├── .github
└── workflows
│ └── email-notification.yml
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── citations.bib
├── examples
├── 01_Creating_Imbalanced_Benchmark_Datasets.ipynb
├── 02_Optimizing_AUROC_with_ResNet20_on_Imbalanced_CIFAR10.ipynb
├── 03_Optimizing_AUPRC_Loss_on_Imbalanced_dataset.ipynb
├── 04_Training_with_Pytorch_Learning_Rate_Scheduling.ipynb
├── 05_Optimizing_AUROC_Loss_with_DenseNet121_on_CheXpert.ipynb
├── 07_Optimizing_Multi_Label_AUROC_Loss_with_DenseNet121_on_CheXpert.ipynb
├── 08_Optimizing_AUROC_Loss_with_DenseNet121_on_Melanoma.ipynb
├── 09_Optimizing_CompositionalAUC_Loss_with_ResNet20_on_CIFAR10.ipynb
├── 10_Optimizing_NDCG_Loss_on_MovieLens20M.ipynb
├── 11_Optimizing_pAUC_Loss_on_Imbalanced_data_wrapper.ipynb
├── 11_Optimizing_pAUC_Loss_with_SOPA_on_Imbalanced_data.ipynb
├── 11_Optimizing_pAUC_Loss_with_SOPAs_on_Imbalanced_data.ipynb
├── 11_Optimizing_pAUC_Loss_with_SOTAs_on_Imbalanced_data.ipynb
├── 12_Optimizing_AUROC_Loss_on_Tabular_Data.ipynb
├── placeholder.md
└── scripts
│ ├── 01_Creating_Imbalanced_Benchmark_Datasets.py
│ ├── 02_optimizing_auroc_with_resnet20_on_imbalanced_cifar10.py
│ ├── 03_optimizing_auprc_loss_on_imbalanced_dataset.py
│ ├── 04_training_with_pytorch_learning_rate_scheduling.py
│ ├── 05_Optimizing_AUROC_loss_with_densenet121_on_CheXpert.py
│ ├── 05_optimizing_auroc_loss_with_densenet121_on_chexpert.py
│ ├── 06_Optimizing_AUROC_loss_with_DenseNet121_on_CIFAR100_in_Federated_Setting_CODASCA.py
│ ├── 07_optimizing_multi_label_auroc_loss_with_densenet121_on_chexpert.py
│ ├── 08_optimizing_auroc_loss_with_densenet121_on_melanoma.py
│ ├── 09_optimizing_compositionalauc_loss_with_resnet20_on_cifar10.py
│ ├── 10_optimizing_ndcg_loss_on_movielens20m.py
│ ├── 11_optimizing_pauc_loss_on_imbalanced_data_wrapper.py
│ ├── 11_optimizing_pauc_loss_with_sopa_on_imbalanced_data.py
│ ├── 11_optimizing_pauc_loss_with_sopas_on_imbalanced_data.py
│ └── 11_optimizing_pauc_loss_with_sotas_on_imbalanced_data.py
├── imgs
└── libauc_logo.png
├── libauc
├── __init__.py
├── datasets
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── breastcancer.py
│ ├── cat_vs_dog.py
│ ├── chexpert.py
│ ├── cifar.py
│ ├── dataset.py
│ ├── folder.py
│ ├── melanoma.py
│ ├── movielens.py
│ ├── musk2.py
│ ├── stl10.py
│ └── webdataset.py
├── losses
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── auc.py
│ ├── contrastive.py
│ ├── losses.py
│ ├── mil.py
│ ├── perf_at_top.py
│ ├── ranking.py
│ └── surrogate.py
├── metrics
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── metrics.py
│ └── metrics_k.py
├── models
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── densenet.py
│ ├── gnn.py
│ ├── mil_models.py
│ ├── neumf.py
│ ├── perceptron.py
│ ├── resnet.py
│ └── resnet_cifar.py
├── optimizers
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── adam.py
│ ├── adamw.py
│ ├── isogclr.py
│ ├── lars.py
│ ├── midam.py
│ ├── pdsca.py
│ ├── pesg.py
│ ├── sgd.py
│ ├── soap.py
│ ├── sogclr.py
│ ├── song.py
│ ├── sopa.py
│ ├── sopa_s.py
│ └── sota_s.py
├── sampler
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── sampler.py
└── utils
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── paper_utils.py
│ └── utils.py
└── setup.py
/.github/workflows/email-notification.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Email Notification
2 |
3 | on:
4 | issues:
5 | types: [opened]
6 |
7 | jobs:
8 | send-email:
9 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
10 |
11 | steps:
12 | - name: Send Email Notification
13 | uses: dawidd6/action-send-mail@v2
14 | with:
15 | server_address: smtp.gmail.com
16 | server_port: 587
17 | username: ${{ secrets.EMAIL_USERNAME }}
18 | password: ${{ secrets.EMAIL_PASSWORD }}
19 | subject: 'New Issue Created'
20 | to: 'yangtia1@gmail.com'
21 | from: 'yangtia1@gmail.com'
22 | body: 'A new issue has been created in your GitHub repository.'
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2023 OptMAI
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 | LibAUC: A Deep Learning Library for X-Risk Optimization
7 | ---
8 |
9 |
10 |  11 |
12 |
13 |
11 |
12 |
13 |  14 |
15 |
16 |
14 |
15 |
16 |  17 |
18 |
19 |
17 |
18 |
19 |  20 |
21 |
22 |
20 |
21 |
22 |  23 |
24 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 | | [**Documentation**](https://docs.libauc.org/)
27 | | [**Installation**](https://libauc.org/installation/)
28 | | [**Website**](https://libauc.org/)
29 | | [**Tutorial**](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/tree/main/examples)
30 | | [**Research**](https://libauc.org/publications/)
31 | | [**Github**](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/) |
32 |
33 |
34 | News
35 | ---
36 |
37 | - [8/14/2024]: **New Version is Available:** We are releasing LibAUC 1.4.0. We offer new optimizers/losses/models and have improved some existing optimizers. For more details, please check the latest [release note](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/releases/).
38 |
39 | - [04/07/2024]: **Bugs fixed:** We fixed a bug in datasets/folder.py by returning a return_index to support SogCLR/iSogCLR for contrastive learning. Fixed incorrect communication with all_gather in GCLoss_v1 and set gamma to original value when u is not 0. None of these were in our experimental code of the paper.
40 |
41 | - [02/11/2024]: **A Bug fixed:** We fixed a bug in the calculation of AUCM loss and MultiLabelAUCM loss (the margin parameter is missed in the original calculation which might cause the loss to be negative). However, it does not affect the learning as the updates are not affected by this. Both the source code and pip install are updated.
42 |
43 | - [06/10/2023]: **LibAUC 1.3.0 is now available!** In this update, we have made improvements and introduced new features. We also release a new documentation website at [https://docs.libauc.org/](https://docs.libauc.org/). Please see the [release notes](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/releases) for details.
44 |
45 |
46 | Why LibAUC?
47 | ---
48 | LibAUC offers an easier way to directly optimize commonly-used performance measures and losses with user-friendly API. LibAUC has broad applications in AI for tackling many challenges, such as **Classification of Imbalanced Data (CID)**, **Learning to Rank (LTR)**, and **Contrastive Learning of Representation (CLR)**. LibAUC provides a unified framework to abstract the optimization of many compositional loss functions, including surrogate losses for AUROC, AUPRC/AP, and partial AUROC that are suitable for CID, surrogate losses for NDCG, top-K NDCG, and listwise losses that are used in LTR, and global contrastive losses for CLR. Here’s an overview:
49 |
50 |
51 | 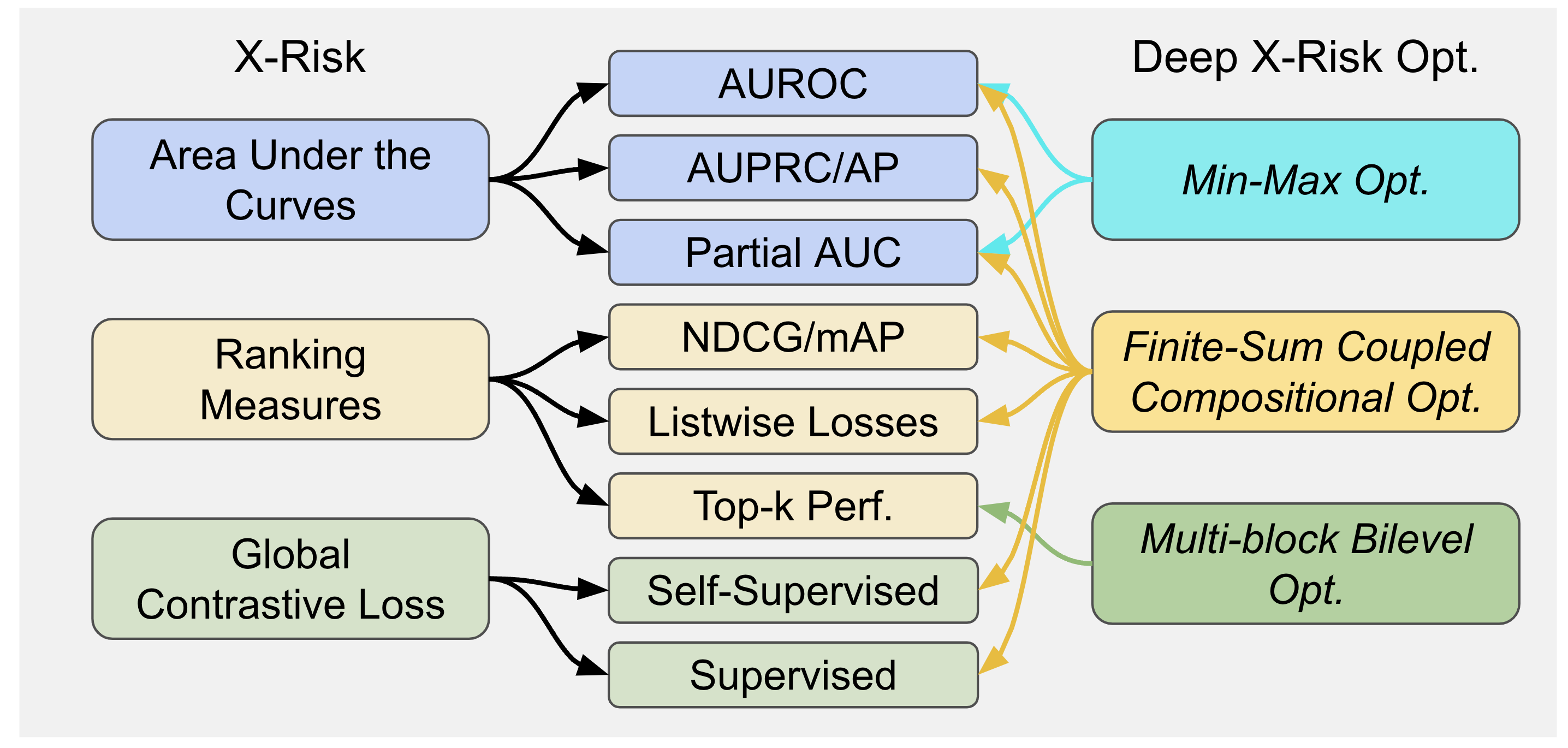 52 |
52 |
53 |
54 |
55 | Installation
56 | --------------
57 | Installing from pip
58 | ```
59 | $ pip install -U libauc
60 | ```
61 |
62 | Installing from source
63 |
64 | ```
65 | $ git clone https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC.git
66 | $ cd LibAUC
67 | $ pip install .
68 | ```
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 | Usage
75 | ---
76 | #### Example training pipline for optimizing X-risk (e.g., AUROC)
77 | ```python
78 | >>> #import our loss and optimizer
79 | >>> from libauc.losses import AUCMLoss
80 | >>> from libauc.optimizers import PESG
81 | >>> #pretraining your model through supervised learning or self-supervised learning
82 | >>> #load a pretrained encoder and random initialize the last linear layer
83 | >>> #define loss & optimizer
84 | >>> Loss = AUCMLoss()
85 | >>> optimizer = PESG()
86 | ...
87 | >>> #training
88 | >>> model.train()
89 | >>> for data, targets in trainloader:
90 | >>> data, targets = data.cuda(), targets.cuda()
91 | logits = model(data)
92 | preds = torch.sigmoid(logits)
93 | loss = Loss(preds, targets)
94 | optimizer.zero_grad()
95 | loss.backward()
96 | optimizer.step()
97 | ...
98 | >>> #update internal parameters
99 | >>> optimizer.update_regularizer()
100 | ```
101 |
102 | Tutorials
103 | -------
104 | ### X-Risk Minimization
105 |
106 | - **Optimizing AUCMLoss**: [[example]](https://docs.libauc.org/examples/auroc.html)
107 | - **Optimizing APLoss**: [[example]](https://docs.libauc.org/examples/auprc.html)
108 | - **Optimizing CompositionalAUCLoss**: [[example]](https://docs.libauc.org/examples/compauc.html)
109 | - **Optimizing pAUCLoss**: [[example]](https://docs.libauc.org/examples/pauc.html)
110 | - **Optimizing MIDAMLoss**: [[example]](https://docs.libauc.org/examples/MIDAM-att-tabular.html)
111 | - **Optimizing NDCGLoss**: [[example]](https://docs.libauc.org/examples/ndcg.html)
112 | - **Optimizing GCLoss (Unimodal)**: [[example]](https://docs.libauc.org/examples/sogclr.html)
113 | - **Optimizing GCLoss (Bimodal)**: [[example]](https://docs.libauc.org/examples/sogclr_gamma.html)
114 |
115 |
116 | Other Applications
117 |
118 | - [Constructing benchmark imbalanced datasets for CIFAR10, CIFAR100, CATvsDOG, STL10](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/blob/main/examples/01_Creating_Imbalanced_Benchmark_Datasets.ipynb)
119 | - [Using LibAUC with PyTorch learning rate scheduler](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/blob/main/examples/04_Training_with_Pytorch_Learning_Rate_Scheduling.ipynb)
120 | - [Optimizing AUROC loss on Chest X-Ray dataset (CheXpert)](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/blob/main/examples/05_Optimizing_AUROC_Loss_with_DenseNet121_on_CheXpert.ipynb)
121 | - [Optimizing AUROC loss on Skin Cancer dataset (Melanoma)](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/blob/main/examples/08_Optimizing_AUROC_Loss_with_DenseNet121_on_Melanoma.ipynb)
122 | - [Optimizing multi-label AUROC loss on Chest X-Ray dataset (CheXpert)](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/blob/main/examples/07_Optimizing_Multi_Label_AUROC_Loss_with_DenseNet121_on_CheXpert.ipynb)
123 | - [Optimizing AUROC loss on Tabular dataset (Credit Fraud)](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/blob/main/examples/12_Optimizing_AUROC_Loss_on_Tabular_Data.ipynb)
124 | - [Optimizing AUROC loss for Federated Learning](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/blob/main/examples/scripts/06_Optimizing_AUROC_loss_with_DenseNet121_on_CIFAR100_in_Federated_Setting_CODASCA.py)
125 | - [Optimizing GCLoss (Bimodal with Cosine Gamma)](https://docs.libauc.org/examples/sogclr_gamma.html)
126 |
127 |
128 |
129 |
130 | Citation
131 | ---------
132 | If you find LibAUC useful in your work, please cite the following papers:
133 | ```
134 | @inproceedings{yuan2023libauc,
135 | title={LibAUC: A Deep Learning Library for X-Risk Optimization},
136 | author={Zhuoning Yuan and Dixian Zhu and Zi-Hao Qiu and Gang Li and Xuanhui Wang and Tianbao Yang},
137 | booktitle={29th SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining},
138 | year={2023}
139 | }
140 | ```
141 | ```
142 | @article{yang2022algorithmic,
143 | title={Algorithmic Foundations of Empirical X-Risk Minimization},
144 | author={Yang, Tianbao},
145 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.00439},
146 | year={2022}
147 | }
148 | ```
149 |
150 | Contact
151 | ----------
152 | For any technical questions, please open a new issue in the Github. If you have any other questions, please contact us via libaucx@gmail.com or tianbao-yang@tamu.edu.
153 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/citations.bib:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | @inproceedings{yuan2023libauc,
2 | title={LibAUC: A Deep Learning Library for X-Risk Optimization},
3 | author={Zhuoning Yuan and Dixian Zhu and Zi-Hao Qiu and Gang Li and Xuanhui Wang and Tianbao Yang},
4 | booktitle={29th SIGKDD Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining},
5 | year={2023}
6 | }
7 |
8 | @article{yang2022algorithmic,
9 | title={Algorithmic Foundation of Deep X-Risk Optimization},
10 | author={Yang, Tianbao},
11 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2206.00439},
12 | year={2022}
13 | }
14 |
15 | @article{yang2022auc,
16 | title={AUC Maximization in the Era of Big Data and AI: A Survey},
17 | author={Yang, Tianbao and Ying, Yiming},
18 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.15046},
19 | year={2022}
20 | }
21 |
22 | @article{yuan2022provable,
23 | title={Provable Stochastic Optimization for Global Contrastive Learning: Small Batch Does Not Harm Performance},
24 | author={Yuan, Zhuoning and Wu, Yuexin and Qiu, Zihao and Du, Xianzhi and Zhang, Lijun and Zhou, Denny and Yang, Tianbao},
25 | booktitle={International Conference on Machine Learning},
26 | year={2022},
27 | organization={PMLR}
28 | }
29 |
30 |
31 | @article{qiu2022large,
32 | title={Large-scale Stochastic Optimization of NDCG Surrogates for Deep Learning with Provable Convergence},
33 | author={Qiu, Zi-Hao and Hu, Quanqi and Zhong, Yongjian and Zhang, Lijun and Yang, Tianbao},
34 | booktitle={International Conference on Machine Learning},
35 | year={2022},
36 | organization={PMLR}
37 | }
38 |
39 | @article{zhu2022auc,
40 | title={When AUC meets DRO: Optimizing Partial AUC for Deep Learning with Non-Convex Convergence Guarantee},
41 | author={Zhu, Dixian and Li, Gang and Wang, Bokun and Wu, Xiaodong and Yang, Tianbao},
42 | booktitle={International Conference on Machine Learning},
43 | year={2022},
44 | organization={PMLR}
45 | }
46 |
47 |
48 | @inproceedings{yuan2021compositional,
49 | title={Compositional Training for End-to-End Deep AUC Maximization},
50 | author={Yuan, Zhuoning and Guo, Zhishuai and Chawla, Nitesh and Yang, Tianbao},
51 | booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations},
52 | year={2022},
53 | organization={PMLR}
54 | }
55 |
56 |
57 | @inproceedings{yuan2021federated,
58 | title={Federated deep AUC maximization for hetergeneous data with a constant communication complexity},
59 | author={Yuan, Zhuoning and Guo, Zhishuai and Xu, Yi and Ying, Yiming and Yang, Tianbao},
60 | booktitle={International Conference on Machine Learning},
61 | pages={12219--12229},
62 | year={2021},
63 | organization={PMLR}
64 | }
65 |
66 | @inproceedings{yuan2021large,
67 | title={Large-scale robust deep auc maximization: A new surrogate loss and empirical studies on medical image classification},
68 | author={Yuan, Zhuoning and Yan, Yan and Sonka, Milan and Yang, Tianbao},
69 | booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
70 | pages={3040--3049},
71 | year={2021}
72 | }
73 | @article{qi2021stochastic,
74 | title={Stochastic optimization of areas under precision-recall curves with provable convergence},
75 | author={Qi, Qi and Luo, Youzhi and Xu, Zhao and Ji, Shuiwang and Yang, Tianbao},
76 | journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
77 | volume={34},
78 | pages={1752--1765},
79 | year={2021}
80 | }
81 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/placeholder.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Code & tutorials will be available soon!
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/01_Creating_Imbalanced_Benchmark_Datasets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Author: Zhuoning Yuan
3 | Contact: yzhuoning@gmail.com
4 | """
5 |
6 | from libauc.datasets import CIFAR10
7 | (train_data, train_label) = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True)
8 | (test_data, test_label) = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False)
9 |
10 | from libauc.datasets import CIFAR100
11 | (train_data, train_label) = CIFAR100(root='./data', train=True)
12 | (test_data, test_label) = CIFAR100(root='./data', train=False)
13 |
14 | from libauc.datasets import CAT_VS_DOG
15 | (train_data, train_label) = CAT_VS_DOG('./data/', train=True)
16 | (test_data, test_label) = CAT_VS_DOG('./data/', train=False)
17 |
18 | from libauc.datasets import STL10
19 | (train_data, train_label) = STL10(root='./data/', split='train') # return numpy array
20 | (test_data, test_label) = STL10(root='./data/', split='test') # return numpy array
21 |
22 | from libauc.utils import ImbalancedDataGenerator
23 |
24 | SEED = 123
25 | imratio = 0.1 # postive_samples/(total_samples)
26 |
27 | from libauc.datasets import CIFAR10
28 | (train_data, train_label) = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True)
29 | (test_data, test_label) = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False)
30 | g = ImbalancedDataGenerator(verbose=True, random_seed=0)
31 | (train_images, train_labels) = g.transform(train_data, train_label, imratio=imratio)
32 | (test_images, test_labels) = g.transform(test_data, test_label, imratio=0.5)
33 |
34 |
35 | import torch
36 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
37 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
38 | import numpy as np
39 | from PIL import Image
40 |
41 | class ImageDataset(Dataset):
42 | def __init__(self, images, targets, image_size=32, crop_size=30, mode='train'):
43 | self.images = images.astype(np.uint8)
44 | self.targets = targets
45 | self.mode = mode
46 | self.transform_train = transforms.Compose([
47 | transforms.ToTensor(),
48 | transforms.RandomCrop((crop_size, crop_size), padding=None),
49 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
50 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
51 | ])
52 | self.transform_test = transforms.Compose([
53 | transforms.ToTensor(),
54 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
55 | ])
56 | def __len__(self):
57 | return len(self.images)
58 |
59 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
60 | image = self.images[idx]
61 | target = self.targets[idx]
62 | image = Image.fromarray(image.astype('uint8'))
63 | if self.mode == 'train':
64 | image = self.transform_train(image)
65 | else:
66 | image = self.transform_test(image)
67 | return image, target
68 |
69 |
70 | trainloader = DataLoader(ImageDataset(train_images, train_labels, mode='train'), batch_size=128, shuffle=True, num_workers=2, pin_memory=True)
71 | testloader = DataLoader(ImageDataset(test_images, test_labels, mode='test'), batch_size=128, shuffle=False, num_workers=2, pin_memory=True)
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/02_optimizing_auroc_with_resnet20_on_imbalanced_cifar10.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """02_Optimizing_AUROC_with_ResNet20_on_Imbalanced_CIFAR10.ipynb
2 |
3 | **Author**: Zhuoning Yuan
4 |
5 | **Introduction**
6 | In this tutorial, you will learn how to quickly train a ResNet20 model by optimizing **AUROC** using our novel [AUCMLoss](https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.03173) and `PESG` optimizer on a binary image classification task on Cifar10. After completion of this tutorial, you should be able to use LibAUC to train your own models on your own datasets.
7 |
8 | **Useful Resources**:
9 | * Website: https://libauc.org
10 | * Github: https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC
11 |
12 | **Reference**:
13 | If you find this tutorial helpful in your work, please acknowledge our library and cite the following paper:
14 | @inproceedings{yuan2021large,
15 | title={Large-scale robust deep auc maximization: A new surrogate loss and empirical studies on medical image classification},
16 | author={Yuan, Zhuoning and Yan, Yan and Sonka, Milan and Yang, Tianbao},
17 | booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
18 | pages={3040--3049},
19 | year={2021}
20 | }
21 | """
22 |
23 |
24 | from libauc.losses import AUCMLoss
25 | from libauc.optimizers import PESG
26 | from libauc.models import resnet20 as ResNet20
27 | from libauc.datasets import CIFAR10
28 | from libauc.utils import ImbalancedDataGenerator
29 | from libauc.sampler import DualSampler
30 | from libauc.metrics import auc_roc_score
31 |
32 | import torch
33 | from PIL import Image
34 | import numpy as np
35 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
36 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
37 | from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
38 |
39 | def set_all_seeds(SEED):
40 | # REPRODUCIBILITY
41 | torch.manual_seed(SEED)
42 | np.random.seed(SEED)
43 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
44 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
45 |
46 |
47 | class ImageDataset(Dataset):
48 | def __init__(self, images, targets, image_size=32, crop_size=30, mode='train'):
49 | self.images = images.astype(np.uint8)
50 | self.targets = targets
51 | self.mode = mode
52 | self.transform_train = transforms.Compose([
53 | transforms.ToTensor(),
54 | transforms.RandomCrop((crop_size, crop_size), padding=None),
55 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
56 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
57 | ])
58 | self.transform_test = transforms.Compose([
59 | transforms.ToTensor(),
60 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
61 | ])
62 | def __len__(self):
63 | return len(self.images)
64 |
65 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
66 | image = self.images[idx]
67 | target = self.targets[idx]
68 | image = Image.fromarray(image.astype('uint8'))
69 | if self.mode == 'train':
70 | image = self.transform_train(image)
71 | else:
72 | image = self.transform_test(image)
73 | return image, target
74 |
75 |
76 | # HyperParameters
77 | SEED = 123
78 | BATCH_SIZE = 128
79 | imratio = 0.1 # for demo
80 | total_epochs = 100
81 | decay_epochs = [50, 75]
82 |
83 | lr = 0.1
84 | margin = 1.0
85 | epoch_decay = 0.003 # refers gamma in the paper
86 | weight_decay = 0.0001
87 |
88 | # oversampling minority class, you can tune it in (0, 0.5]
89 | # e.g., sampling_rate=0.2 is that num of positive samples in mini-batch is sampling_rate*batch_size=13
90 | sampling_rate = 0.2
91 |
92 | # load data as numpy arrays
93 | train_data, train_targets = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True)
94 | test_data, test_targets = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False)
95 |
96 | # generate imbalanced data
97 | generator = ImbalancedDataGenerator(verbose=True, random_seed=0)
98 | (train_images, train_labels) = generator.transform(train_data, train_targets, imratio=imratio)
99 | (test_images, test_labels) = generator.transform(test_data, test_targets, imratio=0.5)
100 |
101 | # data augmentations
102 | trainSet = ImageDataset(train_images, train_labels)
103 | trainSet_eval = ImageDataset(train_images, train_labels, mode='test')
104 | testSet = ImageDataset(test_images, test_labels, mode='test')
105 |
106 | # dataloaders
107 | sampler = DualSampler(trainSet, BATCH_SIZE, sampling_rate=sampling_rate)
108 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainSet, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, sampler=sampler, num_workers=2)
109 | trainloader_eval = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainSet_eval, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
110 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
111 |
112 | """# **Creating models & AUC Optimizer**"""
113 | # You can include sigmoid/l2 activations on model's outputs before computing loss
114 | model = ResNet20(pretrained=False, last_activation=None, num_classes=1)
115 | model = model.cuda()
116 |
117 | # You can also pass Loss.a, Loss.b, Loss.alpha to optimizer (for old version users)
118 | loss_fn = AUCMLoss()
119 | optimizer = PESG(model,
120 | loss_fn=loss_fn,
121 | lr=lr,
122 | momentum=0.9,
123 | margin=margin,
124 | epoch_decay=epoch_decay,
125 | weight_decay=weight_decay)
126 |
127 |
128 | """# **Training**"""
129 | print ('Start Training')
130 | print ('-'*30)
131 |
132 | train_log = []
133 | test_log = []
134 | for epoch in range(total_epochs):
135 | if epoch in decay_epochs:
136 | optimizer.update_regularizer(decay_factor=10) # decrease learning rate by 10x & update regularizer
137 |
138 | train_loss = []
139 | model.train()
140 | for data, targets in trainloader:
141 | data, targets = data.cuda(), targets.cuda()
142 | y_pred = model(data)
143 | y_pred = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
144 | loss = loss_fn(y_pred, targets)
145 | optimizer.zero_grad()
146 | loss.backward()
147 | optimizer.step()
148 | train_loss.append(loss.item())
149 |
150 | # evaluation on train & test sets
151 | model.eval()
152 | train_pred_list = []
153 | train_true_list = []
154 | for train_data, train_targets in trainloader_eval:
155 | train_data = train_data.cuda()
156 | train_pred = model(train_data)
157 | train_pred_list.append(train_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
158 | train_true_list.append(train_targets.numpy())
159 | train_true = np.concatenate(train_true_list)
160 | train_pred = np.concatenate(train_pred_list)
161 | train_auc = auc_roc_score(train_true, train_pred)
162 | train_loss = np.mean(train_loss)
163 |
164 | test_pred_list = []
165 | test_true_list = []
166 | for test_data, test_targets in testloader:
167 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
168 | test_pred = model(test_data)
169 | test_pred_list.append(test_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
170 | test_true_list.append(test_targets.numpy())
171 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true_list)
172 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred_list)
173 | val_auc = auc_roc_score(test_true, test_pred)
174 | model.train()
175 |
176 | # print results
177 | print("epoch: %s, train_loss: %.4f, train_auc: %.4f, test_auc: %.4f, lr: %.4f"%(epoch, train_loss, train_auc, val_auc, optimizer.lr ))
178 | train_log.append(train_auc)
179 | test_log.append(val_auc)
180 |
181 |
182 | """# **Visualization**
183 | Now, let's see the learning curve of optimizing AUROC on train and tes sets.
