('#app')!
101 | app.innerHTML = `
102 | Hello Vite12
103 | 是是是
104 | `
105 | }
106 |
107 |
108 | render()
109 |
110 | if (import.meta.hot) {
111 | import.meta.hot.accept()
112 | }
113 |
114 | // main.ts
115 | import './render.tx'’
116 |
117 | ```
118 |
119 | > 在`render`文件执行执行了`render`函数,这时`accept`就会重新执行这个文件,也就理所当然的触发了`render`函数。这时就不需要我们向`accpet`传递回调函数了。
120 |
121 | #### accept(dep, cb)
122 |
123 | `accept`方法中也可以接收一个`dep`参数,也就是当前页面热更新时所依赖的**子模块的路径**。
124 | 这个`dep`参数,可以是一个单独字符串,也可以是一个字符串数组,当是数组时说明**依赖多个子模块**
125 |
126 | ```ts
127 | //main.ts
128 | import { render } from './render'
129 | import { initsate } from './state'
130 |
131 | render()
132 | initsate()
133 |
134 | if (import.meta.hot) {
135 | import.meta.hot.accept('./render.ts', (mod) => {
136 | console.log(mod, '==')
137 | mod?.render()
138 | })
139 | }
140 | ```
141 |
142 | > `main`模块依赖`render`文件
143 | > 当`render`文件变更时,会接收热更新
144 | > 因为此时没有依赖`state`文件,所以当`state`文件发生变更时会`**reload page**`,而不会热更新。
145 | > 因为此时热更新的边界仅仅是`render`模块,只有`render`模块中的变更才会触发`main`的热更新
146 |
147 | ```ts
148 | //main.ts
149 | import { render } from './render'
150 | import { initsate } from './state'
151 |
152 | render()
153 | initsate()
154 |
155 | if (import.meta.hot) {
156 | import.meta.hot.accept(['./render.ts', './state.ts'], ([mod1, mod2]) => {
157 | console.log(mod1, mod2, '==')
158 | mod1?.render()
159 | mod2?.initsate()
160 | })
161 | }
162 | ```
163 |
164 | > 这时,当`state`模块中的文件发生变化时,就也会触发`main`的热更新了。
165 | > 此时,回调函数中的`mod`为:(因为仅仅变更了`state`模块,所以`mod1`是`undefined`,也就说明`render`模块没有更新,符合预期。
166 | > 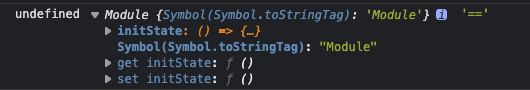
167 |
168 | #### dispose()
169 |
170 | 这个函数就是比较简单。就是在**新模块更新前 旧模块销毁时**的钩子。用来清理掉旧模块中的一些副作用。
171 |
172 | ```ts
173 | const timerId = setInterval(() => {
174 | countEle.innerText = Number(countEle.innerText) + 1 + ''
175 | }, 1000)
176 |
177 | if (import.meta.hot) {
178 | import.meta.hot.dispose((data) => {
179 | // 清理副作用
180 | clearInterval(timerId)
181 | })
182 | }
183 | ```
184 |
185 | > 在我们需要 hmr 的模块中如果有定时器之类的操作,我们热更新后如果不提前销毁定时器,就会重复执行定时,那么可能会出现意想不到效果。
186 |
187 | #### on(event,cb)
188 |
189 | 监听**自定义 `HMR` 事件**。
190 | 自定义 HMR 事件,是在服务端定义发送的。在 vite 中,我们可以在插件中完成这件事。
191 | `vite`插件中提供了[`handleHotUpdate`](https://www.vitejs.net/guide/api-plugin.html#handleHotUpdate)
192 |
193 | ```ts
194 | // vite-plugin.tx
195 | // 省略其他代码
196 | handleHotUpdate({ server }) {
197 | server.ws.send({
198 | type: 'custom',
199 | event: 'xxx-file-change', // 自定义事件名称
200 | data: {} // 携带的信息
201 | })
202 | return []
203 | }
204 |
205 | // client
206 | import.meta.hot.on('xxx-file-change', (payload) => {
207 | console.log(payload)
208 | })
209 | ```
210 |
211 | > [https://github.com/sanyuan0704/island.js/pull/79](https://github.com/sanyuan0704/island.js/pull/79)
212 | > 有时自定义 `hmr` 事件,没有触发页面更新。我们可以利用监听自定义事件,来主动触发页面的`rerender`
213 |
214 | #### data
215 |
216 | 该属性用来共享**同一个模块中**更新前后的数据。
217 | 在这里面绑定的数据,不会被`hmr`影响或重置。
218 |
219 | ```ts
220 | import.meta.hot.data.count = 1
221 | ```
222 |
223 | #### decline()
224 |
225 | 表示此模块不可热更新,如果在传播 HMR 更新时遇到此模块,浏览器应该执行**完全重新加载**。
226 |
227 | #### invalidate()
228 |
229 | 重新加载页面。
230 |
231 | ## 下回书
232 |
233 | :::tip
234 | 请看下一篇[文章](./note/hmr-vite.md)
235 | :::
236 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/note/re-render.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | :::tip
2 | 原文:[在你写 memo()之前](https://overreacted.io/zh-hans/before-you-memo/)
3 | :::
4 |
5 | ## 文章内容
6 |
7 | 大概意思就是在你写`memo()`去优化组件的时候还有两种方式去优化代码。
8 |
9 | ```tsx
10 | import { useState } from 'react'
11 |
12 | export default function App() {
13 | let [color, setColor] = useState('red')
14 | return (
15 |
16 |
setColor(e.target.value)} />
17 |
Hello, world!
