCudaTensor_resizeAs(state, gradInput2, input2);
113 | float * gradOutput_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, gradOutput);
114 | float * gradInput1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, gradInput1);
115 | float * gradInput2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, gradInput2);
116 |
117 | long inputWidthHeight = nInputRows * nInputCols;
118 |
119 | long kernel_radius_ = (kernel_size - 1) / 2;
120 | long border_size_ = max_displacement + kernel_radius_; // size of unreachable border region (on each side)
121 |
122 | long paddedbottomheight = nInputRows;
123 | long paddedbottomwidth = nInputCols + 2 * pad_size;
124 |
125 | long nOutputCols = ceil((float)(paddedbottomwidth - border_size_ * 2) / (float)stride1);
126 | long nOutputRows = ceil((float)(paddedbottomheight - kernel_radius_ * 2) / (float)stride1);
127 |
128 | // Given a center position in image 1, how many displaced positions in -x / +x
129 | // direction do we consider in image2 (neighborhood_grid_width)
130 | long neighborhood_grid_radius_ = max_displacement / stride2;
131 | long neighborhood_grid_width_ = neighborhood_grid_radius_ * 2 + 1;
132 | int x_shift = -neighborhood_grid_radius_;
133 |
134 | // Number of output channels amounts to displacement combinations in X direction only!!
135 | int nOutputPlane = neighborhood_grid_width_; // Same, because 1D X-correlation
136 |
137 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, rbot1, batchSize, nInputPlane, paddedbottomheight, paddedbottomwidth);
138 | THCudaTensor_resize4d(state, rbot2, batchSize, nInputPlane, paddedbottomheight, paddedbottomwidth);
139 |
140 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, rbot1); // added by Jinwei
141 | THCudaTensor_zero(state, rbot2); // added by Jinwei
142 |
143 | float * rbot1_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, rbot1);
144 | float * rbot2_data = THCudaTensor_data(state, rbot2);
145 |
146 | int pwidthheight = paddedbottomwidth * paddedbottomheight;
147 |
148 | cudaStream_t stream = THCState_getCurrentStream(state);
149 |
150 | blob_rearrange_ongpu_1d(input1_data,rbot1_data,batchSize,nInputPlane,nInputCols,nInputRows,inputWidthHeight,pad_size,pwidthheight,stream);
151 |
152 | blob_rearrange_ongpu_1d(input2_data,rbot2_data,batchSize,nInputPlane,nInputCols,nInputRows,inputWidthHeight,pad_size,pwidthheight,stream);
153 |
154 | // CorrelationLayerBackward
155 |
156 | CorrelateDataBackward_ongpu_1d(rbot1_data,rbot2_data,gradOutput_data,gradInput1_data,gradInput2_data,batchSize,nOutputCols,nOutputRows,nOutputPlane,max_displacement,x_shift,neighborhood_grid_width_,kernel_radius_,stride1,stride2,nInputCols,nInputRows,paddedbottomwidth,paddedbottomheight,nInputPlane,pad_size,corr_type_multiply,stream);
157 |
158 | // THCudaTensor_free(state, input1);
159 | // THCudaTensor_free(state, input2);
160 | THCudaTensor_free(state, rbot1);
161 | THCudaTensor_free(state, rbot2);
162 |
163 | return 1;
164 |
165 | }
166 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Learning Rigidity in Dynamic Scenes with a Moving Camera for 3D Motion Field Estimation (ECCV 2018)
2 |
3 | 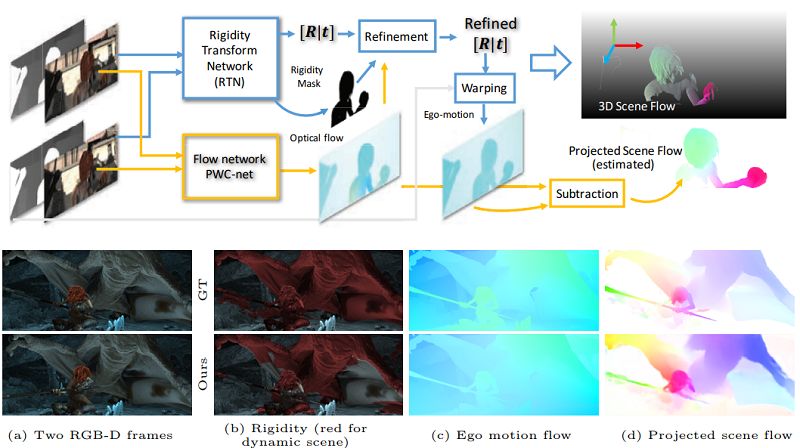
4 |
5 |
6 | ### License ###
7 | Copyright (c) 2018 NVIDIA Corp. All Rights Reserved.
8 | This work is licensed under the [Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial ShareAlike 4.0 License](https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
9 |
10 | ### Project page ###
11 | [NVIDIA Research project page](https://research.nvidia.com/publication/2018-09_Learning-Rigidity-in)
12 |
13 | ### Paper ###
14 | * [ArXiv (PDF)](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.04259.pdf)
15 | * [Video (Youtube)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MnTHkOCY790)
16 |
17 | ### Project members ###
18 |
19 | * [Zhaoyang Lv](https://www.cc.gatech.edu/~zlv30/), Georgia Institute of Technology
20 | * [Kihwan Kim](https://research.nvidia.com/person/kihwan-kim), NVIDIA
21 | * [Alejandro Troccoli](https://research.nvidia.com/person/alejandro-troccoli), NVIDIA
22 | * [Deqing Sun](https://research.nvidia.com/person/deqing-sun), NVIDIA
23 | * [James M. Rehg](https://rehg.org/), Georgia Institute of Technology
24 | * [Jan Kautz](https://research.nvidia.com/person/jan-kautz), NVIDIA
25 |
26 | ## Summary
27 |
28 | This repository includes the implementation of our full inference algorithm, including rigidity network, flow and the refinement optimization.
29 |
30 | The data creation toolkit is located at an independent [REFRESH repository](https://github.com/lvzhaoyang/RefRESH)
31 |
32 | ```
33 | git clone https://github.com/lvzhaoyang/RefRESH
34 | ```
35 |
36 | If you use this code, our generated data, or the dataset creation tool, please cite the following paper:
37 |
38 | **Learning Rigidity in Dynamic Scenes with a Moving Camera for 3D Motion Field Estimation**,
39 | *Zhaoyang Lv, Kihwan Kim, Alejandro Troccoli, Deqing Sun, James M. Rehg, Jan Kautz*,
40 | European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV) 2018
41 |
42 | ```bibtex
43 | @inproceedings{Lv18eccv,
44 | title = {Learning Rigidity in Dynamic Scenes with a Moving Camera for 3D Motion Field Estimation},
45 | author = {Lv, Zhaoyang and Kim, Kihwan and Troccoli, Alejandro and Sun, Deqing and Rehg, James and Kautz, Jan},
46 | booktitle = {ECCV},
47 | year = {2018}
48 | }
49 | ```
50 |
51 | ## Usage
52 |
53 | We provide both Docker-based setup for the containerizaiton and generic setup with conda.
54 |
55 | An inference example is currently available. We are working on a release version of the training code, which will be available soon.
56 |
57 | ## 1. Running with Docker
58 | ### Prerequisites
59 | * Install [nvidia-docker](https://github.com/nvidia/nvidia-docker/wiki/Installation-(version-2.0)).
60 | * Clone [gtsam](https://bitbucket.org/gtborg/gtsam/src/develop/) at **'external_packages/'** folder (do not build it there yet. Docker will build inside the container later).
61 | #### Pretrained model for default inference
62 | Download the following models and put them in the **'weights/'** directory.
63 | * [Rigidity Transform Network Weights][1]: trained on our REFRESH dataset,
64 | * [PWC-net Weights][2]: sequentially trained on FlyingChairs and FlyingThings3D, which is the same weights from [PWC-Net Pytorch][3] repository
65 |
66 |
67 | ### Build with Docker
68 |
69 | ```
70 | docker build . --tag rigidity:1.0
71 | ```
72 | Now go to the **root folder** of this project, and run the run_container.sh script. This is important as we will mount the project folder inside the docker container.
73 |
74 | ```
75 | sudo ./run_container.sh
76 | ```
77 |
78 | ### Run the inference code
79 |
80 | Run the example inference code with default weights with the refinement step and visualization flags:
81 |
82 | ```
83 | /rigidity#python run_inference.py --post_refine --visualize
84 | ```
85 |
86 | Then the output of the testing example (using an example pair from sintel's market_5) will pop up as shown below:
87 | 
88 |
89 | You can also check out the **'results/'** folder to see all saved images.
90 | Optionally you can specify the output folder with ``--output_path``. See more options with ``--h``.
91 |
92 | The estimated pose from the refinment will be shown as:
93 | ```
94 | Estimated two-view transform
95 | [[[ 0.99974869 0.01963792 -0.01081263 -0.04639582]
96 | [-0.01937608 0.9995287 0.02381045 -0.05028503]
97 | [ 0.01127512 -0.02359496 0.99965802 0.44513745]
98 | [ 0. 0. 0. 1. ]]]
99 | ```
100 |
101 |
102 | You can manually choose the network weights if you have another models.
103 |
104 | ```
105 | /rigidity$python run_inference.py --pwc_weights weights/pwc_net_chairs.pth.tar --rigidity_weights weights/rigidity_net.pth.tar --post_refine --visualize
106 |
107 | # to check the help functions
108 | /rigidity$python run_inference.py --help
109 | ```
110 |
111 | ## 2. Running with conda
112 |
113 | The code was developed using Python 2.7 & PyTorch 0.3.1 & Cuda 8.0. We provide an anaconda environment with all dependencies needed.
114 | To run it, please ensure you have the [Anaconda Python 2.7 version](https://www.anaconda.com/download/#linux) installed and set the environment path for **conda**. Then run the following script to automatially set up the environment:
115 |
116 | ```
117 | # create the anaconda environment
118 | conda env create -f setup/rigidity.yml
119 |
120 | # activate the environment
121 | conda activate rigidity
122 |
123 | sh setup/install_for_network.sh
124 | # If you don't need the refinement stage, you can choose not to run this.
125 | # And set the post_refine flag to be false
126 | sh setup/install_for_refinement.sh
127 | ```
128 |
129 | ### Run the inference code
130 |
131 | Download the following pre-trained models and put them in the **'weights/'** directory:
132 |
133 | * [Rigidity Transform Network Weights][1]: trained on our REFRESH dataset
134 | * [PWC-net Weights][2]: sequentially trained on FlyingChairs and FlyingThings3D, which is the same weights from [PWC-Net Pytorch][3] repository
135 |
136 | Please refer to the issue list of [PWC-net/pytorch](https://github.com/NVlabs/PWC-Net/tree/master/PyTorch) if there is any issue w.r.t. the flow models.
137 |
138 | Run the example inference code with default weights the refinement step and visualization:
139 |
140 | ```
141 | python run_inference.py --post_refine --visualize
142 | ```
143 |
144 | Or you can manually choose the network weights
145 |
146 | ```
147 | python run_inference.py --pwc_weights weights/pwc_net_chairs.pth.tar --rigidity_weights weights/rigidity_net.pth.tar --post_refine --visualize
148 |
149 | # to check the help functions
150 | python run_inference.py --help
151 | ```
152 |
153 | To run results for your own inputs, you can use the default simple loader provided in the **run_inference.py** example. You need to set the color images directory, depth images directory (only support *'.dpt'* and *'.png'* format), and a simple pin-hole camera intrinsic parameters ('fx,fy,cx,cy'). For example:
154 |
155 | ```
156 | python run_inference.py --color_dir data/market_5/clean --depth_dir data/market_5/depth --intrinsic 1120,1120,511.5,217.5 --post_refine --visualize
157 | ```
158 |
159 | ### Dataset ###
160 | * The rigidity mask is generated the same as [Optical Flow for Mostly Rigid Scenes, J. Wulff et al, CVPR 2017][4]. As fair comparison, we also use the rigidity mask generated by them. You can download it at [Ground Truth rigidity segmentation for SINTEL][5].
161 | * To download the data we generate for pre-training, check [REFRESH Data Readme][6].
162 |
163 | [1]: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1FkCKnAFuzPa_ndwK01zGaXnL9xKgN2LY
164 | [2]: https://drive.google.com/open?id=1bgcRJKGM0KRREUFjHWeMWQTMsm3sFFZw
165 | [3]: https://github.com/NVlabs/PWC-Net/tree/master/PyTorch
166 | [4]: https://ps.is.tuebingen.mpg.de/research_projects/optical-flow-for-mostly-rigid-scenes
167 | [5]: http://files.is.tue.mpg.de/jwulff/mrflow/sintel_rigiditymaps.zip
168 | [6]: dataset_description.md
169 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/flow2pose_lib/flow2pose.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /**
2 | * Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | * Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | * (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 | *
6 | * Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 | */
8 |
9 | #include
10 | #include
11 | #include
12 |
13 | #include
14 | #include
15 | #include
16 | #include
17 | #include
18 | #include
19 |
20 | #include "flow2pose.h"
21 |
22 | using namespace std;
23 | using namespace gtsam;
24 | using namespace gtsam::noiseModel;
25 |
26 | typedef std::vector Putatives;
27 | typedef boost::shared_ptr sharedPutatives;
28 |
29 | template
30 | T bilinearInterp(const cv::Mat_& src, const double row, const double col) {
31 | int lower_row = std::floor(row);
32 | int upper_row = lower_row < src.rows-1 ? lower_row + 1 : lower_row;
33 | int lower_col = std::floor(col);
34 | int upper_col = lower_col < src.cols-1 ? lower_col + 1 : lower_col;
35 |
36 | // suppose it's 0-1 grid
37 | double r_u = upper_row - row; // row to upper row
38 | double l_r = row - lower_row; // low row to row
39 | double c_u = upper_col - col; // col to upper col
40 | double l_c = col - lower_col; // low col to col
41 |
42 | return src(lower_row, lower_col)*r_u*c_u + src(lower_row, upper_col)*r_u*l_c +
43 | src(upper_row, lower_col)*l_r*c_u + src(upper_row, upper_col)*l_r*l_c;
44 | }
45 |
46 | inline bool within_image(int row, int col, int rows, int cols) {
47 | if (row < 0 || row >= rows || col < 0 || col >= cols) {
48 | return false;
49 | } else {
50 | return true;
51 | }
52 | }
53 |
54 | Flow2Pose::Flow2Pose() {
55 | measurement_noise_model = Diagonal::Sigmas(Vector3(1, 1, 1));
56 | huber_measurement_model = Robust::Create(mEstimator::Huber::Create(huber_threshold, mEstimator::Huber::Scalar), measurement_noise_model);
57 | }
58 |
59 | Point3 invdepth (const Point3& pt, OptionalJacobian<3,3> J_p = boost::none) {
60 | double inv_z = 1 / pt.z();
61 | double inv_z2 = inv_z * inv_z;
62 |
63 | if (J_p) {
64 | *J_p << inv_z, 0, -pt.x() * inv_z2,
65 | 0, inv_z, -pt.y() * inv_z2,
66 | 0, 0, -inv_z2;
67 | }
68 | return Point3(pt.x()*inv_z, pt.y()*inv_z, inv_z);
69 | }
70 |
71 | struct Depth {
72 | double d;
73 | int i;
74 |
75 | Depth(double depth, int index) {
76 | d = depth;
77 | i = index;
78 | }
79 | };
80 |
81 | struct compairDepth {
82 | bool operator()(const Depth&a, const Depth& b) {
83 | return a.d < b.d;
84 | }
85 | } compair_depth;
86 |
87 | gtsam::Pose3 Flow2Pose::calculate_transform(const cv::Mat& v_map0, const cv::Mat& v_map1, const cv::Mat& flow, const cv::Mat& foreground_S0, const cv::Mat& foreground_S1, const cv::Mat& occlusion, const Pose3& pose_init) {
88 | auto rows = v_map0.rows;
89 | auto cols = v_map0.cols;
90 |
91 | vector vertices_0;
92 | vector vertices_1;
93 |
94 | std::vector tmp_depth;
95 | // sharedPutatives putatives(new vector());
96 |
97 | // sparsely sample the flow pairs with pad=4
98 | for (auto row = 8; row < rows-8; row+=4) {
99 | for (auto col = 8; col < cols-8; col+=4) {
100 | // check whether this point is a background point and are not occluded.
