 7 |
7 | 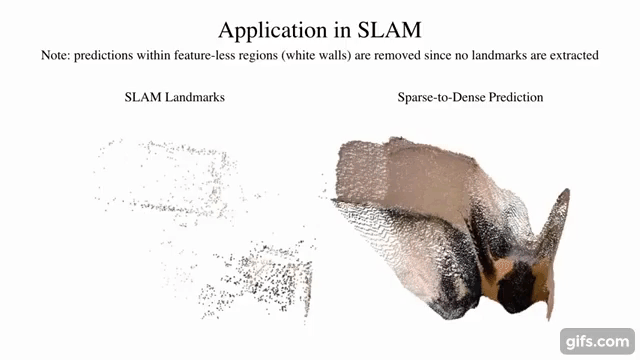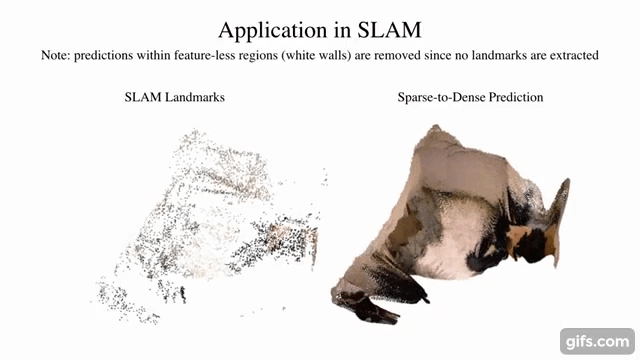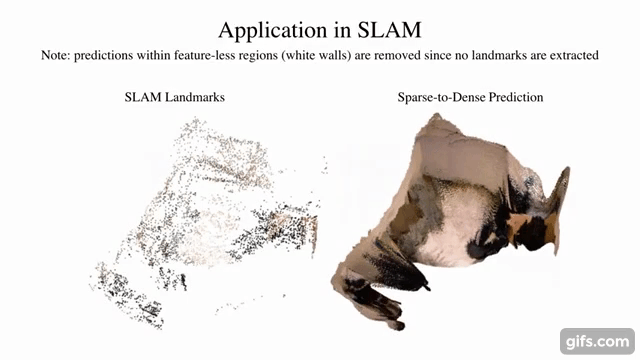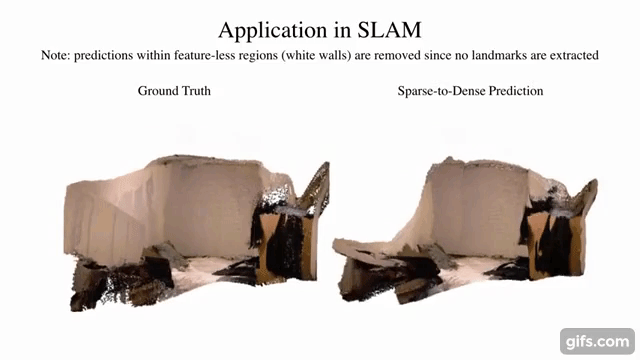 8 |
8 |
6 |  7 |
7 |  8 |
8 |
 87 |
88 | - Error metrics on KITTI dataset:
89 |
90 | | RGB | rms | rel | delta1 | delta2 | delta3 |
91 | |-----------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|
92 | | [Make3D](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5539-depth-map-prediction-from-a-single-image-using-a-multi-scale-deep-network.pdf) | 8.734 | 0.280 | 60.1 | 82.0 | 92.6 |
93 | | [Mancini et al](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.06349.pdf) (_IROS 2016_) | 7.508 | - | 31.8 | 61.7 | 81.3 |
94 | | [Eigen et al](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5539-depth-map-prediction-from-a-single-image-using-a-multi-scale-deep-network.pdf) (_NIPS 2014_) | 7.156 | **0.190** | **69.2** | 89.9 | **96.7** |
95 | | Ours-RGB | **6.266** | 0.208 | 59.1 | **90.0** | 96.2 |
96 |
97 | | RGBd-#samples | rms | rel | delta1 | delta2 | delta3 |
98 | |-----------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|
99 | | [Cadena et al](https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/18d5/f0747a23706a344f1d15b032ea22795324fa.pdf) (_RSS 2016_)-650 | 7.14 | 0.179 | 70.9 | 88.8 | 95.6 |
100 | | Ours-50 | 4.884 | 0.109 | 87.1 | 95.2 | 97.9 |
101 | | [Liao et al](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.02174) (_ICRA 2017_)-225 | 4.50 | 0.113 | 87.4 | 96.0 | 98.4 |
102 | | Ours-100 | 4.303 | 0.095 | 90.0 | 96.3 | 98.3 |
103 | | Ours-200 | 3.851 | 0.083 | 91.9 | 97.0 | 98.6 |
104 | | Ours-500| **3.378** | **0.073** | **93.5** | **97.6** | **98.9** |
105 |
106 |
87 |
88 | - Error metrics on KITTI dataset:
89 |
90 | | RGB | rms | rel | delta1 | delta2 | delta3 |
91 | |-----------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|
92 | | [Make3D](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5539-depth-map-prediction-from-a-single-image-using-a-multi-scale-deep-network.pdf) | 8.734 | 0.280 | 60.1 | 82.0 | 92.6 |
93 | | [Mancini et al](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.06349.pdf) (_IROS 2016_) | 7.508 | - | 31.8 | 61.7 | 81.3 |
94 | | [Eigen et al](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/5539-depth-map-prediction-from-a-single-image-using-a-multi-scale-deep-network.pdf) (_NIPS 2014_) | 7.156 | **0.190** | **69.2** | 89.9 | **96.7** |
95 | | Ours-RGB | **6.266** | 0.208 | 59.1 | **90.0** | 96.2 |
96 |
97 | | RGBd-#samples | rms | rel | delta1 | delta2 | delta3 |
98 | |-----------------------------|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|:-----:|
99 | | [Cadena et al](https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/18d5/f0747a23706a344f1d15b032ea22795324fa.pdf) (_RSS 2016_)-650 | 7.14 | 0.179 | 70.9 | 88.8 | 95.6 |
100 | | Ours-50 | 4.884 | 0.109 | 87.1 | 95.2 | 97.9 |
101 | | [Liao et al](https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.02174) (_ICRA 2017_)-225 | 4.50 | 0.113 | 87.4 | 96.0 | 98.4 |
102 | | Ours-100 | 4.303 | 0.095 | 90.0 | 96.3 | 98.3 |
103 | | Ours-200 | 3.851 | 0.083 | 91.9 | 97.0 | 98.6 |
104 | | Ours-500| **3.378** | **0.073** | **93.5** | **97.6** | **98.9** |
105 |
106 |  107 |
108 | Note: our networks are trained on the KITTI odometry dataset, using only sparse labels from laser measurements.
109 |
110 | ## Citation
111 | If you use our code or method in your work, please consider citing the following:
112 |
113 | @article{Ma2017SparseToDense,
114 | title={Sparse-to-Dense: Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth Samples and a Single Image},
115 | author={Ma, Fangchang and Karaman, Sertac},
116 | booktitle={ICRA},
117 | year={2018}
118 | }
119 | @article{ma2018self,
120 | title={Self-supervised Sparse-to-Dense: Self-supervised Depth Completion from LiDAR and Monocular Camera},
121 | author={Ma, Fangchang and Cavalheiro, Guilherme Venturelli and Karaman, Sertac},
122 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.00275},
123 | year={2018}
124 | }
125 |
126 | Please create a new issue for code-related questions. Pull requests are welcome.
127 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/criteria.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from torch.autograd import Variable
4 |
5 | class MaskedMSELoss(nn.Module):
6 | def __init__(self):
7 | super(MaskedMSELoss, self).__init__()
8 |
9 | def forward(self, pred, target):
10 | assert pred.dim() == target.dim(), "inconsistent dimensions"
11 | valid_mask = (target>0).detach()
12 | diff = target - pred
13 | diff = diff[valid_mask]
14 | self.loss = (diff ** 2).mean()
15 | return self.loss
16 |
17 | class MaskedL1Loss(nn.Module):
18 | def __init__(self):
19 | super(MaskedL1Loss, self).__init__()
20 |
21 | def forward(self, pred, target):
22 | assert pred.dim() == target.dim(), "inconsistent dimensions"
23 | valid_mask = (target>0).detach()
24 | diff = target - pred
25 | diff = diff[valid_mask]
26 | self.loss = diff.abs().mean()
27 | return self.loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import os.path
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import torch.utils.data as data
5 | import h5py
6 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
7 |
8 | IMG_EXTENSIONS = ['.h5',]
9 |
10 | def is_image_file(filename):
11 | return any(filename.endswith(extension) for extension in IMG_EXTENSIONS)
12 |
13 | def find_classes(dir):
14 | classes = [d for d in os.listdir(dir) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(dir, d))]
15 | classes.sort()
16 | class_to_idx = {classes[i]: i for i in range(len(classes))}
17 | return classes, class_to_idx
18 |
19 | def make_dataset(dir, class_to_idx):
20 | images = []
21 | dir = os.path.expanduser(dir)
22 | for target in sorted(os.listdir(dir)):
23 | d = os.path.join(dir, target)
24 | if not os.path.isdir(d):
25 | continue
26 | for root, _, fnames in sorted(os.walk(d)):
27 | for fname in sorted(fnames):
28 | if is_image_file(fname):
29 | path = os.path.join(root, fname)
30 | item = (path, class_to_idx[target])
31 | images.append(item)
32 | return images
33 |
34 | def h5_loader(path):
35 | h5f = h5py.File(path, "r")
36 | rgb = np.array(h5f['rgb'])
37 | rgb = np.transpose(rgb, (1, 2, 0))
38 | depth = np.array(h5f['depth'])
39 | return rgb, depth
40 |
41 | # def rgb2grayscale(rgb):
42 | # return rgb[:,:,0] * 0.2989 + rgb[:,:,1] * 0.587 + rgb[:,:,2] * 0.114
43 |
44 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
45 |
46 | class MyDataloader(data.Dataset):
47 | modality_names = ['rgb', 'rgbd', 'd'] # , 'g', 'gd'
48 | color_jitter = transforms.ColorJitter(0.4, 0.4, 0.4)
49 |
50 | def __init__(self, root, type, sparsifier=None, modality='rgb', loader=h5_loader):
51 | classes, class_to_idx = find_classes(root)
52 | imgs = make_dataset(root, class_to_idx)
53 | assert len(imgs)>0, "Found 0 images in subfolders of: " + root + "\n"
54 | print("Found {} images in {} folder.".format(len(imgs), type))
55 | self.root = root
56 | self.imgs = imgs
57 | self.classes = classes
58 | self.class_to_idx = class_to_idx
59 | if type == 'train':
60 | self.transform = self.train_transform
61 | elif type == 'val':
62 | self.transform = self.val_transform
63 | else:
64 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
65 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
66 | self.loader = loader
67 | self.sparsifier = sparsifier
68 |
69 | assert (modality in self.modality_names), "Invalid modality type: " + modality + "\n" + \
70 | "Supported dataset types are: " + ''.join(self.modality_names)
71 | self.modality = modality
72 |
73 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
74 | raise (RuntimeError("train_transform() is not implemented. "))
75 |
76 | def val_transform(rgb, depth):
77 | raise (RuntimeError("val_transform() is not implemented."))
78 |
79 | def create_sparse_depth(self, rgb, depth):
80 | if self.sparsifier is None:
81 | return depth
82 | else:
83 | mask_keep = self.sparsifier.dense_to_sparse(rgb, depth)
84 | sparse_depth = np.zeros(depth.shape)
85 | sparse_depth[mask_keep] = depth[mask_keep]
86 | return sparse_depth
87 |
88 | def create_rgbd(self, rgb, depth):
89 | sparse_depth = self.create_sparse_depth(rgb, depth)
90 | rgbd = np.append(rgb, np.expand_dims(sparse_depth, axis=2), axis=2)
91 | return rgbd
92 |
93 | def __getraw__(self, index):
94 | """
95 | Args:
96 | index (int): Index
97 |
98 | Returns:
99 | tuple: (rgb, depth) the raw data.
100 | """
101 | path, target = self.imgs[index]
102 | rgb, depth = self.loader(path)
103 | return rgb, depth
104 |
105 | def __getitem__(self, index):
106 | rgb, depth = self.__getraw__(index)
107 |
108 | #print('{:04d} min={:f} max={:f} shape='.format(index, np.amin(depth), np.amax(depth)) + str(depth.shape))
109 |
110 | if self.transform is not None:
111 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
112 | else:
113 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
114 |
115 | #print('{:04d} min={:f} max={:f} shape='.format(index, np.amin(depth_np), np.amax(depth_np)) + str(depth_np.shape))
116 |
117 | # color normalization
118 | # rgb_tensor = normalize_rgb(rgb_tensor)
119 | # rgb_np = normalize_np(rgb_np)
120 |
121 | if self.modality == 'rgb':
122 | input_np = rgb_np
123 | elif self.modality == 'rgbd':
124 | input_np = self.create_rgbd(rgb_np, depth_np)
125 | elif self.modality == 'd':
126 | input_np = self.create_sparse_depth(rgb_np, depth_np)
127 |
128 | input_tensor = to_tensor(input_np)
129 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
130 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
131 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
132 | #print('{:04d} '.format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
133 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
134 | #print('{:04d} '.format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
135 |
136 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
137 |
138 | def __len__(self):
139 | return len(self.imgs)
140 |
141 | # def __get_all_item__(self, index):
142 | # """
143 | # Args:
144 | # index (int): Index
145 |
146 | # Returns:
147 | # tuple: (input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np)
148 | # """
149 | # rgb, depth = self.__getraw__(index)
150 | # if self.transform is not None:
151 | # rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
152 | # else:
153 | # raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
154 |
155 | # # color normalization
156 | # # rgb_tensor = normalize_rgb(rgb_tensor)
157 | # # rgb_np = normalize_np(rgb_np)
158 |
159 | # if self.modality == 'rgb':
160 | # input_np = rgb_np
161 | # elif self.modality == 'rgbd':
162 | # input_np = self.create_rgbd(rgb_np, depth_np)
163 | # elif self.modality == 'd':
164 | # input_np = self.create_sparse_depth(rgb_np, depth_np)
165 |
166 | # input_tensor = to_tensor(input_np)
167 | # while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
168 | # input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
169 | # depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
170 | # depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
171 |
172 | # return input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np
173 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/deepscene_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import re
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
5 |
6 | from imageio import imread
7 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
8 |
9 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
10 |
11 | iheight, iwidth = 472, 872 # original image size (there is some variation in DeepScene dataset)
12 |
13 | class DeepSceneDataset(Dataset):
14 | def __init__(self, root, type='train', train_extra=True):
15 | self.root = root
16 | self.output_size = (224, 224) #(224, 448)
17 |
18 | # search for images
19 | self.rgb_files, self.depth_files = self.gather_images(os.path.join(root, 'rgb'),
20 | os.path.join(root, 'depth_gray'))
21 |
22 | if type == 'train' and train_extra:
23 | extra_root = root + 'extra'
24 | extra_rgb, extra_depth = self.gather_images(os.path.join(extra_root, 'rgb'),
25 | os.path.join(extra_root, 'depth_gray'))
26 |
27 | if len(self.rgb_files) == 0:
28 | raise (RuntimeError("Empty dataset - found no image pairs under \n" + root))
29 |
30 | # determine if 16-bit or 8-bit depth images
31 | self.depth_16 = False
32 |
33 | if imread(self.depth_files[0]).dtype.type is np.uint16:
34 | self.depth_16 = True
35 | self.depth_16_max = 5000 #20000
36 |
37 | print('found {:d} image pairs with {:s}-bit depth under {:s}'.format(len(self.rgb_files), "16" if self.depth_16 else "8", root))
38 |
39 | # setup transforms
40 | if type == 'train':
41 | self.transform = self.train_transform
42 | elif type == 'val':
43 | self.transform = self.val_transform
44 | else:
45 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
46 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
47 |
48 | def gather_images(self, images_path, labels_path):
49 | def sorted_alphanumeric(data):
50 | convert = lambda text: int(text) if text.isdigit() else text.lower()
51 | alphanum_key = lambda key: [ convert(c) for c in re.split('([0-9]+)', key) ]
52 | return sorted(data, key=alphanum_key)
53 |
54 | #print('searching for images under: ')
55 | #print(' ' + images_path)
56 | #print(' ' + labels_path)
57 |
58 | image_files = sorted_alphanumeric(os.listdir(images_path))
59 | label_files = sorted_alphanumeric(os.listdir(labels_path))
60 |
61 | if len(image_files) != len(label_files):
62 | print('warning: images path has a different number of files than labels path')
63 | print(' ({:d} files) - {:s}'.format(len(image_files), images_path))
64 | print(' ({:d} files) - {:s}'.format(len(label_files), labels_path))
65 |
66 | for n in range(len(image_files)):
67 | image_files[n] = os.path.join(images_path, image_files[n])
68 | label_files[n] = os.path.join(labels_path, label_files[n])
69 |
70 | #print('{:s} -> {:s}'.format(image_files[n], label_files[n]))
71 |
72 | return image_files, label_files
73 |
74 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
75 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
76 | depth_np = depth #/ s
77 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
78 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
79 |
80 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
81 | transform = transforms.Compose([
82 | #transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation can be slow
83 | #transforms.Rotate(angle),
84 | #transforms.Resize(s),
85 | #transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
86 | #transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
87 | transforms.Resize(self.output_size)
88 | ])
89 |
90 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
91 | #rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
92 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
93 |
94 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
95 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
96 |
97 | if self.depth_16:
98 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
99 | else:
100 | depth_np = depth_np / 255
101 |
102 | return rgb_np, depth_np
103 |
104 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
105 | depth_np = depth
106 |
107 | transform = transforms.Compose([
108 | #transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight),
109 | #transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
110 | transforms.Resize(self.output_size)
111 | ])
112 |
113 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
114 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
115 |
116 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
117 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
118 |
119 | if self.depth_16:
120 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
121 | else:
122 | depth_np = depth_np / 255
123 |
124 | return rgb_np, depth_np
125 |
126 | def load_rgb(self, index):
127 | return imread(self.rgb_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="RGB")
128 |
129 | def load_depth(self, index):
130 | if self.depth_16:
131 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index])
132 | depth[depth == 65535] = 0 # map 'invalid' to 0
133 | return depth
134 | else:
135 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="L")
136 | #depth[depth == 0] = 255 # map 0 -> 255
137 | return depth
138 |
139 | def __len__(self):
140 | return len(self.rgb_files)
141 |
142 | def __getitem__(self, index):
143 | rgb = self.load_rgb(index)
144 | depth = self.load_depth(index)
145 |
146 | #print(self.rgb_files[index] + str(rgb.shape))
147 | #print(self.depth_files[index] + str(depth.shape))
148 | #print(depth)
149 |
150 | # apply train/val transforms
151 | if self.transform is not None:
152 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
153 | else:
154 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
155 |
156 | # convert from numpy to torch tensors
157 | input_tensor = to_tensor(rgb_np)
158 |
159 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
160 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
161 |
162 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
163 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
164 |
165 | #print("{:04d} rgb = ".format(index) + str(input_tensor.shape))
166 | #print("{:04d} depth = ".format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
167 |
168 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
169 |
170 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/dense_to_sparse.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import cv2
3 |
4 |
5 | def rgb2grayscale(rgb):
6 | return rgb[:, :, 0] * 0.2989 + rgb[:, :, 1] * 0.587 + rgb[:, :, 2] * 0.114
7 |
8 |
9 | class DenseToSparse:
10 | def __init__(self):
11 | pass
12 |
13 | def dense_to_sparse(self, rgb, depth):
14 | pass
15 |
16 | def __repr__(self):
17 | pass
18 |
19 | class UniformSampling(DenseToSparse):
20 | name = "uar"
21 | def __init__(self, num_samples, max_depth=np.inf):
22 | DenseToSparse.__init__(self)
23 | self.num_samples = num_samples
24 | self.max_depth = max_depth
25 |
26 | def __repr__(self):
27 | return "%s{ns=%d,md=%f}" % (self.name, self.num_samples, self.max_depth)
28 |
29 | def dense_to_sparse(self, rgb, depth):
30 | """
31 | Samples pixels with `num_samples`/#pixels probability in `depth`.
32 | Only pixels with a maximum depth of `max_depth` are considered.
33 | If no `max_depth` is given, samples in all pixels
34 | """
35 | mask_keep = depth > 0
36 | if self.max_depth is not np.inf:
37 | mask_keep = np.bitwise_and(mask_keep, depth <= self.max_depth)
38 | n_keep = np.count_nonzero(mask_keep)
39 | if n_keep == 0:
40 | return mask_keep
41 | else:
42 | prob = float(self.num_samples) / n_keep
43 | return np.bitwise_and(mask_keep, np.random.uniform(0, 1, depth.shape) < prob)
44 |
45 |
46 | class SimulatedStereo(DenseToSparse):
47 | name = "sim_stereo"
48 |
49 | def __init__(self, num_samples, max_depth=np.inf, dilate_kernel=3, dilate_iterations=1):
50 | DenseToSparse.__init__(self)
51 | self.num_samples = num_samples
52 | self.max_depth = max_depth
53 | self.dilate_kernel = dilate_kernel
54 | self.dilate_iterations = dilate_iterations
55 |
56 | def __repr__(self):
57 | return "%s{ns=%d,md=%f,dil=%d.%d}" % \
58 | (self.name, self.num_samples, self.max_depth, self.dilate_kernel, self.dilate_iterations)
59 |
60 | # We do not use cv2.Canny, since that applies non max suppression
61 | # So we simply do
62 | # RGB to intensitities
63 | # Smooth with gaussian
64 | # Take simple sobel gradients
65 | # Threshold the edge gradient
66 | # Dilatate
67 | def dense_to_sparse(self, rgb, depth):
68 | gray = rgb2grayscale(rgb)
69 | blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
70 | gx = cv2.Sobel(blurred, cv2.CV_64F, 1, 0, ksize=5)
71 | gy = cv2.Sobel(blurred, cv2.CV_64F, 0, 1, ksize=5)
72 |
73 | depth_mask = np.bitwise_and(depth != 0.0, depth <= self.max_depth)
74 |
75 | edge_fraction = float(self.num_samples) / np.size(depth)
76 |
77 | mag = cv2.magnitude(gx, gy)
78 | min_mag = np.percentile(mag[depth_mask], 100 * (1.0 - edge_fraction))
79 | mag_mask = mag >= min_mag
80 |
81 | if self.dilate_iterations >= 0:
82 | kernel = np.ones((self.dilate_kernel, self.dilate_kernel), dtype=np.uint8)
83 | cv2.dilate(mag_mask.astype(np.uint8), kernel, iterations=self.dilate_iterations)
84 |
85 | mask = np.bitwise_and(mag_mask, depth_mask)
86 | return mask
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/kitti_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
3 | from dataloaders.dataloader import MyDataloader
4 |
5 | class KITTIDataset(MyDataloader):
6 | def __init__(self, root, type, sparsifier=None, modality='rgb'):
7 | super(KITTIDataset, self).__init__(root, type, sparsifier, modality)
8 | self.output_size = (228, 912)
9 |
10 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
11 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
12 | depth_np = depth / s
13 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
14 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
15 |
16 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
17 | transform = transforms.Compose([
18 | transforms.Crop(130, 10, 240, 1200),
19 | transforms.Rotate(angle),
20 | transforms.Resize(s),
21 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
22 | transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
23 | ])
24 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
25 | rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
26 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
27 | # Scipy affine_transform produced RuntimeError when the depth map was
28 | # given as a 'numpy.ndarray'
29 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float32')
30 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
31 |
32 | return rgb_np, depth_np
33 |
34 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
35 | depth_np = depth
36 | transform = transforms.Compose([
37 | transforms.Crop(130, 10, 240, 1200),
38 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
39 | ])
40 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
41 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
42 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float32')
43 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
44 |
45 | return rgb_np, depth_np
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/nyu_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
3 | from dataloaders.dataloader import MyDataloader
4 |
5 | iheight, iwidth = 480, 640 # raw image size
6 |
7 | class NYUDataset(MyDataloader):
8 | def __init__(self, root, type, sparsifier=None, modality='rgb'):
9 | super(NYUDataset, self).__init__(root, type, sparsifier, modality)
10 | self.output_size = (448, 448) #(224, 224) #(228, 304) #(iheight, iwidth)
11 |
12 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
13 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
14 | depth_np = depth / s
15 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
16 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
17 |
18 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
19 | transform = transforms.Compose([
20 | transforms.Resize(480.0 / iheight), #250.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation can be slow
21 | transforms.Rotate(angle),
22 | #transforms.Resize(s), # disabled for 448x448
23 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
24 | transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
25 | ])
26 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
27 | rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
28 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
29 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
30 |
31 | return rgb_np, depth_np
32 |
33 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
34 | depth_np = depth
35 | transform = transforms.Compose([
36 | transforms.Resize(480.0 / iheight), #240.0 / iheight),
37 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
38 | ])
39 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
40 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
41 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
42 |
43 | return rgb_np, depth_np
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/sun_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
4 |
5 | from imageio import imread
6 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
7 |
8 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
9 |
10 | class SunRGBDDataset(Dataset):
11 | def __init__(self, root, type='train', train_extra=True):
12 | self.root = root
13 | self.output_size = (224, 224) #(224, 448)
14 |
15 | # search for images
16 | self.rgb_files, self.depth_files = self.gather_images(os.path.join(root, 'images'),
17 | os.path.join(root, 'depth'))
18 |
19 | if type == 'train' and train_extra:
20 | extra_root = root + 'extra'
21 | extra_rgb, extra_depth = self.gather_images(os.path.join(extra_root, 'images'),
22 | os.path.join(extra_root, 'depth'))
23 |
24 | if len(self.rgb_files) == 0:
25 | raise (RuntimeError("Empty dataset - found no image pairs under \n" + root))
26 |
27 | # determine if 16-bit or 8-bit depth images
28 | self.depth_16 = False
29 |
30 | if imread(self.depth_files[0]).dtype.type is np.uint16:
31 | self.depth_16 = True
32 | self.depth_16_max = 10000
33 |
34 | print('found {:d} image pairs with {:s}-bit depth under {:s}'.format(len(self.rgb_files), "16" if self.depth_16 else "8", root))
35 |
36 | # setup transforms
37 | if type == 'train':
38 | self.transform = self.train_transform
39 | elif type == 'val':
40 | self.transform = self.val_transform
41 | else:
42 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
43 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
44 |
45 | def gather_images(self, images_path, labels_path, max_images=5500):
46 | image_files = []
47 | label_files = []
48 |
49 | for n in range(max_images):
50 | image_filename = os.path.join(images_path, 'img-{:06d}.jpg'.format(n))
51 | label_filename = os.path.join(labels_path, '{:d}.png'.format(n))
52 |
53 | if os.path.isfile(image_filename) and os.path.isfile(label_filename):
54 | image_files.append(image_filename)
55 | label_files.append(label_filename)
56 |
57 | return image_files, label_files
58 |
59 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
60 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
61 | depth_np = depth #/ s
62 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
63 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
64 |
65 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
66 | transform = transforms.Compose([
67 | #transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation can be slow
68 | #transforms.Rotate(angle),
69 | #transforms.Resize(s),
70 | #transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
71 | #transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
72 | transforms.Resize(self.output_size)
73 | ])
74 |
75 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
76 | #rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
77 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
78 |
79 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
80 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
81 |
82 | if self.depth_16:
83 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
84 | else:
85 | depth_np = depth_np / 255
86 |
87 | return rgb_np, depth_np
88 |
89 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
90 | depth_np = depth
91 |
92 | transform = transforms.Compose([
93 | #transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight),
94 | #transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
95 | transforms.Resize(self.output_size)
96 | ])
97 |
98 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
99 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
100 |
101 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
102 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
103 |
104 | if self.depth_16:
105 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
106 | else:
107 | depth_np = depth_np / 255
108 |
109 | return rgb_np, depth_np
110 |
111 | def load_rgb(self, index):
112 | return imread(self.rgb_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="RGB")
113 |
114 | def load_depth(self, index):
115 | if self.depth_16:
116 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index])
117 | depth[depth == 65535] = 0 # map 'invalid' to 0
118 | return depth
119 | else:
120 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="L")
121 | #depth[depth == 0] = 255 # map 0 -> 255
122 | return depth
123 |
124 | def __len__(self):
125 | return len(self.rgb_files)
126 |
127 | def __getitem__(self, index):
128 | rgb = self.load_rgb(index)
129 | depth = self.load_depth(index)
130 |
131 | #print(self.rgb_files[index] + str(rgb.shape))
132 | #print(self.depth_files[index] + str(depth.shape))
133 | #print(depth)
134 |
135 | # apply train/val transforms
136 | if self.transform is not None:
137 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
138 | else:
139 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
140 |
141 | # convert from numpy to torch tensors
142 | input_tensor = to_tensor(rgb_np)
143 |
144 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
145 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
146 |
147 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
148 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
149 |
150 | #print("{:04d} rgb = ".format(index) + str(input_tensor.shape))
151 | #print("{:04d} depth = ".format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
152 |
153 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
154 |
155 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/transforms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | import torch
3 | import math
4 | import random
5 |
6 | from PIL import Image, ImageOps, ImageEnhance
7 | try:
8 | import accimage
9 | except ImportError:
10 | accimage = None
11 |
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import numbers
14 | import types
15 | import collections
16 | import warnings
17 |
18 | import scipy.ndimage.interpolation as itpl
19 | import scipy.misc as misc
20 |
21 |
22 | def _is_numpy_image(img):
23 | return isinstance(img, np.ndarray) and (img.ndim in {2, 3})
24 |
25 | def _is_pil_image(img):
26 | if accimage is not None:
27 | return isinstance(img, (Image.Image, accimage.Image))
28 | else:
29 | return isinstance(img, Image.Image)
30 |
31 | def _is_tensor_image(img):
32 | return torch.is_tensor(img) and img.ndimension() == 3
33 |
34 | def adjust_brightness(img, brightness_factor):
35 | """Adjust brightness of an Image.
