├── resume
├── 公众号-程序员徐公.png
├── 模板1-姓名-公司-Android.docx
├── 模板1-姓名-公司-Android.pdf
├── 模板2-姓名-公司-Android.docx
├── 模板2-姓名-公司-Android.pdf
├── ~$1-姓名-公司-Android.docx
├── 模板2-姓名-公司-Android.md
└── 模板1-姓名-公司-Android.md
├── 剑指offer
├── 【Java】剑指offer(27)二叉树的镜像.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(55-1)二叉树的深度.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(65)不用加减乘除做加法.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(64)求1+2+…+n.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(42)连续子数组的最大和.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(53-3)数组中数值和下标相等的元素.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(30)包含min函数的栈.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(53-2)0到n-1中缺失的数字.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(31)栈的压入、弹出序列.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(33)二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(57-1)和为s的两个数字.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(28)对称的二叉树.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(61)扑克牌的顺子.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(54)二叉搜索树的第k个结点.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(58-2)左旋转字符串.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(66)构建乘积数组.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(68)树中两个结点的最低公共祖先.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(43)从1到n整数中1出现的次数.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(50-1)字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(47)礼物的最大价值.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(45)把数组排成最小的数.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(55-2)平衡二叉树.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(58-1)翻转单词顺序.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(25)合并两个排序的链表.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(26)树的子结构.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(38)字符串的排列.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(56-1)数组中只出现一次的两个数字.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(56-2)数组中唯一只出现一次的数字.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(48)最长不含重复字符的子字符串.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(46)把数字翻译成字符串.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(59-1)滑动窗口的最大值.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(37)序列化二叉树.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(44)数字序列中某一位的数字.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(51)数组中的逆序对.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(52)两个链表的第一个公共结点.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(24)反转链表.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(8)用两个栈实现队列.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(50-2)字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(23)链表中环的入口结点.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(63)股票的最大利润.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(62)圆圈中最后剩下的数字.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(41)数据流中的中位数.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(35)复杂链表的复制.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(53-1)数字在排序数组中出现的次数.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(4)替换空格.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(57-2)为s的连续正数序列.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(29)顺时针打印矩阵.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(36)二叉搜索树与双向链表.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(34)二叉树中和为某一值的路径.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(2)不修改数组找出重复的数字.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(67)把字符串转换成整数.md
├── 目录]《剑指Offer》Java实现.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(7)二叉树的下一个结点.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(14)二进制中1的个数.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(39)数组中出现次数超过一半的数字.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(15)数值的整数次方.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(59-2)队列的最大值.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(12)机器人的运动范围.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(19)正则表达式匹配.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(40)最小的k个数.md
├── 【Java】剑指offer(10)旋转数组的最小数字.md
└── 【Java】剑指offer(5)从尾到头打印链表.md
├── Android基础
└── Android面试必备-http与https协议.md
├── 国内使用chatgpt的使用教程.md
├── 国内使用chatgpt的使用教程(2023 年2月8号,亲测可用).md
└── leetcode
└── ArrayList
└── arraylist-leetcode-list.md
/resume/公众号-程序员徐公.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gdutxiaoxu/AndroidGuide/HEAD/resume/公众号-程序员徐公.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resume/模板1-姓名-公司-Android.docx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gdutxiaoxu/AndroidGuide/HEAD/resume/模板1-姓名-公司-Android.docx
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resume/模板1-姓名-公司-Android.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gdutxiaoxu/AndroidGuide/HEAD/resume/模板1-姓名-公司-Android.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resume/模板2-姓名-公司-Android.docx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gdutxiaoxu/AndroidGuide/HEAD/resume/模板2-姓名-公司-Android.docx
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resume/模板2-姓名-公司-Android.pdf:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gdutxiaoxu/AndroidGuide/HEAD/resume/模板2-姓名-公司-Android.pdf
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resume/~$1-姓名-公司-Android.docx:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | �Microsoft Office User����������������������������������M�i�c�r�o�s�o�f�t� �O�f�f�i�c�e� �U�s�e�r���D�e�s�k�t�o�p�/�g�i�t�P�r�o�j�e�c�t�/�m�y�-�g�i�t�h�u�b�/�A�n�
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resume/模板2-姓名-公司-Android.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 姓名
2 |
3 | 170 7777 7777 | xxx@gmail.com | github.com/xx | www.xx.com
4 |
5 | ---
6 |
7 | ### 个人经历
8 |
9 | #### 20xx/xx—至今
10 |
11 | codeKK2 公司 | Android 资深开发
12 |
13 | 工作描述:带领移动团队负责 xx,取得了什么成绩
14 |
15 | #### 20xx/xx—20xx/xx
16 |
17 | codeKK1 公司 | Android 高级开发
18 |
19 | 工作描述:负责 xx 产品,取得了什么成绩
20 |
21 | #### 20xx/xx—20xx/xx
22 |
23 | XXX 学校 | XX 专业 | 本科
24 |
25 | 专业排名:x/xxx GPA:
26 |
27 |
28 | ---
29 |
30 |
31 | ### 专业技能
32 |
33 | * x 年团队管理经验,x 年开发经验,x 年移动开发经验
34 | * 开源 xx 项目,用于 xx,多少 Star,多少 Contributors
35 | * 博客主要分享 xx xx
36 | * 熟悉 Android 应用框架设计,熟悉 Android 高性能编程及调优
37 | * 熟悉xx 技术点,xx 技术点,xx 技术点
38 |
39 | ---
40 |
41 | ### 项目经验
42 |
43 | #### 20xx/xx—至今 | codeKK2 公司 | XX 项目
44 |
45 | 项目简介:
46 |
47 |
48 | 职责:
49 |
50 | *
51 | *
52 | *
53 |
54 | #### 20xx/xx—至今 | codeKK2 公司 | XX 项目
55 |
56 | 项目简介:
57 |
58 |
59 | 职责:
60 |
61 | *
62 | *
63 | *
64 |
65 | #### 20xx/xx—至今 | codeKK1 公司 | XX 项目
66 |
67 | 项目简介:
68 |
69 |
70 | 职责:
71 |
72 | *
73 | *
74 | *
75 |
76 | ---
77 |
78 | ### 在校经历
79 |
80 | * XX大赛 XX 奖
81 | * XX 系统设计、开发
82 | * XXX 奖学金
83 |
84 |
85 | > 微信公众号:程序员徐公,Android 学习+面试指南:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/AndroidGuide
86 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/resume/模板1-姓名-公司-Android.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## 姓名
2 |
3 | Phone: 170 7777 7777 Email: XXX@gmail.com
4 |
5 | GitHub: github.com/XX Blog: www.XX.com
6 |
7 | ---
8 |
9 | ### 个人经历
10 |
11 | #### 20xx/xx-至今 codeKK2 公司 Android 资深开发
12 |
13 | 带领移动团队负责 xx,取得了什么成绩
14 |
15 | #### 20xx/xx-20xx/xx codeKK1 公司 Android 高级开发
16 |
17 | 负责 xx 产品,取得了什么成绩
18 |
19 | #### 20xx/xx-20xx/xx XX 学校 本科
20 |
21 | xx工程专业
22 |
23 | 专业排名: x/xx GPA:
24 |
25 | ---
26 |
27 | ### 专业技能
28 |
29 |
30 | * x 年团队管理经验,x 年开发经验,x 年移动开发经验
31 | * 开源 xx 项目,用于 xx,多少 Star,多少 Contributors
32 | * 博客主要分享 xx xx
33 | * 熟悉 Android 应用框架设计,熟悉 Android 高性能编程及调优
34 | * 熟悉 xx 技术点,xx 技术点,xx 技术点
35 |
36 | ---
37 |
38 | ### 项目经历
39 |
40 | #### 20xx/xx-20xx/xx XX 项目 codeKK2 公司
41 |
42 | ##### 项目简介:
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 | ##### 职责:
47 |
48 | *
49 |
50 | #### 20xx/xx-20xx/xx XX 项目 codeKK1 公司
51 |
52 | ##### 项目简介:
53 |
54 |
55 |
56 | ##### 职责:
57 |
58 | *
59 | #### 20xx/xx-20xx/xx XX 项目 codeKK1 公司
60 |
61 | ##### 项目简介:
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 | ##### 职责:
66 |
67 | *
68 |
69 | ---
70 |
71 | ### 在校经历
72 |
73 | * XX 比赛 XX 奖
74 | * XX 系统设计、开发
75 | * XXX 奖学金
76 |
77 |
78 | > 微信公众号:程序员徐公,Android 学习+面试指南:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/AndroidGuide
79 |
80 |
81 |
82 |
83 |
84 |
85 |
86 |
87 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(27)二叉树的镜像.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(27) 二叉树的镜像
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 请完成一个函数,输入一个二叉树,该函数输出它的镜像。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 画图可以很清晰地得到思路:先前序遍历,对每个结点交换左右子结点。
16 |
17 | **测试算例** ****
18 |
19 | 1.功能测试(普通二叉树;左斜树;右斜树;一个结点)
20 |
21 | 2.特殊测试(根结点为null;)
22 |
23 | ## **Java代码**
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | //题目:请完成一个函数,输入一个二叉树,该函数输出它的镜像。
28 |
29 | public class MirrorOfBinaryTree {
30 | public class TreeNode {
31 | int val = 0;
32 | TreeNode left = null;
33 | TreeNode right = null;
34 | public TreeNode(int val) {
35 | this.val = val;
36 | }
37 | }
38 |
39 | public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
40 | if(root==null)
41 | return;
42 | //左右子结点交换
43 | TreeNode tempNode = root.left;
44 | root.left=root.right;
45 | root.right=tempNode;
46 |
47 | Mirror(root.left);
48 | Mirror(root.right);
49 | }
50 | }
51 |
52 |
53 | ## **收获**
54 |
55 | 画图使抽象问题形象化,面试时要在编程前先用画图、举例子等来解释思路。
56 |
57 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
58 |
59 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
60 |
61 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(55-1)二叉树的深度.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(55-1) 二叉树的深度
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 输入一棵二叉树的根结点,求该树的深度。从根结点到叶结点依次经过的/结点(含根、叶结点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 简洁理解:
18 |
19 | 树的深度=max(左子树深度,右子树深度)+1,采用递归实现。
20 |
21 | **测试算例** ****
22 |
23 | 1.功能测试(左斜树、右斜树、普通树)
24 |
25 | 2.边界值测试(一个结点)
26 |
27 | 3.特殊测试(null)
28 |
29 | ## **Java代码**
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | //题目:输入一棵二叉树的根结点,求该树的深度。从根结点到叶结点依次经过的
34 | //结点(含根、叶结点)形成树的一条路径,最长路径的长度为树的深度。
35 |
36 | public class TreeDepth {
37 | public class TreeNode {
38 | int val = 0;
39 | TreeNode left = null;
40 | TreeNode right = null;
41 |
42 | public TreeNode(int val) {
43 | this.val = val;
44 | }
45 | }
46 |
47 | public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {
48 | if(root==null)
49 | return 0;
50 | int left=TreeDepth(root.left);
51 | int right=TreeDepth(root.right);
52 | return Math.max(left+1,right+1);
53 | }
54 | }
55 |
56 |
57 | ## **收获**
58 |
59 | 1.深度从递归的角度理解,很赞,要记住。
60 |
61 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
62 |
63 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
64 |
65 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(65)不用加减乘除做加法.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(65) 不用加减乘除做加法
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | [leetcode](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/bu-yong-jia-jian-cheng-chu-zuo-jia-fa-lcof/solution/mian-shi-ti-65-bu-yong-jia-jian-cheng-chu-zuo-ji-7/)
12 |
13 | ## 题目
14 |
15 | 写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用+、-、×、÷四则运算符号。
16 |
17 | ## 思路
18 |
19 | 对数字做运算,除了四则运算外,只剩下位运算了。根据一般情况下的加法步骤,设计如下:
20 |
21 | 1)不考虑进位对每一位相加:1加0,0加1都等于1,而0加0,1加1等于0,所以使用异或^操作;
22 |
23 | 2)计算进位:只有1加1产生进位,所以采用位与 &操作,再左移1位;
24 |
25 | 3)将和与进位相加,即重复前两步操作。结束判断为进位为0。
26 |
27 | **测试代码**
28 |
29 | 1.正负零
30 |
31 | ## **Java代码**
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 | //题目:写一个函数,求两个整数之和,要求在函数体内不得使用+、-、×、÷
36 | //四则运算符号。
37 |
38 | public class AddTwoNumbers {
39 | public int add(int num1,int num2) {
40 | while(num2!=0){
41 | int sum=num1^num2; //没进位的和
42 | int carry=(num1&num2)<<1; //进位
43 | num1=sum;
44 | num2=carry;
45 | }
46 | return num1;
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
50 |
51 | ## **收获**
52 |
53 | 1.熟悉位操作的特性二进制位运算的几个用法:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9971520.html
54 |
55 | 2.记住如何用位操作来进行数字的加减。
56 |
57 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
58 |
59 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
60 |
61 | 
62 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(64)求1+2+…+n.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(64) 求1+2+…+n
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 求1+2+…+n,要求不能使用乘除法、for、while、if、else、switch、case等关键字及条件判断语句(A?B:C)。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 不能使用乘除法,不能使用循环语句、判断语句。可以考虑的有 单目运算符:++和--,双目运算符:+,-,移位运算符
18 | <<和>>,关系运算符>,<等,逻辑运算符&&,||,&,|,^,赋值=
19 |
20 | 最有可能使用到的就是逻辑运算符了。如果记得它们有短路特性的话,就可以当作if来使用了。
21 |
22 | 例如:对于A && B,如果A为假,那么就不执行B了;而如果A为真,就会执行B。
23 |
24 | 对于A || B,如果A为真,那么就会不执行B了;而如果A为假,就会执行B。
25 |
26 | 因此我们使用递归来代替循环,用逻辑运算符&&或者||来代替判断语句。
27 |
28 | 代码实现功能为:当n大于1时,和为f(n)=f(n-1)+n,n=1时,f(n)=1
29 |
30 | ## **Java代码**
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 | //题目:求1+2+…+n,要求不能使用乘除法、for、while、if、else、switch、case
35 | //等关键字及条件判断语句(A?B:C)。
36 |
37 | public class Accumulate {
38 | public int getSum(int n) {
39 | int sum=n;
40 | boolean flag = (n>1) && ((sum+=getSum(n-1))>0);
41 | //上面这句话相当于:
42 | //if(n>1)
43 | // sum+=getSum(n-1);
44 |
45 | //也可以使用||来实现
46 | //boolean flag = (n==1) || ((sum+=getSum(n-1))>0);
47 | return sum;
48 | }
49 | }
50 |
51 |
52 | ## **收获**
53 |
54 | 1.学会利用 &&和||的短路特性来代替判断语句;
55 |
56 | 2.使用短路特性时,记得后面的判断语句要写完整
57 |
58 | 即:不能只写了`(sum+=getSum(n-``1``)),要完整写出`(sum+=getSum(n-``1``))``>``0``
59 |
60 | 还有就是前面要赋值给flag才算完整的语句。
61 |
62 | 3.利用递归来代替循环。
63 |
64 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
65 |
66 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
67 |
68 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(42)连续子数组的最大和.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(42) 连续子数组的最大和
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入一个整型数组,数组里有正数也有负数。数组中一个或连续的多个整/数组成一个子数组。求所有子数组的和的最大值。要求时间复杂度为O(n)。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 分析规律,从第一个数字开始累加,若走到某一个数字时,前面的累加和为负数,说明不能继续累加了,要从当前数字重新开始累加。在累加过程中,将每次累加和的最大值记录下来,遍历完成后,返回该数字。
16 |
17 | **测试算例** ****
18 |
19 | 1.功能测试(输入数组有正有负,全负数,全正数)
20 |
21 | 2.特殊输入测试(null)
22 |
23 | ## **Java代码**
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | //题目:输入一个整型数组,数组里有正数也有负数。数组中一个或连续的多个整
28 | //数组成一个子数组。求所有子数组的和的最大值。要求时间复杂度为O(n)。
29 |
30 | public class GreatestSumOfSubarrays {
31 | boolean InvalidInput = false;
32 | public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] array) {
33 | if(array==null || array.length<=0){
34 | InvalidInput = true;
35 | return 0;
36 | }
37 | InvalidInput = false;
38 | int sum=array[0];
39 | int maxSum=array[0];
40 | for(int i=1;imaxSum)
46 | maxSum=sum;
47 | }
48 | return maxSum;
49 | }
50 | }
51 |
52 |
53 | ## **收获**
54 |
55 | 1.复杂度要求为O(n),考虑是否可以从头开始遍历,找规律。
56 |
57 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
58 |
59 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
60 |
61 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(53-3)数组中数值和下标相等的元素.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(53-3) 数组中数值和下标相等的元素
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 假设一个单调递增的数组里的每个元素都是整数并且是唯一的。请编程实现一个函数找出数组中任意一个数值等于其下标的元素。例如,在数组{-3, -1,1, 3,
14 | 5}中,数字3和它的下标相等。
15 |
16 | ## 思路
17 |
18 | 53-1](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9957949.html)和[53-2:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9958093.html一样,不再从头到尾遍历,由于是排序数组,我们继续考虑使用二分查找算法:
19 |
20 | 1)当中间数字等于其下标时,中间数字即为所求数字;
21 |
22 | 2)当中间数字大于其下标时,在左半部分区域寻找;
23 |
24 | 2)当中间数字小于其下标时,在右半部分区域寻找;
25 |
26 | **测试算例** ****
27 |
28 | 1.功能测试(包含/不包含与下标相等的数字)
29 |
30 | 2.边界值测试(数字位于数组开头、中间或者结尾;仅一个数字数组)
31 |
32 | 2.特殊测试(null)
33 |
34 | ## **Java代码**
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | //题目:假设一个单调递增的数组里的每个元素都是整数并且是唯一的。请编程实
39 | //现一个函数找出数组中任意一个数值等于其下标的元素。例如,在数组{-3, -1,
40 | //1, 3, 5}中,数字3和它的下标相等。
41 |
42 | public class IntegerIdenticalToIndex {
43 | public int getNumberSameAsIndex(int[] arr) {
44 | if(arr==null || arr.length<=0)
45 | return -1; //代表错误
46 | int low=0;
47 | int high=arr.length-1;
48 | while(low<=high) {
49 | int mid= (high+low)>>1;
50 | if(arr[mid]>mid)
51 | high=mid-1;
52 | else if(arr[mid] 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈的最小元素的min函数。在该栈中,调用min、push及pop的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 最初想法是定义一个成员变量min来存放最小元素,但是当最小元素弹出后,min就需要相应改变,所以必须把每次的最小值都存储下来。考虑采用一个辅助栈来存放最小值:
16 |
17 | 栈 3,4,2,5,1
18 |
19 | 辅助栈 3, 3,2,2,1
20 |
21 | (压入时,把每次的最小元素(之前最小元素与新入栈元素的较小值)保存起来放到辅助栈中)
22 |
23 | **测试算例** ****
24 |
25 | 1.新压入数字更大
26 |
27 | 2.新压入数字最小
28 |
29 | 3.弹出数字最小
30 |
31 | 4.弹出数字不是最小
32 |
33 | ## **Java代码**
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 | //题目:定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈的最小元素的min
38 | //函数。在该栈中,调用min、push及pop的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
39 |
40 | public class StackWithMin {
41 |
42 | Stack stack_data=new Stack();
43 | Stack stack_min=new Stack();
44 |
45 | public void push(int node) {
46 | stack_data.push(node);
47 | if(stack_min.empty() || stack_min.peek()>node) {
48 | stack_min.push(node);
49 | }else {
50 | stack_min.push(stack_min.peek());
51 | }
52 | }
53 |
54 | public void pop() {
55 | if(!stack_data.empty()) {
56 | stack_data.pop();
57 | stack_min.pop();
58 | }
59 | }
60 |
61 | public int min() {
62 | return stack_min.peek();
63 | }
64 | }
65 |
66 |
67 | ## **收获**
68 |
69 | 要学会这种情况下辅助栈的用法。
70 |
71 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
72 |
73 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
74 |
75 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(53-2)0到n-1中缺失的数字.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(53-2) 0到n-1中缺失的数字
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 一个长度为n-1的递增排序数组中的所有数字都是唯一的,并且每个数字都在范围0到n-1之内。在范围0到n-1的n个数字中有且只有一个数字不在该数组中,请找出这个数字。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 分析易知,数组形式如下:
18 |
19 | 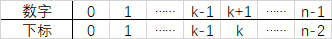
20 |
21 | 如果从头到尾依次比较值与小标是否相等,时间复杂度为O(n),效率低。
22 |
23 | 由于是排序数组,我们继续考虑使用二分查找算法,结合上图可知:
24 |
25 | 当中间数字等于其下标时,我们在后半部分查找;
26 |
27 | 当中间数字不等于其下标时,
28 |
29 | 1)如果中间数字的前一个数字也不等于其下标,则在前半部分查找;
30 |
31 | 2)如果中间数字的前一个数字等于其下标,则说明中间数字的下标即为我们所要找的数字。
32 |
33 | **测试算例** ****
34 |
35 | 1.功能测试(缺失数字位于数组开头、中间或者结尾)
36 |
37 | 2.边界值测试(数字只有0或1)
38 |
39 | 2.特殊测试(null)
40 |
41 | ## **Java代码**
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 | //题目:一个长度为n-1的递增排序数组中的所有数字都是唯一的,并且每个数字
46 | //都在范围0到n-1之内。在范围0到n-1的n个数字中有且只有一个数字不在该数组
47 | //中,请找出这个数字。
48 |
49 | public class MissingNumber {
50 | public int getMissingNumber(int[] arr) {
51 | if(arr==null || arr.length<=0)
52 | return -1;
53 | int low=0;
54 | int high=arr.length-1;
55 | while(low<=high) {
56 | int mid=(low+high)>>1;
57 | if(arr[mid]!=mid) {
58 | if(mid==0 || arr[mid-1]==mid-1)
59 | return mid;
60 | high=mid-1;
61 | }else {
62 | low=mid+1;
63 | }
64 | }
65 | return -1;
66 | }
67 | }
68 |
69 |
70 | ## **收获**
71 |
72 | 1.53-3:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9958138.html#_label3
73 |
74 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
75 |
76 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
77 |
78 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(31)栈的压入、弹出序列.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(31) 栈的压入、弹出序列
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1、2、3、4、5是某栈的压栈序列,序列4、5、3、2、1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但4、3、5、1、2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 建立一个栈,按照压栈序列依次进行入栈操作,按出栈序列的顺序依次弹出数字。在出栈时,若下一个要出栈的数字与栈顶数字相同则弹出。如果压栈序列中的所有数字都入栈后没有完全出栈成功则代表两个序列不匹配,返回false。
16 |
17 | **测试算例** ****
18 |
19 | 1.功能测试(两个数组长度不同;两个数组对应;两个数组不对应)
20 |
21 | 2.特殊测试(数组为空;null;一个数字的数组)
22 |
23 | ## **Java代码**
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | //题目:输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是
28 | //否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如序列1、2、3、4、
29 | //5是某栈的压栈序列,序列4、5、3、2、1是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但
30 | //4、3、5、1、2就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
31 |
32 | public class StackPushPopOrder {
33 | public boolean isPopOrder(int [] pushA,int [] popA) {
34 | if(pushA==null || popA==null)
35 | return false;
36 | Stack stack = new Stack();
37 | //必须提前判断长度是否相等
38 | if(popA.length!=pushA.length || pushA.length==0)
39 | return false;
40 | int popIndex=0;
41 | for(int pushIndex=0; pushIndex 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。如果是则返回true,否则返回false。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 二叉树后序遍历数组的最后一个数为根结点,剩余数字中,小于根结点的数字(即左子树部分)都排在前面,大于根结点的数字(即右子树部分)都排在后面。根据遍历数组的这个特性,可以编写出一个递归函数,用于实现题目所要求的判断功能。
16 |
17 | **测试算例** ****
18 |
19 | 1.功能测试(左斜树;右斜树;能对应的二叉树;不能对应的二叉树序列)
20 |
21 | 2.特殊测试(null;一个结点)
22 |
23 | ## **Java代码**
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | //题目:输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历的结果。
28 | //如果是则返回true,否则返回false。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
29 |
30 | public class SquenceOfBST {
31 | public boolean verifySquenceOfBST(int[] sequence) {
32 | if(sequence== null || sequence.length<=0)
33 | return false;
34 | return verifyCore(sequence, 0, sequence.length-1);
35 | }
36 |
37 | private boolean verifyCore(int[] sequence,int start,int end) {
38 | if(start>=end)
39 | return true;
40 | //判断左子树
41 | int mid=start;
42 | while(sequence[mid] 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字s,在数组中查找两个数,使得它们的和正好是s。如果有多对数字的和等于s,输出任意一对即可。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 从头开始遍历数字,确定一个数字后,对后面的数字遍历,判断和是否为s,这种方法复杂度为O(n^2),效率太低。
18 |
19 | 我们考虑到,如果一个数字比较小,那么另一个数字一定比较大,同时数字为递增排列;所以,我们设置两个指针,一个指针small从第一个数字(最小)出发,另一个指针big从最后一个数字(最大)出发:
20 |
21 | 当small加big的和小于s时,只需要将small指向后一个数字(更大),继续判断;
22 |
23 | 当small加big的和大于s时,只需要将big指向前一个数字(更小),继续判断;
24 |
25 | 当small加big的和等于s时,求解完成。
26 |
27 | 由于是从两边往中间移动,所以不会有跳过的情况,时间复杂度为 **O(n)** 。
28 |
29 | **测试算例** ****
30 |
31 | 1.功能测试(存在/不存在和为s的一对数字)
32 |
33 | 2.特殊输入测试(null)
34 |
35 | ## **Java代码**
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | //题目:输入一个递增排序的数组和一个数字s,在数组中查找两个数,使得它们
40 | //的和正好是s。如果有多对数字的和等于s,输出任意一对即可。
41 |
42 | public class TwoNumbersWithSum {
43 | public ArrayList FindNumbersWithSum(int [] array,int sum) {
44 | ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
45 | if(array==null || array.length<=0)
46 | return list;
47 | int low=0;
48 | int high=array.length-1;
49 | while(low 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 请实现一个函数,用来判断一棵二叉树是不是对称的。如果一棵二叉树和它的镜像一样,那么它是对称的。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 还是画图分析,不用分析根结点,只需要分析左右子树。可以看出,左右子树刚好是呈镜像的两颗二叉树,所以:对左子树采用(父-左-右)的前序遍历,右子树采用(父-右-左)的前序遍历,遍历时判断两个结点位置的值是否相等即可。(也可以这样理解:左树的左子树等于右树的右子树,左树的右子树等于右树的左子树,对应位置刚好相反,判断两子树相反位置上的值是否相等即可)
16 |
17 | **测试算例** ****
18 |
19 | 1.功能测试(对称二叉树;结构不对称二叉树;结构对称但值不对称二叉树)
20 |
21 | 2.特殊测试(根结点为null;单个结点;所有结点的值都相等的二叉树)
22 |
23 | ## **Java代码**
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | //题目:请实现一个函数,用来判断一棵二叉树是不是对称的。如果一棵二叉树和
28 | //它的镜像一样,那么它是对称的。
29 |
30 | public class SymmetricalBinaryTree {
31 | public class TreeNode {
32 | int val = 0;
33 | TreeNode left = null;
34 | TreeNode right = null;
35 | public TreeNode(int val) {
36 | this.val = val;
37 |
38 | }
39 | }
40 |
41 | public boolean isSymmetrical(TreeNode pRoot){
42 | if(pRoot==null)
43 | return true; //根结点为null时,认为是对称二叉树
44 | return isEqual(pRoot.left,pRoot.right);
45 | }
46 |
47 | private boolean isEqual(TreeNode pRoot1,TreeNode pRoot2){
48 | if(pRoot1==null && pRoot2==null)
49 | return true;
50 | if(pRoot1==null || pRoot2==null)
51 | return false;
52 | return pRoot1.val==pRoot2.val
53 | && isEqual(pRoot1.left, pRoot2.right)
54 | && isEqual(pRoot1.right, pRoot2.left);
55 | }
56 | }
57 |
58 |
59 | ## **收获**
60 |
61 | 画图使抽象问题形象化,本题还是相当于对数的遍历算法的理解。
62 |
63 | 这道题主要突破点在于看出左右两个子树数值刚好呈镜像,相反位置对比即可。
64 |
65 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
66 |
67 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
68 |
69 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(61)扑克牌的顺子.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(61) 扑克牌的顺子
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 从扑克牌中随机抽5张牌,判断是不是一个顺子,即这5张牌是不是连续的。2~10为数字本身,A为1,J为11,Q为12,K为13,而大、小王可以看成任意数字。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 输入为大小等于5的数组(大小王记为0),输出为布尔值。具体步骤如下:
18 |
19 | 1)进行对5张牌进行排序;
20 |
21 | 2)找出0的个数;
22 |
23 | 3)算出相邻数字的空缺总数;
24 |
25 | 4)如果0的个数大于等于空缺总数,说明连续,反之不连续;
26 |
27 | 5)记得判断相邻数字是否相等,如果有出现相等,说明不是顺子。
28 |
29 | **测试算例** ****
30 |
31 | 1.功能测试(没有/有一个/多个大小王,有对子,连续/不连续)
32 |
33 | 2.特殊测试(null)
34 |
35 | ## **Java代码**
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | //题目:从扑克牌中随机抽5张牌,判断是不是一个顺子,即这5张牌是不是连续的。
40 | //2~10为数字本身,A为1,J为11,Q为12,K为13,而大、小王可以看成任意数字。
41 |
42 | public class ContinousCards {
43 | public boolean isContinuous(int [] numbers) {
44 | if(numbers==null || numbers.length<=0)
45 | return false;
46 | Arrays.sort(numbers);
47 | int numberOf0 = 0;
48 | int numberOfGap = 0;
49 | for(int i=0;i=numberOfGap) //大于等于,而不是等于!
