├── .python-version
├── day-16
├── .gitignore
├── client
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── test_client.py
│ └── hitl_client.py
├── requirements.txt
├── langgraph_agent
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── checkpointer.py
│ ├── agent.py
│ └── server.py
└── README.md
├── day-01
├── __init__.py
├── README.md
└── main.py
├── day-14
├── host_agent
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── agent.py
├── remote_agent
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── agent.py
├── run_demo.py
└── README.md
├── day-07
├── __init__.py
└── README.md
├── day-08
└── __init__.py
├── day-03
├── __init__.py
├── root_agent.yaml
└── README.md
├── day-02
├── __init__.py
├── root_agent.yaml
└── README.md
├── day-04
├── agent
│ ├── __init__.py
│ └── root_agent.yaml
├── deploy.sh
└── README.md
├── .env.example
├── day-18
├── __init__.py
├── README.md
└── api_registry_demo.py
├── shared
├── __init__.py
└── config.py
├── day-17
├── __init__.py
├── README.md
└── gemini3_flash_thinking.ipynb
├── .gitignore
├── pyproject.toml
├── day-06
├── README.md
└── day06_ide_context.ipynb
├── day-09
├── agent.py
├── main.py
└── day-09-session-rewind.ipynb
├── assets
└── difficulty_curve.svg
├── README.md
├── day-15
├── README.md
└── a2ui.py
└── day-05
├── README.md
└── telemetry_demo.py
/.python-version:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 3.12
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Runtime data
2 | data/
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-01/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Day 01: Introduction to AI Agents."""
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-14/host_agent/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Host Agent - A2A Client
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-14/remote_agent/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Remote Agent - A2A Server
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-07/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 07: Code Execution - Autonomous Problem Solving
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-08/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Day 08: Effective Context Management with ADK Layers."""
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-03/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 03: Gemini 3 + ADK
2 | # Build AI agents with Google Search grounding
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-02/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 02: Hello World with YAML
2 | # This file marks the directory as a valid ADK agent package
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-04/agent/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 04: Source-Based Deployment
2 | # Agent package for deployment to Vertex AI Agent Engine
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.env.example:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Google AI API Key
2 | # Get your key from: https://aistudio.google.com/apikey
3 | GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-18/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 18: Cloud API Registry + ADK
3 |
4 | 核心概念:
5 | - Cloud API Registry = 企业级工具商店
6 | - 管理员统一管理,开发者直接获取已审批的工具
7 | - 简化权限管理和合规性
8 | """
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/shared/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Shared utilities for the 25-Day Agents Course."""
2 |
3 | from .config import load_config, get_api_key
4 |
5 | __all__ = ["load_config", "get_api_key"]
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/client/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 16: A2A Client for LangGraph Agent
3 |
4 | 测试客户端模块
5 | """
6 |
7 | from .test_client import test_langgraph_agent
8 |
9 | __all__ = ["test_langgraph_agent"]
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-02/root_agent.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: search_agent
2 | model: gemini-2.0-flash
3 | description: A helpful assistant that can answer user questions.
4 | instruction: |
5 | You are a helpful assistant that can answer user questions.
6 | Always provide clear and concise responses in the user's language.
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-01/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 01: Introduction to AI Agents
2 |
3 | ## Learning Goals
4 |
5 | - Set up the development environment
6 | - Understand basic concepts of AI Agents
7 | - Make your first API call to Google Gemini
8 |
9 | ## Running
10 |
11 | ```bash
12 | # From project root
13 | uv run python day-01/main.py
14 | ```
15 |
16 | ## Notes
17 |
18 | Add your learning notes here...
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-17/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 17: Gemini 3 Flash - 可配置思考级别
3 |
4 | 学习要点:
5 | 1. ThinkingConfig 配置思考级别
6 | 2. BuiltInPlanner 内置规划器
7 | 3. 不同级别的使用场景
8 | """
9 |
10 | from .thinking_demo import (
11 | create_agent,
12 | agent_minimal,
13 | agent_low,
14 | agent_high,
15 | )
16 |
17 | __all__ = [
18 | "create_agent",
19 | "agent_minimal",
20 | "agent_low",
21 | "agent_high",
22 | ]
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 16: LangGraph + A2A 额外依赖
2 | # 这些依赖是 Day 16 特有的,需要额外安装
3 |
4 | # LangGraph - 图结构 Agent 框架
5 | langgraph>=0.2.0
6 |
7 | # LangChain Google Gemini 集成
8 | langchain-google-genai>=2.0.0
9 |
10 | # LangChain 核心
11 | langchain-core>=0.3.0
12 |
13 | # Human-in-the-Loop 扩展依赖
14 | # FastAPI - REST API 服务
15 | fastapi>=0.104.0
16 |
17 | # Pydantic - 数据验证
18 | pydantic>=2.0.0
19 |
20 | # 可选: SQLite 持久化支持 (生产环境推荐)
21 | # 安装后可使用 CheckpointerType.SQLITE 实现断点续跑
22 | # langgraph-checkpoint-sqlite>=2.0.0
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Python
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 | *.so
6 | .Python
7 | build/
8 | develop-eggs/
9 | dist/
10 | downloads/
11 | eggs/
12 | .eggs/
13 | lib/
14 | lib64/
15 | parts/
16 | sdist/
17 | var/
18 | wheels/
19 | *.egg-info/
20 | .installed.cfg
21 | *.egg
22 |
23 | # Virtual environments
24 | .venv/
25 | venv/
26 | ENV/
27 |
28 | # Environment variables
29 | .env
30 | .env.local
31 |
32 | # IDE
33 | .idea/
34 | .vscode/
35 | *.swp
36 | *.swo
37 |
38 | # Jupyter
39 | .ipynb_checkpoints/
40 |
41 | # Testing
42 | .pytest_cache/
43 | .coverage
44 | htmlcov/
45 |
46 | # UV
47 | uv.lock
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-03/root_agent.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | name: search_agent
2 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
3 | description: A helpful assistant that can search the web for current information.
4 | instruction: |
5 | You are a helpful assistant with access to Google Search.
6 |
7 | Use Google Search when users ask about:
8 | - Current events and news
9 | - Weather information
10 | - Stock prices and market data
11 | - Sports scores and results
12 | - Any time-sensitive information
13 |
14 | Always provide clear, accurate responses based on search results.
15 | Cite your sources when appropriate.
16 | tools:
17 | - name: google_search
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pyproject.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [project]
2 | name = "agents-course"
3 | version = "0.1.0"
4 | description = "25-Day AI Agents Course by Google - Learning Journey"
5 | readme = "README.md"
6 | requires-python = ">=3.11"
7 | dependencies = [
8 | "google-genai>=1.0.0",
9 | "google-adk>=1.0.0",
10 | "python-dotenv>=1.0.0",
11 | "google-generativeai>=0.8.5",
12 | "matplotlib>=3.10.8",
13 | ]
14 |
15 | [project.optional-dependencies]
16 | dev = [
17 | "pytest>=8.0.0",
18 | "ruff>=0.8.0",
19 | ]
20 |
21 | [tool.ruff]
22 | line-length = 100
23 | target-version = "py311"
24 |
25 | [tool.ruff.lint]
26 | select = ["E", "F", "I", "W"]
27 |
28 | [dependency-groups]
29 | dev = [
30 | "pytest>=8.0.0",
31 | "ruff>=0.8.0",
32 | ]
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-01/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Day 01: Getting Started with Google AI Agents.
2 |
3 | This is the first day of the 25-Day AI Agents Course.
4 | """
5 |
6 | import sys
7 | from pathlib import Path
8 |
9 | # Add project root to path for imports
10 | sys.path.insert(0, str(Path(__file__).parent.parent))
11 |
12 | from google import genai
13 |
14 | from shared import get_api_key
15 |
16 |
17 | def main():
18 | """Main entry point for Day 01."""
19 | api_key = get_api_key()
20 | client = genai.Client(api_key=api_key)
21 |
22 | # Example: Simple chat with Gemini
23 | response = client.models.generate_content(
24 | model="gemini-2.0-flash",
25 | contents="Hello! I'm starting the 25-Day AI Agents Course. What will I learn?",
26 | )
27 | print(response.text)
28 |
29 |
30 | if __name__ == "__main__":
31 | main()
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-06/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 6: ADK 在各种 IDE 中的集成
2 |
3 | > 构建 Agent 不应该花一小时配置环境。Agent Starter Pack 已经内置了 ADK 的 IDE 上下文。
4 |
5 | ## 今日要点
6 |
7 | Day 6 讲的是如何为 AI IDE 提供项目上下文,让 AI 助手更好地帮你开发 Agent。
8 |
9 | ## 什么是 llms.txt?
10 |
11 | `llms.txt` 是一种为 LLM 提供项目文档的标准格式,类似于给搜索引擎的 `robots.txt`。
12 |
13 | ## IDE 配置文件
14 |
15 | | IDE | 配置文件 |
16 | |-----|----------|
17 | | Cursor | `.cursorrules` |
18 | | Claude Code | `.claude/instructions.md` |
19 | | Windsurf | `.windsurfrules` |
20 | | 通用 | `llms.txt` |
21 |
22 | ## 运行
23 |
24 | ```bash
25 | # 打开 Jupyter notebook 学习
26 | jupyter notebook day-06/day06_ide_context.ipynb
27 | ```
28 |
29 | ## 资源
30 |
31 | - [llms.txt 规范](https://llmstxt.org/)
32 | - [ADK 文档](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/)
33 | - [Antigravity IDE](https://antigravity.google/)
34 | - [视频](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ep8usBDUTtA)
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-04/agent/root_agent.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 04: Agent for Source-Based Deployment
2 | # This agent is configured for deployment to Vertex AI Agent Engine
3 |
4 | name: deployed_assistant
5 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
6 | description: |
7 | A production-ready assistant deployed to Agent Engine.
8 | Demonstrates source-based deployment with Google Search capability.
9 |
10 | instruction: |
11 | You are a helpful production assistant running on Vertex AI Agent Engine.
12 |
13 | Your capabilities:
14 | - Answer questions about current events using Google Search
15 | - Provide factual information with citations
16 | - Help users with general queries
17 |
18 | Guidelines:
19 | - Always cite your sources when using search results
20 | - Be concise and accurate
21 | - If you don't know something, say so clearly
22 | - Present information in a clear, organized format
23 |
24 | tools:
25 | - name: google_search
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/shared/config.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Configuration utilities for the course."""
2 |
3 | import os
4 | from pathlib import Path
5 |
6 | from dotenv import load_dotenv
7 |
8 |
9 | def load_config() -> None:
10 | """Load environment variables from .env file."""
11 | env_path = Path(__file__).parent.parent / ".env"
12 | load_dotenv(env_path)
13 |
14 |
15 | def get_api_key(key_name: str = "GOOGLE_API_KEY") -> str:
16 | """Get API key from environment variables.
17 |
18 | Args:
19 | key_name: Name of the environment variable containing the API key.
20 |
21 | Returns:
22 | The API key string.
23 |
24 | Raises:
25 | ValueError: If the API key is not found.
26 | """
27 | load_config()
28 | api_key = os.getenv(key_name)
29 | if not api_key:
30 | raise ValueError(
31 | f"{key_name} not found. Please set it in .env file or environment variables."
32 | )
33 | return api_key
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/langgraph_agent/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 16: LangGraph Agent with A2A support
3 |
4 | 这个模块提供了:
5 | 1. 基于 LangGraph 构建的 ReAct Agent (agent.py)
6 | 2. 生产级 Human-in-the-Loop 实现 (hitl_agent.py)
7 | 3. REST API 服务 (server.py)
8 | 4. 状态持久化支持 (checkpointer.py)
9 | """
10 |
11 | from .agent import create_langgraph_agent, run_langgraph, langgraph_adk_agent, app
12 | from .hitl_agent import (
13 | create_hitl_graph,
14 | run_hitl_agent,
15 | resume_after_approval,
16 | RiskLevel,
17 | HITLState,
18 | )
19 | from .checkpointer import (
20 | get_checkpointer,
21 | get_task_store,
22 | TaskStore,
23 | TaskMetadata,
24 | CheckpointerType,
25 | )
26 |
27 | __all__ = [
28 | # 原有的 ReAct Agent
29 | "create_langgraph_agent",
30 | "run_langgraph",
31 | "langgraph_adk_agent",
32 | "app",
33 | # HITL Agent
34 | "create_hitl_graph",
35 | "run_hitl_agent",
36 | "resume_after_approval",
37 | "RiskLevel",
38 | "HITLState",
39 | # Checkpointer
40 | "get_checkpointer",
41 | "get_task_store",
42 | "TaskStore",
43 | "TaskMetadata",
44 | "CheckpointerType",
45 | ]
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-09/agent.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 9: Undo Buttons for your Agents - Session Rewind
2 | #
3 | # ADK 内置了"时间旅行"功能,让你可以实现:
4 | # - 编辑消息(Edit Message)
5 | # - 重新生成(Regenerate)
6 | # - 撤销操作(Undo)
7 |
8 | from google.adk import Agent
9 | from google.adk.tools.tool_context import ToolContext
10 | from google.genai import types
11 |
12 |
13 | async def update_state(tool_context: ToolContext, key: str, value: str) -> dict:
14 | """更新状态值"""
15 | tool_context.state[key] = value
16 | return {"status": f"已更新 '{key}' 为 '{value}'"}
17 |
18 |
19 | async def load_state(tool_context: ToolContext, key: str) -> dict:
20 | """读取状态值"""
21 | return {key: tool_context.state.get(key, "未找到")}
22 |
23 |
24 | async def save_artifact(
25 | tool_context: ToolContext, filename: str, content: str
26 | ) -> dict:
27 | """保存文件内容"""
28 | artifact_bytes = content.encode("utf-8")
29 | artifact_part = types.Part(
30 | inline_data=types.Blob(mime_type="text/plain", data=artifact_bytes)
31 | )
32 | version = await tool_context.save_artifact(filename, artifact_part)
33 | return {"status": "成功", "filename": filename, "version": version}
34 |
35 |
36 | async def load_artifact(tool_context: ToolContext, filename: str) -> dict:
37 | """读取文件内容"""
38 | artifact = await tool_context.load_artifact(filename)
39 | if not artifact:
40 | return {"error": f"文件 '{filename}' 未找到"}
41 | content = artifact.inline_data.data.decode("utf-8")
42 | return {"filename": filename, "content": content}
43 |
44 |
45 | # 创建 Agent
46 | root_agent = Agent(
47 | name="state_agent",
48 | model="gemini-2.0-flash",
49 | instruction="""你是一个状态和文件管理 Agent。
50 |
51 | 你可以:
52 | - 更新状态值 (update_state)
53 | - 读取状态值 (load_state)
54 | - 保存文件 (save_artifact)
55 | - 读取文件 (load_artifact)
56 |
57 | 根据用户的请求使用相应的工具。""",
58 | tools=[
59 | update_state,
60 | load_state,
61 | save_artifact,
62 | load_artifact,
63 | ],
64 | )
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-17/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 17: Gemini 3 Flash - 可配置思考级别
2 |
3 | ## 核心概念
4 |
5 | Gemini 3 Flash 是 Google 最新的快速模型,最大亮点是**可配置的思考级别(Thinking Level)**。
6 |
7 | ### 什么是 Thinking Level?
8 |
9 | 简单说:控制模型"想多久"再回答。
10 |
11 | | 级别 | 特点 | 适用场景 |
12 | |------|------|----------|
13 | | `MINIMAL` | 最快响应,几乎不思考 | 简单问答、聊天 |
14 | | `LOW` | 快速响应,少量推理 | 日常任务、一般查询 |
15 | | `MEDIUM` | 平衡模式 | 中等复杂度任务 |
16 | | `HIGH` | 深度推理,更长思考 | 复杂问题、数学、编程 |
17 |
18 | ### 为什么重要?
19 |
20 | 1. **省钱** - 低思考级别消耗更少 token
21 | 2. **更快** - 简单任务不需要深度思考
22 | 3. **更准** - 复杂任务可以开启深度推理
23 |
24 | ## 在 ADK 中使用
25 |
26 | ```python
27 | from google.adk.agents import Agent
28 | from google.adk.planners import BuiltInPlanner
29 | from google.genai import types
30 |
31 | agent = Agent(
32 | model='gemini-3-flash-preview',
33 | name='my_agent',
34 | instruction="你是一个有用的助手",
35 | planner=BuiltInPlanner(
36 | thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(
37 | thinking_level="LOW" # 可选: MINIMAL, LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH
38 | )
39 | ),
40 | )
41 | ```
42 |
43 | ## 关键配置
44 |
45 | ### ThinkingConfig 参数
46 |
47 | ```python
48 | types.ThinkingConfig(
49 | thinking_level="HIGH" # 思考级别
50 | )
51 | ```
52 |
53 | ### BuiltInPlanner
54 |
55 | - ADK 的内置规划器
56 | - 用于配置模型的思考行为
57 | - 通过 `thinking_config` 传入配置
58 |
59 | ## 与 Gemini 2.5 的区别
60 |
61 | | 特性 | Gemini 2.5 | Gemini 3 |
62 | |------|------------|----------|
63 | | 配置参数 | `thinking_budget` | `thinking_level` |
64 | | 控制方式 | token 预算 | 级别选择 |
65 | | 效率 | 基准 | 平均减少 30% token |
66 |
67 | **注意**: 参数不通用!Gemini 3 用 `thinking_level`,Gemini 2.5 用 `thinking_budget`。
68 |
69 | ## 定价
70 |
71 | - 输入: $0.50 / 百万 token
72 | - 输出: $3.00 / 百万 token
73 | - 比 Gemini 3 Pro 便宜 4 倍
74 |
75 | ## 文件说明
76 |
77 | | 文件 | 说明 |
78 | |------|------|
79 | | `gemini3_flash_thinking.ipynb` | 基础教程 - 思考级别入门 |
80 | | `adaptive_thinking_demo.ipynb` | 扩展案例 - 智能客服自适应思考 |
81 | | `thinking_demo.py` | Python 脚本版本 |
82 |
83 | ## 运行示例
84 |
85 | ```bash
86 | # 安装依赖
87 | pip install google-adk google-genai python-dotenv
88 |
89 | # 设置 API Key
90 | export GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_key_here
91 |
92 | # 运行 Jupyter
93 | jupyter notebook
94 | ```
95 |
96 | ## 参考资料
97 |
98 | - [Gemini 3 Flash 官方公告](https://blog.google/products/gemini/gemini-3-flash/)
99 | - [ADK 模型配置文档](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/agents/models/)
100 | - [多智能体系统指南](https://developers.googleblog.com/developers-guide-to-multi-agent-patterns-in-adk/)
101 | - [TechCrunch 报道](https://techcrunch.com/2025/12/17/google-launches-gemini-3-flash-makes-it-the-default-model-in-the-gemini-app/)
102 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-14/remote_agent/agent.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 14: Remote Agent (A2A Server)
3 |
4 | 这是一个专业的翻译 Agent,通过 A2A 协议对外提供服务。
5 | 其他 Agent 可以通过 A2A 协议调用它来完成翻译任务。
6 |
7 | 运行方式:
8 | python -m remote_agent.agent
9 | 或
10 | uvicorn remote_agent.agent:app --host localhost --port 8001
11 | """
12 |
13 | import os
14 | import sys
15 |
16 | # 添加项目根目录到路径
17 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
18 |
19 | # 加载 .env 文件中的环境变量
20 | from dotenv import load_dotenv
21 | # 从项目根目录加载 .env
22 | project_root = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
23 | load_dotenv(os.path.join(project_root, ".env"))
24 |
25 | from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
26 | from google.adk.a2a.utils.agent_to_a2a import to_a2a
27 |
28 | # ============================================================
29 | # 1. 定义远程 Agent - 专业翻译助手
30 | # ============================================================
31 |
32 | translator_agent = LlmAgent(
33 | name="translator",
34 | description="专业多语言翻译 Agent - 精通中、英、日、韩、法、德等多种语言的翻译服务",
35 | model="gemini-2.0-flash",
36 | instruction="""你是一位专业的多语言翻译专家。
37 |
38 | 你的能力:
39 | - 精通中文、英文、日文、韩文、法文、德文等主流语言
40 | - 能够准确理解原文的语境和文化背景
41 | - 翻译时保持原文的风格和语气
42 | - 可以处理技术文档、商务文件、文学作品等不同类型的内容
43 |
44 | 翻译原则:
45 | 1. 信:准确传达原文的意思
46 | 2. 达:翻译通顺流畅
47 | 3. 雅:保持文字的优美和得体
48 |
49 | 当用户提供文本时:
50 | - 首先识别源语言
51 | - 询问目标语言(如果用户没有指定)
52 | - 提供高质量的翻译结果
53 | - 必要时提供翻译说明或文化背景解释
54 |
55 | 示例:
56 | 用户:请把 "Hello, how are you?" 翻译成中文
57 | 回复:你好,你怎么样?/ 你好,最近好吗?(更口语化的表达)
58 | """,
59 | )
60 |
61 | # ============================================================
62 | # 2. 使用 to_a2a() 将 Agent 转换为 A2A 服务
63 | # ============================================================
64 |
65 | # 关键函数:to_a2a()
66 | # 这是 ADK 提供的便捷方法,只需一行代码即可将 Agent 转换为 A2A 兼容的服务
67 | # 它会自动:
68 | # - 创建 Agent Card(描述 Agent 能力的元数据)
69 | # - 设置 HTTP 端点
70 | # - 处理 A2A 协议的请求/响应转换
71 |
72 | app = to_a2a(
73 | agent=translator_agent,
74 | host="localhost",
75 | port=8001,
76 | protocol="http"
77 | )
78 |
79 | # ============================================================
80 | # 3. 启动服务
81 | # ============================================================
82 |
83 | if __name__ == "__main__":
84 | import uvicorn
85 |
86 | print("=" * 60)
87 | print("Day 14: A2A Remote Agent - 翻译服务")
88 | print("=" * 60)
89 | print()
90 | print("Agent 信息:")
91 | print(f" 名称: {translator_agent.name}")
92 | print(f" 描述: {translator_agent.description}")
93 | print()
94 | print("A2A 服务端点:")
95 | print(" URL: http://localhost:8001")
96 | print(" Agent Card: http://localhost:8001/.well-known/agent.json")
97 | print()
98 | print("提示: 在另一个终端运行 host_agent 来测试 A2A 通信")
99 | print("=" * 60)
100 | print()
101 |
102 | # 启动 uvicorn 服务器
103 | uvicorn.run(app, host="localhost", port=8001)
104 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-07/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 7: LLM 可以执行代码 - 自主问题解决
2 |
3 | > 探索 LLM 如何不仅能编写代码,还能自主执行、调试和优化代码,将其转变为强大的问题解决者。
4 |
5 | ## 今日要点
6 |
7 | Day 7 讲的是 **Code Execution(代码执行)** 功能 - 让 AI Agent 能够在安全的沙箱环境中运行代码,从而实现自主问题解决。
8 |
9 | ## 什么是 Code Execution?
10 |
11 | 传统 LLM 只能**生成**代码,但不能**运行**代码。Code Execution 改变了这一点:
12 |
13 | ```
14 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
15 | │ 没有 Code Execution │
16 | ├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
17 | │ │
18 | │ 用户: "计算 2024 年 1 月 1 日到今天有多少天?" │
19 | │ │
20 | │ AI: "让我算一下... 大约是 350 天左右" ← 可能算错! │
21 | │ │
22 | └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
23 |
24 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
25 | │ 有 Code Execution │
26 | ├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
27 | │ │
28 | │ 用户: "计算 2024 年 1 月 1 日到今天有多少天?" │
29 | │ │
30 | │ AI: [自动生成并执行 Python 代码] │
31 | │ ```python │
32 | │ from datetime import date │
33 | │ days = (date.today() - date(2024, 1, 1)).days │
34 | │ print(f"已经过了 {days} 天") │
35 | │ ``` │
36 | │ 输出: "已经过了 351 天" ← 精确计算! │
37 | │ │
38 | └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
39 | ```
40 |
41 | ## 核心优势
42 |
43 | | 优势 | 说明 |
44 | |------|------|
45 | | **精确计算** | 数学运算由代码执行,避免 LLM 的计算错误 |
46 | | **数据处理** | 可以处理 CSV、JSON 等数据文件 |
47 | | **动态验证** | 生成代码后立即验证是否正确 |
48 | | **迭代调试** | 如果出错,可以自动修复并重试 |
49 |
50 | ## 运行
51 |
52 | ```bash
53 | # 打开 Jupyter notebook 学习
54 | jupyter notebook day-07/code_execution.ipynb
55 | ```
56 |
57 | ## 资源
58 |
59 | - [Code Execution on Vertex AI Agent Engine](https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/docs/agent-engine/code-execution)
60 | - [Tutorial: Get Started with Code Execution](https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/generative-ai/blob/main/agents/agent_engine/tutorial_get_started_with_code_execution.ipynb)
61 | - [Retail AI Location Strategy (Case Study)](https://github.com/google/adk-samples/tree/main/python/agents/retail-ai-location-strategy)
62 | - [视频](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=QH9jK_RkbHc)
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/assets/difficulty_curve.svg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-14/run_demo.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python3
2 | """
3 | Day 14: A2A 协议演示 - 一键运行脚本
4 |
5 | 这个脚本会:
6 | 1. 启动远程 Agent (A2A Server) 在后台
7 | 2. 等待服务就绪
8 | 3. 运行 Host Agent (A2A Client) 进行测试
9 | 4. 清理并退出
10 |
11 | 运行方式:
12 | python run_demo.py
13 | """
14 |
15 | import asyncio
16 | import subprocess
17 | import sys
18 | import time
19 | import os
20 | import signal
21 |
22 | # 确保使用正确的 Python 环境
23 | PYTHON = sys.executable
24 | BASE_DIR = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
25 |
26 |
27 | async def check_server_ready(url: str, max_attempts: int = 30) -> bool:
28 | """检查服务器是否就绪"""
29 | import httpx
30 |
31 | for i in range(max_attempts):
32 | try:
33 | async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
34 | response = await client.get(f"{url}/.well-known/agent.json")
35 | if response.status_code == 200:
36 | print(f" ✅ 服务器就绪!")
37 | return True
38 | except Exception:
39 | pass
40 | print(f" 等待服务器启动... ({i + 1}/{max_attempts})")
41 | await asyncio.sleep(1)
42 | return False
43 |
44 |
45 | async def run_demo():
46 | """运行完整的 A2A 演示"""
47 | print("=" * 60)
48 | print("Day 14: A2A 协议演示")
49 | print("=" * 60)
50 | print()
51 |
52 | server_process = None
53 |
54 | try:
55 | # 步骤 1: 启动远程 Agent
56 | print("📡 步骤 1: 启动远程 Agent (A2A Server)...")
57 | print()
58 |
59 | server_process = subprocess.Popen(
60 | [PYTHON, "-m", "remote_agent.agent"],
61 | cwd=BASE_DIR,
62 | stdout=subprocess.PIPE,
63 | stderr=subprocess.STDOUT,
64 | text=True,
65 | )
66 |
67 | # 等待服务器就绪
68 | print(" 等待服务器启动...")
69 | if not await check_server_ready("http://localhost:8001"):
70 | print(" ❌ 服务器启动失败!")
71 | return
72 |
73 | print()
74 |
75 | # 步骤 2: 运行客户端测试
76 | print("🖥️ 步骤 2: 运行 Host Agent (A2A Client)...")
77 | print()
78 |
79 | # 导入并运行 host agent
80 | sys.path.insert(0, BASE_DIR)
81 | from host_agent.agent import main as host_main
82 | await host_main()
83 |
84 | except KeyboardInterrupt:
85 | print("\n\n⚠️ 用户中断...")
86 |
87 | except Exception as e:
88 | print(f"\n❌ 发生错误: {e}")
89 | import traceback
90 | traceback.print_exc()
91 |
92 | finally:
93 | # 清理
94 | print("\n🧹 清理资源...")
95 | if server_process:
96 | server_process.terminate()
97 | try:
98 | server_process.wait(timeout=5)
99 | except subprocess.TimeoutExpired:
100 | server_process.kill()
101 | print(" 远程 Agent 已停止")
102 |
103 | print()
104 | print("=" * 60)
105 | print("演示结束!")
106 | print("=" * 60)
107 |
108 |
109 | if __name__ == "__main__":
110 | # 检查依赖
111 | try:
112 | import httpx
113 | except ImportError:
114 | print("正在安装 httpx...")
115 | subprocess.run([PYTHON, "-m", "pip", "install", "httpx"], check=True)
116 |
117 | asyncio.run(run_demo())
118 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 25-Day AI Agents Course by Google
2 |
3 | A hands-on learning journey through Google's AI Agents capabilities.
4 |
5 | > **Official Course**: [Advent of Agents 2025](https://adventofagents.com/) - 25 days of Zero to Production-Ready AI Agents on Google Cloud
6 |
7 | ## About This Course
8 |
9 | This is Google Cloud's **Advent of Agents 2025** program - a 25-day journey to master AI Agents using:
10 | - **Gemini 3** - Google's latest AI models
11 | - **Agent Development Kit (ADK)** - Comprehensive agent development platform
12 | - **Agent Engine** - Production deployment infrastructure
13 |
14 | ### Course Highlights
15 | - 🎯 One feature per day, each taking less than 5 minutes to try
16 | - 📋 Copy-paste commands that work out of the box
17 | - 📚 Links to official documentation
18 | - 🆓 100% free
19 |
20 | > 📖 **Prerequisite**: [5-Day AI Agents Intensive Course](https://github.com/anxiong2025/5-Day-AI-Agents-Intensive-Course-with-Google) - Google's foundational course on AI Agents
21 |
22 | ### Difficulty Curve
23 |
24 |
25 |  26 |
26 |
27 |
28 | ## Setup
29 |
30 | ### Prerequisites
31 |
32 | - Python 3.11+
33 | - [uv](https://github.com/astral-sh/uv) package manager
34 |
35 | ### Installation
36 |
37 | ```bash
38 | # Install dependencies
39 | uv sync
40 |
41 | # Create .env file and add your API key
42 | cp .env.example .env
43 | # Edit .env and add your GOOGLE_API_KEY
44 | ```
45 |
46 | ## Project Structure
47 |
48 | ```
49 | .
50 | ├── day-01/ # Day 1: Introduction
51 | ├── day-02/ # Day 2: ...
52 | ├── ...
53 | ├── shared/ # Shared utilities
54 | │ ├── __init__.py
55 | │ └── config.py # Configuration helpers
56 | ├── pyproject.toml # Project dependencies
57 | └── README.md
58 | ```
59 |
60 | ## Daily Progress
61 |
62 | | Day | Topic | Status |
63 | |-----|-------|--------|
64 | | 01 | Introduction to AI Agents | ✅ Done |
65 | | 02 | YAML Agent Configuration | ✅ Done |
66 | | 03 | Gemini Search Agent | ✅ Done |
67 | | 04 | Agent Engine Deployment | ✅ Done |
68 | | 05 | Telemetry & Tracing | ✅ Done |
69 | | 06 | ADK IDE Integration | ✅ Done |
70 | | 07 | Code Execution | ✅ Done |
71 | | 08 | Context Management | ✅ Done |
72 | | 09 | Session Rewind | ✅ Done |
73 | | 10 | Context Caching & Compaction | ✅ Done |
74 | | 11 | Google Managed MCP | ✅ Done |
75 | | 12 | Multimodal Streaming Agents | ✅ Done |
76 | | 13 | Interactions API | ✅ Done |
77 | | 14 | A2A Remote Agents | ✅ Done |
78 | | 15 | Agent-to-UI | ✅ Done |
79 | | 16 | LangGraph + A2A | ✅ Done |
80 | | 17 | Gemini 3 Flash Thinking Levels | ✅ Done |
81 | | 18 | Cloud API Registry + ADK | ✅ Done |
82 | | 19-25 | Enterprise Topics | ⏳ Pending |
83 |
84 | ## Running Daily Exercises
85 |
86 | ```bash
87 | # Run day 1 exercises
88 | uv run python day-01/main.py
89 |
90 | # Run with dev dependencies (for testing)
91 | uv sync --dev
92 | uv run pytest
93 | ```
94 |
95 | ## Resources
96 |
97 | - [Advent of Agents 2025](https://adventofagents.com/) - Official course website
98 | - [Google AI Studio](https://aistudio.google.com/)
99 | - [Gemini API Documentation](https://ai.google.dev/docs)
100 | - [Agent Development Kit (ADK)](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/)
101 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-18/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 18: Cloud API Registry + ADK
2 |
3 | ## 一句话理解
4 |
5 | **Cloud API Registry = 企业级工具商店**
6 |
7 | 以前:每个开发者自己找 API、配置权限、管理工具
8 | 现在:公司统一管理,开发者直接"领取"已审批的工具
9 |
10 | ## 核心概念
11 |
12 | ### 问题:企业开发 Agent 最大的痛点是什么?
