├── .gitignore
├── .travis.yml
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── COPYING
├── COPYING.LESSER
├── FindEigen3.cmake
├── README.md
├── doc
└── Doxyfile
├── include
├── distributions.h
├── libcluster.h
└── probutils.h
├── python
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── FindNumpy.cmake
├── libclusterpy.cpp
├── libclusterpy.h
└── testapi.py
├── src
├── cluster.cpp
├── comutils.cpp
├── comutils.h
├── distributions.cpp
├── mcluster.cpp
├── probutils.cpp
└── scluster.cpp
└── test
├── CMakeLists.txt
├── cluster_test.cpp
├── mcluster_test.cpp
├── scluster_test.cpp
├── scott25.dat
└── testdata.h
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # ignore list for git status etc.
2 | *.mex*
3 | *.user
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.travis.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | language: cpp
2 | dist: trusty
3 | sudo: required
4 |
5 | addons:
6 | apt:
7 | packages:
8 | - cmake
9 | - python3
10 | - python3-dev
11 | - libeigen3-dev
12 | - libboost-all-dev
13 | - libboost-python-dev
14 | - python3-numpy
15 |
16 | install:
17 | - cd /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/
18 | - sudo ln -s libboost_python-py34.so libboost_python3.so
19 | - cd $TRAVIS_BUILD_DIR
20 | - mkdir build
21 | - cd build
22 | - cmake -DBUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE=ON -DBUILD_USE_PYTHON3=ON ..
23 | - make
24 | - sudo make install
25 |
26 | script:
27 | - cd $TRAVIS_BUILD_DIR/build
28 | - ./cluster_test
29 | - ./scluster_test
30 | - ./mcluster_test
31 | - sudo ldconfig
32 | - cd ../python
33 | - python3 testapi.py
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CMakeLists.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | project(cluster)
2 | cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.6)
3 |
4 |
5 | #--------------------------------#
6 | # Includes #
7 | #--------------------------------#
8 |
9 | find_package(Boost REQUIRED)
10 | include_directories(${Boost_INCLUDE_DIRS})
11 | include(${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/FindEigen3.cmake REQUIRED)
12 | include_directories(${EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS})
13 | include(FindOpenMP)
14 |
15 |
16 | #--------------------------------#
17 | # Enforce an out-of-source build #
18 | #--------------------------------#
19 |
20 | string(COMPARE EQUAL "${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}" "${PROJECT_BINARY_DIR}" INSOURCE)
21 | if(INSOURCE)
22 | message(FATAL_ERROR "This project requires an out of source build.")
23 | endif(INSOURCE)
24 |
25 |
26 | #--------------------------------#
27 | # Compiler environment Setup #
28 | #--------------------------------#
29 |
30 | # Some compilation options (changeable from ccmake)
31 | option(BUILD_EXHAUST_SPLIT "Use the exhaustive cluster split heuristic?" off)
32 | option(BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE "Build the python interface?" off)
33 | option(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3 "Use python3 instead of python 2?" on)
34 |
35 | # Locations for source code
36 | set(LIB_SOURCE_DIR ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/src)
37 | set(LIB_INCLUDE_DIR ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/include)
38 | set(TEST_SOURCE_DIR ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/test)
39 | set(PYTHON_SOURCE_DIR ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/python)
40 |
41 | # Locations for binary files
42 | set(LIBRARY_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/lib)
43 | set(EXECUTABLE_OUTPUT_PATH ${PROJECT_SOURCE_DIR}/build)
44 |
45 | # Automatically or from command line set build type
46 | if(NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE)
47 | set(CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE Release CACHE STRING
48 | "Build type options are: None Debug Release RelWithDebInfo MinSizeRel."
49 | FORCE
50 | )
51 | endif(NOT CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE)
52 |
53 | # If we want to use the greedy splitting heuristic, define it here
54 | if(BUILD_EXHAUST_SPLIT)
55 | set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -DEXHAUST_SPLIT")
56 | endif(BUILD_EXHAUST_SPLIT)
57 |
58 | # Python needs row major matrices (for convenience)
59 | if(BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE)
60 | set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -DEIGEN_DEFAULT_TO_ROW_MAJOR")
61 | endif(BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE)
62 |
63 | # Search for OpenMP support for multi-threading
64 | if(OPENMP_FOUND)
65 | set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} ${OpenMP_CXX_FLAGS}")
66 | set(CMAKE_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS
67 | "${CMAKE_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS} ${OpenMP_EXE_LINKER_FLAGS}"
68 | )
69 | # Disable Eigen's parallelisation (this will get in the way of mine)
70 | set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -DEIGEN_DONT_PARALLELIZE")
71 | endif(OPENMP_FOUND)
72 |
73 |
74 | #--------------------------------#
75 | # Library Build Instructions #
76 | #--------------------------------#
77 |
78 | # Make sure we include library headers in compile
79 | include_directories(${LIB_INCLUDE_DIR})
80 |
81 | # Library build instructions
82 | add_library(${PROJECT_NAME} SHARED
83 | ${LIB_INCLUDE_DIR}/libcluster.h
84 | ${LIB_INCLUDE_DIR}/probutils.h
85 | ${LIB_INCLUDE_DIR}/distributions.h
86 | ${LIB_SOURCE_DIR}/distributions.cpp
87 | ${LIB_SOURCE_DIR}/comutils.h
88 | ${LIB_SOURCE_DIR}/comutils.cpp
89 | ${LIB_SOURCE_DIR}/cluster.cpp
90 | ${LIB_SOURCE_DIR}/scluster.cpp
91 | ${LIB_SOURCE_DIR}/mcluster.cpp
92 | ${LIB_SOURCE_DIR}/probutils.cpp
93 | )
94 |
95 | add_definitions("-Wall")
96 |
97 |
98 | #--------------------------------#
99 | # Library Install Instructions #
100 | #--------------------------------#
101 |
102 | if(NOT CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX)
103 | set(CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX "/usr/local" )
104 | endif(NOT CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX)
105 |
106 | install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME} DESTINATION lib)
107 | install(FILES
108 | ${LIB_INCLUDE_DIR}/libcluster.h
109 | ${LIB_INCLUDE_DIR}/probutils.h
110 | ${LIB_INCLUDE_DIR}/distributions.h
111 | DESTINATION include/libcluster
112 | )
113 |
114 |
115 | #--------------------------------#
116 | # Subdirectories to recurse to #
117 | #--------------------------------#
118 |
119 | subdirs(test python)
120 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/COPYING.LESSER:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | GNU LESSER GENERAL PUBLIC LICENSE
2 | Version 3, 29 June 2007
3 |
4 | Copyright (C) 2007 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
5 | Everyone is permitted to copy and distribute verbatim copies
6 | of this license document, but changing it is not allowed.
7 |
8 |
9 | This version of the GNU Lesser General Public License incorporates
10 | the terms and conditions of version 3 of the GNU General Public
11 | License, supplemented by the additional permissions listed below.
12 |
13 | 0. Additional Definitions.
14 |
15 | As used herein, "this License" refers to version 3 of the GNU Lesser
16 | General Public License, and the "GNU GPL" refers to version 3 of the GNU
17 | General Public License.
18 |
19 | "The Library" refers to a covered work governed by this License,
20 | other than an Application or a Combined Work as defined below.
21 |
22 | An "Application" is any work that makes use of an interface provided
23 | by the Library, but which is not otherwise based on the Library.
24 | Defining a subclass of a class defined by the Library is deemed a mode
25 | of using an interface provided by the Library.
26 |
27 | A "Combined Work" is a work produced by combining or linking an
28 | Application with the Library. The particular version of the Library
29 | with which the Combined Work was made is also called the "Linked
30 | Version".
31 |
32 | The "Minimal Corresponding Source" for a Combined Work means the
33 | Corresponding Source for the Combined Work, excluding any source code
34 | for portions of the Combined Work that, considered in isolation, are
35 | based on the Application, and not on the Linked Version.
36 |
37 | The "Corresponding Application Code" for a Combined Work means the
38 | object code and/or source code for the Application, including any data
39 | and utility programs needed for reproducing the Combined Work from the
40 | Application, but excluding the System Libraries of the Combined Work.
41 |
42 | 1. Exception to Section 3 of the GNU GPL.
43 |
44 | You may convey a covered work under sections 3 and 4 of this License
45 | without being bound by section 3 of the GNU GPL.
46 |
47 | 2. Conveying Modified Versions.
48 |
49 | If you modify a copy of the Library, and, in your modifications, a
50 | facility refers to a function or data to be supplied by an Application
51 | that uses the facility (other than as an argument passed when the
52 | facility is invoked), then you may convey a copy of the modified
53 | version:
54 |
55 | a) under this License, provided that you make a good faith effort to
56 | ensure that, in the event an Application does not supply the
57 | function or data, the facility still operates, and performs
58 | whatever part of its purpose remains meaningful, or
59 |
60 | b) under the GNU GPL, with none of the additional permissions of
61 | this License applicable to that copy.
62 |
63 | 3. Object Code Incorporating Material from Library Header Files.
64 |
65 | The object code form of an Application may incorporate material from
66 | a header file that is part of the Library. You may convey such object
67 | code under terms of your choice, provided that, if the incorporated
68 | material is not limited to numerical parameters, data structure
69 | layouts and accessors, or small macros, inline functions and templates
70 | (ten or fewer lines in length), you do both of the following:
71 |
72 | a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the object code that the
73 | Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are
74 | covered by this License.
75 |
76 | b) Accompany the object code with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license
77 | document.
78 |
79 | 4. Combined Works.
80 |
81 | You may convey a Combined Work under terms of your choice that,
82 | taken together, effectively do not restrict modification of the
83 | portions of the Library contained in the Combined Work and reverse
84 | engineering for debugging such modifications, if you also do each of
85 | the following:
86 |
87 | a) Give prominent notice with each copy of the Combined Work that
88 | the Library is used in it and that the Library and its use are
89 | covered by this License.
90 |
91 | b) Accompany the Combined Work with a copy of the GNU GPL and this license
92 | document.
93 |
94 | c) For a Combined Work that displays copyright notices during
95 | execution, include the copyright notice for the Library among
96 | these notices, as well as a reference directing the user to the
97 | copies of the GNU GPL and this license document.
98 |
99 | d) Do one of the following:
100 |
101 | 0) Convey the Minimal Corresponding Source under the terms of this
102 | License, and the Corresponding Application Code in a form
103 | suitable for, and under terms that permit, the user to
104 | recombine or relink the Application with a modified version of
105 | the Linked Version to produce a modified Combined Work, in the
106 | manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL for conveying
107 | Corresponding Source.
108 |
109 | 1) Use a suitable shared library mechanism for linking with the
110 | Library. A suitable mechanism is one that (a) uses at run time
111 | a copy of the Library already present on the user's computer
112 | system, and (b) will operate properly with a modified version
113 | of the Library that is interface-compatible with the Linked
114 | Version.
115 |
116 | e) Provide Installation Information, but only if you would otherwise
117 | be required to provide such information under section 6 of the
118 | GNU GPL, and only to the extent that such information is
119 | necessary to install and execute a modified version of the
120 | Combined Work produced by recombining or relinking the
121 | Application with a modified version of the Linked Version. (If
122 | you use option 4d0, the Installation Information must accompany
123 | the Minimal Corresponding Source and Corresponding Application
124 | Code. If you use option 4d1, you must provide the Installation
125 | Information in the manner specified by section 6 of the GNU GPL
126 | for conveying Corresponding Source.)
127 |
128 | 5. Combined Libraries.
129 |
130 | You may place library facilities that are a work based on the
131 | Library side by side in a single library together with other library
132 | facilities that are not Applications and are not covered by this
133 | License, and convey such a combined library under terms of your
134 | choice, if you do both of the following:
135 |
136 | a) Accompany the combined library with a copy of the same work based
137 | on the Library, uncombined with any other library facilities,
138 | conveyed under the terms of this License.
139 |
140 | b) Give prominent notice with the combined library that part of it
141 | is a work based on the Library, and explaining where to find the
142 | accompanying uncombined form of the same work.
143 |
144 | 6. Revised Versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License.
145 |
146 | The Free Software Foundation may publish revised and/or new versions
147 | of the GNU Lesser General Public License from time to time. Such new
148 | versions will be similar in spirit to the present version, but may
149 | differ in detail to address new problems or concerns.
150 |
151 | Each version is given a distinguishing version number. If the
152 | Library as you received it specifies that a certain numbered version
153 | of the GNU Lesser General Public License "or any later version"
154 | applies to it, you have the option of following the terms and
155 | conditions either of that published version or of any later version
156 | published by the Free Software Foundation. If the Library as you
157 | received it does not specify a version number of the GNU Lesser
158 | General Public License, you may choose any version of the GNU Lesser
159 | General Public License ever published by the Free Software Foundation.
160 |
161 | If the Library as you received it specifies that a proxy can decide
162 | whether future versions of the GNU Lesser General Public License shall
163 | apply, that proxy's public statement of acceptance of any version is
164 | permanent authorization for you to choose that version for the
165 | Library.
166 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/FindEigen3.cmake:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Make sure that we can find Eigen
2 | # This creates the following variables:
3 | # - EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS where to find the library
4 | # - EIGEN_FOUND TRUE if found, FALSE otherwise
5 |
6 | find_path(
7 | EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS Eigen
8 | /usr/local/eigen3
9 | /usr/local/include/eigen3
10 | /usr/include/eigen3
11 | )
12 |
13 | # Check found Eigen
14 | if(EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS)
15 | set(EIGEN_FOUND TRUE)
16 | message(STATUS "Found Eigen: ${EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS}")
17 | else(EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS)
18 | if(EIGEN_FIND_REQUIRED)
19 | set(EIGEN_FOUND FALSE)
20 | message(FATAL_ERROR "Eigen not found")
21 | endif(EIGEN_FIND_REQUIRED)
22 | endif(EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS)
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Libcluster
2 | ==========
3 |
4 | [](https://travis-ci.org/dsteinberg/libcluster)
5 |
6 | ***Author***:
7 | [Daniel Steinberg](http://dsteinberg.github.io/)
8 |
9 | ***License***:
10 | LGPL v3 (See COPYING and COPYING.LESSER)
11 |
12 | ***Overview***:
13 |
14 | This library implements the following algorithms with variational Bayes
15 | learning procedures and efficient cluster splitting heuristics:
16 |
17 | * The Variational Dirichlet Process (VDP) [1, 2, 6]
18 | * The Bayesian Gaussian Mixture Model [3 - 6]
19 | * The Grouped Mixtures Clustering (GMC) model [6]
20 | * The Symmetric Grouped Mixtures Clustering (S-GMC) model [4 - 6]. This is
21 | referred to as Gaussian latent Dirichlet allocation (G-LDA) in [4, 5].
22 | * Simultaneous Clustering Model (SCM) for Multinomial Documents, and Gaussian
23 | Observations [5, 6].
24 | * Multiple-source Clustering Model (MCM) for clustering two observations,
25 | one of an image/document, and multiple of segments/words
26 | simultaneously [4 - 6].
27 | * And more clustering algorithms based on diagonal Gaussian, and
28 | Exponential distributions.
29 |
30 | And also,
31 | * Various functions for evaluating means, standard deviations, covariance,
32 | primary Eigenvalues etc of data.
33 | * Extensible template interfaces for creating new algorithms within the
34 | variational Bayes framework.
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 |  39 |
39 | 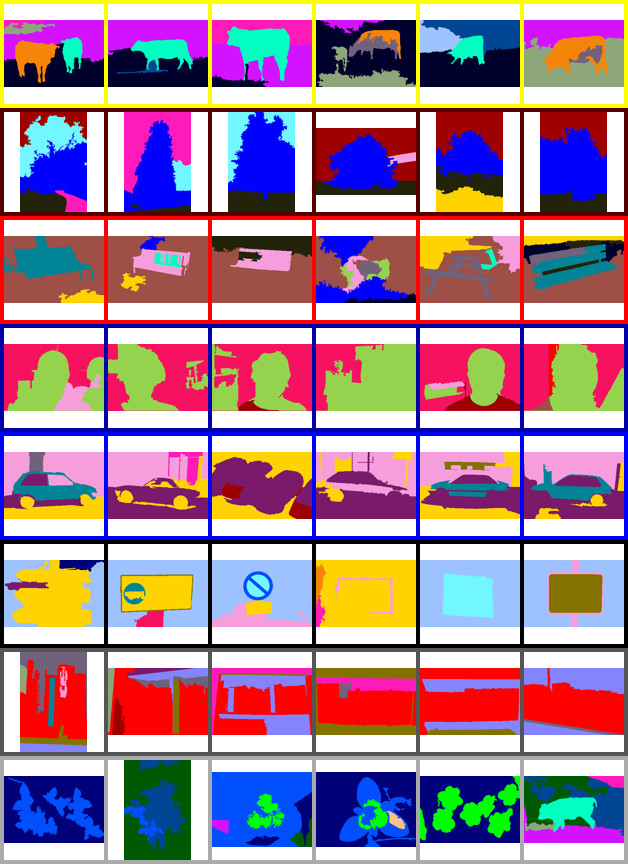 40 |
41 |
42 | An example of using the MCM to simultaneously cluster images and objects within
43 | images for unsupervised scene understanding. See [4 - 6] for more information.
44 |
45 | * * *
46 |
47 |
48 | TABLE OF CONTENTS
49 | -----------------
50 |
51 | * [Dependencies](#dependencies)
52 |
53 | * [Install Instructions](#install-instructions)
54 |
55 | * [C++ Interface](#c-interface)
56 |
57 | * [Python Interface](#python-interface)
58 |
59 | * [General Usability Tips](#general-usability-tips)
60 |
61 | * [References and Citing](#references-and-citing)
62 |
63 |
64 | * * *
65 |
66 |
67 | DEPENDENCIES
68 | ------------
69 |
70 | - Eigen version 3.0 or greater
71 | - Boost version 1.4.x or greater and devel packages (special math functions)
72 | - OpenMP, comes default with most compilers (may need a special version of
73 | [LLVM](http://openmp.llvm.org/)).
74 | - CMake
75 |
76 | For the python interface:
77 |
78 | - Python 2 or 3
79 | - Boost python and boost python devel packages (make sure you have version 2
80 | or 3 for the relevant version of python)
81 | - Numpy (tested with v1.7)
82 |
83 |
84 | INSTALL INSTRUCTIONS
85 | --------------------
86 |
87 | *For Linux and OS X -- I've never tried to build on Windows.*
88 |
89 | To build libcluster:
90 |
91 | 1. Make sure you have CMake installed, and Eigen and Boost preferably in the
92 | usual locations:
93 |
94 | /usr/local/include/eigen3/ or /usr/include/eigen3
95 | /usr/local/include/boost or /usr/include/boost
96 |
97 | 2. Make a build directory where you checked out the source if it does not
98 | already exist, then change into this directory,
99 |
100 | cd {where you checked out the source}
101 | mkdir build
102 | cd build
103 |
104 | 3. To build libcluster, run the following from the build directory:
105 |
106 | cmake ..
107 | make
108 | sudo make install
109 |
110 | This installs:
111 |
112 | libcluster.h /usr/local/include
113 | distributions.h /usr/local/include
114 | probutils.h /usr/local/include
115 | libcluster.* /usr/local/lib (* this is either .dylib or .so)
116 |
117 | 4. Use the doxyfile in {where you checked out the source}/doc to make the
118 | documentation with doxygen:
119 |
120 | doxygen Doxyfile
121 |
122 | **NOTE**: There are few options you can change using ccmake (or the cmake gui),
123 | these include:
124 |
125 | - `BUILD_EXHAUST_SPLIT` (toggle `ON` or `OFF`, default `OFF`) This uses the
126 | exhaustive cluster split heuristic [1, 2] instead of the greedy heuristic [4,
127 | 5] for all algorithms but the SCM and MCM. The greedy heuristic is MUCH
128 | faster, but does give different results. I have yet to determine whether it
129 | is actually worse than the exhaustive method (if it is, it is not by much).
130 | The SCM and MCM only use the greedy split heuristic at this stage.
131 |
132 | - `BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE` (toggle `ON` or `OFF`, default `OFF`) Build the
133 | python interface. This requires boost python, and also uses row-major storage
134 | to be compatible with python.
135 |
136 | - `BUILD_USE_PYTHON3` (toggle `ON` or `OFF`, default `ON`) Use python 3 or 2 to
137 | build the python interface. Make sure you have the relevant python and boost
138 | python libraries installed!
139 |
140 | - `CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX` (default `/usr/local`) The default prefix for
141 | installing the library and binaries.
142 |
143 | - `EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS` (default `/usr/include/eigen3`) Where to look for the
144 | Eigen matrix library.
145 |
146 | **NOTE**: On linux you may have to run `sudo ldconfig` before the system can
147 | find libcluster.so (or just reboot).
148 |
149 | **NOTE**: On Red-Hat based systems, `/usr/local/lib` is not checked unless
150 | added to `/etc/ld.so.conf`! This may lead to "cannot find libcluster.so"
151 | errors.
152 |
153 |
154 | C++ INTERFACE
155 | -------------
156 |
157 | All of the interfaces to this library are documented in `include/libcluster.h`.
158 | There are far too many algorithms to go into here, and I *strongly* recommend
159 | looking at the `test/` directory for example usage, specifically,
160 |
161 | * `cluster_test.cpp` for the group mixture models (GMC etc)
162 | * `scluster_test.cpp` for the SCM
163 | * `mcluster_test.cpp` for the MCM
164 |
165 | Here is an example for regular mixture models, such as the BGMM, which simply
166 | clusters some test data and prints the resulting posterior parameters to the
167 | terminal,
168 |
169 | ```C++
170 |
171 | #include "libcluster.h"
172 | #include "distributions.h"
173 | #include "testdata.h"
174 |
175 |
176 | //
177 | // Namespaces
178 | //
179 |
180 | using namespace std;
181 | using namespace Eigen;
182 | using namespace libcluster;
183 | using namespace distributions;
184 |
185 |
186 | //
187 | // Functions
188 | //
189 |
190 | // Main
191 | int main()
192 | {
193 |
194 | // Populate test data from testdata.h
195 | MatrixXd Xcat;
196 | vMatrixXd X;
197 | makeXdata(Xcat, X);
198 |
199 | // Set up the inputs for the BGMM
200 | Dirichlet weights;
201 | vector clusters;
202 | MatrixXd qZ;
203 |
204 | // Learn the BGMM
205 | double F = learnBGMM(Xcat, qZ, weights, clusters, PRIORVAL, true);
206 |
207 | // Print the posterior parameters
208 | cout << endl << "Cluster Weights:" << endl;
209 | cout << weights.Elogweight().exp().transpose() << endl;
210 |
211 | cout << endl << "Cluster means:" << endl;
212 | for (vector::iterator k=clusters.begin(); k < clusters.end(); ++k)
213 | cout << k->getmean() << endl;
214 |
215 | cout << endl << "Cluster covariances:" << endl;
216 | for (vector::iterator k=clusters.begin(); k < clusters.end(); ++k)
217 | cout << k->getcov() << endl << endl;
218 |
219 | return 0;
220 | }
221 |
222 | ```
223 |
224 | Note that `distributions.h` has also been included. In fact, all of the
225 | algorithms in `libcluster.h` are just wrappers over a few key functions in
226 | `cluster.cpp`, `scluster.cpp` and `mcluster.cpp` that can take in *arbitrary*
227 | distributions as inputs, and so more algorithms potentially exist than
228 | enumerated in `libcluster.h`. If you want to create different algorithms, or
229 | define more cluster distributions (like categorical) have a look at inheriting
230 | the `WeightDist` and `ClusterDist` base classes in `distributions.h`. Depending
231 | on the distributions you use, you may also have to come up with a way to
232 | 'split' clusters. Otherwise you can create an algorithm with a random initial
233 | set of clusters like the MCM at the top level, which then variational Bayes
234 | will prune.
235 |
236 | There are also some generally useful functions included in `probutils.h` when
237 | dealing with mixture models (such as the log-sum-exp trick).
238 |
239 |
240 | PYTHON INTERFACE
241 | ----------------
242 |
243 | ### Installation
244 |
245 | Easy, follow the normal build instructions up to step (4) (if you haven't
246 | already), then from the build directory:
247 |
248 | cmake ..
249 | ccmake .
250 |
251 | Make sure `BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE` is `ON`
252 |
253 | make
254 | sudo make install
255 |
256 | This installs all the same files as step (4), as well as `libclusterpy.so` to
257 | your python staging directory, so it should be on your python path. I.e. just
258 | run
259 |
260 | ```python
261 | import libclusterpy
262 | ```
263 |
264 | **Trouble Shooting**:
265 |
266 | On Fedora 20/21 I have to append `/usr/local/lib` to the file `/etc/ld.so.conf`
267 | to make python find the compiled shared object.
268 |
269 |
270 | ### Usage
271 |
272 | Import the library as
273 |
274 | ```python
275 | import numpy as np
276 | import libclusterpy as lc
277 | ```
278 |
279 | Then for the mixture models, assuming `X` is a numpy array where `X.shape` is
280 | `(N, D)` -- `N` being the number of samples, and `D` being the dimension of
281 | each sample,
282 |
283 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnBGMM(X)
284 |
285 | where `f` is the final free energy value, `qZ` is a distribution over all of
286 | the cluster labels where `qZ.shape` is `(N, K)` and `K` is the number of
287 | clusters (each row of `qZ` sums to 1). Then `w`, `mu` and `cov` the expected
288 | posterior cluster parameters (see the documentation for details. Alternatively,
289 | tuning the `prior` argument can be used to change the number of clusters found,
290 |
291 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnBGMM(X, prior=0.1)
292 |
293 | This interface is common to all of the simple mixture models (i.e. VDP, BGMM
294 | etc).
295 |
296 | For the group mixture models (GMC, SGMC etc) `X` is a *list* of arrays of size
297 | `(Nj, D)` (indexed by j), one for each group/album, `X = [X_1, X_2, ...]`. The
298 | returned `qZ` and `w` are also lists of arrays, one for each group, e.g.,
299 |
300 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnSGMC(X)
301 |
302 | The SCM again has a similar interface to the above models, but now `X` is a
303 | *list of lists of arrays*, `X = [[X_11, X_12, ...], [X_21, X_22, ...], ...]`.
304 | This specifically for modelling situations where `X` is a matrix of all of the
305 | features of, for example, `N_ij` segments in image `ij` in album `j`.
306 |
307 | f, qY, qZ, wi, wij, mu, cov = lc.learnSCM(X)
308 |
309 | Where `qY` is a list of arrays of top-level/image cluster probabilities, `qZ`
310 | is a list of lists of arrays of bottom-level/segment cluster probabilities.
311 | `wi` are the mixture weights (list of arrays) corresponding to the `qY` labels,
312 | and `wij` are the weights (list of lists of arrays) corresponding the `qZ`
313 | labels. This has two optional prior inputs, and a cluster truncation level
314 | (max number of clusters) for the top-level/image clusters,
315 |
316 | f, qY, qZ, wi, wij, mu, cov = lc.learnSCM(X, trunc=10, dirprior=1,
317 | gausprior=0.1)
318 |
319 | Where `dirprior` refers to the top-level cluster prior, and `gausprior` the
320 | bottom-level.
321 |
322 | Finally, the MCM has a similar interface to the MCM, but with an extra input,
323 | `W` which is of the same format as the `X` in the GMC-style models, i.e. it is
324 | a list of arrays of top-level or image features, `W = [W_1, W_2, ...]`. The
325 | usage is,
326 |
327 | f, qY, qZ, wi, wij, mu_t, mu_k, cov_t, cov_k = lc.learnMCM(W, X)
328 |
329 | Here `mu_t` and `cov_t` are the top-level posterior cluster parameters -- these
330 | are both lists of `T` cluster parameters (`T` being the number of clusters
331 | found. Similarly `mu_k` and `cov_k` are lists of `K` bottom-level posterior
332 | cluster parameters. Like the SCM, this has a number of optional inputs,
333 |
334 |
335 | f, qY, qZ, wi, wij, mu_t, mu_k, cov_t, cov_k = lc.learnMCM(W, X, trunc=10,
336 | gausprior_t=1,
337 | gausprior_k=0.1)
338 |
339 | Where `gausprior_t` refers to the top-level cluster prior, and `gausprior_k`
340 | the bottom-level.
341 |
342 | Look at the `libclusterpy` docstrings for more help on usage, and the
343 | `testapi.py` script in the `python` directory for more usage examples.
344 |
345 | **NOTE** if you get the following message when importing libclusterpy:
346 |
347 | ImportError: /lib64/libboost_python.so.1.54.0: undefined symbol: PyClass_Type
348 |
349 | Make sure you have `boost-python3` installed!
350 |
351 |
352 | GENERAL USABILITY TIPS
353 | ----------------------
354 |
355 | When verbose mode is activated you will get output that looks something like
356 | this:
357 |
358 | Learning MODEL X...
359 | --------<=>
360 | ---<==>
361 | --------x<=>
362 | --------------<====>
363 | ----<*>
364 | ---<>
365 | Finished!
366 | Number of clusters = 4
367 | Free Energy = 41225
368 |
369 | What this means:
370 |
371 | * `-` iteration of Variational Bayes (VBE and VBM step)
372 | * `<` cluster splitting has started (model selection)
373 | * `=` found a valid candidate split
374 | * `>` chosen candidate split and testing for inclusion into model
375 | * `x` clusters have been deleted because they became devoid of observations
376 | * `*` clusters (image/document clusters) that are empty have been removed.
377 |
378 | For best clustering results, I have found the following tips may help:
379 |
380 | 1. If clustering runs REALLY slowly then it may be because of hyper-threading.
381 | OpenMP will by default use as many cores available to it as possible, this
382 | includes virtual hyper-threading cores. Unfortunately this may result in
383 | large slow-downs, so try only allowing these functions to use a number of
384 | threads less than or equal to the number of PHYSICAL cores on your machine.
385 |
386 | 2. Garbage in = garbage out. Make sure your assumptions about the data are
387 | reasonable for the type of cluster distribution you use. For instance, if
388 | your observations do not resemble a mixture of Gaussians in feature space,
389 | then it may not be appropriate to use Gaussian clusters.
390 |
391 | 3. For Gaussian clusters: standardising or whitening your data may help, i.e.
392 |
393 | if X is an NxD matrix of observations you wish to cluster, you may get
394 | better results if you use a standardised version of it, X*,
395 |
396 | X_s = C * ( X - mean(X) ) / std(X)
397 |
398 | where `C` is some constant (optional) and the mean and std are for each
399 | column of X.
400 |
401 | You may obtain even better results by using PCA or ZCA whitening on X
402 | (assuming ZERO MEAN data), using python syntax:
403 |
404 | [U, S, V] = svd(cov(X))
405 | X_w = X.dot(U).dot(diag(1. / sqrt(diag(S)))) # PCA Whitening
406 |
407 | Such that
408 |
409 | cov(X_w) = I_D.
410 |
411 | Also, to get some automatic scaling you can multiply the prior by the
412 | PRINCIPAL eigenvector of `cov(X)` (or `cov(X_s)`, `cov(X_w)`).
413 |
414 | **NOTE**: If you use diagonal covariance Gaussians I STRONGLY recommend PCA
415 | or ZCA whitening your data first, otherwise you may end up with hundreds of
416 | clusters!
417 |
418 | 4. For Exponential clusters: Your observations have to be in the range [0,
419 | inf). The clustering solution may also be sensitive to the prior. I find
420 | usually using a prior value that has the approximate magnitude of your data
421 | or more leads to better convergence.
422 |
423 |
424 | * * *
425 |
426 |
427 | REFERENCES AND CITING
428 | ---------------------
429 |
430 | **[1]** K. Kurihara, M. Welling, and N. Vlassis. Accelerated variational
431 | Dirichlet process mixtures, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
432 | vol. 19, p. 761, 2007.
433 |
434 | **[2]** D. M. Steinberg, A. Friedman, O. Pizarro, and S. B. Williams. A
435 | Bayesian nonparametric approach to clustering data from underwater robotic
436 | surveys. In International Symposium on Robotics Research, Flagstaff, AZ, Aug.
437 | 2011.
438 |
439 | **[3]** C. M. Bishop. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Cambridge, UK:
440 | Springer Science+Business Media, 2006.
441 |
442 | **[4]** D. M. Steinberg, O. Pizarro, S. B. Williams. Synergistic Clustering of
443 | Image and Segment Descriptors for Unsupervised Scene Understanding, In
444 | International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, Sydney, NSW, 2013.
445 |
446 | **[5]** D. M. Steinberg, O. Pizarro, S. B. Williams. Hierarchical Bayesian
447 | Models for Unsupervised Scene Understanding. Journal of Computer Vision and
448 | Image Understanding (CVIU). Elsevier, 2014.
449 |
450 | **[6]** D. M. Steinberg, An Unsupervised Approach to Modelling Visual Data, PhD
451 | Thesis, 2013.
452 |
453 | Please consider citing the following if you use this code:
454 |
455 | * VDP: [2, 4, 6]
456 | * BGMM: [5, 6]
457 | * GMC: [6]
458 | * SGMC/GLDA: [4, 5, 6]
459 | * SCM: [5, 6]
460 | * MCM: [4, 5, 6]
461 |
462 | You can find these on my [homepage](http://dsteinberg.github.io/).
463 | Thank you!
464 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/include/distributions.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #ifndef DISTRIBUTIONS_H
22 | #define DISTRIBUTIONS_H
23 |
24 | #include
25 | #include
26 | #include
27 |
28 | //TODO: make all protected variables private and accessed by protected functions
29 | // to improve encapsulation??
30 |
31 | /*! Namespace that implements weight and cluster distributions. */
32 | namespace distributions
33 | {
34 |
35 | //
36 | // Namespace 'symbolic' constants
37 | //
38 |
39 | const double BETAPRIOR = 1.0; //!< beta prior value (Gaussians)
40 | const double NUPRIOR = 1.0; //!< nu prior value (diagonal Gaussians)
41 | const double ALPHA1PRIOR = 1.0; //!< alpha1 prior value (All weight dists)
42 | const double ALPHA2PRIOR = 1.0; //!< alpha2 prior value (SB & Gdir)
43 | const double APRIOR = 1.0; //!< a prior value (Exponential)
44 |
45 |
46 | //
47 | // Useful Typedefs
48 | //
49 |
50 | typedef Eigen::Array ArrayXb; //!< Boolean Array
51 |
52 |
53 | //
54 | // Weight Parameter Distribution classes
55 | //
56 |
57 | /*! \brief To make a new weight class that will work with the algorithm
58 | * templates, your class must have this as the minimum interface.
59 | */
60 | class WeightDist
61 | {
62 | public:
63 |
64 | // WeightDist(), required inherited constructor template
65 |
66 | /*! \brief Update the distribution.
67 | * \param Nk an array of observations counts.
68 | */
69 | virtual void update (const Eigen::ArrayXd& Nk) = 0;
70 |
71 | /*! \brief Evaluate the expectation of the log label weights in the mixtures.
72 | * \returns An array of likelihoods for the labels given the weights
73 | */
74 | virtual const Eigen::ArrayXd& Elogweight () const = 0;
75 |
76 | /*! \brief Get the number of observations contributing to each weight.
77 | * \returns An array the number of observations contributing to each weight.
78 | */
79 | const Eigen::ArrayXd& getNk () const { return this->Nk; }
80 |
81 | /*! \brief Get the free energy contribution of these weights.
82 | * \returns the free energy contribution of these weights
83 | */
84 | virtual double fenergy () const = 0;
85 |
86 | /*! \brief virtual destructor.
87 | */
88 | virtual ~WeightDist() {}
89 |
90 | protected:
91 |
92 | /*! \brief Default constructor to set an empty observation array.
93 | */
94 | WeightDist () : Nk(Eigen::ArrayXd::Zero(1)) {}
95 |
96 | Eigen::ArrayXd Nk; //!< Number of observations making up the weights.
97 | };
98 |
99 |
100 | /*!
101 | * \brief Stick-Breaking (Dirichlet Process) parameter distribution.
102 | */
103 | class StickBreak : public WeightDist
104 | {
105 | public:
106 |
107 | StickBreak ();
108 |
109 | StickBreak (const double concentration);
110 |
111 | void update (const Eigen::ArrayXd& Nk);
112 |
113 | const Eigen::ArrayXd& Elogweight () const { return this->E_logpi; }
114 |
115 | double fenergy () const;
116 |
117 | virtual ~StickBreak () {}
118 |
119 | protected:
120 |
121 | // Prior hyperparameters, expectations etc
122 | double alpha1_p; //!< First prior param \f$ Beta(\alpha_1,\alpha_2) \f$
123 | double alpha2_p; //!< Second prior param \f$ Beta(\alpha_1,\alpha_2) \f$
124 | double F_p; //!< Free energy component dependent on priors only
125 |
126 | // Posterior hyperparameters and expectations
127 | Eigen::ArrayXd alpha1; //!< First posterior param corresp to \f$ \alpha_1 \f$
128 | Eigen::ArrayXd alpha2; //!< Second posterior param corresp to \f$ \alpha_2 \f$
129 | Eigen::ArrayXd E_logv; //!< Stick breaking log expectation
130 | Eigen::ArrayXd E_lognv; //!< Inverse stick breaking log expectation
131 | Eigen::ArrayXd E_logpi; //!< Expected log weights
132 |
133 | // Order tracker
134 | std::vector< std::pair > ordvec; //!< For order specific updates
135 |
136 | private:
137 |
138 | // Do some prior free energy calcs
139 | void priorfcalc (void);
140 | };
141 |
142 |
143 | /*!
144 | * \brief Generalised Dirichlet parameter distribution (truncated stick
145 | * breaking).
146 | */
147 | class GDirichlet : public StickBreak
148 | {
149 | public:
150 |
151 | void update (const Eigen::ArrayXd& Nk);
152 |
153 | double fenergy () const;
154 |
155 | virtual ~GDirichlet () {}
156 |
157 | };
158 |
159 |
160 | /*!
161 | * \brief Dirichlet parameter distribution.
162 | */
163 | class Dirichlet : public WeightDist
164 | {
165 | public:
166 |
167 | Dirichlet ();
168 |
169 | Dirichlet (const double alpha);
170 |
171 | void update (const Eigen::ArrayXd& Nk);
172 |
173 | const Eigen::ArrayXd& Elogweight () const { return this->E_logpi; }
174 |
175 | double fenergy () const;
176 |
177 | virtual ~Dirichlet () {}
178 |
179 | private:
180 |
181 | // Prior hyperparameters, expectations etc
182 | double alpha_p; // Symmetric Dirichlet prior \f$ Dir(\alpha) \f$
183 | double F_p; // Free energy component dependent on priors only
184 |
185 | // Posterior hyperparameters and expectations
186 | Eigen::ArrayXd alpha; // Posterior param corresp to \f$ \alpha \f$
187 | Eigen::ArrayXd E_logpi; // Expected log weights
188 |
189 | };
190 |
191 |
192 | //
193 | // Cluster Parameter Distribution classes
194 | //
195 |
196 | /*! \brief To make a new cluster distribution class that will work with the
197 | * algorithm templates your class must have this as the minimum
198 | * interface.
199 | */
200 | class ClusterDist
201 | {
202 | public:
203 |
204 | /*! \brief Add observations to the cluster without updating the parameters
205 | * (i.e. add to the sufficient statistics)
206 | * \param qZk the observation indicators for this cluster, corresponding to
207 | * X.
208 | * \param X the observations [obs x dims], to add to this cluster according
209 | * to qZk.
210 | */
211 | virtual void addobs (
212 | const Eigen::VectorXd& qZk,
213 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& X
214 | ) = 0;
215 |
216 | /*! \brief Update the cluster parameters from the observations added from
217 | * addobs().
218 | */
219 | virtual void update () = 0;
220 |
221 | /*! \brief Clear the all parameters and observation accumulations from
222 | * addobs().
223 | */
224 | virtual void clearobs () = 0;
225 |
226 | /*! \brief Evaluate the log marginal likelihood of the observations.
227 | * \param X a matrix of observations, [obs x dims].
228 | * \returns An array of likelihoods for the observations given this dist.
229 | */
230 | virtual Eigen::VectorXd Eloglike (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const = 0;
231 |
232 | /*! \brief Get the free energy contribution of these cluster parameters.
233 | * \returns the free energy contribution of these cluster parameters.
234 | */
235 | virtual double fenergy () const = 0;
236 |
237 | /*! \brief Propose a split for the observations given these cluster parameters
238 | * \param X a matrix of observations, [obs x dims], to split.
239 | * \returns a binary array of split assignments.
240 | * \note this needs to consistently split observations between multiple
241 | * subsequent calls, but can change after each update().
242 | */
243 | virtual ArrayXb splitobs (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const = 0;
244 |
245 | /*! \brief Return the number of observations belonging to this cluster.
246 | * \returns the number of observations belonging to this cluster.
247 | */
248 | double getN () const { return this->N; }
249 |
250 | /*! \brief Return the cluster prior value.
251 | * \returns the cluster prior value.
252 | */
253 | double getprior () const { return this->prior; }
254 |
255 | /*! \brief virtual destructor.
256 | */
257 | virtual ~ClusterDist() {}
258 |
259 | protected:
260 |
261 | /*! \brief Constructor that must be called to set the prior and cluster
262 | * dimensionality.
263 | * \param prior the cluster prior.
264 | * \param D the dimensionality of this cluster.
265 | */
266 | ClusterDist (const double prior, const unsigned int D)
267 | : D(D), prior(prior), N(0) {}
268 |
269 | unsigned int D; //!< Dimensionality
270 | double prior; //!< Cluster prior
271 | double N; //!< Number of observations making up this cluster.
272 |
273 | };
274 |
275 |
276 | /*!
277 | * \brief Gaussian-Wishart parameter distribution for full Gaussian clusters.
278 | */
279 | class GaussWish : public ClusterDist
280 | {
281 | public:
282 |
283 | /*! \brief Make a Gaussian-Wishart prior.
284 | *
285 | * \param clustwidth makes the covariance prior \f$ clustwidth \times D
286 | * \times \mathbf{I}_D \f$.
287 | * \param D is the dimensionality of the data
288 | */
289 | GaussWish (const double clustwidth, const unsigned int D);
290 |
291 | void addobs (const Eigen::VectorXd& qZk, const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
292 |
293 | void update ();
294 |
295 | void clearobs ();
296 |
297 | Eigen::VectorXd Eloglike (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
298 |
299 | ArrayXb splitobs (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
300 |
301 | double fenergy () const;
302 |
303 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster mean.
304 | * \returns the expected cluster mean.
305 | */
306 | const Eigen::RowVectorXd& getmean () const { return this->m; }
307 |
308 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster covariance.
309 | * \returns the expected cluster covariance.
310 | */
311 | Eigen::MatrixXd getcov () const { return this->iW/this->nu; }
312 |
313 | virtual ~GaussWish () {}
314 |
315 | private:
316 |
317 | // Prior hyperparameters etc
318 | double nu_p;
319 | double beta_p;
320 | Eigen::RowVectorXd m_p;
321 | Eigen::MatrixXd iW_p;
322 | double logdW_p;
323 | double F_p;
324 |
325 | // Posterior hyperparameters
326 | double nu; // nu, Lambda ~ Wishart(W, nu)
327 | double beta; // beta, mu ~ Normal(m, (beta*Lambda)^-1)
328 | Eigen::RowVectorXd m; // m, mu ~ Normal(m, (beta*Lambda)^-1)
329 | Eigen::MatrixXd iW; // Inverse W, Lambda ~ Wishart(W, nu)
330 | double logdW; // log(det(W))
331 |
332 | // Sufficient Statistics
333 | double N_s;
334 | Eigen::RowVectorXd x_s;
335 | Eigen::MatrixXd xx_s;
336 |
337 | };
338 |
339 |
340 | /*!
341 | * \brief Normal-Gamma parameter distribution for diagonal Gaussian clusters.
342 | */
343 | class NormGamma : public ClusterDist
344 | {
345 | public:
346 |
347 | /*! \brief Make a Normal-Gamma prior.
348 | *
349 | * \param clustwidth makes the covariance prior \f$ clustwidth \times
350 | * \mathbf{I}_D \f$.
351 | * \param D is the dimensionality of the data
352 | */
353 | NormGamma (const double clustwidth, const unsigned int D);
354 |
355 | void addobs (const Eigen::VectorXd& qZk, const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
356 |
357 | void update ();
358 |
359 | void clearobs ();
360 |
361 | Eigen::VectorXd Eloglike (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
362 |
363 | ArrayXb splitobs (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
364 |
365 | double fenergy () const;
366 |
367 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster mean.
368 | * \returns the expected cluster mean.
369 | */
370 | const Eigen::RowVectorXd& getmean () const { return this->m; }
371 |
372 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster covariance.
373 | * \returns the expected cluster covariance (just the diagonal elements).
374 | */
375 | Eigen::RowVectorXd getcov () const { return this->L*this->nu; }
376 |
377 | virtual ~NormGamma () {}
378 |
379 | private:
380 |
381 | // Prior hyperparameters etc
382 | double nu_p;
383 | double beta_p;
384 | Eigen::RowVectorXd m_p;
385 | Eigen::RowVectorXd L_p;
386 | double logL_p;
387 |
388 | // Posterior hyperparameters
389 | double nu;
390 | double beta;
391 | Eigen::RowVectorXd m;
392 | Eigen::RowVectorXd L;
393 | double logL;
394 |
395 | // Sufficient Statistics
396 | double N_s;
397 | Eigen::RowVectorXd x_s;
398 | Eigen::RowVectorXd xx_s;
399 |
400 | };
401 |
402 |
403 | /*!
404 | * \brief Exponential-Gamma parameter distribution for Exponential clusters.
