├── .editorconfig
├── .github
└── workflows
│ ├── close-inactive-issues.yaml
│ ├── main.yaml
│ └── secret-scanning.yaml
├── .gitignore
├── CHANGELOG.md
├── LICENSE
├── Makefile
├── README.md
├── config
├── arg_plate_example.yaml
└── latin_plate_example.yaml
├── docs
├── architecture.md
├── contributing.md
├── index.md
├── installation.md
├── reference.md
└── usage.md
├── fast_plate_ocr
├── __init__.py
├── cli
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── cli.py
│ ├── onnx_converter.py
│ ├── train.py
│ ├── utils.py
│ ├── valid.py
│ ├── visualize_augmentation.py
│ └── visualize_predictions.py
├── common
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── utils.py
├── inference
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── config.py
│ ├── hub.py
│ ├── onnx_inference.py
│ ├── process.py
│ └── utils.py
├── py.typed
└── train
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── data
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── augmentation.py
│ └── dataset.py
│ ├── model
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── config.py
│ ├── custom.py
│ ├── layer_blocks.py
│ └── models.py
│ └── utilities
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── backend_utils.py
│ └── utils.py
├── mkdocs.yml
├── poetry.lock
├── poetry.toml
├── pyproject.toml
└── test
├── __init__.py
├── assets
├── __init__.py
├── test_plate_1.png
└── test_plate_2.png
├── conftest.py
└── fast_lp_ocr
├── __init__.py
├── inference
├── __init__.py
├── test_hub.py
├── test_onnx_inference.py
└── test_process.py
└── train
├── __init__.py
├── test_config.py
├── test_custom.py
├── test_models.py
└── test_utils.py
/.editorconfig:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # EditorConfig: https://EditorConfig.org
2 | root = true
3 |
4 | [*]
5 | charset = utf-8
6 | end_of_line = lf
7 | indent_style = space
8 | trim_trailing_whitespace = true
9 | insert_final_newline = true
10 |
11 | [*.py]
12 | indent_size = 4
13 | max_line_length = 100
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/close-inactive-issues.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Close inactive issues
2 |
3 | on:
4 | schedule:
5 | - cron: "30 1 * * *" # Runs daily at 1:30 AM UTC
6 |
7 | jobs:
8 | close-issues:
9 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
10 | permissions:
11 | issues: write
12 | pull-requests: write
13 | steps:
14 | - uses: actions/stale@v5
15 | with:
16 | days-before-issue-stale: 90 # The number of days old an issue can be before marking it stale
17 | days-before-issue-close: 14 # The number of days to wait to close an issue after it being marked stale
18 | stale-issue-label: "stale"
19 | stale-issue-message: "This issue is stale because it has been open for 90 days with no activity."
20 | close-issue-message: "This issue was closed because it has been inactive for 14 days since being marked as stale."
21 | days-before-pr-stale: -1 # Disables stale behavior for PRs
22 | days-before-pr-close: -1 # Disables closing behavior for PRs
23 | repo-token: ${{ secrets.GITHUB_TOKEN }}
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/main.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: Test and Deploy
2 | on:
3 | push:
4 | branches:
5 | - master
6 | tags:
7 | - 'v*'
8 | pull_request:
9 | branches:
10 | - master
11 | jobs:
12 | test:
13 | name: Test
14 | strategy:
15 | fail-fast: false
16 | matrix:
17 | python-version: [ '3.10', '3.11', '3.12' ]
18 | os: [ ubuntu-latest ]
19 | runs-on: ${{ matrix.os }}
20 | steps:
21 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
22 |
23 | - name: Install poetry
24 | run: pipx install poetry
25 |
26 | - uses: actions/setup-python@v4
27 | with:
28 | python-version: ${{ matrix.python-version }}
29 | cache: 'poetry'
30 |
31 | - name: Install dependencies
32 | run: poetry install --all-extras
33 |
34 | - name: Check format
35 | run: make check_format
36 |
37 | - name: Run linters
38 | run: make lint
39 |
40 | - name: Run tests
41 | run: make test
42 |
43 | publish-to-pypi:
44 | name: Build and Publish to PyPI
45 | needs:
46 | - test
47 | if: "startsWith(github.ref, 'refs/tags/v')"
48 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
49 | environment:
50 | name: pypi
51 | url: https://pypi.org/p/fast-plate-ocr
52 | permissions:
53 | id-token: write
54 | steps:
55 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
56 |
57 | - name: Install poetry
58 | run: pipx install poetry
59 |
60 | - name: Setup Python
61 | uses: actions/setup-python@v3
62 | with:
63 | python-version: '3.10'
64 |
65 | - name: Build a binary wheel
66 | run: poetry build
67 |
68 | - name: Publish distribution 📦 to PyPI
69 | uses: pypa/gh-action-pypi-publish@release/v1
70 |
71 | github-release:
72 | name: Create GitHub release
73 | needs:
74 | - publish-to-pypi
75 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
76 |
77 | permissions:
78 | contents: write
79 |
80 | steps:
81 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
82 |
83 | - name: Check package version matches tag
84 | id: check-version
85 | uses: samuelcolvin/check-python-version@v4.1
86 | with:
87 | version_file_path: 'pyproject.toml'
88 |
89 | - name: Create GitHub Release
90 | env:
91 | GITHUB_TOKEN: ${{ github.token }}
92 | tag: ${{ github.ref_name }}
93 | run: |
94 | gh release create "$tag" \
95 | --repo="$GITHUB_REPOSITORY" \
96 | --title="${GITHUB_REPOSITORY#*/} ${tag#v}" \
97 | --generate-notes
98 |
99 | update_docs:
100 | name: Update documentation
101 | needs:
102 | - github-release
103 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
104 |
105 | steps:
106 | - uses: actions/checkout@v3
107 | with:
108 | fetch-depth: 0
109 |
110 | - name: Install poetry
111 | run: pipx install poetry
112 |
113 | - uses: actions/setup-python@v4
114 | with:
115 | python-version: '3.10'
116 | cache: 'poetry'
117 |
118 | - name: Configure Git user
119 | run: |
120 | git config --local user.email "github-actions[bot]@users.noreply.github.com"
121 | git config --local user.name "github-actions[bot]"
122 |
123 | - name: Retrieve version
124 | id: check-version
125 | uses: samuelcolvin/check-python-version@v4.1
126 | with:
127 | version_file_path: 'pyproject.toml'
128 | skip_env_check: true
129 |
130 | - name: Deploy the docs
131 | run: |
132 | poetry run mike deploy \
133 | --update-aliases \
134 | --push \
135 | --branch docs-site \
136 | ${{ steps.check-version.outputs.VERSION_MAJOR_MINOR }} latest
137 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.github/workflows/secret-scanning.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | on:
2 | push:
3 | branches:
4 | - master
5 | pull_request:
6 | branches:
7 | - master
8 |
9 | name: Secret Leaks
10 | jobs:
11 | trufflehog:
12 | runs-on: ubuntu-latest
13 | steps:
14 | - name: Checkout code
15 | uses: actions/checkout@v4
16 | with:
17 | fetch-depth: 0
18 | - name: Secret Scanning
19 | uses: trufflesecurity/trufflehog@main
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | build/
12 | develop-eggs/
13 | dist/
14 | downloads/
15 | eggs/
16 | .eggs/
17 | lib/
18 | lib64/
19 | parts/
20 | sdist/
21 | var/
22 | wheels/
23 | share/python-wheels/
24 | *.egg-info/
25 | .installed.cfg
26 | *.egg
27 | MANIFEST
28 |
29 | # PyInstaller
30 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
31 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
32 | *.manifest
33 | *.spec
34 |
35 | # Installer logs
36 | pip-log.txt
37 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
38 |
39 | # Unit test / coverage reports
40 | htmlcov/
41 | .tox/
42 | .nox/
43 | .coverage
44 | .coverage.*
45 | .cache
46 | nosetests.xml
47 | coverage.xml
48 | *.cover
49 | *.py,cover
50 | .hypothesis/
51 | .pytest_cache/
52 | cover/
53 |
54 | # Translations
55 | *.mo
56 | *.pot
57 |
58 | # Django stuff:
59 | *.log
60 | local_settings.py
61 | db.sqlite3
62 | db.sqlite3-journal
63 |
64 | # Flask stuff:
65 | instance/
66 | .webassets-cache
67 |
68 | # Scrapy stuff:
69 | .scrapy
70 |
71 | # Sphinx documentation
72 | docs/_build/
73 |
74 | # PyBuilder
75 | .pybuilder/
76 | target/
77 |
78 | # Jupyter Notebook
79 | .ipynb_checkpoints
80 |
81 | # IPython
82 | profile_default/
83 | ipython_config.py
84 |
85 | # pyenv
86 | # For a library or package, you might want to ignore these files since the code is
87 | # intended to run in multiple environments; otherwise, check them in:
88 | # .python-version
89 |
90 | # pipenv
91 | # According to pypa/pipenv#598, it is recommended to include Pipfile.lock in version control.
92 | # However, in case of collaboration, if having platform-specific dependencies or dependencies
93 | # having no cross-platform support, pipenv may install dependencies that don't work, or not
94 | # install all needed dependencies.
95 | #Pipfile.lock
96 |
97 | # poetry
98 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include poetry.lock in version control.
99 | # This is especially recommended for binary packages to ensure reproducibility, and is more
100 | # commonly ignored for libraries.
101 | # https://python-poetry.org/docs/basic-usage/#commit-your-poetrylock-file-to-version-control
102 | #poetry.lock
103 |
104 | # pdm
105 | # Similar to Pipfile.lock, it is generally recommended to include pdm.lock in version control.
106 | #pdm.lock
107 | # pdm stores project-wide configurations in .pdm.toml, but it is recommended to not include it
108 | # in version control.
109 | # https://pdm.fming.dev/#use-with-ide
110 | .pdm.toml
111 |
112 | # PEP 582; used by e.g. github.com/David-OConnor/pyflow and github.com/pdm-project/pdm
113 | __pypackages__/
114 |
115 | # Celery stuff
116 | celerybeat-schedule
117 | celerybeat.pid
118 |
119 | # SageMath parsed files
120 | *.sage.py
121 |
122 | # Environments
123 | .env
124 | .venv
125 | env/
126 | venv/
127 | ENV/
128 | env.bak/
129 | venv.bak/
130 |
131 | # Spyder project settings
132 | .spyderproject
133 | .spyproject
134 |
135 | # Rope project settings
136 | .ropeproject
137 |
138 | # mkdocs documentation
139 | /site
140 |
141 | # mypy
142 | .mypy_cache/
143 | .dmypy.json
144 | dmypy.json
145 |
146 | # Pyre type checker
147 | .pyre/
148 |
149 | # pytype static type analyzer
150 | .pytype/
151 |
152 | # Cython debug symbols
153 | cython_debug/
154 |
155 | # pyenv
156 | .python-version
157 |
158 | # CUDA DNN
159 | cudnn64_7.dll
160 |
161 | # Train folder
162 | train_val_set/
163 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CHANGELOG.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Changelog
2 |
3 | All notable changes to this project will be documented in this file.
4 |
5 | The format is based on [Keep a Changelog](https://keepachangelog.com/en/1.1.0/),
6 | and this project adheres to [Semantic Versioning](https://semver.org/spec/v2.0.0.html).
7 |
8 | ## [0.3.0] - 2024-12-08
9 |
10 | ### Added
11 |
12 | - New Global model using MobileViTV2 trained with data from +65 countries, with 85k+ plates 🚀 .
13 |
14 | [0.2.0]: https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/compare/v0.2.0...v0.3.0
15 |
16 | ## [0.2.0] - 2024-10-14
17 |
18 | ### Added
19 |
20 | - New European model using MobileViTV2 - trained on +40 countries 🚀 .
21 | - Added more logging to train script.
22 |
23 | [0.2.0]: https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/compare/v0.1.6...v0.2.0
24 |
25 | ## [0.1.6] - 2024-05-09
26 |
27 | ### Added
28 |
29 | - Add new Argentinian model trained with more (synthetic) data.
30 | - Add option to visualize only predictions which have low char prob.
31 | - Add onnxsim for simplifying ONNX model when exporting.
32 |
33 | [0.1.6]: https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/compare/v0.1.5...v0.1.6
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2024 ankandrew
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Makefile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Directories
2 | SRC_PATHS := fast_plate_ocr/ test/
3 |
4 | # Tasks
5 | .PHONY: help
6 | help:
7 | @echo "Available targets:"
8 | @echo " help : Show this help message"
9 | @echo " format : Format code using Ruff format"
10 | @echo " check_format : Check code formatting with Ruff format"
11 | @echo " ruff : Run Ruff linter"
12 | @echo " pylint : Run Pylint linter"
13 | @echo " mypy : Run MyPy static type checker"
14 | @echo " lint : Run linters (Ruff, Pylint and Mypy)"
15 | @echo " test : Run tests using pytest"
16 | @echo " checks : Check format, lint, and test"
17 | @echo " clean : Clean up caches and build artifacts"
18 |
19 | .PHONY: format
20 | format:
21 | @echo "==> Sorting imports..."
22 | @# Currently, the Ruff formatter does not sort imports, see https://docs.astral.sh/ruff/formatter/#sorting-imports
23 | @poetry run ruff check --select I --fix $(SRC_PATHS)
24 | @echo "=====> Formatting code..."
25 | @poetry run ruff format $(SRC_PATHS)
26 |
27 | .PHONY: check_format
28 | check_format:
29 | @echo "=====> Checking format..."
30 | @poetry run ruff format --check --diff $(SRC_PATHS)
31 | @echo "=====> Checking imports are sorted..."
32 | @poetry run ruff check --select I --exit-non-zero-on-fix $(SRC_PATHS)
33 |
34 | .PHONY: ruff
35 | ruff:
36 | @echo "=====> Running Ruff..."
37 | @poetry run ruff check $(SRC_PATHS)
38 |
39 | .PHONY: pylint
40 | pylint:
41 | @echo "=====> Running Pylint..."
42 | @poetry run pylint $(SRC_PATHS)
43 |
44 | .PHONY: mypy
45 | mypy:
46 | @echo "=====> Running Mypy..."
47 | @poetry run mypy $(SRC_PATHS)
48 |
49 | .PHONY: lint
50 | lint: ruff pylint mypy
51 |
52 | .PHONY: test
53 | test:
54 | @echo "=====> Running tests..."
55 | @poetry run pytest test/
56 |
57 | .PHONY: clean
58 | clean:
59 | @echo "=====> Cleaning caches..."
60 | @poetry run ruff clean
61 | @rm -rf .cache .pytest_cache .mypy_cache build dist *.egg-info
62 |
63 | checks: format lint test
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Fast & Lightweight License Plate OCR
2 |
3 | [](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/actions)
4 | [](https://keras.io/keras_3/)
5 | [](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/fast-plate-ocr)
6 | [](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/fast-plate-ocr)
7 | [](https://github.com/astral-sh/ruff)
8 | [](https://github.com/pylint-dev/pylint)
9 | [](http://mypy-lang.org/)
10 | [](https://onnx.ai/)
11 | [](https://huggingface.co/spaces/ankandrew/fast-alpr)
12 | [](https://ankandrew.github.io/fast-plate-ocr/)
13 | [](https://pypi.python.org/pypi/fast-plate-ocr)
14 |
15 | 
16 |
17 | ---
18 |
19 | ### Introduction
20 |
21 | **Lightweight** and **fast** OCR models for license plate text recognition. You can train models from scratch or use
22 | the trained models for inference.
23 |
24 | The idea is to use this after a plate object detector, since the OCR expects the cropped plates.
25 |
26 | ### Features
27 |
28 | - **Keras 3 Backend Support**: Compatible with **[TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/)**, **[JAX](https://github.com/google/jax)**, and **[PyTorch](https://pytorch.org/)** backends 🧠
29 | - **Augmentation Variety**: Diverse **augmentations** via **[Albumentations](https://albumentations.ai/)** library 🖼️
30 | - **Efficient Execution**: **Lightweight** models that are cheap to run 💰
31 | - **ONNX Runtime Inference**: **Fast** and **optimized** inference with **[ONNX runtime](https://onnxruntime.ai/)** ⚡
32 | - **User-Friendly CLI**: Simplified **CLI** for **training** and **validating** OCR models 🛠️
33 | - **Model HUB**: Access to a collection of **pre-trained models** ready for inference 🌟
34 |
35 | ### Available Models
36 |
37 | | Model Name | Time b=1
(ms)[1] | Throughput
(plates/second)[1] | Accuracy[2] | Dataset |
38 | |:----------------------------------------:|:--------------------------------:|:----------------------------------------------:|:----------------------:|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
39 | | `argentinian-plates-cnn-model` | 2.1 | 476 | 94.05% | Non-synthetic, plates up to 2020. Dataset [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip). |
40 | | `argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model` | 2.1 | 476 | 94.19% | Plates up to 2020 + synthetic plates. Dataset [arg_plate_dataset_plus_synth.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset_plus_synth.zip). |
41 | | `european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model` | 2.9 | 344 | 92.5%[3] | European plates (from +40 countries, trained on 40k+ plates). |
42 | | 🆕🔥 `global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model` | 2.9 | 344 | 93.3%[4] | Worldwide plates (from +65 countries, trained on 85k+ plates). |
43 |
44 | > [!TIP]
45 | > Try `fast-plate-ocr` pre-trained models in [Hugging Spaces](https://huggingface.co/spaces/ankandrew/fast-alpr).
46 |
47 |
48 | Notes
49 |
50 | _[1] Inference on Mac M1 chip using CPUExecutionProvider. Utilizing CoreMLExecutionProvider accelerates speed by 5x in the CNN models._
51 |
52 | _[2] Accuracy is what we refer to as plate_acc. See [metrics section](#model-metrics)._
53 |
54 | _[3] For detailed accuracy for each country see [results](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_results.json) and the corresponding [val split](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_val.zip) used._
55 |
56 | _[4] For detailed accuracy for each country see [results](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_results.json)._
57 |
58 |
59 |
60 |
61 | Reproduce results
62 |
63 | * Calculate Inference Time:
64 |
65 | ```shell
66 | pip install fast_plate_ocr
67 | ```
68 |
69 | ```python
70 | from fast_plate_ocr import ONNXPlateRecognizer
71 |
72 | m = ONNXPlateRecognizer("argentinian-plates-cnn-model")
73 | m.benchmark()
74 | ```
75 | * Calculate Model accuracy:
76 |
77 | ```shell
78 | pip install fast-plate-ocr[train]
79 | curl -LO https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
80 | curl -LO https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr.keras
81 | curl -LO https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_benchmark.zip
82 | unzip arg_plate_benchmark.zip
83 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
84 | -m arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
85 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml \
86 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
87 | ```
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | ### Inference
92 |
93 | For inference, install:
94 |
95 | ```shell
96 | pip install fast_plate_ocr
97 | ```
98 |
99 | #### Usage
100 |
101 | To predict from disk image:
102 |
103 | ```python
104 | from fast_plate_ocr import ONNXPlateRecognizer
105 |
106 | m = ONNXPlateRecognizer('argentinian-plates-cnn-model')
107 | print(m.run('test_plate.png'))
108 | ```
109 |
110 |
111 | run demo
112 |
113 | 
114 |
115 |
116 |
117 | To run model benchmark:
118 |
119 | ```python
120 | from fast_plate_ocr import ONNXPlateRecognizer
121 |
122 | m = ONNXPlateRecognizer('argentinian-plates-cnn-model')
123 | m.benchmark()
124 | ```
125 |
126 |
127 | benchmark demo
128 |
129 | 
130 |
131 |
132 |
133 | Make sure to check out the [docs](https://ankandrew.github.io/fast-plate-ocr) for more information.
134 |
135 | ### CLI
136 |
137 |  138 |
139 | To train or use the CLI tool, you'll need to install:
140 |
141 | ```shell
142 | pip install fast_plate_ocr[train]
143 | ```
144 |
145 | > [!IMPORTANT]
146 | > Make sure you have installed a supported backend for Keras.
147 |
148 | #### Train Model
149 |
150 | To train the model you will need:
151 |
152 | 1. A configuration used for the OCR model. Depending on your use case, you might have more plate slots or different set
153 | of characters. Take a look at the config for Argentinian license plate as an example:
154 | ```yaml
155 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
156 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
157 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
158 |
159 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
160 | max_plate_slots: 7
161 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
162 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
163 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
164 | pad_char: '_'
165 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
166 | img_height: 70
167 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
168 | img_width: 140
169 | ```
170 | 2. A labeled dataset,
171 | see [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip)
172 | for the expected data format.
173 | 3. Run train script:
174 | ```shell
175 | # You can set the backend to either TensorFlow, JAX or PyTorch
176 | # (just make sure it is installed)
177 | KERAS_BACKEND=tensorflow fast_plate_ocr train \
178 | --annotations path_to_the_train.csv \
179 | --val-annotations path_to_the_val.csv \
180 | --config-file config.yaml \
181 | --batch-size 128 \
182 | --epochs 750 \
183 | --dense \
184 | --early-stopping-patience 100 \
185 | --reduce-lr-patience 50
186 | ```
187 |
188 | You will probably want to change the augmentation pipeline to apply to your dataset.
189 |
190 | In order to do this define an Albumentations pipeline:
191 |
192 | ```python
193 | import albumentations as A
194 |
195 | transform_pipeline = A.Compose(
196 | [
197 | # ...
198 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
199 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
200 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
201 | # ... and any other augmentation ...
202 | ]
203 | )
204 |
205 | # Export to a file (this resultant YAML can be used by the train script)
206 | A.save(transform_pipeline, "./transform_pipeline.yaml", data_format="yaml")
207 | ```
208 |
209 | And then you can train using the custom transformation pipeline with the `--augmentation-path` option.
210 |
211 | #### Visualize Augmentation
212 |
213 | It's useful to visualize the augmentation pipeline before training the model. This helps us to identify
214 | if we should apply more heavy augmentation or less, as it can hurt the model.
215 |
216 | You might want to see the augmented image next to the original, to see how much it changed:
217 |
218 | ```shell
219 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-augmentation \
220 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
221 | --columns 2 \
222 | --show-original \
223 | --augmentation-path '/transform_pipeline.yaml'
224 | ```
225 |
226 | You will see something like:
227 |
228 | 
229 |
230 | #### Validate Model
231 |
232 | After finishing training you can validate the model on a labeled test dataset.
233 |
234 | Example:
235 |
236 | ```shell
237 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
238 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
239 | --config-file arg_plate_example.yaml \
240 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
241 | ```
242 |
243 | #### Visualize Predictions
244 |
245 | Once you finish training your model, you can view the model predictions on raw data with:
246 |
247 | ```shell
248 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-predictions \
249 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
250 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
251 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
252 | ```
253 |
254 | You will see something like:
255 |
256 | 
257 |
258 | #### Export as ONNX
259 |
260 | Exporting the Keras model to ONNX format might be beneficial to speed-up inference time.
261 |
262 | ```shell
263 | fast_plate_ocr export-onnx \
264 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
265 | --output-path arg_cnn_ocr.onnx \
266 | --opset 18 \
267 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
268 | ```
269 |
270 | ### Keras Backend
271 |
272 | To train the model, you can install the ML Framework you like the most. **Keras 3** has
273 | support for **TensorFlow**, **JAX** and **PyTorch** backends.
274 |
275 | To change the Keras backend you can either:
276 |
277 | 1. Export `KERAS_BACKEND` environment variable, i.e. to use JAX for training:
278 | ```shell
279 | KERAS_BACKEND=jax fast_plate_ocr train --config-file ...
280 | ```
281 | 2. Edit your local config file at `~/.keras/keras.json`.
282 |
283 | _Note: You will probably need to install your desired framework for training._
284 |
285 | ### Model Architecture
286 |
287 | The current model architecture is quite simple but effective.
288 | See [cnn_ocr_model](https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/blob/e59b738bad86d269c82101dfe7a3bef49b3a77c7/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py#L23-L23)
289 | for implementation details.
290 |
291 | The model output consists of several heads. Each head represents the prediction of a character of the
292 | plate. If the plate consists of 7 characters at most (`max_plate_slots=7`), then the model would have 7 heads.
293 |
294 | Example of Argentinian plates:
295 |
296 | 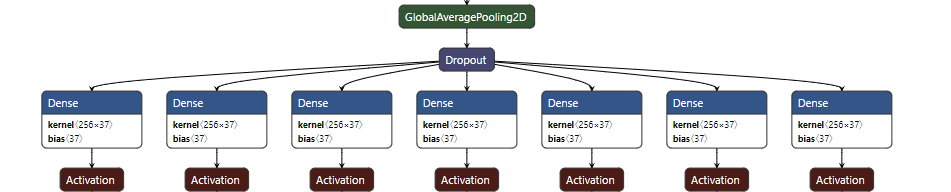
297 |
298 | Each head will output a probability distribution over the `vocabulary` specified during training. So the output
299 | prediction for a single plate will be of shape `(max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)`.
300 |
301 | ### Model Metrics
302 |
303 | During training, you will see the following metrics
304 |
305 | * **plate_acc**: Compute the number of **license plates** that were **fully classified**. For a single plate, if the
306 | ground truth is `ABC123` and the prediction is also `ABC123`, it would score 1. However, if the prediction was
307 | `ABD123`, it would score 0, as **not all characters** were correctly classified.
308 |
309 | * **cat_acc**: Calculate the accuracy of **individual characters** within the license plates that were
310 | **correctly classified**. For example, if the correct label is `ABC123` and the prediction is `ABC133`, it would yield
311 | a precision of 83.3% (5 out of 6 characters correctly classified), rather than 0% as in plate_acc, because it's not
312 | completely classified correctly.
313 |
314 | * **top_3_k**: Calculate how frequently the true character is included in the **top-3 predictions**
315 | (the three predictions with the highest probability).
316 |
317 | ### Contributing
318 |
319 | Contributions to the repo are greatly appreciated. Whether it's bug fixes, feature enhancements, or new models,
320 | your contributions are warmly welcomed.
321 |
322 | To start contributing or to begin development, you can follow these steps:
323 |
324 | 1. Clone repo
325 | ```shell
326 | git clone https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr.git
327 | ```
328 | 2. Install all dependencies using [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/#installation):
329 | ```shell
330 | poetry install --all-extras
331 | ```
332 | 3. To ensure your changes pass linting and tests before submitting a PR:
333 | ```shell
334 | make checks
335 | ```
336 |
337 | If you want to train a model and share it, we'll add it to the HUB 🚀
338 |
339 | If you look to contribute to the repo, some cool things are in the backlog:
340 |
341 | - [ ] Implement [STN](https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02025) using Keras 3 (With `keras.ops`)
342 | - [ ] Implement [SVTRv2](https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.15858).
343 | - [ ] Implement CTC loss function, so we can choose that or CE loss.
344 | - [ ] Extra head for country recognition, making it configurable.
345 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/config/arg_plate_example.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
2 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
3 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
4 |
5 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
6 | max_plate_slots: 7
7 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
8 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
9 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
10 | pad_char: '_'
11 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
12 | img_height: 70
13 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
14 | img_width: 140
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/config/latin_plate_example.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Config example for Latin plates from 70 countries
2 |
3 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
4 | max_plate_slots: 9
5 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
6 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
7 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
8 | pad_char: '_'
9 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
10 | img_height: 70
11 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
12 | img_width: 140
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/architecture.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### ConvNet (CNN) model
2 |
3 | The current model architecture is quite simple but effective. It just consists of a few CNN layers with several output
4 | heads.
5 | See [cnn_ocr_model](https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/blob/e59b738bad86d269c82101dfe7a3bef49b3a77c7/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py#L23-L23)
6 | for implementation details.
7 |
8 | The model output consists of several heads. Each head represents the prediction of a character of the
9 | plate. If the plate consists of 7 characters at most (`max_plate_slots=7`), then the model would have 7 heads.
10 |
11 | Example of Argentinian plates:
12 |
13 | 
14 |
15 | Each head will output a probability distribution over the `vocabulary` specified during training. So the output
16 | prediction for a single plate will be of shape `(max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)`.
17 |
18 | ### Model Metrics
19 |
20 | During training, you will see the following metrics
21 |
22 | * **plate_acc**: Compute the number of **license plates** that were **fully classified**. For a single plate, if the
23 | ground truth is `ABC123` and the prediction is also `ABC123`, it would score 1. However, if the prediction was
24 | `ABD123`, it would score 0, as **not all characters** were correctly classified.
25 |
26 | * **cat_acc**: Calculate the accuracy of **individual characters** within the license plates that were
27 | **correctly classified**. For example, if the correct label is `ABC123` and the prediction is `ABC133`, it would yield
28 | a precision of 83.3% (5 out of 6 characters correctly classified), rather than 0% as in plate_acc, because it's not
29 | completely classified correctly.
30 |
31 | * **top_3_k**: Calculate how frequently the true character is included in the **top-3 predictions**
32 | (the three predictions with the highest probability).
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/contributing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Contributions are greatly appreciated. Whether it's bug fixes, feature enhancements, or new models,
2 | your contributions are warmly welcomed.
3 |
4 | To start contributing or to begin development, you can follow these steps:
5 |
6 | 1. Clone repo
7 | ```shell
8 | git clone https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr.git
9 | ```
10 | 2. Install all dependencies using [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/#installation):
11 | ```shell
12 | poetry install --all-extras
13 | ```
14 | 3. To ensure your changes pass linting and tests before submitting a PR:
15 | ```shell
16 | make checks
17 | ```
18 |
19 | ???+ tip
20 | If you want to train a model and share it, we'll add it to the HUB 🚀
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Fast & Lightweight License Plate OCR
2 |
3 | 
4 |
5 | **FastPlateOCR** is a **lightweight** and **fast** OCR framework for **license plate text recognition**. You can train
6 | models from scratch or use the trained models for inference.
7 |
8 | The idea is to use this after a plate object detector, since the OCR expects the cropped plates.
9 |
10 | ### Features
11 |
12 | - **Keras 3 Backend Support**: Compatible with **TensorFlow**, **JAX**, and **PyTorch** backends 🧠
13 | - **Augmentation Variety**: Diverse augmentations via **Albumentations** library 🖼️
14 | - **Efficient Execution**: **Lightweight** models that are cheap to run 💰
15 | - **ONNX Runtime Inference**: **Fast** and **optimized** inference with ONNX runtime ⚡
16 | - **User-Friendly CLI**: Simplified **CLI** for **training** and **validating** OCR models 🛠️
17 | - **Model HUB**: Access to a collection of pre-trained models ready for inference 🌟
18 |
19 | ### Model Zoo
20 |
21 | We currently have the following available models:
22 |
23 | | Model Name | Time b=1
138 |
139 | To train or use the CLI tool, you'll need to install:
140 |
141 | ```shell
142 | pip install fast_plate_ocr[train]
143 | ```
144 |
145 | > [!IMPORTANT]
146 | > Make sure you have installed a supported backend for Keras.
147 |
148 | #### Train Model
149 |
150 | To train the model you will need:
151 |
152 | 1. A configuration used for the OCR model. Depending on your use case, you might have more plate slots or different set
153 | of characters. Take a look at the config for Argentinian license plate as an example:
154 | ```yaml
155 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
156 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
157 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
158 |
159 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
160 | max_plate_slots: 7
161 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
162 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
163 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
164 | pad_char: '_'
165 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
166 | img_height: 70
167 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
168 | img_width: 140
169 | ```
170 | 2. A labeled dataset,
171 | see [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip)
172 | for the expected data format.
173 | 3. Run train script:
174 | ```shell
175 | # You can set the backend to either TensorFlow, JAX or PyTorch
176 | # (just make sure it is installed)
177 | KERAS_BACKEND=tensorflow fast_plate_ocr train \
178 | --annotations path_to_the_train.csv \
179 | --val-annotations path_to_the_val.csv \
180 | --config-file config.yaml \
181 | --batch-size 128 \
182 | --epochs 750 \
183 | --dense \
184 | --early-stopping-patience 100 \
185 | --reduce-lr-patience 50
186 | ```
187 |
188 | You will probably want to change the augmentation pipeline to apply to your dataset.
189 |
190 | In order to do this define an Albumentations pipeline:
191 |
192 | ```python
193 | import albumentations as A
194 |
195 | transform_pipeline = A.Compose(
196 | [
197 | # ...
198 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
199 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
200 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
201 | # ... and any other augmentation ...
202 | ]
203 | )
204 |
205 | # Export to a file (this resultant YAML can be used by the train script)
206 | A.save(transform_pipeline, "./transform_pipeline.yaml", data_format="yaml")
207 | ```
208 |
209 | And then you can train using the custom transformation pipeline with the `--augmentation-path` option.
210 |
211 | #### Visualize Augmentation
212 |
213 | It's useful to visualize the augmentation pipeline before training the model. This helps us to identify
214 | if we should apply more heavy augmentation or less, as it can hurt the model.
215 |
216 | You might want to see the augmented image next to the original, to see how much it changed:
217 |
218 | ```shell
219 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-augmentation \
220 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
221 | --columns 2 \
222 | --show-original \
223 | --augmentation-path '/transform_pipeline.yaml'
224 | ```
225 |
226 | You will see something like:
227 |
228 | 
229 |
230 | #### Validate Model
231 |
232 | After finishing training you can validate the model on a labeled test dataset.
233 |
234 | Example:
235 |
236 | ```shell
237 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
238 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
239 | --config-file arg_plate_example.yaml \
240 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
241 | ```
242 |
243 | #### Visualize Predictions
244 |
245 | Once you finish training your model, you can view the model predictions on raw data with:
246 |
247 | ```shell
248 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-predictions \
249 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
250 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
251 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
252 | ```
253 |
254 | You will see something like:
255 |
256 | 
257 |
258 | #### Export as ONNX
259 |
260 | Exporting the Keras model to ONNX format might be beneficial to speed-up inference time.
261 |
262 | ```shell
263 | fast_plate_ocr export-onnx \
264 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
265 | --output-path arg_cnn_ocr.onnx \
266 | --opset 18 \
267 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
268 | ```
269 |
270 | ### Keras Backend
271 |
272 | To train the model, you can install the ML Framework you like the most. **Keras 3** has
273 | support for **TensorFlow**, **JAX** and **PyTorch** backends.
274 |
275 | To change the Keras backend you can either:
276 |
277 | 1. Export `KERAS_BACKEND` environment variable, i.e. to use JAX for training:
278 | ```shell
279 | KERAS_BACKEND=jax fast_plate_ocr train --config-file ...
280 | ```
281 | 2. Edit your local config file at `~/.keras/keras.json`.
282 |
283 | _Note: You will probably need to install your desired framework for training._
284 |
285 | ### Model Architecture
286 |
287 | The current model architecture is quite simple but effective.
288 | See [cnn_ocr_model](https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/blob/e59b738bad86d269c82101dfe7a3bef49b3a77c7/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py#L23-L23)
289 | for implementation details.
290 |
291 | The model output consists of several heads. Each head represents the prediction of a character of the
292 | plate. If the plate consists of 7 characters at most (`max_plate_slots=7`), then the model would have 7 heads.
293 |
294 | Example of Argentinian plates:
295 |
296 | 
297 |
298 | Each head will output a probability distribution over the `vocabulary` specified during training. So the output
299 | prediction for a single plate will be of shape `(max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)`.
300 |
301 | ### Model Metrics
302 |
303 | During training, you will see the following metrics
304 |
305 | * **plate_acc**: Compute the number of **license plates** that were **fully classified**. For a single plate, if the
306 | ground truth is `ABC123` and the prediction is also `ABC123`, it would score 1. However, if the prediction was
307 | `ABD123`, it would score 0, as **not all characters** were correctly classified.
308 |
309 | * **cat_acc**: Calculate the accuracy of **individual characters** within the license plates that were
310 | **correctly classified**. For example, if the correct label is `ABC123` and the prediction is `ABC133`, it would yield
311 | a precision of 83.3% (5 out of 6 characters correctly classified), rather than 0% as in plate_acc, because it's not
312 | completely classified correctly.
313 |
314 | * **top_3_k**: Calculate how frequently the true character is included in the **top-3 predictions**
315 | (the three predictions with the highest probability).
316 |
317 | ### Contributing
318 |
319 | Contributions to the repo are greatly appreciated. Whether it's bug fixes, feature enhancements, or new models,
320 | your contributions are warmly welcomed.
321 |
322 | To start contributing or to begin development, you can follow these steps:
323 |
324 | 1. Clone repo
325 | ```shell
326 | git clone https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr.git
327 | ```
328 | 2. Install all dependencies using [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/#installation):
329 | ```shell
330 | poetry install --all-extras
331 | ```
332 | 3. To ensure your changes pass linting and tests before submitting a PR:
333 | ```shell
334 | make checks
335 | ```
336 |
337 | If you want to train a model and share it, we'll add it to the HUB 🚀
338 |
339 | If you look to contribute to the repo, some cool things are in the backlog:
340 |
341 | - [ ] Implement [STN](https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02025) using Keras 3 (With `keras.ops`)
342 | - [ ] Implement [SVTRv2](https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.15858).
