├── excercise
├── P1
│ └── nginx-pod.yml
└── 1-Basic-kubectl
│ ├── nginx-pod.yml
│ └── Readme.md
├── workloads
├── daemonset
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── nginx.yml
│ └── simple-daemonset.yml
├── job
│ ├── paralel-job
│ │ ├── Readme.md
│ │ └── sleep-20s.yml
│ └── uuidgen.yml
├── replicaset
│ └── replicaset.yml
├── deployment
│ ├── nginx-deployment.yml
│ ├── nginx-svc-nodeport.yml
│ └── README.md
└── cronjob
│ └── wget-15min.yml
├── storage
├── localpath - nginx
│ ├── Readme.md
│ ├── pvc.yml
│ ├── nginx-pod.yml
│ └── pv.yml
├── localpath
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── persistentVolumeClaim.yaml
│ ├── redis-example
│ │ ├── redis-pvc.yaml
│ │ ├── redis-pv.yaml
│ │ ├── redispod.yaml
│ │ └── README.md
│ ├── http-pod.yaml
│ └── persistentVolume.yaml
├── resizeable-pv
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── storage-class.yml
│ ├── pvc.yml
│ ├── pv.yml
│ └── pod.yml
├── nfs
│ ├── nfs-server.md
│ ├── pod-using-nfs.yml
│ ├── simple-nfs.yml
│ └── Readme.md
├── emty-dir-accessing-2pod-same-volume
│ ├── readme.md
│ └── ngnix-shared-volume.yml
└── longhorn
│ └── Readme.md
├── installation
├── k3s.md
├── helm-install.sh
├── kubespray.md
├── containerd-installation.md
└── kubeadm-installation.md
├── rbac
└── scenario
│ ├── creating-new-clusteadmin
│ ├── Readme.md
│ ├── 01-serviceacount.yml
│ ├── 02-secret.yml
│ ├── 04-ClusterRolebinding.yml
│ ├── 03-clusterRole.yml
│ └── 05-kubeconfig-creator.sh
│ └── pod-get-resource
│ ├── service-account.yaml
│ ├── role.yml
│ ├── pod.yml
│ ├── rolebinding.yaml
│ └── Readme.md
├── Resource-Limit
├── Namespace-limit
│ ├── Readme.md
│ └── resource-quota.yml
└── Pod-Limit
│ ├── Readme.md
│ └── Nginx.yml
├── keda
└── time-based-scale
│ ├── prometheus
│ ├── Readme.md
│ ├── scale-object.yml
│ └── deployment.yml
│ └── Readme.md
├── PolicyManagement
└── Kyverno
│ ├── Pod.yml
│ ├── policy.yml
│ └── Readme.md
├── ingress
├── apple-orange-ingress
│ ├── Readme.md
│ ├── ingress.yml
│ └── pod.yml
├── README.md
├── nginx-ingress-manifest
│ └── simple-app-ingress.yml
└── nginx-ingress-helm
│ └── Readme.md
├── Resource-Management
├── Limit-Range
│ ├── test-pod.yaml
│ ├── test-pod-exceed.yaml
│ ├── limitrange.yaml
│ └── Readme.md
├── Resource-Quota
│ ├── resource-quota.yaml
│ ├── quota-test-pod.yaml
│ └── Readme.md
├── metric-server
│ └── Readme.md
├── HPA
│ ├── hpa-memory.yml
│ ├── hpa.yml
│ ├── nginx-deployment.yml
│ └── Readme.md
├── VPA
│ ├── Readme.md
│ ├── vpa.yml
│ └── nginx-deployment.yml
└── QOS
│ └── Readme.md
├── secret
├── using-env-from-secret
│ ├── secret.yml
│ ├── nginx-secret-env.yml
│ └── readme.md
└── dockerhub-imagepull-secret
│ └── Readme.md
├── ConfigMap
├── configmap-to-env
│ ├── configmap.yml
│ ├── pod.yml
│ └── Readme.md
├── Configmap-as-volume-redis
│ ├── Readme.md
│ └── redis-manifest-with-cm.yml
├── nginx-configmap
│ └── Readme.md
└── Volume-from-Configmap.yml
├── Network-policy
├── default-deny-np.yml
├── auth-server-np.yml
├── webauth-server.yml
├── web-auth-client.yml
└── README.md
├── sidecar-container
├── Readme.md
├── side-car-tail-log.yml
└── tail-log-with-initcontainer.yml
├── scenario
├── manual-canary-deployment
│ ├── nginx-service.yml
│ ├── nginx-ingress.yml
│ ├── nginx-configmap-canary.yml
│ ├── nginx-configmap-stable.yml
│ ├── Readme.md
│ ├── nginx-canary.yml
│ └── nginx-stable.yml
├── ipnetns-container
│ └── Readme.md
├── curl-kubernetes-object
│ └── Readme.md
├── Creating a ClusterRole to Access a Pod to get pod list in Kubernetes
│ └── README.md
└── turn-dockercompose-to-k8s-manifest
│ └── Readme.md
├── scheduler
├── nodeName
│ └── Readme.md
├── node-affinity
│ └── README.md
├── node-selector
│ └── Readme.md
├── drain
│ └── Readme.md
└── pod-afinity
│ ├── hpa.yml
│ └── Readme.md
├── metalLB
├── nginx-service.yaml
├── nginx-deployment.yml
├── metallb-config.yaml
└── Readme.md
├── audit-log
├── audit-policy.yaml
└── Readme.md
├── statefulset
├── mysql-cluster-scenario
│ ├── readme.md
│ ├── mysql-configmap.yml
│ ├── mysql-service.yml
│ └── mysql-statfulset.yml
└── nginx-scenario
│ ├── README.md
│ ├── pv.yml
│ └── statefulset.yml
├── service
├── external
│ └── varzesh3
│ │ └── Readme.md
├── headless
│ ├── nginx-deployment.yml
│ └── Readme.md
├── LoadBalancer
│ └── Readme.md
├── ClusterIP
│ └── Readme.md
└── NodePort
│ └── Readme.md
├── initcontainer
├── Readme.md
└── Pod-address.yml
├── kwatch
├── nginx-corrupted.yml
└── Readme.md
├── node-affinity
└── node-affinity.yml
├── Monitoring
└── Prometheus
│ ├── scrape-config
│ └── scrape.yaml
│ ├── prometheus-rules
│ └── pod-down.yml
│ ├── app.yml
│ └── Readme.md
├── readiness-liveness
├── liveness-exec
│ └── Readme.md
├── readiness-exec
│ └── Readme.md
├── liveness-http
│ └── Readme.md
├── liveness-grpc
│ └── Readme.md
├── liveness-tcp
│ └── Readme.md
└── startup-prob
│ └── Readme.md
├── Service-Mesh
└── isitio
│ ├── kiali-dashboard
│ └── Readme.md
│ └── canary-deployment
│ ├── Readme.md
│ ├── Virtualservice.yml
│ └── deployment.yml
├── logging
└── side-car
│ ├── fluent-configmap.yml
│ └── deployment-with-fluentd.yml
├── rolebinding
└── Create.md
├── CONTRIBUTING.md
├── enviornment
└── expose-pod-info-with-env
│ └── expose-data-env.yml
├── Static-POD
└── Readme.md
├── etcd
├── etcd.md
├── Readme.md
└── What Configurations are inside of ETCD.MD
├── api-gateway
├── istio-api-gateway
│ └── all-in-one.yml
└── Readme.md
├── PriorityClass
└── Readme.md
├── security
├── gate-keeper
│ └── Readme.md
├── kube-bench
│ └── Readme.md
└── kubescape
│ └── Readme.md
├── multi-container-pattern
├── side-car
│ └── sidecar.yml
└── adaptor
│ └── adaptor.yml
├── README.md
├── helm
└── helm-cheatsheet.md
├── istio
├── installation.sh
└── istio-app.yml
├── kubeconfig-access-for-one-namespace
└── kubeconfig-generator.sh
└── cheat-sheet
└── kubectl.md
/excercise/P1/nginx-pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/daemonset/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath - nginx/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | mkdir -p /mnt/disks/vol1
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/installation/k3s.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | curl -sfL https://get.k3s.io | sh -
3 | ```
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/creating-new-clusteadmin/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | https://devopscube.com/kubernetes-kubeconfig-file/
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Limit/Namespace-limit/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | kubectl apply -f resource-quota.yml
2 | kubectl get resourcequota -n farshad
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 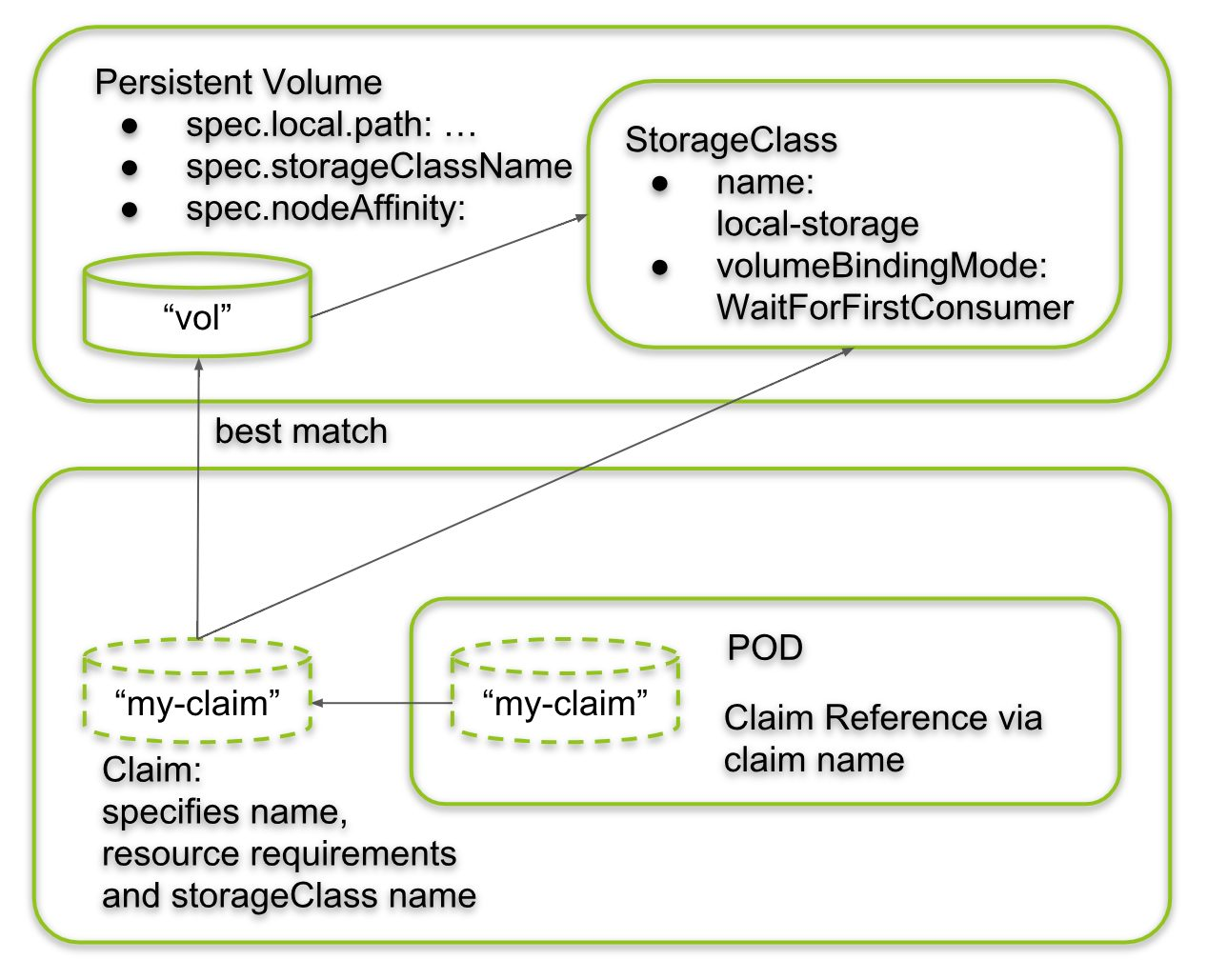
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/resizeable-pv/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## After Applying all of resources##
2 | **Change:**
3 | ``storage: 100Mi`` to ``storage: 200Mi`` in ``pvc.yml``
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/pod-get-resource/service-account.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ServiceAccount
3 | metadata:
4 | name: pod-reader-sa
5 | namespace: default
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/keda/time-based-scale/prometheus/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |  2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/nfs/nfs-server.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apt update && apt install nfs-server
3 | mkdir /exports
4 | echo "/exports *(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)" > /etc/exports
5 | ```
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PolicyManagement/Kyverno/Pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pod
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: nginx
8 | image: nginx
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/creating-new-clusteadmin/01-serviceacount.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ServiceAccount
3 | metadata:
4 | name: devops-cluster-admin
5 | namespace: kube-system
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/apple-orange-ingress/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | curl -H 'Host:packops.local' http://192.168.6.130/apple
3 | ```
4 |
5 | 
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/resizeable-pv/storage-class.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: StorageClass
3 | metadata:
4 | name: localdisk
5 | provisioner: kubernetes.io/no-provisioner
6 | allowVolumeExpansion: true
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Limit-Range/test-pod.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pod
5 | namespace: dev-namespace
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: test-container
9 | image: nginx
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/secret/using-env-from-secret/secret.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Secret
3 | metadata:
4 | name: backend-user
5 | type: Opaque
6 | data:
7 | backend-username: YmFja2VuZC1hZG1pbg== # base64-encoded value of 'backend-admin'
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/configmap-to-env/configmap.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ConfigMap
3 | metadata:
4 | name: simple-config
5 | data:
6 | database_url: "mongodb://db1.packops.dev:27017"
7 | feature_flag: "true"
8 | log_level: "debug"
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/installation/helm-install.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 | VERSION=3.9.0
3 | wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz
4 | tar -xzf helm-v$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz
5 | cp ./linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/ && rm -rf ./linux-amd64
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Limit/Pod-Limit/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | kubectl describe pod nginx-deployment-8c6b98574-27csj -n farshad
4 |
5 |
6 | 
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/default-deny-np.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: NetworkPolicy
3 | metadata:
4 | name: default-deny-ingress
5 | namespace: web-auth
6 | spec:
7 | podSelector: {}
8 | policyTypes:
9 | - Ingress
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sidecar-container/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | in scenario that we want an order for sidecars container or we want order between main container and sidecar we could use sidecar container in initcontainer (main will start after that sequential sidecar will start)
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/excercise/1-Basic-kubectl/nginx-pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # pod.yaml
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | name: my-pod
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: my-container
9 | image: nginx
10 | ports:
11 | - containerPort: 80
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-service.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Service
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-service
5 | spec:
6 | selector:
7 | app: nginx
8 | ports:
9 | - protocol: TCP
10 | port: 80
11 | targetPort: 80
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/pod-get-resource/role.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: Role
3 | metadata:
4 | namespace: default
5 | name: pod-reader
6 | rules:
7 | - apiGroups: [""]
8 | resources: ["pods"]
9 | verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/resizeable-pv/pvc.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pvc
5 | spec:
6 | storageClassName: localdisk
7 | accessModes:
8 | - ReadWriteOnce
9 | resources:
10 | requests:
11 | storage: 100Mi
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath - nginx/pvc.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
3 | metadata:
4 | name: local-pvc
5 | spec:
6 | accessModes:
7 | - ReadWriteOnce
8 | storageClassName: local-storage
9 | resources:
10 | requests:
11 | storage: 5Gi
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/resizeable-pv/pv.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | kind: PersistentVolume
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pv
5 | spec:
6 | storageClassName: localdisk
7 | capacity:
8 | storage: 1Gi
9 | accessModes:
10 | - ReadWriteOnce
11 | hostPath:
12 | path: /etc/output
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/persistentVolumeClaim.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | metadata:
4 | name: my-claim
5 | spec:
6 | accessModes:
7 | - ReadWriteOnce
8 | storageClassName: my-local-storage
9 | resources:
10 | requests:
11 | storage: 5Gi
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/redis-example/redis-pvc.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
3 | metadata:
4 | name: redisdb-pvc
5 | spec:
6 | storageClassName: "pv-local"
7 | accessModes:
8 | - ReadWriteOnce
9 | resources:
10 | requests:
11 | storage: 1Gi
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Limit/Namespace-limit/resource-quota.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ResourceQuota
3 | metadata:
4 | name: mem-cpu-demo
5 | namespace: farshad
6 |
7 | spec:
8 | hard:
9 | requests.cpu: 2
10 | requests.memory: 1Gi
11 | limits.cpu: 3
12 | limits.memory: 2Gi
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/creating-new-clusteadmin/02-secret.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Secret
3 | metadata:
4 | name: devops-cluster-admin-secret
5 | namespace: kube-system
6 | annotations:
7 | kubernetes.io/service-account.name: devops-cluster-admin
8 | type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/redis-example/redis-pv.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolume
3 | metadata:
4 | name: redis-pv
5 | spec:
6 | storageClassName: "pv-local"
7 | capacity:
8 | storage: 1Gi
9 | accessModes:
10 | - ReadWriteOnce
11 | hostPath:
12 | path: "/mnt/data"
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Resource-Quota/resource-quota.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ResourceQuota
3 | metadata:
4 | name: resource-quota
5 | namespace: prod-namespace
6 | spec:
7 | hard:
8 | requests.cpu: "10"
9 | requests.memory: "20Gi"
10 | limits.cpu: "15"
11 | limits.memory: "30Gi"
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/nodeName/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | #nodename-pod.yml
3 | apiVersion: v1
4 | kind: Pod
5 | metadata:
6 | name: nginx
7 | labels:
8 | name: nginx
9 | spec:
10 | containers:
11 | - name: nginx
12 | image: nginx
13 | ports:
14 | - containerPort: 8080
15 | nodeName: node1
16 |
17 | ```
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/pod-get-resource/pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: pod-checker
5 | namespace: default
6 | spec:
7 | serviceAccountName: pod-reader-sa
8 | containers:
9 | - name: kubectl-container
10 | image: bitnami/kubectl:latest
11 | command: ["sleep", "3600"]
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/emty-dir-accessing-2pod-same-volume/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | kubectl apply -f ngnix-shared-volume.yml
3 | kubectl exec -it two-containers -c nginx-container -- /bin/bash
4 | curl localhost
5 | ```
6 | 
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Resource-Quota/quota-test-pod.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: quota-test-pod
5 | namespace: prod-namespace
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: test-container
9 | image: nginx
10 | resources:
11 | requests:
12 | cpu: "1"
13 | memory: "512Mi"
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/metalLB/nginx-service.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Service
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx
5 | spec:
6 | selector:
7 | app: nginx
8 | ports:
9 | - protocol: TCP
10 | port: 80
11 | targetPort: 80
12 | type: LoadBalancer
13 | loadBalancerIP: 192.168.6.210 # Assigning a specific IP from MetalLB's range
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/Configmap-as-volume-redis/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | kubectl apply -f redis-manifest-with-cm.yml
3 | kubectl get cm shared-packops-redis-config -o yaml
4 | kubectl get pods
5 | kubectl exec -it shared-packops-redis-7cddbbf994-k5szl -- bash
6 | redis-cli
7 | ```
8 | ```
9 | cat /redis-master/redis.conf
10 | auth PASSWORD1234P
11 | get keys
12 | ```
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/pod-get-resource/rolebinding.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: RoleBinding
3 | metadata:
4 | name: read-pods
5 | namespace: default
6 | subjects:
7 | - kind: ServiceAccount
8 | name: pod-reader-sa
9 | namespace: default
10 | roleRef:
11 | kind: Role
12 | name: pod-reader
13 | apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/audit-log/audit-policy.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #/etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
2 |
3 | apiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1
4 | kind: Policy
5 | rules:
6 | - level: Metadata
7 | verbs: ["create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
8 | resources:
9 | - group: ""
10 | resources: ["pods", "services", "configmaps"]
11 | - group: "apps"
12 | resources: ["deployments", "statefulsets"]
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/secret/using-env-from-secret/nginx-secret-env.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: env-single-secret
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: envars-test-container
8 | image: nginx
9 | env:
10 | - name: SECRET_USERNAME
11 | valueFrom:
12 | secretKeyRef:
13 | name: backend-user
14 | key: backend-username
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Limit-Range/test-pod-exceed.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pod-exceed
5 | namespace: dev-namespace
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: test-container
9 | image: nginx
10 | resources:
11 | requests:
12 | cpu: "3" # Exceeds the max limit of 2 CPU
13 | memory: "2Gi" # Exceeds the max limit of 1Gi memory
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/metalLB/nginx-deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 2
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: nginx
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx
18 | ports:
19 | - containerPort: 80
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/creating-new-clusteadmin/04-ClusterRolebinding.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: ClusterRoleBinding
3 | metadata:
4 | name: devops-cluster-admin
5 | roleRef:
6 | apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
7 | kind: ClusterRole
8 | name: devops-cluster-admin
9 | subjects:
10 | - kind: ServiceAccount
11 | name: devops-cluster-admin
12 | namespace: kube-system
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/job/paralel-job/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | You can also run a job with parallelism. There are two fields in the spec, called completions and parallelism. completions is set to 1 by default. If you want more than one successful completion, then increase this value. parallelism determines how many pods to launch. A job will not launch more pods than needed for successful completion, even if the parallelism value is greater.
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/statefulset/mysql-cluster-scenario/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/run-replicated-stateful-application/
3 |
4 |
5 | ```
6 | kubectl run mysql-client --image=mysql:5.7 -i --rm --restart=Never --\
7 | mysql -h mysql-0.mysql <> /output/output.log; sleep 10; done']
10 | volumeMounts:
11 | - name: pv-storage
12 | mountPath: /output
13 | volumes:
14 | - name: pv-storage
15 | persistentVolumeClaim:
16 | claimName: test-pvc
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/kwatch/nginx-corrupted.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-failing-deployment
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 1
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: nginx-failing
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: nginx-failing
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx
18 |
19 | command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
20 | args:
21 | - "sleep 60; exit 1"
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/node-affinity/node-affinity.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx
5 | spec:
6 | affinity:
7 | nodeAffinity:
8 | requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
9 | nodeSelectorTerms:
10 | - matchExpressions:
11 | - key: nodename
12 | operator: In
13 | values:
14 | - bi-team
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx
18 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/node-affinity/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Lable a Kubernetes Node
2 | 1- kubectl get nodes
3 |
4 | ```
5 | worker0 Ready 1d v1.13.0 ...,kubernetes.io/hostname=worker0
6 | worker1 Ready 1d v1.13.0 ...,kubernetes.io/hostname=worker1
7 | worker2 Ready 1d v1.13.0 ...,kubernetes.io/hostname=worker2
8 | ```
9 |
10 | 2- kubectl label nodes nodename=bi-team
11 |
12 | 3- kubectl apply -f node-affinity.yml
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/VPA/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | ## install vpa
4 | ```
5 | kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/vpa-release-1.0/vertical-pod-autoscaler/deploy/vpa-v1-crd-gen.yaml
6 | kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/vpa-release-1.0/vertical-pod-autoscaler/deploy/vpa-rbac.yaml
7 | ```
8 | ```
9 | kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
10 | kubectl apply -f nginx-vpa.yaml
11 |
12 | kubectl describe vpa nginx-vpa
13 |
14 | ```
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/http-pod.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: www
5 | labels:
6 | name: www
7 | spec:
8 | containers:
9 | - name: www
10 | image: nginx:alpine
11 | ports:
12 | - containerPort: 80
13 | name: www
14 | volumeMounts:
15 | - name: www-persistent-storage
16 | mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
17 | volumes:
18 | - name: www-persistent-storage
19 | persistentVolumeClaim:
20 | claimName: my-claim
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/node-selector/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1. Label your node
2 | First, you label the node where you want the pod to be scheduled.
