├── FD
├── __init__.py
├── fd_act.py
├── lenet.py
├── linear_regression.py
├── many_fd.py
├── regression.py
└── train_regnet.py
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── image_transformation
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── synthesize_set_cifar.py
└── synthesize_set_coco.py
├── learn
├── __init__.py
├── many_test.py
├── train.py
└── utils.py
└── meta_set
├── main.py
├── mnist.py
└── utils.py
/FD/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Simon4Yan/Meta-set/58e498cc95a879eec369d2ccf8da714baf8480e2/FD/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/FD/fd_act.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import sys
3 |
4 | sys.path.append(".")
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from scipy import linalg
7 | from tqdm import trange
8 |
9 |
10 | def calculate_frechet_distance(mu1, sigma1, mu2, sigma2, eps=1e-6):
11 | """Numpy implementation of the Frechet Distance.
12 | The Frechet distance between two multivariate Gaussians X_1 ~ N(mu_1, C_1)
13 | and X_2 ~ N(mu_2, C_2) is
14 | d^2 = ||mu_1 - mu_2||^2 + Tr(C_1 + C_2 - 2*sqrt(C_1*C_2)).
15 |
16 | Stable version by Dougal J. Sutherland.
17 |
18 | Params:
19 | -- mu1 : Numpy array containing the activations of a layer of the
20 | inception net (like returned by the function 'get_predictions')
21 | for generated samples.
22 | -- mu2 : The sample mean over activations, precalculated on an
23 | representative data set.
24 | -- sigma1: The covariance matrix over activations for generated samples.
25 | -- sigma2: The covariance matrix over activations, precalculated on an
26 | representative data set.
27 |
28 | Returns:
29 | -- : The Frechet Distance.
30 | """
31 |
32 | mu1 = np.atleast_1d(mu1)
33 | mu2 = np.atleast_1d(mu2)
34 |
35 | sigma1 = np.atleast_2d(sigma1)
36 | sigma2 = np.atleast_2d(sigma2)
37 |
38 | assert mu1.shape == mu2.shape, \
39 | 'Training and test mean vectors have different lengths'
40 | assert sigma1.shape == sigma2.shape, \
41 | 'Training and test covariances have different dimensions'
42 |
43 | diff = mu1 - mu2
44 |
45 | # Product might be almost singular
46 | covmean, _ = linalg.sqrtm(sigma1.dot(sigma2), disp=False)
47 | if not np.isfinite(covmean).all():
48 | msg = ('fid calculation produces singular product; '
49 | 'adding %s to diagonal of cov estimates') % eps
50 | print(msg)
51 | offset = np.eye(sigma1.shape[0]) * eps
52 | covmean = linalg.sqrtm((sigma1 + offset).dot(sigma2 + offset))
53 |
54 | # Numerical error might give slight imaginary component
55 | if np.iscomplexobj(covmean):
56 | if not np.allclose(np.diagonal(covmean).imag, 0, atol=1e-3):
57 | m = np.max(np.abs(covmean.imag))
58 | raise ValueError('Imaginary component {}'.format(m))
59 | covmean = covmean.real
60 |
61 | tr_covmean = np.trace(covmean)
62 |
63 | return (diff.dot(diff) + np.trace(sigma1) +
64 | np.trace(sigma2) - 2 * tr_covmean)
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == '__main__':
68 | test_dirs = sorted(os.listdir('../dataset_bg'))
69 | fid_bg = []
70 | m1 = np.load('./dataset_feature/train_mean.npy')
71 | s1 = np.load('./dataset_feature/train_variance.npy')
72 | act1 = np.load('./dataset_feature/train_feature.npy')
73 |
74 | for i in trange(len(test_dirs)):
75 | path = test_dirs[i]
76 | m2 = np.load('./dataset_feature/_%s_mean.npy' % (path))
77 | s2 = np.load('./dataset_feature/_%s_variance.npy' % (path))
78 | act2 = np.load('./dataset_feature/_%s_feature.npy' % (path))
79 | fd_value = calculate_frechet_distance(m1, s1, m2, s2)
80 | print('FD: ', fd_value)
81 | fid_bg.append(fd_value)
82 |
83 | np.save('fd_mnist.npy', fid_bg)
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/FD/lenet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 |
5 |
6 | def init_weights(m):
7 | classname = m.__class__.__name__
8 | if classname.find('Conv2d') != -1 or classname.find('ConvTranspose2d') != -1:
9 | nn.init.kaiming_uniform_(m.weight)
10 | nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
11 | elif classname.find('BatchNorm') != -1:
12 | nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 1.0, 0.02)
13 | nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
14 | elif classname.find('Linear') != -1:
15 | nn.init.xavier_normal_(m.weight)
16 | nn.init.zeros_(m.bias)
17 |
18 |
19 | # For SVHN dataset
20 | class DTN(nn.Module):
21 | def __init__(self):
22 | super(DTN, self).__init__()
23 | self.conv_params = nn.Sequential(
24 | nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=5, stride=2, padding=2),
25 | nn.BatchNorm2d(64),
26 | nn.Dropout2d(0.1),
27 | nn.ReLU(),
28 | nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=5, stride=2, padding=2),
29 | nn.BatchNorm2d(128),
30 | nn.Dropout2d(0.3),
31 | nn.ReLU(),
32 | nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel_size=5, stride=2, padding=2),
33 | nn.BatchNorm2d(256),
34 | nn.Dropout2d(0.5),
35 | nn.ReLU()
36 | )
37 |
38 | self.fc_params = nn.Sequential(
39 | nn.Linear(256 * 4 * 4, 512),
40 | nn.BatchNorm1d(512),
41 | nn.ReLU(),
42 | nn.Dropout()
43 | )
44 |
45 | self.classifier = nn.Linear(512, 10)
46 | self.__in_features = 512
47 |
48 | def forward(self, x):
49 | x = self.conv_params(x)
50 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
51 | x = self.fc_params(x)
52 | y = self.classifier(x)
53 | return x, y
54 |
55 | def output_num(self):
56 | return self.__in_features
57 |
58 |
59 | class LeNet(nn.Module):
60 | def __init__(self):
61 | super(LeNet, self).__init__()
62 | self.conv_params = nn.Sequential(
63 | nn.Conv2d(1, 20, kernel_size=5),
64 | nn.MaxPool2d(2),
65 | nn.ReLU(),
66 | nn.Conv2d(20, 50, kernel_size=5),
67 | nn.Dropout2d(p=0.5),
68 | nn.MaxPool2d(2),
69 | nn.ReLU(),
70 | )
71 |
72 | self.fc_params = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(50 * 4 * 4, 500), nn.ReLU(), nn.Dropout(p=0.5))
73 | self.classifier = nn.Linear(500, 10)
74 | self.__in_features = 500
75 |
76 | def forward(self, x):
77 | x = self.conv_params(x)
78 | x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
79 | x = self.fc_params(x)
80 | y = self.classifier(x)
81 | return x, y
82 |
83 | def output_num(self):
84 | return self.__in_features
85 |
86 |
87 | class Net(nn.Module):
88 | def __init__(self):
89 | super(Net, self).__init__()
90 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3, 1)
91 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1)
92 | self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout2d(0.25)
93 | self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout2d(0.5)
94 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9216, 128)
95 | self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
96 |
97 | def forward(self, x):
98 | x = self.conv1(x)
99 | x = F.relu(x)
100 | x = self.conv2(x)
101 | x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
102 | x = self.dropout1(x)
103 | x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
104 | x = self.fc1(x)
105 | # x = F.relu(x)
106 | # x = self.dropout2(x)
107 | # x = self.fc2(x)
108 | output = x
109 | # output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
110 | return output
111 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/FD/linear_regression.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 | import numpy as np
3 | from scipy import stats
4 | from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
5 | from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
6 | from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
7 | from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
8 |
9 | # data preparation
10 | acc = np.load('./learn/accuracy_mnist.npy')
11 | data = np.load('./FD/fd_mnist.npy').reshape(-1, 1)
12 |
13 | # Choose some sample sets as validation (also used in NN regression)
14 | indice = 30
15 | train_data = data[indice:]
16 | train_acc = acc[indice:]
17 | test_data = train_data[:indice]
18 | test_acc = train_acc[:indice]
19 |
20 | # linear regression
21 | slr = LinearRegression()
22 | slr.fit(train_data, train_acc)
23 | test_pred = slr.predict(test_data)
24 |
25 | # plot training dataset
26 | plt.scatter(train_data, train_acc, color='#0000FF')
27 | plt.plot(train_data, slr.predict(train_data), color='#FF0000')
28 |
29 | ax = plt.gca()
30 | ax.spines['bottom'].set_linewidth(2)
31 | ax.spines['left'].set_linewidth(2)
32 | ax.spines['right'].set_color('none')
33 | ax.spines['top'].set_color('none')
34 | plt.savefig('linear_regression_train.png')
35 | plt.close()
36 |
37 | # plot testing dataset
38 | plt.scatter(test_data, test_acc, color='red')
39 | plt.plot(test_data, slr.predict(test_data), color='blue')
40 | plt.savefig('linear_regression_test.png')
41 |
42 | print('*****'*5)
43 | print('If you could observe the linear correlation from figures, then your implementations are all good!')
44 | print('*****'*5)
45 |
46 | # evaluation with metrics
47 | print('Test on Validation Set..')
48 | R2 = r2_score(test_acc, slr.predict(test_data))
49 | RMSE = mean_squared_error(test_acc, slr.predict(test_data), squared=False)
50 | MAE = mean_absolute_error(test_acc, slr.predict(test_data))
51 | print('\nTest set: R2 :{:.4f} RMSE: {:.4f} MAE: {:.4f}\n'.format(R2, RMSE, MAE))
52 |
53 | # analyze the statistical correlation
54 | rho, pval = stats.spearmanr(test_data, test_acc)
55 | print('\nRank correlation-rho', rho)
56 | print('Rank correlation-pval', pval)
57 |
58 | rho, pval = stats.pearsonr(test_data.reshape(-1, 1), test_acc.reshape(-1, 1))
59 | print('\nPearsons correlation-rho', rho)
60 | print('Pearsons correlation-pval', pval)
61 |
62 | print('*****'*5)
63 | print('\nAll done! Thanks!')
64 | print('*****'*5)
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/FD/many_fd.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import sys
3 |
4 | sys.path.append(".")
5 | from argparse import ArgumentParser, ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
6 |
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import torch
9 | from scipy import linalg
10 | from torchvision import transforms
11 | from tqdm import trange
12 |
13 | from FD.lenet import Net
14 | from learn.utils import MNIST
15 |
16 | try:
17 | from tqdm import tqdm
18 | except ImportError:
19 | # If not tqdm is not available, provide a mock version of it
20 | def tqdm(x):
21 | return x
22 |
23 | parser = ArgumentParser(formatter_class=ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter,
24 | description='PyTorch MNIST FD-Metaset')
25 | parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=128,
26 | help='Batch size to use')
27 | parser.add_argument('--dims', type=int, default=128,
28 | choices=list([128, 9216]),
29 | help=('Dimensionality of Inception features to use. '
30 | 'By default, uses pool3 features'))
31 | parser.add_argument('-c', '--gpu', default='1', type=str,
32 | help='GPU to use (leave blank for CPU only)')
33 |
34 |
35 | def get_activations(files, model, batch_size=50, dims=2048,
36 | cuda=False, overlap=False, verbose=False):
37 | """Calculates the activations of the pool_3 layer for all images.
38 |
39 | Params:
40 | -- files : List of image files paths
41 | -- model : Instance of inception model
42 | -- batch_size : Batch size of images for the model to process at once.