18 |
19 |
I am a very slow component tree.
29 | }
30 | ```
31 |
32 | 上面这个组件现在存在的问题:
33 |
34 | 1. 当我们在`input`中输入`color`后,会导致`App`组件重新渲染,然后`ExpensiveTree`组件虽然不依赖`color`,但是由于父组件`re-render`,他自己也会进行无效的`re-render`
35 |
36 | 为了减少这种无效的`re-render`,我们经常会使用[memo()](https://beta.reactjs.org/apis/react/memo#usage)去包裹组件,来达到缓存组件,减少无效更新的情况。
37 |
38 | ```tsx
39 | import { useState, memo } from 'react'
40 |
41 | export default function App() {
42 | let [color, setColor] = useState('red')
43 | return (
44 | <>
45 | setColor(e.target.value)} />
46 | Hello, world!
47 |
48 |
49 | )
50 | }
51 | // 使用memo
52 | let ExpensiveTree = memo(() => {
53 | let now = performance.now()
54 | while (performance.now() - now < 100) {
55 | // Artificial delay -- do nothing for 100ms
56 | }
57 | return I am a very slow component tree.
58 | })
59 | ```
60 |
61 | 而这篇文章就是讲解另外两种解决思路。
62 |
63 | ### 1. 向下移动 state
64 |
65 | 这个解决方法其实就是将组件粒度变得更细。
66 | 将`state`下沉到与之相关的组件中去,也就是将与该状态相关的组件抽离成一个单独的组件。
67 |
68 | ```tsx
69 | import { useState } from 'react'
70 |
71 | export default function App() {
72 | return (
73 |
74 |
75 |
76 |
77 | )
78 | }
79 |
80 | // 将state下沉到该组件中
81 | function Form() {
82 | let [color, setColor] = useState('red')
83 | return (
84 | <>
85 | setColor(e.target.value)} />
86 | Hello, world!
87 |
88 | )
89 | }
90 |
91 | function ExpensiveTree() {
92 | let now = performance.now()
93 | while (performance.now() - now < 100) {
94 | // Artificial delay -- do nothing for 100ms
95 | }
96 | return I am a very slow component tree.
97 | }
98 | ```
99 |
100 | ### 2. 内容提升
101 |
102 | 像上面那种情况,组件可以单独抽离是因为知道`ExpensiveTree`组件不依赖`color`的状态。
103 | 但是如果我们假设是`App`中的`div`依赖`color`呢。这种情况下其实`ExpensiveTree`组件依然不应该刷新。
104 |
105 | ```tsx
106 | import { useState } from 'react'
107 |
108 | export default function App() {
109 | let [color, setColor] = useState('red')
110 | return (
111 |
112 |
setColor(e.target.value)} />
113 |
Hello, world!
114 |
115 |
I am a very slow component tree.
125 | }
126 | ```
127 |
128 | 这种情况下,我们需要将
129 |
130 | ```tsx
131 | import { useState } from 'react'
132 |
133 | export default function App() {
134 | return (
135 |
136 | Hello, world!
137 |
138 |
139 | )
140 | }
141 |
142 | // 将内容提升到该父组件中
143 | function ColorPicker({ children }) {
144 | let [color, setColor] = useState('red')
145 |
146 | return (
147 |
148 | setColor(e.target.value)} />
149 |
150 | {children}
151 |
152 | )
153 | }
154 |
155 | function ExpensiveTree() {
156 | let now = performance.now()
157 | while (performance.now() - now < 100) {
158 | // Artificial delay -- do nothing for 100ms
159 | }
160 | return I am a very slow component tree.