61 | return true;
62 | return false;
63 | }
64 | }
65 |
66 |
67 | ## **收获**
68 |
69 | 1.这道题中,自己最开始想的是把0插入到空缺当中,当其实只要计算出0的个数和空缺的个数进行比较即可,有时候稍微转换一下思路就豁然开朗了。
70 |
71 | 2.对数组排序,采用Arrays.sort(numbers)方法(快排原理)。
72 |
73 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
74 |
75 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
76 |
77 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(54)二叉搜索树的第k个结点.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(54) 二叉搜索树的第k个结点
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中的第k小的结点。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 设置全局变量index=0,对BST进行中序遍历,每遍历一个结点,index+1,当index=k时,该结点即为所求结点。
16 |
17 | **测试算例** ****
18 |
19 | 1.功能测试(左斜树、右斜树、普通树)
20 |
21 | 2.边界值测试(k=1,k=结点数目)
22 |
23 | 3.特殊测试(null,k <=0,k>结点数目)
24 |
25 | ## **Java代码**
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 | //题目:给定一棵二叉搜索树,请找出其中的第k大的结点。
30 |
31 | public class KthNodeInBST {
32 | public class TreeNode {
33 | int val = 0;
34 | TreeNode left = null;
35 | TreeNode right = null;
36 |
37 | public TreeNode(int val) {
38 | this.val = val;
39 | }
40 | }
41 |
42 | int index=0;
43 |
44 | TreeNode KthNode(TreeNode pRoot, int k){
45 | TreeNode pNode = null;
46 | if(pRoot==null || k<=0)
47 | return pNode;
48 | pNode = getKthNode(pRoot,k);
49 | return pNode;
50 | }
51 |
52 | private TreeNode getKthNode(TreeNode pRoot, int k){
53 | TreeNode kthNode=null;
54 |
55 | if(pRoot.left!=null)
56 | kthNode=getKthNode(pRoot.left,k);
57 |
58 | if(kthNode==null){
59 | index++;
60 | if(k==index)
61 | kthNode = pRoot;
62 | }
63 |
64 | if(kthNode==null && pRoot.right!=null)
65 | kthNode=getKthNode(pRoot.right,k);
66 |
67 | return kthNode;
68 | }
69 | }
70 |
71 |
72 | ## **收获**
73 |
74 | 1.熟练掌握二叉搜索树和中序遍历。
75 |
76 | 2.用中序遍历实现功能时,一定要注意返回值是否满足要求。
77 |
78 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
79 |
80 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
81 |
82 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(58-2)左旋转字符串.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(58-2) 左旋转字符串
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 字符串的左旋转操作是把字符串前面的若干个字符转移到字符串的尾部。请定义一个函数实现字符串左旋转操作的功能。比如输入字符串"abcdefg"和数字2,该函数将返回左旋转2位得到的结果"cdefgab"。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 最初的想法是令chars[i] =
18 | chars[i+n],将后面的数字都往前移,最后面空出的位置放入前面的数字,如abcdef,n=2时,将c放入a的位置,e放入c的位置,a放入e的位置,b也同理,就可以得到cdefab了。但是这没有考虑到最后空出的位置是否正确,例如abcdefg中,同样的方法将会得到cdeba,答案错误,就是因为后面的位置对应不上。思路错误!
19 |
20 | 正确思路:本题思路和上一道翻转单词顺序:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9963135.html的原理一模一样,只是上一道题有空格,这道题没空格,其实这道题还更简单。先分别翻转前半部分字符串和后半部分字符串,最后翻转整个字符串即可。
21 |
22 | **测试算例** ****
23 |
24 | 1.功能测试(对长度为n的字符串,左旋转-1,0,1,2,n-1,n,n+1位)
25 |
26 | 2.边界值测试(null)
27 |
28 | ## **Java代码**
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 | //题目:字符串的左旋转操作是把字符串前面的若干个字符转移到字符串的尾部。
33 | //请定义一个函数实现字符串左旋转操作的功能。比如输入字符串"abcdefg"和数
34 | //字2,该函数将返回左旋转2位得到的结果"cdefgab"。
35 |
36 | public class LeftRotateString {
37 | public String leftRotateString(char[] chars,int n) {
38 | if(chars==null ||chars.length<=0)
39 | return String.valueOf(chars);
40 | if(n<=0 || n>chars.length)
41 | return String.valueOf(chars);
42 | reverse(chars,0,n-1);
43 | reverse(chars,n,chars.length-1);
44 | reverse(chars,0,chars.length-1);
45 | return String.valueOf(chars);
46 | }
47 |
48 | private void reverse(char[] chars, int start,int end){
49 | while(start 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 给定一个数组A[0, 1, …, n-1],请构建一个数组B[0, 1, …, n-1],其中B中的元素B[i] =A[0]×A[1]×…
14 | ×A[i-1]×A[i+1]×…×A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
15 |
16 | ## 思路
17 |
18 | 无法使用除法,正常连乘的话时间复杂度为 **O(n^2)** ,效率非常低。
19 |
20 | 考虑到计算每个B[i]时都会有重复,思考B[i]之间的联系,找出规律,提高效率。
21 |
22 | 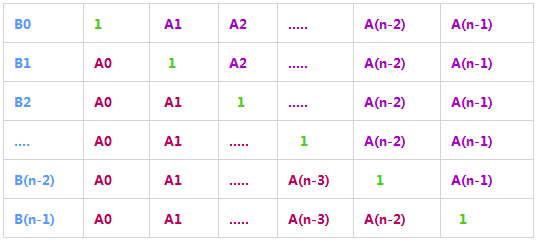
23 |
24 | 图片转构建乘积数组:https://www.cnblogs.com/wxdjss/p/5448990.html
25 |
26 | 如上图所示,可以发现:
27 |
28 | B[i]的左半部分(红色部分)和B[i-1]有关(将B[i]的左半部分乘积看成C[i],有C[i]=C[i-1]*A[i-1]),
29 |
30 | B[i]的右半部分(紫色部分)与B[i+1]有关(将B[i]的右半部分乘积看成D[i],有D[i]=D[i+1]*A[i+1]),
31 |
32 | 因此我们先从0到n-1遍历,计算每个B[i]的左半部分;
33 | 然后定义一个变量temp代表右半部分的乘积,从n-1到0遍历,令B[i]*=temp,而每次的temp与上次的temp关系即为temp*=A[i+1]。
34 |
35 | **测试代码**
36 |
37 | 1.功能测试(正、负、零)
38 |
39 | 2.边界值测试(数组长度为2)
40 |
41 | 3.特殊测试(null,数组长度为1,0)
42 |
43 | ## **Java代码**
44 |
45 |
46 |
47 | //题目:给定一个数组A[0, 1, …, n-1],请构建一个数组B[0, 1, …, n-1],其
48 | //中B中的元素B[i] =A[0]×A[1]×… ×A[i-1]×A[i+1]×…×A[n-1]。不能使用除法。
49 |
50 | public class ConstuctArray {
51 | public int[] multiply(int[] A) {
52 | if(A==null || A.length<2)
53 | return null;
54 | int[] B=new int[A.length];
55 | B[0]=1;
56 | for(int i=1;i=0;i--){
60 | temp*=A[i+1];
61 | B[i]*=temp;
62 | }
63 | return B;
64 | }
65 | }
66 |
67 |
68 | ## **收获**
69 |
70 | 1.考虑到了数组B中的元素间有关系,要进一步分析。本题就是采用画图的方法,将B看成一个矩阵,就能轻易地看出元素之间的关系了。好好学习。
71 |
72 | 2.可以直接从头到尾再从尾到头遍历,不需要创建两个临时数组C[]和D[]。自己写代码时,要尽量设计不用创建太多内存空间。
73 |
74 | 3.如果这道题可以用除法的话,记得除数不能为零!
75 |
76 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
77 |
78 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
79 |
80 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(68)树中两个结点的最低公共祖先.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(68) 树中两个结点的最低公共祖先
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 输入两个树结点,求它们的最低公共祖先。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 该题首先要和面试官确定是否为二叉树,得到肯定答复后,还要确定是否为二叉搜索树,是否有父指针,或者仅仅是普通二叉树。
18 |
19 | 1.树为二叉搜索树时,最低公共祖先结点的大小在两个树结点大小的中间。
20 |
21 | 2.树为普通树时,使用遍历将子结点的信息往上传递。在左右子树中进行查找是否存在两个树结点,如果两个树结点分别在左右子树上,说明该根结点就是它们的最低公共祖先。
22 |
23 | **测试用例**
24 |
25 | 1.功能测试(普通树,左斜树,右斜树)
26 |
27 | 2.特殊测试(null)
28 |
29 | ## **Java代码**
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | /*
34 | * 二叉搜索树
35 | * 利用大小关系即可
36 | */
37 | public TreeNode getLowestCommonParentBST(TreeNode root,TreeNode node1,TreeNode node2) {
38 | while(true) {
39 | if(root==null)
40 | return root;
41 | if(root.valnode1.val && root.val>node2.val)
44 | root=root.right;
45 | else
46 | return root;
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
50 |
51 | /*
52 | * 普通二叉树
53 | * 将下面结点的信息利用递归s往上传递
54 | */
55 | public TreeNode getLowestCommonParent(TreeNode root,TreeNode node1,TreeNode node2) {
56 | if(root==null || root== node1 || root== node2)
57 | return root;
58 | TreeNode left=getLowestCommonParent(root.left, node1, node2);
59 | TreeNode right=getLowestCommonParent(root.right, node1, node2);
60 | return left==null? right:right==null? left:root;
61 | // 上面这句代码就是:
62 | // if(left==null) {
63 | // return right;
64 | // }else {
65 | // if(right==null)
66 | // return left;
67 | // else
68 | // return root;
69 | // }
70 | }
71 |
72 |
73 | ## **收获**
74 |
75 | 1.《剑指OFFER》一书中的方法:普通二叉树时,可以采用链表来存储从根结点到两个树结点的路径,找出两条路径的最后公共结点,就是最低公共祖先。这个方法也要学会。
76 |
77 | 2.这里的方法根据特性:两个树结点分别在左右子树上时,该根结点就是最低公共祖先;非常方便,一定要掌握。
78 |
79 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
80 |
81 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
82 |
83 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(43)从1到n整数中1出现的次数.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(43) 从1到n整数中1出现的次数
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入一个整数n,求从1到n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数。例如输入12,从1到12这些整数中包含1 的数字有1,10,11和12,1一共出现了5次。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 如果是从头到尾遍历(n次),对每一个数字都计算其1的个数(lgn次),则时间复杂度为 **O(nlogn)** ,运算效率太低。因此必须总结规律,提高效率。
16 |
17 | 总结规律如下(思路比《剑指OFFER》一书简单):
18 |
19 | 对于整数n,我们将这个整数分为三部分:当前位数字cur,更高位数字high,更低位数字low,如:对于n=21034,当位数是十位时,cur=3,high=210,low=4。
20 |
21 | 我们从个位到最高位 依次计算每个位置出现1的次数:
22 |
23 | 1)当前位的数字等于0时,例如n=21034,在百位上的数字cur=0,百位上是1的情况有:00100~00199,01100~01199,……,20100~20199。一共有21*100种情况,即high*100;
24 |
25 | 2)当前位的数字等于1时,例如n=21034,在千位上的数字cur=1,千位上是1的情况有:01000~01999,11000~11999,21000~21034。一共有2*1000+(34+1)种情况,即high*1000+(low+1)。
26 |
27 | 3)当前位的数字大于1时,例如n=21034,在十位上的数字cur=3,十位上是1的情况有:00010~00019,……,21010~21019。一共有(210+1)*10种情况,即(high+1)*10。
28 |
29 | 这个方法只需要遍历每个位数,对于整数n,其位数一共有lgn个,所以时间复杂度为 **O(logn)** 。
30 |
31 | **测试算例** ****
32 |
33 | 1.功能测试(3,45,180等)
34 |
35 | 2.边界值测试(0,1等)
36 |
37 | 3.性能测试(输入较大的数字,如1000000等)
38 |
39 | ## **Java代码**
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 | //题目:输入一个整数n,求从1到n这n个整数的十进制表示中1出现的次数。例如
44 | //输入12,从1到12这些整数中包含1 的数字有1,10,11和12,1一共出现了5次。
45 |
46 | public class NumberOf1 {
47 | public int NumberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
48 | int count=0;
49 | for(int i=1;i<=n;i*=10){ //i代表位数
50 | int high=n/(i*10); //更高位数字
51 | int low=(n%i); //更低位数字
52 | int cur=(n/i)%10; //当前位数字
53 | if(cur==0){
54 | count+=high*i;
55 | }else if(cur==1){
56 | count+=high*i+(low+1);
57 | }else{
58 | count+=(high+1)*i;
59 | }
60 | }
61 | return count;
62 | }
63 | }
64 |
65 |
66 | ## **收获**
67 |
68 | 1.找规律要耐心!欲速则不达。
69 |
70 | 2.学会提取不同位置的数字,以及更高、更低位置的数字;学会遍历每个位数的循环。
71 |
72 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
73 |
74 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
75 |
76 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(50-1)字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(50-1) 字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 在字符串中找出第一个只出现一次的字符。如输入"abaccdeff",则输出'b'。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 创建哈希表,键值key为字符,值value为出现次数。第一遍扫描:对每个扫描到的字符的次数加一;第二遍扫描:对每个扫描到的字符通过哈希表查询次数,第一个次数为1的字符即为符合要求的输出。
16 |
17 | 由于字符(char)是长度为8的数据类型,共有256中可能,因此哈希表可以用一个长度为256的数组来代替,数组的下标相当于键值key,对应字符的ASCII码值;数组的值相当于哈希表的值value,用于存放对应字符出现的次数。
18 |
19 | **测试算例** ****
20 |
21 | 1.功能测试(存在/不存在只出现一次的字符;全部都为只出现一次的字符)
22 |
23 | 2.特殊测试(null)
24 |
25 | ## **Java代码**
26 |
27 |
28 |
29 | //题目:在字符串中找出第一个只出现一次的字符。如输入"abaccdeff",则输出
30 | //'b'。
31 |
32 | public class FirstNotRepeatingChar {
33 | public char firstNotRepeatingChar(String str) {
34 | if(str==null)
35 | return '\0';
36 | int[] repetitions = new int[256];
37 | for(int i=0;i<256;i++)
38 | repetitions[i]=0;
39 | for(int i=0;i 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 在一个m×n的棋盘的每一格都放有一个礼物,每个礼物都有一定的价值(价值大于0)。你可以从棋盘的左上角开始拿格子里的礼物,并每次向左或者向下移动一格直到到达棋盘的右下角。给定一个棋盘及其上面的礼物,请计算你最多能拿到多少价值的礼物?
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 动态规划:定义f(i,j)为到达(i,j)位置格子时能拿到的礼物总和的最大值,则有:f(i,j)=max{f(i,j),f(i,j)}+values(i,j)。
16 |
17 | 同上道题一样,如果直接使用递归会产生大量的重复计算,因此,创建辅助的数组来保存中间计算结果。
18 |
19 | 辅助数组不用和m*n的二维数组一样大,只需要保存上一层的最大值就可以。代码中使用长度为列数n的一位数组作为辅助数组,注释部分为二维辅助数组。
20 |
21 | _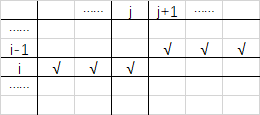_
22 |
23 | 辅助数组只需要存 √ 的部分
24 |
25 | **测试算例** ****
26 |
27 | 1.功能测试(多行多列,一行多列,多行一列,一行一列)
28 |
29 | 2.特殊测试(null)
30 |
31 | ## **Java代码**
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 | //题目:在一个m×n的棋盘的每一格都放有一个礼物,每个礼物都有一定的价值
36 | //(价值大于0)。你可以从棋盘的左上角开始拿格子里的礼物,并每次向左或
37 | //者向下移动一格直到到达棋盘的右下角。给定一个棋盘及其上面的礼物,请计
38 | //算你最多能拿到多少价值的礼物?
39 |
40 | public class MaxValueOfGifts {
41 | public int maxValueOfGifts(int[][] values) {
42 | if(values==null || values.length<=0 ||values[0].length<=0)
43 | return 0;
44 | int rows=values.length;
45 | int cols=values[0].length;
46 | // int[][] maxValue=new int[rows][cols];
47 | int[] maxValue=new int[cols];
48 | for(int i=0;i0)
53 | // up=maxValue[i-1][j];
54 | up=maxValue[j];
55 | if(j>0)
56 | // left=maxValue[i][j-1];
57 | left=maxValue[j-1];
58 | // maxValue[i][j]=Math.max(up, left)+values[i][j];
59 | maxValue[j]=Math.max(up, left)+values[i][j];
60 | }
61 | }
62 | // return maxValue[rows-1][cols-1];
63 | return maxValue[cols-1];
64 | }
65 | }
66 |
67 |
68 | ## **收获**
69 |
70 | 1.动态规划问题,用公式来表示清楚。
71 |
72 | 2.动态规划如果有大量重复计算,可以用循环+辅助空间来提高效率。
73 |
74 | 2.这道题不用二维数组,只需要用一维数组作为辅助空间即可,以后遇到对中间结果的保存问题,看看能否优化辅助空间。
75 |
76 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
77 |
78 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
79 |
80 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(45)把数组排成最小的数.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(45) 把数组排成最小的数
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼接出的所有数字中最小的一个。例如输入数组{3, 32,
12 | 321},则打印出这3个数字能排成的最小数字321323。
13 |
14 | ## 思路
15 |
16 | 不好的方法:求出所有全排列(类字符串的排列:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9869719.html
17 | ),将数字拼起来,最后求出所有的最小值。这效率太低,且没有考虑到大数问题。
18 |
19 | 好的方法:观察规律,自行定义一种排序规则。
20 |
21 | 对于数字m和n,可以拼接成mn和nm,如果mn list, Comparator c)`方法进行排序。Comparator中重写compar()方法来规定比较规则。
27 |
28 | **测试算例** ****
29 |
30 | 1.功能测试(1个数字;多个数字;数字数位有重复)
31 |
32 | 2.特殊测试(null)
33 |
34 | ## **Java代码**
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | //题目:输入一个正整数数组,把数组里所有数字拼接起来排成一个数,打印能拼
39 | //接出的所有数字中最小的一个。例如输入数组{3, 32, 321},则打印出这3个数
40 | //字能排成的最小数字321323。
41 |
42 | public class SortArrayForMinNumber {
43 | public String PrintMinNumber(int [] numbers) {
44 | if(numbers==null || numbers.length<=0)
45 | return "";
46 | ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
47 | for(int number:numbers)
48 | list.add(String.valueOf(number));
49 | Collections.sort(list,new Comparator(){
50 | @Override
51 | public int compare(String s1,String s2){
52 | String a=s1+s2;
53 | String b=s2+s1;
54 | return a.compareTo(b);
55 | }
56 | });
57 | StringBuilder sb= new StringBuilder();
58 | for(String str:list)
59 | sb.append(str);
60 | return sb.toString();
61 | }
62 | }
63 |
64 |
65 | ## **收获**
66 |
67 | 1.记住Collections.` (List list, Comparator c)在重写compare()方法的使用。`
68 |
69 | 2.小心大数问题,用字符串解决大数问题。
70 |
71 | 3.遇到类似排序问题,想想自定排序规则是否更加方便。
72 |
73 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
74 |
75 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
76 |
77 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(55-2)平衡二叉树.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(55-2) 平衡二叉树
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 输入一棵二叉树的根结点,判断该树是不是平衡二叉树。如果某二叉树中任意结点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1,那么它就是一棵平衡二叉树。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 在[(55-1)
18 | 二叉树的深度](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9958736.html)基础上修改:计算树的深度,树的深度=max(左子树深度,右子树深度)+1。在遍历过程中,判断左右子树深度相差是否超过1,如果不平衡,则令树的深度=-1,用来表示树不平衡。最终根据树的深度是否等于-1来确定是否为平衡树。
19 |
20 | **测试算例** ****
21 |
22 | 1.功能测试(左斜树、右斜树、平衡或者不平衡树)
23 |
24 | 3.特殊测试(一个结点,null)
25 |
26 | ## **Java代码**
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 | //题目:输入一棵二叉树的根结点,判断该树是不是平衡二叉树。如果某二叉树中
31 | //任意结点的左右子树的深度相差不超过1,那么它就是一棵平衡二叉树。
32 |
33 | public class BalancedBinaryTree {
34 | public class TreeNode {
35 | int val = 0;
36 | TreeNode left = null;
37 | TreeNode right = null;
38 |
39 | public TreeNode(int val) {
40 | this.val = val;
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
45 | return getDepth(root)!=-1;
46 | }
47 |
48 | public int getDepth(TreeNode root) {
49 | if(root==null) return 0;
50 | int left=getDepth(root.left);
51 | if(left==-1) return -1;
52 | int right=getDepth(root.right);
53 | if(right==-1) return -1;
54 | return Math.abs(left - right) > 1 ? -1 : 1 + Math.max(left, right);
55 | }
56 |
57 | /*
58 | //自己开始想的方法,但是一定要把树给遍历完才行;上面的方法实现了剪枝
59 | boolean isBalanced=true;
60 | public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
61 | TreeDepth(root);
62 | return isBalanced;
63 | }
64 |
65 | public int TreeDepth(TreeNode root) {
66 | if(root==null)
67 | return 0;
68 | int left=TreeDepth(root.left);
69 | int right=TreeDepth(root.right);
70 | if(left-right>1 || right-left>1)
71 | isBalanced=false;
72 | return Math.max(left+1,right+1);
73 | }
74 | */
75 | }
76 |
77 |
78 | ## **收获**
79 |
80 | 1.在判断出树不平衡后,进行剪枝(即代码中直接返回-1,不再对其他子树进行判断),以提高效率。
81 |
82 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
83 |
84 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
85 |
86 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(58-1)翻转单词顺序.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(58-1) 翻转单词顺序
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 输入一个英文句子,翻转句子中单词的顺序,但单词内字符的顺序不变。为简单起见,标点符号和普通字母一样处理。例如输入字符串"I am a student.
14 | ",则输出"student. a am I"。
15 |
16 | ## 思路
17 |
18 | 一开始自己觉得要用split()方法,但这要开辟新的数组,占内存空间,不行。 **
19 | **
20 |
21 | 首先实现翻转整个句子:只需要在首尾两端各放置一个指针,交换指针所指的数字,两端指针往中间移动即可。之后根据空格的位置,对每个单词使用同样的方法翻转即可。
22 |
23 | **测试算例** ****
24 |
25 | 1.功能测试(句子中有一个/多个单词,空格在开头、中间、结尾)
26 |
27 | 2.边界值测试(null,空字符串,句子全为空格)
28 |
29 | ## **Java代码**
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | //题目:输入一个英文句子,翻转句子中单词的顺序,但单词内字符的顺序不变。
34 | //为简单起见,标点符号和普通字母一样处理。例如输入字符串"I am a student. ",
35 | //则输出"student. a am I"。
36 |
37 | public class ReverseWordsInSentence {
38 | public String ReverseSentence(char[] chars) {
39 | if(chars==null || chars.length<=0)
40 | return String.valueOf(chars);
41 | //翻转整个句子
42 | reverseSb(chars,0,chars.length-1);
43 | //翻转单词(指针指向单词的第一个和最后一个)
44 | int start=0;
45 | int end=0;
46 | while(start 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的结点仍然是按照递增排序的。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | **递归实现**
16 | :合并过程中,每次都是从两个链表中找出较小的一个来链接,因此可以采用递归来实现:当任意一个链表为null时,直接链接另一个链表即可;其余情况只需要在两个链表中找出较小的一个结点进行链接,该结点的next值继续通过递归函数来链接。
17 |
18 | **非递归实现:** 非递归实现比较容易想到,直接进行分情况讨论即可,要稍微注意下后面代码中头结点的赋值过程。
19 |
20 | **测试算例** ****
21 |
22 | 1.功能测试(两个链表有多个或一个结点;结点值相同、不同)
23 |
24 | 2.特殊测试(任意一个或者两个链表的头结点为null)
25 |
26 | ## **Java代码**
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 | //题目:输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的结点仍然是按
31 | //照递增排序的。
32 |
33 | public class MergeSortedLists {
34 | public class ListNode{
35 | int val;
36 | ListNode next=null;
37 | public ListNode(int val) {
38 | this.val=val;
39 | }
40 | }
41 |
42 | /*
43 | * 递归版本
44 | */
45 | public ListNode merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
46 | if(list1==null) return list2;
47 | if(list2==null) return list1;
48 | if(list1.val 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 1)先对A树进行遍历,找到与B树的根结点值相同的结点R;
16 |
17 | 2)判断A树中以R为根结点的子树是否包含B树一样的结构。 **
18 | **
19 |
20 | **测试算例** ****
21 |
22 | 1.功能测试(A、B为普通二叉树;B是或者不是A树的子结构)
23 |
24 | 2.特殊测试(任意一个或者两个树的根结点为null;左斜树;右斜树)
25 |
26 | ## **Java代码**
27 |
28 |
29 |
30 | //题目:输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构。
31 |
32 | public class SubstructureInTree {
33 | public class TreeNode{
34 | double val;
35 | TreeNode left = null;
36 | TreeNode right =null;
37 | public TreeNode(int val) {
38 | this.val=val;
39 | }
40 | }
41 |
42 | /*
43 | * 主程序,对每个结点遍历判断
44 | */
45 | public boolean hasSubtree(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
46 | if(root1==null || root2==null)
47 | return false;
48 | // boolean result=false;
49 | // if(equal(root1.val, root2.val)) {
50 | // result = doesTree1HasTree2(root1, root2);
51 | // if(!result)
52 | // result=hasSubtree(root1.left, root2)
53 | // ||hasSubtree(root1.right, root2);
54 | // }
55 | // return result;
56 | //上面几行可以直接写成:
57 | return doesTree1HasTree2(root1, root2)|| hasSubtree(root1.left, root2)
58 | ||hasSubtree(root1.right, root2);
59 | }
60 |
61 | /*
62 | * 判断root结点开始的子树中各个结点是否相同
63 | */
64 | private boolean doesTree1HasTree2(TreeNode root1,TreeNode root2) {
65 | if(root2==null) return true;
66 | if(root1==null) return false;
67 | return equal(root1.val, root2.val) && doesTree1HasTree2(root1.left, root2.left)
68 | && doesTree1HasTree2(root1.right, root2.right);
69 | }
70 |
71 | /*
72 | * 判断两个浮点数是否相等
73 | */
74 | private boolean equal(double num1,double num2) {
75 | if(num1-num2<0.0000001 && num1-num2>-0.0000001 )
76 | return true;
77 | return false;
78 | }
79 | }
80 |
81 |
82 | ## **收获**
83 |
84 | 1.本题相当于对二叉树遍历的拓展,操作过程中,注意null的处理。
85 |
86 | 2.注意判断浮点数相等时有误差,不要直接用“==”判断。
87 |
88 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
89 |
90 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
91 |
92 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(38)字符串的排列.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(38) 字符串的排列
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入一个字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串abc,则打印出由字符a、b、c所能排列出来的所有字符串abc、acb、bac、bca、cab和cba。(本文代码采用ArrayList
12 | 接收返回的字符串,并要求不出现重复字符串)
13 |
14 | ## 思路
15 |
16 | 将字符串看成两部分,一部分是第一个字符,另一部分是后面的所有字符。
17 |
18 | 首先确定第一个字符,该字符可以是字符串中的任意一个;固定第一个字符后,求出后面所有字符的排列(相同步骤,采用递归)。
19 |
20 | 实现第一个字符的改变,只需要将第一个字符和后面所有字符进行交换即可(最早自己想的是从原始字符串拿出第i个字符,然后合并剩下的字符到后面,其实就是个交换的过程,自己开始时想得太复杂了)。要记得字符串输出后要将字符交换回来,变回原始的字符串。
21 |
22 | **测试算例** ****
23 |
24 | 1.功能测试(有多个重复字母的字符串、所有字符相同的字符串、一个字符或者多个字符的普通字符串)
25 |
26 | 2.特殊测试(字符串为null、“”)
27 |
28 | ## **Java代码**
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 | //题目:输入一个字符串,打印出该字符串中字符的所有排列。例如输入字符串abc,
33 | //则打印出由字符a、b、c所能排列出来的所有字符串abc、acb、bac、bca、cab和cba。
34 |
35 | public class StringPermutation {
36 |
37 | public ArrayList Permutation(String str) {
38 | ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
39 | if(str==null || str.length()==0)
40 | return list;
41 | permutationCore(str.toCharArray(),0,list);
42 | Collections.sort(list); //将list中的字符串排序
43 | return list;
44 | }
45 |
46 | private void permutationCore(char[] strArray,int index,ArrayList list){
47 | if(index==strArray.length-1){
48 | if(!list.contains(String.valueOf(strArray))) //判断是否有重复字符串
49 | list.add(String.valueOf(strArray));
50 | }else{
51 | for(int i=index;i 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | [leetcode](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/shu-zu-zhong-shu-zi-chu-xian-de-ci-shu-lcof/solution/zhi-chu-xian-yi-ci-de-liang-ge-shu-zi-by-l25899981/)
6 |
7 | ****
8 |
9 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
10 |
11 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
12 |
13 | ## 题目
14 |
15 | 一个整型数组里除了两个数字之外,其他的数字都出现了两次。请写程序找出这两个只出现一次的数字。要求时间复杂度是O(n),空间复杂度是O(1)。
16 |
17 | ## 思路
18 |
19 | 记住:两个相同的数字异或等于0.