36 |
37 | Args:
38 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
39 | brightness_factor (float): How much to adjust the brightness. Can be
40 | any non negative number. 0 gives a black image, 1 gives the
41 | original image while 2 increases the brightness by a factor of 2.
42 |
43 | Returns:
44 | PIL Image: Brightness adjusted image.
45 | """
46 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
47 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
48 |
49 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Brightness(img)
50 | img = enhancer.enhance(brightness_factor)
51 | return img
52 |
53 |
54 | def adjust_contrast(img, contrast_factor):
55 | """Adjust contrast of an Image.
56 |
57 | Args:
58 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
59 | contrast_factor (float): How much to adjust the contrast. Can be any
60 | non negative number. 0 gives a solid gray image, 1 gives the
61 | original image while 2 increases the contrast by a factor of 2.
62 |
63 | Returns:
64 | PIL Image: Contrast adjusted image.
65 | """
66 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
67 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
68 |
69 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Contrast(img)
70 | img = enhancer.enhance(contrast_factor)
71 | return img
72 |
73 |
74 | def adjust_saturation(img, saturation_factor):
75 | """Adjust color saturation of an image.
76 |
77 | Args:
78 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
79 | saturation_factor (float): How much to adjust the saturation. 0 will
80 | give a black and white image, 1 will give the original image while
81 | 2 will enhance the saturation by a factor of 2.
82 |
83 | Returns:
84 | PIL Image: Saturation adjusted image.
85 | """
86 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
87 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
88 |
89 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Color(img)
90 | img = enhancer.enhance(saturation_factor)
91 | return img
92 |
93 |
94 | def adjust_hue(img, hue_factor):
95 | """Adjust hue of an image.
96 |
97 | The image hue is adjusted by converting the image to HSV and
98 | cyclically shifting the intensities in the hue channel (H).
99 | The image is then converted back to original image mode.
100 |
101 | `hue_factor` is the amount of shift in H channel and must be in the
102 | interval `[-0.5, 0.5]`.
103 |
104 | See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hue for more details on Hue.
105 |
106 | Args:
107 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
108 | hue_factor (float): How much to shift the hue channel. Should be in
109 | [-0.5, 0.5]. 0.5 and -0.5 give complete reversal of hue channel in
110 | HSV space in positive and negative direction respectively.
111 | 0 means no shift. Therefore, both -0.5 and 0.5 will give an image
112 | with complementary colors while 0 gives the original image.
113 |
114 | Returns:
115 | PIL Image: Hue adjusted image.
116 | """
117 | if not(-0.5 <= hue_factor <= 0.5):
118 | raise ValueError('hue_factor is not in [-0.5, 0.5].'.format(hue_factor))
119 |
120 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
121 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
122 |
123 | input_mode = img.mode
124 | if input_mode in {'L', '1', 'I', 'F'}:
125 | return img
126 |
127 | h, s, v = img.convert('HSV').split()
128 |
129 | np_h = np.array(h, dtype=np.uint8)
130 | # uint8 addition take cares of rotation across boundaries
131 | with np.errstate(over='ignore'):
132 | np_h += np.uint8(hue_factor * 255)
133 | h = Image.fromarray(np_h, 'L')
134 |
135 | img = Image.merge('HSV', (h, s, v)).convert(input_mode)
136 | return img
137 |
138 |
139 | def adjust_gamma(img, gamma, gain=1):
140 | """Perform gamma correction on an image.
141 |
142 | Also known as Power Law Transform. Intensities in RGB mode are adjusted
143 | based on the following equation:
144 |
145 | I_out = 255 * gain * ((I_in / 255) ** gamma)
146 |
147 | See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction for more details.
148 |
149 | Args:
150 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
151 | gamma (float): Non negative real number. gamma larger than 1 make the
152 | shadows darker, while gamma smaller than 1 make dark regions
153 | lighter.
154 | gain (float): The constant multiplier.
155 | """
156 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
157 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
158 |
159 | if gamma < 0:
160 | raise ValueError('Gamma should be a non-negative real number')
161 |
162 | input_mode = img.mode
163 | img = img.convert('RGB')
164 |
165 | np_img = np.array(img, dtype=np.float32)
166 | np_img = 255 * gain * ((np_img / 255) ** gamma)
167 | np_img = np.uint8(np.clip(np_img, 0, 255))
168 |
169 | img = Image.fromarray(np_img, 'RGB').convert(input_mode)
170 | return img
171 |
172 |
173 | class Compose(object):
174 | """Composes several transforms together.
175 |
176 | Args:
177 | transforms (list of ``Transform`` objects): list of transforms to compose.
178 |
179 | Example:
180 | >>> transforms.Compose([
181 | >>> transforms.CenterCrop(10),
182 | >>> transforms.ToTensor(),
183 | >>> ])
184 | """
185 |
186 | def __init__(self, transforms):
187 | self.transforms = transforms
188 |
189 | def __call__(self, img):
190 | for t in self.transforms:
191 | img = t(img)
192 | return img
193 |
194 |
195 | class ToTensor(object):
196 | """Convert a ``numpy.ndarray`` to tensor.
197 |
198 | Converts a numpy.ndarray (H x W x C) to a torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W).
199 | """
200 |
201 | def __call__(self, img):
202 | """Convert a ``numpy.ndarray`` to tensor.
203 |
204 | Args:
205 | img (numpy.ndarray): Image to be converted to tensor.
206 |
207 | Returns:
208 | Tensor: Converted image.
209 | """
210 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
211 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
212 |
213 | if isinstance(img, np.ndarray):
214 | # handle numpy array
215 | if img.ndim == 3:
216 | img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose((2, 0, 1)).copy())
217 | elif img.ndim == 2:
218 | img = torch.from_numpy(img.copy())
219 | else:
220 | raise RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
221 |
222 | # backward compatibility
223 | # return img.float().div(255)
224 | return img.float()
225 |
226 |
227 | class NormalizeNumpyArray(object):
228 | """Normalize a ``numpy.ndarray`` with mean and standard deviation.
229 | Given mean: ``(M1,...,Mn)`` and std: ``(M1,..,Mn)`` for ``n`` channels, this transform
230 | will normalize each channel of the input ``numpy.ndarray`` i.e.
231 | ``input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
232 |
233 | Args:
234 | mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
235 | std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
236 | """
237 |
238 | def __init__(self, mean, std):
239 | self.mean = mean
240 | self.std = std
241 |
242 | def __call__(self, img):
243 | """
244 | Args:
245 | img (numpy.ndarray): Image of size (H, W, C) to be normalized.
246 |
247 | Returns:
248 | Tensor: Normalized image.
249 | """
250 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
251 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
252 | # TODO: make efficient
253 | print(img.shape)
254 | for i in range(3):
255 | img[:,:,i] = (img[:,:,i] - self.mean[i]) / self.std[i]
256 | return img
257 |
258 | class NormalizeTensor(object):
259 | """Normalize an tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
260 | Given mean: ``(M1,...,Mn)`` and std: ``(M1,..,Mn)`` for ``n`` channels, this transform
261 | will normalize each channel of the input ``torch.*Tensor`` i.e.
262 | ``input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
263 |
264 | Args:
265 | mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
266 | std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
267 | """
268 |
269 | def __init__(self, mean, std):
270 | self.mean = mean
271 | self.std = std
272 |
273 | def __call__(self, tensor):
274 | """
275 | Args:
276 | tensor (Tensor): Tensor image of size (C, H, W) to be normalized.
277 |
278 | Returns:
279 | Tensor: Normalized Tensor image.
280 | """
281 | if not _is_tensor_image(tensor):
282 | raise TypeError('tensor is not a torch image.')
283 | # TODO: make efficient
284 | for t, m, s in zip(tensor, self.mean, self.std):
285 | t.sub_(m).div_(s)
286 | return tensor
287 |
288 | class Rotate(object):
289 | """Rotates the given ``numpy.ndarray``.
290 |
291 | Args:
292 | angle (float): The rotation angle in degrees.
293 | """
294 |
295 | def __init__(self, angle):
296 | self.angle = angle
297 |
298 | def __call__(self, img):
299 | """
300 | Args:
301 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be rotated.
302 |
303 | Returns:
304 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Rotated image.
305 | """
306 |
307 | # order=0 means nearest-neighbor type interpolation
308 | return itpl.rotate(img, self.angle, reshape=False, prefilter=False, order=0)
309 |
310 |
311 | class Resize(object):
312 | """Resize the the given ``numpy.ndarray`` to the given size.
313 | Args:
314 | size (sequence or int): Desired output size. If size is a sequence like
315 | (h, w), output size will be matched to this. If size is an int,
316 | smaller edge of the image will be matched to this number.
317 | i.e, if height > width, then image will be rescaled to
318 | (size * height / width, size)
319 | interpolation (int, optional): Desired interpolation. Default is
320 | ``PIL.Image.BILINEAR``
321 | """
322 |
323 | def __init__(self, size, interpolation='nearest'):
324 | assert isinstance(size, int) or isinstance(size, float) or \
325 | (isinstance(size, collections.Iterable) and len(size) == 2)
326 | self.size = size
327 | self.interpolation = interpolation
328 |
329 | def __call__(self, img):
330 | """
331 | Args:
332 | img (PIL Image): Image to be scaled.
333 | Returns:
334 | PIL Image: Rescaled image.
335 | """
336 | if img.ndim == 3:
337 | return misc.imresize(img, self.size, self.interpolation)
338 | elif img.ndim == 2:
339 | return misc.imresize(img, self.size, self.interpolation, 'F')
340 | else:
341 | RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
342 |
343 |
344 | class CenterCrop(object):
345 | """Crops the given ``numpy.ndarray`` at the center.
346 |
347 | Args:
348 | size (sequence or int): Desired output size of the crop. If size is an
349 | int instead of sequence like (h, w), a square crop (size, size) is
350 | made.
351 | """
352 |
353 | def __init__(self, size):
354 | if isinstance(size, numbers.Number):
355 | self.size = (int(size), int(size))
356 | else:
357 | self.size = size
358 |
359 | @staticmethod
360 | def get_params(img, output_size):
361 | """Get parameters for ``crop`` for center crop.
362 |
363 | Args:
364 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
365 | output_size (tuple): Expected output size of the crop.
366 |
367 | Returns:
368 | tuple: params (i, j, h, w) to be passed to ``crop`` for center crop.
369 | """
370 | h = img.shape[0]
371 | w = img.shape[1]
372 | th, tw = output_size
373 | i = int(round((h - th) / 2.))
374 | j = int(round((w - tw) / 2.))
375 |
376 | # # randomized cropping
377 | # i = np.random.randint(i-3, i+4)
378 | # j = np.random.randint(j-3, j+4)
379 |
380 | return i, j, th, tw
381 |
382 | def __call__(self, img):
383 | """
384 | Args:
385 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
386 |
387 | Returns:
388 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Cropped image.
389 | """
390 | i, j, h, w = self.get_params(img, self.size)
391 |
392 | """
393 | i: Upper pixel coordinate.
394 | j: Left pixel coordinate.
395 | h: Height of the cropped image.
396 | w: Width of the cropped image.
397 | """
398 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
399 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
400 | if img.ndim == 3:
401 | return img[i:i+h, j:j+w, :]
402 | elif img.ndim == 2:
403 | return img[i:i + h, j:j + w]
404 | else:
405 | raise RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
406 |
407 |
408 | class Lambda(object):
409 | """Apply a user-defined lambda as a transform.
410 |
411 | Args:
412 | lambd (function): Lambda/function to be used for transform.
413 | """
414 |
415 | def __init__(self, lambd):
416 | assert isinstance(lambd, types.LambdaType)
417 | self.lambd = lambd
418 |
419 | def __call__(self, img):
420 | return self.lambd(img)
421 |
422 |
423 | class HorizontalFlip(object):
424 | """Horizontally flip the given ``numpy.ndarray``.
425 |
426 | Args:
427 | do_flip (boolean): whether or not do horizontal flip.
428 |
429 | """
430 |
431 | def __init__(self, do_flip):
432 | self.do_flip = do_flip
433 |
434 | def __call__(self, img):
435 | """
436 | Args:
437 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be flipped.
438 |
439 | Returns:
440 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): flipped image.
441 | """
442 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
443 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
444 |
445 | if self.do_flip:
446 | return np.fliplr(img)
447 | else:
448 | return img
449 |
450 |
451 | class ColorJitter(object):
452 | """Randomly change the brightness, contrast and saturation of an image.
453 |
454 | Args:
455 | brightness (float): How much to jitter brightness. brightness_factor
456 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - brightness), 1 + brightness].
457 | contrast (float): How much to jitter contrast. contrast_factor
458 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - contrast), 1 + contrast].
459 | saturation (float): How much to jitter saturation. saturation_factor
460 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - saturation), 1 + saturation].
461 | hue(float): How much to jitter hue. hue_factor is chosen uniformly from
462 | [-hue, hue]. Should be >=0 and <= 0.5.
463 | """
464 | def __init__(self, brightness=0, contrast=0, saturation=0, hue=0):
465 | self.brightness = brightness
466 | self.contrast = contrast
467 | self.saturation = saturation
468 | self.hue = hue
469 |
470 | @staticmethod
471 | def get_params(brightness, contrast, saturation, hue):
472 | """Get a randomized transform to be applied on image.
473 |
474 | Arguments are same as that of __init__.
475 |
476 | Returns:
477 | Transform which randomly adjusts brightness, contrast and
478 | saturation in a random order.
479 | """
480 | transforms = []
481 | if brightness > 0:
482 | brightness_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - brightness), 1 + brightness)
483 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_brightness(img, brightness_factor)))
484 |
485 | if contrast > 0:
486 | contrast_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - contrast), 1 + contrast)
487 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_contrast(img, contrast_factor)))
488 |
489 | if saturation > 0:
490 | saturation_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - saturation), 1 + saturation)
491 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_saturation(img, saturation_factor)))
492 |
493 | if hue > 0:
494 | hue_factor = np.random.uniform(-hue, hue)
495 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_hue(img, hue_factor)))
496 |
497 | np.random.shuffle(transforms)
498 | transform = Compose(transforms)
499 |
500 | return transform
501 |
502 | def __call__(self, img):
503 | """
504 | Args:
505 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Input image.
506 |
507 | Returns:
508 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Color jittered image.
509 | """
510 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
511 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
512 |
513 | pil = Image.fromarray(img)
514 | transform = self.get_params(self.brightness, self.contrast,
515 | self.saturation, self.hue)
516 | return np.array(transform(pil))
517 |
518 | class Crop(object):
519 | """Crops the given PIL Image to a rectangular region based on a given
520 | 4-tuple defining the left, upper pixel coordinated, hight and width size.
521 |
522 | Args:
523 | a tuple: (upper pixel coordinate, left pixel coordinate, hight, width)-tuple
524 | """
525 |
526 | def __init__(self, i, j, h, w):
527 | """
528 | i: Upper pixel coordinate.
529 | j: Left pixel coordinate.
530 | h: Height of the cropped image.
531 | w: Width of the cropped image.
532 | """
533 | self.i = i
534 | self.j = j
535 | self.h = h
536 | self.w = w
537 |
538 | def __call__(self, img):
539 | """
540 | Args:
541 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
542 | Returns:
543 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Cropped image.
544 | """
545 |
546 | i, j, h, w = self.i, self.j, self.h, self.w
547 |
548 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
549 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
550 | if img.ndim == 3:
551 | return img[i:i + h, j:j + w, :]
552 | elif img.ndim == 2:
553 | return img[i:i + h, j:j + w]
554 | else:
555 | raise RuntimeError(
556 | 'img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
557 |
558 | def __repr__(self):
559 | return self.__class__.__name__ + '(i={0},j={1},h={2},w={3})'.format(
560 | self.i, self.j, self.h, self.w)
561 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/zed_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
4 |
5 | from imageio import imread
6 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
7 |
8 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
9 |
10 | iheight, iwidth = 720, 1280 # raw image size
11 |
12 | class ZEDDataset(Dataset):
13 | def __init__(self, root, type='train'):
14 | self.root = root
15 | self.output_size = (224, 224) #(228, 304)
16 |
17 | # search for images
18 | self.rgb_files = []
19 | self.depth_files = []
20 |
21 | self.gather_images(root, max_images=100000)
22 |
23 | if len(self.rgb_files) == 0:
24 | raise (RuntimeError("Empty dataset - found no image pairs under \n" + root))
25 |
26 | # determine if 16-bit or 8-bit depth images
27 | self.depth_16 = False
28 |
29 | if imread(self.depth_files[0]).dtype.type is np.uint16:
30 | self.depth_16 = True
31 | self.depth_16_max = 5000 #20000
32 |
33 | print('found {:d} image pairs with {:s}-bit depth under {:s}'.format(len(self.rgb_files), "16" if self.depth_16 else "8", root))
34 |
35 | # setup transforms
36 | if type == 'train':
37 | self.transform = self.train_transform
38 | elif type == 'val':
39 | self.transform = self.val_transform
40 | else:
41 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
42 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
43 |
44 | def gather_images(self, img_dir, max_images=999999):
45 | rgb_files = []
46 | depth_files = []
47 |
48 | # search in the current directory
49 | for n in range(max_images):
50 | img_name_rgb = 'left{:06d}.png'.format(n)
51 | img_path_rgb = os.path.join(img_dir, img_name_rgb)
52 |
53 | img_name_depth = 'depth{:06d}.png'.format(n)
54 | img_path_depth = os.path.join(img_dir, img_name_depth)
55 |
56 | if os.path.isfile(img_path_rgb) and os.path.isfile(img_path_depth):
57 | self.rgb_files.append(img_path_rgb)
58 | self.depth_files.append(img_path_depth)
59 |
60 | # search in subdirectories
61 | dir_files = os.listdir(img_dir)
62 |
63 | for dir_name in dir_files:
64 | dir_path = os.path.join(img_dir, dir_name)
65 |
66 | if os.path.isdir(dir_path):
67 | self.gather_images(dir_path, max_images)
68 |
69 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
70 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
71 | depth_np = depth #/ s
72 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
73 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
74 |
75 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
76 | transform = transforms.Compose([
77 | transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation can be slow
78 | #transforms.Rotate(angle),
79 | #transforms.Resize(s),
80 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
81 | transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
82 | ])
83 |
84 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
85 | #rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
86 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
87 |
88 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
89 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
90 |
91 | if self.depth_16:
92 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
93 | else:
94 | depth_np = (255 - depth_np) / 255
95 |
96 | return rgb_np, depth_np
97 |
98 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
99 | depth_np = depth
100 |
101 | transform = transforms.Compose([
102 | transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight),
103 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
104 | ])
105 |
106 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
107 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
108 |
109 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
110 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
111 |
112 | if self.depth_16:
113 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
114 | else:
115 | depth_np = (255 - depth_np) / 255
116 |
117 | return rgb_np, depth_np
118 |
119 | def load_rgb(self, index):
120 | return imread(self.rgb_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="RGB")
121 |
122 | def load_depth(self, index):
123 | if self.depth_16:
124 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index])
125 | depth[depth == 65535] = 0 # map 'invalid' to 0
126 | return depth
127 | else:
128 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="L")
129 | #depth[depth == 0] = 255 # map 0 -> 255
130 | return depth
131 |
132 | def __len__(self):
133 | return len(self.rgb_files)
134 |
135 | def __getitem__(self, index):
136 | rgb = self.load_rgb(index)
137 | depth = self.load_depth(index)
138 |
139 | #print(self.depth_files[index] + str(depth.shape))
140 | #print(depth)
141 |
142 | # apply train/val transforms
143 | if self.transform is not None:
144 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
145 | else:
146 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
147 |
148 | # convert from numpy to torch tensors
149 | input_tensor = to_tensor(rgb_np)
150 |
151 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
152 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
153 |
154 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
155 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
156 |
157 | #print("{:04d} rgb = ".format(index) + str(input_tensor.shape))
158 | #print("{:04d} depth = ".format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
159 |
160 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
161 |
162 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/imagenet/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dusty-nv/pytorch-depth/41d6440dc0a64a4c59dff3daaaea50a1212897b1/imagenet/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/imagenet/mobilenet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import shutil
3 | import time
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | import torch.nn as nn
7 | import torch.nn.parallel
8 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
9 | import torch.optim
10 | import torch.utils.data
11 |
12 | class MobileNet(nn.Module):
13 | def __init__(self, relu6=True):
14 | super(MobileNet, self).__init__()
15 |
16 | def relu(relu6):
17 | if relu6:
18 | return nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
19 | else:
20 | return nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
21 |
22 | def conv_bn(inp, oup, stride, relu6):
23 | return nn.Sequential(
24 | nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),
25 | nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
26 | relu(relu6),
27 | )
28 |
29 | def conv_dw(inp, oup, stride, relu6):
30 | return nn.Sequential(
31 | nn.Conv2d(inp, inp, 3, stride, 1, groups=inp, bias=False),
32 | nn.BatchNorm2d(inp),
33 | relu(relu6),
34 |
35 | nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
36 | nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
37 | relu(relu6),
38 | )
39 |
40 | self.model = nn.Sequential(
41 | conv_bn( 3, 32, 2, relu6),
42 | conv_dw( 32, 64, 1, relu6),
43 | conv_dw( 64, 128, 2, relu6),
44 | conv_dw(128, 128, 1, relu6),
45 | conv_dw(128, 256, 2, relu6),
46 | conv_dw(256, 256, 1, relu6),
47 | conv_dw(256, 512, 2, relu6),
48 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
49 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
50 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
51 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
52 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
53 | conv_dw(512, 1024, 2, relu6),
54 | conv_dw(1024, 1024, 1, relu6),
55 | nn.AvgPool2d(7),
56 | )
57 | self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, 1000)
58 |
59 | def forward(self, x):
60 | x = self.model(x)
61 | #print('pre-view size: ' + str(x.size()))
62 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
63 | #print('post-view size: ' + str(x.size()))
64 | x = self.fc(x)
65 | return x
66 |
67 | def main():
68 | import torchvision.models
69 | model = MobileNet(relu6=True)
70 | model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
71 | model_filename = os.path.join('results', 'imagenet.arch=mobilenet.lr=0.1.bs=256', 'model_best.pth.tar')
72 | if os.path.isfile(model_filename):
73 | print("=> loading Imagenet pretrained model '{}'".format(model_filename))
74 | checkpoint = torch.load(model_filename)
75 | epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
76 | best_prec1 = checkpoint['best_prec1']
77 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
78 | print("=> loaded Imagenet pretrained model '{}' (epoch {}). best_prec1={}".format(model_filename, epoch, best_prec1))
79 |
80 | if __name__ == '__main__':
81 | main()
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import time
3 | import csv
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
8 | import torch.optim
9 |
10 | cudnn.benchmark = True
11 |
12 | from models import ResNet
13 | from models_fast import MobileNetSkipAdd
14 | from metrics import AverageMeter, Result
15 | from dataloaders.dense_to_sparse import UniformSampling, SimulatedStereo
16 |
17 | import criteria
18 | import utils
19 |
20 | args = utils.parse_command()
21 | print(args)
22 |
23 | fieldnames = ['mse', 'rmse', 'absrel', 'lg10', 'mae',
24 | 'delta1', 'delta2', 'delta3',
25 | 'data_time', 'gpu_time']
26 | best_result = Result()
27 | best_result.set_to_worst()
28 |
29 | def create_data_loaders(args):
30 | # Data loading code
31 | print("=> creating data loaders ...")
32 | traindir = os.path.join('data', args.data, 'train')
33 | valdir = os.path.join('data', args.data, 'val')
34 | train_loader = None
35 | val_loader = None
36 |
37 | # sparsifier is a class for generating random sparse depth input from the ground truth
38 | sparsifier = None
39 | max_depth = args.max_depth if args.max_depth >= 0.0 else np.inf
40 | if args.sparsifier == UniformSampling.name:
41 | sparsifier = UniformSampling(num_samples=args.num_samples, max_depth=max_depth)
42 | elif args.sparsifier == SimulatedStereo.name:
43 | sparsifier = SimulatedStereo(num_samples=args.num_samples, max_depth=max_depth)
44 |
45 | if args.data == 'nyudepthv2':
46 | from dataloaders.nyu_dataloader import NYUDataset
47 | if not args.evaluate:
48 | train_dataset = NYUDataset(traindir, type='train',
49 | modality=args.modality, sparsifier=sparsifier)
50 | val_dataset = NYUDataset(valdir, type='val',
51 | modality=args.modality, sparsifier=sparsifier)
52 |
53 | elif args.data == 'kitti':
54 | from dataloaders.kitti_dataloader import KITTIDataset
55 | if not args.evaluate:
56 | train_dataset = KITTIDataset(traindir, type='train',
57 | modality=args.modality, sparsifier=sparsifier)
58 | val_dataset = KITTIDataset(valdir, type='val',
59 | modality=args.modality, sparsifier=sparsifier)
60 |
61 | elif args.data == 'deepscene':
62 | from dataloaders.deepscene_dataloader import DeepSceneDataset
63 | if not args.evaluate:
64 | train_dataset = DeepSceneDataset(traindir, type='train')
65 |
66 | val_dataset = DeepSceneDataset(valdir, type='val')
67 |
68 | elif args.data == 'sun':
69 | from dataloaders.sun_dataloader import SunRGBDDataset
70 | if not args.evaluate:
71 | train_dataset = SunRGBDDataset(traindir, type='train')
72 |
73 | val_dataset = SunRGBDDataset(valdir, type='val')
74 |
75 | elif args.data == 'zed':
76 | from dataloaders.zed_dataloader import ZEDDataset
77 | if not args.evaluate:
78 | train_dataset = ZEDDataset(traindir, type='train')
79 |
80 | val_dataset = ZEDDataset(valdir, type='val')
81 |
82 |
83 | else:
84 | raise RuntimeError('Dataset not found.' +
85 | 'The dataset must be either of nyudepthv2, kitti, or zed.')
86 |
87 | # set batch size to be 1 for validation
88 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
89 | batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True)
90 |
91 | # put construction of train loader here, for those who are interested in testing only
92 | if not args.evaluate:
93 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
94 | train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True,
95 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True, sampler=None,
96 | worker_init_fn=lambda work_id:np.random.seed(work_id))
97 | # worker_init_fn ensures different sampling patterns for each data loading thread
98 |
99 | print("=> data loaders created.")
