res = new ArrayList<>();
18 | for (int i = 0; i <= rowIndex; ++i) {
19 | res.add(1);
20 | for (int j = i - 1; j > 0; --j) {
21 | res.set(j, res.get(j - 1) + res.get(j));
22 | }
23 | }
24 | return res;
25 | }
26 |
27 | public static void main(String[] args) {
28 | Solution solution = new Solution();
29 | System.out.println(solution.getRow(5));
30 | }
31 | }
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_104/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._104;
2 |
3 |
4 | import com.blankj.structure.TreeNode;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/10/09
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Solution {
15 | public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
16 | if (root == null) return 0;
17 | return 1 + Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right));
18 | }
19 |
20 | public static void main(String[] args) {
21 | Solution solution = new Solution();
22 | System.out.println(solution.maxDepth(TreeNode.createTestData("[]")));
23 | System.out.println(solution.maxDepth(TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,3,4,4,3]")));
24 | System.out.println(solution.maxDepth(TreeNode.createTestData("[9,-42,-42,null,76,76,null,null,13,null,13]")));
25 | }
26 | }
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_121/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._121;
2 |
3 |
4 | /**
5 | *
6 | * author: Blankj
7 | * blog : http://blankj.com
8 | * time : 2017/10/11
9 | * desc :
10 | *
11 | */
12 | public class Solution {
13 | public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
14 | int max = 0, minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
15 | for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; ++i) {
16 | if (prices[i] < minPrice) minPrice = prices[i];
17 | int delta = prices[i] - minPrice;
18 | if (delta > max) max = delta;
19 | }
20 | return max;
21 | }
22 |
23 | public static void main(String[] args) {
24 | Solution solution = new Solution();
25 | System.out.println(solution.maxProfit(new int[]{7, 1, 5, 3, 6, 4}));
26 | System.out.println(solution.maxProfit(new int[]{7, 6, 4, 3, 1}));
27 | }
28 | }
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_027/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._027;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/04/31
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
13 | int tail = 0;
14 | for (int i = 0, len = nums.length; i < len; ++i) {
15 | if (nums[i] != val) {
16 | nums[tail++] = nums[i];
17 | }
18 | }
19 | return tail;
20 | }
21 |
22 | public static void main(String[] args) {
23 | Solution solution = new Solution();
24 | int[] data = new int[]{0, 3, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 3};
25 | int len = solution.removeElement(data, 3);
26 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
27 | System.out.print(data[i] + (i == len - 1 ? "" : ", "));
28 | }
29 | }
30 | }
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_112/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._112;
2 |
3 |
4 | import com.blankj.structure.TreeNode;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/10/11
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Solution {
15 | public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
16 | if (root == null) return false;
17 | if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return sum == root.val;
18 | return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
19 | }
20 |
21 | public static void main(String[] args) {
22 | Solution solution = new Solution();
23 | TreeNode testData = TreeNode.createTestData("[5,4,8,11,null,13,4,7,2,null,null,null,1]");
24 | TreeNode.print(testData);
25 | System.out.println(solution.hasPathSum(testData, 22));
26 | }
27 | }
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_543/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._543;
2 |
3 |
4 | import com.blankj.structure.TreeNode;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/10/13
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Solution {
15 | int max = 0;
16 |
17 | public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
18 | helper(root);
19 | return max;
20 | }
21 |
22 | private int helper(TreeNode root) {
23 | if (root == null) return 0;
24 | int l = helper(root.left);
25 | int r = helper(root.right);
26 | if (l + r > max) max = l + r;
27 | return Math.max(l, r) + 1;
28 | }
29 |
30 | public static void main(String[] args) {
31 | Solution solution = new Solution();
32 | System.out.println(solution.diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,3,4,5]")));
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_028/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._028;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/05/01
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
13 | int l1 = haystack.length(), l2 = needle.length();
14 | if (l1 < l2) return -1;
15 | for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
16 | if (i + l2 > l1) return -1;
17 | for (int j = 0; ; j++) {
18 | if (j == l2) return i;
19 | if (haystack.charAt(i + j) != needle.charAt(j)) break;
20 | }
21 | }
22 | }
23 |
24 | public static void main(String[] args) {
25 | Solution solution = new Solution();
26 | System.out.println(solution.strStr("12345", "23"));
27 | System.out.println(solution.strStr("12345", ""));
28 | }
29 | }
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_011/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._011;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/04/23
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public int maxArea(int[] height) {
13 | int l = 0, r = height.length - 1;
14 | int max = 0, h = 0;
15 | while (l < r) {
16 | h = Math.min(height[l], height[r]);
17 | max = Math.max(max, (r - l) * h);
18 | while (height[l] <= h && l < r) ++l;
19 | while (height[r] <= h && l < r) --r;
20 | }
21 | return max;
22 | }
23 |
24 | public static void main(String[] args) {
25 | Solution solution = new Solution();
26 | System.out.println(solution.maxArea(new int[]{1, 2, 4, 3})); // 4
27 | System.out.println(solution.maxArea(new int[]{1, 8, 6, 2, 5, 4, 8, 3, 7}));// 49
28 | }
29 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/031/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Next Permutation][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Implement **next permutation**, which rearranges numbers into the lexicographically next greater permutation of numbers.
6 |
7 | If such arrangement is not possible, it must rearrange it as the lowest possible order (ie, sorted in ascending order).
8 |
9 | The replacement must be **in-place** and use only constant extra memory.
10 |
11 | Here are some examples. Inputs are in the left-hand column and its corresponding outputs are in the right-hand column.
12 |
13 | `1,2,3` → `1,3,2`
14 | `3,2,1` → `1,2,3`
15 | `1,1,5` → `1,5,1`
16 |
17 | **Tags:** Array
18 |
19 |
20 | ## 思路
21 |
22 | 题意是
23 |
24 | ```java
25 |
26 | ```
27 |
28 |
29 | ## 结语
30 |
31 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/next-permutation
36 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_026/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._026;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/04/30
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
13 | int len = nums.length;
14 | if (len <= 1) return len;
15 | int tail = 1;
16 | for (int i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
17 | if (nums[i - 1] != nums[i]) {
18 | nums[tail++] = nums[i];
19 | }
20 | }
21 | return tail;
22 | }
23 |
24 | public static void main(String[] args) {
25 | Solution solution = new Solution();
26 | int[] data = new int[]{0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 3, 3};
27 | int len = solution.removeDuplicates(data);
28 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
29 | System.out.print(data[i] + (i == len - 1 ? "" : ", "));
30 | }
31 | }
32 | }
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_012/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._012;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2018/01/25
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public String intToRoman(int num) {
13 | String M[] = {"", "M", "MM", "MMM"};
14 | String C[] = {"", "C", "CC", "CCC", "CD", "D", "DC", "DCC", "DCCC", "CM"};
15 | String X[] = {"", "X", "XX", "XXX", "XL", "L", "LX", "LXX", "LXXX", "XC"};
16 | String I[] = {"", "I", "II", "III", "IV", "V", "VI", "VII", "VIII", "IX"};
17 | return M[num / 1000] + C[(num % 1000) / 100] + X[(num % 100) / 10] + I[num % 10];
18 | }
19 |
20 | public static void main(String[] args) {
21 | Solution solution = new Solution();
22 | System.out.println(solution.intToRoman(621));// DCXXI
23 | System.out.println(solution.intToRoman(348));// CCCXLVIII
24 | }
25 | }
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_014/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._014;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/04/26
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
13 | int len = strs.length;
14 | if (len == 0) return "";
15 | int minLen = 0x7fffffff;
16 | for (String str : strs) minLen = Math.min(minLen, str.length());
17 | for (int j = 0; j < minLen; ++j)
18 | for (int i = 1; i < len; ++i)
19 | if (strs[0].charAt(j) != strs[i].charAt(j))
20 | return strs[0].substring(0, j);
21 | return strs[0].substring(0, minLen);
22 | }
23 |
24 | public static void main(String[] args) {
25 | Solution solution = new Solution();
26 | System.out.println(solution.longestCommonPrefix(new String[]{"abc", "abcd", "ab"}));
27 | }
28 | }
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_083/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._083;
2 |
3 | import com.blankj.structure.ListNode;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | *
7 | * author: Blankj
8 | * blog : http://blankj.com
9 | * time : 2017/05/10
10 | * desc :
11 | *
12 | */
13 | public class Solution {
14 | public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
15 | if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
16 | ListNode curr = head;
17 | while (curr.next != null) {
18 | if (curr.next.val == curr.val) {
19 | curr.next = curr.next.next;
20 | } else {
21 | curr = curr.next;
22 | }
23 | }
24 | return head;
25 | }
26 |
27 | public static void main(String[] args) {
28 | Solution solution = new Solution();
29 | ListNode.print(solution.deleteDuplicates(ListNode.createTestData("[1,1,2]")));
30 | ListNode.print(solution.deleteDuplicates(ListNode.createTestData("[1,1,2,3,3]")));
31 | }
32 | }
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_035/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._035;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/05/02
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
13 | int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1, mid = (right + left) >> 1;
14 | while (left <= right) {
15 | if (target <= nums[mid]) right = mid - 1;
16 | else left = mid + 1;
17 | mid = (right + left) >> 1;
18 | }
19 | return left;
20 | }
21 |
22 | public static void main(String[] args) {
23 | Solution solution = new Solution();
24 | int[] nums = new int[]{1, 3, 5, 6};
25 | System.out.println(solution.searchInsert(nums, 5));
26 | System.out.println(solution.searchInsert(nums, 2));
27 | System.out.println(solution.searchInsert(nums, 7));
28 | System.out.println(solution.searchInsert(nums, 0));
29 | }
30 | }
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_033/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._033;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/10/16
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
13 | int l = 0, r = nums.length - 1, mid;
14 | while (l <= r) {
15 | mid = l + r >>> 1;
16 | if (nums[mid] == target) return mid;
17 | else if (nums[mid] >= nums[l]) {
18 | if (nums[l] <= target && target < nums[mid]) r = mid - 1;
19 | else l = mid + 1;
20 | } else {
21 | if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[r]) l = mid + 1;
22 | else r = mid - 1;
23 | }
24 | }
25 | return -1;
26 | }
27 |
28 | public static void main(String[] args) {
29 | Solution solution = new Solution();
30 | System.out.println(solution.search(new int[]{2, 1}, 1));
31 | }
32 | }
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_108/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._108;
2 |
3 |
4 | import com.blankj.structure.TreeNode;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/10/09
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Solution {
15 | public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
16 | if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return null;
17 | return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
18 | }
19 |
20 | private TreeNode helper(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
21 | if (left > right) return null;
22 | int mid = (left + right) >>> 1;
23 | TreeNode node = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
24 | node.left = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
25 | node.right = helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
26 | return node;
27 | }
28 |
29 | public static void main(String[] args) {
30 | Solution solution = new Solution();
31 | TreeNode.print(solution.sortedArrayToBST(new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7}));
32 | }
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_088/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._088;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Arrays;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | *
7 | * author: Blankj
8 | * blog : http://blankj.com
9 | * time : 2017/06/01
10 | * desc :
11 | *
12 | */
13 | public class Solution {
14 | public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
15 | int p = m-- + n-- - 1;
16 | while (m >= 0 && n >= 0)
17 | nums1[p--] = nums1[m] > nums2[n] ? nums1[m--] : nums2[n--];
18 | while (n >= 0)
19 | nums1[p--] = nums2[n--];
20 | }
21 |
22 | public static void main(String[] args) {
23 | Solution solution = new Solution();
24 | int[] nums1 = new int[10];
25 | for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
26 | nums1[i] = 2 * i;
27 | }
28 | int[] nums2 = new int[5];
29 | for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
30 | nums2[i] = 2 * i + 1;
31 | }
32 | solution.merge(nums1, 5, nums2, 5);
33 | System.out.println(Arrays.toString(nums1));
34 | }
35 | }
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_110/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._110;
2 |
3 |
4 | import com.blankj.structure.TreeNode;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/10/09
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Solution {
15 | public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
16 | return helper(root) != -1;
17 | }
18 |
19 | private int helper(TreeNode node) {
20 | if (node == null) return 0;
21 | int l = helper(node.left);
22 | if (l == -1) return -1;
23 | int r = helper(node.right);
24 | if (r == -1) return -1;
25 | if (Math.abs(l - r) > 1) return -1;
26 | return 1 + Math.max(l, r);
27 | }
28 |
29 | public static void main(String[] args) {
30 | Solution solution = new Solution();
31 | TreeNode testData = TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,4,4,null,null,5,5]");
32 | TreeNode.print(testData);
33 | System.out.println(solution.isBalanced(testData));
34 | }
35 | }
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_066/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._066;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Arrays;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | *
7 | * author: Blankj
8 | * blog : http://blankj.com
9 | * time : 2017/05/06
10 | * desc :
11 | *
12 | */
13 | public class Solution {
14 | public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
15 | int p = digits.length - 1;
16 | if (digits[p] < 9) {
17 | digits[p] = ++digits[p];
18 | } else {
19 | do {
20 | digits[p--] = 0;
21 | } while (p >= 0 && digits[p] == 9);
22 | if (digits[0] != 0) {
23 | ++digits[p];
24 | } else {
25 | digits = new int[digits.length + 1];
26 | digits[0] = 1;
27 | }
28 | }
29 | return digits;
30 | }
31 |
32 | public static void main(String[] args) {
33 | Solution solution = new Solution();
34 | int[] digits = solution.plusOne(new int[]{9, 9, 9});
35 | System.out.println(Arrays.toString(digits));
36 | }
37 | }
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_100/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._100;
2 |
3 |
4 | import com.blankj.structure.TreeNode;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/10/08
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Solution {
15 | public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
16 | if (p == null || q == null) return p == q;
17 | if (p.val != q.val) return false;
18 | return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
19 | }
20 |
21 | public static void main(String[] args) {
22 | Solution solution = new Solution();
23 | System.out.println(solution.isSameTree(
24 | TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,null,3,null,3]"),
25 | TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,null,3,null,3]"))
26 | );
27 | System.out.println(solution.isSameTree(
28 | TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,null,3,null,3]"),
29 | TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,null,3,null,null]"))
30 | );
31 | }
32 | }
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_029/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._029;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2018/01/31
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {
13 | if (dividend == Integer.MIN_VALUE && divisor == -1) {
14 | return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
15 | }
16 | long dvd = Math.abs((long) dividend);
17 | long dvr = Math.abs((long) divisor);
18 | int res = 0;
19 | while (dvd >= dvr) {
20 | long temp = dvr, multiple = 1;
21 | while (dvd >= temp << 1) {
22 | temp <<= 1;
23 | multiple <<= 1;
24 | }
25 | dvd -= temp;
26 | res += multiple;
27 | }
28 | return (dividend < 0) ^ (divisor < 0) ? -res : res;
29 | }
30 |
31 | public static void main(String[] args) {
32 | Solution solution = new Solution();
33 | System.out.println(solution.divide(-2147483648, 1));
34 | }
35 | }
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_020/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._020;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/04/28
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public boolean isValid(String s) {
13 | char[] stack = new char[s.length() + 1];
14 | int top = 1;
15 | for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
16 | if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{') {
17 | stack[top++] = c;
18 | } else if (c == ')' && stack[--top] != '(') {
19 | return false;
20 | } else if (c == ']' && stack[--top] != '[') {
21 | return false;
22 | } else if (c == '}' && stack[--top] != '{') {
23 | return false;
24 | }
25 | }
26 | return top == 1;
27 | }
28 |
29 | public static void main(String[] args) {
30 | Solution solution = new Solution();
31 | System.out.println(solution.isValid("()[]{}({[]})"));
32 | System.out.println(solution.isValid("(])]"));
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_019/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._019;
2 |
3 | import com.blankj.structure.ListNode;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | *
7 | * author: Blankj
8 | * blog : http://blankj.com
9 | * time : 2017/04/27
10 | * desc :
11 | *
12 | */
13 | public class Solution {
14 | public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
15 | ListNode pre = head;
16 | ListNode afterPreN = head;
17 | while (n-- != 0) {
18 | afterPreN = afterPreN.next;
19 | }
20 | if (afterPreN != null) {
21 | while (afterPreN.next != null) {
22 | pre = pre.next;
23 | afterPreN = afterPreN.next;
24 | }
25 | pre.next = pre.next.next;
26 | } else {
27 | head = head.next;
28 | }
29 | return head;
30 | }
31 |
32 | public static void main(String[] args) {
33 | Solution solution = new Solution();
34 | ListNode.print(solution.removeNthFromEnd(ListNode.createTestData("[1,2,3,4,5]"), 2));
35 | ListNode.print(solution.removeNthFromEnd(ListNode.createTestData("[1]"), 1));
36 | }
37 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_038/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._038;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/05/03
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public String countAndSay(int n) {
13 | String str = "1";
14 | while (--n > 0) {
15 | int times = 1;
16 | StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
17 | char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
18 | int len = chars.length;
19 | for (int j = 1; j < len; j++) {
20 | if (chars[j - 1] == chars[j]) {
21 | times++;
22 | } else {
23 | sb.append(times).append(chars[j - 1]);
24 | times = 1;
25 | }
26 | }
27 | str = sb.append(times).append(chars[len - 1]).toString();
28 | }
29 | return str;
30 | }
31 |
32 | public static void main(String[] args) {
33 | Solution solution = new Solution();
34 | for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
35 | System.out.println(solution.countAndSay(i));
36 | }
37 | }
38 | }
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_118/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._118;
2 |
3 |
4 | import java.util.ArrayList;
5 | import java.util.Collections;
6 | import java.util.List;
7 |
8 | /**
9 | *
10 | * author: Blankj
11 | * blog : http://blankj.com
12 | * time : 2017/10/11
13 | * desc :
14 | *
15 | */
16 | public class Solution {
17 | public List> generate(int numRows) {
18 | if (numRows == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
19 | List> list = new ArrayList<>();
20 | for (int i = 0; i < numRows; ++i) {
21 | List sub = new ArrayList<>();
22 | for (int j = 0; j <= i; ++j) {
23 | if (j == 0 || j == i) {
24 | sub.add(1);
25 | } else {
26 | List upSub = list.get(i - 1);
27 | sub.add(upSub.get(j - 1) + upSub.get(j));
28 | }
29 | }
30 | list.add(sub);
31 | }
32 | return list;
33 | }
34 |
35 | public static void main(String[] args) {
36 | Solution solution = new Solution();
37 | System.out.println(solution.generate(5));
38 | }
39 | }
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_003/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._003;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/10/11
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
13 | int len;
14 | if (s == null || (len = s.length()) == 0) return 0;
15 | int preP = 0, max = 0;
16 | int[] hash = new int[128];
17 | for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
18 | char c = s.charAt(i);
19 | if (hash[c] > preP) {
20 | preP = hash[c];
21 | }
22 | int l = i - preP + 1;
23 | hash[c] = i + 1;
24 | if (l > max) max = l;
25 | }
26 | return max;
27 | }
28 |
29 | public static void main(String[] args) {
30 | Solution solution = new Solution();
31 | System.out.println(solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring("abcabcbb"));
32 | System.out.println(solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring("bbbbb"));
33 | System.out.println(solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring("pwwkew"));
34 | System.out.println(solution.lengthOfLongestSubstring("Abcabcbb"));
35 | }
36 | }
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_021/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._021;
2 |
3 | import com.blankj.structure.ListNode;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | *
7 | * author: Blankj
8 | * blog : http://blankj.com
9 | * time : 2017/04/29
10 | * desc :
11 | *
12 | */
13 | public class Solution {
14 | public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
15 | ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
16 | ListNode temp = head;
17 | while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
18 | if (l1.val < l2.val) {
19 | temp.next = l1;
20 | l1 = l1.next;
21 | } else {
22 | temp.next = l2;
23 | l2 = l2.next;
24 | }
25 | temp = temp.next;
26 | }
27 | temp.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;
28 | return head.next;
29 | }
30 |
31 | public static void main(String[] args) {
32 | Solution solution = new Solution();
33 | ListNode listNode0 = ListNode.createTestData("[1,3,5,7,9]");
34 | ListNode listNode1 = ListNode.createTestData("[2,4,6,8,10]");
35 | ListNode.print(listNode0);
36 | ListNode.print(listNode1);
37 | ListNode.print(solution.mergeTwoLists(listNode0, listNode1));
38 | }
39 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_024/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._024;
2 |
3 | import com.blankj.structure.ListNode;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | *
7 | * author: Blankj
8 | * blog : http://blankj.com
9 | * time : 2018/01/31
10 | * desc :
11 | *
12 | */
13 | public class Solution {
14 | // public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
15 | // if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
16 | // ListNode node = head.next;
17 | // head.next = swapPairs(node.next);
18 | // node.next = head;
19 | // return node;
20 | // }
21 |
22 | public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
23 | ListNode preHead = new ListNode(0), cur = preHead;
24 | preHead.next = head;
25 | while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
26 | ListNode temp = cur.next.next;
27 | cur.next.next = temp.next;
28 | temp.next = cur.next;
29 | cur.next = temp;
30 | cur = cur.next.next;
31 | }
32 | return preHead.next;
33 | }
34 |
35 | public static void main(String[] args) {
36 | Solution solution = new Solution();
37 | ListNode.print(solution.swapPairs(ListNode.createTestData("[1,2,3,4]")));
38 | }
39 | }
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_013/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._013;
2 |
3 | import java.util.HashMap;
4 | import java.util.Map;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/04/25
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Solution {
15 | public int romanToInt(String s) {
16 | Map map = new HashMap<>();
17 | map.put('I', 1);
18 | map.put('V', 5);
19 | map.put('X', 10);
20 | map.put('L', 50);
21 | map.put('C', 100);
22 | map.put('D', 500);
23 | map.put('M', 1000);
24 | int len = s.length();
25 | int sum = map.get(s.charAt(len - 1));
26 | for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
27 | if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) < map.get(s.charAt(i + 1))) {
28 | sum -= map.get(s.charAt(i));
29 | } else {
30 | sum += map.get(s.charAt(i));
31 | }
32 | }
33 | return sum;
34 | }
35 |
36 | public static void main(String[] args) {
37 | Solution solution = new Solution();
38 | System.out.println(solution.romanToInt("DCXXI"));// 621
39 | System.out.println(solution.romanToInt("CCCXLVIII"));// 348
40 | }
41 | }
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_016/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._016;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Arrays;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | *
7 | * author: Blankj
8 | * blog : http://blankj.com
9 | * time : 2018/01/25
10 | * desc :
11 | *
12 | */
13 | public class Solution {
14 | public int threeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target) {
15 | int delta = 0x7fffffff, res = 0;
16 | Arrays.sort(nums);
17 | int len = nums.length - 2;
18 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
19 | int left = i + 1, right = nums.length - 1;
20 | while (left < right) {
21 | int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
22 | int curDelta = Math.abs(sum - target);
23 | if (curDelta == 0) return sum;
24 | if (curDelta < delta) {
25 | delta = curDelta;
26 | res = sum;
27 | }
28 | if (sum > target) --right;
29 | else ++left;
30 | }
31 | }
32 | return res;
33 | }
34 |
35 | public static void main(String[] args) {
36 | Solution solution = new Solution();
37 | System.out.println(solution.threeSumClosest(new int[]{-1, 2, 1, -4}, 1));
38 | }
39 | }
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/058/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Length of Last Word][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a string *s* consists of upper/lower-case alphabets and empty space characters `' '`, return the length of last word in the string.
6 |
7 | If the last word does not exist, return 0.
8 |
9 | **Note:** A word is defined as a character sequence consists of non-space characters only.
10 |
11 | **Example:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Input: "Hello World"
15 | Output: 5
16 | ```
17 |
18 | **Tags:** String
19 |
20 |
21 | ## 思路
22 |
23 | 题意是让你从一个只包含大小字母和空格字符的字符串中得到最后一个单词的长度,很简单,我们倒序遍历,先得到最后一个非空格字符的索引,然后再得到它前面的空格字符索引,两者相减即可。当然,我们使用 API 来完成这件事更加方便,只需一行代码 `return s.trim().length() - s.trim().lastIndexOf(" ") - 1;`,但我相信作者出这道题的目的肯定不是考你 API 的使用,所以我们还是用自己的思路来实现。
24 |
25 | ```java
26 | class Solution {
27 | public int lengthOfLastWord(String s) {
28 | int p = s.length() - 1;
29 | while (p >= 0 && s.charAt(p) == ' ') p--;
30 | int end = p;
31 | while (p >= 0 && s.charAt(p) != ' ') p--;
32 | return end - p;
33 | }
34 | }
35 | ```
36 |
37 |
38 | ## 结语
39 |
40 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
41 |
42 |
43 |
44 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/length-of-last-word
45 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_002/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._002;
2 |
3 | import com.blankj.structure.ListNode;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | *
7 | * author: Blankj
8 | * blog : http://blankj.com
9 | * time : 2017/10/11
10 | * desc :
11 | *
12 | */
13 | public class Solution {
14 | public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
15 | ListNode node = new ListNode(0);
16 | ListNode n1 = l1, n2 = l2, t = node;
17 | int sum = 0;
18 | while (n1 != null || n2 != null) {
19 | sum /= 10;
20 | if (n1 != null) {
21 | sum += n1.val;
22 | n1 = n1.next;
23 | }
24 | if (n2 != null) {
25 | sum += n2.val;
26 | n2 = n2.next;
27 | }
28 | t.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
29 | t = t.next;
30 | }
31 | if (sum / 10 != 0) t.next = new ListNode(1);
32 | return node.next;
33 | }
34 |
35 | public static void main(String[] args) {
36 | Solution solution = new Solution();
37 | ListNode.print(solution.addTwoNumbers(
38 | ListNode.createTestData("[2,4,3]"),
39 | ListNode.createTestData("[5,6,4]")
40 | ));
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/007/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Reverse Integer][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a 32-bit signed integer, reverse digits of an integer.