343 | - [ ] Implement CTC loss function, so we can choose that or CE loss.
344 | - [ ] Extra head for country recognition, making it configurable.
345 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/config/arg_plate_example.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
2 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
3 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
4 |
5 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
6 | max_plate_slots: 7
7 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
8 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
9 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
10 | pad_char: '_'
11 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
12 | img_height: 70
13 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
14 | img_width: 140
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/config/latin_plate_example.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Config example for Latin plates from 70 countries
2 |
3 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
4 | max_plate_slots: 9
5 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
6 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
7 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
8 | pad_char: '_'
9 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
10 | img_height: 70
11 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
12 | img_width: 140
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/architecture.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### ConvNet (CNN) model
2 |
3 | The current model architecture is quite simple but effective. It just consists of a few CNN layers with several output
4 | heads.
5 | See [cnn_ocr_model](https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/blob/e59b738bad86d269c82101dfe7a3bef49b3a77c7/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py#L23-L23)
6 | for implementation details.
7 |
8 | The model output consists of several heads. Each head represents the prediction of a character of the
9 | plate. If the plate consists of 7 characters at most (`max_plate_slots=7`), then the model would have 7 heads.
10 |
11 | Example of Argentinian plates:
12 |
13 | 
14 |
15 | Each head will output a probability distribution over the `vocabulary` specified during training. So the output
16 | prediction for a single plate will be of shape `(max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)`.
17 |
18 | ### Model Metrics
19 |
20 | During training, you will see the following metrics
21 |
22 | * **plate_acc**: Compute the number of **license plates** that were **fully classified**. For a single plate, if the
23 | ground truth is `ABC123` and the prediction is also `ABC123`, it would score 1. However, if the prediction was
24 | `ABD123`, it would score 0, as **not all characters** were correctly classified.
25 |
26 | * **cat_acc**: Calculate the accuracy of **individual characters** within the license plates that were
27 | **correctly classified**. For example, if the correct label is `ABC123` and the prediction is `ABC133`, it would yield
28 | a precision of 83.3% (5 out of 6 characters correctly classified), rather than 0% as in plate_acc, because it's not
29 | completely classified correctly.
30 |
31 | * **top_3_k**: Calculate how frequently the true character is included in the **top-3 predictions**
32 | (the three predictions with the highest probability).
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/contributing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Contributions are greatly appreciated. Whether it's bug fixes, feature enhancements, or new models,
2 | your contributions are warmly welcomed.
3 |
4 | To start contributing or to begin development, you can follow these steps:
5 |
6 | 1. Clone repo
7 | ```shell
8 | git clone https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr.git
9 | ```
10 | 2. Install all dependencies using [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/#installation):
11 | ```shell
12 | poetry install --all-extras
13 | ```
14 | 3. To ensure your changes pass linting and tests before submitting a PR:
15 | ```shell
16 | make checks
17 | ```
18 |
19 | ???+ tip
20 | If you want to train a model and share it, we'll add it to the HUB 🚀
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Fast & Lightweight License Plate OCR
2 |
3 | 
4 |
5 | **FastPlateOCR** is a **lightweight** and **fast** OCR framework for **license plate text recognition**. You can train
6 | models from scratch or use the trained models for inference.
7 |
8 | The idea is to use this after a plate object detector, since the OCR expects the cropped plates.
9 |
10 | ### Features
11 |
12 | - **Keras 3 Backend Support**: Compatible with **TensorFlow**, **JAX**, and **PyTorch** backends 🧠
13 | - **Augmentation Variety**: Diverse augmentations via **Albumentations** library 🖼️
14 | - **Efficient Execution**: **Lightweight** models that are cheap to run 💰
15 | - **ONNX Runtime Inference**: **Fast** and **optimized** inference with ONNX runtime ⚡
16 | - **User-Friendly CLI**: Simplified **CLI** for **training** and **validating** OCR models 🛠️
17 | - **Model HUB**: Access to a collection of pre-trained models ready for inference 🌟
18 |
19 | ### Model Zoo
20 |
21 | We currently have the following available models:
22 |
23 | | Model Name | Time b=1
(ms)[1] | Throughput
(plates/second)[1] | Accuracy[2] | Dataset |
24 | |:----------------------------------------:|:--------------------------------:|:----------------------------------------------:|:----------------------:|:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------:|
25 | | `argentinian-plates-cnn-model` | 2.1 | 476 | 94.05% | Non-synthetic, plates up to 2020. Dataset [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip). |
26 | | `argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model` | 2.1 | 476 | 94.19% | Plates up to 2020 + synthetic plates. Dataset [arg_plate_dataset_plus_synth.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset_plus_synth.zip). |
27 | | `european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model` | 2.9 | 344 | 92.5%[3] | European plates (from +40 countries, trained on 40k+ plates). |
28 | | 🆕🔥 `global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model` | 2.9 | 344 | 93.3%[4] | Worldwide plates (from +65 countries, trained on 85k+ plates). |
29 |
30 | _[1] Inference on Mac M1 chip using CPUExecutionProvider. Utilizing CoreMLExecutionProvider accelerates speed
31 | by 5x in the CNN models._
32 |
33 | _[2] Accuracy is what we refer as plate_acc. See [metrics section](#model-metrics)._
34 |
35 | _[3] For detailed accuracy for each country see [results](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_results.json) and
36 | the corresponding [val split](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_val.zip) used._
37 |
38 | _[4] For detailed accuracy for each country see [results](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_results.json)._
39 |
40 |
41 | Reproduce results.
42 |
43 | Calculate Inference Time:
44 |
45 | ```shell
46 | pip install fast_plate_ocr
47 | ```
48 |
49 | ```python
50 | from fast_plate_ocr import ONNXPlateRecognizer
51 |
52 | m = ONNXPlateRecognizer("argentinian-plates-cnn-model")
53 | m.benchmark()
54 | ```
55 |
56 | Calculate Model accuracy:
57 |
58 | ```shell
59 | pip install fast-plate-ocr[train]
60 | curl -LO https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
61 | curl -LO https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr.keras
62 | curl -LO https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_benchmark.zip
63 | unzip arg_plate_benchmark.zip
64 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
65 | -m arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
66 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml \
67 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
68 | ```
69 |
70 |
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/installation.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### Inference
2 |
3 | For **inference**, install:
4 |
5 | ```shell
6 | pip install fast_plate_ocr
7 | ```
8 |
9 | ### Train
10 |
11 | To **train** or use the **CLI tool**, you'll need to install:
12 |
13 | ```shell
14 | pip install fast_plate_ocr[train]
15 | ```
16 |
17 | ???+ info
18 | You will probably need to **install** your desired framework for training. FastPlateOCR doesn't
19 | enforce you to use any specific framework. See [Keras backend](usage.md#keras-backend) section.
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/reference.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ::: fast_plate_ocr.inference.onnx_inference
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/usage.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### API
2 |
3 | To predict from disk image:
4 |
5 | ```python
6 | from fast_plate_ocr import ONNXPlateRecognizer
7 |
8 | m = ONNXPlateRecognizer('argentinian-plates-cnn-model')
9 | print(m.run('test_plate.png'))
10 | ```
11 |
12 |
13 | Demo
14 |
15 |
16 |

17 |
20 |
21 | To run model benchmark:
22 |
23 | ```python
24 | from fast_plate_ocr import ONNXPlateRecognizer
25 |
26 | m = ONNXPlateRecognizer('argentinian-plates-cnn-model')
27 | m.benchmark()
28 | ```
29 |
30 |
31 | Demo
32 |
33 |
34 |

35 |
38 |
39 | For a full list of options see [Reference](reference.md).
40 |
41 | ### CLI
42 |
43 |  44 |
45 | To train or use the CLI tool, you'll need to install:
46 |
47 | ```shell
48 | pip install fast_plate_ocr[train]
49 | ```
50 |
51 | #### Train Model
52 |
53 | To train the model you will need:
54 |
55 | 1. A configuration used for the OCR model. Depending on your use case, you might have more plate slots or different set
56 | of characters. Take a look at the config for Argentinian license plate as an example:
57 | ```yaml
58 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
59 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
60 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
61 |
62 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
63 | max_plate_slots: 7
64 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
65 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
66 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
67 | pad_char: '_'
68 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
69 | img_height: 70
70 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
71 | img_width: 140
72 | ```
73 | 2. A labeled dataset,
74 | see [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip)
75 | for the expected data format.
76 | 3. Run train script:
77 | ```shell
78 | # You can set the backend to either TensorFlow, JAX or PyTorch
79 | # (just make sure it is installed)
80 | KERAS_BACKEND=tensorflow fast_plate_ocr train \
81 | --annotations path_to_the_train.csv \
82 | --val-annotations path_to_the_val.csv \
83 | --config-file config.yaml \
84 | --batch-size 128 \
85 | --epochs 750 \
86 | --dense \
87 | --early-stopping-patience 100 \
88 | --reduce-lr-patience 50
89 | ```
90 |
91 | You will probably want to change the augmentation pipeline to apply to your dataset.
92 |
93 | In order to do this define an Albumentations pipeline:
94 |
95 | ```python
96 | import albumentations as A
97 |
98 | transform_pipeline = A.Compose(
99 | [
100 | # ...
101 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
102 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
103 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
104 | # ... and any other augmentation ...
105 | ]
106 | )
107 |
108 | # Export to a file (this resultant YAML can be used by the train script)
109 | A.save(transform_pipeline, "./transform_pipeline.yaml", data_format="yaml")
110 | ```
111 |
112 | And then you can train using the custom transformation pipeline with the `--augmentation-path` option.
113 |
114 | #### Visualize Augmentation
115 |
116 | It's useful to visualize the augmentation pipeline before training the model. This helps us to identify
117 | if we should apply more heavy augmentation or less, as it can hurt the model.
118 |
119 | You might want to see the augmented image next to the original, to see how much it changed:
120 |
121 | ```shell
122 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-augmentation \
123 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
124 | --columns 2 \
125 | --show-original \
126 | --augmentation-path '/transform_pipeline.yaml'
127 | ```
128 |
129 | You will see something like:
130 |
131 | 
132 |
133 | #### Validate Model
134 |
135 | After finishing training you can validate the model on a labeled test dataset.
136 |
137 | Example:
138 |
139 | ```shell
140 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
141 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
142 | --config-file arg_plate_example.yaml \
143 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
144 | ```
145 |
146 | #### Visualize Predictions
147 |
148 | Once you finish training your model, you can view the model predictions on raw data with:
149 |
150 | ```shell
151 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-predictions \
152 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
153 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
154 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
155 | ```
156 |
157 | You will see something like:
158 |
159 | 
160 |
161 | #### Export as ONNX
162 |
163 | Exporting the Keras model to ONNX format might be beneficial to speed-up inference time.
164 |
165 | ```shell
166 | fast_plate_ocr export-onnx \
167 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
168 | --output-path arg_cnn_ocr.onnx \
169 | --opset 18 \
170 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
171 | ```
172 |
173 | ### Keras Backend
174 |
175 | To train the model, you can install the ML Framework you like the most. **Keras 3** has
176 | support for **TensorFlow**, **JAX** and **PyTorch** backends.
177 |
178 | To change the Keras backend you can either:
179 |
180 | 1. Export `KERAS_BACKEND` environment variable, i.e. to use JAX for training:
181 | ```shell
182 | KERAS_BACKEND=jax fast_plate_ocr train --config-file ...
183 | ```
184 | 2. Edit your local config file at `~/.keras/keras.json`.
185 |
186 | ???+ tip
187 | **Usually training with JAX and TensorFlow is faster.**
188 |
189 | _Note: You will probably need to install your desired framework for training._
190 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Fast Plate OCR package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.onnx_inference import ONNXPlateRecognizer
6 |
7 | __all__ = ["ONNXPlateRecognizer"]
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/cli/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/cli.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Main CLI used when training a FastPlateOCR model.
3 | """
4 |
5 | try:
6 | import click
7 |
8 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.onnx_converter import export_onnx
9 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.train import train
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.valid import valid
11 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.visualize_augmentation import visualize_augmentation
12 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.visualize_predictions import visualize_predictions
13 | except ImportError as e:
14 | raise ImportError("Make sure to 'pip install fast-plate-ocr[train]' to run this!") from e
15 |
16 |
17 | @click.group(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
18 | def main_cli():
19 | """FastPlateOCR CLI."""
20 |
21 |
22 | main_cli.add_command(visualize_predictions)
23 | main_cli.add_command(visualize_augmentation)
24 | main_cli.add_command(valid)
25 | main_cli.add_command(train)
26 | main_cli.add_command(export_onnx)
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/onnx_converter.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for converting Keras models to ONNX format.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import shutil
8 | from tempfile import NamedTemporaryFile
9 |
10 | import click
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import onnx
13 | import onnxruntime as rt
14 | import onnxsim
15 | import tensorflow as tf
16 | import tf2onnx
17 | from tf2onnx import constants as tf2onnx_constants
18 |
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.common.utils import log_time_taken
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
21 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.utils import load_keras_model
22 |
23 | logging.basicConfig(
24 | level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(message)s", datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
25 | )
26 |
27 |
28 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
29 |
30 |
31 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
32 | @click.option(
33 | "-m",
34 | "--model",
35 | "model_path",
36 | required=True,
37 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
38 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
39 | )
40 | @click.option(
41 | "--output-path",
42 | required=True,
43 | type=str,
44 | help="Output name for ONNX model.",
45 | )
46 | @click.option(
47 | "--simplify/--no-simplify",
48 | default=False,
49 | show_default=True,
50 | help="Simplify ONNX model using onnxsim.",
51 | )
52 | @click.option(
53 | "--config-file",
54 | required=True,
55 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
56 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
57 | )
58 | @click.option(
59 | "--opset",
60 | default=16,
61 | type=click.IntRange(max=max(tf2onnx_constants.OPSET_TO_IR_VERSION)),
62 | show_default=True,
63 | help="Opset version for ONNX.",
64 | )
65 | def export_onnx(
66 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
67 | output_path: str,
68 | simplify: bool,
69 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
70 | opset: int,
71 | ) -> None:
72 | """
73 | Export Keras models to ONNX format.
74 | """
75 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
76 | model = load_keras_model(
77 | model_path,
78 | vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size,
79 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
80 | )
81 | spec = (tf.TensorSpec((None, config.img_height, config.img_width, 1), tf.uint8, name="input"),)
82 | # Convert from Keras to ONNX using tf2onnx library
83 | with NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".onnx") as tmp:
84 | tmp_onnx = tmp.name
85 | model_proto, _ = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(
86 | model,
87 | input_signature=spec,
88 | opset=opset,
89 | output_path=tmp_onnx,
90 | )
91 | if simplify:
92 | logging.info("Simplifying ONNX model ...")
93 | model_simp, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx.load(tmp_onnx))
94 | assert check, "Simplified ONNX model could not be validated!"
95 | onnx.save(model_simp, output_path)
96 | else:
97 | shutil.copy(tmp_onnx, output_path)
98 | output_names = [n.name for n in model_proto.graph.output]
99 | x = np.random.randint(0, 256, size=(1, config.img_height, config.img_width, 1), dtype=np.uint8)
100 | # Run dummy inference and log time taken
101 | m = rt.InferenceSession(output_path)
102 | with log_time_taken("ONNX inference took:"):
103 | onnx_pred = m.run(output_names, {"input": x})
104 | # Check if ONNX and keras have the same results
105 | if not np.allclose(model.predict(x, verbose=0), onnx_pred[0], rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5):
106 | logging.warning("ONNX model output was not close to Keras model for the given tolerance!")
107 | logging.info("Model converted to ONNX! Saved at %s", output_path)
108 |
109 |
110 | if __name__ == "__main__":
111 | export_onnx()
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for training the License Plate OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 | import shutil
7 | from datetime import datetime
8 | from typing import Literal
9 |
10 | import albumentations as A
11 | import click
12 | from keras.src.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, TensorBoard
13 | from keras.src.optimizers import Adam
14 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
15 |
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.utils import print_params, print_train_details
17 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.augmentation import TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
18 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.dataset import LicensePlateDataset
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.custom import (
21 | cat_acc_metric,
22 | cce_loss,
23 | plate_acc_metric,
24 | top_3_k_metric,
25 | )
26 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.models import cnn_ocr_model
27 |
28 | # ruff: noqa: PLR0913
29 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
30 |
31 |
32 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
33 | @click.option(
34 | "--dense/--no-dense",
35 | default=True,
36 | show_default=True,
37 | help="Whether to use Fully Connected layers in model head or not.",
38 | )
39 | @click.option(
40 | "--config-file",
41 | required=True,
42 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
43 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
44 | )
45 | @click.option(
46 | "--annotations",
47 | required=True,
48 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
49 | help="Path pointing to the train annotations CSV file.",
50 | )
51 | @click.option(
52 | "--val-annotations",
53 | required=True,
54 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
55 | help="Path pointing to the train validation CSV file.",
56 | )
57 | @click.option(
58 | "--augmentation-path",
59 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
60 | help="YAML file pointing to the augmentation pipeline saved with Albumentations.save(...)",
61 | )
62 | @click.option(
63 | "--lr",
64 | default=1e-3,
65 | show_default=True,
66 | type=float,
67 | help="Initial learning rate to use.",
68 | )
69 | @click.option(
70 | "--label-smoothing",
71 | default=0.05,
72 | show_default=True,
73 | type=float,
74 | help="Amount of label smoothing to apply.",
75 | )
76 | @click.option(
77 | "--batch-size",
78 | default=128,
79 | show_default=True,
80 | type=int,
81 | help="Batch size for training.",
82 | )
83 | @click.option(
84 | "--num-workers",
85 | default=0,
86 | show_default=True,
87 | type=int,
88 | help="How many subprocesses to load data, used in the torch DataLoader.",
89 | )
90 | @click.option(
91 | "--output-dir",
92 | default="./trained_models",
93 | type=click.Path(dir_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
94 | help="Output directory where model will be saved.",
95 | )
96 | @click.option(
97 | "--epochs",
98 | default=500,
99 | show_default=True,
100 | type=int,
101 | help="Number of training epochs.",
102 | )
103 | @click.option(
104 | "--tensorboard",
105 | "-t",
106 | is_flag=True,
107 | help="Whether to use TensorBoard visualization tool.",
108 | )
109 | @click.option(
110 | "--tensorboard-dir",
111 | "-l",
112 | default="tensorboard_logs",
113 | show_default=True,
114 | type=click.Path(path_type=pathlib.Path),
115 | help="The path of the directory where to save the TensorBoard log files.",
116 | )
117 | @click.option(
118 | "--early-stopping-patience",
119 | default=100,
120 | show_default=True,
121 | type=int,
122 | help="Stop training when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve for X epochs.",
123 | )
124 | @click.option(
125 | "--reduce-lr-patience",
126 | default=60,
127 | show_default=True,
128 | type=int,
129 | help="Patience to reduce the learning rate if 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve within X epochs.",
130 | )
131 | @click.option(
132 | "--reduce-lr-factor",
133 | default=0.85,
134 | show_default=True,
135 | type=float,
136 | help="Reduce the learning rate by this factor when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve.",
137 | )
138 | @click.option(
139 | "--activation",
140 | default="relu",
141 | show_default=True,
142 | type=str,
143 | help="Activation function to use.",
144 | )
145 | @click.option(
146 | "--pool-layer",
147 | default="max",
148 | show_default=True,
149 | type=click.Choice(["max", "avg"]),
150 | help="Choose the pooling layer to use.",
151 | )
152 | @click.option(
153 | "--weights-path",
154 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
155 | help="Path to the pretrained model weights file.",
156 | )
157 | @print_params(table_title="CLI Training Parameters", c1_title="Parameter", c2_title="Details")
158 | def train(
159 | dense: bool,
160 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
161 | annotations: pathlib.Path,
162 | val_annotations: pathlib.Path,
163 | augmentation_path: pathlib.Path | None,
164 | lr: float,
165 | label_smoothing: float,
166 | batch_size: int,
167 | num_workers: int,
168 | output_dir: pathlib.Path,
169 | epochs: int,
170 | tensorboard: bool,
171 | tensorboard_dir: pathlib.Path,
172 | early_stopping_patience: int,
173 | reduce_lr_patience: int,
174 | reduce_lr_factor: float,
175 | activation: str,
176 | pool_layer: Literal["max", "avg"],
177 | weights_path: pathlib.Path | None,
178 | ) -> None:
179 | """
180 | Train the License Plate OCR model.
181 | """
182 | train_augmentation = (
183 | A.load(augmentation_path, data_format="yaml") if augmentation_path else TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
184 | )
185 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
186 | print_train_details(train_augmentation, config.model_dump())
187 | train_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(
188 | annotations_file=annotations,
189 | transform=train_augmentation,
190 | config=config,
191 | )
192 | train_dataloader = DataLoader(
193 | train_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=True
194 | )
195 |
196 | if val_annotations:
197 | val_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(
198 | annotations_file=val_annotations,
199 | config=config,
200 | )
201 | val_dataloader = DataLoader(
202 | val_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=False
203 | )
204 | else:
205 | val_dataloader = None
206 |
207 | # Train
208 | model = cnn_ocr_model(
209 | h=config.img_height,
210 | w=config.img_width,
211 | dense=dense,
212 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
213 | vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size,
214 | activation=activation,
215 | pool_layer=pool_layer,
216 | )
217 |
218 | if weights_path:
219 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
220 |
221 | model.compile(
222 | loss=cce_loss(vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size, label_smoothing=label_smoothing),
223 | optimizer=Adam(lr),
224 | metrics=[
225 | cat_acc_metric(
226 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size
227 | ),
228 | plate_acc_metric(
229 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size
230 | ),
231 | top_3_k_metric(vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size),
232 | ],
233 | )
234 |
235 | output_dir /= datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S")
236 | output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
237 | model_file_path = output_dir / "cnn_ocr-epoch_{epoch:02d}-acc_{val_plate_acc:.3f}.keras"
238 |
239 | # Save params and config used for training
240 | shutil.copy(config_file, output_dir / "config.yaml")
241 | A.save(train_augmentation, output_dir / "train_augmentation.yaml", "yaml")
242 |
243 | callbacks = [
244 | # Reduce the learning rate by 0.5x if 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve within X epochs
245 | ReduceLROnPlateau(
246 | "val_plate_acc",
247 | patience=reduce_lr_patience,
248 | factor=reduce_lr_factor,
249 | min_lr=1e-6,
250 | verbose=1,
251 | ),
252 | # Stop training when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve for X epochs
253 | EarlyStopping(
254 | monitor="val_plate_acc",
255 | patience=early_stopping_patience,
256 | mode="max",
257 | restore_best_weights=False,
258 | verbose=1,
259 | ),
260 | # We don't use EarlyStopping restore_best_weights=True because it won't restore the best
261 | # weights when it didn't manage to EarlyStop but finished all epochs
262 | ModelCheckpoint(
263 | model_file_path,
264 | monitor="val_plate_acc",
265 | mode="max",
266 | save_best_only=True,
267 | verbose=1,
268 | ),
269 | ]
270 |
271 | if tensorboard:
272 | run_dir = tensorboard_dir / datetime.now().strftime("run_%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
273 | run_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
274 | callbacks.append(TensorBoard(log_dir=run_dir))
275 |
276 | model.fit(train_dataloader, epochs=epochs, validation_data=val_dataloader, callbacks=callbacks)
277 |
278 |
279 | if __name__ == "__main__":
280 | train()
281 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utils used for the CLI scripts.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import inspect
6 | import pathlib
7 | from collections.abc import Callable
8 | from functools import wraps
9 | from typing import Any
10 |
11 | import albumentations as A
12 | from rich import box
13 | from rich.console import Console
14 | from rich.pretty import Pretty
15 | from rich.table import Table
16 |
17 |
18 | def print_variables_as_table(
19 | c1_title: str, c2_title: str, title: str = "Variables Table", **kwargs: Any
20 | ) -> None:
21 | """
22 | Prints variables in a formatted table using the rich library.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | c1_title (str): Title of the first column.
26 | c2_title (str): Title of the second column.
27 | title (str): Title of the table.
28 | **kwargs (Any): Variable names and values to be printed.
29 | """
30 | console = Console()
31 | console.print("\n")
32 | table = Table(title=title, show_header=True, header_style="bold blue", box=box.ROUNDED)
33 | table.add_column(c1_title, min_width=20, justify="left", style="bold")
34 | table.add_column(c2_title, min_width=60, justify="left", style="bold")
35 |
36 | for key, value in kwargs.items():
37 | if isinstance(value, pathlib.Path):
38 | value = str(value) # noqa: PLW2901
39 | table.add_row(f"[bold]{key}[/bold]", Pretty(value))
40 |
41 | console.print(table)
42 |
43 |
44 | def print_params(
45 | table_title: str = "Parameters Table", c1_title: str = "Variable", c2_title: str = "Value"
46 | ) -> Callable:
47 | """
48 | A decorator that prints the parameters of a function in a formatted table
49 | using the rich library.
50 |
51 | Args:
52 | c1_title (str, optional): Title of the first column. Defaults to "Variable".
53 | c2_title (str, optional): Title of the second column. Defaults to "Value".
54 | table_title (str, optional): Title of the table. Defaults to "Parameters Table".
55 |
56 | Returns:
57 | Callable: The wrapped function with parameter printing functionality.
58 | """
59 |
60 | def decorator(func: Callable) -> Callable:
61 | @wraps(func)
62 | def wrapper(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> Any:
63 | func_signature = inspect.signature(func)
64 | bound_arguments = func_signature.bind(*args, **kwargs)
65 | bound_arguments.apply_defaults()
66 | params = dict(bound_arguments.arguments.items())
67 | print_variables_as_table(c1_title, c2_title, table_title, **params)
68 | return func(*args, **kwargs)
69 |
70 | return wrapper
71 |
72 | return decorator
73 |
74 |
75 | def print_train_details(augmentation: A.Compose, config: dict[str, Any]) -> None:
76 | console = Console()
77 | console.print("\n")
78 | console.print("[bold blue]Augmentation Pipeline:[/bold blue]")
79 | console.print(Pretty(augmentation))
80 | console.print("\n")
81 | console.print("[bold blue]Configuration:[/bold blue]")
82 | console.print(Pretty(config))
83 | console.print("\n")
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/valid.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for validating trained OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 |
7 | import click
8 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
9 |
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.dataset import LicensePlateDataset
11 |
12 | # Custom metris / losses
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 |
16 |
17 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
18 | @click.option(
19 | "-m",
20 | "--model",
21 | "model_path",
22 | required=True,
23 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
24 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
25 | )
26 | @click.option(
27 | "--config-file",
28 | required=True,
29 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
30 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
31 | )
32 | @click.option(
33 | "-a",
34 | "--annotations",
35 | required=True,
36 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
37 | help="Annotations file used for validation.",
38 | )
39 | @click.option(
40 | "-b",
41 | "--batch-size",
42 | default=1,
43 | show_default=True,
44 | type=int,
45 | help="Batch size.",
46 | )
47 | def valid(
48 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
49 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
50 | annotations: pathlib.Path,
51 | batch_size: int,
52 | ) -> None:
53 | """
54 | Validate the trained OCR model on a labeled set.
55 | """
56 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
57 | model = utils.load_keras_model(
58 | model_path, vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size, max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots
59 | )
60 | val_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(annotations_file=annotations, config=config)
61 | val_dataloader = DataLoader(val_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
62 | model.evaluate(val_dataloader)
63 |
64 |
65 | if __name__ == "__main__":
66 | valid()
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/visualize_augmentation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script to visualize the augmented plates used during training.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 | import random
7 | from math import ceil
8 |
9 | import albumentations as A
10 | import click
11 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import numpy.typing as npt
14 |
15 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.augmentation import TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
17 |
18 |
19 | def _set_seed(seed: int | None) -> None:
20 | """Set random seed for reproducing augmentations."""
21 | if seed:
22 | random.seed(seed)
23 | np.random.seed(seed)
24 |
25 |
26 | def load_images(
27 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
28 | num_images: int,
29 | shuffle: bool,
30 | height: int,
31 | width: int,
32 | augmentation: A.Compose,
33 | ) -> tuple[list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]], list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]]]:
34 | images = utils.load_images_from_folder(
35 | img_dir, height=height, width=width, shuffle=shuffle, limit=num_images
36 | )
37 | augmented_images = [augmentation(image=i)["image"] for i in images]
38 | return images, augmented_images
39 |
40 |
41 | def display_images(
42 | images: list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]],
43 | augmented_images: list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]],
44 | columns: int,
45 | rows: int,
46 | show_original: bool,
47 | ) -> None:
48 | num_images = len(images)
49 | total_plots = rows * columns
50 | num_pages = ceil(num_images / total_plots)
51 | for page in range(num_pages):
52 | _, axs = plt.subplots(rows, columns, figsize=(8, 8))
53 | axs = axs.flatten()
54 | for i, ax in enumerate(axs):
55 | idx = page * total_plots + i
56 | if idx < num_images:
57 | if show_original:
58 | img_to_show = np.concatenate((images[idx], augmented_images[idx]), axis=1)
59 | else:
60 | img_to_show = augmented_images[idx]
61 | ax.imshow(img_to_show, cmap="gray")
62 | ax.axis("off")
63 | else:
64 | ax.axis("off")
65 | plt.tight_layout()
66 | plt.show()
67 |
68 |
69 | # ruff: noqa: PLR0913
70 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
71 |
72 |
73 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
74 | @click.option(
75 | "--img-dir",
76 | "-d",
77 | required=True,
78 | type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
79 | help="Path to the images that will be augmented and visualized.",
80 | )
81 | @click.option(
82 | "--num-images",
83 | "-n",
84 | type=int,
85 | default=1_000,
86 | show_default=True,
87 | help="Maximum number of images to visualize.",
88 | )
89 | @click.option(
90 | "--augmentation-path",
91 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
92 | help="YAML file pointing to the augmentation pipeline saved with Albumentations.save(...)",
93 | )
94 | @click.option(
95 | "--shuffle",
96 | "-s",
97 | is_flag=True,
98 | default=False,
99 | help="Whether to shuffle the images before plotting them.",
100 | )
101 | @click.option(
102 | "--columns",
103 | "-c",
104 | type=int,
105 | default=3,
106 | show_default=True,
107 | help="Number of columns in the grid layout for displaying images.",
108 | )
109 | @click.option(
110 | "--rows",
111 | "-r",
112 | type=int,
113 | default=4,
114 | show_default=True,
115 | help="Number of rows in the grid layout for displaying images.",
116 | )
117 | @click.option(
118 | "--height",
119 | "-h",
120 | type=int,
121 | default=70,
122 | show_default=True,
123 | help="Height to which the images will be resize.",
124 | )
125 | @click.option(
126 | "--width",
127 | "-w",
128 | type=int,
129 | default=140,
130 | show_default=True,
131 | help="Width to which the images will be resize.",
132 | )
133 | @click.option(
134 | "--show-original",
135 | "-o",
136 | is_flag=True,
137 | help="Show the original image along with the augmented one.",
138 | )
139 | @click.option(
140 | "--seed",
141 | type=int,
142 | help="Seed for reproducing augmentations.",
143 | )
144 | def visualize_augmentation(
145 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
146 | num_images: int,
147 | augmentation_path: pathlib.Path | None,
148 | shuffle: bool,
149 | columns: int,
150 | rows: int,
151 | height: int,
152 | width: int,
153 | seed: int | None,
154 | show_original: bool,
155 | ) -> None:
156 | """
157 | Visualize augmentation pipeline applied to raw images.
158 | """
159 | _set_seed(seed)
160 | aug = A.load(augmentation_path, data_format="yaml") if augmentation_path else TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
161 | images, augmented_images = load_images(img_dir, num_images, shuffle, height, width, aug)
162 | display_images(images, augmented_images, columns, rows, show_original)
163 |
164 |
165 | if __name__ == "__main__":
166 | # pylint: disable = no-value-for-parameter
167 | visualize_augmentation()
168 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/visualize_predictions.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for displaying an image with the OCR model predictions.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 |
8 | import click
9 | import cv2
10 | import keras
11 | import numpy as np
12 |
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.utils import postprocess_model_output
16 |
17 | logging.basicConfig(
18 | level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(message)s", datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
19 | )
20 |
21 |
22 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
23 | @click.option(
24 | "-m",
25 | "--model",
26 | "model_path",
27 | required=True,
28 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
29 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
30 | )
31 | @click.option(
32 | "--config-file",
33 | required=True,
34 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
35 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
36 | )
37 | @click.option(
38 | "-d",
39 | "--img-dir",
40 | required=True,
41 | type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=True, file_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
42 | help="Directory containing the images to make predictions from.",
43 | )
44 | @click.option(
45 | "-l",
46 | "--low-conf-thresh",
47 | type=float,
48 | default=0.35,
49 | show_default=True,
50 | help="Threshold for displaying low confidence characters.",
51 | )
52 | @click.option(
53 | "-f",
54 | "--filter-conf",
55 | type=float,
56 | help="Display plates that any of the plate characters are below this number.",
57 | )
58 | def visualize_predictions(
59 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
60 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
61 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
62 | low_conf_thresh: float,
63 | filter_conf: float | None,
64 | ):
65 | """
66 | Visualize OCR model predictions on unlabeled data.
67 | """
68 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
69 | model = utils.load_keras_model(
70 | model_path, vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size, max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots
71 | )
72 | images = utils.load_images_from_folder(
73 | img_dir, width=config.img_width, height=config.img_height
74 | )
75 | for image in images:
76 | x = np.expand_dims(image, 0)
77 | prediction = model(x, training=False)
78 | prediction = keras.ops.stop_gradient(prediction).numpy()
79 | plate, probs = postprocess_model_output(
80 | prediction=prediction,
81 | alphabet=config.alphabet,
82 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
83 | vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size,
84 | )
85 | if not filter_conf or (filter_conf and np.any(probs < filter_conf)):
86 | utils.display_predictions(
87 | image=image, plate=plate, probs=probs, low_conf_thresh=low_conf_thresh
88 | )
89 | cv2.destroyAllWindows()
90 |
91 |
92 | if __name__ == "__main__":
93 | visualize_predictions()
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/common/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/common/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/common/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Common utilities used across the package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import time
7 | from collections.abc import Callable, Iterator
8 | from contextlib import contextmanager
9 |
10 |
11 | @contextmanager
12 | def log_time_taken(process_name: str) -> Iterator[None]:
13 | """
14 | A concise context manager to time code snippets and log the result.
15 |
16 | Usage:
17 | with log_time_taken("process_name"):
18 | # Code snippet to be timed
19 |
20 | :param process_name: Name of the process being timed.
21 | """
22 | time_start: float = time.perf_counter()
23 | try:
24 | yield
25 | finally:
26 | time_end: float = time.perf_counter()
27 | time_elapsed: float = time_end - time_start
28 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
29 | logger.info("Computation time of '%s' = %.3fms", process_name, 1_000 * time_elapsed)
30 |
31 |
32 | @contextmanager
33 | def measure_time() -> Iterator[Callable[[], float]]:
34 | """
35 | A context manager for measuring execution time (in milliseconds) within its code block.
36 |
37 | usage:
38 | with code_timer() as timer:
39 | # Code snippet to be timed
40 | print(f"Code took: {timer()} seconds")
41 | """
42 | start_time = end_time = time.perf_counter()
43 | yield lambda: (end_time - start_time) * 1_000
44 | end_time = time.perf_counter()
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/inference/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Model config reading/parsing for doing inference.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from os import PathLike
6 | from typing import TypedDict
7 |
8 | import yaml
9 |
10 | # pylint: disable=duplicate-code
11 |
12 |
13 | class PlateOCRConfig(TypedDict):
14 | """
15 | Plate OCR Config used for inference.
16 |
17 | This has the same attributes as the one used in the training Pydantic BaseModel. We use this to
18 | avoid having Pydantic as a required dependency of the minimal package install.
19 | """
20 |
21 | max_plate_slots: int
22 | """
23 | Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
24 | """
25 | alphabet: str
26 | """
27 | All the possible character set for the model output.
28 | """
29 | pad_char: str
30 | """
31 | Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS.
32 | """
33 | img_height: int
34 | """
35 | Image height which is fed to the model.
36 | """
37 | img_width: int
38 | """
39 | Image width which is fed to the model.
40 | """
41 |
42 |
43 | def load_config_from_yaml(yaml_file_path: str | PathLike[str]) -> PlateOCRConfig:
44 | """
45 | Read and parse a yaml containing the Plate OCR config.
46 |
47 | Note: This is currently not using Pydantic for parsing/validating to avoid adding it a python
48 | dependency as part of the minimal installation.
