188 |
189 |
190 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/app/src/style.css:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #link {color: #E45635;display:block;font: 12px "Helvetica Neue", Helvetica, Arial, sans-serif;text-align:center; text-decoration: none;}
2 | #link:hover {color: #CCCCCC}
3 |
4 | #link, #link:hover {-webkit-transition: color 0.5s ease-out;-moz-transition: color 0.5s ease-out;-ms-transition: color 0.5s ease-out;-o-transition: color 0.5s ease-out;transition: color 0.5s ease-out;}
5 |
6 | /** BEGIN CSS **/
7 | body {background: #333333;}
8 | @keyframes rotate-loading {
9 | 0% {transform: rotate(0deg);-ms-transform: rotate(0deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(0deg); -o-transform: rotate(0deg); -moz-transform: rotate(0deg);}
10 | 100% {transform: rotate(360deg);-ms-transform: rotate(360deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(360deg); -o-transform: rotate(360deg); -moz-transform: rotate(360deg);}
11 | }
12 |
13 | @-moz-keyframes rotate-loading {
14 | 0% {transform: rotate(0deg);-ms-transform: rotate(0deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(0deg); -o-transform: rotate(0deg); -moz-transform: rotate(0deg);}
15 | 100% {transform: rotate(360deg);-ms-transform: rotate(360deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(360deg); -o-transform: rotate(360deg); -moz-transform: rotate(360deg);}
16 | }
17 |
18 | @-webkit-keyframes rotate-loading {
19 | 0% {transform: rotate(0deg);-ms-transform: rotate(0deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(0deg); -o-transform: rotate(0deg); -moz-transform: rotate(0deg);}
20 | 100% {transform: rotate(360deg);-ms-transform: rotate(360deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(360deg); -o-transform: rotate(360deg); -moz-transform: rotate(360deg);}
21 | }
22 |
23 | @-o-keyframes rotate-loading {
24 | 0% {transform: rotate(0deg);-ms-transform: rotate(0deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(0deg); -o-transform: rotate(0deg); -moz-transform: rotate(0deg);}
25 | 100% {transform: rotate(360deg);-ms-transform: rotate(360deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(360deg); -o-transform: rotate(360deg); -moz-transform: rotate(360deg);}
26 | }
27 |
28 | @keyframes rotate-loading {
29 | 0% {transform: rotate(0deg);-ms-transform: rotate(0deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(0deg); -o-transform: rotate(0deg); -moz-transform: rotate(0deg);}
30 | 100% {transform: rotate(360deg);-ms-transform: rotate(360deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(360deg); -o-transform: rotate(360deg); -moz-transform: rotate(360deg);}
31 | }
32 |
33 | @-moz-keyframes rotate-loading {
34 | 0% {transform: rotate(0deg);-ms-transform: rotate(0deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(0deg); -o-transform: rotate(0deg); -moz-transform: rotate(0deg);}
35 | 100% {transform: rotate(360deg);-ms-transform: rotate(360deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(360deg); -o-transform: rotate(360deg); -moz-transform: rotate(360deg);}
36 | }
37 |
38 | @-webkit-keyframes rotate-loading {
39 | 0% {transform: rotate(0deg);-ms-transform: rotate(0deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(0deg); -o-transform: rotate(0deg); -moz-transform: rotate(0deg);}
40 | 100% {transform: rotate(360deg);-ms-transform: rotate(360deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(360deg); -o-transform: rotate(360deg); -moz-transform: rotate(360deg);}
41 | }
42 |
43 | @-o-keyframes rotate-loading {
44 | 0% {transform: rotate(0deg);-ms-transform: rotate(0deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(0deg); -o-transform: rotate(0deg); -moz-transform: rotate(0deg);}
45 | 100% {transform: rotate(360deg);-ms-transform: rotate(360deg); -webkit-transform: rotate(360deg); -o-transform: rotate(360deg); -moz-transform: rotate(360deg);}
46 | }
47 |
48 | @keyframes loading-text-opacity {
49 | 0% {opacity: 0}
50 | 20% {opacity: 0}
51 | 50% {opacity: 1}
52 | 100%{opacity: 0}
53 | }
54 |
55 | @-moz-keyframes loading-text-opacity {
56 | 0% {opacity: 0}
57 | 20% {opacity: 0}
58 | 50% {opacity: 1}
59 | 100%{opacity: 0}
60 | }
61 |
62 | @-webkit-keyframes loading-text-opacity {
63 | 0% {opacity: 0}
64 | 20% {opacity: 0}
65 | 50% {opacity: 1}
66 | 100%{opacity: 0}
67 | }
68 |
69 | @-o-keyframes loading-text-opacity {
70 | 0% {opacity: 0}
71 | 20% {opacity: 0}
72 | 50% {opacity: 1}
73 | 100%{opacity: 0}
74 | }
75 | .loading-container,
76 | .loading {
77 | height: 100px;
78 | position: relative;
79 | width: 100px;
80 | border-radius: 100%;
81 | }
82 |
83 |
84 | .loading-container { margin: 40px auto }
85 |
86 | .loading {
87 | border: 2px solid transparent;
88 | border-color: transparent #fff transparent #FFF;
89 | -moz-animation: rotate-loading 1.5s linear 0s infinite normal;
90 | -moz-transform-origin: 50% 50%;
91 | -o-animation: rotate-loading 1.5s linear 0s infinite normal;
92 | -o-transform-origin: 50% 50%;
93 | -webkit-animation: rotate-loading 1.5s linear 0s infinite normal;
94 | -webkit-transform-origin: 50% 50%;
95 | animation: rotate-loading 1.5s linear 0s infinite normal;
96 | transform-origin: 50% 50%;
97 | }
98 |
99 | .loading-container:hover .loading {
100 | border-color: transparent #E45635 transparent #E45635;
101 | }
102 | .loading-container:hover .loading,
103 | .loading-container .loading {
104 | -webkit-transition: all 0.5s ease-in-out;
105 | -moz-transition: all 0.5s ease-in-out;
106 | -ms-transition: all 0.5s ease-in-out;
107 | -o-transition: all 0.5s ease-in-out;
108 | transition: all 0.5s ease-in-out;
109 | }
110 |
111 | #loading-text {
112 | -moz-animation: loading-text-opacity 2s linear 0s infinite normal;
113 | -o-animation: loading-text-opacity 2s linear 0s infinite normal;
114 | -webkit-animation: loading-text-opacity 2s linear 0s infinite normal;
115 | animation: loading-text-opacity 2s linear 0s infinite normal;
116 | color: #ffffff;
117 | font-family: "Helvetica Neue, "Helvetica", ""arial";
118 | font-size: 10px;
119 | font-weight: bold;
120 | margin-top: 45px;
121 | opacity: 0;
122 | position: absolute;
123 | text-align: center;
124 | text-transform: uppercase;
125 | top: 0;
126 | width: 100px;
127 | }
128 |
129 | header {
130 | background-color: #666;
131 | padding: 2px;
132 | text-align: center;
133 | font-size: 15px;
134 | color: white;
135 | }
136 | /*.loader {*/
137 | /* border: 16px solid #f3f3f3;*/
138 | /* border-radius: 50%;*/
139 | /* border-top: 16px solid #3498db;*/
140 | /* width: 120px;*/
141 | /* height: 120px;*/
142 | /* -webkit-animation: spin 2s linear infinite; /* Safari */*/
143 | /* animation: spin 2s linear infinite;*/
144 | /* margin: 40 auto;*/
145 | /*}*/
146 | /**/
147 | /**/
148 | /*/* Safari */*/
149 | /*@-webkit-keyframes spin {*/
150 | /* 0% { -webkit-transform: rotate(0deg); }*/
151 | /* 100% { -webkit-transform: rotate(360deg); }*/
152 | /*}*/
153 | /**/
154 | /*@keyframes spin {*/
155 | /* 0% { transform: rotate(0deg); }*/
156 | /* 100% { transform: rotate(360deg); }*/
157 | /*}*/
158 |
159 | a.ca {
160 | color: white;
161 | }
162 | a.ca:hover {
163 | color: white;
164 | }
165 |
166 | body {
167 | /* background: url(bg.jpg) no-repeat center center fixed; */
168 | background-color: rgb(34, 34, 34);
169 | -webkit-background-size: cover;
170 | -moz-background-size: cover;
171 | -o-background-size: cover;
172 | background-size: cover;
173 | }
174 |
175 | hr {
176 | margin-top: 1rem;
177 | margin-bottom: 1rem;
178 | border: 1;
179 | border-top: 1pxsolidrgba(0,0,0,.1);
180 | }
181 |
182 | hr.header1 {
183 | border-top: 1px solid rgb(255, 255, 255);
184 | }
185 |
186 |
187 | .content {
188 | text-align: center;
189 | font-family: 'Open Sans', sans-serif;
190 | color: #fff;
191 | margin: 40px auto;
192 | background: rgb(34, 34, 34);
193 | width: 100%;
194 | max-width: 960px;
195 | border-radius: 5px;
196 | padding-bottom: 32px;
197 | }
198 |
199 | h1, h1 a {
200 | min-height: 50px;
201 | width: 90%;
202 | max-width: 700px;
203 | vertical-align: middle;
204 | text-align: center;
205 | margin: 0 auto;
206 | text-decoration: none;
207 | color: #fff;
208 | padding-top: 10px;
209 | }
210 |
211 | p {
212 | width: 90%;
213 | max-width: 700px;
214 | text-align: left;
215 | margin: 0 auto;
216 | padding-bottom: 32px;
217 | }
218 |
219 | a {
220 | color: white;
221 | }
222 |
223 | th {
224 | color: white;
225 | font-size: 25px;
226 | }
227 |
228 | .latest{
229 | color: rgb(30, 255, 0);
230 | }
231 | .update{
232 | color: rgb(253, 249, 0);
233 | }
234 | .error{
235 | color: rgb(255, 0, 0);
236 | }
237 |
238 |
239 |
240 | .tg {
241 | border-collapse:collapse;border-spacing:0;vertical-align:top;
242 | }
243 | .tg td {
244 | border-color:black;border-style:solid;border-width:0px;font-family:Arial, sans-serif;font-size:14px;
245 | overflow:hidden;padding:10px 5px;word-break:normal;vertical-align:top;
246 | }
247 | .tg th {
248 | border-color:black;border-style:solid;border-width:0px;font-family:Arial, sans-serif;font-size:14px;
249 | font-weight:normal;overflow:hidden;padding:10px 5px;word-break:normal;vertical-align:top;
250 | }
251 | .tg .tg-0lax {
252 | text-align:left;vertical-align:top;
253 | }
254 | * {
255 | box-sizing: border-box;
256 | }
257 |
258 | .row {
259 | margin-left:-5px;
260 | margin-right:-5px;
261 | }
262 |
263 | .column {
264 | float: left;
265 | width: 50%;
266 | padding: 5px;
267 | }
268 | .error {
269 | float: center;
270 | width: 100%;
271 | padding: 5px;
272 | }
273 |
274 | /* Clearfix (clear floats) */
275 | .row::after {
276 | content: "";
277 | clear: both;
278 | display: table;
279 | }
280 |
281 | table {
282 | border-collapse: collapse;
283 | border-spacing: 0;
284 | width: 100%;
285 | border: 0px solid #ddd;
286 | }
287 |
288 | th, td {
289 | text-align: left;
290 | padding: 5px;
291 | color: #fff
292 | }
293 |
294 | tr:nth-child(even) {
295 | background-color: #616161;
296 | color: rgb(100, 21, 21)
297 | }
298 | tr:nth-child(odd) {
299 | background-color: #474747;
300 | color: rgb(100, 21, 21)
301 | }
302 |
303 |
304 | .hide{
305 | display:none;
306 | }
307 | button {
308 | background-color: #474747;
309 | border: none;
310 | color: white;
311 | padding: 4px 40px;
312 | text-align: center;
313 | text-decoration: none;
314 | display: inline-block;
315 | font-size: 16;
316 | border: 2px solid #00000054;
317 | }
318 | slot:not([name]) {
319 | display: none;
320 | }
321 | /* Either the fallback summary (inside the shadow tree), or the slotted main
322 | summary. */
323 | summary,
324 | slot[name=internal-main-summary]::slotted(summary) {
325 | display: list-item;
326 | counter-increment: list-item 0;
327 | list-style: disclosure-closed outside;
328 | }
329 | :host([open]) summary,
330 | :host([open]) slot[name=internal-main-summary]::slotted(summary) {
331 | list-style-type: disclosure-open;
332 | }
333 | :host([open]) slot:not([name]) {
334 | display: revert;
335 | }
336 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # DCW (dockcheck-web) with exporters
2 | A webpage showing available image updates for your running containers.
3 |
4 | Checking for new images at startup, once a day and via the button "Check for updates".
5 |
6 | If dont want gui, just ignore publishing ports.
7 | *working on a non-gui version*.
8 |
9 | ## Exporter (multiple hosts)
10 | [Palleri/DCW-exporter](https://github.com/Palleri/DCW-exporter)
11 |
12 | ## Based on [mag37/dockcheck](https://github.com/mag37/dockcheck)
13 |
14 | >### A script checking updates for docker images without the need of pulling - then having the option to auto-update.
15 |
16 | All cred goes to Mag37 making this amazing script!
17 |
18 | This image use [dockcheck](https://github.com/mag37/dockcheck) provided by Mag37.
19 |
20 |
21 | ## Dependencies:
22 | [regclient/regctl](https://github.com/regclient/regclient) (Licensed under Apache-2.0 License)
23 |
24 | [inotify-tools](https://github.com/inotify-tools/inotify-tools) (Licensed under GPL-2.0 License)
25 |
26 | [APPRISE](https://github.com/caronc/apprise) (Licensed under BSD 3-Clause License)
27 |
28 | ----
29 |
30 | 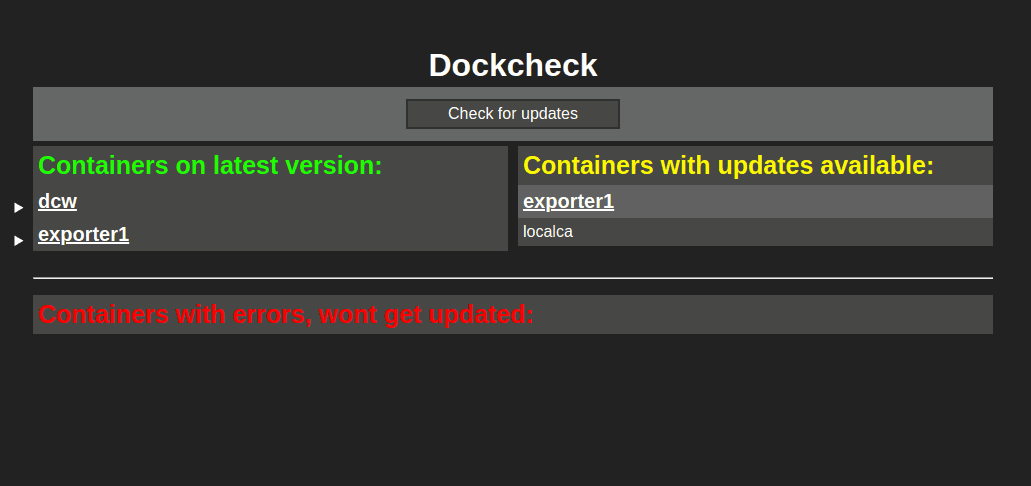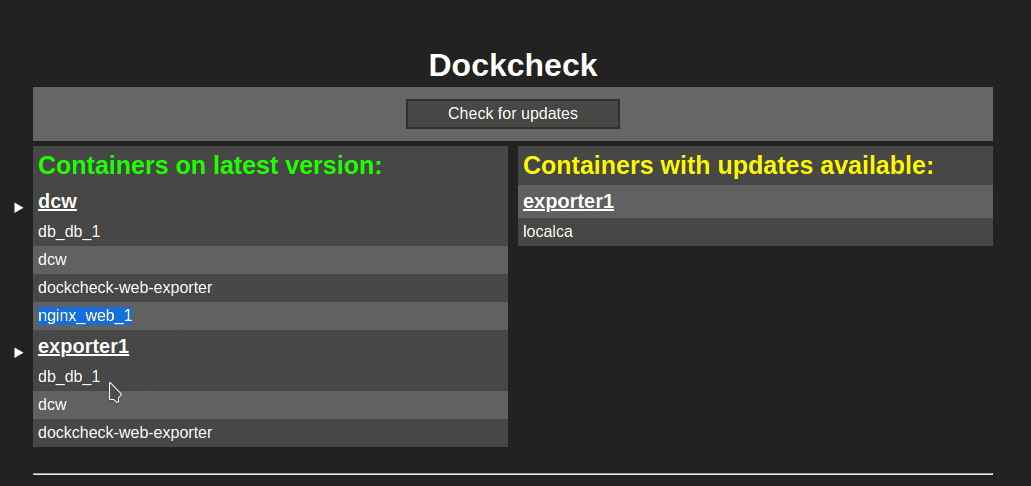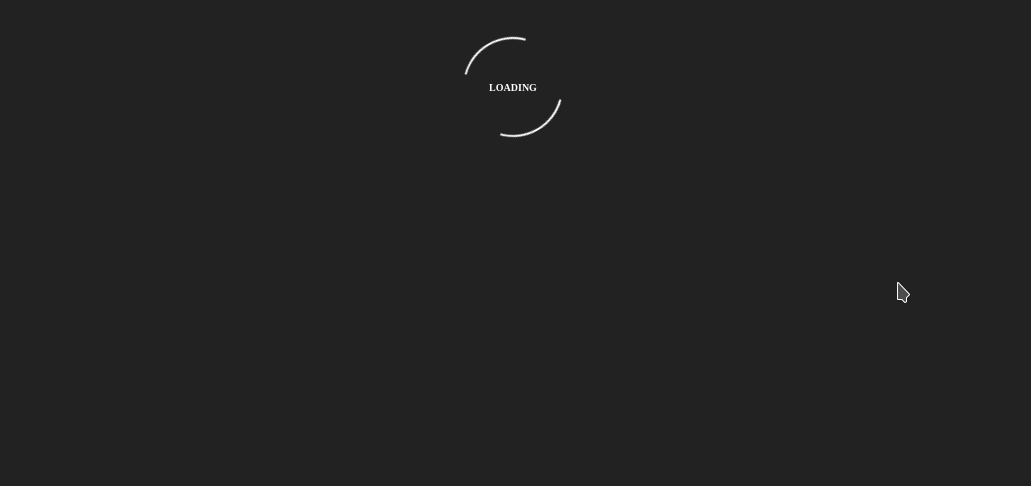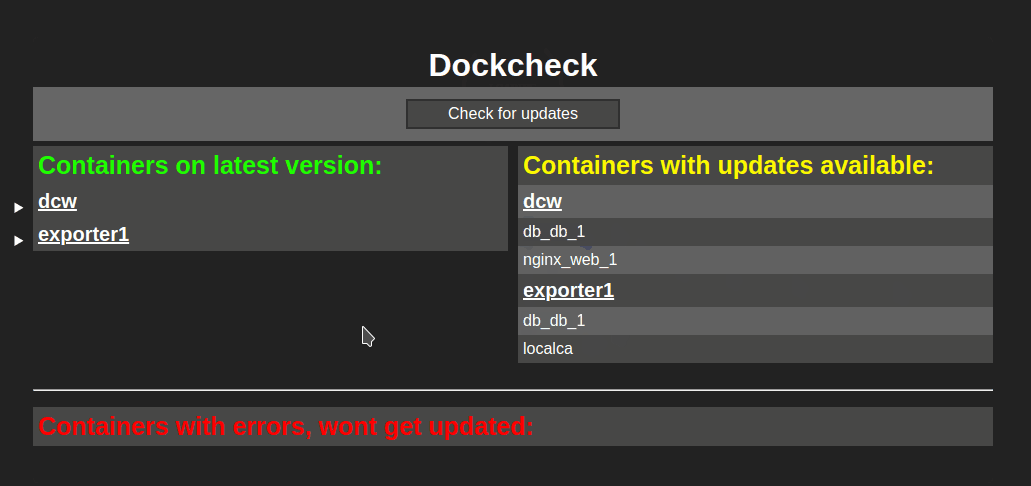
31 |
32 |
33 | docker-compose.yml
34 | ```yml
35 | version: '3.2'
36 | services:
37 | dcw:
38 | container_name: dcw
39 | image: 'palleri/dcw:latest'
40 | hostname: DCW # optional, the hostname will be displayed in the ui
41 | restart: unless-stopped
42 | ports:
43 | - '80:80'
44 | - '5432:5432' # only required with exporters // communication between DCW and exporters
45 | volumes:
46 | - ./data:/var/www/html
47 | - /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro
48 | - /etc/localtime:/etc/localtime:ro
49 | environment:
50 | TOKEN: superSecretPassw0rd # required // Also used by the exporter
51 | NOTIFY: "true" # optional
52 | NOTIFY_URLS: "discord://Dockcheck@xxxxx/xxxxxx" # optional
53 | NOTIFY_DEBUG: true # optional
54 | HTTP_PROXY: "http://proxy.homelab.net:3128" # optional
55 | HTTPS_PROXY: "http://proxy.homelab.net:3128" # optional
56 | EXCLUDE: "nginx,plex,prowlarr" # optional // Exclude containers from being checked for updates
57 | CRON_TIME: "12:56" # optional
58 | ```
59 | The container and exporter are communicating via port tcp/5432
60 |
61 | # Security concern
62 | For more security add the :ro to volumes docker.sock
63 |
64 | Use with care, make sure you keep this container safe and do not publish on the internet.