6 |
7 | **Example 1:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input: 123
11 | Output: 321
12 | ```
13 |
14 | **Example 2:**
15 |
16 | ```
17 | Input: -123
18 | Output: -321
19 | ```
20 |
21 | **Example 3:**
22 |
23 | ```
24 | Input: 120
25 | Output: 21
26 | ```
27 |
28 | **Note:**
29 |
30 | Assume we are dealing with an environment which could only hold integers within the 32-bit signed integer range. For the purpose of this problem, assume that your function returns 0 when the reversed integer overflows.
31 |
32 | **Tags:** Math
33 |
34 |
35 | ## 思路
36 |
37 | 题意是给你一个整型数,求它的逆序整型数,而且有个小坑点,当它的逆序整型数溢出的话,那么就返回 0,用我们代码表示的话可以求得结果保存在 long 中,最后把结果和整型的两个范围比较即可。
38 |
39 | ```java
40 | class Solution {
41 | public int reverse(int x) {
42 | long res = 0;
43 | for (; x != 0; x /= 10)
44 | res = res * 10 + x % 10;
45 | return res > Integer.MAX_VALUE || res < Integer.MIN_VALUE ? 0 : (int) res;
46 | }
47 | }
48 | ```
49 |
50 |
51 | ## 结语
52 |
53 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
54 |
55 |
56 |
57 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-integer
58 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/104/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Maximum Depth of Binary Tree][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a binary tree, find its maximum depth.
6 |
7 | The maximum depth is the number of nodes along the longest path from the root node down to the farthest leaf node.
8 |
9 | **Note:** A leaf is a node with no children.
10 |
11 | **Example:**
12 |
13 | Given binary tree `[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]`,
14 |
15 | ```
16 | 3
17 | / \
18 | 9 20
19 | / \
20 | 15 7
21 | ```
22 |
23 | return its depth = 3.
24 |
25 | **Tags:** Tree, Depth-first Search
26 |
27 |
28 | ## 思路
29 |
30 | 题意是找到二叉树的最大深度,很明显,深搜即可,每深入一次节点加一即可,然后取左右子树的最大深度。
31 |
32 | ```java
33 | /**
34 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
35 | * public class TreeNode {
36 | * int val;
37 | * TreeNode left;
38 | * TreeNode right;
39 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
40 | * }
41 | */
42 | class Solution {
43 | public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
44 | if (root == null) return 0;
45 | return 1 + Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right));
46 | }
47 | }
48 | ```
49 |
50 |
51 | ## 结语
52 |
53 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
54 |
55 |
56 |
57 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
58 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/069/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Sqrt(x)][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Implement `int sqrt(int x)`.
6 |
7 | Compute and return the square root of *x*, where *x* is guaranteed to be a non-negative integer.
8 |
9 | Since the return type is an integer, the decimal digits are truncated and only the integer part of the result is returned.
10 |
11 | **Example 1:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Input: 4
15 | Output: 2
16 | ```
17 |
18 | **Example 2:**
19 |
20 | ```
21 | Input: 8
22 | Output: 2
23 | Explanation: The square root of 8 is 2.82842..., and since
24 | the decimal part is truncated, 2 is returned.
25 | ```
26 |
27 | **Tags:** Binary Search, Math
28 |
29 |
30 | ## 思路
31 |
32 | 题意是求平方根,参考 [牛顿迭代法求平方根](https://wenku.baidu.com/view/6b74c622bcd126fff7050bfe.html),然后再参考维基百科的 [Integer square root](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Integer_square_root#Using_only_integer_division) 即可。
33 |
34 | ```java
35 | class Solution {
36 | public int mySqrt(int x) {
37 | long n = x;
38 | while (n * n > x) {
39 | n = (n + x / n) >> 1;
40 | }
41 | return (int) n;
42 | }
43 | }
44 | ```
45 |
46 |
47 | ## 结语
48 |
49 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/sqrtx
54 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/119/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Pascal's Triangle II][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a non-negative index *k* where *k* ≤ 33, return the *k*th index row of the Pascal's triangle.
6 |
7 | Note that the row index starts from 0.
8 |
9 | 
10 | In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it.
11 |
12 | **Example:**
13 |
14 | ```
15 | Input: 3
16 | Output: [1,3,3,1]
17 | ```
18 |
19 | **Follow up:**
20 |
21 | Could you optimize your algorithm to use only *O*(*k*) extra space?
22 |
23 | **Tags:** Array
24 |
25 |
26 | ## 思路
27 |
28 | 题意是指定输出帕斯卡尔三角形的某一行,模拟即可,优化后的代码如下所示。
29 |
30 | ```java
31 | class Solution {
32 | public List getRow(int rowIndex) {
33 | List res = new ArrayList<>();
34 | for (int i = 0; i <= rowIndex; ++i) {
35 | res.add(1);
36 | for (int j = i - 1; j > 0; --j) {
37 | res.set(j, res.get(j - 1) + res.get(j));
38 | }
39 | }
40 | return res;
41 | }
42 | }
43 | ```
44 |
45 |
46 | ## 结语
47 |
48 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/pascals-triangle-ii
53 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_001/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._001;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Arrays;
4 | import java.util.HashMap;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/04/21
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Solution {
15 | // public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
16 | // for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
17 | // for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; ++j) {
18 | // if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
19 | // return new int[]{i, j};
20 | // }
21 | // }
22 | // }
23 | // return null;
24 | // }
25 |
26 | public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
27 | int len = nums.length;
28 | HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
29 | for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
30 | if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
31 | return new int[]{map.get(nums[i]), i};
32 | }
33 | map.put(target - nums[i], i);
34 | }
35 | return null;
36 | }
37 |
38 | public static void main(String[] args) {
39 | Solution solution = new Solution();
40 | int[] nums = new int[]{2, 7, 11, 15};
41 | int target = 9;
42 | System.out.println(Arrays.toString(solution.twoSum(nums, target)));
43 | }
44 | }
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_107/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._107;
2 |
3 |
4 | import com.blankj.structure.TreeNode;
5 |
6 | import java.util.LinkedList;
7 | import java.util.List;
8 |
9 | /**
10 | *
11 | * author: Blankj
12 | * blog : http://blankj.com
13 | * time : 2017/10/09
14 | * desc :
15 | *
16 | */
17 | public class Solution {
18 | public List> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
19 | List> list = new LinkedList<>();
20 | helper(list, root, 0);
21 | return list;
22 | }
23 |
24 | private void helper(List> list, TreeNode root, int level) {
25 | if (root == null) return;
26 | if (level >= list.size()) {
27 | list.add(0, new LinkedList<>());
28 | }
29 | helper(list, root.left, level + 1);
30 | helper(list, root.right, level + 1);
31 | list.get(list.size() - level - 1).add(root.val);
32 | }
33 |
34 | public static void main(String[] args) {
35 | Solution solution = new Solution();
36 | System.out.println(solution.levelOrderBottom(TreeNode.createTestData("[]")));
37 | System.out.println(solution.levelOrderBottom(TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,3,4,4,3]")));
38 | System.out.println(solution.levelOrderBottom(TreeNode.createTestData("[9,-42,-42,null,76,76,null,null,13,null,13]")));
39 | }
40 | }
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/hard/_025/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.hard._025;
2 |
3 | import com.blankj.structure.ListNode;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | *
7 | * author: Blankj
8 | * blog : http://blankj.com
9 | * time : 2017/10/16
10 | * desc :
11 | *
12 | */
13 | public class Solution {
14 | public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
15 | if (head == null || k == 1) return head;
16 | ListNode node = new ListNode(0), pre = node;
17 | node.next = head;
18 | for (int i = 1; head != null; ++i) {
19 | if (i % k == 0) {
20 | pre = reverse(pre, head.next);
21 | head = pre.next;
22 | } else {
23 | head = head.next;
24 | }
25 | }
26 | return node.next;
27 | }
28 |
29 | private ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode next) {
30 | ListNode head = pre.next;
31 | ListNode move = head.next;
32 | while (move != next) {
33 | head.next = move.next;
34 | move.next = pre.next;
35 | pre.next = move;
36 | move = head.next;
37 | }
38 | return head;
39 | }
40 |
41 | public static void main(String[] args) {
42 | Solution solution = new Solution();
43 | ListNode.print(solution.reverseKGroup(ListNode.createTestData("[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8]"), 3));
44 | }
45 | }
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_009/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._009;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/04/24
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | // public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
13 | // if (x < 0) return false;
14 | // int copyX = x, reverse = 0;
15 | // while (copyX > 0) {
16 | // reverse = reverse * 10 + copyX % 10;
17 | // copyX /= 10;
18 | // }
19 | // return x == reverse;
20 | // }
21 |
22 | public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
23 | if (x < 0 || (x != 0 && x % 10 == 0)) return false;
24 | int halfReverseX = 0;
25 | while (x > halfReverseX) {
26 | halfReverseX = halfReverseX * 10 + x % 10;
27 | x /= 10;
28 | }
29 | return halfReverseX == x || halfReverseX / 10 == x;
30 | }
31 |
32 | public static void main(String[] args) {
33 | Solution solution = new Solution();
34 | System.out.println(solution.isPalindrome(-1));
35 | System.out.println(solution.isPalindrome(10010));
36 |
37 | System.out.println(solution.isPalindrome(0));
38 | System.out.println(solution.isPalindrome(11));
39 | System.out.println(solution.isPalindrome(111));
40 | System.out.println(solution.isPalindrome(222222222));
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/083/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Remove Duplicates from Sorted List][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a sorted linked list, delete all duplicates such that each element appear only *once*.
6 |
7 | **Example 1:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input: 1->1->2
11 | Output: 1->2
12 | ```
13 |
14 | **Example 2:**
15 |
16 | ```
17 | Input: 1->1->2->3->3
18 | Output: 1->2->3
19 | ```
20 |
21 | **Tags:** Linked List
22 |
23 |
24 | ## 思路
25 |
26 | 题意是删除链表中重复的元素,很简单,我们只需要遍历一遍链表,遇到链表中相邻元素相同时,把当前指针指向下下个元素即可。
27 |
28 | ```java
29 | /**
30 | * Definition for singly-linked list.
31 | * public class ListNode {
32 | * int val;
33 | * ListNode next;
34 | * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
35 | * }
36 | */
37 | class Solution {
38 | public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
39 | if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
40 | ListNode curr = head;
41 | while (curr.next != null) {
42 | if (curr.next.val == curr.val) {
43 | curr.next = curr.next.next;
44 | } else {
45 | curr = curr.next;
46 | }
47 | }
48 | return head;
49 | }
50 | }
51 | ```
52 |
53 |
54 | ## 结语
55 |
56 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
57 |
58 |
59 |
60 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list
61 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_043/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._043;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/10/17
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public String multiply(String num1, String num2) {
13 | if (num1.equals("0") || num2.equals("0")) return "0";
14 | int l1 = num1.length(), l2 = num2.length(), l = l1 + l2;
15 | char[] ans = new char[l];
16 | char[] c1 = num1.toCharArray();
17 | char[] c2 = num2.toCharArray();
18 | for (int i = l1 - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
19 | int c = c1[i] - '0';
20 | for (int j = l2 - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
21 | ans[i + j + 1] += c * (c2[j] - '0');
22 | }
23 | }
24 | for (int i = l - 1; i > 0; --i) {
25 | if (ans[i] > 9) {
26 | ans[i - 1] += ans[i] / 10;
27 | ans[i] %= 10;
28 | }
29 | }
30 | StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
31 | int i = 0;
32 | for (; ; ++i) if (ans[i] != 0) break;
33 | for (; i < ans.length; ++i) sb.append((char) (ans[i] + '0'));
34 | return sb.toString();
35 | }
36 |
37 | public static void main(String[] args) {
38 | Solution solution = new Solution();
39 | System.out.println(solution.multiply("132", "19"));
40 | }
41 | }
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/070/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Climbing Stairs][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | You are climbing a stair case. It takes *n* steps to reach to the top.
6 |
7 | Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
8 |
9 | **Note:** Given *n* will be a positive integer.
10 |
11 | **Example 1:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Input: 2
15 | Output: 2
16 | Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
17 | 1. 1 step + 1 step
18 | 2. 2 steps
19 | ```
20 |
21 | **Example 2:**
22 |
23 | ```
24 | Input: 3
25 | Output: 3
26 | Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
27 | 1. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
28 | 2. 1 step + 2 steps
29 | 3. 2 steps + 1 step
30 | ```
31 |
32 | **Tags:** Dynamic Programming
33 |
34 |
35 | ## 思路
36 |
37 | 题意是爬楼梯,每次你只能爬一步或者两步,问到顶层共有多少种方案。我们假设到顶层共有 `f(n)` 种,那么 `f(n) = f(n - 1) + f(n - 2)` 肯定是成立的,意思就是我们迈向顶层的最后一步是在倒数第一级台阶或者在倒数第二级台阶。算法我对空间复杂度进行了优化,因为在迭代过程中只需要两个变量即可。
38 |
39 | ```java
40 | class Solution {
41 | public int climbStairs(int n) {
42 | int a = 1, b = 1;
43 | while (--n > 0) {
44 | b += a;
45 | a = b - a;
46 | }
47 | return b;
48 | }
49 | }
50 | ```
51 |
52 |
53 | ## 结语
54 |
55 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
56 |
57 |
58 |
59 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/climbing-stairs
60 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/050/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Pow(x, n)][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Implement [pow(*x*, *n*)](http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/valarray/pow/), which calculates *x* raised to the power *n* (xn).
6 |
7 | **Example 1:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input: 2.00000, 10
11 | Output: 1024.00000
12 | ```
13 |
14 | **Example 2:**
15 |
16 | ```
17 | Input: 2.10000, 3
18 | Output: 9.26100
19 | ```
20 |
21 | **Example 3:**
22 |
23 | ```
24 | Input: 2.00000, -2
25 | Output: 0.25000
26 | Explanation: 2^-2 = 1/2^2 = 1/4 = 0.25
27 | ```
28 |
29 | **Note:**
30 |
31 | - -100.0 < *x* < 100.0
32 | - *n* is a 32-bit signed integer, within the range [−231, 231 − 1]
33 |
34 | **Tags:** Math, Binary Search
35 |
36 |
37 | ## 思路
38 |
39 | 题意是让你计算 `x^n`,如果直接计算肯定会超时,那么我们可以想到可以使用二分法来降低时间复杂度。
40 |
41 | ```java
42 | class Solution {
43 | public double myPow(double x, int n) {
44 | if (n < 0) return helper(1 / x, -n);
45 | return helper(x, n);
46 | }
47 |
48 | private double helper(double x, int n) {
49 | if (n == 0) return 1;
50 | if (n == 1) return x;
51 | double d = helper(x, n >>> 1);
52 | if (n % 2 == 0) return d * d;
53 | return d * d * x;
54 | }
55 | }
56 | ```
57 |
58 |
59 | ## 结语
60 |
61 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/powx-n
66 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/035/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Search Insert Position][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a sorted array and a target value, return the index if the target is found. If not, return the index where it would be if it were inserted in order.
6 |
7 | You may assume no duplicates in the array.
8 |
9 | **Example 1:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Input: [1,3,5,6], 5
13 | Output: 2
14 | ```
15 |
16 | **Example 2:**
17 |
18 | ```
19 | Input: [1,3,5,6], 2
20 | Output: 1
21 | ```
22 |
23 | **Example 3:**
24 |
25 | ```
26 | Input: [1,3,5,6], 7
27 | Output: 4
28 | ```
29 |
30 | **Example 1:**
31 |
32 | ```
33 | Input: [1,3,5,6], 0
34 | Output: 0
35 | ```
36 |
37 | **Tags:** Array, Binary Search
38 |
39 |
40 | ## 思路
41 |
42 | 题意是让你从一个没有重复元素的已排序数组中找到插入位置的索引。因为数组已排序,所以我们可以想到二分查找法,因为查找到的条件是找到第一个等于或者大于 `target` 的元素的位置,所以二分法略作变动即可。
43 |
44 | ```java
45 | class Solution {
46 | public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
47 | int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1, mid = (right + left) >> 1;
48 | while (left <= right) {
49 | if (target <= nums[mid]) right = mid - 1;
50 | else left = mid + 1;
51 | mid = (right + left) >> 1;
52 | }
53 | return left;
54 | }
55 | }
56 | ```
57 |
58 |
59 | ## 结语
60 |
61 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/search-insert-position
66 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/088/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Merge Sorted Array][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given two sorted integer arrays *nums1* and *nums2*, merge *nums2* into *nums1* as one sorted array.
6 |
7 | **Note:**
8 |
9 | - The number of elements initialized in *nums1* and *nums2* are *m* and *n* respectively.
10 | - You may assume that *nums1* has enough space (size that is greater or equal to *m* + *n*) to hold additional elements from *nums2*.
11 |
12 | **Example:**
13 |
14 | ```
15 | Input:
16 | nums1 = [1,2,3,0,0,0], m = 3
17 | nums2 = [2,5,6], n = 3
18 |
19 | Output: [1,2,2,3,5,6]
20 | ```
21 |
22 | **Tags:** Array, Two Pointers
23 |
24 |
25 | ## 思路
26 |
27 | 题意是给两个已排序的数组 `nums1` 和 `nums2`,合并 `nums2` 到 `nums1` 中,两数组元素个数分别为 `m` 和 `n`,而且 `nums1` 数组的长度足够容纳 `m + n` 个元素,如果我们按顺序排下去,那肯定要开辟一个新数组来保存元素,如果我们选择逆序,这样利用 `nums1` 自身空间足矣,不会出现覆盖的情况,依次把大的元素插入到 `nums1` 的末尾,确保 `nums2` 中的元素全部插入到 `nums1` 即可。
28 |
29 | ```java
30 | class Solution {
31 | public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
32 | int p = m-- + n-- - 1;
33 | while (m >= 0 && n >= 0)
34 | nums1[p--] = nums1[m] > nums2[n] ? nums1[m--] : nums2[n--];
35 | while (n >= 0)
36 | nums1[p--] = nums2[n--];
37 | }
38 | }
39 | ```
40 |
41 |
42 | ## 结语
43 |
44 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
45 |
46 |
47 |
48 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-sorted-array
49 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_049/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._049;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.Arrays;
5 | import java.util.Collections;
6 | import java.util.HashMap;
7 | import java.util.List;
8 | import java.util.Map;
9 |
10 | /**
11 | *
12 | * author: Blankj
13 | * blog : http://blankj.com
14 | * time : 2017/10/18
15 | * desc :
16 | *
17 | */
18 | public class Solution {
19 | public List> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
20 | if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
21 | List> list = new ArrayList<>();
22 | Map hash = new HashMap<>();
23 | int i = 0;
24 | for (String str : strs) {
25 | char[] c = str.toCharArray();
26 | Arrays.sort(c);
27 | String sortStr = String.valueOf(c);
28 | if (!hash.containsKey(sortStr)) {
29 | hash.put(sortStr, i++);
30 | List sub = new ArrayList<>();
31 | sub.add(str);
32 | list.add(sub);
33 | } else {
34 | list.get(hash.get(sortStr)).add(str);
35 | }
36 | }
37 | return list;
38 | }
39 |
40 | public static void main(String[] args) {
41 | Solution solution = new Solution();
42 | System.out.println(solution.groupAnagrams(new String[]{"eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"}));
43 | }
44 | }
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/112/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Path Sum][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a binary tree and a sum, determine if the tree has a root-to-leaf path such that adding up all the values along the path equals the given sum.
6 |
7 | **Note:** A leaf is a node with no children.
8 |
9 | **Example:**
10 |
11 | Given the below binary tree and `sum = 22`,
12 |
13 | ```
14 | 5
15 | / \
16 | 4 8
17 | / / \
18 | 11 13 4
19 | / \ \
20 | 7 2 1
21 | ```
22 |
23 | return true, as there exist a root-to-leaf path `5->4->11->2` which sum is 22.
24 |
25 | **Tags:** Tree, Depth-first Search
26 |
27 |
28 | ## 思路
29 |
30 | 题意是查找二叉树中是否存在从根结点到叶子的路径和为某一值,利用深搜在遇到叶子节点时判断是否满足即可。
31 |
32 |
33 | ```java
34 | /**
35 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
36 | * public class TreeNode {
37 | * int val;
38 | * TreeNode left;
39 | * TreeNode right;
40 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
41 | * }
42 | */
43 | class Solution {
44 | public boolean hasPathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
45 | if (root == null) return false;
46 | if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return sum == root.val;
47 | return hasPathSum(root.left, sum - root.val) || hasPathSum(root.right, sum - root.val);
48 | }
49 | }
50 | ```
51 |
52 |
53 | ## 结语
54 |
55 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
56 |
57 |
58 |
59 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/path-sum
60 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_554/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._554;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.Arrays;
5 | import java.util.HashMap;
6 | import java.util.List;
7 | import java.util.Map;
8 |
9 | /**
10 | *
11 | * author: Blankj
12 | * blog : http://blankj.com
13 | * time : 2017/10/13
14 | * desc :
15 | *
16 | */
17 | public class Solution {
18 | public int leastBricks(List> wall) {
19 | Map map = new HashMap<>();
20 | int width = 0, max = 0;
21 | for (List sub : wall) {
22 | int p = 0;
23 | for (int i = 0, len = sub.size() - 1; i < len; ++i) {
24 | p += sub.get(i);
25 | Integer v = map.get(p);
26 | map.put(p, (v == null ? 0 : v) + 1);
27 | }
28 | }
29 | for (Integer integer : map.values()) {
30 | if (integer > max) max = integer;
31 | }
32 | return wall.size() - max;
33 | }
34 |
35 | public static void main(String[] args) {
36 | Solution solution = new Solution();
37 | List> list = new ArrayList<>();
38 | list.add(Arrays.asList(1, 2, 2, 1));
39 | list.add(Arrays.asList(3, 1, 2));
40 | list.add(Arrays.asList(1, 3, 2));
41 | list.add(Arrays.asList(2, 4));
42 | list.add(Arrays.asList(3, 1, 2));
43 | list.add(Arrays.asList(1, 3, 1, 1));
44 | System.out.println(solution.leastBricks(list));
45 | }
46 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/021/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Merge Two Sorted Lists][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Merge two sorted linked lists and return it as a new list. The new list should be made by splicing together the nodes of the first two lists.
6 |
7 | **Example:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input: 1->2->4, 1->3->4
11 | Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4
12 | ```
13 |
14 | **Tags:** Linked List
15 |
16 |
17 | ## 思路
18 |
19 | 题意是用一个新链表来合并两个已排序的链表,那我们只需要从头开始比较已排序的两个链表,新链表指针每次指向值小的节点,依次比较下去,最后,当其中一个链表到达了末尾,我们只需要把新链表指针指向另一个没有到末尾的链表此时的指针即可。
20 |
21 | ```java
22 | /**
23 | * Definition for singly-linked list.
24 | * public class ListNode {
25 | * int val;
26 | * ListNode next;
27 | * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
28 | * }
29 | */
30 | class Solution {
31 | public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
32 | ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
33 | ListNode temp = head;
34 | while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
35 | if (l1.val < l2.val) {
36 | temp.next = l1;
37 | l1 = l1.next;
38 | } else {
39 | temp.next = l2;
40 | l2 = l2.next;
41 | }
42 | temp = temp.next;
43 | }
44 | temp.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2;
45 | return head.next;
46 | }
47 | }
48 | ```
49 |
50 |
51 | ## 结语
52 |
53 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
54 |
55 |
56 |
57 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists
58 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/014/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Longest Common Prefix][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Write a function to find the longest common prefix string amongst an array of strings.
6 |
7 | If there is no common prefix, return an empty string `""`.
8 |
9 | **Example 1:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Input: ["flower","flow","flight"]
13 | Output: "fl"
14 | ```
15 |
16 | **Example 2:**
17 |
18 | ```
19 | Input: ["dog","racecar","car"]
20 | Output: ""
21 | Explanation: There is no common prefix among the input strings.
22 | ```
23 |
24 | **Note:**
25 |
26 | All given inputs are in lowercase letters `a-z`.
27 |
28 | **Tags:** String
29 |
30 |
31 | ## 思路
32 |
33 | 题意是让你从字符串数组中找出公共前缀,我的想法是找出最短的那个字符串的长度 `minLen`,然后在 `0...minLen` 的范围比较所有字符串,如果比较到有不同的字符,那么直接返回当前索引长度的字符串即可,否则最后返回最短的字符串即可。
34 |
35 | ```java
36 | class Solution {
37 | public String longestCommonPrefix(String[] strs) {
38 | int len = strs.length;
39 | if (len == 0) return "";
40 | int minLen = 0x7fffffff;
41 | for (String str : strs) minLen = Math.min(minLen, str.length());
42 | for (int j = 0; j < minLen; ++j)
43 | for (int i = 1; i < len; ++i)
44 | if (strs[0].charAt(j) != strs[i].charAt(j))
45 | return strs[0].substring(0, j);
46 | return strs[0].substring(0, minLen);
47 | }
48 | }
49 | ```
50 |
51 |
52 | ## 结语
53 |
54 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
55 |
56 |
57 |
58 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-common-prefix
59 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/118/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Pascal's Triangle][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a non-negative integer *numRows*, generate the first *numRows* of Pascal's triangle.
