├── Arithmetic
├── MandelbrotSet.md
├── PartialDifferentialEquations.md
└── WideDeepModel.md
├── BaseLearn
├── README.md
├── Supervisor
│ ├── README.md
│ └── SupervisorEx.py
├── install
│ └── README.md
├── read_data
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── create_data.png
│ ├── n1.csv
│ ├── n2.csv
│ └── read_data.py
├── share_variable
│ ├── README.md
│ └── share_variable.py
├── start
│ ├── README.md
│ └── start.py
├── tensorboard
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── SummayTest.py
│ ├── TensorBoard.py
│ ├── tensorboard_commandline.png
│ ├── tensorboard_example.png
│ └── test_1
│ │ ├── events.out.tfevents.1502120649.NIEBIN
│ │ └── events.out.tfevents.1502121636.NIEBIN
├── tensorboard_image
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── SummayImage.py
│ ├── start_person.jpg
│ ├── sum_image.png
│ └── test_2
│ │ ├── events.out.tfevents.1502182056.NIEBIN
│ │ ├── events.out.tfevents.1502182108.NIEBIN
│ │ ├── events.out.tfevents.1502182134.NIEBIN
│ │ ├── events.out.tfevents.1502185571.NIEBIN
│ │ ├── events.out.tfevents.1502185594.NIEBIN
│ │ ├── events.out.tfevents.1502186495.NIEBIN
│ │ └── events.out.tfevents.1502186504.NIEBIN
├── threads
│ ├── README.md
│ └── threadExample.py
└── variable
│ ├── README.md
│ └── variable.py
├── LICENSE
├── PicClassify
├── Newer
│ ├── README.md
│ └── mnist_softmax.py
├── README.md
├── __init__.py
└── mnist.py
├── README.md
└── Resource
├── README.md
├── thread_queque.png
└── 训练集.png
/Arithmetic/MandelbrotSet.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Mandelbrot Set
2 |
3 | 在此部分,介绍一个使用tensorflow可视化Mandelbrot set的例子。以这个例子表明,tensorflow可用于基础数学。以下内容来源于tensorflow教程部分[Mandelbrot Set](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/mandelbrot),对其进行了翻译和整理。
4 |
5 | 目录:
6 |
7 | * 什么是Mandelbrot set
8 | * 可视化Mandelbrot set
9 |
10 | ## 什么是Mandelbrot set(曼德博集合)?
11 |
12 | Mandelbrot set是在[复平面](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%A4%8D%E5%B9%B3%E9%9D%A2)组成[分形](https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E5%88%86%E5%BD%A2)的点的集合,以美国数学家Mandelbrot命名。
13 |
14 | Mandelbrot set是一个复数点c的集合,任取复平面上的一个点c,若满足:Z(n+1) = Z(n)^2 + c,Z(0)=0,当n不断增大时,|Z(n)|有界,则c属于Mandelbrot set。
15 |
16 | 在实际中,一般取一个较大的n值,迭代计算Z(n)是否有界(小于某个值),若有界则c属于Mandelbrot set。在可视化的时候,可选择在平面上c点的坐标以某种 颜色显示。
17 |
18 | ## 可视化Mandelbrot set
19 |
20 | ### import相关的库
21 |
22 | 导入仿真计算的库
23 |
24 | ```python
25 | import tensorflow as tf
26 | import numpy as np
27 | ```
28 |
29 | 导入可视化的库
30 | ```python
31 | import PIL.Image
32 | from io import BytesIO
33 | from IPython.display import Image, display
34 | ```
35 |
36 | ### 定义一个可视化函数
37 |
38 | ```python
39 | def DisplayFractal(a, fmt='jpeg'):
40 | a_cyclic = (6.28*a/20.0).reshape(list(a.shape)+[1])
41 | img = np.concatenate([10+20*np.cos(a_cyclic),
42 | 30+50*np.sin(a_cyclic),
43 | 155-80*np.cos(a_cyclic)], 2)
44 | img[a==a.max()] = 0
45 | a = img
46 | a = np.uint8(np.clip(a, 0, 255))
47 | f = BytesIO()
48 | PIL.Image.fromarray(a).save(f, fmt)
49 | display(Image(data=f.getvalue()))
50 |
51 | ```
52 |
53 | ### 使用tensorflow进行一些数学计算
54 |
55 | ```python
56 | sess = tf.InteractiveSession() # 打开一个交互式的session,在这个session下进行计算
57 |
58 | Y, X = np.mgrid[-1.3:1.3:0.005, -2:1:0.005] # 创建复平面上点的横纵坐标
59 | Z = X+1j*Y # 复数Z
60 |
61 | xs = tf.constant(Z.astype(np.complex64)) # xs为tf的常量,其值为Z转成np.complex64类型后的值
62 | zs = tf.Variable(xs) # zs为tf中的变量,其初始值为xs
63 | ns = tf.Variable(tf.zeros_like(xs, tf.float32)) # ns为tf中的变量,与xs的shape相同,但值都为0,tf.float32类型。
64 |
65 | tf.global_variables_initializer().run() # 计算前先初始化所有变量
66 |
67 | zs_ = zs*zs + xs # 对应Mandelbrot set的迭代计算公式
68 |
69 | not_diverged = tf.abs(zs_) < 4 # 小于4时即收敛,与zs_的shape相同,但所有值为bool型
70 |
71 | step = tf.group(
72 | zs.assign(zs_), # 将zs_赋值给zs
73 | ns.assign_add(tf.cast(not_diverged, tf.float32)) # ns = ns+not_diverged
74 | )
75 |
76 | for i in range(200):
77 | step.run() # 迭代200次
78 |
79 | ```
80 |
81 | ### 可视化结果
82 |
83 | ```python
84 | DisplayFractal(ns.eval()) # 以上代码在ipython中运行时,并未出现可视化的图片。在jupyter notebook中,出现可视化的结果。
85 | ```
86 | 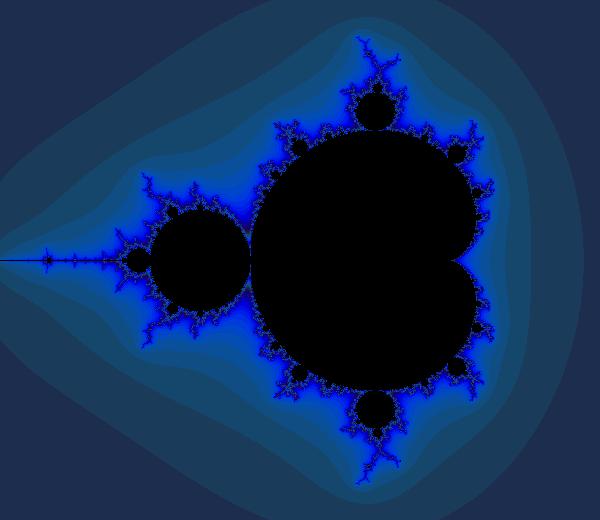
87 |
88 |
89 | 参考文献:
90 |
91 | [1] [曼德布洛特集合简要概述](https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/jj635753(v=vs.85).aspx)
92 |
93 | [2] [tensorflow中的Mandelbrot set教程](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/mandelbrot)
94 |
95 |
96 |
97 |
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Arithmetic/PartialDifferentialEquations.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Partial Differential Equations(偏微分方程)
2 |
3 | TensorFlow不仅仅用于机器学习。在这部分,给出一个使用TensorFlow仿真偏微分方程的例子,模拟一些雨点落在一个方形池塘的水面上。
4 |
5 | 目录
6 |
7 | * 建立基础
8 | * 便于计算的函数
9 | * 定义概率密度函数
10 | * 运行仿真
11 |
12 | ## 建立基础
13 |
14 | 导入一些库
15 | ```python
16 | # 导入用于仿真的库
17 | import tensorflow as tf
18 | import numpy as np
19 |
20 | # 导入用于可视化的库
21 | import PIL.Image
22 | from io import BytesIO
23 | from IPython.display import clear_output, Image, display
24 |
25 | # 用于显示池塘水面状态的函数,水面状态以图像表示
26 | def DisplayArray(a, fmt='jpeg', rng=[0,1]):
27 | """Display an array as a picture."""
