├── .gitignore
├── CONTRIBUTING.md
├── LICENSE
├── README.md
├── experiments
├── constants.py
├── curriculum.py
├── example.py
├── range_evaluation.py
├── training.py
└── utils.py
├── models
├── positional_encodings.py
├── transformer.py
└── transformer_utils.py
├── overview.png
├── requirements.txt
└── tasks
├── cs
├── binary_addition.py
├── binary_multiplication.py
├── bucket_sort.py
├── compute_sqrt.py
├── duplicate_string.py
├── missing_duplicate_string.py
└── odds_first.py
├── dcf
├── modular_arithmetic_brackets.py
├── reverse_string.py
├── solve_equation.py
└── stack_manipulation.py
├── regular
├── cycle_navigation.py
├── even_pairs.py
├── modular_arithmetic.py
└── parity_check.py
└── task.py
/.gitignore:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Byte-compiled / optimized / DLL files
2 | __pycache__/
3 | *.py[cod]
4 | *$py.class
5 |
6 | # Distribution / packaging
7 | .Python
8 | build/
9 | develop-eggs/
10 | dist/
11 | downloads/
12 | eggs/
13 | .eggs/
14 | lib/
15 | lib64/
16 | parts/
17 | sdist/
18 | var/
19 | wheels/
20 | share/python-wheels/
21 | *.egg-info/
22 | .installed.cfg
23 | *.egg
24 | MANIFEST
25 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/CONTRIBUTING.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # How to Contribute
2 |
3 | ## Contributor License Agreement
4 |
5 | Contributions to this project must be accompanied by a Contributor License
6 | Agreement. You (or your employer) retain the copyright to your contribution,
7 | this simply gives us permission to use and redistribute your contributions as
8 | part of the project. Head over to to see
9 | your current agreements on file or to sign a new one.
10 |
11 | You generally only need to submit a CLA once, so if you've already submitted one
12 | (even if it was for a different project), you probably don't need to do it
13 | again.
14 |
15 | ## Code reviews
16 |
17 | All submissions, including submissions by project members, require review. We
18 | use GitHub pull requests for this purpose. Consult
19 | [GitHub Help](https://help.github.com/articles/about-pull-requests/) for more
20 | information on using pull requests.
21 |
22 | ## Community Guidelines
23 |
24 | This project follows [Google's Open Source Community
25 | Guidelines](https://opensource.google/conduct/).
26 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/LICENSE:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | Apache License
3 | Version 2.0, January 2004
4 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/
5 |
6 | TERMS AND CONDITIONS FOR USE, REPRODUCTION, AND DISTRIBUTION
7 |
8 | 1. Definitions.
9 |
10 | "License" shall mean the terms and conditions for use, reproduction,
11 | and distribution as defined by Sections 1 through 9 of this document.
12 |
13 | "Licensor" shall mean the copyright owner or entity authorized by
14 | the copyright owner that is granting the License.
15 |
16 | "Legal Entity" shall mean the union of the acting entity and all
17 | other entities that control, are controlled by, or are under common
18 | control with that entity. For the purposes of this definition,
19 | "control" means (i) the power, direct or indirect, to cause the
20 | direction or management of such entity, whether by contract or
21 | otherwise, or (ii) ownership of fifty percent (50%) or more of the
22 | outstanding shares, or (iii) beneficial ownership of such entity.
23 |
24 | "You" (or "Your") shall mean an individual or Legal Entity
25 | exercising permissions granted by this License.
26 |
27 | "Source" form shall mean the preferred form for making modifications,
28 | including but not limited to software source code, documentation
29 | source, and configuration files.
30 |
31 | "Object" form shall mean any form resulting from mechanical
32 | transformation or translation of a Source form, including but
33 | not limited to compiled object code, generated documentation,
34 | and conversions to other media types.
35 |
36 | "Work" shall mean the work of authorship, whether in Source or
37 | Object form, made available under the License, as indicated by a
38 | copyright notice that is included in or attached to the work
39 | (an example is provided in the Appendix below).
40 |
41 | "Derivative Works" shall mean any work, whether in Source or Object
42 | form, that is based on (or derived from) the Work and for which the
43 | editorial revisions, annotations, elaborations, or other modifications
44 | represent, as a whole, an original work of authorship. For the purposes
45 | of this License, Derivative Works shall not include works that remain
46 | separable from, or merely link (or bind by name) to the interfaces of,
47 | the Work and Derivative Works thereof.
48 |
49 | "Contribution" shall mean any work of authorship, including
50 | the original version of the Work and any modifications or additions
51 | to that Work or Derivative Works thereof, that is intentionally
52 | submitted to Licensor for inclusion in the Work by the copyright owner
53 | or by an individual or Legal Entity authorized to submit on behalf of
54 | the copyright owner. For the purposes of this definition, "submitted"
55 | means any form of electronic, verbal, or written communication sent
56 | to the Licensor or its representatives, including but not limited to
57 | communication on electronic mailing lists, source code control systems,
58 | and issue tracking systems that are managed by, or on behalf of, the
59 | Licensor for the purpose of discussing and improving the Work, but
60 | excluding communication that is conspicuously marked or otherwise
61 | designated in writing by the copyright owner as "Not a Contribution."
62 |
63 | "Contributor" shall mean Licensor and any individual or Legal Entity
64 | on behalf of whom a Contribution has been received by Licensor and
65 | subsequently incorporated within the Work.
66 |
67 | 2. Grant of Copyright License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
68 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
69 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
70 | copyright license to reproduce, prepare Derivative Works of,
71 | publicly display, publicly perform, sublicense, and distribute the
72 | Work and such Derivative Works in Source or Object form.
73 |
74 | 3. Grant of Patent License. Subject to the terms and conditions of
75 | this License, each Contributor hereby grants to You a perpetual,
76 | worldwide, non-exclusive, no-charge, royalty-free, irrevocable
77 | (except as stated in this section) patent license to make, have made,
78 | use, offer to sell, sell, import, and otherwise transfer the Work,
79 | where such license applies only to those patent claims licensable
80 | by such Contributor that are necessarily infringed by their
81 | Contribution(s) alone or by combination of their Contribution(s)
82 | with the Work to which such Contribution(s) was submitted. If You
83 | institute patent litigation against any entity (including a
84 | cross-claim or counterclaim in a lawsuit) alleging that the Work
85 | or a Contribution incorporated within the Work constitutes direct
86 | or contributory patent infringement, then any patent licenses
87 | granted to You under this License for that Work shall terminate
88 | as of the date such litigation is filed.
89 |
90 | 4. Redistribution. You may reproduce and distribute copies of the
91 | Work or Derivative Works thereof in any medium, with or without
92 | modifications, and in Source or Object form, provided that You
93 | meet the following conditions:
94 |
95 | (a) You must give any other recipients of the Work or
96 | Derivative Works a copy of this License; and
97 |
98 | (b) You must cause any modified files to carry prominent notices
99 | stating that You changed the files; and
100 |
101 | (c) You must retain, in the Source form of any Derivative Works
102 | that You distribute, all copyright, patent, trademark, and
103 | attribution notices from the Source form of the Work,
104 | excluding those notices that do not pertain to any part of
105 | the Derivative Works; and
106 |
107 | (d) If the Work includes a "NOTICE" text file as part of its
108 | distribution, then any Derivative Works that You distribute must
109 | include a readable copy of the attribution notices contained
110 | within such NOTICE file, excluding those notices that do not
111 | pertain to any part of the Derivative Works, in at least one
112 | of the following places: within a NOTICE text file distributed
113 | as part of the Derivative Works; within the Source form or
114 | documentation, if provided along with the Derivative Works; or,
115 | within a display generated by the Derivative Works, if and
116 | wherever such third-party notices normally appear. The contents
117 | of the NOTICE file are for informational purposes only and
118 | do not modify the License. You may add Your own attribution
119 | notices within Derivative Works that You distribute, alongside
120 | or as an addendum to the NOTICE text from the Work, provided
121 | that such additional attribution notices cannot be construed
122 | as modifying the License.
123 |
124 | You may add Your own copyright statement to Your modifications and
125 | may provide additional or different license terms and conditions
126 | for use, reproduction, or distribution of Your modifications, or
127 | for any such Derivative Works as a whole, provided Your use,
128 | reproduction, and distribution of the Work otherwise complies with
129 | the conditions stated in this License.
130 |
131 | 5. Submission of Contributions. Unless You explicitly state otherwise,
132 | any Contribution intentionally submitted for inclusion in the Work
133 | by You to the Licensor shall be under the terms and conditions of
134 | this License, without any additional terms or conditions.
135 | Notwithstanding the above, nothing herein shall supersede or modify
136 | the terms of any separate license agreement you may have executed
137 | with Licensor regarding such Contributions.
138 |
139 | 6. Trademarks. This License does not grant permission to use the trade
140 | names, trademarks, service marks, or product names of the Licensor,
141 | except as required for reasonable and customary use in describing the
142 | origin of the Work and reproducing the content of the NOTICE file.
143 |
144 | 7. Disclaimer of Warranty. Unless required by applicable law or
145 | agreed to in writing, Licensor provides the Work (and each
146 | Contributor provides its Contributions) on an "AS IS" BASIS,
147 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or
148 | implied, including, without limitation, any warranties or conditions
149 | of TITLE, NON-INFRINGEMENT, MERCHANTABILITY, or FITNESS FOR A
150 | PARTICULAR PURPOSE. You are solely responsible for determining the
151 | appropriateness of using or redistributing the Work and assume any
152 | risks associated with Your exercise of permissions under this License.
153 |
154 | 8. Limitation of Liability. In no event and under no legal theory,
155 | whether in tort (including negligence), contract, or otherwise,
156 | unless required by applicable law (such as deliberate and grossly
157 | negligent acts) or agreed to in writing, shall any Contributor be
158 | liable to You for damages, including any direct, indirect, special,
159 | incidental, or consequential damages of any character arising as a
160 | result of this License or out of the use or inability to use the
161 | Work (including but not limited to damages for loss of goodwill,
162 | work stoppage, computer failure or malfunction, or any and all
163 | other commercial damages or losses), even if such Contributor
164 | has been advised of the possibility of such damages.
165 |
166 | 9. Accepting Warranty or Additional Liability. While redistributing
167 | the Work or Derivative Works thereof, You may choose to offer,
168 | and charge a fee for, acceptance of support, warranty, indemnity,
169 | or other liability obligations and/or rights consistent with this
170 | License. However, in accepting such obligations, You may act only
171 | on Your own behalf and on Your sole responsibility, not on behalf
172 | of any other Contributor, and only if You agree to indemnify,
173 | defend, and hold each Contributor harmless for any liability
174 | incurred by, or claims asserted against, such Contributor by reason
175 | of your accepting any such warranty or additional liability.
176 |
177 | END OF TERMS AND CONDITIONS
178 |
179 | APPENDIX: How to apply the Apache License to your work.
180 |
181 | To apply the Apache License to your work, attach the following
182 | boilerplate notice, with the fields enclosed by brackets "[]"
183 | replaced with your own identifying information. (Don't include
184 | the brackets!) The text should be enclosed in the appropriate
185 | comment syntax for the file format. We also recommend that a
186 | file or class name and description of purpose be included on the
187 | same "printed page" as the copyright notice for easier
188 | identification within third-party archives.
189 |
190 | Copyright [yyyy] [name of copyright owner]
191 |
192 | Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
193 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
194 | You may obtain a copy of the License at
195 |
196 | http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
197 |
198 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
199 | distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
200 | WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
201 | See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
202 | limitations under the License.
203 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Randomized Positional Encodings Boost Length Generalization of Transformers
2 |
3 |
4 | 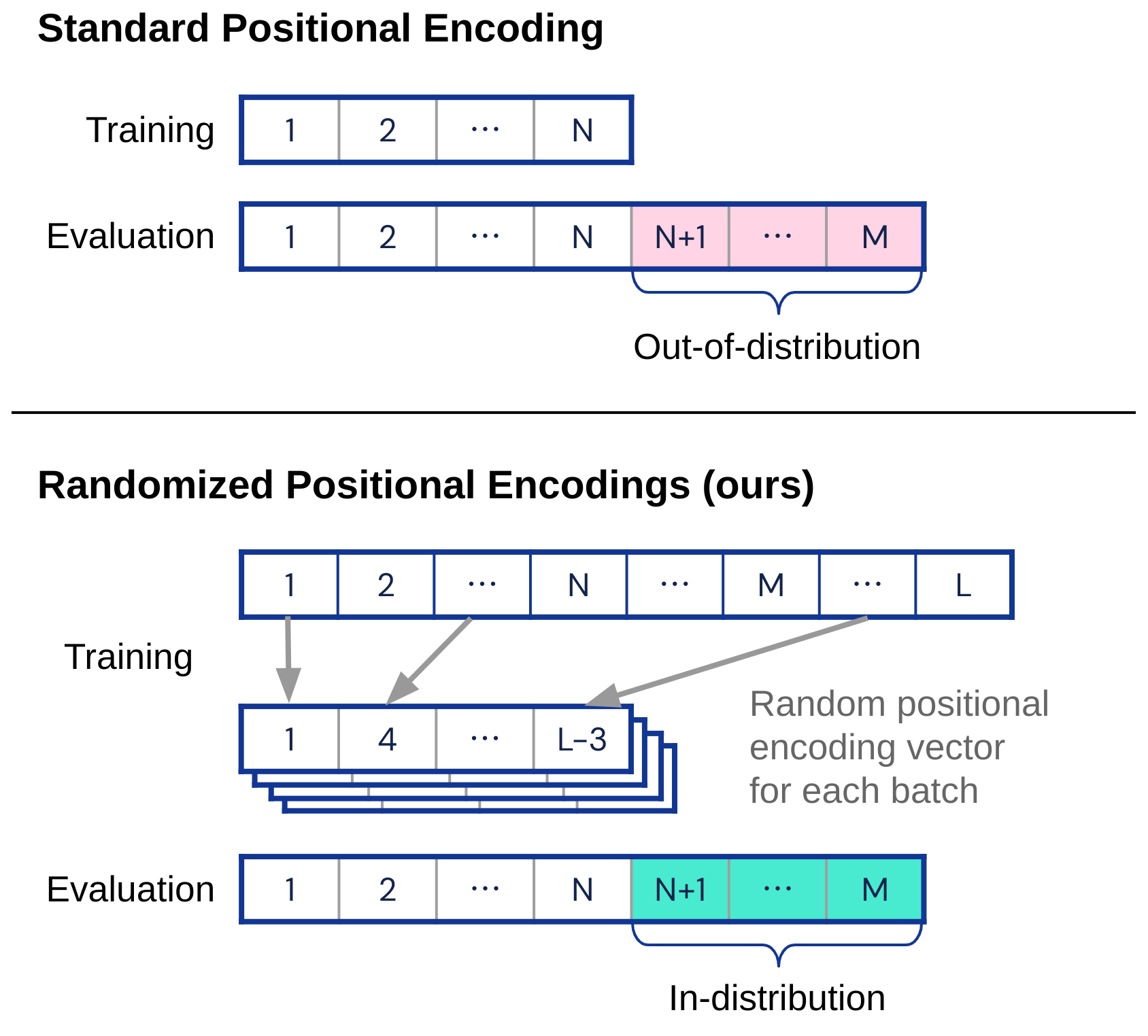 5 |
5 |
6 |
7 | This repository provides an implementation of our ACL 2023 paper [Randomized Positional Encodings Boost Length Generalization of Transformers](https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.16843).
8 |
9 | >Transformers have impressive generalization capabilities on tasks with a fixed context length.
10 | However, they fail to generalize to sequences of arbitrary length, even for seemingly simple tasks such as duplicating a string.
11 | Moreover, simply training on longer sequences is inefficient due to the quadratic computation complexity of the global attention mechanism.
12 | In this work, we demonstrate that this failure mode is linked to positional encodings being out-of-distribution for longer sequences (even for relative encodings) and introduce a novel family of positional encodings that can overcome this problem.
13 | Concretely, our randomized positional encoding scheme simulates the positions of longer sequences and randomly selects an ordered subset to fit the sequence's length.
14 | Our large-scale empirical evaluation of 6000 models across 15 algorithmic reasoning tasks shows that our method allows Transformers to generalize to sequences of unseen length (increasing test accuracy by 12.0% on average).
15 |
16 | It is based on [JAX](https://jax.readthedocs.io) and [Haiku](https://dm-haiku.readthedocs.io) and contains all the code, datasets, and models necessary to reproduce the paper's results.
17 |
18 |
19 | ## Content
20 |
21 | ```
22 | .
23 | ├── models
24 | │ ├── positional_encodings.py
25 | │ ├── transformer.py - Transformer (Vaswani et al., 2017)
26 | │ └── transformer_utils.py
27 | ├── tasks
28 | │ ├── cs - Context-sensitive tasks
29 | │ ├── dcf - Deterministic context-free tasks
30 | │ ├── regular - Regular tasks
31 | │ └── task.py - Abstract `GeneralizationTask`
32 | ├── experiments
33 | | ├── constants.py - Training/Evaluation constants
34 | | ├── curriculum.py - Training curricula (over sequence lengths)
35 | | ├── example.py - Example traning script
36 | | ├── range_evaluation.py - Evaluation loop (test sequences lengths)
37 | | ├── training.py - Training loop
38 | | └── utils.py - Utility functions
39 | ├── README.md
40 | └── requirements.txt - Dependencies
41 | ```
42 |
43 |
44 | ## Installation
45 |
46 | Clone the source code into a local directory:
47 | ```bash
48 | git clone https://github.com/google-deepmind/randomized_positional_encodings.git
49 | cd randomized_positional_encodings
50 | ```
51 |
52 | `pip install -r requirements.txt` will install all required dependencies.
53 | This is best done inside a [conda environment](https://www.anaconda.com/).
54 | To that end, install [Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/download#downloads).
55 | Then, create and activate the conda environment:
56 | ```bash
57 | conda create --name randomized_positional_encodings
58 | conda activate randomized_positional_encodings
59 | ```
60 |
61 | Install `pip` and use it to install all the dependencies:
62 | ```bash
63 | conda install pip
64 | pip install -r requirements.txt
65 | ```
66 |
67 | If you have a GPU available (highly recommended for fast training), then you can install JAX with CUDA support.
68 | ```bash
69 | pip install --upgrade "jax[cuda12_pip]" -f https://storage.googleapis.com/jax-releases/jax_cuda_releases.html
70 | ```
71 | Note that the jax version must correspond to the existing CUDA installation you wish to use (CUDA 12 in the example above).
72 | Please see the [JAX documentation](https://github.com/google/jax#installation) for more details.
73 |
74 |
75 | ## Usage
76 |
77 | Before running any code, make sure to activate the conda environment and set the `PYTHONPATH`:
78 | ```bash
79 | conda activate randomized_positional_encodings
80 | export PYTHONPATH=$(pwd)/..
81 | ```
82 |
83 | We provide an example of a training and evaluation run at:
84 | ```bash
85 | python experiments/example.py
86 | ```
87 |
88 |
89 | ## Citing this work
90 |
91 | ```bibtex
92 | @inproceedings{ruoss2023randomized,
93 | author = {Anian Ruoss and
94 | Gr{\'{e}}goire Del{\'{e}}tang and
95 | Tim Genewein and
96 | Jordi Grau{-}Moya and
97 | R{\'{o}}bert Csord{\'{a}}s and
98 | Mehdi Bennani and
99 | Shane Legg and
100 | Joel Veness},
101 | title = {Randomized Positional Encodings Boost Length Generalization of Transformers},
102 | booktitle = {61st Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics}
103 | year = {2023},
104 | }
105 | ```
106 |
107 |
108 | ## License and disclaimer
109 |
110 | Copyright 2023 DeepMind Technologies Limited
111 |
112 | All software is licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (Apache 2.0);
113 | you may not use this file except in compliance with the Apache 2.0 license.
114 | You may obtain a copy of the Apache 2.0 license at:
115 | https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
116 |
117 | All other materials are licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0
118 | International License (CC-BY). You may obtain a copy of the CC-BY license at:
119 | https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/legalcode
120 |
121 | Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, all software and
122 | materials distributed here under the Apache 2.0 or CC-BY licenses are
123 | distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND,
124 | either express or implied. See the licenses for the specific language governing
125 | permissions and limitations under those licenses.
