├── .gitignore
├── .gitmodules
├── Dockerfile
├── LICENSE.md
├── README.md
├── arguments
└── __init__.py
├── convert.py
├── distill_train.py
├── environment.yml
├── full_eval.py
├── gaussian_renderer
├── __init__.py
├── gaussian_count.py
└── network_gui.py
├── lpipsPyTorch
├── __init__.py
└── modules
│ ├── lpips.py
│ ├── networks.py
│ └── utils.py
├── metrics.py
├── prune.py
├── prune_finetune.py
├── render.py
├── render_video.py
├── scene
├── __init__.py
├── cameras.py
├── colmap_loader.py
├── dataset_readers.py
└── gaussian_model.py
├── scripts
├── run_distill_finetune.sh
├── run_prune_finetune.sh
├── run_prune_pt_finetune.sh
├── run_train_densify_prune.sh
└── run_vectree_quantize.sh
├── static
├── prune_ratio_vs_ssim.svg
└── table5.png
├── submodules
└── simple-knn
│ ├── ext.cpp
│ ├── setup.py
│ ├── simple_knn.cu
│ ├── simple_knn.egg-info
│ ├── PKG-INFO
│ ├── SOURCES.txt
│ ├── dependency_links.txt
│ └── top_level.txt
│ ├── simple_knn.h
│ ├── simple_knn
│ └── .gitkeep
│ ├── spatial.cu
│ └── spatial.h
├── train_densify_prune.py
├── utils
├── camera_utils.py
├── general_utils.py
├── graphics_utils.py
├── image.py
├── image_utils.py
├── logger_utils.py
├── loss_utils.py
├── pose_utils.py
├── save_imp_score.py
├── sh_utils.py
├── system_utils.py
├── tracker_utils.py
└── vgg.py
└── vectree
├── utils.py
├── vectree.py
└── vq.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *.pyc
2 | .vscode
3 | output
4 | build
5 | diff_rasterization/diff_rast.egg-info
6 | diff_rasterization/dist
7 | tensorboard_3d
8 | screenshots
9 | logs_train
10 | vectree/pruned_distilled
11 | vectree/output
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitmodules:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [submodule "submodules/simple-knn"]
2 | path = submodules/simple-knn
3 | url = https://gitlab.inria.fr/bkerbl/simple-knn.git
4 |
5 |
6 | [submodule "submodules/compress-diff-gaussian-rasterization"]
7 | path = submodules/compress-diff-gaussian-rasterization
8 | url = https://github.com/Kevin-2017/compress-diff-gaussian-rasterization.git
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Dockerfile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | FROM nvcr.io/nvidia/pytorch:22.04-py3
2 | RUN conda env create --file environment.yml
3 | RUN bash -c "conda init bash"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Gaussian-Splatting License
2 | ===========================
3 |
4 | **Inria** and **the Max Planck Institut for Informatik (MPII)** hold all the ownership rights on the *Software* named **gaussian-splatting**.
5 | The *Software* is in the process of being registered with the Agence pour la Protection des
6 | Programmes (APP).
7 |
8 | The *Software* is still being developed by the *Licensor*.
9 |
10 | *Licensor*'s goal is to allow the research community to use, test and evaluate
11 | the *Software*.
12 |
13 | ## 1. Definitions
14 |
15 | *Licensee* means any person or entity that uses the *Software* and distributes
16 | its *Work*.
17 |
18 | *Licensor* means the owners of the *Software*, i.e Inria and MPII
19 |
20 | *Software* means the original work of authorship made available under this
21 | License ie gaussian-splatting.
22 |
23 | *Work* means the *Software* and any additions to or derivative works of the
24 | *Software* that are made available under this License.
25 |
26 |
27 | ## 2. Purpose
28 | This license is intended to define the rights granted to the *Licensee* by
29 | Licensors under the *Software*.
30 |
31 | ## 3. Rights granted
32 |
33 | For the above reasons Licensors have decided to distribute the *Software*.
34 | Licensors grant non-exclusive rights to use the *Software* for research purposes
35 | to research users (both academic and industrial), free of charge, without right
36 | to sublicense.. The *Software* may be used "non-commercially", i.e., for research
37 | and/or evaluation purposes only.
38 |
39 | Subject to the terms and conditions of this License, you are granted a
40 | non-exclusive, royalty-free, license to reproduce, prepare derivative works of,
41 | publicly display, publicly perform and distribute its *Work* and any resulting
42 | derivative works in any form.