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 | # Notifications
69 | This image use [apprise](https://github.com/caronc/apprise) for notifications
70 |
71 | ### Environment variables
72 | Set `NOTIFY: true` to enable notifications
73 |
74 | Set `NOTIFY_DEBUG: true` to enable DEBUG mode. Be carefull, your tokens and passwords might be visible in docker logs
75 |
76 | Set `NOTIFY_URLS: "tgram://0123456789:RandomLettersAndNumbers-2morestuff-123456789"`
77 |
78 | Set `EXCLUDE: "nginx,plex,prowlarr"` if you want to exclude containers from being checked for updates
79 | Use the name on each container in comma separated variable
80 |
81 | ### Setup Example for Telegram
82 | Start a chat with `@BotFather` and follow the guided steps.
83 | Create a new bot: `/newbot`
84 | Nickname: `PumpkinsInShorts` Username: `CuriousPlumber`
85 | Note down the token replied: *Use this token to access the HTTP API:*
86 | `0123456789:RandomLettersAndNumbers-2morestuff`
87 |
88 | Now create a new group in Telegram, invite the bot with it's username `@CuriousPlumber`
89 | When in the group, note down the end of the url, eg `web.telegram.org/z/#-123456789` -> `-123456789`
90 | If only using the phone app, invite `@RawDataBot` to the group and it'll post the id.
91 |
92 | Then finally combine the token + the ID of the chatgroup, in this example:
93 | `0123456789:RandomLettersAndNumbers-2morestuff-123456789`
94 | Add that row to the docker-compose.yml
95 | ```yml
96 | version: '3.2'
97 | services:
98 | ...
99 | environment:
100 | NOTIFY: "true"
101 | NOTIFY_URLS: "tgram://0123456789:RandomLettersAndNumbers-2morestuff-123456789"
102 | ...
103 | ```
104 |
105 | ### Setup Example for Discord
106 |
107 | Remove the `api/webhook` from `https://discord.com/api/webhooks/xxxxx/xxxxxx`
108 | To this `discord://xxxxx/xxxxxx`
109 |
110 | Or use it as it is `https://discord.com/api/webhooks/xxxxx/xxxxxx`
111 |
112 | ```yml
113 | version: '3.2'
114 | services:
115 | ...
116 | environment:
117 | NOTIFY: "true"
118 | NOTIFY_URLS: "discord://Dockcheck-web@xxxxx/xxxxxx"
119 | ...
120 | ```
121 |
122 |
123 | ### Example for multiple urls
124 |
125 | ```yml
126 | version: '3.2'
127 | services:
128 | ...
129 | environment:
130 | NOTIFY: "true"
131 | NOTIFY_URLS: "discord://Dockcheck-web@xxxxx/xxxxxx tgram://0123456789:RandomLettersAndNumbers-2morestuff-123456789"
132 | ...
133 | ```
134 |
135 | ### Tested
136 | | Service | Tested | Result |
137 | | --- | :---: | :---: |
138 | | Discord | 2023-02-24 | :heavy_check_mark: |
139 | | Mail | 2023-02-24 | :heavy_check_mark: |
140 | | Telegram | 2023-02-24 | :heavy_check_mark: |
141 | | Gotify | 2023-02-25 | :heavy_check_mark: |
142 | | Matrix | 2023-02-26 | :heavy_check_mark: |
143 | | HomeAssistant | 2023-02-26 | :heavy_check_mark: |
144 |
145 |
146 |
147 |
148 | | Notification Service | Service ID | Default Port | Example Syntax |
149 | | -------------------- | ---------- | ------------ | -------------- |
150 | | [Apprise API](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_apprise_api) | apprise:// or apprises:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | apprise://hostname/Token
151 | | [AWS SES](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_ses) | ses:// | (TCP) 443 | ses://user@domain/AccessKeyID/AccessSecretKey/RegionName ses://user@domain/AccessKeyID/AccessSecretKey/RegionName/email1/email2/emailN
152 | | [Bark](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_bark) | bark:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | bark://hostname bark://hostname/device_key bark://hostname/device_key1/device_key2/device_keyN
153 | | [Boxcar](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_boxcar) | boxcar:// | (TCP) 443 | boxcar://hostname boxcar://hostname/@tag boxcar://hostname/device_token boxcar://hostname/device_token1/device_token2/device_tokenN boxcar://hostname/@tag/@tag2/device_token
154 | | [Discord](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_discord) | discord:// | (TCP) 443 | discord://webhook_id/webhook_token discord://avatar@webhook_id/webhook_token
155 | | [Emby](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_emby) | emby:// or embys:// | (TCP) 8096 | emby://user@hostname/ emby://user:password@hostname
156 | | [Enigma2](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_enigma2) | enigma2:// or enigma2s:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | enigma2://hostname
157 | | [Faast](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_faast) | faast:// | (TCP) 443 | faast://authorizationtoken
158 | | [FCM](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_fcm) | fcm:// | (TCP) 443 | fcm://project@apikey/DEVICE_ID fcm://project@apikey/#TOPIC fcm://project@apikey/DEVICE_ID1/#topic1/#topic2/DEVICE_ID2/
159 | | [Flock](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_flock) | flock:// | (TCP) 443 | flock://token flock://botname@token flock://app_token/u:userid flock://app_token/g:channel_id flock://app_token/u:userid/g:channel_id
160 | | [Gitter](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_gitter) | gitter:// | (TCP) 443 | gitter://token/room gitter://token/room1/room2/roomN
161 | | [Google Chat](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_googlechat) | gchat:// | (TCP) 443 | gchat://workspace/key/token
162 | | [Gotify](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_gotify) | gotify:// or gotifys:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | gotify://hostname/token gotifys://hostname/token?priority=high
163 | | [Growl](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_growl) | growl:// | (UDP) 23053 | growl://hostname growl://hostname:portno growl://password@hostname growl://password@hostname:port**Note**: you can also use the get parameter _version_ which can allow the growl request to behave using the older v1.x protocol. An example would look like: growl://hostname?version=1
164 | | [Guilded](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_guilded) | guilded:// | (TCP) 443 | guilded://webhook_id/webhook_token guilded://avatar@webhook_id/webhook_token
165 | | [Home Assistant](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_homeassistant) | hassio:// or hassios:// | (TCP) 8123 or 443 | hassio://hostname/accesstoken hassio://user@hostname/accesstoken hassio://user:password@hostname:port/accesstoken hassio://hostname/optional/path/accesstoken
166 | | [IFTTT](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_ifttt) | ifttt:// | (TCP) 443 | ifttt://webhooksID/Event ifttt://webhooksID/Event1/Event2/EventN ifttt://webhooksID/Event1/?+Key=Value ifttt://webhooksID/Event1/?-Key=value1
167 | | [Join](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_join) | join:// | (TCP) 443 | join://apikey/device join://apikey/device1/device2/deviceN/ join://apikey/group join://apikey/groupA/groupB/groupN join://apikey/DeviceA/groupA/groupN/DeviceN/
168 | | [KODI](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_kodi) | kodi:// or kodis:// | (TCP) 8080 or 443 | kodi://hostname kodi://user@hostname kodi://user:password@hostname:port
169 | | [Kumulos](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_kumulos) | kumulos:// | (TCP) 443 | kumulos://apikey/serverkey
170 | | [LaMetric Time](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_lametric) | lametric:// | (TCP) 443 | lametric://apikey@device_ipaddr lametric://apikey@hostname:port lametric://client_id@client_secret
171 | | [Line](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_line) | line:// | (TCP) 443 | line://Token@User line://Token/User1/User2/UserN
172 | | [Mailgun](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_mailgun) | mailgun:// | (TCP) 443 | mailgun://user@hostname/apikey mailgun://user@hostname/apikey/email mailgun://user@hostname/apikey/email1/email2/emailN mailgun://user@hostname/apikey/?name="From%20User"
173 | | [Mastodon](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_mastodon) | mastodon:// or mastodons://| (TCP) 80 or 443 | mastodon://access_key@hostname mastodon://access_key@hostname/@user mastodon://access_key@hostname/@user1/@user2/@userN
174 | | [Matrix](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_matrix) | matrix:// or matrixs:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | matrix://hostname matrix://user@hostname matrixs://user:pass@hostname:port/#room_alias matrixs://user:pass@hostname:port/!room_id matrixs://user:pass@hostname:port/#room_alias/!room_id/#room2 matrixs://token@hostname:port/?webhook=matrix matrix://user:token@hostname/?webhook=slack&format=markdown
175 | | [Mattermost](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_mattermost) | mmost:// or mmosts:// | (TCP) 8065 | mmost://hostname/authkey mmost://hostname:80/authkey mmost://user@hostname:80/authkey mmost://hostname/authkey?channel=channel mmosts://hostname/authkey mmosts://user@hostname/authkey
176 | | [Microsoft Teams](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_msteams) | msteams:// | (TCP) 443 | msteams://TokenA/TokenB/TokenC/
177 | | [Misskey](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_misskey) | misskey:// or misskeys://| (TCP) 80 or 443 | misskey://access_token@hostname
178 | | [MQTT](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_mqtt) | mqtt:// or mqtts:// | (TCP) 1883 or 8883 | mqtt://hostname/topic mqtt://user@hostname/topic mqtts://user:pass@hostname:9883/topic
179 | | [Nextcloud](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_nextcloud) | ncloud:// or nclouds:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | ncloud://adminuser:pass@host/User nclouds://adminuser:pass@host/User1/User2/UserN
180 | | [NextcloudTalk](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_nextcloudtalk) | nctalk:// or nctalks:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | nctalk://user:pass@host/RoomId nctalks://user:pass@host/RoomId1/RoomId2/RoomIdN
181 | | [Notica](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_notica) | notica:// | (TCP) 443 | notica://Token/
182 | | [Notifico](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_notifico) | notifico:// | (TCP) 443 | notifico://ProjectID/MessageHook/
183 | | [ntfy](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_ntfy) | ntfy:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | ntfy://topic/ ntfys://topic/
184 | | [Office 365](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_office365) | o365:// | (TCP) 443 | o365://TenantID:AccountEmail/ClientID/ClientSecret o365://TenantID:AccountEmail/ClientID/ClientSecret/TargetEmail o365://TenantID:AccountEmail/ClientID/ClientSecret/TargetEmail1/TargetEmail2/TargetEmailN
185 | | [OneSignal](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_onesignal) | onesignal:// | (TCP) 443 | onesignal://AppID@APIKey/PlayerID onesignal://TemplateID:AppID@APIKey/UserID onesignal://AppID@APIKey/#IncludeSegment onesignal://AppID@APIKey/Email
186 | | [Opsgenie](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_opsgenie) | opsgenie:// | (TCP) 443 | opsgenie://APIKey opsgenie://APIKey/UserID opsgenie://APIKey/#Team opsgenie://APIKey/\*Schedule opsgenie://APIKey/^Escalation
187 | | [PagerDuty](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_pagerduty) | pagerduty:// | (TCP) 443 | pagerduty://IntegrationKey@ApiKey pagerduty://IntegrationKey@ApiKey/Source/Component
188 | | [PagerTree](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_pagertree) | pagertree:// | (TCP) 443 | pagertree://integration_id
189 | | [ParsePlatform](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_parseplatform) | parsep:// or parseps:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | parsep://AppID:MasterKey@Hostname parseps://AppID:MasterKey@Hostname
190 | | [PopcornNotify](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_popcornnotify) | popcorn:// | (TCP) 443 | popcorn://ApiKey/ToPhoneNo popcorn://ApiKey/ToPhoneNo1/ToPhoneNo2/ToPhoneNoN/ popcorn://ApiKey/ToEmail popcorn://ApiKey/ToEmail1/ToEmail2/ToEmailN/ popcorn://ApiKey/ToPhoneNo1/ToEmail1/ToPhoneNoN/ToEmailN
191 | | [Prowl](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_prowl) | prowl:// | (TCP) 443 | prowl://apikey prowl://apikey/providerkey
192 | | [PushBullet](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_pushbullet) | pbul:// | (TCP) 443 | pbul://accesstoken pbul://accesstoken/#channel pbul://accesstoken/A_DEVICE_ID pbul://accesstoken/email@address.com pbul://accesstoken/#channel/#channel2/email@address.net/DEVICE
193 | | [Pushjet](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_pushjet) | pjet:// or pjets:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | pjet://hostname/secret pjet://hostname:port/secret pjets://secret@hostname/secret pjets://hostname:port/secret
194 | | [Push (Techulus)](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_techulus) | push:// | (TCP) 443 | push://apikey/
195 | | [Pushed](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_pushed) | pushed:// | (TCP) 443 | pushed://appkey/appsecret/ pushed://appkey/appsecret/#ChannelAlias pushed://appkey/appsecret/#ChannelAlias1/#ChannelAlias2/#ChannelAliasN pushed://appkey/appsecret/@UserPushedID pushed://appkey/appsecret/@UserPushedID1/@UserPushedID2/@UserPushedIDN
196 | | [Pushover](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_pushover) | pover:// | (TCP) 443 | pover://user@token pover://user@token/DEVICE pover://user@token/DEVICE1/DEVICE2/DEVICEN **Note**: you must specify both your user_id and token
197 | | [PushSafer](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_pushsafer) | psafer:// or psafers:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | psafer://privatekey psafers://privatekey/DEVICE psafer://privatekey/DEVICE1/DEVICE2/DEVICEN
198 | | [Reddit](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_reddit) | reddit:// | (TCP) 443 | reddit://user:password@app_id/app_secret/subreddit reddit://user:password@app_id/app_secret/sub1/sub2/subN
199 | | [Rocket.Chat](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_rocketchat) | rocket:// or rockets:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | rocket://user:password@hostname/RoomID/Channel rockets://user:password@hostname:443/#Channel1/#Channel1/RoomID rocket://user:password@hostname/#Channel rocket://webhook@hostname rockets://webhook@hostname/@User/#Channel
200 | | [Ryver](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_ryver) | ryver:// | (TCP) 443 | ryver://Organization/Token ryver://botname@Organization/Token
201 | | [SendGrid](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_sendgrid) | sendgrid:// | (TCP) 443 | sendgrid://APIToken:FromEmail/ sendgrid://APIToken:FromEmail/ToEmail sendgrid://APIToken:FromEmail/ToEmail1/ToEmail2/ToEmailN/
202 | | [ServerChan](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_serverchan) | schan:// | (TCP) 443 | schan://sendkey/
203 | | [Signal API](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_signal) | signal:// or signals:// | (TCP) 80 or 443 | signal://hostname:port/FromPhoneNo signal://hostname:port/FromPhoneNo/ToPhoneNo signal://hostname:port/FromPhoneNo/ToPhoneNo1/ToPhoneNo2/ToPhoneNoN/
204 | | [SimplePush](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_simplepush) | spush:// | (TCP) 443 | spush://apikey spush://salt:password@apikey spush://apikey?event=Apprise
205 | | [Slack](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_slack) | slack:// | (TCP) 443 | slack://TokenA/TokenB/TokenC/ slack://TokenA/TokenB/TokenC/Channel slack://botname@TokenA/TokenB/TokenC/Channel slack://user@TokenA/TokenB/TokenC/Channel1/Channel2/ChannelN
206 | | [SMTP2Go](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_smtp2go) | smtp2go:// | (TCP) 443 | smtp2go://user@hostname/apikey smtp2go://user@hostname/apikey/email smtp2go://user@hostname/apikey/email1/email2/emailN smtp2go://user@hostname/apikey/?name="From%20User"
207 | | [Streamlabs](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_streamlabs) | strmlabs:// | (TCP) 443 | strmlabs://AccessToken/ strmlabs://AccessToken/?name=name&identifier=identifier&amount=0¤cy=USD
208 | | [SparkPost](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_sparkpost) | sparkpost:// | (TCP) 443 | sparkpost://user@hostname/apikey sparkpost://user@hostname/apikey/email sparkpost://user@hostname/apikey/email1/email2/emailN sparkpost://user@hostname/apikey/?name="From%20User"
209 | | [Spontit](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_spontit) | spontit:// | (TCP) 443 | spontit://UserID@APIKey/ spontit://UserID@APIKey/Channel spontit://UserID@APIKey/Channel1/Channel2/ChannelN
210 | | [Syslog](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_syslog) | syslog:// | (UDP) 514 (_if hostname specified_) | syslog:// syslog://Facility syslog://hostname syslog://hostname/Facility
211 | | [Telegram](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_telegram) | tgram:// | (TCP) 443 | tgram://bottoken/ChatID tgram://bottoken/ChatID1/ChatID2/ChatIDN
212 | | [Twitter](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_twitter) | twitter:// | (TCP) 443 | twitter://CKey/CSecret/AKey/ASecret twitter://user@CKey/CSecret/AKey/ASecret twitter://CKey/CSecret/AKey/ASecret/User1/User2/User2 twitter://CKey/CSecret/AKey/ASecret?mode=tweet
213 | | [Twist](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_twist) | twist:// | (TCP) 443 | twist://pasword:login twist://password:login/#channel twist://password:login/#team:channel twist://password:login/#team:channel1/channel2/#team3:channel
214 | | [XBMC](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_xbmc) | xbmc:// or xbmcs:// | (TCP) 8080 or 443 | xbmc://hostname xbmc://user@hostname xbmc://user:password@hostname:port
215 | | [Webex Teams (Cisco)](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_wxteams) | wxteams:// | (TCP) 443 | wxteams://Token
216 | | [Zulip Chat](https://github.com/caronc/apprise/wiki/Notify_zulip) | zulip:// | (TCP) 443 | zulip://botname@Organization/Token zulip://botname@Organization/Token/Stream zulip://botname@Organization/Token/Email
217 |
218 |
219 | ### Mail
220 | This is what worked for me
221 | * NOTIFY_URL: "mailtos://mail.server.com/?user=testuser@domain.com&pass=xxxx"
222 |
223 | # TODO List
224 | | TODO | Tested | Result | Implemented |
225 | | --- | :---: | :---: | :---: |
226 | | ARM64 and AMD64 Support | 2023-02-23 | :heavy_check_mark: | 2023-02-23 |
227 | | Slim version without webgui (Only notifications) | 2023-02-24 | :heavy_check_mark: | 2023-02-26 |
228 |
229 |
230 | # Future ideas
231 | | Feature | Timeline | Stage |
232 | | --- | :---: | :---: |
233 | | Update via webgui | Unknown (Need Help) | |
234 | | Multiple hosts one gui | 2023-03-* | Alpha |
235 |
236 | * Update via webui
237 | - Need help with how to make docker.sock recreate docker-compose without the need for docker-compose.yml
238 | - Docker remote API good or bad?
