├── README.md
├── Train.py
├── __init__.py
├── evaluations
├── Clefts.py
├── NeuronIds.py
├── SynapticPartners.py
├── __init__.py
├── border_mask.py
├── rand.py
├── synaptic_partners.py
└── voi.py
├── img
├── *Filtered Mask.png
├── *Visualize Boundary.png
├── 6p.png
├── acc.png
├── err.png
├── loss.png
├── n.py
├── res window.png
└── rot.png
├── io
├── CremiFile.py
└── __init__.py
├── models
├── Resnet.py
└── Resnet_3.py
└── type
├── Annotations.py
└── Volume.py
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # CREMIchallenge2017 - Neuron Image Segmentation Task
2 | This is a tentative experiments on solving automated neuron segmentation task using deep learing methods, residual networks.
3 |
4 | See the original challenge post at: https://cremi.org, and leaderboard at: https://cremi.org/leaderboard/
5 |
6 | Use Train.py file o train the models.
7 |
8 |
9 | ## Experimental Restuls
10 | Best at 100 epoch:
11 |
12 | **Acc: 98.88%;**
13 |
14 | **Loss: 0.0298**
15 |
16 | 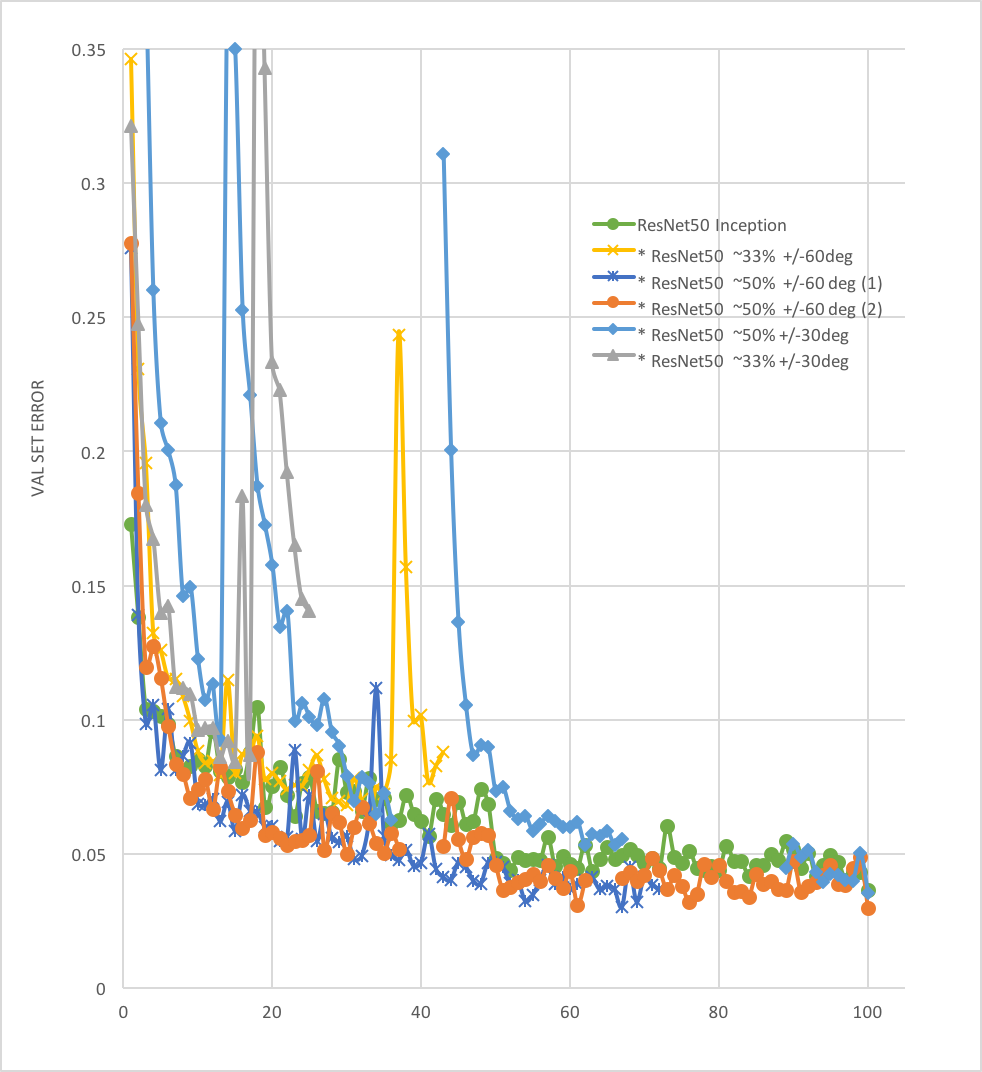 17 |
17 | 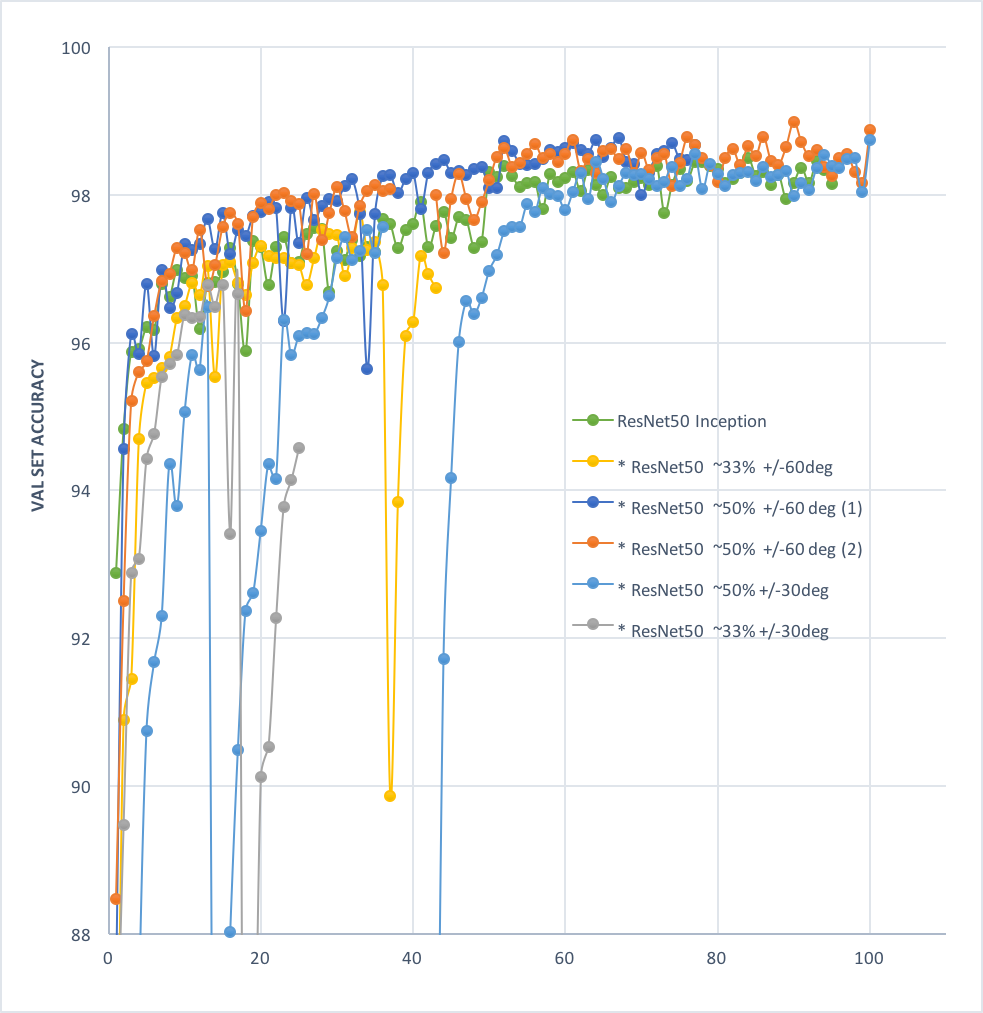 18 |
18 |  19 |
20 | ### Approaches
21 | - For this task, I trained a 2 way classifier to classify the central pixel in 127*127 sample as boudary and non-boundary. The 2-way sofmax layer was applied before the output of the network.
22 | - Reproduced and used **residual network method**. (original: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385, implementation on github: https://github.com/gcr/torch-residual-networks). This has been giving me a great boost in classificaiton results.
23 |
24 | - (see plot below) It was found in preliminary experiments that using a 5-7-5 window for the three conv layers in the bottleneck block of residual net (training on 127*127 sample size, green line) outformed the originally proposed 1-3-1 structure (gray line) by a large margin, so experiments reported above were all trained with the 5-7-5. The position of batch normalization and dropout layer in the block was also changed.
25 |
26 |
19 |
20 | ### Approaches
21 | - For this task, I trained a 2 way classifier to classify the central pixel in 127*127 sample as boudary and non-boundary. The 2-way sofmax layer was applied before the output of the network.
22 | - Reproduced and used **residual network method**. (original: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385, implementation on github: https://github.com/gcr/torch-residual-networks). This has been giving me a great boost in classificaiton results.
23 |
24 | - (see plot below) It was found in preliminary experiments that using a 5-7-5 window for the three conv layers in the bottleneck block of residual net (training on 127*127 sample size, green line) outformed the originally proposed 1-3-1 structure (gray line) by a large margin, so experiments reported above were all trained with the 5-7-5. The position of batch normalization and dropout layer in the block was also changed.
25 |
26 | 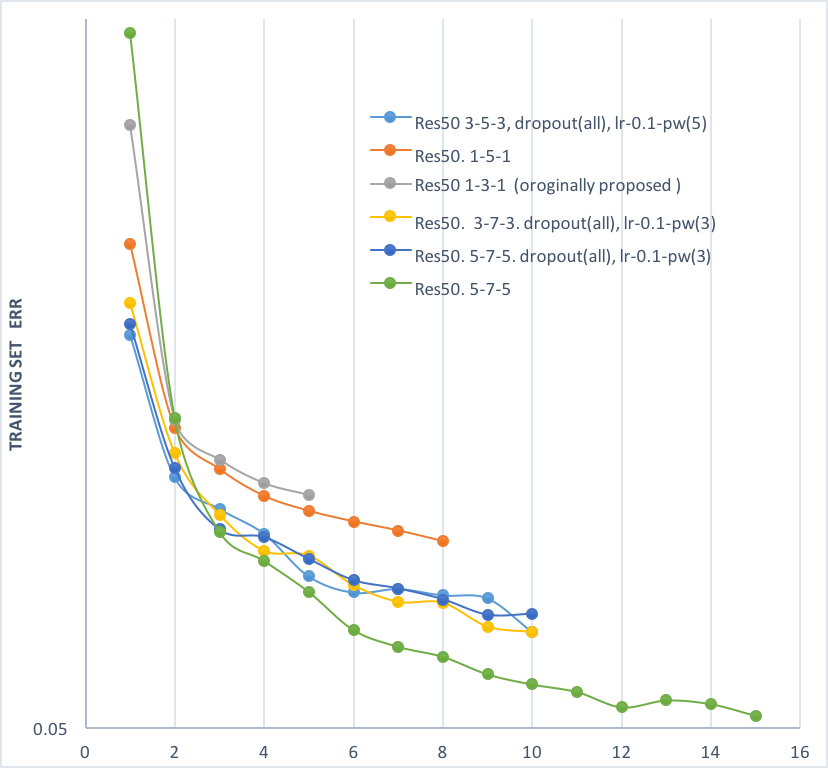 27 |
28 | - **Selectively choose training samples from raw (see figure below)**: the yellow area **X3 dilated boundary** pixels were avoided to be chosen, only green and purple (true boudary, background) pixels will be selected into training batches,.
29 | - **Random rotation techniques**: various augmentation approches were explored, including rand rotations of +/-60, rand +/- 30, on 33.33%, 50% of samples in each batc. rand +/- 60 deg on 50% of samples (see figure below) was found to perform the best so far.
30 |
27 |
28 | - **Selectively choose training samples from raw (see figure below)**: the yellow area **X3 dilated boundary** pixels were avoided to be chosen, only green and purple (true boudary, background) pixels will be selected into training batches,.
29 | - **Random rotation techniques**: various augmentation approches were explored, including rand rotations of +/-60, rand +/- 30, on 33.33%, 50% of samples in each batc. rand +/- 60 deg on 50% of samples (see figure below) was found to perform the best so far.
30 |  31 |
31 |  32 |
32 | 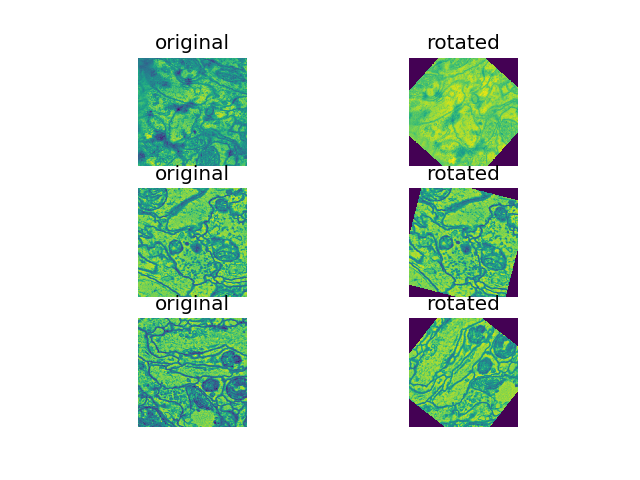 33 |
34 | ### Future work
35 |
36 | - The neighbor area of the boundaries was avoided in this experiment, however the boundary pixels from other organels (intracellular organels) should also be avoided. These pixels could be easily treated as target neuron boundaries which are actually not. The approach to address this challenge can be to pre-train a network to recognize these intracellular boundaries and filter out these pixels when creating training batches for the segmentation task.
37 |
38 | - the raw is originally a 3D image of size 125 * 1250 * 1250. I started by treating each layer in deapth 125 as an independent sample and trained my network with images in 2D sections. However, in later stages of experiments (which i was not able to do due to the time limit of my project), the third deimension should be considered to address the correlation between the neuron pixels at depth.
39 |
40 | ## Dependencies
41 |
42 | * python
43 | * pytorch
44 | * numpy
45 | * matplotlib
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | import torch.optim as optim
5 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
6 | from torch.autograd import Variable
7 |
8 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, TensorDataset
9 | import torchvision
10 | from torchvision import transforms, datasets
11 | import torchvision.models as models
12 | import numpy as np
13 | from tempfile import TemporaryFile
14 | import matplotlib
15 | matplotlib.use('Agg')
16 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
17 | import scipy.ndimage as ndimage
18 | from scipy.ndimage.interpolation import rotate
19 | import time
20 | import os
21 | import random
22 |
23 | from Annotations import *
24 | from Volume import *
25 | from CremiFile import *
26 | from voi import voi
27 | from rand import adapted_rand
28 | plt.style.use('ggplot')
29 |
30 | from models.Resnet_3 import *
31 | from models.Resnet import *
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 | print('')
36 | print('DATASET LOADING ...')
37 | print('')
38 | emdset = CremiFile('sample_B_20160501.hdf', 'r')
39 |
40 | #Check the content of the datafile
41 | print "Has raw: " + str(emdset.has_raw())
42 | print "Has neuron ids: " + str(emdset.has_neuron_ids())
43 | print "Has clefts: " + str(emdset.has_clefts())
44 | print "Has annotations: " + str(emdset.has_annotations())
45 |
46 |
47 | #Read volume and annotation
48 | raw = emdset.read_raw()
49 | neuron_ids = emdset.read_neuron_ids()
50 | clefts = emdset.read_clefts()
51 | annotations = emdset.read_annotations()
52 |
53 | print("")
54 | print "Read raw: " + str(raw) + \
55 | ", resolution " + str(raw.resolution) + \
56 | ", offset " + str(raw.offset) + \
57 | ", data size " + str(raw.data.shape) + \
58 | ("" if raw.comment == None else ", comment \"" + raw.comment + "\"")
59 |
60 | print "Read neuron_ids: " + str(neuron_ids) + \
61 | ", resolution " + str(neuron_ids.resolution) + \
62 | ", offset " + str(neuron_ids.offset) + \
63 | ", data size " + str(neuron_ids.data.shape) + \
64 | ("" if neuron_ids.comment == None else ", comment \"" + neuron_ids.comment + "\"")
65 |
66 | print "Read clefts: " + str(clefts) + \
67 | ", resolution " + str(clefts.resolution) + \
68 | ", offset " + str(clefts.offset) + \
69 | ", data size " + str(clefts.data.shape) + \
70 | ("" if clefts.comment == None else ", comment \"" + clefts.comment + "\"")
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | def mask_filtered(raw, neuron_ids):
76 | """
77 | Image boudnary dilation
78 | Compute mask on each depth for un-selectable dilated(6X) boundary pixels (labeled as value 200.),
79 | the selectable background (0.) and actual boundary (100.) pixels
80 |
81 | return(numpy array): mask of shape 125,1250,1250
82 | """
83 | print ''
84 | print ''
85 | print 'building mask-5X from raw dataset...'
86 | since = time.time()
87 |
88 | d, h, w = raw.data.shape
89 | mask = np.empty([d, h, w]).astype('float32')
90 | for i in range(d):
91 | for j in range(h):
92 | for k in range(w):
93 | pixel = neuron_ids.data[i, j, k]
94 | if check_boundary(pixel, i, j, k, neuron_ids):
95 | mask[i, j, k] = 100
96 | else:
97 | mask[i, j, k] = 0
98 | if (i + 1) % 1 == 0:
99 | print str(0.8 * (i + 1)) + '% done'
100 |
101 | mask_dilated = ndimage.binary_dilation(mask, iterations=7).astype(mask.dtype)
102 | mask_filtered = 200 * mask_dilated - mask
103 |
104 | filter_time = time.time()
105 | time_elapsed = filter_time - since
106 | print('Mask complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format(
107 | time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60))
108 |
109 |
110 | print 'save to maskfile7X.npy'
111 | np.save('maskfile7X.npy', mask_filtered)
112 | print 'saved'
113 |
114 |
115 | def check_boundary(pixel, x, y, z, neuron_ids):
116 | """
117 | Check if a pixel at position (x,y,z) is labeled
118 | as boundary/non-boundary in neuron_ids.
119 |
120 | return(boolean): boundary
121 | """
122 | max_z = neuron_ids.data.shape[2] - 1
123 | max_y = neuron_ids.data.shape[1] - 1
124 | a = neuron_ids.data[x, y, z - 1] if z > 0 else pixel
125 | b = neuron_ids.data[x, y, z + 1] if z < max_z else pixel
126 | c = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z] if y > 0 else pixel
127 | d = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z] if y < max_y else pixel
128 | e = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z - 1] if (y > 0 and z > 0) else pixel
129 | f = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z + 1] if (y > 0 and z < max_z) else pixel
130 | g = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z - 1] if (y < max_y and z > 0) else pixel
131 | h = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z + 1] if (y < max_y and z < max_z) else pixel
132 |
133 | neighbors = [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h]
134 | boundary = False
135 | for neighbor in neighbors:
136 | if pixel != neighbor:
137 | boundary = True
138 |
139 | return boundary
140 |
141 |
142 | # Seed a random number generator
143 | #seed = 24102016
144 | #rng = np.random.RandomState(seed)
145 | def random_rotation(inputs):
146 | """Randomly rotates a subset of images in a batch.
147 | reference: https://github.com/CSTR-Edinburgh/mlpractical/blob/mlp2016-7/master/notebooks/05_Non-linearities_and_regularisation.ipynb
148 |
149 | * chooses 30-50% of the images in the batch at random
150 | * for each image in the 30-50% chosen, rotates the image by a random angle in [-60, 60]
151 | * returns a new array of size (129, 129) in which the rows corresponding to the 25% chosen images are the vectors corresponding to the new randomly rotated images, while the remaining rows correspond to the original images.
152 | Args:
153 | inputs: Input image batch, an array of shape (129, 129).
154 |
155 | Returns:
156 | An array of shape (129, 129) corresponding to a copy
157 | of the original `inputs` array that was randomly selected
158 | to be rotated by a random angle. The original `inputs`
159 | array should not be modified.
160 | """
161 |
162 | new_ims = np.zeros(inputs.shape).astype('float32')
163 | indices = random.randint(-1,1)
164 | angles = random.uniform(-30., 30.)
165 | if indices == 0:
166 | rotate(inputs, angles, output = new_ims, order=1, reshape=False)
167 |
168 | return new_ims
169 |
170 |
171 |
172 |
173 | #mask_filtered(raw, neuron_ids) # used only when the first time of training
174 | mask = np.load('maskfile5X.npy')
175 | print ''
176 | print 'mask loaded'
177 |
178 | class NeuronSegmenDataset(Dataset):
179 | """Raw pixel and its label.
180 | Dataset splitted into 80,000 training and 20,000 validation set
181 | """
182 |
183 | def __init__(self, raw, neuron_ids, mask, phase, transform=None):
184 | """
185 | Args:
186 | raw(Volume): raw
187 | neuron_ids(Volume): neuron segmentation labels
188 | mask(numpy ndarray): filtered mask
189 | phase(String): 'train' or 'val'
190 | transform(callable, optional): optional data augmentation to be applied
191 | """
192 |
193 | self.phase = phase
194 | self.raw = raw
195 | self.neuron_ids = neuron_ids
196 | self.mask = mask
197 | self.transform = transform
198 |
199 | def __len__(self):
200 | """ length of the dataset """
201 | if self.phase == 'train':
202 | x = 80000
203 | else:
204 | x = 20000
205 |
206 | return x
207 |
208 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
209 | """
210 | Return 33*33 patches for each raw pixel at the center
211 | positive if boundary pixel, negative if non-boundary pixel
212 | """
213 | depth = self.raw.data.shape[0]
214 | size = self.raw.data.shape[1]
215 |
216 |
217 | while True:
218 | d = random.randint(0, depth - 1)
219 | h = random.randint(64, size - 65)
220 | w = random.randint(64, size - 65)
221 | ids_pixel = self.neuron_ids.data[d, h, w]
222 | pixel = self.mask[d, h, w]
223 |
224 | if idx % 2 == 0: #control half samples to be boundary pixels
225 | if pixel == 100.:
226 | raw_batch = self.raw.data[d][h - 64:h + 65, w - 64:w + 65].astype(
227 | 'float32') # crop a 129*129 patch
228 |
229 |
230 | if self.transform:
231 | raw_batch = self.transform(raw_batch)
232 |
233 | raw_batch = raw_batch.reshape([1, 129, 129])
234 | raw_batch = torch.from_numpy(raw_batch)
235 | sample = (raw_batch, 0)
236 |
237 | break
238 | elif pixel == 0.: # the other half as non-boundary pixel
239 | raw_batch = self.raw.data[d][h - 64:h + 65, w - 64:w + 65].astype(
240 | 'float32') # crop 33*33 patch
241 | raw_batch = raw_batch.reshape([1, 129, 129])
242 |
243 | if self.transform:
244 | raw_batch = self.transform(raw_batch)
245 |
246 | raw_batch = torch.from_numpy(raw_batch)
247 | sample = (raw_batch, 1)
248 |
249 | break
250 | return sample
251 |
252 |
253 | batch_size = 100
254 | emdset_seg = {x: NeuronSegmenDataset(raw, neuron_ids, mask, x, transform=random_rotation)
255 | for x in ['train', 'val']}
256 | emdset_loaders = {x: DataLoader(emdset_seg[x], batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
257 | for x in ['train', 'val']}
258 | dset_sizes = {x: len(emdset_seg[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']}
259 | dset_classes = ['boundary', 'non-b']
260 | use_gpu = torch.cuda.is_available()
261 |
262 | print "Load num of batches: train " + str(len(emdset_loaders['train'])) + \
263 | ' validation ' + str(len(emdset_loaders['val']))
264 |
265 | print ('done')
266 | print ('')
267 |
268 |
269 | class ConvNet(nn.Module):
270 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel= 3, window =2, padding=1):
271 | super(ConvNet, self).__init__()
272 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
273 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
274 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
275 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
276 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
277 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
278 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
279 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
280 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel, padding=padding)
281 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel, padding=padding)
282 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(window)
283 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(2*2*256, 256)
284 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
285 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
286 | self.linear4 = nn.Linear(128, D_out)
287 |
288 | def forward(self, x):
289 | x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
290 | print "conv 1: " + str(x.data.size())
291 | x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
292 | print "conv 2: " + str(x.data.size())
293 | x = self.pool(x)
294 | print "pool 1: " + str(x.data.size())
295 |
296 | x = F.relu(self.conv3(x))
297 | print "conv 3: " + str(x.data.size())
298 | x = F.relu(self.conv4(x))
299 | print "conv 4: " + str(x.data.size())
300 | x = self.pool(x)
301 | print "pool 2: " + str(x.data.size())
302 |
303 | x = F.relu(self.conv5(x))
304 | print "conv 5: " + str(x.data.size())
305 | x = F.relu(self.conv6(x))
306 | print "conv 6: " + str(x.data.size())
307 | x = self.pool(x)
308 | print "pool 3: " + str(x.data.size())
309 |
310 | x = F.relu(self.conv7(x))
311 | print "conv 7: " + str(x.data.size())
312 | x = F.relu(self.conv8(x))
313 | print "conv 8: " + str(x.data.size())
314 | x = self.pool(x)
315 | print "pool 4: " + str(x.data.size())
316 |
317 | x = x.view(-1, 2*2*256)
318 | x = F.relu(self.linear1(x))
319 |
320 | x = F.relu(self.linear3(x))
321 | x = F.relu(self.linear4(x))
322 |
323 | return x
324 |
325 |
326 |
327 | def exp_lr_scheduler(optimizer, epoch, init_lr=0.001, lr_decay_epoch=10):
328 | """Decay learning rate by a factor of 0.1 every 10 epochs"""
329 | lr = init_lr * (0.1**(epoch // lr_decay_epoch))
330 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
331 | param_group['lr'] = lr
332 |
333 | return optimizer
334 |
335 |
336 | def piecewise_scheduler(optimizer, epoch):
337 | if epoch % 50 ==0 :
338 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
339 | lr = param_group['lr'] / 2
340 | param_group['lr'] = lr
341 |
342 | return optimizer
343 |
344 |
345 |
346 | def train_model (model, criterion, optimizer, lr_scheduler=None, num_epochs=100):
347 | since = time.time()
348 | train_voi_split = np.zeros(num_epochs)
349 | train_voi_merge = np.zeros(num_epochs)
350 | train_rand = np.zeros(num_epochs)
351 |
352 | # iterate over epoch
353 | for epoch in range(num_epochs):
354 | print ('Epoch{}/{}'.format(epoch+1, num_epochs))
355 | print ('-' * 10)
356 |
357 |
358 | # train and validation set
359 | for phase in ['train', 'val']:
360 | if phase == 'train':
361 | if lr_scheduler:
362 | optimizer = lr_scheduler(optimizer, epoch + 1)
363 | model.train(True)
364 | else:
365 | model.train(True)
366 |
367 | running_loss = 0.
368 | running_accuracy = 0.
369 | total = 0
370 |
371 | # iterate over each batch
372 | for i, data in enumerate(emdset_loaders[phase]):
373 | inputs, labels = data
374 | if use_gpu:
375 | model = model.cuda()
376 | inputs, labels = Variable(inputs.cuda()), \
377 | Variable(labels.cuda())
378 | else:
379 | inputs, labels = Variable(inputs), Variable(labels)
380 |
381 |
382 | optimizer.zero_grad() # clean gradients in buffer
383 |
384 | outputs = model(inputs)
385 | _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
386 | loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
387 |
388 |
389 | if phase == 'train':
390 | loss.backward()
391 | optimizer.step()
392 |
393 |
394 | running_loss += loss.data[0]
395 | running_accuracy += (predicted == labels.data).sum()
396 |
397 | # visualize random patches
398 | visualize_pred = True
399 | tt = visualize_pred and epoch == num_epochs-1 and phase == 'val' \
400 | and i+1 == len(emdset_loaders['val'])
401 | if tt:
402 | print('visualizing...')
403 | images_so_far = 0
404 | fig = plt.figure()
405 | for j in [6, 15, 38, 41, 86, 99]:
406 | images_so_far += 1
407 | ax = fig.add_subplot(3, 2, images_so_far)
408 | ax.axis('off')
409 | ax.set_title('Pred: {},\n Labeled: {}'.format(dset_classes[int(predicted.cpu().numpy()[j])],
410 | dset_classes[labels.data[j]]))
411 | ax.imshow(inputs.cpu().data[j].view(129,129).numpy())
412 | fig.savefig('6p.png')
413 | print 'done and saved to 6p.png'
414 |
415 |
416 | # normalize by number of batches
417 | running_loss /= (i + 1)
418 | running_accuracy = 100 * running_accuracy / dset_sizes[phase]
419 |
420 | # print statistics
421 | if epoch % 1 == 0:
422 | print('{} Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(
423 | phase, running_loss, running_accuracy
424 | ))
425 | # print "\tvoi split : " + str(train_voi_split)
426 | # print "\tvoi merge : " + str(train_voi_merge)
427 | # print "\tadapted RAND: " + str(train_rand)
428 |
429 | # Visualize the model. raw, labeled, predicted (optional)
430 | visualize = False
431 | if visualize:
432 | print('')
433 | print('Begin to visualize model..')
434 | visualize_model(model)
435 |
436 | time_elapsed = time.time() - train_time
437 | print('Visualizing complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format(
438 | time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60))
439 |
440 |
441 |
442 | def visualize_model(model, i = 80, s = 300):
443 | """ Args:
444 | model: model
445 | i: depth of the raw image to visualize
446 | s: crop the 1250*1250 image to the size of s*s
447 | """
448 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15,6))
449 |
450 | ax_ori = fig.add_subplot(1,3,1)
451 | ax_lab = fig.add_subplot(1,3,2)
452 | ax_pred = fig.add_subplot(1,3,3)
453 |
454 | ax_ori.imshow(raw.data[i][0:s, 0:s])
455 | ax_ori.set_title('raw')
456 | ax_lab.imshow(neuron_ids.data[i][0:s, 0:s])
457 | ax_lab.set_title('labeled')
458 |
459 |
460 | preds = np.empty([s*s])
461 | for j in range(s*s):
462 | pixel = raw.data[i][j/s, j%s]
463 | input = np.random.uniform(-10000, 0, (1, 1, 33, 33)).astype('float32') ## boundary patch: positive
464 | input[0, 0, 16, 16] = pixel
465 | input = torch.from_numpy(input)
466 |
467 | model.train(False)
468 | if use_gpu:
469 | model = model.cuda()
470 | input = Variable(input.cuda())
471 | else:
472 | input = Variable(input)
473 |
474 | outputs = model(input)
475 | _, pred = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
476 | pred = pred.cpu().numpy()
477 | if pred[0] == 0:
478 | preds[j] = 20000
479 | else:
480 | preds[j] = 100
481 |
482 | if j == 30000:
483 | print '1/3 done'
484 | if j == 60000:
485 | print '2/3 done'
486 |
487 | print preds.reshape(s, s)
488 | ax_pred.imshow(preds.reshape((s,s)))
489 | ax_pred.set_title('predicted')
490 |
491 | ax_lab.axis('off')
492 | ax_ori.axis('off')
493 | ax_pred.axis('off')
494 |
495 | plt.show()
496 | fig.savefig('vi.png')
497 | print('saved as vi.png')
498 |
499 |
500 |
501 |
502 |
503 |
504 | # Train
505 | #-----------------------------------------------------------------------
506 | num_classes = 2
507 | num_epochs = 100
508 | #model = ConvNet(num_classes )
509 | #model = DeepResNet18(num_classes)
510 | #model = DeepResNet34(num_classes )
511 | model = DeepResNet50(num_classes)
512 | #model = DeepResNet101(num_classes )
513 | optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0001)
514 | #optimizer = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[2,4,6,8,10], gamma=0.5)
515 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
516 | print('')
517 | print('START TRAINING ...')
518 | print(time.time())
519 | print('ResNet50. 33% 30deg lr50')
520 | train = train_model(model, criterion, optimizer, lr_scheduler=piecewise_scheduler, num_epochs=num_epochs)
521 |
522 |
523 |
524 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Annotations import *
2 | from Volume import *
3 | from NeuronIds import *
4 | from border_mask import *
5 | from CremiFile import *
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/Clefts.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from scipy import ndimage
3 |
4 | class Clefts:
5 |
6 | def __init__(self, test, truth):
7 |
8 | test_clefts = test
9 | truth_clefts = truth
10 |
11 | self.test_clefts_mask = np.equal(test_clefts.data, 0xffffffffffffffff)
12 | self.truth_clefts_mask = np.equal(truth_clefts.data, 0xffffffffffffffff)
13 |
14 | self.test_clefts_edt = ndimage.distance_transform_edt(self.test_clefts_mask, sampling=test_clefts.resolution)
15 | self.truth_clefts_edt = ndimage.distance_transform_edt(self.truth_clefts_mask, sampling=truth_clefts.resolution)
16 |
17 | def count_false_positives(self, threshold = 200):
18 |
19 | mask1 = np.invert(self.test_clefts_mask)
20 | mask2 = self.truth_clefts_edt > threshold
21 | false_positives = self.truth_clefts_edt[np.logical_and(mask1, mask2)]
22 | return false_positives.size
23 |
24 | def count_false_negatives(self, threshold = 200):
25 |
26 | mask1 = np.invert(self.truth_clefts_mask)
27 | mask2 = self.test_clefts_edt > threshold
28 | false_negatives = self.test_clefts_edt[np.logical_and(mask1, mask2)]
29 | return false_negatives.size
30 |
31 | def acc_false_positives(self):
32 |
33 | mask = np.invert(self.test_clefts_mask)
34 | false_positives = self.truth_clefts_edt[mask]
35 | stats = {
36 | 'mean': np.mean(false_positives),
37 | 'std': np.std(false_positives),
38 | 'max': np.amax(false_positives),
39 | 'count': false_positives.size,
40 | 'median': np.median(false_positives)}
41 | return stats
42 |
43 | def acc_false_negatives(self):
44 |
45 | mask = np.invert(self.truth_clefts_mask)
46 | false_negatives = self.test_clefts_edt[mask]
47 | stats = {
48 | 'mean': np.mean(false_negatives),
49 | 'std': np.std(false_negatives),
50 | 'max': np.amax(false_negatives),
51 | 'count': false_negatives.size,
52 | 'median': np.median(false_negatives)}
53 | return stats
54 |
55 |
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/NeuronIds.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from border_mask import create_border_mask
3 | from voi import voi
4 | from rand import adapted_rand
5 |
6 | class NeuronIds:
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, groundtruth, border_threshold = None):
9 | """Create a new evaluation object for neuron ids against the provided ground truth.
10 |
11 | Parameters
12 | ----------
13 |
14 | groundtruth: Volume
15 | The ground truth volume containing neuron ids.
16 |
17 | border_threshold: None or float, in world units
18 | Pixels within `border_threshold` to a label border in the
19 | same section will be assigned to background and ignored during
20 | the evaluation.