3 | ```
4 | kubectl label nodes disktype=ssd
5 | ```
6 | 2. Pod Specification with Node Selector
7 | Next, you define a pod that will use this node selector:
8 | ```
9 | apiVersion: v1
10 | kind: Pod
11 | metadata:
12 | name: selector
13 | spec:
14 | containers:
15 | - name: my-container
16 | image: nginx
17 | nodeSelector:
18 | disktype: ssd
19 |
20 |
21 | ```
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/configmap-to-env/pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: app-pod
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: app-container
8 | image: nginx
9 | env:
10 | - name: DATABASE_URL
11 | valueFrom:
12 | configMapKeyRef:
13 | name: simple-config
14 | key: database_url
15 | - name: LOG_LEVEL
16 | valueFrom:
17 | configMapKeyRef:
18 | name: simple-config
19 | key: log_level
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-configmap-canary.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ConfigMap
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-config-canary
5 | data:
6 | nginx.conf: |
7 | worker_processes 1;
8 |
9 | events {
10 | worker_connections 1024;
11 | }
12 |
13 | http {
14 | server {
15 | listen 80;
16 | location / {
17 | add_header Content-Type text/plain;
18 | return 200 "Release: Canary";
19 | }
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/auth-server-np.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: NetworkPolicy
3 | metadata:
4 | name: auth-server-ingress
5 | namespace: web-auth
6 | spec:
7 | podSelector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: auth-server
10 | policyTypes:
11 | - Ingress
12 | ingress:
13 | - from:
14 | - namespaceSelector:
15 | matchLabels:
16 | role: auth
17 | podSelector:
18 | matchLabels:
19 | app: auth-client
20 | ports:
21 | - protocol: TCP
22 | port: 80
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Resource-Quota/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | You want to manage resource usage in the prod-namespace by setting both requests and limits. Specifically, you will:
2 |
3 | Limit the total CPU requests in the namespace to 10 CPUs.
4 | Limit the total memory requests in the namespace to 20Gi.
5 | Cap the total CPU limits in the namespace to 15 CPUs.
6 | Cap the total memory limits in the namespace to 30Gi.
7 |
8 | ```
9 | kubectl get resourcequota resource-quota --namespace=prod-namespace --output=yaml
10 | ```
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-configmap-stable.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ConfigMap
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-config-stable
5 | data:
6 | nginx.conf: |
7 | worker_processes 1;
8 |
9 | events {
10 | worker_connections 1024;
11 | }
12 |
13 | http {
14 | server {
15 | listen 80;
16 | location / {
17 | add_header Content-Type text/plain;
18 | return 200 "Release: Stable";
19 | }
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Monitoring/Prometheus/scrape-config/scrape.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1alpha1
2 | kind: ScrapeConfig
3 | metadata:
4 | name: static-targets
5 | namespace: monitoring
6 | labels:
7 | release: kube-prom-stack # must match your Prometheus release label
8 | spec:
9 | staticConfigs:
10 | - targets:
11 | - "10.0.0.5:9100"
12 | - "10.0.0.6:9100"
13 | labels:
14 | job: "node-exporter-external"
15 | environment: "prod"
16 | metricsPath: /metrics
17 | scrapeInterval: 30s
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/HPA/hpa.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #kubectl autoscale deployment nginx-deployment --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
2 | apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
3 | kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
4 | metadata:
5 | name: nginx-hpa
6 | spec:
7 | scaleTargetRef:
8 | apiVersion: apps/v1
9 | kind: Deployment
10 | name: nginx-deployment
11 | minReplicas: 1
12 | maxReplicas: 10
13 | metrics:
14 | - type: Resource
15 | resource:
16 | name: cpu
17 | target:
18 | type: Utilization
19 | averageUtilization: 50
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/VPA/vpa.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: autoscaling.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: VerticalPodAutoscaler
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-vpa
5 | spec:
6 | targetRef:
7 | apiVersion: "apps/v1"
8 | kind: Deployment
9 | name: nginx-deployment
10 | updatePolicy:
11 | updateMode: "Auto"
12 | resourcePolicy:
13 | containerPolicies:
14 | - containerName: "nginx"
15 | minAllowed:
16 | cpu: "50m"
17 | memory: "64Mi"
18 | maxAllowed:
19 | cpu: "500m"
20 | memory: "512Mi"
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/drain/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Cordoning the Node: Prevents new pods from being scheduled on the node.
2 | ```
3 | kubectl cordon
4 | ```
5 | Draining the Node: Evicts all the pods while respecting the configurations.
6 |
7 | ```
8 | kubectl drain --ignore-daemonsets --delete-emptydir-data
9 | ```
10 | Perform Maintenance: After draining, perform any maintenance needed on the node.
11 |
12 | Uncordon the Node (if needed): Allow new pods to be scheduled again.
13 |
14 | ```
15 | kubectl uncordon
16 | ```
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/liveness-exec/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | labels:
6 | test: liveness
7 | name: liveness-exec
8 | spec:
9 | containers:
10 | - name: liveness
11 | image: registry.k8s.io/busybox
12 | args:
13 | - /bin/sh
14 | - -c
15 | - touch /tmp/healthy; sleep 30; rm -f /tmp/healthy; sleep 600
16 | livenessProbe:
17 | exec:
18 | command:
19 | - cat
20 | - /tmp/healthy
21 | initialDelaySeconds: 5
22 | periodSeconds: 5
23 | ```
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/readiness-exec/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 |
3 | apiVersion: v1
4 | kind: Pod
5 | metadata:
6 | labels:
7 | test: liveness
8 | name: liveness-exec
9 | spec:
10 | containers:
11 | - name: liveness
12 | image: registry.k8s.io/busybox
13 | args:
14 | - /bin/sh
15 | - -c
16 | - touch /tmp/healthy; sleep 30; rm -f /tmp/healthy; sleep 600
17 | readinessProbe:
18 | exec:
19 | command:
20 | - cat
21 | - /tmp/healthy
22 | initialDelaySeconds: 5
23 | periodSeconds: 5
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/kwatch/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1- Configmap
2 |
3 | ```
4 | #config.yml
5 | apiVersion: v1
6 | kind: Namespace
7 | metadata:
8 | name: kwatch
9 | ---
10 | apiVersion: v1
11 | kind: ConfigMap
12 | metadata:
13 | name: kwatch
14 | namespace: kwatch
15 | data:
16 | config.yaml: |
17 | alert:
18 | telegram:
19 | token: TOKEN
20 | chatId: CHAT_ID
21 | ```
22 | ```
23 | kubectl apply -f config.yml
24 | ```
25 | 2- Deploy Kwatch
26 | ```
27 | kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abahmed/kwatch/v0.8.4/deploy/deploy.yaml
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/pod-afinity/hpa.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | #kubectl autoscale deployment nginx-deployment --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
3 | apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
4 | kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
5 | metadata:
6 | name: nginx-hpa
7 | spec:
8 | scaleTargetRef:
9 | apiVersion: apps/v1
10 | kind: Deployment
11 | name: nginx-deployment
12 | minReplicas: 1
13 | maxReplicas: 10
14 | metrics:
15 | - type: Resource
16 | resource:
17 | name: cpu
18 | target:
19 | type: Utilization
20 | averageUtilization: 50
21 |
22 | ```
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/liveness-http/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | labels:
6 | test: liveness
7 | name: liveness-http
8 | spec:
9 | containers:
10 | - name: liveness
11 | image: registry.k8s.io/e2e-test-images/agnhost:2.40
12 | args:
13 | - liveness
14 | livenessProbe:
15 | httpGet:
16 | path: /healthz
17 | port: 8080
18 | httpHeaders:
19 | - name: Custom-Header
20 | value: Awesome
21 | initialDelaySeconds: 3
22 | periodSeconds: 3
23 |
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/liveness-grpc/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | name: etcd-with-grpc
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: etcd
9 | image: registry.k8s.io/etcd:3.5.1-0
10 | command: [ "/usr/local/bin/etcd", "--data-dir", "/var/lib/etcd", "--listen-client-urls", "http://0.0.0.0:2379", "--advertise-client-urls", "http://127.0.0.1:2379", "--log-level", "debug"]
11 | ports:
12 | - containerPort: 2379
13 | livenessProbe:
14 | grpc:
15 | port: 2379
16 | initialDelaySeconds: 10
17 |
18 | ```
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/liveness-tcp/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | name: goproxy
6 | labels:
7 | app: goproxy
8 | spec:
9 | containers:
10 | - name: goproxy
11 | image: registry.k8s.io/goproxy:0.1
12 | ports:
13 | - containerPort: 8080
14 | readinessProbe:
15 | tcpSocket:
16 | port: 8080
17 | initialDelaySeconds: 15
18 | periodSeconds: 10
19 | livenessProbe:
20 | tcpSocket:
21 | port: 8080
22 | initialDelaySeconds: 15
23 | periodSeconds: 10
24 |
25 | ```
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath - nginx/pv.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolume
3 | metadata:
4 | name: local-pv
5 | spec:
6 | capacity:
7 | storage: 10Gi
8 | accessModes:
9 | - ReadWriteOnce
10 | persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
11 | storageClassName: local-storage
12 | local:
13 | path: /mnt/disks/vol1
14 | nodeAffinity:
15 | required:
16 | nodeSelectorTerms:
17 | - matchExpressions:
18 | - key: kubernetes.io/hostname
19 | operator: In
20 | values:
21 | - node1
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Service-Mesh/isitio/kiali-dashboard/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Install kiali plugin
2 | ```
3 | git clone https://github.com/istio/istio.git
4 | kubectl apply -f istio/samples/addons
5 | ```
6 |
7 | # make nodeport service for kiali
8 |
9 | ```
10 | apiVersion: v1
11 | kind: Service
12 | metadata:
13 | name: kiali-nodeport
14 | namespace: istio-system
15 | spec:
16 | type: NodePort
17 | ports:
18 | - port: 20001
19 | targetPort: 20001
20 | nodePort: 30001
21 | selector:
22 | app.kubernetes.io/instance: kiali
23 | app.kubernetes.io/name: kiali
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/logging/side-car/fluent-configmap.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ConfigMap
3 | metadata:
4 | name: fluentd-config
5 | data:
6 | fluentd.conf: |
7 |
8 | type tail
9 | format none
10 | path /var/log/1.log
11 | pos_file /var/log/1.log.pos
12 | tag count.format1
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | type tail
17 | format none
18 | path /var/log/2.log
19 | pos_file /var/log/2.log.pos
20 | tag count.format2
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | type google_cloud
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/statefulset/nginx-scenario/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Create Persistent Volume (if you dont have )
3 | create pv and make it default pv in our scenario Our storage is Localpath
4 | ```
5 | kubectl apply pv.yml
6 | ```
7 | ## Make it Default pv
8 | ```
9 | kubectl patch storageclass my-local-storage -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
10 | ```
11 |
12 | # bring up your statefulset
13 | ```
14 | kubectl apply -f statefulset.yml
15 | ```
16 |
17 | # verify your PV and PVC
18 |
19 | ```
20 | kubectl get pv
21 | kubectl get pvc
22 | ```
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/statefulset/nginx-scenario/pv.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolume
3 | metadata:
4 | name: my-local-pv
5 | spec:
6 | capacity:
7 | storage: 500Gi
8 | accessModes:
9 | - ReadWriteOnce
10 | persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
11 | storageClassName: my-local-storage
12 | local:
13 | path: /opt/st
14 | nodeAffinity:
15 | required:
16 | nodeSelectorTerms:
17 | - matchExpressions:
18 | - key: kubernetes.io/hostname
19 | operator: In
20 | values:
21 | - node1
22 | - node2
23 | - node3
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/persistentVolume.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolume
3 | metadata:
4 | name: my-local-pv
5 | spec:
6 | capacity:
7 | storage: 500Gi
8 | accessModes:
9 | - ReadWriteOnce
10 | persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
11 | storageClassName: my-local-storage
12 | local:
13 | path: /opt/st
14 | nodeAffinity:
15 | required:
16 | nodeSelectorTerms:
17 | - matchExpressions:
18 | - key: kubernetes.io/hostname
19 | operator: In
20 | values:
21 | - node1
22 | - node2
23 | - node3
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Monitoring/Prometheus/prometheus-rules/pod-down.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
2 | kind: PrometheusRule
3 | metadata:
4 | labels:
5 | prometheus: kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus
6 | role: alert-rules
7 | name: your-application-name
8 | spec:
9 | groups:
10 | - name: "your-application-name.rules"
11 | rules:
12 | - alert: PodDown
13 | for: 1m
14 | expr: sum(up{job="your-service-monitor-name"}) < 1 or absent(up{job="your-service-monitor-name"})
15 | annotations:
16 | message: The deployment has less than 1 pod running.
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 
3 |
4 | kubectl apply -f nginx-canary.yml
5 | kubectl apply -f nginx-stable.yml
6 | kubectl apply -f nginx-service.yml
7 | kubectl apply -f nginx-configmap-canary.yml
8 | kubectl apply -f nginx-configmap-stable.yml
9 |
10 |
11 | ```
12 | kubectl get svc
13 | ```
14 |
15 | ```
16 | for i in {1..30}; do curl -s http://10.233.57.87 && echo ""; sleep 1; done
17 | ```
18 |
19 | 
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/job/uuidgen.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: batch/v1
2 | kind: Job
3 | metadata:
4 | name: uuidgen
5 | spec:
6 | template:
7 | metadata:
8 | spec:
9 | containers:
10 | - name: ubuntu
11 | image: ubuntu:latest
12 | imagePullPolicy: Always
13 | command: ["bash"]
14 | args:
15 | - -c
16 | - |
17 | apt update
18 | apt install uuid-runtime
19 | for i in {1..10}; do echo `uuidgen`@mailinator.com; done > /tmp/emails.txt
20 | cat /tmp/emails.txt
21 | sleep 60
22 | restartPolicy: OnFailure
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/deployment/nginx-deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-depoyment
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 3
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: webserver
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: webserver
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx:latest
18 | ports:
19 | - containerPort: 80
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/VPA/nginx-deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-deployment
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 1
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: nginx
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx:1.14.2
18 | ports:
19 | - containerPort: 80
20 | resources:
21 | requests:
22 | cpu: "100m"
23 | memory: "128Mi"
24 | limits:
25 | cpu: "200m"
26 | memory: "256Mi"
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/apple-orange-ingress/ingress.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: Ingress
3 | metadata:
4 | name: ingress-packops-local
5 | spec:
6 | ingressClassName: nginx
7 | rules:
8 | - host: packops.local
9 | http:
10 | paths:
11 | - path: /apple
12 | pathType: Prefix
13 | backend:
14 | service:
15 | name: apple-service
16 | port:
17 | number: 5678
18 | - path: /orange
19 | pathType: Prefix
20 | backend:
21 | service:
22 | name: orange-service
23 | port:
24 | number: 5678
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/keda/time-based-scale/prometheus/scale-object.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
2 | kind: ScaledObject
3 | metadata:
4 | name: packops-scaler
5 | namespace: default
6 | spec:
7 | scaleTargetRef:
8 | kind: Deployment
9 | name: nginx-deployment
10 | # minReplicaCount: 2
11 | maxReplicaCount: 10
12 | cooldownPeriod: 10
13 | pollingInterval: 10
14 | triggers:
15 | - type: prometheus
16 | metadata:
17 | serverAddress: http://kube-prom-stack-kube-prome-prometheus.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090
18 | metricName: custom_metric
19 | query: "custom_metric"
20 | threshold: "1"
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/daemonset/nginx.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: DaemonSet
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-da
5 | namespace: devops
6 | labels:
7 | app: nginx-da
8 | spec:
9 | selector:
10 | matchLabels:
11 | app: nginx-da
12 | template:
13 | metadata:
14 | labels:
15 | app: nginx-da
16 | spec:
17 | containers:
18 | - name: nginx-da
19 | image: nginx:alpine
20 | volumeMounts:
21 | - name: localtime
22 | mountPath: /etc/localtime
23 | volumes:
24 | - name: localtime
25 | hostPath:
26 | path: /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Tehran
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/cronjob/wget-15min.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: batch/v1
2 | kind: CronJob
3 | metadata:
4 | namespace: devops
5 | name: packops-cronjob
6 | spec:
7 | schedule: "*/15 * * * *"
8 | jobTemplate:
9 | spec:
10 | template:
11 | spec:
12 | containers:
13 | - name: reference
14 | image: busybox
15 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
16 | command:
17 | - /bin/sh
18 | - -c
19 | - date; echo "This pod Schedule every 15 min"
20 | - wget -q -O - https://packops.ir/wp-cron.php?doing_wp_cron >/dev/null 2>&1
21 | restartPolicy: OnFailure
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/emty-dir-accessing-2pod-same-volume/ngnix-shared-volume.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: two-containers
5 | spec:
6 |
7 | restartPolicy: Never
8 |
9 | volumes:
10 | - name: shared-data
11 | emptyDir: {}
12 |
13 | containers:
14 |
15 | - name: nginx-container
16 | image: nginx
17 | volumeMounts:
18 | - name: shared-data
19 | mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
20 |
21 | - name: debian-container
22 | image: alpine
23 | volumeMounts:
24 | - name: shared-data
25 | mountPath: /pod-data
26 | command: ["/bin/sh"]
27 | args: ["-c", "echo Hello from the debian container > /pod-data/index.html"]
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rolebinding/Create.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | kubectl create rolebinding farshad-admin --clusterrole=admin --user=farshad
3 | ```
4 |
5 | ```
6 | kubectl get RoleBinding -o yaml
7 | ```
8 |
9 | # output would be something like this
10 | ```
11 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
12 | kind: RoleBinding
13 | metadata:
14 | creationTimestamp: "2023-01-15T14:54:47Z"
15 | name: farshad-admin
16 | namespace: default
17 | resourceVersion: "22145"
18 | uid: 6bf97d50-fa9f-4437-b2d0-e1aa1dbe22ae
19 | roleRef:
20 | apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
21 | kind: ClusterRole
22 | name: admin
23 | subjects:
24 | - apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
25 | kind: User
26 | name: farshad
27 |
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/service/LoadBalancer/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Service
4 | metadata:
5 | name: myapp-loadbalancer-service
6 | spec:
7 | type: LoadBalancer
8 | ports:
9 | - port: 80
10 | targetPort: 80
11 | selector:
12 | app: nginx
13 | ---
14 | apiVersion: apps/v1
15 | kind: Deployment
16 | metadata:
17 | name: nginx-deployment
18 | labels:
19 | app: nginx
20 | spec:
21 | replicas: 3
22 | selector:
23 | matchLabels:
24 | app: nginx
25 | template:
26 | metadata:
27 | labels:
28 | app: nginx
29 | spec:
30 | containers:
31 | - name: nginx
32 | image: nginx:latest
33 | ports:
34 | - containerPort: 80
35 | ---
36 |
37 | ```
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/webauth-server.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: web-auth-server
5 | labels:
6 | app: auth-server
7 | namespace: web-auth
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 1
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: auth-server
13 | template:
14 | metadata:
15 | labels:
16 | app: auth-server
17 | spec:
18 | containers:
19 | - name: nginx
20 | image: nginx:1.14.2
21 |
22 | ---
23 |
24 | apiVersion: v1
25 | kind: Service
26 | metadata:
27 | name: web-auth-server-svc
28 | namespace: web-auth
29 | spec:
30 | ports:
31 | - port: 80
32 | protocol: TCP
33 | targetPort: 80
34 | selector:
35 | app: auth-server
36 | type: ClusterIP
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/secret/using-env-from-secret/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Creat a secret name backend-user with key backend-username and value backend-admin
2 | this way
3 | ```
4 | kubectl create secret generic backend-user --from-literal=backend-username='backend-admin'
5 | ```
6 | OR Create it as a manifest
7 | ```
8 | apiVersion: v1
9 | kind: Secret
10 | metadata:
11 | name: backend-user
12 | type: Opaque
13 | data:
14 | backend-username: YmFja2VuZC1hZG1pbg== # base64-encoded value of 'backend-admin'
15 | ```
16 | and apply nginx
17 | ```
18 | kubectl apply nginx-secret-env.yml
19 | ```
20 | Check the env it should have show backend-admin
21 | ```
22 | kubectl exec -i -t env-single-secret -- /bin/sh -c 'echo $SECRET_USERNAME'
23 | ```
24 | ![Uploading image.png…]()
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/web-auth-client.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | labels:
5 | app: auth-client
6 | name: auth-client
7 | namespace: web-auth
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 1
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: auth-client
13 | template:
14 | metadata:
15 | labels:
16 | app: auth-client
17 | spec:
18 | containers:
19 | - name: busybox
20 | image: radial/busyboxplus:curl
21 | command:
22 | - sh
23 | - -c
24 | - while true; do if curl -s -o /dev/null -m 3 web-auth-server-svc; then echo "[SUCCESS]
25 | Successfully reached auth server!"; else echo "[FAIL] Failed to reach auth server!";
26 | fi; sleep 5; done
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/service/ClusterIP/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 
2 |
3 | ```
4 | apiVersion: apps/v1
5 | kind: Deployment
6 | metadata:
7 | name: nginx-deployment
8 | labels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | spec:
11 | replicas: 3
12 | selector:
13 | matchLabels:
14 | app: nginx
15 | template:
16 | metadata:
17 | labels:
18 | app: nginx
19 | spec:
20 | containers:
21 | - name: nginx
22 | image: nginx:latest
23 | ports:
24 | - containerPort: 80
25 | ---
26 | apiVersion: v1
27 | kind: Service
28 | metadata:
29 | name: myapp-clusterip-service
30 | spec:
31 | type: ClusterIP
32 | ports:
33 | - port: 80
34 | targetPort: 80
35 | selector:
36 | app: nginx
37 | ```
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/service/NodePort/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 
2 |
3 | ```
4 | apiVersion: apps/v1
5 | kind: Deployment
6 | metadata:
7 | name: nginx-deployment
8 | labels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | spec:
11 | replicas: 3
12 | selector:
13 | matchLabels:
14 | app: nginx
15 | template:
16 | metadata:
17 | labels:
18 | app: nginx
19 | spec:
20 | containers:
21 | - name: nginx
22 | image: nginx:latest
23 | ports:
24 | - containerPort: 80
25 | ---
26 | apiVersion: v1
27 | kind: Service
28 | metadata:
29 | name: myapp-service
30 | spec:
31 | type: NodePort
32 | ports:
33 | - targetPort: 80
34 | port: 80
35 | nodePort: 30008
36 | selector:
37 | app: nginx
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/statefulset/mysql-cluster-scenario/mysql-service.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Headless service for stable DNS entries of StatefulSet members.
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Service
4 | metadata:
5 | name: mysql
6 | labels:
7 | app: mysql
8 | app.kubernetes.io/name: mysql
9 | spec:
10 | ports:
11 | - name: mysql
12 | port: 3306
13 | clusterIP: None
14 | selector:
15 | app: mysql
16 | ---
17 | # Client service for connecting to any MySQL instance for reads.
18 | # For writes, you must instead connect to the primary: mysql-0.mysql.
19 | apiVersion: v1
20 | kind: Service
21 | metadata:
22 | name: mysql-read
23 | labels:
24 | app: mysql
25 | app.kubernetes.io/name: mysql
26 | readonly: "true"
27 | spec:
28 | ports:
29 | - name: mysql
30 | port: 3306
31 | selector:
32 | app: mysql
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/nfs/pod-using-nfs.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | kind: Pod
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | metadata:
4 | name: pod-using-nfs
5 | spec:
6 | # Add the server as an NFS volume for the pod
7 | volumes:
8 | - name: nfs-volume
9 | nfs:
10 | # URL for the NFS server
11 | server: 10.108.211.244 # Change this!
12 | path: /
13 |
14 | # In this container, we'll mount the NFS volume
15 | # and write the date to a file inside it.
16 | containers:
17 | - name: app
18 | image: alpine
19 |
20 | # Mount the NFS volume in the container
21 | volumeMounts:
22 | - name: nfs-volume
23 | mountPath: /var/nfs
24 |
25 | # Write to a file inside our NFS
26 | command: ["/bin/sh"]
27 | args: ["-c", "while true; do date >> /var/nfs/dates.txt; sleep 5; done"]
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/HPA/nginx-deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-deployment
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 1
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: nginx
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx:1.17.4
18 | ports:
19 | - containerPort: 80
20 | resources:
21 | requests:
22 | cpu: 50m
23 | limits:
24 | cpu: 100m
25 | ---
26 | apiVersion: v1
27 | kind: Service
28 | metadata:
29 | name: nginx-service
30 | labels:
31 | app: nginx
32 | spec:
33 | selector:
34 | app: nginx
35 | ports:
36 | - protocol: TCP
37 | port: 80
38 | targetPort: 80
39 |
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/deployment/nginx-svc-nodeport.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Service
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-svc # create a service with "nginx" name
5 | labels:
6 | app: webserver
7 | spec:
8 | type: NodePort
9 | selector:
10 | app.kubernetes.io/name: MyApp
11 | ports:
12 | - port: 80
13 | # By default and for convenience, the `targetPort` is set to
14 | # the same value as the `port` field.