239 |
240 | # Bugs and fixes
241 |
242 | | Description | Date | Status |
243 | | --- | --- | :---: |
244 | | `Cronjob not working properly` | 2023-01-28 | :heavy_check_mark: |
245 | | `Script not running correctly` | 2023-01-29 | :heavy_check_mark: |
246 | | `Hanging processes` | 2023-01-29 | :heavy_check_mark: |
247 | | `Not displaying in ascending order` | 2023-01-29 | :heavy_check_mark: |
248 | | `Blank/error text on index while script is running` | 2023-01-29 | :heavy_check_mark: |
249 | | `Redirect error while checking for update` | 2023-01-31 | :heavy_check_mark: |
250 |
251 |
252 | -------
253 |
254 |
255 | * Contributors
256 | - [Mag37](https://github.com/Mag37) 👑
257 | - [t0rnis](https://github.com/t0rnis) 🪖🐛
258 | - [aSilentSniper](https://github.com/aSilentSniper)
259 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/app/postgresql.conf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # -----------------------------
2 | # PostgreSQL configuration file
3 | # -----------------------------
4 | #
5 | # This file consists of lines of the form:
6 | #
7 | # name = value
8 | #
9 | # (The "=" is optional.) Whitespace may be used. Comments are introduced with
10 | # "#" anywhere on a line. The complete list of parameter names and allowed
11 | # values can be found in the PostgreSQL documentation.
12 | #
13 | # The commented-out settings shown in this file represent the default values.
14 | # Re-commenting a setting is NOT sufficient to revert it to the default value;
15 | # you need to reload the server.
16 | #
17 | # This file is read on server startup and when the server receives a SIGHUP
18 | # signal. If you edit the file on a running system, you have to SIGHUP the
19 | # server for the changes to take effect, run "pg_ctl reload", or execute
20 | # "SELECT pg_reload_conf()". Some parameters, which are marked below,
21 | # require a server shutdown and restart to take effect.
22 | #
23 | # Any parameter can also be given as a command-line option to the server, e.g.,
24 | # "postgres -c log_connections=on". Some parameters can be changed at run time
25 | # with the "SET" SQL command.
26 | #
27 | # Memory units: B = bytes Time units: us = microseconds
28 | # kB = kilobytes ms = milliseconds
29 | # MB = megabytes s = seconds
30 | # GB = gigabytes min = minutes
31 | # TB = terabytes h = hours
32 | # d = days
33 |
34 |
35 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
36 | # FILE LOCATIONS
37 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
38 |
39 | # The default values of these variables are driven from the -D command-line
40 | # option or PGDATA environment variable, represented here as ConfigDir.
41 |
42 | #data_directory = 'ConfigDir' # use data in another directory
43 | # (change requires restart)
44 | #hba_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_hba.conf' # host-based authentication file
45 | # (change requires restart)
46 | #ident_file = 'ConfigDir/pg_ident.conf' # ident configuration file
47 | # (change requires restart)
48 |
49 | # If external_pid_file is not explicitly set, no extra PID file is written.
50 | #external_pid_file = '' # write an extra PID file
51 | # (change requires restart)
52 |
53 |
54 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
55 | # CONNECTIONS AND AUTHENTICATION
56 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
57 |
58 | # - Connection Settings -
59 |
60 | #listen_addresses = 'localhost' # what IP address(es) to listen on;
61 | # comma-separated list of addresses;
62 | # defaults to 'localhost'; use '*' for all
63 | # (change requires restart)
64 | #port = 5432 # (change requires restart)
65 | max_connections = 100 # (change requires restart)
66 | #superuser_reserved_connections = 3 # (change requires restart)
67 | unix_socket_directories = '/run/postgresql' # comma-separated list of directories
68 | # (change requires restart)
69 | #unix_socket_group = '' # (change requires restart)
70 | #unix_socket_permissions = 0777 # begin with 0 to use octal notation
71 | # (change requires restart)
72 | #bonjour = off # advertise server via Bonjour
73 | # (change requires restart)
74 | #bonjour_name = '' # defaults to the computer name
75 | # (change requires restart)
76 |
77 | # - TCP settings -
78 | # see "man tcp" for details
79 |
80 | #tcp_keepalives_idle = 0 # TCP_KEEPIDLE, in seconds;
81 | # 0 selects the system default
82 | #tcp_keepalives_interval = 0 # TCP_KEEPINTVL, in seconds;
83 | # 0 selects the system default
84 | #tcp_keepalives_count = 0 # TCP_KEEPCNT;
85 | # 0 selects the system default
86 | #tcp_user_timeout = 0 # TCP_USER_TIMEOUT, in milliseconds;
87 | # 0 selects the system default
88 |
89 | #client_connection_check_interval = 0 # time between checks for client
90 | # disconnection while running queries;
91 | # 0 for never
92 |
93 | # - Authentication -
94 |
95 | #authentication_timeout = 1min # 1s-600s
96 | #password_encryption = scram-sha-256 # scram-sha-256 or md5
97 | #db_user_namespace = off
98 |
99 | # GSSAPI using Kerberos
100 | #krb_server_keyfile = 'FILE:${sysconfdir}/krb5.keytab'
101 | #krb_caseins_users = off
102 |
103 | # - SSL -
104 |
105 | #ssl = off
106 | #ssl_ca_file = ''
107 | #ssl_cert_file = 'server.crt'
108 | #ssl_crl_file = ''
109 | #ssl_crl_dir = ''
110 | #ssl_key_file = 'server.key'
111 | #ssl_ciphers = 'HIGH:MEDIUM:+3DES:!aNULL' # allowed SSL ciphers
112 | #ssl_prefer_server_ciphers = on
113 | #ssl_ecdh_curve = 'prime256v1'
114 | #ssl_min_protocol_version = 'TLSv1.2'
115 | #ssl_max_protocol_version = ''
116 | #ssl_dh_params_file = ''
117 | #ssl_passphrase_command = ''
118 | #ssl_passphrase_command_supports_reload = off
119 |
120 |
121 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
122 | # RESOURCE USAGE (except WAL)
123 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
124 |
125 | # - Memory -
126 |
127 | shared_buffers = 128MB # min 128kB
128 | # (change requires restart)
129 | #huge_pages = try # on, off, or try
130 | # (change requires restart)
131 | #huge_page_size = 0 # zero for system default
132 | # (change requires restart)
133 | #temp_buffers = 8MB # min 800kB
134 | #max_prepared_transactions = 0 # zero disables the feature
135 | # (change requires restart)
136 | # Caution: it is not advisable to set max_prepared_transactions nonzero unless
137 | # you actively intend to use prepared transactions.
138 | #work_mem = 4MB # min 64kB
139 | #hash_mem_multiplier = 1.0 # 1-1000.0 multiplier on hash table work_mem
140 | #maintenance_work_mem = 64MB # min 1MB
141 | #autovacuum_work_mem = -1 # min 1MB, or -1 to use maintenance_work_mem
142 | #logical_decoding_work_mem = 64MB # min 64kB
143 | #max_stack_depth = 2MB # min 100kB
144 | #shared_memory_type = mmap # the default is the first option
145 | # supported by the operating system:
146 | # mmap
147 | # sysv
148 | # windows
149 | # (change requires restart)
150 | dynamic_shared_memory_type = posix # the default is the first option
151 | # supported by the operating system:
152 | # posix
153 | # sysv
154 | # windows
155 | # mmap
156 | # (change requires restart)
157 | #min_dynamic_shared_memory = 0MB # (change requires restart)
158 |
159 | # - Disk -
160 |
161 | #temp_file_limit = -1 # limits per-process temp file space
162 | # in kilobytes, or -1 for no limit
163 |
164 | # - Kernel Resources -
165 |
166 | #max_files_per_process = 1000 # min 64
167 | # (change requires restart)
168 |
169 | # - Cost-Based Vacuum Delay -
170 |
171 | #vacuum_cost_delay = 0 # 0-100 milliseconds (0 disables)
172 | #vacuum_cost_page_hit = 1 # 0-10000 credits
173 | #vacuum_cost_page_miss = 2 # 0-10000 credits
174 | #vacuum_cost_page_dirty = 20 # 0-10000 credits
175 | #vacuum_cost_limit = 200 # 1-10000 credits
176 |
177 | # - Background Writer -
178 |
179 | #bgwriter_delay = 200ms # 10-10000ms between rounds
180 | #bgwriter_lru_maxpages = 100 # max buffers written/round, 0 disables
181 | #bgwriter_lru_multiplier = 2.0 # 0-10.0 multiplier on buffers scanned/round
182 | #bgwriter_flush_after = 512kB # measured in pages, 0 disables
183 |
184 | # - Asynchronous Behavior -
185 |
186 | #backend_flush_after = 0 # measured in pages, 0 disables
187 | #effective_io_concurrency = 1 # 1-1000; 0 disables prefetching
188 | #maintenance_io_concurrency = 10 # 1-1000; 0 disables prefetching
189 | #max_worker_processes = 8 # (change requires restart)
190 | #max_parallel_workers_per_gather = 2 # taken from max_parallel_workers
191 | #max_parallel_maintenance_workers = 2 # taken from max_parallel_workers
192 | #max_parallel_workers = 8 # maximum number of max_worker_processes that
193 | # can be used in parallel operations
194 | #parallel_leader_participation = on
195 | #old_snapshot_threshold = -1 # 1min-60d; -1 disables; 0 is immediate
196 | # (change requires restart)
197 |
198 |
199 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
200 | # WRITE-AHEAD LOG
201 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
202 |
203 | # - Settings -
204 |
205 | #wal_level = replica # minimal, replica, or logical
206 | # (change requires restart)
207 | #fsync = on # flush data to disk for crash safety
208 | # (turning this off can cause
209 | # unrecoverable data corruption)
210 | #synchronous_commit = on # synchronization level;
211 | # off, local, remote_write, remote_apply, or on
212 | #wal_sync_method = fsync # the default is the first option
213 | # supported by the operating system:
214 | # open_datasync
215 | # fdatasync (default on Linux and FreeBSD)
216 | # fsync
217 | # fsync_writethrough
218 | # open_sync
219 | #full_page_writes = on # recover from partial page writes
220 | #wal_log_hints = off # also do full page writes of non-critical updates
221 | # (change requires restart)
222 | #wal_compression = off # enable compression of full-page writes
223 | #wal_init_zero = on # zero-fill new WAL files
224 | #wal_recycle = on # recycle WAL files
225 | #wal_buffers = -1 # min 32kB, -1 sets based on shared_buffers
226 | # (change requires restart)
227 | #wal_writer_delay = 200ms # 1-10000 milliseconds
228 | #wal_writer_flush_after = 1MB # measured in pages, 0 disables
229 | #wal_skip_threshold = 2MB
230 |
231 | #commit_delay = 0 # range 0-100000, in microseconds
232 | #commit_siblings = 5 # range 1-1000
233 |
234 | # - Checkpoints -
235 |
236 | #checkpoint_timeout = 5min # range 30s-1d
237 | #checkpoint_completion_target = 0.9 # checkpoint target duration, 0.0 - 1.0
238 | #checkpoint_flush_after = 256kB # measured in pages, 0 disables
239 | #checkpoint_warning = 30s # 0 disables
240 | max_wal_size = 1GB
241 | min_wal_size = 80MB
242 |
243 | # - Archiving -
244 |
245 | #archive_mode = off # enables archiving; off, on, or always
246 | # (change requires restart)
247 | #archive_command = '' # command to use to archive a logfile segment
248 | # placeholders: %p = path of file to archive
249 | # %f = file name only
250 | # e.g. 'test ! -f /mnt/server/archivedir/%f && cp %p /mnt/server/archivedir/%f'
251 | #archive_timeout = 0 # force a logfile segment switch after this
252 | # number of seconds; 0 disables
253 |
254 | # - Archive Recovery -
255 |
256 | # These are only used in recovery mode.
257 |
258 | #restore_command = '' # command to use to restore an archived logfile segment
259 | # placeholders: %p = path of file to restore
260 | # %f = file name only
261 | # e.g. 'cp /mnt/server/archivedir/%f %p'
262 | #archive_cleanup_command = '' # command to execute at every restartpoint
263 | #recovery_end_command = '' # command to execute at completion of recovery
264 |
265 | # - Recovery Target -
266 |
267 | # Set these only when performing a targeted recovery.
268 |
269 | #recovery_target = '' # 'immediate' to end recovery as soon as a
270 | # consistent state is reached
271 | # (change requires restart)
272 | #recovery_target_name = '' # the named restore point to which recovery will proceed
273 | # (change requires restart)
274 | #recovery_target_time = '' # the time stamp up to which recovery will proceed
275 | # (change requires restart)
276 | #recovery_target_xid = '' # the transaction ID up to which recovery will proceed
277 | # (change requires restart)
278 | #recovery_target_lsn = '' # the WAL LSN up to which recovery will proceed
279 | # (change requires restart)
280 | #recovery_target_inclusive = on # Specifies whether to stop:
281 | # just after the specified recovery target (on)
282 | # just before the recovery target (off)
283 | # (change requires restart)
284 | #recovery_target_timeline = 'latest' # 'current', 'latest', or timeline ID
285 | # (change requires restart)
286 | #recovery_target_action = 'pause' # 'pause', 'promote', 'shutdown'
287 | # (change requires restart)
288 |
289 |
290 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
291 | # REPLICATION
292 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
293 |
294 | # - Sending Servers -
295 |
296 | # Set these on the primary and on any standby that will send replication data.
297 |
298 | #max_wal_senders = 10 # max number of walsender processes
299 | # (change requires restart)
300 | #max_replication_slots = 10 # max number of replication slots
301 | # (change requires restart)
302 | #wal_keep_size = 0 # in megabytes; 0 disables
303 | #max_slot_wal_keep_size = -1 # in megabytes; -1 disables
304 | #wal_sender_timeout = 60s # in milliseconds; 0 disables
305 | #track_commit_timestamp = off # collect timestamp of transaction commit
306 | # (change requires restart)
307 |
308 | # - Primary Server -
309 |
310 | # These settings are ignored on a standby server.
311 |
312 | #synchronous_standby_names = '' # standby servers that provide sync rep
313 | # method to choose sync standbys, number of sync standbys,
314 | # and comma-separated list of application_name
315 | # from standby(s); '*' = all
316 | #vacuum_defer_cleanup_age = 0 # number of xacts by which cleanup is delayed
317 |
318 | # - Standby Servers -
319 |
320 | # These settings are ignored on a primary server.
321 |
322 | #primary_conninfo = '' # connection string to sending server
323 | #primary_slot_name = '' # replication slot on sending server
324 | #promote_trigger_file = '' # file name whose presence ends recovery
325 | #hot_standby = on # "off" disallows queries during recovery
326 | # (change requires restart)
327 | #max_standby_archive_delay = 30s # max delay before canceling queries
328 | # when reading WAL from archive;
329 | # -1 allows indefinite delay
330 | #max_standby_streaming_delay = 30s # max delay before canceling queries
331 | # when reading streaming WAL;
332 | # -1 allows indefinite delay
333 | #wal_receiver_create_temp_slot = off # create temp slot if primary_slot_name
334 | # is not set
335 | #wal_receiver_status_interval = 10s # send replies at least this often
336 | # 0 disables
337 | #hot_standby_feedback = off # send info from standby to prevent
338 | # query conflicts
339 | #wal_receiver_timeout = 60s # time that receiver waits for
340 | # communication from primary
341 | # in milliseconds; 0 disables
342 | #wal_retrieve_retry_interval = 5s # time to wait before retrying to
343 | # retrieve WAL after a failed attempt
344 | #recovery_min_apply_delay = 0 # minimum delay for applying changes during recovery
345 |
346 | # - Subscribers -
347 |
348 | # These settings are ignored on a publisher.
349 |
350 | #max_logical_replication_workers = 4 # taken from max_worker_processes
351 | # (change requires restart)
352 | #max_sync_workers_per_subscription = 2 # taken from max_logical_replication_workers
353 |
354 |
355 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
356 | # QUERY TUNING
357 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
358 |
359 | # - Planner Method Configuration -
360 |
361 | #enable_async_append = on
362 | #enable_bitmapscan = on
363 | #enable_gathermerge = on
364 | #enable_hashagg = on
365 | #enable_hashjoin = on
366 | #enable_incremental_sort = on
367 | #enable_indexscan = on
368 | #enable_indexonlyscan = on
369 | #enable_material = on
370 | #enable_memoize = on
371 | #enable_mergejoin = on
372 | #enable_nestloop = on
373 | #enable_parallel_append = on
374 | #enable_parallel_hash = on
375 | #enable_partition_pruning = on
376 | #enable_partitionwise_join = off
377 | #enable_partitionwise_aggregate = off
378 | #enable_seqscan = on
379 | #enable_sort = on
380 | #enable_tidscan = on
381 |
382 | # - Planner Cost Constants -
383 |
384 | #seq_page_cost = 1.0 # measured on an arbitrary scale
385 | #random_page_cost = 4.0 # same scale as above
386 | #cpu_tuple_cost = 0.01 # same scale as above
387 | #cpu_index_tuple_cost = 0.005 # same scale as above
388 | #cpu_operator_cost = 0.0025 # same scale as above
389 | #parallel_setup_cost = 1000.0 # same scale as above
390 | #parallel_tuple_cost = 0.1 # same scale as above
391 | #min_parallel_table_scan_size = 8MB
392 | #min_parallel_index_scan_size = 512kB
393 | #effective_cache_size = 4GB
394 |
395 | #jit_above_cost = 100000 # perform JIT compilation if available
396 | # and query more expensive than this;
397 | # -1 disables
398 | #jit_inline_above_cost = 500000 # inline small functions if query is
399 | # more expensive than this; -1 disables
400 | #jit_optimize_above_cost = 500000 # use expensive JIT optimizations if
401 | # query is more expensive than this;
402 | # -1 disables
403 |
404 | # - Genetic Query Optimizer -
405 |
406 | #geqo = on
407 | #geqo_threshold = 12
408 | #geqo_effort = 5 # range 1-10
409 | #geqo_pool_size = 0 # selects default based on effort
410 | #geqo_generations = 0 # selects default based on effort
411 | #geqo_selection_bias = 2.0 # range 1.5-2.0
412 | #geqo_seed = 0.0 # range 0.0-1.0
413 |
414 | # - Other Planner Options -
415 |
416 | #default_statistics_target = 100 # range 1-10000
417 | #constraint_exclusion = partition # on, off, or partition
418 | #cursor_tuple_fraction = 0.1 # range 0.0-1.0
419 | #from_collapse_limit = 8
420 | #jit = on # allow JIT compilation
421 | #join_collapse_limit = 8 # 1 disables collapsing of explicit
422 | # JOIN clauses
423 | #plan_cache_mode = auto # auto, force_generic_plan or
424 | # force_custom_plan
425 |
426 |
427 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
428 | # REPORTING AND LOGGING
429 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
430 |
431 | # - Where to Log -
432 |
433 | #log_destination = 'stderr' # Valid values are combinations of
434 | # stderr, csvlog, syslog, and eventlog,
435 | # depending on platform. csvlog
436 | # requires logging_collector to be on.