184 | """
185 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
186 | plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (9,5)
187 | x=np.arange(len(train_log))
188 | plt.figure()
189 | plt.plot(x, train_log, LineStyle='-', label='Train Set', linewidth=3)
190 | plt.plot(x, test_log, LineStyle='-', label='Test Set', linewidth=3)
191 | plt.title('AUCMLoss (10% CIFAR10)',fontsize=25)
192 | plt.legend(fontsize=15)
193 | plt.ylabel('AUROC', fontsize=25)
194 | plt.xlabel('Epoch', fontsize=25)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/03_optimizing_auprc_loss_on_imbalanced_dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """03_Optimizing_AUPRC_Loss_on_Imbalanced_dataset.ipynb
2 | # **Optimizing AUPRC Loss on imbalanced dataset**
3 |
4 | **Author**: Gang Li
5 | **Edited by**: Zhuoning Yuan
6 |
7 | In this tutorial, you will learn how to quickly train a Resnet18 model by optimizing **AUPRC** loss with **SOAP** optimizer [[ref]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.08736) on a binary image classification task with CIFAR-10 dataset. After completion of this tutorial, you should be able to use LibAUC to train your own models on your own datasets.
8 |
9 | **Useful Resources**:
10 | * Website: https://libauc.org
11 | * Github: https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC
12 |
13 | **Reference**:
14 | If you find this tutorial helpful, please acknowledge our library and cite the following paper:
15 |
16 | @article{qi2021stochastic,
17 | title={Stochastic Optimization of Areas Under Precision-Recall Curves with Provable Convergence},
18 | author={Qi, Qi and Luo, Youzhi and Xu, Zhao and Ji, Shuiwang and Yang, Tianbao},
19 | journal={Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems},
20 | volume={34},
21 | year={2021}
22 | }
23 | """
24 |
25 | !pip install libauc==1.2.0
26 |
27 | """# **Importing LibAUC**
28 |
29 | Import required packages to use
30 | """
31 |
32 | from libauc.losses import APLoss
33 | from libauc.optimizers import SOAP
34 | from libauc.models import resnet18 as ResNet18
35 | from libauc.datasets import CIFAR10
36 | from libauc.utils import ImbalancedDataGenerator
37 | from libauc.sampler import DualSampler
38 | from libauc.metrics import auc_prc_score
39 |
40 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
41 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
42 | import numpy as np
43 | import torch
44 | from PIL import Image
45 |
46 | """# **Configurations**
47 | **Reproducibility**
48 | The following function `set_all_seeds` limits the number of sources of randomness behaviors, such as model intialization, data shuffling, etcs. However, completely reproducible results are not guaranteed across PyTorch releases [[Ref]](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#:~:text=Completely%20reproducible%20results%20are%20not,even%20when%20using%20identical%20seeds.).
49 | """
50 |
51 | def set_all_seeds(SEED):
52 | # REPRODUCIBILITY
53 | np.random.seed(SEED)
54 | torch.manual_seed(SEED)
55 | torch.cuda.manual_seed(SEED)
56 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
57 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
58 |
59 | """# **Loading datasets**
60 | In this step, , we will use the [CIFAR10](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) as benchmark dataset. Before importing data to `dataloader`, we construct imbalanced version for CIFAR10 by `ImbalanceDataGenerator`. Specifically, it first randomly splits the training data by class ID (e.g., 10 classes) into two even portions as the positive and negative classes, and then it randomly removes some samples from the positive class to make
61 | it imbalanced. We keep the testing set untouched. We refer `imratio` to the ratio of number of positive examples to number of all examples.
62 | """
63 |
64 | train_data, train_targets = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True)
65 | test_data, test_targets = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False)
66 |
67 | imratio = 0.02
68 | generator = ImbalancedDataGenerator(verbose=True, random_seed=2022)
69 | (train_images, train_labels) = generator.transform(train_data, train_targets, imratio=imratio)
70 | (test_images, test_labels) = generator.transform(test_data, test_targets, imratio=0.5)
71 |
72 | """Now that we defined the data input pipeline such as data augmentations. In this tutorials, we use `RandomCrop`, `RandomHorizontalFlip`."""
73 |
74 | class ImageDataset(Dataset):
75 | def __init__(self, images, targets, image_size=32, crop_size=30, mode='train'):
76 | self.images = images.astype(np.uint8)
77 | self.targets = targets
78 | self.mode = mode
79 | self.transform_train = transforms.Compose([
80 | transforms.ToTensor(),
81 | transforms.RandomCrop((crop_size, crop_size), padding=None),
82 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
83 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
84 | ])
85 | self.transform_test = transforms.Compose([
86 | transforms.ToTensor(),
87 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
88 | ])
89 |
90 |
91 | # for loss function
92 | self.pos_indices = np.flatnonzero(targets==1)
93 | self.pos_index_map = {}
94 | for i, idx in enumerate(self.pos_indices):
95 | self.pos_index_map[idx] = i
96 |
97 | def __len__(self):
98 | return len(self.images)
99 |
100 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
101 | image = self.images[idx]
102 | target = self.targets[idx]
103 | image = Image.fromarray(image.astype('uint8'))
104 | if self.mode == 'train':
105 | idx = self.pos_index_map[idx] if idx in self.pos_indices else -1
106 | image = self.transform_train(image)
107 | else:
108 | image = self.transform_test(image)
109 | return idx, image, target
110 |
111 | """We define `dataset`, `DualSampler` and `dataloader` here. By default, we use `batch_size` 64 and we oversample the minority class with `pos:neg=1:1` by setting `sampling_rate=0.5`."""
112 |
113 | batch_size = 64
114 | sampling_rate = 0.5
115 |
116 | trainSet = ImageDataset(train_images, train_labels)
117 | trainSet_eval = ImageDataset(train_images, train_labels,mode='test')
118 | testSet = ImageDataset(test_images, test_labels, mode='test')
119 |
120 | sampler = DualSampler(trainSet, batch_size, sampling_rate=sampling_rate)
121 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainSet, batch_size=batch_size, sampler=sampler, num_workers=2)
122 | trainloader_eval = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainSet_eval, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
123 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
124 |
125 |
126 | # Parameters
127 |
128 | lr = 1e-3
129 | margin = 0.6
130 | gamma = 0.1
131 | weight_decay = 0
132 | total_epoch = 60
133 | decay_epoch = [30]
134 | SEED = 2022
135 |
136 | """# **Model and Loss Setup**
137 | """
138 |
139 | set_all_seeds(SEED)
140 | model = ResNet18(pretrained=False, last_activation=None)
141 | model = model.cuda()
142 |
143 | Loss = APLoss(pos_len=sampler.pos_len, margin=margin, gamma=gamma)
144 | optimizer = SOAP(model.parameters(), lr=lr, mode='adam', weight_decay=weight_decay)
145 |
146 | """# **Training**"""
147 | print ('Start Training')
148 | print ('-'*30)
149 | test_best = 0
150 | train_list, test_list = [], []
151 | for epoch in range(total_epoch):
152 | if epoch in decay_epoch:
153 | optimizer.update_lr(decay_factor=10)
154 | model.train()
155 | for idx, (index, data, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
156 | data, targets = data.cuda(), targets.cuda()
157 | y_pred = model(data)
158 | y_prob = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
159 | loss = Loss(y_prob, targets, index)
160 | optimizer.zero_grad()
161 | loss.backward()
162 | optimizer.step()
163 |
164 | # evaluation
165 | model.eval()
166 | train_pred, train_true = [], []
167 | for i, data in enumerate(trainloader_eval):
168 | _, train_data, train_targets = data
169 | train_data = train_data.cuda()
170 | y_pred = model(train_data)
171 | y_prob = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
172 | train_pred.append(y_prob.cpu().detach().numpy())
173 | train_true.append(train_targets.cpu().detach().numpy())
174 | train_true = np.concatenate(train_true)
175 | train_pred = np.concatenate(train_pred)
176 | train_ap = auc_prc_score(train_true, train_pred)
177 | train_list.append(train_ap)
178 |
179 | test_pred, test_true = [], []
180 | for j, data in enumerate(testloader):
181 | _, test_data, test_targets = data
182 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
183 | y_pred = model(test_data)
184 | y_prob = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
185 | test_pred.append(y_prob.cpu().detach().numpy())
186 | test_true.append(test_targets.numpy())
187 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true)
188 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred)
189 | val_ap = auc_prc_score(test_true, test_pred)
190 | test_list.append(val_ap)
191 | if test_best < val_ap:
192 | test_best = val_ap
193 |
194 | model.train()
195 | print("epoch: %s, train_ap: %.4f, test_ap: %.4f, lr: %.4f, test_best: %.4f"%(epoch, train_ap, val_ap, optimizer.lr, test_best))
196 |
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/04_training_with_pytorch_learning_rate_scheduling.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """04_Training_with_Pytorch_Learning_Rate_Scheduling.ipynb
3 |
4 | **Author**: Zhuoning Yuan
5 | **Introduction**
6 |
7 | In this tutorial, you will learn how to quickly train models using LibAUC with [Pytorch Learning Rate Scheduler](https:/https://www.kaggle.com/code/isbhargav/guide-to-pytorch-learning-rate-scheduling/notebook/). After completion of this tutorial, you should be able to use LibAUC to train your own models on your own datasets.
8 |
9 | **Useful Resources**:
10 | * Website: https://libauc.org
11 | * Github: https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC
12 |
13 | **Reference**:
14 |
15 | If you find this tutorial helpful in your work, please acknowledge our library and cite the following paper:
16 |
17 | @inproceedings{yuan2021large,
18 | title={Large-scale robust deep auc maximization: A new surrogate loss and empirical studies on medical image classification},
19 | author={Yuan, Zhuoning and Yan, Yan and Sonka, Milan and Yang, Tianbao},
20 | booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
21 | pages={3040--3049},
22 | year={2021}
23 | }
24 | """
25 |
26 | """# **Importing AUC Training Pipeline**"""
27 |
28 | from libauc.losses import AUCMLoss
29 | from libauc.optimizers import PESG
30 | from libauc.models import resnet20 as ResNet20
31 | from libauc.datasets import CIFAR10
32 | from libauc.utils import ImbalancedDataGenerator
33 | from libauc.metrics import auc_roc_score
34 |
35 | import torch
36 | from PIL import Image
37 | import numpy as np
38 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
39 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
40 |
41 | class ImageDataset(Dataset):
42 | def __init__(self, images, targets, image_size=32, crop_size=30, mode='train'):
43 | self.images = images.astype(np.uint8)
44 | self.targets = targets
45 | self.mode = mode
46 | self.transform_train = transforms.Compose([
47 | transforms.ToTensor(),
48 | transforms.RandomCrop((crop_size, crop_size), padding=None),
49 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
50 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
51 | ])
52 | self.transform_test = transforms.Compose([
53 | transforms.ToTensor(),
54 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
55 | ])
56 | def __len__(self):
57 | return len(self.images)
58 |
59 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
60 | image = self.images[idx]
61 | target = self.targets[idx]
62 | image = Image.fromarray(image.astype('uint8'))
63 | if self.mode == 'train':
64 | image = self.transform_train(image)
65 | else:
66 | image = self.transform_test(image)
67 | return image, target
68 |
69 | # paramaters
70 | SEED = 123
71 | BATCH_SIZE = 128
72 | imratio = 0.1
73 | lr = 0.1
74 | epoch_decay = 2e-3 # 1/gamma
75 | weight_decay = 1e-4
76 | margin = 1.0
77 |
78 |
79 | # dataloader
80 | (train_data, train_label) = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True)
81 | (test_data, test_label) = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False)
82 |
83 | generator = ImbalancedDataGenerator(verbose=True, random_seed=0)
84 | (train_images, train_labels) = generator.transform(train_data, train_label, imratio=imratio)
85 | (test_images, test_labels) = generator.transform(test_data, test_label, imratio=0.5)
86 |
87 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(ImageDataset(train_images, train_labels), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=True, num_workers=1, pin_memory=True, drop_last=True)
88 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(ImageDataset(test_images, test_labels, mode='test'), batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False, num_workers=1, pin_memory=True)
89 |
90 | # model
91 | model = ResNet20(pretrained=False, num_classes=1)
92 | model = model.cuda()
93 |
94 | # loss & optimizer
95 | loss_fn = AUCMLoss()
96 | optimizer = PESG(model,
97 | loss_fn=loss_fn,
98 | lr=lr,
99 | margin=margin,
100 | epoch_decay=epoch_decay,
101 | weight_decay=weight_decay)
102 |
103 | """# **Pytorch Learning Rate Scheduling**
104 | We will cover three scheduling functions in this section:
105 | * CosineAnnealingLR
106 | * ReduceLROnPlateau
107 | * MultiStepLR
108 |
109 | For more details, please refer to orginal PyTorch [doc](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/optim.html).
110 |
111 | """
112 |
113 | def reset_model():
114 | # loss & optimizer
115 | loss_fn = AUCMLoss()
116 | optimizer = PESG(model,
117 | loss_fn=loss_fn,
118 | lr=lr,
119 | epoch_decay=epoch_decay,
120 | margin=margin,
121 | weight_decay=weight_decay)
122 | return loss_fn, optimizer
123 |
124 | """### CosineAnnealingLR"""
125 |
126 | total_epochs = 10
127 | loss_fn, optimizer = reset_model()
128 | scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, len(trainloader)*total_epochs)
129 |
130 | model.train()
131 | for epoch in range(total_epochs):
132 | for i, (data, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
133 | data, targets = data.cuda(), targets.cuda()
134 | y_pred = model(data)
135 | y_pred = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
136 | loss = loss_fn(y_pred, targets)
137 | optimizer.zero_grad()
138 | loss.backward()
139 | optimizer.step()
140 | scheduler.step()
141 | print("epoch: {}, loss: {:4f}, lr:{:4f}".format(epoch, loss.item(), optimizer.lr))
142 |
143 | """### ReduceLROnPlateau"""
144 |
145 | total_epochs = 20
146 | loss_fn, optimizer = reset_model()
147 | scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau(optimizer,
148 | patience=3,
149 | verbose=True,
150 | factor=0.5,
151 | threshold=0.001,
152 | min_lr=0.00001)
153 |
154 | model.train()
155 | for epoch in range(total_epochs):
156 | for i, (data, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
157 | data, targets = data.cuda(), targets.cuda()
158 | y_pred = model(data)
159 | y_pred = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
160 | loss = loss_fn(y_pred, targets)
161 | optimizer.zero_grad()
162 | loss.backward()
163 | optimizer.step()
164 | scheduler.step(loss)
165 | print("epoch: {}, loss: {:4f}, lr:{:4f}".format(epoch, loss.item(), optimizer.lr))
166 |
167 | """### MultiStepLR"""
168 |
169 | total_epochs = 20
170 | loss_fn, optimizer = reset_model()
171 | scheduler = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[10,15], gamma=0.1)
172 |
173 | # reset model
174 | model.train()
175 | for epoch in range(total_epochs):
176 | for i, (data, targets) in enumerate(trainloader):
177 | data, targets = data.cuda(), targets.cuda()
178 | y_pred = model(data)
179 | y_pred = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
180 | loss = loss_fn(y_pred, targets)
181 | optimizer.zero_grad()
182 | loss.backward()
183 | optimizer.step()
184 | scheduler.step()
185 | print("epoch: {}, loss: {:4f}, lr:{:4f}".format(epoch, loss.item(), optimizer.lr))
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/05_Optimizing_AUROC_loss_with_densenet121_on_CheXpert.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Author: Zhuoning Yuan
3 | Contact: yzhuoning@gmail.com
4 | """
5 |
6 | from libauc.losses import AUCMLoss, CrossEntropyLoss
7 | from libauc.optimizers import PESG, Adam
8 | from libauc.models import DenseNet121, DenseNet169
9 | from libauc.datasets import CheXpert
10 |
11 | import torch
12 | from PIL import Image
13 | import numpy as np
14 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
15 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
16 | from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
17 |
18 |
19 | def set_all_seeds(SEED):
20 | # REPRODUCIBILITY
21 | torch.manual_seed(SEED)
22 | np.random.seed(SEED)
23 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
24 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
25 |
26 | """# **Pretraining**
27 | * Multi-label classification (5 tasks)
28 | * Adam + CrossEntropy Loss
29 | * This step is optional
30 | """
31 |
32 | # dataloader
33 | root = './CheXpert/CheXpert-v1.0-small/'
34 | # Index: -1 denotes multi-label mode including 5 diseases
35 | traindSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'train.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=False, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='train', class_index=-1)
36 | testSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'valid.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=False, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='valid', class_index=-1)
37 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(traindSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=True)
38 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=False)
39 |
40 | # paramaters
41 | SEED = 123
42 | BATCH_SIZE = 32
43 | lr = 1e-4
44 | weight_decay = 1e-5
45 |
46 | # model
47 | set_all_seeds(SEED)
48 | model = DenseNet121(pretrained=True, last_activation=None, activations='relu', num_classes=5)
49 | model = model.cuda()
50 |
51 | # define loss & optimizer
52 | CELoss = CrossEntropyLoss()
53 | optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=weight_decay)
54 |
55 | # training
56 | best_val_auc = 0
57 | for epoch in range(1):
58 | for idx, data in enumerate(trainloader):
59 | train_data, train_labels = data
60 | train_data, train_labels = train_data.cuda(), train_labels.cuda()
61 | y_pred = model(train_data)
62 | loss = CELoss(y_pred, train_labels)
63 | optimizer.zero_grad()
64 | loss.backward()
65 | optimizer.step()
66 |
67 | # validation
68 | if idx % 400 == 0:
69 | model.eval()
70 | with torch.no_grad():
71 | test_pred = []
72 | test_true = []
73 | for jdx, data in enumerate(testloader):
74 | test_data, test_labels = data
75 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
76 | y_pred = model(test_data)
77 | test_pred.append(y_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
78 | test_true.append(test_labels.numpy())
79 |
80 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true)
81 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred)
82 | val_auc_mean = roc_auc_score(test_true, test_pred)
83 | model.train()
84 |
85 | if best_val_auc < val_auc_mean:
86 | best_val_auc = val_auc_mean
87 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'ce_pretrained_model.pth')
88 |
89 | print ('Epoch=%s, BatchID=%s, Val_AUC=%.4f, Best_Val_AUC=%.4f'%(epoch, idx, val_auc_mean, best_val_auc ))
90 |
91 |
92 | """# **Optimizing AUCM Loss**
93 | * Binary Classification
94 | * PESG + AUCM Loss
95 | """
96 |
97 | # parameters
98 | class_id = 1 # 0:Cardiomegaly, 1:Edema, 2:Consolidation, 3:Atelectasis, 4:Pleural Effusion
99 | root = './CheXpert/CheXpert-v1.0-small/'
100 |
101 | # You can set use_upsampling=True and pass the class name by upsampling_cols=['Cardiomegaly'] to do upsampling. This may improve the performance
102 | traindSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'train.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=True, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='train', class_index=class_id)
103 | testSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'valid.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=False, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='valid', class_index=class_id)
104 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(traindSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=True)
105 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=False)
106 |
107 | # paramaters
108 | SEED = 123
109 | BATCH_SIZE = 32
110 | imratio = traindSet.imratio
111 | lr = 0.05 # using smaller learning rate is better
112 | gamma = 500
113 | weight_decay = 1e-5
114 | margin = 1.0
115 |
116 | # model
117 | set_all_seeds(SEED)
118 | model = DenseNet121(pretrained=False, last_activation='sigmoid', activations='relu', num_classes=1)
119 | model = model.cuda()
120 |
121 |
122 | # load pretrained model
123 | if True:
124 | PATH = 'ce_pretrained_model.pth'
125 | state_dict = torch.load(PATH)
126 | state_dict.pop('classifier.weight', None)
127 | state_dict.pop('classifier.bias', None)
128 | model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
129 |
130 |
131 | # define loss & optimizer
132 | Loss = AUCMLoss(imratio=imratio)
133 | optimizer = PESG(model,
134 | a=Loss.a,
135 | b=Loss.b,
136 | alpha=Loss.alpha,
137 | imratio=imratio,
138 | lr=lr,
139 | gamma=gamma,
140 | margin=margin,
141 | weight_decay=weight_decay)
142 |
143 | best_val_auc = 0
144 | for epoch in range(2):
145 | if epoch > 0:
146 | optimizer.update_regularizer(decay_factor=10)
147 | for idx, data in enumerate(trainloader):
148 | train_data, train_labels = data
149 | train_data, train_labels = train_data.cuda(), train_labels.cuda()
150 | y_pred = model(train_data)
151 | loss = Loss(y_pred, train_labels)
152 | optimizer.zero_grad()
153 | loss.backward()
154 | optimizer.step()
155 |
156 | # validation
157 | if idx % 400 == 0:
158 | model.eval()
159 | with torch.no_grad():
160 | test_pred = []
161 | test_true = []
162 | for jdx, data in enumerate(testloader):
163 | test_data, test_label = data
164 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
165 | y_pred = model(test_data)
166 | test_pred.append(y_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
167 | test_true.append(test_label.numpy())
168 |
169 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true)
170 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred)
171 | val_auc = roc_auc_score(test_true, test_pred)
172 | model.train()
173 |
174 | if best_val_auc < val_auc:
175 | best_val_auc = val_auc
176 |
177 | print ('Epoch=%s, BatchID=%s, Val_AUC=%.4f, lr=%.4f'%(epoch, idx, val_auc, optimizer.lr))
178 |
179 | print ('Best Val_AUC is %.4f'%best_val_auc)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/05_optimizing_auroc_loss_with_densenet121_on_chexpert.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """05_Optimizing_AUROC_Loss_with_DenseNet121_on_CheXpert.ipynb
2 |
3 | **Author**: Zhuoning Yuan
4 |
5 | **Introduction**
6 | In this tutorial, you will learn how to quickly train a DenseNet121 model by optimizing **AUROC** using our novel **`AUCMLoss`** and **`PESG`** optimizer on Chest X-Ray dataset, e.g., [CheXpert](https://stanfordmlgroup.github.io/competitions/chexpert/). After completion of this tutorial, you should be able to use LibAUC to train your own models on your own datasets.