13 |
14 | 不是模型,是**工具管理**:
15 | - 哪些 API 可以用?
16 | - 谁有权限用?
17 | - 怎么保证安全合规?
18 |
19 | ### 解决方案:Cloud API Registry
20 |
21 | ```
22 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
23 | │ Cloud API Registry │
24 | │ (企业工具仓库 - 管理员统一管理) │
25 | ├─────────────────────────────────────────┤
26 | │ BigQuery Tool ✅ 已审批 │
27 | │ Cloud Storage ✅ 已审批 │
28 | │ Gmail API ❌ 未授权 │
29 | │ 自定义内部API ✅ 已审批 │
30 | └─────────────────────────────────────────┘
31 | │
32 | ▼
33 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────┐
34 | │ 开发者的 Agent │
35 | │ registry.get_tool("bigquery") │
36 | │ → 直接获取已配置好的工具 │
37 | └─────────────────────────────────────────┘
38 | ```
39 |
40 | ## 两个角色
41 |
42 | | 角色 | 职责 |
43 | |------|------|
44 | | **管理员** | 在 Cloud Console 审批/管理可用工具 |
45 | | **开发者** | 用 `ApiRegistry` 获取已审批的工具 |
46 |
47 | ## 使用步骤
48 |
49 | ### 步骤 1:管理员启用 MCP 服务
50 |
51 | ```bash
52 | # 启用 BigQuery 的 MCP 服务
53 | gcloud beta services mcp enable bigquery.googleapis.com \
54 | --project=YOUR_PROJECT_ID
55 | ```
56 |
57 | ### 步骤 2:开发者使用工具
58 |
59 | ```python
60 | from google.adk import Agent
61 | from google.adk.tools.google_cloud import ApiRegistry
62 |
63 | # 1. 连接到企业的工具仓库
64 | registry = ApiRegistry(project_id="your-project-id")
65 |
66 | # 2. 获取已审批的工具
67 | bq_tool = registry.get_tool("google-bigquery")
68 |
69 | # 3. 给 Agent 装上这个工具
70 | agent = Agent(
71 | model="gemini-3-pro",
72 | tools=[bq_tool]
73 | )
74 | ```
75 |
76 | 就这么简单!不用自己配置 API 密钥、权限等。
77 |
78 | ## 支持的 Google Cloud 工具
79 |
80 | | 工具 | 用途 |
81 | |------|------|
82 | | `google-bigquery` | 数据仓库查询 |
83 | | `google-cloud-storage` | 文件存储 |
84 | | `google-spanner` | 分布式数据库 |
85 | | `google-youtube` | YouTube 数据 |
86 | | 更多... | 持续增加中 |
87 |
88 | ## 核心优势
89 |
90 | ### 1. 统一发现
91 | 所有可用工具在一个地方,不用到处找文档
92 |
93 | ### 2. 集中治理
94 | 管理员控制谁能用什么工具,保证合规
95 |
96 | ### 3. 简化集成
97 | 开发者不用关心底层配置,拿来就用
98 |
99 | ## 与普通方式对比
100 |
101 | ### 以前(手动配置)
102 | ```python
103 | # 需要自己处理认证、配置
104 | from google.cloud import bigquery
105 | client = bigquery.Client(project="xxx", credentials=xxx)
106 | # 还要自己封装成 Agent 工具...
107 | ```
108 |
109 | ### 现在(API Registry)
110 | ```python
111 | # 一行搞定
112 | bq_tool = registry.get_tool("google-bigquery")
113 | ```
114 |
115 | ## 适用场景
116 |
117 | - 企业级 Agent 开发
118 | - 需要统一管理 API 权限
119 | - 多团队协作开发
120 | - 合规性要求高的项目
121 |
122 | ## 前置要求
123 |
124 | 1. Google Cloud 项目
125 | 2. 启用 Cloud API Registry
126 | 3. 配置好 `gcloud` CLI 认证
127 |
128 | ## 参考资料
129 |
130 | - [Cloud API Registry 文档](https://docs.cloud.google.com/api-registry/docs/overview)
131 | - [ADK Cloud API Registry 指南](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/tools/google-cloud/api-registry/)
132 | - [Tool Governance 博客](https://cloud.google.com/blog/products/ai-machine-learning/new-enhanced-tool-governance-in-vertex-ai-agent-builder)
133 | - [官方教程 Notebook](https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/generative-ai/blob/main/agents/agent_engine/tutorial_get_started_with_cloud_api_registry.ipynb)
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-02/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 02: Hello World with YAML
2 |
3 | Build your first AI agent with Gemini 3 in under 5 minutes without writing a single line of code.
4 |
5 | ## Learning Goals
6 |
7 | - Understand ADK Agent Config (YAML-based agents)
8 | - Create a simple agent using YAML configuration
9 | - Use built-in tools like Google Search
10 | - Run and test your agent with `adk web`
11 |
12 | ## Prerequisites
13 |
14 | ```bash
15 | pip install google-adk
16 | ```
17 |
18 | ## Quick Start
19 |
20 | ### 1. Create a YAML-based Agent
21 |
22 | Use the ADK CLI to create a config-based agent:
23 |
24 | ```bash
25 | adk create my_agent --type=config
26 | ```
27 |
28 | This generates:
29 | - `my_agent/root_agent.yaml` - Agent configuration
30 | - `my_agent/.env` - Environment variables
31 |
32 | ### 2. Basic YAML Structure
33 |
34 | ```yaml
35 | name: assistant_agent
36 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
37 | description: A helper agent that can answer users' questions.
38 | instruction: You are an agent to help answer users' various questions.
39 | ```
40 |
41 | ### 3. Run Your Agent
42 |
43 | ```bash
44 | cd day-02
45 | adk web
46 | ```
47 |
48 | Open the browser and select your agent from the dropdown.
49 |
50 | ## YAML Configuration Options
51 |
52 | | Field | Description |
53 | |-------|-------------|
54 | | `name` | Agent identifier |
55 | | `model` | Gemini model to use (e.g., `gemini-2.5-flash`) |
56 | | `description` | Brief description of the agent |
57 | | `instruction` | System prompt / behavior instructions |
58 | | `tools` | List of tools the agent can use |
59 |
60 | ## Built-in Tools
61 |
62 | ADK supports these built-in tools:
63 |
64 | - `google_search` - Search the web for information
65 | - `code_execution` - Execute Python code
66 | - `vertex_ai_search` - Search using Vertex AI
67 |
68 | ## Example: Agent with Google Search
69 |
70 | See [root_agent.yaml](root_agent.yaml) for a working example.
71 |
72 | ```yaml
73 | name: search_agent
74 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
75 | description: A helpful assistant that can search the web.
76 | instruction: |
77 | You are a helpful assistant.
78 | Use Google Search for current events and factual information.
79 | tools:
80 | - google_search
81 | ```
82 |
83 | ## Advanced: Mixing Python with YAML
84 |
85 | You can add custom Python tools to your YAML agent:
86 |
87 | 1. Create `tools.py` in your agent folder:
88 |
89 | ```python
90 | def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
91 | """Get weather for a city."""
92 | return f"The weather in {city} is sunny."
93 | ```
94 |
95 | 2. Reference it in `root_agent.yaml`:
96 |
97 | ```yaml
98 | tools:
99 | - google_search
100 | - tools.get_weather
101 | ```
102 |
103 | ## Advanced: MCP Server Integration
104 |
105 | Connect to an MCP server for additional tools:
106 |
107 | ```yaml
108 | tools:
109 | - type: MCPToolset
110 | stdio_server_params:
111 | command: uvx
112 | args:
113 | - mcp-server-time
114 | ```
115 |
116 | ## Limitations
117 |
118 | - Currently only supports Gemini models
119 | - Some advanced features require Python code
120 | - Experimental feature - API may change
121 |
122 | ## Resources
123 |
124 | - [ADK Agent Config Documentation](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/agents/config/)
125 | - [2-Minute ADK: YAML Tutorial](https://medium.com/google-cloud/2-minute-adk-build-agents-the-easy-way-yaml-a55678d64a75)
126 | - [Third Party MCP Tools in ADK](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/tools/third-party/)
127 | - [ADK Samples Repository](https://github.com/google/adk-samples)
128 |
129 | ## Notes
130 |
131 | Day 2 introduces the no-code approach to building agents using YAML configuration. This is the fastest way to prototype AI agents with Google ADK.
132 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-04/deploy.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 | # Day 04: Source-Based Deployment Script
3 | # Deploy ADK agent to Vertex AI Agent Engine
4 |
5 | set -e
6 |
7 | # Configuration - Update these values
8 | export GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT="${GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT:-your-project-id}"
9 | export GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION="${GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION:-us-central1}"
10 | export STAGING_BUCKET="${STAGING_BUCKET:-gs://your-staging-bucket}"
11 | export AGENT_NAME="deployed_assistant"
12 |
13 | echo "=========================================="
14 | echo "Day 04: Source-Based Deployment"
15 | echo "=========================================="
16 | echo "Project: $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT"
17 | echo "Region: $GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION"
18 | echo "Bucket: $STAGING_BUCKET"
19 | echo "Agent: $AGENT_NAME"
20 | echo "=========================================="
21 |
22 | # Check prerequisites
23 | check_prerequisites() {
24 | echo "Checking prerequisites..."
25 |
26 | # Check gcloud
27 | if ! command -v gcloud &> /dev/null; then
28 | echo "Error: gcloud CLI not found. Install from https://cloud.google.com/sdk/docs/install"
29 | exit 1
30 | fi
31 |
32 | # Check uv
33 | if ! command -v uv &> /dev/null; then
34 | echo "Error: uv not found. Install with: curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh"
35 | exit 1
36 | fi
37 |
38 | # Check adk
39 | if ! command -v adk &> /dev/null; then
40 | echo "Installing google-adk..."
41 | pip install google-adk
42 | fi
43 |
44 | echo "All prerequisites met!"
45 | }
46 |
47 | # Authenticate with Google Cloud
48 | authenticate() {
49 | echo "Authenticating with Google Cloud..."
50 | gcloud auth login
51 | gcloud config set project $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT
52 | gcloud auth application-default login
53 | }
54 |
55 | # Create staging bucket if needed
56 | create_bucket() {
57 | BUCKET_NAME=$(echo $STAGING_BUCKET | sed 's|gs://||')
58 | if ! gsutil ls $STAGING_BUCKET &> /dev/null; then
59 | echo "Creating staging bucket: $STAGING_BUCKET"
60 | gsutil mb -l $GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION $STAGING_BUCKET
61 | else
62 | echo "Staging bucket exists: $STAGING_BUCKET"
63 | fi
64 | }
65 |
66 | # Option 1: Deploy with ADK CLI
67 | deploy_with_adk() {
68 | echo "Deploying with ADK CLI..."
69 | adk deploy agent_engine \
70 | --project $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \
71 | --region $GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION \
72 | --staging_bucket $STAGING_BUCKET \
73 | --trace_to_cloud \
74 | --display_name "$AGENT_NAME" \
75 | --description "Day 04 deployed assistant" \
76 | agent
77 | }
78 |
79 | # Option 2: Enhance existing project with Agent Starter Pack
80 | enhance_project() {
81 | echo "Enhancing project with Agent Starter Pack..."
82 | cd ..
83 | uvx agent-starter-pack enhance --adk -d agent_engine
84 | cd day-04
85 | }
86 |
87 | # Option 3: Create new project with Agent Starter Pack
88 | create_new_project() {
89 | echo "Creating new project with Agent Starter Pack..."
90 | uvx agent-starter-pack create $AGENT_NAME -a adk_base -d agent_engine
91 | }
92 |
93 | # Test locally before deployment
94 | test_locally() {
95 | echo "Testing agent locally..."
96 | cd agent
97 | adk web
98 | }
99 |
100 | # Main menu
101 | main() {
102 | echo ""
103 | echo "Choose an action:"
104 | echo "1) Check prerequisites"
105 | echo "2) Authenticate with Google Cloud"
106 | echo "3) Test agent locally"
107 | echo "4) Deploy with ADK CLI"
108 | echo "5) Enhance project with Agent Starter Pack"
109 | echo "6) Create new project with Agent Starter Pack"
110 | echo "q) Quit"
111 | echo ""
112 | read -p "Enter choice: " choice
113 |
114 | case $choice in
115 | 1) check_prerequisites ;;
116 | 2) authenticate ;;
117 | 3) test_locally ;;
118 | 4)
119 | check_prerequisites
120 | create_bucket
121 | deploy_with_adk
122 | ;;
123 | 5) enhance_project ;;
124 | 6) create_new_project ;;
125 | q) exit 0 ;;
126 | *) echo "Invalid choice" ;;
127 | esac
128 | }
129 |
130 | # Run main menu
131 | main
132 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-09/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env python3
2 | """
3 | Day 9: Undo Buttons for your Agents - Session Rewind 演示
4 |
5 | 这个示例展示了 ADK 的 Session Rewind(会话回溯)功能:
6 | 1. 创建会话并设置初始状态
7 | 2. 修改状态
8 | 3. 使用 rewind 回溯到之前的状态
9 | 4. 验证状态已恢复
10 |
11 | 这个功能可以用来实现:
12 | - "编辑消息" 功能
13 | - "重新生成" 功能
14 | - 任何需要撤销的场景
15 | """
16 |
17 | import asyncio
18 |
19 | import agent
20 | from google.adk.agents.run_config import RunConfig
21 | from google.adk.events.event import Event
22 | from google.adk.runners import InMemoryRunner
23 | from google.genai import types
24 |
25 | APP_NAME = "rewind_demo"
26 | USER_ID = "demo_user"
27 |
28 |
29 | async def call_agent(
30 | runner: InMemoryRunner, user_id: str, session_id: str, prompt: str
31 | ) -> list[Event]:
32 | """调用 Agent 并返回事件列表"""
33 | print(f"\n👤 用户: {prompt}")
34 | content = types.Content(
35 | role="user", parts=[types.Part.from_text(text=prompt)]
36 | )
37 | events = []
38 | async for event in runner.run_async(
39 | user_id=user_id,
40 | session_id=session_id,
41 | new_message=content,
42 | run_config=RunConfig(),
43 | ):
44 | events.append(event)
45 | if event.content and event.author and event.author != "user":
46 | for part in event.content.parts:
47 | if part.text:
48 | print(f" 🤖 Agent: {part.text}")
49 | elif part.function_call:
50 | print(f" 🛠️ 工具调用: {part.function_call.name}")
51 | elif part.function_response:
52 | print(f" 📦 工具响应: {part.function_response.response}")
53 | return events
54 |
55 |
56 | async def main():
57 | """演示 Session Rewind 功能"""
58 | print("=" * 60)
59 | print("🎯 Day 9: Session Rewind (会话回溯) 功能演示")
60 | print("=" * 60)
61 |
62 | # 创建 Runner
63 | runner = InMemoryRunner(
64 | agent=agent.root_agent,
65 | app_name=APP_NAME,
66 | )
67 |
68 | # 创建会话
69 | session = await runner.session_service.create_session(
70 | app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID
71 | )
72 | print(f"\n📝 创建会话: {session.id}")
73 |
74 | # ===== 步骤 1: 初始化状态 =====
75 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
76 | print("步骤 1: 初始化状态")
77 | print("=" * 60)
78 | await call_agent(runner, USER_ID, session.id, "设置状态 color 为 red")
79 | await call_agent(runner, USER_ID, session.id, "保存文件 note.txt 内容为 version1")
80 |
81 | # ===== 步骤 2: 检查当前状态 =====
82 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
83 | print("步骤 2: 检查当前状态")
84 | print("=" * 60)
85 | await call_agent(runner, USER_ID, session.id, "查询状态 color 的值")
86 | await call_agent(runner, USER_ID, session.id, "读取文件 note.txt")
87 |
88 | # ===== 步骤 3: 修改状态 (这是我们要回溯的点) =====
89 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
90 | print("步骤 3: 修改状态 (⚠️ 这是回溯点)")
91 | print("=" * 60)
92 | events_update = await call_agent(
93 | runner, USER_ID, session.id, "更新状态 color 为 blue"
94 | )
95 | rewind_invocation_id = events_update[0].invocation_id
96 | print(f"\n📌 记录回溯点 invocation_id: {rewind_invocation_id}")
97 |
98 | await call_agent(runner, USER_ID, session.id, "保存文件 note.txt 内容为 version2")
99 |
100 | # ===== 步骤 4: 检查修改后的状态 =====
101 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
102 | print("步骤 4: 检查修改后的状态")
103 | print("=" * 60)
104 | await call_agent(runner, USER_ID, session.id, "查询状态 color 的值")
105 | await call_agent(runner, USER_ID, session.id, "读取文件 note.txt")
106 |
107 | # ===== 步骤 5: 执行回溯 =====
108 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
109 | print("步骤 5: ⏪ 执行 REWIND 回溯")
110 | print("=" * 60)
111 | print(f"回溯到 invocation_id: {rewind_invocation_id} 之前...")
112 | await runner.rewind_async(
113 | user_id=USER_ID,
114 | session_id=session.id,
115 | rewind_before_invocation_id=rewind_invocation_id,
116 | )
117 | print("✅ 回溯完成!")
118 |
119 | # ===== 步骤 6: 验证回溯后的状态 =====
120 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
121 | print("步骤 6: 验证回溯后的状态")
122 | print("=" * 60)
123 | await call_agent(runner, USER_ID, session.id, "查询状态 color 的值")
124 | await call_agent(runner, USER_ID, session.id, "读取文件 note.txt")
125 |
126 | # ===== 总结 =====
127 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
128 | print("✨ 演示完成!")
129 | print("=" * 60)
130 | print("""
131 | 🔑 核心要点:
132 | 1. 使用 runner.rewind_async() 可以回溯会话状态
133 | 2. 需要指定 rewind_before_invocation_id 来确定回溯点
134 | 3. 回溯会恢复状态(state)和文件(artifacts)
135 | 4. 这个功能可以用来实现"撤销"、"编辑消息"、"重新生成"等功能
136 |
137 | 📚 文档链接:
138 | - ADK Session Rewind: https://google.github.io/adk-docs/sessions/rewind/
139 | - ADK Runtime Resume: https://google.github.io/adk-docs/runtime/resume/
140 | """)
141 |
142 |
143 | if __name__ == "__main__":
144 | asyncio.run(main())
145 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-15/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 15: A2UI - Agent 生成动态界面
2 |
3 | ## 从一个糟糕的体验说起
4 |
5 | 你开发了一个餐厅推荐 Agent。用户问:"帮我找一家附近的西餐厅"
6 |
7 | Agent 回复:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | 我找到了以下餐厅:
11 | 1. 意大利花园 - 人均 ¥180 - 评分 4.8 - 距离 500m
12 | 2. 牛排工坊 - 人均 ¥280 - 评分 4.5 - 距离 800m
13 | ...
14 | 请告诉我您想选择哪家...
15 | ```
16 |
17 | 用户需要从文字中"脑补"出列表,手动输入选择。
18 |
19 | ## 如果 Agent 能生成 UI 呢?
20 |
21 | ```
22 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
23 | │ 🍽️ 附近的西餐厅 │
24 | ├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
25 | │ 🍕 意大利花园 ¥180 ★4.8 500m [查看] [预订] │
26 | │ 🥩 牛排工坊 ¥280 ★4.5 800m [查看] [预订] │
27 | └─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
28 | ```
29 |
30 | 用户直接点击、筛选、预订。这就是 **A2UI** 要解决的问题。
31 |
32 | ## A2UI 是什么?
33 |
34 | A2UI (Agent-to-User Interface) 是 Google 推出的声明式 UI 协议:
35 |
36 | - **Agent 不生成代码**,只描述"想要什么界面"
37 | - **客户端渲染器** 用预定义的安全组件渲染
38 | - **跨平台**:同一份 JSON 可渲染到 Web、iOS、Android
39 |
40 | ## 快速开始
41 |
42 | ### 1. 进入目录
43 |
44 | ```bash
45 | cd day-15
46 | ```
47 |
48 | ### 2. 启动服务器
49 |
50 | ```bash
51 | uv run python server.py
52 | ```
53 |
54 | 看到以下输出表示启动成功:
55 |
56 | ```
57 | ============================================================
58 | Day 15: A2UI Demo Server
59 | ============================================================
60 |
61 | 🌐 访问: http://localhost:8002
62 |
63 | 功能:
64 | - 输入自然语言描述,生成动态 UI
65 | - 实时渲染 A2UI 组件
66 | - 查看生成的 JSON 结构
67 |
68 | ============================================================
69 | INFO: Uvicorn running on http://localhost:8002
70 | ```
71 |
72 | ### 3. 打开浏览器
73 |
74 | 访问 http://localhost:8002
75 |
76 | ### 4. 试试这些功能
77 |
78 | - 点击快捷按钮:**登录表单**、**餐厅推荐**、**天气卡片**
79 | - 或输入自定义描述:"创建一个用户注册表单"
80 | - 查看右侧生成的 A2UI JSON 结构
81 | - 点击按钮,观察右下角事件日志
82 |
83 | ## 项目结构
84 |
85 | ```
86 | day-15/
87 | ├── README.md # 本文件
88 | ├── a2ui.py # A2UI Python SDK
89 | ├── server.py # Web 服务器 + JS 渲染器
90 | └── day-15-a2ui.ipynb # Jupyter 教程(可选)
91 | ```
92 |
93 | ## 代码示例
94 |
95 | ### 使用 Python SDK
96 |
97 | ```python
98 | from a2ui import A2UI
99 |
100 | # 链式 API 构建界面
101 | ui = (A2UI("login")
102 | .text("title", "用户登录", "h1")
103 | .text_field("username", "/user/name", "用户名")
104 | .text_field("password", "/user/password", "密码")
105 | .button("submit", "登录", "submit_login")
106 | .column("form", ["title", "username", "password", "submit"])
107 | .card("card", "form"))
108 |
109 | # 生成 A2UI JSONL
110 | print(ui.build("card"))
111 | ```
112 |
113 | 输出:
114 |
115 | ```jsonl
116 | {"surfaceUpdate": {"surfaceId": "login", "components": [...]}}
117 | {"beginRendering": {"surfaceId": "login", "root": "card"}}
118 | ```
119 |
120 | ### 使用工厂函数
121 |
122 | ```python
123 | from a2ui import create_restaurant_list, create_weather_card
124 |
125 | # 餐厅列表
126 | restaurants = [
127 | {"name": "意大利花园", "price": 180, "rating": 4.8, "distance": "500m"},
128 | {"name": "牛排工坊", "price": 280, "rating": 4.5, "distance": "800m"},
129 | ]
130 | ui = create_restaurant_list(restaurants)
131 | print(ui.build("main"))
132 |
133 | # 天气卡片
134 | ui = create_weather_card("北京", 25, "晴天", 45)
135 | print(ui.build("card"))
136 | ```
137 |
138 | ### 直接运行测试
139 |
140 | ```bash
141 | uv run python a2ui.py
142 | ```
143 |
144 | ## A2UI 核心概念
145 |
146 | ### 三种消息类型
147 |
148 | | 消息 | 作用 |
149 | |------|------|
150 | | `surfaceUpdate` | 定义 UI 组件及属性 |
151 | | `dataModelUpdate` | 设置数据模型(可选) |
152 | | `beginRendering` | 开始渲染,指定根组件 |
153 |
154 | ### 支持的组件
155 |
156 | | 组件 | 用途 | 示例 |
157 | |------|------|------|
158 | | Text | 文本显示 | 标题、段落 |
159 | | Button | 按钮 | 提交、取消 |
160 | | TextField | 输入框 | 用户名、密码 |
161 | | Column | 垂直布局 | 表单排列 |
162 | | Row | 水平布局 | 按钮组 |
163 | | Card | 卡片容器 | 内容分组 |
164 | | Image | 图片 | 头像、封面 |
165 | | Divider | 分隔线 | 内容分隔 |
166 | | Checkbox | 复选框 | 勾选选项 |
167 |
168 | ### 架构图
169 |
170 | ```
171 | 用户输入 "登录表单"
172 | │
173 | ▼
174 | ┌──────────────┐
175 | │ Gemini │ 理解意图,生成 A2UI JSON
176 | └──────┬───────┘
177 | │
178 | ▼
179 | ┌──────────────┐
180 | │ Python SDK │ a2ui.py 构建组件
181 | └──────┬───────┘
182 | │
183 | ▼
184 | ┌──────────────┐
185 | │ FastAPI │ server.py 提供 API
186 | └──────┬───────┘
187 | │ HTTP
188 | ▼
189 | ┌──────────────┐
190 | │ JS Renderer │ 浏览器渲染真实 UI
191 | └──────────────┘
192 | ```
193 |
194 | ## 与 Gemini 集成
195 |
196 | 服务器会自动检测 `GOOGLE_API_KEY` 环境变量:
197 |
198 | - **有 API Key**:使用 Gemini 动态生成 UI
199 | - **无 API Key**:使用预定义模板(仍可正常演示)
200 |
201 | 设置 API Key:
202 |
203 | ```bash
204 | # 在项目根目录 .env 文件中
205 | GOOGLE_API_KEY=your_api_key_here
206 | ```
207 |
208 | ## 与 Day 14 A2A 的关系
209 |
210 | | Day 14 A2A | Day 15 A2UI |
211 | |------------|-------------|
212 | | Agent 之间如何通信 | Agent 如何向用户展示界面 |
213 | | 协议层 | 表现层 |
214 |
215 | A2UI 消息可以通过 A2A 协议传输,实现多 Agent 协作生成 UI。
216 |
217 | ## 常见问题
218 |
219 | ### Q: 端口 8002 被占用?
220 |
221 | 修改 `server.py` 最后一行的端口号:
222 |
223 | ```python
224 | uvicorn.run(app, host="localhost", port=8003) # 改成其他端口
225 | ```
226 |
227 | ### Q: 提示 ModuleNotFoundError?
228 |
229 | 确保在项目根目录安装了依赖:
230 |
231 | ```bash
232 | cd .. # 回到项目根目录
233 | uv sync
234 | ```
235 |
236 | ### Q: Gemini 生成的 UI 不符合预期?
237 |
238 | 这是正常的,LLM 生成有随机性。可以:
239 | 1. 重新生成
240 | 2. 调整 prompt 描述更具体
241 | 3. 直接使用快捷按钮(使用预定义模板)
242 |
243 | ## 扩展阅读
244 |
245 | - [A2UI 官网](https://a2ui.org/)
246 | - [A2UI GitHub](https://github.com/google/A2UI)
247 | - [A2UI Composer](https://a2ui-editor.ag-ui.com/) - 在线可视化编辑器
248 | - [CopilotKit A2UI 集成](https://www.copilotkit.ai/blog/how-to-build-agent-to-user-interface-a2ui-agents-using-a2a-ag-ui)
249 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-03/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 03: Gemini 3 + ADK
2 |
3 | Build a powerful AI Agent using Gemini 3 and ADK with native support for Google Search grounding, computer use, and real-time streaming.
4 |
5 | ## Learning Goals
6 |
7 | - Use Google Search tool for real-time information grounding
8 | - Understand Gemini 3's native tool capabilities
9 | - Build agents that can access current information
10 | - Learn about search result display requirements
11 |
12 | ## Prerequisites
13 |
14 | ```bash
15 | pip install google-adk
16 | ```
17 |
18 | ## Quick Start
19 |
20 | ### 1. Create Agent with Google Search
21 |
22 | ```yaml
23 | # root_agent.yaml
24 | name: search_agent
25 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
26 | description: An assistant with Google Search capability.
27 | instruction: |
28 | You are a helpful assistant that can search the web.
29 | Use Google Search for current events and factual information.
30 | tools:
31 | - name: google_search
32 | ```
33 |
34 | ### 2. Run Your Agent
35 |
36 | ```bash
37 | cd day-03
38 | adk web
39 | ```
40 |
41 | ## Google Search Tool
42 |
43 | ### Overview
44 |
45 | The `google_search` tool enables agents to perform web searches using Google Search. This provides **grounding** - the ability to access real-time information beyond the model's training data.
46 |
47 | ### Key Features
48 |
49 | | Feature | Description |
50 | |---------|-------------|
51 | | **Real-time data** | Access current news, prices, events |
52 | | **Grounding** | Reduce hallucinations with factual sources |
53 | | **Citations** | Responses include source URLs |
54 | | **Gemini 2+ only** | Requires Gemini 2 or later models |
55 |
56 | ### Python Configuration
57 |
58 | ```python
59 | from google.adk.agents import Agent
60 | from google.adk.tools import google_search
61 |
62 | agent = Agent(
63 | name="search_assistant",
64 | model="gemini-2.5-flash",
65 | instruction="You are a helpful assistant. Use Google Search when needed.",
66 | tools=[google_search]
67 | )
68 | ```
69 |
70 | ### YAML Configuration
71 |
72 | ```yaml
73 | name: search_assistant
74 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
75 | description: An assistant that can search the web.
76 | instruction: |
77 | You are a helpful assistant.
78 | Use Google Search for current events and factual information.
79 | tools:
80 | - name: google_search
81 | ```
82 |
83 | ## Important Limitations
84 |
85 | ### Tool Mixing Rules
86 |
87 | 1. **Built-in tools** (like `google_search`) only work with Gemini models
88 | 2. **Cannot mix** built-in tools with custom Python tools in the same agent
89 | 3. **One built-in tool** per agent (use sub-agents for multiple)
90 |
91 | ### Display Requirements
92 |
93 | When using Google Search grounding in production:
94 | - You must display search suggestions returned in the response
95 | - The UI code (HTML) is in `renderedContent` field
96 | - Follow Google's display policies
97 |
98 | ## Multi-Agent Pattern
99 |
100 | For agents that need both Google Search and custom tools:
101 |
102 | ```yaml
103 | # root_agent.yaml - Coordinator
104 | name: coordinator
105 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
106 | description: Coordinates between search and tools.
107 | instruction: |
108 | Use the search_agent for current information.
109 | Use the calculator_agent for calculations.
110 |
111 | sub_agents:
112 | - name: search_agent
113 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
114 | description: Searches the web.
115 | instruction: Use Google Search to find information.
116 | tools:
117 | - name: google_search
118 |
119 | - name: calculator_agent
120 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
121 | description: Performs calculations.
122 | instruction: Help with math calculations.
123 | tools:
124 | - tools.calculate
125 | ```
126 |
127 | ## Example: News Agent
128 |
129 | ```yaml
130 | name: news_agent
131 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
132 | description: A news assistant that provides current information.
133 | instruction: |
134 | You are a news assistant.
135 |
136 | When users ask about:
137 | - Current events: Use Google Search
138 | - Weather: Use Google Search
139 | - Stock prices: Use Google Search
140 | - Sports scores: Use Google Search
141 |
142 | Always cite your sources and provide links when available.
143 | Present information in a clear, organized format.
144 | tools:
145 | - name: google_search
146 | ```
147 |
148 | ## Resources
149 |
150 | ### Official Documentation
151 | - [ADK Built-in Tools](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/tools/built-in-tools/)
152 | - [Grounding with Google Search](https://ai.google.dev/gemini-api/docs/grounding)
153 | - [ADK Python Repository](https://github.com/google/adk-python)
154 |
155 | ### Tutorials
156 | - [Build an AI Agent with Gemini 3 (Video)](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=9EGtawwvINs&list=PLOU2XLYxmsIJCVXV1bLV7qnT5hilN3YJ7&index=4&t=1s)
157 | - [Gemini 3 Agent Demo (GitHub)](https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/devrel-demos/tree/main/ai-ml/agent-labs/gemini-3-pro-agent-demo)
158 | - [Google Codelabs: Empowering with Tools](https://codelabs.developers.google.com/devsite/codelabs/build-agents-with-adk-empowering-with-tools)
159 |
160 | ### Announcements
161 | - [Gemini 3 Announcement](https://blog.google/products/gemini-3/#gemini-3)
162 | - [Agent Development Kit Blog](https://developers.googleblog.com/en/agent-development-kit-easy-to-build-multi-agent-applications/)
163 |
164 | ## Notes
165 |
166 | Day 3 introduces the Google Search tool, enabling your agents to access real-time information. This is essential for building agents that can answer questions about current events, prices, weather, and other time-sensitive data.