437 |
438 | # This is used when logging to stderr:
439 | #logging_collector = off # Enable capturing of stderr and csvlog
440 | # into log files. Required to be on for
441 | # csvlogs.
442 | # (change requires restart)
443 |
444 | # These are only used if logging_collector is on:
445 | #log_directory = 'log' # directory where log files are written,
446 | # can be absolute or relative to PGDATA
447 | #log_filename = 'postgresql-%Y-%m-%d_%H%M%S.log' # log file name pattern,
448 | # can include strftime() escapes
449 | #log_file_mode = 0600 # creation mode for log files,
450 | # begin with 0 to use octal notation
451 | #log_rotation_age = 1d # Automatic rotation of logfiles will
452 | # happen after that time. 0 disables.
453 | #log_rotation_size = 10MB # Automatic rotation of logfiles will
454 | # happen after that much log output.
455 | # 0 disables.
456 | #log_truncate_on_rotation = off # If on, an existing log file with the
457 | # same name as the new log file will be
458 | # truncated rather than appended to.
459 | # But such truncation only occurs on
460 | # time-driven rotation, not on restarts
461 | # or size-driven rotation. Default is
462 | # off, meaning append to existing files
463 | # in all cases.
464 |
465 | # These are relevant when logging to syslog:
466 | #syslog_facility = 'LOCAL0'
467 | #syslog_ident = 'postgres'
468 | #syslog_sequence_numbers = on
469 | #syslog_split_messages = on
470 |
471 | # This is only relevant when logging to eventlog (Windows):
472 | # (change requires restart)
473 | #event_source = 'PostgreSQL'
474 |
475 | # - When to Log -
476 |
477 | #log_min_messages = warning # values in order of decreasing detail:
478 | # debug5
479 | # debug4
480 | # debug3
481 | # debug2
482 | # debug1
483 | # info
484 | # notice
485 | # warning
486 | # error
487 | # log
488 | # fatal
489 | # panic
490 |
491 | #log_min_error_statement = error # values in order of decreasing detail:
492 | # debug5
493 | # debug4
494 | # debug3
495 | # debug2
496 | # debug1
497 | # info
498 | # notice
499 | # warning
500 | # error
501 | # log
502 | # fatal
503 | # panic (effectively off)
504 |
505 | #log_min_duration_statement = -1 # -1 is disabled, 0 logs all statements
506 | # and their durations, > 0 logs only
507 | # statements running at least this number
508 | # of milliseconds
509 |
510 | #log_min_duration_sample = -1 # -1 is disabled, 0 logs a sample of statements
511 | # and their durations, > 0 logs only a sample of
512 | # statements running at least this number
513 | # of milliseconds;
514 | # sample fraction is determined by log_statement_sample_rate
515 |
516 | #log_statement_sample_rate = 1.0 # fraction of logged statements exceeding
517 | # log_min_duration_sample to be logged;
518 | # 1.0 logs all such statements, 0.0 never logs
519 |
520 |
521 | #log_transaction_sample_rate = 0.0 # fraction of transactions whose statements
522 | # are logged regardless of their duration; 1.0 logs all
523 | # statements from all transactions, 0.0 never logs
524 |
525 | # - What to Log -
526 |
527 | #debug_print_parse = off
528 | #debug_print_rewritten = off
529 | #debug_print_plan = off
530 | #debug_pretty_print = on
531 | #log_autovacuum_min_duration = -1 # log autovacuum activity;
532 | # -1 disables, 0 logs all actions and
533 | # their durations, > 0 logs only
534 | # actions running at least this number
535 | # of milliseconds.
536 | #log_checkpoints = off
537 | #log_connections = off
538 | #log_disconnections = off
539 | #log_duration = off
540 | #log_error_verbosity = default # terse, default, or verbose messages
541 | #log_hostname = off
542 | #log_line_prefix = '%m [%p] ' # special values:
543 | # %a = application name
544 | # %u = user name
545 | # %d = database name
546 | # %r = remote host and port
547 | # %h = remote host
548 | # %b = backend type
549 | # %p = process ID
550 | # %P = process ID of parallel group leader
551 | # %t = timestamp without milliseconds
552 | # %m = timestamp with milliseconds
553 | # %n = timestamp with milliseconds (as a Unix epoch)
554 | # %Q = query ID (0 if none or not computed)
555 | # %i = command tag
556 | # %e = SQL state
557 | # %c = session ID
558 | # %l = session line number
559 | # %s = session start timestamp
560 | # %v = virtual transaction ID
561 | # %x = transaction ID (0 if none)
562 | # %q = stop here in non-session
563 | # processes
564 | # %% = '%'
565 | # e.g. '<%u%%%d> '
566 | #log_lock_waits = off # log lock waits >= deadlock_timeout
567 | #log_recovery_conflict_waits = off # log standby recovery conflict waits
568 | # >= deadlock_timeout
569 | #log_parameter_max_length = -1 # when logging statements, limit logged
570 | # bind-parameter values to N bytes;
571 | # -1 means print in full, 0 disables
572 | #log_parameter_max_length_on_error = 0 # when logging an error, limit logged
573 | # bind-parameter values to N bytes;
574 | # -1 means print in full, 0 disables
575 | #log_statement = 'none' # none, ddl, mod, all
576 | #log_replication_commands = off
577 | #log_temp_files = -1 # log temporary files equal or larger
578 | # than the specified size in kilobytes;
579 | # -1 disables, 0 logs all temp files
580 | log_timezone = 'UTC'
581 |
582 |
583 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
584 | # PROCESS TITLE
585 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
586 |
587 | #cluster_name = '' # added to process titles if nonempty
588 | # (change requires restart)
589 | #update_process_title = on
590 |
591 |
592 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
593 | # STATISTICS
594 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
595 |
596 | # - Query and Index Statistics Collector -
597 |
598 | #track_activities = on
599 | #track_activity_query_size = 1024 # (change requires restart)
600 | #track_counts = on
601 | #track_io_timing = off
602 | #track_wal_io_timing = off
603 | #track_functions = none # none, pl, all
604 | #stats_temp_directory = 'pg_stat_tmp'
605 |
606 |
607 | # - Monitoring -
608 |
609 | #compute_query_id = auto
610 | #log_statement_stats = off
611 | #log_parser_stats = off
612 | #log_planner_stats = off
613 | #log_executor_stats = off
614 |
615 |
616 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
617 | # AUTOVACUUM
618 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
619 |
620 | #autovacuum = on # Enable autovacuum subprocess? 'on'
621 | # requires track_counts to also be on.
622 | #autovacuum_max_workers = 3 # max number of autovacuum subprocesses
623 | # (change requires restart)
624 | #autovacuum_naptime = 1min # time between autovacuum runs
625 | #autovacuum_vacuum_threshold = 50 # min number of row updates before
626 | # vacuum
627 | #autovacuum_vacuum_insert_threshold = 1000 # min number of row inserts
628 | # before vacuum; -1 disables insert
629 | # vacuums
630 | #autovacuum_analyze_threshold = 50 # min number of row updates before
631 | # analyze
632 | #autovacuum_vacuum_scale_factor = 0.2 # fraction of table size before vacuum
633 | #autovacuum_vacuum_insert_scale_factor = 0.2 # fraction of inserts over table
634 | # size before insert vacuum
635 | #autovacuum_analyze_scale_factor = 0.1 # fraction of table size before analyze
636 | #autovacuum_freeze_max_age = 200000000 # maximum XID age before forced vacuum
637 | # (change requires restart)
638 | #autovacuum_multixact_freeze_max_age = 400000000 # maximum multixact age
639 | # before forced vacuum
640 | # (change requires restart)
641 | #autovacuum_vacuum_cost_delay = 2ms # default vacuum cost delay for
642 | # autovacuum, in milliseconds;
643 | # -1 means use vacuum_cost_delay
644 | #autovacuum_vacuum_cost_limit = -1 # default vacuum cost limit for
645 | # autovacuum, -1 means use
646 | # vacuum_cost_limit
647 |
648 |
649 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
650 | # CLIENT CONNECTION DEFAULTS
651 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
652 |
653 | # - Statement Behavior -
654 |
655 | #client_min_messages = notice # values in order of decreasing detail:
656 | # debug5
657 | # debug4
658 | # debug3
659 | # debug2
660 | # debug1
661 | # log
662 | # notice
663 | # warning
664 | # error
665 | #search_path = '"$user", public' # schema names
666 | #row_security = on
667 | #default_table_access_method = 'heap'
668 | #default_tablespace = '' # a tablespace name, '' uses the default
669 | #default_toast_compression = 'pglz' # 'pglz' or 'lz4'
670 | #temp_tablespaces = '' # a list of tablespace names, '' uses
671 | # only default tablespace
672 | #check_function_bodies = on
673 | #default_transaction_isolation = 'read committed'
674 | #default_transaction_read_only = off
675 | #default_transaction_deferrable = off
676 | #session_replication_role = 'origin'
677 | #statement_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled
678 | #lock_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled
679 | #idle_in_transaction_session_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled
680 | #idle_session_timeout = 0 # in milliseconds, 0 is disabled
681 | #vacuum_freeze_table_age = 150000000
682 | #vacuum_freeze_min_age = 50000000
683 | #vacuum_failsafe_age = 1600000000
684 | #vacuum_multixact_freeze_table_age = 150000000
685 | #vacuum_multixact_freeze_min_age = 5000000
686 | #vacuum_multixact_failsafe_age = 1600000000
687 | #bytea_output = 'hex' # hex, escape
688 | #xmlbinary = 'base64'
689 | #xmloption = 'content'
690 | #gin_pending_list_limit = 4MB
691 |
692 | # - Locale and Formatting -
693 |
694 | datestyle = 'iso, mdy'
695 | #intervalstyle = 'postgres'
696 | timezone = 'UTC'
697 | #timezone_abbreviations = 'Default' # Select the set of available time zone
698 | # abbreviations. Currently, there are
699 | # Default
700 | # Australia (historical usage)
701 | # India
702 | # You can create your own file in
703 | # share/timezonesets/.
704 | #extra_float_digits = 1 # min -15, max 3; any value >0 actually
705 | # selects precise output mode
706 | #client_encoding = sql_ascii # actually, defaults to database
707 | # encoding
708 |
709 | # These settings are initialized by initdb, but they can be changed.
710 | lc_messages = 'C' # locale for system error message
711 | # strings
712 | lc_monetary = 'C' # locale for monetary formatting
713 | lc_numeric = 'C' # locale for number formatting
714 | lc_time = 'C' # locale for time formatting
715 |
716 | # default configuration for text search
717 | default_text_search_config = 'pg_catalog.english'
718 |
719 | # - Shared Library Preloading -
720 |
721 | #local_preload_libraries = ''
722 | #session_preload_libraries = ''
723 | #shared_preload_libraries = '' # (change requires restart)
724 | #jit_provider = 'llvmjit' # JIT library to use
725 |
726 | # - Other Defaults -
727 |
728 | #dynamic_library_path = '$libdir'
729 | #gin_fuzzy_search_limit = 0
730 |
731 |
732 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
733 | # LOCK MANAGEMENT
734 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
735 |
736 | #deadlock_timeout = 1s
737 | #max_locks_per_transaction = 64 # min 10
738 | # (change requires restart)
739 | #max_pred_locks_per_transaction = 64 # min 10
740 | # (change requires restart)
741 | #max_pred_locks_per_relation = -2 # negative values mean
742 | # (max_pred_locks_per_transaction
743 | # / -max_pred_locks_per_relation) - 1
744 | #max_pred_locks_per_page = 2 # min 0
745 |
746 |
747 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
748 | # VERSION AND PLATFORM COMPATIBILITY
749 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
750 |
751 | # - Previous PostgreSQL Versions -
752 |
753 | #array_nulls = on
754 | #backslash_quote = safe_encoding # on, off, or safe_encoding
755 | #escape_string_warning = on
756 | #lo_compat_privileges = off
757 | #quote_all_identifiers = off
758 | #standard_conforming_strings = on
759 | #synchronize_seqscans = on
760 |
761 | # - Other Platforms and Clients -
762 |
763 | #transform_null_equals = off
764 |
765 |
766 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
767 | # ERROR HANDLING
768 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
769 |
770 | #exit_on_error = off # terminate session on any error?
771 | #restart_after_crash = on # reinitialize after backend crash?
772 | #data_sync_retry = off # retry or panic on failure to fsync
773 | # data?
774 | # (change requires restart)
775 | #recovery_init_sync_method = fsync # fsync, syncfs (Linux 5.8+)
776 |
777 |
778 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
779 | # CONFIG FILE INCLUDES
780 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
781 |
782 | # These options allow settings to be loaded from files other than the
783 | # default postgresql.conf. Note that these are directives, not variable
784 | # assignments, so they can usefully be given more than once.
785 |
786 | #include_dir = '...' # include files ending in '.conf' from
787 | # a directory, e.g., 'conf.d'
788 | #include_if_exists = '...' # include file only if it exists
789 | #include = '...' # include file
790 |
791 |
792 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
793 | # CUSTOMIZED OPTIONS
794 | #------------------------------------------------------------------------------
795 |
796 | # Add settings for extensions here
797 | listen_addresses='*'
798 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | GNU GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
2 | Version 3, 29 June 2007
3 |
4 | Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
5 | Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
6 | of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
7 |
8 | Preamble
9 |
10 | The GNU General Public License is a free, copyleft license for
11 | software and other kinds of works.
12 |
13 | The licenses for most software and other practical works are designed
14 | to take away your freedom to share and change the works. By contrast,
15 | the GNU General Public License is intended to guarantee your freedom to
16 | share and change all versions of a program--to make sure it remains free
17 | software for all its users. We, the Free Software Foundation, use the
18 | GNU General Public License for most of our software; it applies also to
19 | any other work released this way by its authors. You can apply it to
20 | your programs, too.
21 |
22 | When we speak of free software, we are referring to freedom, not
23 | price. Our General Public Licenses are designed to make sure that you
24 | have the freedom to distribute copies of free software (and charge for
25 | them if you wish), that you receive source code or can get it if you
26 | want it, that you can change the software or use pieces of it in new
27 | free programs, and that you know you can do these things.
28 |
29 | To protect your rights, we need to prevent others from denying you
30 | these rights or asking you to surrender the rights. Therefore, you have
31 | certain responsibilities if you distribute copies of the software, or if
32 | you modify it: responsibilities to respect the freedom of others.
33 |
34 | For example, if you distribute copies of such a program, whether
35 | gratis or for a fee, you must pass on to the recipients the same
36 | freedoms that you received. You must make sure that they, too, receive
37 | or can get the source code. And you must show them these terms so they
38 | know their rights.
39 |
40 | Developers that use the GNU GPL protect your rights with two steps:
41 | (1) assert copyright on the software, and (2) offer you this License
42 | giving you legal permission to copy, distribute and/or modify it.
43 |
44 | For the developers' and authors' protection, the GPL clearly explains
45 | that there is no warranty for this free software. For both users' and
46 | authors' sake, the GPL requires that modified versions be marked as
47 | changed, so that their problems will not be attributed erroneously to
48 | authors of previous versions.
49 |
50 | Some devices are designed to deny users access to install or run
51 | modified versions of the software inside them, although the manufacturer
52 | can do so. This is fundamentally incompatible with the aim of
53 | protecting users' freedom to change the software. The systematic
54 | pattern of such abuse occurs in the area of products for individuals to
55 | use, which is precisely where it is most unacceptable. Therefore, we
56 | have designed this version of the GPL to prohibit the practice for those
57 | products. If such problems arise substantially in other domains, we
58 | stand ready to extend this provision to those domains in future versions
59 | of the GPL, as needed to protect the freedom of users.
60 |
61 | Finally, every program is threatened constantly by software patents.
62 | States should not allow patents to restrict development and use of
63 | software on general-purpose computers, but in those that do, we wish to
64 | avoid the special danger that patents applied to a free program could
65 | make it effectively proprietary. To prevent this, the GPL assures that
66 | patents cannot be used to render the program non-free.
67 |
68 | The precise terms and conditions for copying, distribution and
69 | modification follow.
70 |
71 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS
72 |
73 | 0. Definitions.
74 |
75 | "This License" refers to version 3 of the GNU General Public License.
76 |
77 | "Copyright" also means copyright-like laws that apply to other kinds of
78 | works, such as semiconductor masks.
79 |
80 | "The Program" refers to any copyrightable work licensed under this
81 | License. Each licensee is addressed as "you". "Licensees" and
82 | "recipients" may be individuals or organizations.
83 |
84 | To "modify" a work means to copy from or adapt all or part of the work
85 | in a fashion requiring copyright permission, other than the making of an
86 | exact copy. The resulting work is called a "modified version" of the
87 | earlier work or a work "based on" the earlier work.
88 |
89 | A "covered work" means either the unmodified Program or a work based
90 | on the Program.
91 |
92 | To "propagate" a work means to do anything with it that, without
93 | permission, would make you directly or secondarily liable for
94 | infringement under applicable copyright law, except executing it on a
95 | computer or modifying a private copy. Propagation includes copying,
96 | distribution (with or without modification), making available to the
97 | public, and in some countries other activities as well.
98 |
99 | To "convey" a work means any kind of propagation that enables other
100 | parties to make or receive copies. Mere interaction with a user through
101 | a computer network, with no transfer of a copy, is not conveying.
102 |
103 | An interactive user interface displays "Appropriate Legal Notices"
104 | to the extent that it includes a convenient and prominently visible
105 | feature that (1) displays an appropriate copyright notice, and (2)
106 | tells the user that there is no warranty for the work (except to the
107 | extent that warranties are provided), that licensees may convey the
108 | work under this License, and how to view a copy of this License. If
109 | the interface presents a list of user commands or options, such as a
110 | menu, a prominent item in the list meets this criterion.
111 |
112 | 1. Source Code.
113 |
114 | The "source code" for a work means the preferred form of the work
115 | for making modifications to it. "Object code" means any non-source
116 | form of a work.
117 |
118 | A "Standard Interface" means an interface that either is an official
119 | standard defined by a recognized standards body, or, in the case of
120 | interfaces specified for a particular programming language, one that
121 | is widely used among developers working in that language.
122 |
123 | The "System Libraries" of an executable work include anything, other
124 | than the work as a whole, that (a) is included in the normal form of
125 | packaging a Major Component, but which is not part of that Major
126 | Component, and (b) serves only to enable use of the work with that
127 | Major Component, or to implement a Standard Interface for which an
128 | implementation is available to the public in source code form. A
129 | "Major Component", in this context, means a major essential component
130 | (kernel, window system, and so on) of the specific operating system
131 | (if any) on which the executable work runs, or a compiler used to
132 | produce the work, or an object code interpreter used to run it.
133 |
134 | The "Corresponding Source" for a work in object code form means all
135 | the source code needed to generate, install, and (for an executable
136 | work) run the object code and to modify the work, including scripts to
137 | control those activities. However, it does not include the work's
138 | System Libraries, or general-purpose tools or generally available free
139 | programs which are used unmodified in performing those activities but
140 | which are not part of the work. For example, Corresponding Source
141 | includes interface definition files associated with source files for
142 | the work, and the source code for shared libraries and dynamically
143 | linked subprograms that the work is specifically designed to require,
144 | such as by intimate data communication or control flow between those
145 | subprograms and other parts of the work.
146 |
147 | The Corresponding Source need not include anything that users
148 | can regenerate automatically from other parts of the Corresponding
149 | Source.
150 |
151 | The Corresponding Source for a work in source code form is that
152 | same work.
153 |
154 | 2. Basic Permissions.
155 |
156 | All rights granted under this License are granted for the term of
157 | copyright on the Program, and are irrevocable provided the stated
158 | conditions are met. This License explicitly affirms your unlimited
159 | permission to run the unmodified Program. The output from running a
160 | covered work is covered by this License only if the output, given its
161 | content, constitutes a covered work. This License acknowledges your
162 | rights of fair use or other equivalent, as provided by copyright law.