21 | """
22 |
23 | assert groundtruth.resolution[1] == groundtruth.resolution[2], \
24 | "x and y resolutions of ground truth are not the same (%f != %f)" % \
25 | (groundtruth.resolution[1], groundtruth.resolution[2])
26 |
27 | self.groundtruth = groundtruth
28 | self.border_threshold = border_threshold
29 |
30 | if self.border_threshold:
31 |
32 | print "Computing border mask..."
33 |
34 | self.gt = np.zeros(groundtruth.data.shape, dtype=np.uint64)
35 | create_border_mask(
36 | groundtruth.data,
37 | self.gt,
38 | float(border_threshold)/groundtruth.resolution[1],
39 | np.uint64(-1))
40 | else:
41 | self.gt = np.array(self.groundtruth.data).copy()
42 |
43 | # current voi and rand implementations don't work with np.uint64(-1) as
44 | # background label, so we make it 0 here and bump all other labels
45 | self.gt += 1
46 |
47 | def voi(self, segmentation):
48 |
49 | assert list(segmentation.data.shape) == list(self.groundtruth.data.shape)
50 | assert list(segmentation.resolution) == list(self.groundtruth.resolution)
51 |
52 | print "Computing VOI..."
53 |
54 | return voi(np.array(segmentation.data), self.gt, ignore_groundtruth = [0])
55 |
56 | def adapted_rand(self, segmentation):
57 |
58 | assert list(segmentation.data.shape) == list(self.groundtruth.data.shape)
59 | assert list(segmentation.resolution) == list(self.groundtruth.resolution)
60 |
61 | print "Computing RAND..."
62 |
63 | return adapted_rand(np.array(segmentation.data), self.gt)
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/SynapticPartners.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from synaptic_partners import synaptic_partners_fscore
2 |
3 | class SynapticPartners:
4 |
5 | def __init__(self, matching_threshold = 400):
6 |
7 | self.matching_threshold = matching_threshold
8 |
9 | def fscore(self, rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, all_stats = False):
10 |
11 | return synaptic_partners_fscore(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, self.matching_threshold, all_stats)
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Clefts import *
2 | from NeuronIds import *
3 | from SynapticPartners import *
4 | from border_mask import *
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/border_mask.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import h5py
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import scipy
4 |
5 | def create_border_mask(input_data, target, max_dist, background_label,axis=0):
6 | """
7 | Overlay a border mask with background_label onto input data.
8 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
9 |
10 | Parameters
11 | ----------
12 | input_data : h5py.Dataset or numpy.ndarray - Input data containing neuron ids
13 | target : h5py.Datset or numpy.ndarray - Target which input data overlayed with border mask is written into.
14 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
15 | background_label : int - Border mask will be overlayed using this label.
16 | axis : int - Axis of iteration (perpendicular to 2d images for which mask will be generated)
17 | """
18 | sl = [slice(None) for d in xrange(len(target.shape))]
19 |
20 | for z in xrange(target.shape[axis]):
21 | sl[ axis ] = z
22 | border = create_border_mask_2d(input_data[tuple(sl)], max_dist)
23 | target_slice = input_data[tuple(sl)] if isinstance(input_data,h5py.Dataset) else np.copy(input_data[tuple(sl)])
24 | target_slice[border] = background_label
25 | target[tuple(sl)] = target_slice
26 |
27 | def create_and_write_masked_neuron_ids(in_file, out_file, max_dist, background_label, overwrite=False):
28 | """
29 | Overlay a border mask with background_label onto input data loaded from in_file and write into out_file.
30 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
31 |
32 | Parameters
33 | ----------
34 | in_file : CremiFile - Input file containing neuron ids
35 | out_file : CremiFile - Output file which input data overlayed with border mask is written into.
36 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
37 | background_label : int - Border mask will be overlayed using this label.
38 | overwrite : bool - Overwrite existing data in out_file (True) or do nothing if data is present in out_file (False).
39 | """
40 | if ( not in_file.has_neuron_ids() ) or ( (not overwrite) and out_file.has_neuron_ids() ):
41 | return
42 |
43 | neuron_ids, resolution, offset, comment = in_file.read_neuron_ids()
44 | comment = ('' if comment is None else comment + ' ') + 'Border masked with max_dist=%f' % max_dist
45 |
46 | path = "/volumes/labels/neuron_ids"
47 | group_path = "/".join( path.split("/")[:-1] )
48 | ds_name = path.split("/")[-1]
49 | if ( out_file.has_neuron_ids() ):
50 | del out_file.h5file[path]
51 | if (group_path not in out_file.h5file):
52 | out_file.h5file.create_group(group_path)
53 |
54 | group = out_file.h5file[group_path]
55 | target = group.create_dataset(ds_name, shape=neuron_ids.shape, dtype=neuron_ids.dtype)
56 | target.attrs["resolution"] = resolution
57 | target.attrs["comment"] = comment
58 | if offset != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
59 | target.attrs["offset"] = offset
60 |
61 | create_border_mask(neuron_ids, target, max_dist, background_label)
62 |
63 | def create_border_mask_2d(image, max_dist):
64 | """
65 | Create binary border mask for image.
66 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
67 |
68 | Parameters
69 | ----------
70 | image : numpy.ndarray - Image containing integer labels.
71 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
72 |
73 | Returns
74 | -------
75 | mask : numpy.ndarray - Binary mask of border pixels. Same shape as image.
76 | """
77 | max_dist = max(max_dist, 0)
78 |
79 | padded = np.pad(image, 1, mode='edge')
80 |
81 | border_pixels = np.logical_and(
82 | np.logical_and( image == padded[:-2, 1:-1], image == padded[2:, 1:-1] ),
83 | np.logical_and( image == padded[1:-1, :-2], image == padded[1:-1, 2:] )
84 | )
85 |
86 | distances = scipy.ndimage.distance_transform_edt(
87 | border_pixels,
88 | return_distances=True,
89 | return_indices=False
90 | )
91 |
92 | return distances <= max_dist
93 |
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/rand.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
5 |
6 | # Evaluation code courtesy of Juan Nunez-Iglesias, taken from
7 | # https://github.com/janelia-flyem/gala/blob/master/gala/evaluate.py
8 |
9 | def adapted_rand(seg, gt, all_stats=False):
10 | """Compute Adapted Rand error as defined by the SNEMI3D contest [1]
11 |
12 | Formula is given as 1 - the maximal F-score of the Rand index
13 | (excluding the zero component of the original labels). Adapted
14 | from the SNEMI3D MATLAB script, hence the strange style.
15 |
16 | Parameters
17 | ----------
18 | seg : np.ndarray
19 | the segmentation to score, where each value is the label at that point
20 | gt : np.ndarray, same shape as seg
21 | the groundtruth to score against, where each value is a label
22 | all_stats : boolean, optional
23 | whether to also return precision and recall as a 3-tuple with rand_error
24 |
25 | Returns
26 | -------
27 | are : float
28 | The adapted Rand error; equal to $1 - \frac{2pr}{p + r}$,
29 | where $p$ and $r$ are the precision and recall described below.
30 | prec : float, optional
31 | The adapted Rand precision. (Only returned when `all_stats` is ``True``.)
32 | rec : float, optional
33 | The adapted Rand recall. (Only returned when `all_stats` is ``True``.)
34 |
35 | References
36 | ----------
37 | [1]: http://brainiac2.mit.edu/SNEMI3D/evaluation
38 | """
39 | # segA is truth, segB is query
40 | segA = np.ravel(gt)
41 | segB = np.ravel(seg)
42 | n = segA.size
43 |
44 | n_labels_A = np.amax(segA) + 1
45 | n_labels_B = np.amax(segB) + 1
46 |
47 | ones_data = np.ones(n)
48 |
49 | p_ij = sparse.csr_matrix((ones_data, (segA[:], segB[:])), shape=(n_labels_A, n_labels_B))
50 |
51 | a = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,:]
52 | b = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,1:n_labels_B]
53 | c = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,0].todense()
54 | d = b.multiply(b)
55 |
56 | a_i = np.array(a.sum(1))
57 | b_i = np.array(b.sum(0))
58 |
59 | sumA = np.sum(a_i * a_i)
60 | sumB = np.sum(b_i * b_i) + (np.sum(c) / n)
61 | sumAB = np.sum(d) + (np.sum(c) / n)
62 |
63 | precision = sumAB / sumB
64 | recall = sumAB / sumA
65 |
66 | fScore = 2.0 * precision * recall / (precision + recall)
67 | are = 1.0 - fScore
68 |
69 | if all_stats:
70 | return (are, precision, recall)
71 | else:
72 | return are
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/synaptic_partners.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 | from munkres import Munkres
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | def synaptic_partners_fscore(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold = 400, all_stats = False):
6 | """Compute the f-score of the found synaptic partners.
7 |
8 | Parameters
9 | ----------
10 |
11 | rec_annotations: Annotations, containing found synaptic partners
12 |
13 | gt_annotations: Annotations, containing ground truth synaptic partners
14 |
15 | gt_segmentation: Volume, ground truth neuron segmentation
16 |
17 | matching_threshold: float, world units
18 | Euclidean distance threshold to consider two annotations a potential
19 | match. Annotations that are `matching_threshold` or more untis apart
20 | from each other are not considered as potential matches.
21 |
22 | all_stats: boolean, optional
23 | Whether to also return precision, recall, FP, FN, and matches as a 6-tuple with f-score
24 |
25 | Returns
26 | -------
27 |
28 | fscore: float
29 | The f-score of the found synaptic partners.
30 | precision: float, optional
31 | recall: float, optional
32 | fp: int, optional
33 | fn: int, optional
34 | filtered_matches: list of tuples, optional
35 | The indices of the matches with matching costs.
36 | """
37 |
38 | # get cost matrix
39 | costs = cost_matrix(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold)
40 |
41 | # match using Hungarian method
42 | print "Finding cost-minimal matches..."
43 | munkres = Munkres()
44 | matches = munkres.compute(costs.copy()) # have to copy, because munkres changes the cost matrix...
45 |
46 | filtered_matches = [ (i,j, costs[i][j]) for (i,j) in matches if costs[i][j] <= matching_threshold ]
47 | print str(len(filtered_matches)) + " matches found"
48 |
49 | # unmatched in rec = FP
50 | fp = len(rec_annotations.pre_post_partners) - len(filtered_matches)
51 |
52 | # unmatched in gt = FN
53 | fn = len(gt_annotations.pre_post_partners) - len(filtered_matches)
54 |
55 | # all ground truth elements - FN = TP
56 | tp = len(gt_annotations.pre_post_partners) - fn
57 |
58 | precision = float(tp)/(tp + fp)
59 | recall = float(tp)/(tp + fn)
60 | fscore = 2.0*precision*recall/(precision + recall)
61 |
62 | if all_stats:
63 | return (fscore, precision, recall, fp, fn, filtered_matches)
64 | else:
65 | return fscore
66 |
67 | def cost_matrix(rec, gt, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold):
68 |
69 | print "Computing matching costs..."
70 |
71 | rec_locations = pre_post_locations(rec, gt_segmentation)
72 | gt_locations = pre_post_locations(gt, gt_segmentation)
73 |
74 | rec_labels = pre_post_labels(rec_locations, gt_segmentation)
75 | gt_labels = pre_post_labels(gt_locations, gt_segmentation)
76 |
77 | size = max(len(rec_locations), len(gt_locations))
78 | costs = np.zeros((size, size), dtype=np.float)
79 | costs[:] = 2*matching_threshold
80 | num_potential_matches = 0
81 | for i in range(len(rec_locations)):
82 | for j in range(len(gt_locations)):
83 | c = cost(rec_locations[i], gt_locations[j], rec_labels[i], gt_labels[j], matching_threshold)
84 | costs[i,j] = c
85 | if c <= matching_threshold:
86 | num_potential_matches += 1
87 |
88 | print str(num_potential_matches) + " potential matches found"
89 |
90 | return costs
91 |
92 | def pre_post_locations(annotations, gt_segmentation):
93 | """Get the locations of the annotations relative to the ground truth offset."""
94 |
95 | locations = annotations.locations()
96 | shift = sub(annotations.offset, gt_segmentation.offset)
97 |
98 | return [
99 | (add(annotations.get_annotation(pre_id)[1], shift), add(annotations.get_annotation(post_id)[1], shift)) for (pre_id, post_id) in annotations.pre_post_partners
100 | ]
101 |
102 | def pre_post_labels(locations, segmentation):
103 |
104 | return [ (segmentation[pre], segmentation[post]) for (pre, post) in locations ]
105 |
106 |
107 | def cost(pre_post_location1, pre_post_location2, labels1, labels2, matching_threshold):
108 |
109 | max_cost = 2*matching_threshold
110 |
111 | # pairs do not link the same segments
112 | if labels1 != labels2:
113 | return max_cost
114 |
115 | pre_dist = distance(pre_post_location1[0], pre_post_location2[0])
116 | post_dist = distance(pre_post_location1[1], pre_post_location2[1])
117 |
118 | if pre_dist > matching_threshold or post_dist > matching_threshold:
119 | return max_cost
120 |
121 | return 0.5*(pre_dist + post_dist)
122 |
123 | def distance(a, b):
124 | return np.linalg.norm(np.array(list(a))-np.array(list(b)))
125 |
126 | def add(a, b):
127 | return tuple([a[d] + b[d] for d in range(len(b))])
128 |
129 | def sub(a, b):
130 | return tuple([a[d] - b[d] for d in range(len(b))])
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/voi.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 |
3 | # Evaluation code courtesy of Juan Nunez-Iglesias, taken from
4 | # https://github.com/janelia-flyem/gala/blob/master/gala/evaluate.py
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
8 |
9 | def voi(reconstruction, groundtruth, ignore_reconstruction=[], ignore_groundtruth=[0]):
10 | """Return the conditional entropies of the variation of information metric. [1]
11 |
12 | Let X be a reconstruction, and Y a ground truth labelling. The variation of
13 | information between the two is the sum of two conditional entropies:
14 |
15 | VI(X, Y) = H(X|Y) + H(Y|X).
16 |
17 | The first one, H(X|Y), is a measure of oversegmentation, the second one,
18 | H(Y|X), a measure of undersegmentation. These measures are referred to as
19 | the variation of information split or merge error, respectively.
20 |
21 | Parameters
22 | ----------
23 | seg : np.ndarray, int type, arbitrary shape
24 | A candidate segmentation.
25 | gt : np.ndarray, int type, same shape as `seg`
26 | The ground truth segmentation.
27 | ignore_seg, ignore_gt : list of int, optional
28 | Any points having a label in this list are ignored in the evaluation.
29 | By default, only the label 0 in the ground truth will be ignored.
30 |
31 | Returns
32 | -------
33 | (split, merge) : float
34 | The variation of information split and merge error, i.e., H(X|Y) and H(Y|X)
35 |
36 | References
37 | ----------
38 | [1] Meila, M. (2007). Comparing clusterings - an information based
39 | distance. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 98, 873-895.
40 | """
41 | (hyxg, hxgy) = split_vi(reconstruction, groundtruth, ignore_reconstruction, ignore_groundtruth)
42 | return (hxgy, hyxg)
43 |
44 | def split_vi(x, y=None, ignore_x=[0], ignore_y=[0]):
45 | """Return the symmetric conditional entropies associated with the VI.
46 |
47 | The variation of information is defined as VI(X,Y) = H(X|Y) + H(Y|X).
48 | If Y is the ground-truth segmentation, then H(Y|X) can be interpreted
49 | as the amount of under-segmentation of Y and H(X|Y) is then the amount
50 | of over-segmentation. In other words, a perfect over-segmentation
51 | will have H(Y|X)=0 and a perfect under-segmentation will have H(X|Y)=0.
52 |
53 | If y is None, x is assumed to be a contingency table.
54 |
55 | Parameters
56 | ----------
57 | x : np.ndarray
58 | Label field (int type) or contingency table (float). `x` is
59 | interpreted as a contingency table (summing to 1.0) if and only if `y`
60 | is not provided.
61 | y : np.ndarray of int, same shape as x, optional
62 | A label field to compare to `x`.
63 | ignore_x, ignore_y : list of int, optional
64 | Any points having a label in this list are ignored in the evaluation.
65 | Ignore 0-labeled points by default.
66 |
67 | Returns
68 | -------
69 | sv : np.ndarray of float, shape (2,)
70 | The conditional entropies of Y|X and X|Y.
71 |
72 | See Also
73 | --------
74 | vi
75 | """
76 | _, _, _ , hxgy, hygx, _, _ = vi_tables(x, y, ignore_x, ignore_y)
77 | # false merges, false splits
78 | return np.array([hygx.sum(), hxgy.sum()])
79 |
80 | def vi_tables(x, y=None, ignore_x=[0], ignore_y=[0]):
81 | """Return probability tables used for calculating VI.
82 |
83 | If y is None, x is assumed to be a contingency table.
84 |
85 | Parameters
86 | ----------
87 | x, y : np.ndarray
88 | Either x and y are provided as equal-shaped np.ndarray label fields
89 | (int type), or y is not provided and x is a contingency table
90 | (sparse.csc_matrix) that may or may not sum to 1.
91 | ignore_x, ignore_y : list of int, optional
92 | Rows and columns (respectively) to ignore in the contingency table.
93 | These are labels that are not counted when evaluating VI.
94 |
95 | Returns
96 | -------
97 | pxy : sparse.csc_matrix of float
98 | The normalized contingency table.
99 | px, py, hxgy, hygx, lpygx, lpxgy : np.ndarray of float
100 | The proportions of each label in `x` and `y` (`px`, `py`), the
101 | per-segment conditional entropies of `x` given `y` and vice-versa, the
102 | per-segment conditional probability p log p.
103 | """
104 | if y is not None:
105 | pxy = contingency_table(x, y, ignore_x, ignore_y)
106 | else:
107 | cont = x
108 | total = float(cont.sum())
109 | # normalize, since it is an identity op if already done
110 | pxy = cont / total
111 |
112 | # Calculate probabilities
113 | px = np.array(pxy.sum(axis=1)).ravel()
114 | py = np.array(pxy.sum(axis=0)).ravel()
115 | # Remove zero rows/cols
116 | nzx = px.nonzero()[0]
117 | nzy = py.nonzero()[0]
118 | nzpx = px[nzx]
119 | nzpy = py[nzy]
120 | nzpxy = pxy[nzx, :][:, nzy]
121 |
122 | # Calculate log conditional probabilities and entropies
123 | lpygx = np.zeros(np.shape(px))
124 | lpygx[nzx] = xlogx(divide_rows(nzpxy, nzpx)).sum(axis=1)
125 | # \sum_x{p_{y|x} \log{p_{y|x}}}
126 | hygx = -(px*lpygx) # \sum_x{p_x H(Y|X=x)} = H(Y|X)
127 |
128 | lpxgy = np.zeros(np.shape(py))
129 | lpxgy[nzy] = xlogx(divide_columns(nzpxy, nzpy)).sum(axis=0)
130 | hxgy = -(py*lpxgy)
131 |
132 | return [pxy] + list(map(np.asarray, [px, py, hxgy, hygx, lpygx, lpxgy]))
133 |
134 | def contingency_table(seg, gt, ignore_seg=[0], ignore_gt=[0], norm=True):
135 | """Return the contingency table for all regions in matched segmentations.
136 |
137 | Parameters
138 | ----------
139 | seg : np.ndarray, int type, arbitrary shape
140 | A candidate segmentation.
141 | gt : np.ndarray, int type, same shape as `seg`
142 | The ground truth segmentation.
143 | ignore_seg : list of int, optional
144 | Values to ignore in `seg`. Voxels in `seg` having a value in this list
145 | will not contribute to the contingency table. (default: [0])
146 | ignore_gt : list of int, optional
147 | Values to ignore in `gt`. Voxels in `gt` having a value in this list
148 | will not contribute to the contingency table. (default: [0])
149 | norm : bool, optional
150 | Whether to normalize the table so that it sums to 1.
151 |
152 | Returns
153 | -------
154 | cont : scipy.sparse.csc_matrix
155 | A contingency table. `cont[i, j]` will equal the number of voxels
156 | labeled `i` in `seg` and `j` in `gt`. (Or the proportion of such voxels
157 | if `norm=True`.)
158 | """
159 | segr = seg.ravel()
160 | gtr = gt.ravel()
161 | ignored = np.zeros(segr.shape, np.bool)
162 | data = np.ones(len(gtr))
163 | for i in ignore_seg:
164 | ignored[segr == i] = True
165 | for j in ignore_gt:
166 | ignored[gtr == j] = True
167 | data[ignored] = 0
168 | cont = sparse.coo_matrix((data, (segr, gtr))).tocsc()
169 | if norm:
170 | cont /= float(cont.sum())
171 | return cont
172 |
173 | def divide_columns(matrix, row, in_place=False):
174 | """Divide each column of `matrix` by the corresponding element in `row`.
175 |
176 | The result is as follows: out[i, j] = matrix[i, j] / row[j]
177 |
178 | Parameters
179 | ----------
180 | matrix : np.ndarray, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix, shape (M, N)
181 | The input matrix.
182 | column : a 1D np.ndarray, shape (N,)
183 | The row dividing `matrix`.
184 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
185 | Do the computation in-place.
186 |
187 | Returns
188 | -------
189 | out : same type as `matrix`
190 | The result of the row-wise division.
191 | """
192 | if in_place:
193 | out = matrix
194 | else:
195 | out = matrix.copy()
196 | if type(out) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
197 | if type(out) == sparse.csc_matrix:
198 | convert_to_csc = True
199 | out = out.tocsr()
200 | else:
201 | convert_to_csc = False
202 | row_repeated = np.take(row, out.indices)
203 | nz = out.data.nonzero()
204 | out.data[nz] /= row_repeated[nz]
205 | if convert_to_csc:
206 | out = out.tocsc()
207 | else:
208 | out /= row[np.newaxis, :]
209 | return out
210 |
211 | def divide_rows(matrix, column, in_place=False):
212 | """Divide each row of `matrix` by the corresponding element in `column`.
213 |
214 | The result is as follows: out[i, j] = matrix[i, j] / column[i]
215 |
216 | Parameters
217 | ----------
218 | matrix : np.ndarray, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix, shape (M, N)
219 | The input matrix.
220 | column : a 1D np.ndarray, shape (M,)
221 | The column dividing `matrix`.
222 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
223 | Do the computation in-place.
224 |
225 | Returns
226 | -------
227 | out : same type as `matrix`
228 | The result of the row-wise division.
229 | """
230 | if in_place:
231 | out = matrix
232 | else:
233 | out = matrix.copy()
234 | if type(out) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
235 | if type(out) == sparse.csr_matrix:
236 | convert_to_csr = True
237 | out = out.tocsc()
238 | else:
239 | convert_to_csr = False
240 | column_repeated = np.take(column, out.indices)
241 | nz = out.data.nonzero()
242 | out.data[nz] /= column_repeated[nz]
243 | if convert_to_csr:
244 | out = out.tocsr()
245 | else:
246 | out /= column[:, np.newaxis]
247 | return out
248 |
249 | def xlogx(x, out=None, in_place=False):
250 | """Compute x * log_2(x).
251 |
252 | We define 0 * log_2(0) = 0
253 |
254 | Parameters
255 | ----------
256 | x : np.ndarray or scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix
257 | The input array.
258 | out : same type as x (optional)
259 | If provided, use this array/matrix for the result.
260 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
261 | Operate directly on x.
262 |
263 | Returns
264 | -------
265 | y : same type as x
266 | Result of x * log_2(x).
267 | """
268 | if in_place:
269 | y = x
270 | elif out is None:
271 | y = x.copy()
272 | else:
273 | y = out
274 | if type(y) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
275 | z = y.data
276 | else:
277 | z = y
278 | nz = z.nonzero()
279 | z[nz] *= np.log2(z[nz])
280 | return y
281 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/*Filtered Mask.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/*Filtered Mask.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/*Visualize Boundary.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/*Visualize Boundary.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/6p.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/6p.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/acc.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/acc.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/err.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/err.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/loss.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/loss.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/n.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/res window.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/res window.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/rot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/rot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/io/CremiFile.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import h5py
2 | import numpy as np
3 | from Annotations import *
4 | from Volume import *
5 |
6 | class CremiFile(object):
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, filename, mode):
9 |
10 | self.h5file = h5py.File(filename, mode)
11 |
12 | if mode == "w" or mode == "a":
13 | self.h5file["/"].attrs["file_format"] = "0.2"
14 |
15 | def __create_group(self, group):
16 |
17 | path = "/"
18 | for d in group.split("/"):
19 | path += d + "/"
20 | try:
21 | self.h5file.create_group(path)
22 | except ValueError:
23 | pass
24 |
25 | def __create_dataset(self, path, data, dtype, compression = None):
26 | """Wrapper around h5py's create_dataset. Creates the group, if not
27 | existing. Deletes a previous dataset, if existing and not compatible.
28 | Otherwise, replaces the dataset.
29 | """
30 |
31 | group = "/".join(path.split("/")[:-1])
32 | ds_name = path.split("/")[-1]
33 |
34 | self.__create_group(group)
35 |
36 | if ds_name in self.h5file[group]:
37 |
38 | ds = self.h5file[path]
39 | if ds.dtype == dtype and ds.shape == np.array(data).shape:
40 | print "overwriting existing dataset"
41 | self.h5file[path][:] = data[:]
42 | return
43 |
44 | del self.h5file[path]
45 |
46 | self.h5file.create_dataset(path, data=data, dtype=dtype, compression=compression)
47 |
48 | def write_volume(self, volume, ds_name, dtype):
49 |
50 | self.__create_dataset(ds_name, data=volume.data, dtype=dtype, compression="gzip")
51 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["resolution"] = volume.resolution
52 | if volume.comment is not None:
53 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["comment"] = str(volume.comment)
54 | if tuple(volume.offset) != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
55 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["offset"] = volume.offset
56 |
57 | def read_volume(self, ds_name):
58 |
59 | volume = Volume(self.h5file[ds_name])
60 |
61 | volume.resolution = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["resolution"]
62 | if "offset" in self.h5file[ds_name].attrs:
63 | volume.offset = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["offset"]
64 | if "comment" in self.h5file[ds_name].attrs:
65 | volume.comment = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["comment"]
66 |
67 | return volume
68 |
69 | def __has_volume(self, ds_name):
70 |
71 | return ds_name in self.h5file
72 |
73 | def write_raw(self, raw):
74 | """Write a raw volume.
75 | """
76 |
77 | self.write_volume(raw, "/volumes/raw", np.uint8)
78 |
79 | def write_neuron_ids(self, neuron_ids):
80 | """Write a volume of segmented neurons.
81 | """
82 |
83 | self.write_volume(neuron_ids, "/volumes/labels/neuron_ids", np.uint64)
84 |
85 | def write_clefts(self, clefts):
86 | """Write a volume of segmented synaptic clefts.
87 | """
88 |
89 | self.write_volume(clefts, "/volumes/labels/clefts", np.uint64)
90 |
91 | def write_annotations(self, annotations):
92 | """Write pre- and post-synaptic site annotations.
93 | """
94 |
95 | if len(annotations.ids()) == 0:
96 | return
97 |
98 | self.__create_group("/annotations")
99 | if tuple(annotations.offset) != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
100 | self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs["offset"] = annotations.offset
101 |
102 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/ids", data=annotations.ids(), dtype=np.uint64)
103 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/types", data=annotations.types(), dtype=h5py.special_dtype(vlen=unicode), compression="gzip")
104 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/locations", data=annotations.locations(), dtype=np.double)
105 |
106 | if len(annotations.comments) > 0:
107 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/comments/target_ids", data=annotations.comments.keys(), dtype=np.uint64)
108 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/comments/comments", data=annotations.comments.values(), dtype=h5py.special_dtype(vlen=unicode))
109 |
110 | if len(annotations.pre_post_partners) > 0:
111 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/presynaptic_site/partners", data=annotations.pre_post_partners, dtype=np.uint64)
112 |
113 | def has_raw(self):
114 | """Check if this file contains a raw volume.
115 | """
116 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/raw")
117 |
118 | def has_neuron_ids(self):
119 | """Check if this file contains neuron ids.
120 | """
121 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids")
122 |
123 | def has_neuron_ids_confidence(self):
124 | """Check if this file contains confidence information about neuron ids.
125 | """
126 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids_confidence")
127 |
128 | def has_clefts(self):
129 | """Check if this file contains synaptic clefts.
130 | """
131 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/clefts")
132 |
133 | def has_annotations(self):
134 | """Check if this file contains synaptic partner annotations.
135 | """
136 | return "/annotations" in self.h5file
137 |
138 | def has_segment_annotations(self):
139 | """Check if this file contains segment annotations.
140 | """
141 | return "/annotations" in self.h5file
142 |
143 | def read_raw(self):
144 | """Read the raw volume.
145 | Returns a Volume.
146 | """
147 |
148 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/raw")
149 |
150 | def read_neuron_ids(self):
151 | """Read the volume of segmented neurons.
152 | Returns a Volume.
153 | """
154 |
155 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids")
156 |
157 | def read_neuron_ids_confidence(self):
158 | """Read confidence information about neuron ids.
159 | Returns Confidences.
160 | """
161 |
162 | confidences = Confidences(num_levels=2)
163 | if not self.has_neuron_ids_confidence():
164 | return confidences
165 |
166 | data = self.h5file["/volumes/labels/neuron_ids_confidence"]
167 | i = 0
168 | while i < len(data):
169 | level = data[i]
170 | i += 1
171 | num_ids = data[i]
172 | i += 1
173 | confidences.add_all(level, data[i:i+num_ids])
174 | i += num_ids
175 |
176 | return confidences
177 |
178 | def read_clefts(self):
179 | """Read the volume of segmented synaptic clefts.
180 | Returns a Volume.
181 | """
182 |
183 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/labels/clefts")
184 |
185 | def read_annotations(self):
186 | """Read pre- and post-synaptic site annotations.
187 | """
188 |
189 | annotations = Annotations()
190 |
191 | if not "/annotations" in self.h5file:
192 | return annotations
193 |
194 | offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
195 | if "offset" in self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs:
196 | offset = self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs["offset"]
197 | annotations.offset = offset
198 |
199 | ids = self.h5file["/annotations/ids"]
200 | types = self.h5file["/annotations/types"]
201 | locations = self.h5file["/annotations/locations"]
202 | for i in range(len(ids)):
203 | annotations.add_annotation(ids[i], types[i], locations[i])
204 |
205 | if "comments" in self.h5file["/annotations"]:
206 | ids = self.h5file["/annotations/comments/target_ids"]
207 | comments = self.h5file["/annotations/comments/comments"]
208 | for (id, comment) in zip(ids, comments):
209 | annotations.add_comment(id, comment)
210 |
211 | if "presynaptic_site/partners" in self.h5file["/annotations"]:
212 | pre_post = self.h5file["/annotations/presynaptic_site/partners"]
213 | for (pre, post) in pre_post:
214 | annotations.set_pre_post_partners(pre, post)
215 |
216 | return annotations
217 |
218 | def close(self):
219 |
220 | self.h5file.close()
221 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/io/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from CremiFile import *
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/Resnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
4 |
5 |
6 | def residualLayer2(conv2d1, norm2d, input, nChannels, nOutChannels=False, stride=1, conv2d2=False):
7 | """ Deep Residual Network
8 | https://github.com/gcr/torch-residual-networks
9 |
10 | giving stack of 2 layers as a block providing shortcuts."""
11 |
12 |
13 | if not nOutChannels:
14 | nOutChannels = nChannels
15 | if not conv2d2:
16 | conv2d2 = conv2d1
17 |
18 | # part 1: conv
19 | net = conv2d1(input)
20 | net = norm2d(net) # learnable parameters
21 | net = F.relu(net)
22 | net = conv2d2(net)
23 |
24 |
25 | # part 2: identity / skip connection
26 | skip = input
27 | if stride > 1: # optional downsampling
28 | skip = L.SpatialAveragePooling(1, 1, stride, stride).forward(skip.cpu().data)
29 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
30 | if nOutChannels > nChannels: # optional padding
31 | skip = L.Padding(1, (nOutChannels - nChannels), 3).forward(skip.cpu().data)
32 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
33 | elif nOutChannels < nChannels: # optional narrow
34 | skip = L.Narrow(2, 1, nOutChannels).forward(skip.cpu().data)
35 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
36 |
37 |
38 | # H(x) + x
39 | net = norm2d(net)
40 | #print "skip: " + str(skip.data.size())
41 | #print "net: " + str(net.data.size())
42 | net = torch.add(skip, net)
43 | # net = F.relu(net) # relu here ? see: http://www.gitxiv.com/comments/7rffyqcPLirEEsmpX
44 | #net = norm2d(net) # ==========================BN after add or before ???
45 |
46 | return net
47 |
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 | class DeepResNet18(nn.Module):
55 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=3, padding=1):
56 | super(DeepResNet18, self).__init__()
57 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
58 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
59 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
60 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
61 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
62 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
63 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
64 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
65 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
66 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
67 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
68 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
69 | self.linear = nn.Linear(256, 2)
70 |
71 | def forward(self, x):
72 | # ----> 1, 33, 33
73 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
74 |
75 | # ----> 32, 33, 33 First Group 2X
76 | for i in range(2): x = residualLayer2(self.conv2, self.norm1, x, 32)
77 |
78 | # ----> 64, 17, 17 Second Group 2X
79 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv3, self.norm2, x, 32, 64, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv4)
80 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv4, self.norm2, x, 64)
81 |
82 | # ----> 128, 9, 9 Third Group 2X
83 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv5, self.norm3, x, 64, 128, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv6)
84 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv6, self.norm3, x, 128)
85 |
86 | # ----> 256, 5, 5 Fourth Group 2X
87 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv7, self.norm4, x, 128, 256, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv8)
88 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv8, self.norm4, x, 256)
89 |
90 | # ----> 256, 5, 5 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
91 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(5,5)(x)
92 | x = x.view(-1, 256)
93 | x = self.linear(x)
94 |
95 |
96 | return x
97 |
98 |
99 | class DeepResNet34(nn.Module):
100 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=5, padding=2):
101 | super(DeepResNet34, self).__init__()
102 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
103 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
104 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
105 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
106 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
107 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
108 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
109 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
110 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
111 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
112 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
113 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
114 | self.linear = nn.Linear(256, 2)
115 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
116 |
117 | def forward(self, x):
118 | # ------> 65 * 65
119 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
120 | x = self.pool(x) # ================= max pooling ??