28 | a = (a - rng[0])/float(rng[1] - rng[0])*255
29 | a = np.uint8(np.clip(a, 0, 255))
30 | f = BytesIO()
31 | PIL.Image.fromarray(a).save(f, fmt)
32 | clear_output(wait = True)
33 | display(Image(data=f.getvalue()))
34 |
35 | # 打开一个交互式的session
36 | sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
37 | ```
38 |
39 | ## 便于计算的函数
40 |
41 | ```python
42 | def make_kernel(a):
43 | """转换一个2维数组成一个卷积核"""
44 | a = np.asarray(a)
45 | a = a.reshape(list(a.shape) + [1,1])
46 | return tf.constant(a, dtype=1)
47 |
48 | def simple_conv(x, k):
49 | """一个简单的2维卷积操作"""
50 | x = tf.expand_dims(tf.expand_dims(x, 0), -1)
51 | y = tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d(x, k, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
52 | return y[0, :, :, 0]
53 |
54 | def laplace(x):
55 | """计算一个数组的拉普拉斯变换"""
56 | laplace_k = make_kernel([[0.5, 1.0, 0.5],
57 | [1.0, -6., 1.0],
58 | [0.5, 1.0, 0.5]])
59 | return simple_conv(x, laplace_k)
60 | ```
61 |
62 | 其中,[tf.nn.depthwise_conv2d](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/nn/depthwise_conv2d)的
63 | 图示为
64 |
65 | ## 定义概率密度函数
66 |
67 | 假设池塘的尺寸为N*N,N=500。
68 | ```python
69 | # 池塘的初始状态,初始化为0
70 | u_init = np.zeros([N, N], dtype=np.float32)
71 | ut_init = np.zeros([N, N], dtype=np.float32)
72 | # 用几个随机点表示雨点,落在池塘里
73 | for n in range(40):
74 | a,b = np.random.randint(0, N, 2)
75 | u_init[a,b] = np.random.uniform()
76 | # 显示效果
77 | DisplayArray(u_init, rng=[-0.1, 0.1])
78 | ```
79 | 接下来,定义微分方程。
80 | ```python
81 | # 参数
82 | # eps -- time resolution
83 | # damping -- wave damping
84 | eps = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=())
85 | damping = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=())
86 | # 创建表示仿真状态的变量
87 | U = tf.Variable(u_init)
88 | Ut = tf.Variable(ut_init)
89 | # 离散化的概率密度函数的更新规则
90 | U_ = U + eps * Ut
91 | Ut_ = Ut + eps * (laplace(U) - damping * Ut)
92 | # 更新状态的操作
93 | step = tf.group(
94 | U.assign(U_),
95 | Ut.assign(Ut_))
96 | ```
97 |
98 | ## 运行仿真
99 | ```python
100 | # 初始化所有变量
101 | tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
102 | # 概率密度函数,运行1000次,每一次都输出一个池塘的表面状态结果
103 | for i in range(1000):
104 | # Step simulation
105 | step.run({eps: 0.03, damping: 0.04})
106 | DisplayArray(U.eval(), rng=[-0.1, 0.1])
107 | ```
108 | 最终结果
109 |
110 | 参考文献:
111 | [1]
112 | [tf中几种卷积的介绍](http://qiita.com/YusukeSuzuki@github/items/0764d15b9d0b97ec1e16)
113 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Arithmetic/WideDeepModel.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Tensorflow Wide & Deep Learning Tutorial
2 |
3 | 此部分,简单介绍了一个使用tensorflow在一份数据集上训练wide & deep模型,并使用训练好的模型进行预测的例子。全部内容基于[tf官网例子](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/wide_and_deep)进行了整理。tf官网上该例子的[源代码](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/r1.2/tensorflow/examples/learn/wide_n_deep_tutorial.py),请结合源代码看此部分教程。
4 |
5 | ## 涉及到:
6 | * 数据集:[Census Income Data](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/datasets/Census+Income)
7 | * 模型:Wide & Deep Model [论文](https://arxiv.org/abs/1606.07792),[理论介绍](http://www.shuang0420.com/2017/03/13/%E8%AE%BA%E6%96%87%E7%AC%94%E8%AE%B0%20-%20Wide%20and%20Deep%20Learning%20for%20Recommender%20Systems/)
8 | * pandas(python的一个数据处理库,在这里用于读取数据集)
9 | * tempfile(python的一个临时文件相关的库,在这里用于创建临时文件,关闭后会自动删除)
10 | * [tf.contrib.learn.DNNLinearCombinedClassifier](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/DNNLinearCombinedClassifier)(Wide & Deep Model在tensorflow中的实现)
11 | * [tf.contrib.layers.sparse_column_with_keys](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/sparse_column_with_keys)(tf中处理分类型特征的一种方式,当知道该特征中不同的特征值时使用)
12 | * [tf.contrib.layers.sparse_column_with_hash_bucket](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/sparse_column_with_hash_bucket)(tf中处理分类型特征的另一种方式,如果不知道该特征中不同的特征值时使用,但特征值必须时字符串或整型)
13 | * [tf.contrib.layers.real_valued_column](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/real_valued_column)(tf中处理连续型特征的一种方式)
14 | * [tf.contrib.layers.bucketized_column](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/bucketized_column)(tf中离散化连续型特征的一种方式)
15 | * [tf.contrib.layers.crossed_column](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/crossed_column)(tf中处理交叉特征的一种方式)
16 | * [tf.contrib.layers.embedding_column](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/embedding_column)(tf中embedding稀疏特征,并feed给DNN)
17 |
18 | ## 目录:
19 | * Census Income Data介绍和下载
20 | * Wide & Deep Model简介
21 | * 数据预处理
22 | * 模型的训练和评估
23 |
24 | !!!请注意!!!为避免对有些专有名词翻译的不准确,在这里将不翻译。
25 |
26 | ## 1、 Census Income Data介绍和下载
27 |
28 | ### 1.1、 Census Income Data介绍
29 |
30 | 数据来源于美国1994年人口调查数据库。[数据集介绍](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/adult/adult.names)。
31 |
32 | 样本个数:train=32561, test=16281。
33 | 类别:>50K, <=50K。
34 | 特征个数:14个,其中:
35 | 分类型特征:CATEGORICAL_COLUMNS = ["workclass", "education", "marital_status", "occupation",
36 | "relationship", "race", "gender", "native_country"]
37 | 连续型特征:CONTINUOUS_COLUMNS = ["age", "education_num", "capital_gain", "capital_loss",
38 | "hours_per_week"]
39 |
40 | ### 1.2、Census Income Data下载
41 |
42 | 1) 手动下载,[数据集地址](https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/adult/)
43 |
44 | 2) 使用[源代码](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/r1.2/tensorflow/examples/learn/wide_n_deep_tutorial.py)中的maybe_download函数下载
45 |
46 | ### 2、Wide & Deep Model简介
47 |
48 | 
49 |
50 | 上图左为Wide Model;上图右为Deep Model;上图中为Wide & Deep Model,该模型由两个模型组成:Wide Model(线性模型),Deep Model(DNN模型)。在tensorflow中有该模型的实现:[tf.contrib.learn.DNNLinearCombinedClassifier](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/DNNLinearCombinedClassifier)(模型的理论介绍,可从本篇开头介绍的链接找到)。DNNLinearCombinedClassifier函数的参数有linear_feature_columns,dnn_feature_columns,dnn_hidden_units等。其中linear_feature_columns为模型的wide part的输入,包括sparse features和sparse crossed features(交叉特征);dnn_feature_columns为模型的deep part的输入,包括连续型特征,每一个分类型特征的embedding。
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 | ### 3、数据预处理
55 |
56 | 1) 原数据集中含有缺失值,而模型的输入不能含有缺失值,需去除含有缺失值的样本。在[源代码](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/r1.2/tensorflow/examples/learn/wide_n_deep_tutorial.py)的train_and_eval函数中有相应处理,利用了pandas的dropna函数。
57 |
58 | 我手动下载了数据集,发现其中的缺失值用'?'代替了。我的处理方案时,使用pd.read_csv读取数据集,返回dataframe对象,设为df。
59 |
60 | l = df.apply(lambda x:'?' in x.values, axis=1) # 如果某一行含有'?',则为True,否则为False。
61 | df1 = df.drop(df.loc[l].index) # 利用得到的l来索引df,得到含有'?'的行,然后去除这些行,得到df1。
62 |
63 | 2)对于分类型特征,由于其值本身没有任何意义,一般使用OneHotEncoder来处理。在tensorflow中有相应的函数[tf.contrib.layers.sparse_column_with_keys](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/sparse_column_with_keys),[tf.contrib.layers.sparse_column_with_hash_bucket](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/sparse_column_with_hash_bucket),将分类型特征转成sparse features,这里并没有执行,只是先进行了定义,用于feed给DNN,下面类似的几个函数也是进行类似的定义。
64 |
65 | 将若干个分类型特征组成交叉特征的函数为[tf.contrib.layers.crossed_column](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/crossed_column),特征工程的一种操作。
66 |
67 | 将两个类别转成0和1表示的方法,见源代码中的177和178行。
68 |
69 | 对于有些特征值很多的特征,虽然可将其转成Sparse features,但维度高,还需使用[tf.contrib.layers.embedding_column](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/embedding_column)对其降维转成embedding vecotr,才能作为wide part的输入。对于降维后其维度的确定,可参考
70 | [官网教程的The Deep Model: Neural Network with Embeddings部分](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/wide_and_deep),设置为log2(n)或者k*(n)**(1/4),n为该特征不同的特征值的个数,k为一个小的常数,通常小于10。
71 |
72 | 3)对于连续型特征,使用了函数[tf.contrib.layers.real_valued_column](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/layers/real_valued_column)来处理。
73 |
