\n", 12 | "
Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 13 | "\n", 14 | "
 \n",
17 | "
\n",
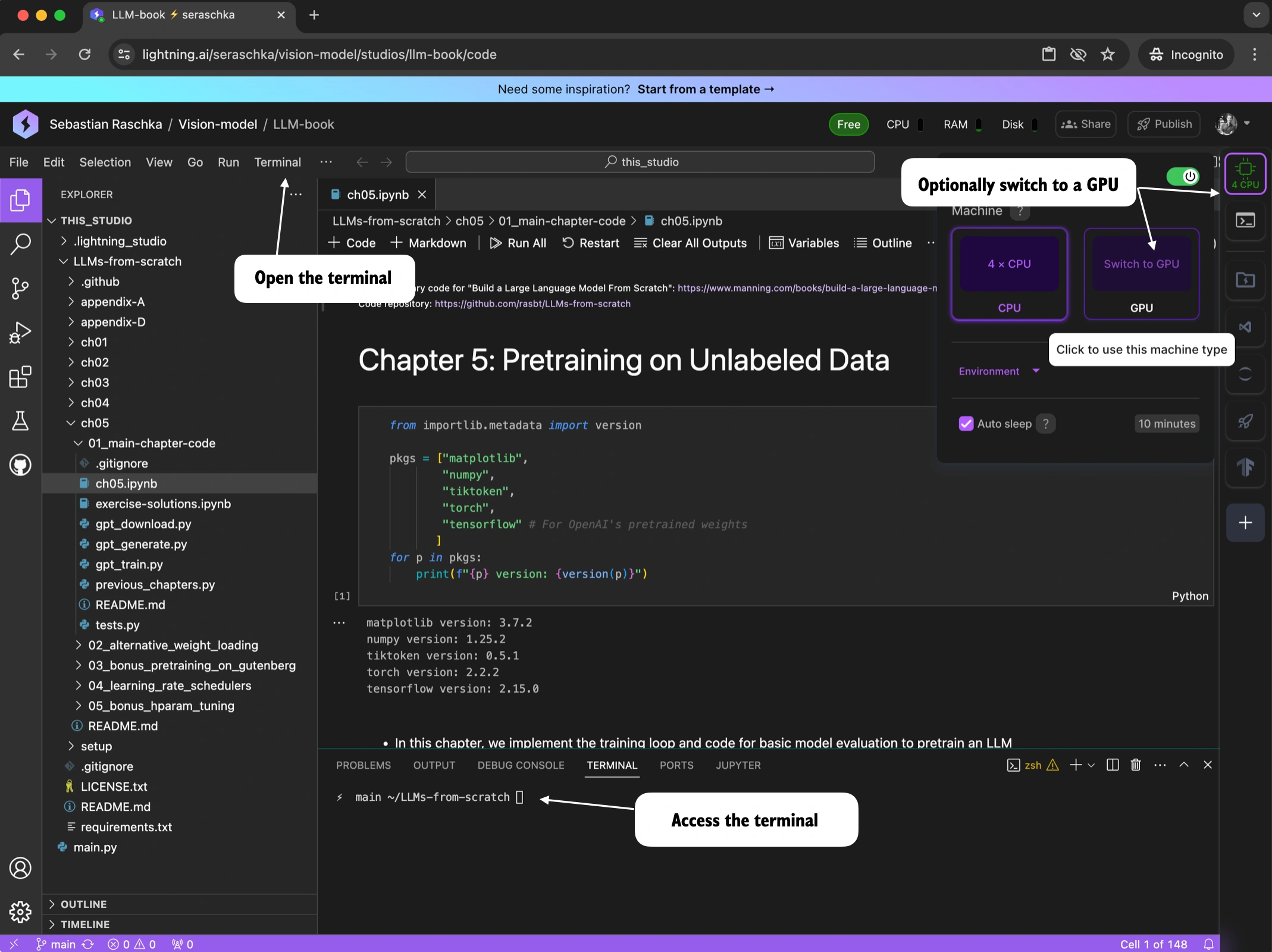
17 | " --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/04_preference-tuning-with-dpo/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 7: Finetuning to Follow Instructions
2 |
3 | - [create-preference-data-ollama.ipynb](create-preference-data-ollama.ipynb): A notebook that creates a synthetic dataset for preference finetuning dataset using Llama 3.1 and Ollama
4 |
5 | - [dpo-from-scratch.ipynb](dpo-from-scratch.ipynb): This notebook implements Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) for LLM alignment
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup/03_optional-docker-environment/.devcontainer/Dockerfile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | FROM pytorch/pytorch:2.0.1-cuda11.7-cudnn8-runtime
2 |
3 | RUN apt-get update && \
4 | apt-get upgrade -y && \
5 | apt-get install -y rsync && \
6 | apt-get install -y git && \
7 | apt-get install -y curl && \
8 | rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
9 |
10 | COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
11 |
12 | RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/03_model-evaluation/scores/llama3-8b-model-2-response.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [76, 85, 67, 90, 20, 98, 22, 96, 40, 80, 40, 20, 90, 98, 80, 92, 98, 98, 95, 99, 55, 99, 80, 90, 20, 4, 98, 4, 40, 95, 14, 44, 95, 44, 80, 4, 4, 40, 95, 80, 98, 95, 92, 98, 68, 20, 20, 60, 95, 90, 98, 0, 20, 80, 20, 80, 92, 98, 98, 20, 95, 100, 95, 85, 98, 4, 40, 98, 98, 65, 20, 76, 100, 67, 44, 92, 75, 97, 27, 98, 20, 60, 90, 96, 67, 98, 80, 10, 80, 98, 100, 40, 92, 98, 20, 98, 98, 20, 20]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | torch >= 2.0.1 # all
2 | jupyterlab >= 4.0 # all
3 | tiktoken >= 0.5.1 # ch02; ch04; ch05
4 | matplotlib >= 3.7.1 # ch04; ch05
5 | tensorflow >= 2.15.0 # ch05
6 | tqdm >= 4.66.1 # ch05; ch07
7 | numpy >= 1.25, < 2.0 # dependency of several other libraries like torch and pandas
8 | pandas >= 2.2.1 # ch06
9 | psutil >= 5.9.5 # ch07; already installed automatically as dependency of torch
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/03_model-evaluation/scores/gpt4-model-2-response.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [0, 100, 0, 100, 0, 100, 0, 100, 0, 0, 50, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 95, 0, 50, 100, 100, 0, 0, 100, 0, 0, 100, 0, 0, 100, 0, 67, 0, 0, 0, 100, 100, 95, 100, 100, 100, 0, 0, 0, 0, 100, 100, 100, 0, 55, 100, 0, 100, 65, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 0, 85, 100, 100, 85, 0, 75, 100, 0, 0, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 0, 50, 100, 100, 0, 100, 0, 0, 100, 85, 100, 0, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 0, 0, 0]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/03_model-evaluation/scores/llama3-8b-model-1-response.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [20, 92, 85, 90, 20, 90, 22, 97, 60, 96, 20, 20, 98, 95, 90, 98, 95, 20, 98, 98, 92, 20, 96, 96, 100, 98, 98, 95, 20, 95, 98, 20, 85, 95, 80, 97, 40, 21, 100, 85, 95, 98, 92, 98, 69, 98, 80, 60, 60, 20, 80, 68, 80, 96, 96, 68, 80, 95, 80, 20, 95, 98, 80, 98, 94, 20, 40, 98, 100, 85, 98, 90, 95, 85, 95, 80, 98, 98, 25, 98, 40, 92, 95, 82, 87, 98, 80, 90, 95, 4, 90, 90, 80, 98, 20, 98, 98, 40, 92, 98]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/03_model-evaluation/scores/gpt4-model-1-response.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [0, 50, 20, 100, 0, 100, 0, 100, 100, 100, 55, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 98, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 85, 100, 0, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 95, 20, 50, 85, 100, 100, 100, 100, 55, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 98, 100, 100, 100, 0, 85, 100, 100, 98, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 0, 100, 100, 0, 0, 100, 50, 100, 100, 10, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 25, 100, 30]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/03_understanding-buffers/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Understanding PyTorch Buffers
2 |
3 | - [understanding-buffers.ipynb](understanding-buffers.ipynb) explains the idea behind PyTorch buffers, which are used to implement the causal attention mechanism in chapter 3
4 |
5 |
6 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/04_preference-tuning-with-dpo/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 7: Finetuning to Follow Instructions
2 |
3 | - [create-preference-data-ollama.ipynb](create-preference-data-ollama.ipynb): A notebook that creates a synthetic dataset for preference finetuning dataset using Llama 3.1 and Ollama
4 |
5 | - [dpo-from-scratch.ipynb](dpo-from-scratch.ipynb): This notebook implements Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) for LLM alignment
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup/03_optional-docker-environment/.devcontainer/Dockerfile:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | FROM pytorch/pytorch:2.0.1-cuda11.7-cudnn8-runtime
2 |
3 | RUN apt-get update && \
4 | apt-get upgrade -y && \
5 | apt-get install -y rsync && \
6 | apt-get install -y git && \
7 | apt-get install -y curl && \
8 | rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
9 |
10 | COPY requirements.txt requirements.txt
11 |
12 | RUN pip install --no-cache-dir -r requirements.txt
13 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/03_model-evaluation/scores/llama3-8b-model-2-response.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [76, 85, 67, 90, 20, 98, 22, 96, 40, 80, 40, 20, 90, 98, 80, 92, 98, 98, 95, 99, 55, 99, 80, 90, 20, 4, 98, 4, 40, 95, 14, 44, 95, 44, 80, 4, 4, 40, 95, 80, 98, 95, 92, 98, 68, 20, 20, 60, 95, 90, 98, 0, 20, 80, 20, 80, 92, 98, 98, 20, 95, 100, 95, 85, 98, 4, 40, 98, 98, 65, 20, 76, 100, 67, 44, 92, 75, 97, 27, 98, 20, 60, 90, 96, 67, 98, 80, 10, 80, 98, 100, 40, 92, 98, 20, 98, 98, 20, 20]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | torch >= 2.0.1 # all
2 | jupyterlab >= 4.0 # all
3 | tiktoken >= 0.5.1 # ch02; ch04; ch05
4 | matplotlib >= 3.7.1 # ch04; ch05
5 | tensorflow >= 2.15.0 # ch05
6 | tqdm >= 4.66.1 # ch05; ch07
7 | numpy >= 1.25, < 2.0 # dependency of several other libraries like torch and pandas
8 | pandas >= 2.2.1 # ch06
9 | psutil >= 5.9.5 # ch07; already installed automatically as dependency of torch
10 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/03_model-evaluation/scores/gpt4-model-2-response.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [0, 100, 0, 100, 0, 100, 0, 100, 0, 0, 50, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 95, 0, 50, 100, 100, 0, 0, 100, 0, 0, 100, 0, 0, 100, 0, 67, 0, 0, 0, 100, 100, 95, 100, 100, 100, 0, 0, 0, 0, 100, 100, 100, 0, 55, 100, 0, 100, 65, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 0, 85, 100, 100, 85, 0, 75, 100, 0, 0, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 0, 50, 100, 100, 0, 100, 0, 0, 100, 85, 100, 0, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 0, 0, 0]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/03_model-evaluation/scores/llama3-8b-model-1-response.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [20, 92, 85, 90, 20, 90, 22, 97, 60, 96, 20, 20, 98, 95, 90, 98, 95, 20, 98, 98, 92, 20, 96, 96, 100, 98, 98, 95, 20, 95, 98, 20, 85, 95, 80, 97, 40, 21, 100, 85, 95, 98, 92, 98, 69, 98, 80, 60, 60, 20, 80, 68, 80, 96, 96, 68, 80, 95, 80, 20, 95, 98, 80, 98, 94, 20, 40, 98, 100, 85, 98, 90, 95, 85, 95, 80, 98, 98, 25, 98, 40, 92, 95, 82, 87, 98, 80, 90, 95, 4, 90, 90, 80, 98, 20, 98, 98, 40, 92, 98]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/03_model-evaluation/scores/gpt4-model-1-response.json:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [0, 50, 20, 100, 0, 100, 0, 100, 100, 100, 55, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 98, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 85, 100, 0, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 95, 20, 50, 85, 100, 100, 100, 100, 55, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 98, 100, 100, 100, 0, 85, 100, 100, 98, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 0, 100, 100, 0, 0, 100, 50, 100, 100, 10, 100, 100, 100, 100, 0, 100, 100, 25, 100, 30]
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/03_understanding-buffers/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Understanding PyTorch Buffers
2 |
3 | - [understanding-buffers.ipynb](understanding-buffers.ipynb) explains the idea behind PyTorch buffers, which are used to implement the causal attention mechanism in chapter 3
4 |
5 |
6 | 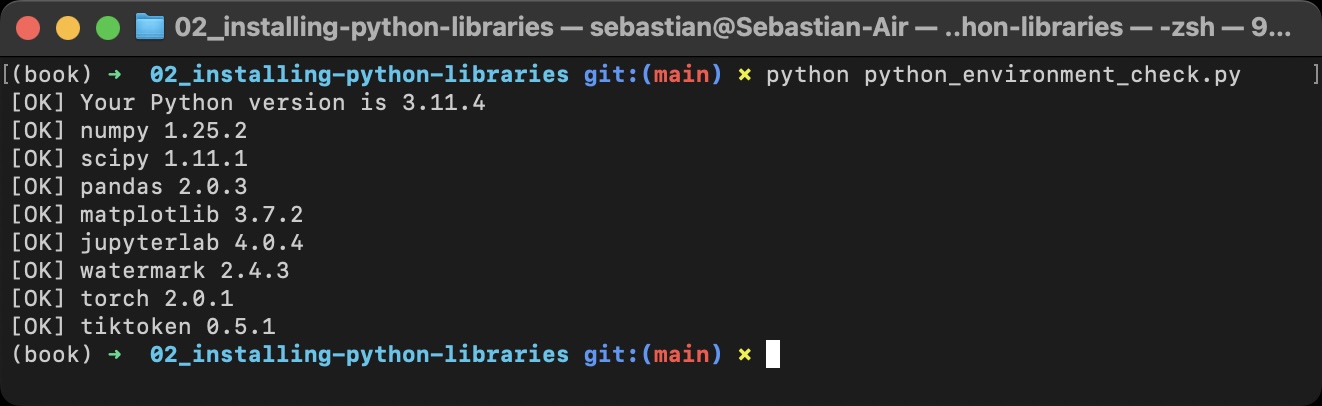 27 |
28 | It's also recommended to check the versions in JupyterLab by running the `python_environment_check.ipynb` in this directory, which should ideally give you the same results as above.
