├── images
├── FIg3.png
├── Fig1.png
└── Fig4.png
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── densenet.py
└── train.py
/images/FIg3.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/HEAD/images/FIg3.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/Fig1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/HEAD/images/Fig1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/Fig4.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/HEAD/images/Fig4.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | BSD 3-Clause License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2017, Andreas Veit
4 | All rights reserved.
5 |
6 | Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
7 | modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions are met:
8 |
9 | * Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright notice, this
10 | list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
11 |
12 | * Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright notice,
13 | this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the documentation
14 | and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
15 |
16 | * Neither the name of the copyright holder nor the names of its
17 | contributors may be used to endorse or promote products derived from
18 | this software without specific prior written permission.
19 |
20 | THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS "AS IS"
21 | AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE
22 | IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE
23 | DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT HOLDER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE
24 | FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL, SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL
25 | DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR
26 | SERVICES; LOSS OF USE, DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER
27 | CAUSED AND ON ANY THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY,
28 | OR TORT (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
29 | OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # A PyTorch Implementation for Densely Connected Convolutional Networks (DenseNets)
2 |
3 | This repository contains a [PyTorch](http://pytorch.org/) implementation of the paper [Densely Connected Convolutional Networks](http://arxiv.org/abs/1608.06993). The code is based on the excellent [PyTorch example for training ResNet on Imagenet](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/imagenet).
4 |
5 | The detault setting for this repo is a DenseNet-BC (with bottleneck layers and channel reduction), 100 layers, a growth rate of 12 and batch size 64.
6 |
7 | The [Official torch implementaion](https://github.com/liuzhuang13/DenseNet) contains further links to implementations in other frameworks.
8 |
9 | Example usage with optional arguments for different hyperparameters (e.g., DenseNet-40-12):
10 | ```sh
11 | $ python train.py --layers 40 --growth 12 --no-bottleneck --reduce 1.0 --name DenseNet-40-12
12 | ```
13 |
14 | ## DenseNets
15 | [DenseNets [1]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.06993) were introduced in late 2016 after to the discoveries by [[2]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1603.09382) and [[3]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1605.06431) that [residual networks [4]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385) exhibit extreme parameter redundancy. DenseNets address this shortcoming by reducing the size of the modules and by introducing more connections between layers. In fact, the output of each layer flows directly as input to all subsequent layers of the same feature dimension as illustrated in their Figure 1 (below). This increases the dependency between the layers and thus reduces redundancy.
16 |
17 | 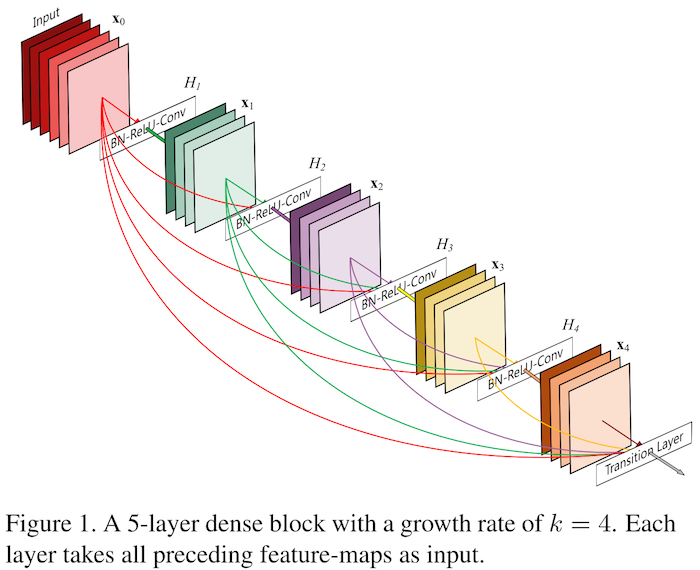 18 |
19 | The improvements in accuracy per parameter are illustrated in their results on ImageNet (Figure 3).
20 |
21 |
18 |
19 | The improvements in accuracy per parameter are illustrated in their results on ImageNet (Figure 3).
20 |
21 |  22 |
23 | ## This implementation
24 | The training code in train.py trains a DenseNet on CIFAR 10 or 100. To train on ImageNet, densenet.py can be copied into the [PyTorch example for training ResNets on Imagenet](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/imagenet), upon which this repo is based. Note that for ImageNet the model contains four dense blocks.
25 |
26 | This implementation is quite _memory efficient requiring between 10% and 20% less memory_ compared to the original torch implementation. We optain a final test error of 4.76 % with DenseNet-BC-100-12 (paper reports 4.51 %) and 5.35 % with DenseNet-40-12 (paper reports 5.24 %).
27 |
28 | This implementation allows for __all model variants__ in the DenseNet paper, i.e., with and without bottleneck, channel reduction, data augmentation and dropout.
29 |
30 | For simple configuration of the model, this repo uses `argparse` so that key hyperparameters can be easily changed.
31 |
32 | Further, this implementation supports [easy checkpointing](https://github.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/blob/master/train.py#L136), keeping track of the best model and [resuming](https://github.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/blob/master/train.py#L103) training from previous checkpoints.
33 |
34 | ### Tracking training progress with TensorBoard
35 | To track training progress, this implementation uses [TensorBoard](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/summaries_and_tensorboard) which offers great ways to track and compare multiple experiments. To track PyTorch experiments in TensorBoard we use [tensorboard_logger](https://github.com/TeamHG-Memex/tensorboard_logger) which can be installed with
36 | ```
37 | pip install tensorboard_logger
38 | ```
39 | Example training curves for DenseNet-BC-100-12 (dark blue) and DenseNet-40-12 (light blue) for training loss and validation accuracy is shown below.
40 |
41 | 
42 |
43 | ### Dependencies
44 | * [PyTorch](http://pytorch.org/)
45 |
46 | optional:
47 | * [tensorboard_logger](https://github.com/TeamHG-Memex/tensorboard_logger)
48 |
49 |
50 | ### Cite
51 | If you use DenseNets in your work, please cite the original paper as:
52 | ```
53 | @article{Huang2016Densely,
54 | author = {Huang, Gao and Liu, Zhuang and Weinberger, Kilian Q.},
55 | title = {Densely Connected Convolutional Networks},
56 | journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.06993},
57 | year = {2016}
58 | }
59 | ```
60 |
61 | If this implementation is useful to you and your project, please also consider to cite or acknowledge this code repository.
62 |
63 | ### References
64 | [1] Huang, G., Liu, Z., Weinberger, K. Q., & van der Maaten, L. (2016). Densely connected convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.06993.