167 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-18/api_registry_demo.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 18: Cloud API Registry + ADK 演示
3 |
4 | 前置要求:
5 | 1. 配置 Google Cloud 项目
6 | 2. 启用 API Registry 和相关服务
7 | 3. 运行: gcloud auth application-default login
8 |
9 | 运行:
10 | python api_registry_demo.py
11 | """
12 |
13 | import os
14 |
15 | # =============================================================================
16 | # 配置
17 | # =============================================================================
18 |
19 | # 从环境变量获取项目 ID,或手动设置
20 | PROJECT_ID = os.getenv("GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT", "your-project-id")
21 |
22 |
23 | # =============================================================================
24 | # 示例 1: 基础用法 - 获取单个工具
25 | # =============================================================================
26 |
27 | def demo_basic_usage():
28 | """
29 | 最简单的用法:从 Registry 获取一个工具
30 | """
31 | from google.adk import Agent
32 | from google.adk.tools.google_cloud import ApiRegistry
33 |
34 | # 1. 连接到 Cloud API Registry
35 | registry = ApiRegistry(project_id=PROJECT_ID)
36 |
37 | # 2. 获取 BigQuery 工具(管理员需要先启用)
38 | bq_tool = registry.get_tool("google-bigquery")
39 |
40 | # 3. 创建带有该工具的 Agent
41 | agent = Agent(
42 | model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
43 | name="data_analyst",
44 | instruction="你是一个数据分析师,可以查询 BigQuery 数据库。",
45 | tools=[bq_tool]
46 | )
47 |
48 | print("✅ Agent 已配置 BigQuery 工具")
49 | return agent
50 |
51 |
52 | # =============================================================================
53 | # 示例 2: 获取多个工具
54 | # =============================================================================
55 |
56 | def demo_multiple_tools():
57 | """
58 | 获取多个已审批的工具
59 | """
60 | from google.adk import Agent
61 | from google.adk.tools.google_cloud import ApiRegistry
62 |
63 | registry = ApiRegistry(project_id=PROJECT_ID)
64 |
65 | # 获取多个工具
66 | tools = [
67 | registry.get_tool("google-bigquery"), # 数据查询
68 | registry.get_tool("google-cloud-storage"), # 文件存储
69 | ]
70 |
71 | agent = Agent(
72 | model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
73 | name="cloud_assistant",
74 | instruction="你是云服务助手,可以查询数据和管理文件。",
75 | tools=tools
76 | )
77 |
78 | print("✅ Agent 已配置多个工具")
79 | return agent
80 |
81 |
82 | # =============================================================================
83 | # 示例 3: 列出所有可用工具
84 | # =============================================================================
85 |
86 | def demo_list_tools():
87 | """
88 | 查看 Registry 中有哪些可用工具
89 | """
90 | from google.adk.tools.google_cloud import ApiRegistry
91 |
92 | registry = ApiRegistry(project_id=PROJECT_ID)
93 |
94 | # 列出所有可用工具
95 | available_tools = registry.list_tools()
96 |
97 | print("📦 可用工具列表:")
98 | for tool in available_tools:
99 | print(f" - {tool.name}: {tool.description}")
100 |
101 | return available_tools
102 |
103 |
104 | # =============================================================================
105 | # 示例 4: 完整工作流程
106 | # =============================================================================
107 |
108 | async def demo_full_workflow():
109 | """
110 | 完整演示:创建 Agent 并执行查询
111 | """
112 | from google.adk import Agent
113 | from google.adk.runners import Runner
114 | from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService
115 | from google.adk.tools.google_cloud import ApiRegistry
116 | from google.genai.types import Content, Part
117 |
118 | # 1. 设置 Registry 和工具
119 | registry = ApiRegistry(project_id=PROJECT_ID)
120 | bq_tool = registry.get_tool("google-bigquery")
121 |
122 | # 2. 创建 Agent
123 | agent = Agent(
124 | model="gemini-3-flash-preview",
125 | name="data_analyst",
126 | instruction="""你是数据分析师。
127 | 用户询问数据问题时,使用 BigQuery 工具查询。
128 | 用中文简洁回答。""",
129 | tools=[bq_tool]
130 | )
131 |
132 | # 3. 运行对话
133 | session_service = InMemorySessionService()
134 | session = await session_service.create_session(
135 | app_name="api_registry_demo",
136 | user_id="demo_user"
137 | )
138 |
139 | runner = Runner(
140 | agent=agent,
141 | app_name="api_registry_demo",
142 | session_service=session_service
143 | )
144 |
145 | # 4. 发送查询
146 | question = "查询公开数据集中 2023 年的数据统计"
147 | user_content = Content(role="user", parts=[Part(text=question)])
148 |
149 | print(f"📝 问题: {question}")
150 | print("-" * 40)
151 |
152 | async for event in runner.run_async(
153 | user_id="demo_user",
154 | session_id=session.id,
155 | new_message=user_content
156 | ):
157 | if hasattr(event, 'content') and event.content:
158 | if hasattr(event.content, 'parts'):
159 | for part in event.content.parts:
160 | if hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:
161 | print(f"🤖 回答: {part.text}")
162 |
163 |
164 | # =============================================================================
165 | # 主程序
166 | # =============================================================================
167 |
168 | if __name__ == "__main__":
169 | print("=" * 50)
170 | print("Day 18: Cloud API Registry + ADK 演示")
171 | print("=" * 50)
172 | print(f"项目 ID: {PROJECT_ID}")
173 | print()
174 |
175 | # 注意:以下代码需要正确配置 Google Cloud 才能运行
176 | # 这里只展示代码结构,实际运行需要:
177 | # 1. 有效的 Google Cloud 项目
178 | # 2. 启用相关 API
179 | # 3. 配置好认证
180 |
181 | print("📌 示例代码已准备好")
182 | print("📌 请确保配置好 Google Cloud 项目后运行")
183 | print()
184 | print("启用 BigQuery MCP 服务:")
185 | print(f" gcloud beta services mcp enable bigquery.googleapis.com --project={PROJECT_ID}")
186 | print()
187 | print("运行完整演示:")
188 | print(" 取消下面的注释并运行")
189 |
190 | # 取消注释运行演示:
191 | # demo_basic_usage()
192 | # demo_multiple_tools()
193 | # demo_list_tools()
194 | # import asyncio
195 | # asyncio.run(demo_full_workflow())
196 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-06/day06_ide_context.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "# Day 6: ADK IDE Integration\n",
8 | "\n",
9 | "> Building agents shouldn't require an hour of environment configuration.\n",
10 | "\n",
11 | "今天学习如何为 AI IDE 提供项目上下文。"
12 | ]
13 | },
14 | {
15 | "cell_type": "markdown",
16 | "metadata": {},
17 | "source": [
18 | "## 1. What is llms.txt?\n",
19 | "\n",
20 | "`llms.txt` 是一种为 LLM 提供项目文档的标准格式,类似于 `robots.txt`。\n",
21 | "\n",
22 | "**支持的 IDE:**\n",
23 | "- Antigravity (Google)\n",
24 | "- Gemini CLI\n",
25 | "- Cursor\n",
26 | "- Firebase Studio\n",
27 | "- Claude Code\n",
28 | "- Windsurf"
29 | ]
30 | },
31 | {
32 | "cell_type": "markdown",
33 | "metadata": {},
34 | "source": [
35 | "## 2. IDE 配置文件对照表\n",
36 | "\n",
37 | "| IDE | 配置文件 |\n",
38 | "|-----|----------|\n",
39 | "| Cursor | `.cursorrules` |\n",
40 | "| Claude Code | `.claude/instructions.md` |\n",
41 | "| Windsurf | `.windsurfrules` |\n",
42 | "| Generic | `llms.txt` |"
43 | ]
44 | },
45 | {
46 | "cell_type": "code",
47 | "execution_count": null,
48 | "metadata": {},
49 | "outputs": [],
50 | "source": [
51 | "from pathlib import Path\n",
52 | "from datetime import datetime"
53 | ]
54 | },
55 | {
56 | "cell_type": "markdown",
57 | "metadata": {},
58 | "source": [
59 | "## 3. 生成 llms.txt"
60 | ]
61 | },
62 | {
63 | "cell_type": "code",
64 | "execution_count": null,
65 | "metadata": {},
66 | "outputs": [],
67 | "source": [
68 | "LLMS_TXT = \"\"\"\\\n",
69 | "# ADK Agent Project\n",
70 | "\n",
71 | "> AI Agent built with Google ADK\n",
72 | "\n",
73 | "## Tech Stack\n",
74 | "- Framework: Google ADK\n",
75 | "- Model: Gemini 2.0 Flash\n",
76 | "- Language: Python 3.11+\n",
77 | "\n",
78 | "## Key Patterns\n",
79 | "\n",
80 | "```python\n",
81 | "from google.adk import Agent, tool\n",
82 | "\n",
83 | "@tool\n",
84 | "def search(query: str) -> str:\n",
85 | " \\\"\\\"\\\"Search for information.\\\"\\\"\\\" \n",
86 | " return results\n",
87 | "\n",
88 | "agent = Agent(\n",
89 | " name=\"my-agent\",\n",
90 | " model=\"gemini-2.0-flash\",\n",
91 | " tools=[search]\n",
92 | ")\n",
93 | "```\n",
94 | "\n",
95 | "## Docs\n",
96 | "- https://google.github.io/adk-docs/\n",
97 | "\"\"\"\n",
98 | "\n",
99 | "print(LLMS_TXT)"
100 | ]
101 | },
102 | {
103 | "cell_type": "markdown",
104 | "metadata": {},
105 | "source": [
106 | "## 4. 生成 .cursorrules"
107 | ]
108 | },
109 | {
110 | "cell_type": "code",
111 | "execution_count": null,
112 | "metadata": {},
113 | "outputs": [],
114 | "source": [
115 | "CURSOR_RULES = \"\"\"\\\n",
116 | "# ADK Development Rules\n",
117 | "\n",
118 | "You are an expert in Google ADK.\n",
119 | "\n",
120 | "## Tech Stack\n",
121 | "- Google ADK + Gemini 2.0 Flash\n",
122 | "- Python 3.11+ with uv\n",
123 | "\n",
124 | "## Code Style\n",
125 | "- Use type hints\n",
126 | "- Write clear tool docstrings (LLM uses them)\n",
127 | "- Handle errors gracefully\n",
128 | "\n",
129 | "## Tool Pattern\n",
130 | "```python\n",
131 | "@tool\n",
132 | "def func(param: str) -> str:\n",
133 | " \\\"\\\"\\\"Clear description for the LLM.\\\"\\\"\\\"\n",
134 | " return result\n",
135 | "```\n",
136 | "\"\"\"\n",
137 | "\n",
138 | "print(CURSOR_RULES)"
139 | ]
140 | },
141 | {
142 | "cell_type": "markdown",
143 | "metadata": {},
144 | "source": [
145 | "## 5. 一键生成所有配置"
146 | ]
147 | },
148 | {
149 | "cell_type": "code",
150 | "execution_count": null,
151 | "metadata": {},
152 | "outputs": [],
153 | "source": [
154 | "def generate_ide_configs(project_root: Path):\n",
155 | " \"\"\"Generate IDE config files for ADK project.\"\"\"\n",
156 | " \n",
157 | " configs = {\n",
158 | " \"llms.txt\": LLMS_TXT,\n",
159 | " \".cursorrules\": CURSOR_RULES,\n",
160 | " \".windsurfrules\": CURSOR_RULES, # Similar format\n",
161 | " }\n",
162 | " \n",
163 | " for filename, content in configs.items():\n",
164 | " path = project_root / filename\n",
165 | " path.write_text(content)\n",
166 | " print(f\"[OK] {filename}\")\n",
167 | " \n",
168 | " # Claude Code\n",
169 | " claude_dir = project_root / \".claude\"\n",
170 | " claude_dir.mkdir(exist_ok=True)\n",
171 | " (claude_dir / \"instructions.md\").write_text(CURSOR_RULES)\n",
172 | " print(f\"[OK] .claude/instructions.md\")"
173 | ]
174 | },
175 | {
176 | "cell_type": "code",
177 | "execution_count": null,
178 | "metadata": {},
179 | "outputs": [],
180 | "source": [
181 | "# 生成配置文件到项目根目录\n",
182 | "project_root = Path.cwd().parent # 从 day-06 回到项目根目录\n",
183 | "print(f\"Project: {project_root}\\n\")\n",
184 | "\n",
185 | "generate_ide_configs(project_root)"
186 | ]
187 | },
188 | {
189 | "cell_type": "markdown",
190 | "metadata": {},
191 | "source": [
192 | "## 6. Key Takeaways\n",
193 | "\n",
194 | "1. **llms.txt** - 为 AI 提供项目上下文的标准格式\n",
195 | "2. **不同 IDE 不同配置文件**,但目标相同\n",
196 | "3. **好的上下文 = 更好的 AI 辅助**\n",
197 | "4. **Agent Starter Pack** 已包含预配置\n",
198 | "\n",
199 | "## Resources\n",
200 | "\n",
201 | "- [llms.txt 规范](https://llmstxt.org/)\n",
202 | "- [ADK 文档](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/)\n",
203 | "- [Antigravity IDE](https://antigravity.google/)\n",
204 | "- [视频教程](https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ep8usBDUTtA)"
205 | ]
206 | }
207 | ],
208 | "metadata": {
209 | "kernelspec": {
210 | "display_name": "Python 3",
211 | "language": "python",
212 | "name": "python3"
213 | },
214 | "language_info": {
215 | "name": "python",
216 | "version": "3.11.0"
217 | }
218 | },
219 | "nbformat": 4,
220 | "nbformat_minor": 4
221 | }
222 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-04/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 04: 基于源代码的部署
2 |
3 | 直接从源代码部署你的 Agent 到 Agent Engine —— 告别序列化的烦恼。
4 |
5 | ## 学习目标
6 |
7 | - 将 ADK Agent 部署到 Vertex AI Agent Engine
8 | - 使用 Agent Starter Pack 进行生产级部署
9 | - 理解 source-based 与 cloudpickle 部署的区别
10 | - 设置 CI/CD 流水线
11 |
12 | ## 前置条件
13 |
14 | ```bash
15 | # 安装 UV 工具(如果还没装的话)
16 | curl -LsSf https://astral.sh/uv/install.sh | sh
17 |
18 | # 安装 Google Cloud CLI
19 | # 参考: https://cloud.google.com/sdk/docs/install
20 | ```
21 |
22 | ## 序列化问题
23 |
24 | 传统的 Agent 部署使用 **cloudpickle** 序列化 Python 对象,经常会遇到问题:
25 |
26 | | 问题 | 描述 |
27 | |------|------|
28 | | **版本不一致** | 开发和生产环境的 cloudpickle 版本不同 |
29 | | **属性缺失** | `AttributeError: Can't get attribute '_class_setstate'` |
30 | | **依赖冲突** | 复杂的依赖关系导致序列化失败 |
31 | | **调试困难** | 序列化错误很难追踪定位 |
32 |
33 | **基于源代码的部署** 直接部署你的源代码,而不是序列化后的对象,从根本上解决这些问题。
34 |
35 | ## 快速开始
36 |
37 | ### 方式一:新建项目
38 |
39 | 创建一个带 Agent Engine 部署配置的新项目:
40 |
41 | ```bash
42 | uvx agent-starter-pack create my-agent -a adk_base -d agent_engine
43 | cd my-agent
44 | ```
45 |
46 | ### 方式二:现有项目
47 |
48 | 为现有的 ADK Agent 添加部署能力:
49 |
50 | ```bash
51 | # 进入包含你 agent 的父目录
52 | cd /path/to/parent
53 |
54 | # 添加部署配置
55 | uvx agent-starter-pack enhance --adk -d agent_engine
56 | ```
57 |
58 | ## 项目结构
59 |
60 | 增强后的项目结构:
61 |
62 | ```
63 | my-agent/
64 | ├── agent/
65 | │ ├── __init__.py
66 | │ ├── agent.py # Agent 代码
67 | │ └── root_agent.yaml # Agent 配置
68 | ├── deployment/
69 | │ ├── terraform/ # 基础设施即代码
70 | │ └── cloudbuild.yaml # CI/CD 流水线
71 | ├── Makefile # 部署命令
72 | ├── pyproject.toml # 依赖配置
73 | └── README.md
74 | ```
75 |
76 | ## 部署到 Agent Engine
77 |
78 | ### 第一步:配置 Google Cloud
79 |
80 | ```bash
81 | # 设置项目
82 | export GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT="your-project-id"
83 | export GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION="us-central1"
84 | export STAGING_BUCKET="gs://your-staging-bucket"
85 |
86 | # 认证
87 | gcloud auth login
88 | gcloud config set project $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT
89 | ```
90 |
91 | ### 第二步:使用 Make 部署
92 |
93 | ```bash
94 | # 部署到 Agent Engine
95 | make deploy
96 | ```
97 |
98 | ### 第三步:使用 ADK CLI 部署
99 |
100 | 也可以直接用 ADK 命令:
101 |
102 | ```bash
103 | adk deploy agent_engine \
104 | --project $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \
105 | --region $GOOGLE_CLOUD_LOCATION \
106 | --staging_bucket $STAGING_BUCKET \
107 | --trace_to_cloud \
108 | --display_name "my-agent" \
109 | --description "我的部署 Agent" \
110 | agent
111 | ```
112 |
113 | ## Agent Starter Pack 功能
114 |
115 | Agent Starter Pack 提供:
116 |
117 | | 功能 | 描述 |
118 | |------|------|
119 | | **CI/CD 流水线** | Cloud Build 或 GitHub Actions |
120 | | **Terraform** | 基础设施即代码 |
121 | | **OpenTelemetry** | 内置追踪和监控 |
122 | | **会话管理** | 有状态对话 |
123 | | **评估框架** | Agent 测试工具 |
124 |
125 | ## 支持的区域
126 |
127 | Agent Engine 在以下区域可用:
128 |
129 | - `us-central1` (爱荷华)
130 | - `us-east1` (南卡罗来纳)
131 | - `europe-west1` (比利时)
132 | - `asia-northeast1` (东京)
133 |
134 | ## 示例:部署搜索 Agent
135 |
136 | ### 1. 创建 Agent
137 |
138 | ```yaml
139 | # agent/root_agent.yaml
140 | name: search_assistant
141 | model: gemini-2.5-flash
142 | description: 部署到 Agent Engine 的搜索助手
143 | instruction: |
144 | 你是一个有帮助的助手。
145 | 使用 Google Search 获取时事和事实信息。
146 | 总是引用你的信息来源。
147 | tools:
148 | - name: google_search
149 | ```
150 |
151 | ### 2. 部署
152 |
153 | ```bash
154 | adk deploy agent_engine \
155 | --project $GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT \
156 | --region us-central1 \
157 | --staging_bucket $STAGING_BUCKET \
158 | --trace_to_cloud \
159 | agent
160 | ```
161 |
162 | ### 3. 测试
163 |
164 | 部署后,你可以通过以下方式与 Agent 交互:
165 | - Google Cloud Console Agent Engine 界面
166 | - REST API
167 | - Python SDK
168 |
169 | ## Python SDK 使用
170 |
171 | 部署后,可以用代码调用你的 Agent:
172 |
173 | ```python
174 | from google.cloud import aiplatform
175 |
176 | # 初始化
177 | aiplatform.init(
178 | project="your-project-id",
179 | location="us-central1"
180 | )
181 |
182 | # 获取已部署的 Agent
183 | agent = aiplatform.Agent("projects/your-project/locations/us-central1/agents/your-agent-id")
184 |
185 | # 创建会话
186 | session = agent.create_session()
187 |
188 | # 与 Agent 对话
189 | response = session.chat("最近有什么 AI 新闻?")
190 | print(response.text)
191 | ```
192 |
193 | ## 监控你的 Agent
194 |
195 | ### Cloud Console
196 |
197 | 在 [Agent Engine Console](https://console.cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/agent-engine) 查看:
198 | - 监控对话
199 | - 查看会话历史
200 | - 追踪性能指标
201 |
202 | ### Cloud Trace
203 |
204 | 使用 `--trace_to_cloud` 参数可获得自动追踪:
205 | - 请求延迟
206 | - 工具执行时间
207 | - 错误追踪
208 |
209 | ## 常见问题排查
210 |
211 | ### 常见错误
212 |
213 | **1. Cloudpickle 版本不匹配**
214 | ```
215 | AttributeError: Can't get attribute '_class_setstate'
216 | ```
217 | 解决方案:确保 `pyproject.toml` 中的 cloudpickle 版本一致
218 |
219 | **2. 区域不支持**
220 | ```
221 | InvalidArgument: Region not supported for Agent Engine
222 | ```
223 | 解决方案:使用支持的区域(us-central1, us-east1 等)
224 |
225 | **3. 依赖缺失**
226 | ```
227 | ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'xxx'
228 | ```
229 | 解决方案:把所有依赖加到 `pyproject.toml`
230 |
231 | ### 先本地调试
232 |
233 | 部署前一定要先本地测试:
234 |
235 | ```bash
236 | # 本地运行
237 | adk web
238 |
239 | # 测试你的 Agent
240 | # 没问题了再部署
241 | ```
242 |
243 | ## Agent Engine vs Cloud Run
244 |
245 | | 特性 | Agent Engine | Cloud Run |
246 | |------|-------------|-----------|
247 | | **会话管理** | 内置 | 需要自己实现 |
248 | | **自动扩缩** | 自动 | 自动 |
249 | | **自定义 UI** | 仅 REST API | 完全灵活 |
250 | | **计费方式** | 按会话 | 按请求 |
251 | | **A2A 协议** | REST API | 直接支持 |
252 |
253 | 选择 **Agent Engine** 如果:
254 | - 想要快速部署
255 | - 需要内置会话管理
256 | - 需要生产监控
257 |
258 | 选择 **Cloud Run** 如果:
259 | - 需要自定义 Web UI
260 | - 需要 A2A 协议支持
261 | - 需要更多基础设施控制
262 |
263 | ## 资源链接
264 |
265 | ### 官方文档
266 | - [ADK 部署指南](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/deploy/)
267 | - [Agent Engine 文档](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/deploy/agent-engine/)
268 | - [Agent Starter Pack](https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/agent-starter-pack)
269 |
270 | ### 教程
271 | - [Source-Based Deployment 视频教程](https://youtu.be/8RjzMG3BKA0)
272 | - [ADK + Agent Engine 多 Agent 应用 (Codelab)](https://codelabs.developers.google.com/multi-agent-app-with-adk)
273 | - [部署多 Agent 系统 (Google Skills)](https://www.skills.google/course_templates/1275)
274 |
275 | ### 快速入门
276 | - [快速入门:ADK + Agent Engine](https://cloud.google.com/agent-builder/agent-engine/quickstart-adk)
277 | - [部署 Agent](https://cloud.google.com/vertex-ai/generative-ai/docs/agent-engine/deploy)
278 |
279 | ## 小结
280 |
281 | Day 4 的核心是 **基于源代码的部署** —— 一种更干净的 Agent 部署方式,避免序列化带来的各种问题。Agent Starter Pack 让这个过程变得简单,提供了生产级的模板和 CI/CD 流水线。
282 |
283 | 关键命令:`uvx agent-starter-pack enhance --adk -d agent_engine` 可以为任何现有的 ADK 项目添加部署能力。
284 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/client/test_client.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 16: A2A Client - 测试 LangGraph Agent
3 |
4 | 这是 A2A 客户端,用于测试 LangGraph Agent 服务。
5 |
6 | 运行前确保:
7 | 1. LangGraph Agent 已在 http://localhost:8016 运行
8 | 2. 运行: python -m client.test_client
9 | """
10 |
11 | import asyncio
12 | import os
13 | import sys
14 |
15 | # 添加项目根目录到路径
16 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
17 |
18 | import httpx
19 | from a2a.client import ClientFactory, ClientConfig
20 | from a2a.types import Role
21 | from a2a.client.helpers import create_text_message_object
22 |
23 | # LangGraph Agent 的 URL
24 | LANGGRAPH_AGENT_URL = "http://localhost:8016"
25 |
26 |
27 | def get_client_config() -> ClientConfig:
28 | """创建不使用代理的客户端配置"""
29 | httpx_client = httpx.AsyncClient(
30 | trust_env=False,
31 | timeout=120.0,
32 | )
33 | return ClientConfig(httpx_client=httpx_client)
34 |
35 |
36 | # ============================================================
37 | # 测试函数
38 | # ============================================================
39 |
40 | async def test_langgraph_agent():
41 | """测试 LangGraph Agent 的 A2A 服务"""
42 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
43 | print("测试 LangGraph + A2A Agent")
44 | print("=" * 60)
45 |
46 | try:
47 | # 1. 连接到 LangGraph Agent
48 | print("\n1️⃣ 连接 LangGraph Agent...")
49 | client = await ClientFactory.connect(
50 | LANGGRAPH_AGENT_URL,
51 | client_config=get_client_config()
52 | )
53 | print(f" ✅ 连接成功!")
54 | print(f" Agent 名称: {client._card.name}")
55 | print(f" Agent 描述: {client._card.description[:60]}...")
56 |
57 | # 显示技能
58 | if client._card.skills:
59 | print(" 技能列表:")
60 | for skill in client._card.skills:
61 | print(f" - {skill.name}: {skill.description}")
62 |
63 | # 2. 测试问答功能
64 | test_questions = [
65 | "什么是 LangGraph?它和 LangChain 有什么关系?",
66 | "请帮我分析:为什么 AI Agent 需要使用图结构来组织工作流?",
67 | "A2A 协议的主要优势是什么?",
68 | ]
69 |
70 | for i, question in enumerate(test_questions, 1):
71 | print(f"\n{'=' * 60}")
72 | print(f"问题 {i}: {question}")
73 | print("=" * 60)
74 |
75 | # 创建消息
76 | message = create_text_message_object(
77 | role=Role.user,
78 | content=question,
79 | )
80 |
81 | # 发送请求并等待响应
82 | print("\n⏳ 等待 Agent 响应...")
83 | result_text = None
84 |
85 | async for event in client.send_message(request=message):
86 | if isinstance(event, tuple) and len(event) >= 1:
87 | task = event[0]
88 |
89 | # 从 Task 的 artifacts 中提取响应
90 | # artifacts[].parts[].root.text 是响应的位置
91 | if task and hasattr(task, 'artifacts') and task.artifacts:
92 | for artifact in task.artifacts:
93 | if hasattr(artifact, 'parts'):
94 | for part in artifact.parts:
95 | # Part 对象有 root 属性,包含 TextPart
96 | if hasattr(part, 'root') and part.root:
97 | if hasattr(part.root, 'text') and part.root.text:
98 | result_text = part.root.text
99 | # 兼容直接访问 text 的情况
100 | elif hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:
101 | result_text = part.text
102 |
103 | if result_text:
104 | print(f"\n🤖 Agent 回答:")
105 | print("-" * 40)
106 | # 格式化输出,每行最多 60 个字符
107 | lines = result_text.split('\n')
108 | for line in lines:
109 | if len(line) > 80:
110 | # 长行分割
111 | words = line.split()
112 | current_line = ""
113 | for word in words:
114 | if len(current_line) + len(word) + 1 <= 80:
115 | current_line += (" " if current_line else "") + word
116 | else:
117 | if current_line:
118 | print(f" {current_line}")
119 | current_line = word
120 | if current_line:
121 | print(f" {current_line}")
122 | else:
123 | print(f" {line}")
124 | print("-" * 40)
125 | else:
126 | print(" ⚠️ 未收到有效响应")
127 |
128 | # 短暂等待,避免请求过快
129 | await asyncio.sleep(1)
130 |
131 | except Exception as e:
132 | print(f"\n❌ 错误: {e}")
133 | import traceback
134 | traceback.print_exc()
135 | print("\n请确保:")
136 | print("1. LangGraph Agent 正在运行 (python -m langgraph_agent.agent)")
137 | print("2. 端口 8016 没有被占用")
138 | print("3. GOOGLE_API_KEY 环境变量已设置")
139 |
140 |
141 | async def check_agent_health():
142 | """检查 Agent 健康状态"""
143 | print("\n检查 Agent 健康状态...")
144 | try:
145 | async with httpx.AsyncClient(trust_env=False) as client:
146 | # 检查 Agent Card
147 | resp = await client.get(f"{LANGGRAPH_AGENT_URL}/.well-known/agent.json")
148 | if resp.status_code == 200:
149 | print("✅ Agent 服务正常运行")
150 | agent_card = resp.json()
151 | print(f" 名称: {agent_card.get('name', 'Unknown')}")
152 | print(f" 版本: {agent_card.get('version', 'Unknown')}")
153 | return True
154 | else:
155 | print(f"⚠️ Agent 响应异常: {resp.status_code}")
156 | return False
157 | except httpx.ConnectError:
158 | print("❌ 无法连接到 Agent 服务")
159 | print(f" 请确保服务正在 {LANGGRAPH_AGENT_URL} 运行")
160 | return False
161 | except Exception as e:
162 | print(f"❌ 检查失败: {e}")
163 | return False
164 |
165 |
166 | # ============================================================
167 | # 主程序
168 | # ============================================================
169 |
170 | async def main():
171 | print("=" * 60)
172 | print("Day 16: LangGraph + A2A 客户端测试")
173 | print("=" * 60)
174 | print()
175 | print(f"目标 Agent: {LANGGRAPH_AGENT_URL}")
176 | print()
177 |
178 | # 先检查健康状态
179 | is_healthy = await check_agent_health()
180 |
181 | if is_healthy:
182 | # 运行测试
183 | await test_langgraph_agent()
184 | else:
185 | print("\n无法进行测试,请先启动 Agent 服务:")
186 | print(" cd day-16")
187 | print(" uv run python -m langgraph_agent.agent")
188 |
189 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
190 | print("测试结束")
191 | print("=" * 60)
192 |
193 |
194 | if __name__ == "__main__":
195 | asyncio.run(main())
196 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/langgraph_agent/checkpointer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Checkpointer 模块 - 状态持久化
3 |
4 | 生产级别的状态持久化实现,支持:
5 | - 内存存储(默认,快速测试)
6 | - SQLite 本地持久化(需要安装 langgraph-checkpoint-sqlite)
7 | - 可扩展到 PostgreSQL/Redis(生产环境)
8 |
9 | 核心功能:
10 | - 保存和恢复 Agent 执行状态
11 | - 支持断点续跑
12 | - 支持 time-travel debugging
13 |
14 | 安装 SQLite 支持:
15 | uv pip install langgraph-checkpoint-sqlite
16 | """
17 |
18 | import os
19 | import json
20 | import sqlite3
21 | import logging
22 | from typing import Optional, Any, Dict
23 | from datetime import datetime
24 | from contextlib import contextmanager
25 | from dataclasses import dataclass, asdict
26 | from enum import Enum
27 |
28 | # LangGraph 的 checkpointer
29 | from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
30 |
31 | # SQLite Saver 是可选的,需要单独安装
32 | try:
33 | from langgraph.checkpoint.sqlite import SqliteSaver
34 | SQLITE_AVAILABLE = True
35 | except ImportError:
36 | SQLITE_AVAILABLE = False
37 | SqliteSaver = None
38 |
39 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
40 |
41 |
42 | class CheckpointerType(Enum):
43 | """Checkpointer 类型"""
44 | MEMORY = "memory"
45 | SQLITE = "sqlite"
46 |
47 |
48 | @dataclass
49 | class TaskMetadata:
50 | """任务元数据 - 用于追踪任务状态"""
51 | task_id: str
52 | thread_id: str
53 | created_at: str
54 | updated_at: str
55 | status: str # pending, waiting_approval, approved, rejected, completed, failed
56 | current_node: Optional[str] = None
57 | pending_action: Optional[str] = None
58 | user_input: Optional[str] = None
59 | error_message: Optional[str] = None
60 |
61 |
62 | class TaskStore:
63 | """
64 | 任务存储 - 管理 Human-in-the-Loop 任务状态
65 |
66 | 与 LangGraph Checkpointer 配合使用:
67 | - Checkpointer: 保存图执行状态
68 | - TaskStore: 保存业务元数据(审批状态、用户输入等)
69 | """
70 |
71 | def __init__(self, db_path: str = "data/tasks.db"):
72 | self.db_path = db_path
73 | self._ensure_db_dir()
74 | self._init_db()
75 |
76 | def _ensure_db_dir(self):
77 | """确保数据库目录存在"""
78 | db_dir = os.path.dirname(self.db_path)
79 | if db_dir and not os.path.exists(db_dir):
80 | os.makedirs(db_dir)
81 | logger.info(f"Created database directory: {db_dir}")
82 |
83 | def _init_db(self):
84 | """初始化数据库表"""
85 | with self._get_connection() as conn:
86 | conn.execute("""
87 | CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tasks (
88 | task_id TEXT PRIMARY KEY,
89 | thread_id TEXT NOT NULL,
90 | created_at TEXT NOT NULL,
91 | updated_at TEXT NOT NULL,
92 | status TEXT NOT NULL,
93 | current_node TEXT,
94 | pending_action TEXT,
95 | user_input TEXT,
96 | error_message TEXT
97 | )
98 | """)
99 | conn.execute("""
100 | CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_tasks_status
101 | ON tasks(status)
102 | """)
103 | conn.execute("""
104 | CREATE INDEX IF NOT EXISTS idx_tasks_thread
105 | ON tasks(thread_id)
106 | """)
107 | conn.commit()
108 | logger.info("Task store initialized")
109 |
110 | @contextmanager
111 | def _get_connection(self):
112 | """获取数据库连接(上下文管理器)"""
113 | conn = sqlite3.connect(self.db_path)
114 | conn.row_factory = sqlite3.Row
115 | try:
116 | yield conn
117 | finally:
118 | conn.close()
119 |
120 | def create_task(self, task_id: str, thread_id: str, user_input: str) -> TaskMetadata:
121 | """创建新任务"""
122 | now = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
123 | task = TaskMetadata(
124 | task_id=task_id,
125 | thread_id=thread_id,
126 | created_at=now,
127 | updated_at=now,
128 | status="pending",
129 | user_input=user_input,
130 | )
131 |
132 | with self._get_connection() as conn:
133 | conn.execute("""
134 | INSERT INTO tasks
135 | (task_id, thread_id, created_at, updated_at, status,
136 | current_node, pending_action, user_input, error_message)
137 | VALUES (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)
138 | """, (
139 | task.task_id, task.thread_id, task.created_at, task.updated_at,
140 | task.status, task.current_node, task.pending_action,
141 | task.user_input, task.error_message
142 | ))
143 | conn.commit()
144 |
145 | logger.info(f"Created task: {task_id}")
146 | return task
147 |
148 | def get_task(self, task_id: str) -> Optional[TaskMetadata]:
149 | """获取任务"""
150 | with self._get_connection() as conn:
151 | row = conn.execute(
152 | "SELECT * FROM tasks WHERE task_id = ?", (task_id,)
153 | ).fetchone()
154 |
155 | if row:
156 | return TaskMetadata(**dict(row))
157 | return None
158 |
159 | def update_task(self, task_id: str, **updates) -> Optional[TaskMetadata]:
160 | """更新任务"""
161 | updates["updated_at"] = datetime.utcnow().isoformat()
162 |
163 | set_clause = ", ".join([f"{k} = ?" for k in updates.keys()])
164 | values = list(updates.values()) + [task_id]
165 |
166 | with self._get_connection() as conn:
167 | conn.execute(
168 | f"UPDATE tasks SET {set_clause} WHERE task_id = ?",
169 | values
170 | )
171 | conn.commit()
172 |
173 | logger.info(f"Updated task {task_id}: {updates}")
174 | return self.get_task(task_id)
175 |
176 | def get_pending_approvals(self) -> list[TaskMetadata]:
177 | """获取所有等待审批的任务"""
178 | with self._get_connection() as conn:
179 | rows = conn.execute(
180 | "SELECT * FROM tasks WHERE status = 'waiting_approval' ORDER BY created_at"
181 | ).fetchall()
182 | return [TaskMetadata(**dict(row)) for row in rows]
183 |
184 | def get_tasks_by_status(self, status: str) -> list[TaskMetadata]:
185 | """按状态获取任务列表"""
186 | with self._get_connection() as conn:
187 | rows = conn.execute(
188 | "SELECT * FROM tasks WHERE status = ? ORDER BY created_at DESC",
189 | (status,)
190 | ).fetchall()
191 | return [TaskMetadata(**dict(row)) for row in rows]
192 |
193 |
194 | def create_checkpointer(
195 | checkpointer_type: CheckpointerType = CheckpointerType.MEMORY,
196 | db_path: str = "data/checkpoints.db"
197 | ) -> Any:
198 | """
199 | 创建 Checkpointer 实例
200 |
201 | Args:
202 | checkpointer_type: 存储类型(默认 MEMORY)
203 | db_path: SQLite 数据库路径(仅 SQLITE 类型需要)
204 |
205 | Returns:
206 | LangGraph Checkpointer 实例
207 |
208 | 注意:
209 | SQLite 需要安装: uv pip install langgraph-checkpoint-sqlite
210 | """
211 | if checkpointer_type == CheckpointerType.MEMORY:
212 | logger.info("Using MemorySaver (data will be lost on restart)")
213 | return MemorySaver()
214 |
215 | elif checkpointer_type == CheckpointerType.SQLITE:
216 | if not SQLITE_AVAILABLE:
217 | logger.warning(
218 | "SQLite checkpointer not available. "
219 | "Install with: uv pip install langgraph-checkpoint-sqlite. "
220 | "Falling back to MemorySaver."
