 29 |
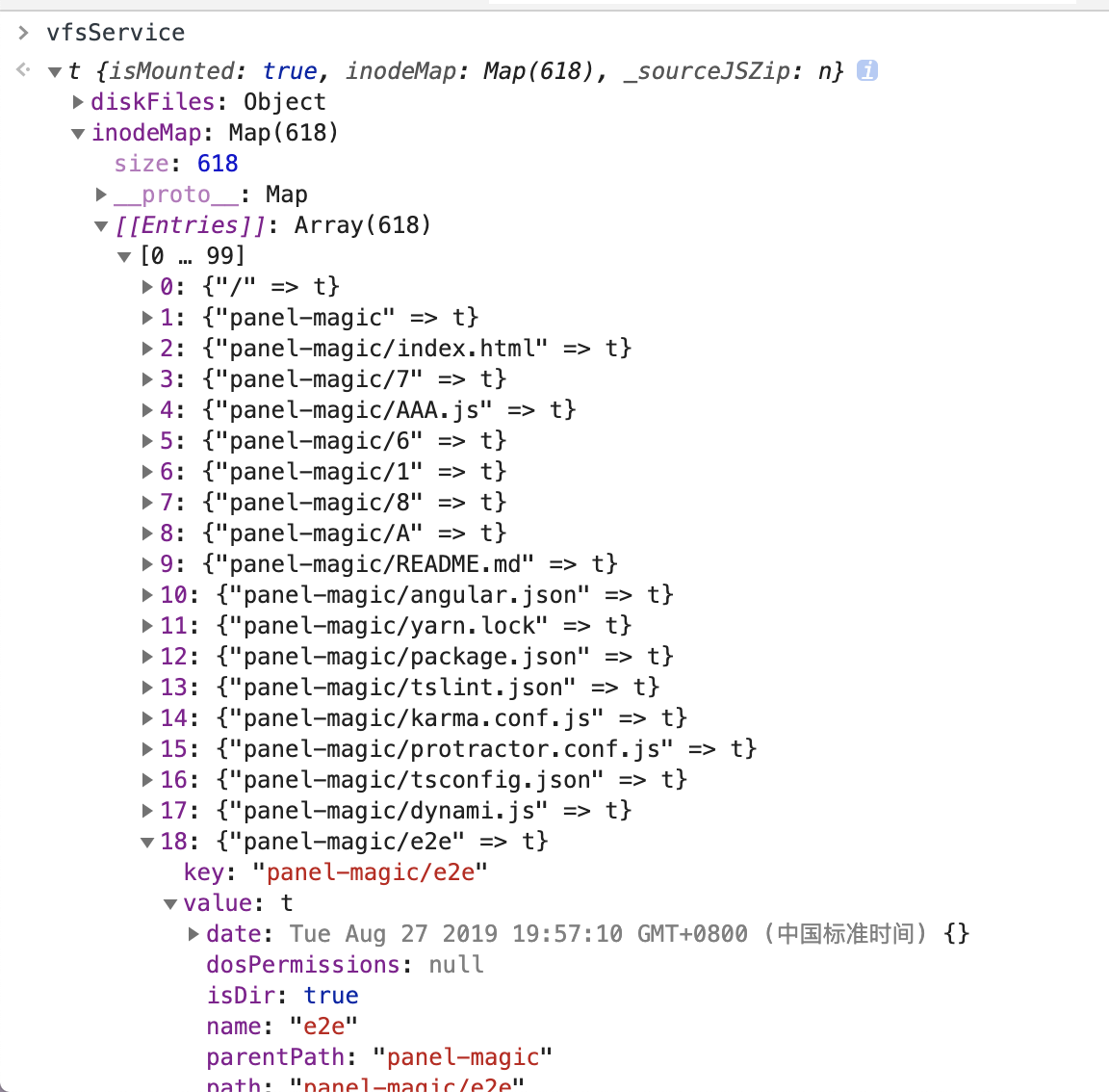
30 | The root directory defaults to '/', you can use the 'ls' method to view all files in a directory, for example
31 |
32 | ```typescript
33 | vfsService.ls('/').then((data: Inode[]) => {
34 | // do it
35 | })
36 | ```
37 |
38 |
29 |
30 | The root directory defaults to '/', you can use the 'ls' method to view all files in a directory, for example
31 |
32 | ```typescript
33 | vfsService.ls('/').then((data: Inode[]) => {
34 | // do it
35 | })
36 | ```
37 |
38 | 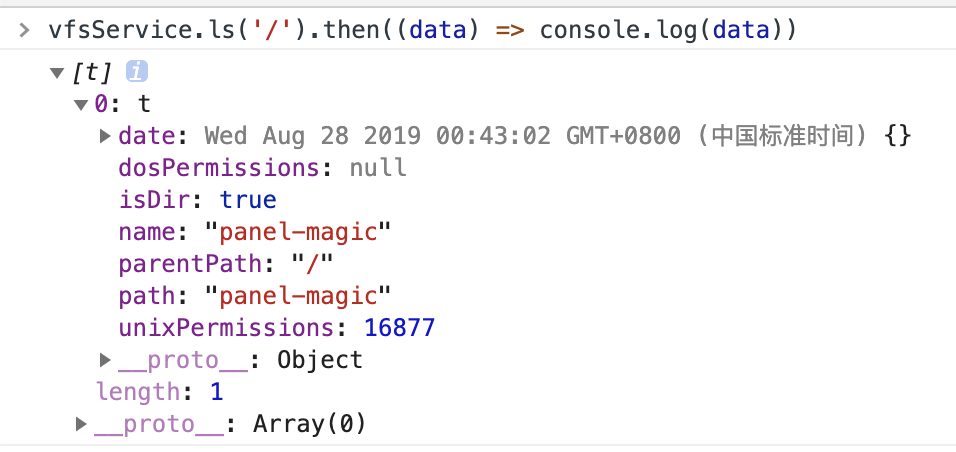 39 |
40 | 🌈enjoy😊🌈
41 |
42 | # api
43 |
44 | ```typescript
45 | interface IVfsable
39 |
40 | 🌈enjoy😊🌈
41 |
42 | # api
43 |
44 | ```typescript
45 | interface IVfsable\n \n
\n );\n};\n\nexport default UploadForm;\n","import { Inode } from \"vfs-frontend\";\n\nexport class TInode extends Inode {\n\n public children!: TInode[]\n\n constructor() {\n super();\n this.init()\n }\n\n public init(): void {\n this.children = []\n }\n\n public setChildren(c: TInode[]): this {\n this.children = c || []\n return this\n }\n\n}\n","import { TInode } from \"./model\";\n\nexport const generateInode = (e: TInode): TInode => {\n return new TInode()\n .setName(e.name)\n .setDate(e.date || new Date())\n .setDosPermissions(e.dosPermissions!)\n .setIsDir(e.isDir)\n .setParentPath(e.parentPath)\n .setPath(e.path)\n .setUnixPermissions(e.unixPermissions!);\n};\n\n// 文件排序\nexport const handleSortFileList = (data: TInode[]): TInode[] => {\n // 比较首字母ACS编码排序\n const sliceData = data.slice(0);\n const sortCharCode = (pre: TInode, cur: TInode): boolean => cur.name.localeCompare(pre.name) > 0;\n const quickSort = (arr: TInode[]): TInode[] => {\n if (arr.length <= 1) return arr;\n const pivotFile = arr.splice(Math.floor(arr.length / 2), 1)[0];\n const left = [];\n const right = [];\n for (let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {\n const currentFile = arr[i];\n if (currentFile.isDir === true && pivotFile.isDir === false) left.push(currentFile);\n else {\n if (currentFile.isDir === pivotFile.isDir) {\n sortCharCode(currentFile, pivotFile) ? left.push(currentFile) : right.push(currentFile);\n } else right.push(currentFile);\n }\n }\n return quickSort(left).concat([pivotFile], quickSort(right));\n };\n const result = quickSort(sliceData);\n return result;\n};\n\nexport const findTreeData = (source: TInode[], target: string): TInode | undefined => {\n const flat = (arr: TInode[]): TInode[] => {\n return arr.reduce(\n (pre: TInode[], cur) =>\n Array.isArray(cur.children) && cur.children.length > 0\n ? pre.concat(flat(cur.children))\n : pre.concat(cur),\n []\n );\n };\n const dimenList = flat(source);\n return dimenList.find(e => e.path === target);\n};\n","import React, { useEffect, useState } from \"react\";\nimport { Tree } from \"antd\";\nimport { TInode } from \"./model\";\nimport { ZipVFSService } from \"vfs-frontend\";\nimport { generateInode, handleSortFileList, findTreeData } from \"./util\";\nimport \"../../file-icons-js.css\";\n\nconst { TreeNode, DirectoryTree } = Tree;\nconst fileIcons = require(\"file-icons-js\");\n\ninterface PropsTreeComp {\n data: TInode[];\n vfsService?: ZipVFSService;\n onLaunchFileDetails?: (d: string) => void;\n}\n\nconst TreeComp = (props: PropsTreeComp): JSX.Element => {\n const { data, vfsService, onLaunchFileDetails } = props;\n\n const [inodeData, setInodeData] = useState\n {inodeData.length ? (\n {renderTreeNodes(inodeData)} \n ) : null}\n
