├── src
├── __init__.py
├── stack.py
├── priorityq.py
├── a_queue.py
├── binheap.py
├── deque.py
├── graph.py
├── linked_list.py
├── dll.py
└── bst.py
├── tox.ini
├── .travis.yml
├── setup.py
├── LICENSE
├── .gitignore
├── tests
├── test_stack.py
├── test_priorityq.py
├── test_binheap.py
├── test_queue.py
├── test_graph.py
├── test_linked_list.py
├── test_bst.py
├── test_deque.py
└── test_dll.py
└── README.md
/src/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tox.ini:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [pytest]
2 | testpaths = tests src
3 |
4 | [tox]
5 | envlist = py27, py35
6 |
7 | [testenv]
8 | commands = py.test tests --cov=src --cov-report term-missing
9 | deps =
10 | pytest
11 | pytest-cov
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.travis.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | language: python
2 | python:
3 | - "2.7"
4 | - "3.5"
5 |
6 | install:
7 | - pip install -e .[test]
8 |
9 | script: py.test tests --cov=tests --cov-report term-missing
10 |
11 | notifications:
12 | email: false
13 |
14 | after_success:
15 | - coveralls
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Setup data structures module."""
2 |
3 |
4 | from setuptools import setup
5 |
6 | setup(
7 | name="Data structures",
8 | description="implementation for common data structures",
9 | version=0.1,
10 | author=["Claire Gatenby"],
11 | author_email=["clairejgatenby@gmail.com"],
12 | licencse="MIT",
13 | package_dir={'': 'src'},
14 | py_modules=[],
15 | extras_require={
16 | "test": ["pytest", "pytest-cov", "tox", 'coveralls']
17 | }
18 | )
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/stack.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Stack implementation in Python."""
2 |
3 | from src.linked_list import LinkedList
4 |
5 |
6 | class Stack(object):
7 | """Implementation of Stack.
8 |
9 | public methods:
10 |
11 | push(value) - Adds a value to the stack.
12 | The parameter is the value to be added to the stack.
13 | pop() - Removes a value from the stack and returns that value.
14 | If the stack is empty, attempts to call pop should raise an exception.
15 |
16 | """
17 |
18 | def __init__(self, data=None):
19 | """Initialization."""
20 | self._stack = LinkedList(data)
21 |
22 | def push(self, val):
23 | """Add val to the stack."""
24 | self._stack.push(val)
25 |
26 | def pop(self):
27 | """Remove item off the stack."""
28 | self._stack.pop()
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | MIT License
2 |
3 | Copyright (c) 2017 Claire Gatenby
4 |
5 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining a copy
6 | of this software and associated documentation files (the "Software"), to deal
7 | in the Software without restriction, including without limitation the rights
8 | to use, copy, modify, merge, publish, distribute, sublicense, and/or sell
9 | copies of the Software, and to permit persons to whom the Software is
10 | furnished to do so, subject to the following conditions:
11 |
12 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be included in all
13 | copies or substantial portions of the Software.
14 |
15 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED "AS IS", WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR
16 | IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY,
17 | FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE
18 | AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER
19 | LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT, TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM,
20 | OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE
21 | SOFTWARE.
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/priorityq.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Python implementation of a priorityq."""
2 |
3 | from src.binheap import Binheap
4 |
5 |
6 | class PriorityQ(object):
7 | """
8 | Priority Q data structure.
9 |
10 | Following methods are supported.
11 |
12 | Insert(value, [priority]): inserts a value into the queue.
13 | Takes an optional argument for that value's priority.
14 | pop(): removes the most important item from the queue
15 | and returns its value.
16 | peek(): returns the most important item without removing it from the queue.
17 | """
18 |
19 | def __init__(self):
20 | """Initialize priorityq."""
21 | self._container = Binheap()
22 |
23 | def insert(self, val, priority=0):
24 | """Insert a val into the queue with an argument for the priority."""
25 | self._container.push((priority, val))
26 |
27 | def pop(self):
28 | """Remove the most important item from the queue."""
29 | to_return = self._container.container[1][1]
30 | if not to_return:
31 | raise(IndexError, 'Can\'t pop from an empty queue.')
32 | self._container.pop()
33 | return to_return
34 |
35 | def peek(self):
36 | """Return the most important item without removing it."""
37 | try:
38 | return self._container.container[1][1]
39 | except IndexError:
40 | return None
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/a_queue.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Implementation of a queue in python."""
2 |
3 |
4 | from src.dll import DoubleLinkedList
5 |
6 |
7 | class Queue(object):
8 | """Implementation of Queue.
9 |
10 | This implementation supports the following public methods:
11 | enqueue(value): adds value to the queue
12 | dequeue(): removes the correct item from the queue and returns its value
13 | (should raise an error if the queue is empty)
14 | peek(): returns the next value in the queue without dequeueing it.
15 | If the queue is empty, returns None
16 | size(): return the size of the queue. Returns 0 if the queue is empty.
17 | """
18 |
19 | def __init__(self, data=None):
20 | """Initialize queue data structure."""
21 | self._container = DoubleLinkedList(data)
22 |
23 | def enqueue(self, val):
24 | """Add a value to the queue."""
25 | self._container.append(val)
26 |
27 | def dequeue(self):
28 | """Remove a value from the front of the queue."""
29 | return self._container.pop()
30 |
31 | def peek(self):
32 | """Return the next value in the queue without dequing it."""
33 | try:
34 | return self._container.head.data
35 | except AttributeError:
36 | return None
37 |
38 | def size(self):
39 | """Return the size of the queue."""
40 | return self._container._length
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # C extensions
7 | *.so
8 |
9 | # Distribution / packaging
10 | .Python
11 | env/
12 | build/
13 | develop-eggs/
14 | dist/
15 | downloads/
16 | eggs/
17 | .eggs/
18 | lib/
19 | lib64/
20 | parts/
21 | sdist/
22 | var/
23 | *.egg-info/
24 | .installed.cfg
25 | *.egg
26 |
27 | # PyInstaller
28 | # Usually these files are written by a python script from a template
29 | # before PyInstaller builds the exe, so as to inject date/other infos into it.
30 | *.manifest
31 | *.spec
32 |
33 | # Installer logs
34 | pip-log.txt
35 | pip-delete-this-directory.txt
36 |
37 | # Unit test / coverage reports
38 | htmlcov/
39 | .tox/
40 | .coverage
41 | .coverage.*
42 | .cache
43 | nosetests.xml
44 | coverage.xml
45 | *,cover
46 | .hypothesis/
47 |
48 | # Translations
49 | *.mo
50 | *.pot
51 |
52 | # Django stuff:
53 | *.log
54 | local_settings.py
55 |
56 | # Flask stuff:
57 | instance/
58 | .webassets-cache
59 |
60 | # Scrapy stuff:
61 | .scrapy
62 |
63 | # Sphinx documentation
64 | docs/_build/
65 |
66 | # PyBuilder
67 | target/
68 |
69 | # IPython Notebook
70 | .ipynb_checkpoints
71 |
72 | # pyenv
73 | .python-version
74 |
75 | # celery beat schedule file
76 | celerybeat-schedule
77 |
78 | # dotenv
79 | .env
80 |
81 | # virtualenv
82 | venv/
83 | ENV/
84 |
85 | # Spyder project settings
86 | .spyderproject
87 |
88 | # Rope project settings
89 | .ropeproject
90 |
91 | standard_tests/
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_stack.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Test for Stack implementation."""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 |
6 | @pytest.fixture
7 | def test_stack():
8 | """Fixture for testing."""
9 | from src.stack import Stack
10 | empty = Stack()
11 | one = Stack(5)
12 | multi = Stack([1, 2, 'three', 4, 5])
13 | return empty, one, multi
14 |
15 |
16 | def test_stack_is_initialized(test_stack):
17 | """Test stack."""
18 | assert test_stack[0]._stack._length is 0
19 |
20 |
21 | def test_empty_stack_push(test_stack):
22 | """Test can push on an empty stack."""
23 | test_stack[0].push(3)
24 | assert test_stack[0]._stack._length is 1
25 |
26 |
27 | def test_stack_of_one_push(test_stack):
28 | """Test can push on an stack of 1."""
29 | test_stack[1].push(2)
30 | assert test_stack[1]._stack.head.data is 2
31 |
32 |
33 | def test_stack_of_multiple_push(test_stack):
34 | """Test can push on an stack of multiple."""
35 | test_stack[2].push(2)
36 | assert test_stack[2]._stack.head.data is 2
37 |
38 |
39 | def test_empty_stack_pop(test_stack):
40 | """Test can pop on an empty stack."""
41 | with pytest.raises(IndexError):
42 | test_stack[0].pop()
43 |
44 |
45 | def test_stack_of_one_pop(test_stack):
46 | """Test can pop on an stack of 1."""
47 | test_stack[1].pop()
48 | assert test_stack[1]._stack.head is None
49 |
50 |
51 | def test_stack_of_multiple_pop(test_stack):
52 | """Test can pop on an stack of multiple."""
53 | test_stack[2].pop()
54 | assert test_stack[2]._stack.head.data is 4
55 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_priorityq.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Testing module for priorityq."""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 |
6 | @pytest.fixture
7 | def test_q():
8 | """Test fixtures of priority qs."""
9 | from src.priorityq import PriorityQ
10 | q0 = PriorityQ()
11 | q1 = PriorityQ()
12 | q1.insert('sgds', 10)
13 | q1.insert('another', 9)
14 | q1.insert('another', 8)
15 | q1.insert('another', 7)
16 | q1.insert('another', 6)
17 | return q0, q1
18 |
19 |
20 | def test_priority_q_insert(test_q):
21 | """Test priorityq insert on a list of none."""
22 | test_q[0].insert('sgds', 10)
23 | assert test_q[0]._container.container[1] == (10, 'sgds')
24 |
25 |
26 | def test_priority_q_insert_multiple(test_q):
27 | """Test priorityq insert multi on a list of none."""
28 | assert test_q[1]._container.container[1] == (10, 'sgds')
29 |
30 |
31 | def test_priority_q_new_highest(test_q):
32 | """Test priorityq changes head with new highest priority."""
33 | test_q[1].insert('highest', 100)
34 | assert test_q[1]._container.container[1] == (100, 'highest')
35 |
36 |
37 | def test_priority_q_pop(test_q):
38 | """Test priority q pop, remove highest priority."""
39 | assert test_q[1].pop() == 'sgds'
40 |
41 |
42 | def test_priority_q_pop_empty(test_q):
43 | """Test priority q pop, raises index error on empty."""
44 | with pytest.raises(IndexError):
45 | test_q[0].pop()
46 |
47 |
48 | def test_peek_returns_highest_priority(test_q):
49 | """Test priority q returns highest value."""
50 | assert test_q[1].peek() == 'sgds'
51 |
52 |
53 | def test_priority_q_peek_empty(test_q):
54 | """Test priority q peek, returns None."""
55 | assert test_q[0].peek() is None
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/binheap.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Python implementation of Binary Heap."""
2 |
3 |
4 | class Binheap(object):
5 | """Python implementation of max binary heap.
6 |
7 | supports the following method
8 |
9 | push(): puts a new value into the heap, maintaining the heap property.
10 | pop(): removes the top value in the heap, maintaining the heap property.
11 | dislplay(): displays the heap as a string representation of a tree.
12 | """
13 |
14 | def __init__(self, data=None):
15 | """Initialize bin heap."""
16 | self.container = [None]
17 | if data:
18 | for val in data:
19 | self.push(val)
20 |
21 | def _balance(self):
22 | """Helper function to balance heap."""
23 | size = len(self.container) - 1
24 | while size // 2 > 0:
25 | if self.container[size] > self.container[size // 2]:
26 | tmp = self.container[size // 2]
27 | self.container[size // 2] = self.container[size]
28 | self.container[size] = tmp
29 | size = size // 2
30 |
31 | def push(self, val):
32 | """Put a new value into the heap."""
33 | self.container.append(val)
34 | self._balance()
35 |
36 | def pop(self):
37 | """Remove the top value of the heap."""
38 | if not self.container:
39 | raise IndexError('Can\'t pop from and empty heap')
40 | self.container.pop(1)
41 | self._balance()
42 |
43 | def display(self):
44 | """Display the heap as a tree."""
45 | cols = []
46 | col = 1
47 | to_show = ''
48 | l = self.container[1:]
49 |
50 | while len(self.container) > col:
51 | cols.append(col)
52 | col *= 2
53 |
54 | for i, v in enumerate(cols):
55 | buff = cols[-1 - i] // 2
56 | to_show += buff * ' '
57 | for idx in range(v):
58 | if l:
59 | to_show += str(l.pop(0)) + ' '
60 | to_show += '\n'
61 |
62 | return to_show
63 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_binheap.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Testing binary Heap."""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 |
6 | @pytest.fixture
7 | def empty_heap():
8 | """Fixture for empty_heap."""
9 | from src.binheap import Binheap
10 | bh = Binheap()
11 | return bh
12 |
13 |
14 | @pytest.fixture
15 | def heap():
16 | """Fixture for a heap."""
17 | from src.binheap import Binheap
18 | bh = Binheap([10, 4, 2, 6, 13, 72, 1, 49])
19 | return bh
20 |
21 |
22 | def test_push_val_to_head(empty_heap):
23 | """Test push first val adds to the head."""
24 | empty_heap.push(3)
25 | assert empty_heap.container == [None, 3]
26 |
27 |
28 | def test_push_val(empty_heap):
29 | """Test push second val adds to the tree."""
30 | empty_heap.push(3)
31 | empty_heap.push(2)
32 | assert empty_heap.container == [None, 3, 2]
33 |
34 |
35 | def test_push_val_large(empty_heap):
36 | """Test push val for larger number."""
37 | empty_heap.push(3)
38 | empty_heap.push(2)
39 | empty_heap.push(1)
40 | empty_heap.push(16)
41 | assert empty_heap.container == [None, 16, 3, 1, 2]
42 |
43 |
44 | def test_push_on_empty(empty_heap):
45 | """Test push on an empty list."""