29 |
30 |
27 |
28 | It's also recommended to check the versions in JupyterLab by running the `python_environment_check.ipynb` in this directory, which should ideally give you the same results as above.
29 |
30 | 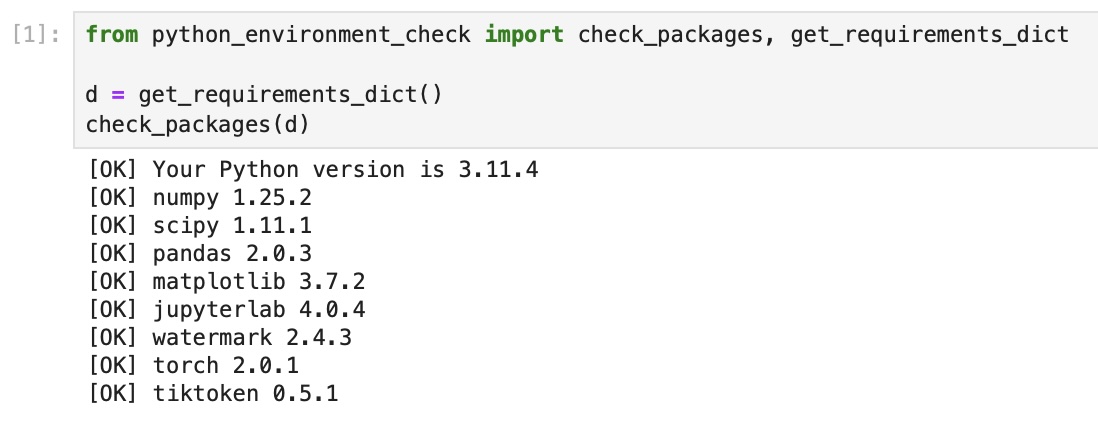 31 |
32 | If you see the following issues, it's likely that your JupyterLab instance is connected to wrong conda environment:
33 |
34 |
31 |
32 | If you see the following issues, it's likely that your JupyterLab instance is connected to wrong conda environment:
33 |
34 | 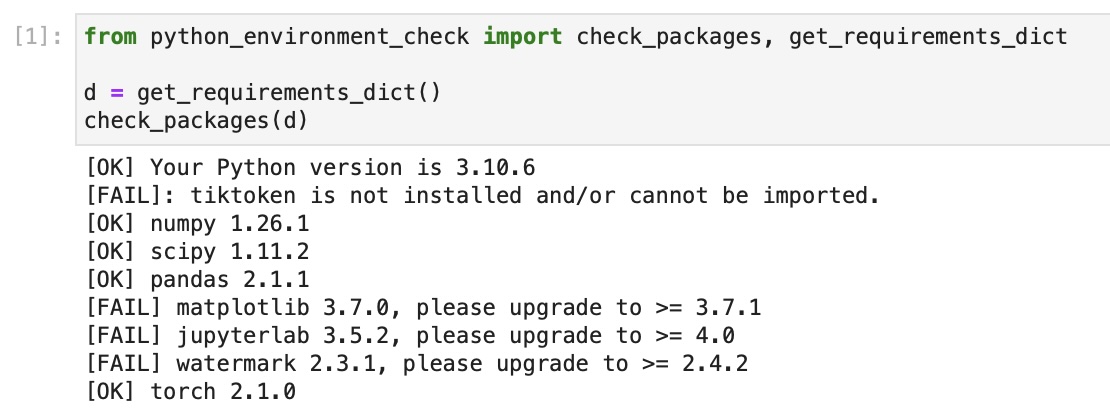 35 |
36 | In this case, you may want to use `watermark` to check if you opened the JupyterLab instance in the right conda environment using the `--conda` flag:
37 |
38 |
35 |
36 | In this case, you may want to use `watermark` to check if you opened the JupyterLab instance in the right conda environment using the `--conda` flag:
37 |
38 | 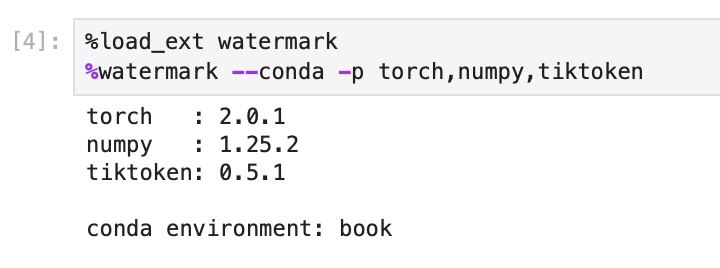 39 |
40 |
41 |
39 |
40 |
41 |  58 |
59 |
60 |
61 | ---
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 |
66 | Any questions? Please feel free to reach out in the [Discussion Forum](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/discussions).
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch05/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 | # File for internal use (unit tests)
7 |
8 | import pytest
9 | from gpt_train import main
10 | import http.client
11 | from urllib.parse import urlparse
12 |
13 |
14 | @pytest.fixture
15 | def gpt_config():
16 | return {
17 | "vocab_size": 50257,
18 | "context_length": 12, # small for testing efficiency
19 | "emb_dim": 32, # small for testing efficiency
20 | "n_heads": 4, # small for testing efficiency
21 | "n_layers": 2, # small for testing efficiency
22 | "drop_rate": 0.1,
23 | "qkv_bias": False
24 | }
25 |
26 |
27 | @pytest.fixture
28 | def other_settings():
29 | return {
30 | "learning_rate": 5e-4,
31 | "num_epochs": 1, # small for testing efficiency
32 | "batch_size": 2,
33 | "weight_decay": 0.1
34 | }
35 |
36 |
37 | def test_main(gpt_config, other_settings):
38 | train_losses, val_losses, tokens_seen, model = main(gpt_config, other_settings)
39 |
40 | assert len(train_losses) == 39, "Unexpected number of training losses"
41 | assert len(val_losses) == 39, "Unexpected number of validation losses"
42 | assert len(tokens_seen) == 39, "Unexpected number of tokens seen"
43 |
44 |
45 | def check_file_size(url, expected_size):
46 | parsed_url = urlparse(url)
47 | if parsed_url.scheme == "https":
48 | conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection(parsed_url.netloc)
49 | else:
50 | conn = http.client.HTTPConnection(parsed_url.netloc)
51 |
52 | conn.request("HEAD", parsed_url.path)
53 | response = conn.getresponse()
54 | if response.status != 200:
55 | return False, f"{url} not accessible"
56 | size = response.getheader("Content-Length")
57 | if size is None:
58 | return False, "Content-Length header is missing"
59 | size = int(size)
60 | if size != expected_size:
61 | return False, f"{url} file has expected size {expected_size}, but got {size}"
62 | return True, f"{url} file size is correct"
63 |
64 |
65 | def test_model_files():
66 | base_url = "https://openaipublic.blob.core.windows.net/gpt-2/models"
67 |
68 | model_size = "124M"
69 | files = {
70 | "checkpoint": 77,
71 | "encoder.json": 1042301,
72 | "hparams.json": 90,
73 | "model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001": 497759232,
74 | "model.ckpt.index": 5215,
75 | "model.ckpt.meta": 471155,
76 | "vocab.bpe": 456318
77 | }
78 |
79 | for file_name, expected_size in files.items():
80 | url = f"{base_url}/{model_size}/{file_name}"
81 | valid, message = check_file_size(url, expected_size)
82 | assert valid, message
83 |
84 | model_size = "355M"
85 | files = {
86 | "checkpoint": 77,
87 | "encoder.json": 1042301,
88 | "hparams.json": 91,
89 | "model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001": 1419292672,
90 | "model.ckpt.index": 10399,
91 | "model.ckpt.meta": 926519,
92 | "vocab.bpe": 456318
93 | }
94 |
95 | for file_name, expected_size in files.items():
96 | url = f"{base_url}/{model_size}/{file_name}"
97 | valid, message = check_file_size(url, expected_size)
98 | assert valid, message
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch06/03_bonus_imdb-classification/download_prepare_dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 | import os
7 | import sys
8 | import tarfile
9 | import time
10 | import urllib.request
11 | import pandas as pd
12 |
13 |
14 | def reporthook(count, block_size, total_size):
15 | global start_time
16 | if count == 0:
17 | start_time = time.time()
18 | else:
19 | duration = time.time() - start_time
20 | progress_size = int(count * block_size)
21 | percent = count * block_size * 100 / total_size
22 |
23 | speed = int(progress_size / (1024 * duration)) if duration else 0
24 | sys.stdout.write(
25 | f"\r{int(percent)}% | {progress_size / (1024**2):.2f} MB "
26 | f"| {speed:.2f} MB/s | {duration:.2f} sec elapsed"
27 | )
28 | sys.stdout.flush()
29 |
30 |
31 | def download_and_extract_dataset(dataset_url, target_file, directory):
32 | if not os.path.exists(directory):
33 | if os.path.exists(target_file):
34 | os.remove(target_file)
35 | urllib.request.urlretrieve(dataset_url, target_file, reporthook)
36 | print("\nExtracting dataset ...")
37 | with tarfile.open(target_file, "r:gz") as tar:
38 | tar.extractall()
39 | else:
40 | print(f"Directory `{directory}` already exists. Skipping download.")
41 |
42 |
43 | def load_dataset_to_dataframe(basepath="aclImdb", labels={"pos": 1, "neg": 0}):
44 | data_frames = [] # List to store each chunk of DataFrame
45 | for subset in ("test", "train"):
46 | for label in ("pos", "neg"):
47 | path = os.path.join(basepath, subset, label)
48 | for file in sorted(os.listdir(path)):
49 | with open(os.path.join(path, file), "r", encoding="utf-8") as infile:
50 | # Create a DataFrame for each file and add it to the list
51 | data_frames.append(pd.DataFrame({"text": [infile.read()], "label": [labels[label]]}))
52 | # Concatenate all DataFrame chunks together
53 | df = pd.concat(data_frames, ignore_index=True)
54 | df = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=123).reset_index(drop=True) # Shuffle the DataFrame
55 | return df
56 |
57 |
58 | def partition_and_save(df, sizes=(35000, 5000, 10000)):
59 | # Shuffle the DataFrame
60 | df_shuffled = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=123).reset_index(drop=True)
61 |
62 | # Get indices for where to split the data
63 | train_end = sizes[0]
64 | val_end = sizes[0] + sizes[1]
65 |
66 | # Split the DataFrame
67 | train = df_shuffled.iloc[:train_end]
68 | val = df_shuffled.iloc[train_end:val_end]
69 | test = df_shuffled.iloc[val_end:]
70 |
71 | # Save to CSV files
72 | train.to_csv("train.csv", index=False)
73 | val.to_csv("validation.csv", index=False)
74 | test.to_csv("test.csv", index=False)
75 |
76 |
77 | if __name__ == "__main__":
78 | dataset_url = "http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz"
79 | print("Downloading dataset ...")
