├── .gitignore
├── LICENSE
├── Neural Networks with Torch (Bay Area Deep Learning School).pdf
├── README.md
└── notebooks
├── Deep Learning with Torch.ipynb
└── Torch & Autograd Basics.ipynb
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Compiled Lua sources
2 | luac.out
3 |
4 | # Notebooks and data
5 | *.ipynb_checkpoints/
6 | *.t7
7 |
8 | # luarocks build files
9 | *.src.rock
10 | *.zip
11 | *.tar.gz
12 | *.key
13 |
14 | # Object files
15 | *.o
16 | *.os
17 | *.ko
18 | *.obj
19 | *.elf
20 |
21 | # Precompiled Headers
22 | *.gch
23 | *.pch
24 |
25 | # Libraries
26 | *.lib
27 | *.a
28 | *.la
29 | *.lo
30 | *.def
31 | *.exp
32 |
33 | # Shared objects (inc. Windows DLLs)
34 | *.dll
35 | *.so
36 | *.so.*
37 | *.dylib
38 |
39 | # Executables
40 | *.exe
41 | *.out
42 | *.app
43 | *.i*86
44 | *.x86_64
45 | *.hex
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Apache License
2 | Version 2.0, January 2004
3 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/
4 |
5 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
6 |
7 | 1. Definitions.
8 |
9 | "License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
10 | and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
11 |
12 | "Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
13 | the copyright owner that is granting the License.
14 |
15 | "Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
16 | other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
17 | control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
18 | "control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
19 | direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
20 | otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
21 | outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
22 |
23 | "You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
24 | exercising permissions granted by this License.
25 |
26 | "Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
27 | including but not limited to software source code, documentation
28 | source, and configuration files.
29 |
30 | "Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
31 | transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
32 | not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
33 | and conversions to other media types.
34 |
35 | "Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
36 | Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
37 | copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
38 | (an example is provided in the Appendix below).
39 |
40 | "Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
41 | form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
42 | editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
43 | represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
44 | of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
45 | separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
46 | the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
47 |
48 | "Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
49 | the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
50 | to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
51 | submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
52 | or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
53 | the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
54 | means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
55 | to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
56 | communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
57 | and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
58 | Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
59 | excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
60 | designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
61 |
62 | "Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
63 | on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
64 | subsequently incorporated within the Work.
65 |
66 | 2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
67 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
68 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
69 | copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
70 | publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
71 | Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
72 |
73 | 3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
74 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
75 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
76 | (except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
77 | use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
78 | where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
79 | by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
80 | Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
81 | with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
82 | institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
83 | cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
84 | or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
85 | or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
86 | granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
87 | as of the date such litigation is filed.
88 |
89 | 4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
90 | Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
91 | modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
92 | meet the following conditions:
93 |
94 | (a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
95 | Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
96 |
97 | (b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
98 | stating that You changed the files; and
99 |
100 | (c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
101 | that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
102 | attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
103 | excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
104 | the Derivative Works; and
105 |
106 | (d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
107 | distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
108 | include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
109 | within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
110 | pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
111 | of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
112 | as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
113 | documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
114 | within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
115 | wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
116 | of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
117 | do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
118 | notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
119 | or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
120 | that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
121 | as modifying the License.
122 |
123 | You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
124 | may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
125 | for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
126 | for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
127 | reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
128 | the conditions stated in this License.
129 |
130 | 5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
131 | any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
132 | by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
133 | this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
134 | Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
135 | the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
136 | with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
137 |
138 | 6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
139 | names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
140 | except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
141 | origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
142 |
143 | 7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
144 | agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
145 | Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
146 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
147 | implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
148 | of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
149 | PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
150 | appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
151 | risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
152 |
153 | 8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
154 | whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
155 | unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
156 | negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
157 | liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
158 | incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
159 | result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
160 | Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
161 | work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
162 | other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
163 | has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
164 |
165 | 9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
166 | the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
167 | and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
168 | or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
169 | License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
170 | on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
171 | of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
172 | defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
173 | incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
174 | of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
175 |
176 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
177 |
178 | APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
179 |
180 | To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
181 | boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "{}"
182 | replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
183 | the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
184 | comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
185 | file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
186 | same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
187 | identification within third-party archives.
188 |
189 | Copyright {yyyy} {name of copyright owner}
190 |
191 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
192 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
193 | You may obtain a copy of the License at
194 |
195 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
196 |
197 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
198 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
199 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
200 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
201 | limitations under the License.
202 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Neural Networks with Torch (Bay Area Deep Learning School).pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/alexbw/bayarea-dl-summerschool/fa79e47331416c90f3caac791bf3b1ec52e60c9a/Neural Networks with Torch (Bay Area Deep Learning School).pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # bayarea-dl-summerschool
2 | Torch notebooks and slides for the Bay Area Deep Learning Summer School
3 |
4 | ## Installation Instructions
5 |
6 | #### Install anaconda if you don't have it (instructions here for OS X)
7 | ```
8 | wget http://repo.continuum.io/miniconda/Miniconda-latest-MacOSX-x86_64.sh
9 | sh Miniconda-latest-MacOSX-x86_64.sh -b -p $HOME/anaconda
10 | ```
11 |
12 | #### Add anaconda to your $PATH
13 | ```
14 | export PATH=$HOME/anaconda/bin:$PATH
15 | ```
16 |
17 | #### Install Lua & Torch
18 | ```
19 | conda install lua=5.2 lua-science -c alexbw
20 | # Although, you could install other Lua versions like 2.0 (LuaJIT), 5.1, 5.2 and 5.3
21 | ```
22 |
23 |
24 | #### Clone this repository and start the notebook server
25 | ```
26 | git clone https://github.com/alexbw/bayarea-dl-summerschool.git
27 | cd bayarea-dl-summerschool
28 | itorch notebook
29 | # Will open a browser tab, then you can navigate to the notebooks
30 | ```
31 |
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/notebooks/Deep Learning with Torch.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {
6 | "slideshow": {
7 | "slide_type": "slide"
8 | }
9 | },
10 | "source": [
11 | "# Hands-on Introduction to Torch\n",
12 | "\n",
13 | "Edited by Ronan Collobert
\n",
14 | "original version by Soumith Chintala\n",
15 | "\n",
16 | "\n",
17 | "\n",
18 | "[Get started](http://ronan.collobert.com/torch/intro.pdf)
\n",
19 | "[Get this itorch notebook](http://ronan.collobert.com/torch/Deep Learning with Torch.ipynb)\n",
20 | "\n",
21 | "Run itorch\n",
22 | "\n",
23 | "```sh\n",
24 | "itorch notebook\n",
25 | "```"
26 | ]
27 | },
28 | {
29 | "cell_type": "markdown",
30 | "metadata": {},
31 | "source": [
32 | "## Goal of this talk\n",
33 | "* Understand torch and the neural networks package at a high-level.\n",
34 | "* Train a small neural network on CPU and GPU"
35 | ]
36 | },
37 | {
38 | "cell_type": "markdown",
39 | "metadata": {},
40 | "source": [
41 | "## What is Torch?"
42 | ]
43 | },
44 | {
45 | "cell_type": "markdown",
46 | "metadata": {},
47 | "source": [
48 | "Torch is an scientific computing framework based on Lua[JIT] with strong CPU and CUDA backends.\n",
49 | "\n",
50 | "Strong points of Torch:\n",
51 | "\n",
52 | "* Efficient Tensor library (like NumPy) with an efficient CUDA backend\n",
53 | "* Neural Networks package -- build arbitrary acyclic computation graphs with automatic differentiation\n",
54 | " * also with fast CUDA and CPU backends\n",
55 | "* Good community and industry support - several hundred community-built and maintained packages.\n",
56 | "* Easy to use Multi-GPU support and parallelizing neural networks\n",
57 | "\n",
58 | "[http://torch.ch](http://torch.ch)
\n",
59 | "[https://github.com/torch/torch7/wiki/Cheatsheet](https://github.com/torch/torch7/wiki/Cheatsheet)"
60 | ]
61 | },
62 | {
63 | "cell_type": "markdown",
64 | "metadata": {},
65 | "source": [
66 | "## Before getting started"
67 | ]
68 | },
69 | {
70 | "cell_type": "markdown",
71 | "metadata": {},
72 | "source": [
73 | "* Based on [Lua](http://lua.org) and C.\n",
74 | "* Currently runs on [LuaJIT](http://luajit.org) (Just-in-time compiler) which is fast and supports FFI.\n",
75 | "* Lua is pretty close to javascript.\n",
76 | " * variables are global by default, unless `local` keyword is used\n",
77 | " * Only has one data structure built-in, a table: `{}`. Doubles as a hash-table and an array.\n",
78 | " * 1-based indexing.\n",
79 | " * `foo:bar()` is the same as `foo.bar(foo)`\n",
80 | " \n",
81 | "* Lua __glues__ C/C++ libraries together\n",
82 | " * __Develop__ fast (scripting language), __run__ fast (minor overhead, C backend)\n",
83 | " \n",
84 | "* The basic brick is the __Tensor__ object\n",
85 | " * n-dimensional array\n",
86 | " * used to store any kind of data\n",
87 | " \n",
88 | "* The __torch__ package provides tensors... _hundred_ of packages are built upon it."