126 |
127 | This is not an official Google product.
128 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/experiments/constants.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Constants for our length generalization experiments."""
17 |
18 | import functools
19 |
20 | from randomized_positional_encodings.experiments import curriculum as curriculum_lib
21 | from randomized_positional_encodings.models import transformer
22 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import binary_addition
23 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import binary_multiplication
24 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import bucket_sort
25 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import compute_sqrt
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import duplicate_string
27 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import missing_duplicate_string
28 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import odds_first
29 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.dcf import modular_arithmetic_brackets
30 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.dcf import reverse_string
31 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.dcf import solve_equation
32 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.dcf import stack_manipulation
33 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.regular import cycle_navigation
34 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.regular import even_pairs
35 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.regular import modular_arithmetic
36 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.regular import parity_check
37 |
38 |
39 | MODEL_BUILDERS = {
40 | 'transformer_encoder': functools.partial(
41 | transformer.make_transformer,
42 | transformer_module=transformer.TransformerEncoder, # pytype: disable=module-attr
43 | ),
44 | }
45 |
46 | CURRICULUM_BUILDERS = {
47 | 'fixed': curriculum_lib.FixedCurriculum,
48 | 'regular_increase': curriculum_lib.RegularIncreaseCurriculum,
49 | 'reverse_exponential': curriculum_lib.ReverseExponentialCurriculum,
50 | 'uniform': curriculum_lib.UniformCurriculum,
51 | }
52 |
53 | TASK_BUILDERS = {
54 | 'even_pairs': even_pairs.EvenPairs,
55 | 'modular_arithmetic': functools.partial(
56 | modular_arithmetic.ModularArithmetic, modulus=5
57 | ),
58 | 'parity_check': parity_check.ParityCheck,
59 | 'cycle_navigation': cycle_navigation.CycleNavigation,
60 | 'stack_manipulation': stack_manipulation.StackManipulation,
61 | 'reverse_string': functools.partial(
62 | reverse_string.ReverseString, vocab_size=2
63 | ),
64 | 'modular_arithmetic_brackets': functools.partial(
65 | modular_arithmetic_brackets.ModularArithmeticBrackets,
66 | modulus=5,
67 | mult=True,
68 | ),
69 | 'solve_equation': functools.partial(
70 | solve_equation.SolveEquation, modulus=5
71 | ),
72 | 'duplicate_string': functools.partial(
73 | duplicate_string.DuplicateString, vocab_size=2
74 | ),
75 | 'missing_duplicate_string': missing_duplicate_string.MissingDuplicateString,
76 | 'odds_first': functools.partial(odds_first.OddsFirst, vocab_size=2),
77 | 'binary_addition': binary_addition.BinaryAddition,
78 | 'binary_multiplication': binary_multiplication.BinaryMultiplication,
79 | 'compute_sqrt': compute_sqrt.ComputeSqrt,
80 | 'bucket_sort': functools.partial(bucket_sort.BucketSort, vocab_size=5),
81 | }
82 |
83 | TASK_LEVELS = {
84 | 'even_pairs': 'regular',
85 | 'modular_arithmetic': 'regular',
86 | 'parity_check': 'regular',
87 | 'cycle_navigation': 'regular',
88 | 'stack_manipulation': 'dcf',
89 | 'reverse_string': 'dcf',
90 | 'modular_arithmetic_brackets': 'dcf',
91 | 'solve_equation': 'dcf',
92 | 'duplicate_string': 'cs',
93 | 'missing_duplicate_string': 'cs',
94 | 'odds_first': 'cs',
95 | 'binary_addition': 'cs',
96 | 'binary_multiplication': 'cs',
97 | 'compute_sqrt': 'cs',
98 | 'bucket_sort': 'cs',
99 | }
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/experiments/curriculum.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Curricula over sequence lengths used to evaluate length generalization.
17 |
18 | Allows to sample different sequence lengths along training. For instance,
19 | one might want to start with length=1 and regularly increase the length by 1,
20 | every 50k steps.
21 | """
22 |
23 | import abc
24 | from collections.abc import Collection
25 | import random
26 |
27 | import numpy as np
28 |
29 |
30 | class Curriculum(abc.ABC):
31 | """Curriculum to sample lengths."""
32 |
33 | @abc.abstractmethod
34 | def sample_sequence_length(self, step: int) -> int:
35 | """Samples a sequence length from the current distribution."""
36 |
37 |
38 | class FixedCurriculum(Curriculum):
39 | """A fixed curriculum, always sampling the same sequence length."""
40 |
41 | def __init__(self, sequence_length: int):
42 | """Initializes.
43 |
44 | Args:
45 | sequence_length: The sequence length to sample.
46 | """
47 | super().__init__()
48 | self._sequence_length = sequence_length
49 |
50 | def sample_sequence_length(self, step: int) -> int:
51 | """Returns a fixed sequence length."""
52 | del step
53 | return self._sequence_length
54 |
55 |
56 | class UniformCurriculum(Curriculum):
57 | """A uniform curriculum, sampling different sequence lengths."""
58 |
59 | def __init__(self, values: Collection[int]):
60 | """Initializes.
61 |
62 | Args:
63 | values: The sequence lengths to sample.
64 | """
65 | super().__init__()
66 | self._values = tuple(values)
67 |
68 | def sample_sequence_length(self, step: int) -> int:
69 | """Returns a sequence length sampled from a uniform distribution."""
70 | del step
71 | return random.choice(self._values)
72 |
73 |
74 | class ReverseExponentialCurriculum(Curriculum):
75 | """A reverse exponential curriculum, sampling different sequence lengths."""
76 |
77 | def __init__(self, values: Collection[int], tau: bool):
78 | """Initializes.
79 |
80 | Args:
81 | values: The sequence lengths to sample.
82 | tau: The exponential rate to use.
83 | """
84 | super().__init__()
85 | self._values = tuple(values)
86 | self._tau = tau
87 |
88 | def sample_sequence_length(self, step: int) -> int:
89 | """Returns a length sampled from a reverse exponential distribution."""
90 | del step
91 | probs = self._tau ** np.array(self._values)
92 | probs = np.array(probs, dtype=np.float32)
93 | probs = probs / np.sum(probs)
94 | return np.random.choice(self._values, p=probs)
95 |
96 |
97 | class RegularIncreaseCurriculum(Curriculum):
98 | """Curriculum for sequence lengths with a regular increase."""
99 |
100 | def __init__(
101 | self,
102 | initial_sequence_length: int,
103 | increase_frequency: int,
104 | increase_amount: int,
105 | sample_all_length: bool,
106 | ):
107 | """Initializes.
108 |
109 | Args:
110 | initial_sequence_length: The value of the sequence length at the beginning
111 | of the curriculum.
112 | increase_frequency: How often we increase the possible sequence length.
113 | increase_amount: The amount of the increase in length.
114 | sample_all_length: Whether to sample all length lower than the current one
115 | or just return the current one.
116 | """
117 | super().__init__()
118 | self._initial_sequence_length = initial_sequence_length
119 | self._increase_frequency = increase_frequency
120 | self._increase_amount = increase_amount
121 | self._sample_all_length = sample_all_length
122 |
123 | def sample_sequence_length(self, step: int) -> int:
124 | """Returns a sequence length from the curriculum with the current step."""
125 | if not self._sample_all_length:
126 | return self._initial_sequence_length + self._increase_amount * (
127 | step // self._increase_frequency
128 | )
129 | return (
130 | self._initial_sequence_length
131 | + self._increase_amount
132 | * np.random.randint(0, step // self._increase_frequency + 1)
133 | )
134 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/experiments/example.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Example script to train and evaluate a network."""
17 |
18 | from absl import app
19 | from absl import flags
20 | import haiku as hk
21 | import jax.numpy as jnp
22 | import numpy as np
23 |
24 | from randomized_positional_encodings.experiments import constants
25 | from randomized_positional_encodings.experiments import curriculum as curriculum_lib
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.experiments import training
27 | from randomized_positional_encodings.experiments import utils
28 |
29 |
30 | _BATCH_SIZE = flags.DEFINE_integer(
31 | 'batch_size',
32 | default=128,
33 | help='Training batch size.',
34 | lower_bound=1,
35 | )
36 | _SEQUENCE_LENGTH = flags.DEFINE_integer(
37 | 'sequence_length',
38 | default=40,
39 | help='Maximum training sequence length.',
40 | lower_bound=1,
41 | )
42 | _TASK = flags.DEFINE_string(
43 | 'task',
44 | default='missing_duplicate_string',
45 | help='Length generalization task (see `constants.py` for other tasks).',
46 | )
47 | _ARCHITECTURE = flags.DEFINE_string(
48 | 'architecture',
49 | default='transformer_encoder',
50 | help='Model architecture (see `constants.py` for other architectures).',
51 | )
52 | _IS_AUTOREGRESSIVE = flags.DEFINE_boolean(
53 | 'is_autoregressive',
54 | default=False,
55 | help='Whether to use autoregressive sampling or not.',
56 | )
57 | _COMPUTATION_STEPS_MULT = flags.DEFINE_integer(
58 | 'computation_steps_mult',
59 | default=0,
60 | help=(
61 | 'The amount of computation tokens to append to the input tape (defined'
62 | ' as a multiple of the input length)'
63 | ),
64 | lower_bound=0,
65 | )
66 | # The architecture parameters depend on the architecture, so we cannot define
67 | # them as via flags. See `constants.py` for the required values.
68 | _ARCHITECTURE_PARAMS = {
69 | 'num_layers': 5,
70 | 'embedding_dim': 64,
71 | 'dropout_prob': 0.1,
72 | 'positional_encodings': 'NOISY_RELATIVE',
73 | 'positional_encodings_params': {'noise_max_length': 2048},
74 | }
75 |
76 |
77 | def main(_) -> None:
78 | # Create the task.
79 | curriculum = curriculum_lib.UniformCurriculum(
80 | values=list(range(1, _SEQUENCE_LENGTH.value + 1))
81 | )
82 | task = constants.TASK_BUILDERS[_TASK.value]()
83 |
84 | # Create the model.
85 | single_output = task.output_length(10) == 1
86 | model = constants.MODEL_BUILDERS[_ARCHITECTURE.value](
87 | output_size=task.output_size,
88 | return_all_outputs=True,
89 | **_ARCHITECTURE_PARAMS,
90 | )
91 | if _IS_AUTOREGRESSIVE.value:
92 | if 'transformer' not in _ARCHITECTURE.value:
93 | model = utils.make_model_with_targets_as_input(
94 | model, _COMPUTATION_STEPS_MULT.value
95 | )
96 | model = utils.add_sampling_to_autoregressive_model(model, single_output)
97 | else:
98 | model = utils.make_model_with_empty_targets(
99 | model, task, _COMPUTATION_STEPS_MULT.value, single_output
100 | )
101 | model = hk.transform(model)
102 |
103 | # Create the loss and accuracy based on the pointwise ones.
104 | def loss_fn(output, target):
105 | loss = jnp.mean(jnp.sum(task.pointwise_loss_fn(output, target), axis=-1))
106 | return loss, {}
107 |
108 | def accuracy_fn(output, target):
109 | mask = task.accuracy_mask(target)
110 | return jnp.sum(mask * task.accuracy_fn(output, target)) / jnp.sum(mask)
111 |
112 | # Create the final training parameters.
113 | training_params = training.ClassicTrainingParams(
114 | seed=0,
115 | model_init_seed=0,
116 | training_steps=10_000,
117 | log_frequency=100,
118 | length_curriculum=curriculum,
119 | batch_size=_BATCH_SIZE.value,
120 | task=task,
121 | model=model,
122 | loss_fn=loss_fn,
123 | learning_rate=1e-3,
124 | l2_weight=0.0,
125 | accuracy_fn=accuracy_fn,
126 | compute_full_range_test=True,
127 | max_range_test_length=100,
128 | range_test_total_batch_size=512,
129 | range_test_sub_batch_size=64,
130 | is_autoregressive=_IS_AUTOREGRESSIVE.value,
131 | )
132 |
133 | training_worker = training.TrainingWorker(training_params, use_tqdm=True)
134 | _, eval_results, _ = training_worker.run()
135 |
136 | # Gather results and print final score.
137 | accuracies = [r['accuracy'] for r in eval_results]
138 | score = np.mean(accuracies[_SEQUENCE_LENGTH.value + 1 :])
139 | print(f'Score: {score}')
140 |
141 |
142 | if __name__ == '__main__':
143 | app.run(main)
144 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/experiments/range_evaluation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Evaluation of a network on sequences of different lengths."""
17 |
18 | import dataclasses
19 | import random
20 | from typing import Any, Callable, Mapping
21 |
22 | from absl import logging
23 | import chex
24 | import haiku as hk
25 | import jax
26 | import jax.numpy as jnp
27 | import numpy as np
28 | import tqdm
29 |
30 | _Batch = Mapping[str, jnp.ndarray]
31 |
32 |
33 | @dataclasses.dataclass
34 | class EvaluationParams:
35 | """The parameters used for range evaluation of networks."""
36 |
37 | model: hk.Transformed
38 | params: chex.ArrayTree
39 |
40 | accuracy_fn: Callable[[jnp.ndarray, jnp.ndarray], jnp.ndarray]
41 | sample_batch: Callable[[chex.Array, int, int], _Batch]
42 |
43 | max_test_length: int
44 | total_batch_size: int
45 | sub_batch_size: int
46 |
47 | is_autoregressive: bool = False
48 |
49 |
50 | def range_evaluation(
51 | eval_params: EvaluationParams,
52 | use_tqdm: bool = False,
53 | ) -> list[Mapping[str, Any]]:
54 | """Evaluates the model on longer, never seen strings and log the results.
55 |
56 | Args:
57 | eval_params: The evaluation parameters, see above.
58 | use_tqdm: Whether to use a progress bar with tqdm.
59 |
60 | Returns:
61 | The list of dicts containing the accuracies.
62 | """
63 | model = eval_params.model
64 | params = eval_params.params
65 |
66 | random.seed(1)
67 | np.random.seed(1)
68 | rng_seq = hk.PRNGSequence(1)
69 |
70 | if eval_params.is_autoregressive:
71 | apply_fn = jax.jit(model.apply, static_argnames=('sample',))
72 | else:
73 | apply_fn = jax.jit(model.apply)
74 |
75 | results = []
76 | lengths = range(1, eval_params.max_test_length + 1)
77 |
78 | if use_tqdm:
79 | lengths = tqdm.tqdm(lengths)
80 |
81 | for length in lengths:
82 | # We need to clear the cache of jitted functions, to avoid overflow as we
83 | # are jitting len(lengths) ones, which can be a lot.
84 | apply_fn.clear_cache()
85 | sub_accuracies = []
86 |
87 | for _ in range(eval_params.total_batch_size // eval_params.sub_batch_size):
88 | batch = eval_params.sample_batch(
89 | next(rng_seq), eval_params.sub_batch_size, length
90 | )
91 |
92 | if eval_params.is_autoregressive:
93 | outputs = apply_fn(
94 | params,
95 | next(rng_seq),
96 | batch['input'],
97 | jnp.empty_like(batch['output']),
98 | sample=True,
99 | )
100 | else:
101 | outputs = apply_fn(params, next(rng_seq), batch['input'])
102 |
103 | sub_accuracies.append(
104 | float(np.mean(eval_params.accuracy_fn(outputs, batch['output'])))
105 | )
106 | log_data = {
107 | 'length': length,
108 | 'accuracy': np.mean(sub_accuracies),
109 | }
110 | logging.info(log_data)
111 | results.append(log_data)
112 | return results
113 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/experiments/training.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Training loop for length generalization experiments."""
17 |
18 | import dataclasses
19 | import functools
20 | import random
21 | from typing import Any, Callable, Mapping, Optional
22 |
23 | from absl import logging
24 | import chex
25 | import haiku as hk
26 | import jax
27 | import jax.numpy as jnp
28 | import numpy as np
29 | import optax
30 | import tqdm
31 |
32 | from randomized_positional_encodings.experiments import curriculum as curriculum_lib
33 | from randomized_positional_encodings.experiments import range_evaluation
34 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task as task_lib
35 |
36 |
37 | _Batch = Mapping[str, jnp.ndarray]
38 | _LossMetrics = Optional[Mapping[str, jnp.ndarray]]
39 | _LossFn = Callable[[chex.Array, chex.Array], tuple[float, _LossMetrics]]
40 | _AccuracyFn = Callable[[chex.Array, chex.Array], float]
41 | _ModelApplyFn = Callable[..., chex.Array]
42 | _MAX_RNGS_RESERVE = 50000
43 |
44 |
45 | @dataclasses.dataclass
46 | class ClassicTrainingParams:
47 | """Parameters needed to train classical architectures."""
48 |
49 | seed: int # Used to sample during forward pass (e.g. from final logits).
50 | model_init_seed: int # Used to initialize model parameters.
51 | training_steps: int
52 | log_frequency: int
53 |
54 | task: task_lib.GeneralizationTask
55 | length_curriculum: curriculum_lib.Curriculum
56 | batch_size: int
57 |
58 | model: hk.Transformed
59 | loss_fn: Callable[[jnp.ndarray, jnp.ndarray], tuple[float, _LossMetrics]]
60 | learning_rate: float
61 | l2_weight: float
62 | test_model: Optional[hk.Transformed] = None
63 | max_grad_norm: float = 1.0
64 | is_autoregressive: bool = False
65 |
66 | compute_full_range_test: bool = False
67 | range_test_total_batch_size: int = 512
68 | range_test_sub_batch_size: int = 64
69 | max_range_test_length: int = 100
70 |
71 | accuracy_fn: Optional[Callable[[jnp.ndarray, jnp.ndarray], jnp.ndarray]] = (
72 | None
73 | )
74 |
75 |
76 | def _apply_loss_and_metrics_fn(
77 | params: hk.Params,
78 | rng_key: chex.PRNGKey,
79 | batch: _Batch,
80 | model_apply_fn: _ModelApplyFn,
81 | loss_fn: _LossFn,
82 | accuracy_fn: _AccuracyFn,
83 | is_autoregressive: bool = False,
84 | ) -> tuple[float, tuple[_LossMetrics, float]]:
85 | """Computes the model output and applies the loss function.
86 |
87 | Depending on whether a model is autoregressive or not, it will have a
88 | different number of input parameters (i.e., autoregressive models also require
89 | the targets as an input).
90 |
91 | Args:
92 | params: The model parameters.
93 | rng_key: The prng key to use for random number generation.
94 | batch: The data (consists of both inputs and outputs).
95 | model_apply_fn: The model function that converts inputs into outputs.
96 | loss_fn: A function that computes the loss for a batch of logits and labels.
97 | accuracy_fn: A function that computes the accuracy for a batch of logits and
98 | labels.
99 | is_autoregressive: Whether the model is autoregressive or not.
100 |
101 | Returns:
102 | The loss of the model for the batch of data, extra loss metrics and the
103 | accuracy, if accuracy_fn is not None.
104 | """
105 | if is_autoregressive:
106 | outputs = model_apply_fn(
107 | params, rng_key, batch["input"], batch["output"], sample=False
108 | )
109 | else:
110 | outputs = model_apply_fn(params, rng_key, batch["input"])
111 |
112 | loss, loss_metrics = loss_fn(outputs, batch["output"])
113 | if accuracy_fn is not None:
114 | accuracy = accuracy_fn(outputs, batch["output"])
115 | else:
116 | accuracy = None
117 | return loss, (loss_metrics, accuracy)
118 |
119 |
120 | @functools.partial(
121 | jax.jit,
122 | static_argnames=(
123 | "model_apply_fn",
124 | "loss_fn",
125 | "accuracy_fn",
126 | "optimizer",
127 | "is_autoregressive",
128 | ),
129 | )
130 | def _update_parameters(
131 | params: hk.Params,
132 | rng_key: chex.PRNGKey,
133 | batch: _Batch,
134 | model_apply_fn: _ModelApplyFn,
135 | loss_fn: _LossFn,
136 | accuracy_fn: _AccuracyFn,
137 | optimizer: optax.GradientTransformation,
138 | opt_state: optax.OptState,
139 | is_autoregressive: bool = False,
140 | ) -> tuple[hk.Params, optax.OptState, tuple[float, _LossMetrics, float]]:
141 | """Applies a single SGD update step to the model parameters.