43 | Make sure that the number of samples is a multiple of
44 | the batch size, otherwise some samples are ignored. This
45 | behavior is retained to match the original FD score
46 | implementation.
47 | -- dims : Dimensionality of features returned by Inception
48 | -- cuda : If set to True, use GPU
49 | -- verbose : If set to True and parameter out_step is given, the number
50 | of calculated batches is reported.
51 | Returns:
52 | -- A numpy array of dimension (num images, dims) that contains the
53 | activations of the given tensor when feeding inception with the
54 | query tensor.
55 | """
56 |
57 | if overlap:
58 | files = './dataset_bg/' + files
59 | test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
60 | MNIST(files, 'test_data.npy', 'test_label.npy', transform=transforms.Compose([
61 | transforms.ToTensor(),
62 | transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,)) # transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
63 | ])),
64 | batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, drop_last=True)
65 | else:
66 | files = './dataset/mnist'
67 | test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
68 | MNIST(files, 'test_data.npy', 'test_label.npy', transform=transforms.Compose([
69 | transforms.ToTensor(),
70 | transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,)) # transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
71 | ])),
72 | batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False, drop_last=True)
73 |
74 | n_batches = len(test_loader.dataset) // batch_size
75 | n_used_imgs = n_batches * batch_size
76 |
77 | pred_arr = np.empty((n_used_imgs, dims))
78 |
79 | for i, data in enumerate(test_loader):
80 | if verbose:
81 | print('\rPropagating batch %d/%d' % (i + 1, n_batches),
82 | end='', flush=True)
83 | start = i * batch_size
84 | end = start + batch_size
85 |
86 | batch, _ = data
87 |
88 | if cuda:
89 | batch = batch.cuda()
90 |
91 | pred = model(batch)
92 |
93 | pred_arr[start:end] = pred.cpu().data.numpy().reshape(batch_size, -1)
94 |
95 | if verbose:
96 | print(' done')
97 |
98 | return pred_arr
99 |
100 |
101 | def calculate_frechet_distance(mu1, sigma1, mu2, sigma2, eps=1e-6):
102 | """Numpy implementation of the Frechet Distance.
103 | The Frechet distance between two multivariate Gaussians X_1 ~ N(mu_1, C_1)
104 | and X_2 ~ N(mu_2, C_2) is
105 | d^2 = ||mu_1 - mu_2||^2 + Tr(C_1 + C_2 - 2*sqrt(C_1*C_2)).
106 |
107 | Stable version by Dougal J. Sutherland.
108 |
109 | Params:
110 | -- mu1 : Numpy array containing the activations of a layer of the
111 | inception net (like returned by the function 'get_predictions')
112 | for generated samples.
113 | -- mu2 : The sample mean over activations, precalculated on an
114 | representative data set.
115 | -- sigma1: The covariance matrix over activations for generated samples.
116 | -- sigma2: The covariance matrix over activations, precalculated on an
117 | representative data set.
118 |
119 | Returns:
120 | -- : The Frechet Distance.
121 | """
122 |
123 | mu1 = np.atleast_1d(mu1)
124 | mu2 = np.atleast_1d(mu2)
125 |
126 | sigma1 = np.atleast_2d(sigma1)
127 | sigma2 = np.atleast_2d(sigma2)
128 |
129 | assert mu1.shape == mu2.shape, \
130 | 'Training and test mean vectors have different lengths'
131 | assert sigma1.shape == sigma2.shape, \
132 | 'Training and test covariances have different dimensions'
133 |
134 | diff = mu1 - mu2
135 |
136 | # Product might be almost singular
137 | covmean, _ = linalg.sqrtm(sigma1.dot(sigma2), disp=False)
138 | if not np.isfinite(covmean).all():
139 | msg = ('fid calculation produces singular product; '
140 | 'adding %s to diagonal of cov estimates') % eps
141 | print(msg)
142 | offset = np.eye(sigma1.shape[0]) * eps
143 | covmean = linalg.sqrtm((sigma1 + offset).dot(sigma2 + offset))
144 |
145 | # Numerical error might give slight imaginary component
146 | if np.iscomplexobj(covmean):
147 | if not np.allclose(np.diagonal(covmean).imag, 0, atol=1e-3):
148 | m = np.max(np.abs(covmean.imag))
149 | raise ValueError('Imaginary component {}'.format(m))
150 | covmean = covmean.real
151 |
152 | tr_covmean = np.trace(covmean)
153 |
154 | return (diff.dot(diff) + np.trace(sigma1) +
155 | np.trace(sigma2) - 2 * tr_covmean)
156 |
157 |
158 | def calculate_activation_statistics(files, model, batch_size=50,
159 | dims=2048, cuda=False, overlap=False):
160 | """Calculation of the statistics used by the FD.
161 | Params:
162 | -- files : List of image files paths
163 | -- model : Instance of inception model
164 | -- batch_size : The images numpy array is split into batches with
165 | batch size batch_size. A reasonable batch size
166 | depends on the hardware.
167 | -- dims : Dimensionality of features returned by Inception
168 | -- cuda : If set to True, use GPU
169 | -- verbose : If set to True and parameter out_step is given, the
170 | number of calculated batches is reported.
171 | Returns:
172 | -- mu : The mean over samples of the activations of the pool_3 layer of
173 | the inception model.
174 | -- sigma : The covariance matrix of the activations of the pool_3 layer of
175 | the inception model.
176 | """
177 | act = get_activations(files, model, batch_size, dims, cuda, overlap)
178 | mu = np.mean(act, axis=0)
179 | sigma = np.cov(act, rowvar=False)
180 | return mu, sigma, act
181 |
182 |
183 | def _compute_statistics_of_path(path, model, batch_size, dims, cuda, overlap):
184 | m, s, act = calculate_activation_statistics(path, model, batch_size,
185 | dims, cuda, overlap)
186 |
187 | return m, s, act
188 |
189 |
190 | def calculate_fid_given_paths(path, batch_size, cuda, dims):
191 | """Calculates the FD of two paths"""
192 | m2, s2, act2 = _compute_statistics_of_path(path, model, batch_size,
193 | dims, cuda, overlap=True)
194 |
195 | return m2, s2, act2
196 |
197 |
198 | if __name__ == '__main__':
199 | args = parser.parse_args()
200 | os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = args.gpu
201 | use_cuda = args.gpu and torch.cuda.is_available()
202 |
203 | model = Net()
204 | # load model_weights
205 | model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./learn/mnist_cnn.pt', map_location=torch.device('cpu')))
206 | if use_cuda:
207 | model.cuda()
208 | model.eval()
209 |
210 | test_dirs = sorted(os.listdir('./dataset_bg'))
211 | feat_path = './FD/dataset_feature/'
212 | try:
213 | os.makedirs(feat_path)
214 | except:
215 | None
216 |
217 | fd_bg = []
218 |
219 | with torch.no_grad():
220 | '''
221 | training dataset (overlap=False--> source dataset)
222 | test dataset (overlap=True--> sample set)
223 | '''
224 | # training dataset (overlap=False--> source dataset)
225 | m1, s1, act1 = _compute_statistics_of_path('', model, args.batch_size,
226 | args.dims, args.gpu != '', overlap=False)
227 |
228 | # saving features of training set
229 | np.save(feat_path + 'train_mean', m1)
230 | np.save(feat_path + 'train_variance', s1)
231 | np.save(feat_path + 'train_feature', act1)
232 |
233 | for i in trange(len(test_dirs)):
234 | path = test_dirs[i]
235 | # test dataset (overlap=True--> sample set)
236 | m2, s2, act2 = calculate_fid_given_paths(path,
237 | args.batch_size,
238 | args.gpu != '',
239 | args.dims)
240 |
241 | fd_value = calculate_frechet_distance(m1, s1, m2, s2)
242 | print('FD: ', fd_value)
243 | fd_bg.append(fd_value)
244 |
245 | # saving features for nn regression
246 | np.save(feat_path + '_%s_mean' % (path), m2)
247 | np.save(feat_path + '_%s_variance' % (path), s2)
248 | np.save(feat_path + '_%s_feature' % (path), act2)
249 |
250 | np.save('./FD/fd_mnist.npy', fd_bg)
251 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/FD/regression.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import sys
2 |
3 | sys.path.append("..")
4 | import torch
5 | import torch.nn as nn
6 | import torch.nn.functional as F
7 | import numpy as np
8 | import torch.utils.data as data
9 | import torch.nn.init as init
10 |
11 |
12 | class RegNet(nn.Module):
13 | def __init__(self):
14 | super(RegNet, self).__init__()
15 | # Batch x Channel x Height x Width; 128- feature dimension
16 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, [128, 1], 1).apply(kaiming_init)
17 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 1, 1, 1).apply(kaiming_init)
18 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(128, 32).apply(kaiming_init)
19 | self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 32).apply(kaiming_init)
20 | self.fc3 = nn.Linear(64 + 1, 32).apply(kaiming_init)
21 | self.fc4 = nn.Linear(32, 1).apply(kaiming_init)
22 | self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout2d(0.15)
23 | self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout2d(0.15)
24 | self.dropout3 = nn.Dropout2d(0.5)
25 |
26 | def forward(self, x, y, f):
27 | # x: cov; y: mean
28 | x = self.conv1(x)
29 | x = F.relu(x)
30 | x = self.conv2(x)
31 | x = F.relu(x)
32 | x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
33 | x = self.fc2(x)
34 | x = F.relu(x)
35 | x = self.dropout1(x)
36 |
37 | y = self.fc1(y)
38 | y = self.dropout2(y)
39 |
40 | z = torch.cat([x, y, f], dim=1) # mean, variance, and fid
41 | z = self.fc3(z)
42 | z = self.dropout3(z)
43 | z = self.fc4(z)
44 |
45 | output = z.view(-1)
46 | return output
47 |
48 |
49 | class REG(data.Dataset):
50 | """
51 | Args:
52 | transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in an PIL image
53 | and returns a transformed version. E.g, ``transforms.RandomCrop``
54 | target_transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in the
55 | target and transforms it.
56 | """
57 |
58 | def __init__(self, path, data, label, fid, transform=None, target_transform=None):
59 | super(REG, self).__init__()
60 | self.transform = transform
61 | self.target_transform = target_transform
62 | self.data = data
63 | self.path = path
64 | self.label_file = label
65 | self.fid = fid
66 |
67 | def __getitem__(self, index):
68 | """
69 | Args:
70 | index (int): Index
71 |
72 | Returns:
73 | tuple: (mean, var, target) where target is index of the target class.
74 | """
75 | mean = np.load(self.path + '_' + self.data[index] + '_mean.npy')
76 | var = np.load(self.path + '_' + self.data[index] + '_variance.npy')
77 |
78 | target = self.label_file[index]
79 | fid = self.fid[index]
80 | fid = torch.as_tensor(fid, dtype=torch.float).view(1)
81 |
82 | mean = torch.as_tensor(mean, dtype=torch.float)
83 | var = torch.as_tensor(var, dtype=torch.float).view(1, 128, 128)
84 |
85 | target = torch.as_tensor(target, dtype=torch.float)
86 | return var, mean, target, fid
87 |
88 | def __len__(self):
89 | return len(self.data)
90 |
91 |
92 | def kaiming_init(m):
93 | if isinstance(m, (nn.Linear, nn.Conv2d)):
94 | init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight)
95 | if m.bias is not None:
96 | m.bias.data.fill_(0)
97 | elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm1d, nn.BatchNorm2d)):
98 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
99 | if m.bias is not None:
100 | m.bias.data.fill_(0)
101 |
102 |
103 | def normal_init(m):
104 | if isinstance(m, (nn.Linear, nn.Conv2d)):
105 | init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.02)
106 | if m.bias is not None:
107 | m.bias.data.fill_(0)
108 | elif isinstance(m, (nn.BatchNorm1d, nn.BatchNorm2d)):
109 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
110 | if m.bias is not None:
111 | m.bias.data.fill_(0)
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/FD/train_regnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import print_function
2 |
3 | import sys
4 |
5 | sys.path.append(".")