100 | return train_loader, val_loader
101 |
102 | def main():
103 | global args, best_result, output_directory, train_csv, test_csv
104 |
105 | # evaluation mode
106 | start_epoch = 0
107 | if args.evaluate:
108 | assert os.path.isfile(args.evaluate), \
109 | "=> no best model found at '{}'".format(args.evaluate)
110 | print("=> loading best model '{}'".format(args.evaluate))
111 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.evaluate)
112 | output_directory = os.path.dirname(args.evaluate)
113 | args = checkpoint['args']
114 | start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
115 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
116 | model = checkpoint['model']
117 | print("=> loaded best model (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
118 | _, val_loader = create_data_loaders(args)
119 | args.evaluate = True
120 | validate(val_loader, model, checkpoint['epoch'], write_to_file=False)
121 | return
122 |
123 | # export to ONNX
124 | elif args.export:
125 | assert os.path.isfile(args.export), \
126 | "=> no best model found at '{}'".format(args.export)
127 | print("=> loading best model '{}'".format(args.export))
128 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.export)
129 | output_directory = os.path.dirname(args.export)
130 | output_filename = args.export + '.onnx'
131 | args = checkpoint['args']
132 | start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
133 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
134 | model = checkpoint['model']
135 | model.export = True
136 | print("=> loaded best model (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
137 | export(model, output_filename, args.data)
138 | return
139 |
140 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
141 | elif args.resume:
142 | chkpt_path = args.resume
143 | assert os.path.isfile(chkpt_path), \
144 | "=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(chkpt_path)
145 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(chkpt_path))
146 | checkpoint = torch.load(chkpt_path)
147 | args = checkpoint['args']
148 | start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
149 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
150 | model = checkpoint['model']
151 | optimizer = checkpoint['optimizer']
152 | output_directory = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(chkpt_path))
153 | print("=> loaded checkpoint (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
154 | train_loader, val_loader = create_data_loaders(args)
155 | args.resume = True
156 |
157 | # transfer learning from a checkpoint
158 | elif args.checkpoint:
159 | chkpt_path = args.checkpoint
160 | assert os.path.isfile(chkpt_path), \
161 | "=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(chkpt_path)
162 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(chkpt_path))
163 | checkpoint = torch.load(chkpt_path)
164 | model = checkpoint['model']
165 | optimizer = checkpoint['optimizer']
166 | print("=> loaded checkpoint (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
167 | train_loader, val_loader = create_data_loaders(args)
168 |
169 | # create new model
170 | else:
171 | train_loader, val_loader = create_data_loaders(args)
172 | print("=> creating Model ({}-{}) ...".format(args.arch, args.decoder))
173 | in_channels = len(args.modality)
174 | if args.arch == 'resnet50':
175 | model = ResNet(layers=50, decoder=args.decoder, output_size=train_loader.dataset.output_size,
176 | in_channels=in_channels, pretrained=args.pretrained)
177 | elif args.arch == 'resnet18':
178 | model = ResNet(layers=18, decoder=args.decoder, output_size=train_loader.dataset.output_size,
179 | in_channels=in_channels, pretrained=args.pretrained)
180 | elif args.arch == 'mobilenet':
181 | model = MobileNetSkipAdd(output_size=train_loader.dataset.output_size,
182 | pretrained=args.pretrained)
183 |
184 | print("=> model created " + str(train_loader.dataset.output_size))
185 |
186 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr, \
187 | momentum=args.momentum, weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
188 |
189 | # model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda() # for multi-gpu training
190 | model = model.cuda()
191 |
192 | # define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
193 | if args.criterion == 'l2':
194 | criterion = criteria.MaskedMSELoss().cuda()
195 | elif args.criterion == 'l1':
196 | criterion = criteria.MaskedL1Loss().cuda()
197 |
198 | # create results folder, if not already exists
199 | output_directory = utils.get_output_directory(args)
200 | if not os.path.exists(output_directory):
201 | os.makedirs(output_directory)
202 | train_csv = os.path.join(output_directory, 'train.csv')
203 | test_csv = os.path.join(output_directory, 'test.csv')
204 | best_txt = os.path.join(output_directory, 'best.txt')
205 |
206 | # create new csv files with only header
207 | if not args.resume:
208 | with open(train_csv, 'w') as csvfile:
209 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
210 | writer.writeheader()
211 | with open(test_csv, 'w') as csvfile:
212 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
213 | writer.writeheader()
214 |
215 | for epoch in range(start_epoch, args.epochs):
216 | utils.adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args.lr)
217 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch) # train for one epoch
218 | result, img_merge = validate(val_loader, model, epoch) # evaluate on validation set
219 |
220 | # remember best rmse and save checkpoint
221 | is_best = result.rmse < best_result.rmse
222 | if is_best:
223 | best_result = result
224 | with open(best_txt, 'w') as txtfile:
225 | txtfile.write("epoch={}\nmse={:.3f}\nrmse={:.3f}\nabsrel={:.3f}\nlg10={:.3f}\nmae={:.3f}\ndelta1={:.3f}\nt_gpu={:.4f}\n".
226 | format(epoch, result.mse, result.rmse, result.absrel, result.lg10, result.mae, result.delta1, result.gpu_time))
227 | if img_merge is not None:
228 | img_filename = output_directory + '/comparison_best.png'
229 | utils.save_image(img_merge, img_filename)
230 |
231 | utils.save_checkpoint({
232 | 'args': args,
233 | 'epoch': epoch,
234 | 'arch': args.arch,
235 | 'model': model,
236 | 'best_result': best_result,
237 | 'optimizer' : optimizer,
238 | }, is_best, epoch, output_directory)
239 |
240 |
241 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
242 | average_meter = AverageMeter()
243 | model.train() # switch to train mode
244 | end = time.time()
245 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
246 |
247 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda()
248 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
249 | data_time = time.time() - end
250 |
251 | # compute pred
252 | end = time.time()
253 | pred = model(input)
254 | loss = criterion(pred, target)
255 | optimizer.zero_grad()
256 | loss.backward() # compute gradient and do SGD step
257 | optimizer.step()
258 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
259 | gpu_time = time.time() - end
260 |
261 | #print('input size: ' + str(input.size()))
262 | #print('output size: ' + str(pred.size()))
263 |
264 | # measure accuracy and record loss
265 | result = Result()
266 | result.evaluate(pred.data, target.data)
267 | average_meter.update(result, gpu_time, data_time, input.size(0))
268 | end = time.time()
269 |
270 | if (i + 1) % args.print_freq == 0:
271 | print('=> output: {}'.format(output_directory))
272 | print('Train Epoch: {0} [{1}/{2}]\t'
273 | 't_Data={data_time:.3f}({average.data_time:.3f}) '
274 | 't_GPU={gpu_time:.3f}({average.gpu_time:.3f})\n\t'
275 | 'RMSE={result.rmse:.2f}({average.rmse:.2f}) '
276 | 'MAE={result.mae:.2f}({average.mae:.2f}) '
277 | 'Delta1={result.delta1:.3f}({average.delta1:.3f}) '
278 | 'REL={result.absrel:.3f}({average.absrel:.3f}) '
279 | 'Lg10={result.lg10:.3f}({average.lg10:.3f}) '.format(
280 | epoch, i+1, len(train_loader), data_time=data_time,
281 | gpu_time=gpu_time, result=result, average=average_meter.average()))
282 |
283 | avg = average_meter.average()
284 | with open(train_csv, 'a') as csvfile:
285 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
286 | writer.writerow({'mse': avg.mse, 'rmse': avg.rmse, 'absrel': avg.absrel, 'lg10': avg.lg10,
287 | 'mae': avg.mae, 'delta1': avg.delta1, 'delta2': avg.delta2, 'delta3': avg.delta3,
288 | 'gpu_time': avg.gpu_time, 'data_time': avg.data_time})
289 |
290 |
291 | def validate(val_loader, model, epoch, write_to_file=True):
292 | average_meter = AverageMeter()
293 | model.eval() # switch to evaluate mode
294 | end = time.time()
295 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
296 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda()
297 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
298 | data_time = time.time() - end
299 |
300 | # compute output
301 | end = time.time()
302 | with torch.no_grad():
303 | pred = model(input)
304 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
305 | gpu_time = time.time() - end
306 |
307 | #print('input size: ' + str(input.size()))
308 | #print('output size: ' + str(pred.size()))
309 |
310 | # measure accuracy and record loss
311 | result = Result()
312 | result.evaluate(pred.data, target.data)
313 | average_meter.update(result, gpu_time, data_time, input.size(0))
314 | end = time.time()
315 |
316 | # save 8 images for visualization
317 | skip = 10 if args.data == 'deepscene' else 50
318 | if args.modality == 'd':
319 | img_merge = None
320 | else:
321 | if args.modality == 'rgb':
322 | rgb = input
323 | elif args.modality == 'rgbd':
324 | rgb = input[:,:3,:,:]
325 | depth = input[:,3:,:,:]
326 |
327 | if i == 0:
328 | if args.modality == 'rgbd':
329 | img_merge = utils.merge_into_row_with_gt(rgb, depth, target, pred)
330 | else:
331 | img_merge = utils.merge_into_row(rgb, target, pred)
332 | elif (i < 8*skip) and (i % skip == 0):
333 | if args.modality == 'rgbd':
334 | row = utils.merge_into_row_with_gt(rgb, depth, target, pred)
335 | else:
336 | row = utils.merge_into_row(rgb, target, pred)
337 | img_merge = utils.add_row(img_merge, row)
338 | elif i == 8*skip:
339 | filename = output_directory + '/comparison_' + str(epoch) + '.png'
340 | utils.save_image(img_merge, filename)
341 |
342 | if (i+1) % args.print_freq == 0:
343 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
344 | 't_GPU={gpu_time:.3f}({average.gpu_time:.3f})\n\t'
345 | 'RMSE={result.rmse:.2f}({average.rmse:.2f}) '
346 | 'MAE={result.mae:.2f}({average.mae:.2f}) '
347 | 'Delta1={result.delta1:.3f}({average.delta1:.3f}) '
348 | 'REL={result.absrel:.3f}({average.absrel:.3f}) '
349 | 'Lg10={result.lg10:.3f}({average.lg10:.3f}) '.format(
350 | i+1, len(val_loader), gpu_time=gpu_time, result=result, average=average_meter.average()))
351 |
352 | avg = average_meter.average()
353 |
354 | print('\n*\n'
355 | 'RMSE={average.rmse:.3f}\n'
356 | 'MAE={average.mae:.3f}\n'
357 | 'Delta1={average.delta1:.3f}\n'
358 | 'REL={average.absrel:.3f}\n'
359 | 'Lg10={average.lg10:.3f}\n'
360 | 't_GPU={time:.3f}\n'.format(
361 | average=avg, time=avg.gpu_time))
362 |
363 | if write_to_file:
364 | with open(test_csv, 'a') as csvfile:
365 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
366 | writer.writerow({'mse': avg.mse, 'rmse': avg.rmse, 'absrel': avg.absrel, 'lg10': avg.lg10,
367 | 'mae': avg.mae, 'delta1': avg.delta1, 'delta2': avg.delta2, 'delta3': avg.delta3,
368 | 'data_time': avg.data_time, 'gpu_time': avg.gpu_time})
369 | return avg, img_merge
370 |
371 |
372 | # export model to ONNX
373 | def export(model, path, dataset):
374 | print('=> exporting ONNX model to: ' + path)
375 | model.eval()
376 |
377 | # set the input size from the dataset
378 | input_size = (1, 3, 448, 448) #(1, 3, 224, 224) #(1, 3, 480, 640) #(1, 3, 228, 304) # nyudepthv2
379 |
380 | if dataset == "kitti":
381 | input_size = (1, 3, 228, 912)
382 |
383 | input = torch.ones(input_size).cuda()
384 | print('=> input resolution: ' + str(input_size))
385 |
386 | # set the input/output layer names
387 | input_names = [ "input_0" ]
388 | output_names = [ "output_0" ]
389 |
390 | print(model)
391 |
392 | # export the model
393 | torch.onnx.export(model, input, path, verbose=True, input_names=input_names, output_names=output_names)
394 | print('=> ONNX model exported to: ' + path)
395 |
396 | if __name__ == '__main__':
397 | main()
398 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/metrics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import math
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | def log10(x):
6 | """Convert a new tensor with the base-10 logarithm of the elements of x. """
7 | return torch.log(x) / math.log(10)
8 |
9 | class Result(object):
10 | def __init__(self):
11 | self.irmse, self.imae = 0, 0
12 | self.mse, self.rmse, self.mae = 0, 0, 0
13 | self.absrel, self.lg10 = 0, 0
14 | self.delta1, self.delta2, self.delta3 = 0, 0, 0
15 | self.data_time, self.gpu_time = 0, 0
16 |
17 | def set_to_worst(self):
18 | self.irmse, self.imae = np.inf, np.inf
19 | self.mse, self.rmse, self.mae = np.inf, np.inf, np.inf
20 | self.absrel, self.lg10 = np.inf, np.inf
21 | self.delta1, self.delta2, self.delta3 = 0, 0, 0
22 | self.data_time, self.gpu_time = 0, 0
23 |
24 | def update(self, irmse, imae, mse, rmse, mae, absrel, lg10, delta1, delta2, delta3, gpu_time, data_time):
25 | self.irmse, self.imae = irmse, imae
26 | self.mse, self.rmse, self.mae = mse, rmse, mae
27 | self.absrel, self.lg10 = absrel, lg10
28 | self.delta1, self.delta2, self.delta3 = delta1, delta2, delta3
29 | self.data_time, self.gpu_time = data_time, gpu_time
30 |
31 | def evaluate(self, output, target):
32 | valid_mask = target>0
33 | output = output[valid_mask]
34 | target = target[valid_mask]
35 |
36 | abs_diff = (output - target).abs()
37 |
38 | self.mse = float((torch.pow(abs_diff, 2)).mean())
39 | self.rmse = math.sqrt(self.mse)
40 | self.mae = float(abs_diff.mean())
41 | self.lg10 = float((log10(output) - log10(target)).abs().mean())
42 | self.absrel = float((abs_diff / target).mean())
43 |
44 | maxRatio = torch.max(output / target, target / output)
45 | self.delta1 = float((maxRatio < 1.25).float().mean())
46 | self.delta2 = float((maxRatio < 1.25 ** 2).float().mean())
47 | self.delta3 = float((maxRatio < 1.25 ** 3).float().mean())
48 | self.data_time = 0
49 | self.gpu_time = 0
50 |
51 | inv_output = 1 / output
52 | inv_target = 1 / target
53 | abs_inv_diff = (inv_output - inv_target).abs()
54 | self.irmse = math.sqrt((torch.pow(abs_inv_diff, 2)).mean())
55 | self.imae = float(abs_inv_diff.mean())
56 |
57 |
58 | class AverageMeter(object):
59 | def __init__(self):
60 | self.reset()
61 |
62 | def reset(self):
63 | self.count = 0.0
64 |
65 | self.sum_irmse, self.sum_imae = 0, 0
66 | self.sum_mse, self.sum_rmse, self.sum_mae = 0, 0, 0
67 | self.sum_absrel, self.sum_lg10 = 0, 0
68 | self.sum_delta1, self.sum_delta2, self.sum_delta3 = 0, 0, 0
69 | self.sum_data_time, self.sum_gpu_time = 0, 0
70 |
71 | def update(self, result, gpu_time, data_time, n=1):
72 | self.count += n
73 |
74 | self.sum_irmse += n*result.irmse
75 | self.sum_imae += n*result.imae
76 | self.sum_mse += n*result.mse
77 | self.sum_rmse += n*result.rmse
78 | self.sum_mae += n*result.mae
79 | self.sum_absrel += n*result.absrel
80 | self.sum_lg10 += n*result.lg10
81 | self.sum_delta1 += n*result.delta1
82 | self.sum_delta2 += n*result.delta2
83 | self.sum_delta3 += n*result.delta3
84 | self.sum_data_time += n*data_time
85 | self.sum_gpu_time += n*gpu_time
86 |
87 | def average(self):
88 | avg = Result()
89 | avg.update(
90 | self.sum_irmse / self.count, self.sum_imae / self.count,
91 | self.sum_mse / self.count, self.sum_rmse / self.count, self.sum_mae / self.count,
92 | self.sum_absrel / self.count, self.sum_lg10 / self.count,
93 | self.sum_delta1 / self.count, self.sum_delta2 / self.count, self.sum_delta3 / self.count,
94 | self.sum_gpu_time / self.count, self.sum_data_time / self.count)
95 | return avg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | import torchvision.models
5 | import collections
6 | import math
7 |
8 | class Unpool(nn.Module):
9 | # Unpool: 2*2 unpooling with zero padding
10 | def __init__(self, num_channels, stride=2):
11 | super(Unpool, self).__init__()
12 |
13 | self.num_channels = num_channels
14 | self.stride = stride
15 |
16 | # create kernel [1, 0; 0, 0]
17 | self.weights = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(num_channels, 1, stride, stride).cuda()) # currently not compatible with running on CPU
18 | self.weights[:,:,0,0] = 1
19 |
20 | def forward(self, x):
21 | return F.conv_transpose2d(x, self.weights, stride=self.stride, groups=self.num_channels)
22 |
23 | def weights_init(m):
24 | # Initialize filters with Gaussian random weights
25 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
26 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
27 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
28 | if m.bias is not None:
29 | m.bias.data.zero_()
30 | elif isinstance(m, nn.ConvTranspose2d):
31 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.in_channels
32 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
33 | if m.bias is not None:
34 | m.bias.data.zero_()
35 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
36 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
37 | m.bias.data.zero_()
38 |
39 | class Decoder(nn.Module):
40 | # Decoder is the base class for all decoders
41 |
42 | names = ['deconv2', 'deconv3', 'upconv', 'upproj']
43 |
44 | def __init__(self):
45 | super(Decoder, self).__init__()
46 |
47 | self.layer1 = None
48 | self.layer2 = None
49 | self.layer3 = None
50 | self.layer4 = None
51 |
52 | def forward(self, x):
53 | x = self.layer1(x)
54 | x = self.layer2(x)
55 | x = self.layer3(x)
56 | x = self.layer4(x)
57 | return x
58 |
59 | class DeConv(Decoder):
60 | def __init__(self, in_channels, kernel_size):
61 | assert kernel_size>=2, "kernel_size out of range: {}".format(kernel_size)
62 | super(DeConv, self).__init__()
63 |
64 | def convt(in_channels):
65 | stride = 2
66 | padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
67 | output_padding = kernel_size % 2
68 | assert -2 - 2*padding + kernel_size + output_padding == 0, "deconv parameters incorrect"
69 |
70 | module_name = "deconv{}".format(kernel_size)
71 | return nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict([
72 | (module_name, nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels,in_channels//2,kernel_size,
73 | stride,padding,output_padding,bias=False)),
74 | ('batchnorm', nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels//2)),
75 | ('relu', nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
76 | ]))
77 |
78 | self.layer1 = convt(in_channels)
79 | self.layer2 = convt(in_channels // 2)
80 | self.layer3 = convt(in_channels // (2 ** 2))
81 | self.layer4 = convt(in_channels // (2 ** 3))
82 |
83 | class UpConv(Decoder):
84 | # UpConv decoder consists of 4 upconv modules with decreasing number of channels and increasing feature map size
85 | def upconv_module(self, in_channels):
86 | # UpConv module: unpool -> 5*5 conv -> batchnorm -> ReLU
87 | upconv = nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict([
88 | ('unpool', Unpool(in_channels)),
89 | ('conv', nn.Conv2d(in_channels,in_channels//2,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False)),
90 | ('batchnorm', nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels//2)),
91 | ('relu', nn.ReLU()),
92 | ]))
93 | return upconv
94 |
95 | def __init__(self, in_channels):
96 | super(UpConv, self).__init__()
97 | self.layer1 = self.upconv_module(in_channels)
98 | self.layer2 = self.upconv_module(in_channels//2)
99 | self.layer3 = self.upconv_module(in_channels//4)
100 | self.layer4 = self.upconv_module(in_channels//8)
101 |
102 | class UpProj(Decoder):
103 | # UpProj decoder consists of 4 upproj modules with decreasing number of channels and increasing feature map size
104 |
105 | class UpProjModule(nn.Module):
106 | # UpProj module has two branches, with a Unpool at the start and a ReLu at the end
107 | # upper branch: 5*5 conv -> batchnorm -> ReLU -> 3*3 conv -> batchnorm
108 | # bottom branch: 5*5 conv -> batchnorm
109 |
110 | def __init__(self, in_channels):
111 | super(UpProj.UpProjModule, self).__init__()
112 | out_channels = in_channels//2
113 | self.unpool = Unpool(in_channels)
114 | self.upper_branch = nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict([
115 | ('conv1', nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False)),
116 | ('batchnorm1', nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)),
117 | ('relu', nn.ReLU()),
118 | ('conv2', nn.Conv2d(out_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False)),
119 | ('batchnorm2', nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)),
120 | ]))
121 | self.bottom_branch = nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict([
122 | ('conv', nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False)),
123 | ('batchnorm', nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)),
124 | ]))
125 | self.relu = nn.ReLU()
126 |
127 | def forward(self, x):
128 | x = self.unpool(x)
129 | x1 = self.upper_branch(x)
130 | x2 = self.bottom_branch(x)
131 | x = x1 + x2
132 | x = self.relu(x)
133 | return x
134 |
135 | def __init__(self, in_channels):
136 | super(UpProj, self).__init__()
137 | self.layer1 = self.UpProjModule(in_channels)
138 | self.layer2 = self.UpProjModule(in_channels//2)
139 | self.layer3 = self.UpProjModule(in_channels//4)
140 | self.layer4 = self.UpProjModule(in_channels//8)
141 |
142 | def choose_decoder(decoder, in_channels):
143 | # iheight, iwidth = 10, 8
144 | if decoder[:6] == 'deconv':
145 | assert len(decoder)==7
146 | kernel_size = int(decoder[6])
147 | return DeConv(in_channels, kernel_size)
148 | elif decoder == "upproj":
149 | return UpProj(in_channels)
150 | elif decoder == "upconv":
151 | return UpConv(in_channels)
152 | else:
153 | assert False, "invalid option for decoder: {}".format(decoder)
154 |
155 |
156 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
157 | def __init__(self, layers, decoder, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True, export=False):
158 |
159 | if layers not in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152]:
160 | raise RuntimeError('Only 18, 34, 50, 101, and 152 layer model are defined for ResNet. Got {}'.format(layers))
161 |
162 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
163 | pretrained_model = torchvision.models.__dict__['resnet{}'.format(layers)](pretrained=pretrained)
164 |
165 | if in_channels == 3:
166 | self.conv1 = pretrained_model._modules['conv1']
167 | self.bn1 = pretrained_model._modules['bn1']
168 | else:
169 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
170 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
171 | weights_init(self.conv1)
172 | weights_init(self.bn1)
173 |
174 | self.output_size = output_size
175 | self.export = export
176 |
177 | self.relu = pretrained_model._modules['relu']
178 | self.maxpool = pretrained_model._modules['maxpool']
179 | self.layer1 = pretrained_model._modules['layer1']
180 | self.layer2 = pretrained_model._modules['layer2']
181 | self.layer3 = pretrained_model._modules['layer3']
182 | self.layer4 = pretrained_model._modules['layer4']
183 |
184 | # clear memory
185 | del pretrained_model
186 |
187 | # define number of intermediate channels
188 | if layers <= 34:
189 | num_channels = 512
190 | elif layers >= 50:
191 | num_channels = 2048
192 |
193 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels,num_channels//2,kernel_size=1,bias=False)
194 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels//2)
195 | self.decoder = choose_decoder(decoder, num_channels//2)
196 |
197 | # setting bias=true doesn't improve accuracy
198 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels//32,1,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False)
199 | self.bilinear = nn.Upsample(size=self.output_size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
200 |
201 | # weight init
202 | self.conv2.apply(weights_init)
203 | self.bn2.apply(weights_init)
204 | self.decoder.apply(weights_init)
205 | self.conv3.apply(weights_init)
206 |
207 | def forward(self, x):
208 | # resnet
209 | x = self.conv1(x)
210 | x = self.bn1(x)
211 | x = self.relu(x)
212 | x = self.maxpool(x)
213 | x = self.layer1(x)
214 | x = self.layer2(x)
215 | x = self.layer3(x)
216 | x = self.layer4(x)
217 |
218 | x = self.conv2(x)
219 | x = self.bn2(x)
220 |
221 | # decoder
222 | x = self.decoder(x)
223 | x = self.conv3(x)
224 |
225 | if not hasattr(self, 'export') or not self.export:
226 | x = self.bilinear(x) # comment out for --export to ONNX mode
227 |
228 | return x
229 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models_fast.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #
2 | # these are the models from FastDepth, which use the training code from sparse-to-dense:
3 | #
4 | # - https://github.com/dwofk/fast-depth/blob/master/models.py
5 | # - https://github.com/dwofk/fast-depth/issues/3#issuecomment-510545490
6 | #
7 | import os
8 | import torch
9 | import torch.nn as nn
10 | import torchvision.models
11 | import collections
12 | import math
13 | import torch.nn.functional as F
14 | import imagenet.mobilenet
15 |
16 | class Identity(nn.Module):
17 | # a dummy identity module
18 | def __init__(self):
19 | super(Identity, self).__init__()
20 |
21 | def forward(self, x):
22 | return x
23 |
24 | class Unpool(nn.Module):
25 | # Unpool: 2*2 unpooling with zero padding
26 | def __init__(self, stride=2):
27 | super(Unpool, self).__init__()
28 |
29 | self.stride = stride
30 |
31 | # create kernel [1, 0; 0, 0]
32 | self.mask = torch.zeros(1, 1, stride, stride)
33 | self.mask[:,:,0,0] = 1
34 |
35 | def forward(self, x):
36 | assert x.dim() == 4
37 | num_channels = x.size(1)
38 | return F.conv_transpose2d(x,
39 | self.mask.detach().type_as(x).expand(num_channels, 1, -1, -1),
40 | stride=self.stride, groups=num_channels)
41 |
42 | def weights_init(m):
43 | # Initialize kernel weights with Gaussian distributions
44 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
45 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
46 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
47 | if m.bias is not None:
48 | m.bias.data.zero_()
49 | elif isinstance(m, nn.ConvTranspose2d):
50 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.in_channels
51 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
52 | if m.bias is not None:
53 | m.bias.data.zero_()
54 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
55 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
56 | m.bias.data.zero_()
57 |
58 | def conv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size):
59 | padding = (kernel_size-1) // 2
60 | assert 2*padding == kernel_size-1, "parameters incorrect. kernel={}, padding={}".format(kernel_size, padding)
61 | return nn.Sequential(
62 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,stride=1,padding=padding,bias=False),
63 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
64 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
65 | )
66 |
67 | def depthwise(in_channels, kernel_size):
68 | padding = (kernel_size-1) // 2
69 | assert 2*padding == kernel_size-1, "parameters incorrect. kernel={}, padding={}".format(kernel_size, padding)
70 | return nn.Sequential(
71 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,in_channels,kernel_size,stride=1,padding=padding,bias=False,groups=in_channels),
72 | nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
73 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
74 | )
75 |
76 | def pointwise(in_channels, out_channels):
77 | return nn.Sequential(
78 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,1,1,0,bias=False),
79 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
80 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
81 | )
82 |
83 | def convt(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size):
84 | stride = 2
85 | padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
86 | output_padding = kernel_size % 2
87 | assert -2 - 2*padding + kernel_size + output_padding == 0, "deconv parameters incorrect"
88 | return nn.Sequential(
89 | nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,
90 | stride,padding,output_padding,bias=False),
91 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
92 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
93 | )
94 |
95 | def convt_dw(channels, kernel_size):
96 | stride = 2
97 | padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
98 | output_padding = kernel_size % 2
99 | assert -2 - 2*padding + kernel_size + output_padding == 0, "deconv parameters incorrect"
100 | return nn.Sequential(
101 | nn.ConvTranspose2d(channels,channels,kernel_size,
102 | stride,padding,output_padding,bias=False,groups=channels),
103 | nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
104 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
105 | )
106 |
107 | def upconv(in_channels, out_channels):
108 | return nn.Sequential(
109 | Unpool(2),
110 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False),
111 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
112 | nn.ReLU(),
113 | )
114 |
115 | class upproj(nn.Module):
116 | # UpProj module has two branches, with a Unpool at the start and a ReLu at the end
117 | # upper branch: 5*5 conv -> batchnorm -> ReLU -> 3*3 conv -> batchnorm
118 | # bottom branch: 5*5 conv -> batchnorm
119 |
120 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
121 | super(upproj, self).__init__()
122 | self.unpool = Unpool(2)
123 | self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
124 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False),
125 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
126 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
127 | nn.Conv2d(out_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),
128 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
129 | )
130 | self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
131 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False),
132 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
133 | )
134 |
135 | def forward(self, x):
136 | x = self.unpool(x)
137 | x1 = self.branch1(x)
138 | x2 = self.branch2(x)
139 | return F.relu(x1 + x2)
140 |
141 | class Decoder(nn.Module):
142 | names = ['deconv{}{}'.format(i,dw) for i in range(3,10,2) for dw in ['', 'dw']]
143 | names.append("upconv")
144 | names.append("upproj")
145 | for i in range(3,10,2):
146 | for dw in ['', 'dw']:
147 | names.append("nnconv{}{}".format(i, dw))
148 | names.append("blconv{}{}".format(i, dw))
149 | names.append("shuffle{}{}".format(i, dw))
150 |
151 | class DeConv(nn.Module):
152 |
153 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, dw):
154 | super(DeConv, self).__init__()
155 | if dw:
156 | self.convt1 = nn.Sequential(
157 | convt_dw(1024, kernel_size),
158 | pointwise(1024, 512))
159 | self.convt2 = nn.Sequential(
160 | convt_dw(512, kernel_size),
161 | pointwise(512, 256))