6 |
7 | 
8 | In Pascal's triangle, each number is the sum of the two numbers directly above it.
9 |
10 | **Example:**
11 |
12 | ```
13 | Input: 5
14 | Output:
15 | [
16 | [1],
17 | [1,1],
18 | [1,2,1],
19 | [1,3,3,1],
20 | [1,4,6,4,1]
21 | ]
22 | ```
23 |
24 | **Tags:** Array
25 |
26 |
27 | ## 思路
28 |
29 | 题意是给出行数,输出帕斯卡尔三角形,很简单的模拟,就不多说了。
30 |
31 | ```java
32 | class Solution {
33 | public List> generate(int numRows) {
34 | if (numRows == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
35 | List> list = new ArrayList<>();
36 | for (int i = 0; i < numRows; ++i) {
37 | List sub = new ArrayList<>();
38 | for (int j = 0; j <= i; ++j) {
39 | if (j == 0 || j == i) {
40 | sub.add(1);
41 | } else {
42 | List upSub = list.get(i - 1);
43 | sub.add(upSub.get(j - 1) + upSub.get(j));
44 | }
45 | }
46 | list.add(sub);
47 | }
48 | return list;
49 | }
50 | }
51 | ```
52 |
53 |
54 | ## 结语
55 |
56 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
57 |
58 |
59 |
60 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/pascals-triangle
61 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/structure/ListNode.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.structure;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/05/18
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class ListNode {
12 |
13 | public int val;
14 | public ListNode next;
15 |
16 | public ListNode(int x) {
17 | val = x;
18 | }
19 |
20 | /**
21 | * 创建测试数据
22 | *
23 | * @param data [XX,XX,XX]
24 | * @return {@link ListNode}
25 | */
26 | public static ListNode createTestData(String data) {
27 | if (data.equals("[]")) return null;
28 | data = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1);
29 | String[] split = data.split(",");
30 | int len = split.length;
31 | ListNode[] listNode = new ListNode[len + 1];
32 | listNode[0] = new ListNode(Integer.valueOf(split[0]));
33 | for (int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
34 | listNode[i] = new ListNode(Integer.valueOf(split[i]));
35 | listNode[i - 1].next = listNode[i];
36 | }
37 | return listNode[0];
38 | }
39 |
40 | public static void print(ListNode listNode) {
41 | if (listNode == null) {
42 | System.out.println("null");
43 | return;
44 | }
45 | StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder("[" + String.valueOf(listNode.val));
46 | ListNode p = listNode.next;
47 | while (p != null) {
48 | str.append(",").append(String.valueOf(p.val));
49 | p = p.next;
50 | }
51 | System.out.println(str.append("]"));
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/003/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Longest Substring Without Repeating Characters][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a string, find the length of the **longest substring** without repeating characters.
6 |
7 | **Examples:**
8 |
9 | Given `"abcabcbb"`, the answer is `"abc"`, which the length is 3.
10 |
11 | Given `"bbbbb"`, the answer is `"b"`, with the length of 1.
12 |
13 | Given `"pwwkew"`, the answer is `"wke"`, with the length of 3. Note that the answer must be a **substring**, `"pwke"` is a *subsequence* and not a substring.
14 |
15 | **Tags:** Hash Table, Two Pointers, String
16 |
17 |
18 | ## 思路
19 |
20 | 题意是计算不带重复字符的最长子字符串的长度,开辟一个 hash 数组来存储该字符上次出现的位置,比如 `hash[a] = 3` 就是代表 `a` 字符前一次出现的索引在 3,遍历该字符串,获取到上次出现的最大索引(只能向前,不能退后),与当前的索引做差获取的就是本次所需长度,从中迭代出最大值就是最终答案。
21 |
22 | ```java
23 | class Solution {
24 | public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
25 | int len;
26 | if (s == null || (len = s.length()) == 0) return 0;
27 | int preP = 0, max = 0;
28 | int[] hash = new int[128];
29 | for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
30 | char c = s.charAt(i);
31 | if (hash[c] > preP) {
32 | preP = hash[c];
33 | }
34 | int l = i - preP + 1;
35 | hash[c] = i + 1;
36 | if (l > max) max = l;
37 | }
38 | return max;
39 | }
40 | }
41 | ```
42 |
43 |
44 | ## 结语
45 |
46 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
47 |
48 |
49 |
50 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters
51 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_111/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._111;
2 |
3 |
4 | import com.blankj.structure.TreeNode;
5 |
6 | import java.util.LinkedList;
7 |
8 | /**
9 | *
10 | * author: Blankj
11 | * blog : http://blankj.com
12 | * time : 2017/10/10
13 | * desc :
14 | *
15 | */
16 | public class Solution {
17 | // public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
18 | // if (root == null) return 0;
19 | // int l = minDepth(root.left);
20 | // int r = minDepth(root.right);
21 | // if (l != 0 && r != 0) return 1 + Math.min(l, r);
22 | // return l + r + 1;
23 | // }
24 |
25 | public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
26 | if (root == null) return 0;
27 | LinkedList q = new LinkedList<>();
28 | q.add(root);
29 | int ans = 1;
30 | while (!q.isEmpty()) {
31 | int size = q.size();
32 | for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
33 | TreeNode node = q.remove();
34 | if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
35 | return ans;
36 | }
37 | if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left);
38 | if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right);
39 | }
40 | ++ans;
41 | }
42 | return 520;
43 | }
44 |
45 | public static void main(String[] args) {
46 | Solution solution = new Solution();
47 | TreeNode testData = TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,4,4,null,null,5,5]");
48 | TreeNode.print(testData);
49 | System.out.println(solution.minDepth(testData));
50 | }
51 | }
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_056/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._056;
2 |
3 | import com.blankj.structure.Interval;
4 |
5 | import java.util.ArrayList;
6 | import java.util.Comparator;
7 | import java.util.List;
8 |
9 | /**
10 | *
11 | * author: Blankj
12 | * blog : http://blankj.com
13 | * time : 2017/10/19
14 | * desc :
15 | *
16 | */
17 | public class Solution {
18 | public List merge(List intervals) {
19 | if (intervals == null || intervals.size() <= 1) return intervals;
20 | intervals.sort(new Comparator() {
21 | @Override
22 | public int compare(Interval o1, Interval o2) {
23 | if (o1.start < o2.start) return -1;
24 | if (o1.start > o2.start) return 1;
25 | return 0;
26 | }
27 | });
28 | List ans = new ArrayList<>();
29 | int start = intervals.get(0).start;
30 | int end = intervals.get(0).end;
31 | for (Interval interval : intervals) {
32 | if (interval.start <= end) {
33 | end = Math.max(end, interval.end);
34 | } else {
35 | ans.add(new Interval(start, end));
36 | start = interval.start;
37 | end = interval.end;
38 | }
39 | }
40 | ans.add(new Interval(start, end));
41 | return ans;
42 | }
43 |
44 | public static void main(String[] args) {
45 | Solution solution = new Solution();
46 | Interval.print(solution.merge(Interval.createTestData("[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]")));
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_053/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._053;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/05/04
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | // public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
13 | // int len = nums.length, dp = nums[0], max = dp;
14 | // for (int i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
15 | // dp = nums[i] + (dp > 0 ? dp : 0);
16 | // if (dp > max) max = dp;
17 | // }
18 | // return max;
19 | // }
20 | public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
21 | return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
22 | }
23 |
24 | private int helper(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
25 | if (left >= right) return nums[left];
26 | int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
27 | int leftAns = helper(nums, left, mid);
28 | int rightAns = helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
29 | int leftMax = nums[mid], rightMax = nums[mid + 1];
30 | int temp = 0;
31 | for (int i = mid; i >= left; --i) {
32 | temp += nums[i];
33 | if (temp > leftMax) leftMax = temp;
34 | }
35 | temp = 0;
36 | for (int i = mid + 1; i <= right; ++i) {
37 | temp += nums[i];
38 | if (temp > rightMax) rightMax = temp;
39 | }
40 | return Math.max(Math.max(leftAns, rightAns), leftMax + rightMax);
41 | }
42 |
43 | public static void main(String[] args) {
44 | Solution solution = new Solution();
45 | int[] nums0 = new int[]{-2, 1, -3, 4, -1, 2, 1, -5, 4};
46 | System.out.println(solution.maxSubArray(nums0));
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/121/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Say you have an array for which the *i*th element is the price of a given stock on day *i*.
6 |
7 | If you were only permitted to complete at most one transaction (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock), design an algorithm to find the maximum profit.
8 |
9 | Note that you cannot sell a stock before you buy one.
10 |
11 | **Example 1:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Input: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
15 | Output: 5
16 | Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5.
17 | Not 7-1 = 6, as selling price needs to be larger than buying price.
18 | ```
19 |
20 | **Example 2:**
21 |
22 | ```
23 | Input: [7,6,4,3,1]
24 | Output: 0
25 | Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
26 | ```
27 |
28 | **Tags:** Array, Dynamic Programmin
29 |
30 |
31 | ## 思路
32 |
33 | 题意是给出一个数组代表每天的股票金额,让你在最多买卖一次的情况下算出最大的收益额,最简单的就是模拟即可,每次记录当前值减去最小值的差值,与上一次的进行比较然后更新最大值即可。
34 |
35 | ```java
36 | class Solution {
37 | public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
38 | int max = 0, minPrice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
39 | for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; ++i) {
40 | if (prices[i] < minPrice) minPrice = prices[i];
41 | int delta = prices[i] - minPrice;
42 | if (delta > max) max = delta;
43 | }
44 | return max;
45 | }
46 | }
47 | ```
48 |
49 |
50 | ## 结语
51 |
52 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
53 |
54 |
55 |
56 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock
57 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/structure/Interval.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.structure;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.List;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/10/19
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Interval {
15 | public int start;
16 | public int end;
17 |
18 | public Interval() {
19 | start = 0;
20 | end = 0;
21 | }
22 |
23 | public Interval(int s, int e) {
24 | start = s;
25 | end = e;
26 | }
27 |
28 | /**
29 | * 创建测试数据
30 | *
31 | * @param data [[X,X],[X,X],[X,X]]
32 | * @return {@link List}
33 | */
34 | public static List createTestData(String data) {
35 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
36 | String[] d = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1).split("],\\[");
37 | for (String s : d) {
38 | String[] sub = s.split(",");
39 | list.add(new Interval(Integer.valueOf(sub[0]), Integer.valueOf(sub[1])));
40 | }
41 | return list;
42 | }
43 |
44 | public static void print(List list) {
45 | if (list == null) {
46 | System.out.println("null");
47 | return;
48 | }
49 | StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
50 | for (Interval interval : list) {
51 | sb.append("[")
52 | .append(interval.start)
53 | .append(",")
54 | .append(interval.end)
55 | .append("],");
56 | }
57 | System.out.println(sb.substring(0, sb.length() - 1));
58 | }
59 | }
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/hard/_004/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.hard._004;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/10/12
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
13 | int len = nums1.length + nums2.length;
14 | if (len % 2 == 0) {
15 | return (helper(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, len / 2) + helper(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, len / 2 + 1)) / 2.0;
16 | }
17 | return helper(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, (len + 1) / 2);
18 | }
19 |
20 | private int helper(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n, int k) {
21 | if (m >= nums1.length) return nums2[n + k - 1];
22 | if (n >= nums2.length) return nums1[m + k - 1];
23 | if (k == 1) return Math.min(nums1[m], nums2[n]);
24 |
25 | int p1 = m + k / 2 - 1;
26 | int p2 = n + k / 2 - 1;
27 | int mid1 = p1 < nums1.length ? nums1[p1] : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
28 | int mid2 = p2 < nums2.length ? nums2[p2] : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
29 | if (mid1 < mid2) {
30 | return helper(nums1, m + k / 2, nums2, n, k - k / 2);
31 | }
32 | return helper(nums1, m, nums2, n + k / 2, k - k / 2);
33 | }
34 |
35 | public static void main(String[] args) {
36 | Solution solution = new Solution();
37 | System.out.println(solution.findMedianSortedArrays(
38 | new int[]{1, 3},
39 | new int[]{2}
40 | ));
41 | System.out.println(solution.findMedianSortedArrays(
42 | new int[]{1, 2},
43 | new int[]{3, 4}
44 | ));
45 | }
46 | }
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/543/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Diameter of Binary Tree][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a binary tree, you need to compute the length of the diameter of the tree. The diameter of a binary tree is the length of the **longest** path between any two nodes in a tree. This path may or may not pass through the root.
6 |
7 | **Example:**
8 | Given a binary tree
9 |
10 | ```
11 | 1
12 | / \
13 | 2 3
14 | / \
15 | 4 5
16 | ```
17 |
18 | Return **3**, which is the length of the path [4,2,1,3] or [5,2,1,3].
19 |
20 | **Note:** The length of path between two nodes is represented by the number of edges between them.
21 |
22 | **Tags:** Tree
23 |
24 |
25 | ## 思路
26 |
27 | 题意是让你算出二叉树中最远的两个节点的距离,分别计算左右子树的最大高度,然后不断迭代出其和的最大值就是最终结果。
28 |
29 | ```java
30 | /**
31 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
32 | * public class TreeNode {
33 | * int val;
34 | * TreeNode left;
35 | * TreeNode right;
36 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
37 | * }
38 | */
39 | class Solution {
40 | int max = 0;
41 |
42 | public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
43 | helper(root);
44 | return max;
45 | }
46 |
47 | private int helper(TreeNode root) {
48 | if (root == null) return 0;
49 | int l = helper(root.left);
50 | int r = helper(root.right);
51 | if (l + r > max) max = l + r;
52 | return Math.max(l, r) + 1;
53 | }
54 | }
55 | ```
56 |
57 |
58 | ## 结语
59 |
60 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
61 |
62 |
63 |
64 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/diameter-of-binary-tree
65 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_015/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._015;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.Arrays;
5 | import java.util.List;
6 |
7 | /**
8 | *
9 | * author: Blankj
10 | * blog : http://blankj.com
11 | * time : 2017/10/14
12 | * desc :
13 | *
14 | */
15 | public class Solution {
16 | public List> threeSum(int[] nums) {
17 | List> list = new ArrayList<>();
18 | int len = nums.length;
19 | if (len < 3) return list;
20 | Arrays.sort(nums);
21 | int max = nums[len - 1];
22 | if (max < 0) return list;
23 | for (int i = 0; i < len - 2; ) {
24 | if (nums[i] > 0) break;
25 | if (nums[i] + 2 * max < 0) {
26 | while (nums[i] == nums[++i] && i < len - 2) ;
27 | continue;
28 | }
29 | int left = i + 1, right = len - 1;
30 | while (left < right) {
31 | int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
32 | if (sum == 0) {
33 | list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]));
34 | while (nums[left] == nums[++left] && left < right) ;
35 | while (nums[right] == nums[--right] && left < right) ;
36 | } else if (sum < 0) ++left;
37 | else --right;
38 | }
39 | while (nums[i] == nums[++i] && i < len - 2) ;
40 | }
41 | return list;
42 | }
43 |
44 | public static void main(String[] args) {
45 | Solution solution = new Solution();
46 | System.out.println(solution.threeSum(new int[]{-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4}));
47 | }
48 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/011/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Container With Most Water][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given *n* non-negative integers *a1*, *a2*, ..., *an*, where each represents a point at coordinate (*i*, *ai*). *n* vertical lines are drawn such that the two endpoints of line *i* is at (*i*, *ai*) and (*i*, 0). Find two lines, which together with x-axis forms a container, such that the container contains the most water.
6 |
7 | Note: You may not slant the container and *n* is at least 2.
8 |
9 | **Tags:** Array, Two Pointers
10 |
11 |
12 | ## 思路
13 |
14 | 题意是给你 *a1*, *a2*, ..., *an* 这 *n* 个数,代表 (*i*, *ai*) 坐标,让你从中找两个点与 x 轴围成的容器可以容纳最多的水。
15 |
16 | 不明白的话可以看数据为 `1 8 6 2 5 4 8 3 7` 所示的图。
17 |
18 | 
19 |
20 | 如果用暴力法求每种情况的结果,其时间复杂度为 O(n^2),相信肯定会超时,我们可以探索下是否有更巧妙的办法呢,题目的标签有双指针,是否就可以想到首尾各放一指针,然后根据条件来收缩。首先计算一次首尾构成的最大面积,然后分析下该移动哪个指针,如果移动大的那个指针的话,那样只会减小面积,所以我们要移动小的那个指针,小的那个指针移动到哪呢?当然是移动到大于之前的值的地方,否则面积不都比之前小么,然后继续更新最大值即可,借助如上分析写出如下代码应该不是什么难事了吧。
21 |
22 |
23 | ```java
24 | class Solution {
25 | public int maxArea(int[] height) {
26 | int l = 0, r = height.length - 1;
27 | int max = 0, h = 0;
28 | while (l < r) {
29 | h = Math.min(height[l], height[r]);
30 | max = Math.max(max, (r - l) * h);
31 | while (height[l] <= h && l < r) ++l;
32 | while (height[r] <= h && l < r) --r;
33 | }
34 | return max;
35 | }
36 | }
37 | ```
38 |
39 |
40 | ## 结语
41 |
42 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/container-with-most-water
47 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_057/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._057;
2 |
3 | import com.blankj.structure.Interval;
4 |
5 | import java.util.ArrayList;
6 | import java.util.Collections;
7 | import java.util.List;
8 |
9 | /**
10 | *
11 | * author: Blankj
12 | * blog : http://blankj.com
13 | * time : 2017/10/24
14 | * desc :
15 | *
16 | */
17 | public class Solution {
18 | public List insert(List intervals, Interval newInterval) {
19 | if (intervals.isEmpty()) return Collections.singletonList(newInterval);
20 | List ans = new ArrayList<>();
21 | int i = 0, len = intervals.size();
22 | for (; i < len; ++i) {
23 | Interval interval = intervals.get(i);
24 | if (interval.end < newInterval.start) ans.add(interval);
25 | else break;
26 | }
27 | for (; i < len; ++i) {
28 | Interval interval = intervals.get(i);
29 | if (interval.start <= newInterval.end) {
30 | newInterval.start = Math.min(newInterval.start, interval.start);
31 | newInterval.end = Math.max(newInterval.end, interval.end);
32 | } else break;
33 | }
34 | ans.add(newInterval);
35 | for (; i < len; ++i) {
36 | ans.add(intervals.get(i));
37 | }
38 | return ans;
39 | }
40 |
41 | public static void main(String[] args) {
42 | Solution solution = new Solution();
43 | Interval.print(solution.insert(Interval.createTestData("[1,3],[6,9]"), new Interval(2, 5)));
44 | Interval.print(solution.insert(Interval.createTestData("[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]"), new Interval(4, 9)));
45 | }
46 | }
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/049/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Group Anagrams][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given an array of strings, group anagrams together.
6 |
7 | **Example:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input: ["eat", "tea", "tan", "ate", "nat", "bat"],
11 | Output:
12 | [
13 | ["ate","eat","tea"],
14 | ["nat","tan"],
15 | ["bat"]
16 | ]
17 | ```
18 |
19 | **Note:**
20 |
21 | - All inputs will be in lowercase.
22 | - The order of your output does not matter.
23 |
24 | **Tags:** Hash Table, String
25 |
26 |
27 | ## 思路
28 |
29 | 题意是给你一组字符串,让你把其中同位异构字符串分组,同位异构字符串就是组成字符串的字符都相同,但是字符放的位置可以不同。既然要分组,那么关键就是如何确定他们是同位异构字符串呢,想到的自然就是对其排序,排序之后他们就都是同一个字符串了,就可以归为一类了,代码如下所示。
30 |
31 | ```java
32 | class Solution {
33 | public List> groupAnagrams(String[] strs) {
34 | if (strs == null || strs.length == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
35 | List> list = new ArrayList<>();
36 | Map hash = new HashMap<>();
37 | int i = 0;
38 | for (String str : strs) {
39 | char[] c = str.toCharArray();
40 | Arrays.sort(c);
41 | String sortStr = String.valueOf(c);
42 | if (!hash.containsKey(sortStr)) {
43 | hash.put(sortStr, i++);
44 | List sub = new ArrayList<>();
45 | sub.add(str);
46 | list.add(sub);
47 | } else {
48 | list.get(hash.get(sortStr)).add(str);
49 | }
50 | }
51 | return list;
52 | }
53 | }
54 | ```
55 |
56 |
57 | ## 结语
58 |
59 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
60 |
61 |
62 |
63 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/group-anagrams
64 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/066/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Plus One][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a **non-empty** array of digits representing a non-negative integer, plus one to the integer.
6 |
7 | The digits are stored such that the most significant digit is at the head of the list, and each element in the array contain a single digit.
8 |
9 | You may assume the integer does not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
10 |
11 | **Example 1:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Input: [1,2,3]
15 | Output: [1,2,4]
16 | Explanation: The array represents the integer 123.
17 | ```
18 |
19 | **Example 2:**
20 |
21 | ```
22 | Input: [4,3,2,1]
23 | Output: [4,3,2,2]
24 | Explanation: The array represents the integer 4321.
25 | ```
26 |
27 | **Tags:** Array, Math
28 |
29 |
30 | ## 思路
31 |
32 | 题意是给你一个数字数组,高位在前,并且首位不为 0 除非这个数组就是 `[0]`,让你给该数组低位加一求其结果,那么我们就模拟小学数学那样进位去算即可,如果一直进位到首位,这种情况也就是都是由 9 组成的数组,此时我们只要 new 出一个多一个长度的数组即可,并把第 0 个元素赋 1 即可。
33 |
34 | ```java
35 | class Solution {
36 | public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
37 | int p = digits.length - 1;
38 | if (digits[p] < 9) {
39 | digits[p] = ++digits[p];
40 | } else {
41 | do {
42 | digits[p--] = 0;
43 | } while (p >= 0 && digits[p] == 9);
44 | if (digits[0] != 0) {
45 | ++digits[p];
46 | } else {
47 | digits = new int[digits.length + 1];
48 | digits[0] = 1;
49 | }
50 | }
51 | return digits;
52 | }
53 | }
54 | ```
55 |
56 |
57 | ## 结语
58 |
59 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
60 |
61 |
62 |
63 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/plus-one
64 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/067/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Add Binary][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given two binary strings, return their sum (also a binary string).
6 |
7 | The input strings are both **non-empty** and contains only characters `1` or `0`.
8 |
9 | **Example 1:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Input: a = "11", b = "1"
13 | Output: "100"
14 | ```
15 |
16 | **Example 2:**
17 |
18 | ```
19 | Input: a = "1010", b = "1011"
20 | Output: "10101"
21 | ```
22 |
23 | **Tags:** Math, String
24 |
25 |
26 | ## 思路
27 |
28 | 题意是给你两个二进制串,求其和的二进制串。我们就按照小学算数那么来做,用 `carry` 表示进位,从后往前算,依次往前,每算出一位就插入到最前面即可,直到把两个二进制串都遍历完即可。
29 |
30 | ```java
31 | class Solution {
32 | public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
33 | StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
34 | int carry = 0, p1 = a.length() - 1, p2 = b.length() - 1;
35 | while (p1 >= 0 && p2 >= 0) {
36 | carry += a.charAt(p1--) - '0';
37 | carry += b.charAt(p2--) - '0';
38 | sb.insert(0, (char) (carry % 2 + '0'));
39 | carry >>= 1;
40 | }
41 | while (p1 >= 0) {
42 | carry += a.charAt(p1--) - '0';
43 | sb.insert(0, (char) (carry % 2 + '0'));
44 | carry >>= 1;
45 | }
46 | while (p2 >= 0) {
47 | carry += b.charAt(p2--) - '0';
48 | sb.insert(0, (char) (carry % 2 + '0'));
49 | carry >>= 1;
50 | }
51 | if (carry == 1) {
52 | sb.insert(0, '1');
53 | }
54 | return sb.toString();
55 | }
56 | }
57 | ```
58 |
59 |
60 | ## 结语
61 |
62 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
63 |
64 |
65 |
66 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/add-binary
67 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_008/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._008;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/04/23
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public int myAtoi(String str) {
13 | int i = 0, ans = 0, sign = 1, len = str.length();
14 | while (i < len && str.charAt(i) == ' ') ++i;
15 | if (i < len && (str.charAt(i) == '-' || str.charAt(i) == '+')) {
16 | sign = str.charAt(i++) == '+' ? 1 : -1;
17 | }
18 | for (; i < len; ++i) {
19 | int tmp = str.charAt(i) - '0';
20 | if (tmp < 0 || tmp > 9) break;
21 | if (ans > Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10
22 | || (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 && (sign == 1 && tmp > 7 || sign == -1 && tmp > 8))) {
23 | return sign == 1 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
24 | } else {
25 | ans = ans * 10 + tmp;
26 | }
27 | }
28 | return sign * ans;
29 | }
30 |
31 | public static void main(String[] args) {
32 | Solution solution = new Solution();
33 | System.out.println(solution.myAtoi(" +1"));
34 | System.out.println(solution.myAtoi(" -1"));
35 | System.out.println(solution.myAtoi(""));
36 | System.out.println(solution.myAtoi("a1"));
37 | System.out.println(solution.myAtoi("100000000000000000000"));
38 | System.out.println(solution.myAtoi("-100000000000000000000"));
39 | System.out.println(solution.myAtoi("-3924x8fc"));
40 | System.out.println(solution.myAtoi(String.valueOf(Integer.MIN_VALUE)));
41 | System.out.println(solution.myAtoi(String.valueOf(Integer.MAX_VALUE)));
42 | }
43 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/028/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Implement strStr()][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Implement [strStr()](http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cstring/strstr/).