6 | import argparse
7 | import os
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn.functional as F
11 | import torch.optim as optim
12 | from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import StepLR
13 | from FD.regression import RegNet
14 | from FD.regression import REG
15 |
16 | from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
17 | from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
18 | from sklearn.metrics import mean_absolute_error
19 |
20 |
21 | def train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch):
22 | model.train()
23 | for batch_idx, (var, mean, target, fid) in enumerate(train_loader):
24 | var, mean, target, fid = var.to(device), mean.to(device), target.to(device), fid.to(device)
25 | optimizer.zero_grad()
26 | output = model(var, mean, fid)
27 | loss = F.mse_loss(output, target)
28 | loss.backward()
29 | optimizer.step()
30 | if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
31 | print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
32 | epoch, batch_idx * len(var), len(train_loader.dataset),
33 | 100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
34 |
35 |
36 | def test(args, model, device, test_loader):
37 | model.eval()
38 | test_loss = 0
39 | pred_acc = []
40 | target_acc = []
41 | with torch.no_grad():
42 | for var, mean, target, fid in test_loader:
43 | var, mean, target, fid = var.to(device), mean.to(device), target.to(device), fid.to(device)
44 | output = model(var, mean, fid)
45 | pred_acc.append(output.cpu())
46 | target_acc.append(target.cpu())
47 | test_loss += F.smooth_l1_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss
48 |
49 | R2 = r2_score(torch.cat(target_acc).numpy(), torch.cat(pred_acc).numpy())
50 | RMSE = mean_squared_error(torch.cat(target_acc).numpy(), torch.cat(pred_acc).numpy(), squared=False)
51 | MAE = mean_absolute_error(torch.cat(target_acc).numpy(), torch.cat(pred_acc).numpy())
52 |
53 | test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
54 | print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f} R2 :{:.4f} RMSE: {:.4f} MAE: {:.4f}\n'.format(test_loss, R2, RMSE, MAE))
55 |
56 |
57 | def main():
58 | '''
59 | few tips:
60 | 1) batch size: 8 or 16, small number of sample sets might use 8;
61 | 2) step_size in scheduler: 20 or 30, small number of sample sets might use 30;
62 | 3) epochs: please use integer multiples of step_size, like 8 * step_size;
63 | Because this project uses Adadelta as optimizer;
64 | 4) how many sample sets? --> more than 2000 would be good for learning RegNet
65 | '''
66 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch NN Regression')
67 | parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=8, metavar='N',
68 | help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')
69 | parser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=1000, metavar='N',
70 | help='input batch size for testing (default: 1000)')
71 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=210, metavar='N',
72 | help='number of epochs to train (default: 14)')
73 | parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=1.0, metavar='LR',
74 | help='learning rate (default: 1.0)')
75 | parser.add_argument('--gamma', type=float, default=0.8, metavar='M',
76 | help='Learning rate step gamma (default: 0.8)')
77 | parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,
78 | help='disables CUDA training')
79 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1, metavar='S',
80 | help='random seed (default: 1)')
81 | parser.add_argument('--log-interval', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
82 | help='how many batches to wait before logging training status')
83 |
84 | parser.add_argument('--save-model', action='store_true', default=True,
85 | help='For Saving the current Model')
86 | args = parser.parse_args()
87 | use_cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
88 |
89 | torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
90 |
91 | device = torch.device("cuda" if use_cuda else "cpu")
92 |
93 | kwargs = {'num_workers': 2, 'pin_memory': True} if use_cuda else {}
94 |
95 | data = sorted(os.listdir('./dataset_bg/'))
96 | acc = np.load('./learn/accuracy_mnist.npy')
97 | fid = np.load('./FD/fd_mnist.npy')
98 | feature_path = './FD/dataset_feature/'
99 |
100 | # select some samplet sets for validation (also used in Linear regression)
101 | index = 30
102 |
103 | train_data = data[index:]
104 | train_acc = acc[index:]
105 | train_fid = fid[index:]
106 |
107 | test_data = data[:index]
108 | test_acc = acc[:index]
109 | test_fid = fid[:index]
110 |
111 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
112 | REG(feature_path, train_data, train_acc, train_fid),
113 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
114 |
115 | test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
116 | REG(feature_path, test_data, test_acc, test_fid),
117 | batch_size=args.test_batch_size, shuffle=False, **kwargs)
118 |
119 | model = RegNet().to(device)
120 | optimizer = optim.Adadelta(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr)
121 | scheduler = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=30, gamma=args.gamma)
122 |
123 | for epoch in range(args.epochs):
124 | train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
125 | test(args, model, device, test_loader)
126 | scheduler.step()
127 | if args.save_model:
128 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./FD/mnist_regnet.pt")
129 |
130 |
131 | if __name__ == '__main__':
132 | main()
133 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2021 Simon4Yan
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Are Labels Always Necessary for Classifier Accuracy Evaluation?
3 | ## [[Paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.02915) [[Project]](http://weijiandeng.xyz/AutoEval/)
4 | 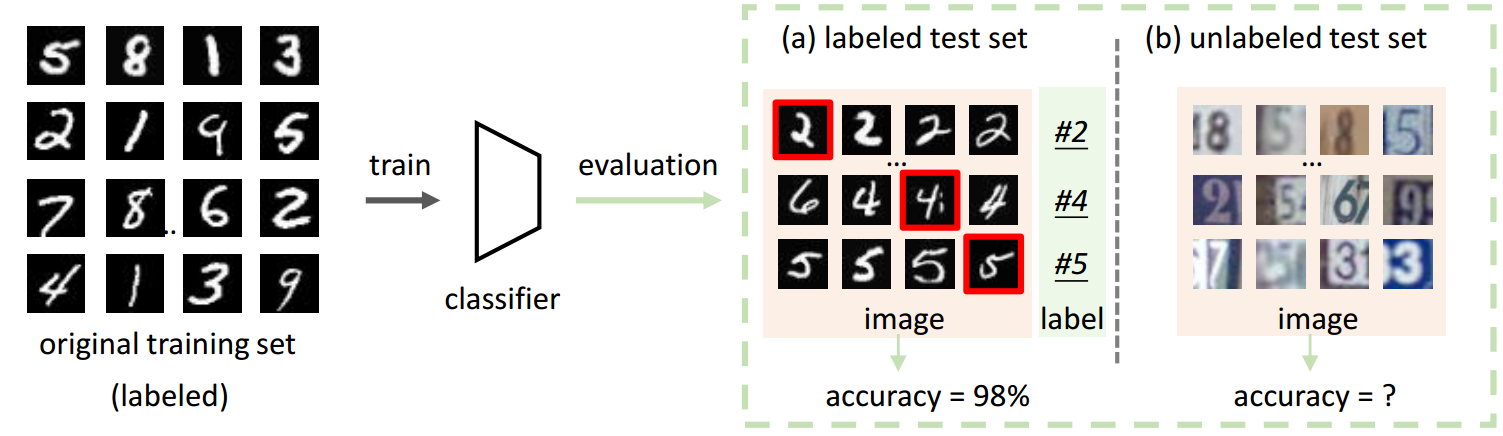
5 |
6 |
7 | ## PyTorch Implementation
8 |
9 | This repository contains:
10 |
11 | - the PyTorch implementation of AutoEavl
12 | - the example on MNIST setup
13 | - FD calculation and two regression methods
14 | - CIFAR-10/CIFAR-100 and COCO Setups (use [imgaug](https://imgaug.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) to generate Meta-set).
15 | Please see ```PROJECT_DIR/image_transformation/```
16 |
17 | Please follow the instruction below to install it and run the experiment demo.
18 |
19 | ### Prerequisites
20 | * Linux (tested on Ubuntu 16.04LTS)
21 | * NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN (tested on GTX 2080 Ti)
22 | * [COCO 2017 Dataset](http://cocodataset.org) (download and unzip to ```PROJECT_DIR/extra_data/```)
23 | * [MNIST dataset-link](https://drive.google.com/file/d/1wq8pIdayAbCu5MBfT1M38BATcShsaaeq/view?usp=sharing) (download and unzip to ```PROJECT_DIR/dataset/```)
24 | * Please use PyTorch1.1 to avoid compilation errors (other versions should be good)
25 | * You might need to change the file paths, and please be sure you change the corresponding paths in the codes as well
26 | * Please see more details about COCO setup in https://github.com/Simon4Yan/Meta-set/issues/2
27 |
28 | ## Getting started
29 | 0. Install dependencies
30 | ```bash
31 | # COCOAPI
32 | cd $DIR/libs
33 | git clone https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi.git
34 | cd cocoapi/PythonAPI
35 | python setup.py build_ext install
36 |
37 | ```
38 | 1. Creat Meta-set
39 | ```bash
40 | # By default it creates 300 sample sets
41 | python meta_set/main.py
42 | ```
43 | 2. Learn classifier
44 | ```bash
45 | # Save as "PROJECT_DIR/learn/mnist_cnn.pt"
46 | python learn/train.py
47 | ```
48 | 3. Test classifier on Meta-set
49 | ```bash
50 | # Get "PROJECT_DIR/learn/accuracy_mnist.npy" file
51 | python learn/many_test.py
52 | ```
53 | 4. Calculate FD on Meta-set
54 | ```bash
55 | # Get "PROJECT_DIR/FD/fd_mnist.npy" file
56 | python FD/many_fd.py
57 | ```
58 | 5. Linear regression
59 | ```bash
60 | # You will see linear_regression_train.png;
61 | # then check if FD and Accuracy have a linear relationship;
62 | # If so, it is all good, and please go back to step 1 and create 3000 sample sets.
63 | python FD/linear_regression.py
64 | ```
65 | 6. Network regression
66 | ```bash
67 | # Please follow the instructions in the script to train the model
68 | # Save as "PROJECT_DIR/FD/mnist_regnet.pt"
69 | python FD/train_regnet.py
70 | ```
71 |
72 | ## Citation
73 | If you use the code in your research, please cite:
74 | ```bibtex
75 | @inproceedings{deng2020labels,
76 | author={Deng, Weijian and Zheng, Liang},
77 | title = {Are Labels Always Necessary for Classifier Accuracy Evaluation?},
78 | booktitle = {Proc. CVPR},
79 | year = {2021},
80 | }
81 | ```
82 |
83 | ## License
84 | MIT
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/image_transformation/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2021 Simon4Yan
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/image_transformation/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Are Labels Always Necessary for Classifier Accuracy Evaluation?
3 |
4 |
5 | ## PyTorch Implementation
6 |
7 | This fold contains:
8 |
9 | - CIFAR-10/CIFAR-100 and COCO Setups (use [imgaug](https://imgaug.readthedocs.io/en/latest/) to generate Meta-set).
10 |
11 | Please follow the instruction below to install it and run the experiment demo.