121 | # ------> 32 * 32
122 | for i in range(3): x = residualLayer2(self.conv2, self.norm1, x, 32)
123 | # ------> 32 * 32
124 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv3, self.norm2, x, 32, 64, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv4)
125 | for i in range(4-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv4, self.norm2, x, 64)
126 |
127 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv5, self.norm3, x, 64, 128, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv6)
128 | for i in range(6-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv6, self.norm3, x, 128)
129 |
130 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv7, self.norm4, x, 128, 256, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv8)
131 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv8, self.norm4, x, 256)
132 |
133 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(8,8)(x)
134 | x = x.view(-1, 256)
135 | x = self.linear(x)
136 |
137 |
138 | return x
139 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/Resnet_3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | class DeepResNet101(nn.Module):
8 |
9 | """using bottle-neck building block """
10 |
11 |
12 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=7, padding=3):
13 | super(DeepResNet101, self).__init__()
14 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
15 | self.conv2_ = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 1, stride=2)
16 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 5, padding=2)
17 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
18 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, 128, 5, padding=2)
19 | self.conv5_ = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 1, stride=2)
20 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 5, padding=2)
21 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
22 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(64, 256, 5, padding=2)
23 | self.conv8_ = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 1, stride=2)
24 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 5, padding=2)
25 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
26 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(128, 512, 5, padding=2)
27 | self.conv11_ = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 1, stride=2)
28 | self.conv11 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, 5, padding=2)
29 | self.conv12 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
30 | self.conv13 = nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, 5, padding=2)
31 |
32 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
33 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
34 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
35 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
36 | self.norm5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
37 | self.norm6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
38 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
39 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 128)
40 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(128, 2)
41 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
42 |
43 | def forward(self, x):
44 | # ----> 1, 129, 129
45 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
46 | x = self.pool(x) # max pooling ? 3x3 s=2
47 |
48 | # ----> 32, 64, 64 First Group
49 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2_, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 32, 32, 128, stride=2)
50 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 128, 32, 128)
51 |
52 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5_, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 128, 64, 256, stride=2)
53 | for i in range(8-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 256, 64, 256)
54 |
55 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8_, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 256, 128, 512, stride=2)
56 | for i in range(36-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 512, 128, 512)
57 |
58 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11_, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 512, 256, 1024, stride=2)
59 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 1024, 256, 1024)
60 |
61 | # ----> 1024, 4, 4 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
62 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(4,4)(x)
63 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
64 | x = self.linear1(x)
65 | x = F.dropout(x) # ==============================
66 | x = self.linear2(x)
67 | x = self.linear3(x)
68 |
69 | return x
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | class DeepResNet50(nn.Module):
76 |
77 | """using bottle-neck building block """
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=7, padding=3): #=============== conv window size 5/22 9:24pm
82 | super(DeepResNet50, self).__init__()
83 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
84 | self.conv2_ = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 1, stride=2)
85 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 5, padding=2)
86 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
87 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, 128, 5, padding=2)
88 | self.conv5_ = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 1, stride=2)
89 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 5, padding=2)
90 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
91 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(64, 256, 5, padding=2)
92 | self.conv8_ = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 1, stride=2)
93 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 5, padding=2)
94 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
95 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(128, 512, 5, padding=2)
96 | self.conv11_ = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 1, stride=2)
97 | self.conv11 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, 5, padding=2)
98 | self.conv12 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
99 | self.conv13 = nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, 5, padding=2)
100 |
101 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
102 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
103 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
104 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
105 | self.norm5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
106 | self.norm6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
107 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
108 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 128)
109 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(128, 2)
110 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
111 |
112 |
113 | def forward(self, x):
114 | # ----> 1, 129, 129
115 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
116 | x = self.pool(x) # ================= max pooling ? better without here
117 |
118 |
119 | # ----> 32, 64, 64 First Group
120 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2_, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 32, 32, 128, stride=2)
121 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 128, 32, 128)
122 |
123 | # ----> 128, 32, 32 Second Group
124 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5_, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 128, 64, 256, stride=2)
125 | for i in range(4-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 256, 64, 256)
126 |
127 | # ----> 256, 16, 16 Third Group
128 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8_, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 256, 128, 512, stride=2)
129 | for i in range(6-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 512, 128, 512)
130 |
131 | # ----> 512, 8,8 Fourth Group
132 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11_, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 512, 256, 1024, stride=2)
133 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 1024, 256, 1024)
134 |
135 | # ----> 1024, 4, 4 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
136 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(4,4)(x)
137 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
138 | x = self.linear1(x)
139 | x = F.dropout(x) # ==============================
140 | x = self.linear2(x)
141 | x = self.linear3(x)
142 |
143 | return x
144 |
145 |
146 | # stack of 3 layers providing shortcuts
147 | def residualLayer3(input, conv2d1, conv2d2, conv2d3, norm2d1, norm2d2, inChannels, hiddenChannels, outChannels, stride=1):
148 | net = conv2d1(input) # 1x1
149 | net = norm2d1(net)
150 | net = F.relu(net)
151 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout within blocks ???? 8.21 9pm
152 |
153 | net = conv2d2(net) # kernel 3x3 or 5x5
154 | net = norm2d1(net)
155 | net = F.relu(net)
156 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout ???? 8.21 9pm
157 |
158 | net = conv2d3(net) # 1x1
159 |
160 | skip = input
161 | #print "input: " + str(skip.data.size())
162 | if stride > 1:
163 | skip = L.SpatialAveragePooling(1, 1, stride, stride).forward(skip.cpu().data)
164 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
165 | if outChannels > inChannels:
166 | skip = L.Padding(1, (outChannels - inChannels), 3).forward(skip.cpu().data)
167 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
168 | elif outChannels < inChannels:
169 | skip = L.Narrow(2, 1, outChannels).forward(skip.cpu().data)
170 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
171 |
172 | #net = norm2d2(net)
173 | #print "skip: " + str(skip.data.size())
174 | #print "net: " + str(net.data.size())
175 | net = norm2d2(torch.add(skip, net)) # ==========================BN after add or before ???
176 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout ????
177 | return net
178 |
179 |
180 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/type/Annotations.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class Annotations:
2 |
3 | def __init__(self, offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)):
4 |
5 | self.__types = {}
6 | self.__locations = {}
7 | self.comments = {}
8 | self.pre_post_partners = []
9 | self.offset = offset
10 |
11 | def __check(self, id):
12 | if not id in self.__types.keys():
13 | raise "there is no annotation with id " + str(id)
14 |
15 | def add_annotation(self, id, type, location):
16 | """Add a new annotation.
17 |
18 | Parameters
19 | ----------
20 |
21 | id: int
22 | The ID of the new annotation.
23 |
24 | type: string
25 | A string denoting the type of the annotation. Use
26 | "presynaptic_site" or "postsynaptic_site" for pre- and
27 | post-synaptic annotations, respectively.
28 |
29 | location: tuple, float
30 | The location of the annotation, relative to the offset.
31 | """
32 |
33 | self.__types[id] = type.encode('utf8')
34 | self.__locations[id] = location
35 |
36 | def add_comment(self, id, comment):
37 | """Add a comment to an annotation.
38 | """
39 |
40 | self.__check(id)
41 | self.comments[id] = comment.encode('utf8')
42 |
43 | def set_pre_post_partners(self, pre_id, post_id):
44 | """Mark two annotations as pre- and post-synaptic partners.
45 | """
46 |
47 | self.__check(pre_id)
48 | self.__check(post_id)
49 | self.pre_post_partners.append((pre_id, post_id))
50 |
51 | def ids(self):
52 | """Get the ids of all annotations.
53 | """
54 |
55 | return self.__types.keys()
56 |
57 | def types(self):
58 | """Get the types of all annotations.
59 | """
60 |
61 | return self.__types.values()
62 |
63 | def locations(self):
64 | """Get the locations of all annotations. Locations are in world units,
65 | relative to the offset.
66 | """
67 |
68 | return self.__locations.values()
69 |
70 | def get_annotation(self, id):
71 | """Get the type and location of an annotation by its id.
72 | """
73 |
74 | self.__check(id)
75 | return (self.__types[id], self.__locations[id])
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/type/Volume.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class Volume():
2 |
3 | def __init__(self, data, resolution = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0), offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0), comment = ""):
4 | self.data = data
5 | self.resolution = resolution
6 | self.offset = offset
7 | self.comment = comment
8 |
9 | def __getitem__(self, location):
10 | """Get the closest value of this volume to the given location. The
11 | location is in world units, relative to the volumes offset.
12 |
13 | This method takes into account the resolution of the volume. An
14 | IndexError exception is raised if the location is not contained in this
15 | volume.
16 |
17 | To access the raw pixel values, use the `data` attribute.
18 | """
19 |
20 | i = tuple([ round(location[d]/self.resolution[d]) for d in range(len(location)) ])
21 |
22 | if min(i) >= 0:
23 | try:
24 | return self.data[i]
25 | except IndexError as e:
26 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume: " + str(e))
27 |
28 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume")
29 |
30 | def __setitem__(self, location, value):
31 | """Set the closest value of this volume to the given location. The
32 | location is in world units, relative to the volumes offset.
33 |
34 | This method takes into account the resolution of the volume. An
35 | IndexError exception is raised if the location is not contained in this
36 | volume.
37 |
38 | To access the raw pixel values, use the `data` attribute.
39 | """
40 |
41 | i = tuple([ round(location[d]/self.resolution[d]) for d in range(len(location)) ])
42 |
43 | if min(i) >= 0:
44 | try:
45 | self.data[i] = value
46 | return
47 | except IndexError as e:
48 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume: " + str(e))
49 |
50 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume")
51 |
52 |
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
33 |
34 | ### Future work
35 |
36 | - The neighbor area of the boundaries was avoided in this experiment, however the boundary pixels from other organels (intracellular organels) should also be avoided. These pixels could be easily treated as target neuron boundaries which are actually not. The approach to address this challenge can be to pre-train a network to recognize these intracellular boundaries and filter out these pixels when creating training batches for the segmentation task.
37 |
38 | - the raw is originally a 3D image of size 125 * 1250 * 1250. I started by treating each layer in deapth 125 as an independent sample and trained my network with images in 2D sections. However, in later stages of experiments (which i was not able to do due to the time limit of my project), the third deimension should be considered to address the correlation between the neuron pixels at depth.
39 |
40 | ## Dependencies
41 |
42 | * python
43 | * pytorch
44 | * numpy
45 | * matplotlib
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | import torch.optim as optim
5 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
6 | from torch.autograd import Variable
7 |
8 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, TensorDataset
9 | import torchvision
10 | from torchvision import transforms, datasets
11 | import torchvision.models as models
12 | import numpy as np
13 | from tempfile import TemporaryFile
14 | import matplotlib
15 | matplotlib.use('Agg')
16 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
17 | import scipy.ndimage as ndimage
18 | from scipy.ndimage.interpolation import rotate
19 | import time
20 | import os
21 | import random
22 |
23 | from Annotations import *
24 | from Volume import *
25 | from CremiFile import *
26 | from voi import voi
27 | from rand import adapted_rand
28 | plt.style.use('ggplot')
29 |
30 | from models.Resnet_3 import *
31 | from models.Resnet import *
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 | print('')
36 | print('DATASET LOADING ...')
37 | print('')
38 | emdset = CremiFile('sample_B_20160501.hdf', 'r')
39 |
40 | #Check the content of the datafile
41 | print "Has raw: " + str(emdset.has_raw())
42 | print "Has neuron ids: " + str(emdset.has_neuron_ids())
43 | print "Has clefts: " + str(emdset.has_clefts())
44 | print "Has annotations: " + str(emdset.has_annotations())
45 |
46 |
47 | #Read volume and annotation
48 | raw = emdset.read_raw()
49 | neuron_ids = emdset.read_neuron_ids()
50 | clefts = emdset.read_clefts()
51 | annotations = emdset.read_annotations()
52 |
53 | print("")
54 | print "Read raw: " + str(raw) + \
55 | ", resolution " + str(raw.resolution) + \
56 | ", offset " + str(raw.offset) + \
57 | ", data size " + str(raw.data.shape) + \
58 | ("" if raw.comment == None else ", comment \"" + raw.comment + "\"")
59 |
60 | print "Read neuron_ids: " + str(neuron_ids) + \
61 | ", resolution " + str(neuron_ids.resolution) + \
62 | ", offset " + str(neuron_ids.offset) + \
63 | ", data size " + str(neuron_ids.data.shape) + \
64 | ("" if neuron_ids.comment == None else ", comment \"" + neuron_ids.comment + "\"")
65 |
66 | print "Read clefts: " + str(clefts) + \
67 | ", resolution " + str(clefts.resolution) + \
68 | ", offset " + str(clefts.offset) + \
69 | ", data size " + str(clefts.data.shape) + \
70 | ("" if clefts.comment == None else ", comment \"" + clefts.comment + "\"")
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | def mask_filtered(raw, neuron_ids):
76 | """
77 | Image boudnary dilation
78 | Compute mask on each depth for un-selectable dilated(6X) boundary pixels (labeled as value 200.),
79 | the selectable background (0.) and actual boundary (100.) pixels
80 |
81 | return(numpy array): mask of shape 125,1250,1250
82 | """
83 | print ''
84 | print ''
85 | print 'building mask-5X from raw dataset...'
86 | since = time.time()
87 |
88 | d, h, w = raw.data.shape
89 | mask = np.empty([d, h, w]).astype('float32')
90 | for i in range(d):
91 | for j in range(h):
92 | for k in range(w):
93 | pixel = neuron_ids.data[i, j, k]
94 | if check_boundary(pixel, i, j, k, neuron_ids):
95 | mask[i, j, k] = 100
96 | else:
97 | mask[i, j, k] = 0
98 | if (i + 1) % 1 == 0:
99 | print str(0.8 * (i + 1)) + '% done'
100 |
101 | mask_dilated = ndimage.binary_dilation(mask, iterations=7).astype(mask.dtype)
102 | mask_filtered = 200 * mask_dilated - mask
103 |
104 | filter_time = time.time()
105 | time_elapsed = filter_time - since
106 | print('Mask complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format(
107 | time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60))
108 |
109 |
110 | print 'save to maskfile7X.npy'
111 | np.save('maskfile7X.npy', mask_filtered)
112 | print 'saved'
113 |
114 |
115 | def check_boundary(pixel, x, y, z, neuron_ids):
116 | """
117 | Check if a pixel at position (x,y,z) is labeled
118 | as boundary/non-boundary in neuron_ids.
119 |
120 | return(boolean): boundary
121 | """
122 | max_z = neuron_ids.data.shape[2] - 1
123 | max_y = neuron_ids.data.shape[1] - 1
124 | a = neuron_ids.data[x, y, z - 1] if z > 0 else pixel
125 | b = neuron_ids.data[x, y, z + 1] if z < max_z else pixel
126 | c = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z] if y > 0 else pixel
127 | d = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z] if y < max_y else pixel
128 | e = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z - 1] if (y > 0 and z > 0) else pixel
129 | f = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z + 1] if (y > 0 and z < max_z) else pixel
130 | g = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z - 1] if (y < max_y and z > 0) else pixel
131 | h = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z + 1] if (y < max_y and z < max_z) else pixel
132 |
133 | neighbors = [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h]
134 | boundary = False
135 | for neighbor in neighbors:
136 | if pixel != neighbor:
137 | boundary = True
138 |
139 | return boundary
140 |
141 |
142 | # Seed a random number generator
143 | #seed = 24102016
144 | #rng = np.random.RandomState(seed)
145 | def random_rotation(inputs):
146 | """Randomly rotates a subset of images in a batch.
147 | reference: https://github.com/CSTR-Edinburgh/mlpractical/blob/mlp2016-7/master/notebooks/05_Non-linearities_and_regularisation.ipynb
148 |
149 | * chooses 30-50% of the images in the batch at random
150 | * for each image in the 30-50% chosen, rotates the image by a random angle in [-60, 60]
151 | * returns a new array of size (129, 129) in which the rows corresponding to the 25% chosen images are the vectors corresponding to the new randomly rotated images, while the remaining rows correspond to the original images.
152 | Args:
153 | inputs: Input image batch, an array of shape (129, 129).
154 |
155 | Returns:
156 | An array of shape (129, 129) corresponding to a copy
157 | of the original `inputs` array that was randomly selected
158 | to be rotated by a random angle. The original `inputs`
159 | array should not be modified.
160 | """
161 |
162 | new_ims = np.zeros(inputs.shape).astype('float32')
163 | indices = random.randint(-1,1)
164 | angles = random.uniform(-30., 30.)
165 | if indices == 0:
166 | rotate(inputs, angles, output = new_ims, order=1, reshape=False)
167 |
168 | return new_ims
169 |
170 |
171 |
172 |
173 | #mask_filtered(raw, neuron_ids) # used only when the first time of training
174 | mask = np.load('maskfile5X.npy')
175 | print ''
176 | print 'mask loaded'
177 |
178 | class NeuronSegmenDataset(Dataset):
179 | """Raw pixel and its label.
180 | Dataset splitted into 80,000 training and 20,000 validation set
181 | """
182 |
183 | def __init__(self, raw, neuron_ids, mask, phase, transform=None):
184 | """
185 | Args:
186 | raw(Volume): raw
187 | neuron_ids(Volume): neuron segmentation labels
188 | mask(numpy ndarray): filtered mask
189 | phase(String): 'train' or 'val'
190 | transform(callable, optional): optional data augmentation to be applied
191 | """
192 |
193 | self.phase = phase
194 | self.raw = raw
195 | self.neuron_ids = neuron_ids
196 | self.mask = mask
197 | self.transform = transform
198 |
199 | def __len__(self):
200 | """ length of the dataset """
201 | if self.phase == 'train':
202 | x = 80000
203 | else:
204 | x = 20000
205 |
206 | return x
207 |
208 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
209 | """
210 | Return 33*33 patches for each raw pixel at the center
211 | positive if boundary pixel, negative if non-boundary pixel
212 | """
213 | depth = self.raw.data.shape[0]
214 | size = self.raw.data.shape[1]
215 |
216 |
217 | while True:
218 | d = random.randint(0, depth - 1)
219 | h = random.randint(64, size - 65)
220 | w = random.randint(64, size - 65)
221 | ids_pixel = self.neuron_ids.data[d, h, w]
222 | pixel = self.mask[d, h, w]
223 |
224 | if idx % 2 == 0: #control half samples to be boundary pixels
225 | if pixel == 100.:
226 | raw_batch = self.raw.data[d][h - 64:h + 65, w - 64:w + 65].astype(
227 | 'float32') # crop a 129*129 patch
228 |
229 |
230 | if self.transform:
231 | raw_batch = self.transform(raw_batch)
232 |
233 | raw_batch = raw_batch.reshape([1, 129, 129])
234 | raw_batch = torch.from_numpy(raw_batch)
235 | sample = (raw_batch, 0)
236 |
237 | break
238 | elif pixel == 0.: # the other half as non-boundary pixel
239 | raw_batch = self.raw.data[d][h - 64:h + 65, w - 64:w + 65].astype(
240 | 'float32') # crop 33*33 patch
241 | raw_batch = raw_batch.reshape([1, 129, 129])
242 |
243 | if self.transform:
244 | raw_batch = self.transform(raw_batch)
245 |
246 | raw_batch = torch.from_numpy(raw_batch)
247 | sample = (raw_batch, 1)
248 |
249 | break
250 | return sample
251 |
252 |
253 | batch_size = 100
254 | emdset_seg = {x: NeuronSegmenDataset(raw, neuron_ids, mask, x, transform=random_rotation)
255 | for x in ['train', 'val']}
256 | emdset_loaders = {x: DataLoader(emdset_seg[x], batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
257 | for x in ['train', 'val']}
258 | dset_sizes = {x: len(emdset_seg[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']}
259 | dset_classes = ['boundary', 'non-b']
260 | use_gpu = torch.cuda.is_available()
261 |
262 | print "Load num of batches: train " + str(len(emdset_loaders['train'])) + \
263 | ' validation ' + str(len(emdset_loaders['val']))
264 |
265 | print ('done')
266 | print ('')
267 |
268 |
269 | class ConvNet(nn.Module):
270 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel= 3, window =2, padding=1):
271 | super(ConvNet, self).__init__()
272 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
273 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
274 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
275 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
276 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
277 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
278 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
279 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
280 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel, padding=padding)
281 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel, padding=padding)
282 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(window)
283 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(2*2*256, 256)
284 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
285 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
286 | self.linear4 = nn.Linear(128, D_out)
287 |
288 | def forward(self, x):
289 | x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
290 | print "conv 1: " + str(x.data.size())
291 | x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
292 | print "conv 2: " + str(x.data.size())
293 | x = self.pool(x)
294 | print "pool 1: " + str(x.data.size())
295 |
296 | x = F.relu(self.conv3(x))
297 | print "conv 3: " + str(x.data.size())
298 | x = F.relu(self.conv4(x))
299 | print "conv 4: " + str(x.data.size())
300 | x = self.pool(x)
301 | print "pool 2: " + str(x.data.size())
302 |
303 | x = F.relu(self.conv5(x))
304 | print "conv 5: " + str(x.data.size())
305 | x = F.relu(self.conv6(x))
306 | print "conv 6: " + str(x.data.size())
307 | x = self.pool(x)
308 | print "pool 3: " + str(x.data.size())
309 |
310 | x = F.relu(self.conv7(x))
311 | print "conv 7: " + str(x.data.size())
312 | x = F.relu(self.conv8(x))
313 | print "conv 8: " + str(x.data.size())
314 | x = self.pool(x)
315 | print "pool 4: " + str(x.data.size())
316 |
317 | x = x.view(-1, 2*2*256)
318 | x = F.relu(self.linear1(x))
319 |
320 | x = F.relu(self.linear3(x))
321 | x = F.relu(self.linear4(x))
322 |
323 | return x
324 |
325 |
326 |
327 | def exp_lr_scheduler(optimizer, epoch, init_lr=0.001, lr_decay_epoch=10):
328 | """Decay learning rate by a factor of 0.1 every 10 epochs"""
329 | lr = init_lr * (0.1**(epoch // lr_decay_epoch))
330 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
331 | param_group['lr'] = lr
332 |
333 | return optimizer
334 |
335 |
336 | def piecewise_scheduler(optimizer, epoch):
337 | if epoch % 50 ==0 :
338 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
339 | lr = param_group['lr'] / 2
340 | param_group['lr'] = lr
341 |
342 | return optimizer
343 |
344 |
345 |
346 | def train_model (model, criterion, optimizer, lr_scheduler=None, num_epochs=100):
347 | since = time.time()
348 | train_voi_split = np.zeros(num_epochs)
349 | train_voi_merge = np.zeros(num_epochs)
350 | train_rand = np.zeros(num_epochs)
351 |
352 | # iterate over epoch
353 | for epoch in range(num_epochs):
354 | print ('Epoch{}/{}'.format(epoch+1, num_epochs))
355 | print ('-' * 10)
356 |
357 |
358 | # train and validation set
359 | for phase in ['train', 'val']:
360 | if phase == 'train':
361 | if lr_scheduler:
362 | optimizer = lr_scheduler(optimizer, epoch + 1)
363 | model.train(True)
364 | else:
365 | model.train(True)
366 |
367 | running_loss = 0.
368 | running_accuracy = 0.
369 | total = 0
370 |
371 | # iterate over each batch
372 | for i, data in enumerate(emdset_loaders[phase]):
373 | inputs, labels = data
374 | if use_gpu:
375 | model = model.cuda()
376 | inputs, labels = Variable(inputs.cuda()), \
377 | Variable(labels.cuda())
378 | else:
379 | inputs, labels = Variable(inputs), Variable(labels)
380 |
381 |
382 | optimizer.zero_grad() # clean gradients in buffer
383 |
384 | outputs = model(inputs)
385 | _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
386 | loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
387 |
388 |
389 | if phase == 'train':
390 | loss.backward()
391 | optimizer.step()
392 |
393 |
394 | running_loss += loss.data[0]
395 | running_accuracy += (predicted == labels.data).sum()
396 |
397 | # visualize random patches
398 | visualize_pred = True
399 | tt = visualize_pred and epoch == num_epochs-1 and phase == 'val' \
400 | and i+1 == len(emdset_loaders['val'])
401 | if tt:
402 | print('visualizing...')
403 | images_so_far = 0
404 | fig = plt.figure()
405 | for j in [6, 15, 38, 41, 86, 99]:
406 | images_so_far += 1
407 | ax = fig.add_subplot(3, 2, images_so_far)
408 | ax.axis('off')
409 | ax.set_title('Pred: {},\n Labeled: {}'.format(dset_classes[int(predicted.cpu().numpy()[j])],
410 | dset_classes[labels.data[j]]))
411 | ax.imshow(inputs.cpu().data[j].view(129,129).numpy())
412 | fig.savefig('6p.png')
413 | print 'done and saved to 6p.png'
414 |
415 |
416 | # normalize by number of batches
417 | running_loss /= (i + 1)
418 | running_accuracy = 100 * running_accuracy / dset_sizes[phase]
419 |
420 | # print statistics
421 | if epoch % 1 == 0:
422 | print('{} Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(
423 | phase, running_loss, running_accuracy
424 | ))
425 | # print "\tvoi split : " + str(train_voi_split)
426 | # print "\tvoi merge : " + str(train_voi_merge)
427 | # print "\tadapted RAND: " + str(train_rand)
428 |
429 | # Visualize the model. raw, labeled, predicted (optional)
430 | visualize = False
431 | if visualize:
432 | print('')
433 | print('Begin to visualize model..')
434 | visualize_model(model)
435 |
436 | time_elapsed = time.time() - train_time
437 | print('Visualizing complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format(
438 | time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60))
439 |
440 |
441 |
442 | def visualize_model(model, i = 80, s = 300):
443 | """ Args:
444 | model: model
445 | i: depth of the raw image to visualize
446 | s: crop the 1250*1250 image to the size of s*s
447 | """
448 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15,6))
449 |
450 | ax_ori = fig.add_subplot(1,3,1)
451 | ax_lab = fig.add_subplot(1,3,2)
452 | ax_pred = fig.add_subplot(1,3,3)
453 |
454 | ax_ori.imshow(raw.data[i][0:s, 0:s])
455 | ax_ori.set_title('raw')
456 | ax_lab.imshow(neuron_ids.data[i][0:s, 0:s])
457 | ax_lab.set_title('labeled')
458 |
459 |
460 | preds = np.empty([s*s])
461 | for j in range(s*s):
462 | pixel = raw.data[i][j/s, j%s]
463 | input = np.random.uniform(-10000, 0, (1, 1, 33, 33)).astype('float32') ## boundary patch: positive
464 | input[0, 0, 16, 16] = pixel
465 | input = torch.from_numpy(input)
466 |
467 | model.train(False)
468 | if use_gpu:
469 | model = model.cuda()
470 | input = Variable(input.cuda())
471 | else:
472 | input = Variable(input)
473 |
474 | outputs = model(input)
475 | _, pred = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
476 | pred = pred.cpu().numpy()
477 | if pred[0] == 0:
478 | preds[j] = 20000
479 | else:
480 | preds[j] = 100
481 |
482 | if j == 30000:
483 | print '1/3 done'
484 | if j == 60000:
485 | print '2/3 done'
486 |
487 | print preds.reshape(s, s)
488 | ax_pred.imshow(preds.reshape((s,s)))
489 | ax_pred.set_title('predicted')
490 |
491 | ax_lab.axis('off')
492 | ax_ori.axis('off')
493 | ax_pred.axis('off')
494 |
495 | plt.show()
496 | fig.savefig('vi.png')
497 | print('saved as vi.png')
498 |
499 |
500 |
501 |
502 |
503 |
504 | # Train
505 | #-----------------------------------------------------------------------
506 | num_classes = 2
507 | num_epochs = 100
508 | #model = ConvNet(num_classes )
509 | #model = DeepResNet18(num_classes)
510 | #model = DeepResNet34(num_classes )
511 | model = DeepResNet50(num_classes)
512 | #model = DeepResNet101(num_classes )
513 | optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0001)
514 | #optimizer = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[2,4,6,8,10], gamma=0.5)
515 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
516 | print('')
517 | print('START TRAINING ...')
518 | print(time.time())
519 | print('ResNet50. 33% 30deg lr50')
520 | train = train_model(model, criterion, optimizer, lr_scheduler=piecewise_scheduler, num_epochs=num_epochs)
521 |
522 |
523 |
524 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Annotations import *
2 | from Volume import *
3 | from NeuronIds import *
4 | from border_mask import *
5 | from CremiFile import *
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/Clefts.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from scipy import ndimage
3 |
4 | class Clefts:
5 |
6 | def __init__(self, test, truth):
7 |
8 | test_clefts = test
9 | truth_clefts = truth
10 |
11 | self.test_clefts_mask = np.equal(test_clefts.data, 0xffffffffffffffff)
12 | self.truth_clefts_mask = np.equal(truth_clefts.data, 0xffffffffffffffff)
13 |
14 | self.test_clefts_edt = ndimage.distance_transform_edt(self.test_clefts_mask, sampling=test_clefts.resolution)
15 | self.truth_clefts_edt = ndimage.distance_transform_edt(self.truth_clefts_mask, sampling=truth_clefts.resolution)
16 |
17 | def count_false_positives(self, threshold = 200):
18 |
19 | mask1 = np.invert(self.test_clefts_mask)
20 | mask2 = self.truth_clefts_edt > threshold
21 | false_positives = self.truth_clefts_edt[np.logical_and(mask1, mask2)]
22 | return false_positives.size
23 |
24 | def count_false_negatives(self, threshold = 200):
25 |
26 | mask1 = np.invert(self.truth_clefts_mask)
27 | mask2 = self.test_clefts_edt > threshold
28 | false_negatives = self.test_clefts_edt[np.logical_and(mask1, mask2)]
29 | return false_negatives.size
30 |
31 | def acc_false_positives(self):
32 |
33 | mask = np.invert(self.test_clefts_mask)
34 | false_positives = self.truth_clefts_edt[mask]
35 | stats = {
36 | 'mean': np.mean(false_positives),
37 | 'std': np.std(false_positives),
38 | 'max': np.amax(false_positives),
39 | 'count': false_positives.size,
40 | 'median': np.median(false_positives)}
41 | return stats
42 |
43 | def acc_false_negatives(self):
44 |
45 | mask = np.invert(self.truth_clefts_mask)
46 | false_negatives = self.test_clefts_edt[mask]
47 | stats = {
48 | 'mean': np.mean(false_negatives),
49 | 'std': np.std(false_negatives),
50 | 'max': np.amax(false_negatives),
51 | 'count': false_negatives.size,
52 | 'median': np.median(false_negatives)}
53 | return stats
54 |
55 |
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/NeuronIds.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from border_mask import create_border_mask
3 | from voi import voi
4 | from rand import adapted_rand
5 |
6 | class NeuronIds:
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, groundtruth, border_threshold = None):
9 | """Create a new evaluation object for neuron ids against the provided ground truth.
10 |
11 | Parameters
12 | ----------
13 |
14 | groundtruth: Volume
15 | The ground truth volume containing neuron ids.
16 |
17 | border_threshold: None or float, in world units
18 | Pixels within `border_threshold` to a label border in the
19 | same section will be assigned to background and ignored during
20 | the evaluation.
21 | """
22 |
23 | assert groundtruth.resolution[1] == groundtruth.resolution[2], \
24 | "x and y resolutions of ground truth are not the same (%f != %f)" % \
25 | (groundtruth.resolution[1], groundtruth.resolution[2])
26 |
27 | self.groundtruth = groundtruth
28 | self.border_threshold = border_threshold
29 |
30 | if self.border_threshold:
31 |
32 | print "Computing border mask..."
33 |
34 | self.gt = np.zeros(groundtruth.data.shape, dtype=np.uint64)
35 | create_border_mask(
36 | groundtruth.data,
37 | self.gt,
38 | float(border_threshold)/groundtruth.resolution[1],
39 | np.uint64(-1))
40 | else:
41 | self.gt = np.array(self.groundtruth.data).copy()
42 |
43 | # current voi and rand implementations don't work with np.uint64(-1) as
44 | # background label, so we make it 0 here and bump all other labels
45 | self.gt += 1
46 |
47 | def voi(self, segmentation):
48 |
49 | assert list(segmentation.data.shape) == list(self.groundtruth.data.shape)
50 | assert list(segmentation.resolution) == list(self.groundtruth.resolution)
51 |
52 | print "Computing VOI..."
53 |
54 | return voi(np.array(segmentation.data), self.gt, ignore_groundtruth = [0])
55 |
56 | def adapted_rand(self, segmentation):
57 |
58 | assert list(segmentation.data.shape) == list(self.groundtruth.data.shape)
59 | assert list(segmentation.resolution) == list(self.groundtruth.resolution)
60 |
61 | print "Computing RAND..."
62 |
63 | return adapted_rand(np.array(segmentation.data), self.gt)
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/SynapticPartners.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from synaptic_partners import synaptic_partners_fscore
2 |
3 | class SynapticPartners:
4 |
5 | def __init__(self, matching_threshold = 400):
6 |
7 | self.matching_threshold = matching_threshold
8 |
9 | def fscore(self, rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, all_stats = False):
10 |
11 | return synaptic_partners_fscore(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, self.matching_threshold, all_stats)
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Clefts import *
2 | from NeuronIds import *
3 | from SynapticPartners import *
4 | from border_mask import *
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/border_mask.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import h5py
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import scipy
4 |
5 | def create_border_mask(input_data, target, max_dist, background_label,axis=0):
6 | """
7 | Overlay a border mask with background_label onto input data.
8 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
9 |
10 | Parameters
11 | ----------
12 | input_data : h5py.Dataset or numpy.ndarray - Input data containing neuron ids
13 | target : h5py.Datset or numpy.ndarray - Target which input data overlayed with border mask is written into.
14 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
15 | background_label : int - Border mask will be overlayed using this label.
16 | axis : int - Axis of iteration (perpendicular to 2d images for which mask will be generated)
17 | """
18 | sl = [slice(None) for d in xrange(len(target.shape))]
19 |
20 | for z in xrange(target.shape[axis]):
21 | sl[ axis ] = z
22 | border = create_border_mask_2d(input_data[tuple(sl)], max_dist)
23 | target_slice = input_data[tuple(sl)] if isinstance(input_data,h5py.Dataset) else np.copy(input_data[tuple(sl)])
24 | target_slice[border] = background_label
25 | target[tuple(sl)] = target_slice
26 |
27 | def create_and_write_masked_neuron_ids(in_file, out_file, max_dist, background_label, overwrite=False):
28 | """
29 | Overlay a border mask with background_label onto input data loaded from in_file and write into out_file.
30 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
31 |
32 | Parameters
33 | ----------
34 | in_file : CremiFile - Input file containing neuron ids
35 | out_file : CremiFile - Output file which input data overlayed with border mask is written into.
36 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
37 | background_label : int - Border mask will be overlayed using this label.
38 | overwrite : bool - Overwrite existing data in out_file (True) or do nothing if data is present in out_file (False).
39 | """
40 | if ( not in_file.has_neuron_ids() ) or ( (not overwrite) and out_file.has_neuron_ids() ):
41 | return
42 |
43 | neuron_ids, resolution, offset, comment = in_file.read_neuron_ids()
44 | comment = ('' if comment is None else comment + ' ') + 'Border masked with max_dist=%f' % max_dist
45 |
46 | path = "/volumes/labels/neuron_ids"
47 | group_path = "/".join( path.split("/")[:-1] )
48 | ds_name = path.split("/")[-1]
49 | if ( out_file.has_neuron_ids() ):
50 | del out_file.h5file[path]
51 | if (group_path not in out_file.h5file):
52 | out_file.h5file.create_group(group_path)
53 |
54 | group = out_file.h5file[group_path]
55 | target = group.create_dataset(ds_name, shape=neuron_ids.shape, dtype=neuron_ids.dtype)
56 | target.attrs["resolution"] = resolution
57 | target.attrs["comment"] = comment
58 | if offset != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
59 | target.attrs["offset"] = offset
60 |
61 | create_border_mask(neuron_ids, target, max_dist, background_label)
62 |
63 | def create_border_mask_2d(image, max_dist):
64 | """
65 | Create binary border mask for image.