74 | 4)[源代码](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/r1.2/tensorflow/examples/learn/wide_n_deep_tutorial.py)的input_fn函数,将传入pandas读取的dataframe对象df的每一列,转成tensorflow中的tensor,并创建特征名与其tensor的Python字典。
75 |
76 | 对于连续型特征,使用tf.constant(df[特征名].values)转成一维的tensor;
77 |
78 | 对于分类型特征,使用[tf.SparseTensor](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/SparseTensor)进行转换。该函数中最重要的三个参数为indice(二维数组,表示dense feature中非0值的下标),values(一维数组,表示feature的非0值),dense_shape(一维数组,表示dense feature的shape)。
79 |
80 | (个人观点:从源代码中tf.SparseTensor的使用来看,对于传递给该函数的每一个分类型特征,indice=[..., [i,0], ...]; value=一个dataframe列的所有值,一维数组;dense_shape=[该列的长度,1]。如果将其转成dense tensor,结果与该列的唯一区别就是维度从一维,变成了二维的[该列的长度,1]。这样的话,并没有达到sparse的特点,请高人指点。)
81 |
82 |
83 | ### 4、 模型的训练和评估
84 |
85 | 在[源代码](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/r1.2/tensorflow/examples/learn/wide_n_deep_tutorial.py)中,build_estimator函数用于创建wide& deep model,返回模型的对象m。
86 |
87 | 然后调用模型的[fit方法](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/DNNLinearCombinedClassifier),传入数据、迭代次数等参数进行训练。
88 |
89 | 调用模型的[evaluate方法](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/DNNLinearCombinedClassifier)进行预测。
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [安装](./install)
2 | [快速入门](./start)
3 | [变量相关的](./variable)
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/Supervisor/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 训练助手
2 | > 当需要做以日计的训练数据 有如下需求
3 | - 处理关机和异常的清除
4 | - 可以从关机或异常中重新运行
5 | - 可以TensorBoard中被监控
6 |
7 | 关键类:[tf.train.Supervisor](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/train/Supervisor)
8 |
9 | ```python
10 | def runSum():
11 | a=tf.constant(12,dtype=tf.int8)
12 | b=tf.constant(10,dtype=tf.int8)
13 | sv=tf.train.Supervisor(logdir="./test1")
14 | with sv.managed_session() as sess:
15 | for i in range(10):
16 | if sv.should_stop():
17 | return
18 | print(sess.run([a,b]))
19 | '''
20 | [12, 10]
21 | [12, 10]
22 | [12, 10]
23 | [12, 10]
24 | [12, 10]
25 | [12, 10]
26 | [12, 10]
27 | [12, 10]
28 | [12, 10]
29 | [12, 10]
30 | '''
31 | ```
32 | [实例代码](./SupervisorEx.py)
33 | - 未完待续
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/Supervisor/SupervisorEx.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # user/bin
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 | import threading
4 | '''
5 | this is test for how to use the Supervisor
6 | '''
7 | def runSum():
8 | a=tf.constant(12,dtype=tf.int8)
9 | b=tf.constant(10,dtype=tf.int8)
10 | sv=tf.train.Supervisor(logdir="./test1")
11 | with sv.managed_session() as sess:
12 | for i in range(10):
13 | if sv.should_stop():
14 | return
15 | print(sess.run([a,b]))
16 |
17 | runSum()
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/install/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 安装window-cpu版本
2 | 1. 安装python3.5.2
3 | > 一定要是这个版本,如果是其他版本会安装不上
4 | 一配置好环境变量
5 | PYTHON_PATH=E:\Tools\Python35\Scripts;E:\Tools\Python35
6 |
7 | 2. 安装tensorflow
8 | 输入命令:pip3 install --upgrade tensorflow
9 | 3. 验证
10 | 命令:import tensorflow as tf
11 | - a.No module named "pywrap_tensorflow"
12 | 解决方案:下载https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=53587
13 | - b.NameError: name 'core' is not defined
14 | - c.NameError: name 'python' is not defined
15 | #### bc重启命令好久好了!!
16 |
17 | ## Mac
18 | 等待你的完成
19 | ## Linux
20 | 等待你的参与
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/read_data/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 读取数据
2 | > 以读取csv文件(可以用excel进行转换 可以作为普通文本打开)为例 如果是普通文件 可以直接用python的接口读取
3 |
4 | - ## 绑定文件
5 | > 将文件放在队列中 创建reader 绑定到队列中 进行操作
6 | > 关键类 TextLineReader
7 | ``` python
8 | filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["n1.csv", "n2.csv"])#将文件扔进管道里面
9 | reader = tf.TextLineReader()
10 | key, value = reader.read(filename_queue)#读取文件的 ,
11 | print("key=",key)# 打印 key= Tensor("ReaderReadV2:0", shape=(), dtype=string)
12 | print("value=",value)#value= Tensor("ReaderReadV2:1", shape=(), dtype=string)
13 | ```
14 |
15 | - ## 特殊格式解析
16 | > 这一步 主要是根据文件格式 选择对应的解析器 对文件进行解析 并根据内容进行特殊处理
17 | > 关键词 tf.decode_csv
18 | ```python
19 | record_defaults = [[1], [1], [1], [1], [1]]
20 | col1, col2, col3, col4, col5 = tf.decode_csv(
21 | value, record_defaults=record_defaults)# 进行解析
22 | print("c1-5=",col1," ",col2," ",col3," ",col4," ",col5)
23 | features = tf.stack([col1, col2, col3, col4])
24 | print("f=",features)
25 | ```
26 |
27 | - ## 读取内容
28 | > 终于到了最关键的一步 前面都是准备工作 ,这才是真正的数据读取 用法也很简单
29 | > 关键字:coordinater,线程 不懂的请参照[队列和线程](https://github.com/TFStudents/Tensorflow/tree/master/BaseLearn/threads)
30 | ```python
31 | with tf.Session() as sess:
32 | # Start populating the filename queue.
33 | coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
34 | threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
35 | for i in range(5):
36 | # Retrieve a single instance:
37 | example, label = sess.run([features, col5])
38 | print(example)
39 | print(label)
40 | coord.request_stop()
41 | coord.join(threads)
42 | ```
43 |
44 | ## 资源
45 | [参考地址](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/reading_data)
46 | [n1.csv](n1.csv)
47 | [n2.csv](n2.csv)
48 | [本实例代码](read_data.py)
49 | 
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/read_data/create_data.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/read_data/create_data.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/read_data/n1.csv:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1,2,3,4,5
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/read_data/n2.csv:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 101,102,103,104,105
2 | 201,203,204,202,205
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/read_data/read_data.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # user/bin
2 |
3 | import tensorflow as tf
4 | import threading
5 | import time
6 | """
7 | n2.csv content
8 | 101,102,103,104,105
9 | 201,203,204,202,205
10 |
11 | n1.csv content
12 | 1,2,3,4,5
13 | """
14 | # 1 read file
15 | filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(["n1.csv", "n2.csv"])
16 | sess=tf.Session()
17 | reader = tf.TextLineReader()
18 | key, value = reader.read(filename_queue)
19 | print("key=",key)
20 | print("value=",value)
21 | # Default values, in case of empty columns. Also specifies the type of the
22 | # decoded result
23 |
24 | # 2 decode file
25 | record_defaults = [[1], [1], [1], [1], [1]]
26 | col1, col2, col3, col4, col5 = tf.decode_csv(
27 | value, record_defaults=record_defaults)
28 | print("c1-5=",col1," ",col2," ",col3," ",col4," ",col5)
29 | features = tf.stack([col1, col2, col3, col4])
30 | print("f=",features)
31 | # 3 get the file content
32 | with tf.Session() as sess:
33 | # Start populating the filename queue.
34 | coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
35 | threads = tf.train.start_queue_runners(coord=coord)
36 | for i in range(5):
37 | # Retrieve a single instance:
38 | example, label = sess.run([features, col5])
39 | print(example)
40 | print(label)
41 | coord.request_stop()
42 | coord.join(threads)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/share_variable/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 共享变量
2 | [share_variable.py](./share_variable.py)
3 | ## 存在问题
4 | - 代码块 A
5 | ```
6 | sess=tf.Session()
7 | def printVariable():
8 | v1=tf.Variable(1,name="v1")
9 | v2=tf.Variable(1,name="v2")
10 | init=tf.global_variables_initializer()#变量的初始化 初始化当前module所有的变量
11 | sess.run(init)
12 | return v1+v2
13 |
14 | a1=printVariable()#两个变量
15 | b1=printVariable()#两个变量 总4个变量
16 | print(sess.run(a1))
17 | print(sess.run(b1))
18 | ```
19 | 当我们运行代码块A时,方法内会产生4个变量,当运算大时,会产生过多的内存消耗,那怎么解决这个问题呢?