49 | """
50 | with open(yaml_file_path, encoding="utf-8") as f_in:
51 | config: PlateOCRConfig = yaml.safe_load(f_in)
52 | return config
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/hub.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utilities function used for doing inference with the OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import shutil
8 | import urllib.request
9 | from http import HTTPStatus
10 | from typing import Literal
11 |
12 | from tqdm.asyncio import tqdm
13 |
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.utils import safe_write
15 |
16 | BASE_URL: str = "https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/releases/download"
17 | OcrModel = Literal[
18 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-model",
19 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model",
20 | "european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model",
21 | "global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model",
22 | ]
23 |
24 |
25 | AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS: dict[OcrModel, tuple[str, str]] = {
26 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-model": (
27 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr.onnx",
28 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml",
29 | ),
30 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model": (
31 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_synth.onnx",
32 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml",
33 | ),
34 | "european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model": (
35 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr.onnx",
36 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_config.yaml",
37 | ),
38 | "global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model": (
39 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr.onnx",
40 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_config.yaml",
41 | ),
42 | }
43 | """Available ONNX models for doing inference."""
44 |
45 | MODEL_CACHE_DIR: pathlib.Path = pathlib.Path.home() / ".cache" / "fast-plate-ocr"
46 | """Default location where models will be stored."""
47 |
48 |
49 | def _download_with_progress(url: str, filename: pathlib.Path) -> None:
50 | """
51 | Download utility function with progress bar.
52 |
53 | :param url: URL of the model to download.
54 | :param filename: Where to save the OCR model.
55 | """
56 | with urllib.request.urlopen(url) as response, safe_write(filename, mode="wb") as out_file:
57 | if response.getcode() != HTTPStatus.OK:
58 | raise ValueError(f"Failed to download file from {url}. Status code: {response.status}")
59 |
60 | file_size = int(response.headers.get("Content-Length", 0))
61 | desc = f"Downloading {filename.name}"
62 |
63 | with tqdm.wrapattr(out_file, "write", total=file_size, desc=desc) as f_out:
64 | shutil.copyfileobj(response, f_out)
65 |
66 |
67 | def download_model(
68 | model_name: OcrModel,
69 | save_directory: pathlib.Path | None = None,
70 | force_download: bool = False,
71 | ) -> tuple[pathlib.Path, pathlib.Path]:
72 | """
73 | Download an OCR model and the config to a given directory.
74 |
75 | :param model_name: Which model to download.
76 | :param save_directory: Directory to save the OCR model. It should point to a folder. If not
77 | supplied, this will point to '~/.cache/'
78 | :param force_download: Force and download the model if it already exists in `save_directory`.
79 | :return: A tuple consisting of (model_downloaded_path, config_downloaded_path).
80 | """
81 | if model_name not in AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS:
82 | available_models = ", ".join(AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS.keys())
83 | raise ValueError(f"Unknown model {model_name}. Use one of [{available_models}]")
84 |
85 | if save_directory is None:
86 | save_directory = MODEL_CACHE_DIR / model_name
87 | elif save_directory.is_file():
88 | raise ValueError(f"Expected a directory, but got {save_directory}")
89 |
90 | save_directory.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
91 |
92 | model_url, config_url = AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS[model_name]
93 | model_filename = save_directory / model_url.split("/")[-1]
94 | config_filename = save_directory / config_url.split("/")[-1]
95 |
96 | if not force_download and model_filename.is_file() and config_filename.is_file():
97 | logging.info(
98 | "Skipping download of '%s' model, already exists at %s",
99 | model_name,
100 | save_directory,
101 | )
102 | return model_filename, config_filename
103 |
104 | # Download the model if not present or if we want to force the download
105 | if force_download or not model_filename.is_file():
106 | logging.info("Downloading model to %s", model_filename)
107 | _download_with_progress(url=model_url, filename=model_filename)
108 |
109 | # Same for the config
110 | if force_download or not config_filename.is_file():
111 | logging.info("Downloading config to %s", config_filename)
112 | _download_with_progress(url=config_url, filename=config_filename)
113 |
114 | return model_filename, config_filename
115 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/onnx_inference.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | ONNX inference module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import os
7 | import pathlib
8 | from collections.abc import Sequence
9 | from typing import Literal
10 |
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import numpy.typing as npt
13 | import onnxruntime as ort
14 | from rich.console import Console
15 | from rich.panel import Panel
16 | from rich.table import Table
17 | from rich.text import Text
18 |
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.common.utils import measure_time
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference import hub
21 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.config import load_config_from_yaml
22 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.hub import OcrModel
23 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.process import postprocess_output, preprocess_image, read_plate_image
24 |
25 |
26 | def _load_image_from_source(
27 | source: str | list[str] | npt.NDArray | list[npt.NDArray],
28 | ) -> npt.NDArray | list[npt.NDArray]:
29 | """
30 | Loads an image from a given source.
31 |
32 | :param source: Path to the input image file, list of paths, or numpy array representing one or
33 | multiple images.
34 | :return: Numpy array representing the input image(s) or a list of numpy arrays.
35 | """
36 | if isinstance(source, str):
37 | # Shape returned (H, W)
38 | return read_plate_image(source)
39 |
40 | if isinstance(source, list):
41 | # Are image paths
42 | if all(isinstance(s, str) for s in source):
43 | # List returned with array item of shape (H, W)
44 | return [read_plate_image(i) for i in source] # type: ignore[arg-type]
45 | # Are list of numpy arrays
46 | if all(isinstance(a, np.ndarray) for a in source):
47 | # List returned with array item of shape (H, W)
48 | return source # type: ignore[return-value]
49 | raise ValueError("Expected source to be a list of `str` or `np.ndarray`!")
50 |
51 | if isinstance(source, np.ndarray):
52 | # Squeeze grayscale channel dimension if supplied
53 | source = source.squeeze()
54 | if source.ndim != 2:
55 | raise ValueError("Expected source array to be of shape (H, W) or (H, W, 1).")
56 | # Shape returned (H, W)
57 | return source
58 |
59 | raise ValueError("Unsupported input type. Only file path or numpy array is supported.")
60 |
61 |
62 | class ONNXPlateRecognizer:
63 | """
64 | ONNX inference class for performing license plates OCR.
65 | """
66 |
67 | def __init__(
68 | self,
69 | hub_ocr_model: OcrModel | None = None,
70 | device: Literal["cuda", "cpu", "auto"] = "auto",
71 | providers: Sequence[str | tuple[str, dict]] | None = None,
72 | sess_options: ort.SessionOptions | None = None,
73 | model_path: str | os.PathLike[str] | None = None,
74 | config_path: str | os.PathLike[str] | None = None,
75 | force_download: bool = False,
76 | ) -> None:
77 | """
78 | Initializes the ONNXPlateRecognizer with the specified OCR model and inference device.
79 |
80 | The current OCR models available from the HUB are:
81 |
82 | - `argentinian-plates-cnn-model`: OCR for Argentinian license plates. Uses fully conv
83 | architecture.
84 | - `argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model`: OCR for Argentinian license plates trained with
85 | synthetic and real data. Uses fully conv architecture.
86 | - `european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model`: OCR for European license plates. Uses MobileVIT-2
87 | for the backbone.
88 | - `global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model`: OCR for Global license plates (+65 countries).
89 | Uses MobileVIT-2 for the backbone.
90 |
91 | Args:
92 | hub_ocr_model: Name of the OCR model to use from the HUB.
93 | device: Device type for inference. Should be one of ('cpu', 'cuda', 'auto'). If
94 | 'auto' mode, the device will be deduced from
95 | `onnxruntime.get_available_providers()`.
96 | providers: Optional sequence of providers in order of decreasing precedence. If not
97 | specified, all available providers are used based on the device argument.
98 | sess_options: Advanced session options for ONNX Runtime.
99 | model_path: Path to ONNX model file to use (In case you want to use a custom one).
100 | config_path: Path to config file to use (In case you want to use a custom one).
101 | force_download: Force and download the model, even if it already exists.
102 | Returns:
103 | None.
104 | """
105 | self.logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
106 |
107 | if providers is not None:
108 | self.providers = providers
109 | self.logger.info("Using custom providers: %s", providers)
110 | else:
111 | if device == "cuda":
112 | self.providers = ["CUDAExecutionProvider"]
113 | elif device == "cpu":
114 | self.providers = ["CPUExecutionProvider"]
115 | elif device == "auto":
116 | self.providers = ort.get_available_providers()
117 | else:
118 | raise ValueError(
119 | f"Device should be one of ('cpu', 'cuda', 'auto'). Got '{device}'."
120 | )
121 |
122 | self.logger.info("Using device '%s' with providers: %s", device, self.providers)
123 |
124 | if model_path and config_path:
125 | model_path = pathlib.Path(model_path)
126 | config_path = pathlib.Path(config_path)
127 | if not model_path.exists() or not config_path.exists():
128 | raise FileNotFoundError("Missing model/config file!")
129 | self.model_name = model_path.stem
130 | elif hub_ocr_model:
131 | self.model_name = hub_ocr_model
132 | model_path, config_path = hub.download_model(
133 | model_name=hub_ocr_model, force_download=force_download
134 | )
135 | else:
136 | raise ValueError(
137 | "Either provide a model from the HUB or a custom model_path and config_path"
138 | )
139 |
140 | self.config = load_config_from_yaml(config_path)
141 | self.model = ort.InferenceSession(
142 | model_path, providers=self.providers, sess_options=sess_options
143 | )
144 | self.logger.info("Using ONNX Runtime with %s.", self.providers)
145 |
146 | def benchmark(self, n_iter: int = 10_000, include_processing: bool = False) -> None:
147 | """
148 | Benchmark time taken to run the OCR model. This reports the average inference time and the
149 | throughput in plates per second.
150 |
151 | Args:
152 | n_iter: The number of iterations to run the benchmark. This determines how many times
153 | the inference will be executed to compute the average performance metrics.
154 | include_processing: Indicates whether the benchmark should include preprocessing and
155 | postprocessing times in the measurement.
156 | """
157 | cum_time = 0.0
158 | x = np.random.randint(
159 | 0, 256, size=(1, self.config["img_height"], self.config["img_width"], 1), dtype=np.uint8
160 | )
161 | for _ in range(n_iter):
162 | with measure_time() as time_taken:
163 | if include_processing:
164 | self.run(x)
165 | else:
166 | self.model.run(None, {"input": x})
167 | cum_time += time_taken()
168 |
169 | avg_time = (cum_time / n_iter) if n_iter > 0 else 0.0
170 | avg_pps = (1_000 / avg_time) if n_iter > 0 else 0.0
171 |
172 | console = Console()
173 | model_info = Panel(
174 | Text(f"Model: {self.model_name}\nProviders: {self.providers}", style="bold green"),
175 | title="Model Information",
176 | border_style="bright_blue",
177 | expand=False,
178 | )
179 | console.print(model_info)
180 | table = Table(title=f"Benchmark for '{self.model_name}' Model", border_style="bright_blue")
181 | table.add_column("Metric", justify="center", style="cyan", no_wrap=True)
182 | table.add_column("Value", justify="center", style="magenta")
183 | table.add_row("Number of Iterations", str(n_iter))
184 | table.add_row("Average Time (ms)", f"{avg_time:.4f}")
185 | table.add_row("Plates Per Second (PPS)", f"{avg_pps:.4f}")
186 | console.print(table)
187 |
188 | def run(
189 | self,
190 | source: str | list[str] | npt.NDArray | list[npt.NDArray],
191 | return_confidence: bool = False,
192 | ) -> tuple[list[str], npt.NDArray] | list[str]:
193 | """
194 | Performs OCR to recognize license plate characters from an image or a list of images.
195 |
196 | Args:
197 | source: The path(s) to the image(s), a numpy array representing an image or a list
198 | of NumPy arrays. If a numpy array is provided, it is expected to already be in
199 | grayscale format, with shape `(H, W) `or `(H, W, 1)`. A list of numpy arrays with
200 | different image sizes may also be provided.
201 | return_confidence: Whether to return confidence scores along with plate predictions.
202 |
203 | Returns:
204 | A list of plates for each input image. If `return_confidence` is True, a numpy
205 | array is returned with the shape `(N, plate_slots)`, where N is the batch size and
206 | each plate slot is the confidence for the recognized license plate character.
207 | """
208 | x = _load_image_from_source(source)
209 | # Preprocess
210 | x = preprocess_image(x, self.config["img_height"], self.config["img_width"])
211 | # Run model
212 | y: list[npt.NDArray] = self.model.run(None, {"input": x})
213 | # Postprocess model output
214 | return postprocess_output(
215 | y[0],
216 | self.config["max_plate_slots"],
217 | self.config["alphabet"],
218 | return_confidence=return_confidence,
219 | )
220 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/process.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utility functions for processing model input/output.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 |
7 | import cv2
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import numpy.typing as npt
10 |
11 |
12 | def read_plate_image(image_path: str) -> npt.NDArray:
13 | """
14 | Read image from disk as a grayscale image.
15 |
16 | :param image_path: The path to the license plate image.
17 | :return: The image as a NumPy array.
18 | """
19 | if not os.path.exists(image_path):
20 | raise ValueError(f"{image_path} file doesn't exist!")
21 | return cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
22 |
23 |
24 | def preprocess_image(
25 | image: npt.NDArray | list[npt.NDArray], img_height: int, img_width: int
26 | ) -> npt.NDArray:
27 | """
28 | Preprocess the image(s), so they're ready to be fed to the model.
29 |
30 | Note: We don't normalize the pixel values between [0, 1] here, because that the model first
31 | layer does that.
32 |
33 | :param image: The image(s) contained in a NumPy array.
34 | :param img_height: The desired height of the resized image.
35 | :param img_width: The desired width of the resized image.
36 | :return: A numpy array with shape (N, H, W, 1).
37 | """
38 | # Add batch dimension: (H, W) -> (1, H, W)
39 | if isinstance(image, np.ndarray):
40 | image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
41 |
42 | imgs = np.array(
43 | [
44 | cv2.resize(im.squeeze(), (img_width, img_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
45 | for im in image
46 | ]
47 | )
48 | # Add channel dimension
49 | imgs = np.expand_dims(imgs, axis=-1)
50 | return imgs
51 |
52 |
53 | def postprocess_output(
54 | model_output: npt.NDArray,
55 | max_plate_slots: int,
56 | model_alphabet: str,
57 | return_confidence: bool = False,
58 | ) -> tuple[list[str], npt.NDArray] | list[str]:
59 | """
60 | Post-processes model output and return license plate string, and optionally the probabilities.
61 |
62 | :param model_output: Output from the model containing predictions.
63 | :param max_plate_slots: Maximum number of characters in a license plate.
64 | :param model_alphabet: Alphabet used by the model for character encoding.
65 | :param return_confidence: Flag to indicate whether to return confidence scores along with plate
66 | predictions.
67 | :return: Decoded license plate characters as a list, optionally with confidence scores. The
68 | confidence scores have shape (N, max_plate_slots) where N is the batch size.
69 | """
70 | predictions = model_output.reshape((-1, max_plate_slots, len(model_alphabet)))
71 | prediction_indices = np.argmax(predictions, axis=-1)
72 | alphabet_array = np.array(list(model_alphabet))
73 | plate_chars = alphabet_array[prediction_indices]
74 | plates: list[str] = np.apply_along_axis("".join, 1, plate_chars).tolist()
75 | if return_confidence:
76 | probs = np.max(predictions, axis=-1)
77 | return plates, probs
78 | return plates
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utilities used around the inference package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | from collections.abc import Iterator
7 | from contextlib import contextmanager
8 | from pathlib import Path
9 | from typing import IO, Any
10 |
11 |
12 | @contextmanager
13 | def safe_write(
14 | file: str | os.PathLike[str],
15 | mode: str = "wb",
16 | encoding: str | None = None,
17 | **kwargs: Any,
18 | ) -> Iterator[IO]:
19 | """
20 | Context manager for safe file writing.
21 |
22 | Opens the specified file for writing and yields a file object.
23 | If an exception occurs during writing, the file is removed before raising the exception.
24 | """
25 | try:
26 | with open(file, mode, encoding=encoding, **kwargs) as f:
27 | yield f
28 | except Exception as e:
29 | Path(file).unlink(missing_ok=True)
30 | raise e
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/py.typed:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/py.typed
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/train/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/data/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/train/data/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/data/augmentation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Augmentations used for training the OCR model.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import albumentations as A
6 | import cv2
7 |
8 | BORDER_COLOR_BLACK: tuple[int, int, int] = (0, 0, 0)
9 |
10 | TRAIN_AUGMENTATION = A.Compose(
11 | [
12 | A.ShiftScaleRotate(
13 | shift_limit=0.06,
14 | scale_limit=0.1,
15 | rotate_limit=9,
16 | border_mode=cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,
17 | value=BORDER_COLOR_BLACK,
18 | p=1,
19 | ),
20 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
21 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
22 | A.OneOf(
23 | [
24 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
25 | A.PixelDropout(dropout_prob=0.01, p=0.2),
26 | ],
27 | p=0.7,
28 | ),
29 | ]
30 | )
31 | """Training augmentations recipe."""
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/data/dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Dataset module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | from os import PathLike
7 |
8 | import albumentations as A
9 | import numpy.typing as npt
10 | import pandas as pd
11 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
12 |
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import PlateOCRConfig
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 |
16 |
17 | class LicensePlateDataset(Dataset):
18 | def __init__(
19 | self,
20 | annotations_file: str | PathLike[str],
21 | config: PlateOCRConfig,
22 | transform: A.Compose | None = None,
23 | ) -> None:
24 | annotations = pd.read_csv(annotations_file)
25 | annotations["image_path"] = (
26 | os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(annotations_file)) + os.sep + annotations["image_path"]
27 | )
28 | assert (
29 | annotations["plate_text"].str.len() <= config.max_plate_slots
30 | ).all(), "Plates are longer than max_plate_slots specified param. Change the parameter."
31 | self.annotations = annotations.to_numpy()
32 | self.config = config
33 | self.transform = transform
34 |
35 | def __len__(self) -> int:
36 | return self.annotations.shape[0]
37 |
38 | def __getitem__(self, idx) -> tuple[npt.NDArray, npt.NDArray]:
39 | image_path, plate_text = self.annotations[idx]
40 | x = utils.read_plate_image(
41 | image_path=image_path,
42 | img_height=self.config.img_height,
43 | img_width=self.config.img_width,
44 | )
45 | y = utils.target_transform(
46 | plate_text=plate_text,
47 | max_plate_slots=self.config.max_plate_slots,
48 | alphabet=self.config.alphabet,
49 | pad_char=self.config.pad_char,
50 | )
51 | if self.transform:
52 | x = self.transform(image=x)["image"]
53 | return x, y
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Config values used throughout the code.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from os import PathLike
6 |
7 | import yaml
8 | from pydantic import BaseModel, computed_field, model_validator
9 |
10 |
11 | class PlateOCRConfig(BaseModel, extra="forbid", frozen=True):
12 | """
13 | Model License Plate OCR config.
14 | """
15 |
16 | max_plate_slots: int
17 | """
18 | Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
19 | """
20 |
21 | alphabet: str
22 | """
23 | All the possible character set for the model output.
24 | """
25 | pad_char: str
26 | """
27 | Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS.
28 | """
29 | img_height: int
30 | """
31 | Image height which is fed to the model.
32 | """
33 | img_width: int
34 | """
35 | Image width which is fed to the model.
36 | """
37 |
38 | @computed_field # type: ignore[misc]
39 | @property
40 | def vocabulary_size(self) -> int:
41 | return len(self.alphabet)
42 |
43 | @model_validator(mode="after")
44 | def check_pad_in_alphabet(self) -> "PlateOCRConfig":
45 | if self.pad_char not in self.alphabet:
46 | raise ValueError("Pad character must be present in model alphabet.")
47 | return self
48 |
49 |
50 | def load_config_from_yaml(yaml_file_path: str | PathLike[str]) -> PlateOCRConfig:
51 | """Read and parse a yaml containing the Plate OCR config."""
52 | with open(yaml_file_path, encoding="utf-8") as f_in:
53 | yaml_content = yaml.safe_load(f_in)
54 | config = PlateOCRConfig(**yaml_content)
55 | return config
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/custom.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Custom metrics and loss functions.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from keras import losses, metrics, ops
6 |
7 |
8 | def cat_acc_metric(max_plate_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int):
9 | """
10 | Categorical accuracy metric.
11 | """
12 |
13 | def cat_acc(y_true, y_pred):
14 | """
15 | This is simply the CategoricalAccuracy for multi-class label problems. Example if the
16 | correct label is ABC123 and ABC133 is predicted, it will not give a precision of 0% like
17 | plate_acc (not completely classified correctly), but 83.3% (5/6).
18 | """
19 | y_true = ops.reshape(y_true, newshape=(-1, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size))
20 | y_pred = ops.reshape(y_pred, newshape=(-1, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size))
21 | return ops.mean(metrics.categorical_accuracy(y_true, y_pred))
22 |
23 | return cat_acc
24 |
25 |
26 | def plate_acc_metric(max_plate_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int):
27 | """
28 | Plate accuracy metric.
29 | """
30 |
31 | def plate_acc(y_true, y_pred):
32 | """
33 | Compute how many plates were correctly classified. For a single plate, if ground truth is
34 | 'ABC 123', and the prediction is 'ABC 123', then this would give a score of 1. If the
35 | prediction was ABD 123, it would score 0.
36 | """
37 | y_true = ops.reshape(y_true, newshape=(-1, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size))
38 | y_pred = ops.reshape(y_pred, newshape=(-1, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size))
39 | et = ops.equal(ops.argmax(y_true, axis=-1), ops.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1))
40 | return ops.mean(ops.cast(ops.all(et, axis=-1, keepdims=False), dtype="float32"))
41 |
42 | return plate_acc
43 |
44 |
45 | def top_3_k_metric(vocabulary_size: int):
46 | """
47 | Top 3 K categorical accuracy metric.
48 | """
49 |
50 | def top_3_k(y_true, y_pred):
51 | """
52 | Calculates how often the true character is found in the 3 predictions with the highest
53 | probability.
54 | """
55 | # Reshape into 2-d
56 | y_true = ops.reshape(y_true, newshape=(-1, vocabulary_size))
57 | y_pred = ops.reshape(y_pred, newshape=(-1, vocabulary_size))
58 | return ops.mean(metrics.top_k_categorical_accuracy(y_true, y_pred, k=3))
59 |
60 | return top_3_k
61 |
62 |
63 | # Custom loss
64 | def cce_loss(vocabulary_size: int, label_smoothing: float = 0.2):
65 | """
66 | Categorical cross-entropy loss.
67 | """
68 |
69 | def cce(y_true, y_pred):
70 | """
71 | Computes the categorical cross-entropy loss.
72 | """
73 | y_true = ops.reshape(y_true, newshape=(-1, vocabulary_size))
74 | y_pred = ops.reshape(y_pred, newshape=(-1, vocabulary_size))
75 | return ops.mean(
76 | losses.categorical_crossentropy(
77 | y_true, y_pred, from_logits=False, label_smoothing=label_smoothing
78 | )
79 | )
80 |
81 | return cce
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/layer_blocks.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Layer blocks used in the OCR model.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from keras import regularizers
6 | from keras.src.layers import (
7 | Activation,
8 | AveragePooling2D,
9 | BatchNormalization,
10 | Conv2D,
11 | MaxPooling2D,
12 | SeparableConv2D,
13 | )
14 |
15 |
16 | def block_no_bn(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
17 | x1 = Conv2D(
18 | kernel_size=k,
19 | filters=n_c,
20 | strides=s,
21 | padding=padding,
22 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
23 | use_bias=False,
24 | )(i)
25 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x1)
26 | return x2, x1
27 |
28 |
29 | def block_no_activation(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same"):
30 | x = Conv2D(
31 | kernel_size=k,
32 | filters=n_c,
33 | strides=s,
34 | padding=padding,
35 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
36 | use_bias=False,
37 | )(i)
38 | x = BatchNormalization()(x)
39 | return x
40 |
41 |
42 | def block_bn(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
43 | x1 = Conv2D(
44 | kernel_size=k,
45 | filters=n_c,
46 | strides=s,
47 | padding=padding,
48 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
49 | use_bias=False,
50 | )(i)
51 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
52 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
53 | return x2, x1
54 |
55 |
56 | def block_bn_no_l2(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
57 | x1 = Conv2D(kernel_size=k, filters=n_c, strides=s, padding=padding, use_bias=False)(i)
58 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
59 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
60 | return x2, x1
61 |
62 |
63 | def block_bn_sep_conv_l2(
64 | i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", depth_multiplier=1, activation: str = "relu"
65 | ):
66 | l2_kernel_reg = regularizers.l2(0.01)
67 | x1 = SeparableConv2D(
68 | kernel_size=k,
69 | filters=n_c,
70 | depth_multiplier=depth_multiplier,
71 | strides=s,
72 | padding=padding,
73 | use_bias=False,
74 | depthwise_regularizer=l2_kernel_reg,
75 | pointwise_regularizer=l2_kernel_reg,
76 | )(i)
77 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
78 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
79 | return x2, x1
80 |
81 |
82 | def block_bn_relu6(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu6"):
83 | x1 = Conv2D(
84 | kernel_size=k,
85 | filters=n_c,
86 | strides=s,
87 | padding=padding,
88 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
89 | use_bias=False,
90 | )(i)
91 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
92 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
93 | return x2, x1
94 |
95 |
96 | def block_bn_relu6_no_l2(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu6"):
97 | x1 = Conv2D(kernel_size=k, filters=n_c, strides=s, padding=padding, use_bias=False)(i)
98 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
99 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
100 | return x2, x1
101 |
102 |
103 | def block_average_conv_down(x, n_c, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
104 | x = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=2, strides=1, padding="valid")(x)
105 | x = Conv2D(
106 | filters=n_c,
107 | kernel_size=3,
108 | strides=2,
109 | padding=padding,
110 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
111 | use_bias=False,
112 | )(x)
113 | x = BatchNormalization()(x)
114 | x = Activation(activation)(x)
115 | return x
116 |
117 |
118 | def block_max_conv_down(x, n_c, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
119 | x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2, strides=1, padding="valid")(x)
120 | x = Conv2D(
121 | filters=n_c,
122 | kernel_size=3,
123 | strides=2,
124 | padding=padding,
125 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
126 | use_bias=False,
127 | )(x)
128 | x = BatchNormalization()(x)
129 | x = Activation(activation)(x)
130 | return x
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Model definitions for the FastLP OCR.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from typing import Literal
6 |
7 | from keras.src.activations import softmax
8 | from keras.src.layers import (
9 | Activation,
10 | Concatenate,
11 | Dense,
12 | Dropout,
13 | GlobalAveragePooling2D,
14 | Input,
15 | Rescaling,
16 | Reshape,
17 | Softmax,
18 | )
19 | from keras.src.models import Model
20 |
21 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.layer_blocks import (
22 | block_average_conv_down,
23 | block_bn,
24 | block_max_conv_down,
25 | block_no_activation,
26 | )
27 |
28 |
29 | def cnn_ocr_model(
30 | h: int,
31 | w: int,
32 | max_plate_slots: int,
33 | vocabulary_size: int,
34 | dense: bool = True,
35 | activation: str = "relu",
36 | pool_layer: Literal["avg", "max"] = "max",
37 | ) -> Model:
38 | """
39 | OCR model implemented with just CNN layers (v2).
40 | """
41 | input_tensor = Input((h, w, 1))
42 | x = Rescaling(1.0 / 255)(input_tensor)
43 | # Pooling-Conv layer
44 | if pool_layer == "avg":
45 | block_pool_conv = block_average_conv_down
46 | elif pool_layer == "max":
47 | block_pool_conv = block_max_conv_down
48 | # Backbone
49 | x = block_pool_conv(x, n_c=32, padding="same", activation=activation)
50 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
51 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
52 | x = block_pool_conv(x, n_c=64, padding="same", activation=activation)
53 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=3, n_c=128, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
54 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=128, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
55 | x = block_pool_conv(x, n_c=128, padding="same", activation=activation)
56 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=3, n_c=128, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
57 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=256, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
58 | x = block_pool_conv(x, n_c=256, padding="same", activation=activation)
59 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=512, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
60 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=1024, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
61 | x = (
62 | head(x, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)
63 | if dense
64 | else head_no_fc(x, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)
65 | )
66 | return Model(inputs=input_tensor, outputs=x)
67 |
68 |
69 | def head(x, max_plate_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int):
70 | """
71 | Model's head with Fully Connected (FC) layers.
72 | """
73 | x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
74 | # dropout for more robust learning
75 | x = Dropout(0.5)(x)
76 | dense_outputs = [
77 | Activation(softmax)(Dense(units=vocabulary_size)(x)) for _ in range(max_plate_slots)
78 | ]
79 | # concat all the dense outputs
80 | x = Concatenate()(dense_outputs)
81 | return x
82 |
83 |
84 | def head_no_fc(x, max_plate_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int):
85 | """
86 | Model's head without Fully Connected (FC) layers.
87 | """
88 | x = block_no_activation(x, k=1, n_c=max_plate_slots * vocabulary_size, s=1, padding="same")
89 | x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
90 | x = Reshape((max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size, 1))(x)
91 | x = Softmax(axis=-2)(x)
92 | return x
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/utilities/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/train/utilities/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/utilities/backend_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utils for Keras supported backends.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | from typing import Literal, TypeAlias
7 |
8 | Framework: TypeAlias = Literal["jax", "tensorflow", "torch"]
9 | """Supported backend frameworks for Keras."""
10 |
11 |
12 | def set_jax_backend() -> None:
13 | """Set Keras backend to jax."""
14 | set_keras_backend("jax")
15 |
16 |
17 | def set_tensorflow_backend() -> None:
18 | """Set Keras backend to tensorflow."""
19 | set_keras_backend("tensorflow")
20 |
21 |
22 | def set_pytorch_backend() -> None:
23 | """Set Keras backend to pytorch."""
24 | set_keras_backend("torch")
25 |
26 |
27 | def set_keras_backend(framework: Framework) -> None:
28 | """Set the Keras backend to a given framework."""
29 | os.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = framework
30 |
31 |
32 | def reload_keras_backend(framework: Framework) -> None:
33 | """Reload the Keras backend with a given framework."""
34 | # pylint: disable=import-outside-toplevel
35 | import keras
36 |
37 | keras.config.set_backend(framework)
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/utilities/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utility functions module
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import random
8 |
9 | import cv2
10 | import keras
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import numpy.typing as npt
13 |
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.custom import (
15 | cat_acc_metric,
16 | cce_loss,
17 | plate_acc_metric,
18 | top_3_k_metric,
19 | )
20 |
21 |
22 | def one_hot_plate(plate: str, alphabet: str) -> list[list[int]]:
23 | return [[0 if char != letter else 1 for char in alphabet] for letter in plate]
24 |
25 |
26 | def target_transform(
27 | plate_text: str,
28 | max_plate_slots: int,
29 | alphabet: str,
30 | pad_char: str,
31 | ) -> npt.NDArray[np.uint8]:
32 | # Pad the plates which length is smaller than 'max_plate_slots'
33 | plate_text = plate_text.ljust(max_plate_slots, pad_char)
34 | # Generate numpy arrays with one-hot encoding of plates
35 | encoded_plate = np.array(one_hot_plate(plate_text, alphabet=alphabet), dtype=np.uint8)
36 | return encoded_plate
37 |
38 |
39 | def read_plate_image(image_path: str, img_height: int, img_width: int) -> npt.NDArray:
40 | """
41 | Read and resize a license plate image.
42 |
43 | :param image_path: The path to the license plate image.
44 | :param img_height: The desired height of the resized image.
45 | :param img_width: The desired width of the resized image.
46 | :return: The resized license plate image as a NumPy array.
47 | """
48 | img = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
49 | img = cv2.resize(img, (img_width, img_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
50 | img = np.expand_dims(img, -1)
51 | return img
52 |
53 |
54 | def load_keras_model(
55 | model_path: str | pathlib.Path,
56 | vocab_size: int,
57 | max_plate_slots: int,
58 | ) -> keras.Model:
59 | """
60 | Utility helper function to load the keras OCR model.
61 | """
62 | custom_objects = {
63 | "cce": cce_loss(vocabulary_size=vocab_size),
64 | "cat_acc": cat_acc_metric(max_plate_slots=max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=vocab_size),
65 | "plate_acc": plate_acc_metric(max_plate_slots=max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=vocab_size),
66 | "top_3_k": top_3_k_metric(vocabulary_size=vocab_size),
67 | }
68 | model = keras.models.load_model(model_path, custom_objects=custom_objects)
69 | return model
70 |
71 |
72 | IMG_EXTENSIONS: set[str] = {".jpg", ".jpeg", ".png", ".bmp", ".gif", ".tiff", ".webp"}
73 | """Valid image extensions for the scope of this script."""
74 |
75 |
76 | def load_images_from_folder(
77 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
78 | width: int,
79 | height: int,
80 | shuffle: bool = False,
81 | limit: int | None = None,
82 | ) -> list[npt.NDArray]:
83 | """
84 | Return all images read from a directory. This uses the same read function used during training.
85 | """
86 | image_paths = sorted(
87 | str(f.resolve()) for f in img_dir.iterdir() if f.is_file() and f.suffix in IMG_EXTENSIONS
88 | )
89 | if limit:
90 | image_paths = image_paths[:limit]
91 | if shuffle:
92 | random.shuffle(image_paths)
93 | images = [read_plate_image(i, img_height=height, img_width=width) for i in image_paths]
94 | return images
95 |
96 |
97 | def postprocess_model_output(
98 | prediction: npt.NDArray,
99 | alphabet: str,
100 | max_plate_slots: int,
101 | vocab_size: int,
102 | ) -> tuple[str, npt.NDArray]:
103 | """
104 | Return plate text and confidence scores from raw model output.
105 | """
106 | prediction = prediction.reshape((max_plate_slots, vocab_size))
107 | probs = np.max(prediction, axis=-1)
108 | prediction = np.argmax(prediction, axis=-1)
109 | plate = "".join([alphabet[x] for x in prediction])
110 | return plate, probs
111 |
112 |
113 | def low_confidence_positions(probs, thresh=0.3) -> npt.NDArray:
114 | """Returns indices of elements in `probs` less than `thresh`, indicating low confidence."""
115 | return np.where(np.array(probs) < thresh)[0]
116 |
117 |
118 | def display_predictions(
119 | image: npt.NDArray,
120 | plate: str,
121 | probs: npt.NDArray,
122 | low_conf_thresh: float,
123 | ) -> None:
124 | """
125 | Display plate and corresponding prediction.
126 | """
127 | plate_str = "".join(plate)
128 | logging.info("Plate: %s", plate_str)
129 | logging.info("Confidence: %s", probs)
130 | image_to_show = cv2.resize(image, None, fx=3, fy=3, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
131 | # Converting to BGR for color text
132 | image_to_show = cv2.cvtColor(image_to_show, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)
133 | # Average probabilities
134 | avg_prob = np.mean(probs) * 100
135 | cv2.putText(
136 | image_to_show,
137 | f"{plate_str} {avg_prob:.{2}f}%",
138 | org=(5, 30),
139 | fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
140 | fontScale=1,
141 | color=(0, 0, 0),
142 | lineType=1,
143 | thickness=6,
144 | )
145 | cv2.putText(
146 | image_to_show,
147 | f"{plate_str} {avg_prob:.{2}f}%",
148 | org=(5, 30),
149 | fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
150 | fontScale=1,
151 | color=(255, 255, 255),
152 | lineType=1,
153 | thickness=2,
154 | )
155 | # Display character with low confidence
156 | low_conf_chars = "Low conf. on: " + " ".join(
157 | [plate[i] for i in low_confidence_positions(probs, thresh=low_conf_thresh)]
158 | )
159 | cv2.putText(
160 | image_to_show,
161 | low_conf_chars,
162 | org=(5, 200),
163 | fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
164 | fontScale=0.7,
165 | color=(0, 0, 220),
166 | lineType=1,
167 | thickness=2,
168 | )
169 | cv2.imshow("plates", image_to_show)
170 | if cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
171 | return
172 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mkdocs.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | site_name: FastPlateOCR
2 | site_author: ankandrew
3 | site_description: Fast & Lightweight License Plate OCR
4 | repo_url: https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr
5 | theme:
6 | name: material
7 | features:
8 | - navigation.instant
9 | - navigation.instant.progress
10 | - search.suggest
11 | - search.highlight
12 | - content.code.copy
13 | palette:
14 | - scheme: default
15 | toggle:
16 | icon: material/lightbulb-outline
17 | name: Switch to dark mode
18 | - scheme: slate
19 | toggle:
20 | icon: material/lightbulb
21 | name: Switch to light mode
22 | nav:
23 | - Introduction: index.md
24 | - Installation: installation.md
25 | - Usage: usage.md
26 | - Architecture: architecture.md
27 | - Contributing: contributing.md
28 | - Reference: reference.md
29 | plugins:
30 | - search
31 | - mike:
32 | alias_type: symlink
33 | canonical_version: latest
34 | - mkdocstrings:
35 | handlers:
36 | python:
37 | paths: [ . ]
38 | options:
39 | members_order: source
40 | separate_signature: true
41 | filters: [ "!^_" ]
42 | docstring_options:
43 | ignore_init_summary: true
44 | merge_init_into_class: true
45 | show_signature_annotations: true
46 | signature_crossrefs: true
47 | extra:
48 | version:
49 | provider: mike
50 | generator: false
51 | markdown_extensions:
52 | - admonition
53 | - pymdownx.highlight:
54 | anchor_linenums: true
55 | line_spans: __span
56 | pygments_lang_class: true
57 | - pymdownx.inlinehilite
58 | - pymdownx.snippets
59 | - pymdownx.details
60 | - pymdownx.superfences
61 | - toc:
62 | permalink: true
63 | title: Page contents
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/poetry.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [virtualenvs]
2 | in-project = true
3 | prefer-active-python = true
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pyproject.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [tool.poetry]
2 | name = "fast-plate-ocr"
3 | version = "0.3.0"
4 | description = "Fast & Lightweight OCR for vehicle license plates."
