├── .gitignore
├── Cheatsheet.png
├── README.md
├── code
├── README.md
├── algs4
│ ├── Alphabet.java
│ ├── Bag.java
│ ├── BinarySearch.java
│ ├── BinaryStdIn.java
│ ├── BinaryStdOut.java
│ ├── Counter.java
│ ├── DepthFirstOrder.java
│ ├── Draw.java
│ ├── DrawListener.java
│ ├── Heap.java
│ ├── HexDump.java
│ ├── In.java
│ ├── IndexMinPQ.java
│ ├── Interval1D.java
│ ├── Interval2D.java
│ ├── MinPQ.java
│ ├── Out.java
│ ├── Particle.java
│ ├── Picture.java
│ ├── PictureDump.java
│ ├── Point2D.java
│ ├── Queue.java
│ ├── SET.java
│ ├── ST.java
│ ├── Stack.java
│ ├── StdDraw.java
│ ├── StdIn.java
│ ├── StdOut.java
│ └── StdRandom.java
├── chapter1_1_Programming_Model
│ ├── BinarySearch.java
│ ├── BouncingBall.java
│ ├── Ex1.java
│ ├── Ex10.java
│ ├── Ex11.java
│ ├── Ex13.java
│ ├── Ex14.java
│ ├── Ex15.java
│ ├── Ex19.java
│ ├── Ex2.java
│ ├── Ex20.java
│ ├── Ex3.java
│ ├── Ex30.java
│ ├── Ex31.java
│ ├── Ex32.java
│ ├── Ex6.java
│ ├── Ex7a.java
│ ├── Ex7b.java
│ ├── Ex7c.java
│ ├── Ex8.java
│ ├── Ex9.java
│ ├── RightTriangle.java
│ ├── Sattolo.java
│ └── StdDrawTest.java
├── chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction
│ ├── Accumulator.java
│ ├── AccumulatorTest.java
│ ├── Cat.java
│ ├── Date.java
│ ├── Flips.java
│ ├── FlipsMax.java
│ ├── Interval2DTest.java
│ ├── Rolls.java
│ ├── StaticSETofInts.java
│ ├── VisualAccumulator.java
│ ├── VisualAccumulatorTest.java
│ ├── WhiteList.java
│ ├── in1.txt
│ └── in2.txt
├── chapter1_3_Bags_Queues_Stacks
│ └── ResizingArrayStack.java
├── chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms
│ ├── DoublingRatio.java
│ ├── DoublingTest.java
│ ├── Stopwatch.java
│ ├── StopwatchTest.java
│ └── ThreeSum.java
├── chapter1_5_Case_Study_Union_Find
│ ├── UF.java
│ └── WeightedQuickUnionUF.java
├── chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts
│ ├── Insertion.java
│ ├── Selection.java
│ ├── Shell.java
│ └── SortCompare.java
├── chapter2_2_Mergesort
│ ├── Merge.java
│ └── MergeBU.java
├── chapter2_3_Quicksort
│ ├── Ex25.java
│ ├── Quick.java
│ └── Quick3way.java
├── chapter2_4_Priority_Queues
│ ├── MaxPQ.java
│ └── TopM.java
├── chapter3_1_Symbol_Tables
│ ├── BinarySearchST.java
│ ├── FrequencyCounter.java
│ └── SequentialSearchST.java
├── chapter3_2_Binary_Search_Trees
│ └── BST.java
├── chapter3_4_Hash_Tables
│ ├── LinearProbingHashST.java
│ └── SeparateChainingHashST.java
├── chapter3_5_Searching_Applications
│ ├── SparseVector.java
│ └── WhiteFilter.java
├── chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs
│ ├── BreadthFirstPaths.java
│ ├── CC.java
│ ├── Cycle.java
│ ├── DegreesOfSeparation.java
│ ├── DepthFirstPaths.java
│ ├── DepthFirstSearch.java
│ ├── Graph.java
│ ├── SymbolGraph.java
│ ├── TestCC.java
│ ├── TestPaths.java
│ ├── TestSearch.java
│ ├── TestSymbolGraph.java
│ └── TwoColor.java
├── chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs
│ ├── DepthFirstOrder.java
│ ├── Digraph.java
│ ├── DirectedCycle.java
│ ├── DirectedDFS.java
│ ├── KosarajuSCC.java
│ ├── SymbolDigraph.java
│ ├── Topological.java
│ └── TransitiveClosure.java
├── chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree
│ ├── Edge.java
│ ├── EdgeWeightedGraph.java
│ ├── KruskalMST.java
│ ├── LazyPrimMST.java
│ ├── PrimMST.java
│ ├── TestMST.java
│ └── UF.java
├── chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths
│ ├── DijkstraSP.java
│ ├── DirectedEdge.java
│ ├── EdgeWeightedDigraph.java
│ ├── SP.java
│ └── TestSP.java
├── chapter5_3_Substring_Search
│ ├── BoyerMoore.java
│ ├── KMP.java
│ └── RabinKarp.java
├── chapter6_3_Suffix_Arrays
│ ├── KWIC.java
│ ├── LRS.java
│ └── SuffixArray.java
└── yuki.config.json
├── docs
├── .nojekyll
├── Context
│ ├── 6.1_事件驱动模拟.md
│ ├── 6.2_B-树.md
│ ├── 6.3_后缀数组.md
│ ├── 6.4_网络流算法.md
│ ├── 6.5_问题规约.md
│ └── 6.6_不可解性.md
├── Fundamentals
│ ├── 1.3_背包、队列和栈.md
│ ├── 1.4_算法分析.md
│ └── 1.5_案例研究:union-find算法.md
├── Graphs
│ ├── 4.1_无向图.md
│ ├── 4.2_有向图.md
│ ├── 4.3_最小生成树.md
│ └── 4.4_最短路径.md
├── README.md
├── Searching
│ ├── 3.1_符号表.md
│ ├── 3.2_二叉查找树.md
│ ├── 3.3_平衡查找树.md
│ ├── 3.4_散列表.md
│ └── 3.5_应用.md
├── Sorting
│ ├── 2.1_初级排序算法.md
│ ├── 2.2_归并排序.md
│ ├── 2.3_快速排序.md
│ ├── 2.4_优先队列.md
│ └── 2.5_应用.md
├── Strings
│ ├── 5.2_单词查找树.md
│ └── 5.3_子字符串查找.md
├── _sidebar.md
└── index.html
├── package.json
├── 每一节可以再看一遍的题.md
└── 相关问题解决方法.md
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Compiled class file
2 | *.class
3 |
4 | # Log file
5 | *.log
6 |
7 | # BlueJ files
8 | *.ctxt
9 |
10 | # Mobile Tools for Java (J2ME)
11 | .mtj.tmp/
12 |
13 | # Package Files #
14 | *.jar
15 | *.war
16 | *.ear
17 | *.zip
18 | *.tar.gz
19 | *.rar
20 |
21 | # virtual machine crash logs, see http://www.java.com/en/download/help/error_hotspot.xml
22 | hs_err_pid*
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Cheatsheet.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/e598780a9ecfe462c72f025fd5f45e052bcf292a/Cheatsheet.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 《算法(第4版)》笔记及代码
2 |
3 | [](http://kyonhuang.top)
4 |
5 | ## 笔记
6 |
7 | 推荐阅览 html 版本的笔记,由 [docsify](https://docsify.js.org/#/zh-cn/) 动态生成文档网站。
8 |
9 | [在线阅览地址](http://kyonhuang.top/Algorithms-notes/)
10 |
11 | ## 目录
12 |
13 | * [《每一节可以再看一遍的题》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/每一节可以再看一遍的题.md)
14 | * [《相关问题解决方法》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/相关问题解决方法.md)
15 |
16 | ### Fundamentals
17 |
18 | * [《1.3_背包、队列和栈》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Fundamentals/1.3_背包、队列和栈.md)
19 | * [《1.4_算法分析》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Fundamentals/1.4_算法分析.md)
20 | * [《1.5_案例研究:union-find算法》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Fundamentals/1.5_案例研究:union-find算法.md)
21 |
22 | ### Sorting
23 |
24 | * [《2.1_初级排序算法》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Sorting/2.1_初级排序算法.md)
25 | * [《2.2_归并排序》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Sorting/2.2_归并排序.md)
26 | * [《2.3_快速排序》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Sorting/2.3_快速排序.md)
27 | * [《2.4_优先队列》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Sorting/2.4_优先队列.md)
28 | * [《2.5_应用》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Sorting/2.5_应用.md)
29 |
30 | ### Searching
31 |
32 | * [《3.1_符号表》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Searching/3.1_符号表.md)
33 | * [《3.2_二叉查找树》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Searching/3.2_二叉查找树.md)
34 | * [《3.3_平衡查找树》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Searching/3.3_平衡查找树.md)
35 | * [《3.4_散列表》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Searching/3.4_散列表.md)
36 | * [《3.5_应用》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Searching/3.5_应用.md)
37 |
38 | ### Graphs
39 |
40 | * [《4.1_无向图》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Graphs/4.1_无向图.md)
41 | * [《4.2_有向图》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Graphs/4.2_有向图.md)
42 | * [《4.3_最小生成树》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Graphs/4.3_最小生成树.md)
43 | * [《4.4_最短路径》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Graphs/4.4_最短路径.md)
44 |
45 | ### Strings
46 |
47 | * [《5.2_单词查找树》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Strings/5.2_单词查找树.md)
48 | * [《5.3_子字符串查找》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Strings/5.3_子字符串查找.md)
49 |
50 | ### Context
51 |
52 | * [《6.3_后缀数组》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Context/6.3_后缀数组.md)
53 | * [《6.4_网络流算法》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Context/6.4_网络流算法.md)
54 | * [《6.5_问题规约》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Context/6.5_问题规约.md)
55 | * [《6.6_不可解性》](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/docs/Context/6.6_不可解性.md)
56 |
57 | ## 代码
58 |
59 | 相关代码详见[代码目录](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code)
60 |
61 | ## Cheatsheet
62 |
63 | [Algorithms and Data Structures Cheatsheet](https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/cheatsheet/)
64 |
65 | 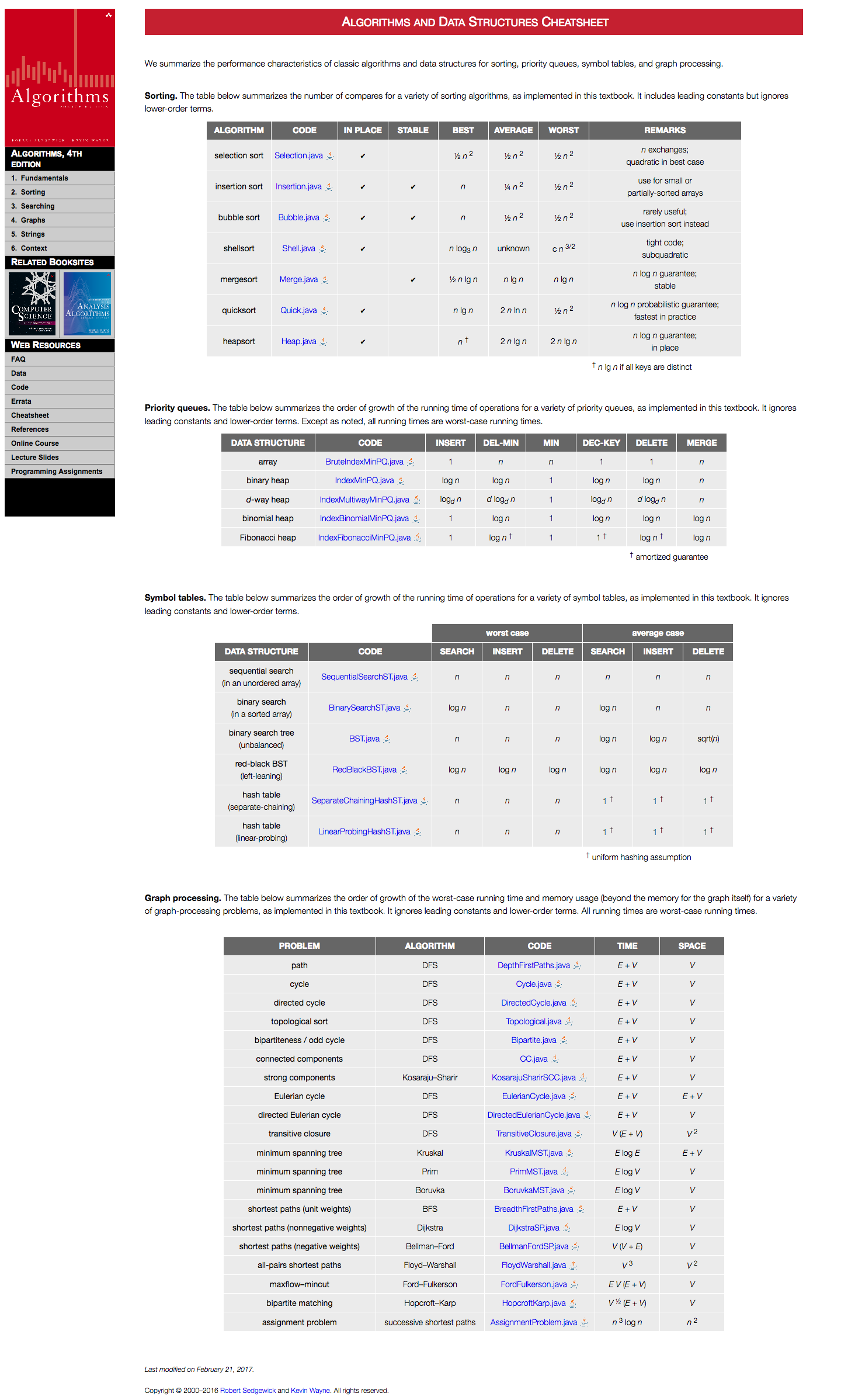
66 |
67 | ## 参考资料
68 |
69 | [算法(第4版)课后练习答案及相关问题解决方案 - 孙强Jimmy的技术博客 - CSDN博客](http://blog.csdn.net/u013541140/article/details/53222770)
70 |
71 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/algs4/Bag.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /******************************************************************************
2 | * Compilation: javac Bag.java
3 | * Execution: java Bag < input.txt
4 | * Dependencies: StdIn.java StdOut.java
5 | *
6 | * A generic bag or multiset, implemented using a singly-linked list.
7 | *
8 | * % more tobe.txt
9 | * to be or not to - be - - that - - - is
10 | *
11 | * % java Bag < tobe.txt
12 | * size of bag = 14
13 | * is
14 | * -
15 | * -
16 | * -
17 | * that
18 | * -
19 | * -
20 | * be
21 | * -
22 | * to
23 | * not
24 | * or
25 | * be
26 | * to
27 | *
28 | ******************************************************************************/
29 |
30 | package algs4;
31 |
32 | import java.util.Iterator;
33 | import java.util.NoSuchElementException;
34 |
35 | /**
36 | * The {@code Bag} class represents a bag (or multiset) of
37 | * generic items. It supports insertion and iterating over the
38 | * items in arbitrary order.
39 | *
40 | * This implementation uses a singly-linked list with a static nested class Node.
41 | * See {@link LinkedBag} for the version from the
42 | * textbook that uses a non-static nested class.
43 | * The add, isEmpty, and size operations
44 | * take constant time. Iteration takes time proportional to the number of items.
45 | *
46 | * For additional documentation, see Section 1.3 of
47 | * Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
48 | *
49 | * @author Robert Sedgewick
50 | * @author Kevin Wayne
51 | *
52 | * @param - the generic type of an item in this bag
53 | */
54 | public class Bag
- implements Iterable
- {
55 | private Node
- first; // beginning of bag
56 | private int n; // number of elements in bag
57 |
58 | // helper linked list class
59 | private static class Node
- {
60 | private Item item;
61 | private Node
- next;
62 | }
63 |
64 | /**
65 | * Initializes an empty bag.
66 | */
67 | public Bag() {
68 | first = null;
69 | n = 0;
70 | }
71 |
72 | /**
73 | * Returns true if this bag is empty.
74 | *
75 | * @return {@code true} if this bag is empty;
76 | * {@code false} otherwise
77 | */
78 | public boolean isEmpty() {
79 | return first == null;
80 | }
81 |
82 | /**
83 | * Returns the number of items in this bag.
84 | *
85 | * @return the number of items in this bag
86 | */
87 | public int size() {
88 | return n;
89 | }
90 |
91 | /**
92 | * Adds the item to this bag.
93 | *
94 | * @param item the item to add to this bag
95 | */
96 | public void add(Item item) {
97 | Node
- oldfirst = first;
98 | first = new Node
- ();
99 | first.item = item;
100 | first.next = oldfirst;
101 | n++;
102 | }
103 |
104 |
105 | /**
106 | * Returns an iterator that iterates over the items in this bag in arbitrary order.
107 | *
108 | * @return an iterator that iterates over the items in this bag in arbitrary order
109 | */
110 | public Iterator
- iterator() {
111 | return new ListIterator
- (first);
112 | }
113 |
114 | // an iterator, doesn't implement remove() since it's optional
115 | private class ListIterator
- implements Iterator
- {
116 | private Node
- current;
117 |
118 | public ListIterator(Node
- first) {
119 | current = first;
120 | }
121 |
122 | public boolean hasNext() { return current != null; }
123 | public void remove() { throw new UnsupportedOperationException(); }
124 |
125 | public Item next() {
126 | if (!hasNext()) throw new NoSuchElementException();
127 | Item item = current.item;
128 | current = current.next;
129 | return item;
130 | }
131 | }
132 |
133 | /**
134 | * Unit tests the {@code Bag} data type.
135 | *
136 | * @param args the command-line arguments
137 | */
138 | public static void main(String[] args) {
139 | Bag bag = new Bag();
140 | while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
141 | String item = StdIn.readString();
142 | bag.add(item);
143 | }
144 |
145 | StdOut.println("size of bag = " + bag.size());
146 | for (String s : bag) {
147 | StdOut.println(s);
148 | }
149 | }
150 |
151 | }
152 |
153 | /******************************************************************************
154 | * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
155 | *
156 | * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
157 | *
158 | * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
159 | * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
160 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
161 | *
162 | *
163 | * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
164 | * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
165 | * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
166 | * (at your option) any later version.
167 | *
168 | * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
169 | * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
170 | * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
171 | * GNU General Public License for more details.
172 | *
173 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
174 | * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
175 | ******************************************************************************/
176 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/algs4/BinarySearch.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /******************************************************************************
2 | * Compilation: javac BinarySearch.java
3 | * Execution: java BinarySearch whitelist.txt < input.txt
4 | * Dependencies: In.java StdIn.java StdOut.java
5 | * Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/11model/tinyW.txt
6 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/11model/tinyT.txt
7 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/11model/largeW.txt
8 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/11model/largeT.txt
9 | *
10 | * % java BinarySearch tinyW.txt < tinyT.txt
11 | * 50
12 | * 99
13 | * 13
14 | *
15 | * % java BinarySearch largeW.txt < largeT.txt | more
16 | * 499569
17 | * 984875
18 | * 295754
19 | * 207807
20 | * 140925
21 | * 161828
22 | * [367,966 total values]
23 | *
24 | ******************************************************************************/
25 |
26 | package algs4;
27 |
28 | import java.util.Arrays;
29 |
30 | /**
31 | * The {@code BinarySearch} class provides a static method for binary
32 | * searching for an integer in a sorted array of integers.
33 | *
34 | * The indexOf operations takes logarithmic time in the worst case.
35 | *
36 | * For additional documentation, see Section 1.1 of
37 | * Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
38 | *
39 | * @author Robert Sedgewick
40 | * @author Kevin Wayne
41 | */
42 | public class BinarySearch {
43 |
44 | /**
45 | * This class should not be instantiated.
46 | */
47 | private BinarySearch() { }
48 |
49 | /**
50 | * Returns the index of the specified key in the specified array.
51 | *
52 | * @param a the array of integers, must be sorted in ascending order
53 | * @param key the search key
54 | * @return index of key in array {@code a} if present; {@code -1} otherwise
55 | */
56 | public static int indexOf(int[] a, int key) {
57 | int lo = 0;
58 | int hi = a.length - 1;
59 | while (lo <= hi) {
60 | // Key is in a[lo..hi] or not present.
61 | int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
62 | if (key < a[mid]) hi = mid - 1;
63 | else if (key > a[mid]) lo = mid + 1;
64 | else return mid;
65 | }
66 | return -1;
67 | }
68 |
69 | /**
70 | * Returns the index of the specified key in the specified array.
71 | * This function is poorly named because it does not give the rank
72 | * if the array has duplicate keys or if the key is not in the array.
73 | *
74 | * @param key the search key
75 | * @param a the array of integers, must be sorted in ascending order
76 | * @return index of key in array {@code a} if present; {@code -1} otherwise
77 | * @deprecated Replaced by {@link #indexOf(int[], int)}.
78 | */
79 | @Deprecated
80 | public static int rank(int key, int[] a) {
81 | return indexOf(a, key);
82 | }
83 |
84 | /**
85 | * Reads in a sequence of integers from the whitelist file, specified as
86 | * a command-line argument; reads in integers from standard input;
87 | * prints to standard output those integers that do not appear in the file.
88 | *
89 | * @param args the command-line arguments
90 | */
91 | public static void main(String[] args) {
92 |
93 | // read the integers from a file
94 | In in = new In(args[0]);
95 | int[] whitelist = in.readAllInts();
96 |
97 | // sort the array
98 | Arrays.sort(whitelist);
99 |
100 | // read integer key from standard input; print if not in whitelist
101 | while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
102 | int key = StdIn.readInt();
103 | if (BinarySearch.indexOf(whitelist, key) == -1)
104 | StdOut.println(key);
105 | }
106 | }
107 | }
108 |
109 | /******************************************************************************
110 | * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
111 | *
112 | * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
113 | *
114 | * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
115 | * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
116 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
117 | *
118 | *
119 | * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
120 | * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
121 | * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
122 | * (at your option) any later version.
123 | *
124 | * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
125 | * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
126 | * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
127 | * GNU General Public License for more details.
128 | *
129 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
130 | * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
131 | ******************************************************************************/
132 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/algs4/Counter.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /******************************************************************************
2 | * Compilation: javac Counter.java
3 | * Execution: java Counter n trials
4 | * Dependencies: StdRandom.java StdOut.java
5 | *
6 | * A mutable data type for an integer counter.
7 | *
8 | * The test clients create n counters and performs trials increment
9 | * operations on random counters.
10 | *
11 | * java Counter 6 600000
12 | * 100140 counter0
13 | * 100273 counter1
14 | * 99848 counter2
15 | * 100129 counter3
16 | * 99973 counter4
17 | * 99637 counter5
18 | *
19 | ******************************************************************************/
20 |
21 | package algs4;
22 |
23 | /**
24 | * The {@code Counter} class is a mutable data type to encapsulate a counter.
25 | *
26 | * For additional documentation,
27 | * see Section 1.2 of
28 | * Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
29 | *
30 | * @author Robert Sedgewick
31 | * @author Kevin Wayne
32 | */
33 | public class Counter implements Comparable {
34 |
35 | private final String name; // counter name
36 | private int count = 0; // current value
37 |
38 | /**
39 | * Initializes a new counter starting at 0, with the given id.
40 | *
41 | * @param id the name of the counter
42 | */
43 | public Counter(String id) {
44 | name = id;
45 | }
46 |
47 | /**
48 | * Increments the counter by 1.
49 | */
50 | public void increment() {
51 | count++;
52 | }
53 |
54 | /**
55 | * Returns the current value of this counter.
56 | *
57 | * @return the current value of this counter
58 | */
59 | public int tally() {
60 | return count;
61 | }
62 |
63 | /**
64 | * Returns a string representation of this counter.
65 | *
66 | * @return a string representation of this counter
67 | */
68 | public String toString() {
69 | return count + " " + name;
70 | }
71 |
72 | /**
73 | * Compares this counter to the specified counter.
74 | *
75 | * @param that the other counter
76 | * @return {@code 0} if the value of this counter equals
77 | * the value of that counter; a negative integer if
78 | * the value of this counter is less than the value of
79 | * that counter; and a positive integer if the value
80 | * of this counter is greater than the value of that
81 | * counter
82 | */
83 | @Override
84 | public int compareTo(Counter that) {
85 | if (this.count < that.count) return -1;
86 | else if (this.count > that.count) return +1;
87 | else return 0;
88 | }
89 |
90 |
91 | /**
92 | * Reads two command-line integers n and trials; creates n counters;
93 | * increments trials counters at random; and prints results.
94 | *
95 | * @param args the command-line arguments
96 | */
97 | public static void main(String[] args) {
98 | int n = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
99 | int trials = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
100 |
101 | // create n counters
102 | Counter[] hits = new Counter[n];
103 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
104 | hits[i] = new Counter("counter" + i);
105 | }
106 |
107 | // increment trials counters at random
108 | for (int t = 0; t < trials; t++) {
109 | hits[StdRandom.uniform(n)].increment();
110 | }
111 |
112 | // print results
113 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
114 | StdOut.println(hits[i]);
115 | }
116 | }
117 | }
118 |
119 | /******************************************************************************
120 | * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
121 | *
122 | * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
123 | *
124 | * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
125 | * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
126 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
127 | *
128 | *
129 | * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
130 | * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
131 | * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
132 | * (at your option) any later version.
133 | *
134 | * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
135 | * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
136 | * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
137 | * GNU General Public License for more details.
138 | *
139 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
140 | * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
141 | ******************************************************************************/
142 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/algs4/DrawListener.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /******************************************************************************
2 | * Compilation: javac DrawListener.java
3 | * Execution: none
4 | * Dependencies: none
5 | *
6 | * Interface that accompanies Draw.java.
7 | ******************************************************************************/
8 |
9 | package algs4;
10 |
11 | public interface DrawListener {
12 |
13 | /**
14 | * Invoked when the mouse has been pressed.
15 | *
16 | * @param x the x-coordinate of the mouse
17 | * @param y the y-coordinate of the mouse
18 | */
19 | void mousePressed(double x, double y);
20 |
21 | /**
22 | * Invoked when the mouse has been dragged.
23 | *
24 | * @param x the x-coordinate of the mouse
25 | * @param y the y-coordinate of the mouse
26 | */
27 | void mouseDragged(double x, double y);
28 |
29 | /**
30 | * Invoked when the mouse has been released.
31 | *
32 | * @param x the x-coordinate of the mouse
33 | * @param y the y-coordinate of the mouse
34 | */
35 | void mouseReleased(double x, double y);
36 |
37 | /**
38 | * Invoked when a key has been typed.
39 | *
40 | * @param c the character typed
41 | */
42 | void keyTyped(char c);
43 |
44 | /**
45 | * Invoked when a key has been pressed.
46 | *
47 | * @param keycode the key combination pressed
48 | */
49 | void keyPressed(int keycode);
50 |
51 | /**
52 | * Invoked when a key has been released.
53 | *
54 | * @param keycode the key combination released
55 | */
56 | void keyReleased(int keycode);
57 | }
58 |
59 | /******************************************************************************
60 | * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
61 | *
62 | * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
63 | *
64 | * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
65 | * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
66 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
67 | *
68 | *
69 | * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
70 | * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
71 | * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
72 | * (at your option) any later version.
73 | *
74 | * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
75 | * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
76 | * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
77 | * GNU General Public License for more details.
78 | *
79 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
80 | * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
81 | ******************************************************************************/
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/algs4/Heap.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /******************************************************************************
2 | * Compilation: javac Heap.java
3 | * Execution: java Heap < input.txt
4 | * Dependencies: StdOut.java StdIn.java
5 | * Data files: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq/tiny.txt
6 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/24pq/words3.txt
7 | *
8 | * Sorts a sequence of strings from standard input using heapsort.
9 | *
10 | * % more tiny.txt
11 | * S O R T E X A M P L E
12 | *
13 | * % java Heap < tiny.txt
14 | * A E E L M O P R S T X [ one string per line ]
15 | *
16 | * % more words3.txt
17 | * bed bug dad yes zoo ... all bad yet
18 | *
19 | * % java Heap < words3.txt
20 | * all bad bed bug dad ... yes yet zoo [ one string per line ]
21 | *
22 | ******************************************************************************/
23 |
24 | package algs4;
25 |
26 | /**
27 | * The {@code Heap} class provides a static methods for heapsorting
28 | * an array.
29 | *
30 | * For additional documentation, see Section 2.4 of
31 | * Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
32 | *
33 | * @author Robert Sedgewick
34 | * @author Kevin Wayne
35 | */
36 | public class Heap {
37 |
38 | // This class should not be instantiated.
39 | private Heap() { }
40 |
41 | /**
42 | * Rearranges the array in ascending order, using the natural order.
43 | * @param pq the array to be sorted
44 | */
45 | public static void sort(Comparable[] pq) {
46 | int n = pq.length;
47 | for (int k = n/2; k >= 1; k--)
48 | sink(pq, k, n);
49 | while (n > 1) {
50 | exch(pq, 1, n--);
51 | sink(pq, 1, n);
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
55 | /***************************************************************************
56 | * Helper functions to restore the heap invariant.
57 | ***************************************************************************/
58 |
59 | private static void sink(Comparable[] pq, int k, int n) {
60 | while (2*k <= n) {
61 | int j = 2*k;
62 | if (j < n && less(pq, j, j+1)) j++;
63 | if (!less(pq, k, j)) break;
64 | exch(pq, k, j);
65 | k = j;
66 | }
67 | }
68 |
69 | /***************************************************************************
70 | * Helper functions for comparisons and swaps.
71 | * Indices are "off-by-one" to support 1-based indexing.
72 | ***************************************************************************/
73 | private static boolean less(Comparable[] pq, int i, int j) {
74 | return pq[i-1].compareTo(pq[j-1]) < 0;
75 | }
76 |
77 | private static void exch(Object[] pq, int i, int j) {
78 | Object swap = pq[i-1];
79 | pq[i-1] = pq[j-1];
80 | pq[j-1] = swap;
81 | }
82 |
83 | // is v < w ?
84 | private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
85 | return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
86 | }
87 |
88 |
89 | /***************************************************************************
90 | * Check if array is sorted - useful for debugging.
91 | ***************************************************************************/
92 | private static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
93 | for (int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
94 | if (less(a[i], a[i-1])) return false;
95 | return true;
96 | }
97 |
98 |
99 | // print array to standard output
100 | private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
101 | for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i++) {
102 | StdOut.println(a[i]);
103 | }
104 | }
105 |
106 | /**
107 | * Reads in a sequence of strings from standard input; heapsorts them;
108 | * and prints them to standard output in ascending order.
109 | *
110 | * @param args the command-line arguments
111 | */
112 | public static void main(String[] args) {
113 | String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
114 | Heap.sort(a);
115 | show(a);
116 | assert isSorted(a);
117 | }
118 | }
119 |
120 | /******************************************************************************
121 | * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
122 | *
123 | * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
124 | *
125 | * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
126 | * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
127 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
128 | *
129 | *
130 | * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
131 | * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
132 | * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
133 | * (at your option) any later version.
134 | *
135 | * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
136 | * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
137 | * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
138 | * GNU General Public License for more details.