101 | // foreground has value 1; occlusion region has value 0
102 | if (foreground_S0.at(row, col) > 1e-2) continue;
103 | if (occlusion.at(row, col) < 1e-2) continue;
104 |
105 | // check whether the mapped points are within the image
106 | const auto& f = flow.at(row, col);
107 | auto row_f = round(row + f[1]);
108 | auto col_f = round(col + f[0]);
109 | if (!within_image(row_f, col_f, rows, cols)) {
110 | continue;
111 | }
112 |
113 | if (bilinearInterp(foreground_S1, row_f, col_f) > 1e-2) {
114 | // remove the pointst that on the second frame foreground
115 | continue;
116 | }
117 |
118 | const auto& v0 = v_map0.at(row, col);
119 | const auto& v1 = bilinearInterp(v_map1, row_f, col_f);
120 | // const auto& v1 = v_map1.at(row_f, col_f);
121 |
122 | // truncate points that are too far away to too near the frustum. This can improve the stability.
123 | if (v0[2] > 5*1e2 || v1[2] > 5*1e2 || v0[2] < 1e-2 || v1[2] < 1e-2) {
124 | continue;
125 | }
126 |
127 | tmp_depth.push_back(Depth(v0[2], vertices_0.size()));
128 | vertices_0.push_back(Point3(v0[0], v0[1], v0[2]));
129 | vertices_1.push_back(Point3(v1[0], v1[1], v1[2]));
130 | }
131 | }
132 |
133 | if (tmp_depth.size() < 10) {
134 | // too few valida points
135 | return pose_init;
136 | }
137 |
138 | // std::sort(tmp_depth.begin(), tmp_depth.end(), compair_depth);
139 |
140 | vector v_list0;
141 | vector v_list1;
142 | // vector putatives;
143 | // Sort and get the top 12000 points near the frustum. It makes the solver much faster.
144 | double error_threshold = 0.0;
145 | auto filtered_num = std::min(12000, int(tmp_depth.size()));
146 | for (auto i = 0; i < filtered_num; i++) {
147 | int index = tmp_depth[i].i;
148 | v_list0.push_back(Point3(vertices_0[index]));
149 | v_list1.push_back(Point3(vertices_1[index]));
150 | // putatives->push_back(Putative(Point3(vertices_0[index]), Point3(vertices_1[index])));
151 | }
152 |
153 | vector inliers(tmp_depth.size(), true);
154 |
155 | error_threshold /= filtered_num;
156 | error_threshold = v_list0[filtered_num/5].norm();
157 | error_threshold = min(error_threshold/10, 15.00);
158 | cout << "the error threshold is: " << error_threshold << endl;
159 |
160 | for (auto i = 0; i < filtered_num; i++) {
161 | if ((v_list0[i] - v_list1[i]).norm() > error_threshold) {
162 | inliers[i] = false;
163 | }
164 | }
165 |
166 | Pose3 pose(pose_init);
167 |
168 | return solve(v_list0, v_list1, pose, inliers);
169 | }
170 |
171 | Pose3 Flow2Pose::solve(const vector& pts1, const vector& pts2, const Pose3& initial_pose, const vector& inliers) {
172 | int total_num = pts1.size();
173 | assert(total_num == pts2.size());
174 |
175 | Symbol var_pose('p', 0);
176 | Pose3_ pose(var_pose);
177 |
178 | ExpressionFactorGraph graph;
179 | // evaluate all the points first
180 |
181 | // add all factors from the list
182 | for(int idx = 0; idx < total_num; idx++) {
183 | if (inliers.size() > 0) {
184 | if(!inliers[idx]) continue;
185 | }
186 |
187 | const Point3& pt1 = pts1[idx];
188 | const Point3& pt2 = pts2[idx];
189 | // set up the factor graph for solving the camera pose
190 | Point3_ pt2_(pt2);
191 | // point 2 that is transformed to point 1
192 | Point3_ pt2_1_ = transform_to(pose, pt2_);
193 |
194 | graph.addExpressionFactor(pt2_1_, pt1, huber_measurement_model);
195 | }
196 |
197 | // specify the uncertainty on the pose
198 | Values initial;
199 | initial.insert(var_pose, initial_pose);
200 |
201 | if (solver_type == Gauss_Newton) {
202 |
203 | static GaussNewtonParams parameters;
204 | parameters.relativeErrorTol = 1e-8;
205 | // Do not perform more than N iteration steps
206 | // parameters.maxIterations = 100;
207 | parameters.verbosity = NonlinearOptimizerParams::ERROR;
208 | GaussNewtonOptimizer optimizer(graph, initial, parameters);
209 |
210 | try {
211 | Values result = optimizer.optimize();
212 | return result.at(var_pose);
213 | } catch (IndeterminantLinearSystemException& e) {
214 | cout << e.what() << endl;
215 | return Pose3();
216 | }
217 |
218 | } else if (solver_type == Levenberg_Marquardt) {
219 | static LevenbergMarquardtParams parameters;
220 | parameters.relativeErrorTol = 1e-8;
221 | // Do not perform more than N iteration steps
222 | parameters.maxIterations = 100;
223 | parameters.verbosity = NonlinearOptimizerParams::ERROR;
224 | parameters.diagonalDamping = true;
225 | LevenbergMarquardtOptimizer optimizer(graph, initial, parameters);
226 |
227 | Values result = optimizer.optimize();
228 | return result.at(var_pose);
229 | } else {
230 | cout << "The solver is not implemented." << endl;
231 | exit(1);
232 | }
233 |
234 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/run_inference.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Copyright (C) 2018 NVIDIA Corporation. All rights reserved.
3 | Licensed under the CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
4 | (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-sa/4.0/legalcode).
5 |
6 | Author: Zhaoyang Lv
7 | """
8 |
9 | import os, sys, time, pickle
10 | import geometry, io_utils
11 | import torch
12 | import torch.nn as nn
13 | import numpy as np
14 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
15 | from scipy.misc import imsave
16 |
17 | from pose_refine import PoseRefine
18 | from math import ceil
19 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
20 | from torch.autograd import Variable
21 | from torchvision import transforms
22 |
23 | from models.PWCNet import pwc_dc_net
24 | from models.RigidityNet import rigidity_transform_net
25 | from SimpleLoader import SimpleLoader
26 |
27 | def check_directory(filename):
28 | target_dir = os.path.dirname(filename)
29 | if not os.path.isdir(target_dir):
30 | os.makedirs(target_dir)
31 |
32 | def check_cuda(data):
33 | if torch.cuda.is_available(): return data.cuda()
34 | else: return data
35 |
36 | def color_normalize(color):
37 | rgb_mean = (0.4914, 0.4822, 0.4465)
38 | rgb_std = (0.2023, 0.1994, 0.2010)
39 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=rgb_mean, std=rgb_std)
40 |
41 | B = color.shape[0]
42 | for idx in range(B):
43 | color[idx] = normalize(color[idx])
44 | return color
45 |
46 | def batch_resize_input(img0, img1):
47 | """ Resize the input for flow-network
48 | """
49 | B, C, H, W = img0.shape
50 | resize_H = int(ceil(H / 64.0)) * 64
51 | resize_W = int(ceil(W / 64.0)) * 64
52 | if H != resize_H or W != resize_W:
53 | resize_img = nn.Upsample(size=(resize_H, resize_W),mode='bilinear')
54 | img0 = resize_img(img0)
55 | img1 = resize_img(img1)
56 |
57 | return img0, img1
58 |
59 | def batch_resize_output(flow, target_size):
60 | """ Resize the output of flow image to match the given resolution
61 | """
62 | H_in, W_in = flow.shape[-2:]
63 | H, W = target_size
64 |
65 | if H_in != H or W_in != W:
66 | resize_flow = nn.Upsample(size=(H, W),mode='bilinear')
67 | scale_H, scale_W = float(H) / H_in, float(W) / W_in
68 | output = resize_flow(flow)
69 | output_flow = output.clone()
70 |
71 | output_flow[:,0,:,:] = output[:,0,:,:] * scale_W
72 | output_flow[:,1,:,:] = output[:,1,:,:] * scale_H
73 |
74 | return output_flow
75 | else:
76 | return flow
77 |
78 | def rigidity_net_forward(net, uvd0, uvd1):
79 | """ Run an forward estimation of the rigidity network
80 | """
81 | input0 = uvd0.clone()
82 | input1 = uvd1.clone()
83 |
84 | # clamp the inverse depth
85 | input0[:,2,:,:] = torch.clamp(input0[:,2,:,:], min=1e-4, max=10)
86 | input1[:,2,:,:] = torch.clamp(input1[:,2,:,:], min=1e-4, max=10)
87 |
88 | data = torch.cat((input0, input1), 1)
89 | data = check_cuda(data)
90 | data = Variable(data, volatile=True)
91 |
92 | pose_feat_map, seg_feat_map = net(data)
93 |
94 | est_pose = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1,1))(pose_feat_map)
95 | B, C, H, W = data.size()
96 | est_pose = est_pose.view([B, -1])
97 |
98 | R = geometry.torch_euler2mat(est_pose[:, 3], est_pose[:, 4], est_pose[:, 5])
99 | t = est_pose[:, :3]
100 |
101 | seg_feat_map = nn.functional.upsample(seg_feat_map, (H,W), mode='bilinear')
102 | seg_map = nn.functional.softmax(seg_feat_map, dim=1)
103 | _, rigidity = torch.max(seg_map, 1)
104 |
105 | return rigidity, [R, t]
106 |
107 | def visualize_flow(flow_tensor, output_path, file_idx, matplot_viz=False):
108 | """ Visualize the pytorch flow results using matplotlib
109 | only visualize the first batch (assume batch-size is 1)
110 | """
111 | np_flow = flow_tensor[0].cpu().numpy()
112 | flow_viz = io_utils.flow_visualize(np_flow)
113 |
114 | filename = "{:}/optical_flow_{:04d}.png".format(output_path, file_idx)
115 | check_directory(filename)
116 | imsave(filename, flow_viz)
117 |
118 | if matplot_viz:
119 | plt.title("optical flow visualization")
120 | plt.imshow(flow_viz)
121 | plt.show()
122 |
123 | def visualize_rigidity(rigidity_tensor, color_tensor,
124 | output_path, file_idx, matplot_viz=False):
125 | """ Visualize the pytorch rigidity results using matplotlib
126 | only visualize the first batch (assume batch-size is 1)
127 | """
128 | image = color_tensor[0].cpu().numpy().transpose((1,2,0))
129 | rigidity = rigidity_tensor[0].cpu().numpy()
130 |
131 | rigidity_viz = io_utils.image_with_mask(image, rigidity)
132 |
133 | filename = "{:}/rigidity_{:04d}.png".format(output_path, file_idx)
134 | check_directory(filename)
135 | imsave(filename, rigidity_viz)
136 |
137 | if matplot_viz:
138 | plt.title("rigidity visualization")
139 | plt.imshow(rigidity_viz)
140 | plt.show()
141 |
142 | def visualize_projected_flow(depth_tensor, flow_tensor, K, T,
143 | output_path, file_idx, matplot_viz=False):
144 | """ Visualize the ego-motion flow and projected scene flow using matplotlib
145 | only visualize the first batch (assume batch-size is 1)
146 | """
147 | origin = np.eye(4)
148 | ego_flow = geometry.np_depth2flow(depth_tensor.cpu().numpy()[0,0], K, origin, K, T[0])[0]
149 | ego_flow_viz = io_utils.flow_visualize(ego_flow)
150 |
151 | proj_scene_flow = flow_tensor[0].cpu().numpy() - ego_flow
152 | proj_scene_flow_viz = io_utils.flow_visualize(proj_scene_flow)
153 |
154 | filename_ego = "{:}/ego_motion_flow_{:04d}.png".format(output_path, file_idx)
155 | filename_proj= "{:}/proj_scene_flow_{:04d}.png".format(output_path, file_idx)
156 | check_directory(filename_ego)
157 | check_directory(filename_proj)
158 | imsave(filename_ego, ego_flow_viz)
159 | imsave(filename_proj, proj_scene_flow_viz)
160 |
161 | if matplot_viz:
162 | f, ax = plt.subplots(2)
163 | ax[0].set_title("ego-motion flow visualization")
164 | ax[0].imshow(ego_flow_viz)
165 | ax[1].set_title("projected scene flow visualization")
166 | ax[1].imshow(proj_scene_flow_viz)
167 |
168 | plt.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.5)
169 | plt.show()
170 |
171 | def run_inference(simple_loader, pwc_net, rigidity_net,
172 | post_refine=True, visualize_output=True, output_path='results'):
173 |
174 | pwc_net = check_cuda(pwc_net)
175 | rigidity_net= check_cuda(rigidity_net)
176 |
177 | pwc_net.eval()
178 | rigidity_net.eval()
179 |
180 | if post_refine:
181 | pose_refine = PoseRefine()
182 |
183 | for batch_idx, batch in enumerate(simple_loader):
184 | color0, color1, depth0, depth1 = [check_cuda(x) for x in batch]
185 |
186 | # run the rigidity network to estimate the forward backward rigidity
187 | uvd0 = geometry.torch_rgbd2uvd(color_normalize(color0.clone()), depth0, K[0], K[1], K[2], K[3])
188 | uvd1 = geometry.torch_rgbd2uvd(color_normalize(color1.clone()), depth1, K[0], K[1], K[2], K[3])
189 |
190 | rigidity_backward,Rt_backward= rigidity_net_forward(rigidity_net, uvd1, uvd0)
191 | rigidity_forward, Rt_forward = rigidity_net_forward(rigidity_net, uvd0, uvd1)
192 |
193 | visualize_rigidity(rigidity_forward.data, color0, output_path, batch_idx, matplot_viz=visualize_output)
194 | # visualize_rigidity(rigidity_backward.data, color1,output_path, batch_idx, matplot_viz=visualize_output)
195 |
196 | # run the pwc-net to estimate the forward backward flow
197 | B, _, H, W = color0.shape
198 | img0, img1 = batch_resize_input(color0, color1)
199 | forward_flow = pwc_net(img0, img1) * 20
200 | backward_flow= pwc_net(img1, img0) * 20
201 | forward_flow = batch_resize_output(forward_flow, target_size=(H, W))
202 | backward_flow= batch_resize_output(backward_flow,target_size=(H, W))
203 |
204 | # visualize the output, finally move it outside of the loop
205 | visualize_flow(forward_flow.data, output_path, batch_idx, matplot_viz=visualize_output)
206 | # visualize_flow(backward_flow.data,output_path, batch_idx, matplot_viz=visualize_output)
207 |
208 | # run the inference refinement
209 | if post_refine:
210 | xyz0 = geometry.torch_depth2xyz(depth0, K[0], K[1], K[2], K[3])
211 | xyz1 = geometry.torch_depth2xyz(depth1, K[0], K[1], K[2], K[3])
212 | # if use indoor data, e.g. TUM, set the maximum depth to 7.5
213 | est_Rt44 = pose_refine.run_batch(
214 | xyz0.cpu().numpy(), xyz1.cpu().numpy(),
215 | rigidity_forward.data.cpu().numpy(),
216 | rigidity_backward.data.cpu().numpy(),
217 | forward_flow.data.cpu().numpy(),
218 | backward_flow.data.cpu().numpy(),
219 | max_depth=None)
220 |
221 | print("Estimated two-view transform")
222 | print(est_Rt44)
223 |
224 | visualize_projected_flow(depth0, forward_flow.data, K, est_Rt44, output_path, batch_idx, matplot_viz=visualize_output)
225 |
226 | if __name__ == '__main__':
227 |
228 | import argparse
229 |
230 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Run the network inference')
231 |
232 | parser.add_argument('--pwc_weights', default='weights/pwc_net_chairs.pth.tar',
233 | type=str, help='the path to pytorch weights of PWC Net')
234 | parser.add_argument('--rigidity_weights', default='weights/rigidity_net.pth.tar',
235 | type=str, help='the path to pytorch weights of Rigidity Transform Net')
236 | parser.add_argument('--visualize', default=False, action='store_true',
237 | help='plot the output')
238 | parser.add_argument('--post_refine', default=False, action='store_true',
239 | help='run the refinement process')
240 | parser.add_argument('--color_dir', default='data/market_5/clean',
241 | help='the directory of color images')
242 | parser.add_argument('--depth_dir', default='data/market_5/depth',
243 | help='the directory of depth images (default SINTEl dpt)')
244 | parser.add_argument('--intrinsic', default='1120,1120,511.5,217.5',
245 | help='Simple pin-hole camera intrinsics, input in the format (fx, fy, cx, cy)')
246 | parser.add_argument('--output_path', default='results',
247 | help='The path to save all the outputs.')
