├── README.md
├── api_examples
├── README.md
└── paddle
│ ├── dataset
│ └── readme.md
│ ├── distributed
│ └── readme.md
│ ├── fluid
│ ├── contrib
│ │ └── readme.md
│ ├── distributed
│ │ └── readme.md
│ ├── dygraph
│ │ └── readme.md
│ ├── layers
│ │ ├── data_0.py
│ │ ├── readme.md
│ │ ├── reduce_sum.py
│ │ └── sequence_pad.py
│ ├── prune_with_input.py
│ ├── pybind
│ │ └── print_tensor.py
│ ├── readme.md
│ ├── tests
│ │ └── readme.md
│ └── transpiler
│ │ └── readme.md
│ ├── libs
│ └── readme.md
│ ├── proto
│ └── readme.md
│ ├── reader
│ └── readme.md
│ ├── readme.md
│ └── utils
│ └── readme.md
└── community_examples
├── README.md
├── fluid_inference
├── README.md
├── compare_onnx_paddle.py
└── paddle_infer.py
├── ner
├── NamedEntityRecognition.md
└── ner.py
└── recompute
├── README.md
└── demo.py
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Examples
2 |
3 | ## example guide
4 | - api_examples: examples for each public api in paddle fluid
5 | - community_examples: community examples contributed by third party developers
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # API Examples书写规范
2 |
3 | ## API Examples的定位是什么?
4 | - 针对每个API提供可跑通的最精简代码,并获得期望的结果
5 | - 用户对API文档理解不够透彻,或者觉得API文档中的代码示例不够全面,开发者可以快速在API Examples中添加示例
6 | - 缓解CI系统的压力,快速修复
7 |
8 | ## 输出规范
9 | - 一个API一个.py文件
10 | - .py文件的格式参考下面的示例
11 | ``` python
12 | # Copyright (c) 2019 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved
13 | #
14 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
15 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
16 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
17 | #
18 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
19 | #
20 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
21 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
22 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
23 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
24 | # limitations under the License.
25 |
26 | # api: paddle.fluid.data
27 | # env: local
28 | # device: gpu
29 | # text:feed-gpu-data
30 |
31 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
32 | import numpy as np
33 |
34 | def gen_data():
35 | return {"x": np.ones((1, 32)).astype('float32')}
36 |
37 | input_x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[32], dtype='float32')
38 | place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0)
39 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
40 | input_val = exe.run(feed=gen_data(),
41 | fetch_list=[input_x.name])
42 | print(input_val)
43 | # [array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
44 | # 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]],
45 | # dtype=float32)]
46 |
47 | ```
48 | - API的全路径名需要在注释中的api字段注明
49 | - API的运行环境需要在env字段中注明,local/distributed
50 | - API的运行设备需要在device字段中注明,gpu/cpu
51 | - API示例需要能够运行,用户能够直接根据代码获得运算结果
52 | - API示例可以起一个名称,作为官网文档的链接文字,代码中用text字段表示
53 |
54 | ## 管理规范
55 | - API示例按照目录结构放置,命名规则为"API名_i.py",其中i为示例序号。即单个API可以有多个示例,按序号编写。
56 | - API examples会根据目录结构,example文件名在官网的API文档中通过链接的方式展现,定期更新做有效性检查。
57 | - API examples对示例是否能够正常运行有要求,会有CI系统每天回归整体示例是否可以运行。
58 | - 通过在官网进行示例展现,我们会统计后台点击数,客观评价API的需求,并对点击数较高的作者进行奖励。
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/dataset/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/dataset/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/distributed/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/distributed/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/contrib/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/fluid/contrib/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/distributed/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/fluid/distributed/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/dygraph/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/fluid/dygraph/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/layers/data_0.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) 2019 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 |