12 |
13 | ### Prerequisites
14 | * Linux (tested on Ubuntu 16.04LTS)
15 | * NVIDIA GPU + CUDA CuDNN (tested on GTX 2080 Ti)
16 | * [COCO 2017 Dataset](http://cocodataset.org) (download and unzip to ```PROJECT_DIR/extra_data/```)
17 | * [CIFAR-10](https://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar.html) (download and unzip to ```PROJECT_DIR/dataset/```)
18 | * You might need to change the file paths, and please be sure you change the corresponding paths in the codes as well
19 |
20 | ## Getting started
21 | 0. Install dependencies
22 | ```bash
23 | # Imgaug (or see https://imgaug.readthedocs.io/en/latest/source/installation.html)
24 | conda config --add channels conda-forge
25 | conda install imgaug
26 | ```
27 |
28 | 1. Customize the image transformations
29 |
30 | ```angular2
31 | # Customize the image transformations for constructing Meta-set. Here, we provide two examples
32 | # Example 1
33 | sometimes = lambda aug: iaa.Sometimes(0.5, aug)
34 | list = [
35 | iaa.pillike.Autocontrast(), # adjust contrast by cutting off p% of lowest/highest histogram values
36 | iaa.Multiply((0.1, 1.9), per_channel=0.2), # make some images brighter and some darker
37 | iaa.pillike.EnhanceColor(), # remove a random fraction of color from input images
38 | iaa.Solarize(0.5, threshold=(32, 128)), # invert the colors
39 | iaa.contrast.LinearContrast((0.5, 2.0), per_channel=0.5), # degrade the quality of images by JPEG-compressing them
40 | sometimes(iaa.Affine(
41 | scale={"x": (0.8, 1.2), "y": (0.8, 1.2)},
42 | translate_percent={"x": (-0.2, 0.2), "y": (-0.2, 0.2)},
43 | rotate=(-30, 30)
44 | )), # add affine transformation
45 | iaa.Sharpen(alpha=(0.1, 1.9)), # apply a sharpening filter kernel to images
46 | ]
47 |
48 | # Example 2
49 | # add more transformations into the list based on the users' need
50 | sometimes = lambda aug: iaa.Sometimes(0.5, aug)
51 | list = [
52 | iaa.pillike.Autocontrast(), # adjust contrast by cutting off p% of lowest/highest histogram values
53 | iaa.Multiply((0.1, 1.9), per_channel=0.2), # make some images brighter and some darker
54 | iaa.pillike.EnhanceColor(), # remove a random fraction of color from input images
55 | iaa.Solarize(0.5, threshold=(32, 128)), # invert the colors
56 | iaa.contrast.LinearContrast((0.5, 2.0), per_channel=0.5), # improve or worsen the contrast of images
57 | sometimes(iaa.Affine(
58 | scale={"x": (0.8, 1.2), "y": (0.8, 1.2)},
59 | translate_percent={"x": (-0.2, 0.2), "y": (-0.2, 0.2)},
60 | rotate=(-30, 30)
61 | )), # add affine transformation
62 | iaa.Sharpen(alpha=(0.0, 1.0)), # apply a sharpening filter kernel to images
63 | iaa.LinearContrast((0.8, 1.2), per_channel=0.5), # improve or worsen the contrast of images
64 | iaa.Rain(speed=(0.1, 0.3)), # add rain to small images
65 | iaa.JpegCompression(compression=(70, 99)), # degrade the quality of images by JPEG-compressing them
66 | iaa.pillike.FilterDetail(), # apply a detail enhancement filter kernel to images
67 | iaa.pillike.EnhanceSharpness(), # alpha-blend two image sources using an alpha/opacity value
68 | iaa.MultiplyHue((0.8, 1.2)), # change the sharpness of images
69 | iaa.Emboss(alpha=(0.0, 0.5), strength=(0.5, 1.0)), # emboss an image, then overlay the results with the original
70 | iaa.AddToSaturation((-25, 25)) # add random values to the saturation of images
71 | ]
72 | ```
73 |
74 | 2. Creat synthetic sets for CIFAR-10 setup
75 | ```bash
76 | # By default it creates 1000 synthetic sets
77 | python image_tranformation/synthesize_set_cifar.py
78 | ```
79 | 3. Creat synthetic sets for COCO setup
80 | ```bash
81 | # By default it creates 1000 synthetic sets
82 | python image_tranformation/synthesize_set_coco.py
83 | ```
84 |
85 | ## Citation
86 | If you use the code in your research, please cite:
87 | ```bibtex
88 | @inproceedings{deng2020labels,
89 | author={Deng, Weijian and Zheng, Liang},
90 | title = {Are Labels Always Necessary for Classifier Accuracy Evaluation?},
91 | booktitle = {Proc. CVPR},
92 | year = {2021},
93 | }
94 | ```
95 |
96 | ## License
97 | MIT
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/image_transformation/synthesize_set_cifar.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import random
3 |
4 | import imgaug as ia
5 | import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import torchvision
8 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
9 | from tqdm import trange
10 |
11 | # ===================================================== #
12 | # ----------- load original dataset ----------- #
13 | # ===================================================== #
14 | '''An example to load original datasets (based on Pytorch's dataloader)'''
15 | NORM = ((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))
16 | te_transforms = transforms.Compose([transforms.ToTensor(),
17 | transforms.Normalize(*NORM)])
18 |
19 | teset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root='/PROJECT_DIR/dataset/',
20 | train=False, download=True, transform=te_transforms)
21 | teset_raw = teset.data
22 | print('Loaded original set')
23 |
24 | # ===================================================== #
25 | # ----------- Image Transformations ----------- #
26 | # ===================================================== #
27 | '''
28 | In our paper, the transformations are:
29 | {Autocontrast, Brightness, Color, ColorSolarize, Contrast, Rotation, Sharpness, TranslateX/Y}
30 | The users can customize the transformation list based on the their own data.
31 | The users can use more transformations for the selection.
32 | We refer the readers to https://imgaug.readthedocs.io/ for more details of transformations.
33 | Here, we provide 3 examples, hope you enjoy it!
34 | '''
35 | # Default
36 | # {Autocontrast, Brightness, Color, ColorSolarize, Contrast, Rotation, Sharpness, TranslateX/Y}
37 | sometimes = lambda aug: iaa.Sometimes(0.5, aug)
38 | list = [
39 | iaa.pillike.Autocontrast(), # adjust contrast by cutting off p% of lowest/highest histogram values
40 | iaa.Multiply((0.1, 1.9), per_channel=0.2), # make some images brighter and some darker
41 | iaa.pillike.EnhanceColor(), # remove a random fraction of color from input images
42 | iaa.Solarize(0.5, threshold=(32, 128)), # invert the colors
43 | iaa.contrast.LinearContrast((0.5, 2.0), per_channel=0.5),
44 | sometimes(iaa.Affine(
45 | scale={"x": (0.8, 1.2), "y": (0.8, 1.2)},
46 | translate_percent={"x": (-0.2, 0.2), "y": (-0.2, 0.2)},
47 | rotate=(-30, 30)
48 | )), # add affine transformation
49 | iaa.Sharpen(alpha=(0.1, 1.0)), # apply a sharpening filter kernel to images
50 | ]
51 |
52 | # GroupA
53 | # list = [
54 | # iaa.Grayscale(alpha=(0.0, 0.5)), # remove colors with varying strengths
55 | # iaa.ElasticTransformation(alpha=(0.5, 2.5), sigma=(0.25, 0.5)), # move pixels locally around with random strengths
56 | # iaa.PiecewiseAffine(scale=(0.01, 0.05)), # distort local areas with varying strength
57 | # iaa.Invert(0.05, per_channel=True), # invert color channels
58 | # iaa.pillike.FilterBlur(), # apply a blur filter kernel to images
59 | # iaa.pillike.EnhanceBrightness(), # change the brightness of images
60 | # iaa.Fog(), # add fog to images
61 | # iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(loc=0, scale=(0.0, 0.025 * 255), per_channel=0.5) # Add gaussian noise to some images
62 | # ]
63 |
64 | # GroupB
65 | # list = [
66 | # iaa.LinearContrast((0.5, 1.5), per_channel=0.5), # improve or worsen the contrast of images
67 | # iaa.Rain(speed=(0.1, 0.5)), # add rain to small images
68 | # iaa.JpegCompression(compression=(70, 99)), # degrade the quality of images by JPEG-compressing them
69 | # iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0.0, 3.0)), # augmenter to blur images using gaussian kernels
70 | # iaa.pillike.EnhanceSharpness(), # alpha-blend two image sources using an alpha/opacity value
71 | # iaa.MultiplyHue((0.5, 1.5)), # change the sharpness of images
72 | # iaa.Emboss(alpha=(0.0, 0.5), strength=(0.5, 1.5)), # emboss an image, then overlay the results with the original
73 | # iaa.AddToSaturation((-50, 50)) # add random values to the saturation of images
74 | # ]
75 |
76 | # add more transformations into the list based on the users' need
77 | # sometimes = lambda aug: iaa.Sometimes(0.5, aug)
78 | # list = [
79 | # iaa.pillike.Autocontrast(), # adjust contrast by cutting off p% of lowest/highest histogram values
80 | # iaa.Multiply((0.1, 1.9), per_channel=0.2), # make some images brighter and some darker
81 | # iaa.pillike.EnhanceColor(), # remove a random fraction of color from input images
82 | # iaa.Solarize(0.5, threshold=(32, 128)), # invert the colors
83 | # iaa.contrast.LinearContrast((0.5, 2.0), per_channel=0.5), # improve or worsen the contrast of images
84 | # sometimes(iaa.Affine(
85 | # scale={"x": (0.8, 1.2), "y": (0.8, 1.2)},
86 | # translate_percent={"x": (-0.2, 0.2), "y": (-0.2, 0.2)},
87 | # rotate=(-30, 30)
88 | # )), # add affine transformation
89 | # iaa.Sharpen(alpha=(0.0, 1.0)), # apply a sharpening filter kernel to images
90 | # iaa.LinearContrast((0.8, 1.2), per_channel=0.5), # improve or worsen the contrast of images
91 | # iaa.Rain(speed=(0.1, 0.3)), # add rain to small images
92 | # iaa.JpegCompression(compression=(70, 99)), # degrade the quality of images by JPEG-compressing them
93 | # iaa.pillike.FilterDetail(), # apply a detail enhancement filter kernel to images
94 | # iaa.pillike.EnhanceSharpness(), # alpha-blend two image sources using an alpha/opacity value
95 | # iaa.MultiplyHue((0.8, 1.2)), # change the sharpness of images
96 | # iaa.Emboss(alpha=(0.0, 0.5), strength=(0.5, 1.0)), # emboss an image, then overlay the results with the original
97 | # iaa.AddToSaturation((-25, 25)) # add random values to the saturation of images
98 | # ]
99 |
100 |
101 | # ===================================================== #
102 | # ----------- Generate Synthetic datasets ----------- #
103 | # ===================================================== #
104 | '''
105 | Generate 800 and 200 synthetic datasets for training and validation, respectively
106 | '''
107 | tesize = 10000
108 | num_sets = 1000
109 | # Change to your path
110 | try:
111 | os.makedirs('/mnt/home/dwj/AutoEval/CIFAR-10_Setup/dataset_GroupA')
112 | except:
113 | print('Alread has this path')
114 |
115 | for num in trange(num_sets):
116 | num_sel = 3 # use more transformation to introduce dataset diversity
117 | list_sel = random.sample(list, int(num_sel))
118 | random.shuffle(list_sel)
119 | seq = iaa.Sequential(list_sel)
120 |
121 | new_data = np.zeros(teset_raw.shape).astype(np.uint8)
122 | for i in range(tesize):
123 | data = teset_raw[i]
124 | ia.seed(i + num * tesize) # add random for each dataset
125 | new_data[i] = seq(image=data)
126 |
127 | np.save('/mnt/home/dwj/AutoEval/CIFAR-10_Setup/dataset_GroupA/new_data_' + str(num).zfill(3), new_data)
128 |
129 | print('Finished, thanks!')
