├── images
├── cycled_linked_list.png
├── binary_search_template.png
└── fast_slow_linked_list.png
├── SUMMARY.md
├── README.md
├── advanced_algorithm
├── quick_select.md
├── three_way_quick_sort.md
├── greedy.md
└── binary_op.md
├── basic_algorithm
├── sort.md
├── slide_window.md
├── disjoin_set.md
├── backtrack.md
├── binary_search.md
└── dp.md
└── data_structure
├── stack_queue.md
├── linked_list.md
└── binary_tree.md
/images/cycled_linked_list.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chienmy/algorithm-pattern-java/HEAD/images/cycled_linked_list.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/binary_search_template.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chienmy/algorithm-pattern-java/HEAD/images/binary_search_template.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/fast_slow_linked_list.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/chienmy/algorithm-pattern-java/HEAD/images/fast_slow_linked_list.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/SUMMARY.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 算法模板——Java版
2 |
3 | ## 数据结构
4 |
5 | - [链表](data_structure/linked_list.md)
6 | - [栈和队列](data_structure/stack_queue.md)
7 | - [二叉树](data_structure/binary_tree.md)
8 |
9 | ## 基础算法
10 |
11 | - [滑动窗口](basic_algorithm/slide_window.md)
12 | - [回溯算法](basic_algorithm/backtrack.md)
13 | - [二分搜索](basic_algorithm/binary_search.md)
14 | - [排序算法](basic_algorithm/sort.md)
15 | - [动态规划](basic_algorithm/dp.md)
16 | - [并查集](basic_algorithm/disjoin_set.md)
17 |
18 | ## 进阶算法
19 |
20 | - [贪心算法](advanced_algorithm/greedy.md)
21 | - [快速选择](advanced_algorithm/quick_select.md)
22 | - [三向切分快速排序](advanced_algorithm/three_way_quick_sort.md)
23 | - [二进制运算](advanced_algorithm/binary_op.md)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 算法模板(Java版)
2 |
3 | > 本项目内容主要参考[算法模板](https://github.com/greyireland/algorithm-pattern),在此感谢原作者的整理与贡献
4 |
5 | 在原项目的基础上,尽量保持了原有的结构划分,并做了一点微小的工作:
6 |
7 | - 代码改写为`java`语言版本
8 | - 调整内容,新增了几种算法
9 | - 补充部分[leetcode中国站](https://leetcode-cn.com/)的题目链接
10 | - 书籍链接:[GitBook](https://chienmy.gitbook.io/algorithm-pattern-java/)
11 |
12 | ## 核心内容
13 |
14 | ### 数据结构
15 |
16 | - [链表](./data_structure/linked_list.md)
17 | - [栈和队列](./data_structure/stack_queue.md)
18 | - [二叉树](./data_structure/binary_tree.md)
19 |
20 | ### 基础算法
21 |
22 | - [滑动窗口](./basic_algorithm/slide_window.md)
23 | - [回溯算法](./basic_algorithm/backtrack.md)
24 | - [二分搜索](./basic_algorithm/binary_search.md)
25 | - [排序算法](./basic_algorithm/sort.md)
26 | - [动态规划](./basic_algorithm/dp.md)
27 | - [并查集](./basic_algorithm/disjoin_set.md)
28 |
29 | ### 进阶算法
30 |
31 | > 此处整理了一些特殊情况下适用的算法
32 |
33 | - [贪心算法](./advanced_algorithm/greedy.md)
34 | - [快速选择](./advanced_algorithm/quick_select.md)
35 | - [三向切分快速排序](./advanced_algorithm/three_way_quick_sort.md)
36 | - [二进制运算](./advanced_algorithm/binary_op.md)
37 |
38 | ## 刷题建议
39 |
40 | 1. 巩固基础:先从数据结构的基础题做起,掌握常见数据结构以及对应操作的实现
41 | 2. 算法专题:推荐按类型刷题,在几天之内做完同一种类型的题目,可以迅速理解
42 | 3. 查漏补缺:对于某些不常见的特殊解法,在最后快速刷掉,务必留下印象
43 |
44 | > ### 欢迎 star 本项目
45 | >
46 | > Github地址:https://github.com/chienmy/algorithm-pattern-java
47 | >
48 | > 本项目采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-相同方式共享 4.0 国际许可协议进行许可。
49 |
50 |  51 |
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/quick_select.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 快速选择
2 |
3 | ## 使用场景
4 |
5 | - 最大/最小的K个数
6 | - 最大/最小的第K个数
7 |
8 | ## 算法思路
9 |
10 | 和快速排序的思路类似,但是不需要得出精确的比较顺序。首先从数组中随机或指定挑选一个元素作为标志,然后将所有比这个标志小的元素放在左边,比标志大的放在右边,最后会有以下三种可能的情况:
11 |
12 | 1. 这个位置就是K,直接返回即可
13 | 2. 这个位置小于K,说明K位置的数在右边
14 | 3. 这个位置大于K,说明K位置的数在左边
15 |
16 | ## 算法实现
17 |
18 | > [215. 数组中的第K个最大元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/)
19 | >
20 | >在未排序的数组中找到第 **k** 个最大的元素。请注意,需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
21 |
22 | ```java
23 | public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
24 | int l = 0;
25 | int r = nums.length - 1;
26 | while (l < r) {
27 | // 对标志两边分别进行处理
28 | int pivot = partition(nums, l, r);
29 | // 标志就是k
30 | if (pivot == nums.length - k) {
31 | break;
32 | }
33 | // k位置在标志的右侧
34 | else if (pivot < nums.length - k) {
35 | l = pivot + 1;
36 | }
37 | // k位置在标志的左侧
38 | else {
39 | r = pivot - 1;
40 | }
41 | }
42 | return nums[nums.length - k];
43 | }
44 |
45 | private int partition(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
46 | int l = start;
47 | int r = end + 1;
48 | // 选择首元素作为比较标志
49 | // 比标志小的放在左边,比标志大的放在右边
50 | while (true) {
51 | while (nums[++l] < nums[start] && l < end);
52 | while (nums[--r] > nums[start] && r > start);
53 | if (l >= r) {
54 | break;
55 | }
56 | swap(nums, l, r);
57 | }
58 | // 将标志交换到中间
59 | swap(nums, start, r);
60 | return r;
61 | }
62 |
63 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
64 | int temp = nums[i];
65 | nums[i] = nums[j];
66 | nums[j] = temp;
67 | }
68 | ```
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/three_way_quick_sort.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 三向切分快速排序
2 |
3 | ## 使用场景
4 |
5 | 待排序数组中含有类别较少但大量重复的元素
6 |
7 | ## 算法思路
8 |
9 | 除前后两个指针外再使用两个额外的指针指向与待选元素相同的元素,遍历后将与待选元素相同的元素置换到数组中间,再对两侧分别进行排序。通过这一方法可以节省元素交换次数。
10 |
11 | ## 算法实现
12 |
13 | ```java
14 | public void sort(int[] nums) {
15 | sort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
16 | }
17 |
18 | private void sort(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
19 | if (left < right) {
20 | // 选择首元素作为比较标志
21 | int temp = nums[left];
22 | // 设置两个指针指向与temp相同的元素范围
23 | int left_p = left;
24 | int right_p = right;
25 | for (int i = left + 1; i <= right_p; ) {
26 | // 根据比较结果进行元素交换
27 | if (nums[i] < temp) {
28 | swap(nums, left_p, i);
29 | left_p++;
30 | i++;
31 | } else if (nums[i] > temp) {
32 | swap(nums, i, right_p);
33 | right_p--;
34 | } else {
35 | i++;
36 | }
37 | }
38 | // 对两侧元素分别进行排序
39 | sort(nums, left, left_p - 1);
40 | sort(nums, right_p + 1, right);
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
45 | int temp = nums[i];
46 | nums[i] = nums[j];
47 | nums[j] = temp;
48 | }
49 | ```
50 |
51 | ## 经典例题
52 |
53 | > [75. 颜色分类](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-colors/)
54 | >
55 | > 给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 `n` 个元素的数组,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
56 | >
57 | > 此题中,我们使用整数 `0`、 `1` 和 `2` 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
58 |
59 | 由于只有三种颜色,所以不需要再对比较标志两侧元素分别排序,对实现代码稍作修改即可。
60 |
61 | ```java
62 | public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
63 | int left = 0;
64 | int mid = 0;
65 | int right = nums.length - 1;
66 | while (mid <= right) {
67 | if (nums[mid] == 0) {
68 | swap(nums, left, mid);
69 | mid++;
70 | left++;
71 | } else if (nums[mid] == 2) {
72 | swap(nums, right, mid);
73 | right--;
74 | } else {
75 | mid++;
76 | }
77 | }
78 | }
79 |
80 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
81 | int temp = nums[i];
82 | nums[i] = nums[j];
83 | nums[j] = temp;
84 | }
85 | ```
86 |
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/greedy.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 贪心算法
2 |
3 | 贪心算法在每一步选择中都采取在当前状态下最好或最优的选择,从而使得结果也是最优解,适合去解决具有最优子结构的问题。
4 |
5 | ## 应用场景
6 |
7 | 最优子结构的特征:
8 |
9 | - 每一次操作对结果直接产生影响
10 | - 不依赖于之前的操作
11 | - 子问题的最优解是全局最优解的一部分
12 |
13 | ## 常见例题
14 |
15 | ### 跳跃游戏
16 |
17 | > [55. 跳跃游戏](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game/)
18 | >
19 | > 给定一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的 第一个下标 。
20 | >
21 | > 数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
22 | >
23 | > 判断你是否能够到达最后一个下标。
24 |
25 | 思路:每个格子`i`作为起跳点最远能跳到`nums[i]`处,所以遍历数组得到最远距离并与数组长度进行比较即可。
26 |
27 | 这题只需要判断能否到达终点而无需给出具体路径,所以不需要用回溯的方法。
28 |
29 | ```java
30 | public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
31 | int maxLen = 0;
32 | for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
33 | // 当前格子已经无法跳到
34 | if (i > maxLen) return false;
35 | // 更新能跳到的最远距离
36 | maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, i + nums[i]);
37 | }
38 | return true;
39 | }
40 | ```
41 |
42 | ### 跳跃游戏 II
43 |
44 | > [45. 跳跃游戏 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game-ii/)
45 | >
46 | >给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
47 | >
48 | >数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
49 | >
50 | >你的目标是使用最少的跳跃次数到达数组的最后一个位置。
51 |
52 | 思路:确保每次跳跃选择的格子都有最远的跳跃范围。
53 |
54 | ```java
55 | public int jump(int[] nums) {
56 | int steps = 0;
57 | int start = 0;
58 | int end = 1;
59 | while (end < nums.length) {
60 | // 确定最远的跳跃范围
61 | int maxPosition = 0;
62 | for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
63 | maxPosition = Math.max(maxPosition, i + nums[i]);
64 | }
65 | start = end;
66 | end = maxPosition + 1;
67 | // 步数增加
68 | steps++;
69 | }
70 | return steps;
71 | }
72 | ```
73 |
74 | ### 分发饼干
75 |
76 | > [455. 分发饼干](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/assign-cookies/)
77 | >
78 | > 对每个孩子 `i`,都有一个胃口值 `g[i]`,这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干 `j`,都有一个尺寸 `s[j]` 。如果 `s[j] >= g[i]`,我们可以将这个饼干 `j` 分配给孩子 `i` ,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是尽可能满足越多数量的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
79 |
80 | 思路:先排序,再贪心,让饼干优先满足胃口更多的孩子
81 |
82 | ```java
83 | public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
84 | Arrays.sort(g);
85 | Arrays.sort(s);
86 | int p = 0;
87 | int q = 0;
88 | while (p < g.length && q < s.length) {
89 | if (g[p] <= s[q]) {
90 | p++;
91 | }
92 | q++;
93 | }
94 | return p;
95 | }
96 | ```
97 |
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/binary_op.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 二进制
2 |
3 | ## 常见二进制操作
4 |
5 | ### 基本操作
6 |
7 | a=0^a=a^0
8 |
9 | 0=a^a
10 |
11 | 由上面两个推导出:a=a^b^b
12 |
13 | ### 交换两个数
14 |
15 | a=a^b
16 |
17 | b=a^b
18 |
19 | a=a^b
20 |
21 | ### 移除最后一个 1
22 |
23 | a=n&(n-1)
24 |
25 | ### 获取最后一个 1
26 |
27 | diff=(n&(n-1))^n
28 |
29 | ## 常见例题
30 |
31 | ### 只出现一次的数字
32 |
33 | > [136. 只出现一次的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number/)
34 | >
35 | > 给定一个**非空**整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
36 |
37 | ```java
38 | public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
39 | // 10 ^ 10 == 00
40 | // 两个相同的数异或变成0
41 | int result = 0;
42 | for (int n : nums) {
43 | result = result ^ n;
44 | }
45 | return result;
46 | }
47 | ```
48 |
49 | ### 只出现一次的数字 II
50 |
51 | > [137. 只出现一次的数字 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number-ii/)
52 | >
53 | > 给定一个**非空**整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现了三次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
54 |
55 | ```java
56 | public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
57 | int result = 0;
58 | // 统计每位1的个数
59 | for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
60 | int sum = 0;
61 | for (int n : nums) {
62 | // 统计1的个数
63 | sum += ((n >> i) & 1);
64 | }
65 | // 还原
66 | result |= ((sum % 3) << i);
67 | }
68 | return result;
69 | }
70 | ```
71 |
72 | ### 只出现一次的数字 III
73 |
74 | > [260. 只出现一次的数字 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number-iii/)
75 | >
76 | > 给定一个整数数组 `nums`,其中恰好有两个元素只出现一次,其余所有元素均出现两次。 找出只出现一次的那两个元素。
77 |
78 | ```java
79 | public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
80 | // 关键点怎么把a^b分成两部分,方案:可以通过diff最后一个1区分
81 | int diff = 0;
82 | for (int n : nums) {
83 | diff ^= n;
84 | }
85 | int[] result = new int[]{diff, diff};
86 | // 去掉末尾的1后异或diff就得到最后一个1的位置
87 | diff = (diff & (diff - 1)) ^ diff;
88 | for (int n : nums) {
89 | if ((diff & n) == 0) {
90 | result[0] ^= n;
91 | } else {
92 | result[1] ^= n;
93 | }
94 | }
95 | return result;
96 | }
97 | ```
98 |
99 | ### 位1的个数
100 |
101 | > [191. 位1的个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-1-bits/)
102 | >
103 | > 编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数,返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 ‘1’ 的个数(也被称为[汉明重量](https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%B1%89%E6%98%8E%E9%87%8D%E9%87%8F))。
104 |
105 | ```java
106 | public int hammingWeight(int n) {
107 | int result = 0;
108 | while (n != 0) {
109 | if ((n & 1) == 1) result++;
110 | n = n >>> 1;
111 | }
112 | return result;
113 | }
114 | ```
115 |
116 | ### 颠倒二进制位
117 |
118 | > [190. 颠倒二进制位](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-bits/)
119 | >
120 | > 颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位。
121 |
122 | 思路:依次颠倒即可
123 |
124 | ```java
125 | public int reverseBits(int n) {
126 | int result = 0;
127 | int p = 31;
128 | while (n != 0) {
129 | result += ((n & 1) << p);
130 | n >>>= 1;
131 | p--;
132 | }
133 | return result;
134 | }
135 | ```
136 |
137 | ### 数字范围按位与
138 |
139 | > [201. 数字范围按位与](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/bitwise-and-of-numbers-range/)
140 | >
141 | > 给定范围 [m, n],其中 0 <= m <= n <= 2147483647,返回此范围内所有数字的按位与(包含 m, n 两端点)。
142 |
143 | 问题转化为求两个给定数字二进制状态下的最长公共前缀,可以用移位判断的思想来做,这里使用另一种`Brian Kernighan`算法:`number`和 `number−1`之间进行按位与运算后,`number`中最右边的1会被抹去变成0。
144 |
145 | ```java
146 | public int rangeBitwiseAnd(int m, int n) {
147 | while (m < n) {
148 | // 抹去最右边的 1
149 | n = n & (n - 1);
150 | }
151 | return n;
152 | }
153 | ```
154 |
155 | ## 注意点
156 |
157 | - Java中区分右移运算和无符号右移运算
158 | - 注意运算顺序,不确定时尽量加上括号
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/sort.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 排序
2 |
3 | ## 常考排序
4 |
5 | ### 快速排序
6 |
7 | ```java
8 | public void quickSort(int[] nums) {
9 | // 思路:把一个数组分为左右两段,左段小于右段
10 | quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
11 | }
12 |
13 | // 原地交换,所以传入交换索引
14 | private void quickSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
15 | if (start < end) {
16 | // 分治法:divide
17 | int pivot = partition(nums, start, end);
18 | quickSort(nums, 0, pivot - 1);
19 | quickSort(nums, pivot + 1, end);
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
23 | // 分区
24 | private int partition(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
25 | // 选取最后一个元素作为基准pivot
26 | int p = nums[end];
27 | int i = start;
28 | // 最后一个值就是基准所以不用比较
29 | for (int j = start; j < end; j++) {
30 | if (nums[j] < p) {
31 | swap(nums, i, j);
32 | i++;
33 | }
34 | }
35 | // 把基准值换到中间
36 | swap(nums, i, end);
37 | return i;
38 | }
39 |
40 | // 交换两个元素
41 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
42 | int temp = nums[i];
43 | nums[i] = nums[j];
44 | nums[j] = temp;
45 | }
46 | ```
47 |
48 | ### 归并排序
49 |
50 | ```java
51 | public void mergeSort(int[] nums) {
52 | mergeSort(nums, 0, nums.length);
53 | }
54 |
55 | private void mergeSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
56 | if (end - start <= 1) {
57 | return;
58 | }
59 | // 分治法:divide 分为两段
60 | int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
61 | mergeSort(nums, start, mid);
62 | mergeSort(nums, mid, end);
63 | // 合并两段数据
64 | merge(nums, start, mid, end);
65 | }
66 |
67 | private void merge(int[] nums, int start, int mid, int end) {
68 | int[] temp = new int[end - start];
69 | // 两边数组合并游标
70 | int l = start;
71 | int r = mid;
72 | int k = 0;
73 | // 注意不能越界
74 | while (l < mid && r < end) {
75 | // 谁小合并谁
76 | if (nums[l] < nums[r]) {
77 | temp[k++] = nums[l++];
78 | } else {
79 | temp[k++] = nums[r++];
80 | }
81 | }
82 | // 剩余部分合并
83 | while (l < mid) {
84 | temp[k++] = nums[l++];
85 | }
86 | while (r < end) {
87 | temp[k++] = nums[r++];
88 | }
89 | // 复制到原数组
90 | for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
91 | nums[i + start] = temp[i];
92 | }
93 | }
94 | ```
95 |
96 | ### 堆排序
97 |
98 | 用数组表示的完全二叉树 complete binary tree
99 |
100 | > 完全二叉树 VS 其他二叉树
101 |
102 | 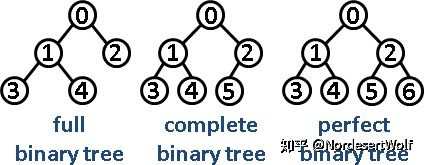
103 |
104 | [动画展示](https://www.bilibili.com/video/av18980178/)
105 |
106 | 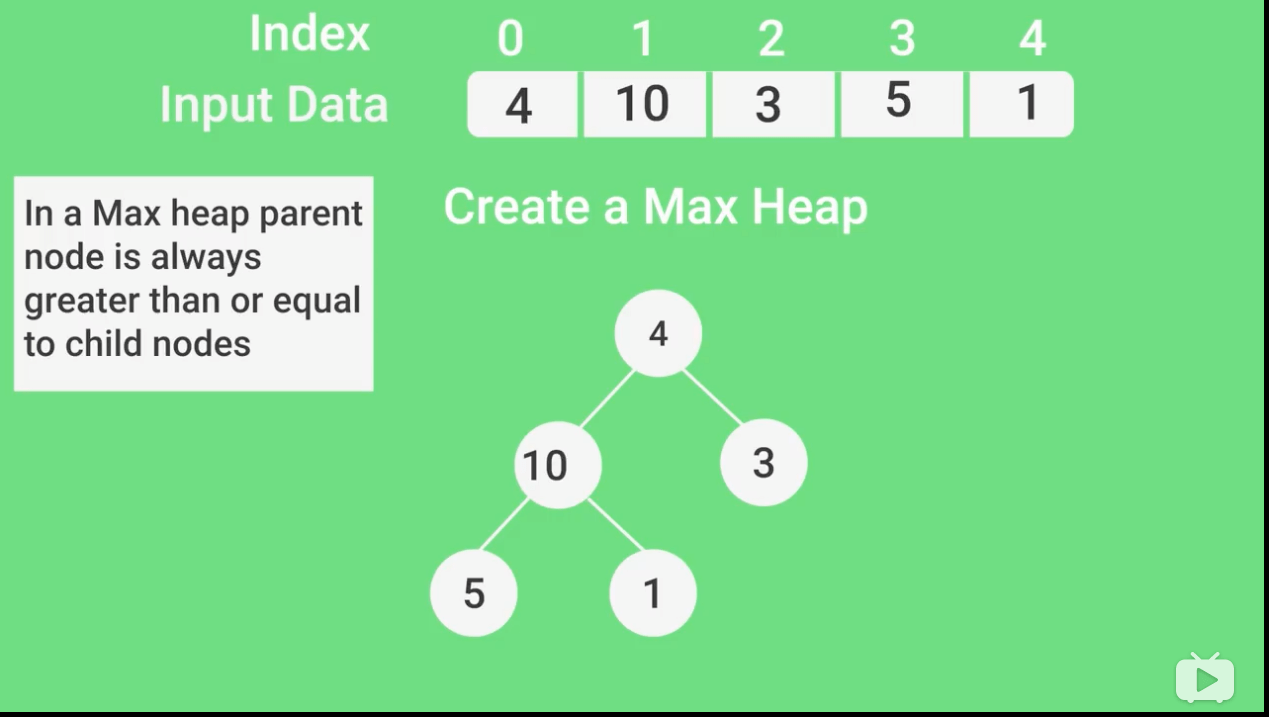
107 |
108 | 核心代码
109 |
110 | ```java
111 | public void heapSort(int[] nums) {
112 | // 1、无序数组nums
113 | // 2、将无序数组nums构建为一个大根堆
114 | for (int i = nums.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
115 | sink(nums, i, nums.length);
116 | }
117 | // 3、交换nums[0]和nums[len(a)-1]
118 | // 4、然后把前面这段数组继续下沉保持堆结构,如此循环即可
119 | for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
120 | // 从后往前填充值
121 | swap(nums, 0, i);
122 | // 前面的长度也减一
123 | sink(nums, 0, i);
124 | }
125 | }
126 |
127 | private void sink(int[] nums, int i, int length) {
128 | while (true) {
129 | // 左节点索引(从0开始,所以左节点为i*2+1)
130 | int l = i * 2 + 1;
131 | // 右节点索引
132 | int r = i * 2 + 2;
133 | // 保存根、左、右三者之间较大值的索引
134 | int index = i;
135 | // 存在左节点,左节点值较大,则取左节点
136 | if (l < length && nums[l] > nums[index]) {
137 | index = l;
138 | }
139 | // 存在右节点,且值较大,取右节点
140 | if (r < length && nums[r] > nums[index]) {
141 | index = r;
142 | }
143 | // 如果根节点较大,则不用下沉
144 | if (index == i) {
145 | break;
146 | }
147 | // 如果根节点较小,则交换值,并继续下沉
148 | swap(nums, i, index);
149 | i = index;
150 | }
151 | }
152 |
153 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
154 | int temp = nums[i];
155 | nums[i] = nums[j];
156 | nums[j] = temp;
157 | }
158 | ```
159 |
160 | ## 参考
161 |
162 | [十大经典排序](https://www.cnblogs.com/onepixel/p/7674659.html)
163 |
164 | [二叉堆](https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo/shu-ju-jie-gou-xi-lie/er-cha-dui-xiang-jie-shi-xian-you-xian-ji-dui-lie)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data_structure/stack_queue.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 栈和队列
2 |
3 | ## 简介
4 |
5 | 栈的特点是后入先出
6 |
7 | 根据这个特点可以临时保存一些数据,之后用到依次再弹出来,常用于树的非递归遍历、 DFS 深度搜索。
8 |
9 | 队列常用于BFS广度搜索,很少单独考察。
10 |
11 | ## 基本应用
12 |
13 | ### 逆波兰表达式求值
14 |
15 | > [150. 逆波兰表达式求值](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/)
16 | >
17 | > **波兰表达式计算** > **输入:** `["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]` > **输出:** 9
18 | >
19 | > **解释:** `((2 + 1) * 3) = 9`
20 |
21 | ```java
22 | public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
23 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
24 | for (String s : tokens) {
25 | if ("+".equals(s) || "-".equals(s) || "*".equals(s) || "/".equals(s)) {
26 | int a = stack.pop();
27 | int b = stack.pop();
28 | if ("+".equals(s)) stack.push(b + a);
29 | else if ("-".equals(s)) stack.push(b - a);
30 | else if ("*".equals(s)) stack.push(b * a);
31 | // 注意:b为被除数,a为除数
32 | else if ("/".equals(s)) stack.push(b / a);
33 | } else {
34 | // 转为数字
35 | stack.push(Integer.parseInt(s));
36 | }
37 | }
38 | return stack.pop();
39 | }
40 | ```
41 |
42 | ### 有效的括号
43 |
44 | > [20. 有效的括号](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/)
45 | >
46 | > 给定一个只包括 `'('`,`')'`,`'{'`,`'}'`,`'['`,`']'` 的字符串 `s` ,判断字符串是否有效。
47 | >
48 | > 有效字符串需满足:
49 | >
50 | > 1. 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
51 | > 2. 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
52 |
53 | ```java
54 | public boolean isValid(String s) {
55 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
56 | for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
57 | if (c == '(') stack.push(')');
58 | else if (c == '[') stack.push(']');
59 | else if (c == '{') stack.push('}');
60 | else if (stack.isEmpty() || c != stack.pop()) {
61 | return false;
62 | }
63 | }
64 | return stack.isEmpty();
65 | }
66 | ```
67 |
68 | ## 单调栈
69 |
70 | 单调栈:栈内元素保持单调递增或单调递减的栈
71 |
72 | **(以单调递增栈为例)**
73 |
74 | 入栈规则:
75 |
76 | - 新元素比栈顶元素小:直接入栈
77 |
78 | - 新元素比栈顶元素大:弹出栈内元素直到栈顶比新元素小(或空栈)
79 |
80 | 出栈意义:
81 |
82 | - 需要出栈时,入栈的新元素是出栈元素右方第一个比出栈元素小的元素
83 |
84 | - 出栈后,新的栈顶是出栈元素左侧最大的数
85 |
86 | 技巧:最后添加一个值为0的哨兵节点,可以在最后强制所有元素出栈。
87 |
88 | 以下分别使用了单调递增栈和单调递减栈
89 |
90 | ### 柱状图中最大的矩形
91 |
92 | > [84. 柱状图中最大的矩形](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/)
93 | >
94 | > 给定 *n* 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
95 | >
96 | > 求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
97 |
98 | ```java
99 | public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
100 | if (heights.length == 0) {
101 | return 0;
102 | }
103 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
104 | int max = 0;
105 | // 当前高度小于栈,则将栈内元素都弹出计算面积
106 | for (int i = 0; i <= heights.length; i++) {
107 | int cur = 0;
108 | if (i < heights.length) {
109 | cur = heights[i];
110 | }
111 | while (stack.size() != 0 && cur <= heights[stack.peek()]) {
112 | int index = stack.pop();
113 | int h = heights[index];
114 | // 计算宽度
115 | int w = i;
116 | if (stack.size() != 0) {
117 | int peek = stack.peek();
118 | w = i - peek - 1;
119 | }
120 | max = Math.max(max, h * w);
121 | }
122 | // 记录索引即可获取对应元素
123 | stack.push(i);
124 | }
125 | return max;
126 | }
127 | ```
128 |
129 | ### 接雨水
130 |
131 | > [42. 接雨水](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/)
132 | >
133 | > 给定 *n* 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
134 |
135 | ```java
136 | public int trap(int[] height) {
137 | int sum = 0;
138 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
139 | int current = 0;
140 | while (current < height.length) {
141 | //如果栈不空并且当前指向的高度大于栈顶高度就一直循环
142 | while (!stack.empty() && height[current] > height[stack.peek()]) {
143 | int h = height[stack.peek()]; //取出要出栈的元素
144 | stack.pop(); //出栈
145 | if (stack.empty()) { // 栈空就出去
146 | break;
147 | }
148 | int distance = current - stack.peek() - 1; //两堵墙之前的距离。
149 | int min = Math.min(height[stack.peek()], height[current]);
150 | sum = sum + distance * (min - h);
151 | }
152 | stack.push(current); //当前指向的墙入栈
153 | current++; //指针后移
154 | }
155 | return sum;
156 | }
157 | ```
158 |
159 | ## 设计类问题
160 |
161 | > [2. 用栈实现队列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/)
162 |
163 | ```java
164 | class MyQueue {
165 |
166 | private Stack stack1 = new Stack<>();
167 | private Stack stack2 = new Stack<>();
168 |
169 | /** Initialize your data structure here. */
170 | public MyQueue() {
171 |
172 |
173 | }
174 |
175 | /** Push element x to the back of queue. */
176 | public void push(int x) {
177 | while (! stack2.isEmpty()) {
178 | int val = stack2.pop();
179 | stack1.push(val);
180 | }
181 | stack1.push(x);
182 | }
183 |
184 | /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
185 | public int pop() {
186 | while (! stack1.isEmpty()) {
187 | int val = stack1.pop();
188 | stack2.push(val);
189 | }
190 | if (stack2.isEmpty()) return -1;
191 | return stack2.pop();
192 | }
193 |
194 | /** Get the front element. */
195 | public int peek() {
196 | while (! stack1.isEmpty()) {
197 | int val = stack1.pop();
198 | stack2.push(val);
199 | }
200 | if (stack2.isEmpty()) return -1;
201 | return stack2.peek();
202 | }
203 |
204 | /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
205 | public boolean empty() {
206 | return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();
207 | }
208 | }
209 | ```
210 |
211 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/slide_window.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 滑动窗口
2 |
3 | ## 模板
4 |
5 | ```cpp
6 | /* 滑动窗口算法框架 */
7 | void slidingWindow(string s, string t) {
8 | unordered_map need, window;
9 | for (char c : t) need[c]++;
10 |
11 | int left = 0, right = 0;
12 | int valid = 0;
13 | while (right < s.size()) {
14 | // c 是将移入窗口的字符
15 | char c = s[right];
16 | // 右移窗口
17 | right++;
18 | // 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
19 | ...
20 |
21 | // 判断左侧窗口是否要收缩
22 | while (window needs shrink) {
23 | // d 是将移出窗口的字符
24 | char d = s[left];
25 | // 左移窗口
26 | left++;
27 | // 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
28 | ...