15 | targetPort: 80
16 | # Optional field
17 | # By default and for convenience, the Kubernetes control plane
18 | # will allocate a port from a range (default: 30000-32767)
19 | nodePort: 30007
20 | selector: # headless service provides to reach pod with podName.serviceName
21 | app: webserver
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-canary.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-canary
5 | labels:
6 | app: nginx
7 | version: canary
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 1
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: nginx
13 | version: canary
14 | template:
15 | metadata:
16 | labels:
17 | app: nginx
18 | version: canary
19 | spec:
20 | containers:
21 | - name: nginx
22 | image: nginx:latest
23 | volumeMounts:
24 | - name: nginx-config-canary
25 | mountPath: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
26 | subPath: nginx.conf
27 | ports:
28 | - containerPort: 80
29 | volumes:
30 | - name: nginx-config-canary
31 | configMap:
32 | name: nginx-config-canary
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-stable.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-stable
5 | labels:
6 | app: nginx
7 | version: stable
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 3
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: nginx
13 | version: stable
14 | template:
15 | metadata:
16 | labels:
17 | app: nginx
18 | version: stable
19 | spec:
20 | containers:
21 | - name: nginx
22 | image: nginx:latest
23 | volumeMounts:
24 | - name: nginx-config-stable
25 | mountPath: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
26 | subPath: nginx.conf
27 | ports:
28 | - containerPort: 80
29 | volumes:
30 | - name: nginx-config-stable
31 | configMap:
32 | name: nginx-config-stable
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sidecar-container/side-car-tail-log.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | $ cat log-shipper-sidecar-deployment.yaml
2 | apiVersion: apps/v1
3 | kind: Deployment
4 | metadata:
5 | name: myapp
6 | labels:
7 | app: myapp
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 1
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: myapp
13 | template:
14 | metadata:
15 | labels:
16 | app: myapp
17 | spec:
18 | containers:
19 | - name: myapp
20 | image: alpine:latest
21 | command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo "logging" > /opt/logs.txt']
22 | volumeMounts:
23 | - name: data
24 | mountPath: /opt
25 | - name: logshipper
26 | image: alpine:latest
27 | command: ['sh', '-c', 'tail /opt/logs.txt']
28 | volumeMounts:
29 | - name: data
30 | mountPath: /opt
31 | volumes:
32 | - name: data
33 | emptyDir: {}
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # install ingress with Hostmode (listen on port 80 )
2 | for accessing on port 80 we need to change deployment to host mode network
3 | i Add this cahnge but for Your Information i just added below hostnetowrk in deploymnet section in manifest ingress-host-mode.yml
4 |
5 | ```
6 | template:
7 | spec:
8 | hostNetwork: true
9 |
10 | ```
11 |
12 | ```
13 | kubectl apply -f ingress-host-mode.yml
14 | kubectl delete -A ValidatingWebhookConfiguration ingress-nginx-admission
15 | ```
16 | # Scale up ingress controler to 3 (in our scenario we have 3 node)
17 | ```
18 | kubectl scale deployments ingress-nginx-controller -n ingress-nginx --replicas 3
19 |
20 | ```
21 |
22 | # apply simple app that listen on 5678 (apple.packops.local)
23 | kubectl -f simple-app-ingress.yml
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 | # Set host apple.packops.local tp kubernetes ip
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/secret/dockerhub-imagepull-secret/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 1- Create imagepullsecret
2 | Create username password based on your dockerhub user pass in this structure :
3 | ```
4 | kubectl create secret docker-registry my-registry-secret \
5 | --docker-server=https://index.docker.io/v1/ \
6 | --docker-username=mrnickfetrat@gmail.com \
7 | --docker-password=PASSS \
8 | --docker-email=mrnickfetrat@gmail.com
9 |
10 | ```
11 | ## 1-1 For cheking you secret
12 | ```
13 | kubectl get secrets my-registry-secret -o yaml
14 | ```
15 | ## 2- create your manifest based on private image that you have on dockerhub
16 | ```
17 | apiVersion: v1
18 | kind: Pod
19 | metadata:
20 | name: my-private-image-pod
21 | spec:
22 | containers:
23 | - name: my-container
24 | image: farshadnikfetrat/hello-nodejs:5918f3e7
25 | imagePullSecrets:
26 | - name: my-registry-secret
27 |
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/ipnetns-container/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | ip netns add packops1-ns
3 | ip netns exec packops1-ns python3 -m http.server 80
4 | ip netns exec packops1-ns ip a
5 |
6 | ip netns list
7 |
8 |
9 | ip netns add packops2-ns
10 | ip netns exec python3 -m http.server 80
11 | ip netns exec packops2-ns ip a
12 |
13 |
14 | sudo ip link add veth-packops1 type veth peer name veth-packops2
15 | sudo ip link set veth-packops1 netns packops1-ns
16 | sudo ip link set veth-packops2 netns packops2-ns
17 |
18 |
19 | sudo ip netns exec packops1-ns /bin/bash
20 | ip addr add 10.0.0.1/24 dev veth-packops1
21 | ip link set veth-packops1 up
22 |
23 |
24 | sudo ip netns exec packops2-ns /bin/bash
25 | ip addr add 10.0.0.2/24 dev veth-packops2
26 | ip link set veth-packops2 up
27 | ```
28 | 
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/apple-orange-ingress/pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | kind: Pod
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | metadata:
4 | name: apple-app
5 | labels:
6 | app: apple
7 | spec:
8 | containers:
9 | - name: apple-app
10 | image: hashicorp/http-echo
11 | args:
12 | - "-text=apple"
13 |
14 | ---
15 |
16 | kind: Service
17 | apiVersion: v1
18 | metadata:
19 | name: apple-service
20 | spec:
21 | selector:
22 | app: apple
23 | ports:
24 | - port: 5678 # Default port for image
25 |
26 | ---
27 | kind: Pod
28 | apiVersion: v1
29 | metadata:
30 | name: orange-app
31 | labels:
32 | app: orange
33 | spec:
34 | containers:
35 | - name: orange-app
36 | image: hashicorp/http-echo
37 | args:
38 | - "-text=orange"
39 |
40 | ---
41 |
42 | kind: Service
43 | apiVersion: v1
44 | metadata:
45 | name: orange-service
46 | spec:
47 | selector:
48 | app: orange
49 | ports:
50 | - port: 5678 # Default port for image
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CONTRIBUTING.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributing to Mastering Kubernetes
2 |
3 | Thank you for considering contributing to the **Mastering Kubernetes** project! We welcome contributions from everyone and appreciate your help in making this project better.
4 |
5 | ## How to Contribute
6 |
7 | Here are some ways you can contribute:
8 |
9 | ### 1. Reporting Issues
10 |
11 | If you encounter any problems or have suggestions for improvements, please open an issue in the [Issues](https://github.com/farshadnick/Mastering-Kubernetes/issues) section of this repository.
12 |
13 | ### 2. Contributing Code
14 |
15 | If you would like to contribute code, please follow these steps:
16 |
17 | 1. **Fork the Repository**
18 | - Click the "Fork" button at the top right of this page to create your own copy of the repository.
19 |
20 | 2. **Clone Your Fork**
21 | ```bash
22 | git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/Mastering-Kubernetes.git
23 | cd Mastering-Kubernetes
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sidecar-container/tail-log-with-initcontainer.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: myapp
5 | labels:
6 | app: myapp
7 | spec:
8 | replicas: 1
9 | selector:
10 | matchLabels:
11 | app: myapp
12 | template:
13 | metadata:
14 | labels:
15 | app: myapp
16 | spec:
17 | containers:
18 | - name: myapp
19 | image: alpine:latest
20 | command: ['sh', '-c', 'while true; do echo "logging" >> /opt/logs.txt; sleep 1; done']
21 | volumeMounts:
22 | - name: data
23 | mountPath: /opt
24 | initContainers:
25 | - name: logshipper
26 | image: alpine:latest
27 | restartPolicy: Always
28 | command: ['sh', '-c', 'tail -F /opt/logs.txt']
29 | volumeMounts:
30 | - name: data
31 | mountPath: /opt
32 | volumes:
33 | - name: data
34 | emptyDir: {}
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/logging/side-car/deployment-with-fluentd.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: counter
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: count
8 | image: busybox:1.28
9 | args:
10 | - /bin/sh
11 | - -c
12 | - >
13 | i=0;
14 | while true;
15 | do
16 | echo "$i: $(date)" >> /var/log/1.log;
17 | echo "$(date) INFO $i" >> /var/log/2.log;
18 | i=$((i+1));
19 | sleep 1;
20 | done
21 | volumeMounts:
22 | - name: varlog
23 | mountPath: /var/log
24 | - name: count-agent
25 | image: registry.k8s.io/fluentd-gcp:1.30
26 | env:
27 | - name: FLUENTD_ARGS
28 | value: -c /etc/fluentd-config/fluentd.conf
29 | volumeMounts:
30 | - name: varlog
31 | mountPath: /var/log
32 | - name: config-volume
33 | mountPath: /etc/fluentd-config
34 | volumes:
35 | - name: varlog
36 | emptyDir: {}
37 | - name: config-volume
38 | configMap:
39 | name: fluentd-config
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | in this Scenario we are going to Block all Trafic in
2 |
3 | # Default Network Policy to Block all incomming Trafic to namespace web-auth
4 | ```
5 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
6 | kind: NetworkPolicy
7 | metadata:
8 | name: default-deny-ingress
9 | namespace: web-auth
10 | spec:
11 | podSelector: {}
12 | policyTypes:
13 | - Ingress
14 | ```
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 | # Network Policy for Permiting Auth-Client to Auth-Server
21 |
22 | ```
23 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
24 | kind: NetworkPolicy
25 | metadata:
26 | name: auth-server-ingress
27 | namespace: web-auth
28 | spec:
29 | podSelector:
30 | matchLabels:
31 | app: auth-server
32 | policyTypes:
33 | - Ingress
34 | ingress:
35 | - from:
36 | - namespaceSelector:
37 | matchLabels:
38 | role: auth
39 | podSelector:
40 | matchLabels:
41 | app: auth-client
42 | ports:
43 | - protocol: TCP
44 | port: 80
45 |
46 |
47 | ```
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/installation/kubespray.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | #write your Kubernetes nodes ip :
3 | #192.168.7.192
4 | #192.168.7.193
5 | #192.168.7.197
6 | ```
7 | # Clone Kubespray
8 | ```
9 | mkdir kubernetes_installation/
10 | cd kubernetes_installation/
11 | git clone https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray.git
12 | cd kubespray/
13 | ```
14 | # install requirements for kubespray
15 | ```
16 | apt update && apt install python3-pip ansible
17 | pip install -r requirements.txt --break-system-packages
18 | pip3 install ruamel.yaml --break-system-packages
19 | # Run it on ALL Nodes
20 | apt install sshpass -y
21 | ```
22 | # Determine Your Kubernetes nodes IP
23 | ```
24 | cp -rfp inventory/sample inventory/mycluster
25 | declare -a IPS=(192.168.7.192 192.168.7.193 192.168.7.197)
26 | CONFIG_FILE=inventory/mycluster/hosts.yaml python3 contrib/inventory_builder/inventory.py ${IPS[@]}
27 | ```
28 | # You will be asked for ssh pass and sudo pass
29 | ```
30 | ansible-playbook -i inventory/mycluster/hosts.yaml --user geek --become -kK cluster.yml
31 | ```
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/initcontainer/Pod-address.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: web-server-pod
5 | spec:
6 | initContainers:
7 | - name: write-ip
8 | image: busybox
9 | command: ["sh", "-c", "echo $MY_POD_IP > /web-content/ip.txt; echo 'Wrote the Pod IP to ip.txt'"]
10 | env:
11 | - name: MY_POD_IP
12 | valueFrom:
13 | fieldRef:
14 | fieldPath: status.podIP
15 | volumeMounts:
16 | - name: web-content
17 | mountPath: /web-content
18 | - name: create-html
19 | image: busybox
20 | command: ["sh", "-c", "echo 'Hello, World! Your Pod IP is: ' > /web-content/index.html; cat /web-content/ip.txt >> /web-content/index.html; echo 'Created index.html with the Pod IP'"]
21 | volumeMounts:
22 | - name: web-content
23 | mountPath: /web-content
24 | containers:
25 | - name: web-container
26 | image: nginx
27 | volumeMounts:
28 | - name: web-content
29 | mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
30 | volumes:
31 | - name: web-content
32 | emptyDir: {}
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/pod-afinity/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Pod Affinity
2 |
3 | Pod Affinity allows you to schedule a pod close to other pods that match specific criteria, usually based on labels. This can be useful for workloads that need to be co-located for performance reasons.
4 | Types of Pod Affinity:
5 |
6 | RequiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: The pod must be scheduled on a node that has the specified other pods running.
7 |
8 | PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: The scheduler tries to place the pod on a node with the specified other pods, but it is not a strict requirement.
9 | ```
10 | apiVersion: v1
11 | kind: Pod
12 | metadata:
13 | name: example-pod
14 | spec:
15 | affinity:
16 | podAffinity:
17 | requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
18 | labelSelector:
19 | matchExpressions:
20 | - key: app
21 | operator: In
22 | values:
23 | - frontend
24 | topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
25 | containers:
26 | - name: nginx
27 | image: nginx
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/service/headless/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # What exactly is a headless service.
2 | It is used for discovering individual pods(especially IPs) which allows another service to interact directly with the Pods instead of a proxy. With NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName, and ClusterIP clients usually connect to the pods through a Service (Kubernetes Services simply visually explained) rather than connecting directly.
3 |
4 | # What does it accomplish?
5 | The requirement is not to make single IP like in the case of other service types. We need all the pod's IP sitting behind the service.
6 |
7 | # What are some legitimate use cases for it?
8 | Create Stateful service.
9 |
10 | Deploying RabbitMQ or Kafka (or any message broker service) to Kubernetes requires a stateful set for RabbitMQ cluster nodes.
11 |
12 | Deployment of Relational databases
13 |
14 |
15 | ```
16 | apiVersion: v1
17 | kind: Service
18 | metadata:
19 | name: headless-svc
20 | spec:
21 | clusterIP: None
22 | selector:
23 | app: nginx
24 | ports:
25 | - protocol: TCP
26 | port: 80
27 | targetPort: 8080
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/curl-kubernetes-object/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Step 1: Create a Service Account
2 | ```
3 | kubectl create serviceaccount my-service-account
4 | ```
5 | ## Step 2: Bind the Service Account to the Appropriate Role
6 | ```
7 | kubectl create rolebinding my-service-account-binding \
8 | --role=view \
9 | --serviceaccount=default:my-service-account \
10 | --namespace=default
11 | ```
12 | ```
13 | kubectl create clusterrolebinding my-service-account-binding \
14 | --clusterrole=view \
15 | --serviceaccount=default:my-service-account
16 | ```
17 | ## Step 3: Create a Token for the Service Account
18 | ```
19 | TOKEN=$(kubectl create token my-service-account)
20 | ```
21 | ## Step 4: Use the Token with curl to Access Kubernetes API
22 | ```
23 | #sample api server address https://127.0.0.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods
24 | curl -X GET "https:///api/v1/namespaces/default/pods" \
25 | -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
26 | -H "Accept: application/json" \
27 | --insecure
28 |
29 | ```
30 |
31 |
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/nfs/nfs-server.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apt update && apt install nfs-server
3 | mkdir /exports
4 | echo "/exports *(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)" > /etc/exports
5 | ```
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PolicyManagement/Kyverno/Pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pod
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: nginx
8 | image: nginx
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/creating-new-clusteadmin/01-serviceacount.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ServiceAccount
3 | metadata:
4 | name: devops-cluster-admin
5 | namespace: kube-system
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/apple-orange-ingress/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | curl -H 'Host:packops.local' http://192.168.6.130/apple
3 | ```
4 |
5 | 
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/resizeable-pv/storage-class.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: storage.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: StorageClass
3 | metadata:
4 | name: localdisk
5 | provisioner: kubernetes.io/no-provisioner
6 | allowVolumeExpansion: true
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Limit-Range/test-pod.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pod
5 | namespace: dev-namespace
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: test-container
9 | image: nginx
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/secret/using-env-from-secret/secret.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Secret
3 | metadata:
4 | name: backend-user
5 | type: Opaque
6 | data:
7 | backend-username: YmFja2VuZC1hZG1pbg== # base64-encoded value of 'backend-admin'
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/configmap-to-env/configmap.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ConfigMap
3 | metadata:
4 | name: simple-config
5 | data:
6 | database_url: "mongodb://db1.packops.dev:27017"
7 | feature_flag: "true"
8 | log_level: "debug"
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/installation/helm-install.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/bash
2 | VERSION=3.9.0
3 | wget https://get.helm.sh/helm-v$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz
4 | tar -xzf helm-v$VERSION-linux-amd64.tar.gz
5 | cp ./linux-amd64/helm /usr/local/bin/ && rm -rf ./linux-amd64
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Limit/Pod-Limit/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | kubectl describe pod nginx-deployment-8c6b98574-27csj -n farshad
4 |
5 |
6 | 
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/default-deny-np.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: NetworkPolicy
3 | metadata:
4 | name: default-deny-ingress
5 | namespace: web-auth
6 | spec:
7 | podSelector: {}
8 | policyTypes:
9 | - Ingress
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sidecar-container/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | in scenario that we want an order for sidecars container or we want order between main container and sidecar we could use sidecar container in initcontainer (main will start after that sequential sidecar will start)
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/excercise/1-Basic-kubectl/nginx-pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # pod.yaml
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | name: my-pod
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: my-container
9 | image: nginx
10 | ports:
11 | - containerPort: 80
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-service.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Service
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-service
5 | spec:
6 | selector:
7 | app: nginx
8 | ports:
9 | - protocol: TCP
10 | port: 80
11 | targetPort: 80
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/pod-get-resource/role.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: Role
3 | metadata:
4 | namespace: default
5 | name: pod-reader
6 | rules:
7 | - apiGroups: [""]
8 | resources: ["pods"]
9 | verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"]
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/resizeable-pv/pvc.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pvc
5 | spec:
6 | storageClassName: localdisk
7 | accessModes:
8 | - ReadWriteOnce
9 | resources:
10 | requests:
11 | storage: 100Mi
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath - nginx/pvc.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
3 | metadata:
4 | name: local-pvc
5 | spec:
6 | accessModes:
7 | - ReadWriteOnce
8 | storageClassName: local-storage
9 | resources:
10 | requests:
11 | storage: 5Gi
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/resizeable-pv/pv.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | kind: PersistentVolume
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pv
5 | spec:
6 | storageClassName: localdisk
7 | capacity:
8 | storage: 1Gi
9 | accessModes:
10 | - ReadWriteOnce
11 | hostPath:
12 | path: /etc/output
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/persistentVolumeClaim.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | metadata:
4 | name: my-claim
5 | spec:
6 | accessModes:
7 | - ReadWriteOnce
8 | storageClassName: my-local-storage
9 | resources:
10 | requests:
11 | storage: 5Gi
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/redis-example/redis-pvc.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
3 | metadata:
4 | name: redisdb-pvc
5 | spec:
6 | storageClassName: "pv-local"
7 | accessModes:
8 | - ReadWriteOnce
9 | resources:
10 | requests:
11 | storage: 1Gi
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Limit/Namespace-limit/resource-quota.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ResourceQuota
3 | metadata:
4 | name: mem-cpu-demo
5 | namespace: farshad
6 |
7 | spec:
8 | hard:
9 | requests.cpu: 2
10 | requests.memory: 1Gi
11 | limits.cpu: 3
12 | limits.memory: 2Gi
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/creating-new-clusteadmin/02-secret.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Secret
3 | metadata:
4 | name: devops-cluster-admin-secret
5 | namespace: kube-system
6 | annotations:
7 | kubernetes.io/service-account.name: devops-cluster-admin
8 | type: kubernetes.io/service-account-token
9 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/redis-example/redis-pv.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolume
3 | metadata:
4 | name: redis-pv
5 | spec:
6 | storageClassName: "pv-local"
7 | capacity:
8 | storage: 1Gi
9 | accessModes:
10 | - ReadWriteOnce
11 | hostPath:
12 | path: "/mnt/data"
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Resource-Quota/resource-quota.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ResourceQuota
3 | metadata:
4 | name: resource-quota
5 | namespace: prod-namespace
6 | spec:
7 | hard:
8 | requests.cpu: "10"
9 | requests.memory: "20Gi"
10 | limits.cpu: "15"
11 | limits.memory: "30Gi"
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/nodeName/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | #nodename-pod.yml
3 | apiVersion: v1
4 | kind: Pod
5 | metadata:
6 | name: nginx
7 | labels:
8 | name: nginx
9 | spec:
10 | containers:
11 | - name: nginx
12 | image: nginx
13 | ports:
14 | - containerPort: 8080
15 | nodeName: node1
16 |
17 | ```
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/pod-get-resource/pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: pod-checker
5 | namespace: default
6 | spec:
7 | serviceAccountName: pod-reader-sa
8 | containers:
9 | - name: kubectl-container
10 | image: bitnami/kubectl:latest
11 | command: ["sleep", "3600"]
12 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/emty-dir-accessing-2pod-same-volume/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | kubectl apply -f ngnix-shared-volume.yml
3 | kubectl exec -it two-containers -c nginx-container -- /bin/bash
4 | curl localhost
5 | ```
6 | 
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Resource-Quota/quota-test-pod.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: quota-test-pod
5 | namespace: prod-namespace
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: test-container
9 | image: nginx
10 | resources:
11 | requests:
12 | cpu: "1"
13 | memory: "512Mi"
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/metalLB/nginx-service.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Service
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx
5 | spec:
6 | selector:
7 | app: nginx
8 | ports:
9 | - protocol: TCP
10 | port: 80
11 | targetPort: 80
12 | type: LoadBalancer
13 | loadBalancerIP: 192.168.6.210 # Assigning a specific IP from MetalLB's range
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/Configmap-as-volume-redis/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | kubectl apply -f redis-manifest-with-cm.yml
3 | kubectl get cm shared-packops-redis-config -o yaml
4 | kubectl get pods
5 | kubectl exec -it shared-packops-redis-7cddbbf994-k5szl -- bash
6 | redis-cli
7 | ```
8 | ```
9 | cat /redis-master/redis.conf
10 | auth PASSWORD1234P
11 | get keys
12 | ```
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/pod-get-resource/rolebinding.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: RoleBinding
3 | metadata:
4 | name: read-pods
5 | namespace: default
6 | subjects:
7 | - kind: ServiceAccount
8 | name: pod-reader-sa
9 | namespace: default
10 | roleRef:
11 | kind: Role
12 | name: pod-reader
13 | apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/audit-log/audit-policy.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #/etc/kubernetes/audit-policy.yaml
2 |
3 | apiVersion: audit.k8s.io/v1
4 | kind: Policy
5 | rules:
6 | - level: Metadata
7 | verbs: ["create", "update", "patch", "delete"]
8 | resources:
9 | - group: ""
10 | resources: ["pods", "services", "configmaps"]
11 | - group: "apps"
12 | resources: ["deployments", "statefulsets"]
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/secret/using-env-from-secret/nginx-secret-env.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: env-single-secret
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: envars-test-container
8 | image: nginx
9 | env:
10 | - name: SECRET_USERNAME
11 | valueFrom:
12 | secretKeyRef:
13 | name: backend-user
14 | key: backend-username
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Limit-Range/test-pod-exceed.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: test-pod-exceed
5 | namespace: dev-namespace
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: test-container
9 | image: nginx
10 | resources:
11 | requests:
12 | cpu: "3" # Exceeds the max limit of 2 CPU
13 | memory: "2Gi" # Exceeds the max limit of 1Gi memory
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/metalLB/nginx-deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 2
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: nginx
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx
18 | ports:
19 | - containerPort: 80
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/creating-new-clusteadmin/04-ClusterRolebinding.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: ClusterRoleBinding
3 | metadata:
4 | name: devops-cluster-admin
5 | roleRef:
6 | apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
7 | kind: ClusterRole
8 | name: devops-cluster-admin
9 | subjects:
10 | - kind: ServiceAccount
11 | name: devops-cluster-admin
12 | namespace: kube-system
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/job/paralel-job/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | You can also run a job with parallelism. There are two fields in the spec, called completions and parallelism. completions is set to 1 by default. If you want more than one successful completion, then increase this value. parallelism determines how many pods to launch. A job will not launch more pods than needed for successful completion, even if the parallelism value is greater.