130 |
131 | # ===================================================== #
132 | # ----------- Load Synthetic datasets ----------- #
133 | # ===================================================== #
134 | # An example to load synthetic datasets (based on Pytorch's dataloader)
135 | '''
136 | for i in range(1000):
137 | teset_raw = np.load('/mnt/home/dwj/AutoEval/CIFAR-10_Setup/dataset_GroupA/new_data_' + str(i).zfill(3)+ '.npy') # your path
138 | teset = torchvision.datasets.CIFAR10(root=YourPATH,
139 | train=False, download=True, transform=te_transforms)
140 | teset.data = teset_raw
141 | teloader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(teset, batch_size=64,
142 | shuffle=False, num_workers=2)
143 | '''
144 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/image_transformation/synthesize_set_coco.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import random
3 |
4 | import cv2
5 | import imgaug as ia
6 | import imgaug.augmenters as iaa
7 | import numpy as np
8 | from pycocotools.coco import COCO
9 | from tqdm import trange
10 |
11 | # ===================================================== #
12 | # ----------- Image Transformations ----------- #
13 | # ===================================================== #
14 |
15 | '''
16 | In our paper, the transformations are:
17 | {Autocontrast, Brightness, Color, ColorSolarize, Contrast, Rotation, Sharpness, TranslateX/Y}.
18 | Other transformations can be also used.
19 | The users can customize the transformation list based on the their own data.
20 | We refer the readers to https://imgaug.readthedocs.io/ for more details of transformations.
21 | Here, we provide 3 examples, hope you enjoy it!
22 | '''
23 | # Default
24 | # {Autocontrast, Brightness, Color, ColorSolarize, Contrast, Rotation, Sharpness, TranslateX/Y}
25 | sometimes = lambda aug: iaa.Sometimes(0.5, aug)
26 | list = [
27 | iaa.pillike.Autocontrast(), # adjust contrast by cutting off p% of lowest/highest histogram values
28 | iaa.Multiply((0.1, 1.9), per_channel=0.2), # make some images brighter and some darker
29 | iaa.pillike.EnhanceColor(), # remove a random fraction of color from input images
30 | iaa.Solarize(0.5, threshold=(32, 128)), # invert the colors
31 | iaa.contrast.LinearContrast((0.5, 2.0), per_channel=0.5),
32 | sometimes(iaa.Affine(
33 | scale={"x": (0.8, 1.2), "y": (0.8, 1.2)},
34 | translate_percent={"x": (-0.2, 0.2), "y": (-0.2, 0.2)},
35 | rotate=(-30, 30)
36 | )), # add affine transformation
37 | iaa.Sharpen(alpha=(0.1, 1.0)), # apply a sharpening filter kernel to images
38 | ]
39 |
40 | # GroupA
41 | # list = [
42 | # iaa.Grayscale(alpha=(0.0, 0.5)), # remove colors with varying strengths
43 | # iaa.ElasticTransformation(alpha=(0.5, 2.5), sigma=(0.25, 0.5)), # move pixels locally around with random strengths
44 | # iaa.PiecewiseAffine(scale=(0.01, 0.05)), # distort local areas with varying strength
45 | # iaa.Invert(0.05, per_channel=True), # invert color channels
46 | # iaa.pillike.FilterBlur(), # apply a blur filter kernel to images
47 | # iaa.pillike.EnhanceBrightness(), # change the brightness of images
48 | # iaa.Fog(), # add fog to images
49 | # iaa.AdditiveGaussianNoise(loc=0, scale=(0.0, 0.025 * 255), per_channel=0.5) # Add gaussian noise to some images
50 | # ]
51 |
52 | # GroupB
53 | # list = [
54 | # iaa.LinearContrast((0.5, 1.5), per_channel=0.5), # improve or worsen the contrast of images
55 | # iaa.Rain(speed=(0.1, 0.5)), # add rain to small images
56 | # iaa.JpegCompression(compression=(70, 99)), # degrade the quality of images by JPEG-compressing them
57 | # iaa.GaussianBlur(sigma=(0.0, 3.0)), # augmenter to blur images using gaussian kernels
58 | # iaa.pillike.EnhanceSharpness(), # alpha-blend two image sources using an alpha/opacity value
59 | # iaa.MultiplyHue((0.5, 1.5)), # change the sharpness of images
60 | # iaa.Emboss(alpha=(0.0, 0.5), strength=(0.5, 1.5)), # emboss an image, then overlay the results with the original
61 | # iaa.AddToSaturation((-50, 50)) # add random values to the saturation of images
62 | # ]
63 |
64 | # add more transformations into the list based on the users' need
65 | # sometimes = lambda aug: iaa.Sometimes(0.5, aug)
66 | # list = [
67 | # iaa.pillike.Autocontrast(), # adjust contrast by cutting off p% of lowest/highest histogram values
68 | # iaa.Multiply((0.1, 1.9), per_channel=0.2), # make some images brighter and some darker
69 | # iaa.pillike.EnhanceColor(), # remove a random fraction of color from input images
70 | # iaa.Solarize(0.5, threshold=(32, 128)), # invert the colors
71 | # iaa.contrast.LinearContrast((0.5, 2.0), per_channel=0.5), # improve or worsen the contrast of images
72 | # sometimes(iaa.Affine(
73 | # scale={"x": (0.8, 1.2), "y": (0.8, 1.2)},
74 | # translate_percent={"x": (-0.2, 0.2), "y": (-0.2, 0.2)},
75 | # rotate=(-30, 30)
76 | # )), # add affine transformation
77 | # iaa.Sharpen(alpha=(0.0, 1.0)), # apply a sharpening filter kernel to images
78 | # iaa.LinearContrast((0.8, 1.2), per_channel=0.5), # improve or worsen the contrast of images
79 | # iaa.Rain(speed=(0.1, 0.3)), # add rain to small images
80 | # iaa.JpegCompression(compression=(70, 99)), # degrade the quality of images by JPEG-compressing them
81 | # iaa.pillike.FilterDetail(), # apply a detail enhancement filter kernel to images
82 | # iaa.pillike.EnhanceSharpness(), # alpha-blend two image sources using an alpha/opacity value
83 | # iaa.MultiplyHue((0.8, 1.2)), # change the sharpness of images
84 | # iaa.Emboss(alpha=(0.0, 0.5), strength=(0.5, 1.0)), # emboss an image, then overlay the results with the original
85 | # iaa.AddToSaturation((-25, 25)) # add random values to the saturation of images
86 | # ]
87 |
88 | # ===================================================== #
89 | # ----------- Load COCO Dataset ----------- #
90 | # ===================================================== #
91 |
92 | dataDir = 'PROJECT_DIR/extra_data' # COCO dataset path, COCO path: PROJECT_DIR/extra_data/
93 | dataType = 'val2014'
94 | annFile = '{}/annotations/instances_{}.json'.format(dataDir, dataType)
95 | coco = COCO(annFile)
96 |
97 | # ===================================================== #
98 | # ----------- Generate Sample Sets ----------- #
99 | # ===================================================== #
100 |
101 | # 12 classes; shared across ImageNet-Pascal-COCO-Caltech
102 | target_list = ['airplane', 'bicycle', 'bird', 'boat', 'bottle',
103 | 'bus', 'car', 'dog', 'horse', 'tv', 'motorcycle', 'person']
104 |
105 | background_path = 'PROJECT_DIR/extra_data/test2014/' # using test set's images as the backgrounds;
106 | background_dir = os.listdir(background_path)
107 | random.shuffle(background_dir)
108 |
109 | # select bbox following the practice in http://ai.bu.edu/visda-2017/
110 | thresh = 120 # for bbox's W and H
111 | crop_pixels = 50
112 | b_thresh = 120 # crop background
113 |
114 | num_sets = 1000 # generate 800 and 200 sample sets for training and validation
115 |
116 | for indice_set in trange(num_sets):
117 | num_sel = 3 # select more transformations to make sample set diverse
118 | list_sel = random.sample(list, int(num_sel))
119 | random.shuffle(list_sel)
120 | seq = iaa.Sequential(list_sel)
121 | save_rb_path = '/mnt/home/dwj/AutoEval/COCO_Setup/coco_dataset_groupA/coco_cls_val_b_' + str(indice_set).zfill(
122 | 5) # the users need to change the path
123 | if not os.path.exists(save_rb_path):
124 | os.makedirs(save_rb_path)
125 |
126 | # randomly choose 20 COCO test images for replacing the background for each sample set
127 | b_indice = np.random.choice(len(background_dir), 20)
128 |
129 | # generate images category by category
130 | # target is the current selected category
131 | for cls_indice, target in enumerate(target_list):
132 | target_rb_dir = save_rb_path + '/' + target
133 | if not os.path.exists(target_rb_dir):
134 | os.makedirs(target_rb_dir)
135 |
136 | im_seq = 1 # how many images are selected for the current category
137 | ss_Id = coco.getCatIds(catNms=[target])[0] # get the category_id of the current category
138 | imgIds = coco.getImgIds(catIds=ss_Id) # find the images that contains the current category
139 |
140 | # handel image that contains the current category
141 | for img_id in imgIds:
142 | imgIds = coco.getImgIds(imgIds=img_id)
143 | img = coco.loadImgs(imgIds)[0]
144 | I = cv2.imread('%s/%s/%s' % (dataDir, dataType, img['file_name']))
145 | hight = I.shape[0]
146 | width = I.shape[1]
147 | # load bbox and segmentation annotations for the current image
148 | annIds = coco.getAnnIds(imgIds=img['id'], catIds=ss_Id, iscrowd=False)
149 | for each_ann_id in annIds:
150 | anns = coco.loadAnns(each_ann_id)
151 | if (len(anns) != 0):
152 | if im_seq <= 600: # select at most 600 images for each category
153 | for ann in anns:
154 | if ann['category_id'] == ss_Id: # choose the object that is from the current category
155 | # crop object
156 | x, y, w, h = ann['bbox']
157 | if w > thresh and h > thresh:
158 | x1 = max(int(float(x)) - crop_pixels, 1)
159 | x2 = min(int(float(x)) + int(float(w)) + crop_pixels, width - 1)
160 | y1 = max(int(float(y)) - crop_pixels, 1)
161 | y2 = min(int(float(y)) + int(float(h)) + crop_pixels, hight - 1)
162 | I_cp = I[y1: y2, x1: x2]
163 | # background replace
164 | np.random.choice(b_indice.shape[0], 1) # choose a background image
165 | background0 = cv2.imread(background_path + '/' + background_dir[
166 | np.random.choice(b_indice, 1)[0]])
167 | try:
168 | # random crop a region from the selected background image
169 | b_y1 = np.random.randint(0, background0.shape[0] - b_thresh - 1)
170 | b_x1 = np.random.randint(0, background0.shape[1] - b_thresh - 1)
171 | background = background0[b_y1: b_y1 + b_thresh, b_x1: b_x1 + b_thresh]
172 | background = cv2.resize(background, (int(x2 - x1), int(y2 - y1)),
173 | interpolation=cv2.INTER_CUBIC)
174 |
175 | # polygon; get object mask
176 | mask = np.zeros([I.shape[0], I.shape[1]], dtype="uint8")
177 | for seg in ann['segmentation']:
178 | poly = np.array(seg).reshape((int(len(seg) / 2), 2))
179 | cv2.polylines(mask, np.int32([poly]), 1, 1)
180 | cv2.fillPoly(mask, np.int32([poly]), 1)
181 | MASK_foreground = np.zeros(I.shape, dtype="uint8")
182 | MASK_background = np.zeros(I.shape, dtype="uint8")
183 | MASK_foreground[:, :, 0] = mask
184 | MASK_foreground[:, :, 1] = mask
185 | MASK_foreground[:, :, 2] = mask
186 | MASK_background[:, :, 0] = np.ones([I.shape[0], I.shape[1]],
187 | dtype="uint8") - mask
188 | MASK_background[:, :, 1] = np.ones([I.shape[0], I.shape[1]],
189 | dtype="uint8") - mask
190 | MASK_background[:, :, 2] = np.ones([I.shape[0], I.shape[1]],
191 | dtype="uint8") - mask
192 | MASK_background_cp = MASK_background[y1: y2, x1: x2]
193 | MASK_foreground_cp = MASK_foreground[y1: y2, x1: x2]
194 |
195 | # paste object on a new background
196 | I_cp_nb = I_cp * MASK_foreground_cp + background * MASK_background_cp
197 |
198 | # apply image transformation to introduce more visual changes
199 | # control the randomness for each dataset
200 | ia.seed(im_seq + cls_indice * 600 + indice_set * 8000)
201 | I_cp_nb = seq(image=I_cp_nb)
202 |
203 | # save image
204 | cv2.imwrite(target_rb_dir + '/' + '{:09d}.jpg'.format(im_seq), I_cp_nb)
205 | # how many images are selected for the current category
206 | im_seq = im_seq + 1
207 | except:
208 | print('jump an object')
209 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/learn/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/Simon4Yan/Meta-set/58e498cc95a879eec369d2ccf8da714baf8480e2/learn/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/learn/many_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import absolute_import
2 | from __future__ import print_function
3 |
4 | import argparse
5 | import os
6 | import sys
7 |
8 | sys.path.append(".")