6 |
7 | Return the index of the first occurrence of needle in haystack, or **-1** if needle is not part of haystack.
8 |
9 | **Example 1:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Input: haystack = "hello", needle = "ll"
13 | Output: 2
14 | ```
15 |
16 | **Example 2:**
17 |
18 | ```
19 | Input: haystack = "aaaaa", needle = "bba"
20 | Output: -1
21 | ```
22 |
23 | **Clarification:**
24 |
25 | What should we return when `needle` is an empty string? This is a great question to ask during an interview.
26 |
27 | For the purpose of this problem, we will return 0 when `needle` is an empty string. This is consistent to C's [strstr()](http://www.cplusplus.com/reference/cstring/strstr/) and Java's [indexOf()](https://docs.oracle.com/javase/7/docs/api/java/lang/String.html#indexOf(java.lang.String)).
28 |
29 | Tags:** Two Pointers, String
30 |
31 |
32 | ## 思路
33 |
34 | 题意是从主串中找到子串的索引,如果找不到则返回-1,当子串长度大于主串,直接返回-1,然后我们只需要遍历比较即可。
35 |
36 | ```java
37 | class Solution {
38 | public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) {
39 | int l1 = haystack.length(), l2 = needle.length();
40 | if (l1 < l2) return -1;
41 | for (int i = 0; ; i++) {
42 | if (i + l2 > l1) return -1;
43 | for (int j = 0; ; j++) {
44 | if (j == l2) return i;
45 | if (haystack.charAt(i + j) != needle.charAt(j)) break;
46 | }
47 | }
48 | }
49 | }
50 | ```
51 |
52 |
53 | ## 结语
54 |
55 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
56 |
57 |
58 |
59 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/implement-strstr
60 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/100/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Same Tree][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given two binary trees, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
6 |
7 | Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical and the nodes have the same value.
8 |
9 | **Example 1:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Input: 1 1
13 | / \ / \
14 | 2 3 2 3
15 |
16 | [1,2,3], [1,2,3]
17 |
18 | Output: true
19 | ```
20 |
21 | **Example 2:**
22 |
23 | ```
24 | Input: 1 1
25 | / \
26 | 2 2
27 |
28 | [1,2], [1,null,2]
29 |
30 | Output: false
31 | ```
32 |
33 | **Example 3:**
34 |
35 | ```
36 | Input: 1 1
37 | / \ / \
38 | 2 1 1 2
39 |
40 | [1,2,1], [1,1,2]
41 |
42 | Output: false
43 | ```
44 |
45 | **Tags:** Tree, Depth-first Search
46 |
47 |
48 | ## 思路
49 |
50 | 题意是比较两棵二叉树是否相同,那么我们就深搜比较各个节点即可。
51 |
52 | ```java
53 | /**
54 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
55 | * public class TreeNode {
56 | * int val;
57 | * TreeNode left;
58 | * TreeNode right;
59 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
60 | * }
61 | */
62 | class Solution {
63 | public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
64 | if (p == null && q == null) return true;
65 | if (p == null || q == null) return false;
66 | if (p.val == q.val) {
67 | return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
68 | }
69 | return false;
70 | }
71 | }
72 | ```
73 |
74 |
75 | ## 结语
76 |
77 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/same-tree
82 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/019/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Remove Nth Node From End of List][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a linked list, remove the *n*-th node from the end of list and return its head.
6 |
7 | **Example:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Given linked list: 1->2->3->4->5, and n = 2.
11 |
12 | After removing the second node from the end, the linked list becomes 1->2->3->5.
13 | ```
14 |
15 | **Note:**
16 |
17 | Given *n* will always be valid.
18 |
19 | **Follow up:**
20 |
21 | Could you do this in one pass?
22 |
23 | **Tags:** Linked List, Two Pointers
24 |
25 |
26 | ## 思路
27 |
28 | 题意是让你删除链表中的倒数第 n 个数,我的解法是利用双指针,这两个指针相差 n 个元素,当后面的指针扫到链表末尾的时候,自然它前面的那个指针所指向的下一个元素就是要删除的元素,即 `pre.next = pre.next.next;`,但是如果一开始后面的指针指向的为空,此时代表的意思就是要删除第一个元素,即 `head = head.next;`。
29 |
30 | ```java
31 | /**
32 | * Definition for singly-linked list.
33 | * public class ListNode {
34 | * int val;
35 | * ListNode next;
36 | * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
37 | * }
38 | */
39 | class Solution {
40 | public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
41 | ListNode pre = head;
42 | ListNode afterPreN = head;
43 | while (n-- != 0) {
44 | afterPreN = afterPreN.next;
45 | }
46 | if (afterPreN != null) {
47 | while (afterPreN.next != null) {
48 | pre = pre.next;
49 | afterPreN = afterPreN.next;
50 | }
51 | pre.next = pre.next.next;
52 | } else {
53 | head = head.next;
54 | }
55 | return head;
56 | }
57 | }
58 | ```
59 |
60 |
61 | ## 结语
62 |
63 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list
68 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_067/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._067;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/05/07
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
13 | StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
14 | int carry = 0, p1 = a.length() - 1, p2 = b.length() - 1;
15 | while (p1 >= 0 && p2 >= 0) {
16 | carry += a.charAt(p1--) - '0';
17 | carry += b.charAt(p2--) - '0';
18 | sb.insert(0, (char) (carry % 2 + '0'));
19 | carry >>= 1;
20 | }
21 | while (p1 >= 0) {
22 | carry += a.charAt(p1--) - '0';
23 | sb.insert(0, (char) (carry % 2 + '0'));
24 | carry >>= 1;
25 | }
26 | while (p2 >= 0) {
27 | carry += b.charAt(p2--) - '0';
28 | sb.insert(0, (char) (carry % 2 + '0'));
29 | carry >>= 1;
30 | }
31 | if (carry == 1) {
32 | sb.insert(0, '1');
33 | }
34 | return sb.toString();
35 | }
36 |
37 | // public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
38 | // StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
39 | // int carry = 0, p1 = a.length() - 1, p2 = b.length() - 1;
40 | // while (p1 >= 0 || p2 >= 0 || carry == 1) {
41 | // carry += p1 >= 0 ? a.charAt(p1--) - '0' : 0;
42 | // carry += p2 >= 0 ? b.charAt(p2--) - '0' : 0;
43 | // sb.insert(0, (char) (carry % 2 + '0'));
44 | // carry >>= 1;
45 | // }
46 | // return sb.print();
47 | // }
48 |
49 | public static void main(String[] args) {
50 | Solution solution = new Solution();
51 | System.out.println(solution.addBinary("11", "1"));
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/002/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Add Two Numbers][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | You are given two **non-empty** linked lists representing two non-negative integers. The digits are stored in **reverse order** and each of their nodes contain a single digit. Add the two numbers and return it as a linked list.
6 |
7 | You may assume the two numbers do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
8 |
9 | **Example**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Input: (2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
13 | Output: 7 -> 0 -> 8
14 | Explanation: 342 + 465 = 807.
15 | ```
16 |
17 | **Tags:** Linked List, Math
18 |
19 |
20 | ## 思路
21 |
22 | 题意我也是看了好久才看懂,就是以链表表示一个数,低位在前,高位在后,所以题中的例子就是 `342 + 465 = 807`,所以我们模拟计算即可。
23 |
24 | ```java
25 | /**
26 | * Definition for singly-linked list.
27 | * public class ListNode {
28 | * int val;
29 | * ListNode next;
30 | * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
31 | * }
32 | */
33 | class Solution {
34 | public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
35 | ListNode node = new ListNode(0);
36 | ListNode n1 = l1, n2 = l2, t = node;
37 | int sum = 0;
38 | while (n1 != null || n2 != null) {
39 | sum /= 10;
40 | if (n1 != null) {
41 | sum += n1.val;
42 | n1 = n1.next;
43 | }
44 | if (n2 != null) {
45 | sum += n2.val;
46 | n2 = n2.next;
47 | }
48 | t.next = new ListNode(sum % 10);
49 | t = t.next;
50 | }
51 | if (sum / 10 != 0) t.next = new ListNode(1);
52 | return node.next;
53 | }
54 | }
55 | ```
56 |
57 |
58 | ## 结语
59 |
60 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
61 |
62 |
63 |
64 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers
65 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_022/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._022;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.Collections;
5 | import java.util.HashMap;
6 | import java.util.List;
7 |
8 | /**
9 | *
10 | * author: Blankj
11 | * blog : http://blankj.com
12 | * time : 2018/01/30
13 | * desc :
14 | *
15 | */
16 | public class Solution {
17 | // public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
18 | // List list = new ArrayList<>();
19 | // helper(list, "", 0, n);
20 | // return list;
21 | // }
22 | //
23 | // private void helper(List list, String str, int rightNeed, int leftRest) {
24 | // if (rightNeed == 0 && leftRest == 0) {
25 | // list.add(str);
26 | // return;
27 | // }
28 | // if (rightNeed > 0) helper(list, str + ")", rightNeed - 1, leftRest);
29 | // if (leftRest > 0) helper(list, str + "(", rightNeed + 1, leftRest - 1);
30 | // }
31 |
32 | public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
33 | HashMap> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
34 | hashMap.put(0, Collections.singletonList(""));
35 | for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
36 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
37 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
38 | for (String fj : hashMap.get(j)) {
39 | for (String fi_j_1 : hashMap.get(i - j - 1)) {
40 | list.add("(" + fj + ")" + fi_j_1);// calculate f(i)
41 | }
42 | }
43 | }
44 | hashMap.put(i, list);
45 | }
46 | return hashMap.get(n);
47 | }
48 |
49 | public static void main(String[] args) {
50 | Solution solution = new Solution();
51 | System.out.println(solution.generateParenthesis(3));
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/016/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [3Sum Closest][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given an array `nums` of *n* integers and an integer `target`, find three integers in `nums` such that the sum is closest to `target`. Return the sum of the three integers. You may assume that each input would have exactly one solution.
6 |
7 | **Example:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Given array nums = [-1, 2, 1, -4], and target = 1.
11 |
12 | The sum that is closest to the target is 2. (-1 + 2 + 1 = 2).
13 | ```
14 |
15 | **Tags:** Array, Two Pointers
16 |
17 |
18 | ## 思路
19 |
20 | 题意是让你从数组中找出最接近 `target` 的三个数的和,该题和 [3Sum][015] 的思路基本一样,先对数组进行排序,然后遍历这个排序数组,用两个指针分别指向当前元素的下一个和数组尾部,判断三者的和与 `target` 的差值来移动两个指针,并更新其结果,当然,如果三者的和直接与 `target` 值相同,那么返回 `target` 结果即可。
21 |
22 | ```java
23 | public class Solution {
24 | public int threeSumClosest(int[] nums, int target) {
25 | int delta = 0x7fffffff, res = 0;
26 | Arrays.sort(nums);
27 | int len = nums.length - 2;
28 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
29 | int left = i + 1, right = nums.length - 1;
30 | while (left < right) {
31 | int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
32 | int curDelta = Math.abs(sum - target);
33 | if (curDelta == 0) return sum;
34 | if (curDelta < delta) {
35 | delta = curDelta;
36 | res = sum;
37 | }
38 | if (sum > target) --right;
39 | else ++left;
40 | }
41 | }
42 | return res;
43 | }
44 | }
45 | ```
46 |
47 |
48 | ## 结语
49 |
50 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 | [015]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode/blob/master/note/015/README.md
55 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum-closest
56 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/110/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Balanced Binary Tree][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a binary tree, determine if it is height-balanced.
6 |
7 | For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as:
8 |
9 | > a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of *every* node never differ by more than 1.
10 |
11 | **Example 1:**
12 |
13 | Given the following tree `[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]`:
14 |
15 | ```
16 | 3
17 | / \
18 | 9 20
19 | / \
20 | 15 7
21 | ```
22 |
23 | Return true.
24 | **Example 2:**
25 |
26 | Given the following tree `[1,2,2,3,3,null,null,4,4]`:
27 |
28 | ```
29 | 1
30 | / \
31 | 2 2
32 | / \
33 | 3 3
34 | / \
35 | 4 4
36 | ```
37 |
38 | Return false.
39 |
40 | **Tags:** Tree, Depth-first Search
41 |
42 |
43 | ## 思路
44 |
45 | 题意是判断一棵二叉树是否是高度平衡的,所谓二叉树高度平衡指的是二叉树的每个节点的两棵子树的高度差都不超过 1,那么我们只需计算左右子树的高度,判断其高度差是否不超过 1 即可,如果超过 1,就代表其不是高度平衡的,立即返回不是即可,我这里用返回 `-1` 代表不是。
46 |
47 | ```java
48 | /**
49 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
50 | * public class TreeNode {
51 | * int val;
52 | * TreeNode left;
53 | * TreeNode right;
54 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
55 | * }
56 | */
57 | class Solution {
58 | public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
59 | return helper(root) != -1;
60 | }
61 |
62 | private int helper(TreeNode node) {
63 | if (node == null) return 0;
64 | int l = helper(node.left);
65 | if (l == -1) return -1;
66 | int r = helper(node.right);
67 | if (r == -1) return -1;
68 | if (Math.abs(l - r) > 1) return -1;
69 | return 1 + Math.max(l, r);
70 | }
71 | }
72 | ```
73 |
74 |
75 | ## 结语
76 |
77 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree
82 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/easy/_101/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.easy._101;
2 |
3 |
4 | import com.blankj.structure.TreeNode;
5 |
6 | import java.util.LinkedList;
7 |
8 | /**
9 | *
10 | * author: Blankj
11 | * blog : http://blankj.com
12 | * time : 2017/10/09
13 | * desc :
14 | *
15 | */
16 | public class Solution {
17 | // public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
18 | // return root == null || helper(root.left, root.right);
19 | // }
20 | //
21 | // private boolean helper(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
22 | // if (left == null || right == null) return left == right;
23 | // if (left.val != right.val) return false;
24 | // return helper(left.left, right.right) && helper(left.right, right.left);
25 | // }
26 |
27 | public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
28 | if (root == null) return true;
29 | LinkedList q = new LinkedList<>();
30 | q.add(root.left);
31 | q.add(root.right);
32 | TreeNode left, right;
33 | while (q.size() > 1) {
34 | left = q.pop();
35 | right = q.pop();
36 | if (left == null && right == null) continue;
37 | if (left == null || right == null) return false;
38 | if (left.val != right.val) return false;
39 | q.add(left.left);
40 | q.add(right.right);
41 | q.add(left.right);
42 | q.add(right.left);
43 | }
44 | return true;
45 | }
46 |
47 | public static void main(String[] args) {
48 | Solution solution = new Solution();
49 | System.out.println(solution.isSymmetric(TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,3,4,4,3]")));
50 | System.out.println(solution.isSymmetric(TreeNode.createTestData("[1,2,2,null,3,null,3]")));
51 | System.out.println(solution.isSymmetric(TreeNode.createTestData("[9,-42,-42,null,76,76,null,null,13,null,13]")));
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/001/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Two Sum][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given an array of integers, return **indices** of the two numbers such that they add up to a specific target.
6 |
7 | You may assume that each input would have ***exactly*** one solution, and you may not use the same element twice.
8 |
9 | **Example:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Given nums = [2, 7, 11, 15], target = 9,
13 |
14 | Because nums[0] + nums[1] = 2 + 7 = 9,
15 | return [0, 1].
16 | ```
17 |
18 | **Tags:** Array, Hash Table
19 |
20 |
21 | ## 思路 0
22 |
23 | 题意是让你从给定的数组中找到两个元素的和为指定值的两个索引,最容易的当然是循环两次,复杂度为 `O(n^2)`,首次提交居然是 2ms,打败了 100% 的提交,谜一样的结果,之后再次提交就再也没跑到过 2ms 了。
24 |
25 | ```java
26 | class Solution {
27 | public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
28 | for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
29 | for (int j = i + 1; j < nums.length; ++j) {
30 | if (nums[i] + nums[j] == target) {
31 | return new int[]{i, j};
32 | }
33 | }
34 | }
35 | return null;
36 | }
37 | }
38 | ```
39 |
40 | ## 思路 1
41 |
42 | 利用 HashMap 作为存储,键为目标值减去当前元素值,索引为值,比如 `i = 0` 时,此时首先要判断 `nums[0] = 2` 是否在 map 中,如果不存在,那么插入键值对 `key = 9 - 2 = 7, value = 0`,之后当 `i = 1` 时,此时判断 `nums[1] = 7` 已存在于 map 中,那么取出该 `value = 0` 作为第一个返回值,当前 `i` 作为第二个返回值,具体代码如下所示。
43 |
44 | ```java
45 | class Solution {
46 | public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
47 | int len = nums.length;
48 | HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
49 | for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
50 | if (map.containsKey(nums[i])) {
51 | return new int[]{map.get(nums[i]), i};
52 | }
53 | map.put(target - nums[i], i);
54 | }
55 | return null;
56 | }
57 | }
58 | ```
59 |
60 |
61 | ## 结语
62 |
63 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
64 |
65 |
66 |
67 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/two-sum
68 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/033/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Search in Rotated Sorted Array][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Suppose an array sorted in ascending order is rotated at some pivot unknown to you beforehand.
6 |
7 | (i.e., `[0,1,2,4,5,6,7]` might become `[4,5,6,7,0,1,2]`).
8 |
9 | You are given a target value to search. If found in the array return its index, otherwise return `-1`.
10 |
11 | You may assume no duplicate exists in the array.
12 |
13 | Your algorithm's runtime complexity must be in the order of *O*(log *n*).
14 |
15 | **Example 1:**
16 |
17 | ```
18 | Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 0
19 | Output: 4
20 | ```
21 |
22 | **Example 2:**
23 |
24 | ```
25 | Input: nums = [4,5,6,7,0,1,2], target = 3
26 | Output: -1
27 | ```
28 |
29 | **Tags:** Arrays, Binary Search
30 |
31 |
32 | ## 思路
33 |
34 | 题意是让你从一个旋转过后的递增序列中寻找给定值,找到返回索引,找不到返回-1,我们在下面这组数据中寻找规律。
35 |
36 | ```
37 | 1 2 4 5 6 7 0
38 | 2 4 5 6 7 0 1
39 | 4 5 6 7 0 1 2
40 | 5 6 7 0 1 2 4
41 | 6 7 0 1 2 4 5
42 | 7 0 1 2 4 5 6
43 | ```
44 |
45 | 由于是旋转一次,所以肯定有一半及以上的序列仍然是具有递增性质的,我们观察到如果中间的数比左面的数大的话,那么左半部分序列是递增的,否则右半部分就是递增的,那么我们就可以确定给定值是否在递增序列中,从而决定取舍哪半边。
46 |
47 |
48 | ```java
49 | class Solution {
50 | public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
51 | int l = 0, r = nums.length - 1, mid;
52 | while (l <= r) {
53 | mid = l + r >>> 1;
54 | if (nums[mid] == target) return mid;
55 | else if (nums[mid] >= nums[l]) {
56 | if (nums[l] <= target && target < nums[mid]) r = mid - 1;
57 | else l = mid + 1;
58 | } else {
59 | if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[r]) l = mid + 1;
60 | else r = mid - 1;
61 | }
62 | }
63 | return -1;
64 | }
65 | }
66 | ```
67 |
68 |
69 | ## 结语
70 |
71 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array
76 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/122/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock II][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Say you have an array for which the *i*th element is the price of a given stock on day *i*.
6 |
7 | Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete as many transactions as you like (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock multiple times).
8 |
9 | **Note:** You may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (i.e., you must sell the stock before you buy again).
10 |
11 | **Example 1:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Input: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
15 | Output: 7
16 | Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 3 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
17 | Then buy on day 4 (price = 3) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-3 = 3.
18 | ```
19 |
20 | **Example 2:**
21 |
22 | ```
23 | Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
24 | Output: 4
25 | Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
26 | Note that you cannot buy on day 1, buy on day 2 and sell them later, as you are
27 | engaging multiple transactions at the same time. You must sell before buying again.
28 | ```
29 |
30 | **Example 3:**
31 |
32 | ```
33 | Input: [7,6,4,3,1]
34 | Output: 0
35 | Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
36 | ```
37 |
38 | **Tags:** Array, Greedy
39 |
40 |
41 | ## 思路
42 |
43 | 题意是给出一个数组代表每天的股票金额,在每天只能买或卖的情况下求出收益最高值,这...,这也太简单了吧,把所有相邻递增的值都加起来即可。
44 |
45 | ```java
46 | class Solution {
47 | public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
48 | int max = 0;
49 | for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; ++i) {
50 | if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1]) max += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
51 | }
52 | return max;
53 | }
54 | }
55 | ```
56 |
57 |
58 | ## 结语
59 |
60 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
61 |
62 |
63 |
64 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/best-time-to-buy-and-sell-stock-ii
65 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/020/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Valid Parentheses][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a string containing just the characters `'('`, `')'`, `'{'`, `'}'`, `'['` and `']'`, determine if the input string is valid.
6 |
7 | An input string is valid if:
8 |
9 | 1. Open brackets must be closed by the same type of brackets.
10 | 2. Open brackets must be closed in the correct order.
11 |
12 | Note that an empty string is also considered valid.
13 |
14 | **Example 1:**
15 |
16 | ```
17 | Input: "()"
18 | Output: true
19 | ```
20 |
21 | **Example 2:**
22 |
23 | ```
24 | Input: "()[]{}"
25 | Output: true
26 | ```
27 |
28 | **Example 3:**
29 |
30 | ```
31 | Input: "(]"
32 | Output: false
33 | ```
34 |
35 | **Example 4:**
36 |
37 | ```
38 | Input: "([)]"
39 | Output: false
40 | ```
41 |
42 | **Example 5:**
43 |
44 | ```
45 | Input: "{[]}"
46 | Output: true
47 | ```
48 |
49 | **Tags:** Stack, String
50 |
51 |
52 | ## 思路
53 |
54 | 题意是判断括号匹配是否正确,很明显,我们可以用栈来解决这个问题,当出现左括号的时候入栈,当遇到右括号时,判断栈顶的左括号是否何其匹配,不匹配的话直接返回 `false` 即可,最终判断是否空栈即可,这里我们可以用数组模拟栈的操作使其操作更快,有个细节注意下 `top = 1;`,从而省去了之后判空的操作和 `top - 1` 导致数组越界的错误。
55 |
56 | ```java
57 | class Solution {
58 | public boolean isValid(String s) {
59 | char[] stack = new char[s.length() + 1];
60 | int top = 1;
61 | for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
62 | if (c == '(' || c == '[' || c == '{') {
63 | stack[top++] = c;
64 | } else if (c == ')' && stack[--top] != '(') {
65 | return false;
66 | } else if (c == ']' && stack[--top] != '[') {
67 | return false;
68 | } else if (c == '}' && stack[--top] != '{') {
69 | return false;
70 | }
71 | }
72 | return top == 1;
73 | }
74 | }
75 | ```
76 |
77 |
78 | ## 结语
79 |
80 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
81 |
82 |
83 |
84 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/valid-parentheses
85 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
86 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/038/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Count and Say][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | The count-and-say sequence is the sequence of integers with the first five terms as following:
6 |
7 | ```
8 | 1. 1
9 | 2. 11
10 | 3. 21
11 | 4. 1211
12 | 5. 111221
13 | ```
14 |
15 | `1` is read off as `"one 1"` or `11`.
16 |
17 | `11` is read off as `"two 1s"` or `21`.
18 |
19 | `21` is read off as `"one 2`, then `one 1"` or `1211`.
20 |
21 | Given an integer *n*, generate the *n*th term of the count-and-say sequence.
22 |
23 | Note: Each term of the sequence of integers will be represented as a string.
24 |
25 | **Example 1:**
26 |
27 | ```
28 | Input: 1
29 | Output: "1"
30 | ```
31 |
32 | **Example 2:**
33 |
34 | ```
35 | Input: 4
36 | Output: "1211"
37 | ```
38 |
39 | **Tags:** String
40 |
41 |
42 | ## 思路
43 |
44 | 题意是数和说,根据如下序列 `1, 11, 21, 1211, 111221, ...`,求第 n 个数,规则很简单,就是数和说,数就是数这个数数字有几个,说就是说这个数,所以 `1` 就是 1 个 1:`11`,`11` 就是有 2 个 1:`21`,`21` 就是 1 个 2、1 个 1:`1211`,可想而知后面就是 `111221`,思路的话就是按这个逻辑模拟出来即可。
45 |
46 | ```java
47 | class Solution {
48 | public String countAndSay(int n) {
49 | String str = "1";
50 | while (--n > 0) {
51 | int times = 1;
52 | StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
53 | char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
54 | int len = chars.length;
55 | for (int j = 1; j < len; j++) {
56 | if (chars[j - 1] == chars[j]) {
57 | times++;
58 | } else {
59 | sb.append(times).append(chars[j - 1]);
60 | times = 1;
61 | }
62 | }
63 | str = sb.append(times).append(chars[len - 1]).toString();
64 | }
65 | return str;
66 | }
67 | }
68 | ```
69 |
70 |
71 | ## 结语
72 |
73 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/count-and-say
78 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/108/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Convert Sorted Array to Binary Search Tree][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given an array where elements are sorted in ascending order, convert it to a height balanced BST.
