├── .gitignore
├── .jshintrc
├── .npmignore
├── .npmrc
├── .travis.yml
├── History.md
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── examples
├── accessible.js
├── blink-led-async.js
├── blink-led-promises.js
├── blink-led.js
├── debounce-button.js
├── light-switch.js
├── light-switch.png
├── mygpio-overlay.dts
├── run-examples
└── wait-for-interrupt.js
├── integration-test
├── blink-led-promises.js
├── blink-led.js
├── change-configuration.js
├── configure-and-check-active-low-defaults.js
├── configure-and-check-active-low.js
├── configure-and-check-input.js
├── configure-and-check-output.js
├── debounce.js
├── dont-reconfigure-direction-part1.js
├── dont-reconfigure-direction-part2.js
├── export-many-times.js
├── high-low.js
├── many-interrupts.js
├── output-with-edge-bug.js
├── performance-async.js
├── performance-interrupt.js
├── performance-sync.js
├── run-performance-tests
├── run-tests
├── wait-for-interrupt.js
└── wait-for-many-interrupts.js
├── onoff.d.ts
├── onoff.js
├── package.json
├── test
├── accessible.js
├── activeLow.js
├── constructor-fails.js
├── constructor.js
├── direction.js
├── edge.js
├── mocks
│ ├── epoll.d.ts
│ ├── epoll.js
│ ├── linux.d.ts
│ └── linux.js
├── read.js
├── readSync.js
├── setActiveLow.js
├── setDirection.js
├── setEdge.js
├── typedefinition.ts
├── utils
│ └── test-promise.js
├── watch-callbacks.js
├── watch-listeners.js
├── write.js
└── writeSync.js
└── tsconfig.json
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *~
2 | .nyc_output
3 | coverage
4 | node_modules
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.jshintrc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "curly": true,
3 | "esversion": 6,
4 | "eqeqeq": true,
5 | "latedef": false,
6 | "noarg": true,
7 | "node": true,
8 | "quotmark": "single",
9 | "strict": "global",
10 | "undef": true,
11 | "varstmt": true,
12 | "globals": {
13 | "afterEach": false,
14 | "beforeEach": false,
15 | "describe": false,
16 | "it": false
17 | }
18 | }
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.npmignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *~
2 | .jshintrc
3 | .nyc_output/
4 | .travis.yml
5 | coverage/
6 | node_modules/
7 | test/
8 | tsconfig.json
9 |
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.npmrc:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | package-lock=false
2 |
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.travis.yml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | os: linux
2 | arch:
3 | - arm64
4 | - ppc64le
5 | - s390x
6 | language: node_js
7 | node_js:
8 | - "16"
9 | - "15"
10 | - "14"
11 | - "12"
12 | - "10"
13 | env:
14 | - CXX=g++-6
15 | addons:
16 | apt:
17 | sources:
18 | - ubuntu-toolchain-r-test
19 | packages:
20 | - g++-6
21 | script:
22 | - npm run lint
23 | - npm test
24 | after_success:
25 | - npm run codecov
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/History.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 6.0.3 - Apr 26 2021
2 | ===================
3 |
4 | * update performance numbers
5 | * add support for node.js 16
6 | * update dependencies
7 |
8 | 6.0.2 - Apr 07 2021
9 | ===================
10 |
11 | * fix accessible property (thank you [@mildsunrise](https://github.com/mildsunrise))
12 | * update dependencies
13 | * add support for node.js 15
14 |
15 | 6.0.1 - Oct 10 2020
16 | ===================
17 |
18 | * switch from coveralls to codecov
19 | * update dependencies
20 | * drop support for node.js 8
21 | * drop support for node.js 13
22 |
23 | 6.0.0 - Apr 23 2020
24 | ===================
25 |
26 | * document the potential of EPERM errors when invoking write methods (fixes [#167](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/167))
27 | * drop support for node.js 6, add support for node.js 14
28 | * avoid calling fs.writeFileSync with numeric data (fixes [#170](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/170))
29 | * update dependencies
30 | * use g++-6 on travis
31 |
32 | 5.0.1 - Dec 24 2019
33 | ===================
34 |
35 | * document node 11 support
36 | * update benchmark results for pi 1, 2, 3 and 4
37 |
38 | 5.0.0 - Sep 22 2019
39 | ===================
40 |
41 | * drop support for node.js v4
42 | * update dependencies (epoll v3.0.0, ts-node v8.4.1, typescript v3.6.3)
43 |
44 | 4.1.4 - Sep 07 2019
45 | ===================
46 |
47 | * update dependencies (epoll v2.0.10, coveralls v3.0.6, mocha v6.2.0, typescript v3.6.2)
48 |
49 | 4.1.3 - Jul 05 2019
50 | ===================
51 |
52 | * avoid recursion in read and write methods (fixes [#156](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/156))
53 |
54 | 4.1.2 - Jun 16 2019
55 | ===================
56 |
57 | * fix export
58 | * refactor promises (thank you [@pizzaisdavid](https://github.com/pizzaisdavid))
59 | * update npm keywords
60 | * update dependencies
61 |
62 | 4.1.1 - Mar 14 2019
63 | ===================
64 |
65 | * simplify constructor
66 | * update dependencies (epoll v2.0.9, jshint v2.10.2, ts-node v8.0.3)
67 |
68 | 4.1.0 - Mar 03 2019
69 | ===================
70 |
71 | * add type definitions for TypeScript (thank you [@saenglert](https://github.com/saenglert))
72 |
73 | 4.0.0 - Feb 28 2019
74 | ===================
75 |
76 | * added Promises to async read/write operations (thank you [@saenglert](https://github.com/saenglert)) - breaking change
77 | * update dependencies (mocha@6.0.2, nyc@13.3.0)
78 |
79 | 3.2.9 - Feb 24 2019
80 | ===================
81 |
82 | * post lcov to coveralls.io
83 |
84 | 3.2.8 - Feb 21 2019
85 | ===================
86 |
87 | * prevent EACCES errors from occurring while waiting for file access permission [#131](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/131)
88 |
89 | 3.2.7 - Feb 17 2019
90 | ===================
91 |
92 | * add code coverage to build
93 | * add more unit tests
94 | * document node 11 support
95 | * only reconfigure direction if needed [#128](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/128)
96 |
97 | 3.2.6 - Feb 09 2019
98 | ===================
99 |
100 | * add travis build
101 |
102 | 3.2.5 - Feb 09 2019
103 | ===================
104 |
105 | * lint with jshint
106 |
107 | 3.2.4 - Feb 09 2019
108 | ===================
109 |
110 | * add .npmignore
111 |
112 | 3.2.3 - Feb 09 2019
113 | ===================
114 |
115 | * update dependencies
116 |
117 | 3.2.2 - Sep 30 2018
118 | ===================
119 |
120 | * add unittests for reading and writing (thank you [@pizzaisdavid](https://github.com/pizzaisdavid))
121 | * update dependencies (epoll v2.0.4, mocha v4.7.0)
122 |
123 | 3.2.1 - Jul 28 2018
124 | ===================
125 |
126 | * code style
127 | * update dependencies (epoll v2.0.3)
128 |
129 | 3.2.0 - Jul 24 2018
130 | ===================
131 |
132 | * add test to ensure HIGH and LOW have the expected values
133 | * add unittests (thank you [@pizzaisdavid](https://github.com/pizzaisdavid))
134 | * set active_low before setting direction in constructor
135 | * add constructor reconfigureDirection option
136 |
137 | 3.1.0 - May 13 2018
138 | ===================
139 |
140 | * replace new Buffer with Buffer.from or Buffer.alloc
141 | * add accessebile property to Gpio class (thank you [@johntalton](https://github.com/johntalton))
142 | * add HIGH and LOW properties to Gpio class (thank you [@johntalton](https://github.com/johntalton))
143 |
144 | 3.0.2 - Apr 07 2018
145 | ===================
146 |
147 | * update dependencies (epoll v2.0.1)
148 | * improve performance tests
149 |
150 | 3.0.1 - Apr 01 2018
151 | ===================
152 |
153 | * create poller for both inputs and outputs
154 | * add test to verify that gpio direction can be changed
155 |
156 | 3.0.0 - Mar 31 2018
157 | ===================
158 |
159 | * add effective debouncing support
160 | * codebase modernized
161 | * remove link to outdated tutorial
162 | * remove undocumented options method
163 |
164 | 2.0.0 - Feb 26 2018
165 | ===================
166 |
167 | * update dependencies (epoll v2.0.0)
168 | * drop support for node.js v0.10, v0.12, v5 and v7
169 |
170 | 1.2.0 - Feb 11 2018
171 | ===================
172 |
173 | * ignore edge argument when instantiating a Gpio for an output
174 |
175 | 1.1.9 - Dec 24 2017
176 | ===================
177 |
178 | * document node 9 support
179 | * update BeagleBone performance numbers
180 | * many documentation improvements
181 | * update BeagleBone Black performance numbers
182 | * update dependencies
183 |
184 | 1.1.8 - Oct 15 2017
185 | ===================
186 |
187 | * update dependencies (epoll v1.0.0)
188 |
189 | 1.1.7 - Aug 26 2017
190 | ===================
191 |
192 | * only check permissions for edge file if edge specified [#77](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/77)
193 |
194 | 1.1.5 - Jul 30 2017
195 | ===================
196 |
197 | * wait until unprivileged file access allowed
198 |
199 | 1.1.4 - Jul 15 2017
200 | ===================
201 |
202 | * improve examples
203 |
204 | 1.1.3 - Jun 18 2017
205 | ===================
206 | * upgrade to epoll v0.1.22
207 | * document related packages
208 |
209 | 1.1.2 - Feb 12 2017
210 | ===================
211 | * documentation improved
212 | * upgrade to epoll v0.1.21
213 |
214 | 1.1.1 - Jun 05 2016
215 | ===================
216 | * avoid exceptions when cape_universal is enabled on the bbb [#50](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/50)
217 |
218 | 1.1.0 - May 04 2016
219 | ===================
220 | * activeLow option
221 | * documentation improved
222 |
223 | 1.0.4 - Jan 29 2016
224 | ===================
225 | * documentation improved
226 | * epoll v0.1.17
227 |
228 | 1.0.3 - Oct 10 2015
229 | ===================
230 | * documentation improved
231 | * epoll v0.1.16
232 |
233 | 1.0.2 - Feb 18 2015
234 | ===================
235 | * documentation improved
236 |
237 | 1.0.1 - Feb 15 2015
238 | ===================
239 | * refactored tests to avoid relying in interrupt generating outputs as linux 3.13 and above no longer supports them
240 | * new wiring for tests and examples
241 | * pullup and pulldown resistor configuration documented
242 |
243 | 1.0.0 - Jan 10 2015
244 | ===================
245 | * use strict mode
246 | * jslint improvements
247 | * updated dependencies: epoll 0.1.4 -> 0.1.10
248 | * new wiring for tests on pi
249 | * GPIO access without superuser privileges on Raspbian
250 |
251 | 0.3.2 - Apr 18 2014
252 | ===================
253 | * Documented BeagleBone Ångström prerequisites
254 | * Updated dependencies: epoll 0.1.2 -> 0.1.4
255 |
256 | 0.3.1 - Mar 22 2014
257 | ===================
258 | * Added setDirection functionality [#19](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/pull/19)
259 | * Added setEdge functionality
260 | * Updated dependencies: epoll 0.1.0 -> 0.1.2
261 |
262 | 0.3.0 - Nov 18 2013
263 | ===================
264 | * Updated dependencies: epoll 0.0.8 -> 0.1.0
265 | * Removed persistentWatch option
266 |
267 | 0.2.3 - Oct 14 2013
268 | ===================
269 |
270 | * Use epoll 0.0.8
271 | * onoff now plays well with the quick2wire gpio-admin and the WiringPi gpio utilities on the Pi [#14](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/14)
272 | * Documentation improved
273 | * New test to monitor interrupt performance
274 | * New light switch example
275 |
276 | 0.2.2 - Oct 05 2013
277 | ===================
278 |
279 | * Use epoll 0.0.7
280 | * Removed timeout hack in many-interrupts test
281 |
282 | 0.2.1 - Sep 25 2013
283 | ===================
284 |
285 | * Use epoll 0.0.3
286 | * Improved five-inputs test
287 |
288 | 0.2.0 - Sep 22 2013
289 | ===================
290 |
291 | * Use epoll module for interrupt detection [#15](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/15)
292 | * 0.11.4+ compatability [#11](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/10)
293 | * One thread for watching all GPIOs rather than one thread per GPIO [#5](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/5)
294 | * Unwatch API added [#4](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/4)
295 |
296 | 0.1.7 - Sep 17 2013
297 | ===================
298 |
299 | * Remove OS limitations for installing [#12](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/12)
300 |
301 | 0.1.6 - July 15 2013
302 | ===================
303 |
304 | * Fixed typos
305 | * Documented how to watch five or more inputs
306 |
307 | 0.1.5 - May 26 2013
308 | ===================
309 |
310 | * Added test with five inputs
311 |
312 | 0.1.0 - Nov 11 2012
313 | ===================
314 |
315 | * Added Gpio objects
316 | * Removed functions, use Gpio objects instead
317 | * Performance improvements
318 | * Synchronous or asynchronous access to a GPIOs value
319 | * Allow applications to handle superuser issues
320 |
321 | 0.0.1 - Oct 28 2012
322 | ===================
323 |
324 | * Initial release
325 |
326 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | (The MIT License)
2 |
3 | Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaining
4 | a copy of this software and associated documentation files (the
5 | 'Software'), to deal in the Software without restriction, including
6 | without limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish,
7 | distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and to
8 | permit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject to
9 | the following conditions:
10 |
11 | The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall be
12 | included in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
13 |
14 | THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED 'AS IS', WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
15 | EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OF
16 | MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT.
17 | IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY
18 | CLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT,
19 | TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THE
20 | SOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
21 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [](https://app.travis-ci.com/github/fivdi/onoff)
2 | [](https://codecov.io/gh/fivdi/onoff)
3 | [](https://www.npmjs.com/package/onoff)
4 | [](https://www.npmjs.com/package/onoff)
5 | [](https://github.com/sindresorhus/awesome-nodejs#hardware)
6 |
7 | # onoff
8 |
9 | GPIO access and interrupt detection with **Node.js** on Linux boards like the
10 | Raspberry Pi or BeagleBone.
11 |
12 | onoff supports Node.js versions 10, 12, 14, 15 and 16.
13 |
14 | ## Contents
15 |
16 | * [Installation](#installation)
17 | * [Usage](#usage)
18 | * [LEDs and Buttons](#leds-and-buttons)
19 | * [Debouncing Buttons](#debouncing-buttons)
20 | * [Blink an LED Using the Synchronous API](#blink-an-led-using-the-synchronous-api)
21 | * [Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Completion Callbacks](#blink-an-led-using-the-asynchronous-api-and-completion-callbacks)
22 | * [Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Promises](#blink-an-led-using-the-asynchronous-api-and-promises)
23 | * [API](#api)
24 | * [How Does onoff Work?](#how-does-onoff-work)
25 | * [Configuring Pullup and Pulldown Resistors](#configuring-pullup-and-pulldown-resistors)
26 | * [Benchmarks](#benchmarks)
27 | * [Related Packages](#related-packages)
28 | * [Additional Information](#additional-information)
29 |
30 | ## Installation
31 |
32 | ```
33 | npm install onoff
34 | ```
35 |
36 | Note that although it's possible to install onoff on non-Linux systems the
37 | functionality offered by onoff is only available on Linux systems.
38 |
39 | ## Usage
40 |
41 | #### LEDs and Buttons
42 | Assume that there's an LED connected to GPIO17 and a momentary push button
43 | connected to GPIO4.
44 |
45 | 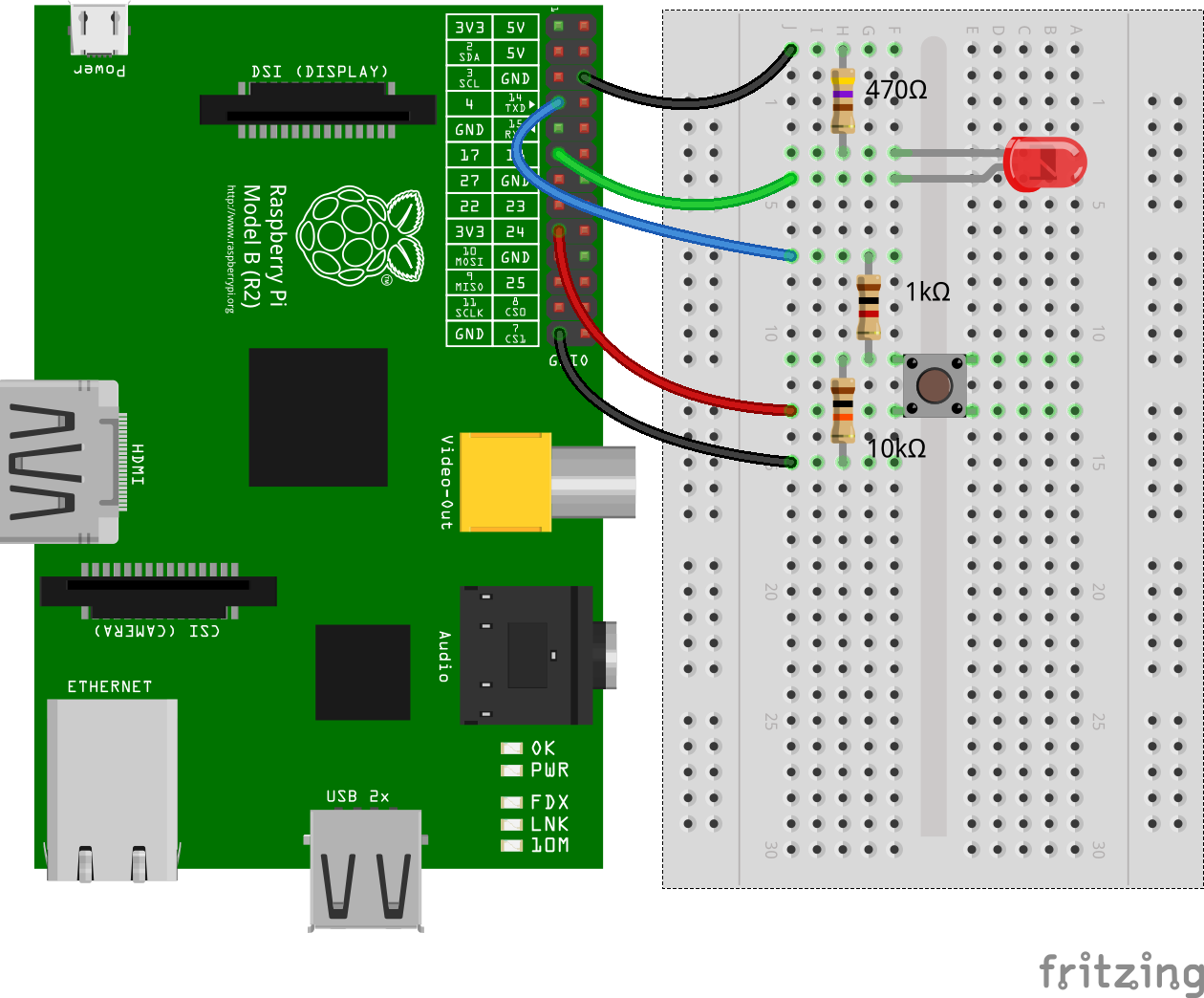 46 |
47 | When the button is pressed the LED should turn on, when it's released the LED
48 | should turn off. This can be achieved with the following code:
49 |
50 | ```js
51 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
52 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
53 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
54 |
55 | button.watch((err, value) => led.writeSync(value));
56 | ```
57 |
58 | Here two Gpio objects are being created. One called led for the LED connected
59 | to GPIO17 which is an output, and one called button for the momentary push
60 | button connected to GPIO4 which is an input. In addition to specifying that
61 | the button is an input, the constructors optional third argument is used to
62 | specify that 'both' rising and falling interrupt edges should be configured
63 | for the button GPIO as both button presses and releases should be handled.
64 |
65 | After everything has been setup correctly, the buttons watch method is used to
66 | specify a callback function to execute every time the button is pressed or
67 | released. The value argument passed to the callback function represents the
68 | state of the button which will be 1 for pressed and 0 for released. This value
69 | is used by the callback to turn the LED on or off using its writeSync method.
70 |
71 | When the above program is running it can be terminated with ctrl-c. However,
72 | it doesn't free its resources. It also ignores the err argument passed to
73 | the callback. Here's a slightly modified variant of the program that handles
74 | ctrl-c gracefully and bails out on error. The resources used by the led and
75 | button Gpio objects are released by invoking their unexport method.
76 |
77 | ```js
78 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
79 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
80 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
81 |
82 | button.watch((err, value) => {
83 | if (err) {
84 | throw err;
85 | }
86 |
87 | led.writeSync(value);
88 | });
89 |
90 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
91 | led.unexport();
92 | button.unexport();
93 | });
94 | ```
95 |
96 | #### Debouncing Buttons
97 | When working with buttons there will often be button bounce issues which
98 | result in the hardware thinking that a button was pressed several times
99 | although it was only pressed once. onoff provides a software debouncing
100 | solution for resolving bounce issues.
101 |
102 | Assume again that there's an LED connected to GPIO17 and a momentary push
103 | button connected to GPIO4.
104 |
105 | When the button is pressed the LED should toggle its state. This is a typical
106 | example of a situation where there will be button bounce issues. The issue can
107 | be resolved by using the debounceTimeout option when creating the Gpio object
108 | for the button. In the below program the debounceTimeout is set to 10
109 | milliseconds. This delays invoking the watch callback for the button while the
110 | button is bouncing. The watch callback will not be invoked until the button
111 | stops bouncing and has been in a stable state for 10 milliseconds.
112 |
113 | ```js
114 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
115 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
116 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
117 |
118 | button.watch((err, value) => {
119 | if (err) {
120 | throw err;
121 | }
122 |
123 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
124 | });
125 |
126 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
127 | led.unexport();
128 | button.unexport();
129 | });
130 | ```
131 |
132 | #### Blink an LED Using the Synchronous API
133 |
134 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the synchronous readSync
135 | and writeSync methods.
136 |
137 | ```js
138 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
139 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
140 |
141 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
142 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 200);
143 |
144 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
145 | setTimeout(_ => {
146 | clearInterval(iv); // Stop blinking
147 | led.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
148 | }, 5000);
149 | ```
150 |
151 | #### Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Completion Callbacks
152 |
153 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the asynchronous read and
154 | write methods and completion callbacks.
155 |
156 | ```js
157 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
158 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
159 | let stopBlinking = false;
160 |
161 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
162 | const blinkLed = _ => {
163 | if (stopBlinking) {
164 | return led.unexport();
165 | }
166 |
167 | led.read((err, value) => { // Asynchronous read
168 | if (err) {
169 | throw err;
170 | }
171 |
172 | led.write(value ^ 1, err => { // Asynchronous write
173 | if (err) {
174 | throw err;
175 | }
176 | });
177 | });
178 |
179 | setTimeout(blinkLed, 200);
180 | };
181 |
182 | blinkLed();
183 |
184 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
185 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
186 | ```
187 |
188 | #### Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Promises
189 |
190 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the asynchronous read and
191 | write methods and Promises.
192 |
193 | ```js
194 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
195 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
196 | let stopBlinking = false;
197 |
198 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
199 | const blinkLed = _ => {
200 | if (stopBlinking) {
201 | return led.unexport();
202 | }
203 |
204 | led.read()
205 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
206 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 200))
207 | .catch(err => console.log(err));
208 | };
209 |
210 | blinkLed();
211 |
212 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
213 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
214 | ```
215 |
216 | #### Check accessibility
217 |
218 | Sometimes it may be necessary to determine if the current system supports
219 | GPIOs programmatically and mock functionality if it doesn't. `Gpio.accessible`
220 | can be used to achieve this.
221 |
222 | ```js
223 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
224 |
225 | const useLed = (led, value) => led.writeSync(value);
226 |
227 | let led;
228 |
229 | if (Gpio.accessible) {
230 | led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
231 | // more real code here
232 | } else {
233 | led = {
234 | writeSync: value => {
235 | console.log('virtual led now uses value: ' + value);
236 | }
237 | };
238 | }
239 |
240 | useLed(led, 1);
241 | ```
242 |
243 | ## API
244 |
245 | ### Class Gpio
246 |
247 | * [Gpio(gpio, direction [, edge] [, options]) - Constructor](#gpiogpio-direction--edge--options)
248 | * [read([callback]) - Read GPIO value asynchronously](#readcallback)
249 | * [readSync() - Read GPIO value synchronously](#readsync)
250 | * [write(value[, callback]) - Write GPIO value asynchronously](#writevalue-callback)
251 | * [writeSync(value) - Write GPIO value synchronously](#writesyncvalue)
252 | * [watch(callback) - Watch for hardware interrupts on the GPIO](#watchcallback)
253 | * [unwatch([callback]) - Stop watching for hardware interrupts on the GPIO](#unwatchcallback)
254 | * [unwatchAll() - Remove all watchers for the GPIO](#unwatchall)
255 | * [direction() - Get GPIO direction](#direction)
256 | * [setDirection(direction) - Set GPIO direction](#setdirectiondirection)
257 | * [edge() - Get GPIO interrupt generating edge](#edge)
258 | * [setEdge(edge) - Set GPIO interrupt generating edge](#setedgeedge)
259 | * [activeLow() - Get GPIO activeLow setting](#activelow)
260 | * [setActiveLow(invert) - Set GPIO activeLow setting](#setactivelowinvert)
261 | * [unexport() - Reverse the effect of exporting the GPIO to userspace](#unexport)
262 | * [static accessible - Determine whether or not GPIO access is possible](#static-accessible)
263 | * [HIGH / LOW - Constants used when reading or writing a GPIO value](#static-high--low)
264 |
265 | ##### Gpio(gpio, direction [, edge] [, options])
266 | - gpio - An unsigned integer specifying the GPIO number.
267 | - direction - A string specifying whether the GPIO should be configured as an
268 | input or output. The valid values are: 'in', 'out', 'high', and 'low'. If 'out'
269 | is specified the GPIO will be configured as an output and the value of the GPIO
270 | will be set to 0. 'high' and 'low' are variants of 'out' that configure the
271 | GPIO as an output with an initial level of 1 or 0 respectively.
272 | - [edge] - An optional string specifying the interrupt generating edge or
273 | edges for an input GPIO. The valid values are: 'none', 'rising', 'falling' or
274 | 'both'. The default value is 'none' indicating that the GPIO will not generate
275 | interrupts. Whether or not interrupts are supported by an input GPIO is GPIO
276 | specific. If interrupts are not supported by a GPIO the edge argument should
277 | not be specified. The edge argument is ignored for output GPIOs.
278 | - [options] - An optional options object.
279 |
280 | Configures the GPIO based on the passed arguments and returns a new Gpio
281 | object that can be used to access the GPIO.
282 |
283 | The following options are supported:
284 | - debounceTimeout - An unsigned integer specifying a millisecond delay. Delays
285 | invoking the watch callback for an interrupt generating input GPIO while the
286 | input is bouncing. The watch callback will not be invoked until the input
287 | stops bouncing and has been in a stable state for debounceTimeout
288 | milliseconds. Optional, if unspecified the input GPIO will not be debounced.
289 | - activeLow - A boolean value specifying whether the values read from or
290 | written to the GPIO should be inverted. The interrupt generating edge for the
291 | GPIO also follow this this setting. The valid values for activeLow are true
292 | and false. Setting activeLow to true inverts. Optional, the default value is
293 | false.
294 | - reconfigureDirection - A boolean value specifying whether the direction for
295 | the GPIO should be reconfigured even though the direction is already
296 | configured correctly. When an application starts, the direction of a GPIO used
297 | by that application may already be configured correctly, for example, from a
298 | previous run of the application. Reconfiguring the direction of that GPIO can
299 | result in unwanted side effects. For example, if a GPIO is already configured
300 | as an output and it is reconfigured as an output by passing 'out' to the
301 | constructor, the value of that output will be set to 0. In some applications
302 | this is not desirable and the value of the output should not be modified. The
303 | reconfigureDirection option can help here. If reconfigureDirection is set to
304 | false the direction of a GPIO that is already correctly configured will not be
305 | reconfigured. Optional, the default value is true.
306 |
307 | GPIOs on Linux are identified by unsigned integers. These are the numbers that
308 | should be passed to the onoff Gpio constructor when exporting GPIOs to
309 | userspace. For example, pin 11 on the Raspberry Pi expansion header
310 | corresponds to GPIO17 in Raspbian Linux. 17 is therefore the number to pass
311 | to the onoff Gpio constructor when using pin 11 on the expansion header.
312 |
313 | ##### read([callback])
314 | - [callback] - An optional completion callback that gets two arguments (err,
315 | value), where err is reserved for an Error object and value is the number 0
316 | or 1 and represents the state of the GPIO.
317 |
318 | Read GPIO value asynchronously. If no completion callback is specified read
319 | returns a Promise which resolves to the value of the GPIO on success or rejects
320 | with an Error object on failure.
321 |
322 | Note that most systems support readback of GPIOs configured as outputs. The
323 | read method can therefore be invoked for any GPIO, irrespective of whether it
324 | was configured as an input or an output. The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are
325 | examples of such systems.
326 |
327 | ##### readSync()
328 | Read GPIO value synchronously. Returns the number 0 or 1 to represent the
329 | state of the GPIO.
330 |
331 | Note that most systems support readback of GPIOs configured as outputs. The
332 | readSync method can therefore be invoked for any GPIO, irrespective of whether
333 | it was configured as an input or an output. The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone
334 | are examples of such systems.
335 |
336 | ##### write(value[, callback])
337 | - value - The number 0 or 1.
338 | - [callback] - An optional completion callback that gets one argument (err),
339 | where err is reserved for an error object.
340 |
341 | Write GPIO value asynchronously. If no completion callback is specified write
342 | returns a Promise that resolves with no value on success or rejects with an
343 | Error object on failure.
344 |
345 | Note that on most systems invoking write for a GPIO configured as an input
346 | will result in an EPERM error indicating that the operation is not permitted.
347 | The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are examples of such systems.
348 |
349 | ##### writeSync(value)
350 | - value - The number 0 or 1.
351 |
352 | Write GPIO value synchronously.
353 |
354 | Note that on most systems invoking writeSync for a GPIO configured as an input
355 | will result in an EPERM error indicating that the operation is not permitted.
356 | The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are examples of such systems.
357 |
358 | ##### watch(callback)
359 | - callback - A callback that gets two arguments (err, value), where err is
360 | reserved for an error object and value is the number 0 or 1 and represents the
361 | state of the GPIO. The value can also be used to determine whether the
362 | interrupt occurred on a rising or falling edge. A value of 0 implies a falling
363 | edge interrupt and a value of 1 implies a rising edge interrupt.
364 |
365 | Watch for hardware interrupts on the GPIO. The edge argument that was passed
366 | to the constructor determines which hardware interrupts to watch for.
367 |
368 | ##### unwatch([callback])
369 | - [callback] - The callback to remove.
370 |
371 | Stop watching for hardware interrupts on the GPIO. If callback is specified,
372 | only that particular callback is removed. Otherwise all callbacks are removed.
373 |
374 | ##### unwatchAll()
375 | Remove all hardware interrupt watchers for the GPIO.
376 |
377 | ##### direction()
378 | Returns the string 'in' or 'out' indicating whether the GPIO is an input or
379 | output.
380 |
381 | ##### setDirection(direction)
382 | - direction - A string specifying whether the GPIO should be configured as an
383 | input or output. The valid values are 'in', 'out', 'high', and 'low'. If 'out'
384 | is specified the GPIO will be configured as an output and the value of the GPIO
385 | will be set to 0. 'high' and 'low' are variants of 'out' that configure the
386 | GPIO as an output with an initial level of 1 or 0 respectively.