9 | import numpy as np
10 | import torch
11 | import torch.nn as nn
12 | import torch.nn.functional as F
13 | from torchvision import transforms
14 | from tqdm import trange
15 |
16 | from learn.utils import MNIST
17 |
18 |
19 | class Net(nn.Module):
20 | def __init__(self):
21 | super(Net, self).__init__()
22 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3, 1)
23 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1)
24 | self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout2d(0.25)
25 | self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout2d(0.5)
26 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9216, 128)
27 | self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
28 |
29 | def forward(self, x):
30 | x = self.conv1(x)
31 | x = F.relu(x)
32 | x = self.conv2(x)
33 | x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
34 | x = self.dropout1(x)
35 | x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
36 | x = self.fc1(x)
37 | x = F.relu(x)
38 | x = self.dropout2(x)
39 | x = self.fc2(x)
40 | output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
41 | return output
42 |
43 |
44 | def test(args, model, device, test_loader):
45 | model.eval()
46 | test_loss = 0
47 | correct = 0
48 | count = 0
49 | with torch.no_grad():
50 | for data, target in test_loader:
51 | data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
52 | output = model(data)
53 | test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss
54 | pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability
55 | correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
56 | count += 1
57 | test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
58 |
59 | print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format(
60 | test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
61 | 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
62 |
63 | return 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)
64 |
65 |
66 | def main():
67 | # Training settings
68 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch MNIST Test-Metaset')
69 | parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64, metavar='N',
70 | help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')
71 | parser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=64, metavar='N',
72 | help='input batch size for testing (default: 1000)')
73 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=14, metavar='N',
74 | help='number of epochs to train (default: 14)')
75 | parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=1.0, metavar='LR',
76 | help='learning rate (default: 1.0)')
77 | parser.add_argument('--gamma', type=float, default=0.7, metavar='M',
78 | help='Learning rate step gamma (default: 0.7)')
79 | parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,
80 | help='disables CUDA training')
81 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1, metavar='S',
82 | help='random seed (default: 1)')
83 | parser.add_argument('--log-interval', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
84 | help='how many batches to wait before logging training status')
85 |
86 | parser.add_argument('--save-model', action='store_true', default=True,
87 | help='For Saving the current Model')
88 | args = parser.parse_args()
89 | use_cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
90 |
91 | torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
92 |
93 | device = torch.device("cuda" if use_cuda else "cpu")
94 |
95 | kwargs = {'num_workers': 8, 'pin_memory': True} if use_cuda else {}
96 |
97 | test_dirs = sorted(os.listdir('./dataset_bg'))
98 |
99 | model = Net().to(device)
100 | model.load_state_dict(torch.load('./learn/mnist_cnn.pt'))
101 | model.eval()
102 |
103 | accuracy = []
104 | with torch.no_grad():
105 | for i in trange(len(test_dirs)):
106 | test_path = './dataset_bg/' + test_dirs[i]
107 |
108 | test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
109 | MNIST(test_path, 'test_data.npy', 'test_label.npy', transform=transforms.Compose([
110 | transforms.ToTensor(),
111 | transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,))
112 | ])),
113 | batch_size=args.test_batch_size, shuffle=False, **kwargs)
114 |
115 | acc = test(args, model, device, test_loader)
116 | accuracy.append(acc)
117 |
118 | # save accuracy file of meta set (all sample sets)
119 | np.save('./learn/accuracy_mnist.npy', accuracy)
120 |
121 |
122 | if __name__ == '__main__':
123 | main()
124 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/learn/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import print_function
2 |
3 | import argparse
4 | import sys
5 | sys.path.append(".")
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.nn.functional as F
9 | import torch.optim as optim
10 | from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import StepLR
11 | from torchvision import transforms
12 |
13 |
14 | from learn.utils import MNIST
15 |
16 |
17 | class Net(nn.Module):
18 | def __init__(self):
19 | super(Net, self).__init__()
20 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 32, 3, 1)
21 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, 3, 1)
22 | self.dropout1 = nn.Dropout2d(0.25)
23 | self.dropout2 = nn.Dropout2d(0.5)
24 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(9216, 128)
25 | self.fc2 = nn.Linear(128, 10)
26 |
27 | def forward(self, x):
28 | x = self.conv1(x)
29 | x = F.relu(x)
30 | x = self.conv2(x)
31 | x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
32 | x = self.dropout1(x)
33 | x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
34 | x = self.fc1(x)
35 | x = F.relu(x)
36 | x = self.dropout2(x)
37 | x = self.fc2(x)
38 | output = F.log_softmax(x, dim=1)
39 | return output
40 |
41 |
42 | def train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch):
43 | model.train()
44 | for batch_idx, (data, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
45 | data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
46 | optimizer.zero_grad()
47 | output = model(data)
48 | loss = F.nll_loss(output, target)
49 | loss.backward()
50 | optimizer.step()
51 | if batch_idx % args.log_interval == 0:
52 | print('Train Epoch: {} [{}/{} ({:.0f}%)]\tLoss: {:.6f}'.format(
53 | epoch, batch_idx * len(data), len(train_loader.dataset),
54 | 100. * batch_idx / len(train_loader), loss.item()))
55 |
56 |
57 | def test(args, model, device, test_loader):
58 | model.eval()
59 | test_loss = 0
60 | correct = 0
61 | with torch.no_grad():
62 | for data, target in test_loader:
63 | data, target = data.to(device), target.to(device)
64 | output = model(data)
65 | test_loss += F.nll_loss(output, target, reduction='sum').item() # sum up batch loss
66 | pred = output.argmax(dim=1, keepdim=True) # get the index of the max log-probability
67 | correct += pred.eq(target.view_as(pred)).sum().item()
68 |
69 | test_loss /= len(test_loader.dataset)
70 |
71 | print('\nTest set: Average loss: {:.4f}, Accuracy: {}/{} ({:.0f}%)\n'.format(
72 | test_loss, correct, len(test_loader.dataset),
73 | 100. * correct / len(test_loader.dataset)))
74 |
75 |
76 | def main():
77 | # Training settings
78 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch MNIST Train')
79 | parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=64, metavar='N',
80 | help='input batch size for training (default: 64)')
81 | parser.add_argument('--test-batch-size', type=int, default=1000, metavar='N',
82 | help='input batch size for testing (default: 1000)')
83 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=14, metavar='N',
84 | help='number of epochs to train (default: 14)')
85 | parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=1.0, metavar='LR',
86 | help='learning rate (default: 1.0)')
87 | parser.add_argument('--gamma', type=float, default=0.7, metavar='M',
88 | help='Learning rate step gamma (default: 0.7)')
89 | parser.add_argument('--no-cuda', action='store_true', default=False,
90 | help='disables CUDA training')
91 | parser.add_argument('--seed', type=int, default=1, metavar='S',
92 | help='random seed (default: 1)')
93 | parser.add_argument('--log-interval', type=int, default=10, metavar='N',
94 | help='how many batches to wait before logging training status')
95 |
96 | parser.add_argument('--save-model', action='store_true', default=True,
97 | help='For Saving the current Model')
98 | args = parser.parse_args()
99 | use_cuda = not args.no_cuda and torch.cuda.is_available()
100 |
101 | torch.manual_seed(args.seed)
102 |
103 | device = torch.device("cuda" if use_cuda else "cpu")
104 |
105 | kwargs = {'num_workers': 1, 'pin_memory': True} if use_cuda else {}
106 |
107 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
108 | MNIST('./dataset/mnist', 'train_data.npy', 'train_label.npy',
109 | transform=transforms.Compose([
110 | transforms.ToTensor(),
111 | transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,)) # transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
112 | ])),
113 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
114 | test_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
115 | MNIST('./dataset/mnist', 'test_data.npy', 'test_label.npy', transform=transforms.Compose([
116 | transforms.ToTensor(),
117 | transforms.Normalize((0.5,), (0.5,)) # transforms.Normalize((0.1307,), (0.3081,))
118 | ])),
119 | batch_size=args.test_batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
120 |
121 | model = Net().to(device)
122 | optimizer = optim.Adadelta(model.parameters(), lr=args.lr)
123 |
124 | scheduler = StepLR(optimizer, step_size=1, gamma=args.gamma)
125 | for epoch in range(1, args.epochs + 1):
126 | train(args, model, device, train_loader, optimizer, epoch)
127 | test(args, model, device, test_loader)
128 | scheduler.step()
129 | if args.save_model:
130 | torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./learn/mnist_cnn.pt")
131 |
132 |
133 | if __name__ == '__main__':
134 | main()
135 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/learn/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import torch.utils.data as data
3 | from PIL import Image
4 |
5 |
6 | class MNIST(data.Dataset):
7 | """`MNIST `_ Dataset.
8 |
9 | Args:
10 | root (string): Root directory of dataset where ``MNIST/processed/training.pt``
11 | and ``MNIST/processed/test.pt`` exist.
12 | train (bool, optional): If True, creates dataset from ``training.pt``,
13 | otherwise from ``test.pt``.
14 | download (bool, optional): If true, downloads the dataset from the internet and
15 | puts it in root directory. If dataset is already downloaded, it is not
16 | downloaded again.
17 | transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in an PIL image
18 | and returns a transformed version. E.g, ``transforms.RandomCrop``
19 | target_transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in the
20 | target and transforms it.
21 | """
22 |
23 | def __init__(self, root, sample_file, label_file, transform=None, target_transform=None):
24 | super(MNIST, self).__init__()
25 | self.transform = transform
26 | self.target_transform = target_transform
27 | self.data = np.load(str(root) + '//' + sample_file)
28 | self.targets = np.load(str(root) + '//' + label_file)
29 |
30 | def __getitem__(self, index):
31 | """
32 | Args:
33 | index (int): Index
34 |
35 | Returns:
36 | tuple: (image, target) where target is index of the target class.