7 |
8 | **Useful Resources**:
9 | * Website: https://libauc.org
10 | * Github: https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC
11 |
12 | **Reference**:
13 | If you find this tutorial helpful in your work, please acknowledge our library and cite the following paper:
14 |
15 | @inproceedings{yuan2021large,
16 | title={Large-scale robust deep auc maximization: A new surrogate loss and empirical studies on medical image classification},
17 | author={Yuan, Zhuoning and Yan, Yan and Sonka, Milan and Yang, Tianbao},
18 | booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
19 | pages={3040--3049},
20 | year={2021}
21 | }
22 | """
23 |
24 | """# **Downloading CheXpert**
25 | * To request dataset access, you need to apply from CheXpert website: https://stanfordmlgroup.github.io/competitions/chexpert/
26 | * In this tutorial, we use the smaller version of dataset with lower image resolution, i.e., *CheXpert-v1.0-small.zip*
27 |
28 | """
29 |
30 | """
31 | # **Importing LibAUC**"""
32 |
33 | from libauc.losses import AUCMLoss, CrossEntropyLoss
34 | from libauc.optimizers import PESG, Adam
35 | from libauc.models import densenet121 as DenseNet121
36 | from libauc.datasets import CheXpert
37 |
38 | import torch
39 | from PIL import Image
40 | import numpy as np
41 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
42 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
43 | from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
44 |
45 | """# **Reproducibility**"""
46 |
47 | def set_all_seeds(SEED):
48 | # REPRODUCIBILITY
49 | torch.manual_seed(SEED)
50 | np.random.seed(SEED)
51 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
52 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
53 |
54 | """# **Pretraining**
55 | * Multi-label classification (5 tasks)
56 | * Adam + CrossEntropy Loss
57 | * This step is optional
58 |
59 |
60 |
61 | """
62 |
63 | # dataloader
64 | root = './CheXpert/CheXpert-v1.0-small/'
65 | # Index: -1 denotes multi-label mode including 5 diseases
66 | traindSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'train.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=False, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='train', class_index=-1)
67 | testSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'valid.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=False, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='valid', class_index=-1)
68 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(traindSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=True)
69 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=False)
70 |
71 | # paramaters
72 | SEED = 123
73 | BATCH_SIZE = 32
74 | lr = 1e-4
75 | weight_decay = 1e-5
76 |
77 | # model
78 | set_all_seeds(SEED)
79 | model = DenseNet121(pretrained=True, last_activation=None, activations='relu', num_classes=5)
80 | model = model.cuda()
81 |
82 | # define loss & optimizer
83 | CELoss = CrossEntropyLoss()
84 | optimizer = Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr, weight_decay=weight_decay)
85 |
86 | # training
87 | best_val_auc = 0
88 | for epoch in range(1):
89 | for idx, data in enumerate(trainloader):
90 | train_data, train_labels = data
91 | train_data, train_labels = train_data.cuda(), train_labels.cuda()
92 | y_pred = model(train_data)
93 | loss = CELoss(y_pred, train_labels)
94 | optimizer.zero_grad()
95 | loss.backward()
96 | optimizer.step()
97 |
98 | # validation
99 | if idx % 400 == 0:
100 | model.eval()
101 | with torch.no_grad():
102 | test_pred = []
103 | test_true = []
104 | for jdx, data in enumerate(testloader):
105 | test_data, test_labels = data
106 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
107 | y_pred = model(test_data)
108 | test_pred.append(y_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
109 | test_true.append(test_labels.numpy())
110 |
111 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true)
112 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred)
113 | val_auc_mean = roc_auc_score(test_true, test_pred)
114 | model.train()
115 |
116 | if best_val_auc < val_auc_mean:
117 | best_val_auc = val_auc_mean
118 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'ce_pretrained_model.pth')
119 |
120 | print ('Epoch=%s, BatchID=%s, Val_AUC=%.4f, Best_Val_AUC=%.4f'%(epoch, idx, val_auc_mean, best_val_auc ))
121 |
122 | """# **Optimizing AUCM Loss**
123 | * Binary Classification
124 | * PESG + AUCM Loss
125 | Note: you can also try other losses in this task, e.g., [CompositionalAUCLoss](https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/blob/main/examples/09_Optimizing_CompositionalAUC_Loss_with_ResNet20_on_CIFAR10.ipynb).
126 | """
127 |
128 | # parameters
129 | class_id = 1 # 0:Cardiomegaly, 1:Edema, 2:Consolidation, 3:Atelectasis, 4:Pleural Effusion
130 | root = './CheXpert/CheXpert-v1.0-small/'
131 |
132 | # You can set use_upsampling=True and pass the class name by upsampling_cols=['Cardiomegaly'] to do upsampling. This may improve the performance
133 | traindSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'train.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=True, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='train', class_index=class_id)
134 | testSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'valid.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=False, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='valid', class_index=class_id)
135 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(traindSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=True)
136 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=False)
137 |
138 | # paramaters
139 | SEED = 123
140 | BATCH_SIZE = 32
141 | imratio = traindSet.imratio
142 | lr = 0.05 # using smaller learning rate is better
143 | epoch_decay = 2e-3
144 | weight_decay = 1e-5
145 | margin = 1.0
146 |
147 | # model
148 | set_all_seeds(SEED)
149 | model = DenseNet121(pretrained=False, last_activation=None, activations='relu', num_classes=1)
150 | model = model.cuda()
151 |
152 |
153 | # load pretrained model
154 | if True:
155 | PATH = 'ce_pretrained_model.pth'
156 | state_dict = torch.load(PATH)
157 | state_dict.pop('classifier.weight', None)
158 | state_dict.pop('classifier.bias', None)
159 | model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
160 |
161 |
162 | # define loss & optimizer
163 | loss_fn = AUCMLoss()
164 | optimizer = PESG(model,
165 | loss_fn=loss_fn,
166 | lr=lr,
167 | margin=margin,
168 | epoch_decay=epoch_decay,
169 | weight_decay=weight_decay)
170 |
171 | best_val_auc = 0
172 | for epoch in range(2):
173 | if epoch > 0:
174 | optimizer.update_regularizer(decay_factor=10)
175 | for idx, data in enumerate(trainloader):
176 | train_data, train_labels = data
177 | train_data, train_labels = train_data.cuda(), train_labels.cuda()
178 | y_pred = model(train_data)
179 | y_pred = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
180 | loss = loss_fn(y_pred, train_labels)
181 | optimizer.zero_grad()
182 | loss.backward()
183 | optimizer.step()
184 |
185 | # validation
186 | if idx % 400 == 0:
187 | model.eval()
188 | with torch.no_grad():
189 | test_pred = []
190 | test_true = []
191 | for jdx, data in enumerate(testloader):
192 | test_data, test_label = data
193 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
194 | y_pred = model(test_data)
195 | test_pred.append(y_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
196 | test_true.append(test_label.numpy())
197 |
198 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true)
199 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred)
200 | val_auc = roc_auc_score(test_true, test_pred)
201 | model.train()
202 |
203 | if best_val_auc < val_auc:
204 | best_val_auc = val_auc
205 |
206 | print ('Epoch=%s, BatchID=%s, Val_AUC=%.4f, lr=%.4f'%(epoch, idx, val_auc, optimizer.lr))
207 |
208 | print ('Best Val_AUC is %.4f'%best_val_auc)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/07_optimizing_multi_label_auroc_loss_with_densenet121_on_chexpert.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | # Optimizing Multi-label AUROC loss on Chest X-Ray Dataset (CheXpert)
3 |
4 | Author: Zhuoning Yuan
5 |
6 | Reference:
7 |
8 | If you find this tutorial helpful in your work, please acknowledge our library and cite the following paper:
9 |
10 | @inproceedings{yuan2021large,
11 | title={Large-scale robust deep auc maximization: A new surrogate loss and empirical studies on medical image classification},
12 | author={Yuan, Zhuoning and Yan, Yan and Sonka, Milan and Yang, Tianbao},
13 | booktitle={Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision},
14 | pages={3040--3049},
15 | year={2021}
16 | }
17 |
18 | @misc{libauc2022,
19 | title={LibAUC: A Deep Learning Library for X-Risk Optimization.},
20 | author={Zhuoning Yuan, Zi-Hao Qiu, Gang Li, Dixian Zhu, Zhishuai Guo, Quanqi Hu, Bokun Wang, Qi Qi, Yongjian Zhong, Tianbao Yang},
21 | year={2022}
22 | }
23 |
24 | """
25 |
26 |
27 | from libauc.losses import AUCM_MultiLabel, CrossEntropyLoss
28 | from libauc.optimizers import PESG, Adam
29 | from libauc.models import densenet121 as DenseNet121
30 | from libauc.datasets import CheXpert
31 | from libauc.metrics import auc_roc_score # for multi-task
32 |
33 | import torch
34 | from PIL import Image
35 | import numpy as np
36 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
37 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
38 | from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
39 | import torch.nn.functional as F
40 |
41 |
42 | def set_all_seeds(SEED):
43 | # REPRODUCIBILITY
44 | torch.manual_seed(SEED)
45 | np.random.seed(SEED)
46 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
47 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
48 |
49 |
50 | # dataloader
51 | root = './CheXpert/CheXpert-v1.0-small/'
52 | # Index: -1 denotes multi-label mode including 5 diseases
53 | traindSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'train.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=False, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='train', class_index=-1, verbose=False)
54 | testSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'valid.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=False, use_frontal=True, image_size=224, mode='valid', class_index=-1, verbose=False)
55 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(traindSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=True)
56 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, shuffle=False)
57 |
58 | # check imbalance ratio for each task
59 | print (traindSet.imratio_list )
60 |
61 | # paramaters
62 | SEED = 123
63 | BATCH_SIZE = 32
64 | lr = 0.1
65 | gamma = 500
66 | weight_decay = 1e-5
67 | margin = 1.0
68 |
69 | # model
70 | set_all_seeds(SEED)
71 | model = DenseNet121(pretrained=True, last_activation=None, activations='relu', num_classes=5)
72 | model = model.cuda()
73 |
74 | # define loss & optimizer
75 | Loss = AUCM_MultiLabel(num_classes=5)
76 | optimizer = PESG(model,
77 | a=Loss.a,
78 | b=Loss.b,
79 | alpha=Loss.alpha,
80 | lr=lr,
81 | gamma=gamma,
82 | margin=margin,
83 | weight_decay=weight_decay, device='cuda')
84 |
85 | # training
86 | best_val_auc = 0
87 | for epoch in range(2):
88 |
89 | if epoch > 0:
90 | optimizer.update_regularizer(decay_factor=10)
91 |
92 | for idx, data in enumerate(trainloader):
93 | train_data, train_labels = data
94 | train_data, train_labels = train_data.cuda(), train_labels.cuda()
95 | y_pred = model(train_data)
96 | y_pred = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
97 | loss = Loss(y_pred, train_labels)
98 | optimizer.zero_grad()
99 | loss.backward()
100 | optimizer.step()
101 |
102 | # validation
103 | if idx % 400 == 0:
104 | model.eval()
105 | with torch.no_grad():
106 | test_pred = []
107 | test_true = []
108 | for jdx, data in enumerate(testloader):
109 | test_data, test_labels = data
110 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
111 | y_pred = model(test_data)
112 | y_pred = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
113 | test_pred.append(y_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
114 | test_true.append(test_labels.numpy())
115 |
116 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true)
117 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred)
118 | val_auc_mean = roc_auc_score(test_true, test_pred)
119 | model.train()
120 |
121 | if best_val_auc < val_auc_mean:
122 | best_val_auc = val_auc_mean
123 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), 'aucm_multi_label_pretrained_model.pth')
124 |
125 | print ('Epoch=%s, BatchID=%s, Val_AUC=%.4f, Best_Val_AUC=%.4f'%(epoch, idx, val_auc_mean, best_val_auc))
126 |
127 |
128 | # show auc roc scores for each task
129 | auc_roc_score(test_true, test_pred)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/08_optimizing_auroc_loss_with_densenet121_on_melanoma.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Author: Zhuoning Yuan
3 | Contact: yzhuoning@gmail.com
4 | """
5 |
6 | """
7 | # **Importing LibAUC**"""
8 |
9 | from libauc.losses import AUCMLoss
10 | from libauc.optimizers import PESG
11 | from libauc.models import DenseNet121, DenseNet169
12 | from libauc.datasets import Melanoma
13 | from libauc.utils import auroc
14 |
15 | import torch
16 | from PIL import Image
17 | import numpy as np
18 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
19 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
20 |
21 | """# **Reproducibility**"""
22 |
23 | def set_all_seeds(SEED):
24 | # REPRODUCIBILITY
25 | torch.manual_seed(SEED)
26 | np.random.seed(SEED)
27 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
28 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
29 |
30 | """# **Data Augmentation**"""
31 |
32 | import albumentations as A
33 | from albumentations.pytorch.transforms import ToTensor
34 |
35 | def augmentations(image_size=256, is_test=True):
36 | # https://www.kaggle.com/vishnus/a-simple-pytorch-starter-code-single-fold-93
37 | imagenet_stats = {'mean':[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], 'std':[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]}
38 | train_tfms = A.Compose([
39 | A.Cutout(p=0.5),
40 | A.RandomRotate90(p=0.5),
41 | A.Flip(p=0.5),
42 | A.OneOf([
43 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.2,
44 | contrast_limit=0.2,
45 | ),
46 | A.HueSaturationValue(
47 | hue_shift_limit=20,
48 | sat_shift_limit=50,
49 | val_shift_limit=50)
50 | ], p=0.5),
51 | A.OneOf([
52 | A.IAAAdditiveGaussianNoise(),
53 | A.GaussNoise(),
54 | ], p=0.5),
55 | A.OneOf([
56 | A.MotionBlur(p=0.2),
57 | A.MedianBlur(blur_limit=3, p=0.1),
58 | A.Blur(blur_limit=3, p=0.1),
59 | ], p=0.5),
60 | A.ShiftScaleRotate(shift_limit=0.0625, scale_limit=0.2, rotate_limit=45, p=0.5),
61 | A.OneOf([
62 | A.OpticalDistortion(p=0.3),
63 | A.GridDistortion(p=0.1),
64 | A.IAAPiecewiseAffine(p=0.3),
65 | ], p=0.5),
66 | ToTensor(normalize=imagenet_stats)
67 | ])
68 |
69 | test_tfms = A.Compose([ToTensor(normalize=imagenet_stats)])
70 | if is_test:
71 | return test_tfms
72 | else:
73 | return train_tfms
74 |
75 | """# **Optimizing AUCM Loss**
76 | * Installation of `albumentations` is required!
77 | """
78 |
79 | # dataset
80 | trainSet = Melanoma(root='./melanoma/', is_test=False, test_size=0.2, transforms=augmentations)
81 | testSet = Melanoma(root='./melanoma/', is_test=True, test_size=0.2, transforms=augmentations)
82 |
83 | # paramaters
84 | SEED = 123
85 | BATCH_SIZE = 64
86 | lr = 0.1
87 | gamma = 500
88 | imratio = trainSet.imratio
89 | weight_decay = 1e-5
90 | margin = 1.0
91 |
92 | # model
93 | set_all_seeds(SEED)
94 | model = DenseNet121(pretrained=True, last_activation=None, activations='relu', num_classes=1)
95 | model = model.cuda()
96 |
97 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainSet, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, num_workers=2, shuffle=True)
98 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, num_workers=2, shuffle=False)
99 |
100 | # load your own pretrained model here
101 | # PATH = 'ce_pretrained_model.pth'
102 | # state_dict = torch.load(PATH)
103 | # state_dict.pop('classifier.weight', None)
104 | # state_dict.pop('classifier.bias', None)
105 | # model.load_state_dict(state_dict, strict=False)
106 |
107 | # define loss & optimizer
108 | Loss = AUCMLoss(imratio=imratio)
109 | optimizer = PESG(model,
110 | a=Loss.a,
111 | b=Loss.b,
112 | alpha=Loss.alpha,
113 | lr=lr,
114 | gamma=gamma,
115 | margin=margin,
116 | weight_decay=weight_decay)
117 |
118 | total_epochs = 16
119 | best_val_auc = 0
120 | for epoch in range(total_epochs):
121 |
122 | # reset stages
123 | if epoch== int(total_epochs*0.5) or epoch== int(total_epochs*0.75):
124 | optimizer.update_regularizer(decay_factor=10)
125 |
126 | # training
127 | for idx, data in enumerate(trainloader):
128 | train_data, train_labels = data
129 | train_data, train_labels = train_data.cuda(), train_labels.cuda()
130 | y_pred = model(train_data)
131 | y_pred = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
132 | loss = Loss(y_pred, train_labels)
133 | optimizer.zero_grad()
134 | loss.backward()
135 | optimizer.step()
136 |
137 | # validation
138 | model.eval()
139 | with torch.no_grad():
140 | test_pred = []
141 | test_true = []
142 | for jdx, data in enumerate(testloader):
143 | test_data, test_label = data
144 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
145 | y_pred = model(test_data)
146 | y_pred = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
147 | test_pred.append(y_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
148 | test_true.append(test_label.numpy())
149 |
150 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true)
151 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred)
152 | val_auc = auroc(test_true, test_pred)
153 | model.train()
154 |
155 | if best_val_auc < val_auc:
156 | best_val_auc = val_auc
157 |
158 | print ('Epoch=%s, Loss=%.4f, Val_AUC=%.4f, lr=%.4f'%(epoch, loss, val_auc, optimizer.lr))
159 |
160 | print ('Best Val_AUC is %.4f'%best_val_auc)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/09_optimizing_compositionalauc_loss_with_resnet20_on_cifar10.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """09_Optimizing_CompositionalAUC_Loss_with_ResNet20_on_CIFAR10.ipynb
2 |
3 | **Author**: Zhuoning Yuan
4 |
5 | **Introduction**
6 | In this tutorial, we will learn how to quickly train a ResNet20 model by optimizing AUC score using our novel compositional training framework [[Ref]](https://openreview.net/forum?id=gPvB4pdu_Z) on an binary image classification task on Cifar10. After completion of this tutorial, you should be able to use LibAUC to train your own models on your own datasets.
7 |
8 | **Useful Resources**
9 | * Website: https://libauc.org
10 | * Github: https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC
11 |
12 |
13 | **References**
14 | If you find this tutorial helpful in your work, please acknowledge our library and cite the following papers:
15 |
16 | @inproceedings{yuan2022compositional,
17 | title={Compositional Training for End-to-End Deep AUC Maximization},
18 | author={Zhuoning Yuan and Zhishuai Guo and Nitesh Chawla and Tianbao Yang},
19 | booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations},
20 | year={2022},
21 | url={https://openreview.net/forum?id=gPvB4pdu_Z}
22 | }
23 |
24 | """
25 |
26 | """# **Importing LibAUC**
27 | Import required packages to use
28 | """
29 |
30 | from libauc.losses import CompositionalAUCLoss
31 | from libauc.optimizers import PDSCA
32 | from libauc.models import resnet20 as ResNet20
33 | from libauc.datasets import CIFAR10, CIFAR100, STL10, CAT_VS_DOG
34 | from libauc.utils import ImbalancedDataGenerator
35 | from libauc.sampler import DualSampler
36 | from libauc.metrics import auc_roc_score
37 |
38 | import torch
39 | from PIL import Image
40 | import numpy as np
41 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
42 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
43 |
44 | """# **Reproducibility**
45 | The following function `set_all_seeds` limits the number of sources of randomness behaviors, such as model intialization, data shuffling, etcs. However, completely reproducible results are not guaranteed across PyTorch releases [[Ref]](https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/notes/randomness.html#:~:text=Completely%20reproducible%20results%20are%20not,even%20when%20using%20identical%20seeds.).
46 | """
47 |
48 | def set_all_seeds(SEED):
49 | # REPRODUCIBILITY
50 | torch.manual_seed(SEED)
51 | np.random.seed(SEED)
52 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
53 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
54 |
55 | """# **Image Dataset**
56 | Now that we defined the data input pipeline such as data augmentations. In this tutorials, we use `RandomCrop`, `RandomHorizontalFlip` as stated in the original paper.
57 | """
58 |
59 | class ImageDataset(Dataset):
60 | def __init__(self, images, targets, image_size=32, crop_size=30, mode='train'):
61 | self.images = images.astype(np.uint8)
62 | self.targets = targets
63 | self.mode = mode
64 | self.transform_train = transforms.Compose([
65 | transforms.ToTensor(),
66 | transforms.RandomCrop((crop_size, crop_size), padding=None),
67 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
68 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
69 | ])
70 | self.transform_test = transforms.Compose([
71 | transforms.ToTensor(),
72 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
73 | ])
74 | def __len__(self):
75 | return len(self.images)
76 |
77 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
78 | image = self.images[idx]
79 | target = self.targets[idx]
80 | image = Image.fromarray(image.astype('uint8'))
81 | if self.mode == 'train':
82 | image = self.transform_train(image)
83 | else:
84 | image = self.transform_test(image)
85 | return image, target
86 |
87 |
88 | # HyperParameters
89 | SEED = 123
90 | dataset = 'C10'
91 | imratio = 0.1
92 | BATCH_SIZE = 128
93 | total_epochs = 100
94 | decay_epochs=[int(total_epochs*0.5), int(total_epochs*0.75)]
95 |
96 | margin = 1.0
97 | lr = 0.1
98 | #lr0 = 0.1 # (default: lr0=lr unless you specify the value and pass it to optimizer)
99 | epoch_decay = 2e-3
100 | weight_decay = 1e-4
101 | beta0 = 0.9 # e.g., [0.999, 0.99, 0.9]
102 | beta1 = 0.9 # e.g., [0.999, 0.99, 0.9]
103 |
104 | sampling_rate = 0.2
105 |
106 |
107 | """# **Loading datasets**
108 | In this step, we will use the [CIFAR10](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/) as benchmark dataset. Before importing data to `dataloader`, we construct imbalanced version for CIFAR10 by `ImbalanceGenerator`. Specifically, it first randomly splits the training data by class ID (e.g., 10 classes) into two even portions as the positive and negative classes, and then it randomly removes some samples from the positive class to make
109 | it imbalanced. We keep the testing set untouched. We refer `imratio` to the ratio of number of positive examples to number of all examples.
110 | """
111 | if dataset == 'C10':
112 | IMG_SIZE = 32
113 | train_data, train_targets = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True)
114 | test_data, test_targets = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False)
115 | elif dataset == 'C100':
116 | IMG_SIZE = 32
117 | train_data, train_targets = CIFAR100(root='./data', train=True)
118 | test_data, test_targets = CIFAR100(root='./data', train=False)
119 | elif dataset == 'STL10':
120 | BATCH_SIZE = 32
121 | IMG_SIZE = 96
122 | train_data, train_targets = STL10(root='./data/', split='train')
123 | test_data, test_targets = STL10(root='./data/', split='test')
124 | elif dataset == 'C2':
125 | IMG_SIZE = 50
126 | train_data, train_targets = CAT_VS_DOG('./data/', train=True)
127 | test_data, test_targets = CAT_VS_DOG('./data/', train=False)
128 |
129 | (train_images, train_labels) = ImbalancedDataGenerator(verbose=True, random_seed=0).transform(train_data, train_targets, imratio=imratio)
130 | (test_images, test_labels) = ImbalancedDataGenerator(verbose=True, random_seed=0).transform(test_data, test_targets, imratio=0.5)
131 |
132 | trainSet = ImageDataset(train_images, train_labels, image_size=IMG_SIZE, crop_size=IMG_SIZE-2)
133 | trainSet_eval = ImageDataset(train_images, train_labels, image_size=IMG_SIZE, crop_size=IMG_SIZE-2, mode='test')
134 | testSet = ImageDataset(test_images, test_labels, image_size=IMG_SIZE, crop_size=IMG_SIZE-2, mode='test')
135 |
136 | # parameters for sampler
137 | sampler = DualSampler(trainSet, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, sampling_rate=sampling_rate)
138 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainSet, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, sampler=sampler, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
139 | trainloader_eval = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainSet_eval, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
140 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE, shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
141 |
142 |
143 | """# **Model, Loss & Optimizer**
144 | Before training, we need to define **model**, **loss function**, **optimizer**.
145 | """
146 | set_all_seeds(123)
147 | model = ResNet20(pretrained=False, last_activation=None, activations='relu', num_classes=1)
148 | model = model.cuda()
149 |
150 | # Compositional Training
151 | loss_fn = CompositionalAUCLoss()
152 | optimizer = PDSCA(model,
153 | loss_fn=loss_fn,
154 | lr=lr,
155 | beta1=beta0,
156 | beta2=beta1,
157 | margin=margin,
158 | epoch_decay=epoch_decay,
159 | weight_decay=weight_decay)
160 |
161 | """# **Training**
162 | Now it's time for training
163 | """
164 | print ('Start Training')
165 | print ('-'*30)
166 |
167 | train_log = []
168 | test_log = []
169 | for epoch in range(total_epochs):
170 | if epoch in decay_epochs:
171 | optimizer.update_regularizer(decay_factor=10, decay_factor0=10) # decrease learning rate by 10x & update regularizer
172 |
173 | train_loss = []
174 | model.train()
175 | for data, targets in trainloader:
176 | data, targets = data.cuda(), targets.cuda()
177 | y_pred = model(data)
178 | loss = loss_fn(y_pred, targets)
179 | optimizer.zero_grad()
180 | loss.backward()
181 | optimizer.step()
182 | train_loss.append(loss.item())
183 |
184 | # evaluation on train & test sets
185 | model.eval()
186 | train_pred_list = []
187 | train_true_list = []
188 | for train_data, train_targets in trainloader_eval:
189 | train_data = train_data.cuda()
190 | train_pred = model(train_data)
191 | train_pred_list.append(train_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
192 | train_true_list.append(train_targets.numpy())
193 | train_true = np.concatenate(train_true_list)
194 | train_pred = np.concatenate(train_pred_list)
195 | train_auc = auc_roc_score(train_true, train_pred)
196 | train_loss = np.mean(train_loss)
197 |
198 | test_pred_list = []
199 | test_true_list = []
200 | for test_data, test_targets in testloader:
201 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
202 | test_pred = model(test_data)
203 | test_pred_list.append(test_pred.cpu().detach().numpy())
204 | test_true_list.append(test_targets.numpy())
205 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true_list)
206 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred_list)
207 | val_auc = auc_roc_score(test_true, test_pred)
208 | model.train()
209 |
210 | # print results
211 | print("epoch: %s, train_loss: %.4f, train_auc: %.4f, test_auc: %.4f, lr: %.4f"%(epoch, train_loss, train_auc, val_auc, optimizer.lr ))
212 | train_log.append(train_auc)
213 | test_log.append(val_auc)
214 |
215 |
216 | """# **Visualization**
217 | Now, let's see the change of AUC scores on training and testing set.
218 | """
219 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
220 | plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (9,5)
221 | x=np.arange(len(train_log))
222 | plt.figure()
223 | plt.plot(x, train_log, LineStyle='-', label='Train Set', linewidth=3)
224 | plt.plot(x, test_log, LineStyle='-', label='Test Set', linewidth=3)
225 | plt.title('CompositionalAUCLoss (10% CIFAR10)',fontsize=25)
226 | plt.legend(fontsize=15)
227 | plt.ylabel('AUROC', fontsize=25)
228 | plt.xlabel('Epoch', fontsize=25)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/scripts/11_optimizing_pauc_loss_with_sopas_on_imbalanced_data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
2 | """11_Optimizing_pAUC_Loss_with_SOPAs_on_Imbalanced_data.ipynb
3 |
4 | Author: Gang Li
5 | Edited by: Zhuoning Yuan
6 |
7 | Introduction
8 |
9 | In this tutorial, we'll show how to use **pAUC_DRO** loss to train a Resnet18 model to maximize the `partial Area Under the Curve (pAUC)` on a binary image classification task with CIFAR-10 dataset. After completion of this tutorial, you should be able to use LibAUC to train your own models on your own datasets.