162 | self.convt3 = nn.Sequential(
163 | convt_dw(256, kernel_size),
164 | pointwise(256, 128))
165 | self.convt4 = nn.Sequential(
166 | convt_dw(128, kernel_size),
167 | pointwise(128, 64))
168 | self.convt5 = nn.Sequential(
169 | convt_dw(64, kernel_size),
170 | pointwise(64, 32))
171 | else:
172 | self.convt1 = convt(1024, 512, kernel_size)
173 | self.convt2 = convt(512, 256, kernel_size)
174 | self.convt3 = convt(256, 128, kernel_size)
175 | self.convt4 = convt(128, 64, kernel_size)
176 | self.convt5 = convt(64, 32, kernel_size)
177 | self.convf = pointwise(32, 1)
178 |
179 | def forward(self, x):
180 | x = self.convt1(x)
181 | x = self.convt2(x)
182 | x = self.convt3(x)
183 | x = self.convt4(x)
184 | x = self.convt5(x)
185 | x = self.convf(x)
186 | return x
187 |
188 |
189 | class UpConv(nn.Module):
190 |
191 | def __init__(self):
192 | super(UpConv, self).__init__()
193 | self.upconv1 = upconv(1024, 512)
194 | self.upconv2 = upconv(512, 256)
195 | self.upconv3 = upconv(256, 128)
196 | self.upconv4 = upconv(128, 64)
197 | self.upconv5 = upconv(64, 32)
198 | self.convf = pointwise(32, 1)
199 |
200 | def forward(self, x):
201 | x = self.upconv1(x)
202 | x = self.upconv2(x)
203 | x = self.upconv3(x)
204 | x = self.upconv4(x)
205 | x = self.upconv5(x)
206 | x = self.convf(x)
207 | return x
208 |
209 | class UpProj(nn.Module):
210 | # UpProj decoder consists of 4 upproj modules with decreasing number of channels and increasing feature map size
211 |
212 | def __init__(self):
213 | super(UpProj, self).__init__()
214 | self.upproj1 = upproj(1024, 512)
215 | self.upproj2 = upproj(512, 256)
216 | self.upproj3 = upproj(256, 128)
217 | self.upproj4 = upproj(128, 64)
218 | self.upproj5 = upproj(64, 32)
219 | self.convf = pointwise(32, 1)
220 |
221 | def forward(self, x):
222 | x = self.upproj1(x)
223 | x = self.upproj2(x)
224 | x = self.upproj3(x)
225 | x = self.upproj4(x)
226 | x = self.upproj5(x)
227 | x = self.convf(x)
228 | return x
229 |
230 | class NNConv(nn.Module):
231 |
232 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, dw):
233 | super(NNConv, self).__init__()
234 | if dw:
235 | self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
236 | depthwise(1024, kernel_size),
237 | pointwise(1024, 512))
238 | self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
239 | depthwise(512, kernel_size),
240 | pointwise(512, 256))
241 | self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
242 | depthwise(256, kernel_size),
243 | pointwise(256, 128))
244 | self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
245 | depthwise(128, kernel_size),
246 | pointwise(128, 64))
247 | self.conv5 = nn.Sequential(
248 | depthwise(64, kernel_size),
249 | pointwise(64, 32))
250 | self.conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
251 | else:
252 | self.conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
253 | self.conv2 = conv(512, 256, kernel_size)
254 | self.conv3 = conv(256, 128, kernel_size)
255 | self.conv4 = conv(128, 64, kernel_size)
256 | self.conv5 = conv(64, 32, kernel_size)
257 | self.conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
258 |
259 | def forward(self, x):
260 | x = self.conv1(x)
261 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
262 |
263 | x = self.conv2(x)
264 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
265 |
266 | x = self.conv3(x)
267 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
268 |
269 | x = self.conv4(x)
270 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
271 |
272 | x = self.conv5(x)
273 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
274 |
275 | x = self.conv6(x)
276 | return x
277 |
278 | class BLConv(NNConv):
279 |
280 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, dw):
281 | super(BLConv, self).__init__(kernel_size, dw)
282 |
283 | def forward(self, x):
284 | x = self.conv1(x)
285 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
286 |
287 | x = self.conv2(x)
288 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
289 |
290 | x = self.conv3(x)
291 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
292 |
293 | x = self.conv4(x)
294 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
295 |
296 | x = self.conv5(x)
297 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
298 |
299 | x = self.conv6(x)
300 | return x
301 |
302 | class ShuffleConv(nn.Module):
303 |
304 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, dw):
305 | super(ShuffleConv, self).__init__()
306 | if dw:
307 | self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
308 | depthwise(256, kernel_size),
309 | pointwise(256, 256))
310 | self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
311 | depthwise(64, kernel_size),
312 | pointwise(64, 64))
313 | self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
314 | depthwise(16, kernel_size),
315 | pointwise(16, 16))
316 | self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
317 | depthwise(4, kernel_size),
318 | pointwise(4, 4))
319 | else:
320 | self.conv1 = conv(256, 256, kernel_size)
321 | self.conv2 = conv(64, 64, kernel_size)
322 | self.conv3 = conv(16, 16, kernel_size)
323 | self.conv4 = conv(4, 4, kernel_size)
324 |
325 | def forward(self, x):
326 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
327 | x = self.conv1(x)
328 |
329 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
330 | x = self.conv2(x)
331 |
332 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
333 | x = self.conv3(x)
334 |
335 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
336 | x = self.conv4(x)
337 |
338 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
339 | return x
340 |
341 | def choose_decoder(decoder):
342 | depthwise = ('dw' in decoder)
343 | if decoder[:6] == 'deconv':
344 | assert len(decoder)==7 or (len(decoder)==9 and 'dw' in decoder)
345 | kernel_size = int(decoder[6])
346 | model = DeConv(kernel_size, depthwise)
347 | elif decoder == "upproj":
348 | model = UpProj()
349 | elif decoder == "upconv":
350 | model = UpConv()
351 | elif decoder[:7] == 'shuffle':
352 | assert len(decoder)==8 or (len(decoder)==10 and 'dw' in decoder)
353 | kernel_size = int(decoder[7])
354 | model = ShuffleConv(kernel_size, depthwise)
355 | elif decoder[:6] == 'nnconv':
356 | assert len(decoder)==7 or (len(decoder)==9 and 'dw' in decoder)
357 | kernel_size = int(decoder[6])
358 | model = NNConv(kernel_size, depthwise)
359 | elif decoder[:6] == 'blconv':
360 | assert len(decoder)==7 or (len(decoder)==9 and 'dw' in decoder)
361 | kernel_size = int(decoder[6])
362 | model = BLConv(kernel_size, depthwise)
363 | else:
364 | assert False, "invalid option for decoder: {}".format(decoder)
365 | model.apply(weights_init)
366 | return model
367 |
368 |
369 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
370 | def __init__(self, layers, decoder, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True):
371 |
372 | if layers not in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152]:
373 | raise RuntimeError('Only 18, 34, 50, 101, and 152 layer model are defined for ResNet. Got {}'.format(layers))
374 |
375 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
376 | self.output_size = output_size
377 | pretrained_model = torchvision.models.__dict__['resnet{}'.format(layers)](pretrained=pretrained)
378 | if not pretrained:
379 | pretrained_model.apply(weights_init)
380 |
381 | if in_channels == 3:
382 | self.conv1 = pretrained_model._modules['conv1']
383 | self.bn1 = pretrained_model._modules['bn1']
384 | else:
385 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
386 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
387 | weights_init(self.conv1)
388 | weights_init(self.bn1)
389 |
390 | self.relu = pretrained_model._modules['relu']
391 | self.maxpool = pretrained_model._modules['maxpool']
392 | self.layer1 = pretrained_model._modules['layer1']
393 | self.layer2 = pretrained_model._modules['layer2']
394 | self.layer3 = pretrained_model._modules['layer3']
395 | self.layer4 = pretrained_model._modules['layer4']
396 |
397 | # clear memory
398 | del pretrained_model
399 |
400 | # define number of intermediate channels
401 | if layers <= 34:
402 | num_channels = 512
403 | elif layers >= 50:
404 | num_channels = 2048
405 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, 1024, 1)
406 | weights_init(self.conv2)
407 | self.decoder = choose_decoder(decoder)
408 |
409 | def forward(self, x):
410 | # resnet
411 | x = self.conv1(x)
412 | x = self.bn1(x)
413 | x = self.relu(x)
414 | x = self.maxpool(x)
415 | x = self.layer1(x)
416 | x = self.layer2(x)
417 | x = self.layer3(x)
418 | x = self.layer4(x)
419 | x = self.conv2(x)
420 |
421 | # decoder
422 | x = self.decoder(x)
423 |
424 | return x
425 |
426 | class MobileNet(nn.Module):
427 | def __init__(self, decoder, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True):
428 |
429 | super(MobileNet, self).__init__()
430 | self.output_size = output_size
431 | mobilenet = imagenet.mobilenet.MobileNet()
432 | if pretrained:
433 | pretrained_path = os.path.join('imagenet', 'results', 'imagenet.arch=mobilenet.lr=0.1.bs=256', 'model_best.pth.tar')
434 | checkpoint = torch.load(pretrained_path)
435 | state_dict = checkpoint['state_dict']
436 |
437 | from collections import OrderedDict
438 | new_state_dict = OrderedDict()
439 | for k, v in state_dict.items():
440 | name = k[7:] # remove `module.`
441 | new_state_dict[name] = v
442 | mobilenet.load_state_dict(new_state_dict)
443 | else:
444 | mobilenet.apply(weights_init)
445 |
446 | if in_channels == 3:
447 | self.mobilenet = nn.Sequential(*(mobilenet.model[i] for i in range(14)))
448 | else:
449 | def conv_bn(inp, oup, stride):
450 | return nn.Sequential(
451 | nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),
452 | nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
453 | nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
454 | )
455 |
456 | self.mobilenet = nn.Sequential(
457 | conv_bn(in_channels, 32, 2),
458 | *(mobilenet.model[i] for i in range(1,14))
459 | )
460 |
461 | self.decoder = choose_decoder(decoder)
462 |
463 | def forward(self, x):
464 | x = self.mobilenet(x)
465 | x = self.decoder(x)
466 | return x
467 |
468 | class ResNetSkipAdd(nn.Module):
469 | def __init__(self, layers, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True):
470 |
471 | if layers not in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152]:
472 | raise RuntimeError('Only 18, 34, 50, 101, and 152 layer model are defined for ResNet. Got {}'.format(layers))
473 |
474 | super(ResNetSkipAdd, self).__init__()
475 | self.output_size = output_size
476 | pretrained_model = torchvision.models.__dict__['resnet{}'.format(layers)](pretrained=pretrained)
477 | if not pretrained:
478 | pretrained_model.apply(weights_init)
479 |
480 | if in_channels == 3:
481 | self.conv1 = pretrained_model._modules['conv1']
482 | self.bn1 = pretrained_model._modules['bn1']
483 | else:
484 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
485 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
486 | weights_init(self.conv1)
487 | weights_init(self.bn1)
488 |
489 | self.relu = pretrained_model._modules['relu']
490 | self.maxpool = pretrained_model._modules['maxpool']
491 | self.layer1 = pretrained_model._modules['layer1']
492 | self.layer2 = pretrained_model._modules['layer2']
493 | self.layer3 = pretrained_model._modules['layer3']
494 | self.layer4 = pretrained_model._modules['layer4']
495 |
496 | # clear memory
497 | del pretrained_model
498 |
499 | # define number of intermediate channels
500 | if layers <= 34:
501 | num_channels = 512
502 | elif layers >= 50:
503 | num_channels = 2048
504 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, 1024, 1)
505 | weights_init(self.conv2)
506 |
507 | kernel_size = 5
508 | self.decode_conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
509 | self.decode_conv2 = conv(512, 256, kernel_size)
510 | self.decode_conv3 = conv(256, 128, kernel_size)
511 | self.decode_conv4 = conv(128, 64, kernel_size)
512 | self.decode_conv5 = conv(64, 32, kernel_size)
513 | self.decode_conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
514 | weights_init(self.decode_conv1)
515 | weights_init(self.decode_conv2)
516 | weights_init(self.decode_conv3)
517 | weights_init(self.decode_conv4)
518 | weights_init(self.decode_conv5)
519 | weights_init(self.decode_conv6)
520 |
521 | def forward(self, x):
522 | # resnet
523 | x = self.conv1(x)
524 | x = self.bn1(x)
525 | x1 = self.relu(x)
526 | # print("x1", x1.size())
527 | x2 = self.maxpool(x1)
528 | # print("x2", x2.size())
529 | x3 = self.layer1(x2)
530 | # print("x3", x3.size())
531 | x4 = self.layer2(x3)
532 | # print("x4", x4.size())
533 | x5 = self.layer3(x4)
534 | # print("x5", x5.size())
535 | x6 = self.layer4(x5)
536 | # print("x6", x6.size())
537 | x7 = self.conv2(x6)
538 |
539 | # decoder
540 | y10 = self.decode_conv1(x7)
541 | # print("y10", y10.size())
542 | y9 = F.interpolate(y10 + x6, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
543 | # print("y9", y9.size())
544 | y8 = self.decode_conv2(y9)
545 | # print("y8", y8.size())
546 | y7 = F.interpolate(y8 + x5, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
547 | # print("y7", y7.size())
548 | y6 = self.decode_conv3(y7)
549 | # print("y6", y6.size())
550 | y5 = F.interpolate(y6 + x4, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
551 | # print("y5", y5.size())
552 | y4 = self.decode_conv4(y5)
553 | # print("y4", y4.size())
554 | y3 = F.interpolate(y4 + x3, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
555 | # print("y3", y3.size())
556 | y2 = self.decode_conv5(y3 + x1)
557 | # print("y2", y2.size())
558 | y1 = F.interpolate(y2, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
559 | # print("y1", y1.size())
560 | y = self.decode_conv6(y1)
561 |
562 | return y
563 |
564 | class ResNetSkipConcat(nn.Module):
565 | def __init__(self, layers, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True):
566 |
567 | if layers not in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152]:
568 | raise RuntimeError('Only 18, 34, 50, 101, and 152 layer model are defined for ResNet. Got {}'.format(layers))
569 |
570 | super(ResNetSkipConcat, self).__init__()
571 | self.output_size = output_size
572 | pretrained_model = torchvision.models.__dict__['resnet{}'.format(layers)](pretrained=pretrained)
573 | if not pretrained:
574 | pretrained_model.apply(weights_init)
575 |
576 | if in_channels == 3:
577 | self.conv1 = pretrained_model._modules['conv1']
578 | self.bn1 = pretrained_model._modules['bn1']
579 | else:
580 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
581 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
582 | weights_init(self.conv1)
583 | weights_init(self.bn1)
584 |
585 | self.relu = pretrained_model._modules['relu']
586 | self.maxpool = pretrained_model._modules['maxpool']
587 | self.layer1 = pretrained_model._modules['layer1']
588 | self.layer2 = pretrained_model._modules['layer2']
589 | self.layer3 = pretrained_model._modules['layer3']
590 | self.layer4 = pretrained_model._modules['layer4']
591 |
592 | # clear memory
593 | del pretrained_model
594 |
595 | # define number of intermediate channels
596 | if layers <= 34:
597 | num_channels = 512
598 | elif layers >= 50:
599 | num_channels = 2048
600 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, 1024, 1)
601 | weights_init(self.conv2)
602 |
603 | kernel_size = 5
604 | self.decode_conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
605 | self.decode_conv2 = conv(768, 256, kernel_size)
606 | self.decode_conv3 = conv(384, 128, kernel_size)
607 | self.decode_conv4 = conv(192, 64, kernel_size)
608 | self.decode_conv5 = conv(128, 32, kernel_size)
609 | self.decode_conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
610 | weights_init(self.decode_conv1)
611 | weights_init(self.decode_conv2)
612 | weights_init(self.decode_conv3)
613 | weights_init(self.decode_conv4)
614 | weights_init(self.decode_conv5)
615 | weights_init(self.decode_conv6)
616 |
617 | def forward(self, x):
618 | # resnet
619 | x = self.conv1(x)
620 | x = self.bn1(x)
621 | x1 = self.relu(x)
622 | # print("x1", x1.size())
623 | x2 = self.maxpool(x1)
624 | # print("x2", x2.size())
625 | x3 = self.layer1(x2)
626 | # print("x3", x3.size())
627 | x4 = self.layer2(x3)
628 | # print("x4", x4.size())
629 | x5 = self.layer3(x4)
630 | # print("x5", x5.size())
631 | x6 = self.layer4(x5)
632 | # print("x6", x6.size())
633 | x7 = self.conv2(x6)
634 |
635 | # decoder
636 | y10 = self.decode_conv1(x7)
637 | # print("y10", y10.size())
638 | y9 = F.interpolate(y10, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
639 | # print("y9", y9.size())
640 | y8 = self.decode_conv2(torch.cat((y9, x5), 1))
641 | # print("y8", y8.size())
642 | y7 = F.interpolate(y8, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
643 | # print("y7", y7.size())
644 | y6 = self.decode_conv3(torch.cat((y7, x4), 1))
645 | # print("y6", y6.size())
646 | y5 = F.interpolate(y6, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
647 | # print("y5", y5.size())
648 | y4 = self.decode_conv4(torch.cat((y5, x3), 1))
649 | # print("y4", y4.size())
650 | y3 = F.interpolate(y4, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
651 | # print("y3", y3.size())
652 | y2 = self.decode_conv5(torch.cat((y3, x1), 1))
653 | # print("y2", y2.size())
654 | y1 = F.interpolate(y2, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
655 | # print("y1", y1.size())
656 | y = self.decode_conv6(y1)
657 |
658 | return y
659 |
660 | class MobileNetSkipAdd(nn.Module):
661 | def __init__(self, output_size, pretrained=True):
662 |
663 | super(MobileNetSkipAdd, self).__init__()
664 | self.output_size = output_size
665 | mobilenet = imagenet.mobilenet.MobileNet()
666 | if pretrained:
667 | pretrained_path = os.path.join('imagenet', 'results', 'imagenet.arch=mobilenet.lr=0.1.bs=256', 'model_best.pth.tar')
668 | checkpoint = torch.load(pretrained_path)
669 | state_dict = checkpoint['state_dict']
670 |
671 | from collections import OrderedDict
672 | new_state_dict = OrderedDict()
673 | for k, v in state_dict.items():
674 | name = k[7:] # remove `module.`
675 | new_state_dict[name] = v
676 | mobilenet.load_state_dict(new_state_dict)
677 | else:
678 | mobilenet.apply(weights_init)
679 |
680 | for i in range(14):
681 | setattr( self, 'conv{}'.format(i), mobilenet.model[i])
682 |
683 | kernel_size = 5
684 | # self.decode_conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
685 | # self.decode_conv2 = conv(512, 256, kernel_size)
686 | # self.decode_conv3 = conv(256, 128, kernel_size)
687 | # self.decode_conv4 = conv(128, 64, kernel_size)
688 | # self.decode_conv5 = conv(64, 32, kernel_size)
689 | self.decode_conv1 = nn.Sequential(
690 | depthwise(1024, kernel_size),
691 | pointwise(1024, 512))
692 | self.decode_conv2 = nn.Sequential(
693 | depthwise(512, kernel_size),
694 | pointwise(512, 256))
695 | self.decode_conv3 = nn.Sequential(
696 | depthwise(256, kernel_size),
697 | pointwise(256, 128))
698 | self.decode_conv4 = nn.Sequential(
699 | depthwise(128, kernel_size),
700 | pointwise(128, 64))
701 | self.decode_conv5 = nn.Sequential(
702 | depthwise(64, kernel_size),
703 | pointwise(64, 32))
704 | self.decode_conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
705 | weights_init(self.decode_conv1)
706 | weights_init(self.decode_conv2)
707 | weights_init(self.decode_conv3)
708 | weights_init(self.decode_conv4)
709 | weights_init(self.decode_conv5)
710 | weights_init(self.decode_conv6)
711 |
712 | def forward(self, x):
713 | # skip connections: dec4: enc1
714 | # dec 3: enc2 or enc3
715 | # dec 2: enc4 or enc5
716 | for i in range(14):
717 | layer = getattr(self, 'conv{}'.format(i))
718 | x = layer(x)
719 | # print("{}: {}".format(i, x.size()))
720 | if i==1:
721 | x1 = x
722 | elif i==3:
723 | x2 = x
724 | elif i==5:
725 | x3 = x
726 | for i in range(1,6):
727 | layer = getattr(self, 'decode_conv{}'.format(i))
728 | x = layer(x)
729 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
730 | if i==4:
731 | x = x + x1
732 | elif i==3:
733 | x = x + x2
734 | elif i==2:
735 | x = x + x3
736 | # print("{}: {}".format(i, x.size()))
737 | x = self.decode_conv6(x)
738 | return x
739 |
740 | class MobileNetSkipConcat(nn.Module):
741 | def __init__(self, output_size, pretrained=True):
742 |
743 | super(MobileNetSkipConcat, self).__init__()
744 | self.output_size = output_size
745 | mobilenet = imagenet.mobilenet.MobileNet()
746 | if pretrained:
747 | pretrained_path = os.path.join('imagenet', 'results', 'imagenet.arch=mobilenet.lr=0.1.bs=256', 'model_best.pth.tar')
748 | checkpoint = torch.load(pretrained_path)
749 | state_dict = checkpoint['state_dict']
750 |
751 | from collections import OrderedDict
752 | new_state_dict = OrderedDict()
753 | for k, v in state_dict.items():
754 | name = k[7:] # remove `module.`
755 | new_state_dict[name] = v
756 | mobilenet.load_state_dict(new_state_dict)
757 | else:
758 | mobilenet.apply(weights_init)
759 |
760 | for i in range(14):
761 | setattr( self, 'conv{}'.format(i), mobilenet.model[i])
762 |
763 | kernel_size = 5
764 | # self.decode_conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
765 | # self.decode_conv2 = conv(512, 256, kernel_size)
766 | # self.decode_conv3 = conv(256, 128, kernel_size)
767 | # self.decode_conv4 = conv(128, 64, kernel_size)
768 | # self.decode_conv5 = conv(64, 32, kernel_size)
769 | self.decode_conv1 = nn.Sequential(
770 | depthwise(1024, kernel_size),
771 | pointwise(1024, 512))
772 | self.decode_conv2 = nn.Sequential(
773 | depthwise(512, kernel_size),
774 | pointwise(512, 256))
775 | self.decode_conv3 = nn.Sequential(
776 | depthwise(512, kernel_size),
777 | pointwise(512, 128))
778 | self.decode_conv4 = nn.Sequential(
779 | depthwise(256, kernel_size),
780 | pointwise(256, 64))
781 | self.decode_conv5 = nn.Sequential(
782 | depthwise(128, kernel_size),
783 | pointwise(128, 32))
784 | self.decode_conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
785 | weights_init(self.decode_conv1)
786 | weights_init(self.decode_conv2)
787 | weights_init(self.decode_conv3)
788 | weights_init(self.decode_conv4)
789 | weights_init(self.decode_conv5)
790 | weights_init(self.decode_conv6)
791 |
792 | def forward(self, x):
793 | # skip connections: dec4: enc1
794 | # dec 3: enc2 or enc3
795 | # dec 2: enc4 or enc5
796 | for i in range(14):
797 | layer = getattr(self, 'conv{}'.format(i))
798 | x = layer(x)
799 | # print("{}: {}".format(i, x.size()))
800 | if i==1:
801 | x1 = x
802 | elif i==3:
803 | x2 = x
804 | elif i==5:
805 | x3 = x
806 | for i in range(1,6):
807 | layer = getattr(self, 'decode_conv{}'.format(i))
808 | # print("{}a: {}".format(i, x.size()))
809 | x = layer(x)
810 | # print("{}b: {}".format(i, x.size()))
811 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
812 | if i==4:
813 | x = torch.cat((x, x1), 1)
814 | elif i==3:
815 | x = torch.cat((x, x2), 1)
816 | elif i==2:
817 | x = torch.cat((x, x3), 1)
818 | # print("{}c: {}".format(i, x.size()))
819 | x = self.decode_conv6(x)
820 | return x
821 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import torch
3 | import shutil
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
6 | from PIL import Image
7 |
8 | cmap = plt.cm.viridis
9 |
10 | def parse_command():
11 | model_names = ['resnet18', 'resnet50', 'mobilenet']
12 | loss_names = ['l1', 'l2']
13 | data_names = ['nyudepthv2', 'kitti', 'deepscene', 'sun', 'zed']
14 | from dataloaders.dense_to_sparse import UniformSampling, SimulatedStereo
15 | sparsifier_names = [x.name for x in [UniformSampling, SimulatedStereo]]
16 | from models import Decoder
17 | decoder_names = Decoder.names
18 | from dataloaders.dataloader import MyDataloader
19 | modality_names = MyDataloader.modality_names
20 |
21 | import argparse
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Sparse-to-Dense')
23 | parser.add_argument('--arch', '-a', metavar='ARCH', default='resnet18', choices=model_names,
24 | help='model architecture: ' + ' | '.join(model_names) + ' (default: resnet18)')
25 | parser.add_argument('--data', metavar='DATA', default='nyudepthv2',
26 | choices=data_names,
27 | help='dataset: ' + ' | '.join(data_names) + ' (default: nyudepthv2)')
28 | parser.add_argument('--modality', '-m', metavar='MODALITY', default='rgb', choices=modality_names,
29 | help='modality: ' + ' | '.join(modality_names) + ' (default: rgb)')
30 | parser.add_argument('-s', '--num-samples', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
31 | help='number of sparse depth samples (default: 0)')
32 | parser.add_argument('--max-depth', default=-1.0, type=float, metavar='D',
33 | help='cut-off depth of sparsifier, negative values means infinity (default: inf [m])')
34 | parser.add_argument('--sparsifier', metavar='SPARSIFIER', default=UniformSampling.name, choices=sparsifier_names,
35 | help='sparsifier: ' + ' | '.join(sparsifier_names) + ' (default: ' + UniformSampling.name + ')')
36 | parser.add_argument('--decoder', '-d', metavar='DECODER', default='deconv2', choices=decoder_names,
37 | help='decoder: ' + ' | '.join(decoder_names) + ' (default: deconv2)')
38 | parser.add_argument('-j', '--workers', default=10, type=int, metavar='N',
39 | help='number of data loading workers (default: 10)')
40 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=15, type=int, metavar='N',
41 | help='number of total epochs to run (default: 15)')
42 | parser.add_argument('-c', '--criterion', metavar='LOSS', default='l1', choices=loss_names,
43 | help='loss function: ' + ' | '.join(loss_names) + ' (default: l1)')
44 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=8, type=int, help='mini-batch size (default: 8)')
45 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.01, type=float,
46 | metavar='LR', help='initial learning rate (default 0.01)')
47 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, metavar='M',
48 | help='momentum')
49 | parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', '--wd', default=1e-4, type=float,
50 | metavar='W', help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)')
51 | parser.add_argument('--print-freq', '-p', default=10, type=int,
52 | metavar='N', help='print frequency (default: 10)')
53 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
54 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
55 | parser.add_argument('--checkpoint', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
56 | help='path to pretrained checkpoint to begin training from')
57 | parser.add_argument('-e', '--evaluate', dest='evaluate', type=str, default='',
58 | help='evaluate model on validation set')
59 | parser.add_argument('--no-pretrain', dest='pretrained', action='store_false',
60 | help='not to use ImageNet pre-trained weights')
61 | parser.add_argument('--export', default='', type=str, help='path to pre-trained model to load to export to ONNX')
62 | parser.set_defaults(pretrained=True)
63 | args = parser.parse_args()
64 | if args.modality == 'rgb' and args.num_samples != 0:
65 | print("number of samples is forced to be 0 when input modality is rgb")
66 | args.num_samples = 0
67 | if args.modality == 'rgb' and args.max_depth != 0.0:
68 | print("max depth is forced to be 0.0 when input modality is rgb/rgbd")
69 | args.max_depth = 0.0
70 | return args
71 |
72 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, epoch, output_directory):
73 | checkpoint_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'checkpoint-' + str(epoch) + '.pth.tar')
74 | torch.save(state, checkpoint_filename)
75 | if is_best:
76 | best_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'model_best.pth.tar')
77 | shutil.copyfile(checkpoint_filename, best_filename)
78 | if epoch > 0:
79 | prev_checkpoint_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'checkpoint-' + str(epoch-1) + '.pth.tar')
80 | if os.path.exists(prev_checkpoint_filename):
81 | os.remove(prev_checkpoint_filename)
82 |
83 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, lr_init):
84 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 every 5 epochs"""
85 | lr = lr_init * (0.1 ** (epoch // 5))
86 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
87 | param_group['lr'] = lr
88 |
89 | def get_output_directory(args):
90 | output_directory = os.path.join('results',
91 | '{}.sparsifier={}.samples={}.modality={}.arch={}.decoder={}.criterion={}.lr={}.bs={}.pretrained={}'.
92 | format(args.data, args.sparsifier, args.num_samples, args.modality, \
93 | args.arch, args.decoder, args.criterion, args.lr, args.batch_size, \
94 | args.pretrained))
95 | return output_directory
96 |
97 |
98 | def colored_depthmap(depth, d_min=None, d_max=None):
99 | if d_min is None:
100 | d_min = np.min(depth)
101 | if d_max is None:
102 | d_max = np.max(depth)
103 | depth_relative = (depth - d_min) / (d_max - d_min)
104 | return 255 * cmap(depth_relative)[:,:,:3] # H, W, C
105 |
106 |
107 | def merge_into_row(input, depth_target, depth_pred):
108 | rgb = 255 * np.transpose(np.squeeze(input.cpu().numpy()), (1,2,0)) # H, W, C
109 | depth_target_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_target.cpu().numpy())
110 | depth_pred_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_pred.data.cpu().numpy())
111 |
112 | d_min = min(np.min(depth_target_cpu), np.min(depth_pred_cpu))
113 | d_max = max(np.max(depth_target_cpu), np.max(depth_pred_cpu))
114 |
115 | print('depth_min {:f} depth_max {:f}'.format(d_min, d_max))
116 |
117 | depth_target_col = colored_depthmap(depth_target_cpu, d_min, d_max)
118 | depth_pred_col = colored_depthmap(depth_pred_cpu, d_min, d_max)
119 | img_merge = np.hstack([rgb, depth_target_col, depth_pred_col])
120 |
121 | return img_merge
122 |
123 |
124 | def merge_into_row_with_gt(input, depth_input, depth_target, depth_pred):
125 | rgb = 255 * np.transpose(np.squeeze(input.cpu().numpy()), (1,2,0)) # H, W, C
126 | depth_input_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_input.cpu().numpy())
127 | depth_target_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_target.cpu().numpy())
128 | depth_pred_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_pred.data.cpu().numpy())
129 |
130 | d_min = min(np.min(depth_input_cpu), np.min(depth_target_cpu), np.min(depth_pred_cpu))
131 | d_max = max(np.max(depth_input_cpu), np.max(depth_target_cpu), np.max(depth_pred_cpu))
132 | depth_input_col = colored_depthmap(depth_input_cpu, d_min, d_max)
133 | depth_target_col = colored_depthmap(depth_target_cpu, d_min, d_max)
134 | depth_pred_col = colored_depthmap(depth_pred_cpu, d_min, d_max)
135 |
136 | img_merge = np.hstack([rgb, depth_input_col, depth_target_col, depth_pred_col])
137 |
138 | return img_merge
139 |
140 |
141 | def add_row(img_merge, row):
142 | return np.vstack([img_merge, row])
143 |
144 |
145 | def save_image(img_merge, filename):
146 | img_merge = Image.fromarray(img_merge.astype('uint8'))
147 | img_merge.save(filename)
148 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
107 |
108 | Note: our networks are trained on the KITTI odometry dataset, using only sparse labels from laser measurements.