15 | # api: paddle.fluid.data
16 | # env: local
17 | # device: gpu
18 | # text:feed-gpu-data
19 |
20 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
21 | import numpy as np
22 |
23 | def gen_data():
24 | return {"x": np.ones((1, 32)).astype('float32')}
25 |
26 | input_x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[32], dtype='float32')
27 | place = fluid.CUDAPlace(0)
28 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
29 | input_val = exe.run(feed=gen_data(),
30 | fetch_list=[input_x.name])
31 | print(input_val)
32 | # [array([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.,
33 | # 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]],
34 | # dtype=float32)]
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/layers/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/fluid/layers/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/layers/reduce_sum.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) 2019 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 |
15 | # api: paddle.fluid.layers.reduce_sum
16 | # env: local
17 | # device: cpu
18 | # text: reduce_sum
19 |
20 |
21 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
22 | import numpy as np
23 |
24 | x = fluid.data(name='x', shape=[2, 4], dtype='float64')
25 |
26 | reduce_sum_no_dim = fluid.layers.reduce_sum(x)
27 | reduce_sum_empty_dim = fluid.layers.reduce_sum(x, dim = [])
28 | reduce_sum_dim_one = fluid.layers.reduce_sum(x, dim = 0)
29 |
30 | place = fluid.CPUPlace()
31 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
32 | feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(feed_list=[x], place=place)
33 | exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
34 |
35 | name_list = [reduce_sum_no_dim,reduce_sum_empty_dim,reduce_sum_dim_one]
36 |
37 | #data = [[np.random.random((2,4)).astype("float64")]]
38 | data = [[[[0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.9],
39 | [0.1, 0.2, 0.6, 0.7]]]]
40 |
41 | print(data)
42 |
43 | sum_no, sum_empty, dim_one = exe.run(
44 | fluid.default_main_program(),
45 | feed=feeder.feed(data),
46 | fetch_list = name_list,
47 | return_numpy=True)
48 |
49 |
50 | print(sum_no) #[3.5]
51 | print(sum_empty) #[3.5]
52 | print(dim_one) #[0.3, 0.5, 1.1, 1.6]
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/layers/sequence_pad.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) 2019 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 |
15 | # api: paddle.fluid.layers.sequence_pad
16 | # env: local
17 | # device: cpu
18 | # text: sequence-pad
19 |
20 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
21 | import numpy
22 |
23 | x = fluid.layers.data(name="question", shape=[1], dtype="int64", lod_level=1)
24 |
25 | # define net here
26 | embed = fluid.layers.embedding(input=x, size=[32, 2],
27 | param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name='emb.w'))
28 |
29 | pad_value = fluid.layers.assign(input=numpy.array([0], dtype=numpy.float32))
30 | z, mask = fluid.layers.sequence_pad(x=embed, pad_value=pad_value)
31 |
32 | place = fluid.CPUPlace()
33 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
34 | feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(feed_list=[x], place=place)
35 | exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
36 |
37 | # prepare a batch of data
38 | data = [([0, 1, 2, 3, 3],), ([0, 1, 2],)]
39 |
40 | mask_out, z_out = exe.run(fluid.default_main_program(),
41 | feed=feeder.feed(data),
42 | fetch_list=[mask, z],
43 | return_numpy=True)
44 |
45 | print(mask_out)
46 | print(z_out)
47 |
48 | #[[5]
49 | # [3]]
50 | #[[[ 0.03990805 -0.10303718]
51 | # [ 0.08801201 -0.30412018]
52 | # [ 0.0706093 -0.18075395]
53 | # [-0.0283702 0.01683199]
54 | # [-0.0283702 0.01683199]]
55 |
56 | # [[ 0.03990805 -0.10303718]
57 | # [ 0.08801201 -0.30412018]
58 | # [ 0.0706093 -0.18075395]
59 | # [ 0. 0. ]
60 | # [ 0. 0. ]]]