65 |
66 | [2] Huang, G., Sun, Y., Liu, Z., Sedra, D., & Weinberger, K. Q. (2016). Deep networks with stochastic depth. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV '16)
67 |
68 | [3] Veit, A., Wilber, M. J., & Belongie, S. (2016). Residual networks behave like ensembles of relatively shallow networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS '16)
69 |
70 | [4] He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR '16)
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/densenet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | import torch.nn as nn
4 | import torch.nn.functional as F
5 |
6 |
7 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
8 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
9 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
10 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
11 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
12 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
13 | padding=1, bias=False)
14 | self.droprate = dropRate
15 | def forward(self, x):
16 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
17 | if self.droprate > 0:
18 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, training=self.training)
19 | return torch.cat([x, out], 1)
20 |
21 | class BottleneckBlock(nn.Module):
22 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
23 | super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()
24 | inter_planes = out_planes * 4
25 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
26 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
27 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
28 | padding=0, bias=False)
29 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_planes)
30 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
31 | padding=1, bias=False)
32 | self.droprate = dropRate
33 | def forward(self, x):
34 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
35 | if self.droprate > 0:
36 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
37 | out = self.conv2(self.relu(self.bn2(out)))
38 | if self.droprate > 0:
39 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
40 | return torch.cat([x, out], 1)
41 |
42 | class TransitionBlock(nn.Module):
43 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
44 | super(TransitionBlock, self).__init__()
45 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
46 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
47 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
48 | padding=0, bias=False)
49 | self.droprate = dropRate
50 | def forward(self, x):
51 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
52 | if self.droprate > 0:
53 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
54 | return F.avg_pool2d(out, 2)
55 |
56 | class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
57 | def __init__(self, nb_layers, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate=0.0):
58 | super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
59 | self.layer = self._make_layer(block, in_planes, growth_rate, nb_layers, dropRate)
60 | def _make_layer(self, block, in_planes, growth_rate, nb_layers, dropRate):
61 | layers = []
62 | for i in range(nb_layers):
63 | layers.append(block(in_planes+i*growth_rate, growth_rate, dropRate))
64 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
65 | def forward(self, x):
66 | return self.layer(x)
67 |
68 | class DenseNet3(nn.Module):
69 | def __init__(self, depth, num_classes, growth_rate=12,
70 | reduction=0.5, bottleneck=True, dropRate=0.0):
71 | super(DenseNet3, self).__init__()
72 | in_planes = 2 * growth_rate
73 | n = (depth - 4) / 3
74 | if bottleneck == True:
75 | n = n/2
76 | block = BottleneckBlock
77 | else:
78 | block = BasicBlock
79 | n = int(n)
80 | # 1st conv before any dense block
81 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, in_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
82 | padding=1, bias=False)
83 | # 1st block
84 | self.block1 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
85 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
86 | self.trans1 = TransitionBlock(in_planes, int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction)), dropRate=dropRate)
87 | in_planes = int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction))
88 | # 2nd block
89 | self.block2 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
90 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
91 | self.trans2 = TransitionBlock(in_planes, int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction)), dropRate=dropRate)
92 | in_planes = int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction))
93 | # 3rd block
94 | self.block3 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
95 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
96 | # global average pooling and classifier
97 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
98 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
99 | self.fc = nn.Linear(in_planes, num_classes)
100 | self.in_planes = in_planes
101 |
102 | for m in self.modules():
103 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
104 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
105 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
106 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
107 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
108 | m.bias.data.zero_()
109 | elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
110 | m.bias.data.zero_()
111 | def forward(self, x):
112 | out = self.conv1(x)
113 | out = self.trans1(self.block1(out))
114 | out = self.trans2(self.block2(out))
115 | out = self.block3(out)
116 | out = self.relu(self.bn1(out))
117 | out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 8)
118 | out = out.view(-1, self.in_planes)
119 | return self.fc(out)
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import shutil
4 | import time
5 |
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.nn.parallel
9 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
10 | import torch.optim
11 | import torch.utils.data
12 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
13 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
14 |
15 | import densenet as dn
16 |
17 | # used for logging to TensorBoard
18 | from tensorboard_logger import configure, log_value
19 |
20 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch DenseNet Training')
21 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=300, type=int,
22 | help='number of total epochs to run')
23 | parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int,
24 | help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
25 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=64, type=int,
26 | help='mini-batch size (default: 64)')
27 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.1, type=float,
28 | help='initial learning rate')
29 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, help='momentum')
30 | parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', '--wd', default=1e-4, type=float,
31 | help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)')
32 | parser.add_argument('--print-freq', '-p', default=10, type=int,
33 | help='print frequency (default: 10)')
34 | parser.add_argument('--layers', default=100, type=int,
35 | help='total number of layers (default: 100)')
36 | parser.add_argument('--growth', default=12, type=int,
37 | help='number of new channels per layer (default: 12)')
38 | parser.add_argument('--droprate', default=0, type=float,
39 | help='dropout probability (default: 0.0)')
40 | parser.add_argument('--no-augment', dest='augment', action='store_false',
41 | help='whether to use standard augmentation (default: True)')
42 | parser.add_argument('--reduce', default=0.5, type=float,
43 | help='compression rate in transition stage (default: 0.5)')
44 | parser.add_argument('--no-bottleneck', dest='bottleneck', action='store_false',
45 | help='To not use bottleneck block')
46 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str,
47 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
48 | parser.add_argument('--name', default='DenseNet_BC_100_12', type=str,
49 | help='name of experiment')
50 | parser.add_argument('--tensorboard',
51 | help='Log progress to TensorBoard', action='store_true')
52 | parser.set_defaults(bottleneck=True)
53 | parser.set_defaults(augment=True)
54 |
55 | best_prec1 = 0
56 |
57 | def main():
58 | global args, best_prec1
59 | args = parser.parse_args()
60 | if args.tensorboard: configure("runs/%s"%(args.name))
61 |
62 | # Data loading code
63 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[x/255.0 for x in [125.3, 123.0, 113.9]],
64 | std=[x/255.0 for x in [63.0, 62.1, 66.7]])
65 |
66 | if args.augment:
67 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
68 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
69 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
70 | transforms.ToTensor(),
71 | normalize,
72 | ])
73 | else:
74 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
75 | transforms.ToTensor(),
76 | normalize,
77 | ])
78 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
79 | transforms.ToTensor(),
80 | normalize
81 | ])
82 |
83 | kwargs = {'num_workers': 1, 'pin_memory': True}
84 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
85 | datasets.CIFAR10('../data', train=True, download=True,
86 | transform=transform_train),
87 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
88 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
89 | datasets.CIFAR10('../data', train=False, transform=transform_test),
90 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
91 |
92 | # create model
93 | model = dn.DenseNet3(args.layers, 10, args.growth, reduction=args.reduce,
94 | bottleneck=args.bottleneck, dropRate=args.droprate)
95 |
96 | # get the number of model parameters
97 | print('Number of model parameters: {}'.format(
98 | sum([p.data.nelement() for p in model.parameters()])))
99 |
100 | # for training on multiple GPUs.
101 | # Use CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 to specify which GPUs to use
102 | # model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
103 | model = model.cuda()
104 |
105 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
106 | if args.resume:
107 | if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
108 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
109 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
110 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
111 | best_prec1 = checkpoint['best_prec1']
112 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
113 | print("=> loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
114 | .format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
115 | else:
116 | print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
117 |
118 | cudnn.benchmark = True
119 |
120 | # define loss function (criterion) and pptimizer
121 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda()
122 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr,
123 | momentum=args.momentum,
124 | nesterov=True,
125 | weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
126 |
127 | for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
128 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch)
129 |
130 | # train for one epoch
131 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
132 |
133 | # evaluate on validation set
134 | prec1 = validate(val_loader, model, criterion, epoch)
135 |
136 | # remember best prec@1 and save checkpoint
137 | is_best = prec1 > best_prec1
138 | best_prec1 = max(prec1, best_prec1)
139 | save_checkpoint({
140 | 'epoch': epoch + 1,
141 | 'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
142 | 'best_prec1': best_prec1,
143 | }, is_best)
144 | print('Best accuracy: ', best_prec1)
145 |
146 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
147 | """Train for one epoch on the training set"""
148 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
149 | losses = AverageMeter()
150 | top1 = AverageMeter()
151 |
152 | # switch to train mode
153 | model.train()
154 |
155 | end = time.time()
156 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
157 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
158 | input = input.cuda()
159 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