142 |
143 | Args:
144 | params: The model parameters.
145 | rng_key: The prng key to use for random number generation.
146 | batch: The data (consists of both inputs and outputs).
147 | model_apply_fn: The model function that converts inputs into outputs.
148 | loss_fn: A function that computes the loss for a batch of logits and labels.
149 | accuracy_fn: A function that computes the accuracy for a batch of logits and
150 | labels.
151 | optimizer: The optimizer that computes the updates from the gradients of the
152 | `loss_fn` with respect to the `params` and the previous `opt_state`.
153 | opt_state: The optimizer state, e.g., momentum for each variable when using
154 | Adam.
155 | is_autoregressive: Whether the model is autoregressive or not.
156 |
157 | Returns:
158 | The updated parameters, the new optimizer state, and the loss, loss metrics
159 | and accuracy.
160 | """
161 | (loss, (metrics, accuracy)), grads = jax.value_and_grad(
162 | _apply_loss_and_metrics_fn, has_aux=True
163 | )(
164 | params,
165 | rng_key,
166 | batch,
167 | model_apply_fn,
168 | loss_fn,
169 | accuracy_fn,
170 | is_autoregressive,
171 | )
172 | updates, new_opt_state = optimizer.update(grads, opt_state, params)
173 | new_params = optax.apply_updates(params, updates)
174 | return new_params, new_opt_state, (loss, metrics, accuracy)
175 |
176 |
177 | class TrainingWorker:
178 | """Training worker."""
179 |
180 | def __init__(
181 | self, training_params: ClassicTrainingParams, use_tqdm: bool = False
182 | ):
183 | """Initializes the worker.
184 |
185 | Args:
186 | training_params: The training parameters.
187 | use_tqdm: Whether to add a progress bar to stdout.
188 | """
189 | self._training_params = training_params
190 | self._use_tqdm = use_tqdm
191 | self._params = None
192 | self._step = 0
193 |
194 | def step_for_evaluator(self) -> int:
195 | return self._step
196 |
197 | def run(
198 | self,
199 | ) -> tuple[list[Mapping[str, Any]], list[Mapping[str, Any]], chex.ArrayTree]:
200 | """Trains the model with the provided config.
201 |
202 | Returns:
203 | Results (various training and validation metrics), module parameters
204 | and router parameters.
205 | """
206 | logging.info("Starting training!")
207 | training_params = self._training_params
208 | rngs_reserve = min(_MAX_RNGS_RESERVE, training_params.training_steps)
209 |
210 | random.seed(training_params.seed)
211 | np.random.seed(training_params.seed)
212 | rng_seq = hk.PRNGSequence(training_params.seed)
213 | rng_seq.reserve(rngs_reserve)
214 |
215 | step = 0
216 |
217 | results = []
218 | model = training_params.model
219 | task = training_params.task
220 | length_curriculum = training_params.length_curriculum
221 |
222 | if training_params.l2_weight is None or training_params.l2_weight == 0:
223 | optimizer = optax.adam(training_params.learning_rate)
224 | else:
225 | optimizer = optax.adamw(
226 | training_params.learning_rate, weight_decay=training_params.l2_weight
227 | )
228 |
229 | optimizer = optax.chain(
230 | optax.clip_by_global_norm(training_params.max_grad_norm), optimizer
231 | )
232 |
233 | dummy_batch = task.sample_batch(
234 | next(rng_seq), length=10, batch_size=training_params.batch_size
235 | )
236 | model_init_rng_key = jax.random.PRNGKey(training_params.model_init_seed)
237 |
238 | if training_params.is_autoregressive:
239 | params = model.init(
240 | model_init_rng_key,
241 | dummy_batch["input"],
242 | dummy_batch["output"],
243 | sample=False,
244 | )
245 | else:
246 | params = model.init(model_init_rng_key, dummy_batch["input"])
247 |
248 | opt_state = optimizer.init(params)
249 | self._params, self._step = params, 0
250 |
251 | steps = range(training_params.training_steps + 1)
252 |
253 | if self._use_tqdm:
254 | steps = tqdm.tqdm(steps)
255 |
256 | for step in steps:
257 | # Randomness handled by either python.random or numpy.
258 | length = length_curriculum.sample_sequence_length(step)
259 | # Randomness handled by either jax, python.random or numpy.
260 | train_batch = task.sample_batch(
261 | next(rng_seq), length=length, batch_size=training_params.batch_size
262 | )
263 | params, opt_state, (train_loss, train_metrics, train_accuracy) = (
264 | _update_parameters(
265 | params=params,
266 | rng_key=next(rng_seq),
267 | batch=train_batch,
268 | model_apply_fn=model.apply,
269 | loss_fn=training_params.loss_fn,
270 | accuracy_fn=training_params.accuracy_fn,
271 | optimizer=optimizer,
272 | opt_state=opt_state,
273 | is_autoregressive=training_params.is_autoregressive,
274 | )
275 | )
276 | self._params, self._step = params, step
277 |
278 | log_freq = training_params.log_frequency
279 | if (log_freq > 0) and (step % log_freq == 0):
280 | log_data = {
281 | "step": step,
282 | "train_loss": float(train_loss),
283 | }
284 | if training_params.accuracy_fn is not None:
285 | log_data["train_accuracy"] = float(train_accuracy)
286 | for key, value in train_metrics.items():
287 | log_data[".".join(["train_metrics", key])] = np.array(value)
288 | logging.info(log_data)
289 | results.append(log_data)
290 |
291 | # We need to access this private attribute since the default reserve size
292 | # can not be edited yet.
293 | if not rng_seq._subkeys: # pylint: disable=protected-access
294 | rng_seq.reserve(rngs_reserve)
295 |
296 | eval_results = list()
297 |
298 | if training_params.compute_full_range_test:
299 | eval_params = range_evaluation.EvaluationParams(
300 | model=training_params.test_model or model,
301 | params=params,
302 | accuracy_fn=training_params.accuracy_fn,
303 | sample_batch=task.sample_batch,
304 | max_test_length=training_params.max_range_test_length,
305 | total_batch_size=training_params.range_test_total_batch_size,
306 | sub_batch_size=training_params.range_test_sub_batch_size,
307 | is_autoregressive=training_params.is_autoregressive,
308 | )
309 | eval_results = range_evaluation.range_evaluation(
310 | eval_params,
311 | use_tqdm=True,
312 | )
313 |
314 | return results, eval_results, params
315 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/experiments/utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Provides utility functions for training and evaluation."""
17 |
18 | import inspect
19 | from typing import Any, Callable
20 |
21 | import chex
22 | import haiku as hk
23 | from jax import nn as jnn
24 | from jax import numpy as jnp
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 |
28 | COMPUTATION_EMPTY_TOKEN = 0
29 | OUTPUT_EMPTY_TOKEN = 1
30 |
31 |
32 | def make_model_with_empty_targets(
33 | model: Callable[[chex.Array], chex.Array],
34 | generalization_task: task.GeneralizationTask,
35 | computation_steps_mult: int = 0,
36 | single_output: bool = False,
37 | ) -> Callable[[chex.Array], chex.Array]:
38 | """Returns a wrapped model that pads the inputs to match the output length.
39 |
40 | For a given input tape `input_tape` of vocabulary size `vocab_size`, the
41 | wrapped model will process a tape of the format
42 | [`input_tape`, `empty_tape`], where the empty tape token is `vocab_size + 1`.
43 | The `empty_tape` has the same length as the task output.
44 |
45 | Args:
46 | model: A model function that converts inputs to outputs.
47 | generalization_task: The task that we train on.
48 | computation_steps_mult: The amount of empty cells to append to the input
49 | tape. This variable is a multiplier and the actual number of cells is
50 | `computation_steps_mult * input_length`.
51 | single_output: Whether to return the squeezed tensor of values.
52 | """
53 |
54 | def new_model(x: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
55 | batch_size, input_length, input_size = x.shape
56 | output_length = generalization_task.output_length(input_length)
57 | extra_dims_onehot = 1 + int(computation_steps_mult > 0)
58 | final_input_size = input_size + extra_dims_onehot
59 |
60 | # Add trailing zeros to account for new final_input_size.
61 | extra_zeros_x = jnp.zeros(
62 | (batch_size, input_length, final_input_size - input_size)
63 | )
64 | x = jnp.concatenate([x, extra_zeros_x], axis=-1)
65 |
66 | computation_tape = jnp.full(
67 | (batch_size, computation_steps_mult * input_length),
68 | fill_value=input_size + COMPUTATION_EMPTY_TOKEN,
69 | )
70 | computation_tape = jnn.one_hot(
71 | computation_tape, num_classes=final_input_size
72 | )
73 |
74 | output_tokens = jnp.full(
75 | (batch_size, output_length),
76 | fill_value=input_size
77 | + OUTPUT_EMPTY_TOKEN
78 | - int(computation_steps_mult == 0),
79 | )
80 | output_tokens = jnn.one_hot(output_tokens, num_classes=final_input_size)
81 | final_input = jnp.concatenate([x, computation_tape, output_tokens], axis=1)
82 |
83 | if 'input_length' in inspect.getfullargspec(model).args:
84 | output = model(final_input, input_length=input_length) # pytype: disable=wrong-keyword-args
85 | else:
86 | output = model(final_input)
87 | output = output[:, -output_length:]
88 | if single_output:
89 | output = jnp.squeeze(output, axis=1)
90 | return output
91 |
92 | return new_model
93 |
94 |
95 | def make_model_with_targets_as_input(
96 | model: Callable[[chex.Array], chex.Array], computation_steps_mult: int = 0
97 | ) -> Callable[[chex.Array, chex.Array], chex.Array]:
98 | """Returns a wrapped model that takes the targets as inputs.
99 |
100 | This function is useful for the autoregressive case where we pass the targets
101 | as inputs to the model. The final input looks like:
102 | [inputs, computation_tokens, output_token, targets]
103 |
104 | Args:
105 | model: A haiku model that takes 'x' as input.
106 | computation_steps_mult: The amount of computation tokens to append to the
107 | input tape. This variable is a multiplier and the actual number of cell is
108 | computation_steps_mult * input_length.
109 | """
110 |
111 | def new_model(x: chex.Array, y: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
112 | """Returns an output from the inputs and targets.
113 |
114 | Args:
115 | x: One-hot input vectors, shape (B, T, input_size).
116 | y: One-hot target output vectors, shape (B, T, output_size).
117 | """
118 | batch_size, input_length, input_size = x.shape
119 | _, output_length, output_size = y.shape
120 | extra_dims_onehot = 1 + int(computation_steps_mult > 0)
121 | final_input_size = max(input_size, output_size) + extra_dims_onehot
122 |
123 | # Add trailing zeros to account for new final_input_size.
124 | extra_zeros_x = jnp.zeros(
125 | (batch_size, input_length, final_input_size - input_size)
126 | )
127 | x = jnp.concatenate([x, extra_zeros_x], axis=-1)
128 | extra_zeros_y = jnp.zeros(
129 | (batch_size, output_length, final_input_size - output_size)
130 | )
131 | y = jnp.concatenate([y, extra_zeros_y], axis=-1)
132 |
133 | computation_tape = jnp.full(
134 | (batch_size, computation_steps_mult * input_length),
135 | fill_value=input_size + COMPUTATION_EMPTY_TOKEN,
136 | )
137 | computation_tape = jnn.one_hot(
138 | computation_tape, num_classes=final_input_size
139 | )
140 |
141 | output_token = jnp.full(
142 | (batch_size, 1),
143 | fill_value=input_size
144 | + OUTPUT_EMPTY_TOKEN
145 | - int(computation_steps_mult == 0),
146 | )
147 | output_token = jnn.one_hot(output_token, num_classes=final_input_size)
148 | final_input = jnp.concatenate(
149 | [x, computation_tape, output_token, y], axis=1
150 | )
151 |
152 | if 'input_length' in inspect.getfullargspec(model).args:
153 | output = model(final_input, input_length=input_length) # pytype: disable=wrong-keyword-args
154 | else:
155 | output = model(final_input)
156 |
157 | return output[:, -output_length - 1 : -1]
158 |
159 | return new_model
160 |
161 |
162 | def add_sampling_to_autoregressive_model(
163 | model: Callable[[chex.Array, chex.Array], chex.Array],
164 | single_output: bool = False,
165 | ) -> Callable[[chex.Array, chex.Array, bool], chex.Array]:
166 | """Adds a 'sample' argument to the model, to use autoregressive sampling."""
167 |
168 | def new_model_with_sampling(
169 | x: chex.Array,
170 | y: chex.Array,
171 | sample: bool,
172 | ) -> chex.Array:
173 | """Returns an autoregressive model if `sample == True and output_size > 1`.
174 |
175 | Args:
176 | x: The input sequences of shape (b, t, i), where i is the input size.
177 | y: The target sequences of shape (b, t, o), where o is the output size.
178 | sample: Whether to evaluate the model using autoregressive decoding.
179 | """
180 | output_length = 1 if len(y.shape) == 2 else y.shape[1]
181 | output_size = y.shape[-1]
182 |
183 | if not sample or output_length == 1:
184 | output = model(x, y)
185 |
186 | else:
187 |
188 | def evaluate_model_autoregressively(
189 | idx: int,
190 | predictions: chex.Array,
191 | ) -> chex.Array:
192 | """Iteratively evaluates the model based on the previous predictions.
193 |
194 | Args:
195 | idx: The index of the target sequence that should be evaluated.
196 | predictions: The logits for the predictions up to but not including
197 | the index `idx`.
198 |
199 | Returns:
200 | The `predictions` array modified only at position `idx` where the
201 | logits for index `idx` have been inserted.
202 | """
203 | one_hot_predictions = jnn.one_hot(
204 | jnp.argmax(predictions, axis=-1),
205 | num_classes=output_size,
206 | )
207 | logits = model(x, one_hot_predictions)
208 | return predictions.at[:, idx].set(logits[:, idx])
209 |
210 | output = hk.fori_loop(
211 | lower=0,
212 | upper=output_length,
213 | body_fun=evaluate_model_autoregressively,
214 | init_val=jnp.empty_like(y),
215 | )
216 |
217 | if single_output:
218 | output = jnp.squeeze(output, axis=1)
219 | return output
220 |
221 | return new_model_with_sampling
222 |
223 |
224 | def update_tree_with_new_containers(
225 | tree: Any, update_dict: dict[str, Any]
226 | ) -> None:
227 | """Updates a dataclass tree in place, adding new containers.
228 |
229 | This method is useful for the nested library to add fields to a tree, for
230 | which containers have not been created.
231 | For instance, if A is a dataclass with attribute architecture_params, and we
232 | want to add the value architecture_params.rnn_model.size, we need to create
233 | the container 'rnn_model' inside architecture_params.
234 |
235 | Args:
236 | tree: An object with attribute (typically a dataclass).
237 | update_dict: A dict of nested updates. See example above.
238 | """
239 | for key in update_dict:
240 | subkeys = key.split('.')
241 | if len(subkeys) >= 2:
242 | # Example: architecture.params.size
243 | for i in range(0, len(subkeys) - 2):
244 | getattr(tree, subkeys[i])[subkeys[i + 1]] = {}
245 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/positional_encodings.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Positional encodings, used in `transformer.py`."""
17 |
18 | import enum
19 | import functools
20 | import math
21 | from typing import Any, Optional, Union
22 |
23 | import chex
24 | import haiku as hk
25 | import jax
26 | import jax.numpy as jnp
27 | import jax.random as jrandom
28 | import numpy as np
29 |
30 |
31 | class PositionalEncodings(enum.Enum):
32 | """Enum for all the positional encodings implemented."""
33 |
34 | NONE = 0
35 | SIN_COS = 1
36 | ALIBI = 2
37 | RELATIVE = 3
38 | ROTARY = 4
39 | LEARNT = 5
40 | NOISY_SIN_COS = 6
41 | NOISY_RELATIVE = 7
42 | NOISY_LEARNT = 8
43 | NOISY_ROTARY = 9
44 | NOISY_ALIBI = 10
45 |
46 |
47 | @chex.dataclass
48 | class SinCosParams:
49 | """Parameters for the classical sin/cos positional encoding."""
50 |
51 | # The maximum wavelength used.
52 | max_time: int = 10_000
53 |
54 |
55 | # We will use this same class for Rotary and Relative.
56 | RotaryParams = SinCosParams
57 | RelativeParams = SinCosParams
58 |
59 |
60 | @chex.dataclass
61 | class LearntParams:
62 | """Parameters for the classical sin/cos positional encoding."""
63 |
64 | # The size of the embedding matrix to use.
65 | max_sequence_length: int
66 |
67 |
68 | @chex.dataclass
69 | class NoisySinCosParams:
70 | """Parameters for the noisy sin/cos positional encoding."""
71 |
72 | # The maximum length to sample.
73 | noise_max_length: int
74 | # The maximum wavelength used.
75 | max_time: int = 10_000
76 |
77 |
78 | @chex.dataclass
79 | class NoisyRelativeParams:
80 | """Parameters for the noisy relative positional encoding."""
81 |
82 | # The maximum length to sample.
83 | noise_max_length: int
84 | # Either randomize the right side and keep the same encodings for the left
85 | # part, keeping the symmetry, or randomize each side independently.
86 | randomize_both_sides: bool = False
87 | # The maximum wavelength used.
88 | max_time: int = 10_000
89 |
90 |
91 | @chex.dataclass
92 | class NoisyLearntParams:
93 | """Parameters for the noisy relative positional encoding."""
94 |
95 | # The maximum length to sample.
96 | noise_max_length: int
97 |
98 |
99 | @chex.dataclass
100 | class NoisyAlibiParams:
101 | """Parameters for the noisy alibi positional encoding."""
102 |
103 | # The maximum length to sample.
104 | noise_max_length: int
105 | # Either randomize the right side and keep the same encodings for the left
106 | # part, maintaining symmetry, or randomize each side independently.
107 | randomize_both_sides: bool = False
108 |
109 |
110 | @chex.dataclass
111 | class NoisyRotaryParams:
112 | """Parameters for the noisy rotary positional encoding."""
113 |
114 | # The maximum length to sample.
115 | noise_max_length: int
116 |
117 |
118 | PositionalEncodingsParams = Union[
119 | SinCosParams,
120 | RelativeParams,
121 | RotaryParams,
122 | LearntParams,
123 | NoisySinCosParams,
124 | NoisyAlibiParams,
125 | NoisyRelativeParams,
126 | NoisyRotaryParams,
127 | NoisyLearntParams,
128 | ]
129 |
130 |
131 | POS_ENC_TABLE = {
132 | 'NONE': PositionalEncodings.NONE,
133 | 'SIN_COS': PositionalEncodings.SIN_COS,
134 | 'ALIBI': PositionalEncodings.ALIBI,
135 | 'RELATIVE': PositionalEncodings.RELATIVE,
136 | 'ROTARY': PositionalEncodings.ROTARY,
137 | 'LEARNT': PositionalEncodings.LEARNT,
138 | 'NOISY_SIN_COS': PositionalEncodings.NOISY_SIN_COS,
139 | 'NOISY_ALIBI': PositionalEncodings.NOISY_ALIBI,
140 | 'NOISY_RELATIVE': PositionalEncodings.NOISY_RELATIVE,
141 | 'NOISY_ROTARY': PositionalEncodings.NOISY_ROTARY,
142 | 'NOISY_LEARNT': PositionalEncodings.NOISY_LEARNT,
143 | }
144 |
145 | POS_ENC_PARAMS_TABLE = {
146 | 'NONE': SinCosParams,
147 | 'SIN_COS': SinCosParams,
148 | 'ALIBI': SinCosParams,
149 | 'RELATIVE': RelativeParams,
150 | 'ROTARY': RotaryParams,
151 | 'LEARNT': LearntParams,
152 | 'NOISY_SIN_COS': NoisySinCosParams,
153 | 'NOISY_ALIBI': NoisyAlibiParams,
154 | 'NOISY_RELATIVE': NoisyRelativeParams,
155 | 'NOISY_ROTARY': NoisyRotaryParams,
156 | 'NOISY_LEARNT': NoisyLearntParams,
157 | }
158 |
159 |
160 | def sinusoid_position_encoding(
161 | sequence_length: int,
162 | hidden_size: int,
163 | max_timescale: float = 1e4,
164 | add_negative_side: bool = False,
165 | ) -> np.ndarray:
166 | """Creates sinusoidal encodings from the original transformer paper.