66 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
67 |
68 | Parameters
69 | ----------
70 | image : numpy.ndarray - Image containing integer labels.
71 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
72 |
73 | Returns
74 | -------
75 | mask : numpy.ndarray - Binary mask of border pixels. Same shape as image.
76 | """
77 | max_dist = max(max_dist, 0)
78 |
79 | padded = np.pad(image, 1, mode='edge')
80 |
81 | border_pixels = np.logical_and(
82 | np.logical_and( image == padded[:-2, 1:-1], image == padded[2:, 1:-1] ),
83 | np.logical_and( image == padded[1:-1, :-2], image == padded[1:-1, 2:] )
84 | )
85 |
86 | distances = scipy.ndimage.distance_transform_edt(
87 | border_pixels,
88 | return_distances=True,
89 | return_indices=False
90 | )
91 |
92 | return distances <= max_dist
93 |
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/rand.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
5 |
6 | # Evaluation code courtesy of Juan Nunez-Iglesias, taken from
7 | # https://github.com/janelia-flyem/gala/blob/master/gala/evaluate.py
8 |
9 | def adapted_rand(seg, gt, all_stats=False):
10 | """Compute Adapted Rand error as defined by the SNEMI3D contest [1]
11 |
12 | Formula is given as 1 - the maximal F-score of the Rand index
13 | (excluding the zero component of the original labels). Adapted
14 | from the SNEMI3D MATLAB script, hence the strange style.
15 |
16 | Parameters
17 | ----------
18 | seg : np.ndarray
19 | the segmentation to score, where each value is the label at that point
20 | gt : np.ndarray, same shape as seg
21 | the groundtruth to score against, where each value is a label
22 | all_stats : boolean, optional
23 | whether to also return precision and recall as a 3-tuple with rand_error
24 |
25 | Returns
26 | -------
27 | are : float
28 | The adapted Rand error; equal to $1 - \frac{2pr}{p + r}$,
29 | where $p$ and $r$ are the precision and recall described below.
30 | prec : float, optional
31 | The adapted Rand precision. (Only returned when `all_stats` is ``True``.)
32 | rec : float, optional
33 | The adapted Rand recall. (Only returned when `all_stats` is ``True``.)
34 |
35 | References
36 | ----------
37 | [1]: http://brainiac2.mit.edu/SNEMI3D/evaluation
38 | """
39 | # segA is truth, segB is query
40 | segA = np.ravel(gt)
41 | segB = np.ravel(seg)
42 | n = segA.size
43 |
44 | n_labels_A = np.amax(segA) + 1
45 | n_labels_B = np.amax(segB) + 1
46 |
47 | ones_data = np.ones(n)
48 |
49 | p_ij = sparse.csr_matrix((ones_data, (segA[:], segB[:])), shape=(n_labels_A, n_labels_B))
50 |
51 | a = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,:]
52 | b = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,1:n_labels_B]
53 | c = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,0].todense()
54 | d = b.multiply(b)
55 |
56 | a_i = np.array(a.sum(1))
57 | b_i = np.array(b.sum(0))
58 |
59 | sumA = np.sum(a_i * a_i)
60 | sumB = np.sum(b_i * b_i) + (np.sum(c) / n)
61 | sumAB = np.sum(d) + (np.sum(c) / n)
62 |
63 | precision = sumAB / sumB
64 | recall = sumAB / sumA
65 |
66 | fScore = 2.0 * precision * recall / (precision + recall)
67 | are = 1.0 - fScore
68 |
69 | if all_stats:
70 | return (are, precision, recall)
71 | else:
72 | return are
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/synaptic_partners.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 | from munkres import Munkres
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | def synaptic_partners_fscore(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold = 400, all_stats = False):
6 | """Compute the f-score of the found synaptic partners.
7 |
8 | Parameters
9 | ----------
10 |
11 | rec_annotations: Annotations, containing found synaptic partners
12 |
13 | gt_annotations: Annotations, containing ground truth synaptic partners
14 |
15 | gt_segmentation: Volume, ground truth neuron segmentation
16 |
17 | matching_threshold: float, world units
18 | Euclidean distance threshold to consider two annotations a potential
19 | match. Annotations that are `matching_threshold` or more untis apart
20 | from each other are not considered as potential matches.
21 |
22 | all_stats: boolean, optional
23 | Whether to also return precision, recall, FP, FN, and matches as a 6-tuple with f-score
24 |
25 | Returns
26 | -------
27 |
28 | fscore: float
29 | The f-score of the found synaptic partners.
30 | precision: float, optional
31 | recall: float, optional
32 | fp: int, optional
33 | fn: int, optional
34 | filtered_matches: list of tuples, optional
35 | The indices of the matches with matching costs.
36 | """
37 |
38 | # get cost matrix
39 | costs = cost_matrix(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold)
40 |
41 | # match using Hungarian method
42 | print "Finding cost-minimal matches..."
43 | munkres = Munkres()
44 | matches = munkres.compute(costs.copy()) # have to copy, because munkres changes the cost matrix...
45 |
46 | filtered_matches = [ (i,j, costs[i][j]) for (i,j) in matches if costs[i][j] <= matching_threshold ]
47 | print str(len(filtered_matches)) + " matches found"
48 |
49 | # unmatched in rec = FP
50 | fp = len(rec_annotations.pre_post_partners) - len(filtered_matches)
51 |
52 | # unmatched in gt = FN
53 | fn = len(gt_annotations.pre_post_partners) - len(filtered_matches)
54 |
55 | # all ground truth elements - FN = TP
56 | tp = len(gt_annotations.pre_post_partners) - fn
57 |
58 | precision = float(tp)/(tp + fp)
59 | recall = float(tp)/(tp + fn)
60 | fscore = 2.0*precision*recall/(precision + recall)
61 |
62 | if all_stats:
63 | return (fscore, precision, recall, fp, fn, filtered_matches)
64 | else:
65 | return fscore
66 |
67 | def cost_matrix(rec, gt, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold):
68 |
69 | print "Computing matching costs..."
70 |
71 | rec_locations = pre_post_locations(rec, gt_segmentation)
72 | gt_locations = pre_post_locations(gt, gt_segmentation)
73 |
74 | rec_labels = pre_post_labels(rec_locations, gt_segmentation)
75 | gt_labels = pre_post_labels(gt_locations, gt_segmentation)
76 |
77 | size = max(len(rec_locations), len(gt_locations))
78 | costs = np.zeros((size, size), dtype=np.float)
79 | costs[:] = 2*matching_threshold
80 | num_potential_matches = 0
81 | for i in range(len(rec_locations)):
82 | for j in range(len(gt_locations)):
83 | c = cost(rec_locations[i], gt_locations[j], rec_labels[i], gt_labels[j], matching_threshold)
84 | costs[i,j] = c
85 | if c <= matching_threshold:
86 | num_potential_matches += 1
87 |
88 | print str(num_potential_matches) + " potential matches found"
89 |
90 | return costs
91 |
92 | def pre_post_locations(annotations, gt_segmentation):
93 | """Get the locations of the annotations relative to the ground truth offset."""
94 |
95 | locations = annotations.locations()
96 | shift = sub(annotations.offset, gt_segmentation.offset)
97 |
98 | return [
99 | (add(annotations.get_annotation(pre_id)[1], shift), add(annotations.get_annotation(post_id)[1], shift)) for (pre_id, post_id) in annotations.pre_post_partners
100 | ]
101 |
102 | def pre_post_labels(locations, segmentation):
103 |
104 | return [ (segmentation[pre], segmentation[post]) for (pre, post) in locations ]
105 |
106 |
107 | def cost(pre_post_location1, pre_post_location2, labels1, labels2, matching_threshold):
108 |
109 | max_cost = 2*matching_threshold
110 |
111 | # pairs do not link the same segments
112 | if labels1 != labels2:
113 | return max_cost
114 |
115 | pre_dist = distance(pre_post_location1[0], pre_post_location2[0])
116 | post_dist = distance(pre_post_location1[1], pre_post_location2[1])
117 |
118 | if pre_dist > matching_threshold or post_dist > matching_threshold:
119 | return max_cost
120 |
121 | return 0.5*(pre_dist + post_dist)
122 |
123 | def distance(a, b):
124 | return np.linalg.norm(np.array(list(a))-np.array(list(b)))
125 |
126 | def add(a, b):
127 | return tuple([a[d] + b[d] for d in range(len(b))])
128 |
129 | def sub(a, b):
130 | return tuple([a[d] - b[d] for d in range(len(b))])
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/voi.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 |
3 | # Evaluation code courtesy of Juan Nunez-Iglesias, taken from
4 | # https://github.com/janelia-flyem/gala/blob/master/gala/evaluate.py
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
8 |
9 | def voi(reconstruction, groundtruth, ignore_reconstruction=[], ignore_groundtruth=[0]):
10 | """Return the conditional entropies of the variation of information metric. [1]
11 |
12 | Let X be a reconstruction, and Y a ground truth labelling. The variation of
13 | information between the two is the sum of two conditional entropies:
14 |
15 | VI(X, Y) = H(X|Y) + H(Y|X).
16 |
17 | The first one, H(X|Y), is a measure of oversegmentation, the second one,
18 | H(Y|X), a measure of undersegmentation. These measures are referred to as
19 | the variation of information split or merge error, respectively.
20 |
21 | Parameters
22 | ----------
23 | seg : np.ndarray, int type, arbitrary shape
24 | A candidate segmentation.
25 | gt : np.ndarray, int type, same shape as `seg`
26 | The ground truth segmentation.
27 | ignore_seg, ignore_gt : list of int, optional
28 | Any points having a label in this list are ignored in the evaluation.
29 | By default, only the label 0 in the ground truth will be ignored.
30 |
31 | Returns
32 | -------
33 | (split, merge) : float
34 | The variation of information split and merge error, i.e., H(X|Y) and H(Y|X)
35 |
36 | References
37 | ----------
38 | [1] Meila, M. (2007). Comparing clusterings - an information based
39 | distance. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 98, 873-895.
40 | """
41 | (hyxg, hxgy) = split_vi(reconstruction, groundtruth, ignore_reconstruction, ignore_groundtruth)
42 | return (hxgy, hyxg)
43 |
44 | def split_vi(x, y=None, ignore_x=[0], ignore_y=[0]):
45 | """Return the symmetric conditional entropies associated with the VI.
46 |
47 | The variation of information is defined as VI(X,Y) = H(X|Y) + H(Y|X).
48 | If Y is the ground-truth segmentation, then H(Y|X) can be interpreted
49 | as the amount of under-segmentation of Y and H(X|Y) is then the amount
50 | of over-segmentation. In other words, a perfect over-segmentation
51 | will have H(Y|X)=0 and a perfect under-segmentation will have H(X|Y)=0.
52 |
53 | If y is None, x is assumed to be a contingency table.
54 |
55 | Parameters
56 | ----------
57 | x : np.ndarray
58 | Label field (int type) or contingency table (float). `x` is
59 | interpreted as a contingency table (summing to 1.0) if and only if `y`
60 | is not provided.
61 | y : np.ndarray of int, same shape as x, optional
62 | A label field to compare to `x`.
63 | ignore_x, ignore_y : list of int, optional
64 | Any points having a label in this list are ignored in the evaluation.
65 | Ignore 0-labeled points by default.
66 |
67 | Returns
68 | -------
69 | sv : np.ndarray of float, shape (2,)
70 | The conditional entropies of Y|X and X|Y.
71 |
72 | See Also
73 | --------
74 | vi
75 | """
76 | _, _, _ , hxgy, hygx, _, _ = vi_tables(x, y, ignore_x, ignore_y)
77 | # false merges, false splits
78 | return np.array([hygx.sum(), hxgy.sum()])
79 |
80 | def vi_tables(x, y=None, ignore_x=[0], ignore_y=[0]):
81 | """Return probability tables used for calculating VI.
82 |
83 | If y is None, x is assumed to be a contingency table.
84 |
85 | Parameters
86 | ----------
87 | x, y : np.ndarray
88 | Either x and y are provided as equal-shaped np.ndarray label fields
89 | (int type), or y is not provided and x is a contingency table
90 | (sparse.csc_matrix) that may or may not sum to 1.
91 | ignore_x, ignore_y : list of int, optional
92 | Rows and columns (respectively) to ignore in the contingency table.
93 | These are labels that are not counted when evaluating VI.
94 |
95 | Returns
96 | -------
97 | pxy : sparse.csc_matrix of float
98 | The normalized contingency table.
99 | px, py, hxgy, hygx, lpygx, lpxgy : np.ndarray of float
100 | The proportions of each label in `x` and `y` (`px`, `py`), the
101 | per-segment conditional entropies of `x` given `y` and vice-versa, the
102 | per-segment conditional probability p log p.
103 | """
104 | if y is not None:
105 | pxy = contingency_table(x, y, ignore_x, ignore_y)
106 | else:
107 | cont = x
108 | total = float(cont.sum())
109 | # normalize, since it is an identity op if already done
110 | pxy = cont / total
111 |
112 | # Calculate probabilities
113 | px = np.array(pxy.sum(axis=1)).ravel()
114 | py = np.array(pxy.sum(axis=0)).ravel()
115 | # Remove zero rows/cols
116 | nzx = px.nonzero()[0]
117 | nzy = py.nonzero()[0]
118 | nzpx = px[nzx]
119 | nzpy = py[nzy]
120 | nzpxy = pxy[nzx, :][:, nzy]
121 |
122 | # Calculate log conditional probabilities and entropies
123 | lpygx = np.zeros(np.shape(px))
124 | lpygx[nzx] = xlogx(divide_rows(nzpxy, nzpx)).sum(axis=1)
125 | # \sum_x{p_{y|x} \log{p_{y|x}}}
126 | hygx = -(px*lpygx) # \sum_x{p_x H(Y|X=x)} = H(Y|X)
127 |
128 | lpxgy = np.zeros(np.shape(py))
129 | lpxgy[nzy] = xlogx(divide_columns(nzpxy, nzpy)).sum(axis=0)
130 | hxgy = -(py*lpxgy)
131 |
132 | return [pxy] + list(map(np.asarray, [px, py, hxgy, hygx, lpygx, lpxgy]))
133 |
134 | def contingency_table(seg, gt, ignore_seg=[0], ignore_gt=[0], norm=True):
135 | """Return the contingency table for all regions in matched segmentations.
136 |
137 | Parameters
138 | ----------
139 | seg : np.ndarray, int type, arbitrary shape
140 | A candidate segmentation.
141 | gt : np.ndarray, int type, same shape as `seg`
142 | The ground truth segmentation.
143 | ignore_seg : list of int, optional
144 | Values to ignore in `seg`. Voxels in `seg` having a value in this list
145 | will not contribute to the contingency table. (default: [0])
146 | ignore_gt : list of int, optional
147 | Values to ignore in `gt`. Voxels in `gt` having a value in this list
148 | will not contribute to the contingency table. (default: [0])
149 | norm : bool, optional
150 | Whether to normalize the table so that it sums to 1.
151 |
152 | Returns
153 | -------
154 | cont : scipy.sparse.csc_matrix
155 | A contingency table. `cont[i, j]` will equal the number of voxels
156 | labeled `i` in `seg` and `j` in `gt`. (Or the proportion of such voxels
157 | if `norm=True`.)
158 | """
159 | segr = seg.ravel()
160 | gtr = gt.ravel()
161 | ignored = np.zeros(segr.shape, np.bool)
162 | data = np.ones(len(gtr))
163 | for i in ignore_seg:
164 | ignored[segr == i] = True
165 | for j in ignore_gt:
166 | ignored[gtr == j] = True
167 | data[ignored] = 0
168 | cont = sparse.coo_matrix((data, (segr, gtr))).tocsc()
169 | if norm:
170 | cont /= float(cont.sum())
171 | return cont
172 |
173 | def divide_columns(matrix, row, in_place=False):
174 | """Divide each column of `matrix` by the corresponding element in `row`.
175 |
176 | The result is as follows: out[i, j] = matrix[i, j] / row[j]
177 |
178 | Parameters
179 | ----------
180 | matrix : np.ndarray, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix, shape (M, N)
181 | The input matrix.
182 | column : a 1D np.ndarray, shape (N,)
183 | The row dividing `matrix`.
184 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
185 | Do the computation in-place.
186 |
187 | Returns
188 | -------
189 | out : same type as `matrix`
190 | The result of the row-wise division.
191 | """
192 | if in_place:
193 | out = matrix
194 | else:
195 | out = matrix.copy()
196 | if type(out) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
197 | if type(out) == sparse.csc_matrix:
198 | convert_to_csc = True
199 | out = out.tocsr()
200 | else:
201 | convert_to_csc = False
202 | row_repeated = np.take(row, out.indices)
203 | nz = out.data.nonzero()
204 | out.data[nz] /= row_repeated[nz]
205 | if convert_to_csc:
206 | out = out.tocsc()
207 | else:
208 | out /= row[np.newaxis, :]
209 | return out
210 |
211 | def divide_rows(matrix, column, in_place=False):
212 | """Divide each row of `matrix` by the corresponding element in `column`.
213 |
214 | The result is as follows: out[i, j] = matrix[i, j] / column[i]
215 |
216 | Parameters
217 | ----------
218 | matrix : np.ndarray, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix, shape (M, N)
219 | The input matrix.
220 | column : a 1D np.ndarray, shape (M,)
221 | The column dividing `matrix`.
222 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
223 | Do the computation in-place.
224 |
225 | Returns
226 | -------
227 | out : same type as `matrix`
228 | The result of the row-wise division.
229 | """
230 | if in_place:
231 | out = matrix
232 | else:
233 | out = matrix.copy()
234 | if type(out) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
235 | if type(out) == sparse.csr_matrix:
236 | convert_to_csr = True
237 | out = out.tocsc()
238 | else:
239 | convert_to_csr = False
240 | column_repeated = np.take(column, out.indices)
241 | nz = out.data.nonzero()
242 | out.data[nz] /= column_repeated[nz]
243 | if convert_to_csr:
244 | out = out.tocsr()
245 | else:
246 | out /= column[:, np.newaxis]
247 | return out
248 |
249 | def xlogx(x, out=None, in_place=False):
250 | """Compute x * log_2(x).
251 |
252 | We define 0 * log_2(0) = 0
253 |
254 | Parameters
255 | ----------
256 | x : np.ndarray or scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix
257 | The input array.
258 | out : same type as x (optional)
259 | If provided, use this array/matrix for the result.
260 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
261 | Operate directly on x.
262 |
263 | Returns
264 | -------
265 | y : same type as x
266 | Result of x * log_2(x).
267 | """
268 | if in_place:
269 | y = x
270 | elif out is None:
271 | y = x.copy()
272 | else:
273 | y = out
274 | if type(y) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
275 | z = y.data
276 | else:
277 | z = y
278 | nz = z.nonzero()
279 | z[nz] *= np.log2(z[nz])
280 | return y
281 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/*Filtered Mask.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/*Filtered Mask.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/*Visualize Boundary.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/*Visualize Boundary.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/6p.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/6p.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/acc.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/acc.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/err.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/err.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/loss.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/loss.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/n.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/res window.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/res window.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/rot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/rot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/io/CremiFile.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import h5py
2 | import numpy as np
3 | from Annotations import *
4 | from Volume import *
5 |
6 | class CremiFile(object):
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, filename, mode):
9 |
10 | self.h5file = h5py.File(filename, mode)
11 |
12 | if mode == "w" or mode == "a":
13 | self.h5file["/"].attrs["file_format"] = "0.2"
14 |
15 | def __create_group(self, group):
16 |
17 | path = "/"
18 | for d in group.split("/"):
19 | path += d + "/"
20 | try:
21 | self.h5file.create_group(path)
22 | except ValueError:
23 | pass
24 |
25 | def __create_dataset(self, path, data, dtype, compression = None):
26 | """Wrapper around h5py's create_dataset. Creates the group, if not
27 | existing. Deletes a previous dataset, if existing and not compatible.
28 | Otherwise, replaces the dataset.
29 | """
30 |
31 | group = "/".join(path.split("/")[:-1])
32 | ds_name = path.split("/")[-1]
33 |
34 | self.__create_group(group)
35 |
36 | if ds_name in self.h5file[group]:
37 |
38 | ds = self.h5file[path]
39 | if ds.dtype == dtype and ds.shape == np.array(data).shape:
40 | print "overwriting existing dataset"
41 | self.h5file[path][:] = data[:]
42 | return
43 |
44 | del self.h5file[path]
45 |
46 | self.h5file.create_dataset(path, data=data, dtype=dtype, compression=compression)
47 |
48 | def write_volume(self, volume, ds_name, dtype):
49 |
50 | self.__create_dataset(ds_name, data=volume.data, dtype=dtype, compression="gzip")
51 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["resolution"] = volume.resolution
52 | if volume.comment is not None:
53 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["comment"] = str(volume.comment)
54 | if tuple(volume.offset) != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
55 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["offset"] = volume.offset
56 |
57 | def read_volume(self, ds_name):
58 |
59 | volume = Volume(self.h5file[ds_name])
60 |
61 | volume.resolution = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["resolution"]
62 | if "offset" in self.h5file[ds_name].attrs:
63 | volume.offset = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["offset"]
64 | if "comment" in self.h5file[ds_name].attrs:
65 | volume.comment = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["comment"]
66 |
67 | return volume
68 |
69 | def __has_volume(self, ds_name):
70 |
71 | return ds_name in self.h5file
72 |
73 | def write_raw(self, raw):
74 | """Write a raw volume.
75 | """
76 |
77 | self.write_volume(raw, "/volumes/raw", np.uint8)
78 |
79 | def write_neuron_ids(self, neuron_ids):
80 | """Write a volume of segmented neurons.
81 | """
82 |
83 | self.write_volume(neuron_ids, "/volumes/labels/neuron_ids", np.uint64)
84 |
85 | def write_clefts(self, clefts):
86 | """Write a volume of segmented synaptic clefts.
87 | """
88 |
89 | self.write_volume(clefts, "/volumes/labels/clefts", np.uint64)
90 |
91 | def write_annotations(self, annotations):
92 | """Write pre- and post-synaptic site annotations.
93 | """
94 |
95 | if len(annotations.ids()) == 0:
96 | return
97 |
98 | self.__create_group("/annotations")
99 | if tuple(annotations.offset) != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
100 | self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs["offset"] = annotations.offset
101 |
102 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/ids", data=annotations.ids(), dtype=np.uint64)
103 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/types", data=annotations.types(), dtype=h5py.special_dtype(vlen=unicode), compression="gzip")
104 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/locations", data=annotations.locations(), dtype=np.double)
105 |
106 | if len(annotations.comments) > 0:
107 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/comments/target_ids", data=annotations.comments.keys(), dtype=np.uint64)
108 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/comments/comments", data=annotations.comments.values(), dtype=h5py.special_dtype(vlen=unicode))
109 |
110 | if len(annotations.pre_post_partners) > 0:
111 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/presynaptic_site/partners", data=annotations.pre_post_partners, dtype=np.uint64)
112 |
113 | def has_raw(self):
114 | """Check if this file contains a raw volume.
115 | """
116 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/raw")
117 |
118 | def has_neuron_ids(self):
119 | """Check if this file contains neuron ids.
120 | """
121 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids")
122 |
123 | def has_neuron_ids_confidence(self):
124 | """Check if this file contains confidence information about neuron ids.
125 | """
126 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids_confidence")
127 |
128 | def has_clefts(self):
129 | """Check if this file contains synaptic clefts.
130 | """
131 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/clefts")
132 |
133 | def has_annotations(self):
134 | """Check if this file contains synaptic partner annotations.
135 | """
136 | return "/annotations" in self.h5file
137 |
138 | def has_segment_annotations(self):
139 | """Check if this file contains segment annotations.
140 | """
141 | return "/annotations" in self.h5file
142 |
143 | def read_raw(self):
144 | """Read the raw volume.
145 | Returns a Volume.
146 | """
147 |
148 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/raw")
149 |
150 | def read_neuron_ids(self):
151 | """Read the volume of segmented neurons.
152 | Returns a Volume.
153 | """
154 |
155 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids")
156 |
157 | def read_neuron_ids_confidence(self):
158 | """Read confidence information about neuron ids.
159 | Returns Confidences.
160 | """
161 |
162 | confidences = Confidences(num_levels=2)
163 | if not self.has_neuron_ids_confidence():
164 | return confidences
165 |
166 | data = self.h5file["/volumes/labels/neuron_ids_confidence"]
167 | i = 0
168 | while i < len(data):
169 | level = data[i]
170 | i += 1
171 | num_ids = data[i]
172 | i += 1
173 | confidences.add_all(level, data[i:i+num_ids])
174 | i += num_ids
175 |
176 | return confidences
177 |
178 | def read_clefts(self):
179 | """Read the volume of segmented synaptic clefts.
180 | Returns a Volume.
181 | """
182 |
183 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/labels/clefts")
184 |
185 | def read_annotations(self):
186 | """Read pre- and post-synaptic site annotations.
187 | """
188 |
189 | annotations = Annotations()
190 |
191 | if not "/annotations" in self.h5file:
192 | return annotations
193 |
194 | offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
195 | if "offset" in self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs:
196 | offset = self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs["offset"]
197 | annotations.offset = offset
198 |
199 | ids = self.h5file["/annotations/ids"]
200 | types = self.h5file["/annotations/types"]
201 | locations = self.h5file["/annotations/locations"]
202 | for i in range(len(ids)):
203 | annotations.add_annotation(ids[i], types[i], locations[i])
204 |
205 | if "comments" in self.h5file["/annotations"]:
206 | ids = self.h5file["/annotations/comments/target_ids"]
207 | comments = self.h5file["/annotations/comments/comments"]
208 | for (id, comment) in zip(ids, comments):
209 | annotations.add_comment(id, comment)
210 |
211 | if "presynaptic_site/partners" in self.h5file["/annotations"]:
212 | pre_post = self.h5file["/annotations/presynaptic_site/partners"]
213 | for (pre, post) in pre_post:
214 | annotations.set_pre_post_partners(pre, post)
215 |
216 | return annotations
217 |
218 | def close(self):
219 |
220 | self.h5file.close()
221 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/io/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from CremiFile import *
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/Resnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
4 |
5 |
6 | def residualLayer2(conv2d1, norm2d, input, nChannels, nOutChannels=False, stride=1, conv2d2=False):
7 | """ Deep Residual Network
8 | https://github.com/gcr/torch-residual-networks
9 |
10 | giving stack of 2 layers as a block providing shortcuts."""
11 |
12 |
13 | if not nOutChannels:
14 | nOutChannels = nChannels
15 | if not conv2d2:
16 | conv2d2 = conv2d1
17 |
18 | # part 1: conv
19 | net = conv2d1(input)
20 | net = norm2d(net) # learnable parameters
21 | net = F.relu(net)
22 | net = conv2d2(net)
23 |
24 |
25 | # part 2: identity / skip connection
26 | skip = input
27 | if stride > 1: # optional downsampling
28 | skip = L.SpatialAveragePooling(1, 1, stride, stride).forward(skip.cpu().data)
29 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
30 | if nOutChannels > nChannels: # optional padding
31 | skip = L.Padding(1, (nOutChannels - nChannels), 3).forward(skip.cpu().data)
32 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
33 | elif nOutChannels < nChannels: # optional narrow
34 | skip = L.Narrow(2, 1, nOutChannels).forward(skip.cpu().data)
35 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
36 |
37 |
38 | # H(x) + x
39 | net = norm2d(net)
40 | #print "skip: " + str(skip.data.size())
41 | #print "net: " + str(net.data.size())
42 | net = torch.add(skip, net)
43 | # net = F.relu(net) # relu here ? see: http://www.gitxiv.com/comments/7rffyqcPLirEEsmpX
44 | #net = norm2d(net) # ==========================BN after add or before ???
45 |
46 | return net
47 |
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 | class DeepResNet18(nn.Module):
55 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=3, padding=1):
56 | super(DeepResNet18, self).__init__()
57 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
58 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
59 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
60 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
61 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
62 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
63 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
64 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
65 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
66 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
67 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
68 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
69 | self.linear = nn.Linear(256, 2)
70 |
71 | def forward(self, x):
72 | # ----> 1, 33, 33
73 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
74 |
75 | # ----> 32, 33, 33 First Group 2X
76 | for i in range(2): x = residualLayer2(self.conv2, self.norm1, x, 32)
77 |
78 | # ----> 64, 17, 17 Second Group 2X
79 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv3, self.norm2, x, 32, 64, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv4)
80 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv4, self.norm2, x, 64)
81 |
82 | # ----> 128, 9, 9 Third Group 2X
83 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv5, self.norm3, x, 64, 128, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv6)
84 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv6, self.norm3, x, 128)
85 |
86 | # ----> 256, 5, 5 Fourth Group 2X
87 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv7, self.norm4, x, 128, 256, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv8)
88 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv8, self.norm4, x, 256)
89 |
90 | # ----> 256, 5, 5 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
91 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(5,5)(x)
92 | x = x.view(-1, 256)
93 | x = self.linear(x)
94 |
95 |
96 | return x
97 |
98 |
99 | class DeepResNet34(nn.Module):
100 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=5, padding=2):
101 | super(DeepResNet34, self).__init__()
102 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
103 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
104 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
105 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
106 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
107 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
108 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
109 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
110 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
111 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
112 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
113 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
114 | self.linear = nn.Linear(256, 2)
115 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
116 |
117 | def forward(self, x):
118 | # ------> 65 * 65
119 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
120 | x = self.pool(x) # ================= max pooling ??
121 | # ------> 32 * 32
122 | for i in range(3): x = residualLayer2(self.conv2, self.norm1, x, 32)
123 | # ------> 32 * 32
124 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv3, self.norm2, x, 32, 64, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv4)
125 | for i in range(4-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv4, self.norm2, x, 64)
126 |
127 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv5, self.norm3, x, 64, 128, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv6)
128 | for i in range(6-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv6, self.norm3, x, 128)
129 |
130 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv7, self.norm4, x, 128, 256, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv8)
131 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv8, self.norm4, x, 256)
132 |
133 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(8,8)(x)
134 | x = x.view(-1, 256)
135 | x = self.linear(x)
136 |
137 |
138 | return x
139 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/Resnet_3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | class DeepResNet101(nn.Module):
8 |
9 | """using bottle-neck building block """
10 |
11 |
12 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=7, padding=3):
13 | super(DeepResNet101, self).__init__()
14 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
15 | self.conv2_ = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 1, stride=2)
16 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 5, padding=2)
17 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
18 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, 128, 5, padding=2)
19 | self.conv5_ = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 1, stride=2)
20 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 5, padding=2)
21 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
22 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(64, 256, 5, padding=2)
23 | self.conv8_ = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 1, stride=2)
24 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 5, padding=2)
25 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
26 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(128, 512, 5, padding=2)
27 | self.conv11_ = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 1, stride=2)
28 | self.conv11 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, 5, padding=2)
29 | self.conv12 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
30 | self.conv13 = nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, 5, padding=2)
31 |
32 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
33 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
34 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
35 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
36 | self.norm5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
37 | self.norm6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
38 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
39 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 128)
40 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(128, 2)
41 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
42 |
43 | def forward(self, x):
44 | # ----> 1, 129, 129
45 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
46 | x = self.pool(x) # max pooling ? 3x3 s=2
47 |
48 | # ----> 32, 64, 64 First Group
49 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2_, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 32, 32, 128, stride=2)
50 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 128, 32, 128)
51 |
52 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5_, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 128, 64, 256, stride=2)
53 | for i in range(8-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 256, 64, 256)
54 |
55 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8_, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 256, 128, 512, stride=2)
56 | for i in range(36-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 512, 128, 512)
57 |
58 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11_, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 512, 256, 1024, stride=2)
59 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 1024, 256, 1024)
60 |
61 | # ----> 1024, 4, 4 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
62 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(4,4)(x)
63 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
64 | x = self.linear1(x)
65 | x = F.dropout(x) # ==============================
66 | x = self.linear2(x)
67 | x = self.linear3(x)
68 |
69 | return x
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | class DeepResNet50(nn.Module):
76 |
77 | """using bottle-neck building block """
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=7, padding=3): #=============== conv window size 5/22 9:24pm
82 | super(DeepResNet50, self).__init__()
83 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
84 | self.conv2_ = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 1, stride=2)
85 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 5, padding=2)
86 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
87 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, 128, 5, padding=2)
88 | self.conv5_ = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 1, stride=2)
89 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 5, padding=2)
90 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
91 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(64, 256, 5, padding=2)
92 | self.conv8_ = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 1, stride=2)
93 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 5, padding=2)
94 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
95 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(128, 512, 5, padding=2)
96 | self.conv11_ = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 1, stride=2)
97 | self.conv11 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, 5, padding=2)
98 | self.conv12 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
99 | self.conv13 = nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, 5, padding=2)
100 |
101 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
102 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
103 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
104 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
105 | self.norm5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
106 | self.norm6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
107 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
108 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 128)
109 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(128, 2)
110 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
111 |
112 |
113 | def forward(self, x):
114 | # ----> 1, 129, 129
115 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
116 | x = self.pool(x) # ================= max pooling ? better without here
117 |
118 |
119 | # ----> 32, 64, 64 First Group
120 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2_, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 32, 32, 128, stride=2)
121 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 128, 32, 128)
122 |
123 | # ----> 128, 32, 32 Second Group
124 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5_, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 128, 64, 256, stride=2)
125 | for i in range(4-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 256, 64, 256)
126 |
127 | # ----> 256, 16, 16 Third Group
128 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8_, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 256, 128, 512, stride=2)
129 | for i in range(6-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 512, 128, 512)
130 |
131 | # ----> 512, 8,8 Fourth Group
132 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11_, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 512, 256, 1024, stride=2)
133 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 1024, 256, 1024)
134 |
135 | # ----> 1024, 4, 4 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
136 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(4,4)(x)
137 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
138 | x = self.linear1(x)
139 | x = F.dropout(x) # ==============================
140 | x = self.linear2(x)
141 | x = self.linear3(x)
142 |
143 | return x
144 |
145 |
146 | # stack of 3 layers providing shortcuts
147 | def residualLayer3(input, conv2d1, conv2d2, conv2d3, norm2d1, norm2d2, inChannels, hiddenChannels, outChannels, stride=1):
148 | net = conv2d1(input) # 1x1
149 | net = norm2d1(net)
150 | net = F.relu(net)
151 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout within blocks ???? 8.21 9pm
152 |
153 | net = conv2d2(net) # kernel 3x3 or 5x5
154 | net = norm2d1(net)
155 | net = F.relu(net)
156 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout ???? 8.21 9pm
157 |
158 | net = conv2d3(net) # 1x1
159 |
160 | skip = input
161 | #print "input: " + str(skip.data.size())
162 | if stride > 1:
163 | skip = L.SpatialAveragePooling(1, 1, stride, stride).forward(skip.cpu().data)
164 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
165 | if outChannels > inChannels:
166 | skip = L.Padding(1, (outChannels - inChannels), 3).forward(skip.cpu().data)
167 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
168 | elif outChannels < inChannels:
169 | skip = L.Narrow(2, 1, outChannels).forward(skip.cpu().data)
170 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
171 |
172 | #net = norm2d2(net)
173 | #print "skip: " + str(skip.data.size())
174 | #print "net: " + str(net.data.size())
175 | net = norm2d2(torch.add(skip, net)) # ==========================BN after add or before ???