160 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
161 |
162 | # compute output
163 | output = model(input_var)
164 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
165 |
166 | # measure accuracy and record loss
167 | prec1 = accuracy(output.data, target, topk=(1,))[0]
168 | losses.update(loss.data[0], input.size(0))
169 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
170 |
171 | # compute gradient and do SGD step
172 | optimizer.zero_grad()
173 | loss.backward()
174 | optimizer.step()
175 |
176 | # measure elapsed time
177 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
178 | end = time.time()
179 |
180 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
181 | print('Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}]\t'
182 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
183 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
184 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})'.format(
185 | epoch, i, len(train_loader), batch_time=batch_time,
186 | loss=losses, top1=top1))
187 | # log to TensorBoard
188 | if args.tensorboard:
189 | log_value('train_loss', losses.avg, epoch)
190 | log_value('train_acc', top1.avg, epoch)
191 |
192 | def validate(val_loader, model, criterion, epoch):
193 | """Perform validation on the validation set"""
194 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
195 | losses = AverageMeter()
196 | top1 = AverageMeter()
197 |
198 | # switch to evaluate mode
199 | model.eval()
200 |
201 | end = time.time()
202 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
203 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
204 | input = input.cuda()
205 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input, volatile=True)
206 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target, volatile=True)
207 |
208 | # compute output
209 | output = model(input_var)
210 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
211 |
212 | # measure accuracy and record loss
213 | prec1 = accuracy(output.data, target, topk=(1,))[0]
214 | losses.update(loss.data[0], input.size(0))
215 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
216 |
217 | # measure elapsed time
218 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
219 | end = time.time()
220 |
221 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
222 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
223 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
224 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
225 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})'.format(
226 | i, len(val_loader), batch_time=batch_time, loss=losses,
227 | top1=top1))
228 |
229 | print(' * Prec@1 {top1.avg:.3f}'.format(top1=top1))
230 | # log to TensorBoard
231 | if args.tensorboard:
232 | log_value('val_loss', losses.avg, epoch)
233 | log_value('val_acc', top1.avg, epoch)
234 | return top1.avg
235 |
236 |
237 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
238 | """Saves checkpoint to disk"""
239 | directory = "runs/%s/"%(args.name)
240 | if not os.path.exists(directory):
241 | os.makedirs(directory)
242 | filename = directory + filename
243 | torch.save(state, filename)
244 | if is_best:
245 | shutil.copyfile(filename, 'runs/%s/'%(args.name) + 'model_best.pth.tar')
246 |
247 | class AverageMeter(object):
248 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
249 | def __init__(self):
250 | self.reset()
251 |
252 | def reset(self):
253 | self.val = 0
254 | self.avg = 0
255 | self.sum = 0
256 | self.count = 0
257 |
258 | def update(self, val, n=1):
259 | self.val = val
260 | self.sum += val * n
261 | self.count += n
262 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
263 |
264 |
265 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch):
266 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 after 150 and 225 epochs"""
267 | lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 150)) * (0.1 ** (epoch // 225))
268 | # log to TensorBoard
269 | if args.tensorboard:
270 | log_value('learning_rate', lr, epoch)
271 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
272 | param_group['lr'] = lr
273 |
274 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
275 | """Computes the precision@k for the specified values of k"""
276 | maxk = max(topk)
277 | batch_size = target.size(0)
278 |
279 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
280 | pred = pred.t()
281 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
282 |
283 | res = []
284 | for k in topk:
285 | correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0)
286 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
287 | return res
288 |
289 | if __name__ == '__main__':
290 | main()
291 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
22 |
23 | ## This implementation
24 | The training code in train.py trains a DenseNet on CIFAR 10 or 100. To train on ImageNet, densenet.py can be copied into the [PyTorch example for training ResNets on Imagenet](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/imagenet), upon which this repo is based. Note that for ImageNet the model contains four dense blocks.
25 |
26 | This implementation is quite _memory efficient requiring between 10% and 20% less memory_ compared to the original torch implementation. We optain a final test error of 4.76 % with DenseNet-BC-100-12 (paper reports 4.51 %) and 5.35 % with DenseNet-40-12 (paper reports 5.24 %).
27 |
28 | This implementation allows for __all model variants__ in the DenseNet paper, i.e., with and without bottleneck, channel reduction, data augmentation and dropout.
29 |
30 | For simple configuration of the model, this repo uses `argparse` so that key hyperparameters can be easily changed.
31 |
32 | Further, this implementation supports [easy checkpointing](https://github.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/blob/master/train.py#L136), keeping track of the best model and [resuming](https://github.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/blob/master/train.py#L103) training from previous checkpoints.
33 |
34 | ### Tracking training progress with TensorBoard
35 | To track training progress, this implementation uses [TensorBoard](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/summaries_and_tensorboard) which offers great ways to track and compare multiple experiments. To track PyTorch experiments in TensorBoard we use [tensorboard_logger](https://github.com/TeamHG-Memex/tensorboard_logger) which can be installed with
36 | ```
37 | pip install tensorboard_logger
38 | ```
39 | Example training curves for DenseNet-BC-100-12 (dark blue) and DenseNet-40-12 (light blue) for training loss and validation accuracy is shown below.
40 |
41 | 
42 |
43 | ### Dependencies
44 | * [PyTorch](http://pytorch.org/)
45 |
46 | optional:
47 | * [tensorboard_logger](https://github.com/TeamHG-Memex/tensorboard_logger)
48 |
49 |
50 | ### Cite
51 | If you use DenseNets in your work, please cite the original paper as:
52 | ```
53 | @article{Huang2016Densely,
54 | author = {Huang, Gao and Liu, Zhuang and Weinberger, Kilian Q.},
55 | title = {Densely Connected Convolutional Networks},
56 | journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.06993},
57 | year = {2016}
58 | }
59 | ```
60 |
61 | If this implementation is useful to you and your project, please also consider to cite or acknowledge this code repository.
62 |
63 | ### References
64 | [1] Huang, G., Liu, Z., Weinberger, K. Q., & van der Maaten, L. (2016). Densely connected convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.06993.
65 |
66 | [2] Huang, G., Sun, Y., Liu, Z., Sedra, D., & Weinberger, K. Q. (2016). Deep networks with stochastic depth. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV '16)
67 |
68 | [3] Veit, A., Wilber, M. J., & Belongie, S. (2016). Residual networks behave like ensembles of relatively shallow networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS '16)
69 |
70 | [4] He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR '16)
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/densenet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | import torch.nn as nn
4 | import torch.nn.functional as F
5 |
6 |
7 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
8 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
9 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
10 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
11 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
12 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
13 | padding=1, bias=False)
14 | self.droprate = dropRate
15 | def forward(self, x):
16 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
17 | if self.droprate > 0:
18 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, training=self.training)
19 | return torch.cat([x, out], 1)
20 |
21 | class BottleneckBlock(nn.Module):
22 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
23 | super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()
24 | inter_planes = out_planes * 4
25 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
26 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
27 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
28 | padding=0, bias=False)
29 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_planes)
30 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
31 | padding=1, bias=False)
32 | self.droprate = dropRate
33 | def forward(self, x):
34 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
35 | if self.droprate > 0:
36 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
37 | out = self.conv2(self.relu(self.bn2(out)))
38 | if self.droprate > 0:
39 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
40 | return torch.cat([x, out], 1)
41 |
42 | class TransitionBlock(nn.Module):
43 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
44 | super(TransitionBlock, self).__init__()
45 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
46 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
47 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
48 | padding=0, bias=False)
49 | self.droprate = dropRate
50 | def forward(self, x):
51 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
52 | if self.droprate > 0:
53 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
54 | return F.avg_pool2d(out, 2)
55 |
56 | class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
57 | def __init__(self, nb_layers, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate=0.0):
58 | super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
59 | self.layer = self._make_layer(block, in_planes, growth_rate, nb_layers, dropRate)
60 | def _make_layer(self, block, in_planes, growth_rate, nb_layers, dropRate):
61 | layers = []
62 | for i in range(nb_layers):
63 | layers.append(block(in_planes+i*growth_rate, growth_rate, dropRate))
64 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
65 | def forward(self, x):
66 | return self.layer(x)
67 |
68 | class DenseNet3(nn.Module):
69 | def __init__(self, depth, num_classes, growth_rate=12,
70 | reduction=0.5, bottleneck=True, dropRate=0.0):
71 | super(DenseNet3, self).__init__()
72 | in_planes = 2 * growth_rate
73 | n = (depth - 4) / 3
74 | if bottleneck == True:
75 | n = n/2
76 | block = BottleneckBlock
77 | else:
78 | block = BasicBlock
79 | n = int(n)
80 | # 1st conv before any dense block
81 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, in_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
82 | padding=1, bias=False)
83 | # 1st block
84 | self.block1 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
85 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
86 | self.trans1 = TransitionBlock(in_planes, int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction)), dropRate=dropRate)
87 | in_planes = int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction))
88 | # 2nd block
89 | self.block2 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
90 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
91 | self.trans2 = TransitionBlock(in_planes, int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction)), dropRate=dropRate)
92 | in_planes = int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction))
93 | # 3rd block
94 | self.block3 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
95 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
96 | # global average pooling and classifier