5 | authors = ["ankandrew <61120139+ankandrew@users.noreply.github.com>"]
6 | readme = "README.md"
7 | repository = "https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/"
8 | documentation = "https://ankandrew.github.io/fast-plate-ocr"
9 | keywords = ["plate-recognition", "license-plate-recognition", "license-plate-ocr"]
10 | license = "MIT"
11 | classifiers = [
12 | "Typing :: Typed",
13 | "Intended Audience :: Developers",
14 | "Intended Audience :: Education",
15 | "Intended Audience :: Science/Research",
16 | "Operating System :: OS Independent",
17 | "Topic :: Software Development",
18 | "Topic :: Scientific/Engineering",
19 | "Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries",
20 | "Topic :: Software Development :: Build Tools",
21 | "Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Artificial Intelligence",
22 | "Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries :: Python Modules",
23 | ]
24 |
25 | [tool.poetry.dependencies]
26 | python = "^3.10"
27 | # Packages required for doing inference
28 | numpy = ">=1.20"
29 | opencv-python = "*"
30 | pyyaml = ">=5.1"
31 | tqdm = "*"
32 | rich = "*"
33 |
34 | # Install onnxruntime-gpu only on systems other than macOS or Raspberry Pi
35 | onnxruntime-gpu = { version = ">=1.19.2", markers = "sys_platform != 'darwin' and platform_machine != 'armv7l' and platform_machine != 'aarch64' and (platform_system == 'Linux' or platform_system == 'Windows')" }
36 | # Fallback to onnxruntime for macOS, Raspberry Pi, and other unsupported platforms
37 | onnxruntime = { version = ">=1.19.2", markers = "sys_platform == 'darwin' or platform_machine == 'armv7l' or platform_machine == 'aarch64'" }
38 |
39 | # Training packages are optional
40 | albumentations = { version = "*", optional = true }
41 | click = { version = "*", optional = true }
42 | keras = { version = ">=3.1.1", optional = true }
43 | matplotlib = { version = "*", optional = true }
44 | pandas = { version = "*", optional = true }
45 | pydantic = { version = "^2.0.0", optional = true }
46 | tensorboard = { version = "*", optional = true }
47 | tensorflow = { version = "*", optional = true }
48 | tf2onnx = { version = "*", optional = true }
49 | torch = { version = "*", optional = true }
50 |
51 | # Optional packages for creating the docs
52 | mkdocs-material = { version = "*", optional = true }
53 | mkdocstrings = {version = "*", extras = ["python"], optional = true}
54 | mike = { version = "*", optional = true }
55 | onnxsim = { version = ">0.4.10", optional = true }
56 |
57 | [tool.poetry.extras]
58 | train = [
59 | "albumentations",
60 | "click",
61 | "keras",
62 | "matplotlib",
63 | "pandas",
64 | "pydantic",
65 | "tensorboard",
66 | "tensorflow",
67 | "tf2onnx",
68 | "torch",
69 | "onnxsim",
70 | ]
71 | docs = ["mkdocs-material", "mkdocstrings", "mike"]
72 |
73 | [tool.poetry.group.test.dependencies]
74 | pytest = "*"
75 |
76 | [tool.poetry.group.dev.dependencies]
77 | mypy = "*"
78 | ruff = "*"
79 | pandas-stubs = "^2.2.0.240218"
80 | pylint = "*"
81 | types-pyyaml = "^6.0.12.20240311"
82 |
83 | [tool.poetry.scripts]
84 | fast_plate_ocr = "fast_plate_ocr.cli.cli:main_cli"
85 |
86 | [tool.ruff]
87 | line-length = 100
88 | target-version = "py310"
89 |
90 | [tool.ruff.lint]
91 | select = [
92 | # pycodestyle
93 | "E",
94 | "W",
95 | # Pyflakes
96 | "F",
97 | # pep8-naming
98 | "N",
99 | # pyupgrade
100 | "UP",
101 | # flake8-bugbear
102 | "B",
103 | # flake8-simplify
104 | "SIM",
105 | # flake8-unused-arguments
106 | "ARG",
107 | # Pylint
108 | "PL",
109 | # Perflint
110 | "PERF",
111 | # Ruff-specific rules
112 | "RUF",
113 | # pandas-vet
114 | "PD",
115 | ]
116 | ignore = ["N812", "PLR2004", "PD011"]
117 | fixable = ["ALL"]
118 | unfixable = []
119 |
120 | [tool.ruff.lint.pylint]
121 | max-args = 8
122 |
123 | [tool.ruff.format]
124 | line-ending = "lf"
125 |
126 | [tool.mypy]
127 | disable_error_code = "import-untyped"
128 | [[tool.mypy.overrides]]
129 | module = ["albumentations"]
130 | ignore_missing_imports = true
131 |
132 | [tool.pylint.typecheck]
133 | generated-members = ["cv2.*"]
134 | signature-mutators = [
135 | "click.decorators.option",
136 | "click.decorators.argument",
137 | "click.decorators.version_option",
138 | "click.decorators.help_option",
139 | "click.decorators.pass_context",
140 | "click.decorators.confirmation_option"
141 | ]
142 |
143 | [tool.pylint.format]
144 | max-line-length = 100
145 |
146 | [tool.pylint."messages control"]
147 | disable = ["missing-class-docstring", "missing-function-docstring", "wrong-import-order"]
148 |
149 | [tool.pylint.design]
150 | max-args = 8
151 | min-public-methods = 1
152 |
153 | [tool.pylint.basic]
154 | no-docstring-rgx = "^__|^test_"
155 |
156 | [build-system]
157 | requires = ["poetry-core"]
158 | build-backend = "poetry.core.masonry.api"
159 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Test package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from pathlib import Path
6 |
7 | PROJECT_ROOT_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/assets/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Assets package used in tests.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 |
7 | ASSETS_DIR = pathlib.Path(__file__).resolve().parent
8 | """Path pointing to test/assets directory"""
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/assets/test_plate_1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/assets/test_plate_1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/assets/test_plate_2.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/assets/test_plate_2.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/conftest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The `conftest.py` file serves as a means of providing fixtures for an entire directory. Fixtures
3 | defined in a `conftest.py` can be used by any test in that package without needing to import them
4 | (pytest will automatically discover them).
5 | """
6 |
7 | import pytest
8 |
9 |
10 | @pytest.fixture(scope="function")
11 | def temp_directory(tmpdir):
12 | """
13 | Example fixture to create a temporary directory for testing.
14 | """
15 | temp_dir = tmpdir.mkdir("temp")
16 | yield temp_dir
17 | temp_dir.remove()
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/fast_lp_ocr/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/test_hub.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Tests for ONNX hub module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from http import HTTPStatus
6 |
7 | import pytest
8 | import requests
9 |
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.hub import AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS
11 |
12 |
13 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS.keys())
14 | def test_model_and_config_urls(model_name):
15 | """
16 | Test to check if the model and config URLs for AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS are valid.
17 | """
18 | model_url, config_url = AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS[model_name]
19 |
20 | for url in [model_url, config_url]:
21 | response = requests.head(url, timeout=5, allow_redirects=True)
22 | assert (
23 | response.status_code == HTTPStatus.OK
24 | ), f"URL {url} is not accessible, got {response.status_code}"
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/test_onnx_inference.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Tests for ONNX inference module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from collections.abc import Iterator
6 |
7 | import cv2
8 | import numpy.typing as npt
9 | import pytest
10 |
11 | from fast_plate_ocr import ONNXPlateRecognizer
12 | from test.assets import ASSETS_DIR
13 |
14 |
15 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module", name="onnx_model")
16 | def onnx_model_fixture() -> Iterator[ONNXPlateRecognizer]:
17 | yield ONNXPlateRecognizer("argentinian-plates-cnn-model", device="cpu")
18 |
19 |
20 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
21 | "input_image, expected_result",
22 | [
23 | # Single image path
24 | (str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_1.png"), 1),
25 | # Multiple Image paths
26 | (
27 | [str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_1.png"), str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_2.png")],
28 | 2,
29 | ),
30 | # NumPy array with single image
31 | (cv2.imread(str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_1.png"), cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE), 1),
32 | # NumPy array with batch images
33 | (
34 | [
35 | cv2.imread(str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_1.png"), cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE),
36 | cv2.imread(str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_2.png"), cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE),
37 | ],
38 | 2,
39 | ),
40 | ],
41 | )
42 | def test_result_from_different_image_sources(
43 | input_image: str | list[str] | npt.NDArray,
44 | expected_result: int,
45 | onnx_model: ONNXPlateRecognizer,
46 | ) -> None:
47 | actual_result = len(onnx_model.run(input_image))
48 | assert actual_result == expected_result
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/test_process.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Tests for inference process module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | import numpy.typing as npt
7 | import pytest
8 |
9 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.process import postprocess_output
10 |
11 |
12 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
13 | "model_output, max_plate_slots, model_alphabet, expected_plates",
14 | [
15 | (
16 | np.array(
17 | [
18 | [[0.5, 0.4, 0.1], [0.2, 0.6, 0.2], [0.1, 0.4, 0.5]],
19 | [[0.1, 0.1, 0.8], [0.2, 0.2, 0.6], [0.1, 0.4, 0.5]],
20 | ],
21 | dtype=np.float32,
22 | ),
23 | 3,
24 | "ABC",
25 | ["ABC", "CCC"],
26 | ),
27 | (
28 | np.array(
29 | [[[0.1, 0.4, 0.5], [0.6, 0.2, 0.2], [0.1, 0.5, 0.4]]],
30 | dtype=np.float32,
31 | ),
32 | 3,
33 | "ABC",
34 | ["CAB"],
35 | ),
36 | ],
37 | )
38 | def test_postprocess_output(
39 | model_output: npt.NDArray,
40 | max_plate_slots: int,
41 | model_alphabet: str,
42 | expected_plates: list[str],
43 | ) -> None:
44 | actual_plate = postprocess_output(model_output, max_plate_slots, model_alphabet)
45 | assert actual_plate == expected_plates
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/test_config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Tests for config module
3 | """
4 |
5 | from pathlib import Path
6 |
7 | import pytest
8 |
9 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import PlateOCRConfig, load_config_from_yaml
10 | from test import PROJECT_ROOT_DIR
11 |
12 |
13 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
14 | "file_path",
15 | [f for f in PROJECT_ROOT_DIR.joinpath("config").iterdir() if f.suffix in (".yaml", ".yml")],
16 | )
17 | def test_yaml_configs(file_path: Path) -> None:
18 | load_config_from_yaml(file_path)
19 |
20 |
21 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
22 | "raw_config",
23 | [
24 | {
25 | "max_plate_slots": 7,
26 | # Pad char not in alphabet, should raise exception
27 | "alphabet": "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ",
28 | "pad_char": "_",
29 | "img_height": 70,
30 | "img_width": 140,
31 | }
32 | ],
33 | )
34 | def test_invalid_config_raises(raw_config: dict) -> None:
35 | with pytest.raises(ValueError):
36 | PlateOCRConfig(**raw_config)
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/test_custom.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Test the custom metric/losses module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | # ruff: noqa: E402
6 | # pylint: disable=wrong-import-position,wrong-import-order,ungrouped-imports
7 | # fmt: off
8 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.backend_utils import set_pytorch_backend
9 |
10 | set_pytorch_backend()
11 | # fmt: on
12 |
13 | import pytest
14 | import torch
15 |
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.custom import cat_acc_metric, plate_acc_metric
17 |
18 |
19 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
20 | "y_true, y_pred, expected_accuracy",
21 | [
22 | (torch.tensor([[[1, 0]] * 6]), torch.tensor([[[0.9, 0.1]] * 6]), 1.0),
23 | ],
24 | )
25 | def test_cat_acc(y_true: torch.Tensor, y_pred: torch.Tensor, expected_accuracy: float) -> None:
26 | actual_accuracy = cat_acc_metric(2, 1)(y_true, y_pred)
27 | assert actual_accuracy == expected_accuracy
28 |
29 |
30 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
31 | "y_true, y_pred, expected_accuracy",
32 | [
33 | (
34 | torch.tensor(
35 | [
36 | [
37 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
38 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
39 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
40 | [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
41 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
42 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
43 | ],
44 | [
45 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
46 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
47 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
48 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
49 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
50 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
51 | ],
52 | ]
53 | ),
54 | torch.tensor(
55 | [
56 | [
57 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
58 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
59 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
60 | [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
61 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
62 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
63 | ],
64 | [
65 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
66 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
67 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
68 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
69 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
70 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
71 | ],
72 | ]
73 | ),
74 | # First batch slice plate was recognized completely correct but second one wasn't
75 | # So 50% of plates were recognized correctly
76 | 0.5,
77 | ),
78 | ],
79 | )
80 | def test_plate_accuracy(
81 | y_true: torch.Tensor, y_pred: torch.Tensor, expected_accuracy: float
82 | ) -> None:
83 | actual_accuracy = plate_acc_metric(y_true.shape[1], y_true.shape[2])(y_true, y_pred).item()
84 | assert actual_accuracy == expected_accuracy
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/test_models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Test OCR models module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pytest
6 | from keras import Input
7 |
8 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model import models
9 |
10 |
11 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
12 | "max_plates_slots, vocabulary_size, expected_hidden_units", [(7, 37, 7 * 37)]
13 | )
14 | def test_head(max_plates_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int, expected_hidden_units: int) -> None:
15 | x = Input((70, 140, 1))
16 | out_tensor = models.head(x, max_plates_slots, vocabulary_size)
17 | actual_hidden_units = out_tensor.shape[-1]
18 | assert actual_hidden_units == expected_hidden_units
19 |
20 |
21 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
22 | "max_plates_slots, vocabulary_size, expected_hidden_units", [(7, 37, 7 * 37)]
23 | )
24 | def test_head_no_fc(
25 | max_plates_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int, expected_hidden_units: int
26 | ) -> None:
27 | x = Input((70, 140, 1))
28 | out_tensor = models.head_no_fc(x, max_plates_slots, vocabulary_size)
29 | actual_hidden_units = out_tensor.shape[1] * out_tensor.shape[2]
30 | assert actual_hidden_units == expected_hidden_units
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/test_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Test utils module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pytest
6 |
7 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
8 |
9 |
10 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
11 | "plate, alphabet, expected_result",
12 | [
13 | (
14 | "AB12",
15 | "ABCD123456",
16 | [
17 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
18 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
19 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
20 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
21 | ],
22 | ),
23 | (
24 | "ABC123",
25 | "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJ",
26 | [
27 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
28 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
29 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
30 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
31 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
32 | [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
33 | ],
34 | ),
35 | ],
36 | )
37 | def test_one_hot_plate(plate: str, alphabet: str, expected_result: list[list[int]]) -> None:
38 | actual_result = utils.one_hot_plate(plate, alphabet)
39 | assert actual_result == expected_result
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
44 |
45 | To train or use the CLI tool, you'll need to install:
46 |
47 | ```shell
48 | pip install fast_plate_ocr[train]
49 | ```
50 |
51 | #### Train Model
52 |
53 | To train the model you will need:
54 |
55 | 1. A configuration used for the OCR model. Depending on your use case, you might have more plate slots or different set
56 | of characters. Take a look at the config for Argentinian license plate as an example:
57 | ```yaml
58 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
59 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
60 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
61 |
62 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
63 | max_plate_slots: 7
64 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
65 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
66 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
67 | pad_char: '_'
68 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
69 | img_height: 70
70 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
71 | img_width: 140
72 | ```
73 | 2. A labeled dataset,
74 | see [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip)
75 | for the expected data format.
76 | 3. Run train script:
77 | ```shell
78 | # You can set the backend to either TensorFlow, JAX or PyTorch
79 | # (just make sure it is installed)
80 | KERAS_BACKEND=tensorflow fast_plate_ocr train \
81 | --annotations path_to_the_train.csv \
82 | --val-annotations path_to_the_val.csv \
83 | --config-file config.yaml \
84 | --batch-size 128 \
85 | --epochs 750 \
86 | --dense \
87 | --early-stopping-patience 100 \
88 | --reduce-lr-patience 50
89 | ```
90 |
91 | You will probably want to change the augmentation pipeline to apply to your dataset.
92 |
93 | In order to do this define an Albumentations pipeline:
94 |
95 | ```python
96 | import albumentations as A
97 |
98 | transform_pipeline = A.Compose(
99 | [
100 | # ...
101 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
102 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
103 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
104 | # ... and any other augmentation ...
105 | ]
106 | )
107 |
108 | # Export to a file (this resultant YAML can be used by the train script)
109 | A.save(transform_pipeline, "./transform_pipeline.yaml", data_format="yaml")
110 | ```
111 |
112 | And then you can train using the custom transformation pipeline with the `--augmentation-path` option.
113 |
114 | #### Visualize Augmentation
115 |
116 | It's useful to visualize the augmentation pipeline before training the model. This helps us to identify
117 | if we should apply more heavy augmentation or less, as it can hurt the model.
118 |
119 | You might want to see the augmented image next to the original, to see how much it changed:
120 |
121 | ```shell
122 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-augmentation \
123 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
124 | --columns 2 \
125 | --show-original \
126 | --augmentation-path '/transform_pipeline.yaml'
127 | ```
128 |
129 | You will see something like:
130 |
131 | 
132 |
133 | #### Validate Model
134 |
135 | After finishing training you can validate the model on a labeled test dataset.
136 |
137 | Example:
138 |
139 | ```shell
140 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
141 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
142 | --config-file arg_plate_example.yaml \
143 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
144 | ```
145 |
146 | #### Visualize Predictions
147 |
148 | Once you finish training your model, you can view the model predictions on raw data with:
149 |
150 | ```shell
151 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-predictions \
152 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
153 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
154 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
155 | ```
156 |
157 | You will see something like:
158 |
159 | 
160 |
161 | #### Export as ONNX
162 |
163 | Exporting the Keras model to ONNX format might be beneficial to speed-up inference time.
164 |
165 | ```shell
166 | fast_plate_ocr export-onnx \
167 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
168 | --output-path arg_cnn_ocr.onnx \
169 | --opset 18 \
170 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
171 | ```
172 |
173 | ### Keras Backend
174 |
175 | To train the model, you can install the ML Framework you like the most. **Keras 3** has
176 | support for **TensorFlow**, **JAX** and **PyTorch** backends.
177 |
178 | To change the Keras backend you can either:
179 |
180 | 1. Export `KERAS_BACKEND` environment variable, i.e. to use JAX for training:
181 | ```shell
182 | KERAS_BACKEND=jax fast_plate_ocr train --config-file ...
183 | ```
184 | 2. Edit your local config file at `~/.keras/keras.json`.
185 |
186 | ???+ tip
187 | **Usually training with JAX and TensorFlow is faster.**
188 |
189 | _Note: You will probably need to install your desired framework for training._
190 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Fast Plate OCR package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.onnx_inference import ONNXPlateRecognizer
6 |
7 | __all__ = ["ONNXPlateRecognizer"]
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/cli/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/cli.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Main CLI used when training a FastPlateOCR model.
3 | """
4 |
5 | try:
6 | import click
7 |
8 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.onnx_converter import export_onnx
9 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.train import train
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.valid import valid
11 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.visualize_augmentation import visualize_augmentation
12 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.visualize_predictions import visualize_predictions
13 | except ImportError as e:
14 | raise ImportError("Make sure to 'pip install fast-plate-ocr[train]' to run this!") from e
15 |
16 |
17 | @click.group(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
18 | def main_cli():
19 | """FastPlateOCR CLI."""
20 |
21 |
22 | main_cli.add_command(visualize_predictions)
23 | main_cli.add_command(visualize_augmentation)
24 | main_cli.add_command(valid)
25 | main_cli.add_command(train)
26 | main_cli.add_command(export_onnx)
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/onnx_converter.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for converting Keras models to ONNX format.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import shutil
8 | from tempfile import NamedTemporaryFile
9 |
10 | import click
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import onnx
13 | import onnxruntime as rt
14 | import onnxsim
15 | import tensorflow as tf
16 | import tf2onnx
17 | from tf2onnx import constants as tf2onnx_constants
18 |
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.common.utils import log_time_taken
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
21 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.utils import load_keras_model
22 |
23 | logging.basicConfig(
24 | level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(message)s", datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
25 | )
26 |
27 |
28 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
29 |
30 |
31 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
32 | @click.option(
33 | "-m",
34 | "--model",
35 | "model_path",
36 | required=True,
37 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
38 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
39 | )
40 | @click.option(
41 | "--output-path",
42 | required=True,
43 | type=str,
44 | help="Output name for ONNX model.",
45 | )
46 | @click.option(
47 | "--simplify/--no-simplify",
48 | default=False,
49 | show_default=True,
50 | help="Simplify ONNX model using onnxsim.",
51 | )
52 | @click.option(
53 | "--config-file",
54 | required=True,
55 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
56 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
57 | )
58 | @click.option(
59 | "--opset",
60 | default=16,
61 | type=click.IntRange(max=max(tf2onnx_constants.OPSET_TO_IR_VERSION)),
62 | show_default=True,
63 | help="Opset version for ONNX.",
64 | )
65 | def export_onnx(
66 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
67 | output_path: str,
68 | simplify: bool,
69 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
70 | opset: int,
71 | ) -> None:
72 | """
73 | Export Keras models to ONNX format.
74 | """
75 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
76 | model = load_keras_model(
77 | model_path,
78 | vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size,
79 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
80 | )
81 | spec = (tf.TensorSpec((None, config.img_height, config.img_width, 1), tf.uint8, name="input"),)
82 | # Convert from Keras to ONNX using tf2onnx library
83 | with NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".onnx") as tmp:
84 | tmp_onnx = tmp.name
85 | model_proto, _ = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(
86 | model,
87 | input_signature=spec,
88 | opset=opset,
89 | output_path=tmp_onnx,
90 | )
91 | if simplify:
92 | logging.info("Simplifying ONNX model ...")
93 | model_simp, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx.load(tmp_onnx))
94 | assert check, "Simplified ONNX model could not be validated!"
95 | onnx.save(model_simp, output_path)
96 | else:
97 | shutil.copy(tmp_onnx, output_path)
98 | output_names = [n.name for n in model_proto.graph.output]
99 | x = np.random.randint(0, 256, size=(1, config.img_height, config.img_width, 1), dtype=np.uint8)
100 | # Run dummy inference and log time taken
101 | m = rt.InferenceSession(output_path)
102 | with log_time_taken("ONNX inference took:"):
103 | onnx_pred = m.run(output_names, {"input": x})
104 | # Check if ONNX and keras have the same results
105 | if not np.allclose(model.predict(x, verbose=0), onnx_pred[0], rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5):
106 | logging.warning("ONNX model output was not close to Keras model for the given tolerance!")
107 | logging.info("Model converted to ONNX! Saved at %s", output_path)
108 |
109 |
110 | if __name__ == "__main__":
111 | export_onnx()
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for training the License Plate OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 | import shutil
7 | from datetime import datetime
8 | from typing import Literal
9 |
10 | import albumentations as A
11 | import click
12 | from keras.src.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, TensorBoard
13 | from keras.src.optimizers import Adam
14 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
15 |
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.utils import print_params, print_train_details
17 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.augmentation import TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
18 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.dataset import LicensePlateDataset
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.custom import (
21 | cat_acc_metric,
22 | cce_loss,
23 | plate_acc_metric,
24 | top_3_k_metric,
25 | )
26 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.models import cnn_ocr_model
27 |
28 | # ruff: noqa: PLR0913
29 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
30 |
31 |
32 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
33 | @click.option(
34 | "--dense/--no-dense",
35 | default=True,
36 | show_default=True,
37 | help="Whether to use Fully Connected layers in model head or not.",
38 | )
39 | @click.option(
40 | "--config-file",
41 | required=True,
42 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
43 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
44 | )
45 | @click.option(
46 | "--annotations",
47 | required=True,
48 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
49 | help="Path pointing to the train annotations CSV file.",
50 | )
51 | @click.option(
52 | "--val-annotations",
53 | required=True,
54 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
55 | help="Path pointing to the train validation CSV file.",
56 | )
57 | @click.option(
58 | "--augmentation-path",
59 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
60 | help="YAML file pointing to the augmentation pipeline saved with Albumentations.save(...)",
61 | )
62 | @click.option(
63 | "--lr",
64 | default=1e-3,
65 | show_default=True,
66 | type=float,
67 | help="Initial learning rate to use.",
68 | )
69 | @click.option(
70 | "--label-smoothing",
71 | default=0.05,
72 | show_default=True,
73 | type=float,
74 | help="Amount of label smoothing to apply.",
75 | )
76 | @click.option(
77 | "--batch-size",
78 | default=128,
79 | show_default=True,
80 | type=int,
81 | help="Batch size for training.",
82 | )
83 | @click.option(
84 | "--num-workers",
85 | default=0,
86 | show_default=True,
87 | type=int,
88 | help="How many subprocesses to load data, used in the torch DataLoader.",
89 | )
90 | @click.option(
91 | "--output-dir",
92 | default="./trained_models",
93 | type=click.Path(dir_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
94 | help="Output directory where model will be saved.",
95 | )
96 | @click.option(
97 | "--epochs",
98 | default=500,
99 | show_default=True,
100 | type=int,
101 | help="Number of training epochs.",
102 | )
103 | @click.option(
104 | "--tensorboard",
105 | "-t",
106 | is_flag=True,
107 | help="Whether to use TensorBoard visualization tool.",
108 | )
109 | @click.option(
110 | "--tensorboard-dir",
111 | "-l",
112 | default="tensorboard_logs",
113 | show_default=True,
114 | type=click.Path(path_type=pathlib.Path),
115 | help="The path of the directory where to save the TensorBoard log files.",
116 | )
117 | @click.option(
118 | "--early-stopping-patience",
119 | default=100,
120 | show_default=True,
121 | type=int,
122 | help="Stop training when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve for X epochs.",
123 | )
124 | @click.option(
125 | "--reduce-lr-patience",
126 | default=60,
127 | show_default=True,
128 | type=int,
129 | help="Patience to reduce the learning rate if 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve within X epochs.",
130 | )
131 | @click.option(
132 | "--reduce-lr-factor",
133 | default=0.85,
134 | show_default=True,
135 | type=float,
136 | help="Reduce the learning rate by this factor when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve.",
137 | )
138 | @click.option(
139 | "--activation",
140 | default="relu",
141 | show_default=True,
142 | type=str,
143 | help="Activation function to use.",
144 | )
145 | @click.option(
146 | "--pool-layer",
147 | default="max",
148 | show_default=True,
149 | type=click.Choice(["max", "avg"]),
150 | help="Choose the pooling layer to use.",
151 | )
152 | @click.option(
153 | "--weights-path",
154 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
155 | help="Path to the pretrained model weights file.",
156 | )
157 | @print_params(table_title="CLI Training Parameters", c1_title="Parameter", c2_title="Details")
158 | def train(
159 | dense: bool,
160 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
161 | annotations: pathlib.Path,
162 | val_annotations: pathlib.Path,
163 | augmentation_path: pathlib.Path | None,
164 | lr: float,
165 | label_smoothing: float,
166 | batch_size: int,
167 | num_workers: int,
168 | output_dir: pathlib.Path,
169 | epochs: int,
170 | tensorboard: bool,
171 | tensorboard_dir: pathlib.Path,
172 | early_stopping_patience: int,
173 | reduce_lr_patience: int,
174 | reduce_lr_factor: float,
175 | activation: str,
176 | pool_layer: Literal["max", "avg"],
177 | weights_path: pathlib.Path | None,
178 | ) -> None:
179 | """
180 | Train the License Plate OCR model.
181 | """
182 | train_augmentation = (
183 | A.load(augmentation_path, data_format="yaml") if augmentation_path else TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
184 | )
185 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
186 | print_train_details(train_augmentation, config.model_dump())
187 | train_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(
188 | annotations_file=annotations,
189 | transform=train_augmentation,
190 | config=config,
191 | )
192 | train_dataloader = DataLoader(
193 | train_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=True
194 | )
195 |
196 | if val_annotations:
197 | val_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(
198 | annotations_file=val_annotations,
199 | config=config,
200 | )
201 | val_dataloader = DataLoader(
202 | val_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=False
203 | )
204 | else:
205 | val_dataloader = None
206 |
207 | # Train
208 | model = cnn_ocr_model(
209 | h=config.img_height,
210 | w=config.img_width,
211 | dense=dense,
212 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
213 | vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size,
214 | activation=activation,
215 | pool_layer=pool_layer,
216 | )
217 |
218 | if weights_path:
219 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
220 |
221 | model.compile(
222 | loss=cce_loss(vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size, label_smoothing=label_smoothing),
223 | optimizer=Adam(lr),
224 | metrics=[
225 | cat_acc_metric(
226 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size
227 | ),
228 | plate_acc_metric(
229 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size
230 | ),
231 | top_3_k_metric(vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size),
232 | ],
233 | )
234 |
235 | output_dir /= datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S")
236 | output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
237 | model_file_path = output_dir / "cnn_ocr-epoch_{epoch:02d}-acc_{val_plate_acc:.3f}.keras"
238 |
239 | # Save params and config used for training
240 | shutil.copy(config_file, output_dir / "config.yaml")
241 | A.save(train_augmentation, output_dir / "train_augmentation.yaml", "yaml")
242 |
243 | callbacks = [
244 | # Reduce the learning rate by 0.5x if 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve within X epochs
245 | ReduceLROnPlateau(
246 | "val_plate_acc",
247 | patience=reduce_lr_patience,
248 | factor=reduce_lr_factor,
249 | min_lr=1e-6,
250 | verbose=1,
251 | ),
252 | # Stop training when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve for X epochs
253 | EarlyStopping(
254 | monitor="val_plate_acc",
255 | patience=early_stopping_patience,
256 | mode="max",
257 | restore_best_weights=False,
258 | verbose=1,
259 | ),
260 | # We don't use EarlyStopping restore_best_weights=True because it won't restore the best
261 | # weights when it didn't manage to EarlyStop but finished all epochs
262 | ModelCheckpoint(
263 | model_file_path,
264 | monitor="val_plate_acc",
265 | mode="max",
266 | save_best_only=True,
267 | verbose=1,
268 | ),
269 | ]
270 |
271 | if tensorboard:
272 | run_dir = tensorboard_dir / datetime.now().strftime("run_%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
273 | run_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
274 | callbacks.append(TensorBoard(log_dir=run_dir))
275 |
276 | model.fit(train_dataloader, epochs=epochs, validation_data=val_dataloader, callbacks=callbacks)
277 |
278 |
279 | if __name__ == "__main__":
280 | train()
281 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utils used for the CLI scripts.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import inspect
6 | import pathlib
7 | from collections.abc import Callable
8 | from functools import wraps
9 | from typing import Any
10 |
11 | import albumentations as A
12 | from rich import box
13 | from rich.console import Console
14 | from rich.pretty import Pretty
15 | from rich.table import Table
16 |
17 |
18 | def print_variables_as_table(
19 | c1_title: str, c2_title: str, title: str = "Variables Table", **kwargs: Any
20 | ) -> None:
21 | """
22 | Prints variables in a formatted table using the rich library.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | c1_title (str): Title of the first column.
26 | c2_title (str): Title of the second column.
27 | title (str): Title of the table.
28 | **kwargs (Any): Variable names and values to be printed.
29 | """
30 | console = Console()
31 | console.print("\n")
32 | table = Table(title=title, show_header=True, header_style="bold blue", box=box.ROUNDED)
33 | table.add_column(c1_title, min_width=20, justify="left", style="bold")
34 | table.add_column(c2_title, min_width=60, justify="left", style="bold")
35 |
36 | for key, value in kwargs.items():
37 | if isinstance(value, pathlib.Path):
38 | value = str(value) # noqa: PLW2901
39 | table.add_row(f"[bold]{key}[/bold]", Pretty(value))
40 |
41 | console.print(table)
42 |
43 |
44 | def print_params(
45 | table_title: str = "Parameters Table", c1_title: str = "Variable", c2_title: str = "Value"
46 | ) -> Callable:
47 | """
48 | A decorator that prints the parameters of a function in a formatted table
49 | using the rich library.
50 |
51 | Args:
52 | c1_title (str, optional): Title of the first column. Defaults to "Variable".
53 | c2_title (str, optional): Title of the second column. Defaults to "Value".
54 | table_title (str, optional): Title of the table. Defaults to "Parameters Table".
55 |
56 | Returns:
57 | Callable: The wrapped function with parameter printing functionality.
58 | """
59 |
60 | def decorator(func: Callable) -> Callable:
61 | @wraps(func)
62 | def wrapper(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> Any:
63 | func_signature = inspect.signature(func)
64 | bound_arguments = func_signature.bind(*args, **kwargs)
65 | bound_arguments.apply_defaults()
66 | params = dict(bound_arguments.arguments.items())
67 | print_variables_as_table(c1_title, c2_title, table_title, **params)
68 | return func(*args, **kwargs)
69 |
70 | return wrapper
71 |
72 | return decorator
73 |
74 |
75 | def print_train_details(augmentation: A.Compose, config: dict[str, Any]) -> None:
76 | console = Console()
77 | console.print("\n")
78 | console.print("[bold blue]Augmentation Pipeline:[/bold blue]")
79 | console.print(Pretty(augmentation))
80 | console.print("\n")
81 | console.print("[bold blue]Configuration:[/bold blue]")
82 | console.print(Pretty(config))
83 | console.print("\n")
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/valid.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for validating trained OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 |
7 | import click
8 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
9 |
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.dataset import LicensePlateDataset
11 |
12 | # Custom metris / losses
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 |
16 |
17 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
18 | @click.option(
19 | "-m",
20 | "--model",
21 | "model_path",
22 | required=True,
23 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
24 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
25 | )
26 | @click.option(
27 | "--config-file",
28 | required=True,
29 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
30 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
31 | )
32 | @click.option(
33 | "-a",
34 | "--annotations",
35 | required=True,
36 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
37 | help="Annotations file used for validation.",
38 | )
39 | @click.option(
40 | "-b",
41 | "--batch-size",
42 | default=1,
43 | show_default=True,
44 | type=int,
45 | help="Batch size.",
46 | )
47 | def valid(
48 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
49 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
50 | annotations: pathlib.Path,
51 | batch_size: int,
52 | ) -> None:
53 | """
54 | Validate the trained OCR model on a labeled set.
55 | """
56 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
57 | model = utils.load_keras_model(
58 | model_path, vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size, max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots
59 | )
60 | val_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(annotations_file=annotations, config=config)
61 | val_dataloader = DataLoader(val_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
62 | model.evaluate(val_dataloader)
63 |
64 |
65 | if __name__ == "__main__":
66 | valid()
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/visualize_augmentation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script to visualize the augmented plates used during training.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 | import random
7 | from math import ceil
8 |
9 | import albumentations as A
10 | import click
11 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import numpy.typing as npt
14 |
15 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.augmentation import TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
17 |
18 |
19 | def _set_seed(seed: int | None) -> None:
20 | """Set random seed for reproducing augmentations."""