89 | ]
90 | },
91 | {
92 | "cell_type": "markdown",
93 | "metadata": {},
94 | "source": [
95 | "## Getting Started\n",
96 | "\n",
97 | "#### Lua Types\n",
98 | "\n",
99 | "Lua has 8 main types:"
100 | ]
101 | },
102 | {
103 | "cell_type": "code",
104 | "execution_count": null,
105 | "metadata": {
106 | "collapsed": false
107 | },
108 | "outputs": [],
109 | "source": [
110 | "print(type(nil))\n",
111 | "print(type(true))\n",
112 | "print(type(10.4*3))\n",
113 | "print(type(\"Hello world\"))\n",
114 | "print(type(function() print(\"Hello world\") end))\n",
115 | "print(type({a=3, b=4}))\n",
116 | "print(type(torch.Tensor()))"
117 | ]
118 | },
119 | {
120 | "cell_type": "markdown",
121 | "metadata": {},
122 | "source": [
123 | "The `thread` type will not be covered by this tutorial.\n",
124 | "Note that `userdata` allows to create C objects (like several Torch objects), and define your own type system over them."
125 | ]
126 | },
127 | {
128 | "cell_type": "markdown",
129 | "metadata": {},
130 | "source": [
131 | "#### Strings, numbers, tables - a tiny introduction"
132 | ]
133 | },
134 | {
135 | "cell_type": "code",
136 | "execution_count": null,
137 | "metadata": {
138 | "collapsed": false
139 | },
140 | "outputs": [],
141 | "source": [
142 | "a = 'hello'"
143 | ]
144 | },
145 | {
146 | "cell_type": "code",
147 | "execution_count": null,
148 | "metadata": {
149 | "collapsed": false
150 | },
151 | "outputs": [],
152 | "source": [
153 | "print(a)"
154 | ]
155 | },
156 | {
157 | "cell_type": "code",
158 | "execution_count": null,
159 | "metadata": {
160 | "collapsed": false
161 | },
162 | "outputs": [],
163 | "source": [
164 | "b = {}"
165 | ]
166 | },
167 | {
168 | "cell_type": "code",
169 | "execution_count": null,
170 | "metadata": {
171 | "collapsed": false
172 | },
173 | "outputs": [],
174 | "source": [
175 | "b[1] = a"
176 | ]
177 | },
178 | {
179 | "cell_type": "code",
180 | "execution_count": null,
181 | "metadata": {
182 | "collapsed": false
183 | },
184 | "outputs": [],
185 | "source": [
186 | "print(b)"
187 | ]
188 | },
189 | {
190 | "cell_type": "code",
191 | "execution_count": null,
192 | "metadata": {
193 | "collapsed": false
194 | },
195 | "outputs": [],
196 | "source": [
197 | "b[2] = 30"
198 | ]
199 | },
200 | {
201 | "cell_type": "code",
202 | "execution_count": null,
203 | "metadata": {
204 | "collapsed": false
205 | },
206 | "outputs": [],
207 | "source": [
208 | "for i=1,#b do -- the # operator is the length operator in Lua\n",
209 | " print(b[i]) \n",
210 | "end"
211 | ]
212 | },
213 | {
214 | "cell_type": "markdown",
215 | "metadata": {},
216 | "source": [
217 | "#### Tensors"
218 | ]
219 | },
220 | {
221 | "cell_type": "code",
222 | "execution_count": null,
223 | "metadata": {
224 | "collapsed": false
225 | },
226 | "outputs": [],
227 | "source": [
228 | "a = torch.Tensor(5,3) -- construct a 5x3 matrix, uninitialized"
229 | ]
230 | },
231 | {
232 | "cell_type": "code",
233 | "execution_count": null,
234 | "metadata": {
235 | "collapsed": false
236 | },
237 | "outputs": [],
238 | "source": [
239 | "a = torch.rand(5,3)\n",
240 | "print(a)"
241 | ]
242 | },
243 | {
244 | "cell_type": "markdown",
245 | "metadata": {},
246 | "source": [
247 | "#### Views\n",
248 | "A tensor is a view over a piece of memory (a storage)"
249 | ]
250 | },
251 | {
252 | "cell_type": "code",
253 | "execution_count": null,
254 | "metadata": {
255 | "collapsed": false
256 | },
257 | "outputs": [],
258 | "source": [
259 | "print(a:storage())"
260 | ]
261 | },
262 | {
263 | "cell_type": "markdown",
264 | "metadata": {},
265 | "source": [
266 | "Torch relies heavily on views:\n",
267 | " - narrow(dim, idx, size)\n",
268 | " - select(dim, idx)\n",
269 | " - unfold(dim, kw, dw)\n",
270 | " - view(dim1, dim2, dim3, ...)\n",
271 | " - index operator [{}]"
272 | ]
273 | },
274 | {
275 | "cell_type": "code",
276 | "execution_count": null,
277 | "metadata": {
278 | "collapsed": false
279 | },
280 | "outputs": [],
281 | "source": [
282 | "print(a:narrow(1, 3, 2))"
283 | ]
284 | },
285 | {
286 | "cell_type": "markdown",
287 | "metadata": {},
288 | "source": [
289 | "Remember that view = *pointer* in a storage"
290 | ]
291 | },
292 | {
293 | "cell_type": "code",
294 | "execution_count": null,
295 | "metadata": {
296 | "collapsed": false
297 | },
298 | "outputs": [],
299 | "source": [
300 | "an = a:narrow(1, 3, 2)\n",
301 | "an:zero()\n",
302 | "print(a)"
303 | ]
304 | },
305 | {
306 | "cell_type": "code",
307 | "execution_count": null,
308 | "metadata": {
309 | "collapsed": false
310 | },
311 | "outputs": [],
312 | "source": [
313 | "a:select(2, 2):fill(3.14)\n",
314 | "print(a)"
315 | ]
316 | },
317 | {
318 | "cell_type": "code",
319 | "execution_count": null,
320 | "metadata": {
321 | "collapsed": false
322 | },
323 | "outputs": [],
324 | "source": [
325 | "print(a:size())\n",
326 | "print(a:stride())\n",
327 | "print(a:storageOffset())"
328 | ]
329 | },
330 | {
331 | "cell_type": "code",
332 | "execution_count": null,
333 | "metadata": {
334 | "collapsed": false
335 | },
336 | "outputs": [],
337 | "source": [
338 | "print(a:select(2, 2):size())\n",
339 | "print(a:select(2, 2):stride())\n",
340 | "print(a:select(2, 2):storageOffset())"
341 | ]
342 | },
343 | {
344 | "cell_type": "markdown",
345 | "metadata": {},
346 | "source": [
347 | "#### Math operations\n",
348 | "\n",
349 | "See [torch documentation](https://github.com/torch/torch7/blob/master/doc/maths.md)\n",
350 | "for a survey on available math operations."