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/prune_with_input.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) 2019 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 |
15 | # api: paddle.fluid.framework.Program._prune_with_input()
16 | # env: local
17 | # device: cpu
18 | # text:prune-with-input
19 |
20 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
21 | import paddle.fluid.optimizer as optimizer
22 | import numpy as np
23 |
24 | def sample_data():
25 | res = []
26 | for i in range(2):
27 | data = np.random.normal(size=(2,))
28 | label = np.random.randint(2, size=(1,))
29 | res.append((data, label))
30 | return res
31 |
32 | x = fluid.layers.data(name='x', shape=[2], dtype='float32')
33 | label = fluid.layers.data(name="label", shape=[1], dtype="int64")
34 |
35 | # define net here
36 | y = fluid.layers.fc(input=[x], size=2, act="softmax")
37 | loss = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=y, label=label)
38 | loss = fluid.layers.mean(x=loss)
39 |
40 | sgd = fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=0.01)
41 | sgd.minimize(loss)
42 |
43 | with open("original_program", "w") as f:
44 | f.write(str(fluid.default_main_program()))
45 |
46 | pruned_program = fluid.default_main_program()._prune_with_input(
47 | feeded_var_names=[y.name, label.name],
48 | targets = [loss])
49 |
50 | with open("pruned_program", "w") as f:
51 | f.write(str(pruned_program))
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/pybind/print_tensor.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) 2019 PaddlePaddle Authors. All Rights Reserved
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 |
15 | # api: paddle.fluid
16 | # env: local
17 | # device: cpu
18 | # text: print-tensor
19 |
20 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
21 | import numpy as np
22 | np.random.seed(9000)
23 |
24 | fluid.default_main_program().random_seed = 9000
25 | fluid.default_startup_program().random_seed = 9000
26 | def gen_data():
27 | return {"x": np.random.random(size=(32, 32)).astype('float32'),
28 | "y": np.random.randint(2, size=(32, 1)).astype('int64')}
29 | def mlp(input_x, input_y, hid_dim=128, label_dim=2):
30 | fc_1 = fluid.layers.fc(input=input_x, size=hid_dim)
31 | prediction = fluid.layers.fc(input=[fc_1], size=label_dim, act='softmax')
32 | cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=prediction, label=input_y)
33 | sum_cost = fluid.layers.reduce_mean(cost)
34 | return sum_cost, fc_1, prediction
35 |
36 | input_x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[32], dtype='float32')
37 | input_y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[1], dtype='int64')
38 | cost, fc_1, pred = mlp(input_x, input_y)
39 |
40 | print("Finished FF")
41 |
42 | sgd = fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.01)
43 | sgd.minimize(cost)
44 |
45 | print("Finished optimize")
46 | place = fluid.CPUPlace()
47 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
48 | exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
49 | step = 10
50 |
51 | with open("main_program.txt", 'w') as f:
52 | f.write(str(fluid.default_main_program()))
53 |
54 | scope = fluid.global_scope()
55 |
56 | for i in range(step):
57 | cost_val = exe.run(feed=gen_data(),
58 | program=fluid.default_main_program(),
59 | fetch_list=[cost.name])
60 | print("step: %d, fc_0.w_0: %s" % (i, scope.var("fc_0.w_0").get_tensor().__array__()))
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/fluid/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/tests/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/fluid/tests/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/fluid/transpiler/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/fluid/transpiler/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/libs/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/libs/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/proto/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/proto/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/reader/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/reader/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api_examples/paddle/utils/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/PaddlePaddle/examples/b75c8324bacca8dcaed09fca221e7c2c3cb39bdd/api_examples/paddle/utils/readme.md