80 | download_and_extract_dataset(dataset_url, "aclImdb_v1.tar.gz", "aclImdb")
81 | print("Creating data frames ...")
82 | df = load_dataset_to_dataframe()
83 | print("Partitioning and saving data frames ...")
84 | partition_and_save(df)
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/01_main-chapter-code/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 7: Finetuning to Follow Instructions
2 |
3 | ### Main Chapter Code
4 |
5 | - [ch07.ipynb](ch07.ipynb) contains all the code as it appears in the chapter
6 | - [previous_chapters.py](previous_chapters.py) is a Python module that contains the GPT model we coded and trained in previous chapters, alongside many utility functions, which we reuse in this chapter
7 | - [gpt_download.py](gpt_download.py) contains the utility functions for downloading the pretrained GPT model weights
8 | - [exercise-solutions.ipynb](exercise-solutions.ipynb) contains the exercise solutions for this chapter
9 |
10 |
11 | ### Optional Code
12 |
13 | - [load-finetuned-model.ipynb](load-finetuned-model.ipynb) is a standalone Jupyter notebook to load the instruction finetuned model we created in this chapter
14 |
15 | - [gpt_instruction_finetuning.py](gpt_instruction_finetuning.py) is a standalone Python script to instruction finetune the model as described in the main chapter (think of it as a chapter summary focused on the finetuning parts)
16 |
17 | Usage:
18 |
19 | ```bash
20 | python gpt_instruction_finetuning.py
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ```
24 | matplotlib version: 3.9.0
25 | tiktoken version: 0.7.0
26 | torch version: 2.3.1
27 | tqdm version: 4.66.4
28 | tensorflow version: 2.16.1
29 | --------------------------------------------------
30 | Training set length: 935
31 | Validation set length: 55
32 | Test set length: 110
33 | --------------------------------------------------
34 | Device: cpu
35 | --------------------------------------------------
36 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/checkpoint
37 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/encoder.json
38 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/hparams.json
39 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001
40 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/model.ckpt.index
41 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/model.ckpt.meta
42 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/vocab.bpe
43 | Loaded model: gpt2-medium (355M)
44 | --------------------------------------------------
45 | Initial losses
46 | Training loss: 3.839039182662964
47 | Validation loss: 3.7619192123413088
48 | Ep 1 (Step 000000): Train loss 2.611, Val loss 2.668
49 | Ep 1 (Step 000005): Train loss 1.161, Val loss 1.131
50 | Ep 1 (Step 000010): Train loss 0.939, Val loss 0.973
51 | ...
52 | Training completed in 15.66 minutes.
53 | Plot saved as loss-plot-standalone.pdf
54 | --------------------------------------------------
55 | Generating responses
56 | 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 110/110 [06:57<00:00, 3.80s/it]
57 | Responses saved as instruction-data-with-response-standalone.json
58 | Model saved as gpt2-medium355M-sft-standalone.pth
59 | ```
60 |
61 | - [ollama_evaluate.py](ollama_evaluate.py) is a standalone Python script to evaluate the responses of the finetuned model as described in the main chapter (think of it as a chapter summary focused on the evaluation parts)
62 |
63 | Usage:
64 |
65 | ```bash
66 | python ollama_evaluate.py --file_path instruction-data-with-response-standalone.json
67 | ```
68 |
69 | ```
70 | Ollama running: True
71 | Scoring entries: 100%|███████████████████████████████████████| 110/110 [01:08<00:00, 1.62it/s]
72 | Number of scores: 110 of 110
73 | Average score: 51.75
74 | ```
75 |
76 | - [exercise_experiments.py](exercise_experiments.py) is an optional scropt that implements the exercise solutions; for more details see [exercise-solutions.ipynb](exercise-solutions.ipynb)
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch05/03_bonus_pretraining_on_gutenberg/prepare_dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 | """
7 | Script that processes the Project Gutenberg files into fewer larger files.
8 | """
9 |
10 | import argparse
11 | import os
12 | import re
13 | from tqdm import tqdm
14 | from gutenberg.src.cleanup import strip_headers
15 |
16 |
17 | def is_english(text, threshold=0.9):
18 | ascii_chars = sum(1 for c in text if ord(c) < 128)
19 | return ascii_chars / len(text) > threshold
20 |
21 |
22 | def combine_files(file_paths, target_dir, max_size_mb=500, separator="<|endoftext|>", fallback_encoding="latin1"):
23 | if not os.path.exists(target_dir):
24 | os.makedirs(target_dir)
25 |
26 | current_content = []
27 | current_size = 0
28 | file_counter = 1
29 |
30 | for file_path in tqdm(file_paths):
31 | try:
32 | with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:
33 | content = file.read()
34 | except UnicodeDecodeError:
35 | # Attempt to read the file with a fallback encoding
36 | tqdm.write(f"Warning: UnicodeDecodeError encountered. Trying fallback encoding for {file_path}")
37 | with open(file_path, "r", encoding=fallback_encoding) as file:
38 | content = file.read()
39 |
40 | if not is_english(content):
41 | tqdm.write(f"Skipping {file_path} as it does not contain primarily English text.")
42 | continue
43 | content = strip_headers(content)
44 |
45 | # Regular expression to replace multiple blank lines with a single blank line
46 | content = re.sub(r'\n\s*\n', '\n\n', content)
47 | estimated_size = len(content.encode("utf-8"))
48 |
49 | if current_size + estimated_size > max_size_mb * 1024 * 1024:
50 | target_file_path = os.path.join(target_dir, f"combined_{file_counter}.txt")
51 | with open(target_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as target_file:
52 | target_file.write(separator.join(current_content))
53 | file_counter += 1
54 | current_content = [content]
55 | current_size = estimated_size
56 | else:
57 | current_content.append(content)
58 | current_size += estimated_size
59 |
60 | if current_content:
61 | target_file_path = os.path.join(target_dir, f"combined_{file_counter}.txt")
62 | with open(target_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as target_file:
63 | target_file.write(separator.join(current_content))
64 | return file_counter
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == "__main__":
68 |
69 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Preprocess and combine text files for pretraining")
70 |
71 | parser.add_argument("--data_dir", type=str, default="gutenberg/data/raw",
72 | help="Directory containing the downloaded raw training data")
73 | parser.add_argument("--max_size_mb", type=int, default=500,
74 | help="The maximum file size for each concatenated file in megabytes")
75 | parser.add_argument("--output_dir", type=str, default="gutenberg_preprocessed",
76 | help="Directory where the preprocessed data will be saved")
77 |
78 | args = parser.parse_args()
79 |
80 | all_files = [os.path.join(path, name) for path, subdirs, files in os.walk(args.data_dir)
81 | for name in files if name.endswith((".txt", ".txt.utf8"))]
82 |
83 | print(f"{len(all_files)} file(s) to process.")
84 | file_counter = combine_files(all_files, args.output_dir, max_size_mb=args.max_size_mb)
85 | print(f"{file_counter} file(s) saved in {os.path.abspath(args.output_dir)}")
86 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup/02_installing-python-libraries/python_environment_check.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 | from importlib.metadata import PackageNotFoundError, import_module
7 | import importlib.metadata
8 | from os.path import dirname, exists, join, realpath
9 | from packaging.version import parse as version_parse
10 | import platform
11 | import sys
12 |
13 | if version_parse(platform.python_version()) < version_parse("3.9"):
14 | print("[FAIL] We recommend Python 3.9 or newer but"
15 | " found version %s" % (sys.version))
16 | else:
17 | print("[OK] Your Python version is %s" % (platform.python_version()))
18 |
19 |
20 | def get_packages(pkgs):
21 | versions = []
22 | for p in pkgs:
23 | try:
24 | imported = import_module(p)
25 | try:
26 | version = (getattr(imported, "__version__", None) or
27 | getattr(imported, "version", None) or
28 | getattr(imported, "version_info", None))
29 | if version is None:
30 | # If common attributes don"t exist, use importlib.metadata
31 | version = importlib.metadata.version(p)
32 | versions.append(version)
33 | except PackageNotFoundError:
34 | # Handle case where package is not installed
35 | versions.append("0.0")
36 | except ImportError:
37 | # Fallback if importlib.import_module fails for unexpected reasons
38 | versions.append("0.0")
39 | return versions
40 |
41 |
42 | def get_requirements_dict():
43 | PROJECT_ROOT = dirname(realpath(__file__))
44 | PROJECT_ROOT_UP_TWO = dirname(dirname(PROJECT_ROOT))
45 | REQUIREMENTS_FILE = join(PROJECT_ROOT_UP_TWO, "requirements.txt")
46 | if not exists(REQUIREMENTS_FILE):
47 | REQUIREMENTS_FILE = join(PROJECT_ROOT, "requirements.txt")
48 |
49 | d = {}
50 | with open(REQUIREMENTS_FILE) as f:
51 | for line in f:
52 | if not line.strip():
53 | continue
54 | if "," in line:
55 | left, right = line.split(",")
56 | lower = right.split("#")[0].strip()
57 | package, _, upper = left.split(" ")
58 | package = package.strip()
59 | _, lower = lower.split(" ")
60 | lower = lower.strip()
61 | upper = upper.strip()
62 | d[package] = (upper, lower)
63 | else:
64 | line = line.split("#")[0].strip()
65 | line = line.split(" ")
66 | line = [ln.strip() for ln in line]
67 | d[line[0]] = line[-1]
68 | return d
69 |
70 |
71 | def check_packages(d):
72 | versions = get_packages(d.keys())
73 |
74 | for (pkg_name, suggested_ver), actual_ver in zip(d.items(), versions):
75 | if isinstance(suggested_ver, tuple):
76 | lower, upper = suggested_ver[0], suggested_ver[1]
77 | else:
78 | lower = suggested_ver
79 | upper = None
80 | if actual_ver == "N/A":
81 | continue
82 | actual_ver = version_parse(actual_ver)
83 | lower = version_parse(lower)
84 | if upper is not None:
85 | upper = version_parse(upper)
86 | if actual_ver < lower and upper is None:
87 | print(f"[FAIL] {pkg_name} {actual_ver}, please upgrade to >= {lower}")
88 | elif actual_ver < lower:
89 | print(f"[FAIL] {pkg_name} {actual_ver}, please upgrade to >= {lower} and < {upper}")
90 | elif upper is not None and actual_ver >= upper:
91 | print(f"[FAIL] {pkg_name} {actual_ver}, please downgrade to >= {lower} and < {upper}")
92 | else:
93 | print(f"[OK] {pkg_name} {actual_ver}")
94 |
95 |
96 | def main():
97 | d = get_requirements_dict()
98 | check_packages(d)
99 |
100 |
101 | if __name__ == "__main__":
102 | main()
103 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch06/03_bonus_imdb-classification/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Additional Experiments Classifying the Sentiment of 50k IMDB Movie Reviews
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Step 1: Install Dependencies
5 |
6 | Install the extra dependencies via
7 |
8 | ```bash
9 | pip install -r requirements-extra.txt
10 | ```
11 |
12 |
13 | ## Step 2: Download Dataset
14 |
15 | The codes are using the 50k movie reviews from IMDb ([dataset source](https://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/)) to predict whether a movie review is positive or negative.
16 |
17 | Run the following code to create the `train.csv`, `validation.csv`, and `test.csv` datasets:
18 |
19 | ```bash
20 | python download_prepare_dataset.py
21 | ```
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 | ## Step 3: Run Models
26 |
27 | The 124M GPT-2 model used in the main chapter, starting with pretrained weights, and finetuning all weights:
28 |
29 | ```bash
30 | python train_gpt.py --trainable_layers "all" --num_epochs 1
31 | ```
32 |
33 | ```
34 | Ep 1 (Step 000000): Train loss 3.706, Val loss 3.853
35 | Ep 1 (Step 000050): Train loss 0.682, Val loss 0.706
36 | ...
37 | Ep 1 (Step 004300): Train loss 0.199, Val loss 0.285
38 | Ep 1 (Step 004350): Train loss 0.188, Val loss 0.208
39 | Training accuracy: 95.62% | Validation accuracy: 95.00%
40 | Training completed in 9.48 minutes.
41 |
42 | Evaluating on the full datasets ...
43 |
44 | Training accuracy: 95.64%
45 | Validation accuracy: 92.32%
46 | Test accuracy: 91.88%
47 | ```
48 |
49 |
50 |
58 |
59 |
60 |
61 | ---
62 |
63 |
64 |
65 |
66 | Any questions? Please feel free to reach out in the [Discussion Forum](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/discussions).