139 | *
140 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
141 | * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
142 | ******************************************************************************/
143 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/algs4/HexDump.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /******************************************************************************
2 | * Compilation: javac HexDump.java
3 | * Execution: java HexDump < file
4 | * Dependencies: BinaryStdIn.java StdOut.java
5 | * Data file: http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/55compression/abra.txt
6 | *
7 | * Reads in a binary file and writes out the bytes in hex, 16 per line.
8 | *
9 | * % more abra.txt
10 | * ABRACADABRA!
11 | *
12 | * % java HexDump 16 < abra.txt
13 | * 41 42 52 41 43 41 44 41 42 52 41 21
14 | * 96 bits
15 | *
16 | *
17 | * Remark
18 | * --------------------------
19 | * - Similar to the Unix utilities od (octal dump) or hexdump (hexadecimal dump).
20 | *
21 | * % od -t x1 < abra.txt
22 | * 0000000 41 42 52 41 43 41 44 41 42 52 41 21
23 | * 0000014
24 | *
25 | ******************************************************************************/
26 |
27 | package algs4;
28 |
29 | /**
30 | * The {@code HexDump} class provides a client for displaying the contents
31 | * of a binary file in hexadecimal.
32 | *
33 | * For additional documentation,
34 | * see Section 5.5 of
35 | * Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
36 | *
37 | * See also {@link BinaryDump} and {@link PictureDump}.
38 | * For more full-featured versions, see the Unix utilities
39 | * {@code od} (octal dump) and {@code hexdump} (hexadecimal dump).
40 | *
41 | *
42 | * @author Robert Sedgewick
43 | * @author Kevin Wayne
44 | */
45 | public class HexDump {
46 |
47 | // Do not instantiate.
48 | private HexDump() { }
49 |
50 | /**
51 | * Reads in a sequence of bytes from standard input and writes
52 | * them to standard output using hexademical notation, k hex digits
53 | * per line, where k is given as a command-line integer (defaults
54 | * to 16 if no integer is specified); also writes the number
55 | * of bits.
56 | *
57 | * @param args the command-line arguments
58 | */
59 | public static void main(String[] args) {
60 | int bytesPerLine = 16;
61 | if (args.length == 1) {
62 | bytesPerLine = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
63 | }
64 |
65 | int i;
66 | for (i = 0; !BinaryStdIn.isEmpty(); i++) {
67 | if (bytesPerLine == 0) {
68 | BinaryStdIn.readChar();
69 | continue;
70 | }
71 | if (i == 0) StdOut.printf("");
72 | else if (i % bytesPerLine == 0) StdOut.printf("\n", i);
73 | else StdOut.print(" ");
74 | char c = BinaryStdIn.readChar();
75 | StdOut.printf("%02x", c & 0xff);
76 | }
77 | if (bytesPerLine != 0) StdOut.println();
78 | StdOut.println((i*8) + " bits");
79 | }
80 | }
81 |
82 | /******************************************************************************
83 | * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
84 | *
85 | * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
86 | *
87 | * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
88 | * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
89 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
90 | *
91 | *
92 | * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
93 | * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
94 | * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
95 | * (at your option) any later version.
96 | *
97 | * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
98 | * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
99 | * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
100 | * GNU General Public License for more details.
101 | *
102 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
103 | * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
104 | ******************************************************************************/
105 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/algs4/PictureDump.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /******************************************************************************
2 | * Compilation: javac PictureDump.java
3 | * Execution: java PictureDump width height < file
4 | * Dependencies: BinaryStdIn.java Picture.java
5 | * Data file: http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/stdlib/abra.txt
6 | *
7 | * Reads in a binary file and writes out the bits as w-by-h picture,
8 | * with the 1 bits in black and the 0 bits in white.
9 | *
10 | * % more abra.txt
11 | * ABRACADABRA!
12 | *
13 | * % java PictureDump 16 6 < abra.txt
14 | *
15 | ******************************************************************************/
16 |
17 | package algs4;
18 |
19 | import java.awt.Color;
20 |
21 |
22 | /**
23 | * The {@code PictureDump} class provides a client for displaying the contents
24 | * of a binary file as a black-and-white picture.
25 | *
26 | * For additional documentation,
27 | * see Section 5.5 of
28 | * Algorithms, 4th Edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
29 | *
30 | * See also {@link BinaryDump} and {@link HexDump}.
31 | *
32 | * @author Robert Sedgewick
33 | * @author Kevin Wayne
34 | */
35 | public class PictureDump {
36 |
37 | // Do not instantiate.
38 | private PictureDump() { }
39 |
40 | /**
41 | * Reads in a sequence of bytes from standard input and draws
42 | * them to standard drawing output as a width-by-height picture,
43 | * using black for 1 and white for 0 (and red for any leftover
44 | * pixels).
45 | *
46 | * @param args the command-line arguments
47 | */
48 | public static void main(String[] args) {
49 | int width = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
50 | int height = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
51 | Picture picture = new Picture(width, height);
52 | for (int row = 0; row < height; row++) {
53 | for (int col = 0; col < width; col++) {
54 | if (!BinaryStdIn.isEmpty()) {
55 | boolean bit = BinaryStdIn.readBoolean();
56 | if (bit) picture.set(col, row, Color.BLACK);
57 | else picture.set(col, row, Color.WHITE);
58 | }
59 | else {
60 | picture.set(col, row, Color.RED);
61 | }
62 | }
63 | }
64 | picture.show();
65 | }
66 | }
67 |
68 | /******************************************************************************
69 | * Copyright 2002-2016, Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne.
70 | *
71 | * This file is part of algs4.jar, which accompanies the textbook
72 | *
73 | * Algorithms, 4th edition by Robert Sedgewick and Kevin Wayne,
74 | * Addison-Wesley Professional, 2011, ISBN 0-321-57351-X.
75 | * http://algs4.cs.princeton.edu
76 | *
77 | *
78 | * algs4.jar is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
79 | * it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
80 | * the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
81 | * (at your option) any later version.
82 | *
83 | * algs4.jar is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
84 | * but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
85 | * MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
86 | * GNU General Public License for more details.
87 | *
88 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
89 | * along with algs4.jar. If not, see http://www.gnu.org/licenses.
90 | ******************************************************************************/
91 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/BinarySearch.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Arrays;
4 | import algs4.*;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | * 二分查找
8 | * @author huang
9 | */
10 | public class BinarySearch {
11 |
12 | public static int rank(int key, int[] a) {
13 | // 数组必须有序
14 | int lo = 0;
15 | int hi = a.length - 1;
16 | while(lo <= hi) {
17 | int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
18 | if(key < a[mid])
19 | hi = mid - 1;
20 | else if(key > a[mid])
21 | lo = mid + 1;
22 | else
23 | return mid;
24 | }
25 | return -1;
26 | }
27 |
28 | public static void main(String[] args) {
29 |
30 | int[] whitelist = In.readInts(args[0]);
31 | Arrays.sort(whitelist);
32 | while(!StdIn.isEmpty()){
33 | int key = StdIn.readInt();
34 | if(rank(key, whitelist) < 0)
35 | StdOut.println(key);
36 | }
37 |
38 | }
39 |
40 | }
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/BouncingBall.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdDraw;
4 |
5 | public class BouncingBall {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | // set the scale of the coordinate system
10 | StdDraw.setXscale(-1.0, 1.0);
11 | StdDraw.setYscale(-1.0, 1.0);
12 | StdDraw.enableDoubleBuffering();
13 |
14 | // initial values
15 | double rx = .480, ry = .860; // position
16 | double vx = .015, vy = .023; // velocity
17 | double radius = .05; // radius
18 |
19 | // main animation loop
20 | while(true) {
21 | // bounce off wall according to law of elastic collision
22 | if(Math.abs(rx + vx) > 1.0 - radius)
23 | vx = -vx;
24 | if(Math.abs(ry + vy) > 1.0 - radius)
25 | vy = -vy;
26 |
27 | // update position
28 | rx = rx + vx;
29 | ry = ry + vy;
30 |
31 | // clear the background
32 | StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.GRAY);
33 | StdDraw.filledSquare(0, 0, 1.0);
34 |
35 | // draw ball on the screen
36 | StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLACK);
37 | StdDraw.filledCircle(rx, ry, radius);
38 |
39 | // display and pause for 20 ms
40 | StdDraw.show();
41 | StdDraw.pause(20);
42 | }
43 |
44 |
45 | }
46 |
47 | }
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex1.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex1 {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | StdOut.println((0 + 15) / 2);
10 | StdOut.println(2.0e-6 * 100000000.1);
11 | StdOut.println(true && false || true && true);
12 |
13 | }
14 |
15 | }
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex10.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex10 {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | int[] a = new int[10];
10 | for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
11 | a[i] = i*i;
12 | for(int i = 9; i >= 0; i--)
13 | StdOut.printf("%d ", a[i]);
14 | }
15 |
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex11.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 |
6 | public class Ex11 {
7 |
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 |
10 | boolean[][] arr = new boolean[7][6];
11 | for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
12 | for(int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
13 | double num = StdRandom.uniform();
14 | if(num > 0.5)
15 | arr[i][j] = true;
16 | else
17 | arr[i][j] = false;
18 | }
19 | }
20 |
21 | printBoolArr(arr);
22 |
23 | }
24 |
25 | public static void printBoolArr (boolean[][] arr) {
26 |
27 | StdOut.print(' ');
28 | for (int i = 0; i < arr[0].length; i++) {
29 | StdOut.print(i);
30 | }
31 | StdOut.println();
32 | for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
33 | StdOut.print(i);
34 | for (int j = 0; j < arr[i].length; j++) {
35 | StdOut.print(arr[i][j] ? '*' : ' ');
36 | }
37 | StdOut.println();
38 | }
39 | }
40 |
41 | }
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex13.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 |
6 | public class Ex13 {
7 |
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 |
10 | int M = 3, N = 4;
11 | int[][] arr = new int[M][N];
12 | for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++)
13 | for (int j = 0; j < arr[0].length; j++)
14 | arr[i][j] = StdRandom.uniform(20);
15 | StdOut.println("oldArr: ");
16 | printArr(arr);
17 | StdOut.println("newArr: ");
18 | printArr(arrReverse(arr));
19 |
20 | }
21 |
22 | public static int[][] arrReverse(int[][] arr) {
23 | int[][] newArr = new int[arr[0].length][arr.length];
24 | for(int i = 0; i < newArr.length; i++)
25 | for(int j = 0; j < newArr[0].length; j++)
26 | newArr[i][j] = arr[j][i];
27 |
28 | return newArr;
29 | }
30 |
31 | public static void printArr(int[][] arr) {
32 | for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
33 | for(int j = 0; j < arr[0].length; j++) {
34 | StdOut.printf("%d ",arr[i][j]);
35 | }
36 | StdOut.println();
37 |
38 | }
39 |
40 | }
41 |
42 | }
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex14.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex14 {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | StdOut.print(lg(8));
10 |
11 | }
12 |
13 | public static int lg(int N) {
14 |
15 | int i = 0;
16 | while(n2(i) <= N)
17 | i++;
18 | return i-1;
19 | }
20 |
21 | public static int n2(int n) {
22 | int result = 1;
23 | for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
24 | result *= 2;
25 | return result;
26 | }
27 |
28 | }
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex15.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex15 {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | int[] arr = {0, 1, 1, 1};
10 | int[] timesArr = histogram(arr, 2);
11 | for(int j = 0; j < timesArr.length; j++) {
12 | StdOut.printf("%d ", timesArr[j]);
13 | }
14 | }
15 |
16 | public static int[] histogram(int[] a, int M) {
17 |
18 | int[] arr = new int[M];
19 | for(int i = 0; i < M; i++){
20 | int times = 0;
21 | for(int j = 0; j < a.length; j++){
22 | if(a[j] == i)
23 | times++;
24 | }
25 | arr[i] = times;
26 | }
27 | return arr;
28 | }
29 |
30 | }
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex19.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex19 {
6 |
7 | static final int M = 100;
8 | static long[] arr = new long[M];
9 |
10 | public static long F(int N) {
11 | if(N == 0)
12 | arr[N] = 0;
13 | else if(N == 1)
14 | arr[N] = 1;
15 | else
16 | arr[N] = arr[N - 1] + arr[N - 2];
17 | return arr[N];
18 | }
19 |
20 | public static void main(String[] args) {
21 | for(int N = 0; N < M; N++)
22 | StdOut.println(N + " " + F(N));
23 | }
24 |
25 | }
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex2.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex2 {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | StdOut.println((1 + 2.236) / 2);
10 | StdOut.println(1 + 2 + 3 + 4.0);
11 | StdOut.println(4.1 >= 4);
12 | StdOut.println(1 + 2 + "3");
13 |
14 | }
15 |
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex20.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex20 {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | StdOut.print(ln10(9));
10 |
11 | }
12 |
13 | public static double ln10(int N) {
14 |
15 | if(N == 1)
16 | return Math.log10(1);
17 | return Math.log10(N) + ln10(N - 1);
18 | }
19 |
20 | }
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex3.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdIn;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | public class Ex3 {
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 | int a = StdIn.readInt();
9 | int b = StdIn.readInt();
10 | int c = StdIn.readInt();
11 | if(a == b && a == c) {
12 | StdOut.println("equal");
13 | } else {
14 | StdOut.println("not equal");
15 | }
16 | }
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex30.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex30 {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | int N = 10;
10 | boolean[][] arr = new boolean [N][N];
11 | setArrBoolean(arr);
12 |
13 | for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
14 | for(int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
15 | StdOut.printf("%b ", arr[i][j]);
16 | }
17 | StdOut.println();
18 | }
19 | }
20 |
21 | public static void setArrBoolean(boolean[][] arr) {
22 | for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
23 | for(int j = 0; j < arr.length; j++) {
24 | arr[i][j] = true;
25 | for(int k = 2; k <= i; k++) {
26 | if((i % k == 0) && (j % k == 0)) {
27 | arr[i][j] = false;
28 | }
29 | }
30 | }
31 | }
32 | }
33 |
34 | }
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex31.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import java.awt.Color;
4 |
5 | import algs4.StdDraw;
6 | import algs4.StdRandom;
7 |
8 | public class Ex31 {
9 |
10 | static class Point {
11 | double x, y;
12 |
13 | public Point(double x, double y) {
14 | super();
15 | this.x = x;
16 | this.y = y;
17 | }
18 | }
19 |
20 | public static void main(String[] args) {
21 |
22 | int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
23 | double p = Double.parseDouble(args[1]);
24 | if(p < 0 || p > 1) {
25 | System.out.println("p is not valid!");
26 | return;
27 | }
28 | Point[] points = new Point[N];
29 | double angle = 360.0 / N;
30 | StdDraw.circle(.5, .5, .5);
31 | StdDraw.setPenRadius(.05);
32 |
33 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
34 | points[i] = new Point(.5 + .5 * Math.cos(angle * i * Math.PI / 180),
35 | .5 + .5 * Math.sin(angle * i * Math.PI / 180));
36 | StdDraw.point(points[i].x, points[i].y);
37 | }
38 |
39 | StdDraw.setPenRadius(.01);
40 | StdDraw.setPenColor(Color.GRAY);
41 |
42 | for(int i = 0; i < N - 1; i++) {
43 | for(int j = i + 1; j < N; j++) {
44 | if(StdRandom.bernoulli(p)) {
45 | StdDraw.line(points[i].x, points[i].y, points[j].x, points[j].y);
46 | }
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
50 | }
51 |
52 | }
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex32.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import java.util.ArrayList;
4 | import java.util.Scanner;
5 |
6 | import algs4.StdDraw;
7 |
8 | public class Ex32 {
9 |
10 | public static void main(String[] args) {
11 |
12 | @SuppressWarnings("resource")
13 | Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
14 | ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
15 | while (scanner.hasNextDouble()) {
16 | list.add(scanner.nextDouble());
17 | }
18 |
19 | int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
20 | double l = Double.parseDouble(args[1]),
21 | r = Double.parseDouble(args[2]);
22 |
23 | double length = (r - l) / N,
24 | start = l;
25 |
26 | while(start < r) {
27 | int height = 0;
28 | for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
29 | if(start <= list.indexOf(i) && list.indexOf(i) < start + length) {
30 | height++;
31 | }
32 | }
33 | StdDraw.filledRectangle(start, height, length / 2, height);
34 | start += length;
35 | }
36 |
37 | }
38 |
39 | }
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex6.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex6 {
6 | public static void main(String[] args) {
7 | int f = 0;
8 | int g = 1;
9 | for(int i = 0; i <= 15; i++){
10 | StdOut.println(f);
11 | f = f + g;
12 | g = f - g;
13 | }
14 | }
15 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex7a.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex7a {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | double t = 9.0;
10 | while(Math.abs(t - 9.0 / t) > .001)
11 | t = (9.0 / t + t) / 2.0;
12 | StdOut.printf("%.5f\n", t);
13 |
14 | }
15 |
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex7b.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex7b {
6 | public static void main(String[] args) {
7 | int sum = 0;
8 | for(int i = 1; i < 1000; i++)
9 | for(int j = 0; j < i; j++)
10 | sum++;
11 | StdOut.println(sum);
12 | }
13 | }
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex7c.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex7c {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | int sum = 0;
10 | for(int i = 1; i < 1000; i *= 2)
11 | for(int j = 0; j < 1000; j++)
12 | sum++;
13 | StdOut.println(sum);
14 |
15 | }
16 |
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex8.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | public class Ex8 {
4 |
5 | public static void main(String[] args) {
6 |
7 | System.out.println('b');
8 | System.out.println('b' + 'c');
9 | System.out.println((char)('a' + 4));
10 |
11 | }
12 |
13 | }
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Ex9.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | public class Ex9 {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 |
9 | int a = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
10 | String result = "";
11 |
12 | for(int n = a; n > 0; n /= 2) {
13 | result = (n % 2) + result;
14 | }
15 |
16 | StdOut.println(result);
17 |
18 | }
19 |
20 | }
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/RightTriangle.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdDraw;
4 |
5 | public class RightTriangle {
6 |
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 | StdDraw.square(.5, .5, .5);
9 | StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.BLUE);
10 | StdDraw.line(.5, .5, .9, .5);
11 | StdDraw.line(.9, .5, .5, .8);
12 | StdDraw.line(.5, .5, .5, .8);
13 | StdDraw.circle(.7, .65, .25);
14 |
15 | }
16 |
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/Sattolo.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdIn;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | public class Sattolo {
7 |
8 | private Sattolo() { }
9 |
10 | public static void cycle(Object[] a) {
11 | int n = a.length;
12 | for(int i = n; i > 1; i--) {
13 | int r = (int)(Math.random() * (i - 1));
14 | Object swap = a[r];
15 | a[r] = a[i - 1];
16 | a[i - 1] = swap;
17 | }
18 | }
19 |
20 | public static void main(String[] args) {
21 | String[] a = StdIn.readAllStrings();
22 |
23 | Sattolo.cycle(a);
24 |
25 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
26 | StdOut.println(a[i]);
27 | }
28 | }
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_1_Programming_Model/StdDrawTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_1_Programming_Model;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Arrays;
4 | import algs4.*;
5 |
6 | public class StdDrawTest {
7 | public static void main(String[] args) {
8 | // int N = 100;
9 | // StdDraw.setXscale(0, N);
10 | // StdDraw.setYscale(0, N*N);
11 | // StdDraw.setPenRadius(.01);
12 | // for(int i = 1; i <= N; i++){
13 | // StdDraw.point(i, i);
14 | // StdDraw.point(i, i*i);
15 | // StdDraw.point(i, i*Math.log(i));
16 | // }
17 |
18 | int N = 50;
19 | double[] a = new double[N];
20 | for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
21 | a[i] = StdRandom.uniform();
22 | }
23 | Arrays.sort(a);
24 | for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
25 | double x = 1.0 * i / N;
26 | double y = a[i] / 2.0;
27 | double rw = 0.5 / N;
28 | double rh = a[i] / 2.0;
29 | StdDraw.filledRectangle(x, y, rw, rh);
30 | }
31 |
32 | }
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/Accumulator.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | public class Accumulator {
4 | private double total;
5 | private int N;
6 | public void addDataValue(double val) {
7 | N++;
8 | total += val;
9 | }
10 | public double mean() {
11 | return total / N;
12 | }
13 | public String toString() {
14 | return "Mean (" + N + " values): " + String.format("%7.5f", mean());
15 | }
16 | }
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/AccumulatorTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 |
6 | public class AccumulatorTest {
7 |
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 |
10 | int T = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
11 | Accumulator a = new Accumulator();
12 | for(int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
13 | a.addDataValue(StdRandom.uniform());
14 | }
15 | StdOut.println(a);
16 |
17 | }
18 | }
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/Cat.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.Out;
5 |
6 | public class Cat {
7 |
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 | // 将所有输入文件复制到输出流(最后一个参数)中
10 | Out out = new Out(args[args.length - 1]);
11 | for(int i = 0; i < args.length - 1; i++) {
12 | // 将第 i 个输入文件复制到输出流中
13 | In in = new In(args[i]);
14 | String str = in.readAll();
15 | out.println(str);
16 | in.close();
17 | }
18 | out.close();
19 |
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/Date.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | public class Date {
4 | private final int month;
5 | private final int day;
6 | private final int year;
7 |
8 | public Date(int m, int d, int y) {
9 | this.month = m;
10 | this.day = d;
11 | this.year = y;
12 | }
13 | public int month() {
14 | return month;
15 | }
16 | public int day() {
17 | return day;
18 | }
19 | public int year() {
20 | return year;
21 | }
22 | public String toString() {
23 | return month() + "/" + day() + "/" + year();
24 | }
25 | public boolean equals(Object x) {
26 | if(this == x)
27 | return true;
28 | if(x == null)
29 | return false;
30 | if(this.getClass() != x.getClass())
31 | return false;
32 | Date that = (Date) x;
33 | if(this.day != that.day)
34 | return false;
35 | if(this.month != that.month)
36 | return false;
37 | if(this.year != that.year)
38 | return false;
39 | return true;
40 | }
41 | }
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/Flips.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Counter;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 | import algs4.StdRandom;
6 |
7 | public class Flips {
8 |
9 | public static void main(String[] args) {
10 |
11 | int T = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
12 | Counter heads = new Counter("heads");
13 | Counter tails = new Counter("tails");
14 | for(int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
15 | if(StdRandom.bernoulli(.5))
16 | heads.increment();
17 | else
18 | tails.increment();
19 | }
20 | StdOut.println(heads);
21 | StdOut.println(tails);
22 | int d = heads.tally() - tails.tally();
23 | StdOut.println("delta: " + Math.abs(d));
24 |
25 | }
26 |
27 | }
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/FlipsMax.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Counter;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 | import algs4.StdRandom;
6 |
7 | public class FlipsMax {
8 |
9 | public static Counter max(Counter x, Counter y) {
10 | if(x.tally() > y.tally()) {
11 | return x;
12 | }
13 | return y;
14 | }
15 |
16 | public static void main(String[] args) {
17 | int T = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
18 | Counter heads = new Counter("heads");
19 | Counter tails = new Counter("tails");
20 | for(int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
21 | if(StdRandom.bernoulli(.5))
22 | heads.increment();
23 | else
24 | tails.increment();
25 | }
26 |
27 | if(heads.tally() == tails.tally())
28 | StdOut.println("Tie");
29 | else
30 | StdOut.println(max(heads, tails) + " wins");
31 | }
32 |
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/Interval2DTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Counter;
4 | import algs4.Interval1D;
5 | import algs4.Interval2D;
6 | import algs4.Point2D;
7 | import algs4.StdOut;
8 |
9 | public class Interval2DTest {
10 |
11 | public static void main(String[] args) {
12 | double xlo = Double.parseDouble(args[0]);
13 | double xhi = Double.parseDouble(args[1]);
14 | double ylo = Double.parseDouble(args[2]);
15 | double yhi = Double.parseDouble(args[3]);
16 | int T = Integer.parseInt(args[4]);
17 |
18 | Interval1D xinterval = new Interval1D(xlo, xhi);
19 | Interval1D yinterval = new Interval1D(ylo, yhi);
20 | Interval2D box = new Interval2D(xinterval, yinterval);
21 | box.draw();
22 |
23 | Counter c = new Counter("hits");
24 | for(int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
25 | double x = Math.random();
26 | double y = Math.random();
27 | Point2D p = new Point2D(x, y);
28 | if(box.contains(p))
29 | c.increment();
30 | else
31 | p.draw();
32 | }
33 | StdOut.println(c);
34 | StdOut.println(box.area());
35 |
36 | }
37 |
38 | }
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/Rolls.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Counter;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 | import algs4.StdRandom;
6 |
7 | public class Rolls {
8 |
9 | public static void main(String[] args) {
10 | int T = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
11 | int SIDES = 6;
12 | Counter[] rolls = new Counter[SIDES + 1];
13 | for(int i = 0; i <= SIDES; i++) {
14 | rolls[i] = new Counter(i + "'s");
15 | }
16 | for(int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
17 | int result = StdRandom.uniform(1, SIDES + 1);
18 | rolls[result].increment();
19 | }
20 | for(int i = 1; i <= SIDES; i++) {
21 | StdOut.println(rolls[i]);
22 | }
23 |
24 | }
25 |
26 | }
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/StaticSETofInts.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Arrays;
4 |
5 | public class StaticSETofInts {
6 | private int[] a;
7 | public StaticSETofInts(int[] keys) {
8 | a = new int[keys.length];
9 | for(int i = 0; i < keys.length; i++) {
10 | a[i] = keys[i]; // 保护性复制
11 | }
12 | Arrays.sort(a);
13 | }
14 | public boolean contains(int key) {
15 | return rank(key) != -1;
16 | }
17 | private int rank(int key) {
18 | // 二分查找
19 | int lo = 0;
20 | int hi = a.length;
21 | while(lo <= hi) {
22 | int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
23 | if(key > a[mid]) {
24 | lo = mid + 1;
25 | }
26 | else if(key < a[mid]) {
27 | hi = mid - 1;
28 | }
29 | else {
30 | return mid;
31 | }
32 | }
33 | return -1;
34 | }
35 | }
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/VisualAccumulator.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdDraw;
4 |
5 | public class VisualAccumulator {
6 | private double total;
7 | private int N;
8 |
9 | public VisualAccumulator(int trials, double max) {
10 | StdDraw.setXscale(0, trials);
11 | StdDraw.setYscale(0, max);
12 | StdDraw.setPenRadius(.005);
13 | }
14 |
15 | public void addDataValue(double val) {
16 | N++;
17 | total += val;
18 | StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.DARK_GRAY);
19 | StdDraw.point(N, val);
20 | StdDraw.setPenColor(StdDraw.RED);
21 | StdDraw.point(N, mean());
22 | }
23 | public double mean() {
24 | return total / N;
25 | }
26 | public String toString() {
27 | return "Mean (" + N + " values): " + String.format("%7.5f", mean());
28 | }
29 | }
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/VisualAccumulatorTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 |
6 | public class VisualAccumulatorTest {
7 |
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 |
10 | int T = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
11 | VisualAccumulator a = new VisualAccumulator(T, 1.0);
12 | for(int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
13 | a.addDataValue(StdRandom.uniform());
14 | }
15 | StdOut.println(a);
16 |
17 | }
18 | }
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/WhiteList.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.StdIn;
5 | import algs4.StdOut;
6 |
7 | public class WhiteList {
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 | int[] w = In.readInts(args[0]);
10 | StaticSETofInts seTofInts = new StaticSETofInts(w);
11 | while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
12 | // 读取键,如果不在白名单中则打印它
13 | int key = StdIn.readInt();
14 | if(!seTofInts.contains(key))
15 | StdOut.println(key);
16 | }
17 | }
18 | }
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/in1.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | This is
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_2_Data_Abstraction/in2.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | a tiny
2 | test.