21 | if seed:
22 | random.seed(seed)
23 | np.random.seed(seed)
24 |
25 |
26 | def load_images(
27 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
28 | num_images: int,
29 | shuffle: bool,
30 | height: int,
31 | width: int,
32 | augmentation: A.Compose,
33 | ) -> tuple[list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]], list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]]]:
34 | images = utils.load_images_from_folder(
35 | img_dir, height=height, width=width, shuffle=shuffle, limit=num_images
36 | )
37 | augmented_images = [augmentation(image=i)["image"] for i in images]
38 | return images, augmented_images
39 |
40 |
41 | def display_images(
42 | images: list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]],
43 | augmented_images: list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]],
44 | columns: int,
45 | rows: int,
46 | show_original: bool,
47 | ) -> None:
48 | num_images = len(images)
49 | total_plots = rows * columns
50 | num_pages = ceil(num_images / total_plots)
51 | for page in range(num_pages):
52 | _, axs = plt.subplots(rows, columns, figsize=(8, 8))
53 | axs = axs.flatten()
54 | for i, ax in enumerate(axs):
55 | idx = page * total_plots + i
56 | if idx < num_images:
57 | if show_original:
58 | img_to_show = np.concatenate((images[idx], augmented_images[idx]), axis=1)
59 | else:
60 | img_to_show = augmented_images[idx]
61 | ax.imshow(img_to_show, cmap="gray")
62 | ax.axis("off")
63 | else:
64 | ax.axis("off")
65 | plt.tight_layout()
66 | plt.show()
67 |
68 |
69 | # ruff: noqa: PLR0913
70 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
71 |
72 |
73 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
74 | @click.option(
75 | "--img-dir",
76 | "-d",
77 | required=True,
78 | type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
79 | help="Path to the images that will be augmented and visualized.",
80 | )
81 | @click.option(
82 | "--num-images",
83 | "-n",
84 | type=int,
85 | default=1_000,
86 | show_default=True,
87 | help="Maximum number of images to visualize.",
88 | )
89 | @click.option(
90 | "--augmentation-path",
91 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
92 | help="YAML file pointing to the augmentation pipeline saved with Albumentations.save(...)",
93 | )
94 | @click.option(
95 | "--shuffle",
96 | "-s",
97 | is_flag=True,
98 | default=False,
99 | help="Whether to shuffle the images before plotting them.",
100 | )
101 | @click.option(
102 | "--columns",
103 | "-c",
104 | type=int,
105 | default=3,
106 | show_default=True,
107 | help="Number of columns in the grid layout for displaying images.",
108 | )
109 | @click.option(
110 | "--rows",
111 | "-r",
112 | type=int,
113 | default=4,
114 | show_default=True,
115 | help="Number of rows in the grid layout for displaying images.",
116 | )
117 | @click.option(
118 | "--height",
119 | "-h",
120 | type=int,
121 | default=70,
122 | show_default=True,
123 | help="Height to which the images will be resize.",
124 | )
125 | @click.option(
126 | "--width",
127 | "-w",
128 | type=int,
129 | default=140,
130 | show_default=True,
131 | help="Width to which the images will be resize.",
132 | )
133 | @click.option(
134 | "--show-original",
135 | "-o",
136 | is_flag=True,
137 | help="Show the original image along with the augmented one.",
138 | )
139 | @click.option(
140 | "--seed",
141 | type=int,
142 | help="Seed for reproducing augmentations.",
143 | )
144 | def visualize_augmentation(
145 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
146 | num_images: int,
147 | augmentation_path: pathlib.Path | None,
148 | shuffle: bool,
149 | columns: int,
150 | rows: int,
151 | height: int,
152 | width: int,
153 | seed: int | None,
154 | show_original: bool,
155 | ) -> None:
156 | """
157 | Visualize augmentation pipeline applied to raw images.
158 | """
159 | _set_seed(seed)
160 | aug = A.load(augmentation_path, data_format="yaml") if augmentation_path else TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
161 | images, augmented_images = load_images(img_dir, num_images, shuffle, height, width, aug)
162 | display_images(images, augmented_images, columns, rows, show_original)
163 |
164 |
165 | if __name__ == "__main__":
166 | # pylint: disable = no-value-for-parameter
167 | visualize_augmentation()
168 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/visualize_predictions.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for displaying an image with the OCR model predictions.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 |
8 | import click
9 | import cv2
10 | import keras
11 | import numpy as np
12 |
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.utils import postprocess_model_output
16 |
17 | logging.basicConfig(
18 | level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(message)s", datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
19 | )
20 |
21 |
22 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
23 | @click.option(
24 | "-m",
25 | "--model",
26 | "model_path",
27 | required=True,
28 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
29 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
30 | )
31 | @click.option(
32 | "--config-file",
33 | required=True,
34 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
35 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
36 | )
37 | @click.option(
38 | "-d",
39 | "--img-dir",
40 | required=True,
41 | type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=True, file_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
42 | help="Directory containing the images to make predictions from.",
43 | )
44 | @click.option(
45 | "-l",
46 | "--low-conf-thresh",
47 | type=float,
48 | default=0.35,
49 | show_default=True,
50 | help="Threshold for displaying low confidence characters.",
51 | )
52 | @click.option(
53 | "-f",
54 | "--filter-conf",
55 | type=float,
56 | help="Display plates that any of the plate characters are below this number.",
57 | )
58 | def visualize_predictions(
59 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
60 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
61 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
62 | low_conf_thresh: float,
63 | filter_conf: float | None,
64 | ):
65 | """
66 | Visualize OCR model predictions on unlabeled data.
67 | """
68 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
69 | model = utils.load_keras_model(
70 | model_path, vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size, max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots
71 | )
72 | images = utils.load_images_from_folder(
73 | img_dir, width=config.img_width, height=config.img_height
74 | )
75 | for image in images:
76 | x = np.expand_dims(image, 0)
77 | prediction = model(x, training=False)
78 | prediction = keras.ops.stop_gradient(prediction).numpy()
79 | plate, probs = postprocess_model_output(
80 | prediction=prediction,
81 | alphabet=config.alphabet,
82 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
83 | vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size,
84 | )
85 | if not filter_conf or (filter_conf and np.any(probs < filter_conf)):
86 | utils.display_predictions(
87 | image=image, plate=plate, probs=probs, low_conf_thresh=low_conf_thresh
88 | )
89 | cv2.destroyAllWindows()
90 |
91 |
92 | if __name__ == "__main__":
93 | visualize_predictions()
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/common/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/common/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/common/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Common utilities used across the package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import time
7 | from collections.abc import Callable, Iterator
8 | from contextlib import contextmanager
9 |
10 |
11 | @contextmanager
12 | def log_time_taken(process_name: str) -> Iterator[None]:
13 | """
14 | A concise context manager to time code snippets and log the result.
15 |
16 | Usage:
17 | with log_time_taken("process_name"):
18 | # Code snippet to be timed
19 |
20 | :param process_name: Name of the process being timed.
21 | """
22 | time_start: float = time.perf_counter()
23 | try:
24 | yield
25 | finally:
26 | time_end: float = time.perf_counter()
27 | time_elapsed: float = time_end - time_start
28 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
29 | logger.info("Computation time of '%s' = %.3fms", process_name, 1_000 * time_elapsed)
30 |
31 |
32 | @contextmanager
33 | def measure_time() -> Iterator[Callable[[], float]]:
34 | """
35 | A context manager for measuring execution time (in milliseconds) within its code block.
36 |
37 | usage:
38 | with code_timer() as timer:
39 | # Code snippet to be timed
40 | print(f"Code took: {timer()} seconds")
41 | """
42 | start_time = end_time = time.perf_counter()
43 | yield lambda: (end_time - start_time) * 1_000
44 | end_time = time.perf_counter()
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/inference/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Model config reading/parsing for doing inference.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from os import PathLike
6 | from typing import TypedDict
7 |
8 | import yaml
9 |
10 | # pylint: disable=duplicate-code
11 |
12 |
13 | class PlateOCRConfig(TypedDict):
14 | """
15 | Plate OCR Config used for inference.
16 |
17 | This has the same attributes as the one used in the training Pydantic BaseModel. We use this to
18 | avoid having Pydantic as a required dependency of the minimal package install.
19 | """
20 |
21 | max_plate_slots: int
22 | """
23 | Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
24 | """
25 | alphabet: str
26 | """
27 | All the possible character set for the model output.
28 | """
29 | pad_char: str
30 | """
31 | Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS.
32 | """
33 | img_height: int
34 | """
35 | Image height which is fed to the model.
36 | """
37 | img_width: int
38 | """
39 | Image width which is fed to the model.
40 | """
41 |
42 |
43 | def load_config_from_yaml(yaml_file_path: str | PathLike[str]) -> PlateOCRConfig:
44 | """
45 | Read and parse a yaml containing the Plate OCR config.
46 |
47 | Note: This is currently not using Pydantic for parsing/validating to avoid adding it a python
48 | dependency as part of the minimal installation.
49 | """
50 | with open(yaml_file_path, encoding="utf-8") as f_in:
51 | config: PlateOCRConfig = yaml.safe_load(f_in)
52 | return config
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/hub.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utilities function used for doing inference with the OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import shutil
8 | import urllib.request
9 | from http import HTTPStatus
10 | from typing import Literal
11 |
12 | from tqdm.asyncio import tqdm
13 |
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.utils import safe_write
15 |
16 | BASE_URL: str = "https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/releases/download"
17 | OcrModel = Literal[
18 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-model",
19 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model",
20 | "european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model",
21 | "global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model",
22 | ]
23 |
24 |
25 | AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS: dict[OcrModel, tuple[str, str]] = {
26 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-model": (
27 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr.onnx",
28 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml",
29 | ),
30 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model": (
31 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_synth.onnx",
32 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml",
33 | ),
34 | "european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model": (
35 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr.onnx",
36 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_config.yaml",
37 | ),
38 | "global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model": (
39 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr.onnx",
40 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_config.yaml",
41 | ),
42 | }
43 | """Available ONNX models for doing inference."""
44 |
45 | MODEL_CACHE_DIR: pathlib.Path = pathlib.Path.home() / ".cache" / "fast-plate-ocr"
46 | """Default location where models will be stored."""
47 |
48 |
49 | def _download_with_progress(url: str, filename: pathlib.Path) -> None:
50 | """
51 | Download utility function with progress bar.
52 |
53 | :param url: URL of the model to download.
54 | :param filename: Where to save the OCR model.
55 | """
56 | with urllib.request.urlopen(url) as response, safe_write(filename, mode="wb") as out_file:
57 | if response.getcode() != HTTPStatus.OK:
58 | raise ValueError(f"Failed to download file from {url}. Status code: {response.status}")
59 |
60 | file_size = int(response.headers.get("Content-Length", 0))
61 | desc = f"Downloading {filename.name}"
62 |
63 | with tqdm.wrapattr(out_file, "write", total=file_size, desc=desc) as f_out:
64 | shutil.copyfileobj(response, f_out)
65 |
66 |
67 | def download_model(
68 | model_name: OcrModel,
69 | save_directory: pathlib.Path | None = None,
70 | force_download: bool = False,
71 | ) -> tuple[pathlib.Path, pathlib.Path]:
72 | """
73 | Download an OCR model and the config to a given directory.
74 |
75 | :param model_name: Which model to download.
76 | :param save_directory: Directory to save the OCR model. It should point to a folder. If not
77 | supplied, this will point to '~/.cache/'
78 | :param force_download: Force and download the model if it already exists in `save_directory`.
79 | :return: A tuple consisting of (model_downloaded_path, config_downloaded_path).
80 | """
81 | if model_name not in AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS:
82 | available_models = ", ".join(AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS.keys())
83 | raise ValueError(f"Unknown model {model_name}. Use one of [{available_models}]")
84 |
85 | if save_directory is None:
86 | save_directory = MODEL_CACHE_DIR / model_name
87 | elif save_directory.is_file():
88 | raise ValueError(f"Expected a directory, but got {save_directory}")
89 |
90 | save_directory.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
91 |
92 | model_url, config_url = AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS[model_name]
93 | model_filename = save_directory / model_url.split("/")[-1]
94 | config_filename = save_directory / config_url.split("/")[-1]
95 |
96 | if not force_download and model_filename.is_file() and config_filename.is_file():
97 | logging.info(
98 | "Skipping download of '%s' model, already exists at %s",
99 | model_name,
100 | save_directory,
101 | )
102 | return model_filename, config_filename
103 |
104 | # Download the model if not present or if we want to force the download
105 | if force_download or not model_filename.is_file():
106 | logging.info("Downloading model to %s", model_filename)
107 | _download_with_progress(url=model_url, filename=model_filename)
108 |
109 | # Same for the config
110 | if force_download or not config_filename.is_file():
111 | logging.info("Downloading config to %s", config_filename)
112 | _download_with_progress(url=config_url, filename=config_filename)
113 |
114 | return model_filename, config_filename
115 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/onnx_inference.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | ONNX inference module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import os
7 | import pathlib
8 | from collections.abc import Sequence
9 | from typing import Literal
10 |
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import numpy.typing as npt
13 | import onnxruntime as ort
14 | from rich.console import Console
15 | from rich.panel import Panel
16 | from rich.table import Table
17 | from rich.text import Text
18 |
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.common.utils import measure_time
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference import hub
21 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.config import load_config_from_yaml
22 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.hub import OcrModel
23 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.process import postprocess_output, preprocess_image, read_plate_image
24 |
25 |
26 | def _load_image_from_source(
27 | source: str | list[str] | npt.NDArray | list[npt.NDArray],
28 | ) -> npt.NDArray | list[npt.NDArray]:
29 | """
30 | Loads an image from a given source.
31 |
32 | :param source: Path to the input image file, list of paths, or numpy array representing one or
33 | multiple images.
34 | :return: Numpy array representing the input image(s) or a list of numpy arrays.
35 | """
36 | if isinstance(source, str):
37 | # Shape returned (H, W)
38 | return read_plate_image(source)
39 |
40 | if isinstance(source, list):
41 | # Are image paths
42 | if all(isinstance(s, str) for s in source):
43 | # List returned with array item of shape (H, W)
44 | return [read_plate_image(i) for i in source] # type: ignore[arg-type]
45 | # Are list of numpy arrays
46 | if all(isinstance(a, np.ndarray) for a in source):
47 | # List returned with array item of shape (H, W)
48 | return source # type: ignore[return-value]
49 | raise ValueError("Expected source to be a list of `str` or `np.ndarray`!")
50 |
51 | if isinstance(source, np.ndarray):
52 | # Squeeze grayscale channel dimension if supplied
53 | source = source.squeeze()
54 | if source.ndim != 2:
55 | raise ValueError("Expected source array to be of shape (H, W) or (H, W, 1).")
56 | # Shape returned (H, W)
57 | return source
58 |
59 | raise ValueError("Unsupported input type. Only file path or numpy array is supported.")
60 |
61 |
62 | class ONNXPlateRecognizer:
63 | """
64 | ONNX inference class for performing license plates OCR.
65 | """
66 |
67 | def __init__(
68 | self,
69 | hub_ocr_model: OcrModel | None = None,
70 | device: Literal["cuda", "cpu", "auto"] = "auto",
71 | providers: Sequence[str | tuple[str, dict]] | None = None,
72 | sess_options: ort.SessionOptions | None = None,
73 | model_path: str | os.PathLike[str] | None = None,
74 | config_path: str | os.PathLike[str] | None = None,
75 | force_download: bool = False,
76 | ) -> None:
77 | """
78 | Initializes the ONNXPlateRecognizer with the specified OCR model and inference device.
79 |
80 | The current OCR models available from the HUB are:
81 |
82 | - `argentinian-plates-cnn-model`: OCR for Argentinian license plates. Uses fully conv
83 | architecture.
84 | - `argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model`: OCR for Argentinian license plates trained with
85 | synthetic and real data. Uses fully conv architecture.
86 | - `european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model`: OCR for European license plates. Uses MobileVIT-2
87 | for the backbone.
88 | - `global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model`: OCR for Global license plates (+65 countries).
89 | Uses MobileVIT-2 for the backbone.
90 |
91 | Args:
92 | hub_ocr_model: Name of the OCR model to use from the HUB.
93 | device: Device type for inference. Should be one of ('cpu', 'cuda', 'auto'). If
94 | 'auto' mode, the device will be deduced from
95 | `onnxruntime.get_available_providers()`.
96 | providers: Optional sequence of providers in order of decreasing precedence. If not
97 | specified, all available providers are used based on the device argument.
98 | sess_options: Advanced session options for ONNX Runtime.
99 | model_path: Path to ONNX model file to use (In case you want to use a custom one).
100 | config_path: Path to config file to use (In case you want to use a custom one).
101 | force_download: Force and download the model, even if it already exists.
102 | Returns:
103 | None.
104 | """
105 | self.logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
106 |
107 | if providers is not None:
108 | self.providers = providers
109 | self.logger.info("Using custom providers: %s", providers)
110 | else:
111 | if device == "cuda":
112 | self.providers = ["CUDAExecutionProvider"]
113 | elif device == "cpu":
114 | self.providers = ["CPUExecutionProvider"]
115 | elif device == "auto":
116 | self.providers = ort.get_available_providers()
117 | else:
118 | raise ValueError(
119 | f"Device should be one of ('cpu', 'cuda', 'auto'). Got '{device}'."
120 | )
121 |
122 | self.logger.info("Using device '%s' with providers: %s", device, self.providers)
123 |
124 | if model_path and config_path:
125 | model_path = pathlib.Path(model_path)
126 | config_path = pathlib.Path(config_path)
127 | if not model_path.exists() or not config_path.exists():
128 | raise FileNotFoundError("Missing model/config file!")
129 | self.model_name = model_path.stem
130 | elif hub_ocr_model:
131 | self.model_name = hub_ocr_model
132 | model_path, config_path = hub.download_model(
133 | model_name=hub_ocr_model, force_download=force_download
134 | )
135 | else:
136 | raise ValueError(
137 | "Either provide a model from the HUB or a custom model_path and config_path"
138 | )
139 |
140 | self.config = load_config_from_yaml(config_path)
141 | self.model = ort.InferenceSession(
142 | model_path, providers=self.providers, sess_options=sess_options
143 | )
144 | self.logger.info("Using ONNX Runtime with %s.", self.providers)
145 |
146 | def benchmark(self, n_iter: int = 10_000, include_processing: bool = False) -> None:
147 | """
148 | Benchmark time taken to run the OCR model. This reports the average inference time and the
149 | throughput in plates per second.
150 |
151 | Args:
152 | n_iter: The number of iterations to run the benchmark. This determines how many times
153 | the inference will be executed to compute the average performance metrics.
154 | include_processing: Indicates whether the benchmark should include preprocessing and
155 | postprocessing times in the measurement.
156 | """
157 | cum_time = 0.0
158 | x = np.random.randint(
159 | 0, 256, size=(1, self.config["img_height"], self.config["img_width"], 1), dtype=np.uint8
160 | )
161 | for _ in range(n_iter):
162 | with measure_time() as time_taken:
163 | if include_processing:
164 | self.run(x)
165 | else:
166 | self.model.run(None, {"input": x})
167 | cum_time += time_taken()
168 |
169 | avg_time = (cum_time / n_iter) if n_iter > 0 else 0.0
170 | avg_pps = (1_000 / avg_time) if n_iter > 0 else 0.0
171 |
172 | console = Console()
173 | model_info = Panel(
174 | Text(f"Model: {self.model_name}\nProviders: {self.providers}", style="bold green"),
175 | title="Model Information",
176 | border_style="bright_blue",
177 | expand=False,
178 | )
179 | console.print(model_info)
180 | table = Table(title=f"Benchmark for '{self.model_name}' Model", border_style="bright_blue")
181 | table.add_column("Metric", justify="center", style="cyan", no_wrap=True)
182 | table.add_column("Value", justify="center", style="magenta")
183 | table.add_row("Number of Iterations", str(n_iter))
184 | table.add_row("Average Time (ms)", f"{avg_time:.4f}")
185 | table.add_row("Plates Per Second (PPS)", f"{avg_pps:.4f}")
186 | console.print(table)
187 |
188 | def run(
189 | self,
190 | source: str | list[str] | npt.NDArray | list[npt.NDArray],
191 | return_confidence: bool = False,
192 | ) -> tuple[list[str], npt.NDArray] | list[str]:
193 | """
194 | Performs OCR to recognize license plate characters from an image or a list of images.
195 |
196 | Args:
197 | source: The path(s) to the image(s), a numpy array representing an image or a list
198 | of NumPy arrays. If a numpy array is provided, it is expected to already be in
199 | grayscale format, with shape `(H, W) `or `(H, W, 1)`. A list of numpy arrays with
200 | different image sizes may also be provided.
201 | return_confidence: Whether to return confidence scores along with plate predictions.
202 |
203 | Returns:
204 | A list of plates for each input image. If `return_confidence` is True, a numpy
205 | array is returned with the shape `(N, plate_slots)`, where N is the batch size and
206 | each plate slot is the confidence for the recognized license plate character.
207 | """
208 | x = _load_image_from_source(source)
209 | # Preprocess
210 | x = preprocess_image(x, self.config["img_height"], self.config["img_width"])
211 | # Run model
212 | y: list[npt.NDArray] = self.model.run(None, {"input": x})
213 | # Postprocess model output
214 | return postprocess_output(
215 | y[0],
216 | self.config["max_plate_slots"],
217 | self.config["alphabet"],
218 | return_confidence=return_confidence,
219 | )
220 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/process.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utility functions for processing model input/output.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 |
7 | import cv2
8 | import numpy as np
9 | import numpy.typing as npt
10 |
11 |
12 | def read_plate_image(image_path: str) -> npt.NDArray:
13 | """
14 | Read image from disk as a grayscale image.
15 |
16 | :param image_path: The path to the license plate image.
17 | :return: The image as a NumPy array.
18 | """
19 | if not os.path.exists(image_path):
20 | raise ValueError(f"{image_path} file doesn't exist!")
21 | return cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
22 |
23 |
24 | def preprocess_image(
25 | image: npt.NDArray | list[npt.NDArray], img_height: int, img_width: int
26 | ) -> npt.NDArray:
27 | """
28 | Preprocess the image(s), so they're ready to be fed to the model.
29 |
30 | Note: We don't normalize the pixel values between [0, 1] here, because that the model first
31 | layer does that.
32 |
33 | :param image: The image(s) contained in a NumPy array.
34 | :param img_height: The desired height of the resized image.
35 | :param img_width: The desired width of the resized image.
36 | :return: A numpy array with shape (N, H, W, 1).
37 | """
38 | # Add batch dimension: (H, W) -> (1, H, W)
39 | if isinstance(image, np.ndarray):
40 | image = np.expand_dims(image, axis=0)
41 |
42 | imgs = np.array(
43 | [
44 | cv2.resize(im.squeeze(), (img_width, img_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
45 | for im in image
46 | ]
47 | )
48 | # Add channel dimension
49 | imgs = np.expand_dims(imgs, axis=-1)
50 | return imgs
51 |
52 |
53 | def postprocess_output(
54 | model_output: npt.NDArray,
55 | max_plate_slots: int,
56 | model_alphabet: str,
57 | return_confidence: bool = False,
58 | ) -> tuple[list[str], npt.NDArray] | list[str]:
59 | """
60 | Post-processes model output and return license plate string, and optionally the probabilities.
61 |
62 | :param model_output: Output from the model containing predictions.
63 | :param max_plate_slots: Maximum number of characters in a license plate.
64 | :param model_alphabet: Alphabet used by the model for character encoding.
65 | :param return_confidence: Flag to indicate whether to return confidence scores along with plate
66 | predictions.
67 | :return: Decoded license plate characters as a list, optionally with confidence scores. The
68 | confidence scores have shape (N, max_plate_slots) where N is the batch size.
69 | """
70 | predictions = model_output.reshape((-1, max_plate_slots, len(model_alphabet)))
71 | prediction_indices = np.argmax(predictions, axis=-1)
72 | alphabet_array = np.array(list(model_alphabet))
73 | plate_chars = alphabet_array[prediction_indices]
74 | plates: list[str] = np.apply_along_axis("".join, 1, plate_chars).tolist()
75 | if return_confidence:
76 | probs = np.max(predictions, axis=-1)
77 | return plates, probs
78 | return plates
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utilities used around the inference package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | from collections.abc import Iterator
7 | from contextlib import contextmanager
8 | from pathlib import Path
9 | from typing import IO, Any
10 |
11 |
12 | @contextmanager
13 | def safe_write(
14 | file: str | os.PathLike[str],
15 | mode: str = "wb",
16 | encoding: str | None = None,
17 | **kwargs: Any,
18 | ) -> Iterator[IO]:
19 | """
20 | Context manager for safe file writing.
21 |
22 | Opens the specified file for writing and yields a file object.
23 | If an exception occurs during writing, the file is removed before raising the exception.
24 | """
25 | try:
26 | with open(file, mode, encoding=encoding, **kwargs) as f:
27 | yield f
28 | except Exception as e:
29 | Path(file).unlink(missing_ok=True)
30 | raise e
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/py.typed:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/py.typed
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/train/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/data/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/train/data/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/data/augmentation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Augmentations used for training the OCR model.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import albumentations as A
6 | import cv2
7 |
8 | BORDER_COLOR_BLACK: tuple[int, int, int] = (0, 0, 0)
9 |
10 | TRAIN_AUGMENTATION = A.Compose(
11 | [
12 | A.ShiftScaleRotate(
13 | shift_limit=0.06,
14 | scale_limit=0.1,
15 | rotate_limit=9,
16 | border_mode=cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT,
17 | value=BORDER_COLOR_BLACK,
18 | p=1,
19 | ),
20 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
21 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
22 | A.OneOf(
23 | [
24 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
25 | A.PixelDropout(dropout_prob=0.01, p=0.2),
26 | ],
27 | p=0.7,
28 | ),
29 | ]
30 | )
31 | """Training augmentations recipe."""
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/data/dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Dataset module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | from os import PathLike
7 |
8 | import albumentations as A
9 | import numpy.typing as npt
10 | import pandas as pd
11 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset
12 |
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import PlateOCRConfig
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 |
16 |
17 | class LicensePlateDataset(Dataset):
18 | def __init__(
19 | self,
20 | annotations_file: str | PathLike[str],
21 | config: PlateOCRConfig,
22 | transform: A.Compose | None = None,
23 | ) -> None:
24 | annotations = pd.read_csv(annotations_file)
25 | annotations["image_path"] = (
26 | os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(annotations_file)) + os.sep + annotations["image_path"]
27 | )
28 | assert (
29 | annotations["plate_text"].str.len() <= config.max_plate_slots
30 | ).all(), "Plates are longer than max_plate_slots specified param. Change the parameter."
31 | self.annotations = annotations.to_numpy()
32 | self.config = config
33 | self.transform = transform
34 |
35 | def __len__(self) -> int:
36 | return self.annotations.shape[0]
37 |
38 | def __getitem__(self, idx) -> tuple[npt.NDArray, npt.NDArray]:
39 | image_path, plate_text = self.annotations[idx]
40 | x = utils.read_plate_image(
41 | image_path=image_path,
42 | img_height=self.config.img_height,
43 | img_width=self.config.img_width,
44 | )
45 | y = utils.target_transform(
46 | plate_text=plate_text,
47 | max_plate_slots=self.config.max_plate_slots,
48 | alphabet=self.config.alphabet,
49 | pad_char=self.config.pad_char,
50 | )
51 | if self.transform:
52 | x = self.transform(image=x)["image"]
53 | return x, y
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Config values used throughout the code.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from os import PathLike
6 |
7 | import yaml
8 | from pydantic import BaseModel, computed_field, model_validator
9 |
10 |
11 | class PlateOCRConfig(BaseModel, extra="forbid", frozen=True):
12 | """
13 | Model License Plate OCR config.
14 | """
15 |
16 | max_plate_slots: int
17 | """
18 | Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
19 | """
20 |
21 | alphabet: str
22 | """
23 | All the possible character set for the model output.
24 | """
25 | pad_char: str
26 | """
27 | Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS.
28 | """
29 | img_height: int
30 | """
31 | Image height which is fed to the model.
32 | """
33 | img_width: int
34 | """
35 | Image width which is fed to the model.
36 | """
37 |
38 | @computed_field # type: ignore[misc]
39 | @property
40 | def vocabulary_size(self) -> int:
41 | return len(self.alphabet)
42 |
43 | @model_validator(mode="after")
44 | def check_pad_in_alphabet(self) -> "PlateOCRConfig":
45 | if self.pad_char not in self.alphabet:
46 | raise ValueError("Pad character must be present in model alphabet.")
47 | return self
48 |
49 |
50 | def load_config_from_yaml(yaml_file_path: str | PathLike[str]) -> PlateOCRConfig:
51 | """Read and parse a yaml containing the Plate OCR config."""
52 | with open(yaml_file_path, encoding="utf-8") as f_in:
53 | yaml_content = yaml.safe_load(f_in)
54 | config = PlateOCRConfig(**yaml_content)
55 | return config
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/custom.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Custom metrics and loss functions.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from keras import losses, metrics, ops
6 |
7 |
8 | def cat_acc_metric(max_plate_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int):
9 | """
10 | Categorical accuracy metric.
11 | """
12 |
13 | def cat_acc(y_true, y_pred):
14 | """
15 | This is simply the CategoricalAccuracy for multi-class label problems. Example if the
16 | correct label is ABC123 and ABC133 is predicted, it will not give a precision of 0% like
17 | plate_acc (not completely classified correctly), but 83.3% (5/6).
18 | """
19 | y_true = ops.reshape(y_true, newshape=(-1, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size))
20 | y_pred = ops.reshape(y_pred, newshape=(-1, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size))
21 | return ops.mean(metrics.categorical_accuracy(y_true, y_pred))
22 |
23 | return cat_acc
24 |
25 |
26 | def plate_acc_metric(max_plate_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int):
27 | """
28 | Plate accuracy metric.
29 | """
30 |
31 | def plate_acc(y_true, y_pred):
32 | """
33 | Compute how many plates were correctly classified. For a single plate, if ground truth is
34 | 'ABC 123', and the prediction is 'ABC 123', then this would give a score of 1. If the
35 | prediction was ABD 123, it would score 0.
36 | """
37 | y_true = ops.reshape(y_true, newshape=(-1, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size))
38 | y_pred = ops.reshape(y_pred, newshape=(-1, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size))
39 | et = ops.equal(ops.argmax(y_true, axis=-1), ops.argmax(y_pred, axis=-1))
40 | return ops.mean(ops.cast(ops.all(et, axis=-1, keepdims=False), dtype="float32"))
41 |
42 | return plate_acc
43 |
44 |
45 | def top_3_k_metric(vocabulary_size: int):
46 | """
47 | Top 3 K categorical accuracy metric.
48 | """
49 |
50 | def top_3_k(y_true, y_pred):
51 | """
52 | Calculates how often the true character is found in the 3 predictions with the highest
53 | probability.
54 | """
55 | # Reshape into 2-d
56 | y_true = ops.reshape(y_true, newshape=(-1, vocabulary_size))
57 | y_pred = ops.reshape(y_pred, newshape=(-1, vocabulary_size))
58 | return ops.mean(metrics.top_k_categorical_accuracy(y_true, y_pred, k=3))
59 |
60 | return top_3_k
61 |
62 |
63 | # Custom loss
64 | def cce_loss(vocabulary_size: int, label_smoothing: float = 0.2):
65 | """
66 | Categorical cross-entropy loss.
67 | """
68 |
69 | def cce(y_true, y_pred):
70 | """
71 | Computes the categorical cross-entropy loss.
72 | """
73 | y_true = ops.reshape(y_true, newshape=(-1, vocabulary_size))
74 | y_pred = ops.reshape(y_pred, newshape=(-1, vocabulary_size))
75 | return ops.mean(
76 | losses.categorical_crossentropy(
77 | y_true, y_pred, from_logits=False, label_smoothing=label_smoothing
78 | )
79 | )
80 |
81 | return cce
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/layer_blocks.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Layer blocks used in the OCR model.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from keras import regularizers
6 | from keras.src.layers import (
7 | Activation,
8 | AveragePooling2D,
9 | BatchNormalization,
10 | Conv2D,
11 | MaxPooling2D,
12 | SeparableConv2D,
13 | )
14 |
15 |
16 | def block_no_bn(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
17 | x1 = Conv2D(
18 | kernel_size=k,
19 | filters=n_c,
20 | strides=s,
21 | padding=padding,
22 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
23 | use_bias=False,
24 | )(i)
25 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x1)
26 | return x2, x1
27 |
28 |
29 | def block_no_activation(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same"):
30 | x = Conv2D(
31 | kernel_size=k,
32 | filters=n_c,
33 | strides=s,
34 | padding=padding,
35 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
36 | use_bias=False,
37 | )(i)
38 | x = BatchNormalization()(x)
39 | return x
40 |
41 |
42 | def block_bn(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
43 | x1 = Conv2D(
44 | kernel_size=k,
45 | filters=n_c,
46 | strides=s,
47 | padding=padding,
48 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
49 | use_bias=False,
50 | )(i)
51 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
52 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
53 | return x2, x1
54 |
55 |
56 | def block_bn_no_l2(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
57 | x1 = Conv2D(kernel_size=k, filters=n_c, strides=s, padding=padding, use_bias=False)(i)
58 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
59 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
60 | return x2, x1
61 |
62 |
63 | def block_bn_sep_conv_l2(
64 | i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", depth_multiplier=1, activation: str = "relu"
65 | ):
66 | l2_kernel_reg = regularizers.l2(0.01)
67 | x1 = SeparableConv2D(
68 | kernel_size=k,
69 | filters=n_c,
70 | depth_multiplier=depth_multiplier,
71 | strides=s,
72 | padding=padding,
73 | use_bias=False,
74 | depthwise_regularizer=l2_kernel_reg,
75 | pointwise_regularizer=l2_kernel_reg,
76 | )(i)
77 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
78 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
79 | return x2, x1
80 |
81 |
82 | def block_bn_relu6(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu6"):
83 | x1 = Conv2D(
84 | kernel_size=k,
85 | filters=n_c,
86 | strides=s,
87 | padding=padding,
88 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
89 | use_bias=False,
90 | )(i)
91 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
92 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
93 | return x2, x1
94 |
95 |
96 | def block_bn_relu6_no_l2(i, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation: str = "relu6"):
97 | x1 = Conv2D(kernel_size=k, filters=n_c, strides=s, padding=padding, use_bias=False)(i)
98 | x2 = BatchNormalization()(x1)
99 | x2 = Activation(activation)(x2)
100 | return x2, x1
101 |
102 |
103 | def block_average_conv_down(x, n_c, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
104 | x = AveragePooling2D(pool_size=2, strides=1, padding="valid")(x)
105 | x = Conv2D(
106 | filters=n_c,
107 | kernel_size=3,
108 | strides=2,
109 | padding=padding,
110 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
111 | use_bias=False,
112 | )(x)
113 | x = BatchNormalization()(x)
114 | x = Activation(activation)(x)
115 | return x
116 |
117 |
118 | def block_max_conv_down(x, n_c, padding="same", activation: str = "relu"):
119 | x = MaxPooling2D(pool_size=2, strides=1, padding="valid")(x)
120 | x = Conv2D(
121 | filters=n_c,
122 | kernel_size=3,
123 | strides=2,
124 | padding=padding,
125 | kernel_regularizer=regularizers.l2(0.01),
126 | use_bias=False,
127 | )(x)
128 | x = BatchNormalization()(x)
129 | x = Activation(activation)(x)
130 | return x
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Model definitions for the FastLP OCR.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from typing import Literal
6 |
7 | from keras.src.activations import softmax
8 | from keras.src.layers import (
9 | Activation,
10 | Concatenate,
11 | Dense,
12 | Dropout,
13 | GlobalAveragePooling2D,
14 | Input,
15 | Rescaling,
16 | Reshape,
17 | Softmax,
18 | )
19 | from keras.src.models import Model
20 |
21 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.layer_blocks import (
22 | block_average_conv_down,
23 | block_bn,
24 | block_max_conv_down,
25 | block_no_activation,
26 | )
27 |
28 |
29 | def cnn_ocr_model(
30 | h: int,
31 | w: int,
32 | max_plate_slots: int,
33 | vocabulary_size: int,
34 | dense: bool = True,
35 | activation: str = "relu",
36 | pool_layer: Literal["avg", "max"] = "max",
37 | ) -> Model:
38 | """
39 | OCR model implemented with just CNN layers (v2).
40 | """
41 | input_tensor = Input((h, w, 1))
42 | x = Rescaling(1.0 / 255)(input_tensor)
43 | # Pooling-Conv layer
44 | if pool_layer == "avg":
45 | block_pool_conv = block_average_conv_down
46 | elif pool_layer == "max":
47 | block_pool_conv = block_max_conv_down
48 | # Backbone
49 | x = block_pool_conv(x, n_c=32, padding="same", activation=activation)
50 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=3, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
51 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=64, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
52 | x = block_pool_conv(x, n_c=64, padding="same", activation=activation)
53 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=3, n_c=128, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
54 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=128, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
55 | x = block_pool_conv(x, n_c=128, padding="same", activation=activation)
56 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=3, n_c=128, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
57 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=256, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
58 | x = block_pool_conv(x, n_c=256, padding="same", activation=activation)
59 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=512, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
60 | x, _ = block_bn(x, k=1, n_c=1024, s=1, padding="same", activation=activation)
61 | x = (
62 | head(x, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)
63 | if dense
64 | else head_no_fc(x, max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)
65 | )
66 | return Model(inputs=input_tensor, outputs=x)
67 |
68 |
69 | def head(x, max_plate_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int):
70 | """
71 | Model's head with Fully Connected (FC) layers.
72 | """
73 | x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
74 | # dropout for more robust learning
75 | x = Dropout(0.5)(x)
76 | dense_outputs = [
77 | Activation(softmax)(Dense(units=vocabulary_size)(x)) for _ in range(max_plate_slots)
78 | ]
79 | # concat all the dense outputs
80 | x = Concatenate()(dense_outputs)
81 | return x
82 |
83 |
84 | def head_no_fc(x, max_plate_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int):
85 | """
86 | Model's head without Fully Connected (FC) layers.
87 | """
88 | x = block_no_activation(x, k=1, n_c=max_plate_slots * vocabulary_size, s=1, padding="same")
89 | x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
90 | x = Reshape((max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size, 1))(x)
91 | x = Softmax(axis=-2)(x)
92 | return x
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/utilities/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/train/utilities/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/utilities/backend_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utils for Keras supported backends.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import os
6 | from typing import Literal, TypeAlias
7 |
8 | Framework: TypeAlias = Literal["jax", "tensorflow", "torch"]
9 | """Supported backend frameworks for Keras."""