29 | }
30 | }
31 | }
32 | ```
33 |
34 | 需要变化的地方
35 |
36 | - 1、右指针右移之后窗口数据更新
37 | - 2、判断窗口是否要收缩
38 | - 3、左指针右移之后窗口数据更新
39 | - 4、根据题意计算结果
40 |
41 | ## 示例
42 |
43 | ### 最小覆盖子串
44 |
45 | > [76. 最小覆盖子串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/)
46 | >
47 | > 给你一个字符串 S、一个字符串 T,请在字符串 S 里面找出:包含 T 所有字母的最小子串
48 |
49 | ```java
50 | public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
51 | // 技巧:用数组代替Map
52 | // 保存滑动窗口字符集
53 | int[] winMap = new int[256];
54 | // 保存需要出现的字符集
55 | int[] tMap = new int[256];
56 | for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
57 | tMap[c]++;
58 | }
59 | // 计算共出现了多少不同的字符
60 | int charNum = 0;
61 | for (int n : tMap) {
62 | if (n > 0) {
63 | charNum++;
64 | }
65 | }
66 | // 滑动窗口左右边界
67 | int left = 0;
68 | int right = 0;
69 | // 匹配数
70 | int match = 0;
71 | // 窗口调整前暂存原窗口边界
72 | int start = 0;
73 | int end = 0;
74 | // 窗口长度的最小值
75 | int minValue = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
76 | while (right < s.length()) {
77 | char c = s.charAt(right);
78 | // 在需要的字符集里面,添加到窗口字符集里面
79 | if (tMap[c] != 0) {
80 | winMap[c]++;
81 | // 如果当前字符的数量匹配需要的字符的数量,则match值+1
82 | if (tMap[c] == winMap[c]) {
83 | match++;
84 | }
85 | }
86 | right++;
87 | // 当所有字符数量都匹配之后,开始缩紧窗口
88 | while (match == charNum) {
89 | // 获取结果
90 | if (right - left < minValue) {
91 | minValue = right - left;
92 | start = left;
93 | end = right;
94 | }
95 | char leftChar = s.charAt(left);
96 | // 左指针指向不在需要字符集则直接跳过
97 | if (tMap[leftChar] != 0) {
98 | // 左指针指向字符数量和需要的字符相等时,右移之后match值就不匹配则减一
99 | if (winMap[leftChar] == tMap[leftChar]) {
100 | match--;
101 | }
102 | winMap[leftChar]--;
103 | }
104 | left++;
105 | }
106 | }
107 | if (minValue == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
108 | return "";
109 | }
110 | return s.substring(start, end);
111 | }
112 | ```
113 |
114 | ### 字符串的排列
115 |
116 | > [567. 字符串的排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutation-in-string/)
117 | >
118 | > 给定两个字符串 **s1** 和 **s2**,写一个函数来判断 **s2** 是否包含 **s1 **的排列。
119 |
120 | ```java
121 | public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {
122 | // 保存滑动窗口字符集
123 | int[] winMap = new int[256];
124 | // 保存需要出现的字符集
125 | int[] tMap = new int[256];
126 | for (char c : s1.toCharArray()) {
127 | tMap[c]++;
128 | }
129 | // 计算共出现了多少不同的字符
130 | int charNum = 0;
131 | for (int n : tMap) {
132 | if (n > 0) {
133 | charNum++;
134 | }
135 | }
136 | // 左右边界
137 | int left = 0;
138 | int right = 0;
139 | // 已经匹配的字母数
140 | int match = 0;
141 |
142 | while (right < s2.length()) {
143 | char c = s2.charAt(right);
144 | right++;
145 | if (tMap[c] != 0) {
146 | winMap[c]++;
147 | if (winMap[c] == tMap[c]) {
148 | match++;
149 | }
150 | }
151 | // 窗口收缩
152 | while (match == charNum) {
153 | c = s2.charAt(left);
154 | if (tMap[c] != 0) {
155 | if (winMap[c] == tMap[c]) {
156 | match--;
157 | }
158 | winMap[c]--;
159 | }
160 | left++;
161 | // 子串是一个排列,即子串长度等于s1
162 | if (right - left + 1 == s1.length()) {
163 | return true;
164 | }
165 | }
166 | }
167 | return false;
168 | }
169 | ```
170 |
171 | ### 找到字符串中所有字母异位词
172 |
173 | > [438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/)
174 | >
175 | > 给定一个字符串 **s **和一个非空字符串 **p**,找到 **s **中所有是 **p **的字母异位词的子串,返回这些子串的起始索引。
176 |
177 | ```java
178 | public List findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
179 | int[] pMap = new int[256];
180 | int[] winMap = new int[256];
181 | int charNum = 0;
182 | for (char c : p.toCharArray()) {
183 | if (pMap[c] == 0) charNum++;
184 | pMap[c]++;
185 | }
186 | int left = 0;
187 | int right = 0;
188 | int match = 0;
189 | List result = new ArrayList<>();
190 | while (right < s.length()) {
191 | char c = s.charAt(right);
192 | right++;
193 | if (pMap[c] != 0) {
194 | winMap[c]++;
195 | if (pMap[c] == winMap[c]) {
196 | match++;
197 | }
198 | }
199 | // 缩紧窗口
200 | while (match == charNum) {
201 | c = s.charAt(left);
202 | if (pMap[c] != 0) {
203 | if (pMap[c] == winMap[c]) {
204 | match--;
205 | }
206 | winMap[c]--;
207 | }
208 | // 当窗口长度和字符串长度匹配时,满足条件
209 | if (right - left == p.length()) {
210 | result.add(left);
211 | }
212 | left++;
213 | }
214 | }
215 | return result;
216 | }
217 | ```
218 |
219 | ### 无重复字符的最长子串
220 |
221 | > [3. 无重复字符的最长子串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/)
222 | >
223 | >给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的**最长子串**的长度。
224 |
225 | ```java
226 | public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
227 | if (s.length() < 2) {
228 | return s.length();
229 | }
230 | int[] winMap = new int[256];
231 | int left = 0;
232 | int right = 0;
233 | int maxLen = 0;
234 | // 1、右指针右移
235 | while (right < s.length()) {
236 | char c = s.charAt(right);
237 | right++;
238 | winMap[c]++;
239 | // 2、根据题意收缩窗口
240 | while (winMap[c] > 1) {
241 | // 3、左指针右移更新窗口
242 | char d = s.charAt(left);
243 | left++;
244 | winMap[d]--;
245 | }
246 | // 4、根据题意计算结果
247 | maxLen = Math.max(right - left, maxLen);
248 | }
249 | return maxLen;
250 | }
251 | ```
252 |
253 | ## 总结
254 |
255 | - 和双指针题目类似,更像双指针的升级版,滑动窗口核心点是维护一个窗口集,根据窗口集来进行处理
256 | - 核心步骤
257 | - right 右移
258 | - 收缩
259 | - left 右移
260 | - 求结果
261 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/disjoin_set.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 并查集
2 |
3 | ## 简介
4 |
5 | 并查集用于处理不相交集合的合并与查询问题,常见操作有:
6 |
7 | - 查询:查询元素属于哪个集合,可用于判断元素是否在一个集合中
8 | - 合并:合并两个集合
9 |
10 | 应用场景:动态连通性的判断,且不需要给出具体路径。
11 |
12 | ## 数据结构
13 |
14 | ### 初始化
15 |
16 | id数组存放的是节点的组号,初始化时将每个节点单独分为一组。
17 |
18 | ```java
19 | private int[] id;
20 |
21 | public DisjoinSet(int size) {
22 | id = new int[size];
23 | for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
24 | id[i] = i;
25 | }
26 | ```
27 |
28 | ### Quick-Find
29 |
30 | 由于使用整数表示节点,可以通过数组实现节点到组编号的映射。
31 |
32 | ```java
33 | public void union(int p, int q) {
34 | // 获得p和q的组号
35 | int pID = id[p];
36 | int qID = id[q];
37 | // 如果两个组号相等,直接返回
38 | if (pID == qID) return;
39 | // 遍历一次,改变组号使他们属于一个组
40 | for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
41 | if (id[i] == pID) id[i] = qID;
42 | count--;
43 | }
44 | ```
45 |
46 | ### Quick-Union
47 |
48 | id数组存放的是节点的父节点索引,根节点的父节点是自身,通过这点判断能到达根节点。
49 |
50 | ```java
51 | private int find(int p) {
52 | // 寻找p节点所在组的根节点,根节点具有性质id[root] = root
53 | while (p != id[p]) p = id[p];
54 | return p;
55 | }
56 | public void union(int p, int q) {
57 | // Give p and q the same root.
58 | int pRoot = find(p);
59 | int qRoot = find(q);
60 | if (pRoot == qRoot)
61 | return;
62 | // 将一棵树(即一个组)变成另外一课树(即一个组)的子树
63 | id[pRoot] = qRoot;
64 | count--;
65 | }
66 | ```
67 |
68 | ### Weighted Quick Union
69 |
70 | 保存两棵树的大小,每次将小的合并到大的树中。
71 |
72 | ## 常见例题
73 |
74 | ### 冗余连接
75 |
76 | > [684. 冗余连接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/redundant-connection/)
77 | >
78 | > 在本问题中, 树指的是一个连通且无环的**无向**图。
79 | >
80 | > 输入一个图,该图由一个有着N个节点 (节点值不重复1, 2, ..., N) 的树及一条附加的边构成。附加的边的两个顶点包含在1到N中间,这条附加的边不属于树中已存在的边。
81 | >
82 | > 结果图是一个以`边`组成的二维数组。每一个`边`的元素是一对`[u, v]` ,满足 `u < v`,表示连接顶点`u` 和`v`的**无向**图的边。
83 | >
84 | > 返回一条可以删去的边,使得结果图是一个有着N个节点的树。如果有多个答案,则返回二维数组中最后出现的边。答案边 `[u, v]` 应满足相同的格式 `u < v`。
85 |
86 | ```java
87 | private int[] parent;
88 | private int[] size;
89 |
90 | private int find(int p) {
91 | while (p != parent[p]) {
92 | parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
93 | p = parent[p];
94 | }
95 | return p;
96 | }
97 |
98 | private boolean union(int p, int q) {
99 | int pRoot = find(p);
100 | int qRoot = find(q);
101 | // 在合并前判断是否属于相同的连通分量
102 | if (pRoot == qRoot) {
103 | return true;
104 | }
105 | // Weighted Quick Union
106 | if (size[pRoot] < size[qRoot]) {
107 | parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
108 | size[qRoot] += size[pRoot];
109 | } else {
110 | parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
111 | size[pRoot] += size[qRoot];
112 | }
113 | return false;
114 | }
115 |
116 | public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
117 | parent = new int[edges.length + 1];
118 | size = new int[edges.length + 1];
119 | // 并查集初始化
120 | for (int i = 0; i < parent.length; i++) {
121 | parent[i] = i;
122 | size[i] = 1;
123 | }
124 | for (int[] arr : edges) {
125 | if (union(arr[0], arr[1])) {
126 | // 如果已经连通说明当前这条边是多余的
127 | return arr;
128 | }
129 | }
130 | return new int[]{};
131 | }
132 | ```
133 |
134 | ### 打砖块
135 |
136 | > [803. 打砖块](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/bricks-falling-when-hit/)
137 | >
138 | >有一个 `m x n` 的二元网格,其中 `1` 表示砖块,`0` 表示空白。砖块 **稳定**(不会掉落)的前提是:
139 | >
140 | >- 一块砖直接连接到网格的顶部,或者
141 | >- 至少有一块相邻(4 个方向之一)砖块 **稳定** 不会掉落时
142 | >
143 | >给你一个数组 `hits` ,这是需要依次消除砖块的位置。每当消除 `hits[i] = (rowi, coli)` 位置上的砖块时,对应位置的砖块(若存在)会消失,然后其他的砖块可能因为这一消除操作而掉落。一旦砖块掉落,它会立即从网格中消失(即,它不会落在其他稳定的砖块上)。
144 | >
145 | >返回一个数组 `result` ,其中 `result[i]` 表示第 `i` 次消除操作对应掉落的砖块数目。
146 | >
147 | >**注意**,消除可能指向是没有砖块的空白位置,如果发生这种情况,则没有砖块掉落。
148 |
149 | 思路:并查集是用于合并连通分量,而砖块消失实质上是拆分连通分量,因此这题应当逆向考虑,即先打碎所有砖块,再从后向前添加砖块(合并连通分量),添加后计算会增加多少个节点与根节点相连。
150 |
151 | 首先给出并查集的定义,`size`既表示连通分量的大小,也用于合并时的权重判断。
152 |
153 | ```java
154 | class DisJoinSet {
155 |
156 | private final int[] parent;
157 | private final int[] size;
158 |
159 | // 初始化并查集,根节点为自身,大小为1
160 | public DisJoinSet(int len) {
161 | parent = new int[len];
162 | size = new int[len];
163 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
164 | parent[i] = i;
165 | size[i] = 1;
166 | }
167 | }
168 |
169 | // 查找连通分量的根节点
170 | public int find(int p) {
171 | while (p != parent[p]) {
172 | parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
173 | p = parent[p];
174 | }
175 | return p;
176 | }
177 |
178 | // 合并两个节点对应的连通分量
179 | public void merge(int p, int q) {
180 | int pRoot = find(p);
181 | int qRoot = find(q);
182 | // 在合并前判断是否属于相同的连通分量
183 | if (pRoot != qRoot) {
184 | if (size[pRoot] < size[qRoot]) {
185 | parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
186 | size[qRoot] += size[pRoot];
187 | } else {
188 | parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
189 | size[pRoot] += size[qRoot];
190 | }
191 | }
192 | }
193 |
194 | // 获取连通分量的大小
195 | public int getSize(int n) {
196 | int root = find(n);
197 | return size[root];
198 | }
199 |
200 | }
201 | ```
202 |
203 | 实际使用中将二维数组映射为一维数组,并在最后增加一项作为“房顶节点”,与其相连的节点均不会下落。下面是算法逻辑:
204 |
205 | ```java
206 | public int[] hitBricks(int[][] grid, int[][] hits) {
207 | int h = grid.length;
208 | int w = grid[0].length;
209 | int[] result = new int[hits.length];
210 | // 保存当前的砖块状态
211 | int[][] status = new int[h][w];
212 | DisJoinSet disJoinSet = new DisJoinSet(h * w + 1);
213 | // 将status初始化为最终的状态
214 | for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
215 | status[i] = grid[i].clone();
216 | }
217 | for (int[] pos : hits) {
218 | status[pos[0]][pos[1]] = 0;
219 | }
220 | // 根据最后的状态构造并查集
221 | for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
222 | for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
223 | if (status[i][j] == 0) {
224 | continue;
225 | }
226 | if (i == 0) {
227 | // 一块砖直接连接到网格的顶部
228 | disJoinSet.merge( h * w, j);
229 | } else {
230 | // 上方有相邻砖块
231 | if (status[i - 1][j] == 1) {
232 | disJoinSet.merge((i - 1) * w + j, i * w + j);
233 | }
234 | // 左侧有相邻砖块
235 | if (j > 0 && status[i][j - 1] == 1) {
236 | disJoinSet.merge(i * w + j - 1, i * w + j);
237 | }
238 | }
239 | }
240 | }
241 | // 从后向前把砖块补上
242 | int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
243 | for (int i = hits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
244 | int r = hits[i][0];
245 | int c = hits[i][1];
246 | if (grid[r][c] == 0) {
247 | result[i] = 0;
248 | } else {
249 | // 添加砖块前与房顶相连通的节点数目
250 | int prev = disJoinSet.getSize(h * w);
251 | // 顶部第一行的情况
252 | if (r == 0) {
253 | disJoinSet.merge(c, h * w);
254 | }
255 | // 处理四周的节点
256 | for (int[] direction : directions) {
257 | int nr = r + direction[0];
258 | int nc = c + direction[1];
259 |
260 | if (nr >= 0 && nr < h && nc >= 0 && nc < w && status[nr][nc] == 1) {
261 | disJoinSet.merge(r * w + c, nr * w + nc);
262 | }
263 | }
264 | // 获得增加的节点数,即为正向操作时这一步下落的节点数
265 | result[i] = Math.max(0, disJoinSet.getSize(h * w) - prev - 1);
266 | status[r][c] = 1;
267 | }
268 | }
269 | return result;
270 | }
271 | ```
272 |
273 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/backtrack.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 回溯算法
2 |
3 | ## 背景
4 |
5 | 回溯法(backtrack)常用于遍历列表所有子集,是 DFS 深度搜索一种,一般用于全排列,穷尽所有可能,遍历的过程实际上是一个决策树的遍历过程。时间复杂度一般 O(N!),它不像动态规划存在重叠子问题可以优化,回溯算法就是纯暴力穷举,复杂度一般都很高。
6 |
7 | ## 模板
8 |
9 | ```go
10 | result = []
11 | func backtrack(选择列表,路径):
12 | if 满足结束条件:
13 | result.add(路径)
14 | return
15 | for 选择 in 选择列表:
16 | 做选择
17 | backtrack(选择列表,路径)
18 | 撤销选择
19 | ```
20 |
21 | 核心就是从选择列表里做一个选择,然后一直递归往下搜索答案,如果遇到路径不通,就返回来撤销这次选择。
22 |
23 | ## 常见例题
24 |
25 | ### 集合类
26 |
27 | #### 子集
28 |
29 | > [78. 子集](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets/)
30 | >
31 | > 给你一个整数数组 `nums` ,数组中的元素 **互不相同** 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
32 |
33 | ```java
34 | public List> subsets(int[] nums) {
35 | // 保存中间结果
36 | List subSet = new ArrayList<>();
37 | // 保存最终结果
38 | List> result = new ArrayList<>();
39 | backtrack(nums, 0, subSet, result);
40 | return result;
41 | }
42 |
43 | // nums 给定的集合
44 | // pos 下次添加到集合中的元素位置索引
45 | // subSet 临时结果集合(每次需要复制保存)
46 | // result 最终结果
47 | private void backtrack(int[] nums, int pos, List subSet, List> result) {
48 | // 把临时结果复制出来保存到最终结果
49 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(subSet));
50 | for (int i = pos; i < nums.length; i++) {
51 | // 选择、处理结果、再撤销选择
52 | subSet.add(nums[i]);
53 | backtrack(nums, i+1, subSet, result);
54 | subSet.remove(subSet.size() - 1);
55 | }
56 | }
57 | ```
58 |
59 | #### 子集 II
60 |
61 | > [90. 子集 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets-ii/)
62 | >
63 | > 给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
64 |
65 | ```java
66 | public List> subsets(int[] nums) {
67 | // 保存中间结果
68 | List subSet = new ArrayList<>();
69 | // 保存最终结果
70 | List> result = new ArrayList<>();
71 | // 先排序
72 | Arrays.sort(nums);
73 | backtrack(nums, 0, subSet, result);
74 | return result;
75 | }
76 |
77 | // nums 给定的集合
78 | // pos 下次添加到集合中的元素位置索引
79 | // subSet 临时结果集合(每次需要复制保存)
80 | // result 最终结果
81 | private void backtrack(int[] nums, int pos, List subSet, List> result) {
82 | // 把临时结果复制出来保存到最终结果
83 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(subSet));
84 | for (int i = pos; i < nums.length; i++) {
85 | // 排序之后,如果再遇到重复元素,则不选择此元素
86 | if (i != pos && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) {
87 | continue;
88 | }
89 | // 选择、处理结果、再撤销选择
90 | subSet.add(nums[i]);
91 | backtrack(nums, i+1, subSet, result);
92 | subSet.remove(subSet.size() - 1);
93 | }
94 | }
95 | ```
96 |
97 | ### 排列类
98 |
99 | #### 全排列
100 |
101 | > [46. 全排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations/)
102 | >
103 | > 给定一个 **没有重复** 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
104 |
105 | 思路:需要记录已经选择过的元素,满足条件的结果才进行返回。这里要注意在做选择时记录,回溯时撤销。
106 |
107 | ```java
108 | public List> permute(int[] nums) {
109 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
110 | List> result = new ArrayList<>();
111 | // 标记这个元素是否已经添加到结果集
112 | boolean[] visited = new boolean[nums.length];
113 | backtrack(nums, visited, list, result);
114 | return result;
115 | }
116 |
117 | // nums 输入集合
118 | // visited 当前递归标记过的元素
119 | // list 临时结果集(路径)
120 | // result 最终结果
121 | private void backtrack(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, List list, List> result) {
122 | if (list.size() == nums.length) {
123 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
124 | return;
125 | }
126 | for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
127 | // 已经添加过的元素,直接跳过
128 | if (visited[i]) {
129 | continue;
130 | }
131 | // 添加元素
132 | list.add(nums[i]);
133 | visited[i] = true;
134 | backtrack(nums, visited, list, result);
135 | // 移除元素
136 | list.remove(list.size() - 1);
137 | visited[i] = false;
138 | }
139 | }
140 | ```
141 |
142 | #### 全排列 II
143 |
144 | > [47. 全排列 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations-ii/)
145 | >
146 | > 给定一个可包含重复数字的序列,返回所有不重复的全排列。
147 |
148 | ```java
149 | public List> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
150 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
151 | List> result = new ArrayList<>();
152 | // 标记这个元素是否已经添加到结果集
153 | boolean[] visited = new boolean[nums.length];
154 | // 先排序
155 | Arrays.sort(nums);
156 | backtrack(nums, visited, list, result);
157 | return result;
158 | }
159 |
160 | // nums 输入集合
161 | // visited 当前递归标记过的元素
162 | // list 临时结果集
163 | // result 最终结果
164 | private void backtrack(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, List list, List> result) {
165 | if (list.size() == nums.length) {
166 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
167 | return;
168 | }
169 | for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
170 | // 已经添加过的元素,直接跳过
171 | if (visited[i]) {
172 | continue;
173 | }
174 | // 上一个元素和当前相同,并且没有访问过就跳过
175 | if (i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && !visited[i-1]) {
176 | continue;
177 | }
178 | list.add(nums[i]);
179 | visited[i] = true;
180 | backtrack(nums, visited, list, result);
181 | list.remove(list.size() - 1);
182 | visited[i] = false;
183 | }
184 | }
185 |
186 | ```
187 |
188 | ### 组合类
189 |
190 | #### 组合总和
191 |
192 | > [39. 组合总和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/)
193 | >
194 | > 给定一个**无重复元素**的数组 `candidates` 和一个目标数 `target` ,找出 `candidates` 中所有可以使数字和为 `target` 的组合。
195 | >
196 | > `candidates` 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
197 | >
198 | > **说明:**
199 | >
200 | > - 所有数字(包括 `target`)都是正整数。
201 | > - 解集不能包含重复的组合。
202 |
203 | ```java
204 | public List> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
205 | List answer = new ArrayList();
206 | List> result = new ArrayList();
207 | // 先排序
208 | Arrays.sort(candidates);
209 | backtrack(candidates, 0, target, answer, result);
210 | return result;
211 | }
212 |
213 | // candidates 输入集合
214 | // pos 当前标记位置,标记前的元素不再考虑
215 | // target 求和目标
216 | // answer 临时解法
217 | // result 最终结果
218 | private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int pos, int target, List answer, List> result) {
219 | if (target == 0) {
220 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(answer));
221 | }
222 | for (int i = pos; i < candidates.length; i++) {
223 | // 剪枝:后续元素都比目标大,直接break(比continue要快)
224 | if (candidates[i] > target) {
225 | break;
226 | }
227 | // 添加元素
228 | answer.add(candidates[i]);
229 | // 元素可以重复取,所以从当前位置继续
230 | backtrack(candidates, i, target - candidates[i], answer, result);
231 | // 移除元素
232 | answer.remove(answer.size() - 1);
233 | }
234 | }
235 | ```
236 |
237 | #### 电话号码的字母组合
238 |
239 | > [17. 电话号码的字母组合](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number/)
240 | >
241 | > 给定一个仅包含数字 `2-9` 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 **任意顺序** 返回。
242 | >
243 | > 数字到字母的映射与电话按键相同
244 |
245 | ```java
246 | // 记录数字到字母的映射
247 | private final static Map map = new HashMap<>();
248 |
249 | static {
250 | map.put('2', "abc");
251 | map.put('3', "def");
252 | map.put('4', "ghi");
253 | map.put('5', "jkl");
254 | map.put('6', "mno");
255 | map.put('7', "pqrs");
256 | map.put('8', "tuv");
257 | map.put('9', "wxyz");
258 | }
259 |
260 | public List letterCombinations(String digits) {
261 | StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
262 | List result = new ArrayList<>();
263 | backtrack(digits, 0, builder, result);
264 | return result;
265 | }
266 |
267 | private void backtrack(String digits, int pos, StringBuilder builder, List result) {
268 | // 结束条件:到达末尾
269 | if (pos == digits.length()) {
270 | // 如果原字符串为空则没有对应的字母组合
271 | if (pos != 0) {
272 | result.add(builder.toString());
273 | }
274 | return;
275 | }
276 | for (char c : map.get(digits.charAt(pos)).toCharArray()) {
277 | builder.append(c);
278 | backtrack(digits, pos + 1, builder, result);
279 | builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1);
280 | }
281 | }
282 | ```
283 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/binary_search.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 二分搜索
2 |
3 | ## 简介
4 |
5 | 给一个**有序数组**和目标值,找第一次/最后一次/任何一次出现的索引,如果没有出现返回-1
6 |
7 | 模板四点要素
8 |
9 | - 1、初始化:start=0、end=len-1
10 | - 2、循环退出条件:start + 1 < end
11 | - 3、比较中点和目标值:A[mid] ==、 <、> target
12 | - 4、判断最后两个元素是否符合:A[start]、A[end] ? target
13 |
14 | 时间复杂度 O(logn),使用场景一般是有序数组的查找
15 |
16 | ### 典型示例
17 |
18 | > [704. 二分查找](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search/)
19 | >
20 | > 给定一个 n 个元素有序的(升序)整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target ,写一个函数搜索 nums 中的 target,如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1。
21 |
22 | ```java
23 | // 二分搜索最常用模板
24 | public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
25 | // 1、初始化left、right
26 | int left = 0;
27 | int right = nums.length - 1;
28 | // 2、处理for循环
29 | while (right - left > 1) {
30 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
31 | // 3、比较nums[mid]和target值
32 | if (nums[mid] == target) {
33 | return mid;
34 | } else if (nums[mid] < target) {
35 | left = mid;
36 | } else {
37 | right = mid;
38 | }
39 | }
40 | // 4、最后剩下两个元素,手动判断
41 | if (nums[left] == target) {
42 | return left;
43 | } else if (nums[right] == target) {
44 | return right;
45 | } else {
46 | return -1;
47 | }
48 | }
49 | ```
50 |
51 | ### 模板
52 |
53 | 大部分二分查找类的题目都可以用这个模板,然后做一点特殊逻辑即可
54 |
55 | 另外二分查找还有一些其他模板如下图,大部分场景模板#3 都能解决问题,而且还能找第一次/最后一次出现的位置,应用更加广泛
56 |
57 | 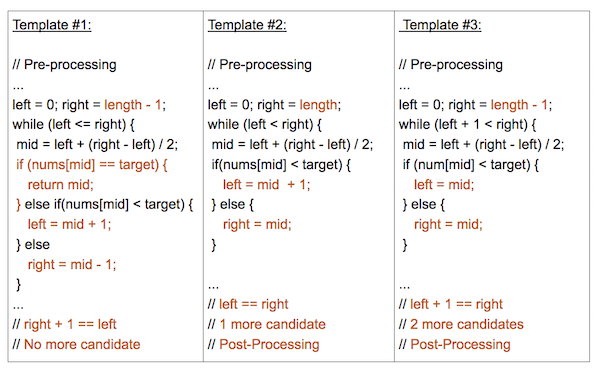
58 |
59 | 所以用模板#3 就对了,详细的对比可以这边文章介绍:[二分搜索模板](https://leetcode-cn.com/explore/learn/card/binary-search/212/template-analysis/847/)
60 |
61 | 如果是最简单的二分搜索,不需要找第一个、最后一个位置、或者是没有重复元素,可以使用模板#1,代码更简洁常见题目
62 |
63 | ## 常见题目
64 |
65 | ### 搜索插入位置
66 |
67 | > [35. 搜索插入位置](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-insert-position/)
68 | >
69 | > 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
70 |
71 | ```java
72 | public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
73 | // 思路:找到第一个 >= target 的元素位置
74 | int left = 0;
75 | int right = nums.length - 1;
76 | while (right - left > 1) {
77 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
78 | if (nums[mid] == target) {
79 | return mid;
80 | } else if (nums[mid] < target) {
81 | left = mid;
82 | } else {
83 | right = mid;
84 | }
85 | }
86 | if (nums[left] >= target) {
87 | return left;
88 | } else if (nums[left] < target && target <= nums[right]) {
89 | return left + 1;
90 | } else {
91 | // 目标值比所有值都大
92 | return right + 1;
93 | }
94 | }
95 | ```
96 |
97 | ### 搜索二维矩阵
98 |
99 | > [74. 搜索二维矩阵](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix/)
100 | >
101 | > 编写一个高效的算法来判断 m x n 矩阵中,是否存在一个目标值。该矩阵具有如下特性:
102 | >
103 | > - 每行中的整数从左到右按升序排列。
104 | > - 每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。
105 |
106 | ```java
107 | public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
108 | // 思路:将2维数组转为1维数组 进行二分搜索
109 | if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
110 | return false;
111 | }
112 | int row = matrix.length;
113 | int col = matrix[0].length;
114 | int left = 0;
115 | int right = row * col - 1;
116 | while (right - left > 1) {
117 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
118 | // 获取2维数组对应值
119 | int val = matrix[mid/col][mid%col];
120 | if (val < target) {
121 | left = mid;
122 | } else if (val > target) {
123 | right = mid;
124 | } else {
125 | return true;
126 | }
127 | }
128 | if (matrix[left/col][left%col] == target || matrix[right/col][right%col] == target) {
129 | return true;
130 | }
131 | return false;
132 | }
133 | ```
134 |
135 | ### 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值
136 |
137 | > [153. 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-minimum-in-rotated-sorted-array/)
138 | >
139 | > 假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
140 | > 请找出其中最小的元素。
141 |
142 | ```java
143 | public int findMin(int[] nums) {
144 | // 思路:最后一个值作为target,然后往左移动,最后比较start、end的值
145 | if (nums.length == 0) {
146 | return -1;
147 | }
148 | int left = 0;
149 | int right = nums.length - 1;
150 | while (right - left > 1) {
151 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
152 | // 最后一个元素值为target
153 | if (nums[mid] > nums[right]) {
154 | left = mid;
155 | } else {
156 | right = mid;
157 | }
158 | }
159 | return Math.min(nums[left], nums[right]);
160 | }
161 | ```
162 |
163 | ### 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值 II
164 |
165 | > [154. 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-minimum-in-rotated-sorted-array-ii/)
166 | >
167 | > 假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转
168 | > ( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
169 | > 请找出其中最小的元素。(包含重复元素)
170 |
171 | ```java
172 | public int findMin(int[] nums) {
173 | // 思路:跳过重复元素,mid值和end值比较,分为两种情况进行处理
174 | if (nums.length == 0) {
175 | return -1;
176 | }
177 | int left = 0;
178 | int right = nums.length - 1;
179 | while (right - left > 1) {
180 | // 去除重复元素
181 | while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
182 | right--;
183 | }
184 | while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {
185 | left++;
186 | }
187 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
188 | // 中间元素和最后一个元素比较(判断中间点落在左边上升区,还是右边上升区)
189 | if (nums[mid] > nums[right]) {
190 | left = mid;
191 | } else {
192 | right = mid;
193 | }
194 | }
195 | return Math.min(nums[left], nums[right]);
196 | }
197 | ```
198 |
199 | ### 搜索旋转排序数组
200 |
201 | > [33. 搜索旋转排序数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/)
202 | >
203 | > 假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。
204 | > ( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
205 | > 搜索一个给定的目标值,如果数组中存在这个目标值,则返回它的索引,否则返回 -1 。
206 | > 你可以假设数组中不存在重复的元素。
207 |
208 | ```java
209 | public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
210 | // 思路:四种情况判断
211 | if (nums.length == 0) {
212 | return -1;
213 | }
214 | int left = 0;
215 | int right = nums.length - 1;
216 | while (right - left > 1) {
217 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
218 | // 相等直接返回
219 | if (nums[mid] == target) {
220 | return mid;
221 | }
222 | // 判断在哪个区间,可能分为四种情况
223 | if (nums[left] < nums[mid]) {
224 | if (nums[left] <= target && target <= nums[mid]) {
225 | right = mid;
226 | } else {
227 | left = mid;
228 | }
229 | } else if (nums[right] > nums[mid]) {
230 | if (nums[right] >= target && target >= nums[mid]) {
231 | left = mid;
232 | } else {
233 | right = mid;
234 | }
235 | }
236 | }
237 | if (nums[left] == target) {
238 | return left;
239 | } else if (nums[right] == target) {
240 | return right;
241 | }
242 | return -1;
243 | }
244 | ```
245 |
246 | 注意点
247 |
248 | > 面试时,可以直接画图进行辅助说明,空讲很容易让大家都比较蒙圈
249 |
250 | ### 搜索旋转排序数组 II
251 |
252 | > [81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array-ii/)
253 | >
254 | > 假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。
255 | > ( 例如,数组 [0,0,1,2,2,5,6] 可能变为 [2,5,6,0,0,1,2] )。
256 | > 编写一个函数来判断给定的目标值是否存在于数组中。若存在返回 true,否则返回 false。(包含重复元素)
257 |
258 | ```java
259 | public boolean search(int[] nums, int target) {
260 | // 思路:四种情况判断
261 | if (nums.length == 0) {
262 | return false;
263 | }
264 | int left = 0;
265 | int right = nums.length - 1;
266 | while (right - left > 1) {
267 | // 去除重复元素
268 | while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
269 | right--;
270 | }
271 | while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {
272 | left++;
273 | }
274 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
275 | // 相等直接返回
276 | if (nums[mid] == target) {
277 | return true;
278 | }
279 | // 判断在哪个区间,可能分为四种情况
280 | if (nums[left] < nums[mid]) {
281 | if (nums[left] <= target && target <= nums[mid]) {
282 | right = mid;
283 | } else {
284 | left = mid;
285 | }
286 | } else if (nums[right] > nums[mid]) {
287 | if (nums[right] >= target && target >= nums[mid]) {
288 | left = mid;
289 | } else {
290 | right = mid;
291 | }
292 | }
293 | }
294 | return (nums[left] == target || nums[right] == target);
295 | }
296 | ```
297 |
298 | ## 总结
299 |
300 | 二分搜索核心四点要素(必背&理解)
301 |
302 | - 1、初始化:start=0、end=len-1
303 | - 2、循环退出条件:start + 1 < end
304 | - 3、比较中点和目标值:A[mid] ==、 <、> target
305 | - 4、判断最后两个元素是否符合:A[start]、A[end] ? target
306 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data_structure/linked_list.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 链表
2 |
3 | ## 提纲
4 |
5 | 链表相关的核心点
6 |
7 | - null 异常处理
8 | - dummy node 哑巴节点
9 | - 快慢指针
10 | - 插入一个节点到排序链表
11 | - 从一个链表中移除一个节点
12 | - 翻转链表
13 | - 合并两个链表
14 | - 找到链表的中间节点
15 |
16 | ## 基本操作
17 |
18 | ### 链表删除
19 |
20 | #### 删除排序链表中的重复元素
21 |
22 | > [83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/)
23 | >
24 | > 给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
25 |
26 | ```java
27 | public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
28 | ListNode p = head;
29 | while (p != null) {
30 | // 全部删除完再移动到下一个元素
31 | while (p.next != null && p.val == p.next.val) {