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_3_Bags_Queues_Stacks/ResizingArrayStack.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_3_Bags_Queues_Stacks;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Iterator;
4 |
5 | public class ResizingArrayStack- implements Iterable
- {
6 | private Item[] a = (Item[]) new Object[1]; // 栈元素
7 | private int N = 0;
8 | public boolean isEmpty() {
9 | return N == 0;
10 | }
11 | public int size() {
12 | return N;
13 | }
14 | public void resize(int max) {
15 | // 将栈移动到一个大小为 max 的新数组
16 | Item[] temp = (Item[]) new Object[max];
17 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
18 | temp[i] = a[i];
19 | a = temp;
20 | }
21 | public void push(Item item) {
22 | if(N == a.length)
23 | resize(2 * a.length);
24 | a[N++] = item;
25 | }
26 | public Item pop() {
27 | Item item = a[--N];
28 | a[N] = null;
29 | if(N > 0 && N == a.length / 4)
30 | resize(a.length / 2);
31 | return item;
32 | }
33 |
34 | @Override
35 | public Iterator
- iterator() {
36 | return new ReverseArrayIterator();
37 | }
38 | private class ReverseArrayIterator implements Iterator
- {
39 | private int i = N;
40 | public boolean hasNext() {
41 | return i > 0;
42 | }
43 | public Item next() {
44 | return a[--i];
45 | }
46 | public void remove() {}
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms/DoublingRatio.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 |
6 | public class DoublingRatio {
7 |
8 | public static double timeTrial(int N) {
9 | // 为处理 N 个随机的六位整数的 ThreeSum.count() 计时
10 | int MAX = 1000000;
11 | int[] a = new int[N];
12 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
13 | a[i] = StdRandom.uniform(-MAX, MAX);
14 | Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
15 | int cnt = ThreeSum.count(a);
16 | return timer.elapsedTime();
17 | }
18 |
19 | public static void main(String[] args) {
20 |
21 | double prev = timeTrial(125);
22 | for(int N = 250; true; N *= 2) {
23 | double time = timeTrial(N);
24 | StdOut.printf("%6d %7.1f ", N, time);
25 | StdOut.printf("%5.1f\n", time/prev);
26 | prev = time;
27 | }
28 |
29 | }
30 |
31 | }
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms/DoublingTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 |
6 | public class DoublingTest {
7 |
8 | public static double timeTrial(int N) {
9 | // 为处理 N 个随机的六位整数的 ThreeSum.count() 计时
10 | int MAX = 1000000;
11 | int[] a = new int[N];
12 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
13 | a[i] = StdRandom.uniform(-MAX, MAX);
14 | Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
15 | int cnt = ThreeSum.count(a);
16 | return timer.elapsedTime();
17 | }
18 |
19 | public static void main(String[] args) {
20 | // 打印运行时间的表格
21 | for(int N = 250; true; N *= 2) {
22 | double time = timeTrial(N);
23 | StdOut.printf("%7d %5.1f\n", N, time);
24 | }
25 |
26 | }
27 |
28 | }
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms/Stopwatch.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms;
2 |
3 | public class Stopwatch {
4 | private final long start;
5 | public Stopwatch() {
6 | start = System.currentTimeMillis();
7 | }
8 | public double elapsedTime() {
9 | long now = System.currentTimeMillis();
10 | return (now - start) / 1000.0;
11 | }
12 | }
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms/StopwatchTest.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 |
6 | public class StopwatchTest {
7 |
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 |
10 | int N = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
11 | int[] a = new int[N];
12 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
13 | a[i] = StdRandom.uniform(-1000000, 1000000);
14 | Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
15 | int cnt = ThreeSum.count(a);
16 | double time = timer.elapsedTime();
17 | StdOut.println(cnt + " triples " + time + " seconds");
18 | }
19 |
20 | }
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms/ThreeSum.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | public class ThreeSum {
7 |
8 | public static int count(int[] a) {
9 | int N = a.length;
10 | int cnt = 0;
11 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
12 | for(int j = i + 1; j < N; j++)
13 | for(int k = j + 1; k < N; k++)
14 | if(a[i] + a[j] + a[k] == 0)
15 | cnt++;
16 | return cnt;
17 | }
18 |
19 | public static void main(String[] args) {
20 | int[] a = In.readInts(args[0]);
21 | StdOut.println(count(a));
22 | }
23 |
24 | }
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_5_Case_Study_Union_Find/UF.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_5_Case_Study_Union_Find;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdIn;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | public class UF {
7 | private int[] id; // 分量id(以触点作为索引)
8 | private int count; // 分量数量
9 |
10 | public UF(int N) {
11 | // 初始化分量 id 数组
12 | count = N;
13 | id = new int[N];
14 | for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
15 | id[i] = i;
16 | }
17 |
18 | public int count() {
19 | return count;
20 | }
21 |
22 | public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
23 | return find(p) == find(q);
24 | }
25 |
26 | /* quick-find 算法 */
27 | // public int find(int p) {
28 | // return id[p];
29 | // }
30 | //
31 | // public void union(int p, int q) {
32 | // // 将 p 和 q 归并到同样的分量中
33 | // int pID = find(p);
34 | // int qID = find(q);
35 | //
36 | // // 如果 p 和 q 已经在相同的分量之中则不需要采取任何行动
37 | // if(pID == qID)
38 | // return;
39 | //
40 | // // 将 p 的分量重命名为 q 的名称
41 | // for(int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
42 | // if(id[i] == pID)
43 | // id[i] = qID;
44 | // count--;
45 | // }
46 |
47 | /* quick-union 算法 */
48 | private int find(int p) {
49 | // 找出分量的名称
50 | while(p != id[p])
51 | p = id[p];
52 | return p;
53 | }
54 |
55 | private void union(int p, int q) {
56 | // 将 p 和 q 的根节点统一
57 | int pRoot = find(p);
58 | int qRoot = find(q);
59 | if(pRoot == qRoot)
60 | return;
61 |
62 | id[pRoot] = qRoot;
63 |
64 | count--;
65 | }
66 |
67 | public static void main(String[] args) {
68 | // 解决由StdIn得到的动态连通性问题
69 | int N = StdIn.readInt(); // 读取触点数量
70 | UF uf = new UF(N); // 初始化 N 个分量
71 | while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
72 | int p = StdIn.readInt();
73 | int q = StdIn.readInt(); // 读取整数对
74 | if (uf.connected(p, q)) // 如果已经连通则忽略
75 | continue;
76 | uf.union(p, q); // 归并分量
77 | StdOut.println(p + " " + q); // 打印连接
78 | }
79 | StdOut.println(uf.count + "components");
80 | }
81 | }
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter1_5_Case_Study_Union_Find/WeightedQuickUnionUF.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter1_5_Case_Study_Union_Find;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | * 加权 quick-union 算法
5 | * @author huang
6 | */
7 | public class WeightedQuickUnionUF {
8 | private int[] id; // 父链接数组(由触点索引)
9 | private int[] sz; // (由触点索引的)各个根节点所对应的分量的大小
10 | private int count; // 连通分量的数量
11 |
12 | public WeightedQuickUnionUF(int N) {
13 | count = N;
14 | id = new int[N];
15 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
16 | id[i] = i;
17 | sz = new int[N];
18 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
19 | sz[i] = 1;
20 | }
21 |
22 | public int count() {
23 | return count;
24 | }
25 |
26 | public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
27 | return find(p) == find(q);
28 | }
29 |
30 | public int find(int p) {
31 | // 跟随链接找到根节点
32 | while(p != id[p])
33 | p = id[p];
34 | return p;
35 | }
36 |
37 | public void union(int p, int q) {
38 | int pRoot = find(p);
39 | int qRoot = find(q);
40 | if(pRoot == qRoot)
41 | return;
42 | // 将小树的根节点连接到大树的根节点
43 | if(sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot]) {
44 | id[pRoot] = qRoot;
45 | sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
46 | }
47 | else {
48 | id[qRoot] = pRoot;
49 | sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
50 | }
51 | count--;
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts/Insertion.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * 插入排序
7 | * @author huang
8 | */
9 | @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unused", "unchecked"})
10 | public class Insertion {
11 | public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
12 | // 将 a[] 按升序排列
13 | int N = a.length;
14 | for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
15 | // 将 a[i] 插入到 a[i-1]、a[i-2]、a[i-3]...之中
16 | /** 有改进空间,见练习 2.1.25 */
17 | for(int j = i; j > 0 && less(a[j], a[j-1]); j--)
18 | exch(a, j, j-1);
19 | }
20 | }
21 |
22 | private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
23 | // 对元素进行比较
24 | return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
25 | }
26 |
27 | private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
28 | // 将元素交换位置
29 | Comparable t = a[i];
30 | a[i] = a[j];
31 | a[j] = t;
32 | }
33 |
34 | private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
35 | // 在单行中打印数组
36 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
37 | StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
38 | StdOut.println();
39 | }
40 |
41 | public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
42 | // 测试数组元素是否有序
43 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
44 | if(less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
45 | return false;
46 | return true;
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts/Selection.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * 选择排序
7 | * @author huang
8 | */
9 | @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unused", "unchecked"})
10 | public class Selection {
11 | public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
12 | // 将 a[] 按升序排列
13 | int N = a.length;
14 | for(int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) {
15 | // 将 a[i] 和 a[i...N]中最小的元素交换
16 | int min = i; // 最小元素的索引
17 | for(int j = i+1; j < N; j++)
18 | if(less(a[j], a[min]))
19 | min = j;
20 | exch(a, i, min);
21 | }
22 | }
23 |
24 | private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
25 | // 对元素进行比较
26 | return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
27 | }
28 |
29 | private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
30 | // 将元素交换位置
31 | Comparable t = a[i];
32 | a[i] = a[j];
33 | a[j] = t;
34 | }
35 |
36 | private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
37 | // 在单行中打印数组
38 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
39 | StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
40 | StdOut.println();
41 | }
42 |
43 | public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
44 | // 测试数组元素是否有序
45 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
46 | if(less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
47 | return false;
48 | return true;
49 | }
50 | }
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts/Shell.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * 希尔排序
7 | * @author huang
8 | */
9 | @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unused", "unchecked"})
10 | public class Shell {
11 | public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
12 | // 将 a[] 按升序排列
13 | int N = a.length;
14 | int h = 1;
15 | while(h < N / 3)
16 | h = 3 * h + 1; // 1, 4, 13, 40, 121, 364, 1093, ...
17 | while(h >= 1) {
18 | // 将数组变为 h 有序
19 | for(int i = h; i < N; i++) {
20 | // 将 a[i] 插入到 a[i-h],a[i-2*h],a[i-3*h]... 之中
21 | for(int j = i; j >= h && less(a[j], a[j -h]); j -= h)
22 | exch(a, j, j-h);
23 | }
24 | h /= 3;
25 | }
26 | }
27 |
28 | private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
29 | // 对元素进行比较
30 | return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
31 | }
32 |
33 | private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
34 | // 将元素交换位置
35 | Comparable t = a[i];
36 | a[i] = a[j];
37 | a[j] = t;
38 | }
39 |
40 | private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
41 | // 在单行中打印数组
42 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
43 | StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
44 | StdOut.println();
45 | }
46 |
47 | public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
48 | // 测试数组元素是否有序
49 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
50 | if(less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
51 | return false;
52 | return true;
53 | }
54 | }
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts/SortCompare.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 | import chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms.Stopwatch;
6 |
7 | /**
8 | * @author huang
9 | * 比较两种排序算法
10 | */
11 | @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes"})
12 | public class SortCompare {
13 | public static double time(String alg, Comparable[] a) {
14 | Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
15 | if(alg.equals("Insertion"))
16 | Insertion.sort(a);
17 | if(alg.equals("Selection"))
18 | Selection.sort(a);
19 | if(alg.equals("Shell"))
20 | Shell.sort(a);
21 | // if(alg.equals("Merge"))
22 | // Merge.sort(a);
23 | // if(alg.equals("Quick"))
24 | // Quick.sort(a);
25 | // if(alg.equals("Heap"))
26 | // Heap.sort(a);
27 | return timer.elapsedTime();
28 | }
29 |
30 | public static double timeRandomInput(String alg, int N, int T) {
31 | // 使用算法 alg 将 T 个长度为 N 的数组排序
32 | double total = 0.0;
33 | Double[] a = new Double[N];
34 | for(int t = 0; t < T; t++) {
35 | // 进行一次测试(生成一个数组并排序)
36 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i ++)
37 | a[i] = StdRandom.uniform(); /** 练习 2.5.31 */
38 | total += time(alg, a);
39 | }
40 | return total;
41 | }
42 |
43 | public static void main(String[] args) {
44 | String alg1 = args[0];
45 | String alg2 = args[1];
46 | int N = Integer.parseInt(args[2]);
47 | int T = Integer.parseInt(args[3]);
48 | double t1 = timeRandomInput(alg1, N, T); // 算法 1 的总时间
49 | double t2 = timeRandomInput(alg2, N, T); // 算法 2 的总时间
50 | StdOut.printf("For %d random Doubles\n %s is", N, alg1);
51 | StdOut.printf(" %.1f times faster than %s\n", t2/t1, alg2);
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_2_Mergesort/Merge.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_2_Mergesort;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * @author huang
7 | * 自顶向下的归并排序
8 | */
9 | @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unused", "unchecked"})
10 | public class Merge {
11 | private static Comparable[] aux; // 归并所需的辅助数组
12 |
13 | public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
14 | aux = new Comparable[a.length];
15 | sort(a, 0, a.length - 1);
16 | }
17 |
18 | private static void sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
19 | // 将数组 a[lo..hi] 排序
20 | if(hi <= lo)
21 | return;
22 | int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
23 | sort(a, lo, mid); // 将左半边排序
24 | sort(a, mid + 1, hi); // 将右半边排序
25 | if(less(a[mid+1], a[mid])) // 为 false 则认为数组已经是有序的,跳过 merge()
26 | merge(a, lo, mid, hi); // 归并结果
27 | }
28 |
29 | public static void merge(Comparable[] a, int lo, int mid, int hi) {
30 | // 将 a[lo..mid] 和 a[mid+1..hi] 归并
31 | int i = lo, j = mid + 1;
32 |
33 | for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) // 将 a[lo..hi] 复制到 aux[lo..hi]
34 | aux[k] = a[k];
35 |
36 | for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k++)
37 | if(i > mid) // 左半边元素用尽
38 | a[k] = aux[j++];
39 | else if(j > hi) // 右半边元素用尽
40 | a[k] = aux[i++];
41 | else if(less(aux[i], aux[j]))
42 | a[k] = aux[i++];
43 | else
44 | a[k] = aux[j++];
45 | }
46 |
47 | private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
48 | // 对元素进行比较
49 | return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
50 | }
51 |
52 | private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
53 | // 将元素交换位置
54 | Comparable t = a[i];
55 | a[i] = a[j];
56 | a[j] = t;
57 | }
58 |
59 | private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
60 | // 在单行中打印数组
61 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
62 | StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
63 | StdOut.println();
64 | }
65 |
66 | public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
67 | // 测试数组元素是否有序
68 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
69 | if(less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
70 | return false;
71 | return true;
72 | }
73 | }
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_2_Mergesort/MergeBU.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_2_Mergesort;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * @author huang
7 | * 自底向上的归并排序
8 | */
9 | @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unused", "unchecked"})
10 | public class MergeBU {
11 | private static Comparable[] aux; // 归并所需的辅助数组
12 |
13 | public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
14 | // 进行 lgN 次两两归并
15 | int N = a.length;
16 | aux = new Comparable[N];
17 | for(int sz = 1; sz < N; sz = sz+sz)
18 | for(int lo = 0; lo < N - sz; lo += sz+sz)
19 | merge(a, lo, lo+sz-1, Math.min(lo+sz+sz-1, N-1)); // 最后一个子数组的大小只有在数组大小是 sz 的偶数倍时才会等于 sz,否则小于 sz
20 | }
21 |
22 | public static void merge(Comparable[] a, int lo, int mid, int hi) {
23 | // 将 a[lo..mid] 和 a[mid+1..hi] 归并
24 | int i = lo, j = mid + 1;
25 |
26 | for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k++) // 将 a[lo..hi] 复制到 aux[lo..hi]
27 | aux[k] = a[k];
28 |
29 | for(int k = lo; k <= hi; k++)
30 | if(i > mid) // 左半边元素用尽
31 | a[k] = aux[j++];
32 | else if(j > hi) // 右半边元素用尽
33 | a[k] = aux[i++];
34 | else if(less(aux[i], aux[j]))
35 | a[k] = aux[i++];
36 | else
37 | a[k] = aux[j++];
38 | }
39 |
40 | private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
41 | // 对元素进行比较
42 | return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
43 | }
44 |
45 | private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
46 | // 将元素交换位置
47 | Comparable t = a[i];
48 | a[i] = a[j];
49 | a[j] = t;
50 | }
51 |
52 | private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
53 | // 在单行中打印数组
54 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
55 | StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
56 | StdOut.println();
57 | }
58 |
59 | public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
60 | // 测试数组元素是否有序
61 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
62 | if(less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
63 | return false;
64 | return true;
65 | }
66 | }
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_3_Quicksort/Ex25.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_3_Quicksort;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 | import chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms.Stopwatch;
6 | import chapter1_4_Analysis_of_Algorithms.ThreeSum;
7 | import chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts.Insertion;
8 | import chapter2_1_Elementary_Sorts.SortCompare;
9 |
10 | /**
11 | * 快速排序切换到插入排序
12 | * @author huang
13 | */
14 | @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unused", "unchecked"})
15 | public class Ex25 {
16 | public static void main(String[] args) {
17 |
18 | for(int N = 1000; N <= 1000000; N *= 10) {
19 | Comparable[] a = new Comparable[N];
20 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
21 | a[i] = StdRandom.uniform(-1000000, 1000000);
22 | for(int M = 0; M <= 30; M++) {
23 | Comparable[] b = a.clone();
24 | Stopwatch timer = new Stopwatch();
25 | sort(b, 1);
26 | double time = timer.elapsedTime();
27 | StdOut.println("Array size: " + N + ", M = " + M + ", time: " + time + " seconds");
28 | }
29 | }
30 | }
31 |
32 | public static void sort(Comparable[] a, int M) {
33 | StdRandom.shuffle(a); // 消除对输入的依赖
34 | sort(a,0, a.length - 1, M);
35 | }
36 |
37 | private static void sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi, int M) {
38 | if(hi <= lo + M) {
39 | insertSort(a, lo, hi);
40 | return;
41 | }
42 | int j = partition(a, lo, hi); // 切分
43 | sort(a, lo, j-1, M); // 将左半部分 a[lo .. j-1]
44 | sort(a, j+1, hi, M); // 将右半部分 a[j+1 .. hi]
45 | }
46 |
47 | private static void insertSort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
48 | int N = a.length;
49 | for(int i = lo; i < hi+1; i++) {
50 | for(int j = i; j > 0 && less(a[j], a[j-1]); j--)
51 | exch(a, j, j-1);
52 | }
53 | }
54 |
55 | private static int partition(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
56 | // 将数组切分为 a[lo .. i-1],a[i],a[i+1 .. hi]
57 | int i = lo, j = hi+1; // 左右扫描指针
58 | Comparable v = a[lo]; // 切分元素
59 | while(true) {
60 | // 扫描左右,检查扫描是否结束并交换元素
61 | while(less(a[++i], v))
62 | if(i == hi)
63 | break;
64 | while(less(v, a[--j]))
65 | if(j == lo)
66 | break;
67 | if(i >= j)
68 | break;
69 | exch(a, i, j);
70 | }
71 | exch(a, lo, j);
72 | return j;
73 | }
74 |
75 | private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
76 | // 对元素进行比较
77 | return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
78 | }
79 |
80 | private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
81 | // 将元素交换位置
82 | Comparable t = a[i];
83 | a[i] = a[j];
84 | a[j] = t;
85 | }
86 |
87 | private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
88 | // 在单行中打印数组
89 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
90 | StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
91 | StdOut.println();
92 | }
93 |
94 | public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
95 | // 测试数组元素是否有序
96 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
97 | if(less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
98 | return false;
99 | return true;
100 | }
101 | }
102 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_3_Quicksort/Quick.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_3_Quicksort;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | * @author huang
8 | * 快速排序
9 | */
10 | @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unused", "unchecked"})
11 | public class Quick {
12 | public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
13 | StdRandom.shuffle(a); // 消除对输入的依赖
14 | sort(a,0, a.length - 1);
15 | }
16 |
17 | private static void sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
18 | if(hi <= lo)
19 | return;
20 | int j = partition(a, lo, hi); // 切分
21 | sort(a, lo, j-1); // 将左半部分 a[lo .. j-1]
22 | sort(a, j+1, hi); // 将右半部分 a[j+1 .. hi]
23 | }
24 |
25 | private static int partition(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
26 | // 将数组切分为 a[lo .. i-1],a[i],a[i+1 .. hi]
27 | int i = lo, j = hi+1; // 左右扫描指针
28 | Comparable v = a[lo]; // 切分元素
29 | while(true) {
30 | // 扫描左右,检查扫描是否结束并交换元素
31 | while(less(a[++i], v))
32 | if(i == hi)
33 | break;
34 | while(less(v, a[--j]))
35 | if(j == lo)
36 | break;
37 | if(i >= j)
38 | break;
39 | exch(a, i, j);
40 | }
41 | exch(a, lo, j);
42 | return j;
43 | }
44 |
45 | private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
46 | // 对元素进行比较
47 | return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
48 | }
49 |
50 | private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
51 | // 将元素交换位置
52 | Comparable t = a[i];
53 | a[i] = a[j];
54 | a[j] = t;
55 | }
56 |
57 | private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
58 | // 在单行中打印数组
59 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
60 | StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
61 | StdOut.println();
62 | }
63 |
64 | public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
65 | // 测试数组元素是否有序
66 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
67 | if(less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
68 | return false;
69 | return true;
70 | }
71 | }
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_3_Quicksort/Quick3way.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_3_Quicksort;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 | import algs4.StdRandom;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | * @author huang
8 | * 三向切分的快速排序
9 | */
10 | @SuppressWarnings({"rawtypes", "unused", "unchecked"})
11 | public class Quick3way {
12 | public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
13 | StdRandom.shuffle(a); // 消除对输入的依赖
14 | sort(a,0, a.length - 1);
15 | }
16 |
17 | private static void sort(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
18 | if(hi <= lo)
19 | return;
20 | int lt = lo, i = lo+1, gt = hi; // lt: b 开始, gt: b 结束, i: c 开始
21 | Comparable v = a[lo];
22 | while(i <= gt) {
23 | int cmp = a[i].compareTo(v);
24 | if(cmp < 0)
25 | exch(a, lt++, i++);
26 | else if(cmp > 0)
27 | exch(a, i, gt--);
28 | else
29 | i++;
30 | } // 现在 a[lo .. lt-1] < v = a[lt .. gt] < a[gt+1 .. hi] 成立
31 | sort(a, lo, lt - 1);
32 | sort(a, gt + 1, hi);
33 | }
34 |
35 | private static int partition(Comparable[] a, int lo, int hi) {
36 | // 将数组切分为 a[lo .. i-1],a[i],a[i+1 .. hi]
37 | int i = lo, j = hi+1; // 左右扫描指针
38 | Comparable v = a[lo]; // 切分元素
39 | while(true) {
40 | // 扫描左右,检查扫描是否结束并交换元素
41 | while(less(a[++i], v))
42 | if(i == hi)
43 | break;