10 |
11 |
12 | def set_jax_backend() -> None:
13 | """Set Keras backend to jax."""
14 | set_keras_backend("jax")
15 |
16 |
17 | def set_tensorflow_backend() -> None:
18 | """Set Keras backend to tensorflow."""
19 | set_keras_backend("tensorflow")
20 |
21 |
22 | def set_pytorch_backend() -> None:
23 | """Set Keras backend to pytorch."""
24 | set_keras_backend("torch")
25 |
26 |
27 | def set_keras_backend(framework: Framework) -> None:
28 | """Set the Keras backend to a given framework."""
29 | os.environ["KERAS_BACKEND"] = framework
30 |
31 |
32 | def reload_keras_backend(framework: Framework) -> None:
33 | """Reload the Keras backend with a given framework."""
34 | # pylint: disable=import-outside-toplevel
35 | import keras
36 |
37 | keras.config.set_backend(framework)
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/train/utilities/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utility functions module
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import random
8 |
9 | import cv2
10 | import keras
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import numpy.typing as npt
13 |
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.custom import (
15 | cat_acc_metric,
16 | cce_loss,
17 | plate_acc_metric,
18 | top_3_k_metric,
19 | )
20 |
21 |
22 | def one_hot_plate(plate: str, alphabet: str) -> list[list[int]]:
23 | return [[0 if char != letter else 1 for char in alphabet] for letter in plate]
24 |
25 |
26 | def target_transform(
27 | plate_text: str,
28 | max_plate_slots: int,
29 | alphabet: str,
30 | pad_char: str,
31 | ) -> npt.NDArray[np.uint8]:
32 | # Pad the plates which length is smaller than 'max_plate_slots'
33 | plate_text = plate_text.ljust(max_plate_slots, pad_char)
34 | # Generate numpy arrays with one-hot encoding of plates
35 | encoded_plate = np.array(one_hot_plate(plate_text, alphabet=alphabet), dtype=np.uint8)
36 | return encoded_plate
37 |
38 |
39 | def read_plate_image(image_path: str, img_height: int, img_width: int) -> npt.NDArray:
40 | """
41 | Read and resize a license plate image.
42 |
43 | :param image_path: The path to the license plate image.
44 | :param img_height: The desired height of the resized image.
45 | :param img_width: The desired width of the resized image.
46 | :return: The resized license plate image as a NumPy array.
47 | """
48 | img = cv2.imread(image_path, cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE)
49 | img = cv2.resize(img, (img_width, img_height), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
50 | img = np.expand_dims(img, -1)
51 | return img
52 |
53 |
54 | def load_keras_model(
55 | model_path: str | pathlib.Path,
56 | vocab_size: int,
57 | max_plate_slots: int,
58 | ) -> keras.Model:
59 | """
60 | Utility helper function to load the keras OCR model.
61 | """
62 | custom_objects = {
63 | "cce": cce_loss(vocabulary_size=vocab_size),
64 | "cat_acc": cat_acc_metric(max_plate_slots=max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=vocab_size),
65 | "plate_acc": plate_acc_metric(max_plate_slots=max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=vocab_size),
66 | "top_3_k": top_3_k_metric(vocabulary_size=vocab_size),
67 | }
68 | model = keras.models.load_model(model_path, custom_objects=custom_objects)
69 | return model
70 |
71 |
72 | IMG_EXTENSIONS: set[str] = {".jpg", ".jpeg", ".png", ".bmp", ".gif", ".tiff", ".webp"}
73 | """Valid image extensions for the scope of this script."""
74 |
75 |
76 | def load_images_from_folder(
77 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
78 | width: int,
79 | height: int,
80 | shuffle: bool = False,
81 | limit: int | None = None,
82 | ) -> list[npt.NDArray]:
83 | """
84 | Return all images read from a directory. This uses the same read function used during training.
85 | """
86 | image_paths = sorted(
87 | str(f.resolve()) for f in img_dir.iterdir() if f.is_file() and f.suffix in IMG_EXTENSIONS
88 | )
89 | if limit:
90 | image_paths = image_paths[:limit]
91 | if shuffle:
92 | random.shuffle(image_paths)
93 | images = [read_plate_image(i, img_height=height, img_width=width) for i in image_paths]
94 | return images
95 |
96 |
97 | def postprocess_model_output(
98 | prediction: npt.NDArray,
99 | alphabet: str,
100 | max_plate_slots: int,
101 | vocab_size: int,
102 | ) -> tuple[str, npt.NDArray]:
103 | """
104 | Return plate text and confidence scores from raw model output.
105 | """
106 | prediction = prediction.reshape((max_plate_slots, vocab_size))
107 | probs = np.max(prediction, axis=-1)
108 | prediction = np.argmax(prediction, axis=-1)
109 | plate = "".join([alphabet[x] for x in prediction])
110 | return plate, probs
111 |
112 |
113 | def low_confidence_positions(probs, thresh=0.3) -> npt.NDArray:
114 | """Returns indices of elements in `probs` less than `thresh`, indicating low confidence."""
115 | return np.where(np.array(probs) < thresh)[0]
116 |
117 |
118 | def display_predictions(
119 | image: npt.NDArray,
120 | plate: str,
121 | probs: npt.NDArray,
122 | low_conf_thresh: float,
123 | ) -> None:
124 | """
125 | Display plate and corresponding prediction.
126 | """
127 | plate_str = "".join(plate)
128 | logging.info("Plate: %s", plate_str)
129 | logging.info("Confidence: %s", probs)
130 | image_to_show = cv2.resize(image, None, fx=3, fy=3, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
131 | # Converting to BGR for color text
132 | image_to_show = cv2.cvtColor(image_to_show, cv2.COLOR_GRAY2RGB)
133 | # Average probabilities
134 | avg_prob = np.mean(probs) * 100
135 | cv2.putText(
136 | image_to_show,
137 | f"{plate_str} {avg_prob:.{2}f}%",
138 | org=(5, 30),
139 | fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
140 | fontScale=1,
141 | color=(0, 0, 0),
142 | lineType=1,
143 | thickness=6,
144 | )
145 | cv2.putText(
146 | image_to_show,
147 | f"{plate_str} {avg_prob:.{2}f}%",
148 | org=(5, 30),
149 | fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
150 | fontScale=1,
151 | color=(255, 255, 255),
152 | lineType=1,
153 | thickness=2,
154 | )
155 | # Display character with low confidence
156 | low_conf_chars = "Low conf. on: " + " ".join(
157 | [plate[i] for i in low_confidence_positions(probs, thresh=low_conf_thresh)]
158 | )
159 | cv2.putText(
160 | image_to_show,
161 | low_conf_chars,
162 | org=(5, 200),
163 | fontFace=cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
164 | fontScale=0.7,
165 | color=(0, 0, 220),
166 | lineType=1,
167 | thickness=2,
168 | )
169 | cv2.imshow("plates", image_to_show)
170 | if cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF == ord("q"):
171 | return
172 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/mkdocs.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | site_name: FastPlateOCR
2 | site_author: ankandrew
3 | site_description: Fast & Lightweight License Plate OCR
4 | repo_url: https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr
5 | theme:
6 | name: material
7 | features:
8 | - navigation.instant
9 | - navigation.instant.progress
10 | - search.suggest
11 | - search.highlight
12 | - content.code.copy
13 | palette:
14 | - scheme: default
15 | toggle:
16 | icon: material/lightbulb-outline
17 | name: Switch to dark mode
18 | - scheme: slate
19 | toggle:
20 | icon: material/lightbulb
21 | name: Switch to light mode
22 | nav:
23 | - Introduction: index.md
24 | - Installation: installation.md
25 | - Usage: usage.md
26 | - Architecture: architecture.md
27 | - Contributing: contributing.md
28 | - Reference: reference.md
29 | plugins:
30 | - search
31 | - mike:
32 | alias_type: symlink
33 | canonical_version: latest
34 | - mkdocstrings:
35 | handlers:
36 | python:
37 | paths: [ . ]
38 | options:
39 | members_order: source
40 | separate_signature: true
41 | filters: [ "!^_" ]
42 | docstring_options:
43 | ignore_init_summary: true
44 | merge_init_into_class: true
45 | show_signature_annotations: true
46 | signature_crossrefs: true
47 | extra:
48 | version:
49 | provider: mike
50 | generator: false
51 | markdown_extensions:
52 | - admonition
53 | - pymdownx.highlight:
54 | anchor_linenums: true
55 | line_spans: __span
56 | pygments_lang_class: true
57 | - pymdownx.inlinehilite
58 | - pymdownx.snippets
59 | - pymdownx.details
60 | - pymdownx.superfences
61 | - toc:
62 | permalink: true
63 | title: Page contents
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/poetry.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [virtualenvs]
2 | in-project = true
3 | prefer-active-python = true
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pyproject.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [tool.poetry]
2 | name = "fast-plate-ocr"
3 | version = "0.3.0"
4 | description = "Fast & Lightweight OCR for vehicle license plates."
5 | authors = ["ankandrew <61120139+ankandrew@users.noreply.github.com>"]
6 | readme = "README.md"
7 | repository = "https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/"
8 | documentation = "https://ankandrew.github.io/fast-plate-ocr"
9 | keywords = ["plate-recognition", "license-plate-recognition", "license-plate-ocr"]
10 | license = "MIT"
11 | classifiers = [
12 | "Typing :: Typed",
13 | "Intended Audience :: Developers",
14 | "Intended Audience :: Education",
15 | "Intended Audience :: Science/Research",
16 | "Operating System :: OS Independent",
17 | "Topic :: Software Development",
18 | "Topic :: Scientific/Engineering",
19 | "Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries",
20 | "Topic :: Software Development :: Build Tools",
21 | "Topic :: Scientific/Engineering :: Artificial Intelligence",
22 | "Topic :: Software Development :: Libraries :: Python Modules",
23 | ]
24 |
25 | [tool.poetry.dependencies]
26 | python = "^3.10"
27 | # Packages required for doing inference
28 | numpy = ">=1.20"
29 | opencv-python = "*"
30 | pyyaml = ">=5.1"
31 | tqdm = "*"
32 | rich = "*"
33 |
34 | # Install onnxruntime-gpu only on systems other than macOS or Raspberry Pi
35 | onnxruntime-gpu = { version = ">=1.19.2", markers = "sys_platform != 'darwin' and platform_machine != 'armv7l' and platform_machine != 'aarch64' and (platform_system == 'Linux' or platform_system == 'Windows')" }
36 | # Fallback to onnxruntime for macOS, Raspberry Pi, and other unsupported platforms
37 | onnxruntime = { version = ">=1.19.2", markers = "sys_platform == 'darwin' or platform_machine == 'armv7l' or platform_machine == 'aarch64'" }
38 |
39 | # Training packages are optional
40 | albumentations = { version = "*", optional = true }
41 | click = { version = "*", optional = true }
42 | keras = { version = ">=3.1.1", optional = true }
43 | matplotlib = { version = "*", optional = true }
44 | pandas = { version = "*", optional = true }
45 | pydantic = { version = "^2.0.0", optional = true }
46 | tensorboard = { version = "*", optional = true }
47 | tensorflow = { version = "*", optional = true }
48 | tf2onnx = { version = "*", optional = true }
49 | torch = { version = "*", optional = true }
50 |
51 | # Optional packages for creating the docs
52 | mkdocs-material = { version = "*", optional = true }
53 | mkdocstrings = {version = "*", extras = ["python"], optional = true}
54 | mike = { version = "*", optional = true }
55 | onnxsim = { version = ">0.4.10", optional = true }
56 |
57 | [tool.poetry.extras]
58 | train = [
59 | "albumentations",
60 | "click",
61 | "keras",
62 | "matplotlib",
63 | "pandas",
64 | "pydantic",
65 | "tensorboard",
66 | "tensorflow",
67 | "tf2onnx",
68 | "torch",
69 | "onnxsim",
70 | ]
71 | docs = ["mkdocs-material", "mkdocstrings", "mike"]
72 |
73 | [tool.poetry.group.test.dependencies]
74 | pytest = "*"
75 |
76 | [tool.poetry.group.dev.dependencies]
77 | mypy = "*"
78 | ruff = "*"
79 | pandas-stubs = "^2.2.0.240218"
80 | pylint = "*"
81 | types-pyyaml = "^6.0.12.20240311"
82 |
83 | [tool.poetry.scripts]
84 | fast_plate_ocr = "fast_plate_ocr.cli.cli:main_cli"
85 |
86 | [tool.ruff]
87 | line-length = 100
88 | target-version = "py310"
89 |
90 | [tool.ruff.lint]
91 | select = [
92 | # pycodestyle
93 | "E",
94 | "W",
95 | # Pyflakes
96 | "F",
97 | # pep8-naming
98 | "N",
99 | # pyupgrade
100 | "UP",
101 | # flake8-bugbear
102 | "B",
103 | # flake8-simplify
104 | "SIM",
105 | # flake8-unused-arguments
106 | "ARG",
107 | # Pylint
108 | "PL",
109 | # Perflint
110 | "PERF",
111 | # Ruff-specific rules
112 | "RUF",
113 | # pandas-vet
114 | "PD",
115 | ]
116 | ignore = ["N812", "PLR2004", "PD011"]
117 | fixable = ["ALL"]
118 | unfixable = []
119 |
120 | [tool.ruff.lint.pylint]
121 | max-args = 8
122 |
123 | [tool.ruff.format]
124 | line-ending = "lf"
125 |
126 | [tool.mypy]
127 | disable_error_code = "import-untyped"
128 | [[tool.mypy.overrides]]
129 | module = ["albumentations"]
130 | ignore_missing_imports = true
131 |
132 | [tool.pylint.typecheck]
133 | generated-members = ["cv2.*"]
134 | signature-mutators = [
135 | "click.decorators.option",
136 | "click.decorators.argument",
137 | "click.decorators.version_option",
138 | "click.decorators.help_option",
139 | "click.decorators.pass_context",
140 | "click.decorators.confirmation_option"
141 | ]
142 |
143 | [tool.pylint.format]
144 | max-line-length = 100
145 |
146 | [tool.pylint."messages control"]
147 | disable = ["missing-class-docstring", "missing-function-docstring", "wrong-import-order"]
148 |
149 | [tool.pylint.design]
150 | max-args = 8
151 | min-public-methods = 1
152 |
153 | [tool.pylint.basic]
154 | no-docstring-rgx = "^__|^test_"
155 |
156 | [build-system]
157 | requires = ["poetry-core"]
158 | build-backend = "poetry.core.masonry.api"
159 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Test package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from pathlib import Path
6 |
7 | PROJECT_ROOT_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/assets/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Assets package used in tests.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 |
7 | ASSETS_DIR = pathlib.Path(__file__).resolve().parent
8 | """Path pointing to test/assets directory"""
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/assets/test_plate_1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/assets/test_plate_1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/assets/test_plate_2.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/assets/test_plate_2.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/conftest.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | The `conftest.py` file serves as a means of providing fixtures for an entire directory. Fixtures
3 | defined in a `conftest.py` can be used by any test in that package without needing to import them
4 | (pytest will automatically discover them).
5 | """
6 |
7 | import pytest
8 |
9 |
10 | @pytest.fixture(scope="function")
11 | def temp_directory(tmpdir):
12 | """
13 | Example fixture to create a temporary directory for testing.
14 | """
15 | temp_dir = tmpdir.mkdir("temp")
16 | yield temp_dir
17 | temp_dir.remove()
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/fast_lp_ocr/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/test_hub.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Tests for ONNX hub module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from http import HTTPStatus
6 |
7 | import pytest
8 | import requests
9 |
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.hub import AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS
11 |
12 |
13 | @pytest.mark.parametrize("model_name", AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS.keys())
14 | def test_model_and_config_urls(model_name):
15 | """
16 | Test to check if the model and config URLs for AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS are valid.
17 | """
18 | model_url, config_url = AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS[model_name]
19 |
20 | for url in [model_url, config_url]:
21 | response = requests.head(url, timeout=5, allow_redirects=True)
22 | assert (
23 | response.status_code == HTTPStatus.OK
24 | ), f"URL {url} is not accessible, got {response.status_code}"
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/test_onnx_inference.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Tests for ONNX inference module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from collections.abc import Iterator
6 |
7 | import cv2
8 | import numpy.typing as npt
9 | import pytest
10 |
11 | from fast_plate_ocr import ONNXPlateRecognizer
12 | from test.assets import ASSETS_DIR
13 |
14 |
15 | @pytest.fixture(scope="module", name="onnx_model")
16 | def onnx_model_fixture() -> Iterator[ONNXPlateRecognizer]:
17 | yield ONNXPlateRecognizer("argentinian-plates-cnn-model", device="cpu")
18 |
19 |
20 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
21 | "input_image, expected_result",
22 | [
23 | # Single image path
24 | (str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_1.png"), 1),
25 | # Multiple Image paths
26 | (
27 | [str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_1.png"), str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_2.png")],
28 | 2,
29 | ),
30 | # NumPy array with single image
31 | (cv2.imread(str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_1.png"), cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE), 1),
32 | # NumPy array with batch images
33 | (
34 | [
35 | cv2.imread(str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_1.png"), cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE),
36 | cv2.imread(str(ASSETS_DIR / "test_plate_2.png"), cv2.IMREAD_GRAYSCALE),
37 | ],
38 | 2,
39 | ),
40 | ],
41 | )
42 | def test_result_from_different_image_sources(
43 | input_image: str | list[str] | npt.NDArray,
44 | expected_result: int,
45 | onnx_model: ONNXPlateRecognizer,
46 | ) -> None:
47 | actual_result = len(onnx_model.run(input_image))
48 | assert actual_result == expected_result
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/inference/test_process.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Tests for inference process module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import numpy as np
6 | import numpy.typing as npt
7 | import pytest
8 |
9 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.process import postprocess_output
10 |
11 |
12 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
13 | "model_output, max_plate_slots, model_alphabet, expected_plates",
14 | [
15 | (
16 | np.array(
17 | [
18 | [[0.5, 0.4, 0.1], [0.2, 0.6, 0.2], [0.1, 0.4, 0.5]],
19 | [[0.1, 0.1, 0.8], [0.2, 0.2, 0.6], [0.1, 0.4, 0.5]],
20 | ],
21 | dtype=np.float32,
22 | ),
23 | 3,
24 | "ABC",
25 | ["ABC", "CCC"],
26 | ),
27 | (
28 | np.array(
29 | [[[0.1, 0.4, 0.5], [0.6, 0.2, 0.2], [0.1, 0.5, 0.4]]],
30 | dtype=np.float32,
31 | ),
32 | 3,
33 | "ABC",
34 | ["CAB"],
35 | ),
36 | ],
37 | )
38 | def test_postprocess_output(
39 | model_output: npt.NDArray,
40 | max_plate_slots: int,
41 | model_alphabet: str,
42 | expected_plates: list[str],
43 | ) -> None:
44 | actual_plate = postprocess_output(model_output, max_plate_slots, model_alphabet)
45 | assert actual_plate == expected_plates
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/test_config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Tests for config module
3 | """
4 |
5 | from pathlib import Path
6 |
7 | import pytest
8 |
9 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import PlateOCRConfig, load_config_from_yaml
10 | from test import PROJECT_ROOT_DIR
11 |
12 |
13 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
14 | "file_path",
15 | [f for f in PROJECT_ROOT_DIR.joinpath("config").iterdir() if f.suffix in (".yaml", ".yml")],
16 | )
17 | def test_yaml_configs(file_path: Path) -> None:
18 | load_config_from_yaml(file_path)
19 |
20 |
21 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
22 | "raw_config",
23 | [
24 | {
25 | "max_plate_slots": 7,
26 | # Pad char not in alphabet, should raise exception
27 | "alphabet": "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ",
28 | "pad_char": "_",
29 | "img_height": 70,
30 | "img_width": 140,
31 | }
32 | ],
33 | )
34 | def test_invalid_config_raises(raw_config: dict) -> None:
35 | with pytest.raises(ValueError):
36 | PlateOCRConfig(**raw_config)
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/test_custom.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Test the custom metric/losses module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | # ruff: noqa: E402
6 | # pylint: disable=wrong-import-position,wrong-import-order,ungrouped-imports
7 | # fmt: off
8 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.backend_utils import set_pytorch_backend
9 |
10 | set_pytorch_backend()
11 | # fmt: on
12 |
13 | import pytest
14 | import torch
15 |
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.custom import cat_acc_metric, plate_acc_metric
17 |
18 |
19 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
20 | "y_true, y_pred, expected_accuracy",
21 | [
22 | (torch.tensor([[[1, 0]] * 6]), torch.tensor([[[0.9, 0.1]] * 6]), 1.0),
23 | ],
24 | )
25 | def test_cat_acc(y_true: torch.Tensor, y_pred: torch.Tensor, expected_accuracy: float) -> None:
26 | actual_accuracy = cat_acc_metric(2, 1)(y_true, y_pred)
27 | assert actual_accuracy == expected_accuracy
28 |
29 |
30 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
31 | "y_true, y_pred, expected_accuracy",
32 | [
33 | (
34 | torch.tensor(
35 | [
36 | [
37 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
38 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
39 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
40 | [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
41 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
42 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
43 | ],
44 | [
45 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
46 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
47 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
48 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
49 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
50 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
51 | ],
52 | ]
53 | ),
54 | torch.tensor(
55 | [
56 | [
57 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
58 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
59 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
60 | [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
61 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
62 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
63 | ],
64 | [
65 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
66 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
67 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
68 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
69 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
70 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
71 | ],
72 | ]
73 | ),
74 | # First batch slice plate was recognized completely correct but second one wasn't
75 | # So 50% of plates were recognized correctly
76 | 0.5,
77 | ),
78 | ],
79 | )
80 | def test_plate_accuracy(
81 | y_true: torch.Tensor, y_pred: torch.Tensor, expected_accuracy: float
82 | ) -> None:
83 | actual_accuracy = plate_acc_metric(y_true.shape[1], y_true.shape[2])(y_true, y_pred).item()
84 | assert actual_accuracy == expected_accuracy
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/test_models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Test OCR models module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pytest
6 | from keras import Input
7 |
8 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model import models
9 |
10 |
11 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
12 | "max_plates_slots, vocabulary_size, expected_hidden_units", [(7, 37, 7 * 37)]
13 | )
14 | def test_head(max_plates_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int, expected_hidden_units: int) -> None:
15 | x = Input((70, 140, 1))
16 | out_tensor = models.head(x, max_plates_slots, vocabulary_size)
17 | actual_hidden_units = out_tensor.shape[-1]
18 | assert actual_hidden_units == expected_hidden_units
19 |
20 |
21 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
22 | "max_plates_slots, vocabulary_size, expected_hidden_units", [(7, 37, 7 * 37)]
23 | )
24 | def test_head_no_fc(
25 | max_plates_slots: int, vocabulary_size: int, expected_hidden_units: int
26 | ) -> None:
27 | x = Input((70, 140, 1))
28 | out_tensor = models.head_no_fc(x, max_plates_slots, vocabulary_size)
29 | actual_hidden_units = out_tensor.shape[1] * out_tensor.shape[2]
30 | assert actual_hidden_units == expected_hidden_units
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/fast_lp_ocr/train/test_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Test utils module.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pytest
6 |
7 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
8 |
9 |
10 | @pytest.mark.parametrize(
11 | "plate, alphabet, expected_result",
12 | [
13 | (
14 | "AB12",
15 | "ABCD123456",
16 | [
17 | [1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
18 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
19 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
20 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
21 | ],
22 | ),
23 | (
24 | "ABC123",
25 | "0123456789ABCDEFGHIJ",
26 | [
27 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
28 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
29 | [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
30 | [0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
31 | [0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
32 | [0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
33 | ],
34 | ),
35 | ],
36 | )
37 | def test_one_hot_plate(plate: str, alphabet: str, expected_result: list[list[int]]) -> None:
38 | actual_result = utils.one_hot_plate(plate, alphabet)
39 | assert actual_result == expected_result
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 17 |
17 |  17 |
17 |  138 |
139 | To train or use the CLI tool, you'll need to install:
140 |
141 | ```shell
142 | pip install fast_plate_ocr[train]
143 | ```
144 |
145 | > [!IMPORTANT]
146 | > Make sure you have installed a supported backend for Keras.
147 |
148 | #### Train Model
149 |
150 | To train the model you will need:
151 |
152 | 1. A configuration used for the OCR model. Depending on your use case, you might have more plate slots or different set
153 | of characters. Take a look at the config for Argentinian license plate as an example:
154 | ```yaml
155 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
156 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
157 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
158 |
159 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
160 | max_plate_slots: 7
161 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
162 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
163 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
164 | pad_char: '_'
165 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
166 | img_height: 70
167 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
168 | img_width: 140
169 | ```
170 | 2. A labeled dataset,
171 | see [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip)
172 | for the expected data format.
173 | 3. Run train script:
174 | ```shell
175 | # You can set the backend to either TensorFlow, JAX or PyTorch
176 | # (just make sure it is installed)
177 | KERAS_BACKEND=tensorflow fast_plate_ocr train \
178 | --annotations path_to_the_train.csv \
179 | --val-annotations path_to_the_val.csv \
180 | --config-file config.yaml \
181 | --batch-size 128 \
182 | --epochs 750 \
183 | --dense \
184 | --early-stopping-patience 100 \
185 | --reduce-lr-patience 50
186 | ```
187 |
188 | You will probably want to change the augmentation pipeline to apply to your dataset.
189 |
190 | In order to do this define an Albumentations pipeline:
191 |
192 | ```python
193 | import albumentations as A
194 |
195 | transform_pipeline = A.Compose(
196 | [
197 | # ...
198 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
199 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
200 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
201 | # ... and any other augmentation ...
202 | ]
203 | )
204 |
205 | # Export to a file (this resultant YAML can be used by the train script)
206 | A.save(transform_pipeline, "./transform_pipeline.yaml", data_format="yaml")
207 | ```
208 |
209 | And then you can train using the custom transformation pipeline with the `--augmentation-path` option.
210 |
211 | #### Visualize Augmentation
212 |
213 | It's useful to visualize the augmentation pipeline before training the model. This helps us to identify
214 | if we should apply more heavy augmentation or less, as it can hurt the model.
215 |
216 | You might want to see the augmented image next to the original, to see how much it changed:
217 |
218 | ```shell
219 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-augmentation \
220 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
221 | --columns 2 \
222 | --show-original \
223 | --augmentation-path '/transform_pipeline.yaml'
224 | ```
225 |
226 | You will see something like:
227 |
228 | 
229 |
230 | #### Validate Model
231 |
232 | After finishing training you can validate the model on a labeled test dataset.
233 |
234 | Example:
235 |
236 | ```shell
237 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
238 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
239 | --config-file arg_plate_example.yaml \
240 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
241 | ```
242 |
243 | #### Visualize Predictions
244 |
245 | Once you finish training your model, you can view the model predictions on raw data with:
246 |
247 | ```shell
248 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-predictions \
249 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
250 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
251 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
252 | ```
253 |
254 | You will see something like:
255 |
256 | 
257 |
258 | #### Export as ONNX
259 |
260 | Exporting the Keras model to ONNX format might be beneficial to speed-up inference time.
261 |
262 | ```shell
263 | fast_plate_ocr export-onnx \
264 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
265 | --output-path arg_cnn_ocr.onnx \
266 | --opset 18 \
267 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
268 | ```
269 |
270 | ### Keras Backend
271 |
272 | To train the model, you can install the ML Framework you like the most. **Keras 3** has
273 | support for **TensorFlow**, **JAX** and **PyTorch** backends.
274 |
275 | To change the Keras backend you can either:
276 |
277 | 1. Export `KERAS_BACKEND` environment variable, i.e. to use JAX for training:
278 | ```shell
279 | KERAS_BACKEND=jax fast_plate_ocr train --config-file ...
280 | ```
281 | 2. Edit your local config file at `~/.keras/keras.json`.
282 |
283 | _Note: You will probably need to install your desired framework for training._
284 |
285 | ### Model Architecture
286 |
287 | The current model architecture is quite simple but effective.
288 | See [cnn_ocr_model](https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/blob/e59b738bad86d269c82101dfe7a3bef49b3a77c7/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py#L23-L23)
289 | for implementation details.
290 |
291 | The model output consists of several heads. Each head represents the prediction of a character of the
292 | plate. If the plate consists of 7 characters at most (`max_plate_slots=7`), then the model would have 7 heads.
293 |
294 | Example of Argentinian plates:
295 |
296 | 
297 |
298 | Each head will output a probability distribution over the `vocabulary` specified during training. So the output
299 | prediction for a single plate will be of shape `(max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)`.
300 |
301 | ### Model Metrics
302 |
303 | During training, you will see the following metrics
304 |
305 | * **plate_acc**: Compute the number of **license plates** that were **fully classified**. For a single plate, if the
306 | ground truth is `ABC123` and the prediction is also `ABC123`, it would score 1. However, if the prediction was
307 | `ABD123`, it would score 0, as **not all characters** were correctly classified.
308 |
309 | * **cat_acc**: Calculate the accuracy of **individual characters** within the license plates that were
310 | **correctly classified**. For example, if the correct label is `ABC123` and the prediction is `ABC133`, it would yield
311 | a precision of 83.3% (5 out of 6 characters correctly classified), rather than 0% as in plate_acc, because it's not
312 | completely classified correctly.
313 |
314 | * **top_3_k**: Calculate how frequently the true character is included in the **top-3 predictions**
315 | (the three predictions with the highest probability).
316 |
317 | ### Contributing
318 |
319 | Contributions to the repo are greatly appreciated. Whether it's bug fixes, feature enhancements, or new models,
320 | your contributions are warmly welcomed.
321 |
322 | To start contributing or to begin development, you can follow these steps:
323 |
324 | 1. Clone repo
325 | ```shell
326 | git clone https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr.git
327 | ```
328 | 2. Install all dependencies using [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/#installation):
329 | ```shell
330 | poetry install --all-extras
331 | ```
332 | 3. To ensure your changes pass linting and tests before submitting a PR:
333 | ```shell
334 | make checks
335 | ```
336 |
337 | If you want to train a model and share it, we'll add it to the HUB 🚀
338 |
339 | If you look to contribute to the repo, some cool things are in the backlog:
340 |
341 | - [ ] Implement [STN](https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02025) using Keras 3 (With `keras.ops`)
342 | - [ ] Implement [SVTRv2](https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.15858).
343 | - [ ] Implement CTC loss function, so we can choose that or CE loss.
344 | - [ ] Extra head for country recognition, making it configurable.
345 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/config/arg_plate_example.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
2 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
3 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
4 |
5 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
6 | max_plate_slots: 7
7 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
8 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
9 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
10 | pad_char: '_'
11 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
12 | img_height: 70
13 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
14 | img_width: 140
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/config/latin_plate_example.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Config example for Latin plates from 70 countries
2 |
3 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
4 | max_plate_slots: 9
5 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
6 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
7 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
8 | pad_char: '_'
9 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
10 | img_height: 70
11 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
12 | img_width: 140
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/architecture.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### ConvNet (CNN) model
2 |
3 | The current model architecture is quite simple but effective. It just consists of a few CNN layers with several output
4 | heads.
5 | See [cnn_ocr_model](https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/blob/e59b738bad86d269c82101dfe7a3bef49b3a77c7/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py#L23-L23)
6 | for implementation details.
7 |
8 | The model output consists of several heads. Each head represents the prediction of a character of the
9 | plate. If the plate consists of 7 characters at most (`max_plate_slots=7`), then the model would have 7 heads.
10 |
11 | Example of Argentinian plates:
12 |
13 | 
14 |
15 | Each head will output a probability distribution over the `vocabulary` specified during training. So the output
16 | prediction for a single plate will be of shape `(max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)`.
17 |
18 | ### Model Metrics
19 |
20 | During training, you will see the following metrics
21 |
22 | * **plate_acc**: Compute the number of **license plates** that were **fully classified**. For a single plate, if the
23 | ground truth is `ABC123` and the prediction is also `ABC123`, it would score 1. However, if the prediction was
24 | `ABD123`, it would score 0, as **not all characters** were correctly classified.
25 |
26 | * **cat_acc**: Calculate the accuracy of **individual characters** within the license plates that were
27 | **correctly classified**. For example, if the correct label is `ABC123` and the prediction is `ABC133`, it would yield
28 | a precision of 83.3% (5 out of 6 characters correctly classified), rather than 0% as in plate_acc, because it's not
29 | completely classified correctly.
30 |
31 | * **top_3_k**: Calculate how frequently the true character is included in the **top-3 predictions**
32 | (the three predictions with the highest probability).
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/contributing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Contributions are greatly appreciated. Whether it's bug fixes, feature enhancements, or new models,
2 | your contributions are warmly welcomed.
3 |
4 | To start contributing or to begin development, you can follow these steps:
5 |
6 | 1. Clone repo
7 | ```shell
8 | git clone https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr.git
9 | ```
10 | 2. Install all dependencies using [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/#installation):
11 | ```shell
12 | poetry install --all-extras
13 | ```
14 | 3. To ensure your changes pass linting and tests before submitting a PR:
15 | ```shell
16 | make checks
17 | ```
18 |
19 | ???+ tip
20 | If you want to train a model and share it, we'll add it to the HUB 🚀
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Fast & Lightweight License Plate OCR
2 |
3 | 
4 |
5 | **FastPlateOCR** is a **lightweight** and **fast** OCR framework for **license plate text recognition**. You can train
6 | models from scratch or use the trained models for inference.
7 |
8 | The idea is to use this after a plate object detector, since the OCR expects the cropped plates.
9 |
10 | ### Features
11 |
12 | - **Keras 3 Backend Support**: Compatible with **TensorFlow**, **JAX**, and **PyTorch** backends 🧠
13 | - **Augmentation Variety**: Diverse augmentations via **Albumentations** library 🖼️
14 | - **Efficient Execution**: **Lightweight** models that are cheap to run 💰
15 | - **ONNX Runtime Inference**: **Fast** and **optimized** inference with ONNX runtime ⚡
16 | - **User-Friendly CLI**: Simplified **CLI** for **training** and **validating** OCR models 🛠️
17 | - **Model HUB**: Access to a collection of pre-trained models ready for inference 🌟
18 |
19 | ### Model Zoo
20 |
21 | We currently have the following available models:
22 |
23 | | Model Name | Time b=1
138 |
139 | To train or use the CLI tool, you'll need to install:
140 |
141 | ```shell
142 | pip install fast_plate_ocr[train]
143 | ```
144 |
145 | > [!IMPORTANT]
146 | > Make sure you have installed a supported backend for Keras.
147 |
148 | #### Train Model
149 |
150 | To train the model you will need:
151 |
152 | 1. A configuration used for the OCR model. Depending on your use case, you might have more plate slots or different set
153 | of characters. Take a look at the config for Argentinian license plate as an example:
154 | ```yaml
155 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
156 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
157 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
158 |
159 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
160 | max_plate_slots: 7
161 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
162 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
163 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
164 | pad_char: '_'
165 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
166 | img_height: 70
167 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
168 | img_width: 140
169 | ```
170 | 2. A labeled dataset,
171 | see [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip)
172 | for the expected data format.
173 | 3. Run train script:
174 | ```shell
175 | # You can set the backend to either TensorFlow, JAX or PyTorch
176 | # (just make sure it is installed)
177 | KERAS_BACKEND=tensorflow fast_plate_ocr train \
178 | --annotations path_to_the_train.csv \
179 | --val-annotations path_to_the_val.csv \
180 | --config-file config.yaml \
181 | --batch-size 128 \
182 | --epochs 750 \
183 | --dense \
184 | --early-stopping-patience 100 \
185 | --reduce-lr-patience 50
186 | ```
187 |
188 | You will probably want to change the augmentation pipeline to apply to your dataset.
189 |
190 | In order to do this define an Albumentations pipeline:
191 |
192 | ```python
193 | import albumentations as A
194 |
195 | transform_pipeline = A.Compose(
196 | [
197 | # ...
198 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
199 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
200 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
201 | # ... and any other augmentation ...
202 | ]
203 | )
204 |
205 | # Export to a file (this resultant YAML can be used by the train script)
206 | A.save(transform_pipeline, "./transform_pipeline.yaml", data_format="yaml")
207 | ```
208 |
209 | And then you can train using the custom transformation pipeline with the `--augmentation-path` option.
210 |
211 | #### Visualize Augmentation
212 |
213 | It's useful to visualize the augmentation pipeline before training the model. This helps us to identify
214 | if we should apply more heavy augmentation or less, as it can hurt the model.
215 |
216 | You might want to see the augmented image next to the original, to see how much it changed:
217 |
218 | ```shell
219 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-augmentation \
220 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
221 | --columns 2 \
222 | --show-original \
223 | --augmentation-path '/transform_pipeline.yaml'
224 | ```
225 |
226 | You will see something like:
227 |
228 | 
229 |
230 | #### Validate Model
231 |
232 | After finishing training you can validate the model on a labeled test dataset.