46 | empty_heap.push(1)
47 | assert empty_heap.container == [None, 1]
48 |
49 |
50 | def test_initialize_iterable(heap):
51 | """Test heap can be initialized with iterable."""
52 | assert heap.container == [None, 72, 49, 13, 10, 6, 2, 1, 4]
53 |
54 |
55 | def test_display(heap):
56 | """Test the display method."""
57 | tree = ' 72 \n 49 13 \n 10 6 2 1 \n4 \n'
58 | assert heap.display() == tree
59 |
60 |
61 | def test_pop(heap):
62 | """Test pop method."""
63 | heap.pop()
64 | assert heap.container == [None, 49, 13, 10, 6, 2, 1, 4]
65 |
66 |
67 | def test_push_pop(heap):
68 | """Test push followed by a pop."""
69 | heap.push(5)
70 | heap.pop()
71 | assert heap.container == [None, 49, 13, 10, 6, 2, 1, 4, 5]
72 |
73 |
74 | def test_pop_empty(empty_heap):
75 | """Test pop on an empty list."""
76 | with pytest.raises(IndexError):
77 | empty_heap.pop()
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/deque.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Python implementation of a deque."""
2 |
3 | from src.dll import DoubleLinkedList
4 |
5 |
6 | class Deque(object):
7 | """Deque data structure.
8 |
9 | Supports the following methods
10 | append(val): adds value to the end of the deque
11 | appendleft(val): adds a value to the front of the deque
12 | pop(): removes a value from the end of the deque and returns it (raises
13 | an exception if the deque is empty)
14 | popleft(): removes a value from the front of the deque and returns it
15 | (raises an exception if the deque is empty)
16 | peek(): returns the next value that would be returned by pop but leaves
17 | the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty)
18 | peekleft(): returns the next value that would be returned by popleft but
19 | leaves the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty)
20 | size(): returns the count of items in the queue (returns 0 if the queue
21 | is empty).
22 | """
23 |
24 | def __init__(self, data=None):
25 | """Initialize deque."""
26 | self._container = DoubleLinkedList(data)
27 |
28 | def append(self, val):
29 | """Add value to the end of the deque."""
30 | self._container.append(val)
31 |
32 | def appendleft(self, val):
33 | """Add a value to the front of the deque."""
34 | self._container.push(val)
35 |
36 | def pop(self):
37 | """Remove a value from the end of the deque and returns it."""
38 | return self._container.shift()
39 |
40 | def popleft(self):
41 | """Remove a value from the front of the deque and returns it."""
42 | return self._container.pop()
43 |
44 | def peek(self):
45 | """Return the next value that would be returned by pop."""
46 | if self._container.head:
47 | return self._container.head.data
48 | return None
49 |
50 | def peekleft(self):
51 | """Return the next value from the front of the deque."""
52 | if self._container.tail:
53 | return self._container.tail.data
54 | return None
55 |
56 | def size(self):
57 | """Return the count of items in the queue."""
58 | return self._container._length
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/graph.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Python implementation of a Graph Data structure."""
2 |
3 |
4 | class Graph(object):
5 | """
6 | Graph implementation.
7 |
8 | Graph data structure supports following methods:
9 |
10 | nodes(): return a list of all nodes in the graph.
11 | edges(): return a list of all edges in the graph.
12 | add_node(n): adds a new node 'n' to the graph.
13 | add_edge(n1, n2): adds a new edge to the graph connecting 'n1' and 'n2', if
14 | either n1 or n2 are not already present in the graph, they should be added.
15 | del_node(n): deletes the node 'n' from the graph, raises an error if no
16 | such node exists.
17 | del_edge(n1, n2): deletes the edge connecting 'n1' and 'n2' from the graph,
18 | raises an error if no such edge exists.
19 | has_node(n): True if node 'n' is contained in the graph, False if not.
20 | neighbors(n): returns the list of all nodes connected to 'n' by edges,
21 | raises an error if n is not in g.
22 | adjacent(n1, n2): returns True if there is an edge connecting n1 and n2,
23 | False if not, raises an error if either of the supplied nodes are not in g.
24 | """
25 |
26 | def __init__(self, data=None):
27 | """Initialize graph."""
28 | self.graph = {}
29 | if data:
30 | for i in data:
31 | self.add_node(i)
32 |
33 | def nodes(self):
34 | """Return a list of all nodes in the graph."""
35 | return list(self.graph.keys())
36 |
37 | def edges(self):
38 | """Return a list of all edges in the graph."""
39 | return [edge for edges in self.graph.values() for edge in edges]
40 |
41 | def add_node(self, n):
42 | """Add a new node to the graph."""
43 | self.graph.setdefault(n, set())
44 |
45 | def add_edge(self, n1, n2):
46 | """Add new edge to the graph."""
47 | self.graph.setdefault(n1, set([n2]))
48 | self.graph.setdefault(n2, set())
49 | self.graph[n1].add(n2)
50 |
51 | def del_node(self, n):
52 | """Delete the node 'n' from the graph."""
53 | del self.graph[n]
54 | for k in self.graph:
55 | self.graph[k].discard(n)
56 |
57 | def del_edge(self, n1, n2):
58 | """Delete the edge connecting n1 and n2."""
59 | self.graph[n1].remove(n2)
60 |
61 | def has_node(self, n):
62 | """Return boolean if 'n' is in the graph."""
63 | return n in self.graph
64 |
65 | def neighbors(self, n):
66 | """Return the list of all nodes connected to n by edges."""
67 | return self.graph[n]
68 |
69 | def adjacent(self, n1, n2):
70 | """Return boolean if there is an edge connecting n1 and n2."""
71 | return n2 in self.neighbors(n1)
72 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_queue.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Testing module for queue data structure."""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 |
6 | @pytest.fixture
7 | def test_queues():
8 | """Fixture for queue tests."""
9 | from src.a_queue import Queue
10 | zero = Queue()
11 | one = Queue(3)
12 | multi = Queue([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
13 | return zero, one, multi
14 |
15 |
16 | def test_enque_adds_data(test_queues):
17 | """Test enque adds data to the tail."""
18 | test_queues[0].enqueue(3)
19 | assert test_queues[0]._container.tail.data is 3
20 |
21 |
22 | def test_enqueue_adds_data_to_tail(test_queues):
23 | """Test enqueue adds to the tail."""
24 | test_queues[1].enqueue(2)
25 | assert test_queues[1]._container.tail.data is 2
26 |
27 |
28 | def test_enqueue_adds_data_to_tail_and_points_to_prev(test_queues):
29 | """Test enqueue adds to the tail and point to prev tail."""
30 | test_queues[1].enqueue(2)
31 | assert test_queues[1]._container.tail.prev.data is 3
32 |
33 |
34 | def test_enque_adds_to_size(test_queues):
35 | """Test enqueue adds size."""
36 | test_queues[2].enqueue(6)
37 | assert test_queues[2]._container._length is 6
38 |
39 |
40 | def test_dequeue_removes_data(test_queues):
41 | """Test dequeue removes data."""
42 | test_queues[1].dequeue()
43 | assert test_queues[1]._container.head is None
44 |
45 |
46 | def test_removes_data_from_head_and_updates_pointer(test_queues):
47 | """Test deque updates pointers."""
48 | test_queues[2].dequeue()
49 | assert test_queues[1]._container.head.data is 3
50 |
51 |
52 | def test_deque_removes_from_size(test_queues):
53 | """Test enqueue adds size."""
54 | test_queues[2].dequeue()
55 | assert test_queues[2]._container._length is 4
56 |
57 |
58 | def test_peek_returns_head(test_queues):
59 | """Test peek returns head of list."""
60 | assert test_queues[2].peek() is 5
61 |
62 |
63 | def test_peek_on_empty(test_queues):
64 | """Test peek returns None when empty."""
65 | assert test_queues[0].peek() is None
66 |
67 |
68 | def test_dequeue_to_get_entire_queue(test_queues):
69 | """Test successive dequeues returns the queue."""
70 | q = []
71 | while test_queues[2]._container._length > 0:
72 | q.append(test_queues[2].dequeue())
73 | assert q == [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
74 |
75 |
76 | def test_dequeue_on_empty_list(test_queues):
77 | """Test dequeue on an empty list."""
78 | with pytest.raises(IndexError):
79 | test_queues[0].dequeue()
80 |
81 |
82 | def test_size_on_empty_queue(test_queues):
83 | """Test size method on empty."""
84 | assert test_queues[0].size() is 0
85 |
86 |
87 | def test_size_on_queue_of_one(test_queues):
88 | """Test size method on a queue of one."""
89 | assert test_queues[1].size() is 1
90 |
91 |
92 | def test_size_on_longer_queue(test_queues):
93 | """Test size method on empty."""
94 | assert test_queues[2].size() is 5
95 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/linked_list.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Implementation of Linked List in Python."""
2 |
3 |
4 | class Node(object):
5 | """Node (data element) object.
6 |
7 | Data attribute for data storage and Next for pointer to next node.
8 | """
9 |
10 | def __init__(self, data, next_node=None):
11 | """Attribute data and next_node."""
12 | self.data = data
13 | self.next = next_node
14 |
15 |
16 | class LinkedList(object):
17 | """Method for linked list.
18 |
19 | push(val) - will insert the value at the head of the list.
20 | pop() - remove the first value off the head and return it.
21 | size() - will return the length of the list.
22 | search(val) - will return the node containing val in the list, if
23 | present, else None
24 | remove(node) - will remove the given node from the list, wherever
25 | it might be (node must be an item in the list)
26 | display() - will return a unicode string representing the list as
27 | if it were a Python tuple literal: "(12, 'sam', 37, 'tango')"
28 | """
29 |
30 | def __init__(self, data=None):
31 | """Linked list initialized with head."""
32 | self._length = 0
33 | self.head = None
34 | try:
35 | for val in data:
36 | self.push(val)
37 | except TypeError:
38 | if data:
39 | self.push(data)
40 |
41 | def push(self, val):
42 | """Insert a value at the head of the list."""
43 | old_head = self.head
44 | self.head = Node(val, old_head)
45 | self._length += 1
46 |
47 | def pop(self):
48 | """Remove the first value and return it."""
49 | if not self.head:
50 | raise IndexError('Cannot pop from an empty list')
51 | to_return = self.head
52 | self.head = self.head.next
53 | self._length -= 1
54 | return to_return.data
55 |
56 | def size(self):
57 | """Return the length of the list."""
58 | return self._length
59 |
60 | def search(self, val):
61 | """Return the node containing val."""
62 | curr = self.head
63 | while curr:
64 | if curr.data == val:
65 | return curr
66 | curr = curr.next
67 |
68 | def remove(self, val):
69 | """Remove node from list if exists."""
70 | curr = self.head
71 | if curr and val is self.head.data:
72 | self.head = self.head.next
73 | self._length -= 1
74 | while curr:
75 | if (curr.next and curr.next.data == val):
76 | curr.next = curr.next.next
77 | self._length -= 1
78 | curr = curr.next
79 |
80 | def display(self):
81 | """Display list as a tuple."""
82 | curr = self.head
83 | display = '('
84 | while curr:
85 | display += str(curr.data) + ', '
86 | curr = curr.next
87 | return display[:-2] + ')'
88 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/dll.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Implementation of a double linked list in Python."""
2 |
3 |
4 | class Node(object):
5 | """Node class for data storage."""
6 |
7 | def __init__(self, data=None, next_node=None, prev=None):
8 | """Initialize Node."""
9 | self.data = data
10 | self.next = next_node
11 | self.prev = prev
12 |
13 | def __repr__(self):
14 | """String representation."""
15 | return "Value: {}".format(self.data)
16 |
17 |
18 | class DoubleLinkedList(object):
19 | """Double linked list impplementation.
20 |
21 | Methods supported
22 | push(val) - will insert the value (val) at the head of the list
23 | append(val) - will append the value (val) at the tail of the list
24 | pop() - will pop the first val off the head of the list and return it.
25 | shift() - will remove the last val from the tail of the list and return it.
26 | remove(val) - will remove the first instance of (val) found in the list,
27 | starting from the head.
28 | """
29 |
30 | def __init__(self, data=None):
31 | """Initialize list."""
32 | self.head = None
33 | self.tail = None
34 | self._length = 0
35 | try:
36 | for val in data:
37 | self.push(val)
38 | except TypeError:
39 | if data:
40 | self.push(data)
41 |
42 | def push(self, val):
43 | """Add val to the head of the list."""
44 | old_head = self.head
45 | self.head = Node(val, next_node=old_head)
46 | if old_head:
47 | old_head.prev = self.head
48 | if not self.tail:
49 | self.tail = self.head
50 | self._length += 1
51 |
52 | def pop(self):
53 | """Remove the val from the head of the list."""
54 | to_return = self.head
55 | if self._length < 1:
56 | raise IndexError('Cannot pop from an empty list.')
57 |
58 | new_head = self.head.next
59 | if new_head:
60 | new_head.prev = None
61 | self.head = new_head
62 | self._length -= 1
63 | if self._length < 1:
64 | self.tail = None
65 | return to_return.data
66 |
67 | def append(self, val):
68 | """Add val to the tail of the list."""
69 | old_tail = self.tail
70 | self.tail = Node(val, prev=old_tail)
71 | if old_tail:
72 | old_tail.next = self.tail
73 | if self._length < 1:
74 | self.head = self.tail
75 | self._length += 1
76 |
77 | def shift(self):
78 | """Remove the val from the tail of the list."""
79 | to_return = self.tail
80 | if self._length < 1:
81 | raise IndexError('Cannot shift from an empty list.')
82 |
83 | new_tail = self.tail.prev
84 | if new_tail:
85 | new_tail.next = None
86 | self.tail = new_tail
87 | self._length -= 1
88 | if self._length < 1:
89 | self.tail = None
90 | return to_return.data
91 |
92 | def remove(self, val):
93 | """Remove first occurance of val from list."""
