├── convnets-keras
├── .gitignore
├── .gitignore~
├── convnetskeras
│ ├── __init__.py
│ ├── __init__.pyc
│ ├── convnets.pyc
│ ├── customlayers.pyc
│ ├── imagenet_tool.pyc
│ ├── data
│ │ └── meta_clsloc.mat
│ ├── imagenet_tool.py
│ ├── customlayers.py
│ ├── convnets.py
│ └── convnets.py~
├── weights
│ └── .gitignore
├── build
│ └── lib.linux-x86_64-2.7
│ │ └── convnetskeras
│ │ ├── __init__.py
│ │ ├── data
│ │ └── meta_clsloc.mat
│ │ ├── imagenet_tool.py
│ │ ├── customlayers.py
│ │ └── convnets.py
├── heatmap_dog.png
├── examples
│ ├── cars.jpg
│ ├── dog.jpg
│ ├── dog2.jpg
│ ├── dog4.jpg
│ ├── 2-Blast.png
│ ├── dog_227.jpg
│ ├── dog_512.jpg
│ ├── heatmap.png
│ ├── 11-Hemat.png
│ └── heatmap_dog.png
├── .ipynb_checkpoints
│ ├── Untitled-checkpoint.ipynb
│ └── Experimental-checkpoint.ipynb
├── setup.py
├── LICENSE.txt
├── README.md
└── Untitled.ipynb
├── Data
└── .gitignore
├── .gitignore
├── Plots
├── accuracy_finetune.png
├── accuracy_scratch.png
├── finetune_vs_scratch_accuracy1.png
└── feature_extraction_convpool_5_accuracy1.png
├── LICENSE
├── Code
├── utils.py
└── alexnet_base.py
└── README.md
/convnets-keras/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Data/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *
2 | !.gitignore
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/.gitignore~:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *.pyc
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Data/*
2 | convnets-keras/weights/*
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/weights/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *
2 | !.gitignore
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/convnetskeras/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Plots/accuracy_finetune.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/Plots/accuracy_finetune.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Plots/accuracy_scratch.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/Plots/accuracy_scratch.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/heatmap_dog.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/heatmap_dog.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/cars.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/cars.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/dog.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/dog.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/dog2.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/dog2.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/dog4.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/dog4.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/2-Blast.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/2-Blast.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/dog_227.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/dog_227.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/dog_512.jpg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/dog_512.jpg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/heatmap.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/heatmap.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/11-Hemat.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/11-Hemat.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Plots/finetune_vs_scratch_accuracy1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/Plots/finetune_vs_scratch_accuracy1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/.ipynb_checkpoints/Untitled-checkpoint.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [],
3 | "metadata": {},
4 | "nbformat": 4,
5 | "nbformat_minor": 0
6 | }
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/examples/heatmap_dog.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/examples/heatmap_dog.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/.ipynb_checkpoints/Experimental-checkpoint.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [],
3 | "metadata": {},
4 | "nbformat": 4,
5 | "nbformat_minor": 0
6 | }
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/__init__.pyc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/__init__.pyc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.pyc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.pyc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/customlayers.pyc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/customlayers.pyc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/imagenet_tool.pyc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/imagenet_tool.pyc
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Plots/feature_extraction_convpool_5_accuracy1.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/Plots/feature_extraction_convpool_5_accuracy1.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/data/meta_clsloc.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/data/meta_clsloc.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/convnetskeras/data/meta_clsloc.mat:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/ashishpatel26/AlexNet-Experiments-Keras/master/convnets-keras/build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/convnetskeras/data/meta_clsloc.mat
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from distutils.core import setup
2 |
3 | setup(name='convnetskeras',
4 | version='0.1',
5 | description='Pre-trained convnets in Keras',
6 | author='Leonard Blier',
7 | author_email='leonard.blier@ens.fr',
8 | packages=['convnetskeras'],
9 | package_dir={'convnetskeras':'convnetskeras'},
10 | package_data={'convnetskeras':["data/*"]},
11 | long_description=open('README.md').read(),
12 | )
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/LICENSE.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Copyright (c) 2016 Heuritech
2 |
3 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
4 |
5 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
6 |
7 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2017
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/imagenet_tool.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 |
3 | from os import listdir
4 | from os.path import isfile, join, dirname
5 |
6 | from scipy.io import loadmat
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | meta_clsloc_file = join(dirname(__file__), "data", "meta_clsloc.mat")
11 |
12 |
13 | synsets = loadmat(meta_clsloc_file)["synsets"][0]
14 |
15 | synsets_imagenet_sorted = sorted([(int(s[0]), str(s[1][0])) for s in synsets[:1000]],
16 | key=lambda v:v[1])
17 |
18 | corr = {}
19 | for j in range(1000):
20 | corr[synsets_imagenet_sorted[j][0]] = j
21 |
22 | corr_inv = {}
23 | for j in range(1,1001):
24 | corr_inv[corr[j]] = j
25 |
26 | def depthfirstsearch(id_, out=None):
27 | if out is None:
28 | out = []
29 | if isinstance(id_, int):
30 | pass
31 | else:
32 | id_ = next(int(s[0]) for s in synsets if s[1][0] == id_)
33 |
34 | out.append(id_)
35 | children = synsets[id_-1][5][0]
36 | for c in children:
37 | depthfirstsearch(int(c), out)
38 | return out
39 |
40 | def synset_to_dfs_ids(synset):
41 | ids = [x for x in depthfirstsearch(synset) if x <= 1000]
42 | ids = [corr[x] for x in ids]
43 | return ids
44 |
45 |
46 | def synset_to_id(synset):
47 | a = next((i for (i,s) in synsets if s == synset), None)
48 | return a
49 |
50 |
51 | def id_to_synset(id_):
52 | return str(synsets[corr_inv[id_]-1][1][0])
53 |
54 |
55 | def id_to_words(id_):
56 | return synsets[corr_inv[id_]-1][2][0]
57 |
58 | def pprint_output(out, n_max_synsets=10):
59 | best_ids = out.argsort()[::-1][:10]
60 | for u in best_ids:
61 | print("%.2f"% round(100*out[u],2)+" : "+id_to_words(u))
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/convnetskeras/imagenet_tool.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 |
3 | from os import listdir
4 | from os.path import isfile, join, dirname
5 |
6 | from scipy.io import loadmat
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 | meta_clsloc_file = join(dirname(__file__), "data", "meta_clsloc.mat")
11 |
12 |
13 | synsets = loadmat(meta_clsloc_file)["synsets"][0]
14 |
15 | synsets_imagenet_sorted = sorted([(int(s[0]), str(s[1][0])) for s in synsets[:1000]],
16 | key=lambda v:v[1])
17 |
18 | corr = {}
19 | for j in range(1000):
20 | corr[synsets_imagenet_sorted[j][0]] = j
21 |
22 | corr_inv = {}
23 | for j in range(1,1001):
24 | corr_inv[corr[j]] = j
25 |
26 | def depthfirstsearch(id_, out=None):
27 | if out is None:
28 | out = []
29 | if isinstance(id_, int):
30 | pass
31 | else:
32 | id_ = next(int(s[0]) for s in synsets if s[1][0] == id_)
33 |
34 | out.append(id_)
35 | children = synsets[id_-1][5][0]
36 | for c in children:
37 | depthfirstsearch(int(c), out)
38 | return out
39 |
40 | def synset_to_dfs_ids(synset):
41 | ids = [x for x in depthfirstsearch(synset) if x <= 1000]
42 | ids = [corr[x] for x in ids]
43 | return ids
44 |
45 |
46 | def synset_to_id(synset):
47 | a = next((i for (i,s) in synsets if s == synset), None)
48 | return a
49 |
50 |
51 | def id_to_synset(id_):
52 | return str(synsets[corr_inv[id_]-1][1][0])
53 |
54 |
55 | def id_to_words(id_):
56 | return synsets[corr_inv[id_]-1][2][0]
57 |
58 | def pprint_output(out, n_max_synsets=10):
59 | best_ids = out.argsort()[::-1][:10]
60 | for u in best_ids:
61 | print("%.2f"% round(100*out[u],2)+" : "+id_to_words(u))
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Code/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
2 |
3 | def append_history(history, h):
4 | '''
5 | This function appends the statistics over epochs
6 | '''
7 | try:
8 | history.history['loss'] = history.history['loss'] + h.history['loss']
9 | history.history['val_loss'] = history.history['val_loss'] + h.history['val_loss']
10 | history.history['acc'] = history.history['acc'] + h.history['acc']
11 | history.history['val_acc'] = history.history['val_acc'] + h.history['val_acc']
12 | except:
13 | history = h
14 |
15 | return history
16 |
17 |
18 | def unfreeze_layer_onwards(model, layer_name):
19 | '''
20 | This layer unfreezes all layers beyond layer_name
21 | '''
22 | trainable = False
23 | for layer in model.layers:
24 | try:
25 | if layer.name == layer_name:
26 | trainable = True
27 | layer.trainable = trainable
28 | except:
29 | continue
30 |
31 | return model
32 |
33 |
34 | def plot_performance(history):
35 | '''
36 | This function plots the train & test accuracy, loss plots
37 | '''
38 |
39 | plt.subplot(1,2,1)
40 | plt.plot(history.history['acc'])
41 | plt.plot(history.history['val_acc'])
42 | plt.title('Accuracy v/s Epochs')
43 | plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
44 | plt.xlabel('Epoch')
45 | plt.legend(['train', 'test'], loc='upper left')
46 |
47 | plt.subplot(1,2,2)
48 | plt.plot(history.history['loss'])
49 | plt.plot(history.history['val_loss'])
50 | plt.title('Loss v/s Epochs')
51 | plt.ylabel('M.S.E Loss')
52 | plt.xlabel('Epoch')
53 | plt.legend(['train', 'test'], loc='upper left')
54 |
55 | plt.tight_layout()
56 | plt.show()
57 |
58 |
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/customlayers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from keras.layers.core import Lambda, Merge
3 | from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D
4 | from keras import backend as K
5 |
6 | from keras.engine import Layer
7 |
8 | def crosschannelnormalization(alpha = 1e-4, k=2, beta=0.75, n=5,**kwargs):
9 | """
10 | This is the function used for cross channel normalization in the original
11 | Alexnet
12 | """
13 | def f(X):
14 | b, ch, r, c = X.shape
15 | half = n // 2
16 | square = K.square(X)
17 | extra_channels = K.spatial_2d_padding(K.permute_dimensions(square, (0,2,3,1))
18 | , (0,half))
19 | extra_channels = K.permute_dimensions(extra_channels, (0,3,1,2))
20 | scale = k
21 | for i in range(n):
22 | scale += alpha * extra_channels[:,i:i+ch,:,:]
23 | scale = scale ** beta
24 | return X / scale
25 |
26 | return Lambda(f, output_shape=lambda input_shape:input_shape,**kwargs)
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 | def splittensor(axis=1, ratio_split=1, id_split=0,**kwargs):
31 | def f(X):
32 | div = X.shape[axis] // ratio_split
33 |
34 | if axis == 0:
35 | output = X[id_split*div:(id_split+1)*div,:,:,:]
36 | elif axis == 1:
37 | output = X[:, id_split*div:(id_split+1)*div, :, :]
38 | elif axis == 2:
39 | output = X[:,:,id_split*div:(id_split+1)*div,:]
40 | elif axis == 3:
41 | output = X[:,:,:,id_split*div:(id_split+1)*div]
42 | else:
43 | raise ValueError("This axis is not possible")
44 |
45 | return output
46 |
47 | def g(input_shape):
48 | output_shape=list(input_shape)
49 | output_shape[axis] = output_shape[axis] // ratio_split
50 | return tuple(output_shape)
51 |
52 | return Lambda(f,output_shape=lambda input_shape:g(input_shape),**kwargs)
53 |
54 |
55 |
56 |
57 | def convolution2Dgroup(n_group, nb_filter, nb_row, nb_col, **kwargs):
58 | def f(input):
59 | return Merge([
60 | Convolution2D(nb_filter//n_group,nb_row,nb_col)(
61 | splittensor(axis=1,
62 | ratio_split=n_group,
63 | id_split=i)(input))
64 | for i in range(n_group)
65 | ],mode='concat',concat_axis=1)
66 |
67 | return f
68 |
69 |
70 | class Softmax4D(Layer):
71 | def __init__(self, axis=-1,**kwargs):
72 | self.axis=axis
73 | super(Softmax4D, self).__init__(**kwargs)
74 |
75 | def build(self,input_shape):
76 | pass
77 |
78 | def call(self, x,mask=None):
79 | e = K.exp(x - K.max(x, axis=self.axis, keepdims=True))
80 | s = K.sum(e, axis=self.axis, keepdims=True)
81 | return e / s
82 |
83 | def get_output_shape_for(self, input_shape):
84 | return input_shape
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/convnetskeras/customlayers.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from keras.layers.core import Lambda, Merge
3 | from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D
4 | from keras import backend as K
5 |
6 | from keras.engine import Layer
7 |
8 | def crosschannelnormalization(alpha = 1e-4, k=2, beta=0.75, n=5,**kwargs):
9 | """
10 | This is the function used for cross channel normalization in the original
11 | Alexnet
12 | """
13 | def f(X):
14 | b, ch, r, c = X.shape
15 | half = n // 2
16 | square = K.square(X)
17 | extra_channels = K.spatial_2d_padding(K.permute_dimensions(square, (0,2,3,1))
18 | , (0,half))
19 | extra_channels = K.permute_dimensions(extra_channels, (0,3,1,2))
20 | scale = k
21 | for i in range(n):
22 | scale += alpha * extra_channels[:,i:i+ch,:,:]
23 | scale = scale ** beta
24 | return X / scale
25 |
26 | return Lambda(f, output_shape=lambda input_shape:input_shape,**kwargs)
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 | def splittensor(axis=1, ratio_split=1, id_split=0,**kwargs):
31 | def f(X):
32 | div = X.shape[axis] // ratio_split
33 |
34 | if axis == 0:
35 | output = X[id_split*div:(id_split+1)*div,:,:,:]
36 | elif axis == 1:
37 | output = X[:, id_split*div:(id_split+1)*div, :, :]
38 | elif axis == 2:
39 | output = X[:,:,id_split*div:(id_split+1)*div,:]
40 | elif axis == 3:
41 | output = X[:,:,:,id_split*div:(id_split+1)*div]
42 | else:
43 | raise ValueError("This axis is not possible")
44 |
45 | return output
46 |
47 | def g(input_shape):
48 | output_shape=list(input_shape)
49 | output_shape[axis] = output_shape[axis] // ratio_split
50 | return tuple(output_shape)
51 |
52 | return Lambda(f,output_shape=lambda input_shape:g(input_shape),**kwargs)
53 |
54 |
55 |
56 |
57 | def convolution2Dgroup(n_group, nb_filter, nb_row, nb_col, **kwargs):
58 | def f(input):
59 | return Merge([
60 | Convolution2D(nb_filter//n_group,nb_row,nb_col)(
61 | splittensor(axis=1,
62 | ratio_split=n_group,
63 | id_split=i)(input))
64 | for i in range(n_group)
65 | ],mode='concat',concat_axis=1)
66 |
67 | return f
68 |
69 |
70 | class Softmax4D(Layer):
71 | def __init__(self, axis=-1,**kwargs):
72 | self.axis=axis
73 | super(Softmax4D, self).__init__(**kwargs)
74 |
75 | def build(self,input_shape):
76 | pass
77 |
78 | def call(self, x,mask=None):
79 | e = K.exp(x - K.max(x, axis=self.axis, keepdims=True))
80 | s = K.sum(e, axis=self.axis, keepdims=True)
81 | return e / s
82 |
83 | def get_output_shape_for(self, input_shape):
84 | return input_shape
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Code/alexnet_base.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | os.environ['THEANO_FLAGS'] = "device=gpu"
3 |
4 | import sys
5 | sys.path.insert(0, '../convnets-keras')
6 |
7 | from keras import backend as K
8 | from theano import tensor as T
9 | from keras.models import Model
10 | from keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, Dropout, Reshape, Permute, Activation, \
11 | Input, merge, Lambda
12 | from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D
13 | from convnetskeras.customlayers import convolution2Dgroup, crosschannelnormalization, \
14 | splittensor, Softmax4D
15 |
16 |
17 | def mean_subtract(img):
18 | img = T.set_subtensor(img[:,0,:,:],img[:,0,:,:] - 123.68)
19 | img = T.set_subtensor(img[:,1,:,:],img[:,1,:,:] - 116.779)
20 | img = T.set_subtensor(img[:,2,:,:],img[:,2,:,:] - 103.939)
21 |
22 | return img / 255.0
23 |
24 | def get_alexnet(input_shape,nb_classes,mean_flag):
25 | # code adapted from https://github.com/heuritech/convnets-keras
26 |
27 | inputs = Input(shape=input_shape)
28 |
29 | if mean_flag:
30 | mean_subtraction = Lambda(mean_subtract, name='mean_subtraction')(inputs)
31 | conv_1 = Convolution2D(96, 11, 11,subsample=(4,4),activation='relu',
32 | name='conv_1', init='he_normal')(mean_subtraction)
33 | else:
34 | conv_1 = Convolution2D(96, 11, 11,subsample=(4,4),activation='relu',
35 | name='conv_1', init='he_normal')(inputs)
36 |
37 | conv_2 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2))(conv_1)
38 | conv_2 = crosschannelnormalization(name="convpool_1")(conv_2)
39 | conv_2 = ZeroPadding2D((2,2))(conv_2)
40 | conv_2 = merge([
41 | Convolution2D(128,5,5,activation="relu",init='he_normal', name='conv_2_'+str(i+1))(
42 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_2)
43 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_2")
44 |
45 | conv_3 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(conv_2)
46 | conv_3 = crosschannelnormalization()(conv_3)
47 | conv_3 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
48 | conv_3 = Convolution2D(384,3,3,activation='relu',name='conv_3',init='he_normal')(conv_3)
49 |
50 | conv_4 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
51 | conv_4 = merge([
52 | Convolution2D(192,3,3,activation="relu", init='he_normal', name='conv_4_'+str(i+1))(
53 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_4)
54 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_4")
55 |
56 | conv_5 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_4)
57 | conv_5 = merge([
58 | Convolution2D(128,3,3,activation="relu",init='he_normal', name='conv_5_'+str(i+1))(
59 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_5)
60 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_5")
61 |
62 | dense_1 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2),name="convpool_5")(conv_5)
63 |
64 | dense_1 = Flatten(name="flatten")(dense_1)
65 | dense_1 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_1',init='he_normal')(dense_1)
66 | dense_2 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_1)
67 | dense_2 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_2',init='he_normal')(dense_2)
68 | dense_3 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_2)
69 | dense_3 = Dense(nb_classes,name='dense_3_new',init='he_normal')(dense_3)
70 |
71 | prediction = Activation("softmax",name="softmax")(dense_3)
72 |
73 | alexnet = Model(input=inputs, output=prediction)
74 |
75 | return alexnet
76 |
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # My experiments with AlexNet, using Keras and Theano
2 | A blog post accompanying this project can be found [here](https://rahulduggal2608.wordpress.com/2017/04/02/alexnet-in-keras/).