233 |
234 | Example:
235 |
236 | ```shell
237 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
238 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
239 | --config-file arg_plate_example.yaml \
240 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
241 | ```
242 |
243 | #### Visualize Predictions
244 |
245 | Once you finish training your model, you can view the model predictions on raw data with:
246 |
247 | ```shell
248 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-predictions \
249 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
250 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
251 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
252 | ```
253 |
254 | You will see something like:
255 |
256 | 
257 |
258 | #### Export as ONNX
259 |
260 | Exporting the Keras model to ONNX format might be beneficial to speed-up inference time.
261 |
262 | ```shell
263 | fast_plate_ocr export-onnx \
264 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
265 | --output-path arg_cnn_ocr.onnx \
266 | --opset 18 \
267 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
268 | ```
269 |
270 | ### Keras Backend
271 |
272 | To train the model, you can install the ML Framework you like the most. **Keras 3** has
273 | support for **TensorFlow**, **JAX** and **PyTorch** backends.
274 |
275 | To change the Keras backend you can either:
276 |
277 | 1. Export `KERAS_BACKEND` environment variable, i.e. to use JAX for training:
278 | ```shell
279 | KERAS_BACKEND=jax fast_plate_ocr train --config-file ...
280 | ```
281 | 2. Edit your local config file at `~/.keras/keras.json`.
282 |
283 | _Note: You will probably need to install your desired framework for training._
284 |
285 | ### Model Architecture
286 |
287 | The current model architecture is quite simple but effective.
288 | See [cnn_ocr_model](https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/blob/e59b738bad86d269c82101dfe7a3bef49b3a77c7/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py#L23-L23)
289 | for implementation details.
290 |
291 | The model output consists of several heads. Each head represents the prediction of a character of the
292 | plate. If the plate consists of 7 characters at most (`max_plate_slots=7`), then the model would have 7 heads.
293 |
294 | Example of Argentinian plates:
295 |
296 | 
297 |
298 | Each head will output a probability distribution over the `vocabulary` specified during training. So the output
299 | prediction for a single plate will be of shape `(max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)`.
300 |
301 | ### Model Metrics
302 |
303 | During training, you will see the following metrics
304 |
305 | * **plate_acc**: Compute the number of **license plates** that were **fully classified**. For a single plate, if the
306 | ground truth is `ABC123` and the prediction is also `ABC123`, it would score 1. However, if the prediction was
307 | `ABD123`, it would score 0, as **not all characters** were correctly classified.
308 |
309 | * **cat_acc**: Calculate the accuracy of **individual characters** within the license plates that were
310 | **correctly classified**. For example, if the correct label is `ABC123` and the prediction is `ABC133`, it would yield
311 | a precision of 83.3% (5 out of 6 characters correctly classified), rather than 0% as in plate_acc, because it's not
312 | completely classified correctly.
313 |
314 | * **top_3_k**: Calculate how frequently the true character is included in the **top-3 predictions**
315 | (the three predictions with the highest probability).
316 |
317 | ### Contributing
318 |
319 | Contributions to the repo are greatly appreciated. Whether it's bug fixes, feature enhancements, or new models,
320 | your contributions are warmly welcomed.
321 |
322 | To start contributing or to begin development, you can follow these steps:
323 |
324 | 1. Clone repo
325 | ```shell
326 | git clone https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr.git
327 | ```
328 | 2. Install all dependencies using [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/#installation):
329 | ```shell
330 | poetry install --all-extras
331 | ```
332 | 3. To ensure your changes pass linting and tests before submitting a PR:
333 | ```shell
334 | make checks
335 | ```
336 |
337 | If you want to train a model and share it, we'll add it to the HUB 🚀
338 |
339 | If you look to contribute to the repo, some cool things are in the backlog:
340 |
341 | - [ ] Implement [STN](https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.02025) using Keras 3 (With `keras.ops`)
342 | - [ ] Implement [SVTRv2](https://arxiv.org/abs/2411.15858).
343 | - [ ] Implement CTC loss function, so we can choose that or CE loss.
344 | - [ ] Extra head for country recognition, making it configurable.
345 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/config/arg_plate_example.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
2 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
3 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
4 |
5 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
6 | max_plate_slots: 7
7 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
8 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
9 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
10 | pad_char: '_'
11 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
12 | img_height: 70
13 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
14 | img_width: 140
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/config/latin_plate_example.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Config example for Latin plates from 70 countries
2 |
3 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
4 | max_plate_slots: 9
5 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
6 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
7 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
8 | pad_char: '_'
9 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
10 | img_height: 70
11 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
12 | img_width: 140
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/architecture.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ### ConvNet (CNN) model
2 |
3 | The current model architecture is quite simple but effective. It just consists of a few CNN layers with several output
4 | heads.
5 | See [cnn_ocr_model](https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/blob/e59b738bad86d269c82101dfe7a3bef49b3a77c7/fast_plate_ocr/train/model/models.py#L23-L23)
6 | for implementation details.
7 |
8 | The model output consists of several heads. Each head represents the prediction of a character of the
9 | plate. If the plate consists of 7 characters at most (`max_plate_slots=7`), then the model would have 7 heads.
10 |
11 | Example of Argentinian plates:
12 |
13 | 
14 |
15 | Each head will output a probability distribution over the `vocabulary` specified during training. So the output
16 | prediction for a single plate will be of shape `(max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size)`.
17 |
18 | ### Model Metrics
19 |
20 | During training, you will see the following metrics
21 |
22 | * **plate_acc**: Compute the number of **license plates** that were **fully classified**. For a single plate, if the
23 | ground truth is `ABC123` and the prediction is also `ABC123`, it would score 1. However, if the prediction was
24 | `ABD123`, it would score 0, as **not all characters** were correctly classified.
25 |
26 | * **cat_acc**: Calculate the accuracy of **individual characters** within the license plates that were
27 | **correctly classified**. For example, if the correct label is `ABC123` and the prediction is `ABC133`, it would yield
28 | a precision of 83.3% (5 out of 6 characters correctly classified), rather than 0% as in plate_acc, because it's not
29 | completely classified correctly.
30 |
31 | * **top_3_k**: Calculate how frequently the true character is included in the **top-3 predictions**
32 | (the three predictions with the highest probability).
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/contributing.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Contributions are greatly appreciated. Whether it's bug fixes, feature enhancements, or new models,
2 | your contributions are warmly welcomed.
3 |
4 | To start contributing or to begin development, you can follow these steps:
5 |
6 | 1. Clone repo
7 | ```shell
8 | git clone https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr.git
9 | ```
10 | 2. Install all dependencies using [Poetry](https://python-poetry.org/docs/#installation):
11 | ```shell
12 | poetry install --all-extras
13 | ```
14 | 3. To ensure your changes pass linting and tests before submitting a PR:
15 | ```shell
16 | make checks
17 | ```
18 |
19 | ???+ tip
20 | If you want to train a model and share it, we'll add it to the HUB 🚀
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Fast & Lightweight License Plate OCR
2 |
3 | 
4 |
5 | **FastPlateOCR** is a **lightweight** and **fast** OCR framework for **license plate text recognition**. You can train
6 | models from scratch or use the trained models for inference.
7 |
8 | The idea is to use this after a plate object detector, since the OCR expects the cropped plates.
9 |
10 | ### Features
11 |
12 | - **Keras 3 Backend Support**: Compatible with **TensorFlow**, **JAX**, and **PyTorch** backends 🧠
13 | - **Augmentation Variety**: Diverse augmentations via **Albumentations** library 🖼️
14 | - **Efficient Execution**: **Lightweight** models that are cheap to run 💰
15 | - **ONNX Runtime Inference**: **Fast** and **optimized** inference with ONNX runtime ⚡
16 | - **User-Friendly CLI**: Simplified **CLI** for **training** and **validating** OCR models 🛠️
17 | - **Model HUB**: Access to a collection of pre-trained models ready for inference 🌟
18 |
19 | ### Model Zoo
20 |
21 | We currently have the following available models:
22 |
23 | | Model Name | Time b=1 17 |
17 |  35 |
35 |  44 |
45 | To train or use the CLI tool, you'll need to install:
46 |
47 | ```shell
48 | pip install fast_plate_ocr[train]
49 | ```
50 |
51 | #### Train Model
52 |
53 | To train the model you will need:
54 |
55 | 1. A configuration used for the OCR model. Depending on your use case, you might have more plate slots or different set
56 | of characters. Take a look at the config for Argentinian license plate as an example:
57 | ```yaml
58 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
59 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
60 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
61 |
62 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
63 | max_plate_slots: 7
64 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
65 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
66 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
67 | pad_char: '_'
68 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
69 | img_height: 70
70 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
71 | img_width: 140
72 | ```
73 | 2. A labeled dataset,
74 | see [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip)
75 | for the expected data format.
76 | 3. Run train script:
77 | ```shell
78 | # You can set the backend to either TensorFlow, JAX or PyTorch
79 | # (just make sure it is installed)
80 | KERAS_BACKEND=tensorflow fast_plate_ocr train \
81 | --annotations path_to_the_train.csv \
82 | --val-annotations path_to_the_val.csv \
83 | --config-file config.yaml \
84 | --batch-size 128 \
85 | --epochs 750 \
86 | --dense \
87 | --early-stopping-patience 100 \
88 | --reduce-lr-patience 50
89 | ```
90 |
91 | You will probably want to change the augmentation pipeline to apply to your dataset.
92 |
93 | In order to do this define an Albumentations pipeline:
94 |
95 | ```python
96 | import albumentations as A
97 |
98 | transform_pipeline = A.Compose(
99 | [
100 | # ...
101 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
102 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
103 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
104 | # ... and any other augmentation ...
105 | ]
106 | )
107 |
108 | # Export to a file (this resultant YAML can be used by the train script)
109 | A.save(transform_pipeline, "./transform_pipeline.yaml", data_format="yaml")
110 | ```
111 |
112 | And then you can train using the custom transformation pipeline with the `--augmentation-path` option.
113 |
114 | #### Visualize Augmentation
115 |
116 | It's useful to visualize the augmentation pipeline before training the model. This helps us to identify
117 | if we should apply more heavy augmentation or less, as it can hurt the model.
118 |
119 | You might want to see the augmented image next to the original, to see how much it changed:
120 |
121 | ```shell
122 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-augmentation \
123 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
124 | --columns 2 \
125 | --show-original \
126 | --augmentation-path '/transform_pipeline.yaml'
127 | ```
128 |
129 | You will see something like:
130 |
131 | 
132 |
133 | #### Validate Model
134 |
135 | After finishing training you can validate the model on a labeled test dataset.
136 |
137 | Example:
138 |
139 | ```shell
140 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
141 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
142 | --config-file arg_plate_example.yaml \
143 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
144 | ```
145 |
146 | #### Visualize Predictions
147 |
148 | Once you finish training your model, you can view the model predictions on raw data with:
149 |
150 | ```shell
151 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-predictions \
152 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
153 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
154 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
155 | ```
156 |
157 | You will see something like:
158 |
159 | 
160 |
161 | #### Export as ONNX
162 |
163 | Exporting the Keras model to ONNX format might be beneficial to speed-up inference time.
164 |
165 | ```shell
166 | fast_plate_ocr export-onnx \
167 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
168 | --output-path arg_cnn_ocr.onnx \
169 | --opset 18 \
170 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
171 | ```
172 |
173 | ### Keras Backend
174 |
175 | To train the model, you can install the ML Framework you like the most. **Keras 3** has
176 | support for **TensorFlow**, **JAX** and **PyTorch** backends.
177 |
178 | To change the Keras backend you can either:
179 |
180 | 1. Export `KERAS_BACKEND` environment variable, i.e. to use JAX for training:
181 | ```shell
182 | KERAS_BACKEND=jax fast_plate_ocr train --config-file ...
183 | ```
184 | 2. Edit your local config file at `~/.keras/keras.json`.
185 |
186 | ???+ tip
187 | **Usually training with JAX and TensorFlow is faster.**
188 |
189 | _Note: You will probably need to install your desired framework for training._
190 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Fast Plate OCR package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.onnx_inference import ONNXPlateRecognizer
6 |
7 | __all__ = ["ONNXPlateRecognizer"]
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/cli/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/cli.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Main CLI used when training a FastPlateOCR model.
3 | """
4 |
5 | try:
6 | import click
7 |
8 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.onnx_converter import export_onnx
9 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.train import train
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.valid import valid
11 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.visualize_augmentation import visualize_augmentation
12 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.visualize_predictions import visualize_predictions
13 | except ImportError as e:
14 | raise ImportError("Make sure to 'pip install fast-plate-ocr[train]' to run this!") from e
15 |
16 |
17 | @click.group(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
18 | def main_cli():
19 | """FastPlateOCR CLI."""
20 |
21 |
22 | main_cli.add_command(visualize_predictions)
23 | main_cli.add_command(visualize_augmentation)
24 | main_cli.add_command(valid)
25 | main_cli.add_command(train)
26 | main_cli.add_command(export_onnx)
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/onnx_converter.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for converting Keras models to ONNX format.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import shutil
8 | from tempfile import NamedTemporaryFile
9 |
10 | import click
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import onnx
13 | import onnxruntime as rt
14 | import onnxsim
15 | import tensorflow as tf
16 | import tf2onnx
17 | from tf2onnx import constants as tf2onnx_constants
18 |
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.common.utils import log_time_taken
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
21 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.utils import load_keras_model
22 |
23 | logging.basicConfig(
24 | level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(message)s", datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
25 | )
26 |
27 |
28 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
29 |
30 |
31 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
32 | @click.option(
33 | "-m",
34 | "--model",
35 | "model_path",
36 | required=True,
37 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
38 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
39 | )
40 | @click.option(
41 | "--output-path",
42 | required=True,
43 | type=str,
44 | help="Output name for ONNX model.",
45 | )
46 | @click.option(
47 | "--simplify/--no-simplify",
48 | default=False,
49 | show_default=True,
50 | help="Simplify ONNX model using onnxsim.",
51 | )
52 | @click.option(
53 | "--config-file",
54 | required=True,
55 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
56 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
57 | )
58 | @click.option(
59 | "--opset",
60 | default=16,
61 | type=click.IntRange(max=max(tf2onnx_constants.OPSET_TO_IR_VERSION)),
62 | show_default=True,
63 | help="Opset version for ONNX.",
64 | )
65 | def export_onnx(
66 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
67 | output_path: str,
68 | simplify: bool,
69 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
70 | opset: int,
71 | ) -> None:
72 | """
73 | Export Keras models to ONNX format.
74 | """
75 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
76 | model = load_keras_model(
77 | model_path,
78 | vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size,
79 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
80 | )
81 | spec = (tf.TensorSpec((None, config.img_height, config.img_width, 1), tf.uint8, name="input"),)
82 | # Convert from Keras to ONNX using tf2onnx library
83 | with NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".onnx") as tmp:
84 | tmp_onnx = tmp.name
85 | model_proto, _ = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(
86 | model,
87 | input_signature=spec,
88 | opset=opset,
89 | output_path=tmp_onnx,
90 | )
91 | if simplify:
92 | logging.info("Simplifying ONNX model ...")
93 | model_simp, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx.load(tmp_onnx))
94 | assert check, "Simplified ONNX model could not be validated!"
95 | onnx.save(model_simp, output_path)
96 | else:
97 | shutil.copy(tmp_onnx, output_path)
98 | output_names = [n.name for n in model_proto.graph.output]
99 | x = np.random.randint(0, 256, size=(1, config.img_height, config.img_width, 1), dtype=np.uint8)
100 | # Run dummy inference and log time taken
101 | m = rt.InferenceSession(output_path)
102 | with log_time_taken("ONNX inference took:"):
103 | onnx_pred = m.run(output_names, {"input": x})
104 | # Check if ONNX and keras have the same results
105 | if not np.allclose(model.predict(x, verbose=0), onnx_pred[0], rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5):
106 | logging.warning("ONNX model output was not close to Keras model for the given tolerance!")
107 | logging.info("Model converted to ONNX! Saved at %s", output_path)
108 |
109 |
110 | if __name__ == "__main__":
111 | export_onnx()
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for training the License Plate OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 | import shutil
7 | from datetime import datetime
8 | from typing import Literal
9 |
10 | import albumentations as A
11 | import click
12 | from keras.src.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, TensorBoard
13 | from keras.src.optimizers import Adam
14 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
15 |
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.utils import print_params, print_train_details
17 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.augmentation import TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
18 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.dataset import LicensePlateDataset
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.custom import (
21 | cat_acc_metric,
22 | cce_loss,
23 | plate_acc_metric,
24 | top_3_k_metric,
25 | )
26 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.models import cnn_ocr_model
27 |
28 | # ruff: noqa: PLR0913
29 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
30 |
31 |
32 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
33 | @click.option(
34 | "--dense/--no-dense",
35 | default=True,
36 | show_default=True,
37 | help="Whether to use Fully Connected layers in model head or not.",
38 | )
39 | @click.option(
40 | "--config-file",
41 | required=True,
42 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
43 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
44 | )
45 | @click.option(
46 | "--annotations",
47 | required=True,
48 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
49 | help="Path pointing to the train annotations CSV file.",
50 | )
51 | @click.option(
52 | "--val-annotations",
53 | required=True,
54 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
55 | help="Path pointing to the train validation CSV file.",
56 | )
57 | @click.option(
58 | "--augmentation-path",
59 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
60 | help="YAML file pointing to the augmentation pipeline saved with Albumentations.save(...)",
61 | )
62 | @click.option(
63 | "--lr",
64 | default=1e-3,
65 | show_default=True,
66 | type=float,
67 | help="Initial learning rate to use.",
68 | )
69 | @click.option(
70 | "--label-smoothing",
71 | default=0.05,
72 | show_default=True,
73 | type=float,
74 | help="Amount of label smoothing to apply.",
75 | )
76 | @click.option(
77 | "--batch-size",
78 | default=128,
79 | show_default=True,
80 | type=int,
81 | help="Batch size for training.",
82 | )
83 | @click.option(
84 | "--num-workers",
85 | default=0,
86 | show_default=True,
87 | type=int,
88 | help="How many subprocesses to load data, used in the torch DataLoader.",
89 | )
90 | @click.option(
91 | "--output-dir",
92 | default="./trained_models",
93 | type=click.Path(dir_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
94 | help="Output directory where model will be saved.",
95 | )
96 | @click.option(
97 | "--epochs",
98 | default=500,
99 | show_default=True,
100 | type=int,
101 | help="Number of training epochs.",
102 | )
103 | @click.option(
104 | "--tensorboard",
105 | "-t",
106 | is_flag=True,
107 | help="Whether to use TensorBoard visualization tool.",
108 | )
109 | @click.option(
110 | "--tensorboard-dir",
111 | "-l",
112 | default="tensorboard_logs",
113 | show_default=True,
114 | type=click.Path(path_type=pathlib.Path),
115 | help="The path of the directory where to save the TensorBoard log files.",
116 | )
117 | @click.option(
118 | "--early-stopping-patience",
119 | default=100,
120 | show_default=True,
121 | type=int,
122 | help="Stop training when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve for X epochs.",
123 | )
124 | @click.option(
125 | "--reduce-lr-patience",
126 | default=60,
127 | show_default=True,
128 | type=int,
129 | help="Patience to reduce the learning rate if 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve within X epochs.",
130 | )
131 | @click.option(
132 | "--reduce-lr-factor",
133 | default=0.85,
134 | show_default=True,
135 | type=float,
136 | help="Reduce the learning rate by this factor when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve.",
137 | )
138 | @click.option(
139 | "--activation",
140 | default="relu",
141 | show_default=True,
142 | type=str,
143 | help="Activation function to use.",
144 | )
145 | @click.option(
146 | "--pool-layer",
147 | default="max",
148 | show_default=True,
149 | type=click.Choice(["max", "avg"]),
150 | help="Choose the pooling layer to use.",
151 | )
152 | @click.option(
153 | "--weights-path",
154 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
155 | help="Path to the pretrained model weights file.",
156 | )
157 | @print_params(table_title="CLI Training Parameters", c1_title="Parameter", c2_title="Details")
158 | def train(
159 | dense: bool,
160 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
161 | annotations: pathlib.Path,
162 | val_annotations: pathlib.Path,
163 | augmentation_path: pathlib.Path | None,
164 | lr: float,
165 | label_smoothing: float,
166 | batch_size: int,
167 | num_workers: int,
168 | output_dir: pathlib.Path,
169 | epochs: int,
170 | tensorboard: bool,
171 | tensorboard_dir: pathlib.Path,
172 | early_stopping_patience: int,
173 | reduce_lr_patience: int,
174 | reduce_lr_factor: float,
175 | activation: str,
176 | pool_layer: Literal["max", "avg"],
177 | weights_path: pathlib.Path | None,
178 | ) -> None:
179 | """
180 | Train the License Plate OCR model.
181 | """
182 | train_augmentation = (
183 | A.load(augmentation_path, data_format="yaml") if augmentation_path else TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
184 | )
185 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
186 | print_train_details(train_augmentation, config.model_dump())
187 | train_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(
188 | annotations_file=annotations,
189 | transform=train_augmentation,
190 | config=config,
191 | )
192 | train_dataloader = DataLoader(
193 | train_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=True
194 | )
195 |
196 | if val_annotations:
197 | val_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(
198 | annotations_file=val_annotations,
199 | config=config,
200 | )
201 | val_dataloader = DataLoader(
202 | val_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=False
203 | )
204 | else:
205 | val_dataloader = None
206 |
207 | # Train
208 | model = cnn_ocr_model(
209 | h=config.img_height,
210 | w=config.img_width,
211 | dense=dense,
212 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
213 | vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size,
214 | activation=activation,
215 | pool_layer=pool_layer,
216 | )
217 |
218 | if weights_path:
219 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
220 |
221 | model.compile(
222 | loss=cce_loss(vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size, label_smoothing=label_smoothing),
223 | optimizer=Adam(lr),
224 | metrics=[
225 | cat_acc_metric(
226 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size
227 | ),
228 | plate_acc_metric(
229 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size
230 | ),
231 | top_3_k_metric(vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size),
232 | ],
233 | )
234 |
235 | output_dir /= datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S")
236 | output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
237 | model_file_path = output_dir / "cnn_ocr-epoch_{epoch:02d}-acc_{val_plate_acc:.3f}.keras"
238 |
239 | # Save params and config used for training
240 | shutil.copy(config_file, output_dir / "config.yaml")
241 | A.save(train_augmentation, output_dir / "train_augmentation.yaml", "yaml")
242 |
243 | callbacks = [
244 | # Reduce the learning rate by 0.5x if 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve within X epochs
245 | ReduceLROnPlateau(
246 | "val_plate_acc",
247 | patience=reduce_lr_patience,
248 | factor=reduce_lr_factor,
249 | min_lr=1e-6,
250 | verbose=1,
251 | ),
252 | # Stop training when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve for X epochs
253 | EarlyStopping(
254 | monitor="val_plate_acc",
255 | patience=early_stopping_patience,
256 | mode="max",
257 | restore_best_weights=False,
258 | verbose=1,
259 | ),
260 | # We don't use EarlyStopping restore_best_weights=True because it won't restore the best
261 | # weights when it didn't manage to EarlyStop but finished all epochs
262 | ModelCheckpoint(
263 | model_file_path,
264 | monitor="val_plate_acc",
265 | mode="max",
266 | save_best_only=True,
267 | verbose=1,
268 | ),
269 | ]
270 |
271 | if tensorboard:
272 | run_dir = tensorboard_dir / datetime.now().strftime("run_%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
273 | run_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
274 | callbacks.append(TensorBoard(log_dir=run_dir))
275 |
276 | model.fit(train_dataloader, epochs=epochs, validation_data=val_dataloader, callbacks=callbacks)
277 |
278 |
279 | if __name__ == "__main__":
280 | train()
281 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utils used for the CLI scripts.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import inspect
6 | import pathlib
7 | from collections.abc import Callable
8 | from functools import wraps
9 | from typing import Any
10 |
11 | import albumentations as A
12 | from rich import box
13 | from rich.console import Console
14 | from rich.pretty import Pretty
15 | from rich.table import Table
16 |
17 |
18 | def print_variables_as_table(
19 | c1_title: str, c2_title: str, title: str = "Variables Table", **kwargs: Any
20 | ) -> None:
21 | """
22 | Prints variables in a formatted table using the rich library.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | c1_title (str): Title of the first column.
26 | c2_title (str): Title of the second column.
27 | title (str): Title of the table.
28 | **kwargs (Any): Variable names and values to be printed.
29 | """
30 | console = Console()
31 | console.print("\n")
32 | table = Table(title=title, show_header=True, header_style="bold blue", box=box.ROUNDED)
33 | table.add_column(c1_title, min_width=20, justify="left", style="bold")
34 | table.add_column(c2_title, min_width=60, justify="left", style="bold")
35 |
36 | for key, value in kwargs.items():
37 | if isinstance(value, pathlib.Path):
38 | value = str(value) # noqa: PLW2901
39 | table.add_row(f"[bold]{key}[/bold]", Pretty(value))
40 |
41 | console.print(table)
42 |
43 |
44 | def print_params(
45 | table_title: str = "Parameters Table", c1_title: str = "Variable", c2_title: str = "Value"
46 | ) -> Callable:
47 | """
48 | A decorator that prints the parameters of a function in a formatted table
49 | using the rich library.
50 |
51 | Args:
52 | c1_title (str, optional): Title of the first column. Defaults to "Variable".
53 | c2_title (str, optional): Title of the second column. Defaults to "Value".
54 | table_title (str, optional): Title of the table. Defaults to "Parameters Table".
55 |
56 | Returns:
57 | Callable: The wrapped function with parameter printing functionality.
58 | """
59 |
60 | def decorator(func: Callable) -> Callable:
61 | @wraps(func)
62 | def wrapper(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> Any:
63 | func_signature = inspect.signature(func)
64 | bound_arguments = func_signature.bind(*args, **kwargs)
65 | bound_arguments.apply_defaults()
66 | params = dict(bound_arguments.arguments.items())
67 | print_variables_as_table(c1_title, c2_title, table_title, **params)
68 | return func(*args, **kwargs)
69 |
70 | return wrapper
71 |
72 | return decorator
73 |
74 |
75 | def print_train_details(augmentation: A.Compose, config: dict[str, Any]) -> None:
76 | console = Console()
77 | console.print("\n")
78 | console.print("[bold blue]Augmentation Pipeline:[/bold blue]")
79 | console.print(Pretty(augmentation))
80 | console.print("\n")
81 | console.print("[bold blue]Configuration:[/bold blue]")
82 | console.print(Pretty(config))
83 | console.print("\n")
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/valid.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for validating trained OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 |
7 | import click
8 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
9 |
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.dataset import LicensePlateDataset
11 |
12 | # Custom metris / losses
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 |
16 |
17 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
18 | @click.option(
19 | "-m",
20 | "--model",
21 | "model_path",
22 | required=True,
23 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
24 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
25 | )
26 | @click.option(
27 | "--config-file",
28 | required=True,
29 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
30 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
31 | )
32 | @click.option(
33 | "-a",
34 | "--annotations",
35 | required=True,
36 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
37 | help="Annotations file used for validation.",
38 | )
39 | @click.option(
40 | "-b",
41 | "--batch-size",
42 | default=1,
43 | show_default=True,
44 | type=int,
45 | help="Batch size.",
46 | )
47 | def valid(
48 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
49 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
50 | annotations: pathlib.Path,
51 | batch_size: int,
52 | ) -> None:
53 | """
54 | Validate the trained OCR model on a labeled set.
55 | """
56 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
57 | model = utils.load_keras_model(
58 | model_path, vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size, max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots
59 | )
60 | val_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(annotations_file=annotations, config=config)
61 | val_dataloader = DataLoader(val_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
62 | model.evaluate(val_dataloader)
63 |
64 |
65 | if __name__ == "__main__":
66 | valid()
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/visualize_augmentation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script to visualize the augmented plates used during training.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 | import random
7 | from math import ceil
8 |
9 | import albumentations as A
10 | import click
11 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import numpy.typing as npt
14 |
15 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.augmentation import TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
17 |
18 |
19 | def _set_seed(seed: int | None) -> None:
20 | """Set random seed for reproducing augmentations."""
21 | if seed:
22 | random.seed(seed)
23 | np.random.seed(seed)
24 |
25 |
26 | def load_images(
27 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
28 | num_images: int,
29 | shuffle: bool,
30 | height: int,
31 | width: int,
32 | augmentation: A.Compose,
33 | ) -> tuple[list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]], list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]]]:
34 | images = utils.load_images_from_folder(
35 | img_dir, height=height, width=width, shuffle=shuffle, limit=num_images
36 | )
37 | augmented_images = [augmentation(image=i)["image"] for i in images]
38 | return images, augmented_images
39 |
40 |
41 | def display_images(
42 | images: list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]],
43 | augmented_images: list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]],
44 | columns: int,
45 | rows: int,
46 | show_original: bool,
47 | ) -> None:
48 | num_images = len(images)
49 | total_plots = rows * columns
50 | num_pages = ceil(num_images / total_plots)
51 | for page in range(num_pages):
52 | _, axs = plt.subplots(rows, columns, figsize=(8, 8))
53 | axs = axs.flatten()
54 | for i, ax in enumerate(axs):
55 | idx = page * total_plots + i
56 | if idx < num_images:
57 | if show_original:
58 | img_to_show = np.concatenate((images[idx], augmented_images[idx]), axis=1)
59 | else:
60 | img_to_show = augmented_images[idx]
61 | ax.imshow(img_to_show, cmap="gray")
62 | ax.axis("off")
63 | else:
64 | ax.axis("off")
65 | plt.tight_layout()
66 | plt.show()
67 |
68 |
69 | # ruff: noqa: PLR0913
70 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
71 |
72 |
73 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
74 | @click.option(
75 | "--img-dir",
76 | "-d",
77 | required=True,
78 | type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
79 | help="Path to the images that will be augmented and visualized.",
80 | )
81 | @click.option(
82 | "--num-images",
83 | "-n",
84 | type=int,
85 | default=1_000,
86 | show_default=True,
87 | help="Maximum number of images to visualize.",
88 | )
89 | @click.option(
90 | "--augmentation-path",
91 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
92 | help="YAML file pointing to the augmentation pipeline saved with Albumentations.save(...)",
93 | )
94 | @click.option(
95 | "--shuffle",
96 | "-s",
97 | is_flag=True,
98 | default=False,
99 | help="Whether to shuffle the images before plotting them.",
100 | )
101 | @click.option(
102 | "--columns",
103 | "-c",
104 | type=int,
105 | default=3,
106 | show_default=True,
107 | help="Number of columns in the grid layout for displaying images.",
108 | )
109 | @click.option(
110 | "--rows",
111 | "-r",
112 | type=int,
113 | default=4,
114 | show_default=True,
115 | help="Number of rows in the grid layout for displaying images.",
116 | )
117 | @click.option(
118 | "--height",
119 | "-h",
120 | type=int,
121 | default=70,
122 | show_default=True,
123 | help="Height to which the images will be resize.",
124 | )
125 | @click.option(
126 | "--width",
127 | "-w",
128 | type=int,
129 | default=140,
130 | show_default=True,
131 | help="Width to which the images will be resize.",
132 | )
133 | @click.option(
134 | "--show-original",
135 | "-o",
136 | is_flag=True,
137 | help="Show the original image along with the augmented one.",
138 | )
139 | @click.option(
140 | "--seed",
141 | type=int,
142 | help="Seed for reproducing augmentations.",
143 | )
144 | def visualize_augmentation(
145 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
146 | num_images: int,
147 | augmentation_path: pathlib.Path | None,
148 | shuffle: bool,
149 | columns: int,
150 | rows: int,
151 | height: int,
152 | width: int,
153 | seed: int | None,
154 | show_original: bool,
155 | ) -> None:
156 | """
157 | Visualize augmentation pipeline applied to raw images.
158 | """
159 | _set_seed(seed)
160 | aug = A.load(augmentation_path, data_format="yaml") if augmentation_path else TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
161 | images, augmented_images = load_images(img_dir, num_images, shuffle, height, width, aug)
162 | display_images(images, augmented_images, columns, rows, show_original)
163 |
164 |
165 | if __name__ == "__main__":
166 | # pylint: disable = no-value-for-parameter
167 | visualize_augmentation()
168 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/visualize_predictions.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for displaying an image with the OCR model predictions.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 |
8 | import click
9 | import cv2
10 | import keras
11 | import numpy as np
12 |
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.utils import postprocess_model_output
16 |
17 | logging.basicConfig(
18 | level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(message)s", datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
19 | )
20 |
21 |
22 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
23 | @click.option(
24 | "-m",
25 | "--model",
26 | "model_path",
27 | required=True,
28 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
29 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
30 | )
31 | @click.option(
32 | "--config-file",
33 | required=True,
34 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
35 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
36 | )
37 | @click.option(
38 | "-d",
39 | "--img-dir",
40 | required=True,
41 | type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=True, file_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
42 | help="Directory containing the images to make predictions from.",
43 | )
44 | @click.option(
45 | "-l",
46 | "--low-conf-thresh",
47 | type=float,
48 | default=0.35,
49 | show_default=True,
50 | help="Threshold for displaying low confidence characters.",
51 | )
52 | @click.option(
53 | "-f",
54 | "--filter-conf",
55 | type=float,
56 | help="Display plates that any of the plate characters are below this number.",
57 | )
58 | def visualize_predictions(
59 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
60 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
61 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
62 | low_conf_thresh: float,
63 | filter_conf: float | None,
64 | ):
65 | """
66 | Visualize OCR model predictions on unlabeled data.
67 | """
68 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
69 | model = utils.load_keras_model(
70 | model_path, vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size, max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots
71 | )
72 | images = utils.load_images_from_folder(
73 | img_dir, width=config.img_width, height=config.img_height
74 | )
75 | for image in images:
76 | x = np.expand_dims(image, 0)
77 | prediction = model(x, training=False)
78 | prediction = keras.ops.stop_gradient(prediction).numpy()
79 | plate, probs = postprocess_model_output(
80 | prediction=prediction,
81 | alphabet=config.alphabet,
82 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
83 | vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size,
84 | )
85 | if not filter_conf or (filter_conf and np.any(probs < filter_conf)):
86 | utils.display_predictions(
87 | image=image, plate=plate, probs=probs, low_conf_thresh=low_conf_thresh
88 | )
89 | cv2.destroyAllWindows()
90 |
91 |
92 | if __name__ == "__main__":
93 | visualize_predictions()
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/common/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/common/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/common/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Common utilities used across the package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import time
7 | from collections.abc import Callable, Iterator
8 | from contextlib import contextmanager
9 |
10 |
11 | @contextmanager
12 | def log_time_taken(process_name: str) -> Iterator[None]:
13 | """
14 | A concise context manager to time code snippets and log the result.
15 |
16 | Usage:
17 | with log_time_taken("process_name"):
18 | # Code snippet to be timed
19 |
20 | :param process_name: Name of the process being timed.
21 | """
22 | time_start: float = time.perf_counter()
23 | try:
24 | yield
25 | finally:
26 | time_end: float = time.perf_counter()
27 | time_elapsed: float = time_end - time_start
28 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
29 | logger.info("Computation time of '%s' = %.3fms", process_name, 1_000 * time_elapsed)
30 |
31 |
32 | @contextmanager
33 | def measure_time() -> Iterator[Callable[[], float]]:
34 | """
35 | A context manager for measuring execution time (in milliseconds) within its code block.
36 |
37 | usage:
38 | with code_timer() as timer:
39 | # Code snippet to be timed
40 | print(f"Code took: {timer()} seconds")
41 | """
42 | start_time = end_time = time.perf_counter()
43 | yield lambda: (end_time - start_time) * 1_000
44 | end_time = time.perf_counter()
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/inference/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Model config reading/parsing for doing inference.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from os import PathLike
6 | from typing import TypedDict
7 |
8 | import yaml
9 |
10 | # pylint: disable=duplicate-code
11 |
12 |
13 | class PlateOCRConfig(TypedDict):
14 | """
15 | Plate OCR Config used for inference.
16 |
17 | This has the same attributes as the one used in the training Pydantic BaseModel. We use this to
18 | avoid having Pydantic as a required dependency of the minimal package install.
19 | """
20 |
21 | max_plate_slots: int
22 | """
23 | Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
24 | """
25 | alphabet: str
26 | """
27 | All the possible character set for the model output.
28 | """
29 | pad_char: str
30 | """
31 | Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS.
32 | """
33 | img_height: int
34 | """
35 | Image height which is fed to the model.
36 | """
37 | img_width: int
38 | """
39 | Image width which is fed to the model.
40 | """
41 |
42 |
43 | def load_config_from_yaml(yaml_file_path: str | PathLike[str]) -> PlateOCRConfig:
44 | """
45 | Read and parse a yaml containing the Plate OCR config.
46 |
47 | Note: This is currently not using Pydantic for parsing/validating to avoid adding it a python
48 | dependency as part of the minimal installation.