161 | }
162 | ```
163 |
164 | 可以看到我们将 App 组件一分为二。
165 | 将于`color`相关的组件放到`ColorPicker`中,然后不相关的作为`children`传给`ColorPicker`组件。
166 | 这样在`ColorPicker`组件`re-render`的时候,**由于**`**App**`**(父组件)中的组件没有变化,所以拿到的**`**children**`**依然是上一次的(没有发生变化的)所以**`**children**`**部分不会**`**re-render**`**。**
167 | 这样就避免了无效的刷新。
168 |
169 | 其实我理解的这里的内容提升,是指将于本次`re-render`无关的组件提升到父组件中去,通过`props`的方法传递给其他组件。这样其他组件在进行`re-render`的时候其实是不会影响到`props`的。
170 |
171 | ## 案例解析
172 |
173 | 这里我们讲完了上面的两种方法,来看一个案例。加深一下印象
174 |
175 | ```tsx
176 | import React, { ReactNode, StrictMode } from 'react'
177 |
178 | import { useValue, MyContext } from './state'
179 | import Counter from './Counter'
180 | import Person from './Person'
181 |
182 | const Provider = ({ children }: { children: ReactNode }) => {children}
183 |
184 | const Body = () => (
185 |
186 |
Counter
187 |
188 |
189 |
Person
190 |
191 |
192 |
221 |
Counter
222 |
223 |
224 |
Person
225 |
226 |
227 |
Helloss Vite12d
540 | \u662F\u662Ffff\u6492\u53D1\u987A\u4E30\u662Fdfd\uFF01sooo\uFF1F
541 | `
542 | }
543 | export const other = () => {
544 | const p = document.querySelector('#p')
545 | p.innerHTML = `
546 | other
547 | `
548 | }
549 | if (import.meta.hot) {
550 | import.meta.hot.data.count = 1
551 | import.meta.hot.accept((mod) => mod?.render())
552 | }
553 | ```
554 |
555 | > `vite:import-analysis` 插件进行注入的
556 |
557 | 可以看到,在我们文件的头部是被注入了`createHotContext`的,并且重写了我们的`import.meta.hot`中的内容为`createHotContext`的返回值。
558 |
559 | 也就是说我们在 21 行使用的 accept 方法是被`createHotContext`重写过的,那我们就来看看`createHotContext`做了什么?
560 |
561 | #### createHotContext
562 |
563 | 其实这个方法的主要任务就是:重写客户端的`import.meta.hot`中的一系列方法。
564 |
565 | ```typescript
566 | const hotModulesMap = new Map()
567 | // 简化后的代码
568 | /**
569 | * ownerPath: 当前文件的相对路径 "/src/render.ts"
570 | **/
571 | export function createHotContext(ownerPath: string): ViteHotContext {
572 | const mod = hotModulesMap.get(ownerPath)
573 | if (mod) {
574 | mod.callbacks = []
575 | }
576 |
577 | // 2. 再来看这个函数
578 | function acceptDeps(deps: string[], callback: HotCallback['fn'] = () => {}) {
579 | // 先查找缓存,如果没缓存,就新建模块相关信息
580 | const mod: HotModule = hotModulesMap.get(ownerPath) || {
581 | id: ownerPath,
582 | callbacks: [],
583 | }
584 | // 修改模块的相关信息
585 | mod.callbacks.push({
586 | deps,
587 | fn: callback,
588 | })
589 | // 将模块信息放入hotModuleMap中
590 | hotModulesMap.set(ownerPath, mod)
591 | }
592 |
593 | // 1. 先来看最终的返回值,就是对上一篇中提到的hmr中的一些API进行重写
594 | const hot: ViteHotContext = {
595 | get data() {
596 | return dataMap.get(ownerPath)
597 | },
598 |
599 | // 我们重点关注这里,重写accept方法
600 | accept(deps?: any, callback?: any) {
601 | // 第一种情况就是,import.meta.accetpt(mod=>{}) 这样写
602 | if (typeof deps === 'function' || !deps) {
603 | // 我们上面的问题,fn就是在这里注入的,这里的deps其实就是我们传入的回调 mod=>{}
604 | acceptDeps([ownerPath], ([mod]) => deps && deps(mod))
605 | } else if (typeof deps === 'string') {
606 | // 第二种情况是,import.meta.accetpt('xxx', mod=>{})
607 | acceptDeps([deps], ([mod]) => callback && callback(mod))
608 | } else if (Array.isArray(deps)) {
609 | // 第三种情况是,import.meta.accetpt(['xxx','xxxx'], mod=>{})
610 | acceptDeps(deps, callback)
611 | } else {
612 | throw new Error(`invalid hot.accept() usage.`)
613 | }
614 | },
615 |
616 | // export names (first arg) are irrelevant on the client side, they're