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/community_examples/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 社区贡献的示例目录
2 |
3 | ## 目录定位
4 | - Paddle的外部社区、内部社区,凡是想贡献一些基于Paddle Fluid的示例的用户均可发起pull request,创建子目录贡献
5 | - 社区中推广的第三方文章、教程中用到的代码,欢迎提交到此目录进行备份,也方便用户获取源码
6 |
7 | ## 贡献规则
8 | - 原则上community_examples下,单个子目录代表一个示例,示例命名由reviewer把关
9 | - 子目录的贡献者负责维护子目录的内容更新、用户的issue、feature request、版本兼容性等问题
10 | - 子目录以接受代码为主,文字部分的说明尽量保持简洁
11 |
12 | ## 基本管理办法
13 | - 示例书写特别规范,用户需求量很大的子目录,会考虑进入官方提供的教程或者示例文档中
14 | - 子目录的owner会放到根目录的authorlist中,方便用户查找原作者
15 | - 管理员会定期review子目录的质量,并与子目录owner沟通更新计划
16 | - 贡献内容数量较多、质量较高的开发者,会进入reviewer list
17 |
18 | ## 项目清单
19 | | 项目名称 | 所用算法 | 作者名称 | 更新时间 |
20 | | ---------------------------------------- | ----------- | ---------- | --------- |
21 | | 手把手教你用 PaddlePaddle 做命名实体识别 | BiGRU + CRF | @huxiaoman77 | 2019.10.8 |
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/community_examples/fluid_inference/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 使用paddle进行预测以及onnx的使用
2 |
3 | 1、训练模型,使用save_inference_model函数保存训练好的模型以及参数,路径为./paddle_infer。
4 |
5 | 2、安装paddle2onnx,并转换模型,得到转换后的onnx文件。
6 |
7 | ```
8 | pip install onnx # 安装onnx
9 | pip install paddle2onnx # 安装paddle2onnx
10 | paddle2onnx --fluid_model paddle_infer --onnx_model onnx_infer # paddle的预测模型转换为onnx
11 | ```
12 |
13 | 3、使用paddle库进行预测,同时和onnx转后的结果进行比较。
14 |
15 | ```
16 | python paddle_infer.py #使用load_inference_model 预测代码
17 | ```
18 |
19 | ```
20 | python compare_onnx_paddle.py #比较paddle转换前后的diff
21 | ```
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/community_examples/fluid_inference/compare_onnx_paddle.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import base64
2 | import getopt
3 | #coding:utf-8
4 | import sys
5 | import os
6 | import json
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
9 | import numpy as np
10 | import json
11 | np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
12 |
13 | val = 'vectors_3*224*224.txt'
14 | vectors = []
15 | file = open(val, 'r')
16 | for line in file.readlines():
17 | datas = line.strip().split(" ")
18 | for d in datas:
19 | vectors.append(float(d))
20 | file.close()
21 | a = np.array(vectors)
22 | print(a.shape)
23 | tensor_img = a.reshape(3,224,224)
24 | tensor_img = tensor_img.astype(np.float32)
25 |
26 | tensor_img = np.expand_dims(tensor_img, axis=0)
27 |
28 | place = fluid.CPUPlace()
29 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
30 | path = "./paddle_infer/"
31 | [inference_program, feed_target_names, fetch_targets] = (fluid.io.load_inference_model(dirname=path, executor=exe))
32 | results = exe.run(inference_program,
33 | feed={feed_target_names[0]: tensor_img},
34 | fetch_list=fetch_targets)[0][0]
35 | paddle_fea = results[:, 0, 0]
36 |
37 | with open("onnx.json",'r') as load_f:
38 | onnx_dict = json.load(load_f)
39 | error = []
40 | onnx_fea = onnx_dict["res_str"]["raw_confidences"]
41 | for index in range(len(onnx_fea)):
42 | _ofea = onnx_fea[index]
43 | _pfea = paddle_fea[index]
44 | error.append(abs(_ofea - _pfea))
45 |
46 | print("max error: {}".format(np.max(error)))
47 | print("accumulate error: {}".format(np.sum(error)))
48 |
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/community_examples/fluid_inference/paddle_infer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python
2 | #coding:utf-8
3 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import sys
6 | import time
7 | import base64
8 | import json
9 | import pyjsonrpc
10 | import urllib2
11 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import cv2
14 | import urllib2
15 | from PIL import Image
16 | import imghdr
17 | import StringIO
18 | np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