176 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout ????
177 | return net
178 |
179 |
180 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/type/Annotations.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class Annotations:
2 |
3 | def __init__(self, offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)):
4 |
5 | self.__types = {}
6 | self.__locations = {}
7 | self.comments = {}
8 | self.pre_post_partners = []
9 | self.offset = offset
10 |
11 | def __check(self, id):
12 | if not id in self.__types.keys():
13 | raise "there is no annotation with id " + str(id)
14 |
15 | def add_annotation(self, id, type, location):
16 | """Add a new annotation.
17 |
18 | Parameters
19 | ----------
20 |
21 | id: int
22 | The ID of the new annotation.
23 |
24 | type: string
25 | A string denoting the type of the annotation. Use
26 | "presynaptic_site" or "postsynaptic_site" for pre- and
27 | post-synaptic annotations, respectively.
28 |
29 | location: tuple, float
30 | The location of the annotation, relative to the offset.
31 | """
32 |
33 | self.__types[id] = type.encode('utf8')
34 | self.__locations[id] = location
35 |
36 | def add_comment(self, id, comment):
37 | """Add a comment to an annotation.
38 | """
39 |
40 | self.__check(id)
41 | self.comments[id] = comment.encode('utf8')
42 |
43 | def set_pre_post_partners(self, pre_id, post_id):
44 | """Mark two annotations as pre- and post-synaptic partners.
45 | """
46 |
47 | self.__check(pre_id)
48 | self.__check(post_id)
49 | self.pre_post_partners.append((pre_id, post_id))
50 |
51 | def ids(self):
52 | """Get the ids of all annotations.
53 | """
54 |
55 | return self.__types.keys()
56 |
57 | def types(self):
58 | """Get the types of all annotations.
59 | """
60 |
61 | return self.__types.values()
62 |
63 | def locations(self):
64 | """Get the locations of all annotations. Locations are in world units,
65 | relative to the offset.
66 | """
67 |
68 | return self.__locations.values()
69 |
70 | def get_annotation(self, id):
71 | """Get the type and location of an annotation by its id.
72 | """
73 |
74 | self.__check(id)
75 | return (self.__types[id], self.__locations[id])
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/type/Volume.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class Volume():
2 |
3 | def __init__(self, data, resolution = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0), offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0), comment = ""):
4 | self.data = data
5 | self.resolution = resolution
6 | self.offset = offset
7 | self.comment = comment
8 |
9 | def __getitem__(self, location):
10 | """Get the closest value of this volume to the given location. The
11 | location is in world units, relative to the volumes offset.
12 |
13 | This method takes into account the resolution of the volume. An
14 | IndexError exception is raised if the location is not contained in this
15 | volume.
16 |
17 | To access the raw pixel values, use the `data` attribute.
18 | """
19 |
20 | i = tuple([ round(location[d]/self.resolution[d]) for d in range(len(location)) ])
21 |
22 | if min(i) >= 0:
23 | try:
24 | return self.data[i]
25 | except IndexError as e:
26 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume: " + str(e))
27 |
28 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume")
29 |
30 | def __setitem__(self, location, value):
31 | """Set the closest value of this volume to the given location. The
32 | location is in world units, relative to the volumes offset.
33 |
34 | This method takes into account the resolution of the volume. An
35 | IndexError exception is raised if the location is not contained in this
36 | volume.
37 |
38 | To access the raw pixel values, use the `data` attribute.
39 | """
40 |
41 | i = tuple([ round(location[d]/self.resolution[d]) for d in range(len(location)) ])
42 |
43 | if min(i) >= 0:
44 | try:
45 | self.data[i] = value
46 | return
47 | except IndexError as e:
48 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume: " + str(e))
49 |
50 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume")
51 |
52 |
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 17 |
17 |  18 |
18 |  19 |
20 | ### Approaches
21 | - For this task, I trained a 2 way classifier to classify the central pixel in 127*127 sample as boudary and non-boundary. The 2-way sofmax layer was applied before the output of the network.
22 | - Reproduced and used **residual network method**. (original: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385, implementation on github: https://github.com/gcr/torch-residual-networks). This has been giving me a great boost in classificaiton results.
23 |
24 | - (see plot below) It was found in preliminary experiments that using a 5-7-5 window for the three conv layers in the bottleneck block of residual net (training on 127*127 sample size, green line) outformed the originally proposed 1-3-1 structure (gray line) by a large margin, so experiments reported above were all trained with the 5-7-5. The position of batch normalization and dropout layer in the block was also changed.
25 |
26 |
19 |
20 | ### Approaches
21 | - For this task, I trained a 2 way classifier to classify the central pixel in 127*127 sample as boudary and non-boundary. The 2-way sofmax layer was applied before the output of the network.
22 | - Reproduced and used **residual network method**. (original: https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385, implementation on github: https://github.com/gcr/torch-residual-networks). This has been giving me a great boost in classificaiton results.
23 |
24 | - (see plot below) It was found in preliminary experiments that using a 5-7-5 window for the three conv layers in the bottleneck block of residual net (training on 127*127 sample size, green line) outformed the originally proposed 1-3-1 structure (gray line) by a large margin, so experiments reported above were all trained with the 5-7-5. The position of batch normalization and dropout layer in the block was also changed.
25 |
26 |  27 |
28 | - **Selectively choose training samples from raw (see figure below)**: the yellow area **X3 dilated boundary** pixels were avoided to be chosen, only green and purple (true boudary, background) pixels will be selected into training batches,.
29 | - **Random rotation techniques**: various augmentation approches were explored, including rand rotations of +/-60, rand +/- 30, on 33.33%, 50% of samples in each batc. rand +/- 60 deg on 50% of samples (see figure below) was found to perform the best so far.
30 |
27 |
28 | - **Selectively choose training samples from raw (see figure below)**: the yellow area **X3 dilated boundary** pixels were avoided to be chosen, only green and purple (true boudary, background) pixels will be selected into training batches,.
29 | - **Random rotation techniques**: various augmentation approches were explored, including rand rotations of +/-60, rand +/- 30, on 33.33%, 50% of samples in each batc. rand +/- 60 deg on 50% of samples (see figure below) was found to perform the best so far.
30 |  31 |
31 |  32 |
32 |  33 |
34 | ### Future work
35 |
36 | - The neighbor area of the boundaries was avoided in this experiment, however the boundary pixels from other organels (intracellular organels) should also be avoided. These pixels could be easily treated as target neuron boundaries which are actually not. The approach to address this challenge can be to pre-train a network to recognize these intracellular boundaries and filter out these pixels when creating training batches for the segmentation task.
37 |
38 | - the raw is originally a 3D image of size 125 * 1250 * 1250. I started by treating each layer in deapth 125 as an independent sample and trained my network with images in 2D sections. However, in later stages of experiments (which i was not able to do due to the time limit of my project), the third deimension should be considered to address the correlation between the neuron pixels at depth.
39 |
40 | ## Dependencies
41 |
42 | * python
43 | * pytorch
44 | * numpy
45 | * matplotlib
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | import torch.optim as optim
5 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
6 | from torch.autograd import Variable
7 |
8 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, TensorDataset
9 | import torchvision
10 | from torchvision import transforms, datasets
11 | import torchvision.models as models
12 | import numpy as np
13 | from tempfile import TemporaryFile
14 | import matplotlib
15 | matplotlib.use('Agg')
16 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
17 | import scipy.ndimage as ndimage
18 | from scipy.ndimage.interpolation import rotate
19 | import time
20 | import os
21 | import random
22 |
23 | from Annotations import *
24 | from Volume import *
25 | from CremiFile import *
26 | from voi import voi
27 | from rand import adapted_rand
28 | plt.style.use('ggplot')
29 |
30 | from models.Resnet_3 import *
31 | from models.Resnet import *
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 | print('')
36 | print('DATASET LOADING ...')
37 | print('')
38 | emdset = CremiFile('sample_B_20160501.hdf', 'r')
39 |
40 | #Check the content of the datafile
41 | print "Has raw: " + str(emdset.has_raw())
42 | print "Has neuron ids: " + str(emdset.has_neuron_ids())
43 | print "Has clefts: " + str(emdset.has_clefts())
44 | print "Has annotations: " + str(emdset.has_annotations())
45 |
46 |
47 | #Read volume and annotation
48 | raw = emdset.read_raw()
49 | neuron_ids = emdset.read_neuron_ids()
50 | clefts = emdset.read_clefts()
51 | annotations = emdset.read_annotations()
52 |
53 | print("")
54 | print "Read raw: " + str(raw) + \
55 | ", resolution " + str(raw.resolution) + \
56 | ", offset " + str(raw.offset) + \
57 | ", data size " + str(raw.data.shape) + \
58 | ("" if raw.comment == None else ", comment \"" + raw.comment + "\"")
59 |
60 | print "Read neuron_ids: " + str(neuron_ids) + \
61 | ", resolution " + str(neuron_ids.resolution) + \
62 | ", offset " + str(neuron_ids.offset) + \
63 | ", data size " + str(neuron_ids.data.shape) + \
64 | ("" if neuron_ids.comment == None else ", comment \"" + neuron_ids.comment + "\"")
65 |
66 | print "Read clefts: " + str(clefts) + \
67 | ", resolution " + str(clefts.resolution) + \
68 | ", offset " + str(clefts.offset) + \
69 | ", data size " + str(clefts.data.shape) + \
70 | ("" if clefts.comment == None else ", comment \"" + clefts.comment + "\"")
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | def mask_filtered(raw, neuron_ids):
76 | """
77 | Image boudnary dilation
78 | Compute mask on each depth for un-selectable dilated(6X) boundary pixels (labeled as value 200.),
79 | the selectable background (0.) and actual boundary (100.) pixels
80 |
81 | return(numpy array): mask of shape 125,1250,1250
82 | """
83 | print ''
84 | print ''
85 | print 'building mask-5X from raw dataset...'
86 | since = time.time()
87 |
88 | d, h, w = raw.data.shape
89 | mask = np.empty([d, h, w]).astype('float32')
90 | for i in range(d):
91 | for j in range(h):
92 | for k in range(w):
93 | pixel = neuron_ids.data[i, j, k]
94 | if check_boundary(pixel, i, j, k, neuron_ids):
95 | mask[i, j, k] = 100
96 | else:
97 | mask[i, j, k] = 0
98 | if (i + 1) % 1 == 0:
99 | print str(0.8 * (i + 1)) + '% done'
100 |
101 | mask_dilated = ndimage.binary_dilation(mask, iterations=7).astype(mask.dtype)
102 | mask_filtered = 200 * mask_dilated - mask
103 |
104 | filter_time = time.time()
105 | time_elapsed = filter_time - since
106 | print('Mask complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format(
107 | time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60))
108 |
109 |
110 | print 'save to maskfile7X.npy'
111 | np.save('maskfile7X.npy', mask_filtered)
112 | print 'saved'
113 |
114 |
115 | def check_boundary(pixel, x, y, z, neuron_ids):
116 | """
117 | Check if a pixel at position (x,y,z) is labeled
118 | as boundary/non-boundary in neuron_ids.
119 |
120 | return(boolean): boundary
121 | """
122 | max_z = neuron_ids.data.shape[2] - 1
123 | max_y = neuron_ids.data.shape[1] - 1
124 | a = neuron_ids.data[x, y, z - 1] if z > 0 else pixel
125 | b = neuron_ids.data[x, y, z + 1] if z < max_z else pixel
126 | c = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z] if y > 0 else pixel
127 | d = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z] if y < max_y else pixel
128 | e = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z - 1] if (y > 0 and z > 0) else pixel
129 | f = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z + 1] if (y > 0 and z < max_z) else pixel
130 | g = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z - 1] if (y < max_y and z > 0) else pixel
131 | h = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z + 1] if (y < max_y and z < max_z) else pixel
132 |
133 | neighbors = [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h]
134 | boundary = False
135 | for neighbor in neighbors:
136 | if pixel != neighbor:
137 | boundary = True
138 |
139 | return boundary
140 |
141 |
142 | # Seed a random number generator
143 | #seed = 24102016
144 | #rng = np.random.RandomState(seed)
145 | def random_rotation(inputs):
146 | """Randomly rotates a subset of images in a batch.
147 | reference: https://github.com/CSTR-Edinburgh/mlpractical/blob/mlp2016-7/master/notebooks/05_Non-linearities_and_regularisation.ipynb
148 |
149 | * chooses 30-50% of the images in the batch at random
150 | * for each image in the 30-50% chosen, rotates the image by a random angle in [-60, 60]
151 | * returns a new array of size (129, 129) in which the rows corresponding to the 25% chosen images are the vectors corresponding to the new randomly rotated images, while the remaining rows correspond to the original images.
152 | Args:
153 | inputs: Input image batch, an array of shape (129, 129).
154 |
155 | Returns:
156 | An array of shape (129, 129) corresponding to a copy
157 | of the original `inputs` array that was randomly selected
158 | to be rotated by a random angle. The original `inputs`
159 | array should not be modified.
160 | """
161 |
162 | new_ims = np.zeros(inputs.shape).astype('float32')
163 | indices = random.randint(-1,1)
164 | angles = random.uniform(-30., 30.)
165 | if indices == 0:
166 | rotate(inputs, angles, output = new_ims, order=1, reshape=False)
167 |
168 | return new_ims
169 |
170 |
171 |
172 |
173 | #mask_filtered(raw, neuron_ids) # used only when the first time of training
174 | mask = np.load('maskfile5X.npy')
175 | print ''
176 | print 'mask loaded'
177 |
178 | class NeuronSegmenDataset(Dataset):
179 | """Raw pixel and its label.
180 | Dataset splitted into 80,000 training and 20,000 validation set
181 | """
182 |
183 | def __init__(self, raw, neuron_ids, mask, phase, transform=None):
184 | """
185 | Args:
186 | raw(Volume): raw
187 | neuron_ids(Volume): neuron segmentation labels
188 | mask(numpy ndarray): filtered mask
189 | phase(String): 'train' or 'val'
190 | transform(callable, optional): optional data augmentation to be applied
191 | """
192 |
193 | self.phase = phase
194 | self.raw = raw
195 | self.neuron_ids = neuron_ids
196 | self.mask = mask
197 | self.transform = transform
198 |
199 | def __len__(self):
200 | """ length of the dataset """
201 | if self.phase == 'train':
202 | x = 80000
203 | else:
204 | x = 20000
205 |
206 | return x
207 |
208 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
209 | """
210 | Return 33*33 patches for each raw pixel at the center
211 | positive if boundary pixel, negative if non-boundary pixel
212 | """
213 | depth = self.raw.data.shape[0]
214 | size = self.raw.data.shape[1]
215 |
216 |
217 | while True:
218 | d = random.randint(0, depth - 1)
219 | h = random.randint(64, size - 65)
220 | w = random.randint(64, size - 65)
221 | ids_pixel = self.neuron_ids.data[d, h, w]
222 | pixel = self.mask[d, h, w]
223 |
224 | if idx % 2 == 0: #control half samples to be boundary pixels
225 | if pixel == 100.:
226 | raw_batch = self.raw.data[d][h - 64:h + 65, w - 64:w + 65].astype(
227 | 'float32') # crop a 129*129 patch
228 |
229 |
230 | if self.transform:
231 | raw_batch = self.transform(raw_batch)
232 |
233 | raw_batch = raw_batch.reshape([1, 129, 129])
234 | raw_batch = torch.from_numpy(raw_batch)
235 | sample = (raw_batch, 0)
236 |
237 | break
238 | elif pixel == 0.: # the other half as non-boundary pixel
239 | raw_batch = self.raw.data[d][h - 64:h + 65, w - 64:w + 65].astype(
240 | 'float32') # crop 33*33 patch
241 | raw_batch = raw_batch.reshape([1, 129, 129])
242 |
243 | if self.transform:
244 | raw_batch = self.transform(raw_batch)
245 |
246 | raw_batch = torch.from_numpy(raw_batch)
247 | sample = (raw_batch, 1)
248 |
249 | break
250 | return sample
251 |
252 |
253 | batch_size = 100
254 | emdset_seg = {x: NeuronSegmenDataset(raw, neuron_ids, mask, x, transform=random_rotation)
255 | for x in ['train', 'val']}
256 | emdset_loaders = {x: DataLoader(emdset_seg[x], batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
257 | for x in ['train', 'val']}
258 | dset_sizes = {x: len(emdset_seg[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']}
259 | dset_classes = ['boundary', 'non-b']
260 | use_gpu = torch.cuda.is_available()
261 |
262 | print "Load num of batches: train " + str(len(emdset_loaders['train'])) + \
263 | ' validation ' + str(len(emdset_loaders['val']))
264 |
265 | print ('done')
266 | print ('')
267 |
268 |
269 | class ConvNet(nn.Module):
270 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel= 3, window =2, padding=1):
271 | super(ConvNet, self).__init__()
272 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
273 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
274 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
275 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
276 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
277 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
278 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
279 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
280 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel, padding=padding)
281 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel, padding=padding)
282 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(window)
283 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(2*2*256, 256)
284 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
285 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
286 | self.linear4 = nn.Linear(128, D_out)
287 |
288 | def forward(self, x):
289 | x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
290 | print "conv 1: " + str(x.data.size())
291 | x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
292 | print "conv 2: " + str(x.data.size())
293 | x = self.pool(x)
294 | print "pool 1: " + str(x.data.size())
295 |
296 | x = F.relu(self.conv3(x))
297 | print "conv 3: " + str(x.data.size())
298 | x = F.relu(self.conv4(x))
299 | print "conv 4: " + str(x.data.size())
300 | x = self.pool(x)
301 | print "pool 2: " + str(x.data.size())
302 |
303 | x = F.relu(self.conv5(x))
304 | print "conv 5: " + str(x.data.size())
305 | x = F.relu(self.conv6(x))
306 | print "conv 6: " + str(x.data.size())
307 | x = self.pool(x)
308 | print "pool 3: " + str(x.data.size())
309 |
310 | x = F.relu(self.conv7(x))
311 | print "conv 7: " + str(x.data.size())
312 | x = F.relu(self.conv8(x))
313 | print "conv 8: " + str(x.data.size())
314 | x = self.pool(x)
315 | print "pool 4: " + str(x.data.size())
316 |
317 | x = x.view(-1, 2*2*256)
318 | x = F.relu(self.linear1(x))
319 |
320 | x = F.relu(self.linear3(x))
321 | x = F.relu(self.linear4(x))
322 |
323 | return x
324 |
325 |
326 |
327 | def exp_lr_scheduler(optimizer, epoch, init_lr=0.001, lr_decay_epoch=10):
328 | """Decay learning rate by a factor of 0.1 every 10 epochs"""
329 | lr = init_lr * (0.1**(epoch // lr_decay_epoch))
330 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
331 | param_group['lr'] = lr
332 |
333 | return optimizer
334 |
335 |
336 | def piecewise_scheduler(optimizer, epoch):
337 | if epoch % 50 ==0 :
338 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
339 | lr = param_group['lr'] / 2
340 | param_group['lr'] = lr
341 |
342 | return optimizer
343 |
344 |
345 |
346 | def train_model (model, criterion, optimizer, lr_scheduler=None, num_epochs=100):
347 | since = time.time()
348 | train_voi_split = np.zeros(num_epochs)
349 | train_voi_merge = np.zeros(num_epochs)
350 | train_rand = np.zeros(num_epochs)
351 |
352 | # iterate over epoch
353 | for epoch in range(num_epochs):
354 | print ('Epoch{}/{}'.format(epoch+1, num_epochs))
355 | print ('-' * 10)
356 |
357 |
358 | # train and validation set
359 | for phase in ['train', 'val']:
360 | if phase == 'train':
361 | if lr_scheduler:
362 | optimizer = lr_scheduler(optimizer, epoch + 1)
363 | model.train(True)
364 | else:
365 | model.train(True)
366 |
367 | running_loss = 0.
368 | running_accuracy = 0.
369 | total = 0
370 |
371 | # iterate over each batch
372 | for i, data in enumerate(emdset_loaders[phase]):
373 | inputs, labels = data
374 | if use_gpu:
375 | model = model.cuda()
376 | inputs, labels = Variable(inputs.cuda()), \
377 | Variable(labels.cuda())
378 | else:
379 | inputs, labels = Variable(inputs), Variable(labels)
380 |
381 |
382 | optimizer.zero_grad() # clean gradients in buffer
383 |
384 | outputs = model(inputs)
385 | _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
386 | loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
387 |
388 |
389 | if phase == 'train':
390 | loss.backward()
391 | optimizer.step()
392 |
393 |
394 | running_loss += loss.data[0]
395 | running_accuracy += (predicted == labels.data).sum()
396 |
397 | # visualize random patches
398 | visualize_pred = True
399 | tt = visualize_pred and epoch == num_epochs-1 and phase == 'val' \
400 | and i+1 == len(emdset_loaders['val'])
401 | if tt:
402 | print('visualizing...')
403 | images_so_far = 0
404 | fig = plt.figure()
405 | for j in [6, 15, 38, 41, 86, 99]:
406 | images_so_far += 1
407 | ax = fig.add_subplot(3, 2, images_so_far)
408 | ax.axis('off')
409 | ax.set_title('Pred: {},\n Labeled: {}'.format(dset_classes[int(predicted.cpu().numpy()[j])],
410 | dset_classes[labels.data[j]]))
411 | ax.imshow(inputs.cpu().data[j].view(129,129).numpy())
412 | fig.savefig('6p.png')
413 | print 'done and saved to 6p.png'
414 |
415 |
416 | # normalize by number of batches
417 | running_loss /= (i + 1)
418 | running_accuracy = 100 * running_accuracy / dset_sizes[phase]
419 |
420 | # print statistics
421 | if epoch % 1 == 0:
422 | print('{} Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(
423 | phase, running_loss, running_accuracy
424 | ))
425 | # print "\tvoi split : " + str(train_voi_split)
426 | # print "\tvoi merge : " + str(train_voi_merge)
427 | # print "\tadapted RAND: " + str(train_rand)
428 |
429 | # Visualize the model. raw, labeled, predicted (optional)
430 | visualize = False
431 | if visualize:
432 | print('')
433 | print('Begin to visualize model..')
434 | visualize_model(model)
435 |
436 | time_elapsed = time.time() - train_time
437 | print('Visualizing complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format(
438 | time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60))
439 |
440 |
441 |
442 | def visualize_model(model, i = 80, s = 300):
443 | """ Args:
444 | model: model
445 | i: depth of the raw image to visualize
446 | s: crop the 1250*1250 image to the size of s*s
447 | """
448 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15,6))
449 |
450 | ax_ori = fig.add_subplot(1,3,1)
451 | ax_lab = fig.add_subplot(1,3,2)
452 | ax_pred = fig.add_subplot(1,3,3)
453 |
454 | ax_ori.imshow(raw.data[i][0:s, 0:s])
455 | ax_ori.set_title('raw')
456 | ax_lab.imshow(neuron_ids.data[i][0:s, 0:s])
457 | ax_lab.set_title('labeled')
458 |
459 |
460 | preds = np.empty([s*s])
461 | for j in range(s*s):
462 | pixel = raw.data[i][j/s, j%s]
463 | input = np.random.uniform(-10000, 0, (1, 1, 33, 33)).astype('float32') ## boundary patch: positive
464 | input[0, 0, 16, 16] = pixel
465 | input = torch.from_numpy(input)
466 |
467 | model.train(False)
468 | if use_gpu:
469 | model = model.cuda()
470 | input = Variable(input.cuda())
471 | else:
472 | input = Variable(input)
473 |
474 | outputs = model(input)
475 | _, pred = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
476 | pred = pred.cpu().numpy()
477 | if pred[0] == 0:
478 | preds[j] = 20000
479 | else:
480 | preds[j] = 100
481 |
482 | if j == 30000:
483 | print '1/3 done'
484 | if j == 60000:
485 | print '2/3 done'
486 |
487 | print preds.reshape(s, s)
488 | ax_pred.imshow(preds.reshape((s,s)))
489 | ax_pred.set_title('predicted')
490 |
491 | ax_lab.axis('off')
492 | ax_ori.axis('off')
493 | ax_pred.axis('off')
494 |
495 | plt.show()
496 | fig.savefig('vi.png')
497 | print('saved as vi.png')
498 |
499 |
500 |
501 |
502 |
503 |
504 | # Train
505 | #-----------------------------------------------------------------------
506 | num_classes = 2
507 | num_epochs = 100
508 | #model = ConvNet(num_classes )
509 | #model = DeepResNet18(num_classes)
510 | #model = DeepResNet34(num_classes )
511 | model = DeepResNet50(num_classes)
512 | #model = DeepResNet101(num_classes )
513 | optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0001)
514 | #optimizer = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[2,4,6,8,10], gamma=0.5)
515 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
516 | print('')
517 | print('START TRAINING ...')
518 | print(time.time())
519 | print('ResNet50. 33% 30deg lr50')
520 | train = train_model(model, criterion, optimizer, lr_scheduler=piecewise_scheduler, num_epochs=num_epochs)
521 |
522 |
523 |
524 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Annotations import *
2 | from Volume import *
3 | from NeuronIds import *
4 | from border_mask import *
5 | from CremiFile import *
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/Clefts.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from scipy import ndimage
3 |
4 | class Clefts:
5 |
6 | def __init__(self, test, truth):
7 |
8 | test_clefts = test
9 | truth_clefts = truth
10 |
11 | self.test_clefts_mask = np.equal(test_clefts.data, 0xffffffffffffffff)
12 | self.truth_clefts_mask = np.equal(truth_clefts.data, 0xffffffffffffffff)
13 |
14 | self.test_clefts_edt = ndimage.distance_transform_edt(self.test_clefts_mask, sampling=test_clefts.resolution)
15 | self.truth_clefts_edt = ndimage.distance_transform_edt(self.truth_clefts_mask, sampling=truth_clefts.resolution)
16 |
17 | def count_false_positives(self, threshold = 200):
18 |
19 | mask1 = np.invert(self.test_clefts_mask)
20 | mask2 = self.truth_clefts_edt > threshold
21 | false_positives = self.truth_clefts_edt[np.logical_and(mask1, mask2)]
22 | return false_positives.size
23 |
24 | def count_false_negatives(self, threshold = 200):
25 |
26 | mask1 = np.invert(self.truth_clefts_mask)
27 | mask2 = self.test_clefts_edt > threshold
28 | false_negatives = self.test_clefts_edt[np.logical_and(mask1, mask2)]
29 | return false_negatives.size
30 |
31 | def acc_false_positives(self):
32 |
33 | mask = np.invert(self.test_clefts_mask)
34 | false_positives = self.truth_clefts_edt[mask]
35 | stats = {
36 | 'mean': np.mean(false_positives),
37 | 'std': np.std(false_positives),
38 | 'max': np.amax(false_positives),
39 | 'count': false_positives.size,
40 | 'median': np.median(false_positives)}
41 | return stats
42 |
43 | def acc_false_negatives(self):
44 |
45 | mask = np.invert(self.truth_clefts_mask)
46 | false_negatives = self.test_clefts_edt[mask]
47 | stats = {
48 | 'mean': np.mean(false_negatives),
49 | 'std': np.std(false_negatives),
50 | 'max': np.amax(false_negatives),
51 | 'count': false_negatives.size,
52 | 'median': np.median(false_negatives)}
53 | return stats
54 |
55 |
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/NeuronIds.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from border_mask import create_border_mask
3 | from voi import voi
4 | from rand import adapted_rand
5 |
6 | class NeuronIds:
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, groundtruth, border_threshold = None):
9 | """Create a new evaluation object for neuron ids against the provided ground truth.
10 |
11 | Parameters
12 | ----------
13 |
14 | groundtruth: Volume
15 | The ground truth volume containing neuron ids.
16 |
17 | border_threshold: None or float, in world units
18 | Pixels within `border_threshold` to a label border in the
19 | same section will be assigned to background and ignored during
20 | the evaluation.
21 | """
22 |
23 | assert groundtruth.resolution[1] == groundtruth.resolution[2], \
24 | "x and y resolutions of ground truth are not the same (%f != %f)" % \
25 | (groundtruth.resolution[1], groundtruth.resolution[2])
26 |
27 | self.groundtruth = groundtruth
28 | self.border_threshold = border_threshold
29 |
30 | if self.border_threshold:
31 |
32 | print "Computing border mask..."
33 |
34 | self.gt = np.zeros(groundtruth.data.shape, dtype=np.uint64)
35 | create_border_mask(
36 | groundtruth.data,
37 | self.gt,
38 | float(border_threshold)/groundtruth.resolution[1],
39 | np.uint64(-1))
40 | else:
41 | self.gt = np.array(self.groundtruth.data).copy()
42 |
43 | # current voi and rand implementations don't work with np.uint64(-1) as
44 | # background label, so we make it 0 here and bump all other labels
45 | self.gt += 1
46 |
47 | def voi(self, segmentation):
48 |
49 | assert list(segmentation.data.shape) == list(self.groundtruth.data.shape)
50 | assert list(segmentation.resolution) == list(self.groundtruth.resolution)
51 |
52 | print "Computing VOI..."
53 |
54 | return voi(np.array(segmentation.data), self.gt, ignore_groundtruth = [0])
55 |
56 | def adapted_rand(self, segmentation):
57 |
58 | assert list(segmentation.data.shape) == list(self.groundtruth.data.shape)
59 | assert list(segmentation.resolution) == list(self.groundtruth.resolution)
60 |
61 | print "Computing RAND..."
62 |
63 | return adapted_rand(np.array(segmentation.data), self.gt)
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/SynapticPartners.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from synaptic_partners import synaptic_partners_fscore
2 |
3 | class SynapticPartners:
4 |
5 | def __init__(self, matching_threshold = 400):
6 |
7 | self.matching_threshold = matching_threshold
8 |
9 | def fscore(self, rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, all_stats = False):
10 |
11 | return synaptic_partners_fscore(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, self.matching_threshold, all_stats)
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Clefts import *
2 | from NeuronIds import *
3 | from SynapticPartners import *
4 | from border_mask import *
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/border_mask.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import h5py
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import scipy
4 |
5 | def create_border_mask(input_data, target, max_dist, background_label,axis=0):
6 | """
7 | Overlay a border mask with background_label onto input data.
8 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
9 |
10 | Parameters
11 | ----------
12 | input_data : h5py.Dataset or numpy.ndarray - Input data containing neuron ids
13 | target : h5py.Datset or numpy.ndarray - Target which input data overlayed with border mask is written into.
14 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
15 | background_label : int - Border mask will be overlayed using this label.
16 | axis : int - Axis of iteration (perpendicular to 2d images for which mask will be generated)
17 | """
18 | sl = [slice(None) for d in xrange(len(target.shape))]
19 |
20 | for z in xrange(target.shape[axis]):
21 | sl[ axis ] = z
22 | border = create_border_mask_2d(input_data[tuple(sl)], max_dist)
23 | target_slice = input_data[tuple(sl)] if isinstance(input_data,h5py.Dataset) else np.copy(input_data[tuple(sl)])
24 | target_slice[border] = background_label
25 | target[tuple(sl)] = target_slice
26 |
27 | def create_and_write_masked_neuron_ids(in_file, out_file, max_dist, background_label, overwrite=False):
28 | """
29 | Overlay a border mask with background_label onto input data loaded from in_file and write into out_file.
30 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
31 |
32 | Parameters
33 | ----------
34 | in_file : CremiFile - Input file containing neuron ids
35 | out_file : CremiFile - Output file which input data overlayed with border mask is written into.
36 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
37 | background_label : int - Border mask will be overlayed using this label.
38 | overwrite : bool - Overwrite existing data in out_file (True) or do nothing if data is present in out_file (False).
39 | """
40 | if ( not in_file.has_neuron_ids() ) or ( (not overwrite) and out_file.has_neuron_ids() ):
41 | return
42 |
43 | neuron_ids, resolution, offset, comment = in_file.read_neuron_ids()
44 | comment = ('' if comment is None else comment + ' ') + 'Border masked with max_dist=%f' % max_dist
45 |
46 | path = "/volumes/labels/neuron_ids"
47 | group_path = "/".join( path.split("/")[:-1] )
48 | ds_name = path.split("/")[-1]
49 | if ( out_file.has_neuron_ids() ):
50 | del out_file.h5file[path]
51 | if (group_path not in out_file.h5file):
52 | out_file.h5file.create_group(group_path)
53 |
54 | group = out_file.h5file[group_path]
55 | target = group.create_dataset(ds_name, shape=neuron_ids.shape, dtype=neuron_ids.dtype)
56 | target.attrs["resolution"] = resolution
57 | target.attrs["comment"] = comment
58 | if offset != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
59 | target.attrs["offset"] = offset
60 |
61 | create_border_mask(neuron_ids, target, max_dist, background_label)
62 |
63 | def create_border_mask_2d(image, max_dist):
64 | """
65 | Create binary border mask for image.
66 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
67 |
68 | Parameters
69 | ----------
70 | image : numpy.ndarray - Image containing integer labels.
71 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
72 |
73 | Returns
74 | -------
75 | mask : numpy.ndarray - Binary mask of border pixels. Same shape as image.
76 | """
77 | max_dist = max(max_dist, 0)
78 |
79 | padded = np.pad(image, 1, mode='edge')
80 |
81 | border_pixels = np.logical_and(
82 | np.logical_and( image == padded[:-2, 1:-1], image == padded[2:, 1:-1] ),
83 | np.logical_and( image == padded[1:-1, :-2], image == padded[1:-1, 2:] )
84 | )
85 |
86 | distances = scipy.ndimage.distance_transform_edt(
87 | border_pixels,
88 | return_distances=True,
89 | return_indices=False
90 | )
91 |
92 | return distances <= max_dist
93 |
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/rand.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
5 |
6 | # Evaluation code courtesy of Juan Nunez-Iglesias, taken from
7 | # https://github.com/janelia-flyem/gala/blob/master/gala/evaluate.py
8 |
9 | def adapted_rand(seg, gt, all_stats=False):
10 | """Compute Adapted Rand error as defined by the SNEMI3D contest [1]
11 |
12 | Formula is given as 1 - the maximal F-score of the Rand index
13 | (excluding the zero component of the original labels). Adapted
14 | from the SNEMI3D MATLAB script, hence the strange style.
15 |
16 | Parameters
17 | ----------
18 | seg : np.ndarray
19 | the segmentation to score, where each value is the label at that point
20 | gt : np.ndarray, same shape as seg
21 | the groundtruth to score against, where each value is a label
22 | all_stats : boolean, optional
23 | whether to also return precision and recall as a 3-tuple with rand_error
24 |
25 | Returns
26 | -------
27 | are : float
28 | The adapted Rand error; equal to $1 - \frac{2pr}{p + r}$,
29 | where $p$ and $r$ are the precision and recall described below.
30 | prec : float, optional
31 | The adapted Rand precision. (Only returned when `all_stats` is ``True``.)
32 | rec : float, optional
33 | The adapted Rand recall. (Only returned when `all_stats` is ``True``.)