2 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/statefulset/mysql-cluster-scenario/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/run-application/run-replicated-stateful-application/
3 |
4 |
5 | ```
6 | kubectl run mysql-client --image=mysql:5.7 -i --rm --restart=Never --\
7 | mysql -h mysql-0.mysql <> /output/output.log; sleep 10; done']
10 | volumeMounts:
11 | - name: pv-storage
12 | mountPath: /output
13 | volumes:
14 | - name: pv-storage
15 | persistentVolumeClaim:
16 | claimName: test-pvc
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/kwatch/nginx-corrupted.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-failing-deployment
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 1
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: nginx-failing
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: nginx-failing
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx
18 |
19 | command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
20 | args:
21 | - "sleep 60; exit 1"
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/node-affinity/node-affinity.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx
5 | spec:
6 | affinity:
7 | nodeAffinity:
8 | requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
9 | nodeSelectorTerms:
10 | - matchExpressions:
11 | - key: nodename
12 | operator: In
13 | values:
14 | - bi-team
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx
18 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/node-affinity/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Lable a Kubernetes Node
2 | 1- kubectl get nodes
3 |
4 | ```
5 | worker0 Ready 1d v1.13.0 ...,kubernetes.io/hostname=worker0
6 | worker1 Ready 1d v1.13.0 ...,kubernetes.io/hostname=worker1
7 | worker2 Ready 1d v1.13.0 ...,kubernetes.io/hostname=worker2
8 | ```
9 |
10 | 2- kubectl label nodes nodename=bi-team
11 |
12 | 3- kubectl apply -f node-affinity.yml
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/VPA/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 | ## install vpa
4 | ```
5 | kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/vpa-release-1.0/vertical-pod-autoscaler/deploy/vpa-v1-crd-gen.yaml
6 | kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/kubernetes/autoscaler/vpa-release-1.0/vertical-pod-autoscaler/deploy/vpa-rbac.yaml
7 | ```
8 | ```
9 | kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
10 | kubectl apply -f nginx-vpa.yaml
11 |
12 | kubectl describe vpa nginx-vpa
13 |
14 | ```
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/http-pod.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: www
5 | labels:
6 | name: www
7 | spec:
8 | containers:
9 | - name: www
10 | image: nginx:alpine
11 | ports:
12 | - containerPort: 80
13 | name: www
14 | volumeMounts:
15 | - name: www-persistent-storage
16 | mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
17 | volumes:
18 | - name: www-persistent-storage
19 | persistentVolumeClaim:
20 | claimName: my-claim
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/node-selector/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1. Label your node
2 | First, you label the node where you want the pod to be scheduled.
3 | ```
4 | kubectl label nodes disktype=ssd
5 | ```
6 | 2. Pod Specification with Node Selector
7 | Next, you define a pod that will use this node selector:
8 | ```
9 | apiVersion: v1
10 | kind: Pod
11 | metadata:
12 | name: selector
13 | spec:
14 | containers:
15 | - name: my-container
16 | image: nginx
17 | nodeSelector:
18 | disktype: ssd
19 |
20 |
21 | ```
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/configmap-to-env/pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: app-pod
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: app-container
8 | image: nginx
9 | env:
10 | - name: DATABASE_URL
11 | valueFrom:
12 | configMapKeyRef:
13 | name: simple-config
14 | key: database_url
15 | - name: LOG_LEVEL
16 | valueFrom:
17 | configMapKeyRef:
18 | name: simple-config
19 | key: log_level
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-configmap-canary.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ConfigMap
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-config-canary
5 | data:
6 | nginx.conf: |
7 | worker_processes 1;
8 |
9 | events {
10 | worker_connections 1024;
11 | }
12 |
13 | http {
14 | server {
15 | listen 80;
16 | location / {
17 | add_header Content-Type text/plain;
18 | return 200 "Release: Canary";
19 | }
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/auth-server-np.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: NetworkPolicy
3 | metadata:
4 | name: auth-server-ingress
5 | namespace: web-auth
6 | spec:
7 | podSelector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: auth-server
10 | policyTypes:
11 | - Ingress
12 | ingress:
13 | - from:
14 | - namespaceSelector:
15 | matchLabels:
16 | role: auth
17 | podSelector:
18 | matchLabels:
19 | app: auth-client
20 | ports:
21 | - protocol: TCP
22 | port: 80
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Resource-Quota/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | You want to manage resource usage in the prod-namespace by setting both requests and limits. Specifically, you will:
2 |
3 | Limit the total CPU requests in the namespace to 10 CPUs.
4 | Limit the total memory requests in the namespace to 20Gi.
5 | Cap the total CPU limits in the namespace to 15 CPUs.
6 | Cap the total memory limits in the namespace to 30Gi.
7 |
8 | ```
9 | kubectl get resourcequota resource-quota --namespace=prod-namespace --output=yaml
10 | ```
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-configmap-stable.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ConfigMap
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-config-stable
5 | data:
6 | nginx.conf: |
7 | worker_processes 1;
8 |
9 | events {
10 | worker_connections 1024;
11 | }
12 |
13 | http {
14 | server {
15 | listen 80;
16 | location / {
17 | add_header Content-Type text/plain;
18 | return 200 "Release: Stable";
19 | }
20 | }
21 | }
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Monitoring/Prometheus/scrape-config/scrape.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1alpha1
2 | kind: ScrapeConfig
3 | metadata:
4 | name: static-targets
5 | namespace: monitoring
6 | labels:
7 | release: kube-prom-stack # must match your Prometheus release label
8 | spec:
9 | staticConfigs:
10 | - targets:
11 | - "10.0.0.5:9100"
12 | - "10.0.0.6:9100"
13 | labels:
14 | job: "node-exporter-external"
15 | environment: "prod"
16 | metricsPath: /metrics
17 | scrapeInterval: 30s
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/HPA/hpa.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #kubectl autoscale deployment nginx-deployment --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
2 | apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
3 | kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
4 | metadata:
5 | name: nginx-hpa
6 | spec:
7 | scaleTargetRef:
8 | apiVersion: apps/v1
9 | kind: Deployment
10 | name: nginx-deployment
11 | minReplicas: 1
12 | maxReplicas: 10
13 | metrics:
14 | - type: Resource
15 | resource:
16 | name: cpu
17 | target:
18 | type: Utilization
19 | averageUtilization: 50
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/VPA/vpa.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: autoscaling.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: VerticalPodAutoscaler
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-vpa
5 | spec:
6 | targetRef:
7 | apiVersion: "apps/v1"
8 | kind: Deployment
9 | name: nginx-deployment
10 | updatePolicy:
11 | updateMode: "Auto"
12 | resourcePolicy:
13 | containerPolicies:
14 | - containerName: "nginx"
15 | minAllowed:
16 | cpu: "50m"
17 | memory: "64Mi"
18 | maxAllowed:
19 | cpu: "500m"
20 | memory: "512Mi"
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/drain/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Cordoning the Node: Prevents new pods from being scheduled on the node.
2 | ```
3 | kubectl cordon
4 | ```
5 | Draining the Node: Evicts all the pods while respecting the configurations.
6 |
7 | ```
8 | kubectl drain --ignore-daemonsets --delete-emptydir-data
9 | ```
10 | Perform Maintenance: After draining, perform any maintenance needed on the node.
11 |
12 | Uncordon the Node (if needed): Allow new pods to be scheduled again.
13 |
14 | ```
15 | kubectl uncordon
16 | ```
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/liveness-exec/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | labels:
6 | test: liveness
7 | name: liveness-exec
8 | spec:
9 | containers:
10 | - name: liveness
11 | image: registry.k8s.io/busybox
12 | args:
13 | - /bin/sh
14 | - -c
15 | - touch /tmp/healthy; sleep 30; rm -f /tmp/healthy; sleep 600
16 | livenessProbe:
17 | exec:
18 | command:
19 | - cat
20 | - /tmp/healthy
21 | initialDelaySeconds: 5
22 | periodSeconds: 5
23 | ```
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/readiness-exec/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 |
3 | apiVersion: v1
4 | kind: Pod
5 | metadata:
6 | labels:
7 | test: liveness
8 | name: liveness-exec
9 | spec:
10 | containers:
11 | - name: liveness
12 | image: registry.k8s.io/busybox
13 | args:
14 | - /bin/sh
15 | - -c
16 | - touch /tmp/healthy; sleep 30; rm -f /tmp/healthy; sleep 600
17 | readinessProbe:
18 | exec:
19 | command:
20 | - cat
21 | - /tmp/healthy
22 | initialDelaySeconds: 5
23 | periodSeconds: 5
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/kwatch/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 1- Configmap
2 |
3 | ```
4 | #config.yml
5 | apiVersion: v1
6 | kind: Namespace
7 | metadata:
8 | name: kwatch
9 | ---
10 | apiVersion: v1
11 | kind: ConfigMap
12 | metadata:
13 | name: kwatch
14 | namespace: kwatch
15 | data:
16 | config.yaml: |
17 | alert:
18 | telegram:
19 | token: TOKEN
20 | chatId: CHAT_ID
21 | ```
22 | ```
23 | kubectl apply -f config.yml
24 | ```
25 | 2- Deploy Kwatch
26 | ```
27 | kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/abahmed/kwatch/v0.8.4/deploy/deploy.yaml
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/pod-afinity/hpa.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | #kubectl autoscale deployment nginx-deployment --cpu-percent=50 --min=1 --max=10
3 | apiVersion: autoscaling/v2
4 | kind: HorizontalPodAutoscaler
5 | metadata:
6 | name: nginx-hpa
7 | spec:
8 | scaleTargetRef:
9 | apiVersion: apps/v1
10 | kind: Deployment
11 | name: nginx-deployment
12 | minReplicas: 1
13 | maxReplicas: 10
14 | metrics:
15 | - type: Resource
16 | resource:
17 | name: cpu
18 | target:
19 | type: Utilization
20 | averageUtilization: 50
21 |
22 | ```
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/liveness-http/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | labels:
6 | test: liveness
7 | name: liveness-http
8 | spec:
9 | containers:
10 | - name: liveness
11 | image: registry.k8s.io/e2e-test-images/agnhost:2.40
12 | args:
13 | - liveness
14 | livenessProbe:
15 | httpGet:
16 | path: /healthz
17 | port: 8080
18 | httpHeaders:
19 | - name: Custom-Header
20 | value: Awesome
21 | initialDelaySeconds: 3
22 | periodSeconds: 3
23 |
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/liveness-grpc/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | name: etcd-with-grpc
6 | spec:
7 | containers:
8 | - name: etcd
9 | image: registry.k8s.io/etcd:3.5.1-0
10 | command: [ "/usr/local/bin/etcd", "--data-dir", "/var/lib/etcd", "--listen-client-urls", "http://0.0.0.0:2379", "--advertise-client-urls", "http://127.0.0.1:2379", "--log-level", "debug"]
11 | ports:
12 | - containerPort: 2379
13 | livenessProbe:
14 | grpc:
15 | port: 2379
16 | initialDelaySeconds: 10
17 |
18 | ```
19 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/liveness-tcp/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Pod
4 | metadata:
5 | name: goproxy
6 | labels:
7 | app: goproxy
8 | spec:
9 | containers:
10 | - name: goproxy
11 | image: registry.k8s.io/goproxy:0.1
12 | ports:
13 | - containerPort: 8080
14 | readinessProbe:
15 | tcpSocket:
16 | port: 8080
17 | initialDelaySeconds: 15
18 | periodSeconds: 10
19 | livenessProbe:
20 | tcpSocket:
21 | port: 8080
22 | initialDelaySeconds: 15
23 | periodSeconds: 10
24 |
25 | ```
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath - nginx/pv.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolume
3 | metadata:
4 | name: local-pv
5 | spec:
6 | capacity:
7 | storage: 10Gi
8 | accessModes:
9 | - ReadWriteOnce
10 | persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
11 | storageClassName: local-storage
12 | local:
13 | path: /mnt/disks/vol1
14 | nodeAffinity:
15 | required:
16 | nodeSelectorTerms:
17 | - matchExpressions:
18 | - key: kubernetes.io/hostname
19 | operator: In
20 | values:
21 | - node1
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Service-Mesh/isitio/kiali-dashboard/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Install kiali plugin
2 | ```
3 | git clone https://github.com/istio/istio.git
4 | kubectl apply -f istio/samples/addons
5 | ```
6 |
7 | # make nodeport service for kiali
8 |
9 | ```
10 | apiVersion: v1
11 | kind: Service
12 | metadata:
13 | name: kiali-nodeport
14 | namespace: istio-system
15 | spec:
16 | type: NodePort
17 | ports:
18 | - port: 20001
19 | targetPort: 20001
20 | nodePort: 30001
21 | selector:
22 | app.kubernetes.io/instance: kiali
23 | app.kubernetes.io/name: kiali
24 | ```
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/logging/side-car/fluent-configmap.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: ConfigMap
3 | metadata:
4 | name: fluentd-config
5 | data:
6 | fluentd.conf: |
7 |
8 | type tail
9 | format none
10 | path /var/log/1.log
11 | pos_file /var/log/1.log.pos
12 | tag count.format1
13 |
14 |
15 |
16 | type tail
17 | format none
18 | path /var/log/2.log
19 | pos_file /var/log/2.log.pos
20 | tag count.format2
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 | type google_cloud
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/statefulset/nginx-scenario/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Create Persistent Volume (if you dont have )
3 | create pv and make it default pv in our scenario Our storage is Localpath
4 | ```
5 | kubectl apply pv.yml
6 | ```
7 | ## Make it Default pv
8 | ```
9 | kubectl patch storageclass my-local-storage -p '{"metadata": {"annotations":{"storageclass.kubernetes.io/is-default-class":"true"}}}'
10 | ```
11 |
12 | # bring up your statefulset
13 | ```
14 | kubectl apply -f statefulset.yml
15 | ```
16 |
17 | # verify your PV and PVC
18 |
19 | ```
20 | kubectl get pv
21 | kubectl get pvc
22 | ```
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/statefulset/nginx-scenario/pv.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolume
3 | metadata:
4 | name: my-local-pv
5 | spec:
6 | capacity:
7 | storage: 500Gi
8 | accessModes:
9 | - ReadWriteOnce
10 | persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
11 | storageClassName: my-local-storage
12 | local:
13 | path: /opt/st
14 | nodeAffinity:
15 | required:
16 | nodeSelectorTerms:
17 | - matchExpressions:
18 | - key: kubernetes.io/hostname
19 | operator: In
20 | values:
21 | - node1
22 | - node2
23 | - node3
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/persistentVolume.yaml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolume
3 | metadata:
4 | name: my-local-pv
5 | spec:
6 | capacity:
7 | storage: 500Gi
8 | accessModes:
9 | - ReadWriteOnce
10 | persistentVolumeReclaimPolicy: Retain
11 | storageClassName: my-local-storage
12 | local:
13 | path: /opt/st
14 | nodeAffinity:
15 | required:
16 | nodeSelectorTerms:
17 | - matchExpressions:
18 | - key: kubernetes.io/hostname
19 | operator: In
20 | values:
21 | - node1
22 | - node2
23 | - node3
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Monitoring/Prometheus/prometheus-rules/pod-down.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
2 | kind: PrometheusRule
3 | metadata:
4 | labels:
5 | prometheus: kube-prometheus-stack-prometheus
6 | role: alert-rules
7 | name: your-application-name
8 | spec:
9 | groups:
10 | - name: "your-application-name.rules"
11 | rules:
12 | - alert: PodDown
13 | for: 1m
14 | expr: sum(up{job="your-service-monitor-name"}) < 1 or absent(up{job="your-service-monitor-name"})
15 | annotations:
16 | message: The deployment has less than 1 pod running.
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 
3 |
4 | kubectl apply -f nginx-canary.yml
5 | kubectl apply -f nginx-stable.yml
6 | kubectl apply -f nginx-service.yml
7 | kubectl apply -f nginx-configmap-canary.yml
8 | kubectl apply -f nginx-configmap-stable.yml
9 |
10 |
11 | ```
12 | kubectl get svc
13 | ```
14 |
15 | ```
16 | for i in {1..30}; do curl -s http://10.233.57.87 && echo ""; sleep 1; done
17 | ```
18 |
19 | 
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/job/uuidgen.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: batch/v1
2 | kind: Job
3 | metadata:
4 | name: uuidgen
5 | spec:
6 | template:
7 | metadata:
8 | spec:
9 | containers:
10 | - name: ubuntu
11 | image: ubuntu:latest
12 | imagePullPolicy: Always
13 | command: ["bash"]
14 | args:
15 | - -c
16 | - |
17 | apt update
18 | apt install uuid-runtime
19 | for i in {1..10}; do echo `uuidgen`@mailinator.com; done > /tmp/emails.txt
20 | cat /tmp/emails.txt
21 | sleep 60
22 | restartPolicy: OnFailure
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/deployment/nginx-deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-depoyment
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 3
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: webserver
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: webserver
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx:latest
18 | ports:
19 | - containerPort: 80
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/VPA/nginx-deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-deployment
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 1
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: nginx
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx:1.14.2
18 | ports:
19 | - containerPort: 80
20 | resources:
21 | requests:
22 | cpu: "100m"
23 | memory: "128Mi"
24 | limits:
25 | cpu: "200m"
26 | memory: "256Mi"
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/apple-orange-ingress/ingress.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
2 | kind: Ingress
3 | metadata:
4 | name: ingress-packops-local
5 | spec:
6 | ingressClassName: nginx
7 | rules:
8 | - host: packops.local
9 | http:
10 | paths:
11 | - path: /apple
12 | pathType: Prefix
13 | backend:
14 | service:
15 | name: apple-service
16 | port:
17 | number: 5678
18 | - path: /orange
19 | pathType: Prefix
20 | backend:
21 | service:
22 | name: orange-service
23 | port:
24 | number: 5678
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/keda/time-based-scale/prometheus/scale-object.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
2 | kind: ScaledObject
3 | metadata:
4 | name: packops-scaler
5 | namespace: default
6 | spec:
7 | scaleTargetRef:
8 | kind: Deployment
9 | name: nginx-deployment
10 | # minReplicaCount: 2
11 | maxReplicaCount: 10
12 | cooldownPeriod: 10
13 | pollingInterval: 10
14 | triggers:
15 | - type: prometheus
16 | metadata:
17 | serverAddress: http://kube-prom-stack-kube-prome-prometheus.monitoring.svc.cluster.local:9090
18 | metricName: custom_metric
19 | query: "custom_metric"
20 | threshold: "1"
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/daemonset/nginx.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: DaemonSet
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-da
5 | namespace: devops
6 | labels:
7 | app: nginx-da
8 | spec:
9 | selector:
10 | matchLabels:
11 | app: nginx-da
12 | template:
13 | metadata:
14 | labels:
15 | app: nginx-da
16 | spec:
17 | containers:
18 | - name: nginx-da
19 | image: nginx:alpine
20 | volumeMounts:
21 | - name: localtime
22 | mountPath: /etc/localtime
23 | volumes:
24 | - name: localtime
25 | hostPath:
26 | path: /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Tehran
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/cronjob/wget-15min.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: batch/v1
2 | kind: CronJob
3 | metadata:
4 | namespace: devops
5 | name: packops-cronjob
6 | spec:
7 | schedule: "*/15 * * * *"
8 | jobTemplate:
9 | spec:
10 | template:
11 | spec:
12 | containers:
13 | - name: reference
14 | image: busybox
15 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
16 | command:
17 | - /bin/sh
18 | - -c
19 | - date; echo "This pod Schedule every 15 min"
20 | - wget -q -O - https://packops.ir/wp-cron.php?doing_wp_cron >/dev/null 2>&1
21 | restartPolicy: OnFailure
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/emty-dir-accessing-2pod-same-volume/ngnix-shared-volume.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: two-containers
5 | spec:
6 |
7 | restartPolicy: Never
8 |
9 | volumes:
10 | - name: shared-data
11 | emptyDir: {}
12 |
13 | containers:
14 |
15 | - name: nginx-container
16 | image: nginx
17 | volumeMounts:
18 | - name: shared-data
19 | mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
20 |
21 | - name: debian-container
22 | image: alpine
23 | volumeMounts:
24 | - name: shared-data
25 | mountPath: /pod-data
26 | command: ["/bin/sh"]
27 | args: ["-c", "echo Hello from the debian container > /pod-data/index.html"]
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rolebinding/Create.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | kubectl create rolebinding farshad-admin --clusterrole=admin --user=farshad
3 | ```
4 |
5 | ```
6 | kubectl get RoleBinding -o yaml
7 | ```
8 |
9 | # output would be something like this
10 | ```
11 | apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
12 | kind: RoleBinding
13 | metadata:
14 | creationTimestamp: "2023-01-15T14:54:47Z"
15 | name: farshad-admin
16 | namespace: default
17 | resourceVersion: "22145"
18 | uid: 6bf97d50-fa9f-4437-b2d0-e1aa1dbe22ae
19 | roleRef:
20 | apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
21 | kind: ClusterRole
22 | name: admin
23 | subjects:
24 | - apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
25 | kind: User
26 | name: farshad
27 |
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/service/LoadBalancer/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Service
4 | metadata:
5 | name: myapp-loadbalancer-service
6 | spec:
7 | type: LoadBalancer
8 | ports:
9 | - port: 80
10 | targetPort: 80
11 | selector:
12 | app: nginx
13 | ---
14 | apiVersion: apps/v1
15 | kind: Deployment
16 | metadata:
17 | name: nginx-deployment
18 | labels:
19 | app: nginx
20 | spec:
21 | replicas: 3
22 | selector:
23 | matchLabels:
24 | app: nginx
25 | template:
26 | metadata:
27 | labels:
28 | app: nginx
29 | spec:
30 | containers:
31 | - name: nginx
32 | image: nginx:latest
33 | ports:
34 | - containerPort: 80
35 | ---
36 |
37 | ```
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/webauth-server.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: web-auth-server
5 | labels:
6 | app: auth-server
7 | namespace: web-auth
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 1
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: auth-server
13 | template:
14 | metadata:
15 | labels:
16 | app: auth-server
17 | spec:
18 | containers:
19 | - name: nginx
20 | image: nginx:1.14.2
21 |
22 | ---
23 |
24 | apiVersion: v1
25 | kind: Service
26 | metadata:
27 | name: web-auth-server-svc
28 | namespace: web-auth
29 | spec:
30 | ports:
31 | - port: 80
32 | protocol: TCP
33 | targetPort: 80
34 | selector:
35 | app: auth-server
36 | type: ClusterIP
37 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/secret/using-env-from-secret/readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | Creat a secret name backend-user with key backend-username and value backend-admin
2 | this way
3 | ```
4 | kubectl create secret generic backend-user --from-literal=backend-username='backend-admin'
5 | ```
6 | OR Create it as a manifest
7 | ```
8 | apiVersion: v1
9 | kind: Secret
10 | metadata:
11 | name: backend-user
12 | type: Opaque
13 | data:
14 | backend-username: YmFja2VuZC1hZG1pbg== # base64-encoded value of 'backend-admin'
15 | ```
16 | and apply nginx
17 | ```
18 | kubectl apply nginx-secret-env.yml
19 | ```
20 | Check the env it should have show backend-admin
21 | ```
22 | kubectl exec -i -t env-single-secret -- /bin/sh -c 'echo $SECRET_USERNAME'
23 | ```
24 | ![Uploading image.png…]()
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/web-auth-client.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | labels:
5 | app: auth-client
6 | name: auth-client
7 | namespace: web-auth
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 1
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: auth-client
13 | template:
14 | metadata:
15 | labels:
16 | app: auth-client
17 | spec:
18 | containers:
19 | - name: busybox
20 | image: radial/busyboxplus:curl
21 | command:
22 | - sh
23 | - -c
24 | - while true; do if curl -s -o /dev/null -m 3 web-auth-server-svc; then echo "[SUCCESS]
25 | Successfully reached auth server!"; else echo "[FAIL] Failed to reach auth server!";
26 | fi; sleep 5; done
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/service/ClusterIP/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 
2 |
3 | ```
4 | apiVersion: apps/v1
5 | kind: Deployment
6 | metadata:
7 | name: nginx-deployment
8 | labels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | spec:
11 | replicas: 3
12 | selector:
13 | matchLabels:
14 | app: nginx
15 | template:
16 | metadata:
17 | labels:
18 | app: nginx
19 | spec:
20 | containers:
21 | - name: nginx
22 | image: nginx:latest
23 | ports:
24 | - containerPort: 80
25 | ---
26 | apiVersion: v1
27 | kind: Service
28 | metadata:
29 | name: myapp-clusterip-service
30 | spec:
31 | type: ClusterIP
32 | ports:
33 | - port: 80
34 | targetPort: 80
35 | selector:
36 | app: nginx
37 | ```
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/service/NodePort/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 
2 |
3 | ```
4 | apiVersion: apps/v1
5 | kind: Deployment
6 | metadata:
7 | name: nginx-deployment
8 | labels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | spec:
11 | replicas: 3
12 | selector:
13 | matchLabels:
14 | app: nginx
15 | template:
16 | metadata:
17 | labels:
18 | app: nginx
19 | spec:
20 | containers:
21 | - name: nginx
22 | image: nginx:latest
23 | ports:
24 | - containerPort: 80
25 | ---
26 | apiVersion: v1
27 | kind: Service
28 | metadata:
29 | name: myapp-service
30 | spec:
31 | type: NodePort
32 | ports:
33 | - targetPort: 80
34 | port: 80
35 | nodePort: 30008
36 | selector:
37 | app: nginx
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/statefulset/mysql-cluster-scenario/mysql-service.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Headless service for stable DNS entries of StatefulSet members.