387 |
388 | Set GPIO direction.
389 |
390 | ##### edge()
391 | Returns the string 'none', 'falling', 'rising', or 'both' indicating the
392 | interrupt generating edge or edges for the GPIO. Whether or not interrupts are
393 | supported by an input GPIO is GPIO specific. If interrupts are not supported
394 | the edge method should not be used. Interrupts are not supported by output
395 | GPIOs.
396 |
397 | ##### setEdge(edge)
398 | - edge - A string specifying the interrupt generating edge or edges for an
399 | input GPIO. The valid values are: 'none', 'rising', 'falling' or 'both'.
400 | Whether or not interrupts are supported by an input GPIO is GPIO specific. If
401 | interrupts are not supported the setEdge method should not be used. Interrupts
402 | are not supported by output GPIOs.
403 |
404 | Set GPIO interrupt generating edge.
405 |
406 | ##### activeLow()
407 | Returns true or false indicating whether or not the values read from or written
408 | to the GPIO are inverted.
409 |
410 | ##### setActiveLow(invert)
411 | - invert - A boolean value specifying whether the values read from or written
412 | to the GPIO should be inverted. The interrupt generating edge for the GPIO also
413 | follow this this setting. The valid values for invert are true and false.
414 | Setting activeLow to true inverts.
415 |
416 | Set GPIO activeLow setting.
417 |
418 | ##### unexport()
419 | Reverse the effect of exporting the GPIO to userspace. A Gpio object should not
420 | be used after invoking its unexport method.
421 |
422 | ##### static accessible
423 | Determine whether or not GPIO access is possible. true if the current process
424 | has the permissions required to export GPIOs to userspace. false otherwise.
425 | Loosely speaking, if this property is true it should be possible for the
426 | current process to create Gpio objects.
427 |
428 | It is notable that while this property may be false indicating that the
429 | current process does not have the permissions required to export GPIOs to
430 | userspace, existing exported GPIOs may still be accessible.
431 |
432 | This property is useful for mocking functionality on computers used for
433 | development that do not provide access to GPIOs.
434 |
435 | This is a static property and should be accessed as `Gpio.accessible`.
436 |
437 | ##### static HIGH / LOW
438 | Constants used when reading or writing a GPIO value. Gpio.HIGH and Gpio.LOW
439 | can be used in place of the numeric constants 1 and 0.
440 |
441 |
442 | ## How Does onoff Work?
443 |
444 | Internally onoff uses sysfs files located at /sys/class/gpio to access GPIOs
445 | and the [epoll package](https://github.com/fivdi/epoll) to detect hardware
446 | interrupts. The Linux GPIO sysfs interface for userspace is documented
447 | [here](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/gpio/sysfs.txt).
448 | It's a relatively simple interface which can be used to ask the Linux kernel
449 | to export control of a GPIO to userspace. After control of a GPIO has been
450 | exported to userspace, the GPIO can be configured as an input or output.
451 | Thereafter, the state of an input can be read, and the state of an output can
452 | be written. Some systems will also allow the state of a output to be read.
453 | The GPIO sysfs interface can also be used for interrupt detection. onoff can
454 | detect several thousand interrupts per second on both the BeagleBone and the
455 | Raspberry Pi.
456 |
457 |
458 | ## Configuring Pullup and Pulldown Resistors
459 |
460 | As mentioned in section [How Does onoff Work](#how-does-onoff-work) the sysfs
461 | interface is used to access GPIOs. The sysfs interface doesn't offer support
462 | for configuring pullup and pulldown resistors on GPIOs.
463 |
464 | There are however many platform specific mechanisms for configuring pullup and
465 | pulldown resistors that are compatible with onoff. onoff itself doesn't use
466 | these mechanisms as one of the goals of onoff is to be platform independent.
467 |
468 | Here we'll take a look at two mechanisms available on the Raspberry Pi for
469 | configuring pullup and pulldown resistors.
470 |
471 | The first point to be aware of is that most GPIOs on a Raspberry Pi have
472 | either their pullup or pulldown resistor activated by default. The defaults
473 | can be seen in Table 6-31 on pages 102 and 103 of the
474 | [BCM2835 ARM Peripherals](http://www.farnell.com/datasheets/1521578.pdf)
475 | documentation.
476 |
477 | #### Using the gpio Command in /boot/config.txt
478 |
479 | On Raspbian 2018-04-18 or later the `gpio` configuration command can be used
480 | in `/boot/config.txt` to configure pullup and pulldown resistors. Further
481 | information is available at
482 | [New "gpio" config command](https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=117&t=208748).
483 |
484 | #### Using Device Tree Overlays
485 |
486 | Device tree overlays can also be used to configure pullup and pulldown
487 | resistors. The Wiki page
488 | [Enabling Pullup and Pulldown Resistors on The Raspberry Pi](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/wiki/Enabling-Pullup-and-Pulldown-Resistors-on-The-Raspberry-Pi)
489 | describes this mechanism in more detail.
490 |
491 | ## Benchmarks
492 |
493 | Three of the onoff tests are used to monitor performance.
494 |
495 | * performance-async.js - determine max. no. of write ops per seconds
496 | * performance-sync.js - determine max. no. of writeSync ops per second
497 | * performance-interrupt.js - determine max. no. of interrupts per second
498 |
499 | The results of these tests are shown in the following tables.
500 |
501 | **Raspberry Pi 4 B, 1.5GHz, Raspberry Pi OS (March 4th 2021, Buster 10.8)**
502 |
503 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
504 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
505 | v16.0.0 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 25124 | 280417 | 20240
506 | v15.14.0 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 24055 | 271149 | 20488
507 | v14.16.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 21669 | 254705 | 19703
508 | v12.22.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 22618 | 318417 | 21122
509 | v10.24.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 22405 | 329927 | 19583
510 |
511 | **Raspberry Pi 3 B, 1.2GHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
512 |
513 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
514 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
515 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 21670 | 207222 | 18328
516 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 23661 | 225758 | 20741
517 |
518 | **Raspberry Pi 2 B, 900MHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
519 |
520 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
521 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
522 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 10769 | 113107 | 10373
523 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 11843 | 129086 | 10536
524 |
525 | **Raspberry Pi 1 B, 700MHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
526 |
527 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
528 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
529 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75+ | 2316 | 26696 | 2112
530 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75+ | 2613 | 33129 | 2225
531 |
532 | **BeagleBone Black, 1GHz, Debian Buster 10.2**
533 |
534 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
535 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
536 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 6855 | 70535 | 5911
537 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 7564 | 79133 | 5920
538 |
539 | **BeagleBone, 720MHz, Debian Buster 10.2**
540 |
541 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
542 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
543 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 5013 | 49741 | 4297
544 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 5400 | 57157 | 4371
545 |
546 | ## Related Packages
547 |
548 | Here are a few links to other hardware specific Node.js packages that may be
549 | of interest.
550 |
551 | * [pigpio](https://github.com/fivdi/pigpio) - Fast GPIO, PWM, servo control, state change notification and interrupt handling on the Raspberry Pi
552 | * [i2c-bus](https://github.com/fivdi/i2c-bus) - I2C serial bus access
553 | * [spi-device](https://github.com/fivdi/spi-device) - SPI serial bus access
554 | * [mcp-spi-adc](https://github.com/fivdi/mcp-spi-adc) - Analog to digital conversion with the MCP3002/4/8, MCP3202/4/8 and MCP3304
555 |
556 | ## Additional Information
557 |
558 | onoff was tested on the following platforms:
559 |
560 | - Raspberry Pi 1, 2, 3 and 4
561 | - Raspbian or Raspberry Pi OS
562 | - BeagleBone, BeagleBone Black and PocketBeagle
563 | - Debian
564 |
565 | The suitability of onoff for a particular Linux board is highly dependent on
566 | how GPIO interfaces are made available on that board. The
567 | [GPIO interfaces](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/gpio/)
568 | documentation describes GPIO access conventions rather than standards that must
569 | be followed so GPIO can vary from platform to platform. For example, onoff
570 | relies on sysfs files located at /sys/class/gpio being available. However,
571 | these sysfs files for userspace GPIO are optional and may not be available on a
572 | particular platform.
573 |
574 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/accessible.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 |
5 | console.log('Gpio functionality accessible on this computer?', Gpio.accessible);
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led-async.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
8 | const blinkLed = _ => {
9 | if (stopBlinking) {
10 | return led.unexport();
11 | }
12 |
13 | led.read((err, value) => { // Asynchronous read
14 | if (err) {
15 | throw err;
16 | }
17 |
18 | led.write(value ^ 1, err => { // Asynchronous write
19 | if (err) {
20 | throw err;
21 | }
22 | });
23 | });
24 |
25 | setTimeout(blinkLed, 200);
26 | };
27 |
28 | blinkLed();
29 |
30 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
31 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
32 |
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led-promises.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
8 | const blinkLed = _ => {
9 | if (stopBlinking) {
10 | return led.unexport();
11 | }
12 |
13 | led.read()
14 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
15 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 200))
16 | .catch(err => console.log(err));
17 | };
18 |
19 | blinkLed();
20 |
21 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
22 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
23 |
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 |
6 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
7 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 200);
8 |
9 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
10 | setTimeout(_ => {
11 | clearInterval(iv); // Stop blinking
12 | led.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
13 | }, 5000);
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/debounce-button.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
6 |
7 | button.watch((err, value) => {
8 | if (err) {
9 | throw err;
10 | }
11 |
12 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
13 | });
14 |
15 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
16 | led.unexport();
17 | button.unexport();
18 | });
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/light-switch.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
6 |
7 | button.watch((err, value) => {
8 | if (err) {
9 | throw err;
10 | }
11 |
12 | led.writeSync(value);
13 | });
14 |
15 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
16 | led.unexport();
17 | button.unexport();
18 | });
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/light-switch.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fivdi/onoff/813da60dd1f3a842a29a8c630243d4f5b7523cc0/examples/light-switch.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/mygpio-overlay.dts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /dts-v1/;
2 | /plugin/;
3 |
4 | / {
5 | compatible = "brcm,bcm2708";
6 |
7 | fragment@0 {
8 | target = <&gpio>;
9 | __overlay__ {
10 | pinctrl-names = "default";
11 | pinctrl-0 = <&my_pins>;
12 |
13 | my_pins: my_pins {
14 | brcm,pins = <7 8 9>; /* gpio no. */
15 | brcm,function = <0 0 0>; /* 0:in, 1:out */
16 | brcm,pull = <1 1 2>; /* 2:up 1:down 0:none */
17 | };
18 | };
19 | };
20 | };
21 |
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/run-examples:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node blink-led
3 | node blink-led-async
4 | node wait-for-interrupt
5 | node light-switch
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/wait-for-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 |
5 | // Export GPIO4 as an interrupt generating input with a debounceTimeout of 10
6 | // milliseconds
7 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
8 |
9 | console.log('Please press the button on GPIO4...');
10 |
11 | // The callback passed to watch will be invoked when the button connected to
12 | // GPIO4 is pressed
13 | button.watch((err, value) => {
14 | if (err) {
15 | throw err;
16 | }
17 |
18 | console.log('Button pressed!, its value was ' + value);
19 |
20 | button.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
21 | });
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/blink-led-promises.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | const blinkLed = _ => {
8 | if (stopBlinking) {
9 | led.unexport();
10 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
11 | return;
12 | }
13 |
14 | led.read()
15 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
16 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 50))
17 | .catch(err => {
18 | console.log(err);
19 | });
20 | };
21 |
22 | blinkLed();
23 |
24 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 2000);
25 |
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/blink-led.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 |
6 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 100);
7 |
8 | setTimeout(_ => {
9 | clearInterval(iv);
10 |
11 | led.writeSync(0);
12 | led.unexport();
13 |
14 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
15 | }, 2000);
16 |
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/change-configuration.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 |
6 | let output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
7 | let input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
8 |
9 | const watchWithSecondConfiguration = _ => {
10 | input.watch((err, value) => {
11 | assert(!err, 'error during interrupt detection');
12 | assert(value === 1, 'expected interrupt on rising edge');
13 |
14 | setTimeout(_ => {
15 | input.unexport();
16 | output.unexport();
17 |
18 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
19 | }, 10);
20 | });
21 |
22 | output.writeSync(1);
23 | };
24 |
25 | const changeConfiguration = _ => {
26 | input.unwatchAll();
27 |
28 | let temp = output;
29 | temp.setDirection('in');
30 | output = input;
31 | input = temp;
32 |
33 | output.setEdge('none');
34 | output.setDirection('out');
35 | output.writeSync(0);
36 | assert(output.direction() === 'out', 'expected direction to be out');
37 | assert(output.edge() === 'none', 'expected edge to be none');
38 | assert(output.readSync() === 0, 'expected value to be 0');
39 |
40 | input.setEdge('rising');
41 | assert(input.direction() === 'in', 'expected direction to be in');
42 | assert(input.edge() === 'rising', 'expected edge to be rising');
43 | assert(input.readSync() === 0, 'expected value to be 0');
44 |
45 | watchWithSecondConfiguration();
46 | };
47 |
48 | const watchWithFirstConfiguration = _ => {
49 | input.watch((err, value) => {
50 | assert(!err, 'error during interrupt detection');
51 | assert(value === 1, 'expected interrupt on rising edge');
52 |
53 | setTimeout(changeConfiguration, 10);
54 | });
55 |
56 | output.writeSync(1);
57 | };
58 |
59 | watchWithFirstConfiguration();
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-active-low-defaults.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | */
7 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
8 | const assert = require('assert');
9 | let input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
10 | let output = new Gpio(8, 'low', {activeLow: true});
11 |
12 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
13 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
14 |
15 | input.unexport();
16 | output.unexport();
17 |
18 | //
19 |
20 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
21 | output = new Gpio(8, 'low', {activeLow: false});
22 |
23 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
24 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
25 |
26 | input.unexport();
27 | output.unexport();
28 |
29 | //
30 |
31 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
32 | output = new Gpio(8, 'high', {activeLow: true});
33 |
34 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
35 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
36 |
37 | input.unexport();
38 | output.unexport();
39 |
40 | //
41 |
42 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
43 | output = new Gpio(8, 'high', {activeLow: false});
44 |
45 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
46 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
47 |
48 | input.unexport();
49 | output.unexport();
50 |
51 | //
52 |
53 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
54 | output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: true});
55 |
56 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
57 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
58 |
59 | input.unexport();
60 | output.unexport();
61 |
62 | //
63 |
64 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
65 | output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: false});
66 |
67 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
68 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
69 |
70 | input.unexport();
71 | output.unexport();
72 |
73 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
74 |
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-active-low.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | */
7 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
8 | const assert = require('assert');
9 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
10 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: true});
11 |
12 | assert(input.activeLow() === false);
13 | assert(output.activeLow() === true);
14 |
15 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
16 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
17 |
18 | output.writeSync(0);
19 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
20 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
21 | output.writeSync(1);
22 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
23 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
24 |
25 | output.setActiveLow(false);
26 | assert(input.activeLow() === false);
27 | assert(output.activeLow() === false);
28 | output.writeSync(0);
29 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
30 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
31 | output.writeSync(1);
32 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
33 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
34 |
35 | input.setActiveLow(true);
36 | assert(input.activeLow() === true);
37 | assert(output.activeLow() === false);
38 | output.writeSync(0);
39 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
40 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
41 | output.writeSync(1);
42 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
43 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
44 |
45 | input.unexport();
46 | output.unexport();
47 |
48 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
49 |
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-input.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const input = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising');
6 |
7 | assert(input.direction() === 'in');
8 | assert(input.edge() === 'rising');
9 |
10 | input.unexport();
11 |
12 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-output.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const output = new Gpio(17, 'out');
6 |
7 | assert(output.direction() === 'out');
8 |
9 | output.writeSync(1);
10 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
11 |
12 | output.writeSync(0);
13 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
14 |
15 | output.write(1, err => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | throw err;
18 | }
19 |
20 | output.read((err, value) => {
21 | if (err) {
22 | throw err;
23 | }
24 |
25 | assert(value === 1);
26 |
27 | output.writeSync(0);
28 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
29 |
30 | output.unexport();
31 |
32 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
33 | });
34 | });
35 |
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/debounce.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
6 | const button = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both', {debounceTimeout: 10});
7 |
8 | let buttonPressedCount = 0;
9 | let buttonReleasedCount = 0;
10 |
11 | const simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce = cb => {
12 | let toggleCount = 0;
13 |
14 | const iv = setInterval(_ => {
15 | if (toggleCount === 19) {
16 | clearInterval(iv);
17 | return cb();
18 | }
19 |
20 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() ^ 1);
21 | toggleCount += 1;
22 | }, 2);
23 | };
24 |
25 | const simulatePressAndReleaseButtonWithBounce = _ => {
26 | simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce(_ => {
27 | setTimeout(_ => {
28 | simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce(_ => {
29 | setTimeout(_ => {
30 | assert(buttonPressedCount === 1);
31 | assert(buttonReleasedCount === 1);
32 |
33 | button.unexport();
34 | output.unexport();
35 |
36 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
37 | }, 20);
38 | });
39 | }, 50);
40 | });
41 | };
42 |
43 | button.watch((err, value) => {
44 | if (err) {
45 | throw err;
46 | }
47 |
48 | if (value === 1) {
49 | buttonPressedCount += 1;
50 | } else if (value === 0) {
51 | buttonReleasedCount += 1;
52 | }
53 | });
54 |
55 | simulatePressAndReleaseButtonWithBounce();
56 |
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/dont-reconfigure-direction-part1.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | *
7 | * This test is part 1 of a two part test.
8 | * For part 2 see dont-reconfigure-direction-part2.js.
9 | *
10 | * Part 1 sets the ouput to 1 and expects to read 1 on the input. Part 1
11 | * doesn't unexport the GPIOs so that part 2 can can ensure that a Gpio output
12 | * object can be constructed without modifying the value of the output. Part 2
13 | * also expects to read one on the input. This is achieved by using the
14 | * reconfigureDirection option.
15 | */
16 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
17 | const assert = require('assert');
18 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
19 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
20 |
21 | output.writeSync(1);
22 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
23 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
24 |
25 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/dont-reconfigure-direction-part2.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | *
7 | * This test is part 2 of a two part test.
8 | * For part 1 see dont-reconfigure-direction-part1.js.
9 | *
10 | * Part 1 sets the ouput to 1 and expects to read 1 on the input. Part 1
11 | * doesn't unexport the GPIOs so that part 2 can can ensure that a Gpio output
12 | * object can be constructed without modifying the value of the output. Part 2
13 | * also expects to read one on the input. This is achieved by using the
14 | * reconfigureDirection option.
15 | */
16 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
17 | const assert = require('assert');
18 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
19 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {reconfigureDirection: false});
20 |
21 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
22 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
23 |
24 | input.unexport();
25 | output.unexport();
26 |
27 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
28 |
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/export-many-times.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | for (let i = 1; i <= 1000000; i += 1) {
6 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
7 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
8 | led.unexport();
9 | if (i % 10 === 0) {
10 | console.log(i);
11 | }
12 | }
13 |
14 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
15 |
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/high-low.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 |
6 | assert(Gpio.HIGH === 1, 'expected Gpio.HIGH to be 1');
7 | assert(Gpio.LOW === 0, 'expected Gpio.LOW to be 0');
8 |
9 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/many-interrupts.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
6 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
7 |
8 | let toggleCount = 0;
9 | let falling = 0;
10 | let rising = 0;
11 |
12 | const toggleOutput = _ => {
13 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() ^ 1);
14 | toggleCount += 1;
15 | };
16 |
17 | const interrupt = (err, value) => {
18 | if (err) {
19 | throw err;
20 | }
21 |
22 | if (value === 1) {
23 | rising += 1;
24 | } else if (value === 0) {
25 | falling += 1;
26 | }
27 |
28 | assert(output.readSync() === value);
29 |
30 | if (rising + falling < 2000) {
31 | toggleOutput();
32 | } else {
33 | assert(toggleCount === 2000);
34 | assert(rising === falling);
35 | assert(rising + falling === toggleCount);
36 |
37 | input.unexport();
38 | output.writeSync(0);
39 | output.unexport();
40 |
41 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
42 | }
43 | };
44 |
45 | input.watch(interrupt);
46 | toggleOutput();
47 |
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/output-with-edge-bug.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | // Test for https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/87
4 | //
5 | // If a Gpio is instantiated for an output GPIO and the edge parameter is
6 | // specified then the edge parameter should be ignored. Attempting to write
7 | // the sysfs edge file for an output GPIO results in an
8 | // "EIO: i/o error, write"
9 |
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 | const assert = require('assert');
12 |
13 | const ensureGpio17Unexported = cb => {
14 | let led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
15 |
16 | led.unexport();
17 |
18 | setTimeout(_ => cb(), 100);
19 | };
20 |
21 | ensureGpio17Unexported(_ => {
22 | let led;
23 |
24 | assert.doesNotThrow(
25 | _ => led = new Gpio(17, 'out', 'both'),
26 | 'can\'t instantiate a Gpio for an output with edge option specified'
27 | );
28 |
29 | led.unexport();
30 |
31 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
32 | });
33 |
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-async.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | const pulseLed = (led, pulseCount, cb) => {
6 | let time = process.hrtime();
7 |
8 | const loop = count => {
9 | if (count === 0) {
10 | time = process.hrtime(time);
11 | const writesPerSecond = pulseCount * 2 / (time[0] + time[1] / 1E9);
12 | return cb(null, writesPerSecond);
13 | }
14 |
15 | led.write(1, err => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | return cb(err);
18 | }
19 |
20 | led.write(0, err => {
21 | if (err) {
22 | return cb(err);
23 | }
24 |
25 | loop(count - 1);
26 | });
27 | });
28 | };
29 |
30 | loop(pulseCount);
31 | };
32 |
33 | const asyncWritesPerSecond = cb => {
34 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
35 | let writes = 0;
36 |
37 | const loop = count => {
38 | if (count === 0) {
39 | led.unexport();
40 | return cb(null, writes / 10);
41 | }
42 |
43 | pulseLed(led, 10000, (err, writesPerSecond) => {
44 | if (err) {
45 | return cb(err);
46 | }
47 |
48 | writes += writesPerSecond;
49 |
50 | loop(count - 1);
51 | });
52 | };
53 |
54 | // Do a dry run first to get the runtime primed
55 | pulseLed(led, 5000, (err, writesPerSecond) => {
56 | if (err) {
57 | return cb(err);
58 | }
59 | loop(10);
60 | });
61 | };
62 |
63 | asyncWritesPerSecond((err, averageWritesPerSecond) => {
64 | if (err) {
65 | throw err;
66 | }
67 |
68 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
69 | console.log(
70 | ' ' + Math.floor(averageWritesPerSecond) + ' async writes per second'
71 | );
72 | });
73 |
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor. GPIO7 is
6 | * an interrupt generating input and GPIO8 is an output. By toggling the state
7 | * of the output an interrupt is generated. The output is toggled as often as
8 | * possible to determine the maximum rate at which interrupts can be handled.
9 | */
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
12 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
13 |
14 | let irqCount = 0;
15 | let iv;
16 |
17 | // Exit handler
18 | const exit = _ => {
19 | input.unexport();
20 | output.unexport();
21 |
22 | clearInterval(iv);
23 | };
24 | process.on('SIGINT', exit);
25 |
26 | // Interrupt handler
27 | input.watch((err, value) => {
28 | if (err) {
29 | exit();
30 | }
31 |
32 | irqCount += 1;
33 |
34 | // Trigger next interrupt by toggling output.
35 | output.writeSync(value === 0 ? 1 : 0);
36 | });
37 |
38 | // Print number of interrupts once a second.
39 | iv = setInterval(_ => {
40 | console.log(irqCount);
41 | irqCount = 0;
42 | }, 1000);
43 |
44 | // Trigger first interrupt by toggling output.
45 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() === 0 ? 1 : 0);
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-sync.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | const pulseLed = (led, pulseCount) => {
6 | let time = process.hrtime();
7 |
8 | for (let i = 0; i !== pulseCount; i += 1) {
9 | led.writeSync(1);
10 | led.writeSync(0);
11 | }
12 |
13 | time = process.hrtime(time);
14 |
15 | const writesPerSecond = pulseCount * 2 / (time[0] + time[1] / 1E9);
16 |
17 | return writesPerSecond;
18 | };
19 |
20 | const syncWritesPerSecond = _ => {
21 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
22 | let writes = 0;
23 |
24 | // Do a dry run first to get the runtime primed
25 | pulseLed(led, 50000);
26 |
27 | for (let i = 0; i !== 10; i += 1) {
28 | writes += pulseLed(led, 100000);
29 | }
30 |
31 | led.unexport();
32 |
33 | return writes / 10;
34 | };
35 |
36 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
37 | console.log(
38 | ' ' + Math.floor(syncWritesPerSecond()) + ' sync writes per second'
39 | );
40 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/run-performance-tests:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node performance-async
3 | node performance-sync
4 | node performance-interrupt
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/run-tests:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node blink-led
3 | node blink-led-promises
4 | node change-configuration
5 | node configure-and-check-active-low
6 | node configure-and-check-active-low-defaults
7 | node configure-and-check-input
8 | node configure-and-check-output
9 | node debounce
10 | node dont-reconfigure-direction-part1
11 | node dont-reconfigure-direction-part2
12 | node high-low
13 | node many-interrupts
14 | node output-with-edge-bug
15 | node wait-for-interrupt
16 | node wait-for-many-interrupts
17 |
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/wait-for-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
6 |
7 | assert(button.direction() === 'in');
8 | assert(button.edge() === 'both');
9 |
10 | console.info('Please press button connected to GPIO #4...');
11 |
12 | button.watch((err, value) => {
13 | if (err) {
14 | throw err;
15 | }
16 |
17 | assert(value === 0 || value === 1);
18 |
19 | button.unexport();
20 |
21 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
22 | console.log(' button pressed, value was ' + value);
23 | });
24 |
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/wait-for-many-interrupts.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {
6 | debounceTimeout : 10
7 | });
8 | let count = 0;
9 |
10 | assert(button.direction() === 'in');
11 | assert(button.edge() === 'rising');
12 |
13 | console.info('Please press button connected to GPIO4 5 times...');
14 |
15 | button.watch((err, value) => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | throw err;
18 | }
19 |
20 | count += 1;
21 |
22 | console.log('button pressed ' + count + ' times, value was ' + value);
23 |
24 | if (count === 5) {
25 | button.unexport();
26 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
27 | }
28 | });
29 |
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/onoff.d.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | export type High = 1;
2 | export type Low = 0;
3 | export type Direction = "in" | "out" | "high" | "low";
4 | export type Edge = "none" | "rising" | "falling" | "both";
5 |
6 | export type Options = {
7 | debounceTimeout?: number,
8 | activeLow?: boolean,
9 | reconfigureDirection?: boolean,
10 | }
11 |
12 | export type BinaryValue = High | Low;
13 | export type ValueCallback = (err: Error | null | undefined, value: BinaryValue) => void;
14 |
15 | export class Gpio {
16 | static HIGH: High;
17 | static LOW: Low;
18 | static accessible: boolean;
19 |
20 | constructor(gpio: number, direction: Direction, edge?: Edge, options?: Options);
21 |
22 | read(callback: ValueCallback): void;
23 | read(): Promise;
24 |
25 | readSync(): BinaryValue;
26 |
27 | write(value: BinaryValue, callback: (err: Error | null | undefined) => void): void;
28 | write(value: BinaryValue): Promise;
29 |
30 | writeSync(value: BinaryValue): void;
31 |
32 | watch(callback: ValueCallback): void;
33 | unwatch(callback?: ValueCallback): void;
34 | unwatchAll(): void;
35 |
36 | direction(): Direction;
37 | setDirection(direction: Direction): void;
38 |
39 | edge(): Edge;
40 | setEdge(edge: Edge): void;
41 |
42 | activeLow(): boolean;
43 | setActiveLow(invert: boolean): void;
44 |
45 | unexport(): void
46 | }
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/onoff.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const fs = require('fs');
4 | const debounce = require('lodash.debounce');
5 | const Epoll = require('epoll').Epoll;
6 |
7 | const GPIO_ROOT_PATH = '/sys/class/gpio/';
8 |
9 | const HIGH_BUF = Buffer.from('1');
10 | const LOW_BUF = Buffer.from('0');
11 |
12 | const HIGH = 1;
13 | const LOW = 0;
14 |
15 | const exportGpio = gpio => {
16 | if (!fs.existsSync(gpio._gpioPath)) {
17 | // The GPIO hasn't been exported yet so export it
18 | fs.writeFileSync(GPIO_ROOT_PATH + 'export', '' + gpio._gpio);
19 |
20 | return false;
21 | }
22 |
23 | // The GPIO has already been exported, perhaps by onoff itself, perhaps
24 | // by quick2wire gpio-admin on the Pi, perhaps by the WiringPi gpio
25 | // utility on the Pi, or perhaps by something else. In any case, an
26 | // attempt is made to set the direction and edge to the requested
27 | // values here. If quick2wire gpio-admin was used for the export, the
28 | // user should have access to both direction and edge files. This is
29 | // important as gpio-admin sets niether direction nor edge. If the
30 | // WiringPi gpio utility was used, the user should have access to edge
31 | // file, but not the direction file. This is also ok as the WiringPi
32 | // gpio utility can set both direction and edge. If there are any
33 | // errors while attempting to perform the modifications, just keep on
34 | // truckin'.
35 | return true;
36 | };
37 |
38 | // Avoid the access permission issue described here:
39 | // https://github.com/raspberrypi/linux/issues/553
40 | // On some syetems udev rules are used to set access permissions on the GPIO
41 | // sysfs files enabling those files to be accessed without root privileges.
42 | // This takes a while so wait for it to complete.
43 | const waitForGpioAccessPermission = (
44 | gpio, direction, edge, gpioPreviouslyExported
45 | ) => {
46 | let permissionRequiredPaths = [
47 | gpio._gpioPath + 'value',
48 | ];
49 |
50 | if (gpioPreviouslyExported === false) {
51 | permissionRequiredPaths.push(gpio._gpioPath + 'direction');
52 | permissionRequiredPaths.push(gpio._gpioPath + 'active_low');
53 |
54 | // On some systems the edge file will not exist if the GPIO does not
55 | // support interrupts
56 | // https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/77#issuecomment-321980735
57 | if (edge && direction === 'in') {
58 | permissionRequiredPaths.push(gpio._gpioPath + 'edge');
59 | }
60 | }
61 |
62 | permissionRequiredPaths.forEach(path => {
63 | let tries = 0;
64 |
65 | while (true) {
66 | try {
67 | tries += 1;
68 | const fd = fs.openSync(path, 'r+');
69 | fs.closeSync(fd);
70 | break;
71 | } catch (e) {
72 | if (tries === 10000) {
73 | throw e;
74 | }
75 | }
76 | }
77 | });
78 | };
79 |
80 | const configureGpio = (
81 | gpio, direction, edge, options, gpioPreviouslyExported
82 | ) => {
83 | const throwIfNeeded = err => {
84 | if (gpioPreviouslyExported === false) {
85 | throw err;
86 | }
87 | };
88 |
89 | try {
90 | if (typeof options.activeLow === 'boolean') {
91 | gpio.setActiveLow(options.activeLow);
92 | }
93 | } catch (err) {
94 | throwIfNeeded(err);
95 | }
96 |
97 | try {
98 | const reconfigureDirection =
99 | typeof options.reconfigureDirection === 'boolean' ?
