├── images
├── ThematicPoem.png
└── ThematicAnalysis.png
├── web_app
├── requirements_app.txt
├── config.py
├── core
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── predictor.py
├── pages
│ ├── Analyze_Poem.py
│ └── Explore_Corpus.py
└── app.py
├── LICENSE
├── .gitignore
├── .dvcignore
├── dvc.yaml
├── src
├── __init__.py
├── utils.py
├── dataset.py
├── data_processing.py
├── segmentation.py
├── hpo.py
├── embedding.py
├── trainer.py
└── model.py
├── test
├── test_data_processing.py
└── test_model.py
└── README.md
/images/ThematicPoem.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NoorBayan/Maqasid/HEAD/images/ThematicPoem.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/ThematicAnalysis.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/NoorBayan/Maqasid/HEAD/images/ThematicAnalysis.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/web_app/requirements_app.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | streamlit==1.33.0
2 | pandas==2.2.1
3 | plotly==5.20.0
4 | torch==2.2.1
5 | scikit-learn==1.4.1.post1
6 | gensim==4.3.2
7 | numpy==1.26.4
8 | pyfarasa==0.1.3
9 | PyYAML==6.0.1
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2025 NoorBayan
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Python Virtual Environments
2 | venv/
3 | /venv/
4 | .venv/
5 | /.venv/
6 | env/
7 | /env/
8 | .env/
9 | /.env/
10 | ENV/
11 | /ENV/
12 |
13 | # Python Bytecode and Cache
14 | __pycache__/
15 | *.pyc
16 | *.pyo
17 | *.pyd
18 | .Python
19 |
20 | # Environment Variables
21 | # The .env.example file SHOULD be committed.
22 | .env
23 | .env.*
24 | !.env.example
25 |
26 | # Large Data and Model Files (Handled by DVC)
27 | # DVC creates small .dvc pointer files which SHOULD be committed.
28 | /data/
29 | /saved_models/
30 |
31 | # Keep the directory structure but ignore the contents initially.
32 | !/data/.gitkeep
33 | !/saved_models/.gitkeep
34 |
35 | # DVC internal cache directory. This should NEVER be committed.
36 | .dvc/cache
37 |
38 | # IDE and Editor Configuration Files
39 | .idea/
40 | .vscode/
41 | *.swp
42 | *.swo
43 |
44 | # Operating System Generated Files
45 | .DS_Store
46 | Thumbs.db
47 | ._*
48 |
49 | # Build, Distribution, and Installation Artifacts
50 | build/
51 | dist/
52 | *.egg-info/
53 | *.egg
54 | *.whl
55 |
56 | # Test and Coverage Reports
57 | .pytest_cache/
58 | htmlcov/
59 | .coverage
60 | *.cover
61 |
62 | # Temporary Files and Logs
63 | *.log
64 | logs/
65 | *.tmp
66 | temp/
67 |
68 | # HPO and Notebook Checkpoints
69 | hpo_results/
70 | hpo_run_example/
71 | .ipynb_checkpoints/
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.dvcignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # ==========================================================
2 | # DVC Ignore File
3 | # ==========================================================
4 | # This file specifies files and directories that DVC should
5 | # ignore and not attempt to track. The syntax is the same
6 | # as .gitignore.
7 |
8 | # --- Directories managed by Git ---
9 | # We explicitly tell DVC to ignore our source code, tests, and web app code,
10 | # as these are handled by Git.
11 | src/
12 | tests/
13 | web_app/
14 | pages/
15 | core/
16 | notebooks/
17 |
18 | # --- Project Configuration and Metadata Files ---
19 | # These are small text files tracked by Git.
20 | .gitignore
21 | .dvcignore
22 | dvc.yaml
23 | dvc.lock
24 | README.md
25 | LICENSE
26 | Makefile
27 | requirements.txt
28 | requirements_app.txt
29 | config.yaml
30 | params.yaml # Common file for DVC pipeline parameters
31 |
32 | # --- Python-related files and directories ---
33 | # These should be ignored by both Git and DVC.
34 | __pycache__/
35 | *.pyc
36 | venv/
37 | .env
38 | .env.example
39 |
40 | # --- Temporary Files and Logs ---
41 | # Ignore any log files generated during pipeline runs.
42 | *.log
43 | logs/
44 |
45 | # --- HPO and Experimentation Artifacts ---
46 | # Ignore temporary outputs from HPO runs that are not the final model.
47 | # The final selected model should be added to DVC manually or via the pipeline.
48 | hpo_results/
49 | hpo_run_example/
50 |
51 | # --- Locally Generated Plots and Reports ---
52 | # Any plots or reports generated for local analysis that are not part of the
53 | # official pipeline outputs.
54 | local_plots/
55 | *.png
56 | *.html
57 |
58 | # --- IDE and OS-specific files ---
59 | .idea/
60 | .vscode/
61 | *.DS_Store
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dvc.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # ==========================================================
2 | # DVC Pipeline Definition
3 | # ==========================================================
4 | # This file defines the stages of the machine learning pipeline.
5 | # To run the entire pipeline, use the command `dvc repro`.
6 |
7 | stages:
8 | # --- Stage 1: Preprocess Raw Data ---
9 | preprocess:
10 | cmd: python scripts/01_preprocess_data.py --input data/raw/diwan_corpus.csv --output data/processed/preprocessed_poems.csv
11 | deps:
12 | - data/raw/diwan_corpus.csv
13 | - scripts/01_preprocess_data.py
14 | - src/poetry_classifier/data_processing.py
15 | outs:
16 | - data/processed/preprocessed_poems.csv
17 |
18 | # --- Stage 2: Train FastText Embeddings ---
19 | train_embeddings:
20 | cmd: python scripts/02_train_embeddings.py --corpus data/processed/preprocessed_poems.csv --output saved_models/embeddings/fasttext_poetry.bin --vector-size ${train_embeddings.vector_size} --epochs ${train_embeddings.epochs}
21 | deps:
22 | - data/processed/preprocessed_poems.csv
23 | - scripts/02_train_embeddings.py
24 | - src/poetry_classifier/embedding.py
25 | params:
26 | - train_embeddings.vector_size
27 | - train_embeddings.epochs
28 | outs:
29 | - saved_models/embeddings/fasttext_poetry.bin
30 |
31 | # --- Stage 3: Prepare Final Datasets (including segmentation and splitting) ---
32 | prepare_final_data:
33 | cmd: python scripts/03_prepare_final_data.py --input data/processed/preprocessed_poems.csv --embedder saved_models/embeddings/fasttext_poetry.bin --output-dir data/annotated --eps ${segment_and_embed.eps}
34 | deps:
35 | - data/processed/preprocessed_poems.csv
36 | - saved_models/embeddings/fasttext_poetry.bin
37 | - scripts/03_prepare_final_data.py
38 | - src/poetry_classifier/segmentation.py
39 | params:
40 | - segment_and_embed.eps
41 | - segment_and_embed.min_samples
42 | outs:
43 | - data/annotated/train.csv
44 | - data/annotated/validation.csv
45 | - data/annotated/test.csv
46 |
47 | # --- Stage 4: Train the Final Classifier Model ---
48 | train_model:
49 | cmd: python scripts/05_train_final_model.py --train-data data/annotated/train.csv --val-data data/annotated/validation.csv --output-dir saved_models/classifier --params-file params.yaml
50 | deps:
51 | - data/annotated/train.csv
52 | - data/annotated/validation.csv
53 | - scripts/05_train_final_model.py
54 | - src/poetry_classifier/model.py
55 | - src/poetry_classifier/trainer.py
56 | - src/poetry_classifier/dataset.py
57 | params:
58 | - train_model
59 | outs:
60 | - saved_models/classifier/best_poetry_classifier.pth
61 | - saved_models/classifier/model_config.json
62 | - reports/training_history.json
63 |
64 | # --- Stage 5: Evaluate the Final Model on the Test Set ---
65 | evaluate:
66 | cmd: python scripts/evaluate.py --model-dir saved_models/classifier --test-data data/annotated/test.csv --output-file reports/metrics.json
67 | deps:
68 | - saved_models/classifier/best_poetry_classifier.pth
69 | - data/annotated/test.csv
70 | - scripts/evaluate.py
71 | metrics:
72 | - reports/metrics.json:
73 | cache: false
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | """
4 | Poetry Classifier Package
5 | =========================
6 |
7 | This package provides a comprehensive toolkit for multi-label thematic classification
8 | of Arabic poetry. It includes modules for data processing, embedding, segmentation,
9 | model definition, and training.
10 |
11 | To get started, you can directly import the main classes from this top-level package.
12 |
13 | Example:
14 | from poetry_classifier import (
15 | PoetryPreprocessor,
16 | PoetryEmbedder,
17 | PoemSegmenter,
18 | HybridPoetryClassifier,
19 | ModelTrainer,
20 | PoetryThematicDataset
21 | )
22 |
23 | This __init__.py file handles:
24 | - Defining package-level metadata like version and author.
25 | - Setting up a default logger for the package.
26 | - Making key classes and functions available at the top level for a cleaner API.
27 | """
28 |
29 | import logging
30 | import os
31 |
32 | # --- Package Metadata ---
33 | # This is a good practice for package management and distribution.
34 | __version__ = "1.0.0"
35 | __author__ = "Your Name / Your Team"
36 | __email__ = "your.email@example.com"
37 |
38 |
39 | # --- Setup a Null Logger ---
40 | # This prevents log messages from being propagated to the root logger if the
41 | # library user has not configured logging. It's a standard practice for libraries.
42 | # The user of the library can then configure logging as they see fit.
43 | logging.getLogger(__name__).addHandler(logging.NullHandler())
44 |
45 |
46 | # --- Cleaner API: Import key classes to the top level ---
47 | # This allows users to import classes directly from the package,
48 | # e.g., `from poetry_classifier import PoetryPreprocessor`
49 | # instead of `from poetry_classifier.data_processing import PoetryPreprocessor`.
50 |
51 | # A try-except block is used here to handle potential circular imports or
52 | # missing dependencies gracefully, although it's less likely with a flat structure.
53 | try:
54 | from .data_processing import PoetryPreprocessor
55 | from .embedding import PoetryEmbedder
56 | from .segmentation import PoemSegmenter
57 | from .model import HybridPoetryClassifier
58 | from .dataset import PoetryThematicDataset
59 | from .trainer import ModelTrainer
60 | from .utils import setup_logging, set_seed, load_config
61 |
62 | except ImportError as e:
63 | # This error might occur if a dependency is not installed.
64 | # For example, if `pyfarasa` is missing, `data_processing` might fail to import.
65 | logging.getLogger(__name__).warning(
66 | f"Could not import all modules from the poetry_classifier package. "
67 | f"Please ensure all dependencies are installed. Original error: {e}"
68 | )
69 |
70 | # --- Define what is exposed with `from poetry_classifier import *` ---
71 | # It's a good practice to explicitly define `__all__` to control what gets imported.
72 | __all__ = [
73 | # Metadata
74 | "__version__",
75 | "__author__",
76 | "__email__",
77 |
78 | # Core Classes
79 | "PoetryPreprocessor",
80 | "PoetryEmbedder",
81 | "PoemSegmenter",
82 | "HybridPoetryClassifier",
83 | "PoetryThematicDataset",
84 | "ModelTrainer",
85 |
86 | # Utility Functions
87 | "setup_logging",
88 | "set_seed",
89 | "load_config"
90 | ]
91 |
92 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
93 | logger.info(f"Poetry Classifier package version {__version__} loaded.")
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/web_app/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import os
4 | import logging
5 | from pathlib import Path
6 |
7 | # Configure a logger specific to the configuration module
8 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
9 |
10 | # --- Dynamic Path Configuration ---
11 | # This is the most robust way to handle paths. It ensures that no matter where
12 | # you run the app from (e.g., from the root directory or from within web_app),
13 | # the paths to your data and models will always be correct.
14 |
15 | try:
16 | # The base directory of the entire project (the parent of 'src' and 'web_app')
17 | # It goes up two levels from this file's location (web_app/config.py -> web_app -> project_root)
18 | PROJECT_ROOT = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent.parent
19 | except NameError:
20 | # Fallback for interactive environments like Jupyter notebooks where __file__ is not defined
21 | PROJECT_ROOT = Path('.').resolve()
22 |
23 | logger.info(f"Project Root determined as: {PROJECT_ROOT}")
24 |
25 |
26 | # --- Helper function for path validation ---
27 | def validate_path(path: Path, description: str):
28 | """Checks if a given path exists and logs a warning if it doesn't."""
29 | if not path.exists():
30 | logger.warning(
31 | f"Configuration Warning: The path for '{description}' does not exist. "
32 | f"Path: '{path}'"
33 | )
34 | return path
35 |
36 |
37 | # ==============================================================================
38 | # 1. MODEL AND DATA PATHS CONFIGURATION
39 | # ==============================================================================
40 | # All paths are constructed relative to the PROJECT_ROOT.
41 |
42 | # --- Saved Models Paths ---
43 | SAVED_MODELS_DIR = PROJECT_ROOT / "saved_models"
44 |
45 | # Classifier model
46 | CLASSIFIER_MODEL_PATH = validate_path(
47 | SAVED_MODELS_DIR / "classifier" / "best_poetry_classifier.pth",
48 | "Classifier Model Weights"
49 | )
50 | CLASSIFIER_CONFIG_PATH = validate_path(
51 | SAVED_MODELS_DIR / "classifier" / "model_config.json",
52 | "Classifier Model Configuration"
53 | )
54 |
55 | # Embedding model
56 | EMBEDDING_MODEL_PATH = validate_path(
57 | SAVED_MODELS_DIR / "embeddings" / "fasttext_poetry.bin",
58 | "FastText Embedding Model"
59 | )
60 |
61 |
62 | # --- Data and Schema Paths ---
63 | DATA_DIR = PROJECT_ROOT / "data"
64 |
65 | # The main annotated corpus for the exploration dashboard
66 | ANNOTATED_CORPUS_PATH = validate_path(
67 | DATA_DIR / "annotated" / "diwan_corpus_annotated.csv",
68 | "Annotated Corpus CSV"
69 | )
70 |
71 | # The hierarchical schema file for mapping labels to names
72 | LABEL_SCHEMA_PATH = validate_path(
73 | DATA_DIR / "schema" / "thematic_schema.json",
74 | "Thematic Schema JSON"
75 | )
76 |
77 | # Example poems for the analysis page
78 | EXAMPLE_POEMS_PATH = validate_path(
79 | PROJECT_ROOT / "web_app" / "static" / "example_poems.json",
80 | "Example Poems JSON"
81 | )
82 |
83 |
84 | # ==============================================================================
85 | # 2. MODEL AND PREDICTION PARAMETERS
86 | # ==============================================================================
87 |
88 | # --- Segmentation Parameters ---
89 | # Hyperparameters for the DBSCAN segmenter used in the predictor.
90 | # These should ideally match the values that yielded the best results in your research.
91 | SEGMENTER_EPS = 0.4
92 | SEGMENTER_MIN_SAMPLES = 1
93 |
94 |
95 | # --- Classification Parameters ---
96 | # The confidence threshold for a theme to be considered "predicted".
97 | # A value between 0.0 and 1.0.
98 | CLASSIFICATION_THRESHOLD = 0.5
99 |
100 |
101 | # ==============================================================================
102 | # 3. WEB APPLICATION UI CONFIGURATION
103 | # ==============================================================================
104 |
105 | # --- Page Titles and Icons ---
106 | # Centralize UI elements for consistency across the app.
107 | APP_TITLE = "Arabic Poetry Thematic Classifier"
108 | APP_ICON = "📜"
109 |
110 | # Page-specific configurations
111 | PAGE_CONFIG = {
112 | "home": {
113 | "title": APP_TITLE,
114 | "icon": APP_ICON
115 | },
116 | "analyze_poem": {
117 | "title": "Analyze a Poem",
118 | "icon": "✍️"
119 | },
120 | "explore_corpus": {
121 | "title": "Explore The Corpus",
122 | "icon": "📚"
123 | }
124 | }
125 |
126 |
127 | # --- UI Defaults ---
128 | # Default values for interactive widgets.
129 | DEFAULT_TOP_K_THEMES = 7
130 | MAX_TOP_K_THEMES = 20
131 |
132 |
133 | # --- External Links ---
134 | # Centralize URLs for easy updates.
135 | RESEARCH_PAPER_URL = "https://your-paper-link.com"
136 | GITHUB_REPO_URL = "https://github.com/your-username/your-repo"
137 |
138 | # ==============================================================================
139 | # END OF CONFIGURATION
140 | # ==============================================================================
141 |
142 | # You could add a final check here if needed, for example:
143 | # if not all([CLASSIFIER_MODEL_PATH.exists(), CLASSIFIER_CONFIG_PATH.exists()]):
144 | # raise FileNotFoundError("Critical model files are missing. The application cannot start.")
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/test_data_processing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import json
4 | import os
5 | import sys
6 | from unittest.mock import MagicMock, patch
7 |
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import pandas as pd
10 | import pytest
11 |
12 | # Add the source directory to the Python path
13 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..', 'src')))
14 |
15 | from poetry_classifier.data_processing import PoetryPreprocessor
16 |
17 | # --- Helper Function to Load Test Data ---
18 |
19 | def load_test_data(file_name: str = "processing_examples.json"):
20 | """Loads test examples from a JSON file."""
21 | current_dir = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
22 | file_path = os.path.join(current_dir, "test_data", file_name)
23 | try:
24 | with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
25 | return json.load(f)
26 | except FileNotFoundError:
27 | pytest.fail(f"Test data file not found at {file_path}. Please create it.")
28 | except json.JSONDecodeError:
29 | pytest.fail(f"Could not decode JSON from {file_path}. Please check its syntax.")
30 |
31 | # Load all test data once, making it available to all tests
32 | test_data = load_test_data()
33 |
34 | # --- Fixtures for Pytest ---
35 |
36 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
37 | def segmentation_map_from_data():
38 | """
39 | Creates the segmentation map for the mock segmenter directly from the test data file.
40 | This fixture is now the single source of truth for the mock's behavior.
41 | """
42 | pipeline_cases = test_data.get("full_pipeline", [])
43 | if not pipeline_cases:
44 | pytest.fail("No 'full_pipeline' cases found in test data file.")