37 | """
38 | if len(self.data.shape) > 3:
39 | img, target = self.data[:, :, :, index], int(self.targets[index])
40 | else:
41 | img, target = self.data[:, :, index], int(self.targets[index])
42 |
43 | # doing this so that it is consistent with all other datasets
44 | # to return a PIL Image
45 | # img = Image.fromarray(img, mode='L')
46 | img = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(img)).convert('RGB') # unit8
47 |
48 | if self.transform is not None:
49 | img = self.transform(img)
50 |
51 | if self.target_transform is not None:
52 | target = self.target_transform(target)
53 |
54 | return img, target
55 |
56 | def __len__(self):
57 | if len(self.data.shape) > 3:
58 | return self.data.shape[3]
59 | else:
60 | return self.data.shape[2]
61 |
62 |
63 | class MNIST_bg(data.Dataset):
64 | """`MNIST `_ Dataset.
65 |
66 | Args:
67 | root (string): Root directory of dataset where ``MNIST/processed/training.pt``
68 | and ``MNIST/processed/test.pt`` exist.
69 | train (bool, optional): If True, creates dataset from ``training.pt``,
70 | otherwise from ``test.pt``.
71 | download (bool, optional): If true, downloads the dataset from the internet and
72 | puts it in root directory. If dataset is already downloaded, it is not
73 | downloaded again.
74 | transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in an PIL image
75 | and returns a transformed version. E.g, ``transforms.RandomCrop``
76 | target_transform (callable, optional): A function/transform that takes in the
77 | target and transforms it.
78 | """
79 |
80 | def __init__(self, root, sample_file, label_file, transform=None, target_transform=None):
81 | super(MNIST_bg, self).__init__()
82 | self.transform = transform
83 | self.target_transform = target_transform
84 | self.data = np.load(str(root) + '//' + sample_file)
85 | self.targets = np.load(str(root) + '//' + label_file)
86 |
87 | def __getitem__(self, index):
88 | """
89 | Args:
90 | index (int): Index
91 |
92 | Returns:
93 | tuple: (image, target) where target is index of the target class.
94 | """
95 | img, target = self.data[:, :, :, index], int(self.targets[index])
96 |
97 | # doing this so that it is consistent with all other datasets
98 | # to return a PIL Image
99 | # img = Image.fromarray(img, mode='L')
100 | img = Image.fromarray(np.uint8(img)).convert('L') # unit8
101 |
102 | if self.transform is not None:
103 | img = self.transform(img)
104 |
105 | if self.target_transform is not None:
106 | target = self.target_transform(target)
107 |
108 | return img, target
109 |
110 | def __len__(self):
111 | return self.data.shape[3]
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/meta_set/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import pathlib
3 | import sys
4 |
5 | sys.path.append(".")
6 | import PIL
7 | import numpy as np
8 | from tqdm import trange
9 |
10 | from meta_set.mnist import loadMnist, random_rotation_new
11 |
12 |
13 | def creat_bg(input_image, img, change_colors=False):
14 | # Rotate image
15 | input_image = random_rotation_new(input_image)
16 | # Extend to RGB
17 | input_image = np.expand_dims(input_image, 2)
18 | input_image = input_image / 255.0
19 | input_image = np.concatenate([input_image, input_image, input_image], axis=2)
20 |
21 | # Convert the MNIST images to binary
22 | img_binary = (input_image > 0.5)
23 |
24 | # Take a random crop of the Lena image (background)
25 | x_c = np.random.randint(0, img.size[0] - 28)
26 | y_c = np.random.randint(0, img.size[1] - 28)
27 | image_bg = img.crop((x_c, y_c, x_c + 28, y_c + 28))
28 | # Conver the image to float between 0 and 1
29 | image_bg = np.asarray(image_bg) / 255.0
30 |
31 | if change_colors:
32 | # Change color distribution; this leads to more diverse changes than transformations
33 | for j in range(3):
34 | image_bg[:, :, j] = (image_bg[:, :, j] + np.random.uniform(0, 1)) / 2.0
35 |
36 | # Invert the colors at the location of the number
37 | image_bg[img_binary] = 1 - image_bg[img_binary]
38 |
39 | image_bg = image_bg / float(np.max(image_bg)) * 255
40 | return image_bg
41 |
42 |
43 | def makeMnistbg(img, num=1):
44 | """
45 | Change the background of MNIST images
46 | Select all testing samples from MNIST
47 | Store in numpy file for fast reading
48 | """
49 |
50 | index = str(num).zfill(5)
51 | np.random.seed(0)
52 |
53 | # Empty arrays
54 | test_data = np.zeros([28, 28, 3, 10000])
55 | test_label = np.zeros([10000])
56 |
57 | train_data = np.zeros([28, 28, 3, 50000])
58 | train_label = np.zeros([50000])
59 |
60 | try:
61 | os.makedirs('./dataset_bg/mnist_bg_%s/images/' % (index))
62 | except:
63 | None
64 |
65 | # testing images
66 | i = 0
67 | for j in range(10000):
68 | sample = all_samples_test[i]
69 |
70 | sample_rot = random_rotation_new(sample[0])
71 | test_data[:, :, :, j] = creat_bg(sample_rot, img)
72 | test_label[j] = sample[1]
73 | i += 1
74 | # save images only for visualization; I use npy file for dataloader
75 | # imsave("./dataset_bg/mnist_bg_%s/images/" % (index) + str(i) + ".jpg", test_data[:, :, :, j])
76 | np.save('./dataset_bg/mnist_bg_%s/test_data' % (index), test_data)
77 | np.save('./dataset_bg/mnist_bg_%s/test_label' % (index), test_label)
78 |
79 |
80 | def makeMnistbg_path(img_paths, num=1):
81 | """
82 | Change the background of MNIST images
83 | Select all testing samples from MNIST
84 | Store in numpy file for fast reading
85 | """
86 | index = str(num).zfill(5)
87 | np.random.seed(0)
88 |
89 | # Empty arrays
90 | test_data = np.zeros([28, 28, 3, 10000])
91 | test_label = np.zeros([10000])
92 |
93 | train_data = np.zeros([28, 28, 3, 50000])
94 | train_label = np.zeros([50000])
95 |
96 | try:
97 | os.makedirs('./dataset_bg/mnist_bg_%s/images/' % (index))
98 | except:
99 | None
100 |
101 | # testing images
102 | i = 0
103 | for j in range(10000):
104 | file = img_paths[np.random.choice(len(img_paths), 1)]
105 | img = PIL.Image.open(file[0])
106 |
107 | sample = all_samples_test[i]
108 | sample_rot = random_rotation_new(sample[0])
109 | test_data[:, :, :, j] = creat_bg(sample_rot, img)
110 | test_label[j] = sample[1]
111 | i += 1
112 | # save images only for visualization; I use npy file for the dataloader
113 | # imsave("./dataset_bg/mnist_bg_%s/images/" % (index) + str(i) + ".jpg", test_data[:, :, :, j])
114 | np.save('./dataset_bg/mnist_bg_%s/test_data' % (index), test_data)
115 | np.save('./dataset_bg/mnist_bg_%s/test_label' % (index), test_label)
116 |
117 |
118 | if __name__ == '__main__':
119 | # ---- load mnist images ----#
120 | mnist_path = './dataset/mnist/'
121 | all_samples_test = loadMnist('test', mnist_path)
122 | all_samples_train = loadMnist('train', mnist_path)
123 |
124 | # ---- coco dataset - using coco training set following the paper ----#
125 | path = './extra_data/train2014/'
126 | path = pathlib.Path(path)
127 | files = sorted(list(path.glob('*.jpg')) + list(path.glob('*.png')) + list(path.glob('*.JPEG')))
128 |
129 | # ---- generate smaple sets ----#
130 | print('==== generating sample sets ====')
131 | num = 200 # the number of sample sets (3000 sample sets; recommend use 200 for check the all codes)
132 | conut = 0
133 |
134 | # two ways of selecting coco images as background, both ways are similar in terms of meta set diversity
135 | # ----------- way 1 ----------- #
136 | for i in trange(num):
137 | try:
138 | img = PIL.Image.open(files[i])
139 | makeMnistbg(img, conut)
140 | conut += 1
141 | except:
142 | print('jump an image!')
143 |
144 | # ----------- way 2 ----------- #
145 | # for _ in trange(num):
146 | # try:
147 | # b_indice = np.random.choice(len( files), 1)
148 | # img_paths = np.array(files)[b_indice]
149 | # makeMnistbg_path(img_paths, conut)
150 | # conut += 1
151 | # except:
152 | # print('jump an image!')
153 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/meta_set/mnist.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import scipy.misc
2 |
3 | from meta_set.utils import *
4 |
5 |
6 | def loadMnist(mode, path):
7 | print('Loading MNIST', mode, 'images')
8 | # Mode = 'train'/'test'
9 | mnist_folder = path
10 |
11 | with open(mnist_folder + mode + '-labels.csv') as f:
12 | path_and_labels = f.readlines()
13 |
14 | samples = []
15 | for entry in path_and_labels:
16 | path = entry.split(',')[0]
17 | label = int(entry.split(',')[1])
18 | img = scipy.misc.imread(mnist_folder + path)
19 |
20 | samples.append([img, label])
21 | return samples
22 |
23 |
24 | def linear_interpolation_2D(input_array, indices, outside_val=0, boundary_correction=True):
25 | # http://stackoverflow.com/questions/6427276/3d-interpolation-of-numpy-arrays-without-scipy
26 | output = np.empty(indices[0].shape)
27 | ind_0 = indices[0, :]
28 | ind_1 = indices[1, :]
29 |
30 | N0, N1 = input_array.shape
31 |
32 | x0_0 = ind_0.astype(np.integer)
33 | x1_0 = ind_1.astype(np.integer)
34 | x0_1 = x0_0 + 1
35 | x1_1 = x1_0 + 1
36 |
37 | # Check if inds are beyond array boundary:
38 | if boundary_correction:
39 | # put all samples outside datacube to 0
40 | inds_out_of_range = (x0_0 < 0) | (x0_1 < 0) | (x1_0 < 0) | (x1_1 < 0) | \
41 | (x0_0 >= N0) | (x0_1 >= N0) | (x1_0 >= N1) | (x1_1 >= N1)
42 |
43 | x0_0[inds_out_of_range] = 0
44 | x1_0[inds_out_of_range] = 0
45 | x0_1[inds_out_of_range] = 0
46 | x1_1[inds_out_of_range] = 0
47 |
48 | w0 = ind_0 - x0_0
49 | w1 = ind_1 - x1_0
50 | # Replace by this...