20 |
21 | 如果数组中只有一个数字只出现一次,我们从头到尾异或每个数字,那么最终的结果刚好是那个只出现一次的数字。
22 |
23 | 而本题里数组中有两个数字只出现一次,如果能够将数组分为两部分,两部分中都只有一个数字只出现一次,那么就可以解决该问题了。
24 |
25 | 求解方法:
26 |
27 | 我们依旧从头到尾异或每个数字,那么最终的结果就是这两个只出现一次的数字的异或结果,由于两个数不同,因此这个结果数字中一定有一位为1,把结果中第一个1的位置记为第n位。因为是两个只出现一次的数字的异或结果,所以
28 | 这两个数字在第n位上的数字一定是1和0。
29 |
30 | 接下来我们根据数组中每个数字的第n位上的数字是否为1来进行分组,恰好能将数组分为两个都只有一个数字只出现一次的数组,对两个数组从头到尾异或,就可以得到这两个数了。
31 |
32 | **测试算例** ****
33 |
34 | 1.功能测试(数组中有多对重复的数字;无重复的数字)
35 |
36 | ## **Java代码**
37 |
38 |
39 |
40 | //题目:一个整型数组里除了两个数字之外,其他的数字都出现了两次。请写程序
41 | //找出这两个只出现一次的数字。要求时间复杂度是O(n),空间复杂度是O(1)。
42 |
43 | public class NumbersAppearOnce {
44 | public void FindNumsAppearOnce(int [] array,int num1[] , int num2[]) {
45 | if(array==null || array.length<2)
46 | return;
47 | int resultExclusiveOR=0;
48 | for(int i=0;i>1; //只有n>>1不完整,要n=n>>1
54 | indexOf1++;
55 | }
56 |
57 | num1[0]=0;
58 | num2[0]=0;
59 | for(int i=0;i>indexOf1)&1)==1)
61 | num1[0]^=array[i];
62 | else
63 | num2[0]^=array[i];
64 | }
65 | }
66 | }
67 |
68 |
69 | ## **收获**
70 |
71 | 1.当一个数字出现两次(或者 **偶数次** )时,用异或^ 可以进行消除。 **一定要牢记 异或的这个功能!**
72 |
73 | 2.将一组数字分为两组,可以根据某位上是否为1来进行分组,即根据和1相与( &1)的结果来进行分组。
74 |
75 | 3.判断某个数x的第n位(如第3位)上是否为1,
76 |
77 | 1)通过 x&00000100 的结果是否为0 来判断。(不能根据是否等于1来判断)
78 |
79 | 2)通过(x>>3)&1 是否为0 来判断
80 |
81 | 4.将某个数x右移m位,一定要写成 **x=x >>m;**而不能只写成 **x >>m;**这个语句
82 |
83 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
84 |
85 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
86 |
87 | 
88 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(56-2)数组中唯一只出现一次的数字.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(56-2) 数组中唯一只出现一次的数字
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | [leetcode 137](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/single-number-ii/solution/xiang-xi-tong-su-de-si-lu-fen-xi-duo-jie-fa-by--31/)
6 | ****
7 |
8 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
9 |
10 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
11 |
12 | ## 题目
13 |
14 | 在一个数组中除了一个数字只出现一次之外,其他数字都出现了三次。请找出那个只出现一次的数字。
15 |
16 | ## 思路
17 |
18 | 这道题中数字出现了三次,无法像[56-1)
19 | 数组中只出现一次的两个数字](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9960018.html)一样通过利用异或位运算进行消除相同个数字。但是仍然可以沿用位运算的思路。
20 |
21 | 将所有数字的二进制表示的对应位都加起来,如果某一位能被三整除,那么只出现一次的数字在该位为0;反之,为1。
22 |
23 | **测试算例** ****
24 |
25 | 1.功能测试(唯一出现的数字是0,正数,负数;重复出现的数字是0,正数,负数)
26 |
27 | ## **Java代码**
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 | //题目:在一个数组中除了一个数字只出现一次之外,其他数字都出现了三次。请
32 | //找出那个只出现一次的数字。
33 |
34 | public class NumberAppearingOnce {
35 | public static int findNumberAppearingOnce(int[] arr) {
36 | if(arr==null || arr.length<=0)
37 | throw new RuntimeException();
38 | int[] bitSum = new int[32];
39 | for(int i=0;i<32;i++)
40 | bitSum[i]=0;
41 | for(int i=0;i=0;j--) {
44 | int bit=arr[i]&bitMask; //注意arr[i]&bitMask不一定等于1或者0,有可能等于00010000
45 | if(bit!=0)
46 | bitSum[j]+=1;
47 | bitMask=bitMask<<1;
48 | }
49 | }
50 | int result=0;
51 | for(int i=0;i<32;i++) {
52 | result=result<<1;
53 | result+=(bitSum[i]%3);
54 | //result=result<<1; //不能放在后面,否则最前面一位就没了
55 | }
56 | return result;
57 | }
58 | }
59 |
60 |
61 | ## **收获**
62 |
63 | 1.判断某个数x的第n位(如第3位)上是否为1,
64 |
65 | 1)通过 x &00000100 的结果是否为0 来判断。(不能根据是否等于1来判断)
66 |
67 | 2)通过(x>>3)&1 是否为0 来判断
68 |
69 | 2.通过number&bitMask的结果是否为0(不能用1判断),bitMask=1不断左移,可以将一个数的二进制存储到32位的数组中。
70 |
71 |
72 |
73 | int number=100;
74 | int bitMask=1;
75 | for(int j=31;j>=0;j--) {
76 | int bit=number&bitMask; //注意arr[i]&bitMask不一定等于1或者0,有可能等于00010000
77 | if(bit!=0)
78 | bits[j]=1;
79 | bitMask=bitMask<<1;
80 | }
81 |
82 | 3.通过以下代码实现二进制转化为数字(注意左移语句的位置):
83 |
84 |
85 |
86 | int result=0;
87 | for(int i=0;i<32;i++) {
88 | result=result<<1;
89 | result+=bits[i];
90 | //result=result<<1; //不能放在后面,否则最前面一位就没了
91 | }
92 |
93 |
94 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
95 |
96 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
97 |
98 | 
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(48)最长不含重复字符的子字符串.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(48) 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 请从字符串中找出一个最长的不包含重复字符的子字符串,计算该最长子字符串的长度。假设字符串中只包含从'a'到'z'的字符。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 动态规划法:定义函数f(i)为:以第i个字符为 **结尾** 的不含重复字符的子字符串的最大长度。
16 |
17 | (1)当第i个字符之前未出现过,则有:f(i)=f(i-1)+1
18 |
19 | (2)当第i个字符之前出现过,记该字符与上次出现的位置距离为d
20 |
21 | 1)如果d<=f(i-1),则有f(i)=d;
22 |
23 | 2)如果d>f(i-1),则有f(i)=f(i-1)+1;
24 |
25 | 我们从第一个字符开始遍历,定义两个int变量preLength和curLength来分别代表f(i-1)和f(i),再创建一个长度为26的pos数组来存放26个字母上次出现的位置,即可根据上述说明进行求解。
26 |
27 | 注意:每次最大长度和字母出现位置要记得更新。
28 |
29 | **另一种思路:** 遍历每个字符,把当前字符看成子字符串的末尾结点,同时更新开头结点,详细代码见[Longest Substring Without
30 | Repeating Characters](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/10071484.html)
31 |
32 | **测试算例** ****
33 |
34 | 1.功能测试(一个或者多个字符,全部字符不同/相同)
35 |
36 | 2.特殊测试(null,空字符串)
37 |
38 | ## **Java代码**
39 |
40 |
41 |
42 | //题目:请从字符串中找出一个最长的不包含重复字符的子字符串,计算该最长子
43 | //字符串的长度。假设字符串中只包含从'a'到'z'的字符。
44 |
45 | public class LongestSubstringWithoutDup {
46 | public static int maxLength(String str) {
47 | if(str==null || str.length()<=0)
48 | return 0;
49 | int preLength=0; //即f(i-1)
50 | int curLength=0; //即f(i)
51 | int maxLength=0;
52 | int[] pos= new int[26]; //用于存放字母上次出现的位置
53 | for(int i=0;ipreLength) {
58 | curLength=preLength+1;
59 | }else {
60 | curLength=i-pos[letterNumber];
61 | }
62 | pos[letterNumber]=i;
63 | if(curLength>maxLength)
64 | maxLength=curLength;
65 | preLength=curLength;
66 | }
67 | return maxLength;
68 | }
69 |
70 | public static void main(String[] args) {
71 | System.out.println(maxLength("arabcacfr")==4);
72 | System.out.println(maxLength("a")==1);
73 | System.out.println(maxLength("aaa")==1);
74 | System.out.println(maxLength("abcdef")==6);
75 | System.out.println(maxLength("")==0);
76 | System.out.println(maxLength(null)==0);
77 | }
78 | }
79 |
80 |
81 | ## **收获**
82 |
83 | 1.函数f(i)为:以第i个字符为 **结尾**
84 | 的不含重复字符的子字符串的最大长度。而不是以第i个字符作为开头。第i个字符作为结尾可以方便与下一个字符进行联系。
85 |
86 | 2.学会用长度为26的数组来存放26个字母所在的位置下标。
87 |
88 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
89 |
90 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
91 |
92 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(46)把数字翻译成字符串.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(46) 把数字翻译成字符串
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 给定一个数字,我们按照如下规则把它翻译为字符串:0翻译成"a",1翻译成"b",……,11翻译成"l",……,25翻译成"z"。一个数字可能有多个翻译。例如12258有5种不同的翻译,它们分别"bccfi",
12 | "bwfi", "bczi", "mcfi" 和 _ _ _"mzi" 。___ 请编程实现一个函数用来计算一个数字有多少种不同的翻译方法。
13 |
14 | ## 思路
15 |
16 | 看到题目,很容易想到使用递归:用f(i)来表示从第i位开始的不同翻译数目,可以得到有:f(i)=f(i+1)+g(i,i+1)*f(i+2)。i和i+1位数字拼起来在10~25范围内时g(i,i+1)的值为1,否则为0。
17 |
18 | 但是存在重复的子问题,所以递归并非最佳方法,我们从数字的末尾开始计算f(i),自下而上解决问题,就可以消除重复的子问题了。先算f(len-1),f(len-2),再根据公式f(i)=f(i+1)+g(i,i+1)*f(i+2)往前逐步推导到f(0),这就是最终要求的结果。
19 |
20 | __
21 |
22 | **测试算例** ****
23 |
24 | 1.功能测试(1个数字;多个数字)
25 |
26 | 2.特殊测试(负数,0,含25、26等)
27 |
28 | ## **Java代码**
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 | //题目:给定一个数字,我们按照如下规则把它翻译为字符串:0翻译成"a",1翻
33 | //译成"b",……,11翻译成"l",……,25翻译成"z"。一个数字可能有多个翻译。例
34 | //如12258有5种不同的翻译,它们分别是"bccfi"、"bwfi"、"bczi"、"mcfi"和
35 | //"mzi"。请编程实现一个函数用来计算一个数字有多少种不同的翻译方法。
36 |
37 | public class TranslateNumbersToStrings {
38 | public int getTranslationCount(int number) {
39 | if(number<0)
40 | return 0;
41 | String sNumber=String.valueOf(number);
42 | int len=sNumber.length();
43 | int[] counts=new int[len];
44 | for(int i=len-1;i>=0;i--) {
45 | if(i==len-1) {
46 | counts[i]=1;
47 | }else {
48 | counts[i]=counts[i+1];
49 | if(canBeTrans(sNumber,i)) {
50 | if(i==len-2)
51 | counts[i]+=1;
52 | else
53 | counts[i]+=counts[i+2];
54 | }
55 | }
56 | }
57 | return counts[0];
58 | }
59 |
60 | private boolean canBeTrans(String sNumber, int i) {
61 | int a=sNumber.charAt(i)-'0';
62 | int b=sNumber.charAt(i+1)-'0';
63 | int convert=a*10+b;
64 | if(convert>=10 && convert<=25)
65 | return true;
66 | return false;
67 | }
68 |
69 | public static void main(String[] args) {
70 | TranslateNumbersToStrings demo= new TranslateNumbersToStrings();
71 | System.out.println(demo.getTranslationCount(0)==1);
72 | System.out.println(demo.getTranslationCount(10)==2);
73 | System.out.println(demo.getTranslationCount(12258)==5);
74 | System.out.println(demo.getTranslationCount(-100)==0);
75 | }
76 | }
77 |
78 |
79 | ## **收获**
80 |
81 | 1.递归方法,我们试着用公式描述会比较清晰
82 |
83 | 2.递归是自上而下解决问题,如果遇到重复的子问题时,考虑自下而上求解,不用递归
84 |
85 | 3.g(i,i+1)不仅要判断 <=25,还要判断>=10,别漏了
86 |
87 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
88 |
89 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
90 |
91 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(59-1)滑动窗口的最大值.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(59-1) 滑动窗口的最大值
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值。例如,如果输入数组{2, 3, 4, 2, 6, 2, 5,
14 | 1}及滑动窗口的大小3,那么一共存在6个滑动窗口,它们的最大值分别为{4, 4, 6, 6, 6, 5}
15 |
16 | ## 思路
17 |
18 | 蛮力直接在每个滑动窗口依次比较找出最大值,时间复杂度太高。
19 |
20 | 我们考虑把每个可能成为最大值的数字记录下来,就可以快速的得到最大值。
21 |
22 | **思路:** 建立一个两端开口的队列,放置 **所有可能是最大值的数字** (存放的其实是对应的下标),且最大值位于队列开头。从头开始扫描数组,
23 |
24 | 如果遇到的数字比队列中所有的数字都大,那么它就是最大值,其它数字不可能是最大值了,将队列中的所有数字清空,放入该数字,该数字位于队列头部;
25 |
26 | 如果遇到的数字比队列中的所有数字都小,那么它还有可能成为之后滑动窗口的最大值,放入队列的末尾;
27 |
28 | 如果遇到的数字比队列中最大值小,最小值大,那么将比它小数字不可能成为最大值了,删除较小的数字,放入该数字。
29 |
30 | 由于滑动窗口有大小,因此,队列头部的数字如果其下标离滑动窗口末尾的距离大于窗口大小,那么也删除队列头部的数字。
31 |
32 | **注** :队列中存放的是下标,以上讲的 队列头部的数字 均指 队列头部的下标所指向的数字。写代码时不要弄混了。
33 |
34 | **测试算例** ****
35 |
36 | 1.功能测试(数组数字递增、递减、无序)
37 |
38 | 2.边界值测试(滑动窗口大小位0、1、大于或者等于数组长度)
39 |
40 | 3.特殊输入测试(null)
41 |
42 | ## **Java代码**
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 | //题目:给定一个数组和滑动窗口的大小,请找出所有滑动窗口里的最大值。例如,
47 | //如果输入数组{2, 3, 4, 2, 6, 2, 5, 1}及滑动窗口的大小3,那么一共存在6个
48 | //滑动窗口,它们的最大值分别为{4, 4, 6, 6, 6, 5},
49 |
50 | public class MaxInSlidingWindow {
51 | public ArrayList maxInWindows(int [] num, int size){
52 | ArrayList max = new ArrayList();
53 | if(num==null || num.length<=0 || size<=0 || size>num.length)
54 | return max;
55 | ArrayDeque indexDeque = new ArrayDeque();
56 |
57 | for(int i=0;i num[indexDeque.getLast()])
59 | indexDeque.removeLast();
60 | indexDeque.addLast(i);
61 | }
62 |
63 | for(int i=size-1;i num[indexDeque.getLast()])
65 | indexDeque.removeLast();
66 | if(!indexDeque.isEmpty() && (i-indexDeque.getFirst())>=size)
67 | indexDeque.removeFirst();
68 | indexDeque.addLast(i);
69 | max.add(num[indexDeque.getFirst()]);
70 | }
71 |
72 | return max;
73 | }
74 | }
75 |
76 |
77 | ## **收获**
78 |
79 | 1.自己最初想到的是只存放最大的数,没有想到可以存放所有可能是最大的数,要记住。
80 |
81 | 2.ArrayDeque——双端队列,要记住。下面是一些常用的方法:
82 |
83 | 
84 |
85 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
86 |
87 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
88 |
89 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(37)序列化二叉树.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(37) 序列化二叉树
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 一般情况下,需要采用前/后序遍历和中序遍历才能确定一个二叉树,但是其实可以只采用前序遍历(从根结点开始),将空结点(null)输出为一个特殊符号(如“$”),就可以确定一个二叉树了。
16 |
17 | 将二叉树序列化为字符串,就是前序遍历的过程,遇见空结点时,序列化为“$”,每个结点间使用逗号分隔开。
18 |
19 | 将字符串反序列化为二叉树,也使用前序遍历,遇见一个新数字(或者$)就建立一个新结点,不过需要注意的是,数字可能不只是个位数字,因此创建了一个全局Int变量index(在字符串上的移动的指针),以便于截取字符串中当前的结点值。(详见代码)
20 |
21 | **测试算例** ****
22 |
23 | 1.功能测试(一个结点;左右斜树;完全二叉树;普通二叉树)
24 |
25 | 2.特殊测试(根结点为null)
26 |
27 | ## **Java代码**
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 | //题目:请实现两个函数,分别用来序列化和反序列化二叉树。
32 |
33 | public class SerializeBinaryTrees {
34 | public class TreeNode {
35 | int val = 0;
36 | TreeNode left = null;
37 | TreeNode right = null;
38 |
39 | public TreeNode(int val) {
40 | this.val = val;
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | String Serialize(TreeNode node) {
45 | StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
46 | if (node == null) {
47 | sb.append("$,");
48 | } else {
49 | sb.append(node.val + ",");
50 | sb.append(Serialize(node.left));
51 | sb.append(Serialize(node.right));
52 | }
53 | return sb.toString();
54 | }
55 |
56 | int index = 0;
57 | TreeNode Deserialize(String str) {
58 | TreeNode node = null;
59 | if (str == null || str.length() == 0)
60 | return node;
61 | int start = index;
62 | while (str.charAt(index) != ',')
63 | index++;
64 | if (!str.substring(start, index).equals("$")) {
65 | node = new TreeNode(Integer.parseInt(str.substring(start, index)));
66 | index++; // 这条语句位置别放错了
67 | node.left = Deserialize(str);
68 | node.right = Deserialize(str);
69 | } else {
70 | index++;
71 | }
72 | return node;
73 | }
74 | }
75 |
76 |
77 | ## **收获**
78 |
79 | 1.记住这种序列化的方式,用于表示二叉树时非常方便。
80 |
81 | 2.字符串中有分割符号时,可以对字符串采用split()方法,变为字符串数组,但是自己觉得数组的保存会消耗一定的空间,因此自己定义了全局变量index,通过substring()方法来截取每一部分的字符串。
82 |
83 | 3.字符串的比较以后尽量用equal来比较。在对某字符串采用substring()方法得到的字符串用==判断会返回false。[substring的==与equal()使用](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9866074.html
84 | "发布于2018-10-28 16:42")
85 |
86 | 4.String 转int 类型采用 `int` `i = Integer.parseInt( s );
87 | 不能用Integer.valueOf(s),这返回的是Integer对象。`
88 |
89 | 5.index++的位置一定不能放错
90 |
91 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
92 |
93 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
94 |
95 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(44)数字序列中某一位的数字.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(44) 数字序列中某一位的数字
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 数字以0123456789101112131415…的格式序列化到一个字符序列中。在这个序列中,第5位(从0开始计数)是5,第13位是1,第19位是4,等等。请写一个函数求任意位对应的数字。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 逐一枚举数字,计算每个数字的位数相加,效率太低。
16 |
17 | 观察规律:
18 |
19 | 个位数的个数一共有10个,即0~9,共占了10*1位数字;
20 |
21 | 两位数的个数一共有90个,即10~99,每个数字占两位,共占了90*2位数字;
22 |
23 | ……
24 |
25 | m位数的个数一共有9*10^(m-1)个,每个数字占m位,占了9*10^(m-1)*m位数字。
26 |
27 | 判断第n个对的数字是属于几位数,再从几位数中进行寻找。
28 |
29 | **测试算例** ****
30 |
31 | 1.功能测试(输入19、1000等)
32 |
33 | 2.边界值测试(输入0、1等)
34 |
35 | ## **Java代码**
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | //题目:数字以0123456789101112131415…的格式序列化到一个字符序列中。在这
40 | //个序列中,第5位(从0开始计数)是5,第13位是1,第19位是4,等等。请写一
41 | //个函数求任意位对应的数字。
42 |
43 | public class DigitsInSequenc {
44 | public int digitAtIndex(int index) {
45 | if(index<0)
46 | return -1;
47 | int m=1; //m位数
48 | while(true) {
49 | int numbers=numbersOfIntegers(m); //m位数的个数
50 | if(index 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 在数组中的两个数字如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 如果遍历数组,对每个数字都和后面的数字比较大小,时间复杂度为O(n^2),效率太低。
16 |
17 | 利归并排序:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9954732.html的思想,先将数组分解成为n个长度为1的子数组,然后进行两两合并同时排好顺序。
18 |
19 | 在对两个子区域合并排序时,记左边区域(下标为start~mid)的指针为i,右边区域(下标为mid+1~end)的指针为j,两个指针都指向该区域内最大的数字,排序时:
20 |
21 | (1)如果i指向的数字大于j指向的数字,说明:逆序对有j-mid个,我们把i指向的数字放入临时创建的排序数组中,然后令i-1,指向该区域前一个数字,继续进行排序;
22 |
23 | (2)如果i指向的数字小于等于j指向的数字,说明暂时不存在逆序对,将j指向的数字放入临时创建的排序数组中,然后令j-1,指向该区域前一个数字,继续进行排序;
24 |
25 | (3)某一子区域数字都放入排序数组后,将另一个子区域剩下的数字放入排序数组中,完成排序;
26 |
27 | (4)最后将排序好的数字按顺序赋值给原始数组的两个子区域,以便合并后的区域与别的区域合并。
28 |
29 | 
30 |
31 | **测试算例** ****
32 |
33 | 1.功能测试(普通数组,递增数组,递减数组,含重复数字)
34 |
35 | 2.边界值测试(数组只有两个数字, **只有一个数字** )
36 |
37 | 2.特殊测试(null)
38 |
39 | ## **Java代码、**
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 | //题目:在数组中的两个数字如果前面一个数字大于后面的数字,则这两个数字组
44 | //成一个逆序对。输入一个数组,求出这个数组中的逆序对的总数。
45 |
46 | public class InversePairs {
47 | public static int inversePairs(int [] array) {
48 | if(array==null || array.length<=0)
49 | return 0;
50 | int count=getCount(array,0,array.length-1);
51 | return count;
52 | }
53 |
54 | private static int getCount(int[] array,int start,int end){
55 | if(start>=end)
56 | return 0;
57 | int mid=(end+start)>>1;
58 | int left=getCount(array,start,mid);
59 | int right=getCount(array,mid+1,end);
60 |
61 | //合并
62 | int count=0;
63 | int i=mid; //左边区域的指针
64 | int j=end; //右边区域的指针
65 | int[] temp= new int[end-start+1]; //临时区域
66 | int k=end-start; //临时区域的指针
67 | while(i>=start && j>=mid+1){
68 | if(array[i]>array[j]){
69 | count+=(j-mid);
70 | temp[k--]=array[i--];
71 | }else{
72 | temp[k--]=array[j--];
73 | }
74 | }
75 | while(i>=start)
76 | temp[k--]=array[i--];
77 | while(j>=mid+1)
78 | temp[k--]=array[j--];
79 | for(k=0;k 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 蛮力法:遍历第一个链表的结点,每到一个结点,就在第二个链表上遍历每个结点,判断是否相等。时间复杂度为O(m*n),效率低;
16 |
17 | 使用栈:由于公共结点出现在尾部,所以用两个栈分别放入两个链表中的结点,从尾结点开始出栈比较。时间复杂度O(m+n),空间复杂度O(m+n)。
18 |
19 | 利用长度关系:计算两个链表的长度之差,长链表先走相差的步数,之后长短链表同时遍历,找到的第一个相同的结点就是第一个公共结点。
20 |
21 | 利用两个指针:一个指针顺序遍历list1和list2,另一个指针顺序遍历list2和list1,(这样两指针能够保证最终同时走到尾结点),两个指针找到的第一个相同结点就是第一个公共结点。
22 |
23 | **测试算例** ****
24 |
25 | 1.功能测试(有/无公共结点;公共结点分别在链表的中间,头结点和尾结点)
26 |
27 | 2.特殊测试(头结点为null)
28 |
29 | ## **完整Java代码**
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | //题目:输入两个链表,找出它们的第一个公共结点。
34 |
35 | public class FirstCommonNodesInLists {
36 | public class ListNode{
37 | int val;
38 | ListNode next = null;
39 | ListNode(int val) {
40 | this.val = val;
41 | }
42 | }
43 |
44 | //方法1:利用长度关系
45 | public ListNode findFirstCommonNode1(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
46 | int length1 = getLength(pHead1);
47 | int length2 = getLength(pHead2);
48 | int lengthDif = length1-length2;
49 | ListNode longList = pHead1;
50 | ListNode shortList = pHead2;
51 | if(lengthDif<0){
52 | longList = pHead2;
53 | shortList = pHead1;
54 | lengthDif = -lengthDif;
55 | }
56 | for(int i=0;i 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头结点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头结点。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 方法一:使用三个指针(pre,p,next)进行实现。令p指向pre,next则是用于防止链表断裂(很简单,详见代码)。
16 |
17 | 方法二(递归):找到最后一个结点作为返回值,递归函数中,找到最后的头结点后,开始进行每个结点next值的转换。
18 |
19 | **测试算例** ****
20 |
21 | 1.功能测试(链表有多个或一个结点)
22 |
23 | 2.特殊测试(头结点为null)
24 |
25 | ## **Java代码**
26 |
27 | 新:
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 | //iteratively
32 | public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
33 | ListNode pre = null;
34 | ListNode cur = head;
35 | while(cur!=null){
36 | ListNode next = cur.next;
37 | cur.next = pre;
38 | pre = cur;
39 | cur = next;
40 | }
41 | return pre;
42 | }
43 | //recursively
44 | public ListNode reverseList1(ListNode head) {
45 | if(head == null || head.next==null)
46 | return head;
47 | ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
48 | head.next.next = head;
49 | head.next = null;
50 | return newHead;
51 | }
52 |
53 |
54 | 旧:
55 |
56 |
57 |
58 | package _24;
59 | /**
60 | *
61 | * @Description 面试题24:反转链表
62 | *
63 | * @author yongh
64 | * @date 2018年10月15日 下午3:24:51
65 | */
66 |
67 | //题目:定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头结点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的
68 | //头结点。
69 |
70 | public class ReverseList {
71 | public class ListNode {
72 | int val;
73 | ListNode next=null;
74 | ListNode(int val){
75 | this.val=val;
76 | }
77 | }
78 |
79 | /*
80 | * 三个指针实现
81 | */
82 | public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
83 | if(head==null)
84 | return null;
85 | ListNode pNode=head;
86 | ListNode preNode=null;
87 | ListNode nextNode=pNode.next;
88 | while(nextNode!=null) {
89 | pNode.next=preNode;
90 | preNode=pNode;
91 | pNode=nextNode;
92 | nextNode=pNode.next;
93 | }
94 | pNode.next=preNode;
95 | return pNode;
96 | }
97 |
98 | /*
99 | * 递归实现
100 | */
101 | public ListNode reverseList2(ListNode head) {
102 | if(head==null || head.next==null)
103 | return head;
104 | ListNode rvsHead=reverseList(head.next);
105 | //找到了最后的头结点后,开始转换每个结点的指向
106 | head.next.next=head;
107 | head.next=null;
108 | return rvsHead;
109 | }
110 |
111 | }
112 |
113 |
114 | ## **收获**
115 |
116 | 1.与链表相关的题目总是涉及大量指针操作,以后遇到链表相关的题目时,多考虑指针的使用。
117 |
118 | 2.递归实现时,第50行:`head.next=``null``; 别忘记了。`
119 |
120 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
121 |
122 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
123 |
124 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(8)用两个栈实现队列.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(8) 用两个栈实现队列
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview **
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 用两个栈实现一个队列。队列的声明如下,请实现它的两个函数appendTail和deleteHead,分别完成在队列尾部插入结点和在队列头部删除结点的功能。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 这道题较简单,自己先试着模拟一下插入删除的过程(在草稿纸上动手画一下):插入肯定是往一个栈stack1中一直插入;删除时,直接出栈无法实现队列的先进先出规则,这时需要将元素从stack1出栈,压到另一个栈stack2中,然后再从stack2中出栈就OK了。需要稍微注意的是:当stack2中还有元素,stack1中的元素不能压进来;当stack2中没元素时,stack1中的所有元素都必须压入stack2中。否则顺序就会被打乱。
16 |
17 | **测试用例**
18 |
19 | 1.往空队列添加删除元素
20 |
21 | 2.往非空队列添加删除元素
22 |
23 | 3.删除至队列为空
24 |
25 | ## **完整Java代码**
26 |
27 | (含测试代码)
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 | import java.util.Stack;
32 |
33 | /**
34 | *
35 | * @Description 用两个栈实现队列
36 | *
37 | * @author yongh
38 | * @date 2018年9月13日 下午2:17:22
39 | */
40 |
41 | // 题目:用两个栈实现一个队列。队列的声明如下,请实现它的两个函数appendTail
42 | // 和deleteHead,分别完成在队列尾部插入结点和在队列头部删除结点的功能。
43 |
44 | public class QueueWithTwoStacks {
45 |
46 | class Queue{
47 | Stack stack1 = new Stack();
48 | Stack stack2 = new Stack();
49 |
50 | /**
51 | * 插入结点
52 | */
53 | public void push(int node) {
54 | stack1.push(node);
55 | }
56 |
57 | /**
58 | * 删除结点
59 | */
60 | public int pop() {
61 | if (stack2.empty()) {
62 | if (stack1.empty())
63 | throw new RuntimeException("队列为空!");
64 | else {
65 | while (!stack1.empty())
66 | stack2.push(stack1.pop());
67 | }
68 | }
69 | return stack2.pop();
70 | }
71 | }
72 |
73 |
74 | //=======测试代码==========
75 |
76 | public void test1() {
77 | Queue queue= new Queue();
78 | queue.push(1);
79 | queue.push(2);
80 | System.out.println(queue.pop());
81 | queue.push(3);
82 | System.out.println(queue.pop());
83 | System.out.println(queue.pop());
84 | }
85 |
86 | /**
87 | * 往空队列删除元素
88 | */
89 | public void test2() {
90 | Queue queue= new Queue();
91 | System.out.println(queue.pop());
92 | }
93 |
94 | public static void main(String[] args) {
95 | QueueWithTwoStacks demo = new QueueWithTwoStacks();
96 | demo.test1();
97 | demo.test2();
98 | }
99 |
100 | }
101 |
102 |
103 | 
104 |
105 |
106 |
107 | 1
108 | 2
109 | 3
110 | Exception in thread "main" java.lang.RuntimeException: 队列为空!