44 | while(less(v, a[--j]))
45 | if(j == lo)
46 | break;
47 | if(i >= j)
48 | break;
49 | exch(a, i, j);
50 | }
51 | exch(a, lo, j);
52 | return j;
53 | }
54 |
55 | private static boolean less(Comparable v, Comparable w) {
56 | // 对元素进行比较
57 | return v.compareTo(w) < 0;
58 | }
59 |
60 | private static void exch(Comparable[] a, int i, int j) {
61 | // 将元素交换位置
62 | Comparable t = a[i];
63 | a[i] = a[j];
64 | a[j] = t;
65 | }
66 |
67 | private static void show(Comparable[] a) {
68 | // 在单行中打印数组
69 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
70 | StdOut.print(a[i] + " ");
71 | StdOut.println();
72 | }
73 |
74 | public static boolean isSorted(Comparable[] a) {
75 | // 测试数组元素是否有序
76 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
77 | if(less(a[i], a[i - 1]))
78 | return false;
79 | return true;
80 | }
81 | }
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_4_Priority_Queues/MaxPQ.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_4_Priority_Queues;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | * 基于堆的优先队列
5 | *
6 | * @author huang
7 | */
8 | public class MaxPQ> {
9 |
10 | private Key[] pq; // 基于堆的完全二叉树
11 | private int N = 0; // 存储于 pq[1 .. N] 中,pq[0] 没有使用
12 |
13 | @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
14 | MaxPQ(int maxN) { // 创建一个初始容量为 max 的优先队列
15 | pq = (Key[]) new Comparable[maxN + 1];
16 | }
17 |
18 | // 向优先队列中插入一个元素
19 | void insert(Key v) {
20 | pq[++N] = v;
21 | swim(N);
22 | }
23 |
24 | // 删除并返回最大元素
25 | public Key delMax() {
26 | Key max = pq[1]; // 从根结点得到最大元素
27 | exch(1, N--); // 将其和最后一个结点交换
28 | pq[N+1] = null; // 防止对象游离
29 | sink(1); // 恢复堆的有序性
30 | return max;
31 | }
32 |
33 | boolean isEmpty() { // 返回队列是否为空
34 | return N == 0;
35 | }
36 |
37 | int size() { // 返回优先队列中的元素个数
38 | return N;
39 | }
40 |
41 | private boolean less(int i, int j) {
42 | return pq[i].compareTo(pq[j]) < 0;
43 | }
44 |
45 | private void exch(int i, int j) {
46 | Key t = pq[i];
47 | pq[i] = pq[j];
48 | pq[j] = t;
49 | }
50 |
51 | // 由下至上的堆有序化(上浮)的实现
52 | private void swim(int k) {
53 | while(k > 1 && less(k/2, k)) {
54 | exch(k/2, k);
55 | k = k/2;
56 | }
57 | }
58 |
59 | // 由上至下的堆有序化(下沉)的实现
60 | private void sink(int k) {
61 | while(2 * k <= N) {
62 | int j = 2 * k;
63 | if(j < N && less(j, j+1))
64 | j++;
65 | if(!less(k, j))
66 | break;
67 | exch(k, j);
68 | k = j;
69 | }
70 | }
71 | }
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter2_4_Priority_Queues/TopM.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter2_4_Priority_Queues;
2 |
3 | import algs4.MinPQ;
4 | import algs4.Stack;
5 | import algs4.StdIn;
6 | import algs4.StdOut;
7 |
8 | public class TopM {
9 | public static void main(String[] args) {
10 | // 打印输入流中最大的 M 行
11 | int M = Integer.parseInt(args[0]);
12 | MinPQ pq = new MinPQ<>(M+1);
13 | while(StdIn.hasNextLine()) {
14 | // 为下一行输入创建一个元素并放入优先队列中
15 | pq.insert(new Transaction(StdIn.readLine()));
16 | if(pq.size() > M)
17 | pq.delMin(); // 如果优先队列中存在 M+1
18 | } // 最大的 M 个元素都在优先队列中
19 |
20 | Stack stack = new Stack();
21 | while(!pq.isEmpty())
22 | stack.push(pq.delMin());
23 | for(Transaction t : stack)
24 | StdOut.println(t);
25 | }
26 | }
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter3_1_Symbol_Tables/BinarySearchST.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter3_1_Symbol_Tables;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Queue;
4 |
5 | @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
6 | public class BinarySearchST, Value> {
7 | private Key[] keys;
8 | private Value[] vals;
9 | private int N;
10 | public BinarySearchST(int capacity) {
11 | keys = (Key[]) new Comparable[capacity];
12 | vals = (Value[]) new Object[capacity];
13 | }
14 |
15 | private void resize(int max) {
16 | // 将栈移动到一个大小为 max 的新数组
17 | Key[] tempKeys = (Key[]) new Comparable[max];
18 | Value[] tempValues = (Value[]) new Object[max];
19 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
20 | tempKeys[i] = keys[i];
21 | tempValues[i] = vals[i];
22 | }
23 | keys = tempKeys;
24 | vals = tempValues;
25 | }
26 |
27 | public int size() {
28 | return N;
29 | }
30 |
31 | public Value get(Key key) {
32 | if(isEmpty())
33 | return null;
34 | int i = rank(key);
35 | if(i < N && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0)
36 | return vals[i];
37 | else
38 | return null;
39 | }
40 |
41 | public boolean isEmpty() {
42 | return N == 0;
43 | }
44 |
45 | public int rank(Key key) {
46 | int lo = 0, hi = N-1;
47 | while(lo <= hi) {
48 | int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
49 | int cmp = key.compareTo(keys[mid]);
50 | if(cmp < 0)
51 | hi = mid - 1;
52 | else if(cmp > 0)
53 | lo = mid + 1;
54 | else
55 | return mid;
56 | }
57 | return lo;
58 | }
59 |
60 | public void put(Key key, Value val) {
61 | // 查找键,找到则更新值,否则创建新的元素
62 | int i = rank(key);
63 | if(i < N && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0) {
64 | vals[i] = val;
65 | return;
66 | }
67 | if(N == keys.length) // 调整数组大小
68 | resize(2 * keys.length);
69 | for(int j = N; j > i; j--) {
70 | keys[j] = keys[j-1];
71 | vals[j] = vals[j-1];
72 | }
73 | keys[i] = key;
74 | vals[i] = val;
75 | N++;
76 | }
77 |
78 | public Key min() {
79 | return keys[0];
80 | }
81 |
82 | public Key max() {
83 | return keys[N-1];
84 | }
85 |
86 | public Key select(int k) {
87 | return keys[k];
88 | }
89 |
90 | public Key ceiling(Key key) {
91 | int i = rank(key);
92 | return keys[i];
93 | }
94 |
95 | // public Key floor(Key key) {
96 | //
97 | // }
98 |
99 | public Key delete(Key key) {
100 | int i = rank(key);
101 | if(!(i < N && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0)) {
102 | return null;
103 | }
104 | if(N < keys.length / 2) // 调整数组大小
105 | resize(keys.length / 2);
106 | for(int j = i; j < N; j++) {
107 | keys[j] = keys[j+1];
108 | vals[j] = vals[j+1];
109 | }
110 | keys[N] = null;
111 | vals[N] = null;
112 | N--;
113 | return key;
114 | }
115 |
116 | public Iterable keys(Key lo, Key hi) {
117 | Queue q = new Queue();
118 | for(int i = rank(lo); i < rank(hi); i++)
119 | q.enqueue(keys[i]);
120 | if(contains(hi))
121 | q.enqueue(keys[rank(hi)]);
122 | return q;
123 | }
124 |
125 | public boolean contains(Key key) {
126 | int i = rank(key);
127 | return i < N && keys[i].compareTo(key) == 0;
128 | }
129 | }
130 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter3_1_Symbol_Tables/FrequencyCounter.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter3_1_Symbol_Tables;
2 |
3 | import algs4.ST;
4 | import algs4.StdIn;
5 | import algs4.StdOut;
6 |
7 | /**
8 | * 符号表的用例
9 | * @author huang
10 | */
11 | public class FrequencyCounter {
12 | public static void main(String[] args) {
13 | int minlen = Integer.parseInt(args[0]); // 最小键长
14 | ST st = new ST();
15 | while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
16 | // 构造符号表并统计频率
17 | String word = StdIn.readString();
18 | if(word.length() < minlen)
19 | continue; // 忽略较短的单词
20 | if(!st.contains(word))
21 | st.put(word, 1);
22 | else
23 | st.put(word, st.get(word)+1);
24 | }
25 | // 找出出现频率最高的单词
26 | String max = " ";
27 | st.put(max, 0);
28 | for(String word : st.keys())
29 | if(st.get(word) > st.get(max))
30 | max = word;
31 | StdOut.println(max + " " + st.get(max));
32 | }
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter3_1_Symbol_Tables/SequentialSearchST.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter3_1_Symbol_Tables;
2 |
3 | public class SequentialSearchST{
4 | private Node first; // 链表首结点
5 | private class Node {
6 | Key key;
7 | Value val;
8 | Node next;
9 | public Node(Key key, Value val, Node next) {
10 | this.key = key;
11 | this.val = val;
12 | this.next = next;
13 | }
14 | }
15 |
16 | public Value get(Key key) {
17 | // 查找给定的键,返回相关联的值
18 | for(Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
19 | if(key.equals(x.key))
20 | return x.val; // 命中
21 | return null; // 未命中
22 | }
23 |
24 | public void put(Key key, Value val) {
25 | // 查找给定的键,找到则更新其值,否则在表中新建结点
26 | for(Node x = first; x != null; x = x.next)
27 | if(key.equals(x.key)) {
28 | x.val = val;
29 | return; // 命中,更新
30 | }
31 | first = new Node(key, val, first); // 未命中,新建结点
32 | }
33 |
34 | }
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter3_2_Binary_Search_Trees/BST.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter3_2_Binary_Search_Trees;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Queue;
4 |
5 | public class BST, Value> {
6 | private Node root; // 二叉查找树的根结点
7 |
8 | private class Node {
9 | private Key key; // 键
10 | private Value val; // 值
11 | private Node left, right; // 指向子树的链接
12 | private int N; // 以该结点为根的子树中的结点总数
13 |
14 | public Node(Key key, Value val, int N) {
15 | this.key = key;
16 | this.val = val;
17 | this.N = N;
18 | }
19 | }
20 |
21 | public int size() {
22 | return size(root);
23 | }
24 |
25 | private int size(Node x) {
26 | if(x == null)
27 | return 0;
28 | else
29 | return x.N;
30 | }
31 |
32 | public Value get(Key key) {
33 | return get(root, key);
34 | }
35 |
36 | private Value get(Node x, Key key) {
37 | // 在以 x 为根结点的子树中查找并返回 key 所对应的值
38 | if(x == null)
39 | return null;
40 | int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
41 | if(cmp < 0)
42 | return get(x.left, key);
43 | else if(cmp > 0)
44 | return get(x.right, key);
45 | else
46 | return x.val;
47 | }
48 |
49 | public void put(Key key, Value val) {
50 | // 查找 key,找到则更新它的值,否则为它创建一个新的结点
51 | root = put(root, key, val);
52 | }
53 |
54 | private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value val) {
55 | // 如果 key 存在于以 x 为根结点的子树中则更新它的值;
56 | // 否则将以 key 和 val 为键值对的新结点插入到该子树中
57 | if(x == null)
58 | return new Node(key, val, 1);
59 | int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
60 | if(cmp < 0)
61 | x.left = put(x.left, key, val);
62 | else if(cmp > 0)
63 | x.right = put(x.right, key, val);
64 | else
65 | x.val = val;
66 | x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
67 | return x;
68 | }
69 |
70 | public Key min() {
71 | return min(root).key;
72 | }
73 |
74 | private Node min(Node x) {
75 | if(x.left == null)
76 | return x;
77 | return min(x.left);
78 | }
79 |
80 | public Key max() {
81 | return max(root).key;
82 | }
83 |
84 | private Node max(Node x) {
85 | if(x.right == null)
86 | return x;
87 | return min(x.right);
88 | }
89 |
90 | public Key floor(Key key) {
91 | Node x = floor(root, key);
92 | if(x == null)
93 | return null;
94 | return x.key;
95 | }
96 |
97 | private Node floor(Node x, Key key) {
98 | if(x == null)
99 | return null;
100 | int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
101 | if(cmp == 0)
102 | return x;
103 | if(cmp < 0)
104 | return floor(x.left, key);
105 | Node t = floor(x.right, key);
106 | if(t != null)
107 | return t;
108 | else
109 | return x;
110 | }
111 |
112 | public Key select(int k) {
113 | return select(root, k).key;
114 | }
115 |
116 | private Node select(Node x, int k) {
117 | // 返回排名为 k 的结点
118 | if(x == null)
119 | return null;
120 | int t = size(x.left);
121 | if(t > k)
122 | return select(x.left, k);
123 | else if(t < k)
124 | return select(x.right, k-t-1);
125 | else
126 | return x;
127 | }
128 |
129 | public int rank(Key key) {
130 | return rank(key, root);
131 | }
132 |
133 | private int rank(Key key, Node x) {
134 | // 返回以 x 为根结点的子树中小于 x.key 的键的数量
135 | if(x == null)
136 | return 0;
137 | int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
138 | if(cmp < 0)
139 | return rank(key, x.left);
140 | else if(cmp > 0)
141 | return 1 + size(x.left) + rank(key, x.left);
142 | else
143 | return size(x.left);
144 | }
145 |
146 | public void deleteMin() {
147 | root = deleteMin(root);
148 | }
149 |
150 | private Node deleteMin(Node x) {
151 | if(x.left == null)
152 | return x.right;
153 | x.left = deleteMin(x.left);
154 | x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
155 | return x;
156 | }
157 |
158 | public void delete(Key key) {
159 | root = delete(root, key);
160 | }
161 |
162 | private Node delete(Node x, Key key) {
163 | if(x == null)
164 | return null;
165 | int cmp = key.compareTo(x.key);
166 | if(cmp < 0)
167 | x.left = delete(x.left, key);
168 | else if(cmp > 0)
169 | x.right = delete(x.right, key);
170 | else {
171 | if(x.right == null)
172 | return x.left;
173 | if(x.left == null)
174 | return x.right;
175 | Node t = x;
176 | x = min(t.right);
177 | x.right = deleteMin(t.right);
178 | x.left = t.left;
179 | }
180 | x.N = size(x.left) + size(x.right) + 1;
181 | return x;
182 | }
183 |
184 | public Iterable keys() {
185 | return keys(min(), max());
186 | }
187 |
188 | public Iterable keys(Key lo, Key hi) {
189 | Queue queue = new Queue();
190 | keys(root, queue, lo, hi);
191 | return queue;
192 | }
193 |
194 | private void keys(Node x, Queue queue, Key lo, Key hi) {
195 | if(x == null)
196 | return;
197 | int cmplo = lo.compareTo(x.key);
198 | int cmphi = hi.compareTo(x.key);
199 | if(cmplo < 0)
200 | keys(x.left, queue, lo, hi);
201 | if(cmplo <= 0 && cmplo >= 0)
202 | queue.enqueue(x.key);
203 | if(cmphi > 0)
204 | keys(x.right, queue, lo, hi);
205 | }
206 |
207 | }
208 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter3_4_Hash_Tables/LinearProbingHashST.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter3_4_Hash_Tables;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Queue;
4 |
5 | @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
6 | public class LinearProbingHashST {
7 | private int N; // 符号表中键值对的总数
8 | private int M = 16; // 线性探测表的大小
9 | private Key[] keys; // 键
10 | private Value[] vals; // 值
11 |
12 | public LinearProbingHashST() {
13 | keys = (Key[]) new Object[M];
14 | vals = (Value[]) new Object[M];
15 | }
16 |
17 | public LinearProbingHashST(int cap) {
18 | this.M = cap;
19 | keys = (Key[]) new Object[M];
20 | vals = (Value[]) new Object[M];
21 | }
22 |
23 | public int size() {
24 | return this.M;
25 | }
26 |
27 | private int hash(Key key) {
28 | return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
29 | }
30 |
31 | private void resize(int cap) {
32 | LinearProbingHashST t;
33 | t = new LinearProbingHashST(cap);
34 | for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
35 | if(keys[i] != null)
36 | t.put(keys[i], vals[i]);
37 | keys = t.keys;
38 | vals = t.vals;
39 | M = t.M;
40 | }
41 |
42 | public void put(Key key, Value val) {
43 | if(N >= M/2)
44 | resize(2 * M);
45 | int i;
46 | for(i = hash(key); keys[i] != null; i = (i + 1) % M)
47 | if(keys[i].equals(key)) {
48 | vals[i] = val;
49 | return;
50 | }
51 | keys[i] = key;
52 | vals[i] = val;
53 | N++;
54 | }
55 |
56 | public Value get(Key key) {
57 | for(int i = hash(key); keys[i] != null; i = (i + 1) % M)
58 | if(keys[i].equals(key))
59 | return vals[i];
60 | return null;
61 | }
62 |
63 | public boolean contains(Key key) {
64 | return get(key) != null;
65 | }
66 |
67 | public void delete(Key key) {
68 | if(!contains(key))
69 | return;
70 | int i = hash(key);
71 | while(!key.equals(keys[i]))
72 | i = (i + 1) % M;
73 | keys[i] = null;
74 | vals[i] = null;
75 | i = (i + 1) % M;
76 | while(keys[i] != null) {
77 | Key keyToRedo = keys[i];
78 | Value valToRedo = vals[i];
79 | keys[i] = null;
80 | vals[i] = null;
81 | N--;
82 | put(keyToRedo, valToRedo);
83 | i = (i + 1) % M;
84 | }
85 | N--;
86 | if(N > 0 && N == M/8)
87 | resize(M/2);
88 | }
89 |
90 | public Iterable keys() {
91 | Queue queue = new Queue();
92 | for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
93 | if(keys[i] != null)
94 | queue.enqueue(keys[i]);
95 | return queue;
96 | }
97 |
98 | }
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter3_4_Hash_Tables/SeparateChainingHashST.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter3_4_Hash_Tables;
2 |
3 | import java.util.Iterator;
4 |
5 | import algs4.Queue;
6 | import chapter3_1_Symbol_Tables.SequentialSearchST;
7 |
8 | @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
9 | public class SeparateChainingHashST {
10 | private int N; // 键值对总数
11 | private int M; // 散列表的大小
12 | private SequentialSearchST[] st; // 存放链表对象的数组
13 |
14 | public SeparateChainingHashST() {
15 | this(997);
16 | }
17 |
18 | public SeparateChainingHashST(int M) {
19 | // 创建 M 条链表
20 | this.M = M;
21 | st = (SequentialSearchST[]) new SequentialSearchST[M];
22 | for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
23 | st[i] = new SequentialSearchST();
24 | }
25 |
26 | private int hash(Key key) {
27 | return (key.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
28 | }
29 |
30 | public Value get(Key key) {
31 | return (Value) st[hash(key)].get(key);
32 | }
33 |
34 | public void put(Key key, Value val) {
35 | st[hash(key)].put(key, val);
36 | }
37 |
38 | public Iterable keys() {
39 | Queue queue = new Queue<>();
40 | for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
41 | for(Iterator iter = (Iterator) st[i].keys(); iter.hasNext();)
42 | queue.enqueue(iter.next());
43 | return queue;
44 | }
45 | }
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter3_5_Searching_Applications/SparseVector.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter3_5_Searching_Applications;
2 |
3 | import chapter3_4_Hash_Tables.LinearProbingHashST;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * @author huang
7 | * 能够完成点乘的稀疏向量
8 | */
9 | public class SparseVector {
10 | private LinearProbingHashST st;
11 | public SparseVector() {
12 | st = new LinearProbingHashST();
13 | }
14 | public int size() {
15 | return st.size();
16 | }
17 | public void put(int i, double x) {
18 | st.put(i, x);
19 | }
20 | public double get(int i) {
21 | if(!st.contains(i))
22 | return 0.0;
23 | return st.get(i);
24 | }
25 | public double dot(double[] that) {
26 | double sum = 0.0;
27 | for(int i : st.keys())
28 | sum += that[i] * this.get(i);
29 | return sum;
30 | }
31 |
32 | }
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter3_5_Searching_Applications/WhiteFilter.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter3_5_Searching_Applications;
2 |
3 | import java.util.HashSet;
4 |
5 | import algs4.In;
6 | import algs4.StdIn;
7 | import algs4.StdOut;
8 |
9 | /**
10 | * @author huang
11 | * 白名单过滤器
12 | */
13 | public class WhiteFilter {
14 | public static void main(String[] args) {
15 | HashSet set;
16 | set = new HashSet();
17 | In in = new In(args[0]);
18 | while(!in.isEmpty())
19 | set.add(in.readString());
20 | while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
21 | String word = StdIn.readString();
22 | if(set.contains(word))
23 | StdOut.print(word + " ");
24 | }
25 | }
26 | }
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/BreadthFirstPaths.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Queue;
4 | import algs4.Stack;
5 |
6 | public class BreadthFirstPaths {
7 | private boolean[] marked; // 到达该顶点的最短路径已知吗?
8 | private int[] edgeTo; // 到达该顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点
9 | private final int s; // 起点
10 |
11 | public BreadthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s) {
12 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
13 | edgeTo = new int[G.V()];
14 | this.s = s;
15 | bfs(G, s);
16 | }
17 |
18 | private void bfs(Graph G, int s) {
19 | Queue queue = new Queue();
20 | marked[s] = true; // 标记起点
21 | queue.enqueue(s); // 将它加入队列
22 | while(!queue.isEmpty()) {
23 | int v = queue.dequeue(); // 从队列中删去下一顶点
24 | for(int w : G.adj(v))
25 | if(!marked[w]) {
26 | edgeTo[w] = v; // 保存最短路径的最后一条边
27 | marked[w] = true; // 标记它,因为最短路径已知
28 | queue.enqueue(w); // 并将它添加到队列中
29 | }
30 | }
31 | }
32 |
33 | public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
34 | return marked[v];
35 | }
36 |
37 | public Iterable pathTo(int v) {
38 | if(!hasPathTo(v))
39 | return null;
40 | Stack path = new Stack<>();
41 | for(int x = v; x != s; x = edgeTo[x])
42 | path.push(x);
43 | path.push(s);
44 | return path;
45 | }
46 | }
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/CC.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | * 查找连通分量
5 | * @author huang
6 | */
7 | public class CC {
8 | private boolean[] marked;
9 | private int[] id;
10 | private int count; // 既用来计量连通分量,同时作为连通分量的下标
11 |
12 | public CC(Graph G) {
13 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
14 | id = new int[G.V()];
15 | for(int s = 0; s < G.V(); s++)
16 | if(!marked[s]) {
17 | dfs(G, s);
18 | count++;
19 | }
20 | }
21 |
22 | private void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
23 | marked[v] = true;
24 | id[v] = count;
25 | for(int w : G.adj(v))
26 | if(!marked[w])
27 | dfs(G, w);
28 | }
29 |
30 | public boolean connected(int v, int w) {
31 | return id[v] == id[w];
32 | }
33 |
34 | public int id(int v) {
35 | return id[v];
36 | }
37 |
38 | public int count() {
39 | return count;
40 | }
41 | }
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/Cycle.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | * 利用深度优先,判断 G 是否是无向图(假设不存在自环或平行边)
5 | * @author huang
6 | */
7 | public class Cycle {
8 | private boolean[] marked;
9 | private boolean hasCycle;
10 | public Cycle(Graph G) {
11 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
12 | for(int s = 0; s < G.V(); s++)
13 | if(!marked[s])
14 | dfs(G, s, s);
15 | }
16 |
17 | private void dfs(Graph G, int v, int u) {
18 | marked[v] = true;
19 | for(int w : G.adj(v)) {
20 | if(!marked[w])
21 | dfs(G, w, v);
22 | else if(w != u) // v 是从 u 深度遍历得到的。因为不存在平行边,所以 w != v 即刻认为遇到了之前遍历过的点(即有环)
23 | hasCycle = true;
24 | }
25 | }
26 |
27 | public boolean hasCycle() {
28 | return hasCycle;
29 | }
30 | }
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/DegreesOfSeparation.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdIn;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | * 间隔的度数
8 | * @author huang
9 | */
10 | public class DegreesOfSeparation {
11 |
12 | public static void main(String[] args) {
13 |
14 | SymbolGraph sGraph = new SymbolGraph(args[0], args[1]);
15 | Graph G = sGraph.G();
16 |
17 | String source = args[2];
18 | if(!sGraph.contains(source)) {
19 | StdOut.println(source + "not in database.");
20 | return;
21 | }
22 |
23 | int s = sGraph.index(source);
24 | BreadthFirstPaths bfs = new BreadthFirstPaths(G, s);
25 |
26 | while(!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
27 | String sink = StdIn.readLine();
28 | if(sGraph.contains(sink)) {
29 | int t = sGraph.index(sink);
30 | if(bfs.hasPathTo(t))
31 | for(int v : bfs.pathTo(t))
32 | StdOut.println(" " + sGraph.name(v));
33 | else
34 | StdOut.println("Not connected");
35 | }
36 | else
37 | StdOut.println("Not in database.");
38 | }
39 |
40 | }
41 |
42 | }
43 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/DepthFirstPaths.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Stack;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * edgeTo[w]=v 表示 v-w 是第一次访问 w 时经过的边
7 | * edgeTo[] 数组是一颗用父链接表示的以 s 为根且含有所有与 s 连通的顶点的树
8 | * @author huang
9 | */
10 | public class DepthFirstPaths {
11 | private boolean[] marked; // 这个顶点上调用过 dfs() 了吗?
12 | private int[] edgeTo; // 从起点到一个顶点的已知路径上的最后一个顶点
13 | private final int s; // 起点
14 |
15 | public DepthFirstPaths(Graph G, int s) {
16 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
17 | edgeTo = new int[G.V()];
18 | this.s = s;
19 | dfs(G, s);
20 | }
21 |
22 | private void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
23 | marked[v] = true;
24 | for(int w : G.adj(v))
25 | if(!marked[w]) {
26 | edgeTo[w] = v;
27 | dfs(G, w);
28 | }
29 | }
30 |
31 | public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
32 | return marked[v];
33 | }
34 |
35 | public Iterable pathTo(int v) {
36 | if(!hasPathTo(v))
37 | return null;
38 | Stack path = new Stack<>();
39 | for(int x = v; x != s; x = edgeTo[x])
40 | path.push(x);
41 | path.push(s);
42 | return path;
43 | }
44 | }
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/DepthFirstSearch.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | public class DepthFirstSearch {
4 | private boolean[] marked;
5 | private int count;
6 |
7 | public DepthFirstSearch(Graph G, int s) {
8 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
9 | dfs(G, s);
10 | }
11 |
12 | private void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
13 | marked[v] = true;
14 | count++;
15 | for(int w : G.adj(v))
16 | if(!marked[w])
17 | dfs(G, w);
18 | }
19 |
20 | public boolean marked(int w) {
21 | return marked[w];
22 | }
23 |
24 | public int count() {
25 | return count;
26 | }
27 | }
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/Graph.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Bag;
4 | import algs4.In;
5 |
6 | public class Graph {
7 | private final int V; // 顶点数目
8 | private int E; // 边的数目
9 | private Bag[] adj; // 邻接表
10 |
11 | @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
12 | public Graph(int V) {
13 | this.V = V;
14 | this.E = 0;
15 | adj = (Bag[]) new Bag[V]; // 创建邻接表