351 | ]
352 | },
353 | {
354 | "cell_type": "code",
355 | "execution_count": null,
356 | "metadata": {
357 | "collapsed": false
358 | },
359 | "outputs": [],
360 | "source": [
361 | "b=torch.rand(3,4)"
362 | ]
363 | },
364 | {
365 | "cell_type": "code",
366 | "execution_count": null,
367 | "metadata": {
368 | "collapsed": false
369 | },
370 | "outputs": [],
371 | "source": [
372 | "-- matrix-matrix multiplication: syntax 1\n",
373 | "a*b "
374 | ]
375 | },
376 | {
377 | "cell_type": "code",
378 | "execution_count": null,
379 | "metadata": {
380 | "collapsed": false
381 | },
382 | "outputs": [],
383 | "source": [
384 | "-- matrix-matrix multiplication: syntax 2\n",
385 | "torch.mm(a,b) "
386 | ]
387 | },
388 | {
389 | "cell_type": "code",
390 | "execution_count": null,
391 | "metadata": {
392 | "collapsed": false
393 | },
394 | "outputs": [],
395 | "source": [
396 | "-- matrix-matrix multiplication: syntax 3\n",
397 | "c=torch.Tensor(5,4)\n",
398 | "c:mm(a,b) -- store the result of a*b in c"
399 | ]
400 | },
401 | {
402 | "cell_type": "markdown",
403 | "metadata": {},
404 | "source": [
405 | "#### CUDA Tensors\n",
406 | "Tensors can be moved onto GPU using the :cuda function"
407 | ]
408 | },
409 | {
410 | "cell_type": "code",
411 | "execution_count": null,
412 | "metadata": {
413 | "collapsed": false
414 | },
415 | "outputs": [],
416 | "source": [
417 | "require 'cutorch';\n",
418 | "a = a:cuda()\n",
419 | "b = b:cuda()\n",
420 | "c = c:cuda()\n",
421 | "c:mm(a,b) -- done on GPU"
422 | ]
423 | },
424 | {
425 | "cell_type": "markdown",
426 | "metadata": {},
427 | "source": [
428 | "#### Functions"
429 | ]
430 | },
431 | {
432 | "cell_type": "code",
433 | "execution_count": null,
434 | "metadata": {
435 | "collapsed": false
436 | },
437 | "outputs": [],
438 | "source": [
439 | "N = 5\n",
440 | "\n",
441 | "-- make sure everybody has the same random seed\n",
442 | "torch.manualSeed(1234)\n",
443 | "\n",
444 | "-- create a random NxN matrix\n",
445 | "A = torch.rand(N, N)\n",
446 | "\n",
447 | "-- make it symmetric positive\n",
448 | "A = A*A:t()\n",
449 | "\n",
450 | "-- make it definite\n",
451 | "A:add(0.001, torch.eye(N))\n",
452 | "\n",
453 | "-- add a linear term\n",
454 | "b = torch.rand(N)\n",
455 | "\n",
456 | "-- create a quadratic form\n",
457 | "function J(x)\n",
458 | " return 0.5*x:dot(A*x)-b:dot(x)\n",
459 | "end"
460 | ]
461 | },
462 | {
463 | "cell_type": "markdown",
464 | "metadata": {},
465 | "source": [
466 | "Function call, here at a random point"
467 | ]
468 | },
469 | {
470 | "cell_type": "code",
471 | "execution_count": null,
472 | "metadata": {
473 | "collapsed": false
474 | },
475 | "outputs": [],
476 | "source": [
477 | "print(J(torch.rand(N)))"
478 | ]
479 | },
480 | {
481 | "cell_type": "markdown",
482 | "metadata": {},
483 | "source": [
484 | "### Exercise: find the minimum of the quadratic function"
485 | ]
486 | },
487 | {
488 | "cell_type": "markdown",
489 | "metadata": {},
490 | "source": [
491 | "#### We can inverse the matrix"
492 | ]
493 | },
494 | {
495 | "cell_type": "code",
496 | "execution_count": null,
497 | "metadata": {
498 | "collapsed": false
499 | },
500 | "outputs": [],
501 | "source": [
502 | "xs = torch.inverse(A)*b\n",
503 | "print(string.format('J(x^*) = %g', J(xs)))"
504 | ]
505 | },
506 | {
507 | "cell_type": "markdown",
508 | "metadata": {},
509 | "source": [
510 | "#### Or we can do a gradient descent!"
511 | ]
512 | },
513 | {
514 | "cell_type": "code",
515 | "execution_count": null,
516 | "metadata": {
517 | "collapsed": false
518 | },
519 | "outputs": [],
520 | "source": [
521 | "function dJ(x)\n",
522 | " return A*x-b\n",
523 | "end"
524 | ]
525 | },
526 | {
527 | "cell_type": "markdown",
528 | "metadata": {},
529 | "source": [
530 | "We define some current solution:"
531 | ]
532 | },
533 | {
534 | "cell_type": "code",
535 | "execution_count": null,
536 | "metadata": {
537 | "collapsed": false
538 | },
539 | "outputs": [],
540 | "source": [
541 | "x = torch.rand(N)"
542 | ]
543 | },
544 | {
545 | "cell_type": "markdown",
546 | "metadata": {},
547 | "source": [
548 | "and then apply gradient descent (with a given learning rate `lr`) for a while:"
549 | ]
550 | },
551 | {
552 | "cell_type": "code",
553 | "execution_count": null,
554 | "metadata": {
555 | "collapsed": false
556 | },
557 | "outputs": [],
558 | "source": [
559 | "lr = 0.01\n",
560 | "for i=1,20000 do\n",
561 | " x = x - dJ(x)*lr\n",
562 | " -- we print the value of the objective function every 1000 iterations\n",
563 | " if i % 1000 == 0 then\n",
564 | " print(string.format('at iter %d J(x) = %f', i, J(x)))\n",
565 | " end\n",
566 | "end"
567 | ]
568 | },
569 | {
570 | "cell_type": "markdown",
571 | "metadata": {},
572 | "source": [
573 | "### Neural Networks\n",
574 | "Neural networks in Torch can be constructed using the `nn` package."
575 | ]
576 | },
577 | {
578 | "cell_type": "code",
579 | "execution_count": null,
580 | "metadata": {
581 | "collapsed": false
582 | },
583 | "outputs": [],
584 | "source": [
585 | "require 'nn';"
586 | ]
587 | },
588 | {
589 | "cell_type": "markdown",
590 | "metadata": {},
591 | "source": [
592 | "`Modules` are the bricks used to build neural networks. Each are themselves neural networks, but can be combined with other networks using `containers` to create complex neural networks"
593 | ]
594 | },
595 | {
596 | "cell_type": "markdown",
597 | "metadata": {},
598 | "source": [
599 | "For example, look at this network that classfies digit images:\n",
600 | "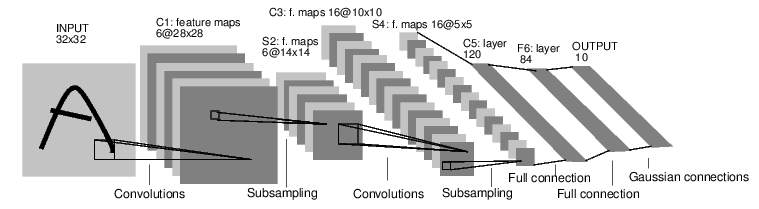"
601 | ]
602 | },
603 | {
604 | "cell_type": "markdown",
605 | "metadata": {},
606 | "source": [
607 | "It is a simple feed-forward network. \n",
608 | "It takes the input, feeds it through several layers one after the other, and then finally gives the output.\n",
609 | "\n",
610 | "Such a network container is `nn.Sequential` which feeds the input through several layers."
611 | ]
612 | },
613 | {
614 | "cell_type": "code",
615 | "execution_count": null,
616 | "metadata": {
617 | "collapsed": false
618 | },
619 | "outputs": [],
620 | "source": [
621 | "net = nn.Sequential()\n",
622 | "\n",
623 | "-- 1 input image channel, 6 output channels, 5x5 convolution kernel\n",
624 | "net:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(1, 6, 5, 5))\n",
625 | "\n",
626 | "-- A max-pooling operation that looks at 2x2 windows and finds the max.\n",
627 | "net:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2,2,2,2))\n",
628 | "\n",
629 | "-- non-linearity\n",
630 | "net:add(nn.Tanh())\n",
631 | "\n",
632 | "-- additional layers\n",
633 | "net:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(6, 16, 5, 5))\n",
634 | "net:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2,2,2,2))\n",
635 | "net:add(nn.Tanh())\n",
636 | "\n",
637 | "-- reshapes from a 3D tensor of 16x5x5 into 1D tensor of 16*5*5\n",
638 | "net:add(nn.View(16*5*5))\n",
639 | "\n",
640 | "-- fully connected layers (matrix multiplication between input and weights)\n",
641 | "net:add(nn.Linear(16*5*5, 120))\n",
642 | "net:add(nn.Tanh())\n",
643 | "net:add(nn.Linear(120, 84))\n",
644 | "net:add(nn.Tanh())\n",
645 | "\n",
646 | "-- 10 is the number of outputs of the network (10 classes)\n",
647 | "net:add(nn.Linear(84, 10))\n",
648 | "print('Lenet5\\n', tostring(net));"
649 | ]
650 | },
651 | {
652 | "cell_type": "markdown",
653 | "metadata": {},
654 | "source": [
655 | "Other examples of nn containers are shown in the figure below:\n",
656 | "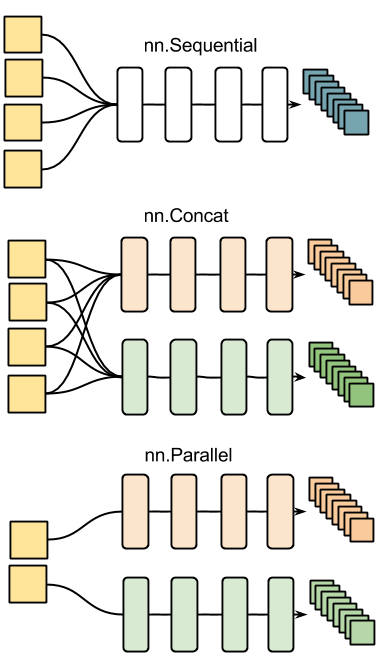\n",
657 | "\n",
658 | "Every neural network module in torch has automatic differentiation.\n",
659 | "It has a `:forward(input)` function that computes the output for a given input, flowing the input through the network.\n",
660 | "and it has a `:backward(input, gradient)` function that will differentiate each neuron in the network w.r.t. the gradient that is passed in. This is done via the chain rule."