32 | p.next = p.next.next;
33 | }
34 | p = p.next;
35 | }
36 | return head;
37 | }
38 | ```
39 |
40 | #### 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
41 |
42 | > [82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/)
43 | >
44 | > 给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现的数字。
45 |
46 | 思路:链表头结点可能被删除,所以用 dummy node 辅助删除
47 |
48 | ```java
49 | public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
50 | if (head == null) {
51 | return null;
52 | }
53 | ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
54 | ListNode p = newHead;
55 | int n = 0;
56 | while (p.next != null && p.next.next != null) {
57 | if (p.next.val == p.next.next.val) {
58 | // 记录已经删除的值,用于后续节点判断
59 | n = p.next.val;
60 | while (p.next != null && p.next.val == n) {
61 | p.next = p.next.next;
62 | }
63 | } else {
64 | p = p.next;
65 | }
66 | }
67 | return newHead.next;
68 | }
69 | ```
70 |
71 | 注意点
72 |
73 | - A->B->C 删除 B,A.next = C
74 | - 删除用一个 Dummy Node 节点辅助(允许头节点可变)
75 | - 访问 X.next 、X.value 一定要保证 X != nil
76 |
77 | ### 链表反转
78 |
79 | #### 反转链表
80 |
81 | > [206. 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
82 | >
83 | > 反转一个单链表。
84 |
85 | 思路:用一个 prev 节点保存向前指针,temp 保存向后的临时指针
86 |
87 | ```java
88 | public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
89 | ListNode pre = null, p = head;
90 | while (p != null) {
91 | // 保存当前head.Next节点,防止重新赋值后被覆盖
92 | // 一轮之后状态:nil<-1 2->3->4
93 | // prev p
94 | ListNode temp = p.next;
95 | p.next = pre;
96 | // pre 移动
97 | pre = p;
98 | // p 移动
99 | p = temp;
100 | }
101 | return pre;
102 | }
103 | ```
104 |
105 | #### 反转链表 II
106 |
107 | > [92. 反转链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/)
108 | >
109 | > 反转从位置 *m* 到 *n* 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
110 |
111 | 思路:先遍历到 m 处,翻转,再拼接后续,注意指针处理
112 |
113 | ```java
114 | public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
115 | // 思路:先遍历到m处,翻转,再拼接后续,注意指针处理
116 | // 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->null, m = 2, n = 4
117 | ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0, head);
118 | ListNode p = newHead;
119 | // 最开始:0(p)->1->2->3->4->5->null
120 | for (int i = 0; i < m-1; i++) {
121 | p = p.next;
122 | }
123 | // 遍历之后: 0->1(p)->2(cur)->3->4->5->null
124 | ListNode pre = null;
125 | ListNode cur = p.next;
126 | for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {
127 | ListNode next = cur.next;
128 | cur.next = pre;
129 | pre = cur;
130 | cur = next;
131 | }
132 | // 循环结束:0->1(p)->2->null 5(cur)->null 4(pre)->3->2->null
133 | p.next.next = cur;
134 | p.next = pre;
135 | return newHead.next;
136 | }
137 | ```
138 |
139 | ### 链表合并
140 |
141 | #### 合并两个有序链表
142 |
143 | > [21. 合并两个有序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/)
144 | >
145 | > 将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
146 |
147 | 思路:通过 dummy node 链表,连接各个元素
148 |
149 | ```java
150 | public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
151 | ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
152 | ListNode p = head;
153 | while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
154 | if (l1.val < l2.val) {
155 | p.next = l1;
156 | l1 = l1.next;
157 | } else {
158 | p.next = l2;
159 | l2 = l2.next;
160 | }
161 | p = p.next;
162 | }
163 | // 连接未处理完节点
164 | p.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
165 | return head.next;
166 | }
167 | ```
168 |
169 | #### 合并K个升序链表
170 |
171 | > [23. 合并K个升序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/)
172 | >
173 | > 给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
174 | >
175 | > 请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
176 |
177 | 思路:使用分治的方法两个两个地合并链表
178 |
179 | ```java
180 | public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
181 | return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
182 | }
183 |
184 | public ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int begin, int end) {
185 | if (begin == end) return lists[begin];
186 | if (begin > end) return null;
187 | int mid = (begin + end) >> 1;
188 | return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, begin, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, end));
189 | }
190 |
191 | public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
192 | // 同上
193 | }
194 | ```
195 |
196 | ## 快慢指针
197 |
198 | ### 链表中点
199 |
200 | 使用两个指针变量,慢指针每次前进一步,快指针每次前进两步。这样当快指针到达链表末尾时,慢指针恰好在链表的中间位置。要注意链表长度为偶数的情况。
201 |
202 | > [876. 链表的中间结点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/)
203 | >
204 | > 给定一个头结点为 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。
205 | >
206 | > 如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
207 |
208 | ```java
209 | public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
210 | ListNode p = head;
211 | ListNode q = head;
212 | while (q != null && q.next != null) {
213 | p = p.next;
214 | q = q.next.next;
215 | }
216 | return p;
217 | }
218 | ```
219 |
220 | #### 重排链表
221 |
222 | > [143. 重排链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-list/)
223 | > 给定一个单链表 L:L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln ,
224 | >
225 | > 将其重新排列后变为: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
226 | >
227 | > 不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
228 |
229 | ```java
230 | public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
231 | if (head == null || head.next == null) return;
232 | // 通过快慢指针找中点
233 | ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
234 | while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
235 | slow = slow.next;
236 | fast = fast.next.next;
237 | }
238 | ListNode p = head;
239 | // 反转链表
240 | ListNode q = reverseList(slow.next);
241 | slow.next = null;
242 | while (p != null && q != null) {
243 | ListNode qNext = q.next;
244 | q.next = p.next;
245 | p.next = q;
246 | p = q.next;
247 | q = qNext;
248 | }
249 | }
250 | ```
251 |
252 |
253 | #### 回文链表
254 |
255 | > [234. 回文链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/)
256 | >
257 | > 请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
258 |
259 | ```java
260 | public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
261 | // fast如果初始化为head.Next则中点在slow.Next
262 | // fast初始化为head,则中点在slow
263 | ListNode slow = head, fast = head, pre = null;
264 | // 这里顺便做了反转链表的操作
265 | while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
266 | fast = fast.next.next;
267 | ListNode next = slow.next;
268 | slow.next = pre;
269 | pre = slow;
270 | slow = next;
271 | }
272 | if (fast != null){
273 | slow = slow.next;
274 | }
275 | // 与另一半链表依次比较
276 | while (slow != null) {
277 | if (slow.val != pre.val) return false;
278 | slow = slow.next;
279 | pre = pre.next;
280 | }
281 | return true;
282 | }
283 | ```
284 |
285 |
286 | ### 结构判断
287 |
288 | #### 环形链表
289 |
290 | > [141. 环形链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
291 | >
292 | > 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
293 | >
294 | > 如果链表中存在环,则返回 `true`。 否则,返回`false`。
295 |
296 | 思路:快慢指针,快慢指针相同则有环,证明:如果有环每走一步快慢指针距离会减 1
297 | 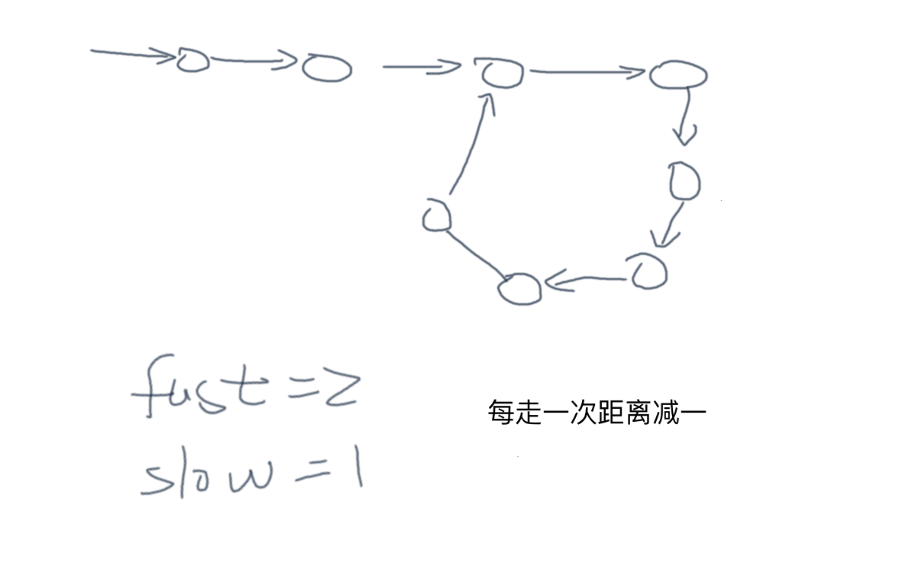
298 |
299 | ```java
300 | public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
301 | ListNode p = head, q = head;
302 | // 思路:快慢指针 快慢指针相同则有环,证明:如果有环每走一步快慢指针距离会减1
303 | while (p != null && q != null && q.next != null) {
304 | p = p.next;
305 | q = q.next.next;
306 | // 比较指针是否相等(不要使用val比较)
307 | if (p == q) {
308 | return true;
309 | }
310 | }
311 | return false;
312 | }
313 | ```
314 |
315 | #### 环形链表 II
316 |
317 | > [142. 环形链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
318 | >
319 | > 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 `null`。
320 |
321 | 思路:快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点
322 | 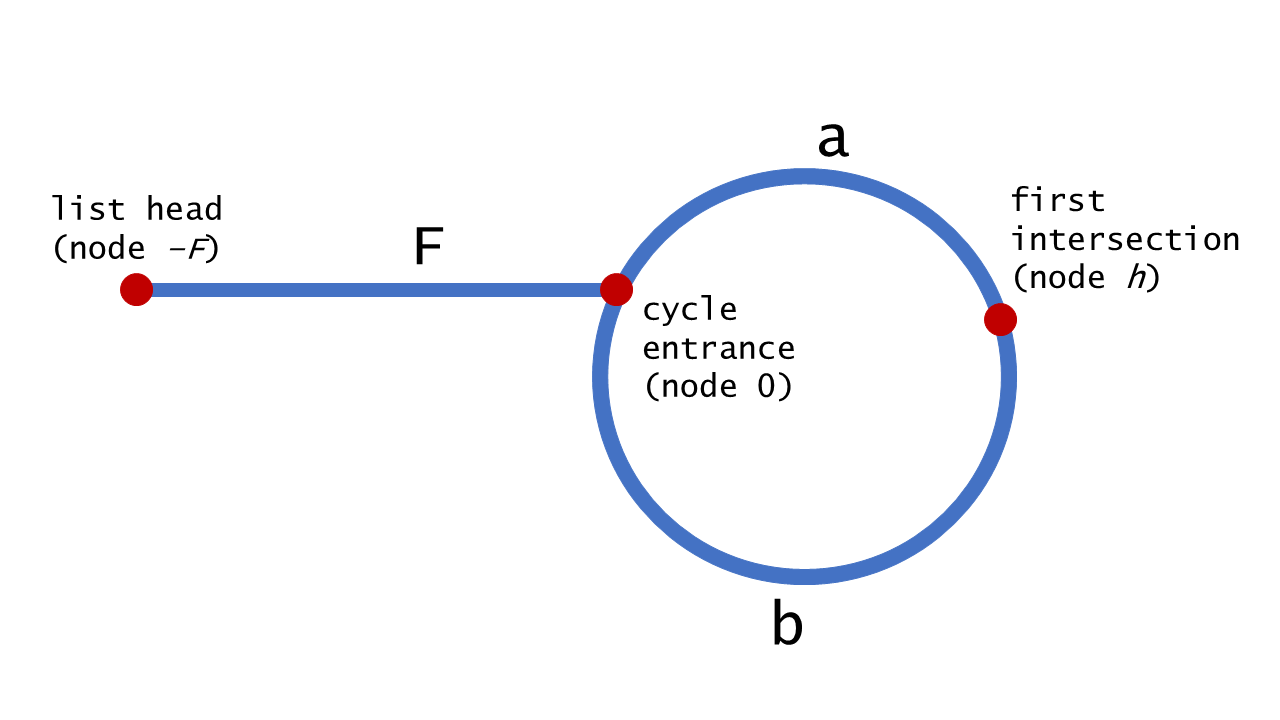
323 |
324 | ```java
325 | public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
326 | // 思路:快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点
327 | ListNode p = head, q = head;
328 | while (p != null && q != null && q.next != null) {
329 | p = p.next;
330 | q = q.next.next;
331 | if (p == q) {
332 | // 指针重新从头开始移动
333 | ListNode m = head;
334 | // 比较指针对象(不要比对指针Val值)
335 | while (m != p) {
336 | m = m.next;
337 | p = p.next;
338 | }
339 | return p;
340 | }
341 | }
342 | return null;
343 | }
344 | ```
345 |
346 | ## 其他
347 |
348 | > [19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/)
349 | >
350 | > 给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 `n` 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。(尝试使用一趟扫描实现)
351 |
352 | ```java
353 | public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
354 | ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0, head);
355 | ListNode p1 = newHead;
356 | ListNode p2 = newHead;
357 | // 提前前进n个位置
358 | while (n >= 0) {
359 | p2 = p2.next;
360 | n--;
361 | }
362 | while (p2 != null) {
363 | p1 = p1.next;
364 | p2 = p2.next;
365 | }
366 | p1.next = p1.next.next;
367 | return newHead.next;
368 | }
369 | ```
370 |
371 | > [138. 复制带随机指针的链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/)
372 | >
373 | > 给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
374 | >
375 | > 要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
376 |
377 | 思路:1、hash 表存储指针,2、复制节点跟在原节点后面
378 |
379 | ```java
380 | public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
381 | if (head == null) {
382 | return null;
383 | }
384 | // 复制节点,紧挨到到后面
385 | // 1->2->3 ==> 1->1'->2->2'->3->3'
386 | Node cur = head;
387 | while (cur != null) {
388 | Node cloneNode = new Node(cur.val);
389 | cloneNode.next = cur.next;
390 | Node temp = cur.next;
391 | cur.next = cloneNode;
392 | cur = temp;
393 | }
394 | // 处理random指针
395 | cur = head;
396 | while (cur != null) {
397 | if (cur.random != null) {
398 | cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
399 | }
400 | cur = cur.next.next;
401 | }
402 | // 分离两个链表
403 | cur = head;
404 | Node cloneHead = cur.next;
405 | while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
406 | Node temp = cur.next;
407 | cur.next = cur.next.next;
408 | cur = temp;
409 | }
410 | // 原始链表头:head 1->2->3
411 | // 克隆的链表头:cloneHead 1'->2'->3'
412 | return cloneHead;
413 | }
414 | ```
415 |
416 | ## 总结
417 |
418 | 链表必须要掌握的一些点,通过下面练习题,基本大部分的链表类的题目都是手到擒来~
419 |
420 | - null 异常处理
421 | - dummy node 哑巴节点
422 | - 快慢指针
423 | - 插入一个节点到排序链表
424 | - 从一个链表中移除一个节点
425 | - 翻转链表
426 | - 合并两个链表
427 | - 找到链表的中间节点
428 | - 链表的末尾指针最后指向null
429 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data_structure/binary_tree.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 二叉树
2 |
3 | ## 二叉树遍历
4 |
5 | **前序遍历**:[144. 二叉树的前序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/)
6 |
7 | 先访问根节点,再前序遍历左子树,再前序遍历右子树
8 |
9 | **中序遍历**:[94. 二叉树的中序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/)
10 |
11 | 先中序遍历左子树,再访问根节点,再中序遍历右子树
12 |
13 | **后序遍历**:[145. 二叉树的后序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/)
14 |
15 | 先后序遍历左子树,再后序遍历右子树,再访问根节点
16 |
17 | 注意点
18 |
19 | - 以根访问顺序决定是什么遍历
20 | - 左子树都比右子树优先遍历
21 |
22 | ### 递归遍历
23 |
24 | ```java
25 | // 递归遍历写法,以前序遍历为例
26 | public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
27 | List result = new LinkedList<>();
28 | traverse(root, result);
29 | return result;
30 | }
31 |
32 | public void traverse(TreeNode p, List result) {
33 | if (p == null) {
34 | return;
35 | }
36 | // 其他遍历调整这里的语句顺序即可
37 | result.add(p.val);
38 | traverse(p.left, result);
39 | traverse(p.right, result);
40 | }
41 | ```
42 |
43 | ### 前序非递归
44 |
45 | ```java
46 | // 通过非递归遍历
47 | public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
48 | List result = new ArrayList<>();
49 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
50 | TreeNode p = root;
51 | while (p != null || ! stack.isEmpty()) {
52 | while (p != null) {
53 | // 前序遍历,所以先保存结果
54 | result.add(p.val);
55 | stack.push(p);
56 | p = p.left;
57 | }
58 | // pop出栈顶元素
59 | if (! stack.isEmpty()) {
60 | p = stack.pop();
61 | p = p.right;
62 | }
63 | }
64 | return result;
65 | }
66 | ```
67 |
68 | ### 中序非递归
69 |
70 | ```java
71 | // 思路:通过stack 保存已经访问的元素,用于原路返回
72 | public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
73 | List result = new LinkedList<>();
74 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
75 | TreeNode p = root;
76 | while (p != null || ! stack.isEmpty()) {
77 | if (p != null) {
78 | stack.push(p);
79 | p = p.left;
80 | } else {
81 | TreeNode node = stack.pop();
82 | result.add(node.val);
83 | p = node.right;
84 | }
85 | }
86 | return result;
87 | }
88 | ```
89 |
90 | ### 后序非递归
91 |
92 | ```java
93 | public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
94 | List result = new ArrayList<>();
95 | Stack stack = new Stack();
96 | TreeNode p = root;
97 | // 通过lastVisit标识右子节点是否已经弹出
98 | TreeNode lastVisit = root;
99 | while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
100 | while (p != null) {
101 | stack.push(p);
102 | p = p.left;
103 | }
104 | //查看当前栈顶元素
105 | p = stack.peek();
106 | //如果其右子树也为空,或者右子树已经访问,则可以访问
107 | if (p.right == null || p.right == lastVisit) {
108 | result.add(p.val);
109 | stack.pop();
110 | // 标记当前这个节点已经弹出过
111 | lastVisit = p;
112 | p = null;
113 | } else {
114 | //否则继续遍历右子树
115 | p = p.right;
116 | }
117 | }
118 | return result;
119 | }
120 | ```
121 |
122 | 注意点
123 |
124 | - 核心就是:根节点必须在右节点弹出之后,再弹出
125 |
126 | ### DFS 深度搜索
127 |
128 | > [257. 二叉树的所有路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/)
129 | >
130 | > 给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
131 |
132 | ```java
133 | public List binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
134 | StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
135 | List paths = new LinkedList<>();
136 | dfs(root, path, paths);
137 | return paths;
138 | }
139 |
140 | public void dfs(TreeNode p, StringBuilder path, List paths) {
141 | if (p == null) {
142 | return;
143 | }
144 | path.append(p.val);
145 | // 当前节点是叶子节点
146 | if (p.left == null && p.right == null) {
147 | // 把路径加入结果
148 | paths.add(path.toString());
149 | } else {
150 | path.append("->");
151 | // 这里需要复制创建新的StringBuilder对象
152 | dfs(p.left, new StringBuilder(path), paths);
153 | dfs(p.right, new StringBuilder(path), paths);
154 | }
155 | }
156 | ```
157 |
158 | ### BFS 层次遍历
159 |
160 | ```java
161 | public List levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
162 | List result = new LinkedList<>();
163 | if (root == null) {
164 | return result;
165 | }
166 | Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
167 | queue.offer(root);
168 | while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
169 | TreeNode p = queue.pop();
170 | result.add(p);
171 | if (p.left != null) {
172 | queue.add(p.left);
173 | numList.add(p.left.val);
174 | }
175 | if (p.right != null) {
176 | queue.add(p.right);
177 | numList.add(p.right.val);
178 | }
179 | }
180 | return result
181 | }
182 | ```
183 |
184 | ## 二叉树分治
185 |
186 | 先分别处理局部,再合并结果
187 |
188 | 分治法模板
189 |
190 | - 递归返回条件
191 | - 分段处理
192 | - 合并结果
193 |
194 | ```java
195 | public ResultType traversal(TreeNode root) {
196 | // null or leaf
197 | if (root == null) {
198 | // do something and return
199 | }
200 | // Divide
201 | ResultType left = traversal(root.Left)
202 | ResultType right = traversal(root.Right)
203 | // Conquer
204 | ResultType result = Merge from left and right
205 | return result
206 | }
207 | ```
208 |
209 | ### 典型示例
210 |
211 | > [98. 验证二叉搜索树](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/)
212 | >
213 | > 给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
214 |
215 | ```java
216 | public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
217 | return divideAndConquer(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
218 | }
219 |
220 | private boolean divideAndConquer(TreeNode p, long min, long max) {
221 | if (p == null) return true;
222 | // 返回条件
223 | if (p.val <= min || max <= p.val) {
224 | return false;
225 | }
226 | // 分治(Divide)
227 | boolean left = divideAndConquer(p.left, min, p.val);
228 | boolean right = divideAndConquer(p.right, p.val, max);
229 | // 合并结果(Conquer)
230 | return left && right;
231 | }
232 | ```
233 |
234 | 注意点:
235 |
236 | > DFS 深度搜索(从上到下) 和分治法区别:前者一般将最终结果通过参数传入,后者一般递归返回结果最后合并
237 |
238 | ### 常见题目
239 |
240 | #### 二叉树的最大深度
241 |
242 | > [104. 二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
243 | >
244 | > 给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
245 | >
246 | > 二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
247 |
248 | 思路:分治法
249 |
250 | ```java
251 | public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
252 | // 返回条件处理
253 | if (root == null) {
254 | return 0;
255 | }
256 | // divide:分左右子树分别计算
257 | // conquer:合并左右子树结果,即取二者中的最大值加一
258 | return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
259 | }
260 | ```
261 |
262 | #### 平衡二叉树
263 |
264 | > [110. 平衡二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/)
265 | >
266 | > 给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
267 |
268 | 思路:分治法,左边平衡 && 右边平衡 && 左右两边高度 <= 1,因为需要返回是否平衡及高度,要么返回两个数据,要么合并两个数据,所以用-1 表示不平衡,>0 表示树高度(二义性:一个变量有两种含义)。
269 |
270 | ```java
271 | public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
272 | return maxDepth(root) >= 0;
273 | }
274 |
275 | private int maxDepth(TreeNode p) {
276 | if (p == null) {
277 | return 0;
278 | }
279 | int left = maxDepth(p.left);
280 | int right = maxDepth(p.right);
281 | if (left < 0 || right < 0 || Math.abs(left - right) > 1) {
282 | return -1;
283 | } else {
284 | return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
285 | }
286 | }
287 | ```
288 |
289 | 注意
290 |
291 | > 一般工程中,结果通过两个变量来返回,不建议用一个变量表示两种含义
292 |
293 | #### 二叉树中的最大路径和
294 |
295 | > [124. 二叉树中的最大路径和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-maximum-path-sum/)
296 | >
297 | > **路径** 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 **至多出现一次** 。该路径 **至少包含一个** 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
298 | >
299 | > **路径和** 是路径中各节点值的总和。
300 | >
301 | > 给你一个二叉树的根节点 `root` ,返回其 **最大路径和** 。
302 |
303 | 思路:分治法,分为三种情况:左子树最大路径和最大,右子树最大路径和最大,左右子树最大加根节点最大,需要保存两个变量:一个保存子树最大路径和,一个保存左右加根节点和,然后比较这个两个变量选择最大值即可
304 |
305 | ```java
306 | public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
307 | return maxSum(root)[1];
308 | }
309 |
310 | // 返回的数组意义:int[0]表示单边最大值,int[1]表示所有情况的最大值(单边或者两个单边+根的值)
311 | private int[] maxSum(TreeNode p) {
312 | // check
313 | if (p == null) {
314 | return new int[]{0, Integer.MIN_VALUE};
315 | }
316 | // Divide
317 | int[] left = maxSum(p.left);
318 | int[] right = maxSum(p.right);
319 | int singleSum, bothSum;
320 | // Conquer
321 | // 求单边最大值
322 | if (left[0] > right[0]) {
323 | singleSum = Math.max(left[0] + p.val, 0);
324 | } else {
325 | singleSum = Math.max(right[0] + p.val, 0);
326 | }
327 | // 求所有情况(两个子树的所有情况、两个单边最大值与根之和)的最大值
328 | bothSum = Math.max(left[1], right[1]);
329 | bothSum = Math.max(bothSum, left[0] + right[0] + p.val);
330 | return new int[]{singleSum, bothSum};
331 | }
332 | ```
333 |
334 | #### 二叉树的最近公共祖先
335 |
336 | > [235. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/)
337 | >
338 | > 给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
339 |
340 | 思路:分治法,有左子树的公共祖先或者有右子树的公共祖先,就返回子树的祖先,否则返回根节点
341 |
342 | ```java
343 | public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
344 | // check
345 | if (root == null) {
346 | return null;
347 | }
348 | // 相等 直接返回root节点即可
349 | if (root == p || root == q) {
350 | return root;
351 | }
352 | // Divide
353 | TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
354 | TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
355 | // Conquer
356 | // 左右两边都不为空,则根节点为祖先
357 | if (left != null && right != null) {
358 | return root;
359 | } else if (left != null) {
360 | return left;
361 | } else {
362 | return right;
363 | }
364 | }
365 | ```
366 |
367 | ## BFS 应用
368 |
369 | ### 常见题目
370 |
371 | #### 二叉树的层序遍历
372 |
373 | > [102. 二叉树的层序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
374 | >
375 | > 给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 **层序遍历** 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)
376 |
377 | 思路:用一个队列记录一层的元素,然后扫描这一层元素添加下一层元素到队列(一个数进去出来一次,所以复杂度 O(logN))
378 |
379 | ```java
380 | public List> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
381 | List> result = new LinkedList<>();
382 | if (root == null) {
383 | return result;
384 | }
385 | LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
386 | LinkedList numList = new LinkedList<>();
387 | queue.add(root);
388 | numList.add(root.val);
389 | while (! queue.isEmpty()) {
390 | // 保存这一层的元素
391 | result.add(numList);
392 | numList = new LinkedList<>();
393 | // 记录当前层有多少元素(遍历当前层,再添加下一层)
394 | int len = queue.size();
395 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
396 | // 出队列
397 | TreeNode p = queue.pop();
398 | if (p.left != null) {
399 | queue.add(p.left);
400 | numList.add(p.left.val);
401 | }
402 | if (p.right != null) {
403 | queue.add(p.right);
404 | numList.add(p.right.val);
405 | }
406 | }
407 | }
408 | return result;
409 | }
410 | ```
411 |
412 | #### 二叉树的层序遍历 II
413 |
414 | > [107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/)
415 | >
416 | > 给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
417 |
418 | 思路:在层级遍历的基础上,翻转一下结果即可,在往result内添加元素之前使用`Collections.reverse`方法翻转列表。
419 |
420 | #### 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
421 |
422 | > [103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/)
423 | >
424 | > 给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层次遍历。Z 字形遍历
425 |
426 | 思路:在层级遍历的基础上,判断这一层是否需要翻转,在往result内添加元素之前加入以下代码:
427 |
428 | ```java
429 | if (result.size() % 2 != 0) {
430 | Collections.reverse(numList);
431 | }
432 | ```
433 |
434 | ## 二叉搜索树应用
435 |
436 | ### 常见题目
437 |
438 | #### 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
439 |
440 | > [701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insert-into-a-binary-search-tree/)
441 | >
442 | > 给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和要插入树中的值,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。
443 |
444 | 思路:找到最后一个叶子节点满足插入条件即可
445 |
446 | ```java
447 | // DFS查找插入位置
448 | public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
449 | if (root == null) {
450 | return new TreeNode(val);
451 | }
452 | if (root.val > val) {
453 | root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
454 | } else {
455 | root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
456 | }
457 | return root;
458 | }
459 | ```
460 |
461 | ## 总结
462 |
463 | - 掌握二叉树递归与非递归遍历
464 | - 理解 DFS 前序遍历与分治法
465 | - 理解 BFS 层次遍历
466 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/dp.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 动态规划
2 |
3 | ## 背景
4 |
5 | > [120. 三角形最小路径和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/triangle/)
6 | >
7 | > 给定一个三角形,找出自顶向下的最小路径和。每一步只能移动到下一行中相邻的结点上。
8 |
9 | 例如,给定三角形:
10 |
11 | ```text
12 | [
13 | [2],
14 | [3,4],
15 | [6,5,7],
16 | [4,1,8,3]
17 | ]
18 | ```
19 |
20 | 自顶向下的最小路径和为 11(即,2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11)。
21 |
22 | ### DFS
23 |
24 | 使用 DFS:
25 |
26 | ```java
27 | // 会超时
28 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
29 | return dfs(0, 0, triangle);
30 | }
31 |
32 | // 返回值表示从x, y处到底部的最小路径和
33 | private int dfs(int x, int y, List> triangle, int[][] saves) {
34 | if (x == triangle.size() - 1) {
35 | return triangle.get(x).get(y);
36 | }
37 | int minLeft = dfs(x + 1, y, triangle, saves);
38 | int minRight = dfs(x + 1, y + 1, triangle, saves);
39 | return Math.min(minLeft, minRight) + triangle.get(x).get(y);
40 | }
41 | ```
42 |
43 | ### DFS的优化
44 |
45 | 优化 DFS,缓存已经被计算的值(称为:记忆化搜索 本质上:动态规划)
46 |
47 | ```java
48 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
49 | int[][] saves = new int[triangle.size()][triangle.size()];
50 | return dfs(0, 0, triangle, saves);
51 | }
52 |
53 | // 使用saves数组记录已经被计算过的值
54 | // 返回值表示从x, y处到底部的最小路径和
55 | private int dfs(int x, int y, List> triangle, int[][] saves) {
56 | if (x == triangle.size() - 1) {
57 | return triangle.get(x).get(y);
58 | }
59 | // 如果已经被计算过则直接返回
60 | if (saves[x][y] != 0) {
61 | return saves[x][y];
62 | }
63 | int minLeft = dfs(x + 1, y, triangle, saves);
64 | int minRight = dfs(x + 1, y + 1, triangle, saves);
65 | // 缓存已经被计算的值
66 | saves[x][y] = Math.min(minLeft, minRight) + triangle.get(x).get(y);
67 | return saves[x][y];
68 | }
69 | ```
70 |
71 | ### 从DFS到动态规划
72 |
73 | 动态规划就是把大问题变成小问题,并解决了小问题重复计算的方法称为动态规划
74 |
75 | 动态规划和 DFS 区别
76 |
77 | - 二叉树 子问题是没有交集,所以大部分二叉树都用递归或者分治法,即 DFS,就可以解决
78 | - 像 triangle 这种是有重复走的情况,**子问题是有交集**,所以可以用动态规划来解决
79 |
80 | #### 自底向上
81 |
82 | ```java
83 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
84 | // 1、状态定义:f[i][j] 表示从i,j出发,到达最后一层的最短路径
85 | int[][] dp = new int[triangle.size()][triangle.size()];
86 | // 2、初始化
87 | for (int i = 0; i < triangle.size(); i++) {
88 | dp[triangle.size() - 1][i] = triangle.get(triangle.size() - 1).get(i);
89 | }
90 | // 3、递推求解
91 | for (int i = triangle.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
92 | for (int j = 0; j < triangle.get(i).size(); j++) {
93 | dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i+1][j], dp[i+1][j+1]) + triangle.get(i).get(j);
94 | }
95 | }
96 | // 4、结果
97 | return dp[0][0];
98 | }
99 | ```
100 |
101 | #### 自顶向下
102 |
103 | ```java
104 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
105 | // 1、状态定义:dp[i][j] 表示从0,0出发,到达i,j的最短路径
106 | int[][] dp = new int[triangle.size()][triangle.size()];
107 | // 2、初始化
108 | dp[0][0] = triangle.get(0).get(0);
109 | for (int i = 1; i < triangle.size(); i++) {
110 | for (int j = 0; j < triangle.get(i).size(); j++) {
111 | // 这里分为三种情况:
112 | // 1、上一层没有左边值
113 | // 2、上一层没有右边值
114 | // 3、其他
115 | if (j == 0) {
116 | dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + triangle.get(i).get(j);
117 | } else if (j == triangle.get(i).size() - 1) {
118 | dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + triangle.get(i).get(j);
119 | } else {
120 | dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j]) + triangle.get(i).get(j);
121 | }
122 | }
123 | }
124 | // 从最后一层中查找最小值
125 | int minValue = dp[triangle.size() - 1][0];
126 | for (int i = 0; i < triangle.size(); i++) {
127 | minValue = Math.min(minValue, dp[triangle.size() - 1][i]);
128 | }
129 | return minValue;
130 | }
131 | ```
132 |
133 | #### 空间优化
134 |
135 | 经过观察发现当前状态只与上一批状态有关,所以二维数组可以优化为一位数组,减少空间占用。
136 |
137 | ```java
138 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
139 | int[] dp = new int[triangle.size()];
140 | for (int i = 0; i < triangle.size(); i++) {
141 | dp[i] = triangle.get(triangle.size() - 1).get(i);
142 | }
143 | for (int i = triangle.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
144 | for (int j = 0; j < triangle.get(i).size(); j++) {
145 | dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j+1]) + triangle.get(i).get(j);
146 | }
147 | }
148 | return dp[0];
149 | }
150 | ```
151 |
152 | 除此之外,也可以覆盖原有数据以实现空间复用。
153 |
154 | ## 使用场景
155 |
156 | 满足两个条件
157 |
158 | - 满足以下条件之一
159 | - 求最大/最小值(Maximum/Minimum )
160 | - 求是否可行(Yes/No )
161 | - 求可行个数(Count(\*) )
162 | - 满足不能排序或者交换(Can not sort / swap )
163 |
164 | 如题:[longest-consecutive-sequence](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence/) 位置可以交换,所以不用动态规划
165 |
166 | ## 四点要素
167 |
168 | 1. **状态 State**
169 | - 灵感,创造力,存储小规模问题的结果
170 | 2. 方程 Function
171 | - 状态之间的联系,怎么通过小的状态,来算大的状态
172 | 3. 初始化 Intialization
173 | - 最极限的小状态是什么, 起点
174 | 4. 答案 Answer
175 | - 最大的那个状态是什么,终点
176 |
177 | ## 常见四种类型
178 |
179 | 1. Matrix DP (10%)
180 | 1. Sequence (40%)
181 | 1. Two Sequences DP (40%)
182 | 1. Backpack (10%)
183 |
184 | > 注意点
185 | >
186 | > - 贪心算法大多题目靠背答案,所以如果能用动态规划就尽量用动规,不用贪心算法
187 |
188 | ### 矩阵类型
189 |
190 | #### 最小路径和
191 |
192 | > [64. 最小路径和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-path-sum/)
193 | >
194 | > 给定一个包含非负整数的 *m* x *n* 网格,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。
195 |
196 | ```java
197 | public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
198 | // dp[i][j] 表示0,0到i,j的最小和
199 | int[] dp = new int[grid[0].length];
200 | // 初始化:用第一行初始化
201 | dp[0] = grid[0][0];
202 | for (int i = 1; i < grid[0].length; i++) {
203 | dp[i] = dp[i-1] + grid[0][i];
204 | }
205 | // 状态转移方程
206 | // 每行第一个元素:
207 | // dp[j] = dp[j](到上一行这个位置的最小和) + grid[i][j];
208 | // 后续元素:
209 | // dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j-1](到左边位置的最小和), dp[j](到上一行这个位置的最小和)) + grid[i][j];
210 | for (int i = 1; i < grid.length; i++) {
211 | for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
212 | if (j == 0) {
213 | dp[j] = dp[j] + grid[i][j];
214 | } else {
215 | dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j-1], dp[j]) + grid[i][j];
216 | }
217 | }
218 | }
219 | // 答案
220 | return dp[grid[0].length - 1];
221 | }
222 | ```
223 |
224 | #### 不同路径
225 |
226 | > [62. 不同路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths/)
227 | >
228 | > 一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。
229 | > 机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为“Finish”)。
230 | >
231 | > 问总共有多少条不同的路径?
