├── .gitignore
├── images
└── grad_disaggregated.png
├── setup.sh
├── README.md
├── fedavg_test.py
└── gradient_disaggregation.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | *~
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/images/grad_disaggregated.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gdisag/gradient_disaggregation/HEAD/images/grad_disaggregated.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | toplevel=`git rev-parse --show-toplevel`
2 | export PYTHONPATH=$PYTHONPATH:$toplevel/
3 | export MKL_NUM_THREADS=1
4 |
5 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Gradient Disaggregation: Breaking Privacy in Federated Learning by Reconstructing the User Participant Matrix
2 |
3 | ## Introduction
4 |
5 | We break the secure aggregation protocol of federated learning by showing that individual model updates may be recovered from sums given access to user summary metrics (specifically, participation frequency across training rounds). Our method, gradient disaggregation, observes multiple rounds of summed updates, then leverages summary metrics to recover individual updates. Read our paper here: https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.06089.
6 |
7 |
8 | 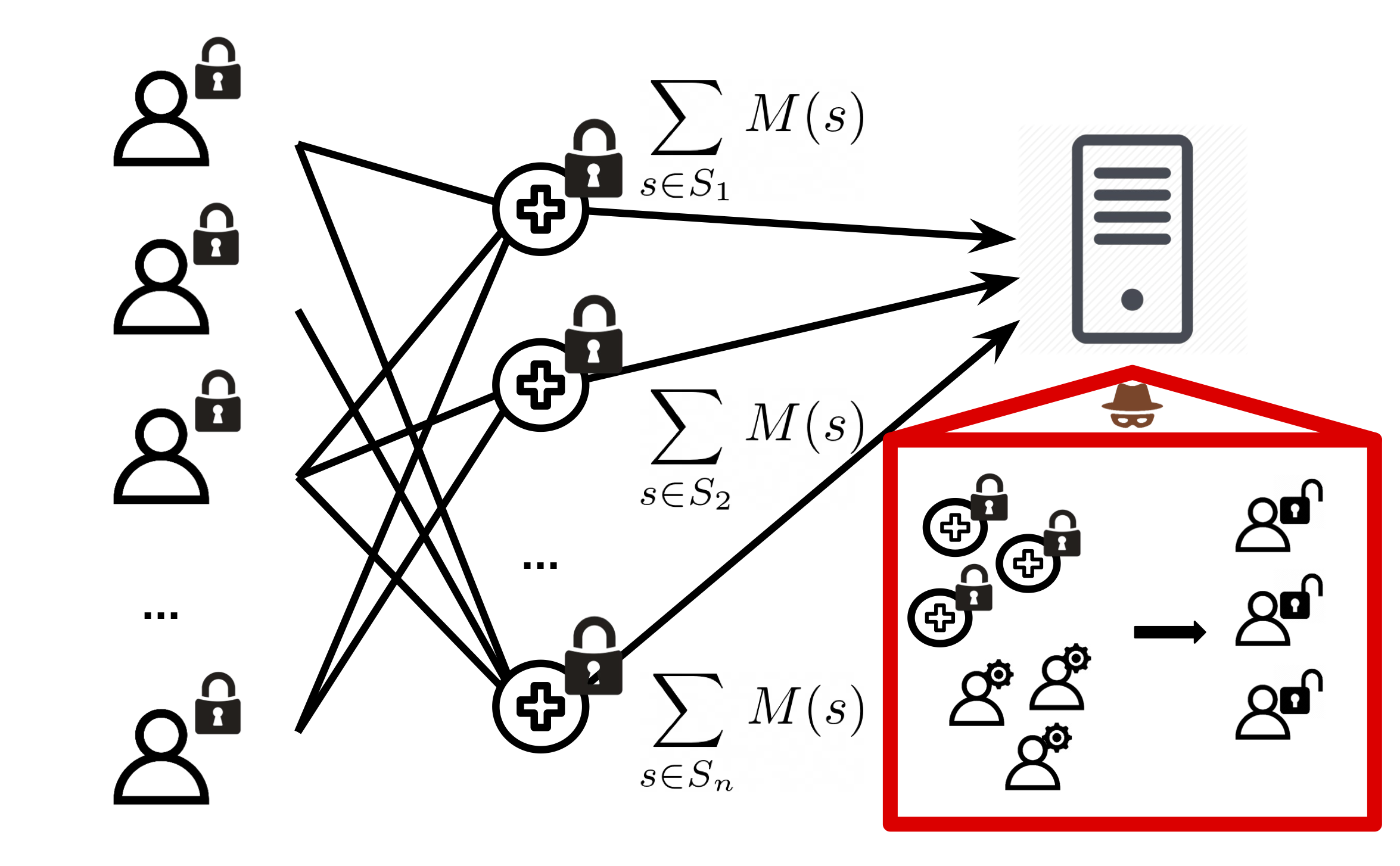 9 |
9 |
10 |
11 | ## Requirements
12 |
13 | ```python
14 | pip install scipy numpy
15 | ```
16 |
17 | ```python
18 | python -m pip install -i https://pypi.gurobi.com gurobipy
19 | ```
20 |
21 | ## Quickstart - Reconstructing Participant Matrix P
22 |
23 | Using the gradient_disaggregation code is fast and easy. Here we demonstrate disaggregating dummy gradients.