100 | options.reconfigureDirection : true;
101 |
102 | const requestedDirection =
103 | direction === 'high' || direction === 'low' ? 'out' : direction;
104 |
105 | if (reconfigureDirection || gpio.direction() !== requestedDirection) {
106 | gpio.setDirection(direction);
107 | }
108 | } catch (err) {
109 | throwIfNeeded(err);
110 | }
111 |
112 | try {
113 | // On some systems writing to the edge file for an output GPIO will
114 | // result in an "EIO, i/o error"
115 | // https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/87
116 | if (edge && direction === 'in') {
117 | gpio.setEdge(edge);
118 | }
119 | } catch (err) {
120 | throwIfNeeded(err);
121 | }
122 | };
123 |
124 | const configureInterruptHandler = gpio => {
125 | // A poller is created for both inputs and outputs. A poller isn't
126 | // actually needed for an output but the setDirection method can be
127 | // invoked to change the direction of a GPIO from output to input and
128 | // then a poller may be needed.
129 | const pollerEventHandler = (err, fd, events) => {
130 | const value = gpio.readSync();
131 |
132 | if ((value === LOW && gpio._fallingEnabled) ||
133 | (value === HIGH && gpio._risingEnabled)) {
134 | gpio._listeners.slice(0).forEach(callback => {
135 | callback(err, value);
136 | });
137 | }
138 | };
139 |
140 | // Read GPIO value before polling to prevent an initial unauthentic
141 | // interrupt
142 | gpio.readSync();
143 |
144 | if (gpio._debounceTimeout > 0) {
145 | const db = debounce(pollerEventHandler, gpio._debounceTimeout);
146 |
147 | gpio._poller = new Epoll((err, fd, events) => {
148 | gpio.readSync(); // Clear interrupt
149 | db(err, fd, events);
150 | });
151 | } else {
152 | gpio._poller = new Epoll(pollerEventHandler);
153 | }
154 | };
155 |
156 | class Gpio {
157 | constructor(gpio, direction, edge, options) {
158 | if (typeof edge === 'object' && !options) {
159 | options = edge;
160 | edge = undefined;
161 | }
162 |
163 | options = options || {};
164 |
165 | this._gpio = gpio;
166 | this._gpioPath = GPIO_ROOT_PATH + 'gpio' + this._gpio + '/';
167 | this._debounceTimeout = options.debounceTimeout || 0;
168 | this._readBuffer = Buffer.alloc(16);
169 | this._readSyncBuffer = Buffer.alloc(16);
170 | this._listeners = [];
171 |
172 | const gpioPreviouslyExported = exportGpio(this);
173 |
174 | waitForGpioAccessPermission(
175 | this, direction, edge, gpioPreviouslyExported
176 | );
177 |
178 | configureGpio(this, direction, edge, options, gpioPreviouslyExported);
179 |
180 | this._valueFd = fs.openSync(this._gpioPath + 'value', 'r+');
181 |
182 | configureInterruptHandler(this);
183 | }
184 |
185 | read(callback) {
186 | const readValue = callback => {
187 | fs.read(this._valueFd, this._readBuffer, 0, 1, 0, (err, bytes, buf) => {
188 | if (typeof callback === 'function') {
189 | if (err) {
190 | return callback(err);
191 | }
192 |
193 | callback(null, convertBufferToBit(buf));
194 | }
195 | });
196 | };
197 |
198 | if (callback) {
199 | readValue(callback);
200 | } else {
201 | return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
202 | readValue((err, value) => {
203 | if (err) {
204 | reject(err);
205 | } else {
206 | resolve(value);
207 | }
208 | });
209 | });
210 | }
211 | }
212 |
213 | readSync() {
214 | fs.readSync(this._valueFd, this._readSyncBuffer, 0, 1, 0);
215 | return convertBufferToBit(this._readSyncBuffer);
216 | }
217 |
218 | write(value, callback) {
219 | const writeValue = (value, callback) => {
220 | const writeBuffer = convertBitToBuffer(value);
221 | fs.write(
222 | this._valueFd, writeBuffer, 0, writeBuffer.length, 0, callback
223 | );
224 | };
225 |
226 | if (callback) {
227 | writeValue(value, callback);
228 | } else {
229 | return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
230 | writeValue(value, err => {
231 | if (err) {
232 | reject(err);
233 | } else {
234 | resolve();
235 | }
236 | });
237 | });
238 | }
239 | }
240 |
241 | writeSync(value) {
242 | const writeBuffer = convertBitToBuffer(value);
243 | fs.writeSync(this._valueFd, writeBuffer, 0, writeBuffer.length, 0);
244 | }
245 |
246 | watch(callback) {
247 | this._listeners.push(callback);
248 |
249 | if (this._listeners.length === 1) {
250 | this._poller.add(this._valueFd, Epoll.EPOLLPRI);
251 | }
252 | }
253 |
254 | unwatch(callback) {
255 | if (this._listeners.length > 0) {
256 | if (typeof callback !== 'function') {
257 | this._listeners = [];
258 | } else {
259 | this._listeners = this._listeners.filter(listener => {
260 | return callback !== listener;
261 | });
262 | }
263 |
264 | if (this._listeners.length === 0) {
265 | this._poller.remove(this._valueFd);
266 | }
267 | }
268 | }
269 |
270 | unwatchAll() {
271 | this.unwatch();
272 | }
273 |
274 | direction() {
275 | return fs.readFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'direction').toString().trim();
276 | }
277 |
278 | setDirection(direction) {
279 | fs.writeFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'direction', direction);
280 | }
281 |
282 | edge() {
283 | return fs.readFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'edge').toString().trim();
284 | }
285 |
286 | setEdge(edge) {
287 | fs.writeFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'edge', edge);
288 |
289 | this._risingEnabled = edge === 'both' || edge === 'rising';
290 | this._fallingEnabled = edge === 'both' || edge === 'falling';
291 | }
292 |
293 | activeLow() {
294 | return convertBufferToBoolean(
295 | fs.readFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'active_low')
296 | );
297 | }
298 |
299 | setActiveLow(invert) {
300 | fs.writeFileSync(
301 | this._gpioPath + 'active_low', convertBooleanToBuffer(!!invert)
302 | );
303 | }
304 |
305 | unexport() {
306 | this.unwatchAll();
307 | fs.closeSync(this._valueFd);
308 | try {
309 | fs.writeFileSync(GPIO_ROOT_PATH + 'unexport', '' + this._gpio);
310 | } catch (ignore) {
311 | // Flow of control always arrives here when cape_universal is enabled on
312 | // the bbb.
313 | }
314 | }
315 |
316 | static get accessible() {
317 | let fd;
318 |
319 | try {
320 | fd = fs.openSync(GPIO_ROOT_PATH + 'export', fs.constants.O_WRONLY);
321 | } catch(e) {
322 | // e.code === 'ENOENT' / 'EACCES' are most common
323 | // though any failure to open will also result in a gpio
324 | // failure to export.
325 | return false;
326 | } finally {
327 | if (fd) {
328 | fs.closeSync(fd);
329 | }
330 | }
331 |
332 | return true;
333 | }
334 | }
335 |
336 | const convertBitToBuffer = bit => convertBooleanToBuffer(bit === HIGH);
337 | const convertBufferToBit =
338 | buffer => convertBufferToBoolean(buffer) ? HIGH : LOW;
339 |
340 | const convertBooleanToBuffer = boolean => boolean ? HIGH_BUF : LOW_BUF;
341 | const convertBufferToBoolean = buffer => buffer[0] === HIGH_BUF[0];
342 |
343 | Gpio.HIGH = HIGH;
344 | Gpio.LOW = LOW;
345 |
346 | module.exports.Gpio = Gpio;
347 |
348 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "name": "onoff",
3 | "version": "6.0.3",
4 | "description": "GPIO access and interrupt detection with Node.js",
5 | "main": "onoff.js",
6 | "types": "onoff.d.ts",
7 | "directories": {
8 | "example": "examples",
9 | "test": "test"
10 | },
11 | "scripts": {
12 | "lint": "jshint onoff.js examples/*.js integration-test/*.js test/*.js test/*/*.js",
13 | "test": "nyc mocha",
14 | "codecov": "nyc report --reporter=text-lcov > coverage.lcov && codecov",
15 | "coverage-report": "nyc report --reporter=html",
16 | "integration-test": "cd integration-test && ./run-tests && cd .."
17 | },
18 | "mocha": {
19 | "extension": [
20 | "js",
21 | "ts"
22 | ],
23 | "require": "ts-node/register"
24 | },
25 | "repository": {
26 | "type": "git",
27 | "url": "https://github.com/fivdi/onoff.git"
28 | },
29 | "homepage": "https://github.com/fivdi/onoff",
30 | "bugs": {
31 | "url": "https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues"
32 | },
33 | "engines": {
34 | "node": ">=10.0.0"
35 | },
36 | "dependencies": {
37 | "epoll": "^4.0.1",
38 | "lodash.debounce": "^4.0.8"
39 | },
40 | "devDependencies": {
41 | "@types/mocha": "^8.2.2",
42 | "@types/mock-require": "^2.0.0",
43 | "codecov": "^3.8.1",
44 | "jshint": "^2.12.0",
45 | "mocha": "^8.3.2",
46 | "mock-fs": "^4.13.0",
47 | "mock-require": "^3.0.3",
48 | "nyc": "^15.1.0",
49 | "ts-node": "^9.1.1",
50 | "typescript": "^4.2.4"
51 | },
52 | "keywords": [
53 | "gpio",
54 | "iot",
55 | "interrupt",
56 | "raspberry",
57 | "raspi",
58 | "rpi",
59 | "pi",
60 | "beaglebone",
61 | "beaglebone-black",
62 | "linux"
63 | ],
64 | "author": "fivdi",
65 | "license": "MIT"
66 | }
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/accessible.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('accessible', () => {
13 | beforeEach(() => {
14 | });
15 |
16 |
17 | it('is accessible', () => {
18 | MockLinux.makeGpioAccessible();
19 | assert.deepEqual(Gpio.accessible, true);
20 | });
21 |
22 | it('is inaccessible', () => {
23 | MockLinux.makeGpioInaccessible();
24 | assert.deepEqual(Gpio.accessible, false);
25 | });
26 |
27 |
28 | afterEach(() => {
29 | MockLinux.restore();
30 | });
31 | });
32 |
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/activeLow.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('activeLow', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('is active high', () => {
24 | MockLinux.writeActiveLow(pin, '1');
25 | const actual = gpio.activeLow();
26 | assert.deepEqual(actual, true);
27 | });
28 |
29 | it('is active low', () => {
30 | MockLinux.writeActiveLow(pin, '0');
31 | const actual = gpio.activeLow();
32 | assert.deepEqual(actual, false);
33 | });
34 |
35 |
36 | afterEach(() => {
37 | gpio.unexport();
38 | MockLinux.restore();
39 | });
40 | });
41 |
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/constructor-fails.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('constructor fails', function () {
13 | let pin;
14 |
15 | this.timeout(10000);
16 |
17 | beforeEach(() => {
18 | pin = 4;
19 | });
20 |
21 |
22 | it('fails to construct input while waiting for access permission', () => {
23 | const expected = 'ENOENT';
24 | let actual;
25 |
26 | MockLinux.gpioWithoutPinFiles();
27 |
28 | try {
29 | const gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
30 | } catch (err) {
31 | actual = err.code;
32 | }
33 |
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 | it('fails to construct output while waiting for access permission', () => {
38 | const expected = 'ENOENT';
39 | let actual;
40 |
41 | MockLinux.gpioWithoutPinFiles();
42 |
43 | try {
44 | const gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
45 | } catch (err) {
46 | actual = err.code;
47 | }
48 |
49 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
50 | });
51 |
52 |
53 | afterEach(() => {
54 | MockLinux.restore();
55 | });
56 | });
57 |
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/constructor.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('constructor', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | });
20 |
21 |
22 | it('creates input', () => {
23 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
24 |
25 | const expected = 'in';
26 | const actual = gpio.direction();
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('creates output', () => {
31 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
32 |
33 | const expected = 'out';
34 | const actual = gpio.direction();
35 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
36 | });
37 |
38 | it('creates active low input', () => {
39 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', {activeLow: true});
40 |
41 | const expected = true;
42 | const actual = gpio.activeLow();
43 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
44 | });
45 |
46 | it('creates active high input', () => {
47 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', {activeLow: false});
48 |
49 | const expected = false;
50 | const actual = gpio.activeLow();
51 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
52 | });
53 |
54 | it('creates input with debounce timeout', () => {
55 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', {debounceTimeout: 10});
56 |
57 | const expected = 10;
58 | const actual = gpio._debounceTimeout;
59 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
60 | });
61 |
62 | it('ignores exceptions thrown by setActiveLow', () => {
63 | const setActiveLow = Gpio.prototype.setActiveLow;
64 | Gpio.prototype.setActiveLow = () => {
65 | throw new Error();
66 | };
67 |
68 | const expected = '';
69 | let actual;
70 |
71 | try {
72 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out', {activeLow: true});
73 | actual = '';
74 | } catch (err) {
75 | actual = 'error thrown by setActiveLow was not ignored';
76 | }
77 |
78 | Gpio.prototype.setActiveLow = setActiveLow;
79 |
80 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
81 | });
82 |
83 | it('ignores exceptions thrown by setDirection', () => {
84 | const setDirection = Gpio.prototype.setDirection;
85 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = () => {
86 | throw new Error();
87 | };
88 |
89 | const expected = '';
90 | let actual;
91 |
92 | try {
93 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
94 | actual = '';
95 | } catch (err) {
96 | actual = 'error thrown by setDirection was not ignored';
97 | }
98 |
99 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = setDirection;
100 |
101 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
102 | });
103 |
104 | it('ignores exceptions thrown by setEdge', () => {
105 | const setEdge = Gpio.prototype.setEdge;
106 | Gpio.prototype.setEdge = () => {
107 | throw new Error();
108 | };
109 |
110 | const expected = '';
111 | let actual;
112 |
113 | try {
114 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
115 | actual = '';
116 | } catch (err) {
117 | actual = 'error thrown by setEdge was not ignored';
118 | }
119 |
120 | Gpio.prototype.setEdge = setEdge;
121 |
122 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
123 | });
124 |
125 | it('does not unnecessarily reconfigure direction', () => {
126 | let setDirectionCalled = false;
127 |
128 | const setDirection = Gpio.prototype.setDirection;
129 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = () => {
130 | setDirectionCalled = true;
131 | };
132 |
133 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', {reconfigureDirection: false});
134 |
135 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = setDirection;
136 |
137 | assert(!setDirectionCalled);
138 | });
139 |
140 | it('reconfigures direction if necessary', () => {
141 | let setDirectionCalled = false;
142 |
143 | const setDirection = Gpio.prototype.setDirection;
144 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = () => {
145 | setDirectionCalled = true;
146 | };
147 |
148 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'high', {reconfigureDirection: false});
149 |
150 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = setDirection;
151 |
152 | assert(setDirectionCalled);
153 | });
154 |
155 |
156 | afterEach(() => {
157 | gpio.unexport();
158 | MockLinux.restore();
159 | });
160 | });
161 |
162 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/direction.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('direction', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | });
20 |
21 |
22 | it('is input', () => {
23 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
24 |
25 | const expected = 'in';
26 | MockLinux.writeDirection(pin, expected);
27 | const actual = gpio.direction();
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | });
30 |
31 | it('is output', () => {
32 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
33 |
34 | const expected = 'out';
35 | MockLinux.writeDirection(pin, expected);
36 | const actual = gpio.direction();
37 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
38 | });
39 |
40 |
41 | afterEach(() => {
42 | gpio.unexport();
43 | MockLinux.restore();
44 | });
45 | });
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/edge.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('edge', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('is rising', () => {
24 | const expected = 'rising';
25 | MockLinux.writeEdge(pin, expected);
26 | const actual = gpio.edge();
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('is falling', () => {
31 | const expected = 'falling';
32 | MockLinux.writeEdge(pin, expected);
33 | const actual = gpio.edge();
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 | it('is both', () => {
38 | const expected = 'both';
39 | MockLinux.writeEdge(pin, expected);
40 | const actual = gpio.edge();
41 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
42 | });
43 |
44 |
45 | afterEach(() => {
46 | gpio.unexport();
47 | MockLinux.restore();
48 | });
49 | });
50 |
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/mocks/epoll.d.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | export class Epoll {
2 | static EPOLLPRI: number;
3 |
4 | constructor(callback: (args: any) => void);
5 |
6 | add(fd: any, events: any): void;
7 |
8 | remove(fd: any): void;
9 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/mocks/epoll.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | class Epoll {
4 | static get EPOLLPRI() { return 2; }
5 |
6 | constructor(callback) {
7 | this._callback = callback;
8 | this._timeout = null;
9 | }
10 |
11 | add(fd, events) {
12 | this._timeout = setTimeout(_ => {
13 | this._callback(null, fd, events);
14 | }, 10);
15 | }
16 |
17 | remove(fd) {
18 | if (this._timeout !== null) {
19 | clearTimeout(this._timeout);
20 | }
21 | }
22 | }
23 |
24 | exports.Epoll = Epoll;
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/mocks/linux.d.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | export function gpio(pin: any): void;
3 |
4 | export function gpioWithoutPinFiles(): void;
5 |
6 | export function makeGpioAccessible(): void;
7 |
8 | export function makeGpioInaccessible(): void;
9 |
10 | export function read(pin: any): any;
11 |
12 | export function write(pin: any, value: any): void;
13 |
14 | export function readDirection(pin: any): any;
15 |
16 | export function writeDirection(pin: any, direction: any): void;
17 |
18 | export function readEdge(pin: void): any;
19 |
20 | export function writeEdge(pin: any, edge: any): void;
21 |
22 | export function readActiveLow(pin: any): any;
23 |
24 | export function writeActiveLow(pin: any, value: any): void;
25 |
26 | export function restore(): void;
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/mocks/linux.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const mockFs = require('mock-fs');
4 | const fs = require('fs');
5 |
6 | function gpio(pin) {
7 | const name = `gpio${pin}`;
8 | mockFs({
9 | '/sys/class/gpio': {
10 | 'export': '',
11 | 'unexport': '',
12 | [name]: {
13 | 'direction': 'in',
14 | 'edge': 'none',
15 | 'active_low': '0',
16 | 'value': '0'
17 | }
18 | }
19 | });
20 | }
21 |
22 | function gpioWithoutPinFiles() {
23 | mockFs({
24 | '/sys/class/gpio': {
25 | 'export': ''
26 | }
27 | });
28 | }
29 |
30 | function makeGpioAccessible() {
31 | mockFs({
32 | '/sys/class/gpio': {
33 | 'export': ''
34 | }
35 | });
36 | }
37 |
38 | function makeGpioInaccessible() {
39 | mockFs({
40 | '/sys/class/gpio': {
41 | }
42 | });
43 | }
44 |
45 | function read(pin) {
46 | return fs.readFileSync('/sys/class/gpio/gpio4/value', { encoding: 'UTF-8' });
47 | }
48 |
49 | function write(pin, value) {
50 | fs.writeFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/value`, value);
51 | }
52 |
53 | function readDirection(pin) {
54 | return fs.readFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/direction`, { encoding: 'UTF-8' });
55 | }
56 |
57 | function writeDirection(pin, direction) {
58 | fs.writeFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/direction`, direction);
59 | }
60 |
61 | function readEdge(pin) {
62 | return fs.readFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/edge`, { encoding: 'UTF-8' });
63 | }
64 |
65 | function writeEdge(pin, edge) {
66 | fs.writeFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/edge`, edge);
67 | }
68 |
69 | function readActiveLow(pin) {
70 | return fs.readFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/active_low`, { encoding: 'UTF-8' });
71 | }
72 |
73 | function writeActiveLow(pin, value) {
74 | fs.writeFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/active_low`, value);
75 | }
76 |
77 | function restore() {
78 | mockFs.restore();
79 | }
80 |
81 | exports.gpio = gpio;
82 | exports.gpioWithoutPinFiles = gpioWithoutPinFiles;
83 | exports.makeGpioAccessible = makeGpioAccessible;
84 | exports.makeGpioInaccessible = makeGpioInaccessible;
85 | exports.read = read;
86 | exports.write = write;
87 | exports.readDirection = readDirection;
88 | exports.writeDirection = writeDirection;
89 | exports.readEdge = readEdge;
90 | exports.writeEdge = writeEdge;
91 | exports.readActiveLow = readActiveLow;
92 | exports.writeActiveLow = writeActiveLow;
93 | exports.restore = restore;
94 |
95 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/read.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 | const TestHelper = require('./utils/test-promise');
8 |
9 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 |
12 |
13 | describe('read', () => {
14 | let gpio;
15 | let pin;
16 |
17 | beforeEach(() => {
18 | pin = 4;
19 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
20 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
21 | });
22 |
23 |
24 | it('reads high', (done) => {
25 | const expected = 1;
26 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
27 | gpio.read((err, actual) => {
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | done();
30 | });
31 | });
32 |
33 | it('reads low', (done) => {
34 | const expected = 0;
35 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
36 | gpio.read((err, actual) => {
37 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
38 | done();
39 | });
40 | });
41 |
42 | it('fails', (done) => {
43 | const expected = 'EBADF';
44 |
45 | const valueFd = gpio._valueFd;
46 | gpio._valueFd = 1e6;
47 |
48 | gpio.read((err, value) => {
49 | gpio._valueFd = valueFd;
50 |
51 | const actual = err.code;
52 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
53 |
54 | done();
55 | });
56 | });
57 |
58 |
59 | afterEach(() => {
60 | gpio.unexport();
61 | MockLinux.restore();
62 | });
63 | });
64 |
65 | describe('read Promise', () => {
66 | let gpio;
67 | let pin;
68 |
69 | beforeEach(() => {
70 | pin = 4;
71 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
72 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
73 | });
74 |
75 | it('reads high', () => {
76 | const expected = 1;
77 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
78 | return gpio.read()
79 | .then(actual => TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected));
80 | });
81 |
82 | it('reads low', () => {
83 | const expected = 0;
84 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
85 | return gpio.read()
86 | .then(actual => TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected));
87 | });
88 |
89 | it('fails', () => {
90 | const expected = 'EBADF';
91 |
92 | const valueFd = gpio._valueFd;
93 | gpio._valueFd = 1e6;
94 |
95 | return gpio.read().catch((err) => {
96 | gpio._valueFd = valueFd;
97 |
98 | const actual = err.code;
99 | return TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected);
100 | });
101 | });
102 |
103 | afterEach(() => {
104 | gpio.unexport();
105 | MockLinux.restore();
106 | });
107 | });
108 |
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/readSync.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('readSync', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('reads high', () => {
24 | const expected = 1;
25 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
26 | const actual = gpio.readSync();
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('reads low', () => {
31 | const expected = 0;
32 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
33 | const actual = gpio.readSync();
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 |
38 | afterEach(() => {
39 | gpio.unexport();
40 | MockLinux.restore();
41 | });
42 | });
43 |
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/setActiveLow.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('setActiveLow', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('is active high', () => {
24 | gpio.setActiveLow(true);
25 | const actual = MockLinux.readActiveLow(pin);
26 | assert.deepEqual(actual, 1);
27 | });
28 |
29 | it('is active low', () => {
30 | gpio.setActiveLow(false);
31 | const actual = MockLinux.readActiveLow(pin);
32 | assert.deepEqual(actual, 0);
33 | });
34 |
35 |
36 | afterEach(() => {
37 | gpio.unexport();
38 | MockLinux.restore();
39 | });
40 | });
41 |
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/setDirection.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('setDirection', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | });
20 |
21 |
22 | it('is input', () => {
23 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
24 |
25 | const expected = 'in';
26 | gpio.setDirection(expected);
27 | const actual = MockLinux.readDirection(pin);
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | });
30 |
31 | it('is output', () => {
32 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
33 |
34 | const expected = 'out';
35 | gpio.setDirection(expected);
36 | const actual = MockLinux.readDirection(pin);
37 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
38 | });
39 |
40 |
41 | afterEach(() => {
42 | gpio.unexport();
43 | MockLinux.restore();
44 | });
45 | });
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/setEdge.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('setEdge', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('is rising', () => {
24 | const expected = 'rising';
25 | gpio.setEdge(expected);
26 | const actual = MockLinux.readEdge(pin);
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('is falling', () => {
31 | const expected = 'out';
32 | gpio.setEdge(expected);
33 | const actual = MockLinux.readEdge(pin);
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 | it('is both', () => {
38 | const expected = 'out';
39 | gpio.setEdge(expected);
40 | const actual = MockLinux.readEdge(pin);
41 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
42 | });
43 |
44 |
45 | afterEach(() => {
46 | gpio.unexport();
47 | MockLinux.restore();
48 | });
49 | });
50 |
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/typedefinition.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import assert = require('assert');
2 | import mockRequire = require('mock-require');
3 | import MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
4 | import MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
5 |
6 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
7 | import { Gpio } from '../onoff';
8 |
9 | describe('definition', () => {
10 | let gpio: Gpio;
11 | let pin: number;
12 |
13 | beforeEach(() => {
14 | pin = 4;
15 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
16 | });
17 |
18 | it('fires rising', (done) => {
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
20 |
21 | const expected = 1;
22 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
23 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
24 | done();
25 | });
26 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
27 | });
28 |
29 | afterEach(() => {
30 | gpio.unexport();
31 | MockLinux.restore();
32 | });
33 | });
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/utils/test-promise.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 |
5 | const shouldEventuallyEqual = (actual, expected) => {
6 | return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
7 | if(actual === expected) {
8 | resolve();
9 | } else {
10 | reject(new Error(
11 | 'Actual value does not equal expected value: Act ' +
12 | actual + ' ' + typeof actual +
13 | ' | Exp ' +
14 | expected + ' ' + typeof expected
15 | ));
16 | }
17 | });
18 | };
19 |
20 | exports.shouldEventuallyEqual = shouldEventuallyEqual;
21 |
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/watch-callbacks.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
6 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 | describe('watch callbacks', () => {
12 | let gpio;
13 | let pin;
14 |
15 | beforeEach(() => {
16 | pin = 4;
17 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
18 | });
19 |
20 | describe('watch', () => {
21 |
22 | it('fires rising', (done) => {
23 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
24 |
25 | const expected = 1;
26 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
27 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | done();
30 | });
31 | });
32 |
33 | it('fires falling', (done) => {
34 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
35 |
36 | const expected = 0;
37 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
38 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
39 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
40 | done();
41 | });
42 | });
43 |
44 | });
45 |
46 | describe('watch with debounce', () => {
47 |
48 | it('fires rising', (done) => {
49 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both', {debounceTimeout: 10});
50 |
51 | const expected = 1;
52 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
53 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
54 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
55 | done();
56 | });
57 | });
58 |
59 | it('fires falling', (done) => {
60 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both', {debounceTimeout: 10});
61 |
62 | const expected = 0;
63 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
64 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
65 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
66 | done();
67 | });
68 | });
69 |
70 | });
71 |
72 | afterEach(() => {
73 | gpio.unexport();
74 | MockLinux.restore();
75 | });
76 | });
77 |
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/watch-listeners.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
6 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('watch listeners', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | const listener1 = (err, value) => {
17 | if (err) {
18 | throw err;
19 | }
20 | console.log(`listener1: value is ${value}`);
21 | };
22 |
23 | const listener2 = (err, value) => {
24 | if (err) {
25 | throw err;
26 | }
27 | console.log(`listener2: value is ${value}`);
28 | };
29 |
30 | beforeEach(() => {
31 | pin = 4;
32 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
33 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
34 | });
35 |
36 | describe('watch', () => {
37 |
38 | it('no listeners', () => {
39 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
40 | });
41 |
42 | it('one listener', () => {
43 | gpio.watch(listener1);
44 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 1);
45 | });
46 |
47 | it('one listener multiple times', () => {
48 | gpio.watch(listener1);
49 | gpio.watch(listener1);
50 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 2);
51 | });
52 |
53 | it('multiple listeners', () => {
54 | gpio.watch(listener1);
55 | gpio.watch(listener2);
56 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 2);
57 | });
58 | });
59 |
60 | describe('unwatch', () => {
61 |
62 | it('no listeners', () => {
63 | gpio.unwatch(listener1);
64 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
65 | });
66 |
67 | it('one listener', () => {
68 | gpio.watch(listener1);
69 | gpio.unwatch(listener1);
70 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
71 | });
72 |
73 | it('one listener, all referneces', () => {
74 | gpio.watch(listener1);
75 | gpio.watch(listener1);
76 | gpio.unwatch(listener1);
77 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
78 | });
79 |
80 | it('mutliple listeners, only remove one', () => {
81 | gpio.watch(listener1);
82 | gpio.watch(listener2);
83 | gpio.unwatch(listener1);
84 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 1);
85 | });
86 | });
87 |
88 | describe('unwatchAll', () => {
89 |
90 | it('no listeners', () => {
91 | gpio.unwatchAll();
92 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
93 | });
94 |
95 |
96 | it('one listener multiple times', () => {
97 | gpio.watch(listener1);
98 | gpio.watch(listener1);
99 | gpio.unwatchAll(listener1);
100 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
101 | });
102 |
103 | it('multiple listeners', () => {
104 | gpio.watch(listener1);
105 | gpio.watch(listener2);
106 | gpio.unwatchAll();
107 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
108 | });
109 | });
110 |
111 | afterEach(() => {
112 | gpio.unexport();
113 | MockLinux.restore();
114 | });
115 | });
116 |
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/write.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
5 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 | const TestHelper = require('./utils/test-promise');
8 |
9 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 |
12 |
13 | describe('write', () => {
14 | let gpio;
15 | let pin;
16 |
17 | beforeEach(() => {
18 | pin = 4;
19 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
20 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
21 | });
22 |
23 |
24 | it('writes high', (done) => {
25 | const expected = 1;
26 | gpio.write(expected, (err) => {
27 | const actual = MockLinux.read(pin);
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | done();
30 | });
31 | });
32 |
33 | it('writes low', (done) => {
34 | const expected = 0;
35 | gpio.write(expected, (err) => {
36 | const actual = MockLinux.read(pin);
37 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
38 | done();
39 | });
40 | });
41 |
42 | afterEach(() => {
43 | gpio.unexport();
44 | MockLinux.restore();
45 | });
46 | });
47 |
48 | describe('write Promise', () => {
49 | let gpio;
50 | let pin;
51 |
52 | beforeEach(() => {
53 | pin = 4;
54 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
55 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
56 | });
57 |
58 | it('writes high', () => {
59 | const expected = 1;
60 | return gpio.write(expected).then(() => {
61 | const actual = parseInt(MockLinux.read(pin));
62 | return TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected);
63 | });
64 | });
65 |
66 | it('writes low', () => {
67 | const expected = 0;
68 | return gpio.write(expected).then(() => {
69 | const actual = parseInt(MockLinux.read(pin));
70 | return TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected);
71 | });
72 | });
73 |
74 | it('write fail',() => {
75 | const expected = 'EBADF';
76 |
77 | const valueFd = gpio._valueFd;
78 | gpio._valueFd = 1e6;
79 |
80 | return gpio.write(1)
81 | .catch((err) => {
82 | gpio._valueFd = valueFd;
83 | const actual = err.code;
84 | return TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected);
85 | });
86 | });
87 |
88 | afterEach(() => {
89 | gpio.unexport();
90 | MockLinux.restore();
91 | });
92 | });
93 |
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/writeSync.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
5 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('writeSync', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('writes high', () => {
24 | const expected = 1;
25 | gpio.writeSync(expected);
26 | const actual = MockLinux.read(pin);
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('writes low', () => {
31 | const expected = 0;
32 | gpio.writeSync(expected);
33 | const actual = MockLinux.read(pin);
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 |
38 | afterEach(() => {
39 | gpio.unexport();
40 | MockLinux.restore();
41 | });
42 | });
43 |
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tsconfig.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "compilerOptions": {
3 | "lib": ["es6", "dom"],
4 | "module": "commonjs",
5 | "sourceMap": true,
6 | "strict": true,
7 | "target": "es6",
8 | },
9 | "exclude": [
10 | "node_modules"
11 | ]
12 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
46 |
47 | When the button is pressed the LED should turn on, when it's released the LED
48 | should turn off. This can be achieved with the following code:
49 |
50 | ```js
51 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
52 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
53 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
54 |
55 | button.watch((err, value) => led.writeSync(value));
56 | ```
57 |
58 | Here two Gpio objects are being created. One called led for the LED connected
59 | to GPIO17 which is an output, and one called button for the momentary push
60 | button connected to GPIO4 which is an input. In addition to specifying that
61 | the button is an input, the constructors optional third argument is used to
62 | specify that 'both' rising and falling interrupt edges should be configured
63 | for the button GPIO as both button presses and releases should be handled.