661 | ]
662 | },
663 | {
664 | "cell_type": "code",
665 | "execution_count": null,
666 | "metadata": {
667 | "collapsed": false
668 | },
669 | "outputs": [],
670 | "source": [
671 | "input = torch.rand(1,32,32) -- pass a random tensor as input to the network"
672 | ]
673 | },
674 | {
675 | "cell_type": "code",
676 | "execution_count": null,
677 | "metadata": {
678 | "collapsed": false
679 | },
680 | "outputs": [],
681 | "source": [
682 | "output = net:forward(input)"
683 | ]
684 | },
685 | {
686 | "cell_type": "code",
687 | "execution_count": null,
688 | "metadata": {
689 | "collapsed": false
690 | },
691 | "outputs": [],
692 | "source": [
693 | "print(output)"
694 | ]
695 | },
696 | {
697 | "cell_type": "code",
698 | "execution_count": null,
699 | "metadata": {
700 | "collapsed": false
701 | },
702 | "outputs": [],
703 | "source": [
704 | "net:zeroGradParameters() -- zero the internal gradient buffers of the network (will come to this later)"
705 | ]
706 | },
707 | {
708 | "cell_type": "code",
709 | "execution_count": null,
710 | "metadata": {
711 | "collapsed": false
712 | },
713 | "outputs": [],
714 | "source": [
715 | "gradInput = net:backward(input, torch.rand(10))"
716 | ]
717 | },
718 | {
719 | "cell_type": "code",
720 | "execution_count": null,
721 | "metadata": {
722 | "collapsed": false
723 | },
724 | "outputs": [],
725 | "source": [
726 | "print(#gradInput)"
727 | ]
728 | },
729 | {
730 | "cell_type": "markdown",
731 | "metadata": {},
732 | "source": [
733 | "One can then update the parameters with"
734 | ]
735 | },
736 | {
737 | "cell_type": "code",
738 | "execution_count": null,
739 | "metadata": {
740 | "collapsed": false
741 | },
742 | "outputs": [],
743 | "source": [
744 | "net:updateParameters(0.001) -- provide a learning rate"
745 | ]
746 | },
747 | {
748 | "cell_type": "markdown",
749 | "metadata": {},
750 | "source": [
751 | "### Criterion: Defining a loss function\n",
752 | "When you want a model to learn to do something, you give it feedback on how well it is doing. This function that computes an objective measure of the model's performance is called a __loss function__.\n",
753 | "\n",
754 | "A typical loss function takes in the model's output and the groundtruth and computes a value that quantifies the model's performance.\n",
755 | "\n",
756 | "The model then corrects itself to have a smaller loss.\n",
757 | "\n",
758 | "In Torch, loss functions are implemented just like neural network modules, and have automatic differentiation. \n",
759 | "They have two functions\n",
760 | " - `forward(input, target)`\n",
761 | " - `backward(input, target)`\n",
762 | "\n",
763 | "For example:"
764 | ]
765 | },
766 | {
767 | "cell_type": "code",
768 | "execution_count": null,
769 | "metadata": {
770 | "collapsed": false
771 | },
772 | "outputs": [],
773 | "source": [
774 | "-- a negative log-likelihood criterion for multi-class classification\n",
775 | "criterion = nn.CrossEntropyCriterion()\n",
776 | "\n",
777 | "-- let's say the groundtruth was class number: 3\n",
778 | "criterion:forward(output, 3)\n",
779 | "gradients = criterion:backward(output, 3)"
780 | ]
781 | },
782 | {
783 | "cell_type": "code",
784 | "execution_count": null,
785 | "metadata": {
786 | "collapsed": false
787 | },
788 | "outputs": [],
789 | "source": [
790 | "gradInput = net:backward(input, gradients)"
791 | ]
792 | },
793 | {
794 | "cell_type": "markdown",
795 | "metadata": {},
796 | "source": [
797 | "#####Review of what you learnt so far\n",
798 | "* Network can have many layers of computation\n",
799 | "* Network takes an input and produces an output in the `:forward` pass\n",
800 | "* Criterion computes the loss of the network, and it's gradients w.r.t. the output of the network.\n",
801 | "* Network takes an (input, gradients) pair in it's `:backward` pass and calculates the gradients w.r.t. each layer (and neuron) in the network.\n",
802 | "\n",
803 | "##### Missing details\n",
804 | "> A neural network layer can have learnable parameters or not.\n",
805 | "\n",
806 | "A convolution layer learns it's convolution kernels to adapt to the input data and the problem being solved. \n",
807 | "A max-pooling layer has no learnable parameters. It only finds the max of local windows.\n",
808 | "\n",
809 | "A layer in torch which has learnable weights, will typically have fields .weight (and optionally, .bias)"
810 | ]
811 | },
812 | {
813 | "cell_type": "code",
814 | "execution_count": null,
815 | "metadata": {
816 | "collapsed": false
817 | },
818 | "outputs": [],
819 | "source": [
820 | "m = nn.SpatialConvolution(1,3,2,2) -- learn 3 2x2 kernels\n",
821 | "print(m.weight) -- initially, the weights are randomly initialized"
822 | ]
823 | },
824 | {
825 | "cell_type": "code",
826 | "execution_count": null,
827 | "metadata": {
828 | "collapsed": false
829 | },
830 | "outputs": [],
831 | "source": [
832 | "print(m.bias) -- The operation in a convolution layer is: output = convolution(input,weight) + bias"
833 | ]
834 | },
835 | {
836 | "cell_type": "markdown",
837 | "metadata": {},
838 | "source": [
839 | "There are also two other important fields in a learnable layer. The gradWeight and gradBias.\n",
840 | "The gradWeight accumulates the gradients w.r.t. each weight in the layer, and the gradBias, w.r.t. each bias in the layer.\n",
841 | "\n",
842 | "#### Training the network\n",
843 | "\n",
844 | "For the network to adjust itself, it typically does this operation (if you do Stochastic Gradient Descent):\n",
845 | "\n",
846 | "> weight = weight - learningRate * gradWeight [equation 1]\n",
847 | "\n",
848 | "This update over time will adjust the network weights such that the output loss is decreasing."
849 | ]
850 | },
851 | {
852 | "cell_type": "markdown",
853 | "metadata": {},
854 | "source": [
855 | "Okay, now it is time to discuss one missing piece. Who visits each layer in your neural network and updates the weight according to Equation 1?\n",
856 | " - You can do your own training loop\n",
857 | " - Pro: easy customization for complicated network\n",
858 | " - Con: code duplication\n",
859 | " \n",
860 | " - You can use existing packages\n",
861 | " - [optim](https://github.com/torch/optim)\n",
862 | " - nn.StochasticGradient\n",
863 | "\n",
864 | "We shall use the simple SGD trainer shipped with the neural network module: [__nn.StochasticGradient__](https://github.com/torch/nn/blob/master/doc/training.md#stochasticgradientmodule-criterion).\n",
865 | "\n",
866 | "It has a function :train(dataset) that takes a given dataset and simply trains your network by showing different samples from your dataset to the network."
867 | ]
868 | },
869 | {
870 | "cell_type": "markdown",
871 | "metadata": {},
872 | "source": [
873 | "### What about data?\n",
874 | "Generally, when you have to deal with image, text, audio or video data, you can use standard functions like: [__image.load__](https://github.com/torch/image#res-imageloadfilename-depth-tensortype) or [__audio.load__](https://github.com/soumith/lua---audio#usage) to load your data into a _torch.Tensor_ or a Lua table, as convenient.\n",
875 | "\n",
876 | "Let us now use some simple data to train our network.\n",
877 | "\n",
878 | "We shall use the CIFAR-10 dataset, which has the classes: 'airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat', 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'. \n",
879 | "The images in CIFAR-10 are of size 3x32x32, i.e. 3-channel color images of 32x32 pixels in size.\n",
880 | "\n",
881 | "\n",
882 | "The dataset has 50,000 training images and 10,000 test images in total.\n",
883 | "\n",
884 | "__We now have 5 steps left to do in training our first torch neural network__\n",
885 | "1. Load and normalize data\n",
886 | "2. Define a Neural Network\n",
887 | "3. Define Loss function\n",
888 | "4. Train network on training data\n",
889 | "5. Test network on test data.\n",
890 | "\n",
891 | "#### 1. Load and normalize data\n",
892 | "\n",
893 | "Today, in the interest of time, we prepared the data before-hand into a 4D torch ByteTensor of size 10000x3x32x32 (training) and 10000x3x32x32 (testing)\n",
894 | "Let us download the data..."
895 | ]
896 | },
897 | {
898 | "cell_type": "code",
899 | "execution_count": null,
900 | "metadata": {
901 | "collapsed": false
902 | },
903 | "outputs": [],
904 | "source": [
905 | "os.execute('wget -c https://s3.amazonaws.com/torch7/data/cifar10torchsmall.zip')\n",
906 | "os.execute('unzip -o cifar10torchsmall.zip')"
907 | ]
908 | },
909 | {
910 | "cell_type": "markdown",
911 | "metadata": {},
912 | "source": [
913 | "And let's inspect it!"