405 | */
406 | class ExpGamma : public ClusterDist
407 | {
408 | public:
409 |
410 | /*! \brief Make a Gamma prior.
411 | *
412 | * \param obsmag is the prior value for b in Gamma(a, b), which works well
413 | * when it is approximately the magnitude of the observation
414 | * dimensions, x_djn.
415 | * \param D is the dimensionality of the data
416 | */
417 | ExpGamma (const double obsmag, const unsigned int D);
418 |
419 | void addobs (const Eigen::VectorXd& qZk, const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
420 |
421 | void update ();
422 |
423 | void clearobs ();
424 |
425 | Eigen::VectorXd Eloglike (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
426 |
427 | ArrayXb splitobs (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
428 |
429 | double fenergy () const;
430 |
431 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster rate parameter, i.e. Exp(E[lambda]),
432 | * where lambda is the rate parameter.
433 | * \returns the expected cluster rate parameter.
434 | */
435 | Eigen::RowVectorXd getrate () { return this->a*this->ib; }
436 |
437 | virtual ~ExpGamma () {}
438 |
439 | private:
440 |
441 | // Prior hyperparameters
442 | double a_p;
443 | double b_p;
444 |
445 | // Posterior hyperparameters etc
446 | double a;
447 | Eigen::RowVectorXd ib; // inverse b
448 | double logb;
449 |
450 | // Sufficient Statistics
451 | double N_s;
452 | Eigen::RowVectorXd x_s;
453 |
454 | };
455 |
456 |
457 | }
458 |
459 | #endif // DISTRIBUTIONS_H
460 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/include/probutils.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #ifndef PROBUTILS_H
22 | #define PROBUTILS_H
23 |
24 | #include
25 | #include
26 | #include
27 |
28 |
29 | //
30 | // Namespaces
31 | //
32 |
33 | /*! \brief Namespace for various linear algebra tools useful for dealing with
34 | * Gaussians and log-probability expressions.
35 | *
36 | * \author Daniel Steinberg
37 | * Australian Centre for Field Robotics
38 | * The University of Sydney
39 | *
40 | * \date 15/02/2011
41 | */
42 | namespace probutils
43 | {
44 |
45 |
46 | //
47 | // Useful Functions
48 | //
49 |
50 | /*! \brief Calculate the column means of a matrix.
51 | *
52 | * \param X an NxD matrix.
53 | * \returns a 1xD row vector of the means of each column of X.
54 | */
55 | Eigen::RowVectorXd mean (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
56 |
57 |
58 | /*! \brief Calculate the column means of a vector of matrices (one mean for
59 | * all data in the matrices).
60 | *
61 | * \param X a vector of N_jxD matrices for j = 1:J.
62 | * \returns a 1xD row vector of the means of each column of X.
63 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if X has inconsistent D between elements.
64 | */
65 | Eigen::RowVectorXd mean (const std::vector& X);
66 |
67 |
68 | /*! \brief Calculate the column standard deviations of a matrix, uses N - 1.
69 | *
70 | * \param X an NxD matrix.
71 | * \returns a 1xD row vector of the standard deviations of each column of X.
72 | */
73 | Eigen::RowVectorXd stdev (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
74 |
75 |
76 | /*! \brief Calculate the covariance of a matrix.
77 | *
78 | * If X is an NxD matrix, then this calculates:
79 | *
80 | * \f[ Cov(X) = \frac{1} {N-1} (X-E[X])^T (X-E[X]) \f]
81 | *
82 | * \param X is a NxD matrix to calculate the covariance of.
83 | * \returns a DxD covariance matrix.
84 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if X is 1xD or less (has one or less
85 | * observations).
86 | */
87 | Eigen::MatrixXd cov (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
88 |
89 |
90 | /*! \brief Calculate the covariance of a vector of matrices (one mean for
91 | * all data in the matrices).
92 | *
93 | * This calculates:
94 | *
95 | * \f[ Cov(X) = \frac{1} {\sum_j N_j-1} \sum_j (X_j-E[X])^T (X_j-E[X]) \f]
96 | *
97 | * \param X is a a vector of N_jxD matrices for j = 1:J.
98 | * \returns a DxD covariance matrix.
99 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if any X_j has one or less observations.
100 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if X has inconsistent D between elements.
101 | */
102 | Eigen::MatrixXd cov (const std::vector& X);
103 |
104 |
105 | /*! \brief Calculate the Mahalanobis distance, (x-mu)' * A^-1 * (x-mu), N
106 | * times.
107 | *
108 | * \param X an NxD matrix of samples/obseravtions.
109 | * \param mu a 1XD vector of means.
110 | * \param A a DxD marix of weights, A must be invertable.
111 | * \returns an Nx1 matrix of distances evaluated for each row of X.
112 | * \throws std::invalid_argument If X, mu and A do not have compatible
113 | * dimensionality, or if A is not PSD.
114 | */
115 | Eigen::VectorXd mahaldist (
116 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& X,
117 | const Eigen::RowVectorXd& mu,
118 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& A
119 | );
120 |
121 |
122 | /*! \brief Perform a log(sum(exp(X))) in a numerically stable fashion.
123 | *
124 | * \param X is a NxK matrix. We wish to sum along the rows (sum out K).
125 | * \returns an Nx1 vector where the log(sum(exp(X))) operation has been
126 | * performed along the rows.
127 | */
128 | Eigen::VectorXd logsumexp (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
129 |
130 |
131 | /*! \brief The eigen power method. Return the principal eigenvalue and
132 | * eigenvector.
133 | *
134 | * \param A is the square DxD matrix to decompose.
135 | * \param eigvec is the Dx1 principal eigenvector (mutable)
136 | * \returns the principal eigenvalue.
137 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if the matrix A is not square
138 | *
139 | */
140 | double eigpower (const Eigen::MatrixXd& A, Eigen::VectorXd& eigvec);
141 |
142 |
143 | /*! \brief Get the log of the determinant of a PSD matrix.
144 | *
145 | * \param A a DxD positive semi-definite matrix.
146 | * \returns log(det(A))
147 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if the matrix A is not square or if it is
148 | * not positive semidefinite.
149 | */
150 | double logdet (const Eigen::MatrixXd& A);
151 |
152 |
153 | /*! \brief Calculate digamma(X) for each element of X.
154 | *
155 | * \param X an NxM matrix
156 | * \returns an NxM matrix for which digamma(X) has been calculated for each
157 | * element
158 | */
159 | Eigen::MatrixXd mxdigamma (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
160 |
161 |
162 | /*! \brief Calculate log(gamma(X)) for each element of X.
163 | *
164 | * \param X an NxM matrix
165 | * \returns an NxM matrix for which log(gamma(X)) has been calculated for
166 | * each element
167 | */
168 | Eigen::MatrixXd mxlgamma (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
169 |
170 | }
171 |
172 | #endif // PROBUTILS_H
173 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/CMakeLists.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | if(BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE)
2 |
3 | message(STATUS "Will build the python interface")
4 | if(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
5 | set(PYCMD "python3")
6 | message(STATUS "Will use python 3")
7 | else(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
8 | set(PYCMD "python2")
9 | message(STATUS "Will use python 2")
10 | endif(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
11 |
12 | # Python needs row major matrices (for convenience)
13 | set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -DEIGEN_DEFAULT_TO_ROW_MAJOR")
14 |
15 |
16 | #--------------------------------#
17 | # Includes #
18 | #--------------------------------#
19 |
20 | if(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
21 | find_package(Boost COMPONENTS python3 REQUIRED)
22 | else(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
23 | find_package(Boost COMPONENTS python REQUIRED)
24 | endif(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
25 |
26 | include(${PYTHON_SOURCE_DIR}/FindNumpy.cmake REQUIRED)
27 | include_directories(${NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR})
28 | find_package(PythonLibs REQUIRED)
29 | include_directories(${PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIRS})
30 |
31 |
32 | #--------------------------------#
33 | # Library Build Instructions #
34 | #--------------------------------#
35 |
36 | add_library(${PROJECT_NAME}py SHARED
37 | ${PYTHON_SOURCE_DIR}/libclusterpy.h
38 | ${PYTHON_SOURCE_DIR}/libclusterpy.cpp
39 | )
40 |
41 | if(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
42 | set(BOOST_PYTHON boost_python3)
43 | else(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
44 | set(BOOST_PYTHON boost_python)
45 | endif(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
46 |
47 | target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}py
48 | ${BOOST_PYTHON}
49 | ${PYTHON_LIBRARIES}
50 | ${Boost_LIBRARIES}
51 | ${PROJECT_NAME}
52 | )
53 |
54 |
55 | #--------------------------------#
56 | # Install Instructions #
57 | #--------------------------------#
58 |
59 | # Get python path
60 | execute_process(COMMAND ${PYCMD} -c
61 | "from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_lib; print(get_python_lib())"
62 | OUTPUT_VARIABLE PYTHON_SITE_PACKAGES OUTPUT_STRIP_TRAILING_WHITESPACE
63 | )
64 |
65 | # Install target
66 | install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}py DESTINATION ${PYTHON_SITE_PACKAGES})
67 |
68 | endif(BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE)
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/FindNumpy.cmake:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # - Find numpy
2 | # Find the native numpy includes
3 | # This module defines
4 | # NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR, where to find numpy/arrayobject.h, etc.
5 | # NUMPY_FOUND, If false, do not try to use numpy headers.
6 |
7 | # This is (modified) from the avogadro project, http://avogadro.cc (GPL)
8 |
9 | if (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR)
10 | # in cache already
11 | set (NUMPY_FIND_QUIETLY TRUE)
12 | endif (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR)
13 |
14 | EXEC_PROGRAM ("${PYCMD}"
15 | ARGS "-c 'import numpy; print(numpy.get_include())'"
16 | OUTPUT_VARIABLE NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR)
17 |
18 |
19 | if (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR MATCHES "Traceback")
20 | # Did not successfully include numpy
21 | set(NUMPY_FOUND FALSE)
22 | else (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR MATCHES "Traceback")
23 | # successful
24 | set (NUMPY_FOUND TRUE)
25 | set (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR ${NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR} CACHE STRING "Numpy include path")
26 | endif (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR MATCHES "Traceback")
27 |
28 | if (NUMPY_FOUND)
29 | if (NOT NUMPY_FIND_QUIETLY)
30 | message (STATUS "Numpy headers found")
31 | endif (NOT NUMPY_FIND_QUIETLY)
32 | else (NUMPY_FOUND)
33 | if (NUMPY_FIND_REQUIRED)
34 | message (FATAL_ERROR "Numpy headers missing")
35 | endif (NUMPY_FIND_REQUIRED)
36 | endif (NUMPY_FOUND)
37 |
38 | MARK_AS_ADVANCED (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR)
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/libclusterpy.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include
22 | #include "distributions.h"
23 | #include "libclusterpy.h"
24 |
25 | //
26 | // Namespaces
27 | //
28 |
29 | using namespace std;
30 | using namespace Eigen;
31 | using namespace distributions;
32 | using namespace libcluster;
33 | using namespace boost::python;
34 | using namespace boost::python::api;
35 |
36 |
37 | //
38 | // Private Functions
39 | //
40 |
41 |
42 | // Convert (memory share) a numpy array to an Eigen MatrixXd
43 | MatrixXd numpy2MatrixXd (const object& X)
44 | {
45 | if (PyArray_Check(X.ptr()) == false)
46 | throw invalid_argument("PyObject is not an array!");
47 |
48 | // Cast PyObject* to PyArrayObject* now we know that it's valid
49 | PyArrayObject* Xptr = (PyArrayObject*) X.ptr();
50 |
51 | if (PyArray_ISFLOAT(Xptr) == false)
52 | throw invalid_argument("PyObject is not an array of floats/doubles!");
53 |
54 | return Map ((double*) PyArray_DATA(Xptr),
55 | PyArray_DIMS(Xptr)[0], PyArray_DIMS(Xptr)[1]);
56 | }
57 |
58 |
59 | // Convert (memory share) a list of numpy arrays to a vector of Eigen MatrixXd
60 | vMatrixXd lnumpy2vMatrixXd (const boost::python::list& X)
61 | {
62 |
63 | vMatrixXd X_;
64 |
65 | for (int i=0; i < len(X); ++i)
66 | X_.push_back(numpy2MatrixXd(X[i]));
67 |
68 | return X_;
69 | }
70 |
71 |
72 | // Convert (memory share) a list of lists of arrays to a vector of vectors of
73 | // matrices
74 | vvMatrixXd llnumpy2vvMatrixXd (const boost::python::list& X)
75 | {
76 |
77 | vvMatrixXd X_;
78 |
79 | for (int i=0; i < len(X); ++i)
80 | {
81 | vMatrixXd Xi_;
82 |
83 | // Compiler complains when try to use lnumpy2vmatrix instead of following
84 | for (int j=0; j < len(X[i]); ++j)
85 | Xi_.push_back(numpy2MatrixXd(X[i][j]));
86 |
87 | X_.push_back(Xi_);
88 | }
89 |
90 | return X_;
91 | }
92 |
93 |
94 | // Get all the means from Gaussian clusters, Kx[1xD] matrices
95 | vMatrixXd getmean (const vector& clusters)
96 | {
97 | vMatrixXd means;
98 |
99 | for (size_t k=0; k < clusters.size(); ++k)
100 | means.push_back(clusters[k].getmean());
101 |
102 | return means;
103 | }
104 |
105 |
106 | // Get all of the covarances of Gaussian clusters, Kx[DxD] matrices
107 | vMatrixXd getcov (const vector& clusters)
108 | {
109 | vMatrixXd covs;
110 |
111 | for (size_t k=0; k < clusters.size(); ++k)
112 | covs.push_back(clusters[k].getcov());
113 |
114 | return covs;
115 | }
116 |
117 |
118 | // Get the expected cluster weights in each of the groups
119 | template
120 | vector getweights (const vector& weights)
121 | {
122 | vector rwgt;
123 | for (size_t k=0; k < weights.size(); ++k)
124 | rwgt.push_back(ArrayXd(weights[k].Elogweight().exp()));
125 |
126 | return rwgt;
127 | }
128 |
129 |
130 | //
131 | // Public Wrappers
132 | //
133 |
134 | // VDP
135 | tuple wrapperVDP (
136 | const object& X,
137 | const float clusterprior,
138 | const int maxclusters,
139 | const bool verbose,
140 | const int nthreads
141 | )
142 | {
143 | // Convert X
144 | const MatrixXd X_ = numpy2MatrixXd(X);
145 |
146 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
147 | MatrixXd qZ;
148 | StickBreak weights;
149 | vector clusters;
150 |
151 | // Do the clustering
152 | double f = learnVDP(X_, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, maxclusters,
153 | verbose, nthreads);
154 |
155 | // Return relevant objects
156 | return make_tuple(f, qZ, ArrayXd(weights.Elogweight().exp()),
157 | getmean(clusters), getcov(clusters));
158 | }
159 |
160 |
161 | // BGMM
162 | tuple wrapperBGMM (
163 | const object& X,
164 | const float clusterprior,
165 | const int maxclusters,
166 | const bool verbose,
167 | const int nthreads
168 | )
169 | {
170 | // Convert X
171 | const MatrixXd X_ = numpy2MatrixXd(X);
172 |
173 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
174 | MatrixXd qZ;
175 | Dirichlet weights;
176 | vector clusters;
177 |
178 | // Do the clustering
179 | double f = learnBGMM(X_, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, maxclusters,
180 | verbose, nthreads);
181 |
182 | // Return relevant objects
183 | return make_tuple(f, qZ, ArrayXd(weights.Elogweight().exp()),
184 | getmean(clusters), getcov(clusters));
185 | }
186 |
187 |
188 | // GMC
189 | tuple wrapperGMC (
190 | const boost::python::list &X,
191 | const float clusterprior,
192 | const int maxclusters,
193 | const bool sparse,
194 | const bool verbose,
195 | const int nthreads
196 | )
197 | {
198 | // Convert X
199 | const vMatrixXd X_ = lnumpy2vMatrixXd(X);
200 |
201 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
202 | vMatrixXd qZ;
203 | vector weights;
204 | vector clusters;
205 |
206 | // Do the clustering
207 | double f = learnGMC(X_, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, maxclusters,
208 | sparse, verbose, nthreads);
209 |
210 | // Return relevant objects
211 | return make_tuple(f, qZ, getweights(weights), getmean(clusters),
212 | getcov(clusters));
213 | }
214 |
215 |
216 | // SGMC
217 | tuple wrapperSGMC (
218 | const boost::python::list &X,
219 | const float clusterprior,
220 | const int maxclusters,
221 | const bool sparse,
222 | const bool verbose,
223 | const int nthreads
224 | )
225 | {
226 | // Convert X
227 | const vMatrixXd X_ = lnumpy2vMatrixXd(X);
228 |
229 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
230 | vMatrixXd qZ;
231 | vector weights;
232 | vector clusters;
233 |
234 | // Do the clustering
235 | double f = learnSGMC(X_, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, maxclusters,
236 | sparse, verbose, nthreads);
237 |
238 | // Return relevant objects
239 | return make_tuple(f, qZ, getweights(weights), getmean(clusters),
240 | getcov(clusters));
241 | }
242 |
243 |
244 | // SCM
245 | tuple wrapperSCM (
246 | const boost::python::list &X,
247 | const float dirprior,
248 | const float gausprior,
249 | const int trunc,
250 | const int maxclusters,
251 | const bool verbose,
252 | const int nthreads
253 | )
254 | {
255 | // Convert X
256 | const vvMatrixXd X_ = llnumpy2vvMatrixXd(X);
257 |
258 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
259 | vMatrixXd qY;
260 | vvMatrixXd qZ;
261 | vector weights_j;
262 | vector weights_t;
263 | vector clusters;
264 |
265 | // Do the clustering
266 | double f = learnSCM(X_, qY, qZ, weights_j, weights_t, clusters, dirprior,
267 | gausprior, trunc, maxclusters, verbose, nthreads);
268 |
269 | // Return relevant objects
270 | return make_tuple(f, qY, qZ, getweights(weights_j),
271 | getweights(weights_t), getmean(clusters), getcov(clusters));
272 | }
273 |
274 |
275 | // MCM
276 | tuple wrapperMCM (
277 | const boost::python::list &W,
278 | const boost::python::list &X,
279 | const float gausprior_t,
280 | const float gausprior_k,
281 | const int trunc,
282 | const int maxclusters,
283 | const bool verbose,
284 | const int nthreads
285 | )
286 | {
287 | // Convert W and X
288 | const vMatrixXd W_ = lnumpy2vMatrixXd(W);
289 | const vvMatrixXd X_ = llnumpy2vvMatrixXd(X);
290 |
291 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
292 | vMatrixXd qY;
293 | vvMatrixXd qZ;
294 | vector weights_j;
295 | vector weights_t;
296 | vector clusters_t;
297 | vector clusters_k;
298 |
299 | // Do the clustering
300 | double f = learnMCM(W_, X_, qY, qZ, weights_j, weights_t, clusters_t,
301 | clusters_k, gausprior_t, gausprior_k, trunc, maxclusters,
302 | verbose, nthreads);
303 |
304 | // Return relevant objects
305 | return make_tuple(f, qY, qZ, getweights(weights_j),
306 | getweights(weights_t), getmean(clusters_t),
307 | getmean(clusters_k), getcov(clusters_t), getcov(clusters_k));
308 | }
309 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/libclusterpy.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #ifndef LIBCLUSTERPY_H
22 | #define LIBCLUSTERPY_H
23 |
24 | #define NPY_NO_DEPRECATED_API NPY_1_7_API_VERSION // Test deprication for v1.7
25 |
26 | #include
27 | #include
28 | #include
29 | #include "libcluster.h"
30 |
31 |
32 | //
33 | // To-python type converters
34 | //
35 |
36 | // Eigen::MatrixXd/ArrayXd (double) to numpy array ([[...]])
37 | template
38 | struct eigen2numpy
39 | {
40 | static PyObject* convert (const M& X)
41 | {
42 | npy_intp arsize[] = {X.rows(), X.cols()};
43 | M* X_ = new M(X); // Copy to persistent array
44 | PyObject* Xp = PyArray_SimpleNewFromData(2, arsize, NPY_DOUBLE, X_->data());
45 |
46 | if (Xp == NULL)
47 | throw std::runtime_error("Cannot convert Eigen matrix to Numpy array!");
48 |
49 | return Xp;
50 | }
51 | };
52 |
53 |
54 | // std::vector to python list [...].
55 | template
56 | struct vector2list
57 | {
58 | static PyObject* convert (const std::vector& X)
59 | {
60 | boost::python::list* Xp = new boost::python::list();
61 |
62 | for (size_t i = 0; i < X.size(); ++i)
63 | Xp->append(X[i]);
64 |
65 | return Xp->ptr();
66 | }
67 | };
68 |
69 |
70 | //
71 | // Wrappers
72 | //
73 |
74 | // VDP
75 | boost::python::tuple wrapperVDP (
76 | const boost::python::api::object& X,
77 | const float clusterprior,
78 | const int maxclusters,
79 | const bool verbose,
80 | const int nthreads
81 | );
82 |
83 |
84 | // BGMM
85 | boost::python::tuple wrapperBGMM (
86 | const boost::python::api::object& X,
87 | const float clusterprior,
88 | const int maxclusters,
89 | const bool verbose,
90 | const int nthreads
91 | );
92 |
93 |
94 | // GMC
95 | boost::python::tuple wrapperGMC (
96 | const boost::python::list& X,
97 | const float clusterprior,
98 | const int maxclusters,
99 | const bool sparse,
100 | const bool verbose,
101 | const int nthreads
102 | );
103 |
104 |
105 | // SGMC
106 | boost::python::tuple wrapperSGMC (
107 | const boost::python::list& X,
108 | const float clusterprior,
109 | const int maxclusters,
110 | const bool sparse,
111 | const bool verbose,
112 | const int nthreads
113 | );
114 |
115 |
116 | // SCM
117 | boost::python::tuple wrapperSCM (
118 | const boost::python::list& X,
119 | const float dirprior,
120 | const float gausprior,
121 | const int trunc,
122 | const int maxclusters,
123 | const bool verbose,
124 | const int nthreads
125 | );
126 |
127 |
128 | // MCM
129 | boost::python::tuple wrapperMCM (
130 | const boost::python::list& W,
131 | const boost::python::list& X,
132 | const float gausprior_t,
133 | const float gausprior_k,
134 | const int trunc,
135 | const int maxclusters,
136 | const bool verbose,
137 | const int nthreads
138 | );
139 |
140 |
141 | //
142 | // Hack for python2/3 numpy return value weirdness
143 | //
144 |
145 | #if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
146 | int*
147 | #else
148 | void
149 | #endif
150 | init_numpy()
151 | {
152 | import_array();
153 | #if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
154 | return NULL;
155 | #endif
156 | }
157 |
158 |
159 | //
160 | // Module definition
161 | //
162 |
163 | BOOST_PYTHON_MODULE (libclusterpy)
164 | {
165 | using namespace boost::python;
166 |
167 | // This will enable user-defined docstrings and python signatures,
168 | // while disabling the C++ signatures
169 | docstring_options local_docstring_options(true, true, false);
170 |
171 |
172 | // set the docstring of the current module scope
173 | const std::string moddoc =
174 | "A collection of structured Bayesian clustering algorithms.\n\n"
175 | "This library contains implementations of a number of variational\n"
176 | "Bayesian clustering algorithms such as the Bayesian Gaussian Mixture\n"
177 | "model of [1], and the Variational Dirichlet process of [2]. Also \n"
178 | "implemented is a latent Dirichlet allocation-like model with a \n"
179 | "Gaussian observation model (GMC [4], SGMC/G-LDA [3, 4, 5]), and more\n"
180 | "highly structured models -- see the SCM and MCM functions [3, 4, 5].\n\n"
181 | "Author: Daniel Steinberg\n"
182 | "\tAustralian Centre for Field Robotics,\n"
183 | "\tThe University of Sydney.\n\n"
184 | "Date: 11/03/2013\n\n"
185 | "License: GPL v3 or later, See LICENSE.\n\n"
186 | " [1] C. M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Cambridge,\n"
187 | "\tUK: pringer Science+Business Media, 2006.\n"
188 | " [2] K. Kurihara, M. Welling, and N. Vlassis, Accelerated variational\n"
189 | "\tDirichlet process mixtures, Advances in Neural Information Processing\n"
190 | "\tSystems, vol. 19, p. 761, 2007.\n"
191 | " [3] D. M. Steinberg, O. Pizarro, S. B. Williams, Synergistic Clustering\n"
192 | "\tof Image and Segment Descriptors for Unsupervised Scene Understanding.\n"
193 | "\tIn International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, Sydney,\n"
194 | "\tNSW, 2013.\n"
195 | " [4] D. M. Steinberg, O. Pizarro, S. B. Williams. Hierarchical\n"
196 | "\tBayesian Models for Unsupervised Scene Understanding. Journal of\n"
197 | "\tComputer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU). Elsevier, 2014.\n"
198 | " [5] D. M. Steinberg, An Unsupervised Approach to Modelling Visual Data,\n"
199 | "\tPhD Thesis, 2013.\n"
200 | " [6] D. M. Steinberg, A. Friedman, O. Pizarro, and S. B. Williams.\n"
201 | "\tA Bayesian nonparametric approach to clustering data from underwater\n"
202 | "\trobotic surveys. In International Symposium on Robotics Research,\n"
203 | "\tFlagstaff, AZ, Aug. 2011.";
204 | scope().attr("__doc__") = moddoc;
205 |
206 |
207 | // To-python converters
208 | init_numpy();
209 | to_python_converter< Eigen::ArrayXd, eigen2numpy >();
210 | to_python_converter< Eigen::MatrixXd, eigen2numpy >();
211 | to_python_converter< std::vector,
212 | vector2list >();
213 | to_python_converter< std::vector,
214 | vector2list >();
215 | to_python_converter< std::vector< std::vector >,
216 | vector2list< std::vector > >();
217 |
218 |
219 | // Common documentation strings -- arguments
220 | const std::string comargs = "\nArguments:\n";
221 | const std::string Xarg =
222 | "\tX: array shape(N,D) the data to be clustered, N are the number of \n"
223 | "\t\tsamples, D the number of dimensions.\n";
224 | const std::string vXarg =
225 | "\tX: list[array shape(N_j,D),...] of len = J which is the data to be\n"
226 | "\t\tclustered, N_j are the number of samples of each group (or list \n"
227 | "\t\telement) j of data, D the number of dimensions.\n";
228 | const std::string vvXarg =
229 | "\tX: list[list[array shape(N_j,D_b),...]] where the outer list is of\n"
230 | "\t\tlen = J, and each inner list is of len = I_j. This is the\n"
231 | "\t\t(bottom-level) data to be clustered, N_ji are the number of samples\n"
232 | "\t\tof each 'document/image' (ji) within each group (j) of data. D_b is\n"
233 | "\t\tthe number of dimensions.\n";
234 | const std::string truncarg =
235 | "\ttrunc: the maximum number of top-level clusters to find. This is the \n"
236 | "\t\ttruncation level, and mostly less top-level clusters than this will\n"
237 | "\t\tbe returned.\n";
238 | const std::string maxclustersarg =
239 | "\tmaxclusters: the maximum number of bottom level clusters to search \n"
240 | "\t\tfor, -1 (default) means no upper bound.\n";
241 | const std::string priorarg =
242 | "\tprior: the prior width of the Gaussian clusters.\n";
243 | const std::string priorkarg =
244 | "\tgausprior_k: the prior width of the bottom-level Gaussian clusters.\n";
245 | const std::string sparsearg =
246 | "\tsparse: do sparse updates? I.e. only update the clusters that have\n"
247 | "\t\tmore than one observation.\n";
248 | const std::string verbarg =
249 | "\tverbose: output clustering status?\n";
250 | const std::string threadarg =
251 | "\tthreads: the number of threads to use.\n";
252 |
253 | // Common documentation strings -- returns
254 | const std::string comrets = "\nReturns:\n";
255 | const std::string fret =
256 | "\tf: float, the free energy learning objective value.\n";
257 | const std::string qZret =
258 | "\tqZ: array shape(N,K), the probability of the observations belonging to\n"
259 | "\t\teach cluster, where K is the number of discovered clusters.\n";
260 | const std::string vqZret =
261 | "\tqZ: list[array shape(N_j,K),...] of len = J, the probability of the\n"
262 | "\t\tobservations in group j belonging to each cluster. Here K is the\n"
263 | "\t\tnumber of discovered clusters.\n";
264 | const std::string vvqZret =
265 | "\tqZ: list[list[array shape(N_j,K),...]] with the outer list of len = J,\n"
266 | "\t\tand each inner list of len = I_j. This is the probability of the\n"
267 | "\t\tbottom-level observations belonging to each cluster. Here K is the\n"
268 | "\t\tnumber of discovered bottom-level clusters.\n";
269 | const std::string vqYret =
270 | "\tqY: list[array shape(N_j,T),...] of len = J, the probability of the\n"
271 | "\t\t'documents' in group j belonging to each top-level cluster. Here T\n"
272 | "\t\tis the number of discovered top-level clusters.\n";
273 | const std::string wret =
274 | "\tw: array shape(K,1), the (expected) Gaussian mixture weights.\n";
275 | const std::string vwret =
276 | "\tw_j: list[array shape(K,1),...] of len = J, the (expected) Gaussian\n"
277 | "\t\tmixture weights of each group, j.\n";
278 | const std::string vwjret =
279 | "\tw_j: list[array shape(T,1),...] of len = J, the (expected) top-level\n"
280 | "\t\tcluster weights of each group, j.\n";
281 | const std::string vwtret =
282 | "\tw_t: list[array shape(K,1),...] of len = T, the (expected) Gaussian\n"
283 | "\t\tmixture weights of each bottom-level cluster within each of the T\n"
284 | "\t\ttop-level clusters.\n";
285 | const std::string muret =
286 | "\tmu: array shape(K,D), the (expected) Gaussian mixture means.\n";
287 | const std::string covret =
288 | "\tcov: list[array shape(D,D),...] of len = K, the (expected) Gaussian\n"
289 | "\t\t mixture covariances.\n";
290 | const std::string mukret =
291 | "\tmu_k: array shape(K,D_b), the (expected) bottom-level Gaussian mixture\n"
292 | "\t\tmeans.\n";
293 | const std::string covkret =
294 | "\tcov_k: list[array shape(D_b,D_b),...] of len = K, the (expected)\n"
295 | "\t\tbottom-level Gaussian mixture covariances.\n";
296 |
297 |
298 | // VDP
299 | const std::string vdpdoc =
300 | "The Variational Dirichlet Process (VDP) of [2].\n\n"
301 | "The VDP is similar to a regular Bayesian GMM, but places a Dirichlet\n"
302 | "process prior over the mixture weights. This is also used in [6].\n"
303 | + comargs + Xarg + priorarg + maxclustersarg + verbarg + threadarg
304 | + comrets + fret + qZret + wret + muret + covret;
305 |
306 | def ("learnVDP", wrapperVDP,
307 | (
308 | arg("X"),
309 | arg("prior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
310 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
311 | arg("verbose") = false,
312 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
313 | ),
314 | vdpdoc.c_str()
315 | );
316 |
317 |
318 | // BGMM
319 | const std::string bgmmdoc =
320 | "The Bayseian Gaussian mixture model (BGMM) described in [1].\n\n"
321 | "This BGMM is similar to a GMM learned with EM, but it places a\n"
322 | "Dirichlet prior over the mixture weights, and Gaussian-Wishart priors\n"
323 | "over the Gaussian clusters. This implementation is similar to [1] but\n"
324 | "also employes the cluster splitting heuristics discussed in [2-5].\n"
325 | + comargs + Xarg + priorarg + maxclustersarg + verbarg + threadarg
326 | + comrets + fret + qZret + wret + muret + covret;
327 |
328 | def ("learnBGMM", wrapperBGMM,
329 | (
330 | arg("X"),
331 | arg("prior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
332 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
333 | arg("verbose") = false,
334 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
335 | ),
336 | bgmmdoc.c_str()
337 | );
338 |
339 |
340 | // GMC
341 | const std::string gmcdoc =
342 | "The Grouped Mixtures Clustering (GMC) algorithm.\n\n"
343 | "This function uses the Grouped Mixtures Clustering model [5] to cluster\n"
344 | "multiple datasets simultaneously with cluster sharing between datasets.\n"
345 | "It uses a Generalised Dirichlet prior over the group mixture weights, and\n"
346 | "a Gaussian-Wishart prior over the cluster parameters. This algorithm is\n"
347 | "similar to a one-level Hierarchical Dirichlet process with Gaussian\n"
348 | "observations.\n"
349 | + comargs + vXarg + priorarg + maxclustersarg+ sparsearg + verbarg
350 | + threadarg
351 | + comrets + fret + vqZret + vwret + muret + covret;
352 |
353 | def ("learnGMC", wrapperGMC,
354 | (
355 | arg("X"),
356 | arg("prior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
357 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
358 | arg("sparse") = false,
359 | arg("verbose") = false,
360 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
361 | ),
362 | gmcdoc.c_str()
363 | );
364 |
365 |
366 | // SGMC
367 | const std::string sgmcdoc =
368 | "The Symmetric Grouped Mixtures Clustering (S-GMC) algorithm.\n\n"
369 | "This function uses the Symmetric Grouped Mixtures Clustering model [5]\n"
370 | "to cluster multiple datasets simultaneously with cluster sharing between\n"
371 | "datasets. It uses a symmetric Dirichlet prior over the group mixture\n"
372 | "weights, and a Gaussian-Wishart prior over the cluster parameters. This\n"
373 | "algorithm is similar to latent Dirichlet allocation with Gaussian\n"
374 | "observations.\n\n"
375 | "It is also referred to as Gaussian Latent Dirichlet Allocation (G-LDA)\n"
376 | "in [3, 4].\n"
377 | + comargs + vXarg + priorarg + maxclustersarg + sparsearg + verbarg
378 | + threadarg
379 | + comrets + fret + vqZret + vwret + muret + covret;
380 |
381 | def ("learnSGMC", wrapperSGMC,
382 | (
383 | arg("X"),
384 | arg("prior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
385 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
386 | arg("sparse") = false,
387 | arg("verbose") = false,
388 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
389 | ),
390 | sgmcdoc.c_str()
391 | );
392 |
393 |
394 | // SCM
395 | const std::string dpriorarg =
396 | "\tdirprior: The top-level Dirichlet prior. This affects the number of\n"
397 | "\t\tclusters found. This may need to turned up high to have an effect.\n";
398 |
399 | const std::string scmdoc =
400 | "The Simultaneous Clustering Model (SCM).\n\n"
401 | "This function implements the Simultaneous Clustering Model algorithm as\n"
402 | "specified by [4, 5]. The SCM uses a Generalised Dirichlet prior on the\n"
403 | "group mixture weights, a Dirichlet prior on the top-level clusters and\n"
404 | "Gaussian bottom-level cluster distributions for observations (with\n"
405 | "Gausian-Wishart priors).\n"
406 | + comargs + vvXarg + dpriorarg + priorkarg + truncarg + maxclustersarg
407 | + verbarg + threadarg
408 | + comrets + fret + vqYret + vvqZret + vwjret + vwtret + mukret + covkret;
409 |
410 | def ("learnSCM", wrapperSCM,
411 | (
412 | arg("X"),
413 | arg("dirprior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
414 | arg("gausprior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
415 | arg("trunc") = libcluster::TRUNC,
416 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
417 | arg("verbose") = false,
418 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
419 | ),
420 | scmdoc.c_str()
421 | );
422 |
423 |
424 | // MCM
425 | const std::string vWarg =
426 | "\tW: list[array shape(I_j,D_t),...] of len = J which is the top-level\n"
427 | "\t\t ('document') data to be clustered, I_j are the number of documents\n"
428 | "\t\tin each group (or list element) j of data, D_t the number of\n"
429 | "\t\tdimensions.\n";
430 | const std::string priortarg =
431 | "\tgausprior_t: the prior width of the top-level Gaussian clusters.\n";
432 | const std::string mutret =
433 | "\tmu_t: array shape(T,D_t), the (expected) top-level Gaussian mixture\n"
434 | "\t\tmeans.\n";
435 | const std::string covtret =
436 | "\tcov_t: list[array shape(D_t,D_t),...] of len = T, the (expected)\n"
437 | "\t\ttop-level Gaussian mixture covariances.\n";
438 |
439 | const std::string mcmdoc =
440 | "The Multiple-source Clustering Model (MCM).\n\n"
441 | "This function implements the Multiple-source Clustering Model algorithm\n"
442 | "as specified by [3-5]. This model jointly cluster both 'document'\n"
443 | "level observations, and 'word' observations. The MCM uses a Generalised\n"
444 | "Dirichlet prior on the group mixture weights, Multinomial-Gaussian \n"
445 | "top-level (document) clusters, and Gaussian bottom-level (word) cluster\n"
446 | "distributions.\n"
447 | + comargs + vWarg + vvXarg + priortarg + priorkarg + truncarg
448 | + maxclustersarg + verbarg + threadarg
449 | + comrets + fret + vqYret + vvqZret + vwjret + vwtret + mutret + mukret
450 | + covtret + covkret;
451 |
452 | def ("learnMCM", wrapperMCM,
453 | (
454 | arg("W"),
455 | arg("X"),
456 | arg("gausprior_t") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
457 | arg("gausprior_k") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
458 | arg("trunc") = libcluster::TRUNC,
459 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
460 | arg("verbose") = false,
461 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
462 | ),
463 | mcmdoc.c_str()
464 | );
465 |
466 | }
467 |
468 | #endif
469 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/testapi.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #! /usr/bin/env python
2 |
3 | # libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
4 | # Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
5 | #
6 | # This file is part of libcluster.
7 | #
8 | # libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
9 | # the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
10 | # Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
11 | # any later version.
12 | #
13 | # libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
14 | # ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
15 | # FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
16 | # for more details.
17 | #
18 | # You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
19 | # along with libcluster. If not, see .
20 |
21 | """ Script to make sure libcluster runs properly using the python API.
22 |
23 | Author: Daniel Steinberg
24 | Date: 13/10/2013
25 |
26 | """
27 |
28 | import numpy as np
29 | import libclusterpy as lc
30 |
31 |
32 | # Top level cluster parameters -- Globals.... whatev...
33 | means = np.array([[0, 0], [5, 5], [-5, -5]])
34 | sigma = [np.eye(2)] * 3
35 | beta = np.array([[1.0 / 3, 1.0 / 3, 1.0 / 3],
36 | [1.0 / 2, 1.0 / 4, 1.0 / 4],
37 | [1.0 / 4, 1.0 / 4, 1.0 / 2]])
38 |
39 |
40 | def testmixtures():
41 | """ The test function. """
42 |
43 | print("Testing mixtures ------------------\n")
44 |
45 | # Create points from clusters
46 | W = gengmm(10000)
47 |
48 | # Test VDP
49 | print("------------ Test VDP -------------")
50 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnVDP(W, verbose=True)
51 | print("")
52 | printgmm(w, mu, cov)
53 |
54 | # Test BGMM
55 | print("------------ Test BGMM ------------")
56 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnBGMM(W, verbose=True)
57 | print("")
58 | printgmm(w, mu, cov)
59 |
60 |
61 | def testgroupmix():
62 |
63 | print("Testing group mixtures ------------\n")
64 |
65 | # Create points from clusters
66 | J = 4 # Groups
67 | W = [gengmm(2000) for j in range(J)]
68 |
69 | # Test GMC
70 | print("------------ Test GMC -------------")
71 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnGMC(W, verbose=True)
72 | print("")
73 | printgmm(w, mu, cov)
74 |
75 | # Test SGMC
76 | print("------------ Test SGMC ------------")
77 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnSGMC(W, verbose=True)
78 | print("")
79 | printgmm(w, mu, cov)
80 |
81 |
82 | def testmultmix():
83 | """ The the models that cluster at multiple levels. Just using J=1. """
84 |
85 | # Generate top-level clusters
86 | I = 200
87 | Ni = 100
88 | betas, Y = gensetweights(I)
89 |
90 | # Create points from clusters
91 | W = np.zeros((I, means.shape[1]))
92 | X = []
93 | for i in range(I):
94 | W[i, :] = np.random.multivariate_normal(means[Y[i]], sigma[Y[i]], 1)
95 | X.append(gengmm(Ni, betas[i, :]))
96 |
97 | # Test SCM
98 | print("------------ Test SCM -------------")
99 | f, qY, qZ, wi, ws, mu, cov = lc.learnSCM([X], trunc=30, verbose=True)
100 | print("")
101 | printgmm(ws, mu, cov)
102 |
103 | # Test MCM
104 | print("------------ Test MCM -------------")
105 | f, qY, qZ, wi, ws, mui, mus, covi, covs = lc.learnMCM([W], [X], trunc=30,
106 | verbose=True)
107 | print("\nTop level mixtures:")
108 | printgmm(wi, mui, covi)
109 | print("Bottom level mixtures:")
110 | printgmm(ws, mus, covs)
111 |
112 |
113 | def gengmm(N, weights=None):
114 | """ Make a random GMM with N observations. """
115 |
116 | K = len(sigma)
117 | pi = np.random.rand(K) if weights is None else weights
118 | pi /= pi.sum()
119 | Nk = np.round(pi * N)
120 | Nk[-1] = N - Nk[0:-1].sum()
121 |
122 | X = [np.random.multivariate_normal(means[k, :], sigma[k], int(Nk[k]))
123 | for k in range(K)]
124 |
125 | return np.concatenate(X)
126 |
127 |
128 | def gensetweights(I):
129 | """ Generate sets of similar weights. """
130 |
131 | T = beta.shape[0]
132 | pi = np.random.rand(T)
133 | pi /= pi.sum()
134 | Nt = np.round(pi * I)
135 | Nt[-1] = I - Nt[0:-1].sum()
136 |
137 | betas = []
138 | Y = []
139 | for t in range(T):
140 | Y += int(Nt[t]) * [t]
141 | betas.append(int(Nt[t]) * [beta[t, :]])
142 |
143 | return np.concatenate(betas), Y
144 |
145 |
146 | def printgmm(W, Mu, Cov):
147 | """ Print the parameters of a GMM. """
148 |
149 | Wnp = np.array(W)
150 |
151 | for i, (mu, cov) in enumerate(zip(Mu, Cov)):
152 |
153 | print("Mixture {0}:".format(i))
154 | if Wnp.ndim == 2:
155 | print(" weight --\n{0}".format(Wnp[i, :]))
156 | elif Wnp.ndim == 3:
157 | print(" group weights --\n{0}".format(Wnp[:, i, :]))
158 | print(" mean --\n{0}\n cov --\n{1}\n".format(mu, cov))
159 |
160 |
161 | if __name__ == "__main__":
162 | testmixtures()
163 | testgroupmix()
164 | testmultmix()
165 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/cluster.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | // TODO:
22 | // - sparse updates sometimes create positive free energy steps.
23 |
24 | #include
25 | #include "libcluster.h"
26 | #include "probutils.h"
27 | #include "distributions.h"
28 | #include "comutils.h"
29 |
30 |
31 | //
32 | // Namespaces
33 | //
34 |
35 | using namespace std;
36 | using namespace Eigen;
37 | using namespace probutils;
38 | using namespace distributions;
39 | using namespace comutils;
40 | using namespace libcluster;
41 |
42 |
43 | //
44 | // Variational Bayes Private Functions
45 | //
46 |
47 |
48 | /* Update the group and model sufficient statistics based on assignments qZj.
49 | *
50 | * mutable: the clusters (add sufficient stats).
51 | * returns: the number of observations in each cluster for this groups.
52 | */
53 | template ArrayXd updateSS (
54 | const MatrixXd& Xj, // Observations in group j
55 | const MatrixXd& qZj, // Observations to group mixture assignments
56 | vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
57 | const bool sparse // Do sparse updates to groups
58 | )
59 | {
60 | const unsigned int K = qZj.cols();
61 |
62 | const ArrayXd Njk = qZj.colwise().sum(); // count obs. in this group
63 | ArrayXi Kful = ArrayXi::Zero(1), // Initialise and set K = 1 defaults
64 | Kemp = ArrayXi::Zero(0);
65 |
66 | // Find empty clusters if sparse
67 | if ( (sparse == false) && (K > 1) )
68 | Kful = ArrayXi::LinSpaced(Sequential, K, 0, K-1);
69 | else if (sparse == true)
70 | arrfind((Njk >= ZEROCUTOFF), Kful, Kemp);
71 |
72 | const unsigned int nKful = Kful.size();
73 |
74 | // Sufficient statistics - with observations
75 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < nKful; ++k)
76 | {
77 | #pragma omp critical
78 | clusters[Kful(k)].addobs(qZj.col(Kful(k)), Xj);
79 | }
80 |
81 | return Njk;
82 | }
83 |
84 |
85 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for each group.
86 | *
87 | * mutable: Group assignment probabilities, qZj
88 | * returns: The complete-data (X,Z) free energy E[log p(X,Z)/q(Z)] for group j.