94 | curr = self.head
95 | while curr:
96 | if curr.data is val:
97 | if self._length is 1:
98 | self.head, self.tail = None, None
99 | elif curr is not self.head and curr is not self.tail:
100 | curr.next.prev, curr.prev.next = curr.prev, curr.next
101 | elif curr is self.head:
102 | self.head, curr.next.prev = curr.next, None
103 | elif curr is self.tail:
104 | self.tail, curr.prev.next = curr.prev, None
105 | self._length -= 1
106 | return
107 | curr = curr.next
108 |
109 | raise ValueError('{} is not in the list'.format(val))
110 |
111 | def _repr(self):
112 | """Return list representation of dll."""
113 | l = []
114 | while True:
115 | try:
116 | popped_data = self.pop()
117 | l.append(popped_data)
118 | except IndexError:
119 | break
120 | return l
121 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_graph.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Test module for graph."""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 |
6 | @pytest.fixture
7 | def test_graph():
8 | """Fixture for graph."""
9 | from src.graph import Graph
10 | g = Graph(['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E'])
11 | g1 = Graph(['A'])
12 | g0 = Graph()
13 | return g0, g1, g
14 |
15 |
16 | def test_nodes_empty(test_graph):
17 | """Test nodes method list."""
18 | assert test_graph[0].nodes() == []
19 |
20 |
21 | def test_nodes_one(test_graph):
22 | """Test nodes method list."""
23 | assert test_graph[1].nodes() == ['A']
24 |
25 |
26 | def test_nodes_graph(test_graph):
27 | """Test nodes method list."""
28 | assert sorted(test_graph[2].nodes()) == ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E']
29 |
30 |
31 | def test_add_nodes(test_graph):
32 | """Test add node adds a node."""
33 | test_graph[0].add_node('A')
34 | assert test_graph[0].nodes() == ['A']
35 |
36 |
37 | def test_add_nodes_dont_duplicate(test_graph):
38 | """Test add node doesn't duplicate."""
39 | test_graph[1].add_node('A')
40 | assert test_graph[1].nodes() == ['A']
41 |
42 |
43 | def test_add_edge_known_nodes(test_graph):
44 | """Test add an edge."""
45 | test_graph[2].add_edge('A', 'B')
46 | assert test_graph[2].graph['A'] == {'B'}
47 |
48 |
49 | def test_add_egde_new_nodes(test_graph):
50 | """Test add an edge with nodes that don't exist."""
51 | test_graph[0].add_edge('A', 'B')
52 | assert test_graph[0].graph == {'A': {'B'}, 'B': set()}
53 |
54 |
55 | def test_edges_full(test_graph):
56 | """Test edges returned in list with edge method."""
57 | test_graph[2].add_edge('A', 'B')
58 | test_graph[2].add_edge('A', 'C')
59 | assert sorted(test_graph[2].edges()) == ['B', 'C']
60 |
61 |
62 | def test_edges_empty(test_graph):
63 | """Test edges method for empty."""
64 | assert test_graph[0].edges() == []
65 |
66 |
67 | def test_remove_edge_full(test_graph):
68 | """Test remove edge full graph."""
69 | test_graph[2].add_edge('A', 'B')
70 | test_graph[2].del_edge('A', 'B')
71 | assert test_graph[2].edges() == []
72 |
73 |
74 | def test_remove_edge_empty(test_graph):
75 | """Test remove edge empty graph."""
76 | with pytest.raises(KeyError):
77 | test_graph[0].del_edge('A', 'B')
78 |
79 |
80 | def test_has_node_true(test_graph):
81 | """Test has node true."""
82 | assert test_graph[2].has_node('A')
83 |
84 |
85 | def test_has_node_false(test_graph):
86 | """Test has node false."""
87 | assert not test_graph[0].has_node('A')
88 |
89 |
90 | def test_has_neighbors_true(test_graph):
91 | """Test neighbors when exist."""
92 | test_graph[2].add_edge('A', 'B')
93 | assert test_graph[2].neighbors('A') == set(['B'])
94 |
95 |
96 | def test_has_neighbors_false(test_graph):
97 | """Test neighbors when there are none."""
98 | assert test_graph[2].neighbors('A') == set()
99 |
100 |
101 | def test_adjacent_true(test_graph):
102 | """Test has node true."""
103 | test_graph[2].add_edge('A', 'B')
104 | assert test_graph[2].adjacent('A', 'B')
105 |
106 |
107 | def test_adjacent_false(test_graph):
108 | """Test ajacent false."""
109 | assert not test_graph[2].adjacent('A', 'B')
110 |
111 |
112 | def test_adjacent_error(test_graph):
113 | """Test adjacent for error."""
114 | with pytest.raises(KeyError):
115 | test_graph[0].adjacent('A', 'B')
116 |
117 |
118 | def test_graph_del_node_empty(test_graph):
119 | """Test graph del node when node isn't there."""
120 | with pytest.raises(KeyError):
121 | test_graph[0].del_node('A')
122 |
123 |
124 | def test_graph_del_node_no_edges(test_graph):
125 | """Test graph del node when node no edges."""
126 | test_graph[1].del_node('A')
127 | assert test_graph[1].graph == {}
128 |
129 |
130 | def test_graph_del_node_with_edges(test_graph):
131 | """Test graph del node with edges."""
132 | test_graph[2].add_edge('A', 'C')
133 | test_graph[2].add_edge('B', 'C')
134 | test_graph[2].add_edge('B', 'C')
135 | test_graph[2].add_edge('A', 'D')
136 | test_graph[2].del_node('C')
137 | assert sorted(test_graph[2].nodes()) == ['A', 'B', 'D', 'E']
138 | assert sorted(test_graph[2].edges()) == ['D']
139 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_linked_list.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Test implementation of a linked list."""
2 |
3 | import sys
4 | import os
5 | import pytest
6 |
7 | myPath = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(__file__))
8 | sys.path.insert(0, myPath + '/../')
9 |
10 |
11 | @pytest.fixture
12 | def test_lists():
13 | """Fixture for linked list tests."""
14 | from src.linked_list import LinkedList
15 | empty = LinkedList()
16 | one = LinkedList(5)
17 | multi = LinkedList([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
18 | return empty, one, multi
19 |
20 |
21 | def test_node_has_data():
22 | """Test node object has data."""
23 | from src.linked_list import Node
24 | ll = Node(5)
25 | assert ll.data is 5 and ll.next is None
26 |
27 |
28 | def test_push_adds_to_the_head(test_lists):
29 | """Test push, adds to the head of the list."""
30 | ll = test_lists[1]
31 | assert ll.head.data is 5
32 |
33 |
34 | def test_ll_has_head(test_lists):
35 | """Test ll with iterable has a head."""
36 | ll = test_lists[2]
37 | assert ll.head.data is 5
38 |
39 |
40 | def test_empty_ll_head_none(test_lists):
41 | """Test empty ll has a head of None."""
42 | assert test_lists[0].head is None
43 |
44 |
45 | def test_size_one(test_lists):
46 | """Test ll of one has length of one."""
47 | assert test_lists[1]._length is 1
48 |
49 |
50 | def test_length_multi(test_lists):
51 | """Test ll of multi has length."""
52 | assert test_lists[2]._length is 5
53 |
54 |
55 | def test_empty_list_length(test_lists):
56 | """Test empty list has no length."""
57 | assert test_lists[0]._length is 0
58 |
59 |
60 | def test_when_push_increases_length(test_lists):
61 | """Test push increases length."""
62 | ll = test_lists[1]
63 | length = ll._length
64 | ll.push(3)
65 | assert ll._length is length + 1
66 |
67 |
68 | def test_pop_multi_list(test_lists):
69 | """Test pop on list of 5."""
70 | ll = test_lists[2]
71 | ll.pop()
72 | assert ll.head.data is 4
73 |
74 |
75 | def test_pop_returns_data(test_lists):
76 | """Test pop method returns data of removed node."""
77 | returned = test_lists[2].pop()
78 | assert returned is 5
79 |
80 |
81 | def test_pop_decreases_length(test_lists):
82 | """Test pop decreases length."""
83 | ll = test_lists[2]
84 | length = ll._length
85 | ll.pop()
86 | assert ll._length is length - 1
87 |
88 |
89 | def test_pop_list_one(test_lists):
90 | """Test pop on list of one."""
91 | test_lists[1].pop()
92 | assert test_lists[1].head is None
93 |
94 |
95 | def test_pop_decreases_length_to_zero(test_lists):
96 | """Test pop decreases length."""
97 | ll = test_lists[1]
98 | length = ll._length
99 | ll.pop()
100 | assert ll._length is length - 1
101 |
102 |
103 | def test_cant_pop_on_empty_list(test_lists):
104 | """Test pop on an empty list raises error."""
105 | with pytest.raises(IndexError, message='Cannot pop from an empty list'):
106 | test_lists[0].pop()
107 |
108 |
109 | def test_size_function(test_lists):
110 | """Test size on empty list."""
111 | assert test_lists[0].size() is 0
112 |
113 |
114 | def test_size_function_list(test_lists):
115 | """Test size on multi list."""
116 | assert test_lists[2].size() is 5
117 |
118 |
119 | def test_size_after_push(test_lists):
120 | """Test size after push."""
121 | ll = test_lists[0]
122 | length = ll.size()
123 | ll.push(4)
124 | assert ll.size() is length + 1
125 |
126 |
127 | def test_size_after_pop(test_lists):
128 | """Test size after pop."""
129 | ll = test_lists[2]
130 | length = ll.size()
131 | ll.pop()
132 | assert ll.size() is length - 1
133 |
134 |
135 | def test_size_after_push_and_pop(test_lists):
136 | """Test size after push and pop."""
137 | ll = test_lists[2]
138 | ll.push(4)
139 | ll.push(2)
140 | ll.pop()
141 | assert ll.size() is 6
142 |
143 |
144 | def test_search_on_list(test_lists):
145 | """Test search returns node."""
146 | assert test_lists[2].search(2).data is 2
147 |
148 |
149 | def test_search_on_list_no_value(test_lists):
150 | """Test search for a list with no val."""
151 | assert test_lists[2].search(9) is None
152 |
153 |
154 | def test_remove_on_list(test_lists):
155 | """Test remove work for node in list."""
156 | test_lists[2].remove(4)
157 | assert test_lists[2].size() is 4
158 |
159 |
160 | def test_remove_second_end_of_list(test_lists):
161 | """Test remove node second last in list."""
162 | test_lists[2].remove(2)
163 | assert test_lists[2].size() is 4
164 |
165 |
166 | def test_remove_on_end_of_list(test_lists):
167 | """Test remove node last in list."""
168 | test_lists[2].remove(1)
169 | assert test_lists[2].size() is 4
170 |
171 |
172 | def test_remove_on_list_with_no_node(test_lists):
173 | """Test remove node that isnt in list."""
174 | test_lists[2].remove(9)
175 | assert test_lists[2].size() is 5
176 |
177 |
178 | def test_remove_on_empty_list(test_lists):
179 | """Test remove from empty list."""
180 | test_lists[0].remove(1)
181 | assert test_lists[0].size() is 0
182 |
183 |
184 | def test_remove_on_list_one_list(test_lists):
185 | """Test remove from list of 1."""
186 | test_lists[1].remove(5)
187 | assert test_lists[1].size() is 0
188 |
189 |
190 | def test_remove_on_start_of_list(test_lists):
191 | """Test remove start node in list."""
192 | test_lists[2].remove(5)
193 | assert test_lists[2].size() is 4
194 |
195 |
196 | def test_display_method(test_lists):
197 | """Test display method."""
198 | assert test_lists[2].display() == '(5, 4, 3, 2, 1)'
199 |
200 |
201 | def test_display_method_one(test_lists):
202 | """Test display method."""
203 | assert test_lists[1].display() == '(5)'
204 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_bst.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Test binary search tree implementation."""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 |
6 | @pytest.fixture
7 | def test_bsts():
8 | """Fixture for bst."""
9 | from src.bst import Bst
10 | empty = Bst()
11 | one = Bst([5])
12 | three = Bst([5, 3, 7])
13 | balance = Bst([5, 3, 2, 4, 9, 7, 10])
14 | leftheavy = Bst([5, 3, 2, 1])
15 | rightheavy = Bst([5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
16 | return empty, one, three, balance, leftheavy, rightheavy
17 |
18 |
19 | @pytest.fixture
20 | def test_traversals():
21 | """Fixture for traversals."""
22 | from src.bst import Bst
23 | fixture = {
24 | 'tree': Bst(['F', 'B', 'A', 'D', 'C', 'E', 'G', 'I', 'H']),
25 | 'empty': Bst(),
26 | 'pre_order': ['F', 'B', 'A', 'D', 'C', 'E', 'G', 'I', 'H'],
27 | 'in_order': ['A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'I'],
28 | 'post_order': ['A', 'C', 'E', 'D', 'B', 'H', 'I', 'G', 'F'],
29 | 'breadth': ['F', 'B', 'G', 'A', 'D', 'I', 'C', 'E', 'H']
30 | }
31 | return fixture
32 |
33 |
34 | def test_node_is_leaf(test_bsts):
35 | """Test node is leaf bst."""
36 | assert test_bsts[1].root._is_leaf()
37 |
38 |
39 | def test_insert_sets_root(test_bsts):
40 | """Test first insert updates root."""
41 | test_bsts[0].insert(5)
42 | assert test_bsts[0].root.val == 5
43 |
44 |
45 | def test_insert_updates_pointers(test_bsts):
46 | """Test insert updates pointers."""
47 | test_bsts[1].insert(3)
48 | assert test_bsts[1].root.left.val == 3
49 | assert test_bsts[1].root.left.parent == test_bsts[1].root
50 |
51 |
52 | def test_insert_smallest_left(test_bsts):
53 | """Test insert the smallest to the left."""
54 | test_bsts[1].insert(3)
55 | assert test_bsts[1].root.left.val < test_bsts[1].root.val
56 |
57 |
58 | def test_insert_largest_right(test_bsts):
59 | """Test insert the largest to the right."""
60 | test_bsts[1].insert(7)
61 | assert test_bsts[1].root.right.val > test_bsts[1].root.val
62 |
63 |
64 | def test_insert_increases_size(test_bsts):
65 | """Test insert increases size."""