10 |
11 | References:
12 |
13 | If you find this tutorial helpful in your work, please acknowledge our library and cite the following papers:
14 | @article{zhu2022auc,
15 | title={When AUC meets DRO: Optimizing Partial AUC for Deep Learning with Non-Convex Convergence Guarantee},
16 | author={Zhu, Dixian and Li, Gang and Wang, Bokun and Wu, Xiaodong and Yang, Tianbao},
17 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2203.00176},
18 | year={2022}
19 | }
20 |
21 | """
22 |
23 | from libauc.losses.auc import pAUC_DRO_Loss
24 | from libauc.optimizers import SOPAs
25 | from libauc.models import resnet18
26 | from libauc.datasets import CIFAR10
27 | from libauc.utils import ImbalancedDataGenerator
28 | from libauc.sampler import DualSampler # data resampling (for binary class)
29 | from libauc.metrics import pauc_roc_score
30 |
31 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
32 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
33 | import numpy as np
34 | import torch
35 | from PIL import Image
36 |
37 |
38 | def set_all_seeds(SEED):
39 | # REPRODUCIBILITY
40 | np.random.seed(SEED)
41 | torch.manual_seed(SEED)
42 | torch.cuda.manual_seed(SEED)
43 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
44 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
45 |
46 |
47 | class ImageDataset(Dataset):
48 | def __init__(self, images, targets, image_size=32, crop_size=30, mode='train'):
49 | self.images = images.astype(np.uint8)
50 | self.targets = targets
51 | self.mode = mode
52 | self.transform_train = transforms.Compose([
53 | transforms.ToTensor(),
54 | transforms.RandomCrop((crop_size, crop_size), padding=None),
55 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
56 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
57 | ])
58 | self.transform_test = transforms.Compose([
59 | transforms.ToTensor(),
60 | transforms.Resize((image_size, image_size)),
61 | ])
62 |
63 | # for loss function
64 | self.pos_indices = np.flatnonzero(targets==1)
65 | self.pos_index_map = {}
66 | for i, idx in enumerate(self.pos_indices):
67 | self.pos_index_map[idx] = i
68 |
69 | def __len__(self):
70 | return len(self.images)
71 |
72 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
73 | image = self.images[idx]
74 | target = self.targets[idx]
75 | image = Image.fromarray(image.astype('uint8'))
76 | if self.mode == 'train':
77 | idx = self.pos_index_map[idx] if idx in self.pos_indices else -1
78 | image = self.transform_train(image)
79 | else:
80 | image = self.transform_test(image)
81 | return image, target, idx
82 |
83 |
84 | # paramaters
85 | SEED = 123
86 | batch_size = 64
87 | total_epochs = 60
88 | weight_decay = 5e-4 # regularization weight decay
89 | lr = 1e-3 # learning rate
90 | eta = 1e1 # learning rate for control negative samples weights
91 | decay_epochs = [20, 40]
92 | decay_factor = 10
93 |
94 | gamma = 0.1
95 | margin = 1.0
96 | Lambda = 1.0
97 |
98 | sampling_rate = 0.5
99 | num_pos = round(sampling_rate*batch_size)
100 | num_neg = batch_size - num_pos
101 |
102 |
103 | train_data, train_targets = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=True)
104 | test_data, test_targets = CIFAR10(root='./data', train=False)
105 |
106 | imratio = 0.2
107 | generator = ImbalancedDataGenerator(shuffle=True, verbose=True, random_seed=0)
108 | (train_images, train_labels) = generator.transform(train_data, train_targets, imratio=imratio)
109 | (test_images, test_labels) = generator.transform(test_data, test_targets, imratio=0.5)
110 |
111 | trainDataset = ImageDataset(train_images, train_labels)
112 | testDataset = ImageDataset(test_images, test_labels, mode='test')
113 |
114 | sampler = DualSampler(trainDataset, batch_size, sampling_rate=sampling_rate)
115 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(trainDataset, batch_size, sampler=sampler, shuffle=False, num_workers=1)
116 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testDataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, num_workers=1)
117 |
118 | """## **Model and Loss setup**"""
119 |
120 | seed = 123
121 | set_all_seeds(seed)
122 | model = resnet18(pretrained=False, num_classes=1, last_activation=None)
123 | model = model.cuda()
124 |
125 | loss_fn = pAUC_DRO_Loss(pos_len=sampler.pos_len, margin=margin, gamma=gamma, Lambda=Lambda)
126 | optimizer = SOPAs(model.parameters(), loss_fn=loss_fn, mode='adam', lr=lr, weight_decay=weight_decay)
127 |
128 |
129 | print ('Start Training')
130 | print ('-'*30)
131 | test_best = 0
132 | train_list, test_list = [], []
133 | for epoch in range(total_epochs):
134 |
135 | if epoch in decay_epochs:
136 | # decrease learning rate by 10x
137 | optimizer.update_lr(decay_factor=10)
138 |
139 | train_pred, train_true = [], []
140 | model.train()
141 | for idx, (data, targets, index) in enumerate(trainloader):
142 | data, targets = data.cuda(), targets.cuda()
143 | y_pred = model(data)
144 | y_prob = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
145 | loss = loss_fn(y_prob, targets, index_p=index) # postive index is selected inside loss function
146 | optimizer.zero_grad()
147 | loss.backward()
148 | optimizer.step()
149 | train_pred.append(y_prob.cpu().detach().numpy())
150 | train_true.append(targets.cpu().detach().numpy())
151 |
152 | train_true = np.concatenate(train_true)
153 | train_pred = np.concatenate(train_pred)
154 | train_pauc = pauc_roc_score(train_true, train_pred, max_fpr=0.3)
155 | train_list.append(train_pauc)
156 |
157 | # evaluation
158 | model.eval()
159 | test_pred, test_true = [], []
160 | for j, data in enumerate(testloader):
161 | test_data, test_targets, index = data
162 | test_data = test_data.cuda()
163 | y_pred = model(test_data)
164 | y_prob = torch.sigmoid(y_pred)
165 | test_pred.append(y_prob.cpu().detach().numpy())
166 | test_true.append(test_targets.numpy())
167 | test_true = np.concatenate(test_true)
168 | test_pred = np.concatenate(test_pred)
169 | val_pauc = pauc_roc_score(test_true, test_pred, max_fpr=0.3)
170 | test_list.append(val_pauc)
171 |
172 | if test_best < val_pauc:
173 | test_best = val_pauc
174 |
175 | model.train()
176 | print("epoch: %s, lr: %.4f, train_pauc: %.4f, test_pauc: %.4f, test_best: %.4f"%(epoch, optimizer.lr, train_pauc, val_pauc, test_best))
177 |
178 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
179 | plt.rcParams["figure.figsize"] = (8,5)
180 | ###
181 | aucm_train= [0.6069506135036445, 0.6978036932301377, 0.7463894673857081, 0.7776219948089698, 0.8027497552574762, 0.8194925184801071, 0.8326414836870717, 0.8418876286652094, 0.8545082542202714, 0.8613377917975251, 0.8663205447982314, 0.8720521974101583, 0.8797435655295311, 0.8809396206077954, 0.8836973394615497, 0.8862993963546479, 0.8907247376100926, 0.8913716767613735, 0.8904567210873551, 0.8936225492461372, 0.9540770048876036, 0.9723488133661535, 0.9781509710156533, 0.9817765145216534, 0.9844834466810455, 0.986610225327087, 0.9881808086925543, 0.9899628359094543, 0.9907810165593278, 0.9914713525781993, 0.9920222707564783, 0.9929317113720121, 0.9935210368721419, 0.993572794854696, 0.9938371343578507, 0.9935073845281966, 0.9947178127253539, 0.9941674834729468, 0.9945044055783974, 0.9948909958585506, 0.9955329256867305, 0.9961777539970935, 0.9958743720990391, 0.9961726341719099, 0.995941568038736, 0.9963039071928088, 0.9965874872432375, 0.9965767861211055, 0.9964081514670973, 0.9963576105770835, 0.9963734406282638, 0.9967885112505668, 0.9964143992297314, 0.9963215825031975, 0.9964172999093988, 0.9968314808643665, 0.9968811317731188, 0.9967179493923207, 0.9970772553897975, 0.9968263538188764]
182 | aucm_test= [0.6624721568627451, 0.6585558039215686, 0.7224398823529412, 0.7461185882352941, 0.7209969411764705, 0.7715108235294117, 0.739145568627451, 0.7252269803921568, 0.7362687450980392, 0.7746165098039216, 0.7529456862745099, 0.8016385098039216, 0.8120752549019608, 0.7091570588235294, 0.7759422745098039, 0.7294065490196078, 0.7001150588235294, 0.761414, 0.7787230980392157, 0.8003133333333334, 0.862998980392157, 0.862715294117647, 0.8590309411764705, 0.8663745098039217, 0.8619192156862745, 0.8615073333333334, 0.8627211764705882, 0.8655584705882353, 0.8625684705882353, 0.8610763921568627, 0.8653654509803922, 0.8593325490196078, 0.8611757254901962, 0.8573677647058824, 0.8564478039215686, 0.8580612549019608, 0.8614994901960784, 0.861043725490196, 0.8583090980392156, 0.853949137254902, 0.8608719215686275, 0.862686431372549, 0.8628177254901961, 0.86389, 0.8628747058823528, 0.8629372549019607, 0.8625298431372549, 0.8619865490196079, 0.8633648235294118, 0.8624133725490196, 0.8632398823529412, 0.863091568627451, 0.8631138823529412, 0.862576, 0.8623480392156863, 0.8626336078431373, 0.8629759607843137, 0.8622864705882353, 0.8625338431372549, 0.8614151372549019]
183 | plt.plot(train_list, label='KLDRO_pAUC Training', linewidth=3)
184 | plt.plot(aucm_train, label='AUCM Training', linewidth=3)
185 | plt.plot(test_list, marker='_' , linestyle='dashed', label='KLDRO_pAUC Test', linewidth=3)
186 | plt.plot(aucm_test, marker='_' , linestyle='dashed', label='AUCM Test', linewidth=3)
187 | plt.title('pAUC Performance(FPR≤0.3)',fontsize=20)
188 | plt.xlabel('Epoch',fontsize=20)
189 | plt.ylabel('pAUC',fontsize=20)
190 | plt.legend(fontsize=15)
191 | plt.show()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/imgs/libauc_logo.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC/53f85d58fef69ca94455a37e27ecf7fb99a8da99/imgs/libauc_logo.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | __version__ = '1.3.0'
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .cifar import *
2 | from .folder import *
3 | from .stl10 import *
4 | from .cat_vs_dog import *
5 | from .chexpert import *
6 | from .melanoma import *
7 | from .movielens import *
8 | from .dataset import *
9 | from .breastcancer import *
10 | from .musk2 import *
11 | from .webdataset import WebDataset
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/breastcancer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import os.path
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from torchvision.datasets.utils import check_integrity, download_url
5 |
6 | def _check_integrity(root, train_list, test_list, base_folder):
7 | for fentry in (train_list + test_list):
8 | filename, md5 = fentry[0], fentry[1]
9 | fpath = os.path.join(root, base_folder, filename)
10 | if not check_integrity(fpath, md5):
11 | return False
12 | print('Files already downloaded and verified')
13 | return True
14 |
15 | def load_data(data_path, MIL_flag=True):
16 | tmp = np.load(data_path, allow_pickle=True) # replace this with an url, file size: 8.8 MB.
17 | Y = tmp['Y']
18 | if MIL_flag == False:
19 | X = tmp['oriX']
20 | X = np.expand_dims(X,axis=1)
21 | else:
22 | X = tmp['X']
23 | X = np.transpose(X,[0,1,4,2,3])
24 | N = Y.shape[0]
25 | ids = np.random.permutation(N)
26 | trN = int(0.9 * N)
27 | tr_ids = ids[:trN]
28 | te_ids = ids[trN:]
29 | train_X = X[tr_ids]
30 | test_X = X[te_ids]
31 | train_Y = Y[tr_ids]
32 | test_Y = Y[te_ids]
33 | print(train_X.shape)
34 | print(train_Y.shape)
35 | print(test_X.shape)
36 | print(test_Y.shape)
37 | return train_X, train_Y, test_X, test_Y
38 |
39 |
40 | def BreastCancer(root='./data/', MIL_flag=True):
41 | r"""
42 | The breast cancer histopathology data from [1]_. The original images can be downloaded at [2]_.
43 |
44 | Args:
45 | flag(bool, required): whether to use data in multiple instance learning format or not, default: False.
46 |
47 | Example:
48 | >>> (train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels) = BreastCancer(flag=False)
49 |
50 | Reference:
51 | .. [1] Gelasca, Elisa Drelie, et al. "Evaluation and benchmark for biological image segmentation."
52 | 2008 15th IEEE international conference on image processing. IEEE, 2008.
53 |
54 | .. [2] https://www.kaggle.com/datasets/andrewmvd/breast-cancer-cell-segmentation?resource=download
55 | """
56 | base_folder = "Breast_Cancer"
57 | url = 'https://github.com/DixianZhu/MIDAM/releases/download/pre-release/breast.npz'
58 | filename = "breast.npz"
59 | train_list = [
60 | ['breast.npz', None],
61 | ]
62 | test_list = []
63 |
64 | # download dataset
65 | if not _check_integrity(root, train_list, test_list, base_folder):
66 | download_url(url=url, root=os.path.join(root, base_folder), filename=filename)
67 |
68 | data_path = os.path.join(root, base_folder, train_list[0][0])
69 | train_data, train_labels, test_data, test_labels = load_data(data_path, MIL_flag=MIL_flag)
70 |
71 | return (train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels)
72 |
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/cat_vs_dog.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import os.path
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from torchvision.datasets.utils import check_integrity, download_and_extract_archive
5 | # reference: https://pytorch.org/vision/0.8/_modules/torchvision/datasets/cifar.html#CIFAR10
6 | # Dataset credit goes to https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=54765
7 |
8 | def _check_integrity(root, train_list, test_list, base_folder):
9 | for fentry in (train_list + test_list):
10 | filename, md5 = fentry[0], fentry[1]
11 | fpath = os.path.join(root, base_folder, filename)
12 | if not check_integrity(fpath, md5):
13 | return False
14 | print('Files already downloaded and verified')
15 | return True
16 |
17 | def load_data(data_path, label_path):
18 | data = np.load(data_path)
19 | targets = np.load(label_path)
20 | return data, targets
21 |
22 | def CAT_VS_DOG(root='./data/', train=True):
23 | base_folder = "cat_vs_dog"
24 | url = 'https://homepage.divms.uiowa.edu/~zhuoning/datasets/cat_vs_dog.tar.gz'
25 | filename = "cat_vs_dog.tar.gz"
26 | train_list = [
27 | ['cat_vs_dog_data.npy', None],
28 | ['cat_vs_dog_label.npy', None],
29 | ]
30 | test_list = []
31 |
32 | # download dataset
33 | if not _check_integrity(root, train_list, test_list, base_folder):
34 | download_and_extract_archive(url=url, download_root=root, filename=filename)
35 |
36 | # train or test set
37 | if train:
38 | data_path = os.path.join(root, base_folder, train_list[0][0])
39 | label_path = os.path.join(root, base_folder, train_list[1][0])
40 | data, targets = load_data(data_path, label_path)
41 | data = data[:-5000]
42 | targets = targets[:-5000]
43 | else:
44 | data_path = os.path.join(root, base_folder, train_list[0][0])
45 | label_path = os.path.join(root, base_folder, train_list[1][0])
46 | data, targets = load_data(data_path, label_path)
47 | data = data[-5000:]
48 | targets = targets[-5000:]
49 |
50 | return data, targets
51 |
52 | if __name__ == '__main__':
53 | data, targets = CAT_VS_DOG('./data/', train=True)
54 | print (data.shape, targets.shape)
55 | data, targets = CAT_VS_DOG('./data/', train=False)
56 | print (data.shape, targets.shape)
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/chexpert.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import torch
3 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
4 | import torchvision.transforms as tfs
5 | import cv2
6 | from PIL import Image
7 | import pandas as pd
8 |
9 | class CheXpert(Dataset):
10 | r"""
11 | Reference:
12 | .. [1] Yuan, Zhuoning, Yan, Yan, Sonka, Milan, and Yang, Tianbao.
13 | "Large-scale robust deep auc maximization: A new surrogate loss and empirical studies on medical image classification."
14 | Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. 2021.
15 | https://arxiv.org/abs/2012.03173
16 | """
17 | def __init__(self,
18 | csv_path,
19 | image_root_path='',
20 | image_size=320,
21 | class_index=0,
22 | use_frontal=True,
23 | use_upsampling=True,
24 | flip_label=False,
25 | shuffle=True,
26 | seed=123,
27 | verbose=False,
28 | transforms=None,
29 | upsampling_cols=['Cardiomegaly', 'Consolidation'],
30 | train_cols=['Cardiomegaly', 'Edema', 'Consolidation', 'Atelectasis', 'Pleural Effusion'],
31 | return_index=False,
32 | mode='train'):
33 |
34 |
35 | # load data from csv
36 | self.df = pd.read_csv(csv_path)
37 | self.df['Path'] = self.df['Path'].str.replace('CheXpert-v1.0-small/', '', regex=True)
38 | self.df['Path'] = self.df['Path'].str.replace('CheXpert-v1.0/', '', regex=True)
39 | if use_frontal:
40 | self.df = self.df[self.df['Frontal/Lateral'] == 'Frontal']
41 |
42 | # upsample selected cols
43 | if use_upsampling:
44 | assert isinstance(upsampling_cols, list), 'Input should be list!'
45 | sampled_df_list = []
46 | for col in upsampling_cols:
47 | print ('Upsampling %s...'%col)
48 | sampled_df_list.append(self.df[self.df[col] == 1])
49 | self.df = pd.concat([self.df] + sampled_df_list, axis=0)
50 |
51 |
52 | # impute missing values
53 | for col in train_cols:
54 | if col in ['Edema', 'Atelectasis']:
55 | self.df[col].replace(-1, 1, inplace=True)
56 | self.df[col].fillna(0, inplace=True)
57 | elif col in ['Cardiomegaly','Consolidation', 'Pleural Effusion']:
58 | self.df[col].replace(-1, 0, inplace=True)
59 | self.df[col].fillna(0, inplace=True)
60 | elif col in ['No Finding', 'Enlarged Cardiomediastinum', 'Lung Opacity', 'Lung Lesion', 'Pneumonia', 'Pneumothorax', 'Pleural Other','Fracture','Support Devices']: # other labels
61 | self.df[col].replace(-1, 0, inplace=True)
62 | self.df[col].fillna(0, inplace=True)
63 | else:
64 | self.df[col].fillna(0, inplace=True)
65 |
66 | self._num_images = len(self.df)
67 |
68 | # 0 --> -1
69 | if flip_label and class_index != -1: # In multi-class mode we disable this option!
70 | self.df.replace(0, -1, inplace=True)
71 |
72 | # shuffle data
73 | if shuffle:
74 | data_index = list(range(self._num_images))
75 | np.random.seed(seed)
76 | np.random.shuffle(data_index)
77 | self.df = self.df.iloc[data_index]
78 |
79 |
80 | #assert class_index in [-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4], 'Out of selection!'
81 | assert image_root_path != '', 'You need to pass the correct location for the dataset!'
82 |
83 | if class_index == -1: # 5 classes
84 | if verbose:
85 | print ('Multi-label mode: True, Number of classes: [%d]'%len(train_cols))
86 | print ('-'*30)
87 | self.select_cols = train_cols
88 | self.value_counts_dict = {}
89 | for class_key, select_col in enumerate(train_cols):
90 | class_value_counts_dict = self.df[select_col].value_counts().to_dict()
91 | self.value_counts_dict[class_key] = class_value_counts_dict
92 | else:
93 | self.select_cols = [train_cols[class_index]] # this var determines the number of classes
94 | self.value_counts_dict = self.df[self.select_cols[0]].value_counts().to_dict()
95 |
96 | self.mode = mode
97 | self.class_index = class_index
98 | self.image_size = image_size
99 | self.transforms = transforms
100 | self.return_index = return_index
101 |
102 | self._images_list = [image_root_path+path for path in self.df['Path'].tolist()]
103 | if class_index != -1:
104 | self.targets = self.df[train_cols].values[:, class_index].tolist()
105 | else:
106 | self.targets = self.df[train_cols].values.tolist()
107 |
108 | if True:
109 | if class_index != -1:
110 | if flip_label:
111 | self.imratio = self.value_counts_dict[1]/(self.value_counts_dict[-1]+self.value_counts_dict[1])
112 | if verbose:
113 | print ('-'*30)
114 | print('Found %s images in total, %s positive images, %s negative images'%(self._num_images, self.value_counts_dict[1], self.value_counts_dict[-1] ))
115 | print ('%s(C%s): imbalance ratio is %.4f'%(self.select_cols[0], class_index, self.imratio ))
116 | print ('-'*30)
117 | else:
118 | self.imratio = self.value_counts_dict[1]/(self.value_counts_dict[0]+self.value_counts_dict[1])
119 | if verbose:
120 | print ('-'*30)
121 | print('Found %s images in total, %s positive images, %s negative images'%(self._num_images, self.value_counts_dict[1], self.value_counts_dict[0] ))
122 | print ('%s(C%s): imbalance ratio is %.4f'%(self.select_cols[0], class_index, self.imratio ))
123 | print ('-'*30)
124 | else:
125 | imratio_list = []
126 | for class_key, select_col in enumerate(train_cols):
127 | try:
128 | imratio = self.value_counts_dict[class_key][1]/(self.value_counts_dict[class_key][0]+self.value_counts_dict[class_key][1])
129 | except:
130 | if len(self.value_counts_dict[class_key]) == 1 :
131 | only_key = list(self.value_counts_dict[class_key].keys())[0]
132 | if only_key == 0:
133 | self.value_counts_dict[class_key][1] = 0
134 | imratio = 0 # no postive samples
135 | else:
136 | self.value_counts_dict[class_key][1] = 0
137 | imratio = 1 # no negative samples
138 |
139 | imratio_list.append(imratio)
140 | if verbose:
141 | #print ('-'*30)
142 | print('Found %s images in total, %s positive images, %s negative images'%(self._num_images, self.value_counts_dict[class_key][1], self.value_counts_dict[class_key][0] ))
143 | print ('%s(C%s): imbalance ratio is %.4f'%(select_col, class_key, imratio ))
144 | print ()
145 | #print ('-'*30)
146 | self.imratio = np.mean(imratio_list)
147 | self.imratio_list = imratio_list
148 |
149 |
150 | @property
151 | def class_counts(self):
152 | return self.value_counts_dict
153 |
154 | @property
155 | def imbalance_ratio(self):
156 | return self.imratio
157 |
158 | @property
159 | def num_classes(self):
160 | return len(self.select_cols)
161 |
162 | @property
163 | def data_size(self):
164 | return self._num_images
165 |
166 | def image_augmentation(self, image):
167 | img_aug = tfs.Compose([tfs.RandomAffine(degrees=(-15, 15), translate=(0.05, 0.05), scale=(0.95, 1.05), fill=128)]) # pytorch 3.7: fillcolor --> fill
168 | image = img_aug(image)
169 | return image
170 |
171 | def __len__(self):
172 | return self._num_images
173 |
174 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
175 |
176 | image = cv2.imread(self._images_list[idx], 0)
177 | image = Image.fromarray(image)
178 | if self.mode == 'train' :
179 | if self.transforms is None:
180 | image = self.image_augmentation(image)
181 | else:
182 | image = self.transforms(image)
183 | image = np.array(image)
184 | image = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)
185 |
186 | # resize and normalize; e.g., ToTensor()
187 | image = cv2.resize(image, dsize=(self.image_size, self.image_size), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
188 | image = image/255.0
189 | __mean__ = np.array([[[0.485, 0.456, 0.406]]])
190 | __std__ = np.array([[[0.229, 0.224, 0.225] ]])
191 | image = (image-__mean__)/__std__
192 | image = image.transpose((2, 0, 1)).astype(np.float32)
193 | if self.class_index != -1: # multi-class mode
194 | label = np.array(self.targets[idx]).reshape(-1).astype(np.float32)
195 | else:
196 | label = np.array(self.targets[idx]).reshape(-1).astype(np.float32)
197 | if self.return_index:
198 | return image, label, idx
199 | return image, label
200 |
201 |
202 | if __name__ == '__main__':
203 | root = '../chexpert/dataset/CheXpert-v1.0-small/'
204 | traindSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'train.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=True, use_frontal=True, image_size=320, mode='train', class_index=0)
205 | testSet = CheXpert(csv_path=root+'valid.csv', image_root_path=root, use_upsampling=False, use_frontal=True, image_size=320, mode='valid', class_index=0)
206 | trainloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(traindSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, drop_last=True, shuffle=True)
207 | testloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(testSet, batch_size=32, num_workers=2, drop_last=False, shuffle=False)
208 |
209 |
210 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os.path
2 | import pickle
3 | from typing import Any, Callable, Optional, Tuple
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from PIL import Image
7 |
8 | from torchvision.datasets.utils import check_integrity, download_and_extract_archive
9 | from torchvision.datasets.vision import VisionDataset
10 |
11 |
12 | class CIFAR10(VisionDataset):
13 | """`CIFAR10 `_ Dataset.
14 |
15 | Args:
16 | root (string): Root directory of dataset where directory
17 | ``cifar-10-batches-py`` exists or will be saved to if download is set to True.
18 | train (bool, optional): If True, creates dataset from training set, otherwise
19 | creates from test set.
20 | transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in an PIL image
21 | and returns a transformed version. E.g, ``transforms.RandomCrop``
22 | target_transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in the
23 | target and transforms it.
24 | download (bool, optional): If true, downloads the dataset from the internet and
25 | puts it in root directory. If dataset is already downloaded, it is not
26 | downloaded again.