3 |
4 | ## Contents
5 | 1. [Motivation](#motivation)
6 | 2. [Requirements](#requirements)
7 | 3. [Experiments](#experiments)
8 | 4. [Results](#results)
9 | 5. [TO-DO](#to-do)
10 | 8. [License](#license)
11 |
12 | ## Motivation
13 | When I first started exploring deep learning (DL) in July 2016, many of the papers I read established their baseline performance using the standard AlexNet model. In part, this could be attributed to the several code examples readily available across all major Deep Learning libraries. Despite its significance, I could not find readily available code examples for training AlexNet in the Keras framework. Through this project, I am sharing my experience of training AlexNet in three very useful scenarios :-
14 |
15 | 1. **Training AlexNet end-to-end** - Also known as training from scratch
16 | 2. **Fine-Tuning the pre-trained AlexNet** - extendable to transfer learning
17 | 3. **Using AlexNet as a feature extractor** - useful for training a classifier such as SVM on top of "Deep" CNN features.
18 |
19 | I have re-used code from a lot of online resources, the two most significant ones being :-
20 | 1. [This](https://blog.keras.io/building-powerful-image-classification-models-using-very-little-data.html) blogpost by the creator of keras - Francois Chollet.
21 | 2. [This](https://github.com/heuritech/convnets-keras) project by Heuritech, which has implemented the AlexNet architecture.
22 |
23 | ## Requirements
24 | This project is compatible with **Python 2.7-3.5**
25 | Make sure you have the following libraries installed.
26 | 1. [Keras](https://keras.io) - A high level neural network library written in python. To install, follow the instructions available [here](https://keras.io/#installation).
27 | 2. [Theano](http://deeplearning.net/software/theano/introduction.html) - A python library to efficiently evaluate/optimize mathematical expressions. To install, follow the instructions available [here](http://deeplearning.net/software/theano/install.html).
28 | 3. [Anaconda](https://docs.continuum.io/) - A package of python libraries which includes several that are absolutely useful for Machine Learning/Data Science. To install, follow the instructions available [here](https://docs.continuum.io/anaconda/install).
29 |
30 | **Note :** If you have a GPU in your machine, you might want to configure Keras and Theano to utilize its resources. For myself, running the code on a K20 GPU resulted in a 10-12x speedup.
31 |
32 |
33 | ## Experiments
34 | - To perform the three tasks outlined in the motivation, first we need to get the dataset. We run our experiments on the dogs v/s cats training dataset available [here](https://www.kaggle.com/c/dogs-vs-cats/data).
35 | - We use 1000 images from each class for training and evaluate on 400 images from each class. Ensure that the images are placed as in the following directory structure.
36 | ```python
37 | Data/
38 | Train/
39 | cats/
40 | cat.0.jpg
41 | cat.1.jpg
42 | .
43 | .
44 | .
45 | cat.999.jpg
46 | dogs/
47 | dog.0.jpg
48 | dog.1.jpg
49 | .
50 | .
51 | .
52 | dog.999.jpg
53 | Test/
54 | cats/
55 | cat.0.jpg
56 | cat.1.jpg
57 | .
58 | .
59 | .
60 | cat.399.jpg
61 | dogs/
62 | dog.0.jpg
63 | dog.1.jpg
64 | .
65 | .
66 | .
67 | dog.399.jpg
68 | ```
69 | - Download the pre-trained weights for alexnet from [here](http://files.heuritech.com/weights/alexnet_weights.h5) and place them in ```convnets-keras/weights/```.
70 | - Once the dataset and weights are in order, navigate to the project root directory, and run the command ```jupyter notebook``` on your shell. This will open a new tab in your browser. Navigate to ```Code/``` and open the file ```AlexNet_Experiments.ipynb```.
71 | - Now you can execute each code cell using ```Shift+Enter``` to generate its output.
72 |
73 | ## Results
74 | **Task 1 : Training from scratch**
75 | 1. Training AlexNet, using stochastic gradient descent with a fixed learning rate of 0.01, for 80 epochs, we acheive a test accuracy of ~84.5%.
76 | 2. In accuracy plot shown below, notice the large gap between the training and testing curves. This suggests that our model is overfitting. This is usually a problem when we have few training examples (~2000 in our case). However, this problem can be partially addressed through finetuning a pre-trained network as we will see in the next subsection.
77 |
78 |  79 |
79 |
80 |
81 | **Task 2 : Fine tuning a pre-trained AlexNet**
82 | 1. CNN's trained on small datasets usually suffer from the problem of overfitting. One of the solutions is to initialize your CNN with weights learnt on a very large dataset and then finetuning the weights on your dataset.
83 | 2. Several papers talk about different strategies for fine-tuning. In this project, I execute the strategy proposed in [this](http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/7426826/) recent paper. The basic strategy is to train layer-wise. So if our network has 5 layers : L1,L2,...,L5. In the first round, we freeze L1-L4 and tune only L5. In the second round, we include L4 in the training. So L4-L5 are allowed to tune for some epochs. The third round includes L3 in the training. So now L3-L5 are tuned. Similarly the training percolates to previous layers.
84 | 2. Training for 80 epochs, using the above strategy, we reach a test accuracy of ~89%. This is almost a 5% jump over training from scratch. The test error plot is shown below.
85 |
86 |  87 |
87 |
88 |
89 | 3. To compare fine-tuning v/s training from scratch, we plot the test accuracies for fine-tuning (Task 2) v/s training from scratch (Task 1) below. Notice how much the accuracy curve for fine-tuning stays above the plot for task 1.
90 |
91 |  92 |
92 |
93 |
94 | **Task 3 : Using AlexNet as a feature extractor**
95 | 1. We train a small ANN consisting of 256 neurons on the features extracted from the last convolutional layer. After training for 80 epochs, we got a test accuracy of ~83%. This is almost as much as the accuracy of AlexNet trained from scratch.
96 | 2. The test accuracy plot shown below reveals massive overfitting as was the case in Task-1.
97 |
98 |  99 |
99 |
100 |
101 | ## TO-DO
102 | 1. The mean subtraction layer (look inside Code/alexnet_base.py) currently uses a theano function - set_subtensor. This introduces a dependancy to install Theano. I would ideally like to use a keras wrapper function which works for both Theano and Tensorflow backends. I'm not sure if such a wrapper exists though. Any suggestions for the corresponding Tensorflow function, so that I could write the Keras wrapper myself?
103 | 2. Use this code to demonstrate performance on a dataset that is significantly different from ImageNet. Maybe a medical imaging dataset?
104 |
105 | ## License
106 | This code is released under the MIT License (refer to the LICENSE file for details).
107 |
108 |
109 |
110 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # convnets-keras
2 |
3 | This repo is regrouping some of of the most used CNN, pre-trained on the ImageNet Dataset, all of them implemented in Keras framework :
4 | - AlexNet : https://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks.pdf
5 | - VGG16 and VGG19 : http://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf
6 |
7 |
8 | We also propose a heatmap option, which allow to detect the location of an object from a given synset.
9 |
10 |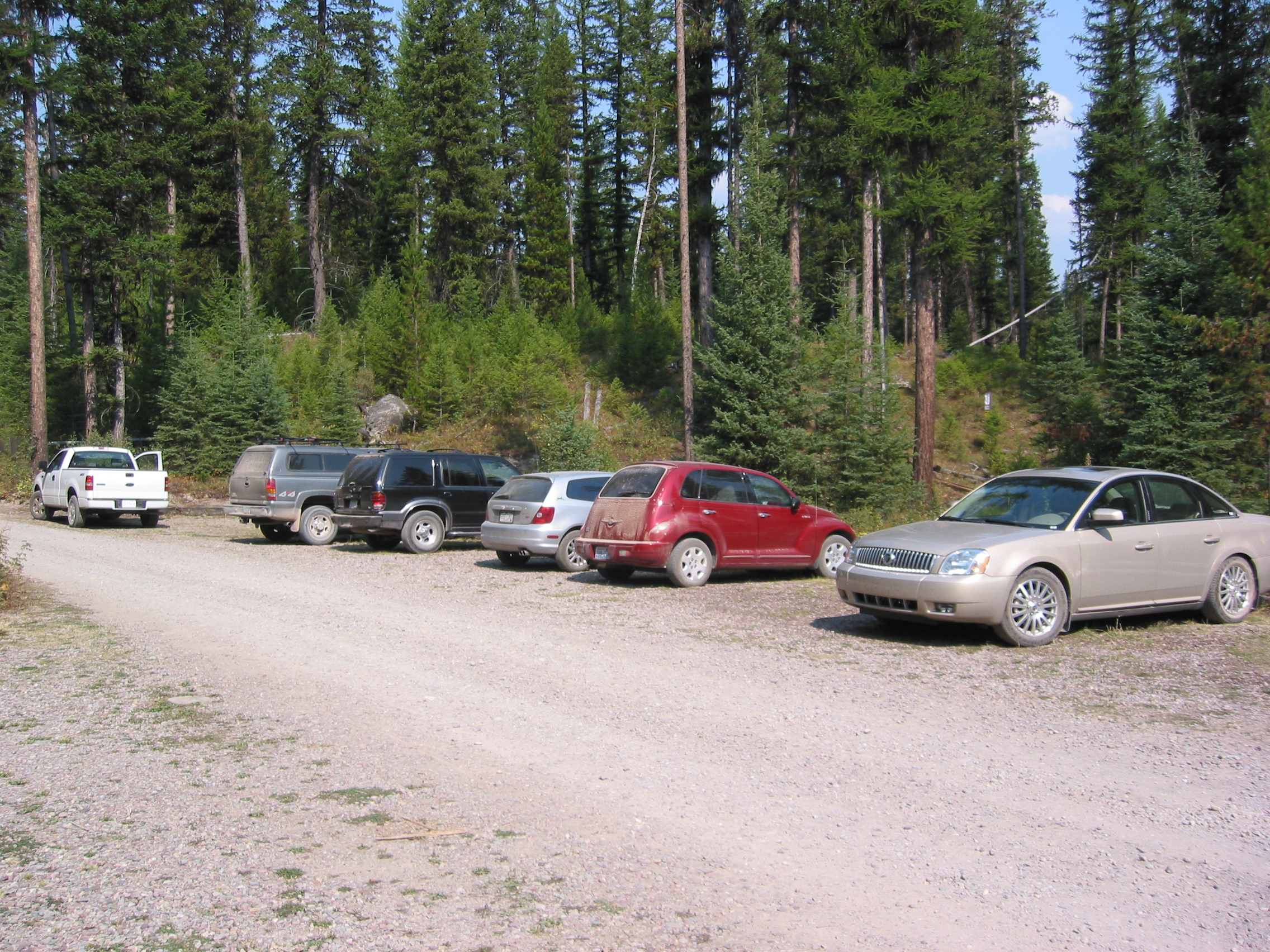  11 |
12 | Here, we detect all the objects linked to the synsets cars, and we produce a heatmap :
13 |
14 |
11 |
12 | Here, we detect all the objects linked to the synsets cars, and we produce a heatmap :
13 |
14 | 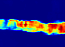 15 |
16 | ## Install
17 | The only dependencies are h5py, Theano and Keras. Run the following commands
18 | ```
19 | pip install --user cython h5py
20 | pip install --user git+https://github.com/Theano/Theano.git
21 | pip install --user git+https://github.com/fchollet/keras.git
22 | ```
23 |
24 | Then, you need to install the convnetskeras module :
25 | ```
26 | git clone https://github.com/heuritech/convnets-keras.git
27 | cd convnets-keras
28 | sudo python setup.py install
29 | ```
30 |
31 | ## Get the weights of the pre-trained networks
32 | The weights can be found here :
33 | * AlexNet weights
34 | * VGG16 weights
35 | * VGG19 weights
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | ## How to use the convnets
40 | **BEWARE** !! : Since the networks have been trained in different settings, the preprocessing is different for the differents networks :
41 | * For the AlexNet, the images (for the mode without the heatmap) have to be of shape (227,227). It is recommended to resize the images with a size of (256,256), and then do a crop of size (227,227). The colors are in RGB order.