67 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch05/01_main-chapter-code/tests.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 | # File for internal use (unit tests)
7 |
8 | import pytest
9 | from gpt_train import main
10 | import http.client
11 | from urllib.parse import urlparse
12 |
13 |
14 | @pytest.fixture
15 | def gpt_config():
16 | return {
17 | "vocab_size": 50257,
18 | "context_length": 12, # small for testing efficiency
19 | "emb_dim": 32, # small for testing efficiency
20 | "n_heads": 4, # small for testing efficiency
21 | "n_layers": 2, # small for testing efficiency
22 | "drop_rate": 0.1,
23 | "qkv_bias": False
24 | }
25 |
26 |
27 | @pytest.fixture
28 | def other_settings():
29 | return {
30 | "learning_rate": 5e-4,
31 | "num_epochs": 1, # small for testing efficiency
32 | "batch_size": 2,
33 | "weight_decay": 0.1
34 | }
35 |
36 |
37 | def test_main(gpt_config, other_settings):
38 | train_losses, val_losses, tokens_seen, model = main(gpt_config, other_settings)
39 |
40 | assert len(train_losses) == 39, "Unexpected number of training losses"
41 | assert len(val_losses) == 39, "Unexpected number of validation losses"
42 | assert len(tokens_seen) == 39, "Unexpected number of tokens seen"
43 |
44 |
45 | def check_file_size(url, expected_size):
46 | parsed_url = urlparse(url)
47 | if parsed_url.scheme == "https":
48 | conn = http.client.HTTPSConnection(parsed_url.netloc)
49 | else:
50 | conn = http.client.HTTPConnection(parsed_url.netloc)
51 |
52 | conn.request("HEAD", parsed_url.path)
53 | response = conn.getresponse()
54 | if response.status != 200:
55 | return False, f"{url} not accessible"
56 | size = response.getheader("Content-Length")
57 | if size is None:
58 | return False, "Content-Length header is missing"
59 | size = int(size)
60 | if size != expected_size:
61 | return False, f"{url} file has expected size {expected_size}, but got {size}"
62 | return True, f"{url} file size is correct"
63 |
64 |
65 | def test_model_files():
66 | base_url = "https://openaipublic.blob.core.windows.net/gpt-2/models"
67 |
68 | model_size = "124M"
69 | files = {
70 | "checkpoint": 77,
71 | "encoder.json": 1042301,
72 | "hparams.json": 90,
73 | "model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001": 497759232,
74 | "model.ckpt.index": 5215,
75 | "model.ckpt.meta": 471155,
76 | "vocab.bpe": 456318
77 | }
78 |
79 | for file_name, expected_size in files.items():
80 | url = f"{base_url}/{model_size}/{file_name}"
81 | valid, message = check_file_size(url, expected_size)
82 | assert valid, message
83 |
84 | model_size = "355M"
85 | files = {
86 | "checkpoint": 77,
87 | "encoder.json": 1042301,
88 | "hparams.json": 91,
89 | "model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001": 1419292672,
90 | "model.ckpt.index": 10399,
91 | "model.ckpt.meta": 926519,
92 | "vocab.bpe": 456318
93 | }
94 |
95 | for file_name, expected_size in files.items():
96 | url = f"{base_url}/{model_size}/{file_name}"
97 | valid, message = check_file_size(url, expected_size)
98 | assert valid, message
99 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch06/03_bonus_imdb-classification/download_prepare_dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 | import os
7 | import sys
8 | import tarfile
9 | import time
10 | import urllib.request
11 | import pandas as pd
12 |
13 |
14 | def reporthook(count, block_size, total_size):
15 | global start_time
16 | if count == 0:
17 | start_time = time.time()
18 | else:
19 | duration = time.time() - start_time
20 | progress_size = int(count * block_size)
21 | percent = count * block_size * 100 / total_size
22 |
23 | speed = int(progress_size / (1024 * duration)) if duration else 0
24 | sys.stdout.write(
25 | f"\r{int(percent)}% | {progress_size / (1024**2):.2f} MB "
26 | f"| {speed:.2f} MB/s | {duration:.2f} sec elapsed"
27 | )
28 | sys.stdout.flush()
29 |
30 |
31 | def download_and_extract_dataset(dataset_url, target_file, directory):
32 | if not os.path.exists(directory):
33 | if os.path.exists(target_file):
34 | os.remove(target_file)
35 | urllib.request.urlretrieve(dataset_url, target_file, reporthook)
36 | print("\nExtracting dataset ...")
37 | with tarfile.open(target_file, "r:gz") as tar:
38 | tar.extractall()
39 | else:
40 | print(f"Directory `{directory}` already exists. Skipping download.")
41 |
42 |
43 | def load_dataset_to_dataframe(basepath="aclImdb", labels={"pos": 1, "neg": 0}):
44 | data_frames = [] # List to store each chunk of DataFrame
45 | for subset in ("test", "train"):
46 | for label in ("pos", "neg"):
47 | path = os.path.join(basepath, subset, label)
48 | for file in sorted(os.listdir(path)):
49 | with open(os.path.join(path, file), "r", encoding="utf-8") as infile:
50 | # Create a DataFrame for each file and add it to the list
51 | data_frames.append(pd.DataFrame({"text": [infile.read()], "label": [labels[label]]}))
52 | # Concatenate all DataFrame chunks together
53 | df = pd.concat(data_frames, ignore_index=True)
54 | df = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=123).reset_index(drop=True) # Shuffle the DataFrame
55 | return df
56 |
57 |
58 | def partition_and_save(df, sizes=(35000, 5000, 10000)):
59 | # Shuffle the DataFrame
60 | df_shuffled = df.sample(frac=1, random_state=123).reset_index(drop=True)
61 |
62 | # Get indices for where to split the data
63 | train_end = sizes[0]
64 | val_end = sizes[0] + sizes[1]
65 |
66 | # Split the DataFrame
67 | train = df_shuffled.iloc[:train_end]
68 | val = df_shuffled.iloc[train_end:val_end]
69 | test = df_shuffled.iloc[val_end:]
70 |
71 | # Save to CSV files
72 | train.to_csv("train.csv", index=False)
73 | val.to_csv("validation.csv", index=False)
74 | test.to_csv("test.csv", index=False)
75 |
76 |
77 | if __name__ == "__main__":
78 | dataset_url = "http://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/aclImdb_v1.tar.gz"
79 | print("Downloading dataset ...")
80 | download_and_extract_dataset(dataset_url, "aclImdb_v1.tar.gz", "aclImdb")
81 | print("Creating data frames ...")
82 | df = load_dataset_to_dataframe()
83 | print("Partitioning and saving data frames ...")
84 | partition_and_save(df)
85 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/01_main-chapter-code/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Chapter 7: Finetuning to Follow Instructions
2 |
3 | ### Main Chapter Code
4 |
5 | - [ch07.ipynb](ch07.ipynb) contains all the code as it appears in the chapter
6 | - [previous_chapters.py](previous_chapters.py) is a Python module that contains the GPT model we coded and trained in previous chapters, alongside many utility functions, which we reuse in this chapter
7 | - [gpt_download.py](gpt_download.py) contains the utility functions for downloading the pretrained GPT model weights
8 | - [exercise-solutions.ipynb](exercise-solutions.ipynb) contains the exercise solutions for this chapter
9 |
10 |
11 | ### Optional Code
12 |
13 | - [load-finetuned-model.ipynb](load-finetuned-model.ipynb) is a standalone Jupyter notebook to load the instruction finetuned model we created in this chapter
14 |
15 | - [gpt_instruction_finetuning.py](gpt_instruction_finetuning.py) is a standalone Python script to instruction finetune the model as described in the main chapter (think of it as a chapter summary focused on the finetuning parts)
16 |
17 | Usage:
18 |
19 | ```bash
20 | python gpt_instruction_finetuning.py
21 | ```
22 |
23 | ```
24 | matplotlib version: 3.9.0
25 | tiktoken version: 0.7.0
26 | torch version: 2.3.1
27 | tqdm version: 4.66.4
28 | tensorflow version: 2.16.1
29 | --------------------------------------------------
30 | Training set length: 935
31 | Validation set length: 55
32 | Test set length: 110
33 | --------------------------------------------------
34 | Device: cpu
35 | --------------------------------------------------
36 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/checkpoint
37 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/encoder.json
38 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/hparams.json
39 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/model.ckpt.data-00000-of-00001
40 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/model.ckpt.index
41 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/model.ckpt.meta
42 | File already exists and is up-to-date: gpt2/355M/vocab.bpe
43 | Loaded model: gpt2-medium (355M)
44 | --------------------------------------------------
45 | Initial losses
46 | Training loss: 3.839039182662964
47 | Validation loss: 3.7619192123413088
48 | Ep 1 (Step 000000): Train loss 2.611, Val loss 2.668
49 | Ep 1 (Step 000005): Train loss 1.161, Val loss 1.131
50 | Ep 1 (Step 000010): Train loss 0.939, Val loss 0.973
51 | ...
52 | Training completed in 15.66 minutes.
53 | Plot saved as loss-plot-standalone.pdf
54 | --------------------------------------------------
55 | Generating responses
56 | 100%|█████████████████████████████████████████████████████████| 110/110 [06:57<00:00, 3.80s/it]
57 | Responses saved as instruction-data-with-response-standalone.json
58 | Model saved as gpt2-medium355M-sft-standalone.pth
59 | ```
60 |
61 | - [ollama_evaluate.py](ollama_evaluate.py) is a standalone Python script to evaluate the responses of the finetuned model as described in the main chapter (think of it as a chapter summary focused on the evaluation parts)
62 |
63 | Usage:
64 |
65 | ```bash
66 | python ollama_evaluate.py --file_path instruction-data-with-response-standalone.json
67 | ```
68 |
69 | ```
70 | Ollama running: True
71 | Scoring entries: 100%|███████████████████████████████████████| 110/110 [01:08<00:00, 1.62it/s]
72 | Number of scores: 110 of 110
73 | Average score: 51.75
74 | ```
75 |
76 | - [exercise_experiments.py](exercise_experiments.py) is an optional scropt that implements the exercise solutions; for more details see [exercise-solutions.ipynb](exercise-solutions.ipynb)
77 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch05/03_bonus_pretraining_on_gutenberg/prepare_dataset.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 | """
7 | Script that processes the Project Gutenberg files into fewer larger files.
8 | """
9 |
10 | import argparse
11 | import os
12 | import re
13 | from tqdm import tqdm
14 | from gutenberg.src.cleanup import strip_headers
15 |
16 |
17 | def is_english(text, threshold=0.9):
18 | ascii_chars = sum(1 for c in text if ord(c) < 128)
19 | return ascii_chars / len(text) > threshold
20 |
21 |
22 | def combine_files(file_paths, target_dir, max_size_mb=500, separator="<|endoftext|>", fallback_encoding="latin1"):
23 | if not os.path.exists(target_dir):
24 | os.makedirs(target_dir)
25 |
26 | current_content = []
27 | current_size = 0
28 | file_counter = 1
29 |
30 | for file_path in tqdm(file_paths):
31 | try:
32 | with open(file_path, "r", encoding="utf-8") as file:
33 | content = file.read()
34 | except UnicodeDecodeError:
35 | # Attempt to read the file with a fallback encoding
36 | tqdm.write(f"Warning: UnicodeDecodeError encountered. Trying fallback encoding for {file_path}")
37 | with open(file_path, "r", encoding=fallback_encoding) as file:
38 | content = file.read()
39 |
40 | if not is_english(content):
41 | tqdm.write(f"Skipping {file_path} as it does not contain primarily English text.")
42 | continue
43 | content = strip_headers(content)
44 |
45 | # Regular expression to replace multiple blank lines with a single blank line
46 | content = re.sub(r'\n\s*\n', '\n\n', content)
47 | estimated_size = len(content.encode("utf-8"))
48 |
49 | if current_size + estimated_size > max_size_mb * 1024 * 1024:
50 | target_file_path = os.path.join(target_dir, f"combined_{file_counter}.txt")
51 | with open(target_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as target_file:
52 | target_file.write(separator.join(current_content))
53 | file_counter += 1
54 | current_content = [content]
55 | current_size = estimated_size
56 | else:
57 | current_content.append(content)
58 | current_size += estimated_size
59 |
60 | if current_content:
61 | target_file_path = os.path.join(target_dir, f"combined_{file_counter}.txt")
62 | with open(target_file_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as target_file:
63 | target_file.write(separator.join(current_content))
64 | return file_counter
65 |
66 |
67 | if __name__ == "__main__":
68 |
69 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description="Preprocess and combine text files for pretraining")
70 |
71 | parser.add_argument("--data_dir", type=str, default="gutenberg/data/raw",
72 | help="Directory containing the downloaded raw training data")
73 | parser.add_argument("--max_size_mb", type=int, default=500,
74 | help="The maximum file size for each concatenated file in megabytes")
75 | parser.add_argument("--output_dir", type=str, default="gutenberg_preprocessed",
76 | help="Directory where the preprocessed data will be saved")
77 |
78 | args = parser.parse_args()
79 |
80 | all_files = [os.path.join(path, name) for path, subdirs, files in os.walk(args.data_dir)
81 | for name in files if name.endswith((".txt", ".txt.utf8"))]
82 |
83 | print(f"{len(all_files)} file(s) to process.")