\n );\n};\n\nexport default TreeComp;\n","import React from \"react\";\n\nimport \"./index.scss\";\n\ninterface PropsDetails {\n content: string;\n}\n\nconst Details = (props: PropsDetails): JSX.Element => {\n const { content } = props;\n return (\n \n
\n );\n};\n\nexport default Details;\n","import React, { useState } from \"react\";\nimport { Layout, Typography, Input, Button, Spin } from \"antd\";\nimport UploadForm from \"../component/upload-form\";\nimport { ZipVFSService, Inode } from \"vfs-frontend\";\nimport TreeComp from \"../component/tree\";\n\nimport \"./index.scss\";\nimport { TInode } from \"../component/tree/model\";\nimport Details from \"../component/details\";\n\nconst vfsService = new ZipVFSService();\n\nconst Page = () => {\n const [treeData, setTreeData] = useState\n
\n {content}\n \n 返回 Blob 数据格式的接口 \n setBlobUrl(e.target.value)}>\n \n
\n );\n };\n\n return (\n \n \n \n \n \n
\n );\n};\n\nexport default Page;\n","// This optional code is used to register a service worker.\n// register() is not called by default.\n\n// This lets the app load faster on subsequent visits in production, and gives\n// it offline capabilities. However, it also means that developers (and users)\n// will only see deployed updates on subsequent visits to a page, after all the\n// existing tabs open on the page have been closed, since previously cached\n// resources are updated in the background.\n\n// To learn more about the benefits of this model and instructions on how to\n// opt-in, read https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA\n\nconst isLocalhost = Boolean(\n window.location.hostname === 'localhost' ||\n // [::1] is the IPv6 localhost address.\n window.location.hostname === '[::1]' ||\n // 127.0.0.1/8 is considered localhost for IPv4.\n window.location.hostname.match(\n /^127(?:\\.(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)){3}$/\n )\n);\n\nexport function register(config) {\n if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' && 'serviceWorker' in navigator) {\n // The URL constructor is available in all browsers that support SW.\n const publicUrl = new URL(process.env.PUBLIC_URL, window.location.href);\n if (publicUrl.origin !== window.location.origin) {\n // Our service worker won't work if PUBLIC_URL is on a different origin\n // from what our page is served on. This might happen if a CDN is used to\n // serve assets; see https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app/issues/2374\n return;\n }\n\n window.addEventListener('load', () => {\n const swUrl = `${process.env.PUBLIC_URL}/service-worker.js`;\n\n if (isLocalhost) {\n // This is running on localhost. Let's check if a service worker still exists or not.