248 |
249 | config = parser.parse_args()
250 |
251 | pwc_net = pwc_dc_net(config.pwc_weights)
252 | rigidity_net = rigidity_transform_net(config.rigidity_weights)
253 |
254 | color_dir = config.color_dir
255 | depth_dir = config.depth_dir
256 | K = [float(x) for x in config.intrinsic.split(',')]
257 |
258 | simple_loader = SimpleLoader(color_dir, depth_dir)
259 | simple_loader = DataLoader(simple_loader, batch_size=1, shuffle=False)
260 |
261 | run_inference(simple_loader, pwc_net, rigidity_net,
262 | post_refine = config.post_refine,
263 | visualize_output = config.visualize,
264 | output_path = config.output_path
265 | )
266 |
267 |
268 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/PWCNet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Implementation of the PWC-DC network for optical flow estimation by Sun et al., 2018
3 |
4 | Author: Jinwei Gu and Zhile Ren
5 | """
6 |
7 | import torch
8 | import torch.nn as nn
9 | from torch.autograd import Variable
10 | import os
11 | os.environ['PYTHON_EGG_CACHE'] = 'tmp/' # a writable directory
12 | from correlation_package.modules.corr import Correlation
13 | import numpy as np
14 |
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 | __all__ = [
20 | 'pwc_dc_net', 'pwc_dc_net_old'
21 | ]
22 |
23 | def conv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1):
24 | return nn.Sequential(
25 | nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
26 | padding=padding, dilation=dilation, bias=True),
27 | nn.LeakyReLU(0.1))
28 |
29 | def predict_flow(in_planes):
30 | return nn.Conv2d(in_planes,2,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=True)
31 |
32 | def deconv(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1):
33 | return nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size, stride, padding, bias=True)
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 | class PWCDCNet(nn.Module):
38 | """
39 | PWC-DC net. add dilation convolution and densenet connections
40 |
41 | """
42 | def __init__(self, md=4):
43 | """
44 | input: md --- maximum displacement (for correlation. default: 4), after warpping
45 |
46 | """
47 | super(PWCDCNet,self).__init__()
48 |
49 | self.conv1a = conv(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
50 | self.conv1aa = conv(16, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
51 | self.conv1b = conv(16, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
52 | self.conv2a = conv(16, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
53 | self.conv2aa = conv(32, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
54 | self.conv2b = conv(32, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
55 | self.conv3a = conv(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
56 | self.conv3aa = conv(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
57 | self.conv3b = conv(64, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
58 | self.conv4a = conv(64, 96, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
59 | self.conv4aa = conv(96, 96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
60 | self.conv4b = conv(96, 96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
61 | self.conv5a = conv(96, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
62 | self.conv5aa = conv(128,128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
63 | self.conv5b = conv(128,128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
64 | self.conv6aa = conv(128,196, kernel_size=3, stride=2)
65 | self.conv6a = conv(196,196, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
66 | self.conv6b = conv(196,196, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
67 |
68 | self.corr = Correlation(pad_size=md, kernel_size=1, max_displacement=md, stride1=1, stride2=1, corr_multiply=1)
69 | self.leakyRELU = nn.LeakyReLU(0.1)
70 |
71 | nd = (2*md+1)**2
72 | dd = np.cumsum([128,128,96,64,32])
73 |
74 | od = nd
75 | self.conv6_0 = conv(od, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
76 | self.conv6_1 = conv(od+dd[0],128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
77 | self.conv6_2 = conv(od+dd[1],96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
78 | self.conv6_3 = conv(od+dd[2],64, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
79 | self.conv6_4 = conv(od+dd[3],32, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
80 | self.predict_flow6 = predict_flow(od+dd[4])
81 | self.deconv6 = deconv(2, 2, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1)
82 | self.upfeat6 = deconv(od+dd[4], 2, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1)
83 |
84 | od = nd+128+4
85 | self.conv5_0 = conv(od, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
86 | self.conv5_1 = conv(od+dd[0],128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
87 | self.conv5_2 = conv(od+dd[1],96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
88 | self.conv5_3 = conv(od+dd[2],64, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
89 | self.conv5_4 = conv(od+dd[3],32, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
90 | self.predict_flow5 = predict_flow(od+dd[4])
91 | self.deconv5 = deconv(2, 2, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1)
92 | self.upfeat5 = deconv(od+dd[4], 2, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1)
93 |
94 | od = nd+96+4
95 | self.conv4_0 = conv(od, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
96 | self.conv4_1 = conv(od+dd[0],128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
97 | self.conv4_2 = conv(od+dd[1],96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
98 | self.conv4_3 = conv(od+dd[2],64, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
99 | self.conv4_4 = conv(od+dd[3],32, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
100 | self.predict_flow4 = predict_flow(od+dd[4])
101 | self.deconv4 = deconv(2, 2, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1)
102 | self.upfeat4 = deconv(od+dd[4], 2, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1)
103 |
104 | od = nd+64+4
105 | self.conv3_0 = conv(od, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
106 | self.conv3_1 = conv(od+dd[0],128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
107 | self.conv3_2 = conv(od+dd[1],96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
108 | self.conv3_3 = conv(od+dd[2],64, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
109 | self.conv3_4 = conv(od+dd[3],32, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
110 | self.predict_flow3 = predict_flow(od+dd[4])
111 | self.deconv3 = deconv(2, 2, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1)
112 | self.upfeat3 = deconv(od+dd[4], 2, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1)
113 |
114 | od = nd+32+4
115 | self.conv2_0 = conv(od, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
116 | self.conv2_1 = conv(od+dd[0],128, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
117 | self.conv2_2 = conv(od+dd[1],96, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
118 | self.conv2_3 = conv(od+dd[2],64, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
119 | self.conv2_4 = conv(od+dd[3],32, kernel_size=3, stride=1)
120 | self.predict_flow2 = predict_flow(od+dd[4])
121 | self.deconv2 = deconv(2, 2, kernel_size=4, stride=2, padding=1)
122 |
123 | self.dc_conv1 = conv(od+dd[4], 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1)
124 | self.dc_conv2 = conv(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=2, dilation=2)
125 | self.dc_conv3 = conv(128, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=4, dilation=4)
126 | self.dc_conv4 = conv(128, 96, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=8, dilation=8)
127 | self.dc_conv5 = conv(96, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=16, dilation=16)
128 | self.dc_conv6 = conv(64, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1)
129 | self.dc_conv7 = predict_flow(32)
130 |
131 | for m in self.modules():
132 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d) or isinstance(m, nn.ConvTranspose2d):
133 | nn.init.kaiming_normal(m.weight.data, mode='fan_in')
134 | if m.bias is not None:
135 | m.bias.data.zero_()
136 |
137 |
138 | def warp(self, x, flo):
139 | """
140 | warp an image/tensor (im2) back to im1, according to the optical flow
141 |
142 | x: [B, C, H, W] (im2)
143 | flo: [B, 2, H, W] flow
144 |
145 | """
146 | B, C, H, W = x.size()
147 | # mesh grid
148 | xx = torch.arange(0, W).view(1,-1).repeat(H,1)
149 | yy = torch.arange(0, H).view(-1,1).repeat(1,W)
150 | xx = xx.view(1,1,H,W).repeat(B,1,1,1)
151 | yy = yy.view(1,1,H,W).repeat(B,1,1,1)
152 | grid = torch.cat((xx,yy),1).float()
153 |
154 | if x.is_cuda:
155 | grid = grid.cuda()
156 | vgrid = Variable(grid) + flo
157 |
158 | # scale grid to [-1,1]
159 | vgrid[:,0,:,:] = 2.0*vgrid[:,0,:,:]/max(W-1,1)-1.0
160 | vgrid[:,1,:,:] = 2.0*vgrid[:,1,:,:]/max(H-1,1)-1.0
161 |
162 | vgrid = vgrid.permute(0,2,3,1)
163 | output = nn.functional.grid_sample(x, vgrid)
164 |
165 | # mask = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.ones(x.size())).cuda()
166 | # mask = nn.functional.grid_sample(mask, vgrid)
167 |
168 | # mask[mask<0.9999] = 0
169 | # mask[mask>0] = 1
170 |
171 | # return output*mask
172 |
173 | return output
174 |
175 | def forward(self,im1,im2):
176 | # im1 = x[:,:3,:,:]
177 | # im2 = x[:,3:,:,:]
178 |
179 | c11 = self.conv1b(self.conv1aa(self.conv1a(im1)))
180 | c21 = self.conv1b(self.conv1aa(self.conv1a(im2)))
181 | c12 = self.conv2b(self.conv2aa(self.conv2a(c11)))
182 | c22 = self.conv2b(self.conv2aa(self.conv2a(c21)))
183 | c13 = self.conv3b(self.conv3aa(self.conv3a(c12)))
184 | c23 = self.conv3b(self.conv3aa(self.conv3a(c22)))
185 | c14 = self.conv4b(self.conv4aa(self.conv4a(c13)))
186 | c24 = self.conv4b(self.conv4aa(self.conv4a(c23)))
187 | c15 = self.conv5b(self.conv5aa(self.conv5a(c14)))
188 | c25 = self.conv5b(self.conv5aa(self.conv5a(c24)))
189 | c16 = self.conv6b(self.conv6a(self.conv6aa(c15)))
190 | c26 = self.conv6b(self.conv6a(self.conv6aa(c25)))
191 |
192 |
193 | corr6 = self.corr(c16, c26)
194 | corr6 = self.leakyRELU(corr6)
195 |
196 |
197 | x = torch.cat((self.conv6_0(corr6), corr6),1)
198 | x = torch.cat((self.conv6_1(x), x),1)
199 | x = torch.cat((self.conv6_2(x), x),1)
200 | x = torch.cat((self.conv6_3(x), x),1)
201 | x = torch.cat((self.conv6_4(x), x),1)
202 | flow6 = self.predict_flow6(x)
203 | up_flow6 = self.deconv6(flow6)
204 | up_feat6 = self.upfeat6(x)
205 |
206 |
207 | warp5 = self.warp(c25, up_flow6*0.625)
208 | corr5 = self.corr(c15, warp5)
209 | corr5 = self.leakyRELU(corr5)
210 | x = torch.cat((corr5, c15, up_flow6, up_feat6), 1)
211 | x = torch.cat((self.conv5_0(x), x),1)
212 | x = torch.cat((self.conv5_1(x), x),1)
213 | x = torch.cat((self.conv5_2(x), x),1)
214 | x = torch.cat((self.conv5_3(x), x),1)
215 | x = torch.cat((self.conv5_4(x), x),1)
216 | flow5 = self.predict_flow5(x)
217 | up_flow5 = self.deconv5(flow5)
218 | up_feat5 = self.upfeat5(x)
219 |
220 |
221 | warp4 = self.warp(c24, up_flow5*1.25)
222 | corr4 = self.corr(c14, warp4)
223 | corr4 = self.leakyRELU(corr4)
224 | x = torch.cat((corr4, c14, up_flow5, up_feat5), 1)
225 | x = torch.cat((self.conv4_0(x), x),1)
226 | x = torch.cat((self.conv4_1(x), x),1)
227 | x = torch.cat((self.conv4_2(x), x),1)
228 | x = torch.cat((self.conv4_3(x), x),1)
229 | x = torch.cat((self.conv4_4(x), x),1)
230 | flow4 = self.predict_flow4(x)
231 | up_flow4 = self.deconv4(flow4)
232 | up_feat4 = self.upfeat4(x)
233 |
234 |
235 | warp3 = self.warp(c23, up_flow4*2.5)
236 | corr3 = self.corr(c13, warp3)
237 | corr3 = self.leakyRELU(corr3)
238 |
239 |
240 | x = torch.cat((corr3, c13, up_flow4, up_feat4), 1)
241 | x = torch.cat((self.conv3_0(x), x),1)
242 | x = torch.cat((self.conv3_1(x), x),1)
243 | x = torch.cat((self.conv3_2(x), x),1)
244 | x = torch.cat((self.conv3_3(x), x),1)
245 | x = torch.cat((self.conv3_4(x), x),1)
246 | flow3 = self.predict_flow3(x)
247 | up_flow3 = self.deconv3(flow3)
248 | up_feat3 = self.upfeat3(x)
249 |
250 |
251 | warp2 = self.warp(c22, up_flow3*5.0)
252 | corr2 = self.corr(c12, warp2)
253 | corr2 = self.leakyRELU(corr2)
254 | x = torch.cat((corr2, c12, up_flow3, up_feat3), 1)
255 | x = torch.cat((self.conv2_0(x), x),1)
256 | x = torch.cat((self.conv2_1(x), x),1)
257 | x = torch.cat((self.conv2_2(x), x),1)
258 | x = torch.cat((self.conv2_3(x), x),1)
259 | x = torch.cat((self.conv2_4(x), x),1)
260 | flow2 = self.predict_flow2(x)
261 |
262 | x = self.dc_conv4(self.dc_conv3(self.dc_conv2(self.dc_conv1(x))))
263 | flow2 += self.dc_conv7(self.dc_conv6(self.dc_conv5(x)))
264 |
265 | if self.training:
266 | return flow2,flow3,flow4,flow5,flow6
267 | else:
268 | return flow2
269 |
270 | def pwc_dc_net(path=None):
271 |
272 | model = PWCDCNet()
273 | if path is not None:
274 | data = torch.load(path)
275 | if 'state_dict' in data.keys():
276 | model.load_state_dict(data['state_dict'])
277 | else:
278 | model.load_state_dict(data)
279 | return model
280 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/flow2pose_lib/pyboost_cv2_converter.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * CV2BoostConverter.cpp
3 | *
4 | * Created on: May 21, 2015
5 | * Author: Gregory Kramida
6 | * Copyright: 2015 Gregory Kramida
7 | */
8 |
9 | #define NO_IMPORT_ARRAY
10 | #define PY_ARRAY_UNIQUE_SYMBOL pbcvt_ARRAY_API
11 | #include "pyboostcvconverter.hpp"
12 | #if CV_VERSION_EPOCH == 2 || (!defined CV_VERSION_EPOCH && CV_VERSION_MAJOR == 2)
13 | namespace pbcvt{
14 | using namespace cv;
15 |
16 | //=================== ERROR HANDLING =========================================================
17 | static int failmsg(const char *fmt, ...)
18 | {
19 | char str[1000];
20 |
21 | va_list ap;
22 | va_start(ap, fmt);
23 | vsnprintf(str, sizeof(str), fmt, ap);
24 | va_end(ap);
25 |
26 | PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, str);
27 | return 0;
28 | }
29 |
30 | static PyObject* failmsgp(const char *fmt, ...)