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Service
4 | metadata:
5 | name: mysql
6 | labels:
7 | app: mysql
8 | app.kubernetes.io/name: mysql
9 | spec:
10 | ports:
11 | - name: mysql
12 | port: 3306
13 | clusterIP: None
14 | selector:
15 | app: mysql
16 | ---
17 | # Client service for connecting to any MySQL instance for reads.
18 | # For writes, you must instead connect to the primary: mysql-0.mysql.
19 | apiVersion: v1
20 | kind: Service
21 | metadata:
22 | name: mysql-read
23 | labels:
24 | app: mysql
25 | app.kubernetes.io/name: mysql
26 | readonly: "true"
27 | spec:
28 | ports:
29 | - name: mysql
30 | port: 3306
31 | selector:
32 | app: mysql
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/nfs/pod-using-nfs.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | kind: Pod
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | metadata:
4 | name: pod-using-nfs
5 | spec:
6 | # Add the server as an NFS volume for the pod
7 | volumes:
8 | - name: nfs-volume
9 | nfs:
10 | # URL for the NFS server
11 | server: 10.108.211.244 # Change this!
12 | path: /
13 |
14 | # In this container, we'll mount the NFS volume
15 | # and write the date to a file inside it.
16 | containers:
17 | - name: app
18 | image: alpine
19 |
20 | # Mount the NFS volume in the container
21 | volumeMounts:
22 | - name: nfs-volume
23 | mountPath: /var/nfs
24 |
25 | # Write to a file inside our NFS
26 | command: ["/bin/sh"]
27 | args: ["-c", "while true; do date >> /var/nfs/dates.txt; sleep 5; done"]
28 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/HPA/nginx-deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-deployment
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 1
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: nginx
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: nginx
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: nginx
17 | image: nginx:1.17.4
18 | ports:
19 | - containerPort: 80
20 | resources:
21 | requests:
22 | cpu: 50m
23 | limits:
24 | cpu: 100m
25 | ---
26 | apiVersion: v1
27 | kind: Service
28 | metadata:
29 | name: nginx-service
30 | labels:
31 | app: nginx
32 | spec:
33 | selector:
34 | app: nginx
35 | ports:
36 | - protocol: TCP
37 | port: 80
38 | targetPort: 80
39 |
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/deployment/nginx-svc-nodeport.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Service
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-svc # create a service with "nginx" name
5 | labels:
6 | app: webserver
7 | spec:
8 | type: NodePort
9 | selector:
10 | app.kubernetes.io/name: MyApp
11 | ports:
12 | - port: 80
13 | # By default and for convenience, the `targetPort` is set to
14 | # the same value as the `port` field.
15 | targetPort: 80
16 | # Optional field
17 | # By default and for convenience, the Kubernetes control plane
18 | # will allocate a port from a range (default: 30000-32767)
19 | nodePort: 30007
20 | selector: # headless service provides to reach pod with podName.serviceName
21 | app: webserver
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-canary.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-canary
5 | labels:
6 | app: nginx
7 | version: canary
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 1
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: nginx
13 | version: canary
14 | template:
15 | metadata:
16 | labels:
17 | app: nginx
18 | version: canary
19 | spec:
20 | containers:
21 | - name: nginx
22 | image: nginx:latest
23 | volumeMounts:
24 | - name: nginx-config-canary
25 | mountPath: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
26 | subPath: nginx.conf
27 | ports:
28 | - containerPort: 80
29 | volumes:
30 | - name: nginx-config-canary
31 | configMap:
32 | name: nginx-config-canary
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/manual-canary-deployment/nginx-stable.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-stable
5 | labels:
6 | app: nginx
7 | version: stable
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 3
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: nginx
13 | version: stable
14 | template:
15 | metadata:
16 | labels:
17 | app: nginx
18 | version: stable
19 | spec:
20 | containers:
21 | - name: nginx
22 | image: nginx:latest
23 | volumeMounts:
24 | - name: nginx-config-stable
25 | mountPath: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
26 | subPath: nginx.conf
27 | ports:
28 | - containerPort: 80
29 | volumes:
30 | - name: nginx-config-stable
31 | configMap:
32 | name: nginx-config-stable
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sidecar-container/side-car-tail-log.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | $ cat log-shipper-sidecar-deployment.yaml
2 | apiVersion: apps/v1
3 | kind: Deployment
4 | metadata:
5 | name: myapp
6 | labels:
7 | app: myapp
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 1
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: myapp
13 | template:
14 | metadata:
15 | labels:
16 | app: myapp
17 | spec:
18 | containers:
19 | - name: myapp
20 | image: alpine:latest
21 | command: ['sh', '-c', 'echo "logging" > /opt/logs.txt']
22 | volumeMounts:
23 | - name: data
24 | mountPath: /opt
25 | - name: logshipper
26 | image: alpine:latest
27 | command: ['sh', '-c', 'tail /opt/logs.txt']
28 | volumeMounts:
29 | - name: data
30 | mountPath: /opt
31 | volumes:
32 | - name: data
33 | emptyDir: {}
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # install ingress with Hostmode (listen on port 80 )
2 | for accessing on port 80 we need to change deployment to host mode network
3 | i Add this cahnge but for Your Information i just added below hostnetowrk in deploymnet section in manifest ingress-host-mode.yml
4 |
5 | ```
6 | template:
7 | spec:
8 | hostNetwork: true
9 |
10 | ```
11 |
12 | ```
13 | kubectl apply -f ingress-host-mode.yml
14 | kubectl delete -A ValidatingWebhookConfiguration ingress-nginx-admission
15 | ```
16 | # Scale up ingress controler to 3 (in our scenario we have 3 node)
17 | ```
18 | kubectl scale deployments ingress-nginx-controller -n ingress-nginx --replicas 3
19 |
20 | ```
21 |
22 | # apply simple app that listen on 5678 (apple.packops.local)
23 | kubectl -f simple-app-ingress.yml
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 | # Set host apple.packops.local tp kubernetes ip
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/secret/dockerhub-imagepull-secret/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 1- Create imagepullsecret
2 | Create username password based on your dockerhub user pass in this structure :
3 | ```
4 | kubectl create secret docker-registry my-registry-secret \
5 | --docker-server=https://index.docker.io/v1/ \
6 | --docker-username=mrnickfetrat@gmail.com \
7 | --docker-password=PASSS \
8 | --docker-email=mrnickfetrat@gmail.com
9 |
10 | ```
11 | ## 1-1 For cheking you secret
12 | ```
13 | kubectl get secrets my-registry-secret -o yaml
14 | ```
15 | ## 2- create your manifest based on private image that you have on dockerhub
16 | ```
17 | apiVersion: v1
18 | kind: Pod
19 | metadata:
20 | name: my-private-image-pod
21 | spec:
22 | containers:
23 | - name: my-container
24 | image: farshadnikfetrat/hello-nodejs:5918f3e7
25 | imagePullSecrets:
26 | - name: my-registry-secret
27 |
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/ipnetns-container/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | ip netns add packops1-ns
3 | ip netns exec packops1-ns python3 -m http.server 80
4 | ip netns exec packops1-ns ip a
5 |
6 | ip netns list
7 |
8 |
9 | ip netns add packops2-ns
10 | ip netns exec python3 -m http.server 80
11 | ip netns exec packops2-ns ip a
12 |
13 |
14 | sudo ip link add veth-packops1 type veth peer name veth-packops2
15 | sudo ip link set veth-packops1 netns packops1-ns
16 | sudo ip link set veth-packops2 netns packops2-ns
17 |
18 |
19 | sudo ip netns exec packops1-ns /bin/bash
20 | ip addr add 10.0.0.1/24 dev veth-packops1
21 | ip link set veth-packops1 up
22 |
23 |
24 | sudo ip netns exec packops2-ns /bin/bash
25 | ip addr add 10.0.0.2/24 dev veth-packops2
26 | ip link set veth-packops2 up
27 | ```
28 | 
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/apple-orange-ingress/pod.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | kind: Pod
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | metadata:
4 | name: apple-app
5 | labels:
6 | app: apple
7 | spec:
8 | containers:
9 | - name: apple-app
10 | image: hashicorp/http-echo
11 | args:
12 | - "-text=apple"
13 |
14 | ---
15 |
16 | kind: Service
17 | apiVersion: v1
18 | metadata:
19 | name: apple-service
20 | spec:
21 | selector:
22 | app: apple
23 | ports:
24 | - port: 5678 # Default port for image
25 |
26 | ---
27 | kind: Pod
28 | apiVersion: v1
29 | metadata:
30 | name: orange-app
31 | labels:
32 | app: orange
33 | spec:
34 | containers:
35 | - name: orange-app
36 | image: hashicorp/http-echo
37 | args:
38 | - "-text=orange"
39 |
40 | ---
41 |
42 | kind: Service
43 | apiVersion: v1
44 | metadata:
45 | name: orange-service
46 | spec:
47 | selector:
48 | app: orange
49 | ports:
50 | - port: 5678 # Default port for image
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CONTRIBUTING.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Contributing to Mastering Kubernetes
2 |
3 | Thank you for considering contributing to the **Mastering Kubernetes** project! We welcome contributions from everyone and appreciate your help in making this project better.
4 |
5 | ## How to Contribute
6 |
7 | Here are some ways you can contribute:
8 |
9 | ### 1. Reporting Issues
10 |
11 | If you encounter any problems or have suggestions for improvements, please open an issue in the [Issues](https://github.com/farshadnick/Mastering-Kubernetes/issues) section of this repository.
12 |
13 | ### 2. Contributing Code
14 |
15 | If you would like to contribute code, please follow these steps:
16 |
17 | 1. **Fork the Repository**
18 | - Click the "Fork" button at the top right of this page to create your own copy of the repository.
19 |
20 | 2. **Clone Your Fork**
21 | ```bash
22 | git clone https://github.com/YOUR-USERNAME/Mastering-Kubernetes.git
23 | cd Mastering-Kubernetes
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/sidecar-container/tail-log-with-initcontainer.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: myapp
5 | labels:
6 | app: myapp
7 | spec:
8 | replicas: 1
9 | selector:
10 | matchLabels:
11 | app: myapp
12 | template:
13 | metadata:
14 | labels:
15 | app: myapp
16 | spec:
17 | containers:
18 | - name: myapp
19 | image: alpine:latest
20 | command: ['sh', '-c', 'while true; do echo "logging" >> /opt/logs.txt; sleep 1; done']
21 | volumeMounts:
22 | - name: data
23 | mountPath: /opt
24 | initContainers:
25 | - name: logshipper
26 | image: alpine:latest
27 | restartPolicy: Always
28 | command: ['sh', '-c', 'tail -F /opt/logs.txt']
29 | volumeMounts:
30 | - name: data
31 | mountPath: /opt
32 | volumes:
33 | - name: data
34 | emptyDir: {}
35 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/logging/side-car/deployment-with-fluentd.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: counter
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: count
8 | image: busybox:1.28
9 | args:
10 | - /bin/sh
11 | - -c
12 | - >
13 | i=0;
14 | while true;
15 | do
16 | echo "$i: $(date)" >> /var/log/1.log;
17 | echo "$(date) INFO $i" >> /var/log/2.log;
18 | i=$((i+1));
19 | sleep 1;
20 | done
21 | volumeMounts:
22 | - name: varlog
23 | mountPath: /var/log
24 | - name: count-agent
25 | image: registry.k8s.io/fluentd-gcp:1.30
26 | env:
27 | - name: FLUENTD_ARGS
28 | value: -c /etc/fluentd-config/fluentd.conf
29 | volumeMounts:
30 | - name: varlog
31 | mountPath: /var/log
32 | - name: config-volume
33 | mountPath: /etc/fluentd-config
34 | volumes:
35 | - name: varlog
36 | emptyDir: {}
37 | - name: config-volume
38 | configMap:
39 | name: fluentd-config
40 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Network-policy/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | in this Scenario we are going to Block all Trafic in
2 |
3 | # Default Network Policy to Block all incomming Trafic to namespace web-auth
4 | ```
5 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
6 | kind: NetworkPolicy
7 | metadata:
8 | name: default-deny-ingress
9 | namespace: web-auth
10 | spec:
11 | podSelector: {}
12 | policyTypes:
13 | - Ingress
14 | ```
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 |
20 | # Network Policy for Permiting Auth-Client to Auth-Server
21 |
22 | ```
23 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
24 | kind: NetworkPolicy
25 | metadata:
26 | name: auth-server-ingress
27 | namespace: web-auth
28 | spec:
29 | podSelector:
30 | matchLabels:
31 | app: auth-server
32 | policyTypes:
33 | - Ingress
34 | ingress:
35 | - from:
36 | - namespaceSelector:
37 | matchLabels:
38 | role: auth
39 | podSelector:
40 | matchLabels:
41 | app: auth-client
42 | ports:
43 | - protocol: TCP
44 | port: 80
45 |
46 |
47 | ```
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/installation/kubespray.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | #write your Kubernetes nodes ip :
3 | #192.168.7.192
4 | #192.168.7.193
5 | #192.168.7.197
6 | ```
7 | # Clone Kubespray
8 | ```
9 | mkdir kubernetes_installation/
10 | cd kubernetes_installation/
11 | git clone https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/kubespray.git
12 | cd kubespray/
13 | ```
14 | # install requirements for kubespray
15 | ```
16 | apt update && apt install python3-pip ansible
17 | pip install -r requirements.txt --break-system-packages
18 | pip3 install ruamel.yaml --break-system-packages
19 | # Run it on ALL Nodes
20 | apt install sshpass -y
21 | ```
22 | # Determine Your Kubernetes nodes IP
23 | ```
24 | cp -rfp inventory/sample inventory/mycluster
25 | declare -a IPS=(192.168.7.192 192.168.7.193 192.168.7.197)
26 | CONFIG_FILE=inventory/mycluster/hosts.yaml python3 contrib/inventory_builder/inventory.py ${IPS[@]}
27 | ```
28 | # You will be asked for ssh pass and sudo pass
29 | ```
30 | ansible-playbook -i inventory/mycluster/hosts.yaml --user geek --become -kK cluster.yml
31 | ```
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/initcontainer/Pod-address.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: web-server-pod
5 | spec:
6 | initContainers:
7 | - name: write-ip
8 | image: busybox
9 | command: ["sh", "-c", "echo $MY_POD_IP > /web-content/ip.txt; echo 'Wrote the Pod IP to ip.txt'"]
10 | env:
11 | - name: MY_POD_IP
12 | valueFrom:
13 | fieldRef:
14 | fieldPath: status.podIP
15 | volumeMounts:
16 | - name: web-content
17 | mountPath: /web-content
18 | - name: create-html
19 | image: busybox
20 | command: ["sh", "-c", "echo 'Hello, World! Your Pod IP is: ' > /web-content/index.html; cat /web-content/ip.txt >> /web-content/index.html; echo 'Created index.html with the Pod IP'"]
21 | volumeMounts:
22 | - name: web-content
23 | mountPath: /web-content
24 | containers:
25 | - name: web-container
26 | image: nginx
27 | volumeMounts:
28 | - name: web-content
29 | mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
30 | volumes:
31 | - name: web-content
32 | emptyDir: {}
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scheduler/pod-afinity/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Pod Affinity
2 |
3 | Pod Affinity allows you to schedule a pod close to other pods that match specific criteria, usually based on labels. This can be useful for workloads that need to be co-located for performance reasons.
4 | Types of Pod Affinity:
5 |
6 | RequiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: The pod must be scheduled on a node that has the specified other pods running.
7 |
8 | PreferredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution: The scheduler tries to place the pod on a node with the specified other pods, but it is not a strict requirement.
9 | ```
10 | apiVersion: v1
11 | kind: Pod
12 | metadata:
13 | name: example-pod
14 | spec:
15 | affinity:
16 | podAffinity:
17 | requiredDuringSchedulingIgnoredDuringExecution:
18 | labelSelector:
19 | matchExpressions:
20 | - key: app
21 | operator: In
22 | values:
23 | - frontend
24 | topologyKey: kubernetes.io/hostname
25 | containers:
26 | - name: nginx
27 | image: nginx
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/service/headless/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # What exactly is a headless service.
2 | It is used for discovering individual pods(especially IPs) which allows another service to interact directly with the Pods instead of a proxy. With NodePort, LoadBalancer, ExternalName, and ClusterIP clients usually connect to the pods through a Service (Kubernetes Services simply visually explained) rather than connecting directly.
3 |
4 | # What does it accomplish?
5 | The requirement is not to make single IP like in the case of other service types. We need all the pod's IP sitting behind the service.
6 |
7 | # What are some legitimate use cases for it?
8 | Create Stateful service.
9 |
10 | Deploying RabbitMQ or Kafka (or any message broker service) to Kubernetes requires a stateful set for RabbitMQ cluster nodes.
11 |
12 | Deployment of Relational databases
13 |
14 |
15 | ```
16 | apiVersion: v1
17 | kind: Service
18 | metadata:
19 | name: headless-svc
20 | spec:
21 | clusterIP: None
22 | selector:
23 | app: nginx
24 | ports:
25 | - protocol: TCP
26 | port: 80
27 | targetPort: 8080
28 | ```
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/curl-kubernetes-object/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Step 1: Create a Service Account
2 | ```
3 | kubectl create serviceaccount my-service-account
4 | ```
5 | ## Step 2: Bind the Service Account to the Appropriate Role
6 | ```
7 | kubectl create rolebinding my-service-account-binding \
8 | --role=view \
9 | --serviceaccount=default:my-service-account \
10 | --namespace=default
11 | ```
12 | ```
13 | kubectl create clusterrolebinding my-service-account-binding \
14 | --clusterrole=view \
15 | --serviceaccount=default:my-service-account
16 | ```
17 | ## Step 3: Create a Token for the Service Account
18 | ```
19 | TOKEN=$(kubectl create token my-service-account)
20 | ```
21 | ## Step 4: Use the Token with curl to Access Kubernetes API
22 | ```
23 | #sample api server address https://127.0.0.1:6443/api/v1/namespaces/default/pods
24 | curl -X GET "https:///api/v1/namespaces/default/pods" \
25 | -H "Authorization: Bearer $TOKEN" \
26 | -H "Accept: application/json" \
27 | --insecure
28 |
29 | ```
30 |
31 |  32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/startup-prob/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: apps/v1
3 | kind: Deployment
4 | metadata:
5 | name: nginx-deployment
6 | spec:
7 | replicas: 1
8 | selector:
9 | matchLabels:
10 | app: nginx
11 | template:
12 | metadata:
13 | labels:
14 | app: nginx
15 | spec:
16 | containers:
17 | - name: nginx
18 | image: nginx:1.23.3
19 | ports:
20 | - containerPort: 80
21 | startupProbe:
22 | httpGet:
23 | path: /
24 | port: 80
25 | initialDelaySeconds: 10
26 | periodSeconds: 5
27 | failureThreshold: 20
28 | ```
29 |
30 | Image: The deployment uses the official nginx:1.23.3 image.
31 |
32 | startupProbe:
33 |
34 | httpGet: The probe checks the root URL / of the nginx server on port 80.
35 | initialDelaySeconds: The probe waits 10 seconds before starting to allow time for nginx to initialize.
36 | periodSeconds: The probe runs every 5 seconds.
37 | failureThreshold: The probe will tolerate up to 20 failures (equivalent to 100 seconds) before considering the container to have failed and triggering a restart.
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/longhorn/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # 1- Install helm
3 | ```
4 | curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
5 | chmod 700 get_helm.sh
6 | ./get_helm.sh
7 | ```
8 | # 1-1 Install longhorn
9 | ```
10 | helm repo add longhorn https://charts.longhorn.io
11 | helm repo update
12 | helm install longhorn longhorn/longhorn --namespace longhorn-system --create-namespace
13 | ```
14 | # 2- Create pod PVC
15 | ```
16 | apiVersion: v1
17 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
18 | metadata:
19 | name: longhorn-pvc
20 | spec:
21 | accessModes:
22 | - ReadWriteOnce
23 | resources:
24 | requests:
25 | storage: 5Gi
26 | storageClassName: longhorn
27 | ```
28 | # 3- Create deployment and Assign pod to pvc
29 | ```
30 | apiVersion: v1
31 | kind: Pod
32 | metadata:
33 | name: longhorn-demo-pod
34 | spec:
35 | containers:
36 | - name: demo-container
37 | image: nginx
38 | volumeMounts:
39 | - mountPath: "/usr/share/nginx/html"
40 | name: longhorn-storage
41 | volumes:
42 | - name: longhorn-storage
43 | persistentVolumeClaim:
44 | claimName: longhorn-pvc
45 |
46 | ```
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Monitoring/Prometheus/app.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: example-app
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 3
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: example-app
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: example-app
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: example-app
17 | image: quay.io/brancz/prometheus-example-app:v0.5.0
18 | ports:
19 | - name: web
20 | containerPort: 8080
21 |
22 | ---
23 | kind: Service
24 | apiVersion: v1
25 | metadata:
26 | name: example-app
27 | labels:
28 | app: example-app
29 | spec:
30 | selector:
31 | app: example-app
32 | ports:
33 | - name: web
34 | port: 8080
35 | ---
36 | apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
37 | kind: ServiceMonitor
38 | metadata:
39 | name: example-app-monitor
40 | labels:
41 | release: kube-prom-stack # Must match the Prometheus serviceMonitorSelector label
42 | app: example-app
43 | spec:
44 | selector:
45 | matchLabels:
46 | app: example-app
47 | endpoints:
48 | - port: web
49 | path: /metrics # Ensure your service exposes metrics here
50 | interval: 30s
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/redis-example/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Connect to the container and write some data.
3 |
4 | Connect to the container and run the redis-cli:
5 | ```
6 | kubectl exec -it redispod redis-cli
7 | ```
8 |
9 | Set the key space server:name and value "redis server":
10 |
11 | ```
12 | SET server:name "redis server"
13 | ```
14 | Run the GET command to verify the value was set:
15 | ```
16 | GET server:name
17 | ```
18 | Exit the redis-cli:
19 | ```
20 | QUIT
21 | ```
22 | Delete `redispod` and create a new pod named `redispod2`.
23 |
24 | Delete the existing redispod:
25 | ```
26 | kubectl delete pod redispod
27 | ```
28 | Open the file redispod.yaml and change line 4 from name: redispod to:
29 | name: redispod2
30 |
31 | Create a new pod named redispod2:
32 | ```
33 | kubectl apply -f redispod.yaml
34 | ```
35 | Verify the volume has persistent data.
36 |
37 | Connect to the container and run redis-cli:
38 | ```
39 | kubectl exec -it redispod2 redis-cli
40 | ```
41 | Run the GET command to retrieve the data written previously:
42 | ```
43 | GET server:name
44 | ```
45 | Exit the redis-cli:
46 | ```
47 | QUIT
48 | ```
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/HPA/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Prequsit
2 | Install metric server with insecure tls mode
3 | ```
4 | wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml
5 | vim components.yaml
6 |
7 | ```
8 | - --kubelet-insecure-tls in args
9 | ```
10 | - --kubelet-insecure-tls
11 | ```
12 | 
13 |
14 | ```
15 | kubectl apply -f components.yaml
16 | kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep metric
17 |
18 | kubectl top pods
19 | kubectl top nodes
20 |
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## 1- Create a deployment with resource limit
24 | ```
25 | kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
26 | ```
27 |
28 | ## 2- Create HPA Rule for it
29 | ```
30 | kubectl apply -f hpa.yml
31 | kubectl get hpa
32 | ```
33 | ```
34 | --cpu-percent=50: Target average CPU utilization across all pods should be 50%.
35 | --min=1: Minimum number of pod replicas is 1.