84 | file_counter = combine_files(all_files, args.output_dir, max_size_mb=args.max_size_mb)
85 | print(f"{file_counter} file(s) saved in {os.path.abspath(args.output_dir)}")
86 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup/02_installing-python-libraries/python_environment_check.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 |
6 | from importlib.metadata import PackageNotFoundError, import_module
7 | import importlib.metadata
8 | from os.path import dirname, exists, join, realpath
9 | from packaging.version import parse as version_parse
10 | import platform
11 | import sys
12 |
13 | if version_parse(platform.python_version()) < version_parse("3.9"):
14 | print("[FAIL] We recommend Python 3.9 or newer but"
15 | " found version %s" % (sys.version))
16 | else:
17 | print("[OK] Your Python version is %s" % (platform.python_version()))
18 |
19 |
20 | def get_packages(pkgs):
21 | versions = []
22 | for p in pkgs:
23 | try:
24 | imported = import_module(p)
25 | try:
26 | version = (getattr(imported, "__version__", None) or
27 | getattr(imported, "version", None) or
28 | getattr(imported, "version_info", None))
29 | if version is None:
30 | # If common attributes don"t exist, use importlib.metadata
31 | version = importlib.metadata.version(p)
32 | versions.append(version)
33 | except PackageNotFoundError:
34 | # Handle case where package is not installed
35 | versions.append("0.0")
36 | except ImportError:
37 | # Fallback if importlib.import_module fails for unexpected reasons
38 | versions.append("0.0")
39 | return versions
40 |
41 |
42 | def get_requirements_dict():
43 | PROJECT_ROOT = dirname(realpath(__file__))
44 | PROJECT_ROOT_UP_TWO = dirname(dirname(PROJECT_ROOT))
45 | REQUIREMENTS_FILE = join(PROJECT_ROOT_UP_TWO, "requirements.txt")
46 | if not exists(REQUIREMENTS_FILE):
47 | REQUIREMENTS_FILE = join(PROJECT_ROOT, "requirements.txt")
48 |
49 | d = {}
50 | with open(REQUIREMENTS_FILE) as f:
51 | for line in f:
52 | if not line.strip():
53 | continue
54 | if "," in line:
55 | left, right = line.split(",")
56 | lower = right.split("#")[0].strip()
57 | package, _, upper = left.split(" ")
58 | package = package.strip()
59 | _, lower = lower.split(" ")
60 | lower = lower.strip()
61 | upper = upper.strip()
62 | d[package] = (upper, lower)
63 | else:
64 | line = line.split("#")[0].strip()
65 | line = line.split(" ")
66 | line = [ln.strip() for ln in line]
67 | d[line[0]] = line[-1]
68 | return d
69 |
70 |
71 | def check_packages(d):
72 | versions = get_packages(d.keys())
73 |
74 | for (pkg_name, suggested_ver), actual_ver in zip(d.items(), versions):
75 | if isinstance(suggested_ver, tuple):
76 | lower, upper = suggested_ver[0], suggested_ver[1]
77 | else:
78 | lower = suggested_ver
79 | upper = None
80 | if actual_ver == "N/A":
81 | continue
82 | actual_ver = version_parse(actual_ver)
83 | lower = version_parse(lower)
84 | if upper is not None:
85 | upper = version_parse(upper)
86 | if actual_ver < lower and upper is None:
87 | print(f"[FAIL] {pkg_name} {actual_ver}, please upgrade to >= {lower}")
88 | elif actual_ver < lower:
89 | print(f"[FAIL] {pkg_name} {actual_ver}, please upgrade to >= {lower} and < {upper}")
90 | elif upper is not None and actual_ver >= upper:
91 | print(f"[FAIL] {pkg_name} {actual_ver}, please downgrade to >= {lower} and < {upper}")
92 | else:
93 | print(f"[OK] {pkg_name} {actual_ver}")
94 |
95 |
96 | def main():
97 | d = get_requirements_dict()
98 | check_packages(d)
99 |
100 |
101 | if __name__ == "__main__":
102 | main()
103 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch06/03_bonus_imdb-classification/README.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Additional Experiments Classifying the Sentiment of 50k IMDB Movie Reviews
2 |
3 |
4 | ## Step 1: Install Dependencies
5 |
6 | Install the extra dependencies via
7 |
8 | ```bash
9 | pip install -r requirements-extra.txt
10 | ```
11 |
12 |
13 | ## Step 2: Download Dataset
14 |
15 | The codes are using the 50k movie reviews from IMDb ([dataset source](https://ai.stanford.edu/~amaas/data/sentiment/)) to predict whether a movie review is positive or negative.
16 |
17 | Run the following code to create the `train.csv`, `validation.csv`, and `test.csv` datasets:
18 |
19 | ```bash
20 | python download_prepare_dataset.py
21 | ```
22 |
23 |
24 |
25 | ## Step 3: Run Models
26 |
27 | The 124M GPT-2 model used in the main chapter, starting with pretrained weights, and finetuning all weights:
28 |
29 | ```bash
30 | python train_gpt.py --trainable_layers "all" --num_epochs 1
31 | ```
32 |
33 | ```
34 | Ep 1 (Step 000000): Train loss 3.706, Val loss 3.853
35 | Ep 1 (Step 000050): Train loss 0.682, Val loss 0.706
36 | ...
37 | Ep 1 (Step 004300): Train loss 0.199, Val loss 0.285
38 | Ep 1 (Step 004350): Train loss 0.188, Val loss 0.208
39 | Training accuracy: 95.62% | Validation accuracy: 95.00%
40 | Training completed in 9.48 minutes.
41 |
42 | Evaluating on the full datasets ...
43 |
44 | Training accuracy: 95.64%
45 | Validation accuracy: 92.32%
46 | Test accuracy: 91.88%
47 | ```
48 |
49 |
50 |  19 |
20 | Depending on your operating system, this should download either an `.sh` (macOS, Linux) or `.exe` file (Windows).
21 |
22 | For the `.sh` file, open your command line terminal and execute the following command
23 |
24 | ```bash
25 | sh ~/Desktop/Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64.sh
26 | ```
27 |
28 | where `Desktop/` is the folder where the Miniforge installer was downloaded to. On your computer, you may have to replace it with `Downloads/`.
29 |
30 |
19 |
20 | Depending on your operating system, this should download either an `.sh` (macOS, Linux) or `.exe` file (Windows).
21 |
22 | For the `.sh` file, open your command line terminal and execute the following command
23 |
24 | ```bash
25 | sh ~/Desktop/Miniforge3-MacOSX-arm64.sh
26 | ```
27 |
28 | where `Desktop/` is the folder where the Miniforge installer was downloaded to. On your computer, you may have to replace it with `Downloads/`.
29 |
30 | 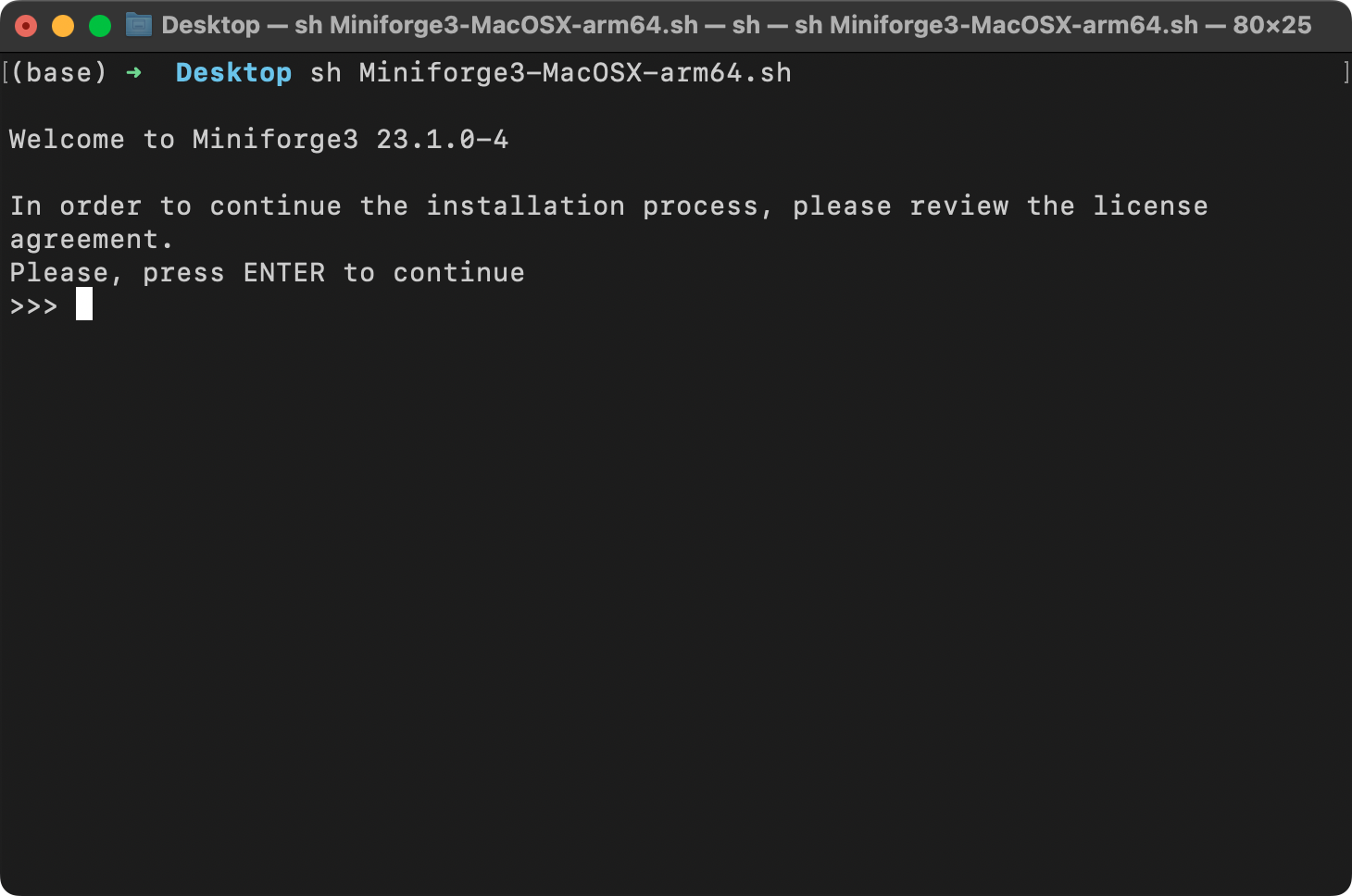 31 |
32 | Next, step through the download instructions, confirming with "Enter".
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | If you work with many packages, Conda can be slow because of its thorough but complex dependency resolution process and the handling of large package indexes and metadata. To speed up Conda, you can use the following setting, which switches to a more efficient Rust reimplementation for solving dependencies:
37 |
38 | ```
39 | conda config --set solver libmamba
40 | ```
41 |
42 |
31 |
32 | Next, step through the download instructions, confirming with "Enter".
33 |
34 |
35 |
36 | If you work with many packages, Conda can be slow because of its thorough but complex dependency resolution process and the handling of large package indexes and metadata. To speed up Conda, you can use the following setting, which switches to a more efficient Rust reimplementation for solving dependencies:
37 |
38 | ```
39 | conda config --set solver libmamba
40 | ```
41 |
42 |  55 |
56 | > Many scientific computing libraries do not immediately support the newest version of Python. Therefore, when installing PyTorch, it's advisable to use a version of Python that is one or two releases older. For instance, if the latest version of Python is 3.13, using Python 3.10 or 3.11 is recommended.
57 |
58 | Next, activate your new virtual environment (you have to do it every time you open a new terminal window or tab):
59 |
60 | ```bash
61 | conda activate LLMs
62 | ```
63 |
64 |
55 |
56 | > Many scientific computing libraries do not immediately support the newest version of Python. Therefore, when installing PyTorch, it's advisable to use a version of Python that is one or two releases older. For instance, if the latest version of Python is 3.13, using Python 3.10 or 3.11 is recommended.