31 | {
32 | char str[1000];
33 |
34 | va_list ap;
35 | va_start(ap, fmt);
36 | vsnprintf(str, sizeof(str), fmt, ap);
37 | va_end(ap);
38 |
39 | PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, str);
40 | return 0;
41 | }
42 |
43 | //=================== THREADING ==============================================================
44 |
45 | class PyAllowThreads
46 | {
47 | public:
48 | PyAllowThreads() :
49 | _state(PyEval_SaveThread()) {
50 | }
51 | ~PyAllowThreads()
52 | {
53 | PyEval_RestoreThread(_state);
54 | }
55 | private:
56 | PyThreadState* _state;
57 | };
58 |
59 | class PyEnsureGIL
60 | {
61 | public:
62 | PyEnsureGIL() :
63 | _state(PyGILState_Ensure()) {
64 | }
65 | ~PyEnsureGIL()
66 | {
67 | PyGILState_Release(_state);
68 | }
69 | private:
70 | PyGILState_STATE _state;
71 | };
72 |
73 | //=================== NUMPY ALLOCATOR FOR OPENCV =============================================
74 | class NumpyAllocator:
75 | public MatAllocator
76 | {
77 | public:
78 | NumpyAllocator() {
79 | }
80 | ~NumpyAllocator() {
81 | }
82 |
83 | void allocate(int dims, const int* sizes, int type, int*& refcount,
84 | uchar*& datastart, uchar*& data, size_t* step) {
85 | PyEnsureGIL gil;
86 |
87 | int depth = CV_MAT_DEPTH(type);
88 | int cn = CV_MAT_CN(type);
89 | const int f = (int) (sizeof(size_t) / 8);
90 | int typenum = depth == CV_8U ? NPY_UBYTE : depth == CV_8S ? NPY_BYTE :
91 | depth == CV_16U ? NPY_USHORT :
92 | depth == CV_16S ? NPY_SHORT :
93 | depth == CV_32S ? NPY_INT :
94 | depth == CV_32F ? NPY_FLOAT :
95 | depth == CV_64F ? NPY_DOUBLE : f * NPY_ULONGLONG + (f ^ 1) * NPY_UINT;
96 | int i;
97 | npy_intp _sizes[CV_MAX_DIM + 1];
98 | for (i = 0; i < dims; i++) {
99 | _sizes[i] = sizes[i];
100 | }
101 |
102 | if (cn > 1) {
103 | _sizes[dims++] = cn;
104 | }
105 |
106 | PyObject* o = PyArray_SimpleNew(dims, _sizes, typenum);
107 |
108 | if (!o) {
109 | CV_Error_(CV_StsError,
110 | ("The numpy array of typenum=%d, ndims=%d can not be created", typenum, dims));
111 | }
112 | refcount = refcountFromPyObject(o);
113 | npy_intp* _strides = PyArray_STRIDES((PyArrayObject*) o);
114 | for( i = 0; i < dims - (cn > 1); i++ )
115 | step[i] = (size_t)_strides[i];
116 | datastart = data = (uchar*)PyArray_DATA((PyArrayObject*) o);
117 | }
118 |
119 | void deallocate(int* refcount, uchar*, uchar*) {
120 | PyEnsureGIL gil;
121 | if (!refcount)
122 | return;
123 | PyObject* o = pyObjectFromRefcount(refcount);
124 | Py_INCREF(o);
125 | Py_DECREF(o);
126 | }
127 | };
128 |
129 | //=================== ALLOCATOR INITIALIZTION ==================================================
130 | NumpyAllocator g_numpyAllocator;
131 |
132 | //=================== STANDALONE CONVERTER FUNCTIONS =========================================
133 |
134 | PyObject* fromMatToNDArray(const Mat& m) {
135 | if( !m.data )
136 | Py_RETURN_NONE;
137 | Mat temp, *p = (Mat*)&m;
138 | if(!p->refcount || p->allocator != &g_numpyAllocator)
139 | {
140 | temp.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
141 | ERRWRAP2(m.copyTo(temp));
142 | p = &temp;
143 | }
144 | p->addref();
145 | return pyObjectFromRefcount(p->refcount);
146 | }
147 |
148 | Mat fromNDArrayToMat(PyObject* o) {
149 | cv::Mat m;
150 | if (!PyArray_Check(o)) {
151 | failmsg("argument is not a numpy array");
152 | if (!m.data)
153 | m.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
154 | } else {
155 | PyArrayObject* oarr = (PyArrayObject*) o;
156 |
157 | bool needcopy = false, needcast = false;
158 | int typenum = PyArray_TYPE(oarr), new_typenum = typenum;
159 | int type = typenum == NPY_UBYTE ? CV_8U : typenum == NPY_BYTE ? CV_8S :
160 | typenum == NPY_USHORT ? CV_16U :
161 | typenum == NPY_SHORT ? CV_16S :
162 | typenum == NPY_INT ? CV_32S :
163 | typenum == NPY_INT32 ? CV_32S :
164 | typenum == NPY_FLOAT ? CV_32F :
165 | typenum == NPY_DOUBLE ? CV_64F : -1;
166 |
167 | if (type < 0) {
168 | if (typenum == NPY_INT64 || typenum == NPY_UINT64
169 | || type == NPY_LONG) {
170 | needcopy = needcast = true;
171 | new_typenum = NPY_INT;
172 | type = CV_32S;
173 | } else {
174 | failmsg("Argument data type is not supported");
175 | m.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
176 | return m;
177 | }
178 | }
179 |
180 | #ifndef CV_MAX_DIM
181 | const int CV_MAX_DIM = 32;
182 | #endif
183 |
184 | int ndims = PyArray_NDIM(oarr);
185 | if (ndims >= CV_MAX_DIM) {
186 | failmsg("Dimensionality of argument is too high");
187 | if (!m.data)
188 | m.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
189 | return m;
190 | }
191 | int size[CV_MAX_DIM + 1];
192 | size_t step[CV_MAX_DIM + 1];
193 | size_t elemsize = CV_ELEM_SIZE1(type);
194 | const npy_intp* _sizes = PyArray_DIMS(oarr);
195 | const npy_intp* _strides = PyArray_STRIDES(oarr);
196 | bool ismultichannel = ndims == 3 && _sizes[2] <= CV_CN_MAX;
197 |
198 | for (int i = ndims - 1; i >= 0 && !needcopy; i--) {
199 | // these checks handle cases of
200 | // a) multi-dimensional (ndims > 2) arrays, as well as simpler 1- and 2-dimensional cases
201 | // b) transposed arrays, where _strides[] elements go in non-descending order
202 | // c) flipped arrays, where some of _strides[] elements are negative
203 | if ((i == ndims - 1 && (size_t) _strides[i] != elemsize)
204 | || (i < ndims - 1 && _strides[i] < _strides[i + 1]))
205 | needcopy = true;
206 | }
207 |
208 | if (ismultichannel && _strides[1] != (npy_intp) elemsize * _sizes[2])
209 | needcopy = true;
210 | if (needcopy) {
211 |
212 | if (needcast) {
213 | o = PyArray_Cast(oarr, new_typenum);
214 | oarr = (PyArrayObject*) o;
215 | } else {
216 | oarr = PyArray_GETCONTIGUOUS(oarr);
217 | o = (PyObject*) oarr;
218 | }
219 |
220 | _strides = PyArray_STRIDES(oarr);
221 | }
222 |
223 | for (int i = 0; i < ndims; i++) {
224 | size[i] = (int) _sizes[i];
225 | step[i] = (size_t) _strides[i];
226 | }
227 |
228 | // handle degenerate case
229 | if (ndims == 0) {
230 | size[ndims] = 1;
231 | step[ndims] = elemsize;
232 | ndims++;
233 | }
234 | if (ismultichannel) {
235 | ndims--;
236 | type |= CV_MAKETYPE(0, size[2]);
237 | }
238 |
239 | m = Mat(ndims, size, type, PyArray_DATA(oarr), step);
240 |
241 | if (m.data){
242 | m.refcount = refcountFromPyObject(o);
243 | if (!needcopy){
244 | m.addref(); // protect the original numpy array from deallocation
245 | // (since Mat destructor will decrement the reference counter)
246 | }
247 | };
248 | m.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
249 | }
250 | return m;
251 | }
252 |
253 | //=================== BOOST CONVERTERS =======================================================
254 |
255 | PyObject* matToNDArrayBoostConverter::convert(Mat const& m) {
256 | if( !m.data )
257 | Py_RETURN_NONE;
258 | Mat temp, *p = (Mat*)&m;
259 | if(!p->refcount || p->allocator != &g_numpyAllocator)
260 | {
261 | temp.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
262 | ERRWRAP2(m.copyTo(temp));
263 | p = &temp;
264 | }
265 | p->addref();
266 | return pyObjectFromRefcount(p->refcount);
267 | }
268 |
269 | matFromNDArrayBoostConverter::matFromNDArrayBoostConverter() {
270 | boost::python::converter::registry::push_back(matFromNDArrayBoostConverter::convertible,
271 | matFromNDArrayBoostConverter::construct,
272 | boost::python::type_id());
273 | }
274 |
275 | /// @brief Check if PyObject is an array and can be converted to OpenCV matrix.
276 | void* matFromNDArrayBoostConverter::convertible(PyObject* object) {
277 |
278 | if (!PyArray_Check(object)) {
279 | return NULL;
280 | }
281 | #ifndef CV_MAX_DIM
282 | const int CV_MAX_DIM = 32;
283 | #endif
284 | PyArrayObject* oarr = (PyArrayObject*) object;
285 |
286 | int typenum = PyArray_TYPE(oarr);
287 | if (typenum != NPY_INT64 && typenum != NPY_UINT64 && typenum != NPY_LONG
288 | && typenum != NPY_UBYTE && typenum != NPY_BYTE
289 | && typenum != NPY_USHORT && typenum != NPY_SHORT
290 | && typenum != NPY_INT && typenum != NPY_INT32
291 | && typenum != NPY_FLOAT && typenum != NPY_DOUBLE) {
292 | return NULL;
293 | }
294 | int ndims = PyArray_NDIM(oarr); //data type not supported
295 |
296 | if (ndims >= CV_MAX_DIM) {
297 | return NULL; //too many dimensions
298 | }
299 |
300 | return object;
301 | }
302 |
303 | /// @brief Construct a Mat from an NDArray object.
304 | void matFromNDArrayBoostConverter::construct(PyObject* object,
305 | boost::python::converter::rvalue_from_python_stage1_data* data) {
306 |
307 | namespace python = boost::python;
308 | // Object is a borrowed reference, so create a handle indicting it is
309 | // borrowed for proper reference counting.
310 | python::handle<> handle(python::borrowed(object));
311 |
312 | // Obtain a handle to the memory block that the converter has allocated
313 | // for the C++ type.
314 | typedef python::converter::rvalue_from_python_storage storage_type;
315 | void* storage = reinterpret_cast(data)->storage.bytes;
316 |
317 | // Allocate the C++ type into the converter's memory block, and assign
318 | // its handle to the converter's convertible variable. The C++
319 | // container is populated by passing the begin and end iterators of
320 | // the python object to the container's constructor.
321 | PyArrayObject* oarr = (PyArrayObject*) object;
322 |
323 | bool needcopy = false, needcast = false;
324 | int typenum = PyArray_TYPE(oarr), new_typenum = typenum;
325 | int type = typenum == NPY_UBYTE ? CV_8U : typenum == NPY_BYTE ? CV_8S :
326 | typenum == NPY_USHORT ? CV_16U :
327 | typenum == NPY_SHORT ? CV_16S :
328 | typenum == NPY_INT ? CV_32S :
329 | typenum == NPY_INT32 ? CV_32S :
330 | typenum == NPY_FLOAT ? CV_32F :
331 | typenum == NPY_DOUBLE ? CV_64F : -1;
332 |
333 | if (type < 0) {
334 | needcopy = needcast = true;
335 | new_typenum = NPY_INT;
336 | type = CV_32S;
337 | }
338 |
339 | #ifndef CV_MAX_DIM
340 | const int CV_MAX_DIM = 32;
341 | #endif
342 | int ndims = PyArray_NDIM(oarr);
343 |
344 | int size[CV_MAX_DIM + 1];
345 | size_t step[CV_MAX_DIM + 1];
346 | size_t elemsize = CV_ELEM_SIZE1(type);
347 | const npy_intp* _sizes = PyArray_DIMS(oarr);
348 | const npy_intp* _strides = PyArray_STRIDES(oarr);
349 | bool ismultichannel = ndims == 3 && _sizes[2] <= CV_CN_MAX;
350 |
351 | for (int i = ndims - 1; i >= 0 && !needcopy; i--) {
352 | // these checks handle cases of
353 | // a) multi-dimensional (ndims > 2) arrays, as well as simpler 1- and 2-dimensional cases
354 | // b) transposed arrays, where _strides[] elements go in non-descending order
355 | // c) flipped arrays, where some of _strides[] elements are negative
356 | if ((i == ndims - 1 && (size_t) _strides[i] != elemsize)
357 | || (i < ndims - 1 && _strides[i] < _strides[i + 1]))
358 | needcopy = true;
359 | }
360 |
361 | if (ismultichannel && _strides[1] != (npy_intp) elemsize * _sizes[2])
362 | needcopy = true;
363 |
364 | if (needcopy) {
365 |
366 | if (needcast) {
367 | object = PyArray_Cast(oarr, new_typenum);
368 | oarr = (PyArrayObject*) object;
369 | } else {
370 | oarr = PyArray_GETCONTIGUOUS(oarr);
371 | object = (PyObject*) oarr;
372 | }
373 |
374 | _strides = PyArray_STRIDES(oarr);
375 | }
376 |
377 | for (int i = 0; i < ndims; i++) {
378 | size[i] = (int) _sizes[i];
379 | step[i] = (size_t) _strides[i];
380 | }
381 |
382 | // handle degenerate case
383 | if (ndims == 0) {
384 | size[ndims] = 1;
385 | step[ndims] = elemsize;
386 | ndims++;
387 | }
388 |
389 | if (ismultichannel) {
390 | ndims--;
391 | type |= CV_MAKETYPE(0, size[2]);
392 | }
393 | if (!needcopy) {
394 | Py_INCREF(object);
395 | }
396 |
397 | cv::Mat* m = new (storage) cv::Mat(ndims, size, type, PyArray_DATA(oarr), step);
398 | if (m->data){
399 | m->refcount = refcountFromPyObject(object);
400 | if (!needcopy){
401 | m->addref(); // protect the original numpy array from deallocation
402 | // (since Mat destructor will decrement the reference counter)
403 | }
404 | };
405 |
406 | m->allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
407 | data->convertible = storage;
408 | }
409 |
410 | } //end namespace pbcvt
411 |
412 | #endif
413 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/flow2pose/flow2pose_lib/pyboost_cv3_converter.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * CV3BoostConverter.cpp
3 | *
4 | * Created on: May 21, 2015
5 | * Author: Gregory Kramida
6 | * Copyright: 2015 Gregory Kramida
7 | */
8 |
9 | #define NO_IMPORT_ARRAY
10 | #define PY_ARRAY_UNIQUE_SYMBOL pbcvt_ARRAY_API
11 | #include "pyboostcvconverter.hpp"
12 | #if CV_VERSION_MAJOR == 3
13 | namespace pbcvt {
14 | using namespace cv;
15 | //=================== ERROR HANDLING =========================================================
16 |
17 | static int failmsg(const char *fmt, ...) {
18 | char str[1000];
19 |
20 | va_list ap;
21 | va_start(ap, fmt);
22 | vsnprintf(str, sizeof(str), fmt, ap);
23 | va_end(ap);
24 |
25 | PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, str);
26 | return 0;
27 | }
28 |
29 | static PyObject* failmsgp(const char *fmt, ...)