221 | )
222 | return MemorySaver()
223 |
224 | # 确保目录存在
225 | db_dir = os.path.dirname(db_path)
226 | if db_dir and not os.path.exists(db_dir):
227 | os.makedirs(db_dir)
228 |
229 | logger.info(f"Using SqliteSaver with database: {db_path}")
230 | # 创建连接
231 | conn = sqlite3.connect(db_path, check_same_thread=False)
232 | return SqliteSaver(conn)
233 |
234 | else:
235 | raise ValueError(f"Unknown checkpointer type: {checkpointer_type}")
236 |
237 |
238 | # 全局单例
239 | _task_store: Optional[TaskStore] = None
240 | _checkpointer: Optional[Any] = None
241 |
242 |
243 | def get_task_store(db_path: str = "data/tasks.db") -> TaskStore:
244 | """获取 TaskStore 单例"""
245 | global _task_store
246 | if _task_store is None:
247 | _task_store = TaskStore(db_path)
248 | return _task_store
249 |
250 |
251 | def get_checkpointer(
252 | checkpointer_type: CheckpointerType = CheckpointerType.SQLITE,
253 | db_path: str = "data/checkpoints.db"
254 | ) -> Any:
255 | """获取 Checkpointer 单例"""
256 | global _checkpointer
257 | if _checkpointer is None:
258 | _checkpointer = create_checkpointer(checkpointer_type, db_path)
259 | return _checkpointer
260 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-05/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 5: Production Observability - 生产级可观测性
2 |
3 | ## 凌晨 3 点的噩梦
4 |
5 | 你的 Agent 上线了,用户反馈"有时候回答很慢"、"偶尔答非所问"。
6 |
7 | 你打开日志,看到的是:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | INFO: Request received
11 | INFO: Response sent
12 | INFO: Request received
13 | INFO: Response sent
14 | ```
15 |
16 | 这能告诉你什么?什么都没有。
17 |
18 | - 哪个请求慢?慢在哪里?
19 | - LLM 调用了几次?每次花了多久?
20 | - Token 消耗多少?成本怎么样?
21 | - 用户问了什么?Agent 答了什么?
22 |
23 | ## 生产环境需要的是可观测性
24 |
25 | Agent Starter Pack 提供了两层可观测性:
26 |
27 | | 层级 | 内容 | 导出目标 | 默认状态 |
28 | |------|------|----------|----------|
29 | | **Agent Telemetry** | 执行追踪、延迟、系统指标 | Cloud Trace | 始终开启 |
30 | | **Prompt-Response Logging** | LLM 交互、Token 使用 | GCS + BigQuery + Cloud Logging | 部署环境开启 |
31 |
32 | ## 快速开始
33 |
34 | ### 1. 创建 Agent 项目
35 |
36 | ```bash
37 | # 使用 agent-starter-pack 创建项目
38 | uvx agent-starter-pack create
39 |
40 | # 选择 adk_base 模板
41 | ```
42 |
43 | ### 2. 本地运行(Telemetry 自动配置)
44 |
45 | ```bash
46 | cd your-agent-project
47 | make playground
48 | ```
49 |
50 | ### 3. 部署到 Cloud Run(完整可观测性)
51 |
52 | ```bash
53 | gcloud config set project YOUR_PROJECT_ID
54 | make deploy
55 | ```
56 |
57 | 部署后,Terraform 会自动配置:
58 | - Cloud Trace 分布式追踪
59 | - GCS 存储 JSONL 日志
60 | - BigQuery 外部表(SQL 查询日志)
61 | - Cloud Logging 专用 bucket
62 |
63 | ## 核心概念
64 |
65 | ### OpenTelemetry 追踪
66 |
67 | ```
68 | 用户请求
69 | │
70 | ▼
71 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────┐
72 | │ Span: handle_request (总耗时 2.5s) │
73 | │ ├── Span: parse_input (50ms) │
74 | │ ├── Span: llm_call_1 (800ms) │
75 | │ │ └── model: gemini-2.0-flash │
76 | │ │ └── tokens: 1500 │
77 | │ ├── Span: tool_execution (600ms) │
78 | │ │ └── tool: search_database │
79 | │ ├── Span: llm_call_2 (900ms) │
80 | │ │ └── model: gemini-2.0-flash │
81 | │ │ └── tokens: 2000 │
82 | │ └── Span: format_response (150ms) │
83 | └─────────────────────────────────────────────┘
84 | ```
85 |
86 | 每个 Span 记录:
87 | - 开始/结束时间
88 | - 父子关系
89 | - 自定义属性(model、tokens 等)
90 | - 错误信息
91 |
92 | ### 隐私保护模式
93 |
94 | 默认使用 `NO_CONTENT` 模式,只记录元数据:
95 |
96 | ```python
97 | # 记录的内容
98 | {
99 | "model": "gemini-2.0-flash",
100 | "input_tokens": 1500,
101 | "output_tokens": 500,
102 | "latency_ms": 800,
103 | "timestamp": "2025-01-15T10:30:00Z"
104 | }
105 |
106 | # 不记录
107 | # - 用户的 prompt
108 | # - LLM 的 response
109 | ```
110 |
111 | 这样既能监控性能,又保护用户隐私。
112 |
113 | ## 代码示例
114 |
115 | ### 基础 Telemetry 配置
116 |
117 | ```python
118 | # app_utils/telemetry.py
119 | import os
120 | import logging
121 |
122 | def setup_telemetry() -> str | None:
123 | """配置 OpenTelemetry 和 GenAI 遥测"""
124 |
125 | bucket = os.environ.get("LOGS_BUCKET_NAME")
126 | capture_content = os.environ.get(
127 | "OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_GENAI_CAPTURE_MESSAGE_CONTENT", "false"
128 | )
129 |
130 | if bucket and capture_content != "false":
131 | logging.info("Prompt-response logging enabled - mode: NO_CONTENT")
132 |
133 | # 设置为 NO_CONTENT 模式(只记录元数据)
134 | os.environ["OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_GENAI_CAPTURE_MESSAGE_CONTENT"] = "NO_CONTENT"
135 | os.environ.setdefault("OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_GENAI_UPLOAD_FORMAT", "jsonl")
136 | os.environ.setdefault("OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_GENAI_COMPLETION_HOOK", "upload")
137 |
138 | # 配置上传路径
139 | path = os.environ.get("GENAI_TELEMETRY_PATH", "completions")
140 | os.environ.setdefault(
141 | "OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_GENAI_UPLOAD_BASE_PATH",
142 | f"gs://{bucket}/{path}",
143 | )
144 | else:
145 | logging.info("Prompt-response logging disabled")
146 |
147 | return bucket
148 | ```
149 |
150 | ### 自定义 Span 添加
151 |
152 | ```python
153 | from opentelemetry import trace
154 |
155 | tracer = trace.get_tracer(__name__)
156 |
157 | async def process_request(request):
158 | with tracer.start_as_current_span("process_request") as span:
159 | # 添加自定义属性
160 | span.set_attribute("user_id", request.user_id)
161 | span.set_attribute("request_type", request.type)
162 |
163 | # 调用 LLM
164 | with tracer.start_as_current_span("llm_call") as llm_span:
165 | response = await model.generate(request.prompt)
166 | llm_span.set_attribute("model", "gemini-2.0-flash")
167 | llm_span.set_attribute("tokens", response.usage.total_tokens)
168 |
169 | return response
170 | ```
171 |
172 | ### 查询 BigQuery 日志
173 |
174 | ```sql
175 | -- 查询过去 24 小时的 LLM 调用统计
176 | SELECT
177 | DATE(timestamp) as date,
178 | model,
179 | COUNT(*) as calls,
180 | AVG(latency_ms) as avg_latency,
181 | SUM(input_tokens + output_tokens) as total_tokens
182 | FROM `your-project.telemetry.genai_logs`
183 | WHERE timestamp > TIMESTAMP_SUB(CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(), INTERVAL 24 HOUR)
184 | GROUP BY date, model
185 | ORDER BY date DESC, calls DESC
186 | ```
187 |
188 | ## 环境配置
189 |
190 | ### 本地开发
191 |
192 | ```bash
193 | # .env 文件
194 | GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT=your-project-id
195 |
196 | # 可选:启用本地 prompt-response 日志
197 | LOGS_BUCKET_NAME=gs://your-bucket
198 | OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_GENAI_CAPTURE_MESSAGE_CONTENT=NO_CONTENT
199 | ```
200 |
201 | ### 生产环境(Terraform 自动配置)
202 |
203 | ```hcl
204 | # 环境变量由 Terraform 自动设置
205 | resource "google_cloud_run_service" "agent" {
206 | template {
207 | spec {
208 | containers {
209 | env {
210 | name = "LOGS_BUCKET_NAME"
211 | value = google_storage_bucket.logs.name
212 | }
213 | env {
214 | name = "OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_GENAI_CAPTURE_MESSAGE_CONTENT"
215 | value = "NO_CONTENT"
216 | }
217 | }
218 | }
219 | }
220 | }
221 | ```
222 |
223 | ## 架构图
224 |
225 | ```
226 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
227 | │ Agent 应用 │
228 | │ ┌──────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐ │
229 | │ │ OpenTelemetry SDK │ │
230 | │ │ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ │ │
231 | │ │ │ Traces │ │ Metrics │ │ Logs │ │ │
232 | │ │ └──────┬──────┘ └──────┬──────┘ └──────┬──────┘ │ │
233 | │ └─────────┼────────────────┼────────────────┼─────────┘ │
234 | └────────────┼────────────────┼────────────────┼────────────┘
235 | │ │ │
236 | ▼ ▼ ▼
237 | ┌───────────┐ ┌───────────┐ ┌───────────────┐
238 | │Cloud Trace│ │Cloud │ │Cloud Logging │
239 | │ │ │Monitoring │ │(10年保留) │
240 | └───────────┘ └───────────┘ └───────┬───────┘
241 | │
242 | ▼
243 | ┌───────────────┐
244 | │ GCS │
245 | │ (JSONL) │
246 | └───────┬───────┘
247 | │
248 | ▼
249 | ┌───────────────┐
250 | │ BigQuery │
251 | │ (外部表/SQL) │
252 | └───────────────┘
253 | ```
254 |
255 | ## 验证部署
256 |
257 | ### 1. 检查 Cloud Trace
258 |
259 | ```bash
260 | # 打开 Cloud Trace 控制台
261 | open "https://console.cloud.google.com/traces/list?project=YOUR_PROJECT_ID"
262 | ```
263 |
264 | ### 2. 检查 GCS 日志
265 |
266 | ```bash
267 | # 列出日志文件
268 | gsutil ls gs://YOUR_BUCKET/completions/
269 |
270 | # 查看日志内容
271 | gsutil cat gs://YOUR_BUCKET/completions/2025/01/15/12/completions_*.jsonl | head -5
272 | ```
273 |
274 | ### 3. BigQuery 查询
275 |
276 | ```bash
277 | # 运行测试查询
278 | bq query --use_legacy_sql=false \
279 | 'SELECT COUNT(*) as total_calls FROM `your-project.telemetry.genai_logs`'
280 | ```
281 |
282 | ## 常见问题
283 |
284 | ### Q: 本地开发时看不到日志?
285 |
286 | 本地开发默认禁用 prompt-response 日志,只有 Cloud Trace 开启。如需启用:
287 |
288 | ```bash
289 | export LOGS_BUCKET_NAME=gs://your-bucket
290 | export OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_GENAI_CAPTURE_MESSAGE_CONTENT=NO_CONTENT
291 | ```
292 |
293 | ### Q: LangGraph 模板支持吗?
294 |
295 | LangGraph 模板只支持 Agent Telemetry(Cloud Trace),不支持 Prompt-Response Logging,因为 SDK 限制。
296 |
297 | ### Q: 如何记录完整的 prompt/response?
298 |
299 | 将环境变量改为 `ALL`(注意隐私合规):
300 |
301 | ```bash
302 | OTEL_INSTRUMENTATION_GENAI_CAPTURE_MESSAGE_CONTENT=ALL
303 | ```
304 |
305 | ## 核心价值
306 |
307 | | 没有可观测性 | 有可观测性 |
308 | |-------------|-----------|
309 | | "用户说慢" → 不知道哪里慢 | 精确定位到某次 LLM 调用耗时 3s |
310 | | "成本超支" → 不知道哪里花的 | Token 使用量按 model/user/time 统计 |
311 | | "有时出错" → 无法复现 | 追踪链完整记录每一步 |
312 |
313 | **生产环境的 Agent,可观测性不是可选项,而是必需品。**
314 |
315 | ## 扩展阅读
316 |
317 | - [Observability Guide](https://googlecloudplatform.github.io/agent-starter-pack/guide/observability.html)
318 | - [Agent Starter Pack GitHub](https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/agent-starter-pack)
319 | - [OpenTelemetry Python](https://opentelemetry.io/docs/languages/python/)
320 | - [Cloud Trace 文档](https://cloud.google.com/trace/docs)
321 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 16: LangGraph + A2A + Human-in-the-Loop
2 |
3 | ## 概述
4 |
5 | 本项目展示了两个核心能力:
6 |
7 | 1. **LangGraph + A2A** - 使用 LangGraph 构建 Agent,通过 ADK 暴露 A2A 服务
8 | 2. **Human-in-the-Loop (HITL)** - 生产级人机协作实现,支持敏感操作审批
9 |
10 | ## 练习场景:企业 AI 助手审批系统
11 |
12 | ### 场景描述
13 |
14 | 企业级构建 AI 助手,该助手可以帮助员工执行各种操作。但出于安全考虑,某些敏感操作需要管理员审批后才能执行。
15 |
16 | ```
17 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
18 | │ 企业 AI 助手审批系统 │
19 | ├─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
20 | │ │
21 | │ 员工请求 AI 分析 管理员审批 执行 │
22 | │ ───────── ──────── ────────── ──── │
23 | │ │
24 | │ "查询销售数据" → 低风险 ────────────────────────→ 直接执行 │
25 | │ │
26 | │ "修改客户信息" → 中风险 → [等待审批] → 批准 ────→ 执行修改 │
27 | │ │ │
28 | │ "删除用户账号" → 高风险 → [等待审批] → 拒绝 ────→ 操作取消 │
29 | │ │ │
30 | │ "批量发送邮件" → 关键级 → [等待审批] → 超时 ────→ 自动拒绝 │
31 | │ │
32 | └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
33 | ```
34 |
35 | ### 真实场景示例
36 |
37 | | 员工请求 | 风险评估 | 处理方式 |
38 | |----------|----------|----------|
39 | | "帮我查一下上个月的销售报表" | `low` | 直接执行,返回数据 |
40 | | "把客户张三的手机号改成 138xxx" | `medium` | 需要审批,防止误操作 |
41 | | "删除离职员工小王的所有数据" | `high` | 必须审批,不可逆操作 |
42 | | "给所有 VIP 客户发送促销邮件" | `critical` | 必须审批,影响范围大 |
43 |
44 | ### 解决的核心问题
45 |
46 | > **Agent 自主性 vs 安全性的平衡**
47 |
48 | - 太自主 → 可能执行危险操作,造成损失
49 | - 太保守 → 每个操作都要审批,效率低下
50 | - **HITL 方案** → AI 自动评估风险,仅对高风险操作要求审批
51 |
52 | ## 核心知识点
53 |
54 | ### LangGraph 三大核心组件
55 |
56 | ```
57 | ┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
58 | │ [START] ──► [Node A] ──► [Node B] ──► [END] │
59 | │ │ ▲ │
60 | │ └──► [Node C]┘ (条件边) │
61 | └─────────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
62 | ```
63 |
64 | | 组件 | 说明 |
65 | |------|------|
66 | | **State** | 共享内存对象,在所有节点间流转 |
67 | | **Nodes** | 执行逻辑的函数,接收状态返回更新 |
68 | | **Edges** | 节点间转换(静态边/条件边) |
69 |
70 | ### Human-in-the-Loop 架构
71 |
72 | ```
73 | ┌─────────┐ ┌──────────┐ ┌─────────────┐ ┌─────────┐
74 | │ Analyze │ ─► │ Classify │ ─► │ Human │ ─► │ Execute │
75 | │ Request │ │ Risk │ │ Review │ │ Action │
76 | └─────────┘ └──────────┘ └─────────────┘ └─────────┘
77 | │ │
78 | │ Low Risk │ Rejected
79 | └─────────────────┴─────────► [END]
80 | ```
81 |
82 | **风险等级:**
83 |
84 | | 等级 | 说明 | 是否审批 |
85 | |------|------|----------|
86 | | `low` | 只读查询,无副作用 | 否 |
87 | | `medium` | 数据修改,可撤销 | 可配置 |
88 | | `high` | 数据删除、外部 API 调用 | 是 |
89 | | `critical` | 支付、批量操作、不可逆 | 是 + 二次确认 |
90 |
91 | **核心特性:**
92 |
93 | - **断点续跑** - 服务重启后可继续执行(需安装 SQLite 支持)
94 | - **超时自动拒绝** - 防止任务无限等待(默认 5 分钟)
95 | - **完整审计日志** - 追踪所有操作
96 | - **状态持久化** - 任务元数据保存到 SQLite
97 |
98 | ## 项目结构
99 |
100 | ```
101 | day-16/
102 | ├── README.md
103 | ├── requirements.txt
104 | ├── langgraph_agent/
105 | │ ├── __init__.py
106 | │ ├── agent.py # LangGraph ReAct Agent + A2A
107 | │ ├── hitl_agent.py # Human-in-the-Loop Agent 核心
108 | │ ├── checkpointer.py # 状态持久化
109 | │ └── server.py # REST API 服务
110 | ├── client/
111 | │ ├── test_client.py # A2A 测试客户端
112 | │ └── hitl_client.py # HITL 交互客户端
113 | └── data/ # 运行时生成
114 | ├── checkpoints.db # LangGraph 状态
115 | └── tasks.db # 任务元数据
116 | ```
117 |
118 | ## 运行示例
119 |
120 | ### 1. 安装依赖
121 |
122 | ```bash
123 | cd day-16
124 | uv pip install -r requirements.txt
125 |
126 | # 可选:安装 SQLite 持久化支持(生产环境推荐)
127 | uv pip install langgraph-checkpoint-sqlite
128 | ```
129 |
130 | ### 2. 运行 HITL 服务
131 |
132 | ```bash
133 | uv run python -m langgraph_agent.server
134 | ```
135 |
136 | 输出:
137 | ```
138 | ============================================================
139 | Day 16: Human-in-the-Loop Agent Server
140 | ============================================================
141 |
142 | 访问地址:
143 | Web UI: http://localhost:8016/ui <- 推荐
144 | API Docs: http://localhost:8016/docs
145 |
146 | 审批超时: 300 秒
147 | ============================================================
148 | ```
149 |
150 | ### 3. 打开 Web UI(推荐)
151 |
152 | 浏览器访问: **http://localhost:8016/ui**
153 |
154 | 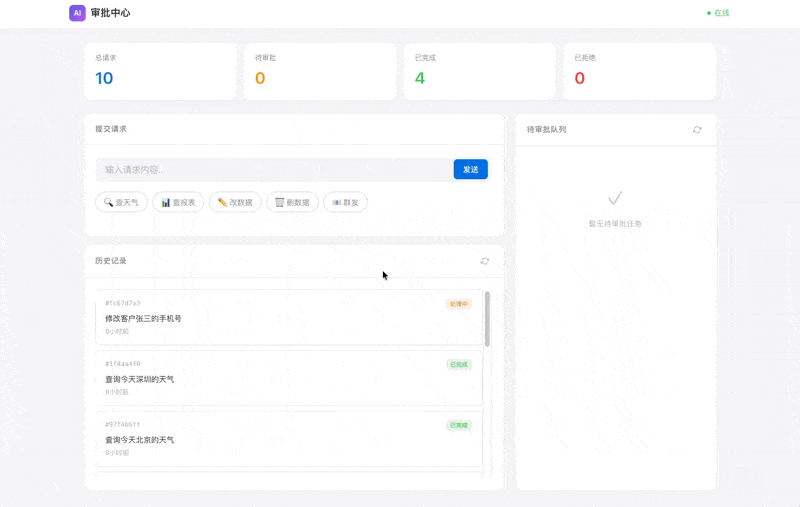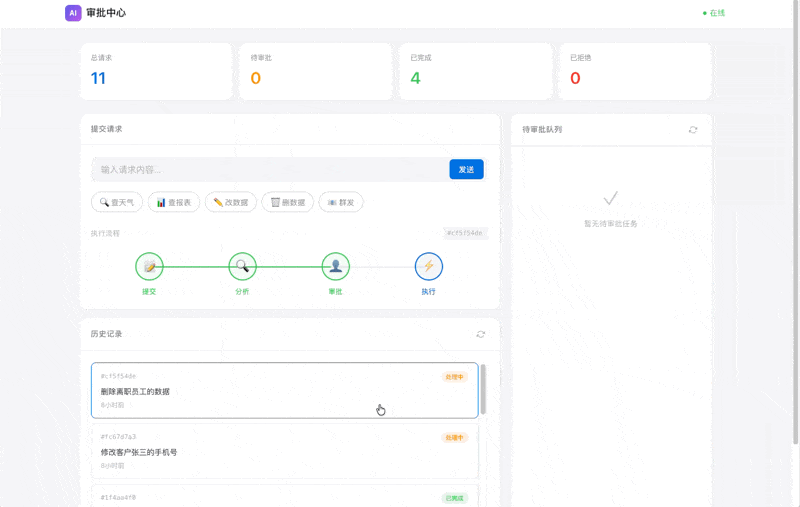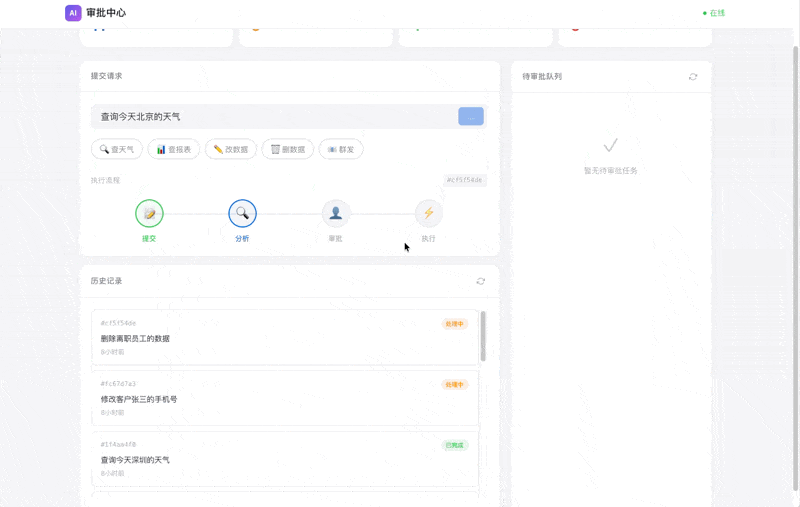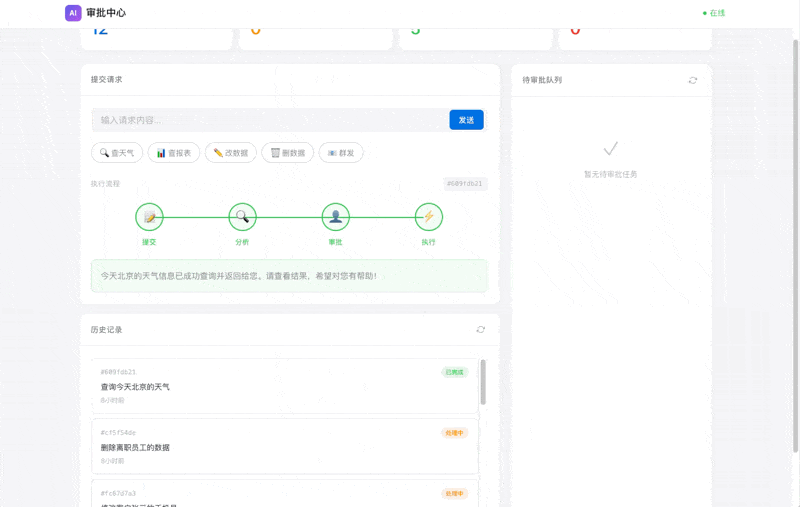
155 |
156 | Web UI 功能:
157 | - 📝 提交请求(带快捷示例按钮)
158 | - ⏳ 查看待审批任务
159 | - ✅❌ 一键批准/拒绝
160 | - 📋 任务历史和统计
161 | - 🔍 点击历史记录查看详情
162 |
163 | ### 4. 或使用命令行客户端
164 |
165 | ```bash
166 | uv run python -m client.hitl_client
167 | ```
168 |
169 | ### 5. 完整演示流程
170 |
171 | ```bash
172 | # 1. 启动服务
173 | uv run python -m langgraph_agent.server
174 |
175 | # 2. 在另一个终端运行客户端,选择 "6. 运行所有演示"
176 | uv run python -m client.hitl_client
177 |
178 | # 演示包括:
179 | # - 低风险任务(查询天气)→ 自动执行
180 | # - 高风险任务(删除数据)→ 等待审批 → 拒绝
181 | # - 中风险任务(发送邮件)→ 等待审批 → 批准
182 | ```
183 |
184 | ### 6. 使用 curl 测试(可选)
185 |
186 | ```bash
187 | # 场景 1: 低风险查询 - 直接返回结果
188 | curl -X POST http://localhost:8016/tasks \
189 | -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
190 | -d '{"message": "查询今天北京的天气"}'
191 |
192 | # 场景 2: 高风险操作 - 需要审批
193 | curl -X POST http://localhost:8016/tasks \
194 | -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
195 | -d '{"message": "删除用户 test@example.com 的所有数据"}'
196 |
197 | # 查看待审批任务
198 | curl http://localhost:8016/tasks/pending
199 |
200 | # 批准任务(替换 {task_id})
201 | curl -X POST http://localhost:8016/tasks/{task_id}/approve \
202 | -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
203 | -d '{"approved": true, "comment": "已确认用户已离职", "approver": "admin"}'
204 |
205 | # 或者拒绝
206 | curl -X POST http://localhost:8016/tasks/{task_id}/reject \
207 | -H "Content-Type: application/json" \
208 | -d '{"approved": false, "comment": "需要先备份数据", "approver": "admin"}'
209 | ```
210 |
211 | ### 5. 运行原有的 A2A 服务
212 |
213 | ```bash
214 | # Terminal 1 - 启动 A2A 服务
215 | uv run python -m langgraph_agent.agent
216 |
217 | # Terminal 2 - 运行测试
218 | uv run python -m client.test_client
219 | ```
220 |
221 | ## 代码核心
222 |
223 | ### 1. HITL Graph 构建
224 |
225 | ```python
226 | from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
227 |
228 | class HITLState(TypedDict):
229 | task_id: str
230 | messages: Annotated[list, add]
231 | risk_level: str
232 | requires_approval: bool
233 | approval_status: str # pending, approved, rejected
234 | final_answer: str
235 |
236 | def create_hitl_graph(checkpointer):
237 | graph = StateGraph(HITLState)
238 |
239 | # 添加节点
240 | graph.add_node("analyze", analyze_request_node)
241 | graph.add_node("human_review", human_review_node)
242 | graph.add_node("execute", execute_action_node)
243 | graph.add_node("respond", generate_response_node)
244 |
245 | # 条件路由:根据风险等级决定是否需要审批
246 | graph.add_conditional_edges(
247 | "analyze",
248 | route_after_analysis,
249 | {"human_review": "human_review", "execute": "execute"}
250 | )
251 |
252 | # 关键:在审批节点前中断,等待外部输入
253 | return graph.compile(
254 | checkpointer=checkpointer,
255 | interrupt_before=["human_review"],
256 | )
257 | ```
258 |
259 | ### 2. 状态持久化
260 |
261 | ```python
262 | from langgraph.checkpoint.memory import MemorySaver
263 | # 或使用 SQLite(需要安装 langgraph-checkpoint-sqlite)
264 | # from langgraph.checkpoint.sqlite import SqliteSaver
265 |
266 | checkpointer = MemorySaver()
267 |
268 | # 图执行时使用 thread_id 区分不同会话
269 | config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "unique-thread-id"}}
270 | result = graph.invoke(initial_state, config)
271 | ```
272 |
273 | ### 3. 审批后恢复执行
274 |
275 | ```python
276 | def resume_after_approval(task_id, thread_id, approved):
277 | graph = create_hitl_graph(checkpointer)
278 | config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": thread_id}}
279 |
280 | # 注入审批结果到图状态
281 | graph.update_state(config, {
282 | "approval_status": "approved" if approved else "rejected"
283 | })
284 |
285 | # 从中断点继续执行
286 | result = graph.invoke(None, config)
287 | return result
288 | ```
289 |
290 | ## 关键学习点
291 |
292 | 1. **interrupt_before** - LangGraph 的中断机制,让图在指定节点前暂停
293 | 2. **Checkpointer** - 状态持久化,支持断点续跑
294 | 3. **update_state** - 外部更新图状态,注入审批结果
295 | 4. **风险评估** - LLM 自动评估操作风险等级
296 | 5. **超时机制** - 后台任务定期检查,超时自动拒绝
297 |
298 | ## API 文档
299 |
300 | 启动服务后访问: http://localhost:8016/docs
301 |
302 | | 端点 | 方法 | 说明 |
303 | |------|------|------|
304 | | `/tasks` | POST | 创建新任务 |
305 | | `/tasks` | GET | 获取任务列表 |
306 | | `/tasks/pending` | GET | 获取待审批任务 |