66 | test_bsts[0].insert(4)
67 | assert test_bsts[0].size() == 1
68 |
69 |
70 | def test_contains_method(test_bsts):
71 | """Test contains on number that exists."""
72 | assert test_bsts[2].contains(5)
73 | assert test_bsts[2].contains(3)
74 | assert test_bsts[2].contains(7)
75 |
76 |
77 | def test_contains_method_no_val(test_bsts):
78 | """Test contains that doesnt exist."""
79 | assert not test_bsts[4].contains(10)
80 |
81 |
82 | def test_depth_method(test_bsts):
83 | """Test depth method."""
84 | depths = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 6]
85 | assert all(tree.depth() == depths[idx]
86 | for idx, tree in enumerate(test_bsts))
87 |
88 |
89 | def test_balance_method(test_bsts):
90 | """Test the balance method."""
91 | balance = [0, 0, 0, 0, 3, -5]
92 | assert all(tree.balance() == balance[idx]
93 | for idx, tree in enumerate(test_bsts))
94 |
95 |
96 | def test_search_method_node_exists(test_bsts):
97 | """Test search method for a node that exists."""
98 | assert all(tree.search(5) for tree in test_bsts[1:])
99 |
100 |
101 | def test_pre_order(test_traversals):
102 | """Test preorder for a traversal."""
103 | path = [i for i in test_traversals['tree'].pre_order()]
104 | assert path == test_traversals['pre_order']
105 |
106 |
107 | def test_in_order(test_traversals):
108 | """Test inorder for a traversal."""
109 | path = [i for i in test_traversals['tree'].in_order()]
110 | assert path == test_traversals['in_order']
111 |
112 |
113 | def test_post_order(test_traversals):
114 | """Test postorder for a traversal."""
115 | path = [i for i in test_traversals['tree'].post_order()]
116 | assert path == test_traversals['post_order']
117 |
118 |
119 | def test_breadth_first(test_traversals):
120 | """Test breadth first for a traversal."""
121 | path = [i for i in test_traversals['tree'].breadth_first()]
122 | assert path == test_traversals['breadth']
123 |
124 |
125 | def test_traversals_none(test_traversals):
126 | """Test traversal when empty."""
127 | path = [i for i in test_traversals['empty'].in_order()]
128 | assert path == []
129 |
130 |
131 | def test_del_false(test_bsts):
132 | """Test delete for a node not in tree."""
133 | size = test_bsts[2].size()
134 | test_bsts[2].delete(1)
135 | assert test_bsts[2].size() == size
136 |
137 |
138 | def test_del_empty_tree(test_bsts):
139 | """Test delete for an empty tree."""
140 | test_bsts[0].delete(1)
141 | assert test_bsts[0].size() == 0
142 |
143 |
144 | def test_remove_leaf_left(test_bsts):
145 | """Test delete leaf on left."""
146 | test_bsts[2].delete(3)
147 | assert not test_bsts[2].contains(3)
148 | assert test_bsts[2].size() is 2
149 |
150 |
151 | def test_remove_leaf_right(test_bsts):
152 | """Test delete leaf on right."""
153 | test_bsts[2].delete(7)
154 | assert not test_bsts[2].contains(7)
155 | assert test_bsts[2].size() is 2
156 |
157 |
158 | def test_remove_leaf_root(test_bsts):
159 | """Test delete leaf that is root."""
160 | test_bsts[1].delete(5)
161 | assert not test_bsts[1].contains(5)
162 | assert test_bsts[1].size() is 0
163 |
164 |
165 | def test_remove_one_child_left(test_bsts):
166 | """Test delete node one child, left."""
167 | test_bsts[4].delete(3)
168 | assert not test_bsts[4].contains(3)
169 | assert test_bsts[4].size() is 3
170 |
171 |
172 | def test_remove_one_child_right(test_bsts):
173 | """Test delete node one child, right."""
174 | test_bsts[5].delete(6)
175 | assert not test_bsts[5].contains(6)
176 | assert test_bsts[5].size() is 5
177 |
178 |
179 | def test_remove_one_child_right_on_left(test_bsts):
180 | """Test delete node that is left child with one child, right."""
181 | test_bsts[1].insert(2)
182 | test_bsts[1].insert(4)
183 | test_bsts[1].delete(2)
184 | assert not test_bsts[1].contains(2)
185 | assert test_bsts[1].size() is 2
186 |
187 |
188 | def test_remove_one_child_left_on_right(test_bsts):
189 | """Test delete node that is right child with one child, left."""
190 | test_bsts[1].insert(7)
191 | test_bsts[1].insert(6)
192 | test_bsts[1].delete(7)
193 | assert not test_bsts[1].contains(7)
194 | assert test_bsts[1].size() is 2
195 |
196 |
197 | def test_remove_one_child_root(test_bsts):
198 | """Test delete node that is root with one child."""
199 | test_bsts[1].insert(7)
200 | test_bsts[1].delete(5)
201 | assert not test_bsts[1].contains(5)
202 | assert test_bsts[1].size() is 1
203 | assert test_bsts[1].root.val is 7
204 |
205 |
206 | def test_delete_two_children(test_bsts):
207 | """Test delete node with two children."""
208 | test_bsts[3].delete(3)
209 | assert not test_bsts[3].contains(3)
210 | assert test_bsts[3].size() is 6
211 |
212 |
213 | def test_delete_two_children_root(test_bsts):
214 | """Test delete node with two children root."""
215 | test_bsts[3].delete(5)
216 | assert not test_bsts[3].contains(5)
217 | assert test_bsts[3].size() is 6
218 | assert test_bsts[3].root.val is 7
219 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_deque.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Test deque implementation."""
2 |
3 |
4 | import pytest
5 |
6 |
7 | @pytest.fixture
8 | def test_deque():
9 | """Deque fixtures."""
10 | from src.deque import Deque
11 | empty = Deque()
12 | one = Deque(3)
13 | multi = Deque([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
14 | return empty, one, multi
15 |
16 |
17 | def test_init_deque_has_data(test_deque):
18 | """Test deque has data."""
19 | assert test_deque[2]._container
20 |
21 |
22 | def test_init_deque_has_head(test_deque):
23 | """Test deque has head."""
24 | assert test_deque[2]._container.head.data is 5
25 |
26 |
27 | def test_init_deque_has_tail(test_deque):
28 | """Test deque has tail."""
29 | assert test_deque[2]._container.tail.data is 1
30 |
31 |
32 | def test_append_adds_data(test_deque):
33 | """Test append adds data to the tail."""
34 | test_deque[0].append(3)
35 | assert test_deque[0]._container.tail.data is 3
36 |
37 |
38 | def test_append_adds_data_to_tail(test_deque):
39 | """Test append adds to the tail."""
40 | test_deque[1].append(2)
41 | assert test_deque[1]._container.tail.data is 2
42 |
43 |
44 | def test_append_adds_data_to_tail_and_points_to_prev(test_deque):
45 | """Test append adds to the tail and point to prev tail."""
46 | test_deque[1].append(2)
47 | assert test_deque[1]._container.tail.prev.data is 3
48 |
49 |
50 | def test_enque_adds_to_size(test_deque):
51 | """Test append adds size."""
52 | test_deque[2].append(6)
53 | assert test_deque[2]._container._length is 6
54 |
55 |
56 | def test_appendleft_increases_length(test_deque):
57 | """Test appendleft increases length."""
58 | test_deque[0].appendleft(2)
59 | assert test_deque[0]._container._length is 1
60 |
61 |
62 | def test_appendleft_updates_head(test_deque):
63 | """Test appendleft updates head."""
64 | test_deque[1].appendleft(6)
65 | assert test_deque[1]._container.head.data is 6
66 |
67 |
68 | def test_appendleft_points_back(test_deque):
69 | """Test old head points to new with prev after a appendleft."""
70 | old_head = test_deque[1]._container.head
71 | test_deque[1].appendleft(6)
72 | assert test_deque[1]._container.head is old_head.prev
73 |
74 |
75 | def test_pop_reduces_length(test_deque):
76 | """Test pop reduces lists."""
77 | old_length = test_deque[2]._container._length
78 | test_deque[2].pop()
79 | assert test_deque[2]._container._length is old_length - 1
80 |
81 |
82 | def test_pop_removes_tail(test_deque):
83 | """Test pop removes tail."""
84 | new_tail = test_deque[2]._container.tail.prev.data
85 | test_deque[2].pop()
86 | assert test_deque[2]._container.tail.data is new_tail
87 |
88 |
89 | def test_pop_removes_next_pointer(test_deque):
90 | """Test pop changes prev pointer."""
91 | test_deque[2].pop()
92 | assert test_deque[2]._container.tail.next is None
93 |
94 |
95 | def test_pop_list_one(test_deque):
96 | """Test pop decreases length."""
97 | test_deque[1].pop()
98 | assert test_deque[1]._container._length is 0
99 |
100 |
101 | def test_cant_pop_on_empty_list(test_deque):
102 | """Test pop on an empty list raises error."""
103 | with pytest.raises(IndexError, message='Cannot pop from an empty list'):
104 | test_deque[0].pop()
105 |
106 |
107 | def test_pop_sequence(test_deque):
108 | """Test that entire sequence is returned by successive pops."""
109 | l = []
110 | while True:
111 | try:
112 | poped_data = test_deque[2].pop()
113 | l.append(poped_data)
114 | except IndexError:
115 | break
116 | assert l == [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
117 |
118 |
119 | def test_pop_append(test_deque):
120 | """Append data and pop it off."""
121 | test_deque[1].append(9)
122 | poped_data = test_deque[1].pop()
123 | assert poped_data is 9
124 |
125 |
126 | def test_popleft_reduces_length(test_deque):
127 | """Test popleft reduces lists."""
128 | old_length = test_deque[2]._container._length
129 | test_deque[2].popleft()
130 | assert test_deque[2]._container._length is old_length - 1
131 |
132 |
133 | def test_popleft_removes_tail(test_deque):
134 | """Test popleft removes head."""
135 | new_head = test_deque[2]._container.head.next.data
136 | test_deque[2].popleft()
137 | assert test_deque[2]._container.head.data is new_head
138 |
139 |
140 | def test_popleft_removes_next_pointer(test_deque):
141 | """Test popleft changes prev pointer."""
142 | test_deque[2].popleft()
143 | assert test_deque[2]._container.head.prev is None
144 |
145 |
146 | def test_popleft_list_one(test_deque):
147 | """Test popleft decreases length."""
148 | test_deque[1].popleft()
149 | assert test_deque[1]._container._length is 0
150 |
151 |
152 | def test_cant_popleft_on_empty_list(test_deque):
153 | """Test popleft on an empty list raises error."""
154 | with pytest.raises(
155 | IndexError, message='Cannot popleft from an empty list'
156 | ):
157 | test_deque[0].popleft()
158 |
159 |
160 | def test_popleft_sequence(test_deque):
161 | """Test that entire sequence is returned by successive poplefts."""
162 | l = []
163 | while True:
164 | try:
165 | poplefted_data = test_deque[2].popleft()
166 | l.append(poplefted_data)
167 | except IndexError:
168 | break
169 | assert l == [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
170 |
171 |
172 | def test_popleft_appendleft(test_deque):
173 | """Append data and popleft it off."""
174 | test_deque[1].appendleft(9)
175 | poplefted_data = test_deque[1].popleft()
176 | assert poplefted_data is 9
177 |
178 |
179 | def test_size_method_append(test_deque):
180 | """Append and test size."""
181 | test_deque[0].append(2)
182 | assert test_deque[0].size() == 1
183 |
184 |
185 | def test_size_method_appendleft(test_deque):
186 | """Appendleft and test size."""
187 | test_deque[0].appendleft(2)
188 | assert test_deque[0].size() == 1
189 |
190 |
191 | def test_size_method_pop(test_deque):
192 | """Pop and test size."""
193 | test_deque[1].pop()
194 | assert test_deque[0].size() == 0
195 |
196 |
197 | def test_size_method_popleft(test_deque):
198 | """Pop and test size."""
199 | test_deque[1].popleft()
200 | assert test_deque[0].size() == 0
201 |
202 |
203 | def test_peek(test_deque):
204 | """Test peek method."""
205 | peek = test_deque[2].peek()
206 | assert peek == test_deque[2]._container.head.data
207 |
208 |
209 | def test_peek_size(test_deque):
210 | """Test peek method does not change size."""
211 | size = test_deque[2].size()
212 | test_deque[2].peek()
213 | assert size == test_deque[2].size()
214 |
215 |
216 | def test_peek_empty(test_deque):
217 | """Test peek method."""
218 | peek = test_deque[0].peek()
219 | assert peek is None
220 |
221 |
222 | def test_peekleft(test_deque):
223 | """Test peekleft method."""
224 | peekleft = test_deque[2].peekleft()
225 | assert peekleft == test_deque[2]._container.tail.data
226 |
227 |
228 | def test_peekleft_size(test_deque):
229 | """Test peekleft method does not change size."""
230 | size = test_deque[2].size()
231 | test_deque[2].peekleft()
232 | assert size == test_deque[2].size()
233 |
234 |
235 | def test_peekleft_empty(test_deque):
236 | """Test peekleft method."""
237 | peekleft = test_deque[0].peekleft()
238 | assert peekleft is None
239 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_dll.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Test double linked list implementation."""
2 |
3 | import pytest
4 |
5 |
6 | @pytest.fixture
7 | def test_lists():
8 | """Dll fixtures."""
9 | from src.dll import DoubleLinkedList
10 | empty = DoubleLinkedList()
11 | one = DoubleLinkedList(3)
12 | multi = DoubleLinkedList([1, 2, 3, 4, 5])
13 | return empty, one, multi
14 |
15 |
16 | def test_node_class():
17 | """Test node class has data."""
18 | from src.dll import Node
19 | node = Node(5)
20 | assert node.data is 5
21 |
22 |
23 | def test_list_of_none(test_lists):
24 | """Test list of none head and tail is none."""