20 | 有如下方案
21 | - 代码块B
22 | ```
23 | v_dict={
24 | "v1":tf.Variable(1,name="v1"),
25 | "v2":tf.Variable(1,name="v2")
26 | }
27 | def printVariable(dicts):
28 | v1=dicts["v1"]
29 | v2=dicts["v2"]
30 | return v1.initialized_value()+v2.initialized_value()
31 | a2=printVariable(v_dict)#两个变量
32 | b2=printVariable(v_dict)#两个变量 总2两个
33 | print(sess.run(a2))
34 | print(sess.run(b2))
35 | ```
36 | 当我们执行两遍printVariable方法时,确实解决了这个问题,只有两个变量,单存在一些问题
37 | 1. 当创建变量时,必须指定一些如类型,形状等参数
38 | 2. 当代码改变时,可能创建的变量会更多
39 |
40 | tensorflow提供了一种更方便的方式提供相应的功能,直接看代码
41 | - 代码块C
42 | ```
43 | def printVariable2():
44 | v1=tf.get_variable("v1",[1],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1))
45 | print("v1.name="+v1.name)
46 | v2=tf.get_variable("v2",[1],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(2))
47 | print("v2.name="+v2.name)
48 | return v1+v2
49 | with tf.variable_scope("boo") as boo:
50 | printVariable2()
51 | print("----------boo--1-----------")
52 | boo.reuse_variables()
53 | printVariable2()
54 | print("----------boo--2-----------")
55 | printVariable2()
56 | print("----------boo--3-----------")
57 | printVariable2()
58 | print("----------boo--4-----------")
59 | printVariable2()
60 | '''
61 | 打印的信息
62 | v1.name=boo/v1:0
63 | v2.name=boo/v2:0
64 | ----------boo--1-----------
65 | v1.name=boo/v1:0
66 | v2.name=boo/v2:0
67 | ----------boo--2-----------
68 | v1.name=boo/v1:0
69 | v2.name=boo/v2:0
70 | ----------boo--3-----------
71 | v1.name=boo/v1:0
72 | v2.name=boo/v2:0
73 | ----------boo--4-----------
74 | v1.name=boo/v1:0
75 | v2.name=boo/v2:0
76 |
77 | '''
78 | ```
79 | 上面虽然调用了好几次,但是变量是共享的,所以只产生了2个变量,而tf就是这么进行变量共享的,先看两个关键函数
80 | ## tf.get_variable
81 | [tf.get_variable](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/get_variable)
82 | - 参数列表
83 | ```
84 | get_variable(
85 | name,
86 | shape=None,
87 | dtype=None,
88 | initializer=None,
89 | regularizer=None,
90 | trainable=True,
91 | collections=None,
92 | caching_device=None,
93 | partitioner=None,
94 | validate_shape=True,
95 | use_resource=None,
96 | custom_getter=None
97 | )
98 | ```
99 | 传入值时,除name外shape也是必须传的
100 | ```
101 | v=tf.get_variable("v1",shape=[1],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1)) #这样一个变量就创建了
102 | ```
103 | - 它是怎么工作的?
104 | 1. 名字: 传入相应参数后,v将会被创建,它的名字就是scope_name+variable_name
105 | 在代码块C中,scope_name="boo",variable_name="v1"或"v2" 则v1的全名就是"boo/v1:0" 参考打印信息
106 | 2. 重用:要确保tf.get_variable_scope().reuse == True ,调用就scope.reuse_variables()就可以了 但不能直接设置为false
107 |
108 | ## tf.variable_scope
109 | [tf.variable_scope](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/variable_scope)
110 | - 参数列表
111 | ```
112 | variable_scope(
113 | name_or_scope,
114 | default_name=None,
115 | values=None,
116 | initializer=None,
117 | regularizer=None,
118 | caching_device=None,
119 | partitioner=None,
120 | custom_getter=None,
121 | reuse=None,
122 | dtype=None,
123 | use_resource=None
124 | )
125 | ```
126 | 一般只传name值就可以了,作用就是为tf.get_variable做名字区分以及重用控制,当然还可以控制initializer
127 | 差不多这些内容就够用了 ,具体细节点击链接看看[本文参考地址](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/variable_scope)
128 |
129 | ## end
130 |
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/share_variable/share_variable.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #user/bin
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 | sess=tf.Session()
4 | print("----------0-------------")
5 | def printVariable():
6 | v1=tf.Variable(1,name="v1")
7 | v2=tf.Variable(1,name="v2")
8 | init=tf.global_variables_initializer()#变量的初始化 初始化当前module所有的变量
9 | sess.run(init)
10 | return v1+v2
11 |
12 | a1=printVariable()#两个变量
13 | b1=printVariable()#两个变量 总4个变量
14 | print(sess.run(a1))
15 | print(sess.run(b1))
16 | print("----------1-------------")
17 | v_dict={
18 | "v1":tf.Variable(1,name="v1"),
19 | "v2":tf.Variable(1,name="v2")
20 | }
21 | def printVariable(dicts):
22 | v1=dicts["v1"]
23 | v2=dicts["v2"]
24 | return v1.initialized_value()+v2.initialized_value()
25 | a2=printVariable(v_dict)#两个变量
26 | b2=printVariable(v_dict)#两个变量 总2两个
27 | print(sess.run(a2))
28 | print(sess.run(b2))
29 |
30 | print("----------2-------------")
31 |
32 | def printVariable2():
33 | v1=tf.get_variable("v1",[1],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(1))
34 | print("v1.name="+v1.name)
35 | v2=tf.get_variable("v2",[1],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(2))
36 | print("v2.name="+v2.name)
37 | return v1+v2
38 | with tf.variable_scope("boo") as boo:
39 | printVariable2()
40 | print("----------boo--1-----------")
41 | boo.reuse_variables()
42 | printVariable2()
43 | print("----------boo--2-----------")
44 | printVariable2()
45 | print("----------boo--3-----------")
46 | printVariable2()
47 | print("----------boo--4-----------")
48 | printVariable2()
49 |
50 | #------------variable_scope--------------------------
51 | def onTestScope():
52 | with tf.variable_scope("boo") as boo:
53 | v=tf.get_variable("v_1",[20],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(2))
54 | print("v.name="+v.name)
55 | print("boo.name="+boo.name)
56 | with tf.variable_scope(boo):
57 | v2=tf.get_variable("v_2",[20],initializer=tf.constant_initializer(3))
58 | v1=v+v2
59 | print("v2.name="+v2.name)
60 | print("v1.name="+v1.name)
61 | return v1
62 | with tf.variable_scope("test") as sc:
63 | onTestScope()
64 | sc.reuse_variables()
65 | onTestScope()
66 |
67 | # with tf.variable_scope("ABC",initializer=tf.constant_initializer(233)):
68 | # v=tf.get_variable("v3",[1])
69 | # with tf.Session() as sess:
70 | # print(sess.run(v.variable_value()))
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/start/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 快速入门
2 | [源码-start.py](./start.py)
3 | ```python
4 | #首先引入tensorflow 代码块是同一.py中
5 | import tensorflow as tf
6 | ```
7 | ## 张量
8 | > 符号 Tensor
9 |
10 | - 阶 rank
11 | > 类似于维度
12 | > 什么是张量?张量相当于表,又有点类似于树
13 |
14 |
15 | | 阶数 |
16 | 维度 |
17 | 实际意义 |
18 | 举例 |
19 |
20 |
21 | | 0 |
22 | 0维张量 |
23 | 标量 |
24 | 2 |
25 |
26 |
27 | | 1 |
28 | 1维张量 |
29 | 向量 |
30 | [1,2] |
31 |
32 |
33 | | 2 |
34 | 2维张量 |
35 | 矩阵 |
36 | [[123,33],[232,21]] |
37 |
38 |
39 | | 3 |
40 | 3维张量 |
41 | 2维张量的向量 |
42 | [[1,2],[123,33]],[[3,5],[7,9]]] |
43 |
44 |
45 | | 4 |
46 | 4维张量 |
47 | 3维张量的向量 |
48 | ~~~ |
49 |
50 |
51 | | 5 |
52 | 5维张量 |
53 | 4维张量的向量 |
54 | ~~~ |
55 |
56 |
57 | | n |
58 | n维张量 |
59 | n-1维张量的向量 |
60 | ~~~ |
61 |
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 |
66 | - 形状 Shape
67 | > 就是张量形状描述 ,长度是张量的阶数
68 |
69 |
70 | | 阶 |
71 | shape |
72 | 举例 |
73 |
74 |
75 | | 0 |
76 | [] |
77 | shape[] |
78 |
79 |
80 | | 1 |
81 | [D0]#D0是数据集 |
82 | shape[233]#D0的个数 |
83 |
84 |
85 | | n |
86 | [D0,....,Dn-1]#D0是数据集 |
87 | shape[D0,....,Dn-1] |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | - 数据类型 type
92 | > 支持所有python 支持的基础数据类型
93 |
94 | - 流图Graph
95 | > 由一系列节点(node)汇聚而成的tf操作(option)
96 |
97 | ## 常量constant
98 | 方法[tf.constant](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/constant)
99 |
100 | - 构造函数
101 | ```python
102 | constant(
103 | value,
104 | dtype=None,
105 | shape=None,
106 | name='Const',
107 | verify_shape=False
108 | )
109 | ```
110 |
111 | - 举例
112 | ```python
113 | node1= tf.constant([True,True])
114 | node2= tf.constant(12)
115 | node3=tf.constant("hello")
116 | node4=tf.constant("world")
117 | print(node1)#打印Tensor("Const:0", shape=(2,), dtype=bool)
118 | print(node2)#打印Tensor("Const_1:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
119 | print(node3)#打印Tensor("Const_2:0", shape=(), dtype=string)
120 | sess=tf.Session()#获取会话
121 | print(sess.run(node1))#打印[True,True]
122 | print(sess.run(node2))#打印12
123 | print(sess.run(node3))#打印b'hello'
124 | print(sess.run(node4))#打印b'world'
125 | #要想获取平常的值如12 必须通过sess.run()进行,不然输入还是tensor格式
126 | ```
127 |
128 | ## 加法
129 | 方法[tf.add](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/add)
130 | [更多数学运算](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_guides/python/math_ops#Arithmetic_Operators)
131 |
132 | - 构造函数
133 | ```python
134 | add(
135 | x,
136 | y,
137 | name=None
138 | )
139 | ```
140 |
141 | - 举例
142 | ```python
143 | node5=tf.constant(-1)
144 | n_add=tf.add(node2,node5)
145 | print(sess.run(n_add))#打印11
146 | node6=tf.constant(-2)
147 | n_add2=node5+node6
148 | print(sess.run(n_add2))#打印-3 说明两种形式的加法也可以的
149 | ```
150 |
151 | ## 占位符
152 | 方法[tf.placeholder](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/placeholder)
153 | 相当于数学函数的右侧的变量
154 | 构造函数
155 | ```python
156 | placeholder(
157 | dtype,
158 | shape=None,
159 | name=None
160 | )
161 | ```
162 | 例子
163 | ```python
164 | p1=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
165 | p2=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
166 | n_add3=p1+p2
167 | a=sess.run(n_add3,{p1:23,p2:32})#用法正确
168 | #a=(n_add3,{p1:23,p2:32})错误 只能和sess一起使用
169 | print(a)#55.0