167 |
168 | The returned values are, for all i < D/2:
169 | array[pos, i] = sin(pos / (max_timescale^(2*i / D)))
170 | array[pos, D/2 + i] = cos(pos / (max_timescale^(2*i / D)))
171 |
172 | Args:
173 | sequence_length: Sequence length.
174 | hidden_size: Dimension of the positional encoding vectors, D. Should be
175 | even.
176 | max_timescale: Maximum timescale for the frequency.
177 | add_negative_side: Whether to also include the positional encodings for
178 | negative positions.
179 |
180 | Returns:
181 | An array of shape [L, D] if add_negative_side is False, else [2 * L, D].
182 | """
183 | if hidden_size % 2 != 0:
184 | raise ValueError(
185 | 'The feature dimension should be even for sin/cos positional encodings.'
186 | )
187 | freqs = np.arange(0, hidden_size, 2)
188 | inv_freq = max_timescale ** (-freqs / hidden_size)
189 | pos_seq = np.arange(
190 | start=-sequence_length if add_negative_side else 0, stop=sequence_length
191 | )
192 | sinusoid_inp = np.einsum('i,j->ij', pos_seq, inv_freq)
193 | return np.concatenate([np.sin(sinusoid_inp), np.cos(sinusoid_inp)], axis=-1)
194 |
195 |
196 | def noisy_fixed_positional_encodings(
197 | fixed_positional_encodings: chex.Array,
198 | sequence_length: int,
199 | rng: Optional[chex.PRNGKey] = None,
200 | ) -> chex.Array:
201 | """Generates noisy positional encodings from fixed positional encodings.
202 |
203 | Randomly samples and orders sequence_length positional encodings from a wider
204 | range [0, noise_max_length) rather than just [0, sequence_length).
205 | The user provides the full_encodings, which should span the entire range
206 | [0, noise_max_length).
207 |
208 | Args:
209 | fixed_positional_encodings: A tensor of shape (noise_max_length,
210 | embedding_size). This is from what the encodings will be sampled.
211 | sequence_length: The length of the output sequence.
212 | rng: Optional rng to use rather than hk.next_rng_key().
213 |
214 | Returns:
215 | A tensor of size [sequence_length, embedding_size].
216 | """
217 | noise_max_length, _ = fixed_positional_encodings.shape
218 | indexes = jrandom.choice(
219 | rng if rng is not None else hk.next_rng_key(),
220 | jnp.arange(noise_max_length),
221 | shape=(sequence_length,),
222 | replace=False,
223 | )
224 | indexes = jnp.sort(indexes)
225 | encodings = fixed_positional_encodings[indexes]
226 | return encodings
227 |
228 |
229 | def _rel_shift_inner(logits: jax.Array, attention_length: int) -> jax.Array:
230 | """Shifts the relative logits.
231 |
232 | This is a more general than the original Transformer-XL implementation as
233 | inputs may also see the future. (The implementation does not rely on a
234 | causal mask removing the upper-right triangle.)
235 |
236 | Given attention length 3 and inputs:
237 | [[-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2],
238 | [-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2],
239 | [-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2]]
240 |
241 | The shifted output is:
242 | [[0, 1, 2],
243 | [-1, 0, 1],
244 | [-2, -1, 0]]
245 |
246 | Args:
247 | logits: input tensor of shape [T_q, T_v + T_q]
248 | attention_length: T_v `int` length of the attention, should be equal to
249 | memory size + sequence length.
250 |
251 | Returns:
252 | A shifted version of the input of size [T_q, T_v]. In each row, a window of
253 | size T_v elements is kept. The window starts at
254 | subsequent row.
255 | """
256 | if logits.ndim != 2:
257 | raise ValueError('`logits` needs to be an array of dimension 2.')
258 | tq, total_len = logits.shape
259 | assert total_len == tq + attention_length
260 | logits = jnp.reshape(logits, [total_len, tq])
261 | logits = jnp.reshape(logits, [total_len, tq])
262 | logits = jax.lax.slice(logits, (1, 0), logits.shape) # logits[1:]
263 | logits = jnp.reshape(logits, [tq, total_len - 1])
264 | # Equiv to logits[:, :attention_length].
265 | logits = jax.lax.slice(logits, (0, 0), (tq, attention_length))
266 | return logits
267 |
268 |
269 | def _rel_shift_causal(logits: jax.Array) -> jax.Array:
270 | """Shifts the relative logits, assuming causal attention.
271 |
272 | Given inputs:
273 | [[-4, -3, -2, -1],
274 | [-4, -3, -2, -1]]
275 |
276 | The shifted (and, later, masked) output is:
277 | [[-3, -2, -1, 0],
278 | [-4, -3, -2, -1]]
279 |
280 | Args:
281 | logits: input tensor of shape [T_q, T_v]
282 |
283 | Returns:
284 | A shifted version of the input of size [T_q, T_v].
285 | """
286 | t1, t2 = logits.shape
287 | # We prepend zeros on the final timescale dimension.
288 | to_pad = jnp.zeros_like(logits[..., :1])
289 | x = jnp.concatenate((to_pad, logits), axis=-1)
290 |
291 | # Reshape trick to shift input.
292 | x = jnp.reshape(x, [t2 + 1, t1])
293 |
294 | # Remove extra time dimension and re-shape.
295 | x = jax.lax.slice(x, [1] + [0] * (x.ndim - 1), x.shape)
296 |
297 | return jnp.reshape(x, [t1, t2])
298 |
299 |
300 | def relative_shift(
301 | logits: jax.Array, attention_length: int, causal: bool = False
302 | ) -> jax.Array:
303 | if causal:
304 | fn = _rel_shift_causal
305 | else:
306 | fn = lambda t: _rel_shift_inner(t, attention_length)
307 | return jax.vmap(jax.vmap(fn))(logits)
308 |
309 |
310 | def apply_rotary_encoding(
311 | x: jnp.ndarray,
312 | position: jnp.ndarray,
313 | max_time: int = 10_000,
314 | noisy: bool = False,
315 | rng: Optional[chex.PRNGKey] = None,
316 | ) -> jnp.ndarray:
317 | """Applies RoPE positional encodings for the input.
318 |
319 | Paper: https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.09864
320 |
321 | Args:
322 | x: The input tensor on which RoPE will be applied. Usually it is either some
323 | queries q or some keys k.
324 | position: The positions to use. Usually it's an arange of the maximum
325 | length.
326 | max_time: Constant used to scale position by in the encodings.
327 | noisy: Whether to use the noisy version.
328 | rng: The rng key to use if the noisy version is used.
329 |
330 | Returns:
331 | A tensor with the same shape as x.
332 | """
333 | # Expand dims for positions to support inputs of shapes BTC or BTHC.
334 | freq_seq = jnp.arange(x.shape[-1] // 2, dtype=jnp.float32)
335 | freq_seq = freq_seq / (x.shape[-1] // 2)
336 | inv_freq = max_time**-freq_seq
337 | inv_freq = jnp.repeat(inv_freq, 2, 0)
338 | # Produce position inputs to periodic functions.
339 | t = position[:, :, None, None] * inv_freq[None, None, None, :]
340 | if noisy:
341 | t = noisy_fixed_positional_encodings(t[0, :, 0], x.shape[1], rng=rng)
342 | t = t[None, :, None, :]
343 | x_rot = jnp.einsum('bthd,dD->bthD', x, _rope_kernel(x.shape[-1], x.dtype))
344 | return x * jnp.cos(t).astype(x.dtype) + jnp.sin(t).astype(x.dtype) * x_rot
345 |
346 |
347 | def _rope_kernel(n: int, dtype: Any) -> np.ndarray:
348 | """Reorders the embedding dimension of an array, to make rotation easier."""
349 | # We implement the equivalent of
350 | # even_dims, odd_dims, = x[..., ::2], x[..., 1::2]
351 | # return jnp.stack((-odd_dims, even_dims), axis=-1).reshape(x.shape)
352 | # with a custom kernel for einsum. This allows the computation to execute
353 | # on the MXU instead of producing a slow gather.
354 | assert n % 2 == 0, n
355 | kernel = np.zeros((n, n), dtype)
356 | for i in range(n):
357 | # Swap each neighbouring pair of values.
358 | if i % 2 == 0:
359 | kernel[i, i + 1] = 1
360 | else:
361 | kernel[i, i - 1] = -1
362 | return kernel
363 |
364 |
365 | def compute_attention_with_relative_encodings(
366 | queries: chex.Array,
367 | keys: chex.Array,
368 | max_time: int = 10_000,
369 | causal: bool = False,
370 | ) -> chex.Array:
371 | """Returns attention with relative positional encodings.
372 |
373 | This code strictly follows what is described in the TransformerXL paper.
374 | https://arxiv.org/pdf/1901.02860.pdf
375 |
376 | Args:
377 | queries: The queries used for attention. Shape (b, t, h, d).
378 | keys: The keys used for attention. Shape (b, T, h, d).
379 | max_time: Constant used to scale position by in the sin/cos encodings.
380 | causal: Whether to use causal attention when shifting the relative logits.
381 |
382 | Returns:
383 | The attention logits. Shape (b, h, t, T).
384 | """
385 | batch_size, k_seq_len, num_heads, num_hiddens = keys.shape
386 | hiddens = num_hiddens * num_heads
387 |
388 | # First compute the content logits.
389 | content_bias = hk.get_parameter(
390 | name='relpos_contentbias',
391 | shape=[num_heads, num_hiddens],
392 | init=hk.initializers.RandomNormal(stddev=0.02),
393 | )
394 | content_logits = jnp.einsum('bthd,bThd->bhtT', queries + content_bias, keys)
395 |
396 | positional_encodings = sinusoid_position_encoding(
397 | sequence_length=k_seq_len,
398 | hidden_size=hiddens,
399 | max_timescale=max_time,
400 | add_negative_side=not causal,
401 | )
402 | positional_encodings = jnp.broadcast_to(
403 | positional_encodings, (batch_size,) + positional_encodings.shape
404 | )
405 | relative_keys = hk.Linear(hiddens, with_bias=False)(positional_encodings)
406 | relative_keys = jnp.reshape(
407 | relative_keys, positional_encodings.shape[:-1] + (num_heads, num_hiddens)
408 | )
409 |
410 | # Then compute the relative part.
411 | relative_bias = hk.get_parameter(
412 | name='relpos_relativebias',
413 | shape=[num_heads, num_hiddens],
414 | init=hk.initializers.RandomNormal(stddev=0.02),
415 | )
416 | relative_logits = jnp.einsum(
417 | 'bthd,bThd->bhtT', queries + relative_bias, relative_keys
418 | )
419 | # We shift the relative logits instead of the positional encoding matrix as
420 | # described in Appendix B of the paper (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1901.02860.pdf).
421 | relative_logits = relative_shift(
422 | relative_logits, attention_length=content_logits.shape[-1], causal=causal
423 | )
424 | assert content_logits.shape == relative_logits.shape
425 | return content_logits + relative_logits
426 |
427 |
428 | def compute_attention_with_noisy_relative_encodings(
429 | queries: chex.Array,
430 | keys: chex.Array,
431 | noise_max_length: int,
432 | randomize_both_sides: bool = False,
433 | max_time: int = 10_000,
434 | causal: bool = False,
435 | ) -> chex.Array:
436 | """Returns attention with *noisy* relative positional encodings.
437 |
438 | This code follows what is described in the TransformerXL paper.
439 | https://arxiv.org/pdf/1901.02860.pdf
440 | However, in this version, the base positional encodings R (which are then
441 | shifted), are randomly sampled and ordered from a wider range than the
442 | sequence length.
443 |
444 | Args:
445 | queries: The queries used for attention. Shape (b, t, h, d).
446 | keys: The keys used for attention. Shape (b, T, h, d).
447 | noise_max_length: The maximum length used to sample the encodings.
448 | randomize_both_sides: Whether to sample the encodings on the left and on the
449 | right of the current token, or just sample from the left and take the
450 | inverted ones for the right part.
451 | max_time: Constant used to scale position by in the sin/cos encodings.
452 | causal: Whether to use causal attention when shifting the relative logits.
453 |
454 | Returns:
455 | The attention logits. Shape (b, h, t, T).
456 | """
457 | batch_size, k_seq_len, num_heads, num_hiddens = keys.shape
458 | hiddens = num_hiddens * num_heads
459 |
460 | # First compute the content logits.
461 | content_bias = hk.get_parameter(
462 | name='relpos_contentbias',
463 | shape=[num_heads, num_hiddens],
464 | init=hk.initializers.RandomNormal(stddev=0.02),
465 | )
466 | content_logits = jnp.einsum('bthd,bThd->bhtT', queries + content_bias, keys)
467 |
468 | # Select random indexes.
469 | # The indexes are in the range
470 | # [-noise_max_length + 1, noise_max_length - 1]
471 | right_indexes = jrandom.choice(
472 | hk.next_rng_key(),
473 | jnp.arange(1, noise_max_length),
474 | shape=(k_seq_len - 1,),
475 | replace=False,
476 | )
477 | right_indexes = jnp.sort(right_indexes)
478 | if randomize_both_sides:
479 | left_indexes = jrandom.choice(
480 | hk.next_rng_key(),
481 | jnp.arange(start=-noise_max_length + 1, stop=0),
482 | shape=(k_seq_len,),
483 | replace=False,
484 | )
485 | left_indexes = jnp.sort(left_indexes)
486 | else:
487 | left_indexes = -right_indexes[::-1]
488 | # The leftmost index is required by position_embedding.relative_shift.
489 | left_indexes = jnp.concatenate([jnp.zeros((1,)), left_indexes])
490 | zero_index = jnp.zeros((1,))
491 | indexes = jnp.concatenate([left_indexes, zero_index, right_indexes])
492 | # We shift the indexes to the range [0, 2*noise_max_length-1], since this
493 | # will be the range of the sin/cos. In this array, the value at index
494 | # noise_max_length is the sin/cos encoding at position 0, which is exactly
495 | # what we want: when doing relative attention, the token should have a fixed
496 | # encoding of position 0 for its own position.
497 | indexes += noise_max_length
498 | indexes = jnp.array(indexes, dtype=jnp.int32)
499 |
500 | positional_encodings = sinusoid_position_encoding(
501 | sequence_length=noise_max_length,
502 | hidden_size=hiddens,
503 | max_timescale=max_time,
504 | )
505 | positional_encodings = jnp.array(positional_encodings, dtype=jnp.float32)
506 | positional_encodings = positional_encodings[indexes]
507 | positional_encodings = jnp.broadcast_to(
508 | positional_encodings, (batch_size,) + positional_encodings.shape
509 | )
510 | relative_keys = hk.Linear(hiddens, with_bias=False)(positional_encodings)
511 | relative_keys = jnp.reshape(
512 | relative_keys, positional_encodings.shape[:-1] + (num_heads, num_hiddens)
513 | )
514 |
515 | # Then compute the relative part.
516 | relative_bias = hk.get_parameter(
517 | name='relpos_relativebias',
518 | shape=[num_heads, num_hiddens],
519 | init=hk.initializers.RandomNormal(stddev=0.02),
520 | )
521 | relative_logits = jnp.einsum(
522 | 'bthd,bThd->bhtT', queries + relative_bias, relative_keys
523 | )
524 | # We shift the relative logits instead of the positional encoding matrix as
525 | # described in Appendix B of the paper (https://arxiv.org/pdf/1901.02860.pdf).
526 | relative_logits = relative_shift(
527 | relative_logits, attention_length=content_logits.shape[-1], causal=causal
528 | )
529 | assert content_logits.shape == relative_logits.shape
530 | return content_logits + relative_logits
531 |
532 |
533 | def _get_alibi_slopes(num_heads: int) -> list[float]:
534 | """Returns the slopes for the different attention heads.
535 |
536 | While this does not exactly match the description of the [ALiBi
537 | paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.12409.pdf), it corresponds to the [official
538 | implementation](https://github.com/ofirpress/attention_with_linear_biases/blob/a06526fbfe557f9148e414b8569dcb97c7b182ba/fairseq/models/transformer.py#L742).
539 |
540 | Args:
541 | num_heads: The number of attention heads to create slopes for.
542 | """
543 |
544 | def get_slopes_power_of_2(n):
545 | start = 2 ** (-(2 ** -(math.log2(n) - 3)))
546 | ratio = start
547 | return [start * ratio**i for i in range(n)]
548 |
549 | if math.log2(num_heads).is_integer():
550 | return get_slopes_power_of_2(num_heads)
551 | else:
552 | closest_power_of_2 = 2 ** math.floor(math.log2(num_heads))
553 | return (
554 | get_slopes_power_of_2(closest_power_of_2)
555 | + _get_alibi_slopes(2 * closest_power_of_2)[0::2][
556 | : num_heads - closest_power_of_2
557 | ]
558 | )
559 |
560 |
561 | def compute_alibi_encodings_biases(
562 | attention_shape: tuple[int, ...]
563 | ) -> chex.Array:
564 | """Returns the biases following the ALiBi method.
565 |
566 | This code strictly follows what is described in the ALiBi paper.
567 | https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.12409.pdf
568 |
569 | Args:
570 | attention_shape: The attention logits shape, without batch size, (h, t, T).
571 |
572 | Returns:
573 | The alibi biases, same shape as the input logits shape.
574 | """
575 | num_heads, q_seq_len, k_seq_len = attention_shape
576 |
577 | # Since we do not use causal masking, the upper triangle of the matrix has to
578 | # be nonzero. Therefore, we set it equal to the lower triangle, but we also
579 | # add a constant factor of 0.5 to the lower triangle, to (arbitrarily) break
580 | # the symmetry (otherwise, the model cannot distinguish left and right).
581 | alibi = np.zeros((q_seq_len, k_seq_len))
582 | alibi -= sum(np.tri(*alibi.shape, k=-i) for i in range(1, q_seq_len))
583 | alibi -= sum(np.tri(*alibi.T.shape, k=-i).T for i in range(1, k_seq_len))
584 | alibi += 0.5 * np.tri(*alibi.shape, k=-1)
585 |
586 | return alibi * jnp.array(_get_alibi_slopes(num_heads))[:, None, None]
587 |
588 |
589 | def compute_noisy_alibi_encodings_biases(
590 | attention_shape: tuple[int, ...],
591 | noise_max_length: int,
592 | randomize_both_sides: bool = False,
593 | ) -> chex.Array:
594 | """Returns the biases following the ALiBi method.
595 |
596 | This code strictly follows what is described in the [ALiBi
597 | paper](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2108.12409.pdf).
598 | However, in this version, the biases are randomly sampled and ordered from a
599 | wider range than the sequence length.
600 |
601 | Args:
602 | attention_shape: The attention logits shape, without batch size, (h, t, T).
603 | noise_max_length: The maximum length used to sample the encodings.
604 | randomize_both_sides: Whether to sample the encodings on the left and on the
605 | right of the current token or just sample from the left and take the
606 | inverted ones for the right part.
607 |
608 | Returns:
609 | The alibi biases, same shape as the input logits shape.