97 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
98 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
99 | self.fc = nn.Linear(in_planes, num_classes)
100 | self.in_planes = in_planes
101 |
102 | for m in self.modules():
103 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
104 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
105 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
106 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
107 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
108 | m.bias.data.zero_()
109 | elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
110 | m.bias.data.zero_()
111 | def forward(self, x):
112 | out = self.conv1(x)
113 | out = self.trans1(self.block1(out))
114 | out = self.trans2(self.block2(out))
115 | out = self.block3(out)
116 | out = self.relu(self.bn1(out))
117 | out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 8)
118 | out = out.view(-1, self.in_planes)
119 | return self.fc(out)
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import shutil
4 | import time
5 |
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.nn.parallel
9 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
10 | import torch.optim
11 | import torch.utils.data
12 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
13 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
14 |
15 | import densenet as dn
16 |
17 | # used for logging to TensorBoard
18 | from tensorboard_logger import configure, log_value
19 |
20 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch DenseNet Training')
21 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=300, type=int,
22 | help='number of total epochs to run')
23 | parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int,
24 | help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
25 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=64, type=int,
26 | help='mini-batch size (default: 64)')
27 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.1, type=float,
28 | help='initial learning rate')
29 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, help='momentum')
30 | parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', '--wd', default=1e-4, type=float,
31 | help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)')
32 | parser.add_argument('--print-freq', '-p', default=10, type=int,
33 | help='print frequency (default: 10)')
34 | parser.add_argument('--layers', default=100, type=int,
35 | help='total number of layers (default: 100)')
36 | parser.add_argument('--growth', default=12, type=int,
37 | help='number of new channels per layer (default: 12)')
38 | parser.add_argument('--droprate', default=0, type=float,
39 | help='dropout probability (default: 0.0)')
40 | parser.add_argument('--no-augment', dest='augment', action='store_false',
41 | help='whether to use standard augmentation (default: True)')
42 | parser.add_argument('--reduce', default=0.5, type=float,
43 | help='compression rate in transition stage (default: 0.5)')
44 | parser.add_argument('--no-bottleneck', dest='bottleneck', action='store_false',
45 | help='To not use bottleneck block')
46 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str,
47 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
48 | parser.add_argument('--name', default='DenseNet_BC_100_12', type=str,
49 | help='name of experiment')
50 | parser.add_argument('--tensorboard',
51 | help='Log progress to TensorBoard', action='store_true')
52 | parser.set_defaults(bottleneck=True)
53 | parser.set_defaults(augment=True)
54 |
55 | best_prec1 = 0
56 |
57 | def main():
58 | global args, best_prec1
59 | args = parser.parse_args()
60 | if args.tensorboard: configure("runs/%s"%(args.name))
61 |
62 | # Data loading code
63 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[x/255.0 for x in [125.3, 123.0, 113.9]],
64 | std=[x/255.0 for x in [63.0, 62.1, 66.7]])
65 |
66 | if args.augment:
67 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
68 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
69 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
70 | transforms.ToTensor(),
71 | normalize,
72 | ])
73 | else:
74 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
75 | transforms.ToTensor(),
76 | normalize,
77 | ])
78 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
79 | transforms.ToTensor(),
80 | normalize
81 | ])
82 |
83 | kwargs = {'num_workers': 1, 'pin_memory': True}
84 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
85 | datasets.CIFAR10('../data', train=True, download=True,
86 | transform=transform_train),
87 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
88 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
89 | datasets.CIFAR10('../data', train=False, transform=transform_test),
90 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
91 |
92 | # create model
93 | model = dn.DenseNet3(args.layers, 10, args.growth, reduction=args.reduce,
94 | bottleneck=args.bottleneck, dropRate=args.droprate)
95 |
96 | # get the number of model parameters
97 | print('Number of model parameters: {}'.format(
98 | sum([p.data.nelement() for p in model.parameters()])))
99 |
100 | # for training on multiple GPUs.
101 | # Use CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 to specify which GPUs to use
102 | # model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
103 | model = model.cuda()
104 |
105 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
106 | if args.resume:
107 | if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
108 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
109 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
110 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
111 | best_prec1 = checkpoint['best_prec1']
112 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
113 | print("=> loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
114 | .format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
115 | else:
116 | print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
117 |
118 | cudnn.benchmark = True
119 |
120 | # define loss function (criterion) and pptimizer
121 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda()
122 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr,
123 | momentum=args.momentum,
124 | nesterov=True,
125 | weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
126 |
127 | for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
128 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch)
129 |
130 | # train for one epoch
131 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
132 |
133 | # evaluate on validation set
134 | prec1 = validate(val_loader, model, criterion, epoch)
135 |
136 | # remember best prec@1 and save checkpoint
137 | is_best = prec1 > best_prec1
138 | best_prec1 = max(prec1, best_prec1)
139 | save_checkpoint({
140 | 'epoch': epoch + 1,
141 | 'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
142 | 'best_prec1': best_prec1,
143 | }, is_best)
144 | print('Best accuracy: ', best_prec1)
145 |
146 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
147 | """Train for one epoch on the training set"""
148 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
149 | losses = AverageMeter()
150 | top1 = AverageMeter()
151 |
152 | # switch to train mode
153 | model.train()
154 |
155 | end = time.time()
156 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
157 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
158 | input = input.cuda()
159 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
160 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
161 |
162 | # compute output
163 | output = model(input_var)
164 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
165 |
166 | # measure accuracy and record loss
167 | prec1 = accuracy(output.data, target, topk=(1,))[0]
168 | losses.update(loss.data[0], input.size(0))
169 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
170 |
171 | # compute gradient and do SGD step
172 | optimizer.zero_grad()
173 | loss.backward()
174 | optimizer.step()
175 |
176 | # measure elapsed time
177 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
178 | end = time.time()
179 |
180 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
181 | print('Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}]\t'
182 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
183 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
184 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})'.format(
185 | epoch, i, len(train_loader), batch_time=batch_time,
186 | loss=losses, top1=top1))
187 | # log to TensorBoard
188 | if args.tensorboard:
189 | log_value('train_loss', losses.avg, epoch)
190 | log_value('train_acc', top1.avg, epoch)
191 |
192 | def validate(val_loader, model, criterion, epoch):
193 | """Perform validation on the validation set"""
194 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
195 | losses = AverageMeter()
196 | top1 = AverageMeter()
197 |
198 | # switch to evaluate mode
199 | model.eval()
200 |
201 | end = time.time()
202 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
203 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
204 | input = input.cuda()
205 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input, volatile=True)
206 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target, volatile=True)
207 |
208 | # compute output
209 | output = model(input_var)
210 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
211 |
212 | # measure accuracy and record loss
213 | prec1 = accuracy(output.data, target, topk=(1,))[0]
214 | losses.update(loss.data[0], input.size(0))
215 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
216 |
217 | # measure elapsed time
218 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
219 | end = time.time()
220 |
221 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
222 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
223 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
224 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
225 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})'.format(
226 | i, len(val_loader), batch_time=batch_time, loss=losses,
227 | top1=top1))
228 |
229 | print(' * Prec@1 {top1.avg:.3f}'.format(top1=top1))
230 | # log to TensorBoard
231 | if args.tensorboard:
232 | log_value('val_loss', losses.avg, epoch)
233 | log_value('val_acc', top1.avg, epoch)
234 | return top1.avg
235 |
236 |
237 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
238 | """Saves checkpoint to disk"""
239 | directory = "runs/%s/"%(args.name)
240 | if not os.path.exists(directory):
241 | os.makedirs(directory)
242 | filename = directory + filename
243 | torch.save(state, filename)
244 | if is_best:
245 | shutil.copyfile(filename, 'runs/%s/'%(args.name) + 'model_best.pth.tar')
246 |
247 | class AverageMeter(object):
248 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
249 | def __init__(self):
250 | self.reset()
251 |
252 | def reset(self):
253 | self.val = 0
254 | self.avg = 0
255 | self.sum = 0
256 | self.count = 0
257 |
258 | def update(self, val, n=1):
259 | self.val = val
260 | self.sum += val * n
261 | self.count += n
262 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
263 |
264 |
265 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch):
266 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 after 150 and 225 epochs"""
267 | lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 150)) * (0.1 ** (epoch // 225))
268 | # log to TensorBoard
269 | if args.tensorboard:
270 | log_value('learning_rate', lr, epoch)
271 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
272 | param_group['lr'] = lr
273 |
274 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
275 | """Computes the precision@k for the specified values of k"""
276 | maxk = max(topk)
277 | batch_size = target.size(0)
278 |
279 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
280 | pred = pred.t()
281 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
282 |
283 | res = []
284 | for k in topk:
285 | correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0)
286 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
287 | return res
288 |
289 | if __name__ == '__main__':
290 | main()
291 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 18 |
19 | The improvements in accuracy per parameter are illustrated in their results on ImageNet (Figure 3).