25 | assert test_lists[0].head is None
26 | assert test_lists[0].tail is None
27 |
28 |
29 | def test_list_of_one(test_lists):
30 | """Test list of one, head is tail."""
31 | assert test_lists[1].head is test_lists[1].tail
32 |
33 |
34 | def test_list_of_five(test_lists):
35 | """Test list of five."""
36 | assert test_lists[2].head.data is 5
37 | assert test_lists[2].tail.data is 1
38 |
39 |
40 | def test_prev_pointer(test_lists):
41 | """Test prev pointer."""
42 | assert test_lists[2].tail.prev.data is 2
43 |
44 |
45 | def test_next_pointer(test_lists):
46 | """Test next pointer."""
47 | assert test_lists[2].head.next.data is 4
48 |
49 |
50 | def test_push_increases_length(test_lists):
51 | """Test push increases length."""
52 | test_lists[0].push(2)
53 | assert test_lists[0]._length is 1
54 |
55 |
56 | def test_push_updates_head(test_lists):
57 | """Test push updates head."""
58 | test_lists[1].push(6)
59 | assert test_lists[1].head.data is 6
60 |
61 |
62 | def test_push_points_back(test_lists):
63 | """Test old head points to new with prev after a push."""
64 | old_head = test_lists[1].head
65 | test_lists[1].push(6)
66 | assert test_lists[1].head is old_head.prev
67 |
68 |
69 | def test_pop_reduces_length(test_lists):
70 | """Test pop reduces lists."""
71 | old_length = test_lists[2]._length
72 | test_lists[2].pop()
73 | assert test_lists[2]._length is old_length - 1
74 |
75 |
76 | def test_pop_removes_head(test_lists):
77 | """Test pop removes head."""
78 | new_head = test_lists[2].head.next.data
79 | test_lists[2].pop()
80 | assert test_lists[2].head.data is new_head
81 |
82 |
83 | def test_pop_removes_prev_pointer(test_lists):
84 | """Test pop changes prev pointer."""
85 | test_lists[2].pop()
86 | assert test_lists[2].head.prev is None
87 |
88 |
89 | def test_pop_list_one(test_lists):
90 | """Test pop decreases length."""
91 | test_lists[1].pop()
92 | assert test_lists[1]._length is 0
93 |
94 |
95 | def test_pop_returns_data(test_lists):
96 | """Test pop returns data."""
97 | assert test_lists[2].pop() is 5
98 |
99 |
100 | def test_cant_pop_on_empty_list(test_lists):
101 | """Test pop on an empty list raises error."""
102 | with pytest.raises(IndexError, message='Cannot pop from an empty list'):
103 | test_lists[0].pop()
104 |
105 |
106 | def test_append_increases_length(test_lists):
107 | """Test append increases length."""
108 | test_lists[0].append(2)
109 | assert test_lists[0]._length is 1
110 |
111 |
112 | def test_append_updates_tail(test_lists):
113 | """Test append updates tail."""
114 | test_lists[1].append(6)
115 | assert test_lists[1].tail.data is 6
116 |
117 |
118 | def test_append_points_back(test_lists):
119 | """Test old tail points to new with prev after a append."""
120 | old_tail = test_lists[1].tail
121 | test_lists[1].append(6)
122 | assert test_lists[1].tail is old_tail.next
123 |
124 |
125 | def test_append_on_empty_list(test_lists):
126 | """Test append updates tail."""
127 | test_lists[0].append(6)
128 | assert test_lists[0].tail.data is 6
129 | assert test_lists[0].head.data is 6
130 |
131 |
132 | def test_append_next_pointer_is_none(test_lists):
133 | """Test append next pointer is none."""
134 | test_lists[2].append(6)
135 | assert test_lists[2].tail.next is None
136 |
137 |
138 | def test_pop_sequence(test_lists):
139 | """Test that entire sequence is returned by successive pops."""
140 | l = []
141 | while True:
142 | try:
143 | popped_data = test_lists[2].pop()
144 | l.append(popped_data)
145 | except IndexError:
146 | break
147 | assert l == [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
148 |
149 |
150 | def test_push_pop(test_lists):
151 | """Push data and pop it off."""
152 | test_lists[1].push(9)
153 | popped_data = test_lists[1].pop()
154 | assert popped_data is 9
155 |
156 |
157 | def test_shift_reduces_length(test_lists):
158 | """Test shift reduces lists."""
159 | old_length = test_lists[2]._length
160 | test_lists[2].shift()
161 | assert test_lists[2]._length is old_length - 1
162 |
163 |
164 | def test_shift_removes_tail(test_lists):
165 | """Test shift removes tail."""
166 | new_tail = test_lists[2].tail.prev.data
167 | test_lists[2].shift()
168 | assert test_lists[2].tail.data is new_tail
169 |
170 |
171 | def test_shift_removes_next_pointer(test_lists):
172 | """Test shift changes prev pointer."""
173 | test_lists[2].shift()
174 | assert test_lists[2].tail.next is None
175 |
176 |
177 | def test_shift_list_one(test_lists):
178 | """Test shift decreases length."""
179 | test_lists[1].shift()
180 | assert test_lists[1]._length is 0
181 |
182 |
183 | def test_cant_shift_on_empty_list(test_lists):
184 | """Test shift on an empty list raises error."""
185 | with pytest.raises(IndexError, message='Cannot shift from an empty list'):
186 | test_lists[0].shift()
187 |
188 |
189 | def test_shift_sequence(test_lists):
190 | """Test that entire sequence is returned by successive shifts."""
191 | l = []
192 | while True:
193 | try:
194 | shifted_data = test_lists[2].shift()
195 | l.append(shifted_data)
196 | except IndexError:
197 | break
198 | assert l == [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
199 |
200 |
201 | def test_shift_append(test_lists):
202 | """Append data and shift it off."""
203 | test_lists[1].append(9)
204 | shifted_data = test_lists[1].shift()
205 | assert shifted_data is 9
206 |
207 |
208 | def test_remove_middle_of_list(test_lists):
209 | """Test remove from middle of list."""
210 | test_lists[2].remove(3)
211 | assert test_lists[2]._repr() == [5, 4, 2, 1]
212 |
213 |
214 | def test_remove_head_of_list(test_lists):
215 | """Test remove from head of list."""
216 | test_lists[2].remove(5)
217 | assert test_lists[2]._repr() == [4, 3, 2, 1]
218 |
219 |
220 | def test_remove_tail_of_list(test_lists):
221 | """Test remove from tail of list."""
222 | test_lists[2].remove(1)
223 | assert test_lists[2]._repr() == [5, 4, 3, 2]
224 |
225 |
226 | def test_remove_middle_decreases_length(test_lists):
227 | """Test remove from middle of list decreases length."""
228 | test_lists[2].remove(3)
229 | assert test_lists[2]._length is 4
230 |
231 |
232 | def test_remove_head_decreases_length(test_lists):
233 | """Test remove from head of list decreases length."""
234 | test_lists[2].remove(5)
235 | assert test_lists[2]._length is 4
236 |
237 |
238 | def test_remove_tail_decreases_length(test_lists):
239 | """Test remove from tail of list decreases length."""
240 | test_lists[2].remove(1)
241 | assert test_lists[2]._length is 4
242 |
243 |
244 | def test_remove_middle_updates_pointers(test_lists):
245 | """Test remove from middle of list updates pointers."""
246 | test_lists[2].remove(3)
247 | assert test_lists[2].head.next.next.data is 2
248 |
249 |
250 | def test_remove_head_pointers(test_lists):
251 | """Test remove from head of list changes pointers."""
252 | test_lists[2].remove(5)
253 | assert test_lists[2].head.data is 4
254 | assert test_lists[2].head.prev is None
255 |
256 |
257 | def test_remove_tail_pointers(test_lists):
258 | """Test remove from tail of list changes pointers."""
259 | test_lists[2].remove(1)
260 | assert test_lists[2].tail.data is 2
261 | assert test_lists[2].tail.next is None
262 |
263 |
264 | def test_remove_list_of_one_length(test_lists):
265 | """Test remove on list of one."""
266 | test_lists[1].remove(3)
267 | assert test_lists[1]._length is 0
268 |
269 |
270 | def test_remove_list_of_one(test_lists):
271 | """Test remove on list of one."""
272 | test_lists[1].remove(3)
273 | assert test_lists[1].head is None
274 | assert test_lists[1].tail is None
275 |
276 |
277 | def test_remove_list_of_none(test_lists):
278 | """Test remove on list of none."""
279 | with pytest.raises(ValueError):
280 | test_lists[0].remove(3)
281 |
282 |
283 | def test_remove_of_list_false(test_lists):
284 | """Test remove from middle of list."""
285 | with pytest.raises(ValueError):
286 | test_lists[2].remove(9)
287 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/bst.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """Python implementation of Binary Search Tree."""
2 |
3 | from src.a_queue import Queue
4 |
5 |
6 | class Node(object):
7 | """Node, or leaf of the BST."""
8 |
9 | def __init__(self, val=None, parent=None):
10 | """Create node object."""
11 | self.val = val
12 | self.right = None
13 | self.left = None
14 | self.parent = parent
15 | self.height = 1
16 |
17 | def _is_leaf(self):
18 | """Return true if a leaf."""
19 | return not (self.right or self.left)
20 |
21 | def _is_interior(self):
22 | """Return true if a interior node."""
23 | return (self.right and self.left)
24 |
25 | def _onlychild(self):
26 | """Return string depending on children."""
27 | if self.left and not self.right:
28 | return 'left'
29 | if self.right and not self.left:
30 | return 'right'
31 |
32 | def _side(self):
33 | """Return if left or right child of parent."""
34 | if self.parent:
35 | return 'left' if self.parent.left == self else 'right'
36 |
37 |
38 | class Bst(object):
39 | """Binary Search Tree.
40 |
41 | Binary Search tree supports the following methods:
42 |
43 | insert(val): will insert the value val into the BST. If val is
44 | already present, it will be ignored.
45 |
46 | search(val): will return the node containing that value, else None
47 |
48 | size(): will return the integer size of the BST (equal to the total
49 | no. of values stored in the tree). It will return 0 if the tree is empty.
50 |
51 | depth(): will return an integer representing the total number of
52 | levels in the tree. If there are no values, depth is 0, if one value the
53 | depth should be 1, if two values it will be 2, if three values it may be
54 | 2 or 3, depending, etc.
55 |
56 | contains(val): will return True if val is in the BST, False if not.
57 |
58 | balance(): will return an integer, positive or negative that represents
59 | how well balanced the tree is. Trees which are higher on the left than
60 | the right should return a positive value, trees which are higher on the
61 | right than the left should return a negative value. An ideally-balanced
62 | tree should return 0.
63 |
64 | in_order(): return a generator that will return the values in the tree
65 | using in-order traversal, one at a time.
66 |
67 | pre_order(): return a generator that will return the values in the tree
68 | using pre-order traversal, one at a time.
69 |
70 | post_order(): return a generator that will return the values in the tree
71 | using post-order traversal, one at a time.
72 |
73 | breadth_first(): return a generator that will return the values in the tree
74 | using breadth frist traversal, one at a time.
75 |
76 | """
77 |
78 | def __init__(self, data=None):
79 | """Initialize tree."""
80 | self._size = 0
81 | self.root = None
82 |
83 | if data:
84 | for i in data:
85 | self.insert(i)
86 |
87 | def insert(self, val):
88 | """Insert val into BST. If val is already present will be ignored."""
89 | if not self.root:
90 | self.root = Node(val)
91 | self._size += 1
92 | else:
93 | self._step(val, self.root)
94 |
95 | def _step(self, val, curr):
96 | """Decide left or right and returns height."""
97 | if val < curr.val:
98 | curr = self._set_child(curr, 'left', val)
99 | elif val > curr.val:
100 | curr = self._set_child(curr, 'right', val)
101 | return curr.height
102 |
103 | def _set_child(self, curr, side, val):
104 | """Helping."""
105 | child = getattr(curr, side)
106 | if child:
107 | count = self._step(val, child)
108 | if curr.height <= count:
109 | curr.height += 1
110 | else:
111 | setattr(curr, side, Node(val, curr))
112 | self._size += 1
113 | if curr.height is 1:
114 | curr.height += 1
115 | return curr
116 |
117 | def search(self, val):
118 | """Return the node containing val."""
119 | curr = self.root
120 | while curr:
121 | if curr.val == val:
122 | return curr
123 | elif val < curr.val:
124 | curr = curr.left
125 | else:
126 | curr = curr.right
127 |
128 | def size(self):
129 | """Return the size of the BST."""
130 | return self._size
131 |
132 | def depth(self):
133 | """Return depth of the BST, representing total levels."""
134 | return 0 if not self.root else self.root.height
135 |
136 | def contains(self, val):
137 | """Return true if val is in the bst."""
138 | return self.search(val) is not None
139 |
140 | def balance(self, tree=None):
141 | """Return an integer of how well the tree is balanced.
142 |
143 | Trees which are higher on the left than the right should return a
144 | positive value, trees which are higher on the right than the left
145 | should return a negative value. An ideally-balanced tree should
146 | return 0.
147 | """
148 | if not tree:
149 | tree = self.root
150 | if not tree:
151 | return 0
152 |
153 | leftbranch = 0 if not tree.left else tree.left.height
154 | rightbranch = 0 if not tree.right else tree.right.height
155 |
156 | return leftbranch - rightbranch
157 |
158 | def pre_order(self, node='root'):
159 | """Depth first pre-order traversal of tree."""
160 | if node is 'root':
161 | node = self.root
162 |
163 | if not node:
164 | return
165 |
166 | yield node.val
167 |
168 | for n in self.pre_order(node=node.left):
169 | yield n
170 | for n in self.pre_order(node=node.right):
171 | yield n
172 |
173 | def in_order(self, node='root'):
174 | """Depth first in-order traversal of tree."""
175 | if node is 'root':
176 | node = self.root
177 |
178 | if not node:
179 | return
180 |
181 | for n in self.in_order(node=node.left):
182 | yield n
183 | yield node.val
184 | for n in self.in_order(node=node.right):
185 | yield n
186 |
187 | def post_order(self, node='root'):
188 | """Depth frist post_order traversal of tree."""