89 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
90 | */
91 | template double vbexpectation (
92 | const MatrixXd& Xj, // Observations in group J
93 | const W& weights, // Group Weight parameter distribution
94 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster parameter distributions
95 | MatrixXd& qZj, // Observations to group mixture assignments
96 | const bool sparse // Do sparse updates to groups
97 | )
98 | {
99 | const int K = clusters.size(),
100 | Nj = Xj.rows();
101 |
102 | // Get log marginal weight likelihoods
103 | const ArrayXd E_logZ = weights.Elogweight();
104 |
105 | // Initialise and set K = 1 defaults for cluster counts
106 | ArrayXi Kful = ArrayXi::Zero(1), Kemp = ArrayXi::Zero(0);
107 |
108 | // Find empty clusters if sparse
109 | if ( (sparse == false) && (K > 1) )
110 | Kful = ArrayXi::LinSpaced(Sequential, K, 0, K-1);
111 | else if (sparse == true)
112 | arrfind((weights.getNk() >= ZEROCUTOFF), Kful, Kemp);
113 |
114 | const int nKful = Kful.size(),
115 | nKemp = Kemp.size();
116 |
117 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs -- allow sparse evaluation
118 | MatrixXd logqZj(Nj, nKful);
119 |
120 | for (int k = 0; k < nKful; ++k)
121 | logqZj.col(k) = E_logZ(Kful(k)) + clusters[Kful(k)].Eloglike(Xj).array();
122 |
123 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
124 | const VectorXd logZzj = logsumexp(logqZj);
125 |
126 | // Make sure qZ is the right size, this is a nop if it is
127 | qZj.resize(Nj, K);
128 |
129 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities -- again allow sparse evaluation
130 | for (int k = 0; k < nKful; ++k)
131 | qZj.col(Kful(k)) = ((logqZj.col(k) - logZzj).array().exp()).matrix();
132 |
133 | // Empty Cluster Responsabilities
134 | for (int k = 0; k < nKemp; ++k)
135 | qZj.col(Kemp(k)).setZero();
136 |
137 | return -logZzj.sum();
138 | }
139 |
140 |
141 | /* Calculates the free energy lower bound for the model parameter distributions.
142 | *
143 | * returns: the free energy of the model
144 | */
145 | template double fenergy (
146 | const vector& weights, // Weight parameter distributions
147 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster parameter distributions
148 | const double Fxz // Free energy from data log-likelihood
149 | )
150 | {
151 | const int K = clusters.size(),
152 | J = weights.size();
153 |
154 | // Free energy of the weight parameter distributions
155 | double Fw = 0;
156 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
157 | Fw += weights[j].fenergy();
158 |
159 | // Free energy of the cluster parameter distributionsreturn
160 | double Fc = 0;
161 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
162 | Fc += clusters[k].fenergy();
163 |
164 | return Fc + Fw + Fxz;
165 | }
166 |
167 |
168 | /* Variational Bayes EM for all group mixtures.
169 | *
170 | * returns: Free energy of the whole model.
171 | * mutable: variational posterior approximations to p(Z|X).
172 | * mutable: the group weight distributions
173 | * mutable: the cluster distributions
174 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
175 | * throws: runtime_error if there is a negative free energy.
176 | */
177 | template double vbem (
178 | const vMatrixXd& X, // Observations
179 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Observations to model mixture assignments
180 | vector& weights, // Group weight distributions
181 | vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
182 | const double clusterprior, // Prior value for cluster distributions
183 | const int maxit = -1, // Max VBEM iterations (-1 = no max, default)
184 | const bool sparse = false, // Do sparse updates to groups (default false)
185 | const bool verbose = false // Verbose output (default false)
186 | )
187 | {
188 | const int J = X.size(),
189 | K = qZ[0].cols();
190 |
191 | // Construct (empty) parameters
192 | weights.resize(J, W());
193 | clusters.resize(K, C(clusterprior, X[0].cols()));
194 |
195 | double F = numeric_limits::max(), Fold;
196 | int i = 0;
197 |
198 | do
199 | {
200 | Fold = F;
201 |
202 | // Clear Suffient Statistics
203 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
204 | clusters[k].clearobs();
205 |
206 | // Update Suff Stats and VBM for weights
207 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
208 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
209 | {
210 | ArrayXd Njk = updateSS(X[j], qZ[j], clusters, sparse);
211 | weights[j].update(Njk);
212 | }
213 |
214 | // VBM for clusters
215 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
216 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
217 | clusters[k].update();
218 |
219 | // VBE
220 | double Fz = 0;
221 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fz)
222 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
223 | Fz += vbexpectation(X[j], weights[j], clusters, qZ[j], sparse);
224 |
225 | // Calculate free energy of model
226 | F = fenergy(weights, clusters, Fz);
227 |
228 | // Check bad free energy step
229 | if ((F-Fold)/abs(Fold) > FENGYDEL)
230 | throw runtime_error("Free energy increase!");
231 |
232 | if (verbose == true) // Notify iteration
233 | cout << '-' << flush;
234 | }
235 | while ( (abs((Fold-F)/Fold) > CONVERGE)
236 | && ( (i++ < maxit) || (maxit < 0) ) );
237 |
238 | return F;
239 | }
240 |
241 |
242 | //
243 | // Model Selection and Heuristics Private Functions
244 | //
245 |
246 |
247 | /* Search in an exhaustive fashion for a mixture split that lowers model free
248 | * energy the most. If no splits are found which lower Free Energy, then
249 | * false is returned, and qZ is not modified.
250 | *
251 | * returns: true if a split was found, false if no splits can be found
252 | * mutable: qZ is augmented with a new split if one is found, otherwise left
253 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions
254 | * throws: runtime_error from its internal VBEM calls
255 | */
256 | #ifdef EXHAUST_SPLIT
257 | template bool split_ex (
258 | const vMatrixXd& X, // Observations
259 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
260 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Probabilities qZ
261 | const double F, // Current model free energy
262 | const int maxclusters, // maximum number of clusters to search for
263 | const bool sparse, // Do sparse updates to groups
264 | const bool verbose // Verbose output
265 | )
266 | {
267 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
268 | K = clusters.size();
269 |
270 | // Check if we have reached the max number of clusters
271 | if ( ((signed) K >= maxclusters) && (maxclusters >= 0) )
272 | return false;
273 |
274 | // Pre allocate big objects for loops (this makes a runtime difference)
275 | double Fbest = numeric_limits::infinity();
276 | vector mapidx(J, ArrayXi());
277 | vMatrixXd qZref(J,MatrixXd()), qZaug(J,MatrixXd()), Xk(J,MatrixXd()), qZbest;
278 |
279 | // Loop through each potential cluster in order and split it
280 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
281 | {
282 | // Don't waste time with clusters that can't really be split min (2:2)
283 | if (clusters[k].getN() < 4)
284 | continue;
285 |
286 | // Now split observations and qZ.
287 | int scount = 0, Mtot = 0;
288 |
289 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Mtot, scount)
290 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
291 | {
292 | // Make COPY of the observations with only relevant data points, p > 0.5
293 | mapidx[j] = partX(X[j], (qZ[j].col(k).array()>0.5), Xk[j]); // Copy :-(
294 | Mtot += Xk[j].rows();
295 |
296 | // Initial cluster split
297 | ArrayXb splitk = clusters[k].splitobs(Xk[j]);
298 | qZref[j].setZero(Xk[j].rows(), 2);
299 | qZref[j].col(0) = (splitk == true).cast(); // Init qZ for split
300 | qZref[j].col(1) = (splitk == false).cast();
301 |
302 | // keep a track of number of splits
303 | scount += splitk.count();
304 | }
305 |
306 | // Don't waste time with clusters that haven't been split sufficiently
307 | if ( (scount < 2) || (scount > (Mtot-2)) )
308 | continue;
309 |
310 | // Refine the split
311 | vector wspl;
312 | vector cspl;
313 | vbem(Xk, qZref, wspl, cspl, clusters[0].getprior(), SPLITITER, sparse);
314 |
315 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
316 | continue;
317 |
318 | // Map the refined splits back to original whole-data problem
319 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
320 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
321 | qZaug[j] = augmentqZ(k, mapidx[j], (qZref[j].col(1).array()>0.5), qZ[j]);
322 |
323 | // Calculate free energy of this split with ALL data (and refine a bit)
324 | double Fsplit = vbem(X, qZaug, wspl, cspl, clusters[0].getprior(), 1,
325 | sparse);
326 |
327 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
328 | continue;
329 |
330 | // Only notify here of split candidates
331 | if (verbose == true)
332 | cout << '=' << flush;
333 |
334 | // Record best splits so far
335 | if (Fsplit < Fbest)
336 | {
337 | qZbest = qZaug;
338 | Fbest = Fsplit;
339 | }
340 | }
341 |
342 | // See if this split actually improves the model
343 | if ( (Fbest < F) && (abs((F-Fbest)/F) > CONVERGE) )
344 | {
345 | qZ = qZbest;
346 | return true;
347 | }
348 | else
349 | return false;
350 | }
351 | #endif
352 |
353 |
354 | /* Search in a greedy fashion for a mixture split that lowers model free
355 | * energy, or return false. An attempt is made at looking for good, untried,
356 | * split candidates first, as soon as a split canditate is found that lowers
357 | * model F, it is returned. This may not be the "best" split, but it is
358 | * certainly faster than an exhaustive search for the "best" split.
359 | *
360 | * returns: true if a split was found, false if no splits can be found
361 | * mutable: qZ is augmented with a new split if one is found, otherwise left
362 | * mutable tally is a tally time a cluster has been unsuccessfully split
363 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions
364 | * throws: runtime_error from its internal VBEM calls
365 | */
366 | #ifndef EXHAUST_SPLIT
367 | template bool split_gr (
368 | const vMatrixXd& X, // Observations
369 | const vector& weights, // Group weight distributions
370 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
371 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Probabilities qZ
372 | vector& tally, // Count of unsuccessful splits
373 | const double F, // Current model free energy
374 | const int maxclusters, // maximum number of clusters to search for
375 | const bool sparse, // Do sparse updates to groups
376 | const bool verbose // Verbose output
377 | )
378 | {
379 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
380 | K = clusters.size();
381 |
382 | // Check if we have reached the max number of clusters
383 | if ( ((signed) K >= maxclusters) && (maxclusters >= 0) )
384 | return false;
385 |
386 | // Split order chooser and cluster parameters
387 | tally.resize(K, 0); // Make sure tally is the right size
388 | vector ord(K);
389 |
390 | // Get cluster parameters and their free energy
391 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
392 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
393 | {
394 | ord[k].k = k;
395 | ord[k].tally = tally[k];
396 | ord[k].Fk = clusters[k].fenergy();
397 | }
398 |
399 | // Get cluster likelihoods
400 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
401 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
402 | {
403 | // Get cluster weights
404 | ArrayXd logpi = weights[j].Elogweight();
405 |
406 | // Add in cluster log-likelihood, weighted by responsability
407 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
408 | {
409 | double LL = qZ[j].col(k).dot((logpi(k)
410 | + clusters[k].Eloglike(X[j]).array()).matrix());
411 |
412 | #pragma omp atomic
413 | ord[k].Fk -= LL;
414 | }
415 | }
416 |
417 | // Sort clusters by split tally, then free energy contributions
418 | sort(ord.begin(), ord.end(), greedcomp);
419 |
420 | // Pre allocate big objects for loops (this makes a runtime difference)
421 | vector mapidx(J, ArrayXi());
422 | vMatrixXd qZref(J, MatrixXd()), qZaug(J,MatrixXd()), Xk(J,MatrixXd());
423 |
424 | // Loop through each potential cluster in order and split it
425 | for (vector::iterator i = ord.begin(); i < ord.end(); ++i)
426 | {
427 | const int k = i->k;
428 |
429 | ++tally[k]; // increase this cluster's unsuccessful split tally by default
430 |
431 | // Don't waste time with clusters that can't really be split min (2:2)
432 | if (clusters[k].getN() < 4)
433 | continue;
434 |
435 | // Now split observations and qZ.
436 | int scount = 0, Mtot = 0;
437 |
438 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Mtot, scount)
439 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
440 | {
441 | // Make COPY of the observations with only relevant data points, p > 0.5
442 | mapidx[j] = partobs(X[j], (qZ[j].col(k).array()>0.5), Xk[j]); // Copy :-(
443 | Mtot += Xk[j].rows();
444 |
445 | // Initial cluster split
446 | ArrayXb splitk = clusters[k].splitobs(Xk[j]);
447 | qZref[j].setZero(Xk[j].rows(), 2);
448 | qZref[j].col(0) = (splitk == true).cast(); // Init qZ for split
449 | qZref[j].col(1) = (splitk == false).cast();
450 |
451 | // keep a track of number of splits
452 | scount += splitk.count();
453 | }
454 |
455 | // Don't waste time with clusters that haven't been split sufficiently
456 | if ( (scount < 2) || (scount > (Mtot-2)) )
457 | continue;
458 |
459 | // Refine the split
460 | vector wspl;
461 | vector cspl;
462 | vbem(Xk, qZref, wspl, cspl, clusters[0].getprior(), SPLITITER, sparse);
463 |
464 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
465 | continue;
466 |
467 | // Map the refined splits back to original whole-data problem
468 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
469 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
470 | qZaug[j] = auglabels(k, mapidx[j], (qZref[j].col(1).array()>0.5), qZ[j]);
471 |
472 | // Calculate free energy of this split with ALL data (and refine a bit)
473 | double Fsplit = vbem(X, qZaug, wspl, cspl, clusters[0].getprior(), 1,
474 | sparse);
475 |
476 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
477 | continue;
478 |
479 | // Only notify here of split candidates
480 | if (verbose == true)
481 | cout << '=' << flush;
482 |
483 | // Test whether this cluster split is a keeper
484 | if ( (Fsplit < F) && (abs((F-Fsplit)/F) > CONVERGE) )
485 | {
486 | qZ = qZaug;
487 | tally[k] = 0; // Reset tally if successfully split
488 | return true;
489 | }
490 | }
491 |
492 | // Failed to find splits
493 | return false;
494 | }
495 | #endif
496 |
497 |
498 | /* Find and remove all empty clusters.
499 | *
500 | * returns: true if any clusters have been deleted, false if all are kept.
501 | * mutable: qZ may have columns deleted if there are empty clusters found.
502 | * mutable: weights if there are empty clusters found.
503 | * mutable: clusters if there are empty clusters found.
504 | */
505 | template bool prune_clusters (
506 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Probabilities qZ
507 | vector& weights, // weights distributions
508 | vector& clusters, // cluster distributions
509 | bool verbose = false // print status
510 | )
511 | {
512 | const unsigned int K = clusters.size(),
513 | J = qZ.size();
514 |
515 | // Look for empty clusters
516 | ArrayXd Nk(K);
517 | for (unsigned int k= 0; k < K; ++k)
518 | Nk(k) = clusters[k].getN();
519 |
520 | // Find location of empty and full clusters
521 | ArrayXi eidx, fidx;
522 | arrfind(Nk.array() < ZEROCUTOFF, eidx, fidx);
523 | const unsigned int nempty = eidx.size();
524 |
525 | // If everything is not empty, return false
526 | if (nempty == 0)
527 | return false;
528 |
529 | if (verbose == true)
530 | cout << '*' << flush;
531 |
532 | // Delete empty cluster suff. stats.
533 | for (int i = (nempty - 1); i >= 0; --i)
534 | clusters.erase(clusters.begin() + eidx(i));
535 |
536 | // Delete empty cluster indicators by copying only full indicators
537 | const unsigned int newK = fidx.size();
538 | vMatrixXd newqZ(J);
539 |
540 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
541 | {
542 | newqZ[j].setZero(qZ[j].rows(), newK);
543 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < newK; ++k)
544 | newqZ[j].col(k) = qZ[j].col(fidx(k));
545 |
546 | weights[j].update(newqZ[j].colwise().sum()); // new weights
547 | }
548 |
549 | qZ = newqZ;
550 |
551 | return true;
552 | }
553 |
554 |
555 | /* The model selection algorithm for a grouped mixture model.
556 | *
557 | * returns: Free energy of the final model
558 | * mutable: qZ the probabilistic observation to cluster assignments
559 | * mutable: the group weight distributions
560 | * mutable: the cluster distributions
561 | * throws: invalid_argument from other functions.
562 | * throws: runtime_error if free energy increases.
563 | */
564 | template double cluster (
565 | const vMatrixXd& X, // Observations
566 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Observations to model mixture assignments
567 | vector& weights, // Group weight distributions
568 | vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
569 | const double clusterprior, // Prior value for cluster distributions
570 | const int maxclusters, // Maximum number of clusters to search for
571 | const bool sparse, // Do sparse updates to groups
572 | const bool verbose, // Verbose output
573 | const unsigned int nthreads // Number of threads for OpenMP to use
574 | )
575 | {
576 | if (nthreads < 1)
577 | throw invalid_argument("Must specify at least one thread for execution!");
578 | omp_set_num_threads(nthreads);
579 |
580 | const unsigned int J = X.size();
581 |
582 | // Initialise indicator variables to just one cluster
583 | qZ.resize(J);
584 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
585 | qZ[j].setOnes(X[j].rows(), 1);
586 |
587 | // Initialise free energy and other loop variables
588 | bool issplit = true;
589 | double F;
590 |
591 | #ifndef EXHAUST_SPLIT
592 | vector tally;
593 | #endif
594 |
595 | // Main loop
596 | while (issplit == true)
597 | {
598 | // VBEM for all groups (throws runtime_error & invalid_argument)
599 | F = vbem(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, -1, sparse, verbose);
600 |
601 | // Remove any empty clusters
602 | prune_clusters(qZ, weights, clusters, verbose);
603 |
604 | // Start cluster splitting
605 | if (verbose == true)
606 | cout << '<' << flush; // Notify start splitting
607 |
608 | // Search for best split, augment qZ if found one
609 | #ifdef EXHAUST_SPLIT
610 | issplit = split_ex(X, clusters, qZ, F, maxclusters, sparse, verbose);
611 | #else
612 | issplit = split_gr(X, weights, clusters, qZ, tally, F, maxclusters,
613 | sparse, verbose);
614 | #endif
615 |
616 | if (verbose == true)
617 | cout << '>' << endl; // Notify end splitting
618 | }
619 |
620 | // Print finished notification if verbose
621 | if (verbose == true)
622 | {
623 | cout << "Finished!" << endl;
624 | cout << "Number of clusters = " << clusters.size() << endl;
625 | cout << "Free energy = " << F << endl;
626 | }
627 |
628 | return F;
629 | }
630 |
631 |
632 | //
633 | // Public Functions
634 | //
635 |
636 | double libcluster::learnVDP (
637 | const MatrixXd& X,
638 | MatrixXd& qZ,
639 | StickBreak& weights,
640 | vector& clusters,
641 | const double clusterprior,
642 | const int maxclusters,
643 | const bool verbose,
644 | const unsigned int nthreads
645 | )
646 | {
647 | if (verbose == true)
648 | cout << "Learning VDP..." << endl; // Print start
649 |
650 | // Make temporary vectors of data to use with cluster()
651 | vMatrixXd vecX(1, X); // copies :-(
652 | vMatrixXd vecqZ;
653 | vector vecweights(1, weights);
654 |
655 | // Perform model learning and selection
656 | double F = cluster(vecX, vecqZ, vecweights, clusters,
657 | clusterprior, maxclusters, false,
658 | verbose, nthreads);
659 |
660 | // Return final Free energy and qZ
661 | qZ = vecqZ[0]; // copies :-(
662 | weights = vecweights[0];
663 | return F;
664 | }
665 |
666 |
667 | double libcluster::learnBGMM (
668 | const MatrixXd& X,
669 | MatrixXd& qZ,
670 | Dirichlet& weights,
671 | vector& clusters,
672 | const double clusterprior,
673 | const int maxclusters,
674 | const bool verbose,
675 | const unsigned int nthreads
676 | )
677 | {
678 | if (verbose == true)
679 | cout << "Learning Bayesian GMM..." << endl; // Print start
680 |
681 | // Make temporary vectors of data to use with cluster()
682 | vMatrixXd vecX(1, X); // copies :-(
683 | vMatrixXd vecqZ;
684 | vector vecweights(1, weights);
685 |
686 | // Perform model learning and selection
687 | double F = cluster(vecX, vecqZ, vecweights, clusters,
688 | clusterprior, maxclusters, false,
689 | verbose, nthreads);
690 |
691 | // Return final Free energy and qZ
692 | qZ = vecqZ[0]; // copies :-(
693 | weights = vecweights[0];
694 | return F;
695 | }
696 |
697 |
698 | double libcluster::learnDGMM (
699 | const MatrixXd& X,
700 | MatrixXd& qZ,
701 | Dirichlet& weights,
702 | vector& clusters,
703 | const double clusterprior,
704 | const int maxclusters,
705 | const bool verbose,
706 | const unsigned int nthreads
707 | )
708 | {
709 | if (verbose == true)
710 | cout << "Learning Bayesian diagonal GMM..." << endl; // Print start
711 |
712 | // Make temporary vectors of data to use with cluster()
713 | vMatrixXd vecX(1, X); // copies :-(
714 | vMatrixXd vecqZ;
715 | vector vecweights(1, weights);
716 |
717 | // Perform model learning and selection
718 | double F = cluster(vecX, vecqZ, vecweights, clusters,
719 | clusterprior, maxclusters, false,
720 | verbose, nthreads);
721 |
722 | // Return final Free energy and qZ
723 | qZ = vecqZ[0]; // copies :-(
724 | weights = vecweights[0];
725 | return F;
726 | }
727 |
728 |
729 | double libcluster::learnBEMM (
730 | const MatrixXd& X,
731 | MatrixXd& qZ,
732 | Dirichlet& weights,
733 | vector& clusters,
734 | const double clusterprior,
735 | const int maxclusters,
736 | const bool verbose,
737 | const unsigned int nthreads
738 | )
739 | {
740 | if ((X.array() < 0).any() == true)
741 | throw invalid_argument("X has to be in the range [0, inf)!");
742 |
743 | if (verbose == true)
744 | cout << "Learning Bayesian EMM..." << endl; // Print start
745 |
746 | // Make temporary vectors of data to use with cluster()
747 | vMatrixXd vecX(1, X); // copies :-(
748 | vMatrixXd vecqZ;
749 | vector vecweights(1, weights);
750 |
751 | // Perform model learning and selection
752 | double F = cluster(vecX, vecqZ, vecweights, clusters,
753 | clusterprior, maxclusters, false,
754 | verbose, nthreads);
755 |
756 | // Return final Free energy and qZ
757 | qZ = vecqZ[0]; // copies :-(
758 | weights = vecweights[0];
759 | return F;
760 | }
761 |
762 |
763 | double libcluster::learnGMC (
764 | const vMatrixXd& X,
765 | vMatrixXd& qZ,
766 | vector& weights,
767 | vector& clusters,
768 | const double clusterprior,
769 | const int maxclusters,
770 | const bool sparse,
771 | const bool verbose,
772 | const unsigned int nthreads
773 | )
774 | {
775 | string spnote = (sparse == true) ? "(sparse) " : "";
776 |
777 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
778 | if (verbose == true)
779 | cout << "Learning " << spnote << "GMC..." << endl;
780 |
781 | return cluster(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior,
782 | maxclusters, sparse, verbose,
783 | nthreads);
784 | }
785 |
786 |
787 | double libcluster::learnSGMC (
788 | const vMatrixXd& X,
789 | vMatrixXd& qZ,
790 | vector& weights,
791 | vector& clusters,
792 | const double clusterprior,
793 | const int maxclusters,
794 | const bool sparse,
795 | const bool verbose,
796 | const unsigned int nthreads
797 | )
798 | {
799 | string spnote = (sparse == true) ? "(sparse) " : "";
800 |
801 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
802 | if (verbose == true)
803 | cout << "Learning " << spnote << "Symmetric GMC..." << endl;
804 |
805 | return cluster(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior,
806 | maxclusters, sparse, verbose, nthreads);
807 | }
808 |
809 |
810 | double libcluster::learnDGMC (
811 | const vMatrixXd& X,
812 | vMatrixXd& qZ,
813 | vector& weights,
814 | vector& clusters,
815 | const double clusterprior,
816 | const int maxclusters,
817 | const bool sparse,
818 | const bool verbose,
819 | const unsigned int nthreads
820 | )
821 | {
822 | string spnote = (sparse == true) ? "(sparse) " : "";
823 |
824 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
825 | if (verbose == true)
826 | cout << "Learning " << spnote << "Diagonal GMC..." << endl;
827 |
828 | return cluster(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior,
829 | maxclusters, sparse, verbose,
830 | nthreads);
831 | }
832 |
833 |
834 | double libcluster::learnEGMC (
835 | const vMatrixXd& X,
836 | vMatrixXd& qZ,
837 | vector& weights,
838 | vector& clusters,
839 | const double clusterprior,
840 | const int maxclusters,
841 | const bool sparse,
842 | const bool verbose,
843 | const unsigned int nthreads
844 | )
845 | {
846 | string spnote = (sparse == true) ? "(sparse) " : "";
847 |
848 | // Check for negative inputs
849 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < X.size(); ++j)
850 | if ((X[j].array() < 0).any() == true)
851 | throw invalid_argument("X has to be in the range [0, inf)!");
852 |
853 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
854 | if (verbose == true)
855 | cout << "Learning " << spnote << "Exponential GMC..." << endl;
856 |
857 | return cluster(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior,
858 | maxclusters, sparse, verbose, nthreads);
859 | }
860 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/comutils.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include "comutils.h"
22 |
23 |
24 | //
25 | // Namespaces
26 | //
27 |
28 | using namespace std;
29 | using namespace Eigen;
30 | using namespace libcluster;
31 | using namespace probutils;
32 | using namespace distributions;
33 |
34 |
35 | //
36 | // Public Functions
37 | //
38 |
39 | void comutils::arrfind (
40 | const ArrayXb& expression,
41 | ArrayXi& indtrue,
42 | ArrayXi& indfalse
43 | )
44 | {
45 | const int N = expression.size(),
46 | M = expression.count();
47 |
48 | indtrue.setZero(M);
49 | indfalse.setZero(N-M);
50 |
51 | for (int n = 0, m = 0, l = 0; n < N; ++n)
52 | expression(n) ? indtrue(m++) = n : indfalse(l++) = n;
53 | }
54 |
55 |
56 | ArrayXi comutils::partobs (
57 | const MatrixXd& X,
58 | const ArrayXb& Xpart,
59 | MatrixXd& Xk
60 | )
61 | {
62 | const int M = Xpart.count();
63 |
64 | ArrayXi pidx, npidx;
65 | comutils::arrfind(Xpart, pidx, npidx);
66 |
67 | Xk.setZero(M, X.cols());
68 | for (int m=0; m < M; ++m) // index copy X to Xk
69 | Xk.row(m) = X.row(pidx(m));
70 |
71 | return pidx;
72 | }
73 |
74 |
75 | MatrixXd comutils::auglabels (
76 | const double k,
77 | const ArrayXi& map,
78 | const ArrayXb& Zsplit,
79 | const MatrixXd& qZ
80 | )
81 | {
82 | const int K = qZ.cols(),
83 | S = Zsplit.count();
84 |
85 | if (Zsplit.size() != map.size())
86 | throw invalid_argument("map and split must be the same size!");
87 |
88 | // Create new qZ for all data with split
89 | MatrixXd qZaug = qZ; // Copy the existing qZ into the new
90 | qZaug.conservativeResize(Eigen::NoChange, K+1);
91 | qZaug.col(K).setZero();
92 |
93 | ArrayXi sidx, nsidx;
94 | comutils::arrfind(Zsplit, sidx, nsidx);
95 |
96 | // Copy split cluster assignments (augment qZ effectively)
97 | for (int s = 0; s < S; ++s)
98 | {
99 | qZaug(map(sidx(s)), K) = qZ(map(sidx(s)), k); // Add new cluster onto end
100 | qZaug(map(sidx(s)), k) = 0;
101 | }
102 |
103 | return qZaug;
104 | }
105 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/comutils.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #ifndef COMUTILS_H
22 | #define COMUTILS_H
23 |
24 | #include
25 | #include
26 | #include
27 | #include "libcluster.h"
28 | #include "probutils.h"
29 | #include "distributions.h"
30 |
31 |
32 | /*! Namespace that implements various common utilities used in the algorithms */
33 | namespace comutils
34 | {
35 |
36 |
37 | //
38 | // Helper structures
39 | //
40 |
41 | /* Triplet that contains the information for choosing a good cluster split
42 | * ordering.
43 | */
44 | struct GreedOrder
45 | {
46 | int k; // Cluster number/index
47 | int tally; // Number of times a cluster has failed to split
48 | double Fk; // The clusters approximate free energy contribution
49 | };
50 |
51 |
52 | //
53 | // Helper functions
54 | //
55 |
56 | /* Compares two GreedOrder triplets and returns which is more optimal to split.
57 | * Precendence is given to less split fail tally, and then to more free energy
58 | * contribution.
59 | */
60 | bool inline greedcomp (const GreedOrder& i, const GreedOrder& j)
61 | {
62 | if (i.tally == j.tally) // If the tally is the same, use the greater Fk
63 | return i.Fk > j.Fk;
64 | else if (i.tally < j.tally) // Otherwise prefer the lower tally
65 | return true;
66 | else
67 | return false;
68 | }
69 |
70 |
71 | /* Find the indices of the ones and zeros in a binary array in the order they
72 | * appear.
73 | *
74 | * mutable: indtrue the indices of the true values in the array "expression"
75 | * mutable: indfalse the indices of the false values in the array "expression"
76 | */
77 | void arrfind (
78 | const distributions::ArrayXb& expression,
79 | Eigen::ArrayXi& indtrue,
80 | Eigen::ArrayXi& indfalse
81 | );
82 |
83 |
84 | /* Partition the observations, X according to a logical array.
85 | *
86 | * mutable: Xk, MxD matrix of observations that have a correspoding 1 in Xpart.
87 | * returns: an Mx1 array of the locations of Xk in X.
88 | */
89 | Eigen::ArrayXi partobs (
90 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& X, // NxD matrix of observations.
91 | const distributions::ArrayXb& Xpart, // Nx1 indicator vector to partition X.
92 | Eigen::MatrixXd& Xk // MxD matrix of obs. beloning to new partition
93 | );
94 |
95 |
96 | /* Augment the assignment matrix, qZ with the split cluster entry.
97 | *
98 | * The new cluster assignments are put in the K+1 th column in the return matrix
99 | * returns: The new observation assignments, [Nx(K+1)].
100 | * throws: std::invalid_argument if map.size() != Zsplit.size().
101 | */
102 | Eigen::MatrixXd auglabels (
103 | const double k, // Cluster to split (i.e. which column of qZ)
104 | const Eigen::ArrayXi& map, // Mapping from array of partitioned obs to qZ
105 | const distributions::ArrayXb& Zsplit, // Boolean array of assignments.
106 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& qZ // [NxK] observation assignment prob. matrix.
107 | );
108 |
109 |
110 | /* Check if any sufficient statistics are empty.
111 | *
112 | * returns: True if any of the sufficient statistics are empty
113 | */
114 | template bool anyempty (const std::vector& clusters)
115 | {
116 | const unsigned int K = clusters.size();
117 |
118 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
119 | if (clusters[k].getN() <= 1)
120 | return true;
121 |
122 | return false;
123 | }
124 |
125 | }
126 |
127 | #endif // COMUTILS_H
128 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/distributions.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include
22 | #include "distributions.h"
23 | #include "probutils.h"
24 |
25 | //
26 | // Namespaces
27 | //
28 |
29 | using namespace std;
30 | using namespace Eigen;
31 | using namespace probutils;
32 | using namespace boost::math;
33 |
34 |
35 | //
36 | // File scope variables
37 | //
38 |
39 | // Define pi
40 | const double pi = constants::pi(); // Boost high precision pi
41 |
42 |
43 | //
44 | // Private Helper Functions
45 | //
46 |
47 | /* Compare an double pair by the double member. Useful
48 | * for sorting an array in descending order while retaining a notion of
49 | * the original order of the array.
50 | *
51 | * returns: true if i.second > j.second.
52 | */
53 | bool inline obscomp (
54 | const std::pair& i, // the first pair to compare.
55 | const std::pair& j // the second pair to compare.
56 | )
57 | {
58 | return i.second > j.second;
59 | }
60 |
61 |
62 | /* Enumerate the dimensions.
63 | *
64 | * returns: 1:D or if D = 1, return 1.
65 | */
66 | ArrayXd enumdims (const int D)
67 | {
68 | ArrayXd l;
69 |
70 | if (D > 1)
71 | l = ArrayXd::LinSpaced(D, 1, D);
72 | else
73 | l.setOnes(1);
74 |
75 | return l;
76 | }
77 |
78 |
79 | //
80 | // Stick-Breaking (Dirichlet Process) weight distribution.
81 | //
82 |
83 | distributions::StickBreak::StickBreak ()
84 | : WeightDist(),
85 | alpha1_p(distributions::ALPHA1PRIOR),
86 | alpha2_p(distributions::ALPHA2PRIOR),
87 | alpha1(ArrayXd::Constant(1, distributions::ALPHA1PRIOR)),
88 | alpha2(ArrayXd::Constant(1, distributions::ALPHA2PRIOR)),
89 | E_logv(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
90 | E_lognv(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
91 | E_logpi(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
92 | ordvec(1, pair(0,0))
93 | {
94 | this->priorfcalc();
95 | }
96 |
97 |
98 | distributions::StickBreak::StickBreak (const double concentration)
99 | : WeightDist(),
100 | alpha2_p(distributions::ALPHA2PRIOR),
101 | alpha2(ArrayXd::Constant(1, distributions::ALPHA2PRIOR)),
102 | E_logv(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
103 | E_lognv(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
104 | E_logpi(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
105 | ordvec(1, pair(0,0))
106 | {
107 | if (concentration <=0)
108 | throw invalid_argument("Concentration parameter has to be > 0!");
109 |
110 | this->alpha1_p = concentration;
111 | this->alpha1 = ArrayXd::Constant(1, concentration);
112 | this->priorfcalc();
113 | }
114 |
115 |
116 | void distributions::StickBreak::priorfcalc (void)
117 | {
118 | // Prior free energy contribution
119 | this->F_p = lgamma(this->alpha1_p) + lgamma(this->alpha2_p)
120 | - lgamma(this->alpha1_p + this->alpha2_p);
121 | }
122 |
123 |
124 | void distributions::StickBreak::update (const ArrayXd& Nk)
125 | {
126 | const int K = Nk.size();
127 |
128 | // Destructively resize members to be the same size as Nk, no-op if same
129 | this->alpha1.resize(K);
130 | this->alpha2.resize(K);
131 | this->E_logv.resize(K);
132 | this->E_lognv.resize(K);
133 | this->E_logpi.resize(K);
134 | this->ordvec.resize(K, pair(-1, -1));
135 |
136 | // Order independent update
137 | this->Nk = Nk;
138 | this->alpha1 = this->alpha1_p + Nk;
139 |
140 | // Get at sort size order of clusters
141 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
142 | {
143 | this->ordvec[k].first = k;
144 | this->ordvec[k].second = Nk(k);
145 | }
146 | sort(this->ordvec.begin(), this->ordvec.end(), obscomp);
147 |
148 | // Now do order dependent updates
149 | const double N = Nk.sum();
150 | double cumNk = 0, cumE_lognv = 0;
151 | for (int idx = 0, k; idx < K; ++idx)
152 | {
153 | k = this->ordvec[idx].first;
154 |
155 | // Alpha 2
156 | cumNk += Nk(k); // Accumulate cluster size sum
157 | this->alpha2(k) = this->alpha2_p + (N - cumNk);
158 |
159 | // Expected stick lengths
160 | double psisum = digamma(this->alpha1(k) + this->alpha2(k));
161 | this->E_logv(k) = digamma(this->alpha1(k)) - psisum;
162 | this->E_lognv(k) = digamma(this->alpha2(k)) - psisum;
163 |
164 | // Expected weights
165 | this->E_logpi(k) = this->E_logv(k) + cumE_lognv;
166 | cumE_lognv += E_lognv(k); // Accumulate log stick length left
167 | }
168 | }
169 |
170 |
171 | double distributions::StickBreak::fenergy () const
172 | {
173 | const int K = this->alpha1.size();
174 |
175 | return K * this->F_p + (mxlgamma(this->alpha1 + this->alpha2).array()
176 | - mxlgamma(this->alpha1).array() - mxlgamma(this->alpha2).array()
177 | + (this->alpha1 - this->alpha1_p) * this->E_logv
178 | + (this->alpha2 - this->alpha2_p) * this->E_lognv).sum();
179 | }
180 |
181 |
182 | //
183 | // Generalised Dirichlet weight distribution.
184 | //
185 |
186 | void distributions::GDirichlet::update (const ArrayXd& Nk)
187 | {
188 | // Call base class (stick breaking) update
189 | this->StickBreak::update(Nk);
190 | const int smallk = (this->ordvec.end() - 1)->first; // Get smallest cluster
191 |
192 | // Set last stick lengths to 1 ( log(0) = 1 ) and adjust log marginal
193 | this->E_logpi(smallk) = this->E_logpi(smallk) - this->E_logv(smallk);
194 | this->E_logv(smallk) = 0; // exp(E[log v_K]) = 1
195 | this->E_lognv(smallk) = 0; // Undefined, but set to zero
196 | }
197 |
198 |
199 | double distributions::GDirichlet::fenergy () const
200 | {
201 | const int K = this->ordvec.size();
202 |
203 | // GDir only has K-1 parameters, so we don't calculate the last F contrib.
204 | double Fpi = 0;
205 | for (int idx = 0, k = 0; idx < K-1; ++idx)
206 | {
207 | k = this->ordvec[idx].first;
208 | Fpi += lgamma(this->alpha1(k) + this->alpha2(k))
209 | - lgamma(this->alpha1(k)) - lgamma(this->alpha2(k))
210 | + (this->alpha1(k) - this->alpha1_p) * this->E_logv(k)
211 | + (this->alpha2(k) - this->alpha2_p) * this->E_lognv(k);
212 | }
213 |
214 | return (K-1) * this->F_p + Fpi;
215 | }
216 |
217 |
218 | //
219 | // Dirichlet weight distribution.
220 | //
221 |
222 | distributions::Dirichlet::Dirichlet ()
223 | : WeightDist(),
224 | alpha_p(distributions::ALPHA1PRIOR),
225 | alpha(ArrayXd::Constant(1, distributions::ALPHA1PRIOR)),
226 | E_logpi(ArrayXd::Zero(1))
227 | {}
228 |
229 |
230 | distributions::Dirichlet::Dirichlet (const double alpha)
231 | : WeightDist(),
232 | E_logpi(ArrayXd::Zero(1))
233 | {
234 | if (alpha <= 0)
235 | throw invalid_argument("Alpha prior must be > 0!");
236 |
237 | alpha_p = alpha;
238 | this->alpha = ArrayXd::Constant(1, alpha);
239 | }
240 |
241 |
242 | void distributions::Dirichlet::update (const ArrayXd& Nk)
243 | {
244 | const int K = Nk.size();
245 |
246 | // Destructively resize members to be the same size as Nk, no-op if same
247 | this->alpha.resize(K);
248 | this->E_logpi.resize(K);
249 |
250 | // Hyperparameter update
251 | this->Nk = Nk;
252 | this->alpha = this->alpha_p + Nk;
253 |
254 | // Expectation update
255 | this->E_logpi = mxdigamma(this->alpha).array() - digamma(this->alpha.sum());
256 | }
257 |
258 |
259 | double distributions::Dirichlet::fenergy () const
260 | {
261 | const int K = this->alpha.size();
262 |
263 | return lgamma(this->alpha.sum()) - (this->alpha_p-1) * this->E_logpi.sum()
264 | + ((this->alpha-1) * this->E_logpi - mxlgamma(this->alpha).array()).sum()
265 | - lgamma(K * this->alpha_p) + K * lgamma(this->alpha_p);
266 | }
267 |
268 |
269 | //
270 | // Gaussian Wishart cluster distribution.
271 | //
272 |
273 | distributions::GaussWish::GaussWish (
274 | const double clustwidth,
275 | const unsigned int D
276 | )
277 | : ClusterDist(clustwidth, D),
278 | nu_p(D),
279 | beta_p(distributions::BETAPRIOR),
280 | m_p(RowVectorXd::Zero(D))
281 | {
282 | if (clustwidth <= 0)
283 | throw invalid_argument("clustwidth must be > 0!");
284 |
285 | // Create Prior
286 | this->iW_p = this->nu_p * this->prior * MatrixXd::Identity(D, D);
287 |
288 | try
289 | { this->logdW_p = -logdet(this->iW_p); }
290 | catch (invalid_argument e)
291 | { throw invalid_argument(string("Creating prior: ").append(e.what())); }
292 |
293 | // Calculate prior free energy contribution
294 | this->F_p = mxlgamma((this->nu_p + 1
295 | - enumdims(this->m_p.cols())).matrix() / 2).sum();
296 |
297 | this->clearobs(); // Empty suff. stats. and set posteriors equal to priors
298 | }
299 |
300 |
301 | void distributions::GaussWish::addobs(const VectorXd& qZk, const MatrixXd& X)
302 | {
303 | if (X.cols() != this->D)
304 | throw invalid_argument("Mismatched dims. of cluster params and obs.!");
305 | if (qZk.rows() != X.rows())
306 | throw invalid_argument("qZk and X ar not the same length!");
307 |
308 | MatrixXd qZkX = qZk.asDiagonal() * X;
309 |
310 | this->N_s += qZk.sum();
311 | this->x_s += qZkX.colwise().sum(); // [1xD] row vector
312 | this->xx_s.noalias() += qZkX.transpose() * X; // [DxD] matrix
313 | }
314 |
315 |
316 | void distributions::GaussWish::update ()
317 | {
318 | // Prepare the Sufficient statistics
319 | RowVectorXd xk = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
320 | if (this->N_s > 0)
321 | xk = this->x_s/this->N_s;
322 | MatrixXd Sk = this->xx_s - xk.transpose() * this->x_s;
323 | RowVectorXd xk_m = xk - this->m_p; // for iW, (xk - m)
324 |
325 | // Update posterior params
326 | this->N = this->N_s;
327 | this->nu = this->nu_p + this->N;
328 | this->beta = this->beta_p + this->N;
329 | this->m = (this->beta_p * this->m_p + this->x_s) / this->beta;
330 | this->iW = this->iW_p + Sk
331 | + (this->beta_p * this->N/this->beta) * xk_m.transpose() * xk_m;
332 |
333 | try
334 | { this->logdW = -logdet(this->iW); }
335 | catch (invalid_argument e)
336 | { throw runtime_error(string("Calc log(det(W)): ").append(e.what())); }
337 | }
338 |
339 |
340 | void distributions::GaussWish::clearobs ()
341 | {
342 | // Reset parameters back to prior values
343 | this->nu = this->nu_p;
344 | this->beta = this->beta_p;
345 | this->m = this->m_p;
346 | this->iW = this->iW_p;
347 | this->logdW = this->logdW_p;
348 |
349 | // Empty sufficient statistics
350 | this->N_s = 0;
351 | this->x_s = RowVectorXd::Zero(D);
352 | this->xx_s = MatrixXd::Zero(D,D);
353 | }
354 |
355 |
356 | VectorXd distributions::GaussWish::Eloglike (const MatrixXd& X) const
357 | {
358 | // Expectations of log Gaussian likelihood
359 | VectorXd E_logX(X.rows());
360 | double sumpsi = mxdigamma((this->nu+1-enumdims(this->D)).matrix()/2).sum();
361 | try
362 | {
363 | E_logX = 0.5 * (sumpsi + this->logdW - this->D * (1/this->beta + log(pi))
364 | - this->nu * mahaldist(X, this->m, this->iW).array()).matrix();
365 | }
366 | catch (invalid_argument e)
367 | { throw(string("Calculating Gaussian likelihood: ").append(e.what())); }
368 |
369 | return E_logX;
370 | }
371 |
372 |
373 | distributions::ArrayXb distributions::GaussWish::splitobs (
374 | const MatrixXd& X
375 | ) const
376 | {
377 |
378 | // Find the principle eigenvector using the power method if not done so
379 | VectorXd eigvec;
380 | eigpower(this->iW, eigvec);
381 |
382 | // 'split' the observations perpendicular to this eigenvector.
383 | return (((X.rowwise() - this->m)
384 | * eigvec.asDiagonal()).array().rowwise().sum()) >= 0;
385 | }
386 |
387 |
388 | double distributions::GaussWish::fenergy () const
389 | {
390 | const ArrayXd l = enumdims(this->D);
391 | double sumpsi = mxdigamma((this->nu + 1 - l).matrix() / 2).sum();
392 |
393 | return this->F_p + (this->D * (this->beta_p/this->beta - 1 - this->nu
394 | - log(this->beta_p/this->beta))
395 | + this->nu * ((this->iW.ldlt().solve(this->iW_p)).trace()
396 | + this->beta_p * mahaldist(this->m, this->m_p, this->iW).coeff(0,0))
397 | + this->nu_p * (this->logdW_p - this->logdW) + this->N*sumpsi)/2
398 | - mxlgamma((this->nu+1-l).matrix() / 2).sum();
399 | }
400 |
401 |
402 | //
403 | // Normal Gamma parameter distribution.