170 | print(sess.run(n_add3,{p1:23,p2:32}))#用法正确 打印55.0
171 | ```
172 |
173 | ## 变量
174 | [tf.Variable](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Variable)
175 |
176 | - 构造函数
177 | ```python
178 | __init__(
179 | initial_value=None,
180 | trainable=True,
181 | collections=None,
182 | validate_shape=True,
183 | caching_device=None,
184 | name=None,
185 | variable_def=None,
186 | dtype=None,
187 | expected_shape=None,
188 | import_scope=None
189 | )
190 | ```
191 |
192 | - 实例
193 | ```python
194 | v1=tf.Variable(12)
195 | v2=tf.Variable(23)#定义一个变量
196 | init = tf.global_variables_initializer()#进去全部变量的初始化
197 | sess.run(init)
198 | x=tf.placeholder(tf.int32)
199 | a_line=v1*x+v2#使用和常量类似
200 | v3=sess.run(a_line,{x:[1,2]})
201 | print(v3)#[35 47]
202 | #重新赋值
203 | v1=tf.assign(v1,-2)
204 | v2=tf.assign(v2,3)
205 | add4=v1+v2
206 | v4=sess.run(add4)
207 | print(v4)#1
208 |
209 | ```
210 | ## END
211 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/start/start.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #user/bin
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 | #---常数----
4 | node1= tf.constant([True,True])
5 | node2= tf.constant(12)
6 | node3=tf.constant("hello")
7 | node4=tf.constant("world")
8 | print(node1)#打印Tensor("Const:0", shape=(2,), dtype=bool)
9 | print(node2)#打印Tensor("Const_1:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
10 | print(node3)#打印Tensor("Const_2:0", shape=(), dtype=string)
11 | #---会话---
12 | sess=tf.Session()#获取会话
13 | print(sess.run(node1))#打印[True,True]
14 | print(sess.run(node2))#打印12
15 | print(sess.run(node3))#打印b'hello'
16 | print(sess.run(node4))#打印b'world'
17 | #---加法----
18 | node5=tf.constant(-1)
19 | n_add=tf.add(node2,node5)
20 | print(sess.run(n_add))#打印11
21 | node6=tf.constant(-2)
22 | n_add2=node5+node6
23 | print(sess.run(n_add2))#打印-3 说明两种形式的加法也可以的
24 | #---占位符---
25 | p1=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
26 | p2=tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
27 | n_add3=p1+p2
28 | a=sess.run(n_add3,{p1:23,p2:32})#用法正确 赋值以json的格式 进行赋值
29 | #a=(n_add3,{p1:23,p2:32})错误 只能和sess一起使用
30 | print(a)#55.0
31 | print(sess.run(n_add3,{p1:23,p2:32}))#用法正确 打印55.0
32 | #---变量---
33 | v1=tf.Variable(12)
34 | v2=tf.Variable(23)#定义一个变量
35 | init = tf.global_variables_initializer()#进去全部变量的初始化
36 | sess.run(init)
37 | x=tf.placeholder(tf.int32)
38 | a_line=v1*x+v2#使用和常量类似
39 | v3=sess.run(a_line,{x:[1,2]})
40 | print(v3)#[35 47]
41 | #重新赋值
42 | v1=tf.assign(v1,-2)
43 | v2=tf.assign(v2,3)
44 | add4=v1+v2
45 | v4=sess.run(add4)
46 | print(v4)#1
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [源码TensorBoard.py](./TensorBoard.py)
2 | # 如何使用TensorBoard
3 | >说明:tensorBoard是Tensorflow的可视化工具
4 | # 使用方法
5 | 1. 构建图并保存到文件
6 | ```python
7 | import tensorflow as tf
8 | node1=tf.constant(2,tf.float32)#定义节点,值为2
9 | node2=tf.constant(3,tf.float32)#定义节点,值为3
10 | node=tf.add(node1,node2)
11 | print(node1)
12 | with tf.Session() as sess:
13 | print(sess.run(node))
14 | tf.summary.merge_all
15 | tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
16 | writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("test_1", sess.graph)
17 |
18 | ```
19 | [生成文件](./test_1)
20 | 2. 显示
21 | > 利用1生成的文件,将视图关系显示出来,在命令行中输入
22 | ```
23 | tensorboard --logdir="./test_1" #这是文件的路径
24 | ```
25 | [运行时可能错误 由于 html5lib 版本问题,可以在anaconda中进行降版本解决此问题](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorboard/pull/589)
26 |
27 | 3. 在浏览器中打开
28 | > 在浏览器中输入:http://192.168.56.1:6006 ,这是自己的电脑IP:6006是端口号
29 | - 而且在步骤2中有提示信息
30 | 
31 | - 效果图
32 | 
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard/SummayTest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard/SummayTest.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard/TensorBoard.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #python
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 | node1=tf.constant(2,tf.float32)#定义节点,值为2
4 | node2=tf.constant(3,tf.float32)#定义节点,值为3
5 | node=tf.add(node1,node2)
6 | print(node1)
7 | with tf.Session() as sess:
8 | print(sess.run(node))
9 | tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
10 | writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("test_1", sess.graph)
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard/tensorboard_commandline.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard/tensorboard_commandline.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard/tensorboard_example.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard/tensorboard_example.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard/test_1/events.out.tfevents.1502120649.NIEBIN:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard/test_1/events.out.tfevents.1502120649.NIEBIN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard/test_1/events.out.tfevents.1502121636.NIEBIN:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard/test_1/events.out.tfevents.1502121636.NIEBIN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Tensorboard显示图片
2 | 基本使用我们会了,那现在来看看怎么使用图片吧。
3 | [实例代码](./SummaryImage.py)
4 | 完全不会使用Tensorboard-[请点击这里](../tensorboard)
5 | 
6 | ### 1. 读取图片
7 |
8 | ```python
9 | image_filename = "start_person.jpg"# 图片地址,这里是放在当前文件夹的
10 | # 获取图片数据
11 | file = open(image_filename, 'rb')
12 | data = file.read()
13 | file.close()
14 | ```
15 | ### 2. 解析图片
16 | 解析图片,并转换为Tensor,这一步很关键,注意这里加一维
17 | ```python
18 | file_img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(data,channels=3) #Tensor("DecodeJpeg:0", shape=(?, ?, 3), dtype=uint8)
19 | file_img=tf.expand_dims(file_img,0)# Tensor("ExpandDims:0", shape=(1, ?, ?, 3), dtype=uint8)
20 | ```
21 | ### 3. 将图片写入文件
22 | ```python
23 | with tf.Session() as sess:
24 | init_op = tf.global_variables_initializer()
25 | sess.run(init_op)
26 | write = tf.summary.FileWriter("./test_2", graph=sess.graph)
27 | img = tf.summary.image("./", tensor=file_img)
28 | img_string = sess.run(img)
29 | write.add_summary(img_string)
30 | ```
31 | [生成文件](./test_2)
32 | ### 4. 在Tensorboard中显示
33 | 在命令行,输入如下命令,在浏览器中输入类http://192.168.56.1:6006 类似 地址进行查看
34 | [参考](../tensorboard)
35 | ```
36 | tensorboard --logdir="./test_2"
37 | ```
38 | ### 5. 结果
39 | 
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/SummayImage.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #user/bin
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 |
4 | def imageTest():
5 | image_filename = "start_person.jpg"# 智能星人的图标
6 | # 获取图片数据
7 | file = open(image_filename, 'rb')
8 | data = file.read()
9 | file.close()
10 | # ---
11 | file_img = tf.image.decode_jpeg(data,channels=3)
12 | print(file_img)
13 | file_img=tf.expand_dims(file_img,0)
14 | print(file_img)
15 | with tf.Session() as sess:
16 | write = tf.summary.FileWriter("./test_2", graph=sess.graph)
17 | img = tf.summary.image("./", tensor=file_img)
18 | img_string = sess.run(img)
19 | write.add_summary(img_string)
20 | imageTest()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/start_person.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/start_person.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/sum_image.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/sum_image.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502182056.NIEBIN:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502182056.NIEBIN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502182108.NIEBIN:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502182108.NIEBIN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502182134.NIEBIN:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502182134.NIEBIN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502185571.NIEBIN:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502185571.NIEBIN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502185594.NIEBIN:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502185594.NIEBIN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502186495.NIEBIN:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502186495.NIEBIN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502186504.NIEBIN:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/BaseLearn/tensorboard_image/test_2/events.out.tfevents.1502186504.NIEBIN
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/threads/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 队列和线程
2 | ## 队列概述
3 | - 多个线程准备实例并放在队列中
4 | - 训练线程 从队列中取出训练操作op
5 | - Session 是多线程的,所以多线程可以使用同一个Session
6 | - 所有的线程都可以一起被关闭 并且当队列停止时要合理关闭
7 |
8 | 设计两个类 一起使用
9 | ## tf.train.Coordinator
10 | > 协作者
11 | > 帮助多线程的合理停止和异常处理
12 | - 实例
13 | ```python
14 | import tensorflow as tf
15 | import threading
16 | import time
17 |
18 | # 创建一个方法 通过coord来控制线程
19 | def MyLoop(coord):
20 | count=0
21 | while not coord.should_stop():
22 | print("count=",count)
23 | count=count+1
24 | time.sleep(1)
25 | if count==10:
26 | print("stop")
27 | coord.request_stop()
28 |
29 | # Main thread: create a coordinator.