232 |
233 | ```java
234 | public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
235 | // dp[i][j] 表示0,0到i,j的路径数
236 | int[] dp = new int[n];
237 | // 初始化:到达第一行的路径数均为1
238 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
239 | dp[i] = 1;
240 | }
241 | for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
242 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
243 | // 每行第一个格子只有一条路到达
244 | if (j == 0) {
245 | dp[j] = 1;
246 | }
247 | // 其他格子可以由左侧或上方的格子到达
248 | else {
249 | dp[j] = dp[j-1] + dp[j];
250 | }
251 | }
252 | }
253 | return dp[n-1];
254 | }
255 | ```
256 |
257 | #### 不同路径 II
258 |
259 | > [63. 不同路径 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths-ii/)
260 | >
261 | > 一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。
262 | > 机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为“Finish”)。
263 | >
264 | > 问总共有多少条不同的路径?
265 | >
266 | > 现在考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?
267 |
268 | ```java
269 | public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
270 | int m = obstacleGrid.length;
271 | int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
272 | int[] dp = new int[n];
273 | // 初始化:遇到障碍前仅有一条路,之后全为0
274 | dp[0] = obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1 ? 0 : 1;
275 | for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
276 | if (obstacleGrid[0][i] == 1) {
277 | dp[i] = 0;
278 | } else {
279 | dp[i] = dp[i-1];
280 | }
281 | }
282 | for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
283 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
284 | // 当前格是障碍,不可达,置为0
285 | if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) {
286 | dp[j] = 0;
287 | continue;
288 | }
289 | if (j > 0) {
290 | dp[j] = dp[j-1] + dp[j];
291 | }
292 | }
293 | }
294 | return dp[n-1];
295 | }
296 | ```
297 |
298 | ### 序列类型
299 |
300 | #### 爬楼梯
301 |
302 | > [70. 爬楼梯](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/)
303 | >
304 | > 假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 *n* 阶你才能到达楼顶。
305 | >
306 | > 每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶?
307 |
308 | ```java
309 | public int climbStairs(int n) {
310 | int[] dp = new int[]{0, 1};
311 | while (n > 0) {
312 | int temp = dp[0] + dp[1];
313 | dp[0] = dp[1];
314 | dp[1] = temp;
315 | n--;
316 | }
317 | return dp[1];
318 | }
319 | ```
320 |
321 | #### 最长递增子序列
322 |
323 | > [300. 最长递增子序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/)
324 | >
325 | > 给定一个无序的整数数组,找到其中最长上升子序列的长度。
326 |
327 | ```java
328 | public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
329 | // dp[i]表示从0到i的最长上升子序列长度
330 | int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
331 | // 初始化:到第一个元素序列长度为1
332 | dp[0] = 1;
333 | for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
334 | // 注意默认为1,即此处最长子序列为自身
335 | int maxLen = 1;
336 | // dp[i] = max(dp[j]) + 1 , nums[j] < nums[i]
337 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
338 | if (nums[j] < nums[i]) {
339 | maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, dp[j] + 1);
340 | }
341 | }
342 | dp[i] = maxLen;
343 | }
344 | int maxNum = 0;
345 | for (int n : dp) {
346 | maxNum = Math.max(maxNum, n);
347 | }
348 | // 答案:dp中的最大值
349 | return maxNum;
350 | }
351 | ```
352 |
353 | #### 单词拆分
354 |
355 | > [139. 单词拆分](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-break/)
356 | >
357 | > 给定一个**非空**字符串 *s* 和一个包含**非空**单词列表的字典 *wordDict*,判定 *s* 是否可以被空格拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
358 |
359 | ```java
360 | public boolean wordBreak(String s, List wordDict) {
361 | // dp[i]表示s[0, i)子串能否被分解
362 | boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
363 | Set wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordDict);
364 | // 初始值:空字符串可以被分解
365 | dp[0] = true;
366 | for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
367 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
368 | // 递推:从i处向前遍历,s[0,j)可以分解且s[j,i)也在集合内
369 | if (dp[j] && wordSet.contains(s.substring(j, i))) {
370 | dp[i] = true;
371 | break;
372 | }
373 | }
374 | }
375 | return dp[s.length()];
376 | }
377 | ```
378 |
379 | 由于分解出的单词长度必定不会超过字典内的最大长度,因此可以利用这一点进行剪枝:
380 |
381 | ```java
382 | public boolean wordBreak(String s, List wordDict) {
383 | // dp[i]表示s[0, i)子串能否被分解
384 | boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
385 | Set wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordDict);
386 | // 计算单词最大长度
387 | int maxLen = 0;
388 | for (String word : wordDict) {
389 | maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, word.length());
390 | }
391 | // 初始值:空字符串可以被分解
392 | dp[0] = true;
393 | for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
394 | // 分解的子串s[j,i)长度不会超过maxLen,注意不能越界
395 | for (int j = Math.max(0, i - maxLen); j < i; j++) {
396 | // 递推:从i处向前遍历,s[0,j)可以分解且s[j,i)也在集合内
397 | if (dp[j] && wordSet.contains(s.substring(j, i))) {
398 | dp[i] = true;
399 | break;
400 | }
401 | }
402 | }
403 | return dp[s.length()];
404 | }
405 | ```
406 |
407 | #### 小结
408 |
409 | 常见处理方式是给 0 位置占位,这样处理问题时一视同仁,初始化则在原来基础上 `length+1`,返回结果 `f[n]`
410 |
411 | - 状态可以为前 i 个
412 | - 初始化 `length+1`
413 | - 取值 `index=i-1`
414 | - 返回值:`f[n]`或者 `f[m][n]`
415 |
416 | ### 双序列类型
417 |
418 | #### 最长公共子序列
419 |
420 | > [1143. 最长公共子序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-common-subsequence/)
421 | >
422 | > 给定两个字符串 text1 和 text2,返回这两个字符串的最长公共子序列。
423 | > 一个字符串的 子序列 是指这样一个新的字符串:它是由原字符串在不改变字符的相对顺序的情况下删除某些字符(也可以不删除任何字符)后组成的新字符串。
424 | > 例如,"ace" 是 "abcde" 的子序列,但 "aec" 不是 "abcde" 的子序列。两个字符串的「公共子序列」是这两个字符串所共同拥有的子序列。
425 |
426 | ```java
427 | public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
428 | // dp[i][j] a前i个和b前j个字符最长公共子序列
429 | // dp[m+1][n+1]
430 | // ' a d c e
431 | // ' 0 0 0 0 0
432 | // a 0 1 1 1 1
433 | // c 0 1 1 2 1
434 | int[][] dp = new int[text1.length() + 1][text2.length() + 1];
435 | for (int i = 1; i <= text1.length(); i++) {
436 | for (int j = 1; j <= text2.length(); j++) {
437 | // 相等取左上元素+1,否则取左或上的较大值
438 | if (text1.charAt(i - 1) == text2.charAt(j - 1)) {
439 | dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
440 | } else {
441 | dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
442 | }
443 | }
444 | }
445 | return dp[text1.length()][text2.length()];
446 | }
447 | ```
448 |
449 | 注意点
450 |
451 | - 从 1 开始遍历到最大长度
452 |
453 | - 索引需要减一
454 |
455 | #### 编辑距离
456 |
457 | > [72. 编辑距离](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/)
458 | >
459 | > 给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
460 | >
461 | > 1. 插入一个字符
462 | > 2. 删除一个字符
463 | > 3. 替换一个字符
464 |
465 | 思路:和上题很类似,相等则不需要操作,否则取删除、插入、替换最小操作次数的值+1
466 |
467 | ```java
468 | // dp[i][j] 表示a字符串的前i个字符编辑为b字符串的前j个字符最少需要多少次操作
469 | // dp[i][j] = OR(dp[i-1][j-1],a[i]==b[j],min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j-1])+1)
470 | public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
471 | int[][] dp = new int[word1.length() + 1][word2.length() + 1];
472 | for (int i = 0; i <= word1.length(); i++) {
473 | dp[i][0] = i;
474 | }
475 | for (int i = 0; i <= word2.length(); i++) {
476 | dp[0][i] = i;
477 | }
478 | for (int i = 1; i <= word1.length(); i++) {
479 | for (int j = 1; j <= word2.length(); j++) {
480 | // 相等则不需要操作
481 | if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {
482 | dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
483 | }
484 | // 否则取删除、插入、替换最小操作次数的值+1
485 | else {
486 | dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]), dp[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1;
487 | }
488 | }
489 | }
490 | return dp[word1.length()][word2.length()];
491 | }
492 | ```
493 |
494 | 说明
495 |
496 | > 另外一种做法:MAXLEN(a,b)-LCS(a,b)
497 |
498 | ### 零钱和背包
499 |
500 | #### 零钱兑换
501 |
502 | > [322. 零钱兑换](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change/)
503 | >
504 | > 给定不同面额的硬币 coins 和一个总金额 amount。编写一个函数来计算可以凑成总金额所需的最少的硬币个数。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1。
505 |
506 | 思路:和其他 DP 不太一样,i 表示钱或者容量
507 |
508 | ```java
509 | public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
510 | // 状态 dp[i]表示金额为i时,组成的最小硬币个数
511 | int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
512 | dp[0] = 0;
513 | for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
514 | // 初始化为最大值
515 | int minNum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
516 | for (int n : coins) {
517 | if (i - n >= 0) {
518 | // 如果上个金额也无法组成,则直接标记
519 | if (dp[i - n] == -1) {
520 | dp[i] = -1;
521 | continue;
522 | } else {
523 | minNum = Math.min(minNum, dp[i - n] + 1);
524 | }
525 | } else if (i % n == 0) {
526 | minNum = i / n;
527 | }
528 | }
529 | dp[i] = (minNum == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : minNum);
530 | }
531 | return dp[amount];
532 | }
533 | ```
534 |
535 | #### 零钱兑换 II
536 |
537 | > [518. 零钱兑换 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change-2/)
538 | >
539 | > 给定不同面额的硬币和一个总金额。写出函数来计算可以凑成总金额的硬币组合数。假设每一种面额的硬币有无限个。
540 |
541 | 先遍历物品再遍历背包 - 组合数
542 |
543 | 先遍历背包再遍历物品 - 排列数
544 |
545 | ```java
546 | public int change(int amount, int[] coins) {
547 | // 状态 dp[i]表示金额为i时,组合的方法数
548 | int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
549 | dp[0] = 1;
550 | // 先遍历物品再遍历背包
551 | for (int n : coins) {
552 | for (int i = n; i <= amount; i++) {
553 | dp[i] += dp[i - n];
554 | }
555 | }
556 | return dp[amount];
557 | }
558 | ```
559 |
560 | #### 分割等和子集
561 |
562 | > [416. 分割等和子集](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/)
563 | >
564 | > 给定一个**只包含正整数**的**非空**数组。是否可以将这个数组分割成两个子集,使得两个子集的元素和相等。
565 |
566 | 等价于0-1背包问题,只不过目标为数组和的一半。状态转移可以参考题解:[动态规划(转换为 0-1 背包问题)](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/solution/0-1-bei-bao-wen-ti-xiang-jie-zhen-dui-ben-ti-de-yo/)。
567 |
568 | ```java
569 | public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {
570 | // 首先计算数组的和
571 | int sum = 0;
572 | for (int n : nums) {
573 | sum += n;
574 | }
575 | // 如果和不是2的倍数则肯定无法分割
576 | if (sum % 2 != 0) {
577 | return false;
578 | }
579 | sum /= 2;
580 | // dp[i][j]表示从数组的[0, i]子区间内挑选一些正整数(每个数只能用一次)使得这些数的和恰好等于j
581 | boolean[][] dp = new boolean[nums.length][sum + 1];
582 | if (nums[0] <= sum) {
583 | dp[0][nums[0]] = true;
584 | }
585 | for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
586 | for (int j = 0; j <= sum; j++) {
587 | // 注意这里的状态转移方程
588 | if (nums[i] == j) {
589 | dp[i][j] = true;
590 | } else if (nums[i] < j) {
591 | dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] || dp[i-1][j-nums[i]];
592 | } else {
593 | dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];
594 | }
595 | }
596 | }
597 | return dp[nums.length - 1][sum];
598 | }
599 | ```
600 |
601 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
51 |
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/quick_select.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 快速选择
2 |
3 | ## 使用场景
4 |
5 | - 最大/最小的K个数
6 | - 最大/最小的第K个数
7 |
8 | ## 算法思路
9 |
10 | 和快速排序的思路类似,但是不需要得出精确的比较顺序。首先从数组中随机或指定挑选一个元素作为标志,然后将所有比这个标志小的元素放在左边,比标志大的放在右边,最后会有以下三种可能的情况:
11 |
12 | 1. 这个位置就是K,直接返回即可
13 | 2. 这个位置小于K,说明K位置的数在右边
14 | 3. 这个位置大于K,说明K位置的数在左边
15 |
16 | ## 算法实现
17 |
18 | > [215. 数组中的第K个最大元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/)
19 | >
20 | >在未排序的数组中找到第 **k** 个最大的元素。请注意,需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
21 |
22 | ```java
23 | public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
24 | int l = 0;
25 | int r = nums.length - 1;
26 | while (l < r) {
27 | // 对标志两边分别进行处理
28 | int pivot = partition(nums, l, r);
29 | // 标志就是k
30 | if (pivot == nums.length - k) {
31 | break;
32 | }
33 | // k位置在标志的右侧
34 | else if (pivot < nums.length - k) {
35 | l = pivot + 1;
36 | }
37 | // k位置在标志的左侧
38 | else {
39 | r = pivot - 1;
40 | }
41 | }
42 | return nums[nums.length - k];
43 | }
44 |
45 | private int partition(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
46 | int l = start;
47 | int r = end + 1;
48 | // 选择首元素作为比较标志
49 | // 比标志小的放在左边,比标志大的放在右边
50 | while (true) {
51 | while (nums[++l] < nums[start] && l < end);
52 | while (nums[--r] > nums[start] && r > start);
53 | if (l >= r) {
54 | break;
55 | }
56 | swap(nums, l, r);
57 | }
58 | // 将标志交换到中间
59 | swap(nums, start, r);
60 | return r;
61 | }
62 |
63 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
64 | int temp = nums[i];
65 | nums[i] = nums[j];
66 | nums[j] = temp;
67 | }
68 | ```
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/three_way_quick_sort.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 三向切分快速排序
2 |
3 | ## 使用场景
4 |
5 | 待排序数组中含有类别较少但大量重复的元素
6 |
7 | ## 算法思路
8 |
9 | 除前后两个指针外再使用两个额外的指针指向与待选元素相同的元素,遍历后将与待选元素相同的元素置换到数组中间,再对两侧分别进行排序。通过这一方法可以节省元素交换次数。
10 |
11 | ## 算法实现
12 |
13 | ```java
14 | public void sort(int[] nums) {
15 | sort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
16 | }
17 |
18 | private void sort(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
19 | if (left < right) {
20 | // 选择首元素作为比较标志
21 | int temp = nums[left];
22 | // 设置两个指针指向与temp相同的元素范围
23 | int left_p = left;
24 | int right_p = right;
25 | for (int i = left + 1; i <= right_p; ) {
26 | // 根据比较结果进行元素交换
27 | if (nums[i] < temp) {
28 | swap(nums, left_p, i);
29 | left_p++;
30 | i++;
31 | } else if (nums[i] > temp) {
32 | swap(nums, i, right_p);
33 | right_p--;
34 | } else {
35 | i++;
36 | }
37 | }
38 | // 对两侧元素分别进行排序
39 | sort(nums, left, left_p - 1);
40 | sort(nums, right_p + 1, right);
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
45 | int temp = nums[i];
46 | nums[i] = nums[j];
47 | nums[j] = temp;
48 | }
49 | ```
50 |
51 | ## 经典例题
52 |
53 | > [75. 颜色分类](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-colors/)
54 | >
55 | > 给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 `n` 个元素的数组,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
56 | >
57 | > 此题中,我们使用整数 `0`、 `1` 和 `2` 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
58 |
59 | 由于只有三种颜色,所以不需要再对比较标志两侧元素分别排序,对实现代码稍作修改即可。
60 |
61 | ```java
62 | public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
63 | int left = 0;
64 | int mid = 0;
65 | int right = nums.length - 1;
66 | while (mid <= right) {
67 | if (nums[mid] == 0) {
68 | swap(nums, left, mid);
69 | mid++;
70 | left++;
71 | } else if (nums[mid] == 2) {
72 | swap(nums, right, mid);
73 | right--;
74 | } else {
75 | mid++;
76 | }
77 | }
78 | }
79 |
80 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
81 | int temp = nums[i];
82 | nums[i] = nums[j];
83 | nums[j] = temp;
84 | }
85 | ```
86 |
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/greedy.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 贪心算法
2 |
3 | 贪心算法在每一步选择中都采取在当前状态下最好或最优的选择,从而使得结果也是最优解,适合去解决具有最优子结构的问题。
4 |
5 | ## 应用场景
6 |
7 | 最优子结构的特征:
8 |
9 | - 每一次操作对结果直接产生影响
10 | - 不依赖于之前的操作
11 | - 子问题的最优解是全局最优解的一部分
12 |
13 | ## 常见例题
14 |
15 | ### 跳跃游戏
16 |
17 | > [55. 跳跃游戏](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game/)
18 | >
19 | > 给定一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的 第一个下标 。
20 | >
21 | > 数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
22 | >
23 | > 判断你是否能够到达最后一个下标。
24 |
25 | 思路:每个格子`i`作为起跳点最远能跳到`nums[i]`处,所以遍历数组得到最远距离并与数组长度进行比较即可。
26 |
27 | 这题只需要判断能否到达终点而无需给出具体路径,所以不需要用回溯的方法。
28 |
29 | ```java
30 | public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
31 | int maxLen = 0;
32 | for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
33 | // 当前格子已经无法跳到
34 | if (i > maxLen) return false;
35 | // 更新能跳到的最远距离
36 | maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, i + nums[i]);
37 | }
38 | return true;
39 | }
40 | ```
41 |
42 | ### 跳跃游戏 II
43 |
44 | > [45. 跳跃游戏 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game-ii/)
45 | >
46 | >给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
47 | >
48 | >数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
49 | >
50 | >你的目标是使用最少的跳跃次数到达数组的最后一个位置。
51 |
52 | 思路:确保每次跳跃选择的格子都有最远的跳跃范围。
53 |
54 | ```java
55 | public int jump(int[] nums) {
56 | int steps = 0;
57 | int start = 0;
58 | int end = 1;
59 | while (end < nums.length) {
60 | // 确定最远的跳跃范围
61 | int maxPosition = 0;
62 | for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
63 | maxPosition = Math.max(maxPosition, i + nums[i]);
64 | }
65 | start = end;
66 | end = maxPosition + 1;
67 | // 步数增加
68 | steps++;
69 | }
70 | return steps;
71 | }
72 | ```
73 |
74 | ### 分发饼干
75 |
76 | > [455. 分发饼干](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/assign-cookies/)
77 | >
78 | > 对每个孩子 `i`,都有一个胃口值 `g[i]`,这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干 `j`,都有一个尺寸 `s[j]` 。如果 `s[j] >= g[i]`,我们可以将这个饼干 `j` 分配给孩子 `i` ,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是尽可能满足越多数量的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
79 |
80 | 思路:先排序,再贪心,让饼干优先满足胃口更多的孩子
81 |
82 | ```java
83 | public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
84 | Arrays.sort(g);
85 | Arrays.sort(s);
86 | int p = 0;
87 | int q = 0;
88 | while (p < g.length && q < s.length) {
89 | if (g[p] <= s[q]) {
90 | p++;
91 | }
92 | q++;
93 | }
94 | return p;
95 | }
96 | ```
97 |
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/binary_op.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 二进制
2 |
3 | ## 常见二进制操作
4 |
5 | ### 基本操作
6 |
7 | a=0^a=a^0
8 |
9 | 0=a^a
10 |
11 | 由上面两个推导出:a=a^b^b
12 |
13 | ### 交换两个数
14 |
15 | a=a^b
16 |
17 | b=a^b
18 |
19 | a=a^b
20 |
21 | ### 移除最后一个 1
22 |
23 | a=n&(n-1)
24 |
25 | ### 获取最后一个 1
26 |
27 | diff=(n&(n-1))^n
28 |
29 | ## 常见例题
30 |
31 | ### 只出现一次的数字
32 |
33 | > [136. 只出现一次的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number/)
34 | >
35 | > 给定一个**非空**整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
36 |
37 | ```java
38 | public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
39 | // 10 ^ 10 == 00
40 | // 两个相同的数异或变成0
41 | int result = 0;
42 | for (int n : nums) {
43 | result = result ^ n;
44 | }
45 | return result;
46 | }
47 | ```
48 |
49 | ### 只出现一次的数字 II
50 |
51 | > [137. 只出现一次的数字 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number-ii/)
52 | >
53 | > 给定一个**非空**整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现了三次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
54 |
55 | ```java
56 | public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
57 | int result = 0;
58 | // 统计每位1的个数
59 | for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
60 | int sum = 0;
61 | for (int n : nums) {
62 | // 统计1的个数
63 | sum += ((n >> i) & 1);
64 | }
65 | // 还原
66 | result |= ((sum % 3) << i);
67 | }
68 | return result;
69 | }
70 | ```
71 |
72 | ### 只出现一次的数字 III
73 |
74 | > [260. 只出现一次的数字 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number-iii/)
75 | >
76 | > 给定一个整数数组 `nums`,其中恰好有两个元素只出现一次,其余所有元素均出现两次。 找出只出现一次的那两个元素。
77 |
78 | ```java
79 | public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
80 | // 关键点怎么把a^b分成两部分,方案:可以通过diff最后一个1区分
81 | int diff = 0;
82 | for (int n : nums) {
83 | diff ^= n;
84 | }
85 | int[] result = new int[]{diff, diff};
86 | // 去掉末尾的1后异或diff就得到最后一个1的位置
87 | diff = (diff & (diff - 1)) ^ diff;
88 | for (int n : nums) {
89 | if ((diff & n) == 0) {
90 | result[0] ^= n;
91 | } else {
92 | result[1] ^= n;
93 | }
94 | }
95 | return result;
96 | }
97 | ```
98 |
99 | ### 位1的个数
100 |
101 | > [191. 位1的个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-1-bits/)
102 | >
103 | > 编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数,返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 ‘1’ 的个数(也被称为[汉明重量](https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%B1%89%E6%98%8E%E9%87%8D%E9%87%8F))。
104 |
105 | ```java
106 | public int hammingWeight(int n) {
107 | int result = 0;
108 | while (n != 0) {
109 | if ((n & 1) == 1) result++;
110 | n = n >>> 1;
111 | }
112 | return result;
113 | }
114 | ```
115 |
116 | ### 颠倒二进制位
117 |
118 | > [190. 颠倒二进制位](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-bits/)
119 | >
120 | > 颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位。
121 |
122 | 思路:依次颠倒即可
123 |
124 | ```java
125 | public int reverseBits(int n) {
126 | int result = 0;
127 | int p = 31;
128 | while (n != 0) {
129 | result += ((n & 1) << p);
130 | n >>>= 1;
131 | p--;
132 | }
133 | return result;
134 | }
135 | ```
136 |
137 | ### 数字范围按位与
138 |
139 | > [201. 数字范围按位与](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/bitwise-and-of-numbers-range/)
140 | >
141 | > 给定范围 [m, n],其中 0 <= m <= n <= 2147483647,返回此范围内所有数字的按位与(包含 m, n 两端点)。
142 |
143 | 问题转化为求两个给定数字二进制状态下的最长公共前缀,可以用移位判断的思想来做,这里使用另一种`Brian Kernighan`算法:`number`和 `number−1`之间进行按位与运算后,`number`中最右边的1会被抹去变成0。
144 |
145 | ```java
146 | public int rangeBitwiseAnd(int m, int n) {
147 | while (m < n) {
148 | // 抹去最右边的 1
149 | n = n & (n - 1);
150 | }
151 | return n;
152 | }
153 | ```
154 |
155 | ## 注意点
156 |
157 | - Java中区分右移运算和无符号右移运算
158 | - 注意运算顺序,不确定时尽量加上括号
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/sort.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 排序
2 |
3 | ## 常考排序
4 |
5 | ### 快速排序
6 |
7 | ```java
8 | public void quickSort(int[] nums) {
9 | // 思路:把一个数组分为左右两段,左段小于右段
10 | quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
11 | }
12 |
13 | // 原地交换,所以传入交换索引
14 | private void quickSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
15 | if (start < end) {
16 | // 分治法:divide
17 | int pivot = partition(nums, start, end);
18 | quickSort(nums, 0, pivot - 1);
19 | quickSort(nums, pivot + 1, end);
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
23 | // 分区
24 | private int partition(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
25 | // 选取最后一个元素作为基准pivot
26 | int p = nums[end];
27 | int i = start;
28 | // 最后一个值就是基准所以不用比较
29 | for (int j = start; j < end; j++) {
30 | if (nums[j] < p) {
31 | swap(nums, i, j);
32 | i++;
33 | }
34 | }
35 | // 把基准值换到中间
36 | swap(nums, i, end);
37 | return i;
38 | }
39 |
40 | // 交换两个元素
41 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
42 | int temp = nums[i];
43 | nums[i] = nums[j];
44 | nums[j] = temp;
45 | }
46 | ```
47 |
48 | ### 归并排序
49 |
50 | ```java
51 | public void mergeSort(int[] nums) {
52 | mergeSort(nums, 0, nums.length);
53 | }
54 |
55 | private void mergeSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
56 | if (end - start <= 1) {
57 | return;
58 | }
59 | // 分治法:divide 分为两段
60 | int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
61 | mergeSort(nums, start, mid);
62 | mergeSort(nums, mid, end);
63 | // 合并两段数据
64 | merge(nums, start, mid, end);
65 | }
66 |
67 | private void merge(int[] nums, int start, int mid, int end) {
68 | int[] temp = new int[end - start];
69 | // 两边数组合并游标
70 | int l = start;
71 | int r = mid;
72 | int k = 0;
73 | // 注意不能越界
74 | while (l < mid && r < end) {
75 | // 谁小合并谁
76 | if (nums[l] < nums[r]) {
77 | temp[k++] = nums[l++];
78 | } else {
79 | temp[k++] = nums[r++];
80 | }
81 | }
82 | // 剩余部分合并
83 | while (l < mid) {
84 | temp[k++] = nums[l++];
85 | }
86 | while (r < end) {
87 | temp[k++] = nums[r++];
88 | }
89 | // 复制到原数组
90 | for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
91 | nums[i + start] = temp[i];
92 | }
93 | }
94 | ```
95 |
96 | ### 堆排序
97 |
98 | 用数组表示的完全二叉树 complete binary tree
99 |
100 | > 完全二叉树 VS 其他二叉树
101 |
102 | 
103 |
104 | [动画展示](https://www.bilibili.com/video/av18980178/)
105 |
106 | 
107 |
108 | 核心代码
109 |
110 | ```java
111 | public void heapSort(int[] nums) {
112 | // 1、无序数组nums
113 | // 2、将无序数组nums构建为一个大根堆
114 | for (int i = nums.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
115 | sink(nums, i, nums.length);
116 | }
117 | // 3、交换nums[0]和nums[len(a)-1]
118 | // 4、然后把前面这段数组继续下沉保持堆结构,如此循环即可
119 | for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
120 | // 从后往前填充值
121 | swap(nums, 0, i);
122 | // 前面的长度也减一
123 | sink(nums, 0, i);
124 | }
125 | }
126 |
127 | private void sink(int[] nums, int i, int length) {
128 | while (true) {
129 | // 左节点索引(从0开始,所以左节点为i*2+1)
130 | int l = i * 2 + 1;
131 | // 右节点索引
132 | int r = i * 2 + 2;
133 | // 保存根、左、右三者之间较大值的索引
134 | int index = i;
135 | // 存在左节点,左节点值较大,则取左节点
136 | if (l < length && nums[l] > nums[index]) {
137 | index = l;
138 | }
139 | // 存在右节点,且值较大,取右节点
140 | if (r < length && nums[r] > nums[index]) {
141 | index = r;
142 | }
143 | // 如果根节点较大,则不用下沉
144 | if (index == i) {
145 | break;
146 | }
147 | // 如果根节点较小,则交换值,并继续下沉
148 | swap(nums, i, index);
149 | i = index;
150 | }
151 | }
152 |
153 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
154 | int temp = nums[i];
155 | nums[i] = nums[j];
156 | nums[j] = temp;
157 | }
158 | ```
159 |
160 | ## 参考
161 |
162 | [十大经典排序](https://www.cnblogs.com/onepixel/p/7674659.html)
163 |
164 | [二叉堆](https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo/shu-ju-jie-gou-xi-lie/er-cha-dui-xiang-jie-shi-xian-you-xian-ji-dui-lie)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data_structure/stack_queue.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 栈和队列
2 |
3 | ## 简介
4 |
5 | 栈的特点是后入先出
6 |
7 | 根据这个特点可以临时保存一些数据,之后用到依次再弹出来,常用于树的非递归遍历、 DFS 深度搜索。
8 |
9 | 队列常用于BFS广度搜索,很少单独考察。
10 |
11 | ## 基本应用
12 |
13 | ### 逆波兰表达式求值
14 |
15 | > [150. 逆波兰表达式求值](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/)
16 | >
17 | > **波兰表达式计算** > **输入:** `["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]` > **输出:** 9
18 | >
19 | > **解释:** `((2 + 1) * 3) = 9`
20 |
21 | ```java
22 | public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
23 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
24 | for (String s : tokens) {
25 | if ("+".equals(s) || "-".equals(s) || "*".equals(s) || "/".equals(s)) {
26 | int a = stack.pop();
27 | int b = stack.pop();
28 | if ("+".equals(s)) stack.push(b + a);
29 | else if ("-".equals(s)) stack.push(b - a);
30 | else if ("*".equals(s)) stack.push(b * a);
31 | // 注意:b为被除数,a为除数
32 | else if ("/".equals(s)) stack.push(b / a);
33 | } else {
34 | // 转为数字
35 | stack.push(Integer.parseInt(s));
36 | }
37 | }
38 | return stack.pop();
39 | }
40 | ```
41 |
42 | ### 有效的括号
43 |
44 | > [20. 有效的括号](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/valid-parentheses/)
45 | >
46 | > 给定一个只包括 `'('`,`')'`,`'{'`,`'}'`,`'['`,`']'` 的字符串 `s` ,判断字符串是否有效。
47 | >
48 | > 有效字符串需满足:
49 | >
50 | > 1. 左括号必须用相同类型的右括号闭合。
51 | > 2. 左括号必须以正确的顺序闭合。
52 |
53 | ```java
54 | public boolean isValid(String s) {
55 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
56 | for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
57 | if (c == '(') stack.push(')');
58 | else if (c == '[') stack.push(']');
59 | else if (c == '{') stack.push('}');
60 | else if (stack.isEmpty() || c != stack.pop()) {
61 | return false;
62 | }
63 | }
64 | return stack.isEmpty();
65 | }
66 | ```
67 |
68 | ## 单调栈
69 |
70 | 单调栈:栈内元素保持单调递增或单调递减的栈
71 |
72 | **(以单调递增栈为例)**
73 |
74 | 入栈规则:
75 |
76 | - 新元素比栈顶元素小:直接入栈
77 |
78 | - 新元素比栈顶元素大:弹出栈内元素直到栈顶比新元素小(或空栈)
79 |
80 | 出栈意义:
81 |
82 | - 需要出栈时,入栈的新元素是出栈元素右方第一个比出栈元素小的元素
83 |
84 | - 出栈后,新的栈顶是出栈元素左侧最大的数
85 |
86 | 技巧:最后添加一个值为0的哨兵节点,可以在最后强制所有元素出栈。
87 |
88 | 以下分别使用了单调递增栈和单调递减栈
89 |
90 | ### 柱状图中最大的矩形
91 |
92 | > [84. 柱状图中最大的矩形](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/largest-rectangle-in-histogram/)
93 | >
94 | > 给定 *n* 个非负整数,用来表示柱状图中各个柱子的高度。每个柱子彼此相邻,且宽度为 1 。
95 | >
96 | > 求在该柱状图中,能够勾勒出来的矩形的最大面积。
97 |
98 | ```java
99 | public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
100 | if (heights.length == 0) {
101 | return 0;
102 | }
103 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
104 | int max = 0;
105 | // 当前高度小于栈,则将栈内元素都弹出计算面积
106 | for (int i = 0; i <= heights.length; i++) {
107 | int cur = 0;
108 | if (i < heights.length) {
109 | cur = heights[i];
110 | }
111 | while (stack.size() != 0 && cur <= heights[stack.peek()]) {
112 | int index = stack.pop();
113 | int h = heights[index];
114 | // 计算宽度
115 | int w = i;
116 | if (stack.size() != 0) {
117 | int peek = stack.peek();
118 | w = i - peek - 1;
119 | }
120 | max = Math.max(max, h * w);
121 | }
122 | // 记录索引即可获取对应元素
123 | stack.push(i);
124 | }
125 | return max;
126 | }
127 | ```
128 |
129 | ### 接雨水
130 |
131 | > [42. 接雨水](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/trapping-rain-water/)
132 | >
133 | > 给定 *n* 个非负整数表示每个宽度为 1 的柱子的高度图,计算按此排列的柱子,下雨之后能接多少雨水。
134 |
135 | ```java
136 | public int trap(int[] height) {
137 | int sum = 0;
138 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
139 | int current = 0;
140 | while (current < height.length) {
141 | //如果栈不空并且当前指向的高度大于栈顶高度就一直循环
142 | while (!stack.empty() && height[current] > height[stack.peek()]) {
143 | int h = height[stack.peek()]; //取出要出栈的元素
144 | stack.pop(); //出栈
145 | if (stack.empty()) { // 栈空就出去
146 | break;
147 | }
148 | int distance = current - stack.peek() - 1; //两堵墙之前的距离。
149 | int min = Math.min(height[stack.peek()], height[current]);
150 | sum = sum + distance * (min - h);
151 | }
152 | stack.push(current); //当前指向的墙入栈
153 | current++; //指针后移
154 | }
155 | return sum;
156 | }
157 | ```
158 |
159 | ## 设计类问题
160 |
161 | > [2. 用栈实现队列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/implement-queue-using-stacks/)
162 |
163 | ```java
164 | class MyQueue {
165 |
166 | private Stack stack1 = new Stack<>();
167 | private Stack stack2 = new Stack<>();
168 |
169 | /** Initialize your data structure here. */
170 | public MyQueue() {
171 |
172 |
173 | }
174 |
175 | /** Push element x to the back of queue. */
176 | public void push(int x) {
177 | while (! stack2.isEmpty()) {
178 | int val = stack2.pop();
179 | stack1.push(val);
180 | }
181 | stack1.push(x);
182 | }
183 |
184 | /** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
185 | public int pop() {
186 | while (! stack1.isEmpty()) {
187 | int val = stack1.pop();
188 | stack2.push(val);
189 | }
190 | if (stack2.isEmpty()) return -1;
191 | return stack2.pop();
192 | }
193 |
194 | /** Get the front element. */
195 | public int peek() {
196 | while (! stack1.isEmpty()) {
197 | int val = stack1.pop();
198 | stack2.push(val);
199 | }
200 | if (stack2.isEmpty()) return -1;
201 | return stack2.peek();
202 | }
203 |
204 | /** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
205 | public boolean empty() {
206 | return stack1.isEmpty() && stack2.isEmpty();
207 | }
208 | }
209 | ```
210 |
211 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/slide_window.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 滑动窗口
2 |
3 | ## 模板
4 |
5 | ```cpp
6 | /* 滑动窗口算法框架 */
7 | void slidingWindow(string s, string t) {
8 | unordered_map need, window;
9 | for (char c : t) need[c]++;
10 |
11 | int left = 0, right = 0;
12 | int valid = 0;
13 | while (right < s.size()) {
14 | // c 是将移入窗口的字符
15 | char c = s[right];
16 | // 右移窗口
17 | right++;
18 | // 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
19 | ...