24 |
25 | Source the setup script.
26 | ```python
27 | source setup.sh
28 | ```
29 |
30 | Import codebase, generate participant matrix P, synthetic gradients G, aggregated gradients P*G, and participation counts. Then call disaggregate to recover P.
31 | ```python
32 | import gradient_disaggregation
33 | import numpy as np
34 |
35 | if __name__ == "__main__":
36 |
37 | num_users = 50
38 | num_rounds = 200
39 | gradient_size = 200
40 |
41 | # Trying to recover this!
42 | G = np.random.uniform(-1, 1, size=(num_users, gradient_size))
43 |
44 | # Trying to recover this! Tells which users participated in which rounds.
45 | P = np.random.choice([0, 1], size=(num_rounds, num_users), p=[.5,.5])
46 |
47 | # Given. Observed aggregated updates
48 | G_agg = P.dot(G)
49 |
50 | # Given. User summary metrics: for all users, we know how many times they participated across each 10 rounds.
51 | constraints = gradient_disaggregation.compute_P_constraints(P, 10)
52 |
53 | # Disaggregate
54 | P_star = gradient_disaggregation.reconstruct_participant_matrix(G_agg, constraints, verbose=True, multiprocess=True)
55 |
56 | diff = np.sum(np.abs(P_star-P))
57 | if diff == 0:
58 | print("Exactly recovered P!")
59 | else:
60 | print("Failed to recover P!")
61 | ```
62 |
63 | ## Reconstructing Aggregated FedAvg Updates
64 |
65 | Gradient disaggregation can disaggregate noisy aggregated model updates (e.g: FedAvg) -- see fedavg_test.py.
66 |
67 | ## Cite
68 |
69 | ```
70 | @inproceedings{lam2021gradient,
71 | title={Gradient Disaggregation: Breaking Privacy in Federated Learning by Reconstructing the User Participant Matrix},
72 | author={Lam, Maximilian and Wei, Gu-Yeon and Brooks, David and Reddi, Vijay Janapa and Mitzenmacher, Michael},
73 | booktitle={Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning},
74 | year={2021}
75 | }
76 | ```
77 |
78 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/fedavg_test.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import gradient_disaggregation
2 | from torch.autograd import grad
3 | from torchvision import models, datasets, transforms
4 | import copy
5 | import numpy as np
6 | import numpy as np
7 | import sys
8 | import torch
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 | import torch.nn as nn
12 | import torch.nn.functional as F
13 | import torch.nn.functional as F
14 | import torch.optim as optim
15 | import torchvision
16 | import torchvision
17 | import torchvision.transforms as transforms
18 |
19 | torch.manual_seed(1234)
20 |
21 | class Net(nn.Module):
22 | def __init__(self, hidden_size=84):
23 | super(Net, self).__init__()
24 | self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 6, 5)
25 | self.pool = nn.MaxPool2d(2, 2)
26 | self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5)
27 | self.fc1 = nn.Linear(16 * 5 * 5, 120)
28 | self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, hidden_size)
29 | self.fc3 = nn.Linear(hidden_size, 10)
30 |
31 | def forward(self, x):
32 | x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv1(x)))
33 | x = self.pool(F.relu(self.conv2(x)))
34 | x = x.view(-1, 16 * 5 * 5)
35 | x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
36 | x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
37 | x = self.fc3(x)
38 | return x
39 |
40 | nclasses = 10
41 | net = Net()
42 | criterion = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
43 | optimizer = optim.SGD(net.parameters(), lr=0.001, momentum=0.9)
44 | transform = transforms.Compose(
45 | [transforms.ToTensor(),