64 |
65 | After everything has been setup correctly, the buttons watch method is used to
66 | specify a callback function to execute every time the button is pressed or
67 | released. The value argument passed to the callback function represents the
68 | state of the button which will be 1 for pressed and 0 for released. This value
69 | is used by the callback to turn the LED on or off using its writeSync method.
70 |
71 | When the above program is running it can be terminated with ctrl-c. However,
72 | it doesn't free its resources. It also ignores the err argument passed to
73 | the callback. Here's a slightly modified variant of the program that handles
74 | ctrl-c gracefully and bails out on error. The resources used by the led and
75 | button Gpio objects are released by invoking their unexport method.
76 |
77 | ```js
78 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
79 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
80 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
81 |
82 | button.watch((err, value) => {
83 | if (err) {
84 | throw err;
85 | }
86 |
87 | led.writeSync(value);
88 | });
89 |
90 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
91 | led.unexport();
92 | button.unexport();
93 | });
94 | ```
95 |
96 | #### Debouncing Buttons
97 | When working with buttons there will often be button bounce issues which
98 | result in the hardware thinking that a button was pressed several times
99 | although it was only pressed once. onoff provides a software debouncing
100 | solution for resolving bounce issues.
101 |
102 | Assume again that there's an LED connected to GPIO17 and a momentary push
103 | button connected to GPIO4.
104 |
105 | When the button is pressed the LED should toggle its state. This is a typical
106 | example of a situation where there will be button bounce issues. The issue can
107 | be resolved by using the debounceTimeout option when creating the Gpio object
108 | for the button. In the below program the debounceTimeout is set to 10
109 | milliseconds. This delays invoking the watch callback for the button while the
110 | button is bouncing. The watch callback will not be invoked until the button
111 | stops bouncing and has been in a stable state for 10 milliseconds.
112 |
113 | ```js
114 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
115 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
116 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
117 |
118 | button.watch((err, value) => {
119 | if (err) {
120 | throw err;
121 | }
122 |
123 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
124 | });
125 |
126 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
127 | led.unexport();
128 | button.unexport();
129 | });
130 | ```
131 |
132 | #### Blink an LED Using the Synchronous API
133 |
134 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the synchronous readSync
135 | and writeSync methods.
136 |
137 | ```js
138 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
139 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
140 |
141 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
142 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 200);
143 |
144 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
145 | setTimeout(_ => {
146 | clearInterval(iv); // Stop blinking
147 | led.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
148 | }, 5000);
149 | ```
150 |
151 | #### Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Completion Callbacks
152 |
153 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the asynchronous read and
154 | write methods and completion callbacks.
155 |
156 | ```js
157 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
158 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
159 | let stopBlinking = false;
160 |
161 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
162 | const blinkLed = _ => {
163 | if (stopBlinking) {
164 | return led.unexport();
165 | }
166 |
167 | led.read((err, value) => { // Asynchronous read
168 | if (err) {
169 | throw err;
170 | }
171 |
172 | led.write(value ^ 1, err => { // Asynchronous write
173 | if (err) {
174 | throw err;
175 | }
176 | });
177 | });
178 |
179 | setTimeout(blinkLed, 200);
180 | };
181 |
182 | blinkLed();
183 |
184 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
185 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
186 | ```
187 |
188 | #### Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Promises
189 |
190 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the asynchronous read and
191 | write methods and Promises.
192 |
193 | ```js
194 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
195 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
196 | let stopBlinking = false;
197 |
198 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
199 | const blinkLed = _ => {
200 | if (stopBlinking) {
201 | return led.unexport();
202 | }
203 |
204 | led.read()
205 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
206 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 200))
207 | .catch(err => console.log(err));
208 | };
209 |
210 | blinkLed();
211 |
212 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
213 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
214 | ```
215 |
216 | #### Check accessibility
217 |
218 | Sometimes it may be necessary to determine if the current system supports
219 | GPIOs programmatically and mock functionality if it doesn't. `Gpio.accessible`
220 | can be used to achieve this.
221 |
222 | ```js
223 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
224 |
225 | const useLed = (led, value) => led.writeSync(value);
226 |
227 | let led;
228 |
229 | if (Gpio.accessible) {
230 | led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
231 | // more real code here
232 | } else {
233 | led = {
234 | writeSync: value => {
235 | console.log('virtual led now uses value: ' + value);
236 | }
237 | };
238 | }
239 |
240 | useLed(led, 1);
241 | ```
242 |
243 | ## API
244 |
245 | ### Class Gpio
246 |
247 | * [Gpio(gpio, direction [, edge] [, options]) - Constructor](#gpiogpio-direction--edge--options)
248 | * [read([callback]) - Read GPIO value asynchronously](#readcallback)
249 | * [readSync() - Read GPIO value synchronously](#readsync)
250 | * [write(value[, callback]) - Write GPIO value asynchronously](#writevalue-callback)
251 | * [writeSync(value) - Write GPIO value synchronously](#writesyncvalue)
252 | * [watch(callback) - Watch for hardware interrupts on the GPIO](#watchcallback)
253 | * [unwatch([callback]) - Stop watching for hardware interrupts on the GPIO](#unwatchcallback)
254 | * [unwatchAll() - Remove all watchers for the GPIO](#unwatchall)
255 | * [direction() - Get GPIO direction](#direction)
256 | * [setDirection(direction) - Set GPIO direction](#setdirectiondirection)
257 | * [edge() - Get GPIO interrupt generating edge](#edge)
258 | * [setEdge(edge) - Set GPIO interrupt generating edge](#setedgeedge)
259 | * [activeLow() - Get GPIO activeLow setting](#activelow)
260 | * [setActiveLow(invert) - Set GPIO activeLow setting](#setactivelowinvert)
261 | * [unexport() - Reverse the effect of exporting the GPIO to userspace](#unexport)
262 | * [static accessible - Determine whether or not GPIO access is possible](#static-accessible)
263 | * [HIGH / LOW - Constants used when reading or writing a GPIO value](#static-high--low)
264 |
265 | ##### Gpio(gpio, direction [, edge] [, options])
266 | - gpio - An unsigned integer specifying the GPIO number.
267 | - direction - A string specifying whether the GPIO should be configured as an
268 | input or output. The valid values are: 'in', 'out', 'high', and 'low'. If 'out'
269 | is specified the GPIO will be configured as an output and the value of the GPIO
270 | will be set to 0. 'high' and 'low' are variants of 'out' that configure the
271 | GPIO as an output with an initial level of 1 or 0 respectively.
272 | - [edge] - An optional string specifying the interrupt generating edge or
273 | edges for an input GPIO. The valid values are: 'none', 'rising', 'falling' or
274 | 'both'. The default value is 'none' indicating that the GPIO will not generate
275 | interrupts. Whether or not interrupts are supported by an input GPIO is GPIO
276 | specific. If interrupts are not supported by a GPIO the edge argument should
277 | not be specified. The edge argument is ignored for output GPIOs.
278 | - [options] - An optional options object.
279 |
280 | Configures the GPIO based on the passed arguments and returns a new Gpio
281 | object that can be used to access the GPIO.
282 |
283 | The following options are supported:
284 | - debounceTimeout - An unsigned integer specifying a millisecond delay. Delays
285 | invoking the watch callback for an interrupt generating input GPIO while the
286 | input is bouncing. The watch callback will not be invoked until the input
287 | stops bouncing and has been in a stable state for debounceTimeout
288 | milliseconds. Optional, if unspecified the input GPIO will not be debounced.
289 | - activeLow - A boolean value specifying whether the values read from or
290 | written to the GPIO should be inverted. The interrupt generating edge for the
291 | GPIO also follow this this setting. The valid values for activeLow are true
292 | and false. Setting activeLow to true inverts. Optional, the default value is
293 | false.
294 | - reconfigureDirection - A boolean value specifying whether the direction for
295 | the GPIO should be reconfigured even though the direction is already
296 | configured correctly. When an application starts, the direction of a GPIO used
297 | by that application may already be configured correctly, for example, from a
298 | previous run of the application. Reconfiguring the direction of that GPIO can
299 | result in unwanted side effects. For example, if a GPIO is already configured
300 | as an output and it is reconfigured as an output by passing 'out' to the
301 | constructor, the value of that output will be set to 0. In some applications
302 | this is not desirable and the value of the output should not be modified. The
303 | reconfigureDirection option can help here. If reconfigureDirection is set to
304 | false the direction of a GPIO that is already correctly configured will not be
305 | reconfigured. Optional, the default value is true.
306 |
307 | GPIOs on Linux are identified by unsigned integers. These are the numbers that
308 | should be passed to the onoff Gpio constructor when exporting GPIOs to
309 | userspace. For example, pin 11 on the Raspberry Pi expansion header
310 | corresponds to GPIO17 in Raspbian Linux. 17 is therefore the number to pass
311 | to the onoff Gpio constructor when using pin 11 on the expansion header.
312 |
313 | ##### read([callback])
314 | - [callback] - An optional completion callback that gets two arguments (err,
315 | value), where err is reserved for an Error object and value is the number 0
316 | or 1 and represents the state of the GPIO.
317 |
318 | Read GPIO value asynchronously. If no completion callback is specified read
319 | returns a Promise which resolves to the value of the GPIO on success or rejects
320 | with an Error object on failure.
321 |
322 | Note that most systems support readback of GPIOs configured as outputs. The
323 | read method can therefore be invoked for any GPIO, irrespective of whether it
324 | was configured as an input or an output. The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are
325 | examples of such systems.
326 |
327 | ##### readSync()
328 | Read GPIO value synchronously. Returns the number 0 or 1 to represent the
329 | state of the GPIO.
330 |
331 | Note that most systems support readback of GPIOs configured as outputs. The
332 | readSync method can therefore be invoked for any GPIO, irrespective of whether
333 | it was configured as an input or an output. The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone
334 | are examples of such systems.
335 |
336 | ##### write(value[, callback])
337 | - value - The number 0 or 1.
338 | - [callback] - An optional completion callback that gets one argument (err),
339 | where err is reserved for an error object.
340 |
341 | Write GPIO value asynchronously. If no completion callback is specified write
342 | returns a Promise that resolves with no value on success or rejects with an
343 | Error object on failure.
344 |
345 | Note that on most systems invoking write for a GPIO configured as an input
346 | will result in an EPERM error indicating that the operation is not permitted.
347 | The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are examples of such systems.
348 |
349 | ##### writeSync(value)
350 | - value - The number 0 or 1.
351 |
352 | Write GPIO value synchronously.
353 |
354 | Note that on most systems invoking writeSync for a GPIO configured as an input
355 | will result in an EPERM error indicating that the operation is not permitted.
356 | The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are examples of such systems.
357 |
358 | ##### watch(callback)
359 | - callback - A callback that gets two arguments (err, value), where err is
360 | reserved for an error object and value is the number 0 or 1 and represents the
361 | state of the GPIO. The value can also be used to determine whether the
362 | interrupt occurred on a rising or falling edge. A value of 0 implies a falling
363 | edge interrupt and a value of 1 implies a rising edge interrupt.
364 |
365 | Watch for hardware interrupts on the GPIO. The edge argument that was passed
366 | to the constructor determines which hardware interrupts to watch for.
367 |
368 | ##### unwatch([callback])
369 | - [callback] - The callback to remove.
370 |
371 | Stop watching for hardware interrupts on the GPIO. If callback is specified,
372 | only that particular callback is removed. Otherwise all callbacks are removed.
373 |
374 | ##### unwatchAll()
375 | Remove all hardware interrupt watchers for the GPIO.
376 |
377 | ##### direction()
378 | Returns the string 'in' or 'out' indicating whether the GPIO is an input or
379 | output.
380 |
381 | ##### setDirection(direction)
382 | - direction - A string specifying whether the GPIO should be configured as an
383 | input or output. The valid values are 'in', 'out', 'high', and 'low'. If 'out'
384 | is specified the GPIO will be configured as an output and the value of the GPIO
385 | will be set to 0. 'high' and 'low' are variants of 'out' that configure the
386 | GPIO as an output with an initial level of 1 or 0 respectively.
387 |
388 | Set GPIO direction.
389 |
390 | ##### edge()
391 | Returns the string 'none', 'falling', 'rising', or 'both' indicating the
392 | interrupt generating edge or edges for the GPIO. Whether or not interrupts are
393 | supported by an input GPIO is GPIO specific. If interrupts are not supported
394 | the edge method should not be used. Interrupts are not supported by output
395 | GPIOs.
396 |
397 | ##### setEdge(edge)
398 | - edge - A string specifying the interrupt generating edge or edges for an
399 | input GPIO. The valid values are: 'none', 'rising', 'falling' or 'both'.
400 | Whether or not interrupts are supported by an input GPIO is GPIO specific. If
401 | interrupts are not supported the setEdge method should not be used. Interrupts
402 | are not supported by output GPIOs.
403 |
404 | Set GPIO interrupt generating edge.
405 |
406 | ##### activeLow()
407 | Returns true or false indicating whether or not the values read from or written
408 | to the GPIO are inverted.
409 |
410 | ##### setActiveLow(invert)
411 | - invert - A boolean value specifying whether the values read from or written
412 | to the GPIO should be inverted. The interrupt generating edge for the GPIO also
413 | follow this this setting. The valid values for invert are true and false.
414 | Setting activeLow to true inverts.
415 |
416 | Set GPIO activeLow setting.
417 |
418 | ##### unexport()
419 | Reverse the effect of exporting the GPIO to userspace. A Gpio object should not
420 | be used after invoking its unexport method.
421 |
422 | ##### static accessible
423 | Determine whether or not GPIO access is possible. true if the current process
424 | has the permissions required to export GPIOs to userspace. false otherwise.
425 | Loosely speaking, if this property is true it should be possible for the
426 | current process to create Gpio objects.
427 |
428 | It is notable that while this property may be false indicating that the
429 | current process does not have the permissions required to export GPIOs to
430 | userspace, existing exported GPIOs may still be accessible.
431 |
432 | This property is useful for mocking functionality on computers used for
433 | development that do not provide access to GPIOs.
434 |
435 | This is a static property and should be accessed as `Gpio.accessible`.
436 |
437 | ##### static HIGH / LOW
438 | Constants used when reading or writing a GPIO value. Gpio.HIGH and Gpio.LOW
439 | can be used in place of the numeric constants 1 and 0.
440 |
441 |
442 | ## How Does onoff Work?
443 |
444 | Internally onoff uses sysfs files located at /sys/class/gpio to access GPIOs
445 | and the [epoll package](https://github.com/fivdi/epoll) to detect hardware
446 | interrupts. The Linux GPIO sysfs interface for userspace is documented
447 | [here](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/gpio/sysfs.txt).
448 | It's a relatively simple interface which can be used to ask the Linux kernel
449 | to export control of a GPIO to userspace. After control of a GPIO has been
450 | exported to userspace, the GPIO can be configured as an input or output.
451 | Thereafter, the state of an input can be read, and the state of an output can
452 | be written. Some systems will also allow the state of a output to be read.
453 | The GPIO sysfs interface can also be used for interrupt detection. onoff can
454 | detect several thousand interrupts per second on both the BeagleBone and the
455 | Raspberry Pi.
456 |
457 |
458 | ## Configuring Pullup and Pulldown Resistors
459 |
460 | As mentioned in section [How Does onoff Work](#how-does-onoff-work) the sysfs
461 | interface is used to access GPIOs. The sysfs interface doesn't offer support
462 | for configuring pullup and pulldown resistors on GPIOs.
463 |
464 | There are however many platform specific mechanisms for configuring pullup and
465 | pulldown resistors that are compatible with onoff. onoff itself doesn't use
466 | these mechanisms as one of the goals of onoff is to be platform independent.
467 |
468 | Here we'll take a look at two mechanisms available on the Raspberry Pi for
469 | configuring pullup and pulldown resistors.
470 |
471 | The first point to be aware of is that most GPIOs on a Raspberry Pi have
472 | either their pullup or pulldown resistor activated by default. The defaults
473 | can be seen in Table 6-31 on pages 102 and 103 of the
474 | [BCM2835 ARM Peripherals](http://www.farnell.com/datasheets/1521578.pdf)
475 | documentation.
476 |
477 | #### Using the gpio Command in /boot/config.txt
478 |
479 | On Raspbian 2018-04-18 or later the `gpio` configuration command can be used
480 | in `/boot/config.txt` to configure pullup and pulldown resistors. Further
481 | information is available at
482 | [New "gpio" config command](https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=117&t=208748).
483 |
484 | #### Using Device Tree Overlays
485 |
486 | Device tree overlays can also be used to configure pullup and pulldown
487 | resistors. The Wiki page
488 | [Enabling Pullup and Pulldown Resistors on The Raspberry Pi](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/wiki/Enabling-Pullup-and-Pulldown-Resistors-on-The-Raspberry-Pi)
489 | describes this mechanism in more detail.
490 |
491 | ## Benchmarks
492 |
493 | Three of the onoff tests are used to monitor performance.
494 |
495 | * performance-async.js - determine max. no. of write ops per seconds
496 | * performance-sync.js - determine max. no. of writeSync ops per second
497 | * performance-interrupt.js - determine max. no. of interrupts per second
498 |
499 | The results of these tests are shown in the following tables.
500 |
501 | **Raspberry Pi 4 B, 1.5GHz, Raspberry Pi OS (March 4th 2021, Buster 10.8)**
502 |
503 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
504 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
505 | v16.0.0 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 25124 | 280417 | 20240
506 | v15.14.0 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 24055 | 271149 | 20488
507 | v14.16.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 21669 | 254705 | 19703
508 | v12.22.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 22618 | 318417 | 21122
509 | v10.24.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 22405 | 329927 | 19583
510 |
511 | **Raspberry Pi 3 B, 1.2GHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
512 |
513 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
514 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
515 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 21670 | 207222 | 18328
516 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 23661 | 225758 | 20741
517 |
518 | **Raspberry Pi 2 B, 900MHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
519 |
520 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
521 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
522 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 10769 | 113107 | 10373
523 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 11843 | 129086 | 10536
524 |
525 | **Raspberry Pi 1 B, 700MHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
526 |
527 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
528 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
529 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75+ | 2316 | 26696 | 2112
530 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75+ | 2613 | 33129 | 2225
531 |
532 | **BeagleBone Black, 1GHz, Debian Buster 10.2**
533 |
534 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
535 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
536 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 6855 | 70535 | 5911
537 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 7564 | 79133 | 5920
538 |
539 | **BeagleBone, 720MHz, Debian Buster 10.2**
540 |
541 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
542 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
543 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 5013 | 49741 | 4297
544 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 5400 | 57157 | 4371
545 |
546 | ## Related Packages
547 |
548 | Here are a few links to other hardware specific Node.js packages that may be
549 | of interest.
550 |
551 | * [pigpio](https://github.com/fivdi/pigpio) - Fast GPIO, PWM, servo control, state change notification and interrupt handling on the Raspberry Pi
552 | * [i2c-bus](https://github.com/fivdi/i2c-bus) - I2C serial bus access
553 | * [spi-device](https://github.com/fivdi/spi-device) - SPI serial bus access
554 | * [mcp-spi-adc](https://github.com/fivdi/mcp-spi-adc) - Analog to digital conversion with the MCP3002/4/8, MCP3202/4/8 and MCP3304
555 |
556 | ## Additional Information
557 |
558 | onoff was tested on the following platforms:
559 |
560 | - Raspberry Pi 1, 2, 3 and 4
561 | - Raspbian or Raspberry Pi OS
562 | - BeagleBone, BeagleBone Black and PocketBeagle
563 | - Debian
564 |
565 | The suitability of onoff for a particular Linux board is highly dependent on
566 | how GPIO interfaces are made available on that board. The
567 | [GPIO interfaces](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/gpio/)
568 | documentation describes GPIO access conventions rather than standards that must
569 | be followed so GPIO can vary from platform to platform. For example, onoff
570 | relies on sysfs files located at /sys/class/gpio being available. However,
571 | these sysfs files for userspace GPIO are optional and may not be available on a
572 | particular platform.
573 |
574 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/accessible.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 |
5 | console.log('Gpio functionality accessible on this computer?', Gpio.accessible);
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led-async.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
8 | const blinkLed = _ => {
9 | if (stopBlinking) {
10 | return led.unexport();
11 | }
12 |
13 | led.read((err, value) => { // Asynchronous read
14 | if (err) {
15 | throw err;
16 | }
17 |
18 | led.write(value ^ 1, err => { // Asynchronous write
19 | if (err) {
20 | throw err;
21 | }
22 | });
23 | });
24 |
25 | setTimeout(blinkLed, 200);
26 | };
27 |
28 | blinkLed();
29 |
30 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
31 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
32 |
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led-promises.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
8 | const blinkLed = _ => {
9 | if (stopBlinking) {
10 | return led.unexport();
11 | }
12 |
13 | led.read()
14 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
15 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 200))
16 | .catch(err => console.log(err));
17 | };
18 |
19 | blinkLed();
20 |
21 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
22 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
23 |
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 |
6 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
7 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 200);
8 |
9 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
10 | setTimeout(_ => {
11 | clearInterval(iv); // Stop blinking
12 | led.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
13 | }, 5000);
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/debounce-button.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
6 |
7 | button.watch((err, value) => {
8 | if (err) {
9 | throw err;
10 | }
11 |
12 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
13 | });
14 |
15 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
16 | led.unexport();
17 | button.unexport();
18 | });
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/light-switch.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
6 |
7 | button.watch((err, value) => {
8 | if (err) {
9 | throw err;
10 | }
11 |
12 | led.writeSync(value);
13 | });
14 |
15 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
16 | led.unexport();
17 | button.unexport();
18 | });
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/light-switch.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fivdi/onoff/813da60dd1f3a842a29a8c630243d4f5b7523cc0/examples/light-switch.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/mygpio-overlay.dts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /dts-v1/;
2 | /plugin/;
3 |
4 | / {
5 | compatible = "brcm,bcm2708";
6 |
7 | fragment@0 {
8 | target = <&gpio>;
9 | __overlay__ {
10 | pinctrl-names = "default";
11 | pinctrl-0 = <&my_pins>;
12 |
13 | my_pins: my_pins {
14 | brcm,pins = <7 8 9>; /* gpio no. */
15 | brcm,function = <0 0 0>; /* 0:in, 1:out */
16 | brcm,pull = <1 1 2>; /* 2:up 1:down 0:none */
17 | };
18 | };
19 | };
20 | };
21 |
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/run-examples:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node blink-led
3 | node blink-led-async
4 | node wait-for-interrupt
5 | node light-switch
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/wait-for-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 |
5 | // Export GPIO4 as an interrupt generating input with a debounceTimeout of 10
6 | // milliseconds
7 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
8 |
9 | console.log('Please press the button on GPIO4...');
10 |
11 | // The callback passed to watch will be invoked when the button connected to
12 | // GPIO4 is pressed
13 | button.watch((err, value) => {
14 | if (err) {
15 | throw err;
16 | }
17 |
18 | console.log('Button pressed!, its value was ' + value);
19 |
20 | button.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
21 | });
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/blink-led-promises.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | const blinkLed = _ => {
8 | if (stopBlinking) {
9 | led.unexport();
10 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
11 | return;
12 | }
13 |
14 | led.read()
15 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
16 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 50))
17 | .catch(err => {
18 | console.log(err);
19 | });
20 | };
21 |
22 | blinkLed();
23 |
24 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 2000);
25 |
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/blink-led.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 |
6 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 100);
7 |
8 | setTimeout(_ => {
9 | clearInterval(iv);
10 |
11 | led.writeSync(0);
12 | led.unexport();
13 |
14 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
15 | }, 2000);
16 |
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/change-configuration.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 |
6 | let output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
7 | let input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
8 |
9 | const watchWithSecondConfiguration = _ => {
10 | input.watch((err, value) => {
11 | assert(!err, 'error during interrupt detection');
12 | assert(value === 1, 'expected interrupt on rising edge');
13 |
14 | setTimeout(_ => {
15 | input.unexport();
16 | output.unexport();
17 |
18 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
19 | }, 10);
20 | });
21 |
22 | output.writeSync(1);
23 | };
24 |
25 | const changeConfiguration = _ => {
26 | input.unwatchAll();
27 |
28 | let temp = output;
29 | temp.setDirection('in');
30 | output = input;
31 | input = temp;
32 |
33 | output.setEdge('none');
34 | output.setDirection('out');
35 | output.writeSync(0);
36 | assert(output.direction() === 'out', 'expected direction to be out');
37 | assert(output.edge() === 'none', 'expected edge to be none');
38 | assert(output.readSync() === 0, 'expected value to be 0');
39 |
40 | input.setEdge('rising');
41 | assert(input.direction() === 'in', 'expected direction to be in');
42 | assert(input.edge() === 'rising', 'expected edge to be rising');
43 | assert(input.readSync() === 0, 'expected value to be 0');
44 |
45 | watchWithSecondConfiguration();
46 | };
47 |
48 | const watchWithFirstConfiguration = _ => {
49 | input.watch((err, value) => {
50 | assert(!err, 'error during interrupt detection');
51 | assert(value === 1, 'expected interrupt on rising edge');
52 |
53 | setTimeout(changeConfiguration, 10);
54 | });
55 |
56 | output.writeSync(1);
57 | };
58 |
59 | watchWithFirstConfiguration();
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-active-low-defaults.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | */
7 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
8 | const assert = require('assert');
9 | let input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
10 | let output = new Gpio(8, 'low', {activeLow: true});
11 |
12 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
13 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
14 |
15 | input.unexport();
16 | output.unexport();
17 |
18 | //
19 |
20 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
21 | output = new Gpio(8, 'low', {activeLow: false});
22 |
23 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
24 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
25 |
26 | input.unexport();
27 | output.unexport();
28 |
29 | //
30 |
31 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
32 | output = new Gpio(8, 'high', {activeLow: true});
33 |
34 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
35 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
36 |
37 | input.unexport();
38 | output.unexport();
39 |
40 | //
41 |
42 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
43 | output = new Gpio(8, 'high', {activeLow: false});
44 |
45 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
46 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
47 |
48 | input.unexport();
49 | output.unexport();
50 |
51 | //
52 |
53 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
54 | output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: true});
55 |
56 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
57 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
58 |
59 | input.unexport();
60 | output.unexport();
61 |
62 | //
63 |
64 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
65 | output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: false});
66 |
67 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
68 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
69 |
70 | input.unexport();
71 | output.unexport();
72 |
73 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
74 |
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-active-low.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | */
7 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
8 | const assert = require('assert');
9 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
10 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: true});
11 |
12 | assert(input.activeLow() === false);
13 | assert(output.activeLow() === true);
14 |
15 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
16 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
17 |
18 | output.writeSync(0);
19 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
20 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
21 | output.writeSync(1);
22 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
23 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
24 |
25 | output.setActiveLow(false);
26 | assert(input.activeLow() === false);
27 | assert(output.activeLow() === false);
28 | output.writeSync(0);
29 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
30 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
31 | output.writeSync(1);
32 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
33 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
34 |
35 | input.setActiveLow(true);
36 | assert(input.activeLow() === true);
37 | assert(output.activeLow() === false);
38 | output.writeSync(0);
39 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
40 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
41 | output.writeSync(1);
42 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
43 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
44 |
45 | input.unexport();
46 | output.unexport();
47 |
48 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
49 |
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-input.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const input = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising');
6 |
7 | assert(input.direction() === 'in');
8 | assert(input.edge() === 'rising');
9 |
10 | input.unexport();
11 |
12 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-output.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const output = new Gpio(17, 'out');
6 |
7 | assert(output.direction() === 'out');
8 |
9 | output.writeSync(1);
10 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
11 |
12 | output.writeSync(0);
13 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
14 |
15 | output.write(1, err => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | throw err;
18 | }
19 |
20 | output.read((err, value) => {
21 | if (err) {
22 | throw err;
23 | }
24 |
25 | assert(value === 1);
26 |
27 | output.writeSync(0);
28 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
29 |
30 | output.unexport();
31 |
32 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
33 | });
34 | });
35 |
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/debounce.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
6 | const button = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both', {debounceTimeout: 10});
7 |
8 | let buttonPressedCount = 0;
9 | let buttonReleasedCount = 0;
10 |
11 | const simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce = cb => {
12 | let toggleCount = 0;
13 |
14 | const iv = setInterval(_ => {
15 | if (toggleCount === 19) {
16 | clearInterval(iv);
17 | return cb();
18 | }
19 |
20 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() ^ 1);
21 | toggleCount += 1;
22 | }, 2);
23 | };
24 |
25 | const simulatePressAndReleaseButtonWithBounce = _ => {
26 | simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce(_ => {
27 | setTimeout(_ => {
28 | simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce(_ => {
29 | setTimeout(_ => {
30 | assert(buttonPressedCount === 1);
31 | assert(buttonReleasedCount === 1);
32 |
33 | button.unexport();
34 | output.unexport();
35 |
36 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
37 | }, 20);
38 | });
39 | }, 50);
40 | });
41 | };
42 |
43 | button.watch((err, value) => {
44 | if (err) {
45 | throw err;
46 | }
47 |
48 | if (value === 1) {
49 | buttonPressedCount += 1;
50 | } else if (value === 0) {
51 | buttonReleasedCount += 1;
52 | }
53 | });
54 |
55 | simulatePressAndReleaseButtonWithBounce();
56 |
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/dont-reconfigure-direction-part1.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | *
7 | * This test is part 1 of a two part test.
8 | * For part 2 see dont-reconfigure-direction-part2.js.
9 | *
10 | * Part 1 sets the ouput to 1 and expects to read 1 on the input. Part 1
11 | * doesn't unexport the GPIOs so that part 2 can can ensure that a Gpio output
12 | * object can be constructed without modifying the value of the output. Part 2
13 | * also expects to read one on the input. This is achieved by using the
14 | * reconfigureDirection option.
15 | */
16 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
17 | const assert = require('assert');
18 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
19 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
20 |
21 | output.writeSync(1);
22 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
23 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
24 |
25 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/dont-reconfigure-direction-part2.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | *
7 | * This test is part 2 of a two part test.
8 | * For part 1 see dont-reconfigure-direction-part1.js.
9 | *
10 | * Part 1 sets the ouput to 1 and expects to read 1 on the input. Part 1
11 | * doesn't unexport the GPIOs so that part 2 can can ensure that a Gpio output
12 | * object can be constructed without modifying the value of the output. Part 2
13 | * also expects to read one on the input. This is achieved by using the
14 | * reconfigureDirection option.