109 |
110 | ## Citation
111 | If you use our code or method in your work, please consider citing the following:
112 |
113 | @article{Ma2017SparseToDense,
114 | title={Sparse-to-Dense: Depth Prediction from Sparse Depth Samples and a Single Image},
115 | author={Ma, Fangchang and Karaman, Sertac},
116 | booktitle={ICRA},
117 | year={2018}
118 | }
119 | @article{ma2018self,
120 | title={Self-supervised Sparse-to-Dense: Self-supervised Depth Completion from LiDAR and Monocular Camera},
121 | author={Ma, Fangchang and Cavalheiro, Guilherme Venturelli and Karaman, Sertac},
122 | journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1807.00275},
123 | year={2018}
124 | }
125 |
126 | Please create a new issue for code-related questions. Pull requests are welcome.
127 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/criteria.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | from torch.autograd import Variable
4 |
5 | class MaskedMSELoss(nn.Module):
6 | def __init__(self):
7 | super(MaskedMSELoss, self).__init__()
8 |
9 | def forward(self, pred, target):
10 | assert pred.dim() == target.dim(), "inconsistent dimensions"
11 | valid_mask = (target>0).detach()
12 | diff = target - pred
13 | diff = diff[valid_mask]
14 | self.loss = (diff ** 2).mean()
15 | return self.loss
16 |
17 | class MaskedL1Loss(nn.Module):
18 | def __init__(self):
19 | super(MaskedL1Loss, self).__init__()
20 |
21 | def forward(self, pred, target):
22 | assert pred.dim() == target.dim(), "inconsistent dimensions"
23 | valid_mask = (target>0).detach()
24 | diff = target - pred
25 | diff = diff[valid_mask]
26 | self.loss = diff.abs().mean()
27 | return self.loss
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import os.path
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import torch.utils.data as data
5 | import h5py
6 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
7 |
8 | IMG_EXTENSIONS = ['.h5',]
9 |
10 | def is_image_file(filename):
11 | return any(filename.endswith(extension) for extension in IMG_EXTENSIONS)
12 |
13 | def find_classes(dir):
14 | classes = [d for d in os.listdir(dir) if os.path.isdir(os.path.join(dir, d))]
15 | classes.sort()
16 | class_to_idx = {classes[i]: i for i in range(len(classes))}
17 | return classes, class_to_idx
18 |
19 | def make_dataset(dir, class_to_idx):
20 | images = []
21 | dir = os.path.expanduser(dir)
22 | for target in sorted(os.listdir(dir)):
23 | d = os.path.join(dir, target)
24 | if not os.path.isdir(d):
25 | continue
26 | for root, _, fnames in sorted(os.walk(d)):
27 | for fname in sorted(fnames):
28 | if is_image_file(fname):
29 | path = os.path.join(root, fname)
30 | item = (path, class_to_idx[target])
31 | images.append(item)
32 | return images
33 |
34 | def h5_loader(path):
35 | h5f = h5py.File(path, "r")
36 | rgb = np.array(h5f['rgb'])
37 | rgb = np.transpose(rgb, (1, 2, 0))
38 | depth = np.array(h5f['depth'])
39 | return rgb, depth
40 |
41 | # def rgb2grayscale(rgb):
42 | # return rgb[:,:,0] * 0.2989 + rgb[:,:,1] * 0.587 + rgb[:,:,2] * 0.114
43 |
44 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
45 |
46 | class MyDataloader(data.Dataset):
47 | modality_names = ['rgb', 'rgbd', 'd'] # , 'g', 'gd'
48 | color_jitter = transforms.ColorJitter(0.4, 0.4, 0.4)
49 |
50 | def __init__(self, root, type, sparsifier=None, modality='rgb', loader=h5_loader):
51 | classes, class_to_idx = find_classes(root)
52 | imgs = make_dataset(root, class_to_idx)
53 | assert len(imgs)>0, "Found 0 images in subfolders of: " + root + "\n"
54 | print("Found {} images in {} folder.".format(len(imgs), type))
55 | self.root = root
56 | self.imgs = imgs
57 | self.classes = classes
58 | self.class_to_idx = class_to_idx
59 | if type == 'train':
60 | self.transform = self.train_transform
61 | elif type == 'val':
62 | self.transform = self.val_transform
63 | else:
64 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
65 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
66 | self.loader = loader
67 | self.sparsifier = sparsifier
68 |
69 | assert (modality in self.modality_names), "Invalid modality type: " + modality + "\n" + \
70 | "Supported dataset types are: " + ''.join(self.modality_names)
71 | self.modality = modality
72 |
73 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
74 | raise (RuntimeError("train_transform() is not implemented. "))
75 |
76 | def val_transform(rgb, depth):
77 | raise (RuntimeError("val_transform() is not implemented."))
78 |
79 | def create_sparse_depth(self, rgb, depth):
80 | if self.sparsifier is None:
81 | return depth
82 | else:
83 | mask_keep = self.sparsifier.dense_to_sparse(rgb, depth)
84 | sparse_depth = np.zeros(depth.shape)
85 | sparse_depth[mask_keep] = depth[mask_keep]
86 | return sparse_depth
87 |
88 | def create_rgbd(self, rgb, depth):
89 | sparse_depth = self.create_sparse_depth(rgb, depth)
90 | rgbd = np.append(rgb, np.expand_dims(sparse_depth, axis=2), axis=2)
91 | return rgbd
92 |
93 | def __getraw__(self, index):
94 | """
95 | Args:
96 | index (int): Index
97 |
98 | Returns:
99 | tuple: (rgb, depth) the raw data.
100 | """
101 | path, target = self.imgs[index]
102 | rgb, depth = self.loader(path)
103 | return rgb, depth
104 |
105 | def __getitem__(self, index):
106 | rgb, depth = self.__getraw__(index)
107 |
108 | #print('{:04d} min={:f} max={:f} shape='.format(index, np.amin(depth), np.amax(depth)) + str(depth.shape))
109 |
110 | if self.transform is not None:
111 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
112 | else:
113 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
114 |
115 | #print('{:04d} min={:f} max={:f} shape='.format(index, np.amin(depth_np), np.amax(depth_np)) + str(depth_np.shape))
116 |
117 | # color normalization
118 | # rgb_tensor = normalize_rgb(rgb_tensor)
119 | # rgb_np = normalize_np(rgb_np)
120 |
121 | if self.modality == 'rgb':
122 | input_np = rgb_np
123 | elif self.modality == 'rgbd':
124 | input_np = self.create_rgbd(rgb_np, depth_np)
125 | elif self.modality == 'd':
126 | input_np = self.create_sparse_depth(rgb_np, depth_np)
127 |
128 | input_tensor = to_tensor(input_np)
129 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
130 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
131 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
132 | #print('{:04d} '.format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
133 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
134 | #print('{:04d} '.format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
135 |
136 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
137 |
138 | def __len__(self):
139 | return len(self.imgs)
140 |
141 | # def __get_all_item__(self, index):
142 | # """
143 | # Args:
144 | # index (int): Index
145 |
146 | # Returns:
147 | # tuple: (input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np)
148 | # """
149 | # rgb, depth = self.__getraw__(index)
150 | # if self.transform is not None:
151 | # rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
152 | # else:
153 | # raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
154 |
155 | # # color normalization
156 | # # rgb_tensor = normalize_rgb(rgb_tensor)
157 | # # rgb_np = normalize_np(rgb_np)
158 |
159 | # if self.modality == 'rgb':
160 | # input_np = rgb_np
161 | # elif self.modality == 'rgbd':
162 | # input_np = self.create_rgbd(rgb_np, depth_np)
163 | # elif self.modality == 'd':
164 | # input_np = self.create_sparse_depth(rgb_np, depth_np)
165 |
166 | # input_tensor = to_tensor(input_np)
167 | # while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
168 | # input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
169 | # depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
170 | # depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
171 |
172 | # return input_tensor, depth_tensor, input_np, depth_np
173 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/deepscene_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import re
3 | import numpy as np
4 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
5 |
6 | from imageio import imread
7 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
8 |
9 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
10 |
11 | iheight, iwidth = 472, 872 # original image size (there is some variation in DeepScene dataset)
12 |
13 | class DeepSceneDataset(Dataset):
14 | def __init__(self, root, type='train', train_extra=True):
15 | self.root = root
16 | self.output_size = (224, 224) #(224, 448)
17 |
18 | # search for images
19 | self.rgb_files, self.depth_files = self.gather_images(os.path.join(root, 'rgb'),
20 | os.path.join(root, 'depth_gray'))
21 |
22 | if type == 'train' and train_extra:
23 | extra_root = root + 'extra'
24 | extra_rgb, extra_depth = self.gather_images(os.path.join(extra_root, 'rgb'),
25 | os.path.join(extra_root, 'depth_gray'))
26 |
27 | if len(self.rgb_files) == 0:
28 | raise (RuntimeError("Empty dataset - found no image pairs under \n" + root))
29 |
30 | # determine if 16-bit or 8-bit depth images
31 | self.depth_16 = False
32 |
33 | if imread(self.depth_files[0]).dtype.type is np.uint16:
34 | self.depth_16 = True
35 | self.depth_16_max = 5000 #20000
36 |
37 | print('found {:d} image pairs with {:s}-bit depth under {:s}'.format(len(self.rgb_files), "16" if self.depth_16 else "8", root))
38 |
39 | # setup transforms
40 | if type == 'train':
41 | self.transform = self.train_transform
42 | elif type == 'val':
43 | self.transform = self.val_transform
44 | else:
45 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
46 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
47 |
48 | def gather_images(self, images_path, labels_path):
49 | def sorted_alphanumeric(data):
50 | convert = lambda text: int(text) if text.isdigit() else text.lower()
51 | alphanum_key = lambda key: [ convert(c) for c in re.split('([0-9]+)', key) ]
52 | return sorted(data, key=alphanum_key)
53 |
54 | #print('searching for images under: ')
55 | #print(' ' + images_path)
56 | #print(' ' + labels_path)
57 |
58 | image_files = sorted_alphanumeric(os.listdir(images_path))
59 | label_files = sorted_alphanumeric(os.listdir(labels_path))
60 |
61 | if len(image_files) != len(label_files):
62 | print('warning: images path has a different number of files than labels path')
63 | print(' ({:d} files) - {:s}'.format(len(image_files), images_path))
64 | print(' ({:d} files) - {:s}'.format(len(label_files), labels_path))
65 |
66 | for n in range(len(image_files)):
67 | image_files[n] = os.path.join(images_path, image_files[n])
68 | label_files[n] = os.path.join(labels_path, label_files[n])
69 |
70 | #print('{:s} -> {:s}'.format(image_files[n], label_files[n]))
71 |
72 | return image_files, label_files
73 |
74 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
75 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
76 | depth_np = depth #/ s
77 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
78 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
79 |
80 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
81 | transform = transforms.Compose([
82 | #transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation can be slow
83 | #transforms.Rotate(angle),
84 | #transforms.Resize(s),
85 | #transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
86 | #transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
87 | transforms.Resize(self.output_size)
88 | ])
89 |
90 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
91 | #rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
92 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
93 |
94 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
95 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
96 |
97 | if self.depth_16:
98 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
99 | else:
100 | depth_np = depth_np / 255
101 |
102 | return rgb_np, depth_np
103 |
104 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
105 | depth_np = depth
106 |
107 | transform = transforms.Compose([
108 | #transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight),
109 | #transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
110 | transforms.Resize(self.output_size)
111 | ])
112 |
113 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
114 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
115 |
116 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
117 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
118 |
119 | if self.depth_16:
120 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
121 | else:
122 | depth_np = depth_np / 255
123 |
124 | return rgb_np, depth_np
125 |
126 | def load_rgb(self, index):
127 | return imread(self.rgb_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="RGB")
128 |
129 | def load_depth(self, index):
130 | if self.depth_16:
131 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index])
132 | depth[depth == 65535] = 0 # map 'invalid' to 0
133 | return depth
134 | else:
135 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="L")
136 | #depth[depth == 0] = 255 # map 0 -> 255
137 | return depth
138 |
139 | def __len__(self):
140 | return len(self.rgb_files)
141 |
142 | def __getitem__(self, index):
143 | rgb = self.load_rgb(index)
144 | depth = self.load_depth(index)
145 |
146 | #print(self.rgb_files[index] + str(rgb.shape))
147 | #print(self.depth_files[index] + str(depth.shape))
148 | #print(depth)
149 |
150 | # apply train/val transforms
151 | if self.transform is not None:
152 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
153 | else:
154 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
155 |
156 | # convert from numpy to torch tensors
157 | input_tensor = to_tensor(rgb_np)
158 |
159 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
160 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
161 |
162 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
163 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
164 |
165 | #print("{:04d} rgb = ".format(index) + str(input_tensor.shape))
166 | #print("{:04d} depth = ".format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
167 |
168 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
169 |
170 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/dense_to_sparse.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import cv2
3 |
4 |
5 | def rgb2grayscale(rgb):
6 | return rgb[:, :, 0] * 0.2989 + rgb[:, :, 1] * 0.587 + rgb[:, :, 2] * 0.114
7 |
8 |
9 | class DenseToSparse:
10 | def __init__(self):
11 | pass
12 |
13 | def dense_to_sparse(self, rgb, depth):
14 | pass
15 |
16 | def __repr__(self):
17 | pass
18 |
19 | class UniformSampling(DenseToSparse):
20 | name = "uar"
21 | def __init__(self, num_samples, max_depth=np.inf):
22 | DenseToSparse.__init__(self)
23 | self.num_samples = num_samples
24 | self.max_depth = max_depth
25 |
26 | def __repr__(self):
27 | return "%s{ns=%d,md=%f}" % (self.name, self.num_samples, self.max_depth)
28 |
29 | def dense_to_sparse(self, rgb, depth):
30 | """
31 | Samples pixels with `num_samples`/#pixels probability in `depth`.
32 | Only pixels with a maximum depth of `max_depth` are considered.
33 | If no `max_depth` is given, samples in all pixels
34 | """
35 | mask_keep = depth > 0
36 | if self.max_depth is not np.inf:
37 | mask_keep = np.bitwise_and(mask_keep, depth <= self.max_depth)
38 | n_keep = np.count_nonzero(mask_keep)
39 | if n_keep == 0:
40 | return mask_keep
41 | else:
42 | prob = float(self.num_samples) / n_keep
43 | return np.bitwise_and(mask_keep, np.random.uniform(0, 1, depth.shape) < prob)
44 |
45 |
46 | class SimulatedStereo(DenseToSparse):
47 | name = "sim_stereo"
48 |
49 | def __init__(self, num_samples, max_depth=np.inf, dilate_kernel=3, dilate_iterations=1):
50 | DenseToSparse.__init__(self)
51 | self.num_samples = num_samples
52 | self.max_depth = max_depth
53 | self.dilate_kernel = dilate_kernel
54 | self.dilate_iterations = dilate_iterations
55 |
56 | def __repr__(self):
57 | return "%s{ns=%d,md=%f,dil=%d.%d}" % \
58 | (self.name, self.num_samples, self.max_depth, self.dilate_kernel, self.dilate_iterations)
59 |
60 | # We do not use cv2.Canny, since that applies non max suppression
61 | # So we simply do
62 | # RGB to intensitities
63 | # Smooth with gaussian
64 | # Take simple sobel gradients
65 | # Threshold the edge gradient
66 | # Dilatate
67 | def dense_to_sparse(self, rgb, depth):
68 | gray = rgb2grayscale(rgb)
69 | blurred = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray, (5, 5), 0)
70 | gx = cv2.Sobel(blurred, cv2.CV_64F, 1, 0, ksize=5)
71 | gy = cv2.Sobel(blurred, cv2.CV_64F, 0, 1, ksize=5)
72 |
73 | depth_mask = np.bitwise_and(depth != 0.0, depth <= self.max_depth)
74 |
75 | edge_fraction = float(self.num_samples) / np.size(depth)
76 |
77 | mag = cv2.magnitude(gx, gy)
78 | min_mag = np.percentile(mag[depth_mask], 100 * (1.0 - edge_fraction))
79 | mag_mask = mag >= min_mag
80 |
81 | if self.dilate_iterations >= 0:
82 | kernel = np.ones((self.dilate_kernel, self.dilate_kernel), dtype=np.uint8)
83 | cv2.dilate(mag_mask.astype(np.uint8), kernel, iterations=self.dilate_iterations)
84 |
85 | mask = np.bitwise_and(mag_mask, depth_mask)
86 | return mask
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/kitti_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
3 | from dataloaders.dataloader import MyDataloader
4 |
5 | class KITTIDataset(MyDataloader):
6 | def __init__(self, root, type, sparsifier=None, modality='rgb'):
7 | super(KITTIDataset, self).__init__(root, type, sparsifier, modality)
8 | self.output_size = (228, 912)
9 |
10 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
11 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
12 | depth_np = depth / s
13 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
14 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
15 |
16 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
17 | transform = transforms.Compose([
18 | transforms.Crop(130, 10, 240, 1200),
19 | transforms.Rotate(angle),
20 | transforms.Resize(s),
21 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
22 | transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
23 | ])
24 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
25 | rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
26 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
27 | # Scipy affine_transform produced RuntimeError when the depth map was
28 | # given as a 'numpy.ndarray'
29 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float32')
30 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
31 |
32 | return rgb_np, depth_np
33 |
34 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
35 | depth_np = depth
36 | transform = transforms.Compose([
37 | transforms.Crop(130, 10, 240, 1200),
38 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
39 | ])
40 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
41 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
42 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float32')
43 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
44 |
45 | return rgb_np, depth_np
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/nyu_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import numpy as np
2 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
3 | from dataloaders.dataloader import MyDataloader
4 |
5 | iheight, iwidth = 480, 640 # raw image size
6 |
7 | class NYUDataset(MyDataloader):
8 | def __init__(self, root, type, sparsifier=None, modality='rgb'):
9 | super(NYUDataset, self).__init__(root, type, sparsifier, modality)
10 | self.output_size = (448, 448) #(224, 224) #(228, 304) #(iheight, iwidth)
11 |
12 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
13 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
14 | depth_np = depth / s
15 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
16 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
17 |
18 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
19 | transform = transforms.Compose([
20 | transforms.Resize(480.0 / iheight), #250.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation can be slow
21 | transforms.Rotate(angle),
22 | #transforms.Resize(s), # disabled for 448x448
23 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
24 | transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
25 | ])
26 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
27 | rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
28 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
29 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
30 |
31 | return rgb_np, depth_np
32 |
33 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
34 | depth_np = depth
35 | transform = transforms.Compose([
36 | transforms.Resize(480.0 / iheight), #240.0 / iheight),
37 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
38 | ])
39 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
40 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
41 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
42 |
43 | return rgb_np, depth_np
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/sun_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
4 |
5 | from imageio import imread
6 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
7 |
8 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
9 |
10 | class SunRGBDDataset(Dataset):
11 | def __init__(self, root, type='train', train_extra=True):
12 | self.root = root
13 | self.output_size = (224, 224) #(224, 448)
14 |
15 | # search for images
16 | self.rgb_files, self.depth_files = self.gather_images(os.path.join(root, 'images'),
17 | os.path.join(root, 'depth'))
18 |
19 | if type == 'train' and train_extra:
20 | extra_root = root + 'extra'
21 | extra_rgb, extra_depth = self.gather_images(os.path.join(extra_root, 'images'),
22 | os.path.join(extra_root, 'depth'))
23 |
24 | if len(self.rgb_files) == 0:
25 | raise (RuntimeError("Empty dataset - found no image pairs under \n" + root))
26 |
27 | # determine if 16-bit or 8-bit depth images
28 | self.depth_16 = False
29 |
30 | if imread(self.depth_files[0]).dtype.type is np.uint16:
31 | self.depth_16 = True
32 | self.depth_16_max = 10000
33 |
34 | print('found {:d} image pairs with {:s}-bit depth under {:s}'.format(len(self.rgb_files), "16" if self.depth_16 else "8", root))
35 |
36 | # setup transforms
37 | if type == 'train':
38 | self.transform = self.train_transform
39 | elif type == 'val':
40 | self.transform = self.val_transform
41 | else:
42 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
43 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
44 |
45 | def gather_images(self, images_path, labels_path, max_images=5500):
46 | image_files = []
47 | label_files = []
48 |
49 | for n in range(max_images):
50 | image_filename = os.path.join(images_path, 'img-{:06d}.jpg'.format(n))
51 | label_filename = os.path.join(labels_path, '{:d}.png'.format(n))
52 |
53 | if os.path.isfile(image_filename) and os.path.isfile(label_filename):
54 | image_files.append(image_filename)
55 | label_files.append(label_filename)
56 |
57 | return image_files, label_files
58 |
59 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
60 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
61 | depth_np = depth #/ s
62 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
63 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
64 |
65 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
66 | transform = transforms.Compose([
67 | #transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation can be slow
68 | #transforms.Rotate(angle),
69 | #transforms.Resize(s),
70 | #transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
71 | #transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
72 | transforms.Resize(self.output_size)
73 | ])
74 |
75 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
76 | #rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
77 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
78 |
79 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
80 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
81 |
82 | if self.depth_16:
83 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
84 | else:
85 | depth_np = depth_np / 255
86 |
87 | return rgb_np, depth_np
88 |
89 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
90 | depth_np = depth
91 |
92 | transform = transforms.Compose([
93 | #transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight),
94 | #transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
95 | transforms.Resize(self.output_size)
96 | ])
97 |
98 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
99 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
100 |
101 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
102 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
103 |
104 | if self.depth_16:
105 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
106 | else:
107 | depth_np = depth_np / 255
108 |
109 | return rgb_np, depth_np
110 |
111 | def load_rgb(self, index):
112 | return imread(self.rgb_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="RGB")
113 |
114 | def load_depth(self, index):
115 | if self.depth_16:
116 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index])
117 | depth[depth == 65535] = 0 # map 'invalid' to 0
118 | return depth
119 | else:
120 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="L")
121 | #depth[depth == 0] = 255 # map 0 -> 255
122 | return depth
123 |
124 | def __len__(self):
125 | return len(self.rgb_files)
126 |
127 | def __getitem__(self, index):
128 | rgb = self.load_rgb(index)
129 | depth = self.load_depth(index)
130 |
131 | #print(self.rgb_files[index] + str(rgb.shape))
132 | #print(self.depth_files[index] + str(depth.shape))
133 | #print(depth)
134 |
135 | # apply train/val transforms
136 | if self.transform is not None:
137 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
138 | else:
139 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
140 |
141 | # convert from numpy to torch tensors
142 | input_tensor = to_tensor(rgb_np)
143 |
144 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
145 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
146 |
147 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
148 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
149 |
150 | #print("{:04d} rgb = ".format(index) + str(input_tensor.shape))
151 | #print("{:04d} depth = ".format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
152 |
153 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
154 |
155 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/transforms.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from __future__ import division
2 | import torch
3 | import math
4 | import random
5 |
6 | from PIL import Image, ImageOps, ImageEnhance
7 | try:
8 | import accimage
9 | except ImportError:
10 | accimage = None
11 |
12 | import numpy as np
13 | import numbers
14 | import types
15 | import collections
16 | import warnings
17 |
18 | import scipy.ndimage.interpolation as itpl
19 | import scipy.misc as misc
20 |
21 |
22 | def _is_numpy_image(img):
23 | return isinstance(img, np.ndarray) and (img.ndim in {2, 3})
24 |
25 | def _is_pil_image(img):
26 | if accimage is not None:
27 | return isinstance(img, (Image.Image, accimage.Image))
28 | else:
29 | return isinstance(img, Image.Image)
30 |
31 | def _is_tensor_image(img):
32 | return torch.is_tensor(img) and img.ndimension() == 3
33 |
34 | def adjust_brightness(img, brightness_factor):
35 | """Adjust brightness of an Image.
36 |
37 | Args:
38 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
39 | brightness_factor (float): How much to adjust the brightness. Can be
40 | any non negative number. 0 gives a black image, 1 gives the
41 | original image while 2 increases the brightness by a factor of 2.
42 |
43 | Returns:
44 | PIL Image: Brightness adjusted image.
45 | """
46 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
47 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
48 |
49 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Brightness(img)
50 | img = enhancer.enhance(brightness_factor)
51 | return img
52 |
53 |
54 | def adjust_contrast(img, contrast_factor):
55 | """Adjust contrast of an Image.
56 |
57 | Args:
58 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
59 | contrast_factor (float): How much to adjust the contrast. Can be any
60 | non negative number. 0 gives a solid gray image, 1 gives the
61 | original image while 2 increases the contrast by a factor of 2.
62 |
63 | Returns:
64 | PIL Image: Contrast adjusted image.
65 | """
66 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
67 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
68 |
69 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Contrast(img)
70 | img = enhancer.enhance(contrast_factor)
71 | return img
72 |
73 |
74 | def adjust_saturation(img, saturation_factor):
75 | """Adjust color saturation of an image.
76 |
77 | Args:
78 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
79 | saturation_factor (float): How much to adjust the saturation. 0 will
80 | give a black and white image, 1 will give the original image while
81 | 2 will enhance the saturation by a factor of 2.
82 |
83 | Returns:
84 | PIL Image: Saturation adjusted image.
85 | """
86 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
87 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
88 |
89 | enhancer = ImageEnhance.Color(img)
90 | img = enhancer.enhance(saturation_factor)
91 | return img
92 |
93 |
94 | def adjust_hue(img, hue_factor):
95 | """Adjust hue of an image.
96 |
97 | The image hue is adjusted by converting the image to HSV and
98 | cyclically shifting the intensities in the hue channel (H).
99 | The image is then converted back to original image mode.
100 |
101 | `hue_factor` is the amount of shift in H channel and must be in the
102 | interval `[-0.5, 0.5]`.
103 |
104 | See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Hue for more details on Hue.
105 |
106 | Args:
107 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
108 | hue_factor (float): How much to shift the hue channel. Should be in
109 | [-0.5, 0.5]. 0.5 and -0.5 give complete reversal of hue channel in
110 | HSV space in positive and negative direction respectively.
111 | 0 means no shift. Therefore, both -0.5 and 0.5 will give an image
112 | with complementary colors while 0 gives the original image.
113 |
114 | Returns:
115 | PIL Image: Hue adjusted image.
116 | """
117 | if not(-0.5 <= hue_factor <= 0.5):
118 | raise ValueError('hue_factor is not in [-0.5, 0.5].'.format(hue_factor))
119 |
120 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
121 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
122 |
123 | input_mode = img.mode
124 | if input_mode in {'L', '1', 'I', 'F'}:
125 | return img
126 |
127 | h, s, v = img.convert('HSV').split()
128 |
129 | np_h = np.array(h, dtype=np.uint8)
130 | # uint8 addition take cares of rotation across boundaries
131 | with np.errstate(over='ignore'):
132 | np_h += np.uint8(hue_factor * 255)
133 | h = Image.fromarray(np_h, 'L')
134 |
135 | img = Image.merge('HSV', (h, s, v)).convert(input_mode)
136 | return img
137 |
138 |
139 | def adjust_gamma(img, gamma, gain=1):
140 | """Perform gamma correction on an image.
141 |
142 | Also known as Power Law Transform. Intensities in RGB mode are adjusted
143 | based on the following equation:
144 |
145 | I_out = 255 * gain * ((I_in / 255) ** gamma)
146 |
147 | See https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gamma_correction for more details.
148 |
149 | Args:
150 | img (PIL Image): PIL Image to be adjusted.
151 | gamma (float): Non negative real number. gamma larger than 1 make the
152 | shadows darker, while gamma smaller than 1 make dark regions
153 | lighter.
154 | gain (float): The constant multiplier.
155 | """
156 | if not _is_pil_image(img):
157 | raise TypeError('img should be PIL Image. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
158 |
159 | if gamma < 0:
160 | raise ValueError('Gamma should be a non-negative real number')
161 |
162 | input_mode = img.mode
163 | img = img.convert('RGB')
164 |
165 | np_img = np.array(img, dtype=np.float32)
166 | np_img = 255 * gain * ((np_img / 255) ** gamma)
167 | np_img = np.uint8(np.clip(np_img, 0, 255))
168 |
169 | img = Image.fromarray(np_img, 'RGB').convert(input_mode)
170 | return img
171 |
172 |
173 | class Compose(object):
174 | """Composes several transforms together.
175 |
176 | Args:
177 | transforms (list of ``Transform`` objects): list of transforms to compose.
178 |
179 | Example:
180 | >>> transforms.Compose([
181 | >>> transforms.CenterCrop(10),
182 | >>> transforms.ToTensor(),
183 | >>> ])
184 | """
185 |
186 | def __init__(self, transforms):
187 | self.transforms = transforms
188 |
189 | def __call__(self, img):
190 | for t in self.transforms:
191 | img = t(img)
192 | return img
193 |
194 |
195 | class ToTensor(object):
196 | """Convert a ``numpy.ndarray`` to tensor.