27 | return_index (bool, optional): returns a tuple containing data, target, and index if return_index is set to True. Otherwise, it returns a tuple containing data and target only (default: ``False``)
28 |
29 | """
30 |
31 | base_folder = "cifar-10-batches-py"
32 | url = "https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz"
33 | filename = "cifar-10-python.tar.gz"
34 | tgz_md5 = "c58f30108f718f92721af3b95e74349a"
35 | train_list = [
36 | ["data_batch_1", "c99cafc152244af753f735de768cd75f"],
37 | ["data_batch_2", "d4bba439e000b95fd0a9bffe97cbabec"],
38 | ["data_batch_3", "54ebc095f3ab1f0389bbae665268c751"],
39 | ["data_batch_4", "634d18415352ddfa80567beed471001a"],
40 | ["data_batch_5", "482c414d41f54cd18b22e5b47cb7c3cb"],
41 | ]
42 |
43 | test_list = [
44 | ["test_batch", "40351d587109b95175f43aff81a1287e"],
45 | ]
46 | meta = {
47 | "filename": "batches.meta",
48 | "key": "label_names",
49 | "md5": "5ff9c542aee3614f3951f8cda6e48888",
50 | }
51 |
52 | def __init__(
53 | self,
54 | root: str,
55 | train: bool = True,
56 | transform: Optional[Callable] = None,
57 | target_transform: Optional[Callable] = None,
58 | download: bool = True,
59 | return_index: bool = False,
60 | ) -> None:
61 |
62 | super().__init__(root, transform=transform, target_transform=target_transform)
63 |
64 | self.train = train # training set or test set
65 |
66 | if download:
67 | self.download()
68 |
69 | if not self._check_integrity():
70 | raise RuntimeError("Dataset not found or corrupted. You can use download=True to download it")
71 |
72 | if self.train:
73 | downloaded_list = self.train_list
74 | else:
75 | downloaded_list = self.test_list
76 |
77 | self.data: Any = []
78 | self.targets = []
79 | self.return_index = return_index
80 |
81 | # now load the picked numpy arrays
82 | for file_name, checksum in downloaded_list:
83 | file_path = os.path.join(self.root, self.base_folder, file_name)
84 | with open(file_path, "rb") as f:
85 | entry = pickle.load(f, encoding="latin1")
86 | self.data.append(entry["data"])
87 | if "labels" in entry:
88 | self.targets.extend(entry["labels"])
89 | else:
90 | self.targets.extend(entry["fine_labels"])
91 |
92 | self.data = np.vstack(self.data).reshape(-1, 3, 32, 32)
93 | self.data = self.data.transpose((0, 2, 3, 1)) # convert to HWC
94 | self.targets = np.array(self.targets).astype(np.int32)
95 |
96 | self._load_meta()
97 |
98 | def _load_meta(self) -> None:
99 | path = os.path.join(self.root, self.base_folder, self.meta["filename"])
100 | if not check_integrity(path, self.meta["md5"]):
101 | raise RuntimeError("Dataset metadata file not found or corrupted. You can use download=True to download it")
102 | with open(path, "rb") as infile:
103 | data = pickle.load(infile, encoding="latin1")
104 | self.classes = data[self.meta["key"]]
105 | self.class_to_idx = {_class: i for i, _class in enumerate(self.classes)}
106 |
107 | def as_array(self):
108 | return self.data, self.targets
109 |
110 | def __getitem__(self, index: int) -> Tuple[Any, Any]:
111 | """
112 | Args:
113 | index (int): Index
114 |
115 | Returns:
116 | tuple: (image, target) where target is index of the target class.
117 | """
118 | img, target = self.data[index], self.targets[index]
119 |
120 | # doing this so that it is consistent with all other datasets
121 | # to return a PIL Image
122 | img = Image.fromarray(img)
123 |
124 | if self.transform is not None:
125 | img = self.transform(img)
126 |
127 | if self.target_transform is not None:
128 | target = self.target_transform(target)
129 |
130 | if self.return_index:
131 | return img, target, index
132 |
133 | return img, target
134 |
135 | def __len__(self) -> int:
136 | return len(self.data)
137 |
138 | def _check_integrity(self) -> bool:
139 | for filename, md5 in self.train_list + self.test_list:
140 | fpath = os.path.join(self.root, self.base_folder, filename)
141 | if not check_integrity(fpath, md5):
142 | return False
143 | return True
144 |
145 | def download(self) -> None:
146 | if self._check_integrity():
147 | print("Files already downloaded and verified")
148 | return
149 | download_and_extract_archive(self.url, self.root, filename=self.filename, md5=self.tgz_md5)
150 |
151 | def extra_repr(self) -> str:
152 | split = "Train" if self.train is True else "Test"
153 | return f"Split: {split}"
154 |
155 |
156 | class CIFAR100(CIFAR10):
157 | """`CIFAR100 `_ Dataset.
158 |
159 | This is a subclass of the `CIFAR10` Dataset.
160 | """
161 |
162 | base_folder = "cifar-100-python"
163 | url = "https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-100-python.tar.gz"
164 | filename = "cifar-100-python.tar.gz"
165 | tgz_md5 = "eb9058c3a382ffc7106e4002c42a8d85"
166 | train_list = [
167 | ["train", "16019d7e3df5f24257cddd939b257f8d"],
168 | ]
169 |
170 | test_list = [
171 | ["test", "f0ef6b0ae62326f3e7ffdfab6717acfc"],
172 | ]
173 | meta = {
174 | "filename": "meta",
175 | "key": "fine_label_names",
176 | "md5": "7973b15100ade9c7d40fb424638fde48",
177 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
2 | from torchvision import transforms
3 | import torch
4 |
5 | class CustomDataset(Dataset):
6 | r"""
7 | Custom Dataset Template for loading numpy array-like data & targets into the PyTorch dataloader.
8 |
9 | Args:
10 | data (numpy.ndarray): numpy array-like data
11 | targets (numpy.ndarray): numpy array-like targets
12 | transform (callable, optional): optional transform to be applied on the training/testing data (default: ``None``)
13 | return_index (bool, optional): returns a tuple containing data, target, and index if return_index is set to True. Otherwise, it returns a tuple containing data and target only (default: ``False``)
14 | """
15 | def __init__(self, data, targets, transform=None, return_index=False):
16 | self.data = data
17 | self.targets = targets
18 | self.transform = transform
19 | self.return_index = return_index
20 | assert len(data) == len(targets), 'The length of data and targets must match!'
21 |
22 | def __len__(self):
23 | return len(self.data)
24 |
25 | def __getitem__(self, index):
26 | try:
27 | sample_id, task_id = index
28 | except:
29 | sample_id, task_id = index, None
30 | data = self.data[sample_id]
31 | target = self.targets[sample_id]
32 | if self.transform:
33 | data = self.transform(data)
34 | if self.return_index:
35 | if task_id != None:
36 | index = (sample_id, task_id)
37 | return data, target, index
38 | return data, target
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/melanoma.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import pandas as pd
3 | from PIL import Image
4 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
5 | import torch
6 | import os
7 |
8 |
9 | def get_augmentations_v1(image_size=256, is_test=True):
10 | import albumentations as A
11 | from albumentations.pytorch.transforms import ToTensor
12 | '''
13 | https://www.kaggle.com/vishnus/a-simple-pytorch-starter-code-single-fold-93
14 | '''
15 | imagenet_stats = {'mean':[0.485, 0.456, 0.406], 'std':[0.229, 0.224, 0.225]}
16 | train_tfms = A.Compose([
17 | A.Cutout(p=0.5),
18 | A.RandomRotate90(p=0.5),
19 | A.Flip(p=0.5),
20 | A.OneOf([
21 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.2,
22 | contrast_limit=0.2,
23 | ),
24 | A.HueSaturationValue(
25 | hue_shift_limit=20,
26 | sat_shift_limit=50,
27 | val_shift_limit=50)
28 | ], p=0.5),
29 | A.OneOf([
30 | A.IAAAdditiveGaussianNoise(),
31 | A.GaussNoise(),
32 | ], p=0.5),
33 | A.OneOf([
34 | A.MotionBlur(p=0.2),
35 | A.MedianBlur(blur_limit=3, p=0.1),
36 | A.Blur(blur_limit=3, p=0.1),
37 | ], p=0.5),
38 | A.ShiftScaleRotate(shift_limit=0.0625, scale_limit=0.2, rotate_limit=45, p=0.5),
39 | A.OneOf([
40 | A.OpticalDistortion(p=0.3),
41 | A.GridDistortion(p=0.1),
42 | A.IAAPiecewiseAffine(p=0.3),
43 | ], p=0.5),
44 | ToTensor(normalize=imagenet_stats)
45 | ])
46 |
47 | test_tfms = A.Compose([
48 | ToTensor(normalize=imagenet_stats)
49 | ])
50 | if is_test:
51 | return test_tfms
52 | else:
53 | return train_tfms
54 |
55 | class Melanoma(Dataset):
56 | r'''
57 | Reference:
58 | - https://www.kaggle.com/cdeotte/jpeg-melanoma-256x256
59 | - https://www.kaggle.com/vishnus/a-simple-pytorch-starter-code-single-fold-93
60 | - https://www.kaggle.com/haqishen/1st-place-soluiton-code-small-ver
61 | '''
62 | def __init__(self, root, test_size=0.2, is_test=False, transforms=None):
63 | assert os.path.isfile(root + '/train.csv'), 'There is no train.csv in %s!'%root
64 | self.data = pd.read_csv(root + '/train.csv')
65 | self.train_df, self.test_df = self.get_train_val_split(self.data, test_size=test_size)
66 | self.is_test = is_test
67 |
68 | if is_test:
69 | self.df = self.test_df.copy()
70 | else:
71 | self.df = self.train_df.copy()
72 |
73 | self._num_images = len(self.df)
74 | self.value_counts_dict = self.df.target.value_counts().to_dict()
75 | self.imratio = self.value_counts_dict[1]/self.value_counts_dict[0]
76 | print ('Found %s image in total, %s postive images, %s negative images.'%(self._num_images, self.value_counts_dict[1], self.value_counts_dict[0]))
77 |
78 | # get path
79 | dir_name = 'train'
80 | self._images_list = [f"{root}/{dir_name}/{img}.jpg" for img in self.df.image_name]
81 | self._labels_list = self.df.target.values.tolist()
82 | if not transforms:
83 | self.transforms = get_augmentations_v1(is_test=is_test)
84 | else:
85 | self.transforms = transforms(is_test=is_test)
86 |
87 | @property
88 | def class_counts(self):
89 | return self.value_counts_dict
90 |
91 | @property
92 | def imbalance_ratio(self):
93 | return self.imratio
94 |
95 | @property
96 | def num_classes(self):
97 | return 1
98 |
99 | def get_train_val_split(self, df, test_size=0.2):
100 | print ('test set split is %s'%test_size)
101 | #Remove Duplicates
102 | df = df[df.tfrecord != -1].reset_index(drop=True)
103 | #We are splitting data based on triple stratified kernel provided here https://www.kaggle.com/c/siim-isic-melanoma-classification/discussion/165526
104 | num_tfrecords = len(df.tfrecord.unique())
105 | train_tf_records = list(range(len(df.tfrecord.unique())))[:-int(num_tfrecords*test_size)]
106 | split_cond = df.tfrecord.apply(lambda x: x in train_tf_records)
107 | train_df = df[split_cond].reset_index()
108 | valid_df = df[~split_cond].reset_index()
109 | return train_df, valid_df
110 |
111 | def __len__(self):
112 | return self.df.shape[0]
113 |
114 | def __getitem__(self,idx):
115 | img_path = self._images_list[idx]
116 | image = Image.open(img_path)
117 | image = self.transforms(**{"image": np.array(image)})["image"]
118 | target = torch.tensor([self._labels_list[idx]],dtype=torch.float32)
119 | return image, target
120 |
121 | if __name__ == '__main__':
122 | trainSet = Melanoma(root='./datasets/256x256/', is_test=False, test_size=0.2)
123 | testSet = Melanoma(root='./datasets/256x256/', is_test=True, test_size=0.2)
124 | bs = 128
125 | train_dl = DataLoader(dataset=trainSet,batch_size=bs,shuffle=True, num_workers=0)
126 |
127 |
128 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/musk2.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import os.path
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from torchvision.datasets.utils import check_integrity, download_url
5 |
6 | def _check_integrity(root, train_list, test_list, base_folder):
7 | for fentry in (train_list + test_list):
8 | filename, md5 = fentry[0], fentry[1]
9 | fpath = os.path.join(root, base_folder, filename)
10 | if not check_integrity(fpath, md5):
11 | return False
12 | print('Files already downloaded and verified')
13 | return True
14 |
15 | def load_data(data_path):
16 | tmp = np.load(data_path, allow_pickle=True) # replace this with an url, file size: 8.8 MB.
17 | train_data = tmp['train_X']
18 | test_data = tmp['test_X']
19 | train_labels = tmp['train_Y'].astype(int)
20 | test_labels = tmp['test_Y'].astype(int)
21 | return train_data, train_labels, test_data, test_labels
22 |
23 |
24 | def MUSK2(root='./data/'):
25 | base_folder = "MUSK2"
26 | url = 'https://github.com/DixianZhu/MIDAM/releases/download/pre-release/musk_2.npz'
27 | filename = "musk_2.npz"
28 | train_list = [
29 | ['musk_2.npz', None],
30 | ]
31 | test_list = []
32 |
33 | # download dataset
34 | if not _check_integrity(root, train_list, test_list, base_folder):
35 | download_url(url=url, root=os.path.join(root, base_folder), filename=filename)
36 |
37 | data_path = os.path.join(root, base_folder, train_list[0][0])
38 | train_data, train_labels, test_data, test_labels = load_data(data_path)
39 |
40 | return (train_data, train_labels), (test_data, test_labels)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/stl10.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import os.path
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from torchvision.datasets.utils import check_integrity, download_and_extract_archive, verify_str_arg
5 | # reference: https://pytorch.org/vision/0.8/_modules/torchvision/datasets/stl10.html#STL10
6 |
7 | def load_file(data_file, labels_file=None):
8 | labels = None
9 | if labels_file:
10 | with open(labels_file, 'rb') as f:
11 | labels = np.fromfile(f, dtype=np.uint8) - 1 # 0-based
12 | with open(data_file, 'rb') as f:
13 | # read whole file in uint8 chunks
14 | everything = np.fromfile(f, dtype=np.uint8)
15 | images = np.reshape(everything, (-1, 3, 96, 96))
16 | images = np.transpose(images, (0, 1, 3, 2))
17 |
18 | return images, labels
19 |
20 | def _check_integrity(root, train_list, test_list, base_folder):
21 | for fentry in (train_list + test_list):
22 | filename, md5 = fentry[0], fentry[1]
23 | fpath = os.path.join(root, base_folder, filename)
24 | if not check_integrity(fpath, md5):
25 | return False
26 | print('Files already downloaded and verified')
27 | return True
28 |
29 | def STL10(root='./data/', split='train'):
30 | base_folder = 'stl10_binary'
31 | url = "http://ai.stanford.edu/~acoates/stl10/stl10_binary.tar.gz"
32 | filename = "stl10_binary.tar.gz"
33 | class_names_file = 'class_names.txt'
34 | folds_list_file = 'fold_indices.txt'
35 | train_list = [
36 | ['train_X.bin', '918c2871b30a85fa023e0c44e0bee87f'],
37 | ['train_y.bin', '5a34089d4802c674881badbb80307741'],
38 | ['unlabeled_X.bin', '5242ba1fed5e4be9e1e742405eb56ca4']
39 | ]
40 |
41 | test_list = [
42 | ['test_X.bin', '7f263ba9f9e0b06b93213547f721ac82'],
43 | ['test_y.bin', '36f9794fa4beb8a2c72628de14fa638e']
44 | ]
45 | splits = ('train', 'train+unlabeled', 'unlabeled', 'test')
46 |
47 | # download dataset
48 | fpath = os.path.join(root, base_folder, filename)
49 | if not _check_integrity(root, train_list, test_list, base_folder):
50 | download_and_extract_archive(url=url, download_root=root, filename=filename)
51 |
52 | # choose which set to load
53 | if split=='train':
54 | path_to_data = os.path.join(root, base_folder, train_list[0][0])
55 | path_to_labels = os.path.join(root, base_folder, train_list[1][0])
56 | data, targets = load_file(path_to_data, path_to_labels)
57 | elif split == 'unlabeled':
58 | path_to_data = os.path.join(root, base_folder, train_list[2][0])
59 | data, _ = load_file(path_to_data)
60 | targets = np.asarray([-1] * data.shape[0])
61 | elif split == 'test':
62 | path_to_data = os.path.join(root, base_folder, test_list[0][0])
63 | path_to_labels = os.path.join(root, base_folder, test_list[1][0])
64 | data, targets = load_file(path_to_data, path_to_labels)
65 | else:
66 | raise ValueError('Out of option!')
67 |
68 | return data, targets
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 | if __name__ == '__main__':
73 | data, targets = STL10(root='./data/', split='test') # return numpy array
74 | print (data.shape, targets.shape)
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/datasets/webdataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Adapted from https://github.com/mlfoundations/open_clip/blob/main/src/training/data.py
2 |
3 | import logging
4 | import random
5 | from multiprocessing import Value
6 | from typing import Dict, Callable, Optional
7 |
8 | from torch.utils.data import get_worker_info
9 | try:
10 | import webdataset as wds
11 | from webdataset.filters import _shuffle
12 | from webdataset.tariterators import base_plus_ext, url_opener, tar_file_expander, valid_sample
13 | except ImportError:
14 | raise ImportError("webdataset is not installed. Please install it by running `pip install webdataset`.")
15 |
16 |
17 | class SharedEpoch:
18 | """Epoch number for distributed training"""
19 | def __init__(self, epoch: int = 0):
20 | self.shared_epoch = Value('i', epoch)
21 |
22 | def set_value(self, epoch):
23 | self.shared_epoch.value = epoch
24 |
25 | def get_value(self):
26 | return self.shared_epoch.value
27 |
28 |
29 | def filter_no_caption_or_no_image(sample):
30 | """Check if sample has caption and image"""
31 | has_caption = ('txt' in sample)
32 | has_image = ('png' in sample or 'jpg' in sample or 'jpeg' in sample or 'webp' in sample)
33 | return has_caption and has_image
34 |
35 |
36 | def log_and_continue(exn):
37 | """Call in an exception handler to ignore any exception, issue a warning, and continue."""
38 | logging.warning(f'Handling webdataset error ({repr(exn)}). Ignoring.')
39 | return True
40 |
41 |
42 | def group_by_keys_nothrow(data, keys=base_plus_ext, lcase=True, suffixes=None, handler=None):
43 | """Return function over iterator that groups key, value pairs into samples.
44 |
45 | :param keys: function that splits the key into key and extension (base_plus_ext)
46 | :param lcase: convert suffixes to lower case (Default value = True)
47 | """
48 | current_sample = None
49 | for filesample in data:
50 | assert isinstance(filesample, dict)
51 | fname, value = filesample["fname"], filesample["data"]
52 | prefix, suffix = keys(fname)
53 | if prefix is None:
54 | continue
55 | if lcase:
56 | suffix = suffix.lower()
57 | # FIXME webdataset version throws if suffix in current_sample, but we have a potential for
58 | # this happening in the current LAION400m dataset if a tar ends with same prefix as the next
59 | # begins, rare, but can happen since prefix aren't unique across tar files in that dataset
60 | if current_sample is None or prefix != current_sample["__key__"] or suffix in current_sample:
61 | if valid_sample(current_sample):
62 | yield current_sample
63 | current_sample = dict(__key__=prefix, __url__=filesample["__url__"])
64 | if suffixes is None or suffix in suffixes:
65 | current_sample[suffix] = value
66 | if valid_sample(current_sample):
67 | yield current_sample
68 |
69 |
70 | def tarfile_to_samples_nothrow(src, handler=log_and_continue):
71 | """A re-implementation of the webdataset impl with group_by_keys that doesn't throw"""
72 | streams = url_opener(src, handler=handler)
73 | files = tar_file_expander(streams, handler=handler)
74 | samples = group_by_keys_nothrow(files, handler=handler)
75 | return samples
76 |
77 |
78 | def pytorch_worker_seed(increment=0):
79 | """Get dataloader worker seed from pytorch"""
80 | worker_info = get_worker_info()
81 | if worker_info is not None:
82 | # favour using the seed already created for pytorch dataloader workers if it exists
83 | seed = worker_info.seed
84 | if increment:
85 | # space out seed increments so they can't overlap across workers in different iterations
86 | seed += increment * max(1, worker_info.num_workers)
87 | return seed
88 | # fallback to wds rank based seed
89 | return wds.utils.pytorch_worker_seed()
90 |
91 |
92 | _SHARD_SHUFFLE_SIZE = 2000
93 | _SHARD_SHUFFLE_INITIAL = 500
94 | _SAMPLE_SHUFFLE_SIZE = 5000
95 | _SAMPLE_SHUFFLE_INITIAL = 1000
96 |
97 |
98 | class detshuffle2(wds.PipelineStage):
99 | """Shuffle according to seed and epoch"""
100 | def __init__(
101 | self,
102 | bufsize=1000,
103 | initial=100,
104 | seed=0,
105 | epoch=-1,
106 | ):
107 | self.bufsize = bufsize
108 | self.initial = initial
109 | self.seed = seed
110 | self.epoch = epoch
111 |
112 | def run(self, src):
113 | if isinstance(self.epoch, SharedEpoch):
114 | epoch = self.epoch.get_value()
115 | else:
116 | # NOTE: this is epoch tracking is problematic in a multiprocess (dataloader workers or train)
117 | # situation as different workers may wrap at different times (or not at all).
118 | self.epoch += 1
119 | epoch = self.epoch
120 | rng = random.Random()
121 | if self.seed < 0:
122 | # If seed is negative, we use the worker's seed, this will be different across all nodes/workers
123 | seed = pytorch_worker_seed(epoch)
124 | else:
125 | # This seed to be deterministic AND the same across all nodes/workers in each epoch
126 | seed = self.seed + epoch
127 | rng.seed(seed)
128 | return _shuffle(src, self.bufsize, self.initial, rng)
129 |
130 |
131 | class WebDataset(wds.DataPipeline):
132 | r"""
133 | An image-text dataset that is stored in webdataset format. For more information on webdataset format,
134 | refer to https://github.com/webdataset/webdataset.
135 |
136 | Args:
137 | input_shards (str): Path to the dataset shards.
138 | is_train (bool): Whether the dataset is for training or evaluation.
139 | batch_size (int): Batch size per worker.
140 | preprocess_img (Callable): Function to preprocess the image.
141 | seed (int): Seed for shuffling the dataset.
142 | epoch (int): Start epoch number.
143 | tokenize (Optional[Callable]): Tokenizer function for the text data.
144 | return_index (bool): Whether to return the index of the data.
145 | """
146 | def __init__(self,
147 | input_shards: str,
148 | is_train: bool,
149 | batch_size: int,
150 | preprocess_img: Callable,
151 | seed: int = 0,
152 | epoch: int = 0,
153 | tokenize: Optional[Callable] = None,
154 | return_index: bool = False,
155 | ):
156 | self.shared_epoch = SharedEpoch(epoch=epoch) # create a shared epoch store to sync epoch to dataloader worker proc
157 | pipeline = [wds.SimpleShardList(input_shards)]
158 |
159 | # at this point we have an iterator over all the shards
160 | if is_train:
161 | pipeline.extend([
162 | detshuffle2(
163 | bufsize=_SHARD_SHUFFLE_SIZE,
164 | initial=_SHARD_SHUFFLE_INITIAL,
165 | seed=seed,
166 | epoch=self.shared_epoch,
167 | ),
168 | wds.split_by_node,
169 | wds.split_by_worker,
170 | ])
171 | pipeline.extend([
172 | # at this point, we have an iterator over the shards assigned to each worker at each node
173 | tarfile_to_samples_nothrow, # wds.tarfile_to_samples(handler=log_and_continue),
174 | wds.shuffle(
175 | bufsize=_SAMPLE_SHUFFLE_SIZE,
176 | initial=_SAMPLE_SHUFFLE_INITIAL,
177 | ),
178 | ])
179 | else:
180 | pipeline.extend([
181 | wds.split_by_worker,
182 | # at this point, we have an iterator over the shards assigned to each worker
183 | wds.tarfile_to_samples(handler=log_and_continue),
184 | ])
185 |
186 | # here we also load the key of data
187 | def json_parse_key(json_dict: Dict) -> int:
188 | return int(json_dict["key"])
189 |
190 | if return_index:
191 | rename = wds.rename(image="jpg;png;jpeg;webp", text="txt", key="json")
192 | if tokenize is not None:
193 | map_dict = wds.map_dict(image=preprocess_img, text=tokenize, key=json_parse_key)
194 | else:
195 | map_dict = wds.map_dict(image=preprocess_img, key=json_parse_key)
196 | to_tuple = wds.to_tuple("image", "text", "key", "key")
197 | else:
198 | rename = wds.rename(image="jpg;png;jpeg;webp", text="txt")
199 | if tokenize is not None:
200 | map_dict = wds.map_dict(image=preprocess_img, text=tokenize)
201 | else:
202 | map_dict = wds.map_dict(image=preprocess_img)
203 | to_tuple = wds.to_tuple("image", "text")
204 | pipeline.extend([
205 | wds.select(filter_no_caption_or_no_image),
206 | wds.decode("pilrgb", handler=log_and_continue),
207 | rename, map_dict, to_tuple,
208 | wds.batched(batch_size, partial=not is_train)
209 | ])
210 |
211 | super().__init__(*pipeline)
212 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/losses/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .auc import *
2 | from .ranking import *
3 | from .contrastive import *
4 | from .mil import *
5 | from .losses import *
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/losses/losses.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | from ..utils.utils import check_tensor_shape
4 |
5 |
6 | class CrossEntropyLoss(torch.nn.Module):
7 | r"""
8 | Cross-Entropy loss with a sigmoid function. This implementation is based on the built-in function
9 | from :obj:`~torch.nn.functional.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits`.
10 |
11 | Example:
12 | >>> loss_fn = CrossEntropyLoss()
13 | >>> preds = torch.randn(32, 1, requires_grad=True)
14 | >>> target = torch.empty(32, dtype=torch.long).random_(1)
15 | >>> loss = loss_fn(preds, target)
16 | >>> loss.backward()
17 |
18 | Reference:
19 | https://pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss.html
20 | """
21 | def __init__(self):
22 | super(CrossEntropyLoss, self).__init__()
23 | self.criterion = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits # with sigmoid
24 |
25 | def forward(self, y_pred, y_true): # TODO: handle the tensor shapes
26 | y_pred = check_tensor_shape(y_pred, (-1, 1))
27 | y_true = check_tensor_shape(y_true, (-1, 1))
28 | return self.criterion(y_pred, y_true)
29 |
30 | class FocalLoss(torch.nn.Module):
31 | r"""
32 | Focal loss with a sigmoid function.
33 |
34 | Args:
35 | alpha (float): weighting factor in range (0,1) to balance positive vs negative examples (Default: ``0.25``).
36 | gamma (float): exponent of the modulating factor (1 - p_t) to balance easy vs hard examples (Default: ``2``).