914 | ]
915 | },
916 | {
917 | "cell_type": "code",
918 | "execution_count": null,
919 | "metadata": {
920 | "collapsed": false
921 | },
922 | "outputs": [],
923 | "source": [
924 | "trainset = torch.load('cifar10-train.t7')\n",
925 | "testset = torch.load('cifar10-test.t7')\n",
926 | "classes = {'airplane', 'automobile', 'bird', 'cat',\n",
927 | " 'deer', 'dog', 'frog', 'horse', 'ship', 'truck'}"
928 | ]
929 | },
930 | {
931 | "cell_type": "code",
932 | "execution_count": null,
933 | "metadata": {
934 | "collapsed": false
935 | },
936 | "outputs": [],
937 | "source": [
938 | "print(trainset)"
939 | ]
940 | },
941 | {
942 | "cell_type": "code",
943 | "execution_count": null,
944 | "metadata": {
945 | "collapsed": false
946 | },
947 | "outputs": [],
948 | "source": [
949 | "print(#trainset.data)"
950 | ]
951 | },
952 | {
953 | "cell_type": "markdown",
954 | "metadata": {},
955 | "source": [
956 | "For fun, let us display an image:"
957 | ]
958 | },
959 | {
960 | "cell_type": "code",
961 | "execution_count": null,
962 | "metadata": {
963 | "collapsed": false
964 | },
965 | "outputs": [],
966 | "source": [
967 | "itorch.image(trainset.data[100]) -- display the 100-th image in dataset\n",
968 | "print(classes[trainset.label[100]])"
969 | ]
970 | },
971 | {
972 | "cell_type": "markdown",
973 | "metadata": {},
974 | "source": [
975 | "Now, to prepare the dataset to be used with __nn.StochasticGradient__, a couple of things have to be done according to it's [documentation](https://github.com/torch/nn/blob/master/doc/training.md#traindataset).\n",
976 | "1. The dataset has to have a :size() function.\n",
977 | "2. The dataset has to have a [i] index operator, so that dataset[i] returns the ith sample in the datset.\n",
978 | "\n",
979 | "Both can be done quickly:"
980 | ]
981 | },
982 | {
983 | "cell_type": "code",
984 | "execution_count": null,
985 | "metadata": {
986 | "collapsed": false
987 | },
988 | "outputs": [],
989 | "source": [
990 | "-- ignore setmetatable() for now, it is a feature beyond the scope of this tutorial.\n",
991 | "-- It sets the index operator.\n",
992 | "\n",
993 | "setmetatable(trainset, \n",
994 | " {__index = function(t, i) \n",
995 | " return {\n",
996 | " t.data[i],\n",
997 | " t.label[i]\n",
998 | " } \n",
999 | " end}\n",
1000 | ");\n",
1001 | "\n",
1002 | "function trainset:size() \n",
1003 | " return self.data:size(1) \n",
1004 | "end\n",
1005 | "\n",
1006 | "-- converts the data from a ByteTensor to a DoubleTensor.\n",
1007 | "trainset.data = trainset.data:double()"
1008 | ]
1009 | },
1010 | {
1011 | "cell_type": "code",
1012 | "execution_count": null,
1013 | "metadata": {
1014 | "collapsed": false
1015 | },
1016 | "outputs": [],
1017 | "source": [
1018 | "print(trainset:size()) -- just to test"
1019 | ]
1020 | },
1021 | {
1022 | "cell_type": "code",
1023 | "execution_count": null,
1024 | "metadata": {
1025 | "collapsed": false
1026 | },
1027 | "outputs": [],
1028 | "source": [
1029 | "print(trainset[33]) -- load sample number 33.\n",
1030 | "itorch.image(trainset[33][1])"
1031 | ]
1032 | },
1033 | {
1034 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1035 | "metadata": {},
1036 | "source": [
1037 | "__One of the most important things you can do in conditioning your data (in general in data-science or machine learning) is to make your data to have a mean of 0.0 and standard-deviation of 1.0.__\n",
1038 | "\n",
1039 | "Let us do that as a final step of our data processing.\n",
1040 | "\n",
1041 | "We are going to do a per-channel normalization"
1042 | ]
1043 | },
1044 | {
1045 | "cell_type": "code",
1046 | "execution_count": null,
1047 | "metadata": {
1048 | "collapsed": false
1049 | },
1050 | "outputs": [],
1051 | "source": [
1052 | "-- remember: our dataset is #samples x #channels x #height x #width\n",
1053 | "-- this picks {all images, 1st channel, all vertical pixels, all horizontal pixels}\n",
1054 | "redChannel = trainset.data:select(2, 1)"
1055 | ]
1056 | },
1057 | {
1058 | "cell_type": "code",
1059 | "execution_count": null,
1060 | "metadata": {
1061 | "collapsed": false
1062 | },
1063 | "outputs": [],
1064 | "source": [
1065 | "print(#redChannel)"
1066 | ]
1067 | },
1068 | {
1069 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1070 | "metadata": {},
1071 | "source": [
1072 | "Moving back to mean-subtraction and standard-deviation based scaling, doing this operation is simple, using the indexing operator that we learnt above:"
1073 | ]
1074 | },
1075 | {
1076 | "cell_type": "code",
1077 | "execution_count": null,
1078 | "metadata": {
1079 | "collapsed": false
1080 | },
1081 | "outputs": [],
1082 | "source": [
1083 | "mean = {} -- store the mean, to normalize the test set in the future\n",
1084 | "stdv = {} -- store the standard-deviation for the future\n",
1085 | "for i=1,3 do -- over each image channel\n",
1086 | " mean[i] = trainset.data:select(2, 1):mean() -- mean estimation\n",
1087 | " print('Channel ' .. i .. ', Mean: ' .. mean[i])\n",
1088 | " trainset.data:select(2, 1):add(-mean[i]) -- mean subtraction\n",
1089 | " \n",
1090 | " stdv[i] = trainset.data:select(2, i):std() -- std estimation\n",
1091 | " print('Channel ' .. i .. ', Standard Deviation: ' .. stdv[i])\n",
1092 | " trainset.data:select(2, i):div(stdv[i]) -- std scaling\n",
1093 | "end"
1094 | ]
1095 | },
1096 | {
1097 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1098 | "metadata": {},
1099 | "source": [
1100 | "Our training data is now normalized and ready to be used.\n",
1101 | "\n",
1102 | "#### 2. Time to define our neural network\n"
1103 | ]
1104 | },
1105 | {
1106 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1107 | "metadata": {},
1108 | "source": [
1109 | "We use here a LeNet-like network, with 3 input channels and threshold units (ReLU):"
1110 | ]
1111 | },
1112 | {
1113 | "cell_type": "code",
1114 | "execution_count": null,
1115 | "metadata": {
1116 | "collapsed": false
1117 | },
1118 | "outputs": [],
1119 | "source": [
1120 | "net = nn.Sequential()\n",
1121 | "net:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(3, 6, 5, 5))\n",
1122 | "net:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2,2,2,2))\n",
1123 | "net:add(nn.Threshold())\n",
1124 | "\n",
1125 | "net:add(nn.SpatialConvolution(6, 16, 5, 5))\n",
1126 | "net:add(nn.SpatialMaxPooling(2,2,2,2))\n",
1127 | "net:add(nn.Threshold())\n",
1128 | "\n",
1129 | "net:add(nn.View(16*5*5))\n",
1130 | "\n",
1131 | "net:add(nn.Linear(16*5*5, 120))\n",
1132 | "net:add(nn.Threshold())\n",
1133 | "net:add(nn.Linear(120, 84))\n",
1134 | "net:add(nn.Threshold())\n",
1135 | "net:add(nn.Linear(84, 10))"
1136 | ]
1137 | },
1138 | {
1139 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1140 | "metadata": {},
1141 | "source": [
1142 | "#### 3. Let us define the Loss function\n",
1143 | "\n",
1144 | "Let us use the cross-entropy classification loss. It is well suited for most classification problems."
1145 | ]
1146 | },
1147 | {
1148 | "cell_type": "code",
1149 | "execution_count": null,
1150 | "metadata": {
1151 | "collapsed": false
1152 | },
1153 | "outputs": [],
1154 | "source": [
1155 | "criterion = nn.CrossEntropyCriterion()"
1156 | ]
1157 | },
1158 | {
1159 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1160 | "metadata": {},
1161 | "source": [
1162 | "#### 4. Train the neural network\n",
1163 | "\n",
1164 | "This is when things start to get interesting. \n",
1165 | "Let us first define an __nn.StochasticGradient__ object. Then we will give our dataset to this object's ___:train___ function, and that will get the ball rolling."