6 |
7 | For this problem, a height-balanced binary tree is defined as a binary tree in which the depth of the two subtrees of *every* node never differ by more than 1.
8 |
9 | **Example:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Given the sorted array: [-10,-3,0,5,9],
13 |
14 | One possible answer is: [0,-3,9,-10,null,5], which represents the following height balanced BST:
15 |
16 | 0
17 | / \
18 | -3 9
19 | / /
20 | -10 5
21 | ```
22 |
23 | **Tags:** Tree, Depth-first Search
24 |
25 |
26 | ## 思路
27 |
28 | 题意是把一个有序数组转化为一棵二叉搜索树,二叉搜索树具有以下性质:
29 |
30 | 1. 若任意节点的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根节点的值;
31 |
32 | 2. 若任意节点的右子树不空,则右子树上所有节点的值均大于它的根节点的值;
33 |
34 | 3. 任意节点的左、右子树也分别为二叉查找树;
35 |
36 | 4. 没有键值相等的节点。
37 |
38 | 所以我们可以用递归来构建一棵二叉搜索树,每次把数组分为两半,把数组中间的值作为其父节点,然后把数组的左右两部分继续构造其左右子树。
39 |
40 |
41 | ```java
42 | /**
43 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
44 | * public class TreeNode {
45 | * int val;
46 | * TreeNode left;
47 | * TreeNode right;
48 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
49 | * }
50 | */
51 | class Solution {
52 | public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
53 | if (nums == null || nums.length == 0) return null;
54 | return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
55 | }
56 |
57 | private TreeNode helper(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
58 | if (left > right) return null;
59 | int mid = (left + right) >>> 1;
60 | TreeNode node = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
61 | node.left = helper(nums, left, mid - 1);
62 | node.right = helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
63 | return node;
64 | }
65 | }
66 | ```
67 |
68 |
69 | ## 结语
70 |
71 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/convert-sorted-array-to-binary-search-tree
76 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/009/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Palindrome Number][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Determine whether an integer is a palindrome. An integer is a palindrome when it reads the same backward as forward.
6 |
7 | **Example 1:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input: 121
11 | Output: true
12 | ```
13 |
14 | **Example 2:**
15 |
16 | ```
17 | Input: -121
18 | Output: false
19 | Explanation: From left to right, it reads -121. From right to left, it becomes 121-. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
20 | ```
21 |
22 | **Example 3:**
23 |
24 | ```
25 | Input: 10
26 | Output: false
27 | Explanation: Reads 01 from right to left. Therefore it is not a palindrome.
28 | ```
29 |
30 | **Follow up:**
31 |
32 | Coud you solve it without converting the integer to a string?
33 |
34 | **Tags:** Math
35 |
36 |
37 | ## 思路 0
38 |
39 | 题意是判断一个有符号整型数是否是回文,也就是逆序过来的整数和原整数相同,首先负数肯定不是,接下来我们分析一下最普通的解法,就是直接算出他的回文数,然后和给定值比较即可。
40 |
41 | ```java
42 | class Solution {
43 | public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
44 | if (x < 0) return false;
45 | int copyX = x, reverse = 0;
46 | while (copyX > 0) {
47 | reverse = reverse * 10 + copyX % 10;
48 | copyX /= 10;
49 | }
50 | return x == reverse;
51 | }
52 | }
53 | ```
54 |
55 | ## 思路 1
56 |
57 | 好好思考下是否需要计算整个长度,比如 1234321,其实不然,我们只需要计算一半的长度即可,就是在计算过程中的那个逆序数比不断除 10 的数大就结束计算即可,但是这也带来了另一个问题,比如 10 的倍数的数 10010,它也会返回 `true`,所以我们需要对 10 的倍数的数再加个判断即可,代码如下所示。
58 |
59 | ```java
60 | class Solution {
61 | public boolean isPalindrome(int x) {
62 | if (x < 0 || (x != 0 && x % 10 == 0)) return false;
63 | int halfReverseX = 0;
64 | while (x > halfReverseX) {
65 | halfReverseX = halfReverseX * 10 + x % 10;
66 | x /= 10;
67 | }
68 | return halfReverseX == x || halfReverseX / 10 == x;
69 | }
70 | }
71 | ```
72 |
73 |
74 | ## 结语
75 |
76 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/palindrome-number
81 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_017/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._017;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Collections;
4 | import java.util.LinkedList;
5 | import java.util.List;
6 |
7 | /**
8 | *
9 | * author: Blankj
10 | * blog : http://blankj.com
11 | * time : 2017/10/15
12 | * desc :
13 | *
14 | */
15 | public class Solution {
16 | // private static String[] map = new String[]{"abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
17 | //
18 | // public List letterCombinations(String digits) {
19 | // if (digits.length() == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
20 | // List list = new ArrayList<>();
21 | // helper(list, digits, "");
22 | // return list;
23 | // }
24 | //
25 | // private void helper(List list, String digits, String ans) {
26 | // if (ans.length() == digits.length()) {
27 | // list.add(ans);
28 | // return;
29 | // }
30 | // for (char c : map[digits.charAt(ans.length()) - '2'].toCharArray()) {
31 | // helper(list, digits, ans + c);
32 | // }
33 | // }
34 |
35 | private static String[] map = new String[]{"abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
36 |
37 | public List letterCombinations(String digits) {
38 | if (digits.length() == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
39 | LinkedList list = new LinkedList<>();
40 | list.add("");
41 | char[] charArray = digits.toCharArray();
42 | for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {
43 | char c = charArray[i];
44 |
45 | while (list.getFirst().length() == i) {
46 | String pop = list.removeFirst();
47 | for (char v : map[c - '2'].toCharArray()) {
48 | list.addLast(pop + v);
49 | }
50 | }
51 | }
52 | return list;
53 | }
54 |
55 | public static void main(String[] args) {
56 | Solution solution = new Solution();
57 | System.out.println(solution.letterCombinations("23"));
58 | }
59 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/015/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [3Sum][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given an array `nums` of *n* integers, are there elements *a*, *b*, *c* in `nums` such that *a* + *b* + *c* = 0? Find all unique triplets in the array which gives the sum of zero.
6 |
7 | **Note:**
8 |
9 | The solution set must not contain duplicate triplets.
10 |
11 | **Example:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Given array nums = [-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4],
15 |
16 | A solution set is:
17 | [
18 | [-1, 0, 1],
19 | [-1, -1, 2]
20 | ]
21 | ```
22 |
23 | **Tags:** Array, Two Pointers
24 |
25 |
26 | ## 思路
27 |
28 | 题意是让你从数组中找出所有三个和为 0 的元素构成的非重复序列,这样的话我们可以把数组先做下排序,然后遍历这个排序数组,用两个指针分别指向当前元素的下一个和数组尾部,判断三者的和与 0 的大小来移动两个指针,其中细节操作就是优化和去重。
29 |
30 | ```java
31 | class Solution {
32 | public List> threeSum(int[] nums) {
33 | List> list = new ArrayList<>();
34 | int len = nums.length;
35 | if (len < 3) return list;
36 | Arrays.sort(nums);
37 | int max = nums[len - 1];
38 | if (max < 0) return list;
39 | for (int i = 0; i < len - 2; ) {
40 | if (nums[i] > 0) break;
41 | if (nums[i] + 2 * max < 0) {
42 | while (nums[i] == nums[++i] && i < len - 2) ;
43 | continue;
44 | }
45 | int left = i + 1, right = len - 1;
46 | while (left < right) {
47 | int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right];
48 | if (sum == 0) {
49 | list.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[left], nums[right]));
50 | while (nums[left] == nums[++left] && left < right) ;
51 | while (nums[right] == nums[--right] && left < right) ;
52 | } else if (sum < 0) ++left;
53 | else --right;
54 | }
55 | while (nums[i] == nums[++i] && i < len - 2) ;
56 | }
57 | return list;
58 | }
59 | }
60 | ```
61 |
62 |
63 | ## 结语
64 |
65 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
66 |
67 |
68 |
69 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/3sum
70 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_006/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._006;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/12/11
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | class Solution {
12 |
13 | // public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
14 | // if (numRows <= 1) return s;
15 | // int len = s.length();
16 | // char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
17 | // int cycle = 2 * (numRows - 1);
18 | // StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
19 | // for (int j = 0; j < len; j += cycle) {
20 | // sb.append(chars[j]);
21 | // }
22 | // for (int i = 1; i < numRows - 1; i++) {
23 | // int step = 2 * i;
24 | // for (int j = i; j < len; j += step) {
25 | // sb.append(chars[j]);
26 | // step = cycle - step;
27 | // }
28 | // }
29 | // for (int j = numRows - 1; j < len; j += cycle) {
30 | // sb.append(chars[j]);
31 | // }
32 | // return sb.toString();
33 | // }
34 |
35 | public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
36 | if (numRows <= 1) return s;
37 | int len = s.length();
38 | char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
39 | StringBuilder[] sbs = new StringBuilder[numRows];
40 | for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
41 | sbs[i] = new StringBuilder();
42 | }
43 | int i = 0;
44 | while (i < len) {
45 | for (int j = 0; j < numRows && i < len; ++j) {
46 | sbs[j].append(chars[i++]);
47 | }
48 | for (int j = numRows - 2; j >= 1 && i < len; --j) {
49 | sbs[j].append(chars[i++]);
50 | }
51 | }
52 | for (i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
53 | sbs[0].append(sbs[i]);
54 | }
55 | return sbs[0].toString();
56 | }
57 |
58 | public static void main(String[] args) {
59 | Solution solution = new Solution();
60 | System.out.println(solution.convert("PAYPALISHIRING", 3));// PAHNAPLSIIGYIR
61 | System.out.println(solution.convert("ABCD", 4));
62 | }
63 | }
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/043/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Multiply Strings][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | 1. Given two non-negative integers `num1` and `num2` represented as strings, return the product of `num1` and `num2`, also represented as a string.
6 |
7 | **Example 1:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input: num1 = "2", num2 = "3"
11 | Output: "6"
12 | ```
13 |
14 | **Example 2:**
15 |
16 | ```
17 | Input: num1 = "123", num2 = "456"
18 | Output: "56088"
19 | ```
20 |
21 | **Note:**
22 |
23 | 1. The length of both `num1` and `num2` is < 110.
24 | 2. Both `num1` and `num2` contain only digits `0-9`.
25 | 3. Both `num1` and `num2` do not contain any leading zero, except the number 0 itself.
26 | 4. You **must not use any built-in BigInteger library** or **convert the inputs to integer** directly.
27 |
28 | **Tags:** Math, String
29 |
30 |
31 | ## 思路
32 |
33 | 题意是让你计算两个非负字符串的乘积,我们模拟小学数学的方式来做,一位一位模拟计算,再各位累加。
34 |
35 | ```java
36 | class Solution {
37 | public String multiply(String num1, String num2) {
38 | if (num1.equals("0") || num2.equals("0")) return "0";
39 | int l1 = num1.length(), l2 = num2.length(), l = l1 + l2;
40 | char[] ans = new char[l];
41 | char[] c1 = num1.toCharArray();
42 | char[] c2 = num2.toCharArray();
43 | for (int i = l1 - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
44 | int c = c1[i] - '0';
45 | for (int j = l2 - 1; j >= 0; --j) {
46 | ans[i + j + 1] += c * (c2[j] - '0');
47 | }
48 | }
49 | for (int i = l - 1; i > 0; --i) {
50 | if (ans[i] > 9) {
51 | ans[i - 1] += ans[i] / 10;
52 | ans[i] %= 10;
53 | }
54 | }
55 | StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
56 | int i = 0;
57 | for (; ; ++i) if (ans[i] != 0) break;
58 | for (; i < ans.length; ++i) sb.append((char) (ans[i] + '0'));
59 | return sb.toString();
60 | }
61 | }
62 | ```
63 |
64 |
65 | ## 结语
66 |
67 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
68 |
69 |
70 |
71 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/multiply-strings
72 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/024/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Swap Nodes in Pairs][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a linked list, swap every two adjacent nodes and return its head.
6 |
7 | **Example:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Given 1->2->3->4, you should return the list as 2->1->4->3.
11 | ```
12 |
13 | **Note:**
14 |
15 | - Your algorithm should use only constant extra space.
16 | - You may **not** modify the values in the list's nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
17 |
18 | **Tags:** Linked List
19 |
20 |
21 | ## 思路 0
22 |
23 | 题意是让你交换链表中相邻的两个节点,最终返回交换后链表的头,限定你空间复杂度为 O(1)。我们可以用递归来算出子集合的结果,递归的终点就是指针指到链表末少于两个元素时,如果不是终点,那么我们就对其两节点进行交换,这里我们需要一个临时节点来作为交换桥梁,就不多说了。
24 |
25 | ```java
26 | /**
27 | * Definition for singly-linked list.
28 | * public class ListNode {
29 | * int val;
30 | * ListNode next;
31 | * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
32 | * }
33 | */
34 | class Solution {
35 | public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
36 | if (head == null || head.next == null) return head;
37 | ListNode node = head.next;
38 | head.next = swapPairs(node.next);
39 | node.next = head;
40 | return node;
41 | }
42 | }
43 | ```
44 |
45 |
46 | ## 思路 1
47 |
48 | 另一种实现方式就是用循环来实现了,两两交换节点,也需要一个临时节点来作为交换桥梁,直到当前指针指到链表末少于两个元素时停止,代码很简单,如下所示。
49 |
50 | ```java
51 | /**
52 | * Definition for singly-linked list.
53 | * public class ListNode {
54 | * int val;
55 | * ListNode next;
56 | * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
57 | * }
58 | */
59 | class Solution {
60 | public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
61 | ListNode preHead = new ListNode(0), cur = preHead;
62 | preHead.next = head;
63 | while (cur.next != null && cur.next.next != null) {
64 | ListNode temp = cur.next.next;
65 | cur.next.next = temp.next;
66 | temp.next = cur.next;
67 | cur.next = temp;
68 | cur = cur.next.next;
69 | }
70 | return preHead.next;
71 | }
72 | }
73 | ```
74 |
75 |
76 | ## 结语
77 |
78 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
79 |
80 |
81 |
82 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/swap-nodes-in-pairs
83 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
84 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/056/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Merge Intervals][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a collection of intervals, merge all overlapping intervals.
6 |
7 | **Example 1:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input: [[1,3],[2,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
11 | Output: [[1,6],[8,10],[15,18]]
12 | Explanation: Since intervals [1,3] and [2,6] overlaps, merge them into [1,6].
13 | ```
14 |
15 | **Example 2:**
16 |
17 | ```
18 | Input: [[1,4],[4,5]]
19 | Output: [[1,5]]
20 | Explanation: Intervals [1,4] and [4,5] are considerred overlapping.
21 | ```
22 |
23 | **Tags:** Array, Sort
24 |
25 |
26 | ## 思路
27 |
28 | 题意是给你一组区间,让你把区间合并成没有交集的一组区间。我们可以把区间按 `start` 进行排序,然后遍历排序后的区间,如果当前的 `start` 小于前者的 `end`,那么说明这两个存在交集,我们取两者中较大的 `end` 即可;否则的话直接插入到结果序列中即可。
29 |
30 | ```java
31 | /**
32 | * Definition for an interval.
33 | * public class Interval {
34 | * int start;
35 | * int end;
36 | * Interval() { start = 0; end = 0; }
37 | * Interval(int s, int e) { start = s; end = e; }
38 | * }
39 | */
40 | class Solution {
41 | public List merge(List intervals) {
42 | if (intervals == null || intervals.size() <= 1) return intervals;
43 | intervals.sort(new Comparator() {
44 | @Override
45 | public int compare(Interval o1, Interval o2) {
46 | if (o1.start < o2.start) return -1;
47 | if (o1.start > o2.start) return 1;
48 | return 0;
49 | }
50 | });
51 | List ans = new ArrayList<>();
52 | int start = intervals.get(0).start;
53 | int end = intervals.get(0).end;
54 | for (Interval interval : intervals) {
55 | if (interval.start <= end) {
56 | end = Math.max(end, interval.end);
57 | } else {
58 | ans.add(new Interval(start, end));
59 | start = interval.start;
60 | end = interval.end;
61 | }
62 | }
63 | ans.add(new Interval(start, end));
64 | return ans;
65 | }
66 | }
67 | ```
68 |
69 |
70 | ## 结语
71 |
72 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-intervals
77 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/medium/_005/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.medium._005;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/11/04
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | // int st, end;
13 | //
14 | // public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
15 | //// st = 0;
16 | //// end = 0;
17 | // int len = s.length();
18 | // if (len <= 1) return s;
19 | // char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
20 | // for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
21 | // helper(chars, i, i);
22 | // helper(chars, i, i + 1);
23 | // }
24 | // return s.substring(st, end + 1);
25 | // }
26 | //
27 | // private void helper(char[] chars, int l, int r) {
28 | // while (l >= 0 && r < chars.length && chars[l] == chars[r]) {
29 | // --l;
30 | // ++r;
31 | // }
32 | // if (end - st < r - l - 2) {
33 | // st = l + 1;
34 | // end = r - 1;
35 | // }
36 | // }
37 |
38 | // public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
39 | // int len = s.length();
40 | // if (len <= 1) return s;
41 | // int st = 0, end = 0;
42 | // char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
43 | // boolean[][] dp = new boolean[len][len];
44 | // for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
45 | // dp[i][i] = true;
46 | // for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
47 | // if (j + 1 == i) {
48 | // dp[j][i] = chars[j] == chars[i];
49 | // } else {
50 | // dp[j][i] = dp[j + 1][i - 1] && chars[j] == chars[i];
51 | // }
52 | // if (dp[j][i] && i - j > end - st) {
53 | // st = j;
54 | // end = i;
55 | // }
56 | // }
57 | // }
58 | // return s.substring(st, end + 1);
59 | // }
60 |
61 | public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
62 |
63 | return s;
64 | }
65 |
66 | public static void main(String[] args) {
67 | Solution solution = new Solution();
68 | System.out.println(solution.longestPalindrome("babad"));
69 | System.out.println(solution.longestPalindrome("cbbd"));
70 |
71 | }
72 | }
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/hard/_068/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.hard._068;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.List;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | *
8 | * author: Blankj
9 | * blog : http://blankj.com
10 | * time : 2017/11/01
11 | * desc :
12 | *
13 | */
14 | public class Solution {
15 |
16 | public List fullJustify(String[] words, int maxWidth) {
17 | int len = words.length;
18 | List ans = new ArrayList<>();
19 | StringBuilder spaces = new StringBuilder();
20 | for (int i = 0; i < maxWidth; ++i) {
21 | spaces.append(" ");
22 | }
23 | int curLen = -1, start = 0;
24 | for (int i = 0; i < len; ++i) {
25 | if (curLen + words[i].length() + 1 <= maxWidth) {
26 | curLen += words[i].length() + 1;
27 | } else {
28 | StringBuilder sub = new StringBuilder(words[start]);
29 | int rest = maxWidth - curLen;
30 | int l = i - start - 1;
31 | if (l <= 0) {
32 | sub.append(spaces.substring(0, rest));
33 | } else {
34 | int m = rest / l + 1;
35 | int mod = rest % l;
36 | for (int j = start + 1; j < i; ++j) {
37 | if (mod-- > 0) {
38 | sub.append(spaces.substring(0, m + 1)).append(words[j]);
39 | } else {
40 | sub.append(spaces.substring(0, m)).append(words[j]);
41 | }
42 | }
43 | }
44 | ans.add(sub.toString());
45 | start = i;
46 | curLen = words[i].length();
47 | }
48 | }
49 | StringBuilder sub = new StringBuilder(words[start]);
50 | for (int i = start + 1; i < len; ++i) {
51 | sub.append(" ").append(words[i]);
52 | }
53 | ans.add(sub + spaces.substring(0, maxWidth - sub.length()));
54 | return ans;
55 | }
56 |
57 | public static void main(String[] args) {
58 | Solution solution = new Solution();
59 | System.out.println(solution.fullJustify(new String[]{"This", "is", "an", "example", "of", "text", "justification."}, 16));
60 | }
61 | }
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/057/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Insert Interval][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a set of *non-overlapping* intervals, insert a new interval into the intervals (merge if necessary).
6 |
7 | You may assume that the intervals were initially sorted according to their start times.
8 |
9 | **Example 1:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Input: intervals = [[1,3],[6,9]], newInterval = [2,5]
13 | Output: [[1,5],[6,9]]
14 | ```
15 |
16 | **Example 2:**
17 |
18 | ```
19 | Input: intervals = [[1,2],[3,5],[6,7],[8,10],[12,16]], newInterval = [4,8]
20 | Output: [[1,2],[3,10],[12,16]]
21 | Explanation: Because the new interval [4,8] overlaps with [3,5],[6,7],[8,10].
22 | ```
23 |
24 | **Tags:** Array, Sort
25 |
26 |
27 | ## 思路
28 |
29 | 题意是给你一组有序区间,和一个待插入区间,让你待插入区间插入到前面的区间中,我们分三步走:
30 |
31 | 1. 首先把有序区间中小于待插入区间的部分加入到结果中;
32 |
33 | 2. 其次是插入待插入区间,如果有交集的话取两者交集的端点值;
34 |
35 | 3. 最后把有序区间中大于待插入区间的部分加入到结果中;
36 |
37 | ```java
38 | /**
39 | * Definition for an interval.
40 | * public class Interval {
41 | * int start;
42 | * int end;
43 | * Interval() { start = 0; end = 0; }
44 | * Interval(int s, int e) { start = s; end = e; }
45 | * }
46 | */
47 | class Solution {
48 | public List insert(List intervals, Interval newInterval) {
49 | if (intervals.isEmpty()) return Collections.singletonList(newInterval);
50 | List ans = new ArrayList<>();
51 | int i = 0, len = intervals.size();
52 | for (; i < len; ++i) {
53 | Interval interval = intervals.get(i);
54 | if (interval.end < newInterval.start) ans.add(interval);
55 | else break;
56 | }
57 | for (; i < len; ++i) {
58 | Interval interval = intervals.get(i);
59 | if (interval.start <= newInterval.end) {
60 | newInterval.start = Math.min(newInterval.start, interval.start);
61 | newInterval.end = Math.max(newInterval.end, interval.end);
62 | } else break;
63 | }
64 | ans.add(newInterval);
65 | for (; i < len; ++i) {
66 | ans.add(intervals.get(i));
67 | }
68 | return ans;
69 | }
70 | }
71 | ```
72 |
73 |
74 | ## 结语
75 |
76 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/insert-interval
81 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/554/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Brick Wall][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | There is a brick wall in front of you. The wall is rectangular and has several rows of bricks. The bricks have the same height but different width. You want to draw a vertical line from the **top** to the **bottom** and cross the **least** bricks.
6 |
7 | The brick wall is represented by a list of rows. Each row is a list of integers representing the width of each brick in this row from left to right.
8 |
9 | If your line go through the edge of a brick, then the brick is not considered as crossed. You need to find out how to draw the line to cross the least bricks and return the number of crossed bricks.
10 |
11 | **You cannot draw a line just along one of the two vertical edges of the wall, in which case the line will obviously cross no bricks.**
12 |
13 | **Example:**
14 |
15 | ```
16 | Input:
17 | [[1,2,2,1],
18 | [3,1,2],
19 | [1,3,2],
20 | [2,4],
21 | [3,1,2],
22 | [1,3,1,1]]
23 | Output: 2
24 | ```
25 |
26 | Explanation:
27 | 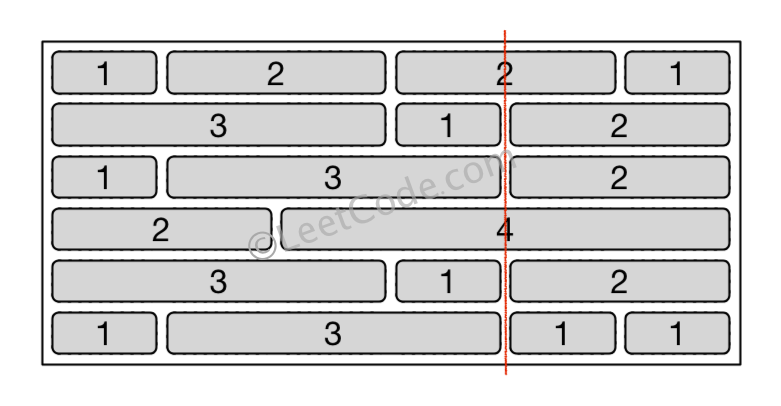
28 |
29 | **Note:**
30 |
31 | 1. The width sum of bricks in different rows are the same and won't exceed INT_MAX.