51 | # input_array.take(np.array([x0_0, x1_0, x2_0]))
52 | output = (input_array[x0_0, x1_0] * (1 - w0) * (1 - w1) +
53 | input_array[x0_1, x1_0] * w0 * (1 - w1) +
54 | input_array[x0_0, x1_1] * (1 - w0) * w1 +
55 | input_array[x0_1, x1_1] * w0 * w1)
56 |
57 | if boundary_correction:
58 | output[inds_out_of_range] = 0
59 |
60 | return output
61 |
62 |
63 | def loadMnistRot():
64 | def load_and_make_list(mode):
65 | data = np.load('mnist_rot/' + mode + '_data.npy')
66 | lbls = np.load('mnist_rot/' + mode + '_label.npy')
67 | data = np.split(data, data.shape[2], 2)
68 | lbls = np.split(lbls, lbls.shape[0], 0)
69 |
70 | return zip(data, lbls)
71 |
72 | train = load_and_make_list('train')
73 | val = load_and_make_list('val')
74 | test = load_and_make_list('test')
75 | return train, val, test
76 |
77 |
78 | def random_rotation(data):
79 | rot = np.random.rand() * 360 # Random rotation
80 | grid = getGrid([28, 28])
81 | grid = rotate_grid_2D(grid, rot)
82 | grid += 13.5
83 | data = linear_interpolation_2D(data, grid)
84 | data = np.reshape(data, [28, 28])
85 | data = data / float(np.max(data)) * 255
86 | return data
87 |
88 |
89 | def random_rotation_new(data):
90 | rot = (-1 + 2 * np.random.rand()) * 15 # Random rotation
91 | grid = getGrid([28, 28])
92 | grid = rotate_grid_2D(grid, rot)
93 | grid += 13.5
94 | data = linear_interpolation_2D(data, grid)
95 | data = np.reshape(data, [28, 28])
96 | data = data / float(np.max(data)) * 255
97 | return data
98 |
99 |
100 | def random_rotation_90(data, degree):
101 | rot = degree # Random rotation
102 | grid = getGrid([28, 28])
103 | grid = rotate_grid_2D(grid, rot)
104 | grid += 13.5
105 | data = linear_interpolation_2D(data, grid)
106 | data = np.reshape(data, [28, 28])
107 | data = (data / float(np.max(data))) * 255
108 | return data
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/meta_set/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | from scipy.linalg import expm, norm
3 | import collections
4 | import itertools
5 | import numpy as np
6 | from torch.autograd import Variable
7 | import torch
8 |
9 |
10 | def ntuple(n):
11 | """ Ensure that input has the correct number of elements """
12 |
13 | def parse(x):
14 | if isinstance(x, collections.Iterable):
15 | return x
16 | return tuple(itertools.repeat(x, n))
17 |
18 | return parse
19 |
20 |
21 | def getGrid(siz):
22 | """ Returns grid with coordinates from -siz[0]/2 : siz[0]/2, -siz[1]/2 : siz[1]/2, ...."""
23 | space = [np.linspace(-(N / 2), (N / 2), N) for N in siz]
24 | mesh = np.meshgrid(*space, indexing='ij')
25 | mesh = [np.expand_dims(ax.ravel(), 0) for ax in mesh]
26 |
27 | return np.concatenate(mesh)
28 |
29 |
30 | def rotate_grid_2D(grid, theta):
31 | """ Rotate grid """
32 | theta = np.deg2rad(theta)
33 |
34 | x0 = grid[0, :] * np.cos(theta) - grid[1, :] * np.sin(theta)
35 | x1 = grid[0, :] * np.sin(theta) + grid[1, :] * np.cos(theta)
36 |
37 | grid[0, :] = x0
38 | grid[1, :] = x1
39 | return grid
40 |
41 |
42 | def rotate_grid_3D(theta, axis, grid):
43 | """ Rotate grid """
44 | theta = np.deg2rad(theta)
45 | axis = np.array(axis)
46 | rot_mat = expm(np.cross(np.eye(3), axis / norm(axis) * theta))
47 | rot_mat = np.expand_dims(rot_mat, 2)
48 | grid = np.transpose(np.expand_dims(grid, 2), [0, 2, 1])
49 |
50 | return np.einsum('ijk,jik->ik', rot_mat, grid)
51 |
52 |
53 | def get_filter_rotation_transforms(kernel_dims, angles):
54 | """ Return the interpolation variables needed to transform a filter by a given number of degrees """
55 |
56 | dim = len(kernel_dims)
57 |
58 | # Make grid (centered around filter-center)
59 | grid = getGrid(kernel_dims)
60 |
61 | # Rotate grid
62 | if dim == 2:
63 | grid = rotate_grid_2D(grid, angles)
64 | elif dim == 3:
65 | grid = rotate_grid_3D(angles[0], [1, 0, 0], grid)
66 | grid = rotate_grid_3D(angles[1], [0, 0, 1], grid)
67 |
68 | # Radius of filter
69 | radius = np.min((np.array(kernel_dims) - 1) / 2.)
70 |
71 | # Mask out samples outside circle
72 | radius = np.expand_dims(radius, -1)
73 | dist_to_center = np.sqrt(np.sum(grid ** 2, axis=0))
74 | mask = dist_to_center >= radius + .0001
75 | mask = 1 - mask
76 |
77 | # Move grid to center
78 | grid += radius
79 |
80 | return compute_interpolation_grids(grid, kernel_dims, mask)
81 |
82 |
83 | def compute_interpolation_grids(grid, kernel_dims, mask):
84 | #######################################################
85 | # The following part is part of nd-linear interpolation
86 |
87 | # Add a small eps to grid so that floor and ceil operations become more stable
88 | grid += 0.000000001
89 |
90 | # Make list where each element represents a dimension
91 | grid = [grid[i, :] for i in range(grid.shape[0])]
92 |
93 | # Get left and right index (integers)
94 | inds_0 = [ind.astype(np.integer) for ind in grid]
95 | inds_1 = [ind + 1 for ind in inds_0]
96 |
97 | # Get weights
98 | weights = [float_ind - int_ind for float_ind, int_ind in zip(grid, inds_0)]
99 |
100 | # Special case for when ind_1 == size (while ind_0 == siz)
101 | # In that case we select ind_0
102 | ind_1_out_of_bounds = np.logical_or.reduce([ind == siz for ind, siz in zip(inds_1, kernel_dims)])
103 | for i in range(len(inds_1)):
104 | inds_1[i][ind_1_out_of_bounds] = 0
105 |
106 | # Get samples that are out of bounds or outside mask
107 | inds_out_of_bounds = np.logical_or.reduce([ind < 0 for ind in itertools.chain(inds_0, inds_1)] + \
108 | [ind >= siz for ind, siz in zip(inds_0, kernel_dims)] + \
109 | [ind >= siz for ind, siz in zip(inds_1, kernel_dims)] +
110 | (1 - mask).astype('bool')
111 | )
112 |
113 | # Set these samples to zero get data from upper-left-corner (which will be put to zero)
114 | for i in range(len(inds_0)):
115 | inds_0[i][inds_out_of_bounds] = 0
116 | inds_1[i][inds_out_of_bounds] = 0
117 |
118 | # Reshape
119 | inds_0 = [np.reshape(ind, [1, 1] + kernel_dims) for ind in inds_0]
120 | inds_1 = [np.reshape(ind, [1, 1] + kernel_dims) for ind in inds_1]
121 | weights = [np.reshape(weight, [1, 1] + kernel_dims) for weight in weights]
122 |
123 | # Make pytorch-tensors of the interpolation variables
124 | inds_0 = [Variable(torch.LongTensor(ind)) for ind in inds_0]
125 | inds_1 = [Variable(torch.LongTensor(ind)) for ind in inds_1]
126 | weights = [Variable(torch.FloatTensor(weight)) for weight in weights]
127 |
128 | # Make mask pytorch tensor
129 | mask = mask.reshape(kernel_dims)
130 | mask = mask.astype('float32')
131 | mask = np.expand_dims(mask, 0)
132 | mask = np.expand_dims(mask, 0)
133 | mask = torch.FloatTensor(mask)
134 |
135 | # Uncomment for nearest interpolation (for debugging)
136 | # inds_1 = [ind*0 for ind in inds_1]
137 | # weights = [weight*0 for weight in weights]
138 |
139 | return inds_0, inds_1, weights, mask
140 |
141 |
142 | def apply_transform(filter, interp_vars, filters_size, old_bilinear_interpolation=True):
143 | """ Apply a transform specified by the interpolation_variables to a filter """
144 |
145 | dim = 2 if len(filter.size()) == 4 else 3
146 |
147 | if dim == 2:
148 | if old_bilinear_interpolation:
149 | [x0_0, x1_0], [x0_1, x1_1], [w0, w1] = interp_vars
150 | rotated_filter = (filter[:, :, x0_0, x1_0] * (1 - w0) * (1 - w1) +
151 | filter[:, :, x0_1, x1_0] * w0 * (1 - w1) +
152 | filter[:, :, x0_0, x1_1] * (1 - w0) * w1 +
153 | filter[:, :, x0_1, x1_1] * w0 * w1)
154 | else:
155 | # Expand dimmentions to fit filter
156 | interp_vars = [[inner_el.expand_as(filter) for inner_el in outer_el] for outer_el in interp_vars]
157 |
158 | [x0_0, x1_0], [x0_1, x1_1], [w0, w1] = interp_vars
159 |
160 | a = torch.gather(torch.gather(filter, 2, x0_0), 3, x1_0) * (1 - w0) * (1 - w1)
161 | b = torch.gather(torch.gather(filter, 2, x0_1), 3, x1_0) * w0 * (1 - w1)
162 | c = torch.gather(torch.gather(filter, 2, x0_0), 3, x1_1) * (1 - w0) * w1
163 | d = torch.gather(torch.gather(filter, 2, x0_1), 3, x1_1) * w0 * w1
164 | rotated_filter = a + b + c + d
165 |
166 | rotated_filter = rotated_filter.view(filter.size()[0], filter.size()[1], filters_size[0], filters_size[1])
167 |
168 | elif dim == 3:
169 | [x0_0, x1_0, x2_0], [x0_1, x1_1, x2_1], [w0, w1, w2] = interp_vars
170 |
171 | rotated_filter = (filter[x0_0, x1_0, x2_0] * (1 - w0) * (1 - w1) * (1 - w2) +
172 | filter[x0_1, x1_0, x2_0] * w0 * (1 - w1) * (1 - w2) +
173 | filter[x0_0, x1_1, x2_0] * (1 - w0) * w1 * (1 - w2) +
174 | filter[x0_1, x1_1, x2_0] * w0 * w1 * (1 - w2) +
175 | filter[x0_0, x1_0, x2_1] * (1 - w0) * (1 - w1) * w2 +
176 | filter[x0_1, x1_0, x2_1] * w0 * (1 - w1) * w2 +
177 | filter[x0_0, x1_1, x2_1] * (1 - w0) * w1 * w2 +
178 | filter[x0_1, x1_1, x2_1] * w0 * w1 * w2)
179 |
180 | rotated_filter = rotated_filter.view(filter.size()[0], filter.size()[1], filters_size[0], filters_size[1],
181 | filters_size[2])
182 |
183 | return rotated_filter
184 |
185 |
186 | if __name__ == '__main__':
187 | """ Test rotation of filter """
188 | import torch.nn as nn
189 | from torch.nn import functional as F
190 | from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
191 | from utils import *
192 |
193 | ks = [9, 9] # Kernel size
194 | angle = 45
195 | interp_vars = get_filter_rotation_transforms(ks, angle)
196 |
197 | w = Variable(torch.ones([1, 1] + ks))
198 | # w[:,:,4,:] = 5
199 | w[:, :, :, 4] = 5
200 | # w[:,:,0,0] = -1
201 |
202 | print(w)
203 | for angle in [0, 90, 45, 180, 65, 10]:
204 | print(angle, 'degrees')
205 | print(apply_transform(w, get_filter_rotation_transforms(ks, angle)[:-1], ks,
206 | old_bilinear_interpolation=True) * Variable(
207 | get_filter_rotation_transforms(ks, angle)[-1]))
208 | print('Difference', torch.sum(apply_transform(w, get_filter_rotation_transforms(ks, angle)[:-1], ks,
209 | old_bilinear_interpolation=False) * Variable(
210 | get_filter_rotation_transforms(ks, angle)[-1]) - apply_transform(w,
211 | get_filter_rotation_transforms(ks, angle)[
212 | :-1], ks,
213 | old_bilinear_interpolation=True) * Variable(
214 | get_filter_rotation_transforms(ks, angle)[-1])))
215 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------