1166 | ]
1167 | },
1168 | {
1169 | "cell_type": "code",
1170 | "execution_count": null,
1171 | "metadata": {
1172 | "collapsed": false
1173 | },
1174 | "outputs": [],
1175 | "source": [
1176 | "trainer = nn.StochasticGradient(net, criterion)\n",
1177 | "trainer.learningRate = 0.001\n",
1178 | "trainer.maxIteration = 5 -- just do 5 epochs of training."
1179 | ]
1180 | },
1181 | {
1182 | "cell_type": "code",
1183 | "execution_count": null,
1184 | "metadata": {
1185 | "collapsed": false
1186 | },
1187 | "outputs": [],
1188 | "source": [
1189 | "trainer:train(trainset)"
1190 | ]
1191 | },
1192 | {
1193 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1194 | "metadata": {},
1195 | "source": [
1196 | "#### 5. Test the network, print accuracy\n",
1197 | "\n",
1198 | "We have trained the network for 5 passes over the training dataset. \n",
1199 | "But we need to check if the network has learnt anything at all. \n",
1200 | "We will check this by predicting the class label that the neural network outputs, and checking it against the ground-truth. If the prediction is correct, we add the sample to the list of correct predictions."
1201 | ]
1202 | },
1203 | {
1204 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1205 | "metadata": {},
1206 | "source": [
1207 | "Okay, first step. Let us display an image from the test set to get familiar."
1208 | ]
1209 | },
1210 | {
1211 | "cell_type": "code",
1212 | "execution_count": null,
1213 | "metadata": {
1214 | "collapsed": false
1215 | },
1216 | "outputs": [],
1217 | "source": [
1218 | "print(classes[testset.label[100]])\n",
1219 | "itorch.image(testset.data[100])"
1220 | ]
1221 | },
1222 | {
1223 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1224 | "metadata": {},
1225 | "source": [
1226 | "Now that we are done with that, let us normalize the test data with the mean and standard-deviation from the training data."
1227 | ]
1228 | },
1229 | {
1230 | "cell_type": "code",
1231 | "execution_count": null,
1232 | "metadata": {
1233 | "collapsed": false
1234 | },
1235 | "outputs": [],
1236 | "source": [
1237 | "testset.data = testset.data:double() -- convert from Byte tensor to Double tensor\n",
1238 | "for i=1,3 do -- over each image channel\n",
1239 | " local channel = testset.data:select(2, i)\n",
1240 | " channel:add(-mean[i]) -- mean subtraction\n",
1241 | " channel:div(stdv[i]) -- std scaling\n",
1242 | " print(string.format('channel %d: mean = %f stdv = %f', i, channel:mean(), channel:std()))\n",
1243 | "end"
1244 | ]
1245 | },
1246 | {
1247 | "cell_type": "code",
1248 | "execution_count": null,
1249 | "metadata": {
1250 | "collapsed": false
1251 | },
1252 | "outputs": [],
1253 | "source": [
1254 | "-- for fun, print the mean and standard-deviation of example-100\n",
1255 | "horse = testset.data[100]\n",
1256 | "print(horse:mean(), horse:std())"
1257 | ]
1258 | },
1259 | {
1260 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1261 | "metadata": {},
1262 | "source": [
1263 | "Okay, now let us see what the neural network thinks these examples above are:"
1264 | ]
1265 | },
1266 | {
1267 | "cell_type": "code",
1268 | "execution_count": null,
1269 | "metadata": {
1270 | "collapsed": false
1271 | },
1272 | "outputs": [],
1273 | "source": [
1274 | "print(classes[testset.label[100]])\n",
1275 | "itorch.image(testset.data[100])\n",
1276 | "predicted = net:forward(testset.data[100])"
1277 | ]
1278 | },
1279 | {
1280 | "cell_type": "code",
1281 | "execution_count": null,
1282 | "metadata": {
1283 | "collapsed": false
1284 | },
1285 | "outputs": [],
1286 | "source": [
1287 | "-- show scores\n",
1288 | "print(predicted)"
1289 | ]
1290 | },
1291 | {
1292 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1293 | "metadata": {},
1294 | "source": [
1295 | "You can see the network predictions. The network assigned a probability to each classes, given the image.\n",
1296 | "\n",
1297 | "To make it clearer, let us tag each probability with it's class-name:"
1298 | ]
1299 | },
1300 | {
1301 | "cell_type": "code",
1302 | "execution_count": null,
1303 | "metadata": {
1304 | "collapsed": false
1305 | },
1306 | "outputs": [],
1307 | "source": [
1308 | "for i=1,predicted:size(1) do\n",
1309 | " print(classes[i], predicted[i])\n",
1310 | "end"
1311 | ]
1312 | },
1313 | {
1314 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1315 | "metadata": {},
1316 | "source": [
1317 | "Alright, fine. How many in total seem to be correct over the test set?"
1318 | ]
1319 | },
1320 | {
1321 | "cell_type": "code",
1322 | "execution_count": null,
1323 | "metadata": {
1324 | "collapsed": false
1325 | },
1326 | "outputs": [],
1327 | "source": [
1328 | "correct = 0\n",
1329 | "for i=1,10000 do\n",
1330 | " local groundtruth = testset.label[i]\n",
1331 | " local prediction = net:forward(testset.data[i])\n",
1332 | " local confidences, indices = torch.sort(prediction, true) -- true means sort in descending order\n",
1333 | " if groundtruth == indices[1] then\n",
1334 | " correct = correct + 1\n",
1335 | " end\n",
1336 | "end"
1337 | ]
1338 | },
1339 | {
1340 | "cell_type": "code",
1341 | "execution_count": null,
1342 | "metadata": {
1343 | "collapsed": false
1344 | },
1345 | "outputs": [],
1346 | "source": [
1347 | "print(correct, 100*correct/10000 .. ' % ')"
1348 | ]
1349 | },
1350 | {
1351 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1352 | "metadata": {},
1353 | "source": [
1354 | "That looks waaay better than chance, which is 10% accuracy (randomly picking a class out of 10 classes). Seems like the network learnt something.\n",
1355 | "\n",
1356 | "Hmmm, what are the classes that performed well, and the classes that did not perform well:"
1357 | ]
1358 | },
1359 | {
1360 | "cell_type": "code",
1361 | "execution_count": null,
1362 | "metadata": {
1363 | "collapsed": false
1364 | },
1365 | "outputs": [],
1366 | "source": [
1367 | "class_performance = {0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0}\n",
1368 | "for i=1,10000 do\n",
1369 | " local groundtruth = testset.label[i]\n",
1370 | " local prediction = net:forward(testset.data[i])\n",
1371 | " local confidences, indices = torch.sort(prediction, true) -- true means sort in descending order\n",
1372 | " if groundtruth == indices[1] then\n",
1373 | " class_performance[groundtruth] = class_performance[groundtruth] + 1\n",
1374 | " end\n",
1375 | "end"
1376 | ]
1377 | },
1378 | {
1379 | "cell_type": "code",
1380 | "execution_count": null,
1381 | "metadata": {
1382 | "collapsed": false
1383 | },
1384 | "outputs": [],
1385 | "source": [
1386 | "for i=1,#classes do\n",
1387 | " print(classes[i], 100*class_performance[i]/1000 .. ' %')\n",
1388 | "end"
1389 | ]
1390 | },
1391 | {
1392 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1393 | "metadata": {},
1394 | "source": [
1395 | "Okay, so what next? How do we run this neural network on GPUs?\n",
1396 | "\n",
1397 | "#### cunn: neural networks on GPUs using CUDA"
1398 | ]
1399 | },
1400 | {
1401 | "cell_type": "code",
1402 | "execution_count": null,
1403 | "metadata": {
1404 | "collapsed": false
1405 | },
1406 | "outputs": [],
1407 | "source": [
1408 | "require 'cunn'"
1409 | ]
1410 | },
1411 | {
1412 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1413 | "metadata": {},
1414 | "source": [
1415 | "The idea is pretty simple. Take a neural network, and transfer it over to GPU:"
1416 | ]
1417 | },
1418 | {
1419 | "cell_type": "code",
1420 | "execution_count": null,
1421 | "metadata": {
1422 | "collapsed": false
1423 | },
1424 | "outputs": [],
1425 | "source": [
1426 | "net = net:cuda()"
1427 | ]
1428 | },
1429 | {
1430 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1431 | "metadata": {},
1432 | "source": [
1433 | "Also, transfer the criterion to GPU:"
1434 | ]
1435 | },
1436 | {
1437 | "cell_type": "code",
1438 | "execution_count": null,
1439 | "metadata": {
1440 | "collapsed": false
1441 | },
1442 | "outputs": [],
1443 | "source": [
1444 | "criterion = criterion:cuda()"
1445 | ]
1446 | },
1447 | {
1448 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1449 | "metadata": {},
1450 | "source": [
1451 | "Ok, now the data:"
1452 | ]
1453 | },
1454 | {
1455 | "cell_type": "code",
1456 | "execution_count": null,
1457 | "metadata": {
1458 | "collapsed": false
1459 | },
1460 | "outputs": [],
1461 | "source": [
1462 | "trainset.data = trainset.data:cuda()"
1463 | ]
1464 | },
1465 | {
1466 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1467 | "metadata": {},
1468 | "source": [
1469 | "Okay, let's train on GPU :) #sosimple"
1470 | ]
1471 | },
1472 | {
1473 | "cell_type": "code",
1474 | "execution_count": null,
1475 | "metadata": {
1476 | "collapsed": false
1477 | },
1478 | "outputs": [],
1479 | "source": [
1480 | "trainer = nn.StochasticGradient(net, criterion)\n",
1481 | "trainer.learningRate = 0.001\n",
1482 | "trainer.maxIteration = 5 -- just do 5 epochs of training."