36 | --max=10: Maximum number of pod replicas is 10.
37 | ```
38 | # 3- Generate Load
39 | ```
40 | apt install apache2-utils -y
41 |
42 | ab -n 190000 -c 1000 http://nginx-service/
43 | ```
44 |
45 | # 4- Verify Scaling
46 | ```
47 | kubectl get hpa
48 | ```
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/enviornment/expose-pod-info-with-env/expose-data-env.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: dapi-envars-fieldref
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: test-container
8 | image: registry.k8s.io/busybox
9 | command: [ "sh", "-c"]
10 | args:
11 | - while true; do
12 | echo -en '\n';
13 | printenv MY_NODE_NAME MY_POD_NAME MY_POD_NAMESPACE;
14 | printenv MY_POD_IP MY_POD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT;
15 | sleep 10;
16 | done;
17 | env:
18 | - name: MY_NODE_NAME
19 | valueFrom:
20 | fieldRef:
21 | fieldPath: spec.nodeName
22 | - name: MY_POD_NAME
23 | valueFrom:
24 | fieldRef:
25 | fieldPath: metadata.name
26 | - name: MY_POD_NAMESPACE
27 | valueFrom:
28 | fieldRef:
29 | fieldPath: metadata.namespace
30 | - name: MY_POD_IP
31 | valueFrom:
32 | fieldRef:
33 | fieldPath: status.podIP
34 | - name: MY_POD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
35 | valueFrom:
36 | fieldRef:
37 | fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName
38 | restartPolicy: Never
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/configmap-to-env/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 1- Create Configmap which contains our config
2 | ```
3 | apiVersion: v1
4 | kind: ConfigMap
5 | metadata:
6 | name: simple-config
7 | data:
8 | database_url: "mongodb://db1.example.net:27017"
9 | feature_flag: "true"
10 | log_level: "debug"
11 |
12 | ```
13 |
14 | ## 1-1 apply it
15 | ```
16 | kubectl apply -f configmap.yml
17 | ```
18 | ## 1-2 Check the Configmap
19 | ```
20 | kubectl get cm
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## 2- Create POD/Deployment to use configmap as env
24 |
25 | ```
26 | apiVersion: v1
27 | kind: Pod
28 | metadata:
29 | name: app-pod
30 | spec:
31 | containers:
32 | - name: app-container
33 | image: nginx
34 | env:
35 | - name: DATABASE_URL
36 | valueFrom:
37 | configMapKeyRef:
38 | name: simple-config
39 | key: database_url
40 | - name: LOG_LEVEL
41 | valueFrom:
42 | configMapKeyRef:
43 | name: simple-config
44 | key: log_level
45 | ```
46 | ```
47 | kubectl apply -f pod.yml
48 | ```
49 | ## 3- Exec in POD and check env
50 | ```
51 | kubectl exec -it app-pod -- bash
52 | printenv | grep DATABASE_URL
53 | printenv | grep LOG_LEVEL
54 | ```
55 |
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Service-Mesh/isitio/canary-deployment/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # install Istio First
2 | ```
3 | # Install istio api crd
4 | kubectl get crd gateways.gateway.networking.k8s.io &> /dev/null || \
5 | { kubectl kustomize "github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/config/crd?ref=v1.1.0" | kubectl apply -f -; }
6 |
7 | curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | sh -
8 | istioctl install --set profile=default
9 |
10 |
11 | ```
12 | ### You should enable istio injector sidecar in order to Monitor Pods traffik
13 | ```
14 | kubectl label namespace istio-injection=enabled
15 |
16 | ```
17 | ### OR add ``istio-injection: enabled`` in manifest
18 |
19 | ```
20 | metadata:
21 | labels:
22 | istio-injection: enabled
23 | ```
24 | # Deploy virtual service and application
25 | ```
26 | kubectl apply -f Virtualservice.yml
27 | kubectl apply -f deployment.yml
28 | ```
29 |
30 | # Curl with Host Header to isiot gateway ingress
31 |
32 | ```
33 | kubectl get svc -n istio-system
34 | curl -H "Host: app1.packops.local" http://10.233.56.67
35 |
36 | for i in {1..1000}; do curl -H "Host: app1.packops.local" http://10.233.56.67; done
37 |
38 | ```
39 |
40 |
32 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/readiness-liveness/startup-prob/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ```
2 | apiVersion: apps/v1
3 | kind: Deployment
4 | metadata:
5 | name: nginx-deployment
6 | spec:
7 | replicas: 1
8 | selector:
9 | matchLabels:
10 | app: nginx
11 | template:
12 | metadata:
13 | labels:
14 | app: nginx
15 | spec:
16 | containers:
17 | - name: nginx
18 | image: nginx:1.23.3
19 | ports:
20 | - containerPort: 80
21 | startupProbe:
22 | httpGet:
23 | path: /
24 | port: 80
25 | initialDelaySeconds: 10
26 | periodSeconds: 5
27 | failureThreshold: 20
28 | ```
29 |
30 | Image: The deployment uses the official nginx:1.23.3 image.
31 |
32 | startupProbe:
33 |
34 | httpGet: The probe checks the root URL / of the nginx server on port 80.
35 | initialDelaySeconds: The probe waits 10 seconds before starting to allow time for nginx to initialize.
36 | periodSeconds: The probe runs every 5 seconds.
37 | failureThreshold: The probe will tolerate up to 20 failures (equivalent to 100 seconds) before considering the container to have failed and triggering a restart.
38 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/longhorn/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # 1- Install helm
3 | ```
4 | curl -fsSL -o get_helm.sh https://raw.githubusercontent.com/helm/helm/main/scripts/get-helm-3
5 | chmod 700 get_helm.sh
6 | ./get_helm.sh
7 | ```
8 | # 1-1 Install longhorn
9 | ```
10 | helm repo add longhorn https://charts.longhorn.io
11 | helm repo update
12 | helm install longhorn longhorn/longhorn --namespace longhorn-system --create-namespace
13 | ```
14 | # 2- Create pod PVC
15 | ```
16 | apiVersion: v1
17 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
18 | metadata:
19 | name: longhorn-pvc
20 | spec:
21 | accessModes:
22 | - ReadWriteOnce
23 | resources:
24 | requests:
25 | storage: 5Gi
26 | storageClassName: longhorn
27 | ```
28 | # 3- Create deployment and Assign pod to pvc
29 | ```
30 | apiVersion: v1
31 | kind: Pod
32 | metadata:
33 | name: longhorn-demo-pod
34 | spec:
35 | containers:
36 | - name: demo-container
37 | image: nginx
38 | volumeMounts:
39 | - mountPath: "/usr/share/nginx/html"
40 | name: longhorn-storage
41 | volumes:
42 | - name: longhorn-storage
43 | persistentVolumeClaim:
44 | claimName: longhorn-pvc
45 |
46 | ```
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Monitoring/Prometheus/app.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: example-app
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 3
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | app: example-app
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | app: example-app
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: example-app
17 | image: quay.io/brancz/prometheus-example-app:v0.5.0
18 | ports:
19 | - name: web
20 | containerPort: 8080
21 |
22 | ---
23 | kind: Service
24 | apiVersion: v1
25 | metadata:
26 | name: example-app
27 | labels:
28 | app: example-app
29 | spec:
30 | selector:
31 | app: example-app
32 | ports:
33 | - name: web
34 | port: 8080
35 | ---
36 | apiVersion: monitoring.coreos.com/v1
37 | kind: ServiceMonitor
38 | metadata:
39 | name: example-app-monitor
40 | labels:
41 | release: kube-prom-stack # Must match the Prometheus serviceMonitorSelector label
42 | app: example-app
43 | spec:
44 | selector:
45 | matchLabels:
46 | app: example-app
47 | endpoints:
48 | - port: web
49 | path: /metrics # Ensure your service exposes metrics here
50 | interval: 30s
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/localpath/redis-example/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Connect to the container and write some data.
3 |
4 | Connect to the container and run the redis-cli:
5 | ```
6 | kubectl exec -it redispod redis-cli
7 | ```
8 |
9 | Set the key space server:name and value "redis server":
10 |
11 | ```
12 | SET server:name "redis server"
13 | ```
14 | Run the GET command to verify the value was set:
15 | ```
16 | GET server:name
17 | ```
18 | Exit the redis-cli:
19 | ```
20 | QUIT
21 | ```
22 | Delete `redispod` and create a new pod named `redispod2`.
23 |
24 | Delete the existing redispod:
25 | ```
26 | kubectl delete pod redispod
27 | ```
28 | Open the file redispod.yaml and change line 4 from name: redispod to:
29 | name: redispod2
30 |
31 | Create a new pod named redispod2:
32 | ```
33 | kubectl apply -f redispod.yaml
34 | ```
35 | Verify the volume has persistent data.
36 |
37 | Connect to the container and run redis-cli:
38 | ```
39 | kubectl exec -it redispod2 redis-cli
40 | ```
41 | Run the GET command to retrieve the data written previously:
42 | ```
43 | GET server:name
44 | ```
45 | Exit the redis-cli:
46 | ```
47 | QUIT
48 | ```
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/HPA/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Prequsit
2 | Install metric server with insecure tls mode
3 | ```
4 | wget https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/metrics-server/releases/latest/download/components.yaml
5 | vim components.yaml
6 |
7 | ```
8 | - --kubelet-insecure-tls in args
9 | ```
10 | - --kubelet-insecure-tls
11 | ```
12 | 
13 |
14 | ```
15 | kubectl apply -f components.yaml
16 | kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep metric
17 |
18 | kubectl top pods
19 | kubectl top nodes
20 |
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## 1- Create a deployment with resource limit
24 | ```
25 | kubectl apply -f nginx-deployment.yaml
26 | ```
27 |
28 | ## 2- Create HPA Rule for it
29 | ```
30 | kubectl apply -f hpa.yml
31 | kubectl get hpa
32 | ```
33 | ```
34 | --cpu-percent=50: Target average CPU utilization across all pods should be 50%.
35 | --min=1: Minimum number of pod replicas is 1.
36 | --max=10: Maximum number of pod replicas is 10.
37 | ```
38 | # 3- Generate Load
39 | ```
40 | apt install apache2-utils -y
41 |
42 | ab -n 190000 -c 1000 http://nginx-service/
43 | ```
44 |
45 | # 4- Verify Scaling
46 | ```
47 | kubectl get hpa
48 | ```
49 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/enviornment/expose-pod-info-with-env/expose-data-env.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Pod
3 | metadata:
4 | name: dapi-envars-fieldref
5 | spec:
6 | containers:
7 | - name: test-container
8 | image: registry.k8s.io/busybox
9 | command: [ "sh", "-c"]
10 | args:
11 | - while true; do
12 | echo -en '\n';
13 | printenv MY_NODE_NAME MY_POD_NAME MY_POD_NAMESPACE;
14 | printenv MY_POD_IP MY_POD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT;
15 | sleep 10;
16 | done;
17 | env:
18 | - name: MY_NODE_NAME
19 | valueFrom:
20 | fieldRef:
21 | fieldPath: spec.nodeName
22 | - name: MY_POD_NAME
23 | valueFrom:
24 | fieldRef:
25 | fieldPath: metadata.name
26 | - name: MY_POD_NAMESPACE
27 | valueFrom:
28 | fieldRef:
29 | fieldPath: metadata.namespace
30 | - name: MY_POD_IP
31 | valueFrom:
32 | fieldRef:
33 | fieldPath: status.podIP
34 | - name: MY_POD_SERVICE_ACCOUNT
35 | valueFrom:
36 | fieldRef:
37 | fieldPath: spec.serviceAccountName
38 | restartPolicy: Never
39 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/configmap-to-env/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 1- Create Configmap which contains our config
2 | ```
3 | apiVersion: v1
4 | kind: ConfigMap
5 | metadata:
6 | name: simple-config
7 | data:
8 | database_url: "mongodb://db1.example.net:27017"
9 | feature_flag: "true"
10 | log_level: "debug"
11 |
12 | ```
13 |
14 | ## 1-1 apply it
15 | ```
16 | kubectl apply -f configmap.yml
17 | ```
18 | ## 1-2 Check the Configmap
19 | ```
20 | kubectl get cm
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## 2- Create POD/Deployment to use configmap as env
24 |
25 | ```
26 | apiVersion: v1
27 | kind: Pod
28 | metadata:
29 | name: app-pod
30 | spec:
31 | containers:
32 | - name: app-container
33 | image: nginx
34 | env:
35 | - name: DATABASE_URL
36 | valueFrom:
37 | configMapKeyRef:
38 | name: simple-config
39 | key: database_url
40 | - name: LOG_LEVEL
41 | valueFrom:
42 | configMapKeyRef:
43 | name: simple-config
44 | key: log_level
45 | ```
46 | ```
47 | kubectl apply -f pod.yml
48 | ```
49 | ## 3- Exec in POD and check env
50 | ```
51 | kubectl exec -it app-pod -- bash
52 | printenv | grep DATABASE_URL
53 | printenv | grep LOG_LEVEL
54 | ```
55 |
56 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Service-Mesh/isitio/canary-deployment/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # install Istio First
2 | ```
3 | # Install istio api crd
4 | kubectl get crd gateways.gateway.networking.k8s.io &> /dev/null || \
5 | { kubectl kustomize "github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/config/crd?ref=v1.1.0" | kubectl apply -f -; }
6 |
7 | curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | sh -
8 | istioctl install --set profile=default
9 |
10 |
11 | ```
12 | ### You should enable istio injector sidecar in order to Monitor Pods traffik
13 | ```
14 | kubectl label namespace istio-injection=enabled
15 |
16 | ```
17 | ### OR add ``istio-injection: enabled`` in manifest
18 |
19 | ```
20 | metadata:
21 | labels:
22 | istio-injection: enabled
23 | ```
24 | # Deploy virtual service and application
25 | ```
26 | kubectl apply -f Virtualservice.yml
27 | kubectl apply -f deployment.yml
28 | ```
29 |
30 | # Curl with Host Header to isiot gateway ingress
31 |
32 | ```
33 | kubectl get svc -n istio-system
34 | curl -H "Host: app1.packops.local" http://10.233.56.67
35 |
36 | for i in {1..1000}; do curl -H "Host: app1.packops.local" http://10.233.56.67; done
37 |
38 | ```
39 |
40 |  41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Static-POD/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | ## Here is a sample YAML file for a static Pod named nginx:
3 | ```
4 | apiVersion: v1
5 | kind: Pod
6 | metadata:
7 | name: nginx
8 | namespace: default
9 | spec:
10 | containers:
11 | - name: nginx
12 | image: nginx:latest
13 | ports:
14 | - containerPort: 80
15 |
16 | ```
17 | ## Place the YAML file in the kubelet manifest directory
18 | The default location for static Pods is usually /etc/kubernetes/manifests/ on the node where the kubelet is running.
19 | ```
20 | sudo mv nginx.yaml /etc/kubernetes/manifests/
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## Key Characteristics of Static Pods:
24 |
25 | Not Managed by the Scheduler: The scheduler does not handle static Pods. Instead, they are placed directly by the kubelet on the node where the manifest file resides.
26 | Defined Locally: Static Pods are defined by placing their YAML manifest files in a specific directory on the node (usually /etc/kubernetes/manifests/).
27 | No API Server Involvement: Although the static Pod’s status can be viewed using kubectl, it is not part of the usual control plane workflows (like Deployments, ReplicaSets).
28 | Managed by the Kubelet: The kubelet continuously monitors the manifest directory and manages the lifecycle of static Pods.
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/nginx-ingress-manifest/simple-app-ingress.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: apple-app
5 | labels:
6 | app: apple
7 | spec:
8 | replicas: 1
9 | selector:
10 | matchLabels:
11 | app: apple
12 | template:
13 | metadata:
14 | labels:
15 | app: apple
16 | spec:
17 | containers:
18 | - name: apple-app
19 | image: hashicorp/http-echo
20 | args:
21 | - "-text=apple"
22 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
23 |
24 |
25 | ---
26 |
27 | kind: Service
28 | apiVersion: v1
29 | metadata:
30 | name: apple-service
31 | spec:
32 | selector:
33 | app: apple
34 | ports:
35 | - port: 5678 # Default port for image
36 |
37 | ---
38 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
39 | kind: Ingress
40 | metadata:
41 | annotations:
42 | app: "apple"
43 | nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 200m
44 | name: "apple-ingress"
45 | spec:
46 | ingressClassName: nginx
47 | rules:
48 | - host: "apple.packops.local"
49 | http:
50 | paths:
51 | - backend:
52 | service:
53 | name: "apple-service"
54 | port:
55 | number: 5678
56 | path: /
57 | pathType: ImplementationSpecific
58 |
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/etcd/etcd.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | etcd is an open source distributed key-value store used to hold and manage the critical information that distributed systems need to keep running. Most notably, it manages the configuration data, state data, and metadata for Kubernetes, the popular container orchestration platform
3 |
4 | **ETCD Benefits**
5 | 1. Fully replicated: Every node in an etcd cluster has access the full data store.
6 | 1. Highly available: etcd is designed to have no single point of failure and gracefully tolerate hardware failures and network partitions.
7 | 1. Reliably consistent: Every data ‘read’ returns the latest data ‘write’ across all clusters.
8 | 1. Fast: etcd has been benchmarked at 10,000 writes per second.
9 | 1. Secure: etcd supports automatic Transport Layer Security (TLS) and optional secure socket layer (SSL) client certificate authentication. Because etcd stores vital and highly sensitive configuration data, administrators should implement role-based access controls within the deployment and ensure that team members interacting with etcd are limited to the least-privileged level of access necessary to perform their jobs.
10 | 1. Simple: Any application, from simple web apps to highly complex container orchestration engines such as Kubernetes, can read or write data to etcd using standard HTTP/JSON tools.
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/creating-new-clusteadmin/05-kubeconfig-creator.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | export SA_SECRET_TOKEN=$(kubectl -n kube-system get secret/devops-cluster-admin-secret -o=go-template='{{.data.token}}' | base64 --decode)
2 |
3 | export CLUSTER_NAME=$(kubectl config current-context)
4 |
5 | export CURRENT_CLUSTER=$(kubectl config view --raw -o=go-template='{{range .contexts}}{{if eq .name "'''${CLUSTER_NAME}'''"}}{{ index .context "cluster" }}{{end}}{{end}}')
6 |
7 | export CLUSTER_CA_CERT=$(kubectl config view --raw -o=go-template='{{range .clusters}}{{if eq .name "'''${CURRENT_CLUSTER}'''"}}"{{with index .cluster "certificate-authority-data" }}{{.}}{{end}}"{{ end }}{{ end }}')
8 |
9 | export CLUSTER_ENDPOINT=$(kubectl config view --raw -o=go-template='{{range .clusters}}{{if eq .name "'''${CURRENT_CLUSTER}'''"}}{{ .cluster.server }}{{end}}{{ end }}')
10 | cat << EOF > devops-cluster-admin-config
11 | apiVersion: v1
12 | kind: Config
13 | current-context: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
14 | contexts:
15 | - name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
16 | context:
17 | cluster: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
18 | user: devops-cluster-admin
19 | clusters:
20 | - name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
21 | cluster:
22 | certificate-authority-data: ${CLUSTER_CA_CERT}
23 | server: ${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}
24 | users:
25 | - name: devops-cluster-admin
26 | user:
27 | token: ${SA_SECRET_TOKEN}
28 | EOF
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/nginx-configmap/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 1- Create configmap with your nginx default config
2 | ```
3 | apiVersion: v1
4 | kind: ConfigMap
5 | metadata:
6 | name: nginx
7 | data:
8 | index.html: |
9 |
10 |
11 | Hello, World
12 |
13 |
14 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Static-POD/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | ## Here is a sample YAML file for a static Pod named nginx:
3 | ```
4 | apiVersion: v1
5 | kind: Pod
6 | metadata:
7 | name: nginx
8 | namespace: default
9 | spec:
10 | containers:
11 | - name: nginx
12 | image: nginx:latest
13 | ports:
14 | - containerPort: 80
15 |
16 | ```
17 | ## Place the YAML file in the kubelet manifest directory
18 | The default location for static Pods is usually /etc/kubernetes/manifests/ on the node where the kubelet is running.
19 | ```
20 | sudo mv nginx.yaml /etc/kubernetes/manifests/
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ## Key Characteristics of Static Pods:
24 |
25 | Not Managed by the Scheduler: The scheduler does not handle static Pods. Instead, they are placed directly by the kubelet on the node where the manifest file resides.
26 | Defined Locally: Static Pods are defined by placing their YAML manifest files in a specific directory on the node (usually /etc/kubernetes/manifests/).
27 | No API Server Involvement: Although the static Pod’s status can be viewed using kubectl, it is not part of the usual control plane workflows (like Deployments, ReplicaSets).
28 | Managed by the Kubelet: The kubelet continuously monitors the manifest directory and manages the lifecycle of static Pods.
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ingress/nginx-ingress-manifest/simple-app-ingress.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: apple-app
5 | labels:
6 | app: apple
7 | spec:
8 | replicas: 1
9 | selector:
10 | matchLabels:
11 | app: apple
12 | template:
13 | metadata:
14 | labels:
15 | app: apple
16 | spec:
17 | containers:
18 | - name: apple-app
19 | image: hashicorp/http-echo
20 | args:
21 | - "-text=apple"
22 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
23 |
24 |
25 | ---
26 |
27 | kind: Service
28 | apiVersion: v1
29 | metadata:
30 | name: apple-service
31 | spec:
32 | selector:
33 | app: apple
34 | ports:
35 | - port: 5678 # Default port for image
36 |
37 | ---
38 | apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
39 | kind: Ingress
40 | metadata:
41 | annotations:
42 | app: "apple"
43 | nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-body-size: 200m
44 | name: "apple-ingress"
45 | spec:
46 | ingressClassName: nginx
47 | rules:
48 | - host: "apple.packops.local"
49 | http:
50 | paths:
51 | - backend:
52 | service:
53 | name: "apple-service"
54 | port:
55 | number: 5678
56 | path: /
57 | pathType: ImplementationSpecific
58 |
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/etcd/etcd.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | etcd is an open source distributed key-value store used to hold and manage the critical information that distributed systems need to keep running. Most notably, it manages the configuration data, state data, and metadata for Kubernetes, the popular container orchestration platform
3 |
4 | **ETCD Benefits**
5 | 1. Fully replicated: Every node in an etcd cluster has access the full data store.
6 | 1. Highly available: etcd is designed to have no single point of failure and gracefully tolerate hardware failures and network partitions.
7 | 1. Reliably consistent: Every data ‘read’ returns the latest data ‘write’ across all clusters.
8 | 1. Fast: etcd has been benchmarked at 10,000 writes per second.
9 | 1. Secure: etcd supports automatic Transport Layer Security (TLS) and optional secure socket layer (SSL) client certificate authentication. Because etcd stores vital and highly sensitive configuration data, administrators should implement role-based access controls within the deployment and ensure that team members interacting with etcd are limited to the least-privileged level of access necessary to perform their jobs.
10 | 1. Simple: Any application, from simple web apps to highly complex container orchestration engines such as Kubernetes, can read or write data to etcd using standard HTTP/JSON tools.
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/rbac/scenario/creating-new-clusteadmin/05-kubeconfig-creator.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | export SA_SECRET_TOKEN=$(kubectl -n kube-system get secret/devops-cluster-admin-secret -o=go-template='{{.data.token}}' | base64 --decode)
2 |
3 | export CLUSTER_NAME=$(kubectl config current-context)
4 |
5 | export CURRENT_CLUSTER=$(kubectl config view --raw -o=go-template='{{range .contexts}}{{if eq .name "'''${CLUSTER_NAME}'''"}}{{ index .context "cluster" }}{{end}}{{end}}')
6 |
7 | export CLUSTER_CA_CERT=$(kubectl config view --raw -o=go-template='{{range .clusters}}{{if eq .name "'''${CURRENT_CLUSTER}'''"}}"{{with index .cluster "certificate-authority-data" }}{{.}}{{end}}"{{ end }}{{ end }}')
8 |
9 | export CLUSTER_ENDPOINT=$(kubectl config view --raw -o=go-template='{{range .clusters}}{{if eq .name "'''${CURRENT_CLUSTER}'''"}}{{ .cluster.server }}{{end}}{{ end }}')
10 | cat << EOF > devops-cluster-admin-config
11 | apiVersion: v1
12 | kind: Config
13 | current-context: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
14 | contexts:
15 | - name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
16 | context:
17 | cluster: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
18 | user: devops-cluster-admin
19 | clusters:
20 | - name: ${CLUSTER_NAME}
21 | cluster:
22 | certificate-authority-data: ${CLUSTER_CA_CERT}
23 | server: ${CLUSTER_ENDPOINT}
24 | users:
25 | - name: devops-cluster-admin
26 | user:
27 | token: ${SA_SECRET_TOKEN}
28 | EOF
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/nginx-configmap/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 1- Create configmap with your nginx default config
2 | ```
3 | apiVersion: v1
4 | kind: ConfigMap
5 | metadata:
6 | name: nginx
7 | data:
8 | index.html: |
9 |
10 |
11 | Hello, World
12 |
13 |
14 | Hello, World from a ConfigMap!