111 |
112 | QueueWithTwoStacks
113 |
114 | ## **收获**
115 |
116 | 1.学会用画图将抽象问题形象化
117 |
118 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview**
119 |
120 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
121 |
122 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(50-2)字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(50-2) 字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。例如,当从字符流中只读出前两个字符"go"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是'g'。当从该字符流中读出前六个字符"google"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是'l'。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 字符只能一个一个从字符流中读出来,因此要定义一个容器来保存字符以及其在字符流中的位置。
16 |
17 | 为尽可能搞笑解决问题,要在O(1)时间内往数据容器中插入字符,及其对应的位置,因此这个数据容器可以用哈希表来实现,以字符的ASCII码作为哈希表的键值key,字符对应的位置作为哈希表的值value。
18 |
19 | 开始时,哈希表的值都初始化为-1,当读取到某个字符时,将位置存入value中,如果之前读取过该字符(即value
20 | >=0),将value赋值为-2,代表重复出现过。最后对哈希表遍历,在value>=0的键值对中找到最小的value,该value即为第一个只出现一次的字符,ASCII码为key的字符即为所求字符。
21 |
22 | **测试算例** ****
23 |
24 | 1.功能测试(读入一个字符;读入多个字符;所有字符都唯一;所有字符重复)
25 |
26 | 2.特殊测试(读入0个字符)
27 |
28 | ## **Java代码**
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 | //题目:请实现一个函数用来找出字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符。例如,当从
33 | //字符流中只读出前两个字符"go"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是'g'。当从该字
34 | //符流中读出前六个字符"google"时,第一个只出现一次的字符是'l'。
35 |
36 | public class FirstCharacterInStream {
37 | private int index;
38 | private int[] occurence;
39 |
40 | public FirstCharacterInStream() { //在构造函数中初始化成员变量
41 | index=0;
42 | occurence = new int[256];
43 | for(int i=0;i<256;i++) {
44 | occurence[i]=-1;
45 | }
46 | }
47 |
48 | public void insert(char ch) {
49 | if(occurence[(int)ch]==-1) {
50 | occurence[(int)ch]=index; //第一次出现
51 | }else if(occurence[(int)ch]>=0) {
52 | occurence[(int)ch]=-2; //已经出现过了
53 | }
54 | index++;
55 | }
56 |
57 | public char getFirst() {
58 | int minIndex=Integer.MAX_VALUE; //最大的integer
59 | char ch='#';
60 | for(int i=0;i<256;i++) {
61 | if(occurence[i]>=0 && occurence[i] 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 一个链表中包含环,如何找出环的入口结点?例如,在图3.8的链表中,环的入口结点是结点3。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 1.确定链表是否有环:通过两个不同速度的指针确定,当两个指针指向同一个结点时,该结点为环中的一个结点。
16 |
17 | 2.确定环中结点的数目n:指针走一圈,边走边计数
18 |
19 | 3.找到环的入口:从头结点开始,通过两个相差为n的指针来得到(即寻找链表中倒数第n个结点)
20 |
21 | 更简单的思路:[【LeetCode】142. Linked List Cycle
22 | II](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9981395.html "发布于2018-11-19 09:21")
23 |
24 | **测试算例** ****
25 |
26 | 1.功能测试(链表包含与不包含环;链表有多个或一个结点)
27 |
28 | 2.特殊测试(头结点为null)
29 |
30 | ## **Java代码**
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 | package _23;
35 | /**
36 | *
37 | * @Description 链表中环的入口结点
38 | *
39 | * @author yongh
40 | * @date 2018年10月15日 下午2:35:14
41 | */
42 |
43 | //题目:一个链表中包含环,如何找出环的入口结点?例如,在图3.8的链表中,
44 | //环的入口结点是结点3。
45 |
46 | /*
47 | * 思路:1.确定链表是否有环:通过两个不同速度的指针确定
48 | * 2.确定环中结点的数目n:指针走一圈,边走边计数
49 | * 3.找到环的入口:从头结点开始,通过两个相差为n的指针来得到(即寻找链表中倒数第n个结点)
50 | */
51 |
52 | public class EntryNodeInListLoop {
53 | public class ListNode {
54 | int val;
55 | ListNode next = null;
56 |
57 | ListNode(int val) {
58 | this.val = val;
59 | }
60 | }
61 |
62 | /*
63 | * 确定链表是否有环,采用快慢指针确定
64 | * 返回值代表快慢指针相遇时的结点,返回null代表链表无环
65 | */
66 | private ListNode meetingNode(ListNode head) {
67 | if(head==null)
68 | return null;
69 | ListNode pSlow=head;
70 | ListNode pFast=head;
71 | while(pFast!=null) {
72 | pSlow=pSlow.next;
73 | pFast=pFast.next;
74 | if(pFast!=null)
75 | pFast=pFast.next;
76 | if(pSlow!=null && pSlow==pFast)
77 | return pSlow;
78 | }
79 | return null;
80 | }
81 |
82 |
83 | /**
84 | * 计算环中入口结点
85 | */
86 | public ListNode entryNodeOfLoop(ListNode head) {
87 | ListNode meetingNode=meetingNode(head);
88 | if(meetingNode==null)
89 | return null;
90 |
91 | //计算环中结点的数目
92 | int count=1; //环中结点的数目
93 | ListNode pNode1 = meetingNode.next;
94 | while(pNode1!=meetingNode){
95 | count++;
96 | pNode1=pNode1.next;
97 | }
98 |
99 | //先移动pNode1,次数为count
100 | pNode1=head;
101 | for(int i=1;i<=count;i++) {
102 | pNode1=pNode1.next;
103 | }
104 | ListNode pNode2=head;
105 | while(pNode1!=pNode2) {
106 | pNode1=pNode1.next;
107 | pNode2=pNode2.next;
108 | }
109 | return pNode1;
110 | }
111 |
112 | }
113 |
114 |
115 | ## **收获**
116 |
117 | 1.通过两个不同速度的指针可以确定链表中是否有环
118 |
119 | 2.相差n步的两个指针可以找到倒数第n个结点链表中倒数第k个结点:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9788286.html)
120 |
121 | 3.复杂问题分解成为几个简单问题(本题分为三步:找出环中任一结点;得到环的个数;找到入口结点)
122 |
123 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
124 |
125 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
126 |
127 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(63)股票的最大利润.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(63) 股票的最大利润
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 假设把某股票的价格按照时间先后顺序存储在数组中,请问买卖交易该股票可能获得的利润是多少?例如一只股票在某些时间节点的价格为{9, 11, 8, 5,7,
14 | 12, 16, 14}。如果我们能在价格为5的时候买入并在价格为16时卖出,则能收获最大的利润11。
15 |
16 | ## 思路
17 |
18 | 遍历每一个数字,并保存之前最小的数字,两者差最大即为最大利润。 **
19 | **
20 |
21 | 值得注意的是,我自己一开始写的代码是默认不能亏本(即可以不买入卖出,利润不能为负数),所以比较简单;但如果可以亏本,最大利润指的是最小的亏损,那么要注意最小数字不能是最后一个。在下面的代码中可以注意比较两种情况的差别。可以考虑的例子如
22 | { 16, 11, 7, 4, 2, 1 }
23 |
24 | **测试算例** ****
25 |
26 | 1.功能测试(数组递增/递减/无序)
27 |
28 | 2.特殊测试(null,空数组)
29 |
30 | 3.边界值测试(数组仅两个数字)
31 |
32 | ## **Java代码**
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | //题目:假设把某股票的价格按照时间先后顺序存储在数组中,请问买卖交易该股
37 | //票可能获得的利润是多少?例如一只股票在某些时间节点的价格为{9, 11, 8, 5,
38 | //7, 12, 16, 14}。如果我们能在价格为5的时候买入并在价格为16时卖出,则能
39 | //收获最大的利润11。
40 |
41 | public class MaximalProfit {
42 | public static int MaxDiff(int[] arr) {
43 | if(arr==null || arr.length<2)
44 | return -1; //error
45 | int min=arr[0];
46 |
47 | //最大利润可以是负数,只要亏损最小就行
48 | int maxDiff=arr[1]-min;
49 | for(int i=1;imaxDiff)
53 | maxDiff=arr[i]-min;
54 | }
55 |
56 | //默认不能亏本,代码简单,上面复杂的代码注意细节
57 | // int maxDiff=0;
58 | // for(int i=1;imaxDiff)
62 | // maxDiff=arr[i]-min;
63 | // }
64 | return maxDiff;
65 | }
66 |
67 |
68 | //简单快速测试下
69 | public static void main(String[] args) {
70 | int[] arr1=null;
71 | System.out.println(MaxDiff(arr1)==-1);
72 |
73 | int[] arr2={ };
74 | System.out.println(MaxDiff(arr2)==-1);
75 |
76 | int[] arr3={ 16, 16, 16, 16, 16 };
77 | System.out.println(MaxDiff(arr3)==0);
78 |
79 | int[] arr4={ 1, 2, 4, 7, 11, 16 };
80 | System.out.println(MaxDiff(arr4)==15);
81 |
82 | int[] arr5={ 16, 11, 7, 4, 2, 1 };
83 | System.out.println(MaxDiff(arr5)==-1);
84 |
85 | int[] arr6={ 9, 11, 5, 7, 16, 1, 4, 2 };
86 | System.out.println(MaxDiff(arr6)==11);
87 |
88 | int[] arr7={ 2,4};
89 | System.out.println(MaxDiff(arr7)==2);
90 |
91 | int[] arr8={ 4,2};
92 | System.out.println(MaxDiff(arr8)==-2);
93 | }
94 | }
95 |
96 |
97 | 
98 |
99 |
100 |
101 | true
102 | true
103 | true
104 | true
105 | true
106 | true
107 | true
108 | true
109 |
110 | MaximalProfit
111 |
112 | ## **收获**
113 |
114 | 1.蛮力法时间复杂度为O(n^2),肯定不对。我们从头到尾遍历,确定规律。可以发现找出之前的最小值即可。
115 |
116 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
117 |
118 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
119 |
120 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Android基础/Android面试必备-http与https协议.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 | ## 前言
6 |
7 | 在讲解 http 与 https 之间的区别之前,我么先来看一下一个常见的面试问题。
8 |
9 | **一次完整的 http 协议请求过程是怎样的**
10 |
11 | 
12 |
13 | 该图片出自 [博客](https://blog.csdn.net/liudong8510/article/details/7908093)
14 |
15 |
16 | ## Http协议的主要特点
17 |
18 | 1. 支持客户/服务器模式
19 | 2. 简单快速:客户向服务端请求服务时,只需传送请求方式和路径。
20 | 3. 灵活:允许传输任意类型的数据对象。由Content-Type加以标记。
21 | 4. 无连接:每次响应一个请求,响应完成以后就断开连接。
22 | 5. 无状态:服务器不保存浏览器的任何信息。每次提交的请求之间没有关联。
23 |
24 |
25 | [怎么理解HTTP协议是无状态的无连接的的协议?](https://www.jianshu.com/p/30744fbd1f01)
26 |
27 | ### 非持续性和持续性
28 |
29 | HTTP1.0默认非持续性;HTTP1.1默认持续性
30 |
31 | 持续性:浏览器和服务器建立TCP连接后,可以请求多个对象
32 |
33 | 非持续性:浏览器和服务器建立TCP连接后,只能请求一个对象
34 |
35 | ### 非流水线和流水线
36 |
37 | 类似于组成里面的流水操作
38 |
39 | * 流水线:不必等到收到服务器的回应就发送下一个报文。
40 | * 非流水线:发出一个报文,等到响应,再发下一个报文。类似TCP。
41 |
42 |
43 | ### http 各个版本之间的区别
44 |
45 | 1.0 与 1.1
46 |
47 | - http1.0一次只能处理一个请求,不能同时收发数据
48 | - http1.1可以处理多个请求,能同时收发数据
49 | - http1.1增加可更多字段,如cache-control,keep-alive.
50 |
51 | 2.0
52 |
53 | - http 2.0采用二进制的格式传送数据,不再使用文本格式传送数据
54 | - http2.0对消息头采用hpack压缩算法,http1.x的版本消息头带有大量的冗余消息
55 | - http2.0 采用多路复用,即用一个tcp连接处理所有的请求,真正意义上做到了并发请求,流还支持优先级和流量控制(HTTP/1.x 虽然通过 pipeline也能并发请求,但是多个请求之间的响应会被阻塞的,所以 pipeline 至今也没有被普及应用,而 HTTP/2 做到了真正的并发请求。同时,流还支持优先级和流量控制。)
56 | - http2.0支持server push,服务端可以主动把css,jsp文件主动推送到客户端,不需要客户端解析HTML,再发送请求,当客户端需要的时候,它已经在客户端了。
57 |
58 |
59 | ### POST和GET的区别
60 |
61 | | Post一般用于更新或者添加资源信息 | Get一般用于查询操作,而且应该是安全和幂等的 |
62 | | ------------- |:-------------:|
63 | | Post更加安全 | Get会把请求的信息放到URL的后面 |
64 | | Post传输量一般无大小限制 | Get不能大于2KB |
65 | | Post执行效率低 | Get执行效率略高 |
66 |
67 |
68 | ### 为什么POST效率低,Get效率高
69 |
70 | * Get将参数拼成URL,放到header消息头里传递
71 | * Post直接以键值对的形式放到消息体中传递。
72 | * 但两者的效率差距很小很小
73 |
74 |
75 | ---
76 |
77 | ## Https
78 |
79 | HTTPS相当于HTTP的安全版本了,是在http的基础之上加上ssl(Secure Socket Layer)
80 |
81 | * 端口号是443
82 | * 是由SSL+Http协议构建的可进行加密传输、身份认证的网络协议。
83 |
84 | https在客户端(浏览器)与服务端(网站)传输加密的数据大概经历一下流程
85 | 1. 客户端将自己的has算法和加密算法发给服务器
86 | 2. 服务器接收到客户端发来的加密算法和has算法,取出自己的加密算法与has算法,并将自己的身份信息以证书的形式发送给客户端,该证书信息包括公钥,网站地址,预计颁发机构等
87 | 3. 客户端收到服务器发来的证书(即公钥),开始验证证书的合法性,如果证书信任,则生成一串随机的字符串数字作为私钥,并将私钥(密文)用证书(服务器的公钥)进行加密,发送给服务器
88 | 4. 服务器收到客户端发来的数据之后,通过服务器自己的私钥进行解密客户端发来的数据(客户端的私钥),(这样双方都拥有私钥)再进行hash检验,如果结果一致,则将客户端发来的字符串(第3个步骤发送过来的字符串)通过加密发送给客户端
89 | 5. 客户端解密,如果一致的话,就使用之前客户端随机生成的字符串进行对称加密算法进行加密
90 |
91 |
92 | 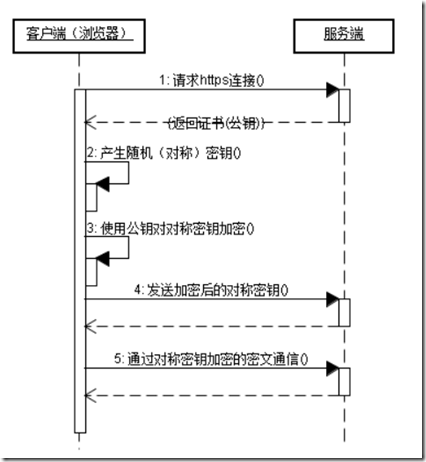
93 |
94 |
95 | ---
96 |
97 |
98 |
99 | ## 推荐阅读
100 |
101 | [聊一聊 Android 中巧妙的位操作](https://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu/article/details/84898590)
102 |
103 | [二分查找的相关算法题](https://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu/article/details/51292440)
104 |
105 | [快速排序的相关算法题(java)](https://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu/article/details/51299994)
106 |
107 | [Android 面试必备 - 计算机网络基本知识(TCP,UDP,Http,https)](https://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu/article/details/97618598)
108 |
109 | [360面试总结(Android)](https://blog.csdn.net/gdutxiaoxu/article/details/52371834)
110 |
111 | 
112 |
113 | **扫一扫,欢迎关注我的公众号 stormjun94。如果你有好的文章,也欢迎你的投稿。**
114 |
115 |
116 |
117 |
118 |
119 |
120 |
121 |
122 |
123 |
124 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(62)圆圈中最后剩下的数字.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(62) 圆圈中最后剩下的数字
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | [leetcode](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/yuan-quan-zhong-zui-hou-sheng-xia-de-shu-zi-lcof/solution/yuan-quan-zhong-zui-hou-sheng-xia-de-shu-zi-by-lee/)
12 |
13 | ## 题目
14 |
15 | 0, 1, …, n-1这n个数字排成一个圆圈,从数字0开始每次从这个圆圈里删除第m个数字。求出这个圆圈里剩下的最后一个数字。
16 |
17 | ## 思路
18 |
19 | **方法一** :采用链表来存放数据,每次对长度取余来实现循环
20 |
21 | 将所有数字放入LinkedList链表中(LinkedList比ArrayList更适合增删操作)。假设当前删除的结点下标为removeIndex,则下一个要删除的结点的下标为:(removeIndex+m-1)%list.size(),通过取余符号可以实现类型循环的操作。
22 |
23 | 注:没必要用循环链表,反而会更麻烦了。
24 |
25 | **方法二:** 数学推导规律
26 |
27 | n个数字的圆圈,不断删除第m个数字,我们把 **最后剩下的数字** 记为 **f(n,m)** 。
28 |
29 | n个数字中第一个被删除的数字是(m-1)%n, 我们记作k, **k=(m-1)%n** 。
30 |
31 | 那么剩下的n-1个数字就变成了:0,1,……k-1,k+1,……,n-1,我们把下一轮第一个数字排在最前面,并且将这个长度为n-1的数组映射到0~n-2。
32 |
33 | 原始数字:k+1,……, n-1, 0, 1,……k-1
34 |
35 | 映射数字:0 ,……,n-k-2, n-k-1, n-k,……n-2
36 |
37 | 把映射数字记为x,原始数字记为y,那么映射数字变回原始数字的公式为 **y=(x+k+1)%n** 。
38 |
39 | 在映射数字中,n-1个数字,不断删除第m个数字,由定义可以知道,最后剩下的数字为 **f(n-1,m)**
40 | 。我们把它变回原始数字,由上一个公式可以得到最后剩下的原始数字是 **( **f(n-1,m)**
41 | +k+1)%n,**而这个数字就是也就是一开始我们标记为的 **f(n,m)** ,所以可以推得递归公式如下:
42 |
43 | ****f(n,m) = **( **f(n-1,m)** +k+1)%n******
44 |
45 | 将 ** ** ** **k=(m-1)%n******** 代入,化简得到:
46 |
47 | ************f(n,m) = **( **f(n-1,m)** +m)%n**************
48 |
49 | **************************f(1,m) = 0**************************
50 |
51 | ************ 代码中可以采用循环或者递归的方法实现该递归公式。时间复杂度为 **O(n)** ,空间复杂度为 **O(1)** 。
52 |
53 | **测试算例** ****
54 |
55 | 1.功能测试(m大于/小于/等于n)
56 |
57 | 2.特殊测试(n、m <=0)
58 |
59 | 3.性能测试(n=4000,n=997)
60 |
61 | ## **Java代码**
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 | //题目:0, 1, …, n-1这n个数字排成一个圆圈,从数字0开始每次从这个圆圈里
66 | //删除第m个数字。求出这个圆圈里剩下的最后一个数字。
67 |
68 | public class LastNumberInCircle {
69 | /*
70 | * 方法一:采用推导出来的方法
71 | */
72 | public int LastRemaining_Solution(int n, int m) {
73 | if(n<1 || m<1)
74 | return -1; //出错
75 | int last=0;
76 | for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
77 | last=(last+m)% i; //这里是i不是n!!!