163 |
164 | You may make, run and propagate covered works that you do not
165 | convey, without conditions so long as your license otherwise remains
166 | in force. You may convey covered works to others for the sole purpose
167 | of having them make modifications exclusively for you, or provide you
168 | with facilities for running those works, provided that you comply with
169 | the terms of this License in conveying all material for which you do
170 | not control copyright. Those thus making or running the covered works
171 | for you must do so exclusively on your behalf, under your direction
172 | and control, on terms that prohibit them from making any copies of
173 | your copyrighted material outside their relationship with you.
174 |
175 | Conveying under any other circumstances is permitted solely under
176 | the conditions stated below. Sublicensing is not allowed; section 10
177 | makes it unnecessary.
178 |
179 | 3. Protecting Users' Legal Rights From Anti-Circumvention Law.
180 |
181 | No covered work shall be deemed part of an effective technological
182 | measure under any applicable law fulfilling obligations under article
183 | 11 of the WIPO copyright treaty adopted on 20 December 1996, or
184 | similar laws prohibiting or restricting circumvention of such
185 | measures.
186 |
187 | When you convey a covered work, you waive any legal power to forbid
188 | circumvention of technological measures to the extent such circumvention
189 | is effected by exercising rights under this License with respect to
190 | the covered work, and you disclaim any intention to limit operation or
191 | modification of the work as a means of enforcing, against the work's
192 | users, your or third parties' legal rights to forbid circumvention of
193 | technological measures.
194 |
195 | 4. Conveying Verbatim Copies.
196 |
197 | You may convey verbatim copies of the Program's source code as you
198 | receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuously and
199 | appropriately publish on each copy an appropriate copyright notice;
200 | keep intact all notices stating that this License and any
201 | non-permissive terms added in accord with section 7 apply to the code;
202 | keep intact all notices of the absence of any warranty; and give all
203 | recipients a copy of this License along with the Program.
204 |
205 | You may charge any price or no price for each copy that you convey,
206 | and you may offer support or warranty protection for a fee.
207 |
208 | 5. Conveying Modified Source Versions.
209 |
210 | You may convey a work based on the Program, or the modifications to
211 | produce it from the Program, in the form of source code under the
212 | terms of section 4, provided that you also meet all of these conditions:
213 |
214 | a) The work must carry prominent notices stating that you modified
215 | it, and giving a relevant date.
216 |
217 | b) The work must carry prominent notices stating that it is
218 | released under this License and any conditions added under section
219 | 7. This requirement modifies the requirement in section 4 to
220 | "keep intact all notices".
221 |
222 | c) You must license the entire work, as a whole, under this
223 | License to anyone who comes into possession of a copy. This
224 | License will therefore apply, along with any applicable section 7
225 | additional terms, to the whole of the work, and all its parts,
226 | regardless of how they are packaged. This License gives no
227 | permission to license the work in any other way, but it does not
228 | invalidate such permission if you have separately received it.
229 |
230 | d) If the work has interactive user interfaces, each must display
231 | Appropriate Legal Notices; however, if the Program has interactive
232 | interfaces that do not display Appropriate Legal Notices, your
233 | work need not make them do so.
234 |
235 | A compilation of a covered work with other separate and independent
236 | works, which are not by their nature extensions of the covered work,
237 | and which are not combined with it such as to form a larger program,
238 | in or on a volume of a storage or distribution medium, is called an
239 | "aggregate" if the compilation and its resulting copyright are not
240 | used to limit the access or legal rights of the compilation's users
241 | beyond what the individual works permit. Inclusion of a covered work
242 | in an aggregate does not cause this License to apply to the other
243 | parts of the aggregate.
244 |
245 | 6. Conveying Non-Source Forms.
246 |
247 | You may convey a covered work in object code form under the terms
248 | of sections 4 and 5, provided that you also convey the
249 | machine-readable Corresponding Source under the terms of this License,
250 | in one of these ways:
251 |
252 | a) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
253 | (including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by the
254 | Corresponding Source fixed on a durable physical medium
255 | customarily used for software interchange.
256 |
257 | b) Convey the object code in, or embodied in, a physical product
258 | (including a physical distribution medium), accompanied by a
259 | written offer, valid for at least three years and valid for as
260 | long as you offer spare parts or customer support for that product
261 | model, to give anyone who possesses the object code either (1) a
262 | copy of the Corresponding Source for all the software in the
263 | product that is covered by this License, on a durable physical
264 | medium customarily used for software interchange, for a price no
265 | more than your reasonable cost of physically performing this
266 | conveying of source, or (2) access to copy the
267 | Corresponding Source from a network server at no charge.
268 |
269 | c) Convey individual copies of the object code with a copy of the
270 | written offer to provide the Corresponding Source. This
271 | alternative is allowed only occasionally and noncommercially, and
272 | only if you received the object code with such an offer, in accord
273 | with subsection 6b.
274 |
275 | d) Convey the object code by offering access from a designated
276 | place (gratis or for a charge), and offer equivalent access to the
277 | Corresponding Source in the same way through the same place at no
278 | further charge. You need not require recipients to copy the
279 | Corresponding Source along with the object code. If the place to
280 | copy the object code is a network server, the Corresponding Source
281 | may be on a different server (operated by you or a third party)
282 | that supports equivalent copying facilities, provided you maintain
283 | clear directions next to the object code saying where to find the
284 | Corresponding Source. Regardless of what server hosts the
285 | Corresponding Source, you remain obligated to ensure that it is
286 | available for as long as needed to satisfy these requirements.
287 |
288 | e) Convey the object code using peer-to-peer transmission, provided
289 | you inform other peers where the object code and Corresponding
290 | Source of the work are being offered to the general public at no
291 | charge under subsection 6d.
292 |
293 | A separable portion of the object code, whose source code is excluded
294 | from the Corresponding Source as a System Library, need not be
295 | included in conveying the object code work.
296 |
297 | A "User Product" is either (1) a "consumer product", which means any
298 | tangible personal property which is normally used for personal, family,
299 | or household purposes, or (2) anything designed or sold for incorporation
300 | into a dwelling. In determining whether a product is a consumer product,
301 | doubtful cases shall be resolved in favor of coverage. For a particular
302 | product received by a particular user, "normally used" refers to a
303 | typical or common use of that class of product, regardless of the status
304 | of the particular user or of the way in which the particular user
305 | actually uses, or expects or is expected to use, the product. A product
306 | is a consumer product regardless of whether the product has substantial
307 | commercial, industrial or non-consumer uses, unless such uses represent
308 | the only significant mode of use of the product.
309 |
310 | "Installation Information" for a User Product means any methods,
311 | procedures, authorization keys, or other information required to install
312 | and execute modified versions of a covered work in that User Product from
313 | a modified version of its Corresponding Source. The information must
314 | suffice to ensure that the continued functioning of the modified object
315 | code is in no case prevented or interfered with solely because
316 | modification has been made.
317 |
318 | If you convey an object code work under this section in, or with, or
319 | specifically for use in, a User Product, and the conveying occurs as
320 | part of a transaction in which the right of possession and use of the
321 | User Product is transferred to the recipient in perpetuity or for a
322 | fixed term (regardless of how the transaction is characterized), the
323 | Corresponding Source conveyed under this section must be accompanied
324 | by the Installation Information. But this requirement does not apply
325 | if neither you nor any third party retains the ability to install
326 | modified object code on the User Product (for example, the work has
327 | been installed in ROM).
328 |
329 | The requirement to provide Installation Information does not include a
330 | requirement to continue to provide support service, warranty, or updates
331 | for a work that has been modified or installed by the recipient, or for
332 | the User Product in which it has been modified or installed. Access to a
333 | network may be denied when the modification itself materially and
334 | adversely affects the operation of the network or violates the rules and
335 | protocols for communication across the network.
336 |
337 | Corresponding Source conveyed, and Installation Information provided,
338 | in accord with this section must be in a format that is publicly
339 | documented (and with an implementation available to the public in
340 | source code form), and must require no special password or key for
341 | unpacking, reading or copying.
342 |
343 | 7. Additional Terms.
344 |
345 | "Additional permissions" are terms that supplement the terms of this
346 | License by making exceptions from one or more of its conditions.
347 | Additional permissions that are applicable to the entire Program shall
348 | be treated as though they were included in this License, to the extent
349 | that they are valid under applicable law. If additional permissions
350 | apply only to part of the Program, that part may be used separately
351 | under those permissions, but the entire Program remains governed by
352 | this License without regard to the additional permissions.
353 |
354 | When you convey a copy of a covered work, you may at your option
355 | remove any additional permissions from that copy, or from any part of
356 | it. (Additional permissions may be written to require their own
357 | removal in certain cases when you modify the work.) You may place
358 | additional permissions on material, added by you to a covered work,
359 | for which you have or can give appropriate copyright permission.
360 |
361 | Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, for material you
362 | add to a covered work, you may (if authorized by the copyright holders of
363 | that material) supplement the terms of this License with terms:
364 |
365 | a) Disclaiming warranty or limiting liability differently from the
366 | terms of sections 15 and 16 of this License; or
367 |
368 | b) Requiring preservation of specified reasonable legal notices or
369 | author attributions in that material or in the Appropriate Legal
370 | Notices displayed by works containing it; or
371 |
372 | c) Prohibiting misrepresentation of the origin of that material, or
373 | requiring that modified versions of such material be marked in
374 | reasonable ways as different from the original version; or
375 |
376 | d) Limiting the use for publicity purposes of names of licensors or
377 | authors of the material; or
378 |
379 | e) Declining to grant rights under trademark law for use of some
380 | trade names, trademarks, or service marks; or
381 |
382 | f) Requiring indemnification of licensors and authors of that
383 | material by anyone who conveys the material (or modified versions of
384 | it) with contractual assumptions of liability to the recipient, for
385 | any liability that these contractual assumptions directly impose on
386 | those licensors and authors.
387 |
388 | All other non-permissive additional terms are considered "further
389 | restrictions" within the meaning of section 10. If the Program as you
390 | received it, or any part of it, contains a notice stating that it is
391 | governed by this License along with a term that is a further
392 | restriction, you may remove that term. If a license document contains
393 | a further restriction but permits relicensing or conveying under this
394 | License, you may add to a covered work material governed by the terms
395 | of that license document, provided that the further restriction does
396 | not survive such relicensing or conveying.
397 |
398 | If you add terms to a covered work in accord with this section, you
399 | must place, in the relevant source files, a statement of the
400 | additional terms that apply to those files, or a notice indicating
401 | where to find the applicable terms.
402 |
403 | Additional terms, permissive or non-permissive, may be stated in the
404 | form of a separately written license, or stated as exceptions;
405 | the above requirements apply either way.
406 |
407 | 8. Termination.
408 |
409 | You may not propagate or modify a covered work except as expressly
410 | provided under this License. Any attempt otherwise to propagate or
411 | modify it is void, and will automatically terminate your rights under
412 | this License (including any patent licenses granted under the third
413 | paragraph of section 11).
414 |
415 | However, if you cease all violation of this License, then your
416 | license from a particular copyright holder is reinstated (a)
417 | provisionally, unless and until the copyright holder explicitly and
418 | finally terminates your license, and (b) permanently, if the copyright
419 | holder fails to notify you of the violation by some reasonable means
420 | prior to 60 days after the cessation.
421 |
422 | Moreover, your license from a particular copyright holder is
423 | reinstated permanently if the copyright holder notifies you of the
424 | violation by some reasonable means, this is the first time you have
425 | received notice of violation of this License (for any work) from that
426 | copyright holder, and you cure the violation prior to 30 days after
427 | your receipt of the notice.
428 |
429 | Termination of your rights under this section does not terminate the
430 | licenses of parties who have received copies or rights from you under
431 | this License. If your rights have been terminated and not permanently
432 | reinstated, you do not qualify to receive new licenses for the same
433 | material under section 10.
434 |
435 | 9. Acceptance Not Required for Having Copies.
436 |
437 | You are not required to accept this License in order to receive or
438 | run a copy of the Program. Ancillary propagation of a covered work
439 | occurring solely as a consequence of using peer-to-peer transmission
440 | to receive a copy likewise does not require acceptance. However,
441 | nothing other than this License grants you permission to propagate or
442 | modify any covered work. These actions infringe copyright if you do
443 | not accept this License. Therefore, by modifying or propagating a
444 | covered work, you indicate your acceptance of this License to do so.
445 |
446 | 10. Automatic Licensing of Downstream Recipients.
447 |
448 | Each time you convey a covered work, the recipient automatically
449 | receives a license from the original licensors, to run, modify and
450 | propagate that work, subject to this License. You are not responsible
451 | for enforcing compliance by third parties with this License.
452 |
453 | An "entity transaction" is a transaction transferring control of an
454 | organization, or substantially all assets of one, or subdividing an
455 | organization, or merging organizations. If propagation of a covered
456 | work results from an entity transaction, each party to that
457 | transaction who receives a copy of the work also receives whatever
458 | licenses to the work the party's predecessor in interest had or could
459 | give under the previous paragraph, plus a right to possession of the
460 | Corresponding Source of the work from the predecessor in interest, if
461 | the predecessor has it or can get it with reasonable efforts.
462 |
463 | You may not impose any further restrictions on the exercise of the
464 | rights granted or affirmed under this License. For example, you may
465 | not impose a license fee, royalty, or other charge for exercise of
466 | rights granted under this License, and you may not initiate litigation
467 | (including a cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that
468 | any patent claim is infringed by making, using, selling, offering for
469 | sale, or importing the Program or any portion of it.
470 |
471 | 11. Patents.
472 |
473 | A "contributor" is a copyright holder who authorizes use under this
474 | License of the Program or a work on which the Program is based. The
475 | work thus licensed is called the contributor's "contributor version".
476 |
477 | A contributor's "essential patent claims" are all patent claims
478 | owned or controlled by the contributor, whether already acquired or
479 | hereafter acquired, that would be infringed by some manner, permitted
480 | by this License, of making, using, or selling its contributor version,
481 | but do not include claims that would be infringed only as a
482 | consequence of further modification of the contributor version. For
483 | purposes of this definition, "control" includes the right to grant
484 | patent sublicenses in a manner consistent with the requirements of
485 | this License.
486 |
487 | Each contributor grants you a non-exclusive, worldwide, royalty-free
488 | patent license under the contributor's essential patent claims, to
489 | make, use, sell, offer for sale, import and otherwise run, modify and
490 | propagate the contents of its contributor version.
491 |
492 | In the following three paragraphs, a "patent license" is any express
493 | agreement or commitment, however denominated, not to enforce a patent
494 | (such as an express permission to practice a patent or covenant not to
495 | sue for patent infringement). To "grant" such a patent license to a
496 | party means to make such an agreement or commitment not to enforce a
497 | patent against the party.
498 |
499 | If you convey a covered work, knowingly relying on a patent license,
500 | and the Corresponding Source of the work is not available for anyone
501 | to copy, free of charge and under the terms of this License, through a
502 | publicly available network server or other readily accessible means,
503 | then you must either (1) cause the Corresponding Source to be so
504 | available, or (2) arrange to deprive yourself of the benefit of the
505 | patent license for this particular work, or (3) arrange, in a manner
506 | consistent with the requirements of this License, to extend the patent
507 | license to downstream recipients. "Knowingly relying" means you have
508 | actual knowledge that, but for the patent license, your conveying the
509 | covered work in a country, or your recipient's use of the covered work
510 | in a country, would infringe one or more identifiable patents in that
511 | country that you have reason to believe are valid.
512 |
513 | If, pursuant to or in connection with a single transaction or
514 | arrangement, you convey, or propagate by procuring conveyance of, a
515 | covered work, and grant a patent license to some of the parties
516 | receiving the covered work authorizing them to use, propagate, modify
517 | or convey a specific copy of the covered work, then the patent license
518 | you grant is automatically extended to all recipients of the covered
519 | work and works based on it.
520 |
521 | A patent license is "discriminatory" if it does not include within
522 | the scope of its coverage, prohibits the exercise of, or is
523 | conditioned on the non-exercise of one or more of the rights that are
524 | specifically granted under this License. You may not convey a covered
525 | work if you are a party to an arrangement with a third party that is
526 | in the business of distributing software, under which you make payment
527 | to the third party based on the extent of your activity of conveying
528 | the work, and under which the third party grants, to any of the
529 | parties who would receive the covered work from you, a discriminatory
530 | patent license (a) in connection with copies of the covered work
531 | conveyed by you (or copies made from those copies), or (b) primarily
532 | for and in connection with specific products or compilations that
533 | contain the covered work, unless you entered into that arrangement,
534 | or that patent license was granted, prior to 28 March 2007.
535 |
536 | Nothing in this License shall be construed as excluding or limiting
537 | any implied license or other defenses to infringement that may
538 | otherwise be available to you under applicable patent law.
539 |
540 | 12. No Surrender of Others' Freedom.
541 |
542 | If conditions are imposed on you (whether by court order, agreement or
543 | otherwise) that contradict the conditions of this License, they do not
544 | excuse you from the conditions of this License. If you cannot convey a
545 | covered work so as to satisfy simultaneously your obligations under this
546 | License and any other pertinent obligations, then as a consequence you may
547 | not convey it at all. For example, if you agree to terms that obligate you
548 | to collect a royalty for further conveying from those to whom you convey
549 | the Program, the only way you could satisfy both those terms and this
550 | License would be to refrain entirely from conveying the Program.
551 |
552 | 13. Use with the GNU Affero General Public License.
553 |
554 | Notwithstanding any other provision of this License, you have
555 | permission to link or combine any covered work with a work licensed
556 | under version 3 of the GNU Affero General Public License into a single
557 | combined work, and to convey the resulting work. The terms of this
558 | License will continue to apply to the part which is the covered work,
559 | but the special requirements of the GNU Affero General Public License,
560 | section 13, concerning interaction through a network will apply to the
561 | combination as such.
562 |
563 | 14. Revised Versions of this License.
564 |
565 | The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions of
566 | the GNU General Public License from time to time. Such new versions will
567 | be similar in spirit to the present version, but may differ in detail to
568 | address new problems or concerns.
569 |
570 | Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
571 | Program specifies that a certain numbered version of the GNU General
572 | Public License "or any later version" applies to it, you have the
573 | option of following the terms and conditions either of that numbered
574 | version or of any later version published by the Free Software
575 | Foundation. If the Program does not specify a version number of the
576 | GNU General Public License, you may choose any version ever published
577 | by the Free Software Foundation.
578 |
579 | If the Program specifies that a proxy can decide which future
580 | versions of the GNU General Public License can be used, that proxy's
581 | public statement of acceptance of a version permanently authorizes you
582 | to choose that version for the Program.
583 |
584 | Later license versions may give you additional or different
585 | permissions. However, no additional obligations are imposed on any
586 | author or copyright holder as a result of your choosing to follow a
587 | later version.
588 |
589 | 15. Disclaimer of Warranty.
590 |
591 | THERE IS NO WARRANTY FOR THE PROGRAM, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY
592 | APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHEN OTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT
593 | HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIES PROVIDE THE PROGRAM "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY
594 | OF ANY KIND, EITHER EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO,
595 | THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR
596 | PURPOSE. THE ENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE PROGRAM
597 | IS WITH YOU. SHOULD THE PROGRAM PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF
598 | ALL NECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR OR CORRECTION.
599 |
600 | 16. Limitation of Liability.
601 |
602 | IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITING
603 | WILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MODIFIES AND/OR CONVEYS
604 | THE PROGRAM AS PERMITTED ABOVE, BE LIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY
605 | GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE
606 | USE OR INABILITY TO USE THE PROGRAM (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF
607 | DATA OR DATA BEING RENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD
608 | PARTIES OR A FAILURE OF THE PROGRAM TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER PROGRAMS),
609 | EVEN IF SUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF
610 | SUCH DAMAGES.