20 |
21 | // 判断左侧窗口是否要收缩
22 | while (window needs shrink) {
23 | // d 是将移出窗口的字符
24 | char d = s[left];
25 | // 左移窗口
26 | left++;
27 | // 进行窗口内数据的一系列更新
28 | ...
29 | }
30 | }
31 | }
32 | ```
33 |
34 | 需要变化的地方
35 |
36 | - 1、右指针右移之后窗口数据更新
37 | - 2、判断窗口是否要收缩
38 | - 3、左指针右移之后窗口数据更新
39 | - 4、根据题意计算结果
40 |
41 | ## 示例
42 |
43 | ### 最小覆盖子串
44 |
45 | > [76. 最小覆盖子串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-window-substring/)
46 | >
47 | > 给你一个字符串 S、一个字符串 T,请在字符串 S 里面找出:包含 T 所有字母的最小子串
48 |
49 | ```java
50 | public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
51 | // 技巧:用数组代替Map
52 | // 保存滑动窗口字符集
53 | int[] winMap = new int[256];
54 | // 保存需要出现的字符集
55 | int[] tMap = new int[256];
56 | for (char c : t.toCharArray()) {
57 | tMap[c]++;
58 | }
59 | // 计算共出现了多少不同的字符
60 | int charNum = 0;
61 | for (int n : tMap) {
62 | if (n > 0) {
63 | charNum++;
64 | }
65 | }
66 | // 滑动窗口左右边界
67 | int left = 0;
68 | int right = 0;
69 | // 匹配数
70 | int match = 0;
71 | // 窗口调整前暂存原窗口边界
72 | int start = 0;
73 | int end = 0;
74 | // 窗口长度的最小值
75 | int minValue = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
76 | while (right < s.length()) {
77 | char c = s.charAt(right);
78 | // 在需要的字符集里面,添加到窗口字符集里面
79 | if (tMap[c] != 0) {
80 | winMap[c]++;
81 | // 如果当前字符的数量匹配需要的字符的数量,则match值+1
82 | if (tMap[c] == winMap[c]) {
83 | match++;
84 | }
85 | }
86 | right++;
87 | // 当所有字符数量都匹配之后,开始缩紧窗口
88 | while (match == charNum) {
89 | // 获取结果
90 | if (right - left < minValue) {
91 | minValue = right - left;
92 | start = left;
93 | end = right;
94 | }
95 | char leftChar = s.charAt(left);
96 | // 左指针指向不在需要字符集则直接跳过
97 | if (tMap[leftChar] != 0) {
98 | // 左指针指向字符数量和需要的字符相等时,右移之后match值就不匹配则减一
99 | if (winMap[leftChar] == tMap[leftChar]) {
100 | match--;
101 | }
102 | winMap[leftChar]--;
103 | }
104 | left++;
105 | }
106 | }
107 | if (minValue == Integer.MAX_VALUE) {
108 | return "";
109 | }
110 | return s.substring(start, end);
111 | }
112 | ```
113 |
114 | ### 字符串的排列
115 |
116 | > [567. 字符串的排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutation-in-string/)
117 | >
118 | > 给定两个字符串 **s1** 和 **s2**,写一个函数来判断 **s2** 是否包含 **s1 **的排列。
119 |
120 | ```java
121 | public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {
122 | // 保存滑动窗口字符集
123 | int[] winMap = new int[256];
124 | // 保存需要出现的字符集
125 | int[] tMap = new int[256];
126 | for (char c : s1.toCharArray()) {
127 | tMap[c]++;
128 | }
129 | // 计算共出现了多少不同的字符
130 | int charNum = 0;
131 | for (int n : tMap) {
132 | if (n > 0) {
133 | charNum++;
134 | }
135 | }
136 | // 左右边界
137 | int left = 0;
138 | int right = 0;
139 | // 已经匹配的字母数
140 | int match = 0;
141 |
142 | while (right < s2.length()) {
143 | char c = s2.charAt(right);
144 | right++;
145 | if (tMap[c] != 0) {
146 | winMap[c]++;
147 | if (winMap[c] == tMap[c]) {
148 | match++;
149 | }
150 | }
151 | // 窗口收缩
152 | while (match == charNum) {
153 | c = s2.charAt(left);
154 | if (tMap[c] != 0) {
155 | if (winMap[c] == tMap[c]) {
156 | match--;
157 | }
158 | winMap[c]--;
159 | }
160 | left++;
161 | // 子串是一个排列,即子串长度等于s1
162 | if (right - left + 1 == s1.length()) {
163 | return true;
164 | }
165 | }
166 | }
167 | return false;
168 | }
169 | ```
170 |
171 | ### 找到字符串中所有字母异位词
172 |
173 | > [438. 找到字符串中所有字母异位词](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-all-anagrams-in-a-string/)
174 | >
175 | > 给定一个字符串 **s **和一个非空字符串 **p**,找到 **s **中所有是 **p **的字母异位词的子串,返回这些子串的起始索引。
176 |
177 | ```java
178 | public List findAnagrams(String s, String p) {
179 | int[] pMap = new int[256];
180 | int[] winMap = new int[256];
181 | int charNum = 0;
182 | for (char c : p.toCharArray()) {
183 | if (pMap[c] == 0) charNum++;
184 | pMap[c]++;
185 | }
186 | int left = 0;
187 | int right = 0;
188 | int match = 0;
189 | List result = new ArrayList<>();
190 | while (right < s.length()) {
191 | char c = s.charAt(right);
192 | right++;
193 | if (pMap[c] != 0) {
194 | winMap[c]++;
195 | if (pMap[c] == winMap[c]) {
196 | match++;
197 | }
198 | }
199 | // 缩紧窗口
200 | while (match == charNum) {
201 | c = s.charAt(left);
202 | if (pMap[c] != 0) {
203 | if (pMap[c] == winMap[c]) {
204 | match--;
205 | }
206 | winMap[c]--;
207 | }
208 | // 当窗口长度和字符串长度匹配时,满足条件
209 | if (right - left == p.length()) {
210 | result.add(left);
211 | }
212 | left++;
213 | }
214 | }
215 | return result;
216 | }
217 | ```
218 |
219 | ### 无重复字符的最长子串
220 |
221 | > [3. 无重复字符的最长子串](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-substring-without-repeating-characters/)
222 | >
223 | >给定一个字符串,请你找出其中不含有重复字符的**最长子串**的长度。
224 |
225 | ```java
226 | public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
227 | if (s.length() < 2) {
228 | return s.length();
229 | }
230 | int[] winMap = new int[256];
231 | int left = 0;
232 | int right = 0;
233 | int maxLen = 0;
234 | // 1、右指针右移
235 | while (right < s.length()) {
236 | char c = s.charAt(right);
237 | right++;
238 | winMap[c]++;
239 | // 2、根据题意收缩窗口
240 | while (winMap[c] > 1) {
241 | // 3、左指针右移更新窗口
242 | char d = s.charAt(left);
243 | left++;
244 | winMap[d]--;
245 | }
246 | // 4、根据题意计算结果
247 | maxLen = Math.max(right - left, maxLen);
248 | }
249 | return maxLen;
250 | }
251 | ```
252 |
253 | ## 总结
254 |
255 | - 和双指针题目类似,更像双指针的升级版,滑动窗口核心点是维护一个窗口集,根据窗口集来进行处理
256 | - 核心步骤
257 | - right 右移
258 | - 收缩
259 | - left 右移
260 | - 求结果
261 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/disjoin_set.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 并查集
2 |
3 | ## 简介
4 |
5 | 并查集用于处理不相交集合的合并与查询问题,常见操作有:
6 |
7 | - 查询:查询元素属于哪个集合,可用于判断元素是否在一个集合中
8 | - 合并:合并两个集合
9 |
10 | 应用场景:动态连通性的判断,且不需要给出具体路径。
11 |
12 | ## 数据结构
13 |
14 | ### 初始化
15 |
16 | id数组存放的是节点的组号,初始化时将每个节点单独分为一组。
17 |
18 | ```java
19 | private int[] id;
20 |
21 | public DisjoinSet(int size) {
22 | id = new int[size];
23 | for(int i = 0; i < size; i++)
24 | id[i] = i;
25 | }
26 | ```
27 |
28 | ### Quick-Find
29 |
30 | 由于使用整数表示节点,可以通过数组实现节点到组编号的映射。
31 |
32 | ```java
33 | public void union(int p, int q) {
34 | // 获得p和q的组号
35 | int pID = id[p];
36 | int qID = id[q];
37 | // 如果两个组号相等,直接返回
38 | if (pID == qID) return;
39 | // 遍历一次,改变组号使他们属于一个组
40 | for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++)
41 | if (id[i] == pID) id[i] = qID;
42 | count--;
43 | }
44 | ```
45 |
46 | ### Quick-Union
47 |
48 | id数组存放的是节点的父节点索引,根节点的父节点是自身,通过这点判断能到达根节点。
49 |
50 | ```java
51 | private int find(int p) {
52 | // 寻找p节点所在组的根节点,根节点具有性质id[root] = root
53 | while (p != id[p]) p = id[p];
54 | return p;
55 | }
56 | public void union(int p, int q) {
57 | // Give p and q the same root.
58 | int pRoot = find(p);
59 | int qRoot = find(q);
60 | if (pRoot == qRoot)
61 | return;
62 | // 将一棵树(即一个组)变成另外一课树(即一个组)的子树
63 | id[pRoot] = qRoot;
64 | count--;
65 | }
66 | ```
67 |
68 | ### Weighted Quick Union
69 |
70 | 保存两棵树的大小,每次将小的合并到大的树中。
71 |
72 | ## 常见例题
73 |
74 | ### 冗余连接
75 |
76 | > [684. 冗余连接](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/redundant-connection/)
77 | >
78 | > 在本问题中, 树指的是一个连通且无环的**无向**图。
79 | >
80 | > 输入一个图,该图由一个有着N个节点 (节点值不重复1, 2, ..., N) 的树及一条附加的边构成。附加的边的两个顶点包含在1到N中间,这条附加的边不属于树中已存在的边。
81 | >
82 | > 结果图是一个以`边`组成的二维数组。每一个`边`的元素是一对`[u, v]` ,满足 `u < v`,表示连接顶点`u` 和`v`的**无向**图的边。
83 | >
84 | > 返回一条可以删去的边,使得结果图是一个有着N个节点的树。如果有多个答案,则返回二维数组中最后出现的边。答案边 `[u, v]` 应满足相同的格式 `u < v`。
85 |
86 | ```java
87 | private int[] parent;
88 | private int[] size;
89 |
90 | private int find(int p) {
91 | while (p != parent[p]) {
92 | parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
93 | p = parent[p];
94 | }
95 | return p;
96 | }
97 |
98 | private boolean union(int p, int q) {
99 | int pRoot = find(p);
100 | int qRoot = find(q);
101 | // 在合并前判断是否属于相同的连通分量
102 | if (pRoot == qRoot) {
103 | return true;
104 | }
105 | // Weighted Quick Union
106 | if (size[pRoot] < size[qRoot]) {
107 | parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
108 | size[qRoot] += size[pRoot];
109 | } else {
110 | parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
111 | size[pRoot] += size[qRoot];
112 | }
113 | return false;
114 | }
115 |
116 | public int[] findRedundantConnection(int[][] edges) {
117 | parent = new int[edges.length + 1];
118 | size = new int[edges.length + 1];
119 | // 并查集初始化
120 | for (int i = 0; i < parent.length; i++) {
121 | parent[i] = i;
122 | size[i] = 1;
123 | }
124 | for (int[] arr : edges) {
125 | if (union(arr[0], arr[1])) {
126 | // 如果已经连通说明当前这条边是多余的
127 | return arr;
128 | }
129 | }
130 | return new int[]{};
131 | }
132 | ```
133 |
134 | ### 打砖块
135 |
136 | > [803. 打砖块](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/bricks-falling-when-hit/)
137 | >
138 | >有一个 `m x n` 的二元网格,其中 `1` 表示砖块,`0` 表示空白。砖块 **稳定**(不会掉落)的前提是:
139 | >
140 | >- 一块砖直接连接到网格的顶部,或者
141 | >- 至少有一块相邻(4 个方向之一)砖块 **稳定** 不会掉落时
142 | >
143 | >给你一个数组 `hits` ,这是需要依次消除砖块的位置。每当消除 `hits[i] = (rowi, coli)` 位置上的砖块时,对应位置的砖块(若存在)会消失,然后其他的砖块可能因为这一消除操作而掉落。一旦砖块掉落,它会立即从网格中消失(即,它不会落在其他稳定的砖块上)。
144 | >
145 | >返回一个数组 `result` ,其中 `result[i]` 表示第 `i` 次消除操作对应掉落的砖块数目。
146 | >
147 | >**注意**,消除可能指向是没有砖块的空白位置,如果发生这种情况,则没有砖块掉落。
148 |
149 | 思路:并查集是用于合并连通分量,而砖块消失实质上是拆分连通分量,因此这题应当逆向考虑,即先打碎所有砖块,再从后向前添加砖块(合并连通分量),添加后计算会增加多少个节点与根节点相连。
150 |
151 | 首先给出并查集的定义,`size`既表示连通分量的大小,也用于合并时的权重判断。
152 |
153 | ```java
154 | class DisJoinSet {
155 |
156 | private final int[] parent;
157 | private final int[] size;
158 |
159 | // 初始化并查集,根节点为自身,大小为1
160 | public DisJoinSet(int len) {
161 | parent = new int[len];
162 | size = new int[len];
163 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
164 | parent[i] = i;
165 | size[i] = 1;
166 | }
167 | }
168 |
169 | // 查找连通分量的根节点
170 | public int find(int p) {
171 | while (p != parent[p]) {
172 | parent[p] = parent[parent[p]];
173 | p = parent[p];
174 | }
175 | return p;
176 | }
177 |
178 | // 合并两个节点对应的连通分量
179 | public void merge(int p, int q) {
180 | int pRoot = find(p);
181 | int qRoot = find(q);
182 | // 在合并前判断是否属于相同的连通分量
183 | if (pRoot != qRoot) {
184 | if (size[pRoot] < size[qRoot]) {
185 | parent[pRoot] = qRoot;
186 | size[qRoot] += size[pRoot];
187 | } else {
188 | parent[qRoot] = pRoot;
189 | size[pRoot] += size[qRoot];
190 | }
191 | }
192 | }
193 |
194 | // 获取连通分量的大小
195 | public int getSize(int n) {
196 | int root = find(n);
197 | return size[root];
198 | }
199 |
200 | }
201 | ```
202 |
203 | 实际使用中将二维数组映射为一维数组,并在最后增加一项作为“房顶节点”,与其相连的节点均不会下落。下面是算法逻辑:
204 |
205 | ```java
206 | public int[] hitBricks(int[][] grid, int[][] hits) {
207 | int h = grid.length;
208 | int w = grid[0].length;
209 | int[] result = new int[hits.length];
210 | // 保存当前的砖块状态
211 | int[][] status = new int[h][w];
212 | DisJoinSet disJoinSet = new DisJoinSet(h * w + 1);
213 | // 将status初始化为最终的状态
214 | for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
215 | status[i] = grid[i].clone();
216 | }
217 | for (int[] pos : hits) {
218 | status[pos[0]][pos[1]] = 0;
219 | }
220 | // 根据最后的状态构造并查集
221 | for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
222 | for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
223 | if (status[i][j] == 0) {
224 | continue;
225 | }
226 | if (i == 0) {
227 | // 一块砖直接连接到网格的顶部
228 | disJoinSet.merge( h * w, j);
229 | } else {
230 | // 上方有相邻砖块
231 | if (status[i - 1][j] == 1) {
232 | disJoinSet.merge((i - 1) * w + j, i * w + j);
233 | }
234 | // 左侧有相邻砖块
235 | if (j > 0 && status[i][j - 1] == 1) {
236 | disJoinSet.merge(i * w + j - 1, i * w + j);
237 | }
238 | }
239 | }
240 | }
241 | // 从后向前把砖块补上
242 | int[][] directions = {{0, 1}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {-1, 0}};
243 | for (int i = hits.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
244 | int r = hits[i][0];
245 | int c = hits[i][1];
246 | if (grid[r][c] == 0) {
247 | result[i] = 0;
248 | } else {
249 | // 添加砖块前与房顶相连通的节点数目
250 | int prev = disJoinSet.getSize(h * w);
251 | // 顶部第一行的情况
252 | if (r == 0) {
253 | disJoinSet.merge(c, h * w);
254 | }
255 | // 处理四周的节点
256 | for (int[] direction : directions) {
257 | int nr = r + direction[0];
258 | int nc = c + direction[1];
259 |
260 | if (nr >= 0 && nr < h && nc >= 0 && nc < w && status[nr][nc] == 1) {
261 | disJoinSet.merge(r * w + c, nr * w + nc);
262 | }
263 | }
264 | // 获得增加的节点数,即为正向操作时这一步下落的节点数
265 | result[i] = Math.max(0, disJoinSet.getSize(h * w) - prev - 1);
266 | status[r][c] = 1;
267 | }
268 | }
269 | return result;
270 | }
271 | ```
272 |
273 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/backtrack.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 回溯算法
2 |
3 | ## 背景
4 |
5 | 回溯法(backtrack)常用于遍历列表所有子集,是 DFS 深度搜索一种,一般用于全排列,穷尽所有可能,遍历的过程实际上是一个决策树的遍历过程。时间复杂度一般 O(N!),它不像动态规划存在重叠子问题可以优化,回溯算法就是纯暴力穷举,复杂度一般都很高。
6 |
7 | ## 模板
8 |
9 | ```go
10 | result = []
11 | func backtrack(选择列表,路径):
12 | if 满足结束条件:
13 | result.add(路径)
14 | return
15 | for 选择 in 选择列表:
16 | 做选择
17 | backtrack(选择列表,路径)
18 | 撤销选择
19 | ```
20 |
21 | 核心就是从选择列表里做一个选择,然后一直递归往下搜索答案,如果遇到路径不通,就返回来撤销这次选择。
22 |
23 | ## 常见例题
24 |
25 | ### 集合类
26 |
27 | #### 子集
28 |
29 | > [78. 子集](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets/)
30 | >
31 | > 给你一个整数数组 `nums` ,数组中的元素 **互不相同** 。返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。
32 |
33 | ```java
34 | public List> subsets(int[] nums) {
35 | // 保存中间结果
36 | List subSet = new ArrayList<>();
37 | // 保存最终结果
38 | List> result = new ArrayList<>();
39 | backtrack(nums, 0, subSet, result);
40 | return result;
41 | }
42 |
43 | // nums 给定的集合
44 | // pos 下次添加到集合中的元素位置索引
45 | // subSet 临时结果集合(每次需要复制保存)
46 | // result 最终结果
47 | private void backtrack(int[] nums, int pos, List subSet, List> result) {
48 | // 把临时结果复制出来保存到最终结果
49 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(subSet));
50 | for (int i = pos; i < nums.length; i++) {
51 | // 选择、处理结果、再撤销选择
52 | subSet.add(nums[i]);
53 | backtrack(nums, i+1, subSet, result);
54 | subSet.remove(subSet.size() - 1);
55 | }
56 | }
57 | ```
58 |
59 | #### 子集 II
60 |
61 | > [90. 子集 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/subsets-ii/)
62 | >
63 | > 给定一个可能包含重复元素的整数数组 nums,返回该数组所有可能的子集(幂集)。说明:解集不能包含重复的子集。
64 |
65 | ```java
66 | public List> subsets(int[] nums) {
67 | // 保存中间结果
68 | List subSet = new ArrayList<>();
69 | // 保存最终结果
70 | List> result = new ArrayList<>();
71 | // 先排序
72 | Arrays.sort(nums);
73 | backtrack(nums, 0, subSet, result);
74 | return result;
75 | }
76 |
77 | // nums 给定的集合
78 | // pos 下次添加到集合中的元素位置索引
79 | // subSet 临时结果集合(每次需要复制保存)
80 | // result 最终结果
81 | private void backtrack(int[] nums, int pos, List subSet, List> result) {
82 | // 把临时结果复制出来保存到最终结果
83 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(subSet));
84 | for (int i = pos; i < nums.length; i++) {
85 | // 排序之后,如果再遇到重复元素,则不选择此元素
86 | if (i != pos && nums[i] == nums[i-1]) {
87 | continue;
88 | }
89 | // 选择、处理结果、再撤销选择
90 | subSet.add(nums[i]);
91 | backtrack(nums, i+1, subSet, result);
92 | subSet.remove(subSet.size() - 1);
93 | }
94 | }
95 | ```
96 |
97 | ### 排列类
98 |
99 | #### 全排列
100 |
101 | > [46. 全排列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations/)
102 | >
103 | > 给定一个 **没有重复** 数字的序列,返回其所有可能的全排列。
104 |
105 | 思路:需要记录已经选择过的元素,满足条件的结果才进行返回。这里要注意在做选择时记录,回溯时撤销。
106 |
107 | ```java
108 | public List> permute(int[] nums) {
109 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
110 | List> result = new ArrayList<>();
111 | // 标记这个元素是否已经添加到结果集
112 | boolean[] visited = new boolean[nums.length];
113 | backtrack(nums, visited, list, result);
114 | return result;
115 | }
116 |
117 | // nums 输入集合
118 | // visited 当前递归标记过的元素
119 | // list 临时结果集(路径)
120 | // result 最终结果
121 | private void backtrack(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, List list, List> result) {
122 | if (list.size() == nums.length) {
123 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
124 | return;
125 | }
126 | for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
127 | // 已经添加过的元素,直接跳过
128 | if (visited[i]) {
129 | continue;
130 | }
131 | // 添加元素
132 | list.add(nums[i]);
133 | visited[i] = true;
134 | backtrack(nums, visited, list, result);
135 | // 移除元素
136 | list.remove(list.size() - 1);
137 | visited[i] = false;
138 | }
139 | }
140 | ```
141 |
142 | #### 全排列 II
143 |
144 | > [47. 全排列 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/permutations-ii/)
145 | >
146 | > 给定一个可包含重复数字的序列,返回所有不重复的全排列。
147 |
148 | ```java
149 | public List> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
150 | List list = new ArrayList<>();
151 | List> result = new ArrayList<>();
152 | // 标记这个元素是否已经添加到结果集
153 | boolean[] visited = new boolean[nums.length];
154 | // 先排序
155 | Arrays.sort(nums);
156 | backtrack(nums, visited, list, result);
157 | return result;
158 | }
159 |
160 | // nums 输入集合
161 | // visited 当前递归标记过的元素
162 | // list 临时结果集
163 | // result 最终结果
164 | private void backtrack(int[] nums, boolean[] visited, List list, List> result) {
165 | if (list.size() == nums.length) {
166 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(list));
167 | return;
168 | }
169 | for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
170 | // 已经添加过的元素,直接跳过
171 | if (visited[i]) {
172 | continue;
173 | }
174 | // 上一个元素和当前相同,并且没有访问过就跳过
175 | if (i != 0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1] && !visited[i-1]) {
176 | continue;
177 | }
178 | list.add(nums[i]);
179 | visited[i] = true;
180 | backtrack(nums, visited, list, result);
181 | list.remove(list.size() - 1);
182 | visited[i] = false;
183 | }
184 | }
185 |
186 | ```
187 |
188 | ### 组合类
189 |
190 | #### 组合总和
191 |
192 | > [39. 组合总和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/combination-sum/)
193 | >
194 | > 给定一个**无重复元素**的数组 `candidates` 和一个目标数 `target` ,找出 `candidates` 中所有可以使数字和为 `target` 的组合。
195 | >
196 | > `candidates` 中的数字可以无限制重复被选取。
197 | >
198 | > **说明:**
199 | >
200 | > - 所有数字(包括 `target`)都是正整数。
201 | > - 解集不能包含重复的组合。
202 |
203 | ```java
204 | public List> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
205 | List answer = new ArrayList();
206 | List> result = new ArrayList();
207 | // 先排序
208 | Arrays.sort(candidates);
209 | backtrack(candidates, 0, target, answer, result);
210 | return result;
211 | }
212 |
213 | // candidates 输入集合
214 | // pos 当前标记位置,标记前的元素不再考虑
215 | // target 求和目标
216 | // answer 临时解法
217 | // result 最终结果
218 | private void backtrack(int[] candidates, int pos, int target, List answer, List> result) {
219 | if (target == 0) {
220 | result.add(new ArrayList<>(answer));
221 | }
222 | for (int i = pos; i < candidates.length; i++) {
223 | // 剪枝:后续元素都比目标大,直接break(比continue要快)
224 | if (candidates[i] > target) {
225 | break;
226 | }
227 | // 添加元素
228 | answer.add(candidates[i]);
229 | // 元素可以重复取,所以从当前位置继续
230 | backtrack(candidates, i, target - candidates[i], answer, result);
231 | // 移除元素
232 | answer.remove(answer.size() - 1);
233 | }
234 | }
235 | ```
236 |
237 | #### 电话号码的字母组合
238 |
239 | > [17. 电话号码的字母组合](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/letter-combinations-of-a-phone-number/)
240 | >
241 | > 给定一个仅包含数字 `2-9` 的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按 **任意顺序** 返回。
242 | >
243 | > 数字到字母的映射与电话按键相同
244 |
245 | ```java
246 | // 记录数字到字母的映射
247 | private final static Map map = new HashMap<>();
248 |
249 | static {
250 | map.put('2', "abc");
251 | map.put('3', "def");
252 | map.put('4', "ghi");
253 | map.put('5', "jkl");
254 | map.put('6', "mno");
255 | map.put('7', "pqrs");
256 | map.put('8', "tuv");
257 | map.put('9', "wxyz");
258 | }
259 |
260 | public List letterCombinations(String digits) {
261 | StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
262 | List result = new ArrayList<>();
263 | backtrack(digits, 0, builder, result);
264 | return result;
265 | }
266 |
267 | private void backtrack(String digits, int pos, StringBuilder builder, List result) {
268 | // 结束条件:到达末尾
269 | if (pos == digits.length()) {
270 | // 如果原字符串为空则没有对应的字母组合
271 | if (pos != 0) {
272 | result.add(builder.toString());
273 | }
274 | return;
275 | }
276 | for (char c : map.get(digits.charAt(pos)).toCharArray()) {
277 | builder.append(c);
278 | backtrack(digits, pos + 1, builder, result);
279 | builder.deleteCharAt(builder.length() - 1);
280 | }
281 | }
282 | ```
283 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/binary_search.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 二分搜索
2 |
3 | ## 简介
4 |
5 | 给一个**有序数组**和目标值,找第一次/最后一次/任何一次出现的索引,如果没有出现返回-1
6 |
7 | 模板四点要素
8 |
9 | - 1、初始化:start=0、end=len-1
10 | - 2、循环退出条件:start + 1 < end
11 | - 3、比较中点和目标值:A[mid] ==、 <、> target
12 | - 4、判断最后两个元素是否符合:A[start]、A[end] ? target
13 |
14 | 时间复杂度 O(logn),使用场景一般是有序数组的查找
15 |
16 | ### 典型示例
17 |
18 | > [704. 二分查找](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-search/)
19 | >
20 | > 给定一个 n 个元素有序的(升序)整型数组 nums 和一个目标值 target ,写一个函数搜索 nums 中的 target,如果目标值存在返回下标,否则返回 -1。
21 |
22 | ```java
23 | // 二分搜索最常用模板
24 | public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
25 | // 1、初始化left、right
26 | int left = 0;
27 | int right = nums.length - 1;
28 | // 2、处理for循环
29 | while (right - left > 1) {
30 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
31 | // 3、比较nums[mid]和target值
32 | if (nums[mid] == target) {
33 | return mid;
34 | } else if (nums[mid] < target) {
35 | left = mid;
36 | } else {
37 | right = mid;
38 | }
39 | }
40 | // 4、最后剩下两个元素,手动判断
41 | if (nums[left] == target) {
42 | return left;
43 | } else if (nums[right] == target) {
44 | return right;
45 | } else {
46 | return -1;
47 | }
48 | }
49 | ```
50 |
51 | ### 模板
52 |
53 | 大部分二分查找类的题目都可以用这个模板,然后做一点特殊逻辑即可
54 |
55 | 另外二分查找还有一些其他模板如下图,大部分场景模板#3 都能解决问题,而且还能找第一次/最后一次出现的位置,应用更加广泛
56 |
57 | 
58 |
59 | 所以用模板#3 就对了,详细的对比可以这边文章介绍:[二分搜索模板](https://leetcode-cn.com/explore/learn/card/binary-search/212/template-analysis/847/)
60 |
61 | 如果是最简单的二分搜索,不需要找第一个、最后一个位置、或者是没有重复元素,可以使用模板#1,代码更简洁常见题目
62 |
63 | ## 常见题目
64 |
65 | ### 搜索插入位置
66 |
67 | > [35. 搜索插入位置](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-insert-position/)
68 | >
69 | > 给定一个排序数组和一个目标值,在数组中找到目标值,并返回其索引。如果目标值不存在于数组中,返回它将会被按顺序插入的位置。
70 |
71 | ```java
72 | public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
73 | // 思路:找到第一个 >= target 的元素位置
74 | int left = 0;
75 | int right = nums.length - 1;
76 | while (right - left > 1) {
77 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
78 | if (nums[mid] == target) {
79 | return mid;
80 | } else if (nums[mid] < target) {
81 | left = mid;
82 | } else {
83 | right = mid;
84 | }
85 | }
86 | if (nums[left] >= target) {
87 | return left;
88 | } else if (nums[left] < target && target <= nums[right]) {
89 | return left + 1;
90 | } else {
91 | // 目标值比所有值都大
92 | return right + 1;
93 | }
94 | }
95 | ```
96 |
97 | ### 搜索二维矩阵
98 |
99 | > [74. 搜索二维矩阵](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-a-2d-matrix/)
100 | >
101 | > 编写一个高效的算法来判断 m x n 矩阵中,是否存在一个目标值。该矩阵具有如下特性:
102 | >
103 | > - 每行中的整数从左到右按升序排列。
104 | > - 每行的第一个整数大于前一行的最后一个整数。
105 |
106 | ```java
107 | public boolean searchMatrix(int[][] matrix, int target) {
108 | // 思路:将2维数组转为1维数组 进行二分搜索
109 | if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
110 | return false;
111 | }
112 | int row = matrix.length;
113 | int col = matrix[0].length;
114 | int left = 0;
115 | int right = row * col - 1;
116 | while (right - left > 1) {
117 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
118 | // 获取2维数组对应值
119 | int val = matrix[mid/col][mid%col];
120 | if (val < target) {
121 | left = mid;
122 | } else if (val > target) {
123 | right = mid;
124 | } else {
125 | return true;
126 | }
127 | }
128 | if (matrix[left/col][left%col] == target || matrix[right/col][right%col] == target) {
129 | return true;
130 | }
131 | return false;
132 | }
133 | ```
134 |
135 | ### 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值
136 |
137 | > [153. 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-minimum-in-rotated-sorted-array/)
138 | >
139 | > 假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
140 | > 请找出其中最小的元素。
141 |
142 | ```java
143 | public int findMin(int[] nums) {
144 | // 思路:最后一个值作为target,然后往左移动,最后比较start、end的值
145 | if (nums.length == 0) {
146 | return -1;
147 | }
148 | int left = 0;
149 | int right = nums.length - 1;
150 | while (right - left > 1) {
151 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