\n checkValidServiceWorker(swUrl, config);\n\n // Add some additional logging to localhost, pointing developers to the\n // service worker/PWA documentation.\n navigator.serviceWorker.ready.then(() => {\n console.log(\n 'This web app is being served cache-first by a service ' +\n 'worker. To learn more, visit https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA'\n );\n });\n } else {\n // Is not localhost. Just register service worker\n registerValidSW(swUrl, config);\n }\n });\n }\n}\n\nfunction registerValidSW(swUrl, config) {\n navigator.serviceWorker\n .register(swUrl)\n .then(registration => {\n registration.onupdatefound = () => {\n const installingWorker = registration.installing;\n if (installingWorker == null) {\n return;\n }\n installingWorker.onstatechange = () => {\n if (installingWorker.state === 'installed') {\n if (navigator.serviceWorker.controller) {\n // At this point, the updated precached content has been fetched,\n // but the previous service worker will still serve the older\n // content until all client tabs are closed.\n console.log(\n 'New content is available and will be used when all ' +\n 'tabs for this page are closed. See https://bit.ly/CRA-PWA.'\n );\n\n // Execute callback\n if (config && config.onUpdate) {\n config.onUpdate(registration);\n }\n } else {\n // At this point, everything has been precached.\n // It's the perfect time to display a\n // \"Content is cached for offline use.\" message.\n console.log('Content is cached for offline use.');\n\n // Execute callback\n if (config && config.onSuccess) {\n config.onSuccess(registration);\n }\n }\n }\n };\n };\n })\n .catch(error => {\n console.error('Error during service worker registration:', error);\n });\n}\n\nfunction checkValidServiceWorker(swUrl, config) {\n // Check if the service worker can be found. If it can't reload the page.\n fetch(swUrl)\n .then(response => {\n // Ensure service worker exists, and that we really are getting a JS file.\n const contentType = response.headers.get('content-type');\n if (\n response.status === 404 ||\n (contentType != null && contentType.indexOf('javascript') === -1)\n ) {\n // No service worker found. Probably a different app. Reload the page.\n navigator.serviceWorker.ready.then(registration => {\n registration.unregister().then(() => {\n window.location.reload();\n });\n });\n } else {\n // Service worker found. Proceed as normal.\n registerValidSW(swUrl, config);\n }\n })\n .catch(() => {\n console.log(\n 'No internet connection found. App is running in offline mode.'\n );\n });\n}\n\nexport function unregister() {\n if ('serviceWorker' in navigator) {\n navigator.serviceWorker.ready.then(registration => {\n registration.unregister();\n });\n }\n}\n","import React from \"react\";\nimport ReactDOM from \"react-dom\";\nimport \"./index.scss\";\nimport Page from \"./page\";\nimport * as serviceWorker from \"./serviceWorker\";\n\nReactDOM.render(\n \n or\n \n {renderFeatchUrlForm()}\n
\n \n \n \n \n
\n \n
\n \n