611 |
612 | 17. Interpretation of Sections 15 and 16.
613 |
614 | If the disclaimer of warranty and limitation of liability provided
615 | above cannot be given local legal effect according to their terms,
616 | reviewing courts shall apply local law that most closely approximates
617 | an absolute waiver of all civil liability in connection with the
618 | Program, unless a warranty or assumption of liability accompanies a
619 | copy of the Program in return for a fee.
620 |
621 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
622 |
623 | How to Apply These Terms to Your New Programs
624 |
625 | If you develop a new program, and you want it to be of the greatest
626 | possible use to the public, the best way to achieve this is to make it
627 | free software which everyone can redistribute and change under these terms.
628 |
629 | To do so, attach the following notices to the program. It is safest
630 | to attach them to the start of each source file to most effectively
631 | state the exclusion of warranty; and each file should have at least
632 | the "copyright" line and a pointer to where the full notice is found.
633 |
634 |
635 | Copyright (C)
636 |
637 | This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
638 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
639 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
640 | (at your option) any later version.
641 |
642 | This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
643 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
644 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
645 | GNU General Public License for more details.
646 |
647 | You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
648 | along with this program. If not, see .
649 |
650 | Also add information on how to contact you by electronic and paper mail.
651 |
652 | If the program does terminal interaction, make it output a short
653 | notice like this when it starts in an interactive mode:
654 |
655 | Copyright (C)
656 | This program comes with ABSOLUTELY NO WARRANTY; for details type `show w'.
657 | This is free software, and you are welcome to redistribute it
658 | under certain conditions; type `show c' for details.
659 |
660 | The hypothetical commands `show w' and `show c' should show the appropriate
661 | parts of the General Public License. Of course, your program's commands
662 | might be different; for a GUI interface, you would use an "about box".
663 |
664 | You should also get your employer (if you work as a programmer) or school,
665 | if any, to sign a "copyright disclaimer" for the program, if necessary.
666 | For more information on this, and how to apply and follow the GNU GPL, see
667 | .
668 |
669 | The GNU General Public License does not permit incorporating your program
670 | into proprietary programs. If your program is a subroutine library, you
671 | may consider it more useful to permit linking proprietary applications with
672 | the library. If this is what you want to do, use the GNU Lesser General
673 | Public License instead of this License. But first, please read
674 | .
675 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/app/php.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [PHP]
2 |
3 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
4 | ; About php.ini ;
5 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
6 | ; PHP's initialization file, generally called php.ini, is responsible for
7 | ; configuring many of the aspects of PHP's behavior.
8 |
9 | ; PHP attempts to find and load this configuration from a number of locations.
10 | ; The following is a summary of its search order:
11 | ; 1. SAPI module specific location.
12 | ; 2. The PHPRC environment variable. (As of PHP 5.2.0)
13 | ; 3. A number of predefined registry keys on Windows (As of PHP 5.2.0)
14 | ; 4. Current working directory (except CLI)
15 | ; 5. The web server's directory (for SAPI modules), or directory of PHP
16 | ; (otherwise in Windows)
17 | ; 6. The directory from the --with-config-file-path compile time option, or the
18 | ; Windows directory (usually C:\windows)
19 | ; See the PHP docs for more specific information.
20 | ; http://php.net/configuration.file
21 |
22 | ; The syntax of the file is extremely simple. Whitespace and lines
23 | ; beginning with a semicolon are silently ignored (as you probably guessed).
24 | ; Section headers (e.g. [Foo]) are also silently ignored, even though
25 | ; they might mean something in the future.
26 |
27 | ; Directives following the section heading [PATH=/www/mysite] only
28 | ; apply to PHP files in the /www/mysite directory. Directives
29 | ; following the section heading [HOST=www.example.com] only apply to
30 | ; PHP files served from www.example.com. Directives set in these
31 | ; special sections cannot be overridden by user-defined INI files or
32 | ; at runtime. Currently, [PATH=] and [HOST=] sections only work under
33 | ; CGI/FastCGI.
34 | ; http://php.net/ini.sections
35 |
36 | ; Directives are specified using the following syntax:
37 | ; directive = value
38 | ; Directive names are *case sensitive* - foo=bar is different from FOO=bar.
39 | ; Directives are variables used to configure PHP or PHP extensions.
40 | ; There is no name validation. If PHP can't find an expected
41 | ; directive because it is not set or is mistyped, a default value will be used.
42 |
43 | ; The value can be a string, a number, a PHP constant (e.g. E_ALL or M_PI), one
44 | ; of the INI constants (On, Off, True, False, Yes, No and None) or an expression
45 | ; (e.g. E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE), a quoted string ("bar"), or a reference to a
46 | ; previously set variable or directive (e.g. ${foo})
47 |
48 | ; Expressions in the INI file are limited to bitwise operators and parentheses:
49 | ; | bitwise OR
50 | ; ^ bitwise XOR
51 | ; & bitwise AND
52 | ; ~ bitwise NOT
53 | ; ! boolean NOT
54 |
55 | ; Boolean flags can be turned on using the values 1, On, True or Yes.
56 | ; They can be turned off using the values 0, Off, False or No.
57 |
58 | ; An empty string can be denoted by simply not writing anything after the equal
59 | ; sign, or by using the None keyword:
60 |
61 | ; foo = ; sets foo to an empty string
62 | ; foo = None ; sets foo to an empty string
63 | ; foo = "None" ; sets foo to the string 'None'
64 |
65 | ; If you use constants in your value, and these constants belong to a
66 | ; dynamically loaded extension (either a PHP extension or a Zend extension),
67 | ; you may only use these constants *after* the line that loads the extension.
68 |
69 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
70 | ; About this file ;
71 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
72 | ; PHP comes packaged with two INI files. One that is recommended to be used
73 | ; in production environments and one that is recommended to be used in
74 | ; development environments.
75 |
76 | ; php.ini-production contains settings which hold security, performance and
77 | ; best practices at its core. But please be aware, these settings may break
78 | ; compatibility with older or less security conscience applications. We
79 | ; recommending using the production ini in production and testing environments.
80 |
81 | ; php.ini-development is very similar to its production variant, except it is
82 | ; much more verbose when it comes to errors. We recommend using the
83 | ; development version only in development environments, as errors shown to
84 | ; application users can inadvertently leak otherwise secure information.
85 |
86 | ; This is the php.ini-production INI file.
87 |
88 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
89 | ; Quick Reference ;
90 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
91 | ; The following are all the settings which are different in either the production
92 | ; or development versions of the INIs with respect to PHP's default behavior.
93 | ; Please see the actual settings later in the document for more details as to why
94 | ; we recommend these changes in PHP's behavior.
95 |
96 | ; display_errors
97 | ; Default Value: On
98 | ; Development Value: On
99 | ; Production Value: Off
100 |
101 | ; display_startup_errors
102 | ; Default Value: Off
103 | ; Development Value: On
104 | ; Production Value: Off
105 |
106 | ; error_reporting
107 | ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED
108 | ; Development Value: E_ALL
109 | ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
110 |
111 | ; log_errors
112 | ; Default Value: Off
113 | ; Development Value: On
114 | ; Production Value: On
115 |
116 | ; max_input_time
117 | ; Default Value: -1 (Unlimited)
118 | ; Development Value: 60 (60 seconds)
119 | ; Production Value: 60 (60 seconds)
120 |
121 | ; output_buffering
122 | ; Default Value: Off
123 | ; Development Value: 4096
124 | ; Production Value: 4096
125 |
126 | ; register_argc_argv
127 | ; Default Value: On
128 | ; Development Value: Off
129 | ; Production Value: Off
130 |
131 | ; request_order
132 | ; Default Value: None
133 | ; Development Value: "GP"
134 | ; Production Value: "GP"
135 |
136 | ; session.gc_divisor
137 | ; Default Value: 100
138 | ; Development Value: 1000
139 | ; Production Value: 1000
140 |
141 | ; session.sid_bits_per_character
142 | ; Default Value: 4
143 | ; Development Value: 5
144 | ; Production Value: 5
145 |
146 | ; short_open_tag
147 | ; Default Value: On
148 | ; Development Value: Off
149 | ; Production Value: Off
150 |
151 | ; variables_order
152 | ; Default Value: "EGPCS"
153 | ; Development Value: "GPCS"
154 | ; Production Value: "GPCS"
155 |
156 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
157 | ; php.ini Options ;
158 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
159 | ; Name for user-defined php.ini (.htaccess) files. Default is ".user.ini"
160 | ;user_ini.filename = ".user.ini"
161 |
162 | ; To disable this feature set this option to an empty value
163 | ;user_ini.filename =
164 |
165 | ; TTL for user-defined php.ini files (time-to-live) in seconds. Default is 300 seconds (5 minutes)
166 | ;user_ini.cache_ttl = 300
167 |
168 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
169 | ; Language Options ;
170 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
171 |
172 | ; Enable the PHP scripting language engine under Apache.
173 | ; http://php.net/engine
174 | engine = On
175 |
176 | ; This directive determines whether or not PHP will recognize code between
177 | ; tags as PHP source which should be processed as such. It is
178 | ; generally recommended that should be used and that this feature
179 | ; should be disabled, as enabling it may result in issues when generating XML
180 | ; documents, however this remains supported for backward compatibility reasons.
181 | ; Note that this directive does not control the would work.
321 | ; http://php.net/syntax-highlighting
322 | ;highlight.string = #DD0000
323 | ;highlight.comment = #FF9900
324 | ;highlight.keyword = #007700
325 | ;highlight.default = #0000BB
326 | ;highlight.html = #000000
327 |
328 | ; If enabled, the request will be allowed to complete even if the user aborts
329 | ; the request. Consider enabling it if executing long requests, which may end up
330 | ; being interrupted by the user or a browser timing out. PHP's default behavior
331 | ; is to disable this feature.
332 | ; http://php.net/ignore-user-abort
333 | ;ignore_user_abort = On
334 |
335 | ; Determines the size of the realpath cache to be used by PHP. This value should
336 | ; be increased on systems where PHP opens many files to reflect the quantity of
337 | ; the file operations performed.
338 | ; Note: if open_basedir is set, the cache is disabled
339 | ; http://php.net/realpath-cache-size
340 | ;realpath_cache_size = 4096k
341 |
342 | ; Duration of time, in seconds for which to cache realpath information for a given
343 | ; file or directory. For systems with rarely changing files, consider increasing this
344 | ; value.
345 | ; http://php.net/realpath-cache-ttl
346 | ;realpath_cache_ttl = 120
347 |
348 | ; Enables or disables the circular reference collector.
349 | ; http://php.net/zend.enable-gc
350 | zend.enable_gc = On
351 |
352 | ; If enabled, scripts may be written in encodings that are incompatible with
353 | ; the scanner. CP936, Big5, CP949 and Shift_JIS are the examples of such
354 | ; encodings. To use this feature, mbstring extension must be enabled.
355 | ; Default: Off
356 | ;zend.multibyte = Off
357 |
358 | ; Allows to set the default encoding for the scripts. This value will be used
359 | ; unless "declare(encoding=...)" directive appears at the top of the script.
360 | ; Only affects if zend.multibyte is set.
361 | ; Default: ""
362 | ;zend.script_encoding =
363 |
364 | ; Allows to include or exclude arguments from stack traces generated for exceptions.
365 | ; In production, it is recommended to turn this setting on to prohibit the output
366 | ; of sensitive information in stack traces
367 | ; Default: Off
368 | zend.exception_ignore_args = On
369 |
370 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
371 | ; Miscellaneous ;
372 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
373 |
374 | ; Decides whether PHP may expose the fact that it is installed on the server
375 | ; (e.g. by adding its signature to the Web server header). It is no security
376 | ; threat in any way, but it makes it possible to determine whether you use PHP
377 | ; on your server or not.
378 | ; http://php.net/expose-php
379 | expose_php = On
380 |
381 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
382 | ; Resource Limits ;
383 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
384 |
385 | ; Maximum execution time of each script, in seconds
386 | ; http://php.net/max-execution-time
387 | ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to 0 for the CLI SAPI
388 | max_execution_time = 0
389 |
390 | ; Maximum amount of time each script may spend parsing request data. It's a good
391 | ; idea to limit this time on productions servers in order to eliminate unexpectedly
392 | ; long running scripts.
393 | ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to -1 for the CLI SAPI
394 | ; Default Value: -1 (Unlimited)
395 | ; Development Value: 60 (60 seconds)
396 | ; Production Value: 60 (60 seconds)
397 | ; http://php.net/max-input-time
398 | max_input_time = -1
399 |
400 | ; Maximum input variable nesting level
401 | ; http://php.net/max-input-nesting-level
402 | ;max_input_nesting_level = 64
403 |
404 | ; How many GET/POST/COOKIE input variables may be accepted
405 | ;max_input_vars = 1000
406 |
407 | ; Maximum amount of memory a script may consume
408 | ; http://php.net/memory-limit
409 | memory_limit = 128M
410 |
411 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
412 | ; Error handling and logging ;
413 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
414 |
415 | ; This directive informs PHP of which errors, warnings and notices you would like
416 | ; it to take action for. The recommended way of setting values for this
417 | ; directive is through the use of the error level constants and bitwise
418 | ; operators. The error level constants are below here for convenience as well as
419 | ; some common settings and their meanings.
420 | ; By default, PHP is set to take action on all errors, notices and warnings EXCEPT
421 | ; those related to E_NOTICE and E_STRICT, which together cover best practices and
422 | ; recommended coding standards in PHP. For performance reasons, this is the
423 | ; recommend error reporting setting. Your production server shouldn't be wasting
424 | ; resources complaining about best practices and coding standards. That's what
425 | ; development servers and development settings are for.
426 | ; Note: The php.ini-development file has this setting as E_ALL. This
427 | ; means it pretty much reports everything which is exactly what you want during
428 | ; development and early testing.
429 | ;
430 | ; Error Level Constants:
431 | ; E_ALL - All errors and warnings (includes E_STRICT as of PHP 5.4.0)
432 | ; E_ERROR - fatal run-time errors
433 | ; E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR - almost fatal run-time errors
434 | ; E_WARNING - run-time warnings (non-fatal errors)
435 | ; E_PARSE - compile-time parse errors
436 | ; E_NOTICE - run-time notices (these are warnings which often result
437 | ; from a bug in your code, but it's possible that it was
438 | ; intentional (e.g., using an uninitialized variable and
439 | ; relying on the fact it is automatically initialized to an
440 | ; empty string)
441 | ; E_STRICT - run-time notices, enable to have PHP suggest changes
442 | ; to your code which will ensure the best interoperability
443 | ; and forward compatibility of your code
444 | ; E_CORE_ERROR - fatal errors that occur during PHP's initial startup
445 | ; E_CORE_WARNING - warnings (non-fatal errors) that occur during PHP's
446 | ; initial startup
447 | ; E_COMPILE_ERROR - fatal compile-time errors
448 | ; E_COMPILE_WARNING - compile-time warnings (non-fatal errors)
449 | ; E_USER_ERROR - user-generated error message
450 | ; E_USER_WARNING - user-generated warning message
451 | ; E_USER_NOTICE - user-generated notice message
452 | ; E_DEPRECATED - warn about code that will not work in future versions
453 | ; of PHP
454 | ; E_USER_DEPRECATED - user-generated deprecation warnings
455 | ;
456 | ; Common Values:
457 | ; E_ALL (Show all errors, warnings and notices including coding standards.)
458 | ; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE (Show all errors, except for notices)
459 | ; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT (Show all errors, except for notices and coding standards warnings.)
460 | ; E_COMPILE_ERROR|E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR|E_ERROR|E_CORE_ERROR (Show only errors)
461 | ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED
462 | ; Development Value: E_ALL
463 | ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
464 | ; http://php.net/error-reporting
465 | #error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT
466 | error_reporting = E_ALL &~ E_NOTICE
467 | ; This directive controls whether or not and where PHP will output errors,
468 | ; notices and warnings too. Error output is very useful during development, but
469 | ; it could be very dangerous in production environments. Depending on the code
470 | ; which is triggering the error, sensitive information could potentially leak
471 | ; out of your application such as database usernames and passwords or worse.
472 | ; For production environments, we recommend logging errors rather than
473 | ; sending them to STDOUT.
474 | ; Possible Values:
475 | ; Off = Do not display any errors
476 | ; stderr = Display errors to STDERR (affects only CGI/CLI binaries!)
477 | ; On or stdout = Display errors to STDOUT
478 | ; Default Value: On
479 | ; Development Value: On
480 | ; Production Value: Off
481 | ; http://php.net/display-errors
482 | display_errors = On
483 |
484 | ; The display of errors which occur during PHP's startup sequence are handled
485 | ; separately from display_errors. PHP's default behavior is to suppress those
486 | ; errors from clients. Turning the display of startup errors on can be useful in
487 | ; debugging configuration problems. We strongly recommend you
488 | ; set this to 'off' for production servers.
489 | ; Default Value: Off
490 | ; Development Value: On
491 | ; Production Value: Off
492 | ; http://php.net/display-startup-errors
493 | display_startup_errors = Off
494 |
495 | ; Besides displaying errors, PHP can also log errors to locations such as a
496 | ; server-specific log, STDERR, or a location specified by the error_log
497 | ; directive found below. While errors should not be displayed on productions
498 | ; servers they should still be monitored and logging is a great way to do that.
499 | ; Default Value: Off
500 | ; Development Value: On
501 | ; Production Value: On
502 | ; http://php.net/log-errors
503 | log_errors = On
504 |
505 | ; Set maximum length of log_errors. In error_log information about the source is
506 | ; added. The default is 1024 and 0 allows to not apply any maximum length at all.
507 | ; http://php.net/log-errors-max-len
508 | log_errors_max_len = 1024
509 |
510 | ; Do not log repeated messages. Repeated errors must occur in same file on same
511 | ; line unless ignore_repeated_source is set true.
512 | ; http://php.net/ignore-repeated-errors
513 | ignore_repeated_errors = Off
514 |
515 | ; Ignore source of message when ignoring repeated messages. When this setting
516 | ; is On you will not log errors with repeated messages from different files or
517 | ; source lines.
518 | ; http://php.net/ignore-repeated-source
519 | ignore_repeated_source = Off
520 |
521 | ; If this parameter is set to Off, then memory leaks will not be shown (on
522 | ; stdout or in the log). This is only effective in a debug compile, and if
523 | ; error reporting includes E_WARNING in the allowed list
524 | ; http://php.net/report-memleaks
525 | report_memleaks = On
526 |
527 | ; This setting is on by default.
528 | ;report_zend_debug = 0
529 |
530 | ; Store the last error/warning message in $php_errormsg (boolean). Setting this value
531 | ; to On can assist in debugging and is appropriate for development servers. It should
532 | ; however be disabled on production servers.
533 | ; This directive is DEPRECATED.
534 | ; Default Value: Off
535 | ; Development Value: Off
536 | ; Production Value: Off
537 | ; http://php.net/track-errors
538 | ;track_errors = Off
539 |
540 | ; Turn off normal error reporting and emit XML-RPC error XML
541 | ; http://php.net/xmlrpc-errors
542 | ;xmlrpc_errors = 0
543 |
544 | ; An XML-RPC faultCode
545 | ;xmlrpc_error_number = 0
546 |
547 | ; When PHP displays or logs an error, it has the capability of formatting the
548 | ; error message as HTML for easier reading. This directive controls whether
549 | ; the error message is formatted as HTML or not.
550 | ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to Off for the CLI SAPI
551 | ; http://php.net/html-errors
552 | ;html_errors = On
553 |
554 | ; If html_errors is set to On *and* docref_root is not empty, then PHP
555 | ; produces clickable error messages that direct to a page describing the error
556 | ; or function causing the error in detail.