46 | transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
47 |
48 | def get_user_datasets(n_users, n_per_user):
49 | d = []
50 | dst = datasets.CIFAR10("~/.torch", download=True, transform=transform)
51 | loader = iter(torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dst, batch_size=1,
52 | shuffle=True))
53 | k = 0
54 | for i in range(n_users):
55 | user_data = []
56 | for j in range(n_per_user):
57 | element, label = next(loader)
58 | element.share_memory_()
59 | label.share_memory_()
60 | element, label = copy.deepcopy(element), copy.deepcopy(label)
61 | user_data.append((element, label))
62 | d.append(user_data)
63 | return d
64 |
65 | def get_params(n):
66 | all_vs = []
67 | for name, param in n.named_parameters():
68 | all_vs.append(param.detach().numpy().flatten())
69 | return np.concatenate(all_vs)
70 |
71 | def count_params(model):
72 | return sum(p.numel() for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad)
73 |
74 | def get_batched_grad_fedavg(user_dataset, local_batchsize, net, epochs=10, momentum=0, lr=1e-2):
75 | copied_net = copy.deepcopy(net)
76 | cur_optimizer = optim.SGD(copied_net.parameters(), lr=lr, momentum=momentum)
77 |
78 | user_dataset_indices = np.random.choice(list(range(len(user_dataset))), size=len(user_dataset), replace=False)
79 | user_dataset = [user_dataset[i] for i in user_dataset_indices]
80 |
81 | for i in range(epochs):
82 | np.random.shuffle(user_dataset)
83 | for j in range(0, len(user_dataset), local_batchsize):
84 |
85 | end = min(j+local_batchsize, len(user_dataset))
86 |
87 | inputs = torch.cat([x[0] for x in user_dataset[j:end]], axis=0)
88 | labels = torch.cat([x[1] for x in user_dataset[j:end]], axis=0)
89 |
90 | cur_optimizer.zero_grad()
91 | outputs = copied_net(inputs)
92 | loss = criterion(outputs, labels)
93 | loss.backward()
94 |
95 | cur_optimizer.step()
96 |
97 | p_net = get_params(net)
98 | p_copied = get_params(copied_net)
99 | diff = p_copied - p_net
100 |
101 | return diff
102 |
103 | def get_batched_grad(user, batchsize, epochs, net, fedavg=True, momentum=0, lr=1e-2):
104 | return get_batched_grad_fedavg(user, batchsize, net, epochs=epochs, momentum=momentum, lr=lr)
105 |
106 | def aggregate_grads(P, user_datasets, batchsize, epochs, momentum=0, lr=1e-2):
107 |
108 | copied_net = copy.deepcopy(net)
109 |
110 | all_grads = []
111 | gradient = get_params(copied_net).shape[-1]
112 | for row in range(P.shape[0]):
113 | print("Aggregating... %d of %d" % (row, P.shape[0]))
114 | sys.stdout.flush()
115 | grads = np.zeros((gradient,))
116 | for col in range(P.shape[1]):
117 | if P[row,col] == 1:
118 | batched_grad = get_batched_grad(user_datasets[col], batchsize, epochs, copied_net, momentum=momentum, lr=lr)
119 | grads += batched_grad
120 | all_grads.append(grads)
121 | return np.stack(all_grads)
122 |
123 | if __name__ == "__main__":
124 | n_users = 20
125 | n_rounds = 60
126 | dataset_size_per_user = 64
127 | batchsize = 16
128 | epochs = 4
129 | granularity = 10
130 |
131 | user_datasets = get_user_datasets(n_users, dataset_size_per_user)
132 | P = np.random.choice([0, 1], size=(n_rounds, n_users), p=[.8, .2])
133 | G_agg = aggregate_grads(P, user_datasets, batchsize, epochs)
134 | constraints = gradient_disaggregation.compute_P_constraints(P, granularity)
135 |
136 | P_star = gradient_disaggregation.reconstruct_participant_matrix(G_agg, constraints, noisy=True, verbose=True)
137 |
138 | diff = np.sum(np.abs(P_star-P))
139 | if diff == 0:
140 | print("Exactly recovered P!")