610 | """
611 | num_heads, q_seq_len, k_seq_len = attention_shape
612 |
613 | sample_positions = functools.partial(
614 | jrandom.choice,
615 | a=jnp.arange(1, noise_max_length),
616 | replace=False,
617 | )
618 |
619 | if randomize_both_sides:
620 | right_positions = sample_positions(
621 | hk.next_rng_key(), shape=(k_seq_len - 1,)
622 | )
623 | left_positions = sample_positions(hk.next_rng_key(), shape=(q_seq_len - 1,))
624 | right_positions = -jnp.sort(right_positions)
625 | left_positions = jnp.sort(-left_positions)
626 |
627 | else:
628 | symmetric_positions = sample_positions(
629 | hk.next_rng_key(), shape=(max(q_seq_len, k_seq_len) - 1,)
630 | )
631 | symmetric_positions = -jnp.sort(symmetric_positions)
632 | right_positions = symmetric_positions[: k_seq_len - 1]
633 | left_positions = jnp.flip(symmetric_positions)[: q_seq_len - 1]
634 |
635 | # Since we do not use causal masking, the upper triangle of the matrix has to
636 | # be nonzero. Therefore, we set it equal to the lower triangle if
637 | # `randomize_both_side` is `False` and to randomly sampled positions
638 | # otherwise, but we also add a constant factor of 0.5 to the lower triangle,
639 | # to (arbitrarily) break the symmetry (otherwise, the model cannot distinguish
640 | # left and right).
641 | left_positions += 0.5
642 |
643 | # We add a dummy value to make the dimensions work for
644 | # position_embedding.relative_shift. The value will be ignored.
645 | left_positions = jnp.concatenate((jnp.empty((1,)), left_positions))
646 |
647 | positions = jnp.concatenate(
648 | (left_positions, jnp.zeros((1,)), right_positions)
649 | )
650 | # position_embedding.relative_shift requires a four-dimensional tensor.
651 | positions = jnp.tile(positions, (1, 1, q_seq_len, 1))
652 |
653 | alibi = relative_shift(
654 | positions,
655 | attention_length=k_seq_len,
656 | causal=False,
657 | )
658 | alibi = jnp.squeeze(alibi, axis=(0, 1))
659 |
660 | return alibi * jnp.array(_get_alibi_slopes(num_heads))[:, None, None]
661 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/transformer.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Transformer model."""
17 |
18 | import dataclasses
19 | from typing import Any, Callable, Optional, Union
20 |
21 | from absl import logging
22 | import chex
23 | import haiku as hk
24 | import jax
25 | import jax.nn as jnn
26 | import jax.numpy as jnp
27 |
28 | from randomized_positional_encodings.models import positional_encodings as pos_encs_lib
29 | from randomized_positional_encodings.models import transformer_utils
30 |
31 |
32 | @chex.dataclass
33 | class TransformerConfig:
34 | """Hyperparameters used in the Transformer architectures."""
35 |
36 | # The dimension of the first embedding.
37 | embedding_dim: int = 64
38 | # The number of multi-head attention layers.
39 | num_layers: int = 5
40 | # The number of heads per layer.
41 | num_heads: int = 8
42 | # The number of hidden neurons per head. If None, it is set to be equal to
43 | # `embedding_dim // num_heads`.
44 | num_hiddens_per_head: Optional[int] = None
45 | # The probability that each element is discarded by the dropout modules.
46 | # None means dropout is not used at all.
47 | dropout_prob: Optional[float] = 0.1
48 | # The parameter initialization scale for the embeddings.
49 | emb_init_scale: float = 0.02
50 | # Whether to use the embeddings rather than raw inputs.
51 | use_embeddings: bool = True
52 | # Whether to use lookup-embeddings, in which case the inputs must be ints.
53 | use_lookup_embeddings: bool = False
54 | # Input vocabulary size, not needed if use_lookup_embeddings is False.
55 | input_vocab_size: Optional[int] = None
56 | # Whether to share embeddings between the Encoder and the Decoder.
57 | share_embeddings: bool = False
58 | # The size of the sliding attention window. See MultiHeadDotProductAttention.
59 | attention_window: Optional[int] = None
60 | # The positional encoding used with default sin/cos (Vaswani et al., 2017).
61 | positional_encodings: pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings = dataclasses.field(
62 | default_factory=lambda: pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.SIN_COS
63 | )
64 | # The parameters for the positional encodings, default sin/cos.
65 | positional_encodings_params: pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodingsParams = (
66 | dataclasses.field(default_factory=pos_encs_lib.SinCosParams)
67 | )
68 | # How much larger the hidden layer of the feedforward network should be
69 | # compared to the `embedding_dim`.
70 | widening_factor: int = 4
71 | # Which activation function to use.
72 | activation_fn: Callable[[jax.Array], jax.Array] = jnn.relu
73 | # Add mask to make causal predictions. All the decoders use causal masking by
74 | # default, this option is only used in the encoder. This is quite unusual but
75 | # can still be useful in some rare cases.
76 | encoder_causal_masking: bool = False
77 | # Which token to use for the beginning of the string. None means an array
78 | # full of zeros will be used.
79 | bos_token: Optional[int] = None
80 | # Used by the chunked transformer.
81 | chunk_context_length: Optional[int] = None
82 |
83 | def __post_init__(self) -> None:
84 | """Runs after the config has been created."""
85 | if self.num_hiddens_per_head is None:
86 | self.num_hiddens_per_head = self.embedding_dim // self.num_heads
87 |
88 | if self.positional_encodings is None:
89 | self.positional_encodings = pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.SIN_COS
90 | self.positional_encodings_params = pos_encs_lib.SinCosParams()
91 | elif self.positional_encodings_params is None:
92 | raise ValueError('No parameters for positional encodings are passed.')
93 | elif not isinstance(
94 | self.positional_encodings, pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings
95 | ) or not isinstance(
96 | self.positional_encodings_params, pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodingsParams
97 | ):
98 | raise ValueError(
99 | "The positional encodings passed are not of the right type. You're"
100 | ' probably passing strings rather than actual objects.'
101 | )
102 |
103 |
104 | class MultiHeadDotProductAttention(hk.Module):
105 | """Multi-head dot-product attention (Vaswani et al., 2017)."""
106 |
107 | def __init__(
108 | self,
109 | num_heads: int,
110 | num_hiddens_per_head: int,
111 | positional_encodings: Optional[pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings] = None,
112 | positional_encodings_params: Optional[
113 | pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodingsParams
114 | ] = None,
115 | attention_window: Optional[int] = None,
116 | name: Optional[str] = None,
117 | ) -> None:
118 | """Initializes the attention module.
119 |
120 | Args:
121 | num_heads: Number of heads to use.
122 | num_hiddens_per_head: Number of hidden neurons per head.
123 | positional_encodings: Which positional encodings to use in the attention.
124 | None means no positional encodings are applied to keys or queries.
125 | positional_encodings_params: Parameters for the positional encodings.
126 | attention_window: Size of the attention sliding window. None means no
127 | sliding window is used (or equivalently, window=full_attention_length).
128 | We attend only on attention_window tokens around a given query token. We
129 | attend to tokens before AND after the query token. If attention_window
130 | is even, we use the value +1.
131 | name: Name of the module.
132 | """
133 | super().__init__(name=name)
134 | self._num_heads = num_heads
135 | self._num_hiddens_per_head = num_hiddens_per_head
136 | self._positional_encodings = positional_encodings
137 | self._attention_window = attention_window
138 | self._positional_encodings_params = (
139 | positional_encodings_params # pytype: disable=annotation-type-mismatch
140 | )
141 |
142 | def __call__(
143 | self,
144 | inputs_q: chex.Array,
145 | inputs_kv: chex.Array,
146 | mask: Optional[chex.Array] = None,
147 | causal: bool = False,
148 | ) -> chex.Array:
149 | """Returns the output of the multi-head attention."""
150 | batch_size, sequence_length, embedding_size = inputs_q.shape
151 |
152 | num_hiddens = self._num_hiddens_per_head * self._num_heads
153 | q = hk.Linear(num_hiddens, with_bias=False)(inputs_q)
154 | k = hk.Linear(num_hiddens, with_bias=False)(inputs_kv)
155 | v = hk.Linear(num_hiddens, with_bias=False)(inputs_kv)
156 | # The second (sequence) dimension is undefined since it can differ between
157 | # queries and keys/values when decoding. Also checking that the inputs have
158 | # the same batch size as the reshape below does not guarantee a failure if
159 | # they are different.
160 | chex.assert_equal_shape_prefix([inputs_q, inputs_kv], prefix_len=1)
161 | new_shape = (batch_size, -1, self._num_heads, self._num_hiddens_per_head)
162 | q = jnp.reshape(q, new_shape)
163 | k = jnp.reshape(k, new_shape)
164 | v = jnp.reshape(v, new_shape)
165 |
166 | # Let b=batch_size, t=seq_len, h=num_heads, and d=num_hiddens_per_head.
167 | if self._positional_encodings == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.RELATIVE:
168 | # We type hint the params to match the if statement, for pytype.
169 | self._positional_encodings_params: pos_encs_lib.RelativeParams
170 | attention = pos_encs_lib.compute_attention_with_relative_encodings(
171 | q, k, self._positional_encodings_params.max_time, causal=causal
172 | )
173 | elif (
174 | self._positional_encodings
175 | == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.NOISY_RELATIVE
176 | ):
177 | if causal:
178 | raise NotImplementedError(
179 | 'Noisy positional encodings not implemented for causal attention.'
180 | )
181 | # We type hint the params to match the if statement, for pytype.
182 | self._positional_encodings_params: pos_encs_lib.NoisyRelativeParams
183 | attention = pos_encs_lib.compute_attention_with_noisy_relative_encodings(
184 | q,
185 | k,
186 | max_time=self._positional_encodings_params.max_time,
187 | noise_max_length=self._positional_encodings_params.noise_max_length,
188 | randomize_both_sides=self._positional_encodings_params.randomize_both_sides,
189 | causal=causal,
190 | )
191 | else:
192 | if self._positional_encodings == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.ROTARY:
193 | q = pos_encs_lib.apply_rotary_encoding(
194 | q, position=jnp.arange(q.shape[1])[None, :]
195 | )
196 | k = pos_encs_lib.apply_rotary_encoding(
197 | k, position=jnp.arange(k.shape[1])[None, :]
198 | )
199 | elif (
200 | self._positional_encodings
201 | == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.NOISY_ROTARY
202 | ):
203 | # We type hint the params to match the if statement, for pytype.
204 | self._positional_encodings_params: pos_encs_lib.NoisyRotaryParams
205 | noise_max_length = self._positional_encodings_params.noise_max_length
206 | # WARNING: This only works with self-attention, ie q.shape==k.shape.
207 | rng = hk.next_rng_key()
208 | q = pos_encs_lib.apply_rotary_encoding(
209 | q,
210 | position=jnp.arange(noise_max_length)[None, :],
211 | noisy=True,
212 | rng=rng,
213 | )
214 | k = pos_encs_lib.apply_rotary_encoding(
215 | k,
216 | position=jnp.arange(noise_max_length)[None, :],
217 | noisy=True,
218 | rng=rng,
219 | )
220 | attention = jnp.einsum('bthd,bThd->bhtT', q, k)
221 | attention *= 1.0 / jnp.sqrt(self._num_hiddens_per_head)
222 |
223 | # ALiBi encodings are not scaled with the 1 / sqrt(d_k) factor.
224 | if self._positional_encodings == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.ALIBI:
225 | attention += pos_encs_lib.compute_alibi_encodings_biases(
226 | attention.shape[1:]
227 | )
228 | if (
229 | self._positional_encodings
230 | == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.NOISY_ALIBI
231 | ):
232 | # We type hint the params to match the if statement, for pytype.
233 | self._positional_encodings_params: pos_encs_lib.NoisyAlibiParams
234 | attention += pos_encs_lib.compute_noisy_alibi_encodings_biases(
235 | attention.shape[1:],
236 | noise_max_length=self._positional_encodings_params.noise_max_length,
237 | randomize_both_sides=self._positional_encodings_params.randomize_both_sides,
238 | )
239 |
240 | if self._attention_window is not None:
241 | # We compute the sliding attention by just applying a mask on the values
242 | # that are outside our window.
243 | attention_mask = transformer_utils.compute_sliding_window_mask(
244 | sequence_length, self._attention_window
245 | )
246 | attention = jnp.where(
247 | attention_mask, attention, jnp.finfo(jnp.float32).min
248 | )
249 |
250 | if mask is not None:
251 | attention = jnp.where(mask, attention, jnp.finfo(jnp.float32).min)
252 |
253 | normalized_attention = jnn.softmax(attention)
254 |
255 | output = jnp.einsum('bhtT,bThd->bthd', normalized_attention, v)
256 | output = jnp.reshape(output, (batch_size, sequence_length, num_hiddens))
257 | return hk.Linear(embedding_size, with_bias=False)(output)
258 |
259 |
260 | class TransformerInit(hk.Module):
261 | """Helper class to avoid repeating the same __init__."""
262 |
263 | def __init__(self, config: TransformerConfig):
264 | """Initializes the module."""
265 | super().__init__()
266 | self._config = config
267 | if self._config.use_lookup_embeddings and self._config.bos_token is None:
268 | raise ValueError("Can't use lookup embeddings with a zero bos_token.")
269 |
270 |
271 | class TransformerEmbedder(TransformerInit):
272 | """A module to embed sequences and add positional encodings if needed."""
273 |
274 | def embed_sequences(self, sequences: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
275 | """Returns embedded sequences, following a linear operation or hk.Embed."""
276 | embs_init = hk.initializers.TruncatedNormal(
277 | stddev=self._config.emb_init_scale
278 | )
279 | if self._config.use_lookup_embeddings:
280 | embeddings_layer = hk.Embed(
281 | vocab_size=self._config.input_vocab_size,
282 | embed_dim=self._config.embedding_dim,
283 | lookup_style=hk.EmbedLookupStyle.ARRAY_INDEX,
284 | w_init=embs_init,
285 | )
286 | integer_sequences = jnp.argmax(sequences, axis=-1)
287 | embeddings = embeddings_layer(integer_sequences)
288 | else:
289 | embeddings_layer = hk.Linear(
290 | self._config.embedding_dim,
291 | with_bias=False,
292 | w_init=embs_init,
293 | )
294 | embeddings = embeddings_layer(sequences)
295 |
296 | embeddings *= jnp.sqrt(self._config.embedding_dim)
297 | return embeddings
298 |
299 | def add_positional_encodings(self, embeddings: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
300 | """Returns new embeddings, which have been added positional encodings.
301 |
302 | The shape of the returned array is (B, T, E), where E is the dimension of
303 | the embeddings (if any are used, otherwise E = F).
304 |
305 | Args:
306 | embeddings: A batch of embeddings, of shape (B, T, F).
307 | """
308 | chex.assert_rank(embeddings, 3)
309 |
310 | _, sequence_length, embedding_size = embeddings.shape
311 |
312 | pos_enc_params = self._config.positional_encodings_params
313 | if (
314 | self._config.positional_encodings
315 | == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.SIN_COS
316 | ):
317 | pos_enc_params: pos_encs_lib.SinCosParams
318 | pos_encodings = pos_encs_lib.sinusoid_position_encoding(
319 | sequence_length=sequence_length,
320 | hidden_size=embedding_size,
321 | max_timescale=pos_enc_params.max_time,
322 | )
323 | h = embeddings + pos_encodings
324 | if self._config.dropout_prob is not None:
325 | h = hk.dropout(hk.next_rng_key(), self._config.dropout_prob, h)
326 | elif (
327 | self._config.positional_encodings
328 | == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.NOISY_SIN_COS
329 | ):
330 | pos_enc_params: pos_encs_lib.NoisySinCosParams
331 | if pos_enc_params.noise_max_length > pos_enc_params.max_time:
332 | logging.warning(
333 | (
334 | 'noise_max_length=%i is larger than max_time=%i, some '
335 | 'positional encodings will be equal.'
336 | ),
337 | pos_enc_params.noise_max_length,
338 | pos_enc_params.max_time,
339 | )
340 | pos_encodings = pos_encs_lib.sinusoid_position_encoding(
341 | sequence_length=pos_enc_params.noise_max_length,
342 | hidden_size=embedding_size,
343 | max_timescale=pos_enc_params.max_time,
344 | )
345 | pos_encodings = jnp.array(pos_encodings)
346 | pos_encodings = pos_encs_lib.noisy_fixed_positional_encodings(
347 | pos_encodings, sequence_length
348 | )
349 | h = embeddings + pos_encodings
350 | if self._config.dropout_prob is not None:
351 | h = hk.dropout(hk.next_rng_key(), self._config.dropout_prob, h)
352 | elif (
353 | self._config.positional_encodings
354 | == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.LEARNT
355 | ):
356 | pos_enc_params: pos_encs_lib.LearntParams
357 | pos_encodings = jnp.arange(sequence_length)
358 | pos_encodings = hk.Embed(
359 | vocab_size=pos_enc_params.max_sequence_length,
360 | embed_dim=embedding_size,
361 | )(pos_encodings)
362 | h = embeddings + pos_encodings
363 | if self._config.dropout_prob is not None:
364 | h = hk.dropout(hk.next_rng_key(), self._config.dropout_prob, h)
365 | elif (
366 | self._config.positional_encodings
367 | == pos_encs_lib.PositionalEncodings.NOISY_LEARNT
368 | ):
369 | pos_enc_params: pos_encs_lib.NoisyLearntParams
370 | pos_encodings = jnp.arange(pos_enc_params.noise_max_length)
371 | pos_encodings = hk.Embed(
372 | vocab_size=pos_enc_params.noise_max_length, embed_dim=embedding_size
373 | )(pos_encodings)
374 | pos_encodings = pos_encs_lib.noisy_fixed_positional_encodings(
375 | pos_encodings, sequence_length
376 | )
377 | h = embeddings + pos_encodings
378 | if self._config.dropout_prob is not None:
379 | h = hk.dropout(hk.next_rng_key(), self._config.dropout_prob, h)
380 | else:
381 | h = embeddings
382 | return h
383 |
384 |
385 | class TransformerEncoder(TransformerInit):
386 | """Transformer Encoder (Vaswani et al., 2017)."""
387 |
388 | def __call__(self, inputs: jnp.ndarray) -> chex.Array:
389 | """Returns the transformer encoder output, shape [B, T, E]."""
390 | batch_size, sequence_length = inputs.shape[:2]
391 | # Embeds the inputs, adds positional encodings.
392 | embedder = TransformerEmbedder(self._config)
393 | embeddings = embedder.embed_sequences(inputs)
394 | h = embedder.add_positional_encodings(embeddings)
395 |
396 | # The causal mask is shared across heads.
397 | if self._config.encoder_causal_masking:
398 | causal_mask = jnp.tril(
399 | jnp.ones((batch_size, 1, sequence_length, sequence_length))
400 | )
401 | else:
402 | causal_mask = None
403 |
404 | for _ in range(self._config.num_layers):
405 | attention = MultiHeadDotProductAttention(
406 | num_heads=self._config.num_heads,
407 | num_hiddens_per_head=self._config.num_hiddens_per_head,
408 | positional_encodings=self._config.positional_encodings,
409 | positional_encodings_params=self._config.positional_encodings_params,
410 | attention_window=self._config.attention_window,
411 | )(
412 | inputs_q=h,
413 | inputs_kv=h,
414 | mask=causal_mask,
415 | causal=self._config.encoder_causal_masking,
416 | )
417 | if self._config.dropout_prob is not None:
418 | attention = hk.dropout(
419 | hk.next_rng_key(), self._config.dropout_prob, attention
420 | )
421 | attention = transformer_utils.layer_norm(h + attention)
422 |
423 | # Position-wise feedforward network.
424 | h = hk.Linear(self._config.embedding_dim * self._config.widening_factor)(
425 | attention
426 | )
427 | h = self._config.activation_fn(h)
428 | h = hk.Linear(self._config.embedding_dim)(h)
429 |
430 | if self._config.dropout_prob is not None:
431 | h = hk.dropout(hk.next_rng_key(), self._config.dropout_prob, h)
432 | h = transformer_utils.layer_norm(h + attention)
433 | return h
434 |
435 |
436 | class ChunkedTransformerEncoder(TransformerInit):
437 | """A Transformer encoder that can handle large histories via chunks.
438 |
439 | We chunk the inputs, moving from a shape (B, T, F) to a shape (B, T/C, C, F),
440 | where C is the length of the chunk. Note that T must be a multiple of C for it
441 | to work. The chunks are then passed independently to the encoder, and all the
442 | outputs are then concatenated together, to return a shape (B, T, E), where E
443 | is the embedding_dim of the TransformerEncoder, see class above.