30 | coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
31 |
32 | # Create 3 threads that run 'MyLoop()'
33 | threads = [threading.Thread(target=MyLoop, args=(coord,)) for i in range(3)]
34 | for t in threads:
35 | t.start() # start a thread
36 | coord.join(threads) # wait util thread stop
37 | ```
38 |
39 | ### tf.train.QueueRunner
40 | > 队列的执行者
41 | > 创建一系列线程,在同一个队列中组织tensors的排队执行
42 | - 实例
43 | ```python
44 | #1 create Runner
45 | b =tf.constant(2,dtype=tf.float16,shape=[1])
46 | que=tf.RandomShuffleQueue(3,1,dtypes=[tf.float16],shapes=())#shapes一定要写 否则会报错
47 | enqueue_op =que.enqueue_many(b)
48 |
49 | qr = tf.train.QueueRunner(que,[enqueue_op])
50 | #2 create Threads
51 | sess=tf.Session()
52 | coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
53 | enqueue_threads = qr.create_threads(sess, coord=coord, start=True)
54 | #3 use coord and queque
55 | inputs=que.dequeue_many(10)+b
56 | for step in range(10):
57 | if coord.should_stop():
58 | break
59 | print("run")
60 | print(sess.run(inputs))
61 | print("this request")
62 | coord.request_stop()
63 | coord.join(enqueue_threads)# wait thread to terminate
64 | ```
65 | 
66 |
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/threads/threadExample.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # python/user
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 | import threading
4 | import time
5 |
6 | #---------------queque sample use------------------------
7 | que=tf.FIFOQueue(3,[tf.int32])
8 | node1= tf.constant([1,1])
9 | que.enqueue_many(node1)
10 | #que.enqueue_many([122])# use the will make error
11 | print(que.dequeue())
12 | print(que.dequeue())
13 | print(que.dequeue())
14 |
15 |
16 | #-----------------Coordinator sample use--------------------
17 | def MyLoop(coord):
18 | count=0
19 | while not coord.should_stop():
20 | print("count=",count)
21 | count=count+1
22 | time.sleep(1)
23 | if count==10:
24 | print("stop")
25 | coord.request_stop()
26 |
27 | # Main thread: create a coordinator.
28 | coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
29 |
30 | # Create 10 threads that run 'MyLoop()'
31 | threads = [threading.Thread(target=MyLoop, args=(coord,)) for i in range(3)]
32 | for t in threads:
33 | t.start() # start a thread
34 | coord.join(threads) # wait util thread stop
35 |
36 | #-----------------QueueRunner example------------------------------------
37 | #1 create Runner
38 | b =tf.constant(2,dtype=tf.float16,shape=[1])
39 | que=tf.RandomShuffleQueue(3,1,dtypes=[tf.float16],shapes=())
40 | enqueue_op =que.enqueue_many(b)
41 |
42 | qr = tf.train.QueueRunner(que,[enqueue_op])
43 | #2 create Threads
44 | sess=tf.Session()
45 | coord = tf.train.Coordinator()
46 | enqueue_threads = qr.create_threads(sess, coord=coord, start=True)
47 | #3 use coord and queque
48 | inputs=que.dequeue_many(10)+b
49 | for step in range(10):
50 | if coord.should_stop():
51 | break
52 | print("run")
53 | print(sess.run(inputs))
54 | print("this request")
55 | coord.request_stop()
56 | coord.join(enqueue_threads)# wait thread to terminate
57 |
58 |
59 |
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/variable/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 变量
2 | [源文件](./variable.py)
3 | 地址[tf.Variable](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/Variable)
4 | ```Python
5 | #文件头先引入
6 | import tensorflow as tf
7 | ```
8 |
9 | ## 如何创建?
10 | - 构造函数
11 | ```Python
12 | __init__(
13 | initial_value=None,
14 | trainable=True,
15 | collections=None,
16 | validate_shape=True,
17 | caching_device=None,
18 | name=None,
19 | variable_def=None,
20 | dtype=None,
21 | expected_shape=None,
22 | import_scope=None
23 | )
24 | ```
25 | 从构造函数中可以看出,可以不传入任何参数,但是必须传入initial_value的值 不然会报错
26 | 其他值可以任意组合传入 如下
27 | ```Python
28 | v1=tf.Variable(0)
29 | v2=tf.Variable("hello world")
30 | ```
31 | - 机器配置
32 | ```Python
33 | # 将变量设置到cpu 0
34 | with tf.device("/cpu:0"):
35 | v = tf.Variable(...)
36 |
37 | #将变量设置到gpu 0
38 | with tf.device("/gpu:0"):
39 | v = tf.Variable(...)
40 | ```
41 |
42 | ## 初始化
43 | 创建变量之后,需调用tf.global_variables_initializer()进行初始化
44 | 才能进行调用 不然会报错的
45 | ```Python
46 | #初始化方式1
47 | init=tf.global_variables_initializer()#变量的初始化 初始化当前module所有的变量
48 | sess=tf.Session()
49 | sess.run(init)
50 | print(v1)#Tensor("Variable/read:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
51 | #初始化方式2
52 | v2=tf.Variable(2)
53 | print(sess.run(v2.initialized_value()))#由于global_variables_initializer 其实不写也可以的
54 | print(v2)# Tensor("Variable_1/read:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
55 | ```
56 | ## 保存及读取变量
57 | ```Python
58 | # 保存session
59 | saver=tf.train.Saver()
60 | saver.save(sess,"./save")
61 | v1=v1.assign(12)
62 | print(sess.run(v1))#重新赋值后打印12
63 |
64 | a=saver.restore(sess,"./save")# 读取模型
65 | print(sess.run("v1:0"))#读取已经保存的变量v1 打印为0
66 | # saver=tf.train.import_meta_graph("save.meta")
67 | # saver.restore(sess,tf.train.latest_checkpoint("./"))
68 | # print(sess.run("v1:0"))# 可以从内存中读取变量v1 打印为0
69 | ```
70 |
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/BaseLearn/variable/variable.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #关于variable
2 | import tensorflow as tf
3 |
4 | v1=tf.Variable(0,name="v1")#变量的创建
5 |
6 | # 将变量设置到cpu 0
7 | #with tf.device("/cpu:0"):
8 | # v = tf.Variable(...)
9 | #将变量设置到gpu 0
10 | #with tf.device("/gpu:0"):
11 | # v = tf.Variable(...)
12 | #初始化方式1
13 | init=tf.global_variables_initializer()#变量的初始化 初始化当前module所有的变量
14 | sess=tf.Session()
15 | sess.run(init)
16 | print(v1)#Tensor("Variable/read:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
17 | #初始化方式2
18 | v2=tf.Variable(2)
19 | print(sess.run(v2.initialized_value()))#由于global_variables_initializer 其实不写也可以的
20 | print(v2)# Tensor("Variable_1/read:0", shape=(), dtype=int32)
21 | # 保存session
22 | saver=tf.train.Saver()
23 | saver.save(sess,"./save")
24 | v1=v1.assign(12)
25 | print(sess.run(v1))#重新赋值后打印12
26 |
27 | a=saver.restore(sess,"./save")# 读取模型
28 | print(sess.run("v1:0"))#读取已经保存的变量v1 打印为0
29 | # saver=tf.train.import_meta_graph("save.meta")
30 | # saver.restore(sess,tf.train.latest_checkpoint("./"))
31 | # print(sess.run("v1:0"))# 可以从内存中读取变量v1 打印为0
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2017 TFStudents
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PicClassify/Newer/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 直接运行程序
2 | 我们先不用看概念,不必知道里面的原理,直接将程序运行起来,看看效果,感受一下手写字体的识别。
3 | 1. ### 训练数据的下载
4 | > [地址](http://yann.lecun.com/exdb/mnist/) 下载如图绿色框内的4个数据,请确保是源文件,不要修改后缀名称
5 | 
6 | 在本地创建一个文件夹如MNIST_TEST(最好和代码同级目录),将下载的4个文件放在其中。
7 | 2. ### 运行py代码
8 | > [mnist_softmax.py源码下载](...)
9 | > 将此源码下载保存到刚才新建的MNIST_TEST 同级目录下。在命令行,直接运行命令
10 | ```
11 | python mnist_softmax.py
12 | ```
13 | 在ipyhon控制台会有如下类似log
14 | ```
15 | runfile('C:/WorkspaceOther/mnist_softmax.py', wdir='C:/WorkspaceOther')
16 | Extracting MNIST_TEST\train-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
17 | Extracting MNIST_TEST\train-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
18 | Extracting MNIST_TEST\t10k-images-idx3-ubyte.gz
19 | Extracting MNIST_TEST\t10k-labels-idx1-ubyte.gz
20 | 0.9192
21 | ```
22 | 使用ipython命令行,可能有如下错误,这是由ipython自身问题,可以忽略。
23 | ```
24 | An exception has occurred, use %tb to see the full traceback.