42 | ```python
43 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
44 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
45 |
46 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(227,227), color_mode="rgb")
47 |
48 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
49 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
50 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
51 |
52 | out = model.predict(im)
53 | ```
54 |
55 | * For the VGG, the images (for the mode without the heatmap) have to be of shape (224,224). It is recommended to resize the images with a size of (256,256), and then do a crop of size (224,224). The colors are in BGR order.
56 | ```python
57 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
58 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
59 |
60 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(224,224), color_mode="bgr")
61 |
62 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
63 | ## For the VGG16, use this command
64 | model = convnet('vgg_16',weights_path="weights/vgg16_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
65 | ## For the VGG19, use this one instead
66 | # model = convnet('vgg_19',weights_path="weights/vgg19_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
67 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
68 |
69 | out = model.predict(im)
70 |
71 | ```
72 |
73 |
74 | ## Performances on ImageNet
75 | The errors are tested on ImageNet validation set.
76 | The prediction time is computed on a GeForce GTX TITAN X, with a Theano backend, and a batch size of 64.
77 |
78 | AlexNet has lower results than the two VGGs, but it is much more lighter and faster, so it can easily be run on a small GPU (like on AWS), or even on a CPU.
79 | ```
80 | Networks | AlexNet | VGG16 | VGG19 |
81 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
82 | Top 1 Error | 42,94% | 32,93% | 32,77% |
83 | Top 5 error | 20,09% | 12,39% | 12,17% |
84 | Top 10 error | 13,84% | 7,77% | 7,80% |
85 | Number of params | 61M | 138M | 144M |
86 | Prediction time, batch of 64 (GPU) | 0.4101s | 0.9645s | 1.0370s |
87 | Prediction time, single image (CPU) | 0.6773s | 1.3353s | 1.5722s |
88 | ```
89 |
90 | ## How to use the heatmap
91 | The heatmap are produced by converting the model into a fully convolutionize model. The fully connected layers are transformed into convolution layers (by using the same weights), so we are able to compute the output of the network on each sub-frame of size (227,227) (or (224,224)) of a bigger picture. This produces a heatmap for each label of the classifier.
92 |
93 | Using the heatmap is almost the same thing than directly classify. We suppose that we want the heatmap of the all the synsets linked with dogs, which are all the children in Wordnet of the synset "n02084071" (see next section to know how to find how we can get all the labels linked with a given synset) :
94 | ```python
95 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
96 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
97 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_dfs_ids
98 |
99 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="bgr")
100 |
101 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
102 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
103 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
104 |
105 | out = model.predict(im)
106 |
107 | s = "n02084071"
108 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
109 | heatmap = out[0,ids].sum(axis=0)
110 |
111 | # Then, we can get the image
112 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
113 | plt.imsave("heatmap_dog.png",heatmap)
114 | ```
115 |
15 |
16 | ## Install
17 | The only dependencies are h5py, Theano and Keras. Run the following commands
18 | ```
19 | pip install --user cython h5py
20 | pip install --user git+https://github.com/Theano/Theano.git
21 | pip install --user git+https://github.com/fchollet/keras.git
22 | ```
23 |
24 | Then, you need to install the convnetskeras module :
25 | ```
26 | git clone https://github.com/heuritech/convnets-keras.git
27 | cd convnets-keras
28 | sudo python setup.py install
29 | ```
30 |
31 | ## Get the weights of the pre-trained networks
32 | The weights can be found here :
33 | * AlexNet weights
34 | * VGG16 weights
35 | * VGG19 weights
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | ## How to use the convnets
40 | **BEWARE** !! : Since the networks have been trained in different settings, the preprocessing is different for the differents networks :
41 | * For the AlexNet, the images (for the mode without the heatmap) have to be of shape (227,227). It is recommended to resize the images with a size of (256,256), and then do a crop of size (227,227). The colors are in RGB order.
42 | ```python
43 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
44 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
45 |
46 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(227,227), color_mode="rgb")
47 |
48 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
49 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
50 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
51 |
52 | out = model.predict(im)
53 | ```
54 |
55 | * For the VGG, the images (for the mode without the heatmap) have to be of shape (224,224). It is recommended to resize the images with a size of (256,256), and then do a crop of size (224,224). The colors are in BGR order.
56 | ```python
57 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
58 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
59 |
60 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(224,224), color_mode="bgr")
61 |
62 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
63 | ## For the VGG16, use this command
64 | model = convnet('vgg_16',weights_path="weights/vgg16_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
65 | ## For the VGG19, use this one instead
66 | # model = convnet('vgg_19',weights_path="weights/vgg19_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
67 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
68 |
69 | out = model.predict(im)
70 |
71 | ```
72 |
73 |
74 | ## Performances on ImageNet
75 | The errors are tested on ImageNet validation set.
76 | The prediction time is computed on a GeForce GTX TITAN X, with a Theano backend, and a batch size of 64.
77 |
78 | AlexNet has lower results than the two VGGs, but it is much more lighter and faster, so it can easily be run on a small GPU (like on AWS), or even on a CPU.
79 | ```
80 | Networks | AlexNet | VGG16 | VGG19 |
81 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
82 | Top 1 Error | 42,94% | 32,93% | 32,77% |
83 | Top 5 error | 20,09% | 12,39% | 12,17% |
84 | Top 10 error | 13,84% | 7,77% | 7,80% |
85 | Number of params | 61M | 138M | 144M |
86 | Prediction time, batch of 64 (GPU) | 0.4101s | 0.9645s | 1.0370s |
87 | Prediction time, single image (CPU) | 0.6773s | 1.3353s | 1.5722s |
88 | ```
89 |
90 | ## How to use the heatmap
91 | The heatmap are produced by converting the model into a fully convolutionize model. The fully connected layers are transformed into convolution layers (by using the same weights), so we are able to compute the output of the network on each sub-frame of size (227,227) (or (224,224)) of a bigger picture. This produces a heatmap for each label of the classifier.
92 |
93 | Using the heatmap is almost the same thing than directly classify. We suppose that we want the heatmap of the all the synsets linked with dogs, which are all the children in Wordnet of the synset "n02084071" (see next section to know how to find how we can get all the labels linked with a given synset) :
94 | ```python
95 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
96 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
97 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_dfs_ids
98 |
99 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="bgr")
100 |
101 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
102 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
103 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
104 |
105 | out = model.predict(im)
106 |
107 | s = "n02084071"
108 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
109 | heatmap = out[0,ids].sum(axis=0)
110 |
111 | # Then, we can get the image
112 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
113 | plt.imsave("heatmap_dog.png",heatmap)
114 | ```
115 |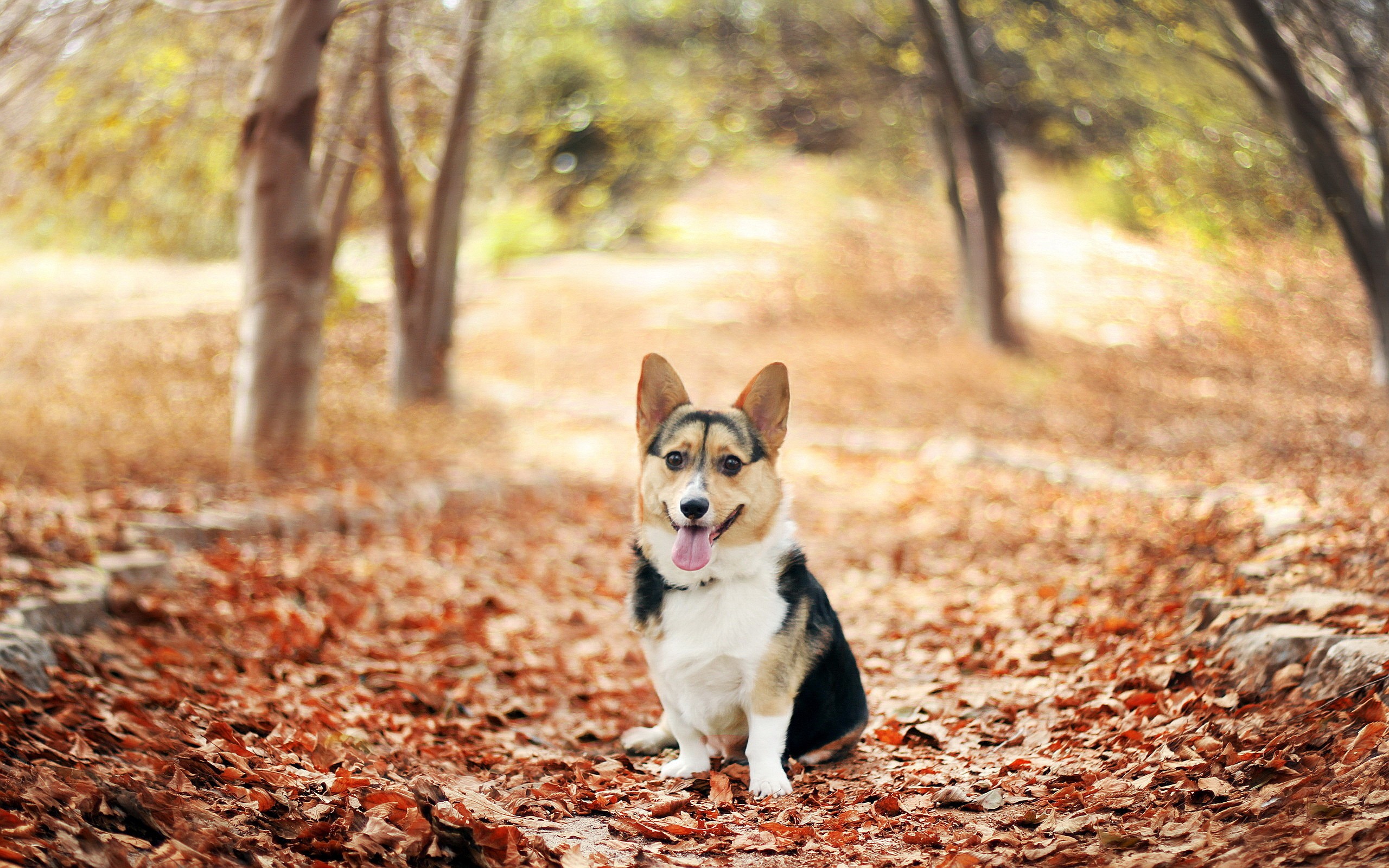  116 |
117 |
116 |
117 |  118 |
119 | ## Useful functions for ImageNet
120 | We propose a few utils function to link the index returned by the networks, and the synsets of ImageNet.
121 |
122 | #### Converting synsets to ids
123 | It can be usefull to use the ids of ImageNet (which can be found on this page , if you want to know the meaning of the classification.
124 | We have two functions : `id_to_synset` and `synset_to_id`
125 | * `id_to_synset` is taking an id of the output of the networks, and returning the WordNet synset
126 | ```python
127 | >>> from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import id_to_synset
128 | >>> id_to_synset(243)
129 | 'n03793489'
130 | ```
131 | * `synset_to_id is doing the inverse operation
132 |
133 | #### Getting all the children of a synset
134 | If you want to detect all cars, you might need to have a classification of higher level than the one given by the wordnets of ImageNet. Indeed, a lot of different synsets are present for different kinds of cars.
135 | We can then choose a synset in the tree, and select all the ids of its children :
136 | ```python
137 | >>>synset_to_dfs_ids("n04576211")
138 | [670, 870, 880, 444, 671, 565, 705, 428, 791, 561, 757, 829, 866, 847, 547, 820, 408, 573, 575, 803, 407, 436, 468, 511, 609, 627, 656, 661, 751, 817, 665, 555, 569, 717, 864, 867, 675, 734, 656, 586, 847, 802, 660, 603, 612, 690]
139 | ```
140 |
141 | ## Credits
142 | * For the AlexNet network, we have adapted the weights that can be found here :
143 | Taylor, Graham; Ding, Weiguang, 2015-03, "Theano-based large-scale visual recognition with multiple GPUs", hdl:10864/10911 University of Guelph Research Data Repository
144 |
145 | * For the VGG networks, we have adapted the code released by baraldilorenzo here : https://gist.github.com/baraldilorenzo/07d7802847aaad0a35d3
146 | We changed it to have the "heatmap" option, and we modified the weights in the same way.
147 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/Untitled.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {
7 | "collapsed": false
8 | },
9 | "outputs": [
10 | {
11 | "name": "stderr",
12 | "output_type": "stream",
13 | "text": [
14 | "Using Theano backend.\n"
15 | ]
16 | },
17 | {
18 | "ename": "IOError",
19 | "evalue": "Unable to open file (Unable to open file: name = 'weights/alexnet_weights.h5', errno = 2, error message = 'no such file or directory', flags = 0, o_flags = 0)",
20 | "output_type": "error",
21 | "traceback": [
22 | "\u001b[1;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
23 | "\u001b[1;31mIOError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
24 | "\u001b[1;32m\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36m\u001b[1;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 5\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 6\u001b[0m \u001b[0msgd\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mSGD\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mlr\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;36m0.1\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mdecay\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;36m1e-6\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmomentum\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;36m0.9\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mnesterov\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mTrue\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m----> 7\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconvnet\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m'alexnet'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m\u001b[0mweights_path\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m\"weights/alexnet_weights.h5\"\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mheatmap\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mFalse\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 8\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mcompile\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0moptimizer\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0msgd\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mloss\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m'mse'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 9\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
25 | "\u001b[1;32m/media/rahul/3828C55728C51532/Cell Classification/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.py\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mconvnet\u001b[1;34m(network, weights_path, heatmap, trainable)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 63\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32melif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mnetwork\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m==\u001b[0m \u001b[1;34m'alexnet'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 64\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconvnet_init\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mAlexNet\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m---> 65\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mconvnet\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconvnet_init\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mweights_path\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mheatmap\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mFalse\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 66\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 67\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mnot\u001b[0m \u001b[0mheatmap\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
26 | "\u001b[1;32m/media/rahul/3828C55728C51532/Cell Classification/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.py\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mAlexNet\u001b[1;34m(weights_path, heatmap)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 274\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 275\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mweights_path\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m--> 276\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mload_weights\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mweights_path\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 277\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 278\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mreturn\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
27 | "\u001b[1;32m/home/rahul/Desktop/CNN_Architecture/keras-master/keras/engine/topology.pyc\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mload_weights\u001b[1;34m(self, filepath)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 2474\u001b[0m '''\n\u001b[0;32m 2475\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mimport\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5py\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m-> 2476\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5py\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mFile\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfilepath\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmode\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m'r'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 2477\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[1;34m'layer_names'\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mnot\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mattrs\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mand\u001b[0m \u001b[1;34m'model_weights'\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 2478\u001b[0m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m[\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m'model_weights'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m]\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
28 | "\u001b[1;32m/home/rahul/anaconda2/lib/python2.7/site-packages/h5py/_hl/files.pyc\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36m__init__\u001b[1;34m(self, name, mode, driver, libver, userblock_size, swmr, **kwds)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 270\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 271\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmake_fapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mdriver\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mlibver\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m**\u001b[0m\u001b[0mkwds\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m--> 272\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mfid\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmake_fid\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mname\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmode\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0muserblock_size\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mswmr\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mswmr\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 273\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 274\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mswmr_support\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
29 | "\u001b[1;32m/home/rahul/anaconda2/lib/python2.7/site-packages/h5py/_hl/files.pyc\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mmake_fid\u001b[1;34m(name, mode, userblock_size, fapl, fcpl, swmr)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 90\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mswmr\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mand\u001b[0m \u001b[0mswmr_support\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 91\u001b[0m \u001b[0mflags\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m|=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5f\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mACC_SWMR_READ\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m---> 92\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mfid\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5f\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mopen\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mname\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mflags\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 93\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32melif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmode\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m==\u001b[0m \u001b[1;34m'r+'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 94\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfid\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5f\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mopen\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mname\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5f\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mACC_RDWR\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
30 | "\u001b[1;32mh5py/_objects.pyx\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mh5py._objects.with_phil.wrapper (-------src-dir-------/h5py/_objects.c:2582)\u001b[1;34m()\u001b[0m\n",
31 | "\u001b[1;32mh5py/_objects.pyx\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mh5py._objects.with_phil.wrapper (-------src-dir-------/h5py/_objects.c:2541)\u001b[1;34m()\u001b[0m\n",
32 | "\u001b[1;32mh5py/h5f.pyx\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mh5py.h5f.open (-------src-dir-------/h5py/h5f.c:1816)\u001b[1;34m()\u001b[0m\n",
33 | "\u001b[1;31mIOError\u001b[0m: Unable to open file (Unable to open file: name = 'weights/alexnet_weights.h5', errno = 2, error message = 'no such file or directory', flags = 0, o_flags = 0)"
34 | ]
35 | }
36 | ],
37 | "source": [
38 | "from keras.optimizers import SGD\n",
39 | "from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet\n",
40 | "\n",
41 | "im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(227,227), color_mode=\"rgb\")\n",
42 | "\n",
43 | "sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)\n",
44 | "model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path=\"weights/alexnet_weights.h5\", heatmap=False)\n",
45 | "model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')\n",
46 | "\n",
47 | "out = model.predict(im)"
48 | ]
49 | }
50 | ],
51 | "metadata": {
52 | "kernelspec": {
53 | "display_name": "Python [Root]",
54 | "language": "python",
55 | "name": "Python [Root]"
56 | },
57 | "language_info": {
58 | "codemirror_mode": {
59 | "name": "ipython",
60 | "version": 2
61 | },
62 | "file_extension": ".py",
63 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
64 | "name": "python",
65 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
66 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython2",
67 | "version": "2.7.12"
68 | }
69 | },
70 | "nbformat": 4,
71 | "nbformat_minor": 0
72 | }
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from keras.models import Sequential, Model
2 | from keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, Dropout, Reshape, Permute, Activation, \
3 | Input, merge
4 | from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D
5 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy.misc import imread, imresize, imsave
8 |
9 | from convnetskeras.customlayers import convolution2Dgroup, crosschannelnormalization, \
10 | splittensor, Softmax4D
11 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_id, id_to_synset,synset_to_dfs_ids
12 |
13 |
14 | def convnet(network, weights_path=None, heatmap=False,
15 | trainable=None):
16 | """
17 | Returns a keras model for a CNN.