78 | }
79 | return last;
80 | }
81 |
82 | /*
83 | * 方法二:采用链表来存放,每次对长度取余来实现循环
84 | */
85 | public int LastRemaining_Solution2(int n, int m) {
86 | if(n<1 || m<1)
87 | return -1; //出错
88 | LinkedList list = new LinkedList();
89 | for(int i=0;i1){
93 | removeIndex=(removeIndex+m-1)%list.size();
94 | list.remove(removeIndex);
95 | }
96 | return list.getFirst();
97 | }
98 | }
99 |
100 |
101 | ## **收获**
102 |
103 | 1.对于下标循环一圈类似的问题,通过%可以很好地实现循环,而不需要我们自己构造循环链表;
104 |
105 | 2.(a%n+b)%n=(a+b)%n
106 |
107 | 3.尽量学会本题的数学方法,特别是要掌握好数字间映射的方法。
108 |
109 | 4.公式法中,`last=(last+m)% i; ``//这里是i不是n!!!`
110 |
111 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
112 |
113 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
114 |
115 | 
116 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(41)数据流中的中位数.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(41) 数据流中的中位数
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 所谓数据流,就是不会一次性读入所有数据,只能一个一个读取,每一步都要求能计算中位数。
16 |
17 | 将读入的数据分为两部分,一部分数字小,另一部分大。小的一部分采用大顶堆存放,大的一部分采用小顶堆存放。当总个数为偶数时,使两个堆的数目相同,则中位数=大顶堆的最大数字与小顶堆的最小数字的平均值;而总个数为奇数时,使小顶堆的个数比大顶堆多一,则中位数=小顶堆的最小数字。
18 |
19 | 因此,插入的步骤如下:
20 |
21 | 1.若已读取的个数为偶数(包括0)时,两个堆的数目已经相同,将新读取的数插入到小顶堆中,从而实现小顶堆的个数多一。但是,如果新读取的数字比大顶堆中最大的数字还小,就不能直接插入到小顶堆中了
22 | ,此时必须将新数字插入到大顶堆中,而将大顶堆中的最大数字插入到小顶堆中,从而实现小顶堆的个数多一。
23 |
24 | 2若已读取的个数为奇数时,小顶堆的个数多一,所以要将新读取数字插入到大顶堆中,此时方法与上面类似。
25 |
26 | **测试算例** ****
27 |
28 | 1.功能测试(读入奇/偶数个数字)
29 |
30 | 2.边界值测试(读入0个、1个、2个数字)
31 |
32 | ## **Java代码**
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | //题目:如何得到一个数据流中的中位数?如果从数据流中读出奇数个数值,那么
37 | //中位数就是所有数值排序之后位于中间的数值。如果从数据流中读出偶数个数值,
38 | //那么中位数就是所有数值排序之后中间两个数的平均值。
39 |
40 | import java.util.PriorityQueue;
41 | import java.util.Comparator;
42 |
43 | public class StreamMedian {
44 | PriorityQueue minHeap = new PriorityQueue(); //小顶堆,默认容量为11
45 | PriorityQueue maxHeap = new PriorityQueue(11,new Comparator(){ //大顶堆,容量11
46 | public int compare(Integer i1,Integer i2){
47 | return i2-i1;
48 | }
49 | });
50 | public void Insert(Integer num) {
51 | if(((minHeap.size()+maxHeap.size())&1)==0){//偶数时,下个数字加入小顶堆
52 | if(!maxHeap.isEmpty() && maxHeap.peek()>num){
53 | maxHeap.offer(num);
54 | num=maxHeap.poll();
55 | }
56 | minHeap.offer(num);
57 | }else{//奇数时,下一个数字放入大顶堆
58 | if(!minHeap.isEmpty() && minHeap.peek() maxHeap = new PriorityQueue(11,new Comparator(){ //大顶堆,容量11
87 | @Override
88 | public int compare(Integer i1,Integer i2){
89 | return i2-i1; //降序排列
90 | }
91 | });
92 |
93 |
94 | PriorityQueue的常用方法有:poll(),offer(Object),size(),peek()等。
95 |
96 | 2.平均值应该定义为double,且(a+b)/ **2.0** 。
97 |
98 | 3.往最大堆中插入数据时间复杂度是O(log _n_ ),获取最大数的时间复杂度是O(1)。
99 |
100 | 4.这道题关键在于分成两个平均分配的部分,奇偶时分别插入到最大最小堆中,利用最大最小堆性质的插入方法要掌握。
101 |
102 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
103 |
104 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
105 |
106 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(35)复杂链表的复制.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(35) 复杂链表的复制
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 请实现函数ComplexListNode* Clone(ComplexListNode*
12 | pHead),复制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个结点除了有一个m_pNext指针指向下一个点外,还有一个m_pSibling
13 | 指向链表中的任意结点或者nullptr。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 思路1:先复制结点,用next链接,最后根据原始结点的sibling指针确定该sibling结点距离头结点的位置,从而对复制结点设置sibling指针。但是该思路对于n个结点的链表,每个结点的sibling都需要O(n)个时间步才能找到,所以时间复杂度为O(n^2)
18 |
19 | 思路2:复制原始结点N创建N’,用next链接。将
20 | 的配对信息存放入一个哈希表中;在设置sibling时,通过哈希表,只需要用O(1)的时间即可找到复制结点的sibling。该方法的时间复杂度为O(n),但空间复杂度为O(n)。
21 |
22 | **思路3**
23 | :复制原始结点N创建N’,将N'链接到N的后面;根据原始结点N的sibling可以快速设置N'结点的sibling,最后将这个长链表拆分成原始链表和复制链表(根据奇偶位置)
24 |
25 | **测试算例** ****
26 |
27 | 1.功能测试(sibling指向自己;链表只有一个结点;sibling指向null或者指向结点)
28 |
29 | 2.特殊测试(头结点为null)
30 |
31 | ## **Java代码**
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 | //题目:请实现函数ComplexListNode* Clone(ComplexListNode* pHead),复
36 | //制一个复杂链表。在复杂链表中,每个结点除了有一个m_pNext指针指向下一个
37 | //结点外,还有一个m_pSibling 指向链表中的任意结点或者nullptr。
38 |
39 |
40 | public class CopyComplexList {
41 | public class ComplexListNode {
42 | int val;
43 | ComplexListNode next = null;
44 | ComplexListNode sibling = null;
45 |
46 | ComplexListNode(int label) {
47 | this.val = label;
48 | }
49 | }
50 |
51 | /*
52 | * 主程序(包含三步)
53 | */
54 | public ComplexListNode cloneList(ComplexListNode head) {
55 | cloneNodes(head); //1.复制结点
56 | connectSiblingNodes(head); //2.设置sibling
57 | return reconnectNodes(head);//3.拆分长链表
58 | }
59 |
60 | /*
61 | * 第一步:复制每个结点,并插入到原始节点的后面
62 | */
63 | private void cloneNodes(ComplexListNode head) {
64 | ComplexListNode pNode=head;
65 | while(pNode!=null) {
66 | ComplexListNode clonedNode=new ComplexListNode(pNode.val);
67 | clonedNode.next=pNode.next;
68 | pNode.next=clonedNode;
69 | pNode=clonedNode.next;
70 | }
71 | }
72 |
73 | /*
74 | * 第二步:根据原结点的sibling,设置复制结点的sibling
75 | */
76 | private void connectSiblingNodes(ComplexListNode head) {
77 | ComplexListNode pNode=head;
78 | while(pNode!=null) {
79 | if(pNode.sibling!=null) //必须考虑到siblingNode==null的情况!
80 | pNode.next.sibling=pNode.sibling.next;
81 | pNode=pNode.next.next;
82 | }
83 | }
84 |
85 | /*
86 | * 第三步:将长链表拆分成原始链表和复制链表(根据奇偶位置)
87 | */
88 | private ComplexListNode reconnectNodes(ComplexListNode head) {
89 | ComplexListNode clonedHead=null;
90 | ComplexListNode clonedNode=null;
91 | ComplexListNode pNode=head;
92 | if(head!=null) {
93 | clonedHead=head.next;
94 | clonedNode=pNode.next;
95 | pNode.next=clonedNode.next;
96 | pNode=pNode.next; //提前将pNode指向下一个结点,方便判断是否为null
97 | }
98 | while(pNode!=null) {
99 | clonedNode.next=pNode.next;
100 | clonedNode=clonedNode.next;
101 | pNode.next=clonedNode.next;
102 | pNode=pNode.next;
103 | }
104 | return clonedHead;
105 | }
106 | }
107 |
108 |
109 | ## **收获**
110 |
111 | 1.涉及链表结点操作,必须时刻注意对null的判断
112 |
113 | 2.复制链表时,在原始结点后面直接插入复制结点,这种方法非常方便,有较高的时间效率,先记住,以后可能会遇到类似的应用
114 |
115 | 3.查找时间复杂度为O(1),可以考虑使用哈希表。哈希表的应用要掌握。
116 |
117 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
118 |
119 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
120 |
121 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/国内使用chatgpt的使用教程.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 国内使用g-pt的方式汇总
2 |
3 | 最近几天OpenAI发布的ChatGPT聊天机器人火出天际了,连着上了各个平台的热搜榜。这个聊天机器人最大的特点是模仿人类说话风格同时回答大量问题。
4 |
5 | 有人说ChatGPT是真正的人工智能,它不仅能和你聊天,还是写小作文,回答问题,甚至帮你写代码。
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | 
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 | **0 ChatGPT可以做什么**
14 |
15 | **写一封情书**
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 | 
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 | **回答各种问题**
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | 
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | 
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 | **帮你写代码**
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 | 
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 | 当然这里展示的也只是ChatGPT功能的冰山一角,更多好玩的玩法需要大家自己去发现。看到这,你是不是也按捺不住想自己玩一把哦。现在我就来教大家如何注册ChatGPT账号。
46 |
47 | **1.准备工作**
48 |
49 | (1)能访问村外的网络环境
50 |
51 | 韩国、新加坡、日本、印度这几个地址最好
52 |
53 | 亲测香港是100%不可行的
54 |
55 | (2)国外手机号
56 |
57 | 一般人肯定没有,有的话直接跳到步骤4去 OpenAI官网注册就行
58 |
59 | 所以我就教大家如何通过第三方接码平台来完成注册(短信费不到2块)
60 |
61 | PS:目前最便宜的注册方式啦
62 |
63 | **2.注册第三方接码平台**
64 |
65 | (有国外手机号的跳转步骤4哦)
66 |
67 | 打开网站:[https://sms-activate.org/cn](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//sms-activate.org/cn)
68 |
69 |
70 |
71 | 
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | 点击右上角的注册按钮:
76 |
77 | 在注册页面输入自己的邮箱账号,设置密码后提交。会给你的邮箱发一条验证邮件,点击邮件中的链接确认即完成注册。
78 |
79 | **3.充值**
80 |
81 | 支持支付宝付款,充值主要是用于接收验证码
82 |
83 | 注册完成后,登录进去,再点击右上角的充值按钮,选择支付宝付款。我们充值0.2美元就够了
84 |
85 |
86 |
87 | 
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | 充值完成后,在页面右上角可以看到账户余额
92 |
93 |
94 |
95 | 
96 |
97 |
98 |
99 | **4.注册OpenAI账号**
100 |
101 | 打开:[https://beta.openai.com/signup](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//beta.openai.com/signup)页面进行相应的账号注册
102 |
103 | 这里注意你的网络环境不能是香港哦,不然会提示不能在当前国家服务
104 |
105 | 在打开的页面输入你的邮箱号(国内邮箱也可以),或者有谷歌账号的用谷歌账号注册也可以
106 |
107 | 输入邮箱号的需要在邮箱收到的邮件内点击验证,然后继续在注册页面填入信息
108 |
109 | **5.输入验证码**
110 |
111 | 上一步输入完信息后点击Continue按钮进行手机验证码校验
112 |
113 |
114 |
115 | 
116 |
117 |
118 |
119 | 有国外手机号的这一步直接输手机号注册啊。
120 |
121 | 没有的,现在就可以用到步骤3里注册的第三方接码平台了。 在平台左侧搜索 openai,然后在下面国家那里找到Indonesia(印度尼西亚),(亲测现在只有印尼是可用的,从销售量看也是印尼卖的最多了)
122 |
123 | 然后加入购物车(这一步就已经买了)
124 |
125 |
126 |
127 | 
128 |
129 |
130 |
131 | 然后等一会出现如下界面 把这里的手机号拷贝出来,输入到上一步中注册OpenAI的界面上,然后点击 Send code按钮,等待验证码短信发送
132 |
133 | PS:注意购买后的短信有效期是20分钟,需要快速操作哦~
134 |
135 |
136 |
137 | 
138 |
139 |
140 |
141 | 再等一会,平台收到验证码短信后会发出提示音,我们把验证码拷贝出来输入到OpenAI的注册界面即可。如下图所示
142 |
143 |
144 |
145 | 
146 |
147 |
148 |
149 | 最后就是注册完成的页面了,这里随便选一个就行
150 |
151 |
152 |
153 | 
154 |
155 |
156 |
157 | 登录体验 账号注册完成了,但是还不知道从哪里去玩?
158 |
159 | 重新登录:[http://chat.openai.com/auth/login](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=http%3A//chat.openai.com/auth/login)
160 |
161 | 然后访问:[http://chat.openai.com/chat](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=http%3A//chat.openai.com/chat)
162 |
163 | 这时你就可以开始尽情和机器人聊天了
164 |
165 | 其他注意 注意香港的网络是无法注册,也无法使用ChatGPT的
166 |
167 | 参考:https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_21834881
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/国内使用chatgpt的使用教程(2023 年2月8号,亲测可用).md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 国内使用g-pt的方式汇总
2 |
3 | 最近几天OpenAI发布的ChatGPT聊天机器人火出天际了,连着上了各个平台的热搜榜。这个聊天机器人最大的特点是模仿人类说话风格同时回答大量问题。
4 |
5 | 有人说ChatGPT是真正的人工智能,它不仅能和你聊天,还是写小作文,回答问题,甚至帮你写代码。
6 |
7 |
8 |
9 | 
10 |
11 |
12 |
13 | **0 ChatGPT可以做什么**
14 |
15 | **写一封情书**
16 |
17 |
18 |
19 | 
20 |
21 |
22 |
23 | **回答各种问题**
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | 
28 |
29 |
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | 
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 | **帮你写代码**
38 |
39 |
40 |
41 | 
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 | 当然这里展示的也只是ChatGPT功能的冰山一角,更多好玩的玩法需要大家自己去发现。看到这,你是不是也按捺不住想自己玩一把哦。现在我就来教大家如何注册ChatGPT账号。
46 |
47 | **1.准备工作**
48 |
49 | (1)能访问村外的网络环境
50 |
51 | 韩国、新加坡、日本、印度这几个地址最好
52 |
53 | 亲测香港是100%不可行的
54 |
55 | (2)国外手机号
56 |
57 | 一般人肯定没有,有的话直接跳到步骤4去 OpenAI官网注册就行
58 |
59 | 所以我就教大家如何通过第三方接码平台来完成注册(短信费不到2块)
60 |
61 | PS:目前最便宜的注册方式啦
62 |
63 | **2.注册第三方接码平台**
64 |
65 | (有国外手机号的跳转步骤4哦)
66 |
67 | 打开网站:[https://sms-activate.org/cn](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//sms-activate.org/cn)
68 |
69 |
70 |
71 | 
72 |
73 |
74 |
75 | 点击右上角的注册按钮:
76 |
77 | 在注册页面输入自己的邮箱账号,设置密码后提交。会给你的邮箱发一条验证邮件,点击邮件中的链接确认即完成注册。
78 |
79 | **3.充值**
80 |
81 | 支持支付宝付款,充值主要是用于接收验证码
82 |
83 | 注册完成后,登录进去,再点击右上角的充值按钮,选择支付宝付款。我们充值0.2美元就够了
84 |
85 |
86 |
87 | 
88 |
89 |
90 |
91 | 充值完成后,在页面右上角可以看到账户余额
92 |
93 |
94 |
95 | 
96 |
97 |
98 |
99 | **4.注册OpenAI账号**
100 |
101 | 打开:[https://beta.openai.com/signup](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=https%3A//beta.openai.com/signup)页面进行相应的账号注册
102 |
103 | 这里注意你的网络环境不能是香港哦,不然会提示不能在当前国家服务
104 |
105 | 在打开的页面输入你的邮箱号(国内邮箱也可以),或者有谷歌账号的用谷歌账号注册也可以
106 |
107 | 输入邮箱号的需要在邮箱收到的邮件内点击验证,然后继续在注册页面填入信息
108 |
109 | **5.输入验证码**
110 |
111 | 上一步输入完信息后点击Continue按钮进行手机验证码校验
112 |
113 |
114 |
115 | 
116 |
117 |
118 |
119 | 有国外手机号的这一步直接输手机号注册啊。
120 |
121 | 没有的,现在就可以用到步骤3里注册的第三方接码平台了。 在平台左侧搜索 openai,然后在下面国家那里找到Indonesia(印度尼西亚),(亲测现在只有印尼是可用的,从销售量看也是印尼卖的最多了)
122 |
123 | 然后加入购物车(这一步就已经买了)
124 |
125 |
126 |
127 | 
128 |
129 |
130 |
131 | 然后等一会出现如下界面 把这里的手机号拷贝出来,输入到上一步中注册OpenAI的界面上,然后点击 Send code按钮,等待验证码短信发送
132 |
133 | PS:注意购买后的短信有效期是20分钟,需要快速操作哦~
134 |
135 |
136 |
137 | 
138 |
139 |
140 |
141 | 再等一会,平台收到验证码短信后会发出提示音,我们把验证码拷贝出来输入到OpenAI的注册界面即可。如下图所示
142 |
143 |
144 |
145 | 
146 |
147 |
148 |
149 | 最后就是注册完成的页面了,这里随便选一个就行
150 |
151 |
152 |
153 | 
154 |
155 |
156 |
157 | 登录体验 账号注册完成了,但是还不知道从哪里去玩?
158 |
159 | 重新登录:[http://chat.openai.com/auth/login](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=http%3A//chat.openai.com/auth/login)
160 |
161 | 然后访问:[http://chat.openai.com/chat](https://link.zhihu.com/?target=http%3A//chat.openai.com/chat)
162 |
163 | 这时你就可以开始尽情和机器人聊天了
164 |
165 | 其他注意 注意香港的网络是无法注册,也无法使用ChatGPT的
166 |
167 | 参考:https://www.thepaper.cn/newsDetail_forward_21834881
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(53-1)数字在排序数组中出现的次数.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(53-1) 数字在排序数组中出现的次数
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | **正文**
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数。例如输入排序数组{1, 2, 3, 3,3, 3, 4, 5}和数字3,由于3在这个数组中出现了4次,因此输出4。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 分析:对于例子来说,如果采用二分法找到某一个3后,再往前遍历和往后遍历到第一个和最后一个3,在长度为n的数组中有可能出现O(n)个3,因此这样的扫描方法时间复杂度为
18 | **O(n)** ,效率与从头到尾扫描一样,速度太慢。
19 |
20 | 这题关键是找到第一个和最后一个3,因此我们尝试改进二分法:中间数字比3大或者小的情况与之前类似,关键是中间数字等于3的情况,这时可以分类讨论如下:
21 |
22 | 1)如果中间数字的前一个数字也等于3,说明第一个3在前面,继续在前半段查找第一个3;
23 |
24 | 2)如果中间数字的前一个数字不等于3,说明该位置是第一个3;
25 |
26 | 3)如果中间数字的后一个数字也等于3,说明最后一个3在后面,继续在后半段查找最后一个3;
27 |
28 | 2)如果中间数字的后一个数字不等于3,说明该位置是最后一个3;
29 |
30 | 附加:牛客网上还有一种算法:如果找数字k的次数,由于数组是整数,可以直接找k-0.5和k+0.5应该在数组中哪个位置,这种方法就不用讨论这么多情况了。(不过double类型的大小比较不知道是否会增加太多时间消耗)。
31 |
32 | **测试算例** ****
33 |
34 | 1.功能测试(数字出现次数为0、1、2等)
35 |
36 | 2.边界值测试(数组只有一个数字,查找数字为第一个或者最后一个)
37 |
38 | 2.特殊测试(null)
39 |
40 | ## **Java代码**
41 |
42 |
43 |
44 | //题目:统计一个数字在排序数组中出现的次数。例如输入排序数组{1, 2, 3, 3,
45 | //3, 3, 4, 5}和数字3,由于3在这个数组中出现了4次,因此输出4。
46 |
47 | public class NumberOfK {
48 | public int GetNumberOfK(int [] array , int k) {
49 | if(array==null || array.length<=0)
50 | return 0;
51 | int firstK = getFirstK(array,0,array.length-1,k);
52 | if(firstK == -1)
53 | return 0;
54 | int lastK = getLastK(array,firstK,array.length-1,k);
55 | return lastK-firstK+1;
56 | }
57 |
58 | private int getFirstK(int[] arr, int start, int end,int k){
59 | if(start>end)
60 | return -1;
61 | int mid = (start+end)>>1;
62 | if(arr[mid]==k){
63 | if( mid == 0 ||arr[mid-1]!=k )
64 | return mid;
65 | else
66 | end = mid-1;
67 | }else if(arr[mid]end)
77 | return -1;
78 | int mid = (start+end)>>1;
79 | if(arr[mid]==k){
80 | if(mid==arr.length-1 || arr[mid+1]!=k )
81 | return mid;
82 | else
83 | start = mid+1;
84 | }else if(arr[mid]>1;
110 | if(arr[mid]>m){
111 | end=mid-1;
112 | }else{
113 | start=mid+1;
114 | }
115 | }
116 | return start;
117 | }
118 |
119 |
120 | ## **收获**
121 |
122 | 1.53-3:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9958138.html#_label3
123 |
124 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
125 |
126 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
127 |
128 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(4)替换空格.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(4) 替换空格
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | _本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。_
6 |
7 | _**更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview**_
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 请实现一个函数,把字符串中的每个空格替换成"%20"。例如输入“We are happy.”,则输出“We%20are%20happy.”。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 首先要询问面试官是新建一个字符串还是在原有的字符串上修改,本题要求 在原有字符串上进行修改。
16 |
17 | 若从前往后依次替换,在每次遇到空格字符时,都需要移动后面O(n)个字符,对于含有O(n)个空格字符的字符串而言,总的时间效率为O(n2)。
18 |
19 | 转变思路:先计算出需要的总长度,然后从后往前进行复制和替换,,则每个字符只需要复制一次即可。时间效率为O(n)。
20 |
21 | **测试用例**
22 |
23 | 1.字符串中无空格
24 |
25 | 2.字符串中含有空格(连续空格,空格在首尾等)
26 |
27 | 3.字符串为空字符串或者为null
28 |
29 | ## **完整Java代码**
30 |
31 | 1.根据牛客网的编程练习参考,方法的输入为StringBuffer(String无法改变长度,所以采用StringBuffer),输出为String。
32 |
33 | 主程序中,可以利用 StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer(str); 来获得字符串的StringBuffer。
34 |
35 | 2.代码中包含测试代码
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | /**
40 | *
41 | * @Description 替换空格
42 | *
43 | * @author yongh
44 | * @date 2018年7月18日 上午11:25:52
45 | */
46 |
47 | // 题目:请实现一个函数,把字符串中的每个空格替换成"%20"。例如输入“We are happy.”,
48 | // 则输出“We%20are%20happy.”。
49 |
50 | public class ReplaceSpaces {
51 |
52 | /**
53 | * 实现空格的替换
54 | */
55 | public String replaceSpace(StringBuffer str) {
56 | if (str == null) {
57 | System.out.println("输入错误!");
58 | return null;
59 | }
60 | int length = str.length();
61 | int indexOfOriginal = length-1;
62 | for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
63 | if (str.charAt(i) == ' ')
64 | length += 2;
65 | }
66 | str.setLength(length);
67 | int indexOfNew = length-1;
68 | while (indexOfNew > indexOfOriginal) {
69 | if (str.charAt(indexOfOriginal) != ' ') {
70 | str.setCharAt(indexOfNew--, str.charAt(indexOfOriginal));
71 | } else {
72 | str.setCharAt(indexOfNew--, '0');
73 | str.setCharAt(indexOfNew--, '2');
74 | str.setCharAt(indexOfNew--, '%');
75 | }
76 | indexOfOriginal--;
77 | }
78 | return str.toString();
79 | }
80 |
81 | // ==================================测试代码==================================
82 |
83 | /**
84 | * 输入为null
85 | */
86 | public void test1() {
87 | System.out.print("Test1:");
88 | StringBuffer sBuffer = null;
89 | String s = replaceSpace(sBuffer);
90 | System.out.println(s);
91 | }
92 |
93 | /**
94 | * 输入为空字符串
95 | */
96 | public void test2() {
97 | System.out.print("Test2:");
98 | StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer("");
99 | String s = replaceSpace(sBuffer);
100 | System.out.println(s);
101 | }
102 |
103 | /**
104 | * 输入字符串无空格
105 | */
106 | public void test3() {
107 | System.out.print("Test3:");
108 | StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer("abc");
109 | String s = replaceSpace(sBuffer);
110 | System.out.println(s);
111 | }
112 |
113 | /**
114 | * 输入字符串为首尾空格,中间连续空格
115 | */
116 | public void test4() {
117 | System.out.print("Test4:");
118 | StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer(" a b c ");
119 | String s = replaceSpace(sBuffer);
120 | System.out.println(s);
121 | }
122 |
123 | public static void main(String[] args) {
124 | ReplaceSpaces rs = new ReplaceSpaces();
125 | rs.test1();
126 | rs.test2();
127 | rs.test3();
128 | rs.test4();
129 | }
130 | }
131 |
132 | 
133 |
134 |
135 |
136 | Test1:输入错误!