404 | //
405 |
406 | distributions::NormGamma::NormGamma (
407 | const double clustwidth,
408 | const unsigned int D
409 | )
410 | : ClusterDist(clustwidth, D),
411 | nu_p(distributions::NUPRIOR),
412 | beta_p(distributions::BETAPRIOR),
413 | m_p(RowVectorXd::Zero(D))
414 | {
415 | if (clustwidth <= 0)
416 | throw invalid_argument("clustwidth must be > 0!");
417 |
418 | // Create Prior
419 | this->L_p = this->nu_p * this->prior * RowVectorXd::Ones(D);
420 | this->logL_p = this->L_p.array().log().sum();
421 |
422 | this->clearobs(); // Empty suff. stats. and set posteriors equal to priors
423 | }
424 |
425 |
426 | void distributions::NormGamma::addobs (const VectorXd& qZk, const MatrixXd& X)
427 | {
428 | if (X.cols() != this->D)
429 | throw invalid_argument("Mismatched dims. of cluster params and obs.!");
430 | if (qZk.rows() != X.rows())
431 | throw invalid_argument("qZk and X ar not the same length!");
432 |
433 | MatrixXd qZkX = qZk.asDiagonal() * X;
434 |
435 | this->N_s += qZk.sum();
436 | this->x_s += qZkX.colwise().sum(); // [1xD]
437 | this->xx_s += (qZkX.array() * X.array()).colwise().sum().matrix(); // [1xD]
438 | }
439 |
440 |
441 | void distributions::NormGamma::update ()
442 | {
443 | // Prepare the Sufficient statistics
444 | RowVectorXd xk = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
445 | RowVectorXd Sk = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
446 | if (this->N_s > 0)
447 | {
448 | xk = this->x_s/this->N_s;
449 | Sk = this->xx_s.array() - this->x_s.array().square()/this->N_s;
450 | }
451 |
452 | // Update posterior params
453 | this->N = this->N_s;
454 | this->beta = this->beta_p + this->N;
455 | this->nu = this->nu_p + this->N/2;
456 | this->m = (this->beta_p * this->m_p + x_s) / this->beta;
457 | this->L = this->L_p + Sk/2 + (this->beta_p * this->N / (2 * this->beta))
458 | * (xk - this->m_p).array().square().matrix();
459 |
460 | if ((this->L.array() <= 0).any())
461 | throw invalid_argument(string("Calc log(L): Variance is zero or less!"));
462 |
463 | this->logL = this->L.array().log().sum();
464 | }
465 |
466 |
467 | void distributions::NormGamma::clearobs ()
468 | {
469 | // Reset parameters back to prior values
470 | this->nu = this->nu_p;
471 | this->beta = this->beta_p;
472 | this->m = this->m_p;
473 | this->L = this->L_p;
474 | this->logL = this->logL_p;
475 |
476 | // Empty sufficient statistics
477 | this->N_s = 0;
478 | this->x_s = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
479 | this->xx_s = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
480 | }
481 |
482 |
483 | VectorXd distributions::NormGamma::Eloglike (const MatrixXd& X) const
484 | {
485 | // Distance evaluation in the exponent
486 | VectorXd Xmdist = (X.rowwise() - this->m).array().square().matrix()
487 | * this->L.array().inverse().matrix().transpose();
488 |
489 | // Expectations of log Gaussian likelihood
490 | return 0.5 * (this->D * (digamma(this->nu) - log(2 * pi) - 1/this->beta)
491 | - this->logL - this->nu * Xmdist.array());
492 | }
493 |
494 |
495 | distributions::ArrayXb distributions::NormGamma::splitobs (
496 | const MatrixXd& X
497 | ) const
498 | {
499 | // Find location of largest element in L, this is the 'eigenvector'
500 | int eigvec;
501 | this->L.maxCoeff(&eigvec);
502 |
503 | // 'split' the observations perpendicular to this 'eigenvector'.
504 | return (X.col(eigvec).array() - this->m(eigvec)) >= 0;
505 | }
506 |
507 |
508 | double distributions::NormGamma::fenergy () const
509 | {
510 | const VectorXd iL = this->L.array().inverse().matrix().transpose();
511 |
512 | return D*(lgamma(this->nu_p) - lgamma(this->nu)
513 | + this->N*digamma(this->nu)/2 - this->nu)
514 | + D/2 * (log(this->beta) - log(this->beta_p) - 1 + this->beta_p/this->beta)
515 | + this->beta_p*this->nu/2*(this->m - this->m_p).array().square().matrix()*iL
516 | + this->nu_p*(this->logL - this->logL_p) + this->nu*this->L_p*iL;
517 | }
518 |
519 |
520 | //
521 | // Exponential Gamma parameter distribution.
522 | //
523 |
524 | distributions::ExpGamma::ExpGamma (const double obsmag, const unsigned int D)
525 | : ClusterDist(obsmag, D),
526 | a_p(distributions::APRIOR),
527 | b_p(obsmag)
528 | {
529 | this->clearobs(); // Empty suff. stats. and set posteriors equal to priors
530 | }
531 |
532 |
533 | void distributions::ExpGamma::addobs (const VectorXd& qZk, const MatrixXd& X)
534 | {
535 | if (X.cols() != this->D)
536 | throw invalid_argument("Mismatched dims. of cluster params and obs.!");
537 | if (qZk.rows() != X.rows())
538 | throw invalid_argument("qZk and X ar not the same length!");
539 |
540 | this->N_s += qZk.sum();
541 | this->x_s += (qZk.asDiagonal() * X).colwise().sum();
542 | }
543 |
544 |
545 | void distributions::ExpGamma::update ()
546 | {
547 | // Update posterior params
548 | this->N = this->N_s;
549 | this->a = this->a_p + this->N;
550 | this->ib = (this->b_p + this->x_s.array()).array().inverse().matrix();
551 | this->logb = - this->ib.array().log().sum();
552 | }
553 |
554 |
555 | void distributions::ExpGamma::clearobs ()
556 | {
557 | // Reset parameters back to prior values
558 | this->a = this->a_p;
559 | this->ib = RowVectorXd::Constant(this->D, 1/this->b_p);
560 | this->logb = this->D * log(this->b_p);
561 |
562 | // Empty sufficient statistics
563 | this->N_s = 0;
564 | this->x_s = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
565 | }
566 |
567 |
568 | VectorXd distributions::ExpGamma::Eloglike (const MatrixXd& X) const
569 | {
570 | return this->D * digamma(this->a) - this->logb
571 | - (this->a * X * this->ib.transpose()).array();
572 | }
573 |
574 |
575 | distributions::ArrayXb distributions::ExpGamma::splitobs (
576 | const MatrixXd& X
577 | ) const
578 | {
579 | ArrayXd XdotL = X * (this->a * this->ib).transpose();
580 | return (XdotL > (XdotL.sum()/XdotL.size()));
581 | }
582 |
583 |
584 | double distributions::ExpGamma::fenergy () const
585 | {
586 | return this->D * ((this->a - this->a_p) * digamma(this->a) - this->a
587 | - this->a_p * log(this->b_p) - lgamma(this->a) + lgamma(this->a_p))
588 | + this->b_p * this->a * this->ib.sum() + this->a_p * this->logb;
589 | }
590 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/mcluster.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include
22 | #include "libcluster.h"
23 | #include "probutils.h"
24 | #include "comutils.h"
25 |
26 |
27 | //
28 | // Namespaces
29 | //
30 |
31 | using namespace std;
32 | using namespace Eigen;
33 | using namespace probutils;
34 | using namespace distributions;
35 | using namespace comutils;
36 | using namespace libcluster;
37 |
38 |
39 | //
40 | // Variational Bayes Private Functions
41 | //
42 |
43 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for weights in each group.
44 | *
45 | * mutable: Top-level cluster assignment probabilities, qYj
46 | * returns: The complete-data free energy, Y and Y+Z dep. terms, for group j.
47 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
48 | */
49 | template double vbeY (
50 | const MatrixXd& Wj, // Top-level observations for group j
51 | const vMatrixXd& qZj, // Bottom-level cluster labels for group j
52 | const WJ& weightsj, // Group top-level cluster weights
53 | const vector& weights_t, // Bottom-level cluster proportion/paramters
54 | const vector& clusters_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
55 | MatrixXd& qYj // Top-level cluster assignments for group j
56 | )
57 | {
58 | const unsigned int T = weights_t.size(),
59 | Ij = qZj.size(),
60 | K = qZj[0].cols();
61 |
62 | // No observations (may happen when splitting)
63 | if (Ij == 0)
64 | return 0;
65 |
66 | // Get log marginal weight likelihoods
67 | const ArrayXd E_logwj = weightsj.Elogweight();
68 |
69 | MatrixXd Njik(Ij, K), logqYj(Ij, T);
70 | ArrayXXd qZjiLike(Ij, T);
71 |
72 | // Get bottom-level cluster counts per "document/image"
73 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < Ij; ++i)
74 | Njik.row(i) = qZj[i].colwise().sum();
75 |
76 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs
77 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
78 | {
79 | qZjiLike.col(t) = Njik * weights_t[t].Elogweight().matrix();
80 | logqYj.col(t) = qZjiLike.col(t) + E_logwj(t)
81 | + clusters_t[t].Eloglike(Wj).array();
82 | }
83 |
84 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
85 | VectorXd logZyj = logsumexp(logqYj);
86 |
87 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities
88 | qYj = (logqYj.colwise() - logZyj).array().exp().matrix();
89 |
90 | return ((qYj.array() * qZjiLike).rowwise().sum() - logZyj.array()).sum();
91 | }
92 |
93 |
94 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for clusters in each "document", ji.
95 | *
96 | * mutable: Bottom-level cluster assignment probabilities, qZji
97 | * returns: The complete-data free energy, Z dep. terms, for group j.
98 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
99 | */
100 | template double vbeZ (
101 | const MatrixXd& Xji, // Observations in i in group j
102 | const RowVectorXd& qYji, // Top-level cluster assignment
103 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
104 | const vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
105 | MatrixXd& qZji // Observation to cluster assignments
106 | )
107 | {
108 | const int K = clusters_k.size(),
109 | Nji = Xji.rows(),
110 | T = weights_t.size();
111 |
112 | // No observations (may happen when splitting)
113 | if (Nji == 0)
114 | return 0;
115 |
116 | // Make top-level cluster global weights from weighted label parameters
117 | RowVectorXd E_logqYljt = RowVectorXd::Zero(K);
118 |
119 | for (int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
120 | E_logqYljt.noalias() += qYji(t) * weights_t[t].Elogweight().matrix();
121 |
122 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs
123 | MatrixXd logqZji = MatrixXd::Zero(Nji, K);
124 |
125 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
126 | logqZji.col(k) = E_logqYljt(k) + clusters_k[k].Eloglike(Xji).array();
127 |
128 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
129 | const VectorXd logZzji = logsumexp(logqZji);
130 |
131 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities
132 | qZji = (logqZji.colwise() - logZzji).array().exp().matrix();
133 |
134 | return -logZzji.sum();
135 | }
136 |
137 |
138 | /* Calculates the free energy lower bound for the model parameter distributions.
139 | *
140 | * returns: the free energy of the model
141 | */
142 | template double fenergy (
143 | const vector& weights_j, // Group top-level cluster weights
144 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster proportion parameters
145 | const vector& clusters_t, // Top-level cluster other parameters
146 | const vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
147 | const double Fyz, // Free energy Y and cross Y-Z terms
148 | const double Fz // Free energy Z terms
149 | )
150 | {
151 | const int T = weights_t.size(),
152 | K = clusters_k.size(),
153 | J = weights_j.size();
154 |
155 | // Class parameter free energy
156 | double Ft = 0;
157 | for (int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
158 | Ft += weights_t[t].fenergy() + clusters_t[t].fenergy();
159 |
160 | // Cluster parameter free energy
161 | double Fk = 0;
162 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
163 | Fk += clusters_k[k].fenergy();
164 |
165 | // Weight parameter free energy
166 | double Fw = 0;
167 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
168 | Fw += weights_j[j].fenergy();
169 |
170 | return Fw + Ft + Fk + Fyz + Fz;
171 | }
172 |
173 |
174 | /* Variational Bayes EM.
175 | *
176 | * returns: Free energy of the whole model.
177 | * mutable: the bottom-level cluster indicators, qZ
178 | * mutable: the top-level cluster indicators, qY
179 | * mutable: model parameters weights_j, weights_t, clusters_k, clusters_t
180 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
181 | * throws: runtime_error if there is a negative free energy.
182 | */
183 | template double vbem (
184 | const vMatrixXd& W, // Top-level observations
185 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Bottom-level observations
186 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level labels
187 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level cluster labels
188 | vector& weights_j, // Group top-level cluster weights
189 | vector& weights_t, // Top-level proportion cluster parameters
190 | vector& clusters_t, // Top-level other cluster parameters
191 | vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
192 | const double prior_t, // Top-level cluster prior
193 | const double prior_k, // Bottom-level cluster prior
194 | const int maxit = -1, // Max VBEM iterations (-1 = no max, default)
195 | const bool verbose = false // Verbose output
196 | )
197 | {
198 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
199 | K = qZ[0][0].cols(),
200 | T = qY[0].cols();
201 |
202 | // Construct (empty) parameters
203 | weights_j.resize(J, WJ());
204 | weights_t.resize(T, WT());
205 | clusters_t.resize(T, CT(prior_t, W[0].cols()));
206 | clusters_k.resize(K, CK(prior_k, X[0][0].cols()));
207 |
208 | // Other loop variables for initialisation
209 | int it = 0;
210 | double F = numeric_limits::max(), Fold;
211 |
212 | do
213 | {
214 | Fold = F;
215 |
216 | MatrixXd Ntk = MatrixXd::Zero(T, K); // Clear Sufficient Stats
217 |
218 | // VBM for top-level cluster weights
219 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
220 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
221 | {
222 | // Accumulate suff. stats for bottom-level cluster counts
223 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
224 | {
225 | MatrixXd Ntkji = qY[j].row(i).transpose() * qZ[j][i].colwise().sum();
226 | #pragma omp critical
227 | Ntk += Ntkji;
228 | }
229 |
230 | weights_j[j].update(qY[j].colwise().sum());
231 | }
232 |
233 | // VBM for top-level cluster parameters and proportions
234 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
235 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
236 | {
237 | clusters_t[t].clearobs(); // Clear Sufficient Stats
238 |
239 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j) // Accumulate sufficient stats
240 | clusters_t[t].addobs(qY[j].col(t), W[j]);
241 |
242 | weights_t[t].update(Ntk.row(t)); // Bottom-level cluster counts.
243 | clusters_t[t].update();
244 | }
245 |
246 | // VBM for bottom-level cluster parameters
247 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
248 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
249 | {
250 | clusters_k[k].clearobs(); // Clear Sufficient Stats
251 |
252 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j) // Accumulate sufficient stats
253 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
254 | clusters_k[k].addobs(qZ[j][i].col(k), X[j][i]);
255 |
256 | clusters_k[k].update(); // Bottom-level observations
257 | }
258 |
259 | // Free energy data fit term accumulators
260 | double Fz = 0, Fyz = 0;
261 |
262 | // VBE for top-level cluster indicators
263 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fyz)
264 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
265 | Fyz += vbeY(W[j], qZ[j], weights_j[j], weights_t, clusters_t,
266 | qY[j]);
267 |
268 | // VBE for bottom-level cluster indicators
269 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
270 | {
271 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fz)
272 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
273 | Fz += vbeZ(X[j][i], qY[j].row(i), weights_t, clusters_k,
274 | qZ[j][i]);
275 | }
276 |
277 | // Calculate free energy of model
278 | F = fenergy(weights_j, weights_t, clusters_t, clusters_k, Fyz,
279 | Fz);
280 |
281 | // Check bad free energy step
282 | if ((F-Fold)/abs(Fold) > libcluster::FENGYDEL)
283 | throw runtime_error("Free energy increase!");
284 |
285 | if (verbose == true) // Notify iteration
286 | cout << '-' << flush;
287 | }
288 | while ( (abs((Fold-F)/Fold) > libcluster::CONVERGE)
289 | && ( (++it < maxit) || (maxit < 0) ) );
290 |
291 | return F;
292 | }
293 |
294 |
295 | //
296 | // Model Selection and Heuristics Private Functions
297 | //
298 |
299 | /* Search in a greedy fashion for a mixture split that lowers model free
300 | * energy, or return false. An attempt is made at looking for good, untried,
301 | * split candidates first, as soon as a split canditate is found that lowers
302 | * model F, it is returned. This may not be the "best" split, but it is
303 | * certainly faster than an exhaustive search for the "best" split.
304 | *
305 | * returns: true if a split was found, false if no splits can be found
306 | * mutable: qZ is augmented with a new split if one is found, otherwise left
307 | * mutable: qY is updated if a new split if one is found, otherwise left
308 | * mutable tally is a tally of times a cluster has been unsuccessfully split
309 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions
310 | * throws: runtime_error from its internal VBEM calls
311 | */
312 | template bool ssplit (
313 | const vMatrixXd& W, // Top-level observations
314 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Bottom-level observations
315 | const vector& clusters_t, // Top-level cluster Distributions
316 | const vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster Distributions
317 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level cluster labels qY
318 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level Cluster labels qZ
319 | vector& tally, // Count of unsuccessful splits
320 | const double F, // Current model free energy
321 | const int maxK, // max number of (bottom) clusters
322 | const bool verbose // Verbose output
323 | )
324 | {
325 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
326 | K = clusters_k.size();
327 |
328 | // Check if we have reached the max number of clusters
329 | if ( ((signed) K >= maxK) && (maxK >= 0) )
330 | return false;
331 |
332 | // Split order chooser and bottom-level cluster parameters
333 | tally.resize(K, 0); // Make sure tally is the right size
334 | vector ord(K);
335 |
336 | // Get cluster parameters and their free energy
337 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
338 | {
339 | ord[k].k = k;
340 | ord[k].tally = tally[k];
341 | ord[k].Fk = clusters_k[k].fenergy();
342 | }
343 |
344 | // Get bottom-level cluster likelihoods
345 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
346 | {
347 | // Add in cluster log-likelihood, weighted by global responsability
348 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
349 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
350 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
351 | {
352 | double LL = qZ[j][i].col(k).dot(clusters_k[k].Eloglike(X[j][i]));
353 |
354 | #pragma omp atomic
355 | ord[k].Fk -= LL;
356 | }
357 | }
358 |
359 | // Sort clusters by split tally, then free energy contributions
360 | sort(ord.begin(), ord.end(), greedcomp);
361 |
362 | // Pre allocate big objects for loops (this makes a runtime difference)
363 | vector< vector > mapidx(J);
364 | vvMatrixXd qZref(J), qZaug(J), Xk(J);
365 |
366 | // Loop through each potential cluster in order and split it
367 | for (vector::iterator ko = ord.begin(); ko < ord.end(); ++ko)
368 | {
369 | const int k = ko->k;
370 |
371 | ++tally[k]; // increase this cluster's unsuccessful split tally by default
372 |
373 | // Don't waste time with clusters that can't really be split min (2:2)
374 | if (clusters_k[k].getN() < 4)
375 | continue;
376 |
377 | // Now split observations and qZ.
378 | int scount = 0, Mtot = 0;
379 |
380 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
381 | {
382 | mapidx[j].resize(X[j].size());
383 | qZref[j].resize(X[j].size());
384 | qZaug[j].resize(X[j].size());
385 | Xk[j].resize(X[j].size());
386 |
387 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Mtot, scount)
388 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
389 | {
390 | // Make COPY of the observations with only relevant data points, p > 0.5
391 | mapidx[j][i] = partobs(X[j][i], (qZ[j][i].col(k).array()>0.5),
392 | Xk[j][i]);
393 | Mtot += Xk[j][i].rows();
394 |
395 | // Initial cluster split
396 | ArrayXb splitk = clusters_k[k].splitobs(Xk[j][i]);
397 | qZref[j][i].setZero(Xk[j][i].rows(), 2);
398 | qZref[j][i].col(0) = (splitk == true).cast();
399 | qZref[j][i].col(1) = (splitk == false).cast();
400 |
401 | // keep a track of number of splits
402 | scount += splitk.count();
403 | }
404 | }
405 |
406 | // Don't waste time with clusters that haven't been split sufficiently
407 | if ( (scount < 2) || (scount > (Mtot-2)) )
408 | continue;
409 |
410 | // Refine the split
411 | vector iwspl;
412 | vector icspl;
413 | vector swspl;
414 | vector scspl;
415 | vMatrixXd qYaug = qY; // Copy :-(
416 | vbem(W, Xk, qYaug, qZref, iwspl, swspl, icspl, scspl,
417 | clusters_t[0].getprior(), clusters_k[0].getprior(), SPLITITER);
418 |
419 | if (anyempty(scspl) == true) // One cluster only
420 | continue;
421 |
422 | // Map the refined splits back to original whole-data problem
423 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
424 | {
425 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
426 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
427 | qZaug[j][i] = auglabels(k, mapidx[j][i],
428 | (qZref[j][i].col(1).array() > 0.5), qZ[j][i]);
429 | }
430 |
431 | // Calculate free energy of this split with ALL data (and refine a bit)
432 | qYaug = qY; // Copy :-(
433 | double Fs = vbem(W, X, qYaug, qZaug, iwspl, swspl, icspl,
434 | scspl, clusters_t[0].getprior(), clusters_k[0].getprior(), 1);
435 |
436 | if (anyempty(scspl) == true) // One cluster only
437 | continue;
438 |
439 | // Only notify here of split candidates
440 | if (verbose == true)
441 | cout << '=' << flush;
442 |
443 | // Test whether this cluster split is a keeper
444 | if ( (Fs < F) && (abs((F-Fs)/F) > CONVERGE) )
445 | {
446 | qY = qYaug;
447 | qZ = qZaug;
448 | tally[k] = 0; // Reset tally if successfully split
449 | return true;
450 | }
451 | }
452 |
453 | // Failed to find splits
454 | return false;
455 | }
456 |
457 |
458 | /* Find and remove all empty top-level clusters.
459 | *
460 | * returns: true if any clusters have been deleted, false if all are kept.
461 | * mutable: qY may have columns deleted if there are empty clusters found.
462 | * mutable: weights_t if there are empty top-level clusters found.
463 | * mutable: clusters_t if there are empty top-level clusters found.
464 | */
465 | template bool prune_clusters_t (
466 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Probabilities qY
467 | vector& weights_t, // Top-level bottom-level cluster proportions
468 | vector& clusters_t, // Top-level clusters
469 | bool verbose = false // print status
470 | )
471 | {
472 | const unsigned int T = weights_t.size(),
473 | J = qY.size();
474 |
475 | // Look for empty clusters
476 | ArrayXd Nt(T);
477 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
478 | Nt(t) = weights_t[t].getNk().sum();
479 |
480 | // Find location of empty and full clusters
481 | ArrayXi eidx, fidx;
482 | arrfind(Nt.array() < 1, eidx, fidx);
483 | const unsigned int nempty = eidx.size();
484 |
485 | // If everything is not empty, return false
486 | if (nempty == 0)
487 | return false;
488 |
489 | if (verbose == true)
490 | cout << '*' << flush;
491 |
492 | // Delete empty clusters
493 | for (int i = (nempty - 1); i >= 0; --i)
494 | {
495 | weights_t.erase(weights_t.begin() + eidx(i));
496 | clusters_t.erase(clusters_t.begin() + eidx(i));
497 | }
498 |
499 | // Delete empty cluster indicators by copying only full indicators
500 | const unsigned int newT = fidx.size();
501 | vMatrixXd newqY(J);
502 |
503 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
504 | {
505 | newqY[j].setZero(qY[j].rows(), newT);
506 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < newT; ++t)
507 | newqY[j].col(t) = qY[j].col(fidx(t));
508 | }
509 |
510 | qY = newqY;
511 |
512 | return true;
513 | }
514 |
515 |
516 | /* The model selection algorithm
517 | *
518 | * returns: Free energy of the final model
519 | * mutable: qY the probabilistic top-level cluster assignments
520 | * mutable: qZ the probabilistic bottom-level cluster assignments
521 | * mutable: The top-level clusters and weights
522 | * mutable: The bottom-level clusters and bottom-level cluster weights
523 | * throws: invalid_argument from other functions
524 | * throws: runtime_error if free energy increases
525 | */
526 | template double mcluster (
527 | const vMatrixXd& W, // Top-level observations
528 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Bottom-level observations
529 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level labels
530 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level labels
531 | vector& weights_j, // Group top-level cluster weights
532 | vector& weights_t, // Tope-level proportion cluster parameters
533 | vector& clusters_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
534 | vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
535 | const double prior_t, // Top-level cluster prior
536 | const double prior_k, // Bottom-level cluster prior
537 | const unsigned int maxT, // Truncation level for top-level clusters
538 | const int maxK, // max number of (bottom) clusters
539 | const bool verbose, // Verbose output
540 | const unsigned int nthreads // Number of threads for OpenMP to use
541 | )
542 | {
543 | if (nthreads < 1)
544 | throw invalid_argument("Must specify at least one thread for execution!");
545 | omp_set_num_threads(nthreads);
546 |
547 | // Do some observation validity checks
548 | if (W.size() != X.size()) // Same number of groups in observations
549 | throw invalid_argument("W and X need to have the same number of groups!");
550 |
551 | const unsigned int J = W.size();
552 |
553 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j) // Same number of images/docs in groups
554 | if ((unsigned) W[j].rows() != X[j].size())
555 | throw invalid_argument("W and X need to have the same number of 'docs'!");
556 |
557 | // Initialise qY randomly and qZ to ones
558 | qY.resize(J);
559 | qZ.resize(J);
560 |
561 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
562 | {
563 | ArrayXXd randm = (ArrayXXd::Random(X[j].size(), maxT)).abs();
564 | ArrayXd norm = randm.rowwise().sum();
565 | qY[j] = (randm.log().colwise() - norm.log()).exp();
566 |
567 | qZ[j].resize(X[j].size());
568 |
569 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
570 | qZ[j][i].setOnes(X[j][i].rows(), 1);
571 | }
572 |
573 | bool emptyclasses = true, split = true;
574 | double F = 0;
575 | vector stally;
576 |
577 | // Main loop
578 | while ((split == true) || (emptyclasses == true))
579 | {
580 |
581 | F = vbem(W, X, qY, qZ, weights_j, weights_t, clusters_t,
582 | clusters_k, prior_t, prior_k, -1, verbose);
583 |
584 | if (verbose == true)
585 | cout << '<' << flush; // Notify start bottom-level cluster search
586 |
587 | if (split == false) // Remove any empty weights
588 | emptyclasses = prune_clusters_t(qY, weights_t, clusters_t,
589 | verbose);
590 | else
591 | split = ssplit(W, X, clusters_t, clusters_k, qY, qZ, stally,
592 | F, maxK, verbose);
593 |
594 | if (verbose == true)
595 | cout << '>' << endl; // Notify end bottom-level cluster search
596 | }
597 |
598 | // Print finished notification if verbose
599 | if (verbose == true)
600 | {
601 | cout << "Finished!" << endl;
602 | cout << "Number of top level clusters = " << clusters_t.size();
603 | cout << ", and bottom level clusters = " << clusters_k.size() << endl;
604 | cout << "Free energy = " << F << endl;
605 | }
606 |
607 | return F;
608 | }
609 |
610 |
611 | //
612 | // Public Functions
613 | //
614 |
615 | double libcluster::learnMCM (
616 | const vMatrixXd& W,
617 | const vvMatrixXd& X,
618 | vMatrixXd& qY,
619 | vvMatrixXd& qZ,
620 | vector& weights_j,
621 | vector& weights_t,
622 | vector& clusters_t,
623 | vector& clusters_k,
624 | const double prior_t,
625 | const double prior_k,
626 | const unsigned int maxT,
627 | const int maxK,
628 | const bool verbose,
629 | const unsigned int nthreads
630 | )
631 | {
632 |
633 | if (verbose == true)
634 | cout << "Learning MCM..." << endl;
635 |
636 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
637 | double F = mcluster(W, X, qY, qZ,
638 | weights_j, weights_t, clusters_t, clusters_k, prior_t, prior_k,
639 | maxT, maxK, verbose, nthreads);
640 |
641 | return F;
642 | }
643 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/probutils.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include "probutils.h"
22 | #include
23 |
24 |
25 | //
26 | // Namespaces
27 | //
28 |
29 |
30 | using namespace std;
31 | using namespace Eigen;
32 |
33 |
34 | //
35 | // Local Constants
36 | //
37 |
38 |
39 | const double EIGCONTHRESH = 1.0e-8f;
40 | const int MAXITER = 100;
41 |
42 |
43 | //
44 | // Public Functions
45 | //
46 |
47 |
48 | RowVectorXd probutils::mean (const MatrixXd& X)
49 | {
50 | return X.colwise().sum()/X.rows();
51 | }
52 |
53 |
54 | RowVectorXd probutils::mean (const vector& X)
55 | {
56 | const int J = X.size(),
57 | D = X[0].cols();
58 | int N = 0;
59 | RowVectorXd mean = RowVectorXd::Zero(D);
60 |
61 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
62 | {
63 | if (X[j].cols() != D)
64 | throw invalid_argument("X dimensions are inconsistent between groups!");
65 |
66 | mean += X[j].colwise().sum();
67 | N += X[j].rows();
68 | }
69 | return mean / N;
70 | }
71 |
72 |
73 | RowVectorXd probutils::stdev (const MatrixXd& X)
74 | {
75 | RowVectorXd meanX = mean(X);
76 | return ((X.rowwise() - meanX).array().square().colwise().sum()
77 | / (X.rows()-1)).sqrt();
78 | }
79 |
80 |
81 | MatrixXd probutils::cov (const MatrixXd& X)
82 | {
83 | if (X.rows() <= 1)
84 | throw invalid_argument("Insufficient no. of observations.");
85 |
86 | MatrixXd X_mu = X.rowwise() - probutils::mean(X); // X - mu
87 | return (X_mu.transpose()*X_mu)/(X.rows()-1); // (X-mu)'*(X-mu)/(N-1)
88 | }
89 |
90 |
91 | MatrixXd probutils::cov (const vector& X)
92 | {
93 | const int J = X.size(),
94 | D = X[0].cols();
95 | int N = 0;
96 | const RowVectorXd mean = probutils::mean(X);
97 | MatrixXd cov = MatrixXd::Zero(D, D),
98 | X_mu;
99 |
100 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
101 | {
102 | if (X[j].rows() <= 1)
103 | throw invalid_argument("Insufficient no. of observations.");
104 | X_mu = X[j].rowwise() - mean;
105 | N += X[j].rows();
106 | cov.noalias() += (X_mu.transpose() * X_mu); // (X_j-mu)'*(X_j-mu)
107 | }
108 |
109 | return cov / (N-1);
110 | }
111 |
112 |
113 | VectorXd probutils::mahaldist (
114 | const MatrixXd& X,
115 | const RowVectorXd& mu,
116 | const MatrixXd& A
117 | )
118 | {
119 | // Check for same number of dimensions, D
120 | if((X.cols() != mu.cols()) || (X.cols() != A.cols()))
121 | throw invalid_argument("Arguments do not have the same dimensionality");
122 |
123 | // Check if A is square
124 | if (A.rows() != A.cols())
125 | throw invalid_argument("Matrix A must be square!");
126 |
127 | // Decompose A
128 | LDLT Aldl(A);
129 |
130 | // Check if A is PD
131 | if ((Aldl.vectorD().array() <= 0).any() == true)
132 | throw invalid_argument("Matrix A is not positive definite");
133 |
134 | // Do the Mahalanobis distance for each sample (N times)
135 | MatrixXd X_mu = (X.rowwise() - mu).transpose();
136 | return ((X_mu.array() * (Aldl.solve(X_mu)).array())
137 | .colwise().sum()).transpose();
138 | }
139 |
140 |
141 | VectorXd probutils::logsumexp (const MatrixXd& X)
142 | {
143 | const VectorXd mx = X.rowwise().maxCoeff(); // Get max of each row
144 |
145 | // Perform the sum(exp(x - mx)) part
146 | ArrayXd se = ((X.colwise() - mx).array().exp()).rowwise().sum();
147 |
148 | // return total log(sum(exp(x))) - hoping for return value optimisation
149 | return (se.log()).matrix() + mx;
150 | }
151 |
152 |
153 | double probutils::eigpower (const MatrixXd& A, VectorXd& eigvec)
154 | {
155 | // Check if A is square
156 | if (A.rows() != A.cols())
157 | throw invalid_argument("Matrix A must be square!");
158 |
159 | // Check if A is a scalar
160 | if (A.rows() == 1)
161 | {
162 | eigvec.setOnes(1);
163 | return A(0,0);
164 | }
165 |
166 | // Initialise working vectors
167 | VectorXd v = VectorXd::LinSpaced(A.rows(), -1, 1);
168 | VectorXd oeigvec(A.rows());
169 |
170 | // Initialise eigenvalue and eigenvectors etc
171 | double eigval = v.norm();
172 | double vdist = numeric_limits::infinity();
173 | eigvec = v/eigval;
174 |
175 | // Loop until eigenvector converges or we reach max iterations
176 | for (int i=0; (vdist>EIGCONTHRESH) && (i.
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include
22 | #include "libcluster.h"
23 | #include "probutils.h"
24 | #include "comutils.h"
25 |
26 |
27 | //
28 | // Namespaces
29 | //
30 |
31 | using namespace std;
32 | using namespace Eigen;
33 | using namespace probutils;
34 | using namespace distributions;
35 | using namespace comutils;
36 | using namespace libcluster;
37 |
38 |
39 | //
40 | // Variational Bayes Private Functions
41 | //
42 |
43 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for weights in each group.
44 | *
45 | * mutable: Top-level cluster assignment probabilities, qYj
46 | * returns: The complete-data free energy, Y and Y+Z dep. terms, for group j.
47 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
48 | */
49 | template double vbeY (
50 | const vMatrixXd& qZj, // Cluster assignments for group j
51 | const WJ& weightsj, // Group top-level cluster weights
52 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
53 | MatrixXd& qYj // Top-level cluster assignments for group j
54 | )
55 | {
56 | const unsigned int T = weights_t.size(),
57 | Ij = qZj.size(),
58 | K = qZj[0].cols();
59 |
60 | // Get log marginal weight likelihoods
61 | const ArrayXd E_logwj = weightsj.Elogweight();
62 |
63 | MatrixXd Njik(Ij, K), logqYj(Ij, T);
64 | ArrayXXd qZjiLike(Ij, T);
65 |
66 | // Get bottom-level cluster counts per top-level cluster
67 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < Ij; ++i)
68 | Njik.row(i) = qZj[i].colwise().sum();
69 |
70 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs
71 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
72 | {
73 | qZjiLike.col(t) = Njik * weights_t[t].Elogweight().matrix();
74 | logqYj.col(t) = E_logwj(t) + qZjiLike.col(t);
75 | }
76 |
77 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
78 | VectorXd logZyj = logsumexp(logqYj);
79 |
80 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities
81 | qYj = (logqYj.colwise() - logZyj).array().exp().matrix();
82 |
83 | return ((qYj.array() * qZjiLike).rowwise().sum() - logZyj.array()).sum();
84 | }
85 |
86 |
87 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for clusters in each "document"
88 | *
89 | * mutable: Bottom-level cluster assignment probabilities, qZji
90 | * returns: The complete-data free energy, Z dep. terms, for group j.
91 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
92 | */
93 | template double vbeZ (
94 | const MatrixXd& Xji, // Observations in i in group j
95 | const RowVectorXd& qYji, // Top-level cluster assignment of this doc
96 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
97 | const vector& clusters, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
98 | MatrixXd& qZji // Observation to cluster assignments
99 | )
100 | {
101 | const int K = clusters.size(),
102 | Nji = Xji.rows(),
103 | T = weights_t.size();
104 |
105 | // Make top-level cluster global weights from weighted label parameters
106 | RowVectorXd E_logqYljt = RowVectorXd::Zero(K);
107 |
108 | for (int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
109 | E_logqYljt.noalias() += qYji(t) * weights_t[t].Elogweight().matrix();
110 |
111 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs
112 | MatrixXd logqZji = MatrixXd::Zero(Nji, K);
113 |
114 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
115 | logqZji.col(k) = E_logqYljt(k) + clusters[k].Eloglike(Xji).array();
116 |
117 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
118 | const VectorXd logZzji = logsumexp(logqZji);
119 |
120 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities
121 | qZji = (logqZji.colwise() - logZzji).array().exp().matrix();
122 |
123 | return -logZzji.sum();
124 | }
125 |
126 |
127 | /* Calculates the free energy lower bound for the model parameter distributions.
128 | *
129 | * returns: the free energy of the model
130 | */
131 | template double fenergy (
132 | const vector& weights_j, // Group top-level cluster weights
133 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
134 | const vector& clusters, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
135 | const double Fyz, // Free energy Y and Z+Y terms
136 | const double Fz // Free energy Z terms
137 | )
138 | {
139 | const int T = weights_t.size(),
140 | K = clusters.size(),
141 | J = weights_j.size();
142 |
143 | // Class parameter free energy
144 | double Fc = 0;
145 | for (int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
146 | Fc += weights_t[t].fenergy();
147 |
148 | // Cluster parameter free energy
149 | double Fk = 0;
150 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
151 | Fk += clusters[k].fenergy();
152 |
153 | // Weight parameter free energy
154 | double Fw = 0;
155 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
156 | Fw += weights_j[j].fenergy();
157 |
158 | return Fw + Fc + Fk + Fyz + Fz;
159 | }
160 |
161 |
162 | /* Variational Bayes EM.
163 | *
164 | * returns: Free energy of the whole model.
165 | * mutable: the bottom-level cluster indicators, qZ
166 | * mutable: the top-level cluster indicators, qY
167 | * mutable: model parameters weights_j, weights_t, clusters
168 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
169 | * throws: runtime_error if there is a negative free energy.
170 | */
171 | template double vbem (
172 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Observations JxIjx[NjixD]
173 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Observations to cluster assigns JxIjx[NjixK]
174 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Indicator to label assignments Jx[IjxT]
175 | vector& weights_j, // Group weight distributions
176 | vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster distributions
177 | vector& clusters, // Bottom-level cluster Distributions
178 | const double prior_t, // Prior value top-level cluster dists.
179 | const double prior_k, // Prior value bottom-level cluster dists.
180 | const int maxit = -1, // Max VBEM iterations (-1 = no max, default)
181 | const bool verbose = false // Verbose output (default false)
182 | )
183 | {
184 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
185 | K = qZ[0][0].cols(),
186 | T = qY[0].cols();
187 |
188 | // Construct (empty) parameters
189 | weights_j.resize(J, WJ());
190 | weights_t.resize(T, WT(prior_t));
191 | clusters.resize(K, C(prior_k, X[0][0].cols()));
192 |
193 | // Other loop variables for initialisation
194 | int it = 0;
195 | double F = numeric_limits::max(), Fold;
196 |
197 | do
198 | {
199 | Fold = F;
200 |
201 | MatrixXd Ntk = MatrixXd::Zero(T, K); // Clear Sufficient Stats
202 |
203 | // VBM for top-level cluster weights
204 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
205 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
206 | {
207 | for(unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
208 | {
209 | MatrixXd Ntkji = qY[j].row(i).transpose() * qZ[j][i].colwise().sum();
210 | #pragma omp critical
211 | Ntk += Ntkji;
212 | }
213 |
214 | weights_j[j].update(qY[j].colwise().sum());
215 | }
216 |
217 | // VBM for top-level cluster parameters
218 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
219 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
220 | weights_t[t].update(Ntk.row(t)); // Weighted multinomials.
221 |
222 | // VBM for bottom-level cluster parameters
223 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
224 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
225 | {
226 | clusters[k].clearobs();
227 |
228 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
229 | for(unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
230 | clusters[k].addobs(qZ[j][i].col(k), X[j][i]);
231 |
232 | clusters[k].update();
233 | }
234 |
235 | double Fz = 0, Fyz = 0;
236 |
237 | // VBE for top-level cluster indicators
238 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fyz)
239 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
240 | Fyz += vbeY(qZ[j], weights_j[j], weights_t, qY[j]);
241 |
242 | // VBE for bottom-level cluster indicators
243 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
244 | {
245 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fz)
246 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
247 | Fz += vbeZ(X[j][i], qY[j].row(i), weights_t, clusters, qZ[j][i]);
248 | }
249 |
250 | // Calculate free energy of model
251 | F = fenergy(weights_j, weights_t, clusters, Fyz, Fz);
252 |
253 | // Check bad free energy step
254 | if ((F-Fold)/abs(Fold) > libcluster::FENGYDEL)
255 | throw runtime_error("Free energy increase!");
256 |
257 | if (verbose == true) // Notify iteration
258 | cout << '-' << flush;
259 | }
260 | while ( (abs((Fold-F)/Fold) > libcluster::CONVERGE)
261 | && ( (++it < maxit) || (maxit < 0) ) );
262 |
263 | return F;
264 | }
265 |
266 |
267 | //
268 | // Model Selection and Heuristics Private Functions
269 | //
270 |
271 | /* Search in a greedy fashion for a mixture split that lowers model free
272 | * energy, or return false. An attempt is made at looking for good, untried,
273 | * split candidates first, as soon as a split canditate is found that lowers
274 | * model F, it is returned. This may not be the "best" split, but it is
275 | * certainly faster than an exhaustive search for the "best" split.
276 | *
277 | * returns: true if a split was found, false if no splits can be found
278 | * mutable: qZ is augmented with a new split if one is found, otherwise left
279 | * mutable: qY is updated if a new split if one is found, otherwise left
280 | * mutable tally is a tally of times a cluster has been unsuccessfully split
281 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions
282 | * throws: runtime_error from its internal VBEM calls
283 | */
284 | template bool split_gr (
285 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Observations
286 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
287 | const double prior_t, // Prior value for top-level clusters
288 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level cluster labels qY
289 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level Cluster labels qZ
290 | vector& tally, // Count of unsuccessful splits
291 | const double F, // Current model free energy
292 | const int maxK, // max number of (bottom) clusters
293 | const bool verbose // Verbose output
294 | )
295 | {
296 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
297 | K = clusters.size();
298 |
299 | // Check if we have reached the max number of clusters
300 | if ( ((signed) K >= maxK) && (maxK >= 0) )
301 | return false;
302 |
303 | // Split order chooser and bottom-level cluster parameters
304 | tally.resize(K, 0); // Make sure tally is the right size
305 | vector ord(K);
306 |
307 | // Get cluster parameters and their free energy
308 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
309 | {
310 | ord[k].k = k;
311 | ord[k].tally = tally[k];
312 | ord[k].Fk = clusters[k].fenergy();
313 | }
314 |
315 | // Get bottom-level cluster likelihoods
316 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
317 | {
318 | // Add in cluster log-likelihood, weighted by global responsability
319 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
320 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
321 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
322 | {
323 | double LL = qZ[j][i].col(k).dot(clusters[k].Eloglike(X[j][i]));
324 |
325 | #pragma omp atomic
326 | ord[k].Fk -= LL;
327 | }
328 | }
329 |
330 | // Sort clusters by split tally, then free energy contributions
331 | sort(ord.begin(), ord.end(), greedcomp);
332 |
333 | // Pre allocate big objects for loops (this makes a runtime difference)
334 | vector< vector > mapidx(J);
335 | vMatrixXd qYref(J);
336 | vvMatrixXd qZref(J), qZaug(J), Xk(J);
337 |
338 | // Loop through each potential cluster in order and split it
339 | for (vector::iterator ko = ord.begin(); ko < ord.end(); ++ko)
340 | {
341 | const int k = ko->k;
342 |
343 | ++tally[k]; // increase this cluster's unsuccessful split tally by default
344 |
345 | // Don't waste time with clusters that can't really be split min (2:2)
346 | if (clusters[k].getN() < 4)
347 | continue;
348 |
349 | // Now split observations and qZ.
350 | int scount = 0, Mtot = 0;
351 |
352 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
353 | {
354 | mapidx[j].resize(X[j].size());
355 | qZref[j].resize(X[j].size());
356 | qZaug[j].resize(X[j].size());
357 | Xk[j].resize(X[j].size());
358 | qYref[j].setOnes(X[j].size(), 1);
359 |
360 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Mtot, scount)
361 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
362 | {
363 | // Make COPY of the observations with only relevant data points, p > 0.5
364 | mapidx[j][i] = partobs(X[j][i], (qZ[j][i].col(k).array() > 0.5),
365 | Xk[j][i]);
366 | Mtot += Xk[j][i].rows();
367 |
368 | // Initial cluster split
369 | ArrayXb splitk = clusters[k].splitobs(Xk[j][i]);
370 | qZref[j][i].setZero(Xk[j][i].rows(), 2);
371 | qZref[j][i].col(0) = (splitk == true).cast();
372 | qZref[j][i].col(1) = (splitk == false).cast();
373 |
374 | // keep a track of number of splits
375 | scount += splitk.count();
376 | }
377 | }
378 |
379 | // Don't waste time with clusters that haven't been split sufficiently
380 | if ( (scount < 2) || (scount > (Mtot-2)) )
381 | continue;
382 |
383 | // Refine the split
384 | vector wspl;
385 | vector lspl;
386 | vector cspl;
387 | vbem(Xk, qZref, qYref, wspl, lspl, cspl, prior_t,
388 | clusters[0].getprior(), SPLITITER);
389 |
390 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
391 | continue;
392 |
393 | // Map the refined splits back to original whole-data problem
394 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
395 | {
396 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
397 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
398 | qZaug[j][i] = auglabels(k, mapidx[j][i],
399 | (qZref[j][i].col(1).array() > 0.5), qZ[j][i]);
400 | }
401 |
402 | // Calculate free energy of this split with ALL data (and refine a bit)
403 | vMatrixXd qYaug = qY; // Copy :-(
404 | double Fs = vbem(X, qZaug, qYaug, wspl, lspl, cspl, prior_t,
405 | clusters[0].getprior(), 1);
406 |
407 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
408 | continue;
409 |
410 | // Only notify here of split candidates
411 | if (verbose == true)
412 | cout << '=' << flush;
413 |
414 | // Test whether this cluster split is a keeper
415 | if ( (Fs < F) && (abs((F-Fs)/F) > CONVERGE) )
416 | {
417 | qY = qYaug;
418 | qZ = qZaug;
419 | tally[k] = 0; // Reset tally if successfully split
420 | return true;
421 | }
422 | }
423 |
424 | // Failed to find splits
425 | return false;
426 | }
427 |
428 | /* Find and remove all empty top-level clusters.