45 |
46 | return {
47 | case['expected_pre_segmentation']: case['expected_final']
48 | for case in pipeline_cases
49 | }
50 |
51 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
52 | def mock_farasa_segmenter(segmentation_map_from_data):
53 | """Mocks the FarasaSegmenter in a purely data-driven way using the segmentation map."""
54 | mock_segmenter = MagicMock()
55 |
56 | def mock_segment(text_to_segment):
57 | return segmentation_map_from_data.get(text_to_segment, text_to_segment)
58 |
59 | mock_segmenter.segment.side_effect = mock_segment
60 | return mock_segmenter
61 |
62 |
63 | @pytest.fixture
64 | def preprocessor(mock_farasa_segmenter):
65 | """Provides a PoetryPreprocessor instance with a mocked FarasaSegmenter."""
66 | with patch('poetry_classifier.data_processing.FarasaSegmenter', return_value=mock_farasa_segmenter):
67 | yield PoetryPreprocessor()
68 |
69 |
70 | # --- Test Cases ---
71 |
72 | class TestPoetryPreprocessor:
73 |
74 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("case", test_data.get("cleaning", []), ids=[c['name'] for c in test_data.get("cleaning", [])])
75 | def test_clean_text(self, preprocessor, case):
76 | """Test the _clean_text method using data-driven cases."""
77 | if 'input' in case and case['input'] is None:
78 | assert preprocessor._clean_text(None) == case['expected']
79 | else:
80 | assert preprocessor._clean_text(case['input']) == case['expected']
81 |
82 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("case", test_data.get("normalization", []), ids=[c['name'] for c in test_data.get("normalization", [])])
83 | def test_normalize_arabic(self, preprocessor, case):
84 | """Test the _normalize_arabic method using data-driven cases."""
85 | assert preprocessor._normalize_arabic(case['input']) == case['expected']
86 |
87 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("case", test_data.get("stopwords", []), ids=[c['name'] for c in test_data.get("stopwords", [])])
88 | def test_remove_stopwords(self, preprocessor, case):
89 | """Test the _remove_stopwords method using data-driven cases."""
90 | assert preprocessor._remove_stopwords(case['input']) == case['expected']
91 |
92 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("case", test_data.get("full_pipeline", []), ids=[c['name'] for c in test_data.get("full_pipeline", [])])
93 | def test_process_text_full_pipeline(self, preprocessor, case):
94 | """Test the end-to-end process_text method using purely data-driven cases."""
95 | processed_output = preprocessor.process_text(case['input'])
96 | assert processed_output == case['expected_final']
97 |
98 | def test_process_dataframe(self, preprocessor):
99 | """Test processing a full pandas DataFrame in a data-driven way."""
100 | pipeline_cases = test_data.get("full_pipeline", [])
101 |
102 | sample_data = {
103 | 'id': [i+1 for i in range(len(pipeline_cases))],
104 | 'raw_verse': [case['input'] for case in pipeline_cases]
105 | }
106 | df = pd.DataFrame(sample_data)
107 |
108 | processed_df = preprocessor.process_dataframe(df, text_column='raw_verse')
109 |
110 | assert 'processed_text' in processed_df.columns
111 | assert len(processed_df) == len(pipeline_cases)
112 | for i, case in enumerate(pipeline_cases):
113 | assert processed_df.loc[i, 'processed_text'] == case['expected_final']
114 |
115 | def test_process_dataframe_with_missing_column(self, preprocessor):
116 | """Test that processing a DataFrame with a missing column raises a ValueError."""
117 | df = pd.DataFrame({'id': [1], 'another_col': ['text']})
118 |
119 | with pytest.raises(ValueError, match="Column 'non_existent_column' not found"):
120 | preprocessor.process_dataframe(df, text_column='non_existent_column')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/web_app/core/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import logging
4 | import time
5 |
6 | import pandas as pd
7 | import streamlit as st
8 |
9 | # Assuming your predictor is in the core directory relative to the web_app folder
10 | from core.predictor import PoetryPredictor
11 |
12 | # Configure logger for this page
13 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
14 |
15 | # --- Page-Specific Configuration ---
16 | st.set_page_config(
17 | page_title="Analyze Poem - Arabic Poetry Classifier",
18 | page_icon="✍️",
19 | layout="wide",
20 | )
21 |
22 | # --- Helper Functions ---
23 |
24 | @st.cache_resource
25 | def get_predictor():
26 | """
27 | Factory function to load and cache the PoetryPredictor instance.
28 | This ensures the model is loaded only once across all pages of the app.
29 | """
30 | try:
31 | return PoetryPredictor()
32 | except Exception as e:
33 | st.error(f"Fatal Error: Could not initialize the model predictor. Please check logs. Error: {e}")
34 | logger.error(f"Failed to load predictor: {e}", exc_info=True)
35 | return None
36 |
37 | def display_results(results: list):
38 | """
39 | Renders the prediction results in a structured and user-friendly format.
40 | """
41 | if not results:
42 | st.warning("The model did not predict any themes above the confidence threshold for the given text.")
43 | return
44 |
45 | st.success("Analysis Complete!")
46 |
47 | # Create a DataFrame for better visualization
48 | # Convert probability to a more readable format
49 | df_data = [
50 | {"Theme": r["theme"], "Confidence": f"{r['probability']:.2%}"}
51 | for r in results
52 | ]
53 | df = pd.DataFrame(df_data)
54 |
55 | st.markdown("#### Predicted Themes:")
56 |
57 | # Use columns for a cleaner layout
58 | col1, col2 = st.columns([2, 1])
59 |
60 | with col1:
61 | st.dataframe(df, use_container_width=True, hide_index=True)
62 |
63 | with col2:
64 | top_theme = results[0]["theme"]
65 | top_prob = results[0]["probability"]
66 | st.metric(label="Top Predicted Theme", value=top_theme, delta=f"{top_prob:.2%}")
67 | st.info("Confidence indicates the model's certainty for each predicted theme.")
68 |
69 | # --- Main Page UI and Logic ---
70 |
71 | def main():
72 | """Main function to render the 'Analyze Poem' page."""
73 |
74 | st.title("✍️ Analyze a New Poem")
75 | st.markdown("Enter the verses of an Arabic poem below to classify its thematic content. "
76 | "For best results, please place each verse on a new line.")
77 |
78 | # --- Load Predictor ---
79 | predictor = get_predictor()
80 | if not predictor:
81 | st.stop() # Stop execution of the page if the predictor failed to load
82 |
83 | # --- UI Components for Analysis ---
84 | st.markdown("---")
85 |
86 | col1, col2 = st.columns(2)
87 |
88 | with col1:
89 | # --- Poem Input Area ---
90 | placeholder_poem = (
91 | "عَلَى قَدْرِ أَهْلِ العَزْمِ تَأْتِي العَزَائِمُ\n"
92 | "وَتَأْتِي عَلَى قَدْرِ الكِرَامِ المَكَارِمُ\n"
93 | "وَتَعْظُمُ فِي عَيْنِ الصَّغِيرِ صِغَارُهَا\n"
94 | "وَتَصْغُرُ فِي عَيْنِ العَظِيمِ العَظَائِمُ"
95 | )
96 | poem_input = st.text_area(
97 | label="**Enter Poem Text Here:**",
98 | value=placeholder_poem,
99 | height=250,
100 | placeholder="Paste or type the poem here..."
101 | )
102 |
103 | with col2:
104 | # --- Analysis Options ---
105 | st.markdown("**Analysis Options**")
106 | top_k = st.slider(
107 | label="Number of top themes to display:",
108 | min_value=1,
109 | max_value=10,
110 | value=5, # Default value
111 | help="Adjust this slider to control how many of the most confident themes are shown."
112 | )
113 |
114 | # The main action button
115 | analyze_button = st.button("Analyze Poem", type="primary", use_container_width=True)
116 |
117 | st.markdown("---")
118 |
119 | # --- Analysis Execution and Output ---
120 | if analyze_button:
121 | # Validate input
122 | if not poem_input or not poem_input.strip():
123 | st.warning("⚠️ Input is empty. Please enter a poem to analyze.")
124 | return # Stop execution for this run
125 |
126 | # Show a spinner while processing
127 | with st.spinner("🔍 Analyzing the poetic essence... Please wait."):
128 | try:
129 | start_time = time.time()
130 |
131 | # Call the predictor
132 | results = predictor.predict(poem_text=poem_input, top_k=top_k)
133 |
134 | end_time = time.time()
135 | logger.info(f"Prediction for input text completed in {end_time - start_time:.2f} seconds.")
136 |
137 | # Display the results
138 | display_results(results)
139 |
140 | except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
141 | # Handle specific, expected errors from the predictor
142 | st.error(f"❌ Input Error: {e}")
143 | logger.warning(f"User input error: {e}")
144 | except Exception as e:
145 | # Handle unexpected errors
146 | st.error("An unexpected error occurred during analysis. Please try again or check the logs.")
147 | logger.error(f"Unexpected prediction error: {e}", exc_info=True)
148 |
149 |
150 | if __name__ == "__main__":
151 | main()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/web_app/pages/Analyze_Poem.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import json
4 | import logging
5 | import os
6 | import time
7 |
8 | import pandas as pd
9 | import plotly.express as px
10 | import streamlit as st
11 |
12 | # Path adjustments for importing from the project's src directory
13 | import sys
14 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..', '..')))
15 |
16 | try:
17 | from web_app.core.predictor import PoetryPredictor
18 | except ImportError:
19 | st.error("Could not import the PoetryPredictor. Ensure the project structure is correct.")
20 | st.stop()
21 |
22 |
23 | # --- Configure logger ---
24 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
25 |
26 |
27 | # --- Page Configuration ---
28 | try:
29 | st.set_page_config(
30 | page_title="Analyze Poem",
31 | page_icon="✍️",
32 | layout="wide",
33 | )
34 | except st.errors.StreamlitAPIException:
35 | pass
36 |
37 |
38 | # --- Caching and Data Loading ---
39 |
40 | @st.cache_resource
41 | def get_predictor():
42 | """Factory function to load and cache the PoetryPredictor instance."""
43 | try:
44 | return PoetryPredictor()
45 | except Exception as e:
46 | logger.error(f"Failed to load predictor: {e}", exc_info=True)
47 | return None
48 |
49 | @st.cache_data
50 | def load_example_poems(file_path: str = "web_app/static/example_poems.json"):
51 | """
52 | Loads example poems from an external JSON file and caches the result.
53 | This makes the app data-driven and easy to update.
54 | """
55 | try:
56 | with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
57 | examples_list = json.load(f)
58 | # Convert list of dicts to a single dict for easy lookup
59 | return {item['key']: item['value'] for item in examples_list}
60 | except (FileNotFoundError, json.JSONDecodeError, KeyError) as e:
61 | logger.error(f"Failed to load or parse example poems from {file_path}: {e}")
62 | st.error("Could not load example poems file.")
63 | return {"Default": "Please add examples to static/example_poems.json"}
64 |
65 |
66 | # --- UI Helper Functions ---
67 |
68 | def render_results(results):
69 | """Renders the analysis results in a visually appealing and informative way."""
70 | if not results:
71 | st.warning("The model did not predict any themes above the confidence threshold.")
72 | return
73 |
74 | st.success("Analysis Complete!")
75 |
76 | df = pd.DataFrame(results)
77 | df['probability_percent'] = df['probability'].apply(lambda p: f"{p:.2%}")
78 |
79 | col1, col2 = st.columns([1, 1])
80 |
81 | with col1:
82 | st.markdown("#### **Top Predicted Themes**")
83 | st.dataframe(
84 | df[['theme', 'probability_percent']],
85 | use_container_width=True,
86 | hide_index=True,
87 | column_config={
88 | "theme": st.column_config.TextColumn("Theme", width="large"),
89 | "probability_percent": st.column_config.TextColumn("Confidence"),
90 | }
91 | )
92 |
93 | with col2:
94 | st.markdown("#### **Confidence Distribution**")
95 | fig = px.bar(
96 | df, x='probability', y='theme', orientation='h', text='probability_percent',
97 | labels={'probability': 'Confidence Score', 'theme': 'Thematic Category'},
98 | )
99 | fig.update_layout(yaxis={'categoryorder':'total ascending'}, showlegend=False, margin=dict(l=0, r=0, t=30, b=0))
100 | fig.update_traces(marker_color='#0068c9', textposition='outside')
101 | st.plotly_chart(fig, use_container_width=True)
102 |
103 |
104 | # --- Main Page Application ---
105 |
106 | def main():
107 | """Main function to render the 'Analyze Poem' page."""
108 |
109 | st.title("✍️ Thematic Analysis of a Poem")
110 | st.markdown("Paste or select an example of Arabic poetry below to classify its thematic content.")
111 |
112 | if "analysis_results" not in st.session_state:
113 | st.session_state.analysis_results = None
114 |
115 | predictor = get_predictor()
116 | example_poems = load_example_poems()
117 |
118 | if predictor is None:
119 | st.error("The analysis model is not available. Application cannot proceed.")
120 | st.stop()
121 |
122 | # --- Input Section ---
123 | st.markdown("---")
124 |
125 | input_col, example_col = st.columns([2, 1])
126 |
127 | with example_col:
128 | st.markdown("##### **Try an Example**")
129 | if example_poems:
130 | selected_example_key = st.selectbox(
131 | "Choose a famous verse:",
132 | options=list(example_poems.keys()),
133 | index=0,
134 | label_visibility="collapsed"
135 | )
136 | # Use the selected key to get the poem text
137 | default_text = example_poems.get(selected_example_key, "")
138 | else:
139 | default_text = "Examples could not be loaded."
140 | st.warning("No examples available.")
141 |
142 | with input_col:
143 | st.markdown("##### **Enter Your Poem**")
144 | poem_input = st.text_area(
145 | "Paste the poem text here, with each verse on a new line.",
146 | value=default_text,
147 | height=200,
148 | key="poem_input_area"
149 | )
150 |
151 | # --- Options and Action Button ---
152 | st.markdown("##### **Analysis Configuration**")
153 | opts_col1, opts_col2 = st.columns([1, 3])
154 | with opts_col1:
155 | top_k = st.number_input(
156 | "Number of themes to show:", min_value=1, max_value=20, value=7,
157 | help="The maximum number of most confident themes to display."
158 | )
159 |
160 | with opts_col2:
161 | analyze_button = st.button("Analyze Poem", type="primary", use_container_width=True)
162 |
163 | # --- Analysis and Result Display Section ---
164 | st.markdown("---")
165 |
166 | if analyze_button:
167 | if not poem_input or not poem_input.strip():
168 | st.warning("⚠️ Please enter a poem to analyze.")
169 | else:
170 | with st.spinner("🔬 Performing deep semantic analysis..."):
171 | try:
172 | results = predictor.predict(poem_text=poem_input, top_k=top_k)
173 | st.session_state.analysis_results = results
174 | except Exception as e:
175 | st.error(f"An unexpected error occurred: {e}")
176 | st.session_state.analysis_results = None
177 |
178 | if st.session_state.analysis_results is not None:
179 | render_results(st.session_state.analysis_results)
180 |
181 | if __name__ == "__main__":
182 | main()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/web_app/app.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import logging
4 | import os
5 | import sys
6 |
7 | import streamlit as st
8 |
9 | # --- Path Setup ---
10 | # Add the project root to the Python path. This allows importing from 'src' and 'web_app.core'.
11 | # This should be done once in the main entry point of the application.
12 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..')))
13 |
14 | try:
15 | from web_app.core.predictor import PoetryPredictor
16 | except ImportError:
17 | # This is a critical failure, the app cannot run without the predictor.
18 | st.error(
19 | "**Fatal Error:** Could not import `PoetryPredictor` from `web_app.core`."
20 | "Please ensure the project structure is correct and all dependencies are installed."
21 | )
22 | st.stop()
23 |
24 |
25 | # --- Application-Wide Configuration ---
26 |
27 | # 1. Page Configuration (must be the first Streamlit command)
28 | st.set_page_config(
29 | page_title="Arabic Poetry Thematic Classifier",
30 | page_icon="📜",
31 | layout="wide",
32 | initial_sidebar_state="expanded",
33 | menu_items={
34 | 'Get Help': 'https://github.com/your-username/your-repo/issues',
35 | 'Report a bug': "https://github.com/your-username/your-repo/issues",
36 | 'About': """
37 | ## Nuanced Thematic Classification of Arabic Poetry
38 | This is an interactive platform demonstrating a deep learning model for classifying themes in Arabic poetry.
39 | Developed as part of our research paper.
40 | """
41 | }
42 | )
43 |
44 | # 2. Setup application-wide logging
45 | # You can use your utility function here if you have one
46 | logging.basicConfig(
47 | level=logging.INFO,
48 | format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
49 | )
50 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
51 |
52 |
53 | # --- Resource Caching ---
54 |
55 | @st.cache_resource
56 | def load_resources():
57 | """
58 | Loads all heavy, application-wide resources once and caches them.
59 | This includes the main model predictor. This function will be called by
60 | all pages to ensure they share the same cached resources.
61 | """
62 | logger.info("Main app: Loading application-wide resources...")
63 | try:
64 | predictor = PoetryPredictor()
65 | logger.info("Main app: PoetryPredictor loaded and cached successfully.")
66 | return {"predictor": predictor}
67 | except Exception as e:
68 | logger.error(f"Main app: A fatal error occurred during resource loading: {e}", exc_info=True)
69 | # Display the error prominently on the main page
70 | st.error(
71 | "**Application Failed to Start**\n\n"
72 | f"A critical error occurred while loading the AI models: **{e}**\n\n"
73 | "Please check the application logs for more details. The app will not be functional."
74 | )
75 | return {"predictor": None}
76 |
77 |
78 | # --- Main Application UI ---
79 |
80 | def main():
81 | """
82 | Renders the main landing page of the application.
83 | This page introduces the project and guides the user to the sub-pages.
84 | """
85 |
86 | # --- Load shared resources ---
87 | # This call ensures that the models are loaded when the user first visits the app.
88 | # The result is cached, so subsequent calls on this or other pages are instantaneous.
89 | resources = load_resources()
90 | if resources["predictor"] is None:
91 | st.stop() # Halt execution if models failed to load.
92 |
93 | # --- Header and Introduction ---
94 | st.title("📜 Nuanced Thematic Classification of Arabic Poetry")
95 |
96 | st.markdown(
97 | """
98 | Welcome to the interactive platform for our research on the thematic analysis of Arabic poetry.