137 | null
138 | Test2:
139 | Test3:abc
140 | Test4:%20a%20b%20%20c%20%20
141 |
142 | ReplaceSpaces
143 |
144 | **收获:** 如果在从前往后进行复制时,需要多次移动数据,则可以考虑从后往前复制,从而减小移动次数,提高效率。
145 |
146 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview**
147 |
148 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
149 |
150 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(57-2)为s的连续正数序列.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(57-2) 为s的连续正数序列
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 输入一个正数s,打印出所有和为s的连续正数序列(至少含有两个数)。例如输入15,由于1+2+3+4+5=4+5+6=7+8=15,所以结果打印出3个连续序列1~5、4~6和7~8。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | **指针法:**
18 |
19 | 类似[(57-1) 和为s的两个数字](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9961940.html
20 | "发布于2018-11-15 10:15")的方法,用两个指针small和big分别代表序列的最大值和最小值。令small从1开始,big从2开始。
21 |
22 | 当从small到big的序列的和小于s时,增加big,使序列包含更多数字;(记得更新序列之和)
23 |
24 | 当从small到big的序列的和大于s时,增加small,使序列去掉较小的数字;(记得更新序列之和)
25 |
26 | 当从small到big的序列的和等于s时,此时得到一个满足题目要求的序列,输出,然后继续将small增大,往后面找新的序列。
27 |
28 | 序列最少两个数字,因此,当small到了s/2时,就可以结束判断了。
29 |
30 | **数学分析法:**
31 |
32 | 参考牛客网](https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/c451a3fd84b64cb19485dad758a55ebe),[丁满历险记:https://www.nowcoder.com/profile/5073898的答案。
33 |
34 | 对于一个长度为n的连续序列,如果它们的和等于s,有:
35 |
36 | 1)当n为奇数时,s/n恰好是连续序列最中间的数字,即n满足 **(n &1)==1 && s%n==0**
37 |
38 | 2)当n为偶数时,s/n恰好是连续序列中间两个数字的平均值,小数部分为0.5,即n满足 **(s%n)*2==n (** 判断条件中包含了n为偶数的判断)
39 |
40 | 得到满足条件的n后,相当于得到了序列的中间数字s/n,所以可以得到第一个数字为 **(s / n) - (n - 1) / 2**
41 | ,结合长度n可以得到所有数字。
42 |
43 | 此外,在什么范围内找n呢?我们知道n至少等于2,那至多等于多少?n最大时,序列从1开始,根据等差数列的求和公式根据等差数列的求和公式:S = (1 + n)
44 | * n / 2,可以得到n应该小于sqrt(2s),所以只需要从n=2到sqrt(2s)来判断满足条件的n,继而输出序列。
45 |
46 | **测试算例** ****
47 |
48 | 1.功能测试(存在/不存在和为s的序列)
49 |
50 | 2.边界值测试(s=3)
51 |
52 | ## **Java代码**
53 |
54 | **方法一:**
55 |
56 |
57 |
58 | //题目:输入一个正数s,打印出所有和为s的连续正数序列(至少含有两个数)。
59 | //例如输入15,由于1+2+3+4+5=4+5+6=7+8=15,所以结果打印出3个连续序列1~5、
60 | //4~6和7~8。
61 |
62 | public class ContinuousSquenceWithSum {
63 | //方法一:采用两个指针的方法
64 | public ArrayList > FindContinuousSequence(int sum) {
65 | ArrayList > sequenceList = new ArrayList >();
66 | if(sum<=0)
67 | return sequenceList;
68 |
69 | int small = 1;
70 | int big = 2;
71 | int curSum = small+big;
72 | while(small <= sum/2){
73 | if(curSum == sum){
74 | ArrayList sequence = new ArrayList();
75 | for(int i=small;i<=big;i++)
76 | sequence.add(i);
77 | sequenceList.add(sequence);
78 | curSum-=small;
79 | small++; //这两行位置先后要注意
80 | }
81 | if(curSum < sum){
82 | big++;
83 | curSum+=big;
84 | }
85 | if(curSum > sum){
86 | curSum-=small;
87 | small++;
88 | }
89 | }
90 | return sequenceList;
91 | }
92 | }
93 |
94 |
95 | 方法二:
96 |
97 |
98 |
99 | //方法二:数学分析法
100 | public ArrayList > FindContinuousSequence(int sum) {
101 | ArrayList > sequenceList = new ArrayList >();
102 | if(sum<=0)
103 | return sequenceList;
104 |
105 | for(int n=(int) Math.sqrt(2*sum);n>=2;n--){
106 | if(((n&1)==1 && sum%n==0) || ((n&1)==0 && (sum%n)*2==n)){
107 | ArrayList sequence = new ArrayList<>();
108 | for (int j = 0, k = (sum / n) - (n - 1) / 2; j < n; j++, k++) {
109 | sequence.add(k);
110 | }
111 | sequenceList.add(sequence);
112 | }
113 | }
114 | return sequenceList;
115 | }
116 |
117 |
118 | ## **收获**
119 |
120 | 1.还是利用两个指针,这个技巧要学会
121 |
122 | 2.代码中求连续序列的和,并没有每次遍历计算,而是根据每次操作的情况而在之前的结果上进行加减,可以提高效率,值得学习
123 |
124 | 3.题目[57-1) 和为s的两个数字](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9961940.html
125 | "发布于2018-11-15 10:15")中的指针是从两端开始,本题指针从1,2开始,注意指针的初始设置。
126 |
127 | 4.方法二中,当s/n的余数为0.5时,s%n的结果是n/2,而不是1。
128 |
129 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
130 |
131 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
132 |
133 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(29)顺时针打印矩阵.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(29) 顺时针打印矩阵
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 每次打印矩阵最外面的一圈(用方法printMatrixInCircle()表示),每次都是这个操作,所以可以采用递归。每次打印矩阵的左上角的横纵坐标相同,即为start,而其余三个角的坐标都与行列数以及start有关,因此只需要for循环即可实现打印。
16 |
17 | 当然,其实只要针对start进行循环判断, start*2的值小于行数和列数时才需要继续打印,这样,通过这个条件,可以用循环来打印每次的最外圈矩阵。
18 |
19 | **测试算例** ****
20 |
21 | 多行多列,单行多列,多行单列,一个数的矩阵,空矩阵,null
22 |
23 | ## **Java代码**
24 |
25 |
26 |
27 | //题目:输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字。
28 |
29 | public class PrintMatrix {
30 | public void printMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
31 | if(matrix==null || matrix.length<=0)
32 | return;
33 | printMatrixInCircle(matrix, 0);
34 | }
35 |
36 | private void printMatrixInCircle(int[][] matrix,int start) {
37 | int row=matrix.length;
38 | int col=matrix[0].length;
39 | int endX=col-1-start;
40 | int endY=row-1-start;
41 | if(endX=start;i--) {
66 | System.out.print(matrix[endY][i]+" ");
67 | }
68 | for(int i=endY-1;i>=start+1;i--) {
69 | System.out.print(matrix[i][start]+" ");
70 | }
71 |
72 | //继续打印更内部的矩阵,令start+1
73 | printMatrixInCircle(matrix, start+1);
74 | }
75 |
76 |
77 | public static void main(String[] args) {
78 | PrintMatrix demo = new PrintMatrix();
79 | int[][] a= {{1,2,3,4},{5,6,7,8},{9,10,11,12},{13,14,15,16}};
80 | // int[][] a= {};
81 | // int[][] a= {{}};
82 | // int[][] a= {{1}};
83 | // int[][] a= {{1,2,3,4}};
84 | // int[][] a= {{1},{2},{3},{4}};
85 | // int[][] a= {{1,2,3},{4,5,6}};
86 | // int[][] a=null;
87 | demo.printMatrix(a);
88 | }
89 |
90 |
91 | 下面的代码是来牛客网:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/9b4c81a02cd34f76be2659fa0d54342a的C++代码:1.采用的是循环;2.在打印一圈时,单行或者单列情况只需要在从右往左打印和从下往上打印时判断是否会出现重复打印(即后面两个for循环)。代码比较简洁。
92 |
93 |
94 |
95 | /*解题思路:顺时针打印就是按圈数循环打印,一圈包含两行或者两列,在打印的时候会
96 | 出现某一圈中只包含一行,要判断从左向右打印和从右向左打印的时候是否会出现重复打印,
97 | 同样只包含一列时,要判断从上向下打印和从下向上打印的时候是否会出现重复打印的情况*/
98 | class Solution {
99 | public:
100 | vector printMatrix(vector > matrix) {
101 | vectorres;
102 | res.clear();
103 | int row=matrix.size();//行数
104 | int collor=matrix[0].size();//列数
105 | //计算打印的圈数
106 | int circle=((row=i)&&(row-i-1!=i);m--)
116 | res.push_back(matrix[row-i-1][m]);
117 | //判断是否会重复打印(从下往上的每一列数据)
118 | for(int n=row-i-2;(n>i)&&(collor-i-1!=i);n--)
119 | res.push_back(matrix[n][i]);}
120 | return res;
121 | }
122 | };
123 |
124 |
125 | ## **收获**
126 |
127 | 1.打印一圈矩阵时,注意单行或者单列时是否会重复打印。
128 |
129 | 2.每一圈矩阵左上角的横纵坐标相等,其余三个角的坐标可以由左上角坐标获得。
130 |
131 | 3.打印矩阵的圈数与其列数或者行数的一半有关。简单但要能想到。
132 |
133 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
134 |
135 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
136 |
137 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(36)二叉搜索树与双向链表.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(36) 二叉搜索树与双向链表
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 二叉搜索树、排序链表,想到使用中序遍历。
16 |
17 | 要实现双向链表,必须知道当前结点的前一个结点。根据中序遍历可以知道,当遍历到根结点的时候,左子树已经转化成了一个排序的链表了,根结点的前一结点就是该链表的最后一个结点(这个结点必须记录下来,将遍历函数的返回值设置为该结点即可),链接根结点和前一个结点,此时链表最后一个结点就是根结点了。再处理右子树,遍历右子树,将右子树的最小结点与根结点链接起来即可。左右子树的转化采用递归即可。
18 |
19 | 大概思想再理一下:首先想一下中序遍历的大概代码结构(先处理左子树,再处理根结点,之后处理右子树),假设左子树处理完了,就要处理根结点,而根结点必须知道左子树的最大结点,所以要用函数返回值记录下来;之后处理右子树,右子树的最小结点(也用中序遍历得到)要和根结点链接。
20 |
21 | 注意搞清楚修改后的中序遍历函数的意义(见代码注释)
22 |
23 | **测试算例** ****
24 |
25 | 1.功能测试(一个结点;左右斜树;完全二叉树;普通二叉树)
26 |
27 | 2.特殊测试(根结点为null)
28 |
29 | ## **Java代码**
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | //题目:输入一棵二叉搜索树,将该二叉搜索树转换成一个排序的双向链表。要求
34 | //不能创建任何新的结点,只能调整树中结点指针的指向。
35 |
36 | public class ConvertBinarySearchTree {
37 | public class TreeNode {
38 | int val = 0;
39 | TreeNode left = null;
40 | TreeNode right = null;
41 |
42 | public TreeNode(int val) {
43 | this.val = val;
44 | }
45 | }
46 |
47 | public TreeNode convert(TreeNode head) {
48 | if(head==null)
49 | return head;
50 | TreeNode lastNodeInList=null;
51 | lastNodeInList=convertHelper(head,lastNodeInList);
52 | TreeNode firstNodeInList=lastNodeInList;
53 | while(firstNodeInList.left!=null) {
54 | firstNodeInList=firstNodeInList.left;
55 | }
56 | return firstNodeInList;
57 | }
58 |
59 | //将以node为根结点的树转化为排序链表,链表头部与lastNode链接,并返回最后一个结点
60 | private TreeNode convertHelper(TreeNode node,TreeNode lastNode) {
61 | //处理左子树,获得最大结点
62 | if(node.left!=null)
63 | lastNode=convertHelper(node.left, lastNode);
64 | //链接最大结点和根结点
65 | node.left=lastNode;
66 | if(lastNode!=null)
67 | lastNode.right=node;
68 | //处理右子树
69 | lastNode=node;
70 | if(node.right!=null)
71 | lastNode=convertHelper(node.right, lastNode);
72 | return lastNode;
73 | }
74 | }
75 |
76 |
77 | 上面的代码是参考《剑指OFFER》写的,下面的代码是复习时重新写过的,思路比较简洁一点。非递归方法的核心是中序遍历非递归实现:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9629940.html#_label1。
78 |
79 |
80 |
81 | public class Solution {
82 | /*
83 | * 递归版本
84 | * 1.已知函数返回的是转换好的双向链表头结点
85 | * 2.左子树处理完后与根结点连接
86 | * 3.右子树处理,也与根结点连接
87 | * 4.最后返回头结点
88 | */
89 | public TreeNode Convert(TreeNode root) {
90 | if (root == null)
91 | return root;
92 | // 处理左子树,获得左子树链表的头结点
93 | TreeNode left = Convert(root.left);
94 | TreeNode p = left;
95 | if (left != null) {
96 | // 找到左子树链表的末尾结点
97 | while (p.right != null)
98 | p = p.right;
99 | // 连接结点
100 | p.right = root;
101 | root.left = p;
102 | }
103 | // 处理右子树,获得右子树链表的头结点
104 | TreeNode right = Convert(root.right);
105 | // 连接结点
106 | if (right != null) {
107 | root.right = right;
108 | right.left = root;
109 | }
110 | return left == null ? root : left;
111 | }
112 |
113 | /* 非递归版本
114 | * 1.利用非递归中序遍历来连接结点
115 | */
116 | public TreeNode Convert1(TreeNode root) {
117 | TreeNode head = null;
118 | TreeNode pre = null;
119 | LinkedList stack = new LinkedList<>();
120 | while (root != null || !stack.isEmpty()) {
121 | // 把root当作指针使用
122 | while (root != null) {
123 | stack.push(root);
124 | root = root.left;
125 | }
126 | TreeNode node = stack.pop();
127 | if (head == null) {
128 | head = node;
129 | pre = node;
130 | } else {
131 | node.left = pre;
132 | pre.right = node;
133 | pre = node; // 别漏写了
134 | }
135 | root = node.right;
136 | }
137 | return head;
138 | }
139 | }
140 |
141 |
142 | ## **收获**
143 |
144 | 题目较复杂时,不要慌。这道题和中序遍历有关,把树分为三部分:根结点、左子树和右子树,思考在中序遍历中根结点应该如何处理,这是关键——要将左子树的最大结点、根结点、右子树的最小结点链接起来。左右子树的处理是相同的,因此采用递归。
145 |
146 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
147 |
148 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
149 |
150 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(34)二叉树中和为某一值的路径.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(34) 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 1.假设找到了其中一条路径,达到叶结点后,由于没有指向父结点的指针,所以必须 **提前创建一个链表** 存储前面经过的结点。
16 |
17 | 2.由于是从根结点出发,所以要想到使用 **前序遍历**
18 |
19 | 3.利用链表存储结点,在该结点完成左右子树的路径搜索后(即递归函数结束,返回到其父结点之前),要 **删除该结点** ,从而记录别的路径。
20 |
21 | **具体实现:**
22 | 通过前序遍历,从根结点出发,每次在链表中存储遍历到的结点,若到达叶子结点,则根据所有结点的和是否等于输入的整数,判断是否打印输出。在当前结点访问结束后,递归函数将会返回到它的父结点,所以在函数退出之前,要删除链表中的当前结点,以确保返回父结点时,储存的路径刚好是从根结点到父结点。
23 |
24 | **改进:**
25 | 书中的代码是根据所有结点的和是否等于输入的整数,判断是否打印输出。其实没有这个必要,只需要在每次遍历到一个结点时,令目标整数等于自己减去当前结点的值,若到达根结点时,最终的目标整数等于0就可以打印输出。(描述得不是很清楚,就是相当于每个结点的目标整数不同,详见代码)
26 |
27 | **测试算例** ****
28 |
29 | 1.功能测试(一条或者多条对应路径;无对应路径;结点值为正负零;)
30 |
31 | 2.特殊测试(根结点为null)
32 |
33 | ## **Java代码**
34 |
35 |
36 |
37 | //题目:输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所
38 | //有路径。从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
39 |
40 | public class PathInTree {
41 | public class TreeNode {
42 | int val = 0;
43 | TreeNode left = null;
44 | TreeNode right = null;
45 | public TreeNode(int val) {
46 | this.val = val;
47 | }
48 | }
49 |
50 | public void findPath(TreeNode root,int target) {
51 | if(root==null)
52 | return;
53 | ArrayList list= new ArrayList<>();
54 | printPath(root, target,list);
55 | }
56 |
57 | private void printPath(TreeNode node,int target,ArrayList list) {
58 | if(node==null)
59 | return;
60 | list.add(node.val);
61 | target-=node.val; //每个结点的target不会受到方法的影响而改变
62 | if(target==0 && node.left==null && node.right==null) { //叶子结点
63 | for (Integer integer : list)
64 | System.out.print(integer+" ");
65 | System.out.println();
66 | }else { //中间结点
67 | printPath(node.left, target, list);
68 | printPath(node.right, target, list);
69 | }
70 | list.remove(list.size()-1);
71 | }
72 |
73 |
74 | 牛客网中题目:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/b736e784e3e34731af99065031301bca?toCommentId=2213961有多两点要求:1.返回类型为ArrayList>,即返回所有路径的集合;2.要求返回的集合中,长度大的靠前。下面是实现的代码:
75 |
76 |
77 |
78 | /*
79 | * 几个要点:
80 | * 1. 将nodeList和pathList定义成全局变量,避免在方法中的多次传递
81 | * 2. 在pathList中添加nodeList时,因为nodeList会不断变化,所以必须新建一个list存入
82 | * 复制ArrayList的方法:newList=new ArrayList(oldList)(复制内容,而不是复制地址,注意与newList=oldList的区分)
83 | * 3. 在当前结点完成左右子树的路径搜索后,记得删除nodeList中的当前结点
84 | * 4. target是基本数据类型int,不会受到方法的影响而改变
85 | */
86 | private ArrayList nodeList= new ArrayList<>();
87 | private ArrayList> pathList = new ArrayList<>();
88 |
89 | public ArrayList> FindPath(TreeNode node,int target) {
90 | if(node==null)
91 | return pathList;
92 | nodeList.add(node.val);
93 | target-=node.val;
94 | if(target==0 && node.left==null && node.right==null) { //叶子结点
95 | //长度大的nodeList插入到pathList的前面
96 | int i=0;
97 | while(i(nodeList)); //nodeList会随方法变化,必须新建一个list存入pathList中!
100 | }else { //不是叶子结点
101 | pathList=FindPath(node.left, target);
102 | pathList=FindPath(node.right, target);
103 | }
104 | nodeList.remove(nodeList.size()-1); //记得删除当前结点
105 | return pathList;
106 | }
107 |
108 |
109 | ## **收获**
110 |
111 | 1.二叉树的许多题目与遍历(包括层序遍历)有关,要深刻理解;根据根结点的位置判断使用哪一种遍历。
112 |
113 | 2.二叉树遍历过程没有父结点指针,要保存路径的话,必须要创建容器存储之前的结点。
114 |
115 | 3.熟悉这道题中在每次递归函数结束前删除当前结点的操作,这可以确保返回到父结点时路径刚好是从根结点到父结点。
116 |
117 | 4.target-=node.val这句代码非常好,多多体会。
118 |
119 | 5.牛客网的那部分代码:在链表中存储一个对象时,如果该对象是不断变化的,则应该创建一个新的对象复制该对象的内容(而不是指向同一个对象),将这个新的对象存储到链表中。。如果直接存储该对象的话,链表中的对象也会不断变化。基本数据类型和String则没有这种问题。说到底其实是存储的是地址还是值的问题这篇文章:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9821916.html讨论了一下。
120 |
121 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
122 |
123 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
124 |
125 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(2)不修改数组找出重复的数字.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(2) 不修改数组找出重复的数字
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | _本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。_
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview**
8 |
9 | ## **题目**
10 |
11 | 在一个长度为n+1的数组里的所有数字都在1到n的范围内,所以数组中至少有一个数字是重复的。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字,但不能修改输入的数组。例如,如果输入长度为8的数组{2,
12 | 3, 5, 4, 3, 2, 6, 7},那么对应的输出是重复的数字2或者3。
13 |
14 | ## **思路**
15 |
16 | 数组长度为n+1,而数字只从1到n,说明
17 | 必定有重复数字。可以由二分查找法拓展:把1~n的数字从中间数字m分成两部分,若前一半1~m的数字数目超过m个,说明重复数字在前一半区间,否则,在后半区间m+1~n。每次在区间中都一分为二,知道找到重复数字。
18 |
19 | **更简单的思路:** 把该数组看作一个链表,下标代表当前结点,值代表next指针,具体参考[Find the Duplicate
20 | Number](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9981582.html),时间复杂度仅为O(n)
21 |
22 | **测试用例**
23 |
24 | 1.数组中带一个或多个重复数字
25 |
26 | 2. 数组中不包含重复的数字
27 |
28 | 3.无效输入测试用例(空数组,数组数字越界等)
29 |
30 | ## **完整Java代码**
31 |
32 | (含测试代码)
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | /**
37 | *
38 | * @Description 不修改数组找出重复的数字
39 | *
40 | * @author yongh
41 | * @date 2018年7月16日 上午11:47:44
42 | */
43 |
44 | /*
45 | * 题目:在一个长度为n+1的数组里的所有数字都在1到n的范围内,所以数组中至
46 | * 少有一个数字是重复的。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字,但不能修改输入的
47 | * 数组。例如,如果输入长度为8的数组{2, 3, 5, 4, 3, 2, 6, 7},那么对应的
48 | * 输出是重复的数字2或者3。
49 | */
50 | public class FindDuplication2 {
51 |
52 | /**
53 | * 找到数组中一个重复的数字
54 | * 返回-1代表无重复数字或者输入无效
55 | */
56 | public int getDuplicate(int[] arr) {
57 | if (arr == null || arr.length <= 0) {
58 | System.out.println("数组输入无效!");
59 | return -1;
60 | }
61 | for (int a : arr) {
62 | if (a < 1 || a > arr.length - 1) {
63 | System.out.println("数字大小超出范围!");
64 | return -1;
65 | }
66 | }
67 | int low = 1;
68 | int high = arr.length - 1; // high即为题目的n
69 | int mid, count;
70 | while (low <= high) {
71 | mid = ((high - low) >> 2) + low;
72 | count = countRange(arr, low, mid);
73 | if (low == high) {
74 | if (count > 1)
75 | return low;
76 | else
77 | break; // 必有重复,应该不会出现这种情况吧?
78 | }
79 | if (count > mid - low + 1) {
80 | high = mid;
81 | } else {
82 | low = mid + 1;
83 | }
84 | }
85 | return -1;
86 | }
87 |
88 | /**
89 | * 返回在[low,high]范围中数字的个数
90 | */
91 | public int countRange(int[] arr, int low, int high) {
92 | if (arr == null)
93 | return 0;
94 |
95 | int count = 0;
96 | for (int a : arr) {
97 | if (a >= low && a <= high)
98 | count++;
99 | }
100 | return count;
101 | }
102 |
103 | // ==================================测试代码==================================
104 | /**
105 | *数组为null
106 | */
107 | public void test1() {
108 | System.out.print("test1:");
109 | int[] a = null;
110 | int dup = getDuplicate(a);
111 | if (dup >= 0)
112 | System.out.println("重复数字为:" + dup);
113 | }
114 |
115 | /**
116 | *数组数字越界
117 | */
118 | public void test2() {
119 | System.out.print("test2:");
120 | int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
121 | int dup = getDuplicate(a);
122 | if (dup >= 0)
123 | System.out.println("重复数字为:" + dup);
124 | }
125 |
126 | /**
127 | *数组带重复数字
128 | */
129 | public void test3() {
130 | System.out.print("test3:");
131 | int[] a = { 1, 2, 3, 2, 4 };
132 | int dup = getDuplicate(a);
133 | if (dup >= 0)
134 | System.out.println("重复数字为:" + dup);
135 | }
136 |
137 | public static void main(String[] args) {
138 | FindDuplication2 f2 = new FindDuplication2();
139 | f2.test1();
140 | f2.test2();
141 | f2.test3();
142 | }
143 | }
144 |
145 |
146 | 
147 | 
148 |
149 |
150 |
151 | test1:数组输入无效!
152 | test2:数字大小超出范围!
153 | test3:重复数字为:2
154 |
155 | FindDuplication2
156 |
157 | ## 复杂度
158 |
159 | 时间复杂度说明:函数countRange()将被调用O(logn)次,每次需要O(n)的时间。
160 |
161 | 时间复杂度:O(nlogn) (while循环为O(logn),coutRange()函数为O(n))
162 |
163 | 空间复杂度:O(1)
164 |
165 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview**
166 |
167 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
168 |
169 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(67)把字符串转换成整数.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(67) 把字符串转换成整数
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | ## 题目
12 |
13 | 请你写一个函数StrToInt,实现把字符串转换成整数这个功能。当然,不能使用atoi或者其他类似的库函数。
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 题目很简单,主要就是实现对每个字符转化为数字,并进行累加即可。但是有很多特殊情况都需要考虑进去,例如null、空字符串、带有正负号、字符不是数字、溢出等等。
18 |
19 | 对于非法的特殊输入,返回值为0,还要用一个全局变量进行标记。
20 |
21 | 写代码时一定要考虑清楚各种测试用例。
22 |
23 | **测试用例**
24 |
25 | 1.功能测试(正、负、零、带有正负号的数字)
26 |
27 | 2.边界值测试(最大正整数,最小负整数)
28 |
29 | 3.特殊测试(null,数空字符串,仅有正负号,非法字符)
30 |
31 | ## **Java代码**
32 |
33 | 今天脑子有点乱,代码总感觉不是很简洁,有点繁琐,但功能是完善的。
34 |
35 | 附注:字符串如果仅有正负号这里认定为非法输入
36 |
37 |
38 |
39 | //题目:请你写一个函数StrToInt,实现把字符串转换成整数这个功能。当然,不
40 | //能使用atoi或者其他类似的库函数。
41 |
42 | public class StringToInt {
43 | static boolean isValid = false;
44 | public static int strToInt(String str) {
45 | if(str == null || str.length()<=0)
46 | return 0;
47 | char[] chars = str.toCharArray();
48 | long num=0; //先用long来存储,以防止越界
49 | boolean minus=false;
50 | for(int i=0; i9){
58 | isValid=false;
59 | return 0;
60 | }
61 | num= (minus==false) ? num*10+a : num*10-a;
62 | isValid=true; //不放在最后面是为了防止str=‘+’的情况被判断为true
63 | if((!minus && num>0x7FFFFFFF)
64 | ||(minus && num<0x80000000)){
65 | isValid=false;
66 | return 0;
67 | }
68 | }
69 | }
70 | return (int)num;
71 | }
72 |
73 | //简单测试下
74 | public static void main(String[] args) {
75 | System.out.println(strToInt("1948243")==1948243);
76 | System.out.println(isValid==true);
77 | System.out.println(strToInt("+1948243")==1948243);
78 | System.out.println(isValid==true);
79 | System.out.println(strToInt("-1948243")==-1948243);
80 | System.out.println(isValid==true);
81 | System.out.println(strToInt("-0")==0);
82 | System.out.println(isValid==true);
83 | System.out.println(strToInt("-194+8243")==0);
84 | System.out.println(isValid==false);
85 | System.out.println(strToInt("")==0);
86 | System.out.println(isValid==false);
87 | System.out.println(strToInt(null)==0);
88 | System.out.println(isValid==false);
89 | System.out.println(strToInt("999999999999999")==0);
90 | System.out.println(isValid==false);
91 | System.out.println(strToInt("+")==0);
92 | System.out.println(isValid==false);
93 |
94 | System.out.println(strToInt("2147483647")==2147483647); //0x7FFFFFFF
95 | System.out.println(isValid==true);
96 | System.out.println(strToInt("2147483648")==0);
97 | System.out.println(isValid==false);
98 |
99 | System.out.println(strToInt("-2147483648")==-2147483648); //0x80000000
100 | System.out.println(isValid==true);
101 | System.out.println(strToInt("-2147483649")==0);
102 | System.out.println(isValid==false);
103 | }
104 | }
105 |
106 |
107 | 
108 |
109 |
110 |
111 | true
112 | true
113 | true
114 | true
115 | true
116 | true
117 | true
118 | true
119 | true
120 | true
121 | true
122 | true
123 | true
124 | true
125 | true
126 | true
127 | true
128 | true
129 | true
130 | true
131 | true
132 | true
133 | true
134 | true
135 | true
136 | true
137 |
138 | StringToInt
139 |
140 | ## **收获**
141 |
142 | 1.熟练掌char类型转化为int类型操作:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9688259.html。
143 |
144 | 2.边界值测试,记住int类型最大正整数为 **0x7FFFFFFF** ,最小负整数为 **0x80000000** 。
145 |
146 | 3.注意到了负号,也要注意到正号。
147 |
148 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
149 |
150 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
151 |
152 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/目录]《剑指Offer》Java实现.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【目录】《剑指Offer》Java实现
2 |
3 | > 作者:华仔要长胖
4 | 来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9637260.html
5 |
6 | 如题:
7 | 1) 找出数组中重复的数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9318604.html
8 | 2) 不修改数组找出重复的数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9318819.html
9 | 3) 二维数组中的查找:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9619591.html
10 | 4) 替换空格:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9328270.html
11 | 5) 从尾到头打印链表:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9622919.html
12 | 6) 重建二叉树:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9635690.html
13 | 7) 二叉树的下一个结点:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9637187.html
14 | 8) 用两个栈实现队列:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9640514.html
15 | 9) 斐波那契数列及青蛙跳台阶问题:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9642411.html
16 | 10) 旋转数组的最小数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9649169.html
17 | 11) 矩阵中的路径:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9655745.html
18 | 12) 机器人的运动范围:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9660324.html
19 | 13) 剪绳子:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9660802.html
20 | 14) 二进制中1的个数:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9662478.html
21 | 15) 数值的整数次方:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9664297.html
22 | 16) 打印1到最大的n位数:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9667104.html
23 | 17) 在O(1)时间删除链表结点:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9669660.html
24 | 18) 删除链表中重复的结点:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9672004.html
25 | 19) 正则表达式匹配:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9684663.html
26 | 20) 表示数值的字符串:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9765589.html
27 | 21) 调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9788193.html
28 | 22) 链表中倒数第k个结点:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9788286.html
29 | 23) 链表中环的入口结点:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9791064.html
30 | 24) 反转链表:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9791485.html
31 | 25) 合并两个排序的链表:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9791945.html
32 | 26) 树的子结构:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9798618.html
33 | 27) 二叉树的镜像:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9798818.html
34 | 28) 对称的二叉树:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9799231.html
35 | 29) 顺时针打印矩阵:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9804640.html
36 | 30) 包含min函数的栈:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9804934.html
37 | 31) 栈的压入、弹出序列:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9806442.html
38 | 32) 从上往下打印二叉树:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9812691.html
39 | 33) 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9819233.html
40 | 34) 二叉树中和为某一值的路径:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9821754.html
41 | 35) 复杂链表的复制:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9858421.html
42 | 36) 二叉搜索树与双向链表:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9860700.html
43 | 37) 序列化二叉树:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9866301.html
44 | 38) 字符串的排列:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9869719.html
45 | 39) 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9938889.html
46 | 40) 最小的k个数:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9944155.html
47 | 41) 数据流中的中位数:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9944993.html
48 | 42) 连续子数组的最大和:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9945510.html
49 | 43) 从1到n整数中1出现的次数:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9947165.html
50 | 44) 数字序列中某一位的数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9948651.html
51 | 45) 把数组排成最小的数:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9949312.html
52 | 46) 把数字翻译成字符串:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9950362.html
53 | 47) 礼物的最大价值:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9950556.html
54 | 48) 最长不含重复字符的子字符串:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9951159.html
55 | 50-1) 字符串中第一个只出现一次的字符:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9954083.html
56 | 50-2) 字符流中第一个只出现一次的字符:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9954206.html
57 | 51)数组中的逆序对:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9955977.html
58 | 52) 两个链表的第一个公共结点:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9956450.html
59 | 53-1) 数字在排序数组中出现的次数:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9957949.html
60 | 53-2) 0到n-1中缺失的数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9958093.html
61 | 53-3) 数组中数值和下标相等的元素:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9958138.html
62 | 54) 二叉搜索树的第k个结点:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9958513.html
63 | 55-1) 二叉树的深度:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9958736.html
64 | 55-2) 平衡二叉树:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9959131.html
65 | 56-1) 数组中只出现一次的两个数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9960018.html
66 | 56-2) 数组中唯一只出现一次的数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9960447.html
67 | 57-1) 和为s的两个数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9961940.html
68 | 57-2) 为s的连续正数序列:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9962159.html
69 | 58-1) 翻转单词顺序:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9963135.html
70 | 58-2) 左旋转字符串:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9963605.html
71 | 59-1) 滑动窗口的最大值:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9964581.html
72 | 59-2) 队列的最大值:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9965541.html
73 | 60) n个骰子的点数:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9967578.html
74 | 61) 扑克牌的顺子:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9968180.html
75 | 62) 圆圈中最后剩下的数字:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9970189.html
76 |
77 | [63) 股票的最大利润
78 | ](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9970538.html)
79 | 64) 求1+2+…+n:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9971111.html
80 | 65) 不用加减乘除做加法:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9971383.html
81 | 66) 构建乘积数组:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9971936.html
82 | 67) 把字符串转换成整数:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9973036.html
83 | 68) 树中两个结点的最低公共祖先:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9975302.html
84 |
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(7)二叉树的下一个结点.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(7) 二叉树的下一个结点
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | _本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。_
6 |
7 | _**更多《 剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview**_
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 给定一棵二叉树和其中的一个结点,如何找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点? 树中的结点除了有两个分别指向左右子结点的指针以外,还有一个指向父结点的指针。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 首先自己在草稿纸上画图,进行分析(不再展开)。可以发现下一个结点的规律为:
16 |
17 | 1.若当前结点有右子树时,其下一个结点为右子树中最左子结点;
18 |
19 | 2.若当前结点无右子树时,
20 |
21 | (1)若当前结点为其父结点的左子结点时,其下一个结点为其父结点;
22 |
23 | (2)若当前结点为其父结点的右子结点时,继续向上遍历父结点的父结点,直到找到一个结点是其父结点的左子结点(与(1)中判断相同),该结点即为下一结点。
24 |
25 | **测试用例**
26 |
27 | 1.正常二叉树
28 |
29 | 2.左斜树、右斜树
30 |
31 | 4.单个结点
32 |
33 | 5.null
34 |
35 | 6.不同位置结点的下一结点(即上面分析的几种情况、无下一节点等情况)
36 |
37 | ## **完整 Java代码**
38 |
39 | (含测试代码)
40 |
41 | 由于树的生成较为繁琐,下面不含全部测试代码,但主体代码已经通过了牛客网中的测试,可以保证没有问题。
42 |
43 |
44 |
45 | /**
46 | *
47 | * @Description 二叉树的下一个结点
48 | *
49 | * @author yongh
50 | * @date 2018年9月12日 下午7:20:45
51 | */
52 |
53 | // 题目:给定一棵二叉树和其中的一个结点,如何找出中序遍历顺序的下一个结点?