49 | """
50 | with open(yaml_file_path, encoding="utf-8") as f_in:
51 | config: PlateOCRConfig = yaml.safe_load(f_in)
52 | return config
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/hub.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utilities function used for doing inference with the OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import shutil
8 | import urllib.request
9 | from http import HTTPStatus
10 | from typing import Literal
11 |
12 | from tqdm.asyncio import tqdm
13 |
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.utils import safe_write
15 |
16 | BASE_URL: str = "https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/releases/download"
17 | OcrModel = Literal[
18 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-model",
19 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model",
20 | "european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model",
21 | "global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model",
22 | ]
23 |
24 |
25 | AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS: dict[OcrModel, tuple[str, str]] = {
26 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-model": (
27 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr.onnx",
28 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml",
29 | ),
30 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model": (
31 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_synth.onnx",
32 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml",
33 | ),
34 | "european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model": (
35 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr.onnx",
36 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_config.yaml",
37 | ),
38 | "global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model": (
39 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr.onnx",
40 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_config.yaml",
41 | ),
42 | }
43 | """Available ONNX models for doing inference."""
44 |
45 | MODEL_CACHE_DIR: pathlib.Path = pathlib.Path.home() / ".cache" / "fast-plate-ocr"
46 | """Default location where models will be stored."""
47 |
48 |
49 | def _download_with_progress(url: str, filename: pathlib.Path) -> None:
50 | """
51 | Download utility function with progress bar.
52 |
53 | :param url: URL of the model to download.
54 | :param filename: Where to save the OCR model.
55 | """
56 | with urllib.request.urlopen(url) as response, safe_write(filename, mode="wb") as out_file:
57 | if response.getcode() != HTTPStatus.OK:
58 | raise ValueError(f"Failed to download file from {url}. Status code: {response.status}")
59 |
60 | file_size = int(response.headers.get("Content-Length", 0))
61 | desc = f"Downloading {filename.name}"
62 |
63 | with tqdm.wrapattr(out_file, "write", total=file_size, desc=desc) as f_out:
64 | shutil.copyfileobj(response, f_out)
65 |
66 |
67 | def download_model(
68 | model_name: OcrModel,
69 | save_directory: pathlib.Path | None = None,
70 | force_download: bool = False,
71 | ) -> tuple[pathlib.Path, pathlib.Path]:
72 | """
73 | Download an OCR model and the config to a given directory.
74 |
75 | :param model_name: Which model to download.
76 | :param save_directory: Directory to save the OCR model. It should point to a folder. If not
77 | supplied, this will point to '~/.cache/
44 |
45 | To train or use the CLI tool, you'll need to install:
46 |
47 | ```shell
48 | pip install fast_plate_ocr[train]
49 | ```
50 |
51 | #### Train Model
52 |
53 | To train the model you will need:
54 |
55 | 1. A configuration used for the OCR model. Depending on your use case, you might have more plate slots or different set
56 | of characters. Take a look at the config for Argentinian license plate as an example:
57 | ```yaml
58 | # Config example for Argentinian License Plates
59 | # The old license plates contain 6 slots/characters (i.e. JUH697)
60 | # and new 'Mercosur' contain 7 slots/characters (i.e. AB123CD)
61 |
62 | # Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
63 | max_plate_slots: 7
64 | # All the possible character set for the model output.
65 | alphabet: '0123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ_'
66 | # Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS. It should still be present in the alphabet.
67 | pad_char: '_'
68 | # Image height which is fed to the model.
69 | img_height: 70
70 | # Image width which is fed to the model.
71 | img_width: 140
72 | ```
73 | 2. A labeled dataset,
74 | see [arg_plate_dataset.zip](https://github.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/releases/download/arg-plates/arg_plate_dataset.zip)
75 | for the expected data format.
76 | 3. Run train script:
77 | ```shell
78 | # You can set the backend to either TensorFlow, JAX or PyTorch
79 | # (just make sure it is installed)
80 | KERAS_BACKEND=tensorflow fast_plate_ocr train \
81 | --annotations path_to_the_train.csv \
82 | --val-annotations path_to_the_val.csv \
83 | --config-file config.yaml \
84 | --batch-size 128 \
85 | --epochs 750 \
86 | --dense \
87 | --early-stopping-patience 100 \
88 | --reduce-lr-patience 50
89 | ```
90 |
91 | You will probably want to change the augmentation pipeline to apply to your dataset.
92 |
93 | In order to do this define an Albumentations pipeline:
94 |
95 | ```python
96 | import albumentations as A
97 |
98 | transform_pipeline = A.Compose(
99 | [
100 | # ...
101 | A.RandomBrightnessContrast(brightness_limit=0.1, contrast_limit=0.1, p=1),
102 | A.MotionBlur(blur_limit=(3, 5), p=0.1),
103 | A.CoarseDropout(max_holes=10, max_height=4, max_width=4, p=0.3),
104 | # ... and any other augmentation ...
105 | ]
106 | )
107 |
108 | # Export to a file (this resultant YAML can be used by the train script)
109 | A.save(transform_pipeline, "./transform_pipeline.yaml", data_format="yaml")
110 | ```
111 |
112 | And then you can train using the custom transformation pipeline with the `--augmentation-path` option.
113 |
114 | #### Visualize Augmentation
115 |
116 | It's useful to visualize the augmentation pipeline before training the model. This helps us to identify
117 | if we should apply more heavy augmentation or less, as it can hurt the model.
118 |
119 | You might want to see the augmented image next to the original, to see how much it changed:
120 |
121 | ```shell
122 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-augmentation \
123 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
124 | --columns 2 \
125 | --show-original \
126 | --augmentation-path '/transform_pipeline.yaml'
127 | ```
128 |
129 | You will see something like:
130 |
131 | 
132 |
133 | #### Validate Model
134 |
135 | After finishing training you can validate the model on a labeled test dataset.
136 |
137 | Example:
138 |
139 | ```shell
140 | fast_plate_ocr valid \
141 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
142 | --config-file arg_plate_example.yaml \
143 | --annotations benchmark/annotations.csv
144 | ```
145 |
146 | #### Visualize Predictions
147 |
148 | Once you finish training your model, you can view the model predictions on raw data with:
149 |
150 | ```shell
151 | fast_plate_ocr visualize-predictions \
152 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
153 | --img-dir benchmark/imgs \
154 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
155 | ```
156 |
157 | You will see something like:
158 |
159 | 
160 |
161 | #### Export as ONNX
162 |
163 | Exporting the Keras model to ONNX format might be beneficial to speed-up inference time.
164 |
165 | ```shell
166 | fast_plate_ocr export-onnx \
167 | --model arg_cnn_ocr.keras \
168 | --output-path arg_cnn_ocr.onnx \
169 | --opset 18 \
170 | --config-file arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml
171 | ```
172 |
173 | ### Keras Backend
174 |
175 | To train the model, you can install the ML Framework you like the most. **Keras 3** has
176 | support for **TensorFlow**, **JAX** and **PyTorch** backends.
177 |
178 | To change the Keras backend you can either:
179 |
180 | 1. Export `KERAS_BACKEND` environment variable, i.e. to use JAX for training:
181 | ```shell
182 | KERAS_BACKEND=jax fast_plate_ocr train --config-file ...
183 | ```
184 | 2. Edit your local config file at `~/.keras/keras.json`.
185 |
186 | ???+ tip
187 | **Usually training with JAX and TensorFlow is faster.**
188 |
189 | _Note: You will probably need to install your desired framework for training._
190 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Fast Plate OCR package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.onnx_inference import ONNXPlateRecognizer
6 |
7 | __all__ = ["ONNXPlateRecognizer"]
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/cli/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/cli.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Main CLI used when training a FastPlateOCR model.
3 | """
4 |
5 | try:
6 | import click
7 |
8 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.onnx_converter import export_onnx
9 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.train import train
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.valid import valid
11 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.visualize_augmentation import visualize_augmentation
12 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.visualize_predictions import visualize_predictions
13 | except ImportError as e:
14 | raise ImportError("Make sure to 'pip install fast-plate-ocr[train]' to run this!") from e
15 |
16 |
17 | @click.group(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
18 | def main_cli():
19 | """FastPlateOCR CLI."""
20 |
21 |
22 | main_cli.add_command(visualize_predictions)
23 | main_cli.add_command(visualize_augmentation)
24 | main_cli.add_command(valid)
25 | main_cli.add_command(train)
26 | main_cli.add_command(export_onnx)
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/onnx_converter.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for converting Keras models to ONNX format.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import shutil
8 | from tempfile import NamedTemporaryFile
9 |
10 | import click
11 | import numpy as np
12 | import onnx
13 | import onnxruntime as rt
14 | import onnxsim
15 | import tensorflow as tf
16 | import tf2onnx
17 | from tf2onnx import constants as tf2onnx_constants
18 |
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.common.utils import log_time_taken
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
21 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.utils import load_keras_model
22 |
23 | logging.basicConfig(
24 | level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(message)s", datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
25 | )
26 |
27 |
28 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
29 |
30 |
31 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
32 | @click.option(
33 | "-m",
34 | "--model",
35 | "model_path",
36 | required=True,
37 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
38 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
39 | )
40 | @click.option(
41 | "--output-path",
42 | required=True,
43 | type=str,
44 | help="Output name for ONNX model.",
45 | )
46 | @click.option(
47 | "--simplify/--no-simplify",
48 | default=False,
49 | show_default=True,
50 | help="Simplify ONNX model using onnxsim.",
51 | )
52 | @click.option(
53 | "--config-file",
54 | required=True,
55 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
56 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
57 | )
58 | @click.option(
59 | "--opset",
60 | default=16,
61 | type=click.IntRange(max=max(tf2onnx_constants.OPSET_TO_IR_VERSION)),
62 | show_default=True,
63 | help="Opset version for ONNX.",
64 | )
65 | def export_onnx(
66 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
67 | output_path: str,
68 | simplify: bool,
69 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
70 | opset: int,
71 | ) -> None:
72 | """
73 | Export Keras models to ONNX format.
74 | """
75 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
76 | model = load_keras_model(
77 | model_path,
78 | vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size,
79 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
80 | )
81 | spec = (tf.TensorSpec((None, config.img_height, config.img_width, 1), tf.uint8, name="input"),)
82 | # Convert from Keras to ONNX using tf2onnx library
83 | with NamedTemporaryFile(suffix=".onnx") as tmp:
84 | tmp_onnx = tmp.name
85 | model_proto, _ = tf2onnx.convert.from_keras(
86 | model,
87 | input_signature=spec,
88 | opset=opset,
89 | output_path=tmp_onnx,
90 | )
91 | if simplify:
92 | logging.info("Simplifying ONNX model ...")
93 | model_simp, check = onnxsim.simplify(onnx.load(tmp_onnx))
94 | assert check, "Simplified ONNX model could not be validated!"
95 | onnx.save(model_simp, output_path)
96 | else:
97 | shutil.copy(tmp_onnx, output_path)
98 | output_names = [n.name for n in model_proto.graph.output]
99 | x = np.random.randint(0, 256, size=(1, config.img_height, config.img_width, 1), dtype=np.uint8)
100 | # Run dummy inference and log time taken
101 | m = rt.InferenceSession(output_path)
102 | with log_time_taken("ONNX inference took:"):
103 | onnx_pred = m.run(output_names, {"input": x})
104 | # Check if ONNX and keras have the same results
105 | if not np.allclose(model.predict(x, verbose=0), onnx_pred[0], rtol=1e-5, atol=1e-5):
106 | logging.warning("ONNX model output was not close to Keras model for the given tolerance!")
107 | logging.info("Model converted to ONNX! Saved at %s", output_path)
108 |
109 |
110 | if __name__ == "__main__":
111 | export_onnx()
112 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for training the License Plate OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 | import shutil
7 | from datetime import datetime
8 | from typing import Literal
9 |
10 | import albumentations as A
11 | import click
12 | from keras.src.callbacks import EarlyStopping, ModelCheckpoint, ReduceLROnPlateau, TensorBoard
13 | from keras.src.optimizers import Adam
14 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
15 |
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.cli.utils import print_params, print_train_details
17 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.augmentation import TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
18 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.dataset import LicensePlateDataset
19 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
20 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.custom import (
21 | cat_acc_metric,
22 | cce_loss,
23 | plate_acc_metric,
24 | top_3_k_metric,
25 | )
26 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.models import cnn_ocr_model
27 |
28 | # ruff: noqa: PLR0913
29 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
30 |
31 |
32 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
33 | @click.option(
34 | "--dense/--no-dense",
35 | default=True,
36 | show_default=True,
37 | help="Whether to use Fully Connected layers in model head or not.",
38 | )
39 | @click.option(
40 | "--config-file",
41 | required=True,
42 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
43 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
44 | )
45 | @click.option(
46 | "--annotations",
47 | required=True,
48 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
49 | help="Path pointing to the train annotations CSV file.",
50 | )
51 | @click.option(
52 | "--val-annotations",
53 | required=True,
54 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
55 | help="Path pointing to the train validation CSV file.",
56 | )
57 | @click.option(
58 | "--augmentation-path",
59 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
60 | help="YAML file pointing to the augmentation pipeline saved with Albumentations.save(...)",
61 | )
62 | @click.option(
63 | "--lr",
64 | default=1e-3,
65 | show_default=True,
66 | type=float,
67 | help="Initial learning rate to use.",
68 | )
69 | @click.option(
70 | "--label-smoothing",
71 | default=0.05,
72 | show_default=True,
73 | type=float,
74 | help="Amount of label smoothing to apply.",
75 | )
76 | @click.option(
77 | "--batch-size",
78 | default=128,
79 | show_default=True,
80 | type=int,
81 | help="Batch size for training.",
82 | )
83 | @click.option(
84 | "--num-workers",
85 | default=0,
86 | show_default=True,
87 | type=int,
88 | help="How many subprocesses to load data, used in the torch DataLoader.",
89 | )
90 | @click.option(
91 | "--output-dir",
92 | default="./trained_models",
93 | type=click.Path(dir_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
94 | help="Output directory where model will be saved.",
95 | )
96 | @click.option(
97 | "--epochs",
98 | default=500,
99 | show_default=True,
100 | type=int,
101 | help="Number of training epochs.",
102 | )
103 | @click.option(
104 | "--tensorboard",
105 | "-t",
106 | is_flag=True,
107 | help="Whether to use TensorBoard visualization tool.",
108 | )
109 | @click.option(
110 | "--tensorboard-dir",
111 | "-l",
112 | default="tensorboard_logs",
113 | show_default=True,
114 | type=click.Path(path_type=pathlib.Path),
115 | help="The path of the directory where to save the TensorBoard log files.",
116 | )
117 | @click.option(
118 | "--early-stopping-patience",
119 | default=100,
120 | show_default=True,
121 | type=int,
122 | help="Stop training when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve for X epochs.",
123 | )
124 | @click.option(
125 | "--reduce-lr-patience",
126 | default=60,
127 | show_default=True,
128 | type=int,
129 | help="Patience to reduce the learning rate if 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve within X epochs.",
130 | )
131 | @click.option(
132 | "--reduce-lr-factor",
133 | default=0.85,
134 | show_default=True,
135 | type=float,
136 | help="Reduce the learning rate by this factor when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve.",
137 | )
138 | @click.option(
139 | "--activation",
140 | default="relu",
141 | show_default=True,
142 | type=str,
143 | help="Activation function to use.",
144 | )
145 | @click.option(
146 | "--pool-layer",
147 | default="max",
148 | show_default=True,
149 | type=click.Choice(["max", "avg"]),
150 | help="Choose the pooling layer to use.",
151 | )
152 | @click.option(
153 | "--weights-path",
154 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
155 | help="Path to the pretrained model weights file.",
156 | )
157 | @print_params(table_title="CLI Training Parameters", c1_title="Parameter", c2_title="Details")
158 | def train(
159 | dense: bool,
160 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
161 | annotations: pathlib.Path,
162 | val_annotations: pathlib.Path,
163 | augmentation_path: pathlib.Path | None,
164 | lr: float,
165 | label_smoothing: float,
166 | batch_size: int,
167 | num_workers: int,
168 | output_dir: pathlib.Path,
169 | epochs: int,
170 | tensorboard: bool,
171 | tensorboard_dir: pathlib.Path,
172 | early_stopping_patience: int,
173 | reduce_lr_patience: int,
174 | reduce_lr_factor: float,
175 | activation: str,
176 | pool_layer: Literal["max", "avg"],
177 | weights_path: pathlib.Path | None,
178 | ) -> None:
179 | """
180 | Train the License Plate OCR model.
181 | """
182 | train_augmentation = (
183 | A.load(augmentation_path, data_format="yaml") if augmentation_path else TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
184 | )
185 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
186 | print_train_details(train_augmentation, config.model_dump())
187 | train_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(
188 | annotations_file=annotations,
189 | transform=train_augmentation,
190 | config=config,
191 | )
192 | train_dataloader = DataLoader(
193 | train_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=True
194 | )
195 |
196 | if val_annotations:
197 | val_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(
198 | annotations_file=val_annotations,
199 | config=config,
200 | )
201 | val_dataloader = DataLoader(
202 | val_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=False
203 | )
204 | else:
205 | val_dataloader = None
206 |
207 | # Train
208 | model = cnn_ocr_model(
209 | h=config.img_height,
210 | w=config.img_width,
211 | dense=dense,
212 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
213 | vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size,
214 | activation=activation,
215 | pool_layer=pool_layer,
216 | )
217 |
218 | if weights_path:
219 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
220 |
221 | model.compile(
222 | loss=cce_loss(vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size, label_smoothing=label_smoothing),
223 | optimizer=Adam(lr),
224 | metrics=[
225 | cat_acc_metric(
226 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size
227 | ),
228 | plate_acc_metric(
229 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots, vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size
230 | ),
231 | top_3_k_metric(vocabulary_size=config.vocabulary_size),
232 | ],
233 | )
234 |
235 | output_dir /= datetime.now().strftime("%Y-%m-%d_%H-%M-%S")
236 | output_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
237 | model_file_path = output_dir / "cnn_ocr-epoch_{epoch:02d}-acc_{val_plate_acc:.3f}.keras"
238 |
239 | # Save params and config used for training
240 | shutil.copy(config_file, output_dir / "config.yaml")
241 | A.save(train_augmentation, output_dir / "train_augmentation.yaml", "yaml")
242 |
243 | callbacks = [
244 | # Reduce the learning rate by 0.5x if 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve within X epochs
245 | ReduceLROnPlateau(
246 | "val_plate_acc",
247 | patience=reduce_lr_patience,
248 | factor=reduce_lr_factor,
249 | min_lr=1e-6,
250 | verbose=1,
251 | ),
252 | # Stop training when 'val_plate_acc' doesn't improve for X epochs
253 | EarlyStopping(
254 | monitor="val_plate_acc",
255 | patience=early_stopping_patience,
256 | mode="max",
257 | restore_best_weights=False,
258 | verbose=1,
259 | ),
260 | # We don't use EarlyStopping restore_best_weights=True because it won't restore the best
261 | # weights when it didn't manage to EarlyStop but finished all epochs
262 | ModelCheckpoint(
263 | model_file_path,
264 | monitor="val_plate_acc",
265 | mode="max",
266 | save_best_only=True,
267 | verbose=1,
268 | ),
269 | ]
270 |
271 | if tensorboard:
272 | run_dir = tensorboard_dir / datetime.now().strftime("run_%Y%m%d_%H%M%S")
273 | run_dir.mkdir(parents=True, exist_ok=True)
274 | callbacks.append(TensorBoard(log_dir=run_dir))
275 |
276 | model.fit(train_dataloader, epochs=epochs, validation_data=val_dataloader, callbacks=callbacks)
277 |
278 |
279 | if __name__ == "__main__":
280 | train()
281 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utils used for the CLI scripts.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import inspect
6 | import pathlib
7 | from collections.abc import Callable
8 | from functools import wraps
9 | from typing import Any
10 |
11 | import albumentations as A
12 | from rich import box
13 | from rich.console import Console
14 | from rich.pretty import Pretty
15 | from rich.table import Table
16 |
17 |
18 | def print_variables_as_table(
19 | c1_title: str, c2_title: str, title: str = "Variables Table", **kwargs: Any
20 | ) -> None:
21 | """
22 | Prints variables in a formatted table using the rich library.
23 |
24 | Args:
25 | c1_title (str): Title of the first column.
26 | c2_title (str): Title of the second column.
27 | title (str): Title of the table.
28 | **kwargs (Any): Variable names and values to be printed.
29 | """
30 | console = Console()
31 | console.print("\n")
32 | table = Table(title=title, show_header=True, header_style="bold blue", box=box.ROUNDED)
33 | table.add_column(c1_title, min_width=20, justify="left", style="bold")
34 | table.add_column(c2_title, min_width=60, justify="left", style="bold")
35 |
36 | for key, value in kwargs.items():
37 | if isinstance(value, pathlib.Path):
38 | value = str(value) # noqa: PLW2901
39 | table.add_row(f"[bold]{key}[/bold]", Pretty(value))
40 |
41 | console.print(table)
42 |
43 |
44 | def print_params(
45 | table_title: str = "Parameters Table", c1_title: str = "Variable", c2_title: str = "Value"
46 | ) -> Callable:
47 | """
48 | A decorator that prints the parameters of a function in a formatted table
49 | using the rich library.
50 |
51 | Args:
52 | c1_title (str, optional): Title of the first column. Defaults to "Variable".
53 | c2_title (str, optional): Title of the second column. Defaults to "Value".
54 | table_title (str, optional): Title of the table. Defaults to "Parameters Table".
55 |
56 | Returns:
57 | Callable: The wrapped function with parameter printing functionality.
58 | """
59 |
60 | def decorator(func: Callable) -> Callable:
61 | @wraps(func)
62 | def wrapper(*args: Any, **kwargs: Any) -> Any:
63 | func_signature = inspect.signature(func)
64 | bound_arguments = func_signature.bind(*args, **kwargs)
65 | bound_arguments.apply_defaults()
66 | params = dict(bound_arguments.arguments.items())
67 | print_variables_as_table(c1_title, c2_title, table_title, **params)
68 | return func(*args, **kwargs)
69 |
70 | return wrapper
71 |
72 | return decorator
73 |
74 |
75 | def print_train_details(augmentation: A.Compose, config: dict[str, Any]) -> None:
76 | console = Console()
77 | console.print("\n")
78 | console.print("[bold blue]Augmentation Pipeline:[/bold blue]")
79 | console.print(Pretty(augmentation))
80 | console.print("\n")
81 | console.print("[bold blue]Configuration:[/bold blue]")
82 | console.print(Pretty(config))
83 | console.print("\n")
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/valid.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for validating trained OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 |
7 | import click
8 | from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
9 |
10 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.dataset import LicensePlateDataset
11 |
12 | # Custom metris / losses
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 |
16 |
17 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
18 | @click.option(
19 | "-m",
20 | "--model",
21 | "model_path",
22 | required=True,
23 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
24 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
25 | )
26 | @click.option(
27 | "--config-file",
28 | required=True,
29 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
30 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
31 | )
32 | @click.option(
33 | "-a",
34 | "--annotations",
35 | required=True,
36 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
37 | help="Annotations file used for validation.",
38 | )
39 | @click.option(
40 | "-b",
41 | "--batch-size",
42 | default=1,
43 | show_default=True,
44 | type=int,
45 | help="Batch size.",
46 | )
47 | def valid(
48 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
49 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
50 | annotations: pathlib.Path,
51 | batch_size: int,
52 | ) -> None:
53 | """
54 | Validate the trained OCR model on a labeled set.
55 | """
56 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
57 | model = utils.load_keras_model(
58 | model_path, vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size, max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots
59 | )
60 | val_torch_dataset = LicensePlateDataset(annotations_file=annotations, config=config)
61 | val_dataloader = DataLoader(val_torch_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=False)
62 | model.evaluate(val_dataloader)
63 |
64 |
65 | if __name__ == "__main__":
66 | valid()
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/visualize_augmentation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script to visualize the augmented plates used during training.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import pathlib
6 | import random
7 | from math import ceil
8 |
9 | import albumentations as A
10 | import click
11 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import numpy.typing as npt
14 |
15 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.data.augmentation import TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
16 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
17 |
18 |
19 | def _set_seed(seed: int | None) -> None:
20 | """Set random seed for reproducing augmentations."""
21 | if seed:
22 | random.seed(seed)
23 | np.random.seed(seed)
24 |
25 |
26 | def load_images(
27 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
28 | num_images: int,
29 | shuffle: bool,
30 | height: int,
31 | width: int,
32 | augmentation: A.Compose,
33 | ) -> tuple[list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]], list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]]]:
34 | images = utils.load_images_from_folder(
35 | img_dir, height=height, width=width, shuffle=shuffle, limit=num_images
36 | )
37 | augmented_images = [augmentation(image=i)["image"] for i in images]
38 | return images, augmented_images
39 |
40 |
41 | def display_images(
42 | images: list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]],
43 | augmented_images: list[npt.NDArray[np.uint8]],
44 | columns: int,
45 | rows: int,
46 | show_original: bool,
47 | ) -> None:
48 | num_images = len(images)
49 | total_plots = rows * columns
50 | num_pages = ceil(num_images / total_plots)
51 | for page in range(num_pages):
52 | _, axs = plt.subplots(rows, columns, figsize=(8, 8))
53 | axs = axs.flatten()
54 | for i, ax in enumerate(axs):
55 | idx = page * total_plots + i
56 | if idx < num_images:
57 | if show_original:
58 | img_to_show = np.concatenate((images[idx], augmented_images[idx]), axis=1)
59 | else:
60 | img_to_show = augmented_images[idx]
61 | ax.imshow(img_to_show, cmap="gray")
62 | ax.axis("off")
63 | else:
64 | ax.axis("off")
65 | plt.tight_layout()
66 | plt.show()
67 |
68 |
69 | # ruff: noqa: PLR0913
70 | # pylint: disable=too-many-arguments,too-many-locals
71 |
72 |
73 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
74 | @click.option(
75 | "--img-dir",
76 | "-d",
77 | required=True,
78 | type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
79 | help="Path to the images that will be augmented and visualized.",
80 | )
81 | @click.option(
82 | "--num-images",
83 | "-n",
84 | type=int,
85 | default=1_000,
86 | show_default=True,
87 | help="Maximum number of images to visualize.",
88 | )
89 | @click.option(
90 | "--augmentation-path",
91 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
92 | help="YAML file pointing to the augmentation pipeline saved with Albumentations.save(...)",
93 | )
94 | @click.option(
95 | "--shuffle",
96 | "-s",
97 | is_flag=True,
98 | default=False,
99 | help="Whether to shuffle the images before plotting them.",
100 | )
101 | @click.option(
102 | "--columns",
103 | "-c",
104 | type=int,
105 | default=3,
106 | show_default=True,
107 | help="Number of columns in the grid layout for displaying images.",
108 | )
109 | @click.option(
110 | "--rows",
111 | "-r",
112 | type=int,
113 | default=4,
114 | show_default=True,
115 | help="Number of rows in the grid layout for displaying images.",
116 | )
117 | @click.option(
118 | "--height",
119 | "-h",
120 | type=int,
121 | default=70,
122 | show_default=True,
123 | help="Height to which the images will be resize.",
124 | )
125 | @click.option(
126 | "--width",
127 | "-w",
128 | type=int,
129 | default=140,
130 | show_default=True,
131 | help="Width to which the images will be resize.",
132 | )
133 | @click.option(
134 | "--show-original",
135 | "-o",
136 | is_flag=True,
137 | help="Show the original image along with the augmented one.",
138 | )
139 | @click.option(
140 | "--seed",
141 | type=int,
142 | help="Seed for reproducing augmentations.",
143 | )
144 | def visualize_augmentation(
145 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
146 | num_images: int,
147 | augmentation_path: pathlib.Path | None,
148 | shuffle: bool,
149 | columns: int,
150 | rows: int,
151 | height: int,
152 | width: int,
153 | seed: int | None,
154 | show_original: bool,
155 | ) -> None:
156 | """
157 | Visualize augmentation pipeline applied to raw images.
158 | """
159 | _set_seed(seed)
160 | aug = A.load(augmentation_path, data_format="yaml") if augmentation_path else TRAIN_AUGMENTATION
161 | images, augmented_images = load_images(img_dir, num_images, shuffle, height, width, aug)
162 | display_images(images, augmented_images, columns, rows, show_original)
163 |
164 |
165 | if __name__ == "__main__":
166 | # pylint: disable = no-value-for-parameter
167 | visualize_augmentation()
168 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/cli/visualize_predictions.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Script for displaying an image with the OCR model predictions.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 |
8 | import click
9 | import cv2
10 | import keras
11 | import numpy as np
12 |
13 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.model.config import load_config_from_yaml
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities import utils
15 | from fast_plate_ocr.train.utilities.utils import postprocess_model_output
16 |
17 | logging.basicConfig(
18 | level=logging.INFO, format="%(asctime)s - %(message)s", datefmt="%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S"
19 | )
20 |
21 |
22 | @click.command(context_settings={"max_content_width": 120})
23 | @click.option(
24 | "-m",
25 | "--model",
26 | "model_path",
27 | required=True,
28 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, dir_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
29 | help="Path to the saved .keras model.",
30 | )
31 | @click.option(
32 | "--config-file",
33 | required=True,
34 | type=click.Path(exists=True, file_okay=True, path_type=pathlib.Path),
35 | help="Path pointing to the model license plate OCR config.",
36 | )
37 | @click.option(
38 | "-d",
39 | "--img-dir",
40 | required=True,
41 | type=click.Path(exists=True, dir_okay=True, file_okay=False, path_type=pathlib.Path),
42 | help="Directory containing the images to make predictions from.",
43 | )
44 | @click.option(
45 | "-l",
46 | "--low-conf-thresh",
47 | type=float,
48 | default=0.35,
49 | show_default=True,
50 | help="Threshold for displaying low confidence characters.",
51 | )
52 | @click.option(
53 | "-f",
54 | "--filter-conf",
55 | type=float,
56 | help="Display plates that any of the plate characters are below this number.",
57 | )
58 | def visualize_predictions(
59 | model_path: pathlib.Path,
60 | config_file: pathlib.Path,
61 | img_dir: pathlib.Path,
62 | low_conf_thresh: float,
63 | filter_conf: float | None,
64 | ):
65 | """
66 | Visualize OCR model predictions on unlabeled data.
67 | """
68 | config = load_config_from_yaml(config_file)
69 | model = utils.load_keras_model(
70 | model_path, vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size, max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots
71 | )
72 | images = utils.load_images_from_folder(
73 | img_dir, width=config.img_width, height=config.img_height
74 | )
75 | for image in images:
76 | x = np.expand_dims(image, 0)
77 | prediction = model(x, training=False)
78 | prediction = keras.ops.stop_gradient(prediction).numpy()
79 | plate, probs = postprocess_model_output(
80 | prediction=prediction,
81 | alphabet=config.alphabet,
82 | max_plate_slots=config.max_plate_slots,
83 | vocab_size=config.vocabulary_size,
84 | )
85 | if not filter_conf or (filter_conf and np.any(probs < filter_conf)):
86 | utils.display_predictions(
87 | image=image, plate=plate, probs=probs, low_conf_thresh=low_conf_thresh
88 | )
89 | cv2.destroyAllWindows()
90 |
91 |
92 | if __name__ == "__main__":
93 | visualize_predictions()
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/common/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/common/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/common/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Common utilities used across the package.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import time
7 | from collections.abc import Callable, Iterator
8 | from contextlib import contextmanager
9 |
10 |
11 | @contextmanager
12 | def log_time_taken(process_name: str) -> Iterator[None]:
13 | """
14 | A concise context manager to time code snippets and log the result.
15 |
16 | Usage:
17 | with log_time_taken("process_name"):
18 | # Code snippet to be timed
19 |
20 | :param process_name: Name of the process being timed.
21 | """
22 | time_start: float = time.perf_counter()
23 | try:
24 | yield
25 | finally:
26 | time_end: float = time.perf_counter()
27 | time_elapsed: float = time_end - time_start
28 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
29 | logger.info("Computation time of '%s' = %.3fms", process_name, 1_000 * time_elapsed)
30 |
31 |
32 | @contextmanager
33 | def measure_time() -> Iterator[Callable[[], float]]:
34 | """
35 | A context manager for measuring execution time (in milliseconds) within its code block.
36 |
37 | usage:
38 | with code_timer() as timer:
39 | # Code snippet to be timed
40 | print(f"Code took: {timer()} seconds")
41 | """
42 | start_time = end_time = time.perf_counter()
43 | yield lambda: (end_time - start_time) * 1_000
44 | end_time = time.perf_counter()
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ankandrew/fast-plate-ocr/49954297c2226ad6c488f6fbfb93169b579b815d/fast_plate_ocr/inference/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Model config reading/parsing for doing inference.
3 | """
4 |
5 | from os import PathLike
6 | from typing import TypedDict
7 |
8 | import yaml
9 |
10 | # pylint: disable=duplicate-code
11 |
12 |
13 | class PlateOCRConfig(TypedDict):
14 | """
15 | Plate OCR Config used for inference.
16 |
17 | This has the same attributes as the one used in the training Pydantic BaseModel. We use this to
18 | avoid having Pydantic as a required dependency of the minimal package install.
19 | """
20 |
21 | max_plate_slots: int
22 | """
23 | Max number of plate slots supported. This represents the number of model classification heads.
24 | """
25 | alphabet: str
26 | """
27 | All the possible character set for the model output.
28 | """
29 | pad_char: str
30 | """
31 | Padding character for plates which length is smaller than MAX_PLATE_SLOTS.
32 | """
33 | img_height: int
34 | """
35 | Image height which is fed to the model.
36 | """
37 | img_width: int
38 | """
39 | Image width which is fed to the model.
40 | """
41 |
42 |
43 | def load_config_from_yaml(yaml_file_path: str | PathLike[str]) -> PlateOCRConfig:
44 | """
45 | Read and parse a yaml containing the Plate OCR config.
46 |
47 | Note: This is currently not using Pydantic for parsing/validating to avoid adding it a python
48 | dependency as part of the minimal installation.
49 | """
50 | with open(yaml_file_path, encoding="utf-8") as f_in:
51 | config: PlateOCRConfig = yaml.safe_load(f_in)
52 | return config
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fast_plate_ocr/inference/hub.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Utilities function used for doing inference with the OCR models.
3 | """
4 |
5 | import logging
6 | import pathlib
7 | import shutil
8 | import urllib.request
9 | from http import HTTPStatus
10 | from typing import Literal
11 |
12 | from tqdm.asyncio import tqdm
13 |
14 | from fast_plate_ocr.inference.utils import safe_write
15 |
16 | BASE_URL: str = "https://github.com/ankandrew/cnn-ocr-lp/releases/download"
17 | OcrModel = Literal[
18 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-model",
19 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model",
20 | "european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model",
21 | "global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model",
22 | ]
23 |
24 |
25 | AVAILABLE_ONNX_MODELS: dict[OcrModel, tuple[str, str]] = {
26 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-model": (
27 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr.onnx",
28 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml",
29 | ),
30 | "argentinian-plates-cnn-synth-model": (
31 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_synth.onnx",
32 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/arg_cnn_ocr_config.yaml",
33 | ),
34 | "european-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model": (
35 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr.onnx",
36 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/european_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_config.yaml",
37 | ),
38 | "global-plates-mobile-vit-v2-model": (
39 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr.onnx",
40 | f"{BASE_URL}/arg-plates/global_mobile_vit_v2_ocr_config.yaml",
41 | ),
42 | }
43 | """Available ONNX models for doing inference."""
44 |
45 | MODEL_CACHE_DIR: pathlib.Path = pathlib.Path.home() / ".cache" / "fast-plate-ocr"
46 | """Default location where models will be stored."""
47 |
48 |
49 | def _download_with_progress(url: str, filename: pathlib.Path) -> None:
50 | """
51 | Download utility function with progress bar.
52 |
53 | :param url: URL of the model to download.
54 | :param filename: Where to save the OCR model.
55 | """
56 | with urllib.request.urlopen(url) as response, safe_write(filename, mode="wb") as out_file:
57 | if response.getcode() != HTTPStatus.OK:
58 | raise ValueError(f"Failed to download file from {url}. Status code: {response.status}")
59 |
60 | file_size = int(response.headers.get("Content-Length", 0))
61 | desc = f"Downloading {filename.name}"
62 |
63 | with tqdm.wrapattr(out_file, "write", total=file_size, desc=desc) as f_out:
64 | shutil.copyfileobj(response, f_out)
65 |
66 |
67 | def download_model(
68 | model_name: OcrModel,
69 | save_directory: pathlib.Path | None = None,
70 | force_download: bool = False,
71 | ) -> tuple[pathlib.Path, pathlib.Path]:
72 | """
73 | Download an OCR model and the config to a given directory.
74 |
75 | :param model_name: Which model to download.
76 | :param save_directory: Directory to save the OCR model. It should point to a folder. If not
77 | supplied, this will point to '~/.cache/