307 | | `/tasks/{id}` | GET | 获取任务详情 |
308 | | `/tasks/{id}/approve` | POST | 批准任务 |
309 | | `/tasks/{id}/reject` | POST | 拒绝任务 |
310 | | `/health` | GET | 健康检查 |
311 |
312 | ## 配置项
313 |
314 | | 环境变量 | 默认值 | 说明 |
315 | |----------|--------|------|
316 | | `GOOGLE_API_KEY` | - | Google AI API Key |
317 | | `APPROVAL_TIMEOUT_SECONDS` | 300 | 审批超时时间(秒) |
318 | | `HITL_SERVER_URL` | http://localhost:8016 | 服务地址 |
319 |
320 | ## 扩展练习
321 |
322 | 1. **添加更多风险类型** - 扩展 `analyze_request_node` 支持更细粒度的风险判断
323 | 2. **接入真实工具** - 将 `execute_action_node` 中的模拟执行替换为真实 API 调用
324 | 3. **添加审批层级** - 高风险需要一级审批,关键级需要二级审批
325 | 4. **集成通知系统** - 待审批时发送 Slack/邮件通知给管理员
326 |
327 | ## 扩展阅读
328 |
329 | - [LangGraph Human-in-the-Loop](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/human_in_the_loop/)
330 | - [LangGraph Checkpointing](https://langchain-ai.github.io/langgraph/concepts/persistence/)
331 | - [A2A Protocol](https://a2a-protocol.org/)
332 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/langgraph_agent/agent.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 16: LangGraph + A2A Agent
3 |
4 | 这个示例展示了如何:
5 | 1. 使用 LangGraph 构建一个 ReAct 推理图
6 | 2. 将其包装为 ADK Agent
7 | 3. 通过 ADK 的 to_a2a() 对外提供 A2A 服务
8 |
9 | 运行方式:
10 | python -m langgraph_agent.agent
11 | """
12 |
13 | import os
14 | import sys
15 | from typing import TypedDict, Annotated, Literal
16 | from operator import add
17 |
18 | # 添加项目根目录到路径
19 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
20 |
21 | # 加载 .env 文件中的环境变量
22 | from dotenv import load_dotenv
23 | project_root = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
24 | load_dotenv(os.path.join(project_root, ".env"))
25 |
26 | # LangGraph 相关导入
27 | from langgraph.graph import StateGraph, END
28 | from langchain_google_genai import ChatGoogleGenerativeAI
29 | from langchain_core.messages import HumanMessage, AIMessage, SystemMessage
30 |
31 | # ADK 相关导入 (用于 A2A 服务)
32 | from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
33 | from google.adk.a2a.utils.agent_to_a2a import to_a2a
34 |
35 |
36 | # ============================================================
37 | # Part 1: LangGraph ReAct Agent 实现
38 | # ============================================================
39 |
40 | class AgentState(TypedDict):
41 | """
42 | LangGraph Agent 的状态定义
43 |
44 | 这是 LangGraph 的核心概念之一:State
45 | 状态在图的所有节点之间共享,每个节点可以读取和更新状态
46 | """
47 | # 消息历史 - 使用 Annotated 和 add 操作符实现消息追加
48 | messages: Annotated[list, add]
49 | # 思考过程记录
50 | thoughts: list
51 | # 最终答案
52 | final_answer: str
53 | # 迭代次数(防止无限循环)
54 | iteration: int
55 |
56 |
57 | def get_llm():
58 | """获取 Google Gemini LLM 实例"""
59 | return ChatGoogleGenerativeAI(
60 | model="gemini-2.0-flash",
61 | google_api_key=os.getenv("GOOGLE_API_KEY"),
62 | temperature=0.7,
63 | )
64 |
65 |
66 | def reasoning_node(state: AgentState) -> dict:
67 | """
68 | 推理节点 - ReAct 模式中的 "Thought" 步骤
69 |
70 | 这是 LangGraph 的核心概念之一:Node
71 | 节点是执行具体逻辑的函数,接收状态,返回状态更新
72 | """
73 | llm = get_llm()
74 |
75 | system_prompt = """你是一个善于分析问题的 AI 助手。
76 |
77 | 请按照以下格式思考:
78 | 1. 分析问题的核心需求
79 | 2. 思考需要什么信息来回答
80 | 3. 决定是直接回答还是需要更多分析
81 |
82 | 如果你已经有足够信息回答问题,请在回复开头加上 [FINAL]
83 | 如果需要继续分析,请在回复开头加上 [CONTINUE]"""
84 |
85 | messages = state.get("messages", [])
86 | thoughts = state.get("thoughts", [])
87 | iteration = state.get("iteration", 0)
88 |
89 | # 构建 LLM 消息
90 | llm_messages = [SystemMessage(content=system_prompt)]
91 |
92 | for msg in messages:
93 | if isinstance(msg, dict):
94 | if msg.get("role") == "user":
95 | llm_messages.append(HumanMessage(content=msg.get("content", "")))
96 | else:
97 | llm_messages.append(AIMessage(content=msg.get("content", "")))
98 | elif isinstance(msg, (HumanMessage, AIMessage)):
99 | llm_messages.append(msg)
100 |
101 | # 添加之前的思考过程
102 | if thoughts:
103 | thought_summary = "\n".join([f"思考 {i+1}: {t}" for i, t in enumerate(thoughts)])
104 | llm_messages.append(SystemMessage(content=f"之前的思考:\n{thought_summary}"))
105 |
106 | # 调用 LLM
107 | response = llm.invoke(llm_messages)
108 | thought = response.content
109 | new_thoughts = thoughts + [thought]
110 |
111 | # 判断是否结束
112 | if "[FINAL]" in thought or iteration >= 2:
113 | return {
114 | "thoughts": new_thoughts,
115 | "iteration": iteration + 1,
116 | }
117 | else:
118 | return {
119 | "thoughts": new_thoughts,
120 | "iteration": iteration + 1,
121 | }
122 |
123 |
124 | def answer_node(state: AgentState) -> dict:
125 | """
126 | 回答节点 - 生成最终答案
127 | """
128 | llm = get_llm()
129 |
130 | messages = state.get("messages", [])
131 | thoughts = state.get("thoughts", [])
132 |
133 | # 提取原始问题
134 | original_question = ""
135 | for msg in messages:
136 | if isinstance(msg, dict) and msg.get("role") == "user":
137 | original_question = msg.get("content", "")
138 | break
139 | elif isinstance(msg, HumanMessage):
140 | original_question = msg.content
141 | break
142 |
143 | # 构建最终回答提示
144 | thought_summary = "\n".join([f"- {t}" for t in thoughts]) if thoughts else "(直接回答)"
145 |
146 | final_prompt = f"""用户问题:{original_question}
147 |
148 | 分析过程:
149 | {thought_summary}
150 |
151 | 请基于以上分析,给出清晰、准确、有帮助的最终回答:"""
152 |
153 | llm_messages = [
154 | SystemMessage(content="你是一个专业的 AI 助手,请简洁明了地回答用户问题。"),
155 | HumanMessage(content=final_prompt),
156 | ]
157 |
158 | response = llm.invoke(llm_messages)
159 |
160 | return {"final_answer": response.content}
161 |
162 |
163 | def should_continue(state: AgentState) -> Literal["continue", "answer"]:
164 | """
165 | 路由函数 - 决定下一步执行哪个节点
166 |
167 | 这是 LangGraph 的核心概念之一:Conditional Edge
168 | 条件边基于当前状态动态决定控制流
169 | """
170 | thoughts = state.get("thoughts", [])
171 | iteration = state.get("iteration", 0)
172 |
173 | if not thoughts:
174 | return "continue"
175 |
176 | last_thought = thoughts[-1] if thoughts else ""
177 |
178 | # 如果达到最大迭代次数或决定回答
179 | if "[FINAL]" in last_thought or iteration >= 2:
180 | return "answer"
181 |
182 | return "continue"
183 |
184 |
185 | def create_langgraph_agent():
186 | """
187 | 创建 LangGraph Agent
188 |
189 | 展示 LangGraph 的核心构建流程:
190 | 1. 创建 StateGraph
191 | 2. 添加节点 (Nodes)
192 | 3. 定义边 (Edges),包括条件边
193 | 4. 设置入口点
194 | 5. 编译图
195 | """
196 | # 创建状态图
197 | graph = StateGraph(AgentState)
198 |
199 | # 添加节点
200 | graph.add_node("reasoning", reasoning_node)
201 | graph.add_node("answer", answer_node)
202 |
203 | # 设置入口点
204 | graph.set_entry_point("reasoning")
205 |
206 | # 添加条件边 - 这是 LangGraph 实现动态控制流的关键
207 | graph.add_conditional_edges(
208 | "reasoning",
209 | should_continue,
210 | {
211 | "continue": "reasoning", # 继续推理
212 | "answer": "answer", # 生成答案
213 | }
214 | )
215 |
216 | # 添加结束边
217 | graph.add_edge("answer", END)
218 |
219 | # 编译图
220 | return graph.compile()
221 |
222 |
223 | def run_langgraph(user_input: str) -> str:
224 | """
225 | 运行 LangGraph Agent
226 |
227 | 这个函数可以被 ADK Agent 的工具调用
228 | """
229 | agent = create_langgraph_agent()
230 |
231 | # 准备输入状态
232 | input_state = {
233 | "messages": [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}],
234 | "thoughts": [],
235 | "final_answer": "",
236 | "iteration": 0,
237 | }
238 |
239 | # 执行图
240 | result = agent.invoke(input_state)
241 |
242 | return result.get("final_answer", "抱歉,我无法处理这个请求。")
243 |
244 |
245 | # ============================================================
246 | # Part 2: 使用 ADK 将 LangGraph Agent 包装为 A2A 服务
247 | # ============================================================
248 |
249 | # 创建 ADK Agent,内部调用 LangGraph
250 | # 这展示了如何将 LangGraph 的复杂推理能力与 ADK 的 A2A 服务能力结合
251 |
252 | langgraph_adk_agent = LlmAgent(
253 | name="langgraph_react_agent",
254 | description="基于 LangGraph 构建的 ReAct 推理 Agent - 能够进行多步骤推理分析,深思熟虑后给出答案",
255 | model="gemini-2.0-flash",
256 | instruction="""你是一个强大的 AI 助手,具有深度推理能力。
257 |
258 | 你的特点:
259 | - 使用 ReAct (Reasoning + Acting) 模式进行思考
260 | - 能够分析复杂问题,进行多步骤推理
261 | - 在回答前会仔细思考,确保答案的准确性和有用性
262 |
263 | 当用户提问时,你会:
264 | 1. 先分析问题的核心需求
265 | 2. 思考需要什么信息或知识来回答
266 | 3. 给出清晰、准确、有帮助的答案
267 |
268 | 你擅长:
269 | - 技术问题解答(编程、架构、AI/ML 等)
270 | - 概念解释和对比分析
271 | - 问题分析和解决方案建议
272 | """,
273 | )
274 |
275 | # 使用 ADK 的 to_a2a() 将 Agent 转换为 A2A 服务
276 | # 这是最简单可靠的方式,ADK 会自动处理所有 A2A 协议细节
277 | app = to_a2a(
278 | agent=langgraph_adk_agent,
279 | host="localhost",
280 | port=8016,
281 | protocol="http"
282 | )
283 |
284 |
285 | # ============================================================
286 | # Part 3: 独立的 LangGraph 演示(不使用 A2A)
287 | # ============================================================
288 |
289 | def demo_langgraph_only():
290 | """
291 | 纯 LangGraph 演示,不涉及 A2A
292 | 用于理解 LangGraph 的工作原理
293 | """
294 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
295 | print("LangGraph ReAct Agent 演示")
296 | print("=" * 60)
297 |
298 | test_questions = [
299 | "什么是 LangGraph?它和 LangChain 有什么关系?",
300 | "解释一下 ReAct 模式是什么?",
301 | ]
302 |
303 | for i, question in enumerate(test_questions, 1):
304 | print(f"\n问题 {i}: {question}")
305 | print("-" * 40)
306 |
307 | answer = run_langgraph(question)
308 | print(f"回答: {answer[:500]}...")
309 | print("-" * 40)
310 |
311 |
312 | # ============================================================
313 | # 主程序
314 | # ============================================================
315 |
316 | if __name__ == "__main__":
317 | import uvicorn
318 | import argparse
319 |
320 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Day 16: LangGraph + A2A")
321 | parser.add_argument("--demo", action="store_true", help="运行纯 LangGraph 演示(不启动 A2A 服务)")
322 | args = parser.parse_args()
323 |
324 | if args.demo:
325 | # 纯 LangGraph 演示模式
326 | demo_langgraph_only()
327 | else:
328 | # A2A 服务模式
329 | print("=" * 60)
330 | print("Day 16: LangGraph + A2A")
331 | print("=" * 60)
332 | print()
333 | print("Agent 信息:")
334 | print(f" 名称: {langgraph_adk_agent.name}")
335 | print(f" 框架: LangGraph + ADK")
336 | print(f" 模式: ReAct (Reasoning + Acting)")
337 | print()
338 | print("A2A 服务端点:")
339 | print(" URL: http://localhost:8016")
340 | print(" Agent Card: http://localhost:8016/.well-known/agent.json")
341 | print()
342 | print("提示:")
343 | print(" - 运行客户端: python -m client.test_client")
344 | print(" - 纯 LangGraph 演示: python -m langgraph_agent.agent --demo")
345 | print("=" * 60)
346 | print()
347 |
348 | # 启动 A2A 服务
349 | uvicorn.run(app, host="localhost", port=8016)
350 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-14/host_agent/agent.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 14: Host Agent (A2A Client)
3 |
4 | 这是主控 Agent,它通过 A2A 协议调用远程的翻译 Agent。
5 | 演示了如何作为 A2A 客户端与远程 Agent 进行通信。
6 |
7 | 运行前确保:
8 | 1. 设置环境变量: export GOOGLE_API_KEY="your-api-key"
9 | 2. 远程 Agent 已经在 http://localhost:8001 运行
10 | 3. 运行: python -m host_agent.agent
11 | """
12 |
13 | import asyncio
14 | import os
15 | import sys
16 | import uuid
17 |
18 | # 添加项目根目录到路径
19 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
20 |
21 | import httpx
22 | from a2a.client import ClientFactory, ClientConfig
23 | from a2a.types import Role
24 | from a2a.client.helpers import create_text_message_object
25 |
26 | # 远程 Agent 的 URL
27 | REMOTE_AGENT_URL = "http://localhost:8001"
28 |
29 |
30 | def get_client_config() -> ClientConfig:
31 | """创建不使用代理的客户端配置"""
32 | # 创建 httpx 客户端,完全禁用代理以避免本地连接问题
33 | # trust_env=False 会忽略环境变量中的代理设置
34 | httpx_client = httpx.AsyncClient(
35 | trust_env=False,
36 | timeout=120.0,
37 | )
38 | return ClientConfig(httpx_client=httpx_client)
39 |
40 |
41 | # ============================================================
42 | # 1. A2A 客户端 - 直接调用远程 Agent
43 | # ============================================================
44 |
45 | async def call_remote_agent_directly(text_to_translate: str, target_language: str = "中文"):
46 | """
47 | 直接使用 A2A 客户端调用远程翻译 Agent
48 |
49 | 这是最基本的 A2A 调用方式,展示了:
50 | - 如何创建 A2A 客户端
51 | - 如何构造请求消息
52 | - 如何处理响应
53 | """
54 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
55 | print("方法 1: 直接调用远程 Agent (A2A Client)")
56 | print("=" * 60)
57 |
58 | # 使用 ClientFactory.connect() 连接远程 Agent
59 | # 这会自动获取 Agent Card 并创建合适的客户端
60 | client = await ClientFactory.connect(REMOTE_AGENT_URL, client_config=get_client_config())
61 |
62 | # 获取 Agent Card 信息 (使用 _card 属性)
63 | print("\n📇 Agent 信息:")
64 | print(f" 名称: {client._card.name}")
65 | print(f" 描述: {client._card.description[:80]}...")
66 | print(f" 技能: {[skill.name for skill in (client._card.skills or [])]}")
67 |
68 | # 构造翻译请求消息
69 | request_text = f"请将以下文本翻译成{target_language}:\n{text_to_translate}"
70 |
71 | print(f"\n📤 发送请求: {request_text[:60]}...")
72 |
73 | # 创建消息对象 (注意: 参数是 content 不是 text)
74 | message = create_text_message_object(
75 | role=Role.user,
76 | content=request_text,
77 | )
78 |
79 | # 发送消息给远程 Agent (注意: 参数是 request 不是 message)
80 | result = None
81 | async for event in client.send_message(request=message):
82 | # 处理返回的事件
83 | # event 是 (Task, TaskEvent) 或 Message 元组
84 | if isinstance(event, tuple) and len(event) >= 2:
85 | task, task_event = event[0], event[1]
86 | if task_event:
87 | # 处理 TaskStatusUpdateEvent 或 TaskArtifactUpdateEvent
88 | if hasattr(task_event, 'status') and task_event.status:
89 | state = task_event.status.state
90 | print(f" [状态] {state}")
91 | if task_event.status.message:
92 | for part in task_event.status.message.parts:
93 | if hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:
94 | result = part.text
95 | elif hasattr(task_event, 'artifact') and task_event.artifact:
96 | for part in task_event.artifact.parts:
97 | if hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:
98 | result = part.text
99 |
100 | if result:
101 | print(f"\n📥 翻译结果:\n {result}")
102 |
103 | return result
104 |
105 |
106 | # ============================================================
107 | # 2. 流式调用 - 实时获取翻译进度
108 | # ============================================================
109 |
110 | async def call_remote_agent_streaming(text_to_translate: str, target_language: str = "中文"):
111 | """
112 | 使用流式模式调用远程 Agent
113 |
114 | 适用于长文本翻译,可以实时看到翻译进度
115 | """
116 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
117 | print("方法 2: 流式调用远程 Agent (Streaming)")
118 | print("=" * 60)
119 |
120 | client = await ClientFactory.connect(REMOTE_AGENT_URL, client_config=get_client_config())
121 |
122 | request_text = f"请将以下文本翻译成{target_language},并提供详细的翻译说明:\n{text_to_translate}"
123 |
124 | print(f"\n📤 发送流式请求...")
125 | print(f" 原文: {text_to_translate[:50]}...")
126 | print("\n📥 实时响应:")
127 |
128 | message = create_text_message_object(
129 | role=Role.user,
130 | content=request_text,
131 | )
132 |
133 | collected_text = []
134 | async for event in client.send_message(request=message):
135 | if isinstance(event, tuple) and len(event) >= 2:
136 | task, task_event = event[0], event[1]
137 | if task_event:
138 | if hasattr(task_event, 'status') and task_event.status:
139 | state = task_event.status.state
140 | print(f" [状态更新] {state}")
141 | if task_event.status.message:
142 | for part in task_event.status.message.parts:
143 | if hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:
144 | collected_text.append(part.text)
145 | print(f" {part.text[:100]}...")
146 | elif hasattr(task_event, 'artifact') and task_event.artifact:
147 | print(" [产出物] ", end="")
148 | for part in task_event.artifact.parts:
149 | if hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:
150 | collected_text.append(part.text)
151 | print(part.text[:100], end="...")
152 | print()
153 |
154 | if collected_text:
155 | print(f"\n 完整结果: {collected_text[-1][:200]}...")
156 |
157 |
158 | # ============================================================
159 | # 3. 多轮对话 - 保持上下文
160 | # ============================================================
161 |
162 | async def multi_turn_conversation():
163 | """
164 | 演示与远程 Agent 的多轮对话
165 |
166 | A2A 支持通过 context_id 保持对话上下文
167 | """
168 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
169 | print("方法 3: 多轮对话 (Multi-turn Conversation)")
170 | print("=" * 60)
171 |
172 | client = await ClientFactory.connect(REMOTE_AGENT_URL, client_config=get_client_config())
173 |
174 | context_id = str(uuid.uuid4()) # 创建会话上下文 ID
175 |
176 | conversations = [
177 | "请翻译:The quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.",
178 | "这句话有什么特别之处吗?",
179 | "能给我一个中文版本的类似句子吗?",
180 | ]
181 |
182 | for i, user_input in enumerate(conversations, 1):
183 | print(f"\n🗣️ 轮次 {i}: {user_input}")
184 |
185 | message = create_text_message_object(
186 | role=Role.user,
187 | content=user_input,
188 | )
189 |
190 | result_text = None
191 | # 注意: 当前 SDK 版本不支持 context_id 参数
192 | # 多轮对话上下文需要通过其他方式管理
193 | async for event in client.send_message(request=message):
194 | if isinstance(event, tuple) and len(event) >= 2:
195 | task, task_event = event[0], event[1]
196 | if task_event:
197 | if hasattr(task_event, 'status') and task_event.status and task_event.status.message:
198 | for part in task_event.status.message.parts:
199 | if hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:
200 | result_text = part.text
201 | elif hasattr(task_event, 'artifact') and task_event.artifact:
202 | for part in task_event.artifact.parts:
203 | if hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:
204 | result_text = part.text
205 |
206 | if result_text:
207 | # 截断显示
208 | display_text = result_text[:300] + "..." if len(result_text) > 300 else result_text
209 | print(f"🤖 回复: {display_text}")
210 |
211 |
212 | # ============================================================
213 | # 简单测试函数
214 | # ============================================================
215 |
216 | async def simple_test():
217 | """最简单的 A2A 调用示例"""
218 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
219 | print("简单测试: A2A 连接和调用")
220 | print("=" * 60)
221 |
222 | # 1. 连接到远程 Agent
223 | print("\n1️⃣ 连接远程 Agent...")
224 | client = await ClientFactory.connect(REMOTE_AGENT_URL, client_config=get_client_config())
225 | print(f" ✅ 连接成功! Agent: {client._card.name}")
226 |
227 | # 2. 发送简单请求
228 | print("\n2️⃣ 发送翻译请求...")
229 | message = create_text_message_object(
230 | role=Role.user,
231 | content="请翻译:Hello World"
232 | )
233 |
234 | print(" 等待响应...")