444 | """
445 |
446 | def __call__(self, inputs: chex.Array) -> jnp.ndarray:
447 | """Calls the chunked transformer encoder."""
448 | batch_size, history_len = inputs.shape[:2]
449 | inputs = transformer_utils.chunk_sequences(
450 | inputs, chunk_length=self._config.chunk_context_length
451 | )
452 | outputs = TransformerEncoder(self._config)(inputs=inputs)
453 | return jnp.reshape(outputs, (batch_size, history_len, outputs.shape[-1]))
454 |
455 |
456 | CallableTransformer = Union[
457 | ChunkedTransformerEncoder,
458 | TransformerEncoder,
459 | ]
460 |
461 |
462 | def make_transformer(
463 | output_size: int,
464 | transformer_module: type[CallableTransformer],
465 | return_all_outputs: bool = False,
466 | **transformer_kwargs,
467 | ) -> Any:
468 | """Returns a transformer predict function."""
469 |
470 | if 'positional_encodings' in transformer_kwargs:
471 | if isinstance(transformer_kwargs['positional_encodings'], str):
472 | transformer_kwargs['positional_encodings_params'] = (
473 | pos_encs_lib.POS_ENC_PARAMS_TABLE[
474 | transformer_kwargs['positional_encodings']
475 | ](**transformer_kwargs['positional_encodings_params'])
476 | )
477 | transformer_kwargs['positional_encodings'] = pos_encs_lib.POS_ENC_TABLE[
478 | transformer_kwargs['positional_encodings']
479 | ]
480 |
481 | config = TransformerConfig(**transformer_kwargs)
482 |
483 | def transformer(*args, **kwargs) -> chex.Array:
484 | output = transformer_module(config=config)(*args, **kwargs)
485 | if not return_all_outputs:
486 | output = output[:, -1, :]
487 | return hk.Linear(output_size)(output)
488 |
489 | return transformer
490 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/models/transformer_utils.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Utils for the transformer architectures."""
17 |
18 | import chex
19 | import haiku as hk
20 | import jax.numpy as jnp
21 |
22 |
23 | def layer_norm(x: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
24 | return hk.LayerNorm(axis=-1, create_scale=True, create_offset=True)(x)
25 |
26 |
27 | def chunk_sequences(sequences: chex.Array, chunk_length: int) -> chex.Array:
28 | """Chunks an array of sequences, on the second (time) dimension.
29 |
30 | Args:
31 | sequences: An array of sequences, of shape (B, T, F).
32 | chunk_length: The length of each chunk.
33 |
34 | Returns:
35 | An array of shape (B, T // chunk_length, chunk_length, F)
36 | Raises:
37 | ValueError if T is not a multiple of chunk_length.
38 | """
39 | chex.assert_rank(sequences, 3)
40 | batch_size, history_len, num_features = sequences.shape
41 | if history_len < chunk_length:
42 | context_length = history_len
43 | elif history_len % chunk_length == 0:
44 | context_length = chunk_length
45 | else:
46 | raise ValueError(
47 | 'The history length should a multiple of the context length. Got'
48 | f' history_length={history_len} and'
49 | f' context_length={chunk_length}'
50 | )
51 |
52 | history_batch_size = history_len // context_length
53 | return jnp.reshape(
54 | sequences,
55 | (batch_size * history_batch_size, context_length, num_features),
56 | )
57 |
58 |
59 | def compute_sliding_window_mask(
60 | sequence_length: int, attention_window: int
61 | ) -> chex.Array:
62 | """Returns a k-diagonal mask for a sliding window.
63 |
64 | Args:
65 | sequence_length: The length of the sequence, which will determine the shape
66 | of the output.
67 | attention_window: The size of the sliding window.
68 |
69 | Returns:
70 | A symmetric matrix of shape (sequence_length, sequence_length),
71 | attention_window-diagonal, with ones on the diagonal and on all the
72 | upper/lower diagonals up to attention_window // 2.
73 |
74 | Raises:
75 | ValueError if attention_window is <= 0.
76 | """
77 | if attention_window <= 0:
78 | raise ValueError(
79 | f'The attention window should be > 0. Got {attention_window}.'
80 | )
81 |
82 | if attention_window == 1:
83 | return jnp.eye(sequence_length, sequence_length)
84 |
85 | attention_mask = jnp.sum(
86 | jnp.stack(
87 | [
88 | jnp.eye(sequence_length, sequence_length, k=k, dtype=jnp.int32)
89 | for k in range(1, attention_window // 2 + 1)
90 | ]
91 | ),
92 | axis=0,
93 | )
94 | attention_mask = attention_mask + jnp.transpose(attention_mask)
95 | attention_mask += jnp.eye(sequence_length, sequence_length)
96 | return attention_mask
97 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/overview.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/google-deepmind/randomized_positional_encodings/f3ef05a7dc2c4f0f71d4efaae3512ccd158b00d7/overview.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | absl-py
2 | chex
3 | dm-haiku
4 | dm-tree
5 | git+https://github.com/deepmind/einshape
6 | jax
7 | numpy
8 | optax
9 | tqdm
10 | typing_extensions
11 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/cs/binary_addition.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Add two binary numbers."""
17 |
18 | import random
19 | from typing import Sequence
20 |
21 | import chex
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 | import numpy as np
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 |
28 |
29 | def numbers_to_variable_length_binary(
30 | numbers: Sequence[int],
31 | lengths: Sequence[int],
32 | little_endian: bool = True,
33 | ) -> list[list[int]]:
34 | """Returns the binary notation of a certain length for a sequence of numbers.
35 |
36 | Args:
37 | numbers: The numbers to be converted to binary.
38 | lengths: The lengths of the binary representations (every number uses its
39 | own length). This argument has no effect if the binary representation is
40 | longer than the specified length.
41 | little_endian: Whether to use little- or big-endian notation.
42 | """
43 | binary_strings = [f'{num:b}'.zfill(len) for num, len in zip(numbers, lengths)]
44 |
45 | if little_endian:
46 | binary_strings = [bin[::-1] for bin in binary_strings]
47 |
48 | return [list(map(int, bin)) for bin in binary_strings]
49 |
50 |
51 | def numbers_to_fixed_length_binary(
52 | numbers: Sequence[int],
53 | length: int,
54 | little_endian: bool = True,
55 | ) -> list[list[int]]:
56 | """Returns the binary notation of a certain length for a sequence of numbers.
57 |
58 | Args:
59 | numbers: The numbers to be converted to binary.
60 | length: The length of the binary representations (all numbers use the same
61 | length). This argument has no effect if the binary representation is
62 | longer than the specified length.
63 | little_endian: Whether to use little- or big-endian notation.
64 | """
65 | return numbers_to_variable_length_binary(
66 | numbers=numbers,
67 | lengths=[length] * len(numbers),
68 | little_endian=little_endian,
69 | )
70 |
71 |
72 | def expression_from_numbers(
73 | numbers_n: Sequence[list[int]],
74 | numbers_m: Sequence[list[int]],
75 | ) -> list[list[int]]:
76 | """Returns an expression with a placeholder value to denote the operation."""
77 | return [n + [2] + m for n, m in zip(numbers_n, numbers_m)]
78 |
79 |
80 | class BinaryAddition(task.GeneralizationTask):
81 | """A task with the goal of summing two numbers in binary (little-endian).
82 |
83 | The input is a string of the form `first_number+second_number` in
84 | (little-endian) binary notation (e.g., `01001+011`). The goal of the agent is
85 | to output the result, also in (little-endian) binary form (i.e., in the
86 | example `18 + 6 = 24 = 00011`). The output is padded with 0s to match the
87 | input length, and the end of the sum is denoted with a termination token
88 | (i.e., the output has values in `{0, 1, 2}`).
89 |
90 | Examples:
91 | 001 + 01101 = 010112000 (4 + 22 = 26)
92 | 1001 + 000001 = 10010120000 (9 + 32 = 41)
93 | """
94 |
95 | def _sample_expressions_and_results(
96 | self,
97 | batch_size: int,
98 | length: int,
99 | ) -> tuple[Sequence[list[int]], Sequence[list[int]]]:
100 | """Samples pairs of numbers and sums them in (little-endian) binary.
101 |
102 | We use Python's bignums, which can represent arbitrary-precision integers to
103 | perform addition of two potentially very large values (roughly of the size
104 | `2 ** (length // 2)`).
105 |
106 | Args:
107 | batch_size: The number of expressions and results to sample.
108 | length: The length of the input expression containing the two numbers and
109 | the separation token.
110 |
111 | Returns:
112 | The expression and the sum of the two numbers. The expression has the
113 | format: `[first_number, 2, second_number]`, where the numbers are in
114 | (little-endian) binary notation. The sum is also in (little-endian) binary
115 | notation, without leading (i.e., ending) zeros.
116 | """
117 | # If `length <= 2`, we just sample a binary value and return it (without
118 | # leading zeros in little-endian notation).
119 | if length <= 2:
120 | # Since `length <= 2`, we can use `np.random`` without overflow errors.
121 | numbers = np.random.randint(0, 2**length - 1, size=(batch_size))
122 | expressions = numbers_to_fixed_length_binary(numbers, length)
123 | results = numbers_to_fixed_length_binary(numbers, 0)
124 | return expressions, results
125 |
126 | # We only use `length - 1` tokens for the two values to account for the `+`.
127 | length_n = np.random.randint(1, length - 1, size=(batch_size,))
128 | length_m = length - 1 - length_n
129 |
130 | integer_n = [random.randint(1, 2 ** int(len_n) - 1) for len_n in length_n]
131 | integer_m = [random.randint(1, 2 ** int(len_m) - 1) for len_m in length_m]
132 |
133 | binary_n = numbers_to_variable_length_binary(integer_n, length_n)
134 | binary_m = numbers_to_variable_length_binary(integer_m, length_m)
135 |
136 | expressions = expression_from_numbers(binary_n, binary_m)
137 |
138 | integer_sum = list(map(sum, zip(integer_n, integer_m)))
139 | results = numbers_to_fixed_length_binary(integer_sum, length=0)
140 |
141 | return expressions, results
142 |
143 | def sample_batch(
144 | self,
145 | rng: chex.PRNGKey,
146 | batch_size: int,
147 | length: int,
148 | ) -> task.Batch:
149 | """Returns a batch of binary additions and their results."""
150 | del rng
151 |
152 | expressions, results = self._sample_expressions_and_results(
153 | batch_size=batch_size, length=length
154 | )
155 | # Append the termination token to the result and pad the result with zeros
156 | # to match the output length (accounting for the termination token).
157 | results = [res + [2] + [0] * (length - len(res)) for res in results]
158 |
159 | expressions = jnp.array(expressions, dtype=jnp.int32)
160 | results = jnp.array(results, dtype=jnp.int32)
161 |
162 | return {
163 | 'input': jnn.one_hot(expressions, self.input_size),
164 | 'output': jnn.one_hot(results, self.output_size),
165 | }
166 |
167 | @property
168 | def input_size(self) -> int:
169 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
170 | return 3
171 |
172 | @property
173 | def output_size(self) -> int:
174 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
175 | return 3
176 |
177 | def output_length(self, input_length: int) -> int:
178 | return input_length + 1
179 |
180 | def accuracy_mask(self, target: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
181 | """Computes a mask that ignores everything after the termination token.
182 |
183 | Args:
184 | target: Target tokens of shape `(batch_size, output_length, output_size)`.
185 |
186 | Returns:
187 | The mask of shape `(batch_size, output_length)`.
188 | """
189 | batch_size, length, _ = target.shape
190 | termination_indices = jnp.argmax(
191 | jnp.argmax(target, axis=-1),
192 | axis=-1,
193 | keepdims=True,
194 | )
195 | indices = jnp.tile(jnp.arange(length), (batch_size, 1))
196 | return indices <= termination_indices
197 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/cs/binary_multiplication.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Multiply two binary numbers."""
17 |
18 | import random
19 | from typing import Sequence
20 |
21 | import chex
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 | import numpy as np
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import binary_addition
28 |
29 |
30 | class BinaryMultiplication(task.GeneralizationTask):
31 | """A task with the goal of multiplying two numbers in binary (little-endian).
32 |
33 | The input is a string of the form `first_number£second_number` in
34 | (little-endian) binary notation (e.g., `01001*011`). The goal of the agent is
35 | to output the result, also in (little-endian) binary form (i.e., in the
36 | example `18 * 6 = 108 = 00110011`). The output is padded with 0s to match the
37 | input length, and the end of the product is denoted with a termination token
38 | (i.e., the output has values in `{0, 1, 2}`).
39 |
40 | Examples:
41 | 001 * 01101 = 000110120 (4 * 22 = 88)
42 | 1001 * 000001 = 00000100120 (9 * 32 = 288)
43 | """
44 |
45 | def _sample_expressions_and_results(
46 | self,
47 | batch_size: int,
48 | length: int,
49 | ) -> tuple[Sequence[list[int]], Sequence[list[int]]]:
50 | """Samples pairs of numbers and multiplies them in (little-endian) binary.
51 |
52 | We use Python's bignums, which can represent arbitrary-precision integers to
53 | perform multiplication of two potentially very large values (roughly of the
54 | size `2 ** (length // 2)`).
55 |
56 | Args:
57 | batch_size: The number of expressions and results to sample.
58 | length: The length of the input expression containing the two numbers and
59 | the separation token.
60 |
61 | Returns:
62 | The expression and the product of the two numbers. The expression has the
63 | format: `[first_number, 2, second_number]`, where the numbers are in
64 | (little-endian) binary notation. The product is also in (little-endian)
65 | binary notation, without leading (i.e., ending) zeros.
66 | """
67 | # If `length <= 2`, we just sample a binary sequence for the expression and
68 | # arbitrarily set the result to a fixed value (`[]` for `length == 1` and
69 | # `[0]` for `length == 2`) to maintain the invariant that the result has
70 | # length has most `length - 1`.
71 | if length <= 2:
72 | # Since `length <= 2`, we can use `np.random`` without overflow errors.
73 | numbers = np.random.randint(0, 2**length - 1, size=(batch_size))
74 | expressions = binary_addition.numbers_to_fixed_length_binary(
75 | numbers, length
76 | )
77 | return expressions, [[0] * (length - 1)] * batch_size
78 |
79 | # We only use `length - 1` tokens for the two values to account for the `*`.
80 | length_n = np.random.randint(1, length - 1, size=(batch_size,))
81 | length_m = length - 1 - length_n
82 |
83 | integer_n = [random.randint(1, 2 ** int(len_n) - 1) for len_n in length_n]
84 | integer_m = [random.randint(1, 2 ** int(len_m) - 1) for len_m in length_m]
85 |
86 | binary_n = binary_addition.numbers_to_variable_length_binary(
87 | integer_n, length_n
88 | )
89 | binary_m = binary_addition.numbers_to_variable_length_binary(
90 | integer_m, length_m
91 | )
92 |
93 | expressions = binary_addition.expression_from_numbers(binary_n, binary_m)
94 |
95 | integer_prod = [int_n * int_m for int_n, int_m in zip(integer_n, integer_m)]
96 | results = binary_addition.numbers_to_fixed_length_binary(
97 | integer_prod, length=0
98 | )
99 |
100 | return expressions, results
101 |
102 | def sample_batch(
103 | self,
104 | rng: chex.PRNGKey,
105 | batch_size: int,
106 | length: int,
107 | ) -> task.Batch:
108 | """Returns a batch of binary multiplications and their results."""
109 | del rng
110 |
111 | expressions, results = self._sample_expressions_and_results(
112 | batch_size=batch_size, length=length
113 | )
114 | # Append the termination token to the result and pad the result with zeros
115 | # to match the output length (accounting for the termination token). The
116 | # binary representation of the result will have at most length
117 | # `#(first_number) + #(second_number)`, where #() denotes the number of
118 | # digits of the binary notation. Since we use the token `2` to separate the
119 | # two numbers in the expression, the result will have length at most
120 | # `length - 1`, and thus by appending the termination token above it will
121 | # have length at most `length`, as desired.
122 | results = [res + [2] + [0] * (length - 1 - len(res)) for res in results]
123 |
124 | expressions = jnp.array(expressions, dtype=jnp.int32)
125 | results = jnp.array(results, dtype=jnp.int32)
126 |
127 | return {
128 | 'input': jnn.one_hot(expressions, self.input_size),
129 | 'output': jnn.one_hot(results, self.output_size),
130 | }
131 |
132 | @property
133 | def input_size(self) -> int:
134 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
135 | return 3
136 |
137 | @property
138 | def output_size(self) -> int:
139 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
140 | return 3
141 |
142 | def output_length(self, input_length: int) -> int:
143 | return input_length
144 |
145 | def accuracy_mask(self, target: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
146 | """Computes a mask that ignores everything after the termination token.
147 |
148 | Args:
149 | target: Target tokens of shape `(batch_size, output_length, output_size)`.
150 |
151 | Returns:
152 | The mask of shape `(batch_size, output_length)`.
153 | """
154 | batch_size, length, _ = target.shape
155 | termination_indices = jnp.argmax(
156 | jnp.argmax(target, axis=-1),
157 | axis=-1,
158 | keepdims=True,
159 | )
160 | indices = jnp.tile(jnp.arange(length), (batch_size, 1))
161 | return indices <= termination_indices
162 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/cs/bucket_sort.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Sort tokens from a fixed alphabet (i.e., bucket sort)."""
17 |
18 | import functools
19 |
20 | import chex
21 | import jax
22 | from jax import nn as jnn
23 | from jax import numpy as jnp
24 | from jax import random as jrandom
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 |
28 |
29 | class BucketSort(task.GeneralizationTask):
30 | """A task with the goal of sorting tokens from a fixed alphabet.
31 |
32 | The input string is composed of tokens from a fixed-size alphabet, i.e.,
33 | `{0, 1, ..., vocab_size - 1}`, and the goal is to return the sorted string (in
34 | lexicographically increasing order).
35 |
36 | Examples:
37 | 10204112 -> 00111224 (with `vocab_size = 5`)
38 | 1110001 -> 0001111 (with `vocab_size = 2`)
39 | """
40 |
41 | def __init__(self, *args, vocab_size: int = 5, **kwargs) -> None:
42 | """Initializes the task.
43 |
44 | Args:
45 | *args: The args for the base task class.
46 | vocab_size: The size of the alphabet.
47 | **kwargs: The kwargs for the base task class.
48 | """
49 | super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
50 | self._vocab_size = vocab_size
51 |
52 | @functools.partial(jax.jit, static_argnums=(0, 2, 3))
53 | def sample_batch(
54 | self,
55 | rng: chex.PRNGKey,
56 | batch_size: int,
57 | length: int,
58 | ) -> task.Batch:
59 | """Returns a batch of strings and tokens sorted by (inc.) occurrence."""
60 | strings = jrandom.randint(
61 | rng, shape=(batch_size, length), minval=0, maxval=self._vocab_size
62 | )
63 | sorted_strings = jnp.sort(strings, axis=-1)
64 |
65 | return {
66 | 'input': jnn.one_hot(strings, num_classes=self.input_size),
67 | 'output': jnn.one_hot(sorted_strings, num_classes=self.output_size),
68 | }
69 |
70 | @property
71 | def input_size(self) -> int:
72 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
73 | return self._vocab_size
74 |
75 | @property
76 | def output_size(self) -> int:
77 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
78 | return self._vocab_size
79 |
80 | def output_length(self, input_length: int) -> int:
81 | """Returns the output length for a given input length."""
82 | return input_length
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/cs/compute_sqrt.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Compute the floor of the square root of a binary number."""
17 |
18 | import math
19 | import random
20 |
21 | import chex
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 |
25 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import binary_addition
27 |
28 |
29 | class ComputeSqrt(task.GeneralizationTask):
30 | """A task with the goal of computing the square root of a binary number.
31 |
32 | The input is a number in binary (big-endian), and the output is the floor of
33 | the square root of this number, also in binary.
34 | Note the output length ie the length of the square root in binary is always
35 | ceil(input_length / 2) (because log(sqrt(x)) = 1/2 log(x)).