20 |
21 |
18 |
19 | The improvements in accuracy per parameter are illustrated in their results on ImageNet (Figure 3).
20 |
21 |  22 |
23 | ## This implementation
24 | The training code in train.py trains a DenseNet on CIFAR 10 or 100. To train on ImageNet, densenet.py can be copied into the [PyTorch example for training ResNets on Imagenet](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/imagenet), upon which this repo is based. Note that for ImageNet the model contains four dense blocks.
25 |
26 | This implementation is quite _memory efficient requiring between 10% and 20% less memory_ compared to the original torch implementation. We optain a final test error of 4.76 % with DenseNet-BC-100-12 (paper reports 4.51 %) and 5.35 % with DenseNet-40-12 (paper reports 5.24 %).
27 |
28 | This implementation allows for __all model variants__ in the DenseNet paper, i.e., with and without bottleneck, channel reduction, data augmentation and dropout.
29 |
30 | For simple configuration of the model, this repo uses `argparse` so that key hyperparameters can be easily changed.
31 |
32 | Further, this implementation supports [easy checkpointing](https://github.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/blob/master/train.py#L136), keeping track of the best model and [resuming](https://github.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/blob/master/train.py#L103) training from previous checkpoints.
33 |
34 | ### Tracking training progress with TensorBoard
35 | To track training progress, this implementation uses [TensorBoard](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/summaries_and_tensorboard) which offers great ways to track and compare multiple experiments. To track PyTorch experiments in TensorBoard we use [tensorboard_logger](https://github.com/TeamHG-Memex/tensorboard_logger) which can be installed with
36 | ```
37 | pip install tensorboard_logger
38 | ```
39 | Example training curves for DenseNet-BC-100-12 (dark blue) and DenseNet-40-12 (light blue) for training loss and validation accuracy is shown below.
40 |
41 | 
42 |
43 | ### Dependencies
44 | * [PyTorch](http://pytorch.org/)
45 |
46 | optional:
47 | * [tensorboard_logger](https://github.com/TeamHG-Memex/tensorboard_logger)
48 |
49 |
50 | ### Cite
51 | If you use DenseNets in your work, please cite the original paper as:
52 | ```
53 | @article{Huang2016Densely,
54 | author = {Huang, Gao and Liu, Zhuang and Weinberger, Kilian Q.},
55 | title = {Densely Connected Convolutional Networks},
56 | journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.06993},
57 | year = {2016}
58 | }
59 | ```
60 |
61 | If this implementation is useful to you and your project, please also consider to cite or acknowledge this code repository.
62 |
63 | ### References
64 | [1] Huang, G., Liu, Z., Weinberger, K. Q., & van der Maaten, L. (2016). Densely connected convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.06993.
65 |
66 | [2] Huang, G., Sun, Y., Liu, Z., Sedra, D., & Weinberger, K. Q. (2016). Deep networks with stochastic depth. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV '16)
67 |
68 | [3] Veit, A., Wilber, M. J., & Belongie, S. (2016). Residual networks behave like ensembles of relatively shallow networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS '16)
69 |
70 | [4] He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR '16)
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/densenet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | import torch.nn as nn
4 | import torch.nn.functional as F
5 |
6 |
7 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
8 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
9 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
10 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
11 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
12 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
13 | padding=1, bias=False)
14 | self.droprate = dropRate
15 | def forward(self, x):
16 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
17 | if self.droprate > 0:
18 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, training=self.training)
19 | return torch.cat([x, out], 1)
20 |
21 | class BottleneckBlock(nn.Module):
22 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
23 | super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()
24 | inter_planes = out_planes * 4
25 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
26 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
27 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
28 | padding=0, bias=False)
29 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_planes)
30 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
31 | padding=1, bias=False)
32 | self.droprate = dropRate
33 | def forward(self, x):
34 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
35 | if self.droprate > 0:
36 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
37 | out = self.conv2(self.relu(self.bn2(out)))
38 | if self.droprate > 0:
39 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
40 | return torch.cat([x, out], 1)
41 |
42 | class TransitionBlock(nn.Module):
43 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
44 | super(TransitionBlock, self).__init__()
45 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
46 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
47 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
48 | padding=0, bias=False)
49 | self.droprate = dropRate
50 | def forward(self, x):
51 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
52 | if self.droprate > 0:
53 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
54 | return F.avg_pool2d(out, 2)
55 |
56 | class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
57 | def __init__(self, nb_layers, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate=0.0):
58 | super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
59 | self.layer = self._make_layer(block, in_planes, growth_rate, nb_layers, dropRate)
60 | def _make_layer(self, block, in_planes, growth_rate, nb_layers, dropRate):
61 | layers = []
62 | for i in range(nb_layers):
63 | layers.append(block(in_planes+i*growth_rate, growth_rate, dropRate))
64 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
65 | def forward(self, x):
66 | return self.layer(x)
67 |
68 | class DenseNet3(nn.Module):
69 | def __init__(self, depth, num_classes, growth_rate=12,
70 | reduction=0.5, bottleneck=True, dropRate=0.0):
71 | super(DenseNet3, self).__init__()
72 | in_planes = 2 * growth_rate
73 | n = (depth - 4) / 3
74 | if bottleneck == True:
75 | n = n/2
76 | block = BottleneckBlock
77 | else:
78 | block = BasicBlock
79 | n = int(n)
80 | # 1st conv before any dense block
81 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, in_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
82 | padding=1, bias=False)
83 | # 1st block
84 | self.block1 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
85 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
86 | self.trans1 = TransitionBlock(in_planes, int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction)), dropRate=dropRate)
87 | in_planes = int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction))
88 | # 2nd block
89 | self.block2 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
90 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
91 | self.trans2 = TransitionBlock(in_planes, int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction)), dropRate=dropRate)
92 | in_planes = int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction))
93 | # 3rd block
94 | self.block3 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
95 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
96 | # global average pooling and classifier
97 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
98 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
99 | self.fc = nn.Linear(in_planes, num_classes)
100 | self.in_planes = in_planes
101 |
102 | for m in self.modules():
103 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
104 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
105 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
106 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
107 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
108 | m.bias.data.zero_()
109 | elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
110 | m.bias.data.zero_()
111 | def forward(self, x):
112 | out = self.conv1(x)
113 | out = self.trans1(self.block1(out))
114 | out = self.trans2(self.block2(out))
115 | out = self.block3(out)
116 | out = self.relu(self.bn1(out))
117 | out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 8)
118 | out = out.view(-1, self.in_planes)
119 | return self.fc(out)
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import shutil
4 | import time
5 |
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.nn.parallel
9 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
10 | import torch.optim
11 | import torch.utils.data
12 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
13 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
14 |
15 | import densenet as dn
16 |
17 | # used for logging to TensorBoard
18 | from tensorboard_logger import configure, log_value
19 |
20 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch DenseNet Training')
21 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=300, type=int,
22 | help='number of total epochs to run')
23 | parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int,
24 | help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
25 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=64, type=int,
26 | help='mini-batch size (default: 64)')
27 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.1, type=float,
28 | help='initial learning rate')
29 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, help='momentum')
30 | parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', '--wd', default=1e-4, type=float,
31 | help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)')
32 | parser.add_argument('--print-freq', '-p', default=10, type=int,
33 | help='print frequency (default: 10)')
34 | parser.add_argument('--layers', default=100, type=int,
35 | help='total number of layers (default: 100)')
36 | parser.add_argument('--growth', default=12, type=int,
37 | help='number of new channels per layer (default: 12)')
38 | parser.add_argument('--droprate', default=0, type=float,
39 | help='dropout probability (default: 0.0)')
40 | parser.add_argument('--no-augment', dest='augment', action='store_false',
41 | help='whether to use standard augmentation (default: True)')
42 | parser.add_argument('--reduce', default=0.5, type=float,
43 | help='compression rate in transition stage (default: 0.5)')
44 | parser.add_argument('--no-bottleneck', dest='bottleneck', action='store_false',
45 | help='To not use bottleneck block')
46 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str,
47 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
48 | parser.add_argument('--name', default='DenseNet_BC_100_12', type=str,
49 | help='name of experiment')
50 | parser.add_argument('--tensorboard',
51 | help='Log progress to TensorBoard', action='store_true')
52 | parser.set_defaults(bottleneck=True)
53 | parser.set_defaults(augment=True)
54 |
55 | best_prec1 = 0
56 |
57 | def main():
58 | global args, best_prec1
59 | args = parser.parse_args()
60 | if args.tensorboard: configure("runs/%s"%(args.name))
61 |
62 | # Data loading code
63 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[x/255.0 for x in [125.3, 123.0, 113.9]],
64 | std=[x/255.0 for x in [63.0, 62.1, 66.7]])
65 |
66 | if args.augment:
67 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
68 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
69 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
70 | transforms.ToTensor(),
71 | normalize,
72 | ])
73 | else:
74 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
75 | transforms.ToTensor(),
76 | normalize,
77 | ])
78 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
79 | transforms.ToTensor(),
80 | normalize
81 | ])
82 |
83 | kwargs = {'num_workers': 1, 'pin_memory': True}
84 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
85 | datasets.CIFAR10('../data', train=True, download=True,
86 | transform=transform_train),
87 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
88 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
89 | datasets.CIFAR10('../data', train=False, transform=transform_test),
90 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
91 |
92 | # create model
93 | model = dn.DenseNet3(args.layers, 10, args.growth, reduction=args.reduce,
94 | bottleneck=args.bottleneck, dropRate=args.droprate)
95 |
96 | # get the number of model parameters
97 | print('Number of model parameters: {}'.format(
98 | sum([p.data.nelement() for p in model.parameters()])))
99 |
100 | # for training on multiple GPUs.