43 |
44 | ## 4. Limitations
45 |
46 | **4.1 Redistribution.** You may reproduce or distribute the *Work* only if (a) you do
47 | so under this License, (b) you include a complete copy of this License with
48 | your distribution, and (c) you retain without modification any copyright,
49 | patent, trademark, or attribution notices that are present in the *Work*.
50 |
51 | **4.2 Derivative Works.** You may specify that additional or different terms apply
52 | to the use, reproduction, and distribution of your derivative works of the *Work*
53 | ("Your Terms") only if (a) Your Terms provide that the use limitation in
54 | Section 2 applies to your derivative works, and (b) you identify the specific
55 | derivative works that are subject to Your Terms. Notwithstanding Your Terms,
56 | this License (including the redistribution requirements in Section 3.1) will
57 | continue to apply to the *Work* itself.
58 |
59 | **4.3** Any other use without of prior consent of Licensors is prohibited. Research
60 | users explicitly acknowledge having received from Licensors all information
61 | allowing to appreciate the adequacy between of the *Software* and their needs and
62 | to undertake all necessary precautions for its execution and use.
63 |
64 | **4.4** The *Software* is provided both as a compiled library file and as source
65 | code. In case of using the *Software* for a publication or other results obtained
66 | through the use of the *Software*, users are strongly encouraged to cite the