152 | // 最后一个元素值为target
153 | if (nums[mid] > nums[right]) {
154 | left = mid;
155 | } else {
156 | right = mid;
157 | }
158 | }
159 | return Math.min(nums[left], nums[right]);
160 | }
161 | ```
162 |
163 | ### 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值 II
164 |
165 | > [154. 寻找旋转排序数组中的最小值 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/find-minimum-in-rotated-sorted-array-ii/)
166 | >
167 | > 假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转
168 | > ( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
169 | > 请找出其中最小的元素。(包含重复元素)
170 |
171 | ```java
172 | public int findMin(int[] nums) {
173 | // 思路:跳过重复元素,mid值和end值比较,分为两种情况进行处理
174 | if (nums.length == 0) {
175 | return -1;
176 | }
177 | int left = 0;
178 | int right = nums.length - 1;
179 | while (right - left > 1) {
180 | // 去除重复元素
181 | while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
182 | right--;
183 | }
184 | while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {
185 | left++;
186 | }
187 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
188 | // 中间元素和最后一个元素比较(判断中间点落在左边上升区,还是右边上升区)
189 | if (nums[mid] > nums[right]) {
190 | left = mid;
191 | } else {
192 | right = mid;
193 | }
194 | }
195 | return Math.min(nums[left], nums[right]);
196 | }
197 | ```
198 |
199 | ### 搜索旋转排序数组
200 |
201 | > [33. 搜索旋转排序数组](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array/)
202 | >
203 | > 假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。
204 | > ( 例如,数组 [0,1,2,4,5,6,7] 可能变为 [4,5,6,7,0,1,2] )。
205 | > 搜索一个给定的目标值,如果数组中存在这个目标值,则返回它的索引,否则返回 -1 。
206 | > 你可以假设数组中不存在重复的元素。
207 |
208 | ```java
209 | public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
210 | // 思路:四种情况判断
211 | if (nums.length == 0) {
212 | return -1;
213 | }
214 | int left = 0;
215 | int right = nums.length - 1;
216 | while (right - left > 1) {
217 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
218 | // 相等直接返回
219 | if (nums[mid] == target) {
220 | return mid;
221 | }
222 | // 判断在哪个区间,可能分为四种情况
223 | if (nums[left] < nums[mid]) {
224 | if (nums[left] <= target && target <= nums[mid]) {
225 | right = mid;
226 | } else {
227 | left = mid;
228 | }
229 | } else if (nums[right] > nums[mid]) {
230 | if (nums[right] >= target && target >= nums[mid]) {
231 | left = mid;
232 | } else {
233 | right = mid;
234 | }
235 | }
236 | }
237 | if (nums[left] == target) {
238 | return left;
239 | } else if (nums[right] == target) {
240 | return right;
241 | }
242 | return -1;
243 | }
244 | ```
245 |
246 | 注意点
247 |
248 | > 面试时,可以直接画图进行辅助说明,空讲很容易让大家都比较蒙圈
249 |
250 | ### 搜索旋转排序数组 II
251 |
252 | > [81. 搜索旋转排序数组 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/search-in-rotated-sorted-array-ii/)
253 | >
254 | > 假设按照升序排序的数组在预先未知的某个点上进行了旋转。
255 | > ( 例如,数组 [0,0,1,2,2,5,6] 可能变为 [2,5,6,0,0,1,2] )。
256 | > 编写一个函数来判断给定的目标值是否存在于数组中。若存在返回 true,否则返回 false。(包含重复元素)
257 |
258 | ```java
259 | public boolean search(int[] nums, int target) {
260 | // 思路:四种情况判断
261 | if (nums.length == 0) {
262 | return false;
263 | }
264 | int left = 0;
265 | int right = nums.length - 1;
266 | while (right - left > 1) {
267 | // 去除重复元素
268 | while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right - 1]) {
269 | right--;
270 | }
271 | while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left + 1]) {
272 | left++;
273 | }
274 | int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
275 | // 相等直接返回
276 | if (nums[mid] == target) {
277 | return true;
278 | }
279 | // 判断在哪个区间,可能分为四种情况
280 | if (nums[left] < nums[mid]) {
281 | if (nums[left] <= target && target <= nums[mid]) {
282 | right = mid;
283 | } else {
284 | left = mid;
285 | }
286 | } else if (nums[right] > nums[mid]) {
287 | if (nums[right] >= target && target >= nums[mid]) {
288 | left = mid;
289 | } else {
290 | right = mid;
291 | }
292 | }
293 | }
294 | return (nums[left] == target || nums[right] == target);
295 | }
296 | ```
297 |
298 | ## 总结
299 |
300 | 二分搜索核心四点要素(必背&理解)
301 |
302 | - 1、初始化:start=0、end=len-1
303 | - 2、循环退出条件:start + 1 < end
304 | - 3、比较中点和目标值:A[mid] ==、 <、> target
305 | - 4、判断最后两个元素是否符合:A[start]、A[end] ? target
306 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data_structure/linked_list.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 链表
2 |
3 | ## 提纲
4 |
5 | 链表相关的核心点
6 |
7 | - null 异常处理
8 | - dummy node 哑巴节点
9 | - 快慢指针
10 | - 插入一个节点到排序链表
11 | - 从一个链表中移除一个节点
12 | - 翻转链表
13 | - 合并两个链表
14 | - 找到链表的中间节点
15 |
16 | ## 基本操作
17 |
18 | ### 链表删除
19 |
20 | #### 删除排序链表中的重复元素
21 |
22 | > [83. 删除排序链表中的重复元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list/)
23 | >
24 | > 给定一个排序链表,删除所有重复的元素,使得每个元素只出现一次。
25 |
26 | ```java
27 | public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
28 | ListNode p = head;
29 | while (p != null) {
30 | // 全部删除完再移动到下一个元素
31 | while (p.next != null && p.val == p.next.val) {
32 | p.next = p.next.next;
33 | }
34 | p = p.next;
35 | }
36 | return head;
37 | }
38 | ```
39 |
40 | #### 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II
41 |
42 | > [82. 删除排序链表中的重复元素 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii/)
43 | >
44 | > 给定一个排序链表,删除所有含有重复数字的节点,只保留原始链表中 没有重复出现的数字。
45 |
46 | 思路:链表头结点可能被删除,所以用 dummy node 辅助删除
47 |
48 | ```java
49 | public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
50 | if (head == null) {
51 | return null;
52 | }
53 | ListNode newHead = new ListNode(-1, head);
54 | ListNode p = newHead;
55 | int n = 0;
56 | while (p.next != null && p.next.next != null) {
57 | if (p.next.val == p.next.next.val) {
58 | // 记录已经删除的值,用于后续节点判断
59 | n = p.next.val;
60 | while (p.next != null && p.next.val == n) {
61 | p.next = p.next.next;
62 | }
63 | } else {
64 | p = p.next;
65 | }
66 | }
67 | return newHead.next;
68 | }
69 | ```
70 |
71 | 注意点
72 |
73 | - A->B->C 删除 B,A.next = C
74 | - 删除用一个 Dummy Node 节点辅助(允许头节点可变)
75 | - 访问 X.next 、X.value 一定要保证 X != nil
76 |
77 | ### 链表反转
78 |
79 | #### 反转链表
80 |
81 | > [206. 反转链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list/)
82 | >
83 | > 反转一个单链表。
84 |
85 | 思路:用一个 prev 节点保存向前指针,temp 保存向后的临时指针
86 |
87 | ```java
88 | public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
89 | ListNode pre = null, p = head;
90 | while (p != null) {
91 | // 保存当前head.Next节点,防止重新赋值后被覆盖
92 | // 一轮之后状态:nil<-1 2->3->4
93 | // prev p
94 | ListNode temp = p.next;
95 | p.next = pre;
96 | // pre 移动
97 | pre = p;
98 | // p 移动
99 | p = temp;
100 | }
101 | return pre;
102 | }
103 | ```
104 |
105 | #### 反转链表 II
106 |
107 | > [92. 反转链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii/)
108 | >
109 | > 反转从位置 *m* 到 *n* 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
110 |
111 | 思路:先遍历到 m 处,翻转,再拼接后续,注意指针处理
112 |
113 | ```java
114 | public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
115 | // 思路:先遍历到m处,翻转,再拼接后续,注意指针处理
116 | // 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->null, m = 2, n = 4
117 | ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0, head);
118 | ListNode p = newHead;
119 | // 最开始:0(p)->1->2->3->4->5->null
120 | for (int i = 0; i < m-1; i++) {
121 | p = p.next;
122 | }
123 | // 遍历之后: 0->1(p)->2(cur)->3->4->5->null
124 | ListNode pre = null;
125 | ListNode cur = p.next;
126 | for (int i = m; i <= n; i++) {
127 | ListNode next = cur.next;
128 | cur.next = pre;
129 | pre = cur;
130 | cur = next;
131 | }
132 | // 循环结束:0->1(p)->2->null 5(cur)->null 4(pre)->3->2->null
133 | p.next.next = cur;
134 | p.next = pre;
135 | return newHead.next;
136 | }
137 | ```
138 |
139 | ### 链表合并
140 |
141 | #### 合并两个有序链表
142 |
143 | > [21. 合并两个有序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists/)
144 | >
145 | > 将两个升序链表合并为一个新的升序链表并返回。新链表是通过拼接给定的两个链表的所有节点组成的。
146 |
147 | 思路:通过 dummy node 链表,连接各个元素
148 |
149 | ```java
150 | public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
151 | ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
152 | ListNode p = head;
153 | while (l1 != null && l2 != null) {
154 | if (l1.val < l2.val) {
155 | p.next = l1;
156 | l1 = l1.next;
157 | } else {
158 | p.next = l2;
159 | l2 = l2.next;
160 | }
161 | p = p.next;
162 | }
163 | // 连接未处理完节点
164 | p.next = l1 == null ? l2 : l1;
165 | return head.next;
166 | }
167 | ```
168 |
169 | #### 合并K个升序链表
170 |
171 | > [23. 合并K个升序链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists/)
172 | >
173 | > 给你一个链表数组,每个链表都已经按升序排列。
174 | >
175 | > 请你将所有链表合并到一个升序链表中,返回合并后的链表。
176 |
177 | 思路:使用分治的方法两个两个地合并链表
178 |
179 | ```java
180 | public ListNode mergeKLists(ListNode[] lists) {
181 | return merge(lists, 0, lists.length - 1);
182 | }
183 |
184 | public ListNode merge(ListNode[] lists, int begin, int end) {
185 | if (begin == end) return lists[begin];
186 | if (begin > end) return null;
187 | int mid = (begin + end) >> 1;
188 | return mergeTwoLists(merge(lists, begin, mid), merge(lists, mid + 1, end));
189 | }
190 |
191 | public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
192 | // 同上
193 | }
194 | ```
195 |
196 | ## 快慢指针
197 |
198 | ### 链表中点
199 |
200 | 使用两个指针变量,慢指针每次前进一步,快指针每次前进两步。这样当快指针到达链表末尾时,慢指针恰好在链表的中间位置。要注意链表长度为偶数的情况。
201 |
202 | > [876. 链表的中间结点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list/)
203 | >
204 | > 给定一个头结点为 head 的非空单链表,返回链表的中间结点。
205 | >
206 | > 如果有两个中间结点,则返回第二个中间结点。
207 |
208 | ```java
209 | public ListNode middleNode(ListNode head) {
210 | ListNode p = head;
211 | ListNode q = head;
212 | while (q != null && q.next != null) {
213 | p = p.next;
214 | q = q.next.next;
215 | }
216 | return p;
217 | }
218 | ```
219 |
220 | #### 重排链表
221 |
222 | > [143. 重排链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-list/)
223 | > 给定一个单链表 L:L0→L1→…→Ln-1→Ln ,
224 | >
225 | > 将其重新排列后变为: L0→Ln→L1→Ln-1→L2→Ln-2→…
226 | >
227 | > 不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
228 |
229 | ```java
230 | public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
231 | if (head == null || head.next == null) return;
232 | // 通过快慢指针找中点
233 | ListNode slow = head, fast = head;
234 | while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
235 | slow = slow.next;
236 | fast = fast.next.next;
237 | }
238 | ListNode p = head;
239 | // 反转链表
240 | ListNode q = reverseList(slow.next);
241 | slow.next = null;
242 | while (p != null && q != null) {
243 | ListNode qNext = q.next;
244 | q.next = p.next;
245 | p.next = q;
246 | p = q.next;
247 | q = qNext;
248 | }
249 | }
250 | ```
251 |
252 |
253 | #### 回文链表
254 |
255 | > [234. 回文链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list/)
256 | >
257 | > 请判断一个链表是否为回文链表。
258 |
259 | ```java
260 | public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
261 | // fast如果初始化为head.Next则中点在slow.Next
262 | // fast初始化为head,则中点在slow
263 | ListNode slow = head, fast = head, pre = null;
264 | // 这里顺便做了反转链表的操作
265 | while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
266 | fast = fast.next.next;
267 | ListNode next = slow.next;
268 | slow.next = pre;
269 | pre = slow;
270 | slow = next;
271 | }
272 | if (fast != null){
273 | slow = slow.next;
274 | }
275 | // 与另一半链表依次比较
276 | while (slow != null) {
277 | if (slow.val != pre.val) return false;
278 | slow = slow.next;
279 | pre = pre.next;
280 | }
281 | return true;
282 | }
283 | ```
284 |
285 |
286 | ### 结构判断
287 |
288 | #### 环形链表
289 |
290 | > [141. 环形链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle/)
291 | >
292 | > 给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
293 | >
294 | > 如果链表中存在环,则返回 `true`。 否则,返回`false`。
295 |
296 | 思路:快慢指针,快慢指针相同则有环,证明:如果有环每走一步快慢指针距离会减 1
297 | 
298 |
299 | ```java
300 | public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {
301 | ListNode p = head, q = head;
302 | // 思路:快慢指针 快慢指针相同则有环,证明:如果有环每走一步快慢指针距离会减1
303 | while (p != null && q != null && q.next != null) {
304 | p = p.next;
305 | q = q.next.next;
306 | // 比较指针是否相等(不要使用val比较)
307 | if (p == q) {
308 | return true;
309 | }
310 | }
311 | return false;
312 | }
313 | ```
314 |
315 | #### 环形链表 II
316 |
317 | > [142. 环形链表 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii/)
318 | >
319 | > 给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 `null`。
320 |
321 | 思路:快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点
322 | 
323 |
324 | ```java
325 | public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
326 | // 思路:快慢指针,快慢相遇之后,慢指针回到头,快慢指针步调一致一起移动,相遇点即为入环点
327 | ListNode p = head, q = head;
328 | while (p != null && q != null && q.next != null) {
329 | p = p.next;
330 | q = q.next.next;
331 | if (p == q) {
332 | // 指针重新从头开始移动
333 | ListNode m = head;
334 | // 比较指针对象(不要比对指针Val值)
335 | while (m != p) {
336 | m = m.next;
337 | p = p.next;
338 | }
339 | return p;
340 | }
341 | }
342 | return null;
343 | }
344 | ```
345 |
346 | ## 其他
347 |
348 | > [19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list/)
349 | >
350 | > 给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 `n` 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。(尝试使用一趟扫描实现)
351 |
352 | ```java
353 | public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
354 | ListNode newHead = new ListNode(0, head);
355 | ListNode p1 = newHead;
356 | ListNode p2 = newHead;
357 | // 提前前进n个位置
358 | while (n >= 0) {
359 | p2 = p2.next;
360 | n--;
361 | }
362 | while (p2 != null) {
363 | p1 = p1.next;
364 | p2 = p2.next;
365 | }
366 | p1.next = p1.next.next;
367 | return newHead.next;
368 | }
369 | ```
370 |
371 | > [138. 复制带随机指针的链表](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer/)
372 | >
373 | > 给定一个链表,每个节点包含一个额外增加的随机指针,该指针可以指向链表中的任何节点或空节点。
374 | >
375 | > 要求返回这个链表的 深拷贝。
376 |
377 | 思路:1、hash 表存储指针,2、复制节点跟在原节点后面
378 |
379 | ```java
380 | public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
381 | if (head == null) {
382 | return null;
383 | }
384 | // 复制节点,紧挨到到后面
385 | // 1->2->3 ==> 1->1'->2->2'->3->3'
386 | Node cur = head;
387 | while (cur != null) {
388 | Node cloneNode = new Node(cur.val);
389 | cloneNode.next = cur.next;
390 | Node temp = cur.next;
391 | cur.next = cloneNode;
392 | cur = temp;
393 | }
394 | // 处理random指针
395 | cur = head;
396 | while (cur != null) {
397 | if (cur.random != null) {
398 | cur.next.random = cur.random.next;
399 | }
400 | cur = cur.next.next;
401 | }
402 | // 分离两个链表
403 | cur = head;
404 | Node cloneHead = cur.next;
405 | while (cur != null && cur.next != null) {
406 | Node temp = cur.next;
407 | cur.next = cur.next.next;
408 | cur = temp;
409 | }
410 | // 原始链表头:head 1->2->3
411 | // 克隆的链表头:cloneHead 1'->2'->3'
412 | return cloneHead;
413 | }
414 | ```
415 |
416 | ## 总结
417 |
418 | 链表必须要掌握的一些点,通过下面练习题,基本大部分的链表类的题目都是手到擒来~
419 |
420 | - null 异常处理
421 | - dummy node 哑巴节点
422 | - 快慢指针
423 | - 插入一个节点到排序链表
424 | - 从一个链表中移除一个节点
425 | - 翻转链表
426 | - 合并两个链表
427 | - 找到链表的中间节点
428 | - 链表的末尾指针最后指向null
429 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data_structure/binary_tree.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 二叉树
2 |
3 | ## 二叉树遍历
4 |
5 | **前序遍历**:[144. 二叉树的前序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-preorder-traversal/)
6 |
7 | 先访问根节点,再前序遍历左子树,再前序遍历右子树
8 |
9 | **中序遍历**:[94. 二叉树的中序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/)
10 |
11 | 先中序遍历左子树,再访问根节点,再中序遍历右子树
12 |
13 | **后序遍历**:[145. 二叉树的后序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-postorder-traversal/)
14 |
15 | 先后序遍历左子树,再后序遍历右子树,再访问根节点
16 |
17 | 注意点
18 |
19 | - 以根访问顺序决定是什么遍历
20 | - 左子树都比右子树优先遍历
21 |
22 | ### 递归遍历
23 |
24 | ```java
25 | // 递归遍历写法,以前序遍历为例
26 | public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
27 | List result = new LinkedList<>();
28 | traverse(root, result);
29 | return result;
30 | }
31 |
32 | public void traverse(TreeNode p, List result) {
33 | if (p == null) {
34 | return;
35 | }
36 | // 其他遍历调整这里的语句顺序即可
37 | result.add(p.val);
38 | traverse(p.left, result);
39 | traverse(p.right, result);
40 | }
41 | ```
42 |
43 | ### 前序非递归
44 |
45 | ```java
46 | // 通过非递归遍历
47 | public List preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
48 | List result = new ArrayList<>();
49 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
50 | TreeNode p = root;
51 | while (p != null || ! stack.isEmpty()) {
52 | while (p != null) {
53 | // 前序遍历,所以先保存结果
54 | result.add(p.val);
55 | stack.push(p);
56 | p = p.left;
57 | }
58 | // pop出栈顶元素
59 | if (! stack.isEmpty()) {
60 | p = stack.pop();
61 | p = p.right;
62 | }
63 | }
64 | return result;
65 | }
66 | ```
67 |
68 | ### 中序非递归
69 |
70 | ```java
71 | // 思路:通过stack 保存已经访问的元素,用于原路返回
72 | public List inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
73 | List result = new LinkedList<>();
74 | Stack stack = new Stack<>();
75 | TreeNode p = root;
76 | while (p != null || ! stack.isEmpty()) {
77 | if (p != null) {
78 | stack.push(p);
79 | p = p.left;
80 | } else {
81 | TreeNode node = stack.pop();
82 | result.add(node.val);
83 | p = node.right;
84 | }
85 | }
86 | return result;
87 | }
88 | ```
89 |
90 | ### 后序非递归
91 |
92 | ```java
93 | public List postorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
94 | List result = new ArrayList<>();
95 | Stack stack = new Stack();
96 | TreeNode p = root;
97 | // 通过lastVisit标识右子节点是否已经弹出
98 | TreeNode lastVisit = root;
99 | while (p != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
100 | while (p != null) {
101 | stack.push(p);
102 | p = p.left;
103 | }
104 | //查看当前栈顶元素
105 | p = stack.peek();
106 | //如果其右子树也为空,或者右子树已经访问,则可以访问
107 | if (p.right == null || p.right == lastVisit) {
108 | result.add(p.val);
109 | stack.pop();
110 | // 标记当前这个节点已经弹出过
111 | lastVisit = p;
112 | p = null;
113 | } else {
114 | //否则继续遍历右子树
115 | p = p.right;
116 | }
117 | }
118 | return result;
119 | }
120 | ```
121 |
122 | 注意点
123 |
124 | - 核心就是:根节点必须在右节点弹出之后,再弹出
125 |
126 | ### DFS 深度搜索
127 |
128 | > [257. 二叉树的所有路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-paths/)
129 | >
130 | > 给定一个二叉树,返回所有从根节点到叶子节点的路径。
131 |
132 | ```java
133 | public List binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
134 | StringBuilder path = new StringBuilder();
135 | List paths = new LinkedList<>();
136 | dfs(root, path, paths);
137 | return paths;
138 | }
139 |
140 | public void dfs(TreeNode p, StringBuilder path, List paths) {
141 | if (p == null) {
142 | return;
143 | }
144 | path.append(p.val);
145 | // 当前节点是叶子节点
146 | if (p.left == null && p.right == null) {
147 | // 把路径加入结果
148 | paths.add(path.toString());
149 | } else {
150 | path.append("->");
151 | // 这里需要复制创建新的StringBuilder对象
152 | dfs(p.left, new StringBuilder(path), paths);
153 | dfs(p.right, new StringBuilder(path), paths);
154 | }
155 | }
156 | ```
157 |
158 | ### BFS 层次遍历
159 |
160 | ```java
161 | public List levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
162 | List result = new LinkedList<>();
163 | if (root == null) {
164 | return result;
165 | }
166 | Queue queue = new LinkedList<>();
167 | queue.offer(root);
168 | while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
169 | TreeNode p = queue.pop();
170 | result.add(p);
171 | if (p.left != null) {
172 | queue.add(p.left);
173 | numList.add(p.left.val);
174 | }
175 | if (p.right != null) {
176 | queue.add(p.right);
177 | numList.add(p.right.val);
178 | }
179 | }
180 | return result
181 | }
182 | ```
183 |
184 | ## 二叉树分治
185 |
186 | 先分别处理局部,再合并结果
187 |
188 | 分治法模板
189 |
190 | - 递归返回条件
191 | - 分段处理
192 | - 合并结果
193 |
194 | ```java
195 | public ResultType traversal(TreeNode root) {
196 | // null or leaf
197 | if (root == null) {
198 | // do something and return
199 | }
200 | // Divide
201 | ResultType left = traversal(root.Left)
202 | ResultType right = traversal(root.Right)
203 | // Conquer
204 | ResultType result = Merge from left and right
205 | return result
206 | }
207 | ```
208 |
209 | ### 典型示例
210 |
211 | > [98. 验证二叉搜索树](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/validate-binary-search-tree/)
212 | >
213 | > 给定一个二叉树,判断其是否是一个有效的二叉搜索树。
214 |
215 | ```java
216 | public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
217 | return divideAndConquer(root, Long.MIN_VALUE, Long.MAX_VALUE);
218 | }
219 |
220 | private boolean divideAndConquer(TreeNode p, long min, long max) {
221 | if (p == null) return true;
222 | // 返回条件
223 | if (p.val <= min || max <= p.val) {
224 | return false;
225 | }
226 | // 分治(Divide)
227 | boolean left = divideAndConquer(p.left, min, p.val);
228 | boolean right = divideAndConquer(p.right, p.val, max);
229 | // 合并结果(Conquer)
230 | return left && right;
231 | }
232 | ```
233 |
234 | 注意点:
235 |
236 | > DFS 深度搜索(从上到下) 和分治法区别:前者一般将最终结果通过参数传入,后者一般递归返回结果最后合并
237 |
238 | ### 常见题目
239 |
240 | #### 二叉树的最大深度
241 |
242 | > [104. 二叉树的最大深度](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree/)
243 | >
244 | > 给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
245 | >
246 | > 二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
247 |
248 | 思路:分治法
249 |
250 | ```java
251 | public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
252 | // 返回条件处理
253 | if (root == null) {
254 | return 0;
255 | }
256 | // divide:分左右子树分别计算
257 | // conquer:合并左右子树结果,即取二者中的最大值加一
258 | return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1;
259 | }
260 | ```
261 |
262 | #### 平衡二叉树
263 |
264 | > [110. 平衡二叉树](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/balanced-binary-tree/)
265 | >
266 | > 给定一个二叉树,判断它是否是高度平衡的二叉树。
267 |
268 | 思路:分治法,左边平衡 && 右边平衡 && 左右两边高度 <= 1,因为需要返回是否平衡及高度,要么返回两个数据,要么合并两个数据,所以用-1 表示不平衡,>0 表示树高度(二义性:一个变量有两种含义)。
269 |
270 | ```java
271 | public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
272 | return maxDepth(root) >= 0;
273 | }
274 |
275 | private int maxDepth(TreeNode p) {
276 | if (p == null) {
277 | return 0;
278 | }
279 | int left = maxDepth(p.left);
280 | int right = maxDepth(p.right);
281 | if (left < 0 || right < 0 || Math.abs(left - right) > 1) {
282 | return -1;
283 | } else {
284 | return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
285 | }
286 | }
287 | ```
288 |
289 | 注意
290 |
291 | > 一般工程中,结果通过两个变量来返回,不建议用一个变量表示两种含义
292 |
293 | #### 二叉树中的最大路径和
294 |
295 | > [124. 二叉树中的最大路径和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-maximum-path-sum/)
296 | >
297 | > **路径** 被定义为一条从树中任意节点出发,沿父节点-子节点连接,达到任意节点的序列。同一个节点在一条路径序列中 **至多出现一次** 。该路径 **至少包含一个** 节点,且不一定经过根节点。
298 | >
299 | > **路径和** 是路径中各节点值的总和。
300 | >
301 | > 给你一个二叉树的根节点 `root` ,返回其 **最大路径和** 。
302 |
303 | 思路:分治法,分为三种情况:左子树最大路径和最大,右子树最大路径和最大,左右子树最大加根节点最大,需要保存两个变量:一个保存子树最大路径和,一个保存左右加根节点和,然后比较这个两个变量选择最大值即可
304 |
305 | ```java
306 | public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
307 | return maxSum(root)[1];
308 | }
309 |
310 | // 返回的数组意义:int[0]表示单边最大值,int[1]表示所有情况的最大值(单边或者两个单边+根的值)
311 | private int[] maxSum(TreeNode p) {
312 | // check
313 | if (p == null) {
314 | return new int[]{0, Integer.MIN_VALUE};
315 | }
316 | // Divide
317 | int[] left = maxSum(p.left);
318 | int[] right = maxSum(p.right);
319 | int singleSum, bothSum;
320 | // Conquer
321 | // 求单边最大值
322 | if (left[0] > right[0]) {
323 | singleSum = Math.max(left[0] + p.val, 0);
324 | } else {
325 | singleSum = Math.max(right[0] + p.val, 0);
326 | }
327 | // 求所有情况(两个子树的所有情况、两个单边最大值与根之和)的最大值
328 | bothSum = Math.max(left[1], right[1]);
329 | bothSum = Math.max(bothSum, left[0] + right[0] + p.val);
330 | return new int[]{singleSum, bothSum};
331 | }
332 | ```
333 |
334 | #### 二叉树的最近公共祖先
335 |
336 | > [235. 二叉树的最近公共祖先](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/lowest-common-ancestor-of-a-binary-tree/)
337 | >
338 | > 给定一个二叉树, 找到该树中两个指定节点的最近公共祖先。
339 |
340 | 思路:分治法,有左子树的公共祖先或者有右子树的公共祖先,就返回子树的祖先,否则返回根节点
341 |
342 | ```java
343 | public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
344 | // check
345 | if (root == null) {
346 | return null;
347 | }
348 | // 相等 直接返回root节点即可
349 | if (root == p || root == q) {
350 | return root;
351 | }
352 | // Divide
353 | TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor(root.left, p, q);
354 | TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor(root.right, p, q);
355 | // Conquer
356 | // 左右两边都不为空,则根节点为祖先
357 | if (left != null && right != null) {
358 | return root;
359 | } else if (left != null) {
360 | return left;
361 | } else {
362 | return right;
363 | }
364 | }
365 | ```
366 |