235 | async for event in client.send_message(request=message):
236 | if isinstance(event, tuple) and len(event) >= 2:
237 | task, task_event = event[0], event[1]
238 | if task_event:
239 | if hasattr(task_event, 'artifact') and task_event.artifact:
240 | for part in task_event.artifact.parts:
241 | if hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:
242 | print(f"\n3️⃣ 收到翻译结果: {part.text}")
243 |
244 |
245 | # ============================================================
246 | # 主程序
247 | # ============================================================
248 |
249 | async def main():
250 | print("=" * 60)
251 | print("Day 14: A2A Host Agent - 调用远程翻译服务")
252 | print("=" * 60)
253 | print()
254 | print(f"远程 Agent URL: {REMOTE_AGENT_URL}")
255 | print("确保远程 Agent 已运行: python -m remote_agent.agent")
256 | print()
257 |
258 | try:
259 | # 首先进行简单测试
260 | await simple_test()
261 |
262 | # 方法 1: 直接调用
263 | await call_remote_agent_directly(
264 | "Hello, World! Welcome to the Agent2Agent protocol.",
265 | "中文"
266 | )
267 |
268 | # 再测试一个中译英
269 | await call_remote_agent_directly(
270 | "人工智能正在改变我们的生活方式。",
271 | "英文"
272 | )
273 |
274 | # 方法 2: 流式调用
275 | await call_remote_agent_streaming(
276 | "Artificial Intelligence (AI) is transforming industries worldwide. "
277 | "From healthcare to finance, AI systems are automating tasks.",
278 | "中文"
279 | )
280 |
281 | # 方法 3: 多轮对话
282 | await multi_turn_conversation()
283 |
284 | except Exception as e:
285 | print(f"\n❌ 错误: {e}")
286 | import traceback
287 | traceback.print_exc()
288 | print("\n请确保:")
289 | print("1. 远程 Agent 正在运行 (python -m remote_agent.agent)")
290 | print("2. 端口 8001 没有被占用")
291 | print("3. GOOGLE_API_KEY 环境变量已设置")
292 |
293 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
294 | print("演示结束")
295 | print("=" * 60)
296 |
297 |
298 | if __name__ == "__main__":
299 | asyncio.run(main())
300 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-15/a2ui.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | A2UI Python SDK - Agent-to-User Interface 生成器
3 |
4 | 这个模块提供了生成 A2UI JSONL 的 Python API。
5 | A2UI 是 Google 推出的声明式 UI 协议,让 Agent 能安全地生成动态界面。
6 | """
7 |
8 | import json
9 | from typing import List, Dict, Any, Optional, Union
10 | from dataclasses import dataclass, field
11 |
12 |
13 | @dataclass
14 | class A2UIComponent:
15 | """A2UI 组件"""
16 | id: str
17 | type: str
18 | props: Dict[str, Any] = field(default_factory=dict)
19 |
20 | def to_dict(self) -> Dict:
21 | return {
22 | "id": self.id,
23 | "component": {self.type: self.props}
24 | }
25 |
26 |
27 | class A2UI:
28 | """
29 | A2UI 消息构建器
30 |
31 | 使用链式 API 构建 A2UI JSONL 消息。
32 |
33 | 示例:
34 | ui = A2UI("my-surface")
35 | ui.text("title", "Hello World", "h1")
36 | ui.button("btn", "Click Me", "on_click")
37 | ui.column("main", ["title", "btn"])
38 | print(ui.build("main"))
39 | """
40 |
41 | def __init__(self, surface_id: str):
42 | self.surface_id = surface_id
43 | self.components: List[A2UIComponent] = []
44 | self.data: Dict[str, Any] = {}
45 |
46 | # ========== 基础组件 ==========
47 |
48 | def text(self, id: str, content: str, hint: str = "body") -> 'A2UI':
49 | """
50 | 添加文本组件
51 |
52 | Args:
53 | id: 组件唯一标识
54 | content: 文本内容
55 | hint: 用途提示 (h1, h2, h3, body, caption)
56 | """
57 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(
58 | id=id,
59 | type="Text",
60 | props={
61 | "text": {"literalString": content},
62 | "usageHint": hint
63 | }
64 | ))
65 | return self
66 |
67 | def text_binding(self, id: str, path: str, hint: str = "body") -> 'A2UI':
68 | """添加数据绑定的文本"""
69 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(
70 | id=id,
71 | type="Text",
72 | props={
73 | "text": {"path": path},
74 | "usageHint": hint
75 | }
76 | ))
77 | return self
78 |
79 | def button(self, id: str, label: str, action: str, style: str = "filled") -> 'A2UI':
80 | """
81 | 添加按钮组件
82 |
83 | Args:
84 | id: 组件唯一标识
85 | label: 按钮文字
86 | action: 点击时触发的动作名
87 | style: 按钮样式 (filled, outlined, text)
88 | """
89 | label_id = f"{id}__label"
90 | self.text(label_id, label)
91 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(
92 | id=id,
93 | type="Button",
94 | props={
95 | "child": label_id,
96 | "action": {"name": action},
97 | "style": style
98 | }
99 | ))
100 | return self
101 |
102 | def text_field(self, id: str, path: str, label: str = "",
103 | placeholder: str = "", multiline: bool = False) -> 'A2UI':
104 | """
105 | 添加文本输入框
106 |
107 | Args:
108 | id: 组件唯一标识
109 | path: 数据绑定路径 (如 /user/name)
110 | label: 标签文字
111 | placeholder: 占位符
112 | multiline: 是否多行
113 | """
114 | props = {"value": {"path": path}}
115 | if label:
116 | props["labelText"] = {"literalString": label}
117 | if placeholder:
118 | props["hintText"] = {"literalString": placeholder}
119 | if multiline:
120 | props["maxLines"] = 5
121 |
122 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(id=id, type="TextField", props=props))
123 | return self
124 |
125 | def checkbox(self, id: str, path: str, label: str) -> 'A2UI':
126 | """添加复选框"""
127 | label_id = f"{id}__label"
128 | self.text(label_id, label)
129 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(
130 | id=id,
131 | type="Checkbox",
132 | props={
133 | "value": {"path": path},
134 | "label": label_id
135 | }
136 | ))
137 | return self
138 |
139 | def image(self, id: str, url: str, alt: str = "") -> 'A2UI':
140 | """添加图片"""
141 | props = {"source": {"literalString": url}}
142 | if alt:
143 | props["altText"] = {"literalString": alt}
144 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(id=id, type="Image", props=props))
145 | return self
146 |
147 | def divider(self, id: str) -> 'A2UI':
148 | """添加分隔线"""
149 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(id=id, type="Divider", props={}))
150 | return self
151 |
152 | def spacer(self, id: str, size: int = 16) -> 'A2UI':
153 | """添加间距"""
154 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(
155 | id=id,
156 | type="Spacer",
157 | props={"size": size}
158 | ))
159 | return self
160 |
161 | # ========== 布局组件 ==========
162 |
163 | def column(self, id: str, children: List[str],
164 | align: str = "start", gap: int = 8) -> 'A2UI':
165 | """
166 | 垂直布局容器
167 |
168 | Args:
169 | id: 组件唯一标识
170 | children: 子组件 ID 列表
171 | align: 对齐方式 (start, center, end, stretch)
172 | gap: 子组件间距
173 | """
174 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(
175 | id=id,
176 | type="Column",
177 | props={
178 | "children": children,
179 | "mainAxisAlignment": align,
180 | "spacing": gap
181 | }
182 | ))
183 | return self
184 |
185 | def row(self, id: str, children: List[str],
186 | align: str = "start", gap: int = 8) -> 'A2UI':
187 | """水平布局容器"""
188 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(
189 | id=id,
190 | type="Row",
191 | props={
192 | "children": children,
193 | "mainAxisAlignment": align,
194 | "spacing": gap
195 | }
196 | ))
197 | return self
198 |
199 | def card(self, id: str, child: str, elevation: int = 1) -> 'A2UI':
200 | """卡片容器"""
201 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(
202 | id=id,
203 | type="Card",
204 | props={
205 | "child": child,
206 | "elevation": elevation
207 | }
208 | ))
209 | return self
210 |
211 | def container(self, id: str, child: str,
212 | padding: int = 16,
213 | background: str = None) -> 'A2UI':
214 | """通用容器"""
215 | props = {
216 | "child": child,
217 | "padding": padding
218 | }
219 | if background:
220 | props["backgroundColor"] = background
221 | self.components.append(A2UIComponent(id=id, type="Container", props=props))
222 | return self
223 |
224 | # ========== 数据 ==========
225 |
226 | def set_data(self, path: str, value: Any) -> 'A2UI':
227 | """
228 | 设置数据模型
229 |
230 | Args:
231 | path: 数据路径 (如 "user" 或 "user.name")
232 | value: 数据值 (字符串、数字或字典)
233 | """
234 | self.data[path] = value
235 | return self
236 |
237 | # ========== 生成 ==========
238 |
239 | def build(self, root_id: str) -> str:
240 | """
241 | 生成 A2UI JSONL
242 |
243 | Args:
244 | root_id: 根组件 ID
245 |
246 | Returns:
247 | JSONL 格式的字符串,每行一个 JSON 对象
248 | """
249 | lines = []
250 |
251 | # 1. surfaceUpdate
252 | lines.append(json.dumps({
253 | "surfaceUpdate": {
254 | "surfaceId": self.surface_id,
255 | "components": [c.to_dict() for c in self.components]
256 | }
257 | }, ensure_ascii=False))
258 |
259 | # 2. dataModelUpdate (可选)
260 | if self.data:
261 | contents = []
262 | for key, value in self.data.items():
263 | if isinstance(value, dict):
264 | contents.append({
265 | "key": key,
266 | "valueMap": [
267 | {"key": k, "valueString": str(v)}
268 | for k, v in value.items()
269 | ]
270 | })
271 | else:
272 | contents.append({"key": key, "valueString": str(value)})
273 |
274 | lines.append(json.dumps({
275 | "dataModelUpdate": {
276 | "surfaceId": self.surface_id,
277 | "contents": contents
278 | }
279 | }, ensure_ascii=False))
280 |
281 | # 3. beginRendering
282 | lines.append(json.dumps({
283 | "beginRendering": {
284 | "surfaceId": self.surface_id,
285 | "root": root_id
286 | }
287 | }, ensure_ascii=False))
288 |
289 | return "\n".join(lines)
290 |
291 | def to_json(self, root_id: str) -> Dict:
292 | """返回结构化的 JSON 对象(用于 API 响应)"""
293 | return {
294 | "surface_id": self.surface_id,
295 | "components": [c.to_dict() for c in self.components],
296 | "data": self.data,
297 | "root": root_id
298 | }
299 |
300 |
301 | # ========== 便捷工厂函数 ==========
302 |
303 | def create_login_form() -> A2UI:
304 | """创建登录表单"""
305 | return (A2UI("login")
306 | .text("title", "用户登录", "h1")
307 | .text_field("username", "/user/username", "用户名", "请输入用户名")
308 | .text_field("password", "/user/password", "密码", "请输入密码")
309 | .button("submit", "登录", "submit_login")
310 | .column("form", ["title", "username", "password", "submit"], gap=16)
311 | .card("card", "form"))
312 |
313 |
314 | def create_restaurant_list(restaurants: List[Dict]) -> A2UI:
315 | """创建餐厅列表"""
316 | ui = A2UI("restaurants")
317 | ui.text("title", "🍱 附近的餐厅", "h1")
318 |
319 | cards = []
320 | for i, r in enumerate(restaurants):
321 | prefix = f"r{i}"
322 | ui.text(f"{prefix}-name", r.get("name", ""), "h2")
323 | ui.text(f"{prefix}-info", f"¥{r.get('price', 0)} · ★{r.get('rating', 0)} · {r.get('distance', '')}")
324 | ui.button(f"{prefix}-view", "查看", f"view_{i}", "outlined")
325 | ui.button(f"{prefix}-book", "预订", f"book_{i}", "filled")
326 | ui.row(f"{prefix}-actions", [f"{prefix}-view", f"{prefix}-book"], gap=8)
327 | ui.column(f"{prefix}-content", [f"{prefix}-name", f"{prefix}-info", f"{prefix}-actions"], gap=8)
328 | ui.card(f"{prefix}-card", f"{prefix}-content")
329 | cards.append(f"{prefix}-card")
330 |
331 | ui.column("list", cards, gap=16)
332 | ui.column("main", ["title", "list"], gap=24)
333 | return ui
334 |
335 |
336 | def create_weather_card(city: str, temp: int, condition: str, humidity: int) -> A2UI:
337 | """创建天气卡片"""
338 | return (A2UI("weather")
339 | .text("title", f"🌤️ {city}天气", "h1")
340 | .text("temp", f"{temp}°C", "h2")
341 | .text("condition", condition)
342 | .text("humidity", f"湿度 {humidity}%")
343 | .button("refresh", "刷新", "refresh_weather", "outlined")
344 | .column("info", ["title", "temp", "condition", "humidity", "refresh"], gap=12)
345 | .card("card", "info"))
346 |
347 |
348 | # ========== 测试 ==========
349 |
350 | if __name__ == "__main__":
351 | # 测试餐厅列表
352 | restaurants = [
353 | {"name": "意大利花园", "price": 180, "rating": 4.8, "distance": "500m"},
354 | {"name": "牛排工坊", "price": 280, "rating": 4.5, "distance": "800m"},
355 | {"name": "巴黎小馆", "price": 150, "rating": 4.9, "distance": "1.2km"},
356 | ]
357 |
358 | ui = create_restaurant_list(restaurants)
359 | print("=== A2UI JSONL ===")
360 | print(ui.build("main"))
361 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-09/day-09-session-rewind.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "# Day 9: ⏪ Undo Buttons for your Agents\n",
8 | "\n",
9 | "> Building an \"Edit Message\" or \"Regenerate\" feature shouldn't require complex database migrations. In the ADK, time travel is built-in.\n",
10 | "\n",
11 | "## 今日目标\n",
12 | "\n",
13 | "学习 ADK 的 **Session Rewind** 功能,实现:\n",
14 | "- 编辑消息 (Edit Message)\n",
15 | "- 重新生成 (Regenerate)\n",
16 | "- 撤销操作 (Undo)\n",
17 | "\n",
18 | "## 官方资源\n",
19 | "\n",
20 | "- [ADK Sessions Rewind](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/sessions/rewind/)\n",
21 | "- [ADK Runtime Resume](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/runtime/resume/)\n",
22 | "- [官方示例代码](https://github.com/google/adk-python/blob/main/contributing/samples/rewind_session/main.py)"
23 | ]
24 | },
25 | {
26 | "cell_type": "markdown",
27 | "metadata": {},
28 | "source": [
29 | "## 1. 环境准备"
30 | ]
31 | },
32 | {
33 | "cell_type": "code",
34 | "execution_count": null,
35 | "metadata": {},
36 | "outputs": [],
37 | "source": [
38 | "import sys\n",
39 | "sys.path.insert(0, '..')\n",
40 | "\n",
41 | "from shared.config import load_env\n",
42 | "load_env()"
43 | ]
44 | },
45 | {
46 | "cell_type": "code",
47 | "execution_count": null,
48 | "metadata": {},
49 | "outputs": [],
50 | "source": [
51 | "from google.adk import Agent\n",
52 | "from google.adk.tools.tool_context import ToolContext\n",
53 | "from google.adk.agents.run_config import RunConfig\n",
54 | "from google.adk.runners import InMemoryRunner\n",
55 | "from google.genai import types"
56 | ]
57 | },
58 | {
59 | "cell_type": "markdown",
60 | "metadata": {},
61 | "source": [
62 | "## 2. 定义工具函数\n",
63 | "\n",
64 | "我们创建一个可以管理状态和文件的 Agent,用来演示回溯功能。"
65 | ]
66 | },
67 | {
68 | "cell_type": "code",
69 | "execution_count": null,
70 | "metadata": {},
71 | "outputs": [],
72 | "source": [
73 | "async def update_state(tool_context: ToolContext, key: str, value: str) -> dict:\n",
74 | " \"\"\"更新状态值\"\"\"\n",
75 | " tool_context.state[key] = value\n",
76 | " return {\"status\": f\"已更新 '{key}' 为 '{value}'\"}\n",
77 | "\n",
78 | "\n",
79 | "async def load_state(tool_context: ToolContext, key: str) -> dict:\n",
80 | " \"\"\"读取状态值\"\"\"\n",
81 | " return {key: tool_context.state.get(key, \"未找到\")}\n",
82 | "\n",
83 | "\n",
84 | "async def save_artifact(tool_context: ToolContext, filename: str, content: str) -> dict:\n",
85 | " \"\"\"保存文件内容\"\"\"\n",
86 | " artifact_bytes = content.encode(\"utf-8\")\n",
87 | " artifact_part = types.Part(\n",
88 | " inline_data=types.Blob(mime_type=\"text/plain\", data=artifact_bytes)\n",
89 | " )\n",
90 | " version = await tool_context.save_artifact(filename, artifact_part)\n",
91 | " return {\"status\": \"成功\", \"filename\": filename, \"version\": version}\n",
92 | "\n",
93 | "\n",
94 | "async def load_artifact(tool_context: ToolContext, filename: str) -> dict:\n",
95 | " \"\"\"读取文件内容\"\"\"\n",
96 | " artifact = await tool_context.load_artifact(filename)\n",
97 | " if not artifact:\n",
98 | " return {\"error\": f\"文件 '{filename}' 未找到\"}\n",
99 | " content = artifact.inline_data.data.decode(\"utf-8\")\n",
100 | " return {\"filename\": filename, \"content\": content}"
101 | ]
102 | },
103 | {
104 | "cell_type": "markdown",
105 | "metadata": {},
106 | "source": [
107 | "## 3. 创建 Agent"
108 | ]
109 | },
110 | {
111 | "cell_type": "code",
112 | "execution_count": null,
113 | "metadata": {},
114 | "outputs": [],
115 | "source": [
116 | "state_agent = Agent(\n",
117 | " name=\"state_agent\",\n",
118 | " model=\"gemini-2.0-flash\",\n",
119 | " instruction=\"\"\"你是一个状态和文件管理 Agent。\n",
120 | "\n",
121 | "你可以:\n",
122 | "- 更新状态值 (update_state)\n",
123 | "- 读取状态值 (load_state)\n",
124 | "- 保存文件 (save_artifact)\n",
125 | "- 读取文件 (load_artifact)\n",
126 | "\n",
127 | "根据用户的请求使用相应的工具。用中文回复。\"\"\",\n",
128 | " tools=[\n",
129 | " update_state,\n",
130 | " load_state,\n",
131 | " save_artifact,\n",
132 | " load_artifact,\n",
133 | " ],\n",
134 | ")\n",
135 | "\n",
136 | "print(\"✅ Agent 创建成功\")"
137 | ]
138 | },
139 | {
140 | "cell_type": "markdown",
141 | "metadata": {},
142 | "source": [
143 | "## 4. 创建辅助函数"
144 | ]
145 | },
146 | {
147 | "cell_type": "code",
148 | "execution_count": null,
149 | "metadata": {},
150 | "outputs": [],
151 | "source": [
152 | "APP_NAME = \"rewind_demo\"\n",
153 | "USER_ID = \"demo_user\"\n",
154 | "\n",
155 | "\n",
156 | "async def call_agent(runner, session_id: str, prompt: str):\n",
157 | " \"\"\"调用 Agent 并打印结果\"\"\"\n",
158 | " print(f\"\\n👤 用户: {prompt}\")\n",
159 | " content = types.Content(\n",
160 | " role=\"user\", parts=[types.Part.from_text(text=prompt)]\n",
161 | " )\n",
162 | " events = []\n",
163 | " async for event in runner.run_async(\n",
164 | " user_id=USER_ID,\n",
165 | " session_id=session_id,\n",
166 | " new_message=content,\n",
167 | " run_config=RunConfig(),\n",
168 | " ):\n",
169 | " events.append(event)\n",
170 | " if event.content and event.author and event.author != \"user\":\n",
171 | " for part in event.content.parts:\n",
172 | " if part.text:\n",
173 | " print(f\" 🤖 Agent: {part.text}\")\n",
174 | " elif part.function_call:\n",
175 | " print(f\" 🛠️ 工具调用: {part.function_call.name}({part.function_call.args})\")\n",
176 | " elif part.function_response:\n",
177 | " print(f\" 📦 工具响应: {part.function_response.response}\")\n",
178 | " return events"
179 | ]
180 | },
181 | {
182 | "cell_type": "markdown",
183 | "metadata": {},
184 | "source": [
185 | "## 5. Session Rewind 演示\n",
186 | "\n",
187 | "### 5.1 创建 Runner 和 Session"
188 | ]
189 | },
190 | {
191 | "cell_type": "code",
192 | "execution_count": null,
193 | "metadata": {},
194 | "outputs": [],
195 | "source": [
196 | "# 创建 Runner\n",
197 | "runner = InMemoryRunner(\n",
198 | " agent=state_agent,\n",
199 | " app_name=APP_NAME,\n",
200 | ")\n",
201 | "\n",
202 | "# 创建会话\n",
203 | "session = await runner.session_service.create_session(\n",
204 | " app_name=APP_NAME, user_id=USER_ID\n",
205 | ")\n",
206 | "print(f\"📝 创建会话: {session.id}\")"
207 | ]
208 | },
209 | {
210 | "cell_type": "markdown",
211 | "metadata": {},
212 | "source": [
213 | "### 5.2 步骤 1: 初始化状态"
214 | ]
215 | },
216 | {
217 | "cell_type": "code",
218 | "execution_count": null,
219 | "metadata": {},
220 | "outputs": [],
221 | "source": [
222 | "# 设置初始状态\n",
223 | "await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"设置状态 color 为 red\")"
224 | ]
225 | },
226 | {
227 | "cell_type": "code",
228 | "execution_count": null,
229 | "metadata": {},
230 | "outputs": [],
231 | "source": [
232 | "# 保存初始文件\n",
233 | "await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"保存文件 note.txt 内容为 version1\")"
234 | ]
235 | },
236 | {
237 | "cell_type": "markdown",
238 | "metadata": {},
239 | "source": [
240 | "### 5.3 步骤 2: 确认当前状态"
241 | ]
242 | },
243 | {
244 | "cell_type": "code",
245 | "execution_count": null,
246 | "metadata": {},
247 | "outputs": [],
248 | "source": [
249 | "await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"查询状态 color 的值\")"
250 | ]
251 | },
252 | {
253 | "cell_type": "code",
254 | "execution_count": null,
255 | "metadata": {},
256 | "outputs": [],
257 | "source": [
258 | "await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"读取文件 note.txt\")"
259 | ]
260 | },
261 | {
262 | "cell_type": "markdown",
263 | "metadata": {},
264 | "source": [
265 | "### 5.4 步骤 3: 修改状态 ⚠️ 这是回溯点"
266 | ]
267 | },
268 | {
269 | "cell_type": "code",
270 | "execution_count": null,
271 | "metadata": {},
272 | "outputs": [],
273 | "source": [
274 | "# 这次修改是我们后面要撤销的\n",
275 | "events_update = await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"更新状态 color 为 blue\")\n",
276 | "\n",
277 | "# 记录这个操作的 invocation_id,用于后续回溯\n",
278 | "rewind_invocation_id = events_update[0].invocation_id\n",
279 | "print(f\"\\n📌 记录回溯点 invocation_id: {rewind_invocation_id}\")"
280 | ]
281 | },
282 | {
283 | "cell_type": "code",
284 | "execution_count": null,
285 | "metadata": {},
286 | "outputs": [],
287 | "source": [
288 | "# 再保存新版本的文件\n",
289 | "await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"保存文件 note.txt 内容为 version2\")"
290 | ]
291 | },
292 | {
293 | "cell_type": "markdown",
294 | "metadata": {},
295 | "source": [
296 | "### 5.5 步骤 4: 确认修改后的状态"
297 | ]
298 | },
299 | {
300 | "cell_type": "code",
301 | "execution_count": null,
302 | "metadata": {},
303 | "outputs": [],
304 | "source": [
305 | "await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"查询状态 color 的值\")"
306 | ]
307 | },
308 | {
309 | "cell_type": "code",
310 | "execution_count": null,
311 | "metadata": {},
312 | "outputs": [],
313 | "source": [
314 | "await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"读取文件 note.txt\")"
315 | ]
316 | },
317 | {
318 | "cell_type": "markdown",
319 | "metadata": {},
320 | "source": [
321 | "### 5.6 步骤 5: ⏪ 执行 REWIND!\n",
322 | "\n",
323 | "现在我们要回溯到 \"color = blue\" 那次修改之前的状态。"
324 | ]
325 | },
326 | {
327 | "cell_type": "code",
328 | "execution_count": null,
329 | "metadata": {},
330 | "outputs": [],
331 | "source": [
332 | "print(f\"⏪ 回溯到 invocation_id: {rewind_invocation_id} 之前...\")\n",
333 | "\n",
334 | "await runner.rewind_async(\n",
335 | " user_id=USER_ID,\n",
336 | " session_id=session.id,\n",
337 | " rewind_before_invocation_id=rewind_invocation_id,\n",
338 | ")\n",
339 | "\n",
340 | "print(\"✅ 回溯完成!\")"
341 | ]
342 | },
343 | {
344 | "cell_type": "markdown",
345 | "metadata": {},
346 | "source": [
347 | "### 5.7 步骤 6: 验证回溯后的状态\n",
348 | "\n",
349 | "回溯后,状态应该恢复到:\n",
350 | "- color = **red** (而不是 blue)\n",
351 | "- note.txt = **version1** (而不是 version2)"
352 | ]
353 | },
354 | {
355 | "cell_type": "code",
356 | "execution_count": null,
357 | "metadata": {},
358 | "outputs": [],
359 | "source": [
360 | "await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"查询状态 color 的值\")"
361 | ]
362 | },
363 | {
364 | "cell_type": "code",
365 | "execution_count": null,
366 | "metadata": {},
367 | "outputs": [],
368 | "source": [
369 | "await call_agent(runner, session.id, \"读取文件 note.txt\")"
370 | ]
371 | },
372 | {
373 | "cell_type": "markdown",
374 | "metadata": {},
375 | "source": [
376 | "## 6. 总结\n",
377 | "\n",
378 | "### 🔑 核心要点\n",
379 | "\n",
380 | "1. **`runner.rewind_async()`** - 回溯会话到指定的 invocation 之前\n",
381 | "2. **`rewind_before_invocation_id`** - 指定回溯点的 ID\n",
382 | "3. **完整恢复** - 回溯会同时恢复 state(状态)和 artifacts(文件)\n",
383 | "\n",
384 | "### 💡 应用场景\n",
385 | "\n",
386 | "| 功能 | 实现方式 |\n",
387 | "|------|----------|\n",
388 | "| 编辑消息 | 回溯到该消息之前,然后发送新消息 |\n",
389 | "| 重新生成 | 回溯到上一个用户消息之前,然后重新运行 |\n",
390 | "| 撤销操作 | 回溯到操作之前 |\n",
391 | "| 分支对话 | 回溯到某个点,然后走不同的路径 |\n",
392 | "\n",
393 | "### 📚 参考链接\n",
394 | "\n",
395 | "- [ADK Sessions Rewind 文档](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/sessions/rewind/)\n",
396 | "- [ADK Runtime Resume 文档](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/runtime/resume/)\n",
397 | "- [官方示例代码](https://github.com/google/adk-python/blob/main/contributing/samples/rewind_session/main.py)"
398 | ]
399 | }
400 | ],
401 | "metadata": {
402 | "kernelspec": {
403 | "display_name": "Python 3",
404 | "language": "python",
405 | "name": "python3"
406 | },
407 | "language_info": {
408 | "name": "python",
409 | "version": "3.11.0"
410 | }
411 | },
412 | "nbformat": 4,
413 | "nbformat_minor": 4
414 | }
415 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-05/telemetry_demo.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Day 5: Production Observability Demo
3 |
4 | 演示如何在 Agent 中集成 OpenTelemetry 进行可观测性监控。
5 | 这是一个简化版本,展示核心概念。
6 |
7 | 实际生产中请使用 Agent Starter Pack 的完整 telemetry 模块。
8 | """
9 |
10 | import os
11 | import time
12 | import json
13 | import logging
14 | from datetime import datetime
15 | from typing import Optional
16 | from dataclasses import dataclass, field, asdict
17 |
18 | # 配置日志
19 | logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO, format='%(asctime)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s')
20 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
21 |
22 |
23 | # ============================================================
24 | # Span 数据结构
25 | # ============================================================
26 |
27 | @dataclass
28 | class Span:
29 | """表示一个追踪 Span"""
30 | name: str
31 | trace_id: str
32 | span_id: str
33 | parent_id: Optional[str] = None
34 | start_time: float = field(default_factory=time.time)
35 | end_time: Optional[float] = None
36 | attributes: dict = field(default_factory=dict)
37 | status: str = "OK"
38 |
39 | def end(self):
40 | self.end_time = time.time()
41 |
42 | @property
43 | def duration_ms(self) -> float:
44 | if self.end_time:
45 | return (self.end_time - self.start_time) * 1000
46 | return 0
47 |
48 | def set_attribute(self, key: str, value):
49 | self.attributes[key] = value
50 |
51 | def to_dict(self) -> dict:
52 | return {
53 | "name": self.name,
54 | "trace_id": self.trace_id,
55 | "span_id": self.span_id,
56 | "parent_id": self.parent_id,
57 | "start_time": datetime.fromtimestamp(self.start_time).isoformat(),
58 | "end_time": datetime.fromtimestamp(self.end_time).isoformat() if self.end_time else None,
59 | "duration_ms": self.duration_ms,
60 | "attributes": self.attributes,
61 | "status": self.status
62 | }
63 |
64 |
65 | # ============================================================
66 | # 简化版 Tracer
67 | # ============================================================
68 |
69 | class SimpleTracer:
70 | """简化版追踪器,用于演示概念"""
71 |
72 | def __init__(self, service_name: str):
73 | self.service_name = service_name
74 | self.spans: list[Span] = []
75 | self._current_span: Optional[Span] = None
76 | self._trace_id = self._generate_id()
77 |
78 | def _generate_id(self) -> str:
79 | import random
80 | return hex(random.getrandbits(64))[2:]
81 |
82 | def start_span(self, name: str) -> Span:
83 | """开始一个新的 Span"""
84 | span = Span(
85 | name=name,
86 | trace_id=self._trace_id,
87 | span_id=self._generate_id(),
88 | parent_id=self._current_span.span_id if self._current_span else None
89 | )
90 | span.set_attribute("service.name", self.service_name)
91 | self.spans.append(span)
92 | self._current_span = span
93 | return span
94 |
95 | def end_span(self, span: Span):
96 | """结束一个 Span"""
97 | span.end()
98 | # 恢复到父 Span
99 | if span.parent_id:
100 | for s in reversed(self.spans):
101 | if s.span_id == span.parent_id:
102 | self._current_span = s
103 | break
104 | else:
105 | self._current_span = None
106 |
107 | def get_trace_summary(self) -> dict:
108 | """获取追踪摘要"""
109 | return {
110 | "trace_id": self._trace_id,
111 | "service": self.service_name,
112 | "total_spans": len(self.spans),
113 | "spans": [s.to_dict() for s in self.spans]
114 | }
115 |
116 |
117 | # ============================================================
118 | # GenAI Telemetry 记录器
119 | # ============================================================
120 |
121 | @dataclass
122 | class GenAITelemetryRecord:
123 | """GenAI 调用遥测记录"""
124 | timestamp: str
125 | model: str
126 | input_tokens: int
127 | output_tokens: int
128 | latency_ms: float
129 | status: str = "success"
130 | # NO_CONTENT 模式下不记录以下字段
131 | # prompt: str = ""
132 | # response: str = ""
133 |
134 |
135 | class GenAITelemetryLogger:
136 | """GenAI 遥测记录器(模拟 GCS 上传)"""
137 |
138 | def __init__(self, bucket_name: Optional[str] = None, capture_content: str = "NO_CONTENT"):
139 | self.bucket_name = bucket_name
140 | self.capture_content = capture_content
141 | self.records: list[GenAITelemetryRecord] = []
142 |
143 | if bucket_name:
144 | logger.info(f"GenAI Telemetry enabled - bucket: {bucket_name}, mode: {capture_content}")
145 | else:
146 | logger.info("GenAI Telemetry disabled (no bucket configured)")
147 |
148 | def log_completion(self, model: str, input_tokens: int, output_tokens: int,
149 | latency_ms: float, status: str = "success"):
150 | """记录一次 LLM 调用"""
151 | record = GenAITelemetryRecord(
152 | timestamp=datetime.utcnow().isoformat() + "Z",
153 | model=model,
154 | input_tokens=input_tokens,
155 | output_tokens=output_tokens,
156 | latency_ms=latency_ms,
157 | status=status
158 | )
159 | self.records.append(record)
160 |
161 | # 模拟上传到 GCS(实际中使用 JSONL 格式)
162 | if self.bucket_name:
163 | logger.info(f"[Telemetry] {model}: {input_tokens}+{output_tokens} tokens, {latency_ms:.0f}ms")
164 |
165 | def export_jsonl(self) -> str:
166 | """导出为 JSONL 格式"""
167 | lines = []
168 | for record in self.records:
169 | lines.append(json.dumps(asdict(record)))
170 | return "\n".join(lines)
171 |
172 | def get_summary(self) -> dict:
173 | """获取统计摘要"""
174 | if not self.records:
175 | return {"total_calls": 0}
176 |
177 | total_input = sum(r.input_tokens for r in self.records)
178 | total_output = sum(r.output_tokens for r in self.records)
179 | avg_latency = sum(r.latency_ms for r in self.records) / len(self.records)
180 |
181 | return {
182 | "total_calls": len(self.records),
183 | "total_input_tokens": total_input,
184 | "total_output_tokens": total_output,
185 | "total_tokens": total_input + total_output,
186 | "avg_latency_ms": round(avg_latency, 2)
187 | }
188 |
189 |
190 | # ============================================================
191 | # 模拟 Agent 执行
192 | # ============================================================
193 |
194 | class MockLLM:
195 | """模拟 LLM 调用"""
196 |
197 | def __init__(self, model: str = "gemini-2.0-flash"):
198 | self.model = model
199 |
200 | def generate(self, prompt: str) -> dict:
201 | """模拟生成响应"""
202 | # 模拟延迟
203 | time.sleep(0.1 + len(prompt) * 0.001)
204 |
205 | return {
206 | "text": f"这是对 '{prompt[:20]}...' 的回复",
207 | "usage": {
208 | "input_tokens": len(prompt) * 2,
209 | "output_tokens": 50 + len(prompt)
210 | }
211 | }
212 |
213 |
214 | def simulate_agent_request(tracer: SimpleTracer, telemetry: GenAITelemetryLogger,
215 | llm: MockLLM, user_input: str):
216 | """模拟一次 Agent 请求处理"""
217 |
218 | # 主 Span
219 | main_span = tracer.start_span("agent.handle_request")
220 | main_span.set_attribute("user_input_length", len(user_input))
221 |
222 | try:
223 | # 解析输入
224 | parse_span = tracer.start_span("agent.parse_input")
225 | time.sleep(0.02) # 模拟解析
226 | tracer.end_span(parse_span)
227 |
228 | # 第一次 LLM 调用(理解意图)
229 | llm_span_1 = tracer.start_span("llm.generate")
230 | llm_span_1.set_attribute("model", llm.model)
231 | llm_span_1.set_attribute("purpose", "intent_understanding")
232 |
233 | start = time.time()
234 | response1 = llm.generate(f"理解用户意图: {user_input}")
235 | latency1 = (time.time() - start) * 1000
236 |
237 | llm_span_1.set_attribute("input_tokens", response1["usage"]["input_tokens"])
238 | llm_span_1.set_attribute("output_tokens", response1["usage"]["output_tokens"])
239 | tracer.end_span(llm_span_1)
240 |
241 | telemetry.log_completion(
242 | model=llm.model,
243 | input_tokens=response1["usage"]["input_tokens"],
244 | output_tokens=response1["usage"]["output_tokens"],
245 | latency_ms=latency1
246 | )
247 |
248 | # 工具执行
249 | tool_span = tracer.start_span("tool.execute")
250 | tool_span.set_attribute("tool_name", "search_database")
251 | time.sleep(0.05) # 模拟工具执行
252 | tracer.end_span(tool_span)
253 |
254 | # 第二次 LLM 调用(生成回复)
255 | llm_span_2 = tracer.start_span("llm.generate")
256 | llm_span_2.set_attribute("model", llm.model)
257 | llm_span_2.set_attribute("purpose", "response_generation")
258 |
259 | start = time.time()
260 | response2 = llm.generate(f"基于搜索结果回复: {user_input}")
261 | latency2 = (time.time() - start) * 1000
262 |
263 | llm_span_2.set_attribute("input_tokens", response2["usage"]["input_tokens"])
264 | llm_span_2.set_attribute("output_tokens", response2["usage"]["output_tokens"])
265 | tracer.end_span(llm_span_2)
266 |
267 | telemetry.log_completion(
268 | model=llm.model,
269 | input_tokens=response2["usage"]["input_tokens"],
270 | output_tokens=response2["usage"]["output_tokens"],
271 | latency_ms=latency2
272 | )
273 |
274 | # 格式化响应
275 | format_span = tracer.start_span("agent.format_response")
276 | time.sleep(0.01)
277 | tracer.end_span(format_span)
278 |
279 | main_span.set_attribute("status", "success")
280 |
281 | except Exception as e:
282 | main_span.set_attribute("status", "error")
283 | main_span.set_attribute("error.message", str(e))
284 | main_span.status = "ERROR"
285 |
286 | finally:
287 | tracer.end_span(main_span)
288 |
289 |
290 | # ============================================================
291 | # 演示
292 | # ============================================================
293 |
294 | def main():
295 | print("=" * 60)
296 | print("Day 5: Production Observability Demo")
297 | print("=" * 60)
298 | print()
299 |
300 | # 初始化组件
301 | tracer = SimpleTracer(service_name="my-agent")
302 | telemetry = GenAITelemetryLogger(
303 | bucket_name="gs://demo-bucket/logs", # 模拟 bucket
304 | capture_content="NO_CONTENT"
305 | )
306 | llm = MockLLM(model="gemini-2.0-flash")
307 |
308 | # 模拟多个请求
309 | requests = [
310 | "北京今天天气怎么样?",
311 | "帮我找一家附近评分高的西餐厅",
312 | "解释一下什么是 OpenTelemetry"
313 | ]
314 |
315 | print("\n📨 处理用户请求...")