15 |
16 |
17 |
18 | ```
19 | ## 2- Create deployment that Include configmap and map it to nginx
20 | ```
21 | apiVersion: apps/v1
22 | kind: Deployment
23 | metadata:
24 | name: nginx
25 | spec:
26 | replicas: 1
27 | selector:
28 | matchLabels:
29 | app: nginx
30 | template:
31 | metadata:
32 | labels:
33 | app: nginx
34 | spec:
35 | containers:
36 | - name: nginx
37 | image: nginx
38 | volumeMounts:
39 | - name: nginx-files
40 | mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
41 | volumes:
42 | - name: nginx-files
43 | configMap:
44 | name: nginx
45 |
46 | ---
47 | apiVersion: v1
48 | kind: Service
49 | metadata:
50 | name: nginx-service
51 | spec:
52 | selector:
53 | app: nginx
54 | ports:
55 | - protocol: TCP
56 | port: 80
57 | targetPort: 80
58 |
59 | ```
60 |
61 | 
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/Creating a ClusterRole to Access a Pod to get pod list in Kubernetes/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | 
3 |
4 | ## Create SA and namespace`
5 | ```
6 | kubectl create namespace packops
7 | kubectl create namespace web
8 |
9 | kubectl create serviceaccount sa-read -n packops
10 | ```
11 | ## Create a ClusterRole
12 | ```
13 | kubectl create clusterrole pod-reader --verb=get,list --resource=pod
14 |
15 | ```
16 |
17 | ## Create Cluster Rolbinding
18 |
19 | ```
20 | kubectl create clusterrolebinding pod-crb --clusterrole=pod-reader --serviceaccount=packops:sa-read
21 | ```
22 | ## Create Pod to Verify it
23 | ```
24 | apiVersion: v1
25 | kind: Pod
26 | metadata:
27 | name: kubectlpod
28 | namespace: packops
29 | spec:
30 | serviceAccountName: sa-read
31 | containers:
32 | - name: kubectl
33 | image: bitnami/kubectl:latest
34 | command: ["sleep", "9999999"]
35 | restartPolicy: Always
36 |
37 |
38 | ```
39 | # Create a simple nginx in web namespace
40 | ```
41 | kubectl run nginx --image=nginx --namespace=web
42 |
43 | ```
44 | ```
45 | kubectl exec -it kubectlpod -n packops -- sh
46 | kubectl get pods -n web
47 | ```
48 | 
49 |
50 |
51 |
52 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/nfs/simple-nfs.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: PersistentVolume
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nfs
5 | spec:
6 | capacity:
7 | storage: 100Mi
8 | accessModes:
9 | - ReadWriteOnce
10 | nfs:
11 | server: 192.168.5.242
12 | path: "/exports"
13 | mountOptions:
14 | - nfsvers=4.2
15 | ---
16 | apiVersion: v1
17 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
18 | metadata:
19 | name: nfs
20 | spec:
21 | accessModes:
22 | - ReadWriteOnce
23 | storageClassName: ""
24 | resources:
25 | requests:
26 | storage: 1Mi
27 | volumeName: nfs
28 |
29 | ---
30 |
31 | apiVersion: apps/v1
32 | kind: Deployment
33 | metadata:
34 | name: nfs-busybox
35 | spec:
36 | replicas: 3
37 | selector:
38 | matchLabels:
39 | name: nfs-busybox
40 | template:
41 | metadata:
42 | labels:
43 | name: nfs-busybox
44 | spec:
45 | containers:
46 | - image: busybox
47 | command:
48 | - sh
49 | - -c
50 | - 'while true; do date > /mnt/index.html; hostname >> /mnt/index.html; sleep $(($RANDOM % 5 + 5)); done'
51 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
52 | name: busybox
53 | volumeMounts:
54 | # name must match the volume name below
55 | - name: nfs
56 | mountPath: "/mnt"
57 | volumes:
58 | - name: nfs
59 | persistentVolumeClaim:
60 | claimName: nfs
61 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/keda/time-based-scale/prometheus/deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: web-app
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 1
7 | selector:
8 | matchLabels:
9 | label: packops
10 | template:
11 | metadata:
12 | labels:
13 | label: packops
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: web-app
17 | image: farshadnikfetrat/prom-request:3
18 | ports:
19 | - containerPort: 8080
20 | env:
21 | - name: PROMETHEUS_METRICS_PORT
22 | value: "8080"
23 | ---
24 | apiVersion: apps/v1
25 | kind: Deployment
26 | metadata:
27 | name: nginx-deployment
28 | labels:
29 | app: nginx
30 | spec:
31 | replicas: 1
32 | selector:
33 | matchLabels:
34 | app: nginx
35 | template:
36 | metadata:
37 | labels:
38 | app: nginx
39 | spec:
40 | containers:
41 | - name: nginx
42 | image: nginx:latest
43 | ports:
44 | - containerPort: 80
45 |
46 |
47 | ---
48 | apiVersion: v1
49 | kind: Service
50 | metadata:
51 | annotations:
52 | prometheus.io/port: "metrics"
53 | prometheus.io/scrape: "true"
54 | name: web-app
55 | labels:
56 | label: svc-packops
57 | spec:
58 | selector:
59 | label: packops
60 | ports:
61 | - port: 80
62 | protocol: TCP
63 | targetPort: 8080
64 | name: "metrics"
65 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Service-Mesh/isitio/canary-deployment/Virtualservice.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
2 | kind: Gateway
3 | metadata:
4 | name: my-app-gateway
5 | spec:
6 | selector:
7 | istio: ingressgateway
8 | servers:
9 | - port:
10 | number: 80
11 | name: http
12 | protocol: HTTP
13 | hosts:
14 | - "app1.packops.local"
15 | - "app2.packops.local"
16 | ---
17 | apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
18 | kind: VirtualService
19 | metadata:
20 | name: my-app
21 | spec:
22 | hosts:
23 | - "app1.packops.local"
24 | - "app2.packops.local"
25 | gateways:
26 | - my-app-gateway
27 | http:
28 | - match:
29 | - headers:
30 | host:
31 | exact: "app1.packops.local"
32 | route:
33 | - destination:
34 | host: my-app-v1.default.svc.cluster.local
35 | port:
36 | number: 80
37 | weight: 80
38 | - destination:
39 | host: my-app-v2.default.svc.cluster.local
40 | port:
41 | number: 80
42 | weight: 20
43 | - match:
44 | - headers:
45 | host:
46 | exact: "app2.packops.local"
47 | route:
48 | - destination:
49 | host: my-app-v2.default.svc.cluster.local
50 | port:
51 | number: 80
52 | weight: 80
53 | - destination:
54 | host: my-app-v1.default.svc.cluster.local
55 | port:
56 | number: 80
57 | weight: 20
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/Limit-Range/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | You are managing a Kubernetes namespace called dev-namespace, and you want to ensure that all containers in this namespace have appropriate resource limits and requests. Specifically, you want to:
2 |
3 | - Set a minimum resource request of 100m CPU and 128Mi memory for every container.
4 | - Set a maximum resource limit of 2 CPU and 1Gi memory for any container.
5 | - Provide default values of 200m CPU and 256Mi memory if a container doesn't specify any resource requests or limits.
6 |
7 | Apply the LimitRange:
8 |
9 | Apply the LimitRange to your dev-namespace:
10 | ```
11 | kubectl apply -f limitrange.yaml
12 | ```
13 |
14 | Create a Pod without Resource Requests or Limits:
15 |
16 | Now, create a Pod in the dev-namespace without specifying any resource requests or limits to see the default values being applied:
17 | ```
18 | kubectl apply -f test-pod.yaml
19 | ```
20 |
21 | Check the Applied Resource Requests and Limits:
22 | ```
23 | kubectl get pod test-pod -n dev-namespace -o jsonpath='{.spec.containers[0].resources}'
24 | ```
25 |
26 | Out out must be something like that :
27 | {"limits":{"cpu":"200m","memory":"256Mi"},"requests":{"cpu":"100m","memory":"128Mi"}}
28 |
29 | Try to Create pod more than limitation :
30 |
31 | ```
32 | kubectl apply -f test-pod-exceed.yaml
33 | ```
34 |
35 | The Kubernetes API server will reject this Pod creation because it exceeds the limits set by the LimitRange.
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/api-gateway/istio-api-gateway/all-in-one.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ---
2 | apiVersion: v1
3 | kind: Namespace
4 | metadata:
5 | name: demo-gateway
6 | ---
7 | apiVersion: v1
8 | kind: Pod
9 | metadata:
10 | name: http-echo
11 | namespace: demo-gateway
12 | labels:
13 | app: http-echo
14 | spec:
15 | containers:
16 | - name: echo
17 | image: hashicorp/http-echo
18 | args:
19 | - "-text=Hello from Gateway API!"
20 | ports:
21 | - containerPort: 5678
22 | ---
23 | apiVersion: v1
24 | kind: Service
25 | metadata:
26 | name: http-echo
27 | namespace: demo-gateway
28 | spec:
29 | selector:
30 | app: http-echo
31 | ports:
32 | - protocol: TCP
33 | port: 80
34 | targetPort: 5678
35 | ---
36 | # Gateway definition
37 | apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
38 | kind: Gateway
39 | metadata:
40 | name: demo-gateway
41 | namespace: demo-gateway
42 | spec:
43 | gatewayClassName: istio # or nginx, or gke-l7-global-external-managed, depending on your cluster
44 | listeners:
45 | - name: http
46 | protocol: HTTP
47 | port: 80
48 | ---
49 | # Route definition
50 | apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
51 | kind: HTTPRoute
52 | metadata:
53 | name: echo-route
54 | namespace: demo-gateway
55 | spec:
56 | parentRefs:
57 | - name: demo-gateway
58 | rules:
59 | - matches:
60 | - path:
61 | type: PathPrefix
62 | value: /
63 | backendRefs:
64 | - name: http-echo
65 | port: 80
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/keda/time-based-scale/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 1- Install keda
2 | ```
3 | kubectl apply --force-conflicts --server-side -f https://github.com/kedacore/keda/releases/download/v2.12.0/keda-2.12.0.yaml
4 | kubectl get pods -n keda
5 |
6 | ```
7 |
8 | ## 2- Create an deployment that you want to scale
9 | ```
10 | # nginx-deployment.yaml
11 | apiVersion: apps/v1
12 | kind: Deployment
13 | metadata:
14 | name: nginx-deployment
15 | namespace: default
16 | spec:
17 | replicas: 1
18 | selector:
19 | matchLabels:
20 | app: nginx
21 | template:
22 | metadata:
23 | labels:
24 | app: nginx
25 | spec:
26 | containers:
27 | - name: nginx
28 | image: nginx
29 | ports:
30 | - containerPort: 80
31 |
32 | ```
33 | ## 3- Create object scale rule
34 | ```
35 | apiVersion: keda.sh/v1alpha1
36 | kind: ScaledObject
37 | metadata:
38 | name: time-based-scaler2
39 | namespace: default
40 | spec:
41 | scaleTargetRef:
42 | name: nginx-deployment
43 | kind: Deployment
44 | apiVersion: apps/v1
45 | minReplicaCount: 1
46 | maxReplicaCount: 3
47 | cooldownPeriod: 30
48 | triggers:
49 | - type: cron
50 | metadata:
51 | # Required
52 | timezone: Asia/Tehran # The acceptable values would be a value from the IANA Time Zone Database.
53 | start: 6 1 * * * # At 6:00 AM
54 | end: 20 1 * * * # At 8:00 PM
55 | desiredReplicas: "3"
56 |
57 | ```
58 |
59 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/scenario/turn-dockercompose-to-k8s-manifest/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Here is docker-compose which need to be turned to kubernetes manifest
2 | ```
3 | services:
4 | redis-leader:
5 | container_name: redis-leader
6 | image: redis
7 | ports:
8 | - "6379"
9 |
10 | redis-replica:
11 | container_name: redis-replica
12 | image: redis
13 | ports:
14 | - "6379"
15 | command: redis-server --replicaof redis-leader 6379 --dir /tmp
16 |
17 | web:
18 | container_name: web
19 | image: quay.io/kompose/web
20 | ports:
21 | - "8080:8080"
22 | environment:
23 | - GET_HOSTS_FROM=dns
24 | labels:
25 | kompose.service.type: LoadBalancer
26 |
27 | ```
28 | ## Install Kompose
29 | ```
30 | curl -L https://github.com/kubernetes/kompose/releases/download/v1.34.0/kompose-linux-amd64 -o kompose
31 | ```
32 | ## Covert to k8s manifest
33 | ```
34 | kompose convert
35 | ```
36 | ```
37 | INFO Kubernetes file "redis-leader-service.yaml" created
38 | INFO Kubernetes file "redis-replica-service.yaml" created
39 | INFO Kubernetes file "web-tcp-service.yaml" created
40 | INFO Kubernetes file "redis-leader-deployment.yaml" created
41 | INFO Kubernetes file "redis-replica-deployment.yaml" created
42 | INFO Kubernetes file "web-deployment.yaml" created
43 | ```
44 |
45 | ```
46 | kubectl apply -f web-tcp-service.yaml,redis-leader-service.yaml,redis-replica-service.yaml,web-deployment.yaml,redis-leader-deployment.yaml,redis-replica-deployment.yaml
47 | ```
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Limit/Pod-Limit/Nginx.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx-deployment
5 | spec:
6 | replicas: 2
7 | strategy:
8 | type: Recreate
9 | revisionHistoryLimit: 100
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: farshad
13 | template:
14 | metadata:
15 | labels:
16 | test: a
17 | app: farshad
18 | spec:
19 | containers:
20 | - name: nginx
21 | image: nginx:latest
22 | resources:
23 | requests:
24 | memory: "64Mi"
25 | cpu: "250m"
26 | limits:
27 | memory: "128Mi"
28 | cpu: "500m"
29 | ports:
30 | - containerPort: 80
31 | ---
32 | apiVersion: v1
33 | kind: Service
34 | metadata:
35 | name: nginx-svc # create a service with "nginx" name
36 | labels:
37 | app: farshad
38 | spec:
39 | type: NodePort
40 | selector:
41 | app.kubernetes.io/name: MyApp
42 | ports:
43 | - port: 80
44 | # By default and for convenience, the `targetPort` is set to
45 | # the same value as the `port` field.
46 | targetPort: 80
47 | # Optional field
48 | # By default and for convenience, the Kubernetes control plane
49 | # will allocate a port from a range (default: 30000-32767)
50 | nodePort: 30007
51 | selector: # headless service provides to reach pod with podName.serviceName
52 | app: farshad
53 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/PriorityClass/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # How to use priority and preemption
2 | ## To use priority and preemption:
3 | ### 1-Add one or more PriorityClasses.
4 | ### 2-Create Pods withpriorityClassName set to one of the added PriorityClasses.
5 |
6 | # PriorityClass
7 | A PriorityClass is a non-namespaced object that defines a mapping from a priority class name to the integer value of the priority (higher the value, the higher the priority)
8 | In Kubernetes, the default priority for pods is zero if no PriorityClass
9 | ```
10 | apiVersion: scheduling.k8s.io/v1
11 | kind: PriorityClass
12 | metadata:
13 | name: high-priority
14 | value: 1000
15 | globalDefault: false
16 | description: This is a very high priority Pod class
17 |
18 | ```
19 | # Assing PriorityClass to POD or deployment
20 |
21 | ```
22 | # Deployment
23 | apiVersion: apps/v1
24 | kind: Deployment
25 | metadata:
26 | name: random-generator-deployment
27 | spec:
28 | replicas: 3
29 | selector:
30 | matchLabels:
31 | app: random-generator
32 | template:
33 | metadata:
34 | labels:
35 | app: random-generator
36 | spec:
37 | containers:
38 | - image: k8spatterns/random-generator:1.0
39 | name: random-generator
40 | priorityClassName: high-priority
41 | ```
42 | # OR You Can Assign it to an Deployment
43 | ```
44 | #POD
45 | apiVersion: v1
46 | kind: Pod
47 | metadata:
48 | name: random-generator
49 | labels:
50 | env: random-generator
51 | spec:
52 | containers:
53 | - image: k8spatterns/random-generator:1.0
54 | name: random-generator
55 | priorityClassName: high-priority
56 |
57 | ```
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Service-Mesh/isitio/canary-deployment/deployment.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # my-app-v1.yaml
2 | apiVersion: apps/v1
3 | kind: Deployment
4 | metadata:
5 | name: my-app-v1
6 | spec:
7 | replicas: 1
8 | selector:
9 | matchLabels:
10 | app: my-app
11 | version: v1
12 | template:
13 | metadata:
14 | labels:
15 | app: my-app
16 | version: v1
17 | annotations:
18 | sidecar.istio.io/inject: "true" # Enable Istio sidecar injection
19 | spec:
20 | containers:
21 | - name: my-app
22 | image: hashicorp/http-echo
23 | args:
24 | - "-text=my-app v1"
25 | ports:
26 | - containerPort: 5678
27 | ---
28 | apiVersion: v1
29 | kind: Service
30 | metadata:
31 | name: my-app-v1
32 | spec:
33 | selector:
34 | app: my-app
35 | ports:
36 | - port: 80
37 | targetPort: 5678
38 |
39 | ---
40 | apiVersion: v1
41 | kind: Service
42 | metadata:
43 | name: my-app-v2
44 | spec:
45 | selector:
46 | app: my-app-v2
47 | ports:
48 | - port: 80
49 | targetPort: 5678
50 | ---
51 | # my-app-v2.yaml
52 | apiVersion: apps/v1
53 | kind: Deployment
54 | metadata:
55 | name: my-app-v2
56 | spec:
57 | replicas: 1
58 | selector:
59 | matchLabels:
60 | app: my-app-v2
61 | version: v2
62 | template:
63 | metadata:
64 | labels:
65 | app: my-app-v2
66 | version: v2
67 | annotations:
68 | sidecar.istio.io/inject: "true" # Enable Istio sidecar injection
69 | spec:
70 | containers:
71 | - name: my-app-v2
72 | image: hashicorp/http-echo
73 | args:
74 | - "-text=my-app v2"
75 | ports:
76 | - containerPort: 5678
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/statefulset/nginx-scenario/statefulset.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Service
3 | metadata:
4 | name: nginx # create a service with "nginx" name
5 | labels:
6 | app: nginx
7 | spec:
8 | ports:
9 | - port: 80
10 | name: web # create headless service if clusterIP:None
11 | clusterIP: None # when requesting service name, service returns one of the IP of pods
12 | selector: # headless service provides to reach pod with podName.serviceName
13 | app: nginx # selects/binds to app:nginx (defined in: spec > template > metadata > labels > app:nginx)
14 | ---
15 | apiVersion: apps/v1
16 | kind: StatefulSet
17 | metadata:
18 | name: web # statefulset name: web
19 | spec:
20 | serviceName: nginx # binds/selects service (defined in metadata > name: nginx)
21 | replicas: 3
22 | selector:
23 | matchLabels:
24 | app: nginx
25 | template:
26 | metadata:
27 | labels:
28 | app: nginx
29 | spec:
30 | containers:
31 | - name: nginx
32 | image: nginx
33 | ports:
34 | - containerPort: 80
35 | name: web
36 | volumeMounts:
37 | - name: www
38 | mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html
39 | volumeClaimTemplates:
40 | - metadata:
41 | name: www
42 | spec:
43 | accessModes: [ "ReadWriteOnce" ] # creates PVCs for each pod automatically
44 | resources: # hence, each node has own PV
45 | requests:
46 | storage: 512Mi
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/storage/nfs/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 1- Install nfs server on a node
2 | ```
3 | apt update && apt install nfs-server
4 | mkdir /exports
5 | echo "/exports *(rw,sync,no_subtree_check)" > /etc/exports
6 | ```
7 | ## 2- install nfs-common on all workers in order to connect to nfs server
8 | ```
9 | apt update && apt install nfs-common
10 | ```
11 |
12 | ## 3- Create PV and PVC
13 | ```
14 | apiVersion: v1
15 | kind: PersistentVolume
16 | metadata:
17 | name: nfs
18 | spec:
19 | capacity:
20 | storage: 100Mi
21 | accessModes:
22 | - ReadWriteOnce
23 | nfs:
24 | server: 192.168.5.242
25 | path: "/exports"
26 | mountOptions:
27 | - nfsvers=4.2
28 | ---
29 | apiVersion: v1
30 | kind: PersistentVolumeClaim
31 | metadata:
32 | name: nfs
33 | spec:
34 | accessModes:
35 | - ReadWriteOnce
36 | storageClassName: ""
37 | resources:
38 | requests:
39 | storage: 1Mi
40 | volumeName: nfs
41 |
42 | ```
43 |
44 | ## 4- Create pod that using pvc
45 | ```
46 | apiVersion: apps/v1
47 | kind: Deployment
48 | metadata:
49 | name: nfs-busybox
50 | spec:
51 | replicas: 3
52 | selector:
53 | matchLabels:
54 | name: nfs-busybox
55 | template:
56 | metadata:
57 | labels:
58 | name: nfs-busybox
59 | spec:
60 | containers:
61 | - image: busybox
62 | command:
63 | - sh
64 | - -c
65 | - 'while true; do date >> /mnt/index.html; hostname >> /mnt/index.html; sleep $(($RANDOM % 5 + 5)); done'
66 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
67 | name: busybox
68 | volumeMounts:
69 | # name must match the volume name below
70 | - name: nfs
71 | mountPath: "/mnt"
72 | volumes:
73 | - name: nfs
74 | persistentVolumeClaim:
75 | claimName: nfs
76 | ```
77 |
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/workloads/daemonset/simple-daemonset.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: DaemonSet
3 | metadata:
4 | name: logdaemonset
5 | labels:
6 | app: fluentd-logging
7 | spec:
8 | selector:
9 | matchLabels: # label selector should be same labels in the template (template > metadata > labels)
10 | name: fluentd-elasticsearch
11 | template:
12 | metadata:
13 | labels:
14 | name: fluentd-elasticsearch
15 | spec:
16 | tolerations:
17 | - key: node-role.kubernetes.io/master # this toleration is to have the daemonset runnable on master nodes
18 | effect: NoSchedule # remove it if your masters can't run pods
19 | containers:
20 | - name: fluentd-elasticsearch
21 | image: quay.io/fluentd_elasticsearch/fluentd:v2.5.2 # installing fluentd elasticsearch on each nodes
22 | resources:
23 | limits:
24 | memory: 200Mi # resource limitations configured
25 | requests:
26 | cpu: 100m
27 | memory: 200Mi
28 | volumeMounts: # definition of volumeMounts for each pod
29 | - name: varlog
30 | mountPath: /var/log
31 | - name: varlibdockercontainers
32 | mountPath: /var/lib/docker/containers
33 | readOnly: true
34 | terminationGracePeriodSeconds: 30
35 | volumes: # ephemerial volumes on node (hostpath defined)
36 | - name: varlog
37 | hostPath:
38 | path: /var/log
39 | - name: varlibdockercontainers
40 | hostPath:
41 | path: /var/lib/docker/containers
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/Configmap-as-volume-redis/redis-manifest-with-cm.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | name: shared-packops-redis
5 | labels:
6 | app: shared-packops-redis
7 | spec:
8 | replicas: 1
9 | selector:
10 | matchLabels:
11 | app: shared-packops-redis
12 | template:
13 | metadata:
14 | labels:
15 | app: shared-packops-redis
16 | spec:
17 | containers:
18 | - name: redis
19 | image: redis:6
20 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
21 | command:
22 | - redis-server
23 | - /redis-master/redis.conf
24 | ports:
25 | - containerPort: 6379
26 | name: redis-port
27 | protocol: TCP
28 | env:
29 | - name: MASTER
30 | value: "true"
31 | resources:
32 | limits:
33 | cpu: "1"
34 | memory: "1Gi"
35 | volumeMounts:
36 | - name: redis-config
37 | mountPath: /redis-master/redis.conf
38 | subPath: redis.conf
39 | volumes:
40 | - name: redis-config
41 | configMap:
42 | name: shared-packops-redis-config
43 | ---
44 | apiVersion: v1
45 | kind: Service
46 | metadata:
47 | name: shared-packops-redis-svc
48 | labels:
49 | app: shared-packops-redis
50 | spec:
51 | ports:
52 | - name: redis-port
53 | port: 6379
54 | protocol: TCP
55 | targetPort: 6379
56 | selector:
57 | app: shared-packops-redis
58 | type: ClusterIP
59 | ---
60 | apiVersion: v1
61 | kind: ConfigMap
62 | metadata:
63 | name: shared-packops-redis-config
64 | data:
65 | redis.conf: |-
66 | maxmemory 800mb
67 | maxmemory-policy allkeys-lru
68 | appendonly no
69 | requirepass PASSWORD1234P
70 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/installation/containerd-installation.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 1- Disable Swap on Your Linux
2 | Comment out Line swap.image in **/etc/fstab**
3 | ```
4 | swapoff -a
5 | ```
6 | # 2- Make this two module available in k8s moudles
7 | ```
8 | cat <
9 |
10 | ```
11 | +--------------------+
12 | | |
13 | | Service Account |
14 | | pod-reader-sa |
15 | | Namespace: default|
16 | | |
17 | +----------+---------+
18 | |
19 | |
20 | v
21 | +------------------------------------+
22 | | |
23 | | Role |
24 | | pod-reader |
25 | | rules: |
26 | | - apiGroups: [""] |
27 | | resources: ["pods"] |
28 | | verbs: ["get", "watch", "list"] |
29 | | Namespace: default |
30 | | |
31 | +----------+-------------------------+
32 | |
33 | |
34 | v
35 | +-------------------------------+
36 | | |
37 | | RoleBinding |
38 | | read-pods |
39 | | Namespace: default |
40 | | - kind: ServiceAccount |
41 | | name: pod-reader-sa |
42 | | namespace: default |
43 | | roleRef: |
44 | | kind: Role |
45 | | name: pod-reader |
46 | | |
47 | +----------+---------------------+
48 | |
49 | |
50 | v
51 | +--------------------+
52 | | |
53 | | Pod |
54 | | pod-checker |
55 | | Namespace: default|
56 | | Service Account: |
57 | | pod-reader-sa |
58 | | |
59 | +--------------------+
60 |
61 | Relationship:
62 | - Service Account is bound to the Role via RoleBinding.