36 |
37 | Examples:
38 | 100101 = 37 -> square root is 6.08... -> floor(6.08) = 6 -> 101
39 | 111 = 7 -> square root is 2.64 -> floor(2.64) = 2 -> 10
40 | """
41 |
42 | def sample_batch(
43 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
44 | ) -> task.Batch:
45 | """Returns a batch of binary numbers and their square roots, in binary."""
46 | del rng
47 | numbers = [random.randint(1, 2**length - 1) for _ in range(batch_size)]
48 | binary_numbers = binary_addition.numbers_to_fixed_length_binary(
49 | numbers, length=length, little_endian=False
50 | )
51 |
52 | sqrts = list(map(math.isqrt, numbers))
53 | binary_sqrts = binary_addition.numbers_to_fixed_length_binary(
54 | sqrts, length=self.output_length(length), little_endian=False
55 | )
56 |
57 | binary_numbers = jnp.array(binary_numbers, jnp.int32)
58 | binary_sqrts = jnp.array(binary_sqrts, jnp.int32)
59 |
60 | inputs = jnn.one_hot(binary_numbers, self.input_size)
61 | output = jnn.one_hot(binary_sqrts, self.output_size)
62 | return {'input': inputs, 'output': output}
63 |
64 | @property
65 | def input_size(self) -> int:
66 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
67 | return 2
68 |
69 | @property
70 | def output_size(self) -> int:
71 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
72 | return 2
73 |
74 | def output_length(self, input_length: int) -> int:
75 | return math.ceil(input_length / 2)
76 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/cs/duplicate_string.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Duplicate a string."""
17 |
18 | import functools
19 |
20 | import chex
21 | import jax
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 | import jax.random as jrandom
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 |
28 |
29 | class DuplicateString(task.GeneralizationTask):
30 | """A task with the goal of duplicating a string.
31 |
32 | The input is a string s_1 ... s_n composed of symbols from a finite set S. The
33 | output is the same string outputted twice without any separator, ie:
34 | s_1 ... s_n s_1 ... s_n
35 |
36 | Examples:
37 | 101 -> 101 101
38 | 111111 -> 111111 111111
39 |
40 | In the paper, we use only binary strings (ie S = {0, 1}).
41 | Note that the sampling is jittable so this task is fast.
42 | """
43 |
44 | def __init__(self, vocab_size: int, *args, duplication: int = 2, **kwargs):
45 | """Initializes the remember_string task.
46 |
47 | Args:
48 | vocab_size: The size of the alphabet.
49 | *args: Args for the base task class.
50 | duplication: Number of times the string should be duplicated.
51 | **kwargs: Kwargs for the base task class.
52 | """
53 | super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
54 |
55 | self._vocab_size = vocab_size
56 | self._duplication = duplication
57 |
58 | @functools.partial(jax.jit, static_argnums=(0, 2, 3))
59 | def sample_batch(
60 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
61 | ) -> task.Batch:
62 | """Returns a batch of strings and their copies."""
63 | strings = jrandom.randint(
64 | rng, shape=(batch_size, length), minval=0, maxval=self._vocab_size
65 | )
66 | one_hot_strings = jnn.one_hot(strings, num_classes=self._vocab_size)
67 | output = jnp.concatenate([one_hot_strings] * self._duplication, axis=1)
68 | return {"input": one_hot_strings, "output": output}
69 |
70 | @property
71 | def input_size(self) -> int:
72 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
73 | return self._vocab_size
74 |
75 | @property
76 | def output_size(self) -> int:
77 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
78 | return self._vocab_size
79 |
80 | def output_length(self, input_length: int) -> int:
81 | """Returns the output length for a given input length."""
82 | return self._duplication * input_length
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/cs/missing_duplicate_string.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Predict the missing symbol in a duplicated string."""
17 |
18 | import functools
19 |
20 | import chex
21 | import jax
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 | import jax.random as jrandom
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 |
28 |
29 | class MissingDuplicateString(task.GeneralizationTask):
30 | """A task with the goal of finding the missing symbol in a duplicated string.
31 |
32 | Given a binary string that is presented twice with exactly one element omitted
33 | (denoted by the placeholder token `2`), predict the value of that element.
34 | Thus, an agent trying to solve this task needs to recognize the underlying
35 | duplicated string to be able to produce the correct output.
36 | If the length is odd, the duplicated strings of length `length // 2` are
37 | padded with the empty token `3`.
38 |
39 | Examples
40 | 01100210 -> 1 (the substring is 0110, so the missing value is 1)
41 | 1011213 -> 0 (the subtring is 101, so the missing value is 0)
42 | """
43 |
44 | @functools.partial(jax.jit, static_argnums=(0, 2, 3))
45 | def sample_batch(
46 | self,
47 | rng: chex.PRNGKey,
48 | batch_size: int,
49 | length: int,
50 | ) -> task.Batch:
51 | """Returns a batch of strings and the expected class."""
52 | # For `length == 1`, we cannot meaningfully define substrings of length
53 | # `length // 2`, so we arbitrarily set the inputs and outputs to `1`.
54 | if length == 1:
55 | return {
56 | 'input': jnn.one_hot(
57 | jnp.ones((batch_size, length)), num_classes=self.input_size
58 | ),
59 | 'output': jnn.one_hot(
60 | jnp.ones((batch_size,)), num_classes=self.output_size
61 | ),
62 | }
63 |
64 | strings_rng, indices_rng = jrandom.split(rng)
65 | strings = jrandom.randint(
66 | strings_rng, shape=(batch_size, length // 2), minval=0, maxval=2
67 | )
68 | duplicated_strings = jnp.concatenate((strings, strings), axis=-1)
69 | indices = jrandom.randint(
70 | indices_rng,
71 | shape=(batch_size,),
72 | minval=0,
73 | maxval=duplicated_strings.shape[1],
74 | )
75 | output = jax.vmap(lambda x, y: x[y])(duplicated_strings, indices)
76 | masked_strings = jax.vmap(lambda x, y: x.at[y].set(2))(
77 | duplicated_strings, indices
78 | )
79 |
80 | # If `length` is odd, we pad the strings with the empty token `3` at the end
81 | # to ensure that the final input length is equal to `length` given the two
82 | # substrings of length `length // 2`.
83 | padding = jnp.full((batch_size, length % 2), fill_value=3)
84 | padded_strings = jnp.concatenate((masked_strings, padding), axis=-1)
85 |
86 | return {
87 | 'input': jnn.one_hot(padded_strings, num_classes=self.input_size),
88 | 'output': jnn.one_hot(output, num_classes=self.output_size),
89 | }
90 |
91 | @property
92 | def input_size(self) -> int:
93 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
94 | return 4
95 |
96 | @property
97 | def output_size(self) -> int:
98 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
99 | return 2
100 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/cs/odds_first.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Sort a string by the parity of the indices (odd indices first)."""
17 |
18 | import functools
19 |
20 | import chex
21 | import jax
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 | import jax.random as jrandom
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 |
28 |
29 | class OddsFirst(task.GeneralizationTask):
30 | """A task with the goal of outputting a string's tokens at odd indices first.
31 |
32 | The input is a string s_1 ... s_n composed of symbols from a finite set S. The
33 | output is the same string, but where the values at odd indexes have been put
34 | first: s_1 s_3 s_5 ... s_2 s_4 s_6 ...
35 |
36 | Examples:
37 | 00110101 -> 0100 0111
38 | 110 -> 10 1
39 |
40 | In the paper, we use only binary strings (ie S = {0, 1}).
41 | Note that the sampling is jittable so this task is fast.
42 | """
43 |
44 | def __init__(self, vocab_size: int, *args, **kwargs):
45 | """Initializes the odds_first task.
46 |
47 | Args:
48 | vocab_size: The size of the alphabet.
49 | *args: Args for the base task class.
50 | **kwargs: Kwargs for the base task class.
51 | """
52 | super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
53 |
54 | self._vocab_size = vocab_size
55 |
56 | @functools.partial(jax.jit, static_argnums=(0, 2, 3))
57 | def sample_batch(
58 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
59 | ) -> task.Batch:
60 | """Returns a batch of strings and their outputs."""
61 | strings = jrandom.randint(
62 | rng, shape=(batch_size, length), minval=0, maxval=self._vocab_size
63 | )
64 | one_hot_strings = jnn.one_hot(strings, num_classes=self._vocab_size)
65 | output = jnp.concatenate(
66 | [one_hot_strings[:, 1::2], one_hot_strings[:, ::2]], axis=1
67 | )
68 | return {"input": one_hot_strings, "output": output}
69 |
70 | @property
71 | def input_size(self) -> int:
72 | """Returns the input size for the model."""
73 | return self._vocab_size
74 |
75 | @property
76 | def output_size(self) -> int:
77 | """Returns the output size for the model."""
78 | return self._vocab_size
79 |
80 | def output_length(self, input_length: int) -> int:
81 | """Returns the output length for the model."""
82 | return input_length
83 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/dcf/modular_arithmetic_brackets.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Modular arithmetic with brackets."""
17 |
18 | import collections
19 | from typing import Sequence
20 |
21 | import chex
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import numpy as np
24 | import tqdm
25 | import tree
26 |
27 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
28 |
29 |
30 | def generate_one_expression_and_result(
31 | modulus: int, length: int, mult: bool = False
32 | ) -> tuple[str, int]:
33 | """Returns a modular arithmetic expression with brackets, and its result.
34 |
35 | The values in the expression are in {0, 1, ..., modulus-1}. The allowed
36 | operations are either {+, -} (mult=False) or {+, -, *} (mult=True).
37 |
38 | Args:
39 | modulus: The modulus to use for the expression.
40 | length: The length of the expression.
41 | mult: Whether to include the multiplication operator in the expressions.
42 |
43 | Raises:
44 | ValueError if length < 1.
45 | """
46 |
47 | # Generates a terminal (digit).
48 | def gen_terminal():
49 | terminal = np.random.randint(low=0, high=modulus)
50 | return str(terminal), terminal
51 |
52 | # If length is less than 1, issue an error.
53 | if length < 1:
54 | raise ValueError(f"Can't generate expressions of length < 1. Got {length}.")
55 |
56 | # If length is less than 5, generate a digit d, -d, (d), or (-d).
57 | if length == 1:
58 | return gen_terminal()
59 | elif length == 2:
60 | term_str, term_val = gen_terminal()
61 | return '-' + term_str, -term_val % modulus
62 | elif length == 3:
63 | term_str, term_val = gen_terminal()
64 | return '(' + term_str + ')', term_val
65 | elif length == 4:
66 | term_str, term_val = gen_terminal()
67 | return '(-' + term_str + ')', -term_val % modulus
68 |
69 | # If length is >= 5, sample an operator with brackets.
70 |
71 | # First split the length into a left and right part.
72 | left_length = np.random.randint(low=1, high=length - 3)
73 | right_length = length - (left_length + 3)
74 | left_str, left_val = generate_one_expression_and_result(
75 | modulus, left_length, mult=mult
76 | )
77 | right_str, right_val = generate_one_expression_and_result(
78 | modulus, right_length, mult=mult
79 | )
80 |
81 | # Now sample an operator and return.
82 | maxop = 3 if mult else 2
83 | op = np.random.randint(low=0, high=maxop)
84 | if op == 0:
85 | return (
86 | '(' + left_str + '+' + right_str + ')',
87 | (left_val + right_val) % modulus,
88 | )
89 | elif op == 1:
90 | return (
91 | '(' + left_str + '-' + right_str + ')',
92 | (left_val - right_val) % modulus,
93 | )
94 | else:
95 | return (
96 | '(' + left_str + '*' + right_str + ')',
97 | (left_val * right_val) % modulus,
98 | )
99 |
100 |
101 | def generate_raw_dataset(
102 | n: int,
103 | lengths: Sequence[int],
104 | modulus: int,
105 | mult: bool = False,
106 | with_tqdm: bool = False,
107 | ) -> dict[int, dict[str, np.ndarray]]:
108 | """Generates a dataset of maths expressions with brackets, and their results.
109 |
110 | Args:
111 | n: The number of datapoints in the dataset.
112 | lengths: The lengths of the sequences to generate. n is evenly distributed
113 | over these lengths.
114 | modulus: Modulus used to compute the expressions.
115 | mult: Whether to include the multiplication operator in the expressions.
116 | with_tqdm: As the computation might be long, whether to add a tqdm progress
117 | bar or not.
118 |
119 | Returns:
120 | A dict which keys are the passed lengths, and the values are dicts with keys
121 | 'equations' and 'solutions', and values are the data numpy arrays.
122 | """
123 | alphabet_to_int = {
124 | '+': modulus,
125 | '-': modulus + 1,
126 | '*': modulus + 2,
127 | '(': modulus + 3,
128 | ')': modulus + 4,
129 | 'x': modulus + 5,
130 | '=': modulus + 6,
131 | }
132 | for x in range(modulus):
133 | alphabet_to_int[str(x)] = x
134 |
135 | sequences = collections.defaultdict(
136 | lambda: { # pylint: disable=g-long-lambda
137 | 'expressions': [],
138 | 'results': [],
139 | }
140 | )
141 | range_lengths = tqdm.tqdm(lengths) if with_tqdm else lengths
142 | for length in range_lengths:
143 | for _ in range(n // len(lengths)):
144 | seq, label = generate_one_expression_and_result(modulus, length, mult)
145 | seq = [alphabet_to_int[x] for x in seq]
146 | sequences[length]['expressions'].append(seq)
147 | sequences[length]['results'].append(label)
148 | sequences = tree.traverse(
149 | lambda l: np.array(l, dtype=np.int32) if isinstance(l, list) else l,
150 | sequences,
151 | top_down=False,
152 | )
153 | return dict(sequences)
154 |
155 |
156 | class ModularArithmeticBrackets(task.GeneralizationTask):
157 | """A task with the goal of reducing an arithmetic expression with brackets."""
158 |
159 | def __init__(self, modulus: int, *args, mult: bool = False, **kwargs):
160 | super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
161 | self._modulus = modulus
162 | self._mult = mult
163 |
164 | def sample_batch(
165 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
166 | ) -> task.Batch:
167 | """Returns a batch of inputs/outputs."""
168 | np.random.seed(rng[0])
169 | batch = generate_raw_dataset(
170 | batch_size, lengths=[length], modulus=self._modulus, mult=self._mult
171 | )[length]
172 | inputs = jnn.one_hot(batch['expressions'], self.input_size)
173 | output = jnn.one_hot(batch['results'], self.output_size)
174 | return {'input': inputs, 'output': output}
175 |
176 | @property
177 | def input_size(self) -> int:
178 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
179 | return self._modulus + 6
180 |
181 | @property
182 | def output_size(self) -> int:
183 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
184 | return self._modulus
185 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/dcf/reverse_string.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Compute the reverse of an input string."""
17 |
18 | import functools
19 |
20 | import chex
21 | import jax
22 | import jax.numpy as jnp
23 |
24 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
25 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.cs import duplicate_string
26 |
27 |
28 | class ReverseString(duplicate_string.DuplicateString):
29 | """A task with the goal of reversing a given string.
30 |
31 | The input is a string s_1 ... s_n composed of symbols from a finite set S. The
32 | output is the string, reversed, ie s_n ... s_1.
33 |
34 | Examples:
35 | 011010 -> 010110
36 | 123021 -> 120321
37 |
38 | In the paper, we use only binary strings (ie S = {0, 1}).
39 | Note that the sampling is jittable so this task is fast.
40 | """
41 |
42 | @functools.partial(jax.jit, static_argnums=(0, 2, 3))
43 | def sample_batch(
44 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
45 | ) -> task.Batch:
46 | """Returns a batch of strings and their reversed version."""
47 | batch = super().sample_batch(rng, batch_size, length)
48 | batch['output'] = jnp.flip(batch['input'], axis=1)
49 | return batch
50 |
51 | def output_length(self, input_length: int) -> int:
52 | """Returns the output length for a given input length."""
53 | return input_length
54 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/dcf/solve_equation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Solve for the value of an unknown variable in an equation."""
17 |
18 | import collections
19 | from typing import Sequence
20 |
21 | import chex
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 | import numpy as np
25 | import tqdm
26 | import tree
27 |
28 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
29 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks.dcf import modular_arithmetic_brackets as mab
30 |
31 |
32 | def generate_equation_and_solution(
33 | modulus: int, length: int, mult: bool = False
34 | ) -> tuple[str, int]:
35 | """Returns a modular arithmetic equation with brackets, and its solution.
36 |
37 | The values are in {0, 1, ..., modulus-1}, and the unknown
38 | value is x. The allowed operations are either {+, -} (mult=False) or
39 | {+, -, *} (mult=True).
40 | Warning: if mult=True, x might have multiple valid solutions.
41 |
42 | Args:
43 | modulus: The modulus to use for the expression.
44 | length: The length of the expression.
45 | mult: Whether to include the multiplication operator in the expressions.
46 |
47 | Raises:
48 | ValueError if the length is < 3.
49 | """
50 |
51 | # Generate the expression.
52 | expr, val = mab.generate_one_expression_and_result(
53 | modulus, length - 2, mult=mult
54 | )
55 |
56 | # Replace random digit with 'x'.
57 | idx = np.random.randint(low=0, high=len(expr))
58 | digits = [str(n) for n in range(modulus)]
59 | while expr[idx] not in digits:
60 | idx = (idx + 1) % (length - 2)
61 | solution = int(expr[idx])
62 | equation = expr[:idx] + 'x' + expr[idx + 1 :] + '=' + str(val)
63 |
64 | return equation, solution
65 |
66 |
67 | def generate_raw_dataset(
68 | n: int,
69 | lengths: Sequence[int],
70 | modulus: int,
71 | mult: bool = False,
72 | with_tqdm: bool = False,
73 | ) -> dict[int, dict[str, np.ndarray]]:
74 | """Generates a dataset of equations and their solutions.
75 |
76 | Args:
77 | n: The number of datapoints in the dataset.
78 | lengths: The lengths of the sequences to generate. n is evenly distributed
79 | over these lengths.
80 | modulus: Modulus used to compute the expressions.
81 | mult: Whether to include the multiplication operator in the expressions.
82 | with_tqdm: As the computation might be long, whether to add a tqdm progress
83 | bar or not.
84 |
85 | Returns:
86 | A dict which keys are the passed lengths, and the values are dicts with keys
87 | 'equations' and 'solutions', and values are the data numpy arrays.
88 | """
89 | alphabet_to_int = {
90 | '+': modulus,
91 | '-': modulus + 1,
92 | '(': modulus + 2,
93 | ')': modulus + 3,
94 | 'x': modulus + 4,
95 | '=': modulus + 5,
96 | }
97 | for x in range(modulus):
98 | alphabet_to_int[str(x)] = x
99 |
100 | sequences = collections.defaultdict(
101 | lambda: { # pylint: disable=g-long-lambda
102 | 'equations': [],
103 | 'solutions': [],
104 | }
105 | )
106 | range_lengths = tqdm.tqdm(lengths) if with_tqdm else lengths
107 | for length in range_lengths:
108 | for _ in range(n // len(lengths)):
109 | seq, label = generate_equation_and_solution(modulus, length, mult=mult)
110 | seq = [alphabet_to_int[x] for x in seq]
111 | sequences[length]['equations'].append(seq)
112 | sequences[length]['solutions'].append(label)
113 | # Convert the list of numbers we have to arrays at the leaves.
114 | sequences = tree.traverse(
115 | lambda l: np.array(l, dtype=np.int32) if isinstance(l, list) else l,
116 | sequences,
117 | top_down=False,
118 | )
119 | return dict(sequences)
120 |
121 |
122 | class SolveEquation(task.GeneralizationTask):
123 | """A task with the goal of solving an modular equation for an unknown."""
124 |
125 | def __init__(self, modulus: int, *args, **kwargs):
126 | super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
127 | self._modulus = modulus
128 |
129 | def sample_batch(
130 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
131 | ) -> task.Batch:
132 | """Returns a batch of inputs/outputs."""