197 |
198 | Converts a numpy.ndarray (H x W x C) to a torch.FloatTensor of shape (C x H x W).
199 | """
200 |
201 | def __call__(self, img):
202 | """Convert a ``numpy.ndarray`` to tensor.
203 |
204 | Args:
205 | img (numpy.ndarray): Image to be converted to tensor.
206 |
207 | Returns:
208 | Tensor: Converted image.
209 | """
210 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
211 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
212 |
213 | if isinstance(img, np.ndarray):
214 | # handle numpy array
215 | if img.ndim == 3:
216 | img = torch.from_numpy(img.transpose((2, 0, 1)).copy())
217 | elif img.ndim == 2:
218 | img = torch.from_numpy(img.copy())
219 | else:
220 | raise RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
221 |
222 | # backward compatibility
223 | # return img.float().div(255)
224 | return img.float()
225 |
226 |
227 | class NormalizeNumpyArray(object):
228 | """Normalize a ``numpy.ndarray`` with mean and standard deviation.
229 | Given mean: ``(M1,...,Mn)`` and std: ``(M1,..,Mn)`` for ``n`` channels, this transform
230 | will normalize each channel of the input ``numpy.ndarray`` i.e.
231 | ``input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
232 |
233 | Args:
234 | mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
235 | std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
236 | """
237 |
238 | def __init__(self, mean, std):
239 | self.mean = mean
240 | self.std = std
241 |
242 | def __call__(self, img):
243 | """
244 | Args:
245 | img (numpy.ndarray): Image of size (H, W, C) to be normalized.
246 |
247 | Returns:
248 | Tensor: Normalized image.
249 | """
250 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
251 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
252 | # TODO: make efficient
253 | print(img.shape)
254 | for i in range(3):
255 | img[:,:,i] = (img[:,:,i] - self.mean[i]) / self.std[i]
256 | return img
257 |
258 | class NormalizeTensor(object):
259 | """Normalize an tensor image with mean and standard deviation.
260 | Given mean: ``(M1,...,Mn)`` and std: ``(M1,..,Mn)`` for ``n`` channels, this transform
261 | will normalize each channel of the input ``torch.*Tensor`` i.e.
262 | ``input[channel] = (input[channel] - mean[channel]) / std[channel]``
263 |
264 | Args:
265 | mean (sequence): Sequence of means for each channel.
266 | std (sequence): Sequence of standard deviations for each channel.
267 | """
268 |
269 | def __init__(self, mean, std):
270 | self.mean = mean
271 | self.std = std
272 |
273 | def __call__(self, tensor):
274 | """
275 | Args:
276 | tensor (Tensor): Tensor image of size (C, H, W) to be normalized.
277 |
278 | Returns:
279 | Tensor: Normalized Tensor image.
280 | """
281 | if not _is_tensor_image(tensor):
282 | raise TypeError('tensor is not a torch image.')
283 | # TODO: make efficient
284 | for t, m, s in zip(tensor, self.mean, self.std):
285 | t.sub_(m).div_(s)
286 | return tensor
287 |
288 | class Rotate(object):
289 | """Rotates the given ``numpy.ndarray``.
290 |
291 | Args:
292 | angle (float): The rotation angle in degrees.
293 | """
294 |
295 | def __init__(self, angle):
296 | self.angle = angle
297 |
298 | def __call__(self, img):
299 | """
300 | Args:
301 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be rotated.
302 |
303 | Returns:
304 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Rotated image.
305 | """
306 |
307 | # order=0 means nearest-neighbor type interpolation
308 | return itpl.rotate(img, self.angle, reshape=False, prefilter=False, order=0)
309 |
310 |
311 | class Resize(object):
312 | """Resize the the given ``numpy.ndarray`` to the given size.
313 | Args:
314 | size (sequence or int): Desired output size. If size is a sequence like
315 | (h, w), output size will be matched to this. If size is an int,
316 | smaller edge of the image will be matched to this number.
317 | i.e, if height > width, then image will be rescaled to
318 | (size * height / width, size)
319 | interpolation (int, optional): Desired interpolation. Default is
320 | ``PIL.Image.BILINEAR``
321 | """
322 |
323 | def __init__(self, size, interpolation='nearest'):
324 | assert isinstance(size, int) or isinstance(size, float) or \
325 | (isinstance(size, collections.Iterable) and len(size) == 2)
326 | self.size = size
327 | self.interpolation = interpolation
328 |
329 | def __call__(self, img):
330 | """
331 | Args:
332 | img (PIL Image): Image to be scaled.
333 | Returns:
334 | PIL Image: Rescaled image.
335 | """
336 | if img.ndim == 3:
337 | return misc.imresize(img, self.size, self.interpolation)
338 | elif img.ndim == 2:
339 | return misc.imresize(img, self.size, self.interpolation, 'F')
340 | else:
341 | RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
342 |
343 |
344 | class CenterCrop(object):
345 | """Crops the given ``numpy.ndarray`` at the center.
346 |
347 | Args:
348 | size (sequence or int): Desired output size of the crop. If size is an
349 | int instead of sequence like (h, w), a square crop (size, size) is
350 | made.
351 | """
352 |
353 | def __init__(self, size):
354 | if isinstance(size, numbers.Number):
355 | self.size = (int(size), int(size))
356 | else:
357 | self.size = size
358 |
359 | @staticmethod
360 | def get_params(img, output_size):
361 | """Get parameters for ``crop`` for center crop.
362 |
363 | Args:
364 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
365 | output_size (tuple): Expected output size of the crop.
366 |
367 | Returns:
368 | tuple: params (i, j, h, w) to be passed to ``crop`` for center crop.
369 | """
370 | h = img.shape[0]
371 | w = img.shape[1]
372 | th, tw = output_size
373 | i = int(round((h - th) / 2.))
374 | j = int(round((w - tw) / 2.))
375 |
376 | # # randomized cropping
377 | # i = np.random.randint(i-3, i+4)
378 | # j = np.random.randint(j-3, j+4)
379 |
380 | return i, j, th, tw
381 |
382 | def __call__(self, img):
383 | """
384 | Args:
385 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
386 |
387 | Returns:
388 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Cropped image.
389 | """
390 | i, j, h, w = self.get_params(img, self.size)
391 |
392 | """
393 | i: Upper pixel coordinate.
394 | j: Left pixel coordinate.
395 | h: Height of the cropped image.
396 | w: Width of the cropped image.
397 | """
398 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
399 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
400 | if img.ndim == 3:
401 | return img[i:i+h, j:j+w, :]
402 | elif img.ndim == 2:
403 | return img[i:i + h, j:j + w]
404 | else:
405 | raise RuntimeError('img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
406 |
407 |
408 | class Lambda(object):
409 | """Apply a user-defined lambda as a transform.
410 |
411 | Args:
412 | lambd (function): Lambda/function to be used for transform.
413 | """
414 |
415 | def __init__(self, lambd):
416 | assert isinstance(lambd, types.LambdaType)
417 | self.lambd = lambd
418 |
419 | def __call__(self, img):
420 | return self.lambd(img)
421 |
422 |
423 | class HorizontalFlip(object):
424 | """Horizontally flip the given ``numpy.ndarray``.
425 |
426 | Args:
427 | do_flip (boolean): whether or not do horizontal flip.
428 |
429 | """
430 |
431 | def __init__(self, do_flip):
432 | self.do_flip = do_flip
433 |
434 | def __call__(self, img):
435 | """
436 | Args:
437 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be flipped.
438 |
439 | Returns:
440 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): flipped image.
441 | """
442 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
443 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
444 |
445 | if self.do_flip:
446 | return np.fliplr(img)
447 | else:
448 | return img
449 |
450 |
451 | class ColorJitter(object):
452 | """Randomly change the brightness, contrast and saturation of an image.
453 |
454 | Args:
455 | brightness (float): How much to jitter brightness. brightness_factor
456 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - brightness), 1 + brightness].
457 | contrast (float): How much to jitter contrast. contrast_factor
458 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - contrast), 1 + contrast].
459 | saturation (float): How much to jitter saturation. saturation_factor
460 | is chosen uniformly from [max(0, 1 - saturation), 1 + saturation].
461 | hue(float): How much to jitter hue. hue_factor is chosen uniformly from
462 | [-hue, hue]. Should be >=0 and <= 0.5.
463 | """
464 | def __init__(self, brightness=0, contrast=0, saturation=0, hue=0):
465 | self.brightness = brightness
466 | self.contrast = contrast
467 | self.saturation = saturation
468 | self.hue = hue
469 |
470 | @staticmethod
471 | def get_params(brightness, contrast, saturation, hue):
472 | """Get a randomized transform to be applied on image.
473 |
474 | Arguments are same as that of __init__.
475 |
476 | Returns:
477 | Transform which randomly adjusts brightness, contrast and
478 | saturation in a random order.
479 | """
480 | transforms = []
481 | if brightness > 0:
482 | brightness_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - brightness), 1 + brightness)
483 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_brightness(img, brightness_factor)))
484 |
485 | if contrast > 0:
486 | contrast_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - contrast), 1 + contrast)
487 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_contrast(img, contrast_factor)))
488 |
489 | if saturation > 0:
490 | saturation_factor = np.random.uniform(max(0, 1 - saturation), 1 + saturation)
491 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_saturation(img, saturation_factor)))
492 |
493 | if hue > 0:
494 | hue_factor = np.random.uniform(-hue, hue)
495 | transforms.append(Lambda(lambda img: adjust_hue(img, hue_factor)))
496 |
497 | np.random.shuffle(transforms)
498 | transform = Compose(transforms)
499 |
500 | return transform
501 |
502 | def __call__(self, img):
503 | """
504 | Args:
505 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Input image.
506 |
507 | Returns:
508 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Color jittered image.
509 | """
510 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
511 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
512 |
513 | pil = Image.fromarray(img)
514 | transform = self.get_params(self.brightness, self.contrast,
515 | self.saturation, self.hue)
516 | return np.array(transform(pil))
517 |
518 | class Crop(object):
519 | """Crops the given PIL Image to a rectangular region based on a given
520 | 4-tuple defining the left, upper pixel coordinated, hight and width size.
521 |
522 | Args:
523 | a tuple: (upper pixel coordinate, left pixel coordinate, hight, width)-tuple
524 | """
525 |
526 | def __init__(self, i, j, h, w):
527 | """
528 | i: Upper pixel coordinate.
529 | j: Left pixel coordinate.
530 | h: Height of the cropped image.
531 | w: Width of the cropped image.
532 | """
533 | self.i = i
534 | self.j = j
535 | self.h = h
536 | self.w = w
537 |
538 | def __call__(self, img):
539 | """
540 | Args:
541 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Image to be cropped.
542 | Returns:
543 | img (numpy.ndarray (C x H x W)): Cropped image.
544 | """
545 |
546 | i, j, h, w = self.i, self.j, self.h, self.w
547 |
548 | if not(_is_numpy_image(img)):
549 | raise TypeError('img should be ndarray. Got {}'.format(type(img)))
550 | if img.ndim == 3:
551 | return img[i:i + h, j:j + w, :]
552 | elif img.ndim == 2:
553 | return img[i:i + h, j:j + w]
554 | else:
555 | raise RuntimeError(
556 | 'img should be ndarray with 2 or 3 dimensions. Got {}'.format(img.ndim))
557 |
558 | def __repr__(self):
559 | return self.__class__.__name__ + '(i={0},j={1},h={2},w={3})'.format(
560 | self.i, self.j, self.h, self.w)
561 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dataloaders/zed_dataloader.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import numpy as np
3 | import dataloaders.transforms as transforms
4 |
5 | from imageio import imread
6 | from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
7 |
8 | to_tensor = transforms.ToTensor()
9 |
10 | iheight, iwidth = 720, 1280 # raw image size
11 |
12 | class ZEDDataset(Dataset):
13 | def __init__(self, root, type='train'):
14 | self.root = root
15 | self.output_size = (224, 224) #(228, 304)
16 |
17 | # search for images
18 | self.rgb_files = []
19 | self.depth_files = []
20 |
21 | self.gather_images(root, max_images=100000)
22 |
23 | if len(self.rgb_files) == 0:
24 | raise (RuntimeError("Empty dataset - found no image pairs under \n" + root))
25 |
26 | # determine if 16-bit or 8-bit depth images
27 | self.depth_16 = False
28 |
29 | if imread(self.depth_files[0]).dtype.type is np.uint16:
30 | self.depth_16 = True
31 | self.depth_16_max = 5000 #20000
32 |
33 | print('found {:d} image pairs with {:s}-bit depth under {:s}'.format(len(self.rgb_files), "16" if self.depth_16 else "8", root))
34 |
35 | # setup transforms
36 | if type == 'train':
37 | self.transform = self.train_transform
38 | elif type == 'val':
39 | self.transform = self.val_transform
40 | else:
41 | raise (RuntimeError("Invalid dataset type: " + type + "\n"
42 | "Supported dataset types are: train, val"))
43 |
44 | def gather_images(self, img_dir, max_images=999999):
45 | rgb_files = []
46 | depth_files = []
47 |
48 | # search in the current directory
49 | for n in range(max_images):
50 | img_name_rgb = 'left{:06d}.png'.format(n)
51 | img_path_rgb = os.path.join(img_dir, img_name_rgb)
52 |
53 | img_name_depth = 'depth{:06d}.png'.format(n)
54 | img_path_depth = os.path.join(img_dir, img_name_depth)
55 |
56 | if os.path.isfile(img_path_rgb) and os.path.isfile(img_path_depth):
57 | self.rgb_files.append(img_path_rgb)
58 | self.depth_files.append(img_path_depth)
59 |
60 | # search in subdirectories
61 | dir_files = os.listdir(img_dir)
62 |
63 | for dir_name in dir_files:
64 | dir_path = os.path.join(img_dir, dir_name)
65 |
66 | if os.path.isdir(dir_path):
67 | self.gather_images(dir_path, max_images)
68 |
69 | def train_transform(self, rgb, depth):
70 | s = np.random.uniform(1.0, 1.5) # random scaling
71 | depth_np = depth #/ s
72 | angle = np.random.uniform(-5.0, 5.0) # random rotation degrees
73 | do_flip = np.random.uniform(0.0, 1.0) < 0.5 # random horizontal flip
74 |
75 | # perform 1st step of data augmentation
76 | transform = transforms.Compose([
77 | transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight), # this is for computational efficiency, since rotation can be slow
78 | #transforms.Rotate(angle),
79 | #transforms.Resize(s),
80 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
81 | transforms.HorizontalFlip(do_flip)
82 | ])
83 |
84 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
85 | #rgb_np = self.color_jitter(rgb_np) # random color jittering
86 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
87 |
88 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
89 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
90 |
91 | if self.depth_16:
92 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
93 | else:
94 | depth_np = (255 - depth_np) / 255
95 |
96 | return rgb_np, depth_np
97 |
98 | def val_transform(self, rgb, depth):
99 | depth_np = depth
100 |
101 | transform = transforms.Compose([
102 | transforms.Resize(240.0 / iheight),
103 | transforms.CenterCrop(self.output_size),
104 | ])
105 |
106 | rgb_np = transform(rgb)
107 | rgb_np = np.asfarray(rgb_np, dtype='float') / 255
108 |
109 | depth_np = transform(depth_np)
110 | depth_np = np.asfarray(depth_np, dtype='float')
111 |
112 | if self.depth_16:
113 | depth_np = depth_np / self.depth_16_max
114 | else:
115 | depth_np = (255 - depth_np) / 255
116 |
117 | return rgb_np, depth_np
118 |
119 | def load_rgb(self, index):
120 | return imread(self.rgb_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="RGB")
121 |
122 | def load_depth(self, index):
123 | if self.depth_16:
124 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index])
125 | depth[depth == 65535] = 0 # map 'invalid' to 0
126 | return depth
127 | else:
128 | depth = imread(self.depth_files[index], as_gray=False, pilmode="L")
129 | #depth[depth == 0] = 255 # map 0 -> 255
130 | return depth
131 |
132 | def __len__(self):
133 | return len(self.rgb_files)
134 |
135 | def __getitem__(self, index):
136 | rgb = self.load_rgb(index)
137 | depth = self.load_depth(index)
138 |
139 | #print(self.depth_files[index] + str(depth.shape))
140 | #print(depth)
141 |
142 | # apply train/val transforms
143 | if self.transform is not None:
144 | rgb_np, depth_np = self.transform(rgb, depth)
145 | else:
146 | raise(RuntimeError("transform not defined"))
147 |
148 | # convert from numpy to torch tensors
149 | input_tensor = to_tensor(rgb_np)
150 |
151 | while input_tensor.dim() < 3:
152 | input_tensor = input_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
153 |
154 | depth_tensor = to_tensor(depth_np)
155 | depth_tensor = depth_tensor.unsqueeze(0)
156 |
157 | #print("{:04d} rgb = ".format(index) + str(input_tensor.shape))
158 | #print("{:04d} depth = ".format(index) + str(depth_tensor.shape))
159 |
160 | return input_tensor, depth_tensor
161 |
162 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/imagenet/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dusty-nv/pytorch-depth/41d6440dc0a64a4c59dff3daaaea50a1212897b1/imagenet/__init__.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/imagenet/mobilenet.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import shutil
3 | import time
4 |
5 | import torch
6 | import torch.nn as nn
7 | import torch.nn.parallel
8 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
9 | import torch.optim
10 | import torch.utils.data
11 |
12 | class MobileNet(nn.Module):
13 | def __init__(self, relu6=True):
14 | super(MobileNet, self).__init__()
15 |
16 | def relu(relu6):
17 | if relu6:
18 | return nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
19 | else:
20 | return nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
21 |
22 | def conv_bn(inp, oup, stride, relu6):
23 | return nn.Sequential(
24 | nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),
25 | nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
26 | relu(relu6),
27 | )
28 |
29 | def conv_dw(inp, oup, stride, relu6):
30 | return nn.Sequential(
31 | nn.Conv2d(inp, inp, 3, stride, 1, groups=inp, bias=False),
32 | nn.BatchNorm2d(inp),
33 | relu(relu6),
34 |
35 | nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 1, 1, 0, bias=False),
36 | nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
37 | relu(relu6),
38 | )
39 |
40 | self.model = nn.Sequential(
41 | conv_bn( 3, 32, 2, relu6),
42 | conv_dw( 32, 64, 1, relu6),
43 | conv_dw( 64, 128, 2, relu6),
44 | conv_dw(128, 128, 1, relu6),
45 | conv_dw(128, 256, 2, relu6),
46 | conv_dw(256, 256, 1, relu6),
47 | conv_dw(256, 512, 2, relu6),
48 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
49 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
50 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
51 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
52 | conv_dw(512, 512, 1, relu6),
53 | conv_dw(512, 1024, 2, relu6),
54 | conv_dw(1024, 1024, 1, relu6),
55 | nn.AvgPool2d(7),
56 | )
57 | self.fc = nn.Linear(1024, 1000)
58 |
59 | def forward(self, x):
60 | x = self.model(x)
61 | #print('pre-view size: ' + str(x.size()))
62 | x = x.view(-1, 1024)
63 | #print('post-view size: ' + str(x.size()))
64 | x = self.fc(x)
65 | return x
66 |
67 | def main():
68 | import torchvision.models
69 | model = MobileNet(relu6=True)
70 | model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda()
71 | model_filename = os.path.join('results', 'imagenet.arch=mobilenet.lr=0.1.bs=256', 'model_best.pth.tar')
72 | if os.path.isfile(model_filename):
73 | print("=> loading Imagenet pretrained model '{}'".format(model_filename))
74 | checkpoint = torch.load(model_filename)
75 | epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
76 | best_prec1 = checkpoint['best_prec1']
77 | model.load_state_dict(checkpoint['state_dict'])
78 | print("=> loaded Imagenet pretrained model '{}' (epoch {}). best_prec1={}".format(model_filename, epoch, best_prec1))
79 |
80 | if __name__ == '__main__':
81 | main()
82 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/main.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import time
3 | import csv
4 | import numpy as np
5 |
6 | import torch
7 | import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
8 | import torch.optim
9 |
10 | cudnn.benchmark = True
11 |
12 | from models import ResNet
13 | from models_fast import MobileNetSkipAdd
14 | from metrics import AverageMeter, Result
15 | from dataloaders.dense_to_sparse import UniformSampling, SimulatedStereo
16 |
17 | import criteria
18 | import utils
19 |
20 | args = utils.parse_command()
21 | print(args)
22 |
23 | fieldnames = ['mse', 'rmse', 'absrel', 'lg10', 'mae',
24 | 'delta1', 'delta2', 'delta3',
25 | 'data_time', 'gpu_time']
26 | best_result = Result()
27 | best_result.set_to_worst()
28 |
29 | def create_data_loaders(args):
30 | # Data loading code
31 | print("=> creating data loaders ...")
32 | traindir = os.path.join('data', args.data, 'train')
33 | valdir = os.path.join('data', args.data, 'val')
34 | train_loader = None
35 | val_loader = None
36 |
37 | # sparsifier is a class for generating random sparse depth input from the ground truth
38 | sparsifier = None
39 | max_depth = args.max_depth if args.max_depth >= 0.0 else np.inf
40 | if args.sparsifier == UniformSampling.name:
41 | sparsifier = UniformSampling(num_samples=args.num_samples, max_depth=max_depth)
42 | elif args.sparsifier == SimulatedStereo.name:
43 | sparsifier = SimulatedStereo(num_samples=args.num_samples, max_depth=max_depth)
44 |
45 | if args.data == 'nyudepthv2':
46 | from dataloaders.nyu_dataloader import NYUDataset
47 | if not args.evaluate:
48 | train_dataset = NYUDataset(traindir, type='train',
49 | modality=args.modality, sparsifier=sparsifier)
50 | val_dataset = NYUDataset(valdir, type='val',
51 | modality=args.modality, sparsifier=sparsifier)
52 |
53 | elif args.data == 'kitti':
54 | from dataloaders.kitti_dataloader import KITTIDataset
55 | if not args.evaluate:
56 | train_dataset = KITTIDataset(traindir, type='train',
57 | modality=args.modality, sparsifier=sparsifier)
58 | val_dataset = KITTIDataset(valdir, type='val',
59 | modality=args.modality, sparsifier=sparsifier)
60 |
61 | elif args.data == 'deepscene':
62 | from dataloaders.deepscene_dataloader import DeepSceneDataset
63 | if not args.evaluate:
64 | train_dataset = DeepSceneDataset(traindir, type='train')
65 |
66 | val_dataset = DeepSceneDataset(valdir, type='val')
67 |
68 | elif args.data == 'sun':
69 | from dataloaders.sun_dataloader import SunRGBDDataset
70 | if not args.evaluate:
71 | train_dataset = SunRGBDDataset(traindir, type='train')
72 |
73 | val_dataset = SunRGBDDataset(valdir, type='val')
74 |
75 | elif args.data == 'zed':
76 | from dataloaders.zed_dataloader import ZEDDataset
77 | if not args.evaluate:
78 | train_dataset = ZEDDataset(traindir, type='train')
79 |
80 | val_dataset = ZEDDataset(valdir, type='val')
81 |
82 |
83 | else:
84 | raise RuntimeError('Dataset not found.' +
85 | 'The dataset must be either of nyudepthv2, kitti, or zed.')
86 |
87 | # set batch size to be 1 for validation
88 | val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
89 | batch_size=1, shuffle=False, num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True)
90 |
91 | # put construction of train loader here, for those who are interested in testing only
92 | if not args.evaluate:
93 | train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(
94 | train_dataset, batch_size=args.batch_size, shuffle=True,
95 | num_workers=args.workers, pin_memory=True, sampler=None,
96 | worker_init_fn=lambda work_id:np.random.seed(work_id))
97 | # worker_init_fn ensures different sampling patterns for each data loading thread
98 |
99 | print("=> data loaders created.")
100 | return train_loader, val_loader
101 |
102 | def main():
103 | global args, best_result, output_directory, train_csv, test_csv
104 |
105 | # evaluation mode
106 | start_epoch = 0
107 | if args.evaluate:
108 | assert os.path.isfile(args.evaluate), \
109 | "=> no best model found at '{}'".format(args.evaluate)
110 | print("=> loading best model '{}'".format(args.evaluate))
111 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.evaluate)
112 | output_directory = os.path.dirname(args.evaluate)
113 | args = checkpoint['args']
114 | start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
115 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
116 | model = checkpoint['model']
117 | print("=> loaded best model (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
118 | _, val_loader = create_data_loaders(args)
119 | args.evaluate = True
120 | validate(val_loader, model, checkpoint['epoch'], write_to_file=False)
121 | return
122 |
123 | # export to ONNX
124 | elif args.export:
125 | assert os.path.isfile(args.export), \
126 | "=> no best model found at '{}'".format(args.export)
127 | print("=> loading best model '{}'".format(args.export))
128 | checkpoint = torch.load(args.export)
129 | output_directory = os.path.dirname(args.export)
130 | output_filename = args.export + '.onnx'
131 | args = checkpoint['args']
132 | start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
133 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
134 | model = checkpoint['model']
135 | model.export = True
136 | print("=> loaded best model (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
137 | export(model, output_filename, args.data)
138 | return
139 |
140 | # optionally resume from a checkpoint
141 | elif args.resume:
142 | chkpt_path = args.resume
143 | assert os.path.isfile(chkpt_path), \
144 | "=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(chkpt_path)
145 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(chkpt_path))
146 | checkpoint = torch.load(chkpt_path)
147 | args = checkpoint['args']
148 | start_epoch = checkpoint['epoch'] + 1
149 | best_result = checkpoint['best_result']
150 | model = checkpoint['model']
151 | optimizer = checkpoint['optimizer']
152 | output_directory = os.path.dirname(os.path.abspath(chkpt_path))
153 | print("=> loaded checkpoint (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
154 | train_loader, val_loader = create_data_loaders(args)
155 | args.resume = True
156 |
157 | # transfer learning from a checkpoint
158 | elif args.checkpoint:
159 | chkpt_path = args.checkpoint
160 | assert os.path.isfile(chkpt_path), \
161 | "=> no checkpoint found at '{}'".format(chkpt_path)
162 | print("=> loading checkpoint '{}'".format(chkpt_path))
163 | checkpoint = torch.load(chkpt_path)
164 | model = checkpoint['model']
165 | optimizer = checkpoint['optimizer']
166 | print("=> loaded checkpoint (epoch {})".format(checkpoint['epoch']))
167 | train_loader, val_loader = create_data_loaders(args)
168 |
169 | # create new model
170 | else:
171 | train_loader, val_loader = create_data_loaders(args)
172 | print("=> creating Model ({}-{}) ...".format(args.arch, args.decoder))
173 | in_channels = len(args.modality)
174 | if args.arch == 'resnet50':
175 | model = ResNet(layers=50, decoder=args.decoder, output_size=train_loader.dataset.output_size,
176 | in_channels=in_channels, pretrained=args.pretrained)
177 | elif args.arch == 'resnet18':
178 | model = ResNet(layers=18, decoder=args.decoder, output_size=train_loader.dataset.output_size,
179 | in_channels=in_channels, pretrained=args.pretrained)
180 | elif args.arch == 'mobilenet':
181 | model = MobileNetSkipAdd(output_size=train_loader.dataset.output_size,
182 | pretrained=args.pretrained)
183 |
184 | print("=> model created " + str(train_loader.dataset.output_size))
185 |
186 | optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), args.lr, \
187 | momentum=args.momentum, weight_decay=args.weight_decay)
188 |
189 | # model = torch.nn.DataParallel(model).cuda() # for multi-gpu training
190 | model = model.cuda()
191 |
192 | # define loss function (criterion) and optimizer
193 | if args.criterion == 'l2':
194 | criterion = criteria.MaskedMSELoss().cuda()
195 | elif args.criterion == 'l1':
196 | criterion = criteria.MaskedL1Loss().cuda()
197 |
198 | # create results folder, if not already exists
199 | output_directory = utils.get_output_directory(args)
200 | if not os.path.exists(output_directory):
201 | os.makedirs(output_directory)
202 | train_csv = os.path.join(output_directory, 'train.csv')
203 | test_csv = os.path.join(output_directory, 'test.csv')
204 | best_txt = os.path.join(output_directory, 'best.txt')
205 |
206 | # create new csv files with only header
207 | if not args.resume:
208 | with open(train_csv, 'w') as csvfile:
209 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
210 | writer.writeheader()
211 | with open(test_csv, 'w') as csvfile:
212 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
213 | writer.writeheader()
214 |
215 | for epoch in range(start_epoch, args.epochs):
216 | utils.adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, args.lr)
217 | train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch) # train for one epoch
218 | result, img_merge = validate(val_loader, model, epoch) # evaluate on validation set
219 |
220 | # remember best rmse and save checkpoint
221 | is_best = result.rmse < best_result.rmse
222 | if is_best:
223 | best_result = result
224 | with open(best_txt, 'w') as txtfile:
225 | txtfile.write("epoch={}\nmse={:.3f}\nrmse={:.3f}\nabsrel={:.3f}\nlg10={:.3f}\nmae={:.3f}\ndelta1={:.3f}\nt_gpu={:.4f}\n".