99 | This application serves as a practical demonstration of our hybrid deep learning model,
100 | designed to understand the rich and complex themes inherent in this literary tradition.
101 | """
102 | )
103 |
104 | st.info(
105 | "**👈 To get started, please select a tool from the sidebar on the left.**",
106 | icon="ℹ️"
107 | )
108 |
109 | # --- Page Navigation Guide ---
110 | st.header("Available Tools")
111 |
112 | col1, col2 = st.columns(2)
113 |
114 | with col1:
115 | with st.container(border=True):
116 | st.markdown("#### ✍️ Analyze a New Poem")
117 | st.markdown(
118 | "Input your own Arabic poetry verses or choose from our examples to get an "
119 | "instant thematic analysis, complete with confidence scores for each predicted theme."
120 | )
121 |
122 | with col2:
123 | with st.container(border=True):
124 | st.markdown("#### 📚 Explore the Corpus")
125 | st.markdown(
126 | "Dive into our richly annotated dataset. Use interactive filters to explore "
127 | "thematic trends across different poets, historical eras, and literary genres."
128 | )
129 |
130 | st.markdown("---")
131 |
132 | # --- Project Background and Resources ---
133 | st.header("About The Project")
134 |
135 | with st.expander("Click here to learn more about the project's methodology and contributions"):
136 | st.markdown(
137 | """
138 | This project was born out of the need to address the significant challenges in the computational
139 | analysis of Arabic poetry, namely its thematic complexity, frequent thematic overlap, and the
140 | scarcity of comprehensively annotated data.
141 |
142 | #### Key Contributions:
143 | 1. **A Novel Annotated Corpus:** We meticulously created a large-scale, multi-label Arabic poetry corpus,
144 | annotated according to a new, literature-grounded hierarchical thematic taxonomy and validated by domain experts.
145 |
146 | 2. **An Optimized Hybrid Model:** We developed a hybrid deep learning model that synergistically integrates
147 | Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for local feature extraction with Bidirectional Long Short-Term
148 | Memory (Bi-LSTM) networks for sequential context modeling. This model leverages custom FastText embeddings
149 | trained from scratch on our poetic corpus.
150 |
151 | 3. **This Interactive Platform:** This web application makes our model and data accessible, fostering
152 | more sophisticated, data-driven research in Arabic digital humanities.
153 | """
154 | )
155 |
156 | st.markdown("#### Project Links")
157 | st.link_button("📄 View the Research Paper", "https://your-paper-link.com")
158 | st.link_button("💻 Browse the Source Code on GitHub", "https://github.com/your-username/your-repo")
159 |
160 | # --- Sidebar Content ---
161 | st.sidebar.success("Select a page above to begin.")
162 | st.sidebar.markdown("---")
163 | st.sidebar.info(
164 | "This application is a research prototype. "
165 | "For questions or feedback, please open an issue on our GitHub repository."
166 | )
167 |
168 |
169 | if __name__ == "__main__":
170 | main()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import json
4 | import logging
5 | import os
6 | import pickle
7 | import random
8 | from typing import Any, Dict, List, Optional
9 |
10 | import numpy as np
11 | import torch
12 | import yaml
13 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader, Dataset
14 |
15 |
16 | # Configure a root logger for the utility functions
17 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
18 |
19 |
20 | def setup_logging(level: int = logging.INFO, log_file: Optional[str] = None):
21 | """
22 | Sets up a standardized logging configuration for the entire project.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | level (int): The logging level (e.g., logging.INFO, logging.DEBUG).
26 | log_file (Optional[str]): Path to a file to save logs. If None, logs to console only.
27 | """
28 | log_format = '%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
29 |
30 | # Get the root logger
31 | root_logger = logging.getLogger()
32 | root_logger.setLevel(level)
33 |
34 | # Clear existing handlers to avoid duplicate logs
35 | if root_logger.hasHandlers():
36 | root_logger.handlers.clear()
37 |
38 | # Console handler
39 | console_handler = logging.StreamHandler()
40 | console_handler.setFormatter(logging.Formatter(log_format))
41 | root_logger.addHandler(console_handler)
42 |
43 | # File handler
44 | if log_file:
45 | try:
46 | # Ensure directory exists
47 | os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(log_file), exist_ok=True)
48 | file_handler = logging.FileHandler(log_file, mode='a', encoding='utf-8')
49 | file_handler.setFormatter(logging.Formatter(log_format))
50 | root_logger.addHandler(file_handler)
51 | logger.info(f"Logging is set up. Logs will also be saved to {log_file}")
52 | except Exception as e:
53 | logger.error(f"Failed to set up file logger at {log_file}. Error: {e}")
54 |
55 | logger.info(f"Logging level set to {logging.getLevelName(level)}.")
56 |
57 |
58 | def set_seed(seed: int = 42):
59 | """
60 | Sets the random seed for reproducibility across all relevant libraries.
61 |
62 | Args:
63 | seed (int): The seed value.
64 | """
65 | random.seed(seed)
66 | np.random.seed(seed)
67 | torch.manual_seed(seed)
68 | if torch.cuda.is_available():
69 | torch.cuda.manual_seed(seed)
70 | torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed) # if you are using multi-GPU.
71 | # The following two lines are needed for full reproducibility with CUDA
72 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
73 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
74 | logger.info(f"Random seed set to {seed} for reproducibility.")
75 |
76 |
77 | def load_config(config_path: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
78 | """
79 | Loads a configuration file in YAML format.
80 |
81 | Args:
82 | config_path (str): The path to the YAML configuration file.
83 |
84 | Returns:
85 | Dict[str, Any]: A dictionary containing the configuration.
86 |
87 | Raises:
88 | FileNotFoundError: If the config file does not exist.
89 | yaml.YAMLError: If the file is not a valid YAML.
90 | """
91 | logger.info(f"Loading configuration from {config_path}")
92 | try:
93 | with open(config_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
94 | config = yaml.safe_load(f)
95 | if not isinstance(config, dict):
96 | raise TypeError("Configuration file content is not a dictionary.")
97 | return config
98 | except FileNotFoundError:
99 | logger.error(f"Configuration file not found at: {config_path}")
100 | raise
101 | except yaml.YAMLError as e:
102 | logger.error(f"Error parsing YAML file at {config_path}. Please check syntax. Error: {e}")
103 | raise
104 | except TypeError as e:
105 | logger.error(f"Error in config file structure: {e}")
106 | raise
107 |
108 |
109 | def save_object(obj: Any, filepath: str):
110 | """
111 | Saves a Python object to a file using pickle.
112 |
113 | Args:
114 | obj (Any): The Python object to save.
115 | filepath (str): The path where the object will be saved.
116 | """
117 | logger.info(f"Saving object to {filepath}")
118 | try:
119 | # Ensure the directory exists
120 | os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(filepath), exist_ok=True)
121 | with open(filepath, 'wb') as f:
122 | pickle.dump(obj, f)
123 | except (IOError, pickle.PicklingError) as e:
124 | logger.error(f"Failed to save object to {filepath}. Error: {e}")
125 | raise
126 |
127 |
128 | def load_object(filepath: str) -> Any:
129 | """
130 |
131 | Loads a Python object from a pickle file.
132 |
133 | Args:
134 | filepath (str): The path to the pickle file.
135 |
136 | Returns:
137 | Any: The loaded Python object.
138 | """
139 | logger.info(f"Loading object from {filepath}")
140 | try:
141 | with open(filepath, 'rb') as f:
142 | obj = pickle.load(f)
143 | return obj
144 | except FileNotFoundError:
145 | logger.error(f"Object file not found at: {filepath}")
146 | raise
147 | except (IOError, pickle.UnpicklingError) as e:
148 | logger.error(f"Failed to load object from {filepath}. Error: {e}")
149 | raise
150 |
151 |
152 | # --- Data Handling Utilities ---
153 |
154 | class PoetryDataset(Dataset):
155 | """
156 | A custom PyTorch Dataset for poetry classification.
157 | Assumes data is pre-processed and consists of feature tensors and label tensors.
158 | """
159 | def __init__(self, features: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor], labels: Union[np.ndarray, torch.Tensor]):
160 | if len(features) != len(labels):
161 | raise ValueError("Features and labels must have the same length.")
162 |
163 | self.features = torch.tensor(features, dtype=torch.float32) if isinstance(features, np.ndarray) else features
164 | self.labels = torch.tensor(labels, dtype=torch.float32) if isinstance(labels, np.ndarray) else labels
165 | logger.info(f"Dataset created with {len(self.features)} samples.")
166 |
167 | def __len__(self) -> int:
168 | return len(self.features)
169 |
170 | def __getitem__(self, idx: int) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
171 | return self.features[idx], self.labels[idx]
172 |
173 |
174 | def pad_collate_fn(batch: List[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]], pad_value: float = 0.0) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
175 | """
176 | A custom collate_fn for a DataLoader to handle padding of sequences with variable lengths.
177 | This is crucial if your poems (or segments) have different numbers of vectors.
178 |
179 | Args:
180 | batch (List[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]]): A list of (features, label) tuples.
181 | pad_value (float): The value to use for padding.
182 |
183 | Returns:
184 | Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]: Padded features and their corresponding labels.
185 | """
186 | # Separate features and labels
187 | features, labels = zip(*batch)
188 |
189 | # Pad the features (sequences)
190 | # torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence handles padding efficiently
191 | features_padded = torch.nn.utils.rnn.pad_sequence(features, batch_first=True, padding_value=pad_value)
192 |
193 | # Stack the labels
194 | labels = torch.stack(labels, 0)
195 |
196 | return features_padded, labels
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/web_app/pages/Explore_Corpus.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import logging
4 | from typing import List
5 |
6 | import pandas as pd
7 | import plotly.express as px
8 | import streamlit as st
9 |
10 | # Configure logger for this page
11 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
12 |
13 |
14 | # --- Page Configuration ---
15 | try:
16 | st.set_page_config(
17 | page_title="Explore The Corpus",
18 | page_icon="📚",
19 | layout="wide",
20 | )
21 | except st.errors.StreamlitAPIException:
22 | # This error is expected if set_page_config is already called in the main app.py
23 | pass
24 |
25 |
26 | # --- Caching and Data Loading ---
27 |
28 | @st.cache_data
29 | def load_annotated_corpus(file_path: str = "data/annotated/diwan_corpus_annotated.csv") -> pd.DataFrame:
30 | """
31 | Loads the main annotated corpus from a CSV file and caches it.
32 | This function is the single source of truth for the dashboard's data.
33 | """
34 | try:
35 | logger.info(f"Loading annotated corpus from {file_path}...")
36 | df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
37 | # Basic validation
38 | if 'poet_name' not in df.columns or 'era' not in df.columns:
39 | raise ValueError("Required columns 'poet_name' or 'era' not found.")
40 | logger.info(f"Corpus loaded successfully with {len(df)} poems.")
41 | return df
42 | except FileNotFoundError:
43 | st.error(f"Data file not found at '{file_path}'. Please ensure the annotated corpus is available.")
44 | logger.error(f"Data file not found: {file_path}")
45 | return pd.DataFrame() # Return empty dataframe to prevent crash
46 | except Exception as e:
47 | st.error(f"An error occurred while loading the data: {e}")
48 | logger.error(f"Error loading corpus: {e}", exc_info=True)
49 | return pd.DataFrame()
50 |
51 |
52 | @st.cache_data
53 | def get_theme_columns(df: pd.DataFrame) -> List[str]:
54 | """Extracts theme column names from the DataFrame."""
55 | return [col for col in df.columns if col.startswith('theme_')]
56 |
57 |
58 | # --- UI and Plotting Functions ---
59 |
60 | def display_main_metrics(df: pd.DataFrame, theme_cols: List[str]):
61 | """Displays key statistics about the corpus."""
62 | st.header("Corpus Overview")
63 |
64 | col1, col2, col3, col4 = st.columns(4)
65 | col1.metric("Total Poems", f"{len(df):,}")
66 | col2.metric("Unique Poets", f"{df['poet_name'].nunique():,}")
67 | col3.metric("Historical Eras", f"{df['era'].nunique():,}")
68 | col4.metric("Annotated Themes", f"{len(theme_cols):,}")
69 |
70 |
71 | def display_theme_distribution(df: pd.DataFrame, theme_cols: List[str]):
72 | """Calculates and displays the overall distribution of themes."""
73 | st.subheader("Overall Theme Distribution")
74 |
75 | if not theme_cols:
76 | st.warning("No theme columns found to analyze.")
77 | return
78 |
79 | # Calculate theme counts
80 | theme_counts = df[theme_cols].sum().sort_values(ascending=False)
81 | theme_counts.index = theme_counts.index.str.replace('theme_', '') # Clean up names for display
82 |
83 | # Create a bar chart
84 | fig = px.bar(
85 | theme_counts,
86 | x=theme_counts.values,
87 | y=theme_counts.index,
88 | orientation='h',
89 | labels={'x': 'Number of Poems', 'y': 'Theme'},
90 | title="Frequency of Each Theme in the Corpus"
91 | )
92 | fig.update_layout(yaxis={'categoryorder': 'total ascending'})
93 | st.plotly_chart(fig, use_container_width=True)
94 |
95 |
96 | def display_interactive_filters(df: pd.DataFrame, theme_cols: List[str]):
97 | """Creates and manages the interactive filters in the sidebar."""
98 | st.sidebar.header("🔍 Interactive Filters")
99 |
100 | # Theme filter
101 | # Clean up names for the multiselect widget
102 | cleaned_theme_names = [name.replace('theme_', '') for name in theme_cols]
103 | selected_themes_cleaned = st.sidebar.multiselect(
104 | "Filter by Theme(s):",
105 | options=cleaned_theme_names,
106 | help="Select one or more themes to view poems containing them."
107 | )
108 | # Map back to original column names
109 | selected_themes_original = ['theme_' + name for name in selected_themes_cleaned]
110 |
111 | # Poet filter
112 | all_poets = sorted(df['poet_name'].unique())
113 | selected_poets = st.sidebar.multiselect(
114 | "Filter by Poet(s):",
115 | options=all_poets
116 | )
117 |
118 | # Era filter
119 | all_eras = sorted(df['era'].unique())
120 | selected_eras = st.sidebar.multiselect(
121 | "Filter by Era(s):",
122 | options=all_eras
123 | )
124 |
125 | return selected_themes_original, selected_poets, selected_eras
126 |
127 |
128 | def apply_filters(df: pd.DataFrame, themes: List[str], poets: List[str], eras: List[str]) -> pd.DataFrame:
129 | """Applies the selected filters to the DataFrame."""
130 | filtered_df = df.copy()
131 |
132 | # Apply theme filter (poems must contain ALL selected themes)
133 | if themes:
134 | for theme in themes:
135 | filtered_df = filtered_df[filtered_df[theme] == 1]
136 |
137 | # Apply poet filter
138 | if poets:
139 | filtered_df = filtered_df[filtered_df['poet_name'].isin(poets)]
140 |
141 | # Apply era filter
142 | if eras:
143 | filtered_df = filtered_df[filtered_df['era'].isin(eras)]
144 |
145 | return filtered_df
146 |
147 |
148 | # --- Main Page Application ---
149 |
150 | def main():
151 | """Main function to render the 'Explore Corpus' page."""
152 |
153 | st.title("📚 Explore the Annotated Poetry Corpus")
154 | st.markdown(
155 | "This interactive dashboard allows you to explore the thematic landscape of our annotated "
156 | "Arabic poetry corpus. Use the filters in the sidebar to drill down into the data."
157 | )
158 | st.markdown("---")
159 |
160 | # Load data
161 | corpus_df = load_annotated_corpus()
162 |
163 | # Stop if data loading failed
164 | if corpus_df.empty:
165 | st.warning("Cannot display dashboard because the data could not be loaded.")
166 | st.stop()
167 |
168 | theme_columns = get_theme_columns(corpus_df)
169 |
170 | # Display widgets and get filter selections
171 | selected_themes, selected_poets, selected_eras = display_interactive_filters(corpus_df, theme_columns)
172 |
173 | # Apply filters
174 | filtered_data = apply_filters(corpus_df, selected_themes, selected_poets, selected_eras)
175 |
176 | # --- Main Content Area ---
177 |
178 | # Display high-level stats of the *original* corpus
179 | display_main_metrics(corpus_df, theme_columns)
180 | st.markdown("---")
181 |
182 | # Display analysis based on the *filtered* data
183 | st.header("Filtered Results")
184 | st.write(f"**Showing {len(filtered_data)} of {len(corpus_df)} poems based on your selections.**")
185 |
186 | if len(filtered_data) > 0:
187 | # Display theme distribution for the filtered subset
188 | display_theme_distribution(filtered_data, theme_columns)
189 |
190 | # Display a sample of the filtered data
191 | st.subheader("Filtered Data Sample")
192 | st.dataframe(
193 | filtered_data[['poet_name', 'era', 'poem_text']].head(20),
194 | use_container_width=True,
195 | hide_index=True
196 | )
197 | else:
198 | st.info("No poems match the selected filter criteria. Please broaden your search.")
199 |
200 |
201 | if __name__ == "__main__":
202 | main()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import logging
4 | from typing import Tuple, List, Optional, Union
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import pandas as pd
8 | import torch
9 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
10 |
11 | # Configure logging
12 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
13 |
14 |
15 | class PoetryThematicDataset(Dataset):
16 | """
17 | A robust, custom PyTorch Dataset for the Arabic Poetry Thematic Classification task.
18 |
19 | This class is responsible for:
20 | 1. Loading data from a CSV file.
21 | 2. Validating the necessary columns.
22 | 3. Converting data into PyTorch Tensors.
23 | 4. Optionally caching the processed data in memory for faster access during training.
24 | """
25 |
26 | def __init__(
27 | self,
28 | csv_path: str,
29 | vector_column: str,
30 | label_columns: List[str],
31 | text_column: Optional[str] = None,
32 | use_caching: bool = True
33 | ):
34 | """
35 | Initializes the Dataset.
36 |
37 | Args:
38 | csv_path (str): Path to the CSV file containing the dataset (e.g., train.csv).
39 | vector_column (str): The name of the column containing the pre-computed segment embeddings.
40 | The data in this column should be list-like or array-like.