54 | // 树中的结点除了有两个分别指向左右子结点的指针以外,还有一个指向父结点的指针。
55 |
56 | public class NextNodeInBinaryTrees {
57 | private class TreeLinkNode {
58 | int val;
59 | TreeLinkNode left = null;
60 | TreeLinkNode right = null;
61 | TreeLinkNode parent = null;
62 |
63 | TreeLinkNode(int val) {
64 | this.val = val;
65 | }
66 | }
67 |
68 | public TreeLinkNode GetNext(TreeLinkNode pNode) {
69 | if (pNode == null) {
70 | System.out.print("结点为null ");
71 | return null;
72 | }
73 | if (pNode.right != null) {
74 | pNode = pNode.right;
75 | while(pNode.left!=null)
76 | pNode=pNode.left;
77 | return pNode;
78 | }
79 | while(pNode.parent !=null){
80 | if(pNode==pNode.parent .left)
81 | return pNode.parent;
82 | pNode=pNode.parent;
83 | }
84 | return null;
85 | }
86 |
87 |
88 | // ==================================测试代码==================================
89 | //创建树较为繁琐,未包括所有测试代码。
90 | public void test1() {
91 | TreeLinkNode node = null;
92 | TreeLinkNode nextNode = GetNext(node);
93 | if(nextNode!=null)
94 | System.out.println(nextNode.val);
95 | else
96 | System.out.println("无下一结点");
97 | }
98 |
99 | public void test2() {
100 | TreeLinkNode node1 = new TreeLinkNode(1);
101 | TreeLinkNode node2 = new TreeLinkNode(2);
102 | TreeLinkNode node3 = new TreeLinkNode(3);
103 | TreeLinkNode node4 = new TreeLinkNode(4);
104 | node1.left = node2;
105 | node1.right = node3;
106 | node2.parent = node1;
107 | node3.parent = node1;
108 | node4.left=node1;
109 | node1.parent=node4;
110 | TreeLinkNode nextNodeOf1=GetNext(node1);
111 | TreeLinkNode nextNodeOf2=GetNext(node2);
112 | TreeLinkNode nextNodeOf3=GetNext(node3);
113 | TreeLinkNode nextNodeOf4=GetNext(node4);
114 | if(nextNodeOf1!=null)
115 | System.out.println("1结点的下一个结点值为:"+nextNodeOf1.val);
116 | else
117 | System.out.println("1结点无下一结点");
118 | if(nextNodeOf2!=null)
119 | System.out.println("2结点的下一个结点值为:"+nextNodeOf2.val);
120 | else
121 | System.out.println("2结点无下一结点");
122 | if(nextNodeOf3!=null)
123 | System.out.println("3结点的下一个结点值为:"+nextNodeOf3.val);
124 | else
125 | System.out.println("3结点无下一结点");
126 | if(nextNodeOf4!=null)
127 | System.out.println("4结点的下一个结点值为:"+nextNodeOf4.val);
128 | else
129 | System.out.println("4结点无下一结点");
130 | }
131 |
132 | public static void main(String[] args) {
133 | NextNodeInBinaryTrees demo = new NextNodeInBinaryTrees();
134 | System.out.print("test1:");
135 | demo.test1();
136 | System.out.print("test2:");
137 | demo.test2();
138 | }
139 | }
140 |
141 |
142 | 
143 |
144 |
145 |
146 | test1:结点为null 无下一结点
147 | test2:1结点的下一个结点值为:3
148 | 2结点的下一个结点值为:1
149 | 3结点的下一个结点值为:4
150 | 4结点无下一结点
151 |
152 | NextNodeInBinaryTrees
153 |
154 | ## **收获**
155 |
156 | 1.在面对复杂问题时要学会画图和举例分析
157 |
158 | 2.在分情况讨论时,一定要考虑到所有情况,这些都是在写代码前需要考虑到的。
159 |
160 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview**
161 |
162 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
163 |
164 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(14)二进制中1的个数.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(14) 二进制中1的个数
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 请实现一个函数,输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。例如把9表示成二进制是1001,有2位是1。因此如果输入9,该函数输出2。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 遇到与二进制有关的题目,应该想到位运算(与、或、异或、左移、右移)。
16 |
17 | 方法一:”与运算“有一个性质:通过与对应位上为1,其余位为0的数进行与运算,可以某一整数指定位上的值。这道题中,先把整数n与1做与运算,判断最低位是否为1;接着把1左移一位,与n做与运算,可以判断次低位是否为1……反复左移,即可对每一个位置都进行判断,从而可以获得1的个数。这种方法需要循环判断32次。
18 |
19 | 方法二(better):如果一个整数不为0,把这个整数减1,那么原来处在整数最右边的1就会变为0,原来在1后面的所有的0都会变成1。其余所有位将不会受到影响。再把原来的整数和减去1之后的结果做与运算,从原来整数最右边一个1那一位开始所有位都会变成0。因此,把一个整数减1,再和原来的整数做与运算,会把该整数最右边的1变成0。这种方法,整数中有几个1,就只需要循环判断几次。
20 |
21 | **测试用例**
22 |
23 | 1.正数(包括边界值1、0x7FFFFFFF)
24 |
25 | 2.负数(包括边界值0x80000000、0xFFFFFFFF)
26 |
27 | 3.0
28 |
29 | ## **完整Java代码**
30 |
31 | (含测试代码)
32 |
33 |
34 |
35 | /**
36 | *
37 | * @Description 面试题15:二进制中1的个数
38 | *
39 | * @author yongh
40 | * @date 2018年9月17日 下午3:01:16
41 | */
42 |
43 | // 题目:请实现一个函数,输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。例如
44 | // 把9表示成二进制是1001,有2位是1。因此如果输入9,该函数输出2。
45 |
46 | public class NumberOf1InBinary {
47 | public int NumberOf1_Solution1(int n) {
48 | int count = 0;
49 | int flag = 1;
50 | while (flag != 0) {
51 | if ((flag & n) != 0)
52 | count++;
53 | flag = flag << 1;
54 | }
55 | return count;
56 | }
57 |
58 | public int NumberOf1_Solution2(int n) {
59 | int count = 0;
60 | while (n != 0) {
61 | count++;
62 | n = (n - 1) & n;
63 | }
64 | return count;
65 | }
66 |
67 | // =========测试代码=========
68 |
69 | void test(String testName, int n, int expected) {
70 | if (testName != null)
71 | System.out.println(testName + ":");
72 | if (NumberOf1_Solution1(n) == expected) {
73 | System.out.print(" soluton1:" + "passed ");
74 | } else {
75 | System.out.print(" solution1:" + "failed ");
76 | }
77 |
78 | if (NumberOf1_Solution2(n) == expected) {
79 | System.out.println("soluton2:" + "passed ");
80 | } else {
81 | System.out.println("solution2:" + "failed ");
82 | }
83 | }
84 |
85 | void test1() {
86 | test("Test for 0", 0, 0);
87 | }
88 |
89 | void test2() {
90 | test("Test for 1", 1, 1);
91 | }
92 |
93 | void test3() {
94 | test("Test for 10", 10, 2);
95 | }
96 |
97 | void test4() {
98 | test("Test for 0x7FFFFFFF", 0x7FFFFFFF, 31);
99 | }
100 |
101 | void test5() {
102 | test("Test for 0xFFFFFFFF", 0xFFFFFFFF, 32);
103 | }
104 |
105 | void test6() {
106 | test("Test for 0x80000000", 0x80000000, 1);
107 | }
108 |
109 | public static void main(String[] args) {
110 | NumberOf1InBinary demo = new NumberOf1InBinary();
111 | demo.test1();
112 | demo.test2();
113 | demo.test3();
114 | demo.test4();
115 | demo.test5();
116 | demo.test6();
117 | }
118 | }
119 |
120 |
121 | 
122 |
123 |
124 |
125 | Test for 0:
126 | soluton1:passed soluton2:passed
127 | Test for 1:
128 | soluton1:passed soluton2:passed
129 | Test for 10:
130 | soluton1:passed soluton2:passed
131 | Test for 0x7FFFFFFF:
132 | soluton1:passed soluton2:passed
133 | Test for 0xFFFFFFFF:
134 | soluton1:passed soluton2:passed
135 | Test for 0x80000000:
136 | soluton1:passed soluton2:passed
137 |
138 | NumberOf1InBinary
139 |
140 | ## **收获**
141 |
142 | 1.与二进制有关的题目要往位运算方面想,复习一下二进制位运算的几个用法:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9971520.html
143 |
144 | 2.注意: **负数右移还是负数!** 即如果对n=0x8000
145 | 0000右移,最高位的1是不会变的。如果这道题目通过令n=n>>1来计算n中1的个数,该数最终会变成0xFFFF FFFF而陷入死循环!
146 |
147 | 3. **把一个整数减1,再和原来的整数做与运算,会把该整数最右边的1变成0。** 这种方法一定要牢牢记住,很多情况下都可能用到,例如:
148 |
149 | _1)一句话判断一个整数是否为2的整数次方;_
150 |
151 | _2)对两个整数m和n,计算需要改变m二进制表示中的几位才能得到n。_
152 |
153 | 4.与数字操作有关的题目,测试时注意边界值的问题。对于32位数字,其正数的边界值为1、0x7FFFFFFF,负数的边界值为0x80000000、0xFFFFFFFF。
154 |
155 | 5.几个细节问题
156 |
157 | 1)flag=flag <<1,而不是只写一句flag<<1;
158 |
159 | 2)flag&n!=0,而非flag&n==1; 也就不能写成count+=(flag&1)了
160 |
161 | 3)if语句中,不能写为if(flag&n!=0) ,而要写成 if((flag&n)!=0),需要注意一下
162 |
163 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
164 |
165 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
166 |
167 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(39)数组中出现次数超过一半的数字.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(39) 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例如输入一个长度为9的数组{1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 5, 4,
12 | 2}。由于数字2在数组中出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。
13 |
14 | ## 思路
15 |
16 | **思路一:** 数字次数超过一半,则说明:排序之后数组中间的数字一定就是所求的数字。
17 |
18 | 利用partition()函数获得某一随机数字,其余数字按大小排在该数字的左右。若该数字下标刚好为n/2,则该数字即为所求数字;若小于n/2,则在右边部分继续查找;反之,左边部分查找。
19 |
20 | **思路二:** 数字次数超过一半,则说明:该数字出现的次数比其他数字之和还多
21 |
22 | 遍历数组过程中保存两个值:一个是数组中某一数字,另一个是次数。遍历到下一个数字时,若与保存数字相同,则次数加1,反之减1。若次数=0,则保存下一个数字,次数重新设置为1。由于要找的数字出现的次数比其他数字之和还多,那么要找的数字肯定是最后一次把次数设置为1的数字。
23 |
24 | 也可以这样理解(来源牛客网:https://www.nowcoder.com/questionTerminal/e8a1b01a2df14cb2b228b30ee6a92163cm问前程:https://www.nowcoder.com/profile/429784):
25 |
26 | 采用阵地攻守的思想:
27 | 第一个数字作为第一个士兵,守阵地;count = 1;
28 | 遇到相同元素,count++;
29 | 遇到不相同元素,即为敌人,同归于尽,count--;当遇到count为0的情况,又以新的i值作为守阵地的士兵,继续下去,到最后还留在阵地上的士兵,
30 | **有可能是** 主元素。
31 | 再加一次循环,记录这个士兵的个数看是否大于数组一般即可。
32 |
33 | **测试算例** ****
34 |
35 | 1.功能测试(存在或者不存在超过数组长度一半的数字)
36 |
37 | 2.特殊测试(null、1个数字)
38 |
39 | ## **Java代码**
40 |
41 |
42 |
43 | //题目:数组中有一个数字出现的次数超过数组长度的一半,请找出这个数字。例
44 | //如输入一个长度为9的数组{1, 2, 3, 2, 2, 2, 5, 4, 2}。由于数字2在数组中
45 | //出现了5次,超过数组长度的一半,因此输出2。
46 |
47 | public class MoreThanHalfNumber {
48 | boolean isInputInvalid = true;
49 |
50 | //方法一:partition方法
51 | public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int [] array) {
52 | if(array==null ||array.length<=0)
53 | return 0;
54 | int low=0;
55 | int high=array.length-1;
56 | int index=partition(array,low,high);
57 | while(index!=array.length>>1){
58 | if(index>1){
59 | low=index+1;
60 | index=partition(array,low,high);
61 | }else{
62 | high=index-1;
63 | index=partition(array,low,high);
64 | }
65 | }
66 | //判断次数是否超过一半
67 | int num=array[index];
68 | int times=0;
69 | for(int i=0;iarray.length){
75 | isInputInvalid=false;
76 | return num;
77 | }
78 | return 0;
79 | }
80 |
81 | private int partition(int[] array,int low ,int high){
82 | int pivotKey=array[low];
83 | while(low=pivotKey)
85 | high--;
86 | int temp=array[low];
87 | array[low]=array[high];
88 | array[high]=temp;
89 | while(low0){
115 | int times=0;
116 | for(int i=0;iarray.length){
122 | isInputInvalid=false;
123 | return num;
124 | }
125 | }
126 | return 0;
127 | }
128 | }
129 |
130 |
131 | ## **收获**
132 |
133 | 1.length/2 用 length >>1 来代替,具有更高的效率;
134 |
135 | 2.本题中,找到了所求数字,别忘记 **判断该数字的次数是否超过一半** 。
136 |
137 | 3.题目所要求的返回值为int,所以如果数组不满足要求时,无法通过返回值来告知是否出错,所以这道题设置了一个全局变量来进行判断。调用该方法时,需要记得对全局变量进行检查。
138 |
139 | 4.方法一中,采用了partition()函数,该函数会改变修改的数组,因此在面试的时候,需要和面试官讨论是否可以修改数组。
140 |
141 | 5.两种方法的时间复杂度均为O(n)。
142 |
143 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
144 |
145 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
146 |
147 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(15)数值的整数次方.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(15) 数值的整数次方
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 实现函数double Power(double base, int
12 | exponent),求base的exponent次方。不得使用库函数,同时不需要考虑大数问题。
13 |
14 | ## 思路
15 |
16 | 这道题很容易实现,但需要注意以下陷阱:1)0的负数次方不存在;2)0的0次方没有数学意义;3)要考虑exponent为负数的情况。所以可以对exponent进行分类讨论,在对base是否为0进行讨论。
17 |
18 | **测试用例**
19 |
20 | 指数和底数都分别设置为正负数和0.
21 |
22 | ## **完整Java代码**
23 |
24 | (含测试代码)
25 |
26 |
27 |
28 | /**
29 | *
30 | * @Description 面试题16:数值的整数次方
31 | *
32 | * @author yongh
33 | * @date 2018年9月17日 下午5:17:35
34 | */
35 |
36 | // 题目:实现函数double Power(double base, int exponent),求base的exponent
37 | // 次方。不得使用库函数,同时不需要考虑大数问题。
38 |
39 | public class Power {
40 |
41 | boolean IsInvalid = false;//用全局变量标记是否出错
42 |
43 | public double power(double base, int exponent) {
44 | IsInvalid = false;
45 | double result; // double类型
46 | if (exponent > 0) {
47 | result = powerCore(base, exponent);
48 | } else if (exponent < 0) {
49 | if (base == 0) {
50 | IsInvalid = true; //0的负数次方不存在
51 | return 0;
52 | }
53 | result = 1 / powerCore(base, -exponent);
54 | } else {
55 | return 1; //这里0的0次方输出为1
56 | }
57 | return result;
58 | }
59 |
60 | private double powerCore(double base, int exponent) {
61 | if (exponent == 1)
62 | return base;
63 | if (exponent == 0)
64 | return 1;
65 | double result = powerCore(base, exponent >> 1);
66 | result *= result;
67 | if ((exponent & 0x1) == 1)
68 | result *= base;
69 | return result;
70 | }
71 |
72 | // ========测试代码========
73 | void test(String testName, double base, int exponent, double expected, boolean expectedFlag) {
74 | if (testName != null)
75 | System.out.print(testName + ":");
76 | if (power(base, exponent) == expected && IsInvalid == expectedFlag) {
77 | System.out.println("passed.");
78 | } else {
79 | System.out.println("failed.");
80 | }
81 | }
82 |
83 | void test1() {
84 | test("test1", 0, 6, 0, false);
85 | }
86 |
87 | void test2() {
88 | test("test2", 0, -6, 0, true);
89 | }
90 |
91 | void test3() {
92 | test("test3", 0, 0, 1, false);
93 | }
94 |
95 | void test4() {
96 | test("test4", 2, 6, 64, false);
97 | }
98 |
99 | void test5() {
100 | test("test5", 2, -3, 0.125, false);
101 | }
102 |
103 | void test6() {
104 | test("test6", 5, 0, 1, false);
105 | }
106 |
107 | void test7() {
108 | test("test7", -2, 6, 64, false);
109 | }
110 |
111 | public static void main(String[] args) {
112 | Power demo = new Power();
113 | demo.test1();
114 | demo.test2();
115 | demo.test3();
116 | demo.test4();
117 | demo.test5();
118 | demo.test6();
119 | demo.test7();
120 | }
121 |
122 | }
123 |
124 |
125 | 
126 |
127 |
128 |
129 | test1:passed.
130 | test2:passed.
131 | test3:passed.
132 | test4:passed.
133 | test5:passed.
134 | test6:passed.
135 | test7:passed.
136 |
137 | Power
138 |
139 | **非递归实现乘方:**
140 |
141 | 上面的powerCore()方法可改写如下:
142 |
143 |
144 |
145 | /**
146 | * 非递归实现乘方
147 | */
148 | private double powerCore2(double base, int exponent) {
149 | double result=1;
150 | while(exponent!=0) {
151 | if((exponent&0x1)==1)
152 | result*=base;
153 | exponent>>=1;
154 | base*=base; //指数右移一位,则底数翻倍
155 | //举例:10^1101 = 10^0001*10^0100*10^1000
156 | //即10^1+10^4+10^8
157 | }
158 | return result;
159 | }
160 |
161 |
162 | ## **收获**
163 |
164 | 这道题虽然简单,但很有价值,收获如下:
165 |
166 | 1.double类型好像是不能直接用等号判断,因为存在误差(这里暂时用==好像没问题,不确定)
167 |
168 | 2.完全掌握快速做乘方的诀窍:涉及到求解某数的n次方问题时,可以采用递归来完成,即利用以下公式:
169 |
170 | 
171 |
172 | 3.使用右移运算符 >>代替除以2,有较高的效率: **exponent >> 1**
173 |
174 | 4.使用位与运算符代替求余运算符%判断奇偶数,有较高的效率: **if ((exponent & 0x1) == 1)**
175 |
176 | (第三第四条以后在除以2时和判断奇偶时一定要下意识就能想到)
177 |
178 | 5.不要忽略底数为0而指数为负的情况。
179 |
180 | 6.非递归实现乘方,其本质是根据指数与2的倍数关系来对底数进行操作。
181 |
182 | 7. **if ((exponent & 0x1) == 1) **里面的小括号一定不能忘记!
183 |
184 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
185 |
186 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
187 |
188 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(59-2)队列的最大值.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(59-2) 队列的最大值
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | ****
6 |
7 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
8 |
9 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
10 |
11 | [leetcode](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/dui-lie-de-zui-da-zhi-lcof/solution/mian-shi-ti-59-ii-javashi-xian-yuan-li-he-mian-shi/)
12 |
13 | ## 题目
14 |
15 | 请定义一个队列并实现函数max得到队列里的最大值,要求函数max、push_back和pop_front的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
16 |
17 | ## 思路
18 |
19 | 滑动窗口的最大值:https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9964581.html一题相似,利用一个双端队列来存储当前队列里的最大值以及之后可能的最大值。
20 |
21 | 在定义题目要求功能的队列时,除了定义一个队列data存储数值,还需额外用一个队列maxmium存储可能的最大值;此外,还要定义一个数据结构,用于存放数据以及当前的index值,用于删除操作时确定是否删除maxmium中最大值。
22 |
23 | 具体实现见代码,代码进行了一些测试,应该没有什么问题。
24 |
25 | **测试算例** ****
26 |
27 | 尾部插入不同大小数字,删除头部数字。插入删除同时获取最大值。
28 |
29 | ## **Java代码**
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | import java.util.ArrayDeque;
34 |
35 | //题目:请定义一个队列并实现函数max得到队列里的最大值,要求函数max、
36 | //push_back和pop_front的时间复杂度都是O(1)。
37 |
38 | public class QueueWithMax {
39 | private ArrayDeque data = new ArrayDeque();
40 | private ArrayDeque maximum = new ArrayDeque();
41 | private class InternalData{
42 | int number;
43 | int index;
44 | public InternalData(int number,int index) {
45 | this.number=number;
46 | this.index=index;
47 | }
48 | }
49 | private int curIndex;
50 |
51 | public void push_back(int number) {
52 | InternalData curData = new InternalData(number,curIndex);
53 | data.addLast(curData);
54 |
55 | while(!maximum.isEmpty() && maximum.getLast().number data时,别忘记了new
152 | ArrayDeque();否则在插入数据时,会抛出NPE异常。
153 |
154 | 2.进行删除操作时,注意是否队列是否为空。
155 |
156 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
157 |
158 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
159 |
160 | 
161 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(12)机器人的运动范围.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(12) 机器人的运动范围
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 地上有一个m行n列的方格。一个机器人从坐标(0,
12 | 0)的格子开始移动,它每一次可以向左、右、上、下移动一格,但不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格(35,
13 | 37),因为3+5+3+7=18。但它不能进入方格(35, 38),因为3+5+3+8=19。请问该机器人能够到达多少个格子?
14 |
15 | ## 思路
16 |
17 | 与[【Java】 剑指offer(11)
18 | 矩阵中的路径](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9655745.html)类似,也采用回溯法,先判断机器人能否进入(i,j),再判断周围4个格子。这题返回的是int值。
19 |
20 | **测试用例**
21 |
22 | 1.功能测试(多行多列矩阵,k为正数)
23 |
24 | 2.边界值测试(矩阵只有一行或一列;k=0)
25 |
26 | 3.特殊输入测试(k为负数)
27 |
28 | ## **完整Java代码**
29 |
30 | (含测试代码,测试代码引用于RobotMove.cpp:https://github.com/zhedahht/CodingInterviewChinese2/blob/master/13_RobotMove/RobotMove.cpp)
31 |
32 |
33 |
34 | /**
35 | *
36 | * @Description 面试题13:机器人的运动范围
37 | *
38 | * @author yongh
39 | * @date 2018年9月17日 上午8:33:07
40 | */
41 |
42 | // 题目:地上有一个m行n列的方格。一个机器人从坐标(0, 0)的格子开始移动,它
43 | // 每一次可以向左、右、上、下移动一格,但不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和
44 | // 大于k的格子。例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格(35, 37),因为3+5+3+7=18。
45 | // 但它不能进入方格(35, 38),因为3+5+3+8=19。请问该机器人能够到达多少个格子?
46 |
47 | public class RobotMove {
48 | public int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols) {
49 | if (rows <= 0 || cols <= 0 || threshold < 0)
50 | return 0;
51 |
52 | boolean[] isVisited = new boolean[rows * cols];
53 | int count = movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, 0, 0, isVisited);// 用两种方法试一下
54 | return count;
55 | }
56 |
57 | private int movingCountCore(int threshold, int rows, int cols, int row, int col, boolean[] isVisited) {
58 | if (row < 0 || col < 0 || row >= rows || col >= cols || isVisited[row * cols + col]
59 | || cal(row) + cal(col) > threshold)
60 | return 0;
61 | isVisited[row * cols + col] = true;
62 | return 1 + movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row - 1, col, isVisited)
63 | + movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row + 1, col, isVisited)
64 | + movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row, col - 1, isVisited)
65 | + movingCountCore(threshold, rows, cols, row, col + 1, isVisited);
66 | }
67 |
68 | private int cal(int num) {
69 | int sum = 0;
70 | while (num > 0) {
71 | sum += num % 10;
72 | num /= 10;
73 | }
74 | return sum;
75 | }
76 |
77 | // ========测试代码=========
78 | void test(String testName, int threshold, int rows, int cols, int expected) {
79 | if (testName != null)
80 | System.out.print(testName + ":");
81 |
82 | if (movingCount(threshold, rows, cols) == expected)
83 | System.out.println("Passed.");
84 | else
85 | System.out.println("Failed.");
86 | }
87 |
88 | // 方格多行多列
89 | void test1() {
90 | test("Test1", 5, 10, 10, 21);
91 | }
92 |
93 | // 方格多行多列
94 | void test2() {
95 | test("Test2", 15, 20, 20, 359);
96 | }
97 |
98 | // 方格只有一行,机器人只能到达部分方格
99 | void test3() {
100 | test("Test3", 10, 1, 100, 29);
101 | }
102 |
103 | // 方格只有一行,机器人能到达所有方格
104 | void test4() {
105 | test("Test4", 10, 1, 10, 10);
106 | }
107 |
108 | // 方格只有一列,机器人只能到达部分方格
109 | void test5() {
110 | test("Test5", 15, 100, 1, 79);
111 | }
112 |
113 | // 方格只有一列,机器人能到达所有方格
114 | void test6() {
115 | test("Test6", 15, 10, 1, 10);
116 | }
117 |
118 | // 方格只有一行一列
119 | void test7() {
120 | test("Test7", 15, 1, 1, 1);
121 | }
122 |
123 | // 方格只有一行一列
124 | void test8() {
125 | test("Test8", 0, 1, 1, 1);
126 | }
127 |
128 | // 机器人不能进入任意一个方格
129 | void test9() {
130 | test("Test9", -10, 10, 10, 0);
131 | }
132 |
133 | public static void main(String[] args) {
134 | RobotMove demo = new RobotMove();
135 | demo.test1();
136 | demo.test2();
137 | demo.test3();
138 | demo.test4();
139 | demo.test5();
140 | demo.test6();
141 | demo.test7();
142 | demo.test8();
143 | demo.test9();
144 | }
145 |
146 | }
147 |
148 |
149 | 
150 |
151 |
152 |
153 | Test1:Passed.