316 | print("-" * 60)
317 |
318 | for req in requests:
319 | print(f"\n用户: {req}")
320 | simulate_agent_request(tracer, telemetry, llm, req)
321 |
322 | # 输出追踪结果
323 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
324 | print("📊 Trace Summary (类似 Cloud Trace)")
325 | print("=" * 60)
326 |
327 | trace_data = tracer.get_trace_summary()
328 | print(f"\nTrace ID: {trace_data['trace_id']}")
329 | print(f"Service: {trace_data['service']}")
330 | print(f"Total Spans: {trace_data['total_spans']}")
331 |
332 | print("\nSpans:")
333 | for span in trace_data['spans']:
334 | indent = " " if span['parent_id'] else ""
335 | print(f"{indent}├── {span['name']}: {span['duration_ms']:.1f}ms")
336 | for key, value in span['attributes'].items():
337 | if key not in ['service.name']:
338 | print(f"{indent}│ └── {key}: {value}")
339 |
340 | # 输出遥测摘要
341 | print("\n" + "=" * 60)
342 | print("📈 GenAI Telemetry Summary (类似 BigQuery 查询结果)")
343 | print("=" * 60)
344 |
345 | summary = telemetry.get_summary()
346 | print(f"""
347 | Total LLM Calls: {summary['total_calls']}
348 | Total Tokens: {summary['total_tokens']}
349 | - Input: {summary['total_input_tokens']}
350 | - Output: {summary['total_output_tokens']}
351 | Avg Latency: {summary['avg_latency_ms']}ms
352 | """)
353 |
354 | # 输出 JSONL 格式
355 | print("=" * 60)
356 | print("📄 JSONL Export (类似 GCS 日志文件)")
357 | print("=" * 60)
358 | print()
359 | print(telemetry.export_jsonl())
360 | print()
361 |
362 | print("=" * 60)
363 | print("✅ Demo 完成")
364 | print("=" * 60)
365 | print("""
366 | 实际生产中:
367 | - Traces 导出到 Cloud Trace,可视化查看调用链
368 | - JSONL 上传到 GCS,通过 BigQuery 外部表查询
369 | - 可以按 model、时间、user 等维度分析 Token 消耗和延迟
370 | """)
371 |
372 |
373 | if __name__ == "__main__":
374 | main()
375 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-17/gemini3_flash_thinking.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "# Day 17: Gemini 3 Flash - 可配置思考级别\n",
8 | "\n",
9 | "Gemini 3 Flash 最大亮点:**Thinking Level(思考级别)**\n",
10 | "\n",
11 | "简单说:控制模型\"想多久\"再回答。"
12 | ]
13 | },
14 | {
15 | "cell_type": "markdown",
16 | "metadata": {},
17 | "source": [
18 | "## 1. 思考级别一览\n",
19 | "\n",
20 | "| 级别 | 特点 | 适用场景 |\n",
21 | "|------|------|----------|\n",
22 | "| `MINIMAL` | 最快响应 | 简单问答、聊天 |\n",
23 | "| `LOW` | 快速 + 少量推理 | 日常任务 |\n",
24 | "| `MEDIUM` | 平衡模式 | 中等复杂度 |\n",
25 | "| `HIGH` | 深度推理 | 数学、编程、复杂问题 |"
26 | ]
27 | },
28 | {
29 | "cell_type": "markdown",
30 | "metadata": {},
31 | "source": [
32 | "## 2. 环境准备"
33 | ]
34 | },
35 | {
36 | "cell_type": "code",
37 | "execution_count": 1,
38 | "metadata": {},
39 | "outputs": [],
40 | "source": [
41 | "import os\n",
42 | "from dotenv import load_dotenv\n",
43 | "\n",
44 | "load_dotenv()\n",
45 | "\n",
46 | "# 确认 API Key 已设置\n",
47 | "assert os.getenv(\"GOOGLE_API_KEY\"), \"请设置 GOOGLE_API_KEY\""
48 | ]
49 | },
50 | {
51 | "cell_type": "code",
52 | "execution_count": 2,
53 | "metadata": {},
54 | "outputs": [],
55 | "source": [
56 | "from google.adk.agents import Agent\n",
57 | "from google.adk.planners import BuiltInPlanner\n",
58 | "from google.adk.runners import Runner\n",
59 | "from google.adk.sessions import InMemorySessionService\n",
60 | "from google.genai import types\n",
61 | "from google.genai.types import Content, Part"
62 | ]
63 | },
64 | {
65 | "cell_type": "markdown",
66 | "metadata": {},
67 | "source": [
68 | "## 3. 核心配置:ThinkingConfig\n",
69 | "\n",
70 | "关键代码就这几行:"
71 | ]
72 | },
73 | {
74 | "cell_type": "code",
75 | "execution_count": 3,
76 | "metadata": {},
77 | "outputs": [
78 | {
79 | "name": "stdout",
80 | "output_type": "stream",
81 | "text": [
82 | "思考级别: ThinkingLevel.LOW\n"
83 | ]
84 | }
85 | ],
86 | "source": [
87 | "# 配置思考级别\n",
88 | "thinking_config = types.ThinkingConfig(\n",
89 | " thinking_level=\"LOW\" # 可选: MINIMAL, LOW, MEDIUM, HIGH\n",
90 | ")\n",
91 | "\n",
92 | "# 创建规划器\n",
93 | "planner = BuiltInPlanner(thinking_config=thinking_config)\n",
94 | "\n",
95 | "print(f\"思考级别: {thinking_config.thinking_level}\")"
96 | ]
97 | },
98 | {
99 | "cell_type": "markdown",
100 | "metadata": {},
101 | "source": [
102 | "## 4. 定义工具"
103 | ]
104 | },
105 | {
106 | "cell_type": "code",
107 | "execution_count": 4,
108 | "metadata": {},
109 | "outputs": [],
110 | "source": [
111 | "def get_current_time(city: str) -> dict:\n",
112 | " \"\"\"获取指定城市的当前时间\"\"\"\n",
113 | " times = {\n",
114 | " \"北京\": \"22:30\",\n",
115 | " \"东京\": \"23:30\", \n",
116 | " \"纽约\": \"09:30\",\n",
117 | " \"伦敦\": \"14:30\",\n",
118 | " }\n",
119 | " time = times.get(city, \"10:00\")\n",
120 | " return {\"city\": city, \"time\": time}\n",
121 | "\n",
122 | "\n",
123 | "def calculate(expression: str) -> dict:\n",
124 | " \"\"\"计算数学表达式\"\"\"\n",
125 | " try:\n",
126 | " result = eval(expression)\n",
127 | " return {\"expression\": expression, \"result\": result}\n",
128 | " except Exception as e:\n",
129 | " return {\"error\": str(e)}"
130 | ]
131 | },
132 | {
133 | "cell_type": "markdown",
134 | "metadata": {},
135 | "source": [
136 | "## 5. 创建 Agent 工厂函数"
137 | ]
138 | },
139 | {
140 | "cell_type": "code",
141 | "execution_count": 5,
142 | "metadata": {},
143 | "outputs": [
144 | {
145 | "name": "stdout",
146 | "output_type": "stream",
147 | "text": [
148 | "✅ 工厂函数已定义\n"
149 | ]
150 | }
151 | ],
152 | "source": [
153 | "def create_agent(thinking_level: str) -> Agent:\n",
154 | " \"\"\"创建指定思考级别的 Agent\"\"\"\n",
155 | " return Agent(\n",
156 | " model='gemini-3-flash-preview',\n",
157 | " name=f'agent_{thinking_level.lower()}',\n",
158 | " instruction=\"你是一个有用的助手。请用中文简洁回答。\",\n",
159 | " tools=[get_current_time, calculate],\n",
160 | " planner=BuiltInPlanner(\n",
161 | " thinking_config=types.ThinkingConfig(\n",
162 | " thinking_level=thinking_level\n",
163 | " )\n",
164 | " ),\n",
165 | " )\n",
166 | "\n",
167 | "print(\"✅ 工厂函数已定义\")"
168 | ]
169 | },
170 | {
171 | "cell_type": "markdown",
172 | "metadata": {},
173 | "source": [
174 | "## 6. 运行辅助函数(含思考过程显示)\n",
175 | "\n",
176 | "关键:通过 `event.content.parts` 中的 `thought` 属性获取思考内容"
177 | ]
178 | },
179 | {
180 | "cell_type": "code",
181 | "execution_count": 6,
182 | "metadata": {},
183 | "outputs": [
184 | {
185 | "name": "stdout",
186 | "output_type": "stream",
187 | "text": [
188 | "✅ 辅助函数已定义(支持显示思考过程)\n"
189 | ]
190 | }
191 | ],
192 | "source": [
193 | "session_service = InMemorySessionService()\n",
194 | "\n",
195 | "async def ask(agent: Agent, question: str, show_thinking: bool = True) -> str:\n",
196 | " \"\"\"\n",
197 | " 向 Agent 提问并返回回答\n",
198 | " \n",
199 | " 参数:\n",
200 | " show_thinking: 是否显示思考过程\n",
201 | " \"\"\"\n",
202 | " session = await session_service.create_session(\n",
203 | " app_name=\"day17_demo\",\n",
204 | " user_id=\"demo_user\"\n",
205 | " )\n",
206 | " \n",
207 | " runner = Runner(\n",
208 | " agent=agent,\n",
209 | " app_name=\"day17_demo\", \n",
210 | " session_service=session_service\n",
211 | " )\n",
212 | " \n",
213 | " user_content = Content(role=\"user\", parts=[Part(text=question)])\n",
214 | " \n",
215 | " response = \"\"\n",
216 | " thinking = \"\"\n",
217 | " \n",
218 | " async for event in runner.run_async(\n",
219 | " user_id=\"demo_user\",\n",
220 | " session_id=session.id,\n",
221 | " new_message=user_content\n",
222 | " ):\n",
223 | " if hasattr(event, 'content') and event.content:\n",
224 | " if hasattr(event.content, 'parts'):\n",
225 | " for part in event.content.parts:\n",
226 | " # 获取思考过程\n",
227 | " if hasattr(part, 'thought') and part.thought:\n",
228 | " thinking += part.text if hasattr(part, 'text') else \"\"\n",
229 | " # 获取最终回答\n",
230 | " elif hasattr(part, 'text') and part.text:\n",
231 | " response += part.text\n",
232 | " \n",
233 | " # 显示思考过程\n",
234 | " if show_thinking and thinking:\n",
235 | " print(f\"💭 思考过程:\\n{thinking}\\n\")\n",
236 | " print(\"-\" * 40)\n",
237 | " \n",
238 | " return response\n",
239 | "\n",
240 | "print(\"✅ 辅助函数已定义(支持显示思考过程)\")"
241 | ]
242 | },
243 | {
244 | "cell_type": "markdown",
245 | "metadata": {},
246 | "source": [
247 | "## 7. 测试:LOW 级别(日常使用推荐)"
248 | ]
249 | },
250 | {
251 | "cell_type": "code",
252 | "execution_count": 7,
253 | "metadata": {},
254 | "outputs": [
255 | {
256 | "name": "stderr",
257 | "output_type": "stream",
258 | "text": [
259 | "Warning: there are non-text parts in the response: ['function_call'], returning concatenated text result from text parts. Check the full candidates.content.parts accessor to get the full model response.\n"
260 | ]
261 | },
262 | {
263 | "name": "stdout",
264 | "output_type": "stream",
265 | "text": [
266 | "🤖 [LOW] 回答: 现在北京时间是 22:30。\n"
267 | ]
268 | }
269 | ],
270 | "source": [
271 | "agent_low = create_agent(\"LOW\")\n",
272 | "\n",
273 | "response = await ask(agent_low, \"北京现在几点?\")\n",
274 | "print(f\"🤖 [LOW] 回答: {response}\")"
275 | ]
276 | },
277 | {
278 | "cell_type": "markdown",
279 | "metadata": {},
280 | "source": [
281 | "## 8. 测试:HIGH 级别(复杂推理)"
282 | ]
283 | },
284 | {
285 | "cell_type": "code",
286 | "execution_count": 8,
287 | "metadata": {},
288 | "outputs": [
289 | {
290 | "name": "stdout",
291 | "output_type": "stream",
292 | "text": [
293 | "🤖 [HIGH] 回答: 北京晚上10点(22:00),纽约是当日**上午10点**(目前处于夏令时)。如果是冬令时,则为上午9点。\n",
294 | "\n",
295 | "**时差原因:**\n",
296 | "1. **地球自转**:地球自西向东自转,不同经度的地区看到日出的时间不同。\n",
297 | "2. **时区划分**:为统一时间,全球分为24个时区。北京位于**东八区 (UTC+8)**,纽约位于**西五区 (UTC-5)**。\n",
298 | "3. **夏令时**:纽约在夏季会进入夏令时,将时钟拨快一小时(变为UTC-4),因此两地目前的时差为12小时。\n"
299 | ]
300 | }
301 | ],
302 | "source": [
303 | "agent_high = create_agent(\"HIGH\")\n",
304 | "\n",
305 | "response = await ask(agent_high, \"如果北京是晚上10点,纽约是什么时候?解释时差原因。\")\n",
306 | "print(f\"🤖 [HIGH] 回答: {response}\")"
307 | ]
308 | },
309 | {
310 | "cell_type": "markdown",
311 | "metadata": {},
312 | "source": [
313 | "## 9. 测试:数学计算"
314 | ]
315 | },
316 | {
317 | "cell_type": "code",
318 | "execution_count": 9,
319 | "metadata": {},
320 | "outputs": [
321 | {
322 | "name": "stdout",
323 | "output_type": "stream",
324 | "text": [
325 | "🤖 [LOW] 回答: 结果是 126。\n"
326 | ]
327 | }
328 | ],
329 | "source": [
330 | "response = await ask(agent_low, \"计算 (15 * 8) + (42 / 7)\")\n",
331 | "print(f\"🤖 [LOW] 回答: {response}\")"
332 | ]
333 | },
334 | {
335 | "cell_type": "markdown",
336 | "metadata": {},
337 | "source": [
338 | "## 10. 查看思考过程对比\n",
339 | "\n",
340 | "HIGH 级别会有更详细的思考过程:"
341 | ]
342 | },
343 | {
344 | "cell_type": "code",
345 | "execution_count": 10,
346 | "metadata": {},
347 | "outputs": [
348 | {
349 | "name": "stdout",
350 | "output_type": "stream",
351 | "text": [
352 | "🔵 LOW 级别思考:\n",
353 | "🤖 回答: 1000 除以 7 约等于 142.86。\n"
354 | ]
355 | }
356 | ],
357 | "source": [
358 | "print(\"🔵 LOW 级别思考:\")\n",
359 | "agent_low = create_agent(\"LOW\")\n",
360 | "response = await ask(agent_low, \"1000 除以 7 等于多少?保留两位小数。\", show_thinking=True)\n",
361 | "print(f\"🤖 回答: {response}\")"
362 | ]
363 | },
364 | {
365 | "cell_type": "code",
366 | "execution_count": 11,
367 | "metadata": {},
368 | "outputs": [
369 | {
370 | "name": "stdout",
371 | "output_type": "stream",
372 | "text": [
373 | "🔴 HIGH 级别思考:\n",
374 | "🤖 回答: 1000 除以 7 等于 142.86。\n"
375 | ]
376 | }
377 | ],
378 | "source": [
379 | "print(\"🔴 HIGH 级别思考:\")\n",
380 | "agent_high = create_agent(\"HIGH\")\n",
381 | "response = await ask(agent_high, \"1000 除以 7 等于多少?保留两位小数。\", show_thinking=True)\n",
382 | "print(f\"🤖 回答: {response}\")"
383 | ]
384 | },
385 | {
386 | "cell_type": "markdown",
387 | "metadata": {},
388 | "source": [
389 | "## 11. 总结\n",
390 | "\n",
391 | "### 选择建议\n",
392 | "\n",
393 | "```\n",
394 | "简单聊天 → MINIMAL(最省钱最快)\n",
395 | "日常任务 → LOW(推荐默认)\n",
396 | "分析任务 → MEDIUM\n",
397 | "复杂推理 → HIGH(最准但最慢)\n",
398 | "```\n",
399 | "\n",
400 | "### 思考过程显示\n",
401 | "\n",
402 | "```python\n",
403 | "# part.thought = True 表示这是思考内容\n",
404 | "for part in event.content.parts:\n",
405 | " if hasattr(part, 'thought') and part.thought:\n",
406 | " print(\"思考:\", part.text)\n",
407 | "```\n",
408 | "\n",
409 | "### 与 Gemini 2.5 的区别\n",
410 | "\n",
411 | "| 版本 | 参数 | 方式 |\n",
412 | "|------|------|------|\n",
413 | "| Gemini 3 | `thinking_level` | 级别选择 |\n",
414 | "| Gemini 2.5 | `thinking_budget` | token 预算 |\n",
415 | "\n",
416 | "**注意:参数不能混用!**"
417 | ]
418 | },
419 | {
420 | "cell_type": "markdown",
421 | "metadata": {},
422 | "source": [
423 | "## 参考资料\n",
424 | "\n",
425 | "- [Gemini 3 Flash 官方公告](https://blog.google/products/gemini/gemini-3-flash/)\n",
426 | "- [ADK 模型配置文档](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/agents/models/)\n",
427 | "- [TechCrunch 报道](https://techcrunch.com/2025/12/17/google-launches-gemini-3-flash-makes-it-the-default-model-in-the-gemini-app/)"
428 | ]
429 | }
430 | ],
431 | "metadata": {
432 | "kernelspec": {
433 | "display_name": ".venv",
434 | "language": "python",
435 | "name": "python3"
436 | },
437 | "language_info": {
438 | "codemirror_mode": {
439 | "name": "ipython",
440 | "version": 3
441 | },
442 | "file_extension": ".py",
443 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
444 | "name": "python",
445 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
446 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
447 | "version": "3.12.11"
448 | }
449 | },
450 | "nbformat": 4,
451 | "nbformat_minor": 4
452 | }
453 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-14/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Day 14: 使用 A2A 协议连接 Agents
2 |
3 | ## 概述
4 |
5 | 今天我们学习 **Agent2Agent (A2A)** 协议 - 一个开放标准,允许不同的 AI Agents 之间进行通信和协作,无论它们使用什么框架或语言。
6 |
7 | ## A2A 协议核心概念
8 |
9 | ### 什么是 A2A?
10 |
11 | A2A (Agent-to-Agent) 是 Google 推出的开放协议,解决了一个关键问题:**如何让不同团队、不同框架构建的 Agents 互相协作?**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | ┌─────────────────┐ A2A 协议 ┌─────────────────┐
15 | │ Host Agent │ ◄──────────────────────► │ Remote Agent │
16 | │ (客户端) │ JSON-RPC over HTTP │ (服务端) │
17 | │ ADK/LangChain │ │ ADK/其他框架 │
18 | └─────────────────┘ └─────────────────┘
19 | ```
20 |
21 | ### A2A 的核心组件
22 |
23 | 1. **Agent Card** - Agent 的"名片"
24 | - 描述 Agent 的能力、技能
25 | - 提供 RPC URL 端点
26 | - 类似于 API 文档
27 | - 可通过 `/.well-known/agent-card.json` 访问
28 |
29 | 2. **Task** - 任务单元
30 | - 客户端向服务端发送的工作请求
31 | - 包含 message (消息) 和 context (上下文)
32 | - 有状态流转:submitted → working → completed/failed
33 |
34 | 3. **Message** - 消息
35 | - 包含多个 Parts (文本、文件、数据等)
36 | - 支持角色区分 (user/agent)
37 |
38 | ### A2A vs MCP
39 |
40 | | 特性 | A2A | MCP |
41 | |------|-----|-----|
42 | | 目的 | Agent 之间通信 | Agent 访问外部工具/数据 |
43 | | 通信方向 | Agent ↔ Agent | Agent → 工具/数据源 |
44 | | 复杂度 | 支持复杂任务流 | 简单的请求/响应 |
45 | | 状态管理 | 有状态 (Task 生命周期) | 无状态 |
46 |
47 | ## 项目结构
48 |
49 | ```
50 | day-14/
51 | ├── README.md
52 | ├── remote_agent/ # 远程 Agent (A2A 服务端)
53 | │ ├── __init__.py
54 | │ └── agent.py # 提供专业翻译服务的 Agent
55 | ├── host_agent/ # 主机 Agent (A2A 客户端)
56 | │ ├── __init__.py
57 | │ └── agent.py # 调用远程 Agent 的主 Agent
58 | └── run_demo.py # 演示脚本
59 | ```
60 |
61 | ## 前提条件
62 |
63 | API Key 已在项目根目录 `.env` 文件中配置,代码会自动加载。
64 |
65 | ## 运行示例 (请按顺序操作)
66 |
67 | ### 第一步:启动服务端 (Terminal 1)
68 |
69 | ```bash
70 | cd day-14
71 | uv run python -m remote_agent.agent
72 | ```
73 |
74 | > 也可以使用 `python3 -m remote_agent.agent`
75 |
76 | 看到以下输出表示服务端启动成功:
77 | ```
78 | ============================================================
79 | Day 14: A2A Remote Agent - 翻译服务
80 | ============================================================
81 | Agent 信息:
82 | 名称: translator
83 | A2A 服务端点:
84 | URL: http://localhost:8001
85 | ============================================================
86 | INFO: Uvicorn running on http://localhost:8001
87 | ```
88 |
89 | ### 第二步:运行客户端 (Terminal 2)
90 |
91 | **新开一个终端**,运行:
92 |
93 | ```bash
94 | cd day-14
95 | uv run python -m host_agent.agent
96 | ```
97 |
98 | > 也可以使用 `python3 -m host_agent.agent`
99 |
100 | 客户端会连接服务端,发送翻译请求,你会看到翻译结果。
101 |
102 | ### 运行效果
103 |
104 | 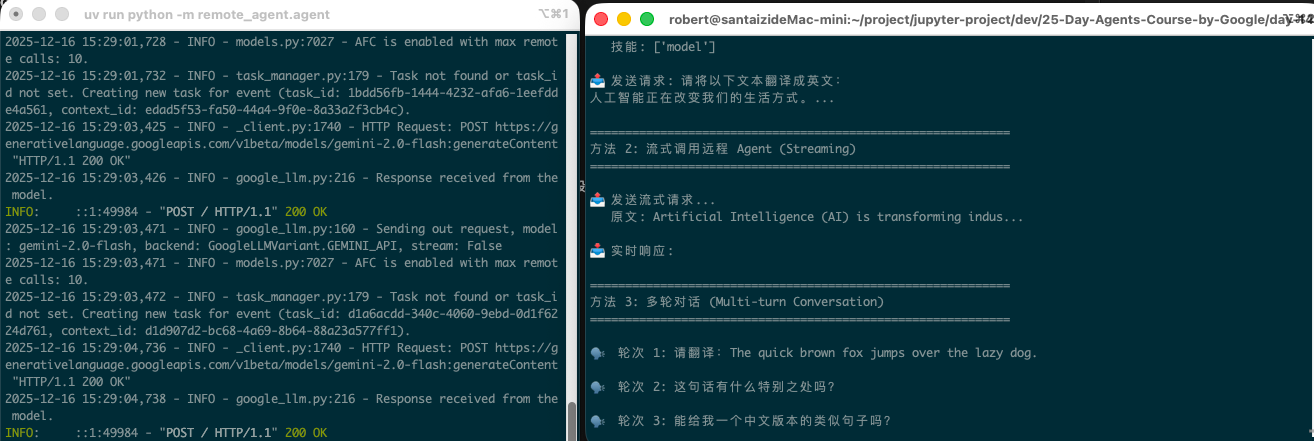
105 |
106 | 左侧是服务端 (Remote Agent),右侧是客户端 (Host Agent) 的运行输出。
107 |
108 | ### 验证服务
109 |
110 | 在任意终端执行:
111 | ```bash
112 | curl http://localhost:8001/.well-known/agent-card.json
113 | ```
114 |
115 | ### 关闭服务
116 |
117 | 在服务端终端按 `Ctrl+C` 即可关闭。
118 |
119 | ## 代码详解
120 |
121 | ### Remote Agent (服务端) - 关键代码
122 |
123 | ```python
124 | from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
125 | from google.adk.a2a.utils.agent_to_a2a import to_a2a
126 |
127 | # 创建一个专业翻译 Agent
128 | translator = LlmAgent(
129 | name="translator",
130 | description="专业多语言翻译 Agent",
131 | model="gemini-2.0-flash",
132 | instruction="你是专业翻译,精通中英日韩等语言..."
133 | )
134 |
135 | # 一行代码转换为 A2A 服务!
136 | app = to_a2a(translator, host="localhost", port=8001)
137 |
138 | # 启动服务
139 | if __name__ == "__main__":
140 | import uvicorn
141 | uvicorn.run(app, host="localhost", port=8001)
142 | ```
143 |
144 | ### Host Agent (客户端) - 关键代码
145 |
146 | ```python
147 | import httpx
148 | from a2a.client import ClientFactory, ClientConfig
149 | from a2a.types import Role
150 | from a2a.client.helpers import create_text_message_object
151 |
152 | # 创建无代理的 HTTP 客户端配置
153 | def get_client_config():
154 | httpx_client = httpx.AsyncClient(
155 | trust_env=False, # 禁用代理
156 | timeout=120.0,
157 | )
158 | return ClientConfig(httpx_client=httpx_client)
159 |
160 | # 连接远程 Agent
161 | client = await ClientFactory.connect(
162 | "http://localhost:8001",
163 | client_config=get_client_config()
164 | )
165 |
166 | # 创建消息
167 | message = create_text_message_object(
168 | role=Role.user,
169 | content="请翻译:Hello World"
170 | )
171 |
172 | # 发送请求并处理响应
173 | async for event in client.send_message(request=message):
174 | if isinstance(event, tuple):
175 | task, task_event = event[0], event[1]
176 | if task_event and hasattr(task_event, 'artifact'):
177 | for part in task_event.artifact.parts:
178 | if hasattr(part, 'text'):
179 | print(f"翻译结果: {part.text}")
180 | ```
181 |
182 | ## 关键学习点
183 |
184 | 1. **`to_a2a()` 函数** - ADK 提供的便捷方法,将任何 Agent 转换为 A2A 服务
185 | 2. **Agent Card** - 自动从 Agent 元数据生成,描述 Agent 能力
186 | 3. **ClientFactory.connect()** - A2A SDK 提供的连接方法,自动获取 Agent Card
187 | 4. **Task 状态流** - submitted → working → completed/failed
188 | 5. **跨框架互操作** - A2A 是协议标准,不限于 ADK
189 |
190 | ## API 快速参考
191 |
192 | ### 服务端 API
193 |
194 | | 函数 | 描述 |
195 | |------|------|
196 | | `to_a2a(agent, host, port)` | 将 ADK Agent 转换为 A2A 服务 |
197 |
198 | ### 客户端 API
199 |
200 | | 函数/类 | 描述 |
201 | |---------|------|
202 | | `ClientFactory.connect(url)` | 连接远程 A2A Agent |
203 | | `create_text_message_object(role, content)` | 创建文本消息 |
204 | | `client.send_message(request)` | 发送消息并获取响应流 |
205 |
206 | ## 客户端功能演示
207 |
208 | 当前 `host_agent/agent.py` 实现了 3 种 A2A 调用方式:
209 |
210 | ### 方法 1: 直接调用 (`call_remote_agent_directly`)
211 |
212 | 最基本的 A2A 调用模式:
213 | - 连接远程 Agent
214 | - 发送单次请求
215 | - 等待并获取完整响应
216 |
217 | ```python
218 | client = await ClientFactory.connect(url, client_config=config)
219 | message = create_text_message_object(role=Role.user, content="请翻译...")
220 | async for event in client.send_message(request=message):
221 | # 处理响应
222 | ```
223 |
224 | ### 方法 2: 流式调用 (`call_remote_agent_streaming`)
225 |
226 | 适用于长文本,实时获取响应:
227 | - 边处理边显示结果
228 | - 可以看到任务状态变化 (submitted → working → completed)
229 |
230 | ### 方法 3: 多轮对话 (`multi_turn_conversation`)
231 |
232 | 演示连续对话场景:
233 | - 发送多个相关问题
234 | - 每次都创建新的请求
235 |
236 | > **注意**: 当前 SDK 版本不支持 `context_id` 参数,多轮对话上下文需要应用层自行管理。
237 |
238 | ## 扩展方向
239 |
240 | 基于当前代码,你可以尝试以下扩展:
241 |
242 | ### 1. 添加更多远程 Agent
243 |
244 | ```python
245 | # 创建多个专业 Agent
246 | code_agent = await ClientFactory.connect("http://localhost:8002") # 代码助手
247 | math_agent = await ClientFactory.connect("http://localhost:8003") # 数学助手
248 |
249 | # 根据任务类型选择合适的 Agent
250 | if "翻译" in user_request:
251 | agent = translator_agent
252 | elif "代码" in user_request:
253 | agent = code_agent
254 | ```
255 |
256 | ### 2. Agent 编排 (Orchestration)
257 |
258 | ```python
259 | async def translate_and_summarize(text: str):
260 | """先翻译再总结"""
261 | # 调用翻译 Agent
262 | translated = await call_agent(translator_url, f"翻译: {text}")
263 | # 调用总结 Agent
264 | summary = await call_agent(summarizer_url, f"总结: {translated}")
265 | return summary
266 | ```
267 |
268 | ### 3. 并行调用多个 Agent
269 |
270 | ```python
271 | import asyncio
272 |
273 | async def parallel_translate(text: str):
274 | """同时翻译成多种语言"""
275 | tasks = [
276 | call_remote_agent(text, "中文"),
277 | call_remote_agent(text, "日文"),
278 | call_remote_agent(text, "韩文"),
279 | ]
280 | results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
281 | return dict(zip(["中文", "日文", "韩文"], results))
282 | ```
283 |
284 | ### 4. 错误重试机制
285 |
286 | ```python
287 | async def call_with_retry(client, message, max_retries=3):
288 | for attempt in range(max_retries):
289 | try:
290 | async for event in client.send_message(request=message):
291 | yield event
292 | return
293 | except Exception as e:
294 | if attempt == max_retries - 1:
295 | raise
296 | await asyncio.sleep(2 ** attempt) # 指数退避
297 | ```
298 |
299 | ### 5. 健康检查
300 |
301 | ```python
302 | async def health_check(url: str) -> bool:
303 | """检查远程 Agent 是否可用"""
304 | try:
305 | async with httpx.AsyncClient(trust_env=False) as client:
306 | resp = await client.get(f"{url}/.well-known/agent-card.json")
307 | return resp.status_code == 200
308 | except:
309 | return False
310 | ```
311 |
312 | ### 6. 创建新的远程 Agent (服务端扩展)
313 |
314 | 在 `remote_agent/` 目录下创建新的 Agent 服务:
315 |
316 | ```python
317 | # remote_agent/code_reviewer.py
318 | from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
319 | from google.adk.a2a.utils.agent_to_a2a import to_a2a
320 |
321 | code_reviewer = LlmAgent(
322 | name="code_reviewer",
323 | description="专业代码审查 Agent - 检查代码质量、安全漏洞和最佳实践",
324 | model="gemini-2.0-flash",
325 | instruction="""你是一位资深的代码审查专家。
326 |
327 | 你的职责:
328 | - 检查代码逻辑错误和潜在 bug
329 | - 识别安全漏洞 (SQL注入、XSS等)
330 | - 评估代码可读性和可维护性
331 | - 建议性能优化方案
332 | - 检查是否符合最佳实践
333 |
334 | 输出格式:
335 | 1. 问题概述
336 | 2. 具体问题列表 (严重程度: 高/中/低)
337 | 3. 改进建议
338 | """,
339 | )
340 |
341 | app = to_a2a(agent=code_reviewer, host="localhost", port=8002, protocol="http")
342 |
343 | if __name__ == "__main__":
344 | import uvicorn
345 | uvicorn.run(app, host="localhost", port=8002)
346 | ```
347 |
348 | ### 7. 构建 Agent 注册中心
349 |
350 | ```python
351 | # agent_registry.py
352 | class AgentRegistry:
353 | """简单的 Agent 注册中心"""
354 |
355 | def __init__(self):
356 | self.agents = {}
357 |
358 | async def register(self, name: str, url: str):
359 | """注册一个 Agent"""
360 | if await self.health_check(url):
361 | client = await ClientFactory.connect(url, client_config=get_client_config())
362 | self.agents[name] = {
363 | "url": url,
364 | "client": client,
365 | "card": client._card,
366 | }
367 | return True
368 | return False
369 |
370 | async def health_check(self, url: str) -> bool:
371 | try:
372 | async with httpx.AsyncClient(trust_env=False) as client:
373 | resp = await client.get(f"{url}/.well-known/agent-card.json")
374 | return resp.status_code == 200
375 | except:
376 | return False
377 |
378 | def get(self, name: str):
379 | """获取已注册的 Agent"""
380 | return self.agents.get(name)
381 |
382 | def list_agents(self):
383 | """列出所有可用的 Agent"""
384 | return {
385 | name: {
386 | "url": info["url"],
387 | "description": info["card"].description,
388 | }
389 | for name, info in self.agents.items()
390 | }
391 |
392 | # 使用示例
393 | registry = AgentRegistry()
394 | await registry.register("translator", "http://localhost:8001")
395 | await registry.register("code_reviewer", "http://localhost:8002")
396 |
397 | # 根据任务智能选择 Agent
398 | translator = registry.get("translator")
399 | ```
400 |
401 | ### 8. 带工具的远程 Agent
402 |
403 | ```python
404 | # remote_agent/weather_agent.py
405 | from google.adk.agents import LlmAgent
406 | from google.adk.tools import FunctionTool
407 |
408 | def get_weather(city: str) -> str:
409 | """获取城市天气 (模拟)"""
410 | # 实际应用中可以调用真实天气 API
411 | weather_data = {
412 | "北京": "晴天,25°C",
413 | "上海": "多云,28°C",
414 | "东京": "小雨,22°C",
415 | }
416 | return weather_data.get(city, f"{city} 天气数据暂无")
417 |
418 | weather_tool = FunctionTool(func=get_weather)
419 |
420 | weather_agent = LlmAgent(
421 | name="weather_assistant",
422 | description="天气查询 Agent - 提供全球城市天气信息",
423 | model="gemini-2.0-flash",
424 | instruction="你是天气助手,帮助用户查询天气信息。",
425 | tools=[weather_tool],
426 | )
427 |
428 | app = to_a2a(agent=weather_agent, host="localhost", port=8003, protocol="http")
429 | ```
430 |
431 | ## 实战项目想法
432 |
433 | ### 项目 1: 多语言文档翻译系统
434 |
435 | ```
436 | 用户 → Host Agent → 翻译 Agent (中文)
437 | → 翻译 Agent (日文)
438 | → 翻译 Agent (韩文)
439 | → 汇总结果返回用户
440 | ```
441 |
442 | ### 项目 2: 代码审查流水线
443 |
444 | ```
445 | 代码提交 → 代码审查 Agent → 安全扫描 Agent → 性能分析 Agent → 生成报告
446 | ```
447 |
448 | ### 项目 3: 智能客服系统
449 |
450 | ```
451 | 用户问题 → 路由 Agent (分析问题类型)
452 | ├→ FAQ Agent (常见问题)
453 | ├→ 技术支持 Agent (技术问题)
454 | └→ 订单 Agent (订单相关)
455 | ```
456 |
457 | ### 项目 4: 研究助手
458 |
459 | ```
460 | 研究主题 → 搜索 Agent (收集资料)
461 | → 总结 Agent (提取要点)
462 | → 写作 Agent (生成报告)
463 | ```
464 |
465 | ## 常见问题
466 |
467 | ### Q: 服务启动但客户端连接失败?
468 | A: 检查是否有代理设置。使用 `httpx.AsyncClient(trust_env=False)` 禁用代理。
469 |
470 | ### Q: 看到 "Missing key inputs argument" 错误?
471 | A: 确保设置了 `GOOGLE_API_KEY` 环境变量。
472 |
473 | ### Q: Agent Card 端点是什么?