1483 | ]
1484 | },
1485 | {
1486 | "cell_type": "code",
1487 | "execution_count": null,
1488 | "metadata": {
1489 | "collapsed": false
1490 | },
1491 | "outputs": [],
1492 | "source": [
1493 | "trainer:train(trainset)"
1494 | ]
1495 | },
1496 | {
1497 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1498 | "metadata": {},
1499 | "source": [
1500 | "Why dont we notice MASSIVE speedup compared to CPU?\n",
1501 | "Because your network is realllly small (and because my laptop sux). \n",
1502 | "\n",
1503 | "**Exercise:** Try increasing the size of the network (argument 1 and 2 of nn.SpatialConvolution(...), see what kind of speedup you get."
1504 | ]
1505 | },
1506 | {
1507 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1508 | "metadata": {},
1509 | "source": [
1510 | "__Goals achieved:__\n",
1511 | " * Understand torch and the neural networks package at a high-level.\n",
1512 | " * Train a small neural network on CPU and GPU"
1513 | ]
1514 | },
1515 | {
1516 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1517 | "metadata": {},
1518 | "source": [
1519 | "### Where do I go next?"
1520 | ]
1521 | },
1522 | {
1523 | "cell_type": "markdown",
1524 | "metadata": {},
1525 | "source": [
1526 | "* Build crazy graphs of networks, without writing any graphs explicitly: https://github.com/twitter/autograd\n",
1527 | "* Train on imagenet with multiple GPUs: https://github.com/soumith/imagenet-multiGPU.torch\n",
1528 | "* Train recurrent networks with LSTM on text: https://github.com/wojzaremba/lstm\n",
1529 | "\n",
1530 | "* More demos and tutorials: https://github.com/torch/torch7/wiki/Cheatsheet\n",
1531 | "\n",
1532 | "* Chat with developers of Torch: http://gitter.im/torch/torch7\n",
1533 | "* Ask for help: http://groups.google.com/forum/#!forum/torch7"
1534 | ]
1535 | }
1536 | ],
1537 | "metadata": {
1538 | "kernelspec": {
1539 | "display_name": "iTorch",
1540 | "language": "lua",
1541 | "name": "itorch"
1542 | },
1543 | "language_info": {
1544 | "name": "lua",
1545 | "version": "5.2"
1546 | }
1547 | },
1548 | "nbformat": 4,
1549 | "nbformat_minor": 0
1550 | }
1551 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/notebooks/Torch & Autograd Basics.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "### Torch Basics"
8 | ]
9 | },
10 | {
11 | "cell_type": "code",
12 | "execution_count": null,
13 | "metadata": {
14 | "collapsed": false
15 | },
16 | "outputs": [],
17 | "source": [
18 | "-- Scalar & tensor arithmetic\n",
19 | "A = torch.eye(3)\n",
20 | "b = 4\n",
21 | "c = 2\n",
22 | "print(A*b - c)"
23 | ]
24 | },
25 | {
26 | "cell_type": "code",
27 | "execution_count": null,
28 | "metadata": {
29 | "collapsed": false
30 | },
31 | "outputs": [],
32 | "source": [
33 | "-- Max\n",
34 | "print(torch.max(torch.FloatTensor{1,3,5}))"
35 | ]
36 | },
37 | {
38 | "cell_type": "code",
39 | "execution_count": null,
40 | "metadata": {
41 | "collapsed": false
42 | },
43 | "outputs": [],
44 | "source": [
45 | "-- Clamp\n",
46 | "torch.clamp(torch.range(0,4),0,2)"
47 | ]
48 | },
49 | {
50 | "cell_type": "code",
51 | "execution_count": null,
52 | "metadata": {
53 | "collapsed": false
54 | },
55 | "outputs": [],
56 | "source": [
57 | "-- Matrix multiply\n",
58 | "A = torch.eye(3)\n",
59 | "B = torch.ones(3,1)*3\n",
60 | "print(A*B)"
61 | ]
62 | },
63 | {
64 | "cell_type": "code",
65 | "execution_count": null,
66 | "metadata": {
67 | "collapsed": false
68 | },
69 | "outputs": [],
70 | "source": [
71 | "-- Boolean fns\n",
72 | "A = torch.range(1,5)\n",
73 | "print(torch.le(A,3))"
74 | ]
75 | },
76 | {
77 | "cell_type": "markdown",
78 | "metadata": {},
79 | "source": [
80 | "### Scientific Computing Basics"
81 | ]
82 | },
83 | {
84 | "cell_type": "code",
85 | "execution_count": null,
86 | "metadata": {
87 | "collapsed": false
88 | },
89 | "outputs": [],
90 | "source": [
91 | "-- Special functions\n",
92 | "require 'cephes'\n",
93 | "print(cephes.gamma(0.5))"
94 | ]
95 | },
96 | {
97 | "cell_type": "code",
98 | "execution_count": null,
99 | "metadata": {
100 | "collapsed": false
101 | },
102 | "outputs": [],
103 | "source": [
104 | "print(cephes.atan2(3,1))"
105 | ]
106 | },
107 | {
108 | "cell_type": "code",
109 | "execution_count": null,
110 | "metadata": {
111 | "collapsed": false
112 | },
113 | "outputs": [],
114 | "source": [
115 | "-- Sampling from a distribution\n",
116 | "require 'randomkit'\n",
117 | "a = torch.zeros(10000)\n",
118 | "randomkit.negative_binomial(a,9,0.3)"
119 | ]
120 | },
121 | {
122 | "cell_type": "code",
123 | "execution_count": null,
124 | "metadata": {
125 | "collapsed": false
126 | },
127 | "outputs": [],
128 | "source": [
129 | "Plot = require 'itorch.Plot'\n",
130 | "local p = Plot()\n",
131 | " :histogram(a,80,1,80)\n",
132 | " :title(\"Histogram of Draws From Negative Binomial\")\n",
133 | " :draw();"
134 | ]
135 | },
136 | {
137 | "cell_type": "markdown",
138 | "metadata": {},
139 | "source": [
140 | "### Memory-layout"
141 | ]
142 | },
143 | {
144 | "cell_type": "code",
145 | "execution_count": null,
146 | "metadata": {
147 | "collapsed": true
148 | },
149 | "outputs": [],
150 | "source": [
151 | "a = torch.DoubleTensor(4, 6) -- DoubleTensor, uninitialized memory\n",
152 | "a:uniform() -- fills \"a\" with uniform noise with mean=0, stdev=1"
153 | ]
154 | },
155 | {
156 | "cell_type": "code",
157 | "execution_count": null,
158 | "metadata": {
159 | "collapsed": false
160 | },
161 | "outputs": [],
162 | "source": [
163 | "print(a)"
164 | ]
165 | },
166 | {
167 | "cell_type": "code",
168 | "execution_count": null,
169 | "metadata": {
170 | "collapsed": true
171 | },
172 | "outputs": [],
173 | "source": [
174 | "b = a:select(1, 3) -- Select from the 1st axis (rows), \n",
175 | " -- the 3rd set of entries"
176 | ]
177 | },
178 | {
179 | "cell_type": "code",
180 | "execution_count": null,
181 | "metadata": {
182 | "collapsed": false
183 | },
184 | "outputs": [],
185 | "source": [
186 | "print(b)"
187 | ]
188 | },
189 | {
190 | "cell_type": "code",
191 | "execution_count": null,
192 | "metadata": {
193 | "collapsed": false
194 | },
195 | "outputs": [],
196 | "source": [
197 | "b:fill(3);"
198 | ]
199 | },
200 | {
201 | "cell_type": "code",
202 | "execution_count": null,
203 | "metadata": {
204 | "collapsed": false
205 | },
206 | "outputs": [],
207 | "source": [
208 | "print(b)"
209 | ]
210 | },
211 | {
212 | "cell_type": "code",
213 | "execution_count": null,
214 | "metadata": {
215 | "collapsed": false
216 | },
217 | "outputs": [],
218 | "source": [
219 | "print(a) -- Look at the 3rd row! It's been filled with 3."