34 |
35 | References
36 | ----------
37 | [1]: http://brainiac2.mit.edu/SNEMI3D/evaluation
38 | """
39 | # segA is truth, segB is query
40 | segA = np.ravel(gt)
41 | segB = np.ravel(seg)
42 | n = segA.size
43 |
44 | n_labels_A = np.amax(segA) + 1
45 | n_labels_B = np.amax(segB) + 1
46 |
47 | ones_data = np.ones(n)
48 |
49 | p_ij = sparse.csr_matrix((ones_data, (segA[:], segB[:])), shape=(n_labels_A, n_labels_B))
50 |
51 | a = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,:]
52 | b = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,1:n_labels_B]
53 | c = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,0].todense()
54 | d = b.multiply(b)
55 |
56 | a_i = np.array(a.sum(1))
57 | b_i = np.array(b.sum(0))
58 |
59 | sumA = np.sum(a_i * a_i)
60 | sumB = np.sum(b_i * b_i) + (np.sum(c) / n)
61 | sumAB = np.sum(d) + (np.sum(c) / n)
62 |
63 | precision = sumAB / sumB
64 | recall = sumAB / sumA
65 |
66 | fScore = 2.0 * precision * recall / (precision + recall)
67 | are = 1.0 - fScore
68 |
69 | if all_stats:
70 | return (are, precision, recall)
71 | else:
72 | return are
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/synaptic_partners.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 | from munkres import Munkres
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | def synaptic_partners_fscore(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold = 400, all_stats = False):
6 | """Compute the f-score of the found synaptic partners.
7 |
8 | Parameters
9 | ----------
10 |
11 | rec_annotations: Annotations, containing found synaptic partners
12 |
13 | gt_annotations: Annotations, containing ground truth synaptic partners
14 |
15 | gt_segmentation: Volume, ground truth neuron segmentation
16 |
17 | matching_threshold: float, world units
18 | Euclidean distance threshold to consider two annotations a potential
19 | match. Annotations that are `matching_threshold` or more untis apart
20 | from each other are not considered as potential matches.
21 |
22 | all_stats: boolean, optional
23 | Whether to also return precision, recall, FP, FN, and matches as a 6-tuple with f-score
24 |
25 | Returns
26 | -------
27 |
28 | fscore: float
29 | The f-score of the found synaptic partners.
30 | precision: float, optional
31 | recall: float, optional
32 | fp: int, optional
33 | fn: int, optional
34 | filtered_matches: list of tuples, optional
35 | The indices of the matches with matching costs.
36 | """
37 |
38 | # get cost matrix
39 | costs = cost_matrix(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold)
40 |
41 | # match using Hungarian method
42 | print "Finding cost-minimal matches..."
43 | munkres = Munkres()
44 | matches = munkres.compute(costs.copy()) # have to copy, because munkres changes the cost matrix...
45 |
46 | filtered_matches = [ (i,j, costs[i][j]) for (i,j) in matches if costs[i][j] <= matching_threshold ]
47 | print str(len(filtered_matches)) + " matches found"
48 |
49 | # unmatched in rec = FP
50 | fp = len(rec_annotations.pre_post_partners) - len(filtered_matches)
51 |
52 | # unmatched in gt = FN
53 | fn = len(gt_annotations.pre_post_partners) - len(filtered_matches)
54 |
55 | # all ground truth elements - FN = TP
56 | tp = len(gt_annotations.pre_post_partners) - fn
57 |
58 | precision = float(tp)/(tp + fp)
59 | recall = float(tp)/(tp + fn)
60 | fscore = 2.0*precision*recall/(precision + recall)
61 |
62 | if all_stats:
63 | return (fscore, precision, recall, fp, fn, filtered_matches)
64 | else:
65 | return fscore
66 |
67 | def cost_matrix(rec, gt, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold):
68 |
69 | print "Computing matching costs..."
70 |
71 | rec_locations = pre_post_locations(rec, gt_segmentation)
72 | gt_locations = pre_post_locations(gt, gt_segmentation)
73 |
74 | rec_labels = pre_post_labels(rec_locations, gt_segmentation)
75 | gt_labels = pre_post_labels(gt_locations, gt_segmentation)
76 |
77 | size = max(len(rec_locations), len(gt_locations))
78 | costs = np.zeros((size, size), dtype=np.float)
79 | costs[:] = 2*matching_threshold
80 | num_potential_matches = 0
81 | for i in range(len(rec_locations)):
82 | for j in range(len(gt_locations)):
83 | c = cost(rec_locations[i], gt_locations[j], rec_labels[i], gt_labels[j], matching_threshold)
84 | costs[i,j] = c
85 | if c <= matching_threshold:
86 | num_potential_matches += 1
87 |
88 | print str(num_potential_matches) + " potential matches found"
89 |
90 | return costs
91 |
92 | def pre_post_locations(annotations, gt_segmentation):
93 | """Get the locations of the annotations relative to the ground truth offset."""
94 |
95 | locations = annotations.locations()
96 | shift = sub(annotations.offset, gt_segmentation.offset)
97 |
98 | return [
99 | (add(annotations.get_annotation(pre_id)[1], shift), add(annotations.get_annotation(post_id)[1], shift)) for (pre_id, post_id) in annotations.pre_post_partners
100 | ]
101 |
102 | def pre_post_labels(locations, segmentation):
103 |
104 | return [ (segmentation[pre], segmentation[post]) for (pre, post) in locations ]
105 |
106 |
107 | def cost(pre_post_location1, pre_post_location2, labels1, labels2, matching_threshold):
108 |
109 | max_cost = 2*matching_threshold
110 |
111 | # pairs do not link the same segments
112 | if labels1 != labels2:
113 | return max_cost
114 |
115 | pre_dist = distance(pre_post_location1[0], pre_post_location2[0])
116 | post_dist = distance(pre_post_location1[1], pre_post_location2[1])
117 |
118 | if pre_dist > matching_threshold or post_dist > matching_threshold:
119 | return max_cost
120 |
121 | return 0.5*(pre_dist + post_dist)
122 |
123 | def distance(a, b):
124 | return np.linalg.norm(np.array(list(a))-np.array(list(b)))
125 |
126 | def add(a, b):
127 | return tuple([a[d] + b[d] for d in range(len(b))])
128 |
129 | def sub(a, b):
130 | return tuple([a[d] - b[d] for d in range(len(b))])
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/voi.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 |
3 | # Evaluation code courtesy of Juan Nunez-Iglesias, taken from
4 | # https://github.com/janelia-flyem/gala/blob/master/gala/evaluate.py
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
8 |
9 | def voi(reconstruction, groundtruth, ignore_reconstruction=[], ignore_groundtruth=[0]):
10 | """Return the conditional entropies of the variation of information metric. [1]
11 |
12 | Let X be a reconstruction, and Y a ground truth labelling. The variation of
13 | information between the two is the sum of two conditional entropies:
14 |
15 | VI(X, Y) = H(X|Y) + H(Y|X).
16 |
17 | The first one, H(X|Y), is a measure of oversegmentation, the second one,
18 | H(Y|X), a measure of undersegmentation. These measures are referred to as
19 | the variation of information split or merge error, respectively.
20 |
21 | Parameters
22 | ----------
23 | seg : np.ndarray, int type, arbitrary shape
24 | A candidate segmentation.
25 | gt : np.ndarray, int type, same shape as `seg`
26 | The ground truth segmentation.
27 | ignore_seg, ignore_gt : list of int, optional
28 | Any points having a label in this list are ignored in the evaluation.
29 | By default, only the label 0 in the ground truth will be ignored.
30 |
31 | Returns
32 | -------
33 | (split, merge) : float
34 | The variation of information split and merge error, i.e., H(X|Y) and H(Y|X)
35 |
36 | References
37 | ----------
38 | [1] Meila, M. (2007). Comparing clusterings - an information based
39 | distance. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 98, 873-895.
40 | """
41 | (hyxg, hxgy) = split_vi(reconstruction, groundtruth, ignore_reconstruction, ignore_groundtruth)
42 | return (hxgy, hyxg)
43 |
44 | def split_vi(x, y=None, ignore_x=[0], ignore_y=[0]):
45 | """Return the symmetric conditional entropies associated with the VI.
46 |
47 | The variation of information is defined as VI(X,Y) = H(X|Y) + H(Y|X).
48 | If Y is the ground-truth segmentation, then H(Y|X) can be interpreted
49 | as the amount of under-segmentation of Y and H(X|Y) is then the amount
50 | of over-segmentation. In other words, a perfect over-segmentation
51 | will have H(Y|X)=0 and a perfect under-segmentation will have H(X|Y)=0.
52 |
53 | If y is None, x is assumed to be a contingency table.
54 |
55 | Parameters
56 | ----------
57 | x : np.ndarray
58 | Label field (int type) or contingency table (float). `x` is
59 | interpreted as a contingency table (summing to 1.0) if and only if `y`
60 | is not provided.
61 | y : np.ndarray of int, same shape as x, optional
62 | A label field to compare to `x`.
63 | ignore_x, ignore_y : list of int, optional
64 | Any points having a label in this list are ignored in the evaluation.
65 | Ignore 0-labeled points by default.
66 |
67 | Returns
68 | -------
69 | sv : np.ndarray of float, shape (2,)
70 | The conditional entropies of Y|X and X|Y.
71 |
72 | See Also
73 | --------
74 | vi
75 | """
76 | _, _, _ , hxgy, hygx, _, _ = vi_tables(x, y, ignore_x, ignore_y)
77 | # false merges, false splits
78 | return np.array([hygx.sum(), hxgy.sum()])
79 |
80 | def vi_tables(x, y=None, ignore_x=[0], ignore_y=[0]):
81 | """Return probability tables used for calculating VI.
82 |
83 | If y is None, x is assumed to be a contingency table.
84 |
85 | Parameters
86 | ----------
87 | x, y : np.ndarray
88 | Either x and y are provided as equal-shaped np.ndarray label fields
89 | (int type), or y is not provided and x is a contingency table
90 | (sparse.csc_matrix) that may or may not sum to 1.
91 | ignore_x, ignore_y : list of int, optional
92 | Rows and columns (respectively) to ignore in the contingency table.
93 | These are labels that are not counted when evaluating VI.
94 |
95 | Returns
96 | -------
97 | pxy : sparse.csc_matrix of float
98 | The normalized contingency table.
99 | px, py, hxgy, hygx, lpygx, lpxgy : np.ndarray of float
100 | The proportions of each label in `x` and `y` (`px`, `py`), the
101 | per-segment conditional entropies of `x` given `y` and vice-versa, the
102 | per-segment conditional probability p log p.
103 | """
104 | if y is not None:
105 | pxy = contingency_table(x, y, ignore_x, ignore_y)
106 | else:
107 | cont = x
108 | total = float(cont.sum())
109 | # normalize, since it is an identity op if already done
110 | pxy = cont / total
111 |
112 | # Calculate probabilities
113 | px = np.array(pxy.sum(axis=1)).ravel()
114 | py = np.array(pxy.sum(axis=0)).ravel()
115 | # Remove zero rows/cols
116 | nzx = px.nonzero()[0]
117 | nzy = py.nonzero()[0]
118 | nzpx = px[nzx]
119 | nzpy = py[nzy]
120 | nzpxy = pxy[nzx, :][:, nzy]
121 |
122 | # Calculate log conditional probabilities and entropies
123 | lpygx = np.zeros(np.shape(px))
124 | lpygx[nzx] = xlogx(divide_rows(nzpxy, nzpx)).sum(axis=1)
125 | # \sum_x{p_{y|x} \log{p_{y|x}}}
126 | hygx = -(px*lpygx) # \sum_x{p_x H(Y|X=x)} = H(Y|X)
127 |
128 | lpxgy = np.zeros(np.shape(py))
129 | lpxgy[nzy] = xlogx(divide_columns(nzpxy, nzpy)).sum(axis=0)
130 | hxgy = -(py*lpxgy)
131 |
132 | return [pxy] + list(map(np.asarray, [px, py, hxgy, hygx, lpygx, lpxgy]))
133 |
134 | def contingency_table(seg, gt, ignore_seg=[0], ignore_gt=[0], norm=True):
135 | """Return the contingency table for all regions in matched segmentations.
136 |
137 | Parameters
138 | ----------
139 | seg : np.ndarray, int type, arbitrary shape
140 | A candidate segmentation.
141 | gt : np.ndarray, int type, same shape as `seg`
142 | The ground truth segmentation.
143 | ignore_seg : list of int, optional
144 | Values to ignore in `seg`. Voxels in `seg` having a value in this list
145 | will not contribute to the contingency table. (default: [0])
146 | ignore_gt : list of int, optional
147 | Values to ignore in `gt`. Voxels in `gt` having a value in this list
148 | will not contribute to the contingency table. (default: [0])
149 | norm : bool, optional
150 | Whether to normalize the table so that it sums to 1.
151 |
152 | Returns
153 | -------
154 | cont : scipy.sparse.csc_matrix
155 | A contingency table. `cont[i, j]` will equal the number of voxels
156 | labeled `i` in `seg` and `j` in `gt`. (Or the proportion of such voxels
157 | if `norm=True`.)
158 | """
159 | segr = seg.ravel()
160 | gtr = gt.ravel()
161 | ignored = np.zeros(segr.shape, np.bool)
162 | data = np.ones(len(gtr))
163 | for i in ignore_seg:
164 | ignored[segr == i] = True
165 | for j in ignore_gt:
166 | ignored[gtr == j] = True
167 | data[ignored] = 0
168 | cont = sparse.coo_matrix((data, (segr, gtr))).tocsc()
169 | if norm:
170 | cont /= float(cont.sum())
171 | return cont
172 |
173 | def divide_columns(matrix, row, in_place=False):
174 | """Divide each column of `matrix` by the corresponding element in `row`.
175 |
176 | The result is as follows: out[i, j] = matrix[i, j] / row[j]
177 |
178 | Parameters
179 | ----------
180 | matrix : np.ndarray, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix, shape (M, N)
181 | The input matrix.
182 | column : a 1D np.ndarray, shape (N,)
183 | The row dividing `matrix`.
184 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
185 | Do the computation in-place.
186 |
187 | Returns
188 | -------
189 | out : same type as `matrix`
190 | The result of the row-wise division.
191 | """
192 | if in_place:
193 | out = matrix
194 | else:
195 | out = matrix.copy()
196 | if type(out) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
197 | if type(out) == sparse.csc_matrix:
198 | convert_to_csc = True
199 | out = out.tocsr()
200 | else:
201 | convert_to_csc = False
202 | row_repeated = np.take(row, out.indices)
203 | nz = out.data.nonzero()
204 | out.data[nz] /= row_repeated[nz]
205 | if convert_to_csc:
206 | out = out.tocsc()
207 | else:
208 | out /= row[np.newaxis, :]
209 | return out
210 |
211 | def divide_rows(matrix, column, in_place=False):
212 | """Divide each row of `matrix` by the corresponding element in `column`.
213 |
214 | The result is as follows: out[i, j] = matrix[i, j] / column[i]
215 |
216 | Parameters
217 | ----------
218 | matrix : np.ndarray, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix, shape (M, N)
219 | The input matrix.
220 | column : a 1D np.ndarray, shape (M,)
221 | The column dividing `matrix`.
222 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
223 | Do the computation in-place.
224 |
225 | Returns
226 | -------
227 | out : same type as `matrix`
228 | The result of the row-wise division.
229 | """
230 | if in_place:
231 | out = matrix
232 | else:
233 | out = matrix.copy()
234 | if type(out) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
235 | if type(out) == sparse.csr_matrix:
236 | convert_to_csr = True
237 | out = out.tocsc()
238 | else:
239 | convert_to_csr = False
240 | column_repeated = np.take(column, out.indices)
241 | nz = out.data.nonzero()
242 | out.data[nz] /= column_repeated[nz]
243 | if convert_to_csr:
244 | out = out.tocsr()
245 | else:
246 | out /= column[:, np.newaxis]
247 | return out
248 |
249 | def xlogx(x, out=None, in_place=False):
250 | """Compute x * log_2(x).
251 |
252 | We define 0 * log_2(0) = 0
253 |
254 | Parameters
255 | ----------
256 | x : np.ndarray or scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix
257 | The input array.
258 | out : same type as x (optional)
259 | If provided, use this array/matrix for the result.
260 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
261 | Operate directly on x.
262 |
263 | Returns
264 | -------
265 | y : same type as x
266 | Result of x * log_2(x).
267 | """
268 | if in_place:
269 | y = x
270 | elif out is None:
271 | y = x.copy()
272 | else:
273 | y = out
274 | if type(y) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
275 | z = y.data
276 | else:
277 | z = y
278 | nz = z.nonzero()
279 | z[nz] *= np.log2(z[nz])
280 | return y
281 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/*Filtered Mask.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/*Filtered Mask.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/*Visualize Boundary.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/*Visualize Boundary.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/6p.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/6p.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/acc.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/acc.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/err.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/err.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/loss.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/loss.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/n.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/res window.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/res window.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/rot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/rot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/io/CremiFile.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import h5py
2 | import numpy as np
3 | from Annotations import *
4 | from Volume import *
5 |
6 | class CremiFile(object):
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, filename, mode):
9 |
10 | self.h5file = h5py.File(filename, mode)
11 |
12 | if mode == "w" or mode == "a":
13 | self.h5file["/"].attrs["file_format"] = "0.2"
14 |
15 | def __create_group(self, group):
16 |
17 | path = "/"
18 | for d in group.split("/"):
19 | path += d + "/"
20 | try:
21 | self.h5file.create_group(path)
22 | except ValueError:
23 | pass
24 |
25 | def __create_dataset(self, path, data, dtype, compression = None):
26 | """Wrapper around h5py's create_dataset. Creates the group, if not
27 | existing. Deletes a previous dataset, if existing and not compatible.
28 | Otherwise, replaces the dataset.
29 | """
30 |
31 | group = "/".join(path.split("/")[:-1])
32 | ds_name = path.split("/")[-1]
33 |
34 | self.__create_group(group)
35 |
36 | if ds_name in self.h5file[group]:
37 |
38 | ds = self.h5file[path]
39 | if ds.dtype == dtype and ds.shape == np.array(data).shape:
40 | print "overwriting existing dataset"
41 | self.h5file[path][:] = data[:]
42 | return
43 |
44 | del self.h5file[path]
45 |
46 | self.h5file.create_dataset(path, data=data, dtype=dtype, compression=compression)
47 |
48 | def write_volume(self, volume, ds_name, dtype):
49 |
50 | self.__create_dataset(ds_name, data=volume.data, dtype=dtype, compression="gzip")
51 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["resolution"] = volume.resolution
52 | if volume.comment is not None:
53 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["comment"] = str(volume.comment)
54 | if tuple(volume.offset) != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
55 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["offset"] = volume.offset
56 |
57 | def read_volume(self, ds_name):
58 |
59 | volume = Volume(self.h5file[ds_name])
60 |
61 | volume.resolution = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["resolution"]
62 | if "offset" in self.h5file[ds_name].attrs:
63 | volume.offset = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["offset"]
64 | if "comment" in self.h5file[ds_name].attrs:
65 | volume.comment = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["comment"]
66 |
67 | return volume
68 |
69 | def __has_volume(self, ds_name):
70 |
71 | return ds_name in self.h5file
72 |
73 | def write_raw(self, raw):
74 | """Write a raw volume.
75 | """
76 |
77 | self.write_volume(raw, "/volumes/raw", np.uint8)
78 |
79 | def write_neuron_ids(self, neuron_ids):
80 | """Write a volume of segmented neurons.
81 | """
82 |
83 | self.write_volume(neuron_ids, "/volumes/labels/neuron_ids", np.uint64)
84 |
85 | def write_clefts(self, clefts):
86 | """Write a volume of segmented synaptic clefts.
87 | """
88 |
89 | self.write_volume(clefts, "/volumes/labels/clefts", np.uint64)
90 |
91 | def write_annotations(self, annotations):
92 | """Write pre- and post-synaptic site annotations.
93 | """
94 |
95 | if len(annotations.ids()) == 0:
96 | return
97 |
98 | self.__create_group("/annotations")
99 | if tuple(annotations.offset) != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
100 | self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs["offset"] = annotations.offset
101 |
102 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/ids", data=annotations.ids(), dtype=np.uint64)
103 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/types", data=annotations.types(), dtype=h5py.special_dtype(vlen=unicode), compression="gzip")
104 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/locations", data=annotations.locations(), dtype=np.double)
105 |
106 | if len(annotations.comments) > 0:
107 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/comments/target_ids", data=annotations.comments.keys(), dtype=np.uint64)
108 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/comments/comments", data=annotations.comments.values(), dtype=h5py.special_dtype(vlen=unicode))
109 |
110 | if len(annotations.pre_post_partners) > 0:
111 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/presynaptic_site/partners", data=annotations.pre_post_partners, dtype=np.uint64)
112 |
113 | def has_raw(self):
114 | """Check if this file contains a raw volume.
115 | """
116 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/raw")
117 |
118 | def has_neuron_ids(self):
119 | """Check if this file contains neuron ids.
120 | """
121 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids")
122 |
123 | def has_neuron_ids_confidence(self):
124 | """Check if this file contains confidence information about neuron ids.
125 | """
126 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids_confidence")
127 |
128 | def has_clefts(self):
129 | """Check if this file contains synaptic clefts.
130 | """
131 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/clefts")
132 |
133 | def has_annotations(self):
134 | """Check if this file contains synaptic partner annotations.
135 | """
136 | return "/annotations" in self.h5file
137 |
138 | def has_segment_annotations(self):
139 | """Check if this file contains segment annotations.
140 | """
141 | return "/annotations" in self.h5file
142 |
143 | def read_raw(self):
144 | """Read the raw volume.
145 | Returns a Volume.
146 | """
147 |
148 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/raw")
149 |
150 | def read_neuron_ids(self):
151 | """Read the volume of segmented neurons.
152 | Returns a Volume.
153 | """
154 |
155 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids")
156 |
157 | def read_neuron_ids_confidence(self):
158 | """Read confidence information about neuron ids.
159 | Returns Confidences.
160 | """
161 |
162 | confidences = Confidences(num_levels=2)
163 | if not self.has_neuron_ids_confidence():
164 | return confidences
165 |
166 | data = self.h5file["/volumes/labels/neuron_ids_confidence"]
167 | i = 0
168 | while i < len(data):
169 | level = data[i]
170 | i += 1
171 | num_ids = data[i]
172 | i += 1
173 | confidences.add_all(level, data[i:i+num_ids])
174 | i += num_ids
175 |
176 | return confidences
177 |
178 | def read_clefts(self):
179 | """Read the volume of segmented synaptic clefts.
180 | Returns a Volume.
181 | """
182 |
183 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/labels/clefts")
184 |
185 | def read_annotations(self):
186 | """Read pre- and post-synaptic site annotations.
187 | """
188 |
189 | annotations = Annotations()
190 |
191 | if not "/annotations" in self.h5file:
192 | return annotations
193 |
194 | offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
195 | if "offset" in self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs:
196 | offset = self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs["offset"]
197 | annotations.offset = offset
198 |
199 | ids = self.h5file["/annotations/ids"]
200 | types = self.h5file["/annotations/types"]
201 | locations = self.h5file["/annotations/locations"]
202 | for i in range(len(ids)):
203 | annotations.add_annotation(ids[i], types[i], locations[i])
204 |
205 | if "comments" in self.h5file["/annotations"]:
206 | ids = self.h5file["/annotations/comments/target_ids"]
207 | comments = self.h5file["/annotations/comments/comments"]
208 | for (id, comment) in zip(ids, comments):
209 | annotations.add_comment(id, comment)
210 |
211 | if "presynaptic_site/partners" in self.h5file["/annotations"]:
212 | pre_post = self.h5file["/annotations/presynaptic_site/partners"]
213 | for (pre, post) in pre_post:
214 | annotations.set_pre_post_partners(pre, post)
215 |
216 | return annotations
217 |
218 | def close(self):
219 |
220 | self.h5file.close()
221 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/io/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from CremiFile import *
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/Resnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
4 |
5 |
6 | def residualLayer2(conv2d1, norm2d, input, nChannels, nOutChannels=False, stride=1, conv2d2=False):
7 | """ Deep Residual Network
8 | https://github.com/gcr/torch-residual-networks
9 |
10 | giving stack of 2 layers as a block providing shortcuts."""
11 |
12 |
13 | if not nOutChannels:
14 | nOutChannels = nChannels
15 | if not conv2d2:
16 | conv2d2 = conv2d1
17 |
18 | # part 1: conv
19 | net = conv2d1(input)
20 | net = norm2d(net) # learnable parameters
21 | net = F.relu(net)
22 | net = conv2d2(net)
23 |
24 |
25 | # part 2: identity / skip connection
26 | skip = input
27 | if stride > 1: # optional downsampling
28 | skip = L.SpatialAveragePooling(1, 1, stride, stride).forward(skip.cpu().data)
29 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
30 | if nOutChannels > nChannels: # optional padding
31 | skip = L.Padding(1, (nOutChannels - nChannels), 3).forward(skip.cpu().data)
32 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
33 | elif nOutChannels < nChannels: # optional narrow
34 | skip = L.Narrow(2, 1, nOutChannels).forward(skip.cpu().data)
35 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
36 |
37 |
38 | # H(x) + x
39 | net = norm2d(net)
40 | #print "skip: " + str(skip.data.size())
41 | #print "net: " + str(net.data.size())
42 | net = torch.add(skip, net)
43 | # net = F.relu(net) # relu here ? see: http://www.gitxiv.com/comments/7rffyqcPLirEEsmpX
44 | #net = norm2d(net) # ==========================BN after add or before ???
45 |
46 | return net
47 |
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 | class DeepResNet18(nn.Module):
55 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=3, padding=1):
56 | super(DeepResNet18, self).__init__()
57 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
58 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
59 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
60 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
61 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
62 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
63 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
64 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
65 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
66 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
67 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
68 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
69 | self.linear = nn.Linear(256, 2)
70 |
71 | def forward(self, x):
72 | # ----> 1, 33, 33
73 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
74 |
75 | # ----> 32, 33, 33 First Group 2X
76 | for i in range(2): x = residualLayer2(self.conv2, self.norm1, x, 32)
77 |
78 | # ----> 64, 17, 17 Second Group 2X
79 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv3, self.norm2, x, 32, 64, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv4)
80 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv4, self.norm2, x, 64)
81 |
82 | # ----> 128, 9, 9 Third Group 2X
83 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv5, self.norm3, x, 64, 128, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv6)
84 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv6, self.norm3, x, 128)
85 |
86 | # ----> 256, 5, 5 Fourth Group 2X
87 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv7, self.norm4, x, 128, 256, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv8)
88 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv8, self.norm4, x, 256)
89 |
90 | # ----> 256, 5, 5 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
91 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(5,5)(x)
92 | x = x.view(-1, 256)
93 | x = self.linear(x)
94 |
95 |
96 | return x
97 |
98 |
99 | class DeepResNet34(nn.Module):
100 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=5, padding=2):
101 | super(DeepResNet34, self).__init__()
102 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
103 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
104 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
105 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
106 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
107 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
108 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
109 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
110 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
111 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
112 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
113 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
114 | self.linear = nn.Linear(256, 2)
115 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
116 |
117 | def forward(self, x):
118 | # ------> 65 * 65
119 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
120 | x = self.pool(x) # ================= max pooling ??
121 | # ------> 32 * 32
122 | for i in range(3): x = residualLayer2(self.conv2, self.norm1, x, 32)
123 | # ------> 32 * 32
124 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv3, self.norm2, x, 32, 64, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv4)
125 | for i in range(4-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv4, self.norm2, x, 64)
126 |
127 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv5, self.norm3, x, 64, 128, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv6)
128 | for i in range(6-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv6, self.norm3, x, 128)
129 |
130 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv7, self.norm4, x, 128, 256, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv8)
131 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv8, self.norm4, x, 256)
132 |
133 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(8,8)(x)
134 | x = x.view(-1, 256)
135 | x = self.linear(x)
136 |
137 |
138 | return x
139 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/Resnet_3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | class DeepResNet101(nn.Module):
8 |
9 | """using bottle-neck building block """
10 |
11 |
12 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=7, padding=3):
13 | super(DeepResNet101, self).__init__()
14 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
15 | self.conv2_ = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 1, stride=2)
16 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 5, padding=2)
17 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
18 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, 128, 5, padding=2)
19 | self.conv5_ = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 1, stride=2)
20 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 5, padding=2)
21 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
22 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(64, 256, 5, padding=2)
23 | self.conv8_ = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 1, stride=2)
24 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 5, padding=2)
25 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
26 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(128, 512, 5, padding=2)
27 | self.conv11_ = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 1, stride=2)
28 | self.conv11 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, 5, padding=2)
29 | self.conv12 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
30 | self.conv13 = nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, 5, padding=2)
31 |
32 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
33 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
34 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
35 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
36 | self.norm5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
37 | self.norm6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
38 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
39 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 128)
40 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(128, 2)
41 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
42 |
43 | def forward(self, x):
44 | # ----> 1, 129, 129
45 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
46 | x = self.pool(x) # max pooling ? 3x3 s=2
47 |
48 | # ----> 32, 64, 64 First Group
49 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2_, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 32, 32, 128, stride=2)
50 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 128, 32, 128)
51 |
52 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5_, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 128, 64, 256, stride=2)
53 | for i in range(8-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 256, 64, 256)
54 |
55 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8_, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 256, 128, 512, stride=2)
56 | for i in range(36-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 512, 128, 512)
57 |
58 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11_, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 512, 256, 1024, stride=2)
59 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 1024, 256, 1024)
60 |
61 | # ----> 1024, 4, 4 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
62 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(4,4)(x)
63 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
64 | x = self.linear1(x)
65 | x = F.dropout(x) # ==============================
66 | x = self.linear2(x)
67 | x = self.linear3(x)
68 |
69 | return x
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | class DeepResNet50(nn.Module):
76 |
77 | """using bottle-neck building block """
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=7, padding=3): #=============== conv window size 5/22 9:24pm
82 | super(DeepResNet50, self).__init__()
83 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
84 | self.conv2_ = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 1, stride=2)
85 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 5, padding=2)
86 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
87 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, 128, 5, padding=2)
88 | self.conv5_ = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 1, stride=2)
89 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 5, padding=2)
90 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
91 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(64, 256, 5, padding=2)
92 | self.conv8_ = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 1, stride=2)
93 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 5, padding=2)
94 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
95 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(128, 512, 5, padding=2)
96 | self.conv11_ = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 1, stride=2)
97 | self.conv11 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, 5, padding=2)
98 | self.conv12 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
99 | self.conv13 = nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, 5, padding=2)
100 |
101 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
102 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
103 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
104 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
105 | self.norm5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
106 | self.norm6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
107 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
108 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 128)
109 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(128, 2)
110 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
111 |
112 |
113 | def forward(self, x):
114 | # ----> 1, 129, 129
115 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
116 | x = self.pool(x) # ================= max pooling ? better without here
117 |
118 |
119 | # ----> 32, 64, 64 First Group
120 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2_, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 32, 32, 128, stride=2)
121 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 128, 32, 128)
122 |
123 | # ----> 128, 32, 32 Second Group
124 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5_, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 128, 64, 256, stride=2)
125 | for i in range(4-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 256, 64, 256)
126 |
127 | # ----> 256, 16, 16 Third Group
128 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8_, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 256, 128, 512, stride=2)
129 | for i in range(6-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 512, 128, 512)
130 |
131 | # ----> 512, 8,8 Fourth Group
132 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11_, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 512, 256, 1024, stride=2)
133 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 1024, 256, 1024)
134 |
135 | # ----> 1024, 4, 4 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
136 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(4,4)(x)
137 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
138 | x = self.linear1(x)
139 | x = F.dropout(x) # ==============================
140 | x = self.linear2(x)
141 | x = self.linear3(x)
142 |
143 | return x
144 |
145 |
146 | # stack of 3 layers providing shortcuts
147 | def residualLayer3(input, conv2d1, conv2d2, conv2d3, norm2d1, norm2d2, inChannels, hiddenChannels, outChannels, stride=1):
148 | net = conv2d1(input) # 1x1
149 | net = norm2d1(net)
150 | net = F.relu(net)
151 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout within blocks ???? 8.21 9pm
152 |
153 | net = conv2d2(net) # kernel 3x3 or 5x5
154 | net = norm2d1(net)
155 | net = F.relu(net)
156 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout ???? 8.21 9pm
157 |
158 | net = conv2d3(net) # 1x1
159 |
160 | skip = input
161 | #print "input: " + str(skip.data.size())
162 | if stride > 1:
163 | skip = L.SpatialAveragePooling(1, 1, stride, stride).forward(skip.cpu().data)
164 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
165 | if outChannels > inChannels:
166 | skip = L.Padding(1, (outChannels - inChannels), 3).forward(skip.cpu().data)
167 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
168 | elif outChannels < inChannels:
169 | skip = L.Narrow(2, 1, outChannels).forward(skip.cpu().data)
170 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
171 |
172 | #net = norm2d2(net)
173 | #print "skip: " + str(skip.data.size())
174 | #print "net: " + str(net.data.size())
175 | net = norm2d2(torch.add(skip, net)) # ==========================BN after add or before ???
176 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout ????
177 | return net
178 |
179 |
180 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/type/Annotations.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class Annotations:
2 |
3 | def __init__(self, offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)):
4 |
5 | self.__types = {}
6 | self.__locations = {}
7 | self.comments = {}
8 | self.pre_post_partners = []
9 | self.offset = offset
10 |
11 | def __check(self, id):
12 | if not id in self.__types.keys():
13 | raise "there is no annotation with id " + str(id)
14 |
15 | def add_annotation(self, id, type, location):
16 | """Add a new annotation.
17 |
18 | Parameters
19 | ----------
20 |
21 | id: int
22 | The ID of the new annotation.
23 |
24 | type: string
25 | A string denoting the type of the annotation. Use
26 | "presynaptic_site" or "postsynaptic_site" for pre- and
27 | post-synaptic annotations, respectively.
28 |
29 | location: tuple, float
30 | The location of the annotation, relative to the offset.
31 | """
32 |
33 | self.__types[id] = type.encode('utf8')
34 | self.__locations[id] = location
35 |
36 | def add_comment(self, id, comment):
37 | """Add a comment to an annotation.
38 | """
39 |
40 | self.__check(id)
41 | self.comments[id] = comment.encode('utf8')
42 |
43 | def set_pre_post_partners(self, pre_id, post_id):
44 | """Mark two annotations as pre- and post-synaptic partners.
45 | """
46 |
47 | self.__check(pre_id)
48 | self.__check(post_id)
49 | self.pre_post_partners.append((pre_id, post_id))
50 |
51 | def ids(self):
52 | """Get the ids of all annotations.
53 | """
54 |
55 | return self.__types.keys()
56 |
57 | def types(self):
58 | """Get the types of all annotations.
59 | """
60 |
61 | return self.__types.values()
62 |
63 | def locations(self):
64 | """Get the locations of all annotations. Locations are in world units,
65 | relative to the offset.
66 | """
67 |
68 | return self.__locations.values()
69 |
70 | def get_annotation(self, id):
71 | """Get the type and location of an annotation by its id.