18 |
19 | BEWARE !! : Since the different convnets have been trained in different settings, they don't take
20 | data of the same shape. You should change the arguments of preprocess_image_batch for each CNN :
21 | * For AlexNet, the data are of shape (227,227), and the colors in the RGB order (default)
22 | * For VGG16 and VGG19, the data are of shape (224,224), and the colors in the BGR order
23 |
24 | It can also be used to look at the hidden layers of the model.
25 |
26 | It can be used that way :
27 | >>> im = preprocess_image_batch(['cat.jpg'])
28 |
29 | >>> # Test pretrained model
30 | >>> model = convnet('vgg_16', 'weights/vgg16_weights.h5')
31 | >>> sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
32 | >>> model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='categorical_crossentropy')
33 | >>> out = model.predict(im)
34 |
35 | Parameters
36 | --------------
37 | network: str
38 | The type of network chosen. For the moment, can be 'vgg_16' or 'vgg_19'
39 |
40 | weights_path: str
41 | Location of the pre-trained model. If not given, the model will be trained
42 |
43 | heatmap: bool
44 | Says wether the fully connected layers are transformed into Convolution2D layers,
45 | to produce a heatmap instead of a
46 |
47 |
48 | Returns
49 | ---------------
50 | model:
51 | The keras model for this convnet
52 |
53 | output_dict:
54 | Dict of feature layers, asked for in output_layers.
55 | """
56 |
57 |
58 | # Select the network
59 | if network == 'vgg_16':
60 | convnet_init = VGG_16
61 | elif network == 'vgg_19':
62 | convnet_init = VGG_19
63 | elif network == 'alexnet':
64 | convnet_init = AlexNet
65 | convnet = convnet_init(weights_path, heatmap=False)
66 |
67 | if not heatmap:
68 | return convnet
69 | else:
70 | convnet_heatmap = convnet_init(heatmap=True)
71 |
72 | for layer in convnet_heatmap.layers:
73 | if layer.name.startswith("conv"):
74 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
75 | layer.set_weights(orig_layer.get_weights())
76 | elif layer.name.startswith("dense"):
77 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
78 | W,b = orig_layer.get_weights()
79 | n_filter,previous_filter,ax1,ax2 = layer.get_weights()[0].shape
80 | new_W = W.reshape((previous_filter,ax1,ax2,n_filter))
81 | new_W = new_W.transpose((3,0,1,2))
82 | new_W = new_W[:,:,::-1,::-1]
83 | layer.set_weights([new_W,b])
84 | return convnet_heatmap
85 |
86 | return model
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | def VGG_16(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
92 | model = Sequential()
93 | if heatmap:
94 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
95 | else:
96 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
97 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
98 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
99 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
100 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
101 |
102 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
103 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
104 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
105 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
106 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
107 |
108 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
109 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
110 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
111 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
112 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
113 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
114 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
115 |
116 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
117 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
118 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
119 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
120 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
121 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
122 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
123 |
124 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
125 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
126 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
127 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
128 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
129 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
130 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
131 |
132 | if heatmap:
133 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
134 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
135 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
136 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
137 | else:
138 | model.add(Flatten(name="flatten"))
139 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
140 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
141 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
142 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
143 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
144 | model.add(Activation("softmax",name="softmax"))
145 |
146 | if weights_path:
147 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
148 | return model
149 |
150 |
151 |
152 |
153 | def VGG_19(weights_path=None,heatmap=False):
154 | model = Sequential()
155 |
156 | if heatmap:
157 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
158 | else:
159 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
160 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
161 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
162 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
163 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
164 |
165 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
166 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
167 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
168 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
169 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
170 |
171 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
172 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
173 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
174 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
175 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
176 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
177 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
178 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_4'))
179 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
180 |
181 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
182 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
183 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
184 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
185 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
186 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
187 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
188 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_4'))
189 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
190 |
191 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
192 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
193 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
194 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
195 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
196 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
197 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
198 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_4'))
199 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
200 |
201 | if heatmap:
202 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
203 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
204 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
205 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
206 | else:
207 | model.add(Flatten())
208 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
209 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
210 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
211 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
212 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
213 | model.add(Activation("softmax"))
214 |
215 | if weights_path:
216 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
217 |
218 | return model
219 |
220 |
221 |
222 | def AlexNet(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
223 | if heatmap:
224 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,None,None))
225 | else:
226 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,227,227))
227 |
228 | conv_1 = Convolution2D(96, 11, 11,subsample=(4,4),activation='relu',
229 | name='conv_1')(inputs)
230 |
231 | conv_2 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2))(conv_1)
232 | conv_2 = crosschannelnormalization(name="convpool_1")(conv_2)
233 | conv_2 = ZeroPadding2D((2,2))(conv_2)
234 | conv_2 = merge([
235 | Convolution2D(128,5,5,activation="relu",name='conv_2_'+str(i+1))(
236 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_2)
237 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_2")
238 |
239 | conv_3 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(conv_2)
240 | conv_3 = crosschannelnormalization()(conv_3)
241 | conv_3 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
242 | conv_3 = Convolution2D(384,3,3,activation='relu',name='conv_3')(conv_3)
243 |
244 | conv_4 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
245 | conv_4 = merge([
246 | Convolution2D(192,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_4_'+str(i+1))(
247 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_4)
248 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_4")
249 |
250 | conv_5 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_4)
251 | conv_5 = merge([
252 | Convolution2D(128,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_5_'+str(i+1))(
253 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_5)
254 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_5")
255 |
256 | dense_1 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2),name="convpool_5")(conv_5)
257 |
258 | if heatmap:
259 | dense_1 = Convolution2D(4096,6,6,activation="relu",name="dense_1")(dense_1)
260 | dense_2 = Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2")(dense_1)
261 | dense_3 = Convolution2D(1000, 1,1,name="dense_3")(dense_2)
262 | prediction = Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax")(dense_3)
263 | else:
264 | dense_1 = Flatten(name="flatten")(dense_1)
265 | dense_1 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_1')(dense_1)
266 | dense_2 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_1)
267 | dense_2 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_2')(dense_2)
268 | dense_3 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_2)
269 | dense_3 = Dense(1000,name='dense_3')(dense_3)
270 | prediction = Activation("softmax",name="softmax")(dense_3)
271 |
272 |
273 | model = Model(input=inputs, output=prediction)
274 |
275 | if weights_path:
276 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
277 |
278 | return model
279 |
280 |
281 |
282 |
283 | def preprocess_image_batch(image_paths, img_size=None, crop_size=None, color_mode="rgb", out=None):
284 | img_list = []
285 |
286 | for im_path in image_paths:
287 | img = imread(im_path, mode='RGB')
288 | if img_size:
289 | img = imresize(img,img_size)
290 |
291 | img = img.astype('float32')
292 | # We normalize the colors (in RGB space) with the empirical means on the training set
293 | img[:, :, 0] -= 123.68
294 | img[:, :, 1] -= 116.779
295 | img[:, :, 2] -= 103.939
296 | # We permute the colors to get them in the BGR order
297 | if color_mode=="bgr":
298 | img[:,:,[0,1,2]] = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]
299 | img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
300 |
301 | if crop_size:
302 | img = img[:,(img_size[0]-crop_size[0])//2:(img_size[0]+crop_size[0])//2
303 | ,(img_size[1]-crop_size[1])//2:(img_size[1]+crop_size[1])//2]
304 |
305 | img_list.append(img)
306 |
307 | try:
308 | img_batch = np.stack(img_list, axis=0)
309 | except:
310 | raise ValueError('when img_size and crop_size are None, images'
311 | ' in image_paths must have the same shapes.')
312 |
313 | if out is not None and hasattr(out, 'append'):
314 | out.append(img_batch)
315 | else:
316 | return img_batch
317 |
318 |
319 |
320 |
321 |
322 | if __name__ == "__main__":
323 | ### Here is a script to compute the heatmap of the dog synsets.
324 | ## We find the synsets corresponding to dogs on ImageNet website
325 | s = "n02084071"
326 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
327 | # Most of the synsets are not in the subset of the synsets used in ImageNet recognition task.
328 | ids = np.array([id_ for id_ in ids if id_ is not None])
329 |
330 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="rgb")
331 |
332 | # Test pretrained model
333 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
334 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
335 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
336 |
337 |
338 | out = model.predict(im)
339 | heatmap = out[0,ids,:,:].sum(axis=0)
340 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.py~:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from keras.models import Sequential, Model
2 | from keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, Dropout, Reshape, Permute, Activation, \
3 | Input, merge
4 | from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D
5 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy.misc import imread, imresize, imsave
8 |
9 | from convnetskeras.customlayers import convolution2Dgroup, crosschannelnormalization, \
10 | splittensor, Softmax4D
11 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_id, id_to_synset,synset_to_dfs_ids
12 |
13 |
14 | def convnet(network, weights_path=None, heatmap=False,
15 | trainable=None):
16 | """
17 | Returns a keras model for a CNN.
18 |
19 | BEWARE !! : Since the different convnets have been trained in different settings, they don't take
20 | data of the same shape. You should change the arguments of preprocess_image_batch for each CNN :
21 | * For AlexNet, the data are of shape (227,227), and the colors in the RGB order (default)
22 | * For VGG16 and VGG19, the data are of shape (224,224), and the colors in the BGR order
23 |
24 | It can also be used to look at the hidden layers of the model.
25 |
26 | It can be used that way :
27 | >>> im = preprocess_image_batch(['cat.jpg'])
28 |
29 | >>> # Test pretrained model
30 | >>> model = convnet('vgg_16', 'weights/vgg16_weights.h5')
31 | >>> sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
32 | >>> model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='categorical_crossentropy')
33 | >>> out = model.predict(im)
34 |
35 | Parameters
36 | --------------
37 | network: str
38 | The type of network chosen. For the moment, can be 'vgg_16' or 'vgg_19'
39 |
40 | weights_path: str
41 | Location of the pre-trained model. If not given, the model will be trained
42 |
43 | heatmap: bool
44 | Says wether the fully connected layers are transformed into Convolution2D layers,
45 | to produce a heatmap instead of a
46 |
47 |
48 | Returns
49 | ---------------
50 | model:
51 | The keras model for this convnet
52 |
53 | output_dict:
54 | Dict of feature layers, asked for in output_layers.