57 |
58 | Next, activate your new virtual environment (you have to do it every time you open a new terminal window or tab):
59 |
60 | ```bash
61 | conda activate LLMs
62 | ```
63 |
64 | 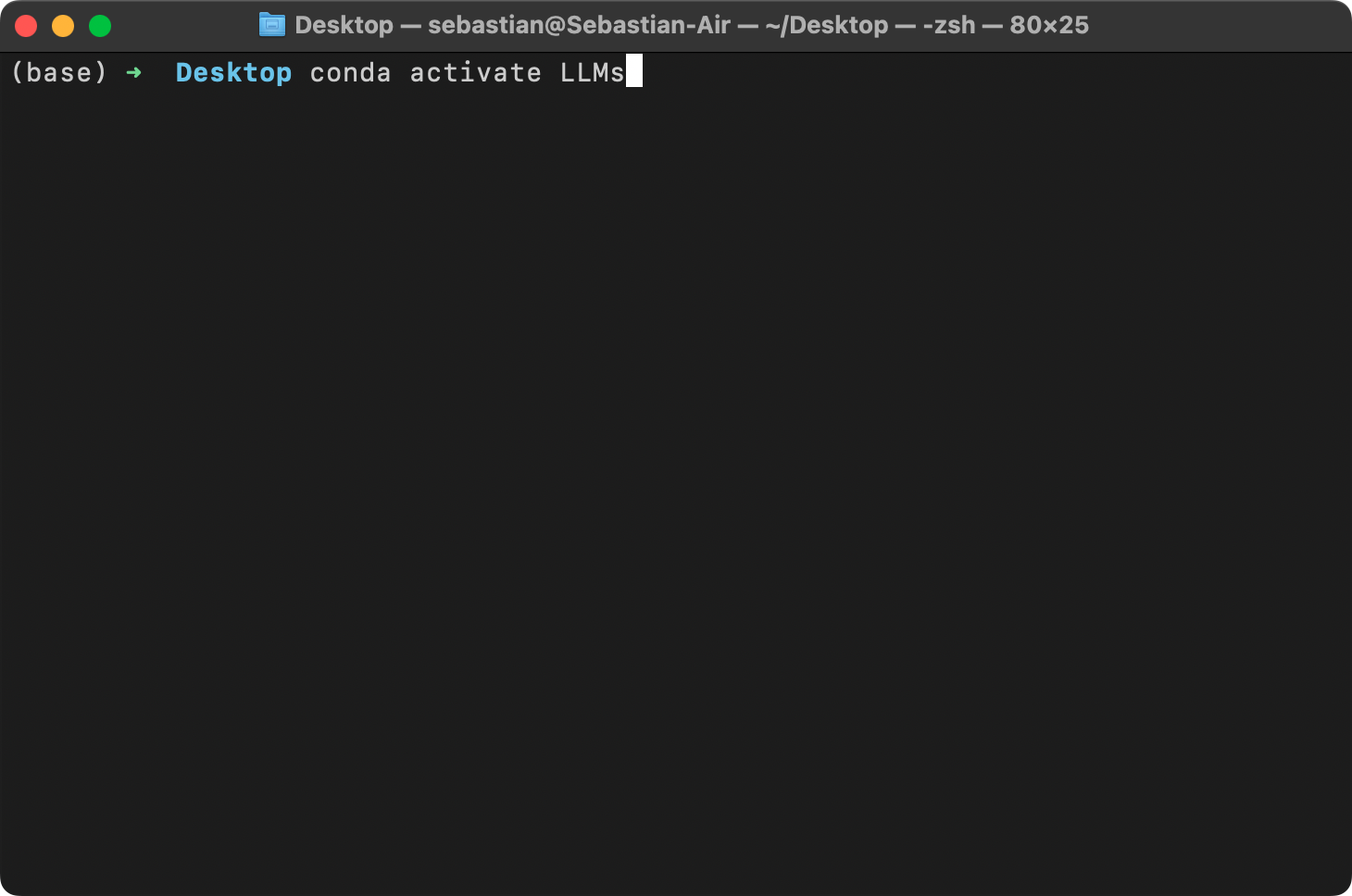 65 |
66 |
65 |
66 | 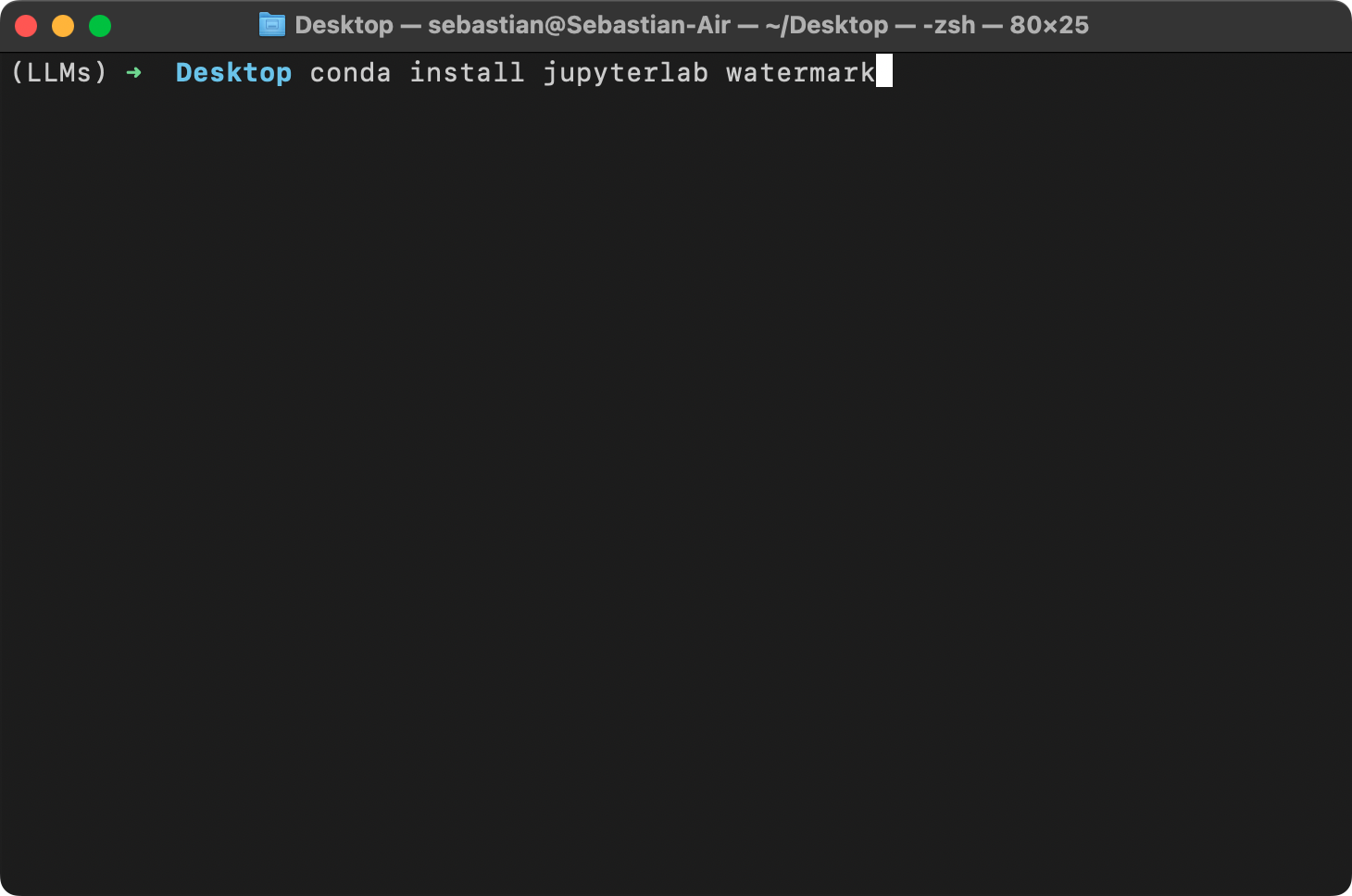 87 |
88 |
89 |
90 | You can also still use `pip` to install libraries. By default, `pip` should be linked to your new `LLms` conda environment:
91 |
92 |
87 |
88 |
89 |
90 | You can also still use `pip` to install libraries. By default, `pip` should be linked to your new `LLms` conda environment:
91 |
92 | 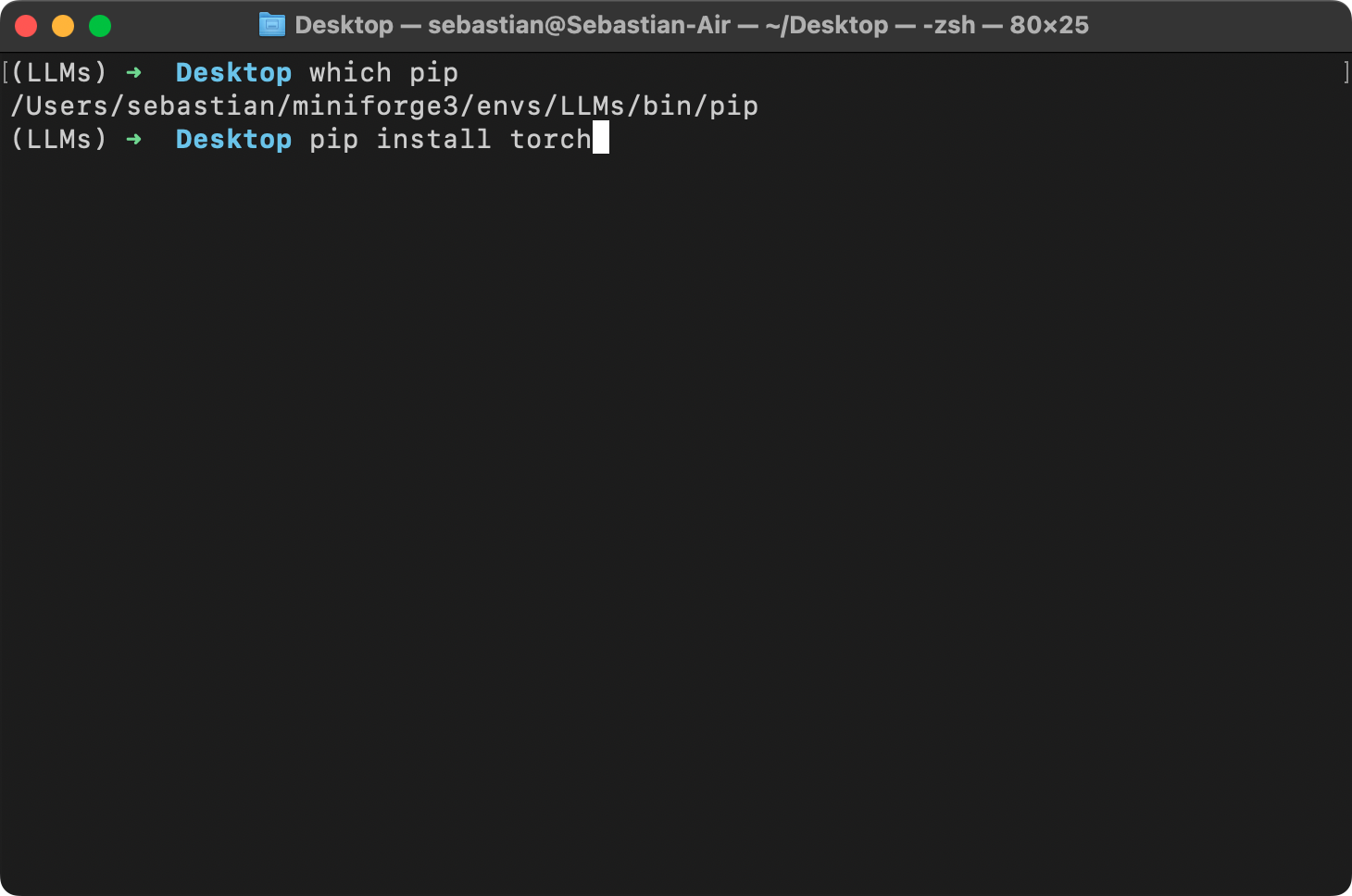 93 |
94 |
93 |
94 | 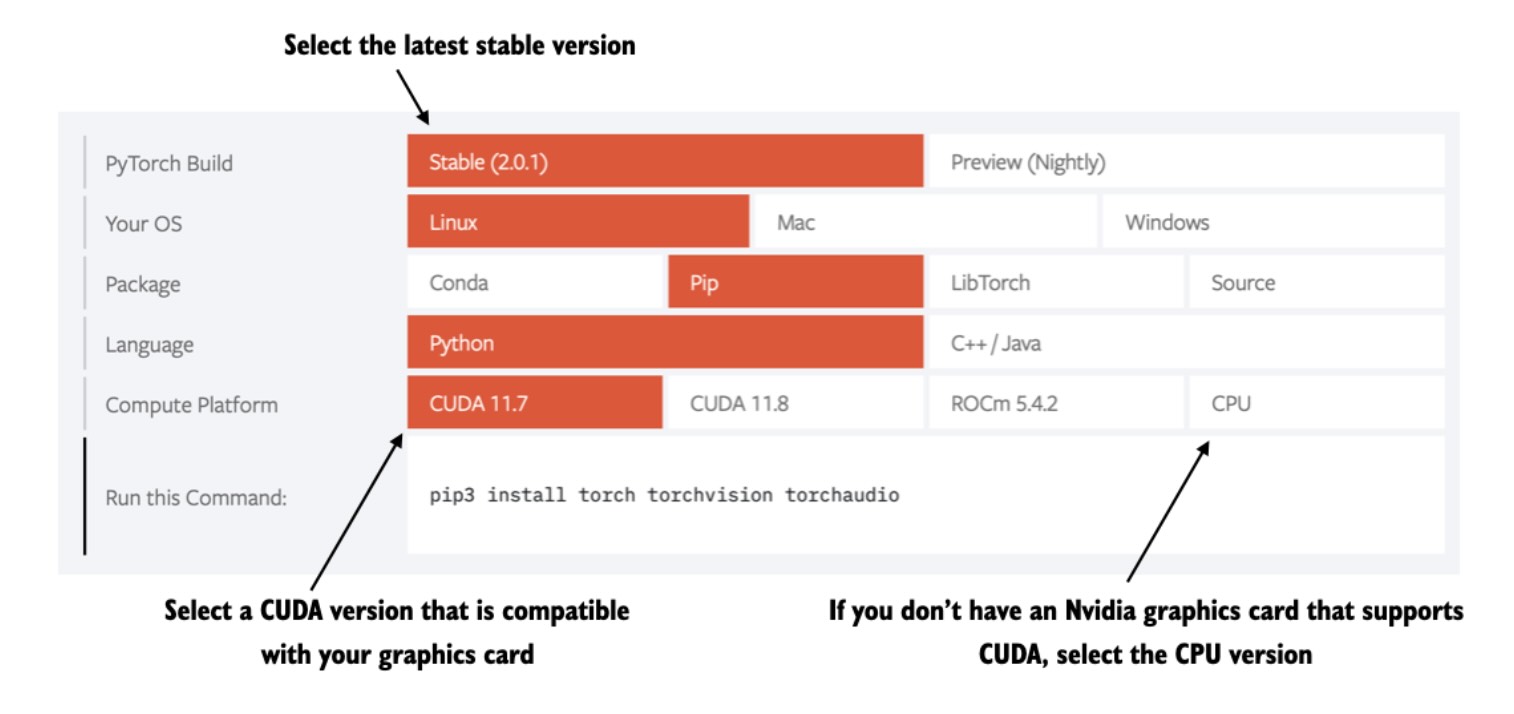 110 |
111 |
112 |
113 | ---
114 |
115 |
116 |
117 |
118 | Any questions? Please feel free to reach out in the [Discussion Forum](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/discussions).