72 | """
73 |
74 | self.__check(id)
75 | return (self.__types[id], self.__locations[id])
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/type/Volume.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class Volume():
2 |
3 | def __init__(self, data, resolution = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0), offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0), comment = ""):
4 | self.data = data
5 | self.resolution = resolution
6 | self.offset = offset
7 | self.comment = comment
8 |
9 | def __getitem__(self, location):
10 | """Get the closest value of this volume to the given location. The
11 | location is in world units, relative to the volumes offset.
12 |
13 | This method takes into account the resolution of the volume. An
14 | IndexError exception is raised if the location is not contained in this
15 | volume.
16 |
17 | To access the raw pixel values, use the `data` attribute.
18 | """
19 |
20 | i = tuple([ round(location[d]/self.resolution[d]) for d in range(len(location)) ])
21 |
22 | if min(i) >= 0:
23 | try:
24 | return self.data[i]
25 | except IndexError as e:
26 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume: " + str(e))
27 |
28 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume")
29 |
30 | def __setitem__(self, location, value):
31 | """Set the closest value of this volume to the given location. The
32 | location is in world units, relative to the volumes offset.
33 |
34 | This method takes into account the resolution of the volume. An
35 | IndexError exception is raised if the location is not contained in this
36 | volume.
37 |
38 | To access the raw pixel values, use the `data` attribute.
39 | """
40 |
41 | i = tuple([ round(location[d]/self.resolution[d]) for d in range(len(location)) ])
42 |
43 | if min(i) >= 0:
44 | try:
45 | self.data[i] = value
46 | return
47 | except IndexError as e:
48 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume: " + str(e))
49 |
50 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume")
51 |
52 |
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
33 |
34 | ### Future work
35 |
36 | - The neighbor area of the boundaries was avoided in this experiment, however the boundary pixels from other organels (intracellular organels) should also be avoided. These pixels could be easily treated as target neuron boundaries which are actually not. The approach to address this challenge can be to pre-train a network to recognize these intracellular boundaries and filter out these pixels when creating training batches for the segmentation task.
37 |
38 | - the raw is originally a 3D image of size 125 * 1250 * 1250. I started by treating each layer in deapth 125 as an independent sample and trained my network with images in 2D sections. However, in later stages of experiments (which i was not able to do due to the time limit of my project), the third deimension should be considered to address the correlation between the neuron pixels at depth.
39 |
40 | ## Dependencies
41 |
42 | * python
43 | * pytorch
44 | * numpy
45 | * matplotlib
46 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Train.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | import torch.optim as optim
5 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
6 | from torch.autograd import Variable
7 |
8 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader, TensorDataset
9 | import torchvision
10 | from torchvision import transforms, datasets
11 | import torchvision.models as models
12 | import numpy as np
13 | from tempfile import TemporaryFile
14 | import matplotlib
15 | matplotlib.use('Agg')
16 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
17 | import scipy.ndimage as ndimage
18 | from scipy.ndimage.interpolation import rotate
19 | import time
20 | import os
21 | import random
22 |
23 | from Annotations import *
24 | from Volume import *
25 | from CremiFile import *
26 | from voi import voi
27 | from rand import adapted_rand
28 | plt.style.use('ggplot')
29 |
30 | from models.Resnet_3 import *
31 | from models.Resnet import *
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 | print('')
36 | print('DATASET LOADING ...')
37 | print('')
38 | emdset = CremiFile('sample_B_20160501.hdf', 'r')
39 |
40 | #Check the content of the datafile
41 | print "Has raw: " + str(emdset.has_raw())
42 | print "Has neuron ids: " + str(emdset.has_neuron_ids())
43 | print "Has clefts: " + str(emdset.has_clefts())
44 | print "Has annotations: " + str(emdset.has_annotations())
45 |
46 |
47 | #Read volume and annotation
48 | raw = emdset.read_raw()
49 | neuron_ids = emdset.read_neuron_ids()
50 | clefts = emdset.read_clefts()
51 | annotations = emdset.read_annotations()
52 |
53 | print("")
54 | print "Read raw: " + str(raw) + \
55 | ", resolution " + str(raw.resolution) + \
56 | ", offset " + str(raw.offset) + \
57 | ", data size " + str(raw.data.shape) + \
58 | ("" if raw.comment == None else ", comment \"" + raw.comment + "\"")
59 |
60 | print "Read neuron_ids: " + str(neuron_ids) + \
61 | ", resolution " + str(neuron_ids.resolution) + \
62 | ", offset " + str(neuron_ids.offset) + \
63 | ", data size " + str(neuron_ids.data.shape) + \
64 | ("" if neuron_ids.comment == None else ", comment \"" + neuron_ids.comment + "\"")
65 |
66 | print "Read clefts: " + str(clefts) + \
67 | ", resolution " + str(clefts.resolution) + \
68 | ", offset " + str(clefts.offset) + \
69 | ", data size " + str(clefts.data.shape) + \
70 | ("" if clefts.comment == None else ", comment \"" + clefts.comment + "\"")
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | def mask_filtered(raw, neuron_ids):
76 | """
77 | Image boudnary dilation
78 | Compute mask on each depth for un-selectable dilated(6X) boundary pixels (labeled as value 200.),
79 | the selectable background (0.) and actual boundary (100.) pixels
80 |
81 | return(numpy array): mask of shape 125,1250,1250
82 | """
83 | print ''
84 | print ''
85 | print 'building mask-5X from raw dataset...'
86 | since = time.time()
87 |
88 | d, h, w = raw.data.shape
89 | mask = np.empty([d, h, w]).astype('float32')
90 | for i in range(d):
91 | for j in range(h):
92 | for k in range(w):
93 | pixel = neuron_ids.data[i, j, k]
94 | if check_boundary(pixel, i, j, k, neuron_ids):
95 | mask[i, j, k] = 100
96 | else:
97 | mask[i, j, k] = 0
98 | if (i + 1) % 1 == 0:
99 | print str(0.8 * (i + 1)) + '% done'
100 |
101 | mask_dilated = ndimage.binary_dilation(mask, iterations=7).astype(mask.dtype)
102 | mask_filtered = 200 * mask_dilated - mask
103 |
104 | filter_time = time.time()
105 | time_elapsed = filter_time - since
106 | print('Mask complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format(
107 | time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60))
108 |
109 |
110 | print 'save to maskfile7X.npy'
111 | np.save('maskfile7X.npy', mask_filtered)
112 | print 'saved'
113 |
114 |
115 | def check_boundary(pixel, x, y, z, neuron_ids):
116 | """
117 | Check if a pixel at position (x,y,z) is labeled
118 | as boundary/non-boundary in neuron_ids.
119 |
120 | return(boolean): boundary
121 | """
122 | max_z = neuron_ids.data.shape[2] - 1
123 | max_y = neuron_ids.data.shape[1] - 1
124 | a = neuron_ids.data[x, y, z - 1] if z > 0 else pixel
125 | b = neuron_ids.data[x, y, z + 1] if z < max_z else pixel
126 | c = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z] if y > 0 else pixel
127 | d = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z] if y < max_y else pixel
128 | e = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z - 1] if (y > 0 and z > 0) else pixel
129 | f = neuron_ids.data[x, y - 1, z + 1] if (y > 0 and z < max_z) else pixel
130 | g = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z - 1] if (y < max_y and z > 0) else pixel
131 | h = neuron_ids.data[x, y + 1, z + 1] if (y < max_y and z < max_z) else pixel
132 |
133 | neighbors = [a, b, c, d, e, f, g, h]
134 | boundary = False
135 | for neighbor in neighbors:
136 | if pixel != neighbor:
137 | boundary = True
138 |
139 | return boundary
140 |
141 |
142 | # Seed a random number generator
143 | #seed = 24102016
144 | #rng = np.random.RandomState(seed)
145 | def random_rotation(inputs):
146 | """Randomly rotates a subset of images in a batch.
147 | reference: https://github.com/CSTR-Edinburgh/mlpractical/blob/mlp2016-7/master/notebooks/05_Non-linearities_and_regularisation.ipynb
148 |
149 | * chooses 30-50% of the images in the batch at random
150 | * for each image in the 30-50% chosen, rotates the image by a random angle in [-60, 60]
151 | * returns a new array of size (129, 129) in which the rows corresponding to the 25% chosen images are the vectors corresponding to the new randomly rotated images, while the remaining rows correspond to the original images.
152 | Args:
153 | inputs: Input image batch, an array of shape (129, 129).
154 |
155 | Returns:
156 | An array of shape (129, 129) corresponding to a copy
157 | of the original `inputs` array that was randomly selected
158 | to be rotated by a random angle. The original `inputs`
159 | array should not be modified.
160 | """
161 |
162 | new_ims = np.zeros(inputs.shape).astype('float32')
163 | indices = random.randint(-1,1)
164 | angles = random.uniform(-30., 30.)
165 | if indices == 0:
166 | rotate(inputs, angles, output = new_ims, order=1, reshape=False)
167 |
168 | return new_ims
169 |
170 |
171 |
172 |
173 | #mask_filtered(raw, neuron_ids) # used only when the first time of training
174 | mask = np.load('maskfile5X.npy')
175 | print ''
176 | print 'mask loaded'
177 |
178 | class NeuronSegmenDataset(Dataset):
179 | """Raw pixel and its label.
180 | Dataset splitted into 80,000 training and 20,000 validation set
181 | """
182 |
183 | def __init__(self, raw, neuron_ids, mask, phase, transform=None):
184 | """
185 | Args:
186 | raw(Volume): raw
187 | neuron_ids(Volume): neuron segmentation labels
188 | mask(numpy ndarray): filtered mask
189 | phase(String): 'train' or 'val'
190 | transform(callable, optional): optional data augmentation to be applied
191 | """
192 |
193 | self.phase = phase
194 | self.raw = raw
195 | self.neuron_ids = neuron_ids
196 | self.mask = mask
197 | self.transform = transform
198 |
199 | def __len__(self):
200 | """ length of the dataset """
201 | if self.phase == 'train':
202 | x = 80000
203 | else:
204 | x = 20000
205 |
206 | return x
207 |
208 | def __getitem__(self, idx):
209 | """
210 | Return 33*33 patches for each raw pixel at the center
211 | positive if boundary pixel, negative if non-boundary pixel
212 | """
213 | depth = self.raw.data.shape[0]
214 | size = self.raw.data.shape[1]
215 |
216 |
217 | while True:
218 | d = random.randint(0, depth - 1)
219 | h = random.randint(64, size - 65)
220 | w = random.randint(64, size - 65)
221 | ids_pixel = self.neuron_ids.data[d, h, w]
222 | pixel = self.mask[d, h, w]
223 |
224 | if idx % 2 == 0: #control half samples to be boundary pixels
225 | if pixel == 100.:
226 | raw_batch = self.raw.data[d][h - 64:h + 65, w - 64:w + 65].astype(
227 | 'float32') # crop a 129*129 patch
228 |
229 |
230 | if self.transform:
231 | raw_batch = self.transform(raw_batch)
232 |
233 | raw_batch = raw_batch.reshape([1, 129, 129])
234 | raw_batch = torch.from_numpy(raw_batch)
235 | sample = (raw_batch, 0)
236 |
237 | break
238 | elif pixel == 0.: # the other half as non-boundary pixel
239 | raw_batch = self.raw.data[d][h - 64:h + 65, w - 64:w + 65].astype(
240 | 'float32') # crop 33*33 patch
241 | raw_batch = raw_batch.reshape([1, 129, 129])
242 |
243 | if self.transform:
244 | raw_batch = self.transform(raw_batch)
245 |
246 | raw_batch = torch.from_numpy(raw_batch)
247 | sample = (raw_batch, 1)
248 |
249 | break
250 | return sample
251 |
252 |
253 | batch_size = 100
254 | emdset_seg = {x: NeuronSegmenDataset(raw, neuron_ids, mask, x, transform=random_rotation)
255 | for x in ['train', 'val']}
256 | emdset_loaders = {x: DataLoader(emdset_seg[x], batch_size=batch_size, shuffle=True)
257 | for x in ['train', 'val']}
258 | dset_sizes = {x: len(emdset_seg[x]) for x in ['train', 'val']}
259 | dset_classes = ['boundary', 'non-b']
260 | use_gpu = torch.cuda.is_available()
261 |
262 | print "Load num of batches: train " + str(len(emdset_loaders['train'])) + \
263 | ' validation ' + str(len(emdset_loaders['val']))
264 |
265 | print ('done')
266 | print ('')
267 |
268 |
269 | class ConvNet(nn.Module):
270 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel= 3, window =2, padding=1):
271 | super(ConvNet, self).__init__()
272 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
273 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
274 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
275 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
276 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
277 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
278 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
279 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
280 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(256, 512, kernel, padding=padding)
281 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(512, 512, kernel, padding=padding)
282 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(window)
283 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(2*2*256, 256)
284 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 256)
285 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(256, 128)
286 | self.linear4 = nn.Linear(128, D_out)
287 |
288 | def forward(self, x):
289 | x = F.relu(self.conv1(x))
290 | print "conv 1: " + str(x.data.size())
291 | x = F.relu(self.conv2(x))
292 | print "conv 2: " + str(x.data.size())
293 | x = self.pool(x)
294 | print "pool 1: " + str(x.data.size())
295 |
296 | x = F.relu(self.conv3(x))
297 | print "conv 3: " + str(x.data.size())
298 | x = F.relu(self.conv4(x))
299 | print "conv 4: " + str(x.data.size())
300 | x = self.pool(x)
301 | print "pool 2: " + str(x.data.size())
302 |
303 | x = F.relu(self.conv5(x))
304 | print "conv 5: " + str(x.data.size())
305 | x = F.relu(self.conv6(x))
306 | print "conv 6: " + str(x.data.size())
307 | x = self.pool(x)
308 | print "pool 3: " + str(x.data.size())
309 |
310 | x = F.relu(self.conv7(x))
311 | print "conv 7: " + str(x.data.size())
312 | x = F.relu(self.conv8(x))
313 | print "conv 8: " + str(x.data.size())
314 | x = self.pool(x)
315 | print "pool 4: " + str(x.data.size())
316 |
317 | x = x.view(-1, 2*2*256)
318 | x = F.relu(self.linear1(x))
319 |
320 | x = F.relu(self.linear3(x))
321 | x = F.relu(self.linear4(x))
322 |
323 | return x
324 |
325 |
326 |
327 | def exp_lr_scheduler(optimizer, epoch, init_lr=0.001, lr_decay_epoch=10):
328 | """Decay learning rate by a factor of 0.1 every 10 epochs"""
329 | lr = init_lr * (0.1**(epoch // lr_decay_epoch))
330 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
331 | param_group['lr'] = lr
332 |
333 | return optimizer
334 |
335 |
336 | def piecewise_scheduler(optimizer, epoch):
337 | if epoch % 50 ==0 :
338 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
339 | lr = param_group['lr'] / 2
340 | param_group['lr'] = lr
341 |
342 | return optimizer
343 |
344 |
345 |
346 | def train_model (model, criterion, optimizer, lr_scheduler=None, num_epochs=100):
347 | since = time.time()
348 | train_voi_split = np.zeros(num_epochs)
349 | train_voi_merge = np.zeros(num_epochs)
350 | train_rand = np.zeros(num_epochs)
351 |
352 | # iterate over epoch
353 | for epoch in range(num_epochs):
354 | print ('Epoch{}/{}'.format(epoch+1, num_epochs))
355 | print ('-' * 10)
356 |
357 |
358 | # train and validation set
359 | for phase in ['train', 'val']:
360 | if phase == 'train':
361 | if lr_scheduler:
362 | optimizer = lr_scheduler(optimizer, epoch + 1)
363 | model.train(True)
364 | else:
365 | model.train(True)
366 |
367 | running_loss = 0.
368 | running_accuracy = 0.
369 | total = 0
370 |
371 | # iterate over each batch
372 | for i, data in enumerate(emdset_loaders[phase]):
373 | inputs, labels = data
374 | if use_gpu:
375 | model = model.cuda()
376 | inputs, labels = Variable(inputs.cuda()), \
377 | Variable(labels.cuda())
378 | else:
379 | inputs, labels = Variable(inputs), Variable(labels)
380 |
381 |
382 | optimizer.zero_grad() # clean gradients in buffer
383 |
384 | outputs = model(inputs)
385 | _, predicted = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
386 | loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
387 |
388 |
389 | if phase == 'train':
390 | loss.backward()
391 | optimizer.step()
392 |
393 |
394 | running_loss += loss.data[0]
395 | running_accuracy += (predicted == labels.data).sum()
396 |
397 | # visualize random patches
398 | visualize_pred = True
399 | tt = visualize_pred and epoch == num_epochs-1 and phase == 'val' \
400 | and i+1 == len(emdset_loaders['val'])
401 | if tt:
402 | print('visualizing...')
403 | images_so_far = 0
404 | fig = plt.figure()
405 | for j in [6, 15, 38, 41, 86, 99]:
406 | images_so_far += 1
407 | ax = fig.add_subplot(3, 2, images_so_far)
408 | ax.axis('off')
409 | ax.set_title('Pred: {},\n Labeled: {}'.format(dset_classes[int(predicted.cpu().numpy()[j])],
410 | dset_classes[labels.data[j]]))
411 | ax.imshow(inputs.cpu().data[j].view(129,129).numpy())
412 | fig.savefig('6p.png')
413 | print 'done and saved to 6p.png'
414 |
415 |
416 | # normalize by number of batches
417 | running_loss /= (i + 1)
418 | running_accuracy = 100 * running_accuracy / dset_sizes[phase]
419 |
420 | # print statistics
421 | if epoch % 1 == 0:
422 | print('{} Loss: {:.4f} Acc: {:.4f}'.format(
423 | phase, running_loss, running_accuracy
424 | ))
425 | # print "\tvoi split : " + str(train_voi_split)
426 | # print "\tvoi merge : " + str(train_voi_merge)
427 | # print "\tadapted RAND: " + str(train_rand)
428 |
429 | # Visualize the model. raw, labeled, predicted (optional)
430 | visualize = False
431 | if visualize:
432 | print('')
433 | print('Begin to visualize model..')
434 | visualize_model(model)
435 |
436 | time_elapsed = time.time() - train_time
437 | print('Visualizing complete in {:.0f}m {:.0f}s'.format(
438 | time_elapsed // 60, time_elapsed % 60))
439 |
440 |
441 |
442 | def visualize_model(model, i = 80, s = 300):
443 | """ Args:
444 | model: model
445 | i: depth of the raw image to visualize
446 | s: crop the 1250*1250 image to the size of s*s
447 | """
448 | fig = plt.figure(figsize=(15,6))
449 |
450 | ax_ori = fig.add_subplot(1,3,1)
451 | ax_lab = fig.add_subplot(1,3,2)
452 | ax_pred = fig.add_subplot(1,3,3)
453 |
454 | ax_ori.imshow(raw.data[i][0:s, 0:s])
455 | ax_ori.set_title('raw')
456 | ax_lab.imshow(neuron_ids.data[i][0:s, 0:s])
457 | ax_lab.set_title('labeled')
458 |
459 |
460 | preds = np.empty([s*s])
461 | for j in range(s*s):
462 | pixel = raw.data[i][j/s, j%s]
463 | input = np.random.uniform(-10000, 0, (1, 1, 33, 33)).astype('float32') ## boundary patch: positive
464 | input[0, 0, 16, 16] = pixel
465 | input = torch.from_numpy(input)
466 |
467 | model.train(False)
468 | if use_gpu:
469 | model = model.cuda()
470 | input = Variable(input.cuda())
471 | else:
472 | input = Variable(input)
473 |
474 | outputs = model(input)
475 | _, pred = torch.max(outputs.data, 1)
476 | pred = pred.cpu().numpy()
477 | if pred[0] == 0:
478 | preds[j] = 20000
479 | else:
480 | preds[j] = 100
481 |
482 | if j == 30000:
483 | print '1/3 done'
484 | if j == 60000:
485 | print '2/3 done'
486 |
487 | print preds.reshape(s, s)
488 | ax_pred.imshow(preds.reshape((s,s)))
489 | ax_pred.set_title('predicted')
490 |
491 | ax_lab.axis('off')
492 | ax_ori.axis('off')
493 | ax_pred.axis('off')
494 |
495 | plt.show()
496 | fig.savefig('vi.png')
497 | print('saved as vi.png')
498 |
499 |
500 |
501 |
502 |
503 |
504 | # Train
505 | #-----------------------------------------------------------------------
506 | num_classes = 2
507 | num_epochs = 100
508 | #model = ConvNet(num_classes )
509 | #model = DeepResNet18(num_classes)
510 | #model = DeepResNet34(num_classes )
511 | model = DeepResNet50(num_classes)
512 | #model = DeepResNet101(num_classes )
513 | optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1, momentum=0.9, weight_decay=0.0001)
514 | #optimizer = torch.optim.lr_scheduler.MultiStepLR(optimizer, milestones=[2,4,6,8,10], gamma=0.5)
515 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
516 | print('')
517 | print('START TRAINING ...')
518 | print(time.time())
519 | print('ResNet50. 33% 30deg lr50')
520 | train = train_model(model, criterion, optimizer, lr_scheduler=piecewise_scheduler, num_epochs=num_epochs)
521 |
522 |
523 |
524 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Annotations import *
2 | from Volume import *
3 | from NeuronIds import *
4 | from border_mask import *
5 | from CremiFile import *
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/Clefts.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from scipy import ndimage
3 |
4 | class Clefts:
5 |
6 | def __init__(self, test, truth):
7 |
8 | test_clefts = test
9 | truth_clefts = truth
10 |
11 | self.test_clefts_mask = np.equal(test_clefts.data, 0xffffffffffffffff)
12 | self.truth_clefts_mask = np.equal(truth_clefts.data, 0xffffffffffffffff)
13 |
14 | self.test_clefts_edt = ndimage.distance_transform_edt(self.test_clefts_mask, sampling=test_clefts.resolution)
15 | self.truth_clefts_edt = ndimage.distance_transform_edt(self.truth_clefts_mask, sampling=truth_clefts.resolution)
16 |
17 | def count_false_positives(self, threshold = 200):
18 |
19 | mask1 = np.invert(self.test_clefts_mask)
20 | mask2 = self.truth_clefts_edt > threshold
21 | false_positives = self.truth_clefts_edt[np.logical_and(mask1, mask2)]
22 | return false_positives.size
23 |
24 | def count_false_negatives(self, threshold = 200):
25 |
26 | mask1 = np.invert(self.truth_clefts_mask)
27 | mask2 = self.test_clefts_edt > threshold
28 | false_negatives = self.test_clefts_edt[np.logical_and(mask1, mask2)]
29 | return false_negatives.size
30 |
31 | def acc_false_positives(self):
32 |
33 | mask = np.invert(self.test_clefts_mask)
34 | false_positives = self.truth_clefts_edt[mask]
35 | stats = {
36 | 'mean': np.mean(false_positives),
37 | 'std': np.std(false_positives),
38 | 'max': np.amax(false_positives),
39 | 'count': false_positives.size,
40 | 'median': np.median(false_positives)}
41 | return stats
42 |
43 | def acc_false_negatives(self):
44 |
45 | mask = np.invert(self.truth_clefts_mask)
46 | false_negatives = self.test_clefts_edt[mask]
47 | stats = {
48 | 'mean': np.mean(false_negatives),
49 | 'std': np.std(false_negatives),
50 | 'max': np.amax(false_negatives),
51 | 'count': false_negatives.size,
52 | 'median': np.median(false_negatives)}
53 | return stats
54 |
55 |
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/NeuronIds.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | from border_mask import create_border_mask
3 | from voi import voi
4 | from rand import adapted_rand
5 |
6 | class NeuronIds:
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, groundtruth, border_threshold = None):
9 | """Create a new evaluation object for neuron ids against the provided ground truth.
10 |
11 | Parameters
12 | ----------
13 |
14 | groundtruth: Volume
15 | The ground truth volume containing neuron ids.
16 |
17 | border_threshold: None or float, in world units
18 | Pixels within `border_threshold` to a label border in the
19 | same section will be assigned to background and ignored during
20 | the evaluation.
21 | """
22 |
23 | assert groundtruth.resolution[1] == groundtruth.resolution[2], \
24 | "x and y resolutions of ground truth are not the same (%f != %f)" % \
25 | (groundtruth.resolution[1], groundtruth.resolution[2])
26 |
27 | self.groundtruth = groundtruth
28 | self.border_threshold = border_threshold
29 |
30 | if self.border_threshold:
31 |
32 | print "Computing border mask..."
33 |
34 | self.gt = np.zeros(groundtruth.data.shape, dtype=np.uint64)
35 | create_border_mask(
36 | groundtruth.data,
37 | self.gt,
38 | float(border_threshold)/groundtruth.resolution[1],
39 | np.uint64(-1))
40 | else:
41 | self.gt = np.array(self.groundtruth.data).copy()
42 |
43 | # current voi and rand implementations don't work with np.uint64(-1) as
44 | # background label, so we make it 0 here and bump all other labels
45 | self.gt += 1
46 |
47 | def voi(self, segmentation):
48 |
49 | assert list(segmentation.data.shape) == list(self.groundtruth.data.shape)
50 | assert list(segmentation.resolution) == list(self.groundtruth.resolution)
51 |
52 | print "Computing VOI..."
53 |
54 | return voi(np.array(segmentation.data), self.gt, ignore_groundtruth = [0])
55 |
56 | def adapted_rand(self, segmentation):
57 |
58 | assert list(segmentation.data.shape) == list(self.groundtruth.data.shape)
59 | assert list(segmentation.resolution) == list(self.groundtruth.resolution)
60 |
61 | print "Computing RAND..."
62 |
63 | return adapted_rand(np.array(segmentation.data), self.gt)
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/SynapticPartners.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from synaptic_partners import synaptic_partners_fscore
2 |
3 | class SynapticPartners:
4 |
5 | def __init__(self, matching_threshold = 400):
6 |
7 | self.matching_threshold = matching_threshold
8 |
9 | def fscore(self, rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, all_stats = False):
10 |
11 | return synaptic_partners_fscore(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, self.matching_threshold, all_stats)
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from Clefts import *
2 | from NeuronIds import *
3 | from SynapticPartners import *
4 | from border_mask import *
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/border_mask.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import h5py
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import scipy
4 |
5 | def create_border_mask(input_data, target, max_dist, background_label,axis=0):
6 | """
7 | Overlay a border mask with background_label onto input data.
8 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
9 |
10 | Parameters
11 | ----------
12 | input_data : h5py.Dataset or numpy.ndarray - Input data containing neuron ids
13 | target : h5py.Datset or numpy.ndarray - Target which input data overlayed with border mask is written into.
14 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
15 | background_label : int - Border mask will be overlayed using this label.
16 | axis : int - Axis of iteration (perpendicular to 2d images for which mask will be generated)
17 | """
18 | sl = [slice(None) for d in xrange(len(target.shape))]
19 |
20 | for z in xrange(target.shape[axis]):
21 | sl[ axis ] = z
22 | border = create_border_mask_2d(input_data[tuple(sl)], max_dist)
23 | target_slice = input_data[tuple(sl)] if isinstance(input_data,h5py.Dataset) else np.copy(input_data[tuple(sl)])
24 | target_slice[border] = background_label
25 | target[tuple(sl)] = target_slice
26 |
27 | def create_and_write_masked_neuron_ids(in_file, out_file, max_dist, background_label, overwrite=False):
28 | """
29 | Overlay a border mask with background_label onto input data loaded from in_file and write into out_file.
30 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
31 |
32 | Parameters
33 | ----------
34 | in_file : CremiFile - Input file containing neuron ids
35 | out_file : CremiFile - Output file which input data overlayed with border mask is written into.
36 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
37 | background_label : int - Border mask will be overlayed using this label.
38 | overwrite : bool - Overwrite existing data in out_file (True) or do nothing if data is present in out_file (False).
39 | """
40 | if ( not in_file.has_neuron_ids() ) or ( (not overwrite) and out_file.has_neuron_ids() ):
41 | return
42 |
43 | neuron_ids, resolution, offset, comment = in_file.read_neuron_ids()
44 | comment = ('' if comment is None else comment + ' ') + 'Border masked with max_dist=%f' % max_dist
45 |
46 | path = "/volumes/labels/neuron_ids"
47 | group_path = "/".join( path.split("/")[:-1] )
48 | ds_name = path.split("/")[-1]
49 | if ( out_file.has_neuron_ids() ):
50 | del out_file.h5file[path]
51 | if (group_path not in out_file.h5file):
52 | out_file.h5file.create_group(group_path)
53 |
54 | group = out_file.h5file[group_path]
55 | target = group.create_dataset(ds_name, shape=neuron_ids.shape, dtype=neuron_ids.dtype)
56 | target.attrs["resolution"] = resolution
57 | target.attrs["comment"] = comment
58 | if offset != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
59 | target.attrs["offset"] = offset
60 |
61 | create_border_mask(neuron_ids, target, max_dist, background_label)
62 |
63 | def create_border_mask_2d(image, max_dist):
64 | """
65 | Create binary border mask for image.
66 | A pixel is part of a border if one of its 4-neighbors has different label.
67 |
68 | Parameters
69 | ----------
70 | image : numpy.ndarray - Image containing integer labels.
71 | max_dist : int or float - Maximum distance from border for pixels to be included into the mask.
72 |
73 | Returns
74 | -------
75 | mask : numpy.ndarray - Binary mask of border pixels. Same shape as image.
76 | """
77 | max_dist = max(max_dist, 0)
78 |
79 | padded = np.pad(image, 1, mode='edge')
80 |
81 | border_pixels = np.logical_and(
82 | np.logical_and( image == padded[:-2, 1:-1], image == padded[2:, 1:-1] ),
83 | np.logical_and( image == padded[1:-1, :-2], image == padded[1:-1, 2:] )
84 | )
85 |
86 | distances = scipy.ndimage.distance_transform_edt(
87 | border_pixels,
88 | return_distances=True,
89 | return_indices=False
90 | )
91 |
92 | return distances <= max_dist
93 |
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/rand.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 |
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
5 |
6 | # Evaluation code courtesy of Juan Nunez-Iglesias, taken from
7 | # https://github.com/janelia-flyem/gala/blob/master/gala/evaluate.py
8 |
9 | def adapted_rand(seg, gt, all_stats=False):
10 | """Compute Adapted Rand error as defined by the SNEMI3D contest [1]
11 |
12 | Formula is given as 1 - the maximal F-score of the Rand index
13 | (excluding the zero component of the original labels). Adapted
14 | from the SNEMI3D MATLAB script, hence the strange style.
15 |
16 | Parameters
17 | ----------
18 | seg : np.ndarray
19 | the segmentation to score, where each value is the label at that point
20 | gt : np.ndarray, same shape as seg
21 | the groundtruth to score against, where each value is a label
22 | all_stats : boolean, optional
23 | whether to also return precision and recall as a 3-tuple with rand_error
24 |
25 | Returns
26 | -------
27 | are : float
28 | The adapted Rand error; equal to $1 - \frac{2pr}{p + r}$,
29 | where $p$ and $r$ are the precision and recall described below.
30 | prec : float, optional
31 | The adapted Rand precision. (Only returned when `all_stats` is ``True``.)
32 | rec : float, optional
33 | The adapted Rand recall. (Only returned when `all_stats` is ``True``.)
34 |
35 | References
36 | ----------
37 | [1]: http://brainiac2.mit.edu/SNEMI3D/evaluation
38 | """
39 | # segA is truth, segB is query
40 | segA = np.ravel(gt)
41 | segB = np.ravel(seg)
42 | n = segA.size
43 |
44 | n_labels_A = np.amax(segA) + 1
45 | n_labels_B = np.amax(segB) + 1
46 |
47 | ones_data = np.ones(n)
48 |
49 | p_ij = sparse.csr_matrix((ones_data, (segA[:], segB[:])), shape=(n_labels_A, n_labels_B))
50 |
51 | a = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,:]
52 | b = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,1:n_labels_B]
53 | c = p_ij[1:n_labels_A,0].todense()
54 | d = b.multiply(b)
55 |
56 | a_i = np.array(a.sum(1))
57 | b_i = np.array(b.sum(0))
58 |
59 | sumA = np.sum(a_i * a_i)
60 | sumB = np.sum(b_i * b_i) + (np.sum(c) / n)
61 | sumAB = np.sum(d) + (np.sum(c) / n)
62 |
63 | precision = sumAB / sumB
64 | recall = sumAB / sumA
65 |
66 | fScore = 2.0 * precision * recall / (precision + recall)
67 | are = 1.0 - fScore
68 |
69 | if all_stats:
70 | return (are, precision, recall)
71 | else:
72 | return are
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/synaptic_partners.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 | from munkres import Munkres
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | def synaptic_partners_fscore(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold = 400, all_stats = False):
6 | """Compute the f-score of the found synaptic partners.
7 |
8 | Parameters
9 | ----------
10 |
11 | rec_annotations: Annotations, containing found synaptic partners
12 |
13 | gt_annotations: Annotations, containing ground truth synaptic partners
14 |
15 | gt_segmentation: Volume, ground truth neuron segmentation
16 |
17 | matching_threshold: float, world units
18 | Euclidean distance threshold to consider two annotations a potential
19 | match. Annotations that are `matching_threshold` or more untis apart
20 | from each other are not considered as potential matches.
21 |
22 | all_stats: boolean, optional
23 | Whether to also return precision, recall, FP, FN, and matches as a 6-tuple with f-score
24 |
25 | Returns
26 | -------
27 |
28 | fscore: float
29 | The f-score of the found synaptic partners.
30 | precision: float, optional
31 | recall: float, optional
32 | fp: int, optional
33 | fn: int, optional
34 | filtered_matches: list of tuples, optional
35 | The indices of the matches with matching costs.
36 | """
37 |
38 | # get cost matrix
39 | costs = cost_matrix(rec_annotations, gt_annotations, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold)
40 |
41 | # match using Hungarian method
42 | print "Finding cost-minimal matches..."
43 | munkres = Munkres()
44 | matches = munkres.compute(costs.copy()) # have to copy, because munkres changes the cost matrix...
45 |
46 | filtered_matches = [ (i,j, costs[i][j]) for (i,j) in matches if costs[i][j] <= matching_threshold ]
47 | print str(len(filtered_matches)) + " matches found"
48 |
49 | # unmatched in rec = FP
50 | fp = len(rec_annotations.pre_post_partners) - len(filtered_matches)
51 |
52 | # unmatched in gt = FN
53 | fn = len(gt_annotations.pre_post_partners) - len(filtered_matches)
54 |
55 | # all ground truth elements - FN = TP
56 | tp = len(gt_annotations.pre_post_partners) - fn
57 |
58 | precision = float(tp)/(tp + fp)
59 | recall = float(tp)/(tp + fn)
60 | fscore = 2.0*precision*recall/(precision + recall)
61 |
62 | if all_stats:
63 | return (fscore, precision, recall, fp, fn, filtered_matches)
64 | else:
65 | return fscore
66 |
67 | def cost_matrix(rec, gt, gt_segmentation, matching_threshold):
68 |
69 | print "Computing matching costs..."