189 | if node is 'root':
190 | node = self.root
191 |
192 | if not node:
193 | return
194 |
195 | for n in self.post_order(node=node.left):
196 | yield n
197 | for n in self.post_order(node=node.right):
198 | yield n
199 | yield node.val
200 |
201 | def breadth_first(self):
202 | """Breadth first traversal of tree."""
203 | q = Queue()
204 | q.enqueue(self.root)
205 | while q.peek():
206 | node = q.dequeue()
207 | yield node.val
208 | if node.left:
209 | q.enqueue(node.left)
210 | if node.right:
211 | q.enqueue(node.right)
212 |
213 | def delete(self, val):
214 | """Remove a node from the tree."""
215 | if self._size < 1 or not self.contains(val):
216 | return
217 |
218 | node = self.search(val)
219 |
220 | if node._is_leaf(): # no children
221 | if node.parent:
222 | setattr(node.parent, node._side(), None)
223 | else:
224 | self.root = None
225 |
226 | elif node._is_interior(): # two children
227 | next_node = self._find_replacement(node)
228 | self._size += 1
229 | self.delete(next_node.val)
230 | node.val = next_node.val
231 |
232 | else: # one children
233 | child = getattr(node, node._onlychild())
234 | if node.parent:
235 | child.parent = node.parent
236 | setattr(node.parent, node._side(), child)
237 | else:
238 | self.root = child
239 |
240 | self._size -= 1
241 |
242 | def _find_replacement(self, node):
243 | """Find left most node of right subtree."""
244 | if node.right:
245 | return self._findmin(node.right)
246 | else:
247 | if node.parent:
248 | if node._side() is 'left':
249 | return self.parent
250 | else:
251 | node.parent.right = None
252 | tmp = self._find_replacement(node.parent)
253 | node.parent.right = node
254 | return tmp
255 |
256 | def _findmin(self, node):
257 | """Find min of subtree, Min is always left most node."""
258 | while node.left:
259 | node = node.left
260 | return node
261 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Data-Structures [](https://travis-ci.org/clair3st/Data-Structures) [](https://coveralls.io/github/clair3st/Data-Structures?branch=master)
2 | Implementation of simple data structures in Python.
3 |
4 | _____________
5 |
6 | ## Linked List
7 |
8 | A singly linked list is made of nodes which contain a reference (or pointer) to the next node in the list and data. They are one of the simpliest data structures and can be used to implement other abstract data types including lists, stacks, queues etc.
9 |
10 | 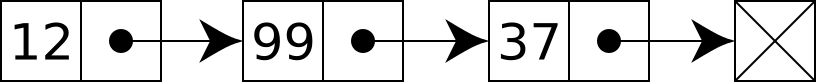
11 |
12 | Advatange of a Linked list is a dynamic data structure which can grow while program is running (unlike arrays). Insertion and deletion methods are easy to implement, and it is a simple building block for other more complex data structures.
13 |
14 | The disadvantages of using a linked list is they use more memory than an array. Nodes must be read in order from the head to the tail (sequential access). Hard to reverse traverse a single linked list.
15 |
16 | - **Module:** [linked_list.py](src/linked_list.py)
17 |
18 | - **Tests:** [test_linked_list.py](tests/test_linked_list.py)
19 |
20 | - **Resources:**
21 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/linked_list.html
22 | http://greenteapress.com/thinkpython/html/chap17.html
23 | https://medium.freecodecamp.com/a-gentle-introduction-to-data-structures-how-linked-lists-work-5adc793897dd#.34gncxsx5
24 |
25 | The list implementation supports the following methods:
26 |
27 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
28 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
29 | | **push(val)** | insert the value ‘val’ at the head of the list. | O(1) |
30 | | **pop()** | removes the first value off the head of the list and return it | O(1) |
31 | | **size()** | return the length of the list | O(1) |
32 | | **search(val)** | return the node containing ‘val’ in the list, if present, else None | O(n) |
33 | | **remove(node)** | remove the given node from the list, wherever it might be (node must be an item in the list) | O(n) |
34 | | **display()** | return a unicode string representing the list as if it were a Python tuple literal: “(12, ‘sam’, 37, ‘tango’)” | O(n) |
35 |
36 | ___________________
37 |
38 | ## Stack
39 |
40 | A stack is a collection of nodes with operations occuring at one end only. It behaves like a real-world stack or pile of books - books can only be taken from or placed on the top of the pile in a First In Last Out (LIFO) operations.
41 |
42 | 
43 |
44 | Stacks are handy for remembering state eg undo and redo
45 |
46 | - **Module:** [stack.py](src/stack.py)
47 |
48 | - **Tests:** [test_stack.py](tests/test_stack.py)
49 |
50 | - **Resources:**
51 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/stack.html
52 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stack_(abstract_data_type)
53 | https://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Data_Structures/Stacks_and_Queues
54 |
55 |
56 | The Stack implementation supports the following methods:
57 |
58 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
59 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
60 | | **push(val)** | insert the value ‘val’ at the head of the stack. | O(1) |
61 | | **pop()** | removes the first value off the head of the stack and return it | O(1) |
62 |
63 | _____________
64 |
65 | ## Double Linked List
66 |
67 | A doubly linked list is made of nodes which contain a reference (or pointer) to the next node in the list, and the previous node in the list plus data.
68 |
69 | 
70 |
71 | Advatange of a doubly linked list is two directional pointers allow traversal of the list in either direction.
72 |
73 | The disadvantages of using a doubly linked list is they use more memory than a singly linked list and adding or removing a node requires changing more pointers.
74 |
75 | - **Module:** [dll.py](src/dll.py)
76 |
77 | - **Tests:** [test_dll.py](tests/test_dll.py)
78 |
79 | - **Resources:**
80 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/doubly_linked_list.html
81 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/double_linked_list.html
82 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Doubly_linked_list
83 |
84 |
85 | The list implementation supports the following methods:
86 |
87 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
88 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
89 | | **push(val)** | will insert the value ‘val’ at the head of the list. | O(1) |
90 | | **pop()** | will pop the first value off the head of the list and return it | O(1) |
91 | | **append(val)** | will insert the value ‘val’ at the tail of the list. | O(1) |
92 | | **shift()** | will pop the first value off the tail of the list and return it | O(1) |
93 | | **remove(val)** | will remove the first instance of ‘val’ found in the list, starting from the head. If ‘val’ is not present, it will raise an appropriate Python exception. | O(n) |
94 |
95 | _____________
96 |
97 |
98 | ## Queue
99 |
100 | A queue is an ordered collection of nodes with operations only allowing the addition of new nodes to the tail and removing nodes from the head of the collection. The Queue is called a First In First Out (FIFO) data structure for this reason.
101 |
102 | 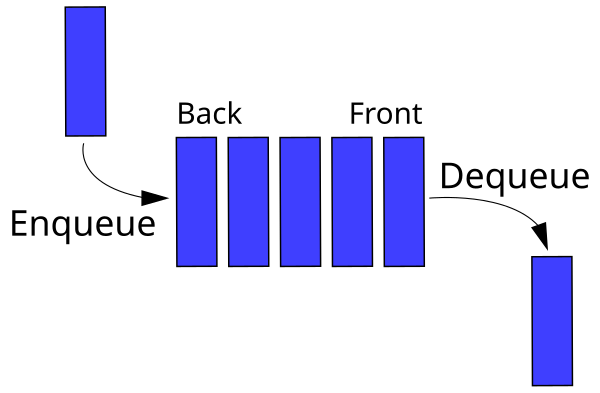 103 |
104 | Queues are used in computer science exactly like they are in the physical world, that is, they are a buffer and store data until it will later get processed. They have limited access (only insert at the tail) and they can always be added to (the length is unlimited).
105 |
106 | - **Module:** [a_queue.py](src/a_queue.py)
107 |
108 | - **Tests:** [test_queue.py](tests/test_queue.py)
109 |
110 | - **Resources:**
111 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/queue.html
112 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/queue.html
113 | http://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Queue_(data_structure).html
114 |
115 |
116 | The Queue implementation supports the following methods:
117 |
118 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
119 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
120 | | **enqueue(value)** | adds value to the queue | O(1) |
121 | | **dequeue()** | removes the correct item from the queue and returns its value (should raise an error if the queue is empty) | O(1) |
122 | | **peek()** | returns the next value in the queue without dequeueing it. If the queue is empty, returns None | O(1) |
123 | | **size()** | return the size of the queue. Should return 0 if the queue is empty | O(1) |
124 |
125 | _____________
126 |
127 | ## Deque
128 |
129 | Deque is a queue that can be accessed from both ends.
130 |
131 | 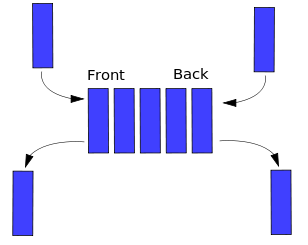
132 |
133 | Deques are useful when modeling any kind of real-world waiting line. This is where entities (bits, people, cars, words, particles etc) arrive with a certain frequency and the front of the line is serviced at a different frequency.
134 |
135 | - **Module:** [deque.py](src/deque.py)
136 |
137 | - **Tests:** [test_deque.py](tests/test_deque.py)
138 |
139 | - **Resources:**
140 | http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3880254/why-do-we-need-deque-data-structures-in-the-real-world
141 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/deque.html
142 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/deque.html
143 |
144 | The Deque implementation supports the following methods:
145 |
146 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
147 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
148 | | **append(val)** | adds value to the end of the deque | O(1) |
149 | | **appendleft(val)** | adds a value to the front of the deque | O(1) |
150 | | **pop()** | removes a value from the end of the deque and returns it (raises an exception if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
151 | | **popleft()** | removes a value from the front of the deque and returns it (raises an exception if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
152 | | **peek()** | returns the next value that would be returned by pop but leaves the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
153 | | **peekleft()** | returns the next value that would be returned by popleft but leaves the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
154 | | **size()** | returns the count of items in the queue (returns 0 if the queue is empty) | O(1) |
155 |
156 | _____________
157 |
158 | ## Binary Heap
159 |
160 | A binary heap is a heap data structure that takes the form of a binary tree. Heaps where the parent node is greater than or equal to the child node are called max-heaps; those where it is less than or equal to are called min-heaps.
161 |
162 | Heaps are commonly implemented with an array. Any binary tree can be stored in an array, but because a binary heap is always a complete binary tree (only the bottom layer can be partially unfilled), it can be stored compactly. No space is required for pointers; instead, the parent and children of each node can be found by arithmetic on array indices.
163 |
164 | 
165 |
166 | The advantages of a binary heap is due to the heap property it provides efficient search. I also sorts the tree in place and is easy to retrieve top N items
167 |
168 |
169 | - **Module:** [binheap.py](src/binheap.py)
170 |
171 | - **Tests:** [test_binheap.py](tests/test_binheap.py)
172 |
173 | - **Resources:**
174 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/heap.html
175 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/binary_heap.html
176 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_heap
177 |
178 | The heap implementation supports the following methods:
179 |
180 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
181 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
182 | | **push(val)** | puts a new value into the heap, maintaining the heap property. | Ave: O(1), Worst: O(log n) |
183 | | **pop()** | removes the “top” value in the heap, maintaining the heap property. | O(log n) |
184 | | **display()** | returns a string representation of the tree | O(n) |
185 |
186 | _____________
187 |
188 | ## Priority Queue
189 |
190 | Priority Q is like a regular queue with the added element of a 'priority'. Elements with a higher priority is severed before elements of a lower priority. If two elements have the same priority they are served based on their order in the queue.
191 |
192 |
103 |
104 | Queues are used in computer science exactly like they are in the physical world, that is, they are a buffer and store data until it will later get processed. They have limited access (only insert at the tail) and they can always be added to (the length is unlimited).
105 |
106 | - **Module:** [a_queue.py](src/a_queue.py)
107 |
108 | - **Tests:** [test_queue.py](tests/test_queue.py)
109 |
110 | - **Resources:**
111 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/queue.html
112 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/queue.html
113 | http://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Queue_(data_structure).html
114 |
115 |
116 | The Queue implementation supports the following methods:
117 |
118 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
119 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
120 | | **enqueue(value)** | adds value to the queue | O(1) |
121 | | **dequeue()** | removes the correct item from the queue and returns its value (should raise an error if the queue is empty) | O(1) |
122 | | **peek()** | returns the next value in the queue without dequeueing it. If the queue is empty, returns None | O(1) |
123 | | **size()** | return the size of the queue. Should return 0 if the queue is empty | O(1) |
124 |
125 | _____________
126 |
127 | ## Deque
128 |
129 | Deque is a queue that can be accessed from both ends.
130 |
131 | 
132 |
133 | Deques are useful when modeling any kind of real-world waiting line. This is where entities (bits, people, cars, words, particles etc) arrive with a certain frequency and the front of the line is serviced at a different frequency.
134 |
135 | - **Module:** [deque.py](src/deque.py)
136 |
137 | - **Tests:** [test_deque.py](tests/test_deque.py)
138 |
139 | - **Resources:**
140 | http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3880254/why-do-we-need-deque-data-structures-in-the-real-world
141 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/deque.html
142 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/deque.html
143 |
144 | The Deque implementation supports the following methods:
145 |
146 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
147 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
148 | | **append(val)** | adds value to the end of the deque | O(1) |
149 | | **appendleft(val)** | adds a value to the front of the deque | O(1) |
150 | | **pop()** | removes a value from the end of the deque and returns it (raises an exception if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
151 | | **popleft()** | removes a value from the front of the deque and returns it (raises an exception if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
152 | | **peek()** | returns the next value that would be returned by pop but leaves the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
153 | | **peekleft()** | returns the next value that would be returned by popleft but leaves the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
154 | | **size()** | returns the count of items in the queue (returns 0 if the queue is empty) | O(1) |
155 |
156 | _____________
157 |
158 | ## Binary Heap
159 |
160 | A binary heap is a heap data structure that takes the form of a binary tree. Heaps where the parent node is greater than or equal to the child node are called max-heaps; those where it is less than or equal to are called min-heaps.