367 | ## BFS 应用
368 |
369 | ### 常见题目
370 |
371 | #### 二叉树的层序遍历
372 |
373 | > [102. 二叉树的层序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal/)
374 | >
375 | > 给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按 **层序遍历** 得到的节点值。 (即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)
376 |
377 | 思路:用一个队列记录一层的元素,然后扫描这一层元素添加下一层元素到队列(一个数进去出来一次,所以复杂度 O(logN))
378 |
379 | ```java
380 | public List> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
381 | List> result = new LinkedList<>();
382 | if (root == null) {
383 | return result;
384 | }
385 | LinkedList queue = new LinkedList<>();
386 | LinkedList numList = new LinkedList<>();
387 | queue.add(root);
388 | numList.add(root.val);
389 | while (! queue.isEmpty()) {
390 | // 保存这一层的元素
391 | result.add(numList);
392 | numList = new LinkedList<>();
393 | // 记录当前层有多少元素(遍历当前层,再添加下一层)
394 | int len = queue.size();
395 | for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
396 | // 出队列
397 | TreeNode p = queue.pop();
398 | if (p.left != null) {
399 | queue.add(p.left);
400 | numList.add(p.left.val);
401 | }
402 | if (p.right != null) {
403 | queue.add(p.right);
404 | numList.add(p.right.val);
405 | }
406 | }
407 | }
408 | return result;
409 | }
410 | ```
411 |
412 | #### 二叉树的层序遍历 II
413 |
414 | > [107. 二叉树的层序遍历 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal-ii/)
415 | >
416 | > 给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值自底向上的层次遍历。 (即按从叶子节点所在层到根节点所在的层,逐层从左向右遍历)
417 |
418 | 思路:在层级遍历的基础上,翻转一下结果即可,在往result内添加元素之前使用`Collections.reverse`方法翻转列表。
419 |
420 | #### 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历
421 |
422 | > [103. 二叉树的锯齿形层序遍历](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-zigzag-level-order-traversal/)
423 | >
424 | > 给定一个二叉树,返回其节点值的锯齿形层次遍历。Z 字形遍历
425 |
426 | 思路:在层级遍历的基础上,判断这一层是否需要翻转,在往result内添加元素之前加入以下代码:
427 |
428 | ```java
429 | if (result.size() % 2 != 0) {
430 | Collections.reverse(numList);
431 | }
432 | ```
433 |
434 | ## 二叉搜索树应用
435 |
436 | ### 常见题目
437 |
438 | #### 二叉搜索树中的插入操作
439 |
440 | > [701. 二叉搜索树中的插入操作](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insert-into-a-binary-search-tree/)
441 | >
442 | > 给定二叉搜索树(BST)的根节点和要插入树中的值,将值插入二叉搜索树。 返回插入后二叉搜索树的根节点。
443 |
444 | 思路:找到最后一个叶子节点满足插入条件即可
445 |
446 | ```java
447 | // DFS查找插入位置
448 | public TreeNode insertIntoBST(TreeNode root, int val) {
449 | if (root == null) {
450 | return new TreeNode(val);
451 | }
452 | if (root.val > val) {
453 | root.left = insertIntoBST(root.left, val);
454 | } else {
455 | root.right = insertIntoBST(root.right, val);
456 | }
457 | return root;
458 | }
459 | ```
460 |
461 | ## 总结
462 |
463 | - 掌握二叉树递归与非递归遍历
464 | - 理解 DFS 前序遍历与分治法
465 | - 理解 BFS 层次遍历
466 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/dp.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 动态规划
2 |
3 | ## 背景
4 |
5 | > [120. 三角形最小路径和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/triangle/)
6 | >
7 | > 给定一个三角形,找出自顶向下的最小路径和。每一步只能移动到下一行中相邻的结点上。
8 |
9 | 例如,给定三角形:
10 |
11 | ```text
12 | [
13 | [2],
14 | [3,4],
15 | [6,5,7],
16 | [4,1,8,3]
17 | ]
18 | ```
19 |
20 | 自顶向下的最小路径和为 11(即,2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11)。
21 |
22 | ### DFS
23 |
24 | 使用 DFS:
25 |
26 | ```java
27 | // 会超时
28 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
29 | return dfs(0, 0, triangle);
30 | }
31 |
32 | // 返回值表示从x, y处到底部的最小路径和
33 | private int dfs(int x, int y, List> triangle, int[][] saves) {
34 | if (x == triangle.size() - 1) {
35 | return triangle.get(x).get(y);
36 | }
37 | int minLeft = dfs(x + 1, y, triangle, saves);
38 | int minRight = dfs(x + 1, y + 1, triangle, saves);
39 | return Math.min(minLeft, minRight) + triangle.get(x).get(y);
40 | }
41 | ```
42 |
43 | ### DFS的优化
44 |
45 | 优化 DFS,缓存已经被计算的值(称为:记忆化搜索 本质上:动态规划)
46 |
47 | ```java
48 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
49 | int[][] saves = new int[triangle.size()][triangle.size()];
50 | return dfs(0, 0, triangle, saves);
51 | }
52 |
53 | // 使用saves数组记录已经被计算过的值
54 | // 返回值表示从x, y处到底部的最小路径和
55 | private int dfs(int x, int y, List> triangle, int[][] saves) {
56 | if (x == triangle.size() - 1) {
57 | return triangle.get(x).get(y);
58 | }
59 | // 如果已经被计算过则直接返回
60 | if (saves[x][y] != 0) {
61 | return saves[x][y];
62 | }
63 | int minLeft = dfs(x + 1, y, triangle, saves);
64 | int minRight = dfs(x + 1, y + 1, triangle, saves);
65 | // 缓存已经被计算的值
66 | saves[x][y] = Math.min(minLeft, minRight) + triangle.get(x).get(y);
67 | return saves[x][y];
68 | }
69 | ```
70 |
71 | ### 从DFS到动态规划
72 |
73 | 动态规划就是把大问题变成小问题,并解决了小问题重复计算的方法称为动态规划
74 |
75 | 动态规划和 DFS 区别
76 |
77 | - 二叉树 子问题是没有交集,所以大部分二叉树都用递归或者分治法,即 DFS,就可以解决
78 | - 像 triangle 这种是有重复走的情况,**子问题是有交集**,所以可以用动态规划来解决
79 |
80 | #### 自底向上
81 |
82 | ```java
83 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
84 | // 1、状态定义:f[i][j] 表示从i,j出发,到达最后一层的最短路径
85 | int[][] dp = new int[triangle.size()][triangle.size()];
86 | // 2、初始化
87 | for (int i = 0; i < triangle.size(); i++) {
88 | dp[triangle.size() - 1][i] = triangle.get(triangle.size() - 1).get(i);
89 | }
90 | // 3、递推求解
91 | for (int i = triangle.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
92 | for (int j = 0; j < triangle.get(i).size(); j++) {
93 | dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i+1][j], dp[i+1][j+1]) + triangle.get(i).get(j);
94 | }
95 | }
96 | // 4、结果
97 | return dp[0][0];
98 | }
99 | ```
100 |
101 | #### 自顶向下
102 |
103 | ```java
104 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
105 | // 1、状态定义:dp[i][j] 表示从0,0出发,到达i,j的最短路径
106 | int[][] dp = new int[triangle.size()][triangle.size()];
107 | // 2、初始化
108 | dp[0][0] = triangle.get(0).get(0);
109 | for (int i = 1; i < triangle.size(); i++) {
110 | for (int j = 0; j < triangle.get(i).size(); j++) {
111 | // 这里分为三种情况:
112 | // 1、上一层没有左边值
113 | // 2、上一层没有右边值
114 | // 3、其他
115 | if (j == 0) {
116 | dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + triangle.get(i).get(j);
117 | } else if (j == triangle.get(i).size() - 1) {
118 | dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + triangle.get(i).get(j);
119 | } else {
120 | dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i-1][j-1], dp[i-1][j]) + triangle.get(i).get(j);
121 | }
122 | }
123 | }
124 | // 从最后一层中查找最小值
125 | int minValue = dp[triangle.size() - 1][0];
126 | for (int i = 0; i < triangle.size(); i++) {
127 | minValue = Math.min(minValue, dp[triangle.size() - 1][i]);
128 | }
129 | return minValue;
130 | }
131 | ```
132 |
133 | #### 空间优化
134 |
135 | 经过观察发现当前状态只与上一批状态有关,所以二维数组可以优化为一位数组,减少空间占用。
136 |
137 | ```java
138 | public int minimumTotal(List> triangle) {
139 | int[] dp = new int[triangle.size()];
140 | for (int i = 0; i < triangle.size(); i++) {
141 | dp[i] = triangle.get(triangle.size() - 1).get(i);
142 | }
143 | for (int i = triangle.size() - 2; i >= 0; i--) {
144 | for (int j = 0; j < triangle.get(i).size(); j++) {
145 | dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j], dp[j+1]) + triangle.get(i).get(j);
146 | }
147 | }
148 | return dp[0];
149 | }
150 | ```
151 |
152 | 除此之外,也可以覆盖原有数据以实现空间复用。
153 |
154 | ## 使用场景
155 |
156 | 满足两个条件
157 |
158 | - 满足以下条件之一
159 | - 求最大/最小值(Maximum/Minimum )
160 | - 求是否可行(Yes/No )
161 | - 求可行个数(Count(\*) )
162 | - 满足不能排序或者交换(Can not sort / swap )
163 |
164 | 如题:[longest-consecutive-sequence](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-consecutive-sequence/) 位置可以交换,所以不用动态规划
165 |
166 | ## 四点要素
167 |
168 | 1. **状态 State**
169 | - 灵感,创造力,存储小规模问题的结果
170 | 2. 方程 Function
171 | - 状态之间的联系,怎么通过小的状态,来算大的状态
172 | 3. 初始化 Intialization
173 | - 最极限的小状态是什么, 起点
174 | 4. 答案 Answer
175 | - 最大的那个状态是什么,终点
176 |
177 | ## 常见四种类型
178 |
179 | 1. Matrix DP (10%)
180 | 1. Sequence (40%)
181 | 1. Two Sequences DP (40%)
182 | 1. Backpack (10%)
183 |
184 | > 注意点
185 | >
186 | > - 贪心算法大多题目靠背答案,所以如果能用动态规划就尽量用动规,不用贪心算法
187 |
188 | ### 矩阵类型
189 |
190 | #### 最小路径和
191 |
192 | > [64. 最小路径和](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-path-sum/)
193 | >
194 | > 给定一个包含非负整数的 *m* x *n* 网格,请找出一条从左上角到右下角的路径,使得路径上的数字总和为最小。
195 |
196 | ```java
197 | public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
198 | // dp[i][j] 表示0,0到i,j的最小和
199 | int[] dp = new int[grid[0].length];
200 | // 初始化:用第一行初始化
201 | dp[0] = grid[0][0];
202 | for (int i = 1; i < grid[0].length; i++) {
203 | dp[i] = dp[i-1] + grid[0][i];
204 | }
205 | // 状态转移方程
206 | // 每行第一个元素:
207 | // dp[j] = dp[j](到上一行这个位置的最小和) + grid[i][j];
208 | // 后续元素:
209 | // dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j-1](到左边位置的最小和), dp[j](到上一行这个位置的最小和)) + grid[i][j];
210 | for (int i = 1; i < grid.length; i++) {
211 | for (int j = 0; j < grid[0].length; j++) {
212 | if (j == 0) {
213 | dp[j] = dp[j] + grid[i][j];
214 | } else {
215 | dp[j] = Math.min(dp[j-1], dp[j]) + grid[i][j];
216 | }
217 | }
218 | }
219 | // 答案
220 | return dp[grid[0].length - 1];
221 | }
222 | ```
223 |
224 | #### 不同路径
225 |
226 | > [62. 不同路径](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths/)
227 | >
228 | > 一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。
229 | > 机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为“Finish”)。
230 | >
231 | > 问总共有多少条不同的路径?
232 |
233 | ```java
234 | public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
235 | // dp[i][j] 表示0,0到i,j的路径数
236 | int[] dp = new int[n];
237 | // 初始化:到达第一行的路径数均为1
238 | for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
239 | dp[i] = 1;
240 | }
241 | for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
242 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
243 | // 每行第一个格子只有一条路到达
244 | if (j == 0) {
245 | dp[j] = 1;
246 | }
247 | // 其他格子可以由左侧或上方的格子到达
248 | else {
249 | dp[j] = dp[j-1] + dp[j];
250 | }
251 | }
252 | }
253 | return dp[n-1];
254 | }
255 | ```
256 |
257 | #### 不同路径 II
258 |
259 | > [63. 不同路径 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/unique-paths-ii/)
260 | >
261 | > 一个机器人位于一个 m x n 网格的左上角 (起始点在下图中标记为“Start” )。
262 | > 机器人每次只能向下或者向右移动一步。机器人试图达到网格的右下角(在下图中标记为“Finish”)。
263 | >
264 | > 问总共有多少条不同的路径?
265 | >
266 | > 现在考虑网格中有障碍物。那么从左上角到右下角将会有多少条不同的路径?
267 |
268 | ```java
269 | public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
270 | int m = obstacleGrid.length;
271 | int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
272 | int[] dp = new int[n];
273 | // 初始化:遇到障碍前仅有一条路,之后全为0
274 | dp[0] = obstacleGrid[0][0] == 1 ? 0 : 1;
275 | for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
276 | if (obstacleGrid[0][i] == 1) {
277 | dp[i] = 0;
278 | } else {
279 | dp[i] = dp[i-1];
280 | }
281 | }
282 | for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
283 | for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
284 | // 当前格是障碍,不可达,置为0
285 | if (obstacleGrid[i][j] == 1) {
286 | dp[j] = 0;
287 | continue;
288 | }
289 | if (j > 0) {
290 | dp[j] = dp[j-1] + dp[j];
291 | }
292 | }
293 | }
294 | return dp[n-1];
295 | }
296 | ```
297 |
298 | ### 序列类型
299 |
300 | #### 爬楼梯
301 |
302 | > [70. 爬楼梯](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/climbing-stairs/)
303 | >
304 | > 假设你正在爬楼梯。需要 *n* 阶你才能到达楼顶。
305 | >
306 | > 每次你可以爬 1 或 2 个台阶。你有多少种不同的方法可以爬到楼顶?
307 |
308 | ```java
309 | public int climbStairs(int n) {
310 | int[] dp = new int[]{0, 1};
311 | while (n > 0) {
312 | int temp = dp[0] + dp[1];
313 | dp[0] = dp[1];
314 | dp[1] = temp;
315 | n--;
316 | }
317 | return dp[1];
318 | }
319 | ```
320 |
321 | #### 最长递增子序列
322 |
323 | > [300. 最长递增子序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-increasing-subsequence/)
324 | >
325 | > 给定一个无序的整数数组,找到其中最长上升子序列的长度。
326 |
327 | ```java
328 | public int lengthOfLIS(int[] nums) {
329 | // dp[i]表示从0到i的最长上升子序列长度
330 | int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
331 | // 初始化:到第一个元素序列长度为1
332 | dp[0] = 1;
333 | for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
334 | // 注意默认为1,即此处最长子序列为自身
335 | int maxLen = 1;
336 | // dp[i] = max(dp[j]) + 1 , nums[j] < nums[i]
337 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
338 | if (nums[j] < nums[i]) {
339 | maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, dp[j] + 1);
340 | }
341 | }
342 | dp[i] = maxLen;
343 | }
344 | int maxNum = 0;
345 | for (int n : dp) {
346 | maxNum = Math.max(maxNum, n);
347 | }
348 | // 答案:dp中的最大值
349 | return maxNum;
350 | }
351 | ```
352 |
353 | #### 单词拆分
354 |
355 | > [139. 单词拆分](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/word-break/)
356 | >
357 | > 给定一个**非空**字符串 *s* 和一个包含**非空**单词列表的字典 *wordDict*,判定 *s* 是否可以被空格拆分为一个或多个在字典中出现的单词。
358 |
359 | ```java
360 | public boolean wordBreak(String s, List wordDict) {
361 | // dp[i]表示s[0, i)子串能否被分解
362 | boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
363 | Set wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordDict);
364 | // 初始值:空字符串可以被分解
365 | dp[0] = true;
366 | for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
367 | for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
368 | // 递推:从i处向前遍历,s[0,j)可以分解且s[j,i)也在集合内
369 | if (dp[j] && wordSet.contains(s.substring(j, i))) {
370 | dp[i] = true;
371 | break;
372 | }
373 | }
374 | }
375 | return dp[s.length()];
376 | }
377 | ```
378 |
379 | 由于分解出的单词长度必定不会超过字典内的最大长度,因此可以利用这一点进行剪枝:
380 |
381 | ```java
382 | public boolean wordBreak(String s, List wordDict) {
383 | // dp[i]表示s[0, i)子串能否被分解
384 | boolean[] dp = new boolean[s.length() + 1];
385 | Set wordSet = new HashSet<>(wordDict);
386 | // 计算单词最大长度
387 | int maxLen = 0;
388 | for (String word : wordDict) {
389 | maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, word.length());
390 | }
391 | // 初始值:空字符串可以被分解
392 | dp[0] = true;
393 | for (int i = 1; i <= s.length(); i++) {
394 | // 分解的子串s[j,i)长度不会超过maxLen,注意不能越界
395 | for (int j = Math.max(0, i - maxLen); j < i; j++) {
396 | // 递推:从i处向前遍历,s[0,j)可以分解且s[j,i)也在集合内
397 | if (dp[j] && wordSet.contains(s.substring(j, i))) {
398 | dp[i] = true;
399 | break;
400 | }
401 | }
402 | }
403 | return dp[s.length()];
404 | }
405 | ```
406 |
407 | #### 小结
408 |
409 | 常见处理方式是给 0 位置占位,这样处理问题时一视同仁,初始化则在原来基础上 `length+1`,返回结果 `f[n]`
410 |
411 | - 状态可以为前 i 个
412 | - 初始化 `length+1`
413 | - 取值 `index=i-1`
414 | - 返回值:`f[n]`或者 `f[m][n]`
415 |
416 | ### 双序列类型
417 |
418 | #### 最长公共子序列
419 |
420 | > [1143. 最长公共子序列](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/longest-common-subsequence/)
421 | >
422 | > 给定两个字符串 text1 和 text2,返回这两个字符串的最长公共子序列。
423 | > 一个字符串的 子序列 是指这样一个新的字符串:它是由原字符串在不改变字符的相对顺序的情况下删除某些字符(也可以不删除任何字符)后组成的新字符串。
424 | > 例如,"ace" 是 "abcde" 的子序列,但 "aec" 不是 "abcde" 的子序列。两个字符串的「公共子序列」是这两个字符串所共同拥有的子序列。
425 |
426 | ```java
427 | public int longestCommonSubsequence(String text1, String text2) {
428 | // dp[i][j] a前i个和b前j个字符最长公共子序列
429 | // dp[m+1][n+1]
430 | // ' a d c e
431 | // ' 0 0 0 0 0
432 | // a 0 1 1 1 1
433 | // c 0 1 1 2 1
434 | int[][] dp = new int[text1.length() + 1][text2.length() + 1];
435 | for (int i = 1; i <= text1.length(); i++) {
436 | for (int j = 1; j <= text2.length(); j++) {
437 | // 相等取左上元素+1,否则取左或上的较大值
438 | if (text1.charAt(i - 1) == text2.charAt(j - 1)) {
439 | dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
440 | } else {
441 | dp[i][j] = Math.max(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]);
442 | }
443 | }
444 | }
445 | return dp[text1.length()][text2.length()];
446 | }
447 | ```
448 |
449 | 注意点
450 |
451 | - 从 1 开始遍历到最大长度
452 |
453 | - 索引需要减一
454 |
455 | #### 编辑距离
456 |
457 | > [72. 编辑距离](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/edit-distance/)
458 | >
459 | > 给你两个单词 word1 和 word2,请你计算出将 word1 转换成 word2 所使用的最少操作数 。你可以对一个单词进行如下三种操作:
460 | >
461 | > 1. 插入一个字符
462 | > 2. 删除一个字符
463 | > 3. 替换一个字符
464 |
465 | 思路:和上题很类似,相等则不需要操作,否则取删除、插入、替换最小操作次数的值+1
466 |
467 | ```java
468 | // dp[i][j] 表示a字符串的前i个字符编辑为b字符串的前j个字符最少需要多少次操作
469 | // dp[i][j] = OR(dp[i-1][j-1],a[i]==b[j],min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j-1])+1)
470 | public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
471 | int[][] dp = new int[word1.length() + 1][word2.length() + 1];
472 | for (int i = 0; i <= word1.length(); i++) {
473 | dp[i][0] = i;
474 | }
475 | for (int i = 0; i <= word2.length(); i++) {
476 | dp[0][i] = i;
477 | }
478 | for (int i = 1; i <= word1.length(); i++) {
479 | for (int j = 1; j <= word2.length(); j++) {
480 | // 相等则不需要操作
481 | if (word1.charAt(i - 1) == word2.charAt(j - 1)) {
482 | dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j - 1];
483 | }
484 | // 否则取删除、插入、替换最小操作次数的值+1
485 | else {
486 | dp[i][j] = Math.min(Math.min(dp[i - 1][j], dp[i][j - 1]), dp[i - 1][j - 1]) + 1;
487 | }
488 | }
489 | }
490 | return dp[word1.length()][word2.length()];
491 | }
492 | ```
493 |
494 | 说明
495 |
496 | > 另外一种做法:MAXLEN(a,b)-LCS(a,b)
497 |
498 | ### 零钱和背包
499 |
500 | #### 零钱兑换
501 |
502 | > [322. 零钱兑换](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change/)
503 | >
504 | > 给定不同面额的硬币 coins 和一个总金额 amount。编写一个函数来计算可以凑成总金额所需的最少的硬币个数。如果没有任何一种硬币组合能组成总金额,返回 -1。
505 |
506 | 思路:和其他 DP 不太一样,i 表示钱或者容量
507 |
508 | ```java
509 | public int coinChange(int[] coins, int amount) {
510 | // 状态 dp[i]表示金额为i时,组成的最小硬币个数
511 | int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
512 | dp[0] = 0;
513 | for (int i = 1; i <= amount; i++) {
514 | // 初始化为最大值
515 | int minNum = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
516 | for (int n : coins) {
517 | if (i - n >= 0) {
518 | // 如果上个金额也无法组成,则直接标记
519 | if (dp[i - n] == -1) {
520 | dp[i] = -1;
521 | continue;
522 | } else {
523 | minNum = Math.min(minNum, dp[i - n] + 1);
524 | }
525 | } else if (i % n == 0) {
526 | minNum = i / n;
527 | }
528 | }
529 | dp[i] = (minNum == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : minNum);
530 | }
531 | return dp[amount];
532 | }
533 | ```
534 |
535 | #### 零钱兑换 II
536 |
537 | > [518. 零钱兑换 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/coin-change-2/)
538 | >
539 | > 给定不同面额的硬币和一个总金额。写出函数来计算可以凑成总金额的硬币组合数。假设每一种面额的硬币有无限个。
540 |
541 | 先遍历物品再遍历背包 - 组合数
542 |
543 | 先遍历背包再遍历物品 - 排列数
544 |
545 | ```java
546 | public int change(int amount, int[] coins) {
547 | // 状态 dp[i]表示金额为i时,组合的方法数
548 | int[] dp = new int[amount + 1];
549 | dp[0] = 1;
550 | // 先遍历物品再遍历背包
551 | for (int n : coins) {
552 | for (int i = n; i <= amount; i++) {
553 | dp[i] += dp[i - n];
554 | }
555 | }
556 | return dp[amount];
557 | }
558 | ```
559 |
560 | #### 分割等和子集
561 |
562 | > [416. 分割等和子集](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/)
563 | >
564 | > 给定一个**只包含正整数**的**非空**数组。是否可以将这个数组分割成两个子集,使得两个子集的元素和相等。
565 |
566 | 等价于0-1背包问题,只不过目标为数组和的一半。状态转移可以参考题解:[动态规划(转换为 0-1 背包问题)](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-equal-subset-sum/solution/0-1-bei-bao-wen-ti-xiang-jie-zhen-dui-ben-ti-de-yo/)。
567 |
568 | ```java
569 | public boolean canPartition(int[] nums) {
570 | // 首先计算数组的和
571 | int sum = 0;
572 | for (int n : nums) {
573 | sum += n;
574 | }
575 | // 如果和不是2的倍数则肯定无法分割
576 | if (sum % 2 != 0) {
577 | return false;
578 | }
579 | sum /= 2;
580 | // dp[i][j]表示从数组的[0, i]子区间内挑选一些正整数(每个数只能用一次)使得这些数的和恰好等于j
581 | boolean[][] dp = new boolean[nums.length][sum + 1];
582 | if (nums[0] <= sum) {
583 | dp[0][nums[0]] = true;
584 | }
585 | for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
586 | for (int j = 0; j <= sum; j++) {
587 | // 注意这里的状态转移方程
588 | if (nums[i] == j) {
589 | dp[i][j] = true;
590 | } else if (nums[i] < j) {
591 | dp[i][j] = dp[i - 1][j] || dp[i-1][j-nums[i]];
592 | } else {
593 | dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j];
594 | }
595 | }
596 | }
597 | return dp[nums.length - 1][sum];
598 | }
599 | ```
600 |
601 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 51 |
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/quick_select.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 快速选择
2 |
3 | ## 使用场景
4 |
5 | - 最大/最小的K个数
6 | - 最大/最小的第K个数
7 |
8 | ## 算法思路
9 |
10 | 和快速排序的思路类似,但是不需要得出精确的比较顺序。首先从数组中随机或指定挑选一个元素作为标志,然后将所有比这个标志小的元素放在左边,比标志大的放在右边,最后会有以下三种可能的情况:
11 |
12 | 1. 这个位置就是K,直接返回即可
13 | 2. 这个位置小于K,说明K位置的数在右边
14 | 3. 这个位置大于K,说明K位置的数在左边
15 |
16 | ## 算法实现
17 |
18 | > [215. 数组中的第K个最大元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/)
19 | >
20 | >在未排序的数组中找到第 **k** 个最大的元素。请注意,需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
21 |
22 | ```java
23 | public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
24 | int l = 0;
25 | int r = nums.length - 1;
26 | while (l < r) {
27 | // 对标志两边分别进行处理
28 | int pivot = partition(nums, l, r);
29 | // 标志就是k
30 | if (pivot == nums.length - k) {
31 | break;
32 | }
33 | // k位置在标志的右侧
34 | else if (pivot < nums.length - k) {
35 | l = pivot + 1;
36 | }
37 | // k位置在标志的左侧
38 | else {
39 | r = pivot - 1;
40 | }
41 | }
42 | return nums[nums.length - k];
43 | }
44 |
45 | private int partition(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
46 | int l = start;
47 | int r = end + 1;
48 | // 选择首元素作为比较标志
49 | // 比标志小的放在左边,比标志大的放在右边
50 | while (true) {
51 | while (nums[++l] < nums[start] && l < end);
52 | while (nums[--r] > nums[start] && r > start);
53 | if (l >= r) {
54 | break;
55 | }
56 | swap(nums, l, r);
57 | }
58 | // 将标志交换到中间
59 | swap(nums, start, r);
60 | return r;
61 | }
62 |
63 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
64 | int temp = nums[i];
65 | nums[i] = nums[j];
66 | nums[j] = temp;
67 | }
68 | ```
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/three_way_quick_sort.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 三向切分快速排序
2 |
3 | ## 使用场景
4 |
5 | 待排序数组中含有类别较少但大量重复的元素
6 |
7 | ## 算法思路
8 |
9 | 除前后两个指针外再使用两个额外的指针指向与待选元素相同的元素,遍历后将与待选元素相同的元素置换到数组中间,再对两侧分别进行排序。通过这一方法可以节省元素交换次数。
10 |
11 | ## 算法实现
12 |
13 | ```java
14 | public void sort(int[] nums) {
15 | sort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
16 | }
17 |
18 | private void sort(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
19 | if (left < right) {
20 | // 选择首元素作为比较标志
21 | int temp = nums[left];
22 | // 设置两个指针指向与temp相同的元素范围
23 | int left_p = left;
24 | int right_p = right;
25 | for (int i = left + 1; i <= right_p; ) {
26 | // 根据比较结果进行元素交换
27 | if (nums[i] < temp) {
28 | swap(nums, left_p, i);
29 | left_p++;
30 | i++;
31 | } else if (nums[i] > temp) {
32 | swap(nums, i, right_p);
33 | right_p--;
34 | } else {
35 | i++;
36 | }
37 | }
38 | // 对两侧元素分别进行排序
39 | sort(nums, left, left_p - 1);
40 | sort(nums, right_p + 1, right);
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
45 | int temp = nums[i];
46 | nums[i] = nums[j];
47 | nums[j] = temp;
48 | }
49 | ```
50 |
51 | ## 经典例题
52 |
53 | > [75. 颜色分类](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-colors/)
54 | >
55 | > 给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 `n` 个元素的数组,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
56 | >
57 | > 此题中,我们使用整数 `0`、 `1` 和 `2` 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
58 |
59 | 由于只有三种颜色,所以不需要再对比较标志两侧元素分别排序,对实现代码稍作修改即可。
60 |
61 | ```java
62 | public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
63 | int left = 0;
64 | int mid = 0;
65 | int right = nums.length - 1;
66 | while (mid <= right) {
67 | if (nums[mid] == 0) {
68 | swap(nums, left, mid);
69 | mid++;
70 | left++;
71 | } else if (nums[mid] == 2) {
72 | swap(nums, right, mid);
73 | right--;
74 | } else {
75 | mid++;
76 | }
77 | }
78 | }
79 |
80 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
81 | int temp = nums[i];
82 | nums[i] = nums[j];
83 | nums[j] = temp;
84 | }
85 | ```
86 |
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/greedy.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 贪心算法
2 |
3 | 贪心算法在每一步选择中都采取在当前状态下最好或最优的选择,从而使得结果也是最优解,适合去解决具有最优子结构的问题。
4 |
5 | ## 应用场景
6 |
7 | 最优子结构的特征:
8 |
9 | - 每一次操作对结果直接产生影响
10 | - 不依赖于之前的操作
11 | - 子问题的最优解是全局最优解的一部分
12 |
13 | ## 常见例题
14 |
15 | ### 跳跃游戏
16 |
17 | > [55. 跳跃游戏](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game/)
18 | >
19 | > 给定一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的 第一个下标 。
20 | >
21 | > 数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
22 | >
23 | > 判断你是否能够到达最后一个下标。
24 |
25 | 思路:每个格子`i`作为起跳点最远能跳到`nums[i]`处,所以遍历数组得到最远距离并与数组长度进行比较即可。
26 |
27 | 这题只需要判断能否到达终点而无需给出具体路径,所以不需要用回溯的方法。
28 |
29 | ```java
30 | public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
31 | int maxLen = 0;