15 | */
16 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
17 | const assert = require('assert');
18 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
19 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {reconfigureDirection: false});
20 |
21 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
22 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
23 |
24 | input.unexport();
25 | output.unexport();
26 |
27 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
28 |
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/export-many-times.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | for (let i = 1; i <= 1000000; i += 1) {
6 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
7 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
8 | led.unexport();
9 | if (i % 10 === 0) {
10 | console.log(i);
11 | }
12 | }
13 |
14 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
15 |
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/high-low.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 |
6 | assert(Gpio.HIGH === 1, 'expected Gpio.HIGH to be 1');
7 | assert(Gpio.LOW === 0, 'expected Gpio.LOW to be 0');
8 |
9 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/many-interrupts.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
6 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
7 |
8 | let toggleCount = 0;
9 | let falling = 0;
10 | let rising = 0;
11 |
12 | const toggleOutput = _ => {
13 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() ^ 1);
14 | toggleCount += 1;
15 | };
16 |
17 | const interrupt = (err, value) => {
18 | if (err) {
19 | throw err;
20 | }
21 |
22 | if (value === 1) {
23 | rising += 1;
24 | } else if (value === 0) {
25 | falling += 1;
26 | }
27 |
28 | assert(output.readSync() === value);
29 |
30 | if (rising + falling < 2000) {
31 | toggleOutput();
32 | } else {
33 | assert(toggleCount === 2000);
34 | assert(rising === falling);
35 | assert(rising + falling === toggleCount);
36 |
37 | input.unexport();
38 | output.writeSync(0);
39 | output.unexport();
40 |
41 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
42 | }
43 | };
44 |
45 | input.watch(interrupt);
46 | toggleOutput();
47 |
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/output-with-edge-bug.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | // Test for https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/87
4 | //
5 | // If a Gpio is instantiated for an output GPIO and the edge parameter is
6 | // specified then the edge parameter should be ignored. Attempting to write
7 | // the sysfs edge file for an output GPIO results in an
8 | // "EIO: i/o error, write"
9 |
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 | const assert = require('assert');
12 |
13 | const ensureGpio17Unexported = cb => {
14 | let led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
15 |
16 | led.unexport();
17 |
18 | setTimeout(_ => cb(), 100);
19 | };
20 |
21 | ensureGpio17Unexported(_ => {
22 | let led;
23 |
24 | assert.doesNotThrow(
25 | _ => led = new Gpio(17, 'out', 'both'),
26 | 'can\'t instantiate a Gpio for an output with edge option specified'
27 | );
28 |
29 | led.unexport();
30 |
31 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
32 | });
33 |
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-async.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | const pulseLed = (led, pulseCount, cb) => {
6 | let time = process.hrtime();
7 |
8 | const loop = count => {
9 | if (count === 0) {
10 | time = process.hrtime(time);
11 | const writesPerSecond = pulseCount * 2 / (time[0] + time[1] / 1E9);
12 | return cb(null, writesPerSecond);
13 | }
14 |
15 | led.write(1, err => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | return cb(err);
18 | }
19 |
20 | led.write(0, err => {
21 | if (err) {
22 | return cb(err);
23 | }
24 |
25 | loop(count - 1);
26 | });
27 | });
28 | };
29 |
30 | loop(pulseCount);
31 | };
32 |
33 | const asyncWritesPerSecond = cb => {
34 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
35 | let writes = 0;
36 |
37 | const loop = count => {
38 | if (count === 0) {
39 | led.unexport();
40 | return cb(null, writes / 10);
41 | }
42 |
43 | pulseLed(led, 10000, (err, writesPerSecond) => {
44 | if (err) {
45 | return cb(err);
46 | }
47 |
48 | writes += writesPerSecond;
49 |
50 | loop(count - 1);
51 | });
52 | };
53 |
54 | // Do a dry run first to get the runtime primed
55 | pulseLed(led, 5000, (err, writesPerSecond) => {
56 | if (err) {
57 | return cb(err);
58 | }
59 | loop(10);
60 | });
61 | };
62 |
63 | asyncWritesPerSecond((err, averageWritesPerSecond) => {
64 | if (err) {
65 | throw err;
66 | }
67 |
68 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
69 | console.log(
70 | ' ' + Math.floor(averageWritesPerSecond) + ' async writes per second'
71 | );
72 | });
73 |
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor. GPIO7 is
6 | * an interrupt generating input and GPIO8 is an output. By toggling the state
7 | * of the output an interrupt is generated. The output is toggled as often as
8 | * possible to determine the maximum rate at which interrupts can be handled.
9 | */
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
12 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
13 |
14 | let irqCount = 0;
15 | let iv;
16 |
17 | // Exit handler
18 | const exit = _ => {
19 | input.unexport();
20 | output.unexport();
21 |
22 | clearInterval(iv);
23 | };
24 | process.on('SIGINT', exit);
25 |
26 | // Interrupt handler
27 | input.watch((err, value) => {
28 | if (err) {
29 | exit();
30 | }
31 |
32 | irqCount += 1;
33 |
34 | // Trigger next interrupt by toggling output.
35 | output.writeSync(value === 0 ? 1 : 0);
36 | });
37 |
38 | // Print number of interrupts once a second.
39 | iv = setInterval(_ => {
40 | console.log(irqCount);
41 | irqCount = 0;
42 | }, 1000);
43 |
44 | // Trigger first interrupt by toggling output.
45 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() === 0 ? 1 : 0);
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-sync.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | const pulseLed = (led, pulseCount) => {
6 | let time = process.hrtime();
7 |
8 | for (let i = 0; i !== pulseCount; i += 1) {
9 | led.writeSync(1);
10 | led.writeSync(0);
11 | }
12 |
13 | time = process.hrtime(time);
14 |
15 | const writesPerSecond = pulseCount * 2 / (time[0] + time[1] / 1E9);
16 |
17 | return writesPerSecond;
18 | };
19 |
20 | const syncWritesPerSecond = _ => {
21 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
22 | let writes = 0;
23 |
24 | // Do a dry run first to get the runtime primed
25 | pulseLed(led, 50000);
26 |
27 | for (let i = 0; i !== 10; i += 1) {
28 | writes += pulseLed(led, 100000);
29 | }
30 |
31 | led.unexport();
32 |
33 | return writes / 10;
34 | };
35 |
36 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
37 | console.log(
38 | ' ' + Math.floor(syncWritesPerSecond()) + ' sync writes per second'
39 | );
40 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/run-performance-tests:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node performance-async
3 | node performance-sync
4 | node performance-interrupt
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/run-tests:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node blink-led
3 | node blink-led-promises
4 | node change-configuration
5 | node configure-and-check-active-low
6 | node configure-and-check-active-low-defaults
7 | node configure-and-check-input
8 | node configure-and-check-output
9 | node debounce
10 | node dont-reconfigure-direction-part1
11 | node dont-reconfigure-direction-part2
12 | node high-low
13 | node many-interrupts
14 | node output-with-edge-bug
15 | node wait-for-interrupt
16 | node wait-for-many-interrupts
17 |
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/wait-for-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
6 |
7 | assert(button.direction() === 'in');
8 | assert(button.edge() === 'both');
9 |
10 | console.info('Please press button connected to GPIO #4...');
11 |
12 | button.watch((err, value) => {
13 | if (err) {
14 | throw err;
15 | }
16 |
17 | assert(value === 0 || value === 1);
18 |
19 | button.unexport();
20 |
21 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
22 | console.log(' button pressed, value was ' + value);
23 | });
24 |
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/wait-for-many-interrupts.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {
6 | debounceTimeout : 10
7 | });
8 | let count = 0;
9 |
10 | assert(button.direction() === 'in');
11 | assert(button.edge() === 'rising');
12 |
13 | console.info('Please press button connected to GPIO4 5 times...');
14 |
15 | button.watch((err, value) => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | throw err;
18 | }
19 |
20 | count += 1;
21 |
22 | console.log('button pressed ' + count + ' times, value was ' + value);
23 |
24 | if (count === 5) {
25 | button.unexport();
26 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
27 | }
28 | });
29 |
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/onoff.d.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | export type High = 1;
2 | export type Low = 0;
3 | export type Direction = "in" | "out" | "high" | "low";
4 | export type Edge = "none" | "rising" | "falling" | "both";
5 |
6 | export type Options = {
7 | debounceTimeout?: number,
8 | activeLow?: boolean,
9 | reconfigureDirection?: boolean,
10 | }
11 |
12 | export type BinaryValue = High | Low;
13 | export type ValueCallback = (err: Error | null | undefined, value: BinaryValue) => void;
14 |
15 | export class Gpio {
16 | static HIGH: High;
17 | static LOW: Low;
18 | static accessible: boolean;
19 |
20 | constructor(gpio: number, direction: Direction, edge?: Edge, options?: Options);
21 |
22 | read(callback: ValueCallback): void;
23 | read(): Promise;
24 |
25 | readSync(): BinaryValue;
26 |
27 | write(value: BinaryValue, callback: (err: Error | null | undefined) => void): void;
28 | write(value: BinaryValue): Promise;
29 |
30 | writeSync(value: BinaryValue): void;
31 |
32 | watch(callback: ValueCallback): void;
33 | unwatch(callback?: ValueCallback): void;
34 | unwatchAll(): void;
35 |
36 | direction(): Direction;
37 | setDirection(direction: Direction): void;
38 |
39 | edge(): Edge;
40 | setEdge(edge: Edge): void;
41 |
42 | activeLow(): boolean;
43 | setActiveLow(invert: boolean): void;
44 |
45 | unexport(): void
46 | }
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/onoff.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const fs = require('fs');
4 | const debounce = require('lodash.debounce');
5 | const Epoll = require('epoll').Epoll;
6 |
7 | const GPIO_ROOT_PATH = '/sys/class/gpio/';
8 |
9 | const HIGH_BUF = Buffer.from('1');
10 | const LOW_BUF = Buffer.from('0');
11 |
12 | const HIGH = 1;
13 | const LOW = 0;
14 |
15 | const exportGpio = gpio => {
16 | if (!fs.existsSync(gpio._gpioPath)) {
17 | // The GPIO hasn't been exported yet so export it
18 | fs.writeFileSync(GPIO_ROOT_PATH + 'export', '' + gpio._gpio);
19 |
20 | return false;
21 | }
22 |
23 | // The GPIO has already been exported, perhaps by onoff itself, perhaps
24 | // by quick2wire gpio-admin on the Pi, perhaps by the WiringPi gpio
25 | // utility on the Pi, or perhaps by something else. In any case, an
26 | // attempt is made to set the direction and edge to the requested
27 | // values here. If quick2wire gpio-admin was used for the export, the
28 | // user should have access to both direction and edge files. This is
29 | // important as gpio-admin sets niether direction nor edge. If the
30 | // WiringPi gpio utility was used, the user should have access to edge
31 | // file, but not the direction file. This is also ok as the WiringPi
32 | // gpio utility can set both direction and edge. If there are any
33 | // errors while attempting to perform the modifications, just keep on
34 | // truckin'.
35 | return true;
36 | };
37 |
38 | // Avoid the access permission issue described here:
39 | // https://github.com/raspberrypi/linux/issues/553
40 | // On some syetems udev rules are used to set access permissions on the GPIO
41 | // sysfs files enabling those files to be accessed without root privileges.
42 | // This takes a while so wait for it to complete.
43 | const waitForGpioAccessPermission = (
44 | gpio, direction, edge, gpioPreviouslyExported
45 | ) => {
46 | let permissionRequiredPaths = [
47 | gpio._gpioPath + 'value',
48 | ];
49 |
50 | if (gpioPreviouslyExported === false) {
51 | permissionRequiredPaths.push(gpio._gpioPath + 'direction');
52 | permissionRequiredPaths.push(gpio._gpioPath + 'active_low');
53 |
54 | // On some systems the edge file will not exist if the GPIO does not
55 | // support interrupts
56 | // https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/77#issuecomment-321980735
57 | if (edge && direction === 'in') {
58 | permissionRequiredPaths.push(gpio._gpioPath + 'edge');
59 | }
60 | }
61 |
62 | permissionRequiredPaths.forEach(path => {
63 | let tries = 0;
64 |
65 | while (true) {
66 | try {
67 | tries += 1;
68 | const fd = fs.openSync(path, 'r+');
69 | fs.closeSync(fd);
70 | break;
71 | } catch (e) {
72 | if (tries === 10000) {
73 | throw e;
74 | }
75 | }
76 | }
77 | });
78 | };
79 |
80 | const configureGpio = (
81 | gpio, direction, edge, options, gpioPreviouslyExported
82 | ) => {
83 | const throwIfNeeded = err => {
84 | if (gpioPreviouslyExported === false) {
85 | throw err;
86 | }
87 | };
88 |
89 | try {
90 | if (typeof options.activeLow === 'boolean') {
91 | gpio.setActiveLow(options.activeLow);
92 | }
93 | } catch (err) {
94 | throwIfNeeded(err);
95 | }
96 |
97 | try {
98 | const reconfigureDirection =
99 | typeof options.reconfigureDirection === 'boolean' ?
100 | options.reconfigureDirection : true;
101 |
102 | const requestedDirection =
103 | direction === 'high' || direction === 'low' ? 'out' : direction;
104 |
105 | if (reconfigureDirection || gpio.direction() !== requestedDirection) {
106 | gpio.setDirection(direction);
107 | }
108 | } catch (err) {
109 | throwIfNeeded(err);
110 | }
111 |
112 | try {
113 | // On some systems writing to the edge file for an output GPIO will
114 | // result in an "EIO, i/o error"
115 | // https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/87
116 | if (edge && direction === 'in') {
117 | gpio.setEdge(edge);
118 | }
119 | } catch (err) {
120 | throwIfNeeded(err);
121 | }
122 | };
123 |
124 | const configureInterruptHandler = gpio => {
125 | // A poller is created for both inputs and outputs. A poller isn't
126 | // actually needed for an output but the setDirection method can be
127 | // invoked to change the direction of a GPIO from output to input and
128 | // then a poller may be needed.
129 | const pollerEventHandler = (err, fd, events) => {
130 | const value = gpio.readSync();
131 |
132 | if ((value === LOW && gpio._fallingEnabled) ||
133 | (value === HIGH && gpio._risingEnabled)) {
134 | gpio._listeners.slice(0).forEach(callback => {
135 | callback(err, value);
136 | });
137 | }
138 | };
139 |
140 | // Read GPIO value before polling to prevent an initial unauthentic
141 | // interrupt
142 | gpio.readSync();
143 |
144 | if (gpio._debounceTimeout > 0) {
145 | const db = debounce(pollerEventHandler, gpio._debounceTimeout);
146 |
147 | gpio._poller = new Epoll((err, fd, events) => {
148 | gpio.readSync(); // Clear interrupt
149 | db(err, fd, events);
150 | });
151 | } else {
152 | gpio._poller = new Epoll(pollerEventHandler);
153 | }
154 | };
155 |
156 | class Gpio {
157 | constructor(gpio, direction, edge, options) {
158 | if (typeof edge === 'object' && !options) {
159 | options = edge;
160 | edge = undefined;
161 | }
162 |
163 | options = options || {};
164 |
165 | this._gpio = gpio;
166 | this._gpioPath = GPIO_ROOT_PATH + 'gpio' + this._gpio + '/';
167 | this._debounceTimeout = options.debounceTimeout || 0;
168 | this._readBuffer = Buffer.alloc(16);
169 | this._readSyncBuffer = Buffer.alloc(16);
170 | this._listeners = [];
171 |
172 | const gpioPreviouslyExported = exportGpio(this);
173 |
174 | waitForGpioAccessPermission(
175 | this, direction, edge, gpioPreviouslyExported
176 | );
177 |
178 | configureGpio(this, direction, edge, options, gpioPreviouslyExported);
179 |
180 | this._valueFd = fs.openSync(this._gpioPath + 'value', 'r+');
181 |
182 | configureInterruptHandler(this);
183 | }
184 |
185 | read(callback) {
186 | const readValue = callback => {
187 | fs.read(this._valueFd, this._readBuffer, 0, 1, 0, (err, bytes, buf) => {
188 | if (typeof callback === 'function') {
189 | if (err) {
190 | return callback(err);
191 | }
192 |
193 | callback(null, convertBufferToBit(buf));
194 | }
195 | });
196 | };
197 |
198 | if (callback) {
199 | readValue(callback);
200 | } else {
201 | return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
202 | readValue((err, value) => {
203 | if (err) {
204 | reject(err);
205 | } else {
206 | resolve(value);
207 | }
208 | });
209 | });
210 | }
211 | }
212 |
213 | readSync() {
214 | fs.readSync(this._valueFd, this._readSyncBuffer, 0, 1, 0);
215 | return convertBufferToBit(this._readSyncBuffer);
216 | }
217 |
218 | write(value, callback) {
219 | const writeValue = (value, callback) => {
220 | const writeBuffer = convertBitToBuffer(value);
221 | fs.write(
222 | this._valueFd, writeBuffer, 0, writeBuffer.length, 0, callback
223 | );
224 | };
225 |
226 | if (callback) {
227 | writeValue(value, callback);
228 | } else {
229 | return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
230 | writeValue(value, err => {
231 | if (err) {
232 | reject(err);
233 | } else {
234 | resolve();
235 | }
236 | });
237 | });
238 | }
239 | }
240 |
241 | writeSync(value) {
242 | const writeBuffer = convertBitToBuffer(value);
243 | fs.writeSync(this._valueFd, writeBuffer, 0, writeBuffer.length, 0);
244 | }
245 |
246 | watch(callback) {
247 | this._listeners.push(callback);
248 |
249 | if (this._listeners.length === 1) {
250 | this._poller.add(this._valueFd, Epoll.EPOLLPRI);
251 | }
252 | }
253 |
254 | unwatch(callback) {
255 | if (this._listeners.length > 0) {
256 | if (typeof callback !== 'function') {
257 | this._listeners = [];
258 | } else {
259 | this._listeners = this._listeners.filter(listener => {
260 | return callback !== listener;
261 | });
262 | }
263 |
264 | if (this._listeners.length === 0) {
265 | this._poller.remove(this._valueFd);
266 | }
267 | }
268 | }
269 |
270 | unwatchAll() {
271 | this.unwatch();
272 | }
273 |
274 | direction() {
275 | return fs.readFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'direction').toString().trim();
276 | }
277 |
278 | setDirection(direction) {
279 | fs.writeFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'direction', direction);
280 | }
281 |
282 | edge() {
283 | return fs.readFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'edge').toString().trim();
284 | }
285 |
286 | setEdge(edge) {
287 | fs.writeFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'edge', edge);
288 |
289 | this._risingEnabled = edge === 'both' || edge === 'rising';
290 | this._fallingEnabled = edge === 'both' || edge === 'falling';
291 | }
292 |
293 | activeLow() {
294 | return convertBufferToBoolean(
295 | fs.readFileSync(this._gpioPath + 'active_low')
296 | );
297 | }
298 |
299 | setActiveLow(invert) {
300 | fs.writeFileSync(
301 | this._gpioPath + 'active_low', convertBooleanToBuffer(!!invert)
302 | );
303 | }
304 |
305 | unexport() {
306 | this.unwatchAll();
307 | fs.closeSync(this._valueFd);
308 | try {
309 | fs.writeFileSync(GPIO_ROOT_PATH + 'unexport', '' + this._gpio);
310 | } catch (ignore) {
311 | // Flow of control always arrives here when cape_universal is enabled on
312 | // the bbb.
313 | }
314 | }
315 |
316 | static get accessible() {
317 | let fd;
318 |
319 | try {
320 | fd = fs.openSync(GPIO_ROOT_PATH + 'export', fs.constants.O_WRONLY);
321 | } catch(e) {
322 | // e.code === 'ENOENT' / 'EACCES' are most common
323 | // though any failure to open will also result in a gpio
324 | // failure to export.
325 | return false;
326 | } finally {
327 | if (fd) {
328 | fs.closeSync(fd);
329 | }
330 | }
331 |
332 | return true;
333 | }
334 | }
335 |
336 | const convertBitToBuffer = bit => convertBooleanToBuffer(bit === HIGH);
337 | const convertBufferToBit =
338 | buffer => convertBufferToBoolean(buffer) ? HIGH : LOW;
339 |
340 | const convertBooleanToBuffer = boolean => boolean ? HIGH_BUF : LOW_BUF;
341 | const convertBufferToBoolean = buffer => buffer[0] === HIGH_BUF[0];
342 |
343 | Gpio.HIGH = HIGH;
344 | Gpio.LOW = LOW;
345 |
346 | module.exports.Gpio = Gpio;
347 |
348 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/package.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "name": "onoff",
3 | "version": "6.0.3",
4 | "description": "GPIO access and interrupt detection with Node.js",
5 | "main": "onoff.js",
6 | "types": "onoff.d.ts",
7 | "directories": {
8 | "example": "examples",
9 | "test": "test"
10 | },
11 | "scripts": {
12 | "lint": "jshint onoff.js examples/*.js integration-test/*.js test/*.js test/*/*.js",
13 | "test": "nyc mocha",
14 | "codecov": "nyc report --reporter=text-lcov > coverage.lcov && codecov",
15 | "coverage-report": "nyc report --reporter=html",
16 | "integration-test": "cd integration-test && ./run-tests && cd .."
17 | },
18 | "mocha": {
19 | "extension": [
20 | "js",
21 | "ts"
22 | ],
23 | "require": "ts-node/register"
24 | },
25 | "repository": {
26 | "type": "git",
27 | "url": "https://github.com/fivdi/onoff.git"
28 | },
29 | "homepage": "https://github.com/fivdi/onoff",
30 | "bugs": {
31 | "url": "https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues"
32 | },
33 | "engines": {
34 | "node": ">=10.0.0"
35 | },
36 | "dependencies": {
37 | "epoll": "^4.0.1",
38 | "lodash.debounce": "^4.0.8"
39 | },
40 | "devDependencies": {
41 | "@types/mocha": "^8.2.2",
42 | "@types/mock-require": "^2.0.0",
43 | "codecov": "^3.8.1",
44 | "jshint": "^2.12.0",
45 | "mocha": "^8.3.2",
46 | "mock-fs": "^4.13.0",
47 | "mock-require": "^3.0.3",
48 | "nyc": "^15.1.0",
49 | "ts-node": "^9.1.1",
50 | "typescript": "^4.2.4"
51 | },
52 | "keywords": [
53 | "gpio",
54 | "iot",
55 | "interrupt",
56 | "raspberry",
57 | "raspi",
58 | "rpi",
59 | "pi",
60 | "beaglebone",
61 | "beaglebone-black",
62 | "linux"
63 | ],
64 | "author": "fivdi",
65 | "license": "MIT"
66 | }
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/accessible.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('accessible', () => {
13 | beforeEach(() => {
14 | });
15 |
16 |
17 | it('is accessible', () => {
18 | MockLinux.makeGpioAccessible();
19 | assert.deepEqual(Gpio.accessible, true);
20 | });
21 |
22 | it('is inaccessible', () => {
23 | MockLinux.makeGpioInaccessible();
24 | assert.deepEqual(Gpio.accessible, false);
25 | });
26 |
27 |
28 | afterEach(() => {
29 | MockLinux.restore();
30 | });
31 | });
32 |
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/activeLow.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('activeLow', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('is active high', () => {
24 | MockLinux.writeActiveLow(pin, '1');
25 | const actual = gpio.activeLow();
26 | assert.deepEqual(actual, true);
27 | });
28 |
29 | it('is active low', () => {
30 | MockLinux.writeActiveLow(pin, '0');
31 | const actual = gpio.activeLow();
32 | assert.deepEqual(actual, false);
33 | });
34 |
35 |
36 | afterEach(() => {
37 | gpio.unexport();
38 | MockLinux.restore();
39 | });
40 | });
41 |
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/constructor-fails.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('constructor fails', function () {
13 | let pin;
14 |
15 | this.timeout(10000);
16 |
17 | beforeEach(() => {
18 | pin = 4;
19 | });
20 |
21 |
22 | it('fails to construct input while waiting for access permission', () => {
23 | const expected = 'ENOENT';
24 | let actual;
25 |
26 | MockLinux.gpioWithoutPinFiles();
27 |
28 | try {
29 | const gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
30 | } catch (err) {
31 | actual = err.code;
32 | }
33 |
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 | it('fails to construct output while waiting for access permission', () => {
38 | const expected = 'ENOENT';
39 | let actual;
40 |
41 | MockLinux.gpioWithoutPinFiles();
42 |
43 | try {
44 | const gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
45 | } catch (err) {
46 | actual = err.code;
47 | }
48 |
49 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
50 | });
51 |
52 |
53 | afterEach(() => {
54 | MockLinux.restore();
55 | });
56 | });
57 |
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/constructor.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('constructor', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | });
20 |
21 |
22 | it('creates input', () => {
23 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
24 |
25 | const expected = 'in';
26 | const actual = gpio.direction();
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('creates output', () => {
31 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
32 |
33 | const expected = 'out';
34 | const actual = gpio.direction();
35 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
36 | });
37 |
38 | it('creates active low input', () => {
39 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', {activeLow: true});
40 |
41 | const expected = true;
42 | const actual = gpio.activeLow();
43 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
44 | });
45 |
46 | it('creates active high input', () => {
47 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', {activeLow: false});
48 |
49 | const expected = false;
50 | const actual = gpio.activeLow();
51 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
52 | });
53 |
54 | it('creates input with debounce timeout', () => {
55 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', {debounceTimeout: 10});
56 |
57 | const expected = 10;
58 | const actual = gpio._debounceTimeout;
59 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
60 | });
61 |
62 | it('ignores exceptions thrown by setActiveLow', () => {
63 | const setActiveLow = Gpio.prototype.setActiveLow;
64 | Gpio.prototype.setActiveLow = () => {
65 | throw new Error();
66 | };
67 |
68 | const expected = '';
69 | let actual;
70 |
71 | try {
72 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out', {activeLow: true});
73 | actual = '';
74 | } catch (err) {
75 | actual = 'error thrown by setActiveLow was not ignored';
76 | }
77 |
78 | Gpio.prototype.setActiveLow = setActiveLow;
79 |
80 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
81 | });
82 |
83 | it('ignores exceptions thrown by setDirection', () => {
84 | const setDirection = Gpio.prototype.setDirection;
85 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = () => {
86 | throw new Error();
87 | };
88 |
89 | const expected = '';
90 | let actual;
91 |
92 | try {
93 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
94 | actual = '';
95 | } catch (err) {
96 | actual = 'error thrown by setDirection was not ignored';
97 | }
98 |
99 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = setDirection;
100 |
101 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
102 | });
103 |
104 | it('ignores exceptions thrown by setEdge', () => {
105 | const setEdge = Gpio.prototype.setEdge;
106 | Gpio.prototype.setEdge = () => {
107 | throw new Error();
108 | };
109 |
110 | const expected = '';
111 | let actual;
112 |
113 | try {
114 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
115 | actual = '';
116 | } catch (err) {
117 | actual = 'error thrown by setEdge was not ignored';
118 | }
119 |
120 | Gpio.prototype.setEdge = setEdge;
121 |
122 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
123 | });
124 |
125 | it('does not unnecessarily reconfigure direction', () => {
126 | let setDirectionCalled = false;
127 |
128 | const setDirection = Gpio.prototype.setDirection;
129 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = () => {
130 | setDirectionCalled = true;
131 | };
132 |
133 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', {reconfigureDirection: false});
134 |
135 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = setDirection;
136 |
137 | assert(!setDirectionCalled);
138 | });
139 |
140 | it('reconfigures direction if necessary', () => {
141 | let setDirectionCalled = false;
142 |
143 | const setDirection = Gpio.prototype.setDirection;
144 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = () => {
145 | setDirectionCalled = true;
146 | };
147 |
148 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'high', {reconfigureDirection: false});
149 |
150 | Gpio.prototype.setDirection = setDirection;
151 |
152 | assert(setDirectionCalled);
153 | });
154 |
155 |
156 | afterEach(() => {
157 | gpio.unexport();
158 | MockLinux.restore();
159 | });
160 | });
161 |
162 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/direction.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('direction', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | });
20 |
21 |
22 | it('is input', () => {
23 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
24 |
25 | const expected = 'in';
26 | MockLinux.writeDirection(pin, expected);
27 | const actual = gpio.direction();
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | });
30 |
31 | it('is output', () => {
32 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
33 |
34 | const expected = 'out';
35 | MockLinux.writeDirection(pin, expected);
36 | const actual = gpio.direction();
37 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
38 | });
39 |
40 |
41 | afterEach(() => {
42 | gpio.unexport();
43 | MockLinux.restore();
44 | });
45 | });
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/edge.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('edge', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('is rising', () => {
24 | const expected = 'rising';
25 | MockLinux.writeEdge(pin, expected);
26 | const actual = gpio.edge();
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('is falling', () => {
31 | const expected = 'falling';
32 | MockLinux.writeEdge(pin, expected);
33 | const actual = gpio.edge();
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 | it('is both', () => {
38 | const expected = 'both';
39 | MockLinux.writeEdge(pin, expected);
40 | const actual = gpio.edge();
41 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
42 | });
43 |
44 |
45 | afterEach(() => {
46 | gpio.unexport();
47 | MockLinux.restore();
48 | });
49 | });
50 |
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/mocks/epoll.d.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | export class Epoll {
2 | static EPOLLPRI: number;
3 |
4 | constructor(callback: (args: any) => void);
5 |
6 | add(fd: any, events: any): void;
7 |
8 | remove(fd: any): void;
9 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/mocks/epoll.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | class Epoll {
4 | static get EPOLLPRI() { return 2; }
5 |
6 | constructor(callback) {
7 | this._callback = callback;
8 | this._timeout = null;
9 | }
10 |
11 | add(fd, events) {
12 | this._timeout = setTimeout(_ => {
13 | this._callback(null, fd, events);
14 | }, 10);
15 | }
16 |
17 | remove(fd) {
18 | if (this._timeout !== null) {
19 | clearTimeout(this._timeout);
20 | }
21 | }
22 | }
23 |
24 | exports.Epoll = Epoll;
25 |
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/mocks/linux.d.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | export function gpio(pin: any): void;
3 |
4 | export function gpioWithoutPinFiles(): void;
5 |
6 | export function makeGpioAccessible(): void;
7 |
8 | export function makeGpioInaccessible(): void;
9 |
10 | export function read(pin: any): any;
11 |
12 | export function write(pin: any, value: any): void;
13 |
14 | export function readDirection(pin: any): any;
15 |
16 | export function writeDirection(pin: any, direction: any): void;
17 |
18 | export function readEdge(pin: void): any;
19 |
20 | export function writeEdge(pin: any, edge: any): void;
21 |
22 | export function readActiveLow(pin: any): any;
23 |
24 | export function writeActiveLow(pin: any, value: any): void;
25 |
26 | export function restore(): void;
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/mocks/linux.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const mockFs = require('mock-fs');
4 | const fs = require('fs');
5 |
6 | function gpio(pin) {
7 | const name = `gpio${pin}`;
8 | mockFs({
9 | '/sys/class/gpio': {
10 | 'export': '',
11 | 'unexport': '',
12 | [name]: {
13 | 'direction': 'in',
14 | 'edge': 'none',
15 | 'active_low': '0',
16 | 'value': '0'
17 | }
18 | }
19 | });
20 | }
21 |
22 | function gpioWithoutPinFiles() {
23 | mockFs({
24 | '/sys/class/gpio': {
25 | 'export': ''
26 | }
27 | });
28 | }
29 |
30 | function makeGpioAccessible() {
31 | mockFs({
32 | '/sys/class/gpio': {
33 | 'export': ''
34 | }
35 | });
36 | }
37 |
38 | function makeGpioInaccessible() {
39 | mockFs({
40 | '/sys/class/gpio': {
41 | }
42 | });
43 | }
44 |
45 | function read(pin) {
46 | return fs.readFileSync('/sys/class/gpio/gpio4/value', { encoding: 'UTF-8' });
47 | }
48 |
49 | function write(pin, value) {
50 | fs.writeFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/value`, value);
51 | }
52 |
53 | function readDirection(pin) {
54 | return fs.readFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/direction`, { encoding: 'UTF-8' });
55 | }
56 |
57 | function writeDirection(pin, direction) {
58 | fs.writeFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/direction`, direction);
59 | }
60 |
61 | function readEdge(pin) {
62 | return fs.readFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/edge`, { encoding: 'UTF-8' });
63 | }
64 |
65 | function writeEdge(pin, edge) {
66 | fs.writeFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/edge`, edge);
67 | }
68 |
69 | function readActiveLow(pin) {
70 | return fs.readFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/active_low`, { encoding: 'UTF-8' });
71 | }
72 |
73 | function writeActiveLow(pin, value) {
74 | fs.writeFileSync(`/sys/class/gpio/gpio${pin}/active_low`, value);
75 | }
76 |
77 | function restore() {
78 | mockFs.restore();
79 | }
80 |
81 | exports.gpio = gpio;
82 | exports.gpioWithoutPinFiles = gpioWithoutPinFiles;
83 | exports.makeGpioAccessible = makeGpioAccessible;
84 | exports.makeGpioInaccessible = makeGpioInaccessible;
85 | exports.read = read;
86 | exports.write = write;
87 | exports.readDirection = readDirection;
88 | exports.writeDirection = writeDirection;
89 | exports.readEdge = readEdge;
90 | exports.writeEdge = writeEdge;
91 | exports.readActiveLow = readActiveLow;
92 | exports.writeActiveLow = writeActiveLow;
93 | exports.restore = restore;
94 |
95 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/read.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 | const TestHelper = require('./utils/test-promise');
8 |
9 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 |
12 |
13 | describe('read', () => {
14 | let gpio;
15 | let pin;
16 |
17 | beforeEach(() => {
18 | pin = 4;
19 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
20 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
21 | });
22 |
23 |
24 | it('reads high', (done) => {
25 | const expected = 1;
26 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
27 | gpio.read((err, actual) => {
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | done();
30 | });
31 | });
32 |
33 | it('reads low', (done) => {
34 | const expected = 0;
35 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
36 | gpio.read((err, actual) => {
37 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
38 | done();