161 |
162 | Heaps are commonly implemented with an array. Any binary tree can be stored in an array, but because a binary heap is always a complete binary tree (only the bottom layer can be partially unfilled), it can be stored compactly. No space is required for pointers; instead, the parent and children of each node can be found by arithmetic on array indices.
163 |
164 | 
165 |
166 | The advantages of a binary heap is due to the heap property it provides efficient search. I also sorts the tree in place and is easy to retrieve top N items
167 |
168 |
169 | - **Module:** [binheap.py](src/binheap.py)
170 |
171 | - **Tests:** [test_binheap.py](tests/test_binheap.py)
172 |
173 | - **Resources:**
174 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/heap.html
175 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/binary_heap.html
176 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_heap
177 |
178 | The heap implementation supports the following methods:
179 |
180 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
181 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
182 | | **push(val)** | puts a new value into the heap, maintaining the heap property. | Ave: O(1), Worst: O(log n) |
183 | | **pop()** | removes the “top” value in the heap, maintaining the heap property. | O(log n) |
184 | | **display()** | returns a string representation of the tree | O(n) |
185 |
186 | _____________
187 |
188 | ## Priority Queue
189 |
190 | Priority Q is like a regular queue with the added element of a 'priority'. Elements with a higher priority is severed before elements of a lower priority. If two elements have the same priority they are served based on their order in the queue.
191 |
192 |  193 |
194 | Priority Queues are very useful for situations when you need to process items in a particular order, but not necessarily in full sorted order and not all at the same time.
195 |
196 |
197 | - **Module:** [priorityq.py](src/priorityq.py)
198 |
199 | - **Tests:** [test_priorityq.py](tests/test_priorityq.py)
200 |
201 | - **Resources:**
202 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/priority_queue.html
203 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Priority_queue
204 |
205 | The priorityq implementation supports the following methods:
206 |
207 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
208 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
209 | | **insert(val, [priority])** | puts a new value into the queue, maintaining the heap property. | O(log n) |
210 | | **pop()** | removes the most important item from the queue. | O(log n) |
211 | | **peek()** | returns the most important item without removing it from the queue | O(1) |
212 |
213 | _____________
214 |
215 | ## Graph
216 |
217 | Graphs allow for a representation of relationship between different nodes. There are two parts to a graph, the nodes themselves and the connections (referred to as edges) which represent the relationship between each node. Connections can be directed (the relationship exists in only one direction) or undirected (the relationship exisits in both directions)
218 |
219 |  
220 |
221 | - **Module:** [graph.py](src/graph.py)
222 |
223 | - **Tests:** [test_graph.py](tests/test_graph.py)
224 |
225 | - **Resources:**
226 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/graph_1.html?highlight=graph
227 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_(abstract_data_type)
228 | https://medium.freecodecamp.com/a-gentle-introduction-to-data-structures-how-graphs-work-a223d9ef8837
229 |
230 | The graph implementation supports the following methods:
231 |
232 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
233 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
234 | | **nodes()** | return a list of all nodes in the graph. | O(n) |
235 | | **edges()** | return a list of all edges in the graph. | O(n) |
236 | | **add_node(n)** | adds a new node 'n' to the graph. | O(1) |
237 | | **add_edge(n1, n2)** | adds a new edge to the graph connecting 'n1' and 'n2', if either n1 or n2 are not already present in the graph, they should be added. | O(1) |
238 | | **del_node(n)** | deletes the node 'n' from the graph, raises an error if no such node exists. | O(1) |
239 | | **del_edge(n1, n2)** | deletes the edge connecting 'n1' and 'n2' from the graph, raises an error if no such edge exists. | O(1) |
240 | | **has_node(n1, n2)** | True if node 'n' is contained in the graph, False if not. | O(1) |
241 | | **neighbors(n1, n2)** | returns the list of all nodes connected to 'n' by edges, raises an error if n is not in g. | O(1) |
242 | | **adjacent(n1, n2)** | returns True if there is an edge connecting n1 and n2, False if not, raises an error if either of the supplied nodes are not in g. | O(1) |
243 |
244 | _____________
245 |
246 | ## Binary Search Tree
247 |
248 | Binary Search Tree (BST) is a data structure used to map from key to value. A binary search tree relies on the property that keys that are less than the parent are found in the left subtree, and keys that are greater than the parent are found in the right subtree.
249 |
250 | If the tree is empty, then a new node inserted into the tree becomes the tree’s root. The next node inserted will have its key compared to the key of the root node. If lower, it will occupy the “left” attribute of the root node. If higher, it occupies the “right” attribute. If a node tries to occupy the “left” or “right” attribute of the root and that attribute is already occupied, it moves down the tree to that node and has its key compared again.
251 |
252 | 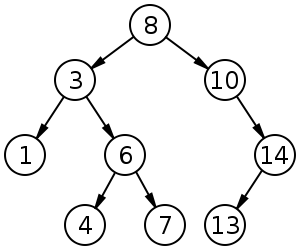
253 |
254 | Binary Search Trees are a popular data structure choice in computing because of its efficient sorting and searching of data. On average, each comparison allows searching to ignore half of the tree. As such, each search takes time proportional to the logarithm of the number of items stored in the tree.
255 |
256 | - **Module:** [bst.py](src/bst.py)
257 |
258 | - **Tests:** [test_bst.py](tests/test_bst.py)
259 |
260 | - **Resources:**
261 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d6/assignments/bst_1.html
262 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/bst_3_traversals.html
263 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/bst_3_delete.html
264 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d6/lectures/binary_search_tree1.html
265 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal
266 |
267 | This BST implementation `Bst()` supports the following methods.
268 |
269 | Method | Description | Time Complexity
270 | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:
271 | **insert(val)** | insert the value val into the BST. If val is already present, it will be ignored. | Best: O(log n),
193 |
194 | Priority Queues are very useful for situations when you need to process items in a particular order, but not necessarily in full sorted order and not all at the same time.
195 |
196 |
197 | - **Module:** [priorityq.py](src/priorityq.py)
198 |
199 | - **Tests:** [test_priorityq.py](tests/test_priorityq.py)
200 |
201 | - **Resources:**
202 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/priority_queue.html
203 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Priority_queue
204 |
205 | The priorityq implementation supports the following methods:
206 |
207 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
208 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
209 | | **insert(val, [priority])** | puts a new value into the queue, maintaining the heap property. | O(log n) |
210 | | **pop()** | removes the most important item from the queue. | O(log n) |
211 | | **peek()** | returns the most important item without removing it from the queue | O(1) |
212 |
213 | _____________
214 |
215 | ## Graph
216 |
217 | Graphs allow for a representation of relationship between different nodes. There are two parts to a graph, the nodes themselves and the connections (referred to as edges) which represent the relationship between each node. Connections can be directed (the relationship exists in only one direction) or undirected (the relationship exisits in both directions)
218 |
219 |  
220 |
221 | - **Module:** [graph.py](src/graph.py)
222 |
223 | - **Tests:** [test_graph.py](tests/test_graph.py)
224 |
225 | - **Resources:**
226 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/graph_1.html?highlight=graph
227 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_(abstract_data_type)
228 | https://medium.freecodecamp.com/a-gentle-introduction-to-data-structures-how-graphs-work-a223d9ef8837
229 |
230 | The graph implementation supports the following methods:
231 |
232 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
233 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
234 | | **nodes()** | return a list of all nodes in the graph. | O(n) |
235 | | **edges()** | return a list of all edges in the graph. | O(n) |
236 | | **add_node(n)** | adds a new node 'n' to the graph. | O(1) |
237 | | **add_edge(n1, n2)** | adds a new edge to the graph connecting 'n1' and 'n2', if either n1 or n2 are not already present in the graph, they should be added. | O(1) |
238 | | **del_node(n)** | deletes the node 'n' from the graph, raises an error if no such node exists. | O(1) |
239 | | **del_edge(n1, n2)** | deletes the edge connecting 'n1' and 'n2' from the graph, raises an error if no such edge exists. | O(1) |
240 | | **has_node(n1, n2)** | True if node 'n' is contained in the graph, False if not. | O(1) |
241 | | **neighbors(n1, n2)** | returns the list of all nodes connected to 'n' by edges, raises an error if n is not in g. | O(1) |
242 | | **adjacent(n1, n2)** | returns True if there is an edge connecting n1 and n2, False if not, raises an error if either of the supplied nodes are not in g. | O(1) |
243 |
244 | _____________
245 |
246 | ## Binary Search Tree
247 |
248 | Binary Search Tree (BST) is a data structure used to map from key to value. A binary search tree relies on the property that keys that are less than the parent are found in the left subtree, and keys that are greater than the parent are found in the right subtree.
249 |
250 | If the tree is empty, then a new node inserted into the tree becomes the tree’s root. The next node inserted will have its key compared to the key of the root node. If lower, it will occupy the “left” attribute of the root node. If higher, it occupies the “right” attribute. If a node tries to occupy the “left” or “right” attribute of the root and that attribute is already occupied, it moves down the tree to that node and has its key compared again.
251 |
252 | 
253 |
254 | Binary Search Trees are a popular data structure choice in computing because of its efficient sorting and searching of data. On average, each comparison allows searching to ignore half of the tree. As such, each search takes time proportional to the logarithm of the number of items stored in the tree.
255 |
256 | - **Module:** [bst.py](src/bst.py)
257 |
258 | - **Tests:** [test_bst.py](tests/test_bst.py)
259 |
260 | - **Resources:**
261 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d6/assignments/bst_1.html
262 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/bst_3_traversals.html
263 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/bst_3_delete.html
264 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d6/lectures/binary_search_tree1.html
265 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal
266 |
267 | This BST implementation `Bst()` supports the following methods.
268 |
269 | Method | Description | Time Complexity
270 | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:
271 | **insert(val)** | insert the value val into the BST. If val is already present, it will be ignored. | Best: O(log n),
Worst: O(n)
272 | **search(val)** | return the node containing that value, else None | Best: O(log n),
Worst: O(n)
273 | **size()** | will return the integer size of the BST (equal to the total number of values stored in the tree). It will return 0 if the tree is empty. | O(1)
274 | **depth()** | will return an integer representing the total number of levels in the tree. If there are no values, depth is 0, if one value the depth should be 1, if two values it will be 2, if three values it may be 2 or 3, depending, etc. | O(1)
275 | **contians(val)** | will return True if val is in the BST, False if not | Best: O(log n),
Worst: O(n)
276 | **balance()** | will return an integer, positive or negative that represents how well balanced the tree is. Trees which are higher on the left than the right should return a positive value, trees which are higher on the right than the left should return a negative value. An ideally-balanced tree should return 0. | O(1)
277 | **in_order():** |return a generator that will return the values in the tree using in-order traversal, one at a time. | O(n)
278 | **pre_order():** |return a generator that will return the values in the tree using pre-order traversal, one at a time. | O(n)
279 | **post_order():** | return a generator that will return the values in the tree using post-order traversal, one at a time. | O(n)
280 | **breadth_first():** | return a generator that will return the values in the tree using breadth frist traversal, one at a time. | O(n)
281 | **delete(val):** |removes a node from the list. | O(logn)
282 |
283 |
284 | **Tree traversals**
285 |
286 | This is the process of visiting each node in the tree once. Trees may be traversed in multiple ways so the output of nodes depends on the method used.
287 |
288 | - Depth first Traversals:
289 | - Pre-order traversal: F, B, A, D, C, E, G, I, H.
290 | 
291 | - In-order traversal: A, B, C, D, E, F, G, H, I.
292 | 
293 | - Post-order traversal: A, C, E, D, B, H, I, G, F.
294 | 
295 | - Breadth first Traversal:
296 | - Level-order: F, B, G, A, D, I, C, E, H.
297 | 
298 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 103 |
104 | Queues are used in computer science exactly like they are in the physical world, that is, they are a buffer and store data until it will later get processed. They have limited access (only insert at the tail) and they can always be added to (the length is unlimited).
105 |
106 | - **Module:** [a_queue.py](src/a_queue.py)
107 |
108 | - **Tests:** [test_queue.py](tests/test_queue.py)
109 |
110 | - **Resources:**
111 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/queue.html
112 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/queue.html
113 | http://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Queue_(data_structure).html
114 |
115 |
116 | The Queue implementation supports the following methods:
117 |
118 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
119 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
120 | | **enqueue(value)** | adds value to the queue | O(1) |
121 | | **dequeue()** | removes the correct item from the queue and returns its value (should raise an error if the queue is empty) | O(1) |
122 | | **peek()** | returns the next value in the queue without dequeueing it. If the queue is empty, returns None | O(1) |
123 | | **size()** | return the size of the queue. Should return 0 if the queue is empty | O(1) |
124 |
125 | _____________
126 |
127 | ## Deque
128 |
129 | Deque is a queue that can be accessed from both ends.
130 |
131 | 
132 |
133 | Deques are useful when modeling any kind of real-world waiting line. This is where entities (bits, people, cars, words, particles etc) arrive with a certain frequency and the front of the line is serviced at a different frequency.
134 |
135 | - **Module:** [deque.py](src/deque.py)
136 |
137 | - **Tests:** [test_deque.py](tests/test_deque.py)
138 |
139 | - **Resources:**
140 | http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3880254/why-do-we-need-deque-data-structures-in-the-real-world
141 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/deque.html
142 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/deque.html
143 |
144 | The Deque implementation supports the following methods:
145 |
146 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
147 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
148 | | **append(val)** | adds value to the end of the deque | O(1) |
149 | | **appendleft(val)** | adds a value to the front of the deque | O(1) |
150 | | **pop()** | removes a value from the end of the deque and returns it (raises an exception if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
151 | | **popleft()** | removes a value from the front of the deque and returns it (raises an exception if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
152 | | **peek()** | returns the next value that would be returned by pop but leaves the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
153 | | **peekleft()** | returns the next value that would be returned by popleft but leaves the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
154 | | **size()** | returns the count of items in the queue (returns 0 if the queue is empty) | O(1) |
155 |
156 | _____________
157 |
158 | ## Binary Heap
159 |
160 | A binary heap is a heap data structure that takes the form of a binary tree. Heaps where the parent node is greater than or equal to the child node are called max-heaps; those where it is less than or equal to are called min-heaps.