16 | for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
17 | adj[v] = new Bag();
18 | }
19 | public Graph(In in) {
20 | this(in.readInt()); // 读取 V 并将图初始化
21 | int E = in.readInt(); // 读取 E
22 | for(int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
23 | // 添加一条边
24 | int v = in.readInt(); // 读取一个顶点
25 | int w = in.readInt(); // 读取另一个顶点
26 | addEdge(v, w); // 添加一条连接它们的边
27 | }
28 | }
29 | public int V() {
30 | return V;
31 | }
32 | public int E() {
33 | return E;
34 | }
35 | public void addEdge(int v, int w) {
36 | adj[v].add(w);
37 | adj[w].add(v);
38 | E++;
39 | }
40 | public Iterable adj(int v) {
41 | return adj[v];
42 | }
43 | }
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/SymbolGraph.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.ST;
5 |
6 | public class SymbolGraph {
7 |
8 | private ST st; // 符号名 -> 索引
9 | private String[] keys; // 索引 -> 符号名
10 | private Graph G; // 使用索引表示顶点的图
11 |
12 | public SymbolGraph(String filename, String delim) {
13 | st = new ST();
14 | In in = new In(filename); // 第一遍
15 | while(in.hasNextLine()) {
16 | String[] a = in.readLine().split(delim); // 读取字符串
17 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
18 | if(!st.contains(a[i]))
19 | st.put(a[i], st.size());
20 | }
21 | keys = new String[st.size()]; // 用来获得顶点名的反向索引是一个数组
22 |
23 | for(String name : st.keys())
24 | keys[st.get(name)] = name;
25 |
26 | G = new Graph(st.size());
27 | in = new In(filename); // 第二遍
28 | while(in.hasNextLine()) { // 构造图
29 | String[] a = in.readLine().split(delim); // 将每一行的第一个顶点和该行的其他顶点相连
30 | int v = st.get(a[0]);
31 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
32 | G.addEdge(v, st.get(a[i]));
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
36 | // key 是一个顶点吗
37 | boolean contains(String key) {
38 | return st.contains(key);
39 | }
40 |
41 | // key 的索引
42 | int index(String key) {
43 | return st.get(key);
44 | }
45 |
46 | // 索引 v 的顶点名
47 | String name(int v) {
48 | return keys[v];
49 | }
50 |
51 | // 隐藏的 Graph 对象
52 | Graph G() {
53 | return G;
54 | }
55 | }
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/TestCC.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Bag;
4 | import algs4.In;
5 | import algs4.StdOut;
6 |
7 | /**
8 | * 找出一幅图的所有连通分量
9 | * @author huang
10 | */
11 | public class TestCC {
12 | @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
13 | public static void main(String[] args) {
14 | Graph G = new Graph(new In(args[0]));
15 | CC cc = new CC(G);
16 |
17 | int M = cc.count();
18 | StdOut.println(M + " components");
19 |
20 | Bag[] components;
21 | components = (Bag[]) new Bag[M];
22 | for(int i = 0; i < M; i++)
23 | components[i] = new Bag();
24 | for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
25 | components[cc.id(v)].add(v);
26 | for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
27 | for(int v : components[i])
28 | StdOut.print(v + " ");
29 | StdOut.println();
30 | }
31 |
32 | }
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/TestPaths.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | * 单点路径问题
8 | * @author huang
9 | */
10 | public class TestPaths {
11 |
12 | public static void main(String[] args) {
13 |
14 | Graph G = new Graph(new In(args[0]));
15 | int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
16 | DepthFirstPaths search = new DepthFirstPaths(G, s);
17 | for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
18 | StdOut.print(s + " to " + v + ": ");
19 | if(search.hasPathTo(v))
20 | for(int x : search.pathTo(v))
21 | if(x == s)
22 | StdOut.print(x);
23 | else
24 | StdOut.print("-" + x);
25 | StdOut.println();
26 | }
27 | }
28 |
29 | }
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/TestSearch.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | public class TestSearch {
7 |
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 | Graph G = new Graph(new In(args[0]));
10 | int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
11 | Search search = new Search(G, s);
12 |
13 | for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
14 | if(search.marked(v))
15 | StdOut.println(v + " ");
16 | StdOut.println();
17 |
18 | if(search.count() != G.V())
19 | StdOut.print("NOT ");
20 | StdOut.println("connected");
21 |
22 | }
23 |
24 | }
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/TestSymbolGraph.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdIn;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | public class TestSymbolGraph {
7 |
8 | public static void main(String[] args) {
9 | String filename = args[0];
10 | String delim = args[1];
11 | SymbolGraph sGraph = new SymbolGraph(filename, delim);
12 |
13 | Graph G = sGraph.G();
14 |
15 | while(StdIn.hasNextLine()) {
16 | String source = StdIn.readLine();
17 | for(int w : G.adj(sGraph.index(source)))
18 | StdOut.println(" " + sGraph.name(w));
19 | }
20 | }
21 |
22 | }
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/TwoColor.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | * 判断 G 是否为二分图
5 | * @author huang
6 | */
7 | public class TwoColor {
8 | private boolean[] marked;
9 | private boolean[] color;
10 | private boolean isTwoColorable = true;
11 | public TwoColor(Graph G) {
12 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
13 | color = new boolean[G.V()];
14 | for(int s = 0; s < G.V(); s++)
15 | if(!marked[s])
16 | dfs(G, s);
17 | }
18 |
19 | private void dfs(Graph G, int v) {
20 | marked[v] = true;
21 | for(int w : G.adj(v))
22 | if(!marked[w]) {
23 | color[w] = !color[v];
24 | dfs(G, w);
25 | }
26 | else if(color[w] == color[v])
27 | isTwoColorable = false;
28 | }
29 |
30 | public boolean isBipartite() {
31 | return isTwoColorable;
32 | }
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/DepthFirstOrder.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Queue;
4 | import algs4.Stack;
5 |
6 | public class DepthFirstOrder {
7 | private boolean[] marked;
8 | private Queue pre; // 所有顶点的前序排列
9 | private Queue post; // 所有顶点的后序排列
10 | private Stack reversePost; // 所有顶点的逆后序排列
11 |
12 | public DepthFirstOrder(Digraph G) {
13 | pre = new Queue<>();
14 | post = new Queue<>();
15 | reversePost = new Stack<>();
16 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
17 |
18 | for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
19 | if(!marked[v])
20 | dfs(G, v);
21 | }
22 |
23 | private void dfs(Digraph G, int v) {
24 | pre.enqueue(v);
25 |
26 | marked[v] = true;
27 | for(int w : G.adj(v))
28 | if(!marked[w])
29 | dfs(G, w);
30 | post.enqueue(v);
31 | reversePost.push(v);
32 | }
33 |
34 | public Iterable pre() {
35 | return pre;
36 | }
37 |
38 | public Iterable post() {
39 | return post;
40 | }
41 |
42 | public Iterable reversePost() {
43 | return reversePost;
44 | }
45 | }
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/Digraph.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Bag;
4 | import algs4.In;
5 |
6 | public class Digraph {
7 |
8 | private final int V;
9 | private int E;
10 | private Bag[] adj;
11 |
12 | @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
13 | public Digraph(int V) { // 创建一幅含有 V 个顶点但没有边的有向图
14 | this.V = V;
15 | this.E = 0;
16 | adj = (Bag[]) new Bag[V];
17 | for(int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
18 | adj[v] = new Bag();
19 | }
20 | }
21 |
22 | public Digraph(In in) { // 从输入流 in 中读取一幅有向图
23 | this(in.readInt()); // 读取 V 并将图初始化
24 | int E = in.readInt(); // 读取 E
25 | for(int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
26 | // 添加一条边
27 | int v = in.readInt(); // 读取一个顶点
28 | int w = in.readInt(); // 读取另一个顶点
29 | addEdge(v, w); // 添加一条连接它们的边
30 | }
31 | }
32 |
33 | public int V() { // 顶点总数
34 | return V;
35 | }
36 |
37 | public int E() { // 边的总数
38 | return E;
39 | }
40 |
41 | void addEdge(int v, int w) { // 向有向图中添加一条边 v -> w
42 | adj[v].add(w);
43 | E++;
44 | }
45 |
46 | public Iterable adj(int v) { // 由 v 指出的边所连接的所有顶点
47 | return adj[v];
48 | }
49 |
50 | public Digraph reverse() { // 该图的反向图
51 | Digraph R = new Digraph(V);
52 | for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
53 | for(int w : adj(v))
54 | R.addEdge(w, v);
55 | return R;
56 | }
57 |
58 | }
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/DirectedCycle.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Stack;
4 |
5 | public class DirectedCycle {
6 | private boolean[] marked;
7 | private int[] edgeTo;
8 | private Stack cycle; // 有向环中的所有顶点(如果存在)
9 | private boolean[] onStack; // 递归调用的栈上的所有顶点
10 |
11 | public DirectedCycle(Digraph G) {
12 | onStack = new boolean[G.V()];
13 | edgeTo = new int[G.V()];
14 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
15 | for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++) {
16 | if(!marked[v])
17 | dfs(G, v);
18 | }
19 | }
20 |
21 | private void dfs(Digraph G, int v) {
22 | onStack[v] = true;
23 | marked[v] = true;
24 | for(int w : G.adj(v))
25 | if(this.hasCycle())
26 | return;
27 | else if(!marked[w]) {
28 | edgeTo[w] = v;
29 | dfs(G, w);
30 | }
31 | else if(onStack[w]) {
32 | cycle = new Stack();
33 | for(int x = v; x != w; x = edgeTo[x])
34 | cycle.push(x);
35 | cycle.push(w);
36 | cycle.push(v);
37 | }
38 | onStack[v] = false;
39 | }
40 |
41 | public boolean hasCycle() {
42 | return cycle != null;
43 | }
44 |
45 | public Iterable cycle() {
46 | return cycle;
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/DirectedDFS.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Bag;
4 | import algs4.In;
5 | import algs4.StdOut;
6 |
7 | /*
8 | * 深度优先搜索,解决单点可达性和多点可达性问题
9 | */
10 | public class DirectedDFS {
11 | private boolean[] marked;
12 |
13 | public DirectedDFS(Digraph G, int s) {
14 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
15 | dfs(G, s);
16 | }
17 |
18 | public DirectedDFS(Digraph G, Iterable sources) {
19 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
20 | for(int s : sources)
21 | if(!marked[s])
22 | dfs(G, s);
23 | }
24 |
25 | private void dfs(Digraph G, int v) {
26 | marked[v] = true;
27 | for(int w : G.adj(v))
28 | if(!marked[w])
29 | dfs(G, w);
30 | }
31 |
32 | public boolean marked(int v) {
33 | return marked[v];
34 | }
35 |
36 | public static void main(String[] args) {
37 | Digraph G = new Digraph(new In(args[0]));
38 |
39 | Bag sources = new Bag();
40 | for(int i = 1; i < args.length; i++)
41 | sources.add(Integer.parseInt(args[i]));
42 |
43 | DirectedDFS reachable = new DirectedDFS(G, sources);
44 |
45 | for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
46 | if(reachable.marked(v))
47 | StdOut.print(v + " ");
48 | StdOut.println();
49 | }
50 | }
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/KosarajuSCC.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs;
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * 计算强连通分量的 Kosaraju 算法
5 | */
6 | public class KosarajuSCC {
7 | private boolean[] marked; // 已访问过的顶点
8 | private int[] id; // 强连通分量的标识符
9 | private int count; // 强连通分量的数量
10 |
11 | public KosarajuSCC(Digraph G) {
12 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
13 | id = new int[G.V()];
14 | DepthFirstOrder order = new DepthFirstOrder(G.reverse());
15 | for(int s : order.reversePost())
16 | if(!marked[s]) {
17 | dfs(G, s);
18 | count++;
19 | }
20 | }
21 |
22 | private void dfs(Digraph G, int v) {
23 | marked[v] = true;
24 | id[v] = count;
25 | for(int w : G.adj(v))
26 | if(!marked[w])
27 | dfs(G, w);
28 | }
29 |
30 | public boolean stronglyConnected(int v, int w) {
31 | return id[v] == id[w];
32 | }
33 |
34 | public int id(int v) {
35 | return id[v];
36 | }
37 |
38 | public int count() {
39 | return count;
40 | }
41 | }
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/SymbolDigraph.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.ST;
5 |
6 | public class SymbolDigraph {
7 |
8 | private ST st; // 符号名 -> 索引
9 | private String[] keys; // 索引 -> 符号名
10 | private Digraph G; // 使用索引表示顶点的图
11 |
12 | public SymbolDigraph(String filename, String delim) {
13 | st = new ST();
14 | In in = new In(filename); // 第一遍
15 | while(in.hasNextLine()) {
16 | String[] a = in.readLine().split(delim); // 读取字符串
17 | for(int i = 0; i < a.length; i++)
18 | if(!st.contains(a[i]))
19 | st.put(a[i], st.size());
20 | }
21 | keys = new String[st.size()]; // 用来获得顶点名的反向索引是一个数组
22 |
23 | for(String name : st.keys())
24 | keys[st.get(name)] = name;
25 |
26 | G = new Digraph(st.size());
27 | in = new In(filename); // 第二遍
28 | while(in.hasNextLine()) { // 构造图
29 | String[] a = in.readLine().split(delim); // 将每一行的第一个顶点和该行的其他顶点相连
30 | int v = st.get(a[0]);
31 | for(int i = 1; i < a.length; i++)
32 | G.addEdge(v, st.get(a[i]));
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
36 | // key 是一个顶点吗
37 | boolean contains(String key) {
38 | return st.contains(key);
39 | }
40 |
41 | // key 的索引
42 | int index(String key) {
43 | return st.get(key);
44 | }
45 |
46 | // 索引 v 的顶点名
47 | public String name(int v) {
48 | return keys[v];
49 | }
50 |
51 | // 隐藏的 Digraph 对象
52 | public Digraph G() {
53 | return G;
54 | }
55 | }
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/Topological.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | /*
6 | * 拓扑排序
7 | */
8 | public class Topological {
9 | private Iterable order; // 顶点的拓扑排序
10 |
11 | public Topological(Digraph G) {
12 | DirectedCycle cyclefinder = new DirectedCycle(G);
13 | if(!cyclefinder.hasCycle()) {
14 | DepthFirstOrder dfs = new DepthFirstOrder(G);
15 | order = dfs.reversePost(); // 一幅有向无环图的拓扑顺序即为所有顶点的逆后序排列
16 | }
17 | }
18 |
19 | public Iterable order() {
20 | return order;
21 | }
22 |
23 | public boolean isDAG() {
24 | return order != null;
25 | }
26 |
27 | public static void main(String[] args) {
28 | String filename = args[0];
29 | String separator = args[1];
30 | SymbolDigraph sGraph = new SymbolDigraph(filename, separator);
31 |
32 | Topological top = new Topological(sGraph.G());
33 |
34 | for(int v : top.order())
35 | StdOut.println(sGraph.name(v));
36 | }
37 | }
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/TransitiveClosure.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs;
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * 有向图顶点对可达性
5 | */
6 | public class TransitiveClosure {
7 | private DirectedDFS[] all;
8 | public TransitiveClosure(Digraph G) {
9 | all = new DirectedDFS[G.V()];
10 | for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
11 | all[v] = new DirectedDFS(G, v);
12 | }
13 |
14 | public boolean reachable(int v, int w) {
15 | return all[v].marked(w);
16 | }
17 | }
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/Edge.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree;
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * 带权重的边
5 | */
6 | public class Edge implements Comparable {
7 | private final int v; // 顶点之一
8 | private final int w; // 另一个顶点
9 | private final double weight; // 边的权重
10 |
11 | public Edge(int v, int w, double weight) {
12 | this.v = v;
13 | this.w = w;
14 | this.weight = weight;
15 | }
16 |
17 | public double weight() {
18 | return weight;
19 | }
20 |
21 | // 边两端的顶点之一
22 | public int either() {
23 | return v;
24 | }
25 |
26 | // 另一个顶点
27 | public int other(int vertex) {
28 | if(vertex == v)
29 | return w;
30 | else if(vertex == w)
31 | return v;
32 | else
33 | throw new RuntimeException("Inconsistent edge");
34 | }
35 |
36 | public int compareTo(Edge that) {
37 | if(this.weight() < that.weight())
38 | return -1;
39 | else if(this.weight() > that.weight())
40 | return +1;
41 | else
42 | return 0;
43 | }
44 |
45 | public String toString() {
46 | return String.format("%d-%d %.2f", v, w, weight);
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/EdgeWeightedGraph.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Bag;
4 | import algs4.In;
5 |
6 | /*
7 | * 加权无向图
8 | */
9 | public class EdgeWeightedGraph {
10 | private final int V; // 顶点总数
11 | private int E; // 边的总数
12 | private Bag[] adj; // 邻接表
13 |
14 | @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
15 | public EdgeWeightedGraph(int V) {
16 | this.V = V;
17 | this.E = 0;
18 | adj = (Bag[]) new Bag[V];
19 | for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
20 | adj[v] = new Bag();
21 | }
22 |
23 | public EdgeWeightedGraph(In in) {
24 | this(in.readInt()); // 读取 V 并将图初始化
25 | int E = in.readInt(); // 读取 E
26 | for(int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
27 | // 添加一条边
28 | int v = in.readInt(); // 读取一个顶点
29 | int w = in.readInt(); // 读取另一个顶点
30 | double weight = in.readDouble(); // 读取权重
31 | Edge e = new Edge(v, w, weight);
32 | addEdge(e); // 添加一条连接它们的边
33 | }
34 | }
35 |
36 | public int V() {
37 | return V;
38 | }
39 |
40 | public int E() {
41 | return E;
42 | }
43 |
44 | public void addEdge(Edge e) {
45 | int v = e.either(),
46 | w = e.other(v);
47 | adj[v].add(e);
48 | adj[w].add(e);
49 | E++;
50 | }
51 |
52 | public Iterable adj(int v) {
53 | return adj[v];
54 | }
55 |
56 | // 图的所有边
57 | public Iterable edges() {
58 | Bag b = new Bag();
59 | for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
60 | for(Edge e : adj[v])
61 | if(e.other(v) > v)
62 | b.add(e);
63 | return b;
64 | }
65 |
66 | }
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/KruskalMST.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree;
2 |
3 | import algs4.MinPQ;
4 | import algs4.Queue;
5 |
6 | public class KruskalMST {
7 | private Queue mst;
8 |
9 | public KruskalMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
10 | mst = new Queue();
11 | MinPQ pq = new MinPQ();
12 | for(Edge e : G.edges())
13 | pq.insert(e);
14 | UF uf = new UF(G.V());
15 |
16 | while(!pq.isEmpty() && mst.size() < G.V() - 1) {
17 | Edge e = pq.delMin(); // 从 pq 得到权重最小的边和它的顶点
18 | int v = e.either(), w = e.other(v);
19 | if(uf.connected(v, w))
20 | continue; // 忽略失效的边
21 | uf.union(v, w); // 合并分量
22 | mst.enqueue(e); // 将边添加到最小生成树中
23 | }
24 | }
25 |
26 | public Iterable edges() {
27 | return mst;
28 | }
29 |
30 | public double weight() {
31 |
32 | }
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/LazyPrimMST.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree;
2 |
3 | import java.beans.Visibility;
4 |
5 | import algs4.MinPQ;
6 | import algs4.Queue;
7 |
8 | /*
9 | * 最小生成树的 Prim 算法的延时实现
10 | */
11 | public class LazyPrimMST {
12 | private boolean[] marked; // 最小生成树的顶点
13 | private Queue mst; // 最小生成树的边
14 | private MinPQ pq; // 横切边(包括失效的边)
15 |
16 | public LazyPrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
17 | pq = new MinPQ();
18 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
19 | mst = new Queue();
20 |
21 | visit(G, 0);
22 | while(!pq.isEmpty()) {
23 | Edge e = pq.delMin(); // 从 pq 中得到权重最小的边
24 |
25 | int v = e.either(),
26 | w = e.other(v);
27 | if(marked[v] && marked[w])
28 | continue; // 跳过失效的边
29 | mst.enqueue(e); // 将边加入到树中
30 | if(!marked[v]) // 将顶点(v 或 w)添加到树中
31 | visit(G, v);
32 | if(!marked[w])
33 | visit(G, w);
34 | }
35 | }
36 |
37 | private void visit(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v) {
38 | // 标记顶点 v 并将所有连接 v 和未被标记顶点的边加入 pq
39 | marked[v] = true;
40 | for(Edge e : G.adj(v))
41 | if(!marked[e.other(v)])
42 | pq.insert(e);
43 | }
44 |
45 | public Iterable edges() {
46 | return mst;
47 | }
48 |
49 | public double weight() {
50 |
51 | }
52 | }
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/PrimMST.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree;
2 |
3 | import algs4.IndexMinPQ;
4 |
5 | /*
6 | * 最小生成树的 Prim(即时版本)
7 | */
8 | public class PrimMST {
9 | private Edge[] edgeTo; // 距离树最近的边
10 | private double[] distTo; // distTo[w] = edgeTo[w].weight()
11 | private boolean[] marked; // 如果 v 在树中则为 true
12 | private IndexMinPQ pq; // 有效的横切边
13 |
14 | public PrimMST(EdgeWeightedGraph G) {
15 | edgeTo = new Edge[G.V()];
16 | distTo = new double[G.V()];
17 | marked = new boolean[G.V()];
18 | for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
19 | distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
20 | pq = new IndexMinPQ(G.V());
21 |
22 | distTo[0] = 0.0;
23 | pq.insert(0, 0.0); // 用顶点 0 和权重 0 初始化 pq
24 | while(!pq.isEmpty())
25 | visit(G, pq.delMin()); // 将最近的顶点添加到树中
26 | }
27 |
28 | private void visit(EdgeWeightedGraph G, int v) {
29 | // 将顶点 v 添加到树中,更新数据
30 | marked[v] = true;
31 | for(Edge e : G.adj(v)) {
32 | int w = e.other(v);
33 | if(marked[w]) // v-w 失效
34 | continue;
35 | if(e.weight() < distTo[w]) {
36 | // 连接 w 和树的最佳边 Edge 变为 e
37 | edgeTo[w] = e;
38 | distTo[w] = e.weight();
39 | if(pq.contains(w))
40 | pq.change(w, distTo[w]);
41 | else
42 | pq.insert(w, distTo[w]);
43 | }
44 | }
45 | }
46 |
47 | public Iterable edges() {
48 |
49 | }
50 |
51 | public double weight() {
52 |
53 | }
54 | }
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/TestMST.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | /*
7 | * 最小生成树测试
8 | */
9 | public class TestMST {
10 |
11 | public static void main(String[] args) {
12 |
13 | In in = new In(args[0]);
14 | EdgeWeightedGraph G;
15 | G = new EdgeWeightedGraph(in);
16 |
17 | MST mst = new MST(G);
18 | for(Edge e : mst.edges())
19 | StdOut.println(e);
20 | StdOut.println(mst.weight());
21 |
22 | }
23 |
24 | }
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/UF.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdIn;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | public class UF {
7 | private int[] id; // 分量id(以触点作为索引)
8 | private int count; // 分量数量
9 |
10 | public UF(int N) {
11 | // 初始化分量 id 数组
12 | count = N;
13 | id = new int[N];
14 | for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
15 | id[i] = i;
16 | }
17 |
18 | public int count() {
19 | return count;
20 | }
21 |
22 | public boolean connected(int p, int q) {
23 | return find(p) == find(q);
24 | }
25 |
26 | /* quick-find 算法 */
27 | // public int find(int p) {
28 | // return id[p];
29 | // }
30 | //
31 | // public void union(int p, int q) {
32 | // // 将 p 和 q 归并到同样的分量中
33 | // int pID = find(p);
34 | // int qID = find(q);
35 | //
36 | // // 如果 p 和 q 已经在相同的分量之中则不需要采取任何行动
37 | // if(pID == qID)
38 | // return;
39 | //
40 | // // 将 p 的分量重命名为 q 的名称
41 | // for(int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
42 | // if(id[i] == pID)
43 | // id[i] = qID;
44 | // count--;
45 | // }
46 |
47 | /* quick-union 算法 */
48 | private int find(int p) {
49 | // 找出分量的名称
50 | while(p != id[p])
51 | p = id[p];
52 | return p;
53 | }
54 |
55 | public void union(int p, int q) {
56 | // 将 p 和 q 的根节点统一
57 | int pRoot = find(p);
58 | int qRoot = find(q);
59 | if(pRoot == qRoot)
60 | return;
61 |
62 | id[pRoot] = qRoot;
63 |
64 | count--;
65 | }
66 |
67 | public static void main(String[] args) {
68 | // 解决由StdIn得到的动态连通性问题
69 | int N = StdIn.readInt(); // 读取触点数量
70 | UF uf = new UF(N); // 初始化 N 个分量
71 | while (!StdIn.isEmpty()) {
72 | int p = StdIn.readInt();
73 | int q = StdIn.readInt(); // 读取整数对
74 | if (uf.connected(p, q)) // 如果已经连通则忽略
75 | continue;
76 | uf.union(p, q); // 归并分量
77 | StdOut.println(p + " " + q); // 打印连接
78 | }
79 | StdOut.println(uf.count + "components");
80 | }
81 | }
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths/DijkstraSP.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths;
2 |
3 | import algs4.IndexMinPQ;
4 | import algs4.Stack;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | * @author huang
8 | * 最短路径的 Dijkstra 算法
9 | */
10 | public class DijkstraSP implements SP {
11 | private DirectedEdge[] edgeTo;
12 | private double[] distTo;
13 | private IndexMinPQ pq;
14 |
15 | public DijkstraSP(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int s) {
16 | edgeTo = new DirectedEdge[G.V()];
17 | distTo = new double[G.V()];
18 | pq = new IndexMinPQ(G.V());
19 | for(int v = 0; v < G.V(); v++)
20 | distTo[v] = Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
21 | distTo[s] = 0.0;
22 |
23 | pq.insert(s, 0.0);
24 | while(!pq.isEmpty())
25 | relax(G, pq.delMin());
26 | }
27 |
28 | private void relax(EdgeWeightedDigraph G, int v) {
29 | for(DirectedEdge e : G.adj(v)) {
30 | int w = e.to();
31 | if(distTo[w] > distTo[w] + e.weight()) {
32 | distTo[w] = distTo[v] + e.weight();
33 | edgeTo[w] = e;
34 | if(pq.contains(w))
35 | pq.change(w, distTo[w]);
36 | else
37 | pq.insert(w, distTo[w]);
38 | }
39 | }
40 | }
41 |
42 | public double distTo(int v) {
43 | return distTo[v];
44 | }
45 |
46 | public boolean hasPathTo(int v) {
47 | return distTo[v] < Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY;
48 | }
49 |
50 | public Iterable pathTo(int v) {
51 | if(!hasPathTo(v))
52 | return null;
53 | Stack path = new Stack();
54 | for(DirectedEdge e = edgeTo[v]; e != null; e = edgeTo[e.from()])
55 | path.push(e);
56 | return path;
57 | }
58 | }
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths/DirectedEdge.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | * @author huang
5 | * 加权有向边的数据类型
6 | */
7 | public class DirectedEdge {
8 | private final int v; // 边的起点
9 | private final int w; // 边的终点