429 | *
430 | * returns: true if any clusters have been deleted, false if all are kept.
431 | * mutable: qY may have columns deleted if there are empty weights found.
432 | * mutable: weights_t if there are empty top-level clusters found.
433 | */
434 | template bool prune_clusters_t (
435 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Probabilities qY
436 | vector& weights_t, // weights distributions
437 | bool verbose = false // print status
438 | )
439 | {
440 | const unsigned int T = weights_t.size(),
441 | J = qY.size();
442 |
443 | // Look for empty clusters
444 | ArrayXd Nt(T);
445 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
446 | Nt(t) = weights_t[t].getNk().sum();
447 |
448 | // Find location of empty and full clusters
449 | ArrayXi eidx, fidx;
450 | arrfind(Nt.array() < 1, eidx, fidx);
451 | const unsigned int nempty = eidx.size();
452 |
453 | // If everything is not empty, return false
454 | if (nempty == 0)
455 | return false;
456 |
457 | if (verbose == true)
458 | cout << '*' << flush;
459 |
460 | // Delete empty cluster suff. stats.
461 | for (int i = (nempty - 1); i >= 0; --i)
462 | weights_t.erase(weights_t.begin() + eidx(i));
463 |
464 | // Delete empty cluster indicators by copying only full indicators
465 | const unsigned int newT = fidx.size();
466 | vMatrixXd newqY(J);
467 |
468 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
469 | {
470 | newqY[j].setZero(qY[j].rows(), newT);
471 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < newT; ++t)
472 | newqY[j].col(t) = qY[j].col(fidx(t));
473 | }
474 |
475 | qY = newqY;
476 |
477 | return true;
478 | }
479 |
480 |
481 | /* The model selection algorithm
482 | *
483 | * returns: Free energy of the final model
484 | * mutable: qY the probabilistic top-level cluster assignments
485 | * mutable: qZ the probabilistic observation to bottom-level cluster assigns.
486 | * mutable: the top-level cluster weights and parameters.
487 | * mutable: the bottom-level cluster weights and parameters.
488 | * throws: invalid_argument from other functions.
489 | * throws: runtime_error if free energy increases.
490 | */
491 | template double scluster (
492 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Observations
493 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level cluster assignments
494 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level cluster assignments
495 | vector& weights_j, // Group weight distributions
496 | vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster distributions
497 | vector& clusters, // Bottom-level cluster Distributions
498 | const double prior_t, // Prior value for top-level cluster dists.
499 | const double prior_k, // Prior value for bottom-level cluster dists.
500 | const unsigned int maxT, // Truncation level for number of weights
501 | const int maxK, // max number of (bottom) clusters
502 | const bool verbose, // Verbose output
503 | const unsigned int nthreads // Number of threads for OpenMP to use
504 | )
505 | {
506 | if (nthreads < 1)
507 | throw invalid_argument("Must specify at least one thread for execution!");
508 | omp_set_num_threads(nthreads);
509 |
510 | const unsigned int J = X.size();
511 | unsigned int Itot = 0;
512 |
513 | // Randomly initialise qY and initialise qZ to ones
514 | qY.resize(J);
515 | qZ.resize(J);
516 |
517 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
518 | {
519 | const unsigned int Ij = X[j].size();
520 |
521 | ArrayXXd randm = (ArrayXXd::Random(Ij, maxT)).abs();
522 | ArrayXd norm = randm.rowwise().sum();
523 | qY[j] = (randm.log().colwise() - norm.log()).exp();
524 |
525 | qZ[j].resize(Ij);
526 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < Ij; ++i)
527 | qZ[j][i].setOnes(X[j][i].rows(), 1);
528 |
529 | Itot += Ij;
530 | }
531 |
532 | // Some input argument checking
533 | if (maxT > Itot)
534 | throw invalid_argument("maxT must be less than the number of documents of"
535 | "X!");
536 |
537 | // Initialise free energy and other loop variables
538 | bool issplit = true, emptyclasses = true;
539 | double F = 0;
540 | vector tally;
541 |
542 | // Main loop
543 | while ((issplit == true) || (emptyclasses == true))
544 | {
545 | // Variational Bayes
546 | F = vbem(X, qZ, qY, weights_j, weights_t, clusters, prior_t,
547 | prior_k, -1, verbose);
548 |
549 | // Start model search heuristics
550 | if (verbose == true)
551 | cout << '<' << flush; // Notify start search
552 |
553 | if (issplit == false) // Remove any empty weights
554 | emptyclasses = prune_clusters_t(qY, weights_t, verbose);
555 | else // Search for best split, augment qZ if found one
556 | issplit = split_gr(X, clusters, prior_t, qY, qZ, tally, F, maxK,
557 | verbose);
558 |
559 | if (verbose == true)
560 | cout << '>' << endl; // Notify end search
561 | }
562 |
563 | // Print finished notification if verbose
564 | if (verbose == true)
565 | {
566 | cout << "Finished!" << endl;
567 | cout << "Number of top level clusters = " << weights_t.size();
568 | cout << ", and bottom level clusters = " << clusters.size() << endl;
569 | cout << "Free energy = " << F << endl;
570 | }
571 |
572 | return F;
573 | }
574 |
575 |
576 | //
577 | // Public Functions
578 | //
579 |
580 | double libcluster::learnSCM (
581 | const vvMatrixXd& X,
582 | vMatrixXd& qY,
583 | vvMatrixXd& qZ,
584 | vector& weights_j,
585 | vector& weights_t,
586 | vector& clusters,
587 | const double dirprior,
588 | const double gausprior,
589 | const unsigned int maxT,
590 | const int maxK,
591 | const bool verbose,
592 | const unsigned int nthreads
593 | )
594 | {
595 |
596 | if (verbose == true)
597 | cout << "Learning SCM..." << endl;
598 |
599 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
600 | double F = scluster(X, qY, qZ,
601 | weights_j, weights_t, clusters, dirprior, gausprior, maxT,
602 | maxK, verbose, nthreads);
603 |
604 | return F;
605 | }
606 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/CMakeLists.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Test executable build instructions
2 |
3 | # Make Cluster models batch test executable (test VDP and GMC)
4 | add_executable(cluster_test
5 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/cluster_test.cpp
6 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/testdata.h
7 | )
8 |
9 | target_link_libraries(cluster_test ${PROJECT_NAME})
10 |
11 | # Make Topic models batch test executable
12 | add_executable(scluster_test
13 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/scluster_test.cpp
14 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/testdata.h
15 | )
16 |
17 | target_link_libraries(scluster_test ${PROJECT_NAME})
18 |
19 | # Make Topic models batch test executable
20 | add_executable(mcluster_test
21 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/mcluster_test.cpp
22 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/testdata.h
23 | )
24 |
25 | target_link_libraries(mcluster_test ${PROJECT_NAME})
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/cluster_test.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include "libcluster.h"
22 | #include "distributions.h"
23 | #include "testdata.h"
24 |
25 |
26 | //
27 | // Namespaces
28 | //
29 |
30 |
31 | using namespace std;
32 | using namespace Eigen;
33 | using namespace libcluster;
34 | using namespace distributions;
35 |
36 |
37 | // Main
38 | int main()
39 | {
40 |
41 | // Populate test data from testdata.h
42 | MatrixXd Xcat;
43 | vMatrixXd X;
44 | makeXdata(Xcat, X);
45 |
46 | // GMC
47 | vector weights;
48 | vector
40 |
41 |
42 | An example of using the MCM to simultaneously cluster images and objects within
43 | images for unsupervised scene understanding. See [4 - 6] for more information.
44 |
45 | * * *
46 |
47 |
48 | TABLE OF CONTENTS
49 | -----------------
50 |
51 | * [Dependencies](#dependencies)
52 |
53 | * [Install Instructions](#install-instructions)
54 |
55 | * [C++ Interface](#c-interface)
56 |
57 | * [Python Interface](#python-interface)
58 |
59 | * [General Usability Tips](#general-usability-tips)
60 |
61 | * [References and Citing](#references-and-citing)
62 |
63 |
64 | * * *
65 |
66 |
67 | DEPENDENCIES
68 | ------------
69 |
70 | - Eigen version 3.0 or greater
71 | - Boost version 1.4.x or greater and devel packages (special math functions)
72 | - OpenMP, comes default with most compilers (may need a special version of
73 | [LLVM](http://openmp.llvm.org/)).
74 | - CMake
75 |
76 | For the python interface:
77 |
78 | - Python 2 or 3
79 | - Boost python and boost python devel packages (make sure you have version 2
80 | or 3 for the relevant version of python)
81 | - Numpy (tested with v1.7)
82 |
83 |
84 | INSTALL INSTRUCTIONS
85 | --------------------
86 |
87 | *For Linux and OS X -- I've never tried to build on Windows.*
88 |
89 | To build libcluster:
90 |
91 | 1. Make sure you have CMake installed, and Eigen and Boost preferably in the
92 | usual locations:
93 |
94 | /usr/local/include/eigen3/ or /usr/include/eigen3
95 | /usr/local/include/boost or /usr/include/boost
96 |
97 | 2. Make a build directory where you checked out the source if it does not
98 | already exist, then change into this directory,
99 |
100 | cd {where you checked out the source}
101 | mkdir build
102 | cd build
103 |
104 | 3. To build libcluster, run the following from the build directory:
105 |
106 | cmake ..
107 | make
108 | sudo make install
109 |
110 | This installs:
111 |
112 | libcluster.h /usr/local/include
113 | distributions.h /usr/local/include
114 | probutils.h /usr/local/include
115 | libcluster.* /usr/local/lib (* this is either .dylib or .so)
116 |
117 | 4. Use the doxyfile in {where you checked out the source}/doc to make the
118 | documentation with doxygen:
119 |
120 | doxygen Doxyfile
121 |
122 | **NOTE**: There are few options you can change using ccmake (or the cmake gui),
123 | these include:
124 |
125 | - `BUILD_EXHAUST_SPLIT` (toggle `ON` or `OFF`, default `OFF`) This uses the
126 | exhaustive cluster split heuristic [1, 2] instead of the greedy heuristic [4,
127 | 5] for all algorithms but the SCM and MCM. The greedy heuristic is MUCH
128 | faster, but does give different results. I have yet to determine whether it
129 | is actually worse than the exhaustive method (if it is, it is not by much).
130 | The SCM and MCM only use the greedy split heuristic at this stage.
131 |
132 | - `BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE` (toggle `ON` or `OFF`, default `OFF`) Build the
133 | python interface. This requires boost python, and also uses row-major storage
134 | to be compatible with python.
135 |
136 | - `BUILD_USE_PYTHON3` (toggle `ON` or `OFF`, default `ON`) Use python 3 or 2 to
137 | build the python interface. Make sure you have the relevant python and boost
138 | python libraries installed!
139 |
140 | - `CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX` (default `/usr/local`) The default prefix for
141 | installing the library and binaries.
142 |
143 | - `EIGEN_INCLUDE_DIRS` (default `/usr/include/eigen3`) Where to look for the
144 | Eigen matrix library.
145 |
146 | **NOTE**: On linux you may have to run `sudo ldconfig` before the system can
147 | find libcluster.so (or just reboot).
148 |
149 | **NOTE**: On Red-Hat based systems, `/usr/local/lib` is not checked unless
150 | added to `/etc/ld.so.conf`! This may lead to "cannot find libcluster.so"
151 | errors.
152 |
153 |
154 | C++ INTERFACE
155 | -------------
156 |
157 | All of the interfaces to this library are documented in `include/libcluster.h`.
158 | There are far too many algorithms to go into here, and I *strongly* recommend
159 | looking at the `test/` directory for example usage, specifically,
160 |
161 | * `cluster_test.cpp` for the group mixture models (GMC etc)
162 | * `scluster_test.cpp` for the SCM
163 | * `mcluster_test.cpp` for the MCM
164 |
165 | Here is an example for regular mixture models, such as the BGMM, which simply
166 | clusters some test data and prints the resulting posterior parameters to the
167 | terminal,
168 |
169 | ```C++
170 |
171 | #include "libcluster.h"
172 | #include "distributions.h"
173 | #include "testdata.h"
174 |
175 |
176 | //
177 | // Namespaces
178 | //
179 |
180 | using namespace std;
181 | using namespace Eigen;
182 | using namespace libcluster;
183 | using namespace distributions;
184 |
185 |
186 | //
187 | // Functions
188 | //
189 |
190 | // Main
191 | int main()
192 | {
193 |
194 | // Populate test data from testdata.h
195 | MatrixXd Xcat;
196 | vMatrixXd X;
197 | makeXdata(Xcat, X);
198 |
199 | // Set up the inputs for the BGMM
200 | Dirichlet weights;
201 | vector clusters;
202 | MatrixXd qZ;
203 |
204 | // Learn the BGMM
205 | double F = learnBGMM(Xcat, qZ, weights, clusters, PRIORVAL, true);
206 |
207 | // Print the posterior parameters
208 | cout << endl << "Cluster Weights:" << endl;
209 | cout << weights.Elogweight().exp().transpose() << endl;
210 |
211 | cout << endl << "Cluster means:" << endl;
212 | for (vector::iterator k=clusters.begin(); k < clusters.end(); ++k)
213 | cout << k->getmean() << endl;
214 |
215 | cout << endl << "Cluster covariances:" << endl;
216 | for (vector::iterator k=clusters.begin(); k < clusters.end(); ++k)
217 | cout << k->getcov() << endl << endl;
218 |
219 | return 0;
220 | }
221 |
222 | ```
223 |
224 | Note that `distributions.h` has also been included. In fact, all of the
225 | algorithms in `libcluster.h` are just wrappers over a few key functions in
226 | `cluster.cpp`, `scluster.cpp` and `mcluster.cpp` that can take in *arbitrary*
227 | distributions as inputs, and so more algorithms potentially exist than
228 | enumerated in `libcluster.h`. If you want to create different algorithms, or
229 | define more cluster distributions (like categorical) have a look at inheriting
230 | the `WeightDist` and `ClusterDist` base classes in `distributions.h`. Depending
231 | on the distributions you use, you may also have to come up with a way to
232 | 'split' clusters. Otherwise you can create an algorithm with a random initial
233 | set of clusters like the MCM at the top level, which then variational Bayes
234 | will prune.
235 |
236 | There are also some generally useful functions included in `probutils.h` when
237 | dealing with mixture models (such as the log-sum-exp trick).
238 |
239 |
240 | PYTHON INTERFACE
241 | ----------------
242 |
243 | ### Installation
244 |
245 | Easy, follow the normal build instructions up to step (4) (if you haven't
246 | already), then from the build directory:
247 |
248 | cmake ..
249 | ccmake .
250 |
251 | Make sure `BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE` is `ON`
252 |
253 | make
254 | sudo make install
255 |
256 | This installs all the same files as step (4), as well as `libclusterpy.so` to
257 | your python staging directory, so it should be on your python path. I.e. just
258 | run
259 |
260 | ```python
261 | import libclusterpy
262 | ```
263 |
264 | **Trouble Shooting**:
265 |
266 | On Fedora 20/21 I have to append `/usr/local/lib` to the file `/etc/ld.so.conf`
267 | to make python find the compiled shared object.
268 |
269 |
270 | ### Usage
271 |
272 | Import the library as
273 |
274 | ```python
275 | import numpy as np
276 | import libclusterpy as lc
277 | ```
278 |
279 | Then for the mixture models, assuming `X` is a numpy array where `X.shape` is
280 | `(N, D)` -- `N` being the number of samples, and `D` being the dimension of
281 | each sample,
282 |
283 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnBGMM(X)
284 |
285 | where `f` is the final free energy value, `qZ` is a distribution over all of
286 | the cluster labels where `qZ.shape` is `(N, K)` and `K` is the number of
287 | clusters (each row of `qZ` sums to 1). Then `w`, `mu` and `cov` the expected
288 | posterior cluster parameters (see the documentation for details. Alternatively,
289 | tuning the `prior` argument can be used to change the number of clusters found,
290 |
291 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnBGMM(X, prior=0.1)
292 |
293 | This interface is common to all of the simple mixture models (i.e. VDP, BGMM
294 | etc).
295 |
296 | For the group mixture models (GMC, SGMC etc) `X` is a *list* of arrays of size
297 | `(Nj, D)` (indexed by j), one for each group/album, `X = [X_1, X_2, ...]`. The
298 | returned `qZ` and `w` are also lists of arrays, one for each group, e.g.,
299 |
300 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnSGMC(X)
301 |
302 | The SCM again has a similar interface to the above models, but now `X` is a
303 | *list of lists of arrays*, `X = [[X_11, X_12, ...], [X_21, X_22, ...], ...]`.
304 | This specifically for modelling situations where `X` is a matrix of all of the
305 | features of, for example, `N_ij` segments in image `ij` in album `j`.
306 |
307 | f, qY, qZ, wi, wij, mu, cov = lc.learnSCM(X)
308 |
309 | Where `qY` is a list of arrays of top-level/image cluster probabilities, `qZ`
310 | is a list of lists of arrays of bottom-level/segment cluster probabilities.
311 | `wi` are the mixture weights (list of arrays) corresponding to the `qY` labels,
312 | and `wij` are the weights (list of lists of arrays) corresponding the `qZ`
313 | labels. This has two optional prior inputs, and a cluster truncation level
314 | (max number of clusters) for the top-level/image clusters,
315 |
316 | f, qY, qZ, wi, wij, mu, cov = lc.learnSCM(X, trunc=10, dirprior=1,
317 | gausprior=0.1)
318 |
319 | Where `dirprior` refers to the top-level cluster prior, and `gausprior` the
320 | bottom-level.
321 |
322 | Finally, the MCM has a similar interface to the MCM, but with an extra input,
323 | `W` which is of the same format as the `X` in the GMC-style models, i.e. it is
324 | a list of arrays of top-level or image features, `W = [W_1, W_2, ...]`. The
325 | usage is,
326 |
327 | f, qY, qZ, wi, wij, mu_t, mu_k, cov_t, cov_k = lc.learnMCM(W, X)
328 |
329 | Here `mu_t` and `cov_t` are the top-level posterior cluster parameters -- these
330 | are both lists of `T` cluster parameters (`T` being the number of clusters
331 | found. Similarly `mu_k` and `cov_k` are lists of `K` bottom-level posterior
332 | cluster parameters. Like the SCM, this has a number of optional inputs,
333 |
334 |
335 | f, qY, qZ, wi, wij, mu_t, mu_k, cov_t, cov_k = lc.learnMCM(W, X, trunc=10,
336 | gausprior_t=1,
337 | gausprior_k=0.1)
338 |
339 | Where `gausprior_t` refers to the top-level cluster prior, and `gausprior_k`
340 | the bottom-level.
341 |
342 | Look at the `libclusterpy` docstrings for more help on usage, and the
343 | `testapi.py` script in the `python` directory for more usage examples.
344 |
345 | **NOTE** if you get the following message when importing libclusterpy:
346 |
347 | ImportError: /lib64/libboost_python.so.1.54.0: undefined symbol: PyClass_Type
348 |
349 | Make sure you have `boost-python3` installed!
350 |
351 |
352 | GENERAL USABILITY TIPS
353 | ----------------------
354 |
355 | When verbose mode is activated you will get output that looks something like
356 | this:
357 |
358 | Learning MODEL X...
359 | --------<=>
360 | ---<==>
361 | --------x<=>
362 | --------------<====>
363 | ----<*>
364 | ---<>
365 | Finished!
366 | Number of clusters = 4
367 | Free Energy = 41225
368 |
369 | What this means:
370 |
371 | * `-` iteration of Variational Bayes (VBE and VBM step)
372 | * `<` cluster splitting has started (model selection)
373 | * `=` found a valid candidate split
374 | * `>` chosen candidate split and testing for inclusion into model
375 | * `x` clusters have been deleted because they became devoid of observations
376 | * `*` clusters (image/document clusters) that are empty have been removed.
377 |
378 | For best clustering results, I have found the following tips may help:
379 |
380 | 1. If clustering runs REALLY slowly then it may be because of hyper-threading.
381 | OpenMP will by default use as many cores available to it as possible, this
382 | includes virtual hyper-threading cores. Unfortunately this may result in
383 | large slow-downs, so try only allowing these functions to use a number of
384 | threads less than or equal to the number of PHYSICAL cores on your machine.
385 |
386 | 2. Garbage in = garbage out. Make sure your assumptions about the data are
387 | reasonable for the type of cluster distribution you use. For instance, if
388 | your observations do not resemble a mixture of Gaussians in feature space,
389 | then it may not be appropriate to use Gaussian clusters.
390 |
391 | 3. For Gaussian clusters: standardising or whitening your data may help, i.e.
392 |
393 | if X is an NxD matrix of observations you wish to cluster, you may get
394 | better results if you use a standardised version of it, X*,
395 |
396 | X_s = C * ( X - mean(X) ) / std(X)
397 |
398 | where `C` is some constant (optional) and the mean and std are for each
399 | column of X.
400 |
401 | You may obtain even better results by using PCA or ZCA whitening on X
402 | (assuming ZERO MEAN data), using python syntax:
403 |
404 | [U, S, V] = svd(cov(X))
405 | X_w = X.dot(U).dot(diag(1. / sqrt(diag(S)))) # PCA Whitening
406 |
407 | Such that
408 |
409 | cov(X_w) = I_D.
410 |
411 | Also, to get some automatic scaling you can multiply the prior by the
412 | PRINCIPAL eigenvector of `cov(X)` (or `cov(X_s)`, `cov(X_w)`).
413 |
414 | **NOTE**: If you use diagonal covariance Gaussians I STRONGLY recommend PCA
415 | or ZCA whitening your data first, otherwise you may end up with hundreds of
416 | clusters!
417 |
418 | 4. For Exponential clusters: Your observations have to be in the range [0,
419 | inf). The clustering solution may also be sensitive to the prior. I find
420 | usually using a prior value that has the approximate magnitude of your data
421 | or more leads to better convergence.
422 |
423 |
424 | * * *
425 |
426 |
427 | REFERENCES AND CITING
428 | ---------------------
429 |
430 | **[1]** K. Kurihara, M. Welling, and N. Vlassis. Accelerated variational
431 | Dirichlet process mixtures, Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,
432 | vol. 19, p. 761, 2007.
433 |
434 | **[2]** D. M. Steinberg, A. Friedman, O. Pizarro, and S. B. Williams. A
435 | Bayesian nonparametric approach to clustering data from underwater robotic
436 | surveys. In International Symposium on Robotics Research, Flagstaff, AZ, Aug.
437 | 2011.
438 |
439 | **[3]** C. M. Bishop. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Cambridge, UK:
440 | Springer Science+Business Media, 2006.
441 |
442 | **[4]** D. M. Steinberg, O. Pizarro, S. B. Williams. Synergistic Clustering of
443 | Image and Segment Descriptors for Unsupervised Scene Understanding, In
444 | International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, Sydney, NSW, 2013.
445 |
446 | **[5]** D. M. Steinberg, O. Pizarro, S. B. Williams. Hierarchical Bayesian
447 | Models for Unsupervised Scene Understanding. Journal of Computer Vision and
448 | Image Understanding (CVIU). Elsevier, 2014.
449 |
450 | **[6]** D. M. Steinberg, An Unsupervised Approach to Modelling Visual Data, PhD
451 | Thesis, 2013.
452 |
453 | Please consider citing the following if you use this code:
454 |
455 | * VDP: [2, 4, 6]
456 | * BGMM: [5, 6]
457 | * GMC: [6]
458 | * SGMC/GLDA: [4, 5, 6]
459 | * SCM: [5, 6]
460 | * MCM: [4, 5, 6]
461 |
462 | You can find these on my [homepage](http://dsteinberg.github.io/).
463 | Thank you!
464 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/include/distributions.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #ifndef DISTRIBUTIONS_H
22 | #define DISTRIBUTIONS_H
23 |
24 | #include
25 | #include
26 | #include
27 |
28 | //TODO: make all protected variables private and accessed by protected functions
29 | // to improve encapsulation??
30 |
31 | /*! Namespace that implements weight and cluster distributions. */
32 | namespace distributions
33 | {
34 |
35 | //
36 | // Namespace 'symbolic' constants
37 | //
38 |
39 | const double BETAPRIOR = 1.0; //!< beta prior value (Gaussians)
40 | const double NUPRIOR = 1.0; //!< nu prior value (diagonal Gaussians)
41 | const double ALPHA1PRIOR = 1.0; //!< alpha1 prior value (All weight dists)
42 | const double ALPHA2PRIOR = 1.0; //!< alpha2 prior value (SB & Gdir)
43 | const double APRIOR = 1.0; //!< a prior value (Exponential)
44 |
45 |
46 | //
47 | // Useful Typedefs
48 | //
49 |
50 | typedef Eigen::Array ArrayXb; //!< Boolean Array
51 |
52 |
53 | //
54 | // Weight Parameter Distribution classes
55 | //
56 |
57 | /*! \brief To make a new weight class that will work with the algorithm
58 | * templates, your class must have this as the minimum interface.
59 | */
60 | class WeightDist
61 | {
62 | public:
63 |
64 | // WeightDist(), required inherited constructor template
65 |
66 | /*! \brief Update the distribution.
67 | * \param Nk an array of observations counts.
68 | */
69 | virtual void update (const Eigen::ArrayXd& Nk) = 0;
70 |
71 | /*! \brief Evaluate the expectation of the log label weights in the mixtures.
72 | * \returns An array of likelihoods for the labels given the weights
73 | */
74 | virtual const Eigen::ArrayXd& Elogweight () const = 0;
75 |
76 | /*! \brief Get the number of observations contributing to each weight.
77 | * \returns An array the number of observations contributing to each weight.
78 | */
79 | const Eigen::ArrayXd& getNk () const { return this->Nk; }
80 |
81 | /*! \brief Get the free energy contribution of these weights.
82 | * \returns the free energy contribution of these weights
83 | */
84 | virtual double fenergy () const = 0;
85 |
86 | /*! \brief virtual destructor.
87 | */
88 | virtual ~WeightDist() {}
89 |
90 | protected:
91 |
92 | /*! \brief Default constructor to set an empty observation array.
93 | */
94 | WeightDist () : Nk(Eigen::ArrayXd::Zero(1)) {}
95 |
96 | Eigen::ArrayXd Nk; //!< Number of observations making up the weights.
97 | };
98 |
99 |
100 | /*!
101 | * \brief Stick-Breaking (Dirichlet Process) parameter distribution.
102 | */
103 | class StickBreak : public WeightDist
104 | {
105 | public:
106 |
107 | StickBreak ();
108 |
109 | StickBreak (const double concentration);
110 |
111 | void update (const Eigen::ArrayXd& Nk);
112 |
113 | const Eigen::ArrayXd& Elogweight () const { return this->E_logpi; }
114 |
115 | double fenergy () const;
116 |
117 | virtual ~StickBreak () {}
118 |
119 | protected:
120 |
121 | // Prior hyperparameters, expectations etc
122 | double alpha1_p; //!< First prior param \f$ Beta(\alpha_1,\alpha_2) \f$
123 | double alpha2_p; //!< Second prior param \f$ Beta(\alpha_1,\alpha_2) \f$
124 | double F_p; //!< Free energy component dependent on priors only
125 |
126 | // Posterior hyperparameters and expectations
127 | Eigen::ArrayXd alpha1; //!< First posterior param corresp to \f$ \alpha_1 \f$
128 | Eigen::ArrayXd alpha2; //!< Second posterior param corresp to \f$ \alpha_2 \f$
129 | Eigen::ArrayXd E_logv; //!< Stick breaking log expectation
130 | Eigen::ArrayXd E_lognv; //!< Inverse stick breaking log expectation
131 | Eigen::ArrayXd E_logpi; //!< Expected log weights
132 |
133 | // Order tracker
134 | std::vector< std::pair > ordvec; //!< For order specific updates
135 |
136 | private:
137 |
138 | // Do some prior free energy calcs
139 | void priorfcalc (void);
140 | };
141 |
142 |
143 | /*!
144 | * \brief Generalised Dirichlet parameter distribution (truncated stick
145 | * breaking).
146 | */
147 | class GDirichlet : public StickBreak
148 | {
149 | public:
150 |
151 | void update (const Eigen::ArrayXd& Nk);
152 |
153 | double fenergy () const;
154 |
155 | virtual ~GDirichlet () {}
156 |
157 | };
158 |
159 |
160 | /*!
161 | * \brief Dirichlet parameter distribution.
162 | */
163 | class Dirichlet : public WeightDist
164 | {
165 | public:
166 |
167 | Dirichlet ();
168 |
169 | Dirichlet (const double alpha);
170 |
171 | void update (const Eigen::ArrayXd& Nk);
172 |
173 | const Eigen::ArrayXd& Elogweight () const { return this->E_logpi; }
174 |
175 | double fenergy () const;
176 |
177 | virtual ~Dirichlet () {}
178 |
179 | private:
180 |
181 | // Prior hyperparameters, expectations etc
182 | double alpha_p; // Symmetric Dirichlet prior \f$ Dir(\alpha) \f$
183 | double F_p; // Free energy component dependent on priors only
184 |
185 | // Posterior hyperparameters and expectations
186 | Eigen::ArrayXd alpha; // Posterior param corresp to \f$ \alpha \f$
187 | Eigen::ArrayXd E_logpi; // Expected log weights
188 |
189 | };
190 |
191 |
192 | //
193 | // Cluster Parameter Distribution classes
194 | //
195 |
196 | /*! \brief To make a new cluster distribution class that will work with the
197 | * algorithm templates your class must have this as the minimum
198 | * interface.
199 | */
200 | class ClusterDist
201 | {
202 | public:
203 |
204 | /*! \brief Add observations to the cluster without updating the parameters
205 | * (i.e. add to the sufficient statistics)
206 | * \param qZk the observation indicators for this cluster, corresponding to
207 | * X.
208 | * \param X the observations [obs x dims], to add to this cluster according
209 | * to qZk.
210 | */
211 | virtual void addobs (
212 | const Eigen::VectorXd& qZk,
213 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& X
214 | ) = 0;
215 |
216 | /*! \brief Update the cluster parameters from the observations added from
217 | * addobs().
218 | */
219 | virtual void update () = 0;
220 |
221 | /*! \brief Clear the all parameters and observation accumulations from
222 | * addobs().
223 | */
224 | virtual void clearobs () = 0;
225 |
226 | /*! \brief Evaluate the log marginal likelihood of the observations.
227 | * \param X a matrix of observations, [obs x dims].
228 | * \returns An array of likelihoods for the observations given this dist.
229 | */
230 | virtual Eigen::VectorXd Eloglike (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const = 0;
231 |
232 | /*! \brief Get the free energy contribution of these cluster parameters.
233 | * \returns the free energy contribution of these cluster parameters.
234 | */
235 | virtual double fenergy () const = 0;
236 |
237 | /*! \brief Propose a split for the observations given these cluster parameters
238 | * \param X a matrix of observations, [obs x dims], to split.
239 | * \returns a binary array of split assignments.
240 | * \note this needs to consistently split observations between multiple
241 | * subsequent calls, but can change after each update().
242 | */
243 | virtual ArrayXb splitobs (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const = 0;
244 |
245 | /*! \brief Return the number of observations belonging to this cluster.
246 | * \returns the number of observations belonging to this cluster.
247 | */
248 | double getN () const { return this->N; }
249 |
250 | /*! \brief Return the cluster prior value.
251 | * \returns the cluster prior value.
252 | */
253 | double getprior () const { return this->prior; }
254 |
255 | /*! \brief virtual destructor.
256 | */
257 | virtual ~ClusterDist() {}
258 |
259 | protected:
260 |
261 | /*! \brief Constructor that must be called to set the prior and cluster
262 | * dimensionality.
263 | * \param prior the cluster prior.
264 | * \param D the dimensionality of this cluster.
265 | */
266 | ClusterDist (const double prior, const unsigned int D)
267 | : D(D), prior(prior), N(0) {}
268 |
269 | unsigned int D; //!< Dimensionality
270 | double prior; //!< Cluster prior
271 | double N; //!< Number of observations making up this cluster.
272 |
273 | };
274 |
275 |
276 | /*!
277 | * \brief Gaussian-Wishart parameter distribution for full Gaussian clusters.
278 | */
279 | class GaussWish : public ClusterDist
280 | {
281 | public:
282 |
283 | /*! \brief Make a Gaussian-Wishart prior.
284 | *
285 | * \param clustwidth makes the covariance prior \f$ clustwidth \times D
286 | * \times \mathbf{I}_D \f$.
287 | * \param D is the dimensionality of the data
288 | */
289 | GaussWish (const double clustwidth, const unsigned int D);
290 |
291 | void addobs (const Eigen::VectorXd& qZk, const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
292 |
293 | void update ();
294 |
295 | void clearobs ();
296 |
297 | Eigen::VectorXd Eloglike (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
298 |
299 | ArrayXb splitobs (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
300 |
301 | double fenergy () const;
302 |
303 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster mean.
304 | * \returns the expected cluster mean.
305 | */
306 | const Eigen::RowVectorXd& getmean () const { return this->m; }
307 |
308 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster covariance.
309 | * \returns the expected cluster covariance.
310 | */
311 | Eigen::MatrixXd getcov () const { return this->iW/this->nu; }
312 |
313 | virtual ~GaussWish () {}
314 |
315 | private:
316 |
317 | // Prior hyperparameters etc
318 | double nu_p;
319 | double beta_p;
320 | Eigen::RowVectorXd m_p;
321 | Eigen::MatrixXd iW_p;
322 | double logdW_p;
323 | double F_p;
324 |
325 | // Posterior hyperparameters
326 | double nu; // nu, Lambda ~ Wishart(W, nu)
327 | double beta; // beta, mu ~ Normal(m, (beta*Lambda)^-1)
328 | Eigen::RowVectorXd m; // m, mu ~ Normal(m, (beta*Lambda)^-1)
329 | Eigen::MatrixXd iW; // Inverse W, Lambda ~ Wishart(W, nu)
330 | double logdW; // log(det(W))
331 |
332 | // Sufficient Statistics
333 | double N_s;
334 | Eigen::RowVectorXd x_s;
335 | Eigen::MatrixXd xx_s;
336 |
337 | };
338 |
339 |
340 | /*!
341 | * \brief Normal-Gamma parameter distribution for diagonal Gaussian clusters.
342 | */
343 | class NormGamma : public ClusterDist
344 | {
345 | public:
346 |
347 | /*! \brief Make a Normal-Gamma prior.
348 | *
349 | * \param clustwidth makes the covariance prior \f$ clustwidth \times
350 | * \mathbf{I}_D \f$.
351 | * \param D is the dimensionality of the data
352 | */
353 | NormGamma (const double clustwidth, const unsigned int D);
354 |
355 | void addobs (const Eigen::VectorXd& qZk, const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
356 |
357 | void update ();
358 |
359 | void clearobs ();
360 |
361 | Eigen::VectorXd Eloglike (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
362 |
363 | ArrayXb splitobs (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
364 |
365 | double fenergy () const;
366 |
367 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster mean.
368 | * \returns the expected cluster mean.
369 | */
370 | const Eigen::RowVectorXd& getmean () const { return this->m; }
371 |
372 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster covariance.
373 | * \returns the expected cluster covariance (just the diagonal elements).
374 | */
375 | Eigen::RowVectorXd getcov () const { return this->L*this->nu; }
376 |
377 | virtual ~NormGamma () {}
378 |
379 | private:
380 |
381 | // Prior hyperparameters etc
382 | double nu_p;
383 | double beta_p;
384 | Eigen::RowVectorXd m_p;
385 | Eigen::RowVectorXd L_p;
386 | double logL_p;
387 |
388 | // Posterior hyperparameters
389 | double nu;
390 | double beta;
391 | Eigen::RowVectorXd m;
392 | Eigen::RowVectorXd L;
393 | double logL;
394 |
395 | // Sufficient Statistics
396 | double N_s;
397 | Eigen::RowVectorXd x_s;
398 | Eigen::RowVectorXd xx_s;
399 |
400 | };
401 |
402 |
403 | /*!
404 | * \brief Exponential-Gamma parameter distribution for Exponential clusters.
405 | */
406 | class ExpGamma : public ClusterDist
407 | {
408 | public:
409 |
410 | /*! \brief Make a Gamma prior.
411 | *
412 | * \param obsmag is the prior value for b in Gamma(a, b), which works well
413 | * when it is approximately the magnitude of the observation
414 | * dimensions, x_djn.
415 | * \param D is the dimensionality of the data
416 | */
417 | ExpGamma (const double obsmag, const unsigned int D);
418 |
419 | void addobs (const Eigen::VectorXd& qZk, const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
420 |
421 | void update ();
422 |
423 | void clearobs ();
424 |
425 | Eigen::VectorXd Eloglike (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
426 |
427 | ArrayXb splitobs (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X) const;
428 |
429 | double fenergy () const;
430 |
431 | /*! \brief Get the estimated cluster rate parameter, i.e. Exp(E[lambda]),
432 | * where lambda is the rate parameter.
433 | * \returns the expected cluster rate parameter.
434 | */
435 | Eigen::RowVectorXd getrate () { return this->a*this->ib; }
436 |
437 | virtual ~ExpGamma () {}
438 |
439 | private:
440 |
441 | // Prior hyperparameters
442 | double a_p;
443 | double b_p;
444 |
445 | // Posterior hyperparameters etc
446 | double a;
447 | Eigen::RowVectorXd ib; // inverse b
448 | double logb;
449 |
450 | // Sufficient Statistics
451 | double N_s;
452 | Eigen::RowVectorXd x_s;
453 |
454 | };
455 |
456 |
457 | }
458 |
459 | #endif // DISTRIBUTIONS_H
460 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/include/probutils.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #ifndef PROBUTILS_H
22 | #define PROBUTILS_H
23 |
24 | #include
25 | #include
26 | #include
27 |
28 |
29 | //
30 | // Namespaces
31 | //
32 |
33 | /*! \brief Namespace for various linear algebra tools useful for dealing with
34 | * Gaussians and log-probability expressions.
35 | *
36 | * \author Daniel Steinberg
37 | * Australian Centre for Field Robotics
38 | * The University of Sydney
39 | *
40 | * \date 15/02/2011
41 | */
42 | namespace probutils
43 | {
44 |
45 |
46 | //
47 | // Useful Functions
48 | //
49 |
50 | /*! \brief Calculate the column means of a matrix.
51 | *
52 | * \param X an NxD matrix.
53 | * \returns a 1xD row vector of the means of each column of X.
54 | */
55 | Eigen::RowVectorXd mean (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
56 |
57 |
58 | /*! \brief Calculate the column means of a vector of matrices (one mean for
59 | * all data in the matrices).
60 | *
61 | * \param X a vector of N_jxD matrices for j = 1:J.
62 | * \returns a 1xD row vector of the means of each column of X.
63 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if X has inconsistent D between elements.
64 | */
65 | Eigen::RowVectorXd mean (const std::vector& X);
66 |
67 |
68 | /*! \brief Calculate the column standard deviations of a matrix, uses N - 1.
69 | *
70 | * \param X an NxD matrix.
71 | * \returns a 1xD row vector of the standard deviations of each column of X.
72 | */
73 | Eigen::RowVectorXd stdev (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
74 |
75 |
76 | /*! \brief Calculate the covariance of a matrix.
77 | *
78 | * If X is an NxD matrix, then this calculates:
79 | *
80 | * \f[ Cov(X) = \frac{1} {N-1} (X-E[X])^T (X-E[X]) \f]
81 | *
82 | * \param X is a NxD matrix to calculate the covariance of.
83 | * \returns a DxD covariance matrix.
84 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if X is 1xD or less (has one or less
85 | * observations).
86 | */
87 | Eigen::MatrixXd cov (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
88 |
89 |
90 | /*! \brief Calculate the covariance of a vector of matrices (one mean for
91 | * all data in the matrices).
92 | *
93 | * This calculates:
94 | *
95 | * \f[ Cov(X) = \frac{1} {\sum_j N_j-1} \sum_j (X_j-E[X])^T (X_j-E[X]) \f]
96 | *
97 | * \param X is a a vector of N_jxD matrices for j = 1:J.
98 | * \returns a DxD covariance matrix.
99 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if any X_j has one or less observations.
100 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if X has inconsistent D between elements.
101 | */
102 | Eigen::MatrixXd cov (const std::vector& X);
103 |
104 |
105 | /*! \brief Calculate the Mahalanobis distance, (x-mu)' * A^-1 * (x-mu), N
106 | * times.
107 | *
108 | * \param X an NxD matrix of samples/obseravtions.
109 | * \param mu a 1XD vector of means.
110 | * \param A a DxD marix of weights, A must be invertable.
111 | * \returns an Nx1 matrix of distances evaluated for each row of X.
112 | * \throws std::invalid_argument If X, mu and A do not have compatible
113 | * dimensionality, or if A is not PSD.
114 | */
115 | Eigen::VectorXd mahaldist (
116 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& X,
117 | const Eigen::RowVectorXd& mu,
118 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& A
119 | );
120 |
121 |
122 | /*! \brief Perform a log(sum(exp(X))) in a numerically stable fashion.
123 | *
124 | * \param X is a NxK matrix. We wish to sum along the rows (sum out K).
125 | * \returns an Nx1 vector where the log(sum(exp(X))) operation has been
126 | * performed along the rows.
127 | */
128 | Eigen::VectorXd logsumexp (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
129 |
130 |
131 | /*! \brief The eigen power method. Return the principal eigenvalue and
132 | * eigenvector.
133 | *
134 | * \param A is the square DxD matrix to decompose.
135 | * \param eigvec is the Dx1 principal eigenvector (mutable)
136 | * \returns the principal eigenvalue.
137 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if the matrix A is not square
138 | *
139 | */
140 | double eigpower (const Eigen::MatrixXd& A, Eigen::VectorXd& eigvec);
141 |
142 |
143 | /*! \brief Get the log of the determinant of a PSD matrix.
144 | *
145 | * \param A a DxD positive semi-definite matrix.
146 | * \returns log(det(A))
147 | * \throws std::invalid_argument if the matrix A is not square or if it is
148 | * not positive semidefinite.
149 | */
150 | double logdet (const Eigen::MatrixXd& A);
151 |
152 |
153 | /*! \brief Calculate digamma(X) for each element of X.
154 | *
155 | * \param X an NxM matrix
156 | * \returns an NxM matrix for which digamma(X) has been calculated for each
157 | * element
158 | */
159 | Eigen::MatrixXd mxdigamma (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
160 |
161 |
162 | /*! \brief Calculate log(gamma(X)) for each element of X.
163 | *
164 | * \param X an NxM matrix
165 | * \returns an NxM matrix for which log(gamma(X)) has been calculated for
166 | * each element
167 | */
168 | Eigen::MatrixXd mxlgamma (const Eigen::MatrixXd& X);
169 |
170 | }
171 |
172 | #endif // PROBUTILS_H
173 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/CMakeLists.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | if(BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE)
2 |
3 | message(STATUS "Will build the python interface")
4 | if(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
5 | set(PYCMD "python3")
6 | message(STATUS "Will use python 3")
7 | else(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
8 | set(PYCMD "python2")
9 | message(STATUS "Will use python 2")
10 | endif(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
11 |
12 | # Python needs row major matrices (for convenience)
13 | set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -DEIGEN_DEFAULT_TO_ROW_MAJOR")
14 |
15 |
16 | #--------------------------------#
17 | # Includes #
18 | #--------------------------------#
19 |
20 | if(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
21 | find_package(Boost COMPONENTS python3 REQUIRED)
22 | else(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
23 | find_package(Boost COMPONENTS python REQUIRED)
24 | endif(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
25 |
26 | include(${PYTHON_SOURCE_DIR}/FindNumpy.cmake REQUIRED)
27 | include_directories(${NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR})
28 | find_package(PythonLibs REQUIRED)
29 | include_directories(${PYTHON_INCLUDE_DIRS})
30 |
31 |
32 | #--------------------------------#
33 | # Library Build Instructions #
34 | #--------------------------------#
35 |
36 | add_library(${PROJECT_NAME}py SHARED
37 | ${PYTHON_SOURCE_DIR}/libclusterpy.h
38 | ${PYTHON_SOURCE_DIR}/libclusterpy.cpp
39 | )
40 |
41 | if(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
42 | set(BOOST_PYTHON boost_python3)
43 | else(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
44 | set(BOOST_PYTHON boost_python)
45 | endif(BUILD_USE_PYTHON3)
46 |
47 | target_link_libraries(${PROJECT_NAME}py
48 | ${BOOST_PYTHON}
49 | ${PYTHON_LIBRARIES}
50 | ${Boost_LIBRARIES}
51 | ${PROJECT_NAME}
52 | )
53 |
54 |
55 | #--------------------------------#
56 | # Install Instructions #
57 | #--------------------------------#
58 |
59 | # Get python path
60 | execute_process(COMMAND ${PYCMD} -c
61 | "from distutils.sysconfig import get_python_lib; print(get_python_lib())"
62 | OUTPUT_VARIABLE PYTHON_SITE_PACKAGES OUTPUT_STRIP_TRAILING_WHITESPACE
63 | )
64 |
65 | # Install target
66 | install(TARGETS ${PROJECT_NAME}py DESTINATION ${PYTHON_SITE_PACKAGES})
67 |
68 | endif(BUILD_PYTHON_INTERFACE)
69 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/FindNumpy.cmake:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # - Find numpy
2 | # Find the native numpy includes
3 | # This module defines
4 | # NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR, where to find numpy/arrayobject.h, etc.
5 | # NUMPY_FOUND, If false, do not try to use numpy headers.