39 | });
40 | });
41 |
42 | it('fails', (done) => {
43 | const expected = 'EBADF';
44 |
45 | const valueFd = gpio._valueFd;
46 | gpio._valueFd = 1e6;
47 |
48 | gpio.read((err, value) => {
49 | gpio._valueFd = valueFd;
50 |
51 | const actual = err.code;
52 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
53 |
54 | done();
55 | });
56 | });
57 |
58 |
59 | afterEach(() => {
60 | gpio.unexport();
61 | MockLinux.restore();
62 | });
63 | });
64 |
65 | describe('read Promise', () => {
66 | let gpio;
67 | let pin;
68 |
69 | beforeEach(() => {
70 | pin = 4;
71 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
72 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
73 | });
74 |
75 | it('reads high', () => {
76 | const expected = 1;
77 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
78 | return gpio.read()
79 | .then(actual => TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected));
80 | });
81 |
82 | it('reads low', () => {
83 | const expected = 0;
84 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
85 | return gpio.read()
86 | .then(actual => TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected));
87 | });
88 |
89 | it('fails', () => {
90 | const expected = 'EBADF';
91 |
92 | const valueFd = gpio._valueFd;
93 | gpio._valueFd = 1e6;
94 |
95 | return gpio.read().catch((err) => {
96 | gpio._valueFd = valueFd;
97 |
98 | const actual = err.code;
99 | return TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected);
100 | });
101 | });
102 |
103 | afterEach(() => {
104 | gpio.unexport();
105 | MockLinux.restore();
106 | });
107 | });
108 |
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/readSync.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('readSync', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('reads high', () => {
24 | const expected = 1;
25 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
26 | const actual = gpio.readSync();
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('reads low', () => {
31 | const expected = 0;
32 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
33 | const actual = gpio.readSync();
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 |
38 | afterEach(() => {
39 | gpio.unexport();
40 | MockLinux.restore();
41 | });
42 | });
43 |
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/setActiveLow.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('setActiveLow', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('is active high', () => {
24 | gpio.setActiveLow(true);
25 | const actual = MockLinux.readActiveLow(pin);
26 | assert.deepEqual(actual, 1);
27 | });
28 |
29 | it('is active low', () => {
30 | gpio.setActiveLow(false);
31 | const actual = MockLinux.readActiveLow(pin);
32 | assert.deepEqual(actual, 0);
33 | });
34 |
35 |
36 | afterEach(() => {
37 | gpio.unexport();
38 | MockLinux.restore();
39 | });
40 | });
41 |
42 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/setDirection.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('setDirection', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | });
20 |
21 |
22 | it('is input', () => {
23 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'out');
24 |
25 | const expected = 'in';
26 | gpio.setDirection(expected);
27 | const actual = MockLinux.readDirection(pin);
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | });
30 |
31 | it('is output', () => {
32 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
33 |
34 | const expected = 'out';
35 | gpio.setDirection(expected);
36 | const actual = MockLinux.readDirection(pin);
37 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
38 | });
39 |
40 |
41 | afterEach(() => {
42 | gpio.unexport();
43 | MockLinux.restore();
44 | });
45 | });
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/setEdge.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('setEdge', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('is rising', () => {
24 | const expected = 'rising';
25 | gpio.setEdge(expected);
26 | const actual = MockLinux.readEdge(pin);
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('is falling', () => {
31 | const expected = 'out';
32 | gpio.setEdge(expected);
33 | const actual = MockLinux.readEdge(pin);
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 | it('is both', () => {
38 | const expected = 'out';
39 | gpio.setEdge(expected);
40 | const actual = MockLinux.readEdge(pin);
41 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
42 | });
43 |
44 |
45 | afterEach(() => {
46 | gpio.unexport();
47 | MockLinux.restore();
48 | });
49 | });
50 |
51 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/typedefinition.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import assert = require('assert');
2 | import mockRequire = require('mock-require');
3 | import MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
4 | import MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
5 |
6 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
7 | import { Gpio } from '../onoff';
8 |
9 | describe('definition', () => {
10 | let gpio: Gpio;
11 | let pin: number;
12 |
13 | beforeEach(() => {
14 | pin = 4;
15 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
16 | });
17 |
18 | it('fires rising', (done) => {
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
20 |
21 | const expected = 1;
22 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
23 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
24 | done();
25 | });
26 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
27 | });
28 |
29 | afterEach(() => {
30 | gpio.unexport();
31 | MockLinux.restore();
32 | });
33 | });
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/utils/test-promise.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 |
5 | const shouldEventuallyEqual = (actual, expected) => {
6 | return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
7 | if(actual === expected) {
8 | resolve();
9 | } else {
10 | reject(new Error(
11 | 'Actual value does not equal expected value: Act ' +
12 | actual + ' ' + typeof actual +
13 | ' | Exp ' +
14 | expected + ' ' + typeof expected
15 | ));
16 | }
17 | });
18 | };
19 |
20 | exports.shouldEventuallyEqual = shouldEventuallyEqual;
21 |
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/watch-callbacks.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
6 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 | describe('watch callbacks', () => {
12 | let gpio;
13 | let pin;
14 |
15 | beforeEach(() => {
16 | pin = 4;
17 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
18 | });
19 |
20 | describe('watch', () => {
21 |
22 | it('fires rising', (done) => {
23 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
24 |
25 | const expected = 1;
26 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
27 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | done();
30 | });
31 | });
32 |
33 | it('fires falling', (done) => {
34 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
35 |
36 | const expected = 0;
37 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
38 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
39 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
40 | done();
41 | });
42 | });
43 |
44 | });
45 |
46 | describe('watch with debounce', () => {
47 |
48 | it('fires rising', (done) => {
49 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both', {debounceTimeout: 10});
50 |
51 | const expected = 1;
52 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
53 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
54 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
55 | done();
56 | });
57 | });
58 |
59 | it('fires falling', (done) => {
60 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both', {debounceTimeout: 10});
61 |
62 | const expected = 0;
63 | MockLinux.write(pin, '' + expected);
64 | gpio.watch((err, actual) => {
65 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
66 | done();
67 | });
68 | });
69 |
70 | });
71 |
72 | afterEach(() => {
73 | gpio.unexport();
74 | MockLinux.restore();
75 | });
76 | });
77 |
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/watch-listeners.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
5 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
6 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('watch listeners', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | const listener1 = (err, value) => {
17 | if (err) {
18 | throw err;
19 | }
20 | console.log(`listener1: value is ${value}`);
21 | };
22 |
23 | const listener2 = (err, value) => {
24 | if (err) {
25 | throw err;
26 | }
27 | console.log(`listener2: value is ${value}`);
28 | };
29 |
30 | beforeEach(() => {
31 | pin = 4;
32 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
33 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in', 'both');
34 | });
35 |
36 | describe('watch', () => {
37 |
38 | it('no listeners', () => {
39 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
40 | });
41 |
42 | it('one listener', () => {
43 | gpio.watch(listener1);
44 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 1);
45 | });
46 |
47 | it('one listener multiple times', () => {
48 | gpio.watch(listener1);
49 | gpio.watch(listener1);
50 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 2);
51 | });
52 |
53 | it('multiple listeners', () => {
54 | gpio.watch(listener1);
55 | gpio.watch(listener2);
56 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 2);
57 | });
58 | });
59 |
60 | describe('unwatch', () => {
61 |
62 | it('no listeners', () => {
63 | gpio.unwatch(listener1);
64 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
65 | });
66 |
67 | it('one listener', () => {
68 | gpio.watch(listener1);
69 | gpio.unwatch(listener1);
70 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
71 | });
72 |
73 | it('one listener, all referneces', () => {
74 | gpio.watch(listener1);
75 | gpio.watch(listener1);
76 | gpio.unwatch(listener1);
77 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
78 | });
79 |
80 | it('mutliple listeners, only remove one', () => {
81 | gpio.watch(listener1);
82 | gpio.watch(listener2);
83 | gpio.unwatch(listener1);
84 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 1);
85 | });
86 | });
87 |
88 | describe('unwatchAll', () => {
89 |
90 | it('no listeners', () => {
91 | gpio.unwatchAll();
92 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
93 | });
94 |
95 |
96 | it('one listener multiple times', () => {
97 | gpio.watch(listener1);
98 | gpio.watch(listener1);
99 | gpio.unwatchAll(listener1);
100 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
101 | });
102 |
103 | it('multiple listeners', () => {
104 | gpio.watch(listener1);
105 | gpio.watch(listener2);
106 | gpio.unwatchAll();
107 | assert.deepEqual(gpio._listeners.length, 0);
108 | });
109 | });
110 |
111 | afterEach(() => {
112 | gpio.unexport();
113 | MockLinux.restore();
114 | });
115 | });
116 |
117 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/write.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
5 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 | const TestHelper = require('./utils/test-promise');
8 |
9 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 |
12 |
13 | describe('write', () => {
14 | let gpio;
15 | let pin;
16 |
17 | beforeEach(() => {
18 | pin = 4;
19 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
20 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
21 | });
22 |
23 |
24 | it('writes high', (done) => {
25 | const expected = 1;
26 | gpio.write(expected, (err) => {
27 | const actual = MockLinux.read(pin);
28 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
29 | done();
30 | });
31 | });
32 |
33 | it('writes low', (done) => {
34 | const expected = 0;
35 | gpio.write(expected, (err) => {
36 | const actual = MockLinux.read(pin);
37 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
38 | done();
39 | });
40 | });
41 |
42 | afterEach(() => {
43 | gpio.unexport();
44 | MockLinux.restore();
45 | });
46 | });
47 |
48 | describe('write Promise', () => {
49 | let gpio;
50 | let pin;
51 |
52 | beforeEach(() => {
53 | pin = 4;
54 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
55 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
56 | });
57 |
58 | it('writes high', () => {
59 | const expected = 1;
60 | return gpio.write(expected).then(() => {
61 | const actual = parseInt(MockLinux.read(pin));
62 | return TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected);
63 | });
64 | });
65 |
66 | it('writes low', () => {
67 | const expected = 0;
68 | return gpio.write(expected).then(() => {
69 | const actual = parseInt(MockLinux.read(pin));
70 | return TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected);
71 | });
72 | });
73 |
74 | it('write fail',() => {
75 | const expected = 'EBADF';
76 |
77 | const valueFd = gpio._valueFd;
78 | gpio._valueFd = 1e6;
79 |
80 | return gpio.write(1)
81 | .catch((err) => {
82 | gpio._valueFd = valueFd;
83 | const actual = err.code;
84 | return TestHelper.shouldEventuallyEqual(actual, expected);
85 | });
86 | });
87 |
88 | afterEach(() => {
89 | gpio.unexport();
90 | MockLinux.restore();
91 | });
92 | });
93 |
94 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/test/writeSync.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const MockLinux = require('./mocks/linux');
5 | const mockRequire = require('mock-require');
6 | const MockEpoll = require('./mocks/epoll');
7 |
8 | mockRequire('epoll', MockEpoll);
9 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
10 |
11 |
12 | describe('writeSync', () => {
13 | let gpio;
14 | let pin;
15 |
16 | beforeEach(() => {
17 | pin = 4;
18 | MockLinux.gpio(pin);
19 | gpio = new Gpio(pin, 'in');
20 | });
21 |
22 |
23 | it('writes high', () => {
24 | const expected = 1;
25 | gpio.writeSync(expected);
26 | const actual = MockLinux.read(pin);
27 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
28 | });
29 |
30 | it('writes low', () => {
31 | const expected = 0;
32 | gpio.writeSync(expected);
33 | const actual = MockLinux.read(pin);
34 | assert.deepEqual(actual, expected);
35 | });
36 |
37 |
38 | afterEach(() => {
39 | gpio.unexport();
40 | MockLinux.restore();
41 | });
42 | });
43 |
44 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tsconfig.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "compilerOptions": {
3 | "lib": ["es6", "dom"],
4 | "module": "commonjs",
5 | "sourceMap": true,
6 | "strict": true,
7 | "target": "es6",
8 | },
9 | "exclude": [
10 | "node_modules"
11 | ]
12 | }
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 46 |
47 | When the button is pressed the LED should turn on, when it's released the LED
48 | should turn off. This can be achieved with the following code:
49 |
50 | ```js
51 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
52 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
53 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
54 |
55 | button.watch((err, value) => led.writeSync(value));
56 | ```
57 |
58 | Here two Gpio objects are being created. One called led for the LED connected
59 | to GPIO17 which is an output, and one called button for the momentary push
60 | button connected to GPIO4 which is an input. In addition to specifying that
61 | the button is an input, the constructors optional third argument is used to
62 | specify that 'both' rising and falling interrupt edges should be configured
63 | for the button GPIO as both button presses and releases should be handled.
64 |
65 | After everything has been setup correctly, the buttons watch method is used to
66 | specify a callback function to execute every time the button is pressed or
67 | released. The value argument passed to the callback function represents the
68 | state of the button which will be 1 for pressed and 0 for released. This value
69 | is used by the callback to turn the LED on or off using its writeSync method.
70 |
71 | When the above program is running it can be terminated with ctrl-c. However,
72 | it doesn't free its resources. It also ignores the err argument passed to
73 | the callback. Here's a slightly modified variant of the program that handles
74 | ctrl-c gracefully and bails out on error. The resources used by the led and
75 | button Gpio objects are released by invoking their unexport method.
76 |
77 | ```js
78 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
79 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
80 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
81 |
82 | button.watch((err, value) => {
83 | if (err) {
84 | throw err;
85 | }
86 |
87 | led.writeSync(value);
88 | });
89 |
90 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
91 | led.unexport();
92 | button.unexport();
93 | });
94 | ```
95 |
96 | #### Debouncing Buttons
97 | When working with buttons there will often be button bounce issues which
98 | result in the hardware thinking that a button was pressed several times
99 | although it was only pressed once. onoff provides a software debouncing
100 | solution for resolving bounce issues.
101 |
102 | Assume again that there's an LED connected to GPIO17 and a momentary push
103 | button connected to GPIO4.
104 |
105 | When the button is pressed the LED should toggle its state. This is a typical
106 | example of a situation where there will be button bounce issues. The issue can
107 | be resolved by using the debounceTimeout option when creating the Gpio object
108 | for the button. In the below program the debounceTimeout is set to 10
109 | milliseconds. This delays invoking the watch callback for the button while the
110 | button is bouncing. The watch callback will not be invoked until the button
111 | stops bouncing and has been in a stable state for 10 milliseconds.
112 |
113 | ```js
114 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
115 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
116 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
117 |
118 | button.watch((err, value) => {
119 | if (err) {
120 | throw err;
121 | }
122 |
123 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
124 | });
125 |
126 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
127 | led.unexport();
128 | button.unexport();
129 | });
130 | ```
131 |
132 | #### Blink an LED Using the Synchronous API
133 |
134 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the synchronous readSync
135 | and writeSync methods.
136 |
137 | ```js
138 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
139 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
140 |
141 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
142 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 200);
143 |
144 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
145 | setTimeout(_ => {
146 | clearInterval(iv); // Stop blinking
147 | led.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
148 | }, 5000);
149 | ```
150 |
151 | #### Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Completion Callbacks
152 |
153 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the asynchronous read and
154 | write methods and completion callbacks.
155 |
156 | ```js
157 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
158 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
159 | let stopBlinking = false;
160 |
161 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
162 | const blinkLed = _ => {
163 | if (stopBlinking) {
164 | return led.unexport();
165 | }
166 |
167 | led.read((err, value) => { // Asynchronous read
168 | if (err) {
169 | throw err;
170 | }
171 |
172 | led.write(value ^ 1, err => { // Asynchronous write
173 | if (err) {
174 | throw err;
175 | }
176 | });
177 | });
178 |
179 | setTimeout(blinkLed, 200);
180 | };
181 |
182 | blinkLed();
183 |
184 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
185 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
186 | ```
187 |
188 | #### Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Promises
189 |
190 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the asynchronous read and
191 | write methods and Promises.
192 |
193 | ```js
194 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
195 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
196 | let stopBlinking = false;
197 |
198 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
199 | const blinkLed = _ => {
200 | if (stopBlinking) {
201 | return led.unexport();
202 | }
203 |
204 | led.read()
205 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
206 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 200))
207 | .catch(err => console.log(err));
208 | };
209 |
210 | blinkLed();
211 |
212 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
213 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
214 | ```
215 |
216 | #### Check accessibility
217 |
218 | Sometimes it may be necessary to determine if the current system supports
219 | GPIOs programmatically and mock functionality if it doesn't. `Gpio.accessible`
220 | can be used to achieve this.
221 |
222 | ```js
223 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
224 |
225 | const useLed = (led, value) => led.writeSync(value);
226 |
227 | let led;
228 |
229 | if (Gpio.accessible) {
230 | led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
231 | // more real code here
232 | } else {
233 | led = {
234 | writeSync: value => {
235 | console.log('virtual led now uses value: ' + value);
236 | }
237 | };
238 | }
239 |
240 | useLed(led, 1);
241 | ```
242 |
243 | ## API
244 |
245 | ### Class Gpio
246 |
247 | * [Gpio(gpio, direction [, edge] [, options]) - Constructor](#gpiogpio-direction--edge--options)
248 | * [read([callback]) - Read GPIO value asynchronously](#readcallback)
249 | * [readSync() - Read GPIO value synchronously](#readsync)
250 | * [write(value[, callback]) - Write GPIO value asynchronously](#writevalue-callback)
251 | * [writeSync(value) - Write GPIO value synchronously](#writesyncvalue)
252 | * [watch(callback) - Watch for hardware interrupts on the GPIO](#watchcallback)
253 | * [unwatch([callback]) - Stop watching for hardware interrupts on the GPIO](#unwatchcallback)
254 | * [unwatchAll() - Remove all watchers for the GPIO](#unwatchall)
255 | * [direction() - Get GPIO direction](#direction)
256 | * [setDirection(direction) - Set GPIO direction](#setdirectiondirection)
257 | * [edge() - Get GPIO interrupt generating edge](#edge)
258 | * [setEdge(edge) - Set GPIO interrupt generating edge](#setedgeedge)
259 | * [activeLow() - Get GPIO activeLow setting](#activelow)
260 | * [setActiveLow(invert) - Set GPIO activeLow setting](#setactivelowinvert)
261 | * [unexport() - Reverse the effect of exporting the GPIO to userspace](#unexport)
262 | * [static accessible - Determine whether or not GPIO access is possible](#static-accessible)
263 | * [HIGH / LOW - Constants used when reading or writing a GPIO value](#static-high--low)
264 |
265 | ##### Gpio(gpio, direction [, edge] [, options])
266 | - gpio - An unsigned integer specifying the GPIO number.
267 | - direction - A string specifying whether the GPIO should be configured as an
268 | input or output. The valid values are: 'in', 'out', 'high', and 'low'. If 'out'
269 | is specified the GPIO will be configured as an output and the value of the GPIO
270 | will be set to 0. 'high' and 'low' are variants of 'out' that configure the
271 | GPIO as an output with an initial level of 1 or 0 respectively.
272 | - [edge] - An optional string specifying the interrupt generating edge or
273 | edges for an input GPIO. The valid values are: 'none', 'rising', 'falling' or
274 | 'both'. The default value is 'none' indicating that the GPIO will not generate
275 | interrupts. Whether or not interrupts are supported by an input GPIO is GPIO
276 | specific. If interrupts are not supported by a GPIO the edge argument should
277 | not be specified. The edge argument is ignored for output GPIOs.
278 | - [options] - An optional options object.
279 |
280 | Configures the GPIO based on the passed arguments and returns a new Gpio
281 | object that can be used to access the GPIO.
282 |
283 | The following options are supported:
284 | - debounceTimeout - An unsigned integer specifying a millisecond delay. Delays
285 | invoking the watch callback for an interrupt generating input GPIO while the
286 | input is bouncing. The watch callback will not be invoked until the input
287 | stops bouncing and has been in a stable state for debounceTimeout
288 | milliseconds. Optional, if unspecified the input GPIO will not be debounced.
289 | - activeLow - A boolean value specifying whether the values read from or
290 | written to the GPIO should be inverted. The interrupt generating edge for the
291 | GPIO also follow this this setting. The valid values for activeLow are true
292 | and false. Setting activeLow to true inverts. Optional, the default value is
293 | false.
294 | - reconfigureDirection - A boolean value specifying whether the direction for
295 | the GPIO should be reconfigured even though the direction is already
296 | configured correctly. When an application starts, the direction of a GPIO used
297 | by that application may already be configured correctly, for example, from a
298 | previous run of the application. Reconfiguring the direction of that GPIO can
299 | result in unwanted side effects. For example, if a GPIO is already configured
300 | as an output and it is reconfigured as an output by passing 'out' to the
301 | constructor, the value of that output will be set to 0. In some applications
302 | this is not desirable and the value of the output should not be modified. The
303 | reconfigureDirection option can help here. If reconfigureDirection is set to
304 | false the direction of a GPIO that is already correctly configured will not be
305 | reconfigured. Optional, the default value is true.
306 |
307 | GPIOs on Linux are identified by unsigned integers. These are the numbers that
308 | should be passed to the onoff Gpio constructor when exporting GPIOs to
309 | userspace. For example, pin 11 on the Raspberry Pi expansion header
310 | corresponds to GPIO17 in Raspbian Linux. 17 is therefore the number to pass
311 | to the onoff Gpio constructor when using pin 11 on the expansion header.
312 |
313 | ##### read([callback])
314 | - [callback] - An optional completion callback that gets two arguments (err,
315 | value), where err is reserved for an Error object and value is the number 0
316 | or 1 and represents the state of the GPIO.
317 |
318 | Read GPIO value asynchronously. If no completion callback is specified read
319 | returns a Promise which resolves to the value of the GPIO on success or rejects
320 | with an Error object on failure.
321 |
322 | Note that most systems support readback of GPIOs configured as outputs. The
323 | read method can therefore be invoked for any GPIO, irrespective of whether it
324 | was configured as an input or an output. The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are
325 | examples of such systems.
326 |
327 | ##### readSync()
328 | Read GPIO value synchronously. Returns the number 0 or 1 to represent the
329 | state of the GPIO.
330 |
331 | Note that most systems support readback of GPIOs configured as outputs. The
332 | readSync method can therefore be invoked for any GPIO, irrespective of whether
333 | it was configured as an input or an output. The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone
334 | are examples of such systems.
335 |
336 | ##### write(value[, callback])
337 | - value - The number 0 or 1.
338 | - [callback] - An optional completion callback that gets one argument (err),
339 | where err is reserved for an error object.
340 |
341 | Write GPIO value asynchronously. If no completion callback is specified write
342 | returns a Promise that resolves with no value on success or rejects with an
343 | Error object on failure.
344 |
345 | Note that on most systems invoking write for a GPIO configured as an input
346 | will result in an EPERM error indicating that the operation is not permitted.
347 | The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are examples of such systems.
348 |
349 | ##### writeSync(value)
350 | - value - The number 0 or 1.
351 |
352 | Write GPIO value synchronously.
353 |
354 | Note that on most systems invoking writeSync for a GPIO configured as an input
355 | will result in an EPERM error indicating that the operation is not permitted.
356 | The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are examples of such systems.
357 |
358 | ##### watch(callback)
359 | - callback - A callback that gets two arguments (err, value), where err is
360 | reserved for an error object and value is the number 0 or 1 and represents the
361 | state of the GPIO. The value can also be used to determine whether the
362 | interrupt occurred on a rising or falling edge. A value of 0 implies a falling
363 | edge interrupt and a value of 1 implies a rising edge interrupt.
364 |
365 | Watch for hardware interrupts on the GPIO. The edge argument that was passed
366 | to the constructor determines which hardware interrupts to watch for.
367 |
368 | ##### unwatch([callback])
369 | - [callback] - The callback to remove.
370 |
371 | Stop watching for hardware interrupts on the GPIO. If callback is specified,
372 | only that particular callback is removed. Otherwise all callbacks are removed.
373 |
374 | ##### unwatchAll()
375 | Remove all hardware interrupt watchers for the GPIO.
376 |
377 | ##### direction()
378 | Returns the string 'in' or 'out' indicating whether the GPIO is an input or
379 | output.
380 |
381 | ##### setDirection(direction)
382 | - direction - A string specifying whether the GPIO should be configured as an
383 | input or output. The valid values are 'in', 'out', 'high', and 'low'. If 'out'
384 | is specified the GPIO will be configured as an output and the value of the GPIO
385 | will be set to 0. 'high' and 'low' are variants of 'out' that configure the
386 | GPIO as an output with an initial level of 1 or 0 respectively.
387 |
388 | Set GPIO direction.
389 |
390 | ##### edge()
391 | Returns the string 'none', 'falling', 'rising', or 'both' indicating the
392 | interrupt generating edge or edges for the GPIO. Whether or not interrupts are
393 | supported by an input GPIO is GPIO specific. If interrupts are not supported
394 | the edge method should not be used. Interrupts are not supported by output
395 | GPIOs.
396 |
397 | ##### setEdge(edge)
398 | - edge - A string specifying the interrupt generating edge or edges for an
399 | input GPIO. The valid values are: 'none', 'rising', 'falling' or 'both'.
400 | Whether or not interrupts are supported by an input GPIO is GPIO specific. If
401 | interrupts are not supported the setEdge method should not be used. Interrupts
402 | are not supported by output GPIOs.
403 |
404 | Set GPIO interrupt generating edge.
405 |
406 | ##### activeLow()
407 | Returns true or false indicating whether or not the values read from or written
408 | to the GPIO are inverted.
409 |
410 | ##### setActiveLow(invert)
411 | - invert - A boolean value specifying whether the values read from or written
412 | to the GPIO should be inverted. The interrupt generating edge for the GPIO also
413 | follow this this setting. The valid values for invert are true and false.
414 | Setting activeLow to true inverts.
415 |
416 | Set GPIO activeLow setting.
417 |
418 | ##### unexport()
419 | Reverse the effect of exporting the GPIO to userspace. A Gpio object should not
420 | be used after invoking its unexport method.
421 |
422 | ##### static accessible
423 | Determine whether or not GPIO access is possible. true if the current process
424 | has the permissions required to export GPIOs to userspace. false otherwise.
425 | Loosely speaking, if this property is true it should be possible for the
426 | current process to create Gpio objects.
427 |
428 | It is notable that while this property may be false indicating that the
429 | current process does not have the permissions required to export GPIOs to
430 | userspace, existing exported GPIOs may still be accessible.
431 |
432 | This property is useful for mocking functionality on computers used for
433 | development that do not provide access to GPIOs.
434 |
435 | This is a static property and should be accessed as `Gpio.accessible`.
436 |
437 | ##### static HIGH / LOW
438 | Constants used when reading or writing a GPIO value. Gpio.HIGH and Gpio.LOW
439 | can be used in place of the numeric constants 1 and 0.
440 |
441 |
442 | ## How Does onoff Work?
443 |
444 | Internally onoff uses sysfs files located at /sys/class/gpio to access GPIOs
445 | and the [epoll package](https://github.com/fivdi/epoll) to detect hardware
446 | interrupts. The Linux GPIO sysfs interface for userspace is documented
447 | [here](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/gpio/sysfs.txt).
448 | It's a relatively simple interface which can be used to ask the Linux kernel
449 | to export control of a GPIO to userspace. After control of a GPIO has been
450 | exported to userspace, the GPIO can be configured as an input or output.
451 | Thereafter, the state of an input can be read, and the state of an output can
452 | be written. Some systems will also allow the state of a output to be read.
453 | The GPIO sysfs interface can also be used for interrupt detection. onoff can
454 | detect several thousand interrupts per second on both the BeagleBone and the
455 | Raspberry Pi.
456 |
457 |
458 | ## Configuring Pullup and Pulldown Resistors
459 |
460 | As mentioned in section [How Does onoff Work](#how-does-onoff-work) the sysfs
461 | interface is used to access GPIOs. The sysfs interface doesn't offer support
462 | for configuring pullup and pulldown resistors on GPIOs.
463 |
464 | There are however many platform specific mechanisms for configuring pullup and
465 | pulldown resistors that are compatible with onoff. onoff itself doesn't use
466 | these mechanisms as one of the goals of onoff is to be platform independent.
467 |
468 | Here we'll take a look at two mechanisms available on the Raspberry Pi for
469 | configuring pullup and pulldown resistors.
470 |
471 | The first point to be aware of is that most GPIOs on a Raspberry Pi have
472 | either their pullup or pulldown resistor activated by default. The defaults
473 | can be seen in Table 6-31 on pages 102 and 103 of the
474 | [BCM2835 ARM Peripherals](http://www.farnell.com/datasheets/1521578.pdf)
475 | documentation.
476 |
477 | #### Using the gpio Command in /boot/config.txt
478 |
479 | On Raspbian 2018-04-18 or later the `gpio` configuration command can be used
480 | in `/boot/config.txt` to configure pullup and pulldown resistors. Further
481 | information is available at
482 | [New "gpio" config command](https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=117&t=208748).
483 |
484 | #### Using Device Tree Overlays
485 |
486 | Device tree overlays can also be used to configure pullup and pulldown
487 | resistors. The Wiki page
488 | [Enabling Pullup and Pulldown Resistors on The Raspberry Pi](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/wiki/Enabling-Pullup-and-Pulldown-Resistors-on-The-Raspberry-Pi)
489 | describes this mechanism in more detail.
490 |
491 | ## Benchmarks
492 |
493 | Three of the onoff tests are used to monitor performance.
494 |
495 | * performance-async.js - determine max. no. of write ops per seconds
496 | * performance-sync.js - determine max. no. of writeSync ops per second
497 | * performance-interrupt.js - determine max. no. of interrupts per second
498 |
499 | The results of these tests are shown in the following tables.