141 | else:
142 | print("Failed to recover P!")
143 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/gradient_disaggregation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Please export MKL_NUM_THREADS=1 if multiprocess disaggregating
2 |
3 | from numpy.linalg import svd
4 | import copy
5 | import numpy as np
6 | import random
7 | import scipy
8 | import scipy.linalg
9 | import sys
10 | import time
11 | import gurobipy as gp
12 | from gurobipy import GRB
13 | import multiprocessing as mp
14 | import os
15 |
16 | np.set_printoptions(threshold=sys.maxsize)
17 |
18 | def relative_err(A, B):
19 | return np.mean(np.abs(A-B)/(np.abs(B)+1e-9))
20 |
21 | def generate_A(r, n):
22 | return np.random.normal(0,1,size=(r,n))
23 |
24 | def generate_T(m, r, sparsity=.2):
25 | return np.float32(np.rint(np.random.uniform(0, 1, (m, r)) <= sparsity))
26 |
27 | def nullspace(A, atol=1e-13, rtol=0):
28 | A = np.atleast_2d(A)
29 | u, s, vh = svd(A)
30 | tol = max(atol, rtol * s[0])
31 | nnz = (s >= tol).sum()
32 | ns = vh[nnz:].conj().T
33 | return ns
34 |
35 | def compute_P_constraints(T, log_intervals):
36 | # From T, extract all log data that we need
37 | # - Number of participants per round
38 | # - Per user participation ums across rounds
39 | r = T.shape[1]
40 | m = T.shape[0]
41 | round_points = np.sum(T, axis=1)
42 | participant_points = []
43 | for user_id in range(r):
44 | user_participation_vector = T[:,user_id]
45 | interval = 0
46 | individual_participant_points = []
47 | while interval < m:
48 | n_participated = np.sum(user_participation_vector[interval:interval+log_intervals])
49 | individual_participant_points.append(((interval,interval+log_intervals), n_participated))
50 | interval += log_intervals
51 | participant_points.append(individual_participant_points)
52 | return participant_points
53 |
54 | def disaggregate_grads(grads, participant_points, interval=None, gt=None, gt_P=None, verbose=False, noisy=True, override_dim_to_use=None):
55 |
56 | def intersects(x, y):
57 | return not (x[1] < y[0] or y[1] < x[0]) and (x[1] <= y[1] and x[0] >= y[0])
58 |
59 | # Params
60 | nrounds, ndim = grads.shape
61 | nusers = len(participant_points)
62 |
63 | # Try to determine interval from participant constraints
64 | max_interval = max([x[0][1]-x[0][0] for y in participant_points for x in y])
65 | interval = max(nusers*5,max_interval*10) if interval is None else interval
66 | interval = min(interval, grads.shape[0])
67 |
68 | # Calculate dimension based on matrix rank
69 | if override_dim_to_use is not None:
70 | ndim_to_use = override_dim_to_use
71 | else:
72 | ndim_to_use = min(ndim, max(nrounds, nusers))
73 | for ndim_to_use in range(max(nrounds,nusers), ndim, (ndim-max(nrounds,nusers))//10):
74 | if np.linalg.matrix_rank(grads[0:interval,0:ndim_to_use]) >= nusers:
75 | break
76 | ndim_to_use = ndim
77 |
78 | # Disaggregate gradients averaging over rounds
79 | disaggregated = 0
80 | c = 0
81 | all_P = []
82 | for total, row in list(enumerate(range(0, nrounds, interval))):
83 | if verbose:
84 | print("Set %d of %d" % (total, nrounds//interval))
85 | lower,upper = row,row+interval
86 | upper = min(upper, nrounds)
87 | cutoff_start = 0
88 | if upper-lower < interval:
89 | cutoff_start = np.abs((upper-interval)-lower)
90 | lower = upper-interval
91 |
92 | aggregated_chunk = grads[lower:upper,0:ndim_to_use]
93 | filtered_participant_points = [[y for y in x if intersects(y[0], (lower,upper))] for x in participant_points]
94 | filtered_participant_points = [[((y[0][0]-lower, y[0][1]-lower), y[1]) for y in x] for x in filtered_participant_points]
95 | Ps = reconstruct_participant_matrix(aggregated_chunk, filtered_participant_points, verbose=verbose, noisy=noisy)