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_bonus_efficient-multihead-attention/ch03.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 | #
6 | # This file contains the relevant code from chapter 3 that is going to be used
7 | # in forthcoming chapters.
8 |
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 |
12 |
13 | class CausalAttention(nn.Module):
14 |
15 | def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, qkv_bias=False):
16 | super().__init__()
17 | self.d_out = d_out
18 | self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
19 | self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
20 | self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
21 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) # New
22 | self.register_buffer('mask', torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length), diagonal=1)) # New
23 |
24 | def forward(self, x):
25 | b, num_tokens, d_in = x.shape # New batch dimension b
26 | keys = self.W_key(x)
27 | queries = self.W_query(x)
28 | values = self.W_value(x)
29 |
30 | attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(1, 2) # Changed transpose
31 | attn_scores.masked_fill_( # New, _ ops are in-place
32 | self.mask.bool()[:num_tokens, :num_tokens], -torch.inf)
33 | attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1)
34 | attn_weights = self.dropout(attn_weights) # New
35 |
36 | context_vec = attn_weights @ values
37 | return context_vec
38 |
39 |
40 | class MultiHeadAttentionWrapper(nn.Module):
41 |
42 | def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, num_heads, qkv_bias=False):
43 | super().__init__()
44 | self.heads = nn.ModuleList(
45 | [CausalAttention(d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, qkv_bias)
46 | for _ in range(num_heads)]
47 | )
48 | self.out_proj = nn.Linear(d_out*num_heads, d_out*num_heads)
49 |
50 | def forward(self, x):
51 | context_vec = torch.cat([head(x) for head in self.heads], dim=-1)
52 | return self.out_proj(context_vec)
53 |
54 |
55 | class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
56 | def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, num_heads, qkv_bias=False):
57 | super().__init__()
58 | assert d_out % num_heads == 0, "d_out must be divisible by num_heads"
59 |
60 | self.d_out = d_out
61 | self.num_heads = num_heads
62 | self.head_dim = d_out // num_heads # Reduce the projection dim to match desired output dim
63 |
64 | self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
65 | self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
66 | self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
67 | self.out_proj = nn.Linear(d_out, d_out) # Linear layer to combine head outputs
68 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
69 | self.register_buffer('mask', torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length), diagonal=1))
70 |
71 | def forward(self, x):
72 | b, num_tokens, d_in = x.shape
73 |
74 | keys = self.W_key(x) # Shape: (b, num_tokens, d_out)
75 | queries = self.W_query(x)
76 | values = self.W_value(x)
77 |
78 | # We implicitly split the matrix by adding a `num_heads` dimension
79 | # Unroll last dim: (b, num_tokens, d_out) -> (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim)
80 | keys = keys.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
81 | values = values.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
82 | queries = queries.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
83 |
84 | # Transpose: (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim) -> (b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim)
85 | keys = keys.transpose(1, 2)
86 | queries = queries.transpose(1, 2)
87 | values = values.transpose(1, 2)
88 |
89 | # Compute scaled dot-product attention (aka self-attention) with a causal mask
90 | attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(2, 3) # Dot product for each head
91 |
92 | # Original mask truncated to the number of tokens and converted to boolean
93 | mask_bool = self.mask.bool()[:num_tokens, :num_tokens]
94 |
95 | # Use the mask to fill attention scores
96 | attn_scores.masked_fill_(mask_bool, -torch.inf)
97 |
98 | attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1)
99 | attn_weights = self.dropout(attn_weights)
100 |
101 | # Shape: (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim)
102 | context_vec = (attn_weights @ values).transpose(1, 2)
103 |
104 | # Combine heads, where self.d_out = self.num_heads * self.head_dim
105 | context_vec = context_vec.contiguous().view(b, num_tokens, self.d_out)
106 | context_vec = self.out_proj(context_vec) # optional projection
107 |
108 | return context_vec
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch04/02_performance-analysis/flops-analysis.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "
110 |
111 |
112 |
113 | ---
114 |
115 |
116 |
117 |
118 | Any questions? Please feel free to reach out in the [Discussion Forum](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/discussions).
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch03/02_bonus_efficient-multihead-attention/ch03.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
2 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
3 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
4 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
5 | #
6 | # This file contains the relevant code from chapter 3 that is going to be used
7 | # in forthcoming chapters.
8 |
9 | import torch
10 | import torch.nn as nn
11 |
12 |
13 | class CausalAttention(nn.Module):
14 |
15 | def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, qkv_bias=False):
16 | super().__init__()
17 | self.d_out = d_out
18 | self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
19 | self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
20 | self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
21 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) # New
22 | self.register_buffer('mask', torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length), diagonal=1)) # New
23 |
24 | def forward(self, x):
25 | b, num_tokens, d_in = x.shape # New batch dimension b
26 | keys = self.W_key(x)
27 | queries = self.W_query(x)
28 | values = self.W_value(x)
29 |
30 | attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(1, 2) # Changed transpose
31 | attn_scores.masked_fill_( # New, _ ops are in-place
32 | self.mask.bool()[:num_tokens, :num_tokens], -torch.inf)
33 | attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1)
34 | attn_weights = self.dropout(attn_weights) # New
35 |
36 | context_vec = attn_weights @ values
37 | return context_vec
38 |
39 |
40 | class MultiHeadAttentionWrapper(nn.Module):
41 |
42 | def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, num_heads, qkv_bias=False):
43 | super().__init__()
44 | self.heads = nn.ModuleList(
45 | [CausalAttention(d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, qkv_bias)
46 | for _ in range(num_heads)]
47 | )
48 | self.out_proj = nn.Linear(d_out*num_heads, d_out*num_heads)
49 |
50 | def forward(self, x):
51 | context_vec = torch.cat([head(x) for head in self.heads], dim=-1)
52 | return self.out_proj(context_vec)
53 |
54 |
55 | class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module):
56 | def __init__(self, d_in, d_out, context_length, dropout, num_heads, qkv_bias=False):
57 | super().__init__()
58 | assert d_out % num_heads == 0, "d_out must be divisible by num_heads"
59 |
60 | self.d_out = d_out
61 | self.num_heads = num_heads
62 | self.head_dim = d_out // num_heads # Reduce the projection dim to match desired output dim
63 |
64 | self.W_query = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
65 | self.W_key = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
66 | self.W_value = nn.Linear(d_in, d_out, bias=qkv_bias)
67 | self.out_proj = nn.Linear(d_out, d_out) # Linear layer to combine head outputs
68 | self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout)
69 | self.register_buffer('mask', torch.triu(torch.ones(context_length, context_length), diagonal=1))
70 |
71 | def forward(self, x):
72 | b, num_tokens, d_in = x.shape
73 |
74 | keys = self.W_key(x) # Shape: (b, num_tokens, d_out)
75 | queries = self.W_query(x)
76 | values = self.W_value(x)
77 |
78 | # We implicitly split the matrix by adding a `num_heads` dimension
79 | # Unroll last dim: (b, num_tokens, d_out) -> (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim)
80 | keys = keys.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
81 | values = values.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
82 | queries = queries.view(b, num_tokens, self.num_heads, self.head_dim)
83 |
84 | # Transpose: (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim) -> (b, num_heads, num_tokens, head_dim)
85 | keys = keys.transpose(1, 2)
86 | queries = queries.transpose(1, 2)
87 | values = values.transpose(1, 2)
88 |
89 | # Compute scaled dot-product attention (aka self-attention) with a causal mask
90 | attn_scores = queries @ keys.transpose(2, 3) # Dot product for each head
91 |
92 | # Original mask truncated to the number of tokens and converted to boolean
93 | mask_bool = self.mask.bool()[:num_tokens, :num_tokens]
94 |
95 | # Use the mask to fill attention scores
96 | attn_scores.masked_fill_(mask_bool, -torch.inf)
97 |
98 | attn_weights = torch.softmax(attn_scores / keys.shape[-1]**0.5, dim=-1)
99 | attn_weights = self.dropout(attn_weights)
100 |
101 | # Shape: (b, num_tokens, num_heads, head_dim)
102 | context_vec = (attn_weights @ values).transpose(1, 2)
103 |
104 | # Combine heads, where self.d_out = self.num_heads * self.head_dim
105 | context_vec = context_vec.contiguous().view(b, num_tokens, self.d_out)
106 | context_vec = self.out_proj(context_vec) # optional projection
107 |
108 | return context_vec
109 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch04/02_performance-analysis/flops-analysis.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "| \n",
10 | "\n",
11 | "Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka \n", 12 | " Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 13 | "\n", 14 | " | \n",
15 | "\n",
16 | " \n",
17 | " \n",
17 | " | \n",
18 | "
 79 |
80 |
81 |
82 | ## Using Google Colab
83 |
84 | To use a Google Colab environment in the cloud, head over to [https://colab.research.google.com/](https://colab.research.google.com/) and open the respective chapter notebook from the GitHub menu or by dragging the notebook into the *Upload* field as shown in the figure below.
85 |
86 |
79 |
80 |
81 |
82 | ## Using Google Colab
83 |
84 | To use a Google Colab environment in the cloud, head over to [https://colab.research.google.com/](https://colab.research.google.com/) and open the respective chapter notebook from the GitHub menu or by dragging the notebook into the *Upload* field as shown in the figure below.