500 |
501 | **Raspberry Pi 4 B, 1.5GHz, Raspberry Pi OS (March 4th 2021, Buster 10.8)**
502 |
503 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
504 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
505 | v16.0.0 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 25124 | 280417 | 20240
506 | v15.14.0 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 24055 | 271149 | 20488
507 | v14.16.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 21669 | 254705 | 19703
508 | v12.22.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 22618 | 318417 | 21122
509 | v10.24.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 22405 | 329927 | 19583
510 |
511 | **Raspberry Pi 3 B, 1.2GHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
512 |
513 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
514 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
515 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 21670 | 207222 | 18328
516 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 23661 | 225758 | 20741
517 |
518 | **Raspberry Pi 2 B, 900MHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
519 |
520 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
521 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
522 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 10769 | 113107 | 10373
523 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 11843 | 129086 | 10536
524 |
525 | **Raspberry Pi 1 B, 700MHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
526 |
527 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
528 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
529 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75+ | 2316 | 26696 | 2112
530 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75+ | 2613 | 33129 | 2225
531 |
532 | **BeagleBone Black, 1GHz, Debian Buster 10.2**
533 |
534 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
535 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
536 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 6855 | 70535 | 5911
537 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 7564 | 79133 | 5920
538 |
539 | **BeagleBone, 720MHz, Debian Buster 10.2**
540 |
541 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
542 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
543 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 5013 | 49741 | 4297
544 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 5400 | 57157 | 4371
545 |
546 | ## Related Packages
547 |
548 | Here are a few links to other hardware specific Node.js packages that may be
549 | of interest.
550 |
551 | * [pigpio](https://github.com/fivdi/pigpio) - Fast GPIO, PWM, servo control, state change notification and interrupt handling on the Raspberry Pi
552 | * [i2c-bus](https://github.com/fivdi/i2c-bus) - I2C serial bus access
553 | * [spi-device](https://github.com/fivdi/spi-device) - SPI serial bus access
554 | * [mcp-spi-adc](https://github.com/fivdi/mcp-spi-adc) - Analog to digital conversion with the MCP3002/4/8, MCP3202/4/8 and MCP3304
555 |
556 | ## Additional Information
557 |
558 | onoff was tested on the following platforms:
559 |
560 | - Raspberry Pi 1, 2, 3 and 4
561 | - Raspbian or Raspberry Pi OS
562 | - BeagleBone, BeagleBone Black and PocketBeagle
563 | - Debian
564 |
565 | The suitability of onoff for a particular Linux board is highly dependent on
566 | how GPIO interfaces are made available on that board. The
567 | [GPIO interfaces](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/gpio/)
568 | documentation describes GPIO access conventions rather than standards that must
569 | be followed so GPIO can vary from platform to platform. For example, onoff
570 | relies on sysfs files located at /sys/class/gpio being available. However,
571 | these sysfs files for userspace GPIO are optional and may not be available on a
572 | particular platform.
573 |
574 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/accessible.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 |
5 | console.log('Gpio functionality accessible on this computer?', Gpio.accessible);
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led-async.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
8 | const blinkLed = _ => {
9 | if (stopBlinking) {
10 | return led.unexport();
11 | }
12 |
13 | led.read((err, value) => { // Asynchronous read
14 | if (err) {
15 | throw err;
16 | }
17 |
18 | led.write(value ^ 1, err => { // Asynchronous write
19 | if (err) {
20 | throw err;
21 | }
22 | });
23 | });
24 |
25 | setTimeout(blinkLed, 200);
26 | };
27 |
28 | blinkLed();
29 |
30 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
31 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
32 |
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led-promises.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
8 | const blinkLed = _ => {
9 | if (stopBlinking) {
10 | return led.unexport();
11 | }
12 |
13 | led.read()
14 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
15 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 200))
16 | .catch(err => console.log(err));
17 | };
18 |
19 | blinkLed();
20 |
21 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
22 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
23 |
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 |
6 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
7 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 200);
8 |
9 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
10 | setTimeout(_ => {
11 | clearInterval(iv); // Stop blinking
12 | led.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
13 | }, 5000);
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/debounce-button.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
6 |
7 | button.watch((err, value) => {
8 | if (err) {
9 | throw err;
10 | }
11 |
12 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
13 | });
14 |
15 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
16 | led.unexport();
17 | button.unexport();
18 | });
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/light-switch.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
6 |
7 | button.watch((err, value) => {
8 | if (err) {
9 | throw err;
10 | }
11 |
12 | led.writeSync(value);
13 | });
14 |
15 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
16 | led.unexport();
17 | button.unexport();
18 | });
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/light-switch.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fivdi/onoff/813da60dd1f3a842a29a8c630243d4f5b7523cc0/examples/light-switch.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/mygpio-overlay.dts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /dts-v1/;
2 | /plugin/;
3 |
4 | / {
5 | compatible = "brcm,bcm2708";
6 |
7 | fragment@0 {
8 | target = <&gpio>;
9 | __overlay__ {
10 | pinctrl-names = "default";
11 | pinctrl-0 = <&my_pins>;
12 |
13 | my_pins: my_pins {
14 | brcm,pins = <7 8 9>; /* gpio no. */
15 | brcm,function = <0 0 0>; /* 0:in, 1:out */
16 | brcm,pull = <1 1 2>; /* 2:up 1:down 0:none */
17 | };
18 | };
19 | };
20 | };
21 |
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/run-examples:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node blink-led
3 | node blink-led-async
4 | node wait-for-interrupt
5 | node light-switch
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/wait-for-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 |
5 | // Export GPIO4 as an interrupt generating input with a debounceTimeout of 10
6 | // milliseconds
7 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
8 |
9 | console.log('Please press the button on GPIO4...');
10 |
11 | // The callback passed to watch will be invoked when the button connected to
12 | // GPIO4 is pressed
13 | button.watch((err, value) => {
14 | if (err) {
15 | throw err;
16 | }
17 |
18 | console.log('Button pressed!, its value was ' + value);
19 |
20 | button.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
21 | });
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/blink-led-promises.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | const blinkLed = _ => {
8 | if (stopBlinking) {
9 | led.unexport();
10 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
11 | return;
12 | }
13 |
14 | led.read()
15 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
16 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 50))
17 | .catch(err => {
18 | console.log(err);
19 | });
20 | };
21 |
22 | blinkLed();
23 |
24 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 2000);
25 |
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/blink-led.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 |
6 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 100);
7 |
8 | setTimeout(_ => {
9 | clearInterval(iv);
10 |
11 | led.writeSync(0);
12 | led.unexport();
13 |
14 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
15 | }, 2000);
16 |
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/change-configuration.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 |
6 | let output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
7 | let input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
8 |
9 | const watchWithSecondConfiguration = _ => {
10 | input.watch((err, value) => {
11 | assert(!err, 'error during interrupt detection');
12 | assert(value === 1, 'expected interrupt on rising edge');
13 |
14 | setTimeout(_ => {
15 | input.unexport();
16 | output.unexport();
17 |
18 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
19 | }, 10);
20 | });
21 |
22 | output.writeSync(1);
23 | };
24 |
25 | const changeConfiguration = _ => {
26 | input.unwatchAll();
27 |
28 | let temp = output;
29 | temp.setDirection('in');
30 | output = input;
31 | input = temp;
32 |
33 | output.setEdge('none');
34 | output.setDirection('out');
35 | output.writeSync(0);
36 | assert(output.direction() === 'out', 'expected direction to be out');
37 | assert(output.edge() === 'none', 'expected edge to be none');
38 | assert(output.readSync() === 0, 'expected value to be 0');
39 |
40 | input.setEdge('rising');
41 | assert(input.direction() === 'in', 'expected direction to be in');
42 | assert(input.edge() === 'rising', 'expected edge to be rising');
43 | assert(input.readSync() === 0, 'expected value to be 0');
44 |
45 | watchWithSecondConfiguration();
46 | };
47 |
48 | const watchWithFirstConfiguration = _ => {
49 | input.watch((err, value) => {
50 | assert(!err, 'error during interrupt detection');
51 | assert(value === 1, 'expected interrupt on rising edge');
52 |
53 | setTimeout(changeConfiguration, 10);
54 | });
55 |
56 | output.writeSync(1);
57 | };
58 |
59 | watchWithFirstConfiguration();
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-active-low-defaults.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | */
7 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
8 | const assert = require('assert');
9 | let input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
10 | let output = new Gpio(8, 'low', {activeLow: true});
11 |
12 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
13 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
14 |
15 | input.unexport();
16 | output.unexport();
17 |
18 | //
19 |
20 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
21 | output = new Gpio(8, 'low', {activeLow: false});
22 |
23 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
24 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
25 |
26 | input.unexport();
27 | output.unexport();
28 |
29 | //
30 |
31 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
32 | output = new Gpio(8, 'high', {activeLow: true});
33 |
34 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
35 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
36 |
37 | input.unexport();
38 | output.unexport();
39 |
40 | //
41 |
42 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
43 | output = new Gpio(8, 'high', {activeLow: false});
44 |
45 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
46 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
47 |
48 | input.unexport();
49 | output.unexport();
50 |
51 | //
52 |
53 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
54 | output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: true});
55 |
56 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
57 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
58 |
59 | input.unexport();
60 | output.unexport();
61 |
62 | //
63 |
64 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
65 | output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: false});
66 |
67 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
68 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
69 |
70 | input.unexport();
71 | output.unexport();
72 |
73 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
74 |
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-active-low.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | */
7 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
8 | const assert = require('assert');
9 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
10 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: true});
11 |
12 | assert(input.activeLow() === false);
13 | assert(output.activeLow() === true);
14 |
15 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
16 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
17 |
18 | output.writeSync(0);
19 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
20 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
21 | output.writeSync(1);
22 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
23 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
24 |
25 | output.setActiveLow(false);
26 | assert(input.activeLow() === false);
27 | assert(output.activeLow() === false);
28 | output.writeSync(0);
29 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
30 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
31 | output.writeSync(1);
32 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
33 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
34 |
35 | input.setActiveLow(true);
36 | assert(input.activeLow() === true);
37 | assert(output.activeLow() === false);
38 | output.writeSync(0);
39 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
40 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
41 | output.writeSync(1);
42 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
43 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
44 |
45 | input.unexport();
46 | output.unexport();
47 |
48 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
49 |
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-input.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const input = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising');
6 |
7 | assert(input.direction() === 'in');
8 | assert(input.edge() === 'rising');
9 |
10 | input.unexport();
11 |
12 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-output.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const output = new Gpio(17, 'out');
6 |
7 | assert(output.direction() === 'out');
8 |
9 | output.writeSync(1);
10 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
11 |
12 | output.writeSync(0);
13 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
14 |
15 | output.write(1, err => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | throw err;
18 | }
19 |
20 | output.read((err, value) => {
21 | if (err) {
22 | throw err;
23 | }
24 |
25 | assert(value === 1);
26 |
27 | output.writeSync(0);
28 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
29 |
30 | output.unexport();
31 |
32 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
33 | });
34 | });
35 |
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/debounce.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
6 | const button = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both', {debounceTimeout: 10});
7 |
8 | let buttonPressedCount = 0;
9 | let buttonReleasedCount = 0;
10 |
11 | const simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce = cb => {
12 | let toggleCount = 0;
13 |
14 | const iv = setInterval(_ => {
15 | if (toggleCount === 19) {
16 | clearInterval(iv);
17 | return cb();
18 | }
19 |
20 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() ^ 1);
21 | toggleCount += 1;
22 | }, 2);
23 | };
24 |
25 | const simulatePressAndReleaseButtonWithBounce = _ => {
26 | simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce(_ => {
27 | setTimeout(_ => {
28 | simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce(_ => {
29 | setTimeout(_ => {
30 | assert(buttonPressedCount === 1);
31 | assert(buttonReleasedCount === 1);
32 |
33 | button.unexport();
34 | output.unexport();
35 |
36 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
37 | }, 20);
38 | });
39 | }, 50);
40 | });
41 | };
42 |
43 | button.watch((err, value) => {
44 | if (err) {
45 | throw err;
46 | }
47 |
48 | if (value === 1) {
49 | buttonPressedCount += 1;
50 | } else if (value === 0) {
51 | buttonReleasedCount += 1;
52 | }
53 | });
54 |
55 | simulatePressAndReleaseButtonWithBounce();
56 |
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/dont-reconfigure-direction-part1.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | *
7 | * This test is part 1 of a two part test.
8 | * For part 2 see dont-reconfigure-direction-part2.js.
9 | *
10 | * Part 1 sets the ouput to 1 and expects to read 1 on the input. Part 1
11 | * doesn't unexport the GPIOs so that part 2 can can ensure that a Gpio output
12 | * object can be constructed without modifying the value of the output. Part 2
13 | * also expects to read one on the input. This is achieved by using the
14 | * reconfigureDirection option.
15 | */
16 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
17 | const assert = require('assert');
18 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
19 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
20 |
21 | output.writeSync(1);
22 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
23 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
24 |
25 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/dont-reconfigure-direction-part2.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | *
7 | * This test is part 2 of a two part test.
8 | * For part 1 see dont-reconfigure-direction-part1.js.
9 | *
10 | * Part 1 sets the ouput to 1 and expects to read 1 on the input. Part 1
11 | * doesn't unexport the GPIOs so that part 2 can can ensure that a Gpio output
12 | * object can be constructed without modifying the value of the output. Part 2
13 | * also expects to read one on the input. This is achieved by using the
14 | * reconfigureDirection option.
15 | */
16 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
17 | const assert = require('assert');
18 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
19 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {reconfigureDirection: false});
20 |
21 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
22 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
23 |
24 | input.unexport();
25 | output.unexport();
26 |
27 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
28 |
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/export-many-times.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | for (let i = 1; i <= 1000000; i += 1) {
6 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
7 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
8 | led.unexport();
9 | if (i % 10 === 0) {
10 | console.log(i);
11 | }
12 | }
13 |
14 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
15 |
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/high-low.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 |
6 | assert(Gpio.HIGH === 1, 'expected Gpio.HIGH to be 1');
7 | assert(Gpio.LOW === 0, 'expected Gpio.LOW to be 0');
8 |
9 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/many-interrupts.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
6 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
7 |
8 | let toggleCount = 0;
9 | let falling = 0;
10 | let rising = 0;
11 |
12 | const toggleOutput = _ => {
13 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() ^ 1);
14 | toggleCount += 1;
15 | };
16 |
17 | const interrupt = (err, value) => {
18 | if (err) {
19 | throw err;
20 | }
21 |
22 | if (value === 1) {
23 | rising += 1;
24 | } else if (value === 0) {
25 | falling += 1;
26 | }
27 |
28 | assert(output.readSync() === value);
29 |
30 | if (rising + falling < 2000) {
31 | toggleOutput();
32 | } else {
33 | assert(toggleCount === 2000);
34 | assert(rising === falling);
35 | assert(rising + falling === toggleCount);
36 |
37 | input.unexport();
38 | output.writeSync(0);
39 | output.unexport();
40 |
41 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
42 | }
43 | };
44 |
45 | input.watch(interrupt);
46 | toggleOutput();
47 |
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/output-with-edge-bug.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | // Test for https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/87
4 | //
5 | // If a Gpio is instantiated for an output GPIO and the edge parameter is
6 | // specified then the edge parameter should be ignored. Attempting to write
7 | // the sysfs edge file for an output GPIO results in an
8 | // "EIO: i/o error, write"
9 |
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 | const assert = require('assert');
12 |
13 | const ensureGpio17Unexported = cb => {
14 | let led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
15 |
16 | led.unexport();
17 |
18 | setTimeout(_ => cb(), 100);
19 | };
20 |
21 | ensureGpio17Unexported(_ => {
22 | let led;
23 |
24 | assert.doesNotThrow(
25 | _ => led = new Gpio(17, 'out', 'both'),
26 | 'can\'t instantiate a Gpio for an output with edge option specified'
27 | );
28 |
29 | led.unexport();
30 |
31 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
32 | });
33 |
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-async.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | const pulseLed = (led, pulseCount, cb) => {
6 | let time = process.hrtime();
7 |
8 | const loop = count => {
9 | if (count === 0) {
10 | time = process.hrtime(time);
11 | const writesPerSecond = pulseCount * 2 / (time[0] + time[1] / 1E9);
12 | return cb(null, writesPerSecond);
13 | }
14 |
15 | led.write(1, err => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | return cb(err);
18 | }
19 |
20 | led.write(0, err => {
21 | if (err) {
22 | return cb(err);
23 | }
24 |
25 | loop(count - 1);
26 | });
27 | });
28 | };
29 |
30 | loop(pulseCount);
31 | };
32 |
33 | const asyncWritesPerSecond = cb => {
34 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
35 | let writes = 0;
36 |
37 | const loop = count => {
38 | if (count === 0) {
39 | led.unexport();
40 | return cb(null, writes / 10);
41 | }
42 |
43 | pulseLed(led, 10000, (err, writesPerSecond) => {
44 | if (err) {
45 | return cb(err);
46 | }
47 |
48 | writes += writesPerSecond;
49 |
50 | loop(count - 1);
51 | });
52 | };
53 |
54 | // Do a dry run first to get the runtime primed
55 | pulseLed(led, 5000, (err, writesPerSecond) => {
56 | if (err) {
57 | return cb(err);
58 | }
59 | loop(10);
60 | });
61 | };
62 |
63 | asyncWritesPerSecond((err, averageWritesPerSecond) => {
64 | if (err) {
65 | throw err;
66 | }
67 |
68 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
69 | console.log(
70 | ' ' + Math.floor(averageWritesPerSecond) + ' async writes per second'
71 | );
72 | });
73 |
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor. GPIO7 is
6 | * an interrupt generating input and GPIO8 is an output. By toggling the state
7 | * of the output an interrupt is generated. The output is toggled as often as
8 | * possible to determine the maximum rate at which interrupts can be handled.
9 | */
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
12 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
13 |
14 | let irqCount = 0;
15 | let iv;
16 |
17 | // Exit handler
18 | const exit = _ => {
19 | input.unexport();
20 | output.unexport();
21 |
22 | clearInterval(iv);
23 | };
24 | process.on('SIGINT', exit);
25 |
26 | // Interrupt handler
27 | input.watch((err, value) => {
28 | if (err) {
29 | exit();
30 | }
31 |
32 | irqCount += 1;
33 |
34 | // Trigger next interrupt by toggling output.
35 | output.writeSync(value === 0 ? 1 : 0);
36 | });
37 |
38 | // Print number of interrupts once a second.
39 | iv = setInterval(_ => {
40 | console.log(irqCount);
41 | irqCount = 0;
42 | }, 1000);
43 |
44 | // Trigger first interrupt by toggling output.
45 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() === 0 ? 1 : 0);
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-sync.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | const pulseLed = (led, pulseCount) => {
6 | let time = process.hrtime();
7 |
8 | for (let i = 0; i !== pulseCount; i += 1) {
9 | led.writeSync(1);
10 | led.writeSync(0);
11 | }
12 |
13 | time = process.hrtime(time);
14 |
15 | const writesPerSecond = pulseCount * 2 / (time[0] + time[1] / 1E9);
16 |
17 | return writesPerSecond;
18 | };
19 |
20 | const syncWritesPerSecond = _ => {
21 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
22 | let writes = 0;
23 |
24 | // Do a dry run first to get the runtime primed
25 | pulseLed(led, 50000);
26 |
27 | for (let i = 0; i !== 10; i += 1) {
28 | writes += pulseLed(led, 100000);
29 | }
30 |
31 | led.unexport();
32 |
33 | return writes / 10;
34 | };
35 |
36 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
37 | console.log(
38 | ' ' + Math.floor(syncWritesPerSecond()) + ' sync writes per second'
39 | );
40 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/run-performance-tests:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node performance-async
3 | node performance-sync
4 | node performance-interrupt
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/run-tests:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node blink-led
3 | node blink-led-promises
4 | node change-configuration
5 | node configure-and-check-active-low
6 | node configure-and-check-active-low-defaults
7 | node configure-and-check-input
8 | node configure-and-check-output
9 | node debounce
10 | node dont-reconfigure-direction-part1
11 | node dont-reconfigure-direction-part2
12 | node high-low
13 | node many-interrupts
14 | node output-with-edge-bug
15 | node wait-for-interrupt
16 | node wait-for-many-interrupts
17 |
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/wait-for-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
6 |
7 | assert(button.direction() === 'in');
8 | assert(button.edge() === 'both');
9 |
10 | console.info('Please press button connected to GPIO #4...');
11 |
12 | button.watch((err, value) => {
13 | if (err) {
14 | throw err;
15 | }
16 |
17 | assert(value === 0 || value === 1);
18 |
19 | button.unexport();
20 |
21 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
22 | console.log(' button pressed, value was ' + value);
23 | });
24 |
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/wait-for-many-interrupts.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {
6 | debounceTimeout : 10
7 | });
8 | let count = 0;
9 |
10 | assert(button.direction() === 'in');
11 | assert(button.edge() === 'rising');
12 |
13 | console.info('Please press button connected to GPIO4 5 times...');
14 |
15 | button.watch((err, value) => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | throw err;
18 | }
19 |
20 | count += 1;
21 |
22 | console.log('button pressed ' + count + ' times, value was ' + value);
23 |
24 | if (count === 5) {
25 | button.unexport();
26 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
27 | }
28 | });
29 |
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/onoff.d.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | export type High = 1;
2 | export type Low = 0;
3 | export type Direction = "in" | "out" | "high" | "low";
4 | export type Edge = "none" | "rising" | "falling" | "both";
5 |
6 | export type Options = {
7 | debounceTimeout?: number,
8 | activeLow?: boolean,
9 | reconfigureDirection?: boolean,
10 | }
11 |
12 | export type BinaryValue = High | Low;
13 | export type ValueCallback = (err: Error | null | undefined, value: BinaryValue) => void;
14 |
15 | export class Gpio {
16 | static HIGH: High;
17 | static LOW: Low;
18 | static accessible: boolean;
19 |
20 | constructor(gpio: number, direction: Direction, edge?: Edge, options?: Options);
21 |
22 | read(callback: ValueCallback): void;
23 | read(): Promise
46 |
47 | When the button is pressed the LED should turn on, when it's released the LED
48 | should turn off. This can be achieved with the following code:
49 |
50 | ```js
51 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
52 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
53 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
54 |
55 | button.watch((err, value) => led.writeSync(value));
56 | ```
57 |
58 | Here two Gpio objects are being created. One called led for the LED connected
59 | to GPIO17 which is an output, and one called button for the momentary push
60 | button connected to GPIO4 which is an input. In addition to specifying that
61 | the button is an input, the constructors optional third argument is used to
62 | specify that 'both' rising and falling interrupt edges should be configured
63 | for the button GPIO as both button presses and releases should be handled.
64 |
65 | After everything has been setup correctly, the buttons watch method is used to
66 | specify a callback function to execute every time the button is pressed or
67 | released. The value argument passed to the callback function represents the
68 | state of the button which will be 1 for pressed and 0 for released. This value
69 | is used by the callback to turn the LED on or off using its writeSync method.
70 |
71 | When the above program is running it can be terminated with ctrl-c. However,
72 | it doesn't free its resources. It also ignores the err argument passed to
73 | the callback. Here's a slightly modified variant of the program that handles
74 | ctrl-c gracefully and bails out on error. The resources used by the led and
75 | button Gpio objects are released by invoking their unexport method.
76 |
77 | ```js
78 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
79 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
80 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
81 |
82 | button.watch((err, value) => {
83 | if (err) {
84 | throw err;
85 | }
86 |
87 | led.writeSync(value);
88 | });
89 |
90 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
91 | led.unexport();
92 | button.unexport();
93 | });
94 | ```
95 |
96 | #### Debouncing Buttons
97 | When working with buttons there will often be button bounce issues which
98 | result in the hardware thinking that a button was pressed several times
99 | although it was only pressed once. onoff provides a software debouncing
100 | solution for resolving bounce issues.
101 |
102 | Assume again that there's an LED connected to GPIO17 and a momentary push
103 | button connected to GPIO4.
104 |
105 | When the button is pressed the LED should toggle its state. This is a typical
106 | example of a situation where there will be button bounce issues. The issue can
107 | be resolved by using the debounceTimeout option when creating the Gpio object
108 | for the button. In the below program the debounceTimeout is set to 10
109 | milliseconds. This delays invoking the watch callback for the button while the
110 | button is bouncing. The watch callback will not be invoked until the button
111 | stops bouncing and has been in a stable state for 10 milliseconds.
112 |
113 | ```js
114 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
115 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
116 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
117 |
118 | button.watch((err, value) => {
119 | if (err) {
120 | throw err;
121 | }
122 |
123 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
124 | });
125 |
126 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
127 | led.unexport();
128 | button.unexport();
129 | });
130 | ```
131 |
132 | #### Blink an LED Using the Synchronous API
133 |
134 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the synchronous readSync
135 | and writeSync methods.
136 |
137 | ```js
138 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
139 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
140 |
141 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
142 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 200);
143 |
144 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
145 | setTimeout(_ => {
146 | clearInterval(iv); // Stop blinking
147 | led.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
148 | }, 5000);
149 | ```
150 |
151 | #### Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Completion Callbacks
152 |
153 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the asynchronous read and
154 | write methods and completion callbacks.
155 |
156 | ```js
157 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
158 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
159 | let stopBlinking = false;
160 |
161 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
162 | const blinkLed = _ => {
163 | if (stopBlinking) {
164 | return led.unexport();
165 | }
166 |
167 | led.read((err, value) => { // Asynchronous read
168 | if (err) {
169 | throw err;
170 | }
171 |
172 | led.write(value ^ 1, err => { // Asynchronous write
173 | if (err) {
174 | throw err;
175 | }
176 | });
177 | });
178 |
179 | setTimeout(blinkLed, 200);
180 | };
181 |
182 | blinkLed();
183 |
184 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
185 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
186 | ```
187 |
188 | #### Blink an LED Using the Asynchronous API and Promises
189 |
190 | Blink an LED connected to GPIO17 for 5 seconds using the asynchronous read and
191 | write methods and Promises.
192 |
193 | ```js
194 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
195 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
196 | let stopBlinking = false;
197 |
198 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
199 | const blinkLed = _ => {
200 | if (stopBlinking) {
201 | return led.unexport();
202 | }
203 |
204 | led.read()
205 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
206 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 200))
207 | .catch(err => console.log(err));
208 | };
209 |
210 | blinkLed();
211 |
212 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
213 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
214 | ```
215 |
216 | #### Check accessibility
217 |
218 | Sometimes it may be necessary to determine if the current system supports
219 | GPIOs programmatically and mock functionality if it doesn't. `Gpio.accessible`
220 | can be used to achieve this.
221 |
222 | ```js
223 | const Gpio = require('onoff').Gpio;
224 |
225 | const useLed = (led, value) => led.writeSync(value);
226 |
227 | let led;
228 |
229 | if (Gpio.accessible) {
230 | led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
231 | // more real code here
232 | } else {
233 | led = {
234 | writeSync: value => {
235 | console.log('virtual led now uses value: ' + value);
236 | }
237 | };
238 | }
239 |
240 | useLed(led, 1);
241 | ```
242 |
243 | ## API
244 |
245 | ### Class Gpio
246 |
247 | * [Gpio(gpio, direction [, edge] [, options]) - Constructor](#gpiogpio-direction--edge--options)
248 | * [read([callback]) - Read GPIO value asynchronously](#readcallback)
249 | * [readSync() - Read GPIO value synchronously](#readsync)
250 | * [write(value[, callback]) - Write GPIO value asynchronously](#writevalue-callback)
251 | * [writeSync(value) - Write GPIO value synchronously](#writesyncvalue)
252 | * [watch(callback) - Watch for hardware interrupts on the GPIO](#watchcallback)
253 | * [unwatch([callback]) - Stop watching for hardware interrupts on the GPIO](#unwatchcallback)
254 | * [unwatchAll() - Remove all watchers for the GPIO](#unwatchall)
255 | * [direction() - Get GPIO direction](#direction)
256 | * [setDirection(direction) - Set GPIO direction](#setdirectiondirection)
257 | * [edge() - Get GPIO interrupt generating edge](#edge)
258 | * [setEdge(edge) - Set GPIO interrupt generating edge](#setedgeedge)
259 | * [activeLow() - Get GPIO activeLow setting](#activelow)
260 | * [setActiveLow(invert) - Set GPIO activeLow setting](#setactivelowinvert)
261 | * [unexport() - Reverse the effect of exporting the GPIO to userspace](#unexport)
262 | * [static accessible - Determine whether or not GPIO access is possible](#static-accessible)
263 | * [HIGH / LOW - Constants used when reading or writing a GPIO value](#static-high--low)
264 |
265 | ##### Gpio(gpio, direction [, edge] [, options])
266 | - gpio - An unsigned integer specifying the GPIO number.
267 | - direction - A string specifying whether the GPIO should be configured as an
268 | input or output. The valid values are: 'in', 'out', 'high', and 'low'. If 'out'
269 | is specified the GPIO will be configured as an output and the value of the GPIO
270 | will be set to 0. 'high' and 'low' are variants of 'out' that configure the
271 | GPIO as an output with an initial level of 1 or 0 respectively.
272 | - [edge] - An optional string specifying the interrupt generating edge or
273 | edges for an input GPIO. The valid values are: 'none', 'rising', 'falling' or
274 | 'both'. The default value is 'none' indicating that the GPIO will not generate
275 | interrupts. Whether or not interrupts are supported by an input GPIO is GPIO
276 | specific. If interrupts are not supported by a GPIO the edge argument should
277 | not be specified. The edge argument is ignored for output GPIOs.
278 | - [options] - An optional options object.
279 |
280 | Configures the GPIO based on the passed arguments and returns a new Gpio
281 | object that can be used to access the GPIO.
282 |
283 | The following options are supported:
284 | - debounceTimeout - An unsigned integer specifying a millisecond delay. Delays
285 | invoking the watch callback for an interrupt generating input GPIO while the
286 | input is bouncing. The watch callback will not be invoked until the input
287 | stops bouncing and has been in a stable state for debounceTimeout
288 | milliseconds. Optional, if unspecified the input GPIO will not be debounced.
289 | - activeLow - A boolean value specifying whether the values read from or
290 | written to the GPIO should be inverted. The interrupt generating edge for the
291 | GPIO also follow this this setting. The valid values for activeLow are true
292 | and false. Setting activeLow to true inverts. Optional, the default value is
293 | false.
294 | - reconfigureDirection - A boolean value specifying whether the direction for
295 | the GPIO should be reconfigured even though the direction is already
296 | configured correctly. When an application starts, the direction of a GPIO used
297 | by that application may already be configured correctly, for example, from a
298 | previous run of the application. Reconfiguring the direction of that GPIO can
299 | result in unwanted side effects. For example, if a GPIO is already configured
300 | as an output and it is reconfigured as an output by passing 'out' to the
301 | constructor, the value of that output will be set to 0. In some applications
302 | this is not desirable and the value of the output should not be modified. The
303 | reconfigureDirection option can help here. If reconfigureDirection is set to
304 | false the direction of a GPIO that is already correctly configured will not be
305 | reconfigured. Optional, the default value is true.
306 |
307 | GPIOs on Linux are identified by unsigned integers. These are the numbers that
308 | should be passed to the onoff Gpio constructor when exporting GPIOs to
309 | userspace. For example, pin 11 on the Raspberry Pi expansion header
310 | corresponds to GPIO17 in Raspbian Linux. 17 is therefore the number to pass
311 | to the onoff Gpio constructor when using pin 11 on the expansion header.
312 |
313 | ##### read([callback])
314 | - [callback] - An optional completion callback that gets two arguments (err,
315 | value), where err is reserved for an Error object and value is the number 0
316 | or 1 and represents the state of the GPIO.
317 |
318 | Read GPIO value asynchronously. If no completion callback is specified read
319 | returns a Promise which resolves to the value of the GPIO on success or rejects
320 | with an Error object on failure.
321 |
322 | Note that most systems support readback of GPIOs configured as outputs. The
323 | read method can therefore be invoked for any GPIO, irrespective of whether it
324 | was configured as an input or an output. The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are
325 | examples of such systems.
326 |
327 | ##### readSync()
328 | Read GPIO value synchronously. Returns the number 0 or 1 to represent the
329 | state of the GPIO.