474 | A: 标准端点是 `/.well-known/agent-card.json`(旧版本是 `/.well-known/agent.json`)。
475 |
476 | ## 扩展阅读
477 |
478 | - [A2A Protocol Spec](https://a2a-protocol.org/)
479 | - [ADK A2A Docs](https://google.github.io/adk-docs/a2a/)
480 | - [Agent Starter Pack](https://github.com/GoogleCloudPlatform/agent-starter-pack)
481 | - [Prototype to Production Whitepaper](https://www.kaggle.com/whitepaper-prototype-to-production)
482 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/client/hitl_client.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Human-in-the-Loop 客户端
3 |
4 | 交互式客户端,演示完整的 Human-in-the-Loop 流程:
5 | 1. 提交任务请求
6 | 2. 查看待审批任务
7 | 3. 审批或拒绝任务
8 | 4. 查看执行结果
9 |
10 | 运行方式:
11 | python -m client.hitl_client
12 | """
13 |
14 | import asyncio
15 | import sys
16 | import os
17 | from typing import Optional
18 |
19 | # 添加项目根目录到路径
20 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
21 |
22 | import httpx
23 |
24 | # HITL Server URL
25 | HITL_SERVER_URL = os.getenv("HITL_SERVER_URL", "http://localhost:8016")
26 |
27 |
28 | class HITLClient:
29 | """Human-in-the-Loop 客户端"""
30 |
31 | def __init__(self, base_url: str = HITL_SERVER_URL):
32 | self.base_url = base_url
33 | self.client = httpx.AsyncClient(
34 | base_url=base_url,
35 | timeout=120.0,
36 | trust_env=False,
37 | )
38 |
39 | async def close(self):
40 | """关闭客户端"""
41 | await self.client.aclose()
42 |
43 | async def health_check(self) -> bool:
44 | """健康检查"""
45 | try:
46 | resp = await self.client.get("/health")
47 | return resp.status_code == 200
48 | except Exception:
49 | return False
50 |
51 | async def create_task(self, message: str) -> dict:
52 | """创建新任务"""
53 | resp = await self.client.post(
54 | "/tasks",
55 | json={"message": message},
56 | )
57 | resp.raise_for_status()
58 | return resp.json()
59 |
60 | async def list_tasks(self, status: Optional[str] = None) -> dict:
61 | """获取任务列表"""
62 | params = {}
63 | if status:
64 | params["status"] = status
65 | resp = await self.client.get("/tasks", params=params)
66 | resp.raise_for_status()
67 | return resp.json()
68 |
69 | async def get_pending_approvals(self) -> dict:
70 | """获取待审批任务"""
71 | resp = await self.client.get("/tasks/pending")
72 | resp.raise_for_status()
73 | return resp.json()
74 |
75 | async def get_task(self, task_id: str) -> dict:
76 | """获取任务详情"""
77 | resp = await self.client.get(f"/tasks/{task_id}")
78 | resp.raise_for_status()
79 | return resp.json()
80 |
81 | async def approve_task(
82 | self,
83 | task_id: str,
84 | comment: str = "",
85 | approver: str = "user",
86 | ) -> dict:
87 | """批准任务"""
88 | resp = await self.client.post(
89 | f"/tasks/{task_id}/approve",
90 | json={
91 | "approved": True,
92 | "comment": comment,
93 | "approver": approver,
94 | },
95 | )
96 | resp.raise_for_status()
97 | return resp.json()
98 |
99 | async def reject_task(
100 | self,
101 | task_id: str,
102 | comment: str = "",
103 | approver: str = "user",
104 | ) -> dict:
105 | """拒绝任务"""
106 | resp = await self.client.post(
107 | f"/tasks/{task_id}/reject",
108 | json={
109 | "approved": False,
110 | "comment": comment,
111 | "approver": approver,
112 | },
113 | )
114 | resp.raise_for_status()
115 | return resp.json()
116 |
117 |
118 | # ============================================================
119 | # 交互式演示
120 | # ============================================================
121 |
122 | def print_header(title: str):
123 | """打印标题"""
124 | print()
125 | print("=" * 60)
126 | print(f" {title}")
127 | print("=" * 60)
128 |
129 |
130 | def print_task(task: dict, show_details: bool = False):
131 | """打印任务信息"""
132 | print(f" ID: {task.get('task_id', 'N/A')[:8]}...")
133 | print(f" 状态: {task.get('status', 'N/A')}")
134 | if task.get('pending_action'):
135 | print(f" 待执行: {task.get('pending_action')}")
136 | if task.get('user_input'):
137 | print(f" 用户输入: {task.get('user_input')[:50]}...")
138 | if show_details:
139 | print(f" 创建时间: {task.get('created_at', 'N/A')}")
140 | print(f" 更新时间: {task.get('updated_at', 'N/A')}")
141 |
142 |
143 | async def demo_low_risk():
144 | """演示低风险任务(自动执行)"""
145 | print_header("场景 1: 低风险任务 - 自动执行")
146 | print(" 请求: 查询今天的天气")
147 | print("-" * 60)
148 |
149 | client = HITLClient()
150 | try:
151 | result = await client.create_task("查询今天北京的天气")
152 | print(f"\n 任务创建成功!")
153 | print(f" Task ID: {result.get('task_id', 'N/A')[:8]}...")
154 | print(f" 状态: {result.get('status')}")
155 | print(f" 需要审批: {result.get('requires_approval')}")
156 | print(f" 风险等级: {result.get('risk_level')}")
157 | print()
158 | print(f" 响应: {result.get('message')[:200]}...")
159 | except Exception as e:
160 | print(f" ❌ 错误: {e}")
161 | finally:
162 | await client.close()
163 |
164 |
165 | async def demo_high_risk():
166 | """演示高风险任务(需要审批)"""
167 | print_header("场景 2: 高风险任务 - 需要审批")
168 | print(" 请求: 删除所有用户数据")
169 | print("-" * 60)
170 |
171 | client = HITLClient()
172 | try:
173 | # 创建任务
174 | result = await client.create_task("请帮我删除所有用户数据")
175 | task_id = result.get('task_id')
176 |
177 | print(f"\n 任务创建成功!")
178 | print(f" Task ID: {task_id[:8]}...")
179 | print(f" 状态: {result.get('status')}")
180 | print(f" 需要审批: {result.get('requires_approval')}")
181 | print(f" 风险等级: {result.get('risk_level')}")
182 | print(f" 待执行操作: {result.get('action_description')}")
183 | print()
184 | print(f" 消息: {result.get('message')}")
185 |
186 | if result.get('status') == 'waiting_approval':
187 | print()
188 | print("-" * 60)
189 | print(" 任务等待审批中...")
190 | print("-" * 60)
191 |
192 | # 模拟人工审批决策
193 | print()
194 | print(" [模拟审批] 这是一个危险操作,拒绝执行")
195 |
196 | # 拒绝任务
197 | reject_result = await client.reject_task(
198 | task_id,
199 | comment="操作过于危险,不允许批量删除用户数据",
200 | approver="security_admin",
201 | )
202 |
203 | print()
204 | print(f" 审批结果: {reject_result.get('status')}")
205 | print(f" 响应: {reject_result.get('result', 'N/A')[:200]}...")
206 |
207 | except Exception as e:
208 | print(f" ❌ 错误: {e}")
209 | finally:
210 | await client.close()
211 |
212 |
213 | async def demo_approved_task():
214 | """演示审批通过的任务"""
215 | print_header("场景 3: 审批通过的任务")
216 | print(" 请求: 发送一封邮件给用户")
217 | print("-" * 60)
218 |
219 | client = HITLClient()
220 | try:
221 | # 创建任务
222 | result = await client.create_task("发送一封欢迎邮件给新注册的用户 test@example.com")
223 | task_id = result.get('task_id')
224 |
225 | print(f"\n 任务创建成功!")
226 | print(f" Task ID: {task_id[:8]}...")
227 | print(f" 状态: {result.get('status')}")
228 | print(f" 需要审批: {result.get('requires_approval')}")
229 | print(f" 风险等级: {result.get('risk_level')}")
230 |
231 | if result.get('status') == 'waiting_approval':
232 | print()
233 | print("-" * 60)
234 | print(" 任务等待审批中...")
235 | print("-" * 60)
236 |
237 | # 模拟人工审批决策
238 | print()
239 | print(" [模拟审批] 邮件内容合规,批准发送")
240 |
241 | # 批准任务
242 | approve_result = await client.approve_task(
243 | task_id,
244 | comment="邮件内容已审核,批准发送",
245 | approver="content_reviewer",
246 | )
247 |
248 | print()
249 | print(f" 审批结果: {approve_result.get('status')}")
250 | print(f" 执行结果: {approve_result.get('result', 'N/A')[:200]}...")
251 |
252 | except Exception as e:
253 | print(f" ❌ 错误: {e}")
254 | finally:
255 | await client.close()
256 |
257 |
258 | async def demo_list_tasks():
259 | """演示任务列表查询"""
260 | print_header("任务列表查询")
261 |
262 | client = HITLClient()
263 | try:
264 | # 获取所有任务
265 | result = await client.list_tasks()
266 | tasks = result.get('tasks', [])
267 |
268 | print(f"\n 共 {result.get('total', 0)} 个任务:")
269 | print("-" * 60)
270 |
271 | for task in tasks[:5]: # 只显示前 5 个
272 | print()
273 | print_task(task)
274 |
275 | if len(tasks) > 5:
276 | print(f"\n ... 还有 {len(tasks) - 5} 个任务")
277 |
278 | # 获取待审批任务
279 | pending = await client.get_pending_approvals()
280 | pending_tasks = pending.get('tasks', [])
281 |
282 | if pending_tasks:
283 | print()
284 | print("-" * 60)
285 | print(f" 待审批任务: {len(pending_tasks)} 个")
286 | print("-" * 60)
287 | for task in pending_tasks:
288 | print()
289 | print_task(task)
290 |
291 | except Exception as e:
292 | print(f" ❌ 错误: {e}")
293 | finally:
294 | await client.close()
295 |
296 |
297 | async def interactive_mode():
298 | """交互模式"""
299 | print_header("交互模式")
300 | print(" 输入命令与 HITL Agent 交互")
301 | print()
302 | print(" 可用命令:")
303 | print(" send - 发送请求")
304 | print(" list - 查看任务列表")
305 | print(" pending - 查看待审批任务")
306 | print(" approve - 批准任务")
307 | print(" reject - 拒绝任务")
308 | print(" detail - 查看任务详情")
309 | print(" quit - 退出")
310 | print()
311 |
312 | client = HITLClient()
313 |
314 | try:
315 | while True:
316 | try:
317 | user_input = input("HITL> ").strip()
318 | if not user_input:
319 | continue
320 |
321 | parts = user_input.split(maxsplit=1)
322 | command = parts[0].lower()
323 | args = parts[1] if len(parts) > 1 else ""
324 |
325 | if command == "quit" or command == "exit":
326 | print("再见!")
327 | break
328 |
329 | elif command == "send":
330 | if not args:
331 | print("请输入消息内容")
332 | continue
333 | result = await client.create_task(args)
334 | print(f"\n任务 ID: {result.get('task_id')}")
335 | print(f"状态: {result.get('status')}")
336 | print(f"风险等级: {result.get('risk_level')}")
337 | print(f"响应: {result.get('message')[:300]}...")
338 |
339 | elif command == "list":
340 | result = await client.list_tasks()
341 | tasks = result.get('tasks', [])
342 | print(f"\n共 {len(tasks)} 个任务:")
343 | for task in tasks[:10]:
344 | print(f" [{task.get('status'):15}] {task.get('task_id')[:8]}... - {task.get('user_input', '')[:30]}...")
345 |
346 | elif command == "pending":
347 | result = await client.get_pending_approvals()
348 | tasks = result.get('tasks', [])
349 | if tasks:
350 | print(f"\n待审批任务 ({len(tasks)} 个):")
351 | for task in tasks:
352 | print(f" {task.get('task_id')[:8]}... - {task.get('pending_action', '')[:50]}...")
353 | else:
354 | print("\n没有待审批的任务")
355 |
356 | elif command == "approve":
357 | if not args:
358 | print("请输入任务 ID")
359 | continue
360 | comment = input("审批意见 (可选): ").strip()
361 | result = await client.approve_task(args, comment)
362 | print(f"\n审批结果: {result.get('status')}")
363 | print(f"响应: {result.get('result', 'N/A')[:300]}...")
364 |
365 | elif command == "reject":
366 | if not args:
367 | print("请输入任务 ID")
368 | continue
369 | comment = input("拒绝原因: ").strip()
370 | result = await client.reject_task(args, comment)
371 | print(f"\n审批结果: {result.get('status')}")
372 | print(f"响应: {result.get('result', 'N/A')[:300]}...")
373 |
374 | elif command == "detail":
375 | if not args:
376 | print("请输入任务 ID")
377 | continue
378 | result = await client.get_task(args)
379 | task = result.get('task', {})
380 | print(f"\n任务详情:")
381 | print(f" ID: {task.get('task_id')}")
382 | print(f" 状态: {task.get('status')}")
383 | print(f" 用户输入: {task.get('user_input')}")
384 | print(f" 待执行: {task.get('pending_action')}")
385 | print(f" 创建时间: {task.get('created_at')}")
386 | if result.get('state'):
387 | state = result['state']
388 | print(f" 风险等级: {state.get('risk_level')}")
389 | print(f" 分析: {state.get('analysis', '')[:100]}...")
390 |
391 | else:
392 | print(f"未知命令: {command}")
393 |
394 | except KeyboardInterrupt:
395 | print("\n再见!")
396 | break
397 | except Exception as e:
398 | print(f"错误: {e}")
399 |
400 | finally:
401 | await client.close()
402 |
403 |
404 | async def main():
405 | """主程序"""
406 | print("=" * 60)
407 | print(" Day 16: Human-in-the-Loop Client")
408 | print("=" * 60)
409 | print()
410 | print(f"服务地址: {HITL_SERVER_URL}")
411 |
412 | # 健康检查
413 | client = HITLClient()
414 | try:
415 | is_healthy = await client.health_check()
416 | if not is_healthy:
417 | print()
418 | print("❌ 无法连接到 HITL 服务")
419 | print(" 请确保服务正在运行:")
420 | print(" python -m langgraph_agent.server")
421 | return
422 | print("✅ 服务连接正常")
423 | finally:
424 | await client.close()
425 |
426 | print()
427 | print("选择演示模式:")
428 | print(" 1. 低风险任务演示 (自动执行)")
429 | print(" 2. 高风险任务演示 (需要审批)")
430 | print(" 3. 审批通过演示")
431 | print(" 4. 查看任务列表")
432 | print(" 5. 交互模式")
433 | print(" 6. 运行所有演示")
434 | print(" q. 退出")
435 | print()
436 |
437 | choice = input("请选择 (1-6/q): ").strip()
438 |
439 | if choice == "1":
440 | await demo_low_risk()
441 | elif choice == "2":
442 | await demo_high_risk()
443 | elif choice == "3":
444 | await demo_approved_task()
445 | elif choice == "4":
446 | await demo_list_tasks()
447 | elif choice == "5":
448 | await interactive_mode()
449 | elif choice == "6":
450 | await demo_low_risk()
451 | await asyncio.sleep(1)
452 | await demo_high_risk()
453 | await asyncio.sleep(1)
454 | await demo_approved_task()
455 | await asyncio.sleep(1)
456 | await demo_list_tasks()
457 | elif choice.lower() == "q":
458 | print("再见!")
459 | else:
460 | print("无效选择")
461 |
462 | print()
463 | print("=" * 60)
464 | print(" 演示结束")
465 | print("=" * 60)
466 |
467 |
468 | if __name__ == "__main__":
469 | asyncio.run(main())
470 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/day-16/langgraph_agent/server.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | Human-in-the-Loop Server - 生产级 API 服务
3 |
4 | 提供完整的 REST API:
5 | - POST /tasks - 创建新任务
6 | - GET /tasks - 获取任务列表
7 | - GET /tasks/{id} - 获取任务详情
8 | - POST /tasks/{id}/approve - 批准任务
9 | - POST /tasks/{id}/reject - 拒绝任务
10 | - GET /tasks/pending - 获取待审批任务
11 |
12 | 同时提供 A2A 协议支持。
13 |
14 | 运行方式:
15 | python -m langgraph_agent.server
16 | """
17 |
18 | import os
19 | import sys
20 | import asyncio
21 | import logging
22 | from typing import Optional
23 | from datetime import datetime, timedelta
24 | from contextlib import asynccontextmanager
25 |
26 | from fastapi import FastAPI, HTTPException, BackgroundTasks
27 | from fastapi.middleware.cors import CORSMiddleware
28 | from fastapi.staticfiles import StaticFiles
29 | from fastapi.responses import FileResponse
30 | from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
31 |
32 | # 添加项目根目录到路径
33 | sys.path.insert(0, os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
34 |
35 | from dotenv import load_dotenv
36 | project_root = os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))))
37 | load_dotenv(os.path.join(project_root, ".env"))
38 |
39 | from langgraph_agent.hitl_agent import (
40 | run_hitl_agent,
41 | resume_after_approval,
42 | create_hitl_graph,
43 | )
44 | from langgraph_agent.checkpointer import (
45 | get_task_store,
46 | get_checkpointer,
47 | TaskMetadata,
48 | )
49 |
50 | # 配置日志
51 | logging.basicConfig(
52 | level=logging.INFO,
53 | format="%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s - %(message)s",
54 | )
55 | logger = logging.getLogger(__name__)
56 |
57 |
58 | # ============================================================
59 | # Pydantic Models
60 | # ============================================================
61 |
62 | class TaskCreateRequest(BaseModel):
63 | """创建任务请求"""
64 | message: str = Field(..., description="用户输入的消息")
65 | metadata: Optional[dict] = Field(default=None, description="额外元数据")
66 |
67 |
68 | class TaskCreateResponse(BaseModel):
69 | """创建任务响应"""
70 | task_id: str
71 | thread_id: str
72 | status: str
73 | requires_approval: bool
74 | risk_level: Optional[str] = None
75 | action_description: Optional[str] = None
76 | message: str
77 |
78 |
79 | class ApprovalRequest(BaseModel):
80 | """审批请求"""
81 | approved: bool = Field(..., description="是否批准")
82 | comment: Optional[str] = Field(default="", description="审批意见")
83 | approver: Optional[str] = Field(default="system", description="审批人")
84 |
85 |
86 | class ApprovalResponse(BaseModel):
87 | """审批响应"""
88 | task_id: str
89 | status: str
90 | result: Optional[str] = None
91 | message: str
92 |
93 |
94 | class TaskInfo(BaseModel):
95 | """任务信息"""
96 | task_id: str
97 | thread_id: str
98 | status: str
99 | created_at: str
100 | updated_at: str
101 | current_node: Optional[str] = None
102 | pending_action: Optional[str] = None
103 | user_input: Optional[str] = None
104 | error_message: Optional[str] = None
105 |
106 |
107 | class TaskListResponse(BaseModel):
108 | """任务列表响应"""
109 | tasks: list[TaskInfo]
110 | total: int
111 |
112 |
113 | class TaskDetailResponse(BaseModel):
114 | """任务详情响应"""
115 | task: TaskInfo
116 | state: Optional[dict] = None
117 |
118 |
119 | # ============================================================
120 | # 超时检查后台任务
121 | # ============================================================
122 |
123 | # 审批超时时间(秒)
124 | APPROVAL_TIMEOUT_SECONDS = int(os.getenv("APPROVAL_TIMEOUT_SECONDS", "300")) # 默认 5 分钟
125 |
126 | async def check_approval_timeouts():
127 | """
128 | 后台任务:检查审批超时
129 |
130 | 每隔一段时间检查等待审批的任务,超时的自动拒绝
131 | """
132 | while True:
133 | try:
134 | task_store = get_task_store()
135 | pending_tasks = task_store.get_pending_approvals()
136 |
137 | for task in pending_tasks:
138 | # 检查是否超时
139 | created_at = datetime.fromisoformat(task.created_at)
140 | timeout_at = created_at + timedelta(seconds=APPROVAL_TIMEOUT_SECONDS)
141 |
142 | if datetime.utcnow() > timeout_at:
143 | logger.warning(f"Task {task.task_id} approval timeout, auto-rejecting")
144 |
145 | # 自动拒绝
146 | try:
147 | resume_after_approval(
148 | task_id=task.task_id,
149 | thread_id=task.thread_id,
150 | approved=False,
151 | comment="审批超时,自动拒绝",
152 | approver="system_timeout",
153 | )
154 | task_store.update_task(task.task_id, status="timeout")
155 | except Exception as e:
156 | logger.error(f"Failed to auto-reject task {task.task_id}: {e}")
157 |
158 | except Exception as e:
159 | logger.error(f"Error in timeout check: {e}")
160 |
161 | # 每 30 秒检查一次
162 | await asyncio.sleep(30)
163 |
164 |
165 | # ============================================================
166 | # FastAPI App
167 | # ============================================================
168 |
169 | @asynccontextmanager
170 | async def lifespan(app: FastAPI):
171 | """应用生命周期管理"""
172 | # 启动时
173 | logger.info("Starting HITL Server...")
174 | logger.info(f"Approval timeout: {APPROVAL_TIMEOUT_SECONDS} seconds")
175 |
176 | # 启动超时检查后台任务
177 | timeout_task = asyncio.create_task(check_approval_timeouts())
178 |
179 | yield
180 |
181 | # 关闭时
182 | logger.info("Shutting down HITL Server...")
183 | timeout_task.cancel()
184 | try:
185 | await timeout_task
186 | except asyncio.CancelledError:
187 | pass
188 |
189 |
190 | app = FastAPI(
191 | title="Human-in-the-Loop Agent API",
192 | description="生产级 Human-in-the-Loop Agent 服务",
193 | version="1.0.0",
194 | lifespan=lifespan,
195 | )
196 |
197 | # CORS 配置
198 | app.add_middleware(
199 | CORSMiddleware,
200 | allow_origins=["*"], # 生产环境应该限制
201 | allow_credentials=True,
202 | allow_methods=["*"],
203 | allow_headers=["*"],
204 | )
205 |
206 | # 静态文件服务(Web UI)
207 | STATIC_DIR = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), "static")
208 | if os.path.exists(STATIC_DIR):
209 | app.mount("/static", StaticFiles(directory=STATIC_DIR), name="static")
210 |
211 |
212 | # ============================================================
213 | # Web UI 入口
214 | # ============================================================
215 |
216 | @app.get("/ui", tags=["Web UI"])
217 | async def web_ui():
218 | """Web UI 入口页面"""
219 | index_path = os.path.join(STATIC_DIR, "index.html")
220 | if os.path.exists(index_path):
221 | return FileResponse(index_path)
222 | raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail="Web UI not found")
223 |
224 |
225 | # ============================================================
226 | # API 端点
227 | # ============================================================
228 |
229 | @app.post("/tasks", response_model=TaskCreateResponse, tags=["Tasks"])
230 | async def create_task(request: TaskCreateRequest, background_tasks: BackgroundTasks):
231 | """
232 | 创建新任务
233 |
234 | 流程:
235 | 1. 分析用户请求
236 | 2. 评估风险等级
237 | 3. 如果需要审批,返回等待审批状态
238 | 4. 如果不需要审批,直接执行并返回结果
239 | """
240 | try:
241 | logger.info(f"Creating task for: {request.message[:50]}...")
242 |
243 | # 运行 Agent
244 | result = run_hitl_agent(request.message)
245 |
246 | task_id = result["task_id"]
247 | thread_id = result["thread_id"]
248 | status = result["status"]
249 | agent_result = result.get("result", {})
250 |
251 | # 提取关键信息
252 | requires_approval = agent_result.get("requires_approval", False)
253 | risk_level = agent_result.get("risk_level", "")
254 | action_plan = agent_result.get("action_plan", {})
255 | action_description = action_plan.get("description", "")
256 | final_answer = agent_result.get("final_answer", "")
257 |
258 | # 根据状态返回不同消息
259 | if status == "waiting_approval":
260 | message = f"任务需要审批。风险等级: {risk_level},操作: {action_description}"
261 | elif status == "completed":
262 | message = final_answer or "任务已完成"
263 | else:
264 | message = f"任务状态: {status}"
265 |
266 | return TaskCreateResponse(
267 | task_id=task_id,
268 | thread_id=thread_id,
269 | status=status,
270 | requires_approval=requires_approval,
271 | risk_level=risk_level,
272 | action_description=action_description,
273 | message=message,
274 | )
275 |
276 | except Exception as e:
277 | logger.error(f"Failed to create task: {e}")
278 | raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
279 |
280 |
281 | @app.get("/tasks", response_model=TaskListResponse, tags=["Tasks"])
282 | async def list_tasks(status: Optional[str] = None, limit: int = 50):
283 | """
284 | 获取任务列表
285 |
286 | 可选参数:
287 | - status: 按状态筛选 (pending, waiting_approval, approved, rejected, completed, failed)
288 | - limit: 返回数量限制
289 | """
290 | try:
291 | task_store = get_task_store()
292 |
293 | if status:
294 | tasks = task_store.get_tasks_by_status(status)
295 | else:
296 | # 获取所有任务(通过获取各状态的任务合并)
297 | all_tasks = []
298 | for s in ["pending", "waiting_approval", "approved", "rejected", "completed", "failed", "timeout"]:
299 | all_tasks.extend(task_store.get_tasks_by_status(s))
300 | # 按创建时间排序
301 | tasks = sorted(all_tasks, key=lambda t: t.created_at, reverse=True)
302 |
303 | # 限制数量
304 | tasks = tasks[:limit]
305 |
306 | return TaskListResponse(
307 | tasks=[
308 | TaskInfo(
309 | task_id=t.task_id,
310 | thread_id=t.thread_id,
311 | status=t.status,
312 | created_at=t.created_at,
313 | updated_at=t.updated_at,
314 | current_node=t.current_node,
315 | pending_action=t.pending_action,
316 | user_input=t.user_input,
317 | error_message=t.error_message,
318 | )
319 | for t in tasks
320 | ],
321 | total=len(tasks),
322 | )
323 |
324 | except Exception as e:
325 | logger.error(f"Failed to list tasks: {e}")
326 | raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
327 |
328 |
329 | @app.get("/tasks/pending", response_model=TaskListResponse, tags=["Tasks"])
330 | async def get_pending_approvals():
331 | """获取所有待审批的任务"""
332 | try:
333 | task_store = get_task_store()
334 | tasks = task_store.get_pending_approvals()
335 |
336 | return TaskListResponse(
337 | tasks=[
338 | TaskInfo(
339 | task_id=t.task_id,
340 | thread_id=t.thread_id,
341 | status=t.status,
342 | created_at=t.created_at,
343 | updated_at=t.updated_at,
344 | current_node=t.current_node,
345 | pending_action=t.pending_action,
346 | user_input=t.user_input,
347 | error_message=t.error_message,
348 | )
349 | for t in tasks
350 | ],
351 | total=len(tasks),
352 | )
353 |
354 | except Exception as e:
355 | logger.error(f"Failed to get pending approvals: {e}")
356 | raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
357 |
358 |
359 | @app.get("/tasks/{task_id}", response_model=TaskDetailResponse, tags=["Tasks"])
360 | async def get_task(task_id: str):
361 | """获取任务详情"""
362 | try:
363 | task_store = get_task_store()
364 | task = task_store.get_task(task_id)
365 |
366 | if not task:
367 | raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail=f"Task {task_id} not found")
368 |
369 | # 获取图状态(如果有)
370 | state = None
371 | try:
372 | checkpointer = get_checkpointer()
373 | config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": task.thread_id}}
374 | graph = create_hitl_graph(checkpointer)
375 | state_snapshot = graph.get_state(config)
376 | if state_snapshot:
377 | state = dict(state_snapshot.values) if state_snapshot.values else None
378 | except Exception as e:
379 | logger.warning(f"Failed to get state for task {task_id}: {e}")
380 |
381 | return TaskDetailResponse(
382 | task=TaskInfo(
383 | task_id=task.task_id,
384 | thread_id=task.thread_id,
385 | status=task.status,
386 | created_at=task.created_at,
387 | updated_at=task.updated_at,
388 | current_node=task.current_node,
389 | pending_action=task.pending_action,
390 | user_input=task.user_input,
391 | error_message=task.error_message,
392 | ),
393 | state=state,
394 | )
395 |
396 | except HTTPException:
397 | raise
398 | except Exception as e:
399 | logger.error(f"Failed to get task {task_id}: {e}")
400 | raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
401 |
402 |
403 | @app.post("/tasks/{task_id}/approve", response_model=ApprovalResponse, tags=["Approval"])
404 | async def approve_task(task_id: str, request: ApprovalRequest):
405 | """
406 | 审批任务(批准)
407 |
408 | 批准后,任务将继续执行
409 | """
410 | if not request.approved:
411 | raise HTTPException(
412 | status_code=400,
413 | detail="Use /tasks/{task_id}/reject for rejection"
414 | )
415 |
416 | return await _process_approval(task_id, True, request.comment, request.approver)
417 |
418 |
419 | @app.post("/tasks/{task_id}/reject", response_model=ApprovalResponse, tags=["Approval"])
420 | async def reject_task(task_id: str, request: ApprovalRequest):
421 | """
422 | 审批任务(拒绝)
423 |
424 | 拒绝后,任务将终止并返回拒绝原因
425 | """
426 | return await _process_approval(task_id, False, request.comment, request.approver)
427 |
428 |
429 | async def _process_approval(
430 | task_id: str,
431 | approved: bool,
432 | comment: str,
433 | approver: str,
434 | ) -> ApprovalResponse:
435 | """处理审批"""
436 | try:
437 | task_store = get_task_store()
438 | task = task_store.get_task(task_id)
439 |
440 | if not task:
441 | raise HTTPException(status_code=404, detail=f"Task {task_id} not found")
442 |
443 | if task.status != "waiting_approval":
444 | raise HTTPException(
445 | status_code=400,
446 | detail=f"Task is not waiting for approval. Current status: {task.status}"
447 | )
448 |
449 | logger.info(f"Processing approval for task {task_id}: approved={approved}")
450 |
451 | # 恢复执行
452 | result = resume_after_approval(
453 | task_id=task_id,
454 | thread_id=task.thread_id,
455 | approved=approved,
456 | comment=comment or "",
457 | approver=approver or "system",
458 | )
459 |
460 | # 获取最终结果
461 | agent_result = result.get("result", {})
462 | final_answer = agent_result.get("final_answer", "")
463 |
464 | action = "批准" if approved else "拒绝"
465 | return ApprovalResponse(
466 | task_id=task_id,
467 | status=result["status"],
468 | result=final_answer,
469 | message=f"任务已{action}",
470 | )
471 |
472 | except HTTPException:
473 | raise
474 | except Exception as e:
475 | logger.error(f"Failed to process approval for {task_id}: {e}")
476 | raise HTTPException(status_code=500, detail=str(e))
477 |
478 |
479 | # ============================================================
480 | # 健康检查
481 | # ============================================================
482 |
483 | @app.get("/health", tags=["System"])
484 | async def health_check():
485 | """健康检查"""
486 | return {
487 | "status": "healthy",
488 | "timestamp": datetime.utcnow().isoformat(),
489 | "approval_timeout_seconds": APPROVAL_TIMEOUT_SECONDS,
490 | }
491 |
492 |
493 | @app.get("/", tags=["System"])
494 | async def root():
495 | """API 根路径"""
496 | return {
497 | "name": "Human-in-the-Loop Agent API",
498 | "version": "1.0.0",
499 | "web_ui": "/ui",
500 | "docs": "/docs",
501 | "endpoints": {
502 | "create_task": "POST /tasks",
503 | "list_tasks": "GET /tasks",
504 | "pending_approvals": "GET /tasks/pending",
505 | "get_task": "GET /tasks/{task_id}",
506 | "approve": "POST /tasks/{task_id}/approve",
507 | "reject": "POST /tasks/{task_id}/reject",
508 | }
509 | }
510 |
511 |
512 | # ============================================================
513 | # 主程序
514 | # ============================================================
515 |
516 | if __name__ == "__main__":
517 | import uvicorn
518 |
519 | print("=" * 60)
520 | print("Day 16: Human-in-the-Loop Agent Server")
521 | print("=" * 60)
522 | print()
523 | print("访问地址:")
524 | print(" Web UI: http://localhost:8016/ui <- 推荐")
525 | print(" API Docs: http://localhost:8016/docs")
526 | print()
527 | print("API 端点:")
528 | print(" POST /tasks - 创建新任务")
529 | print(" GET /tasks - 获取任务列表")
530 | print(" GET /tasks/pending - 获取待审批任务")
531 | print(" POST /tasks/{id}/approve - 批准任务")
532 | print(" POST /tasks/{id}/reject - 拒绝任务")
533 | print()
534 | print(f"审批超时: {APPROVAL_TIMEOUT_SECONDS} 秒")
535 | print("=" * 60)
536 | print()
537 |
538 | uvicorn.run(app, host="localhost", port=8016)
539 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
26 |