41 | label_columns (List[str]): A list of column names representing the multi-label targets.
42 | text_column (Optional[str]): The name of the column containing the original text.
43 | Useful for debugging and analysis, but not used by the model.
44 | use_caching (bool): If True, the entire dataset will be loaded and converted to tensors
45 | in memory upon initialization for faster access. Recommended for
46 | datasets that fit in RAM.
47 | """
48 | super().__init__()
49 |
50 | self.csv_path = csv_path
51 | self.vector_column = vector_column
52 | self.label_columns = label_columns
53 | self.text_column = text_column
54 | self.use_caching = use_caching
55 |
56 | self.data = self._load_and_validate_data()
57 | self.num_samples = len(self.data)
58 |
59 | self._cached_data: Optional[List[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]]] = None
60 | if self.use_caching:
61 | logger.info("Caching enabled. Pre-loading and converting all data to tensors...")
62 | self._cache_data()
63 | logger.info(f"Successfully cached {self.num_samples} samples.")
64 |
65 | logger.info(f"Dataset initialized from {csv_path}. Found {self.num_samples} samples.")
66 |
67 | def _load_and_validate_data(self) -> pd.DataFrame:
68 | """Loads the CSV file and validates its structure."""
69 | try:
70 | df = pd.read_csv(self.csv_path)
71 | except FileNotFoundError:
72 | logger.error(f"Dataset file not found at: {self.csv_path}")
73 | raise
74 | except Exception as e:
75 | logger.error(f"Failed to read CSV file at {self.csv_path}. Error: {e}")
76 | raise
77 |
78 | # Validate required columns
79 | required_cols = [self.vector_column] + self.label_columns
80 | if self.text_column:
81 | required_cols.append(self.text_column)
82 |
83 | missing_cols = [col for col in required_cols if col not in df.columns]
84 | if missing_cols:
85 | raise ValueError(f"Missing required columns in {self.csv_path}: {missing_cols}")
86 |
87 | return df
88 |
89 | def _parse_row(self, index: int) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, Optional[str]]:
90 | """
91 | Parses a single row from the DataFrame and converts it to tensors.
92 |
93 | Returns:
94 | A tuple of (feature_tensor, label_tensor, optional_text).
95 | """
96 | row = self.data.iloc[index]
97 |
98 | # --- Process Features (Vectors) ---
99 | try:
100 | # Vectors might be stored as string representations of lists, e.g., '[1, 2, 3]'
101 | # We need to handle this safely.
102 | vector_data = row[self.vector_column]
103 | if isinstance(vector_data, str):
104 | # A common case when reading from CSV
105 | import json
106 | feature_list = json.loads(vector_data)
107 | else:
108 | # Assumes it's already a list or numpy array
109 | feature_list = vector_data
110 |
111 | features = torch.tensor(feature_list, dtype=torch.float32)
112 |
113 | except Exception as e:
114 | logger.error(f"Failed to parse vector data at index {index} from column '{self.vector_column}'. Error: {e}")
115 | # Return a dummy tensor to avoid crashing the loader, or raise an error
116 | # For now, we'll raise to highlight the data quality issue.
117 | raise TypeError(f"Invalid data format in vector column at index {index}") from e
118 |
119 | # --- Process Labels ---
120 | try:
121 | labels = row[self.label_columns].values.astype(np.float32)
122 | labels = torch.from_numpy(labels)
123 | except Exception as e:
124 | logger.error(f"Failed to parse label data at index {index}. Error: {e}")
125 | raise TypeError(f"Invalid data format in label columns at index {index}") from e
126 |
127 | # --- Process Optional Text ---
128 | text = row[self.text_column] if self.text_column else None
129 |
130 | return features, labels, text
131 |
132 | def _cache_data(self):
133 | """Pre-processes and stores all samples in a list for fast retrieval."""
134 | self._cached_data = []
135 | for i in range(self.num_samples):
136 | try:
137 | # We only cache features and labels, not the text, to save memory
138 | features, labels, _ = self._parse_row(i)
139 | self._cached_data.append((features, labels))
140 | except TypeError as e:
141 | logger.error(f"Skipping sample at index {i} due to parsing error: {e}")
142 | # In a real scenario, you might want to handle this more gracefully,
143 | # e.g., by removing bad samples from self.data
144 | continue
145 |
146 | def __len__(self) -> int:
147 | """Returns the total number of samples in the dataset."""
148 | return self.num_samples
149 |
150 | def __getitem__(self, index: int) -> Union[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], Dict]:
151 | """
152 | Retrieves a single sample from the dataset.
153 |
154 | If caching is enabled, it fetches pre-processed tensors from memory.
155 | Otherwise, it parses the row from the DataFrame on the fly.
156 |
157 | Returns:
158 | If text_column is provided, returns a dictionary.
159 | Otherwise, returns a tuple of (features, labels).
160 | This dictionary format is more flexible and explicit.
161 | """
162 | if self.use_caching and self._cached_data:
163 | if index >= len(self._cached_data):
164 | raise IndexError(f"Index {index} out of range for cached data of size {len(self._cached_data)}")
165 | features, labels = self._cached_data[index]
166 |
167 | # If text is needed, we still have to fetch it from the DataFrame
168 | if self.text_column:
169 | text = self.data.iloc[index][self.text_column]
170 | return {"features": features, "labels": labels, "text": text}
171 | else:
172 | return features, labels
173 | else:
174 | # Process on the fly
175 | features, labels, text = self._parse_row(index)
176 | if self.text_column:
177 | return {"features": features, "labels": labels, "text": text}
178 | else:
179 | return features, labels
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/data_processing.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import pandas as pd
4 | import re
5 | import string
6 | import logging
7 | from typing import List, Optional
8 |
9 | # Set up logging
10 | logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
11 |
12 | try:
13 | from pyfarasa.segmenter import FarasaSegmenter
14 | except ImportError:
15 | logging.error("pyfarasa is not installed. Please install it using 'pip install pyfarasa'.")
16 | # You might want to raise the error to stop execution if Farasa is critical
17 | # raise ImportError("pyfarasa is not installed.")
18 | FarasaSegmenter = None # Set to None to handle cases where it's not present
19 |
20 |
21 | class PoetryPreprocessor:
22 | """
23 | A robust class to preprocess Arabic poetry text.
24 | Handles cleaning, normalization, stopword removal, and morphological segmentation.
25 | Includes error handling and logging.
26 | """
27 |
28 | def __init__(self, stopwords_path: Optional[str] = None):
29 | """
30 | Initializes the preprocessor, setting up the Farasa segmenter and loading stopwords.
31 |
32 | Args:
33 | stopwords_path (Optional[str]): Path to a file containing custom stopwords, one per line.
34 | If None, a default internal list is used.
35 | """
36 | self.segmenter = self._initialize_farasa()
37 | self.stopwords = self._load_stopwords(stopwords_path)
38 |
39 | def _initialize_farasa(self):
40 | """
41 | Initializes the FarasaSegmenter and handles potential errors if pyfarasa is not installed
42 | or if the JAR files are not found.
43 | """
44 | if FarasaSegmenter is None:
45 | logging.warning("FarasaSegmenter is not available. Segmentation step will be skipped.")
46 | return None
47 | try:
48 | # interactive=True avoids re-initializing the JVM for each call, making it much faster.
49 | return FarasaSegmenter(interactive=True)
50 | except Exception as e:
51 | logging.error(f"Failed to initialize FarasaSegmenter. Error: {e}")
52 | logging.warning("Segmentation step will be skipped. Ensure Java is installed and Farasa's dependencies are correct.")
53 | return None
54 |
55 | def _load_stopwords(self, path: Optional[str]) -> List[str]:
56 | """
57 | Loads stopwords from a specified file path or returns a default list.
58 | """
59 | if path:
60 | try:
61 | with open(path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
62 | stopwords = [line.strip() for line in f if line.strip()]
63 | logging.info(f"Successfully loaded {len(stopwords)} stopwords from {path}.")
64 | return stopwords
65 | except FileNotFoundError:
66 | logging.error(f"Stopwords file not found at {path}. Falling back to default list.")
67 |
68 | # Fallback to default list
69 | logging.info("Using default internal stopwords list.")
70 | return [
71 | "من", "في", "على", "إلى", "عن", "و", "ف", "ثم", "أو", "ب", "ك", "ل",
72 | "يا", "ما", "لا", "إن", "أن", "كان", "قد", "لقد", "لكن", "هذا", "هذه",
73 | "ذلك", "تلك", "هنا", "هناك", "هو", "هي", "هم", "هن", "أنا", "نحن",
74 | "أنت", "أنتي", "أنتما", "أنتن", "الذي", "التي", "الذين", "اللاتي",
75 | "كل", "بعض", "غير", "سوى", "مثل", "كيف", "متى", "أين", "كم", "أي",
76 | "حتى", "إذ", "إذا", "إذن", "بعد", "قبل", "حين", "بين", "مع", "عند"
77 | ]
78 |
79 | def _clean_text(self, text: str) -> str:
80 | """
81 | Applies basic cleaning to the text: removes diacritics, non-Arabic chars,
82 | tatweel, and extra whitespaces.
83 | Handles non-string inputs gracefully.
84 | """
85 | if not isinstance(text, str):
86 | logging.warning(f"Input is not a string (type: {type(text)}), returning empty string.")
87 | return ""
88 |
89 | # 1. Remove diacritics (tashkeel)
90 | text = re.sub(r'[\u064B-\u0652]', '', text)
91 |
92 | # 2. Remove tatweel (elongation)
93 | text = re.sub(r'\u0640', '', text)
94 |
95 | # 3. Remove punctuation and non-Arabic characters (keeps only Arabic letters and spaces)
96 | # This regex is more comprehensive and includes a wider range of punctuation.
97 | arabic_only_pattern = re.compile(r'[^\u0621-\u064A\s]')
98 | text = arabic_only_pattern.sub('', text)
99 |
100 | # 4. Remove extra whitespaces
101 | text = re.sub(r'\s+', ' ', text).strip()
102 |
103 | return text
104 |
105 | def _normalize_arabic(self, text: str) -> str:
106 | """
107 | Normalizes Arabic characters: unifies Alef forms, Yaa/Alef Maqsura, and Taa Marbuta.
108 | """
109 | text = re.sub(r'[إأآ]', 'ا', text)
110 | text = re.sub(r'ى', 'ي', text)
111 | text = re.sub(r'ة', 'ه', text)
112 | return text
113 |
114 | def _remove_stopwords(self, text: str) -> str:
115 | """Removes stopwords from a space-tokenized text."""
116 | words = text.split()
117 | filtered_words = [word for word in words if word not in self.stopwords]
118 | return " ".join(filtered_words)
119 |
120 | def _segment_text(self, text: str) -> str:
121 | """
122 |
123 | Segments the text using the initialized Farasa segmenter.
124 | Returns the original text if the segmenter is not available.
125 | """
126 | if self.segmenter and text:
127 | try:
128 | # Farasa returns a single string with '+' delimiters.
129 | segmented_text = self.segmenter.segment(text)
130 | return segmented_text
131 | except Exception as e:
132 | logging.error(f"Error during Farasa segmentation for text: '{text[:50]}...'. Error: {e}")
133 | return text # Return original text on error
134 | return text # Return original text if no segmenter or empty text
135 |
136 | def process_text(self, text: str) -> str:
137 | """
138 |
139 | Applies the full preprocessing pipeline to a single string of text.
140 | The order of operations is crucial for correctness and efficiency.
141 | """
142 | # 1. Clean first to remove noise
143 | cleaned_text = self._clean_text(text)
144 |
145 | # 2. Normalize characters
146 | normalized_text = self._normalize_arabic(cleaned_text)
147 |
148 | # 3. Remove stopwords
149 | no_stopwords_text = self._remove_stopwords(normalized_text)
150 |
151 | # 4. Segment the remaining text using Farasa
152 | segmented_text = self._segment_text(no_stopwords_text)
153 |
154 | return segmented_text
155 |
156 | def process_dataframe(self, df: pd.DataFrame, text_column: str, new_column_name: str = 'processed_text') -> pd.DataFrame:
157 | """
158 | Applies the full preprocessing pipeline to a pandas DataFrame column.
159 | Includes a progress log for large dataframes.
160 |
161 | Args:
162 | df (pd.DataFrame): The input DataFrame.
163 | text_column (str): The name of the column containing the text to process.
164 | new_column_name (str): The name for the new column with processed text.
165 |
166 | Returns:
167 | pd.DataFrame: DataFrame with the new processed text column.
168 | """
169 | if text_column not in df.columns:
170 | logging.error(f"Column '{text_column}' not found in the DataFrame. Available columns: {df.columns.tolist()}")
171 | raise ValueError(f"Column '{text_column}' not found.")
172 |
173 | df_copy = df.copy()
174 |
175 | logging.info(f"Starting preprocessing for column '{text_column}' in a DataFrame with {len(df_copy)} rows.")
176 |
177 | # Using .apply() is convenient. For very large datasets, consider swifter or Dask for parallelization.
178 | df_copy[new_column_name] = df_copy[text_column].apply(self.process_text)
179 |
180 | logging.info("Finished preprocessing the DataFrame.")
181 |
182 | # Check for empty results which might indicate an issue.
183 | empty_results = df_copy[df_copy[new_column_name] == ''].shape[0]
184 | if empty_results > 0:
185 | logging.warning(f"{empty_results} rows resulted in an empty string after processing. Please check your data and preprocessing steps.")
186 |
187 | return df_copy
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/test_model.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import json
4 | import os
5 | import sys
6 |
7 | import pytest
8 | import torch
9 | import torch.nn as nn
10 |
11 | # Add the source directory to the Python path
12 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..', 'src')))
13 |
14 | from poetry_classifier.model import HybridPoetryClassifier
15 |
16 | # --- Fixtures for Pytest ---
17 |
18 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
19 | def default_model_config():
20 | """Provides a default, valid configuration for the model."""
21 | return {
22 | "input_dim": 100,
23 | "num_classes": 10,
24 | "cnn_filters": 32,
25 | "cnn_kernel_sizes": [2, 3, 4],
26 | "lstm_hidden_dim": 50,
27 | "lstm_layers": 1,
28 | "dropout_rate": 0.3,
29 | }
30 |
31 | @pytest.fixture
32 | def model(default_model_config):
33 | """Provides a default instance of the HybridPoetryClassifier."""
34 | return HybridPoetryClassifier(**default_model_config)
35 |
36 | @pytest.fixture
37 | def dummy_input_batch():
38 | """Provides a dummy input batch tensor for testing the forward pass."""
39 | batch_size = 8
40 | seq_len = 15
41 | input_dim = 100
42 | # Create a random tensor of the expected shape
43 | return torch.randn(batch_size, seq_len, input_dim)
44 |
45 |
46 | # --- Test Cases ---
47 |
48 | class TestHybridPoetryClassifier:
49 |
50 | def test_initialization_success(self, model, default_model_config):
51 | """Test that the model initializes correctly with valid parameters."""
52 | assert model is not None
53 | assert isinstance(model, nn.Module)
54 | # Check if the configuration is stored correctly
55 | for key, value in default_model_config.items():
56 | assert model.config[key] == value
57 |
58 | # Check if sub-modules are created
59 | assert isinstance(model.convs, nn.ModuleList)
60 | assert len(model.convs) == len(default_model_config["cnn_kernel_sizes"])
61 | assert isinstance(model.lstm, nn.LSTM)
62 | assert isinstance(model.fc, nn.Linear)
63 |
64 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("invalid_config, error_msg", [
65 | ({"dropout_rate": 1.1}, "Dropout rate must be in"),
66 | ({"dropout_rate": -0.1}, "Dropout rate must be in"),
67 | ({"input_dim": 0}, "Dimensions, filters, and layer counts must be positive integers"),
68 | ({"cnn_kernel_sizes": [2, 0, 3]}, "cnn_kernel_sizes must be a list of positive integers"),
69 | ({"cnn_kernel_sizes": "not a list"}, "cnn_kernel_sizes must be a list"),
70 | ])
71 | def test_initialization_failure(self, default_model_config, invalid_config, error_msg):
72 | """Test that the model raises ValueError with invalid configuration parameters."""
73 | config = default_model_config.copy()
74 | config.update(invalid_config)
75 |
76 | with pytest.raises(ValueError, match=error_msg):
77 | HybridPoetryClassifier(**config)
78 |
79 | def test_forward_pass_output_shape(self, model, dummy_input_batch, default_model_config):
80 | """Test the forward pass and ensure the output shape is correct."""
81 | model.eval() # Set to evaluation mode
82 | with torch.no_grad():
83 | output = model(dummy_input_batch)
84 |
85 | expected_batch_size = dummy_input_batch.shape[0]
86 | expected_num_classes = default_model_config["num_classes"]
87 |
88 | assert isinstance(output, torch.Tensor)
89 | assert output.shape == (expected_batch_size, expected_num_classes)
90 |
91 | def test_forward_pass_with_different_batch_sizes(self, model):
92 | """Test that the model handles different batch sizes correctly."""
93 | model.eval()
94 | with torch.no_grad():
95 | # Test with batch size 1
96 | input_bs1 = torch.randn(1, 15, 100)
97 | output_bs1 = model(input_bs1)
98 | assert output_bs1.shape == (1, 10)
99 |
100 | # Test with a larger batch size
101 | input_bs32 = torch.randn(32, 15, 100)
102 | output_bs32 = model(input_bs32)
103 | assert output_bs32.shape == (32, 10)
104 |
105 | def test_forward_pass_invalid_input_dim(self, model):
106 | """Test that the model raises an error for input with incorrect dimensions."""
107 | # 2D input instead of 3D
108 | invalid_input = torch.randn(8, 100)
109 | with pytest.raises(ValueError, match="Expected 3D input tensor"):
110 | model(invalid_input)
111 |
112 | def test_trainability_and_gradient_flow(self, model, dummy_input_batch, default_model_config):
113 | """
114 | Perform a single training step to ensure that gradients are computed and
115 | model parameters are updated.