67 | corresponding publications as explained in the documentation of the *Software*.
68 |
69 | ## 5. Disclaimer
70 |
71 | THE USER CANNOT USE, EXPLOIT OR DISTRIBUTE THE *SOFTWARE* FOR COMMERCIAL PURPOSES
72 | WITHOUT PRIOR AND EXPLICIT CONSENT OF LICENSORS. YOU MUST CONTACT INRIA FOR ANY
73 | UNAUTHORIZED USE: stip-sophia.transfert@inria.fr . ANY SUCH ACTION WILL
74 | CONSTITUTE A FORGERY. THIS *SOFTWARE* IS PROVIDED "AS IS" WITHOUT ANY WARRANTIES
75 | OF ANY NATURE AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, WITH REGARDS TO COMMERCIAL
76 | USE, PROFESSIONNAL USE, LEGAL OR NOT, OR OTHER, OR COMMERCIALISATION OR
77 | ADAPTATION. UNLESS EXPLICITLY PROVIDED BY LAW, IN NO EVENT, SHALL INRIA OR THE
78 | AUTHOR BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR
79 | CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE
80 | GOODS OR SERVICES, LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION)
81 | HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT
82 | LIABILITY, OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR
83 | IN CONNECTION WITH THE *SOFTWARE* OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE *SOFTWARE*.
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LightGaussian: Unbounded 3D Gaussian Compression with 15x Reduction and 200+ FPS
2 |
3 |
4 |  5 |
5 |  6 |
6 |  7 |
7 |  8 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 |
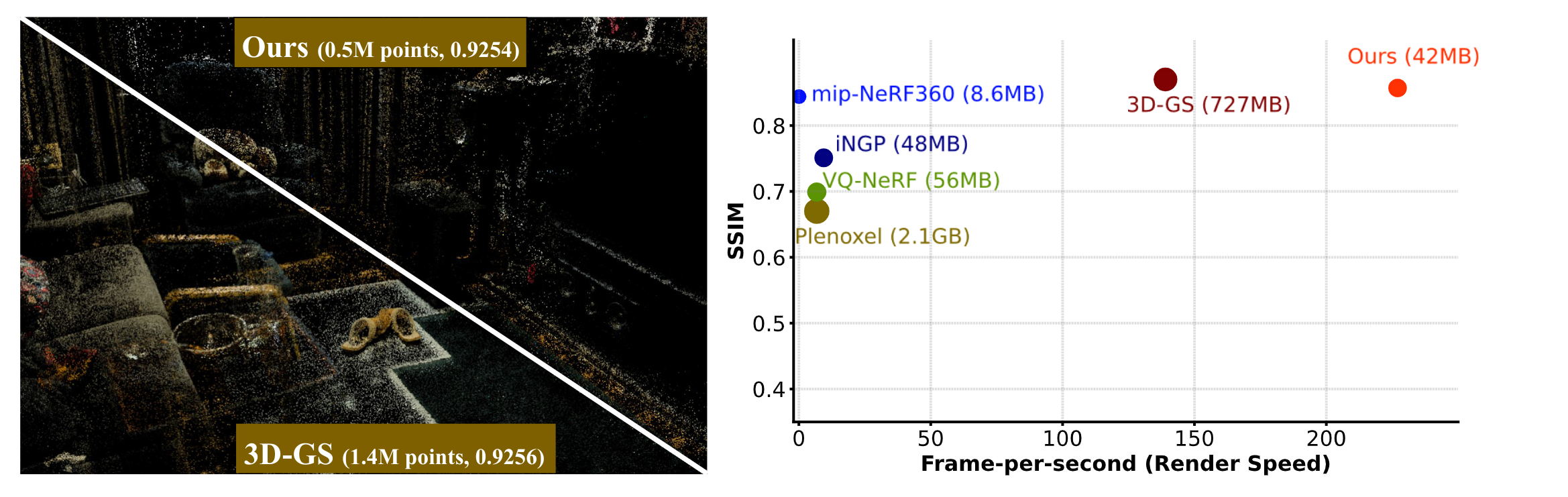
13 |
18 |

19 |
23 |
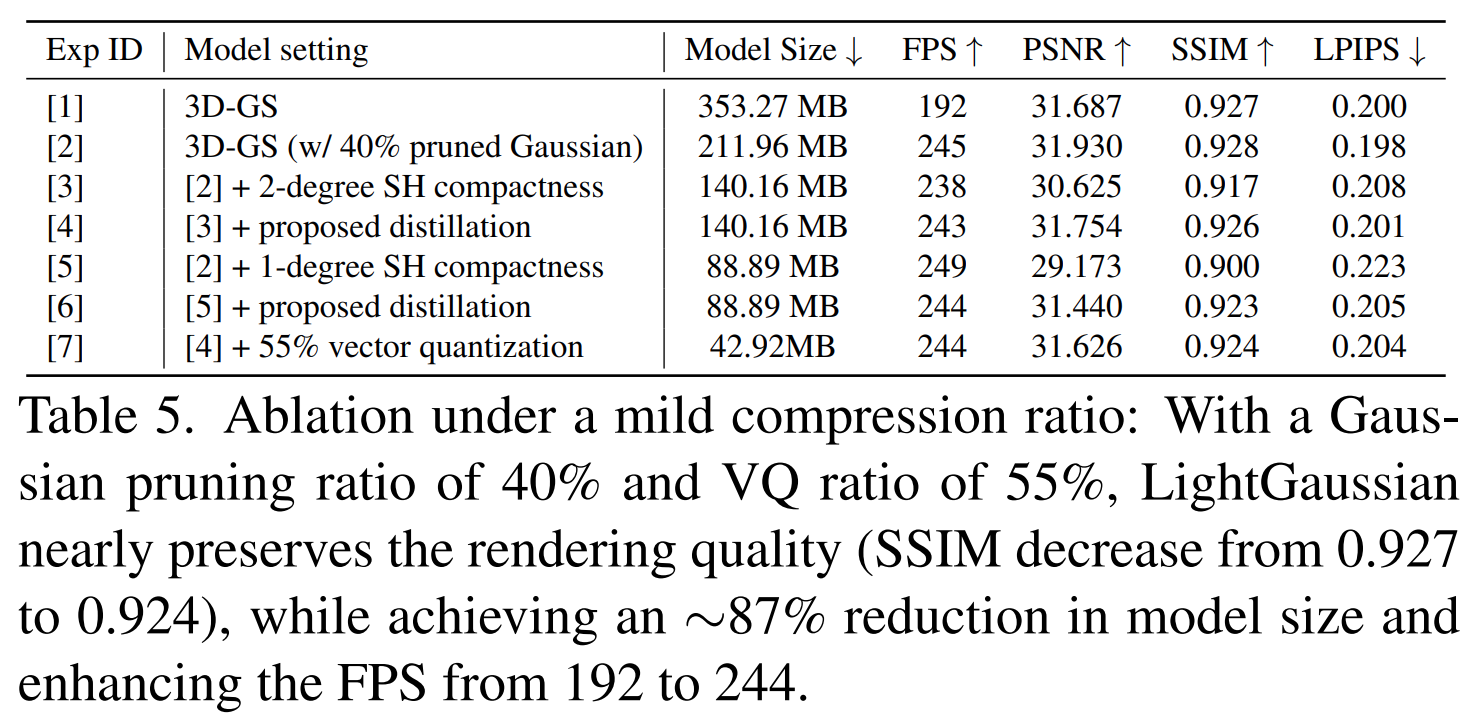
24 |
 5 |
5 |  6 |
6 |  7 |
7 |  8 |
8 |  13 |
13 |  24 |
24 |