6 |
7 | # This is (modified) from the avogadro project, http://avogadro.cc (GPL)
8 |
9 | if (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR)
10 | # in cache already
11 | set (NUMPY_FIND_QUIETLY TRUE)
12 | endif (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR)
13 |
14 | EXEC_PROGRAM ("${PYCMD}"
15 | ARGS "-c 'import numpy; print(numpy.get_include())'"
16 | OUTPUT_VARIABLE NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR)
17 |
18 |
19 | if (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR MATCHES "Traceback")
20 | # Did not successfully include numpy
21 | set(NUMPY_FOUND FALSE)
22 | else (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR MATCHES "Traceback")
23 | # successful
24 | set (NUMPY_FOUND TRUE)
25 | set (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR ${NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR} CACHE STRING "Numpy include path")
26 | endif (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR MATCHES "Traceback")
27 |
28 | if (NUMPY_FOUND)
29 | if (NOT NUMPY_FIND_QUIETLY)
30 | message (STATUS "Numpy headers found")
31 | endif (NOT NUMPY_FIND_QUIETLY)
32 | else (NUMPY_FOUND)
33 | if (NUMPY_FIND_REQUIRED)
34 | message (FATAL_ERROR "Numpy headers missing")
35 | endif (NUMPY_FIND_REQUIRED)
36 | endif (NUMPY_FOUND)
37 |
38 | MARK_AS_ADVANCED (NUMPY_INCLUDE_DIR)
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/libclusterpy.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include
22 | #include "distributions.h"
23 | #include "libclusterpy.h"
24 |
25 | //
26 | // Namespaces
27 | //
28 |
29 | using namespace std;
30 | using namespace Eigen;
31 | using namespace distributions;
32 | using namespace libcluster;
33 | using namespace boost::python;
34 | using namespace boost::python::api;
35 |
36 |
37 | //
38 | // Private Functions
39 | //
40 |
41 |
42 | // Convert (memory share) a numpy array to an Eigen MatrixXd
43 | MatrixXd numpy2MatrixXd (const object& X)
44 | {
45 | if (PyArray_Check(X.ptr()) == false)
46 | throw invalid_argument("PyObject is not an array!");
47 |
48 | // Cast PyObject* to PyArrayObject* now we know that it's valid
49 | PyArrayObject* Xptr = (PyArrayObject*) X.ptr();
50 |
51 | if (PyArray_ISFLOAT(Xptr) == false)
52 | throw invalid_argument("PyObject is not an array of floats/doubles!");
53 |
54 | return Map ((double*) PyArray_DATA(Xptr),
55 | PyArray_DIMS(Xptr)[0], PyArray_DIMS(Xptr)[1]);
56 | }
57 |
58 |
59 | // Convert (memory share) a list of numpy arrays to a vector of Eigen MatrixXd
60 | vMatrixXd lnumpy2vMatrixXd (const boost::python::list& X)
61 | {
62 |
63 | vMatrixXd X_;
64 |
65 | for (int i=0; i < len(X); ++i)
66 | X_.push_back(numpy2MatrixXd(X[i]));
67 |
68 | return X_;
69 | }
70 |
71 |
72 | // Convert (memory share) a list of lists of arrays to a vector of vectors of
73 | // matrices
74 | vvMatrixXd llnumpy2vvMatrixXd (const boost::python::list& X)
75 | {
76 |
77 | vvMatrixXd X_;
78 |
79 | for (int i=0; i < len(X); ++i)
80 | {
81 | vMatrixXd Xi_;
82 |
83 | // Compiler complains when try to use lnumpy2vmatrix instead of following
84 | for (int j=0; j < len(X[i]); ++j)
85 | Xi_.push_back(numpy2MatrixXd(X[i][j]));
86 |
87 | X_.push_back(Xi_);
88 | }
89 |
90 | return X_;
91 | }
92 |
93 |
94 | // Get all the means from Gaussian clusters, Kx[1xD] matrices
95 | vMatrixXd getmean (const vector& clusters)
96 | {
97 | vMatrixXd means;
98 |
99 | for (size_t k=0; k < clusters.size(); ++k)
100 | means.push_back(clusters[k].getmean());
101 |
102 | return means;
103 | }
104 |
105 |
106 | // Get all of the covarances of Gaussian clusters, Kx[DxD] matrices
107 | vMatrixXd getcov (const vector& clusters)
108 | {
109 | vMatrixXd covs;
110 |
111 | for (size_t k=0; k < clusters.size(); ++k)
112 | covs.push_back(clusters[k].getcov());
113 |
114 | return covs;
115 | }
116 |
117 |
118 | // Get the expected cluster weights in each of the groups
119 | template
120 | vector getweights (const vector& weights)
121 | {
122 | vector rwgt;
123 | for (size_t k=0; k < weights.size(); ++k)
124 | rwgt.push_back(ArrayXd(weights[k].Elogweight().exp()));
125 |
126 | return rwgt;
127 | }
128 |
129 |
130 | //
131 | // Public Wrappers
132 | //
133 |
134 | // VDP
135 | tuple wrapperVDP (
136 | const object& X,
137 | const float clusterprior,
138 | const int maxclusters,
139 | const bool verbose,
140 | const int nthreads
141 | )
142 | {
143 | // Convert X
144 | const MatrixXd X_ = numpy2MatrixXd(X);
145 |
146 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
147 | MatrixXd qZ;
148 | StickBreak weights;
149 | vector clusters;
150 |
151 | // Do the clustering
152 | double f = learnVDP(X_, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, maxclusters,
153 | verbose, nthreads);
154 |
155 | // Return relevant objects
156 | return make_tuple(f, qZ, ArrayXd(weights.Elogweight().exp()),
157 | getmean(clusters), getcov(clusters));
158 | }
159 |
160 |
161 | // BGMM
162 | tuple wrapperBGMM (
163 | const object& X,
164 | const float clusterprior,
165 | const int maxclusters,
166 | const bool verbose,
167 | const int nthreads
168 | )
169 | {
170 | // Convert X
171 | const MatrixXd X_ = numpy2MatrixXd(X);
172 |
173 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
174 | MatrixXd qZ;
175 | Dirichlet weights;
176 | vector clusters;
177 |
178 | // Do the clustering
179 | double f = learnBGMM(X_, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, maxclusters,
180 | verbose, nthreads);
181 |
182 | // Return relevant objects
183 | return make_tuple(f, qZ, ArrayXd(weights.Elogweight().exp()),
184 | getmean(clusters), getcov(clusters));
185 | }
186 |
187 |
188 | // GMC
189 | tuple wrapperGMC (
190 | const boost::python::list &X,
191 | const float clusterprior,
192 | const int maxclusters,
193 | const bool sparse,
194 | const bool verbose,
195 | const int nthreads
196 | )
197 | {
198 | // Convert X
199 | const vMatrixXd X_ = lnumpy2vMatrixXd(X);
200 |
201 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
202 | vMatrixXd qZ;
203 | vector weights;
204 | vector clusters;
205 |
206 | // Do the clustering
207 | double f = learnGMC(X_, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, maxclusters,
208 | sparse, verbose, nthreads);
209 |
210 | // Return relevant objects
211 | return make_tuple(f, qZ, getweights(weights), getmean(clusters),
212 | getcov(clusters));
213 | }
214 |
215 |
216 | // SGMC
217 | tuple wrapperSGMC (
218 | const boost::python::list &X,
219 | const float clusterprior,
220 | const int maxclusters,
221 | const bool sparse,
222 | const bool verbose,
223 | const int nthreads
224 | )
225 | {
226 | // Convert X
227 | const vMatrixXd X_ = lnumpy2vMatrixXd(X);
228 |
229 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
230 | vMatrixXd qZ;
231 | vector weights;
232 | vector clusters;
233 |
234 | // Do the clustering
235 | double f = learnSGMC(X_, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, maxclusters,
236 | sparse, verbose, nthreads);
237 |
238 | // Return relevant objects
239 | return make_tuple(f, qZ, getweights(weights), getmean(clusters),
240 | getcov(clusters));
241 | }
242 |
243 |
244 | // SCM
245 | tuple wrapperSCM (
246 | const boost::python::list &X,
247 | const float dirprior,
248 | const float gausprior,
249 | const int trunc,
250 | const int maxclusters,
251 | const bool verbose,
252 | const int nthreads
253 | )
254 | {
255 | // Convert X
256 | const vvMatrixXd X_ = llnumpy2vvMatrixXd(X);
257 |
258 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
259 | vMatrixXd qY;
260 | vvMatrixXd qZ;
261 | vector weights_j;
262 | vector weights_t;
263 | vector clusters;
264 |
265 | // Do the clustering
266 | double f = learnSCM(X_, qY, qZ, weights_j, weights_t, clusters, dirprior,
267 | gausprior, trunc, maxclusters, verbose, nthreads);
268 |
269 | // Return relevant objects
270 | return make_tuple(f, qY, qZ, getweights(weights_j),
271 | getweights(weights_t), getmean(clusters), getcov(clusters));
272 | }
273 |
274 |
275 | // MCM
276 | tuple wrapperMCM (
277 | const boost::python::list &W,
278 | const boost::python::list &X,
279 | const float gausprior_t,
280 | const float gausprior_k,
281 | const int trunc,
282 | const int maxclusters,
283 | const bool verbose,
284 | const int nthreads
285 | )
286 | {
287 | // Convert W and X
288 | const vMatrixXd W_ = lnumpy2vMatrixXd(W);
289 | const vvMatrixXd X_ = llnumpy2vvMatrixXd(X);
290 |
291 | // Pre-allocate some stuff
292 | vMatrixXd qY;
293 | vvMatrixXd qZ;
294 | vector weights_j;
295 | vector weights_t;
296 | vector clusters_t;
297 | vector clusters_k;
298 |
299 | // Do the clustering
300 | double f = learnMCM(W_, X_, qY, qZ, weights_j, weights_t, clusters_t,
301 | clusters_k, gausprior_t, gausprior_k, trunc, maxclusters,
302 | verbose, nthreads);
303 |
304 | // Return relevant objects
305 | return make_tuple(f, qY, qZ, getweights(weights_j),
306 | getweights(weights_t), getmean(clusters_t),
307 | getmean(clusters_k), getcov(clusters_t), getcov(clusters_k));
308 | }
309 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/libclusterpy.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #ifndef LIBCLUSTERPY_H
22 | #define LIBCLUSTERPY_H
23 |
24 | #define NPY_NO_DEPRECATED_API NPY_1_7_API_VERSION // Test deprication for v1.7
25 |
26 | #include
27 | #include
28 | #include
29 | #include "libcluster.h"
30 |
31 |
32 | //
33 | // To-python type converters
34 | //
35 |
36 | // Eigen::MatrixXd/ArrayXd (double) to numpy array ([[...]])
37 | template
38 | struct eigen2numpy
39 | {
40 | static PyObject* convert (const M& X)
41 | {
42 | npy_intp arsize[] = {X.rows(), X.cols()};
43 | M* X_ = new M(X); // Copy to persistent array
44 | PyObject* Xp = PyArray_SimpleNewFromData(2, arsize, NPY_DOUBLE, X_->data());
45 |
46 | if (Xp == NULL)
47 | throw std::runtime_error("Cannot convert Eigen matrix to Numpy array!");
48 |
49 | return Xp;
50 | }
51 | };
52 |
53 |
54 | // std::vector to python list [...].
55 | template
56 | struct vector2list
57 | {
58 | static PyObject* convert (const std::vector& X)
59 | {
60 | boost::python::list* Xp = new boost::python::list();
61 |
62 | for (size_t i = 0; i < X.size(); ++i)
63 | Xp->append(X[i]);
64 |
65 | return Xp->ptr();
66 | }
67 | };
68 |
69 |
70 | //
71 | // Wrappers
72 | //
73 |
74 | // VDP
75 | boost::python::tuple wrapperVDP (
76 | const boost::python::api::object& X,
77 | const float clusterprior,
78 | const int maxclusters,
79 | const bool verbose,
80 | const int nthreads
81 | );
82 |
83 |
84 | // BGMM
85 | boost::python::tuple wrapperBGMM (
86 | const boost::python::api::object& X,
87 | const float clusterprior,
88 | const int maxclusters,
89 | const bool verbose,
90 | const int nthreads
91 | );
92 |
93 |
94 | // GMC
95 | boost::python::tuple wrapperGMC (
96 | const boost::python::list& X,
97 | const float clusterprior,
98 | const int maxclusters,
99 | const bool sparse,
100 | const bool verbose,
101 | const int nthreads
102 | );
103 |
104 |
105 | // SGMC
106 | boost::python::tuple wrapperSGMC (
107 | const boost::python::list& X,
108 | const float clusterprior,
109 | const int maxclusters,
110 | const bool sparse,
111 | const bool verbose,
112 | const int nthreads
113 | );
114 |
115 |
116 | // SCM
117 | boost::python::tuple wrapperSCM (
118 | const boost::python::list& X,
119 | const float dirprior,
120 | const float gausprior,
121 | const int trunc,
122 | const int maxclusters,
123 | const bool verbose,
124 | const int nthreads
125 | );
126 |
127 |
128 | // MCM
129 | boost::python::tuple wrapperMCM (
130 | const boost::python::list& W,
131 | const boost::python::list& X,
132 | const float gausprior_t,
133 | const float gausprior_k,
134 | const int trunc,
135 | const int maxclusters,
136 | const bool verbose,
137 | const int nthreads
138 | );
139 |
140 |
141 | //
142 | // Hack for python2/3 numpy return value weirdness
143 | //
144 |
145 | #if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
146 | int*
147 | #else
148 | void
149 | #endif
150 | init_numpy()
151 | {
152 | import_array();
153 | #if PY_MAJOR_VERSION >= 3
154 | return NULL;
155 | #endif
156 | }
157 |
158 |
159 | //
160 | // Module definition
161 | //
162 |
163 | BOOST_PYTHON_MODULE (libclusterpy)
164 | {
165 | using namespace boost::python;
166 |
167 | // This will enable user-defined docstrings and python signatures,
168 | // while disabling the C++ signatures
169 | docstring_options local_docstring_options(true, true, false);
170 |
171 |
172 | // set the docstring of the current module scope
173 | const std::string moddoc =
174 | "A collection of structured Bayesian clustering algorithms.\n\n"
175 | "This library contains implementations of a number of variational\n"
176 | "Bayesian clustering algorithms such as the Bayesian Gaussian Mixture\n"
177 | "model of [1], and the Variational Dirichlet process of [2]. Also \n"
178 | "implemented is a latent Dirichlet allocation-like model with a \n"
179 | "Gaussian observation model (GMC [4], SGMC/G-LDA [3, 4, 5]), and more\n"
180 | "highly structured models -- see the SCM and MCM functions [3, 4, 5].\n\n"
181 | "Author: Daniel Steinberg\n"
182 | "\tAustralian Centre for Field Robotics,\n"
183 | "\tThe University of Sydney.\n\n"
184 | "Date: 11/03/2013\n\n"
185 | "License: GPL v3 or later, See LICENSE.\n\n"
186 | " [1] C. M. Bishop, Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning. Cambridge,\n"
187 | "\tUK: pringer Science+Business Media, 2006.\n"
188 | " [2] K. Kurihara, M. Welling, and N. Vlassis, Accelerated variational\n"
189 | "\tDirichlet process mixtures, Advances in Neural Information Processing\n"
190 | "\tSystems, vol. 19, p. 761, 2007.\n"
191 | " [3] D. M. Steinberg, O. Pizarro, S. B. Williams, Synergistic Clustering\n"
192 | "\tof Image and Segment Descriptors for Unsupervised Scene Understanding.\n"
193 | "\tIn International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV). IEEE, Sydney,\n"
194 | "\tNSW, 2013.\n"
195 | " [4] D. M. Steinberg, O. Pizarro, S. B. Williams. Hierarchical\n"
196 | "\tBayesian Models for Unsupervised Scene Understanding. Journal of\n"
197 | "\tComputer Vision and Image Understanding (CVIU). Elsevier, 2014.\n"
198 | " [5] D. M. Steinberg, An Unsupervised Approach to Modelling Visual Data,\n"
199 | "\tPhD Thesis, 2013.\n"
200 | " [6] D. M. Steinberg, A. Friedman, O. Pizarro, and S. B. Williams.\n"
201 | "\tA Bayesian nonparametric approach to clustering data from underwater\n"
202 | "\trobotic surveys. In International Symposium on Robotics Research,\n"
203 | "\tFlagstaff, AZ, Aug. 2011.";
204 | scope().attr("__doc__") = moddoc;
205 |
206 |
207 | // To-python converters
208 | init_numpy();
209 | to_python_converter< Eigen::ArrayXd, eigen2numpy >();
210 | to_python_converter< Eigen::MatrixXd, eigen2numpy >();
211 | to_python_converter< std::vector,
212 | vector2list >();
213 | to_python_converter< std::vector,
214 | vector2list >();
215 | to_python_converter< std::vector< std::vector >,
216 | vector2list< std::vector > >();
217 |
218 |
219 | // Common documentation strings -- arguments
220 | const std::string comargs = "\nArguments:\n";
221 | const std::string Xarg =
222 | "\tX: array shape(N,D) the data to be clustered, N are the number of \n"
223 | "\t\tsamples, D the number of dimensions.\n";
224 | const std::string vXarg =
225 | "\tX: list[array shape(N_j,D),...] of len = J which is the data to be\n"
226 | "\t\tclustered, N_j are the number of samples of each group (or list \n"
227 | "\t\telement) j of data, D the number of dimensions.\n";
228 | const std::string vvXarg =
229 | "\tX: list[list[array shape(N_j,D_b),...]] where the outer list is of\n"
230 | "\t\tlen = J, and each inner list is of len = I_j. This is the\n"
231 | "\t\t(bottom-level) data to be clustered, N_ji are the number of samples\n"
232 | "\t\tof each 'document/image' (ji) within each group (j) of data. D_b is\n"
233 | "\t\tthe number of dimensions.\n";
234 | const std::string truncarg =
235 | "\ttrunc: the maximum number of top-level clusters to find. This is the \n"
236 | "\t\ttruncation level, and mostly less top-level clusters than this will\n"
237 | "\t\tbe returned.\n";
238 | const std::string maxclustersarg =
239 | "\tmaxclusters: the maximum number of bottom level clusters to search \n"
240 | "\t\tfor, -1 (default) means no upper bound.\n";
241 | const std::string priorarg =
242 | "\tprior: the prior width of the Gaussian clusters.\n";
243 | const std::string priorkarg =
244 | "\tgausprior_k: the prior width of the bottom-level Gaussian clusters.\n";
245 | const std::string sparsearg =
246 | "\tsparse: do sparse updates? I.e. only update the clusters that have\n"
247 | "\t\tmore than one observation.\n";
248 | const std::string verbarg =
249 | "\tverbose: output clustering status?\n";
250 | const std::string threadarg =
251 | "\tthreads: the number of threads to use.\n";
252 |
253 | // Common documentation strings -- returns
254 | const std::string comrets = "\nReturns:\n";
255 | const std::string fret =
256 | "\tf: float, the free energy learning objective value.\n";
257 | const std::string qZret =
258 | "\tqZ: array shape(N,K), the probability of the observations belonging to\n"
259 | "\t\teach cluster, where K is the number of discovered clusters.\n";
260 | const std::string vqZret =
261 | "\tqZ: list[array shape(N_j,K),...] of len = J, the probability of the\n"
262 | "\t\tobservations in group j belonging to each cluster. Here K is the\n"
263 | "\t\tnumber of discovered clusters.\n";
264 | const std::string vvqZret =
265 | "\tqZ: list[list[array shape(N_j,K),...]] with the outer list of len = J,\n"
266 | "\t\tand each inner list of len = I_j. This is the probability of the\n"
267 | "\t\tbottom-level observations belonging to each cluster. Here K is the\n"
268 | "\t\tnumber of discovered bottom-level clusters.\n";
269 | const std::string vqYret =
270 | "\tqY: list[array shape(N_j,T),...] of len = J, the probability of the\n"
271 | "\t\t'documents' in group j belonging to each top-level cluster. Here T\n"
272 | "\t\tis the number of discovered top-level clusters.\n";
273 | const std::string wret =
274 | "\tw: array shape(K,1), the (expected) Gaussian mixture weights.\n";
275 | const std::string vwret =
276 | "\tw_j: list[array shape(K,1),...] of len = J, the (expected) Gaussian\n"
277 | "\t\tmixture weights of each group, j.\n";
278 | const std::string vwjret =
279 | "\tw_j: list[array shape(T,1),...] of len = J, the (expected) top-level\n"
280 | "\t\tcluster weights of each group, j.\n";
281 | const std::string vwtret =
282 | "\tw_t: list[array shape(K,1),...] of len = T, the (expected) Gaussian\n"
283 | "\t\tmixture weights of each bottom-level cluster within each of the T\n"
284 | "\t\ttop-level clusters.\n";
285 | const std::string muret =
286 | "\tmu: array shape(K,D), the (expected) Gaussian mixture means.\n";
287 | const std::string covret =
288 | "\tcov: list[array shape(D,D),...] of len = K, the (expected) Gaussian\n"
289 | "\t\t mixture covariances.\n";
290 | const std::string mukret =
291 | "\tmu_k: array shape(K,D_b), the (expected) bottom-level Gaussian mixture\n"
292 | "\t\tmeans.\n";
293 | const std::string covkret =
294 | "\tcov_k: list[array shape(D_b,D_b),...] of len = K, the (expected)\n"
295 | "\t\tbottom-level Gaussian mixture covariances.\n";
296 |
297 |
298 | // VDP
299 | const std::string vdpdoc =
300 | "The Variational Dirichlet Process (VDP) of [2].\n\n"
301 | "The VDP is similar to a regular Bayesian GMM, but places a Dirichlet\n"
302 | "process prior over the mixture weights. This is also used in [6].\n"
303 | + comargs + Xarg + priorarg + maxclustersarg + verbarg + threadarg
304 | + comrets + fret + qZret + wret + muret + covret;
305 |
306 | def ("learnVDP", wrapperVDP,
307 | (
308 | arg("X"),
309 | arg("prior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
310 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
311 | arg("verbose") = false,
312 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
313 | ),
314 | vdpdoc.c_str()
315 | );
316 |
317 |
318 | // BGMM
319 | const std::string bgmmdoc =
320 | "The Bayseian Gaussian mixture model (BGMM) described in [1].\n\n"
321 | "This BGMM is similar to a GMM learned with EM, but it places a\n"
322 | "Dirichlet prior over the mixture weights, and Gaussian-Wishart priors\n"
323 | "over the Gaussian clusters. This implementation is similar to [1] but\n"
324 | "also employes the cluster splitting heuristics discussed in [2-5].\n"
325 | + comargs + Xarg + priorarg + maxclustersarg + verbarg + threadarg
326 | + comrets + fret + qZret + wret + muret + covret;
327 |
328 | def ("learnBGMM", wrapperBGMM,
329 | (
330 | arg("X"),
331 | arg("prior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
332 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
333 | arg("verbose") = false,
334 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
335 | ),
336 | bgmmdoc.c_str()
337 | );
338 |
339 |
340 | // GMC
341 | const std::string gmcdoc =
342 | "The Grouped Mixtures Clustering (GMC) algorithm.\n\n"
343 | "This function uses the Grouped Mixtures Clustering model [5] to cluster\n"
344 | "multiple datasets simultaneously with cluster sharing between datasets.\n"
345 | "It uses a Generalised Dirichlet prior over the group mixture weights, and\n"
346 | "a Gaussian-Wishart prior over the cluster parameters. This algorithm is\n"
347 | "similar to a one-level Hierarchical Dirichlet process with Gaussian\n"
348 | "observations.\n"
349 | + comargs + vXarg + priorarg + maxclustersarg+ sparsearg + verbarg
350 | + threadarg
351 | + comrets + fret + vqZret + vwret + muret + covret;
352 |
353 | def ("learnGMC", wrapperGMC,
354 | (
355 | arg("X"),
356 | arg("prior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
357 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
358 | arg("sparse") = false,
359 | arg("verbose") = false,
360 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
361 | ),
362 | gmcdoc.c_str()
363 | );
364 |
365 |
366 | // SGMC
367 | const std::string sgmcdoc =
368 | "The Symmetric Grouped Mixtures Clustering (S-GMC) algorithm.\n\n"
369 | "This function uses the Symmetric Grouped Mixtures Clustering model [5]\n"
370 | "to cluster multiple datasets simultaneously with cluster sharing between\n"
371 | "datasets. It uses a symmetric Dirichlet prior over the group mixture\n"
372 | "weights, and a Gaussian-Wishart prior over the cluster parameters. This\n"
373 | "algorithm is similar to latent Dirichlet allocation with Gaussian\n"
374 | "observations.\n\n"
375 | "It is also referred to as Gaussian Latent Dirichlet Allocation (G-LDA)\n"
376 | "in [3, 4].\n"
377 | + comargs + vXarg + priorarg + maxclustersarg + sparsearg + verbarg
378 | + threadarg
379 | + comrets + fret + vqZret + vwret + muret + covret;
380 |
381 | def ("learnSGMC", wrapperSGMC,
382 | (
383 | arg("X"),
384 | arg("prior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
385 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
386 | arg("sparse") = false,
387 | arg("verbose") = false,
388 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
389 | ),
390 | sgmcdoc.c_str()
391 | );
392 |
393 |
394 | // SCM
395 | const std::string dpriorarg =
396 | "\tdirprior: The top-level Dirichlet prior. This affects the number of\n"
397 | "\t\tclusters found. This may need to turned up high to have an effect.\n";
398 |
399 | const std::string scmdoc =
400 | "The Simultaneous Clustering Model (SCM).\n\n"
401 | "This function implements the Simultaneous Clustering Model algorithm as\n"
402 | "specified by [4, 5]. The SCM uses a Generalised Dirichlet prior on the\n"
403 | "group mixture weights, a Dirichlet prior on the top-level clusters and\n"
404 | "Gaussian bottom-level cluster distributions for observations (with\n"
405 | "Gausian-Wishart priors).\n"
406 | + comargs + vvXarg + dpriorarg + priorkarg + truncarg + maxclustersarg
407 | + verbarg + threadarg
408 | + comrets + fret + vqYret + vvqZret + vwjret + vwtret + mukret + covkret;
409 |
410 | def ("learnSCM", wrapperSCM,
411 | (
412 | arg("X"),
413 | arg("dirprior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
414 | arg("gausprior") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
415 | arg("trunc") = libcluster::TRUNC,
416 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
417 | arg("verbose") = false,
418 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
419 | ),
420 | scmdoc.c_str()
421 | );
422 |
423 |
424 | // MCM
425 | const std::string vWarg =
426 | "\tW: list[array shape(I_j,D_t),...] of len = J which is the top-level\n"
427 | "\t\t ('document') data to be clustered, I_j are the number of documents\n"
428 | "\t\tin each group (or list element) j of data, D_t the number of\n"
429 | "\t\tdimensions.\n";
430 | const std::string priortarg =
431 | "\tgausprior_t: the prior width of the top-level Gaussian clusters.\n";
432 | const std::string mutret =
433 | "\tmu_t: array shape(T,D_t), the (expected) top-level Gaussian mixture\n"
434 | "\t\tmeans.\n";
435 | const std::string covtret =
436 | "\tcov_t: list[array shape(D_t,D_t),...] of len = T, the (expected)\n"
437 | "\t\ttop-level Gaussian mixture covariances.\n";
438 |
439 | const std::string mcmdoc =
440 | "The Multiple-source Clustering Model (MCM).\n\n"
441 | "This function implements the Multiple-source Clustering Model algorithm\n"
442 | "as specified by [3-5]. This model jointly cluster both 'document'\n"
443 | "level observations, and 'word' observations. The MCM uses a Generalised\n"
444 | "Dirichlet prior on the group mixture weights, Multinomial-Gaussian \n"
445 | "top-level (document) clusters, and Gaussian bottom-level (word) cluster\n"
446 | "distributions.\n"
447 | + comargs + vWarg + vvXarg + priortarg + priorkarg + truncarg
448 | + maxclustersarg + verbarg + threadarg
449 | + comrets + fret + vqYret + vvqZret + vwjret + vwtret + mutret + mukret
450 | + covtret + covkret;
451 |
452 | def ("learnMCM", wrapperMCM,
453 | (
454 | arg("W"),
455 | arg("X"),
456 | arg("gausprior_t") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
457 | arg("gausprior_k") = libcluster::PRIORVAL,
458 | arg("trunc") = libcluster::TRUNC,
459 | arg("maxclusters") = -1,
460 | arg("verbose") = false,
461 | arg("threads") = omp_get_max_threads()
462 | ),
463 | mcmdoc.c_str()
464 | );
465 |
466 | }
467 |
468 | #endif
469 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/python/testapi.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #! /usr/bin/env python
2 |
3 | # libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
4 | # Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
5 | #
6 | # This file is part of libcluster.
7 | #
8 | # libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
9 | # the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
10 | # Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
11 | # any later version.
12 | #
13 | # libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
14 | # ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
15 | # FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
16 | # for more details.
17 | #
18 | # You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
19 | # along with libcluster. If not, see .
20 |
21 | """ Script to make sure libcluster runs properly using the python API.
22 |
23 | Author: Daniel Steinberg
24 | Date: 13/10/2013
25 |
26 | """
27 |
28 | import numpy as np
29 | import libclusterpy as lc
30 |
31 |
32 | # Top level cluster parameters -- Globals.... whatev...
33 | means = np.array([[0, 0], [5, 5], [-5, -5]])
34 | sigma = [np.eye(2)] * 3
35 | beta = np.array([[1.0 / 3, 1.0 / 3, 1.0 / 3],
36 | [1.0 / 2, 1.0 / 4, 1.0 / 4],
37 | [1.0 / 4, 1.0 / 4, 1.0 / 2]])
38 |
39 |
40 | def testmixtures():
41 | """ The test function. """
42 |
43 | print("Testing mixtures ------------------\n")
44 |
45 | # Create points from clusters
46 | W = gengmm(10000)
47 |
48 | # Test VDP
49 | print("------------ Test VDP -------------")
50 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnVDP(W, verbose=True)
51 | print("")
52 | printgmm(w, mu, cov)
53 |
54 | # Test BGMM
55 | print("------------ Test BGMM ------------")
56 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnBGMM(W, verbose=True)
57 | print("")
58 | printgmm(w, mu, cov)
59 |
60 |
61 | def testgroupmix():
62 |
63 | print("Testing group mixtures ------------\n")
64 |
65 | # Create points from clusters
66 | J = 4 # Groups
67 | W = [gengmm(2000) for j in range(J)]
68 |
69 | # Test GMC
70 | print("------------ Test GMC -------------")
71 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnGMC(W, verbose=True)
72 | print("")
73 | printgmm(w, mu, cov)
74 |
75 | # Test SGMC
76 | print("------------ Test SGMC ------------")
77 | f, qZ, w, mu, cov = lc.learnSGMC(W, verbose=True)
78 | print("")
79 | printgmm(w, mu, cov)
80 |
81 |
82 | def testmultmix():
83 | """ The the models that cluster at multiple levels. Just using J=1. """
84 |
85 | # Generate top-level clusters
86 | I = 200
87 | Ni = 100
88 | betas, Y = gensetweights(I)
89 |
90 | # Create points from clusters
91 | W = np.zeros((I, means.shape[1]))
92 | X = []
93 | for i in range(I):
94 | W[i, :] = np.random.multivariate_normal(means[Y[i]], sigma[Y[i]], 1)
95 | X.append(gengmm(Ni, betas[i, :]))
96 |
97 | # Test SCM
98 | print("------------ Test SCM -------------")
99 | f, qY, qZ, wi, ws, mu, cov = lc.learnSCM([X], trunc=30, verbose=True)
100 | print("")
101 | printgmm(ws, mu, cov)
102 |
103 | # Test MCM
104 | print("------------ Test MCM -------------")
105 | f, qY, qZ, wi, ws, mui, mus, covi, covs = lc.learnMCM([W], [X], trunc=30,
106 | verbose=True)
107 | print("\nTop level mixtures:")
108 | printgmm(wi, mui, covi)
109 | print("Bottom level mixtures:")
110 | printgmm(ws, mus, covs)
111 |
112 |
113 | def gengmm(N, weights=None):
114 | """ Make a random GMM with N observations. """
115 |
116 | K = len(sigma)
117 | pi = np.random.rand(K) if weights is None else weights
118 | pi /= pi.sum()
119 | Nk = np.round(pi * N)
120 | Nk[-1] = N - Nk[0:-1].sum()
121 |
122 | X = [np.random.multivariate_normal(means[k, :], sigma[k], int(Nk[k]))
123 | for k in range(K)]
124 |
125 | return np.concatenate(X)
126 |
127 |
128 | def gensetweights(I):
129 | """ Generate sets of similar weights. """
130 |
131 | T = beta.shape[0]
132 | pi = np.random.rand(T)
133 | pi /= pi.sum()
134 | Nt = np.round(pi * I)
135 | Nt[-1] = I - Nt[0:-1].sum()
136 |
137 | betas = []
138 | Y = []
139 | for t in range(T):
140 | Y += int(Nt[t]) * [t]
141 | betas.append(int(Nt[t]) * [beta[t, :]])
142 |
143 | return np.concatenate(betas), Y
144 |
145 |
146 | def printgmm(W, Mu, Cov):
147 | """ Print the parameters of a GMM. """
148 |
149 | Wnp = np.array(W)
150 |
151 | for i, (mu, cov) in enumerate(zip(Mu, Cov)):
152 |
153 | print("Mixture {0}:".format(i))
154 | if Wnp.ndim == 2:
155 | print(" weight --\n{0}".format(Wnp[i, :]))
156 | elif Wnp.ndim == 3:
157 | print(" group weights --\n{0}".format(Wnp[:, i, :]))
158 | print(" mean --\n{0}\n cov --\n{1}\n".format(mu, cov))
159 |
160 |
161 | if __name__ == "__main__":
162 | testmixtures()
163 | testgroupmix()
164 | testmultmix()
165 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/cluster.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | // TODO:
22 | // - sparse updates sometimes create positive free energy steps.
23 |
24 | #include
25 | #include "libcluster.h"
26 | #include "probutils.h"
27 | #include "distributions.h"
28 | #include "comutils.h"
29 |
30 |
31 | //
32 | // Namespaces
33 | //
34 |
35 | using namespace std;
36 | using namespace Eigen;
37 | using namespace probutils;
38 | using namespace distributions;
39 | using namespace comutils;
40 | using namespace libcluster;
41 |
42 |
43 | //
44 | // Variational Bayes Private Functions
45 | //
46 |
47 |
48 | /* Update the group and model sufficient statistics based on assignments qZj.
49 | *
50 | * mutable: the clusters (add sufficient stats).
51 | * returns: the number of observations in each cluster for this groups.
52 | */
53 | template ArrayXd updateSS (
54 | const MatrixXd& Xj, // Observations in group j
55 | const MatrixXd& qZj, // Observations to group mixture assignments
56 | vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
57 | const bool sparse // Do sparse updates to groups
58 | )
59 | {
60 | const unsigned int K = qZj.cols();
61 |
62 | const ArrayXd Njk = qZj.colwise().sum(); // count obs. in this group
63 | ArrayXi Kful = ArrayXi::Zero(1), // Initialise and set K = 1 defaults
64 | Kemp = ArrayXi::Zero(0);
65 |
66 | // Find empty clusters if sparse
67 | if ( (sparse == false) && (K > 1) )
68 | Kful = ArrayXi::LinSpaced(Sequential, K, 0, K-1);
69 | else if (sparse == true)
70 | arrfind((Njk >= ZEROCUTOFF), Kful, Kemp);
71 |
72 | const unsigned int nKful = Kful.size();
73 |
74 | // Sufficient statistics - with observations
75 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < nKful; ++k)
76 | {
77 | #pragma omp critical
78 | clusters[Kful(k)].addobs(qZj.col(Kful(k)), Xj);
79 | }
80 |
81 | return Njk;
82 | }
83 |
84 |
85 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for each group.
86 | *
87 | * mutable: Group assignment probabilities, qZj
88 | * returns: The complete-data (X,Z) free energy E[log p(X,Z)/q(Z)] for group j.
89 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
90 | */
91 | template double vbexpectation (
92 | const MatrixXd& Xj, // Observations in group J
93 | const W& weights, // Group Weight parameter distribution
94 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster parameter distributions
95 | MatrixXd& qZj, // Observations to group mixture assignments
96 | const bool sparse // Do sparse updates to groups
97 | )
98 | {
99 | const int K = clusters.size(),
100 | Nj = Xj.rows();
101 |
102 | // Get log marginal weight likelihoods
103 | const ArrayXd E_logZ = weights.Elogweight();
104 |
105 | // Initialise and set K = 1 defaults for cluster counts
106 | ArrayXi Kful = ArrayXi::Zero(1), Kemp = ArrayXi::Zero(0);
107 |
108 | // Find empty clusters if sparse
109 | if ( (sparse == false) && (K > 1) )
110 | Kful = ArrayXi::LinSpaced(Sequential, K, 0, K-1);
111 | else if (sparse == true)
112 | arrfind((weights.getNk() >= ZEROCUTOFF), Kful, Kemp);
113 |
114 | const int nKful = Kful.size(),
115 | nKemp = Kemp.size();
116 |
117 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs -- allow sparse evaluation
118 | MatrixXd logqZj(Nj, nKful);
119 |
120 | for (int k = 0; k < nKful; ++k)
121 | logqZj.col(k) = E_logZ(Kful(k)) + clusters[Kful(k)].Eloglike(Xj).array();
122 |
123 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
124 | const VectorXd logZzj = logsumexp(logqZj);
125 |
126 | // Make sure qZ is the right size, this is a nop if it is
127 | qZj.resize(Nj, K);
128 |
129 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities -- again allow sparse evaluation
130 | for (int k = 0; k < nKful; ++k)
131 | qZj.col(Kful(k)) = ((logqZj.col(k) - logZzj).array().exp()).matrix();
132 |
133 | // Empty Cluster Responsabilities
134 | for (int k = 0; k < nKemp; ++k)
135 | qZj.col(Kemp(k)).setZero();
136 |
137 | return -logZzj.sum();
138 | }
139 |
140 |
141 | /* Calculates the free energy lower bound for the model parameter distributions.
142 | *
143 | * returns: the free energy of the model
144 | */
145 | template double fenergy (
146 | const vector& weights, // Weight parameter distributions
147 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster parameter distributions
148 | const double Fxz // Free energy from data log-likelihood
149 | )
150 | {
151 | const int K = clusters.size(),
152 | J = weights.size();
153 |
154 | // Free energy of the weight parameter distributions
155 | double Fw = 0;
156 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
157 | Fw += weights[j].fenergy();
158 |
159 | // Free energy of the cluster parameter distributionsreturn
160 | double Fc = 0;
161 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
162 | Fc += clusters[k].fenergy();
163 |
164 | return Fc + Fw + Fxz;
165 | }
166 |
167 |
168 | /* Variational Bayes EM for all group mixtures.
169 | *
170 | * returns: Free energy of the whole model.
171 | * mutable: variational posterior approximations to p(Z|X).
172 | * mutable: the group weight distributions
173 | * mutable: the cluster distributions
174 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
175 | * throws: runtime_error if there is a negative free energy.
176 | */
177 | template double vbem (
178 | const vMatrixXd& X, // Observations
179 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Observations to model mixture assignments
180 | vector& weights, // Group weight distributions
181 | vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
182 | const double clusterprior, // Prior value for cluster distributions
183 | const int maxit = -1, // Max VBEM iterations (-1 = no max, default)
184 | const bool sparse = false, // Do sparse updates to groups (default false)
185 | const bool verbose = false // Verbose output (default false)
186 | )
187 | {
188 | const int J = X.size(),
189 | K = qZ[0].cols();
190 |
191 | // Construct (empty) parameters
192 | weights.resize(J, W());
193 | clusters.resize(K, C(clusterprior, X[0].cols()));
194 |
195 | double F = numeric_limits::max(), Fold;
196 | int i = 0;
197 |
198 | do
199 | {
200 | Fold = F;
201 |
202 | // Clear Suffient Statistics
203 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
204 | clusters[k].clearobs();
205 |
206 | // Update Suff Stats and VBM for weights
207 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
208 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
209 | {
210 | ArrayXd Njk = updateSS(X[j], qZ[j], clusters, sparse);
211 | weights[j].update(Njk);
212 | }
213 |
214 | // VBM for clusters
215 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
216 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
217 | clusters[k].update();
218 |
219 | // VBE
220 | double Fz = 0;
221 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fz)
222 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
223 | Fz += vbexpectation(X[j], weights[j], clusters, qZ[j], sparse);
224 |
225 | // Calculate free energy of model
226 | F = fenergy(weights, clusters, Fz);
227 |
228 | // Check bad free energy step
229 | if ((F-Fold)/abs(Fold) > FENGYDEL)
230 | throw runtime_error("Free energy increase!");
231 |
232 | if (verbose == true) // Notify iteration
233 | cout << '-' << flush;
234 | }
235 | while ( (abs((Fold-F)/Fold) > CONVERGE)
236 | && ( (i++ < maxit) || (maxit < 0) ) );
237 |
238 | return F;
239 | }
240 |
241 |
242 | //
243 | // Model Selection and Heuristics Private Functions
244 | //
245 |
246 |
247 | /* Search in an exhaustive fashion for a mixture split that lowers model free
248 | * energy the most. If no splits are found which lower Free Energy, then
249 | * false is returned, and qZ is not modified.
250 | *
251 | * returns: true if a split was found, false if no splits can be found
252 | * mutable: qZ is augmented with a new split if one is found, otherwise left
253 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions
254 | * throws: runtime_error from its internal VBEM calls
255 | */
256 | #ifdef EXHAUST_SPLIT
257 | template bool split_ex (
258 | const vMatrixXd& X, // Observations
259 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
260 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Probabilities qZ
261 | const double F, // Current model free energy
262 | const int maxclusters, // maximum number of clusters to search for
263 | const bool sparse, // Do sparse updates to groups
264 | const bool verbose // Verbose output
265 | )
266 | {
267 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
268 | K = clusters.size();
269 |
270 | // Check if we have reached the max number of clusters
271 | if ( ((signed) K >= maxclusters) && (maxclusters >= 0) )
272 | return false;
273 |
274 | // Pre allocate big objects for loops (this makes a runtime difference)
275 | double Fbest = numeric_limits::infinity();
276 | vector mapidx(J, ArrayXi());
277 | vMatrixXd qZref(J,MatrixXd()), qZaug(J,MatrixXd()), Xk(J,MatrixXd()), qZbest;
278 |
279 | // Loop through each potential cluster in order and split it
280 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
281 | {
282 | // Don't waste time with clusters that can't really be split min (2:2)
283 | if (clusters[k].getN() < 4)
284 | continue;
285 |
286 | // Now split observations and qZ.
287 | int scount = 0, Mtot = 0;
288 |
289 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Mtot, scount)
290 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
291 | {
292 | // Make COPY of the observations with only relevant data points, p > 0.5
293 | mapidx[j] = partX(X[j], (qZ[j].col(k).array()>0.5), Xk[j]); // Copy :-(
294 | Mtot += Xk[j].rows();
295 |
296 | // Initial cluster split
297 | ArrayXb splitk = clusters[k].splitobs(Xk[j]);
298 | qZref[j].setZero(Xk[j].rows(), 2);
299 | qZref[j].col(0) = (splitk == true).cast(); // Init qZ for split
300 | qZref[j].col(1) = (splitk == false).cast();
301 |
302 | // keep a track of number of splits
303 | scount += splitk.count();
304 | }
305 |
306 | // Don't waste time with clusters that haven't been split sufficiently
307 | if ( (scount < 2) || (scount > (Mtot-2)) )
308 | continue;
309 |
310 | // Refine the split
311 | vector wspl;
312 | vector cspl;
313 | vbem(Xk, qZref, wspl, cspl, clusters[0].getprior(), SPLITITER, sparse);
314 |
315 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
316 | continue;
317 |
318 | // Map the refined splits back to original whole-data problem
319 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
320 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
321 | qZaug[j] = augmentqZ(k, mapidx[j], (qZref[j].col(1).array()>0.5), qZ[j]);
322 |
323 | // Calculate free energy of this split with ALL data (and refine a bit)
324 | double Fsplit = vbem(X, qZaug, wspl, cspl, clusters[0].getprior(), 1,
325 | sparse);
326 |
327 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
328 | continue;
329 |
330 | // Only notify here of split candidates
331 | if (verbose == true)
332 | cout << '=' << flush;
333 |
334 | // Record best splits so far
335 | if (Fsplit < Fbest)
336 | {
337 | qZbest = qZaug;
338 | Fbest = Fsplit;
339 | }
340 | }
341 |
342 | // See if this split actually improves the model
343 | if ( (Fbest < F) && (abs((F-Fbest)/F) > CONVERGE) )
344 | {
345 | qZ = qZbest;
346 | return true;
347 | }
348 | else
349 | return false;
350 | }
351 | #endif
352 |
353 |
354 | /* Search in a greedy fashion for a mixture split that lowers model free
355 | * energy, or return false. An attempt is made at looking for good, untried,
356 | * split candidates first, as soon as a split canditate is found that lowers
357 | * model F, it is returned. This may not be the "best" split, but it is
358 | * certainly faster than an exhaustive search for the "best" split.