10 | private final double weight; // 边的权重
11 |
12 | public DirectedEdge(int v, int w, double weight) {
13 | this.v = v;
14 | this.w = w;
15 | this.weight = weight;
16 | }
17 |
18 | public double weight() {
19 | return weight;
20 | }
21 |
22 | public int from() {
23 | return v;
24 | }
25 |
26 | public int to() {
27 | return w;
28 | }
29 |
30 | public String toString() {
31 | return String.format("%d->%d %.2f", v, w, weight);
32 | }
33 | }
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths/EdgeWeightedDigraph.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths;
2 |
3 | import algs4.Bag;
4 | import algs4.In;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | * @author huang
8 | * 加权有向图的数据类型
9 | */
10 | public class EdgeWeightedDigraph {
11 | private final int V; // 顶点总数
12 | private int E; // 边的总数
13 | private Bag[] adj; // 邻接表
14 |
15 | @SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
16 | public EdgeWeightedDigraph(int V) {
17 | this.V = V;
18 | this.E = 0;
19 | adj = (Bag[]) new Bag[V];
20 | for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
21 | adj[v] = new Bag();
22 | }
23 |
24 | public EdgeWeightedDigraph(In in) {
25 | this(in.readInt());
26 | int E = in.readInt();
27 | for(int i = 0; i < E; i++) {
28 | DirectedEdge edge = new DirectedEdge(in.readInt(), in.readInt(), in.readDouble());
29 | addEdge(edge);
30 | }
31 | }
32 |
33 | public int V() {
34 | return V;
35 | }
36 |
37 | public int E() {
38 | return E;
39 | }
40 |
41 | public void addEdge(DirectedEdge e) {
42 | adj[e.from()].add(e);
43 | E++;
44 | }
45 |
46 | public Iterable adj(int v) {
47 | return adj[v];
48 | }
49 |
50 | public Iterable edges() {
51 | Bag bag = new Bag<>();
52 | for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
53 | for(DirectedEdge e : adj[v])
54 | bag.add(e);
55 | return bag;
56 | }
57 |
58 | }
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths/SP.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths;
2 |
3 | /**
4 | * @author huang
5 | * 最短路径的 API
6 | */
7 | public interface SP {
8 | // 从顶点 s 到 v 的距离,如果不存在则路径为无穷大
9 | double distTo(int v);
10 | // 是否存在从顶点 s 到 v 的路径
11 | boolean hasPathTo(int v);
12 | // 从顶点 s 到 v 的路径,如果不存在则为 null
13 | Iterable pathTo(int v);
14 | }
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths/TestSP.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter4_4_Shortest_Paths;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | * @author huang
8 | * 最短路径测试
9 | */
10 | public class TestSP {
11 | public static void main(String[] args) {
12 | EdgeWeightedDigraph G;
13 | G = new EdgeWeightedDigraph(new In(args[0]));
14 | int s = Integer.parseInt(args[1]);
15 | SP sp = new DijkstraSP(G, s);
16 |
17 | for(int t = 0; t < G.V(); t++) {
18 | StdOut.print(s + " to " + t);
19 | StdOut.printf(" (%4.2f): ", sp.distTo(t));
20 | if(sp.hasPathTo(t))
21 | for(DirectedEdge e : sp.pathTo(t))
22 | StdOut.print(e + " ");
23 | StdOut.println();
24 | }
25 | }
26 | }
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter5_3_Substring_Search/BoyerMoore.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter5_3_Substring_Search;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * @author huang
7 | * Boyer-Moore 字符串查找算法(启发式地处理不匹配地字符)
8 | */
9 | public class BoyerMoore {
10 |
11 | private int[] right;
12 | private String pat;
13 |
14 | // 计算跳跃表
15 | public BoyerMoore(String pat) {
16 | this.pat = pat;
17 | int M = pat.length();
18 | int R = 256;
19 | right = new int[R];
20 | for(int c = 0; c < R; c++)
21 | right[c] = -1; // 不包含在模式字符串中的字符的值为 -1
22 | for(int j = 0; j < M; j++) // 包含在模式字符串中的字符的值为
23 | right[pat.charAt(j)] = j; // 它在其中出现的最右位置
24 | }
25 |
26 | // 在 txt 中查找模式字符串
27 | public int search(String txt) {
28 | int N = txt.length();
29 | int M = pat.length();
30 | int skip;
31 | for(int i = 0; i <= N-M; i += skip) {
32 | // 模式字符串和文本在位置 i 匹配吗?
33 | skip = 0;
34 | for(int j = M-1; j >= 0; j--)
35 | if(pat.charAt(j) != txt.charAt(i+j)) {
36 | skip = j - right[txt.charAt(i+j)];
37 | if(skip < 1)
38 | skip = 1;
39 | break;
40 | }
41 | if(skip == 0)
42 | return i; // 找到匹配
43 | }
44 | return N; // 未找到匹配
45 | }
46 |
47 | public static void main(String[] args) {
48 | String pat = args[0];
49 | String txt = args[1];
50 | BoyerMoore bm = new BoyerMoore(pat);
51 | StdOut.println("text: " + txt);
52 | int offset = bm.search(txt);
53 | StdOut.print("pattern: ");
54 | for(int i = 0; i < offset; i++)
55 | StdOut.print(" ");
56 | StdOut.println(pat);
57 | }
58 |
59 | }
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter5_3_Substring_Search/KMP.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter5_3_Substring_Search;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdOut;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * @author huang
7 | * Knuth-Morris-Pratt 字符串查找算法
8 | */
9 | public class KMP {
10 |
11 | private String pat;
12 | private int[][] dfa;
13 | public KMP(String pat) {
14 | this.pat = pat;
15 | int M = pat.length();
16 | int R = 256;
17 | dfa = new int[R][M];
18 | dfa[pat.charAt(0)][0] = 1;
19 | for(int X = 0, j = 1; j < M; j++) {
20 | // 计算 dfa[][j]
21 | for(int ch = 0; ch < R; ch++)
22 | dfa[ch][j] = dfa[ch][X]; // 复制匹配失败情况下的值
23 | dfa[pat.charAt(j)][j] = j+1; // 设置匹配成功情况下的值
24 | X = dfa[pat.charAt(j)][X]; // 更新重启状态
25 | }
26 | }
27 |
28 | public int search(String txt) {
29 | int i, j, N = txt.length(), M = pat.length();
30 | for(i = 0, j = 0; i < N && j < M; i++)
31 | j = dfa[txt.charAt(i)][j];
32 | if(j == M)
33 | return i - M; // 找到匹配(到达模式字符串的结尾)
34 | else
35 | return N; // 未找到匹配(到达文本字符串的结尾)
36 | }
37 |
38 | public static void main(String[] args) {
39 | String pat = args[0];
40 | String txt = args[1];
41 | KMP kmp = new KMP(pat);
42 | StdOut.println("text: " + txt);
43 | int offset = kmp.search(txt);
44 | StdOut.print("pattern: ");
45 | for(int i = 0; i < offset; i++)
46 | StdOut.print(" ");
47 | StdOut.println(pat);
48 | }
49 |
50 | }
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter5_3_Substring_Search/RabinKarp.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter5_3_Substring_Search;
2 |
3 | import java.math.BigInteger;
4 | import java.util.Random;
5 |
6 | import algs4.StdOut;
7 |
8 | /**
9 | * @author huang
10 | * Rabin-Karp 指纹字符串查找算法
11 | */
12 | public class RabinKarp {
13 | private String pat; /**仅拉斯维加斯算法需要**/ // 模式字符串
14 | private long patHash; // 模式字符串的散列值
15 | private int M; // 模式字符串的长度
16 | private long Q; // 一个很大的素数
17 | private int R = 256; // 字母表的大小
18 | private long RM; // R^(M-1) % Q
19 |
20 | public RabinKarp(String pat) {
21 | this.pat = pat; /**仅拉斯维加斯算法需要**/ // 保存模式字符串
22 | this.M = pat.length();
23 | Q = longRandomPrime();
24 | RM = 1;
25 | for(int i = 1; i <= M-1; i++) // 计算 R^(M-1) % Q
26 | RM = (R * RM) % Q; // 用于减去第一个数字时的计算
27 | patHash = hash(pat, M);
28 | }
29 |
30 | public boolean check(int i) { // 蒙特卡洛算法直接返回 true
31 | return true; // 对于拉斯维加斯算法,检查模式与 txt(i..i-M+1) 匹配
32 | }
33 |
34 | private long hash(String key, int M) { // Horner 方法计算 key[0..M-1] 的散列值
35 | long h = 0;
36 | for(int j = 0; j < M; j++)
37 | h = (R * h + key.charAt(j)) % Q;
38 | return h;
39 | }
40 |
41 | private int search(String txt) {
42 | int N = txt.length();
43 | long txtHash = hash(txt, M);
44 | if(patHash == txtHash && check(0)) // 一开始就匹配成功
45 | return 0;
46 | for(int i = M; i < N; i++) { // 减去第一个数字,加上最后一个数字,再次检查匹配
47 | txtHash = (txtHash + Q - RM*txt.charAt(i-M) % Q) % Q;
48 | txtHash = (txtHash*R + txt.charAt(i)) % Q;
49 | if(patHash == txtHash)
50 | if(check(i - M + 1))
51 | return i - M + 1;
52 | }
53 | return N;
54 | }
55 |
56 | /**
57 | * Exercise 5.3.33
58 | */
59 | private static long longRandomPrime() {
60 | BigInteger prime = BigInteger.probablePrime(31, new Random());
61 | return prime.longValue();
62 | }
63 |
64 | public static void main(String[] args) {
65 | String pat = args[0];
66 | String txt = args[1];
67 | RabinKarp rk = new RabinKarp(pat);
68 | StdOut.println("text: " + txt);
69 | int offset = rk.search(txt);
70 | StdOut.print("pattern: ");
71 | for (int i = 0; i < offset; i++) {
72 | StdOut.print(" ");
73 | }
74 | StdOut.println(pat);
75 | }
76 | }
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter6_3_Suffix_Arrays/KWIC.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter6_3_Suffix_Arrays;
2 |
3 | import algs4.In;
4 | import algs4.StdIn;
5 | import algs4.StdOut;
6 |
7 | /**
8 | * @author huang
9 | * keyword-in-context
10 | * 上下文的关键词的索引用例
11 | */
12 | public class KWIC {
13 | public static void main(String[] args) {
14 | In in = new In(args[0]);
15 | int context = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); // 关键词的前后若干个字符
16 |
17 | String text = in.readAll().replaceAll("\\s+", " ");
18 | int N = text.length();
19 | SuffixArray sa = new SuffixArray(text);
20 |
21 | while(StdIn.hasNextLine()) {
22 | String q = StdIn.readLine();
23 | for(int i = sa.rank(q); i < N && sa.select(i).startsWith(q); i++) {
24 | int from = Math.max(0, sa.index(i) - context);
25 | int to = Math.min(N-1, from + q.length() + 2 * context);
26 | StdOut.println(text.substring(from, to));
27 | }
28 | StdOut.println();
29 | }
30 | }
31 | }
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter6_3_Suffix_Arrays/LRS.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter6_3_Suffix_Arrays;
2 |
3 | import algs4.StdIn;
4 | import algs4.StdOut;
5 |
6 | /**
7 | * @author huang
8 | * 最长重复子字符串算法的用例
9 | */
10 | public class LRS {
11 | public static void main(String[] args) {
12 | String text = StdIn.readAll();
13 | int N = text.length();
14 | SuffixArray sa = new SuffixArray(text);
15 | String lrs = "";
16 | for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
17 | int length = sa.lcp(i);
18 | if(length > lrs.length())
19 | lrs = sa.select(i).substring(0, length);
20 | }
21 | StdOut.println(lrs);
22 | }
23 | }
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/chapter6_3_Suffix_Arrays/SuffixArray.java:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package chapter6_3_Suffix_Arrays;
2 |
3 | import chapter2_3_Quicksort.Quick3way;
4 |
5 | /**
6 | * @author huang
7 | * 后缀数组(初级实现)
8 | */
9 | public class SuffixArray {
10 | private final String[] suffixes; // 后缀数组
11 | private final int N; // 字符串(和数组)的长度
12 |
13 | public SuffixArray(String s) {
14 | N = s.length();
15 | suffixes = new String[N];
16 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
17 | suffixes[i] = s.substring(i);
18 | Quick3way.sort(suffixes);
19 | }
20 |
21 | public int length() {
22 | return N;
23 | }
24 |
25 | public String select(int i) {
26 | return suffixes[i];
27 | }
28 |
29 | public int index(int i) {
30 | return N - suffixes[i].length();
31 | }
32 |
33 | private static int lcp(String s, String t) {
34 | int N = Math.min(s.length(), t.length());
35 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
36 | if(s.charAt(i) != t.charAt(i))
37 | return i;
38 | return N;
39 | }
40 |
41 | public int lcp(int i) {
42 | return lcp(suffixes[i], suffixes[i-1]);
43 | }
44 |
45 | public int rank(String key) {
46 | // 二分查找
47 | int lo = 0, hi = N - 1;
48 | while(lo <= hi) {
49 | int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
50 | int cmp = key.compareTo(suffixes[mid]);
51 | if(cmp < 0)
52 | hi = mid - 1;
53 | else if(cmp > 0)
54 | lo = mid + 1;
55 | else
56 | return mid;
57 | }
58 | return lo;
59 | }
60 | }
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/code/yuki.config.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "title": "代码目录",
3 | "repository": {
4 | "index": "https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes",
5 | "branch": "master/code"
6 | },
7 | "startLevel": 2,
8 | "ignore": {
9 | "dir": [".git"],
10 | "extname": [".md"],
11 | "file": [
12 | "yuki.config.json",
13 | ".gitignore",
14 | "README.md",
15 | ".DS_Store"
16 | ]
17 | }
18 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/.nojekyll:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/e598780a9ecfe462c72f025fd5f45e052bcf292a/docs/.nojekyll
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Context/6.1_事件驱动模拟.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 6.1 事件驱动模拟
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | ### 性能
6 |
7 | 对 N 个能够相互碰撞的粒子系统,**基于事件的模拟**在初始化时最多需要 N^2 次优先队列操作,在碰撞时最多需要 N 次优先队列操作(且对于每个无效的事件都需要一次额外的操作)。
8 |
9 | 2.4 节的优先队列实现保证每次操作都是对数级别,因此每次碰撞所需时间是线性对数级别的。
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Context/6.2_B-树.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 6.2 B- 树
2 |
3 | 作用:快速访问大量数据中的特定元素
4 |
5 | ### 成本模型
6 |
7 | 我们用**页**表示一块连续的数据,用**探查**表示访问一个页。因此外部查找算法的成本模型为**页的访问**次数(无论读写)。
8 |
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Context/6.3_后缀数组.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 6.3 后缀数组
2 |
3 | * 问题描述:在长度为数百万个字符的字符串中找出其**最长重复子字符串**。
4 | * 暴力解法:将字符串中每个起始位置为 i 的子字符串与另一个起始位置为 j 的子字符串相比较,记录匹配的最长子字符串。运行时间至少是字符串长度的**平方**级别。
5 |
6 | ### 后缀排序
7 |
8 | 方法:
9 |
10 | 1. 用 Java 的`substring()`方法创建一个由字符串 s 的所有后缀字符串(由字符串的所有位置开始得到的后缀字符串)组成的数组;
11 | 2. 将该数组排序,**最长重复子字符串会出现在数组中的相邻位置**;
12 | 3. 遍历排序后的数组一遍即可在相邻元素中找到最长的公共前缀。
13 |
14 | ### 应用:定位字符串
15 |
16 | 通过后缀排序和二分查找,我们可以迅速在大量文本中定位某个特定的子字符串(例如使用文本编辑器或浏览网页时)。
17 |
18 | ### 后缀数组的 API
19 |
20 | | public class SuffixArray | 说明 |
21 | | :----: | :----: |
22 | | SuffixArray(String text) | 为文本 text 构造后缀数组 |
23 | | int length() | 文本 text 的长度 |
24 | | String select(int i) | 后缀数组中的第 i 个元素(0 <= i <= N-1) |
25 | | int index(int i) | select(i) 的索引(0 <= i <= N-1) |
26 | | int lcp(int i) | select(i) 和 select(i-1) 的最长公共前缀的长度(1 <= i <= N-1) |
27 | | int rank(String key) | 小于键 key 的后缀数量 |
28 |
29 | ### 用例
30 |
31 | 最长重复子字符串算法的用例:
32 |
33 | ```java
34 | /**
35 | * @author huang
36 | * 最长重复子字符串算法的用例
37 | */
38 | public class LRS {
39 | public static void main(String[] args) {
40 | String text = StdIn.readAll();
41 | int N = text.length();
42 | SuffixArray sa = new SuffixArray(text);
43 | String lrs = "";
44 | for(int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
45 | int length = sa.lcp(i);
46 | if(length > lrs.length())
47 | lrs = sa.select(i).substring(0, length);
48 | }
49 | StdOut.println(lrs);
50 | }
51 | }
52 | ```
53 |
54 | 上下文的关键词的索引用例:
55 |
56 | ```java
57 | /**
58 | * @author huang
59 | * keyword-in-context
60 | * 上下文的关键词的索引用例
61 | */
62 | public class KWIC {
63 | public static void main(String[] args) {
64 | In in = new In(args[0]);
65 | int context = Integer.parseInt(args[1]); // 关键词的前后若干个字符
66 |
67 | String text = in.readAll().replaceAll("\\s+", " ");
68 | int N = text.length();
69 | SuffixArray sa = new SuffixArray(text);
70 |
71 | while(StdIn.hasNextLine()) {
72 | String q = StdIn.readLine();
73 | for(int i = sa.rank(q); i < N && sa.select(i).startsWith(q); i++) {
74 | int from = Math.max(0, sa.index(i) - context);
75 | int to = Math.min(N-1, from + q.length() + 2 * context);
76 | StdOut.println(text.substring(from, to));
77 | }
78 | StdOut.println();
79 | }
80 | }
81 | }
82 | ```
83 |
84 | ### 代码实现
85 |
86 | ```java
87 | /**
88 | * @author huang
89 | * 后缀数组(初级实现)
90 | */
91 | public class SuffixArray {
92 | private final String[] suffixes; // 后缀数组
93 | private final int N; // 字符串(和数组)的长度
94 |
95 | public SuffixArray(String s) {
96 | N = s.length();
97 | suffixes = new String[N];
98 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
99 | suffixes[i] = s.substring(i);
100 | Quick3way.sort(suffixes);
101 | }
102 |
103 | public int length() {
104 | return N;
105 | }
106 |
107 | public String select(int i) {
108 | return suffixes[i];
109 | }
110 |
111 | // 后缀字符串的长度说明其起始位置
112 | public int index(int i) {
113 | return N - suffixes[i].length();
114 | }
115 |
116 | private static int lcp(String s, String t) {
117 | int N = Math.min(s.length(), t.length());
118 | for(int i = 0; i < N; i++)
119 | if(s.charAt(i) != t.charAt(i))
120 | return i;
121 | return N;
122 | }
123 |
124 | public int lcp(int i) {
125 | return lcp(suffixes[i], suffixes[i-1]);
126 | }
127 |
128 | public int rank(String key) {
129 | // 二分查找
130 | int lo = 0, hi = N - 1;
131 | while(lo <= hi) {
132 | int mid = lo + (hi - lo) / 2;
133 | int cmp = key.compareTo(suffixes[mid]);
134 | if(cmp < 0)
135 | hi = mid - 1;
136 | else if(cmp > 0)
137 | lo = mid + 1;
138 | else
139 | return mid;
140 | }
141 | return lo;
142 | }
143 | }
144 | ```
145 |
146 | ### 性能
147 |
148 | 使用三向字符串快速排序,构造长度为 N 的随机字符串的后缀数组,平均所需的空间与 N 成正比,字符比较次数与 ~2NlnN 成正比(渐近于将 N 个随机字符串排序的成本)。
149 |
150 | ### 改进思路
151 |
152 | SuffixArray 的初级实现在最坏情况下性能糟糕,因为排序和查找最长重复子字符串所需的时间都可能是平方级别。
153 |
154 | Winter 算法可以在**线性时间**内解决最长重复子字符串问题,其基础是构造一棵由所有后缀字符串组成的字典查找树。显然在解决许多实际问题时,该算法对空间要求较大。
155 |
156 | [Manber 算法](https://algs4.cs.princeton.edu/63suffix/Manber.java.html)在线性对数时间内构造后缀数组,并有一个同时完成预处理和对后缀数组排序以支持**常数时间**的`lcp()`方法。
157 |
158 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Context/6.4_网络流算法.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 6.4 网络流算法
2 |
3 | ### 定义
4 |
5 | * 一个**流量网络**是一张边的权重(这里称为**容量**)为正的加权有向图。
6 | * 一个 **st- 流量网络**有两个已知的顶点,即起点 s 和终点 t。
7 | * st- 流量网络中的 **st- 流量配置**是由一组和每条边相关联的值组成的集合,这个值被称为**边的流量**。如果所有边的流量均小于边的容量且满足每个顶点的**局部平衡**(即净流量 = 流入量 - 流出量 = 0,s 和 t 除外),那么就称这种流量配置方案是**可行的**。
8 | * **最大流量问题**:给定一个 st- 流量网络,找到一种 st- 流量配置,使得从 s 到 t 的流量最大化。
9 |
10 | ### API
11 |
12 | FlowEdge 并不基于之前的 DirectedEdge,因为需要使每条边都出现在它的两个顶点的邻接表中才能实现剩余网络。**剩余网络**能够增减流量并检测一条边是否已经饱和(无法再增大流量)或者是否为空(无法再减小流量)。
13 |
14 | 流量网络中的边的 API:
15 |
16 | | public class FlowEdge | 说明 |
17 | | :----: | :----: |
18 | | FlowEdge(int v, int w, double cap) | |
19 | | int from() | 这条边的起始顶点 |
20 | | int to() | 这条边的目的顶点 |
21 | | int other(int v) | 边的另一个顶点 |
22 | | double capacity() | 边的容量 |
23 | | double flow() | 边中的流量 |
24 | | double residualCapacityTo(int v) | v 的剩余流量 |
25 | | double addResidualFlowTo(int v, double delta) | 将 v 的流量增加 delta |
26 | | String toString() | 对象的字符串表示 |
27 |
28 | 流量网络的 API:
29 |
30 | | public class FlowNetwork | 说明 |
31 | | :----: | :----: |
32 | | FlowNetwork(int V) | 创建一个含有 V 个顶点的空网格 |
33 | | FlowNetwork(In in) | 从输入流中构造流量网络 |
34 | | int V() | 顶点总数 |
35 | | int E() | 边的总数 |
36 | | void addEdge(FlowEdge e) | 向流量网络中添加边 e |
37 | | Iterable adj(int v) | 从 v 指出的边 |
38 | | Iterable edges() | 流量网络中的所有边 |
39 | | String toString() | 对象的字符串表示 |
40 |
41 | ### Ford-Fulkerson 算法
42 |
43 | 一种计算网络中流量分配的方法:
44 |
45 | 1. 找到任一条从起点到终点的有向路径,增大流量为该路径上所有边中未使用容量的最小值;
46 | 2. 找到另一条路径,如此反复,直到所有从起点到终点的路径上至少有一条边是饱和的。
47 |
48 | 上述方法只在某些情况下能够计算出网络中的最大流量。因此我们将依据变为网络所对应的无向图中从起点到终点的路径。
49 |
50 | 一些概念如下:
51 |
52 | * 正向边:沿着路径从起点向终点前进时,经过方向与流量方向相同的边;
53 | * 逆向边:经过方向与流量方向相反的边;
54 | * **增广路径**:满足所有正向边非饱和、所有逆向边非空的路径。
55 |
56 | **Ford-Fulkerson 最大流量算法**:网络中的初始流量为 0,沿着任意从起点到终点(且不含有饱和的正向边或是空逆向边)的增光路径增大流量,直到网络中不存在这样的路径为止。
57 |
58 | ### 证明:最大流-最小切分定理
59 |
60 | **st- 切分**:一个将顶点 s 和顶点 t 分配于不同集合中的切分。
61 |
62 | **最大流-最小切分定理**:令 f 为一个 st- 流量网络,以下三种条件是等价的:
63 |
64 | * 存在某个 st- 切分,其容量和 f 的流量相等;
65 | * f 到达了最大流量;
66 | * f 中已经不存在任何增广路径。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Context/6.5_问题规约.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 6.5 问题归约
2 |
3 | 将很多看似复杂的问题归约为简单的问题,再用特定算法解决。
4 |
5 | 但是注意不要犯下“Maslow 的锤子”的错误:沉迷于若干问题解决模型,从而妨碍发现更好的解决方法。
6 |
7 | ### 排序问题
8 |
9 | 以下问题可以被归约为排序问题:
10 |
11 | * 寻找中位数;
12 | * 统计不同的值;
13 | * 最小平均完成时间的调度问题。
14 |
15 | ### 最短路径问题
16 |
17 | 以下问题能够归约为加权图中的最短路径问题:
18 |
19 | * 非负权重的无向图中的单点最短路径问题;
20 | * 优先级限制下的并行调度问题;
21 | * 套汇问题。
22 |
23 | ### 最大流量问题
24 |
25 | 以下问题可以归约为最大流量问题:
26 |
27 | * 就业安置;
28 | * 产品配送;
29 | * 网络可靠性。
30 |
31 | ### 线性规划
32 |
33 | 运筹学的基础之一是**线性规划(Linear Programming,LP)**:给定一个由 M 个**线性不等式**组成的集合和含有 N 个决策变量的线性等式,以及一个由该 N 个决策变量组成的线性**目标函数**,找出能够使目标函数的值最大化的一组变量值,或者证明不存在这样的赋值方案。
34 |
35 |
 36 |
37 | 以下问题均可归约为线性规划问题:
38 |
39 | * 最大流量问题;
40 | * 最短路径问题;
41 | * 许多许多其他问题。
42 |
43 | “许多许多其他问题”的含义如下:
44 |
45 | 1. 添加约束条件和扩展线性规划模型非常简单;
46 | 2. 问题的归约是有传递性的;
47 | 3. **各种最优化问题都能够直接构造为线性规划问题**。
48 |
49 | 解决线性规划问题的高效算法:
50 |
51 | * 单纯形法(Simplex Algorithm);
52 | * 椭球法(Ellipsoid Algorithm);
53 | * 内点法(Interior Point Methods)。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Context/6.6_不可解性.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 6.6 不可解性
2 |
3 | 一台“图灵机”就是一台能够读取输入、变换状态和打印输出的有限状态机。它来自于两个重要的思想:
4 |
5 | * 普遍性:图灵机可以模拟所有物理可实现的计算设备。这被称为**丘奇-图灵论题**。
6 | * 可计算性:图灵机无法解决的问题是存在的。
7 |
8 | 还有第三个关于计算设备效率的思想:
9 |
10 | * **扩展的丘奇-图灵论题**:在任意计算设备上解决某个问题的某个程序所需的运行时间的增长数量级都是在图灵机上(或是任意其他计算设备上)解决该问题的某个程序的多项式倍数。
11 |
12 | 最近几年,量子计算的概念使得一些研究者开始怀疑扩展的丘奇-图灵论题的正确性。
13 |
14 | ### 指数级别的运行时间
15 |
16 | 不可解性理论的目的在于将能够区别**多项式时间内**解决的问题和**在最坏情况下(可能)需要指数级别(2^N)时间**才能解决的问题。
17 |
18 | 一般认为,指数时间的算法无法保证在合理的时间内解决规模超过(例如)100 的问题。
19 |
20 | ### 搜索问题
21 |
22 | * **搜索问题**:有解且**验证它的解的正确性**所需的时间不会超过输入规模的多项式的问题(只与解的验证有关);
23 | * **解决**了一个搜索问题:一个算法给出了一个解或已证明解不存在;
24 | * **NP**:所有搜索问题的集合。
25 | * **P**:能够在多项式时间内**解决**的所有搜索问题的集合。或者说,能够保证在合理时间范围内解决的所有问题的集合。一般来说,用**不可解**来表示不包含在集合 P 中的问题。
26 |
27 | 虽然在技术上并不等价,但**搜索问题**、**决定性问题**(解是否存在)、**最优化问题**(最优解是什么)一般都能够相互归约。
28 |
29 | ### 非确定性
30 |
31 | NP 中的 N 表示的是**非确定性(nondeterminism)**。其意思是断言当一个算法面对若干个选项时,它有能力“猜出”正确的选项。在图灵机中,非确定性只是定义为一个给定状态和一个给定输入时的两个不同的后继状态,解则是能够得到期望结果的所有路径。
32 |
33 | 非确定性看似强大,但没人能**证明**它能够帮助解决任何问题。这就导致人们始终探寻一个问题的答案:
34 |
35 | **P=NP 成立吗?**
36 |
37 | 因为许多重要的实际问题都属于 NP 但不一定属于 P(即已知的最快确定性算法需要指数级别的时间)。如果能够证明它不属于 P,就可以放弃寻找高效率的算法;反之则存在发现某种高效算法的可能性。
38 |
39 | ### 多项式时间问题的相互归约
40 |
41 | 证明问题 A 是可以归约为问题 B 的:
42 |
43 | 1. 将 A 的实例归约为 B 的实例;
44 | 2. 解决 B 的实例;
45 | 3. 将 B 的实例的解归约为 A 的实例的解。
46 |
47 | 因此,如果一个问题 A 已知是难以解决的,且 A 在多项式时间内能够归约为问题 B,那么问题 B 必然也是难以解决的。
48 |
49 | ### NP-完全性
50 |
51 | 若 NP 中的所有问题都能在多项式时间内归纳为搜索问题 A,那么则称问题 A 是 **NP-完全的**。
52 |
53 | NP-完全问题的意思是,我们不期望能够找到多项式时间的算法。
54 |
55 | ### Cook-Levin 定理
56 |
57 | Cook-Levin 定理:布尔可满足性问题是 NP-完全的。
58 |
59 | Cook-Levin 定理,加上围绕各种 NP-完全问题所进行的多项式时间内的归约,得到两种可能性:
60 |
61 | * 或者 P=NP,即所有搜索问题都能够在多项式时间内得到解决;
62 | * 或者 P 不等于 NP,即存在某些搜索问题无法在多项式时间内得到解决。
63 |
64 | 无论 P=NP 是否成立,目前的实际状态是所有 NP-完全问题的已知最佳算法在最坏情况下都需要指数级别的时间。
65 |
66 | ### 处理 NP-完全性
67 |
68 | 要证明 NP 中的一个问题是 NP-完全的,需要证明某个已知的 NP-完全问题能够在多项式时间内归约为它。如果成功,则说明找到一个高效算法是不可能的。
69 |
70 | 处理 NP-完全性的一些尝试:
71 |
72 | 1. 修改问题,寻找“近似”算法来给出接近但非最佳的解:欧几里得旅行销售员问题、梯度下降;
73 | 2. 给出一种能够有效解决实际应用中所出现的问题的实例算法;
74 | 3. 使用“回溯法”来避免检查所有可能的解,以期找到尽可能“高效”的指数级别算法。
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Fundamentals/1.3_背包、队列和栈.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 1.3 背包、队列和栈
2 |
3 | ## 可迭代的集合类型
4 |
5 | foreach 语句:
6 |
7 | ```java
8 | Queue collection = new Queue();
9 |
10 | for(Transaction t : collection) {
11 | StdOut.println(t);
12 | }
13 | ```
14 |
15 | ## 背包
16 |
17 | 背包是一种**不支持从中删除元素**的集合数据类型。迭代的顺序不确定且与用例无关,因此使用 Bag 可以说明**元素的处理顺序不重要**。
18 |
19 | ## 先进先出队列
20 |
21 | 任何服务性策略的基本原则都是公平,先进先出策略准则是优先服务等待最久的人。
22 |
23 | 在应用中使用队列的主要原因是在用集合保存元素的同时**保存他们的相对顺序**。
24 |
25 | ## 栈的实现思路
26 |
27 | 1. 先用数组实现一个只能处理 String 值、要求用例指定一个容量且不支持迭代的栈。
28 | 2. 修改以实现一个**泛型**的栈。
29 | 3. 在`push()`和`pop()`方法中增加容量判断来调用`resize()`方法。`resize()`方法将栈移动到一个新的大小为 max 的数组中并返回,这样可以**调整数组大小**。
30 | 4. 之前`pop()`的实现仅仅是对 index 的操纵,被弹出的元素的引用仍然存在于数组中,但实际上已成**孤儿**,不会再被访问。这时应将其设置为`null`,让内存被回收。
31 | 5. 集合类数据类型的基本操作之一就是能够使用 Java 的 foreach 语句通过**迭代**遍历并处理集合中的每个元素。
32 |
33 | 任意可迭代的集合数据类型中都需要实现:
34 | * 集合数据类型必须实现一个`iterator()`方法并返回一个`Iterator`对象;
35 | * `Iterator`类必须包含两个方法:`hasNext()`和`next()`。
36 |
37 | ```java
38 | // implement Iterable
36 |
37 | 以下问题均可归约为线性规划问题:
38 |
39 | * 最大流量问题;
40 | * 最短路径问题;
41 | * 许多许多其他问题。
42 |
43 | “许多许多其他问题”的含义如下:
44 |
45 | 1. 添加约束条件和扩展线性规划模型非常简单;
46 | 2. 问题的归约是有传递性的;
47 | 3. **各种最优化问题都能够直接构造为线性规划问题**。
48 |
49 | 解决线性规划问题的高效算法:
50 |
51 | * 单纯形法(Simplex Algorithm);
52 | * 椭球法(Ellipsoid Algorithm);
53 | * 内点法(Interior Point Methods)。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Context/6.6_不可解性.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 6.6 不可解性
2 |
3 | 一台“图灵机”就是一台能够读取输入、变换状态和打印输出的有限状态机。它来自于两个重要的思想:
4 |
5 | * 普遍性:图灵机可以模拟所有物理可实现的计算设备。这被称为**丘奇-图灵论题**。
6 | * 可计算性:图灵机无法解决的问题是存在的。
7 |
8 | 还有第三个关于计算设备效率的思想:
9 |
10 | * **扩展的丘奇-图灵论题**:在任意计算设备上解决某个问题的某个程序所需的运行时间的增长数量级都是在图灵机上(或是任意其他计算设备上)解决该问题的某个程序的多项式倍数。
11 |
12 | 最近几年,量子计算的概念使得一些研究者开始怀疑扩展的丘奇-图灵论题的正确性。
13 |
14 | ### 指数级别的运行时间
15 |
16 | 不可解性理论的目的在于将能够区别**多项式时间内**解决的问题和**在最坏情况下(可能)需要指数级别(2^N)时间**才能解决的问题。
17 |
18 | 一般认为,指数时间的算法无法保证在合理的时间内解决规模超过(例如)100 的问题。
19 |
20 | ### 搜索问题
21 |
22 | * **搜索问题**:有解且**验证它的解的正确性**所需的时间不会超过输入规模的多项式的问题(只与解的验证有关);
23 | * **解决**了一个搜索问题:一个算法给出了一个解或已证明解不存在;
24 | * **NP**:所有搜索问题的集合。
25 | * **P**:能够在多项式时间内**解决**的所有搜索问题的集合。或者说,能够保证在合理时间范围内解决的所有问题的集合。一般来说,用**不可解**来表示不包含在集合 P 中的问题。
26 |
27 | 虽然在技术上并不等价,但**搜索问题**、**决定性问题**(解是否存在)、**最优化问题**(最优解是什么)一般都能够相互归约。
28 |
29 | ### 非确定性
30 |
31 | NP 中的 N 表示的是**非确定性(nondeterminism)**。其意思是断言当一个算法面对若干个选项时,它有能力“猜出”正确的选项。在图灵机中,非确定性只是定义为一个给定状态和一个给定输入时的两个不同的后继状态,解则是能够得到期望结果的所有路径。
32 |
33 | 非确定性看似强大,但没人能**证明**它能够帮助解决任何问题。这就导致人们始终探寻一个问题的答案:
34 |
35 | **P=NP 成立吗?**
36 |
37 | 因为许多重要的实际问题都属于 NP 但不一定属于 P(即已知的最快确定性算法需要指数级别的时间)。如果能够证明它不属于 P,就可以放弃寻找高效率的算法;反之则存在发现某种高效算法的可能性。
38 |
39 | ### 多项式时间问题的相互归约
40 |
41 | 证明问题 A 是可以归约为问题 B 的:
42 |
43 | 1. 将 A 的实例归约为 B 的实例;
44 | 2. 解决 B 的实例;