63 | - Pod uses the Service Account to get permissions defined by the Role.
64 |
65 | ```
66 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ConfigMap/Volume-from-Configmap.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: apps/v1
2 | kind: Deployment
3 | metadata:
4 | labels:
5 | app: stream-enrich
6 | name: stream-enrich
7 | namespace: demo
8 | spec:
9 | replicas: 1
10 | selector:
11 | matchLabels:
12 | app: stream-enrich
13 | strategy:
14 | rollingUpdate:
15 | maxSurge: 25%
16 | maxUnavailable: 25%
17 | type: RollingUpdate
18 | template:
19 | metadata:
20 | labels:
21 | app: stream-enrich
22 | spec:
23 | containers:
24 | - args:
25 | - --config
26 | - /snowplow/config/config.hocon
27 | - --resolver
28 | - file:/snowplow/config/resolver.json
29 | - --enrichments
30 | - file:/snowplow/config/enrichments
31 | env:
32 | - name: SP_JAVA_OPTS
33 | value: -Xms512m -Xmx512m
34 | image: hub.indraproject.ir/hubproxy/snowplow/stream-enrich-kafka:0.21.0
35 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
36 | name: stream-enrich
37 | resources:
38 | limits:
39 | cpu: 800m
40 | memory: 1Gi
41 | requests:
42 | cpu: 800m
43 | memory: 1Gi
44 | volumeMounts:
45 | - name: stream-enrich
46 | mountPath: /snowplow/config/config.hocon
47 | subPath: config.hocon
48 |
49 | - name: resolver
50 | mountPath: /snowplow/config/resolver.json
51 | subPath: resolver.json
52 |
53 | - name: enrichments
54 | mountPath: /snowplow/config/enrichments/anon_ip.json
55 | subPath: anon_ip.json
56 |
57 | restartPolicy: Always
58 | volumes:
59 | - name: stream-enrich
60 | configMap:
61 | name: stream-enrich-config
62 |
63 | - name: resolver
64 | configMap:
65 | name: resolver-enrich-config
66 |
67 | - name: enrichments
68 | configMap:
69 | name: enrichments-enrich-config
70 |
71 | ---
72 | apiVersion: v1
73 | kind: ConfigMap
74 | metadata:
75 | name: enrichments-enrich-config
76 | data:
77 | config.hocon: |
78 | enemies=aliens
79 | lives=3
80 | enemies.cheat=true
81 | enemies.cheat.level=noGoodRotten
82 |
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/security/kube-bench/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | What Kube-bench does for us ?
2 |
3 | Kube-bench runs tests to verify that your Kubernetes installation meets these security benchmarks. It provides detailed output on the areas where your cluster complies with the benchmark and highlights the aspects that need attention. This automated auditing tool is invaluable for system administrators, DevOps teams, and security professionals who aim to maintain robust security postures for their Kubernetes environments.
4 |
5 | In this article, we will delve into the functionality of Kube-bench, explore its key features, and demonstrate how to effectively use it to enhance the security of your Kubernetes clusters. Whether you're a seasoned Kubernetes administrator or a newcomer to the world of container orchestration, understanding and utilizing Kube-bench is an essential step in fortifying your infrastructure against potential security threats.
6 |
7 |
8 | How does kube-bench work ?
9 |
10 | Kube-bench runs a simple kubernetes job in order to check cis security check
11 |
12 | so all thing that we need to do is deploy that job.
13 |
14 | there are lots of kube-bench job for different environment like EKS, GKE ...
15 |
16 | here is kube-bench git repo you can find jobs there:
17 |
18 | https://github.com/aquasecurity/kube-bench/tree/main
19 |
20 |
21 | but in my scenario i've installed 3 node kubernetes cluster on bare-metal so wee need to do :
22 | ```
23 | $ kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/aquasecurity/kube-bench/main/job.yaml
24 |
25 | $ kubectl get pods
26 | NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
27 | kube-bench-j76s9 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 3s
28 |
29 | # Wait for a few seconds for the job to complete
30 | $ kubectl get pods
31 | NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
32 | kube-bench-j76s9 0/1 Completed 0 11s
33 |
34 | # The results are held in the pod's logs
35 | kubectl logs kube-bench-j76s9
36 | [INFO] 1 Master Node Security Configuration
37 | [INFO] 1.1 API Server
38 | ...
39 | ```
40 | Finally you can see the Test's result
41 |
42 | 
43 |
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/multi-container-pattern/side-car/sidecar.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Example YAML configuration for the sidecar pattern.
2 |
3 | # It defines a main application container which writes
4 | # the current date to a log file every five seconds.
5 |
6 | # The sidecar container is nginx serving that log file.
7 | # (In practice, your sidecar is likely to be a log collection
8 | # container that uploads to external storage.)
9 |
10 | # To run:
11 | # kubectl apply -f pod.yaml
12 |
13 | # Once the pod is running:
14 | #
15 | # (Connect to the sidecar pod)
16 | # kubectl exec pod-with-sidecar -c sidecar-container -it bash
17 | #
18 | # (Install curl on the sidecar)
19 | # apt-get update && apt-get install curl
20 | #
21 | # (Access the log file via the sidecar)
22 | # curl 'http://localhost:80/app.txt'
23 |
24 | apiVersion: v1
25 | kind: Pod
26 | metadata:
27 | name: pod-with-sidecar
28 | spec:
29 | # Create a volume called 'shared-logs' that the
30 | # app and sidecar share.
31 | volumes:
32 | - name: shared-logs
33 | emptyDir: {}
34 |
35 | # In the sidecar pattern, there is a main application
36 | # container and a sidecar container.
37 | containers:
38 |
39 | # Main application container
40 | - name: app-container
41 | # Simple application: write the current date
42 | # to the log file every five seconds
43 | image: alpine # alpine is a simple Linux OS image
44 | command: ["/bin/sh"]
45 | args: ["-c", "while true; do date >> /var/log/app.txt; sleep 5;done"]
46 |
47 | # Mount the pod's shared log file into the app
48 | # container. The app writes logs here.
49 | volumeMounts:
50 | - name: shared-logs
51 | mountPath: /var/log
52 |
53 | # Sidecar container
54 | - name: sidecar-container
55 | # Simple sidecar: display log files using nginx.
56 | # In reality, this sidecar would be a custom image
57 | # that uploads logs to a third-party or storage service.
58 | image: nginx:1.7.9
59 | ports:
60 | - containerPort: 80
61 |
62 | # Mount the pod's shared log file into the sidecar
63 | # container. In this case, nginx will serve the files
64 | # in this directory.
65 | volumeMounts:
66 | - name: shared-logs
67 | mountPath: /usr/share/nginx/html # nginx-specific mount path
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/etcd/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # ETCD for Beginners
2 |
3 | In this section, we will take a quick look at introduction to ETCD for beginners.
4 | - What is ETCD?
5 | - What is a Key-Value Store?
6 | - How to get started quickly with ETCD?
7 | - How to operate ETCD?
8 |
9 | ## What is a ETCD?
10 | - ETCD is a distributed reliable key-value store that is simple, secure & Fast.
11 |
12 | ## What is a Key-Value Store
13 | - Traditionally, databases have been in tabular format, you must have heard about SQL or Relational databases. They store data in rows and columns
14 |
15 | 
16 |
17 | - A Key-Value Store stores information in a Key and Value format.
18 |
19 | 
20 |
21 | ## Install ETCD
22 | - It's easy to install and get started with **`ETCD`**.
23 | - Download the relevant binary for your operating system from github releases page (https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/releases)
24 |
25 | For Example: To download ETCD v3.5.6, run the below curl command
26 |
27 | ```
28 | $ curl -LO https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/releases/download/v3.5.6/etcd-v3.5.6-linux-amd64.tar.gz
29 | ```
30 | - Extract it.
31 | ```
32 | $ tar xvzf etcd-v3.5.6-linux-amd64.tar.gz
33 | ```
34 | - Run the ETCD Service
35 | ```
36 | $ ./etcd
37 | ```
38 | - When you start **`ETCD`** it will by default listen on port **`2379`**
39 | - The default client that comes with **`ETCD`** is the [**`etcdctl`**](https://github.com/etcd-io/etcd/tree/main/etcdctl) client. You can use it to store and retrieve key-value pairs.
40 | ```
41 | Syntax: To Store a Key-Value pair
42 | $ ./etcdctl put key1 value1
43 | ```
44 | ```
45 | Syntax: To retrieve the stored data
46 | $ ./etcdctl get key1
47 | ```
48 | ```
49 | Syntax: To view more commands. Run etcdctl without any arguments
50 | $ ./etcdctl
51 | ```
52 |
53 | 
54 |
55 | K8s Reference Docs:
56 | - https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/
57 | - https://etcd.io/docs/
58 | - https://kubernetes.io/docs/tasks/administer-cluster/configure-upgrade-etcd/
59 |
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Resource-Management/QOS/Readme.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | In Kubernetes, Quality of Service (QoS) classes provide a way to categorize pods based on their resource requirements and guarantees. This classification helps Kubernetes prioritize and manage resources more efficiently, especially during times of resource contention.
2 |
3 | Importance of QoS Classes
4 |
5 | Resource Management: QoS classes help Kubernetes make better decisions about scheduling and resource allocation. Higher priority is given to Guaranteed pods over Burstable and BestEffort pods.
6 | Eviction Policies: During resource contention, Kubernetes evicts pods based on their QoS class. BestEffort pods are evicted first, followed by Burstable pods, and finally Guaranteed pods.
7 | Performance Optimization: By categorizing pods based on their resource requirements, Kubernetes can ensure that critical applications receive the necessary resources to function correctly, while less critical applications use resources more flexibly.
8 |
9 | | QoS Class | Description | Resource Requirements | Eviction Priority | Use Case |
10 | |--------------|---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------------------------------------------|---------------------------------------|----------------------------------------------------|
11 | | Guaranteed | Provides strong resource guarantees. All containers must have equal `requests` and `limits`. | `requests` and `limits` must be specified and equal for all containers. | Last to be evicted | Critical workloads requiring guaranteed resources |
12 | | Burstable | Offers flexible resource usage with some guarantees. At least one container must have a `request`. | At least one container must have `requests` for CPU or memory. | Evicted before Guaranteed, after BestEffort | Workloads that can tolerate some resource variability |
13 | | BestEffort | No resource guarantees. No `requests` or `limits` specified for any container. | No `requests` or `limits` specified. | First to be evicted | Non-critical workloads with minimal resource needs |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Mastering Kubernetes: A Comprehensive Repo for CKA Exam
2 | Welcome to the **Mastering Kubernetes** repository! This project is designed to help you prepare for the Certified Kubernetes Administrator (CKA) exam and deepen your understanding of Kubernetes.
3 |
4 |

5 |
- Easier to automate and version control |
12 | | **Cons** | - Error-prone
- Less consistent and repeatable | - Steeper learning curve
- Less immediate control |
13 | | **Examples** | - `kubectl run nginx --image=nginx`
- `kubectl delete pod my-pod` | - `kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml`
- `kubectl apply -f service.yaml` |
14 | | **Learning Curve** | Lower | Higher |
15 | | **Version Control** | Less straightforward | Natural fit for version control systems (e.g., Git) |
16 |
17 |
18 | # Kubectl Cheat Sheet
19 |
20 | | **Command** | **Description** |
21 | |-----------------------------------------------|------------------------------------------------------------|
22 | | `kubectl version` | Display the Kubernetes version |
23 | | `kubectl cluster-info` | Display cluster information |
24 | | `kubectl get nodes` | List all nodes in the cluster |
25 | | `kubectl describe node ` | Display detailed information about a specific node |
26 | | `kubectl get pods` | List all Pods in the default namespace |
27 | | `kubectl get pods --all-namespaces` | List all Pods in all namespaces |
28 | | `kubectl get pods -n ` | List all Pods in a specific namespace |
29 | | `kubectl describe pod ` | Display detailed information about a specific Pod |
30 | | `kubectl logs ` | Print the logs for a container in a Pod |
31 | | `kubectl exec -it -- /bin/bash` | Execute a command in a container in a Pod |
32 | | `kubectl get services` | List all Services in the default namespace |
33 | | `kubectl get svc` | Shorthand for `kubectl get services` |
34 | | `kubectl describe svc ` | Display detailed information about a specific Service |
35 | | `kubectl get deployments` | List all Deployments in the default namespace |
36 | | `kubectl describe deployment `| Display detailed information about a specific Deployment |
37 | | `kubectl get replicasets` | List all ReplicaSets in the default namespace |
38 | | `kubectl get rs` | Shorthand for `kubectl get replicasets` |
39 | | `kubectl describe rs ` | Display detailed information about a specific ReplicaSet |
40 | | `kubectl get namespaces` | List all namespaces |
41 | | `kubectl get ns` | Shorthand for `kubectl get namespaces` |
42 | | `kubectl create namespace ` | Create a new namespace |
43 | | `kubectl delete namespace ` | Delete a namespace |
44 | | `kubectl apply -f ` | Apply a configuration to a resource by filename or stdin |
45 | | `kubectl create -f ` | Create a resource from a file |
46 | | `kubectl delete -f ` | Delete a resource from a file |
47 | | `kubectl edit ` | Edit a resource on the server |
48 | | `kubectl scale --replicas= deployment/` | Scale a deployment to a specified number of replicas |
49 | | `kubectl rollout status deployment/` | Watch the rollout status of a deployment |
50 | | `kubectl rollout undo deployment/` | Undo a deployment to a previous revision |
51 | | `kubectl get configmaps` | List all ConfigMaps in the default namespace |
52 | | `kubectl describe configmap ` | Display detailed information about a specific ConfigMap |
53 | | `kubectl get secrets` | List all Secrets in the default namespace |
54 | | `kubectl describe secret ` | Display detailed information about a specific Secret |
55 | | `kubectl get pv` | List all PersistentVolumes |
56 | | `kubectl get pvc` | List all PersistentVolumeClaims in the default namespace |
57 | | `kubectl describe pvc ` | Display detailed information about a specific PVC |
58 | | `kubectl get events` | List all events in the default namespace |
59 | | `kubectl top nodes` | Display resource (CPU/memory) usage of nodes |
60 | | `kubectl top pods` | Display resource (CPU/memory) usage of Pods |
61 |
62 | ## Tips
63 | - Replace `` with the type of resource you are managing, such as `pod`, `service`, `deployment`, etc.
64 | - Replace `` with the name of the specific resource.
65 | - Replace `` with the namespace you want to interact with.
66 | - Use `-o wide` with `get` commands to get more detailed output.
67 | - Use `-o yaml` or `-o json` to get the output in YAML or JSON format, respectively.
68 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/istio/istio-app.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | apiVersion: v1
2 | kind: Service
3 | metadata:
4 | name: details
5 | labels:
6 | app: details
7 | service: details
8 | spec:
9 | ports:
10 | - port: 9080
11 | name: http
12 | selector:
13 | app: details
14 | ---
15 | apiVersion: v1
16 | kind: ServiceAccount
17 | metadata:
18 | name: bookinfo-details
19 | labels:
20 | account: details
21 | ---
22 | apiVersion: apps/v1
23 | kind: Deployment
24 | metadata:
25 | name: details-v1
26 | labels:
27 | app: details
28 | version: v1
29 | spec:
30 | replicas: 1
31 | selector:
32 | matchLabels:
33 | app: details
34 | version: v1
35 | template:
36 | metadata:
37 | labels:
38 | app: details
39 | version: v1
40 | spec:
41 | serviceAccountName: bookinfo-details
42 | containers:
43 | - name: details
44 | image: docker.io/istio/examples-bookinfo-details-v1:1.17.0
45 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
46 | ports:
47 | - containerPort: 9080
48 | securityContext:
49 | runAsUser: 1000
50 | ---
51 | ##################################################################################################
52 | # Ratings service
53 | ##################################################################################################
54 | apiVersion: v1
55 | kind: Service
56 | metadata:
57 | name: ratings
58 | labels:
59 | app: ratings
60 | service: ratings
61 | spec:
62 | ports:
63 | - port: 9080
64 | name: http
65 | selector:
66 | app: ratings
67 | ---
68 | apiVersion: v1
69 | kind: ServiceAccount
70 | metadata:
71 | name: bookinfo-ratings
72 | labels:
73 | account: ratings
74 | ---
75 | apiVersion: apps/v1
76 | kind: Deployment
77 | metadata:
78 | name: ratings-v1
79 | labels:
80 | app: ratings
81 | version: v1
82 | spec:
83 | replicas: 1
84 | selector:
85 | matchLabels:
86 | app: ratings
87 | version: v1
88 | template:
89 | metadata:
90 | labels:
91 | app: ratings
92 | version: v1
93 | spec:
94 | serviceAccountName: bookinfo-ratings
95 | containers:
96 | - name: ratings
97 | image: docker.io/istio/examples-bookinfo-ratings-v1:1.17.0
98 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
99 | ports:
100 | - containerPort: 9080
101 | securityContext:
102 | runAsUser: 1000
103 | ---
104 | ##################################################################################################
105 | # Reviews service
106 | ##################################################################################################
107 | apiVersion: v1
108 | kind: Service
109 | metadata:
110 | name: reviews
111 | labels:
112 | app: reviews
113 | service: reviews
114 | spec:
115 | ports:
116 | - port: 9080
117 | name: http
118 | selector:
119 | app: reviews
120 | ---
121 | apiVersion: v1
122 | kind: ServiceAccount
123 | metadata:
124 | name: bookinfo-reviews
125 | labels:
126 | account: reviews
127 | ---
128 | apiVersion: apps/v1
129 | kind: Deployment
130 | metadata:
131 | name: reviews-v1
132 | labels:
133 | app: reviews
134 | version: v1
135 | spec:
136 | replicas: 1
137 | selector:
138 | matchLabels:
139 | app: reviews
140 | version: v1
141 | template:
142 | metadata:
143 | labels:
144 | app: reviews
145 | version: v1
146 | spec:
147 | serviceAccountName: bookinfo-reviews
148 | containers:
149 | - name: reviews
150 | image: docker.io/istio/examples-bookinfo-reviews-v1:1.17.0
151 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
152 | env:
153 | - name: LOG_DIR
154 | value: "/tmp/logs"
155 | ports:
156 | - containerPort: 9080
157 | volumeMounts:
158 | - name: tmp
159 | mountPath: /tmp
160 | - name: wlp-output
161 | mountPath: /opt/ibm/wlp/output
162 | securityContext:
163 | runAsUser: 1000
164 | volumes:
165 | - name: wlp-output
166 | emptyDir: {}
167 | - name: tmp
168 | emptyDir: {}
169 | ---
170 | apiVersion: apps/v1
171 | kind: Deployment
172 | metadata:
173 | name: reviews-v2
174 | labels:
175 | app: reviews
176 | version: v2
177 | spec:
178 | replicas: 1
179 | selector:
180 | matchLabels:
181 | app: reviews
182 | version: v2
183 | template:
184 | metadata:
185 | labels:
186 | app: reviews
187 | version: v2
188 | spec:
189 | serviceAccountName: bookinfo-reviews
190 | containers:
191 | - name: reviews
192 | image: docker.io/istio/examples-bookinfo-reviews-v2:1.17.0
193 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
194 | env:
195 | - name: LOG_DIR
196 | value: "/tmp/logs"
197 | ports:
198 | - containerPort: 9080
199 | volumeMounts:
200 | - name: tmp
201 | mountPath: /tmp
202 | - name: wlp-output
203 | mountPath: /opt/ibm/wlp/output
204 | securityContext:
205 | runAsUser: 1000
206 | volumes:
207 | - name: wlp-output
208 | emptyDir: {}
209 | - name: tmp
210 | emptyDir: {}
211 | ---
212 | apiVersion: apps/v1
213 | kind: Deployment
214 | metadata:
215 | name: reviews-v3
216 | labels:
217 | app: reviews
218 | version: v3
219 | spec:
220 | replicas: 1
221 | selector:
222 | matchLabels:
223 | app: reviews
224 | version: v3
225 | template:
226 | metadata:
227 | labels:
228 | app: reviews
229 | version: v3
230 | spec:
231 | serviceAccountName: bookinfo-reviews
232 | containers:
233 | - name: reviews
234 | image: docker.io/istio/examples-bookinfo-reviews-v3:1.17.0
235 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
236 | env:
237 | - name: LOG_DIR
238 | value: "/tmp/logs"
239 | ports:
240 | - containerPort: 9080
241 | volumeMounts:
242 | - name: tmp
243 | mountPath: /tmp
244 | - name: wlp-output
245 | mountPath: /opt/ibm/wlp/output
246 | securityContext:
247 | runAsUser: 1000
248 | volumes:
249 | - name: wlp-output
250 | emptyDir: {}
251 | - name: tmp
252 | emptyDir: {}
253 | ---
254 | ##################################################################################################
255 | # Productpage services
256 | ##################################################################################################
257 | apiVersion: v1
258 | kind: Service
259 | metadata:
260 | name: productpage
261 | labels:
262 | app: productpage
263 | service: productpage
264 | spec:
265 | ports:
266 | - port: 9080
267 | name: http
268 | selector:
269 | app: productpage
270 | ---
271 | apiVersion: v1
272 | kind: ServiceAccount
273 | metadata:
274 | name: bookinfo-productpage
275 | labels:
276 | account: productpage
277 | ---
278 | apiVersion: apps/v1
279 | kind: Deployment
280 | metadata:
281 | name: productpage-v1
282 | labels:
283 | app: productpage
284 | version: v1
285 | spec:
286 | replicas: 1
287 | selector:
288 | matchLabels:
289 | app: productpage
290 | version: v1
291 | template:
292 | metadata:
293 | labels:
294 | app: productpage
295 | version: v1
296 | spec:
297 | serviceAccountName: bookinfo-productpage
298 | containers:
299 | - name: productpage
300 | image: docker.io/istio/examples-bookinfo-productpage-v1:1.17.0
301 | imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
302 | ports:
303 | - containerPort: 9080
304 | volumeMounts:
305 | - name: tmp
306 | mountPath: /tmp
307 | securityContext:
308 | runAsUser: 1000
309 | volumes:
310 | - name: tmp
311 | emptyDir: {}
312 | ---
313 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 5 |
5 |