154 | Test2:Passed.
155 | Test3:Passed.
156 | Test4:Passed.
157 | Test5:Passed.
158 | Test6:Passed.
159 | Test7:Passed.
160 | Test8:Passed.
161 | Test9:Passed.
162 |
163 | RobotMove
164 |
165 | ## **收获**
166 |
167 | 1.计算数位之和时,要注意数字不一定是十位数,可能是百位、千位甚至更多,所以cal()函数别写成计算十位数的方法了。
168 |
169 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
170 |
171 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
172 |
173 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/leetcode/ArrayList/arraylist-leetcode-list.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | > 下面是leetcode中包含链表的题目:
3 |
4 | #### 删除类题目
5 | | 序号 | 题目 | 难度 | 代码 |
6 | | ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | ---- |
7 | | 19 | [Remove Nth Node From End of List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list) | medium | java |
8 | | 82 | [Remove Duplicates from Sorted List II ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list-ii) | Medium | java |
9 | | 83 | [Remove Duplicates from Sorted List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-duplicates-from-sorted-list) | Easy | java |
10 | | 203 | [Remove Linked List Elements ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/remove-linked-list-elements) | Easy | java |
11 | | 237 | [Delete Node in a Linked List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list) | Easy | java |
12 | #### 翻转类题目
13 | | 序号 | 题目 | 难度 | 代码 |
14 | | ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | ---- |
15 | | 25 | [Reverse Nodes in k-Group ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group) | Hard | java |
16 | | 61 | [Rotate List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/rotate-list) | Medium | java |
17 | | 92 | [Reverse Linked List II ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list-ii) | Medium | java |
18 | | 206 | [Reverse Linked List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reverse-linked-list) | Easy | java |
19 | #### 合并链表
20 | | 序号 | 题目 | 难度 | 代码 |
21 | | ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | ---- |
22 | | 2 | [Add Two Numbers ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers) | medium | java |
23 | | 21 | [Merge Two Sorted Lists ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists) | Easy | java |
24 | | 23 | [Merge k Sorted Lists ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/merge-k-sorted-lists) | Hard | java |
25 | | 445 | [Add Two Numbers II ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers-ii) | Medium | java |
26 | #### 环
27 | | 序号 | 题目 | 难度 | 代码 |
28 | | ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | ---- |
29 | | 141 | [Linked List Cycle ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle) | Easy | java |
30 | | 142 | [Linked List Cycle II ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-cycle-ii) | Medium | java |
31 | | 708 | [Insert into a Cyclic Sorted List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insert-into-a-cyclic-sorted-list) | Medium | java |
32 | #### 拆分链表
33 | | 序号 | 题目 | 难度 | 代码 |
34 | | ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | ---- |
35 | | 725 | [Split Linked List in Parts ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/split-linked-list-in-parts) | Medium | java |
36 | | 86 | [Partition List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/partition-list) | Medium | java |
37 | #### 排序链表
38 | | 序号 | 题目 | 难度 | 代码 |
39 | | ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | ---- |
40 | | 143 | [Reorder List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/reorder-list) | Medium | java |
41 | | 147 | [Insertion Sort List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/insertion-sort-list) | Medium | java |
42 | | 148 | [Sort List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/sort-list) | Medium | java |
43 | #### 基础
44 | | 序号 | 题目 | 难度 | 代码 |
45 | | ---- | ------------------------------------------------------------ | ------ | ---- |
46 | | 109 | [Convert Sorted List to Binary Search Tree ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-sorted-list-to-binary-search-tree) | Medium | java |
47 | | 138 | [Copy List with Random Pointer ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/copy-list-with-random-pointer) | Medium | |
48 | | 160 | [Intersection of Two Linked Lists ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists) | Easy | java |
49 | | 234 | [Palindrome Linked List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/palindrome-linked-list) | Easy | java |
50 | | 328 | [Odd Even Linked List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/odd-even-linked-list) | Medium | java |
51 | | 369 | [Plus One Linked List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/plus-one-linked-list) | Medium | java |
52 | | 379 | [Design Phone Directory ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-phone-directory) | Medium | java |
53 | | 426 | [Convert Binary Search Tree to Sorted Doubly Linked List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/convert-binary-search-tree-to-sorted-doubly-linked-list) | Medium | java |
54 | | 430 | [Flatten a Multilevel Doubly Linked List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/flatten-a-multilevel-doubly-linked-list) | Medium | java |
55 | | 707 | [Design Linked List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/design-linked-list) | Easy | java |
56 | | 817 | [Linked List Components ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/linked-list-components) | Medium | java |
57 | | 876 | [Middle of the Linked List ](https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/middle-of-the-linked-list) | Easy | java |
58 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(19)正则表达式匹配.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(19) 正则表达式匹配
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 请实现一个函数用来匹配包含'.'和'*'的正则表达式。模式中的字符'.'表示任意一个字符,而'*'表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(含0次)。在本题中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式。例如,字符串"aaa"与模式"a.a"和"ab\*ac\*a"匹配,但与"aa.a"及"ab\*a"均不匹配。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | 使用函数matchCore(char[] str, int indexOfStr, char[] pattern, int indexOfPattern)
16 | 来实现每一步的比较(递归)。
17 |
18 | (1)当模式中第二个字符不为“*”时:若当前字符相等,则字符串和模式都后移一个字符,继续调用函数进行比较;若不相等,则返回false。
19 |
20 | (2)当模式中第二个字符为“*”时:若当前字符不相等,则模式后移两个字符,继续比较;若当前字符相等,则有三种情况:
21 |
22 | 1)字符串字符位置不变,模式后移两个字符,继续比较; //x*被忽略
23 |
24 | 2)字符串后移一个字符,模式后移两个字符,继续比较;
25 |
26 | 3)字符串后移一个字符,模式字符位置不变,继续比较。
27 |
28 | 三种情况使用“||”进行并列比较。
29 |
30 | **注意点**
31 |
32 | 时刻要注意数组是否越界!
33 |
34 | **测试算例**
35 |
36 | 1.功能测试(模式中包含普通字符、“.”、“*”;匹配情况;不匹配情况)
37 |
38 | 2.特殊测试(null,空字符串)
39 |
40 | ## **完整Java代码**
41 |
42 | (含测试代码)
43 |
44 |
45 |
46 | package _19;
47 |
48 | /**
49 | *
50 | * @Description 面试题19:正则表达式匹配
51 | *
52 | * @author yongh
53 | * @date 2018年9月21日 上午8:12:06
54 | */
55 |
56 | // 题目:请实现一个函数用来匹配包含'.'和'*'的正则表达式。模式中的字符'.'
57 | // 表示任意一个字符,而'*'表示它前面的字符可以出现任意次(含0次)。在本题
58 | // 中,匹配是指字符串的所有字符匹配整个模式。例如,字符串"aaa"与模式"a.a"
59 | // 和"ab*ac*a"匹配,但与"aa.a"及"ab*a"均不匹配。
60 |
61 | public class RegularExpressions {
62 | public boolean match(char[] str, char[] pattern) {
63 | if (str == null || pattern == null)
64 | return false;
65 | return matchCore(str, 0, pattern, 0);
66 | }
67 |
68 | private boolean matchCore(char[] str, int indexOfStr, char[] pattern, int indexOfPattern) {
69 | if (indexOfStr == str.length && indexOfPattern == pattern.length)
70 | return true;
71 | if (indexOfStr < str.length && indexOfPattern == pattern.length)
72 | return false;
73 | if (indexOfPattern + 1 < pattern.length && pattern[indexOfPattern + 1] == '*') {
74 | if ((indexOfStr < str.length && pattern[indexOfPattern] == '.')
75 | || (indexOfStr < str.length && pattern[indexOfPattern] == str[indexOfStr])) {
76 | return matchCore(str, indexOfStr, pattern, indexOfPattern + 2)
77 | || matchCore(str, indexOfStr + 1, pattern, indexOfPattern)
78 | || matchCore(str, indexOfStr + 1, pattern, indexOfPattern + 2);
79 | } else {
80 | return matchCore(str, indexOfStr, pattern, indexOfPattern + 2);
81 | }
82 | }
83 | if (indexOfStr < str.length && (pattern[indexOfPattern] == str[indexOfStr] || pattern[indexOfPattern] == '.'))
84 | return matchCore(str, indexOfStr + 1, pattern, indexOfPattern + 1);
85 | return false;
86 | }
87 |
88 | // ==========测试代码=========
89 | void test(String testName, char[] str, char[] pattern, boolean expected) {
90 | System.out.print(testName + ":");
91 | if (match(str, pattern) == expected)
92 | System.out.println("passed!");
93 | else
94 | System.out.println("failed!");
95 | }
96 |
97 | void test1() {
98 | char[] str = {};
99 | char[] pattern = { '.' };
100 | test("test1", str, pattern, false);
101 | }
102 |
103 | void test2() {
104 | char[] str = {};
105 | char[] pattern = { '.', '*' };
106 | test("test2", str, pattern, true);
107 | }
108 |
109 | void test3() {
110 | char[] str = { 'a' };
111 | char[] pattern = { '.', '*' };
112 | test("test3", str, pattern, true);
113 | }
114 |
115 | void test4() {
116 | char[] str = {};
117 | char[] pattern = {};
118 | test("test4", str, pattern, true);
119 | }
120 |
121 | void test5() {
122 | char[] str = null;
123 | char[] pattern = null;
124 | test("test5", str, pattern, false);
125 | }
126 |
127 | void test6() {
128 | char[] str = { 'a', 'b', 'b' };
129 | char[] pattern = { 'a', 'b', 'b', '*', 'b' };
130 | test("test6", str, pattern, true);
131 | }
132 |
133 | void test7() {
134 | char[] str = { 'a' };
135 | char[] pattern = { 'a', 'a', '*' };
136 | test("test7", str, pattern, true);
137 | }
138 |
139 | public static void main(String[] args) {
140 | RegularExpressions demo = new RegularExpressions();
141 | demo.test1();
142 | demo.test2();
143 | demo.test3();
144 | demo.test4();
145 | demo.test5();
146 | demo.test6();
147 | demo.test7();
148 | }
149 | }
150 |
151 |
152 | 
153 |
154 |
155 |
156 | test1:passed!
157 | test2:passed!
158 | test3:passed!
159 | test4:passed!
160 | test5:passed!
161 | test6:passed!
162 | test7:passed!
163 |
164 | RegularExpressions
165 |
166 | ## **收获**
167 |
168 | 1.涉及到数组的情况下,一定要时刻注意数组越界问题!
169 |
170 | 2.对于每一步都是采用相同判断方法的题目,可以采用递归函数来实现
171 |
172 | 3.思维一定要全面,把握住关键矛盾,将每种情况考虑清楚。例如这道题,关键就在于第二个字符是否为“*”,确定关键问题后,分析清楚每一种情况即可
173 |
174 | 4.代码第29行的 indexOfStr < str.length 一定要记得加,否则可能会出现重复执行第32行的情况。
175 |
176 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
177 |
178 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
179 |
180 | 
181 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(40)最小的k个数.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(40) 最小的k个数
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入n个整数,找出其中最小的k个数。例如输入4、5、1、6、2、7、3、8这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1、2、3、4。
12 |
13 | ## 思路
14 |
15 | **思路一:** 同[剑指offer(39)
16 | 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字](https://www.cnblogs.com/yongh/p/9938889.html)中使用partition()方法,基于数组的第k个数字调整,使得更小的k个数字都在数组左边即可。
17 |
18 | **思路二:**
19 | 依次遍历n个整数,用一个容器存放最小的k个数字,每遇到比容器中最大的数字还小的数字时,将最大值替换为该数字。容器可以使用最大堆或者红黑树来实现。本文根据堆排序的原理来实现。
20 |
21 | **测试算例** ****
22 |
23 | 1.功能测试(数组中存在/不存在重复数字)
24 |
25 | 2.边界值测试(k=1或者等于数组长度)
26 |
27 | 2.特殊测试(null、k <1、k大于数组长度)
28 |
29 | ## **Java代码**
30 |
31 |
32 |
33 | //题目:输入n个整数,找出其中最小的k个数。例如输入4、5、1、6、2、7、3、8
34 | //这8个数字,则最小的4个数字是1、2、3、4。
35 |
36 | public class KLeastNumbers {
37 |
38 | /*
39 | * 方法一:采用partition()
40 | */
41 | public ArrayList GetLeastNumbers_Solution1(int [] input, int k) {
42 | ArrayList leastNumbers = new ArrayList();
43 | while(input==null || k<=0 || k>input.length)
44 | return leastNumbers;
45 | int start=0;
46 | int end=input.length-1;
47 | int index=partition(input,start,end);
48 | while(index!=k-1){
49 | if(index=pivotKey)
67 | end--;
68 | swap(arr,start,end);
69 | while(start GetLeastNumbers_Solution2(int [] input, int k) {
86 | ArrayList leastNumbers = new ArrayList();
87 | while(input==null || k<=0 || k>input.length)
88 | return leastNumbers;
89 | int[] numbers=new int[k]; //用于放最小的k个数
90 | for(int i=0;i=0;i--){
93 | adjustHeap(numbers,i,k-1);//将数组构造成最大堆形式
94 | }
95 | for(int i=k;iarr[child])
112 | child++;
113 | if(arr[child] GetLeastNumbers_Solution(int [] input, int k) {
129 | ArrayList list = new ArrayList<>();
130 | if(input==null || input.length heap = new PriorityQueue<>(k,(i1, i2)->(i2-i1));
133 | for(int i=0; iinput[i]){
137 | heap.poll();
138 | heap.offer(input[i]);
139 | }
140 | }
141 | for(int i: heap)
142 | list.add(i);
143 | return list;
144 | }
145 |
146 |
147 | ## **收获**
148 |
149 | 1.k小于等于0的情况别忘记了
150 |
151 | 2.方法二,只需要在原始数组中进行读入操作,而所有的写操作和判断都是在容器中进行的,不用反复读取原始数组,思想非常好。
152 |
153 | 3.记得要弄清楚是否可以改变原始输入的数组。
154 |
155 | 4.partition函数:即是快速排序的基础,也可以用来查找n个数中第k大的数字。
156 |
157 | 5.当涉及到频繁查找和替换最大最小值时,二叉树是非常合适的数据结构,要能想到堆和二叉树。
158 |
159 | 6\. PriorityQueue重点:
160 |
161 | * 大顶堆与小顶堆的构建: new Comporator()
162 |
163 | * 如何插值: heap.offer(e)
164 |
165 | * 如何获取堆顶的值: heap.peek(), heap.poll()
166 |
167 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
168 |
169 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
170 |
171 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(10)旋转数组的最小数字.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(10) 旋转数组的最小数字
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | 本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个递增排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。例如数组{3, 4, 5, 1,
12 | 2}为{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
13 |
14 | ## 思路
15 |
16 | 数组在一定程度上是排序的,很容易分析出:可以采用二分法来寻找最小数字。
17 |
18 | 但是这里面有一些陷阱:
19 |
20 | 1.递增排序数组的本身是自己的旋转,则最小数字是第一个数字
21 |
22 | 2.中间数字与首尾数字大小相等,如{1,0,1,1,1,1}和{1,1,1,1,0,1},无法采用二分法,只能顺序查找。
23 |
24 | **测试用例**
25 |
26 | 1.功能测试(正常旋转数组,中间有或者无重复数字)
27 |
28 | 2.边界值测试(升序数组,1个数字的数组)
29 |
30 | 3.特殊输入测试(null,空数组)
31 |
32 | ## **完整Java代码**
33 |
34 | (含测试代码)
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | /**
39 | *
40 | * @Description 旋转数组的最小数字
41 | *
42 | * @author yongh
43 | * @date 2018年9月14日 下午8:30:29
44 | */
45 |
46 | // 题目:把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。
47 | // 输入一个递增排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。例如数组
48 | // {3, 4, 5, 1, 2}为{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
49 |
50 | public class MinNumberInRotatedArray {
51 | public int minNumberInRotateArray(int[] array) {
52 | if (array == null || array.length <= 0) // 空数组或null时返回0
53 | return 0;
54 | int low = 0;
55 | int high = array.length - 1;
56 | int mid = (low + high) / 2;
57 | //升序数组
58 | if (array[low] < array[high])
59 | return array[low];
60 | //中间数字与首尾数字相等
61 | if (array[mid] == array[high] && array[mid] == array[low]) {
62 | for (int i = 1; i <= high; i++) {
63 | if (array[i] < array[i - 1])
64 | return array[i];
65 | }
66 | return array[low];
67 | }
68 | //正常情况
69 | while (low < high) {
70 | if (high - low == 1)
71 | break;
72 | mid = (low + high) / 2;
73 | if (array[mid] <= array[high])
74 | high = mid;
75 | if (array[mid] > array[high])
76 | low = mid;
77 | }
78 | return array[high]; // 别错写成了return high; !!
79 | }
80 |
81 | // =======测试代码======
82 | public void test1() {
83 | int[] array = null;
84 | System.out.println("test1:" + minNumberInRotateArray(array));
85 | }
86 |
87 | public void test2() {
88 | int[] array = {};
89 | System.out.println("test2:" + minNumberInRotateArray(array));
90 | }
91 |
92 | public void test3() {
93 | int[] array = { 1 };
94 | System.out.println("test3:" + minNumberInRotateArray(array));
95 | }
96 |
97 | public void test4() {
98 | int[] array = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
99 | System.out.println("test4:" + minNumberInRotateArray(array));
100 | }
101 |
102 | public void test5() {
103 | int[] array = { 2, 2, 2, 2, 1, 2 };
104 | System.out.println("test5:" + minNumberInRotateArray(array));
105 | }
106 |
107 | public void test6() {
108 | int[] array = { 2, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2 };
109 | System.out.println("test6:" + minNumberInRotateArray(array));
110 | }
111 |
112 | public void test7() {
113 | int[] array = { 6, 6, 8, 9, 10, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5, 6 };
114 | System.out.println("test7:" + minNumberInRotateArray(array));
115 | }
116 |
117 | public static void main(String[] args) {
118 | MinNumberInRotatedArray demo = new MinNumberInRotatedArray();
119 | demo.test1();
120 | demo.test2();
121 | demo.test3();
122 | demo.test4();
123 | demo.test5();
124 | demo.test6();
125 | demo.test7();
126 | }
127 | }
128 |
129 |
130 | 
131 |
132 |
133 |
134 | test1:0
135 | test2:0
136 | test3:1
137 | test4:1
138 | test5:1
139 | test6:1
140 | test7:1
141 |
142 | MinNumberInRotatedArray
143 |
144 | **代码学习**
145 |
146 | 下面的代码是牛客网中FINACK:https://www.nowcoder.com/profile/519819写的代码,非常简略。在保证可读性的情况下,希望自己也能早日写出简洁高效的代码。
147 |
148 |
149 |
150 | public class Solution {
151 | public int minNumberInRotateArray(int [] array) {
152 | int low = 0 ; int high = array.length - 1;
153 | while(low < high){
154 | int mid = low + (high - low) / 2;
155 | if(array[mid] > array[high]){
156 | low = mid + 1;
157 | }else if(array[mid] == array[high]){
158 | high = high - 1;
159 | }else{
160 | high = mid;
161 | }
162 | }
163 | return array[low];
164 | }
165 | }
166 |
167 |
168 | 注意这段代码的一些细节:
169 |
170 | 1.使用low=mid+1,而不是low=mid,最终会使得low=high(即最小值位置)而跳出循环;
171 |
172 | 2.使用high=mid,而不是high=mid-1,因为有可能mid就是最小值点,不能减1;
173 |
174 | 3.升序数组的情况可以直接在循环中一起搞定,不用单独列出来判断(自己的代码还可以改进)
175 |
176 | 小瑕疵:
177 |
178 | 1.该程序在array[mid] = array[high]时直接顺序查找。但其实这还有可能可以用二分法的,除非还满足array[mid] =
179 | array[low],才只能使用顺序查找。所以可以先排除掉必须顺序查找的情况(类似自己上面的程序,提前判断掉),之后就可以直接删除else
180 | if(array[mid] == array[high]){high = high - 1;这两行了。
181 |
182 | 2.缺少null的判断。
183 |
184 | ## **收获**
185 |
186 | 1.对于一些涉及数组的方法(如二分法等),可以用low和high,mid等来定义下标,但是,输出时如果要求输出数据值array[low],不要错写成下标low了。
187 |
188 | 2.思维一定要考虑全面,特别是接触到一个新的概念时,要注意到一些特例,如递增排序数组的本身是自己的旋转、相同数字数组等。
189 |
190 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview ******
191 |
192 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
193 |
194 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/剑指offer/【Java】剑指offer(5)从尾到头打印链表.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # 【Java】 剑指offer(5) 从尾到头打印链表
2 |
3 | > 作者:gdutxiaoxu
微信公众号:徐公码字(stormjun94)
来源:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview
4 |
5 | _本文参考自《剑指offer》一书,代码采用Java语言。_
6 |
7 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview**
8 |
9 | ## 题目
10 |
11 | 输入一个链表的头结点,从尾到头反过来打印出每个结点的值。结点定义如下:
12 |
13 |
14 |
15 | public class ListNode {
16 | int val;
17 | ListNode next = null;
18 |
19 | ListNode(int val) {
20 | this.val = val;
21 | }
22 | }
23 |
24 | ## 思路
25 |
26 | 结点遍历顺序只能从头到尾,但是输出的顺序却为从尾到头,是典型的“后进先出”问题,这就要联想到使用栈,从而也可以联想到使用递归。
27 |
28 | **测试用例**
29 |
30 | 1.功能测试(单个结点链表,多个结点链表)
31 |
32 | 2.特殊输入测试(链表为空)
33 |
34 | ## **完整Java代码**
35 |
36 |
37 |
38 | import java.util.Stack;
39 |
40 | /**
41 | *
42 | * @Description 从尾到头打印链表
43 | *
44 | * @author yongh
45 | * @date 2018年9月10日 下午7:07:23
46 | */
47 |
48 | //题目:输入一个链表的头结点,从尾到头反过来打印出每个结点的值。
49 |
50 | public class PrintListInReversedOrder {
51 | class ListNode{
52 | int key;
53 | ListNode next;
54 | public ListNode(int key) {
55 | this.key=key;
56 | this.next=null;
57 | }
58 | }
59 |
60 | // 采用栈
61 | public void printListReversingly_Iteratively(ListNode node) {
62 | Stack stack = new Stack();
63 | while (node!= null) {
64 | stack.push(node);
65 | node=node.next;
66 | }
67 | while(!stack.empty()) {
68 | System.out.println(stack.pop().key);
69 | }
70 | }
71 |
72 | //采用递归
73 | public void printListReversingly_Recursively(ListNode node) {
74 | if(node!=null) {
75 | printListReversingly_Recursively(node.next);
76 | System.out.println(node.key);
77 | }else
78 | return;
79 |
80 | }
81 |
82 |
83 | // ==================================测试代码==================================
84 | /**
85 | * 链表为空
86 | */
87 | public void test1() {
88 | ListNode aListNode = null;
89 | System.out.println("采用栈:");
90 | printListReversingly_Iteratively(aListNode);
91 | System.out.println("采用递归:");
92 | printListReversingly_Recursively(aListNode);
93 | }
94 |
95 | /**
96 | * 多个结点链表
97 | */
98 | public void test2() {
99 | ListNode ListNode1 = new ListNode(1);
100 | ListNode ListNode2 = new ListNode(2);
101 | ListNode ListNode3 = new ListNode(3);
102 | ListNode ListNode4 = new ListNode(4);
103 | ListNode ListNode5 = new ListNode(5);
104 | ListNode1.next=ListNode2;
105 | ListNode2.next=ListNode3;
106 | ListNode3.next=ListNode4;
107 | ListNode4.next=ListNode5;
108 | System.out.println("采用栈:");
109 | printListReversingly_Iteratively(ListNode1);
110 | System.out.println("采用递归:");
111 | printListReversingly_Recursively(ListNode1);
112 | }
113 |
114 | /**
115 | * 单个结点链表
116 | */
117 | public void test3() {
118 | ListNode ListNode1 = new ListNode(1);
119 | System.out.println("采用栈:");
120 | printListReversingly_Iteratively(ListNode1);
121 | System.out.println("采用递归:");
122 | printListReversingly_Recursively(ListNode1);
123 | }
124 |
125 | public static void main(String[] args) {
126 | PrintListInReversedOrder demo = new PrintListInReversedOrder();
127 | System.out.println("test1:");
128 | demo.test1();
129 | System.out.println("test2:");
130 | demo.test2();
131 | System.out.println("test3:");
132 | demo.test3();
133 | }
134 | }
135 |
136 |
137 | 
138 |
139 |
140 |
141 | test1:
142 | 采用栈:
143 | 采用递归:
144 | test2:
145 | 采用栈:
146 | 5
147 | 4
148 | 3
149 | 2
150 | 1
151 | 采用递归:
152 | 5
153 | 4
154 | 3
155 | 2
156 | 1
157 | test3:
158 | 采用栈:
159 | 1
160 | 采用递归:
161 | 1
162 |
163 | PrintListInReversedOrder
164 |
165 | 递归部分代码也可以像下面这样写,注意体会不同的递归写法:
166 |
167 |
168 |
169 | // 采用递归
170 | public void printListReversingly_Recursively(ListNode node) {
171 | // if(node!=null) {
172 | // printListReversingly_Recursively(node.next);
173 | // System.out.println(node.key);
174 | // }else
175 | // return;
176 | if (node != null) {
177 | if (node.next != null) {
178 | printListReversingly_Recursively(node.next);
179 | }
180 | System.out.println(node.key);
181 | }
182 | }
183 |
184 |
185 | ====================================================================
186 |
187 | 在牛客网中提交的代码如下(参考自grass_stars:https://www.nowcoder.com/profile/146839 的代码):
188 |
189 |
190 |
191 | public class Solution {
192 | ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList();
193 | public ArrayList printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
194 | if (listNode != null) {
195 | this.printListFromTailToHead(listNode.next);
196 | arrayList.add(listNode.val);
197 | }
198 | return arrayList;
199 | }
200 | }
201 |
202 |
203 | 上面代码采用的递归,非常简洁,很值得学习。
204 |
205 | ## **收获**
206 |
207 | 1.对于“后进先出”问题,要快速想到”栈“,也同时想到递归。
208 |
209 | 2.采用递归时,返回的函数值不一定要有赋值操作,只要实现了遍历的作用就可以了,上面牛客网的代码可以多多学习。
210 |
211 | **更多《剑指Offer》Java实现合集:https://github.com/gdutxiaoxu/Android_interview**
212 |
213 | 扫一扫,关注我的微信公众号徐公码字(stormjun94),一起敲代码,一起吹水,书写属于自己的人生。
214 |
215 | 
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------