330 |
331 | Note that most systems support readback of GPIOs configured as outputs. The
332 | readSync method can therefore be invoked for any GPIO, irrespective of whether
333 | it was configured as an input or an output. The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone
334 | are examples of such systems.
335 |
336 | ##### write(value[, callback])
337 | - value - The number 0 or 1.
338 | - [callback] - An optional completion callback that gets one argument (err),
339 | where err is reserved for an error object.
340 |
341 | Write GPIO value asynchronously. If no completion callback is specified write
342 | returns a Promise that resolves with no value on success or rejects with an
343 | Error object on failure.
344 |
345 | Note that on most systems invoking write for a GPIO configured as an input
346 | will result in an EPERM error indicating that the operation is not permitted.
347 | The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are examples of such systems.
348 |
349 | ##### writeSync(value)
350 | - value - The number 0 or 1.
351 |
352 | Write GPIO value synchronously.
353 |
354 | Note that on most systems invoking writeSync for a GPIO configured as an input
355 | will result in an EPERM error indicating that the operation is not permitted.
356 | The Raspberry Pi and BeagleBone are examples of such systems.
357 |
358 | ##### watch(callback)
359 | - callback - A callback that gets two arguments (err, value), where err is
360 | reserved for an error object and value is the number 0 or 1 and represents the
361 | state of the GPIO. The value can also be used to determine whether the
362 | interrupt occurred on a rising or falling edge. A value of 0 implies a falling
363 | edge interrupt and a value of 1 implies a rising edge interrupt.
364 |
365 | Watch for hardware interrupts on the GPIO. The edge argument that was passed
366 | to the constructor determines which hardware interrupts to watch for.
367 |
368 | ##### unwatch([callback])
369 | - [callback] - The callback to remove.
370 |
371 | Stop watching for hardware interrupts on the GPIO. If callback is specified,
372 | only that particular callback is removed. Otherwise all callbacks are removed.
373 |
374 | ##### unwatchAll()
375 | Remove all hardware interrupt watchers for the GPIO.
376 |
377 | ##### direction()
378 | Returns the string 'in' or 'out' indicating whether the GPIO is an input or
379 | output.
380 |
381 | ##### setDirection(direction)
382 | - direction - A string specifying whether the GPIO should be configured as an
383 | input or output. The valid values are 'in', 'out', 'high', and 'low'. If 'out'
384 | is specified the GPIO will be configured as an output and the value of the GPIO
385 | will be set to 0. 'high' and 'low' are variants of 'out' that configure the
386 | GPIO as an output with an initial level of 1 or 0 respectively.
387 |
388 | Set GPIO direction.
389 |
390 | ##### edge()
391 | Returns the string 'none', 'falling', 'rising', or 'both' indicating the
392 | interrupt generating edge or edges for the GPIO. Whether or not interrupts are
393 | supported by an input GPIO is GPIO specific. If interrupts are not supported
394 | the edge method should not be used. Interrupts are not supported by output
395 | GPIOs.
396 |
397 | ##### setEdge(edge)
398 | - edge - A string specifying the interrupt generating edge or edges for an
399 | input GPIO. The valid values are: 'none', 'rising', 'falling' or 'both'.
400 | Whether or not interrupts are supported by an input GPIO is GPIO specific. If
401 | interrupts are not supported the setEdge method should not be used. Interrupts
402 | are not supported by output GPIOs.
403 |
404 | Set GPIO interrupt generating edge.
405 |
406 | ##### activeLow()
407 | Returns true or false indicating whether or not the values read from or written
408 | to the GPIO are inverted.
409 |
410 | ##### setActiveLow(invert)
411 | - invert - A boolean value specifying whether the values read from or written
412 | to the GPIO should be inverted. The interrupt generating edge for the GPIO also
413 | follow this this setting. The valid values for invert are true and false.
414 | Setting activeLow to true inverts.
415 |
416 | Set GPIO activeLow setting.
417 |
418 | ##### unexport()
419 | Reverse the effect of exporting the GPIO to userspace. A Gpio object should not
420 | be used after invoking its unexport method.
421 |
422 | ##### static accessible
423 | Determine whether or not GPIO access is possible. true if the current process
424 | has the permissions required to export GPIOs to userspace. false otherwise.
425 | Loosely speaking, if this property is true it should be possible for the
426 | current process to create Gpio objects.
427 |
428 | It is notable that while this property may be false indicating that the
429 | current process does not have the permissions required to export GPIOs to
430 | userspace, existing exported GPIOs may still be accessible.
431 |
432 | This property is useful for mocking functionality on computers used for
433 | development that do not provide access to GPIOs.
434 |
435 | This is a static property and should be accessed as `Gpio.accessible`.
436 |
437 | ##### static HIGH / LOW
438 | Constants used when reading or writing a GPIO value. Gpio.HIGH and Gpio.LOW
439 | can be used in place of the numeric constants 1 and 0.
440 |
441 |
442 | ## How Does onoff Work?
443 |
444 | Internally onoff uses sysfs files located at /sys/class/gpio to access GPIOs
445 | and the [epoll package](https://github.com/fivdi/epoll) to detect hardware
446 | interrupts. The Linux GPIO sysfs interface for userspace is documented
447 | [here](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/gpio/sysfs.txt).
448 | It's a relatively simple interface which can be used to ask the Linux kernel
449 | to export control of a GPIO to userspace. After control of a GPIO has been
450 | exported to userspace, the GPIO can be configured as an input or output.
451 | Thereafter, the state of an input can be read, and the state of an output can
452 | be written. Some systems will also allow the state of a output to be read.
453 | The GPIO sysfs interface can also be used for interrupt detection. onoff can
454 | detect several thousand interrupts per second on both the BeagleBone and the
455 | Raspberry Pi.
456 |
457 |
458 | ## Configuring Pullup and Pulldown Resistors
459 |
460 | As mentioned in section [How Does onoff Work](#how-does-onoff-work) the sysfs
461 | interface is used to access GPIOs. The sysfs interface doesn't offer support
462 | for configuring pullup and pulldown resistors on GPIOs.
463 |
464 | There are however many platform specific mechanisms for configuring pullup and
465 | pulldown resistors that are compatible with onoff. onoff itself doesn't use
466 | these mechanisms as one of the goals of onoff is to be platform independent.
467 |
468 | Here we'll take a look at two mechanisms available on the Raspberry Pi for
469 | configuring pullup and pulldown resistors.
470 |
471 | The first point to be aware of is that most GPIOs on a Raspberry Pi have
472 | either their pullup or pulldown resistor activated by default. The defaults
473 | can be seen in Table 6-31 on pages 102 and 103 of the
474 | [BCM2835 ARM Peripherals](http://www.farnell.com/datasheets/1521578.pdf)
475 | documentation.
476 |
477 | #### Using the gpio Command in /boot/config.txt
478 |
479 | On Raspbian 2018-04-18 or later the `gpio` configuration command can be used
480 | in `/boot/config.txt` to configure pullup and pulldown resistors. Further
481 | information is available at
482 | [New "gpio" config command](https://www.raspberrypi.org/forums/viewtopic.php?f=117&t=208748).
483 |
484 | #### Using Device Tree Overlays
485 |
486 | Device tree overlays can also be used to configure pullup and pulldown
487 | resistors. The Wiki page
488 | [Enabling Pullup and Pulldown Resistors on The Raspberry Pi](https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/wiki/Enabling-Pullup-and-Pulldown-Resistors-on-The-Raspberry-Pi)
489 | describes this mechanism in more detail.
490 |
491 | ## Benchmarks
492 |
493 | Three of the onoff tests are used to monitor performance.
494 |
495 | * performance-async.js - determine max. no. of write ops per seconds
496 | * performance-sync.js - determine max. no. of writeSync ops per second
497 | * performance-interrupt.js - determine max. no. of interrupts per second
498 |
499 | The results of these tests are shown in the following tables.
500 |
501 | **Raspberry Pi 4 B, 1.5GHz, Raspberry Pi OS (March 4th 2021, Buster 10.8)**
502 |
503 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
504 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
505 | v16.0.0 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 25124 | 280417 | 20240
506 | v15.14.0 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 24055 | 271149 | 20488
507 | v14.16.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 21669 | 254705 | 19703
508 | v12.22.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 22618 | 318417 | 21122
509 | v10.24.1 | v6.0.3 | 5.10.17-v7l+ | 22405 | 329927 | 19583
510 |
511 | **Raspberry Pi 3 B, 1.2GHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
512 |
513 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
514 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
515 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 21670 | 207222 | 18328
516 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 23661 | 225758 | 20741
517 |
518 | **Raspberry Pi 2 B, 900MHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
519 |
520 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
521 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
522 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 10769 | 113107 | 10373
523 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75-v7l+ | 11843 | 129086 | 10536
524 |
525 | **Raspberry Pi 1 B, 700MHz, Raspbian Buster 10.1**
526 |
527 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
528 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
529 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75+ | 2316 | 26696 | 2112
530 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.75+ | 2613 | 33129 | 2225
531 |
532 | **BeagleBone Black, 1GHz, Debian Buster 10.2**
533 |
534 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
535 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
536 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 6855 | 70535 | 5911
537 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 7564 | 79133 | 5920
538 |
539 | **BeagleBone, 720MHz, Debian Buster 10.2**
540 |
541 | node | onoff | kernel | write / sec | writeSync / sec | interrupts / sec
542 | :---: | :---: | :---: | ---: | ---: | ---:
543 | v12.14.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 5013 | 49741 | 4297
544 | v10.18.0 | v5.0.0 | 4.19.79-ti-r30 | 5400 | 57157 | 4371
545 |
546 | ## Related Packages
547 |
548 | Here are a few links to other hardware specific Node.js packages that may be
549 | of interest.
550 |
551 | * [pigpio](https://github.com/fivdi/pigpio) - Fast GPIO, PWM, servo control, state change notification and interrupt handling on the Raspberry Pi
552 | * [i2c-bus](https://github.com/fivdi/i2c-bus) - I2C serial bus access
553 | * [spi-device](https://github.com/fivdi/spi-device) - SPI serial bus access
554 | * [mcp-spi-adc](https://github.com/fivdi/mcp-spi-adc) - Analog to digital conversion with the MCP3002/4/8, MCP3202/4/8 and MCP3304
555 |
556 | ## Additional Information
557 |
558 | onoff was tested on the following platforms:
559 |
560 | - Raspberry Pi 1, 2, 3 and 4
561 | - Raspbian or Raspberry Pi OS
562 | - BeagleBone, BeagleBone Black and PocketBeagle
563 | - Debian
564 |
565 | The suitability of onoff for a particular Linux board is highly dependent on
566 | how GPIO interfaces are made available on that board. The
567 | [GPIO interfaces](https://www.kernel.org/doc/Documentation/gpio/)
568 | documentation describes GPIO access conventions rather than standards that must
569 | be followed so GPIO can vary from platform to platform. For example, onoff
570 | relies on sysfs files located at /sys/class/gpio being available. However,
571 | these sysfs files for userspace GPIO are optional and may not be available on a
572 | particular platform.
573 |
574 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/accessible.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 |
5 | console.log('Gpio functionality accessible on this computer?', Gpio.accessible);
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led-async.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
8 | const blinkLed = _ => {
9 | if (stopBlinking) {
10 | return led.unexport();
11 | }
12 |
13 | led.read((err, value) => { // Asynchronous read
14 | if (err) {
15 | throw err;
16 | }
17 |
18 | led.write(value ^ 1, err => { // Asynchronous write
19 | if (err) {
20 | throw err;
21 | }
22 | });
23 | });
24 |
25 | setTimeout(blinkLed, 200);
26 | };
27 |
28 | blinkLed();
29 |
30 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
31 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
32 |
33 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led-promises.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
8 | const blinkLed = _ => {
9 | if (stopBlinking) {
10 | return led.unexport();
11 | }
12 |
13 | led.read()
14 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
15 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 200))
16 | .catch(err => console.log(err));
17 | };
18 |
19 | blinkLed();
20 |
21 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
22 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 5000);
23 |
24 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/blink-led.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out'); // Export GPIO17 as an output
5 |
6 | // Toggle the state of the LED connected to GPIO17 every 200ms
7 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 200);
8 |
9 | // Stop blinking the LED after 5 seconds
10 | setTimeout(_ => {
11 | clearInterval(iv); // Stop blinking
12 | led.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
13 | }, 5000);
14 |
15 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/debounce-button.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
6 |
7 | button.watch((err, value) => {
8 | if (err) {
9 | throw err;
10 | }
11 |
12 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
13 | });
14 |
15 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
16 | led.unexport();
17 | button.unexport();
18 | });
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/light-switch.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
6 |
7 | button.watch((err, value) => {
8 | if (err) {
9 | throw err;
10 | }
11 |
12 | led.writeSync(value);
13 | });
14 |
15 | process.on('SIGINT', _ => {
16 | led.unexport();
17 | button.unexport();
18 | });
19 |
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/light-switch.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/fivdi/onoff/813da60dd1f3a842a29a8c630243d4f5b7523cc0/examples/light-switch.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/mygpio-overlay.dts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /dts-v1/;
2 | /plugin/;
3 |
4 | / {
5 | compatible = "brcm,bcm2708";
6 |
7 | fragment@0 {
8 | target = <&gpio>;
9 | __overlay__ {
10 | pinctrl-names = "default";
11 | pinctrl-0 = <&my_pins>;
12 |
13 | my_pins: my_pins {
14 | brcm,pins = <7 8 9>; /* gpio no. */
15 | brcm,function = <0 0 0>; /* 0:in, 1:out */
16 | brcm,pull = <1 1 2>; /* 2:up 1:down 0:none */
17 | };
18 | };
19 | };
20 | };
21 |
22 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/run-examples:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node blink-led
3 | node blink-led-async
4 | node wait-for-interrupt
5 | node light-switch
6 |
7 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/examples/wait-for-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio; // Gpio class
4 |
5 | // Export GPIO4 as an interrupt generating input with a debounceTimeout of 10
6 | // milliseconds
7 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {debounceTimeout: 10});
8 |
9 | console.log('Please press the button on GPIO4...');
10 |
11 | // The callback passed to watch will be invoked when the button connected to
12 | // GPIO4 is pressed
13 | button.watch((err, value) => {
14 | if (err) {
15 | throw err;
16 | }
17 |
18 | console.log('Button pressed!, its value was ' + value);
19 |
20 | button.unexport(); // Unexport GPIO and free resources
21 | });
22 |
23 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/blink-led-promises.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 | let stopBlinking = false;
6 |
7 | const blinkLed = _ => {
8 | if (stopBlinking) {
9 | led.unexport();
10 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
11 | return;
12 | }
13 |
14 | led.read()
15 | .then(value => led.write(value ^ 1))
16 | .then(_ => setTimeout(blinkLed, 50))
17 | .catch(err => {
18 | console.log(err);
19 | });
20 | };
21 |
22 | blinkLed();
23 |
24 | setTimeout(_ => stopBlinking = true, 2000);
25 |
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/blink-led.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
5 |
6 | const iv = setInterval(_ => led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1), 100);
7 |
8 | setTimeout(_ => {
9 | clearInterval(iv);
10 |
11 | led.writeSync(0);
12 | led.unexport();
13 |
14 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
15 | }, 2000);
16 |
17 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/change-configuration.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 |
6 | let output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
7 | let input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
8 |
9 | const watchWithSecondConfiguration = _ => {
10 | input.watch((err, value) => {
11 | assert(!err, 'error during interrupt detection');
12 | assert(value === 1, 'expected interrupt on rising edge');
13 |
14 | setTimeout(_ => {
15 | input.unexport();
16 | output.unexport();
17 |
18 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
19 | }, 10);
20 | });
21 |
22 | output.writeSync(1);
23 | };
24 |
25 | const changeConfiguration = _ => {
26 | input.unwatchAll();
27 |
28 | let temp = output;
29 | temp.setDirection('in');
30 | output = input;
31 | input = temp;
32 |
33 | output.setEdge('none');
34 | output.setDirection('out');
35 | output.writeSync(0);
36 | assert(output.direction() === 'out', 'expected direction to be out');
37 | assert(output.edge() === 'none', 'expected edge to be none');
38 | assert(output.readSync() === 0, 'expected value to be 0');
39 |
40 | input.setEdge('rising');
41 | assert(input.direction() === 'in', 'expected direction to be in');
42 | assert(input.edge() === 'rising', 'expected edge to be rising');
43 | assert(input.readSync() === 0, 'expected value to be 0');
44 |
45 | watchWithSecondConfiguration();
46 | };
47 |
48 | const watchWithFirstConfiguration = _ => {
49 | input.watch((err, value) => {
50 | assert(!err, 'error during interrupt detection');
51 | assert(value === 1, 'expected interrupt on rising edge');
52 |
53 | setTimeout(changeConfiguration, 10);
54 | });
55 |
56 | output.writeSync(1);
57 | };
58 |
59 | watchWithFirstConfiguration();
60 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-active-low-defaults.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | */
7 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
8 | const assert = require('assert');
9 | let input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
10 | let output = new Gpio(8, 'low', {activeLow: true});
11 |
12 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
13 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
14 |
15 | input.unexport();
16 | output.unexport();
17 |
18 | //
19 |
20 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
21 | output = new Gpio(8, 'low', {activeLow: false});
22 |
23 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
24 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
25 |
26 | input.unexport();
27 | output.unexport();
28 |
29 | //
30 |
31 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
32 | output = new Gpio(8, 'high', {activeLow: true});
33 |
34 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
35 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
36 |
37 | input.unexport();
38 | output.unexport();
39 |
40 | //
41 |
42 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
43 | output = new Gpio(8, 'high', {activeLow: false});
44 |
45 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
46 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
47 |
48 | input.unexport();
49 | output.unexport();
50 |
51 | //
52 |
53 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
54 | output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: true});
55 |
56 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
57 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
58 |
59 | input.unexport();
60 | output.unexport();
61 |
62 | //
63 |
64 | input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
65 | output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: false});
66 |
67 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
68 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
69 |
70 | input.unexport();
71 | output.unexport();
72 |
73 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
74 |
75 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-active-low.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | */
7 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
8 | const assert = require('assert');
9 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
10 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {activeLow: true});
11 |
12 | assert(input.activeLow() === false);
13 | assert(output.activeLow() === true);
14 |
15 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
16 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
17 |
18 | output.writeSync(0);
19 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
20 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
21 | output.writeSync(1);
22 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
23 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
24 |
25 | output.setActiveLow(false);
26 | assert(input.activeLow() === false);
27 | assert(output.activeLow() === false);
28 | output.writeSync(0);
29 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
30 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
31 | output.writeSync(1);
32 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
33 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
34 |
35 | input.setActiveLow(true);
36 | assert(input.activeLow() === true);
37 | assert(output.activeLow() === false);
38 | output.writeSync(0);
39 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
40 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
41 | output.writeSync(1);
42 | assert(input.readSync() === 0);
43 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
44 |
45 | input.unexport();
46 | output.unexport();
47 |
48 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
49 |
50 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-input.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const input = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising');
6 |
7 | assert(input.direction() === 'in');
8 | assert(input.edge() === 'rising');
9 |
10 | input.unexport();
11 |
12 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
13 |
14 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/configure-and-check-output.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const output = new Gpio(17, 'out');
6 |
7 | assert(output.direction() === 'out');
8 |
9 | output.writeSync(1);
10 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
11 |
12 | output.writeSync(0);
13 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
14 |
15 | output.write(1, err => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | throw err;
18 | }
19 |
20 | output.read((err, value) => {
21 | if (err) {
22 | throw err;
23 | }
24 |
25 | assert(value === 1);
26 |
27 | output.writeSync(0);
28 | assert(output.readSync() === 0);
29 |
30 | output.unexport();
31 |
32 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
33 | });
34 | });
35 |
36 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/debounce.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
6 | const button = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both', {debounceTimeout: 10});
7 |
8 | let buttonPressedCount = 0;
9 | let buttonReleasedCount = 0;
10 |
11 | const simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce = cb => {
12 | let toggleCount = 0;
13 |
14 | const iv = setInterval(_ => {
15 | if (toggleCount === 19) {
16 | clearInterval(iv);
17 | return cb();
18 | }
19 |
20 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() ^ 1);
21 | toggleCount += 1;
22 | }, 2);
23 | };
24 |
25 | const simulatePressAndReleaseButtonWithBounce = _ => {
26 | simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce(_ => {
27 | setTimeout(_ => {
28 | simulateToggleButtonStateWithBounce(_ => {
29 | setTimeout(_ => {
30 | assert(buttonPressedCount === 1);
31 | assert(buttonReleasedCount === 1);
32 |
33 | button.unexport();
34 | output.unexport();
35 |
36 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
37 | }, 20);
38 | });
39 | }, 50);
40 | });
41 | };
42 |
43 | button.watch((err, value) => {
44 | if (err) {
45 | throw err;
46 | }
47 |
48 | if (value === 1) {
49 | buttonPressedCount += 1;
50 | } else if (value === 0) {
51 | buttonReleasedCount += 1;
52 | }
53 | });
54 |
55 | simulatePressAndReleaseButtonWithBounce();
56 |
57 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/dont-reconfigure-direction-part1.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | *
7 | * This test is part 1 of a two part test.
8 | * For part 2 see dont-reconfigure-direction-part2.js.
9 | *
10 | * Part 1 sets the ouput to 1 and expects to read 1 on the input. Part 1
11 | * doesn't unexport the GPIOs so that part 2 can can ensure that a Gpio output
12 | * object can be constructed without modifying the value of the output. Part 2
13 | * also expects to read one on the input. This is achieved by using the
14 | * reconfigureDirection option.
15 | */
16 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
17 | const assert = require('assert');
18 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
19 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
20 |
21 | output.writeSync(1);
22 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
23 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
24 |
25 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
26 |
27 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/dont-reconfigure-direction-part2.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor.
6 | *
7 | * This test is part 2 of a two part test.
8 | * For part 1 see dont-reconfigure-direction-part1.js.
9 | *
10 | * Part 1 sets the ouput to 1 and expects to read 1 on the input. Part 1
11 | * doesn't unexport the GPIOs so that part 2 can can ensure that a Gpio output
12 | * object can be constructed without modifying the value of the output. Part 2
13 | * also expects to read one on the input. This is achieved by using the
14 | * reconfigureDirection option.
15 | */
16 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
17 | const assert = require('assert');
18 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in');
19 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out', {reconfigureDirection: false});
20 |
21 | assert(input.readSync() === 1);
22 | assert(output.readSync() === 1);
23 |
24 | input.unexport();
25 | output.unexport();
26 |
27 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
28 |
29 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/export-many-times.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | for (let i = 1; i <= 1000000; i += 1) {
6 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
7 | led.writeSync(led.readSync() ^ 1);
8 | led.unexport();
9 | if (i % 10 === 0) {
10 | console.log(i);
11 | }
12 | }
13 |
14 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
15 |
16 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/high-low.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 |
6 | assert(Gpio.HIGH === 1, 'expected Gpio.HIGH to be 1');
7 | assert(Gpio.LOW === 0, 'expected Gpio.LOW to be 0');
8 |
9 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
10 |
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/many-interrupts.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const assert = require('assert');
4 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
5 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
6 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
7 |
8 | let toggleCount = 0;
9 | let falling = 0;
10 | let rising = 0;
11 |
12 | const toggleOutput = _ => {
13 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() ^ 1);
14 | toggleCount += 1;
15 | };
16 |
17 | const interrupt = (err, value) => {
18 | if (err) {
19 | throw err;
20 | }
21 |
22 | if (value === 1) {
23 | rising += 1;
24 | } else if (value === 0) {
25 | falling += 1;
26 | }
27 |
28 | assert(output.readSync() === value);
29 |
30 | if (rising + falling < 2000) {
31 | toggleOutput();
32 | } else {
33 | assert(toggleCount === 2000);
34 | assert(rising === falling);
35 | assert(rising + falling === toggleCount);
36 |
37 | input.unexport();
38 | output.writeSync(0);
39 | output.unexport();
40 |
41 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
42 | }
43 | };
44 |
45 | input.watch(interrupt);
46 | toggleOutput();
47 |
48 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/output-with-edge-bug.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | // Test for https://github.com/fivdi/onoff/issues/87
4 | //
5 | // If a Gpio is instantiated for an output GPIO and the edge parameter is
6 | // specified then the edge parameter should be ignored. Attempting to write
7 | // the sysfs edge file for an output GPIO results in an
8 | // "EIO: i/o error, write"
9 |
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 | const assert = require('assert');
12 |
13 | const ensureGpio17Unexported = cb => {
14 | let led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
15 |
16 | led.unexport();
17 |
18 | setTimeout(_ => cb(), 100);
19 | };
20 |
21 | ensureGpio17Unexported(_ => {
22 | let led;
23 |
24 | assert.doesNotThrow(
25 | _ => led = new Gpio(17, 'out', 'both'),
26 | 'can\'t instantiate a Gpio for an output with edge option specified'
27 | );
28 |
29 | led.unexport();
30 |
31 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
32 | });
33 |
34 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-async.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | const pulseLed = (led, pulseCount, cb) => {
6 | let time = process.hrtime();
7 |
8 | const loop = count => {
9 | if (count === 0) {
10 | time = process.hrtime(time);
11 | const writesPerSecond = pulseCount * 2 / (time[0] + time[1] / 1E9);
12 | return cb(null, writesPerSecond);
13 | }
14 |
15 | led.write(1, err => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | return cb(err);
18 | }
19 |
20 | led.write(0, err => {
21 | if (err) {
22 | return cb(err);
23 | }
24 |
25 | loop(count - 1);
26 | });
27 | });
28 | };
29 |
30 | loop(pulseCount);
31 | };
32 |
33 | const asyncWritesPerSecond = cb => {
34 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
35 | let writes = 0;
36 |
37 | const loop = count => {
38 | if (count === 0) {
39 | led.unexport();
40 | return cb(null, writes / 10);
41 | }
42 |
43 | pulseLed(led, 10000, (err, writesPerSecond) => {
44 | if (err) {
45 | return cb(err);
46 | }
47 |
48 | writes += writesPerSecond;
49 |
50 | loop(count - 1);
51 | });
52 | };
53 |
54 | // Do a dry run first to get the runtime primed
55 | pulseLed(led, 5000, (err, writesPerSecond) => {
56 | if (err) {
57 | return cb(err);
58 | }
59 | loop(10);
60 | });
61 | };
62 |
63 | asyncWritesPerSecond((err, averageWritesPerSecond) => {
64 | if (err) {
65 | throw err;
66 | }
67 |
68 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
69 | console.log(
70 | ' ' + Math.floor(averageWritesPerSecond) + ' async writes per second'
71 | );
72 | });
73 |
74 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | /*
4 | * In this test, GPIO7 is connected to one end of a 1kΩ current limiting
5 | * resistor and GPIO8 is connected to the other end of the resistor. GPIO7 is
6 | * an interrupt generating input and GPIO8 is an output. By toggling the state
7 | * of the output an interrupt is generated. The output is toggled as often as
8 | * possible to determine the maximum rate at which interrupts can be handled.
9 | */
10 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
11 | const input = new Gpio(7, 'in', 'both');
12 | const output = new Gpio(8, 'out');
13 |
14 | let irqCount = 0;
15 | let iv;
16 |
17 | // Exit handler
18 | const exit = _ => {
19 | input.unexport();
20 | output.unexport();
21 |
22 | clearInterval(iv);
23 | };
24 | process.on('SIGINT', exit);
25 |
26 | // Interrupt handler
27 | input.watch((err, value) => {
28 | if (err) {
29 | exit();
30 | }
31 |
32 | irqCount += 1;
33 |
34 | // Trigger next interrupt by toggling output.
35 | output.writeSync(value === 0 ? 1 : 0);
36 | });
37 |
38 | // Print number of interrupts once a second.
39 | iv = setInterval(_ => {
40 | console.log(irqCount);
41 | irqCount = 0;
42 | }, 1000);
43 |
44 | // Trigger first interrupt by toggling output.
45 | output.writeSync(output.readSync() === 0 ? 1 : 0);
46 |
47 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/performance-sync.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 |
5 | const pulseLed = (led, pulseCount) => {
6 | let time = process.hrtime();
7 |
8 | for (let i = 0; i !== pulseCount; i += 1) {
9 | led.writeSync(1);
10 | led.writeSync(0);
11 | }
12 |
13 | time = process.hrtime(time);
14 |
15 | const writesPerSecond = pulseCount * 2 / (time[0] + time[1] / 1E9);
16 |
17 | return writesPerSecond;
18 | };
19 |
20 | const syncWritesPerSecond = _ => {
21 | const led = new Gpio(17, 'out');
22 | let writes = 0;
23 |
24 | // Do a dry run first to get the runtime primed
25 | pulseLed(led, 50000);
26 |
27 | for (let i = 0; i !== 10; i += 1) {
28 | writes += pulseLed(led, 100000);
29 | }
30 |
31 | led.unexport();
32 |
33 | return writes / 10;
34 | };
35 |
36 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
37 | console.log(
38 | ' ' + Math.floor(syncWritesPerSecond()) + ' sync writes per second'
39 | );
40 |
41 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/run-performance-tests:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node performance-async
3 | node performance-sync
4 | node performance-interrupt
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/run-tests:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/bin/sh
2 | node blink-led
3 | node blink-led-promises
4 | node change-configuration
5 | node configure-and-check-active-low
6 | node configure-and-check-active-low-defaults
7 | node configure-and-check-input
8 | node configure-and-check-output
9 | node debounce
10 | node dont-reconfigure-direction-part1
11 | node dont-reconfigure-direction-part2
12 | node high-low
13 | node many-interrupts
14 | node output-with-edge-bug
15 | node wait-for-interrupt
16 | node wait-for-many-interrupts
17 |
18 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/wait-for-interrupt.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'both');
6 |
7 | assert(button.direction() === 'in');
8 | assert(button.edge() === 'both');
9 |
10 | console.info('Please press button connected to GPIO #4...');
11 |
12 | button.watch((err, value) => {
13 | if (err) {
14 | throw err;
15 | }
16 |
17 | assert(value === 0 || value === 1);
18 |
19 | button.unexport();
20 |
21 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
22 | console.log(' button pressed, value was ' + value);
23 | });
24 |
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/integration-test/wait-for-many-interrupts.js:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | 'use strict';
2 |
3 | const Gpio = require('../onoff').Gpio;
4 | const assert = require('assert');
5 | const button = new Gpio(4, 'in', 'rising', {
6 | debounceTimeout : 10
7 | });
8 | let count = 0;
9 |
10 | assert(button.direction() === 'in');
11 | assert(button.edge() === 'rising');
12 |
13 | console.info('Please press button connected to GPIO4 5 times...');
14 |
15 | button.watch((err, value) => {
16 | if (err) {
17 | throw err;
18 | }
19 |
20 | count += 1;
21 |
22 | console.log('button pressed ' + count + ' times, value was ' + value);
23 |
24 | if (count === 5) {
25 | button.unexport();
26 | console.log('ok - ' + __filename);
27 | }
28 | });
29 |
30 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/onoff.d.ts:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | export type High = 1;
2 | export type Low = 0;
3 | export type Direction = "in" | "out" | "high" | "low";
4 | export type Edge = "none" | "rising" | "falling" | "both";
5 |
6 | export type Options = {
7 | debounceTimeout?: number,
8 | activeLow?: boolean,
9 | reconfigureDirection?: boolean,
10 | }
11 |
12 | export type BinaryValue = High | Low;
13 | export type ValueCallback = (err: Error | null | undefined, value: BinaryValue) => void;
14 |
15 | export class Gpio {
16 | static HIGH: High;
17 | static LOW: Low;
18 | static accessible: boolean;
19 |
20 | constructor(gpio: number, direction: Direction, edge?: Edge, options?: Options);
21 |
22 | read(callback: ValueCallback): void;
23 | read(): Promise