133 | np.random.seed(rng[0])
134 | if length < 3:
135 | return {
136 | 'input': jnn.one_hot(
137 | jnp.zeros((batch_size, length)), num_classes=self.input_size
138 | ),
139 | 'output': jnn.one_hot(
140 | jnp.zeros((batch_size,)), num_classes=self.output_size
141 | ),
142 | }
143 | batch = generate_raw_dataset(
144 | batch_size, lengths=[length], modulus=self._modulus
145 | )[length]
146 | inputs = jnn.one_hot(batch['equations'], self.input_size)
147 | output = jnn.one_hot(batch['solutions'], self.output_size)
148 | return {'input': inputs, 'output': output}
149 |
150 | @property
151 | def input_size(self) -> int:
152 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
153 | return self._modulus + 6
154 |
155 | @property
156 | def output_size(self) -> int:
157 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
158 | return self._modulus
159 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/dcf/stack_manipulation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Manipulate an input stack, using the input actions."""
17 |
18 | import chex
19 | import jax.nn as jnn
20 | import jax.numpy as jnp
21 | import numpy as np
22 |
23 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
24 |
25 |
26 | class StackManipulation(task.GeneralizationTask):
27 | """A task with the goal of following instructions and returning the end stack.
28 |
29 | The input is composed of a stack of 0s and 1s followed by a sequence of
30 | instructions POP/PUSH 0/PUSH 1 (represented by 2s/3s/4s). The input stack is
31 | given bottom-to-top, and the agent needs to execute the instructions given
32 | (left-to-rigth) and output the final stack top-to-bottom (i.e., as if it were
33 | popping the final stack). If a POP action is to be called on an empty stack,
34 | the action is ignored. The output is padded with 0s to match the input length
35 | + 1 (to accommodate for the termination token), and the end of the final stack
36 | is denoted with the termination symbol 2 (i.e., the output has values in {0,
37 | 1, 2}).
38 |
39 | Examples:
40 | 0 1 1 0 PUSH 1 POP POP
41 | initial 0 1 1 0 (the stack is received bottom-to-top)
42 | PUSH 1 0 1 1 0 1
43 | POP 0 1 1 0
44 | POP 0 1 1
45 | -> 1 1 0 2 0 0 0 0 (the stack is returned top-to-bottom)
46 |
47 | 1 1 0 POP POP POP
48 | initial 1 1 0
49 | POP 1 1
50 | POP 1
51 | POP
52 | -> 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 (the stack is empty and padded with zeros)
53 | """
54 |
55 | def _sample_expression_and_result(
56 | self, length: int
57 | ) -> tuple[np.ndarray, list[int]]:
58 | """Returns an expression with stack instructions, and the result stack."""
59 | if length == 1:
60 | value = np.random.randint(low=0, high=2, size=(1,))
61 | return value, list(value)
62 |
63 | # Initialize the stack content and the actions (POP/PUSH).
64 | stack_length = np.random.randint(low=1, high=length)
65 | stack = np.random.randint(low=0, high=2, size=(stack_length,))
66 | actions = np.random.randint(low=2, high=5, size=(length - stack_length,))
67 |
68 | # Apply the actions on the stack.
69 | current_stack = list(stack)
70 |
71 | for action in actions:
72 | if action == 2: # POP
73 | if current_stack:
74 | current_stack.pop()
75 | elif action in [3, 4]: # PUSH a 0 (case 3) or a 1 (case 4)
76 | current_stack.append(action - 3)
77 |
78 | return np.concatenate([stack, actions]), current_stack[::-1]
79 |
80 | def sample_batch(
81 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
82 | ) -> task.Batch:
83 | """Returns a batch of strings and the expected class."""
84 | np.random.seed(rng[0])
85 | expressions, results = [], []
86 | for _ in range(batch_size):
87 | expression, result = self._sample_expression_and_result(length)
88 | expressions.append(expression)
89 | # Append the termination token to the result.
90 | result += [self.output_size - 1]
91 | # Pad the result with zeros to match the input length (accounting for the
92 | # termination token).
93 | result += [0] * (length + 1 - len(result))
94 | results.append(result)
95 | expressions = jnp.array(expressions)
96 | results = jnp.array(results)
97 |
98 | inputs = jnn.one_hot(expressions, self.input_size)
99 | output = jnn.one_hot(results, self.output_size)
100 | return {'input': inputs, 'output': output}
101 |
102 | @property
103 | def input_size(self) -> int:
104 | """Returns the input size for the models.
105 |
106 | The value is 5 because we have two possible tokens in the stack (0, 1), plus
107 | three tokens to describe the PUSH 0, PUSH 1, and POP actions.
108 | """
109 | return 5
110 |
111 | @property
112 | def output_size(self) -> int:
113 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
114 | return 3
115 |
116 | def output_length(self, input_length: int) -> int:
117 | """Returns the output length of the task."""
118 | return input_length + 1
119 |
120 | def accuracy_mask(self, target: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
121 | """Computes mask that ignores everything after the termination tokens.
122 |
123 | Args:
124 | target: Target tokens of shape `(batch_size, output_length, output_size)`.
125 |
126 | Returns:
127 | The mask of shape `(batch_size, output_length)`.
128 | """
129 | batch_size, length, _ = target.shape
130 | termination_indices = jnp.argmax(
131 | jnp.argmax(target, axis=-1),
132 | axis=-1,
133 | keepdims=True,
134 | )
135 | indices = jnp.tile(jnp.arange(length), (batch_size, 1))
136 | return indices <= termination_indices
137 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/regular/cycle_navigation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Compute the final state after randomly walking on a circle."""
17 |
18 | import functools
19 |
20 | import chex
21 | import jax
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 | import jax.random as jrandom
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 |
28 |
29 | class CycleNavigation(task.GeneralizationTask):
30 | """A task with the goal of computing the final state on a circle.
31 |
32 | The input is a string of actions, composed of 0s, 1s or -1s. The actions give
33 | directions to take on a finite length circle (0 is for stay, 1 is for right,
34 | -1 is for left). The goal is to give the final position on the circle after
35 | all the actions have been taken. The agent starts at position 0.
36 |
37 | By default, the length the circle is 5.
38 |
39 | Examples:
40 | 1 -1 0 -1 -1 -> -2 = class 3
41 | 1 1 1 -1 -> 2 = class 2
42 |
43 | Note that the sampling is jittable so it is fast.
44 | """
45 |
46 | @property
47 | def _cycle_length(self) -> int:
48 | """Returns the cycle length, number of possible states."""
49 | return 5
50 |
51 | @functools.partial(jax.jit, static_argnums=(0, 2, 3))
52 | def sample_batch(
53 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
54 | ) -> task.Batch:
55 | """Returns a batch of strings and the expected class."""
56 | actions = jrandom.randint(
57 | rng, shape=(batch_size, length), minval=0, maxval=3
58 | )
59 | final_states = jnp.sum(actions - 1, axis=1) % self._cycle_length
60 | final_states = jnn.one_hot(final_states, num_classes=self.output_size)
61 | one_hot_strings = jnn.one_hot(actions, num_classes=self.input_size)
62 | return {"input": one_hot_strings, "output": final_states}
63 |
64 | @property
65 | def input_size(self) -> int:
66 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
67 | return 3
68 |
69 | @property
70 | def output_size(self) -> int:
71 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
72 | return self._cycle_length
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/regular/even_pairs.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Compute whether the number of 01's and 10's is even."""
17 |
18 | import functools
19 |
20 | import chex
21 | import jax
22 | from jax import nn as jnn
23 | from jax import numpy as jnp
24 | from jax import random as jrandom
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 |
28 |
29 | class EvenPairs(task.GeneralizationTask):
30 | """A task with the goal of checking whether the number of 01s and 10s is even.
31 |
32 | The input is a binary string, composed of 0s and 1s. If the result is even,
33 | the class is 0, otherwise it's one.
34 |
35 | Examples:
36 | 001110 -> 1 '10' and 1 '01' -> class 0
37 | 0101001 -> 2 '10' and 3 '01' -> class 1
38 |
39 | Note the sampling is jittable so this task is fast.
40 | """
41 |
42 | @functools.partial(jax.jit, static_argnums=(0, 2, 3))
43 | def sample_batch(
44 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
45 | ) -> task.Batch:
46 | """Returns a batch of strings and the expected class."""
47 | strings = jrandom.randint(
48 | rng,
49 | shape=(batch_size, length),
50 | minval=0,
51 | maxval=2,
52 | )
53 | one_hot_strings = jnn.one_hot(strings, num_classes=2)
54 | unequal_pairs = jnp.logical_xor(strings[:, :-1], strings[:, 1:])
55 | odd_unequal_pairs = jnp.sum(unequal_pairs, axis=-1) % 2
56 | return {
57 | 'input': one_hot_strings,
58 | 'output': jnn.one_hot(odd_unequal_pairs, num_classes=self.output_size),
59 | }
60 |
61 | @property
62 | def input_size(self) -> int:
63 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
64 | return 2
65 |
66 | @property
67 | def output_size(self) -> int:
68 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
69 | return 2
70 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/regular/modular_arithmetic.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Modular arithmetic without brackets.
17 |
18 | Note this allows to generate samples using a jittable function, and is therefore
19 | much faster than its 'brackets' counterpart, which requires to simulate the full
20 | CF grammar, non-jittable.
21 | """
22 |
23 | import functools
24 | from typing import Optional, Sequence
25 |
26 | import chex
27 | import jax
28 | import jax.nn as jnn
29 | import jax.numpy as jnp
30 | import jax.random as jrandom
31 |
32 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
33 |
34 | OP_BY_CHARACTER = {'+': 0, '-': 1, '*': 2, '_': 3}
35 |
36 |
37 | def _replace_subtractions(expression: chex.Array, modulus: int) -> chex.Array:
38 | """Replaces subtractions in an expression by additions with the inverse.
39 |
40 | e.g. the expression [1, -, 3] results in [1, +, -3].
41 |
42 | Args:
43 | expression: Encoded expression (a 1D array of integers) in which to replace
44 | subtractions.
45 | modulus: The modulus to use for the modular arithmetic.
46 |
47 | Returns:
48 | The expression with all subtractions replaced by additions with the inverse.
49 | """
50 | if expression.size < 2:
51 | return expression
52 |
53 | mask = expression == modulus + OP_BY_CHARACTER['-']
54 | subtract_replaced = jnp.where(
55 | mask, modulus + OP_BY_CHARACTER['+'], expression
56 | )
57 | return subtract_replaced.at[2:].multiply(1 - 2 * mask[1:-1])
58 |
59 |
60 | def _perform_multiplications(
61 | expression: chex.Array, modulus: int
62 | ) -> chex.Array:
63 | """Performs all multiplications in an expression containing only + and *.
64 |
65 | This is done at fixed length and the result is zero-padded to achieve this.
66 | Since the result of performing multiplications is an expression containing
67 | only + operators, the operators are dropped from the output. For example, the
68 | expression [1, +, 3, *, 4] results in [1, 12, 0].
69 |
70 | Args:
71 | expression: Encoded expression in which to perform multiplications.
72 | modulus: The modulus to use for the modular arithmetic.
73 |
74 | Returns:
75 | An array with the results of the multiplications (potentially zero-padded).
76 | """
77 | term_ids = jnp.cumsum(expression == modulus + OP_BY_CHARACTER['+'])[::2]
78 | # Segment_prod can only be jit-compiled with a fixed number of segments.
79 | # Therefore, we have to set to the maximum number of terms possible and
80 | # mask out superfluous segment results with zeros afterwards.
81 | maximum_term_number = expression.shape[0] // 2 + 1
82 | products = jax.ops.segment_prod(
83 | expression[::2],
84 | term_ids,
85 | num_segments=maximum_term_number,
86 | indices_are_sorted=True,
87 | )
88 | valid_segment_mask = jnp.arange(maximum_term_number) <= term_ids[-1]
89 | return products * valid_segment_mask
90 |
91 |
92 | def _replace_blanks(expression: chex.Array, modulus: int) -> chex.Array:
93 | """Replaces blank symbols in expression with either `+` or `0`.
94 |
95 | Depending on whether the blank symbol is at the position of an operator or a
96 | residual, the blank symbol is replaced with a `+` operator or a `0`.
97 |
98 | Args:
99 | expression: Encoded expression in which to replace blank symbols.
100 | modulus: The modulus to use for the modular arithmetic.
101 |
102 | Returns:
103 | An array with blank symbols replaced by either `+` or `0`.
104 | """
105 | mask = expression == OP_BY_CHARACTER['_'] + modulus
106 | operator_mask = mask.at[::2].set(False) # pytype: disable=attribute-error # numpy-scalars
107 | residual_mask = mask.at[1::2].set(False) # pytype: disable=attribute-error # numpy-scalars
108 |
109 | blanks_replaced = jnp.where(
110 | operator_mask, OP_BY_CHARACTER['+'] + modulus, expression
111 | )
112 | blanks_replaced = jnp.where(residual_mask, 0, blanks_replaced)
113 | return blanks_replaced
114 |
115 |
116 | def _evaluate_expression(expression: chex.Array, modulus: int) -> chex.Array:
117 | """Returns the result of evaluating a modular arithmetic expression."""
118 | expression = _replace_blanks(expression, modulus)
119 | expression = _replace_subtractions(expression, modulus)
120 | additive_terms = _perform_multiplications(expression, modulus)
121 | return jnp.sum(additive_terms) % modulus
122 |
123 |
124 | class ModularArithmetic(task.GeneralizationTask):
125 | """A task with the goal of reducing a simple arithmetic expression.
126 |
127 | The input is a string, composed of numbers (in {0, ..., modulus-1}), and
128 | operators (in {+, -, *}). The output is the reduced value of this expression,
129 | which is also in {0, ..., modulus-1}.
130 |
131 | Examples (modulo 5):
132 | 1 + 2 * 3 = 2
133 | 1 - 1 - 1 = 4
134 | 0 * 1 + 4 * 3 - 2 = 0
135 |
136 | Note that the input strings are always of odd length.
137 | """
138 |
139 | def __init__(
140 | self,
141 | modulus: int,
142 | *args,
143 | operators: Optional[Sequence[str]] = None,
144 | **kwargs
145 | ):
146 | """Initializes the modular arithmetic task.
147 |
148 | Args:
149 | modulus: The modulus used for the computation.
150 | *args: Args for the base task class.
151 | operators: Operators to be used in the sequences. By default it's None,
152 | meaning all operators available are used.
153 | **kwargs: Kwargs for the base task class.
154 | """
155 | super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
156 |
157 | self._modulus = modulus
158 | if operators is None:
159 | operators = ('+', '*', '-')
160 | self._operators = [OP_BY_CHARACTER[op] for op in operators]
161 |
162 | @functools.partial(jax.jit, static_argnums=(0, 2, 3))
163 | def sample_batch(
164 | self,
165 | rng: chex.PRNGKey,
166 | batch_size: int,
167 | length: int,
168 | ) -> task.Batch:
169 | """Returns a batch of modular arithmetic expressions and their labels.
170 |
171 | Args:
172 | rng: The jax random number generator.
173 | batch_size: The size of the batch returned.
174 | length: The length of the sequence. As this length must be odd for the
175 | modular arithmetic dataset, if it's not, we force it to be by
176 | subtracting one to the length passed.
177 | """
178 | # Subtracting one to the length if it's not odd already.
179 | if length % 2 != 1:
180 | length -= 1
181 |
182 | batch = jnp.empty((batch_size, length), dtype=int)
183 | rng1, rng2 = jax.random.split(rng)
184 | remainders = jax.random.randint(
185 | rng1, (batch_size, length // 2 + 1), 0, self._modulus
186 | )
187 | ops = self._modulus + jnp.array(self._operators)
188 |
189 | operations = jrandom.choice(rng2, ops, (batch_size, length // 2))
190 | batch = batch.at[:, ::2].set(remainders)
191 | expressions = batch.at[:, 1::2].set(operations)
192 |
193 | evaluate = functools.partial(_evaluate_expression, modulus=self._modulus)
194 | labels = jax.vmap(evaluate)(expressions)
195 | labels = jnn.one_hot(labels, self._modulus)
196 | one_hot_expressions = jnn.one_hot(
197 | expressions, self._modulus + len(OP_BY_CHARACTER)
198 | )
199 | return {'input': one_hot_expressions, 'output': labels}
200 |
201 | @property
202 | def input_size(self) -> int:
203 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
204 | return self._modulus + len(OP_BY_CHARACTER)
205 |
206 | @property
207 | def output_size(self) -> int:
208 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
209 | return self._modulus
210 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/regular/parity_check.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Compute whether the number of 1s in a string is even."""
17 |
18 | import functools
19 |
20 | import chex
21 | import jax
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 | import jax.random as jrandom
25 |
26 | from randomized_positional_encodings.tasks import task
27 |
28 |
29 | class ParityCheck(task.GeneralizationTask):
30 | """A task with the goal of counting the number of '1' in a string, modulo 2.
31 |
32 | The input is a string, composed of 0s and 1s. If the result is even, the class
33 | is 0, otherwise it's 1.
34 |
35 | Examples:
36 | 1010100 -> 3 1s (odd) -> class 1
37 | 01111 -> 4 1s (even) -> class 0
38 |
39 | Note that the sampling is jittable so this task is fast.
40 | """
41 |
42 | @functools.partial(jax.jit, static_argnums=(0, 2, 3))
43 | def sample_batch(
44 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
45 | ) -> task.Batch:
46 | """Returns a batch of strings and the expected class."""
47 | strings = jrandom.randint(
48 | rng, shape=(batch_size, length), minval=0, maxval=2
49 | )
50 | n_b = jnp.sum(strings, axis=1) % 2
51 | n_b = jnn.one_hot(n_b, num_classes=2)
52 | one_hot_strings = jnn.one_hot(strings, num_classes=2)
53 | return {"input": one_hot_strings, "output": n_b}
54 |
55 | @property
56 | def input_size(self) -> int:
57 | """Returns the input size for the models."""
58 | return 2
59 |
60 | @property
61 | def output_size(self) -> int:
62 | """Returns the output size for the models."""
63 | return 2
64 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tasks/task.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright 2024 DeepMind Technologies Limited
2 | #
3 | # Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
4 | # you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
5 | # You may obtain a copy of the License at
6 | #
7 | # http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
8 | #
9 | # Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
10 | # distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
11 | # WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
12 | # See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
13 | # limitations under the License.
14 | # ==============================================================================
15 |
16 | """Base class for length generalization tasks."""
17 |
18 | import abc
19 | from typing import TypedDict
20 |
21 | import chex
22 | import jax.nn as jnn
23 | import jax.numpy as jnp
24 |
25 | Batch = TypedDict('Batch', {'input': chex.Array, 'output': chex.Array})
26 |
27 |
28 | class GeneralizationTask(abc.ABC):
29 | """A task for the generalization project.
30 |
31 | Exposes a sample_batch method, and some details about input/output sizes,
32 | losses and accuracies.
33 | """
34 |
35 | @abc.abstractmethod
36 | def sample_batch(
37 | self, rng: chex.PRNGKey, batch_size: int, length: int
38 | ) -> Batch:
39 | """Returns a batch of inputs/outputs."""
40 |
41 | def pointwise_loss_fn(
42 | self, output: chex.Array, target: chex.Array
43 | ) -> chex.Array:
44 | """Returns the pointwise loss between an output and a target."""
45 | return -target * jnn.log_softmax(output)
46 |
47 | def accuracy_fn(self, output: chex.Array, target: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
48 | """Returns the accuracy between an output and a target."""
49 | return (jnp.argmax(output, axis=-1) == jnp.argmax(target, axis=-1)).astype(
50 | jnp.float32
51 | )
52 |
53 | def accuracy_mask(self, target: chex.Array) -> chex.Array:
54 | """Returns a mask to compute the accuracies, to remove the superfluous ones."""
55 | # Target is a shape of shape (B, T, C) where C is the number of classes.
56 | # We want a mask per input (B, T), so we take this shape.
57 | return jnp.ones(target.shape[:-1])
58 |
59 | @property
60 | @abc.abstractmethod
61 | def input_size(self) -> int:
62 | """Returns the size of the input of the models trained on this task."""
63 |
64 | @property
65 | @abc.abstractmethod
66 | def output_size(self) -> int:
67 | """Returns the size of the output of the models trained on this task."""
68 |
69 | def output_length(self, input_length: int) -> int:
70 | """Returns the length of the output, given an input length."""
71 | del input_length
72 | return 1
73 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
 5 |
5 |  5 |
5 |