19 |
20 | def proc_img(img, centercrop=True):
21 | #img = open(name, 'rb').read()
22 | resize = 256
23 | #crop = 224
24 | if imghdr.what("", img) == "gif":
25 | buff_in = StringIO.StringIO(img)
26 | img = Image.open(buff_in)
27 | first_frame = Image.new("RGBA", img.size)
28 | first_frame.paste(img, (0, 0), img.convert('RGBA'))
29 | buff_out = StringIO.StringIO()
30 | first_frame.save(buff_out, "PNG")
31 | img = buff_out.getvalue()
32 | buff_in.close()
33 | buff_out.close()
34 | image_raw = np.asarray(bytearray(img), dtype="uint8")
35 | img = cv2.imdecode(image_raw, cv2.IMREAD_COLOR)
36 | # center crop, hold aspect ratio
37 | if img.shape[0] >= img.shape[1]:
38 | img = cv2.resize(img, (resize, img.shape[0] * resize / img.shape[1]))
39 | if centercrop:
40 | start = (img.shape[0]-resize)/2
41 | img = img[start:start+resize, :, :]
42 | elif img.shape[0] < img.shape[1]:
43 | img = cv2.resize(img, (img.shape[1] * resize / img.shape[0], resize))
44 | if centercrop:
45 | start = (img.shape[1]-resize)/2
46 | img = img[:, start:start+resize, :]
47 | img = img[:, :, ::-1] # BGR to RGB
48 | img = img.astype('float32')
49 | img -= np.array([0.485, 0.456, 0.406]) * 255.0
50 | img /= np.array([0.229, 0.224, 0.225]) * 255.0
51 | img = img.transpose(2, 0, 1) # NCHW
52 | img = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
53 | return img
54 |
55 |
56 | path = "./paddle_infer/" # paddle save inference model
57 | file = "./imagenet/part-00000" # dataset for inference, base64 format
58 |
59 | place = fluid.CPUPlace()
60 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
61 | [inference_program, feed_target_names, fetch_targets] = fluid.io.load_inference_model(dirname=path, executor=exe)
62 |
63 | fea_mat = []
64 | with open(file, 'r') as f:
65 | #for line in sys.stdin:
66 | for line in f.xreadlines():
67 | try:
68 | temp = line.strip().split('\t')
69 | img_base641 = base64.b64decode(temp[1].replace('-','+').replace('_','/'))
70 |
71 | img = proc_img(img_base641)
72 |
73 | t = time.time()
74 | fea = exe.run(inference_program,
75 | feed={feed_target_names[0]: img},
76 | fetch_list=fetch_targets)[0][0]
77 | fea /= np.linalg.norm(fea)
78 | feature1 = np.array(fea, dtype='float16')
79 | fea_mat.append(feature1[:,0,0])
80 | #print(list(feature1))
81 | # print "%s\t%s\t%s\t%s" % (temp[0], temp[1], temp[2], list(feature1))
82 | except Exception, e:
83 | print >> sys.stderr, str(e), temp[0]
84 |
85 | np.save("paddle_result.npy", fea_mat)
86 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/community_examples/ner/NamedEntityRecognition.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 手把手教你用 PaddlePaddle 做命名实体识别
2 |
3 |
4 | ****命名实体识别(Named Entity Recognition,NER)是 NLP 几个经典任务之一,通俗易懂的来说,他就是从一段文本中抽取出需求的关键词,如地名,人名等。
5 |
6 | 如上图所示,Google、IBM、Baidu 这些都是企业名、Chinese、U.S. 都是地名。就科学研究来说,命名实体是非常通用的技术,类似任务型对话中的槽位识别(Slot Filling)、基础语言学中的语义角色标注(Semantic Role Labelling)都变相地使用了命名实体识别的技术;而就工业应用而言,命名实体其实就是序列标注(Sequential Tagging),是除分类外最值得信赖和应用最广的技术,例如智能客服、网络文本分析,关键词提取等。
7 |
8 | 下面我们先带您了解一些 Gated RNN 和 CRF 的背景知识,然后再教您一步一步用 Paddle Paddle 实现一个命名实体任务。另外,我们采用经典的 CoNLL 数据集。
9 |
10 | ## Part-1:RNN 基础知识
11 |
12 | 循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Networks,RNN)是有效建模有时序特征输入的方式。它的原理实际上非常简单,可以被以下简单的张量公式建模:
13 |
14 | $$\vec{h}_t = f(\vec{x}_t, \vec{h}_{t-1})$$
15 | $$\vec{y}_t = g(\vec{h}_t)$$
16 |
17 | 其中函数 f, g 是自定的,可以非线性,也可以就是简单的线性变换,比较常用的是:
18 |
19 |
20 | $$\vec{h}_t = ReLU(W_{xh}\vec{x}_t + W_{hh}\vec{h}_{t-1})$$
21 | $$\vec{y}_t = W_{hy}\vec{h}_t$$
22 |
23 | 虽然理论上 RNN 能建模无限长的序列,但因为很多数值计算(如梯度弥散、过拟合等)的原因致使 RNN 实际能收容的长度很小。等等类似的原因催生了门机制。
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | 大量实验证明,基于门机制(Gate Mechanism)可以一定程度上缓解 RNN 的梯度弥散、过拟合等问题。LSTM 是最广为应用的 Gated RNN,它的结构如下:
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | 如上图所示,运算 tanh(取值 -1 ~ 1) 和 α(Sigmoid,取值 0 – 1)表示控制滤过信息的 “门”。网上关于这些门有很多解释,可以参考这篇[博文](https://colah.github.io/posts/2015-08-Understanding-LSTMs/)。
34 |