32 | for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
33 | // 当前格子已经无法跳到
34 | if (i > maxLen) return false;
35 | // 更新能跳到的最远距离
36 | maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, i + nums[i]);
37 | }
38 | return true;
39 | }
40 | ```
41 |
42 | ### 跳跃游戏 II
43 |
44 | > [45. 跳跃游戏 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game-ii/)
45 | >
46 | >给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
47 | >
48 | >数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
49 | >
50 | >你的目标是使用最少的跳跃次数到达数组的最后一个位置。
51 |
52 | 思路:确保每次跳跃选择的格子都有最远的跳跃范围。
53 |
54 | ```java
55 | public int jump(int[] nums) {
56 | int steps = 0;
57 | int start = 0;
58 | int end = 1;
59 | while (end < nums.length) {
60 | // 确定最远的跳跃范围
61 | int maxPosition = 0;
62 | for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
63 | maxPosition = Math.max(maxPosition, i + nums[i]);
64 | }
65 | start = end;
66 | end = maxPosition + 1;
67 | // 步数增加
68 | steps++;
69 | }
70 | return steps;
71 | }
72 | ```
73 |
74 | ### 分发饼干
75 |
76 | > [455. 分发饼干](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/assign-cookies/)
77 | >
78 | > 对每个孩子 `i`,都有一个胃口值 `g[i]`,这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干 `j`,都有一个尺寸 `s[j]` 。如果 `s[j] >= g[i]`,我们可以将这个饼干 `j` 分配给孩子 `i` ,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是尽可能满足越多数量的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
79 |
80 | 思路:先排序,再贪心,让饼干优先满足胃口更多的孩子
81 |
82 | ```java
83 | public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
84 | Arrays.sort(g);
85 | Arrays.sort(s);
86 | int p = 0;
87 | int q = 0;
88 | while (p < g.length && q < s.length) {
89 | if (g[p] <= s[q]) {
90 | p++;
91 | }
92 | q++;
93 | }
94 | return p;
95 | }
96 | ```
97 |
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/binary_op.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 二进制
2 |
3 | ## 常见二进制操作
4 |
5 | ### 基本操作
6 |
7 | a=0^a=a^0
8 |
9 | 0=a^a
10 |
11 | 由上面两个推导出:a=a^b^b
12 |
13 | ### 交换两个数
14 |
15 | a=a^b
16 |
17 | b=a^b
18 |
19 | a=a^b
20 |
21 | ### 移除最后一个 1
22 |
23 | a=n&(n-1)
24 |
25 | ### 获取最后一个 1
26 |
27 | diff=(n&(n-1))^n
28 |
29 | ## 常见例题
30 |
31 | ### 只出现一次的数字
32 |
33 | > [136. 只出现一次的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number/)
34 | >
35 | > 给定一个**非空**整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
36 |
37 | ```java
38 | public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
39 | // 10 ^ 10 == 00
40 | // 两个相同的数异或变成0
41 | int result = 0;
42 | for (int n : nums) {
43 | result = result ^ n;
44 | }
45 | return result;
46 | }
47 | ```
48 |
49 | ### 只出现一次的数字 II
50 |
51 | > [137. 只出现一次的数字 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number-ii/)
52 | >
53 | > 给定一个**非空**整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现了三次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
54 |
55 | ```java
56 | public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
57 | int result = 0;
58 | // 统计每位1的个数
59 | for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
60 | int sum = 0;
61 | for (int n : nums) {
62 | // 统计1的个数
63 | sum += ((n >> i) & 1);
64 | }
65 | // 还原
66 | result |= ((sum % 3) << i);
67 | }
68 | return result;
69 | }
70 | ```
71 |
72 | ### 只出现一次的数字 III
73 |
74 | > [260. 只出现一次的数字 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number-iii/)
75 | >
76 | > 给定一个整数数组 `nums`,其中恰好有两个元素只出现一次,其余所有元素均出现两次。 找出只出现一次的那两个元素。
77 |
78 | ```java
79 | public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
80 | // 关键点怎么把a^b分成两部分,方案:可以通过diff最后一个1区分
81 | int diff = 0;
82 | for (int n : nums) {
83 | diff ^= n;
84 | }
85 | int[] result = new int[]{diff, diff};
86 | // 去掉末尾的1后异或diff就得到最后一个1的位置
87 | diff = (diff & (diff - 1)) ^ diff;
88 | for (int n : nums) {
89 | if ((diff & n) == 0) {
90 | result[0] ^= n;
91 | } else {
92 | result[1] ^= n;
93 | }
94 | }
95 | return result;
96 | }
97 | ```
98 |
99 | ### 位1的个数
100 |
101 | > [191. 位1的个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-1-bits/)
102 | >
103 | > 编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数,返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 ‘1’ 的个数(也被称为[汉明重量](https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%B1%89%E6%98%8E%E9%87%8D%E9%87%8F))。
104 |
105 | ```java
106 | public int hammingWeight(int n) {
107 | int result = 0;
108 | while (n != 0) {
109 | if ((n & 1) == 1) result++;
110 | n = n >>> 1;
111 | }
112 | return result;
113 | }
114 | ```
115 |
116 | ### 颠倒二进制位
117 |
118 | > [190. 颠倒二进制位](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-bits/)
119 | >
120 | > 颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位。
121 |
122 | 思路:依次颠倒即可
123 |
124 | ```java
125 | public int reverseBits(int n) {
126 | int result = 0;
127 | int p = 31;
128 | while (n != 0) {
129 | result += ((n & 1) << p);
130 | n >>>= 1;
131 | p--;
132 | }
133 | return result;
134 | }
135 | ```
136 |
137 | ### 数字范围按位与
138 |
139 | > [201. 数字范围按位与](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/bitwise-and-of-numbers-range/)
140 | >
141 | > 给定范围 [m, n],其中 0 <= m <= n <= 2147483647,返回此范围内所有数字的按位与(包含 m, n 两端点)。
142 |
143 | 问题转化为求两个给定数字二进制状态下的最长公共前缀,可以用移位判断的思想来做,这里使用另一种`Brian Kernighan`算法:`number`和 `number−1`之间进行按位与运算后,`number`中最右边的1会被抹去变成0。
144 |
145 | ```java
146 | public int rangeBitwiseAnd(int m, int n) {
147 | while (m < n) {
148 | // 抹去最右边的 1
149 | n = n & (n - 1);
150 | }
151 | return n;
152 | }
153 | ```
154 |
155 | ## 注意点
156 |
157 | - Java中区分右移运算和无符号右移运算
158 | - 注意运算顺序,不确定时尽量加上括号
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/sort.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 排序
2 |
3 | ## 常考排序
4 |
5 | ### 快速排序
6 |
7 | ```java
8 | public void quickSort(int[] nums) {
9 | // 思路:把一个数组分为左右两段,左段小于右段
10 | quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
11 | }
12 |
13 | // 原地交换,所以传入交换索引
14 | private void quickSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
15 | if (start < end) {
16 | // 分治法:divide
17 | int pivot = partition(nums, start, end);
18 | quickSort(nums, 0, pivot - 1);
19 | quickSort(nums, pivot + 1, end);
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
23 | // 分区
24 | private int partition(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
25 | // 选取最后一个元素作为基准pivot
26 | int p = nums[end];
27 | int i = start;
28 | // 最后一个值就是基准所以不用比较
29 | for (int j = start; j < end; j++) {
30 | if (nums[j] < p) {
31 | swap(nums, i, j);
32 | i++;
33 | }
34 | }
35 | // 把基准值换到中间
36 | swap(nums, i, end);
37 | return i;
38 | }
39 |
40 | // 交换两个元素
41 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
42 | int temp = nums[i];
43 | nums[i] = nums[j];
44 | nums[j] = temp;
45 | }
46 | ```
47 |
48 | ### 归并排序
49 |
50 | ```java
51 | public void mergeSort(int[] nums) {
52 | mergeSort(nums, 0, nums.length);
53 | }
54 |
55 | private void mergeSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
56 | if (end - start <= 1) {
57 | return;
58 | }
59 | // 分治法:divide 分为两段
60 | int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
61 | mergeSort(nums, start, mid);
62 | mergeSort(nums, mid, end);
63 | // 合并两段数据
64 | merge(nums, start, mid, end);
65 | }
66 |
67 | private void merge(int[] nums, int start, int mid, int end) {
68 | int[] temp = new int[end - start];
69 | // 两边数组合并游标
70 | int l = start;
71 | int r = mid;
72 | int k = 0;
73 | // 注意不能越界
74 | while (l < mid && r < end) {
75 | // 谁小合并谁
76 | if (nums[l] < nums[r]) {
77 | temp[k++] = nums[l++];
78 | } else {
79 | temp[k++] = nums[r++];
80 | }
81 | }
82 | // 剩余部分合并
83 | while (l < mid) {
84 | temp[k++] = nums[l++];
85 | }
86 | while (r < end) {
87 | temp[k++] = nums[r++];
88 | }
89 | // 复制到原数组
90 | for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
91 | nums[i + start] = temp[i];
92 | }
93 | }
94 | ```
95 |
96 | ### 堆排序
97 |
98 | 用数组表示的完全二叉树 complete binary tree
99 |
100 | > 完全二叉树 VS 其他二叉树
101 |
102 | 
103 |
104 | [动画展示](https://www.bilibili.com/video/av18980178/)
105 |
106 | 
107 |
108 | 核心代码
109 |
110 | ```java
111 | public void heapSort(int[] nums) {
112 | // 1、无序数组nums
113 | // 2、将无序数组nums构建为一个大根堆
114 | for (int i = nums.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
115 | sink(nums, i, nums.length);
116 | }
117 | // 3、交换nums[0]和nums[len(a)-1]
118 | // 4、然后把前面这段数组继续下沉保持堆结构,如此循环即可
119 | for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
120 | // 从后往前填充值
121 | swap(nums, 0, i);
122 | // 前面的长度也减一
123 | sink(nums, 0, i);
124 | }
125 | }
126 |
127 | private void sink(int[] nums, int i, int length) {
128 | while (true) {
129 | // 左节点索引(从0开始,所以左节点为i*2+1)
130 | int l = i * 2 + 1;
131 | // 右节点索引
132 | int r = i * 2 + 2;
133 | // 保存根、左、右三者之间较大值的索引
134 | int index = i;
135 | // 存在左节点,左节点值较大,则取左节点
136 | if (l < length && nums[l] > nums[index]) {
137 | index = l;
138 | }
139 | // 存在右节点,且值较大,取右节点
140 | if (r < length && nums[r] > nums[index]) {
141 | index = r;
142 | }
143 | // 如果根节点较大,则不用下沉
144 | if (index == i) {
145 | break;
146 | }
147 | // 如果根节点较小,则交换值,并继续下沉
148 | swap(nums, i, index);
149 | i = index;
150 | }
151 | }
152 |
153 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
154 | int temp = nums[i];
155 | nums[i] = nums[j];
156 | nums[j] = temp;
157 | }
158 | ```
159 |
160 | ## 参考
161 |
162 | [十大经典排序](https://www.cnblogs.com/onepixel/p/7674659.html)
163 |
164 | [二叉堆](https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo/shu-ju-jie-gou-xi-lie/er-cha-dui-xiang-jie-shi-xian-you-xian-ji-dui-lie)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data_structure/stack_queue.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 栈和队列
2 |
3 | ## 简介
4 |
5 | 栈的特点是后入先出
6 |
7 | 根据这个特点可以临时保存一些数据,之后用到依次再弹出来,常用于树的非递归遍历、 DFS 深度搜索。
8 |
9 | 队列常用于BFS广度搜索,很少单独考察。
10 |
11 | ## 基本应用
12 |
13 | ### 逆波兰表达式求值
14 |
15 | > [150. 逆波兰表达式求值](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/)
16 | >
17 | > **波兰表达式计算** > **输入:** `["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]` > **输出:** 9
18 | >
19 | > **解释:** `((2 + 1) * 3) = 9`
20 |
21 | ```java
22 | public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
23 | Stack
51 |
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/quick_select.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 快速选择
2 |
3 | ## 使用场景
4 |
5 | - 最大/最小的K个数
6 | - 最大/最小的第K个数
7 |
8 | ## 算法思路
9 |
10 | 和快速排序的思路类似,但是不需要得出精确的比较顺序。首先从数组中随机或指定挑选一个元素作为标志,然后将所有比这个标志小的元素放在左边,比标志大的放在右边,最后会有以下三种可能的情况:
11 |
12 | 1. 这个位置就是K,直接返回即可
13 | 2. 这个位置小于K,说明K位置的数在右边
14 | 3. 这个位置大于K,说明K位置的数在左边
15 |
16 | ## 算法实现
17 |
18 | > [215. 数组中的第K个最大元素](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/kth-largest-element-in-an-array/)
19 | >
20 | >在未排序的数组中找到第 **k** 个最大的元素。请注意,需要找的是数组排序后的第 k 个最大的元素,而不是第 k 个不同的元素。
21 |
22 | ```java
23 | public int findKthLargest(int[] nums, int k) {
24 | int l = 0;
25 | int r = nums.length - 1;
26 | while (l < r) {
27 | // 对标志两边分别进行处理
28 | int pivot = partition(nums, l, r);
29 | // 标志就是k
30 | if (pivot == nums.length - k) {
31 | break;
32 | }
33 | // k位置在标志的右侧
34 | else if (pivot < nums.length - k) {
35 | l = pivot + 1;
36 | }
37 | // k位置在标志的左侧
38 | else {
39 | r = pivot - 1;
40 | }
41 | }
42 | return nums[nums.length - k];
43 | }
44 |
45 | private int partition(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
46 | int l = start;
47 | int r = end + 1;
48 | // 选择首元素作为比较标志
49 | // 比标志小的放在左边,比标志大的放在右边
50 | while (true) {
51 | while (nums[++l] < nums[start] && l < end);
52 | while (nums[--r] > nums[start] && r > start);
53 | if (l >= r) {
54 | break;
55 | }
56 | swap(nums, l, r);
57 | }
58 | // 将标志交换到中间
59 | swap(nums, start, r);
60 | return r;
61 | }
62 |
63 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
64 | int temp = nums[i];
65 | nums[i] = nums[j];
66 | nums[j] = temp;
67 | }
68 | ```
69 |
70 |
71 |
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/three_way_quick_sort.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 三向切分快速排序
2 |
3 | ## 使用场景
4 |
5 | 待排序数组中含有类别较少但大量重复的元素
6 |
7 | ## 算法思路
8 |
9 | 除前后两个指针外再使用两个额外的指针指向与待选元素相同的元素,遍历后将与待选元素相同的元素置换到数组中间,再对两侧分别进行排序。通过这一方法可以节省元素交换次数。
10 |
11 | ## 算法实现
12 |
13 | ```java
14 | public void sort(int[] nums) {
15 | sort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
16 | }
17 |
18 | private void sort(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
19 | if (left < right) {
20 | // 选择首元素作为比较标志
21 | int temp = nums[left];
22 | // 设置两个指针指向与temp相同的元素范围
23 | int left_p = left;
24 | int right_p = right;
25 | for (int i = left + 1; i <= right_p; ) {
26 | // 根据比较结果进行元素交换
27 | if (nums[i] < temp) {
28 | swap(nums, left_p, i);
29 | left_p++;
30 | i++;
31 | } else if (nums[i] > temp) {
32 | swap(nums, i, right_p);
33 | right_p--;
34 | } else {
35 | i++;
36 | }
37 | }
38 | // 对两侧元素分别进行排序
39 | sort(nums, left, left_p - 1);
40 | sort(nums, right_p + 1, right);
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
45 | int temp = nums[i];
46 | nums[i] = nums[j];
47 | nums[j] = temp;
48 | }
49 | ```
50 |
51 | ## 经典例题
52 |
53 | > [75. 颜色分类](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-colors/)
54 | >
55 | > 给定一个包含红色、白色和蓝色,一共 `n` 个元素的数组,原地对它们进行排序,使得相同颜色的元素相邻,并按照红色、白色、蓝色顺序排列。
56 | >
57 | > 此题中,我们使用整数 `0`、 `1` 和 `2` 分别表示红色、白色和蓝色。
58 |
59 | 由于只有三种颜色,所以不需要再对比较标志两侧元素分别排序,对实现代码稍作修改即可。
60 |
61 | ```java
62 | public void sortColors(int[] nums) {
63 | int left = 0;
64 | int mid = 0;
65 | int right = nums.length - 1;
66 | while (mid <= right) {
67 | if (nums[mid] == 0) {
68 | swap(nums, left, mid);
69 | mid++;
70 | left++;
71 | } else if (nums[mid] == 2) {
72 | swap(nums, right, mid);
73 | right--;
74 | } else {
75 | mid++;
76 | }
77 | }
78 | }
79 |
80 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
81 | int temp = nums[i];
82 | nums[i] = nums[j];
83 | nums[j] = temp;
84 | }
85 | ```
86 |
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/greedy.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 贪心算法
2 |
3 | 贪心算法在每一步选择中都采取在当前状态下最好或最优的选择,从而使得结果也是最优解,适合去解决具有最优子结构的问题。
4 |
5 | ## 应用场景
6 |
7 | 最优子结构的特征:
8 |
9 | - 每一次操作对结果直接产生影响
10 | - 不依赖于之前的操作
11 | - 子问题的最优解是全局最优解的一部分
12 |
13 | ## 常见例题
14 |
15 | ### 跳跃游戏
16 |
17 | > [55. 跳跃游戏](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game/)
18 | >
19 | > 给定一个非负整数数组 nums ,你最初位于数组的 第一个下标 。
20 | >
21 | > 数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
22 | >
23 | > 判断你是否能够到达最后一个下标。
24 |
25 | 思路:每个格子`i`作为起跳点最远能跳到`nums[i]`处,所以遍历数组得到最远距离并与数组长度进行比较即可。
26 |
27 | 这题只需要判断能否到达终点而无需给出具体路径,所以不需要用回溯的方法。
28 |
29 | ```java
30 | public boolean canJump(int[] nums) {
31 | int maxLen = 0;
32 | for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
33 | // 当前格子已经无法跳到
34 | if (i > maxLen) return false;
35 | // 更新能跳到的最远距离
36 | maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, i + nums[i]);
37 | }
38 | return true;
39 | }
40 | ```
41 |
42 | ### 跳跃游戏 II
43 |
44 | > [45. 跳跃游戏 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/jump-game-ii/)
45 | >
46 | >给定一个非负整数数组,你最初位于数组的第一个位置。
47 | >
48 | >数组中的每个元素代表你在该位置可以跳跃的最大长度。
49 | >
50 | >你的目标是使用最少的跳跃次数到达数组的最后一个位置。
51 |
52 | 思路:确保每次跳跃选择的格子都有最远的跳跃范围。
53 |
54 | ```java
55 | public int jump(int[] nums) {
56 | int steps = 0;
57 | int start = 0;
58 | int end = 1;
59 | while (end < nums.length) {
60 | // 确定最远的跳跃范围
61 | int maxPosition = 0;
62 | for (int i = start; i < end; i++) {
63 | maxPosition = Math.max(maxPosition, i + nums[i]);
64 | }
65 | start = end;
66 | end = maxPosition + 1;
67 | // 步数增加
68 | steps++;
69 | }
70 | return steps;
71 | }
72 | ```
73 |
74 | ### 分发饼干
75 |
76 | > [455. 分发饼干](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/assign-cookies/)
77 | >
78 | > 对每个孩子 `i`,都有一个胃口值 `g[i]`,这是能让孩子们满足胃口的饼干的最小尺寸;并且每块饼干 `j`,都有一个尺寸 `s[j]` 。如果 `s[j] >= g[i]`,我们可以将这个饼干 `j` 分配给孩子 `i` ,这个孩子会得到满足。你的目标是尽可能满足越多数量的孩子,并输出这个最大数值。
79 |
80 | 思路:先排序,再贪心,让饼干优先满足胃口更多的孩子
81 |
82 | ```java
83 | public int findContentChildren(int[] g, int[] s) {
84 | Arrays.sort(g);
85 | Arrays.sort(s);
86 | int p = 0;
87 | int q = 0;
88 | while (p < g.length && q < s.length) {
89 | if (g[p] <= s[q]) {
90 | p++;
91 | }
92 | q++;
93 | }
94 | return p;
95 | }
96 | ```
97 |
98 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/advanced_algorithm/binary_op.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 二进制
2 |
3 | ## 常见二进制操作
4 |
5 | ### 基本操作
6 |
7 | a=0^a=a^0
8 |
9 | 0=a^a
10 |
11 | 由上面两个推导出:a=a^b^b
12 |
13 | ### 交换两个数
14 |
15 | a=a^b
16 |
17 | b=a^b
18 |
19 | a=a^b
20 |
21 | ### 移除最后一个 1
22 |
23 | a=n&(n-1)
24 |
25 | ### 获取最后一个 1
26 |
27 | diff=(n&(n-1))^n
28 |
29 | ## 常见例题
30 |
31 | ### 只出现一次的数字
32 |
33 | > [136. 只出现一次的数字](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number/)
34 | >
35 | > 给定一个**非空**整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现两次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
36 |
37 | ```java
38 | public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
39 | // 10 ^ 10 == 00
40 | // 两个相同的数异或变成0
41 | int result = 0;
42 | for (int n : nums) {
43 | result = result ^ n;
44 | }
45 | return result;
46 | }
47 | ```
48 |
49 | ### 只出现一次的数字 II
50 |
51 | > [137. 只出现一次的数字 II](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number-ii/)
52 | >
53 | > 给定一个**非空**整数数组,除了某个元素只出现一次以外,其余每个元素均出现了三次。找出那个只出现了一次的元素。
54 |
55 | ```java
56 | public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
57 | int result = 0;
58 | // 统计每位1的个数
59 | for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
60 | int sum = 0;
61 | for (int n : nums) {
62 | // 统计1的个数
63 | sum += ((n >> i) & 1);
64 | }
65 | // 还原
66 | result |= ((sum % 3) << i);
67 | }
68 | return result;
69 | }
70 | ```
71 |
72 | ### 只出现一次的数字 III
73 |
74 | > [260. 只出现一次的数字 III](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number-iii/)
75 | >
76 | > 给定一个整数数组 `nums`,其中恰好有两个元素只出现一次,其余所有元素均出现两次。 找出只出现一次的那两个元素。
77 |
78 | ```java
79 | public int[] singleNumber(int[] nums) {
80 | // 关键点怎么把a^b分成两部分,方案:可以通过diff最后一个1区分
81 | int diff = 0;
82 | for (int n : nums) {
83 | diff ^= n;
84 | }
85 | int[] result = new int[]{diff, diff};
86 | // 去掉末尾的1后异或diff就得到最后一个1的位置
87 | diff = (diff & (diff - 1)) ^ diff;
88 | for (int n : nums) {
89 | if ((diff & n) == 0) {
90 | result[0] ^= n;
91 | } else {
92 | result[1] ^= n;
93 | }
94 | }
95 | return result;
96 | }
97 | ```
98 |
99 | ### 位1的个数
100 |
101 | > [191. 位1的个数](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/number-of-1-bits/)
102 | >
103 | > 编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数,返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 ‘1’ 的个数(也被称为[汉明重量](https://baike.baidu.com/item/%E6%B1%89%E6%98%8E%E9%87%8D%E9%87%8F))。
104 |
105 | ```java
106 | public int hammingWeight(int n) {
107 | int result = 0;
108 | while (n != 0) {
109 | if ((n & 1) == 1) result++;
110 | n = n >>> 1;
111 | }
112 | return result;
113 | }
114 | ```
115 |
116 | ### 颠倒二进制位
117 |
118 | > [190. 颠倒二进制位](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-bits/)
119 | >
120 | > 颠倒给定的 32 位无符号整数的二进制位。
121 |
122 | 思路:依次颠倒即可
123 |
124 | ```java
125 | public int reverseBits(int n) {
126 | int result = 0;
127 | int p = 31;
128 | while (n != 0) {
129 | result += ((n & 1) << p);
130 | n >>>= 1;
131 | p--;
132 | }
133 | return result;
134 | }
135 | ```
136 |
137 | ### 数字范围按位与
138 |
139 | > [201. 数字范围按位与](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/bitwise-and-of-numbers-range/)
140 | >
141 | > 给定范围 [m, n],其中 0 <= m <= n <= 2147483647,返回此范围内所有数字的按位与(包含 m, n 两端点)。
142 |
143 | 问题转化为求两个给定数字二进制状态下的最长公共前缀,可以用移位判断的思想来做,这里使用另一种`Brian Kernighan`算法:`number`和 `number−1`之间进行按位与运算后,`number`中最右边的1会被抹去变成0。
144 |
145 | ```java
146 | public int rangeBitwiseAnd(int m, int n) {
147 | while (m < n) {
148 | // 抹去最右边的 1
149 | n = n & (n - 1);
150 | }
151 | return n;
152 | }
153 | ```
154 |
155 | ## 注意点
156 |
157 | - Java中区分右移运算和无符号右移运算
158 | - 注意运算顺序,不确定时尽量加上括号
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/basic_algorithm/sort.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 排序
2 |
3 | ## 常考排序
4 |
5 | ### 快速排序
6 |
7 | ```java
8 | public void quickSort(int[] nums) {
9 | // 思路:把一个数组分为左右两段,左段小于右段
10 | quickSort(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
11 | }
12 |
13 | // 原地交换,所以传入交换索引
14 | private void quickSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
15 | if (start < end) {
16 | // 分治法:divide
17 | int pivot = partition(nums, start, end);
18 | quickSort(nums, 0, pivot - 1);
19 | quickSort(nums, pivot + 1, end);
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
23 | // 分区
24 | private int partition(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
25 | // 选取最后一个元素作为基准pivot
26 | int p = nums[end];
27 | int i = start;
28 | // 最后一个值就是基准所以不用比较
29 | for (int j = start; j < end; j++) {
30 | if (nums[j] < p) {
31 | swap(nums, i, j);
32 | i++;
33 | }
34 | }
35 | // 把基准值换到中间
36 | swap(nums, i, end);
37 | return i;
38 | }
39 |
40 | // 交换两个元素
41 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
42 | int temp = nums[i];
43 | nums[i] = nums[j];
44 | nums[j] = temp;
45 | }
46 | ```
47 |
48 | ### 归并排序
49 |
50 | ```java
51 | public void mergeSort(int[] nums) {
52 | mergeSort(nums, 0, nums.length);
53 | }
54 |
55 | private void mergeSort(int[] nums, int start, int end) {
56 | if (end - start <= 1) {
57 | return;
58 | }
59 | // 分治法:divide 分为两段
60 | int mid = start + (end - start) / 2;
61 | mergeSort(nums, start, mid);
62 | mergeSort(nums, mid, end);
63 | // 合并两段数据
64 | merge(nums, start, mid, end);
65 | }
66 |
67 | private void merge(int[] nums, int start, int mid, int end) {
68 | int[] temp = new int[end - start];
69 | // 两边数组合并游标
70 | int l = start;
71 | int r = mid;
72 | int k = 0;
73 | // 注意不能越界
74 | while (l < mid && r < end) {
75 | // 谁小合并谁
76 | if (nums[l] < nums[r]) {
77 | temp[k++] = nums[l++];
78 | } else {
79 | temp[k++] = nums[r++];
80 | }
81 | }
82 | // 剩余部分合并
83 | while (l < mid) {
84 | temp[k++] = nums[l++];
85 | }
86 | while (r < end) {
87 | temp[k++] = nums[r++];
88 | }
89 | // 复制到原数组
90 | for (int i = 0; i < temp.length; i++) {
91 | nums[i + start] = temp[i];
92 | }
93 | }
94 | ```
95 |
96 | ### 堆排序
97 |
98 | 用数组表示的完全二叉树 complete binary tree
99 |
100 | > 完全二叉树 VS 其他二叉树
101 |
102 | 
103 |
104 | [动画展示](https://www.bilibili.com/video/av18980178/)
105 |
106 | 
107 |
108 | 核心代码
109 |
110 | ```java
111 | public void heapSort(int[] nums) {
112 | // 1、无序数组nums
113 | // 2、将无序数组nums构建为一个大根堆
114 | for (int i = nums.length / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
115 | sink(nums, i, nums.length);
116 | }
117 | // 3、交换nums[0]和nums[len(a)-1]
118 | // 4、然后把前面这段数组继续下沉保持堆结构,如此循环即可
119 | for (int i = nums.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
120 | // 从后往前填充值
121 | swap(nums, 0, i);
122 | // 前面的长度也减一
123 | sink(nums, 0, i);
124 | }
125 | }
126 |
127 | private void sink(int[] nums, int i, int length) {
128 | while (true) {
129 | // 左节点索引(从0开始,所以左节点为i*2+1)
130 | int l = i * 2 + 1;
131 | // 右节点索引
132 | int r = i * 2 + 2;
133 | // 保存根、左、右三者之间较大值的索引
134 | int index = i;
135 | // 存在左节点,左节点值较大,则取左节点
136 | if (l < length && nums[l] > nums[index]) {
137 | index = l;
138 | }
139 | // 存在右节点,且值较大,取右节点
140 | if (r < length && nums[r] > nums[index]) {
141 | index = r;
142 | }
143 | // 如果根节点较大,则不用下沉
144 | if (index == i) {
145 | break;
146 | }
147 | // 如果根节点较小,则交换值,并继续下沉
148 | swap(nums, i, index);
149 | i = index;
150 | }
151 | }
152 |
153 | private void swap(int[] nums, int i, int j) {
154 | int temp = nums[i];
155 | nums[i] = nums[j];
156 | nums[j] = temp;
157 | }
158 | ```
159 |
160 | ## 参考
161 |
162 | [十大经典排序](https://www.cnblogs.com/onepixel/p/7674659.html)
163 |
164 | [二叉堆](https://labuladong.gitbook.io/algo/shu-ju-jie-gou-xi-lie/er-cha-dui-xiang-jie-shi-xian-you-xian-ji-dui-lie)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/data_structure/stack_queue.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 栈和队列
2 |
3 | ## 简介
4 |
5 | 栈的特点是后入先出
6 |
7 | 根据这个特点可以临时保存一些数据,之后用到依次再弹出来,常用于树的非递归遍历、 DFS 深度搜索。
8 |
9 | 队列常用于BFS广度搜索,很少单独考察。
10 |
11 | ## 基本应用
12 |
13 | ### 逆波兰表达式求值
14 |
15 | > [150. 逆波兰表达式求值](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/evaluate-reverse-polish-notation/)
16 | >
17 | > **波兰表达式计算** > **输入:** `["2", "1", "+", "3", "*"]` > **输出:** 9
18 | >
19 | > **解释:** `((2 + 1) * 3) = 9`
20 |
21 | ```java
22 | public int evalRPN(String[] tokens) {
23 | Stack