32 |
33 | 2. The number of bricks in each row is in range [1,10,000]. The height of wall is in range [1,10,000]. Total number of bricks of the wall won't exceed 20,000.
34 |
35 | **Tags:** Hash Table
36 |
37 |
38 | ## 思路
39 |
40 | 题意根据图示已经描述得很清楚了,就是在从底部到顶部,求最少交叉的数量,我们可以把每堵墙可以穿过的地方保存到哈希表中,每次遇到哈希表中的值加一,代表就是这条路不用交叉的数量,最终我们可以算出不用交叉的最大值,让总墙数减去其值就是最少交叉的数量。
41 |
42 | ```java
43 | class Solution {
44 | public int leastBricks(List> wall) {
45 | Map map = new HashMap<>();
46 | int width = 0, max = 0;
47 | for (List sub : wall) {
48 | int p = 0;
49 | for (int i = 0, len = sub.size() - 1; i < len; ++i) {
50 | p += sub.get(i);
51 | Integer v = map.get(p);
52 | map.put(p, (v == null ? 0 : v) + 1);
53 | }
54 | }
55 | for (Integer integer : map.values()) {
56 | if (integer > max) max = integer;
57 | }
58 | return wall.size() - max;
59 | }
60 | }
61 | ```
62 |
63 |
64 | ## 结语
65 |
66 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
67 |
68 |
69 |
70 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/brick-wall
71 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/053/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Maximum Subarray][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given an integer array `nums`, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return its sum.
6 |
7 | **Example:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
11 | Output: 6
12 | Explanation: [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
13 | ```
14 |
15 | **Follow up:**
16 |
17 | If you have figured out the O(*n*) solution, try coding another solution using the divide and conquer approach, which is more subtle.
18 |
19 | **Tags:** Array, Divide and Conquer, Dynamic Programming
20 |
21 |
22 | ## 思路 0
23 |
24 | 题意是求数组中子数组的最大和,这种最优问题一般第一时间想到的就是动态规划,我们可以这样想,当部分序列和大于零的话就一直加下一个元素即可,并和当前最大值进行比较,如果出现部分序列小于零的情况,那肯定就是从当前元素算起。其转移方程就是 `dp[i] = nums[i] + (dp[i - 1] > 0 ? dp[i - 1] : 0);`,由于我们不需要保留 dp 状态,故可以优化空间复杂度为 1,即 `dp = nums[i] + (dp > 0 ? dp : 0);`。
25 |
26 | ```java
27 | class Solution {
28 | public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
29 | int len = nums.length, dp = nums[0], max = dp;
30 | for (int i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
31 | dp = nums[i] + (dp > 0 ? dp : 0);
32 | if (dp > max) max = dp;
33 | }
34 | return max;
35 | }
36 | }
37 | ```
38 |
39 | ## 思路 1
40 |
41 | 题目也给了我们另一种思路,就是分治,所谓分治就是把问题分割成更小的,最后再合并即可,我们把 `nums` 一分为二先,那么就有两种情况,一种最大序列包括中间的值,一种就是不包括,也就是在左边或者右边;当最大序列在中间的时候那我们就把它两侧的最大和算出即可;当在两侧的话就继续分治即可。
42 |
43 | ```java
44 | class Solution {
45 | public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
46 | return helper(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
47 | }
48 |
49 | private int helper(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
50 | if (left >= right) return nums[left];
51 | int mid = (left + right) >> 1;
52 | int leftAns = helper(nums, left, mid);
53 | int rightAns = helper(nums, mid + 1, right);
54 | int leftMax = nums[mid], rightMax = nums[mid + 1];
55 | int temp = 0;
56 | for (int i = mid; i >= left; --i) {
57 | temp += nums[i];
58 | if (temp > leftMax) leftMax = temp;
59 | }
60 | temp = 0;
61 | for (int i = mid + 1; i <= right; ++i) {
62 | temp += nums[i];
63 | if (temp > rightMax) rightMax = temp;
64 | }
65 | return Math.max(Math.max(leftAns, rightAns), leftMax + rightMax);
66 | }
67 | }
68 | ```
69 |
70 |
71 | ## 结语
72 |
73 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/maximum-subarray
78 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
79 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/026/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Remove Duplicates from Sorted Array][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a sorted array *nums*, remove the duplicates [**in-place**](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm) such that each element appear only *once* and return the new length.
6 |
7 | Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by **modifying the input array [in-place](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm)** with O(1) extra memory.
8 |
9 | **Example 1:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | Given nums = [1,1,2],
13 |
14 | Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 1 and 2 respectively.
15 |
16 | It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
17 | ```
18 |
19 | **Example 2:**
20 |
21 | ```
22 | Given nums = [0,0,1,1,1,2,2,3,3,4],
23 |
24 | Your function should return length = 5, with the first five elements of nums being modified to 0, 1, 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
25 |
26 | It doesn't matter what values are set beyond the returned length.
27 | ```
28 |
29 | **Clarification:**
30 |
31 | Confused why the returned value is an integer but your answer is an array?
32 |
33 | Note that the input array is passed in by **reference**, which means modification to the input array will be known to the caller as well.
34 |
35 | Internally you can think of this:
36 |
37 | ```
38 | // nums is passed in by reference. (i.e., without making a copy)
39 | int len = removeDuplicates(nums);
40 |
41 | // any modification to nums in your function would be known by the caller.
42 | // using the length returned by your function, it prints the first len elements.
43 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
44 | print(nums[i]);
45 | }
46 | ```
47 |
48 | **Tags:** Array, Two Pointers
49 |
50 |
51 | ## 思路
52 |
53 | 题意是让你从一个有序的数组中移除重复的元素,并返回之后数组的长度。我的思路是判断长度小于等于 1 的话直接返回原长度即可,否则的话遍历一遍数组,用一个 `tail` 变量指向尾部,如果后面的元素和前面的元素不同,就让 `tail` 变量加一,最后返回 `tail` 即可。
54 |
55 | ```java
56 | class Solution {
57 | public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
58 | int len = nums.length;
59 | if (len <= 1) return len;
60 | int tail = 1;
61 | for (int i = 1; i < len; ++i) {
62 | if (nums[i - 1] != nums[i]) {
63 | nums[tail++] = nums[i];
64 | }
65 | }
66 | return tail;
67 | }
68 | }
69 | ```
70 |
71 |
72 | ## 结语
73 |
74 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
75 |
76 |
77 |
78 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-array
79 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
80 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/111/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Minimum Depth of Binary Tree][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a binary tree, find its minimum depth.
6 |
7 | The minimum depth is the number of nodes along the shortest path from the root node down to the nearest leaf node.
8 |
9 | **Note:** A leaf is a node with no children.
10 |
11 | **Example:**
12 |
13 | Given binary tree `[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]`,
14 |
15 | ```
16 | 3
17 | / \
18 | 9 20
19 | / \
20 | 15 7
21 | ```
22 |
23 | return its minimum depth = 2.
24 |
25 | **Tags:** Tree, Depth-first Search, Breadth-first Search
26 |
27 |
28 | ## 思路 0
29 |
30 | 题意是查找二叉树的最小深度,也就是找到从根结点到叶子节点的最小深度,最容易想到的当然是深搜,如果节点的左右深度都不是 0 的话,说明该节点含有左右子树,所以它的最小高度就是 1 加上其左右子树高度较小者,否则如果左子树为空或者右子树为空或者两者都为空,那么就是 1 加上非空子树高度。
31 |
32 | ```java
33 | /**
34 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
35 | * public class TreeNode {
36 | * int val;
37 | * TreeNode left;
38 | * TreeNode right;
39 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
40 | * }
41 | */
42 | class Solution {
43 | public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
44 | if (root == null) return 0;
45 | int l = minDepth(root.left);
46 | int r = minDepth(root.right);
47 | if (l != 0 && r != 0) return 1 + Math.min(l, r);
48 | return l + r + 1;
49 | }
50 | }
51 | ```
52 |
53 | ## 思路 1
54 |
55 | 第二种思路就是利用宽搜了,搜索到该层有叶子节点,那就返回该层宽度即可。
56 |
57 | ```java
58 | /**
59 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
60 | * public class TreeNode {
61 | * int val;
62 | * TreeNode left;
63 | * TreeNode right;
64 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
65 | * }
66 | */
67 | class Solution {
68 | public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
69 | if (root == null) return 0;
70 | LinkedList q = new LinkedList<>();
71 | q.add(root);
72 | int ans = 1;
73 | while (!q.isEmpty()) {
74 | int size = q.size();
75 | for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
76 | TreeNode node = q.remove();
77 | if (node.left == null && node.right == null) {
78 | return ans;
79 | }
80 | if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left);
81 | if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right);
82 | }
83 | ++ans;
84 | }
85 | return 520;
86 | }
87 | }
88 | ```
89 |
90 |
91 | ## 结语
92 |
93 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
94 |
95 |
96 |
97 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree
98 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/027/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Remove Element][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given an array *nums* and a value *val*, remove all instances of that value [**in-place**](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm) and return the new length.
6 |
7 | Do not allocate extra space for another array, you must do this by **modifying the input array [in-place](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/In-place_algorithm) ** with O(1) extra memory.
8 |
9 | The order of elements can be changed. It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the new length.
10 |
11 | **Example 1:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Given nums = [3,2,2,3], val = 3,
15 |
16 | Your function should return length = 2, with the first two elements of nums being 2.
17 |
18 | It doesn't matter what you leave beyond the returned length.
19 | ```
20 |
21 | **Example 2:**
22 |
23 | ```
24 | Given nums = [0,1,2,2,3,0,4,2], val = 2,
25 |
26 | Your function should return length = 5, with the first five elements of nums containing 0, 1, 3, 0, and 4.
27 |
28 | Note that the order of those five elements can be arbitrary.
29 |
30 | It doesn't matter what values are set beyond the returned length.
31 | ```
32 |
33 | **Clarification:**
34 |
35 | Confused why the returned value is an integer but your answer is an array?
36 |
37 | Note that the input array is passed in by **reference**, which means modification to the input array will be known to the caller as well.
38 |
39 | Internally you can think of this:
40 |
41 | ```
42 | // nums is passed in by reference. (i.e., without making a copy)
43 | int len = removeElement(nums, val);
44 |
45 | // any modification to nums in your function would be known by the caller.
46 | // using the length returned by your function, it prints the first len elements.
47 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
48 | print(nums[i]);
49 | }
50 | ```
51 |
52 | **Tags:** Array, Two Pointers
53 |
54 |
55 | ## 思路
56 |
57 | 题意是移除数组中值等于 `val` 的元素,并返回之后数组的长度,并且题目中指定空间复杂度为 O(1),我的思路是用 `tail` 标记尾部,遍历该数组时当索引元素不等于 `val` 时,`tail` 加一,尾部指向当前元素,最后返回 `tail` 即可。
58 |
59 | ```java
60 | class Solution {
61 | public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
62 | int tail = 0;
63 | for (int i = 0, len = nums.length; i < len; ++i) {
64 | if (nums[i] != val) {
65 | nums[tail++] = nums[i];
66 | }
67 | }
68 | return tail;
69 | }
70 | }
71 | ```
72 |
73 |
74 | ## 结语
75 |
76 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
77 |
78 |
79 |
80 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/remove-element
81 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/hard/_023/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.hard._023;
2 |
3 | import com.blankj.structure.ListNode;
4 |
5 | import java.util.Comparator;
6 | import java.util.PriorityQueue;
7 |
8 | /**
9 | *
10 | * author: Blankj
11 | * blog : http://blankj.com
12 | * time : 2017/10/15
13 | * desc :
14 | *
15 | */
16 | public class Solution {
17 | // public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
18 | // if (lists.length == 0) return null;
19 | // return helper(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
20 | // }
21 | //
22 | // private ListNode helper(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {
23 | // if (left >= right) return lists[left];
24 | // int mid = left + right >>> 1;
25 | // ListNode l0 = helper(lists, left, mid);
26 | // ListNode l1 = helper(lists, mid + 1, right);
27 | // return merge2Lists(l0, l1);
28 | // }
29 | //
30 | // private ListNode merge2Lists(ListNode l0, ListNode l1) {
31 | // ListNode node = new ListNode(0), tmp = node;
32 | // while (l0 != null && l1 != null) {
33 | // if (l0.val <= l1.val) {
34 | // tmp.next = new ListNode(l0.val);
35 | // l0 = l0.next;
36 | // } else {
37 | // tmp.next = new ListNode(l1.val);
38 | // l1 = l1.next;
39 | // }
40 | // tmp = tmp.next;
41 | // }
42 | // tmp.next = l0 != null ? l0 : l1;
43 | // return node.next;
44 | // }
45 |
46 | public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
47 | if (lists.length == 0) return null;
48 | PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue<>(lists.length, new Comparator() {
49 | @Override
50 | public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2) {
51 | if (o1.val < o2.val) return -1;
52 | else if (o1.val == o2.val) return 0;
53 | else return 1;
54 | }
55 | });
56 | ListNode node = new ListNode(0), tmp = node;
57 | for (ListNode l : lists) {
58 | if (l != null) queue.add(l);
59 | }
60 | while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
61 | tmp.next = queue.poll();
62 | tmp = tmp.next;
63 | if (tmp.next != null) queue.add(tmp.next);
64 | }
65 | return node.next;
66 | }
67 |
68 | public static void main(String[] args) {
69 | Solution solution = new Solution();
70 | ListNode.print(solution.mergeKLists(new ListNode[]{
71 | ListNode.createTestData("[1,3,5,7]"),
72 | ListNode.createTestData("[2,4,6]")
73 | }));
74 | }
75 | }
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/022/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Generate Parentheses][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given *n* pairs of parentheses, write a function to generate all combinations of well-formed parentheses.
6 |
7 | For example, given *n* = 3, a solution set is:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | [
11 | "((()))",
12 | "(()())",
13 | "(())()",
14 | "()(())",
15 | "()()()"
16 | ]
17 | ```
18 |
19 | **Tags:** String, Backtracking
20 |
21 |
22 | ## 思路 0
23 |
24 | 题意是给你 `n` 值,让你找到所有格式正确的圆括号匹配组,题目中已经给出了 `n = 3` 的所有结果。遇到这种问题,第一直觉就是用到递归或者堆栈,我们选取递归来解决,也就是 `helper` 函数的功能,从参数上来看肯定很好理解了,`leftRest` 代表还有几个左括号可以用,`rightNeed` 代表还需要几个右括号才能匹配,初始状态当然是 `rightNeed = 0, leftRest = n`,递归的终止状态就是 `rightNeed == 0 && leftRest == 0`,也就是左右括号都已匹配完毕,然后把 `str` 加入到链表中即可。
25 |
26 | ```java
27 | class Solution {
28 | public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
29 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
30 | helper(list, "", 0, n);
31 | return list;
32 | }
33 |
34 | private void helper(List list, String str, int rightNeed, int leftRest) {
35 | if (rightNeed == 0 && leftRest == 0) {
36 | list.add(str);
37 | return;
38 | }
39 | if (rightNeed > 0) helper(list, str + ")", rightNeed - 1, leftRest);
40 | if (leftRest > 0) helper(list, str + "(", rightNeed + 1, leftRest - 1);
41 | }
42 | }
43 | ```
44 |
45 |
46 | ## 思路 1
47 |
48 | 另一种实现方式就是迭代的思想了,我们来找寻其规律如下所示:
49 |
50 | ```
51 | f(0): “”
52 |
53 | f(1): “(“f(0)”)”
54 |
55 | f(2): "(“f(0)”)"f(1), “(“f(1)”)”
56 |
57 | f(3): "(“f(0)”)"f(2), "(“f(1)”)"f(1), “(“f(2)”)”
58 | ...
59 | ```
60 |
61 | 可以递推出 `f(n) = "(“f(0)”)"f(n-1) , "(“f(1)”)"f(n-2) "(“f(2)”)"f(n-3) … "(“f(i)”)“f(n-1-i) … “(f(n-1)”)”`
62 |
63 | 根据如上递推式写出如下代码应该不难了吧。
64 |
65 | ```java
66 | class Solution {
67 | public List generateParenthesis(int n) {
68 | HashMap> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
69 | hashMap.put(0, Collections.singletonList(""));
70 | for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
71 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
72 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
73 | for (String fj : hashMap.get(j)) {
74 | for (String fi_j_1 : hashMap.get(i - j - 1)) {
75 | list.add("(" + fj + ")" + fi_j_1);// calculate f(i)
76 | }
77 | }
78 | }
79 | hashMap.put(i, list);
80 | }
81 | return hashMap.get(n);
82 | }
83 | }
84 | ```
85 |
86 |
87 | ## 结语
88 |
89 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
90 |
91 |
92 |
93 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/generate-parentheses
94 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
95 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/029/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Divide Two Integers][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given two integers `dividend` and `divisor`, divide two integers without using multiplication, division and mod operator.
6 |
7 | Return the quotient after dividing `dividend` by `divisor`.
8 |
9 | The integer division should truncate toward zero.
10 |
11 | **Example 1:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Input: dividend = 10, divisor = 3
15 | Output: 3
16 | ```
17 |
18 | **Example 2:**
19 |
20 | ```
21 | Input: dividend = 7, divisor = -3
22 | Output: -2
23 | ```
24 |
25 | **Note:**
26 |
27 | - Both dividend and divisor will be 32-bit signed integers.
28 | - The divisor will never be 0.
29 | - Assume we are dealing with an environment which could only store integers within the 32-bit signed integer range: [−231, 231 − 1]. For the purpose of this problem, assume that your function returns 231 − 1 when the division result overflows.
30 |
31 | **Tags:** Math, Binary Search
32 |
33 |
34 | ## 思路
35 |
36 | 题意是让你算两个整型数相除后的结果,如果结果溢出就返回 `MAX_INT`,但不能使用乘、除、余的操作符,如果是用加减操作符的话肯定会超时哈,这样的话我们就只能想到位操作符了。
37 |
38 | 首先,我们分析下溢出的情况,也就是当被除数为 `Integer.MIN_VALUE`,除数为 `-1` 时会溢出,因为 `|Integer.MIN_VALUE| = Integer.MAX_VALUE + 1`。
39 |
40 | 然后,我们把除数和被除数都转为 `long` 类型的正数去做下一步操作,我这里以 `22` 和 `3` 相除为例子,因为 `22 >= 3`,我们对 `3` 进行左移一位,也就是乘 2,结果为 `6`,比 `22` 小,我们继续对 `6` 左移一位结果为 `12`,还是比 `22` 小,我们继续对 `12` 左移一位为 `24`,比 `22` 大,这时我们可以分析出,`22` 肯定比 `3` 的 `4` 倍要大,`4` 是怎么来的?因为我们左移了两次,也就是 `1 << 2 = 4`,此时我们记下这个 `4`,然后让 `22 - 3 * 4 = 10`,因为 `10 >= 3`,对 `10` 和 `3` 进行同样的操作,我们可以得到 `2`,此时加上上次的 `4`,和为 `6`,也就是 `22` 比 `3` 的 `6` 倍要大,此时还剩余 `10 - 6 = 4`,因为 `4 >= 3`,所以对 `4` 和 `3` 进行同样的操作,我们发现并不能对 `3` 进行左移了,因为 `4 >= 3`,所以 `1` 倍还是有的,所以加上最后的 `1`,结果为 `6 + 1 = 7`,也就是 `22` 整除 `3` 结果为 `7`。
41 |
42 | 最终,我们对结果赋予符号位即可,根据以上思路来书写如下代码应该不是难事了吧。
43 |
44 | ```java
45 | class Solution {
46 | public int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {
47 | if (dividend == Integer.MIN_VALUE && divisor == -1) {
48 | return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
49 | }
50 | long dvd = Math.abs((long) dividend);
51 | long dvr = Math.abs((long) divisor);
52 | int res = 0;
53 | while (dvd >= dvr) {
54 | long temp = dvr, multiple = 1;
55 | while (dvd >= temp << 1) {
56 | temp <<= 1;
57 | multiple <<= 1;
58 | }
59 | dvd -= temp;
60 | res += multiple;
61 | }
62 | return (dividend < 0) ^ (divisor < 0) ? -res : res;
63 | }
64 | }
65 | ```
66 |
67 |
68 | ## 结语
69 |
70 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/divide-two-integers
75 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/structure/TreeNode.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.structure;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/06/05
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class TreeNode {
12 |
13 | public int val;
14 | public TreeNode left;
15 | public TreeNode right;
16 |
17 | public TreeNode(int x) {
18 | val = x;
19 | }
20 |
21 | /**
22 | * 创建测试数据
23 | *
24 | * @param data [XX,XX,null,xx]
25 | * @return {@link TreeNode}
26 | */
27 | public static TreeNode createTestData(String data) {
28 | if (data.equals("[]")) return null;
29 | data = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1);
30 | String[] split = data.split(",");
31 | int len = len = split.length;
32 | TreeNode[] treeNodes = new TreeNode[len];
33 | data = data.substring(1, data.length() - 1);
34 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
35 | if (!split[i].equals("null")) {
36 | treeNodes[i] = new TreeNode(Integer.valueOf(split[i]));
37 | }
38 | }
39 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
40 | if (treeNodes[i] != null) {
41 | int leftIndex = i * 2 + 1;
42 | if (leftIndex < len) {
43 | treeNodes[i].left = treeNodes[leftIndex];
44 | }
45 | int rightIndex = leftIndex + 1;
46 | if (rightIndex < len) {
47 | treeNodes[i].right = treeNodes[rightIndex];
48 | }
49 | }
50 | }
51 | return treeNodes[0];
52 | }
53 |
54 | private static final String space = " ";
55 |
56 | /**
57 | * 竖向打印二叉树
58 | *
59 | * @param root 二叉树根节点
60 | */
61 | public static void print(TreeNode root) {
62 | print(root, 0);
63 | }
64 |
65 | private static void print(TreeNode node, int deep) {
66 | if (node == null) {
67 | printSpace(deep);
68 | System.out.println("#");
69 | return;
70 | }
71 | print(node.right, deep + 1);
72 | printSpace(deep);
73 | printNode(node.val);
74 | print(node.left, deep + 1);
75 | }
76 |
77 | private static void printSpace(int count) {
78 | for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
79 | System.out.printf(space);
80 | }
81 | }
82 |
83 | private static void printNode(int val) {
84 | StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder(val + "<");
85 | int spaceNum = space.length() - res.length();
86 | for (int i = 0; i < spaceNum; i++) {
87 | res.append(" ");
88 | }
89 | System.out.println(res);
90 | }
91 | }
92 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/017/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Letter Combinations of a Phone Number][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a digit string, return all possible letter combinations that the number could represent.
6 |
7 | A mapping of digit to letters (just like on the telephone buttons) is given below.
8 |
9 | 
10 |
11 | **Example:**
12 |
13 | ```
14 | Input: "23"
15 | Output: ["ad", "ae", "af", "bd", "be", "bf", "cd", "ce", "cf"].
16 | ```
17 |
18 | **Note:**
19 |
20 | Although the above answer is in lexicographical order, your answer could be in any order you want.
21 |
22 | **Tags:** String, Backtracking
23 |
24 |
25 | ## 思路 0
26 |
27 | 题意是给你按键,让你组合出所有不同结果,首先想到的肯定是回溯了,对每个按键的所有情况进行回溯,回溯的终点就是结果字符串长度和按键长度相同。
28 |
29 | ```java
30 | class Solution {
31 | private static String[] map = new String[]{"abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
32 |
33 | public List letterCombinations(String digits) {
34 | if (digits.length() == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
35 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
36 | helper(list, digits, "");
37 | return list;
38 | }
39 |
40 | private void helper(List list, String digits, String ans) {
41 | if (ans.length() == digits.length()) {
42 | list.add(ans);
43 | return;
44 | }
45 | for (char c : map[digits.charAt(ans.length()) - '2'].toCharArray()) {
46 | helper(list, digits, ans + c);
47 | }
48 | }
49 | }
50 | ```
51 |
52 | ## 思路 1
53 |
54 | 还有一种思路就是利用队列,根据上一次队列中的值,该值拼接当前可选值来不断迭代其结果,具体代码如下。
55 |
56 | ```java
57 | class Solution {
58 | private static String[] map = new String[]{"abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl", "mno", "pqrs", "tuv", "wxyz"};
59 |
60 | public List letterCombinations(String digits) {
61 | if (digits.length() == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
62 | LinkedList list = new LinkedList<>();
63 | list.add("");
64 | char[] charArray = digits.toCharArray();
65 | for (int i = 0; i < charArray.length; i++) {
66 | char c = charArray[i];
67 | while (list.getFirst().length() == i) {
68 | String pop = list.removeFirst();
69 | for (char v : map[c - '2'].toCharArray()) {
70 | list.addLast(pop + v);
71 | }
72 | }
73 | }
74 | return list;
75 | }
76 | }
77 | ```
78 |
79 |
80 | ## 结语
81 |
82 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
83 |
84 |
85 |
86 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number
87 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
88 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/101/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Symmetric Tree][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a binary tree, check whether it is a mirror of itself (ie, symmetric around its center).
6 |
7 | For example, this binary tree `[1,2,2,3,4,4,3]` is symmetric:
8 |
9 | ```
10 | 1
11 | / \
12 | 2 2
13 | / \ / \
14 | 3 4 4 3
15 | ```
16 |
17 | But the following `[1,2,2,null,3,null,3]` is not:
18 |
19 | ```
20 | 1
21 | / \
22 | 2 2
23 | \ \
24 | 3 3
25 | ```
26 |
27 | **Note:**
28 |
29 | Bonus points if you could solve it both recursively and iteratively.