35 | 除了 LSTM 外,GRU(Gated Recurrent Unit) 也是一种常用的 Gated RNN:
36 |
37 | > + 由于结构相对简单,相比起 LSTM,GRU 的计算速度更快;
38 | > + 由于参数较少,在小样本数据及上,GRU 的泛化效果更好;
39 |
40 | 事实上,一些类似机器阅读的任务要求高效计算,大家都会采用 GRU。甚至现在有很多工作开始为了效率而采用 Transformer 的结构。可以参考这篇[论文](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1804.09541.pdf)。
41 |
42 | ## Part-2:CRF 基础知识
43 |
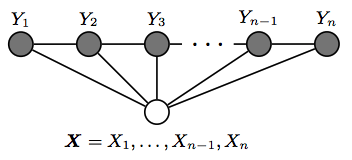
44 | > 给定输入 $X=(x_1,x_2,⋯,x_n)$,一般 RNN 模型输出标注序列 $Y=(y_1,y_2,⋯,y_n)$ 的办法就是简单的贪心,在每个词上做 argmax,忽略了类别之间的时序依存关系。
45 |
46 |
47 |
48 |
49 |
50 | 线性链条件随机场(Linear Chain Conditional Random Field),是基于马尔科夫性建模时序序列的有效方法。算法上可以利用损失 l(x)=-log(exp〖(x〗)) 的函数特点做前向计算;用维特比算法(实际上是动态规划,因此比贪心解码肯定好)做逆向解码。
51 |
52 | 形式上,给定发射特征(由 RNN 编码器获得)矩阵 E 和转移(CRF 参数矩阵,需要在计算图中被损失函数反向优化)矩阵 T,可计算给定输入输出的匹配得分:
53 |
54 | $$ score(X,y)=\sum_{i,y_i} E_{i,y_i} + \sum_i T_{y_i,y_{i+1}} $$
55 |
56 | 其中 X 是输入词序列,y 是预测的 label 序列。然后使以下目标最大化:
57 |
58 | $$ P(y_{gold} | X) = exp(s(X, y_{gold})) / \sum_{y \in Y_s} exp(s(X, y)) $$
59 |
60 | 以上就是 CRF 的核心原理。当然要实现一个 CRF,尤其是支持 batch 的 CRF,难度非常高,非常容易出 BUG 或低效的问题。之前笔者用 Pytorch 时就非常不便,一方面手动实现不是特别方便,另一方面用截取开源代码接口不好用。然而 PaddlePaddle 就很棒,它原生的提供了 CRF 的接口,同时支持损失函数计算和反向解码等功能。
61 |
62 | ## Part-3:建模思路
63 |
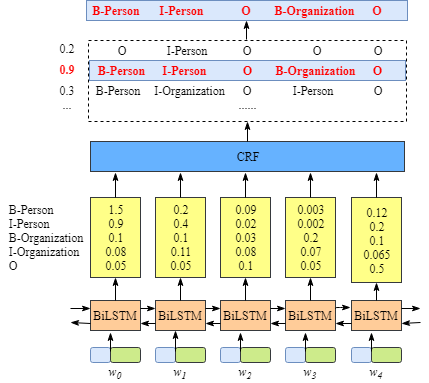
64 | **我们数据简单来说就是一句话。目前比较流行建模序列标注的方法是 BIO 标注,其中 B 表示 Begin,即标签的起始;I 表示 In,即标签的内部;O 表示 other,即非标签词。如下面图所示,低端的 w_i,0≤i≤4 表示输入,顶端的输出表示 BIO 标注。
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 |
69 |
70 | 模型的结构也如上图所示,我们首先用 Bi-GRU(忽略图中的 LSTM) 循环编码以获取输入序列的特征,然后再用 CRF 优化解码序列,从而达到比单用 RNNs 更好的效果。
71 |
72 | ## Part-4:PaddlePaddle实现
73 |
74 | 终于到了动手的部分。本节将会一步一步教您如何用 PaddlePaddle 实现 BiGRU + CRF 做序列标注。由于是demo,我们力求简单,让您能够将精力放到最核心的地方!
75 |
76 | ```python
77 | # 导入 PaddlePaddle 函数库.
78 | import paddle
79 | from paddle import fluid
80 |
81 | # 导入内置的 CoNLL 数据集.
82 | from paddle.dataset import conll05
83 |
84 | # 获取数据集的内置字典信息.
85 | word_dict, _, label_dict = conll05.get_dict()
86 |
87 | WORD_DIM = 32 # 超参数: 词向量维度.
88 | BATCH_SIZE = 10 # 训练时 BATCH 大小.
89 | EPOCH_NUM = 20 # 迭代轮数数目.
90 | HIDDEN_DIM = 512 # 模型隐层大小.
91 | LEARNING_RATE = 1e-1 # 模型学习率大小.
92 |
93 | # 设置输入 word 和目标 label 的变量.
94 | word = fluid.layers.data(name='word_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
95 | target = fluid.layers.data(name='target', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
96 |
97 | # 将词用 embedding 表示并通过线性层.
98 | embedding = fluid.layers.embedding(size=[len(word_dict), WORD_DIM], input=word,
99 | param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name="emb", trainable=False))
100 | hidden_0 = fluid.layers.fc(input=embedding, size=HIDDEN_DIM, act="tanh")
101 |
102 | # 用 RNNs 得到输入的提取特征并做变换.
103 | hidden_1 = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(
104 | input=hidden_0, size=HIDDEN_DIM,
105 | gate_activation='sigmoid',
106 | candidate_activation='relu',
107 | cell_activation='sigmoid')
108 | feature_out = fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden_1, size=len(label_dict), act='tanh')
109 |
110 | # 调用内置 CRF 函数并做状态转换解码.
111 | crf_cost = fluid.layers.linear_chain_crf(
112 | input=feature_out, label=target,
113 | param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name='crfw', learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE))
114 | avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(crf_cost)
115 |
116 | # 调用 SGD 优化函数并优化平均损失函数.
117 | fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE).minimize(avg_cost)
118 |
119 | # 声明 PaddlePaddle 的计算引擎.
120 | place = fluid.CPUPlace()
121 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
122 | main_program = fluid.default_main_program()
123 | exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
124 |
125 | # 由于是 DEMO 因此用测试集训练模型.
126 | feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(feed_list=[word, target], place=place)
127 | shuffle_loader = paddle.reader.shuffle(paddle.dataset.conll05.test(), buf_size=8192)
128 | train_data = paddle.batch(shuffle_loader, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
129 |
130 | # 按 FOR 循环迭代训练模型并打印损失.