55 | """
56 |
57 |
58 | # Select the network
59 | if network == 'vgg_16':
60 | convnet_init = VGG_16
61 | elif network == 'vgg_19':
62 | convnet_init = VGG_19
63 | elif network == 'alexnet':
64 | convnet_init = AlexNet
65 | convnet = convnet_init(weights_path, heatmap=False)
66 |
67 | if not heatmap:
68 | return convnet
69 | else:
70 | convnet_heatmap = convnet_init(heatmap=True)
71 |
72 | for layer in convnet_heatmap.layers:
73 | if layer.name.startswith("conv"):
74 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
75 | layer.set_weights(orig_layer.get_weights())
76 | elif layer.name.startswith("dense"):
77 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
78 | W,b = orig_layer.get_weights()
79 | n_filter,previous_filter,ax1,ax2 = layer.get_weights()[0].shape
80 | new_W = W.reshape((previous_filter,ax1,ax2,n_filter))
81 | new_W = new_W.transpose((3,0,1,2))
82 | new_W = new_W[:,:,::-1,::-1]
83 | layer.set_weights([new_W,b])
84 | return convnet_heatmap
85 |
86 | return model
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | def VGG_16(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
92 | model = Sequential()
93 | if heatmap:
94 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
95 | else:
96 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
97 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
98 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
99 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
100 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
101 |
102 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
103 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
104 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
105 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
106 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
107 |
108 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
109 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
110 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
111 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
112 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
113 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
114 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
115 |
116 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
117 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
118 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
119 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
120 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
121 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
122 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
123 |
124 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
125 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
126 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
127 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
128 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
129 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
130 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
131 |
132 | if heatmap:
133 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
134 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
135 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
136 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
137 | else:
138 | model.add(Flatten(name="flatten"))
139 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
140 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
141 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
142 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
143 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
144 | model.add(Activation("softmax",name="softmax"))
145 |
146 | if weights_path:
147 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
148 | return model
149 |
150 |
151 |
152 |
153 | def VGG_19(weights_path=None,heatmap=False):
154 | model = Sequential()
155 |
156 | if heatmap:
157 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
158 | else:
159 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
160 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
161 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
162 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
163 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
164 |
165 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
166 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
167 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
168 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
169 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
170 |
171 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
172 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
173 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
174 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
175 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
176 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
177 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
178 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_4'))
179 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
180 |
181 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
182 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
183 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
184 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
185 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
186 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
187 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
188 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_4'))
189 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
190 |
191 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
192 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
193 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
194 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
195 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
196 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
197 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
198 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_4'))
199 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
200 |
201 | if heatmap:
202 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
203 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
204 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
205 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
206 | else:
207 | model.add(Flatten())
208 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
209 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
210 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
211 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
212 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
213 | model.add(Activation("softmax"))
214 |
215 | if weights_path:
216 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
217 |
218 | return model
219 |
220 |
221 |
222 | def AlexNet(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
223 | if heatmap:
224 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,None,None))
225 | else:
226 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,227,227))
227 |
228 | conv_1 = Convolution2D(96, 11, 11,subsample=(4,4),activation='relu',
229 | name='conv_1')(inputs)
230 |
231 | conv_2 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2))(conv_1)
232 | conv_2 = crosschannelnormalization(name="convpool_1")(conv_2)
233 | conv_2 = ZeroPadding2D((2,2))(conv_2)
234 | conv_2 = merge([
235 | Convolution2D(128,5,5,activation="relu",name='conv_2_'+str(i+1))(
236 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_2)
237 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_2")
238 |
239 | conv_3 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(conv_2)
240 | conv_3 = crosschannelnormalization()(conv_3)
241 | conv_3 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
242 | conv_3 = Convolution2D(384,3,3,activation='relu',name='conv_3')(conv_3)
243 |
244 | conv_4 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
245 | conv_4 = merge([
246 | Convolution2D(192,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_4_'+str(i+1))(
247 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_4)
248 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_4")
249 |
250 | conv_5 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_4)
251 | conv_5 = merge([
252 | Convolution2D(128,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_5_'+str(i+1))(
253 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_5)
254 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_5")
255 |
256 | dense_1 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2),name="convpool_5")(conv_5)
257 |
258 | if heatmap:
259 | dense_1 = Convolution2D(4096,6,6,activation="relu",name="dense_1")(dense_1)
260 | dense_2 = Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2")(dense_1)
261 | dense_3 = Convolution2D(1000, 1,1,name="dense_3")(dense_2)
262 | prediction = Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax")(dense_3)
263 | else:
264 | dense_1 = Flatten(name="flatten")(dense_1)
265 | dense_1 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_1')(dense_1)
266 | dense_2 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_1)
267 | dense_2 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_2')(dense_2)
268 | dense_3 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_2)
269 | dense_3 = Dense(1000,name='dense_3')(dense_3)
270 | prediction = Activation("softmax",name="softmax")(dense_3)
271 |
272 |
273 | model = Model(input=inputs, output=prediction)
274 |
275 | if weights_path:
276 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
277 |
278 | return model
279 |
280 |
281 |
282 |
283 | def preprocess_image_batch(image_paths, img_size=None, crop_size=None, color_mode="rgb", out=None):
284 | img_list = []
285 |
286 | for im_path in image_paths:
287 | img = imread(im_path, mode='RGB')
288 | if img_size:
289 | img = imresize(img,img_size)
290 |
291 | img = img.astype('float32')
292 | # We normalize the colors (in RGB space) with the empirical means on the training set
293 | img[:, :, 0] -= 123.68
294 | img[:, :, 1] -= 116.779
295 | img[:, :, 2] -= 103.939
296 | # We permute the colors to get them in the BGR order
297 | if color_mode=="bgr":
298 | img[:,:,[0,1,2]] = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]
299 | img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
300 |
301 | if crop_size:
302 | img = img[:,(img_size[0]-crop_size[0])//2:(img_size[0]+crop_size[0])//2
303 | ,(img_size[1]-crop_size[1])//2:(img_size[1]+crop_size[1])//2]
304 |
305 | img_list.append(img)
306 |
307 | try:
308 | img_batch = np.stack(img_list, axis=0)
309 | except:
310 | raise ValueError('when img_size and crop_size are None, images'
311 | ' in image_paths must have the same shapes.')
312 |
313 | if out is not None and hasattr(out, 'append'):
314 | out.append(img_batch)
315 | else:
316 | return img_batch
317 |
318 |
319 |
320 |
321 |
322 | if __name__ == "__main__":
323 | ### Here is a script to compute the heatmap of the dog synsets.
324 | ## We find the synsets corresponding to dogs on ImageNet website
325 | s = "n02084071"
326 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
327 | # Most of the synsets are not in the subset of the synsets used in ImageNet recognition task.
328 | ids = np.array([id_ for id_ in ids if id_ is not None])
329 |
330 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="rgb")
331 |
332 | # Test pretrained model
333 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
334 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
335 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
336 |
337 |
338 | out = model.predict(im)
339 | heatmap = out[0,ids,:,:].sum(axis=0)
340 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/convnetskeras/convnets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from keras.models import Sequential, Model
2 | from keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, Dropout, Reshape, Permute, Activation, \
3 | Input, merge
4 | from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D
5 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy.misc import imread, imresize, imsave
8 |
9 | from convnetskeras.customlayers import convolution2Dgroup, crosschannelnormalization, \
10 | splittensor, Softmax4D
11 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_id, id_to_synset,synset_to_dfs_ids
12 |
13 |
14 | def convnet(network, weights_path=None, heatmap=False,
15 | trainable=None):
16 | """
17 | Returns a keras model for a CNN.
18 |
19 | BEWARE !! : Since the different convnets have been trained in different settings, they don't take
20 | data of the same shape. You should change the arguments of preprocess_image_batch for each CNN :
21 | * For AlexNet, the data are of shape (227,227), and the colors in the RGB order (default)
22 | * For VGG16 and VGG19, the data are of shape (224,224), and the colors in the BGR order
23 |
24 | It can also be used to look at the hidden layers of the model.
25 |
26 | It can be used that way :
27 | >>> im = preprocess_image_batch(['cat.jpg'])
28 |
29 | >>> # Test pretrained model
30 | >>> model = convnet('vgg_16', 'weights/vgg16_weights.h5')
31 | >>> sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
32 | >>> model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='categorical_crossentropy')
33 | >>> out = model.predict(im)
34 |
35 | Parameters
36 | --------------
37 | network: str
38 | The type of network chosen. For the moment, can be 'vgg_16' or 'vgg_19'
39 |
40 | weights_path: str
41 | Location of the pre-trained model. If not given, the model will be trained
42 |
43 | heatmap: bool
44 | Says wether the fully connected layers are transformed into Convolution2D layers,
45 | to produce a heatmap instead of a
46 |
47 |
48 | Returns
49 | ---------------
50 | model:
51 | The keras model for this convnet
52 |
53 | output_dict:
54 | Dict of feature layers, asked for in output_layers.
55 | """
56 |
57 |
58 | # Select the network
59 | if network == 'vgg_16':
60 | convnet_init = VGG_16
61 | elif network == 'vgg_19':
62 | convnet_init = VGG_19
63 | elif network == 'alexnet':
64 | convnet_init = AlexNet
65 | convnet = convnet_init(weights_path, heatmap=False)
66 |
67 | if not heatmap:
68 | return convnet
69 | else:
70 | convnet_heatmap = convnet_init(heatmap=True)
71 |
72 | for layer in convnet_heatmap.layers:
73 | if layer.name.startswith("conv"):
74 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
75 | layer.set_weights(orig_layer.get_weights())
76 | elif layer.name.startswith("dense"):
77 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
78 | W,b = orig_layer.get_weights()
79 | n_filter,previous_filter,ax1,ax2 = layer.get_weights()[0].shape
80 | new_W = W.reshape((previous_filter,ax1,ax2,n_filter))
81 | new_W = new_W.transpose((3,0,1,2))
82 | new_W = new_W[:,:,::-1,::-1]
83 | layer.set_weights([new_W,b])
84 | return convnet_heatmap
85 |
86 | return model
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | def VGG_16(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
92 | model = Sequential()
93 | if heatmap:
94 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
95 | else:
96 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
97 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
98 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
99 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
100 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
101 |
102 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
103 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
104 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
105 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
106 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
107 |
108 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
109 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
110 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
111 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
112 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
113 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
114 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
115 |
116 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
117 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
118 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
119 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
120 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
121 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
122 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
123 |
124 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
125 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
126 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
127 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
128 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
129 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
130 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
131 |
132 | if heatmap:
133 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
134 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
135 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
136 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
137 | else:
138 | model.add(Flatten(name="flatten"))
139 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
140 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
141 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
142 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
143 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
144 | model.add(Activation("softmax",name="softmax"))
145 |
146 | if weights_path:
147 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
148 | return model
149 |
150 |
151 |
152 |
153 | def VGG_19(weights_path=None,heatmap=False):
154 | model = Sequential()
155 |
156 | if heatmap:
157 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
158 | else:
159 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
160 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
161 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
162 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
163 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
164 |
165 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
166 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
167 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
168 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
169 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
170 |
171 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
172 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
173 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
174 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
175 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
176 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
177 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
178 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_4'))
179 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
180 |
181 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
182 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
183 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
184 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
185 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
186 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
187 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
188 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_4'))
189 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
190 |
191 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
192 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
193 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
194 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
195 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
196 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
197 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
198 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_4'))
199 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
200 |
201 | if heatmap:
202 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
203 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
204 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
205 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
206 | else:
207 | model.add(Flatten())
208 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
209 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
210 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
211 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
212 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
213 | model.add(Activation("softmax"))
214 |
215 | if weights_path:
216 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
217 |
218 | return model
219 |
220 |
221 |
222 | def AlexNet(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
223 | if heatmap:
224 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,None,None))
225 | else:
226 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,227,227))
227 |
228 | conv_1 = Convolution2D(96, 11, 11,subsample=(4,4),activation='relu',
229 | name='conv_1')(inputs)
230 |
231 | conv_2 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2))(conv_1)
232 | conv_2 = crosschannelnormalization(name="convpool_1")(conv_2)
233 | conv_2 = ZeroPadding2D((2,2))(conv_2)
234 | conv_2 = merge([
235 | Convolution2D(128,5,5,activation="relu",name='conv_2_'+str(i+1))(
236 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_2)
237 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_2")
238 |
239 | conv_3 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(conv_2)
240 | conv_3 = crosschannelnormalization()(conv_3)
241 | conv_3 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
242 | conv_3 = Convolution2D(384,3,3,activation='relu',name='conv_3')(conv_3)
243 |
244 | conv_4 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
245 | conv_4 = merge([
246 | Convolution2D(192,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_4_'+str(i+1))(
247 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_4)
248 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_4")
249 |
250 | conv_5 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_4)
251 | conv_5 = merge([
252 | Convolution2D(128,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_5_'+str(i+1))(
253 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_5)
254 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_5")
255 |
256 | dense_1 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2),name="convpool_5")(conv_5)
257 |
258 | if heatmap:
259 | dense_1 = Convolution2D(4096,6,6,activation="relu",name="dense_1")(dense_1)
260 | dense_2 = Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2")(dense_1)
261 | dense_3 = Convolution2D(1000, 1,1,name="dense_3")(dense_2)
262 | prediction = Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax")(dense_3)
263 | else:
264 | dense_1 = Flatten(name="flatten")(dense_1)
265 | dense_1 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_1')(dense_1)
266 | dense_2 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_1)
267 | dense_2 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_2')(dense_2)
268 | dense_3 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_2)
269 | dense_3 = Dense(1000,name='dense_3')(dense_3)
270 | prediction = Activation("softmax",name="softmax")(dense_3)
271 |
272 |
273 | model = Model(input=inputs, output=prediction)
274 |
275 | if weights_path:
276 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
277 |
278 | return model
279 |
280 |
281 |
282 |
283 | def preprocess_image_batch(image_paths, img_size=None, crop_size=None, color_mode="rgb", out=None):
284 | img_list = []
285 |
286 | for im_path in image_paths:
287 | img = imread(im_path, mode='RGB')
288 | if img_size:
289 | img = imresize(img,img_size)
290 |
291 | img = img.astype('float32')
292 | # We normalize the colors (in RGB space) with the empirical means on the training set
293 | img[:, :, 0] -= 123.68
294 | img[:, :, 1] -= 116.779
295 | img[:, :, 2] -= 103.939
296 | # We permute the colors to get them in the BGR order
297 | if color_mode=="bgr":
298 | img[:,:,[0,1,2]] = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]
299 | img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
300 |
301 | if crop_size:
302 | img = img[:,(img_size[0]-crop_size[0])//2:(img_size[0]+crop_size[0])//2
303 | ,(img_size[1]-crop_size[1])//2:(img_size[1]+crop_size[1])//2]
304 |
305 | img_list.append(img)
306 |
307 | try:
308 | img_batch = np.stack(img_list, axis=0)
309 | except:
310 | raise ValueError('when img_size and crop_size are None, images'
311 | ' in image_paths must have the same shapes.')
312 |
313 | if out is not None and hasattr(out, 'append'):
314 | out.append(img_batch)
315 | else:
316 | return img_batch
317 |
318 |
319 |
320 |
321 |
322 | if __name__ == "__main__":
323 | ### Here is a script to compute the heatmap of the dog synsets.
324 | ## We find the synsets corresponding to dogs on ImageNet website
325 | s = "n02084071"
326 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
327 | # Most of the synsets are not in the subset of the synsets used in ImageNet recognition task.
328 | ids = np.array([id_ for id_ in ids if id_ is not None])
329 |
330 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="rgb")
331 |
332 | # Test pretrained model
333 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
334 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
335 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
336 |
337 |
338 | out = model.predict(im)
339 | heatmap = out[0,ids,:,:].sum(axis=0)
340 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
118 |
119 | ## Useful functions for ImageNet
120 | We propose a few utils function to link the index returned by the networks, and the synsets of ImageNet.
121 |
122 | #### Converting synsets to ids
123 | It can be usefull to use the ids of ImageNet (which can be found on this page , if you want to know the meaning of the classification.
124 | We have two functions : `id_to_synset` and `synset_to_id`
125 | * `id_to_synset` is taking an id of the output of the networks, and returning the WordNet synset
126 | ```python
127 | >>> from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import id_to_synset
128 | >>> id_to_synset(243)
129 | 'n03793489'
130 | ```
131 | * `synset_to_id is doing the inverse operation
132 |
133 | #### Getting all the children of a synset
134 | If you want to detect all cars, you might need to have a classification of higher level than the one given by the wordnets of ImageNet. Indeed, a lot of different synsets are present for different kinds of cars.
135 | We can then choose a synset in the tree, and select all the ids of its children :
136 | ```python
137 | >>>synset_to_dfs_ids("n04576211")
138 | [670, 870, 880, 444, 671, 565, 705, 428, 791, 561, 757, 829, 866, 847, 547, 820, 408, 573, 575, 803, 407, 436, 468, 511, 609, 627, 656, 661, 751, 817, 665, 555, 569, 717, 864, 867, 675, 734, 656, 586, 847, 802, 660, 603, 612, 690]
139 | ```
140 |
141 | ## Credits
142 | * For the AlexNet network, we have adapted the weights that can be found here :
143 | Taylor, Graham; Ding, Weiguang, 2015-03, "Theano-based large-scale visual recognition with multiple GPUs", hdl:10864/10911 University of Guelph Research Data Repository
144 |
145 | * For the VGG networks, we have adapted the code released by baraldilorenzo here : https://gist.github.com/baraldilorenzo/07d7802847aaad0a35d3
146 | We changed it to have the "heatmap" option, and we modified the weights in the same way.