226 | format(epoch, result.mse, result.rmse, result.absrel, result.lg10, result.mae, result.delta1, result.gpu_time))
227 | if img_merge is not None:
228 | img_filename = output_directory + '/comparison_best.png'
229 | utils.save_image(img_merge, img_filename)
230 |
231 | utils.save_checkpoint({
232 | 'args': args,
233 | 'epoch': epoch,
234 | 'arch': args.arch,
235 | 'model': model,
236 | 'best_result': best_result,
237 | 'optimizer' : optimizer,
238 | }, is_best, epoch, output_directory)
239 |
240 |
241 | def train(train_loader, model, criterion, optimizer, epoch):
242 | average_meter = AverageMeter()
243 | model.train() # switch to train mode
244 | end = time.time()
245 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(train_loader):
246 |
247 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda()
248 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
249 | data_time = time.time() - end
250 |
251 | # compute pred
252 | end = time.time()
253 | pred = model(input)
254 | loss = criterion(pred, target)
255 | optimizer.zero_grad()
256 | loss.backward() # compute gradient and do SGD step
257 | optimizer.step()
258 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
259 | gpu_time = time.time() - end
260 |
261 | #print('input size: ' + str(input.size()))
262 | #print('output size: ' + str(pred.size()))
263 |
264 | # measure accuracy and record loss
265 | result = Result()
266 | result.evaluate(pred.data, target.data)
267 | average_meter.update(result, gpu_time, data_time, input.size(0))
268 | end = time.time()
269 |
270 | if (i + 1) % args.print_freq == 0:
271 | print('=> output: {}'.format(output_directory))
272 | print('Train Epoch: {0} [{1}/{2}]\t'
273 | 't_Data={data_time:.3f}({average.data_time:.3f}) '
274 | 't_GPU={gpu_time:.3f}({average.gpu_time:.3f})\n\t'
275 | 'RMSE={result.rmse:.2f}({average.rmse:.2f}) '
276 | 'MAE={result.mae:.2f}({average.mae:.2f}) '
277 | 'Delta1={result.delta1:.3f}({average.delta1:.3f}) '
278 | 'REL={result.absrel:.3f}({average.absrel:.3f}) '
279 | 'Lg10={result.lg10:.3f}({average.lg10:.3f}) '.format(
280 | epoch, i+1, len(train_loader), data_time=data_time,
281 | gpu_time=gpu_time, result=result, average=average_meter.average()))
282 |
283 | avg = average_meter.average()
284 | with open(train_csv, 'a') as csvfile:
285 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
286 | writer.writerow({'mse': avg.mse, 'rmse': avg.rmse, 'absrel': avg.absrel, 'lg10': avg.lg10,
287 | 'mae': avg.mae, 'delta1': avg.delta1, 'delta2': avg.delta2, 'delta3': avg.delta3,
288 | 'gpu_time': avg.gpu_time, 'data_time': avg.data_time})
289 |
290 |
291 | def validate(val_loader, model, epoch, write_to_file=True):
292 | average_meter = AverageMeter()
293 | model.eval() # switch to evaluate mode
294 | end = time.time()
295 | for i, (input, target) in enumerate(val_loader):
296 | input, target = input.cuda(), target.cuda()
297 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
298 | data_time = time.time() - end
299 |
300 | # compute output
301 | end = time.time()
302 | with torch.no_grad():
303 | pred = model(input)
304 | torch.cuda.synchronize()
305 | gpu_time = time.time() - end
306 |
307 | #print('input size: ' + str(input.size()))
308 | #print('output size: ' + str(pred.size()))
309 |
310 | # measure accuracy and record loss
311 | result = Result()
312 | result.evaluate(pred.data, target.data)
313 | average_meter.update(result, gpu_time, data_time, input.size(0))
314 | end = time.time()
315 |
316 | # save 8 images for visualization
317 | skip = 10 if args.data == 'deepscene' else 50
318 | if args.modality == 'd':
319 | img_merge = None
320 | else:
321 | if args.modality == 'rgb':
322 | rgb = input
323 | elif args.modality == 'rgbd':
324 | rgb = input[:,:3,:,:]
325 | depth = input[:,3:,:,:]
326 |
327 | if i == 0:
328 | if args.modality == 'rgbd':
329 | img_merge = utils.merge_into_row_with_gt(rgb, depth, target, pred)
330 | else:
331 | img_merge = utils.merge_into_row(rgb, target, pred)
332 | elif (i < 8*skip) and (i % skip == 0):
333 | if args.modality == 'rgbd':
334 | row = utils.merge_into_row_with_gt(rgb, depth, target, pred)
335 | else:
336 | row = utils.merge_into_row(rgb, target, pred)
337 | img_merge = utils.add_row(img_merge, row)
338 | elif i == 8*skip:
339 | filename = output_directory + '/comparison_' + str(epoch) + '.png'
340 | utils.save_image(img_merge, filename)
341 |
342 | if (i+1) % args.print_freq == 0:
343 | print('Test: [{0}/{1}]\t'
344 | 't_GPU={gpu_time:.3f}({average.gpu_time:.3f})\n\t'
345 | 'RMSE={result.rmse:.2f}({average.rmse:.2f}) '
346 | 'MAE={result.mae:.2f}({average.mae:.2f}) '
347 | 'Delta1={result.delta1:.3f}({average.delta1:.3f}) '
348 | 'REL={result.absrel:.3f}({average.absrel:.3f}) '
349 | 'Lg10={result.lg10:.3f}({average.lg10:.3f}) '.format(
350 | i+1, len(val_loader), gpu_time=gpu_time, result=result, average=average_meter.average()))
351 |
352 | avg = average_meter.average()
353 |
354 | print('\n*\n'
355 | 'RMSE={average.rmse:.3f}\n'
356 | 'MAE={average.mae:.3f}\n'
357 | 'Delta1={average.delta1:.3f}\n'
358 | 'REL={average.absrel:.3f}\n'
359 | 'Lg10={average.lg10:.3f}\n'
360 | 't_GPU={time:.3f}\n'.format(
361 | average=avg, time=avg.gpu_time))
362 |
363 | if write_to_file:
364 | with open(test_csv, 'a') as csvfile:
365 | writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldnames)
366 | writer.writerow({'mse': avg.mse, 'rmse': avg.rmse, 'absrel': avg.absrel, 'lg10': avg.lg10,
367 | 'mae': avg.mae, 'delta1': avg.delta1, 'delta2': avg.delta2, 'delta3': avg.delta3,
368 | 'data_time': avg.data_time, 'gpu_time': avg.gpu_time})
369 | return avg, img_merge
370 |
371 |
372 | # export model to ONNX
373 | def export(model, path, dataset):
374 | print('=> exporting ONNX model to: ' + path)
375 | model.eval()
376 |
377 | # set the input size from the dataset
378 | input_size = (1, 3, 448, 448) #(1, 3, 224, 224) #(1, 3, 480, 640) #(1, 3, 228, 304) # nyudepthv2
379 |
380 | if dataset == "kitti":
381 | input_size = (1, 3, 228, 912)
382 |
383 | input = torch.ones(input_size).cuda()
384 | print('=> input resolution: ' + str(input_size))
385 |
386 | # set the input/output layer names
387 | input_names = [ "input_0" ]
388 | output_names = [ "output_0" ]
389 |
390 | print(model)
391 |
392 | # export the model
393 | torch.onnx.export(model, input, path, verbose=True, input_names=input_names, output_names=output_names)
394 | print('=> ONNX model exported to: ' + path)
395 |
396 | if __name__ == '__main__':
397 | main()
398 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/metrics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import math
3 | import numpy as np
4 |
5 | def log10(x):
6 | """Convert a new tensor with the base-10 logarithm of the elements of x. """
7 | return torch.log(x) / math.log(10)
8 |
9 | class Result(object):
10 | def __init__(self):
11 | self.irmse, self.imae = 0, 0
12 | self.mse, self.rmse, self.mae = 0, 0, 0
13 | self.absrel, self.lg10 = 0, 0
14 | self.delta1, self.delta2, self.delta3 = 0, 0, 0
15 | self.data_time, self.gpu_time = 0, 0
16 |
17 | def set_to_worst(self):
18 | self.irmse, self.imae = np.inf, np.inf
19 | self.mse, self.rmse, self.mae = np.inf, np.inf, np.inf
20 | self.absrel, self.lg10 = np.inf, np.inf
21 | self.delta1, self.delta2, self.delta3 = 0, 0, 0
22 | self.data_time, self.gpu_time = 0, 0
23 |
24 | def update(self, irmse, imae, mse, rmse, mae, absrel, lg10, delta1, delta2, delta3, gpu_time, data_time):
25 | self.irmse, self.imae = irmse, imae
26 | self.mse, self.rmse, self.mae = mse, rmse, mae
27 | self.absrel, self.lg10 = absrel, lg10
28 | self.delta1, self.delta2, self.delta3 = delta1, delta2, delta3
29 | self.data_time, self.gpu_time = data_time, gpu_time
30 |
31 | def evaluate(self, output, target):
32 | valid_mask = target>0
33 | output = output[valid_mask]
34 | target = target[valid_mask]
35 |
36 | abs_diff = (output - target).abs()
37 |
38 | self.mse = float((torch.pow(abs_diff, 2)).mean())
39 | self.rmse = math.sqrt(self.mse)
40 | self.mae = float(abs_diff.mean())
41 | self.lg10 = float((log10(output) - log10(target)).abs().mean())
42 | self.absrel = float((abs_diff / target).mean())
43 |
44 | maxRatio = torch.max(output / target, target / output)
45 | self.delta1 = float((maxRatio < 1.25).float().mean())
46 | self.delta2 = float((maxRatio < 1.25 ** 2).float().mean())
47 | self.delta3 = float((maxRatio < 1.25 ** 3).float().mean())
48 | self.data_time = 0
49 | self.gpu_time = 0
50 |
51 | inv_output = 1 / output
52 | inv_target = 1 / target
53 | abs_inv_diff = (inv_output - inv_target).abs()
54 | self.irmse = math.sqrt((torch.pow(abs_inv_diff, 2)).mean())
55 | self.imae = float(abs_inv_diff.mean())
56 |
57 |
58 | class AverageMeter(object):
59 | def __init__(self):
60 | self.reset()
61 |
62 | def reset(self):
63 | self.count = 0.0
64 |
65 | self.sum_irmse, self.sum_imae = 0, 0
66 | self.sum_mse, self.sum_rmse, self.sum_mae = 0, 0, 0
67 | self.sum_absrel, self.sum_lg10 = 0, 0
68 | self.sum_delta1, self.sum_delta2, self.sum_delta3 = 0, 0, 0
69 | self.sum_data_time, self.sum_gpu_time = 0, 0
70 |
71 | def update(self, result, gpu_time, data_time, n=1):
72 | self.count += n
73 |
74 | self.sum_irmse += n*result.irmse
75 | self.sum_imae += n*result.imae
76 | self.sum_mse += n*result.mse
77 | self.sum_rmse += n*result.rmse
78 | self.sum_mae += n*result.mae
79 | self.sum_absrel += n*result.absrel
80 | self.sum_lg10 += n*result.lg10
81 | self.sum_delta1 += n*result.delta1
82 | self.sum_delta2 += n*result.delta2
83 | self.sum_delta3 += n*result.delta3
84 | self.sum_data_time += n*data_time
85 | self.sum_gpu_time += n*gpu_time
86 |
87 | def average(self):
88 | avg = Result()
89 | avg.update(
90 | self.sum_irmse / self.count, self.sum_imae / self.count,
91 | self.sum_mse / self.count, self.sum_rmse / self.count, self.sum_mae / self.count,
92 | self.sum_absrel / self.count, self.sum_lg10 / self.count,
93 | self.sum_delta1 / self.count, self.sum_delta2 / self.count, self.sum_delta3 / self.count,
94 | self.sum_gpu_time / self.count, self.sum_data_time / self.count)
95 | return avg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import torch
2 | import torch.nn as nn
3 | import torch.nn.functional as F
4 | import torchvision.models
5 | import collections
6 | import math
7 |
8 | class Unpool(nn.Module):
9 | # Unpool: 2*2 unpooling with zero padding
10 | def __init__(self, num_channels, stride=2):
11 | super(Unpool, self).__init__()
12 |
13 | self.num_channels = num_channels
14 | self.stride = stride
15 |
16 | # create kernel [1, 0; 0, 0]
17 | self.weights = torch.autograd.Variable(torch.zeros(num_channels, 1, stride, stride).cuda()) # currently not compatible with running on CPU
18 | self.weights[:,:,0,0] = 1
19 |
20 | def forward(self, x):
21 | return F.conv_transpose2d(x, self.weights, stride=self.stride, groups=self.num_channels)
22 |
23 | def weights_init(m):
24 | # Initialize filters with Gaussian random weights
25 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
26 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
27 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
28 | if m.bias is not None:
29 | m.bias.data.zero_()
30 | elif isinstance(m, nn.ConvTranspose2d):
31 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.in_channels
32 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
33 | if m.bias is not None:
34 | m.bias.data.zero_()
35 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
36 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
37 | m.bias.data.zero_()
38 |
39 | class Decoder(nn.Module):
40 | # Decoder is the base class for all decoders
41 |
42 | names = ['deconv2', 'deconv3', 'upconv', 'upproj']
43 |
44 | def __init__(self):
45 | super(Decoder, self).__init__()
46 |
47 | self.layer1 = None
48 | self.layer2 = None
49 | self.layer3 = None
50 | self.layer4 = None
51 |
52 | def forward(self, x):
53 | x = self.layer1(x)
54 | x = self.layer2(x)
55 | x = self.layer3(x)
56 | x = self.layer4(x)
57 | return x
58 |
59 | class DeConv(Decoder):
60 | def __init__(self, in_channels, kernel_size):
61 | assert kernel_size>=2, "kernel_size out of range: {}".format(kernel_size)
62 | super(DeConv, self).__init__()
63 |
64 | def convt(in_channels):
65 | stride = 2
66 | padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
67 | output_padding = kernel_size % 2
68 | assert -2 - 2*padding + kernel_size + output_padding == 0, "deconv parameters incorrect"
69 |
70 | module_name = "deconv{}".format(kernel_size)
71 | return nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict([
72 | (module_name, nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels,in_channels//2,kernel_size,
73 | stride,padding,output_padding,bias=False)),
74 | ('batchnorm', nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels//2)),
75 | ('relu', nn.ReLU(inplace=True)),
76 | ]))
77 |
78 | self.layer1 = convt(in_channels)
79 | self.layer2 = convt(in_channels // 2)
80 | self.layer3 = convt(in_channels // (2 ** 2))
81 | self.layer4 = convt(in_channels // (2 ** 3))
82 |
83 | class UpConv(Decoder):
84 | # UpConv decoder consists of 4 upconv modules with decreasing number of channels and increasing feature map size
85 | def upconv_module(self, in_channels):
86 | # UpConv module: unpool -> 5*5 conv -> batchnorm -> ReLU
87 | upconv = nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict([
88 | ('unpool', Unpool(in_channels)),
89 | ('conv', nn.Conv2d(in_channels,in_channels//2,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False)),
90 | ('batchnorm', nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels//2)),
91 | ('relu', nn.ReLU()),
92 | ]))
93 | return upconv
94 |
95 | def __init__(self, in_channels):
96 | super(UpConv, self).__init__()
97 | self.layer1 = self.upconv_module(in_channels)
98 | self.layer2 = self.upconv_module(in_channels//2)
99 | self.layer3 = self.upconv_module(in_channels//4)
100 | self.layer4 = self.upconv_module(in_channels//8)
101 |
102 | class UpProj(Decoder):
103 | # UpProj decoder consists of 4 upproj modules with decreasing number of channels and increasing feature map size
104 |
105 | class UpProjModule(nn.Module):
106 | # UpProj module has two branches, with a Unpool at the start and a ReLu at the end
107 | # upper branch: 5*5 conv -> batchnorm -> ReLU -> 3*3 conv -> batchnorm
108 | # bottom branch: 5*5 conv -> batchnorm
109 |
110 | def __init__(self, in_channels):
111 | super(UpProj.UpProjModule, self).__init__()
112 | out_channels = in_channels//2
113 | self.unpool = Unpool(in_channels)
114 | self.upper_branch = nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict([
115 | ('conv1', nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False)),
116 | ('batchnorm1', nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)),
117 | ('relu', nn.ReLU()),
118 | ('conv2', nn.Conv2d(out_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False)),
119 | ('batchnorm2', nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)),
120 | ]))
121 | self.bottom_branch = nn.Sequential(collections.OrderedDict([
122 | ('conv', nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False)),
123 | ('batchnorm', nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels)),
124 | ]))
125 | self.relu = nn.ReLU()
126 |
127 | def forward(self, x):
128 | x = self.unpool(x)
129 | x1 = self.upper_branch(x)
130 | x2 = self.bottom_branch(x)
131 | x = x1 + x2
132 | x = self.relu(x)
133 | return x
134 |
135 | def __init__(self, in_channels):
136 | super(UpProj, self).__init__()
137 | self.layer1 = self.UpProjModule(in_channels)
138 | self.layer2 = self.UpProjModule(in_channels//2)
139 | self.layer3 = self.UpProjModule(in_channels//4)
140 | self.layer4 = self.UpProjModule(in_channels//8)
141 |
142 | def choose_decoder(decoder, in_channels):
143 | # iheight, iwidth = 10, 8
144 | if decoder[:6] == 'deconv':
145 | assert len(decoder)==7
146 | kernel_size = int(decoder[6])
147 | return DeConv(in_channels, kernel_size)
148 | elif decoder == "upproj":
149 | return UpProj(in_channels)
150 | elif decoder == "upconv":
151 | return UpConv(in_channels)
152 | else:
153 | assert False, "invalid option for decoder: {}".format(decoder)
154 |
155 |
156 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
157 | def __init__(self, layers, decoder, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True, export=False):
158 |
159 | if layers not in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152]:
160 | raise RuntimeError('Only 18, 34, 50, 101, and 152 layer model are defined for ResNet. Got {}'.format(layers))
161 |
162 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
163 | pretrained_model = torchvision.models.__dict__['resnet{}'.format(layers)](pretrained=pretrained)
164 |
165 | if in_channels == 3:
166 | self.conv1 = pretrained_model._modules['conv1']
167 | self.bn1 = pretrained_model._modules['bn1']
168 | else:
169 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
170 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
171 | weights_init(self.conv1)
172 | weights_init(self.bn1)
173 |
174 | self.output_size = output_size
175 | self.export = export
176 |
177 | self.relu = pretrained_model._modules['relu']
178 | self.maxpool = pretrained_model._modules['maxpool']
179 | self.layer1 = pretrained_model._modules['layer1']
180 | self.layer2 = pretrained_model._modules['layer2']
181 | self.layer3 = pretrained_model._modules['layer3']
182 | self.layer4 = pretrained_model._modules['layer4']
183 |
184 | # clear memory
185 | del pretrained_model
186 |
187 | # define number of intermediate channels
188 | if layers <= 34:
189 | num_channels = 512
190 | elif layers >= 50:
191 | num_channels = 2048
192 |
193 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels,num_channels//2,kernel_size=1,bias=False)
194 | self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_channels//2)
195 | self.decoder = choose_decoder(decoder, num_channels//2)
196 |
197 | # setting bias=true doesn't improve accuracy
198 | self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels//32,1,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False)
199 | self.bilinear = nn.Upsample(size=self.output_size, mode='bilinear', align_corners=True)
200 |
201 | # weight init
202 | self.conv2.apply(weights_init)
203 | self.bn2.apply(weights_init)
204 | self.decoder.apply(weights_init)
205 | self.conv3.apply(weights_init)
206 |
207 | def forward(self, x):
208 | # resnet
209 | x = self.conv1(x)
210 | x = self.bn1(x)
211 | x = self.relu(x)
212 | x = self.maxpool(x)
213 | x = self.layer1(x)
214 | x = self.layer2(x)
215 | x = self.layer3(x)
216 | x = self.layer4(x)
217 |
218 | x = self.conv2(x)
219 | x = self.bn2(x)
220 |
221 | # decoder
222 | x = self.decoder(x)
223 | x = self.conv3(x)
224 |
225 | if not hasattr(self, 'export') or not self.export:
226 | x = self.bilinear(x) # comment out for --export to ONNX mode
227 |
228 | return x
229 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models_fast.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #
2 | # these are the models from FastDepth, which use the training code from sparse-to-dense:
3 | #
4 | # - https://github.com/dwofk/fast-depth/blob/master/models.py
5 | # - https://github.com/dwofk/fast-depth/issues/3#issuecomment-510545490
6 | #
7 | import os
8 | import torch
9 | import torch.nn as nn
10 | import torchvision.models
11 | import collections
12 | import math
13 | import torch.nn.functional as F
14 | import imagenet.mobilenet
15 |
16 | class Identity(nn.Module):
17 | # a dummy identity module
18 | def __init__(self):
19 | super(Identity, self).__init__()
20 |
21 | def forward(self, x):
22 | return x
23 |
24 | class Unpool(nn.Module):
25 | # Unpool: 2*2 unpooling with zero padding
26 | def __init__(self, stride=2):
27 | super(Unpool, self).__init__()
28 |
29 | self.stride = stride
30 |
31 | # create kernel [1, 0; 0, 0]
32 | self.mask = torch.zeros(1, 1, stride, stride)
33 | self.mask[:,:,0,0] = 1
34 |
35 | def forward(self, x):
36 | assert x.dim() == 4
37 | num_channels = x.size(1)
38 | return F.conv_transpose2d(x,
39 | self.mask.detach().type_as(x).expand(num_channels, 1, -1, -1),
40 | stride=self.stride, groups=num_channels)
41 |
42 | def weights_init(m):
43 | # Initialize kernel weights with Gaussian distributions
44 | if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):
45 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels
46 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
47 | if m.bias is not None:
48 | m.bias.data.zero_()
49 | elif isinstance(m, nn.ConvTranspose2d):
50 | n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.in_channels
51 | m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n))
52 | if m.bias is not None:
53 | m.bias.data.zero_()
54 | elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):
55 | m.weight.data.fill_(1)
56 | m.bias.data.zero_()
57 |
58 | def conv(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size):
59 | padding = (kernel_size-1) // 2
60 | assert 2*padding == kernel_size-1, "parameters incorrect. kernel={}, padding={}".format(kernel_size, padding)
61 | return nn.Sequential(
62 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,stride=1,padding=padding,bias=False),
63 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
64 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
65 | )
66 |
67 | def depthwise(in_channels, kernel_size):
68 | padding = (kernel_size-1) // 2
69 | assert 2*padding == kernel_size-1, "parameters incorrect. kernel={}, padding={}".format(kernel_size, padding)
70 | return nn.Sequential(
71 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,in_channels,kernel_size,stride=1,padding=padding,bias=False,groups=in_channels),
72 | nn.BatchNorm2d(in_channels),
73 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
74 | )
75 |
76 | def pointwise(in_channels, out_channels):
77 | return nn.Sequential(
78 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,1,1,0,bias=False),
79 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
80 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
81 | )
82 |
83 | def convt(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size):
84 | stride = 2
85 | padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
86 | output_padding = kernel_size % 2
87 | assert -2 - 2*padding + kernel_size + output_padding == 0, "deconv parameters incorrect"
88 | return nn.Sequential(
89 | nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size,
90 | stride,padding,output_padding,bias=False),
91 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
92 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
93 | )
94 |
95 | def convt_dw(channels, kernel_size):
96 | stride = 2
97 | padding = (kernel_size - 1) // 2
98 | output_padding = kernel_size % 2
99 | assert -2 - 2*padding + kernel_size + output_padding == 0, "deconv parameters incorrect"
100 | return nn.Sequential(
101 | nn.ConvTranspose2d(channels,channels,kernel_size,
102 | stride,padding,output_padding,bias=False,groups=channels),
103 | nn.BatchNorm2d(channels),
104 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
105 | )
106 |
107 | def upconv(in_channels, out_channels):
108 | return nn.Sequential(
109 | Unpool(2),
110 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False),
111 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
112 | nn.ReLU(),
113 | )
114 |
115 | class upproj(nn.Module):
116 | # UpProj module has two branches, with a Unpool at the start and a ReLu at the end
117 | # upper branch: 5*5 conv -> batchnorm -> ReLU -> 3*3 conv -> batchnorm
118 | # bottom branch: 5*5 conv -> batchnorm
119 |
120 | def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels):
121 | super(upproj, self).__init__()
122 | self.unpool = Unpool(2)
123 | self.branch1 = nn.Sequential(
124 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False),
125 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
126 | nn.ReLU(inplace=True),
127 | nn.Conv2d(out_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=3,stride=1,padding=1,bias=False),
128 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
129 | )
130 | self.branch2 = nn.Sequential(
131 | nn.Conv2d(in_channels,out_channels,kernel_size=5,stride=1,padding=2,bias=False),
132 | nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
133 | )
134 |
135 | def forward(self, x):
136 | x = self.unpool(x)
137 | x1 = self.branch1(x)
138 | x2 = self.branch2(x)
139 | return F.relu(x1 + x2)
140 |
141 | class Decoder(nn.Module):
142 | names = ['deconv{}{}'.format(i,dw) for i in range(3,10,2) for dw in ['', 'dw']]
143 | names.append("upconv")
144 | names.append("upproj")
145 | for i in range(3,10,2):
146 | for dw in ['', 'dw']:
147 | names.append("nnconv{}{}".format(i, dw))
148 | names.append("blconv{}{}".format(i, dw))
149 | names.append("shuffle{}{}".format(i, dw))
150 |
151 | class DeConv(nn.Module):
152 |
153 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, dw):
154 | super(DeConv, self).__init__()
155 | if dw:
156 | self.convt1 = nn.Sequential(
157 | convt_dw(1024, kernel_size),
158 | pointwise(1024, 512))
159 | self.convt2 = nn.Sequential(
160 | convt_dw(512, kernel_size),
161 | pointwise(512, 256))
162 | self.convt3 = nn.Sequential(
163 | convt_dw(256, kernel_size),
164 | pointwise(256, 128))
165 | self.convt4 = nn.Sequential(
166 | convt_dw(128, kernel_size),
167 | pointwise(128, 64))
168 | self.convt5 = nn.Sequential(
169 | convt_dw(64, kernel_size),
170 | pointwise(64, 32))
171 | else:
172 | self.convt1 = convt(1024, 512, kernel_size)
173 | self.convt2 = convt(512, 256, kernel_size)
174 | self.convt3 = convt(256, 128, kernel_size)
175 | self.convt4 = convt(128, 64, kernel_size)
176 | self.convt5 = convt(64, 32, kernel_size)
177 | self.convf = pointwise(32, 1)
178 |
179 | def forward(self, x):
180 | x = self.convt1(x)
181 | x = self.convt2(x)
182 | x = self.convt3(x)
183 | x = self.convt4(x)
184 | x = self.convt5(x)
185 | x = self.convf(x)
186 | return x
187 |
188 |
189 | class UpConv(nn.Module):
190 |
191 | def __init__(self):
192 | super(UpConv, self).__init__()
193 | self.upconv1 = upconv(1024, 512)
194 | self.upconv2 = upconv(512, 256)
195 | self.upconv3 = upconv(256, 128)
196 | self.upconv4 = upconv(128, 64)
197 | self.upconv5 = upconv(64, 32)
198 | self.convf = pointwise(32, 1)
199 |
200 | def forward(self, x):
201 | x = self.upconv1(x)
202 | x = self.upconv2(x)
203 | x = self.upconv3(x)
204 | x = self.upconv4(x)
205 | x = self.upconv5(x)
206 | x = self.convf(x)
207 | return x
208 |
209 | class UpProj(nn.Module):
210 | # UpProj decoder consists of 4 upproj modules with decreasing number of channels and increasing feature map size
211 |
212 | def __init__(self):
213 | super(UpProj, self).__init__()
214 | self.upproj1 = upproj(1024, 512)
215 | self.upproj2 = upproj(512, 256)
216 | self.upproj3 = upproj(256, 128)
217 | self.upproj4 = upproj(128, 64)
218 | self.upproj5 = upproj(64, 32)
219 | self.convf = pointwise(32, 1)
220 |
221 | def forward(self, x):
222 | x = self.upproj1(x)
223 | x = self.upproj2(x)
224 | x = self.upproj3(x)
225 | x = self.upproj4(x)
226 | x = self.upproj5(x)
227 | x = self.convf(x)
228 | return x
229 |
230 | class NNConv(nn.Module):
231 |
232 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, dw):
233 | super(NNConv, self).__init__()
234 | if dw:
235 | self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
236 | depthwise(1024, kernel_size),
237 | pointwise(1024, 512))
238 | self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
239 | depthwise(512, kernel_size),
240 | pointwise(512, 256))
241 | self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
242 | depthwise(256, kernel_size),
243 | pointwise(256, 128))
244 | self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
245 | depthwise(128, kernel_size),
246 | pointwise(128, 64))
247 | self.conv5 = nn.Sequential(
248 | depthwise(64, kernel_size),
249 | pointwise(64, 32))