131 | batch_id = 0
132 | for pass_id in range(EPOCH_NUM):
133 | for data in train_data():
134 | data = [[d[0], d[-1]] for d in data]
135 | cost = exe.run(main_program, feed=feeder.feed(data), fetch_list=[avg_cost])
136 |
137 | if batch_id % 10 == 0:
138 | print("avg_cost:\t" + str(cost[0][0]))
139 | batch_id = batch_id + 1
140 |
141 | ```
142 |
143 | 输出结果:
144 |
145 | ```bash
146 | [==================================================]l05st/conll05st%2FwordDict.txt not found, downloading http://paddlemodels.bj.bcebos.com/conll05st%2FwordDict.txt
147 | [==================================================]l05st/conll05st%2FverbDict.txt not found, downloading http://paddlemodels.bj.bcebos.com/conll05st%2FverbDict.txt
148 | [==================================================]l05st/conll05st%2FtargetDict.txt not found, downloading http://paddlemodels.bj.bcebos.com/conll05st%2FtargetDict.txt
149 |
150 |
151 |
152 | [==================================================]l05st/conll05st-tests.tar.gz not found, downloading http://paddlemodels.bj.bcebos.com/conll05st/conll05st-tests.tar.gz
153 | avg_cost: 150.293
154 | avg_cost: 102.468956
155 | avg_cost: 55.6771
156 | avg_cost: 45.3841
157 | avg_cost: 55.393227
158 | avg_cost: 47.93234
159 | avg_cost: 43.970863
160 | avg_cost: 46.385117
161 | avg_cost: 41.363853
162 | avg_cost: 46.78142
163 | avg_cost: 57.744774
164 | avg_cost: 33.612484
165 | avg_cost: 30.556072
166 | avg_cost: 36.819237
167 | avg_cost: 37.627037
168 | avg_cost: 38.523487
169 | avg_cost: 38.453724
170 | avg_cost: 47.136696
171 | avg_cost: 39.19741
172 | avg_cost: 36.097908
173 | avg_cost: 38.043354
174 | avg_cost: 25.416252
175 | avg_cost: 22.22056
176 | avg_cost: 45.511017
177 | avg_cost: 36.31049
178 | avg_cost: 33.19769
179 | avg_cost: 37.441
180 | avg_cost: 34.272476
181 | avg_cost: 25.608454
182 | avg_cost: 27.278118
183 | avg_cost: 32.817966
184 | avg_cost: 25.00168
185 | avg_cost: 36.707935
186 | avg_cost: 27.87775
187 | avg_cost: 31.61958
188 | avg_cost: 33.14825
189 | avg_cost: 34.09555
190 | avg_cost: 24.461145
191 | avg_cost: 33.34344
192 | avg_cost: 29.01653
193 | avg_cost: 36.376263
194 |
195 | ```
196 |
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/community_examples/ner/ner.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python3
2 | # -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
3 |
4 | ' BiGRU + CRF '
5 |
6 | __author__ = 'huxiaoman77'
7 |
8 | # 导入 PaddlePaddle 函数库.
9 | import paddle
10 | from paddle import fluid
11 |
12 | # 导入内置的 CoNLL 数据集.
13 | from paddle.dataset import conll05
14 |
15 | # 获取数据集的内置字典信息.
16 | word_dict, _, label_dict = conll05.get_dict()
17 |
18 | WORD_DIM = 32 # 超参数: 词向量维度.
19 | BATCH_SIZE = 10 # 训练时 BATCH 大小.
20 | EPOCH_NUM = 20 # 迭代轮数数目.
21 | HIDDEN_DIM = 512 # 模型隐层大小.
22 | LEARNING_RATE = 1e-1 # 模型学习率大小.
23 |
24 | # 设置输入 word 和目标 label 的变量.
25 | word = fluid.layers.data(name='word_data', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
26 | target = fluid.layers.data(name='target', shape=[1], dtype='int64', lod_level=1)
27 |
28 | # 将词用 embedding 表示并通过线性层.
29 | embedding = fluid.layers.embedding(size=[len(word_dict), WORD_DIM], input=word,
30 | param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name="emb", trainable=False))
31 | hidden_0 = fluid.layers.fc(input=embedding, size=HIDDEN_DIM, act="tanh")
32 |
33 | # 用 RNNs 得到输入的提取特征并做变换.
34 | hidden_1 = fluid.layers.dynamic_lstm(
35 | input=hidden_0, size=HIDDEN_DIM,
36 | gate_activation='sigmoid',
37 | candidate_activation='relu',
38 | cell_activation='sigmoid')
39 | feature_out = fluid.layers.fc(input=hidden_1, size=len(label_dict), act='tanh')
40 |
41 | # 调用内置 CRF 函数并做状态转换解码.