147 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/Untitled.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {
7 | "collapsed": false
8 | },
9 | "outputs": [
10 | {
11 | "name": "stderr",
12 | "output_type": "stream",
13 | "text": [
14 | "Using Theano backend.\n"
15 | ]
16 | },
17 | {
18 | "ename": "IOError",
19 | "evalue": "Unable to open file (Unable to open file: name = 'weights/alexnet_weights.h5', errno = 2, error message = 'no such file or directory', flags = 0, o_flags = 0)",
20 | "output_type": "error",
21 | "traceback": [
22 | "\u001b[1;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
23 | "\u001b[1;31mIOError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
24 | "\u001b[1;32m\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36m\u001b[1;34m()\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 5\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 6\u001b[0m \u001b[0msgd\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mSGD\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mlr\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;36m0.1\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mdecay\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;36m1e-6\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmomentum\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;36m0.9\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mnesterov\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mTrue\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m----> 7\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconvnet\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m'alexnet'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m\u001b[0mweights_path\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m\"weights/alexnet_weights.h5\"\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mheatmap\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mFalse\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 8\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mcompile\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0moptimizer\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0msgd\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mloss\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m'mse'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 9\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
25 | "\u001b[1;32m/media/rahul/3828C55728C51532/Cell Classification/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.py\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mconvnet\u001b[1;34m(network, weights_path, heatmap, trainable)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 63\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32melif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mnetwork\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m==\u001b[0m \u001b[1;34m'alexnet'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 64\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconvnet_init\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mAlexNet\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m---> 65\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mconvnet\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mconvnet_init\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mweights_path\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mheatmap\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mFalse\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 66\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 67\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mnot\u001b[0m \u001b[0mheatmap\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
26 | "\u001b[1;32m/media/rahul/3828C55728C51532/Cell Classification/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.py\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mAlexNet\u001b[1;34m(weights_path, heatmap)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 274\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 275\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mweights_path\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m--> 276\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mload_weights\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mweights_path\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 277\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 278\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mreturn\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmodel\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
27 | "\u001b[1;32m/home/rahul/Desktop/CNN_Architecture/keras-master/keras/engine/topology.pyc\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mload_weights\u001b[1;34m(self, filepath)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 2474\u001b[0m '''\n\u001b[0;32m 2475\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mimport\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5py\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m-> 2476\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5py\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mFile\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfilepath\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmode\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m'r'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 2477\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[1;34m'layer_names'\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mnot\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mattrs\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mand\u001b[0m \u001b[1;34m'model_weights'\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32min\u001b[0m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 2478\u001b[0m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mf\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m[\u001b[0m\u001b[1;34m'model_weights'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m]\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
28 | "\u001b[1;32m/home/rahul/anaconda2/lib/python2.7/site-packages/h5py/_hl/files.pyc\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36m__init__\u001b[1;34m(self, name, mode, driver, libver, userblock_size, swmr, **kwds)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 270\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 271\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmake_fapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mdriver\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mlibver\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m**\u001b[0m\u001b[0mkwds\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m--> 272\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mfid\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmake_fid\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mname\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmode\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0muserblock_size\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mswmr\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mswmr\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 273\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 274\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mswmr_support\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
29 | "\u001b[1;32m/home/rahul/anaconda2/lib/python2.7/site-packages/h5py/_hl/files.pyc\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mmake_fid\u001b[1;34m(name, mode, userblock_size, fapl, fcpl, swmr)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 90\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mswmr\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32mand\u001b[0m \u001b[0mswmr_support\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 91\u001b[0m \u001b[0mflags\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m|=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5f\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mACC_SWMR_READ\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m---> 92\u001b[1;33m \u001b[0mfid\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5f\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mopen\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mname\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mflags\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m\u001b[0;32m 93\u001b[0m \u001b[1;32melif\u001b[0m \u001b[0mmode\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m==\u001b[0m \u001b[1;34m'r+'\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m:\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m 94\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfid\u001b[0m \u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5f\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mopen\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m(\u001b[0m\u001b[0mname\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mh5f\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m.\u001b[0m\u001b[0mACC_RDWR\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m,\u001b[0m \u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m=\u001b[0m\u001b[0mfapl\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m)\u001b[0m\u001b[1;33m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n",
30 | "\u001b[1;32mh5py/_objects.pyx\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mh5py._objects.with_phil.wrapper (-------src-dir-------/h5py/_objects.c:2582)\u001b[1;34m()\u001b[0m\n",
31 | "\u001b[1;32mh5py/_objects.pyx\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mh5py._objects.with_phil.wrapper (-------src-dir-------/h5py/_objects.c:2541)\u001b[1;34m()\u001b[0m\n",
32 | "\u001b[1;32mh5py/h5f.pyx\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36mh5py.h5f.open (-------src-dir-------/h5py/h5f.c:1816)\u001b[1;34m()\u001b[0m\n",
33 | "\u001b[1;31mIOError\u001b[0m: Unable to open file (Unable to open file: name = 'weights/alexnet_weights.h5', errno = 2, error message = 'no such file or directory', flags = 0, o_flags = 0)"
34 | ]
35 | }
36 | ],
37 | "source": [
38 | "from keras.optimizers import SGD\n",
39 | "from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet\n",
40 | "\n",
41 | "im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(227,227), color_mode=\"rgb\")\n",
42 | "\n",
43 | "sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)\n",
44 | "model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path=\"weights/alexnet_weights.h5\", heatmap=False)\n",
45 | "model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')\n",
46 | "\n",
47 | "out = model.predict(im)"
48 | ]
49 | }
50 | ],
51 | "metadata": {
52 | "kernelspec": {
53 | "display_name": "Python [Root]",
54 | "language": "python",
55 | "name": "Python [Root]"
56 | },
57 | "language_info": {
58 | "codemirror_mode": {
59 | "name": "ipython",
60 | "version": 2
61 | },
62 | "file_extension": ".py",
63 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
64 | "name": "python",
65 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
66 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython2",
67 | "version": "2.7.12"
68 | }
69 | },
70 | "nbformat": 4,
71 | "nbformat_minor": 0
72 | }
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from keras.models import Sequential, Model
2 | from keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, Dropout, Reshape, Permute, Activation, \
3 | Input, merge
4 | from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D
5 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy.misc import imread, imresize, imsave
8 |
9 | from convnetskeras.customlayers import convolution2Dgroup, crosschannelnormalization, \
10 | splittensor, Softmax4D
11 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_id, id_to_synset,synset_to_dfs_ids
12 |
13 |
14 | def convnet(network, weights_path=None, heatmap=False,
15 | trainable=None):
16 | """
17 | Returns a keras model for a CNN.
18 |
19 | BEWARE !! : Since the different convnets have been trained in different settings, they don't take
20 | data of the same shape. You should change the arguments of preprocess_image_batch for each CNN :
21 | * For AlexNet, the data are of shape (227,227), and the colors in the RGB order (default)
22 | * For VGG16 and VGG19, the data are of shape (224,224), and the colors in the BGR order
23 |
24 | It can also be used to look at the hidden layers of the model.
25 |
26 | It can be used that way :
27 | >>> im = preprocess_image_batch(['cat.jpg'])
28 |
29 | >>> # Test pretrained model
30 | >>> model = convnet('vgg_16', 'weights/vgg16_weights.h5')
31 | >>> sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
32 | >>> model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='categorical_crossentropy')
33 | >>> out = model.predict(im)
34 |
35 | Parameters
36 | --------------
37 | network: str
38 | The type of network chosen. For the moment, can be 'vgg_16' or 'vgg_19'
39 |
40 | weights_path: str
41 | Location of the pre-trained model. If not given, the model will be trained
42 |
43 | heatmap: bool
44 | Says wether the fully connected layers are transformed into Convolution2D layers,
45 | to produce a heatmap instead of a
46 |
47 |
48 | Returns
49 | ---------------
50 | model:
51 | The keras model for this convnet
52 |
53 | output_dict:
54 | Dict of feature layers, asked for in output_layers.
55 | """
56 |
57 |
58 | # Select the network
59 | if network == 'vgg_16':
60 | convnet_init = VGG_16
61 | elif network == 'vgg_19':
62 | convnet_init = VGG_19
63 | elif network == 'alexnet':
64 | convnet_init = AlexNet
65 | convnet = convnet_init(weights_path, heatmap=False)
66 |
67 | if not heatmap:
68 | return convnet
69 | else:
70 | convnet_heatmap = convnet_init(heatmap=True)
71 |
72 | for layer in convnet_heatmap.layers:
73 | if layer.name.startswith("conv"):
74 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
75 | layer.set_weights(orig_layer.get_weights())
76 | elif layer.name.startswith("dense"):
77 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
78 | W,b = orig_layer.get_weights()
79 | n_filter,previous_filter,ax1,ax2 = layer.get_weights()[0].shape
80 | new_W = W.reshape((previous_filter,ax1,ax2,n_filter))
81 | new_W = new_W.transpose((3,0,1,2))
82 | new_W = new_W[:,:,::-1,::-1]
83 | layer.set_weights([new_W,b])
84 | return convnet_heatmap
85 |
86 | return model
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | def VGG_16(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
92 | model = Sequential()
93 | if heatmap:
94 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
95 | else:
96 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
97 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
98 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
99 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
100 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
101 |
102 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
103 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
104 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
105 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
106 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
107 |
108 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
109 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
110 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
111 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
112 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
113 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
114 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
115 |
116 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
117 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
118 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
119 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
120 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
121 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
122 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
123 |
124 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
125 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
126 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
127 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
128 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
129 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
130 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
131 |
132 | if heatmap:
133 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
134 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
135 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
136 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
137 | else:
138 | model.add(Flatten(name="flatten"))
139 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
140 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
141 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
142 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
143 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
144 | model.add(Activation("softmax",name="softmax"))
145 |
146 | if weights_path:
147 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
148 | return model
149 |
150 |
151 |
152 |
153 | def VGG_19(weights_path=None,heatmap=False):
154 | model = Sequential()
155 |
156 | if heatmap:
157 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
158 | else:
159 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
160 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
161 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
162 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
163 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
164 |
165 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
166 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
167 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
168 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
169 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
170 |
171 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
172 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
173 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
174 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
175 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
176 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
177 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
178 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_4'))
179 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
180 |
181 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
182 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
183 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
184 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
185 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
186 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
187 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
188 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_4'))
189 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
190 |
191 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
192 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
193 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
194 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
195 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
196 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
197 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
198 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_4'))
199 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
200 |
201 | if heatmap:
202 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
203 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
204 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
205 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
206 | else:
207 | model.add(Flatten())
208 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
209 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
210 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
211 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
212 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
213 | model.add(Activation("softmax"))
214 |
215 | if weights_path:
216 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
217 |
218 | return model
219 |
220 |
221 |
222 | def AlexNet(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
223 | if heatmap:
224 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,None,None))
225 | else:
226 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,227,227))
227 |
228 | conv_1 = Convolution2D(96, 11, 11,subsample=(4,4),activation='relu',
229 | name='conv_1')(inputs)
230 |
231 | conv_2 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2))(conv_1)
232 | conv_2 = crosschannelnormalization(name="convpool_1")(conv_2)
233 | conv_2 = ZeroPadding2D((2,2))(conv_2)
234 | conv_2 = merge([
235 | Convolution2D(128,5,5,activation="relu",name='conv_2_'+str(i+1))(
236 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_2)
237 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_2")
238 |
239 | conv_3 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(conv_2)
240 | conv_3 = crosschannelnormalization()(conv_3)
241 | conv_3 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
242 | conv_3 = Convolution2D(384,3,3,activation='relu',name='conv_3')(conv_3)
243 |
244 | conv_4 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
245 | conv_4 = merge([
246 | Convolution2D(192,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_4_'+str(i+1))(
247 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_4)
248 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_4")
249 |
250 | conv_5 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_4)
251 | conv_5 = merge([
252 | Convolution2D(128,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_5_'+str(i+1))(
253 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_5)
254 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_5")
255 |
256 | dense_1 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2),name="convpool_5")(conv_5)
257 |
258 | if heatmap:
259 | dense_1 = Convolution2D(4096,6,6,activation="relu",name="dense_1")(dense_1)
260 | dense_2 = Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2")(dense_1)
261 | dense_3 = Convolution2D(1000, 1,1,name="dense_3")(dense_2)
262 | prediction = Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax")(dense_3)
263 | else:
264 | dense_1 = Flatten(name="flatten")(dense_1)
265 | dense_1 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_1')(dense_1)
266 | dense_2 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_1)
267 | dense_2 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_2')(dense_2)
268 | dense_3 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_2)
269 | dense_3 = Dense(1000,name='dense_3')(dense_3)
270 | prediction = Activation("softmax",name="softmax")(dense_3)
271 |
272 |
273 | model = Model(input=inputs, output=prediction)
274 |
275 | if weights_path:
276 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
277 |
278 | return model
279 |
280 |
281 |
282 |
283 | def preprocess_image_batch(image_paths, img_size=None, crop_size=None, color_mode="rgb", out=None):
284 | img_list = []
285 |
286 | for im_path in image_paths:
287 | img = imread(im_path, mode='RGB')
288 | if img_size:
289 | img = imresize(img,img_size)
290 |
291 | img = img.astype('float32')
292 | # We normalize the colors (in RGB space) with the empirical means on the training set
293 | img[:, :, 0] -= 123.68
294 | img[:, :, 1] -= 116.779
295 | img[:, :, 2] -= 103.939
296 | # We permute the colors to get them in the BGR order
297 | if color_mode=="bgr":
298 | img[:,:,[0,1,2]] = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]
299 | img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
300 |
301 | if crop_size:
302 | img = img[:,(img_size[0]-crop_size[0])//2:(img_size[0]+crop_size[0])//2
303 | ,(img_size[1]-crop_size[1])//2:(img_size[1]+crop_size[1])//2]
304 |
305 | img_list.append(img)
306 |
307 | try:
308 | img_batch = np.stack(img_list, axis=0)
309 | except:
310 | raise ValueError('when img_size and crop_size are None, images'
311 | ' in image_paths must have the same shapes.')
312 |
313 | if out is not None and hasattr(out, 'append'):
314 | out.append(img_batch)
315 | else:
316 | return img_batch
317 |
318 |
319 |
320 |
321 |
322 | if __name__ == "__main__":
323 | ### Here is a script to compute the heatmap of the dog synsets.
324 | ## We find the synsets corresponding to dogs on ImageNet website
325 | s = "n02084071"
326 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
327 | # Most of the synsets are not in the subset of the synsets used in ImageNet recognition task.
328 | ids = np.array([id_ for id_ in ids if id_ is not None])
329 |
330 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="rgb")
331 |
332 | # Test pretrained model
333 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
334 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
335 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
336 |
337 |
338 | out = model.predict(im)
339 | heatmap = out[0,ids,:,:].sum(axis=0)
340 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/convnetskeras/convnets.py~:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from keras.models import Sequential, Model
2 | from keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, Dropout, Reshape, Permute, Activation, \
3 | Input, merge
4 | from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D
5 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy.misc import imread, imresize, imsave
8 |
9 | from convnetskeras.customlayers import convolution2Dgroup, crosschannelnormalization, \
10 | splittensor, Softmax4D
11 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_id, id_to_synset,synset_to_dfs_ids
12 |
13 |
14 | def convnet(network, weights_path=None, heatmap=False,
15 | trainable=None):
16 | """
17 | Returns a keras model for a CNN.
18 |
19 | BEWARE !! : Since the different convnets have been trained in different settings, they don't take
20 | data of the same shape. You should change the arguments of preprocess_image_batch for each CNN :
21 | * For AlexNet, the data are of shape (227,227), and the colors in the RGB order (default)
22 | * For VGG16 and VGG19, the data are of shape (224,224), and the colors in the BGR order
23 |
24 | It can also be used to look at the hidden layers of the model.
25 |
26 | It can be used that way :
27 | >>> im = preprocess_image_batch(['cat.jpg'])
28 |
29 | >>> # Test pretrained model
30 | >>> model = convnet('vgg_16', 'weights/vgg16_weights.h5')
31 | >>> sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
32 | >>> model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='categorical_crossentropy')
33 | >>> out = model.predict(im)
34 |
35 | Parameters
36 | --------------
37 | network: str
38 | The type of network chosen. For the moment, can be 'vgg_16' or 'vgg_19'
39 |
40 | weights_path: str
41 | Location of the pre-trained model. If not given, the model will be trained
42 |
43 | heatmap: bool
44 | Says wether the fully connected layers are transformed into Convolution2D layers,
45 | to produce a heatmap instead of a
46 |
47 |
48 | Returns
49 | ---------------
50 | model:
51 | The keras model for this convnet
52 |
53 | output_dict:
54 | Dict of feature layers, asked for in output_layers.