30 |
31 | **Tags:** Tree, Depth-first Search, Breadth-first Search
32 |
33 |
34 | ## 思路 0
35 |
36 | 题意是判断一棵二叉树是否左右对称,首先想到的是深搜,比较根结点的左右两棵子树是否对称,如果左右子树的值相同,那么再分别对左子树的左节点和右子树的右节点,左子树的右节点和右子树的左节点做比较即可。
37 |
38 | ```java
39 | /**
40 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
41 | * public class TreeNode {
42 | * int val;
43 | * TreeNode left;
44 | * TreeNode right;
45 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
46 | * }
47 | */
48 | class Solution {
49 | public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
50 | return root == null || helper(root.left, root.right);
51 | }
52 |
53 | public boolean helper(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
54 | if (left == null || right == null) return left == right;
55 | if (left.val != right.val) return false;
56 | return helper(left.left, right.right) && helper(left.right, right.left);
57 | }
58 | }
59 | ```
60 |
61 | ## 思路 1
62 |
63 | 第二种思路就是宽搜了,宽搜肯定要用到队列,Java 中可用 `LinkedList` 替代,也是要做到左子树的左节点和右子树的右节点,左子树的右节点和右子树的左节点做比较即可。
64 |
65 | ```java
66 | /**
67 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
68 | * public class TreeNode {
69 | * int val;
70 | * TreeNode left;
71 | * TreeNode right;
72 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
73 | * }
74 | */
75 | class Solution {
76 | public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
77 | if (root == null) return true;
78 | LinkedList q = new LinkedList<>();
79 | q.add(root.left);
80 | q.add(root.right);
81 | TreeNode left, right;
82 | while (q.size() > 1) {
83 | left = q.pop();
84 | right = q.pop();
85 | if (left == null && right == null) continue;
86 | if (left == null || right == null) return false;
87 | if (left.val != right.val) return false;
88 | q.add(left.left);
89 | q.add(right.right);
90 | q.add(left.right);
91 | q.add(right.left);
92 | }
93 | return true;
94 | }
95 | }
96 | ```
97 |
98 |
99 | ## 结语
100 |
101 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
102 |
103 |
104 |
105 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/symmetric-tree
106 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
107 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/025/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Reverse Nodes in k-Group][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a linked list, reverse the nodes of a linked list *k* at a time and return its modified list.
6 |
7 | *k* is a positive integer and is less than or equal to the length of the linked list. If the number of nodes is not a multiple of *k* then left-out nodes in the end should remain as it is.
8 |
9 |
10 | **Example:**
11 |
12 | Given this linked list: `1->2->3->4->5`
13 |
14 | For *k* = 2, you should return: `2->1->4->3->5`
15 |
16 | For *k* = 3, you should return: `3->2->1->4->5`
17 |
18 | **Note:**
19 |
20 | - Only constant extra memory is allowed.
21 | - You may not alter the values in the list's nodes, only nodes itself may be changed.
22 |
23 | **Tags:** Linked List
24 |
25 |
26 | ## 思路
27 |
28 | 题意是让你以 `k` 个元素为一组来翻转链表,最后不足 `k` 个的话不需要翻转,最传统的思路就是每遇到 `k` 个元素,对其 `k` 个元素进行翻转,而难点就是在此,下面介绍其原理,我们以例子中的 `k = 3` 为例,其 `pre` 和 `next` 如下所示。
29 |
30 | ```
31 | 0->1->2->3->4->5
32 | | |
33 | pre next
34 | ```
35 |
36 | 我们要做的就是把 `pre` 和 `next` 之间的元素逆序,思想是依次从第二个元素到第 `k` 个元素,依次把它插入到 `pre` 后面,过程如下。
37 |
38 | ```
39 | head move
40 | | |
41 | 0->1->2->3->4->5
42 | | |
43 | pre next
44 |
45 | head move
46 | | |
47 | 0->2->1->3->4->5
48 | | |
49 | pre next
50 |
51 | head move
52 | | |
53 | 0->3->2->1->4->5
54 | | |
55 | pre next
56 | ```
57 |
58 | 好了,根据原理,那写出代码就不难了。
59 |
60 | ```java
61 | /**
62 | * Definition for singly-linked list.
63 | * public class ListNode {
64 | * int val;
65 | * ListNode next;
66 | * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
67 | * }
68 | */
69 | class Solution {
70 | public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {
71 | if (head == null || k == 1) return head;
72 | ListNode node = new ListNode(0), pre = node;
73 | node.next = head;
74 | for (int i = 1; head != null; ++i) {
75 | if (i % k == 0) {
76 | pre = reverse(pre, head.next);
77 | head = pre.next;
78 | } else {
79 | head = head.next;
80 | }
81 | }
82 | return node.next;
83 | }
84 |
85 | private ListNode reverse(ListNode pre, ListNode next) {
86 | ListNode head = pre.next;
87 | ListNode move = head.next;
88 | while (move != next) {
89 | head.next = move.next;
90 | move.next = pre.next;
91 | pre.next = move;
92 | move = head.next;
93 | }
94 | return head;
95 | }
96 | }
97 | ```
98 |
99 |
100 | ## 结语
101 |
102 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
103 |
104 |
105 |
106 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group
107 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
108 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/004/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Median of Two Sorted Arrays][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | There are two sorted arrays **nums1** and **nums2** of size m and n respectively.
6 |
7 | Find the median of the two sorted arrays. The overall run time complexity should be O(log (m+n)).
8 |
9 | **Example 1:**
10 |
11 | ```
12 | nums1 = [1, 3]
13 | nums2 = [2]
14 |
15 | The median is 2.0
16 | ```
17 |
18 | **Example 2:**
19 |
20 | ```
21 | nums1 = [1, 2]
22 | nums2 = [3, 4]
23 |
24 | The median is (2 + 3)/2 = 2.5
25 | ```
26 |
27 | **Tags:** Array, Binary Search, Divide and Conquer
28 |
29 |
30 | ## 思路
31 |
32 | 题意是给你两个已排序的递增数组,让你找出其中位数。
33 |
34 | 乍一看这题并不是很难,因为两序列有序,所以我们很容想到时间复杂度为 `O(m + n)` 的做法:依次取出两数组中较小的元素,然后找到中间的元素即可。但这题要求的时间复杂度为 `O(log(m + n))`,那么我们自然而然地就能想到二分查找法进行求解。
35 |
36 | 题目是让找两数组的中位数,我们可以泛化为求两数组中第 `k` 大的元素,那么,求中位数就是其中的一个特例而已。`helper` 函数所起到的作用就是求两数组中第 `k` 大的元素,下面来解释其原理:
37 |
38 | 假设数组分别记为 `A`,`B`,当前需要搜索第 `k` 大的数,于是我们可以考虑从数组 `A` 中取出前 `m` 个元素,从数组 `B` 中取出前 `k - m` 个元素。由于数组 `A`,`B` 分别排序,则 `A[m - 1]` 大于从数组 `A` 中取出的其他所有元素,`B[k - m - 1]` 大于数组 `B` 中取出的其他所有元素。此时,尽管取出元素之间的相对大小关系不确定,但 `A[m - 1]` 与 `B[k - m - 1]` 的较大者一定是这 `k` 个元素中最大的。那么,较小的那个元素一定不是第 `k` 大的,这里留给读者自己想象。
39 |
40 | 为叙述方便,假设 `A[m - 1]` 是较小的那个元素,那么我们可以把 `A[0]`,`A[1]`...`A[m - 1]` 排除掉,并且更新 `k` 值为 `k - m`,也就是下一次就是从剩余的元素中寻找第 `k - m` 大的元素,这样,我们就完成了一次范围缩小,同理进行下一轮的操作。
41 |
42 | 那么什么时候停止操作呢?分两种情况:
43 |
44 | 1. 当某个数组的数都被取完了,那么直接返回另一个数组的后 `k` 个元素即可。
45 |
46 | 2. 当 `k = 1` 时,也就是只需再找一个数即可,也就是取两者当前较小的那个即可。
47 |
48 | 特别地,我们选取 `m = k / 2`,下面是我画的草图,希望能帮助大家理解。
49 |
50 | 
51 |
52 | 借助上面的理论,你能写出相关代码了吗?
53 |
54 | ```java
55 | class Solution {
56 | public double findMedianSortedArrays(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
57 | int len = nums1.length + nums2.length;
58 | if (len % 2 == 0) {
59 | return (helper(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, len / 2) + helper(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, len / 2 + 1)) / 2.0;
60 | }
61 | return helper(nums1, 0, nums2, 0, (len + 1) / 2);
62 | }
63 |
64 | private int helper(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n, int k) {
65 | if (m >= nums1.length) return nums2[n + k - 1];
66 | if (n >= nums2.length) return nums1[m + k - 1];
67 | if (k == 1) return Math.min(nums1[m], nums2[n]);
68 |
69 | int p1 = m + k / 2 - 1;
70 | int p2 = n + k / 2 - 1;
71 | int mid1 = p1 < nums1.length ? nums1[p1] : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
72 | int mid2 = p2 < nums2.length ? nums2[p2] : Integer.MAX_VALUE;
73 | if (mid1 < mid2) {
74 | return helper(nums1, m + k / 2, nums2, n, k - k / 2);
75 | }
76 | return helper(nums1, m, nums2, n + k / 2, k - k / 2);
77 | }
78 | }
79 | ```
80 |
81 |
82 | ## 结语
83 |
84 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
85 |
86 |
87 |
88 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/median-of-two-sorted-arrays
89 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
90 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/107/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given a binary tree, return the *bottom-up level order* traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from left to right, level by level from leaf to root).
6 |
7 | For example:
8 |
9 | Given binary tree `[3,9,20,null,null,15,7]`,
10 |
11 | ```
12 | 3
13 | / \
14 | 9 20
15 | / \
16 | 15 7
17 | ```
18 |
19 | return its bottom-up level order traversal as:
20 |
21 | ```
22 | [
23 | [15,7],
24 | [9,20],
25 | [3]
26 | ]
27 | ```
28 |
29 | **Tags:** Tree, Breadth-first Search
30 |
31 |
32 | ## 思路 0
33 |
34 | 题意是从下往上按层遍历二叉树,每一层是从左到右,按层遍历,很明显,宽搜第一时间符合,因为是从下往上,所以插入的时候每次插到链表头即可。
35 |
36 | ```java
37 | /**
38 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
39 | * public class TreeNode {
40 | * int val;
41 | * TreeNode left;
42 | * TreeNode right;
43 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
44 | * }
45 | */
46 | class Solution {
47 | public List> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
48 | if (root == null) return Collections.emptyList();
49 | List> list = new LinkedList<>();
50 | LinkedList q = new LinkedList<>();
51 | q.add(root);
52 | while(!q.isEmpty()) {
53 | int size = q.size();
54 | List sub = new LinkedList();
55 | for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
56 | TreeNode node = q.remove();
57 | sub.add(node.val);
58 | if (node.left != null) q.add(node.left);
59 | if (node.right != null) q.add(node.right);
60 | }
61 | list.add(0, sub);
62 | }
63 | return list;
64 | }
65 | }
66 | ```
67 |
68 | ## 思路 1
69 |
70 | 另一种思路就是深搜,深搜的时候同时记录深度,然后在相应的层插入节点值即可。
71 |
72 | ```java
73 | /**
74 | * Definition for a binary tree node.
75 | * public class TreeNode {
76 | * int val;
77 | * TreeNode left;
78 | * TreeNode right;
79 | * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
80 | * }
81 | */
82 | class Solution {
83 | public List> levelOrderBottom(TreeNode root) {
84 | List> list = new LinkedList<>();
85 | helper(list, root, 0);
86 | return list;
87 | }
88 |
89 | private void helper(List> list, TreeNode root, int level) {
90 | if (root == null) return;
91 | if (level >= list.size()) {
92 | list.add(0, new LinkedList<>());
93 | }
94 | helper(list, root.left, level + 1);
95 | helper(list, root.right, level + 1);
96 | list.get(list.size() - level - 1).add(root.val);
97 | }
98 | }
99 | ```
100 |
101 |
102 | ## 结语
103 |
104 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
105 |
106 |
107 |
108 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii
109 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
110 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/012/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Integer to Roman][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: `I`, `V`, `X`, `L`, `C`, `D` and `M`.
6 |
7 | ```
8 | Symbol Value
9 | I 1
10 | V 5
11 | X 10
12 | L 50
13 | C 100
14 | D 500
15 | M 1000
16 | ```
17 |
18 | For example, two is written as `II` in Roman numeral, just two one's added together. Twelve is written as, `XII`, which is simply `X` + `II`. The number twenty seven is written as `XXVII`, which is `XX` + `V` + `II`.
19 |
20 | Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not `IIII`. Instead, the number four is written as `IV`. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as `IX`. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
21 |
22 | - `I` can be placed before `V` (5) and `X` (10) to make 4 and 9.
23 | - `X` can be placed before `L` (50) and `C` (100) to make 40 and 90.
24 | - `C` can be placed before `D` (500) and `M` (1000) to make 400 and 900.
25 |
26 | Given an integer, convert it to a roman numeral. Input is guaranteed to be within the range from 1 to 3999.
27 |
28 | **Example 1:**
29 |
30 | ```
31 | Input: 3
32 | Output: "III"
33 | ```
34 |
35 | **Example 2:**
36 |
37 | ```
38 | Input: 4
39 | Output: "IV"
40 | ```
41 |
42 | **Example 3:**
43 |
44 | ```
45 | Input: 9
46 | Output: "IX"
47 | ```
48 |
49 | **Example 4:**
50 |
51 | ```
52 | Input: 58
53 | Output: "LVIII"
54 | Explanation: C = 100, L = 50, XXX = 30 and III = 3.
55 | ```
56 |
57 | **Example 5:**
58 |
59 | ```
60 | Input: 1994
61 | Output: "MCMXCIV"
62 | Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
63 | ```
64 |
65 | **Tags:** Math, String
66 |
67 |
68 | ## 思路
69 |
70 | 题意是整型数转罗马数字,范围从 1 到 3999,查看下百度百科的罗马数字介绍如下:
71 |
72 | * 相同的数字连写,所表示的数等于这些数字相加得到的数,如 Ⅲ=3;
73 |
74 | * 小的数字在大的数字的右边,所表示的数等于这些数字相加得到的数,如 Ⅷ=8、Ⅻ=12;
75 |
76 | * 小的数字(限于 Ⅰ、X 和 C)在大的数字的左边,所表示的数等于大数减小数得到的数,如 Ⅳ=4、Ⅸ=9。
77 |
78 | 那么我们可以把整数的每一位分离出来,让其每一位都用相应的罗马数字位表示,最终拼接完成。比如 `621` 我们可以分离百、十、个分别为 `6`、`2`、`1`,那么 `600` 对应的罗马数字是 `DC`,`20` 对应的罗马数字是 `XX`,`1` 对应的罗马数字是 `I`,所以最终答案便是 `DCXXI`。
79 |
80 | ```java
81 | class Solution {
82 | public String intToRoman(int num) {
83 | String M[] = {"", "M", "MM", "MMM"};
84 | String C[] = {"", "C", "CC", "CCC", "CD", "D", "DC", "DCC", "DCCC", "CM"};
85 | String X[] = {"", "X", "XX", "XXX", "XL", "L", "LX", "LXX", "LXXX", "XC"};
86 | String I[] = {"", "I", "II", "III", "IV", "V", "VI", "VII", "VIII", "IX"};
87 | return M[num / 1000] + C[(num % 1000) / 100] + X[(num % 100) / 10] + I[num % 10];
88 | }
89 | }
90 | ```
91 |
92 |
93 | ## 结语
94 |
95 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
96 |
97 |
98 |
99 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/integer-to-roman
100 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
101 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/013/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Roman to Integer][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Roman numerals are represented by seven different symbols: `I`, `V`, `X`, `L`, `C`, `D` and `M`.
6 |
7 | ```
8 | Symbol Value
9 | I 1
10 | V 5
11 | X 10
12 | L 50
13 | C 100
14 | D 500
15 | M 1000
16 | ```
17 |
18 | For example, two is written as `II` in Roman numeral, just two one's added together. Twelve is written as, `XII`, which is simply `X` + `II`. The number twenty seven is written as `XXVII`, which is `XX` + `V` + `II`.
19 |
20 | Roman numerals are usually written largest to smallest from left to right. However, the numeral for four is not `IIII`. Instead, the number four is written as `IV`. Because the one is before the five we subtract it making four. The same principle applies to the number nine, which is written as `IX`. There are six instances where subtraction is used:
21 |
22 | - `I` can be placed before `V` (5) and `X` (10) to make 4 and 9.
23 | - `X` can be placed before `L` (50) and `C` (100) to make 40 and 90.
24 | - `C` can be placed before `D` (500) and `M` (1000) to make 400 and 900.
25 |
26 | Given a roman numeral, convert it to an integer. Input is guaranteed to be within the range from 1 to 3999.
27 |
28 | **Example 1:**
29 |
30 | ```
31 | Input: "III"
32 | Output: 3
33 | ```
34 |
35 | **Example 2:**
36 |
37 | ```
38 | Input: "IV"
39 | Output: 4
40 | ```
41 |
42 | **Example 3:**
43 |
44 | ```
45 | Input: "IX"
46 | Output: 9
47 | ```
48 |
49 | **Example 4:**
50 |
51 | ```
52 | Input: "LVIII"
53 | Output: 58
54 | Explanation: C = 100, L = 50, XXX = 30 and III = 3.
55 | ```
56 |
57 | **Example 5:**
58 |
59 | ```
60 | Input: "MCMXCIV"
61 | Output: 1994
62 | Explanation: M = 1000, CM = 900, XC = 90 and IV = 4.
63 | ```
64 |
65 | **Tags:** Math, String
66 |
67 |
68 | ## 思路
69 |
70 | 题意是罗马数字转整型数,范围从 1 到 3999,查看下百度百科的罗马数字介绍如下:
71 |
72 | * 相同的数字连写,所表示的数等于这些数字相加得到的数,如 Ⅲ=3;
73 |
74 | * 小的数字在大的数字的右边,所表示的数等于这些数字相加得到的数,如 Ⅷ=8、Ⅻ=12;
75 |
76 | * 小的数字(限于 Ⅰ、X 和 C)在大的数字的左边,所表示的数等于大数减小数得到的数,如 Ⅳ=4、Ⅸ=9。
77 |
78 | 那么我们可以利用 map 来完成罗马数字的 7 个数字符号:I、V、X、L、C、D、M 和整数的映射关系,然后根据上面的解释来模拟完成即可。
79 |
80 | ```java
81 | class Solution {
82 | public int romanToInt(String s) {
83 | Map map = new HashMap<>();
84 | map.put('I', 1);
85 | map.put('V', 5);
86 | map.put('X', 10);
87 | map.put('L', 50);
88 | map.put('C', 100);
89 | map.put('D', 500);
90 | map.put('M', 1000);
91 | int len = s.length();
92 | int sum = map.get(s.charAt(len - 1));
93 | for (int i = len - 2; i >= 0; --i) {
94 | if (map.get(s.charAt(i)) < map.get(s.charAt(i + 1))) {
95 | sum -= map.get(s.charAt(i));
96 | } else {
97 | sum += map.get(s.charAt(i));
98 | }
99 | }
100 | return sum;
101 | }
102 | }
103 | ```
104 |
105 |
106 | ## 结语
107 |
108 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
109 |
110 |
111 |
112 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/roman-to-integer
113 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
114 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/hard/_030/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.hard._030;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.Collections;
5 | import java.util.HashMap;
6 | import java.util.HashSet;
7 | import java.util.List;
8 | import java.util.Map;
9 | import java.util.Set;
10 |
11 | /**
12 | *
13 | * author: Blankj
14 | * blog : http://blankj.com
15 | * time : 2018/02/01
16 | * desc :
17 | *
18 | */
19 | public class Solution {
20 | public List findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
21 | if (s == null) return Collections.emptyList();
22 | int len = s.length();
23 | if (len == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
24 | int wordsSize = words.length;
25 | if (wordsSize == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
26 | int wordLen = words[0].length(), end = len - wordsSize * wordLen;
27 | if (end < 0) return Collections.emptyList();
28 | Map countMap = new HashMap<>();
29 | for (String word : words) {
30 | countMap.put(word, countMap.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
31 | }
32 | List res = new ArrayList<>();
33 | Set ignores = new HashSet<>();
34 | for (int i = 0; i <= end; ++i) {
35 | if (ignores.contains(i)) continue;
36 | Map findMap = new HashMap<>();
37 | int st = i, count = 0;
38 | List ignore = new ArrayList<>();
39 | for (int j = 0; ; ++j) {
40 | int cur = i + j * wordLen;
41 | if (cur + wordLen > len) break;
42 | String word = s.substring(cur, cur + wordLen);
43 | if (countMap.containsKey(word)) {
44 | findMap.put(word, findMap.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
45 | ++count;
46 | while (findMap.get(word) > countMap.get(word)) {
47 | ignore.add(st);
48 | String tmp = s.substring(st, st += wordLen);
49 | findMap.put(tmp, findMap.get(tmp) - 1);
50 | --count;
51 | }
52 | if (count == wordsSize) {
53 | ignore.add(st);
54 | res.add(st);
55 | String tmp = s.substring(st, st += wordLen);
56 | findMap.put(tmp, findMap.get(tmp) - 1);
57 | --count;
58 | }
59 | } else {
60 | for (int k = i; k <= cur; k += wordLen) {
61 | ignore.add(k);
62 | }
63 | break;
64 | }
65 | }
66 | ignores.addAll(ignore);
67 | }
68 | return res;
69 | }
70 |
71 | public static void main(String[] args) {
72 | Solution solution = new Solution();
73 | System.out.println(solution.findSubstring("wordgoodgoodgoodbestword", new String[]{"word", "good", "best", "good"}));
74 | System.out.println(solution.findSubstring("barfoothefoobarman", new String[]{"foo", "bar"}));
75 | System.out.println(solution.findSubstring("barfoofoobarthefoobarman", new String[]{"bar", "foo", "the"}));
76 | }
77 | }
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/023/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Merge k Sorted Lists][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Merge *k* sorted linked lists and return it as one sorted list. Analyze and describe its complexity.
6 |
7 | **Example:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input:
11 | [
12 | 1->4->5,
13 | 1->3->4,
14 | 2->6
15 | ]
16 | Output: 1->1->2->3->4->4->5->6
17 | ```
18 |
19 | **Tags:** Linked List, Divide and Conquer, Heap
20 |
21 |
22 | ## 思路 0
23 |
24 | 题意是合并多个已排序的链表,分析并描述其复杂度,我们可以用分治法来两两合并他们,假设 `k` 为总链表个数,`N` 为总元素个数,那么其时间复杂度为 `O(Nlogk)`。
25 |
26 | ```java
27 | /**
28 | * Definition for singly-linked list.
29 | * public class ListNode {
30 | * int val;
31 | * ListNode next;
32 | * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
33 | * }
34 | */
35 | class Solution {
36 | public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
37 | if (lists.length == 0) return null;
38 | return helper(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
39 | }
40 |
41 | private ListNode helper(ListNode[] lists, int left, int right) {
42 | if (left >= right) return lists[left];
43 | int mid = left + right >>> 1;
44 | ListNode l0 = helper(lists, left, mid);
45 | ListNode l1 = helper(lists, mid + 1, right);
46 | return merge2Lists(l0, l1);
47 | }
48 |
49 | private ListNode merge2Lists(ListNode l0, ListNode l1) {
50 | ListNode node = new ListNode(0), tmp = node;
51 | while (l0 != null && l1 != null) {
52 | if (l0.val <= l1.val) {
53 | tmp.next = new ListNode(l0.val);
54 | l0 = l0.next;
55 | } else {
56 | tmp.next = new ListNode(l1.val);
57 | l1 = l1.next;
58 | }
59 | tmp = tmp.next;
60 | }
61 | tmp.next = l0 != null ? l0 : l1;
62 | return node.next;
63 | }
64 | }
65 | ```
66 |
67 | ## 思路 1
68 |
69 | 还有另一种思路是利用优先队列,该数据结构用到的是堆排序,所以对总链表个数为 `k` 的复杂度为 `logk`,总元素为个数为 `N` 的话,其时间复杂度也为 `O(Nlogk)`。
70 |
71 | ```java
72 | /**
73 | * Definition for singly-linked list.