116 | """
117 | model.train() # Set to training mode
118 |
119 | # Create a dummy loss function and optimizer
120 | optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=1e-3)
121 | criterion = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
122 |
123 | # Get a dummy target
124 | dummy_target = torch.randint(0, 2, (dummy_input_batch.shape[0], default_model_config["num_classes"])).float()
125 |
126 | # Get initial parameter values to check for updates
127 | initial_param_sum = sum(p.sum() for p in model.parameters())
128 |
129 | # --- Single training step ---
130 | optimizer.zero_grad()
131 | output = model(dummy_input_batch)
132 | loss = criterion(output, dummy_target)
133 | loss.backward()
134 |
135 | # Check if gradients are computed for the final layer
136 | assert model.fc.weight.grad is not None
137 | assert model.fc.weight.grad.ne(0).any() # Check that gradient is not all zeros
138 |
139 | optimizer.step()
140 |
141 | # Check if parameters have been updated
142 | final_param_sum = sum(p.sum() for p in model.parameters())
143 | assert initial_param_sum != final_param_sum
144 |
145 | def test_save_and_load_model(self, model, dummy_input_batch, tmp_path):
146 | """
147 | Test the model's save and load functionality.
148 | - Save the model state and config.
149 | - Load it back into a new model instance.
150 | - Verify that the new model produces the same output as the original.
151 | """
152 | model.eval()
153 |
154 | # Define paths for saving
155 | model_path = tmp_path / "test_model.pth"
156 | config_path = tmp_path / "test_config.json"
157 |
158 | # Save the model
159 | model.save_model(str(model_path), str(config_path))
160 |
161 | assert os.path.exists(model_path)
162 | assert os.path.exists(config_path)
163 |
164 | # Load the model into a new instance
165 | loaded_model = HybridPoetryClassifier.from_pretrained(str(model_path), str(config_path))
166 | loaded_model.eval()
167 |
168 | assert isinstance(loaded_model, HybridPoetryClassifier)
169 |
170 | # --- Verification ---
171 | # 1. Check that the configurations are identical
172 | with open(config_path, 'r') as f:
173 | saved_config = json.load(f)
174 | assert model.config == saved_config
175 | assert loaded_model.config == saved_config
176 |
177 | # 2. Check that the state dictionaries are identical
178 | assert all(
179 | torch.equal(p1, p2) for p1, p2 in zip(model.state_dict().values(), loaded_model.state_dict().values())
180 | )
181 |
182 | # 3. Most importantly, check that they produce the same output for the same input
183 | with torch.no_grad():
184 | original_output = model(dummy_input_batch)
185 | loaded_output = loaded_model(dummy_input_batch)
186 |
187 | assert torch.allclose(original_output, loaded_output, atol=1e-6)
188 |
189 | def test_device_movement(self, model, dummy_input_batch):
190 | """Test that the model can be moved to CUDA if available."""
191 | if not torch.cuda.is_available():
192 | pytest.skip("CUDA not available, skipping device movement test.")
193 |
194 | # Move model and data to GPU
195 | device = torch.device("cuda")
196 | model.to(device)
197 | gpu_input = dummy_input_batch.to(device)
198 |
199 | # Check if parameters are on the correct device
200 | assert next(model.parameters()).is_cuda
201 |
202 | # Perform a forward pass on GPU
203 | model.eval()
204 | with torch.no_grad():
205 | try:
206 | output = model(gpu_input)
207 | assert output.is_cuda
208 | except Exception as e:
209 | pytest.fail(f"Forward pass on GPU failed: {e}")
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/web_app/core/predictor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import json
4 | import logging
5 | import os
6 | import sys
7 | from typing import List, Dict, Any
8 |
9 | import numpy as np
10 | import streamlit as st
11 | import torch
12 |
13 | # Add project root to path for src imports
14 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.abspath(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..', '..')))
15 |
16 | from src.poetry_classifier.data_processing import PoetryPreprocessor
17 | from src.poetry_classifier.embedding import PoetryEmbedder
18 | from src.poetry_classifier.model import HybridPoetryClassifier
19 | from src.poetry_classifier.segmentation import PoemSegmenter
20 |
21 | # Import configurations
22 | from web_app.config import (
23 | MODEL_PATH, CONFIG_PATH, EMBEDDING_PATH, LABEL_MAPPING_PATH,
24 | SEGMENTER_EPS, SEGMENTER_MIN_SAMPLES, CLASSIFICATION_THRESHOLD
25 | )
26 |
27 | # Configure logger
28 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
29 |
30 |
31 | class PoetryPredictor:
32 | """
33 | A professional, robust, and efficient predictor class for the Arabic Poetry Classifier.
34 |
35 | This class encapsulates the entire prediction pipeline, from text preprocessing to
36 | returning formatted thematic predictions. It is designed to be a singleton-like
37 | resource within a Streamlit application, loading heavy models only once.
38 | """
39 |
40 | def __init__(self):
41 | """
42 | Initializes the predictor by loading all necessary components (preprocessor, models, etc.).
43 | Relies on Streamlit's caching mechanisms passed via factory functions.
44 | """
45 | logger.info("Initializing PoetryPredictor...")
46 | self.device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
47 |
48 | # Load components using factory methods decorated with Streamlit caching
49 | self.preprocessor = self._load_preprocessor()
50 | self.embedder = self._load_embedder()
51 | self.segmenter = self._load_segmenter()
52 | self.classifier = self._load_classifier()
53 | self.label_map = self._load_label_map()
54 |
55 | logger.info(f"PoetryPredictor initialized successfully on device: {self.device}")
56 |
57 | # The following methods use Streamlit's caching.
58 | # The `_self` argument is a convention to make these methods cacheable
59 | # when called from an instance.
60 | @st.cache_resource
61 | def _load_preprocessor(_self) -> PoetryPreprocessor:
62 | logger.info("Loading PoetryPreprocessor...")
63 | return PoetryPreprocessor()
64 |
65 | @st.cache_resource
66 | def _load_embedder(_self) -> PoetryEmbedder:
67 | logger.info(f"Loading PoetryEmbedder from {EMBEDDING_PATH}...")
68 | embedder = PoetryEmbedder()
69 | embedder.load_model(EMBEDDING_PATH)
70 | return embedder
71 |
72 | @st.cache_resource
73 | def _load_segmenter(_self) -> PoemSegmenter:
74 | logger.info(f"Loading PoemSegmenter with eps={SEGMENTER_EPS}, min_samples={SEGMENTER_MIN_SAMPLES}...")
75 | return PoemSegmenter(eps=SEGMENTER_EPS, min_samples=SEGMENTER_MIN_SAMPLES)
76 |
77 | @st.cache_resource
78 | def _load_classifier(_self) -> HybridPoetryClassifier:
79 | logger.info(f"Loading HybridPoetryClassifier from {MODEL_PATH}...")
80 | model = HybridPoetryClassifier.from_pretrained(MODEL_PATH, CONFIG_PATH, device=_self.device)
81 | return model
82 |
83 | @st.cache_data
84 | def _load_label_map(_self) -> Dict[int, str]:
85 | logger.info(f"Loading label map from {LABEL_MAPPING_PATH}...")
86 | try:
87 | # This is a placeholder for how you might load your schema.
88 | # Assuming the JSON has a structure that can be mapped to {index: name}.
89 | # You will need to adapt this to your actual schema file structure.
90 | with open(LABEL_MAPPING_PATH, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
91 | schema = json.load(f)
92 | # Example of extracting leaf nodes from a hierarchical schema
93 | label_map = {}
94 | index = 0
95 | def extract_leaves(node):
96 | nonlocal index
97 | if "subcategories" not in node or not node["subcategories"]:
98 | label_map[index] = node["name"]
99 | index += 1
100 | else:
101 | for sub_node in node["subcategories"]:
102 | extract_leaves(sub_node)
103 |
104 | # Assuming your schema is a list of root nodes
105 | for root_node in schema:
106 | extract_leaves(root_node)
107 |
108 | if not label_map:
109 | raise ValueError("Label map is empty. Check schema file and parsing logic.")
110 |
111 | return label_map
112 | except (FileNotFoundError, KeyError, ValueError) as e:
113 | logger.error(f"Failed to load or parse the label map: {e}")
114 | # Fallback to generic labels if loading fails
115 | num_classes = _self._load_classifier().config['num_classes']
116 | return {i: f"Theme_{i+1}" for i in range(num_classes)}
117 |
118 | def _preprocess_text(self, text: str) -> List[str]:
119 | """Splits text into verses and applies preprocessing."""
120 | if not isinstance(text, str) or not text.strip():
121 | raise ValueError("Input text must be a non-empty string.")
122 |
123 | verses = [v.strip() for v in text.split('\n') if v.strip()]
124 | if not verses:
125 | raise ValueError("No valid verses found in the input text after cleaning.")
126 |
127 | return [self.preprocessor.process_text(v) for v in verses]
128 |
129 | def _embed_and_segment(self, processed_verses: List[str]) -> np.ndarray:
130 | """
131 | Embeds verses, segments them, and returns a single feature vector for the poem.
132 | This part can be enhanced to produce segment-level features.
133 | """
134 | if not processed_verses:
135 | raise ValueError("Cannot embed an empty list of processed verses.")
136 |
137 | # For simplicity, we create a single feature vector for the whole poem.
138 | # This averages all verse embeddings.
139 | full_processed_text = " ".join(processed_verses)
140 | poem_embedding = self.embedder.get_document_vector(full_processed_text)
141 |
142 | if poem_embedding is None:
143 | raise RuntimeError("Embedding model failed to produce a vector.")
144 |
145 | return poem_embedding
146 |
147 | def _classify(self, feature_vector: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
148 | """Runs the feature vector through the classifier model."""
149 | # Model expects a batch, so we add batch and sequence dimensions
150 | input_tensor = torch.tensor(feature_vector, dtype=torch.float32)
151 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).to(self.device)
152 |
153 | self.classifier.eval()
154 | with torch.no_grad():
155 | logits = self.classifier(input_tensor)
156 | probabilities = torch.sigmoid(logits).squeeze().cpu().numpy()
157 | return probabilities
158 |
159 | def predict(self, poem_text: str, top_k: int = 5) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
160 | """
161 | The main prediction pipeline. Orchestrates all steps.
162 |
163 | Args:
164 | poem_text (str): The raw Arabic poetry text.
165 | top_k (int): The number of top themes to return. If None, returns all.
166 |
167 | Returns:
168 | A list of dictionaries, each containing the theme name and its probability.
169 | """
170 | try:
171 | logger.info("Starting a new prediction...")
172 |
173 | # 1. Preprocess
174 | processed_verses = self._preprocess_text(poem_text)
175 |
176 | # 2. Embed
177 | poem_embedding = self._embed_and_segment(processed_verses)
178 |
179 | # 3. Classify
180 | probabilities = self._classify(poem_embedding)
181 |
182 | # 4. Format results
183 | results = []
184 | for i, prob in enumerate(probabilities):
185 | if prob > CLASSIFICATION_THRESHOLD:
186 | results.append({
187 | "theme": self.label_map.get(i, f"Unknown_Theme_{i}"),
188 | "probability": float(prob)
189 | })
190 |
191 | # Sort by probability in descending order
192 | sorted_results = sorted(results, key=lambda x: x['probability'], reverse=True)
193 |
194 | logger.info(f"Prediction successful. Found {len(sorted_results)} themes above threshold.")
195 |
196 | return sorted_results[:top_k] if top_k else sorted_results
197 |
198 | except (ValueError, TypeError) as e:
199 | logger.warning(f"Prediction failed due to invalid input: {e}")
200 | raise # Re-raise to be caught by the UI
201 | except Exception as e:
202 | logger.error(f"An unexpected error occurred in the prediction pipeline: {e}", exc_info=True)
203 | raise RuntimeError("An internal error occurred during analysis.") from e
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/segmentation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import logging
4 | from typing import List, Dict, Tuple, Any
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import pandas as pd
8 | from sklearn.cluster import DBSCAN
9 | from sklearn.metrics import davies_bouldin_score
10 | from sklearn.exceptions import NotFittedError
11 |
12 | # Configure logging
13 | logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
14 |
15 |
16 | class PoemSegmenter:
17 | """
18 | A class for segmenting poems into thematically coherent units using DBSCAN clustering
19 | on verse-level semantic embeddings. It also provides tools for evaluating clustering quality.
20 | """
21 |
22 | def __init__(self, eps: float = 0.5, min_samples: int = 2):
23 | """
24 | Initializes the PoemSegmenter with DBSCAN hyperparameters.
25 |
26 | Args:
27 | eps (float): The maximum distance between two samples for one to be considered as in the neighborhood of the other.
28 | This is the most important DBSCAN parameter.
29 | min_samples (int): The number of samples in a neighborhood for a point to be considered as a core point.
30 | """
31 | if eps <= 0:
32 | raise ValueError("DBSCAN 'eps' parameter must be positive.")
33 | if min_samples < 1:
34 | raise ValueError("DBSCAN 'min_samples' parameter must be at least 1.")
35 |
36 | self.eps = eps
37 | self.min_samples = min_samples
38 | self.dbscan = DBSCAN(eps=self.eps, min_samples=self.min_samples, metric='cosine')
39 | logging.info(f"PoemSegmenter initialized with DBSCAN(eps={self.eps}, min_samples={self.min_samples}, metric='cosine').")
40 |
41 | def _validate_embeddings(self, embeddings: np.ndarray) -> bool:
42 | """
43 | Validates the input embeddings to ensure they are in the correct format.
44 | """
45 | if not isinstance(embeddings, np.ndarray):
46 | logging.error("Embeddings must be a numpy array.")
47 | return False
48 | if embeddings.ndim != 2:
49 | logging.error(f"Embeddings must be a 2D array, but got shape {embeddings.shape}.")
50 | return False
51 | if embeddings.shape[0] < self.min_samples:
52 | logging.warning(f"Number of verses ({embeddings.shape[0]}) is less than min_samples ({self.min_samples}). "
53 | "All points may be classified as noise.")
54 | return True
55 |
56 | def segment_poem(self, verse_embeddings: np.ndarray) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, Dict[str, Any]]:
57 | """
58 | Segments a single poem into topical units based on its verse embeddings.
59 |
60 | Args:
61 | verse_embeddings (np.ndarray): A 2D numpy array where each row is the embedding for a verse.
62 |
63 | Returns:
64 | Tuple[np.ndarray, Dict[str, Any]]:
65 | - A numpy array of cluster labels for each verse. Label -1 indicates noise (a transitional verse).
66 | - A dictionary containing clustering metrics (number of clusters, noise points, Davies-Bouldin Index).
67 | """
68 | if not self._validate_embeddings(verse_embeddings):
69 | raise ValueError("Invalid embeddings format.")
70 |
71 | try:
72 | # Fit DBSCAN to the embeddings
73 | self.dbscan.fit(verse_embeddings)
74 | labels = self.dbscan.labels_
75 | except Exception as e:
76 | logging.error(f"An error occurred during DBSCAN fitting: {e}")
77 | # Return a result indicating failure (e.g., all noise)
78 | return np.full(verse_embeddings.shape[0], -1), {'error': str(e)}
79 |
80 | # --- Calculate Metrics ---
81 | metrics = {}
82 | # Number of clusters in labels, ignoring noise if present.
83 | n_clusters = len(set(labels)) - (1 if -1 in labels else 0)
84 | n_noise = np.sum(labels == -1)
85 |
86 | metrics['num_clusters'] = n_clusters
87 | metrics['num_noise_points'] = n_noise
88 | metrics['total_points'] = len(labels)
89 |
90 | # Davies-Bouldin score can only be calculated if there is more than 1 cluster.
91 | if n_clusters > 1:
92 | try:
93 | db_index = davies_bouldin_score(verse_embeddings, labels)
94 | metrics['davies_bouldin_index'] = db_index
95 | except ValueError as e:
96 | logging.warning(f"Could not calculate Davies-Bouldin Index: {e}")
97 | metrics['davies_bouldin_index'] = None
98 | else:
99 | metrics['davies_bouldin_index'] = None
100 | logging.info(f"Davies-Bouldin Index not calculated (requires at least 2 clusters, found {n_clusters}).")
101 |
102 | logging.debug(f"Segmentation complete. Found {n_clusters} clusters and {n_noise} noise points.")
103 |
104 | return labels, metrics
105 |
106 | def group_verses_by_segment(self, verses: List[str], labels: np.ndarray) -> List[Dict[str, Any]]:
107 | """
108 | Groups original verse texts into segments based on the clustering labels.
109 |
110 | Args:
111 | verses (List[str]): The original list of verse texts.
112 | labels (np.ndarray): The cluster labels from `segment_poem`.
113 |
114 | Returns:
115 | List[Dict[str, Any]]: A list of segments. Each segment is a dictionary
116 | containing the 'segment_label' and a list of 'verses'.
117 | Noise points are grouped into their own individual segments.
118 | """
119 | if len(verses) != len(labels):
120 | raise ValueError("The number of verses must match the number of labels.")
121 |
122 | segments = {}
123 | noise_count = 0
124 |
125 | for i, label in enumerate(labels):
126 | if label == -1:
127 | # Treat each noise point as a separate, transitional segment
128 | segment_id = f"noise_{noise_count}"
129 | noise_count += 1
130 | else:
131 | segment_id = f"segment_{label}"
132 |
133 | if segment_id not in segments:
134 | segments[segment_id] = {'segment_label': label, 'verses': []}
135 |
136 | segments[segment_id]['verses'].append(verses[i])
137 |
138 | # Convert the dictionary of segments to a list, maintaining order if possible (though DBSCAN is not ordered).
139 | # We sort by the original segment label to keep some consistency.
140 | # This is an approximation of order. For true order, one would need to post-process.
141 | sorted_segments = sorted(segments.values(), key=lambda x: str(x['segment_label']))
142 |
143 | return sorted_segments
144 |
145 | def process_poem_df(self, df: pd.DataFrame, poem_id_col: str, verse_text_col: str, vector_col: str) -> pd.DataFrame:
146 | """
147 | Processes a DataFrame containing multiple poems, segmenting each one.
148 |
149 | Args:
150 | df (pd.DataFrame): DataFrame with columns for poem ID, verse text, and verse vectors.
151 | poem_id_col (str): The column name for the poem identifier.
152 | verse_text_col (str): The column name for the verse text.
153 | vector_col (str): The column name for the verse embeddings.
154 |
155 | Returns:
156 | pd.DataFrame: A new DataFrame with segmentation results for each poem, including
157 | labels, metrics, and grouped segments.