161 |
162 | Heaps are commonly implemented with an array. Any binary tree can be stored in an array, but because a binary heap is always a complete binary tree (only the bottom layer can be partially unfilled), it can be stored compactly. No space is required for pointers; instead, the parent and children of each node can be found by arithmetic on array indices.
163 |
164 | 
165 |
166 | The advantages of a binary heap is due to the heap property it provides efficient search. I also sorts the tree in place and is easy to retrieve top N items
167 |
168 |
169 | - **Module:** [binheap.py](src/binheap.py)
170 |
171 | - **Tests:** [test_binheap.py](tests/test_binheap.py)
172 |
173 | - **Resources:**
174 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/heap.html
175 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/binary_heap.html
176 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_heap
177 |
178 | The heap implementation supports the following methods:
179 |
180 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
181 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
182 | | **push(val)** | puts a new value into the heap, maintaining the heap property. | Ave: O(1), Worst: O(log n) |
183 | | **pop()** | removes the “top” value in the heap, maintaining the heap property. | O(log n) |
184 | | **display()** | returns a string representation of the tree | O(n) |
185 |
186 | _____________
187 |
188 | ## Priority Queue
189 |
190 | Priority Q is like a regular queue with the added element of a 'priority'. Elements with a higher priority is severed before elements of a lower priority. If two elements have the same priority they are served based on their order in the queue.
191 |
192 |
103 |
104 | Queues are used in computer science exactly like they are in the physical world, that is, they are a buffer and store data until it will later get processed. They have limited access (only insert at the tail) and they can always be added to (the length is unlimited).
105 |
106 | - **Module:** [a_queue.py](src/a_queue.py)
107 |
108 | - **Tests:** [test_queue.py](tests/test_queue.py)
109 |
110 | - **Resources:**
111 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/queue.html
112 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/queue.html
113 | http://www.princeton.edu/~achaney/tmve/wiki100k/docs/Queue_(data_structure).html
114 |
115 |
116 | The Queue implementation supports the following methods:
117 |
118 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
119 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
120 | | **enqueue(value)** | adds value to the queue | O(1) |
121 | | **dequeue()** | removes the correct item from the queue and returns its value (should raise an error if the queue is empty) | O(1) |
122 | | **peek()** | returns the next value in the queue without dequeueing it. If the queue is empty, returns None | O(1) |
123 | | **size()** | return the size of the queue. Should return 0 if the queue is empty | O(1) |
124 |
125 | _____________
126 |
127 | ## Deque
128 |
129 | Deque is a queue that can be accessed from both ends.
130 |
131 | 
132 |
133 | Deques are useful when modeling any kind of real-world waiting line. This is where entities (bits, people, cars, words, particles etc) arrive with a certain frequency and the front of the line is serviced at a different frequency.
134 |
135 | - **Module:** [deque.py](src/deque.py)
136 |
137 | - **Tests:** [test_deque.py](tests/test_deque.py)
138 |
139 | - **Resources:**
140 | http://stackoverflow.com/questions/3880254/why-do-we-need-deque-data-structures-in-the-real-world
141 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/deque.html
142 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/deque.html
143 |
144 | The Deque implementation supports the following methods:
145 |
146 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
147 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
148 | | **append(val)** | adds value to the end of the deque | O(1) |
149 | | **appendleft(val)** | adds a value to the front of the deque | O(1) |
150 | | **pop()** | removes a value from the end of the deque and returns it (raises an exception if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
151 | | **popleft()** | removes a value from the front of the deque and returns it (raises an exception if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
152 | | **peek()** | returns the next value that would be returned by pop but leaves the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
153 | | **peekleft()** | returns the next value that would be returned by popleft but leaves the value in the deque (returns None if the deque is empty) | O(1) |
154 | | **size()** | returns the count of items in the queue (returns 0 if the queue is empty) | O(1) |
155 |
156 | _____________
157 |
158 | ## Binary Heap
159 |
160 | A binary heap is a heap data structure that takes the form of a binary tree. Heaps where the parent node is greater than or equal to the child node are called max-heaps; those where it is less than or equal to are called min-heaps.
161 |
162 | Heaps are commonly implemented with an array. Any binary tree can be stored in an array, but because a binary heap is always a complete binary tree (only the bottom layer can be partially unfilled), it can be stored compactly. No space is required for pointers; instead, the parent and children of each node can be found by arithmetic on array indices.
163 |
164 | 
165 |
166 | The advantages of a binary heap is due to the heap property it provides efficient search. I also sorts the tree in place and is easy to retrieve top N items
167 |
168 |
169 | - **Module:** [binheap.py](src/binheap.py)
170 |
171 | - **Tests:** [test_binheap.py](tests/test_binheap.py)
172 |
173 | - **Resources:**
174 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/lectures/heap.html
175 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/binary_heap.html
176 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Binary_heap
177 |
178 | The heap implementation supports the following methods:
179 |
180 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
181 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
182 | | **push(val)** | puts a new value into the heap, maintaining the heap property. | Ave: O(1), Worst: O(log n) |
183 | | **pop()** | removes the “top” value in the heap, maintaining the heap property. | O(log n) |
184 | | **display()** | returns a string representation of the tree | O(n) |
185 |
186 | _____________
187 |
188 | ## Priority Queue
189 |
190 | Priority Q is like a regular queue with the added element of a 'priority'. Elements with a higher priority is severed before elements of a lower priority. If two elements have the same priority they are served based on their order in the queue.
191 |
192 |  193 |
194 | Priority Queues are very useful for situations when you need to process items in a particular order, but not necessarily in full sorted order and not all at the same time.
195 |
196 |
197 | - **Module:** [priorityq.py](src/priorityq.py)
198 |
199 | - **Tests:** [test_priorityq.py](tests/test_priorityq.py)
200 |
201 | - **Resources:**
202 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/priority_queue.html
203 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Priority_queue
204 |
205 | The priorityq implementation supports the following methods:
206 |
207 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
208 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
209 | | **insert(val, [priority])** | puts a new value into the queue, maintaining the heap property. | O(log n) |
210 | | **pop()** | removes the most important item from the queue. | O(log n) |
211 | | **peek()** | returns the most important item without removing it from the queue | O(1) |
212 |
213 | _____________
214 |
215 | ## Graph
216 |
217 | Graphs allow for a representation of relationship between different nodes. There are two parts to a graph, the nodes themselves and the connections (referred to as edges) which represent the relationship between each node. Connections can be directed (the relationship exists in only one direction) or undirected (the relationship exisits in both directions)
218 |
219 |  
220 |
221 | - **Module:** [graph.py](src/graph.py)
222 |
223 | - **Tests:** [test_graph.py](tests/test_graph.py)
224 |
225 | - **Resources:**
226 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/graph_1.html?highlight=graph
227 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_(abstract_data_type)
228 | https://medium.freecodecamp.com/a-gentle-introduction-to-data-structures-how-graphs-work-a223d9ef8837
229 |
230 | The graph implementation supports the following methods:
231 |
232 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
233 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
234 | | **nodes()** | return a list of all nodes in the graph. | O(n) |
235 | | **edges()** | return a list of all edges in the graph. | O(n) |
236 | | **add_node(n)** | adds a new node 'n' to the graph. | O(1) |
237 | | **add_edge(n1, n2)** | adds a new edge to the graph connecting 'n1' and 'n2', if either n1 or n2 are not already present in the graph, they should be added. | O(1) |
238 | | **del_node(n)** | deletes the node 'n' from the graph, raises an error if no such node exists. | O(1) |
239 | | **del_edge(n1, n2)** | deletes the edge connecting 'n1' and 'n2' from the graph, raises an error if no such edge exists. | O(1) |
240 | | **has_node(n1, n2)** | True if node 'n' is contained in the graph, False if not. | O(1) |
241 | | **neighbors(n1, n2)** | returns the list of all nodes connected to 'n' by edges, raises an error if n is not in g. | O(1) |
242 | | **adjacent(n1, n2)** | returns True if there is an edge connecting n1 and n2, False if not, raises an error if either of the supplied nodes are not in g. | O(1) |
243 |
244 | _____________
245 |
246 | ## Binary Search Tree
247 |
248 | Binary Search Tree (BST) is a data structure used to map from key to value. A binary search tree relies on the property that keys that are less than the parent are found in the left subtree, and keys that are greater than the parent are found in the right subtree.
249 |
250 | If the tree is empty, then a new node inserted into the tree becomes the tree’s root. The next node inserted will have its key compared to the key of the root node. If lower, it will occupy the “left” attribute of the root node. If higher, it occupies the “right” attribute. If a node tries to occupy the “left” or “right” attribute of the root and that attribute is already occupied, it moves down the tree to that node and has its key compared again.
251 |
252 | 
253 |
254 | Binary Search Trees are a popular data structure choice in computing because of its efficient sorting and searching of data. On average, each comparison allows searching to ignore half of the tree. As such, each search takes time proportional to the logarithm of the number of items stored in the tree.
255 |
256 | - **Module:** [bst.py](src/bst.py)
257 |
258 | - **Tests:** [test_bst.py](tests/test_bst.py)
259 |
260 | - **Resources:**
261 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d6/assignments/bst_1.html
262 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/bst_3_traversals.html
263 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/bst_3_delete.html
264 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d6/lectures/binary_search_tree1.html
265 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal
266 |
267 | This BST implementation `Bst()` supports the following methods.
268 |
269 | Method | Description | Time Complexity
270 | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:
271 | **insert(val)** | insert the value val into the BST. If val is already present, it will be ignored. | Best: O(log n),
193 |
194 | Priority Queues are very useful for situations when you need to process items in a particular order, but not necessarily in full sorted order and not all at the same time.
195 |
196 |
197 | - **Module:** [priorityq.py](src/priorityq.py)
198 |
199 | - **Tests:** [test_priorityq.py](tests/test_priorityq.py)
200 |
201 | - **Resources:**
202 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/priority_queue.html
203 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Priority_queue
204 |
205 | The priorityq implementation supports the following methods:
206 |
207 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
208 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
209 | | **insert(val, [priority])** | puts a new value into the queue, maintaining the heap property. | O(log n) |
210 | | **pop()** | removes the most important item from the queue. | O(log n) |
211 | | **peek()** | returns the most important item without removing it from the queue | O(1) |
212 |
213 | _____________
214 |
215 | ## Graph
216 |
217 | Graphs allow for a representation of relationship between different nodes. There are two parts to a graph, the nodes themselves and the connections (referred to as edges) which represent the relationship between each node. Connections can be directed (the relationship exists in only one direction) or undirected (the relationship exisits in both directions)
218 |
219 |  
220 |
221 | - **Module:** [graph.py](src/graph.py)
222 |
223 | - **Tests:** [test_graph.py](tests/test_graph.py)
224 |
225 | - **Resources:**
226 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/graph_1.html?highlight=graph
227 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Graph_(abstract_data_type)
228 | https://medium.freecodecamp.com/a-gentle-introduction-to-data-structures-how-graphs-work-a223d9ef8837
229 |
230 | The graph implementation supports the following methods:
231 |
232 | | Method | Description | Time Complexity |
233 | | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:|
234 | | **nodes()** | return a list of all nodes in the graph. | O(n) |
235 | | **edges()** | return a list of all edges in the graph. | O(n) |
236 | | **add_node(n)** | adds a new node 'n' to the graph. | O(1) |
237 | | **add_edge(n1, n2)** | adds a new edge to the graph connecting 'n1' and 'n2', if either n1 or n2 are not already present in the graph, they should be added. | O(1) |
238 | | **del_node(n)** | deletes the node 'n' from the graph, raises an error if no such node exists. | O(1) |
239 | | **del_edge(n1, n2)** | deletes the edge connecting 'n1' and 'n2' from the graph, raises an error if no such edge exists. | O(1) |
240 | | **has_node(n1, n2)** | True if node 'n' is contained in the graph, False if not. | O(1) |
241 | | **neighbors(n1, n2)** | returns the list of all nodes connected to 'n' by edges, raises an error if n is not in g. | O(1) |
242 | | **adjacent(n1, n2)** | returns True if there is an edge connecting n1 and n2, False if not, raises an error if either of the supplied nodes are not in g. | O(1) |
243 |
244 | _____________
245 |
246 | ## Binary Search Tree
247 |
248 | Binary Search Tree (BST) is a data structure used to map from key to value. A binary search tree relies on the property that keys that are less than the parent are found in the left subtree, and keys that are greater than the parent are found in the right subtree.
249 |
250 | If the tree is empty, then a new node inserted into the tree becomes the tree’s root. The next node inserted will have its key compared to the key of the root node. If lower, it will occupy the “left” attribute of the root node. If higher, it occupies the “right” attribute. If a node tries to occupy the “left” or “right” attribute of the root and that attribute is already occupied, it moves down the tree to that node and has its key compared again.
251 |
252 | 
253 |
254 | Binary Search Trees are a popular data structure choice in computing because of its efficient sorting and searching of data. On average, each comparison allows searching to ignore half of the tree. As such, each search takes time proportional to the logarithm of the number of items stored in the tree.
255 |
256 | - **Module:** [bst.py](src/bst.py)
257 |
258 | - **Tests:** [test_bst.py](tests/test_bst.py)
259 |
260 | - **Resources:**
261 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d6/assignments/bst_1.html
262 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/bst_3_traversals.html
263 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d5/assignments/bst_3_delete.html
264 | https://codefellows.github.io/sea-python-401d6/lectures/binary_search_tree1.html
265 | https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal
266 |
267 | This BST implementation `Bst()` supports the following methods.
268 |
269 | Method | Description | Time Complexity
270 | ------------- |-------------| :---------------:
271 | **insert(val)** | insert the value val into the BST. If val is already present, it will be ignored. | Best: O(log n),