55 | """
56 |
57 |
58 | # Select the network
59 | if network == 'vgg_16':
60 | convnet_init = VGG_16
61 | elif network == 'vgg_19':
62 | convnet_init = VGG_19
63 | elif network == 'alexnet':
64 | convnet_init = AlexNet
65 | convnet = convnet_init(weights_path, heatmap=False)
66 |
67 | if not heatmap:
68 | return convnet
69 | else:
70 | convnet_heatmap = convnet_init(heatmap=True)
71 |
72 | for layer in convnet_heatmap.layers:
73 | if layer.name.startswith("conv"):
74 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
75 | layer.set_weights(orig_layer.get_weights())
76 | elif layer.name.startswith("dense"):
77 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
78 | W,b = orig_layer.get_weights()
79 | n_filter,previous_filter,ax1,ax2 = layer.get_weights()[0].shape
80 | new_W = W.reshape((previous_filter,ax1,ax2,n_filter))
81 | new_W = new_W.transpose((3,0,1,2))
82 | new_W = new_W[:,:,::-1,::-1]
83 | layer.set_weights([new_W,b])
84 | return convnet_heatmap
85 |
86 | return model
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | def VGG_16(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
92 | model = Sequential()
93 | if heatmap:
94 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
95 | else:
96 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
97 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
98 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
99 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
100 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
101 |
102 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
103 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
104 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
105 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
106 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
107 |
108 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
109 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
110 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
111 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
112 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
113 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
114 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
115 |
116 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
117 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
118 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
119 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
120 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
121 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
122 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
123 |
124 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
125 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
126 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
127 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
128 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
129 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
130 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
131 |
132 | if heatmap:
133 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
134 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
135 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
136 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
137 | else:
138 | model.add(Flatten(name="flatten"))
139 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
140 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
141 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
142 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
143 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
144 | model.add(Activation("softmax",name="softmax"))
145 |
146 | if weights_path:
147 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
148 | return model
149 |
150 |
151 |
152 |
153 | def VGG_19(weights_path=None,heatmap=False):
154 | model = Sequential()
155 |
156 | if heatmap:
157 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
158 | else:
159 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
160 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
161 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
162 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
163 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
164 |
165 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
166 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
167 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
168 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
169 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
170 |
171 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
172 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
173 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
174 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
175 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
176 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
177 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
178 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_4'))
179 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
180 |
181 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
182 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
183 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
184 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
185 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
186 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
187 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
188 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_4'))
189 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
190 |
191 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
192 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
193 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
194 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
195 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
196 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
197 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
198 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_4'))
199 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
200 |
201 | if heatmap:
202 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
203 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
204 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
205 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
206 | else:
207 | model.add(Flatten())
208 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
209 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
210 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
211 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
212 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
213 | model.add(Activation("softmax"))
214 |
215 | if weights_path:
216 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
217 |
218 | return model
219 |
220 |
221 |
222 | def AlexNet(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
223 | if heatmap:
224 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,None,None))
225 | else:
226 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,227,227))
227 |
228 | conv_1 = Convolution2D(96, 11, 11,subsample=(4,4),activation='relu',
229 | name='conv_1')(inputs)
230 |
231 | conv_2 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2))(conv_1)
232 | conv_2 = crosschannelnormalization(name="convpool_1")(conv_2)
233 | conv_2 = ZeroPadding2D((2,2))(conv_2)
234 | conv_2 = merge([
235 | Convolution2D(128,5,5,activation="relu",name='conv_2_'+str(i+1))(
236 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_2)
237 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_2")
238 |
239 | conv_3 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(conv_2)
240 | conv_3 = crosschannelnormalization()(conv_3)
241 | conv_3 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
242 | conv_3 = Convolution2D(384,3,3,activation='relu',name='conv_3')(conv_3)
243 |
244 | conv_4 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
245 | conv_4 = merge([
246 | Convolution2D(192,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_4_'+str(i+1))(
247 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_4)
248 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_4")
249 |
250 | conv_5 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_4)
251 | conv_5 = merge([
252 | Convolution2D(128,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_5_'+str(i+1))(
253 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_5)
254 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_5")
255 |
256 | dense_1 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2),name="convpool_5")(conv_5)
257 |
258 | if heatmap:
259 | dense_1 = Convolution2D(4096,6,6,activation="relu",name="dense_1")(dense_1)
260 | dense_2 = Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2")(dense_1)
261 | dense_3 = Convolution2D(1000, 1,1,name="dense_3")(dense_2)
262 | prediction = Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax")(dense_3)
263 | else:
264 | dense_1 = Flatten(name="flatten")(dense_1)
265 | dense_1 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_1')(dense_1)
266 | dense_2 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_1)
267 | dense_2 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_2')(dense_2)
268 | dense_3 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_2)
269 | dense_3 = Dense(1000,name='dense_3')(dense_3)
270 | prediction = Activation("softmax",name="softmax")(dense_3)
271 |
272 |
273 | model = Model(input=inputs, output=prediction)
274 |
275 | if weights_path:
276 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
277 |
278 | return model
279 |
280 |
281 |
282 |
283 | def preprocess_image_batch(image_paths, img_size=None, crop_size=None, color_mode="rgb", out=None):
284 | img_list = []
285 |
286 | for im_path in image_paths:
287 | img = imread(im_path, mode='RGB')
288 | if img_size:
289 | img = imresize(img,img_size)
290 |
291 | img = img.astype('float32')
292 | # We normalize the colors (in RGB space) with the empirical means on the training set
293 | img[:, :, 0] -= 123.68
294 | img[:, :, 1] -= 116.779
295 | img[:, :, 2] -= 103.939
296 | # We permute the colors to get them in the BGR order
297 | if color_mode=="bgr":
298 | img[:,:,[0,1,2]] = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]
299 | img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
300 |
301 | if crop_size:
302 | img = img[:,(img_size[0]-crop_size[0])//2:(img_size[0]+crop_size[0])//2
303 | ,(img_size[1]-crop_size[1])//2:(img_size[1]+crop_size[1])//2]
304 |
305 | img_list.append(img)
306 |
307 | try:
308 | img_batch = np.stack(img_list, axis=0)
309 | except:
310 | raise ValueError('when img_size and crop_size are None, images'
311 | ' in image_paths must have the same shapes.')
312 |
313 | if out is not None and hasattr(out, 'append'):
314 | out.append(img_batch)
315 | else:
316 | return img_batch
317 |
318 |
319 |
320 |
321 |
322 | if __name__ == "__main__":
323 | ### Here is a script to compute the heatmap of the dog synsets.
324 | ## We find the synsets corresponding to dogs on ImageNet website
325 | s = "n02084071"
326 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
327 | # Most of the synsets are not in the subset of the synsets used in ImageNet recognition task.
328 | ids = np.array([id_ for id_ in ids if id_ is not None])
329 |
330 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="rgb")
331 |
332 | # Test pretrained model
333 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
334 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
335 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
336 |
337 |
338 | out = model.predict(im)
339 | heatmap = out[0,ids,:,:].sum(axis=0)
340 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/build/lib.linux-x86_64-2.7/convnetskeras/convnets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from keras.models import Sequential, Model
2 | from keras.layers import Flatten, Dense, Dropout, Reshape, Permute, Activation, \
3 | Input, merge
4 | from keras.layers.convolutional import Convolution2D, MaxPooling2D, ZeroPadding2D
5 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
6 | import numpy as np
7 | from scipy.misc import imread, imresize, imsave
8 |
9 | from convnetskeras.customlayers import convolution2Dgroup, crosschannelnormalization, \
10 | splittensor, Softmax4D
11 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_id, id_to_synset,synset_to_dfs_ids
12 |
13 |
14 | def convnet(network, weights_path=None, heatmap=False,
15 | trainable=None):
16 | """
17 | Returns a keras model for a CNN.
18 |
19 | BEWARE !! : Since the different convnets have been trained in different settings, they don't take
20 | data of the same shape. You should change the arguments of preprocess_image_batch for each CNN :
21 | * For AlexNet, the data are of shape (227,227), and the colors in the RGB order (default)
22 | * For VGG16 and VGG19, the data are of shape (224,224), and the colors in the BGR order
23 |
24 | It can also be used to look at the hidden layers of the model.
25 |
26 | It can be used that way :
27 | >>> im = preprocess_image_batch(['cat.jpg'])
28 |
29 | >>> # Test pretrained model
30 | >>> model = convnet('vgg_16', 'weights/vgg16_weights.h5')
31 | >>> sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
32 | >>> model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='categorical_crossentropy')
33 | >>> out = model.predict(im)
34 |
35 | Parameters
36 | --------------
37 | network: str
38 | The type of network chosen. For the moment, can be 'vgg_16' or 'vgg_19'
39 |
40 | weights_path: str
41 | Location of the pre-trained model. If not given, the model will be trained
42 |
43 | heatmap: bool
44 | Says wether the fully connected layers are transformed into Convolution2D layers,
45 | to produce a heatmap instead of a
46 |
47 |
48 | Returns
49 | ---------------
50 | model:
51 | The keras model for this convnet
52 |
53 | output_dict:
54 | Dict of feature layers, asked for in output_layers.
55 | """
56 |
57 |
58 | # Select the network
59 | if network == 'vgg_16':
60 | convnet_init = VGG_16
61 | elif network == 'vgg_19':
62 | convnet_init = VGG_19
63 | elif network == 'alexnet':
64 | convnet_init = AlexNet
65 | convnet = convnet_init(weights_path, heatmap=False)
66 |
67 | if not heatmap:
68 | return convnet
69 | else:
70 | convnet_heatmap = convnet_init(heatmap=True)
71 |
72 | for layer in convnet_heatmap.layers:
73 | if layer.name.startswith("conv"):
74 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
75 | layer.set_weights(orig_layer.get_weights())
76 | elif layer.name.startswith("dense"):
77 | orig_layer = convnet.get_layer(layer.name)
78 | W,b = orig_layer.get_weights()
79 | n_filter,previous_filter,ax1,ax2 = layer.get_weights()[0].shape
80 | new_W = W.reshape((previous_filter,ax1,ax2,n_filter))
81 | new_W = new_W.transpose((3,0,1,2))
82 | new_W = new_W[:,:,::-1,::-1]
83 | layer.set_weights([new_W,b])
84 | return convnet_heatmap
85 |
86 | return model
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | def VGG_16(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
92 | model = Sequential()
93 | if heatmap:
94 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
95 | else:
96 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
97 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
98 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
99 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
100 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
101 |
102 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
103 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
104 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
105 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
106 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
107 |
108 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
109 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
110 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
111 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
112 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
113 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
114 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
115 |
116 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
117 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
118 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
119 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
120 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
121 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
122 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
123 |
124 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
125 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
126 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
127 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
128 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
129 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
130 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
131 |
132 | if heatmap:
133 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
134 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
135 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
136 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
137 | else:
138 | model.add(Flatten(name="flatten"))
139 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
140 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
141 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
142 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
143 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
144 | model.add(Activation("softmax",name="softmax"))
145 |
146 | if weights_path:
147 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
148 | return model
149 |
150 |
151 |
152 |
153 | def VGG_19(weights_path=None,heatmap=False):
154 | model = Sequential()
155 |
156 | if heatmap:
157 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,None,None)))
158 | else:
159 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1),input_shape=(3,224,224)))
160 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_1'))
161 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
162 | model.add(Convolution2D(64, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv1_2'))
163 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
164 |
165 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
166 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_1'))
167 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
168 | model.add(Convolution2D(128, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv2_2'))
169 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
170 |
171 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
172 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_1'))
173 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
174 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_2'))
175 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
176 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_3'))
177 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
178 | model.add(Convolution2D(256, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv3_4'))
179 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
180 |
181 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
182 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_1'))
183 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
184 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_2'))
185 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
186 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_3'))
187 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
188 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv4_4'))
189 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
190 |
191 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
192 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_1'))
193 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
194 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_2'))
195 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
196 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_3'))
197 | model.add(ZeroPadding2D((1,1)))
198 | model.add(Convolution2D(512, 3, 3, activation='relu', name='conv5_4'))
199 | model.add(MaxPooling2D((2,2), strides=(2,2)))
200 |
201 | if heatmap:
202 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,7,7,activation="relu",name="dense_1"))
203 | model.add(Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2"))
204 | model.add(Convolution2D(1000,1,1,name="dense_3"))
205 | model.add(Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax"))
206 | else:
207 | model.add(Flatten())
208 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_1'))
209 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
210 | model.add(Dense(4096, activation='relu', name='dense_2'))
211 | model.add(Dropout(0.5))
212 | model.add(Dense(1000, name='dense_3'))
213 | model.add(Activation("softmax"))
214 |
215 | if weights_path:
216 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
217 |
218 | return model
219 |
220 |
221 |
222 | def AlexNet(weights_path=None, heatmap=False):
223 | if heatmap:
224 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,None,None))
225 | else:
226 | inputs = Input(shape=(3,227,227))
227 |
228 | conv_1 = Convolution2D(96, 11, 11,subsample=(4,4),activation='relu',
229 | name='conv_1')(inputs)
230 |
231 | conv_2 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2))(conv_1)
232 | conv_2 = crosschannelnormalization(name="convpool_1")(conv_2)
233 | conv_2 = ZeroPadding2D((2,2))(conv_2)
234 | conv_2 = merge([
235 | Convolution2D(128,5,5,activation="relu",name='conv_2_'+str(i+1))(
236 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_2)
237 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_2")
238 |
239 | conv_3 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2, 2))(conv_2)
240 | conv_3 = crosschannelnormalization()(conv_3)
241 | conv_3 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
242 | conv_3 = Convolution2D(384,3,3,activation='relu',name='conv_3')(conv_3)
243 |
244 | conv_4 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_3)
245 | conv_4 = merge([
246 | Convolution2D(192,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_4_'+str(i+1))(
247 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_4)
248 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_4")
249 |
250 | conv_5 = ZeroPadding2D((1,1))(conv_4)
251 | conv_5 = merge([
252 | Convolution2D(128,3,3,activation="relu",name='conv_5_'+str(i+1))(
253 | splittensor(ratio_split=2,id_split=i)(conv_5)
254 | ) for i in range(2)], mode='concat',concat_axis=1,name="conv_5")
255 |
256 | dense_1 = MaxPooling2D((3, 3), strides=(2,2),name="convpool_5")(conv_5)
257 |
258 | if heatmap:
259 | dense_1 = Convolution2D(4096,6,6,activation="relu",name="dense_1")(dense_1)
260 | dense_2 = Convolution2D(4096,1,1,activation="relu",name="dense_2")(dense_1)
261 | dense_3 = Convolution2D(1000, 1,1,name="dense_3")(dense_2)
262 | prediction = Softmax4D(axis=1,name="softmax")(dense_3)
263 | else:
264 | dense_1 = Flatten(name="flatten")(dense_1)
265 | dense_1 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_1')(dense_1)
266 | dense_2 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_1)
267 | dense_2 = Dense(4096, activation='relu',name='dense_2')(dense_2)
268 | dense_3 = Dropout(0.5)(dense_2)
269 | dense_3 = Dense(1000,name='dense_3')(dense_3)
270 | prediction = Activation("softmax",name="softmax")(dense_3)
271 |
272 |
273 | model = Model(input=inputs, output=prediction)
274 |
275 | if weights_path:
276 | model.load_weights(weights_path)
277 |
278 | return model
279 |
280 |
281 |
282 |
283 | def preprocess_image_batch(image_paths, img_size=None, crop_size=None, color_mode="rgb", out=None):
284 | img_list = []
285 |
286 | for im_path in image_paths:
287 | img = imread(im_path, mode='RGB')
288 | if img_size:
289 | img = imresize(img,img_size)
290 |
291 | img = img.astype('float32')
292 | # We normalize the colors (in RGB space) with the empirical means on the training set
293 | img[:, :, 0] -= 123.68
294 | img[:, :, 1] -= 116.779
295 | img[:, :, 2] -= 103.939
296 | # We permute the colors to get them in the BGR order
297 | if color_mode=="bgr":
298 | img[:,:,[0,1,2]] = img[:,:,[2,1,0]]
299 | img = img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
300 |
301 | if crop_size:
302 | img = img[:,(img_size[0]-crop_size[0])//2:(img_size[0]+crop_size[0])//2
303 | ,(img_size[1]-crop_size[1])//2:(img_size[1]+crop_size[1])//2]
304 |
305 | img_list.append(img)
306 |
307 | try:
308 | img_batch = np.stack(img_list, axis=0)
309 | except:
310 | raise ValueError('when img_size and crop_size are None, images'
311 | ' in image_paths must have the same shapes.')