101 | # Use CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 to specify which GPUs to use
102 | # model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
103 | model = model.cuda()
104 |
105 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
106 | if args.resume:
107 | if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
108 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
109 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
110 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
111 | best_prec1 = checkpoint['best_prec1']
112 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
113 | print("=> loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
114 | .format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
115 | else:
116 | print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
117 |
118 | cudnn.benchmark = True
119 |
120 | # define loss function (criterion) and pptimizer
121 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda()
122 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr,
123 | momentum=args.momentum,
124 | nesterov=True,
125 | weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
126 |
127 | for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
128 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch)
129 |
130 | # train for one epoch
131 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
132 |
133 | # evaluate on validation set
134 | prec1 = validate(val_loader, model, criterion, epoch)
135 |
136 | # remember best prec@1 and save checkpoint
137 | is_best = prec1 > best_prec1
138 | best_prec1 = max(prec1, best_prec1)
139 | save_checkpoint({
140 | 'epoch': epoch + 1,
141 | 'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
142 | 'best_prec1': best_prec1,
143 | }, is_best)
144 | print('Best accuracy: ', best_prec1)
145 |
146 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
147 | """Train for one epoch on the training set"""
148 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
149 | losses = AverageMeter()
150 | top1 = AverageMeter()
151 |
152 | # switch to train mode
153 | model.train()
154 |
155 | end = time.time()
156 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
157 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
158 | input = input.cuda()
159 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
160 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
161 |
162 | # compute output
163 | output = model(input_var)
164 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
165 |
166 | # measure accuracy and record loss
167 | prec1 = accuracy(output.data, target, topk=(1,))[0]
168 | losses.update(loss.data[0], input.size(0))
169 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
170 |
171 | # compute gradient and do SGD step
172 | optimizer.zero_grad()
173 | loss.backward()
174 | optimizer.step()
175 |
176 | # measure elapsed time
177 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
178 | end = time.time()
179 |
180 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
181 | print('Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}]\t'
182 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
183 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
184 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})'.format(
185 | epoch, i, len(train_loader), batch_time=batch_time,
186 | loss=losses, top1=top1))
187 | # log to TensorBoard
188 | if args.tensorboard:
189 | log_value('train_loss', losses.avg, epoch)
190 | log_value('train_acc', top1.avg, epoch)
191 |
192 | def validate(val_loader, model, criterion, epoch):
193 | """Perform validation on the validation set"""
194 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
195 | losses = AverageMeter()
196 | top1 = AverageMeter()
197 |
198 | # switch to evaluate mode
199 | model.eval()
200 |
201 | end = time.time()
202 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
203 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
204 | input = input.cuda()
205 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input, volatile=True)
206 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target, volatile=True)
207 |
208 | # compute output
209 | output = model(input_var)
210 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
211 |
212 | # measure accuracy and record loss
213 | prec1 = accuracy(output.data, target, topk=(1,))[0]
214 | losses.update(loss.data[0], input.size(0))
215 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
216 |
217 | # measure elapsed time
218 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
219 | end = time.time()
220 |
221 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
222 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
223 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
224 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
225 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})'.format(
226 | i, len(val_loader), batch_time=batch_time, loss=losses,
227 | top1=top1))
228 |
229 | print(' * Prec@1 {top1.avg:.3f}'.format(top1=top1))
230 | # log to TensorBoard
231 | if args.tensorboard:
232 | log_value('val_loss', losses.avg, epoch)
233 | log_value('val_acc', top1.avg, epoch)
234 | return top1.avg
235 |
236 |
237 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
238 | """Saves checkpoint to disk"""
239 | directory = "runs/%s/"%(args.name)
240 | if not os.path.exists(directory):
241 | os.makedirs(directory)
242 | filename = directory + filename
243 | torch.save(state, filename)
244 | if is_best:
245 | shutil.copyfile(filename, 'runs/%s/'%(args.name) + 'model_best.pth.tar')
246 |
247 | class AverageMeter(object):
248 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
249 | def __init__(self):
250 | self.reset()
251 |
252 | def reset(self):
253 | self.val = 0
254 | self.avg = 0
255 | self.sum = 0
256 | self.count = 0
257 |
258 | def update(self, val, n=1):
259 | self.val = val
260 | self.sum += val * n
261 | self.count += n
262 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
263 |
264 |
265 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch):
266 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 after 150 and 225 epochs"""
267 | lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 150)) * (0.1 ** (epoch // 225))
268 | # log to TensorBoard
269 | if args.tensorboard:
270 | log_value('learning_rate', lr, epoch)
271 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
272 | param_group['lr'] = lr
273 |
274 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
275 | """Computes the precision@k for the specified values of k"""
276 | maxk = max(topk)
277 | batch_size = target.size(0)
278 |
279 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
280 | pred = pred.t()
281 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
282 |
283 | res = []
284 | for k in topk:
285 | correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0)
286 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
287 | return res
288 |
289 | if __name__ == '__main__':
290 | main()
291 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
22 |
23 | ## This implementation
24 | The training code in train.py trains a DenseNet on CIFAR 10 or 100. To train on ImageNet, densenet.py can be copied into the [PyTorch example for training ResNets on Imagenet](https://github.com/pytorch/examples/tree/master/imagenet), upon which this repo is based. Note that for ImageNet the model contains four dense blocks.
25 |
26 | This implementation is quite _memory efficient requiring between 10% and 20% less memory_ compared to the original torch implementation. We optain a final test error of 4.76 % with DenseNet-BC-100-12 (paper reports 4.51 %) and 5.35 % with DenseNet-40-12 (paper reports 5.24 %).
27 |
28 | This implementation allows for __all model variants__ in the DenseNet paper, i.e., with and without bottleneck, channel reduction, data augmentation and dropout.