74 | * public class ListNode {
75 | * int val;
76 | * ListNode next;
77 | * ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
78 | * }
79 | */
80 | class Solution {
81 | public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
82 | if (lists.length == 0) return null;
83 | PriorityQueue queue = new PriorityQueue<>(lists.length, new Comparator() {
84 | @Override
85 | public int compare(ListNode o1, ListNode o2) {
86 | if (o1.val < o2.val) return -1;
87 | else if (o1.val == o2.val) return 0;
88 | else return 1;
89 | }
90 | });
91 | ListNode node = new ListNode(0), tmp = node;
92 | for (ListNode l : lists) {
93 | if (l != null) queue.add(l);
94 | }
95 | while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
96 | tmp.next = queue.poll();
97 | tmp = tmp.next;
98 | if (tmp.next != null) queue.add(tmp.next);
99 | }
100 | return node.next;
101 | }
102 | }
103 | ```
104 |
105 |
106 | ## 结语
107 |
108 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
109 |
110 |
111 |
112 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists
113 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
114 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/com/blankj/hard/_010/Solution.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package com.blankj.hard._010;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | *
5 | * author: Blankj
6 | * blog : http://blankj.com
7 | * time : 2017/10/13
8 | * desc :
9 | *
10 | */
11 | public class Solution {
12 | // public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
13 | // if (p.isEmpty()) return s.isEmpty();
14 | // if (p.length() == 1) {
15 | // return s.length() == 1 && (p.charAt(0) == s.charAt(0) || p.charAt(0) == '.');
16 | // }
17 | // if (p.charAt(1) != '*') {
18 | // if (s.isEmpty()) return false;
19 | // return (p.charAt(0) == s.charAt(0) || p.charAt(0) == '.')
20 | // && isMatch(s.substring(1), p.substring(1));
21 | // }
22 | // // match 1 or more preceding element
23 | // while (!s.isEmpty() && (p.charAt(0) == s.charAt(0) || p.charAt(0) == '.')) {
24 | // if (isMatch(s, p.substring(2))) return true;
25 | // s = s.substring(1);
26 | // }
27 | // // match 0 preceding element
28 | // return isMatch(s, p.substring(2));
29 | // }
30 | //
31 | // public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
32 | // if (p.isEmpty()) return s.isEmpty();
33 | // if (p.length() > 1 && p.charAt(1) == '*') {
34 | // return isMatch(s, p.substring(2))
35 | // || (!s.isEmpty() && (p.charAt(0) == s.charAt(0) || p.charAt(0) == '.')
36 | // && isMatch(s.substring(1), p));
37 | // }
38 | // return !s.isEmpty() && (p.charAt(0) == s.charAt(0) || p.charAt(0) == '.')
39 | // && isMatch(s.substring(1), p.substring(1));
40 | // }
41 |
42 | public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
43 | if (p.length() == 0) return s.length() == 0;
44 | int sL = s.length(), pL = p.length();
45 | boolean[][] dp = new boolean[sL + 1][pL + 1];
46 | char[] sc = s.toCharArray(), pc = p.toCharArray();
47 | dp[0][0] = true;
48 | for (int i = 2; i <= pL; ++i) {
49 | if (pc[i - 1] == '*' && dp[0][i - 2]) {
50 | dp[0][i] = true;
51 | }
52 | }
53 | for (int i = 1; i <= sL; ++i) {
54 | for (int j = 1; j <= pL; ++j) {
55 | if (pc[j - 1] == '.' || pc[j - 1] == sc[i - 1]) {
56 | dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
57 | }
58 | if (pc[j - 1] == '*') {
59 | if (pc[j - 2] == sc[i - 1] || pc[j - 2] == '.') {
60 | dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] || dp[i][j - 2];
61 | } else {
62 | dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 2];
63 | }
64 | }
65 | }
66 | }
67 | return dp[sL][pL];
68 | }
69 |
70 | public static void main(String[] args) {
71 | Solution solution = new Solution();
72 | System.out.println(solution.isMatch("aa", "a")); // false
73 | System.out.println(solution.isMatch("aa", "aa")); // true
74 | System.out.println(solution.isMatch("aaa", "aa")); // false
75 | System.out.println(solution.isMatch("aa", "a*")); // true
76 | System.out.println(solution.isMatch("aa", ".*")); // true
77 | System.out.println(solution.isMatch("ab", ".*")); // true
78 | System.out.println(solution.isMatch("aab", "c*a*b"));// true
79 | }
80 | }
81 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Companies.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # LeetCode companies
2 |
3 | ### Google
4 | ```
5 | 4,10,17,20,22,23,31,42,44,50,54,56,57,66,128,133,139,140,146,155,158
6 | 159,162,163,166,173,200,208,212,214,218,224,228,230,231,239,240,246
7 | 247,249,251,253,257,259,261,266,269,270,271,272,274,276,279,280,281
8 | 282,284,286,288,289,293,294,295,297,298,302,305,308,309,310,312,313
9 | 314,315,316,317,318,320,321,323,324,326,327,329,330,331,332,336,340
10 | 341,345,346,348,351,353,354,356,357,358,359,360,361,362,363,368,369
11 | 370,373,374,375,377,378,379,380,382,388,389,391,393,394,397,399,400
12 | 401,402,406,407,408,409,411,415,417,418,421,422,425,444,447,448,451
13 | 459,460,463,465,469,471,474,475,480,481-487,490,493,494,498,501,503
14 | 505,506,514,520,521,522,524,526,527,530,531,533,534,535,541,542,543
15 | 544,545,551,552,560,562,568,569,572
16 | ```
17 |
18 | ### Facebook
19 | ```
20 | 1,10,13,15,17,20,23,25,26,28,33,38,43,44,49,50,56,57,67,68,69,71,75,76
21 | 78,79,80,85,88,90,91,98,102,117,121,125,127,128,133,139,146,157,158,161
22 | 168,173,200,206,208,209,210,211,215,218,221,234,235,236,238,252,253,257
23 | 261,265,269,273,274,275,277,278,282,283,285,286,297,301,311,314,325,334
24 | 341,377,380,398,404,410,461,477,494,523,525,534,535,543,554
25 | ```
26 |
27 | ### Linkedin
28 | ```
29 | 1,21,23,33,34,46,47,50,53,56,57,65,68,76,101-104,127,149,150,152
30 | 156,170,173,18,198,205,236,238,243,244,245,254,256,277,297,311,339
31 | 364,366,367,464,515
32 | ```
33 |
34 | ### Microsoft
35 | ```
36 | 1,2,4,5,8,13,15,20,21,23-26,28,33,46,47,48,53-56,71,73,75,79,88,91
37 | 94,98,101,102,103,106,112,114,116,117,121,124,125,138,141,146,151,153
38 | 160,162,165,168,171,173,174,186,189,191,200,204,206,208,212,213,215
39 | 218,232,235,236,237,238,258,268,270,273,285,297,300,333,348,365,387
40 | 419,445,452,513,567
41 | ```
42 |
43 | ### Amazon
44 | ```
45 | 1,2,3,5,8,15,1,20,21,,23,42,48,49,73,78,89,98,102,119,121,126,127,138
46 | 139,141,146,155,160,167,186,199,200,204,206,215,234,235,236,238,239,240
47 | 242,297,355,380,387,396,414,438,449,451,459,460,508,516,517,529,532,534
48 | 535,536,537,538,545,579
49 | ```
50 |
51 | ### Uber
52 | ```
53 | 1,8,10,13,17,22,23,24,33,36,37,39,49,54,76,78,91,104,121,125,133,138
54 | 139,140,146,155,161,171,186,202,206,208,230,242,249,254,262,266,290
55 | 291,297,337,373,380,432,450,516,534,535
56 | ```
57 |
58 | ### Yelp
59 | ```
60 | 1,3,14,49,56,126,127,151,206,207,218,242,347,380,381,564
61 | ```
62 |
63 | ### Apple
64 | ```
65 | 1,4,7,21,28,36,42,48,69,70,102,104,118,149,151,165,190,191,206,207,215
66 | 221,236,237,238,240,257,284,383
67 | ```
68 |
69 | ### Bloomberg
70 | ```
71 | 1,2,3,5,7,8,11,13,15,16,20,24,26,33,42,49,50,53,56,62,63,69,79,88,98,100,101,102
72 | 103,105,110,113,117,121,122,131,138,139,141,146,151,155,158,160,172,189,206,208
73 | 215,225,230,232,266,268,2774,283,287,297,386,387,445,556
74 | ```
75 |
76 | ### Yahoo
77 | ```
78 | 1,4,13,104,139,141,146,206,217,284,297,479,491
79 | ```
80 |
81 | ### Airbnb
82 | ```
83 | 1,2,10,20,23,68,108,136,160,190,198,202,212,217,219,220,221,227,251
84 | 269,336,385,415
85 | ```
86 |
87 | ### Snapchat
88 | ```
89 | 36,37,39,40,44,76,96,127,140,146,151,155,161,206,253,269,270,289,312,314,
90 | 377,402,403,439,527
91 | ```
92 |
93 | ### Two Sigma
94 | ```
95 | 44,289,342,349,547
96 | ```
97 |
98 | ### Indeed
99 | ```
100 | 453,563
101 | ```
102 |
103 | ### Mathworks
104 | ```
105 | 500,566
106 | ```
107 |
108 | ### Alibaba
109 | ```
110 | 548,555
111 | ```
112 |
113 | ### Baidu
114 | ```
115 | 124,395,397,410,413,446,488,576
116 | ```
117 |
118 | ### Zappos
119 | ```
120 | 557
121 | ```
122 |
123 | ### eBay
124 | ```
125 | 416,572
126 | ```
127 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/008/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [String to Integer (atoi)][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Implement `atoi` which converts a string to an integer.
6 |
7 | The function first discards as many whitespace characters as necessary until the first non-whitespace character is found. Then, starting from this character, takes an optional initial plus or minus sign followed by as many numerical digits as possible, and interprets them as a numerical value.
8 |
9 | The string can contain additional characters after those that form the integral number, which are ignored and have no effect on the behavior of this function.
10 |
11 | If the first sequence of non-whitespace characters in str is not a valid integral number, or if no such sequence exists because either str is empty or it contains only whitespace characters, no conversion is performed.
12 |
13 | If no valid conversion could be performed, a zero value is returned.
14 |
15 | **Note:**
16 |
17 | - Only the space character `' '` is considered as whitespace character.
18 | - Assume we are dealing with an environment which could only store integers within the 32-bit signed integer range: [−231, 231 − 1]. If the numerical value is out of the range of representable values, INT_MAX (231 − 1) or INT_MIN (−231) is returned.
19 |
20 | **Example 1:**
21 |
22 | ```
23 | Input: "42"
24 | Output: 42
25 | ```
26 |
27 | **Example 2:**
28 |
29 | ```
30 | Input: " -42"
31 | Output: -42
32 | Explanation: The first non-whitespace character is '-', which is the minus sign.
33 | Then take as many numerical digits as possible, which gets 42.
34 | ```
35 |
36 | **Example 3:**
37 |
38 | ```
39 | Input: "4193 with words"
40 | Output: 4193
41 | Explanation: Conversion stops at digit '3' as the next character is not a numerical digit.
42 | ```
43 |
44 | **Example 4:**
45 |
46 | ```
47 | Input: "words and 987"
48 | Output: 0
49 | Explanation: The first non-whitespace character is 'w', which is not a numerical
50 | digit or a +/- sign. Therefore no valid conversion could be performed.
51 | ```
52 |
53 | **Example 5:**
54 |
55 | ```
56 | Input: "-91283472332"
57 | Output: -2147483648
58 | Explanation: The number "-91283472332" is out of the range of a 32-bit signed integer.
59 | Thefore INT_MIN (−2^31) is returned.
60 | ```
61 |
62 | **Tags:** Math, String
63 |
64 |
65 | ## 思路
66 |
67 | 题意是把一个字符串转为整型,但要注意所给的要求,先去除最前面的空格,然后判断正负数,注意正数可能包含 `+`,如果之后存在非数字或全为空则返回 `0`,而如果合法的值超过 int 表示的最大范围,则根据正负号返回 `INT_MAX` 或 `INT_MIN`。
68 |
69 | ```java
70 | class Solution {
71 | public int myAtoi(String str) {
72 | int i = 0, ans = 0, sign = 1, len = str.length();
73 | while (i < len && str.charAt(i) == ' ') ++i;
74 | if (i < len && (str.charAt(i) == '-' || str.charAt(i) == '+')) {
75 | sign = str.charAt(i++) == '+' ? 1 : -1;
76 | }
77 | for (; i < len; ++i) {
78 | int tmp = str.charAt(i) - '0';
79 | if (tmp < 0 || tmp > 9) break;
80 | if (ans > Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10
81 | || (ans == Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10 && (sign == 1 && tmp > 7 || sign == -1 && tmp > 8))) {
82 | return sign == 1 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
83 | } else {
84 | ans = ans * 10 + tmp;
85 | }
86 | }
87 | return sign * ans;
88 | }
89 | }
90 | ```
91 |
92 |
93 | ## 结语
94 |
95 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
96 |
97 |
98 |
99 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/string-to-integer-atoi
100 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
101 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/006/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [ZigZag Conversion][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | The string `"PAYPALISHIRING"` is written in a zigzag pattern on a given number of rows like this: (you may want to display this pattern in a fixed font for better legibility)
6 |
7 | ```
8 | P A H N
9 | A P L S I I G
10 | Y I R
11 | ```
12 |
13 | And then read line by line: `"PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"`
14 |
15 | Write the code that will take a string and make this conversion given a number of rows:
16 |
17 | ```
18 | string convert(string s, int numRows);
19 | ```
20 |
21 | **Example 1:**
22 |
23 | ```
24 | Input: s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 3
25 | Output: "PAHNAPLSIIGYIR"
26 | ```
27 |
28 | **Example 2:**
29 |
30 | ```
31 | Input: s = "PAYPALISHIRING", numRows = 4
32 | Output: "PINALSIGYAHRPI"
33 | Explanation:
34 |
35 | P I N
36 | A L S I G
37 | Y A H R
38 | P I
39 | ```
40 |
41 | **Tags:** String
42 |
43 |
44 | ## 思路 0
45 |
46 | 题意是让你把字符串按波浪形排好,然后返回横向读取的字符串。
47 |
48 | 听不懂的话,看下面的表示应该就明白了:
49 |
50 | ```
51 | 0 2n-2 4n-4
52 | 1 2n-3 2n-1 4n-5 4n-5
53 | 2 2n-4 2n 4n-6 .
54 | . . . . .
55 | . n+1 . 3n-1 .
56 | n-2 n 3n-4 3n-2 5n-6
57 | n-1 3n-3 5n-5
58 | ```
59 |
60 | 那么我们可以根据上面找规律,可以看到波峰和波谷是单顶点的,它们周期是 `2 * (n - 1)`,单独处理即可;中间的部分每个周期会出现两次,规律很好找,留给读者自己想象,不懂的可以结合以下代码。
61 |
62 | ```java
63 | class Solution {
64 | public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
65 | if (numRows <= 1) return s;
66 | int len = s.length();
67 | char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
68 | int cycle = 2 * (numRows - 1);
69 | StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
70 | for (int j = 0; j < len; j += cycle) {
71 | sb.append(chars[j]);
72 | }
73 | for (int i = 1; i < numRows - 1; i++) {
74 | int step = 2 * i;
75 | for (int j = i; j < len; j += step) {
76 | sb.append(chars[j]);
77 | step = cycle - step;
78 | }
79 | }
80 | for (int j = numRows - 1; j < len; j += cycle) {
81 | sb.append(chars[j]);
82 | }
83 | return sb.toString();
84 | }
85 | }
86 | ```
87 |
88 |
89 | ## 思路 1
90 |
91 | 另外一种思路就是开辟相应行数的 `StringBuilder` 对象,然后模拟波浪生成的样子分别插入到相应的 `StringBuilder` 对象,比较直白简单,具体代码如下。
92 |
93 | ```java
94 | class Solution {
95 | public String convert(String s, int numRows) {
96 | if (numRows <= 1) return s;
97 | int len = s.length();
98 | char[] chars = s.toCharArray();
99 | StringBuilder[] sbs = new StringBuilder[numRows];
100 | for (int i = 0; i < numRows; i++) {
101 | sbs[i] = new StringBuilder();
102 | }
103 | int i = 0;
104 | while (i < len) {
105 | for (int j = 0; j < numRows && i < len; ++j) {
106 | sbs[j].append(chars[i++]);
107 | }
108 | for (int j = numRows - 2; j >= 1 && i < len; --j) {
109 | sbs[j].append(chars[i++]);
110 | }
111 | }
112 | for (i = 1; i < numRows; i++) {
113 | sbs[0].append(sbs[i]);
114 | }
115 | return sbs[0].toString();
116 | }
117 | }
118 | ```
119 |
120 |
121 | ## 结语
122 |
123 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
124 |
125 |
126 |
127 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/zigzag-conversion
128 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
129 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/030/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Substring with Concatenation of All Words][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | You are given a string, **s**, and a list of words, **words**, that are all of the same length. Find all starting indices of substring(s) in **s** that is a concatenation of each word in **words** exactly once and without any intervening characters.
6 |
7 | **Example 1:**
8 |
9 | ```
10 | Input:
11 | s = "barfoothefoobarman",
12 | words = ["foo","bar"]
13 | Output: [0,9]
14 | Explanation: Substrings starting at index 0 and 9 are "barfoor" and "foobar" respectively.
15 | The output order does not matter, returning [9,0] is fine too.
16 | ```
17 |
18 | **Example 2:**
19 |
20 | ```
21 | Input:
22 | s = "wordgoodgoodgoodbestword",
23 | words = ["word","good","best","word"]
24 | Output: []
25 | ```
26 |
27 | **Tags:** Hash Table, Two Pointers, String
28 |
29 |
30 | ## 思路
31 |
32 | 题意是给一个字符串 `s` 和等长度的单词数组 `words`,我们要找到的就是在 `s` 串中由所有单词组成的子串的索引(不要求顺序),不明白的话看下例子也就理解了,比如例子 1 的结果 [0, 9]:[`barfoo`,`foobar`] 就是符合的子串。
33 |
34 | 我们把 `words` 每个单词出现的次数都存入到一个 `map` 中,然后遍历 `s` 串,依次截取单词长度的子串做比较,如果都符合那就加入结果,如果不符合,我们要把和它相关联的不符合的都剔除掉,这样在之后的遍历就可以跳过该位置从而达到优化的目的。
35 |
36 | ```java
37 | public class Solution {
38 | public List findSubstring(String s, String[] words) {
39 | if (s == null) return Collections.emptyList();
40 | int len = s.length();
41 | if (len == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
42 | int wordsSize = words.length;
43 | if (wordsSize == 0) return Collections.emptyList();
44 | int wordLen = words[0].length(), end = len - wordsSize * wordLen;
45 | if (end < 0) return Collections.emptyList();
46 | Map countMap = new HashMap<>();
47 | for (String word : words) {
48 | countMap.put(word, countMap.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
49 | }
50 | List res = new ArrayList<>();
51 | Set ignores = new HashSet<>();
52 | for (int i = 0; i <= end; ++i) {
53 | if (ignores.contains(i)) continue;
54 | Map findMap = new HashMap<>();
55 | int st = i, count = 0;
56 | List ignore = new ArrayList<>();
57 | for (int j = 0; ; ++j) {
58 | int cur = i + j * wordLen;
59 | if (cur + wordLen > len) break;
60 | String word = s.substring(cur, cur + wordLen);
61 | if (countMap.containsKey(word)) {
62 | findMap.put(word, findMap.getOrDefault(word, 0) + 1);
63 | ++count;
64 | while (findMap.get(word) > countMap.get(word)) {
65 | ignore.add(st);
66 | String tmp = s.substring(st, st += wordLen);
67 | findMap.put(tmp, findMap.get(tmp) - 1);
68 | --count;
69 | }
70 | if (count == wordsSize) {
71 | ignore.add(st);
72 | res.add(st);
73 | String tmp = s.substring(st, st += wordLen);
74 | findMap.put(tmp, findMap.get(tmp) - 1);
75 | --count;
76 | }
77 | } else {
78 | for (int k = i; k <= cur; k += wordLen) {
79 | ignore.add(k);
80 | }
81 | break;
82 | }
83 | }
84 | ignores.addAll(ignore);
85 | }
86 | return res;
87 | }
88 | }
89 | ```
90 |
91 |
92 | ## 结语
93 |
94 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
95 |
96 |
97 |
98 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/substring-with-concatenation-of-all-words
99 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/note/044/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # [Wildcard Matching][title]
2 |
3 | ## Description
4 |
5 | Given an input string (`s`) and a pattern (`p`), implement wildcard pattern matching with support for `'?'` and `'*'`.
6 |
7 | ```
8 | '?' Matches any single character.
9 | '*' Matches any sequence of characters (including the empty sequence).
10 | ```
11 |
12 | The matching should cover the **entire** input string (not partial).
13 |
14 | **Note:**
15 |
16 | - `s` could be empty and contains only lowercase letters `a-z`.
17 | - `p` could be empty and contains only lowercase letters `a-z`, and characters like `?` or `*`.
18 |
19 | **Example 1:**
20 |
21 | ```
22 | Input:
23 | s = "aa"
24 | p = "a"
25 | Output: false
26 | Explanation: "a" does not match the entire string "aa".
27 | ```
28 |
29 | **Example 2:**
30 |
31 | ```
32 | Input:
33 | s = "aa"
34 | p = "*"
35 | Output: true
36 | Explanation: '*' matches any sequence.
37 | ```
38 |
39 | **Example 3:**
40 |
41 | ```
42 | Input:
43 | s = "cb"
44 | p = "?a"
45 | Output: false
46 | Explanation: '?' matches 'c', but the second letter is 'a', which does not match 'b'.
47 | ```
48 |
49 | **Example 4:**
50 |
51 | ```
52 | Input:
53 | s = "adceb"
54 | p = "*a*b"
55 | Output: true
56 | Explanation: The first '*' matches the empty sequence, while the second '*' matches the substring "dce".
57 | ```
58 |
59 | **Example 5:**
60 |
61 | ```
62 | Input:
63 | s = "acdcb"
64 | p = "a*c?b"
65 | Output: false
66 | ```
67 |
68 | **Tags:** String, Dynamic Programming, Backtracking, Greedy
69 |
70 |
71 | ## 思路 0
72 |
73 | 题意是让让你从判断 `s` 字符串是否通配符匹配于 `p`,这道题和[Regular Expression Matching][010]很是相似,区别在于 `*`,正则匹配的 `*` 不能单独存在,前面必须具有一个字符,其意义是表明前面的这个字符个数可以是任意个数,包括 0 个;而通配符的 `*` 是可以随意出现的,跟前面字符没有任何关系,其作用是可以表示任意字符串。在此我们可以利用 *贪心算法* 来解决这个问题,需要两个额外指针 `p` 和 `match` 来分别记录最后一个 `*` 的位置和 `*` 匹配到 `s` 字符串的位置,其贪心体现在如果遇到 `*`,那就尽可能取匹配后方的内容,如果匹配失败,那就回到上一个遇到 `*` 的位置来继续贪心。
74 |
75 | ```java
76 | class Solution {
77 | public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
78 | if (p.length() == 0) return s.length() == 0;
79 | int si = 0, pi = 0, match = 0, star = -1;
80 | int sl = s.length(), pl = p.length();
81 | char[] sc = s.toCharArray(), pc = p.toCharArray();
82 | while (si < sl) {
83 | if (pi < pl && (pc[pi] == sc[si] || pc[pi] == '?')) {
84 | si++;
85 | pi++;
86 | } else if (pi < pl && pc[pi] == '*') {
87 | star = pi++;
88 | match = si;
89 | } else if (star != -1) {
90 | si = ++match;
91 | pi = star + 1;
92 | } else return false;
93 | }
94 | while (pi < pl && pc[pi] == '*') pi++;
95 | return pi == pl;
96 | }
97 | }
98 | ```
99 |
100 |
101 | ## 思路 1
102 |
103 | 另一种思路就是动态规划了,我们定义 `dp[i][j]` 的真假来表示 `s[0..i)` 是否匹配 `p[0..j)`,其状态转移方程如下所示:
104 |
105 | * 如果 `p[j - 1] != '*'`,`P[i][j] = P[i - 1][j - 1] && (s[i - 1] == p[j - 1] || p[j - 1] == '?');`
106 |
107 | * 如果 `p[j - 1] == '*'`,`P[i][j] = P[i][j - 1] || P[i - 1][j]`
108 |
109 | ```java
110 | class Solution {
111 | public boolean isMatch(String s, String p) {
112 | if (p.length() == 0) return s.length() == 0;
113 | int sl = s.length(), pl = p.length();
114 | boolean[][] dp = new boolean[sl + 1][pl + 1];
115 | char[] sc = s.toCharArray(), pc = p.toCharArray();
116 | dp[0][0] = true;
117 | for (int i = 1; i <= pl; ++i) {
118 | if (pc[i - 1] == '*') dp[0][i] = dp[0][i - 1];
119 | }
120 | for (int i = 1; i <= sl; ++i) {
121 | for (int j = 1; j <= pl; ++j) {
122 | if (pc[j - 1] != '*') {
123 | dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] && (sc[i - 1] == pc[j - 1] || pc[j - 1] == '?');
124 | } else {
125 | dp[i][j] = dp[i][j - 1] || dp[i - 1][j];
126 | }
127 | }
128 | }
129 | return dp[sl][pl];
130 | }
131 | }
132 | ```
133 |
134 |
135 | ## 结语
136 |
137 | 如果你同我一样热爱数据结构、算法、LeetCode,可以关注我 GitHub 上的 LeetCode 题解:[awesome-java-leetcode][ajl]
138 |
139 |
140 |
141 | [010]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode/blob/master/note/010/README.md
142 | [title]: https://leetcode.com/problems/wildcard-matching
143 | [ajl]: https://github.com/Blankj/awesome-java-leetcode
144 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------