30 | {
31 | char str[1000];
32 |
33 | va_list ap;
34 | va_start(ap, fmt);
35 | vsnprintf(str, sizeof(str), fmt, ap);
36 | va_end(ap);
37 |
38 | PyErr_SetString(PyExc_TypeError, str);
39 | return 0;
40 | }
41 |
42 | //=================== THREADING ==============================================================
43 | class PyAllowThreads {
44 | public:
45 | PyAllowThreads() :
46 | _state(PyEval_SaveThread()) {
47 | }
48 | ~PyAllowThreads() {
49 | PyEval_RestoreThread(_state);
50 | }
51 | private:
52 | PyThreadState* _state;
53 | };
54 |
55 | class PyEnsureGIL {
56 | public:
57 | PyEnsureGIL() :
58 | _state(PyGILState_Ensure()) {
59 | }
60 | ~PyEnsureGIL() {
61 | PyGILState_Release(_state);
62 | }
63 | private:
64 | PyGILState_STATE _state;
65 | };
66 |
67 | enum {
68 | ARG_NONE = 0, ARG_MAT = 1, ARG_SCALAR = 2
69 | };
70 |
71 | class NumpyAllocator:
72 | public MatAllocator {
73 | public:
74 | NumpyAllocator() {
75 | stdAllocator = Mat::getStdAllocator();
76 | }
77 | ~NumpyAllocator() {
78 | }
79 |
80 | UMatData* allocate(PyObject* o, int dims, const int* sizes, int type,
81 | size_t* step) const {
82 | UMatData* u = new UMatData(this);
83 | u->data = u->origdata = (uchar*) PyArray_DATA((PyArrayObject*) o);
84 | npy_intp* _strides = PyArray_STRIDES((PyArrayObject*) o);
85 | for (int i = 0; i < dims - 1; i++)
86 | step[i] = (size_t) _strides[i];
87 | step[dims - 1] = CV_ELEM_SIZE(type);
88 | u->size = sizes[0] * step[0];
89 | u->userdata = o;
90 | return u;
91 | }
92 |
93 | UMatData* allocate(int dims0, const int* sizes, int type, void* data,
94 | size_t* step, int flags, UMatUsageFlags usageFlags) const {
95 | if (data != 0) {
96 | CV_Error(Error::StsAssert, "The data should normally be NULL!");
97 | // probably this is safe to do in such extreme case
98 | return stdAllocator->allocate(dims0, sizes, type, data, step, flags,
99 | usageFlags);
100 | }
101 | PyEnsureGIL gil;
102 |
103 | int depth = CV_MAT_DEPTH(type);
104 | int cn = CV_MAT_CN(type);
105 | const int f = (int) (sizeof(size_t) / 8);
106 | int typenum =
107 | depth == CV_8U ? NPY_UBYTE :
108 | depth == CV_8S ? NPY_BYTE :
109 | depth == CV_16U ? NPY_USHORT :
110 | depth == CV_16S ? NPY_SHORT :
111 | depth == CV_32S ? NPY_INT :
112 | depth == CV_32F ? NPY_FLOAT :
113 | depth == CV_64F ?
114 | NPY_DOUBLE :
115 | f * NPY_ULONGLONG + (f ^ 1) * NPY_UINT;
116 | int i, dims = dims0;
117 | cv::AutoBuffer _sizes(dims + 1);
118 | for (i = 0; i < dims; i++)
119 | _sizes[i] = sizes[i];
120 | if (cn > 1)
121 | _sizes[dims++] = cn;
122 | PyObject* o = PyArray_SimpleNew(dims, _sizes, typenum);
123 | if (!o)
124 | CV_Error_(Error::StsError,
125 | ("The numpy array of typenum=%d, ndims=%d can not be created", typenum, dims));
126 | return allocate(o, dims0, sizes, type, step);
127 | }
128 |
129 | bool allocate(UMatData* u, int accessFlags,
130 | UMatUsageFlags usageFlags) const {
131 | return stdAllocator->allocate(u, accessFlags, usageFlags);
132 | }
133 |
134 | void deallocate(UMatData* u) const {
135 | if (u) {
136 | PyEnsureGIL gil;
137 | PyObject* o = (PyObject*) u->userdata;
138 | Py_XDECREF(o);
139 | delete u;
140 | }
141 | }
142 |
143 | const MatAllocator* stdAllocator;
144 | };
145 |
146 | //=================== ALLOCATOR INITIALIZTION ==================================================
147 | NumpyAllocator g_numpyAllocator;
148 |
149 | //=================== STANDALONE CONVERTER FUNCTIONS =========================================
150 |
151 | PyObject* fromMatToNDArray(const Mat& m) {
152 | if (!m.data)
153 | Py_RETURN_NONE;
154 | Mat temp,
155 | *p = (Mat*) &m;
156 | if (!p->u || p->allocator != &g_numpyAllocator) {
157 | temp.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
158 | ERRWRAP2(m.copyTo(temp));
159 | p = &temp;
160 | }
161 | PyObject* o = (PyObject*) p->u->userdata;
162 | Py_INCREF(o);
163 | return o;
164 | }
165 |
166 | Mat fromNDArrayToMat(PyObject* o) {
167 | cv::Mat m;
168 | bool allowND = true;
169 | if (!PyArray_Check(o)) {
170 | failmsg("argument is not a numpy array");
171 | if (!m.data)
172 | m.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
173 | } else {
174 | PyArrayObject* oarr = (PyArrayObject*) o;
175 |
176 | bool needcopy = false, needcast = false;
177 | int typenum = PyArray_TYPE(oarr), new_typenum = typenum;
178 | int type = typenum == NPY_UBYTE ? CV_8U : typenum == NPY_BYTE ? CV_8S :
179 | typenum == NPY_USHORT ? CV_16U :
180 | typenum == NPY_SHORT ? CV_16S :
181 | typenum == NPY_INT ? CV_32S :
182 | typenum == NPY_INT32 ? CV_32S :
183 | typenum == NPY_FLOAT ? CV_32F :
184 | typenum == NPY_DOUBLE ? CV_64F : -1;
185 |
186 | if (type < 0) {
187 | if (typenum == NPY_INT64 || typenum == NPY_UINT64
188 | || type == NPY_LONG) {
189 | needcopy = needcast = true;
190 | new_typenum = NPY_INT;
191 | type = CV_32S;
192 | } else {
193 | failmsg("Argument data type is not supported");
194 | m.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
195 | return m;
196 | }
197 | }
198 |
199 | #ifndef CV_MAX_DIM
200 | const int CV_MAX_DIM = 32;
201 | #endif
202 |
203 | int ndims = PyArray_NDIM(oarr);
204 | if (ndims >= CV_MAX_DIM) {
205 | failmsg("Dimensionality of argument is too high");
206 | if (!m.data)
207 | m.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
208 | return m;
209 | }
210 |
211 | int size[CV_MAX_DIM + 1];
212 | size_t step[CV_MAX_DIM + 1];
213 | size_t elemsize = CV_ELEM_SIZE1(type);
214 | const npy_intp* _sizes = PyArray_DIMS(oarr);
215 | const npy_intp* _strides = PyArray_STRIDES(oarr);
216 | bool ismultichannel = ndims == 3 && _sizes[2] <= CV_CN_MAX;
217 |
218 | for (int i = ndims - 1; i >= 0 && !needcopy; i--) {
219 | // these checks handle cases of
220 | // a) multi-dimensional (ndims > 2) arrays, as well as simpler 1- and 2-dimensional cases
221 | // b) transposed arrays, where _strides[] elements go in non-descending order
222 | // c) flipped arrays, where some of _strides[] elements are negative
223 | if ((i == ndims - 1 && (size_t) _strides[i] != elemsize)
224 | || (i < ndims - 1 && _strides[i] < _strides[i + 1]))
225 | needcopy = true;
226 | }
227 |
228 | if (ismultichannel && _strides[1] != (npy_intp) elemsize * _sizes[2])
229 | needcopy = true;
230 |
231 | if (needcopy) {
232 |
233 | if (needcast) {
234 | o = PyArray_Cast(oarr, new_typenum);
235 | oarr = (PyArrayObject*) o;
236 | } else {
237 | oarr = PyArray_GETCONTIGUOUS(oarr);
238 | o = (PyObject*) oarr;
239 | }
240 |
241 | _strides = PyArray_STRIDES(oarr);
242 | }
243 |
244 | for (int i = 0; i < ndims; i++) {
245 | size[i] = (int) _sizes[i];
246 | step[i] = (size_t) _strides[i];
247 | }
248 |
249 | // handle degenerate case
250 | if (ndims == 0) {
251 | size[ndims] = 1;
252 | step[ndims] = elemsize;
253 | ndims++;
254 | }
255 |
256 | if (ismultichannel) {
257 | ndims--;
258 | type |= CV_MAKETYPE(0, size[2]);
259 | }
260 |
261 | if (ndims > 2 && !allowND) {
262 | failmsg("%s has more than 2 dimensions");
263 | } else {
264 |
265 | m = Mat(ndims, size, type, PyArray_DATA(oarr), step);
266 | m.u = g_numpyAllocator.allocate(o, ndims, size, type, step);
267 | m.addref();
268 |
269 | if (!needcopy) {
270 | Py_INCREF(o);
271 | }
272 | }
273 | m.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
274 | }
275 | return m;
276 | }
277 |
278 | //=================== BOOST CONVERTERS =======================================================
279 |
280 | PyObject* matToNDArrayBoostConverter::convert(Mat const& m) {
281 | if (!m.data)
282 | Py_RETURN_NONE;
283 | Mat temp,
284 | *p = (Mat*) &m;
285 | if (!p->u || p->allocator != &g_numpyAllocator)
286 | {
287 | temp.allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
288 | ERRWRAP2(m.copyTo(temp));
289 | p = &temp;
290 | }
291 | PyObject* o = (PyObject*) p->u->userdata;
292 | Py_INCREF(o);
293 | return o;
294 | }
295 |
296 | matFromNDArrayBoostConverter::matFromNDArrayBoostConverter() {
297 | boost::python::converter::registry::push_back(convertible, construct,
298 | boost::python::type_id());
299 | }
300 |
301 | /// @brief Check if PyObject is an array and can be converted to OpenCV matrix.
302 | void* matFromNDArrayBoostConverter::convertible(PyObject* object) {
303 | if (!PyArray_Check(object)) {
304 | return NULL;
305 | }
306 | #ifndef CV_MAX_DIM
307 | const int CV_MAX_DIM = 32;
308 | #endif
309 | PyArrayObject* oarr = (PyArrayObject*) object;
310 |
311 | int typenum = PyArray_TYPE(oarr);
312 | if (typenum != NPY_INT64 && typenum != NPY_UINT64 && typenum != NPY_LONG
313 | && typenum != NPY_UBYTE && typenum != NPY_BYTE
314 | && typenum != NPY_USHORT && typenum != NPY_SHORT
315 | && typenum != NPY_INT && typenum != NPY_INT32
316 | && typenum != NPY_FLOAT && typenum != NPY_DOUBLE) {
317 | return NULL;
318 | }
319 | int ndims = PyArray_NDIM(oarr); //data type not supported
320 |
321 | if (ndims >= CV_MAX_DIM) {
322 | return NULL; //too many dimensions
323 | }
324 | return object;
325 | }
326 |
327 | /// @brief Construct a Mat from an NDArray object.
328 | void matFromNDArrayBoostConverter::construct(PyObject* object,
329 | boost::python::converter::rvalue_from_python_stage1_data* data) {
330 | namespace python = boost::python;
331 | // Object is a borrowed reference, so create a handle indicting it is
332 | // borrowed for proper reference counting.
333 | python::handle<> handle(python::borrowed(object));
334 |
335 | // Obtain a handle to the memory block that the converter has allocated
336 | // for the C++ type.
337 | typedef python::converter::rvalue_from_python_storage storage_type;
338 | void* storage = reinterpret_cast(data)->storage.bytes;
339 |
340 | // Allocate the C++ type into the converter's memory block, and assign
341 | // its handle to the converter's convertible variable. The C++
342 | // container is populated by passing the begin and end iterators of
343 | // the python object to the container's constructor.