45 | 3. 将 B 的实例的解归约为 A 的实例的解。
46 |
47 | 因此,如果一个问题 A 已知是难以解决的,且 A 在多项式时间内能够归约为问题 B,那么问题 B 必然也是难以解决的。
48 |
49 | ### NP-完全性
50 |
51 | 若 NP 中的所有问题都能在多项式时间内归纳为搜索问题 A,那么则称问题 A 是 **NP-完全的**。
52 |
53 | NP-完全问题的意思是,我们不期望能够找到多项式时间的算法。
54 |
55 | ### Cook-Levin 定理
56 |
57 | Cook-Levin 定理:布尔可满足性问题是 NP-完全的。
58 |
59 | Cook-Levin 定理,加上围绕各种 NP-完全问题所进行的多项式时间内的归约,得到两种可能性:
60 |
61 | * 或者 P=NP,即所有搜索问题都能够在多项式时间内得到解决;
62 | * 或者 P 不等于 NP,即存在某些搜索问题无法在多项式时间内得到解决。
63 |
64 | 无论 P=NP 是否成立,目前的实际状态是所有 NP-完全问题的已知最佳算法在最坏情况下都需要指数级别的时间。
65 |
66 | ### 处理 NP-完全性
67 |
68 | 要证明 NP 中的一个问题是 NP-完全的,需要证明某个已知的 NP-完全问题能够在多项式时间内归约为它。如果成功,则说明找到一个高效算法是不可能的。
69 |
70 | 处理 NP-完全性的一些尝试:
71 |
72 | 1. 修改问题,寻找“近似”算法来给出接近但非最佳的解:欧几里得旅行销售员问题、梯度下降;
73 | 2. 给出一种能够有效解决实际应用中所出现的问题的实例算法;
74 | 3. 使用“回溯法”来避免检查所有可能的解,以期找到尽可能“高效”的指数级别算法。
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Fundamentals/1.3_背包、队列和栈.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 1.3 背包、队列和栈
2 |
3 | ## 可迭代的集合类型
4 |
5 | foreach 语句:
6 |
7 | ```java
8 | Queue collection = new Queue();
9 |
10 | for(Transaction t : collection) {
11 | StdOut.println(t);
12 | }
13 | ```
14 |
15 | ## 背包
16 |
17 | 背包是一种**不支持从中删除元素**的集合数据类型。迭代的顺序不确定且与用例无关,因此使用 Bag 可以说明**元素的处理顺序不重要**。
18 |
19 | ## 先进先出队列
20 |
21 | 任何服务性策略的基本原则都是公平,先进先出策略准则是优先服务等待最久的人。
22 |
23 | 在应用中使用队列的主要原因是在用集合保存元素的同时**保存他们的相对顺序**。
24 |
25 | ## 栈的实现思路
26 |
27 | 1. 先用数组实现一个只能处理 String 值、要求用例指定一个容量且不支持迭代的栈。
28 | 2. 修改以实现一个**泛型**的栈。
29 | 3. 在`push()`和`pop()`方法中增加容量判断来调用`resize()`方法。`resize()`方法将栈移动到一个新的大小为 max 的数组中并返回,这样可以**调整数组大小**。
30 | 4. 之前`pop()`的实现仅仅是对 index 的操纵,被弹出的元素的引用仍然存在于数组中,但实际上已成**孤儿**,不会再被访问。这时应将其设置为`null`,让内存被回收。
31 | 5. 集合类数据类型的基本操作之一就是能够使用 Java 的 foreach 语句通过**迭代**遍历并处理集合中的每个元素。
32 |
33 | 任意可迭代的集合数据类型中都需要实现:
34 | * 集合数据类型必须实现一个`iterator()`方法并返回一个`Iterator`对象;
35 | * `Iterator`类必须包含两个方法:`hasNext()`和`next()`。
36 |
37 | ```java
38 | // implement Iterable - 对应的接口
39 | public interface Iterable
- {
40 | Iterator
- iterator();
41 | }
42 | ```
43 |
44 | ```java
45 | // 集合数据类型需要实现 iterator 方法
46 | import java.util.Iterator;
47 |
48 | // iterator 方法并返回一个 Iterator 对象
49 | public Iterator
- iterator() {
50 | return new ReverseArrayIterator();
51 | }
52 | ```
53 |
54 | ```java
55 | // 迭代器接口
56 | public interface Iterator
- {
57 | boolean hasNext();
58 | Item next();
59 | void remove();
60 | }
61 | ```
62 |
63 | ```java
64 | // ReverseArrayIterator 的实现
65 | private class ReverseArrayIterator implements Iterator
- {
66 | private int i = N;
67 |
68 | public boolean hasNext() { return i > 0; }
69 | public Item next() { return a[--i]; }
70 | public void remove() {}
71 | }
72 | ```
73 |
74 | 这样,无需知晓类的实现细节也能使用迭代。
75 |
76 | ## 栈实现的分析
77 |
78 | 以上实现几乎达到了任意集合类型实现的最佳性能:
79 |
80 | * 每项操作的用时都与集合大小无关;
81 | * 空间需求总是不超过集合大小乘以一个整数。
82 |
83 | 但以上实现的缺点在于`push()`和`pop()`操作会调整数组的大小:这项操作的耗时和栈大小成正比。
84 |
85 | 使用链表来实现可以克服这个缺点,使操作所需时间总是和集合的大小无关。
86 |
87 | ## 基础数据结构——数组与链表
88 |
89 | | 数据结构 | 优点 | 缺点 |
90 | | :----: | :----: | :----: |
91 | | 数组 | 通过索引可以直接访问任意元素 | 在初始化时就需要知道元素的数量 |
92 | | 链表 | 使用的空间大小和元素数量成正比 | 需要通过引用访问任意元素 |
93 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Fundamentals/1.4_算法分析.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 1.4 算法分析
2 |
3 | ## 数学模型
4 |
5 | 我们用`~f(N)`表示所有随着 N 的增大除以 f(N) 的结果趋近于 1 的函数,用`g(N)~f(N)`表示`g(N)/f(N)`随着 N 的增大趋近于 1。则 f(N) 为 g(N) 的增长的**数量级**。
6 |
7 | 对于大多数程序,得到其运行时间的数学模型所需的步骤如下:
8 |
9 | * 确定**输入模型***(自己的理解:输入的数据,重要的是数据规模)*,定义问题的规模;
10 | * 识别**内循环**;
11 | * 根据内循环中的操作确定**成本模型***(自己的理解:耗时间的操作)*;
12 | * 对于给定的输入,判断这些操作的执行频率。
13 |
14 | 一般来说,我们希望为各种基础问题找到对数级别、线性级别或是线性对数级别(NlogN)的算法。
15 |
16 | ### 重要资料
17 |
18 | p116.表1.4.5 算法中的常见函数/表1.4.6 算法分析中常用的近似函数
19 |
20 | 
21 |
22 | ## 内存
23 |
24 | ### 对象
25 |
26 | 要知道一个对象所使用的内存量,需要将所有实例变量使用的内存与**对象本身的开销(一般是 16 字节)**相加。这些开销包括一个指向对象的类的引用、垃圾收集信息以及同步信息。另外,一般内存的使用都会被**填充为 8 字节(64 位计算机中的机器字)的倍数**。
27 |
28 | ### 链表
29 |
30 | 嵌套的非静态(内部)类,还需要额外的 8 字节(用于一个指向外部类的引用)。
31 |
32 | ### 数组
33 |
34 | 一个**原始数据类型**的数组一般需要 24 字节的头信息(16 字节的对象开销,*4 字节用于保存长度*以及 4 填充字节)再加上保存值所需的内存。
35 |
36 | 一个**对象**的数组就是一个对象的引用的数组。例如一个含有 N 个 Date 对象的数组需要使用 24 字节(数组开销)加上 8N 字节(所有引用)加上每个对象的 32 字节,共 (24 + 40N) 字节。
37 |
38 | **二维数组**是一个数组的数组(每个数组都是一个对象)。例如一个 M * N 的 double 类型的二维数组需要使用 24 字节(数组的数组的开销)加上 8M 字节(所有元素数组的引用)加上 24M 字节(所有元素数组的开销)加上 8MN 字节(M 个长度为 N 的 double 类型的数组),总共(8MN + 32M + 24)~ 8MN 字节。
39 |
40 | ### 字符串
41 |
42 | Java 中 String 的标准实现含有 4 个实例变量:一个指向字符数组的引用(8 字节)和 3 个 int 值(各 4 字节)。第一个 int 值描述的是字符数组中的偏移量,第二个 int 值是一个计数器(字符串的长度),第三个 int 值是一个散列值(在某些情况下节省一些计算)。因此,**每个 String 对象共会使用 40 字节**(16 字节表示对象,3 个 int 实例变量共 12 字节,加上数组引用的 8 字节和 4 个填充字节),这是除字符数组之外字符串所需的内存空间。
43 |
44 | 一个长度为 N 的 String 对象一般需要使用 40 字节(String 对象本身)加上(24 + 2N)字节(字符数组),总共(64 + 2N)字节。
45 |
46 | 调用`substring()`方法创建子字符串时,重用了相同的 value[] 数组,因此只会使用 40 字节的内存。即**一个子字符串所需的额外内存是一个常数,构造一个子字符串所需的时间也是常数**。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Fundamentals/1.5_案例研究:union-find算法.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 1.5 案例研究:union-find 算法
2 |
3 | ## 动态连通性
4 |
5 | 动态连通性问题:设计一个数据结构来保存程序已知的所有整数对的足够多的信息,并用它们来判断一对新对象是否是相连的。
6 |
7 | 解决该问题的算法被称为 union-find。成本模型:在研究实现 union-find 的 API 的各种算法时,我们统计的是**数组的访问次数**(访问任意数组元素的次数,无论读写)。
8 |
9 | 路径压缩的加权 quick-union 算法是最优的算法,但并非所有操作*都能在常数时间内完成*。
10 |
11 | ## 展望
12 |
13 | 研究各种基础问题的基本步骤:
14 |
15 | 1. 完整而详细地定义问题,找出解决问题所必需的基本抽象操作并定义一份 API。
16 | 2. 简洁地实现一种初级算法,给出一个精心组织的开发用例并使用实际数据作为输入。
17 | 3. 当实现所能解决的问题的最大规模达不到期望时决定改进还是放弃。
18 | 4. 逐步改进实现,通过经验性分析或(和)数学分析验证改进后的效果。
19 | 5. 用更高层次的抽象表示数据结构或算法来设计更高级的改进版本。
20 | 6. 如果可能,尽量为最坏情况下的性能提供保证,但在处理普通数据时也要有良好的性能。
21 | 7. 在适当的时候将更细致的深入研究留给有经验的研究者并继续解决下一个问题。
22 |
23 | ## 看一下别人的总结
24 |
25 | [算法(1):Union-Find | Weber](http://binweber.top/2018/02/15/algs_1/)
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Graphs/4.1_无向图.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 4.1 无向图
2 |
3 | ## 术语表
4 |
5 | * 自环:一条连接一个顶点和其自身的边;
6 | * 平行边:连接同一对顶点的两条边;
7 | * 多重图:含有平行边的图;
8 | * 简单图:没有平行边或自环的图;
9 | * 子图:由一幅图的所有边的一个子集(以及它们所依附的所有顶点)组成的图;
10 |
11 | * **路径**:由边顺序连接的一系列顶点;
12 | * 简单路径:一条没有重复顶点的路径;
13 | * 环:一条至少含有一条边且起点与终点相同的路径;
14 | * 简单环:一条(除了起点和终点必须相同之外)不含有重复顶点和边的环;
15 |
16 | * 连通图:从任意一个顶点都存在一条路径到达另一个任意顶点的图;
17 | * 一幅**非连通的图**由若干连通的部分组成,它们都是其极大连通子图。一般来说,**要处理一张图就需要一个个地处理它的连通分量(子图)**;
18 |
19 | * 树:一幅无环连通图;
20 | * 森林:互不相连的树组成的集合;
21 | * 连通图的生成树:它的一幅子图,它含有图中的所有顶点且是一棵树;
22 | * 图的生成树森林:它的所有连通子图的生成树的集合;
23 |
24 | * 图的密度:已经连接的**顶点对**占所有可能被连接的**顶点对**的比例;
25 |
26 | * 二分图:一种能将所有结点分成两部分的图,其中图的每条边所连接的两个顶点都分别属于不同的部分;
27 |
28 | ## 树的数学性质
29 |
30 | 当且仅当一幅含有 V 个结点的图 G 满足下列 5 个条件之一时,它就是一棵树:
31 |
32 | * G 有 V-1 条边且不含有环;
33 | * G 有 V-1 条边且是连通的;
34 | * G 是连通的,但删除任意一条边都会使它不再连通;
35 | * G 是无环图,但添加任意一条边都会产生一条环;
36 | * G 中的任意一对顶点之间仅存在一条简单路径。
37 |
38 | ## 图的表示方法
39 |
40 | * 邻接矩阵
41 | * 边的数组
42 | * 邻接表数组
43 |
44 | ## 深度优先搜索(DFS)
45 |
46 | ### 实现方法
47 |
48 | 在访问其中一个顶点时:
49 |
50 | * 将它**标记为已访问**;
51 | * 递归地访问它的所有没被标记过的邻居顶点。
52 |
53 | ### 命题
54 |
55 | * 深度优先搜索标记与起点连通的所有顶点所需的时间和顶点的度数之和成正比。
56 | * 深度优先搜素中每条边都会被访问两次。
57 | * 深度优先搜索的预处理使用的时间和空间与 V+E 成正比,且可以在常数时间内处理关于图的连通性查询。
58 |
59 | ### 解决问题
60 |
61 | * 连通性:两个给定的顶点是否连通;
62 | * 单点路径:能够解决**找出**两个给定顶点间的路径的问题;
63 | * 检测环:给定的图是否为无环图;
64 | * 双色问题:给定的图是否为二分图;
65 |
66 | ## 广度优先搜索(BFS)
67 |
68 | ### 实现方法
69 |
70 | 使用一个队列来保存所有已经被标记过但其邻接表还未被检查过的顶点。先将起点加入队列,然后重复以下步骤直到队列为空:
71 |
72 | * 取队列中的下一个顶点 v 并标记它;
73 | * 将与 v 相邻的所有未被标记过的顶点加入队列。
74 |
75 | ### 命题
76 |
77 | * 广度优先搜索所需时间在最坏情况下和 V+E 成正比。
78 |
79 | ## 总结
80 |
81 | 问题 | 解决方法
82 | :-----------: | :-----------:
83 | 单点连通性 | [DepthFirstSearch](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/DepthFirstSearch.java)
84 | 单点路径 | [DepthFirstPaths](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/DepthFirstPaths.java)
85 | 单点最短路径 | [BreadthFirstPaths](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/BreadthFirstPaths.java)
86 | 连通性 | [CC](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/CC.java)、union-find
87 | 检测环 | [Cycle](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/Cycle.java)
88 | 双色问题(图的二分性) | [TwoColor](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_1_Undirected_Graphs/TwoColor.java)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Graphs/4.2_有向图.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 4.2 有向图
2 |
3 | ## 有向图中的可达性
4 |
5 | 单点可达性:存在一条从顶点 s 到达顶点 v 的**有向路径**。
6 |
7 | ### 标记-清除的垃圾收集
8 |
9 | 标记-清除的垃圾回收策略会对每个对象保留一个位做垃圾收集之用。它会**周期性地运行一个类似于 DirectedDFS 的有向图可达性算法**来标记所有**可以被访问到**的对象,然后清理所有对象,回收**没有被标记**的对象,以腾出内存供新的对象使用。
10 |
11 | ## 拓扑排序
12 |
13 | * 当且仅当一幅有向图是无环图时才能进行拓扑排序。
14 | * 一幅有向无环图的拓扑顺序即为所有顶点的**逆后序排列**(证明见 p376)。
15 |
16 | 顶点的三种排列顺序:
17 |
18 | * 前序:在递归调用之前将顶点加入队列。
19 | * 后序:在递归调用之后将顶点加入队列。
20 | * **逆后序**:在递归调用之**后**将顶点压入**栈**。
21 |
22 | 命题:Topological 类的实现使用了**深度优先搜索**对有向无环图进行拓扑排序,所需时间和 **V+E 成正比**。
23 |
24 | 证明:第一遍深度优先搜索保证了不存在有向环,第二遍深度优先搜索产生了顶点的逆后序排列,两次搜索都访问了所有的顶点和所有的边。
25 |
26 | ## 有向图中的强连通性
27 |
28 | ### 定义
29 |
30 | * 如果两个顶点 v 和 w 是互相可达的,则称它们为**强连通**的。
31 | * 如果一幅有向图中的**任意**两个顶点都是强连通的,则称这幅有向图也是**强连通**的。
32 | * **强连通分量**:相互均为强连通的顶点的最大子集。
33 |
34 | 两个顶点是强连通的当且仅当它们都在一个普通的有向环中。
35 |
36 | ### Kosaraju 算法
37 |
38 | Kosaraju 算法用于在有向图中高效计算强连通分量,具体操作(证明见 p381):
39 |
40 | 1. 在给定的一幅有向图 G 中,使用 DepthFirstOrder(深度优先搜索)来计算它的反向图 G^R 的逆后序排列。
41 | 2. 在 G 中进行标准的深度优先搜索,但是要按照刚才计算得到的顺序而非标准的顺序来访问所有未被标记的顶点。
42 | 3. 在构造函数中,所有在同一个递归 dfs() 调用中被访问到的顶点都在同一个**强连通分量**中。
43 |
44 | 命题:Kosaraju 算法的预处理所需的**时间和空间与 V+E 成正比**且支持常数时间的有向图强连通性的查询。
45 |
46 | 证明:该算法会处理有向图的反向图并进行两次深度优先搜索。这三步所需的时间都与 V+E 成正比。反向复制一幅有向图所需的空间与 V+E 成正比。
47 |
48 | ### 传递闭包
49 |
50 | 定义:有向图 G 的**传递闭包**是由相同的一组顶点组成的另一幅有向图,在传递闭包中存在一条从 v 指向 w 的边当且仅当在 G 中 w 是从 v 可达的。
51 |
52 | 根据约定,每个顶点对于自己都是可达的,因此传递闭包会含有 V 个自环。
53 |
54 | 一般来说,一幅有向图的传递闭包中所含的边比原图多得多。因为传递闭包一般都很稠密,我们通常将它们表示为一个布尔值矩阵,其中 v 行 w 列的值为 true 当且仅当 w 是从 v 可达的。
55 |
56 | 书上提供的 TransitiveClosure **不适用**于在实际应用中可能遇到的大型有向图,因为**构造函数所需的空间和 V^2 成正比,所需的时间和 V(V+E) 成正比**。
57 |
58 | 目前,我们还没有找到用远小于平方级别的空间支持常数级别的查询的一般解决方案。
59 |
60 | ## 总结
61 |
62 | 问题 | 解决方法
63 | :-----------: | :-----------:
64 | 单点和多点的可达性 | [DirectedDFS](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/DirectedDFS.java)
65 | 单点有向路径 | DepthFirstDirectedPaths
66 | 单点最短有向路径 | BreadthFirstDirectedPaths
67 | 有向环检测 | [DirectedCycle](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/DirectedCycle.java)
68 | 深度优先的顶点排序 | [DepthFirstOrder](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/DepthFirstOrder.java)
69 | 优先级限制下的调度问题 | [Topological](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/Topological.java)
70 | 拓扑排序 | [Topological](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/Topological.java)
71 | 强连通行 | [KosarajuSCC](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/KosarajuSCC.java)
72 | 顶点对的可达性 | [TransitiveClosure](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_2_Directed_Graphs/TransitiveClosure.java)
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Graphs/4.3_最小生成树.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 4.3 最小生成树
2 |
3 | 本节研究最小生成树问题:给定一幅**加权无向图**,找到它的一棵最小生成树。
4 |
5 | ## 术语表
6 |
7 | * 图的**生成树**:它的一棵含有其所有顶点的无环连通子图。
8 | * 一幅**加权图**的**最小生成树(MST)**:它的一棵权值(树中所有边的权值之和)最小的生成树。
9 |
10 | ## 约定
11 |
12 | * 只考虑连通性。
13 | * 边的权重不一定表示距离。
14 | * 边的权重可能是 0 或者负数。
15 | * 所有边的权重都各不相同。
16 |
17 | ## 原理
18 |
19 | ### 切分定理
20 |
21 | #### 原理
22 |
23 | * 用一条边连接树中的任意两个顶点都会产生一个新的环;
24 | * 从树中删去一条边将会得到两棵独立的树。
25 |
26 | #### 定义
27 |
28 | * 图的一种**切分**:将图的所有顶点分为两个非空且不重叠的两个集合;
29 | * **横切边**:一条连接两个属于不同集合的顶点的边。
30 |
31 | #### 命题(切分定理)
32 |
33 | 在一幅加权图中,给定任意的切分,它的**横切边中的权重最小者**必然属于图的最小生成树。
34 |
35 | #### 证明
36 |
37 | 反证法。详见 p392。
38 |
39 | ### 最小生成树的贪心算法
40 |
41 | #### 命题
42 |
43 | 下面这种方法会将含有 V 个顶点的任意加权连通图中属于最小生成树的边标记为黑色:
44 |
45 | 初始状态下所有边均为灰色,找到一种切分,它产生的横切边均不为黑色。将它权重最小的横切边标记为黑色。反复,直到标记了 V-1 条黑色边为止。
46 |
47 | ## Prim 算法
48 |
49 | 每一步都会为一棵生长中的树添加一条边。一开始这棵树只有一个顶点,然后会向它添加 V-1 条边,每次总是将下一条**连接树中的顶点与不在树中的顶点且权重最小的边**加入树中(即由树中的顶点所定义的切分中的一条横切边)。
50 |
51 | ### 延时实现
52 |
53 | Prim 算法的延时实现使用了一条优先队列来保存所有的横切边、一个由顶点索引的数组来标记树的顶点以及一条队列来保存最小生成树的边。这种延时实现会在优先队列中**保留**失效的边。
54 |
55 | #### 开销
56 |
57 | Prim 算法的延时实现计算一幅含有 V 个顶点和 E 条边的连通加权无向图的最小生成树所需的**空间与 E 成正比**,所需的**时间与 ElogE 成正比(最坏情况)**。
58 |
59 | **证明**:
60 |
61 | 优先队列中最多可能有 E 条边,这就是空间需求的上限。
62 |
63 | 算法的瓶颈在于优先队列的`insert()`和`delMin()`方法中比较边的权重的次数。在最坏情况下,一次插入的成本为 ~lgE,删除最小元素的成本为 ~2lgE。因为最多只能插入 E 条边,删除 E 次最小元素,因此所需的时间与 ElogE 成正比(最坏情况)。
64 |
65 | ### 即时实现
66 |
67 | 我们感兴趣的只是连接树顶点和非树顶点中**权重最小**的边。当我们将顶点 v 添加到树中时,对于每个非树顶点 w 产生的变化只可能使得 w 到最小生成树的距离更近。因此,我们只需要在优先队列中保存每个非树顶点 w 的一条边:**将它与树中顶点连接起来的权重最小的那条边**。
68 |
69 | Prim 算法的即时实现将有效的横切边保存在了一条索引优先队列中。
70 |
71 | #### 开销
72 |
73 | Prim 算法的即时实现计算一幅含有 V 个顶点和 E 条边的连通加权无向图的最小生成树所需的**空间与 V 成正比**,所需的**时间与 ElogV 成正比(最坏情况)**。
74 |
75 | **证明**:
76 |
77 | 因为优先队列中的顶点树最多为 V,且使用了三条由顶点索引的数组,所以所需的空间的上限和 V 成正比。
78 |
79 | 算法会进行 V 次插入操作,V 次删除最小元素的操作和(在最坏情况下)E 次改变优先级的操作。已知在基于堆实现的索引优先队列中所有这些操作的增长数量级为 logV,所以将所有这些加起来可知算法所需时间和 ElogV 成正比。
80 |
81 | ## Kruskal 算法
82 |
83 | 按照边的权重顺序(从小到大)处理它们,将边加入最小生成树中,**加入的边不会与已经加入的边构成环**,直到树中含有 V-1 条边为止。我们从一片由 V 棵单顶点的树构成的森林开始并不断将两颗树合并(用可以找到的最短边),直到只剩下一棵树,它就是最小生成树。
84 |
85 | #### 开销
86 |
87 | Kruskal 算法的计算一幅含有 V 个顶点和 E 条边的连通加权无向图的最小生成树所需的**空间与 E 成正比**,所需的**时间与 ElogE 成正比(最坏情况)**。
88 |
89 | **证明**:
90 |
91 | 算法的实现在构造函数中使用所有边初始化优先队列,成本最多为 E 次比较。
92 |
93 | 优先队列构造完成后,其余的部分和 Prim 算法完全相同。优先队列中最多可能含有 E 条边,即所需的空间的上限。每次操作的成本最多为 2lgE 次比较,这就是时间上限的由来。
94 |
95 | ## 总结与展望
96 |
97 | 各种最小生成树算法 V 个顶点 E 条边,最坏情况下的增长数量级:
98 |
99 | 算法 | 空间 | 时间
100 | :----------- | :-----------: | :-----------
101 | [延时的 Prim 算法](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/LazyPrimMST.java) | E | ElogE
102 | [即时的 Prim 算法](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/PrimMST.java) | V | ElogV
103 | [Kruskal](https://github.com/bighuang624/Algorithms-notes/blob/master/code/chapter4_3_Minimum_Spanning_Tree/KruskalMST.java) | E | ElogE
104 | Fredman-Tarjan | V | E+VlogV
105 | Chazelle | V | 非常接近但还没有达到 E
106 | 理想情况 | V | E?
107 |
108 | 一方面,目前还没有理论能够证明,不存在能在线性时间内得到任意图的最小生成树的算法;另一方面,发明能够在线性时间内计算稀疏图的最小生成树的算法仍然没有进展。
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Graphs/4.4_最短路径.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 4.4 最短路径
2 |
3 | 本节研究最短路径问题:找到从一个顶点到达另一个顶点的**成本最小**的路径。
4 |
5 | ## 最短路径的性质
6 |
7 | ### 需要解决的问题
8 |
9 | * 并不是所有顶点都是可达的:为了简化问题,约定图都是强连通的(每个顶点从另外任意一个顶点都是可达的)。
10 | * 负权重会使问题更复杂:经典 Bellman-Ford 算法可以解决。
11 | * 最短路径一般都是简单的:我们的算法会忽略构成环的零权重边,因此找到的最短路径都不会含有环。
12 | * 可能存在平行边和自环:平行边中权重最小者才会被选中,权重为零的自环会被忽略。
13 |
14 | ### 最短路径树(SPT)
15 |
16 | **定义**:给定一幅加权有向图和一个顶点 s,以 s 为起点的一棵**最短路径树**是图的一幅子图,它包含 s 和从 s 可达的所有顶点。这棵有向树的根结点为 s,树的每条路径都是有向图中的一条最短路径。
17 |
18 | ## 加权有向图的数据结构
19 |
20 | ### 最短路径的数据结构
21 |
22 | 表示最短路径所需的数据结构:
23 |
24 | * **最短路径树中的边**:和深度优先搜索、广度优先搜索和 Prim 算法一样,使用一个**由顶点索引的 DirectedEdge 对象的父链接数组 edgeTo[]**,其中 edgeTo[v] 的值为树中连接 v 和它的父结点的边(也是从 s 到 v 的最短路径上的最后一条边)。
25 | * **到达起点的距离**:使用一个**由顶点索引的数组 distTo[]**,其中 distTo[v] 为从 s 到 v 的已知最短路径的长度。
26 |
27 | 约定(s 是寻找的起点):
28 |
29 | * edgeTo[s] 的值为 null,distTo[s] 的值为 0。
30 | * 从起点到不可达的顶点的距离均为`Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY`。
31 |
32 | ### 边的松弛
33 |
34 | **放松**边 v->w 意味着检查从 s 到 w 的最短路径是否是先从 s 到 v,然后再由 v 到 w。如果是,则根据这个情况更新数据结构中的内容。
35 |
36 | 边的放松操作之后可能出现两种情况:
37 |
38 | * 边失效(`distTo[w] <= distTo[v] + e.weight()`);
39 | * v->w 就是到达 w 的最短路径,更新 edgeTo[w] 和 distTo[w](这可能会使另一些边失效,但也有可能产生一些新的有效边)。
40 |
41 | 实际上,实现会放松从一个给定顶点指出的所有边。
42 |
43 | ## 最短路径算法的理论基础
44 |
45 |
46 | ## Dijkstra 算法
47 |
48 | Dijkstra 算法能够解决**边权重非负**的加权有向图的单起点最短路径问题。
49 |
50 | 思想:**每次添加离起点最近的非树顶点**。
51 |
52 | ### 数据结构
53 |
54 | ### 开销
55 |
56 | 在一幅含有 V 个顶点和 E 条边的加权有向图中,使用 Dijkstra 算法计算根结点为给定起点的最短路径树所需的**空间与 E 成正比**,所需的**时间与 ElogE 成正比(最坏情况)**。
57 |
58 | ### 与 Prim 算法的比较
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
《算法(第4版)》笔记
2 |
3 | 
4 |
5 |
6 |

7 |
[LinearProbingHashST]() | 能够快速地查找和插入常见类型的数据 |
65 |
66 |
67 |
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Searching/3.2_二叉查找树.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 3.2 二叉查找树
2 |
3 | **定义**:一棵**二叉查找树(BST,或二叉搜索树)**是一棵二叉树,其中每个结点都含有一个 Comparable 的键(以及相关联的值)且每个结点的键都大于其左子树中的任意结点的键而小于右子树的任意结点的键。
4 |
5 | ## 基本实现
6 |
7 | ### 数据表示
8 |
9 | 二叉查找树上的一个结点,**左链接**指向一棵**小于**该结点的所有键组成的二叉查找树,**右链接**指向一棵由**大于**该结点的所有键组成的二叉查找树。
10 |
11 | ### 查找
12 |
13 | 在二叉查找树中查找一个键的递归算法:如果树是空的,则查找未命中;如果被查找的键和根结点的键相等,查找命中,否则我们就(递归地)在适当的子树中继续查找。如果被查找的键较小就选择左子树,较大则选择右子树。
14 |
15 | ### 删除*
16 |
17 | 对于删除一个拥有两个子结点的情况,在删除结点 x 后用它的**后继结点**填补它的位置。因为 x 有一个右子结点,因此它的后继结点就是**其右子树中的最小结点**。这样的替换仍然能保证树的有序性,因为 x.key 和它的后继结点的键之间不存在其他的键。
18 |
19 | 用 4 个简单的步骤能够完成将 x 替换为它的后继结点的任务:
20 |
21 | 1. 将指向即将被删除的结点的链接保存为 t;
22 | 2. 将 x 指向它的后继结点`min(t.right)`;
23 | 3. 将 x 的**右链接**(原本指向一棵所有结点都大于 x.key 的二叉查找树)指向`deleteMin(t.right)`,也就是在删除后所有结点仍然大于 x.key 的子二叉查找树;
24 | 4. 将 x 的**左链接**(本为空)设为 t.left(其下所有的键都小于被删除的结点和它的后继结点)。
25 |
26 | 对于某些大规模的实际应用,这种方法可能会有一点性能上的问题。
27 |
28 | ## 分析
29 |
30 | 使用二叉查找树的算法的运行时间取决于树的形状,而树的形状又取决于键被插入的先后顺序。
31 |
32 | * **最好**情况:一棵含有 N 个结点的树是完全平衡的,每条空链接和根结点的距离都为 ~lgN。
33 | * **最坏**情况:搜索路径上可能有 N 个结点。
34 |
35 | 在由 N 个随机键构造的二叉查找树中,查找命中平均所需的比较次数为 ~2lnN(约 1.39 lgN)。
36 |
37 | 在由 N 个随机键构造的二叉查找树中插入操作和查找未命中平均所需的比较次数为 ~2lnN(约 1.39 lgN)。
38 |
39 | ## 简单的符号表实现的成本总结
40 |
41 | | 算法(数据结构) | N 次插入后最坏情况下的查找成本 | N 次插入后最坏情况下的插入成本 | N 次随机插入后平均情况下的查找成本 | N 次随机插入后平均情况下的查找成本 | 是否高效支持有序性相关的操作
42 | | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: |
43 | | 顺序查找(无序链表) | N | N | N/2 | N | 否
44 | | 二分查找(有序数组) | lgN | 2N | lgN | N | 是
45 | | 二叉树查找(二叉查找树) | N | N | 1.39lgN | 1.39lgN | 是
46 |
47 | 随机键构造的二叉查找树的平均高度为树中结点数的对数级别。而对于不随机的构造树的键,有**平衡二叉查找树**来保证无论键的插入顺序如何,树的高度都将是总键数的对数。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Searching/3.3_平衡查找树.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 3.3 平衡查找树
2 |
3 | 前几种算法在最坏情况下的性能还是很糟糕。本节中介绍一种二分查找树并能保证无论如何构造它,它的运行时间都是对数级别的。
4 |
5 | 理想情况下,我们希望能够保持二分查找树的平衡性,以使树高为 ~lgN,这样就能保证所有查找都能在 ~lgN 次比较内结束。
6 |
7 | ## 2-3 查找树
8 |
9 | **定义**:一棵 **2-3 查找树**或为一棵空树,或由以下结点组成:
10 |
11 | * **2-结点**,含有一个键(及其对应的值)和两条链接,左链接指向的 2-3 树中的键都小于该结点,右链接指向的 2-3 树中的键都大于该结点;
12 | * **3-结点**,含有两个键(及其对应的值)和三条链接,左链接指向的 2-3 树中的键都小于该结点,**中链接**指向的 2-3 树中的键都位于该结点的两个键之间,右链接指向的 2-3 树中的键都大于该结点。
13 |
14 | 将指向一棵空树的链接称为**空链接**,一棵**完美平衡**的 2-3 查找树中的所有空链接到根结点的距离都应该是相同的。
15 |
16 | ### 插入
17 |
18 | 在一棵大小为 N 的 2-3 树中,查找和插入操作访问的结点必然不超过 lgN 个。
19 |
20 | ##
21 |
22 | 尽管可以用不同的数据类型表示 2-结点和 3-结点,但这种直白的表示方法需要维护两种不同类型不同类型的结点,将被查找的键和结点中的每个键进行比较,将链接和其中信息从一种结点复制到另一种结点,
23 |
24 | ## 红黑二叉查找树
25 |
26 | **定义**:**红黑树**是含有红黑链接并满足下列条件的二叉查找树:
27 |
28 | * 红链接均为左链接;
29 | * 没有任何一个结点同时和两条红链接相连;
30 | * 该树是**完美黑色平衡**的,即任意空链接到根结点的路径上的黑链接数量相同。
31 |
32 | **红链接**将两个 2-结点连接起来构成一个 3-结点,**黑链接**则是 2-3 树中的普通链接。确切来说,3-结点被表示为由一条**左斜**的红色链接相连的两个 2-结点(其中一个是另一个的左子结点)。
33 |
34 | ## 各种符号表实现的成本总结
35 |
36 | | 算法(数据结构) | N 次插入后最坏情况下的查找成本 | N 次插入后最坏情况下的插入成本 | N 次随机插入后平均情况下的查找成本 | N 次随机插入后平均情况下的查找成本 | 是否高效支持有序性相关的操作
37 | | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: |
38 | | 顺序查找(无序链表) | N | N | N/2 | N | 否
39 | | 二分查找(有序数组) | lgN | 2N | lgN | N | 是
40 | | 二叉树查找(BST) | N | N | 1.39lgN | 1.39lgN | 是
41 | | 2-3 树查找(红黑树) | 2lgN | 2lgN | lgN | lgN | 是
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Searching/3.4_散列表.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 3.4 散列表
2 |
3 | 使用散列的查找算法分为两步:
4 |
5 | 1. 使用**散列函数**将被查找的键转化为数组的一个索引;
6 | 2. **处理碰撞冲突**。
7 |
8 | 两种解决碰撞的方法:**拉链法**和**线性探测法**。
9 |
10 | 散列表是算法在**时间**和**空间**上做出权衡的经典例子,只需要调整散列算法的参数就可以在空间和时间之间做出取舍。使用散列表可以实现在一般应用中拥有(均摊后)**常数级别**的查找和插入操作的符号表。
11 |
12 | ## 散列函数
13 |
14 | 如果我们有一个能够保存 M 个键值对的数组,则需要能够将**任意键**转化为**该数组范围内的索引([0, M-1] 范围内的整数)**的**散列函数**,这个散列函数应该**易于计算**并且能够**均匀分布**所有的键。
15 |
16 | ### 键为正整数
17 |
18 | 将**整数**散列的最常用方法是**除留余数法**:选择大小为**素数**(特别地,不是 2 的幂) M 的数组,对于任意正整数 k,计算 k 除以 M 的余数。
19 |
20 | 如果 M 不是素数,可能无法均匀地散列散列值。
21 |
22 | ### 键为浮点数
23 |
24 | 两种方法:
25 |
26 | * 对于 0 到 1 之间的实数,可以乘以 M 并四舍五入得到一个 0 至 M-1 之间的索引值。但这种方式会使键的高位起的作用更大,最低位对散列的结果没有影响;
27 | * 将键表示二进制数,然后使用除留余数法(Java 使用同样的方法)。
28 |
29 | ### 键为字符串
30 |
31 | 一种叫 Horner 方法的经典算法用 N 次乘法、加法和取余来计算一个字符串的散列值。
32 |
33 | ```java
34 | int hash = 0;
35 | for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
36 | hash = (R * hash + s.charAt(i)) % M;
37 | ```
38 |
39 | 只要 R 足够小,不造成溢出(这里我认为是指 int 类型的溢出),那么结果就能够落在 0 到 M-1 之内。
40 |
41 | ### 键为组合
42 |
43 | 可以用 String 类型一样的方法进行混合处理。例如对于由两个数字表示的 day、两个数字表示的 month、四个数字表示的 year 所构成的键类型 Date,可以这样计算散列值:
44 |
45 | ```java
46 | int hash = (((day * R + month) % M) * R + year) % M;
47 | ```
48 |
49 | ### Java 的相关处理
50 |
51 | Java 令所有数据类型都继承了一个能够返回一个 32 比特整数的`hashCode()`方法,且每一种数据类型的`hashCode()`方法都必须和`equals()`方法一致,即`a.equals(b) == true`说明`a.hashCode() == b.hashCode()`(但反过来不一定成立)。
52 |
53 | 如果要为自定义的数据类型定义散列函数,需要同时重写`hashCode()`和`equals()`两个方法。
54 |
55 | ### 将`hashCode()`的返回值转化为数组索引
56 |
57 | 因为需要的是数组索引而非一个 32 位的整数,在实现中会将默认的`hashCode()`方法和除留余数法结合产生一个 0 到 M-1 的整数:
58 |
59 | ```java
60 | private int hash(Key k) {
61 | return (x.hashCode() & 0x7fffffff) % M;
62 | }
63 | ```
64 |
65 | 这段代码会将符号位屏蔽(将一个 32 位整数变为一个 31 位非负整数),然后用除留余数法计算它除以 M 的余数。
66 |
67 | ### 软缓存
68 |
69 | 如果散列值的计算很耗时,可以考虑将**每个键的散列值缓存起来**,即在每个键中使用一个 hash 变量来保存它的`hashCode()`的返回值。
70 |
71 | ### 小结
72 |
73 | 总的来说,要为一个数据类型实现一个优秀的散列方法需要满足三个条件:
74 |
75 | * 一致性:等价的键必然产生相等的散列值;
76 | * 高效性:计算简便;
77 | * 均匀性:均匀地散列所有的键。
78 |
79 | 其中,保证均匀性的最好方法是保证键的每一位都在散列值的计算中起到了相同的作用。
80 |
81 | 实现散列函数时有一个指导思想,称作**均匀散列假设**:我们使用的散列函数能够均匀并独立地将所有的键散布于 0 到 M-1 之间。这是一个实际无法达到的理想模型。
82 |
83 | ## 基于拉链法的散列表
84 |
85 | **拉链法**:将大小为 M 的数组中的每个元素指向一条链表,链表中的每个结点都存储了散列值为该元素的索引的键值对。
86 |
87 | 查找分两步:首先根据散列值找到对应的链表,然后沿着链表顺序查找相应的键。
88 |
89 | 命题:在一张含有 M 条链表和 N 个键的散列表中,(在均匀散列假设成立的前提下)任意一条链表中的键的数量均在 N/M 的常数因子范围内的概率无限趋向于 1。
90 |
91 | 性质:在一张含有 M 条链表和 N 个键的散列表中,未命中查找和插入操作所需的比较次数为 ~N/M。
92 |
93 | ### 散列表的大小
94 |
95 | 选择适当的数组大小 M,既不会因为空链表而浪费大量内存,也不会因为链表太长而在查找上浪费太多时间。拉链法的一个**好处**是这并不是关键性的选择,对性能的影响没有那么大。
96 |
97 | 一种更可靠的方案是动态调整链表数组的大小,这样无论在符号表中有多少键值对都能保证链表较短。
98 |
99 | ### 有序性相关的操作
100 |
101 | 散列最主要的目的在于均匀地将键散布开来,因此在计算散列后键的顺序信息就丢失了。如果要执行有序性相关的操作,散列表不是最合适的选择,因为这些操作的运行时间都会是线性的。
102 |
103 | ## 基于线性探测法的散列表
104 |
105 | 实现散列表的另一种方式是用大小为 M 的数组保存 N 个键值对,其中 M > N,需要依靠数组中的**空位**解决碰撞冲突。基于这种策略的所有方法被统称为**开放地址**散列表,其中最简单的是**线性探测法**:当碰撞发生时(当一个键的散列值已经被另一个不同的键占用),直接检查散列表中的下一个位置(将索引值加 1)。这样的线性探测可能会产生三种结果:
106 |
107 | * 命中,该位置的键和被查找的键相同;
108 | * 未命中,键为空(该位置没有键);
109 | * 继续查找,该位置的键和被查找的键不同。
110 |
111 | ### 删除操作
112 |
113 | 实现删除操作时,直接将该键所在的位置设为 null 是不行的,因为这会使得在此位置之后的元素无法被查找。因此,我们需要将簇中被删除的右侧的所有键重新插入散列表。
114 |
115 | 和拉链法一样,开放地址类的散列表的性能也依赖于 a = N/M 的比值,但意义有所不同。我们将 a 称为散列表的**使用率**:
116 |
117 | * 对于基于拉链法的散列表,a 是每条链表的长度,因此一般大于 1;
118 | * 对于基于线性探测的散列表,a 是表中已被占用的空间的比例,不可能大于 1,且不允许达到 1(散列表被占满,未命中的查找会导致无限循环)。会动态调整保证使用率在 1/8 到 1/2 之间。
119 |
120 | ### 键簇
121 |
122 | 线性探测的平均成本取决于**元素在插入数组后聚集成的一组连续的条目**,也叫做**键簇**。短小的键簇才能保证较高的效率。
123 |
124 | 基于均匀散列假设,数组的每个位置都有相同的可能性被插入一个新键,长键簇更长的可能性比短键簇更大,因为新建的散列值无论落在簇中的任何位置都会使簇的长度加 1。
125 |
126 | ### 性能分析
127 |
128 | 在一张大小为 M 并含有 N = aM 个键的基于线性探测的散列表中,基于均匀散列假设,
129 |
130 | * 命中的查找所需的探测次数为:~1/2 (1 + 1/(1 - a))
131 | * 未命中的查找所需的探测次数为:~1/2 (1 + 1/(1 - a)^2)
132 |
133 | ## 调整数组大小
134 |
135 | 动态调整数组大小可以为我们保证 a 不大于 1/2。
136 |
137 | * 对于拉链法,如果能够准确估计用例所需的散列表的大小 N,调整数组的工作不是必须的,选取一个适当的 M 即可;
138 | * 对于线性探测法,调整数组的大小是必须的,因为当用例插入的键值对数量超过预期时,它的查找时间不仅会变得非常长,还会在散列表被填满时进入无限循环。
139 |
140 | 假设一张散列表能够自己调整数组的大小,初始为空。基于均匀散列假设,执行任意顺序的 t 次**查找**、**插入**和**删除**操作所需的时间和 t 成正比,所使用的内存量总是在表中的键的总数的常数因子范围内。
141 |
142 | ## 总结
143 |
144 | ### 符号表的内存使用
145 |
146 | | 方法 | N 个元素所需的内存(引用类型) |
147 | | :--: | :--: |
148 | | 基于拉链法的散列表 | ~48N+32M |
149 | | 基于线性探测的散列表 | 在 ~32N 和 ~128N 之间 |
150 | | 各种二叉查找树 | ~56N |
151 |
152 | ### 散列表无法达到理论最优性能原因
153 |
154 | * 每种类型的键都需要一个优秀的散列函数;
155 | * 性能保证来自于散列函数的质量;
156 | * 散列函数的计算可能复杂而且昂贵;
157 | * 难以支持有序性相关的符号表操作。
158 |
159 |
160 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Searching/3.5_应用.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 3.5 应用
2 |
3 | ## 对符号表实现的选择
4 |
5 | | 算法(数据结构) | N 次插入后最坏情况下的查找成本 | N 次插入后最坏情况下的插入成本 | N 次随机插入后平均情况下的查找成本 | N 次随机插入后平均情况下的查找成本 | 是否高效支持有序性相关的操作
6 | | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: |
7 | | 顺序查找(无序链表) | N | N | N/2 | N | 否
8 | | 二分查找(有序数组) | lgN | 2N | lgN | N | 是
9 | | 二叉树查找(BST) | N | N | 1.39lgN | 1.39lgN | 是
10 | | 2-3 树查找(红黑树) | 2lgN | 2lgN | lgN | lgN | 是
11 | | 拉链法*(链表数组) | 0 && less(a[j], a[j-1]); j--)
106 | exch(a, j, j-1);
107 | }
108 | }
109 | ```
110 |
111 | 对于随机排列的长度为 N 且主键不重复的数组,平均情况下插入排序需要 ~N^2/4 次比较以及 ~N^2/4 次交换。最坏情况下需要 ~N^2/2 次比较和 ~N^2/2 次交换,最好情况下需要 N-1 次比较和 0 次交换。
112 |
113 | 插入排序所需的时间取决于输入中元素的初始顺序。因此,插入排序对于**部分有序**的数组十分高效,也很适应小规模数组。
114 |
115 | 选择排序和插入排序的可视化对比:
116 |
117 | 
118 |
119 | ## 希尔排序
120 |
121 | **希尔排序**是一种基于插入排序的快速的排序算法,为了加快速度简单地改进了插入排序,交换不相邻的元素以对数组的局部进行排序,并最终用插入排序将局部有序的数组排序。
122 |
123 | **思想**:使数组中任意间隔为 h 的元素都是有序的。这样的数组被称为 **h 有序数组**。换句话说,一个 h 有序数组就是 h 个互相独立的有序数组编织在一起的一个数组。
124 |
125 | 
126 |
127 | 希尔排序更高效的原因是它权衡了子数组的规模和有序性。排序之初各个子数组都很短,排序之后的子数组都是部分有序的,这两种情况都很适合插入排序。
128 |
129 | 使用递增序列 1,4,13,40,121,364...的希尔排序所需的比较次数不会超出 N 的若干倍乘以递增序列的长度。
130 |
131 | 希尔排序的代码量很小,且不需要使用额外的内存空间。对于中等大小的数组,它的运行时间是可以接受的。
132 |
133 | ```java
134 | public static void sort(Comparable[] a) {
135 | // 将 a[] 按升序排列
136 | int N = a.length;
137 | int h = 1;
138 | while(h < N / 3)
139 | h = 3 * h + 1; // 1, 4, 13, 40, 121, 364, 1093, ...