37 |
38 | Example:
39 | >>> loss_fn = FocalLoss(alpha=0.25, gamma=2.0)
40 | >>> preds = torch.randn(32, 1, requires_grad=True)
41 | >>> target = torch.empty(32, dtype=torch.long).random_(1)
42 | >>> loss = loss_fn(preds, target)
43 | >>> loss.backward()
44 |
45 | Reference:
46 | .. [1] Lin, Tsung-Yi and Goyal, Priya and Girshick, Ross and He, Kaiming and Doll{\'a}r, Piotr.
47 | "Focal loss for dense object detection."
48 | Proceedings of the IEEE international conference on computer vision. 2017.
49 | """
50 | def __init__(self, alpha=.25, gamma=2, device=None):
51 | super(FocalLoss, self).__init__()
52 | if not device:
53 | self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
54 | else:
55 | self.device = device
56 | self.alpha = torch.tensor([alpha, 1-alpha]).to(self.device)
57 | self.gamma = torch.tensor([gamma]).to(self.device)
58 |
59 | def forward(self, y_pred, y_true):
60 | y_pred = check_tensor_shape(y_pred, (-1, 1))
61 | y_true = check_tensor_shape(y_true, (-1, 1))
62 | BCE_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(y_pred, y_true, reduction='none')
63 | y_true = y_true.type(torch.long)
64 | at = self.alpha.gather(0, y_true.data.view(-1))
65 | pt = torch.exp(-BCE_loss)
66 | F_loss = at*(1-pt)**self.gamma * BCE_loss
67 | return F_loss.mean()
68 |
69 |
70 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/losses/perf_at_top.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | from .surrogate import get_surrogate_loss
4 | from ..utils.utils import check_tensor_shape
5 |
6 | class Top_Push_Loss(torch.nn.Module):
7 | """
8 | Partial AUC loss based on Top Push Loss to optimize One-way Partial AUROC (OPAUC).
9 |
10 | Args:
11 | pos_len (int): number of positive examples in the training data
12 | num_neg (int): number of negative samples for each mini-batch
13 | margin: margin used in surrogate loss (default: ``squared_hinge``)
14 | alpha: upper bound of False Positive Rate (FPR) used for optimizing pAUC (default: ``0``).
15 | beta (float): upper bound of False Positive Rate (FPR) used for optimizing pAUC (default: ``0.2``).
16 |
17 | Reference:
18 | [1] Zhu, Dixian and Li, Gang and Wang, Bokun and Wu, Xiaodong and Yang, Tianbao.
19 | "When AUC meets DRO: Optimizing Partial AUC for Deep Learning with Non-Convex Convergence Guarantee."
20 | In International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 27548-27573. PMLR, 2022.
21 | https://proceedings.mlr.press/v162/zhu22g.html
22 |
23 | """
24 | def __init__(self,
25 | pos_len,
26 | num_neg,
27 | margin=1.0,
28 | beta=0.2,
29 | surrogate_loss='squared_hinge'):
30 |
31 | super(Top_Push_Loss, self).__init__()
32 | self.beta = 1/num_neg # choose hardest negative samples in mini-batch
33 | self.eta = 1.0
34 | self.num_neg = num_neg
35 | self.pos_len = pos_len
36 | self.u_pos = torch.tensor([0.0]*pos_len).reshape(-1, 1).cuda()
37 | self.margin = margin
38 | self.surrogate_loss = get_surrogate_loss(surrogate_loss)
39 |
40 | def forward(self, y_pred, y_true, index, auto=True):
41 | if auto:
42 | self.num_neg = (y_true == 0).float().sum()
43 | assert self.num_neg > 0, 'There is no negative sample in the data!'
44 | y_pred = check_tensor_shape(y_pred, (-1, 1))
45 | y_true = check_tensor_shape(y_true, (-1, 1))
46 | index = check_tensor_shape(index, (-1,))
47 | pos_mask = (y_true == 1).squeeze()
48 | neg_mask = (y_true == 0).squeeze()
49 | assert sum(pos_mask) > 0, "Input data has no positive sample! Please use 'libauc.sampler.DualSampler' for data resampling!"
50 | if len(index) == len(y_pred):
51 | index = index[pos_mask] # indices for positive samples
52 | f_ps = y_pred[pos_mask] # shape: (len(f_ps), 1)
53 | f_ns = y_pred[neg_mask].squeeze() # shape: (len(f_ns))
54 | surr_loss = self.surrogate_loss(self.margin, f_ps - f_ns) # shape: (len(f_ps), len(f_ns))
55 | p = loss > self.u_pos[index]
56 | self.u_pos[index] = self.u_pos[index]-self.eta/self.pos_len*(1 - p.sum(dim=1, keepdim=True)/(self.beta*self.num_neg))
57 | p.detach_()
58 | loss = torch.mean(p * loss) / self.beta
59 | return loss
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/losses/surrogate.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 |
3 | __all__ = ['squared_loss',
4 | 'squared_hinge_loss',
5 | 'hinge_loss',
6 | 'logistic_loss',
7 | 'barrier_hinge_loss',
8 | 'get_surrogate_loss']
9 |
10 |
11 | def squared_loss(margin, t):
12 | r"""
13 | Squared Loss. The loss can be described as:
14 |
15 | .. math::
16 |
17 | L_\text{squared}(t, m) = (m - t)^2
18 |
19 | where ``m`` is the margin hyper-parameter.
20 | """
21 | return (margin - t)** 2
22 |
23 | def squared_hinge_loss(margin, t):
24 | r"""
25 | Squared Hinge Loss. The loss can be described as:
26 |
27 | .. math::
28 | L_\text{squared_hinge}(t, m) = \max(m - t, 0)^2
29 |
30 | where ``m`` is the margin hyper-parameter.
31 | """
32 | return torch.max(margin - t, torch.zeros_like(t)) ** 2
33 |
34 | def hinge_loss(margin, t):
35 | r"""
36 | Hinge Loss. The loss can be described as:
37 |
38 | .. math::
39 |
40 | L_\text{hinge}(t, m) = \max(m - t, 0)
41 |
42 | where ``m`` is the margin hyper-parameter.
43 | """
44 | return torch.max(margin - t, torch.zeros_like(t))
45 |
46 | def logistic_loss(scale, t):
47 | r"""
48 | Logistic Loss. The loss can be described as:
49 |
50 | .. math::
51 | L_\text{logistic}(t, s) = \log(1 + e^{-st})
52 |
53 | where ``s`` is the scaling hyper-parameter.
54 | """
55 | return torch.log(1+torch.exp(-scale*t))
56 |
57 | def barrier_hinge_loss(hparam, t):
58 | r"""
59 | Barrier Hinge Loss. The loss can be described as:
60 |
61 | .. math::
62 | L_\text{barrier_hinge}(t, s, m) = \max(−s(m + t) + m, \max(s(t − m), m − t))
63 |
64 | where ``m`` is the margin hyper-parameter and ``s`` is the the scaling hyper-parameter.
65 |
66 | Reference:
67 | .. [1] Charoenphakdee, Nontawat, Jongyeong Lee, and Masashi Sugiyama. "On symmetric losses for learning from corrupted labels." International Conference on Machine Learning. PMLR, 2019.
68 | """
69 | m,s = hparam
70 | loss = torch.maximum(-s * (m + t) + m, torch.maximum(m - t, s* (t - rm)))
71 | return loss
72 |
73 | def get_surrogate_loss(loss_name='squared_hinge'):
74 | r"""
75 | A wrapper to call a specific surrogate loss function.
76 |
77 | Args:
78 | loss_name (str): type of surrogate loss function to fetch, including 'squared_hinge', 'squared', 'logistic', 'barrier_hinge' (default: ``'squared_hinge'``).
79 | """
80 | assert f'{loss_name}_loss' in __all__, f'{loss_name} is not implemented'
81 | if loss_name == 'squared_hinge':
82 | surr_loss = squared_hinge_loss
83 | elif loss_name == 'squared':
84 | surr_loss = squared_loss
85 | elif loss_name == 'logistic':
86 | surr_loss = logistic_loss
87 | elif loss_name == 'barrier_hinge':
88 | surr_loss = barrier_hinge_loss
89 | else:
90 | raise ValueError('Out of options!')
91 | return surr_loss
92 |
93 |
94 |
95 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/metrics/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .metrics_k import *
2 | from .metrics import *
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/metrics/metrics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from sklearn.metrics import roc_auc_score
2 | from sklearn.metrics import average_precision_score
3 | import numpy as np
4 | from ..utils.utils import check_array_type, check_tensor_shape, check_array_shape, select_mean
5 |
6 |
7 | def auc_roc_score(y_true, y_pred, reduction='mean', **kwargs):
8 | r"""Evaluation function of AUROC"""
9 | y_true = check_array_type(y_true)
10 | y_pred = check_array_type(y_pred)
11 | num_labels = y_true.shape[-1] if len(y_true.shape) == 2 else 1
12 | y_true = check_array_shape(y_true, (-1, num_labels))
13 | y_pred = check_array_shape(y_pred, (-1, num_labels))
14 | assert reduction in ['mean', None, 'None'], 'Input is not valid!'
15 | if y_pred.shape[-1] != 1 and len(y_pred.shape) > 1:
16 | class_auc_list = []
17 | for i in range(y_pred.shape[-1]):
18 | try:
19 | local_auc = roc_auc_score(y_true[:, i], y_pred[:, i], **kwargs)
20 | class_auc_list.append(local_auc)
21 | except:
22 | # edge case: no positive samples in the data set
23 | class_auc_list.append(-1.0) # if only one class
24 | if reduction == 'mean':
25 | return select_mean(class_auc_list, threshold=0) # return non-negative mean
26 | return class_auc_list
27 | return roc_auc_score(y_true, y_pred, **kwargs)
28 |
29 |
30 | def auc_prc_score(y_true, y_pred, reduction='mean', **kwargs):
31 | r"""Evaluation function of AUPRC"""
32 | y_true = check_array_type(y_true)
33 | y_pred = check_array_type(y_pred)
34 | num_labels = y_true.shape[-1] if len(y_true.shape) == 2 else 1
35 | y_true = check_array_shape(y_true, (-1, num_labels))
36 | y_pred = check_array_shape(y_pred, (-1, num_labels))
37 | if y_pred.shape[-1] != 1 and len(y_pred.shape)>1:
38 | class_auc_list = []
39 | for i in range(y_pred.shape[-1]):
40 | try:
41 | local_auc = average_precision_score(y_true[:, i], y_pred[:, i])
42 | class_auc_list.append(local_auc)
43 | except:
44 | # edge case: no positive samples in the data set
45 | class_auc_list.append(-1.0)
46 | if reduction == 'mean':
47 | return select_mean(class_auc_list)
48 | return class_auc_list
49 | return average_precision_score(y_true, y_pred, **kwargs)
50 |
51 |
52 | def pauc_roc_score(y_true, y_pred, max_fpr=1.0, min_tpr=0.0, reduction='mean', **kwargs):
53 | r"""Evaluation function of pAUROC"""
54 | y_true = check_array_type(y_true)
55 | y_pred = check_array_type(y_pred)
56 | #num_labels = y_true.shape[-1] if len(y_true) == 2 else 1
57 | y_true = check_array_shape(y_true, (-1,))
58 | y_pred = check_array_shape(y_pred, (-1,))
59 |
60 | # TODO: multi-label support
61 | if min_tpr == 0:
62 | # One-way Partial AUC (OPAUC)
63 | return roc_auc_score(y_true, y_pred, max_fpr=max_fpr, **kwargs)
64 |
65 | # Two-way Partial AUC (TPAUC)
66 | pos_idx = np.where(y_true == 1)[0]
67 | neg_idx = np.where(y_true != 1)[0]
68 | num_pos = round(len(pos_idx)*(1-min_tpr))
69 | num_neg = round(len(neg_idx)*max_fpr)
70 | num_pos = 1 if num_pos < 1 else num_pos
71 | num_neg = 1 if num_neg < 1 else num_neg
72 | if len(pos_idx)==1:
73 | selected_pos = [0]
74 | else:
75 | selected_pos = np.argpartition(y_pred[pos_idx], num_pos)[:num_pos]
76 | if len(neg_idx)==1:
77 | selected_neg = [0]
78 | else:
79 | selected_neg = np.argpartition(-y_pred[neg_idx], num_neg)[:num_neg]
80 | selected_target = np.concatenate((y_true[pos_idx][selected_pos], y_true[neg_idx][selected_neg]))
81 | selected_pred = np.concatenate((y_pred[pos_idx][selected_pos], y_pred[neg_idx][selected_neg]))
82 | return roc_auc_score(selected_target, selected_pred, **kwargs)
83 |
84 | # TODO: automatic detect classificaiton task or ranking task?
85 | def evaluator(y_true, y_pred, metrics=['auroc', 'auprc', 'pauroc'], return_str=False, format='%.4f(%s)', **kwargs):
86 | results = {}
87 | if 'auroc' in metrics:
88 | results['auroc'] = auc_roc_score(y_true, y_pred)
89 | if 'auprc' in metrics:
90 | results['auprc'] = auc_prc_score(y_true, y_pred)
91 | if 'pauroc' in metrics:
92 | results['pauroc'] = pauc_roc_score(y_true, y_pred, **kwargs) # e.g., max_fpr=0.3
93 | if return_str:
94 | output = []
95 | for key, value in results.items():
96 | output.append(format%(value, key))
97 | return ','.join(output)
98 | return results
99 |
100 |
101 | if __name__ == '__main__':
102 | # import numpy as np
103 | preds = [0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8, 0.9, 1.0]
104 | labels = [1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0]
105 |
106 | print (roc_auc_score(labels, preds))
107 | print (average_precision_score(labels, preds))
108 |
109 |
110 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/metrics/metrics_k.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 |
3 | def check_array_type(array):
4 | # convert to array type
5 | if not isinstance(array, (np.ndarray, np.generic)):
6 | array = np.array(array)
7 | return array
8 |
9 | def check_array_shape(array, shape):
10 | # check array shape
11 | array = check_array_type(array)
12 | if array.size == 0:
13 | raise ValueError("Array is empty.")
14 | if array.shape != shape and len(array.shape) != 1:
15 | try:
16 | array = array.reshape(shape)
17 | except ValueError as e:
18 | raise ValueError(f"Could not reshape array of shape {array.shape} to {shape}.") from e
19 | return array
20 |
21 | # Reference: https://www.kaggle.com/code/nandeshwar/mean-average-precision-map-k-metric-explained-code
22 | def precision_and_recall_at_k(y_true, y_pred, k, pos_label=1, **kwargs):
23 | # referece: https://github.com/NicolasHug/Surprise/blob/master/examples/precision_recall_at_k.py
24 | def calc_metrics(y_true, y_pred):
25 | y_true = y_true == pos_label
26 | desc_sort_order = np.argsort(y_pred)[::-1]
27 | y_true_sorted = y_true[desc_sort_order]
28 | true_positives = y_true_sorted[:k].sum()
29 | total_positives = sum(y_true)
30 |
31 | precision_k = true_positives / min(k, total_positives)
32 | recall_k = true_positives / total_positives
33 | return precision_k, recall_k
34 |
35 | y_true = check_array_shape(y_true, (-1, 1))
36 | y_pred = check_array_shape(y_pred, (-1, 1))
37 |
38 | if y_true.shape[-1] != 1 and len(y_true.shape) > 1:
39 | metrics_list = [calc_metrics(y_true[:, i], y_pred[:, i]) for i in range(y_true.shape[-1])]
40 | precision_k_list, recall_k_list = zip(*metrics_list)
41 | return precision_k_list, recall_k_list
42 | else:
43 | y_true = y_true.flatten()
44 | y_pred = y_pred.flatten()
45 | precision_k, recall_k = calc_metrics(y_true, y_pred)
46 | return precision_k, recall_k
47 |
48 | def precision_at_k(y_true, y_pred, k, pos_label=1, **kwargs):
49 | r"""Evaluation function of Precision@K"""
50 | precision_k, _ = precision_and_recall_at_k(y_true, y_pred, k, pos_label=1, **kwargs)
51 | return precision_k
52 |
53 | def recall_at_k(y_true, y_pred, k, pos_label=1, **kwargs):
54 | r"""Evaluation function of Recall@K"""
55 | _, recall_k = precision_and_recall_at_k(y_true, y_pred, k, pos_label=1, **kwargs)
56 | return recall_k
57 |
58 | def ap_at_k(y_true, y_pred, k=10):
59 | r"""Evaluation function of AveragePrecision@K"""
60 | # adapted from https://github.com/benhamner/Metrics/blob/master/Python/ml_metrics/average_precision.py
61 | y_true = check_array_shape(y_true, (-1,))
62 | y_pred = check_array_shape(y_pred, (-1,))
63 | if len(y_pred)>k:
64 | y_pred = y_pred[:k]
65 | score = 0.0
66 | num_hits = 0.0
67 | for i,p in enumerate(y_pred):
68 | if p in y_true and p not in y_pred[:i]:
69 | num_hits += 1.0
70 | score += num_hits / (i+1.0)
71 | return score / min(len(y_true), k)
72 |
73 | def map_at_k(y_true, y_pred, k=10):
74 | r"""Evaluation function of meanAveragePrecision@K"""
75 | # adapted from https://github.com/benhamner/Metrics/blob/master/Python/ml_metrics/average_precision.py
76 | assert len(y_true.shape) == 2 and len(y_true.shape) == 2
77 | assert k > 0, 'Value of k is not valid!'
78 | if isinstance(y_true, np.ndarray):
79 | y_true = y_true.tolist()
80 | if isinstance(y_pred, np.ndarray):
81 | y_pred = y_pred.tolist()
82 | return np.mean([ap_at_k(a,p,k) for a,p in zip(y_true, y_pred)])
83 |
84 |
85 | def ndcg_at_k(y_true, y_pred, k=5):
86 | r"""
87 | Evaluation function of NDCG@K
88 | """
89 | assert isinstance(y_pred, np.ndarray)
90 | assert isinstance(y_true, np.ndarray)
91 | assert len(y_pred.shape) == 2 and len(y_pred.shape) == 2
92 |
93 | num_of_users, num_pos_items = y_true.shape
94 | sorted_ratings = -np.sort(-y_true) # descending order !!
95 | discounters = np.tile([np.log2(i+1) for i in range(1, 1+num_pos_items)], (num_of_users, 1))
96 | normalizer_mat = (np.exp2(sorted_ratings) - 1) / discounters
97 |
98 | sort_idx = (-y_pred).argsort(axis=1) # index of sorted predictions (max->min)
99 | gt_rank = np.array([np.argwhere(sort_idx == i)[:, 1]+1 for i in range(num_pos_items)]).T # rank of the ground-truth (start from 1)
100 | hit = (gt_rank <= k)
101 |
102 | # calculate the normalizer first
103 | normalizer = np.sum(normalizer_mat[:, :k], axis=1)
104 | # calculate DCG
105 | DCG = np.sum(((np.exp2(y_true) - 1) / np.log2(gt_rank+1)) * hit.astype(float), axis=1)
106 | return np.mean(DCG / normalizer)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/models/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .densenet import *
2 | from .resnet import *
3 | from .resnet_cifar import *
4 | from .neumf import *
5 | from .perceptron import *
6 | from .mil_models import *
7 | from .gnn import *
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/models/mil_models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | import torch.nn.init as init
5 |
6 | from torch.autograd import Variable
7 |
8 |
9 | class FFNN(torch.nn.Module):
10 | r"""
11 | The basic 3-layer-MLP in multiple instance learning experiments utilized from [1]_.
12 |
13 | Args:
14 | input_dim (int, required): input data dimension.
15 | hidden_sizes (list[int], required): number of nurons for the hidden layers.
16 | num_class (int, required): number of class for model prediction, default: 1.
17 | last_activation (str, optional): the activation function for the output layer.
18 |
19 | Example:
20 | >>> model = FFNN_stoc_att(num_classes=1, dims=DIMS)
21 |
22 | Reference:
23 | .. [1] Dixian Zhu, Bokun Wang, Zhi Chen, Yaxing Wang, Milan Sonka, Xiaodong Wu, Tianbao Yang
24 | "Provable Multi-instance Deep AUC Maximization with Stochastic Pooling."
25 | In International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. xxxxx-xxxxx. PMLR, 2023.
26 | https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.08040
27 | """
28 | def __init__(self, input_dim=29, hidden_sizes=(16,), last_activation=None, num_classes=1):
29 | super(FFNN, self).__init__()
30 | self.inputs = torch.nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_sizes[0])
31 | self.last_activation = last_activation
32 | layers = []
33 | for i in range(len(hidden_sizes)-1):
34 | layers.append(torch.nn.Linear(hidden_sizes[i], hidden_sizes[i+1]))
35 | layers.append(nn.ReLU())
36 | self.layers = nn.Sequential(*layers)
37 | self.classifer = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_sizes[-1], num_classes)
38 | def forward(self, x):
39 | x = torch.tanh(self.inputs(x))
40 | x = self.layers(x)
41 | if self.last_activation is None:
42 | return self.classifer(x)
43 | elif self.last_activation == 'sigmoid':
44 | return torch.sigmoid(self.classifer(x))
45 |
46 |
47 | class FFNN_stoc_att(nn.Module):
48 | r"""
49 | The basic 3-layer-MLP with an extra attention module that generates importance weights for combining the instance-level hidden features for each bag under multiple instance learning setting [1]_.
50 |
51 | Args:
52 | input_dim (int, required): input data dimension.
53 | hidden_sizes (list[int], required): number of nurons for the hidden layers.
54 | num_class (int, required): number of class for model prediction, default: 1.
55 |
56 | Example:
57 | >>> model = FFNN_stoc_att(num_classes=1, dims=DIMS)
58 |
59 | Reference:
60 | .. [1] Dixian Zhu, Bokun Wang, Zhi Chen, Yaxing Wang, Milan Sonka, Xiaodong Wu, Tianbao Yang
61 | "Provable Multi-instance Deep AUC Maximization with Stochastic Pooling."
62 | In International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. xxxxx-xxxxx. PMLR, 2023.
63 | https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.08040
64 | """
65 | def __init__(self, input_dim=29, hidden_sizes=(16,), num_classes=1):
66 | super(FFNN_stoc_att, self).__init__()
67 | self.inputs = torch.nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_sizes[0])
68 | layers = []
69 | for i in range(len(hidden_sizes)-1):
70 | layers.append(torch.nn.Linear(hidden_sizes[i], hidden_sizes[i+1]))
71 | layers.append(nn.ReLU())
72 | self.layers = nn.Sequential(*layers)
73 | self.classifer = torch.nn.Linear(hidden_sizes[-1], num_classes)
74 | self.attention = nn.Sequential(
75 | nn.Linear(hidden_sizes[-1], hidden_sizes[-1]),
76 | nn.Tanh(),
77 | nn.Linear(hidden_sizes[-1], 1)
78 | )
79 |
80 | self.apply(_weights_init)
81 | print('model initialized')
82 |
83 |
84 | def forward(self, x):
85 | x = torch.tanh(self.inputs(x))
86 | x = self.layers(x)
87 | weights = self.attention(x)
88 | weights = torch.exp(weights)
89 | out = self.classifer(x)
90 | return out, weights
91 |
92 |
93 |
94 | def _weights_init(m):
95 | classname = m.__class__.__name__
96 | if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) or isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
97 | init.xavier_normal_(m.weight)
98 |
99 | class LambdaLayer(nn.Module):
100 | def __init__(self, lambd):
101 | super(LambdaLayer, self).__init__()
102 | self.lambd = lambd
103 |
104 | def forward(self, x):
105 | return self.lambd(x)
106 |
107 |
108 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
109 | expansion = 1
110 |
111 | def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1, option='A'):
112 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
113 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
114 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
115 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
116 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
117 |
118 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
119 | if stride != 1 or in_planes != planes:
120 | if option == 'A':
121 | """
122 | For CIFAR10 ResNet paper uses option A.
123 | """
124 | self.shortcut = LambdaLayer(lambda x:
125 | F.pad(x[:, :, ::2, ::2], (0, 0, 0, 0, planes//4, planes//4), "constant", 0))
126 | elif option == 'B':
127 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
128 | nn.Conv2d(in_planes, self.expansion * planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
129 | nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion * planes)
130 | )
131 |
132 | def forward(self, x):
133 | out = activation_func(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
134 | out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out))
135 | out += self.shortcut(x)
136 | out = activation_func(out)
137 | return out
138 |
139 |
140 |
141 | class ResNet_stoc_att(nn.Module):
142 | r"""
143 | The ResNet [2,3,4]_ with an extra attention module that generates importance weights for combining the instance-level hidden features for each bag under multiple instance learning setting [1]_.
144 |
145 | Args:
146 | block (torch.nn.module, required): block module for ResNet.
147 | num_blocks (list[int], required): number of nurons for the hidden layer.
148 | inchannels (int, required): the number of channels for the input image, default: 3.
149 | num_classes (int, required): the model prediction class number, default: 1.
150 |
151 | Example:
152 | >>> model = ResNet_stoc_att(block=BasicBlock, num_blocks=[3,3,3], inchannels=3, num_classes=1)
153 |
154 | Reference:
155 | .. [1] Dixian Zhu, Bokun Wang, Zhi Chen, Yaxing Wang, Milan Sonka, Xiaodong Wu, Tianbao Yang
156 | "Provable Multi-instance Deep AUC Maximization with Stochastic Pooling."