344 | PyArrayObject* oarr = (PyArrayObject*) object;
345 |
346 | bool needcopy = false, needcast = false;
347 | int typenum = PyArray_TYPE(oarr), new_typenum = typenum;
348 | int type = typenum == NPY_UBYTE ? CV_8U : typenum == NPY_BYTE ? CV_8S :
349 | typenum == NPY_USHORT ? CV_16U :
350 | typenum == NPY_SHORT ? CV_16S :
351 | typenum == NPY_INT ? CV_32S :
352 | typenum == NPY_INT32 ? CV_32S :
353 | typenum == NPY_FLOAT ? CV_32F :
354 | typenum == NPY_DOUBLE ? CV_64F : -1;
355 |
356 | if (type < 0) {
357 | needcopy = needcast = true;
358 | new_typenum = NPY_INT;
359 | type = CV_32S;
360 | }
361 |
362 | #ifndef CV_MAX_DIM
363 | const int CV_MAX_DIM = 32;
364 | #endif
365 | int ndims = PyArray_NDIM(oarr);
366 |
367 | int size[CV_MAX_DIM + 1];
368 | size_t step[CV_MAX_DIM + 1];
369 | size_t elemsize = CV_ELEM_SIZE1(type);
370 | const npy_intp* _sizes = PyArray_DIMS(oarr);
371 | const npy_intp* _strides = PyArray_STRIDES(oarr);
372 | bool ismultichannel = ndims == 3 && _sizes[2] <= CV_CN_MAX;
373 |
374 | for (int i = ndims - 1; i >= 0 && !needcopy; i--) {
375 | // these checks handle cases of
376 | // a) multi-dimensional (ndims > 2) arrays, as well as simpler 1- and 2-dimensional cases
377 | // b) transposed arrays, where _strides[] elements go in non-descending order
378 | // c) flipped arrays, where some of _strides[] elements are negative
379 | if ((i == ndims - 1 && (size_t) _strides[i] != elemsize)
380 | || (i < ndims - 1 && _strides[i] < _strides[i + 1]))
381 | needcopy = true;
382 | }
383 |
384 | if (ismultichannel && _strides[1] != (npy_intp) elemsize * _sizes[2])
385 | needcopy = true;
386 |
387 | if (needcopy) {
388 |
389 | if (needcast) {
390 | object = PyArray_Cast(oarr, new_typenum);
391 | oarr = (PyArrayObject*) object;
392 | } else {
393 | oarr = PyArray_GETCONTIGUOUS(oarr);
394 | object = (PyObject*) oarr;
395 | }
396 |
397 | _strides = PyArray_STRIDES(oarr);
398 | }
399 |
400 | for (int i = 0; i < ndims; i++) {
401 | size[i] = (int) _sizes[i];
402 | step[i] = (size_t) _strides[i];
403 | }
404 |
405 | // handle degenerate case
406 | if (ndims == 0) {
407 | size[ndims] = 1;
408 | step[ndims] = elemsize;
409 | ndims++;
410 | }
411 |
412 | if (ismultichannel) {
413 | ndims--;
414 | type |= CV_MAKETYPE(0, size[2]);
415 | }
416 | if (!needcopy) {
417 | Py_INCREF(object);
418 | }
419 |
420 | cv::Mat* m = new (storage) cv::Mat(ndims, size, type, PyArray_DATA(oarr), step);
421 | m->u = g_numpyAllocator.allocate(object, ndims, size, type, step);
422 | m->allocator = &g_numpyAllocator;
423 | m->addref();
424 | data->convertible = storage;
425 | }
426 |
427 | } //end namespace pbcvt
428 | #endif
429 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr1d_cuda_kernel.cu:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include
2 | #include
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 | #include "corr1d_cuda_kernel.h"
6 |
7 | #define ROUND_OFF 50000
8 |
9 | #define CUDA_NUM_THREADS 1024
10 | #define WARPS_PER_BLOCK 1
11 | #define THREADS_PER_WARP 32
12 |
13 | #define CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(i, n) for (int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; i < (n); i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x)
14 |
15 | #define GET_BLOCKS(n, t) (n+t-1) / t
16 |
17 | // == Dimension rearrangement Kernel
18 | __global__ void blob_rearrange_kernel2_1d(const float *in, float *out, int num, int channels, int width, int height, int widthheight, int padding, int pwidthheight)
19 | {
20 | int xy = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
21 | if(xy>=widthheight)
22 | return;
23 |
24 | int ch = blockIdx.y;
25 | int n = blockIdx.z;
26 |
27 |
28 | float value=in[(n*channels+ch)*widthheight+xy];
29 |
30 | __syncthreads();
31 |
32 | int xpad = (xy % width + padding);
33 | int ypad = (xy / width + 0);
34 | int xypad = ypad * (width+2*padding) + xpad;
35 |
36 | out[(n*pwidthheight+xypad)*channels + ch] = value;
37 | }
38 |
39 | void blob_rearrange_ongpu_1d(const float *in, float *out, int num, int channels, int width, int height, int widthheight, int padding, int pwidthheight, cudaStream_t stream)
40 | {
41 | int threads_per_block=16;
42 | dim3 totalBlocksRearr((widthheight-1)/threads_per_block+1, channels, num);
43 |
44 | cudaError_t err;
45 |
46 | blob_rearrange_kernel2_1d<<>>
47 | (in, out, num, channels, width, height, widthheight, padding, pwidthheight);
48 |
49 | err = cudaGetLastError();
50 | if(cudaSuccess != err)
51 | {
52 | fprintf(stderr, "cudaCheckError() failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(err));
53 | exit(-1);
54 | }
55 | }
56 |
57 | // == Correlation Kernel
58 |
59 | __global__ void CorrelateData_1d(const int nthreads, int num, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels, int topcount,
60 | int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int kernel_size, int stride1, int stride2,
61 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int bottomchannels,
62 | const float *bottom0, const float *bottom1, float *top)
63 | {
64 | extern __shared__ char patch_data_char[];
65 |
66 | float *patch_data = (float *)patch_data_char;
67 |
68 | // First (upper left) position of kernel upper-left corner in current center position of neighborhood in image 1
69 | int x1 = blockIdx.x*stride1 + max_displacement;
70 | int y1 = blockIdx.y*stride1;
71 | int item = blockIdx.z;
72 | int ch_off = threadIdx.x;
73 |
74 | // Load 3D patch into shared shared memory
75 | for(int j = 0; j < kernel_size; j++) { // HEIGHT
76 | for(int i = 0; i < kernel_size; i++) { // WIDTH
77 | int ji_off = ((j * kernel_size) + i) * bottomchannels;
78 | for(int ch = ch_off; ch < bottomchannels; ch += (WARPS_PER_BLOCK*THREADS_PER_WARP)) { // CHANNELS
79 | int idx1 = ((item * bottomheight + y1+j) * bottomwidth + x1+i) * bottomchannels + ch;
80 | int idxPatchData = ji_off + ch;
81 | patch_data[idxPatchData] = bottom0[idx1];
82 | }
83 | }
84 | }
85 |
86 | __syncthreads();
87 |
88 | __shared__ float sum[WARPS_PER_BLOCK*THREADS_PER_WARP];
89 |
90 | // Compute correlation
91 | for(int top_channel = 0; top_channel < topchannels; top_channel++) {
92 | sum[ch_off] = 0;
93 |
94 | int s2o = (top_channel % neighborhood_grid_width + x_shift) * stride2;
95 |
96 | for(int j = 0; j < kernel_size; j++) { // HEIGHT
97 | for(int i = 0; i < kernel_size; i++) { // WIDTH
98 | int ji_off = ((j * kernel_size) + i) * bottomchannels;
99 | for(int ch = ch_off; ch < bottomchannels; ch += (WARPS_PER_BLOCK*THREADS_PER_WARP)) { // CHANNELS
100 | int x2 = x1 + s2o;
101 |
102 | int idxPatchData = ji_off + ch;
103 | int idx2 = ((item * bottomheight + y1+j) * bottomwidth + x2+i) * bottomchannels + ch;
104 | //int idx2 = ((item * bottomheight + y1+j) * bottomwidth + x1+i) * bottomchannels + ch;
105 |
106 | //printf("x1 %d x2 %d bh %d bw %d bc %d i %d ch %d y1 %d idx2 %d\n", x1, x2, bottomheight, bottomwidth, bottomchannels, item, ch, y1, idx2);
107 |
108 | sum[ch_off] += patch_data[idxPatchData] * bottom1[idx2];
109 | }
110 | }
111 | }
112 |
113 | __syncthreads();
114 |
115 | if(ch_off == 0) {
116 | float total_sum = 0;
117 | for(int idx = 0; idx < WARPS_PER_BLOCK*THREADS_PER_WARP; idx++) {
118 | total_sum += sum[idx];
119 | }
120 | //printf("ch_off %d sum %f\n", ch_off, total_sum);
121 | const int sumelems = kernel_size*kernel_size*bottomchannels;
122 | const int index = ((top_channel*topheight + blockIdx.y)*topwidth)+blockIdx.x;
123 | top[index + item*topcount] = total_sum / (float)sumelems;
124 | }
125 | }
126 |
127 |
128 | // Aggregate
129 | }
130 |
131 | __global__ void CorrelateDataSubtract_1d(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels, int topcount,
132 | int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
133 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int bottomchannels,
134 | const float *bottom0, const float *bottom1, float *top)
135 | {
136 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
137 | int x = index % topwidth; //w-pos
138 | int y = (index / topwidth) % topheight; //h-pos
139 | int c = (index / topwidth / topheight) % topchannels; //channels
140 |
141 | // Offset of patch in image 2
142 | int s2o = (c % neighborhood_grid_width + x_shift) * stride2;
143 |
144 | // First (upper left) position of kernel center in current neighborhood in image 1
145 | int x1 = x*stride1 + kernel_radius + max_displacement;
146 | int y1 = y*stride1 + kernel_radius + 0;
147 |
148 | // Iterate through 3D patch
149 | float sum = 0;
150 | for(int j = -kernel_radius; j <= kernel_radius; j++) { // HEIGHT
151 | for(int i = -kernel_radius; i <= kernel_radius; i++) { // WIDTH
152 | for(int l = 0; l < bottomchannels; l++) { // CHANNELS
153 | // Calculate position in image 2
154 | int x2 = x1 + s2o;
155 | int y2 = y1;
156 |
157 | // Indices in bottom data: (CH=l,W=x2,H=y2,N)
158 | int idx1 = ((item * bottomheight + y1+j) * bottomwidth + x1+i) * bottomchannels + l;
159 | int idx2 = ((item * bottomheight + y2+j) * bottomwidth + x2+i) * bottomchannels + l;
160 |
161 | // Do the correlation:
162 | sum += fabsf(bottom0[idx1] - bottom1[idx2]);
163 | }
164 | }
165 | }
166 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
167 | top[index + item*topcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
168 | }
169 |
170 | }
171 |
172 | void CorrelateData_ongpu_1d(const float *rbot1, const float *rbot2, float *output, int batchSize, int nOutputCols, int nOutputRows, int nOutputPlane, int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width_, int kernel_radius_, int kernel_size, int stride1, int stride2, int paddedbottomwidth, int paddedbottomheight, int nInputPlane, int corr_type_multiply, cudaStream_t stream)
173 | {
174 |
175 | dim3 threadsPerBlock(THREADS_PER_WARP * WARPS_PER_BLOCK);
176 |
177 | int shared_memory_per_block = (kernel_size*kernel_size)*nInputPlane;
178 |
179 | int outputCount = nOutputCols * nOutputRows * nOutputPlane;
180 | int outputThreadCount = outputCount;
181 |
182 | if (corr_type_multiply == 1) {
183 |
184 | dim3 totalBlocksCorr(nOutputCols, nOutputRows, batchSize);
185 |
186 | CorrelateData_1d<<>>(
187 | outputThreadCount,
188 | batchSize, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane, outputCount,
189 | max_displacement, x_shift,
190 | neighborhood_grid_width_, kernel_radius_, kernel_size,
191 | stride1, stride2,
192 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane,
193 | rbot1, rbot2, output
194 | );
195 | } else {
196 |
197 | for (int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++) {
198 |
199 | CorrelateDataSubtract_1d<<>>(
200 | outputThreadCount,
201 | batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane, outputCount,
202 | max_displacement, x_shift, neighborhood_grid_width_,
203 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2,
204 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane,
205 | rbot1, rbot2, output
206 | );
207 | }
208 | }
209 | }
210 |
211 | // == Correlation Backward Pass Kernel (For Blob 0)
212 |
213 | __global__ void CorrelateDataBackward0_1d(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels,
214 | int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
215 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int pbottomwidth, int pbottomheight, int bottomchannels, int bottomcount, int pad_size,
216 | float *bottom0diff, const float *bottom1, const float *topdiff)
217 | {
218 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
219 | int n = index % bottomchannels; //channels
220 | int l = (index / bottomchannels) % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
221 | int m = (index / bottomchannels / bottomwidth) % bottomheight; //h-pos
222 |
223 | //Get X,Y ranges and clamp
224 | // round_off is a trick to enable integer division with ceil, even for negative numbers
225 | // We use a large offset, for the inner part not to become negative.
226 | const int round_off = ROUND_OFF;
227 | const int round_off_s1 = stride1 * round_off;
228 |
229 | // We add round_off before_s1 the int division and subtract round_off after it, to ensure the formula matches ceil behavior:
230 | int xmin = (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement) / stride1
231 | int ymin = (m - 2*kernel_radius - 0 + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement) / stride1
232 |
233 | // Same here:
234 | int xmax = (l - max_displacement + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (l - max_displacement) / stride1
235 | int ymax = (m - 0 + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (m - max_displacement) / stride1
236 |
237 |
238 | float sum = 0;
239 | if(xmax>=0 && ymax>=0 && (xmin<=topwidth-1) && (ymin<=topheight-1))
240 | {
241 | xmin = max(0,xmin);
242 | xmax = min(topwidth-1,xmax);
243 |
244 | ymin = max(0,ymin);
245 | ymax = min(topheight-1,ymax);
246 |
247 | {
248 | for(int o = x_shift; o < x_shift + neighborhood_grid_width; o++) {
249 |
250 | // Get bottom1 data:
251 | int s2o = stride2 * o;
252 | int idxbot1 = ((item * pbottomheight + m) * pbottomwidth + (l+s2o)) * bottomchannels + n;
253 | float bot1tmp = bottom1[idxbot1]; // bottom1[l+s2o,m,n]
254 |
255 | // Index offset for topdiff in following loops:
256 | int op = (o-x_shift); // index [o,p]
257 | int idxopoffset = (item * topchannels + op);
258 |
259 | for(int y = ymin; y <= ymax; y++) {
260 | for(int x = xmin; x <= xmax; x++) {
261 | int idxtopdiff = (idxopoffset * topheight + y) * topwidth + x; // topdiff[x,y,o,p]
262 | sum += topdiff[idxtopdiff] * bot1tmp;
263 | }
264 | }
265 | }
266 | }
267 | }
268 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
269 | const int bot0index = ((n * bottomheight) + m) * bottomwidth + (l-pad_size);
270 | bottom0diff[bot0index + item*bottomcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
271 | }
272 |
273 | }
274 |
275 | // == Correlation Backward Pass Kernel (For Blob 1)
276 | __global__ void CorrelateDataBackward1_1d(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels,
277 | int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
278 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int pbottomwidth, int pbottomheight, int bottomchannels, int bottomcount, int pad_size,
279 | const float *bottom0, float *bottom1diff, const float *topdiff)
280 | {
281 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
282 | //int l = index % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
283 | //int m = (index / bottomwidth) % bottomheight + pad_size; //h-pos
284 | //int n = (index / bottomwidth / bottomheight) % bottomchannels; //channels
285 | int n = index % bottomchannels; //channels
286 | int l = (index / bottomchannels) % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
287 | int m = (index / bottomchannels / bottomwidth) % bottomheight; //h-pos
288 |
289 | // round_off is a trick to enable integer division with ceil, even for negative numbers
290 | // We use a large offset, for the inner part not to become negative.
291 | const int round_off = ROUND_OFF;
292 | const int round_off_s1 = stride1 * round_off;
293 |
294 | float sum = 0;
295 | {
296 | for(int o = x_shift; o < x_shift + neighborhood_grid_width; o++) {
297 |
298 | int s2o = stride2 * o;
299 |
300 | //Get X,Y ranges and clamp
301 | // We add round_off before_s1 the int division and subtract round_off after it, to ensure the formula matches ceil behavior:
302 | int xmin = (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
303 | int ymin = (m - 2*kernel_radius - 0 - 0 + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
304 |
305 | // Same here:
306 | int xmax = (l - max_displacement - s2o + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (l - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
307 | int ymax = (m - 0 - 0 + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (m - max_displacement - s2p) / stride1
308 |
309 | if(xmax>=0 && ymax>=0 && (xmin<=topwidth-1) && (ymin<=topheight-1))
310 | {
311 | xmin = max(0,xmin);
312 | xmax = min(topwidth-1,xmax);
313 |
314 | ymin = max(0,ymin);
315 | ymax = min(topheight-1,ymax);
316 |
317 | // Get bottom0 data:
318 | int idxbot0 = ((item * pbottomheight + m) * pbottomwidth + (l-s2o)) * bottomchannels + n;
319 | float bot0tmp = bottom0[idxbot0]; // bottom1[l+s2o,m,n]
320 |
321 | // Index offset for topdiff in following loops:
322 | int op = (o-x_shift); // index [o,p]
323 | int idxOpOffset = (item * topchannels + op);
324 |
325 | for(int y = ymin; y <= ymax; y++) {
326 | for(int x = xmin; x <= xmax; x++) {
327 | int idxtopdiff = (idxOpOffset * topheight + y) * topwidth + x; // topdiff[x,y,o,p]
328 | sum += topdiff[idxtopdiff] * bot0tmp;
329 | }
330 | }
331 | }
332 | }
333 | }
334 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
335 | const int bot1index = ((n * bottomheight) + m) * bottomwidth + (l-pad_size);
336 | bottom1diff[bot1index + item*bottomcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
337 | }
338 |
339 | }
340 |
341 | // == Correlation Kernel Subtraction
342 |
343 |
344 | // == Correlation Backward Pass Kernel (For Blob 0)
345 | __global__ void CorrelateDataBackward0Subtract_1d(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels,
346 | int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
347 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int pbottomwidth, int pbottomheight, int bottomchannels, int bottomcount, int pad_size,
348 | float *bottom0diff, const float *bottom0, const float *bottom1, const float *topdiff)
349 | {
350 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
351 | int l = index % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
352 | int m = (index / bottomwidth) % bottomheight; //h-pos
353 | int n = (index / bottomwidth / bottomheight) % bottomchannels; //channels
354 |
355 | //Get X,Y ranges and clamp
356 | // round_off is a trick to enable integer division with ceil, even for negative numbers
357 | // We use a large offset, for the inner part not to become negative.