29 |
30 | For simple configuration of the model, this repo uses `argparse` so that key hyperparameters can be easily changed.
31 |
32 | Further, this implementation supports [easy checkpointing](https://github.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/blob/master/train.py#L136), keeping track of the best model and [resuming](https://github.com/andreasveit/densenet-pytorch/blob/master/train.py#L103) training from previous checkpoints.
33 |
34 | ### Tracking training progress with TensorBoard
35 | To track training progress, this implementation uses [TensorBoard](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/summaries_and_tensorboard) which offers great ways to track and compare multiple experiments. To track PyTorch experiments in TensorBoard we use [tensorboard_logger](https://github.com/TeamHG-Memex/tensorboard_logger) which can be installed with
36 | ```
37 | pip install tensorboard_logger
38 | ```
39 | Example training curves for DenseNet-BC-100-12 (dark blue) and DenseNet-40-12 (light blue) for training loss and validation accuracy is shown below.
40 |
41 | 
42 |
43 | ### Dependencies
44 | * [PyTorch](http://pytorch.org/)
45 |
46 | optional:
47 | * [tensorboard_logger](https://github.com/TeamHG-Memex/tensorboard_logger)
48 |
49 |
50 | ### Cite
51 | If you use DenseNets in your work, please cite the original paper as:
52 | ```
53 | @article{Huang2016Densely,
54 | author = {Huang, Gao and Liu, Zhuang and Weinberger, Kilian Q.},
55 | title = {Densely Connected Convolutional Networks},
56 | journal = {arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.06993},
57 | year = {2016}
58 | }
59 | ```
60 |
61 | If this implementation is useful to you and your project, please also consider to cite or acknowledge this code repository.
62 |
63 | ### References
64 | [1] Huang, G., Liu, Z., Weinberger, K. Q., & van der Maaten, L. (2016). Densely connected convolutional networks. arXiv preprint arXiv:1608.06993.
65 |
66 | [2] Huang, G., Sun, Y., Liu, Z., Sedra, D., & Weinberger, K. Q. (2016). Deep networks with stochastic depth. In European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV '16)
67 |
68 | [3] Veit, A., Wilber, M. J., & Belongie, S. (2016). Residual networks behave like ensembles of relatively shallow networks. In Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems (NIPS '16)
69 |
70 | [4] He, K., Zhang, X., Ren, S., & Sun, J. (2016). Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR '16)
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/densenet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import math
2 | import torch
3 | import torch.nn as nn
4 | import torch.nn.functional as F
5 |
6 |
7 | class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
8 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
9 | super(BasicBlock, self).__init__()
10 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
11 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
12 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
13 | padding=1, bias=False)
14 | self.droprate = dropRate
15 | def forward(self, x):
16 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
17 | if self.droprate > 0:
18 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, training=self.training)
19 | return torch.cat([x, out], 1)
20 |
21 | class BottleneckBlock(nn.Module):
22 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
23 | super(BottleneckBlock, self).__init__()
24 | inter_planes = out_planes * 4
25 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
26 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
27 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, inter_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
28 | padding=0, bias=False)
29 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(inter_planes)
30 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(inter_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
31 | padding=1, bias=False)
32 | self.droprate = dropRate
33 | def forward(self, x):
34 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
35 | if self.droprate > 0:
36 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
37 | out = self.conv2(self.relu(self.bn2(out)))
38 | if self.droprate > 0:
39 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
40 | return torch.cat([x, out], 1)
41 |
42 | class TransitionBlock(nn.Module):
43 | def __init__(self, in_planes, out_planes, dropRate=0.0):
44 | super(TransitionBlock, self).__init__()
45 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
46 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
47 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=1,
48 | padding=0, bias=False)
49 | self.droprate = dropRate
50 | def forward(self, x):
51 | out = self.conv1(self.relu(self.bn1(x)))
52 | if self.droprate > 0:
53 | out = F.dropout(out, p=self.droprate, inplace=False, training=self.training)
54 | return F.avg_pool2d(out, 2)
55 |
56 | class DenseBlock(nn.Module):
57 | def __init__(self, nb_layers, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate=0.0):
58 | super(DenseBlock, self).__init__()
59 | self.layer = self._make_layer(block, in_planes, growth_rate, nb_layers, dropRate)
60 | def _make_layer(self, block, in_planes, growth_rate, nb_layers, dropRate):
61 | layers = []
62 | for i in range(nb_layers):
63 | layers.append(block(in_planes+i*growth_rate, growth_rate, dropRate))
64 | return nn.Sequential(*layers)
65 | def forward(self, x):
66 | return self.layer(x)
67 |
68 | class DenseNet3(nn.Module):
69 | def __init__(self, depth, num_classes, growth_rate=12,
70 | reduction=0.5, bottleneck=True, dropRate=0.0):
71 | super(DenseNet3, self).__init__()
72 | in_planes = 2 * growth_rate
73 | n = (depth - 4) / 3
74 | if bottleneck == True:
75 | n = n/2
76 | block = BottleneckBlock
77 | else:
78 | block = BasicBlock
79 | n = int(n)
80 | # 1st conv before any dense block
81 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, in_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=1,
82 | padding=1, bias=False)
83 | # 1st block
84 | self.block1 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
85 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
86 | self.trans1 = TransitionBlock(in_planes, int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction)), dropRate=dropRate)
87 | in_planes = int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction))
88 | # 2nd block
89 | self.block2 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
90 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
91 | self.trans2 = TransitionBlock(in_planes, int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction)), dropRate=dropRate)
92 | in_planes = int(math.floor(in_planes*reduction))
93 | # 3rd block
94 | self.block3 = DenseBlock(n, in_planes, growth_rate, block, dropRate)
95 | in_planes = int(in_planes+n*growth_rate)
96 | # global average pooling and classifier
97 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(in_planes)
98 | self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
99 | self.fc = nn.Linear(in_planes, num_classes)
100 | self.in_planes = in_planes
101 |
102 | for m in self.modules():
103 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
104 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
105 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
106 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
107 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
108 | m.bias.data.zero_()
109 | elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
110 | m.bias.data.zero_()
111 | def forward(self, x):
112 | out = self.conv1(x)
113 | out = self.trans1(self.block1(out))
114 | out = self.trans2(self.block2(out))
115 | out = self.block3(out)
116 | out = self.relu(self.bn1(out))
117 | out = F.avg_pool2d(out, 8)
118 | out = out.view(-1, self.in_planes)
119 | return self.fc(out)
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import argparse
2 | import os
3 | import shutil
4 | import time
5 |
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.nn as nn
8 | import torch.nn.parallel
9 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
10 | import torch.optim
11 | import torch.utils.data
12 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
13 | import torchvision.datasets as datasets
14 |
15 | import densenet as dn
16 |
17 | # used for logging to TensorBoard
18 | from tensorboard_logger import configure, log_value
19 |
20 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='PyTorch DenseNet Training')
21 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=300, type=int,
22 | help='number of total epochs to run')
23 | parser.add_argument('--start-epoch', default=0, type=int,
24 | help='manual epoch number (useful on restarts)')
25 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=64, type=int,
26 | help='mini-batch size (default: 64)')
27 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.1, type=float,
28 | help='initial learning rate')
29 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, help='momentum')
30 | parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', '--wd', default=1e-4, type=float,
31 | help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)')
32 | parser.add_argument('--print-freq', '-p', default=10, type=int,
33 | help='print frequency (default: 10)')
34 | parser.add_argument('--layers', default=100, type=int,
35 | help='total number of layers (default: 100)')
36 | parser.add_argument('--growth', default=12, type=int,
37 | help='number of new channels per layer (default: 12)')
38 | parser.add_argument('--droprate', default=0, type=float,
39 | help='dropout probability (default: 0.0)')
40 | parser.add_argument('--no-augment', dest='augment', action='store_false',
41 | help='whether to use standard augmentation (default: True)')
42 | parser.add_argument('--reduce', default=0.5, type=float,
43 | help='compression rate in transition stage (default: 0.5)')
44 | parser.add_argument('--no-bottleneck', dest='bottleneck', action='store_false',
45 | help='To not use bottleneck block')
46 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str,
47 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
48 | parser.add_argument('--name', default='DenseNet_BC_100_12', type=str,
49 | help='name of experiment')
50 | parser.add_argument('--tensorboard',
51 | help='Log progress to TensorBoard', action='store_true')
52 | parser.set_defaults(bottleneck=True)
53 | parser.set_defaults(augment=True)
54 |
55 | best_prec1 = 0
56 |
57 | def main():
58 | global args, best_prec1
59 | args = parser.parse_args()
60 | if args.tensorboard: configure("runs/%s"%(args.name))
61 |
62 | # Data loading code
63 | normalize = transforms.Normalize(mean=[x/255.0 for x in [125.3, 123.0, 113.9]],
64 | std=[x/255.0 for x in [63.0, 62.1, 66.7]])
65 |
66 | if args.augment:
67 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
68 | transforms.RandomCrop(32, padding=4),
69 | transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
70 | transforms.ToTensor(),
71 | normalize,
72 | ])
73 | else:
74 | transform_train = transforms.Compose([
75 | transforms.ToTensor(),
76 | normalize,
77 | ])
78 | transform_test = transforms.Compose([
79 | transforms.ToTensor(),
80 | normalize
81 | ])
82 |
83 | kwargs = {'num_workers': 1, 'pin_memory': True}
84 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
85 | datasets.CIFAR10('../data', train=True, download=True,
86 | transform=transform_train),
87 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
88 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
89 | datasets.CIFAR10('../data', train=False, transform=transform_test),
90 | batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True, **kwargs)
91 |
92 | # create model
93 | model = dn.DenseNet3(args.layers, 10, args.growth, reduction=args.reduce,
94 | bottleneck=args.bottleneck, dropRate=args.droprate)
95 |
96 | # get the number of model parameters
97 | print('Number of model parameters: {}'.format(
98 | sum([p.data.nelement() for p in model.parameters()])))
99 |
100 | # for training on multiple GPUs.