42 | crf_cost = fluid.layers.linear_chain_crf(
43 | input=feature_out, label=target,
44 | param_attr=fluid.ParamAttr(name='crfw', learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE))
45 | avg_cost = fluid.layers.mean(crf_cost)
46 |
47 | # 调用 SGD 优化函数并优化平均损失函数.
48 | fluid.optimizer.SGD(learning_rate=LEARNING_RATE).minimize(avg_cost)
49 |
50 | # 声明 PaddlePaddle 的计算引擎.
51 | place = fluid.CPUPlace()
52 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
53 | main_program = fluid.default_main_program()
54 | exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
55 |
56 | # 由于是 DEMO 因此用测试集训练模型.
57 | feeder = fluid.DataFeeder(feed_list=[word, target], place=place)
58 | shuffle_loader = paddle.reader.shuffle(paddle.dataset.conll05.test(), buf_size=8192)
59 | train_data = paddle.batch(shuffle_loader, batch_size=BATCH_SIZE)
60 |
61 | # 按 FOR 循环迭代训练模型并打印损失.
62 | batch_id = 0
63 | for pass_id in range(EPOCH_NUM):
64 | for data in train_data():
65 | data = [[d[0], d[-1]] for d in data]
66 | cost = exe.run(main_program, feed=feeder.feed(data), fetch_list=[avg_cost])
67 |
68 | if batch_id % 10 == 0:
69 | print("avg_cost:\t" + str(cost[0][0]))
70 | batch_id = batch_id + 1
71 |
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/community_examples/recompute/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | This demo belongs to the Forward Recomputation Backpropagation Document.
3 |
4 | Expected output of this demo is like:
5 |
6 | ```shell
7 | name: "x"
8 | type {
9 | type: LOD_TENSOR
10 | lod_tensor {
11 | tensor {
12 | data_type: FP32
13 | dims: -1
14 | dims: 32
15 | }
16 | lod_level: 0
17 | }
18 | }
19 | persistable: false
20 |
21 | Finished FF
22 | Finished optimize
23 | step=0 cost=0.740719
24 | step=1 cost=1.113626
25 | step=2 cost=0.699762
26 | step=3 cost=0.663064
27 | step=4 cost=0.785782
28 | step=5 cost=0.655717
29 | step=6 cost=0.722237
30 | step=7 cost=0.699711
31 | step=8 cost=0.698443
32 | step=9 cost=0.698395
33 | ```
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/community_examples/recompute/demo.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import paddle.fluid as fluid
2 | import numpy as np
3 | np.random.seed(9000)
4 |
5 | fluid.default_main_program().random_seed = 9000
6 | fluid.default_startup_program().random_seed = 9000
7 |
8 | def gen_data():
9 | return {"x": np.random.random(size=(32, 32)).astype('float32'),
10 | "y": np.random.randint(2, size=(32, 1)).astype('int64')}
11 |
12 | def mlp(input_x, input_y, hid_dim=128, label_dim=2):
13 | print(input_x)
14 | fc_1 = fluid.layers.fc(input=input_x, size=hid_dim, act='relu')
15 | fc_2 = fluid.layers.fc(input=fc_1, size=hid_dim, act='relu')
16 | fc_3 = fluid.layers.fc(input=fc_2, size=hid_dim, act='relu')
17 | prediction = fluid.layers.fc(input=[fc_3], size=label_dim, act='softmax')
18 | cost = fluid.layers.cross_entropy(input=prediction, label=input_y)
19 | sum_cost = fluid.layers.reduce_mean(cost)
20 | return sum_cost, fc_1, prediction
21 |
22 | input_x = fluid.layers.data(name="x", shape=[32], dtype='float32')
23 | input_y = fluid.layers.data(name="y", shape=[1], dtype='int64')
24 | cost, fc_1, pred = mlp(input_x, input_y)
25 |
26 | print("Finished FF")
27 |
28 | sgd = fluid.optimizer.Adam(learning_rate=0.01)
29 | sgd = fluid.optimizer.RecomputeOptimizer(sgd)
30 | sgd._set_checkpoints([fc_1, pred])
31 | sgd.minimize(cost)
32 |
33 | print("Finished optimize")
34 | place = fluid.CPUPlace()
35 | exe = fluid.Executor(place)
36 | exe.run(fluid.default_startup_program())
37 | step = 10
38 |
39 | with open("main_program.txt", 'w') as f:
40 | f.write(str(fluid.default_main_program()))
41 |
42 | for i in range(step):
43 | cost_val = exe.run(feed=gen_data(),
44 | program=fluid.default_main_program(),
45 | fetch_list=[cost.name])
46 | print("step=%d cost=%f" % (i, cost_val[0]))
47 |
48 | fluid.io.save_inference_model("model", ["x", "y"], [cost], exe,
49 | export_for_deployment=False)
50 |
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------