358 | const int round_off = ROUND_OFF;
359 | const int round_off_s1 = stride1 * round_off;
360 |
361 | // We add round_off before_s1 the int division and subtract round_off after it, to ensure the formula matches ceil behavior:
362 | int xmin = (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement) / stride1
363 | int ymin = (m - 2*kernel_radius - 0 + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement) / stride1
364 |
365 | // Same here:
366 | int xmax = (l - max_displacement + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (l - max_displacement) / stride1
367 | int ymax = (m - 0 + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (m - max_displacement) / stride1
368 |
369 |
370 | float sum = 0;
371 | if(xmax>=0 && ymax>=0 && (xmin<=topwidth-1) && (ymin<=topheight-1))
372 | {
373 | xmin = max(0,xmin);
374 | xmax = min(topwidth-1,xmax);
375 |
376 | ymin = max(0,ymin);
377 | ymax = min(topheight-1,ymax);
378 |
379 | {
380 | for(int o = x_shift; o < x_shift + neighborhood_grid_width; o++) {
381 |
382 | // Get bottom1 data:
383 | int s2o = stride2 * o;
384 | int idxbot = ((item * pbottomheight + (m)) * pbottomwidth + (l+s2o)) * bottomchannels + n;
385 | float bot0tmp = bottom0[idxbot]; // bottom0[l+s2o,m,n]
386 | float bot1tmp = bottom1[idxbot]; // bottom1[l+s2o,m,n]
387 | float sign = (bot0tmp >= bot1tmp) ? float(1.0) : float(-1.0);
388 |
389 | // Index offset for topdiff in following loops:
390 | int op = (o-x_shift); // index [o,p]
391 | int idxopoffset = (item * topchannels + op);
392 |
393 | for(int y = ymin; y <= ymax; y++) {
394 | for(int x = xmin; x <= xmax; x++) {
395 | int idxtopdiff = (idxopoffset * topheight + y) * topwidth + x; // topdiff[x,y,o,p]
396 | sum += topdiff[idxtopdiff] * sign;
397 | }
398 | }
399 | }
400 | }
401 | }
402 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
403 | bottom0diff[index + item*bottomcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
404 | }
405 |
406 | }
407 |
408 |
409 | // == Correlation Backward Pass Kernel (For Blob 1)
410 | __global__ void CorrelateDataBackward1Subtract_1d(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels,
411 | int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
412 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int pbottomwidth, int pbottomheight, int bottomchannels, int bottomcount, int pad_size,
413 | const float *bottom0, const float *bottom1, float *bottom1diff, const float *topdiff)
414 | {
415 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
416 | int l = index % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
417 | int m = (index / bottomwidth) % bottomheight; //h-pos
418 | int n = (index / bottomwidth / bottomheight) % bottomchannels; //channels
419 |
420 | // round_off is a trick to enable integer division with ceil, even for negative numbers
421 | // We use a large offset, for the inner part not to become negative.
422 | const int round_off = ROUND_OFF;
423 | const int round_off_s1 = stride1 * round_off;
424 |
425 | float sum = 0;
426 | {
427 | for(int o = x_shift; o < x_shift + neighborhood_grid_width; o++) {
428 |
429 | int s2o = stride2 * o;
430 |
431 | //Get X,Y ranges and clamp
432 | // We add round_off before_s1 the int division and subtract round_off after it, to ensure the formula matches ceil behavior:
433 | int xmin = (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
434 | int ymin = (m - 2*kernel_radius - 0 - 0 + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
435 |
436 | // Same here:
437 | int xmax = (l - max_displacement - s2o + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (l - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
438 | int ymax = (m - 0 - 0 + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (m - max_displacement - s2p) / stride1
439 |
440 | if(xmax>=0 && ymax>=0 && (xmin<=topwidth-1) && (ymin<=topheight-1))
441 | {
442 | xmin = max(0,xmin);
443 | xmax = min(topwidth-1,xmax);
444 |
445 | ymin = max(0,ymin);
446 | ymax = min(topheight-1,ymax);
447 |
448 | // Get bottom0 data:
449 | int idxbot = ((item * pbottomheight + (m)) * pbottomwidth + (l-s2o)) * bottomchannels + n;
450 | float bot0tmp = bottom0[idxbot]; // bottom0[l+s2o,m,n]
451 | float bot1tmp = bottom1[idxbot]; // bottom1[l+s2o,m,n]
452 | float sign = (bot0tmp >= bot1tmp) ? float(-1.0) : float(1.0);
453 |
454 | // Index offset for topdiff in following loops:
455 | int op = (o-x_shift); // index [o,p]
456 | int idxOpOffset = (item * topchannels + op);
457 |
458 | for(int y = ymin; y <= ymax; y++) {
459 | for(int x = xmin; x <= xmax; x++) {
460 | int idxtopdiff = (idxOpOffset * topheight + y) * topwidth + x; // topdiff[x,y,o,p]
461 | sum += topdiff[idxtopdiff] * sign;
462 | }
463 | }
464 | }
465 | }
466 | }
467 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
468 | bottom1diff[index + item*bottomcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
469 | }
470 |
471 | }
472 |
473 | void CorrelateDataBackward_ongpu_1d(const float *rbot1, const float *rbot2, const float *gradOutput, float *gradInput1, float *gradInput2, int batchSize, int nOutputCols, int nOutputRows, int nOutputPlane, int max_displacement, int x_shift, int neighborhood_grid_width_, int kernel_radius_, int stride1, int stride2, int nInputCols, int nInputRows, int paddedbottomwidth, int paddedbottomheight, int nInputPlane, int pad_size, int corr_type_multiply, cudaStream_t stream)
474 | {
475 | int inputCount = nInputPlane * nInputRows * nInputCols;
476 | int botThreadCount = inputCount;
477 |
478 | if (corr_type_multiply == 1) {
479 |
480 | // == Run kernel Backward 0
481 | for (int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++) {
482 | //Bottom0
483 | CorrelateDataBackward0_1d<<>>(
484 | botThreadCount,
485 | batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane,
486 | max_displacement, x_shift, neighborhood_grid_width_,
487 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2, nInputCols, nInputRows,
488 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane, inputCount, pad_size,
489 | gradInput1, rbot2, gradOutput
490 | );
491 |
492 | }
493 |
494 | // == Run kernel Backward 1
495 | for (int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++) {
496 | CorrelateDataBackward1_1d<<>>(
497 | botThreadCount, batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane,
498 | max_displacement, x_shift, neighborhood_grid_width_,
499 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2, nInputCols, nInputRows,
500 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane, inputCount, pad_size,
501 | rbot1, gradInput2, gradOutput
502 | );
503 | }
504 |
505 | } else {
506 |
507 | for ( int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++ ) {
508 |
509 | //Bottom0
510 | CorrelateDataBackward0Subtract_1d<<>> (
511 | botThreadCount,
512 | batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane,
513 | max_displacement, x_shift, neighborhood_grid_width_,
514 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2, nInputCols, nInputRows,
515 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane, inputCount, pad_size,
516 | gradInput1, rbot1, rbot2, gradOutput
517 | );
518 | }
519 |
520 | for (int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++ ) {
521 |
522 | //Bottom0
523 | CorrelateDataBackward1Subtract_1d<<>>(
524 | botThreadCount,
525 | batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane,
526 | max_displacement, x_shift, neighborhood_grid_width_,
527 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2, nInputCols, nInputRows,
528 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane, inputCount, pad_size,
529 | rbot1, rbot2, gradInput2, gradOutput
530 | );
531 | }
532 | }
533 | }
534 |
535 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/external_packages/correlation-pytorch-master/correlation-pytorch/correlation_package/src/corr_cuda_kernel.cu:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #include
2 | #include
3 | #include
4 | #include
5 | #include "corr_cuda_kernel.h"
6 |
7 | #define ROUND_OFF 50000
8 |
9 | #define CUDA_NUM_THREADS 1024
10 | #define WARPS_PER_BLOCK 1
11 | #define THREADS_PER_WARP 32
12 |
13 | #define CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(i, n) for (int i = blockIdx.x * blockDim.x + threadIdx.x; i < (n); i += blockDim.x * gridDim.x)
14 |
15 | #define GET_BLOCKS(n, t) (n+t-1) / t
16 |
17 | // == Dimension rearrangement Kernel
18 | __global__ void blob_rearrange_kernel2(const float *in, float *out, int num, int channels, int width, int height, int widthheight, int padding, int pwidthheight)
19 | {
20 | int xy = blockIdx.x*blockDim.x + threadIdx.x;
21 | if(xy>=widthheight)
22 | return;
23 |
24 | int ch = blockIdx.y;
25 | int n = blockIdx.z;
26 |
27 |
28 | float value=in[(n*channels+ch)*widthheight+xy];
29 |
30 | __syncthreads();
31 |
32 | int xpad = (xy % width + padding);
33 | int ypad = (xy / width + padding);
34 | int xypad = ypad * (width+2*padding) + xpad;
35 |
36 | out[(n*pwidthheight+xypad)*channels + ch] = value;
37 | }
38 |
39 | void blob_rearrange_ongpu(const float *in, float *out, int num, int channels, int width, int height, int widthheight, int padding, int pwidthheight, cudaStream_t stream)
40 | {
41 | int threads_per_block=16;
42 | dim3 totalBlocksRearr((widthheight-1)/threads_per_block+1, channels, num);
43 |
44 | cudaError_t err;
45 |
46 | blob_rearrange_kernel2<<>>
47 | (in, out, num, channels, width, height, widthheight, padding, pwidthheight);
48 |
49 | err = cudaGetLastError();
50 | if(cudaSuccess != err)
51 | {
52 | fprintf(stderr, "cudaCheckError() failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(err));
53 | exit(-1);
54 | }
55 | }
56 |
57 | // == Correlation Kernel
58 |
59 | __global__ void CorrelateData(const int nthreads, int num, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels, int topcount,
60 | int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int kernel_size, int stride1, int stride2,
61 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int bottomchannels,
62 | const float *bottom0, const float *bottom1, float *top)
63 | {
64 | extern __shared__ char patch_data_char[];
65 |
66 | float *patch_data = (float *)patch_data_char;
67 |
68 | // First (upper left) position of kernel upper-left corner in current center position of neighborhood in image 1
69 | int x1 = blockIdx.x*stride1 + max_displacement;
70 | int y1 = blockIdx.y*stride1 + max_displacement;
71 | int item = blockIdx.z;
72 | int ch_off = threadIdx.x;
73 |
74 | // Load 3D patch into shared shared memory
75 | for(int j = 0; j < kernel_size; j++) { // HEIGHT
76 | for(int i = 0; i < kernel_size; i++) { // WIDTH
77 | int ji_off = ((j * kernel_size) + i) * bottomchannels;
78 | for(int ch = ch_off; ch < bottomchannels; ch += (WARPS_PER_BLOCK*THREADS_PER_WARP)) { // CHANNELS
79 | int idx1 = ((item * bottomheight + y1+j) * bottomwidth + x1+i) * bottomchannels + ch;
80 | int idxPatchData = ji_off + ch;
81 | patch_data[idxPatchData] = bottom0[idx1];
82 | }
83 | }
84 | }
85 |
86 | __syncthreads();
87 |
88 | __shared__ float sum[WARPS_PER_BLOCK*THREADS_PER_WARP];
89 |
90 | // Compute correlation
91 | for(int top_channel = 0; top_channel < topchannels; top_channel++) {
92 | sum[ch_off] = 0;
93 |
94 | int s2o = (top_channel % neighborhood_grid_width - neighborhood_grid_radius) * stride2;
95 | int s2p = (top_channel / neighborhood_grid_width - neighborhood_grid_radius) * stride2;
96 |
97 | for(int j = 0; j < kernel_size; j++) { // HEIGHT
98 | for(int i = 0; i < kernel_size; i++) { // WIDTH
99 | int ji_off = ((j * kernel_size) + i) * bottomchannels;
100 | for(int ch = ch_off; ch < bottomchannels; ch += (WARPS_PER_BLOCK*THREADS_PER_WARP)) { // CHANNELS
101 | int x2 = x1 + s2o;
102 | int y2 = y1 + s2p;
103 |
104 | int idxPatchData = ji_off + ch;
105 | int idx2 = ((item * bottomheight + y2+j) * bottomwidth + x2+i) * bottomchannels + ch;
106 |
107 | sum[ch_off] += patch_data[idxPatchData] * bottom1[idx2];
108 | }
109 | }
110 | }
111 |
112 | __syncthreads();
113 |
114 | if(ch_off == 0) {
115 | float total_sum = 0;
116 | for(int idx = 0; idx < WARPS_PER_BLOCK*THREADS_PER_WARP; idx++) {
117 | total_sum += sum[idx];
118 | }
119 | const int sumelems = kernel_size*kernel_size*bottomchannels;
120 | const int index = ((top_channel*topheight + blockIdx.y)*topwidth)+blockIdx.x;
121 | top[index + item*topcount] = total_sum / (float)sumelems;
122 | }
123 | }
124 |
125 |
126 | // Aggregate
127 | }
128 |
129 | __global__ void CorrelateDataSubtract(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels, int topcount,
130 | int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
131 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int bottomchannels,
132 | const float *bottom0, const float *bottom1, float *top)
133 | {
134 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
135 | int x = index % topwidth; //w-pos
136 | int y = (index / topwidth) % topheight; //h-pos
137 | int c = (index / topwidth / topheight) % topchannels; //channels
138 |
139 | // Offset of patch in image 2
140 | int s2o = (c % neighborhood_grid_width - neighborhood_grid_radius) * stride2;
141 | int s2p = (c / neighborhood_grid_width - neighborhood_grid_radius) * stride2;
142 |
143 | // First (upper left) position of kernel center in current neighborhood in image 1
144 | int x1 = x*stride1 + kernel_radius + max_displacement;
145 | int y1 = y*stride1 + kernel_radius + max_displacement;
146 |
147 | // Iterate through 3D patch
148 | float sum = 0;
149 | for(int j = -kernel_radius; j <= kernel_radius; j++) { // HEIGHT
150 | for(int i = -kernel_radius; i <= kernel_radius; i++) { // WIDTH
151 | for(int l = 0; l < bottomchannels; l++) { // CHANNELS
152 | // Calculate position in image 2
153 | int x2 = x1 + s2o;
154 | int y2 = y1 + s2p;
155 |
156 | // Indices in bottom data: (CH=l,W=x2,H=y2,N)
157 | int idx1 = ((item * bottomheight + y1+j) * bottomwidth + x1+i) * bottomchannels + l;
158 | int idx2 = ((item * bottomheight + y2+j) * bottomwidth + x2+i) * bottomchannels + l;
159 |
160 | // Do the correlation:
161 | sum += fabsf(bottom0[idx1] - bottom1[idx2]);
162 | }
163 | }
164 | }
165 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
166 | top[index + item*topcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
167 | }
168 |
169 | }
170 |
171 | void CorrelateData_ongpu(const float *rbot1, const float *rbot2, float *output, int batchSize, int nOutputCols, int nOutputRows, int nOutputPlane, int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius_, int neighborhood_grid_width_, int kernel_radius_, int kernel_size, int stride1, int stride2, int paddedbottomwidth, int paddedbottomheight, int nInputPlane, int corr_type_multiply, cudaStream_t stream)
172 | {
173 |
174 | dim3 threadsPerBlock(THREADS_PER_WARP * WARPS_PER_BLOCK);
175 |
176 | int shared_memory_per_block = (kernel_size*kernel_size)*nInputPlane;
177 |
178 | int outputCount = nOutputCols * nOutputRows * nOutputPlane;
179 | int outputThreadCount = outputCount;
180 |
181 | if (corr_type_multiply == 1) {
182 |
183 | dim3 totalBlocksCorr(nOutputCols, nOutputRows, batchSize);
184 |
185 | CorrelateData<<>>(
186 | outputThreadCount,
187 | batchSize, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane, outputCount,
188 | max_displacement, neighborhood_grid_radius_,
189 | neighborhood_grid_width_, kernel_radius_, kernel_size,
190 | stride1, stride2,
191 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane,
192 | rbot1, rbot2, output
193 | );
194 | } else {
195 |
196 | for (int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++) {
197 |
198 | CorrelateDataSubtract<<>>(
199 | outputThreadCount,
200 | batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane, outputCount,
201 | max_displacement, neighborhood_grid_radius_, neighborhood_grid_width_,
202 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2,
203 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane,
204 | rbot1, rbot2, output
205 | );
206 | }
207 | }
208 | }
209 |
210 | // == Correlation Backward Pass Kernel (For Blob 0)
211 |
212 | __global__ void CorrelateDataBackward0(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels,
213 | int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
214 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int pbottomwidth, int pbottomheight, int bottomchannels, int bottomcount, int pad_size,
215 | float *bottom0diff, const float *bottom1, const float *topdiff)
216 | {
217 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
218 | int n = index % bottomchannels; //channels
219 | int l = (index / bottomchannels) % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
220 | int m = (index / bottomchannels / bottomwidth) % bottomheight + pad_size; //h-pos
221 |
222 | //Get X,Y ranges and clamp
223 | // round_off is a trick to enable integer division with ceil, even for negative numbers
224 | // We use a large offset, for the inner part not to become negative.