158 | """
159 | required_cols = [poem_id_col, verse_text_col, vector_col]
160 | if not all(col in df.columns for col in required_cols):
161 | raise ValueError(f"DataFrame must contain the following columns: {required_cols}")
162 |
163 | results = []
164 |
165 | # Group by poem ID to process each poem individually
166 | for poem_id, group in df.groupby(poem_id_col):
167 | logging.info(f"Segmenting poem ID: {poem_id}")
168 |
169 | verses = group[verse_text_col].tolist()
170 | # Stack the list of arrays into a single 2D array
171 | embeddings = np.vstack(group[vector_col].values)
172 |
173 | try:
174 | labels, metrics = self.segment_poem(embeddings)
175 | grouped_segments = self.group_verses_by_segment(verses, labels)
176 |
177 | results.append({
178 | poem_id_col: poem_id,
179 | 'segmentation_labels': labels,
180 | 'segmentation_metrics': metrics,
181 | 'thematic_segments': grouped_segments
182 | })
183 | except Exception as e:
184 | logging.error(f"Failed to process poem ID {poem_id}: {e}")
185 | results.append({
186 | poem_id_col: poem_id,
187 | 'segmentation_labels': None,
188 | 'segmentation_metrics': {'error': str(e)},
189 | 'thematic_segments': None
190 | })
191 |
192 | if not results:
193 | logging.warning("Processing completed with no results. Check if the input DataFrame was empty.")
194 | return pd.DataFrame()
195 |
196 | return pd.DataFrame(results)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | 📜 Maqasid (مقاصد) 📜
4 |
5 |
6 | A Deep Learning Framework for Nuanced Thematic Classification of Arabic Poetry
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |  11 |
12 |
13 |
11 |
12 |
13 |  14 |
15 |
16 |
14 |
15 |
16 |  17 |
18 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
27 |
28 |  29 |
29 |
30 |
31 | ---
32 |
33 | ## 📖 Table of Contents
34 |
35 | - [✨ Key Features](#-key-features)
36 | - [⚡ Project Structure](#-project-structure)
37 | - [📊 The Mana Corpus](#-the-mana-corpus)
38 | - [🔬 Interactive Exploration with Google Colab](#-interactive-exploration-with-google-colab)
39 | - [📦 Technology Stack](#-technology-stack)
40 | - [🚀 Getting Started](#-getting-started)
41 | - [📜 How to Cite](#-how-to-cite)
42 | - [📄 License](#-license)
43 | ---
44 |
45 | ## ✨ Key Features
46 |
47 | - **Multi-Label Classification:** Accurately assigns multiple, co-occurring themes to a single poem, reflecting its true literary nature.
48 | - **Hierarchical Thematic Schema:** A novel taxonomy based on seven authoritative works of Arabic literary criticism, capturing thematic nuances with up to four levels of specificity.
49 | - **Poetry-Specific Embeddings:** Utilizes a custom `FastText` model trained from scratch on our poetry corpus to understand archaic and metaphorical language.
50 | - **Reproducible MLOps Pipeline:** The entire project is structured with modern MLOps practices, using `DVC` for data versioning to ensure full reproducibility.
51 | - **Interactive Tools:** A user-friendly web application and a Google Colab notebook for model demonstration and in-depth corpus exploration.
52 |
53 | ---
54 |
55 | ### ⚡ Project Structure
56 |
57 | The repository is organized into several key directories, each serving a specific purpose to ensure modularity and clarity.
58 |
59 | ```
60 | /
61 | ├── src/ # Contains the core source code of the Maqasid framework,
62 | │ # including data processing, model architecture, and training logic.
63 | │
64 | ├── web_app/ # Source code for the interactive Streamlit web application,
65 | │ # which provides a user-friendly interface for the model.
66 | │
67 | ├── test/ # Includes unit and integration tests to ensure the reliability
68 | │ # and correctness of the framework's components.
69 | │
70 | ├── images/ # Static image assets used in the documentation and web app.
71 | │
72 | ├── .dvc/ # Directory for DVC metadata (not shown in repo view).
73 | ├── dvc.yaml # Defines the stages of the DVC data pipeline.
74 | └── README.md # This documentation file.
75 |
76 | ```
77 |
78 | ---
79 |
80 | ## 📊 The Mana Corpus
81 |
82 | The **Maqasid** framework was trained and evaluated on the **Mana (مَعنَى) Corpus**, a large-scale, thematically annotated dataset of Arabic poetry developed as part of this research. The corpus is a key contribution of our work and is hosted in its own dedicated repository.
83 |
84 | It features a gold-standard, expert-annotated set and a large, computationally-annotated extension.
85 |
86 | ➡️ **[Explore and Download the Mana Corpus Here](https://github.com/NoorBayan/Mana)**
87 |
88 | For all details regarding the corpus structure, metadata, and usage, please refer to the documentation in the Mana repository.
89 |
90 | ---
91 |
92 | ## 🔬 Interactive Exploration with Google Colab
93 |
94 | To enhance the accessibility and promote hands-on analysis of the **Maqasid Corpus**, we have developed an interactive Google Colab notebook. This tool empowers anyone—from students to seasoned researchers—to visually explore, filter, and analyze the dataset directly in their browser with zero setup.
95 |
96 | ➡️ **[Open the Interactive Explorer in Google Colab](https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1Z6r-Q37jYzyjHcR-nAtRXRfr9BTAWLYG?usp=drive_link)**
97 |
98 | The notebook features two powerful, user-friendly dashboards:
99 |
100 | #### 1. Thematic Poem Browser
101 |
102 | This dashboard provides an intuitive way to navigate the corpus through its rich thematic hierarchy. It allows you to:
103 |
104 | - **Drill-Down Through Themes**: Start from broad categories (e.g., "Love Poetry") and progressively narrow your focus to highly specific sub-themes (e.g., "Chaste Love" → "Love from a distance").
105 | - **Instantly Access Poems**: As you select a theme, the interface immediately populates a list of all poems annotated with that specific theme.
106 | - **View Detailed Poem Analysis**: Clicking on a poem reveals its full text, essential metadata (poet, era), and an interactive pie chart that visualizes its complete thematic composition.
107 |
108 |
109 | The interactive poem browser in action, allowing users to filter poems by theme and view a detailed analysis with a dynamic chart.
110 |
111 | 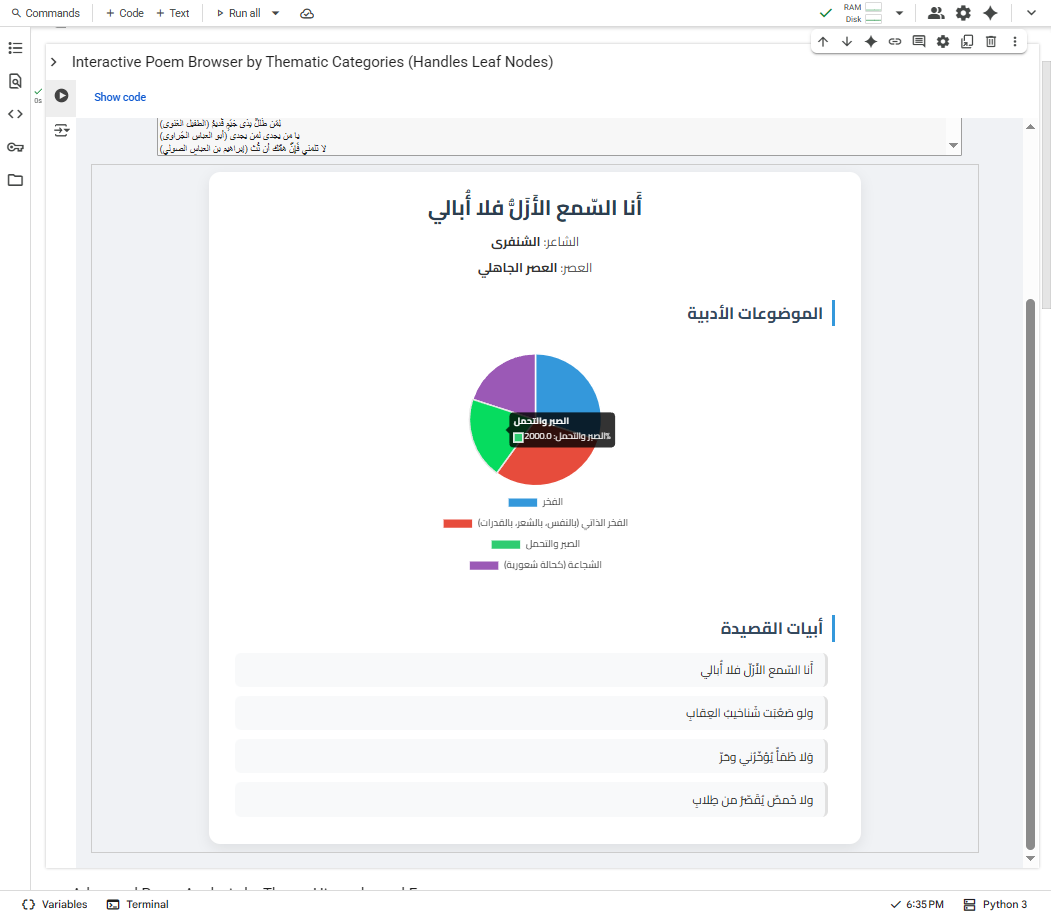 112 |
112 |
113 |
114 | #### 2. Cross-Era Thematic Analysis Dashboard
115 |
116 | Designed for comparative literary studies, this advanced analytical tool enables data-driven investigation into the evolution of poetic themes across different historical periods. Its key functionalities include:
117 |
118 | - **Targeted Analysis**: Select a primary theme (e.g., "Praise Poetry") and a specific historical era (e.g., "Umayyad Period") to focus your inquiry.
119 | - **Dynamic Visualization**: The tool automatically generates a series of hierarchical bar charts that break down the chosen theme into its sub-themes, displaying the frequency of each within the selected era.
120 | - **Uncover Literary Trends**: This dashboard facilitates empirical answers to complex research questions, such as: *"Which sub-themes of Satire were most prevalent in the Abbasid era compared to the Modern era?"*
121 |
122 |
123 | The Cross-Era Analysis Dashboard generating hierarchical bar charts to compare sub-theme frequencies within a selected era.
124 |
125 | 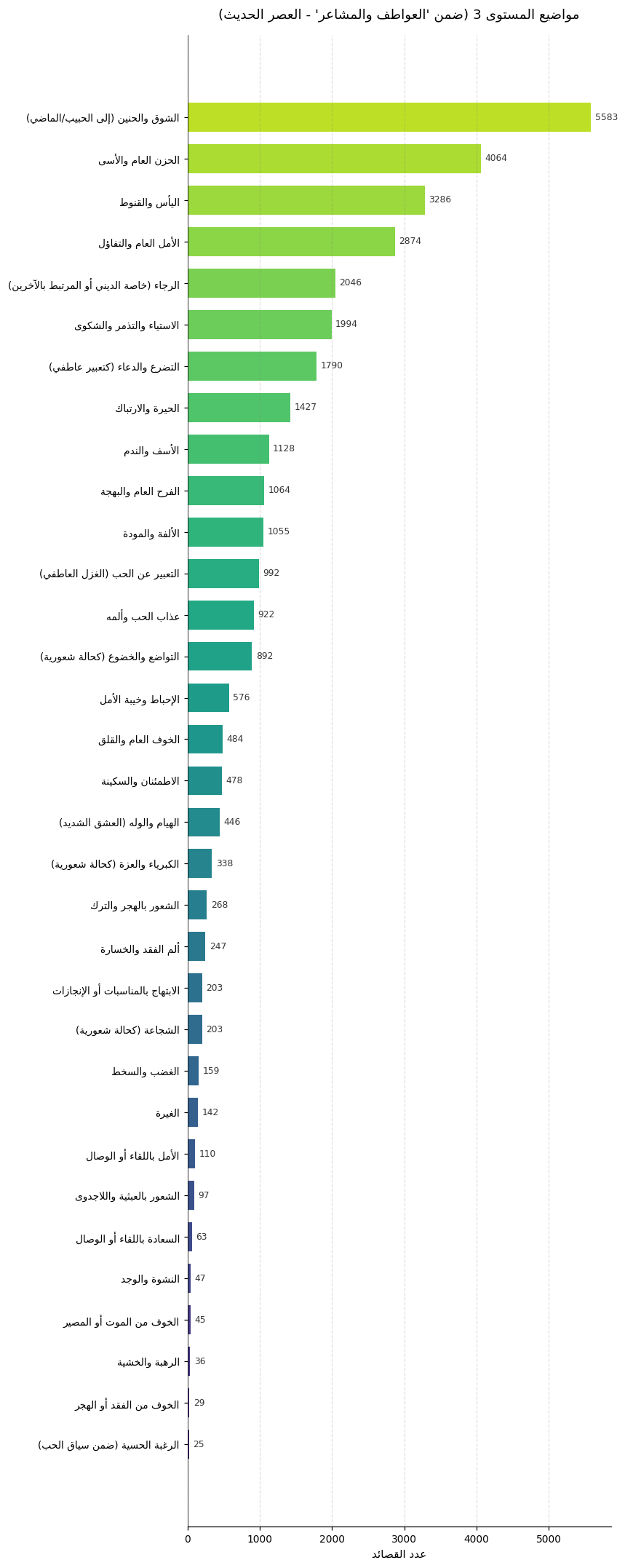 126 |
126 |
127 |
128 | This powerful feature transforms the Maqasid Corpus from a static dataset into a dynamic laboratory for literary and historical inquiry.
129 |
130 | ---
131 |
132 | ## 📦 Technology Stack
133 |
134 | - **Backend & ML:** Python, PyTorch, Gensim, Scikit-learn
135 | - **Web Framework & Notebooks:** Streamlit, Google Colab, Plotly
136 | - **Data Versioning:** DVC
137 | - **HPO:** Optuna
138 | - **Code Quality:** Black, isort, Flake8
139 | - **Testing:** Pytest
140 |
141 | ---
142 |
143 | ## 🚀 Getting Started
144 |
145 | Follow these instructions to set up and run the project on your local machine.
146 |
147 | ### Prerequisites
148 |
149 | - [Python 3.9+](https://www.python.org/downloads/)
150 | - [Java Development Kit (JDK)](https://www.oracle.com/java/technologies/downloads/) (required by `pyfarasa`)
151 | - [Git](https://git-scm.com/downloads/) & [DVC](https://dvc.org/doc/install)
152 |
153 | ### Installation and Setup
154 |
155 | 1. **Clone the Repository**
156 | ```bash
157 | git clone https://github.com/your-username/maqasid.git
158 | cd maqasid
159 | ```
160 |
161 | 2. **Create and Activate a Virtual Environment**
162 | ```bash
163 | python -m venv venv
164 | # On Windows: venv\Scripts\activate
165 | # On macOS/Linux: source venv/bin/activate
166 | ```
167 |
168 | 3. **Install Dependencies**
169 | ```bash
170 | pip install -r requirements.txt
171 | ```
172 |
173 | 4. **Pull Data and Models with DVC**
174 | *This step downloads the large data and model files tracked by DVC.*
175 | ```bash
176 | dvc pull
177 | ```
178 |
179 | 5. **Run the Interactive Web Application**
180 | ```bash
181 | streamlit run web_app/app.py
182 | ```
183 | Your browser should open a new tab with the **Maqasid** dashboard!
184 |
185 | ---
186 |
187 | ### 📜 How to Cite
188 |
189 | If you use the Maqasid framework or the associated corpus in your research, please cite our paper:
190 |
191 | *(Once the paper is published, add the full BibTeX citation here. For now, you can use a placeholder.)*
192 |
193 | ```
194 | bibtex
195 | @article{Al-anazi2025Maqasid,
196 | author = {Your Authors},
197 | title = {Maqasid: A Hybrid CNN-BiLSTM Framework for Nuanced Thematic Classification of Arabic Poetry},
198 | journal = {IEEE Access},
199 | year = {2025 (Forthcoming)}
200 | }
201 |
202 | ```
203 |
204 | ---
205 |
206 | ## 📄 License
207 |
208 | This project is licensed under the MIT License. See the [LICENSE](LICENSE) file for more details.
209 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/hpo.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import logging
4 | import os
5 | import sys
6 |
7 | import optuna
8 | import torch
9 | from torch.optim import Adam, AdamW
10 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
11 |
12 | # Add src to path to allow direct imports
13 | # This is necessary if you run the script directly
14 | sys.path.append(os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), '..'))
15 |
16 | from poetry_classifier.model import HybridPoetryClassifier
17 | from poetry_classifier.trainer import ModelTrainer
18 | from poetry_classifier.dataset import PoetryThematicDataset
19 | from poetry_classifier.utils import set_seed
20 |
21 | # Configure logging
22 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
23 |
24 |
25 | def objective(trial: optuna.trial.Trial, hpo_config: dict) -> float:
26 | """
27 | The objective function for Optuna to optimize.
28 | This function defines a single trial of HPO:
29 | 1. Suggests a set of hyperparameters.
30 | 2. Builds a model with these hyperparameters.
31 | 3. Trains and evaluates the model.
32 | 4. Reports the final performance metric to Optuna.
33 |
34 | Args:
35 | trial (optuna.trial.Trial): An Optuna trial object.
36 | hpo_config (dict): A dictionary containing fixed configurations for HPO
37 | (e.g., data paths, input/output dimensions).
38 |
39 | Returns:
40 | float: The performance metric to be optimized (e.g., validation F1-score).