250 | self.conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
251 | else:
252 | self.conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
253 | self.conv2 = conv(512, 256, kernel_size)
254 | self.conv3 = conv(256, 128, kernel_size)
255 | self.conv4 = conv(128, 64, kernel_size)
256 | self.conv5 = conv(64, 32, kernel_size)
257 | self.conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
258 |
259 | def forward(self, x):
260 | x = self.conv1(x)
261 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
262 |
263 | x = self.conv2(x)
264 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
265 |
266 | x = self.conv3(x)
267 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
268 |
269 | x = self.conv4(x)
270 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
271 |
272 | x = self.conv5(x)
273 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
274 |
275 | x = self.conv6(x)
276 | return x
277 |
278 | class BLConv(NNConv):
279 |
280 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, dw):
281 | super(BLConv, self).__init__(kernel_size, dw)
282 |
283 | def forward(self, x):
284 | x = self.conv1(x)
285 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
286 |
287 | x = self.conv2(x)
288 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
289 |
290 | x = self.conv3(x)
291 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
292 |
293 | x = self.conv4(x)
294 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
295 |
296 | x = self.conv5(x)
297 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='bilinear', align_corners=False)
298 |
299 | x = self.conv6(x)
300 | return x
301 |
302 | class ShuffleConv(nn.Module):
303 |
304 | def __init__(self, kernel_size, dw):
305 | super(ShuffleConv, self).__init__()
306 | if dw:
307 | self.conv1 = nn.Sequential(
308 | depthwise(256, kernel_size),
309 | pointwise(256, 256))
310 | self.conv2 = nn.Sequential(
311 | depthwise(64, kernel_size),
312 | pointwise(64, 64))
313 | self.conv3 = nn.Sequential(
314 | depthwise(16, kernel_size),
315 | pointwise(16, 16))
316 | self.conv4 = nn.Sequential(
317 | depthwise(4, kernel_size),
318 | pointwise(4, 4))
319 | else:
320 | self.conv1 = conv(256, 256, kernel_size)
321 | self.conv2 = conv(64, 64, kernel_size)
322 | self.conv3 = conv(16, 16, kernel_size)
323 | self.conv4 = conv(4, 4, kernel_size)
324 |
325 | def forward(self, x):
326 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
327 | x = self.conv1(x)
328 |
329 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
330 | x = self.conv2(x)
331 |
332 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
333 | x = self.conv3(x)
334 |
335 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
336 | x = self.conv4(x)
337 |
338 | x = F.pixel_shuffle(x, 2)
339 | return x
340 |
341 | def choose_decoder(decoder):
342 | depthwise = ('dw' in decoder)
343 | if decoder[:6] == 'deconv':
344 | assert len(decoder)==7 or (len(decoder)==9 and 'dw' in decoder)
345 | kernel_size = int(decoder[6])
346 | model = DeConv(kernel_size, depthwise)
347 | elif decoder == "upproj":
348 | model = UpProj()
349 | elif decoder == "upconv":
350 | model = UpConv()
351 | elif decoder[:7] == 'shuffle':
352 | assert len(decoder)==8 or (len(decoder)==10 and 'dw' in decoder)
353 | kernel_size = int(decoder[7])
354 | model = ShuffleConv(kernel_size, depthwise)
355 | elif decoder[:6] == 'nnconv':
356 | assert len(decoder)==7 or (len(decoder)==9 and 'dw' in decoder)
357 | kernel_size = int(decoder[6])
358 | model = NNConv(kernel_size, depthwise)
359 | elif decoder[:6] == 'blconv':
360 | assert len(decoder)==7 or (len(decoder)==9 and 'dw' in decoder)
361 | kernel_size = int(decoder[6])
362 | model = BLConv(kernel_size, depthwise)
363 | else:
364 | assert False, "invalid option for decoder: {}".format(decoder)
365 | model.apply(weights_init)
366 | return model
367 |
368 |
369 | class ResNet(nn.Module):
370 | def __init__(self, layers, decoder, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True):
371 |
372 | if layers not in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152]:
373 | raise RuntimeError('Only 18, 34, 50, 101, and 152 layer model are defined for ResNet. Got {}'.format(layers))
374 |
375 | super(ResNet, self).__init__()
376 | self.output_size = output_size
377 | pretrained_model = torchvision.models.__dict__['resnet{}'.format(layers)](pretrained=pretrained)
378 | if not pretrained:
379 | pretrained_model.apply(weights_init)
380 |
381 | if in_channels == 3:
382 | self.conv1 = pretrained_model._modules['conv1']
383 | self.bn1 = pretrained_model._modules['bn1']
384 | else:
385 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
386 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
387 | weights_init(self.conv1)
388 | weights_init(self.bn1)
389 |
390 | self.relu = pretrained_model._modules['relu']
391 | self.maxpool = pretrained_model._modules['maxpool']
392 | self.layer1 = pretrained_model._modules['layer1']
393 | self.layer2 = pretrained_model._modules['layer2']
394 | self.layer3 = pretrained_model._modules['layer3']
395 | self.layer4 = pretrained_model._modules['layer4']
396 |
397 | # clear memory
398 | del pretrained_model
399 |
400 | # define number of intermediate channels
401 | if layers <= 34:
402 | num_channels = 512
403 | elif layers >= 50:
404 | num_channels = 2048
405 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, 1024, 1)
406 | weights_init(self.conv2)
407 | self.decoder = choose_decoder(decoder)
408 |
409 | def forward(self, x):
410 | # resnet
411 | x = self.conv1(x)
412 | x = self.bn1(x)
413 | x = self.relu(x)
414 | x = self.maxpool(x)
415 | x = self.layer1(x)
416 | x = self.layer2(x)
417 | x = self.layer3(x)
418 | x = self.layer4(x)
419 | x = self.conv2(x)
420 |
421 | # decoder
422 | x = self.decoder(x)
423 |
424 | return x
425 |
426 | class MobileNet(nn.Module):
427 | def __init__(self, decoder, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True):
428 |
429 | super(MobileNet, self).__init__()
430 | self.output_size = output_size
431 | mobilenet = imagenet.mobilenet.MobileNet()
432 | if pretrained:
433 | pretrained_path = os.path.join('imagenet', 'results', 'imagenet.arch=mobilenet.lr=0.1.bs=256', 'model_best.pth.tar')
434 | checkpoint = torch.load(pretrained_path)
435 | state_dict = checkpoint['state_dict']
436 |
437 | from collections import OrderedDict
438 | new_state_dict = OrderedDict()
439 | for k, v in state_dict.items():
440 | name = k[7:] # remove `module.`
441 | new_state_dict[name] = v
442 | mobilenet.load_state_dict(new_state_dict)
443 | else:
444 | mobilenet.apply(weights_init)
445 |
446 | if in_channels == 3:
447 | self.mobilenet = nn.Sequential(*(mobilenet.model[i] for i in range(14)))
448 | else:
449 | def conv_bn(inp, oup, stride):
450 | return nn.Sequential(
451 | nn.Conv2d(inp, oup, 3, stride, 1, bias=False),
452 | nn.BatchNorm2d(oup),
453 | nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
454 | )
455 |
456 | self.mobilenet = nn.Sequential(
457 | conv_bn(in_channels, 32, 2),
458 | *(mobilenet.model[i] for i in range(1,14))
459 | )
460 |
461 | self.decoder = choose_decoder(decoder)
462 |
463 | def forward(self, x):
464 | x = self.mobilenet(x)
465 | x = self.decoder(x)
466 | return x
467 |
468 | class ResNetSkipAdd(nn.Module):
469 | def __init__(self, layers, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True):
470 |
471 | if layers not in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152]:
472 | raise RuntimeError('Only 18, 34, 50, 101, and 152 layer model are defined for ResNet. Got {}'.format(layers))
473 |
474 | super(ResNetSkipAdd, self).__init__()
475 | self.output_size = output_size
476 | pretrained_model = torchvision.models.__dict__['resnet{}'.format(layers)](pretrained=pretrained)
477 | if not pretrained:
478 | pretrained_model.apply(weights_init)
479 |
480 | if in_channels == 3:
481 | self.conv1 = pretrained_model._modules['conv1']
482 | self.bn1 = pretrained_model._modules['bn1']
483 | else:
484 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
485 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
486 | weights_init(self.conv1)
487 | weights_init(self.bn1)
488 |
489 | self.relu = pretrained_model._modules['relu']
490 | self.maxpool = pretrained_model._modules['maxpool']
491 | self.layer1 = pretrained_model._modules['layer1']
492 | self.layer2 = pretrained_model._modules['layer2']
493 | self.layer3 = pretrained_model._modules['layer3']
494 | self.layer4 = pretrained_model._modules['layer4']
495 |
496 | # clear memory
497 | del pretrained_model
498 |
499 | # define number of intermediate channels
500 | if layers <= 34:
501 | num_channels = 512
502 | elif layers >= 50:
503 | num_channels = 2048
504 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, 1024, 1)
505 | weights_init(self.conv2)
506 |
507 | kernel_size = 5
508 | self.decode_conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
509 | self.decode_conv2 = conv(512, 256, kernel_size)
510 | self.decode_conv3 = conv(256, 128, kernel_size)
511 | self.decode_conv4 = conv(128, 64, kernel_size)
512 | self.decode_conv5 = conv(64, 32, kernel_size)
513 | self.decode_conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
514 | weights_init(self.decode_conv1)
515 | weights_init(self.decode_conv2)
516 | weights_init(self.decode_conv3)
517 | weights_init(self.decode_conv4)
518 | weights_init(self.decode_conv5)
519 | weights_init(self.decode_conv6)
520 |
521 | def forward(self, x):
522 | # resnet
523 | x = self.conv1(x)
524 | x = self.bn1(x)
525 | x1 = self.relu(x)
526 | # print("x1", x1.size())
527 | x2 = self.maxpool(x1)
528 | # print("x2", x2.size())
529 | x3 = self.layer1(x2)
530 | # print("x3", x3.size())
531 | x4 = self.layer2(x3)
532 | # print("x4", x4.size())
533 | x5 = self.layer3(x4)
534 | # print("x5", x5.size())
535 | x6 = self.layer4(x5)
536 | # print("x6", x6.size())
537 | x7 = self.conv2(x6)
538 |
539 | # decoder
540 | y10 = self.decode_conv1(x7)
541 | # print("y10", y10.size())
542 | y9 = F.interpolate(y10 + x6, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
543 | # print("y9", y9.size())
544 | y8 = self.decode_conv2(y9)
545 | # print("y8", y8.size())
546 | y7 = F.interpolate(y8 + x5, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
547 | # print("y7", y7.size())
548 | y6 = self.decode_conv3(y7)
549 | # print("y6", y6.size())
550 | y5 = F.interpolate(y6 + x4, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
551 | # print("y5", y5.size())
552 | y4 = self.decode_conv4(y5)
553 | # print("y4", y4.size())
554 | y3 = F.interpolate(y4 + x3, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
555 | # print("y3", y3.size())
556 | y2 = self.decode_conv5(y3 + x1)
557 | # print("y2", y2.size())
558 | y1 = F.interpolate(y2, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
559 | # print("y1", y1.size())
560 | y = self.decode_conv6(y1)
561 |
562 | return y
563 |
564 | class ResNetSkipConcat(nn.Module):
565 | def __init__(self, layers, output_size, in_channels=3, pretrained=True):
566 |
567 | if layers not in [18, 34, 50, 101, 152]:
568 | raise RuntimeError('Only 18, 34, 50, 101, and 152 layer model are defined for ResNet. Got {}'.format(layers))
569 |
570 | super(ResNetSkipConcat, self).__init__()
571 | self.output_size = output_size
572 | pretrained_model = torchvision.models.__dict__['resnet{}'.format(layers)](pretrained=pretrained)
573 | if not pretrained:
574 | pretrained_model.apply(weights_init)
575 |
576 | if in_channels == 3:
577 | self.conv1 = pretrained_model._modules['conv1']
578 | self.bn1 = pretrained_model._modules['bn1']
579 | else:
580 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
581 | self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
582 | weights_init(self.conv1)
583 | weights_init(self.bn1)
584 |
585 | self.relu = pretrained_model._modules['relu']
586 | self.maxpool = pretrained_model._modules['maxpool']
587 | self.layer1 = pretrained_model._modules['layer1']
588 | self.layer2 = pretrained_model._modules['layer2']
589 | self.layer3 = pretrained_model._modules['layer3']
590 | self.layer4 = pretrained_model._modules['layer4']
591 |
592 | # clear memory
593 | del pretrained_model
594 |
595 | # define number of intermediate channels
596 | if layers <= 34:
597 | num_channels = 512
598 | elif layers >= 50:
599 | num_channels = 2048
600 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(num_channels, 1024, 1)
601 | weights_init(self.conv2)
602 |
603 | kernel_size = 5
604 | self.decode_conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
605 | self.decode_conv2 = conv(768, 256, kernel_size)
606 | self.decode_conv3 = conv(384, 128, kernel_size)
607 | self.decode_conv4 = conv(192, 64, kernel_size)
608 | self.decode_conv5 = conv(128, 32, kernel_size)
609 | self.decode_conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
610 | weights_init(self.decode_conv1)
611 | weights_init(self.decode_conv2)
612 | weights_init(self.decode_conv3)
613 | weights_init(self.decode_conv4)
614 | weights_init(self.decode_conv5)
615 | weights_init(self.decode_conv6)
616 |
617 | def forward(self, x):
618 | # resnet
619 | x = self.conv1(x)
620 | x = self.bn1(x)
621 | x1 = self.relu(x)
622 | # print("x1", x1.size())
623 | x2 = self.maxpool(x1)
624 | # print("x2", x2.size())
625 | x3 = self.layer1(x2)
626 | # print("x3", x3.size())
627 | x4 = self.layer2(x3)
628 | # print("x4", x4.size())
629 | x5 = self.layer3(x4)
630 | # print("x5", x5.size())
631 | x6 = self.layer4(x5)
632 | # print("x6", x6.size())
633 | x7 = self.conv2(x6)
634 |
635 | # decoder
636 | y10 = self.decode_conv1(x7)
637 | # print("y10", y10.size())
638 | y9 = F.interpolate(y10, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
639 | # print("y9", y9.size())
640 | y8 = self.decode_conv2(torch.cat((y9, x5), 1))
641 | # print("y8", y8.size())
642 | y7 = F.interpolate(y8, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
643 | # print("y7", y7.size())
644 | y6 = self.decode_conv3(torch.cat((y7, x4), 1))
645 | # print("y6", y6.size())
646 | y5 = F.interpolate(y6, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
647 | # print("y5", y5.size())
648 | y4 = self.decode_conv4(torch.cat((y5, x3), 1))
649 | # print("y4", y4.size())
650 | y3 = F.interpolate(y4, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
651 | # print("y3", y3.size())
652 | y2 = self.decode_conv5(torch.cat((y3, x1), 1))
653 | # print("y2", y2.size())
654 | y1 = F.interpolate(y2, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
655 | # print("y1", y1.size())
656 | y = self.decode_conv6(y1)
657 |
658 | return y
659 |
660 | class MobileNetSkipAdd(nn.Module):
661 | def __init__(self, output_size, pretrained=True):
662 |
663 | super(MobileNetSkipAdd, self).__init__()
664 | self.output_size = output_size
665 | mobilenet = imagenet.mobilenet.MobileNet()
666 | if pretrained:
667 | pretrained_path = os.path.join('imagenet', 'results', 'imagenet.arch=mobilenet.lr=0.1.bs=256', 'model_best.pth.tar')
668 | checkpoint = torch.load(pretrained_path)
669 | state_dict = checkpoint['state_dict']
670 |
671 | from collections import OrderedDict
672 | new_state_dict = OrderedDict()
673 | for k, v in state_dict.items():
674 | name = k[7:] # remove `module.`
675 | new_state_dict[name] = v
676 | mobilenet.load_state_dict(new_state_dict)
677 | else:
678 | mobilenet.apply(weights_init)
679 |
680 | for i in range(14):
681 | setattr( self, 'conv{}'.format(i), mobilenet.model[i])
682 |
683 | kernel_size = 5
684 | # self.decode_conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
685 | # self.decode_conv2 = conv(512, 256, kernel_size)
686 | # self.decode_conv3 = conv(256, 128, kernel_size)
687 | # self.decode_conv4 = conv(128, 64, kernel_size)
688 | # self.decode_conv5 = conv(64, 32, kernel_size)
689 | self.decode_conv1 = nn.Sequential(
690 | depthwise(1024, kernel_size),
691 | pointwise(1024, 512))
692 | self.decode_conv2 = nn.Sequential(
693 | depthwise(512, kernel_size),
694 | pointwise(512, 256))
695 | self.decode_conv3 = nn.Sequential(
696 | depthwise(256, kernel_size),
697 | pointwise(256, 128))
698 | self.decode_conv4 = nn.Sequential(
699 | depthwise(128, kernel_size),
700 | pointwise(128, 64))
701 | self.decode_conv5 = nn.Sequential(
702 | depthwise(64, kernel_size),
703 | pointwise(64, 32))
704 | self.decode_conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
705 | weights_init(self.decode_conv1)
706 | weights_init(self.decode_conv2)
707 | weights_init(self.decode_conv3)
708 | weights_init(self.decode_conv4)
709 | weights_init(self.decode_conv5)
710 | weights_init(self.decode_conv6)
711 |
712 | def forward(self, x):
713 | # skip connections: dec4: enc1
714 | # dec 3: enc2 or enc3
715 | # dec 2: enc4 or enc5
716 | for i in range(14):
717 | layer = getattr(self, 'conv{}'.format(i))
718 | x = layer(x)
719 | # print("{}: {}".format(i, x.size()))
720 | if i==1:
721 | x1 = x
722 | elif i==3:
723 | x2 = x
724 | elif i==5:
725 | x3 = x
726 | for i in range(1,6):
727 | layer = getattr(self, 'decode_conv{}'.format(i))
728 | x = layer(x)
729 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
730 | if i==4:
731 | x = x + x1
732 | elif i==3:
733 | x = x + x2
734 | elif i==2:
735 | x = x + x3
736 | # print("{}: {}".format(i, x.size()))
737 | x = self.decode_conv6(x)
738 | return x
739 |
740 | class MobileNetSkipConcat(nn.Module):
741 | def __init__(self, output_size, pretrained=True):
742 |
743 | super(MobileNetSkipConcat, self).__init__()
744 | self.output_size = output_size
745 | mobilenet = imagenet.mobilenet.MobileNet()
746 | if pretrained:
747 | pretrained_path = os.path.join('imagenet', 'results', 'imagenet.arch=mobilenet.lr=0.1.bs=256', 'model_best.pth.tar')
748 | checkpoint = torch.load(pretrained_path)
749 | state_dict = checkpoint['state_dict']
750 |
751 | from collections import OrderedDict
752 | new_state_dict = OrderedDict()
753 | for k, v in state_dict.items():
754 | name = k[7:] # remove `module.`
755 | new_state_dict[name] = v
756 | mobilenet.load_state_dict(new_state_dict)
757 | else:
758 | mobilenet.apply(weights_init)
759 |
760 | for i in range(14):
761 | setattr( self, 'conv{}'.format(i), mobilenet.model[i])
762 |
763 | kernel_size = 5
764 | # self.decode_conv1 = conv(1024, 512, kernel_size)
765 | # self.decode_conv2 = conv(512, 256, kernel_size)
766 | # self.decode_conv3 = conv(256, 128, kernel_size)
767 | # self.decode_conv4 = conv(128, 64, kernel_size)
768 | # self.decode_conv5 = conv(64, 32, kernel_size)
769 | self.decode_conv1 = nn.Sequential(
770 | depthwise(1024, kernel_size),
771 | pointwise(1024, 512))
772 | self.decode_conv2 = nn.Sequential(
773 | depthwise(512, kernel_size),
774 | pointwise(512, 256))
775 | self.decode_conv3 = nn.Sequential(
776 | depthwise(512, kernel_size),
777 | pointwise(512, 128))
778 | self.decode_conv4 = nn.Sequential(
779 | depthwise(256, kernel_size),
780 | pointwise(256, 64))
781 | self.decode_conv5 = nn.Sequential(
782 | depthwise(128, kernel_size),
783 | pointwise(128, 32))
784 | self.decode_conv6 = pointwise(32, 1)
785 | weights_init(self.decode_conv1)
786 | weights_init(self.decode_conv2)
787 | weights_init(self.decode_conv3)
788 | weights_init(self.decode_conv4)
789 | weights_init(self.decode_conv5)
790 | weights_init(self.decode_conv6)
791 |
792 | def forward(self, x):
793 | # skip connections: dec4: enc1
794 | # dec 3: enc2 or enc3
795 | # dec 2: enc4 or enc5
796 | for i in range(14):
797 | layer = getattr(self, 'conv{}'.format(i))
798 | x = layer(x)
799 | # print("{}: {}".format(i, x.size()))
800 | if i==1:
801 | x1 = x
802 | elif i==3:
803 | x2 = x
804 | elif i==5:
805 | x3 = x
806 | for i in range(1,6):
807 | layer = getattr(self, 'decode_conv{}'.format(i))
808 | # print("{}a: {}".format(i, x.size()))
809 | x = layer(x)
810 | # print("{}b: {}".format(i, x.size()))
811 | x = F.interpolate(x, scale_factor=2, mode='nearest')
812 | if i==4:
813 | x = torch.cat((x, x1), 1)
814 | elif i==3:
815 | x = torch.cat((x, x2), 1)
816 | elif i==2:
817 | x = torch.cat((x, x3), 1)
818 | # print("{}c: {}".format(i, x.size()))
819 | x = self.decode_conv6(x)
820 | return x
821 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import os
2 | import torch
3 | import shutil
4 | import numpy as np
5 | import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
6 | from PIL import Image
7 |
8 | cmap = plt.cm.viridis
9 |
10 | def parse_command():
11 | model_names = ['resnet18', 'resnet50', 'mobilenet']
12 | loss_names = ['l1', 'l2']
13 | data_names = ['nyudepthv2', 'kitti', 'deepscene', 'sun', 'zed']
14 | from dataloaders.dense_to_sparse import UniformSampling, SimulatedStereo
15 | sparsifier_names = [x.name for x in [UniformSampling, SimulatedStereo]]
16 | from models import Decoder
17 | decoder_names = Decoder.names
18 | from dataloaders.dataloader import MyDataloader
19 | modality_names = MyDataloader.modality_names
20 |
21 | import argparse
22 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Sparse-to-Dense')
23 | parser.add_argument('--arch', '-a', metavar='ARCH', default='resnet18', choices=model_names,
24 | help='model architecture: ' + ' | '.join(model_names) + ' (default: resnet18)')
25 | parser.add_argument('--data', metavar='DATA', default='nyudepthv2',
26 | choices=data_names,
27 | help='dataset: ' + ' | '.join(data_names) + ' (default: nyudepthv2)')
28 | parser.add_argument('--modality', '-m', metavar='MODALITY', default='rgb', choices=modality_names,
29 | help='modality: ' + ' | '.join(modality_names) + ' (default: rgb)')
30 | parser.add_argument('-s', '--num-samples', default=0, type=int, metavar='N',
31 | help='number of sparse depth samples (default: 0)')
32 | parser.add_argument('--max-depth', default=-1.0, type=float, metavar='D',
33 | help='cut-off depth of sparsifier, negative values means infinity (default: inf [m])')
34 | parser.add_argument('--sparsifier', metavar='SPARSIFIER', default=UniformSampling.name, choices=sparsifier_names,
35 | help='sparsifier: ' + ' | '.join(sparsifier_names) + ' (default: ' + UniformSampling.name + ')')
36 | parser.add_argument('--decoder', '-d', metavar='DECODER', default='deconv2', choices=decoder_names,
37 | help='decoder: ' + ' | '.join(decoder_names) + ' (default: deconv2)')
38 | parser.add_argument('-j', '--workers', default=10, type=int, metavar='N',
39 | help='number of data loading workers (default: 10)')
40 | parser.add_argument('--epochs', default=15, type=int, metavar='N',
41 | help='number of total epochs to run (default: 15)')
42 | parser.add_argument('-c', '--criterion', metavar='LOSS', default='l1', choices=loss_names,
43 | help='loss function: ' + ' | '.join(loss_names) + ' (default: l1)')
44 | parser.add_argument('-b', '--batch-size', default=8, type=int, help='mini-batch size (default: 8)')
45 | parser.add_argument('--lr', '--learning-rate', default=0.01, type=float,
46 | metavar='LR', help='initial learning rate (default 0.01)')
47 | parser.add_argument('--momentum', default=0.9, type=float, metavar='M',
48 | help='momentum')
49 | parser.add_argument('--weight-decay', '--wd', default=1e-4, type=float,
50 | metavar='W', help='weight decay (default: 1e-4)')
51 | parser.add_argument('--print-freq', '-p', default=10, type=int,
52 | metavar='N', help='print frequency (default: 10)')
53 | parser.add_argument('--resume', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
54 | help='path to latest checkpoint (default: none)')
55 | parser.add_argument('--checkpoint', default='', type=str, metavar='PATH',
56 | help='path to pretrained checkpoint to begin training from')
57 | parser.add_argument('-e', '--evaluate', dest='evaluate', type=str, default='',
58 | help='evaluate model on validation set')
59 | parser.add_argument('--no-pretrain', dest='pretrained', action='store_false',
60 | help='not to use ImageNet pre-trained weights')
61 | parser.add_argument('--export', default='', type=str, help='path to pre-trained model to load to export to ONNX')
62 | parser.set_defaults(pretrained=True)
63 | args = parser.parse_args()
64 | if args.modality == 'rgb' and args.num_samples != 0:
65 | print("number of samples is forced to be 0 when input modality is rgb")
66 | args.num_samples = 0
67 | if args.modality == 'rgb' and args.max_depth != 0.0:
68 | print("max depth is forced to be 0.0 when input modality is rgb/rgbd")
69 | args.max_depth = 0.0
70 | return args
71 |
72 | def save_checkpoint(state, is_best, epoch, output_directory):
73 | checkpoint_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'checkpoint-' + str(epoch) + '.pth.tar')
74 | torch.save(state, checkpoint_filename)
75 | if is_best:
76 | best_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'model_best.pth.tar')
77 | shutil.copyfile(checkpoint_filename, best_filename)
78 | if epoch > 0:
79 | prev_checkpoint_filename = os.path.join(output_directory, 'checkpoint-' + str(epoch-1) + '.pth.tar')
80 | if os.path.exists(prev_checkpoint_filename):
81 | os.remove(prev_checkpoint_filename)
82 |
83 | def adjust_learning_rate(optimizer, epoch, lr_init):
84 | """Sets the learning rate to the initial LR decayed by 10 every 5 epochs"""
85 | lr = lr_init * (0.1 ** (epoch // 5))
86 | for param_group in optimizer.param_groups:
87 | param_group['lr'] = lr
88 |
89 | def get_output_directory(args):
90 | output_directory = os.path.join('results',
91 | '{}.sparsifier={}.samples={}.modality={}.arch={}.decoder={}.criterion={}.lr={}.bs={}.pretrained={}'.
92 | format(args.data, args.sparsifier, args.num_samples, args.modality, \
93 | args.arch, args.decoder, args.criterion, args.lr, args.batch_size, \
94 | args.pretrained))
95 | return output_directory
96 |
97 |
98 | def colored_depthmap(depth, d_min=None, d_max=None):
99 | if d_min is None:
100 | d_min = np.min(depth)
101 | if d_max is None:
102 | d_max = np.max(depth)
103 | depth_relative = (depth - d_min) / (d_max - d_min)
104 | return 255 * cmap(depth_relative)[:,:,:3] # H, W, C
105 |
106 |
107 | def merge_into_row(input, depth_target, depth_pred):
108 | rgb = 255 * np.transpose(np.squeeze(input.cpu().numpy()), (1,2,0)) # H, W, C
109 | depth_target_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_target.cpu().numpy())
110 | depth_pred_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_pred.data.cpu().numpy())
111 |
112 | d_min = min(np.min(depth_target_cpu), np.min(depth_pred_cpu))
113 | d_max = max(np.max(depth_target_cpu), np.max(depth_pred_cpu))
114 |
115 | print('depth_min {:f} depth_max {:f}'.format(d_min, d_max))
116 |
117 | depth_target_col = colored_depthmap(depth_target_cpu, d_min, d_max)
118 | depth_pred_col = colored_depthmap(depth_pred_cpu, d_min, d_max)
119 | img_merge = np.hstack([rgb, depth_target_col, depth_pred_col])
120 |
121 | return img_merge
122 |
123 |
124 | def merge_into_row_with_gt(input, depth_input, depth_target, depth_pred):
125 | rgb = 255 * np.transpose(np.squeeze(input.cpu().numpy()), (1,2,0)) # H, W, C
126 | depth_input_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_input.cpu().numpy())
127 | depth_target_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_target.cpu().numpy())
128 | depth_pred_cpu = np.squeeze(depth_pred.data.cpu().numpy())
129 |
130 | d_min = min(np.min(depth_input_cpu), np.min(depth_target_cpu), np.min(depth_pred_cpu))
131 | d_max = max(np.max(depth_input_cpu), np.max(depth_target_cpu), np.max(depth_pred_cpu))
132 | depth_input_col = colored_depthmap(depth_input_cpu, d_min, d_max)
133 | depth_target_col = colored_depthmap(depth_target_cpu, d_min, d_max)
134 | depth_pred_col = colored_depthmap(depth_pred_cpu, d_min, d_max)
135 |
136 | img_merge = np.hstack([rgb, depth_input_col, depth_target_col, depth_pred_col])
137 |
138 | return img_merge
139 |
140 |
141 | def add_row(img_merge, row):
142 | return np.vstack([img_merge, row])
143 |
144 |
145 | def save_image(img_merge, filename):
146 | img_merge = Image.fromarray(img_merge.astype('uint8'))
147 | img_merge.save(filename)
148 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------