157 | In International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. xxxxx-xxxxx. PMLR, 2023. https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.08040
158 |
159 | .. [2] Kaiming He, Xiangyu Zhang, Shaoqing Ren, Jian Sun "Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition." arXiv:1512.03385
160 |
161 | .. [3] https://github.com/pytorch/vision/blob/master/torchvision/models/resnet.py
162 |
163 | .. [4] https://github.com/akamaster/pytorch_resnet_cifar10/tree/master
164 | """
165 | def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, inchannels=3, num_classes=1):
166 | super(ResNet_stoc_att, self).__init__()
167 | self.in_planes = 16
168 | self.inchannels = inchannels
169 |
170 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inchannels, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
171 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
172 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, num_blocks[0], stride=1)
173 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, num_blocks[1], stride=2)
174 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_blocks[2], stride=2)
175 | self.attention = nn.Sequential(
176 | nn.Linear(64, 128),
177 | nn.Tanh(),
178 | nn.Linear(128, 1)
179 | )
180 | self.linear = nn.Linear(64, num_classes)
181 |
182 | self.apply(_weights_init)
183 |
184 | self.bnlast = nn.BatchNorm1d(1)
185 |
186 | def init_weights(self):
187 | self.apply(_weights_init)
188 |
189 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, num_blocks, stride):
190 | strides = [stride] + [1]*(num_blocks-1)
191 | layers = []
192 | for stride in strides:
193 | layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, stride))
194 | self.in_planes = planes * block.expansion
195 |
196 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
197 |
198 | def forward(self, x):
199 | batch_size = x.shape[0]
200 | x = x.view(-1,self.inchannels,x.shape[2],x.shape[3])
201 | out = activation_func(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
202 | out = self.layer1(out)
203 | out = self.layer2(out)
204 | out = self.layer3(out)
205 |
206 | out = F.avg_pool2d(out, (out.size()[2],out.size()[3]))
207 | out = out.view(out.size()[0], -1)
208 | weights = self.attention(out)
209 | weights = torch.exp(weights)
210 | out = self.linear(out)
211 | return out, weights
212 |
213 |
214 |
215 | def ResNet20_stoc_att(activations='relu', **kwargs):
216 | global activation_func
217 | activation_func = F.relu if activations=='relu' else F.elu
218 | return ResNet_stoc_att(BasicBlock, [3, 3, 3], **kwargs)
219 |
220 |
221 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/models/neumf.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # This implementation is from https://github.com/hexiangnan/neural_collaborative_filtering
2 |
3 | import torch
4 | import torch.nn as nn
5 | import logging
6 |
7 | class NeuMF(nn.Module):
8 | r"""
9 | NeuMF is a widely-used model for recommender systems.
10 |
11 | args:
12 | user_num (int): the number of users in the dataset
13 | item_num (int): the number of items in the dataset
14 | dropout (float, optional): dropout ratio for the model
15 | emb_size (int, optional): embedding size of the model
16 | layers (string, optional): describe the layer information of the model
17 |
18 | Reference:
19 | .. [1] He, X., Liao, L., Zhang, H., Nie, L., Hu, X., and Chua, T.
20 | Neural Collaborative Filtering
21 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.05031
22 | """
23 | def __init__(self, user_num: int, item_num: int, dropout: float=0.2, emb_size: int=64, layers: str='[64]'):
24 | super(NeuMF, self).__init__()
25 | self.user_num = user_num
26 | self.item_num = item_num
27 | self.emb_size = emb_size
28 | self.dropout = dropout
29 | self.layers = eval(layers)
30 |
31 | self.mf_u_embeddings = nn.Embedding(self.user_num, self.emb_size)
32 | self.mf_i_embeddings = nn.Embedding(self.item_num, self.emb_size)
33 | self.mlp_u_embeddings = nn.Embedding(self.user_num, self.emb_size)
34 | self.mlp_i_embeddings = nn.Embedding(self.item_num, self.emb_size)
35 |
36 | self.mlp = nn.ModuleList([])
37 | pre_size = 2 * self.emb_size
38 | for i, layer_size in enumerate(self.layers):
39 | self.mlp.append(nn.Linear(pre_size, layer_size))
40 | pre_size = layer_size
41 | self.dropout_layer = nn.Dropout(p=self.dropout)
42 | self.prediction = nn.Linear(pre_size + self.emb_size, 1, bias=False)
43 |
44 | def reset_last_layer(self):
45 | self.prediction.reset_parameters()
46 |
47 | @staticmethod
48 | def init_weights(m):
49 | if 'Linear' in str(type(m)):
50 | nn.init.normal_(m.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
51 | if m.bias is not None:
52 | nn.init.normal_(m.bias, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
53 | elif 'Embedding' in str(type(m)):
54 | nn.init.normal_(m.weight, mean=0.0, std=0.01)
55 |
56 | def save_model(self, model_path=None):
57 | if model_path is None:
58 | model_path = self.model_path
59 | torch.save(self.state_dict(), model_path)
60 |
61 | def load_model(self, model_path=None):
62 | if model_path is None:
63 | model_path = self.model_path
64 | self.load_state_dict(torch.load(model_path))
65 | logging.info('Load model from ' + model_path)
66 |
67 | def forward(self, feed_dict):
68 | u_ids = feed_dict['user_id'].long() # [batch_size]
69 | i_ids = feed_dict['item_id'].long() # [batch_size, -1]
70 |
71 | u_ids = u_ids.unsqueeze(-1).repeat((1, i_ids.shape[1])) # [batch_size, -1]
72 |
73 | mf_u_vectors = self.mf_u_embeddings(u_ids)
74 | mf_i_vectors = self.mf_i_embeddings(i_ids)
75 | mlp_u_vectors = self.mlp_u_embeddings(u_ids)
76 | mlp_i_vectors = self.mlp_i_embeddings(i_ids)
77 |
78 | mf_vector = mf_u_vectors * mf_i_vectors
79 | mlp_vector = torch.cat([mlp_u_vectors, mlp_i_vectors], dim=-1)
80 | for layer in self.mlp:
81 | mlp_vector = layer(mlp_vector).relu()
82 | mlp_vector = self.dropout_layer(mlp_vector)
83 |
84 | output_vector = torch.cat([mf_vector, mlp_vector], dim=-1)
85 | prediction = self.prediction(output_vector)
86 | return {'prediction': prediction.view(feed_dict['batch_size'], -1)}
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/models/perceptron.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch import nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | class MLP(torch.nn.Module):
8 | r"""
9 | An implementation of Multilayer Perceptron (MLP).
10 | """
11 | def __init__(self, input_dim=29, hidden_sizes=(16,), activation='relu', num_classes=1):
12 | super().__init__()
13 | self.hidden_sizes = hidden_sizes
14 | if sum(self.hidden_sizes) > 0: # multi-layer model
15 | self.inputs = torch.nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_sizes[0])
16 | layers = []
17 | for i in range(len(hidden_sizes)-1):
18 | layers.append(torch.nn.Linear(hidden_sizes[i], hidden_sizes[i+1]))
19 | if activation=='relu':
20 | layers.append(nn.ReLU())
21 | elif activation=='elu':
22 | layers.append(nn.ELU())
23 | else:
24 | pass
25 | self.layers = nn.Sequential(*layers)
26 | classifier_input_dim = hidden_sizes[-1]
27 | else: # linear model
28 | classifier_input_dim = input_dim
29 | self.classifer = torch.nn.Linear(classifier_input_dim, num_classes)
30 |
31 | def forward(self, x):
32 | """forward pass"""
33 | if sum(self.hidden_sizes) > 0:
34 | x = self.inputs(x)
35 | x = self.layers(x)
36 | return self.classifer(x)
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/models/resnet_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # This implementation is adapted from https://github.com/akamaster/pytorch_resnet_cifar10/tree/master.
2 |
3 | import torch
4 | import torch.nn as nn
5 | import torch.nn.functional as F
6 | import torch.nn.init as init
7 |
8 | from torch.autograd import Variable
9 |
10 | __all__ = ['ResNet', 'resnet20', 'resnet32', 'resnet44', 'resnet56', 'resnet110', 'resnet1202']
11 |
12 |
13 | def _weights_init(m):
14 | classname = m.__class__.__name__
15 | #print(classname)
16 | if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) or isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
17 | #init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight)
18 | init.xavier_normal_(m.weight)
19 |
20 | class LambdaLayer(nn.Module):
21 | def __init__(self, lambd):
22 | super(LambdaLayer, self).__init__()
23 | self.lambd = lambd
24 |
25 | def forward(self, x):
26 | return self.lambd(x)
27 |
28 | from torch.nn import Parameter
29 | class NormedLinear(nn.Module):
30 |
31 | def __init__(self, in_features, out_features):
32 | super(NormedLinear, self).__init__()
33 | self.weight = Parameter(torch.Tensor(in_features, out_features))
34 | self.weight.data.uniform_(-1, 1).renorm_(2, 1, 1e-5).mul_(1e5)
35 |
36 | def forward(self, x):
37 | out = F.normalize(x, dim=1).mm(F.normalize(self.weight, dim=0))
38 | return out
39 |
40 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
41 | expansion = 1
42 |
43 | def __init__(self, in_planes, planes, stride=1, option='A'):
44 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
45 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
46 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
47 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
48 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
49 |
50 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
51 | if stride != 1 or in_planes != planes:
52 | if option == 'A':
53 | """
54 | For CIFAR10 ResNet paper uses option A.
55 | """
56 | self.shortcut = LambdaLayer(lambda x:
57 | F.pad(x[:, :, ::2, ::2], (0, 0, 0, 0, planes//4, planes//4), "constant", 0))
58 | elif option == 'B':
59 | self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
60 | nn.Conv2d(in_planes, self.expansion * planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False),
61 | nn.BatchNorm2d(self.expansion * planes)
62 | )
63 |
64 | def forward(self, x):
65 | out = activation_func(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
66 | out = self.bn2(self.conv2(out))
67 | out += self.shortcut(x)
68 | out = activation_func(out)
69 | return out
70 |
71 |
72 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
73 | def __init__(self, block, num_blocks, num_classes=1, last_activation='sigmoid', pretrained=False):
74 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
75 | self.in_planes = 16
76 |
77 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 16, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False)
78 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(16)
79 | self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 16, num_blocks[0], stride=1)
80 | self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 32, num_blocks[1], stride=2)
81 | self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 64, num_blocks[2], stride=2)
82 | self.linear = nn.Linear(64, num_classes)
83 |
84 | self.apply(_weights_init)
85 | self.last_activation = last_activation
86 | if self.last_activation is not None:
87 | self.sigmoid = nn.Sigmoid()
88 |
89 | def _make_layer(self, block, planes, num_blocks, stride):
90 | strides = [stride] + [1]*(num_blocks-1)
91 | layers = []
92 | for stride in strides:
93 | layers.append(block(self.in_planes, planes, stride))
94 | self.in_planes = planes * block.expansion
95 |
96 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
97 |
98 | def forward(self, x):
99 | out = activation_func(self.bn1(self.conv1(x)))
100 | out = self.layer1(out)
101 | out = self.layer2(out)
102 | out = self.layer3(out)
103 |
104 | out = F.avg_pool2d(out, out.size()[3])
105 | out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
106 | out = self.linear(out)
107 | if self.last_activation == 'sigmoid':
108 | out = self.sigmoid(out)
109 | elif self.last_activation == 'none' or self.last_activation==None:
110 | out = out
111 | elif self.last_activation == 'l2':
112 | out= F.normalize(out,dim=0,p=2)
113 | else:
114 | out = self.sigmoid(out)
115 | return out
116 |
117 |
118 | def resnet20(pretrained=False, activations='relu', last_activation=None, **kwargs):
119 | global activation_func
120 | activation_func = F.relu if activations=='relu' else F.elu
121 | # print (activation_func)
122 | return ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 3, 3], last_activation=last_activation, **kwargs)
123 |
124 |
125 | def resnet32(pretrained=False, activations='relu', last_activation=None, **kwargs):
126 | global activation_func
127 | activation_func = F.relu if activations=='relu' else F.elu
128 | # print (activation_func)
129 | return ResNet(BasicBlock, [5, 5, 5], last_activation=last_activation, **kwargs)
130 |
131 |
132 | def resnet44(pretrained=False, activations='relu', last_activation=None, **kwargs):
133 | global activation_func
134 | activation_func = F.relu if activations=='relu' else F.elu
135 | # print (activation_func)
136 | return ResNet(BasicBlock, [7, 7, 7], last_activation=last_activation, **kwargs)
137 |
138 |
139 | def resnet56(pretrained=False, activations='relu', last_activation=None, **kwargs):
140 | global activation_func
141 | activation_func = F.relu if activations=='relu' else F.elu
142 | # print (activation_func)
143 | return ResNet(BasicBlock, [9, 9, 9], last_activation=last_activation, **kwargs)
144 |
145 |
146 | def resnet110(pretrained=False, activations='relu', last_activation=None, **kwargs):
147 | global activation_func
148 | activation_func = F.relu if activations=='relu' else F.elu
149 | # print (activation_func)
150 | return ResNet(BasicBlock, [18, 18, 18], last_activation=last_activation, **kwargs)
151 |
152 |
153 | def resnet1202(pretrained=False, activations='relu', last_activation=None, **kwargs):
154 | global activation_func
155 | activation_func = F.relu if activations=='relu' else F.elu
156 | # print (activation_func)
157 | return ResNet(BasicBlock, [200, 200, 200], last_activation=last_activation, **kwargs)
158 |
159 |
160 | def test(net):
161 | import numpy as np
162 | total_params = 0
163 |
164 | for x in filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad, net.parameters()):
165 | total_params += np.prod(x.data.numpy().shape)
166 | print("Total number of params", total_params)
167 | print("Total layers", len(list(filter(lambda p: p.requires_grad and len(p.data.size())>1, net.parameters()))))
168 |
169 |
170 | # alias
171 | ResNet20 = resnet20
172 | ResNet32 = resnet32
173 | ResNet44 = resnet44
174 | ResNet56 = resnet56
175 | ResNet110 = resnet110
176 | ResNet1202 = resnet1202
177 |
178 | if __name__ == "__main__":
179 | for net_name in __all__:
180 | if net_name.startswith('resnet'):
181 | print(net_name)
182 | test(globals()[net_name]())
183 | print()
184 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/optimizers/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LibAUC optimizers
2 | from .pesg import *
3 | from .pdsca import *
4 | from .soap import *
5 | from .sopa import *
6 | from .sopa_s import *
7 | from .sota_s import *
8 | from .song import *
9 | from .sogclr import *
10 | from .isogclr import *
11 | from .midam import *
12 |
13 | # PyTorch optimizers
14 | from .sgd import *
15 | from .adam import *
16 | from .adamw import *
17 | from .lars import *
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/optimizers/adam.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 |
4 | class Adam(torch.optim.Optimizer):
5 | r"""Implements Adam algorithm. This code is adapted from `PyTorch codebase `__.
6 |
7 | It has been proposed in `Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization`_.
8 | The implementation of the L2 penalty follows changes proposed in
9 | `Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization`_.
10 |
11 | Arguments:
12 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize
13 | lr (float): learning rate (default: ``1e-3``)
14 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
15 | running averages of gradient and its square (default: ``(0.9, 0.999)``)
16 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
17 | numerical stability (default: ``1e-8``)
18 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: ``0``)
19 | epoch_decay (float, optional): epoch decay (epoch-wise l2 penalty) (default: ``0.0``)
20 | amsgrad (boolean, optional): whether to use the AMSGrad variant of this
21 | algorithm from the paper `On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond`_
22 | (default: ``False``)
23 | device (torch.device, optional): the device used for optimization, e.g., 'cpu' or 'cuda' (default: ``None``)
24 |
25 | .. _Adam\: A Method for Stochastic Optimization:
26 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
27 | .. _Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization:
28 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101
29 | .. _On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond:
30 | https://openreview.net/forum?id=ryQu7f-RZ
31 | """
32 |
33 | def __init__(self,
34 | params,
35 | lr=1e-3,
36 | betas=(0.9, 0.999),
37 | eps=1e-8,
38 | clip_value=1.0,
39 | epoch_decay=0,
40 | weight_decay=0,
41 | amsgrad=False,
42 | verbose=True,
43 | device=None,
44 | **kwargs):
45 | if not device:
46 | self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
47 | else:
48 | self.device = device
49 |
50 | if not 0.0 <= lr:
51 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
52 | if not 0.0 <= eps:
53 | raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
54 | if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
55 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
56 | if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
57 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
58 | if not 0.0 <= weight_decay:
59 | raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
60 |
61 | self.params = list(params)
62 | self.lr = lr
63 |
64 | self.model_ref = self.__init_model_ref__(self.params) if epoch_decay > 0 else None
65 | self.model_acc = self.__init_model_acc__(self.params) if epoch_decay > 0 else None
66 |
67 | self.T = 0 # for epoch_decay
68 | self.steps = 0 # total optim steps
69 | self.verbose = verbose # print updates for lr/regularizer
70 |
71 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps,
72 | weight_decay=weight_decay, epoch_decay=epoch_decay, amsgrad=amsgrad,
73 | clip_value=clip_value, model_ref=self.model_ref, model_acc=self.model_acc)
74 | super(Adam, self).__init__(self.params, defaults)
75 |
76 | def __setstate__(self, state):
77 | super(Adam, self).__setstate__(state)
78 | for group in self.param_groups:
79 | group.setdefault('amsgrad', False)
80 |
81 | def __init_model_ref__(self, params):
82 | model_ref = []
83 | if not isinstance(params, list):
84 | params = list(params)
85 | for var in params:
86 | if var is not None:
87 | model_ref.append(torch.empty(var.shape).normal_(mean=0, std=0.01).to(self.device))
88 | return model_ref
89 |
90 | def __init_model_acc__(self, params):
91 | model_acc = []
92 | if not isinstance(params, list):
93 | params = list(params)
94 | for var in params:
95 | if var is not None:
96 | model_acc.append(torch.zeros(var.shape, dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device, requires_grad=False).to(self.device))
97 | return model_acc
98 |
99 | @torch.no_grad()
100 | def step(self, closure=None):
101 | """Performs a single optimization step.
102 |
103 | Arguments:
104 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
105 | and returns the loss.
106 | """
107 | loss = None
108 | if closure is not None:
109 | with torch.enable_grad():
110 | loss = closure()
111 |
112 | for group in self.param_groups:
113 | self.lr = group['lr']
114 | model_ref = group['model_ref']
115 | model_acc = group['model_acc']
116 | epoch_decay = group['epoch_decay']
117 | clip_value = group['clip_value']
118 | weight_decay = group['weight_decay']
119 |
120 | for i, p in enumerate(group['params']):
121 | if p.grad is None:
122 | continue
123 | if epoch_decay > 0:
124 | grad = torch.clamp(p.grad.data , -clip_value, clip_value) + epoch_decay*(p.data - model_ref[i].data) + weight_decay*p.data
125 | else:
126 | grad = torch.clamp(p.grad.data , -clip_value, clip_value) + weight_decay*p.data
127 | if grad.is_sparse:
128 | raise RuntimeError('Adam does not support sparse gradients, please consider SparseAdam instead')
129 | amsgrad = group['amsgrad']
130 | state = self.state[p]
131 |
132 | # State initialization
133 | if len(state) == 0:
134 | state['step'] = 0
135 | # Exponential moving average of gradient values
136 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
137 | # Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
138 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
139 | if amsgrad:
140 | # Maintains max of all exp. moving avg. of sq. grad. values
141 | state['max_exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
142 |
143 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
144 | if amsgrad:
145 | max_exp_avg_sq = state['max_exp_avg_sq']
146 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
147 |
148 | state['step'] += 1
149 | bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
150 | bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
151 |
152 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
153 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(grad, alpha=1 - beta1)
154 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - beta2)
155 | if amsgrad:
156 | # Maintains the maximum of all 2nd moment running avg. till now
157 | torch.max(max_exp_avg_sq, exp_avg_sq, out=max_exp_avg_sq)
158 | # Use the max. for normalizing running avg. of gradient
159 | denom = (max_exp_avg_sq.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
160 | else:
161 | denom = (exp_avg_sq.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
162 |
163 | step_size = self.lr / bias_correction1
164 |
165 | p.addcdiv_(exp_avg, denom, value=-step_size)
166 | if epoch_decay > 0:
167 | model_acc[i].data = model_acc[i].data + p.data
168 |
169 | self.T += 1
170 | self.steps += 1
171 | return loss
172 |
173 | def update_lr(self, decay_factor=None):
174 | r"""Updates learning rate given a decay factor."""
175 | if decay_factor != None:
176 | self.param_groups[0]['lr'] = self.param_groups[0]['lr']/decay_factor
177 | if self.verbose:
178 | print ('Reducing learning rate to %.5f !'%(self.param_groups[0]['lr']))
179 |
180 | def update_regularizer(self, decay_factor=None):
181 | r"""Updates learning rate given a decay factor and resets epoch-decay regularizer."""
182 | if decay_factor != None:
183 | self.param_groups[0]['lr'] = self.param_groups[0]['lr']/decay_factor
184 | if self.verbose:
185 | print ('Reducing learning rate to %.5f @ T=%s!'%(self.param_groups[0]['lr'], self.steps))
186 | if self.verbose:
187 | print ('Updating regularizer @ T=%s!'%(self.steps))
188 | for i, param in enumerate(self.model_ref):
189 | self.model_ref[i].data = self.model_acc[i].data/self.T
190 | for i, param in enumerate(self.model_acc):
191 | self.model_acc[i].data = torch.zeros(param.shape, dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device, requires_grad=False).to(self.device)
192 | self.T = 0
193 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/optimizers/adamw.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 |
4 | class AdamW(torch.optim.Optimizer):
5 | r"""Implements AdamW algorithm. This code is adapated from `PyTorch codebase `__.
6 |
7 | The original Adam algorithm was proposed in `Adam: A Method for Stochastic Optimization`_.
8 | The AdamW variant was proposed in `Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization`_.
9 | Arguments:
10 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize
11 | lr (float): learning rate (default: ``1e-3``)
12 | betas (Tuple[float, float], optional): coefficients used for computing
13 | running averages of gradient and its square (default: ``(0.9, 0.999)``)
14 | eps (float, optional): term added to the denominator to improve
15 | numerical stability (default: 1e-8)
16 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay coefficient (default: ``1e-2``)
17 | epoch_decay (float, optional): epoch decay (epoch-wise l2 penalty) (default: ``0.0``)
18 | amsgrad (boolean, optional): whether to use the AMSGrad variant of this
19 | algorithm from the paper `On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond`_
20 | (default: False)
21 | device (torch.device, optional): the device used for optimization, e.g., 'cpu' or 'cuda' (default: ``None``).
22 |
23 | .. _Adam\: A Method for Stochastic Optimization:
24 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980
25 | .. _Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization:
26 | https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101
27 | .. _On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond:
28 | https://openreview.net/forum?id=ryQu7f-RZ
29 | """
30 |
31 | def __init__(self,
32 | params,
33 | lr=1e-3,
34 | betas=(0.9, 0.999),
35 | eps=1e-8,
36 | clip_value=10.0,
37 | epoch_decay=0,
38 | weight_decay=1e-2,
39 | amsgrad=False,
40 | verbose=False,
41 | device=None,
42 | **kwargs):
43 |
44 | if not device:
45 | self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
46 | else:
47 | self.device = device
48 | if not 0.0 <= lr:
49 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
50 | if not 0.0 <= eps:
51 | raise ValueError("Invalid epsilon value: {}".format(eps))
52 | if not 0.0 <= betas[0] < 1.0:
53 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 0: {}".format(betas[0]))
54 | if not 0.0 <= betas[1] < 1.0:
55 | raise ValueError("Invalid beta parameter at index 1: {}".format(betas[1]))
56 | if not 0.0 <= weight_decay:
57 | raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
58 |
59 | self.params = list(params)
60 | self.lr = lr
61 | self.model_ref = self.__init_model_ref__(self.params) if epoch_decay > 0 else None
62 | self.model_acc = self.__init_model_acc__(self.params) if epoch_decay > 0 else None
63 | self.T = 0 # for epoch_decay
64 | self.steps = 0 # total optim steps
65 | self.verbose = verbose # print updates for lr/regularizer
66 |
67 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, betas=betas, eps=eps,
68 | weight_decay=weight_decay, epoch_decay=epoch_decay, amsgrad=amsgrad,
69 | clip_value=clip_value, model_ref=self.model_ref, model_acc=self.model_acc)
70 |
71 | super(AdamW, self).__init__(self.params, defaults)
72 |
73 | def __setstate__(self, state):
74 | super(AdamW, self).__setstate__(state)
75 | for group in self.param_groups:
76 | group.setdefault('amsgrad', False)
77 |
78 | def __init_model_ref__(self, params):
79 | model_ref = []
80 | if not isinstance(params, list):
81 | params = list(params)
82 | for var in params:
83 | if var is not None:
84 | model_ref.append(torch.empty(var.shape).normal_(mean=0, std=0.01).to(self.device))
85 | return model_ref
86 |
87 | def __init_model_acc__(self, params):
88 | model_acc = []
89 | if not isinstance(params, list):
90 | params = list(params)
91 | for var in params:
92 | if var is not None:
93 | model_acc.append(torch.zeros(var.shape, dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device, requires_grad=False).to(self.device))
94 | return model_acc
95 |
96 | @torch.no_grad()
97 | def step(self, closure=None):
98 | """Performs a single optimization step.
99 | Arguments:
100 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
101 | and returns the loss.
102 | """
103 | loss = None
104 | if closure is not None:
105 | with torch.enable_grad():
106 | loss = closure()
107 |
108 | for group in self.param_groups:
109 | self.lr = group['lr']
110 |
111 | model_ref = group['model_ref']
112 | model_acc = group['model_acc']
113 | epoch_decay = group['epoch_decay']
114 | clip_value = group['clip_value']
115 |
116 | for i, p in enumerate(group['params']):
117 | if p.grad is None:
118 | continue
119 |
120 | # Perform stepweight decay
121 | p.mul_(1 - self.lr * group['weight_decay'])
122 |
123 | # Perform optimization step
124 | if epoch_decay > 0:
125 | grad = torch.clamp(p.grad.data , -clip_value, clip_value) + epoch_decay*(p.data - model_ref[i].data) #p.grad
126 | else:
127 | grad = torch.clamp(p.grad.data , -clip_value, clip_value)
128 |
129 | if grad.is_sparse:
130 | raise RuntimeError('AdamW does not support sparse gradients')
131 | amsgrad = group['amsgrad']
132 |
133 | state = self.state[p]
134 |
135 | # State initialization
136 | if len(state) == 0:
137 | state['step'] = 0
138 | # Exponential moving average of gradient values
139 | state['exp_avg'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
140 | # Exponential moving average of squared gradient values
141 | state['exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
142 | if amsgrad:
143 | # Maintains max of all exp. moving avg. of sq. grad. values
144 | state['max_exp_avg_sq'] = torch.zeros_like(p, memory_format=torch.preserve_format)
145 |
146 | exp_avg, exp_avg_sq = state['exp_avg'], state['exp_avg_sq']
147 | if amsgrad:
148 | max_exp_avg_sq = state['max_exp_avg_sq']
149 | beta1, beta2 = group['betas']
150 |
151 | state['step'] += 1
152 | bias_correction1 = 1 - beta1 ** state['step']
153 | bias_correction2 = 1 - beta2 ** state['step']
154 |
155 | # Decay the first and second moment running average coefficient
156 | exp_avg.mul_(beta1).add_(grad, alpha=1 - beta1)
157 | exp_avg_sq.mul_(beta2).addcmul_(grad, grad, value=1 - beta2)
158 | if amsgrad:
159 | # Maintains the maximum of all 2nd moment running avg. till now
160 | torch.maximum(max_exp_avg_sq, exp_avg_sq, out=max_exp_avg_sq)
161 | # Use the max. for normalizing running avg. of gradient
162 | denom = (max_exp_avg_sq.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
163 | else:
164 | denom = (exp_avg_sq.sqrt() / math.sqrt(bias_correction2)).add_(group['eps'])
165 |
166 | step_size = self.lr / bias_correction1
167 |
168 | p.addcdiv_(exp_avg, denom, value=-step_size)
169 | if epoch_decay > 0:
170 | model_acc[i].data = model_acc[i].data + p.data
171 |
172 | self.T += 1
173 | self.steps += 1
174 | return loss
175 |
176 | def update_lr(self, decay_factor=None):
177 | r"""Updates learning rate given a decay factor."""