41 | """
42 | set_seed(42) # Ensure reproducibility for each trial
43 |
44 | try:
45 | # --- 1. Suggest Hyperparameters ---
46 | logger.info(f"--- Starting Trial {trial.number} ---")
47 |
48 | # Optimizer selection
49 | optimizer_name = trial.suggest_categorical("optimizer", ["Adam", "AdamW"])
50 | learning_rate = trial.suggest_float("lr", 1e-5, 1e-2, log=True)
51 |
52 | # Model architecture
53 | cnn_filters = trial.suggest_categorical("cnn_filters", [64, 128, 256])
54 | # Example of suggesting combinations of kernel sizes
55 | kernel_sizes_str = trial.suggest_categorical("cnn_kernel_sizes", ["[2,3,4]", "[3,4,5]", "[2,4,6]"])
56 | cnn_kernel_sizes = eval(kernel_sizes_str)
57 |
58 | lstm_hidden_dim = trial.suggest_categorical("lstm_hidden_dim", [64, 128, 256])
59 | lstm_layers = trial.suggest_int("lstm_layers", 1, 2)
60 | dropout_rate = trial.suggest_float("dropout", 0.1, 0.5)
61 |
62 | # Training related
63 | batch_size = trial.suggest_categorical("batch_size", [16, 32, 64])
64 |
65 | # --- 2. Load Data ---
66 | # Assuming data paths are fixed and provided in hpo_config
67 | train_dataset = PoetryThematicDataset(
68 | csv_path=hpo_config['train_data_path'],
69 | vector_column=hpo_config['vector_column'],
70 | label_columns=hpo_config['label_columns']
71 | )
72 | val_dataset = PoetryThematicDataset(
73 | csv_path=hpo_config['val_data_path'],
74 | vector_column=hpo_config['vector_column'],
75 | label_columns=hpo_config['label_columns']
76 | )
77 |
78 | train_loader = DataLoader(train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
79 | val_loader = DataLoader(val_dataset, batch_size=batch_size)
80 |
81 | # --- 3. Build Model and Optimizer ---
82 | device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
83 |
84 | model = HybridPoetryClassifier(
85 | input_dim=hpo_config['input_dim'],
86 | num_classes=len(hpo_config['label_columns']),
87 | cnn_filters=cnn_filters,
88 | cnn_kernel_sizes=cnn_kernel_sizes,
89 | lstm_hidden_dim=lstm_hidden_dim,
90 | lstm_layers=lstm_layers,
91 | dropout_rate=dropout_rate
92 | ).to(device)
93 |
94 | optimizer = getattr(torch.optim, optimizer_name)(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
95 | criterion = torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss()
96 |
97 | # --- 4. Train and Evaluate ---
98 | trainer_config = {
99 | 'epochs': hpo_config.get('epochs_per_trial', 15), # Limit epochs for HPO
100 | 'checkpoint_dir': os.path.join(hpo_config['hpo_output_dir'], f'trial_{trial.number}'),
101 | 'model_name': 'best_model.pth',
102 | 'early_stopping_patience': hpo_config.get('patience', 3),
103 | 'classification_threshold': 0.5
104 | }
105 |
106 | trainer = ModelTrainer(
107 | model=model,
108 | train_loader=train_loader,
109 | val_loader=val_loader,
110 | optimizer=optimizer,
111 | criterion=criterion,
112 | device=device,
113 | config=trainer_config
114 | )
115 |
116 | # --- Integrate with Optuna's Pruning ---
117 | # We need to adapt the trainer to report intermediate values.
118 | # For simplicity, here we'll just run the full training and get the best F1.
119 | # A more advanced integration would involve callbacks.
120 | history = trainer.train()
121 |
122 | # Check if training was successful
123 | if not history or not history['val_f1']:
124 | logger.warning(f"Trial {trial.number} did not produce any validation results. Returning a low score.")
125 | return 0.0 # Return a poor score to penalize this trial
126 |
127 | best_val_f1 = max(history['val_f1'])
128 | logger.info(f"--- Trial {trial.number} Finished --- Best Val F1: {best_val_f1:.4f}")
129 |
130 | return best_val_f1
131 |
132 | except Exception as e:
133 | logger.error(f"Trial {trial.number} failed with an exception: {e}", exc_info=True)
134 | # Return a poor score to indicate failure, but allow the study to continue.
135 | return 0.0
136 |
137 |
138 | def run_hpo(hpo_config: dict):
139 | """
140 | Main function to orchestrate the hyperparameter optimization process.
141 |
142 | Args:
143 | hpo_config (dict): Main configuration for the HPO study.
144 | """
145 | n_trials = hpo_config.get('n_trials', 50)
146 | output_dir = hpo_config.get('hpo_output_dir', 'hpo_results')
147 |
148 | os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
149 |
150 | # --- Create an Optuna Study ---
151 | # We want to maximize the F1-score, so the direction is 'maximize'.
152 | study = optuna.create_study(
153 | direction="maximize",
154 | pruner=optuna.pruners.MedianPruner(n_warmup_steps=5), # Prune unpromising trials early
155 | study_name="arabic_poetry_classification_hpo"
156 | )
157 |
158 | logger.info(f"Starting HPO study with {n_trials} trials...")
159 |
160 | # The lambda function is used to pass the fixed hpo_config to the objective function.
161 | study.optimize(lambda trial: objective(trial, hpo_config), n_trials=n_trials, timeout=hpo_config.get('timeout_seconds', None))
162 |
163 | # --- Print and Save Results ---
164 | logger.info("HPO study finished.")
165 |
166 | # Best trial
167 | best_trial = study.best_trial
168 | logger.info(f"Best trial number: {best_trial.number}")
169 | logger.info(f"Best value (max F1-score): {best_trial.value:.4f}")
170 | logger.info("Best hyperparameters:")
171 | for key, value in best_trial.params.items():
172 | logger.info(f" {key}: {value}")
173 |
174 | # Save results to a CSV file
175 | results_df = study.trials_dataframe()
176 | results_csv_path = os.path.join(output_dir, "hpo_results.csv")
177 | results_df.to_csv(results_csv_path, index=False)
178 | logger.info(f"Full HPO results saved to {results_csv_path}")
179 |
180 | # --- Visualization ---
181 | # This requires installing plotly: pip install plotly
182 | try:
183 | fig_hist = optuna.visualization.plot_optimization_history(study)
184 | fig_hist.write_image(os.path.join(output_dir, "optimization_history.png"))
185 |
186 | fig_slice = optuna.visualization.plot_slice(study)
187 | fig_slice.write_image(os.path.join(output_dir, "slice_plot.png"))
188 |
189 | fig_importance = optuna.visualization.plot_param_importances(study)
190 | fig_importance.write_image(os.path.join(output_dir, "param_importances.png"))
191 |
192 | logger.info(f"Visualization plots saved to {output_dir}")
193 | except (ImportError, Exception) as e:
194 | logger.warning(f"Could not generate visualization plots. Is plotly installed? Error: {e}")
195 |
196 | if __name__ == '__main__':
197 | # This is an example of how to run the HPO script.
198 | # In a real project, this config would be loaded from a YAML file.
199 |
200 | # Dummy data for demonstration. Replace with your actual data paths.
201 | # Creating dummy files for the script to run without errors.
202 | dummy_data = {
203 | 'vector': [[0.1]*10 for _ in range(100)],
204 | 'label_1': [0, 1]*50,
205 | 'label_2': [1, 0]*50
206 | }
207 | import pandas as pd
208 | os.makedirs('data/annotated', exist_ok=True)
209 | pd.DataFrame(dummy_data).to_csv('data/annotated/dummy_train.csv', index=False)
210 | pd.DataFrame(dummy_data).to_csv('data/annotated/dummy_val.csv', index=False)
211 |
212 | hpo_main_config = {
213 | 'train_data_path': 'data/annotated/dummy_train.csv',
214 | 'val_data_path': 'data/annotated/dummy_val.csv',
215 | 'vector_column': 'vector',
216 | 'label_columns': ['label_1', 'label_2'],
217 | 'input_dim': 10, # Must match the dummy data vector size
218 | 'n_trials': 10, # Use a small number for quick testing
219 | 'epochs_per_trial': 3,
220 | 'patience': 2,
221 | 'hpo_output_dir': 'hpo_run_example'
222 | }
223 |
224 | run_hpo(hpo_main_config)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/embedding.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import logging
4 | import os
5 | from typing import List, Optional, Union
6 |
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import pandas as pd
9 | from gensim.models.fasttext import FastText
10 | from gensim.models.keyedvectors import FastTextKeyedVectors
11 |
12 | # Configure logging
13 | logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
14 |
15 |
16 | class PoetryEmbedder:
17 | """
18 | A comprehensive class for training, loading, and using FastText embeddings
19 | tailored for Arabic poetry. This class handles the end-to-end embedding process,
20 | from training on a corpus to generating document-level vectors.
21 | """
22 |
23 | def __init__(self, model: Optional[FastTextKeyedVectors] = None):
24 | """
25 | Initializes the PoetryEmbedder.
26 |
27 | Args:
28 | model (Optional[FastTextKeyedVectors]): A pre-loaded Gensim FastText model.
29 | If None, a model must be loaded or trained.
30 | """
31 | self.model = model
32 | if self.model:
33 | self.vector_size = self.model.vector_size
34 | logging.info(f"Embedder initialized with a pre-loaded model of vector size {self.vector_size}.")
35 | else:
36 | self.vector_size = None
37 | logging.info("Embedder initialized without a model. Load or train a model before use.")
38 |
39 | def train_model(
40 | self,
41 | corpus_path: str,
42 | text_column: str,
43 | save_path: str,
44 | vector_size: int = 300,
45 | window: int = 5,
46 | min_count: int = 2,
47 | workers: int = -1,
48 | epochs: int = 10
49 | ):
50 | """
51 | Trains a new FastText model from a text corpus (CSV file).
52 |
53 | Args:
54 | corpus_path (str): Path to the training corpus CSV file.
55 | text_column (str): The column name in the CSV containing the preprocessed text.
56 | save_path (str): Path to save the trained model (.bin file).
57 | vector_size (int): Dimensionality of the word vectors.
58 | window (int): The maximum distance between the current and predicted word within a sentence.
59 | min_count (int): Ignores all words with a total frequency lower than this.
60 | workers (int): Use these many worker threads to train the model. -1 means use all available cores.
61 | epochs (int): Number of iterations (epochs) over the corpus.
62 | """
63 | logging.info(f"Starting FastText model training from corpus: {corpus_path}")
64 |
65 | try:
66 | df = pd.read_csv(corpus_path)
67 | if text_column not in df.columns:
68 | raise ValueError(f"Column '{text_column}' not found in {corpus_path}.")
69 |
70 | # Gensim's FastText expects a list of lists of tokens.
71 | sentences = df[text_column].dropna().str.split().tolist()
72 | logging.info(f"Training on {len(sentences)} sentences/documents.")
73 |
74 | except FileNotFoundError:
75 | logging.error(f"Corpus file not found at {corpus_path}.")
76 | raise
77 | except Exception as e:
78 | logging.error(f"Failed to read or process corpus file: {e}")
79 | raise
80 |
81 | if not sentences:
82 | logging.error("The processed corpus is empty. Cannot train the model.")
83 | return
84 |
85 | # Determine the number of workers
86 | if workers == -1:
87 | try:
88 | workers = os.cpu_count() or 4
89 | logging.info(f"Using {workers} CPU cores for training.")
90 | except NotImplementedError:
91 | workers = 4 # Fallback
92 | logging.warning("Could not determine CPU count. Defaulting to 4 workers.")
93 |
94 | # Train the model
95 | logging.info("Training FastText model...")
96 | model = FastText(
97 | sentences=sentences,
98 | vector_size=vector_size,
99 | window=window,
100 | min_count=min_count,
101 | workers=workers,
102 | epochs=epochs,
103 | sg=1 # Use skip-gram
104 | )
105 | logging.info("Model training completed.")
106 |
107 | # Save the model
108 | try:
109 | # Create directory if it doesn't exist
110 | os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(save_path), exist_ok=True)
111 | model.save(save_path)
112 | logging.info(f"Model successfully saved to {save_path}")
113 |
114 | # Load the trained model into the instance
115 | self.load_model(save_path)
116 |
117 | except Exception as e:
118 | logging.error(f"Failed to save the model to {save_path}: {e}")
119 | raise
120 |
121 | def load_model(self, model_path: str):
122 | """
123 | Loads a pre-trained FastText model from a .bin file.
124 |
125 | Args:
126 | model_path (str): Path to the .bin model file.
127 | """
128 | logging.info(f"Loading FastText model from {model_path}...")
129 | try:
130 | # We load only the KeyedVectors to save memory if we don't need to continue training.
131 | self.model = FastText.load(model_path).wv
132 | self.vector_size = self.model.vector_size
133 | logging.info(f"Model loaded successfully. Vector size: {self.vector_size}.")
134 | except FileNotFoundError:
135 | logging.error(f"Model file not found at {model_path}.")
136 | raise
137 | except Exception as e:
138 | logging.error(f"An error occurred while loading the model: {e}")
139 | raise
140 |
141 | def get_word_vector(self, word: str) -> Optional[np.ndarray]:
142 | """
143 | Retrieves the vector for a single word. Returns None if the word is not in vocabulary.
144 |
145 | Args:
146 | word (str): The word to look up.
147 |
148 | Returns:
149 | Optional[np.ndarray]: The word vector, or None if the model is not loaded.
150 | """
151 | if not self.model:
152 | logging.error("Model is not loaded. Cannot get word vector.")
153 | return None
154 |
155 | if word in self.model:
156 | return self.model[word]
157 | else:
158 | # FastText can generate vectors for out-of-vocabulary words
159 | # by using its subword information.
160 | logging.debug(f"Word '{word}' is OOV, generating vector from subwords.")
161 | return self.model[word]
162 |
163 | def get_document_vector(self, text: Union[str, List[str]], strategy: str = 'mean') -> Optional[np.ndarray]:
164 | """
165 | Generates a single vector representation for a document (a string or a list of words).
166 |
167 | Args:
168 | text (Union[str, List[str]]): The input text. Can be a single string or a list of pre-tokenized words.
169 | strategy (str): The strategy to aggregate word vectors. Currently only 'mean' is supported.
170 |
171 | Returns:
172 | Optional[np.ndarray]: A single vector for the document, or None if no valid words are found or model is not loaded.
173 | """
174 | if not self.model:
175 | logging.error("Model is not loaded. Cannot generate document vector.")
176 | return None
177 |
178 | if isinstance(text, str):
179 | tokens = text.split()
180 | elif isinstance(text, list):
181 | tokens = text
182 | else:
183 | logging.error(f"Input text must be a string or a list of strings, but got {type(text)}.")
184 | return None
185 |
186 | if not tokens:
187 | logging.warning("Input text is empty. Returning a zero vector.")
188 | return np.zeros(self.vector_size)
189 |
190 | word_vectors = []
191 | for token in tokens:
192 | # We don't check for OOV because FastText handles it.
193 | word_vectors.append(self.model[token])
194 |
195 | if not word_vectors:
196 | logging.warning(f"No valid word vectors found for the input text: '{' '.join(tokens)[:50]}...'. Returning a zero vector.")
197 | return np.zeros(self.vector_size)
198 |
199 | if strategy == 'mean':
200 | return np.mean(word_vectors, axis=0)
201 | else:
202 | logging.error(f"Unsupported aggregation strategy: '{strategy}'. Only 'mean' is available.")
203 | raise ValueError(f"Unsupported aggregation strategy: '{strategy}'")
204 |
205 | def embed_dataframe_column(self, df: pd.DataFrame, text_column: str, new_column_name: str = 'doc_vector') -> pd.DataFrame:
206 | """
207 | Applies document embedding to a DataFrame column.
208 |
209 | Args:
210 | df (pd.DataFrame): The input DataFrame.
211 | text_column (str): The column containing the preprocessed text.
212 | new_column_name (str): Name for the new column containing document vectors.
213 |
214 | Returns:
215 | pd.DataFrame: The DataFrame with the new vector column.
216 | """
217 | if not self.model:
218 | logging.error("Model is not loaded. Cannot embed DataFrame.")
219 | raise RuntimeError("Model must be loaded before embedding a DataFrame.")
220 |
221 | if text_column not in df.columns:
222 | logging.error(f"Column '{text_column}' not found in the DataFrame.")
223 | raise ValueError(f"Column '{text_column}' not found.")
224 |
225 | logging.info(f"Generating document vectors for column '{text_column}'...")
226 | df_copy = df.copy()
227 | df_copy[new_column_name] = df_copy[text_column].apply(
228 | lambda x: self.get_document_vector(x) if pd.notna(x) else np.zeros(self.vector_size)
229 | )
230 | logging.info("Finished generating document vectors.")
231 | return df_copy
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/trainer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import logging
4 | import os
5 | import time
6 | from typing import Dict, Any
7 |
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | from torch.optim import Adam
12 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
13 | from tqdm import tqdm
14 | from sklearn.metrics import precision_recall_f1_score, hamming_loss
15 |
16 | # Configure logging
17 | logging.basicConfig(
18 | level=logging.INFO,
19 | format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
20 | )
21 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
22 |
23 |
24 | class ModelTrainer:
25 | """
26 | A robust trainer class for PyTorch models, specifically designed for multi-label text classification.
27 | This class encapsulates the training and evaluation loops, metric calculation, early stopping,
28 | and model checkpointing.
29 | """
30 |
31 | def __init__(
32 | self,
33 | model: nn.Module,
34 | train_loader: DataLoader,
35 | val_loader: DataLoader,
36 | optimizer: torch.optim.Optimizer,
37 | criterion: nn.Module,
38 | device: torch.device,
39 | config: Dict[str, Any]
40 | ):
41 | """
42 | Initializes the ModelTrainer.
43 |
44 | Args:
45 | model (nn.Module): The PyTorch model to be trained.
46 | train_loader (DataLoader): DataLoader for the training set.
47 | val_loader (DataLoader): DataLoader for the validation set.
48 | optimizer (torch.optim.Optimizer): The optimizer for training (e.g., Adam).
49 | criterion (nn.Module): The loss function (e.g., nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss).
50 | device (torch.device): The device to run training on ('cpu' or 'cuda').
51 | config (Dict[str, Any]): A dictionary containing training configurations, including:
52 | - 'epochs' (int): Total number of training epochs.
53 | - 'checkpoint_dir' (str): Directory to save model checkpoints.
54 | - 'model_name' (str): Name for the saved model file.
55 | - 'early_stopping_patience' (int): Patience for early stopping.
56 | - 'classification_threshold' (float): Threshold for converting probabilities to binary predictions.
57 | """
58 | self.model = model.to(device)
59 | self.train_loader = train_loader
60 | self.val_loader = val_loader
61 | self.optimizer = optimizer
62 | self.criterion = criterion
63 | self.device = device
64 | self.config = config
65 |
66 | # Extract config values with defaults
67 | self.epochs = self.config.get('epochs', 20)
68 | self.checkpoint_dir = self.config.get('checkpoint_dir', 'saved_models/classifier/')
69 | self.model_name = self.config.get('model_name', 'best_poetry_classifier.pth')
70 | self.patience = self.config.get('early_stopping_patience', 5)
71 | self.threshold = self.config.get('classification_threshold', 0.5)
72 |
73 | # Early stopping attributes
74 | self.best_val_f1 = -1.0
75 | self.epochs_no_improve = 0
76 |
77 | # Ensure checkpoint directory exists
78 | os.makedirs(self.checkpoint_dir, exist_ok=True)
79 |
80 | logger.info("ModelTrainer initialized successfully.")