359 | *
360 | * returns: true if a split was found, false if no splits can be found
361 | * mutable: qZ is augmented with a new split if one is found, otherwise left
362 | * mutable tally is a tally time a cluster has been unsuccessfully split
363 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions
364 | * throws: runtime_error from its internal VBEM calls
365 | */
366 | #ifndef EXHAUST_SPLIT
367 | template bool split_gr (
368 | const vMatrixXd& X, // Observations
369 | const vector& weights, // Group weight distributions
370 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
371 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Probabilities qZ
372 | vector& tally, // Count of unsuccessful splits
373 | const double F, // Current model free energy
374 | const int maxclusters, // maximum number of clusters to search for
375 | const bool sparse, // Do sparse updates to groups
376 | const bool verbose // Verbose output
377 | )
378 | {
379 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
380 | K = clusters.size();
381 |
382 | // Check if we have reached the max number of clusters
383 | if ( ((signed) K >= maxclusters) && (maxclusters >= 0) )
384 | return false;
385 |
386 | // Split order chooser and cluster parameters
387 | tally.resize(K, 0); // Make sure tally is the right size
388 | vector ord(K);
389 |
390 | // Get cluster parameters and their free energy
391 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
392 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
393 | {
394 | ord[k].k = k;
395 | ord[k].tally = tally[k];
396 | ord[k].Fk = clusters[k].fenergy();
397 | }
398 |
399 | // Get cluster likelihoods
400 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
401 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
402 | {
403 | // Get cluster weights
404 | ArrayXd logpi = weights[j].Elogweight();
405 |
406 | // Add in cluster log-likelihood, weighted by responsability
407 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
408 | {
409 | double LL = qZ[j].col(k).dot((logpi(k)
410 | + clusters[k].Eloglike(X[j]).array()).matrix());
411 |
412 | #pragma omp atomic
413 | ord[k].Fk -= LL;
414 | }
415 | }
416 |
417 | // Sort clusters by split tally, then free energy contributions
418 | sort(ord.begin(), ord.end(), greedcomp);
419 |
420 | // Pre allocate big objects for loops (this makes a runtime difference)
421 | vector mapidx(J, ArrayXi());
422 | vMatrixXd qZref(J, MatrixXd()), qZaug(J,MatrixXd()), Xk(J,MatrixXd());
423 |
424 | // Loop through each potential cluster in order and split it
425 | for (vector::iterator i = ord.begin(); i < ord.end(); ++i)
426 | {
427 | const int k = i->k;
428 |
429 | ++tally[k]; // increase this cluster's unsuccessful split tally by default
430 |
431 | // Don't waste time with clusters that can't really be split min (2:2)
432 | if (clusters[k].getN() < 4)
433 | continue;
434 |
435 | // Now split observations and qZ.
436 | int scount = 0, Mtot = 0;
437 |
438 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Mtot, scount)
439 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
440 | {
441 | // Make COPY of the observations with only relevant data points, p > 0.5
442 | mapidx[j] = partobs(X[j], (qZ[j].col(k).array()>0.5), Xk[j]); // Copy :-(
443 | Mtot += Xk[j].rows();
444 |
445 | // Initial cluster split
446 | ArrayXb splitk = clusters[k].splitobs(Xk[j]);
447 | qZref[j].setZero(Xk[j].rows(), 2);
448 | qZref[j].col(0) = (splitk == true).cast(); // Init qZ for split
449 | qZref[j].col(1) = (splitk == false).cast();
450 |
451 | // keep a track of number of splits
452 | scount += splitk.count();
453 | }
454 |
455 | // Don't waste time with clusters that haven't been split sufficiently
456 | if ( (scount < 2) || (scount > (Mtot-2)) )
457 | continue;
458 |
459 | // Refine the split
460 | vector wspl;
461 | vector cspl;
462 | vbem(Xk, qZref, wspl, cspl, clusters[0].getprior(), SPLITITER, sparse);
463 |
464 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
465 | continue;
466 |
467 | // Map the refined splits back to original whole-data problem
468 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
469 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
470 | qZaug[j] = auglabels(k, mapidx[j], (qZref[j].col(1).array()>0.5), qZ[j]);
471 |
472 | // Calculate free energy of this split with ALL data (and refine a bit)
473 | double Fsplit = vbem(X, qZaug, wspl, cspl, clusters[0].getprior(), 1,
474 | sparse);
475 |
476 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
477 | continue;
478 |
479 | // Only notify here of split candidates
480 | if (verbose == true)
481 | cout << '=' << flush;
482 |
483 | // Test whether this cluster split is a keeper
484 | if ( (Fsplit < F) && (abs((F-Fsplit)/F) > CONVERGE) )
485 | {
486 | qZ = qZaug;
487 | tally[k] = 0; // Reset tally if successfully split
488 | return true;
489 | }
490 | }
491 |
492 | // Failed to find splits
493 | return false;
494 | }
495 | #endif
496 |
497 |
498 | /* Find and remove all empty clusters.
499 | *
500 | * returns: true if any clusters have been deleted, false if all are kept.
501 | * mutable: qZ may have columns deleted if there are empty clusters found.
502 | * mutable: weights if there are empty clusters found.
503 | * mutable: clusters if there are empty clusters found.
504 | */
505 | template bool prune_clusters (
506 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Probabilities qZ
507 | vector& weights, // weights distributions
508 | vector& clusters, // cluster distributions
509 | bool verbose = false // print status
510 | )
511 | {
512 | const unsigned int K = clusters.size(),
513 | J = qZ.size();
514 |
515 | // Look for empty clusters
516 | ArrayXd Nk(K);
517 | for (unsigned int k= 0; k < K; ++k)
518 | Nk(k) = clusters[k].getN();
519 |
520 | // Find location of empty and full clusters
521 | ArrayXi eidx, fidx;
522 | arrfind(Nk.array() < ZEROCUTOFF, eidx, fidx);
523 | const unsigned int nempty = eidx.size();
524 |
525 | // If everything is not empty, return false
526 | if (nempty == 0)
527 | return false;
528 |
529 | if (verbose == true)
530 | cout << '*' << flush;
531 |
532 | // Delete empty cluster suff. stats.
533 | for (int i = (nempty - 1); i >= 0; --i)
534 | clusters.erase(clusters.begin() + eidx(i));
535 |
536 | // Delete empty cluster indicators by copying only full indicators
537 | const unsigned int newK = fidx.size();
538 | vMatrixXd newqZ(J);
539 |
540 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
541 | {
542 | newqZ[j].setZero(qZ[j].rows(), newK);
543 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < newK; ++k)
544 | newqZ[j].col(k) = qZ[j].col(fidx(k));
545 |
546 | weights[j].update(newqZ[j].colwise().sum()); // new weights
547 | }
548 |
549 | qZ = newqZ;
550 |
551 | return true;
552 | }
553 |
554 |
555 | /* The model selection algorithm for a grouped mixture model.
556 | *
557 | * returns: Free energy of the final model
558 | * mutable: qZ the probabilistic observation to cluster assignments
559 | * mutable: the group weight distributions
560 | * mutable: the cluster distributions
561 | * throws: invalid_argument from other functions.
562 | * throws: runtime_error if free energy increases.
563 | */
564 | template double cluster (
565 | const vMatrixXd& X, // Observations
566 | vMatrixXd& qZ, // Observations to model mixture assignments
567 | vector& weights, // Group weight distributions
568 | vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
569 | const double clusterprior, // Prior value for cluster distributions
570 | const int maxclusters, // Maximum number of clusters to search for
571 | const bool sparse, // Do sparse updates to groups
572 | const bool verbose, // Verbose output
573 | const unsigned int nthreads // Number of threads for OpenMP to use
574 | )
575 | {
576 | if (nthreads < 1)
577 | throw invalid_argument("Must specify at least one thread for execution!");
578 | omp_set_num_threads(nthreads);
579 |
580 | const unsigned int J = X.size();
581 |
582 | // Initialise indicator variables to just one cluster
583 | qZ.resize(J);
584 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
585 | qZ[j].setOnes(X[j].rows(), 1);
586 |
587 | // Initialise free energy and other loop variables
588 | bool issplit = true;
589 | double F;
590 |
591 | #ifndef EXHAUST_SPLIT
592 | vector tally;
593 | #endif
594 |
595 | // Main loop
596 | while (issplit == true)
597 | {
598 | // VBEM for all groups (throws runtime_error & invalid_argument)
599 | F = vbem(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior, -1, sparse, verbose);
600 |
601 | // Remove any empty clusters
602 | prune_clusters(qZ, weights, clusters, verbose);
603 |
604 | // Start cluster splitting
605 | if (verbose == true)
606 | cout << '<' << flush; // Notify start splitting
607 |
608 | // Search for best split, augment qZ if found one
609 | #ifdef EXHAUST_SPLIT
610 | issplit = split_ex(X, clusters, qZ, F, maxclusters, sparse, verbose);
611 | #else
612 | issplit = split_gr(X, weights, clusters, qZ, tally, F, maxclusters,
613 | sparse, verbose);
614 | #endif
615 |
616 | if (verbose == true)
617 | cout << '>' << endl; // Notify end splitting
618 | }
619 |
620 | // Print finished notification if verbose
621 | if (verbose == true)
622 | {
623 | cout << "Finished!" << endl;
624 | cout << "Number of clusters = " << clusters.size() << endl;
625 | cout << "Free energy = " << F << endl;
626 | }
627 |
628 | return F;
629 | }
630 |
631 |
632 | //
633 | // Public Functions
634 | //
635 |
636 | double libcluster::learnVDP (
637 | const MatrixXd& X,
638 | MatrixXd& qZ,
639 | StickBreak& weights,
640 | vector& clusters,
641 | const double clusterprior,
642 | const int maxclusters,
643 | const bool verbose,
644 | const unsigned int nthreads
645 | )
646 | {
647 | if (verbose == true)
648 | cout << "Learning VDP..." << endl; // Print start
649 |
650 | // Make temporary vectors of data to use with cluster()
651 | vMatrixXd vecX(1, X); // copies :-(
652 | vMatrixXd vecqZ;
653 | vector vecweights(1, weights);
654 |
655 | // Perform model learning and selection
656 | double F = cluster(vecX, vecqZ, vecweights, clusters,
657 | clusterprior, maxclusters, false,
658 | verbose, nthreads);
659 |
660 | // Return final Free energy and qZ
661 | qZ = vecqZ[0]; // copies :-(
662 | weights = vecweights[0];
663 | return F;
664 | }
665 |
666 |
667 | double libcluster::learnBGMM (
668 | const MatrixXd& X,
669 | MatrixXd& qZ,
670 | Dirichlet& weights,
671 | vector& clusters,
672 | const double clusterprior,
673 | const int maxclusters,
674 | const bool verbose,
675 | const unsigned int nthreads
676 | )
677 | {
678 | if (verbose == true)
679 | cout << "Learning Bayesian GMM..." << endl; // Print start
680 |
681 | // Make temporary vectors of data to use with cluster()
682 | vMatrixXd vecX(1, X); // copies :-(
683 | vMatrixXd vecqZ;
684 | vector vecweights(1, weights);
685 |
686 | // Perform model learning and selection
687 | double F = cluster(vecX, vecqZ, vecweights, clusters,
688 | clusterprior, maxclusters, false,
689 | verbose, nthreads);
690 |
691 | // Return final Free energy and qZ
692 | qZ = vecqZ[0]; // copies :-(
693 | weights = vecweights[0];
694 | return F;
695 | }
696 |
697 |
698 | double libcluster::learnDGMM (
699 | const MatrixXd& X,
700 | MatrixXd& qZ,
701 | Dirichlet& weights,
702 | vector& clusters,
703 | const double clusterprior,
704 | const int maxclusters,
705 | const bool verbose,
706 | const unsigned int nthreads
707 | )
708 | {
709 | if (verbose == true)
710 | cout << "Learning Bayesian diagonal GMM..." << endl; // Print start
711 |
712 | // Make temporary vectors of data to use with cluster()
713 | vMatrixXd vecX(1, X); // copies :-(
714 | vMatrixXd vecqZ;
715 | vector vecweights(1, weights);
716 |
717 | // Perform model learning and selection
718 | double F = cluster(vecX, vecqZ, vecweights, clusters,
719 | clusterprior, maxclusters, false,
720 | verbose, nthreads);
721 |
722 | // Return final Free energy and qZ
723 | qZ = vecqZ[0]; // copies :-(
724 | weights = vecweights[0];
725 | return F;
726 | }
727 |
728 |
729 | double libcluster::learnBEMM (
730 | const MatrixXd& X,
731 | MatrixXd& qZ,
732 | Dirichlet& weights,
733 | vector& clusters,
734 | const double clusterprior,
735 | const int maxclusters,
736 | const bool verbose,
737 | const unsigned int nthreads
738 | )
739 | {
740 | if ((X.array() < 0).any() == true)
741 | throw invalid_argument("X has to be in the range [0, inf)!");
742 |
743 | if (verbose == true)
744 | cout << "Learning Bayesian EMM..." << endl; // Print start
745 |
746 | // Make temporary vectors of data to use with cluster()
747 | vMatrixXd vecX(1, X); // copies :-(
748 | vMatrixXd vecqZ;
749 | vector vecweights(1, weights);
750 |
751 | // Perform model learning and selection
752 | double F = cluster(vecX, vecqZ, vecweights, clusters,
753 | clusterprior, maxclusters, false,
754 | verbose, nthreads);
755 |
756 | // Return final Free energy and qZ
757 | qZ = vecqZ[0]; // copies :-(
758 | weights = vecweights[0];
759 | return F;
760 | }
761 |
762 |
763 | double libcluster::learnGMC (
764 | const vMatrixXd& X,
765 | vMatrixXd& qZ,
766 | vector& weights,
767 | vector& clusters,
768 | const double clusterprior,
769 | const int maxclusters,
770 | const bool sparse,
771 | const bool verbose,
772 | const unsigned int nthreads
773 | )
774 | {
775 | string spnote = (sparse == true) ? "(sparse) " : "";
776 |
777 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
778 | if (verbose == true)
779 | cout << "Learning " << spnote << "GMC..." << endl;
780 |
781 | return cluster(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior,
782 | maxclusters, sparse, verbose,
783 | nthreads);
784 | }
785 |
786 |
787 | double libcluster::learnSGMC (
788 | const vMatrixXd& X,
789 | vMatrixXd& qZ,
790 | vector& weights,
791 | vector& clusters,
792 | const double clusterprior,
793 | const int maxclusters,
794 | const bool sparse,
795 | const bool verbose,
796 | const unsigned int nthreads
797 | )
798 | {
799 | string spnote = (sparse == true) ? "(sparse) " : "";
800 |
801 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
802 | if (verbose == true)
803 | cout << "Learning " << spnote << "Symmetric GMC..." << endl;
804 |
805 | return cluster(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior,
806 | maxclusters, sparse, verbose, nthreads);
807 | }
808 |
809 |
810 | double libcluster::learnDGMC (
811 | const vMatrixXd& X,
812 | vMatrixXd& qZ,
813 | vector& weights,
814 | vector& clusters,
815 | const double clusterprior,
816 | const int maxclusters,
817 | const bool sparse,
818 | const bool verbose,
819 | const unsigned int nthreads
820 | )
821 | {
822 | string spnote = (sparse == true) ? "(sparse) " : "";
823 |
824 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
825 | if (verbose == true)
826 | cout << "Learning " << spnote << "Diagonal GMC..." << endl;
827 |
828 | return cluster(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior,
829 | maxclusters, sparse, verbose,
830 | nthreads);
831 | }
832 |
833 |
834 | double libcluster::learnEGMC (
835 | const vMatrixXd& X,
836 | vMatrixXd& qZ,
837 | vector& weights,
838 | vector& clusters,
839 | const double clusterprior,
840 | const int maxclusters,
841 | const bool sparse,
842 | const bool verbose,
843 | const unsigned int nthreads
844 | )
845 | {
846 | string spnote = (sparse == true) ? "(sparse) " : "";
847 |
848 | // Check for negative inputs
849 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < X.size(); ++j)
850 | if ((X[j].array() < 0).any() == true)
851 | throw invalid_argument("X has to be in the range [0, inf)!");
852 |
853 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
854 | if (verbose == true)
855 | cout << "Learning " << spnote << "Exponential GMC..." << endl;
856 |
857 | return cluster(X, qZ, weights, clusters, clusterprior,
858 | maxclusters, sparse, verbose, nthreads);
859 | }
860 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/comutils.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include "comutils.h"
22 |
23 |
24 | //
25 | // Namespaces
26 | //
27 |
28 | using namespace std;
29 | using namespace Eigen;
30 | using namespace libcluster;
31 | using namespace probutils;
32 | using namespace distributions;
33 |
34 |
35 | //
36 | // Public Functions
37 | //
38 |
39 | void comutils::arrfind (
40 | const ArrayXb& expression,
41 | ArrayXi& indtrue,
42 | ArrayXi& indfalse
43 | )
44 | {
45 | const int N = expression.size(),
46 | M = expression.count();
47 |
48 | indtrue.setZero(M);
49 | indfalse.setZero(N-M);
50 |
51 | for (int n = 0, m = 0, l = 0; n < N; ++n)
52 | expression(n) ? indtrue(m++) = n : indfalse(l++) = n;
53 | }
54 |
55 |
56 | ArrayXi comutils::partobs (
57 | const MatrixXd& X,
58 | const ArrayXb& Xpart,
59 | MatrixXd& Xk
60 | )
61 | {
62 | const int M = Xpart.count();
63 |
64 | ArrayXi pidx, npidx;
65 | comutils::arrfind(Xpart, pidx, npidx);
66 |
67 | Xk.setZero(M, X.cols());
68 | for (int m=0; m < M; ++m) // index copy X to Xk
69 | Xk.row(m) = X.row(pidx(m));
70 |
71 | return pidx;
72 | }
73 |
74 |
75 | MatrixXd comutils::auglabels (
76 | const double k,
77 | const ArrayXi& map,
78 | const ArrayXb& Zsplit,
79 | const MatrixXd& qZ
80 | )
81 | {
82 | const int K = qZ.cols(),
83 | S = Zsplit.count();
84 |
85 | if (Zsplit.size() != map.size())
86 | throw invalid_argument("map and split must be the same size!");
87 |
88 | // Create new qZ for all data with split
89 | MatrixXd qZaug = qZ; // Copy the existing qZ into the new
90 | qZaug.conservativeResize(Eigen::NoChange, K+1);
91 | qZaug.col(K).setZero();
92 |
93 | ArrayXi sidx, nsidx;
94 | comutils::arrfind(Zsplit, sidx, nsidx);
95 |
96 | // Copy split cluster assignments (augment qZ effectively)
97 | for (int s = 0; s < S; ++s)
98 | {
99 | qZaug(map(sidx(s)), K) = qZ(map(sidx(s)), k); // Add new cluster onto end
100 | qZaug(map(sidx(s)), k) = 0;
101 | }
102 |
103 | return qZaug;
104 | }
105 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/comutils.h:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #ifndef COMUTILS_H
22 | #define COMUTILS_H
23 |
24 | #include
25 | #include
26 | #include
27 | #include "libcluster.h"
28 | #include "probutils.h"
29 | #include "distributions.h"
30 |
31 |
32 | /*! Namespace that implements various common utilities used in the algorithms */
33 | namespace comutils
34 | {
35 |
36 |
37 | //
38 | // Helper structures
39 | //
40 |
41 | /* Triplet that contains the information for choosing a good cluster split
42 | * ordering.
43 | */
44 | struct GreedOrder
45 | {
46 | int k; // Cluster number/index
47 | int tally; // Number of times a cluster has failed to split
48 | double Fk; // The clusters approximate free energy contribution
49 | };
50 |
51 |
52 | //
53 | // Helper functions
54 | //
55 |
56 | /* Compares two GreedOrder triplets and returns which is more optimal to split.
57 | * Precendence is given to less split fail tally, and then to more free energy
58 | * contribution.
59 | */
60 | bool inline greedcomp (const GreedOrder& i, const GreedOrder& j)
61 | {
62 | if (i.tally == j.tally) // If the tally is the same, use the greater Fk
63 | return i.Fk > j.Fk;
64 | else if (i.tally < j.tally) // Otherwise prefer the lower tally
65 | return true;
66 | else
67 | return false;
68 | }
69 |
70 |
71 | /* Find the indices of the ones and zeros in a binary array in the order they
72 | * appear.
73 | *
74 | * mutable: indtrue the indices of the true values in the array "expression"
75 | * mutable: indfalse the indices of the false values in the array "expression"
76 | */
77 | void arrfind (
78 | const distributions::ArrayXb& expression,
79 | Eigen::ArrayXi& indtrue,
80 | Eigen::ArrayXi& indfalse
81 | );
82 |
83 |
84 | /* Partition the observations, X according to a logical array.
85 | *
86 | * mutable: Xk, MxD matrix of observations that have a correspoding 1 in Xpart.
87 | * returns: an Mx1 array of the locations of Xk in X.
88 | */
89 | Eigen::ArrayXi partobs (
90 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& X, // NxD matrix of observations.
91 | const distributions::ArrayXb& Xpart, // Nx1 indicator vector to partition X.
92 | Eigen::MatrixXd& Xk // MxD matrix of obs. beloning to new partition
93 | );
94 |
95 |
96 | /* Augment the assignment matrix, qZ with the split cluster entry.
97 | *
98 | * The new cluster assignments are put in the K+1 th column in the return matrix
99 | * returns: The new observation assignments, [Nx(K+1)].
100 | * throws: std::invalid_argument if map.size() != Zsplit.size().
101 | */
102 | Eigen::MatrixXd auglabels (
103 | const double k, // Cluster to split (i.e. which column of qZ)
104 | const Eigen::ArrayXi& map, // Mapping from array of partitioned obs to qZ
105 | const distributions::ArrayXb& Zsplit, // Boolean array of assignments.
106 | const Eigen::MatrixXd& qZ // [NxK] observation assignment prob. matrix.
107 | );
108 |
109 |
110 | /* Check if any sufficient statistics are empty.
111 | *
112 | * returns: True if any of the sufficient statistics are empty
113 | */
114 | template bool anyempty (const std::vector& clusters)
115 | {
116 | const unsigned int K = clusters.size();
117 |
118 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
119 | if (clusters[k].getN() <= 1)
120 | return true;
121 |
122 | return false;
123 | }
124 |
125 | }
126 |
127 | #endif // COMUTILS_H
128 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/distributions.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include
22 | #include "distributions.h"
23 | #include "probutils.h"
24 |
25 | //
26 | // Namespaces
27 | //
28 |
29 | using namespace std;
30 | using namespace Eigen;
31 | using namespace probutils;
32 | using namespace boost::math;
33 |
34 |
35 | //
36 | // File scope variables
37 | //
38 |
39 | // Define pi
40 | const double pi = constants::pi(); // Boost high precision pi
41 |
42 |
43 | //
44 | // Private Helper Functions
45 | //
46 |
47 | /* Compare an double pair by the double member. Useful
48 | * for sorting an array in descending order while retaining a notion of
49 | * the original order of the array.
50 | *
51 | * returns: true if i.second > j.second.
52 | */
53 | bool inline obscomp (
54 | const std::pair& i, // the first pair to compare.
55 | const std::pair& j // the second pair to compare.
56 | )
57 | {
58 | return i.second > j.second;
59 | }
60 |
61 |
62 | /* Enumerate the dimensions.
63 | *
64 | * returns: 1:D or if D = 1, return 1.
65 | */
66 | ArrayXd enumdims (const int D)
67 | {
68 | ArrayXd l;
69 |
70 | if (D > 1)
71 | l = ArrayXd::LinSpaced(D, 1, D);
72 | else
73 | l.setOnes(1);
74 |
75 | return l;
76 | }
77 |
78 |
79 | //
80 | // Stick-Breaking (Dirichlet Process) weight distribution.
81 | //
82 |
83 | distributions::StickBreak::StickBreak ()
84 | : WeightDist(),
85 | alpha1_p(distributions::ALPHA1PRIOR),
86 | alpha2_p(distributions::ALPHA2PRIOR),
87 | alpha1(ArrayXd::Constant(1, distributions::ALPHA1PRIOR)),
88 | alpha2(ArrayXd::Constant(1, distributions::ALPHA2PRIOR)),
89 | E_logv(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
90 | E_lognv(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
91 | E_logpi(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
92 | ordvec(1, pair(0,0))
93 | {
94 | this->priorfcalc();
95 | }
96 |
97 |
98 | distributions::StickBreak::StickBreak (const double concentration)
99 | : WeightDist(),
100 | alpha2_p(distributions::ALPHA2PRIOR),
101 | alpha2(ArrayXd::Constant(1, distributions::ALPHA2PRIOR)),
102 | E_logv(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
103 | E_lognv(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
104 | E_logpi(ArrayXd::Zero(1)),
105 | ordvec(1, pair(0,0))
106 | {
107 | if (concentration <=0)
108 | throw invalid_argument("Concentration parameter has to be > 0!");
109 |
110 | this->alpha1_p = concentration;
111 | this->alpha1 = ArrayXd::Constant(1, concentration);
112 | this->priorfcalc();
113 | }
114 |
115 |
116 | void distributions::StickBreak::priorfcalc (void)
117 | {
118 | // Prior free energy contribution
119 | this->F_p = lgamma(this->alpha1_p) + lgamma(this->alpha2_p)
120 | - lgamma(this->alpha1_p + this->alpha2_p);
121 | }
122 |
123 |
124 | void distributions::StickBreak::update (const ArrayXd& Nk)
125 | {
126 | const int K = Nk.size();
127 |
128 | // Destructively resize members to be the same size as Nk, no-op if same
129 | this->alpha1.resize(K);
130 | this->alpha2.resize(K);
131 | this->E_logv.resize(K);
132 | this->E_lognv.resize(K);
133 | this->E_logpi.resize(K);
134 | this->ordvec.resize(K, pair(-1, -1));
135 |
136 | // Order independent update
137 | this->Nk = Nk;
138 | this->alpha1 = this->alpha1_p + Nk;
139 |
140 | // Get at sort size order of clusters
141 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
142 | {
143 | this->ordvec[k].first = k;
144 | this->ordvec[k].second = Nk(k);
145 | }
146 | sort(this->ordvec.begin(), this->ordvec.end(), obscomp);
147 |
148 | // Now do order dependent updates
149 | const double N = Nk.sum();
150 | double cumNk = 0, cumE_lognv = 0;
151 | for (int idx = 0, k; idx < K; ++idx)
152 | {
153 | k = this->ordvec[idx].first;
154 |
155 | // Alpha 2
156 | cumNk += Nk(k); // Accumulate cluster size sum
157 | this->alpha2(k) = this->alpha2_p + (N - cumNk);
158 |
159 | // Expected stick lengths
160 | double psisum = digamma(this->alpha1(k) + this->alpha2(k));
161 | this->E_logv(k) = digamma(this->alpha1(k)) - psisum;
162 | this->E_lognv(k) = digamma(this->alpha2(k)) - psisum;
163 |
164 | // Expected weights
165 | this->E_logpi(k) = this->E_logv(k) + cumE_lognv;
166 | cumE_lognv += E_lognv(k); // Accumulate log stick length left
167 | }
168 | }
169 |
170 |
171 | double distributions::StickBreak::fenergy () const
172 | {
173 | const int K = this->alpha1.size();
174 |
175 | return K * this->F_p + (mxlgamma(this->alpha1 + this->alpha2).array()
176 | - mxlgamma(this->alpha1).array() - mxlgamma(this->alpha2).array()
177 | + (this->alpha1 - this->alpha1_p) * this->E_logv
178 | + (this->alpha2 - this->alpha2_p) * this->E_lognv).sum();
179 | }
180 |
181 |
182 | //
183 | // Generalised Dirichlet weight distribution.
184 | //
185 |
186 | void distributions::GDirichlet::update (const ArrayXd& Nk)
187 | {
188 | // Call base class (stick breaking) update
189 | this->StickBreak::update(Nk);
190 | const int smallk = (this->ordvec.end() - 1)->first; // Get smallest cluster
191 |
192 | // Set last stick lengths to 1 ( log(0) = 1 ) and adjust log marginal
193 | this->E_logpi(smallk) = this->E_logpi(smallk) - this->E_logv(smallk);
194 | this->E_logv(smallk) = 0; // exp(E[log v_K]) = 1
195 | this->E_lognv(smallk) = 0; // Undefined, but set to zero
196 | }
197 |
198 |
199 | double distributions::GDirichlet::fenergy () const
200 | {
201 | const int K = this->ordvec.size();
202 |
203 | // GDir only has K-1 parameters, so we don't calculate the last F contrib.
204 | double Fpi = 0;
205 | for (int idx = 0, k = 0; idx < K-1; ++idx)
206 | {
207 | k = this->ordvec[idx].first;
208 | Fpi += lgamma(this->alpha1(k) + this->alpha2(k))
209 | - lgamma(this->alpha1(k)) - lgamma(this->alpha2(k))
210 | + (this->alpha1(k) - this->alpha1_p) * this->E_logv(k)
211 | + (this->alpha2(k) - this->alpha2_p) * this->E_lognv(k);
212 | }
213 |
214 | return (K-1) * this->F_p + Fpi;
215 | }
216 |
217 |
218 | //
219 | // Dirichlet weight distribution.
220 | //
221 |
222 | distributions::Dirichlet::Dirichlet ()
223 | : WeightDist(),
224 | alpha_p(distributions::ALPHA1PRIOR),
225 | alpha(ArrayXd::Constant(1, distributions::ALPHA1PRIOR)),
226 | E_logpi(ArrayXd::Zero(1))
227 | {}
228 |
229 |
230 | distributions::Dirichlet::Dirichlet (const double alpha)
231 | : WeightDist(),
232 | E_logpi(ArrayXd::Zero(1))
233 | {
234 | if (alpha <= 0)
235 | throw invalid_argument("Alpha prior must be > 0!");
236 |
237 | alpha_p = alpha;
238 | this->alpha = ArrayXd::Constant(1, alpha);
239 | }
240 |
241 |
242 | void distributions::Dirichlet::update (const ArrayXd& Nk)
243 | {
244 | const int K = Nk.size();
245 |
246 | // Destructively resize members to be the same size as Nk, no-op if same
247 | this->alpha.resize(K);
248 | this->E_logpi.resize(K);
249 |
250 | // Hyperparameter update
251 | this->Nk = Nk;
252 | this->alpha = this->alpha_p + Nk;
253 |
254 | // Expectation update
255 | this->E_logpi = mxdigamma(this->alpha).array() - digamma(this->alpha.sum());
256 | }
257 |
258 |
259 | double distributions::Dirichlet::fenergy () const
260 | {
261 | const int K = this->alpha.size();
262 |
263 | return lgamma(this->alpha.sum()) - (this->alpha_p-1) * this->E_logpi.sum()
264 | + ((this->alpha-1) * this->E_logpi - mxlgamma(this->alpha).array()).sum()
265 | - lgamma(K * this->alpha_p) + K * lgamma(this->alpha_p);
266 | }
267 |
268 |
269 | //
270 | // Gaussian Wishart cluster distribution.
271 | //
272 |
273 | distributions::GaussWish::GaussWish (
274 | const double clustwidth,
275 | const unsigned int D
276 | )
277 | : ClusterDist(clustwidth, D),
278 | nu_p(D),
279 | beta_p(distributions::BETAPRIOR),
280 | m_p(RowVectorXd::Zero(D))
281 | {
282 | if (clustwidth <= 0)
283 | throw invalid_argument("clustwidth must be > 0!");
284 |
285 | // Create Prior
286 | this->iW_p = this->nu_p * this->prior * MatrixXd::Identity(D, D);
287 |
288 | try
289 | { this->logdW_p = -logdet(this->iW_p); }
290 | catch (invalid_argument e)
291 | { throw invalid_argument(string("Creating prior: ").append(e.what())); }
292 |
293 | // Calculate prior free energy contribution
294 | this->F_p = mxlgamma((this->nu_p + 1
295 | - enumdims(this->m_p.cols())).matrix() / 2).sum();
296 |
297 | this->clearobs(); // Empty suff. stats. and set posteriors equal to priors
298 | }
299 |
300 |
301 | void distributions::GaussWish::addobs(const VectorXd& qZk, const MatrixXd& X)
302 | {
303 | if (X.cols() != this->D)
304 | throw invalid_argument("Mismatched dims. of cluster params and obs.!");
305 | if (qZk.rows() != X.rows())
306 | throw invalid_argument("qZk and X ar not the same length!");
307 |
308 | MatrixXd qZkX = qZk.asDiagonal() * X;
309 |
310 | this->N_s += qZk.sum();
311 | this->x_s += qZkX.colwise().sum(); // [1xD] row vector
312 | this->xx_s.noalias() += qZkX.transpose() * X; // [DxD] matrix
313 | }
314 |
315 |
316 | void distributions::GaussWish::update ()
317 | {
318 | // Prepare the Sufficient statistics
319 | RowVectorXd xk = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
320 | if (this->N_s > 0)
321 | xk = this->x_s/this->N_s;
322 | MatrixXd Sk = this->xx_s - xk.transpose() * this->x_s;
323 | RowVectorXd xk_m = xk - this->m_p; // for iW, (xk - m)
324 |
325 | // Update posterior params
326 | this->N = this->N_s;
327 | this->nu = this->nu_p + this->N;
328 | this->beta = this->beta_p + this->N;
329 | this->m = (this->beta_p * this->m_p + this->x_s) / this->beta;
330 | this->iW = this->iW_p + Sk
331 | + (this->beta_p * this->N/this->beta) * xk_m.transpose() * xk_m;
332 |
333 | try
334 | { this->logdW = -logdet(this->iW); }
335 | catch (invalid_argument e)
336 | { throw runtime_error(string("Calc log(det(W)): ").append(e.what())); }
337 | }
338 |
339 |
340 | void distributions::GaussWish::clearobs ()
341 | {
342 | // Reset parameters back to prior values
343 | this->nu = this->nu_p;
344 | this->beta = this->beta_p;
345 | this->m = this->m_p;
346 | this->iW = this->iW_p;
347 | this->logdW = this->logdW_p;
348 |
349 | // Empty sufficient statistics
350 | this->N_s = 0;
351 | this->x_s = RowVectorXd::Zero(D);
352 | this->xx_s = MatrixXd::Zero(D,D);
353 | }
354 |
355 |
356 | VectorXd distributions::GaussWish::Eloglike (const MatrixXd& X) const
357 | {
358 | // Expectations of log Gaussian likelihood
359 | VectorXd E_logX(X.rows());
360 | double sumpsi = mxdigamma((this->nu+1-enumdims(this->D)).matrix()/2).sum();
361 | try
362 | {
363 | E_logX = 0.5 * (sumpsi + this->logdW - this->D * (1/this->beta + log(pi))
364 | - this->nu * mahaldist(X, this->m, this->iW).array()).matrix();
365 | }
366 | catch (invalid_argument e)
367 | { throw(string("Calculating Gaussian likelihood: ").append(e.what())); }
368 |
369 | return E_logX;
370 | }
371 |
372 |
373 | distributions::ArrayXb distributions::GaussWish::splitobs (
374 | const MatrixXd& X
375 | ) const
376 | {
377 |
378 | // Find the principle eigenvector using the power method if not done so
379 | VectorXd eigvec;
380 | eigpower(this->iW, eigvec);
381 |
382 | // 'split' the observations perpendicular to this eigenvector.
383 | return (((X.rowwise() - this->m)
384 | * eigvec.asDiagonal()).array().rowwise().sum()) >= 0;
385 | }
386 |
387 |
388 | double distributions::GaussWish::fenergy () const
389 | {
390 | const ArrayXd l = enumdims(this->D);
391 | double sumpsi = mxdigamma((this->nu + 1 - l).matrix() / 2).sum();
392 |
393 | return this->F_p + (this->D * (this->beta_p/this->beta - 1 - this->nu
394 | - log(this->beta_p/this->beta))
395 | + this->nu * ((this->iW.ldlt().solve(this->iW_p)).trace()
396 | + this->beta_p * mahaldist(this->m, this->m_p, this->iW).coeff(0,0))
397 | + this->nu_p * (this->logdW_p - this->logdW) + this->N*sumpsi)/2
398 | - mxlgamma((this->nu+1-l).matrix() / 2).sum();
399 | }
400 |
401 |
402 | //
403 | // Normal Gamma parameter distribution.
404 | //
405 |
406 | distributions::NormGamma::NormGamma (
407 | const double clustwidth,
408 | const unsigned int D
409 | )
410 | : ClusterDist(clustwidth, D),
411 | nu_p(distributions::NUPRIOR),
412 | beta_p(distributions::BETAPRIOR),
413 | m_p(RowVectorXd::Zero(D))
414 | {
415 | if (clustwidth <= 0)
416 | throw invalid_argument("clustwidth must be > 0!");
417 |
418 | // Create Prior
419 | this->L_p = this->nu_p * this->prior * RowVectorXd::Ones(D);
420 | this->logL_p = this->L_p.array().log().sum();
421 |
422 | this->clearobs(); // Empty suff. stats. and set posteriors equal to priors
423 | }
424 |
425 |
426 | void distributions::NormGamma::addobs (const VectorXd& qZk, const MatrixXd& X)
427 | {
428 | if (X.cols() != this->D)
429 | throw invalid_argument("Mismatched dims. of cluster params and obs.!");
430 | if (qZk.rows() != X.rows())
431 | throw invalid_argument("qZk and X ar not the same length!");
432 |
433 | MatrixXd qZkX = qZk.asDiagonal() * X;
434 |
435 | this->N_s += qZk.sum();
436 | this->x_s += qZkX.colwise().sum(); // [1xD]
437 | this->xx_s += (qZkX.array() * X.array()).colwise().sum().matrix(); // [1xD]
438 | }
439 |
440 |
441 | void distributions::NormGamma::update ()
442 | {
443 | // Prepare the Sufficient statistics
444 | RowVectorXd xk = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
445 | RowVectorXd Sk = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
446 | if (this->N_s > 0)
447 | {
448 | xk = this->x_s/this->N_s;
449 | Sk = this->xx_s.array() - this->x_s.array().square()/this->N_s;
450 | }
451 |
452 | // Update posterior params
453 | this->N = this->N_s;
454 | this->beta = this->beta_p + this->N;
455 | this->nu = this->nu_p + this->N/2;
456 | this->m = (this->beta_p * this->m_p + x_s) / this->beta;
457 | this->L = this->L_p + Sk/2 + (this->beta_p * this->N / (2 * this->beta))
458 | * (xk - this->m_p).array().square().matrix();
459 |
460 | if ((this->L.array() <= 0).any())
461 | throw invalid_argument(string("Calc log(L): Variance is zero or less!"));
462 |
463 | this->logL = this->L.array().log().sum();
464 | }
465 |
466 |
467 | void distributions::NormGamma::clearobs ()
468 | {
469 | // Reset parameters back to prior values
470 | this->nu = this->nu_p;
471 | this->beta = this->beta_p;
472 | this->m = this->m_p;
473 | this->L = this->L_p;
474 | this->logL = this->logL_p;
475 |
476 | // Empty sufficient statistics
477 | this->N_s = 0;
478 | this->x_s = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
479 | this->xx_s = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
480 | }
481 |
482 |
483 | VectorXd distributions::NormGamma::Eloglike (const MatrixXd& X) const
484 | {
485 | // Distance evaluation in the exponent
486 | VectorXd Xmdist = (X.rowwise() - this->m).array().square().matrix()
487 | * this->L.array().inverse().matrix().transpose();
488 |
489 | // Expectations of log Gaussian likelihood
490 | return 0.5 * (this->D * (digamma(this->nu) - log(2 * pi) - 1/this->beta)
491 | - this->logL - this->nu * Xmdist.array());
492 | }
493 |
494 |
495 | distributions::ArrayXb distributions::NormGamma::splitobs (
496 | const MatrixXd& X
497 | ) const
498 | {
499 | // Find location of largest element in L, this is the 'eigenvector'
500 | int eigvec;
501 | this->L.maxCoeff(&eigvec);
502 |
503 | // 'split' the observations perpendicular to this 'eigenvector'.
504 | return (X.col(eigvec).array() - this->m(eigvec)) >= 0;
505 | }
506 |
507 |
508 | double distributions::NormGamma::fenergy () const
509 | {
510 | const VectorXd iL = this->L.array().inverse().matrix().transpose();
511 |
512 | return D*(lgamma(this->nu_p) - lgamma(this->nu)
513 | + this->N*digamma(this->nu)/2 - this->nu)
514 | + D/2 * (log(this->beta) - log(this->beta_p) - 1 + this->beta_p/this->beta)
515 | + this->beta_p*this->nu/2*(this->m - this->m_p).array().square().matrix()*iL
516 | + this->nu_p*(this->logL - this->logL_p) + this->nu*this->L_p*iL;
517 | }
518 |
519 |
520 | //
521 | // Exponential Gamma parameter distribution.
522 | //
523 |
524 | distributions::ExpGamma::ExpGamma (const double obsmag, const unsigned int D)
525 | : ClusterDist(obsmag, D),
526 | a_p(distributions::APRIOR),
527 | b_p(obsmag)
528 | {
529 | this->clearobs(); // Empty suff. stats. and set posteriors equal to priors
530 | }
531 |
532 |
533 | void distributions::ExpGamma::addobs (const VectorXd& qZk, const MatrixXd& X)
534 | {
535 | if (X.cols() != this->D)
536 | throw invalid_argument("Mismatched dims. of cluster params and obs.!");
537 | if (qZk.rows() != X.rows())
538 | throw invalid_argument("qZk and X ar not the same length!");
539 |
540 | this->N_s += qZk.sum();
541 | this->x_s += (qZk.asDiagonal() * X).colwise().sum();
542 | }
543 |
544 |
545 | void distributions::ExpGamma::update ()
546 | {
547 | // Update posterior params
548 | this->N = this->N_s;
549 | this->a = this->a_p + this->N;
550 | this->ib = (this->b_p + this->x_s.array()).array().inverse().matrix();
551 | this->logb = - this->ib.array().log().sum();
552 | }
553 |
554 |
555 | void distributions::ExpGamma::clearobs ()
556 | {
557 | // Reset parameters back to prior values
558 | this->a = this->a_p;
559 | this->ib = RowVectorXd::Constant(this->D, 1/this->b_p);
560 | this->logb = this->D * log(this->b_p);
561 |
562 | // Empty sufficient statistics
563 | this->N_s = 0;
564 | this->x_s = RowVectorXd::Zero(this->D);
565 | }
566 |
567 |
568 | VectorXd distributions::ExpGamma::Eloglike (const MatrixXd& X) const
569 | {
570 | return this->D * digamma(this->a) - this->logb
571 | - (this->a * X * this->ib.transpose()).array();
572 | }
573 |
574 |
575 | distributions::ArrayXb distributions::ExpGamma::splitobs (
576 | const MatrixXd& X
577 | ) const
578 | {
579 | ArrayXd XdotL = X * (this->a * this->ib).transpose();
580 | return (XdotL > (XdotL.sum()/XdotL.size()));
581 | }
582 |
583 |
584 | double distributions::ExpGamma::fenergy () const
585 | {
586 | return this->D * ((this->a - this->a_p) * digamma(this->a) - this->a
587 | - this->a_p * log(this->b_p) - lgamma(this->a) + lgamma(this->a_p))
588 | + this->b_p * this->a * this->ib.sum() + this->a_p * this->logb;
589 | }
590 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/mcluster.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include
22 | #include "libcluster.h"
23 | #include "probutils.h"
24 | #include "comutils.h"
25 |
26 |
27 | //
28 | // Namespaces
29 | //
30 |
31 | using namespace std;
32 | using namespace Eigen;
33 | using namespace probutils;
34 | using namespace distributions;
35 | using namespace comutils;
36 | using namespace libcluster;
37 |
38 |
39 | //
40 | // Variational Bayes Private Functions
41 | //
42 |
43 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for weights in each group.
44 | *
45 | * mutable: Top-level cluster assignment probabilities, qYj
46 | * returns: The complete-data free energy, Y and Y+Z dep. terms, for group j.
47 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
48 | */
49 | template double vbeY (
50 | const MatrixXd& Wj, // Top-level observations for group j
51 | const vMatrixXd& qZj, // Bottom-level cluster labels for group j
52 | const WJ& weightsj, // Group top-level cluster weights
53 | const vector& weights_t, // Bottom-level cluster proportion/paramters
54 | const vector& clusters_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
55 | MatrixXd& qYj // Top-level cluster assignments for group j
56 | )
57 | {
58 | const unsigned int T = weights_t.size(),
59 | Ij = qZj.size(),
60 | K = qZj[0].cols();
61 |
62 | // No observations (may happen when splitting)
63 | if (Ij == 0)
64 | return 0;
65 |
66 | // Get log marginal weight likelihoods
67 | const ArrayXd E_logwj = weightsj.Elogweight();
68 |
69 | MatrixXd Njik(Ij, K), logqYj(Ij, T);
70 | ArrayXXd qZjiLike(Ij, T);
71 |
72 | // Get bottom-level cluster counts per "document/image"
73 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < Ij; ++i)
74 | Njik.row(i) = qZj[i].colwise().sum();
75 |
76 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs
77 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
78 | {
79 | qZjiLike.col(t) = Njik * weights_t[t].Elogweight().matrix();
80 | logqYj.col(t) = qZjiLike.col(t) + E_logwj(t)
81 | + clusters_t[t].Eloglike(Wj).array();
82 | }
83 |
84 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
85 | VectorXd logZyj = logsumexp(logqYj);
86 |
87 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities
88 | qYj = (logqYj.colwise() - logZyj).array().exp().matrix();
89 |
90 | return ((qYj.array() * qZjiLike).rowwise().sum() - logZyj.array()).sum();
91 | }
92 |
93 |
94 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for clusters in each "document", ji.
95 | *
96 | * mutable: Bottom-level cluster assignment probabilities, qZji
97 | * returns: The complete-data free energy, Z dep. terms, for group j.