312 |
313 | if out is not None and hasattr(out, 'append'):
314 | out.append(img_batch)
315 | else:
316 | return img_batch
317 |
318 |
319 |
320 |
321 |
322 | if __name__ == "__main__":
323 | ### Here is a script to compute the heatmap of the dog synsets.
324 | ## We find the synsets corresponding to dogs on ImageNet website
325 | s = "n02084071"
326 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
327 | # Most of the synsets are not in the subset of the synsets used in ImageNet recognition task.
328 | ids = np.array([id_ for id_ in ids if id_ is not None])
329 |
330 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="rgb")
331 |
332 | # Test pretrained model
333 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
334 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
335 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
336 |
337 |
338 | out = model.predict(im)
339 | heatmap = out[0,ids,:,:].sum(axis=0)
340 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 79 |
79 |  79 |
79 |  87 |
87 |  92 |
92 |  99 |
99 |  11 |
12 | Here, we detect all the objects linked to the synsets cars, and we produce a heatmap :
13 |
14 |
11 |
12 | Here, we detect all the objects linked to the synsets cars, and we produce a heatmap :
13 |
14 |  15 |
16 | ## Install
17 | The only dependencies are h5py, Theano and Keras. Run the following commands
18 | ```
19 | pip install --user cython h5py
20 | pip install --user git+https://github.com/Theano/Theano.git
21 | pip install --user git+https://github.com/fchollet/keras.git
22 | ```
23 |
24 | Then, you need to install the convnetskeras module :
25 | ```
26 | git clone https://github.com/heuritech/convnets-keras.git
27 | cd convnets-keras
28 | sudo python setup.py install
29 | ```
30 |
31 | ## Get the weights of the pre-trained networks
32 | The weights can be found here :
33 | * AlexNet weights
34 | * VGG16 weights
35 | * VGG19 weights
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | ## How to use the convnets
40 | **BEWARE** !! : Since the networks have been trained in different settings, the preprocessing is different for the differents networks :
41 | * For the AlexNet, the images (for the mode without the heatmap) have to be of shape (227,227). It is recommended to resize the images with a size of (256,256), and then do a crop of size (227,227). The colors are in RGB order.
42 | ```python
43 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
44 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
45 |
46 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(227,227), color_mode="rgb")
47 |
48 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
49 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
50 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
51 |
52 | out = model.predict(im)
53 | ```
54 |
55 | * For the VGG, the images (for the mode without the heatmap) have to be of shape (224,224). It is recommended to resize the images with a size of (256,256), and then do a crop of size (224,224). The colors are in BGR order.
56 | ```python
57 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
58 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
59 |
60 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(224,224), color_mode="bgr")
61 |
62 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
63 | ## For the VGG16, use this command
64 | model = convnet('vgg_16',weights_path="weights/vgg16_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
65 | ## For the VGG19, use this one instead
66 | # model = convnet('vgg_19',weights_path="weights/vgg19_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
67 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
68 |
69 | out = model.predict(im)
70 |
71 | ```
72 |
73 |
74 | ## Performances on ImageNet
75 | The errors are tested on ImageNet validation set.
76 | The prediction time is computed on a GeForce GTX TITAN X, with a Theano backend, and a batch size of 64.
77 |
78 | AlexNet has lower results than the two VGGs, but it is much more lighter and faster, so it can easily be run on a small GPU (like on AWS), or even on a CPU.
79 | ```
80 | Networks | AlexNet | VGG16 | VGG19 |
81 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
82 | Top 1 Error | 42,94% | 32,93% | 32,77% |
83 | Top 5 error | 20,09% | 12,39% | 12,17% |
84 | Top 10 error | 13,84% | 7,77% | 7,80% |
85 | Number of params | 61M | 138M | 144M |
86 | Prediction time, batch of 64 (GPU) | 0.4101s | 0.9645s | 1.0370s |
87 | Prediction time, single image (CPU) | 0.6773s | 1.3353s | 1.5722s |
88 | ```
89 |
90 | ## How to use the heatmap
91 | The heatmap are produced by converting the model into a fully convolutionize model. The fully connected layers are transformed into convolution layers (by using the same weights), so we are able to compute the output of the network on each sub-frame of size (227,227) (or (224,224)) of a bigger picture. This produces a heatmap for each label of the classifier.
92 |
93 | Using the heatmap is almost the same thing than directly classify. We suppose that we want the heatmap of the all the synsets linked with dogs, which are all the children in Wordnet of the synset "n02084071" (see next section to know how to find how we can get all the labels linked with a given synset) :
94 | ```python
95 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
96 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
97 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_dfs_ids
98 |
99 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="bgr")
100 |
101 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
102 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
103 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
104 |
105 | out = model.predict(im)
106 |
107 | s = "n02084071"
108 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
109 | heatmap = out[0,ids].sum(axis=0)
110 |
111 | # Then, we can get the image
112 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
113 | plt.imsave("heatmap_dog.png",heatmap)
114 | ```
115 |
15 |
16 | ## Install
17 | The only dependencies are h5py, Theano and Keras. Run the following commands
18 | ```
19 | pip install --user cython h5py
20 | pip install --user git+https://github.com/Theano/Theano.git
21 | pip install --user git+https://github.com/fchollet/keras.git
22 | ```
23 |
24 | Then, you need to install the convnetskeras module :
25 | ```
26 | git clone https://github.com/heuritech/convnets-keras.git
27 | cd convnets-keras
28 | sudo python setup.py install
29 | ```
30 |
31 | ## Get the weights of the pre-trained networks
32 | The weights can be found here :
33 | * AlexNet weights
34 | * VGG16 weights
35 | * VGG19 weights
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | ## How to use the convnets
40 | **BEWARE** !! : Since the networks have been trained in different settings, the preprocessing is different for the differents networks :
41 | * For the AlexNet, the images (for the mode without the heatmap) have to be of shape (227,227). It is recommended to resize the images with a size of (256,256), and then do a crop of size (227,227). The colors are in RGB order.
42 | ```python
43 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
44 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
45 |
46 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(227,227), color_mode="rgb")
47 |
48 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
49 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
50 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
51 |
52 | out = model.predict(im)
53 | ```
54 |
55 | * For the VGG, the images (for the mode without the heatmap) have to be of shape (224,224). It is recommended to resize the images with a size of (256,256), and then do a crop of size (224,224). The colors are in BGR order.
56 | ```python
57 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
58 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
59 |
60 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'],img_size=(256,256), crop_size=(224,224), color_mode="bgr")
61 |
62 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
63 | ## For the VGG16, use this command
64 | model = convnet('vgg_16',weights_path="weights/vgg16_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
65 | ## For the VGG19, use this one instead
66 | # model = convnet('vgg_19',weights_path="weights/vgg19_weights.h5", heatmap=False)
67 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
68 |
69 | out = model.predict(im)
70 |
71 | ```
72 |
73 |
74 | ## Performances on ImageNet
75 | The errors are tested on ImageNet validation set.
76 | The prediction time is computed on a GeForce GTX TITAN X, with a Theano backend, and a batch size of 64.
77 |
78 | AlexNet has lower results than the two VGGs, but it is much more lighter and faster, so it can easily be run on a small GPU (like on AWS), or even on a CPU.
79 | ```
80 | Networks | AlexNet | VGG16 | VGG19 |
81 | -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
82 | Top 1 Error | 42,94% | 32,93% | 32,77% |
83 | Top 5 error | 20,09% | 12,39% | 12,17% |
84 | Top 10 error | 13,84% | 7,77% | 7,80% |
85 | Number of params | 61M | 138M | 144M |
86 | Prediction time, batch of 64 (GPU) | 0.4101s | 0.9645s | 1.0370s |
87 | Prediction time, single image (CPU) | 0.6773s | 1.3353s | 1.5722s |
88 | ```
89 |
90 | ## How to use the heatmap
91 | The heatmap are produced by converting the model into a fully convolutionize model. The fully connected layers are transformed into convolution layers (by using the same weights), so we are able to compute the output of the network on each sub-frame of size (227,227) (or (224,224)) of a bigger picture. This produces a heatmap for each label of the classifier.
92 |
93 | Using the heatmap is almost the same thing than directly classify. We suppose that we want the heatmap of the all the synsets linked with dogs, which are all the children in Wordnet of the synset "n02084071" (see next section to know how to find how we can get all the labels linked with a given synset) :
94 | ```python
95 | from keras.optimizers import SGD
96 | from convnetskeras.convnets import preprocess_image_batch, convnet
97 | from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import synset_to_dfs_ids
98 |
99 | im = preprocess_image_batch(['examples/dog.jpg'], color_mode="bgr")
100 |
101 | sgd = SGD(lr=0.1, decay=1e-6, momentum=0.9, nesterov=True)
102 | model = convnet('alexnet',weights_path="weights/alexnet_weights.h5", heatmap=True)
103 | model.compile(optimizer=sgd, loss='mse')
104 |
105 | out = model.predict(im)
106 |
107 | s = "n02084071"
108 | ids = synset_to_dfs_ids(s)
109 | heatmap = out[0,ids].sum(axis=0)
110 |
111 | # Then, we can get the image
112 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
113 | plt.imsave("heatmap_dog.png",heatmap)
114 | ```
115 |  116 |
117 |
116 |
117 |  118 |
119 | ## Useful functions for ImageNet
120 | We propose a few utils function to link the index returned by the networks, and the synsets of ImageNet.
121 |
122 | #### Converting synsets to ids
123 | It can be usefull to use the ids of ImageNet (which can be found on this page , if you want to know the meaning of the classification.
124 | We have two functions : `id_to_synset` and `synset_to_id`
125 | * `id_to_synset` is taking an id of the output of the networks, and returning the WordNet synset
126 | ```python
127 | >>> from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import id_to_synset
128 | >>> id_to_synset(243)
129 | 'n03793489'
130 | ```
131 | * `synset_to_id is doing the inverse operation
132 |
133 | #### Getting all the children of a synset
134 | If you want to detect all cars, you might need to have a classification of higher level than the one given by the wordnets of ImageNet. Indeed, a lot of different synsets are present for different kinds of cars.
135 | We can then choose a synset in the tree, and select all the ids of its children :
136 | ```python
137 | >>>synset_to_dfs_ids("n04576211")
138 | [670, 870, 880, 444, 671, 565, 705, 428, 791, 561, 757, 829, 866, 847, 547, 820, 408, 573, 575, 803, 407, 436, 468, 511, 609, 627, 656, 661, 751, 817, 665, 555, 569, 717, 864, 867, 675, 734, 656, 586, 847, 802, 660, 603, 612, 690]
139 | ```
140 |
141 | ## Credits
142 | * For the AlexNet network, we have adapted the weights that can be found here :
143 | Taylor, Graham; Ding, Weiguang, 2015-03, "Theano-based large-scale visual recognition with multiple GPUs", hdl:10864/10911 University of Guelph Research Data Repository
144 |
145 | * For the VGG networks, we have adapted the code released by baraldilorenzo here : https://gist.github.com/baraldilorenzo/07d7802847aaad0a35d3
146 | We changed it to have the "heatmap" option, and we modified the weights in the same way.
147 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/Untitled.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {
7 | "collapsed": false
8 | },
9 | "outputs": [
10 | {
11 | "name": "stderr",
12 | "output_type": "stream",
13 | "text": [
14 | "Using Theano backend.\n"
15 | ]
16 | },
17 | {
18 | "ename": "IOError",
19 | "evalue": "Unable to open file (Unable to open file: name = 'weights/alexnet_weights.h5', errno = 2, error message = 'no such file or directory', flags = 0, o_flags = 0)",
20 | "output_type": "error",
21 | "traceback": [
22 | "\u001b[1;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
23 | "\u001b[1;31mIOError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
24 | "\u001b[1;32m
118 |
119 | ## Useful functions for ImageNet
120 | We propose a few utils function to link the index returned by the networks, and the synsets of ImageNet.
121 |
122 | #### Converting synsets to ids
123 | It can be usefull to use the ids of ImageNet (which can be found on this page , if you want to know the meaning of the classification.
124 | We have two functions : `id_to_synset` and `synset_to_id`
125 | * `id_to_synset` is taking an id of the output of the networks, and returning the WordNet synset
126 | ```python
127 | >>> from convnetskeras.imagenet_tool import id_to_synset
128 | >>> id_to_synset(243)
129 | 'n03793489'
130 | ```
131 | * `synset_to_id is doing the inverse operation
132 |
133 | #### Getting all the children of a synset
134 | If you want to detect all cars, you might need to have a classification of higher level than the one given by the wordnets of ImageNet. Indeed, a lot of different synsets are present for different kinds of cars.
135 | We can then choose a synset in the tree, and select all the ids of its children :
136 | ```python
137 | >>>synset_to_dfs_ids("n04576211")
138 | [670, 870, 880, 444, 671, 565, 705, 428, 791, 561, 757, 829, 866, 847, 547, 820, 408, 573, 575, 803, 407, 436, 468, 511, 609, 627, 656, 661, 751, 817, 665, 555, 569, 717, 864, 867, 675, 734, 656, 586, 847, 802, 660, 603, 612, 690]
139 | ```
140 |
141 | ## Credits
142 | * For the AlexNet network, we have adapted the weights that can be found here :
143 | Taylor, Graham; Ding, Weiguang, 2015-03, "Theano-based large-scale visual recognition with multiple GPUs", hdl:10864/10911 University of Guelph Research Data Repository
144 |
145 | * For the VGG networks, we have adapted the code released by baraldilorenzo here : https://gist.github.com/baraldilorenzo/07d7802847aaad0a35d3
146 | We changed it to have the "heatmap" option, and we modified the weights in the same way.
147 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/convnets-keras/Untitled.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {
7 | "collapsed": false
8 | },
9 | "outputs": [
10 | {
11 | "name": "stderr",
12 | "output_type": "stream",
13 | "text": [
14 | "Using Theano backend.\n"
15 | ]
16 | },
17 | {
18 | "ename": "IOError",
19 | "evalue": "Unable to open file (Unable to open file: name = 'weights/alexnet_weights.h5', errno = 2, error message = 'no such file or directory', flags = 0, o_flags = 0)",
20 | "output_type": "error",
21 | "traceback": [
22 | "\u001b[1;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
23 | "\u001b[1;31mIOError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
24 | "\u001b[1;32m