25 |
26 | SystemExit
27 |
28 | C:\DevelopTools\Anaconda\envs\tensorflow\lib\site-packages\IPython\core\interactiveshell.py:2870: UserWarning: To exit: use 'exit', 'quit', or Ctrl-D.
29 | warn("To exit: use 'exit', 'quit', or Ctrl-D.", stacklevel=1)
30 | ```
31 | # 解释代码及原理
32 | > 直接根据就运行顺序开始走起,引包就不讲了
33 | - ### 训练集文件地址
34 | ```python
35 | FLAGS = None
36 | DEFAULT_PATH="MNIST_TEST"
37 | ```
38 | 由于源文件和训练集是同级目录,所以只需“MNIST_TEST”,如果不在,则这里填写训练集路径就可以了
39 |
40 | - ### 读取参数并启动main
41 | ```
42 | if __name__ == '__main__':
43 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() #就是对命令行的参数进行解析及添加
44 | parser.add_argument('--data_dir', type=str, default=DEFAULT_PATH,
45 | help='Directory for storing input data')
46 | FLAGS, unparsed = parser.parse_known_args()
47 | tf.app.run(main=main, argv=[sys.argv[0]] + unparsed) #启动main(_)函数
48 | ```
49 | [argparse.ArgumentParser更多知识参考](https://docs.python.org/2/howto/argparse.html)
50 |
51 | - ### 读取数据
52 | ```
53 | mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(FLAGS.data_dir, one_hot=True)
54 | ```
55 | 这才是真正的读取数据,tf已经封装了,其实FLAGS.data_dir的值为训练集的文件夹即"MNIST_TEST",如果本地为空,系统会自动帮你下载,感兴趣可以看看源码。
56 | ### 至于数据集本身,是由一定像素的如28x28的手写数字图片,转换而成的特殊数据类型,至于怎么制作这样的图片,制作属于自己的数据集,这是个问题,再另外的章节再一起探讨。我有这样的计划,再每学一个实例的时候,先把基本的流程及核心原理弄懂,然后对应疑惑的问题进行整理,后面再深入的研究探讨。并且在章节的末尾会留下问题,如果你对某个问题感兴趣,可以提交出来,让大家学习参考。*
57 |
58 | - ### 创建模型
59 | ```
60 | x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])#None代表可以是任何长度
61 | W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
62 | b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
63 | y = tf.matmul(x, W) + b #线性方程
64 |
65 | y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])# 占位符
66 | ```
67 | 你可以理解为平面中的直线方程,只是这里是多维的。机器学习的目标就是找到这一个一组参数来描述我们的数字特征。
68 | 为什么这里是784?是因为我们的输入28x28=784的像素。
69 | 为什么是10维?是因为数字0-9总共10个。
70 | x与W相乘会得到一个 与b一样的长度的一维向量。【None代表可以是任何长度】
71 | 至于这个方程代表什么含义,y代表的输出0-9,而y的右边代表输入经过神经网络的矩阵计算。
72 | 如何更深地理解此方程,请参考地址:
73 | [感知机](https://hit-scir.gitbooks.io/neural-networks-and-deep-learning-zh_cn/content/chap1/c1s1.html)和
74 | [sigmoid神经元](https://hit-scir.gitbooks.io/neural-networks-and-deep-learning-zh_cn/content/chap1/c1s2.html)
75 | 看完后你可能就会对这个方程有很深的认识。
76 |
77 | - ### 错误的评估之交叉熵
78 | ```
79 | cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(
80 | tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_, logits=y))
81 | train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
82 | ```
83 | y_是数据集中已经确定的数,y是评估模型,就是目标函数,是一个表达式,cross_entropy是交叉熵,用来评估错误率,这个值越小,代表错误率越低.
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PicClassify/Newer/mnist_softmax.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2015 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """A very simple MNIST classifier.
17 |
18 | See extensive documentation at
19 | https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/mnist/beginners
20 | """
21 | from __future__ import absolute_import
22 | from __future__ import division
23 | from __future__ import print_function
24 |
25 | import argparse
26 | import sys
27 |
28 | from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
29 |
30 | import tensorflow as tf
31 |
32 | FLAGS = None
33 | DEFAULT_PATH="MNIST_TEST"
34 |
35 | def main(_):
36 | # Import data
37 | mnist = input_data.read_data_sets(FLAGS.data_dir, one_hot=True)
38 |
39 | # Create the model
40 | x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 784])
41 | W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784, 10]))
42 | b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
43 | y = tf.matmul(x, W) + b #
44 |
45 | # Define loss and optimizer
46 | y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 10])
47 |
48 | # The raw formulation of cross-entropy,
49 | #
50 | # tf.reduce_mean(-tf.reduce_sum(y_ * tf.log(tf.nn.softmax(y)),
51 | # reduction_indices=[1]))
52 | #
53 | # can be numerically unstable.
54 | #
55 | # So here we use tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits on the raw
56 | # outputs of 'y', and then average across the batch.
57 | cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(
58 | tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_, logits=y))
59 | train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.5).minimize(cross_entropy)
60 |
61 | sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
62 | tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
63 | # Train
64 | for _ in range(1000):
65 | batch_xs, batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(100)
66 | sess.run(train_step, feed_dict={x: batch_xs, y_: batch_ys})
67 |
68 | # Test trained model
69 | correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y, 1), tf.argmax(y_, 1))
70 | accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
71 | print(sess.run(accuracy, feed_dict={x: mnist.test.images,
72 | y_: mnist.test.labels}))
73 | writer = tf.summary.FileWriter("test_1", sess.graph)
74 |
75 | if __name__ == '__main__':
76 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
77 | parser.add_argument('--data_dir', type=str, default=DEFAULT_PATH,
78 | help='Directory for storing input data')
79 | FLAGS, unparsed = parser.parse_known_args()
80 | tf.app.run(main=main, argv=[sys.argv[0]] + unparsed)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PicClassify/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 图片识别
2 |
3 | 图片识别用于识别图片属于哪一类物体,本质是图片的分类问题(机器学习主要用于两方面,回归和分类),此处以MNIST为例以数字识别介绍图片识别.
4 |
5 | ## 1. 环境
6 | python 2.7
7 | tensorflow 1.2.1
8 |
9 | ## 2. 程序说明
10 | 程序使用 tensorflow branch r1.2 中的https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/r1.2/tensorflow/examples/learn/mnist.py
11 |
12 | $ ./minst.py
13 | 本程序采用两种方式进行训练,一种为LinearClassifier,另一种为cnn,其中cnn有进行两层卷积,下面进行详细说明.
14 |
15 | ### 2.1 LinearClassifier
16 | ```python
17 | feature_columns = learn.infer_real_valued_columns_from_input(
18 | mnist.train.images)
19 | classifier = learn.LinearClassifier(
20 | feature_columns=feature_columns, n_classes=10)
21 | classifier.fit(mnist.train.images,
22 | mnist.train.labels.astype(np.int32),
23 | batch_size=100,
24 | steps=1000)
25 | score = metrics.accuracy_score(mnist.test.labels,
26 | list(classifier.predict(mnist.test.images)))
27 | print('Accuracy: {0:f}'.format(score))
28 | ```
29 | LinearClassifier较易理解,不进一步说明
30 |
31 | ### 2.2 cnn
32 |
33 | cnn 部分主要包括卷积层,池化层和全连接层,详细介绍如下:
34 |
35 | #### 2.2.1 池化层
36 | ```python
37 | def max_pool_2x2(tensor_in):
38 | return tf.nn.max_pool(
39 | tensor_in, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
40 | ```
41 |
42 | 池化使用过滤器为大小为2*2, 使用max_pooling,长和宽的步长均为2,padding方式为'SAME',所以池化后图片大小变为原来的一半.
43 |
44 | #### 2.2.2 卷积层
45 | ```python
46 | def conv_model(feature, target, mode):
47 | """2-layer convolution model."""
48 | # Convert the target to a one-hot tensor of shape (batch_size, 10) and
49 | # with a on-value of 1 for each one-hot vector of length 10.
50 | target = tf.one_hot(tf.cast(target, tf.int32), 10, 1, 0)
51 |
52 | # Reshape feature to 4d tensor with 2nd and 3rd dimensions being
53 | # image width and height final dimension being the number of color channels.
54 | feature = tf.reshape(feature, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
55 |
56 | # First conv layer will compute 32 features for each 5x5 patch
57 | with tf.variable_scope('conv_layer1'):
58 | h_conv1 = layers.convolution2d(
59 | feature, 32, kernel_size=[5, 5], activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
60 | h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
61 |
62 | # Second conv layer will compute 64 features for each 5x5 patch.
63 | with tf.variable_scope('conv_layer2'):
64 | h_conv2 = layers.convolution2d(
65 | h_pool1, 64, kernel_size=[5, 5], activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
66 | h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
67 | # reshape tensor into a batch of vectors
68 | h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
69 |
70 | # Densely connected layer with 1024 neurons.
71 | h_fc1 = layers.dropout(
72 | layers.fully_connected(
73 | h_pool2_flat, 1024, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu),
74 | keep_prob=0.5,
75 | is_training=mode == tf.contrib.learn.ModeKeys.TRAIN)
76 |
77 | # Compute logits (1 per class) and compute loss.