98 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
99 | */
100 | template double vbeZ (
101 | const MatrixXd& Xji, // Observations in i in group j
102 | const RowVectorXd& qYji, // Top-level cluster assignment
103 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
104 | const vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
105 | MatrixXd& qZji // Observation to cluster assignments
106 | )
107 | {
108 | const int K = clusters_k.size(),
109 | Nji = Xji.rows(),
110 | T = weights_t.size();
111 |
112 | // No observations (may happen when splitting)
113 | if (Nji == 0)
114 | return 0;
115 |
116 | // Make top-level cluster global weights from weighted label parameters
117 | RowVectorXd E_logqYljt = RowVectorXd::Zero(K);
118 |
119 | for (int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
120 | E_logqYljt.noalias() += qYji(t) * weights_t[t].Elogweight().matrix();
121 |
122 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs
123 | MatrixXd logqZji = MatrixXd::Zero(Nji, K);
124 |
125 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
126 | logqZji.col(k) = E_logqYljt(k) + clusters_k[k].Eloglike(Xji).array();
127 |
128 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
129 | const VectorXd logZzji = logsumexp(logqZji);
130 |
131 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities
132 | qZji = (logqZji.colwise() - logZzji).array().exp().matrix();
133 |
134 | return -logZzji.sum();
135 | }
136 |
137 |
138 | /* Calculates the free energy lower bound for the model parameter distributions.
139 | *
140 | * returns: the free energy of the model
141 | */
142 | template double fenergy (
143 | const vector& weights_j, // Group top-level cluster weights
144 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster proportion parameters
145 | const vector& clusters_t, // Top-level cluster other parameters
146 | const vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
147 | const double Fyz, // Free energy Y and cross Y-Z terms
148 | const double Fz // Free energy Z terms
149 | )
150 | {
151 | const int T = weights_t.size(),
152 | K = clusters_k.size(),
153 | J = weights_j.size();
154 |
155 | // Class parameter free energy
156 | double Ft = 0;
157 | for (int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
158 | Ft += weights_t[t].fenergy() + clusters_t[t].fenergy();
159 |
160 | // Cluster parameter free energy
161 | double Fk = 0;
162 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
163 | Fk += clusters_k[k].fenergy();
164 |
165 | // Weight parameter free energy
166 | double Fw = 0;
167 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
168 | Fw += weights_j[j].fenergy();
169 |
170 | return Fw + Ft + Fk + Fyz + Fz;
171 | }
172 |
173 |
174 | /* Variational Bayes EM.
175 | *
176 | * returns: Free energy of the whole model.
177 | * mutable: the bottom-level cluster indicators, qZ
178 | * mutable: the top-level cluster indicators, qY
179 | * mutable: model parameters weights_j, weights_t, clusters_k, clusters_t
180 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
181 | * throws: runtime_error if there is a negative free energy.
182 | */
183 | template double vbem (
184 | const vMatrixXd& W, // Top-level observations
185 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Bottom-level observations
186 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level labels
187 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level cluster labels
188 | vector& weights_j, // Group top-level cluster weights
189 | vector& weights_t, // Top-level proportion cluster parameters
190 | vector& clusters_t, // Top-level other cluster parameters
191 | vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
192 | const double prior_t, // Top-level cluster prior
193 | const double prior_k, // Bottom-level cluster prior
194 | const int maxit = -1, // Max VBEM iterations (-1 = no max, default)
195 | const bool verbose = false // Verbose output
196 | )
197 | {
198 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
199 | K = qZ[0][0].cols(),
200 | T = qY[0].cols();
201 |
202 | // Construct (empty) parameters
203 | weights_j.resize(J, WJ());
204 | weights_t.resize(T, WT());
205 | clusters_t.resize(T, CT(prior_t, W[0].cols()));
206 | clusters_k.resize(K, CK(prior_k, X[0][0].cols()));
207 |
208 | // Other loop variables for initialisation
209 | int it = 0;
210 | double F = numeric_limits::max(), Fold;
211 |
212 | do
213 | {
214 | Fold = F;
215 |
216 | MatrixXd Ntk = MatrixXd::Zero(T, K); // Clear Sufficient Stats
217 |
218 | // VBM for top-level cluster weights
219 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
220 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
221 | {
222 | // Accumulate suff. stats for bottom-level cluster counts
223 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
224 | {
225 | MatrixXd Ntkji = qY[j].row(i).transpose() * qZ[j][i].colwise().sum();
226 | #pragma omp critical
227 | Ntk += Ntkji;
228 | }
229 |
230 | weights_j[j].update(qY[j].colwise().sum());
231 | }
232 |
233 | // VBM for top-level cluster parameters and proportions
234 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
235 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
236 | {
237 | clusters_t[t].clearobs(); // Clear Sufficient Stats
238 |
239 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j) // Accumulate sufficient stats
240 | clusters_t[t].addobs(qY[j].col(t), W[j]);
241 |
242 | weights_t[t].update(Ntk.row(t)); // Bottom-level cluster counts.
243 | clusters_t[t].update();
244 | }
245 |
246 | // VBM for bottom-level cluster parameters
247 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
248 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
249 | {
250 | clusters_k[k].clearobs(); // Clear Sufficient Stats
251 |
252 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j) // Accumulate sufficient stats
253 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
254 | clusters_k[k].addobs(qZ[j][i].col(k), X[j][i]);
255 |
256 | clusters_k[k].update(); // Bottom-level observations
257 | }
258 |
259 | // Free energy data fit term accumulators
260 | double Fz = 0, Fyz = 0;
261 |
262 | // VBE for top-level cluster indicators
263 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fyz)
264 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
265 | Fyz += vbeY(W[j], qZ[j], weights_j[j], weights_t, clusters_t,
266 | qY[j]);
267 |
268 | // VBE for bottom-level cluster indicators
269 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
270 | {
271 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fz)
272 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
273 | Fz += vbeZ(X[j][i], qY[j].row(i), weights_t, clusters_k,
274 | qZ[j][i]);
275 | }
276 |
277 | // Calculate free energy of model
278 | F = fenergy(weights_j, weights_t, clusters_t, clusters_k, Fyz,
279 | Fz);
280 |
281 | // Check bad free energy step
282 | if ((F-Fold)/abs(Fold) > libcluster::FENGYDEL)
283 | throw runtime_error("Free energy increase!");
284 |
285 | if (verbose == true) // Notify iteration
286 | cout << '-' << flush;
287 | }
288 | while ( (abs((Fold-F)/Fold) > libcluster::CONVERGE)
289 | && ( (++it < maxit) || (maxit < 0) ) );
290 |
291 | return F;
292 | }
293 |
294 |
295 | //
296 | // Model Selection and Heuristics Private Functions
297 | //
298 |
299 | /* Search in a greedy fashion for a mixture split that lowers model free
300 | * energy, or return false. An attempt is made at looking for good, untried,
301 | * split candidates first, as soon as a split canditate is found that lowers
302 | * model F, it is returned. This may not be the "best" split, but it is
303 | * certainly faster than an exhaustive search for the "best" split.
304 | *
305 | * returns: true if a split was found, false if no splits can be found
306 | * mutable: qZ is augmented with a new split if one is found, otherwise left
307 | * mutable: qY is updated if a new split if one is found, otherwise left
308 | * mutable tally is a tally of times a cluster has been unsuccessfully split
309 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions
310 | * throws: runtime_error from its internal VBEM calls
311 | */
312 | template bool ssplit (
313 | const vMatrixXd& W, // Top-level observations
314 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Bottom-level observations
315 | const vector& clusters_t, // Top-level cluster Distributions
316 | const vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster Distributions
317 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level cluster labels qY
318 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level Cluster labels qZ
319 | vector& tally, // Count of unsuccessful splits
320 | const double F, // Current model free energy
321 | const int maxK, // max number of (bottom) clusters
322 | const bool verbose // Verbose output
323 | )
324 | {
325 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
326 | K = clusters_k.size();
327 |
328 | // Check if we have reached the max number of clusters
329 | if ( ((signed) K >= maxK) && (maxK >= 0) )
330 | return false;
331 |
332 | // Split order chooser and bottom-level cluster parameters
333 | tally.resize(K, 0); // Make sure tally is the right size
334 | vector ord(K);
335 |
336 | // Get cluster parameters and their free energy
337 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
338 | {
339 | ord[k].k = k;
340 | ord[k].tally = tally[k];
341 | ord[k].Fk = clusters_k[k].fenergy();
342 | }
343 |
344 | // Get bottom-level cluster likelihoods
345 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
346 | {
347 | // Add in cluster log-likelihood, weighted by global responsability
348 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
349 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
350 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
351 | {
352 | double LL = qZ[j][i].col(k).dot(clusters_k[k].Eloglike(X[j][i]));
353 |
354 | #pragma omp atomic
355 | ord[k].Fk -= LL;
356 | }
357 | }
358 |
359 | // Sort clusters by split tally, then free energy contributions
360 | sort(ord.begin(), ord.end(), greedcomp);
361 |
362 | // Pre allocate big objects for loops (this makes a runtime difference)
363 | vector< vector > mapidx(J);
364 | vvMatrixXd qZref(J), qZaug(J), Xk(J);
365 |
366 | // Loop through each potential cluster in order and split it
367 | for (vector::iterator ko = ord.begin(); ko < ord.end(); ++ko)
368 | {
369 | const int k = ko->k;
370 |
371 | ++tally[k]; // increase this cluster's unsuccessful split tally by default
372 |
373 | // Don't waste time with clusters that can't really be split min (2:2)
374 | if (clusters_k[k].getN() < 4)
375 | continue;
376 |
377 | // Now split observations and qZ.
378 | int scount = 0, Mtot = 0;
379 |
380 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
381 | {
382 | mapidx[j].resize(X[j].size());
383 | qZref[j].resize(X[j].size());
384 | qZaug[j].resize(X[j].size());
385 | Xk[j].resize(X[j].size());
386 |
387 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Mtot, scount)
388 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
389 | {
390 | // Make COPY of the observations with only relevant data points, p > 0.5
391 | mapidx[j][i] = partobs(X[j][i], (qZ[j][i].col(k).array()>0.5),
392 | Xk[j][i]);
393 | Mtot += Xk[j][i].rows();
394 |
395 | // Initial cluster split
396 | ArrayXb splitk = clusters_k[k].splitobs(Xk[j][i]);
397 | qZref[j][i].setZero(Xk[j][i].rows(), 2);
398 | qZref[j][i].col(0) = (splitk == true).cast();
399 | qZref[j][i].col(1) = (splitk == false).cast();
400 |
401 | // keep a track of number of splits
402 | scount += splitk.count();
403 | }
404 | }
405 |
406 | // Don't waste time with clusters that haven't been split sufficiently
407 | if ( (scount < 2) || (scount > (Mtot-2)) )
408 | continue;
409 |
410 | // Refine the split
411 | vector iwspl;
412 | vector icspl;
413 | vector swspl;
414 | vector scspl;
415 | vMatrixXd qYaug = qY; // Copy :-(
416 | vbem(W, Xk, qYaug, qZref, iwspl, swspl, icspl, scspl,
417 | clusters_t[0].getprior(), clusters_k[0].getprior(), SPLITITER);
418 |
419 | if (anyempty(scspl) == true) // One cluster only
420 | continue;
421 |
422 | // Map the refined splits back to original whole-data problem
423 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
424 | {
425 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
426 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
427 | qZaug[j][i] = auglabels(k, mapidx[j][i],
428 | (qZref[j][i].col(1).array() > 0.5), qZ[j][i]);
429 | }
430 |
431 | // Calculate free energy of this split with ALL data (and refine a bit)
432 | qYaug = qY; // Copy :-(
433 | double Fs = vbem(W, X, qYaug, qZaug, iwspl, swspl, icspl,
434 | scspl, clusters_t[0].getprior(), clusters_k[0].getprior(), 1);
435 |
436 | if (anyempty(scspl) == true) // One cluster only
437 | continue;
438 |
439 | // Only notify here of split candidates
440 | if (verbose == true)
441 | cout << '=' << flush;
442 |
443 | // Test whether this cluster split is a keeper
444 | if ( (Fs < F) && (abs((F-Fs)/F) > CONVERGE) )
445 | {
446 | qY = qYaug;
447 | qZ = qZaug;
448 | tally[k] = 0; // Reset tally if successfully split
449 | return true;
450 | }
451 | }
452 |
453 | // Failed to find splits
454 | return false;
455 | }
456 |
457 |
458 | /* Find and remove all empty top-level clusters.
459 | *
460 | * returns: true if any clusters have been deleted, false if all are kept.
461 | * mutable: qY may have columns deleted if there are empty clusters found.
462 | * mutable: weights_t if there are empty top-level clusters found.
463 | * mutable: clusters_t if there are empty top-level clusters found.
464 | */
465 | template bool prune_clusters_t (
466 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Probabilities qY
467 | vector& weights_t, // Top-level bottom-level cluster proportions
468 | vector& clusters_t, // Top-level clusters
469 | bool verbose = false // print status
470 | )
471 | {
472 | const unsigned int T = weights_t.size(),
473 | J = qY.size();
474 |
475 | // Look for empty clusters
476 | ArrayXd Nt(T);
477 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
478 | Nt(t) = weights_t[t].getNk().sum();
479 |
480 | // Find location of empty and full clusters
481 | ArrayXi eidx, fidx;
482 | arrfind(Nt.array() < 1, eidx, fidx);
483 | const unsigned int nempty = eidx.size();
484 |
485 | // If everything is not empty, return false
486 | if (nempty == 0)
487 | return false;
488 |
489 | if (verbose == true)
490 | cout << '*' << flush;
491 |
492 | // Delete empty clusters
493 | for (int i = (nempty - 1); i >= 0; --i)
494 | {
495 | weights_t.erase(weights_t.begin() + eidx(i));
496 | clusters_t.erase(clusters_t.begin() + eidx(i));
497 | }
498 |
499 | // Delete empty cluster indicators by copying only full indicators
500 | const unsigned int newT = fidx.size();
501 | vMatrixXd newqY(J);
502 |
503 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
504 | {
505 | newqY[j].setZero(qY[j].rows(), newT);
506 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < newT; ++t)
507 | newqY[j].col(t) = qY[j].col(fidx(t));
508 | }
509 |
510 | qY = newqY;
511 |
512 | return true;
513 | }
514 |
515 |
516 | /* The model selection algorithm
517 | *
518 | * returns: Free energy of the final model
519 | * mutable: qY the probabilistic top-level cluster assignments
520 | * mutable: qZ the probabilistic bottom-level cluster assignments
521 | * mutable: The top-level clusters and weights
522 | * mutable: The bottom-level clusters and bottom-level cluster weights
523 | * throws: invalid_argument from other functions
524 | * throws: runtime_error if free energy increases
525 | */
526 | template double mcluster (
527 | const vMatrixXd& W, // Top-level observations
528 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Bottom-level observations
529 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level labels
530 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level labels
531 | vector& weights_j, // Group top-level cluster weights
532 | vector& weights_t, // Tope-level proportion cluster parameters
533 | vector& clusters_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
534 | vector& clusters_k, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
535 | const double prior_t, // Top-level cluster prior
536 | const double prior_k, // Bottom-level cluster prior
537 | const unsigned int maxT, // Truncation level for top-level clusters
538 | const int maxK, // max number of (bottom) clusters
539 | const bool verbose, // Verbose output
540 | const unsigned int nthreads // Number of threads for OpenMP to use
541 | )
542 | {
543 | if (nthreads < 1)
544 | throw invalid_argument("Must specify at least one thread for execution!");
545 | omp_set_num_threads(nthreads);
546 |
547 | // Do some observation validity checks
548 | if (W.size() != X.size()) // Same number of groups in observations
549 | throw invalid_argument("W and X need to have the same number of groups!");
550 |
551 | const unsigned int J = W.size();
552 |
553 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j) // Same number of images/docs in groups
554 | if ((unsigned) W[j].rows() != X[j].size())
555 | throw invalid_argument("W and X need to have the same number of 'docs'!");
556 |
557 | // Initialise qY randomly and qZ to ones
558 | qY.resize(J);
559 | qZ.resize(J);
560 |
561 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
562 | {
563 | ArrayXXd randm = (ArrayXXd::Random(X[j].size(), maxT)).abs();
564 | ArrayXd norm = randm.rowwise().sum();
565 | qY[j] = (randm.log().colwise() - norm.log()).exp();
566 |
567 | qZ[j].resize(X[j].size());
568 |
569 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
570 | qZ[j][i].setOnes(X[j][i].rows(), 1);
571 | }
572 |
573 | bool emptyclasses = true, split = true;
574 | double F = 0;
575 | vector stally;
576 |
577 | // Main loop
578 | while ((split == true) || (emptyclasses == true))
579 | {
580 |
581 | F = vbem(W, X, qY, qZ, weights_j, weights_t, clusters_t,
582 | clusters_k, prior_t, prior_k, -1, verbose);
583 |
584 | if (verbose == true)
585 | cout << '<' << flush; // Notify start bottom-level cluster search
586 |
587 | if (split == false) // Remove any empty weights
588 | emptyclasses = prune_clusters_t(qY, weights_t, clusters_t,
589 | verbose);
590 | else
591 | split = ssplit(W, X, clusters_t, clusters_k, qY, qZ, stally,
592 | F, maxK, verbose);
593 |
594 | if (verbose == true)
595 | cout << '>' << endl; // Notify end bottom-level cluster search
596 | }
597 |
598 | // Print finished notification if verbose
599 | if (verbose == true)
600 | {
601 | cout << "Finished!" << endl;
602 | cout << "Number of top level clusters = " << clusters_t.size();
603 | cout << ", and bottom level clusters = " << clusters_k.size() << endl;
604 | cout << "Free energy = " << F << endl;
605 | }
606 |
607 | return F;
608 | }
609 |
610 |
611 | //
612 | // Public Functions
613 | //
614 |
615 | double libcluster::learnMCM (
616 | const vMatrixXd& W,
617 | const vvMatrixXd& X,
618 | vMatrixXd& qY,
619 | vvMatrixXd& qZ,
620 | vector& weights_j,
621 | vector& weights_t,
622 | vector& clusters_t,
623 | vector& clusters_k,
624 | const double prior_t,
625 | const double prior_k,
626 | const unsigned int maxT,
627 | const int maxK,
628 | const bool verbose,
629 | const unsigned int nthreads
630 | )
631 | {
632 |
633 | if (verbose == true)
634 | cout << "Learning MCM..." << endl;
635 |
636 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
637 | double F = mcluster(W, X, qY, qZ,
638 | weights_j, weights_t, clusters_t, clusters_k, prior_t, prior_k,
639 | maxT, maxK, verbose, nthreads);
640 |
641 | return F;
642 | }
643 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/src/probutils.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include "probutils.h"
22 | #include
23 |
24 |
25 | //
26 | // Namespaces
27 | //
28 |
29 |
30 | using namespace std;
31 | using namespace Eigen;
32 |
33 |
34 | //
35 | // Local Constants
36 | //
37 |
38 |
39 | const double EIGCONTHRESH = 1.0e-8f;
40 | const int MAXITER = 100;
41 |
42 |
43 | //
44 | // Public Functions
45 | //
46 |
47 |
48 | RowVectorXd probutils::mean (const MatrixXd& X)
49 | {
50 | return X.colwise().sum()/X.rows();
51 | }
52 |
53 |
54 | RowVectorXd probutils::mean (const vector& X)
55 | {
56 | const int J = X.size(),
57 | D = X[0].cols();
58 | int N = 0;
59 | RowVectorXd mean = RowVectorXd::Zero(D);
60 |
61 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
62 | {
63 | if (X[j].cols() != D)
64 | throw invalid_argument("X dimensions are inconsistent between groups!");
65 |
66 | mean += X[j].colwise().sum();
67 | N += X[j].rows();
68 | }
69 | return mean / N;
70 | }
71 |
72 |
73 | RowVectorXd probutils::stdev (const MatrixXd& X)
74 | {
75 | RowVectorXd meanX = mean(X);
76 | return ((X.rowwise() - meanX).array().square().colwise().sum()
77 | / (X.rows()-1)).sqrt();
78 | }
79 |
80 |
81 | MatrixXd probutils::cov (const MatrixXd& X)
82 | {
83 | if (X.rows() <= 1)
84 | throw invalid_argument("Insufficient no. of observations.");
85 |
86 | MatrixXd X_mu = X.rowwise() - probutils::mean(X); // X - mu
87 | return (X_mu.transpose()*X_mu)/(X.rows()-1); // (X-mu)'*(X-mu)/(N-1)
88 | }
89 |
90 |
91 | MatrixXd probutils::cov (const vector& X)
92 | {
93 | const int J = X.size(),
94 | D = X[0].cols();
95 | int N = 0;
96 | const RowVectorXd mean = probutils::mean(X);
97 | MatrixXd cov = MatrixXd::Zero(D, D),
98 | X_mu;
99 |
100 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
101 | {
102 | if (X[j].rows() <= 1)
103 | throw invalid_argument("Insufficient no. of observations.");
104 | X_mu = X[j].rowwise() - mean;
105 | N += X[j].rows();
106 | cov.noalias() += (X_mu.transpose() * X_mu); // (X_j-mu)'*(X_j-mu)
107 | }
108 |
109 | return cov / (N-1);
110 | }
111 |
112 |
113 | VectorXd probutils::mahaldist (
114 | const MatrixXd& X,
115 | const RowVectorXd& mu,
116 | const MatrixXd& A
117 | )
118 | {
119 | // Check for same number of dimensions, D
120 | if((X.cols() != mu.cols()) || (X.cols() != A.cols()))
121 | throw invalid_argument("Arguments do not have the same dimensionality");
122 |
123 | // Check if A is square
124 | if (A.rows() != A.cols())
125 | throw invalid_argument("Matrix A must be square!");
126 |
127 | // Decompose A
128 | LDLT Aldl(A);
129 |
130 | // Check if A is PD
131 | if ((Aldl.vectorD().array() <= 0).any() == true)
132 | throw invalid_argument("Matrix A is not positive definite");
133 |
134 | // Do the Mahalanobis distance for each sample (N times)
135 | MatrixXd X_mu = (X.rowwise() - mu).transpose();
136 | return ((X_mu.array() * (Aldl.solve(X_mu)).array())
137 | .colwise().sum()).transpose();
138 | }
139 |
140 |
141 | VectorXd probutils::logsumexp (const MatrixXd& X)
142 | {
143 | const VectorXd mx = X.rowwise().maxCoeff(); // Get max of each row
144 |
145 | // Perform the sum(exp(x - mx)) part
146 | ArrayXd se = ((X.colwise() - mx).array().exp()).rowwise().sum();
147 |
148 | // return total log(sum(exp(x))) - hoping for return value optimisation
149 | return (se.log()).matrix() + mx;
150 | }
151 |
152 |
153 | double probutils::eigpower (const MatrixXd& A, VectorXd& eigvec)
154 | {
155 | // Check if A is square
156 | if (A.rows() != A.cols())
157 | throw invalid_argument("Matrix A must be square!");
158 |
159 | // Check if A is a scalar
160 | if (A.rows() == 1)
161 | {
162 | eigvec.setOnes(1);
163 | return A(0,0);
164 | }
165 |
166 | // Initialise working vectors
167 | VectorXd v = VectorXd::LinSpaced(A.rows(), -1, 1);
168 | VectorXd oeigvec(A.rows());
169 |
170 | // Initialise eigenvalue and eigenvectors etc
171 | double eigval = v.norm();
172 | double vdist = numeric_limits::infinity();
173 | eigvec = v/eigval;
174 |
175 | // Loop until eigenvector converges or we reach max iterations
176 | for (int i=0; (vdist>EIGCONTHRESH) && (i.
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include
22 | #include "libcluster.h"
23 | #include "probutils.h"
24 | #include "comutils.h"
25 |
26 |
27 | //
28 | // Namespaces
29 | //
30 |
31 | using namespace std;
32 | using namespace Eigen;
33 | using namespace probutils;
34 | using namespace distributions;
35 | using namespace comutils;
36 | using namespace libcluster;
37 |
38 |
39 | //
40 | // Variational Bayes Private Functions
41 | //
42 |
43 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for weights in each group.
44 | *
45 | * mutable: Top-level cluster assignment probabilities, qYj
46 | * returns: The complete-data free energy, Y and Y+Z dep. terms, for group j.
47 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
48 | */
49 | template double vbeY (
50 | const vMatrixXd& qZj, // Cluster assignments for group j
51 | const WJ& weightsj, // Group top-level cluster weights
52 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
53 | MatrixXd& qYj // Top-level cluster assignments for group j
54 | )
55 | {
56 | const unsigned int T = weights_t.size(),
57 | Ij = qZj.size(),
58 | K = qZj[0].cols();
59 |
60 | // Get log marginal weight likelihoods
61 | const ArrayXd E_logwj = weightsj.Elogweight();
62 |
63 | MatrixXd Njik(Ij, K), logqYj(Ij, T);
64 | ArrayXXd qZjiLike(Ij, T);
65 |
66 | // Get bottom-level cluster counts per top-level cluster
67 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < Ij; ++i)
68 | Njik.row(i) = qZj[i].colwise().sum();
69 |
70 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs
71 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
72 | {
73 | qZjiLike.col(t) = Njik * weights_t[t].Elogweight().matrix();
74 | logqYj.col(t) = E_logwj(t) + qZjiLike.col(t);
75 | }
76 |
77 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
78 | VectorXd logZyj = logsumexp(logqYj);
79 |
80 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities
81 | qYj = (logqYj.colwise() - logZyj).array().exp().matrix();
82 |
83 | return ((qYj.array() * qZjiLike).rowwise().sum() - logZyj.array()).sum();
84 | }
85 |
86 |
87 | /* The Variational Bayes Expectation step for clusters in each "document"
88 | *
89 | * mutable: Bottom-level cluster assignment probabilities, qZji
90 | * returns: The complete-data free energy, Z dep. terms, for group j.
91 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
92 | */
93 | template double vbeZ (
94 | const MatrixXd& Xji, // Observations in i in group j
95 | const RowVectorXd& qYji, // Top-level cluster assignment of this doc
96 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
97 | const vector& clusters, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
98 | MatrixXd& qZji // Observation to cluster assignments
99 | )
100 | {
101 | const int K = clusters.size(),
102 | Nji = Xji.rows(),
103 | T = weights_t.size();
104 |
105 | // Make top-level cluster global weights from weighted label parameters
106 | RowVectorXd E_logqYljt = RowVectorXd::Zero(K);
107 |
108 | for (int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
109 | E_logqYljt.noalias() += qYji(t) * weights_t[t].Elogweight().matrix();
110 |
111 | // Find Expectations of log joint observation probs
112 | MatrixXd logqZji = MatrixXd::Zero(Nji, K);
113 |
114 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
115 | logqZji.col(k) = E_logqYljt(k) + clusters[k].Eloglike(Xji).array();
116 |
117 | // Log normalisation constant of log observation likelihoods
118 | const VectorXd logZzji = logsumexp(logqZji);
119 |
120 | // Normalise and Compute Responsibilities
121 | qZji = (logqZji.colwise() - logZzji).array().exp().matrix();
122 |
123 | return -logZzji.sum();
124 | }
125 |
126 |
127 | /* Calculates the free energy lower bound for the model parameter distributions.
128 | *
129 | * returns: the free energy of the model
130 | */
131 | template double fenergy (
132 | const vector& weights_j, // Group top-level cluster weights
133 | const vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster parameters
134 | const vector& clusters, // Bottom-level cluster parameters
135 | const double Fyz, // Free energy Y and Z+Y terms
136 | const double Fz // Free energy Z terms
137 | )
138 | {
139 | const int T = weights_t.size(),
140 | K = clusters.size(),
141 | J = weights_j.size();
142 |
143 | // Class parameter free energy
144 | double Fc = 0;
145 | for (int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
146 | Fc += weights_t[t].fenergy();
147 |
148 | // Cluster parameter free energy
149 | double Fk = 0;
150 | for (int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
151 | Fk += clusters[k].fenergy();
152 |
153 | // Weight parameter free energy
154 | double Fw = 0;
155 | for (int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
156 | Fw += weights_j[j].fenergy();
157 |
158 | return Fw + Fc + Fk + Fyz + Fz;
159 | }
160 |
161 |
162 | /* Variational Bayes EM.
163 | *
164 | * returns: Free energy of the whole model.
165 | * mutable: the bottom-level cluster indicators, qZ
166 | * mutable: the top-level cluster indicators, qY
167 | * mutable: model parameters weights_j, weights_t, clusters
168 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions.
169 | * throws: runtime_error if there is a negative free energy.
170 | */
171 | template double vbem (
172 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Observations JxIjx[NjixD]
173 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Observations to cluster assigns JxIjx[NjixK]
174 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Indicator to label assignments Jx[IjxT]
175 | vector& weights_j, // Group weight distributions
176 | vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster distributions
177 | vector& clusters, // Bottom-level cluster Distributions
178 | const double prior_t, // Prior value top-level cluster dists.
179 | const double prior_k, // Prior value bottom-level cluster dists.
180 | const int maxit = -1, // Max VBEM iterations (-1 = no max, default)
181 | const bool verbose = false // Verbose output (default false)
182 | )
183 | {
184 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
185 | K = qZ[0][0].cols(),
186 | T = qY[0].cols();
187 |
188 | // Construct (empty) parameters
189 | weights_j.resize(J, WJ());
190 | weights_t.resize(T, WT(prior_t));
191 | clusters.resize(K, C(prior_k, X[0][0].cols()));
192 |
193 | // Other loop variables for initialisation
194 | int it = 0;
195 | double F = numeric_limits::max(), Fold;
196 |
197 | do
198 | {
199 | Fold = F;
200 |
201 | MatrixXd Ntk = MatrixXd::Zero(T, K); // Clear Sufficient Stats
202 |
203 | // VBM for top-level cluster weights
204 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
205 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
206 | {
207 | for(unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
208 | {
209 | MatrixXd Ntkji = qY[j].row(i).transpose() * qZ[j][i].colwise().sum();
210 | #pragma omp critical
211 | Ntk += Ntkji;
212 | }
213 |
214 | weights_j[j].update(qY[j].colwise().sum());
215 | }
216 |
217 | // VBM for top-level cluster parameters
218 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
219 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
220 | weights_t[t].update(Ntk.row(t)); // Weighted multinomials.
221 |
222 | // VBM for bottom-level cluster parameters
223 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
224 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
225 | {
226 | clusters[k].clearobs();
227 |
228 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
229 | for(unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
230 | clusters[k].addobs(qZ[j][i].col(k), X[j][i]);
231 |
232 | clusters[k].update();
233 | }
234 |
235 | double Fz = 0, Fyz = 0;
236 |
237 | // VBE for top-level cluster indicators
238 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fyz)
239 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
240 | Fyz += vbeY(qZ[j], weights_j[j], weights_t, qY[j]);
241 |
242 | // VBE for bottom-level cluster indicators
243 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
244 | {
245 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Fz)
246 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
247 | Fz += vbeZ(X[j][i], qY[j].row(i), weights_t, clusters, qZ[j][i]);
248 | }
249 |
250 | // Calculate free energy of model
251 | F = fenergy(weights_j, weights_t, clusters, Fyz, Fz);
252 |
253 | // Check bad free energy step
254 | if ((F-Fold)/abs(Fold) > libcluster::FENGYDEL)
255 | throw runtime_error("Free energy increase!");
256 |
257 | if (verbose == true) // Notify iteration
258 | cout << '-' << flush;
259 | }
260 | while ( (abs((Fold-F)/Fold) > libcluster::CONVERGE)
261 | && ( (++it < maxit) || (maxit < 0) ) );
262 |
263 | return F;
264 | }
265 |
266 |
267 | //
268 | // Model Selection and Heuristics Private Functions
269 | //
270 |
271 | /* Search in a greedy fashion for a mixture split that lowers model free
272 | * energy, or return false. An attempt is made at looking for good, untried,
273 | * split candidates first, as soon as a split canditate is found that lowers
274 | * model F, it is returned. This may not be the "best" split, but it is
275 | * certainly faster than an exhaustive search for the "best" split.
276 | *
277 | * returns: true if a split was found, false if no splits can be found
278 | * mutable: qZ is augmented with a new split if one is found, otherwise left
279 | * mutable: qY is updated if a new split if one is found, otherwise left
280 | * mutable tally is a tally of times a cluster has been unsuccessfully split
281 | * throws: invalid_argument rethrown from other functions
282 | * throws: runtime_error from its internal VBEM calls
283 | */
284 | template bool split_gr (
285 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Observations
286 | const vector& clusters, // Cluster Distributions
287 | const double prior_t, // Prior value for top-level clusters
288 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level cluster labels qY
289 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level Cluster labels qZ
290 | vector& tally, // Count of unsuccessful splits
291 | const double F, // Current model free energy
292 | const int maxK, // max number of (bottom) clusters
293 | const bool verbose // Verbose output
294 | )
295 | {
296 | const unsigned int J = X.size(),
297 | K = clusters.size();
298 |
299 | // Check if we have reached the max number of clusters
300 | if ( ((signed) K >= maxK) && (maxK >= 0) )
301 | return false;
302 |
303 | // Split order chooser and bottom-level cluster parameters
304 | tally.resize(K, 0); // Make sure tally is the right size
305 | vector ord(K);
306 |
307 | // Get cluster parameters and their free energy
308 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
309 | {
310 | ord[k].k = k;
311 | ord[k].tally = tally[k];
312 | ord[k].Fk = clusters[k].fenergy();
313 | }
314 |
315 | // Get bottom-level cluster likelihoods
316 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
317 | {
318 | // Add in cluster log-likelihood, weighted by global responsability
319 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
320 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
321 | for (unsigned int k = 0; k < K; ++k)
322 | {
323 | double LL = qZ[j][i].col(k).dot(clusters[k].Eloglike(X[j][i]));
324 |
325 | #pragma omp atomic
326 | ord[k].Fk -= LL;
327 | }
328 | }
329 |
330 | // Sort clusters by split tally, then free energy contributions
331 | sort(ord.begin(), ord.end(), greedcomp);
332 |
333 | // Pre allocate big objects for loops (this makes a runtime difference)
334 | vector< vector > mapidx(J);
335 | vMatrixXd qYref(J);
336 | vvMatrixXd qZref(J), qZaug(J), Xk(J);
337 |
338 | // Loop through each potential cluster in order and split it
339 | for (vector::iterator ko = ord.begin(); ko < ord.end(); ++ko)
340 | {
341 | const int k = ko->k;
342 |
343 | ++tally[k]; // increase this cluster's unsuccessful split tally by default
344 |
345 | // Don't waste time with clusters that can't really be split min (2:2)
346 | if (clusters[k].getN() < 4)
347 | continue;
348 |
349 | // Now split observations and qZ.
350 | int scount = 0, Mtot = 0;
351 |
352 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
353 | {
354 | mapidx[j].resize(X[j].size());
355 | qZref[j].resize(X[j].size());
356 | qZaug[j].resize(X[j].size());
357 | Xk[j].resize(X[j].size());
358 | qYref[j].setOnes(X[j].size(), 1);
359 |
360 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided) reduction(+ : Mtot, scount)
361 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
362 | {
363 | // Make COPY of the observations with only relevant data points, p > 0.5
364 | mapidx[j][i] = partobs(X[j][i], (qZ[j][i].col(k).array() > 0.5),
365 | Xk[j][i]);
366 | Mtot += Xk[j][i].rows();
367 |
368 | // Initial cluster split
369 | ArrayXb splitk = clusters[k].splitobs(Xk[j][i]);
370 | qZref[j][i].setZero(Xk[j][i].rows(), 2);
371 | qZref[j][i].col(0) = (splitk == true).cast();
372 | qZref[j][i].col(1) = (splitk == false).cast();
373 |
374 | // keep a track of number of splits
375 | scount += splitk.count();
376 | }
377 | }
378 |
379 | // Don't waste time with clusters that haven't been split sufficiently
380 | if ( (scount < 2) || (scount > (Mtot-2)) )
381 | continue;
382 |
383 | // Refine the split
384 | vector wspl;
385 | vector lspl;
386 | vector cspl;
387 | vbem(Xk, qZref, qYref, wspl, lspl, cspl, prior_t,
388 | clusters[0].getprior(), SPLITITER);
389 |
390 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
391 | continue;
392 |
393 | // Map the refined splits back to original whole-data problem
394 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
395 | {
396 | #pragma omp parallel for schedule(guided)
397 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < X[j].size(); ++i)
398 | qZaug[j][i] = auglabels(k, mapidx[j][i],
399 | (qZref[j][i].col(1).array() > 0.5), qZ[j][i]);
400 | }
401 |
402 | // Calculate free energy of this split with ALL data (and refine a bit)
403 | vMatrixXd qYaug = qY; // Copy :-(
404 | double Fs = vbem(X, qZaug, qYaug, wspl, lspl, cspl, prior_t,
405 | clusters[0].getprior(), 1);
406 |
407 | if (anyempty(cspl) == true) // One cluster only
408 | continue;
409 |
410 | // Only notify here of split candidates
411 | if (verbose == true)
412 | cout << '=' << flush;
413 |
414 | // Test whether this cluster split is a keeper
415 | if ( (Fs < F) && (abs((F-Fs)/F) > CONVERGE) )
416 | {
417 | qY = qYaug;
418 | qZ = qZaug;
419 | tally[k] = 0; // Reset tally if successfully split
420 | return true;
421 | }
422 | }
423 |
424 | // Failed to find splits
425 | return false;
426 | }
427 |
428 | /* Find and remove all empty top-level clusters.
429 | *
430 | * returns: true if any clusters have been deleted, false if all are kept.
431 | * mutable: qY may have columns deleted if there are empty weights found.
432 | * mutable: weights_t if there are empty top-level clusters found.
433 | */
434 | template bool prune_clusters_t (
435 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Probabilities qY
436 | vector& weights_t, // weights distributions
437 | bool verbose = false // print status
438 | )
439 | {
440 | const unsigned int T = weights_t.size(),
441 | J = qY.size();
442 |
443 | // Look for empty clusters
444 | ArrayXd Nt(T);
445 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < T; ++t)
446 | Nt(t) = weights_t[t].getNk().sum();
447 |
448 | // Find location of empty and full clusters
449 | ArrayXi eidx, fidx;
450 | arrfind(Nt.array() < 1, eidx, fidx);
451 | const unsigned int nempty = eidx.size();
452 |
453 | // If everything is not empty, return false
454 | if (nempty == 0)
455 | return false;
456 |
457 | if (verbose == true)
458 | cout << '*' << flush;
459 |
460 | // Delete empty cluster suff. stats.
461 | for (int i = (nempty - 1); i >= 0; --i)
462 | weights_t.erase(weights_t.begin() + eidx(i));
463 |
464 | // Delete empty cluster indicators by copying only full indicators
465 | const unsigned int newT = fidx.size();
466 | vMatrixXd newqY(J);
467 |
468 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
469 | {
470 | newqY[j].setZero(qY[j].rows(), newT);
471 | for (unsigned int t = 0; t < newT; ++t)
472 | newqY[j].col(t) = qY[j].col(fidx(t));
473 | }
474 |
475 | qY = newqY;
476 |
477 | return true;
478 | }
479 |
480 |
481 | /* The model selection algorithm
482 | *
483 | * returns: Free energy of the final model
484 | * mutable: qY the probabilistic top-level cluster assignments
485 | * mutable: qZ the probabilistic observation to bottom-level cluster assigns.
486 | * mutable: the top-level cluster weights and parameters.
487 | * mutable: the bottom-level cluster weights and parameters.
488 | * throws: invalid_argument from other functions.
489 | * throws: runtime_error if free energy increases.
490 | */
491 | template double scluster (
492 | const vvMatrixXd& X, // Observations
493 | vMatrixXd& qY, // Top-level cluster assignments
494 | vvMatrixXd& qZ, // Bottom-level cluster assignments
495 | vector& weights_j, // Group weight distributions
496 | vector& weights_t, // Top-level cluster distributions
497 | vector& clusters, // Bottom-level cluster Distributions
498 | const double prior_t, // Prior value for top-level cluster dists.
499 | const double prior_k, // Prior value for bottom-level cluster dists.
500 | const unsigned int maxT, // Truncation level for number of weights
501 | const int maxK, // max number of (bottom) clusters
502 | const bool verbose, // Verbose output
503 | const unsigned int nthreads // Number of threads for OpenMP to use
504 | )
505 | {
506 | if (nthreads < 1)
507 | throw invalid_argument("Must specify at least one thread for execution!");
508 | omp_set_num_threads(nthreads);
509 |
510 | const unsigned int J = X.size();
511 | unsigned int Itot = 0;
512 |
513 | // Randomly initialise qY and initialise qZ to ones
514 | qY.resize(J);
515 | qZ.resize(J);
516 |
517 | for (unsigned int j = 0; j < J; ++j)
518 | {
519 | const unsigned int Ij = X[j].size();
520 |
521 | ArrayXXd randm = (ArrayXXd::Random(Ij, maxT)).abs();
522 | ArrayXd norm = randm.rowwise().sum();
523 | qY[j] = (randm.log().colwise() - norm.log()).exp();
524 |
525 | qZ[j].resize(Ij);
526 | for (unsigned int i = 0; i < Ij; ++i)
527 | qZ[j][i].setOnes(X[j][i].rows(), 1);
528 |
529 | Itot += Ij;
530 | }
531 |
532 | // Some input argument checking
533 | if (maxT > Itot)
534 | throw invalid_argument("maxT must be less than the number of documents of"
535 | "X!");
536 |
537 | // Initialise free energy and other loop variables
538 | bool issplit = true, emptyclasses = true;
539 | double F = 0;
540 | vector tally;
541 |
542 | // Main loop
543 | while ((issplit == true) || (emptyclasses == true))
544 | {
545 | // Variational Bayes
546 | F = vbem(X, qZ, qY, weights_j, weights_t, clusters, prior_t,
547 | prior_k, -1, verbose);
548 |
549 | // Start model search heuristics
550 | if (verbose == true)
551 | cout << '<' << flush; // Notify start search
552 |
553 | if (issplit == false) // Remove any empty weights
554 | emptyclasses = prune_clusters_t(qY, weights_t, verbose);
555 | else // Search for best split, augment qZ if found one
556 | issplit = split_gr(X, clusters, prior_t, qY, qZ, tally, F, maxK,
557 | verbose);
558 |
559 | if (verbose == true)
560 | cout << '>' << endl; // Notify end search
561 | }
562 |
563 | // Print finished notification if verbose
564 | if (verbose == true)
565 | {
566 | cout << "Finished!" << endl;
567 | cout << "Number of top level clusters = " << weights_t.size();
568 | cout << ", and bottom level clusters = " << clusters.size() << endl;
569 | cout << "Free energy = " << F << endl;
570 | }
571 |
572 | return F;
573 | }
574 |
575 |
576 | //
577 | // Public Functions
578 | //
579 |
580 | double libcluster::learnSCM (
581 | const vvMatrixXd& X,
582 | vMatrixXd& qY,
583 | vvMatrixXd& qZ,
584 | vector& weights_j,
585 | vector& weights_t,
586 | vector& clusters,
587 | const double dirprior,
588 | const double gausprior,
589 | const unsigned int maxT,
590 | const int maxK,
591 | const bool verbose,
592 | const unsigned int nthreads
593 | )
594 | {
595 |
596 | if (verbose == true)
597 | cout << "Learning SCM..." << endl;
598 |
599 | // Model selection and Variational Bayes learning
600 | double F = scluster(X, qY, qZ,
601 | weights_j, weights_t, clusters, dirprior, gausprior, maxT,
602 | maxK, verbose, nthreads);
603 |
604 | return F;
605 | }
606 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/CMakeLists.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Test executable build instructions
2 |
3 | # Make Cluster models batch test executable (test VDP and GMC)
4 | add_executable(cluster_test
5 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/cluster_test.cpp
6 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/testdata.h
7 | )
8 |
9 | target_link_libraries(cluster_test ${PROJECT_NAME})
10 |
11 | # Make Topic models batch test executable
12 | add_executable(scluster_test
13 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/scluster_test.cpp
14 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/testdata.h
15 | )
16 |
17 | target_link_libraries(scluster_test ${PROJECT_NAME})
18 |
19 | # Make Topic models batch test executable
20 | add_executable(mcluster_test
21 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/mcluster_test.cpp
22 | ${TEST_SOURCE_DIR}/testdata.h
23 | )
24 |
25 | target_link_libraries(mcluster_test ${PROJECT_NAME})
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/cluster_test.cpp:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /*
2 | * libcluster -- A collection of hierarchical Bayesian clustering algorithms.
3 | * Copyright (C) 2013 Daniel M. Steinberg (daniel.m.steinberg@gmail.com)
4 | *
5 | * This file is part of libcluster.
6 | *
7 | * libcluster is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under
8 | * the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public License as published by the Free
9 | * Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option)
10 | * any later version.
11 | *
12 | * libcluster is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT
13 | * ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or
14 | * FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU Lesser General Public License
15 | * for more details.
16 | *
17 | * You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public License
18 | * along with libcluster. If not, see .
19 | */
20 |
21 | #include "libcluster.h"
22 | #include "distributions.h"
23 | #include "testdata.h"
24 |
25 |
26 | //
27 | // Namespaces
28 | //
29 |
30 |
31 | using namespace std;
32 | using namespace Eigen;
33 | using namespace libcluster;
34 | using namespace distributions;
35 |
36 |
37 | // Main
38 | int main()
39 | {
40 |
41 | // Populate test data from testdata.h
42 | MatrixXd Xcat;
43 | vMatrixXd X;
44 | makeXdata(Xcat, X);
45 |
46 | // GMC
47 | vector weights;
48 | vector 39 |
39 |  40 |
40 |  39 |
39 |  40 |
40 |