557 | ; You can download a copy of the PHP manual from http://php.net/docs
558 | ; and change docref_root to the base URL of your local copy including the
559 | ; leading '/'. You must also specify the file extension being used including
560 | ; the dot. PHP's default behavior is to leave these settings empty, in which
561 | ; case no links to documentation are generated.
562 | ; Note: Never use this feature for production boxes.
563 | ; http://php.net/docref-root
564 | ; Examples
565 | ;docref_root = "/phpmanual/"
566 |
567 | ; http://php.net/docref-ext
568 | ;docref_ext = .html
569 |
570 | ; String to output before an error message. PHP's default behavior is to leave
571 | ; this setting blank.
572 | ; http://php.net/error-prepend-string
573 | ; Example:
574 | ;error_prepend_string = ""
575 |
576 | ; String to output after an error message. PHP's default behavior is to leave
577 | ; this setting blank.
578 | ; http://php.net/error-append-string
579 | ; Example:
580 | ;error_append_string = ""
581 |
582 | ; Log errors to specified file. PHP's default behavior is to leave this value
583 | ; empty.
584 | ; http://php.net/error-log
585 | ; Example:
586 | ;error_log = php_errors.log
587 | ; Log errors to syslog (Event Log on Windows).
588 | ;error_log = syslog
589 |
590 | ; The syslog ident is a string which is prepended to every message logged
591 | ; to syslog. Only used when error_log is set to syslog.
592 | ;syslog.ident = php
593 |
594 | ; The syslog facility is used to specify what type of program is logging
595 | ; the message. Only used when error_log is set to syslog.
596 | ;syslog.facility = user
597 |
598 | ; Set this to disable filtering control characters (the default).
599 | ; Some loggers only accept NVT-ASCII, others accept anything that's not
600 | ; control characters. If your logger accepts everything, then no filtering
601 | ; is needed at all.
602 | ; Allowed values are:
603 | ; ascii (all printable ASCII characters and NL)
604 | ; no-ctrl (all characters except control characters)
605 | ; all (all characters)
606 | ; raw (like "all", but messages are not split at newlines)
607 | ; http://php.net/syslog.filter
608 | ;syslog.filter = ascii
609 |
610 | ;windows.show_crt_warning
611 | ; Default value: 0
612 | ; Development value: 0
613 | ; Production value: 0
614 |
615 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
616 | ; Data Handling ;
617 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
618 |
619 | ; The separator used in PHP generated URLs to separate arguments.
620 | ; PHP's default setting is "&".
621 | ; http://php.net/arg-separator.output
622 | ; Example:
623 | ;arg_separator.output = "&"
624 |
625 | ; List of separator(s) used by PHP to parse input URLs into variables.
626 | ; PHP's default setting is "&".
627 | ; NOTE: Every character in this directive is considered as separator!
628 | ; http://php.net/arg-separator.input
629 | ; Example:
630 | ;arg_separator.input = ";&"
631 |
632 | ; This directive determines which super global arrays are registered when PHP
633 | ; starts up. G,P,C,E & S are abbreviations for the following respective super
634 | ; globals: GET, POST, COOKIE, ENV and SERVER. There is a performance penalty
635 | ; paid for the registration of these arrays and because ENV is not as commonly
636 | ; used as the others, ENV is not recommended on productions servers. You
637 | ; can still get access to the environment variables through getenv() should you
638 | ; need to.
639 | ; Default Value: "EGPCS"
640 | ; Development Value: "GPCS"
641 | ; Production Value: "GPCS";
642 | ; http://php.net/variables-order
643 | variables_order = "GPCS"
644 |
645 | ; This directive determines which super global data (G,P & C) should be
646 | ; registered into the super global array REQUEST. If so, it also determines
647 | ; the order in which that data is registered. The values for this directive
648 | ; are specified in the same manner as the variables_order directive,
649 | ; EXCEPT one. Leaving this value empty will cause PHP to use the value set
650 | ; in the variables_order directive. It does not mean it will leave the super
651 | ; globals array REQUEST empty.
652 | ; Default Value: None
653 | ; Development Value: "GP"
654 | ; Production Value: "GP"
655 | ; http://php.net/request-order
656 | request_order = "GP"
657 |
658 | ; This directive determines whether PHP registers $argv & $argc each time it
659 | ; runs. $argv contains an array of all the arguments passed to PHP when a script
660 | ; is invoked. $argc contains an integer representing the number of arguments
661 | ; that were passed when the script was invoked. These arrays are extremely
662 | ; useful when running scripts from the command line. When this directive is
663 | ; enabled, registering these variables consumes CPU cycles and memory each time
664 | ; a script is executed. For performance reasons, this feature should be disabled
665 | ; on production servers.
666 | ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to On for the CLI SAPI
667 | ; Default Value: On
668 | ; Development Value: Off
669 | ; Production Value: Off
670 | ; http://php.net/register-argc-argv
671 | register_argc_argv = Off
672 |
673 | ; When enabled, the ENV, REQUEST and SERVER variables are created when they're
674 | ; first used (Just In Time) instead of when the script starts. If these
675 | ; variables are not used within a script, having this directive on will result
676 | ; in a performance gain. The PHP directive register_argc_argv must be disabled
677 | ; for this directive to have any effect.
678 | ; http://php.net/auto-globals-jit
679 | auto_globals_jit = On
680 |
681 | ; Whether PHP will read the POST data.
682 | ; This option is enabled by default.
683 | ; Most likely, you won't want to disable this option globally. It causes $_POST
684 | ; and $_FILES to always be empty; the only way you will be able to read the
685 | ; POST data will be through the php://input stream wrapper. This can be useful
686 | ; to proxy requests or to process the POST data in a memory efficient fashion.
687 | ; http://php.net/enable-post-data-reading
688 | ;enable_post_data_reading = Off
689 |
690 | ; Maximum size of POST data that PHP will accept.
691 | ; Its value may be 0 to disable the limit. It is ignored if POST data reading
692 | ; is disabled through enable_post_data_reading.
693 | ; http://php.net/post-max-size
694 | post_max_size = 8M
695 |
696 | ; Automatically add files before PHP document.
697 | ; http://php.net/auto-prepend-file
698 | auto_prepend_file =
699 |
700 | ; Automatically add files after PHP document.
701 | ; http://php.net/auto-append-file
702 | auto_append_file =
703 |
704 | ; By default, PHP will output a media type using the Content-Type header. To
705 | ; disable this, simply set it to be empty.
706 | ;
707 | ; PHP's built-in default media type is set to text/html.
708 | ; http://php.net/default-mimetype
709 | default_mimetype = "text/html"
710 |
711 | ; PHP's default character set is set to UTF-8.
712 | ; http://php.net/default-charset
713 | default_charset = "UTF-8"
714 |
715 | ; PHP internal character encoding is set to empty.
716 | ; If empty, default_charset is used.
717 | ; http://php.net/internal-encoding
718 | ;internal_encoding =
719 |
720 | ; PHP input character encoding is set to empty.
721 | ; If empty, default_charset is used.
722 | ; http://php.net/input-encoding
723 | ;input_encoding =
724 |
725 | ; PHP output character encoding is set to empty.
726 | ; If empty, default_charset is used.
727 | ; See also output_buffer.
728 | ; http://php.net/output-encoding
729 | ;output_encoding =
730 |
731 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
732 | ; Paths and Directories ;
733 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
734 |
735 | ; UNIX: "/path1:/path2"
736 | include_path = ".:/usr/share/php7"
737 | ;
738 | ; Windows: "\path1;\path2"
739 | ;include_path = ".;c:\php\includes"
740 | ;
741 | ; PHP's default setting for include_path is ".;/path/to/php/pear"
742 | ; http://php.net/include-path
743 |
744 | ; The root of the PHP pages, used only if nonempty.
745 | ; if PHP was not compiled with FORCE_REDIRECT, you SHOULD set doc_root
746 | ; if you are running php as a CGI under any web server (other than IIS)
747 | ; see documentation for security issues. The alternate is to use the
748 | ; cgi.force_redirect configuration below
749 | ; http://php.net/doc-root
750 | doc_root =
751 |
752 | ; The directory under which PHP opens the script using /~username used only
753 | ; if nonempty.
754 | ; http://php.net/user-dir
755 | user_dir =
756 |
757 | ; Directory in which the loadable extensions (modules) reside.
758 | ; http://php.net/extension-dir
759 | ;extension_dir = "./"
760 | ; On windows:
761 | ;extension_dir = "ext"
762 |
763 | ; Directory where the temporary files should be placed.
764 | ; Defaults to the system default (see sys_get_temp_dir)
765 | ;sys_temp_dir = "/tmp"
766 |
767 | ; Whether or not to enable the dl() function. The dl() function does NOT work
768 | ; properly in multithreaded servers, such as IIS or Zeus, and is automatically
769 | ; disabled on them.
770 | ; http://php.net/enable-dl
771 | enable_dl = Off
772 |
773 | ; cgi.force_redirect is necessary to provide security running PHP as a CGI under
774 | ; most web servers. Left undefined, PHP turns this on by default. You can
775 | ; turn it off here AT YOUR OWN RISK
776 | ; **You CAN safely turn this off for IIS, in fact, you MUST.**
777 | ; http://php.net/cgi.force-redirect
778 | ;cgi.force_redirect = 1
779 |
780 | ; if cgi.nph is enabled it will force cgi to always sent Status: 200 with
781 | ; every request. PHP's default behavior is to disable this feature.
782 | ;cgi.nph = 1
783 |
784 | ; if cgi.force_redirect is turned on, and you are not running under Apache or Netscape
785 | ; (iPlanet) web servers, you MAY need to set an environment variable name that PHP
786 | ; will look for to know it is OK to continue execution. Setting this variable MAY
787 | ; cause security issues, KNOW WHAT YOU ARE DOING FIRST.
788 | ; http://php.net/cgi.redirect-status-env
789 | ;cgi.redirect_status_env =
790 |
791 | ; cgi.fix_pathinfo provides *real* PATH_INFO/PATH_TRANSLATED support for CGI. PHP's
792 | ; previous behaviour was to set PATH_TRANSLATED to SCRIPT_FILENAME, and to not grok
793 | ; what PATH_INFO is. For more information on PATH_INFO, see the cgi specs. Setting
794 | ; this to 1 will cause PHP CGI to fix its paths to conform to the spec. A setting
795 | ; of zero causes PHP to behave as before. Default is 1. You should fix your scripts
796 | ; to use SCRIPT_FILENAME rather than PATH_TRANSLATED.
797 | ; http://php.net/cgi.fix-pathinfo
798 | ;cgi.fix_pathinfo=1
799 |
800 | ; if cgi.discard_path is enabled, the PHP CGI binary can safely be placed outside
801 | ; of the web tree and people will not be able to circumvent .htaccess security.
802 | ;cgi.discard_path=1
803 |
804 | ; FastCGI under IIS supports the ability to impersonate
805 | ; security tokens of the calling client. This allows IIS to define the
806 | ; security context that the request runs under. mod_fastcgi under Apache
807 | ; does not currently support this feature (03/17/2002)
808 | ; Set to 1 if running under IIS. Default is zero.
809 | ; http://php.net/fastcgi.impersonate
810 | ;fastcgi.impersonate = 1
811 |
812 | ; Disable logging through FastCGI connection. PHP's default behavior is to enable
813 | ; this feature.
814 | ;fastcgi.logging = 0
815 |
816 | ; cgi.rfc2616_headers configuration option tells PHP what type of headers to
817 | ; use when sending HTTP response code. If set to 0, PHP sends Status: header that
818 | ; is supported by Apache. When this option is set to 1, PHP will send
819 | ; RFC2616 compliant header.
820 | ; Default is zero.
821 | ; http://php.net/cgi.rfc2616-headers
822 | ;cgi.rfc2616_headers = 0
823 |
824 | ; cgi.check_shebang_line controls whether CGI PHP checks for line starting with #!
825 | ; (shebang) at the top of the running script. This line might be needed if the
826 | ; script support running both as stand-alone script and via PHP CGI<. PHP in CGI
827 | ; mode skips this line and ignores its content if this directive is turned on.
828 | ; http://php.net/cgi.check-shebang-line
829 | ;cgi.check_shebang_line=1
830 |
831 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
832 | ; File Uploads ;
833 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
834 |
835 | ; Whether to allow HTTP file uploads.
836 | ; http://php.net/file-uploads
837 | file_uploads = On
838 |
839 | ; Temporary directory for HTTP uploaded files (will use system default if not
840 | ; specified).
841 | ; http://php.net/upload-tmp-dir
842 | ;upload_tmp_dir =
843 |
844 | ; Maximum allowed size for uploaded files.
845 | ; http://php.net/upload-max-filesize
846 | upload_max_filesize = 2M
847 |
848 | ; Maximum number of files that can be uploaded via a single request
849 | max_file_uploads = 20
850 |
851 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
852 | ; Fopen wrappers ;
853 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
854 |
855 | ; Whether to allow the treatment of URLs (like http:// or ftp://) as files.
856 | ; http://php.net/allow-url-fopen
857 | allow_url_fopen = On
858 |
859 | ; Whether to allow include/require to open URLs (like http:// or ftp://) as files.
860 | ; http://php.net/allow-url-include
861 | allow_url_include = Off
862 |
863 | ; Define the anonymous ftp password (your email address). PHP's default setting
864 | ; for this is empty.
865 | ; http://php.net/from
866 | ;from="john@doe.com"
867 |
868 | ; Define the User-Agent string. PHP's default setting for this is empty.
869 | ; http://php.net/user-agent
870 | ;user_agent="PHP"
871 |
872 | ; Default timeout for socket based streams (seconds)
873 | ; http://php.net/default-socket-timeout
874 | default_socket_timeout = 60
875 |
876 | ; If your scripts have to deal with files from Macintosh systems,
877 | ; or you are running on a Mac and need to deal with files from
878 | ; unix or win32 systems, setting this flag will cause PHP to
879 | ; automatically detect the EOL character in those files so that
880 | ; fgets() and file() will work regardless of the source of the file.
881 | ; http://php.net/auto-detect-line-endings
882 | ;auto_detect_line_endings = Off
883 |
884 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
885 | ; Dynamic Extensions ;
886 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
887 |
888 | ; If you wish to have an extension loaded automatically, use the following
889 | ; syntax:
890 | ;
891 | ; extension=modulename
892 | ;
893 | ; For example:
894 | ;
895 | ; extension=mysqli
896 | ;
897 | ; When the extension library to load is not located in the default extension
898 | ; directory, You may specify an absolute path to the library file:
899 | ;
900 | ; extension=/path/to/extension/mysqli.so
901 | ;
902 | ; Note : The syntax used in previous PHP versions ('extension=.so' and
903 | ; 'extension='php_.dll') is supported for legacy reasons and may be
904 | ; deprecated in a future PHP major version. So, when it is possible, please
905 | ; move to the new ('extension=) syntax.
906 | ;
907 | ; Notes for Windows environments :
908 | ;
909 | ; - Many DLL files are located in the extensions/ (PHP 4) or ext/ (PHP 5+)
910 | ; extension folders as well as the separate PECL DLL download (PHP 5+).
911 | ; Be sure to appropriately set the extension_dir directive.
912 | ;
913 | ;extension=bz2
914 | ;extension=curl
915 | ;extension=ffi
916 | ;extension=ftp
917 | ;extension=fileinfo
918 | ;extension=gd2
919 | ;extension=gettext
920 | ;extension=gmp
921 | ;extension=intl
922 | ;extension=imap
923 | ;extension=ldap
924 | ;extension=mbstring
925 | ;extension=exif ; Must be after mbstring as it depends on it
926 | ;extension=mysqli
927 | ;extension=oci8_12c ; Use with Oracle Database 12c Instant Client
928 | ;extension=odbc
929 | ;extension=openssl
930 | ;extension=pdo_firebird
931 | ;extension=pdo_mysql
932 | ;extension=pdo_oci
933 | ;extension=pdo_odbc
934 | ;extension=pdo_pgsql
935 | ;extension=pdo_sqlite
936 | ;extension=pgsql
937 | ;extension=shmop
938 |
939 | ; The MIBS data available in the PHP distribution must be installed.
940 | ; See http://www.php.net/manual/en/snmp.installation.php
941 | ;extension=snmp
942 |
943 | ;extension=soap
944 | ;extension=sockets
945 | ;extension=sodium
946 | ;extension=sqlite3
947 | ;extension=tidy
948 | ;extension=xmlrpc
949 | ;extension=xsl
950 |
951 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
952 | ; Module Settings ;
953 | ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;
954 |
955 | [CLI Server]
956 | ; Whether the CLI web server uses ANSI color coding in its terminal output.
957 | cli_server.color = On
958 |
959 | [Date]
960 | ; Defines the default timezone used by the date functions
961 | ; http://php.net/date.timezone
962 | ;date.timezone =
963 |
964 | ; http://php.net/date.default-latitude
965 | ;date.default_latitude = 31.7667
966 |
967 | ; http://php.net/date.default-longitude
968 | ;date.default_longitude = 35.2333
969 |
970 | ; http://php.net/date.sunrise-zenith
971 | ;date.sunrise_zenith = 90.583333
972 |
973 | ; http://php.net/date.sunset-zenith
974 | ;date.sunset_zenith = 90.583333
975 |
976 | [filter]
977 | ; http://php.net/filter.default
978 | ;filter.default = unsafe_raw
979 |
980 | ; http://php.net/filter.default-flags
981 | ;filter.default_flags =
982 |
983 | [iconv]
984 | ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global input_encoding instead.
985 | ; If empty, default_charset or input_encoding or iconv.input_encoding is used.
986 | ; The precedence is: default_charset < input_encoding < iconv.input_encoding
987 | ;iconv.input_encoding =
988 |
989 | ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global internal_encoding instead.
990 | ; If empty, default_charset or internal_encoding or iconv.internal_encoding is used.
991 | ; The precedence is: default_charset < internal_encoding < iconv.internal_encoding
992 | ;iconv.internal_encoding =
993 |
994 | ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global output_encoding instead.
995 | ; If empty, default_charset or output_encoding or iconv.output_encoding is used.
996 | ; The precedence is: default_charset < output_encoding < iconv.output_encoding
997 | ; To use an output encoding conversion, iconv's output handler must be set
998 | ; otherwise output encoding conversion cannot be performed.
999 | ;iconv.output_encoding =
1000 |
1001 | [imap]
1002 | ; rsh/ssh logins are disabled by default. Use this INI entry if you want to
1003 | ; enable them. Note that the IMAP library does not filter mailbox names before
1004 | ; passing them to rsh/ssh command, thus passing untrusted data to this function
1005 | ; with rsh/ssh enabled is insecure.
1006 | ;imap.enable_insecure_rsh=0
1007 |
1008 | [intl]
1009 | ;intl.default_locale =
1010 | ; This directive allows you to produce PHP errors when some error
1011 | ; happens within intl functions. The value is the level of the error produced.
1012 | ; Default is 0, which does not produce any errors.
1013 | ;intl.error_level = E_WARNING
1014 | ;intl.use_exceptions = 0
1015 |
1016 | [sqlite3]
1017 | ; Directory pointing to SQLite3 extensions
1018 | ; http://php.net/sqlite3.extension-dir
1019 | ;sqlite3.extension_dir =
1020 |
1021 | ; SQLite defensive mode flag (only available from SQLite 3.26+)
1022 | ; When the defensive flag is enabled, language features that allow ordinary
1023 | ; SQL to deliberately corrupt the database file are disabled. This forbids
1024 | ; writing directly to the schema, shadow tables (eg. FTS data tables), or
1025 | ; the sqlite_dbpage virtual table.