140 | while(h >= 1) {
141 | // 将数组变为 h 有序
142 | for(int i = h; i < N; i++) {
143 | // 将 a[i] 插入到 a[i-h],a[i-2*h],a[i-3*h]... 之中
144 | for(int j = i; j >= h && less(a[j], a[j -h]); j -= h)
145 | exch(a, j, j-h);
146 | }
147 | h /= 3;
148 | }
149 | }
150 | ```
151 |
152 |
153 |
154 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Sorting/2.2_归并排序.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 2.2 归并排序
2 |
3 | **归并**:将两个有序的数组归并成一个更大的有序数组。
4 |
5 | 归并排序能保证将任意长度为 N 的数组排序所需时间和 NlogN 成正比;但主要缺点是所需的额外空间和 N 成正比。
6 |
7 | 每一次归并将涉及的所有元素复制到一个辅助数组中,再把归并的结果放回原数组中。
8 |
9 | ## 自顶向下的归并排序
10 |
11 | 归并算法是算法设计中**分治思想**的典型应用。
12 |
13 | **比较次数**:对于长度为 N 的任意数组,自顶向下的归并排序需要 1/2NlgN 至 NlgN 次比较。
14 |
15 | 注:N = 2 ^ n ==> n = lgN
16 |
17 | **访问数组次数**:对于长度为 N 的任意数组,自顶向下的归并排序最多需要访问数组 6NlgN 次。
18 |
19 | ### 性能优化点
20 |
21 | #### 对小规模子数组使用插入排序
22 |
23 | **递归**会使**小规模问题**中方法的调用过于频繁,所以改进对它们的处理方法就能改进整个算法。
24 |
25 | 对排序来说,插入排序(或选择排序)可能在小数组上比归并排序更快。
26 |
27 | ## 自底向上的归并排序
28 |
29 | 对于长度为 N 的任意数组,自底向上的归并排序需要 1/2NlgN 至 NlgN 次比较,最多需要访问数组 6NlgN 次。
30 |
31 | 自底向上的归并排序比较适合用**链表**组织的数据。将链表按大小为 1 的子链表进行排序,然后是大小为 2 的子链表,然后是大小为 4 的子链表等。这种方法只需要重新组织链表链接就能将链表**原地**排序。
32 |
33 | ## 排序算法的复杂度
34 |
35 | **命题**:没有任何基于比较的算法能够保证使用少于 lg(N!) ~ NlgN 次比较将长度为 N 的数组排序。
36 |
37 | **证明**:
38 |
39 | 假设没有重复的主键(因为这是所有排序算法的必要需求)。N 个不同的主键会有 N! 种不同的排列。
40 |
41 | 任何基于比较的排序算法都对应着一颗高 h 的比较树,其中`N! <= 叶子结点的数量 <= 2^h`。h 的值就是最坏情况下的比较次数,因此对不等式的两边取对数可得到任意算法的比较次数至少是 lgN!。
42 |
43 | 根据斯特灵公式可得 lgN! ~ NlgN。
44 |
45 | 注:斯特灵公式:`lgN! = lg1 + lg2 + ... + lgN ~ NlgN`
46 |
47 | 归并排序是一种渐进最优的基于比较排序的算法。也就是说,归并排序在最坏情况下的比较次数和任意基于比较的排序算法所需的最少比较次数都是 ~NlgN。
48 |
49 |
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Sorting/2.3_快速排序.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 2.3 快速排序
2 |
3 | **特点:**
4 |
5 | * 原地排序(只需要一个很小的辅助栈);
6 | * 将长度为 N 的数组排序所需的时间和 NlgN 成正比。
7 |
8 | ## 基本算法
9 |
10 | 快速排序的**切分**方法:
11 |
12 | 一般策略是先随意地选取 a[lo] 作为**切分元素**,即那个会被排定的元素,然后我们从数组的左端开始向右扫描直到找到一个**大于等于**它的元素,再从数组的右端开始向左扫描直到找到一个小于等于它的元素。这两个元素显然是没有排定的,因此我们交换它们的位置。
13 |
14 | 如此继续,我们就可以保证左指针 i 的左侧元素都不大于切分元素,右指针 j 的右侧元素都不小于切分元素。当两个指针相遇时,我们只需要将切分元素 a[lo] 和左子数组最右侧的元素(a[j])交换然后返回 j 即可。
15 |
16 | ## 性能特点
17 |
18 | 快速排序的两个速度优势:
19 |
20 | 1. 切分方法的内循环会用一个递增的索引将数组元素和一个定值比较,而归并排序、希尔排序等还在内循环中移动数据;
21 | 2. 比较次数少。
22 |
23 | 将长度为 N 的无重复数组排序,快速排序平均需要 ~2NlnN 次比较(以及 1/6 的交换)。
24 |
25 | ### 潜在缺点
26 |
27 | 快速排序的最好情况是每次都正好能将数组对半分。而**在切分不平衡**时,这个程序可能会最多需要约 **N^2/2** 次比较。例如,如果第一次从最小的元素切分,第二次从第二小的元素切分,如此这般,每次调用只会移除一个元素。
28 |
29 | 因此,我们在快速排序前将数组随机排序,以避免上述情况。
30 |
31 | ## 算法改进
32 |
33 | ### 切换到插入排序
34 |
35 | 和大多数递归排序算法一样,改进快速排序性能的一个简单办法基于以下两点:
36 |
37 | * 对于小数组,快速排序比插入排序慢;
38 | * 因为递归,快速排序的`sort()`方法在小数组中也会调用自己。
39 |
40 | 因此,在排序**小数组**时应该切换到插入排序。
41 |
42 | ### 三取样切分
43 |
44 | 使用子数组中的一小部分元素的中位数来切分数组。这样做得到的切分更好,但代价是需要计算中位数。
45 |
46 | ### 熵最优的排序
47 |
48 | 在**有大量重复元素**的情况下,快速排序的递归性会使元素全部重复的子数组经常出现,这就有很大的改进潜力,将当前实现的线性对数级的性能提高到**线性级别**。
49 |
50 | 一个简单的想法是将数组切分为**三部分**,分别对应小于、等于和大于切分元素的数组元素。这种做法被称为“三向切分”。
51 |
52 | 命题 1:不存在任何基于比较的排序算法能够保证在 NH-N 次比较之内将 N 个元素排序,其中 H 为由主键值出现频率定义的香农信息量。
53 |
54 | 命题 2:对于大小为 N 的数组,三向切分的快速排序需要 ~(2ln2)NH 次比较。其中 H 为由主键值出现频率定义的香农信息量。
55 |
56 | **香农信息素**是对信息含量的一种标准的度量方法。给定包含 k 个不同值的 N 个主键,对于从 1 到 k 的每个 i,定义 fi 为第 i 个主键值出现的次数,pi 为 fi/N,即为随机抽取一个数组元素时第 i 个主键值出现的概率。那么所有主键的**香农信息素**可以定义为:
57 |
58 | H = -(p1lgp1 + p2lgp2 + .. + pklgpk)
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Sorting/2.4_优先队列.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 2.4 优先队列
2 |
3 | 优先队列最重要的操作就是**插入元素**和**删除最大元素**。
4 |
5 | **应用场景:**在某些数据处理的场合,**总数据量太大**(可以认为输入是无限的),无法排序(甚至无法全部装进内存)。如果将每个新的输入和已知的 M 个最大(或最小)元素比较,除非 M 较小,否则这种比较的代价会非常高昂。如果有了**优先队列**,就只用一个能存储 M 个元素的队列即可。
6 |
7 | ## 初级实现
8 |
9 | * 数组实现(无序):惰性方法,仅在必要的时候找出最大元素;
10 | * 数组实现(有序):积极方法:在插入时就保持列表有序,使后续操作更高效;
11 | * 链表表示法
12 |
13 | 在上述优先队列的初级实现中,**删除最大元素**和**插入元素**这两个操作之一在最坏情况下需要**线性**时间来完成。
14 |
15 | | 数据结构 | 插入元素 | 删除最大元素 |
16 | | :----: | :----: | :----: |
17 | | 有序数组 | N | 1 |
18 | | 无序数组 | 1 | N |
19 | | 堆 | logN | logN |
20 | | 理想情况 | 1 | 1 |
21 |
22 | ## 堆的定义
23 |
24 | 当一棵二叉树的每个结点都**大于等于**它的两个子结点时,它被称为**堆有序**。
25 |
26 | 根结点是堆有序的二叉树中的最大结点。
27 |
28 | ### 二叉堆表示法
29 |
30 | 如果使用指针来表示堆有序的二叉树,那么每个元素都需要**三个指针**来找到它的上下结点。
31 |
32 | 但使用完全二叉树,只需要数组而不需要指针就可以表示,十分方便。具体方法是将二叉树的结点按照**层级顺序**放入数组中。
33 |
34 | **定义**:**二叉堆**(后文简称为堆)是一组能够用堆有序的完全二叉树排序的元素,并在数组中按照层级储存(不使用数组的第一个位置)。
35 |
36 | 在一个堆中,位置`k`的结点的父结点的位置为`⌊k/2⌋`,子结点位置分别为`2k`和`2k+1`。
37 |
38 | **高性能的原因**:利用在数组中无需指针即可沿树上下移动的便利。
39 |
40 | 注:完全二叉树:除最后一层外,每一层上的结点数均达到最大值;在最后一层上只缺少右边的若干结点。
41 |
42 | 一棵大小为 N 的完全二叉树的高度为`⌊lgN⌋`。
43 |
44 | ## 堆的算法
45 |
46 | **堆的有序化**:打破堆的状态,然后再遍历堆并按照要求将堆的状态恢复。
47 |
48 | **插入元素**时,将新元素加到数组末尾,增加堆的大小并让这个新元素上浮到合适的位置。
49 |
50 | **删除最大元素**时,从数组顶端删去最大的元素并将数组的最后一个元素放到顶端,减小堆的大小并让这个元素下沉到合适的位置。
51 |
52 | 这样,**删除最大元素**和**插入元素**这两个操作的用时和队列的大小仅成**对数**关系。对于一个含有 N 个元素的基于堆的优先队列,插入元素操作只需不超过 (lgN+1) 次比较,删除最大元素的操作需要不超过 2lgN 次比较。
53 |
54 | ## 堆排序
55 |
56 | 用下沉操作由 N 个元素构造堆只需少于 2N 次比较以及少于 N 次交换。
57 |
58 | 将 N 个元素排序,堆排序只需少于 (2NlgN+2N) 次比较(以及一半次数的交换)。
59 |
60 | ### 特点
61 |
62 | **堆排序的优点**:所知的唯一能够同时最优地利用空间和时间的方法;
63 |
64 | **堆排序的缺点**:**无法利用缓存**。数组元素很少和相邻的其他元素进行比较,因此缓存未命中的次数要远远高于大多数比较都在相邻元素间进行的算法(如快速排序、归并排序、希尔排序)。
65 |
66 | **堆排序的使用场景**:当空间十分紧张时(例如在嵌入式系统或低成本的移动设备中)很流行,但现代系统的许多应用很少使用它。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Sorting/2.5_应用.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 2.5 应用
2 |
3 | ## 稳定性
4 |
5 | 如果一个排序算法能够保留数组中**重复元素的相对位置**则可以被称为是**稳定**的。
6 |
7 | * 稳定的排序算法:插入排序、归并排序
8 | * 不稳定的排序算法:选择排序、希尔排序、快速排序和堆排序
9 |
10 | 一般只有在稳定性是必要的情况下,稳定的排序算法才有优势。
11 |
12 | ## 各种排序算法的性能特点
13 |
14 | | 算法 | 是否稳定 | 是否为原地排序 | 时间复杂度 | 空间复杂度 | 备注
15 | | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: | :----: |
16 | | 选择排序 | 否 | 是 | N^2 | 1 |
17 | | 插入排序 | 是 | 是 | 介于 N 和 N^2 之间 | 1 | 取决于输入元素的排列情况
18 | | 希尔排序 | 否 | 是 | NlogN? | 1 |
19 | | 快速排序 | 否 | 是 | NlogN | lgN | 运行效率由概率提供保证
20 | | 三向快速排序 | 否 | 是 | 介于 N 和 NlogN 之间 | lgN | 运行效率由概率保证,同时也取决于输入元素的分布情况
21 | | 归并排序 | 是 | 否 | NlogN | N |
22 | | 堆排序 | 否 | 是 | NlogN | 1 |
23 |
24 | 快速排序是最快的通用排序算法。
25 |
26 | ### Java 系统库的排序算法
27 |
28 | Java 的系统程序员选择对**原始数据**类型使用(三向切分的)快速排序,对**引用类型**使用归并排序。暗示着用速度和空间(对于原始数据类型)来换取稳定性(对于引用类型)。
29 |
30 |
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Strings/5.2_单词查找树.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 5.2 单词查找树
2 |
3 | * 查找命中所需的时间与被查找的键的长度成正比;
4 | * 查找未命中只需检查若干个字符。
5 |
6 | ## 单词查找树
7 |
8 | 单词查找树是由链接的结点所组成的数据结构,这些链接可能为空,也可能指向其他结点。每个结点都含有 R 条链接,其中 R 为字母表的大小(即字母表中字母的数量)。
9 |
10 | **值为空的结点在符号表中没有对应的键,它们的存在是为了简化单词查找树中的查找操作。**
11 |
12 | ### 查找操作
13 |
14 | ### 插入操作
15 |
16 | ### 结点的表示
17 |
18 | ## 单词查找树的性质
19 |
20 | 单词查找树的链表结构(形状)和键的插入或删除顺序无关:对于任意给定的一组键,其单词查找树都是唯一的。
21 |
22 | ## 三向单词查找树
23 |
24 | ## 总结
25 |
26 | 如果空间足够,R 向单词查找树的速度是最快的,能够在**常数**次字符比较内完成查找。
27 |
28 | 对应大型字母表,R 向单词查找树所需的空间可能无法满足时,三向查找树是最佳的选择,因为它对“字符”比较次数是**对数级别**的比较,而二叉查找树中键的比较次数是对数级别的。
29 |
30 | 
31 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/_sidebar.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | - **第 1 章 基础**
2 | - 1.1 基础编程模型
3 | - 1.2 数据抽象
4 | - [1.3 背包、队列和栈](Fundamentals/1.3_背包、队列和栈)
5 | - [1.4 算法分析](Fundamentals/1.4_算法分析)
6 | - [1.5 案例研究:union-find算法](Fundamentals/1.5_案例研究:union-find算法)
7 | - **第 2 章 排序**
8 | - [2.1 初级排序算法](Sorting/2.1_初级排序算法)
9 | - [2.2 归并排序](Sorting/2.2_归并排序)
10 | - [2.3 快速排序](Sorting/2.3_快速排序)
11 | - [2.4 优先队列](Sorting/2.4_优先队列)
12 | - [2.5 应用](Sorting/2.5_应用)
13 | - **第 3 章 查找**
14 | - [3.1 符号表](Searching/3.1_符号表)
15 | - [3.2 二叉查找树](Searching/3.2_二叉查找树)
16 | - [3.3 平衡查找树](Searching/3.3_平衡查找树)
17 | - [3.4 散列表](Searching/3.4_散列表)
18 | - [3.5 应用](Searching/3.5_应用)
19 | - **第 4 章 图**
20 | - [4.1 无向图](Graphs/4.1_无向图)
21 | - [4.2 有向图](Graphs/4.2_有向图)
22 | - [4.3 最小生成树](Graphs/4.3_最小生成树)
23 | - [4.4 最短路径](Graphs/4.4_最短路径)
24 | - **第 5 章 字符串**
25 | - 5.1 字符串排序
26 | - [5.2 单词查找树](Strings/5.2_单词查找树)
27 | - [5.3 子字符串查找](Strings/5.3_子字符串查找)
28 | - 5.4 正则表达式
29 | - 5.5 数据压缩
30 | - **第 6 章 背景**
31 | - [6.1 事件驱动模拟](Context/6.1_事件驱动模拟)
32 | - [6.2 B- 树](Context/6.2_B-树)
33 | - [6.3 后缀数组](Context/6.3_后缀数组)
34 | - [6.4 网络流算法](Context/6.4_网络流算法)
35 | - [6.5 问题规约](Context/6.5_问题规约)
36 | - [6.6 不可解性](Context/6.6_不可解性)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.html:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | 《算法(第4版)》笔记
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 |
10 |
11 |
12 | 加载中...
13 |
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "name": "Algorithms-notes",
3 | "version": "1.0.0",
4 | "description": "《算法(第4版)》笔记",
5 | "main": "index.js",
6 | "scripts": {
7 | "test": "echo \"Error: no test specified\" && exit 1",
8 | "preupdate": "cd code && yuki && cd .. && git add docs code README.md",
9 | "update": "git commit -m",
10 | "postupdate": "git push origin master"
11 | },
12 | "repository": {
13 | "type": "git",
14 | "url": "git+https://github.com/bighuang624/LeetCode-everyday.git"
15 | },
16 | "author": "",
17 | "license": "ISC",
18 | "bugs": {
19 | "url": "https://github.com/bighuang624/LeetCode-everyday/issues"
20 | },
21 | "homepage": "https://github.com/bighuang624/LeetCode-everyday#readme"
22 | }
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/每一节可以再看一遍的题.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 每一节可以再看一遍的题
2 |
3 | ### 1.1
4 |
5 | 1.1.9 将一个正整数 N 用二进制表示并转换为一个 String 类型的 s
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/相关问题解决方法.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Eclipse命令行参数使用
2 |
3 | Run---->Run Configurations----->右边 Arguments 里 Program arguments 中写。
4 |
5 | 如果写的是文件,默认该文件要放在项目的根目录里。当然也可以换位置,勾选 Working directory 的 Other,然后选择文件目录即可。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 36 |
37 | 以下问题均可归约为线性规划问题:
38 |
39 | * 最大流量问题;
40 | * 最短路径问题;
41 | * 许多许多其他问题。
42 |
43 | “许多许多其他问题”的含义如下:
44 |
45 | 1. 添加约束条件和扩展线性规划模型非常简单;
46 | 2. 问题的归约是有传递性的;
47 | 3. **各种最优化问题都能够直接构造为线性规划问题**。
48 |
49 | 解决线性规划问题的高效算法:
50 |
51 | * 单纯形法(Simplex Algorithm);
52 | * 椭球法(Ellipsoid Algorithm);
53 | * 内点法(Interior Point Methods)。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Context/6.6_不可解性.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 6.6 不可解性
2 |
3 | 一台“图灵机”就是一台能够读取输入、变换状态和打印输出的有限状态机。它来自于两个重要的思想:
4 |
5 | * 普遍性:图灵机可以模拟所有物理可实现的计算设备。这被称为**丘奇-图灵论题**。
6 | * 可计算性:图灵机无法解决的问题是存在的。
7 |
8 | 还有第三个关于计算设备效率的思想:
9 |
10 | * **扩展的丘奇-图灵论题**:在任意计算设备上解决某个问题的某个程序所需的运行时间的增长数量级都是在图灵机上(或是任意其他计算设备上)解决该问题的某个程序的多项式倍数。
11 |
12 | 最近几年,量子计算的概念使得一些研究者开始怀疑扩展的丘奇-图灵论题的正确性。
13 |
14 | ### 指数级别的运行时间
15 |
16 | 不可解性理论的目的在于将能够区别**多项式时间内**解决的问题和**在最坏情况下(可能)需要指数级别(2^N)时间**才能解决的问题。
17 |
18 | 一般认为,指数时间的算法无法保证在合理的时间内解决规模超过(例如)100 的问题。
19 |
20 | ### 搜索问题
21 |
22 | * **搜索问题**:有解且**验证它的解的正确性**所需的时间不会超过输入规模的多项式的问题(只与解的验证有关);
23 | * **解决**了一个搜索问题:一个算法给出了一个解或已证明解不存在;
24 | * **NP**:所有搜索问题的集合。
25 | * **P**:能够在多项式时间内**解决**的所有搜索问题的集合。或者说,能够保证在合理时间范围内解决的所有问题的集合。一般来说,用**不可解**来表示不包含在集合 P 中的问题。
26 |
27 | 虽然在技术上并不等价,但**搜索问题**、**决定性问题**(解是否存在)、**最优化问题**(最优解是什么)一般都能够相互归约。
28 |
29 | ### 非确定性
30 |
31 | NP 中的 N 表示的是**非确定性(nondeterminism)**。其意思是断言当一个算法面对若干个选项时,它有能力“猜出”正确的选项。在图灵机中,非确定性只是定义为一个给定状态和一个给定输入时的两个不同的后继状态,解则是能够得到期望结果的所有路径。
32 |
33 | 非确定性看似强大,但没人能**证明**它能够帮助解决任何问题。这就导致人们始终探寻一个问题的答案:
34 |
35 | **P=NP 成立吗?**
36 |
37 | 因为许多重要的实际问题都属于 NP 但不一定属于 P(即已知的最快确定性算法需要指数级别的时间)。如果能够证明它不属于 P,就可以放弃寻找高效率的算法;反之则存在发现某种高效算法的可能性。
38 |
39 | ### 多项式时间问题的相互归约
40 |
41 | 证明问题 A 是可以归约为问题 B 的:
42 |
43 | 1. 将 A 的实例归约为 B 的实例;
44 | 2. 解决 B 的实例;
45 | 3. 将 B 的实例的解归约为 A 的实例的解。
46 |
47 | 因此,如果一个问题 A 已知是难以解决的,且 A 在多项式时间内能够归约为问题 B,那么问题 B 必然也是难以解决的。
48 |
49 | ### NP-完全性
50 |
51 | 若 NP 中的所有问题都能在多项式时间内归纳为搜索问题 A,那么则称问题 A 是 **NP-完全的**。
52 |
53 | NP-完全问题的意思是,我们不期望能够找到多项式时间的算法。
54 |
55 | ### Cook-Levin 定理
56 |
57 | Cook-Levin 定理:布尔可满足性问题是 NP-完全的。
58 |
59 | Cook-Levin 定理,加上围绕各种 NP-完全问题所进行的多项式时间内的归约,得到两种可能性:
60 |
61 | * 或者 P=NP,即所有搜索问题都能够在多项式时间内得到解决;
62 | * 或者 P 不等于 NP,即存在某些搜索问题无法在多项式时间内得到解决。
63 |
64 | 无论 P=NP 是否成立,目前的实际状态是所有 NP-完全问题的已知最佳算法在最坏情况下都需要指数级别的时间。
65 |
66 | ### 处理 NP-完全性
67 |
68 | 要证明 NP 中的一个问题是 NP-完全的,需要证明某个已知的 NP-完全问题能够在多项式时间内归约为它。如果成功,则说明找到一个高效算法是不可能的。
69 |
70 | 处理 NP-完全性的一些尝试:
71 |
72 | 1. 修改问题,寻找“近似”算法来给出接近但非最佳的解:欧几里得旅行销售员问题、梯度下降;
73 | 2. 给出一种能够有效解决实际应用中所出现的问题的实例算法;
74 | 3. 使用“回溯法”来避免检查所有可能的解,以期找到尽可能“高效”的指数级别算法。
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Fundamentals/1.3_背包、队列和栈.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 1.3 背包、队列和栈
2 |
3 | ## 可迭代的集合类型
4 |
5 | foreach 语句:
6 |
7 | ```java
8 | Queue
36 |
37 | 以下问题均可归约为线性规划问题:
38 |
39 | * 最大流量问题;
40 | * 最短路径问题;
41 | * 许多许多其他问题。
42 |
43 | “许多许多其他问题”的含义如下:
44 |
45 | 1. 添加约束条件和扩展线性规划模型非常简单;
46 | 2. 问题的归约是有传递性的;
47 | 3. **各种最优化问题都能够直接构造为线性规划问题**。
48 |
49 | 解决线性规划问题的高效算法:
50 |
51 | * 单纯形法(Simplex Algorithm);
52 | * 椭球法(Ellipsoid Algorithm);
53 | * 内点法(Interior Point Methods)。
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Context/6.6_不可解性.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 6.6 不可解性
2 |
3 | 一台“图灵机”就是一台能够读取输入、变换状态和打印输出的有限状态机。它来自于两个重要的思想:
4 |
5 | * 普遍性:图灵机可以模拟所有物理可实现的计算设备。这被称为**丘奇-图灵论题**。
6 | * 可计算性:图灵机无法解决的问题是存在的。
7 |
8 | 还有第三个关于计算设备效率的思想:
9 |
10 | * **扩展的丘奇-图灵论题**:在任意计算设备上解决某个问题的某个程序所需的运行时间的增长数量级都是在图灵机上(或是任意其他计算设备上)解决该问题的某个程序的多项式倍数。
11 |
12 | 最近几年,量子计算的概念使得一些研究者开始怀疑扩展的丘奇-图灵论题的正确性。
13 |
14 | ### 指数级别的运行时间
15 |
16 | 不可解性理论的目的在于将能够区别**多项式时间内**解决的问题和**在最坏情况下(可能)需要指数级别(2^N)时间**才能解决的问题。
17 |
18 | 一般认为,指数时间的算法无法保证在合理的时间内解决规模超过(例如)100 的问题。
19 |
20 | ### 搜索问题
21 |
22 | * **搜索问题**:有解且**验证它的解的正确性**所需的时间不会超过输入规模的多项式的问题(只与解的验证有关);
23 | * **解决**了一个搜索问题:一个算法给出了一个解或已证明解不存在;
24 | * **NP**:所有搜索问题的集合。
25 | * **P**:能够在多项式时间内**解决**的所有搜索问题的集合。或者说,能够保证在合理时间范围内解决的所有问题的集合。一般来说,用**不可解**来表示不包含在集合 P 中的问题。
26 |
27 | 虽然在技术上并不等价,但**搜索问题**、**决定性问题**(解是否存在)、**最优化问题**(最优解是什么)一般都能够相互归约。
28 |
29 | ### 非确定性
30 |
31 | NP 中的 N 表示的是**非确定性(nondeterminism)**。其意思是断言当一个算法面对若干个选项时,它有能力“猜出”正确的选项。在图灵机中,非确定性只是定义为一个给定状态和一个给定输入时的两个不同的后继状态,解则是能够得到期望结果的所有路径。
32 |
33 | 非确定性看似强大,但没人能**证明**它能够帮助解决任何问题。这就导致人们始终探寻一个问题的答案:
34 |
35 | **P=NP 成立吗?**
36 |
37 | 因为许多重要的实际问题都属于 NP 但不一定属于 P(即已知的最快确定性算法需要指数级别的时间)。如果能够证明它不属于 P,就可以放弃寻找高效率的算法;反之则存在发现某种高效算法的可能性。
38 |
39 | ### 多项式时间问题的相互归约
40 |
41 | 证明问题 A 是可以归约为问题 B 的:
42 |
43 | 1. 将 A 的实例归约为 B 的实例;
44 | 2. 解决 B 的实例;
45 | 3. 将 B 的实例的解归约为 A 的实例的解。
46 |
47 | 因此,如果一个问题 A 已知是难以解决的,且 A 在多项式时间内能够归约为问题 B,那么问题 B 必然也是难以解决的。
48 |
49 | ### NP-完全性
50 |
51 | 若 NP 中的所有问题都能在多项式时间内归纳为搜索问题 A,那么则称问题 A 是 **NP-完全的**。
52 |
53 | NP-完全问题的意思是,我们不期望能够找到多项式时间的算法。
54 |
55 | ### Cook-Levin 定理
56 |
57 | Cook-Levin 定理:布尔可满足性问题是 NP-完全的。
58 |
59 | Cook-Levin 定理,加上围绕各种 NP-完全问题所进行的多项式时间内的归约,得到两种可能性:
60 |
61 | * 或者 P=NP,即所有搜索问题都能够在多项式时间内得到解决;
62 | * 或者 P 不等于 NP,即存在某些搜索问题无法在多项式时间内得到解决。
63 |
64 | 无论 P=NP 是否成立,目前的实际状态是所有 NP-完全问题的已知最佳算法在最坏情况下都需要指数级别的时间。
65 |
66 | ### 处理 NP-完全性
67 |
68 | 要证明 NP 中的一个问题是 NP-完全的,需要证明某个已知的 NP-完全问题能够在多项式时间内归约为它。如果成功,则说明找到一个高效算法是不可能的。
69 |
70 | 处理 NP-完全性的一些尝试:
71 |
72 | 1. 修改问题,寻找“近似”算法来给出接近但非最佳的解:欧几里得旅行销售员问题、梯度下降;
73 | 2. 给出一种能够有效解决实际应用中所出现的问题的实例算法;
74 | 3. 使用“回溯法”来避免检查所有可能的解,以期找到尽可能“高效”的指数级别算法。
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/Fundamentals/1.3_背包、队列和栈.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 1.3 背包、队列和栈
2 |
3 | ## 可迭代的集合类型
4 |
5 | foreach 语句:
6 |
7 | ```java
8 | Queue 7 |
7 | 