96 | if len(Ps) == 1:
97 | P = Ps[0]
98 | all_P.append(P[cutoff_start:,:])
99 | disaggregated += np.linalg.lstsq(P, grads[lower:upper,:], rcond=None)[0]
100 | c += 1
101 | if gt_P is not None:
102 | ham_dist = np.sum(np.abs(gt_P[lower:upper,:]-P))
103 | if verbose:
104 | print("Ham distance of P Matrix: %f" % ham_dist)
105 | if gt is not None:
106 | rel_err = relative_err(disaggregated/c, gt)
107 | if verbose:
108 | print("Relative Error vs Ground Truth: %f" % rel_err)
109 |
110 | if c == 0:
111 | return float("inf")
112 | return disaggregated / c, np.concatenate(all_P, axis=0)
113 |
114 | def reconstruct_participant_matrix(D, participant_points,
115 | top_k=None, verbose=False, noisy=False, column_timelimit=None,
116 | exit_after_tle=False, multiprocess=True):
117 | # D - T*Grads where T is the user participant matrix
118 | # participant_points - array of (round #, count), where count is
119 | # the cumulative number of participations by
120 | # the specific user at round #
121 | # round_point - number of participants per round
122 |
123 | # Candidates for participant vectors
124 |
125 | if not multiprocess:
126 | participant_vectors = []
127 | n_possibilities_per_user = []
128 | statuses = []
129 | cached_space = None
130 | nrounds = D.shape[0]
131 | for i, individual_participant_point in enumerate(participant_points):
132 | if top_k is not None and len(participant_vectors) >= top_k:
133 | break
134 | if verbose:
135 | print("Reconstructing: %d of %d" % (i,len(participant_points)))
136 | p_vector, model, cached_space = compute_participant_candidate_vectors(D, individual_participant_point, nrounds, len(participant_points), noisy=noisy, timelimit=column_timelimit, cached_space=cached_space)
137 | if model.status == GRB.TIME_LIMIT and exit_after_tle:
138 | if verbose:
139 | print("Time limit exceeded")
140 | return []
141 | participant_vectors.append(p_vector)
142 | n_possibilities_per_user.append(len(p_vector))
143 | if verbose:
144 | print("Obtained candidate vector for user %d" % (i))
145 | sys.stdout.flush()
146 | if len(p_vector) <= 0:
147 | return []
148 |
149 | if verbose:
150 | print("# of candidate vectors per user: %s" % str(n_possibilities_per_user))
151 |
152 | # Naive method -- just stack and return
153 | naive = np.stack([x[0] for x in participant_vectors]).T
154 | return [np.rint(naive)]
155 |
156 | # Multiprocessing code
157 | nrounds = D.shape[0]
158 | nusers = len(participant_points)
159 |
160 | cached_space = compute_space(D, nusers, noisy=noisy)
161 | arguments = []
162 | for i, participant_point in enumerate(participant_points):
163 | arguments.append((i, None, participant_point, nrounds, nusers, noisy, column_timelimit, False,cached_space, verbose, exit_after_tle))
164 | if top_k is not None:
165 | arguments = arguments[:top_k]
166 |
167 | cores = mp.cpu_count()
168 | pool = mp.Pool(processes=cores)
169 | try:
170 | indices_and_participant_vectors = pool.imap_unordered(compute_participant_candidate_vectors_multicore_wrapper, arguments)
171 | indices_and_participant_vectors = sorted(indices_and_participant_vectors, key=lambda x:x[0])
172 | participant_vectors = [x[1] for x in indices_and_participant_vectors]
173 | except Exception:
174 | if verbose:
175 | print("Timelimit exceeded on one of the workers. Exiting")
176 | pool.close()
177 | pool.terminate()
178 | participant_vectors = [np.zeros((1,nrounds)) for i in range(nusers)]
179 | else:
180 | pool.close()
181 | pool.join()
182 |
183 | participant_vectors = np.concatenate([x for x in participant_vectors], axis=0).T
184 | return [np.rint(participant_vectors)]
185 |