225 | const int round_off = ROUND_OFF;
226 | const int round_off_s1 = stride1 * round_off;
227 |
228 | // We add round_off before_s1 the int division and subtract round_off after it, to ensure the formula matches ceil behavior:
229 | int xmin = (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement) / stride1
230 | int ymin = (m - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement) / stride1
231 |
232 | // Same here:
233 | int xmax = (l - max_displacement + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (l - max_displacement) / stride1
234 | int ymax = (m - max_displacement + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (m - max_displacement) / stride1
235 |
236 |
237 | float sum = 0;
238 | if(xmax>=0 && ymax>=0 && (xmin<=topwidth-1) && (ymin<=topheight-1))
239 | {
240 | xmin = max(0,xmin);
241 | xmax = min(topwidth-1,xmax);
242 |
243 | ymin = max(0,ymin);
244 | ymax = min(topheight-1,ymax);
245 |
246 | for(int p = -neighborhood_grid_radius; p <= neighborhood_grid_radius; p++) {
247 | for(int o = -neighborhood_grid_radius; o <= neighborhood_grid_radius; o++) {
248 |
249 | // Get bottom1 data:
250 | int s2o = stride2 * o;
251 | int s2p = stride2 * p;
252 | int idxbot1 = ((item * pbottomheight + (m+s2p)) * pbottomwidth + (l+s2o)) * bottomchannels + n;
253 | float bot1tmp = bottom1[idxbot1]; // bottom1[l+s2o,m+s2p,n]
254 |
255 | // Index offset for topdiff in following loops:
256 | int op = (p+neighborhood_grid_radius) * neighborhood_grid_width + (o+neighborhood_grid_radius); // index [o,p]
257 | int idxopoffset = (item * topchannels + op);
258 |
259 | for(int y = ymin; y <= ymax; y++) {
260 | for(int x = xmin; x <= xmax; x++) {
261 | int idxtopdiff = (idxopoffset * topheight + y) * topwidth + x; // topdiff[x,y,o,p]
262 | sum += topdiff[idxtopdiff] * bot1tmp;
263 | }
264 | }
265 | }
266 | }
267 | }
268 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
269 | const int bot0index = ((n * bottomheight) + (m-pad_size)) * bottomwidth + (l-pad_size);
270 | bottom0diff[bot0index + item*bottomcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
271 | }
272 |
273 | }
274 |
275 | // == Correlation Backward Pass Kernel (For Blob 1)
276 | __global__ void CorrelateDataBackward1(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels,
277 | int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
278 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int pbottomwidth, int pbottomheight, int bottomchannels, int bottomcount, int pad_size,
279 | const float *bottom0, float *bottom1diff, const float *topdiff)
280 | {
281 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
282 | //int l = index % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
283 | //int m = (index / bottomwidth) % bottomheight + pad_size; //h-pos
284 | //int n = (index / bottomwidth / bottomheight) % bottomchannels; //channels
285 | int n = index % bottomchannels; //channels
286 | int l = (index / bottomchannels) % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
287 | int m = (index / bottomchannels / bottomwidth) % bottomheight + pad_size; //h-pos
288 |
289 | // round_off is a trick to enable integer division with ceil, even for negative numbers
290 | // We use a large offset, for the inner part not to become negative.
291 | const int round_off = ROUND_OFF;
292 | const int round_off_s1 = stride1 * round_off;
293 |
294 | float sum = 0;
295 | for(int p = -neighborhood_grid_radius; p <= neighborhood_grid_radius; p++) {
296 | for(int o = -neighborhood_grid_radius; o <= neighborhood_grid_radius; o++) {
297 |
298 | int s2o = stride2 * o;
299 | int s2p = stride2 * p;
300 |
301 | //Get X,Y ranges and clamp
302 | // We add round_off before_s1 the int division and subtract round_off after it, to ensure the formula matches ceil behavior:
303 | int xmin = (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
304 | int ymin = (m - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2p + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
305 |
306 | // Same here:
307 | int xmax = (l - max_displacement - s2o + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (l - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
308 | int ymax = (m - max_displacement - s2p + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (m - max_displacement - s2p) / stride1
309 |
310 | if(xmax>=0 && ymax>=0 && (xmin<=topwidth-1) && (ymin<=topheight-1))
311 | {
312 | xmin = max(0,xmin);
313 | xmax = min(topwidth-1,xmax);
314 |
315 | ymin = max(0,ymin);
316 | ymax = min(topheight-1,ymax);
317 |
318 | // Get bottom0 data:
319 | int idxbot0 = ((item * pbottomheight + (m-s2p)) * pbottomwidth + (l-s2o)) * bottomchannels + n;
320 | float bot0tmp = bottom0[idxbot0]; // bottom1[l+s2o,m+s2p,n]
321 |
322 | // Index offset for topdiff in following loops:
323 | int op = (p+neighborhood_grid_radius) * neighborhood_grid_width + (o+neighborhood_grid_radius); // index [o,p]
324 | int idxOpOffset = (item * topchannels + op);
325 |
326 | for(int y = ymin; y <= ymax; y++) {
327 | for(int x = xmin; x <= xmax; x++) {
328 | int idxtopdiff = (idxOpOffset * topheight + y) * topwidth + x; // topdiff[x,y,o,p]
329 | sum += topdiff[idxtopdiff] * bot0tmp;
330 | }
331 | }
332 | }
333 | }
334 | }
335 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
336 | const int bot1index = ((n * bottomheight) + (m-pad_size)) * bottomwidth + (l-pad_size);
337 | bottom1diff[bot1index + item*bottomcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
338 | }
339 |
340 | }
341 |
342 | // == Correlation Kernel Subtraction
343 |
344 |
345 | // == Correlation Backward Pass Kernel (For Blob 0)
346 | __global__ void CorrelateDataBackward0Subtract(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels,
347 | int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
348 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int pbottomwidth, int pbottomheight, int bottomchannels, int bottomcount, int pad_size,
349 | float *bottom0diff, const float *bottom0, const float *bottom1, const float *topdiff)
350 | {
351 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
352 | int l = index % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
353 | int m = (index / bottomwidth) % bottomheight + pad_size; //h-pos
354 | int n = (index / bottomwidth / bottomheight) % bottomchannels; //channels
355 |
356 | //Get X,Y ranges and clamp
357 | // round_off is a trick to enable integer division with ceil, even for negative numbers
358 | // We use a large offset, for the inner part not to become negative.
359 | const int round_off = ROUND_OFF;
360 | const int round_off_s1 = stride1 * round_off;
361 |
362 | // We add round_off before_s1 the int division and subtract round_off after it, to ensure the formula matches ceil behavior:
363 | int xmin = (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement) / stride1
364 | int ymin = (m - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement) / stride1
365 |
366 | // Same here:
367 | int xmax = (l - max_displacement + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (l - max_displacement) / stride1
368 | int ymax = (m - max_displacement + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (m - max_displacement) / stride1
369 |
370 |
371 | float sum = 0;
372 | if(xmax>=0 && ymax>=0 && (xmin<=topwidth-1) && (ymin<=topheight-1))
373 | {
374 | xmin = max(0,xmin);
375 | xmax = min(topwidth-1,xmax);
376 |
377 | ymin = max(0,ymin);
378 | ymax = min(topheight-1,ymax);
379 |
380 | for(int p = -neighborhood_grid_radius; p <= neighborhood_grid_radius; p++) {
381 | for(int o = -neighborhood_grid_radius; o <= neighborhood_grid_radius; o++) {
382 |
383 | // Get bottom1 data:
384 | int s2o = stride2 * o;
385 | int s2p = stride2 * p;
386 | int idxbot = ((item * pbottomheight + (m+s2p)) * pbottomwidth + (l+s2o)) * bottomchannels + n;
387 | float bot0tmp = bottom0[idxbot]; // bottom0[l+s2o,m+s2p,n]
388 | float bot1tmp = bottom1[idxbot]; // bottom1[l+s2o,m+s2p,n]
389 | float sign = (bot0tmp >= bot1tmp) ? float(1.0) : float(-1.0);
390 |
391 | // Index offset for topdiff in following loops:
392 | int op = (p+neighborhood_grid_radius) * neighborhood_grid_width + (o+neighborhood_grid_radius); // index [o,p]
393 | int idxopoffset = (item * topchannels + op);
394 |
395 | for(int y = ymin; y <= ymax; y++) {
396 | for(int x = xmin; x <= xmax; x++) {
397 | int idxtopdiff = (idxopoffset * topheight + y) * topwidth + x; // topdiff[x,y,o,p]
398 | sum += topdiff[idxtopdiff] * sign;
399 | }
400 | }
401 | }
402 | }
403 | }
404 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
405 | bottom0diff[index + item*bottomcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
406 | }
407 |
408 | }
409 |
410 |
411 | // == Correlation Backward Pass Kernel (For Blob 1)
412 | __global__ void CorrelateDataBackward1Subtract(const int nthreads, int num, int item, int topwidth, int topheight, int topchannels,
413 | int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius, int neighborhood_grid_width, int kernel_radius, int stride1, int stride2,
414 | int bottomwidth, int bottomheight, int pbottomwidth, int pbottomheight, int bottomchannels, int bottomcount, int pad_size,
415 | const float *bottom0, const float *bottom1, float *bottom1diff, const float *topdiff)
416 | {
417 | CUDA_KERNEL_LOOP(index, nthreads) {
418 | int l = index % bottomwidth + pad_size; //w-pos
419 | int m = (index / bottomwidth) % bottomheight + pad_size; //h-pos
420 | int n = (index / bottomwidth / bottomheight) % bottomchannels; //channels
421 |
422 | // round_off is a trick to enable integer division with ceil, even for negative numbers
423 | // We use a large offset, for the inner part not to become negative.
424 | const int round_off = ROUND_OFF;
425 | const int round_off_s1 = stride1 * round_off;
426 |
427 | float sum = 0;
428 | for(int p = -neighborhood_grid_radius; p <= neighborhood_grid_radius; p++) {
429 | for(int o = -neighborhood_grid_radius; o <= neighborhood_grid_radius; o++) {
430 |
431 | int s2o = stride2 * o;
432 | int s2p = stride2 * p;
433 |
434 | //Get X,Y ranges and clamp
435 | // We add round_off before_s1 the int division and subtract round_off after it, to ensure the formula matches ceil behavior:
436 | int xmin = (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
437 | int ymin = (m - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2p + round_off_s1 - 1) / stride1 + 1 - round_off; // ceil (l - 2*kernel_radius - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
438 |
439 | // Same here:
440 | int xmax = (l - max_displacement - s2o + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (l - max_displacement - s2o) / stride1
441 | int ymax = (m - max_displacement - s2p + round_off_s1) / stride1 - round_off; // floor (m - max_displacement - s2p) / stride1
442 |
443 | if(xmax>=0 && ymax>=0 && (xmin<=topwidth-1) && (ymin<=topheight-1))
444 | {
445 | xmin = max(0,xmin);
446 | xmax = min(topwidth-1,xmax);
447 |
448 | ymin = max(0,ymin);
449 | ymax = min(topheight-1,ymax);
450 |
451 | // Get bottom0 data:
452 | int idxbot = ((item * pbottomheight + (m-s2p)) * pbottomwidth + (l-s2o)) * bottomchannels + n;
453 | float bot0tmp = bottom0[idxbot]; // bottom0[l+s2o,m+s2p,n]
454 | float bot1tmp = bottom1[idxbot]; // bottom1[l+s2o,m+s2p,n]
455 | float sign = (bot0tmp >= bot1tmp) ? float(-1.0) : float(1.0);
456 |
457 | // Index offset for topdiff in following loops:
458 | int op = (p+neighborhood_grid_radius) * neighborhood_grid_width + (o+neighborhood_grid_radius); // index [o,p]
459 | int idxOpOffset = (item * topchannels + op);
460 |
461 | for(int y = ymin; y <= ymax; y++) {
462 | for(int x = xmin; x <= xmax; x++) {
463 | int idxtopdiff = (idxOpOffset * topheight + y) * topwidth + x; // topdiff[x,y,o,p]
464 | sum += topdiff[idxtopdiff] * sign;
465 | }
466 | }
467 | }
468 | }
469 | }
470 | const int sumelems = (kernel_radius*2+1)*(kernel_radius*2+1)*bottomchannels;
471 | bottom1diff[index + item*bottomcount] = sum / (float)sumelems;
472 | }
473 |
474 | }
475 |
476 | void CorrelateDataBackward_ongpu(const float *rbot1, const float *rbot2, const float *gradOutput, float *gradInput1, float *gradInput2, int batchSize, int nOutputCols, int nOutputRows, int nOutputPlane, int max_displacement, int neighborhood_grid_radius_, int neighborhood_grid_width_, int kernel_radius_, int stride1, int stride2, int nInputCols, int nInputRows, int paddedbottomwidth, int paddedbottomheight, int nInputPlane, int pad_size, int corr_type_multiply, cudaStream_t stream)
477 | {
478 | int inputCount = nInputPlane * nInputRows * nInputCols;
479 | int botThreadCount = inputCount;
480 |
481 | if (corr_type_multiply == 1) {
482 |
483 | // == Run kernel Backward 0
484 | for (int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++) {
485 | //Bottom0
486 | CorrelateDataBackward0<<>>(
487 | botThreadCount,
488 | batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane,
489 | max_displacement, neighborhood_grid_radius_, neighborhood_grid_width_,
490 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2, nInputCols, nInputRows,
491 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane, inputCount, pad_size,
492 | gradInput1, rbot2, gradOutput
493 | );
494 |
495 | }
496 |
497 | // == Run kernel Backward 1
498 | for (int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++) {
499 | CorrelateDataBackward1<<>>(
500 | botThreadCount, batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane,
501 | max_displacement, neighborhood_grid_radius_, neighborhood_grid_width_,
502 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2, nInputCols, nInputRows,
503 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane, inputCount, pad_size,
504 | rbot1, gradInput2, gradOutput
505 | );
506 | }
507 |
508 | } else {
509 |
510 | for ( int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++ ) {
511 |
512 | //Bottom0
513 | CorrelateDataBackward0Subtract<<>> (
514 | botThreadCount,
515 | batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane,
516 | max_displacement, neighborhood_grid_radius_, neighborhood_grid_width_,
517 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2, nInputCols, nInputRows,
518 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane, inputCount, pad_size,
519 | gradInput1, rbot1, rbot2, gradOutput
520 | );
521 | }
522 |
523 | for (int n = 0; n < batchSize; n++ ) {
524 |
525 | //Bottom0
526 | CorrelateDataBackward1Subtract<<>>(
527 | botThreadCount,
528 | batchSize, n, nOutputCols, nOutputRows, nOutputPlane,
529 | max_displacement, neighborhood_grid_radius_, neighborhood_grid_width_,
530 | kernel_radius_, stride1, stride2, nInputCols, nInputRows,
531 | paddedbottomwidth, paddedbottomheight, nInputPlane, inputCount, pad_size,
532 | rbot1, rbot2, gradInput2, gradOutput
533 | );
534 | }
535 | }
536 | }
537 |
538 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
|