220 | ]
221 | },
222 | {
223 | "cell_type": "markdown",
224 | "metadata": {},
225 | "source": [
226 | "### Autograd"
227 | ]
228 | },
229 | {
230 | "cell_type": "code",
231 | "execution_count": null,
232 | "metadata": {
233 | "collapsed": false
234 | },
235 | "outputs": [],
236 | "source": [
237 | "-- Arithmetic is no problem\n",
238 | "grad = require 'autograd'\n",
239 | "function f(a,b,c)\n",
240 | " return a + b * c\n",
241 | "end\n",
242 | "df = grad(f)\n",
243 | "da, val = df(3.5, 2.1, 1.1)\n",
244 | "print(\"Value: \"..val)\n",
245 | "print(\"Gradient: \"..da)"
246 | ]
247 | },
248 | {
249 | "cell_type": "code",
250 | "execution_count": null,
251 | "metadata": {
252 | "collapsed": false
253 | },
254 | "outputs": [],
255 | "source": [
256 | "-- If statements are no problem\n",
257 | "grad = require 'autograd'\n",
258 | "function f(a,b,c)\n",
259 | " if b > c then\n",
260 | " return a * math.sin(b)\n",
261 | " else\n",
262 | " return a + b * c\n",
263 | " end\n",
264 | "end\n",
265 | "g = grad(f)\n",
266 | "da, val = g(3.5, 2.1, 1.1)\n",
267 | "print(\"Value: \"..val)\n",
268 | "print(\"Gradient: \"..da)"
269 | ]
270 | },
271 | {
272 | "cell_type": "code",
273 | "execution_count": null,
274 | "metadata": {
275 | "collapsed": false
276 | },
277 | "outputs": [],
278 | "source": [
279 | "-- Of course, works with tensors\n",
280 | "grad = require 'autograd'\n",
281 | "function f(a,b,c)\n",
282 | " if torch.sum(b) > torch.sum(c) then\n",
283 | " return torch.sum(torch.cmul(a,torch.sin(b)))\n",
284 | " else\n",
285 | " return torch.sum(a + torch.cmul(b,c))\n",
286 | " end\n",
287 | "end\n",
288 | "g = grad(f)\n",
289 | "a = torch.randn(3,3)\n",
290 | "b = torch.eye(3,3)\n",
291 | "c = torch.randn(3,3)\n",
292 | "da, val = g(a,b,c)\n",
293 | "print(\"Value: \"..val)\n",
294 | "print(\"Gradient: \")\n",
295 | "print(da)"
296 | ]
297 | },
298 | {
299 | "cell_type": "code",
300 | "execution_count": null,
301 | "metadata": {
302 | "collapsed": false
303 | },
304 | "outputs": [],
305 | "source": [
306 | "-- Autograd for loop\n",
307 | "function f(a,b)\n",
308 | " for i=1,b do\n",
309 | " a = a*a\n",
310 | " end\n",
311 | " return a\n",
312 | "end\n",
313 | "g = grad(f)\n",
314 | "da, val = g(3,2)\n",
315 | "print(\"Value: \"..val)\n",
316 | "print(\"Gradient: \"..da)"
317 | ]
318 | },
319 | {
320 | "cell_type": "code",
321 | "execution_count": null,
322 | "metadata": {
323 | "collapsed": false
324 | },
325 | "outputs": [],
326 | "source": [
327 | "-- Autograd recursive function\n",
328 | "function f(a,b)\n",
329 | " if b == 0 then\n",
330 | " return a\n",
331 | " else\n",
332 | " return f(a*a,b-1)\n",
333 | " end\n",
334 | "end\n",
335 | "g = grad(f)\n",
336 | "da, val = g(3,2)\n",
337 | "print(\"Value: \"..val)\n",
338 | "print(\"Gradient: \"..da)"
339 | ]
340 | },
341 | {
342 | "cell_type": "code",
343 | "execution_count": null,
344 | "metadata": {
345 | "collapsed": false
346 | },
347 | "outputs": [],
348 | "source": [
349 | "-- New ops aren't a problem\n",
350 | "function f(a)\n",
351 | " return torch.sum(torch.floor(torch.pow(a,3)))\n",
352 | "end\n",
353 | "g = grad(f)\n",
354 | "da, val = g(torch.eye(3))\n",
355 | "print(\"Value: \"..val)\n",
356 | "print(\"Gradient:\")\n",
357 | "print(da)"
358 | ]
359 | },
360 | {
361 | "cell_type": "code",
362 | "execution_count": null,
363 | "metadata": {
364 | "collapsed": true
365 | },
366 | "outputs": [],
367 | "source": [
368 | "-- New ops aren't a problem\n",
369 | "grad = require 'autograd'\n",
370 | "special = {}\n",
371 | "special.floor = function(x) return torch.floor(x) end\n",
372 | "-- Overload our new mini-module, called \"special\"\n",
373 | "grad.overload.module(\"special\",special,function(module)\n",
374 | " -- Define a gradient for the member function \"floor\"\n",
375 | " module.gradient(\"floor\", {\n",
376 | " -- Here's our new partial derivative\n",
377 | " -- (if we had two arguments, \n",
378 | " -- we'd define two functions)\n",
379 | " function(g,ans,x) \n",
380 | " return g\n",
381 | " end\n",
382 | " })\n",
383 | " end)"
384 | ]
385 | },
386 | {
387 | "cell_type": "code",
388 | "execution_count": null,
389 | "metadata": {
390 | "collapsed": false
391 | },
392 | "outputs": [],
393 | "source": [
394 | "function f(a)\n",
395 | " return torch.sum(special.floor(torch.pow(a,3)))\n",
396 | "end\n",
397 | "g = grad(f)\n",
398 | "da, val = g(torch.eye(3))\n",
399 | "print(\"Value: \"..val)\n",
400 | "print(\"Gradient:\")\n",
401 | "print(da)"
402 | ]
403 | },
404 | {
405 | "cell_type": "code",
406 | "execution_count": null,
407 | "metadata": {
408 | "collapsed": false
409 | },
410 | "outputs": [],
411 | "source": [
412 | "function f(a,b)\n",
413 | " c = a * b\n",
414 | " if c > 0 then\n",
415 | " d = torch.log(c)\n",
416 | " else\n",
417 | " d = torch.sin(c)\n",
418 | " end\n",
419 | " return d\n",
420 | "end\n",
421 | "print(f(2,3))"
422 | ]
423 | },
424 | {
425 | "cell_type": "code",
426 | "execution_count": null,
427 | "metadata": {
428 | "collapsed": false
429 | },
430 | "outputs": [],
431 | "source": [
432 | "function f(a,b,c)\n",
433 | " if b > c then\n",
434 | " d = a * math.sin(b)\n",
435 | " else\n",
436 | " d = a + b * c\n",
437 | " end\n",
438 | " return d\n",
439 | "end\n",
440 | "print(f(3,2,1))"
441 | ]
442 | },
443 | {
444 | "cell_type": "code",
445 | "execution_count": null,
446 | "metadata": {
447 | "collapsed": false
448 | },
449 | "outputs": [],
450 | "source": [
451 | "grad = require 'autograd'\n",
452 | "g = grad(f)\n",
453 | "print(g(3,2,1))"
454 | ]
455 | },
456 | {
457 | "cell_type": "raw",
458 | "metadata": {
459 | "collapsed": true
460 | },
461 | "source": [
462 | "-- Representation of \"Wengert list\" or \"program\" trace of the evaluation of g(3,2,1)\n",
463 | "a = 3\n",
464 | "\n",
465 | "b = 2\n",
466 | "\n",
467 | "c = 1\n",
468 | "\n",
469 | "d = a * math.sin(b) = 2.728\n",
470 | "\n",
471 | "return 2.728"
472 | ]
473 | },
474 | {
475 | "cell_type": "raw",
476 | "metadata": {
477 | "collapsed": true
478 | },
479 | "source": [
480 | "-- \"Forward mode\" augmentation of the above program trace, for calculation of dd/da\n",
481 | "a = 3\n",
482 | "da = 1\n",
483 | "b = 2\n",
484 | "db = 0\n",
485 | "c = 1\n",
486 | "dc = 0\n",
487 | "d = a * math.sin(b) = 2.728\n",
488 | "dd = math.sin(b) = 0.909\n",
489 | "return 0.909"
490 | ]
491 | },
492 | {
493 | "cell_type": "raw",
494 | "metadata": {
495 | "collapsed": true
496 | },
497 | "source": [
498 | "-- \"Reverse mode\" augmentation of the above program trace, for calculation of dd/da\n",
499 | "a = 3\n",
500 | "b = 2\n",
501 | "c = 1\n",
502 | "d = a * math.sin(b) = 2.728\n",
503 | "dd = 1\n",
504 | "da = dd * math.sin(b) = 0.909\n",
505 | "return 0.909, 2.728"
506 | ]
507 | }
508 | ],
509 | "metadata": {
510 | "kernelspec": {
511 | "display_name": "iTorch",
512 | "language": "lua",
513 | "name": "itorch"
514 | },
515 | "language_info": {
516 | "name": "lua",
517 | "version": "5.2"
518 | }
519 | },
520 | "nbformat": 4,
521 | "nbformat_minor": 0
522 | }
523 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------