101 | # Use CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0,1 to specify which GPUs to use
102 | # model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
103 | model = model.cuda()
104 |
105 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
106 | if args.resume:
107 | if os.path.isfile(args.resume):
108 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(args.resume))
109 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.resume)
110 | args.start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
111 | best_prec1 = checkpoint['best_prec1']
112 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
113 | print("=> loaded checkpoint '{}' (epoch {})"
114 | .format(args.resume, checkpoint['epoch']))
115 | else:
116 | print("=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(args.resume))
117 |
118 | cudnn.benchmark = True
119 |
120 | # define loss function (criterion) and pptimizer
121 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss().cuda()
122 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr,
123 | momentum=args.momentum,
124 | nesterov=True,
125 | weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
126 |
127 | for epoch in range(args.start_epoch, args.epochs):
128 | adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch)
129 |
130 | # train for one epoch
131 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch)
132 |
133 | # evaluate on validation set
134 | prec1 = validate(val_loader, model, criterion, epoch)
135 |
136 | # remember best prec@1 and save checkpoint
137 | is_best = prec1 > best_prec1
138 | best_prec1 = max(prec1, best_prec1)
139 | save_checkpoint({
140 | 'epoch': epoch + 1,
141 | 'state_dict': model.state_dict(),
142 | 'best_prec1': best_prec1,
143 | }, is_best)
144 | print('Best accuracy: ', best_prec1)
145 |
146 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
147 | """Train for one epoch on the training set"""
148 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
149 | losses = AverageMeter()
150 | top1 = AverageMeter()
151 |
152 | # switch to train mode
153 | model.train()
154 |
155 | end = time.time()
156 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
157 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
158 | input = input.cuda()
159 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input)
160 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target)
161 |
162 | # compute output
163 | output = model(input_var)
164 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
165 |
166 | # measure accuracy and record loss
167 | prec1 = accuracy(output.data, target, topk=(1,))[0]
168 | losses.update(loss.data[0], input.size(0))
169 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
170 |
171 | # compute gradient and do SGD step
172 | optimizer.zero_grad()
173 | loss.backward()
174 | optimizer.step()
175 |
176 | # measure elapsed time
177 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
178 | end = time.time()
179 |
180 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
181 | print('Epoch: [{0}][{1}/{2}]\t'
182 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
183 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
184 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})'.format(
185 | epoch, i, len(train_loader), batch_time=batch_time,
186 | loss=losses, top1=top1))
187 | # log to TensorBoard
188 | if args.tensorboard:
189 | log_value('train_loss', losses.avg, epoch)
190 | log_value('train_acc', top1.avg, epoch)
191 |
192 | def validate(val_loader, model, criterion, epoch):
193 | """Perform validation on the validation set"""
194 | batch_time = AverageMeter()
195 | losses = AverageMeter()
196 | top1 = AverageMeter()
197 |
198 | # switch to evaluate mode
199 | model.eval()
200 |
201 | end = time.time()
202 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
203 | target = target.cuda(async=True)
204 | input = input.cuda()
205 | input_var = torch.autograd.Variable(input, volatile=True)
206 | target_var = torch.autograd.Variable(target, volatile=True)
207 |
208 | # compute output
209 | output = model(input_var)
210 | loss = criterion(output, target_var)
211 |
212 | # measure accuracy and record loss
213 | prec1 = accuracy(output.data, target, topk=(1,))[0]
214 | losses.update(loss.data[0], input.size(0))
215 | top1.update(prec1[0], input.size(0))
216 |
217 | # measure elapsed time
218 | batch_time.update(time.time() - end)
219 | end = time.time()
220 |
221 | if i % args.print_freq == 0:
222 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
223 | 'Time {batch_time.val:.3f} ({batch_time.avg:.3f})\t'
224 | 'Loss {loss.val:.4f} ({loss.avg:.4f})\t'
225 | 'Prec@1 {top1.val:.3f} ({top1.avg:.3f})'.format(
226 | i, len(val_loader), batch_time=batch_time, loss=losses,
227 | top1=top1))
228 |
229 | print(' * Prec@1 {top1.avg:.3f}'.format(top1=top1))
230 | # log to TensorBoard
231 | if args.tensorboard:
232 | log_value('val_loss', losses.avg, epoch)
233 | log_value('val_acc', top1.avg, epoch)
234 | return top1.avg
235 |
236 |
237 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, filename='checkpoint.pth.tar'):
238 | """Saves checkpoint to disk"""
239 | directory = "runs/%s/"%(args.name)
240 | if not os.path.exists(directory):
241 | os.makedirs(directory)
242 | filename = directory + filename
243 | torch.save(state, filename)
244 | if is_best:
245 | shutil.copyfile(filename, 'runs/%s/'%(args.name) + 'model_best.pth.tar')
246 |
247 | class AverageMeter(object):
248 | """Computes and stores the average and current value"""
249 | def __init__(self):
250 | self.reset()
251 |
252 | def reset(self):
253 | self.val = 0
254 | self.avg = 0
255 | self.sum = 0
256 | self.count = 0
257 |
258 | def update(self, val, n=1):
259 | self.val = val
260 | self.sum += val * n
261 | self.count += n
262 | self.avg = self.sum / self.count
263 |
264 |
265 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch):
266 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 after 150 and 225 epochs"""
267 | lr = args.lr * (0.1 ** (epoch // 150)) * (0.1 ** (epoch // 225))
268 | # log to TensorBoard
269 | if args.tensorboard:
270 | log_value('learning_rate', lr, epoch)
271 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
272 | param_group['lr'] = lr
273 |
274 | def accuracy(output, target, topk=(1,)):
275 | """Computes the precision@k for the specified values of k"""
276 | maxk = max(topk)
277 | batch_size = target.size(0)
278 |
279 | _, pred = output.topk(maxk, 1, True, True)
280 | pred = pred.t()
281 | correct = pred.eq(target.view(1, -1).expand_as(pred))
282 |
283 | res = []
284 | for k in topk:
285 | correct_k = correct[:k].view(-1).float().sum(0)
286 | res.append(correct_k.mul_(100.0 / batch_size))
287 | return res
288 |
289 | if __name__ == '__main__':
290 | main()
291 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------