186 | def compute_space(D, nusers, noisy=True):
187 |
188 | # We use SVD to handle noisy gradients
189 | if noisy:
190 | u,s,vh = np.linalg.svd(D, full_matrices=False)
191 | cutoff = sorted(list(s.flatten()), reverse=True)[nusers]
192 | s[s= r)
271 |
272 | participant_points = compute_P_constraints(T, log_intervals)
273 |
274 | # Solve
275 | T_reconstructed_candidates = reconstruct_participant_matrix(D, participant_points, verbose=True)
276 | T_reconstructed = T_reconstructed_candidates[0]
277 | err = np.linalg.norm(T_reconstructed-T)
278 | print("Error between reconstructed vs truth: %f" %
279 | err)
280 | assert(err <= 1e-5)
281 |
282 | def test_recover_grad_sanity():
283 |
284 | # m - number of rounds
285 | # r - number of users
286 | # n - dimension of gradient
287 | # sparsity - percent participate per round
288 | # log_intervals - every log_intervals rounds will log how many times a user participated
289 | m = 5000
290 | r = 80
291 | n = 400
292 | sparsity=.1
293 | log_intervals = 2*int(1/sparsity)
294 |
295 | # Create data
296 | user_grads = np.random.normal(0, 1, size=(r,n))
297 |
298 | # Construct rounds
299 | P = []
300 | aggregated = []
301 | total = 0
302 | for round in range(m):
303 | row = generate_T(1, r, sparsity=sparsity)
304 | with_noise = user_grads + np.random.normal(0, .2, size=user_grads.shape)
305 | total += with_noise
306 | row_grads = row.dot(with_noise)
307 | P.append(row)
308 | aggregated.append(row_grads)
309 | P = np.concatenate(P, axis=0)
310 | aggregated = np.concatenate(aggregated, axis=0)
311 |
312 | print("Number of rounds: %d" % m)
313 | print("Number of users: %d" % r)
314 | print("Number of grad dims: %d" % n)
315 | print("Rank of participant matrix: %d" % np.linalg.matrix_rank(P))
316 | assert(np.linalg.matrix_rank(P) >= r)
317 |
318 | participant_points = compute_P_constraints(P, log_intervals)
319 |
320 | disaggregated, P = disaggregate_grads(aggregated, participant_points, verbose=True, gt=user_grads, gt_P=P)
321 | rel_err = relative_err(disaggregated, user_grads)
322 | print("Relative Error (percentage): %f" % rel_err)
323 |
324 |
325 | def test_recover_grad():
326 |
327 | # m - number of rounds
328 | # r - number of users
329 | # n - dimension of gradient
330 | # sparsity - percent participate per round
331 | # log_intervals - every log_intervals rounds will log how many times a user participated
332 | m = 400
333 | r = 40
334 | n = 400
335 | sparsity=.5
336 | log_intervals = int(1/sparsity)*5
337 | noise = .2
338 | mat_intervals = 100
339 |
340 | # Create data
341 | A = np.random.normal(1, .1, size=(r,n))
342 | Ds = []
343 | Ts = []
344 | for i in range(0, m, mat_intervals):
345 | random_noise = np.random.normal(0, noise, size=(r,n))
346 | T = generate_T(mat_intervals,r,sparsity=sparsity)
347 | Ts.append(T)
348 | Ds.append(T.dot(A+random_noise))
349 | D = np.concatenate(Ds, axis=0)
350 | T = np.concatenate(Ts, axis=0)
351 |
352 |
353 | print("Number of rounds: %d" % m)
354 | print("Number of users: %d" % r)
355 | print("Number of grad dims: %d" % n)
356 | print("Rank of participant matrix: %d" % np.linalg.matrix_rank(T))
357 | assert(np.linalg.matrix_rank(T) >= r)
358 |
359 | participant_points = compute_P_constraints(T, log_intervals)
360 |
361 | disaggregated, P = disaggregate_grads(D, participant_points, verbose=True, gt=A, interval=mat_intervals)
362 | rel_err = relative_err(disaggregated, A)
363 | print("Relative Error (percentage): %f" % rel_err)
364 |
365 | if __name__=="__main__":
366 |
367 | np.random.seed(0)
368 | #test_recover_p()
369 | #test_recover_grad()
370 | test_recover_grad_sanity()
371 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 9 |
9 |  9 |
9 |