1026 | ; https://www.sqlite.org/c3ref/c_dbconfig_defensive.html
1027 | ; (for older SQLite versions, this flag has no use)
1028 | ;sqlite3.defensive = 1
1029 |
1030 | [Pcre]
1031 | ; PCRE library backtracking limit.
1032 | ; http://php.net/pcre.backtrack-limit
1033 | ;pcre.backtrack_limit=100000
1034 |
1035 | ; PCRE library recursion limit.
1036 | ; Please note that if you set this value to a high number you may consume all
1037 | ; the available process stack and eventually crash PHP (due to reaching the
1038 | ; stack size limit imposed by the Operating System).
1039 | ; http://php.net/pcre.recursion-limit
1040 | ;pcre.recursion_limit=100000
1041 |
1042 | ; Enables or disables JIT compilation of patterns. This requires the PCRE
1043 | ; library to be compiled with JIT support.
1044 | ;pcre.jit=1
1045 |
1046 | [Pdo]
1047 | ; Whether to pool ODBC connections. Can be one of "strict", "relaxed" or "off"
1048 | ; http://php.net/pdo-odbc.connection-pooling
1049 | ;pdo_odbc.connection_pooling=strict
1050 |
1051 | ;pdo_odbc.db2_instance_name
1052 |
1053 | [PDO_SQLITE]
1054 | ;extension=pdo_sqlite.so
1055 |
1056 | [Pdo_mysql]
1057 | ; Default socket name for local MySQL connects. If empty, uses the built-in
1058 | ; MySQL defaults.
1059 | pdo_mysql.default_socket=
1060 |
1061 | [Phar]
1062 | ; http://php.net/phar.readonly
1063 | ;phar.readonly = On
1064 |
1065 | ; http://php.net/phar.require-hash
1066 | ;phar.require_hash = On
1067 |
1068 | ;phar.cache_list =
1069 |
1070 | [mail function]
1071 | ; For Win32 only.
1072 | ; http://php.net/smtp
1073 | SMTP = localhost
1074 | ; http://php.net/smtp-port
1075 | smtp_port = 25
1076 |
1077 | ; For Win32 only.
1078 | ; http://php.net/sendmail-from
1079 | ;sendmail_from = me@example.com
1080 |
1081 | ; For Unix only. You may supply arguments as well (default: "sendmail -t -i").
1082 | ; http://php.net/sendmail-path
1083 | ;sendmail_path =
1084 |
1085 | ; Force the addition of the specified parameters to be passed as extra parameters
1086 | ; to the sendmail binary. These parameters will always replace the value of
1087 | ; the 5th parameter to mail().
1088 | ;mail.force_extra_parameters =
1089 |
1090 | ; Add X-PHP-Originating-Script: that will include uid of the script followed by the filename
1091 | mail.add_x_header = Off
1092 |
1093 | ; The path to a log file that will log all mail() calls. Log entries include
1094 | ; the full path of the script, line number, To address and headers.
1095 | ;mail.log =
1096 | ; Log mail to syslog (Event Log on Windows).
1097 | ;mail.log = syslog
1098 |
1099 | [ODBC]
1100 | ; http://php.net/odbc.default-db
1101 | ;odbc.default_db = Not yet implemented
1102 |
1103 | ; http://php.net/odbc.default-user
1104 | ;odbc.default_user = Not yet implemented
1105 |
1106 | ; http://php.net/odbc.default-pw
1107 | ;odbc.default_pw = Not yet implemented
1108 |
1109 | ; Controls the ODBC cursor model.
1110 | ; Default: SQL_CURSOR_STATIC (default).
1111 | ;odbc.default_cursortype
1112 |
1113 | ; Allow or prevent persistent links.
1114 | ; http://php.net/odbc.allow-persistent
1115 | odbc.allow_persistent = On
1116 |
1117 | ; Check that a connection is still valid before reuse.
1118 | ; http://php.net/odbc.check-persistent
1119 | odbc.check_persistent = On
1120 |
1121 | ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit.
1122 | ; http://php.net/odbc.max-persistent
1123 | odbc.max_persistent = -1
1124 |
1125 | ; Maximum number of links (persistent + non-persistent). -1 means no limit.
1126 | ; http://php.net/odbc.max-links
1127 | odbc.max_links = -1
1128 |
1129 | ; Handling of LONG fields. Returns number of bytes to variables. 0 means
1130 | ; passthru.
1131 | ; http://php.net/odbc.defaultlrl
1132 | odbc.defaultlrl = 4096
1133 |
1134 | ; Handling of binary data. 0 means passthru, 1 return as is, 2 convert to char.
1135 | ; See the documentation on odbc_binmode and odbc_longreadlen for an explanation
1136 | ; of odbc.defaultlrl and odbc.defaultbinmode
1137 | ; http://php.net/odbc.defaultbinmode
1138 | odbc.defaultbinmode = 1
1139 |
1140 | [MySQLi]
1141 |
1142 | ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit.
1143 | ; http://php.net/mysqli.max-persistent
1144 | mysqli.max_persistent = -1
1145 |
1146 | ; Allow accessing, from PHP's perspective, local files with LOAD DATA statements
1147 | ; http://php.net/mysqli.allow_local_infile
1148 | ;mysqli.allow_local_infile = On
1149 |
1150 | ; Allow or prevent persistent links.
1151 | ; http://php.net/mysqli.allow-persistent
1152 | mysqli.allow_persistent = On
1153 |
1154 | ; Maximum number of links. -1 means no limit.
1155 | ; http://php.net/mysqli.max-links
1156 | mysqli.max_links = -1
1157 |
1158 | ; Default port number for mysqli_connect(). If unset, mysqli_connect() will use
1159 | ; the $MYSQL_TCP_PORT or the mysql-tcp entry in /etc/services or the
1160 | ; compile-time value defined MYSQL_PORT (in that order). Win32 will only look
1161 | ; at MYSQL_PORT.
1162 | ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-port
1163 | mysqli.default_port = 3306
1164 |
1165 | ; Default socket name for local MySQL connects. If empty, uses the built-in
1166 | ; MySQL defaults.
1167 | ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-socket
1168 | mysqli.default_socket =
1169 |
1170 | ; Default host for mysqli_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode).
1171 | ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-host
1172 | mysqli.default_host =
1173 |
1174 | ; Default user for mysqli_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode).
1175 | ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-user
1176 | mysqli.default_user =
1177 |
1178 | ; Default password for mysqli_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode).
1179 | ; Note that this is generally a *bad* idea to store passwords in this file.
1180 | ; *Any* user with PHP access can run 'echo get_cfg_var("mysqli.default_pw")
1181 | ; and reveal this password! And of course, any users with read access to this
1182 | ; file will be able to reveal the password as well.
1183 | ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-pw
1184 | mysqli.default_pw =
1185 |
1186 | ; Allow or prevent reconnect
1187 | mysqli.reconnect = Off
1188 |
1189 | [mysqlnd]
1190 | ; Enable / Disable collection of general statistics by mysqlnd which can be
1191 | ; used to tune and monitor MySQL operations.
1192 | mysqlnd.collect_statistics = On
1193 |
1194 | ; Enable / Disable collection of memory usage statistics by mysqlnd which can be
1195 | ; used to tune and monitor MySQL operations.
1196 | mysqlnd.collect_memory_statistics = Off
1197 |
1198 | ; Records communication from all extensions using mysqlnd to the specified log
1199 | ; file.
1200 | ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.debug
1201 | ;mysqlnd.debug =
1202 |
1203 | ; Defines which queries will be logged.
1204 | ;mysqlnd.log_mask = 0
1205 |
1206 | ; Default size of the mysqlnd memory pool, which is used by result sets.
1207 | ;mysqlnd.mempool_default_size = 16000
1208 |
1209 | ; Size of a pre-allocated buffer used when sending commands to MySQL in bytes.
1210 | ;mysqlnd.net_cmd_buffer_size = 2048
1211 |
1212 | ; Size of a pre-allocated buffer used for reading data sent by the server in
1213 | ; bytes.
1214 | ;mysqlnd.net_read_buffer_size = 32768
1215 |
1216 | ; Timeout for network requests in seconds.
1217 | ;mysqlnd.net_read_timeout = 31536000
1218 |
1219 | ; SHA-256 Authentication Plugin related. File with the MySQL server public RSA
1220 | ; key.
1221 | ;mysqlnd.sha256_server_public_key =
1222 |
1223 | [OCI8]
1224 |
1225 | ; Connection: Enables privileged connections using external
1226 | ; credentials (OCI_SYSOPER, OCI_SYSDBA)
1227 | ; http://php.net/oci8.privileged-connect
1228 | ;oci8.privileged_connect = Off
1229 |
1230 | ; Connection: The maximum number of persistent OCI8 connections per
1231 | ; process. Using -1 means no limit.
1232 | ; http://php.net/oci8.max-persistent
1233 | ;oci8.max_persistent = -1
1234 |
1235 | ; Connection: The maximum number of seconds a process is allowed to
1236 | ; maintain an idle persistent connection. Using -1 means idle
1237 | ; persistent connections will be maintained forever.
1238 | ; http://php.net/oci8.persistent-timeout
1239 | ;oci8.persistent_timeout = -1
1240 |
1241 | ; Connection: The number of seconds that must pass before issuing a
1242 | ; ping during oci_pconnect() to check the connection validity. When
1243 | ; set to 0, each oci_pconnect() will cause a ping. Using -1 disables
1244 | ; pings completely.
1245 | ; http://php.net/oci8.ping-interval
1246 | ;oci8.ping_interval = 60
1247 |
1248 | ; Connection: Set this to a user chosen connection class to be used
1249 | ; for all pooled server requests with Oracle 11g Database Resident
1250 | ; Connection Pooling (DRCP). To use DRCP, this value should be set to
1251 | ; the same string for all web servers running the same application,
1252 | ; the database pool must be configured, and the connection string must
1253 | ; specify to use a pooled server.
1254 | ;oci8.connection_class =
1255 |
1256 | ; High Availability: Using On lets PHP receive Fast Application
1257 | ; Notification (FAN) events generated when a database node fails. The
1258 | ; database must also be configured to post FAN events.
1259 | ;oci8.events = Off
1260 |
1261 | ; Tuning: This option enables statement caching, and specifies how
1262 | ; many statements to cache. Using 0 disables statement caching.
1263 | ; http://php.net/oci8.statement-cache-size
1264 | ;oci8.statement_cache_size = 20
1265 |
1266 | ; Tuning: Enables statement prefetching and sets the default number of
1267 | ; rows that will be fetched automatically after statement execution.
1268 | ; http://php.net/oci8.default-prefetch
1269 | ;oci8.default_prefetch = 100
1270 |
1271 | ; Compatibility. Using On means oci_close() will not close
1272 | ; oci_connect() and oci_new_connect() connections.
1273 | ; http://php.net/oci8.old-oci-close-semantics
1274 | ;oci8.old_oci_close_semantics = Off
1275 |
1276 | [PostgreSQL]
1277 | ; Allow or prevent persistent links.
1278 | ; http://php.net/pgsql.allow-persistent
1279 | pgsql.allow_persistent = On
1280 |
1281 | ; Detect broken persistent links always with pg_pconnect().
1282 | ; Auto reset feature requires a little overheads.
1283 | ; http://php.net/pgsql.auto-reset-persistent
1284 | pgsql.auto_reset_persistent = Off
1285 |
1286 | ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit.
1287 | ; http://php.net/pgsql.max-persistent
1288 | pgsql.max_persistent = -1
1289 |
1290 | ; Maximum number of links (persistent+non persistent). -1 means no limit.
1291 | ; http://php.net/pgsql.max-links
1292 | pgsql.max_links = -1
1293 |
1294 | ; Ignore PostgreSQL backends Notice message or not.
1295 | ; Notice message logging require a little overheads.
1296 | ; http://php.net/pgsql.ignore-notice
1297 | pgsql.ignore_notice = 0
1298 |
1299 | ; Log PostgreSQL backends Notice message or not.
1300 | ; Unless pgsql.ignore_notice=0, module cannot log notice message.
1301 | ; http://php.net/pgsql.log-notice
1302 | pgsql.log_notice = 0
1303 |
1304 | [bcmath]
1305 | ; Number of decimal digits for all bcmath functions.
1306 | ; http://php.net/bcmath.scale
1307 | bcmath.scale = 0
1308 |
1309 | [browscap]
1310 | ; http://php.net/browscap
1311 | ;browscap = extra/browscap.ini
1312 |
1313 | [Session]
1314 | ; Handler used to store/retrieve data.
1315 | ; http://php.net/session.save-handler
1316 | session.save_handler = files
1317 |
1318 | ; Argument passed to save_handler. In the case of files, this is the path
1319 | ; where data files are stored. Note: Windows users have to change this
1320 | ; variable in order to use PHP's session functions.
1321 | ;
1322 | ; The path can be defined as:
1323 | ;
1324 | ; session.save_path = "N;/path"
1325 | ;
1326 | ; where N is an integer. Instead of storing all the session files in
1327 | ; /path, what this will do is use subdirectories N-levels deep, and
1328 | ; store the session data in those directories. This is useful if
1329 | ; your OS has problems with many files in one directory, and is
1330 | ; a more efficient layout for servers that handle many sessions.
1331 | ;
1332 | ; NOTE 1: PHP will not create this directory structure automatically.
1333 | ; You can use the script in the ext/session dir for that purpose.
1334 | ; NOTE 2: See the section on garbage collection below if you choose to
1335 | ; use subdirectories for session storage
1336 | ;
1337 | ; The file storage module creates files using mode 600 by default.
1338 | ; You can change that by using
1339 | ;
1340 | ; session.save_path = "N;MODE;/path"
1341 | ;
1342 | ; where MODE is the octal representation of the mode. Note that this
1343 | ; does not overwrite the process's umask.
1344 | ; http://php.net/session.save-path
1345 | ;session.save_path = "/tmp"
1346 |
1347 | ; Whether to use strict session mode.
1348 | ; Strict session mode does not accept an uninitialized session ID, and
1349 | ; regenerates the session ID if the browser sends an uninitialized session ID.
1350 | ; Strict mode protects applications from session fixation via a session adoption
1351 | ; vulnerability. It is disabled by default for maximum compatibility, but
1352 | ; enabling it is encouraged.
1353 | ; https://wiki.php.net/rfc/strict_sessions
1354 | session.use_strict_mode = 0
1355 |
1356 | ; Whether to use cookies.
1357 | ; http://php.net/session.use-cookies
1358 | session.use_cookies = 1
1359 |
1360 | ; http://php.net/session.cookie-secure
1361 | ;session.cookie_secure =
1362 |
1363 | ; This option forces PHP to fetch and use a cookie for storing and maintaining
1364 | ; the session id. We encourage this operation as it's very helpful in combating
1365 | ; session hijacking when not specifying and managing your own session id. It is
1366 | ; not the be-all and end-all of session hijacking defense, but it's a good start.
1367 | ; http://php.net/session.use-only-cookies
1368 | session.use_only_cookies = 1
1369 |
1370 | ; Name of the session (used as cookie name).
1371 | ; http://php.net/session.name
1372 | session.name = PHPSESSID
1373 |
1374 | ; Initialize session on request startup.
1375 | ; http://php.net/session.auto-start
1376 | session.auto_start = 0
1377 |
1378 | ; Lifetime in seconds of cookie or, if 0, until browser is restarted.
1379 | ; http://php.net/session.cookie-lifetime
1380 | session.cookie_lifetime = 0
1381 |
1382 | ; The path for which the cookie is valid.
1383 | ; http://php.net/session.cookie-path
1384 | session.cookie_path = /
1385 |
1386 | ; The domain for which the cookie is valid.
1387 | ; http://php.net/session.cookie-domain
1388 | session.cookie_domain =
1389 |
1390 | ; Whether or not to add the httpOnly flag to the cookie, which makes it
1391 | ; inaccessible to browser scripting languages such as JavaScript.
1392 | ; http://php.net/session.cookie-httponly
1393 | session.cookie_httponly =
1394 |
1395 | ; Add SameSite attribute to cookie to help mitigate Cross-Site Request Forgery (CSRF/XSRF)
1396 | ; Current valid values are "Strict", "Lax" or "None". When using "None",
1397 | ; make sure to include the quotes, as `none` is interpreted like `false` in ini files.
1398 | ; https://tools.ietf.org/html/draft-west-first-party-cookies-07
1399 | session.cookie_samesite =
1400 |
1401 | ; Handler used to serialize data. php is the standard serializer of PHP.
1402 | ; http://php.net/session.serialize-handler
1403 | session.serialize_handler = php
1404 |
1405 | ; Defines the probability that the 'garbage collection' process is started on every
1406 | ; session initialization. The probability is calculated by using gc_probability/gc_divisor,
1407 | ; e.g. 1/100 means there is a 1% chance that the GC process starts on each request.
1408 | ; Default Value: 1
1409 | ; Development Value: 1
1410 | ; Production Value: 1
1411 | ; http://php.net/session.gc-probability
1412 | session.gc_probability = 1
1413 |
1414 | ; Defines the probability that the 'garbage collection' process is started on every
1415 | ; session initialization. The probability is calculated by using gc_probability/gc_divisor,
1416 | ; e.g. 1/100 means there is a 1% chance that the GC process starts on each request.
1417 | ; For high volume production servers, using a value of 1000 is a more efficient approach.
1418 | ; Default Value: 100
1419 | ; Development Value: 1000
1420 | ; Production Value: 1000
1421 | ; http://php.net/session.gc-divisor
1422 | session.gc_divisor = 1000
1423 |
1424 | ; After this number of seconds, stored data will be seen as 'garbage' and
1425 | ; cleaned up by the garbage collection process.
1426 | ; http://php.net/session.gc-maxlifetime
1427 | session.gc_maxlifetime = 1440
1428 |
1429 | ; NOTE: If you are using the subdirectory option for storing session files
1430 | ; (see session.save_path above), then garbage collection does *not*
1431 | ; happen automatically. You will need to do your own garbage
1432 | ; collection through a shell script, cron entry, or some other method.
1433 | ; For example, the following script is the equivalent of setting
1434 | ; session.gc_maxlifetime to 1440 (1440 seconds = 24 minutes):
1435 | ; find /path/to/sessions -cmin +24 -type f | xargs rm
1436 |
1437 | ; Check HTTP Referer to invalidate externally stored URLs containing ids.
1438 | ; HTTP_REFERER has to contain this substring for the session to be
1439 | ; considered as valid.
1440 | ; http://php.net/session.referer-check
1441 | session.referer_check =
1442 |
1443 | ; Set to {nocache,private,public,} to determine HTTP caching aspects
1444 | ; or leave this empty to avoid sending anti-caching headers.
1445 | ; http://php.net/session.cache-limiter
1446 | session.cache_limiter = nocache
1447 |
1448 | ; Document expires after n minutes.
1449 | ; http://php.net/session.cache-expire
1450 | session.cache_expire = 180
1451 |
1452 | ; trans sid support is disabled by default.
1453 | ; Use of trans sid may risk your users' security.
1454 | ; Use this option with caution.
1455 | ; - User may send URL contains active session ID
1456 | ; to other person via. email/irc/etc.
1457 | ; - URL that contains active session ID may be stored
1458 | ; in publicly accessible computer.
1459 | ; - User may access your site with the same session ID
1460 | ; always using URL stored in browser's history or bookmarks.
1461 | ; http://php.net/session.use-trans-sid
1462 | session.use_trans_sid = 0
1463 |
1464 | ; Set session ID character length. This value could be between 22 to 256.
1465 | ; Shorter length than default is supported only for compatibility reason.
1466 | ; Users should use 32 or more chars.
1467 | ; http://php.net/session.sid-length
1468 | ; Default Value: 32
1469 | ; Development Value: 26
1470 | ; Production Value: 26
1471 | session.sid_length = 26
1472 |
1473 | ; The URL rewriter will look for URLs in a defined set of HTML tags.
1474 | ;