78 | logits = layers.fully_connected(h_fc1, 10, activation_fn=None)
79 | loss = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(target, logits)
80 |
81 | # Create a tensor for training op.
82 | train_op = layers.optimize_loss(
83 | loss,
84 | tf.contrib.framework.get_global_step(),
85 | optimizer='SGD',
86 | learning_rate=0.001)
87 |
88 | return tf.argmax(logits, 1), loss, train_op
89 |
90 | ```
91 | 该卷积层使用两层卷积,卷基层使用的过滤器大小为5*5,padding方式为'SAME',激活函数使用relu,损失函数为SGD;
92 | * 第一层卷积输入为28*28,卷积后的大小为28*28,设置输出的深度为32;然后经过池化层处理后深度为32,大小为14*14;
93 | * 第二层卷积输入为14*14,卷积后的大小为14*14,深度为64,经过池化处理后深度仍为64,大小为7*7
94 | * 在两层卷积和池化后加一个全连接层,全连接层使用1024核.
95 | * 在全连接后使用softmax进行分类
96 |
97 | #### 2.2.3 cnn调用
98 | ```python
99 | ### Convolutional network
100 | classifier = learn.Estimator(model_fn=conv_model)
101 | classifier.fit(mnist.train.images,
102 | mnist.train.labels,
103 | batch_size=100,
104 | steps=20000)
105 | score = metrics.accuracy_score(mnist.test.labels,
106 | list(classifier.predict(mnist.test.images)))
107 | print('Accuracy: {0:f}'.format(score))
108 | ```
109 |
110 | ### 2.3 运行结果
111 | LinearClassifier方法在测试集上正确率为0.921600,cnn在测试集上正确率为0.967500
112 |
113 |
114 | __以上为个人理解,如有错误请指正,感谢!!!__
115 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PicClassify/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/python
2 | # encoding: utf-8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PicClassify/mnist.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/python
2 | # encoding: utf-8
3 |
4 | """This showcases how simple it is to build image classification networks.
5 | It follows description from this TensorFlow tutorial:
6 | https://www.tensorflow.org/versions/master/tutorials/mnist/pros/index.html#deep-mnist-for-experts
7 | """
8 |
9 | from __future__ import absolute_import
10 | from __future__ import division
11 | from __future__ import print_function
12 |
13 | import numpy as np
14 | from sklearn import metrics
15 | import tensorflow as tf
16 |
17 | layers = tf.contrib.layers
18 | learn = tf.contrib.learn
19 |
20 |
21 | def max_pool_2x2(tensor_in):
22 | return tf.nn.max_pool(
23 | tensor_in, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
24 |
25 |
26 | def conv_model(feature, target, mode):
27 | """2-layer convolution model."""
28 | # Convert the target to a one-hot tensor of shape (batch_size, 10) and
29 | # with a on-value of 1 for each one-hot vector of length 10.
30 | target = tf.one_hot(tf.cast(target, tf.int32), 10, 1, 0)
31 |
32 | # Reshape feature to 4d tensor with 2nd and 3rd dimensions being
33 | # image width and height final dimension being the number of color channels.
34 | feature = tf.reshape(feature, [-1, 28, 28, 1])
35 |
36 | # First conv layer will compute 32 features for each 5x5 patch
37 | with tf.variable_scope('conv_layer1'):
38 | h_conv1 = layers.convolution2d(
39 | feature, 32, kernel_size=[5, 5], activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
40 | h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
41 |
42 | # Second conv layer will compute 64 features for each 5x5 patch.
43 | with tf.variable_scope('conv_layer2'):
44 | h_conv2 = layers.convolution2d(
45 | h_pool1, 64, kernel_size=[5, 5], activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
46 | h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
47 | # reshape tensor into a batch of vectors
48 | h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7 * 7 * 64])
49 |
50 | # Densely connected layer with 1024 neurons.
51 | h_fc1 = layers.dropout(
52 | layers.fully_connected(
53 | h_pool2_flat, 1024, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu),
54 | keep_prob=0.5,
55 | is_training=mode == tf.contrib.learn.ModeKeys.TRAIN)
56 |
57 | # Compute logits (1 per class) and compute loss.
58 | logits = layers.fully_connected(h_fc1, 10, activation_fn=None)
59 | loss = tf.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(target, logits)
60 |
61 | # Create a tensor for training op.
62 | train_op = layers.optimize_loss(
63 | loss,
64 | tf.contrib.framework.get_global_step(),
65 | optimizer='SGD',
66 | learning_rate=0.001)
67 |
68 | return tf.argmax(logits, 1), loss, train_op
69 |
70 |
71 | def main(unused_args):
72 | ### Download and load MNIST dataset.
73 | mnist = learn.datasets.load_dataset('mnist')
74 |
75 | ### Linear classifier.
76 | feature_columns = learn.infer_real_valued_columns_from_input(
77 | mnist.train.images)
78 | classifier = learn.LinearClassifier(
79 | feature_columns=feature_columns, n_classes=10)
80 | classifier.fit(mnist.train.images,
81 | mnist.train.labels.astype(np.int32),
82 | batch_size=100,
83 | steps=1000)
84 | score = metrics.accuracy_score(mnist.test.labels,
85 | list(classifier.predict(mnist.test.images)))
86 | print('Accuracy: {0:f}'.format(score))
87 |
88 | ### Convolutional network
89 | classifier = learn.Estimator(model_fn=conv_model)
90 | classifier.fit(mnist.train.images,
91 | mnist.train.labels,
92 | batch_size=100,
93 | steps=20000)
94 | score = metrics.accuracy_score(mnist.test.labels,
95 | list(classifier.predict(mnist.test.images)))
96 | print('Accuracy: {0:f}'.format(score))
97 |
98 |
99 | if __name__ == '__main__':
100 | tf.app.run()
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Tensorflow 实例
2 | ## 基础
3 |
4 | - [安装](BaseLearn/install)
5 | - [简单上手](BaseLearn/start)
6 | - 变量
7 | > [创建-初始化](BaseLearn/variable)
8 | > [共享变量](BaseLearn/share_variable)
9 | - [多线程和队列](BaseLearn/threads)
10 | - [读取数据](BaseLearn/read_data)
11 | - [训练助手](BaseLearn/Supervisor)
12 | - TensorBoard的使用
13 | > 1. [显示graph](BaseLearn/tensorboard)
14 | > 2. [显示图片](BaseLearn/tensorboard_image)
15 | - 调试
16 | > [Mnist为例](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/debugger)-[未完]
17 | > [机器学习为例](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/tfdbg-tflearn)
18 | - [元图](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/meta_graph)
19 | - [保存模型](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/saved_model_cli)
20 | - [版本解释](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/version_semantics)
21 | - [数据版本](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/data_versions)
22 |
23 | ## 初级实例
24 | [参考资料](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started)
25 | > ### 跑实例时 一步步解析每一行代码,包括每一个变量,每一个函数 每一步的运行结果写在后面注释里面
26 | - [mnist新手](./PicClassify/Newer/)
27 | - [mnist专家](./PicClassify)
28 | - [神经网络](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/mnist/mechanics)
29 | - 机器学习
30 | > [快速入门](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/tflearn)
31 | > [输入函数](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/input_fn)
32 | > [日志和监测](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/monitors)
33 | - TensorBoard
34 | > [可视化学习](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/summaries_and_tensorboard)
35 | > [嵌入可视化](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/embedding_viz)
36 | > [图像化](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/graph_viz)
37 | > [直方图](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/tensorboard_histograms)
38 | ## 算法相关
39 | - [GPU的使用](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/using_gpu)[聂彬-认领]
40 | - [图片识别](./PicClassify)[张夏旭-认领]-完成
41 | - [迁移学习](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/image_retraining)-[魏杨-认领]
42 | - 卷积神经网络-[魏杨-认领]
43 | > [创建](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/layers)
44 | > [高级](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/deep_cnn)
45 | - [词的向量化](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/word2vec)[聂彬-认领]
46 | - [循环神经网络](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/recurrent)[聂彬-认领]
47 | - [序列到序列模型](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/seq2seq)[张夏旭-认领]
48 | - [大型线性模型](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/linear)
49 | - [线性模型实例](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/wide)
50 | - [深度学习](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/wide_and_deep)-[王凯-认领]
51 | - [Mandelbrot Set](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/mandelbrot)-[王凯-认领]
52 | - [偏微分方程](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/pdes)-[王凯-认领]
53 |
54 |
55 | [参考资料](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide)
56 | ### 本项目为开源项目:由[Tensorflow学生会]管理更新,TF爱好者参与
57 | - 一个DNN的分类例子
58 | 介绍内容:构造一个四层的DNN,用Python读取一份分类数据,并feed给DNN。一步步解析每一行代码,包括每一个变量,每一个函数
59 | - 一个CNN的分类例子(MNIST)
60 | 介绍内容:给出代码,并一步步解析每一行代码,包括每一个变量,每一个函数。
61 | - 转换image成tfrecord的例子
62 | - 读tfrecords,并训练网络使用tfrecords
63 |
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 |
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 | - end 其他需要修改的 大家提出来
74 |
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 这是图片资源
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource/thread_queque.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/Resource/thread_queque.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource/训练集.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/TFStudents/TensorFlowExample/6278f8b3d2c61e45c95ec47a10fa47e61472bf55/Resource/训练集.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------