178 | if decay_factor != None:
179 | self.param_groups[0]['lr'] = self.param_groups[0]['lr']/decay_factor
180 | if self.verbose:
181 | print ('Reducing learning rate to %.5f !'%(self.param_groups[0]['lr']))
182 |
183 | def update_regularizer(self, decay_factor=None):
184 | r"""Updates learning rate given a decay factor and resets epoch-decay regularizer."""
185 | if decay_factor != None:
186 | self.param_groups[0]['lr'] = self.param_groups[0]['lr']/decay_factor
187 | if self.verbose:
188 | print ('Reducing learning rate to %.5f @ T=%s!'%(self.param_groups[0]['lr'], self.steps))
189 | if self.verbose:
190 | print ('Updating regularizer @ T=%s!'%(self.steps))
191 | for i, param in enumerate(self.model_ref):
192 | self.model_ref[i].data = self.model_acc[i].data/self.T
193 | for i, param in enumerate(self.model_acc):
194 | self.model_acc[i].data = torch.zeros(param.shape, dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device, requires_grad=False).to(self.device)
195 | self.T = 0
196 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/optimizers/lars.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Facebook, Inc. and its affiliates.
2 | # All rights reserved.
3 |
4 | # This source code is licensed under the license found in the
5 | # LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree.
6 |
7 | import torch
8 |
9 |
10 | class LARS(torch.optim.Optimizer):
11 | """
12 | LARS optimizer, no rate scaling or weight decay for parameters <= 1D. This code is adapated from `MOCOv3 codebase `__.
13 | """
14 | def __init__(self, params, lr=0, weight_decay=0, momentum=0.9, trust_coefficient=0.001):
15 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, weight_decay=weight_decay, momentum=momentum, trust_coefficient=trust_coefficient)
16 | super().__init__(params, defaults)
17 |
18 | @torch.no_grad()
19 | def step(self):
20 | for g in self.param_groups:
21 | for p in g['params']:
22 | dp = p.grad
23 |
24 | if dp is None:
25 | continue
26 |
27 | if p.ndim > 1: # if not normalization gamma/beta or bias
28 | dp = dp.add(p, alpha=g['weight_decay'])
29 | param_norm = torch.norm(p)
30 | update_norm = torch.norm(dp)
31 | one = torch.ones_like(param_norm)
32 | q = torch.where(param_norm > 0.,
33 | torch.where(update_norm > 0,
34 | (g['trust_coefficient'] * param_norm / update_norm), one),
35 | one)
36 | dp = dp.mul(q)
37 |
38 | param_state = self.state[p]
39 | if 'mu' not in param_state:
40 | param_state['mu'] = torch.zeros_like(p)
41 | mu = param_state['mu']
42 | mu.mul_(g['momentum']).add_(dp)
43 | p.add_(mu, alpha=-g['lr'])
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/optimizers/midam.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer, required
4 |
5 | class MIDAM(torch.optim.Optimizer):
6 | r"""
7 | MIDAM (Multiple Instance Deep AUC Maximization) is used for optimizing the :obj:`~libauc.losses.MIDAMLoss` (softmax or attention pooling based AUC loss).
8 |
9 | Notice that :math:`h(\mathbf w; \mathcal X_i)=f_2(f_1 (\mathbf w;\mathcal X_i))` is the bag-level prediction after the pooling operation. Denote that the moving average estimation for bag-level prediction for i-th bag at t-th iteration as :math:`s_i^t`. The gradients estimation are:
10 |
11 | .. math::
12 | G^t_{1,\mathbf w} = \hat{\mathbb E}_{i\in\mathcal S_+^t}\nabla f_1(\mathbf w^t; \mathcal B_{i}^t) \nabla f_2(s^{t-1}_i)\nabla_1 f( f_2(s^{t-1}_i), a^t),
13 |
14 | .. math::
15 | G^t_{2,\mathbf w} = \hat{\mathbb E}_{i\in\mathcal S_-^t}\nabla f_1(\mathbf w^t; \mathcal B_{i}^t) \nabla f_2(s^{t-1}_i)\nabla_1 f( f_2(s^{t-1}_i), b^t),
16 |
17 | .. math::
18 | G^t_{3,\mathbf w} = \alpha^t \cdot\left(\hat{\mathbb E}_{i\in\mathcal S_-^t}\nabla f_1(\mathbf w^t; \mathcal B_{i}^t) \nabla f_2(s^{t-1}_i)\right. \left.- \hat{\mathbb E}_{i\in\mathcal S_+^t}\nabla f_1(\mathbf w^t; \mathcal B_{i}^t) \nabla f_2(s^{t-1}_i)\right),
19 |
20 | .. math::
21 | G^t_{1,a} = \hat{\mathbb E}_{i\in\mathcal S_+^t} \nabla_2 f( f_2(s^{t-1}_i), a^t),
22 |
23 | .. math::
24 | G^t_{2, b} =\hat{\mathbb E}_{i\in\mathcal S_-^t} \nabla_2 f( f_2(s^{t-1}_i), b^t),
25 |
26 | .. math::
27 | G^t_{3,\alpha} = c+ \hat{\mathbb E}_{i\in\mathcal S_-^t}f_2(s^{t-1}_i) - \hat{\mathbb E}_{i\in\mathcal S_+^t}f_2(s^{t-1}_i),
28 |
29 | The key update steps for the stochastic optimization are summarized as follows:
30 |
31 | 1. Initialize :math:`\mathbf s^0=0, \mathbf v^0=\mathbf 0, a=0, b=0, \mathbf w`
32 | 2. For :math:`t=1, \ldots, T`:
33 | 3. :math:`\hspace{5mm}` Sample a batch of positive bags :math:`\mathcal S_+^t\subset\mathcal D_+` and a batch of negative bags :math:`\mathcal S_-^t\subset\mathcal D_-`.
34 | 4. :math:`\hspace{5mm}` For each :math:`i \in \mathcal S^t=\mathcal S_+^t\cup \mathcal S_-^t`:
35 | 5. :math:`\hspace{5mm}` Sample a mini-batch of instances :math:`\mathcal B^t_i\subset\mathcal X_i` and update:
36 |
37 | .. math::
38 |
39 | s^t_i = (1-\gamma_0)s^{t-1}_i + \gamma_0 f_1(\mathbf w^t; \mathcal B_{i}^t)
40 |
41 | 6. :math:`\hspace{5mm}` Update stochastic gradient estimator of :math:`(\mathbf w, a, b)`:
42 |
43 | .. math::
44 | \mathbf v_1^t =\beta_1\mathbf v_1^{t-1} + (1-\beta_1)(G^t_{1,\mathbf w} + G^t_{2,\mathbf w} + G^t_{3,\mathbf w})
45 |
46 | .. math::
47 | \mathbf v_2^t =\beta_1\mathbf v_2^{t-1} + (1-\beta_1)G^t_{1,a}
48 |
49 | .. math::
50 | \mathbf v_3^t =\beta_1\mathbf v_3^{t-1} + (1-\beta_1)G^t_{2,b}
51 |
52 | 6. :math:`\hspace{5mm}` Update :math:`(\mathbf w^{t+1}, a^{t+1}, b^{t+1}) = (\mathbf w^t, a^t, b^t) - \eta \mathbf v^t` (or Adam style)
53 | 7. :math:`\hspace{5mm}` Update :math:`\alpha^{t+1} = \Pi_{\Omega}[\alpha^t + \eta' (G^t_{3,\alpha} - \alpha^t)]`
54 |
55 | For more details, please refer to the paper `Provable Multi-instance Deep AUC Maximization with Stochastic Pooling.`
56 |
57 | Args:
58 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize
59 | loss_fn (callable): loss function used for optimization (default: ``None``)
60 | lr (float): learning rate (default: ``0.1``)
61 | momentum (float, optional): momentum factor for 'sgd' mode (default: ``0.1``)
62 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: ``1e-5``)
63 | device (torch.device, optional): the device used for optimization, e.g., 'cpu' or 'cuda' (default: ``None``)
64 |
65 | Example:
66 | >>> optimizer = libauc.optimizers.MIDAM(params=model.parameters(), loss_fn=loss_fn, lr=0.1, momentum=0.1)
67 | >>> optimizer.zero_grad()
68 | >>> loss_fn(model(input), target).backward()
69 | >>> optimizer.step()
70 |
71 |
72 | Reference:
73 | .. [1] Dixian Zhu, Bokun Wang, Zhi Chen, Yaxing Wang, Milan Sonka, Xiaodong Wu, Tianbao Yang
74 | "Provable Multi-instance Deep AUC Maximization with Stochastic Pooling."
75 | In International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. xxxxx-xxxxx. PMLR, 2023.
76 | https://prepare-arxiv?
77 | """
78 |
79 | def __init__(self, params, loss_fn, lr=required, momentum=0, weight_decay=0, device=None):
80 | if lr is not required and lr < 0.0:
81 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
82 | if momentum < 0.0:
83 | raise ValueError("Invalid momentum value: {}".format(momentum))
84 | if weight_decay < 0.0:
85 | raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
86 |
87 | self.a = None
88 | self.b = None
89 | self.alpha = None
90 | self.margin = None
91 | try:
92 | self.a = loss_fn.a
93 | self.b = loss_fn.b
94 | self.alpha = loss_fn.alpha
95 | self.margin = loss_fn.margin
96 | except:
97 | print('AUCMLoss is not found!')
98 |
99 | self.params = list(params)
100 | if self.a is not None and self.b is not None:
101 | self.params = self.params + [self.a, self.b]
102 | if device is None:
103 | self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
104 | self.lr = lr
105 | self.T = 0
106 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, momentum=momentum, margin=self.margin, a=self.a, b=self.b, alpha=self.alpha, weight_decay=weight_decay)
107 | super(MIDAM, self).__init__(self.params, defaults)
108 |
109 |
110 | def __setstate__(self, state):
111 | super(SGD, self).__setstate__(state)
112 | for group in self.param_groups:
113 | group.setdefault('nesterov', False)
114 |
115 |
116 | @torch.no_grad()
117 | def step(self, closure=None):
118 | """Performs a single optimization step.
119 |
120 | Arguments:
121 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
122 | and returns the loss.
123 | """
124 | loss = None
125 | if closure is not None:
126 | with torch.enable_grad():
127 | loss = closure()
128 |
129 | for group in self.param_groups:
130 | weight_decay = group['weight_decay']
131 | momentum = group['momentum']
132 | self.lr = group['lr']
133 | alpha = group['alpha']
134 | m = group['margin']
135 | a = group['a']
136 | b = group['b']
137 |
138 | for i, p in enumerate(group['params']):
139 | if p.grad is None:
140 | continue
141 | d_p = p.grad
142 | if weight_decay != 0:
143 | d_p = d_p.add(p, alpha=weight_decay)
144 | if momentum != 0:
145 | param_state = self.state[p]
146 | if 'momentum_buffer' not in param_state:
147 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer'] = torch.clone(d_p).detach()
148 | else:
149 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer']
150 | buf.mul_(momentum).add_(d_p, alpha=1 - momentum)
151 | d_p = buf
152 |
153 | p.add_(d_p, alpha=-group['lr'])
154 |
155 | if alpha is not None:
156 | alpha.data = torch.clip(alpha.data + group['lr']*((m + b.data - a.data)-alpha.data), min=0.0)
157 | self.T = self.T + 1
158 | return loss
159 |
160 | def update_lr(self, decay_factor=None):
161 | if decay_factor != None:
162 | self.param_groups[0]['lr'] = self.param_groups[0]['lr']/decay_factor
163 | print('Reducing learning rate to %.5f @ T=%s!'%(self.param_groups[0]['lr'], self.T))
164 | print('Updating regularizer @ T=%s!'%(self.T))
165 |
166 | def __setstate__(self, state):
167 | super(SGD, self).__setstate__(state)
168 | for group in self.param_groups:
169 | group.setdefault('nesterov', False)
170 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/optimizers/sgd.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | from torch.optim.optimizer import Optimizer, required
3 |
4 | class SGD(torch.optim.Optimizer):
5 | r"""Implements stochastic gradient descent (optionally with momentum). This code is adapted from `PyTorch codebase `__.
6 |
7 | Nesterov momentum is based on the formula from
8 | `On the importance of initialization and momentum in deep learning`__.
9 |
10 | Args:
11 | params (iterable): iterable of parameters to optimize
12 | lr (float): learning rate
13 | momentum (float, optional): momentum factor (default: ``0``)
14 | weight_decay (float, optional): weight decay (L2 penalty) (default: ``0``)
15 | epoch_decay (float, optional): epoch decay (epoch-wise l2 penalty) (default: ``0.0``)
16 | dampening (float, optional): dampening for momentum (default: ``0.0``)
17 | nesterov (bool, optional): enables Nesterov momentum (default: ``False)``
18 | device (torch.device, optional): the device used for optimization, e.g., 'cpu' or 'cuda' (default: ``None``).
19 |
20 | Example:
21 | >>> optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9)
22 | >>> optimizer.zero_grad()
23 | >>> loss_fn(model(input), target).backward()
24 | >>> optimizer.step()
25 |
26 | __ http://www.cs.toronto.edu/%7Ehinton/absps/momentum.pdf
27 |
28 | .. note::
29 | The implementation of SGD with Momentum/Nesterov subtly differs from
30 | Sutskever et. al. and implementations in some other frameworks.
31 |
32 | Considering the specific case of Momentum, the update can be written as
33 |
34 | .. math::
35 | \begin{aligned}
36 | v_{t+1} & = \mu * v_{t} + g_{t+1}, \\
37 | p_{t+1} & = p_{t} - \text{lr} * v_{t+1},
38 | \end{aligned}
39 |
40 | where :math:`p`, :math:`g`, :math:`v` and :math:`\mu` denote the
41 | parameters, gradient, velocity, and momentum respectively.
42 |
43 | This is in contrast to Sutskever et. al. and
44 | other frameworks which employ an update of the form
45 |
46 | .. math::
47 | \begin{aligned}
48 | v_{t+1} & = \mu * v_{t} + \text{lr} * g_{t+1}, \\
49 | p_{t+1} & = p_{t} - v_{t+1}.
50 | \end{aligned}
51 |
52 | The Nesterov version is analogously modified.
53 | """
54 |
55 | def __init__(self,
56 | params,
57 | lr=required,
58 | momentum=0,
59 | dampening=0,
60 | clip_value=1.0,
61 | epoch_decay=0,
62 | weight_decay=0,
63 | nesterov=False,
64 | verbose=True,
65 | device=None,
66 | **kwargs):
67 | if not device:
68 | self.device = torch.device('cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu')
69 | else:
70 | self.device = device
71 |
72 | if lr is not required and lr < 0.0:
73 | raise ValueError("Invalid learning rate: {}".format(lr))
74 | if momentum < 0.0:
75 | raise ValueError("Invalid momentum value: {}".format(momentum))
76 | if weight_decay < 0.0:
77 | raise ValueError("Invalid weight_decay value: {}".format(weight_decay))
78 |
79 | self.params = list(params)
80 | self.lr = lr
81 |
82 | self.model_ref = self.__init_model_ref__(self.params) if epoch_decay > 0 else None
83 | self.model_acc = self.__init_model_acc__(self.params) if epoch_decay > 0 else None
84 |
85 | self.T = 0 # for epoch_decay
86 | self.steps = 0 # total optim steps
87 | self.verbose = verbose # print updates for lr/regularizer
88 |
89 | defaults = dict(lr=lr, momentum=momentum, dampening=dampening,
90 | weight_decay=weight_decay, epoch_decay=epoch_decay, nesterov=nesterov,
91 | clip_value=clip_value, model_ref=self.model_ref, model_acc=self.model_acc)
92 | if nesterov and (momentum <= 0 or dampening != 0):
93 | raise ValueError("Nesterov momentum requires a momentum and zero dampening")
94 | super(SGD, self).__init__(self.params, defaults)
95 |
96 | def __setstate__(self, state):
97 | super(SGD, self).__setstate__(state)
98 | for group in self.param_groups:
99 | group.setdefault('nesterov', False)
100 |
101 | def __init_model_ref__(self, params):
102 | model_ref = []
103 | if not isinstance(params, list):
104 | params = list(params)
105 | for var in params:
106 | if var is not None:
107 | model_ref.append(torch.empty(var.shape).normal_(mean=0, std=0.01).to(self.device))
108 | return model_ref
109 |
110 | def __init_model_acc__(self, params):
111 | model_acc = []
112 | if not isinstance(params, list):
113 | params = list(params)
114 | for var in params:
115 | if var is not None:
116 | model_acc.append(torch.zeros(var.shape, dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device, requires_grad=False).to(self.device))
117 | return model_acc
118 |
119 | @torch.no_grad()
120 | def step(self, closure=None):
121 | """Performs a single optimization step.
122 |
123 | Arguments:
124 | closure (callable, optional): A closure that reevaluates the model
125 | and returns the loss.
126 | """
127 | loss = None
128 | if closure is not None:
129 | with torch.enable_grad():
130 | loss = closure()
131 |
132 | for group in self.param_groups:
133 | self.lr = group['lr']
134 | momentum = group['momentum']
135 | dampening = group['dampening']
136 | nesterov = group['nesterov']
137 |
138 | epoch_decay = group['epoch_decay']
139 | clip_value = group['clip_value']
140 | weight_decay = group['weight_decay']
141 | model_ref = group['model_ref']
142 | model_acc = group['model_acc']
143 |
144 | for i, p in enumerate(group['params']):
145 | if p.grad is None:
146 | continue
147 | if epoch_decay > 0:
148 | d_p = torch.clamp(p.grad.data , -clip_value, clip_value) + epoch_decay*(p.data - model_ref[i].data) + weight_decay*p.data
149 | else:
150 | d_p = torch.clamp(p.grad.data , -clip_value, clip_value) + weight_decay*p.data
151 | if momentum != 0:
152 | param_state = self.state[p]
153 | if 'momentum_buffer' not in param_state:
154 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer'] = torch.clone(d_p).detach()
155 | else:
156 | buf = param_state['momentum_buffer']
157 | buf.mul_(momentum).add_(d_p, alpha=1 - dampening)
158 | if nesterov:
159 | d_p = d_p.add(buf, alpha=momentum)
160 | else:
161 | d_p = buf
162 |
163 | p.add_(d_p, alpha=-self.lr)
164 | if epoch_decay > 0:
165 | model_acc[i].data = model_acc[i].data + p.data
166 |
167 | self.T += 1
168 | self.steps += 1
169 | return loss
170 |
171 | def update_lr(self, decay_factor=None):
172 | r"""Updates learning rate given a decay factor."""
173 | if decay_factor != None:
174 | self.param_groups[0]['lr'] = self.param_groups[0]['lr']/decay_factor
175 | if self.verbose:
176 | print ('Reducing learning rate to %.5f !'%(self.param_groups[0]['lr']))
177 |
178 | def update_regularizer(self, decay_factor=None):
179 | r"""Updates learning rate given a decay factor and resets epoch-decay regularizer."""
180 | if decay_factor != None:
181 | self.param_groups[0]['lr'] = self.param_groups[0]['lr']/decay_factor
182 | if self.verbose:
183 | print ('Reducing learning rate to %.5f @ T=%s!'%(self.param_groups[0]['lr'], self.steps))
184 | if self.verbose:
185 | print ('Updating regularizer @ T=%s!'%(self.steps))
186 | for i, param in enumerate(self.model_ref):
187 | self.model_ref[i].data = self.model_acc[i].data/self.T
188 | for i, param in enumerate(self.model_acc):
189 | self.model_acc[i].data = torch.zeros(param.shape, dtype=torch.float32, device=self.device, requires_grad=False).to(self.device)
190 | self.T = 0
191 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/sampler/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .sampler import *
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/utils/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from .utils import *
2 | from .paper_utils import *
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/libauc/utils/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import datetime
4 | import os
5 | import sys
6 | import time
7 | import random
8 | import shutil
9 | import numpy as np
10 | from collections import Counter
11 | from tqdm import tqdm, trange
12 |
13 | def set_all_seeds(SEED):
14 | # for reproducibility
15 | torch.manual_seed(SEED)
16 | np.random.seed(SEED)
17 | random.seed(SEED)
18 | torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic = True
19 | torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
20 |
21 | def check_tensor_shape(tensor, shape):
22 | # check tensor shape
23 | if not torch.is_tensor(tensor):
24 | raise ValueError('Input is not a valid torch tensor!')
25 | if not isinstance(shape, (tuple, list, int)):
26 | raise ValueError("Shape must be a tuple, an integer or a list!")
27 | if isinstance(shape, int):
28 | shape = torch.Size([shape])
29 | tensor_shape = tensor.shape
30 | if len(tensor_shape) != len(shape):
31 | tensor = tensor.reshape(shape)
32 | return tensor
33 |
34 | def check_array_type(array):
35 | # convert to array type
36 | if not isinstance(array, (np.ndarray, np.generic)):
37 | array = np.array(array)
38 | return array
39 |
40 | def check_array_shape(array, shape):
41 | # check array shape
42 | array = check_array_type(array)
43 | if array.size == 0:
44 | raise ValueError("Array is empty.")
45 | if array.shape != shape and len(array.shape) != 1:
46 | try:
47 | array = array.reshape(shape)
48 | except ValueError as e:
49 | raise ValueError(f"Could not reshape array of shape {array.shape} to {shape}.") from e
50 | return array
51 |
52 | def check_class_labels(labels):
53 | # check if labels are valid
54 | labels = check_array_type(labels)
55 | unique_values = np.unique(labels)
56 | num_classes = len(unique_values)
57 | if not np.all(unique_values == np.arange(num_classes)):
58 | raise ValueError("Labels should be integer values starting from 0.")
59 |
60 | def select_mean(array, threshold=0):
61 | # select elements for average based on threshold
62 | array = check_array_type(array)
63 | select_array = array[array >= threshold]
64 | if len(select_array) != 0:
65 | return np.mean(select_array)
66 | else:
67 | return None
68 |
69 | def check_imbalance_ratio(labels):
70 | # check data imbalance ratio for the labels
71 | labels = check_array_type(labels)
72 | check_class_labels(labels)
73 |
74 | # Flatten the labels array if it's 2D (n, 1)
75 | if len(labels.shape) > 1 and labels.shape[1] == 1:
76 | labels = labels.flatten()
77 |
78 | num_samples = len(labels)
79 | class_counts = Counter(labels)
80 |
81 | for class_label, count in class_counts.items():
82 | class_ratio = count / num_samples
83 | print (f'#SAMPLES: {num_samples}, CLASS {class_label:.1f} COUNT: {count}, CLASS RATIO: {class_ratio:.4f}')
84 |
85 | def get_time():
86 | return datetime.datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H:%M:%S")
87 |
88 | class ImbalancedDataGenerator(object):
89 | def __init__(self, imratio=None, shuffle=True, random_seed=0, verbose=False):
90 | self.imratio = imratio
91 | self.shuffle = shuffle
92 | self.random_seed = random_seed
93 | self.verbose = verbose
94 |
95 | @staticmethod
96 | def _get_split_index(num_classes):
97 | split_index = num_classes // 2 - 1
98 | if split_index < 0:
99 | raise NotImplementedError
100 | return split_index
101 |
102 | @staticmethod
103 | def _get_class_num(targets):
104 | return np.unique(targets).size
105 |
106 | def transform(self, data, targets, imratio=None):
107 | data = check_array_type(data)
108 | targets = check_array_type(targets)
109 | targets = np.maximum(targets, 0)
110 | if imratio is not None:
111 | self.imratio = imratio
112 | if self.imratio is None:
113 | raise ValueError("imratio is None.")
114 | assert self.imratio > 0 and self.imratio <= 0.5, 'imratio needs to be in (0, 0.5)!'
115 |
116 | if self.shuffle:
117 | np.random.seed(self.random_seed)
118 | idx = np.random.permutation(len(targets))
119 | data, targets = data[idx], targets[idx]
120 |
121 | num_classes = self._get_class_num(targets)
122 | split_index = self._get_split_index(num_classes)
123 | targets = np.where(targets <= split_index, 0, 1)
124 |
125 | if self.imratio < 0.5:
126 | neg_ids = np.where(targets == 0)[0]
127 | pos_ids = np.where(targets == 1)[0]
128 | pos_ids = pos_ids[:int((self.imratio / (1 - self.imratio)) * len(neg_ids))]
129 | idx = np.concatenate([neg_ids, pos_ids])
130 | data, targets = data[idx], targets[idx]
131 | targets = targets.reshape(-1, 1).astype(np.float32)
132 |
133 | if self.shuffle:
134 | np.random.seed(self.random_seed)
135 | idx = np.random.permutation(len(targets))
136 | data, targets = data[idx], targets[idx]
137 |
138 | if self.verbose:
139 | check_imbalance_ratio(targets)
140 |
141 | return data, targets
142 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import setuptools
2 |
3 | with open("README.md", "r") as fh:
4 | long_description = fh.read()
5 |
6 | setuptools.setup(
7 | name="libauc",
8 | version="1.4.0",
9 | author="Zhuoning Yuan, Tianbao Yang",
10 | description="LibAUC: A Deep Learning Library for X-Risk Optimization",
11 | long_description=long_description,
12 | long_description_content_type="text/markdown",
13 | url="https://github.com/Optimization-AI/LibAUC",
14 | packages=setuptools.find_packages(),
15 | classifiers=[
16 | "Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
17 | "License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
18 | "Operating System :: OS Independent",
19 | ],
20 | python_requires=">=3.8",
21 | install_requires = [
22 | 'torch',
23 | 'torchvision',
24 | 'numpy',
25 | 'tqdm',
26 | 'scipy',
27 | 'pandas',
28 | 'Pillow',
29 | 'scikit-learn',
30 | 'opencv-python',
31 | 'torch_geometric',
32 | 'ogb',
33 | 'webdataset']
34 | )
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------







 52 |
52 |