617 | // extracted in the server for propagation
618 | acceptExports(_: string | readonly string[], callback?: any) {
619 | acceptDeps([ownerPath], callback && (([mod]) => callback(mod)))
620 | },
621 |
622 | dispose(cb) {
623 | disposeMap.set(ownerPath, cb)
624 | },
625 |
626 | // @ts-expect-error untyped
627 | prune(cb: (data: any) => void) {
628 | pruneMap.set(ownerPath, cb)
629 | },
630 |
631 | decline() {},
632 |
633 | // tell the server to re-perform hmr propagation from this module as root
634 | invalidate() {
635 | notifyListeners('vite:invalidate', { path: ownerPath })
636 | this.send('vite:invalidate', { path: ownerPath })
637 | },
638 |
639 | // custom events
640 | on(event, cb) {
641 | const addToMap = (map: Map) => {
642 | const existing = map.get(event) || []
643 | existing.push(cb)
644 | map.set(event, existing)
645 | }
646 | addToMap(customListenersMap)
647 | addToMap(newListeners)
648 | },
649 |
650 | send(event, data) {
651 | messageBuffer.push(JSON.stringify({ type: 'custom', event, data }))
652 | sendMessageBuffer()
653 | },
654 | }
655 |
656 | return hot
657 | }
658 | ```
659 |
660 | 对于上面这个的`createHotContext`函数我们分为两部分来看:
661 |
662 | 1. 先看返回值`hot`, 这里总结来说就是重写上一篇中我们提到过的`hmr`相关的`API`。 我们重点关注`accept`函数,这里对`accept`函数的三种不同使用方式进行处理:
663 | 1. 第一种情况就是:`import.meta.accetpt(mod=>{})`
664 | 2. 第二种情况是:`import.meta.accetpt('xxx', mod=>{})`
665 | 3. 第三种情况是:`import.meta.accetpt(['xxx','xxxx'], mod=>{})`
666 | 2. 然后再看在返回值里重写`accept`方法时,用到了一个新的方法`acceptDeps`。这个方法其实就是更新`hotModulesMap`信息的。
667 |
668 | **参数:**
669 |
670 | 1. `deps`: 第一种情况下,其实就是传入的本身的路径,其他情况下是在`accpet`中主动声明的依赖
671 | 2. `callback`:
672 |
673 | 1. 第一种情况下,是重新注入的`([mod]) => deps && deps(mod)`,这里的`deps`其实就是我们传入的回调`mod=>{}`
674 | 2. 第二种情况下,也是重新注入的`([mod]) => callback && callback(mod)`,这里的`callback`是我们在 accept 中传入的第二个参数`import.meta.accetpt('xxx', mod=>{})`
675 | 3. 第三种情况就没怎么处理,将两个参数依次传入就好了
676 |
677 | > 我们上面的疑问 ❓:
678 | > 这个 fn 是哪里来的? 其实就是在重新 accpet 时
679 | > `acceptDeps([ownerPath], ([mod]) => deps && deps(mod))`中注入的
680 |
681 | 然后我们最后再来看一下在`queueUpdat`中调度任务最后执行的方法
682 |
683 | ```typescript
684 | // qualifiedCallbacks: {
685 | // "deps": [
686 | // "/src/render.ts"
687 | // ],
688 | // "fn": ([mod]) => deps && deps(mod)
689 | // }
690 | for (const { deps, fn } of qualifiedCallbacks) {
691 | fn(deps.map((dep) => moduleMap.get(dep)))
692 | }
693 | ```
694 |
695 | - `fn`: 就是我们上面解析的`acceptDeps`中的第二个参数`callback`
696 | - `moduleMap.get(dep)`: 获取到的是一个模块的信息`Module`
697 | - 所以最终`fn([mod])` ===>` ([mod]) => cb(mod)`(`cb`就是我们在`accept`中传入的)
698 |
699 | #### 在哪里注入的 createContext
700 |
701 | ```typescript
702 | // vite/src/node/plugins/importAnalysis.ts
703 | if (hasHMR && !ssr) {
704 | debugHmr(`${isSelfAccepting ? `[self-accepts]` : isPartiallySelfAccepting ? `[accepts-exports]` : acceptedUrls.size ? `[accepts-deps]` : `[detected api usage]`} ${prettyImporter}`)
705 | // inject hot context
706 | str().prepend(
707 | `import { createHotContext as __vite__createHotContext } from "${clientPublicPath}";` + `import.meta.hot = __vite__createHotContext(${JSON.stringify(normalizeHmrUrl(importerModule.url))});`
708 | )
709 | }
710 | ```
711 |
712 | ## 总结
713 |
714 | 
715 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 Liuqh's Note
Liuqh's Note Liuqh's Note
Liuqh's Note![]() 近期有更新 】
近期有更新 】