70 |
71 | rec_locations = pre_post_locations(rec, gt_segmentation)
72 | gt_locations = pre_post_locations(gt, gt_segmentation)
73 |
74 | rec_labels = pre_post_labels(rec_locations, gt_segmentation)
75 | gt_labels = pre_post_labels(gt_locations, gt_segmentation)
76 |
77 | size = max(len(rec_locations), len(gt_locations))
78 | costs = np.zeros((size, size), dtype=np.float)
79 | costs[:] = 2*matching_threshold
80 | num_potential_matches = 0
81 | for i in range(len(rec_locations)):
82 | for j in range(len(gt_locations)):
83 | c = cost(rec_locations[i], gt_locations[j], rec_labels[i], gt_labels[j], matching_threshold)
84 | costs[i,j] = c
85 | if c <= matching_threshold:
86 | num_potential_matches += 1
87 |
88 | print str(num_potential_matches) + " potential matches found"
89 |
90 | return costs
91 |
92 | def pre_post_locations(annotations, gt_segmentation):
93 | """Get the locations of the annotations relative to the ground truth offset."""
94 |
95 | locations = annotations.locations()
96 | shift = sub(annotations.offset, gt_segmentation.offset)
97 |
98 | return [
99 | (add(annotations.get_annotation(pre_id)[1], shift), add(annotations.get_annotation(post_id)[1], shift)) for (pre_id, post_id) in annotations.pre_post_partners
100 | ]
101 |
102 | def pre_post_labels(locations, segmentation):
103 |
104 | return [ (segmentation[pre], segmentation[post]) for (pre, post) in locations ]
105 |
106 |
107 | def cost(pre_post_location1, pre_post_location2, labels1, labels2, matching_threshold):
108 |
109 | max_cost = 2*matching_threshold
110 |
111 | # pairs do not link the same segments
112 | if labels1 != labels2:
113 | return max_cost
114 |
115 | pre_dist = distance(pre_post_location1[0], pre_post_location2[0])
116 | post_dist = distance(pre_post_location1[1], pre_post_location2[1])
117 |
118 | if pre_dist > matching_threshold or post_dist > matching_threshold:
119 | return max_cost
120 |
121 | return 0.5*(pre_dist + post_dist)
122 |
123 | def distance(a, b):
124 | return np.linalg.norm(np.array(list(a))-np.array(list(b)))
125 |
126 | def add(a, b):
127 | return tuple([a[d] + b[d] for d in range(len(b))])
128 |
129 | def sub(a, b):
130 | return tuple([a[d] - b[d] for d in range(len(b))])
131 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/evaluations/voi.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # coding=utf-8
2 |
3 | # Evaluation code courtesy of Juan Nunez-Iglesias, taken from
4 | # https://github.com/janelia-flyem/gala/blob/master/gala/evaluate.py
5 |
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import scipy.sparse as sparse
8 |
9 | def voi(reconstruction, groundtruth, ignore_reconstruction=[], ignore_groundtruth=[0]):
10 | """Return the conditional entropies of the variation of information metric. [1]
11 |
12 | Let X be a reconstruction, and Y a ground truth labelling. The variation of
13 | information between the two is the sum of two conditional entropies:
14 |
15 | VI(X, Y) = H(X|Y) + H(Y|X).
16 |
17 | The first one, H(X|Y), is a measure of oversegmentation, the second one,
18 | H(Y|X), a measure of undersegmentation. These measures are referred to as
19 | the variation of information split or merge error, respectively.
20 |
21 | Parameters
22 | ----------
23 | seg : np.ndarray, int type, arbitrary shape
24 | A candidate segmentation.
25 | gt : np.ndarray, int type, same shape as `seg`
26 | The ground truth segmentation.
27 | ignore_seg, ignore_gt : list of int, optional
28 | Any points having a label in this list are ignored in the evaluation.
29 | By default, only the label 0 in the ground truth will be ignored.
30 |
31 | Returns
32 | -------
33 | (split, merge) : float
34 | The variation of information split and merge error, i.e., H(X|Y) and H(Y|X)
35 |
36 | References
37 | ----------
38 | [1] Meila, M. (2007). Comparing clusterings - an information based
39 | distance. Journal of Multivariate Analysis 98, 873-895.
40 | """
41 | (hyxg, hxgy) = split_vi(reconstruction, groundtruth, ignore_reconstruction, ignore_groundtruth)
42 | return (hxgy, hyxg)
43 |
44 | def split_vi(x, y=None, ignore_x=[0], ignore_y=[0]):
45 | """Return the symmetric conditional entropies associated with the VI.
46 |
47 | The variation of information is defined as VI(X,Y) = H(X|Y) + H(Y|X).
48 | If Y is the ground-truth segmentation, then H(Y|X) can be interpreted
49 | as the amount of under-segmentation of Y and H(X|Y) is then the amount
50 | of over-segmentation. In other words, a perfect over-segmentation
51 | will have H(Y|X)=0 and a perfect under-segmentation will have H(X|Y)=0.
52 |
53 | If y is None, x is assumed to be a contingency table.
54 |
55 | Parameters
56 | ----------
57 | x : np.ndarray
58 | Label field (int type) or contingency table (float). `x` is
59 | interpreted as a contingency table (summing to 1.0) if and only if `y`
60 | is not provided.
61 | y : np.ndarray of int, same shape as x, optional
62 | A label field to compare to `x`.
63 | ignore_x, ignore_y : list of int, optional
64 | Any points having a label in this list are ignored in the evaluation.
65 | Ignore 0-labeled points by default.
66 |
67 | Returns
68 | -------
69 | sv : np.ndarray of float, shape (2,)
70 | The conditional entropies of Y|X and X|Y.
71 |
72 | See Also
73 | --------
74 | vi
75 | """
76 | _, _, _ , hxgy, hygx, _, _ = vi_tables(x, y, ignore_x, ignore_y)
77 | # false merges, false splits
78 | return np.array([hygx.sum(), hxgy.sum()])
79 |
80 | def vi_tables(x, y=None, ignore_x=[0], ignore_y=[0]):
81 | """Return probability tables used for calculating VI.
82 |
83 | If y is None, x is assumed to be a contingency table.
84 |
85 | Parameters
86 | ----------
87 | x, y : np.ndarray
88 | Either x and y are provided as equal-shaped np.ndarray label fields
89 | (int type), or y is not provided and x is a contingency table
90 | (sparse.csc_matrix) that may or may not sum to 1.
91 | ignore_x, ignore_y : list of int, optional
92 | Rows and columns (respectively) to ignore in the contingency table.
93 | These are labels that are not counted when evaluating VI.
94 |
95 | Returns
96 | -------
97 | pxy : sparse.csc_matrix of float
98 | The normalized contingency table.
99 | px, py, hxgy, hygx, lpygx, lpxgy : np.ndarray of float
100 | The proportions of each label in `x` and `y` (`px`, `py`), the
101 | per-segment conditional entropies of `x` given `y` and vice-versa, the
102 | per-segment conditional probability p log p.
103 | """
104 | if y is not None:
105 | pxy = contingency_table(x, y, ignore_x, ignore_y)
106 | else:
107 | cont = x
108 | total = float(cont.sum())
109 | # normalize, since it is an identity op if already done
110 | pxy = cont / total
111 |
112 | # Calculate probabilities
113 | px = np.array(pxy.sum(axis=1)).ravel()
114 | py = np.array(pxy.sum(axis=0)).ravel()
115 | # Remove zero rows/cols
116 | nzx = px.nonzero()[0]
117 | nzy = py.nonzero()[0]
118 | nzpx = px[nzx]
119 | nzpy = py[nzy]
120 | nzpxy = pxy[nzx, :][:, nzy]
121 |
122 | # Calculate log conditional probabilities and entropies
123 | lpygx = np.zeros(np.shape(px))
124 | lpygx[nzx] = xlogx(divide_rows(nzpxy, nzpx)).sum(axis=1)
125 | # \sum_x{p_{y|x} \log{p_{y|x}}}
126 | hygx = -(px*lpygx) # \sum_x{p_x H(Y|X=x)} = H(Y|X)
127 |
128 | lpxgy = np.zeros(np.shape(py))
129 | lpxgy[nzy] = xlogx(divide_columns(nzpxy, nzpy)).sum(axis=0)
130 | hxgy = -(py*lpxgy)
131 |
132 | return [pxy] + list(map(np.asarray, [px, py, hxgy, hygx, lpygx, lpxgy]))
133 |
134 | def contingency_table(seg, gt, ignore_seg=[0], ignore_gt=[0], norm=True):
135 | """Return the contingency table for all regions in matched segmentations.
136 |
137 | Parameters
138 | ----------
139 | seg : np.ndarray, int type, arbitrary shape
140 | A candidate segmentation.
141 | gt : np.ndarray, int type, same shape as `seg`
142 | The ground truth segmentation.
143 | ignore_seg : list of int, optional
144 | Values to ignore in `seg`. Voxels in `seg` having a value in this list
145 | will not contribute to the contingency table. (default: [0])
146 | ignore_gt : list of int, optional
147 | Values to ignore in `gt`. Voxels in `gt` having a value in this list
148 | will not contribute to the contingency table. (default: [0])
149 | norm : bool, optional
150 | Whether to normalize the table so that it sums to 1.
151 |
152 | Returns
153 | -------
154 | cont : scipy.sparse.csc_matrix
155 | A contingency table. `cont[i, j]` will equal the number of voxels
156 | labeled `i` in `seg` and `j` in `gt`. (Or the proportion of such voxels
157 | if `norm=True`.)
158 | """
159 | segr = seg.ravel()
160 | gtr = gt.ravel()
161 | ignored = np.zeros(segr.shape, np.bool)
162 | data = np.ones(len(gtr))
163 | for i in ignore_seg:
164 | ignored[segr == i] = True
165 | for j in ignore_gt:
166 | ignored[gtr == j] = True
167 | data[ignored] = 0
168 | cont = sparse.coo_matrix((data, (segr, gtr))).tocsc()
169 | if norm:
170 | cont /= float(cont.sum())
171 | return cont
172 |
173 | def divide_columns(matrix, row, in_place=False):
174 | """Divide each column of `matrix` by the corresponding element in `row`.
175 |
176 | The result is as follows: out[i, j] = matrix[i, j] / row[j]
177 |
178 | Parameters
179 | ----------
180 | matrix : np.ndarray, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix, shape (M, N)
181 | The input matrix.
182 | column : a 1D np.ndarray, shape (N,)
183 | The row dividing `matrix`.
184 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
185 | Do the computation in-place.
186 |
187 | Returns
188 | -------
189 | out : same type as `matrix`
190 | The result of the row-wise division.
191 | """
192 | if in_place:
193 | out = matrix
194 | else:
195 | out = matrix.copy()
196 | if type(out) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
197 | if type(out) == sparse.csc_matrix:
198 | convert_to_csc = True
199 | out = out.tocsr()
200 | else:
201 | convert_to_csc = False
202 | row_repeated = np.take(row, out.indices)
203 | nz = out.data.nonzero()
204 | out.data[nz] /= row_repeated[nz]
205 | if convert_to_csc:
206 | out = out.tocsc()
207 | else:
208 | out /= row[np.newaxis, :]
209 | return out
210 |
211 | def divide_rows(matrix, column, in_place=False):
212 | """Divide each row of `matrix` by the corresponding element in `column`.
213 |
214 | The result is as follows: out[i, j] = matrix[i, j] / column[i]
215 |
216 | Parameters
217 | ----------
218 | matrix : np.ndarray, scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix, shape (M, N)
219 | The input matrix.
220 | column : a 1D np.ndarray, shape (M,)
221 | The column dividing `matrix`.
222 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
223 | Do the computation in-place.
224 |
225 | Returns
226 | -------
227 | out : same type as `matrix`
228 | The result of the row-wise division.
229 | """
230 | if in_place:
231 | out = matrix
232 | else:
233 | out = matrix.copy()
234 | if type(out) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
235 | if type(out) == sparse.csr_matrix:
236 | convert_to_csr = True
237 | out = out.tocsc()
238 | else:
239 | convert_to_csr = False
240 | column_repeated = np.take(column, out.indices)
241 | nz = out.data.nonzero()
242 | out.data[nz] /= column_repeated[nz]
243 | if convert_to_csr:
244 | out = out.tocsr()
245 | else:
246 | out /= column[:, np.newaxis]
247 | return out
248 |
249 | def xlogx(x, out=None, in_place=False):
250 | """Compute x * log_2(x).
251 |
252 | We define 0 * log_2(0) = 0
253 |
254 | Parameters
255 | ----------
256 | x : np.ndarray or scipy.sparse.csc_matrix or csr_matrix
257 | The input array.
258 | out : same type as x (optional)
259 | If provided, use this array/matrix for the result.
260 | in_place : bool (optional, default False)
261 | Operate directly on x.
262 |
263 | Returns
264 | -------
265 | y : same type as x
266 | Result of x * log_2(x).
267 | """
268 | if in_place:
269 | y = x
270 | elif out is None:
271 | y = x.copy()
272 | else:
273 | y = out
274 | if type(y) in [sparse.csc_matrix, sparse.csr_matrix]:
275 | z = y.data
276 | else:
277 | z = y
278 | nz = z.nonzero()
279 | z[nz] *= np.log2(z[nz])
280 | return y
281 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/*Filtered Mask.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/*Filtered Mask.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/*Visualize Boundary.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/*Visualize Boundary.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/6p.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/6p.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/acc.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/acc.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/err.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/err.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/loss.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/loss.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/n.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/res window.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/res window.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/img/rot.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/celisun/Deep_learning_automated__neuron_segmentation/68bc9adb2e19ad2ca53ac72236176d274c07e3c7/img/rot.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/io/CremiFile.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import h5py
2 | import numpy as np
3 | from Annotations import *
4 | from Volume import *
5 |
6 | class CremiFile(object):
7 |
8 | def __init__(self, filename, mode):
9 |
10 | self.h5file = h5py.File(filename, mode)
11 |
12 | if mode == "w" or mode == "a":
13 | self.h5file["/"].attrs["file_format"] = "0.2"
14 |
15 | def __create_group(self, group):
16 |
17 | path = "/"
18 | for d in group.split("/"):
19 | path += d + "/"
20 | try:
21 | self.h5file.create_group(path)
22 | except ValueError:
23 | pass
24 |
25 | def __create_dataset(self, path, data, dtype, compression = None):
26 | """Wrapper around h5py's create_dataset. Creates the group, if not
27 | existing. Deletes a previous dataset, if existing and not compatible.
28 | Otherwise, replaces the dataset.
29 | """
30 |
31 | group = "/".join(path.split("/")[:-1])
32 | ds_name = path.split("/")[-1]
33 |
34 | self.__create_group(group)
35 |
36 | if ds_name in self.h5file[group]:
37 |
38 | ds = self.h5file[path]
39 | if ds.dtype == dtype and ds.shape == np.array(data).shape:
40 | print "overwriting existing dataset"
41 | self.h5file[path][:] = data[:]
42 | return
43 |
44 | del self.h5file[path]
45 |
46 | self.h5file.create_dataset(path, data=data, dtype=dtype, compression=compression)
47 |
48 | def write_volume(self, volume, ds_name, dtype):
49 |
50 | self.__create_dataset(ds_name, data=volume.data, dtype=dtype, compression="gzip")
51 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["resolution"] = volume.resolution
52 | if volume.comment is not None:
53 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["comment"] = str(volume.comment)
54 | if tuple(volume.offset) != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
55 | self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["offset"] = volume.offset
56 |
57 | def read_volume(self, ds_name):
58 |
59 | volume = Volume(self.h5file[ds_name])
60 |
61 | volume.resolution = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["resolution"]
62 | if "offset" in self.h5file[ds_name].attrs:
63 | volume.offset = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["offset"]
64 | if "comment" in self.h5file[ds_name].attrs:
65 | volume.comment = self.h5file[ds_name].attrs["comment"]
66 |
67 | return volume
68 |
69 | def __has_volume(self, ds_name):
70 |
71 | return ds_name in self.h5file
72 |
73 | def write_raw(self, raw):
74 | """Write a raw volume.
75 | """
76 |
77 | self.write_volume(raw, "/volumes/raw", np.uint8)
78 |
79 | def write_neuron_ids(self, neuron_ids):
80 | """Write a volume of segmented neurons.
81 | """
82 |
83 | self.write_volume(neuron_ids, "/volumes/labels/neuron_ids", np.uint64)
84 |
85 | def write_clefts(self, clefts):
86 | """Write a volume of segmented synaptic clefts.
87 | """
88 |
89 | self.write_volume(clefts, "/volumes/labels/clefts", np.uint64)
90 |
91 | def write_annotations(self, annotations):
92 | """Write pre- and post-synaptic site annotations.
93 | """
94 |
95 | if len(annotations.ids()) == 0:
96 | return
97 |
98 | self.__create_group("/annotations")
99 | if tuple(annotations.offset) != (0.0, 0.0, 0.0):
100 | self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs["offset"] = annotations.offset
101 |
102 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/ids", data=annotations.ids(), dtype=np.uint64)
103 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/types", data=annotations.types(), dtype=h5py.special_dtype(vlen=unicode), compression="gzip")
104 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/locations", data=annotations.locations(), dtype=np.double)
105 |
106 | if len(annotations.comments) > 0:
107 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/comments/target_ids", data=annotations.comments.keys(), dtype=np.uint64)
108 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/comments/comments", data=annotations.comments.values(), dtype=h5py.special_dtype(vlen=unicode))
109 |
110 | if len(annotations.pre_post_partners) > 0:
111 | self.__create_dataset("/annotations/presynaptic_site/partners", data=annotations.pre_post_partners, dtype=np.uint64)
112 |
113 | def has_raw(self):
114 | """Check if this file contains a raw volume.
115 | """
116 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/raw")
117 |
118 | def has_neuron_ids(self):
119 | """Check if this file contains neuron ids.
120 | """
121 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids")
122 |
123 | def has_neuron_ids_confidence(self):
124 | """Check if this file contains confidence information about neuron ids.
125 | """
126 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids_confidence")
127 |
128 | def has_clefts(self):
129 | """Check if this file contains synaptic clefts.
130 | """
131 | return self.__has_volume("/volumes/labels/clefts")
132 |
133 | def has_annotations(self):
134 | """Check if this file contains synaptic partner annotations.
135 | """
136 | return "/annotations" in self.h5file
137 |
138 | def has_segment_annotations(self):
139 | """Check if this file contains segment annotations.
140 | """
141 | return "/annotations" in self.h5file
142 |
143 | def read_raw(self):
144 | """Read the raw volume.
145 | Returns a Volume.
146 | """
147 |
148 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/raw")
149 |
150 | def read_neuron_ids(self):
151 | """Read the volume of segmented neurons.
152 | Returns a Volume.
153 | """
154 |
155 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/labels/neuron_ids")
156 |
157 | def read_neuron_ids_confidence(self):
158 | """Read confidence information about neuron ids.
159 | Returns Confidences.
160 | """
161 |
162 | confidences = Confidences(num_levels=2)
163 | if not self.has_neuron_ids_confidence():
164 | return confidences
165 |
166 | data = self.h5file["/volumes/labels/neuron_ids_confidence"]
167 | i = 0
168 | while i < len(data):
169 | level = data[i]
170 | i += 1
171 | num_ids = data[i]
172 | i += 1
173 | confidences.add_all(level, data[i:i+num_ids])
174 | i += num_ids
175 |
176 | return confidences
177 |
178 | def read_clefts(self):
179 | """Read the volume of segmented synaptic clefts.
180 | Returns a Volume.
181 | """
182 |
183 | return self.read_volume("/volumes/labels/clefts")
184 |
185 | def read_annotations(self):
186 | """Read pre- and post-synaptic site annotations.
187 | """
188 |
189 | annotations = Annotations()
190 |
191 | if not "/annotations" in self.h5file:
192 | return annotations
193 |
194 | offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)
195 | if "offset" in self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs:
196 | offset = self.h5file["/annotations"].attrs["offset"]
197 | annotations.offset = offset
198 |
199 | ids = self.h5file["/annotations/ids"]
200 | types = self.h5file["/annotations/types"]
201 | locations = self.h5file["/annotations/locations"]
202 | for i in range(len(ids)):
203 | annotations.add_annotation(ids[i], types[i], locations[i])
204 |
205 | if "comments" in self.h5file["/annotations"]:
206 | ids = self.h5file["/annotations/comments/target_ids"]
207 | comments = self.h5file["/annotations/comments/comments"]
208 | for (id, comment) in zip(ids, comments):
209 | annotations.add_comment(id, comment)
210 |
211 | if "presynaptic_site/partners" in self.h5file["/annotations"]:
212 | pre_post = self.h5file["/annotations/presynaptic_site/partners"]
213 | for (pre, post) in pre_post:
214 | annotations.set_pre_post_partners(pre, post)
215 |
216 | return annotations
217 |
218 | def close(self):
219 |
220 | self.h5file.close()
221 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/io/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from CremiFile import *
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/Resnet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
4 |
5 |
6 | def residualLayer2(conv2d1, norm2d, input, nChannels, nOutChannels=False, stride=1, conv2d2=False):
7 | """ Deep Residual Network
8 | https://github.com/gcr/torch-residual-networks
9 |
10 | giving stack of 2 layers as a block providing shortcuts."""
11 |
12 |
13 | if not nOutChannels:
14 | nOutChannels = nChannels
15 | if not conv2d2:
16 | conv2d2 = conv2d1
17 |
18 | # part 1: conv
19 | net = conv2d1(input)
20 | net = norm2d(net) # learnable parameters
21 | net = F.relu(net)
22 | net = conv2d2(net)
23 |
24 |
25 | # part 2: identity / skip connection
26 | skip = input
27 | if stride > 1: # optional downsampling
28 | skip = L.SpatialAveragePooling(1, 1, stride, stride).forward(skip.cpu().data)
29 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
30 | if nOutChannels > nChannels: # optional padding
31 | skip = L.Padding(1, (nOutChannels - nChannels), 3).forward(skip.cpu().data)
32 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
33 | elif nOutChannels < nChannels: # optional narrow
34 | skip = L.Narrow(2, 1, nOutChannels).forward(skip.cpu().data)
35 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
36 |
37 |
38 | # H(x) + x
39 | net = norm2d(net)
40 | #print "skip: " + str(skip.data.size())
41 | #print "net: " + str(net.data.size())
42 | net = torch.add(skip, net)
43 | # net = F.relu(net) # relu here ? see: http://www.gitxiv.com/comments/7rffyqcPLirEEsmpX
44 | #net = norm2d(net) # ==========================BN after add or before ???
45 |
46 | return net
47 |
48 |
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
53 |
54 | class DeepResNet18(nn.Module):
55 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=3, padding=1):
56 | super(DeepResNet18, self).__init__()
57 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
58 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
59 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
60 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
61 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
62 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
63 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
64 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
65 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
66 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
67 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
68 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
69 | self.linear = nn.Linear(256, 2)
70 |
71 | def forward(self, x):
72 | # ----> 1, 33, 33
73 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
74 |
75 | # ----> 32, 33, 33 First Group 2X
76 | for i in range(2): x = residualLayer2(self.conv2, self.norm1, x, 32)
77 |
78 | # ----> 64, 17, 17 Second Group 2X
79 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv3, self.norm2, x, 32, 64, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv4)
80 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv4, self.norm2, x, 64)
81 |
82 | # ----> 128, 9, 9 Third Group 2X
83 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv5, self.norm3, x, 64, 128, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv6)
84 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv6, self.norm3, x, 128)
85 |
86 | # ----> 256, 5, 5 Fourth Group 2X
87 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv7, self.norm4, x, 128, 256, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv8)
88 | for i in range(2-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv8, self.norm4, x, 256)
89 |
90 | # ----> 256, 5, 5 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
91 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(5,5)(x)
92 | x = x.view(-1, 256)
93 | x = self.linear(x)
94 |
95 |
96 | return x
97 |
98 |
99 | class DeepResNet34(nn.Module):
100 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=5, padding=2):
101 | super(DeepResNet34, self).__init__()
102 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
103 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
104 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
105 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
106 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
107 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
108 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(128, 256, kernel, stride =2, padding=padding)
109 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
110 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
111 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
112 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
113 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
114 | self.linear = nn.Linear(256, 2)
115 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
116 |
117 | def forward(self, x):
118 | # ------> 65 * 65
119 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
120 | x = self.pool(x) # ================= max pooling ??
121 | # ------> 32 * 32
122 | for i in range(3): x = residualLayer2(self.conv2, self.norm1, x, 32)
123 | # ------> 32 * 32
124 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv3, self.norm2, x, 32, 64, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv4)
125 | for i in range(4-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv4, self.norm2, x, 64)
126 |
127 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv5, self.norm3, x, 64, 128, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv6)
128 | for i in range(6-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv6, self.norm3, x, 128)
129 |
130 | x = residualLayer2(self.conv7, self.norm4, x, 128, 256, stride=2, conv2d2=self.conv8)
131 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer2(self.conv8, self.norm4, x, 256)
132 |
133 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(8,8)(x)
134 | x = x.view(-1, 256)
135 | x = self.linear(x)
136 |
137 |
138 | return x
139 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/Resnet_3.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch.nn as nn
2 | import torch.nn.functional as F
3 | import torch.legacy.nn as L
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 | class DeepResNet101(nn.Module):
8 |
9 | """using bottle-neck building block """
10 |
11 |
12 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=7, padding=3):
13 | super(DeepResNet101, self).__init__()
14 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
15 | self.conv2_ = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 1, stride=2)
16 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 5, padding=2)
17 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
18 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, 128, 5, padding=2)
19 | self.conv5_ = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 1, stride=2)
20 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 5, padding=2)
21 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
22 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(64, 256, 5, padding=2)
23 | self.conv8_ = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 1, stride=2)
24 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 5, padding=2)
25 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
26 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(128, 512, 5, padding=2)
27 | self.conv11_ = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 1, stride=2)
28 | self.conv11 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, 5, padding=2)
29 | self.conv12 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
30 | self.conv13 = nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, 5, padding=2)
31 |
32 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
33 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
34 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
35 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
36 | self.norm5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
37 | self.norm6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
38 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
39 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 128)
40 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(128, 2)
41 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
42 |
43 | def forward(self, x):
44 | # ----> 1, 129, 129
45 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
46 | x = self.pool(x) # max pooling ? 3x3 s=2
47 |
48 | # ----> 32, 64, 64 First Group
49 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2_, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 32, 32, 128, stride=2)
50 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 128, 32, 128)
51 |
52 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5_, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 128, 64, 256, stride=2)
53 | for i in range(8-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 256, 64, 256)
54 |
55 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8_, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 256, 128, 512, stride=2)
56 | for i in range(36-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 512, 128, 512)
57 |
58 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11_, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 512, 256, 1024, stride=2)
59 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 1024, 256, 1024)
60 |
61 | # ----> 1024, 4, 4 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
62 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(4,4)(x)
63 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
64 | x = self.linear1(x)
65 | x = F.dropout(x) # ==============================
66 | x = self.linear2(x)
67 | x = self.linear3(x)
68 |
69 | return x
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | class DeepResNet50(nn.Module):
76 |
77 | """using bottle-neck building block """
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 | def __init__(self, D_out, kernel=7, padding=3): #=============== conv window size 5/22 9:24pm
82 | super(DeepResNet50, self).__init__()
83 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
84 | self.conv2_ = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, 1, stride=2)
85 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(128, 32, 5, padding=2)
86 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(32, 32, kernel, padding=padding)
87 | self.conv4 = nn.Conv2d(32, 128, 5, padding=2)
88 | self.conv5_ = nn.Conv2d(128, 64, 1, stride=2)
89 | self.conv5 = nn.Conv2d(256, 64, 5, padding=2)
90 | self.conv6 = nn.Conv2d(64, 64, kernel, padding=padding)
91 | self.conv7 = nn.Conv2d(64, 256, 5, padding=2)
92 | self.conv8_ = nn.Conv2d(256, 128, 1, stride=2)
93 | self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(512, 128, 5, padding=2)
94 | self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(128, 128, kernel, padding=padding)
95 | self.conv10 = nn.Conv2d(128, 512, 5, padding=2)
96 | self.conv11_ = nn.Conv2d(512, 256, 1, stride=2)
97 | self.conv11 = nn.Conv2d(1024, 256, 5, padding=2)
98 | self.conv12 = nn.Conv2d(256, 256, kernel, padding=padding)
99 | self.conv13 = nn.Conv2d(256, 1024, 5, padding=2)
100 |
101 | self.norm1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(32)
102 | self.norm2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
103 | self.norm3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(128)
104 | self.norm4 = nn.BatchNorm2d(256)
105 | self.norm5 = nn.BatchNorm2d(512)
106 | self.norm6 = nn.BatchNorm2d(1024)
107 | self.linear1 = nn.Linear(1024, 512)
108 | self.linear2 = nn.Linear(512, 128)
109 | self.linear3 = nn.Linear(128, 2)
110 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(3, stride=2)
111 |
112 |
113 | def forward(self, x):
114 | # ----> 1, 129, 129
115 | x = F.relu(self.norm1(self.conv1(x)))
116 | x = self.pool(x) # ================= max pooling ? better without here
117 |
118 |
119 | # ----> 32, 64, 64 First Group
120 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2_, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 32, 32, 128, stride=2)
121 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv2, self.conv3, self.conv4, self.norm1, self.norm3, 128, 32, 128)
122 |
123 | # ----> 128, 32, 32 Second Group
124 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5_, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 128, 64, 256, stride=2)
125 | for i in range(4-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv5, self.conv6, self.conv7, self.norm2, self.norm4, 256, 64, 256)
126 |
127 | # ----> 256, 16, 16 Third Group
128 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8_, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 256, 128, 512, stride=2)
129 | for i in range(6-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv8, self.conv9, self.conv10, self.norm3, self.norm5, 512, 128, 512)
130 |
131 | # ----> 512, 8,8 Fourth Group
132 | x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11_, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 512, 256, 1024, stride=2)
133 | for i in range(3-1): x = residualLayer3(x, self.conv11, self.conv12, self.conv13, self.norm4, self.norm6, 1024, 256, 1024)
134 |
135 | # ----> 1024, 4, 4 Pooling, Linear, Softmax
136 | x = nn.AvgPool2d(4,4)(x)
137 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
138 | x = self.linear1(x)
139 | x = F.dropout(x) # ==============================
140 | x = self.linear2(x)
141 | x = self.linear3(x)
142 |
143 | return x
144 |
145 |
146 | # stack of 3 layers providing shortcuts
147 | def residualLayer3(input, conv2d1, conv2d2, conv2d3, norm2d1, norm2d2, inChannels, hiddenChannels, outChannels, stride=1):
148 | net = conv2d1(input) # 1x1
149 | net = norm2d1(net)
150 | net = F.relu(net)
151 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout within blocks ???? 8.21 9pm
152 |
153 | net = conv2d2(net) # kernel 3x3 or 5x5
154 | net = norm2d1(net)
155 | net = F.relu(net)
156 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout ???? 8.21 9pm
157 |
158 | net = conv2d3(net) # 1x1
159 |
160 | skip = input
161 | #print "input: " + str(skip.data.size())
162 | if stride > 1:
163 | skip = L.SpatialAveragePooling(1, 1, stride, stride).forward(skip.cpu().data)
164 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
165 | if outChannels > inChannels:
166 | skip = L.Padding(1, (outChannels - inChannels), 3).forward(skip.cpu().data)
167 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
168 | elif outChannels < inChannels:
169 | skip = L.Narrow(2, 1, outChannels).forward(skip.cpu().data)
170 | skip = Variable(skip.cuda())
171 |
172 | #net = norm2d2(net)
173 | #print "skip: " + str(skip.data.size())
174 | #print "net: " + str(net.data.size())
175 | net = norm2d2(torch.add(skip, net)) # ==========================BN after add or before ???
176 | net = F.dropout(net) # ========================== dropout ????
177 | return net
178 |
179 |
180 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/type/Annotations.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class Annotations:
2 |
3 | def __init__(self, offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0)):
4 |
5 | self.__types = {}
6 | self.__locations = {}
7 | self.comments = {}
8 | self.pre_post_partners = []
9 | self.offset = offset
10 |
11 | def __check(self, id):
12 | if not id in self.__types.keys():
13 | raise "there is no annotation with id " + str(id)
14 |
15 | def add_annotation(self, id, type, location):
16 | """Add a new annotation.
17 |
18 | Parameters
19 | ----------
20 |
21 | id: int
22 | The ID of the new annotation.
23 |
24 | type: string
25 | A string denoting the type of the annotation. Use
26 | "presynaptic_site" or "postsynaptic_site" for pre- and
27 | post-synaptic annotations, respectively.
28 |
29 | location: tuple, float
30 | The location of the annotation, relative to the offset.
31 | """
32 |
33 | self.__types[id] = type.encode('utf8')
34 | self.__locations[id] = location
35 |
36 | def add_comment(self, id, comment):
37 | """Add a comment to an annotation.
38 | """
39 |
40 | self.__check(id)
41 | self.comments[id] = comment.encode('utf8')
42 |
43 | def set_pre_post_partners(self, pre_id, post_id):
44 | """Mark two annotations as pre- and post-synaptic partners.
45 | """
46 |
47 | self.__check(pre_id)
48 | self.__check(post_id)
49 | self.pre_post_partners.append((pre_id, post_id))
50 |
51 | def ids(self):
52 | """Get the ids of all annotations.
53 | """
54 |
55 | return self.__types.keys()
56 |
57 | def types(self):
58 | """Get the types of all annotations.
59 | """
60 |
61 | return self.__types.values()
62 |
63 | def locations(self):
64 | """Get the locations of all annotations. Locations are in world units,
65 | relative to the offset.
66 | """
67 |
68 | return self.__locations.values()
69 |
70 | def get_annotation(self, id):
71 | """Get the type and location of an annotation by its id.
72 | """
73 |
74 | self.__check(id)
75 | return (self.__types[id], self.__locations[id])
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/type/Volume.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | class Volume():
2 |
3 | def __init__(self, data, resolution = (1.0, 1.0, 1.0), offset = (0.0, 0.0, 0.0), comment = ""):
4 | self.data = data
5 | self.resolution = resolution
6 | self.offset = offset
7 | self.comment = comment
8 |
9 | def __getitem__(self, location):
10 | """Get the closest value of this volume to the given location. The
11 | location is in world units, relative to the volumes offset.
12 |
13 | This method takes into account the resolution of the volume. An
14 | IndexError exception is raised if the location is not contained in this
15 | volume.
16 |
17 | To access the raw pixel values, use the `data` attribute.
18 | """
19 |
20 | i = tuple([ round(location[d]/self.resolution[d]) for d in range(len(location)) ])
21 |
22 | if min(i) >= 0:
23 | try:
24 | return self.data[i]
25 | except IndexError as e:
26 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume: " + str(e))
27 |
28 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume")
29 |
30 | def __setitem__(self, location, value):
31 | """Set the closest value of this volume to the given location. The
32 | location is in world units, relative to the volumes offset.
33 |
34 | This method takes into account the resolution of the volume. An
35 | IndexError exception is raised if the location is not contained in this
36 | volume.
37 |
38 | To access the raw pixel values, use the `data` attribute.
39 | """
40 |
41 | i = tuple([ round(location[d]/self.resolution[d]) for d in range(len(location)) ])
42 |
43 | if min(i) >= 0:
44 | try:
45 | self.data[i] = value
46 | return
47 | except IndexError as e:
48 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume: " + str(e))
49 |
50 | raise IndexError("location " + str(location) + " does not lie inside volume")
51 |
52 |
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------