81 |
82 | def _train_one_epoch(self) -> float:
83 | """Runs a single training epoch."""
84 | self.model.train()
85 | total_loss = 0
86 |
87 | # Progress bar for visual feedback
88 | progress_bar = tqdm(self.train_loader, desc="Training", leave=False)
89 |
90 | for batch in progress_bar:
91 | # Unpack batch and move to device
92 | # Assuming batch is a tuple/list: (inputs, labels)
93 | try:
94 | inputs, labels = batch
95 | inputs = inputs.to(self.device)
96 | labels = labels.to(self.device).float()
97 | except ValueError as e:
98 | logger.error(f"Error unpacking batch. Ensure DataLoader yields (inputs, labels). Error: {e}")
99 | continue # Skip this batch
100 |
101 | # --- Forward Pass ---
102 | self.optimizer.zero_grad()
103 | outputs = self.model(inputs)
104 |
105 | # --- Loss Calculation ---
106 | loss = self.criterion(outputs, labels)
107 |
108 | # --- Backward Pass and Optimization ---
109 | loss.backward()
110 | torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.model.parameters(), max_norm=1.0) # Gradient clipping
111 | self.optimizer.step()
112 |
113 | total_loss += loss.item()
114 | progress_bar.set_postfix(loss=f"{loss.item():.4f}")
115 |
116 | return total_loss / len(self.train_loader)
117 |
118 | def _evaluate(self, data_loader: DataLoader) -> Dict[str, float]:
119 | """Runs evaluation on a given DataLoader."""
120 | self.model.eval()
121 | total_loss = 0
122 | all_preds = []
123 | all_labels = []
124 |
125 | with torch.no_grad():
126 | progress_bar = tqdm(data_loader, desc="Evaluating", leave=False)
127 | for batch in progress_bar:
128 | try:
129 | inputs, labels = batch
130 | inputs = inputs.to(self.device)
131 | labels = labels.to(self.device).float()
132 | except ValueError as e:
133 | logger.error(f"Error unpacking batch during evaluation. Error: {e}")
134 | continue
135 |
136 | outputs = self.model(inputs)
137 | loss = self.criterion(outputs, labels)
138 | total_loss += loss.item()
139 |
140 | # Convert logits to probabilities and then to binary predictions
141 | preds = torch.sigmoid(outputs) > self.threshold
142 |
143 | # Append to lists for overall metric calculation
144 | all_preds.append(preds.cpu().numpy())
145 | all_labels.append(labels.cpu().numpy())
146 |
147 | # Concatenate all batch results
148 | try:
149 | all_preds = np.concatenate(all_preds, axis=0)
150 | all_labels = np.concatenate(all_labels, axis=0)
151 | except ValueError:
152 | logger.error("Evaluation resulted in empty predictions or labels. Check your data loader.")
153 | return {'loss': 0, 'precision': 0, 'recall': 0, 'f1_score': 0, 'hamming_loss': 1}
154 |
155 | # Calculate metrics
156 | # Use macro average to treat all classes equally, important for imbalanced datasets
157 | precision, recall, f1, _ = precision_recall_f1_score(all_labels, all_preds, average='macro', zero_division=0)
158 |
159 | # Hamming loss is useful for multi-label classification
160 | h_loss = hamming_loss(all_labels, all_preds)
161 |
162 | return {
163 | 'loss': total_loss / len(data_loader),
164 | 'precision': precision,
165 | 'recall': recall,
166 | 'f1_score': f1,
167 | 'hamming_loss': h_loss
168 | }
169 |
170 | def _early_stopping(self, val_f1: float) -> bool:
171 | """
172 | Checks for early stopping condition and saves the best model.
173 |
174 | Returns:
175 | bool: True if training should stop, False otherwise.
176 | """
177 | if val_f1 > self.best_val_f1:
178 | self.best_val_f1 = val_f1
179 | self.epochs_no_improve = 0
180 | # Save the best model
181 | best_model_path = os.path.join(self.checkpoint_dir, self.model_name)
182 | try:
183 | torch.save(self.model.state_dict(), best_model_path)
184 | logger.info(f"New best model saved to {best_model_path} with F1-score: {val_f1:.4f}")
185 | except Exception as e:
186 | logger.error(f"Failed to save best model: {e}")
187 | return False
188 | else:
189 | self.epochs_no_improve += 1
190 | if self.epochs_no_improve >= self.patience:
191 | logger.info(f"Early stopping triggered after {self.patience} epochs with no improvement.")
192 | return True
193 | return False
194 |
195 | def train(self) -> Dict[str, Any]:
196 | """
197 | Executes the full training and validation loop for the specified number of epochs.
198 | Implements early stopping.
199 |
200 | Returns:
201 | Dict[str, Any]: A dictionary containing training history and best model path.
202 | """
203 | history = {
204 | 'train_loss': [],
205 | 'val_loss': [],
206 | 'val_f1': [],
207 | 'best_model_path': None
208 | }
209 |
210 | logger.info(f"Starting training for {self.epochs} epochs on device '{self.device}'.")
211 | start_time = time.time()
212 |
213 | try:
214 | for epoch in range(self.epochs):
215 | epoch_start_time = time.time()
216 |
217 | # --- Training ---
218 | train_loss = self._train_one_epoch()
219 | history['train_loss'].append(train_loss)
220 |
221 | # --- Validation ---
222 | val_metrics = self._evaluate(self.val_loader)
223 | val_loss = val_metrics['loss']
224 | val_f1 = val_metrics['f1_score']
225 | history['val_loss'].append(val_loss)
226 | history['val_f1'].append(val_f1)
227 |
228 | epoch_duration = time.time() - epoch_start_time
229 |
230 | logger.info(
231 | f"Epoch {epoch+1}/{self.epochs} | "
232 | f"Train Loss: {train_loss:.4f} | "
233 | f"Val Loss: {val_loss:.4f} | "
234 | f"Val F1: {val_f1:.4f} | "
235 | f"Val Precision: {val_metrics['precision']:.4f} | "
236 | f"Val Recall: {val_metrics['recall']:.4f} | "
237 | f"Duration: {epoch_duration:.2f}s"
238 | )
239 |
240 | # --- Early Stopping Check ---
241 | if self._early_stopping(val_f1):
242 | break
243 |
244 | total_duration = time.time() - start_time
245 | logger.info(f"Training finished in {total_duration:.2f} seconds.")
246 |
247 | history['best_model_path'] = os.path.join(self.checkpoint_dir, self.model_name)
248 |
249 | return history
250 |
251 | except KeyboardInterrupt:
252 | logger.warning("Training interrupted by user.")
253 | return history
254 | except Exception as e:
255 | logger.error(f"An unexpected error occurred during training: {e}", exc_info=True)
256 | raise # Re-raise the exception after logging for debugging
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/model.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 |
3 | import json
4 | import logging
5 | from typing import List, Dict, Any, Union
6 |
7 | import torch
8 | import torch.nn as nn
9 |
10 | # Configure logging for clear and informative output
11 | logging.basicConfig(
12 | level=logging.INFO,
13 | format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s'
14 | )
15 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
16 |
17 |
18 | class HybridPoetryClassifier(nn.Module):
19 | """
20 | A robust and flexible hybrid deep learning model combining CNNs and a Bi-LSTM network
21 | for multi-label thematic classification of Arabic poetry.
22 |
23 | This enhanced version includes rigorous input validation, flexible forward pass,
24 | and clear configuration management for production-ready use.
25 |
26 | Architecture:
27 | 1. Input: Sequences of semantic segment embeddings (batch, seq_len, input_dim).
28 | 2. 1D CNNs: Parallel convolutions with different kernel sizes to capture local features.
29 | Padding is applied to maintain sequence length for the smaller kernels.
30 | 3. Activation & Pooling: ReLU activation followed by Max-over-time pooling.
31 | 4. Bi-LSTM: Processes concatenated CNN features to model sequential context.
32 | 5. Output: A fully connected layer with a Sigmoid activation (handled by loss function)
33 | for independent multi-label predictions.
34 | """
35 |
36 | def __init__(
37 | self,
38 | input_dim: int,
39 | num_classes: int,
40 | cnn_filters: int,
41 | cnn_kernel_sizes: List[int],
42 | lstm_hidden_dim: int,
43 | lstm_layers: int = 1,
44 | dropout_rate: float = 0.5,
45 | ):
46 | """
47 | Initializes the HybridPoetryClassifier model.
48 |
49 | Args:
50 | input_dim (int): The dimension of input embeddings.
51 | num_classes (int): The number of output classes (thematic labels).
52 | cnn_filters (int): The number of filters for each CNN kernel.
53 | cnn_kernel_sizes (List[int]): A list of kernel sizes for parallel CNNs.
54 | lstm_hidden_dim (int): The number of hidden units in the Bi-LSTM per direction.
55 | lstm_layers (int): The number of Bi-LSTM layers.
56 | dropout_rate (float): The dropout probability for regularization.
57 | """
58 | super(HybridPoetryClassifier, self).__init__()
59 |
60 | # --- Rigorous Input Validation ---
61 | self._validate_constructor_args(
62 | input_dim, num_classes, cnn_filters, cnn_kernel_sizes,
63 | lstm_hidden_dim, lstm_layers, dropout_rate
64 | )
65 |
66 | # Store configuration for saving and loading
67 | self.config = {
68 | 'input_dim': input_dim,
69 | 'num_classes': num_classes,
70 | 'cnn_filters': cnn_filters,
71 | 'cnn_kernel_sizes': cnn_kernel_sizes,
72 | 'lstm_hidden_dim': lstm_hidden_dim,
73 | 'lstm_layers': lstm_layers,
74 | 'dropout_rate': dropout_rate,
75 | }
76 |
77 | # --- CNN Layers ---
78 | # We use a ModuleList to hold the parallel convolutional layers.
79 | # Padding is added to handle sequences shorter than the kernel size.
80 | # padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2 for 'same' padding on one side.
81 | self.convs = nn.ModuleList([
82 | nn.Conv1d(
83 | in_channels=input_dim,
84 | out_channels=cnn_filters,
85 | kernel_size=k,
86 | padding=(k - 1) // 2 # Add padding to preserve length for pooling
87 | ) for k in cnn_kernel_sizes
88 | ])
89 |
90 | # --- Bi-LSTM Layer ---
91 | lstm_input_dim = len(cnn_kernel_sizes) * cnn_filters
92 | self.lstm = nn.LSTM(
93 | input_size=lstm_input_dim,
94 | hidden_size=lstm_hidden_dim,
95 | num_layers=lstm_layers,
96 | bidirectional=True,
97 | batch_first=True,
98 | dropout=dropout_rate if lstm_layers > 1 else 0.0
99 | )
100 |
101 | # --- Dropout and Output Layer ---
102 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout_rate)
103 |
104 | # The input to the final linear layer is the concatenated output of the Bi-LSTM
105 | self.fc = nn.Linear(lstm_hidden_dim * 2, num_classes)
106 |
107 | logger.info("HybridPoetryClassifier model initialized successfully.")
108 | self.log_model_summary()
109 |
110 | def _validate_constructor_args(self, *args):
111 | """A helper method to centralize constructor argument validation."""
112 | (input_dim, num_classes, cnn_filters, cnn_kernel_sizes,
113 | lstm_hidden_dim, lstm_layers, dropout_rate) = args
114 |
115 | if not all(isinstance(i, int) and i > 0 for i in [input_dim, num_classes, cnn_filters, lstm_hidden_dim, lstm_layers]):
116 | raise ValueError("Dimensions, filters, and layer counts must be positive integers.")
117 | if not (isinstance(cnn_kernel_sizes, list) and all(isinstance(k, int) and k > 0 for k in cnn_kernel_sizes)):
118 | raise ValueError("cnn_kernel_sizes must be a list of positive integers.")
119 | if not (0.0 <= dropout_rate < 1.0):
120 | raise ValueError(f"Dropout rate must be in [0.0, 1.0), but got {dropout_rate}.")
121 |
122 |
123 | def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
124 | """
125 | Defines the forward pass of the model.
126 |
127 | Args:
128 | x (torch.Tensor): The input tensor of shape (batch_size, seq_len, input_dim).
129 | `seq_len` corresponds to the number of thematic segments in a poem.
130 |
131 | Returns:
132 | torch.Tensor: The output tensor of raw logits of shape (batch_size, num_classes).
133 | """
134 | if x.dim() != 3:
135 | raise ValueError(f"Expected 3D input tensor (batch, seq_len, dim), but got {x.dim()}D.")
136 |
137 | # --- CNN Path ---
138 | # Permute input for Conv1d: (batch, seq_len, input_dim) -> (batch, input_dim, seq_len)
139 | x_permuted = x.permute(0, 2, 1)
140 |
141 | # Apply convolutions and activation
142 | conv_outputs = [torch.relu(conv(x_permuted)) for conv in self.convs]
143 |
144 | # Max-over-time pooling: pool over the sequence dimension
145 | # The output of each pool is (batch, cnn_filters)
146 | pooled_outputs = [torch.max(conv, dim=2)[0] for conv in conv_outputs]
147 |
148 | # Concatenate features from all parallel CNNs
149 | # Shape: (batch, len(cnn_kernel_sizes) * cnn_filters)
150 | cnn_features = torch.cat(pooled_outputs, dim=1)
151 |
152 | # --- Bi-LSTM Path ---
153 | # Add a sequence dimension of 1 for the LSTM, treating CNN output as a single time step
154 | # Shape: (batch, 1, lstm_input_dim)
155 | lstm_input = self.dropout(cnn_features.unsqueeze(1))
156 |
157 | # LSTM forward pass
158 | # lstm_output shape: (batch, seq_len=1, num_directions * hidden_dim)
159 | lstm_output, (hidden, cell) = self.lstm(lstm_input)
160 |
161 | # Squeeze to remove the sequence dimension of 1
162 | # Shape: (batch, 2 * lstm_hidden_dim)
163 | lstm_final_output = lstm_output.squeeze(1)
164 |
165 | # --- Output Path ---
166 | final_features = self.dropout(lstm_final_output)
167 | logits = self.fc(final_features)
168 |
169 | return logits
170 |
171 | def save_model(self, model_path: str, config_path: str):
172 | """Saves the model's state_dict and its configuration to disk."""
173 | logger.info(f"Saving model to {model_path} and config to {config_path}")
174 | try:
175 | # Ensure directory exists
176 | os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(model_path), exist_ok=True)
177 | os.makedirs(os.path.dirname(config_path), exist_ok=True)
178 |
179 | torch.save(self.state_dict(), model_path)
180 |
181 | with open(config_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
182 | json.dump(self.config, f, ensure_ascii=False, indent=4)
183 | logger.info("Model and configuration saved successfully.")
184 |
185 | except IOError as e:
186 | logger.error(f"IOError saving model: Could not write to path. Check permissions. Error: {e}")
187 | raise
188 | except Exception as e:
189 | logger.error(f"An unexpected error occurred while saving the model: {e}")
190 | raise
191 |
192 | @classmethod
193 | def from_pretrained(cls, model_path: str, config_path: str, device: Union[str, torch.device] = 'cpu'):
194 | """Loads a model from a saved state_dict and a configuration file."""
195 | logger.info(f"Loading model from {model_path} and config from {config_path}")
196 | try:
197 | with open(config_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
198 | config = json.load(f)
199 | except FileNotFoundError:
200 | logger.error(f"Configuration file not found at {config_path}")
201 | raise
202 | except json.JSONDecodeError:
203 | logger.error(f"Could not decode JSON from config file at {config_path}")
204 | raise
205 |
206 | # Instantiate the model with the loaded configuration
207 | model = cls(**config)
208 |
209 | # Determine device
210 | device = torch.device(device if torch.cuda.is_available() and device == 'cuda' else 'cpu')
211 |
212 | try:
213 | # Load the state dictionary onto the specified device
214 | model.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path, map_location=device))
215 | logger.info(f"Model state_dict loaded successfully from {model_path}")
216 | except FileNotFoundError:
217 | logger.error(f"Model state_dict file not found at {model_path}")
218 | raise
219 | except RuntimeError as e:
220 | logger.error(f"RuntimeError loading state_dict. This often means the model architecture in the code "
221 | f"does not match the saved weights. Check your config. Error: {e}")
222 | raise
223 |
224 | model.to(device)
225 | model.eval() # Set to evaluation mode by default after loading
226 | logger.info(f"Model loaded on device: '{device}' and set to evaluation mode.")
227 | return model
228 |
229 | def log_model_summary(self):
230 | """Logs a formatted summary of the model's architecture and parameter count."""
231 | total_params = sum(p.numel() for p in self.parameters())
232 | trainable_params = sum(p.numel() for p in self.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
233 |
234 | summary = f"""
235 | ================================================================
236 | Model: {self.__class__.__name__}
237 | ----------------------------------------------------------------
238 | Configuration:
239 | {json.dumps(self.config, indent=4)}
240 | ----------------------------------------------------------------
241 | Total Parameters: {total_params:,}
242 | Trainable Parameters: {trainable_params:,}
243 | ================================================================
244 | """
245 | logger.info(summary)
246 |
247 | def freeze_layers(self, layers_to_freeze: List[str]):
248 | """
249 | Freezes specified layers of the model to prevent them from being trained.
250 | Helpful for fine-tuning.
251 |
252 | Args:
253 | layers_to_freeze (List[str]): A list of layer names to freeze, e.g., ['convs', 'lstm'].
254 | """
255 | logger.warning(f"Freezing layers: {layers_to_freeze}")
256 | for name, param in self.named_parameters():
257 | # Check if the parameter's name starts with any of the specified layer names
258 | if any(name.startswith(layer_name) for layer_name in layers_to_freeze):
259 | param.requires_grad = False
260 |
261 | # Re-log the summary to show the new trainable parameter count
262 | self.log_model_summary()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 29 |
29 |  112 |
112 |  126 |
126 |