85 |
86 | 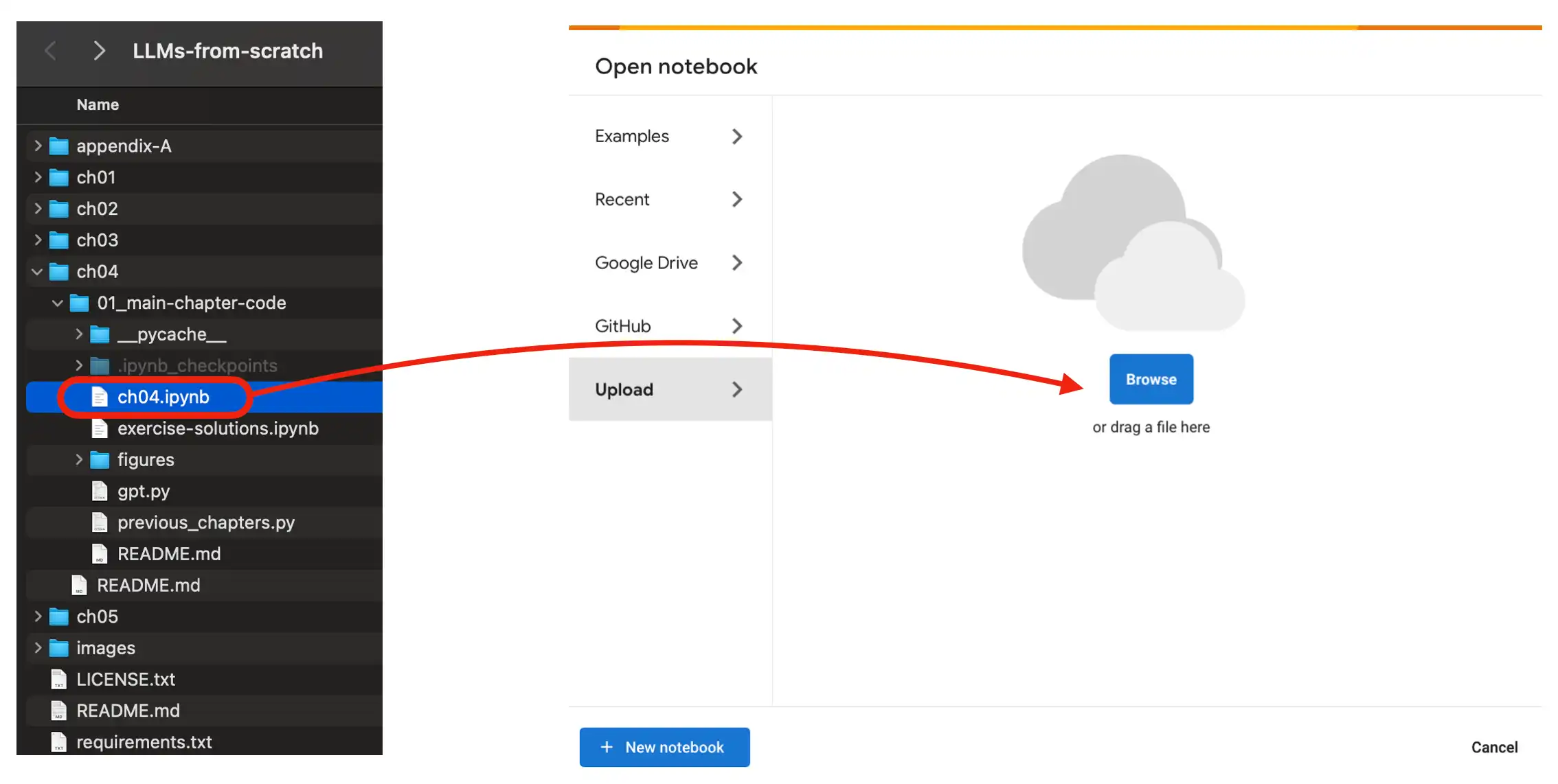 87 |
88 |
89 | Also make sure you upload the relevant files (dataset files and .py files the notebook is importing from) to the Colab environment as well, as shown below.
90 |
91 |
87 |
88 |
89 | Also make sure you upload the relevant files (dataset files and .py files the notebook is importing from) to the Colab environment as well, as shown below.
90 |
91 | 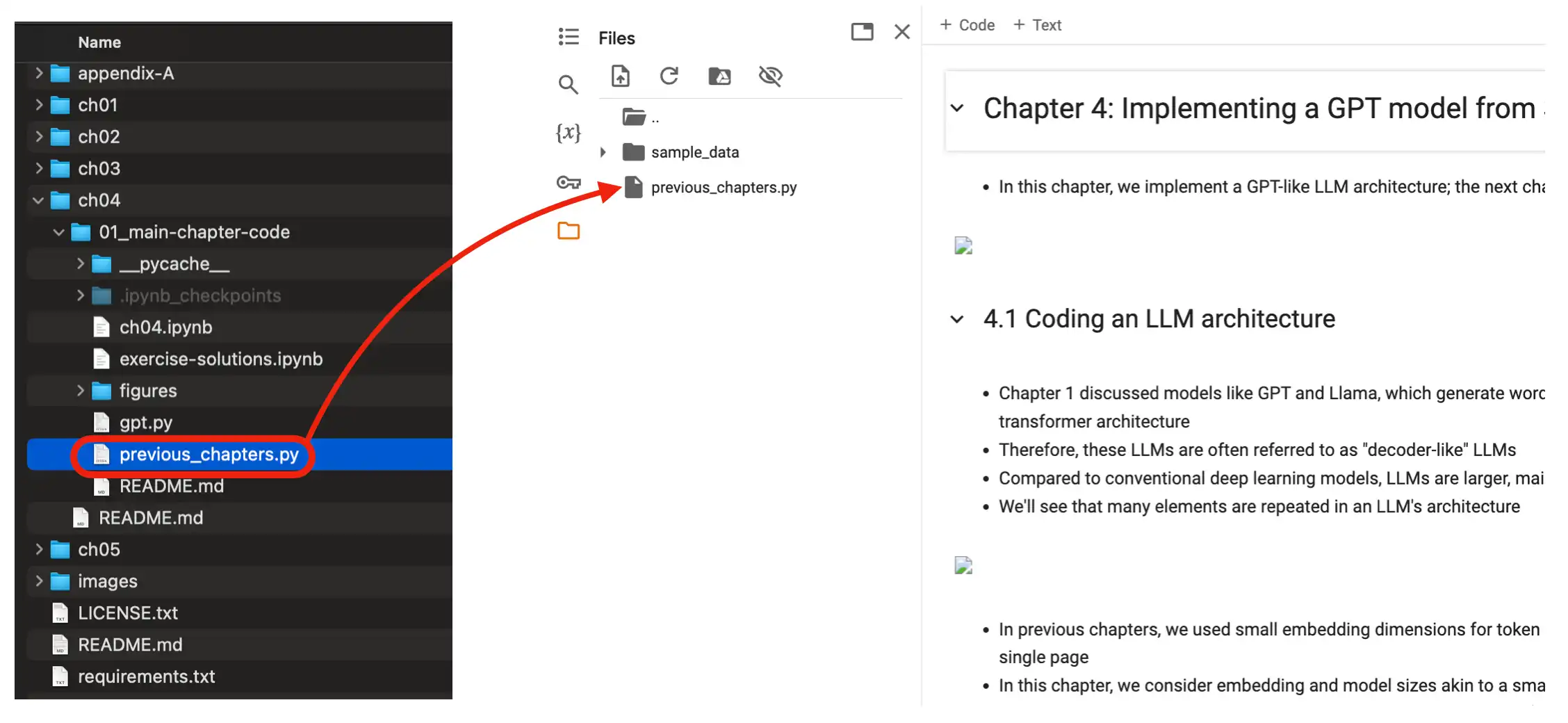 92 |
93 |
94 | You can optionally run the code on a GPU by changing the *Runtime* as illustrated in the figure below.
95 |
96 |
92 |
93 |
94 | You can optionally run the code on a GPU by changing the *Runtime* as illustrated in the figure below.
95 |
96 | 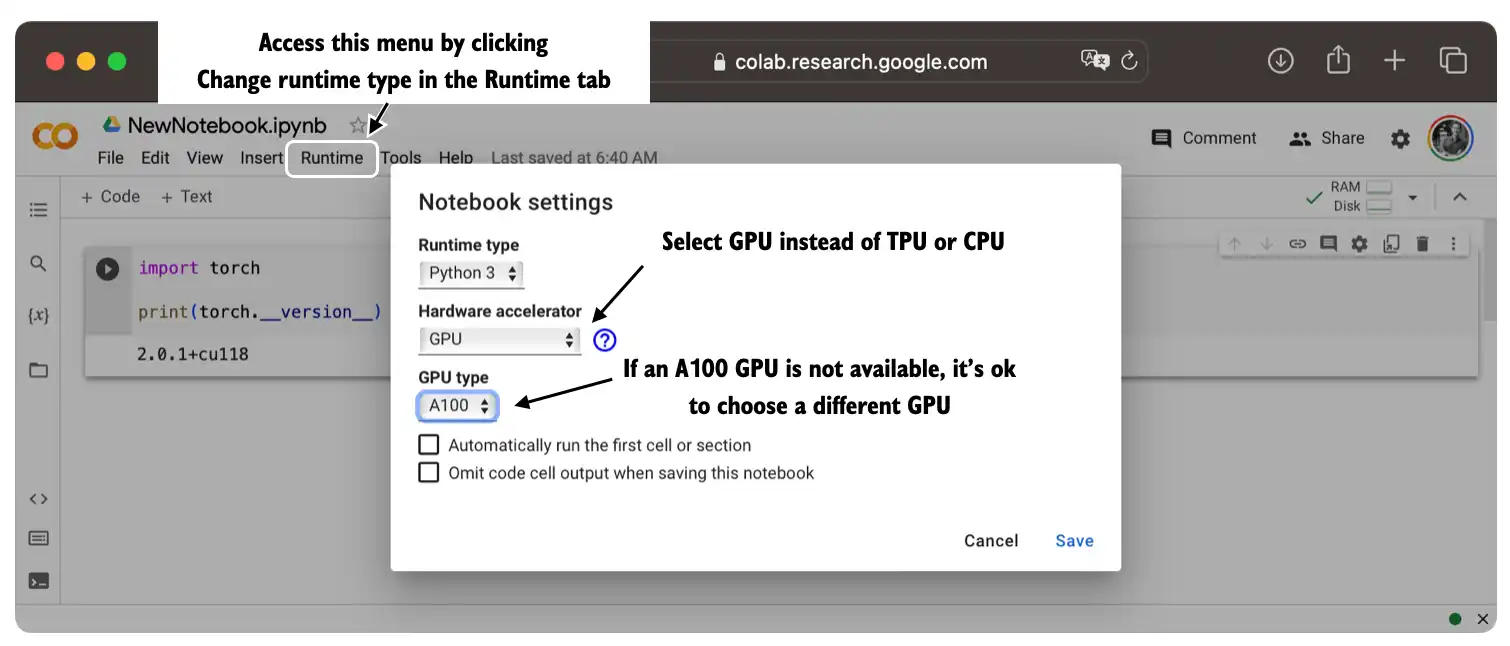 97 |
98 |
99 |
100 |
101 | # Questions?
102 |
103 | If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to reach out via the [Discussions](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/discussions) forum in this GitHub repository.
104 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/02_dataset-utilities/find-near-duplicates.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
3 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
4 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
5 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
6 |
7 | import argparse
8 | import json
9 | import re
10 | from sklearn import __version__ as sklearn_version
11 | from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
12 | from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
13 |
14 |
15 | # Sample JSON dataset
16 | example_data = [
17 | {"instruction": "What is the capital of Italy?",
18 | "input": "", "output": "The capital of Italy is Rome."
19 | },
20 | {"instruction": "What's the capital city of Italy?",
21 | "input": "", "output": "The capital city is Rome."
22 | },
23 | {"instruction": "Identify the main verb in the sentence: 'The cat sleeps on the couch.'",
24 | "input": "", "output": "The verb is 'sleeps'."
25 | },
26 | {"instruction": "Identify the verb in the following sentence: The cat sleeps on the couch.",
27 | "input": "", "output": "The verb in the sentence is \"sleeps.\""
28 | },
29 | # ...
30 | ]
31 |
32 |
33 | def preprocess_text(text):
34 | # Lowercase the text
35 | text = text.lower()
36 | # Remove punctuation
37 | text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', '', text)
38 | return text
39 |
40 |
41 | def find_near_duplicates(json_data, threshold=0.75, key="instruction"):
42 | """The higher the threshold, the more similar the texts have to be to match"""
43 |
44 | # Extract instructions
45 | text = [preprocess_text(item[key]) for item in json_data if item[key]]
46 | near_duplicates = []
47 | indices_to_remove = set()
48 |
49 | if not text:
50 | return {}, near_duplicates
51 |
52 | # Vectorize the text data
53 | vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=None, analyzer='char', ngram_range=(1, 3))
54 | tfidf_matrix = vectorizer.fit_transform(text)
55 |
56 | # Compute cosine similarity between each pair of entries
57 | cos_sim_matrix = cosine_similarity(tfidf_matrix)
58 |
59 | # Find pairs of near-duplicate instructions based on the threshold
60 |
61 | for i in range(len(cos_sim_matrix)):
62 | for j in range(i+1, len(cos_sim_matrix)):
63 | if cos_sim_matrix[i, j] > threshold:
64 | if len(json_data[i][key]) <= 1 or len(json_data[j][key]) <= 1:
65 | continue
66 | near_duplicates.append((json_data[i], json_data[j], cos_sim_matrix[i, j]))
67 | if key in ("input", "output"): # Don't remove duplicates based on the instruction
68 | indices_to_remove.add(j) # Mark the second entry for removal
69 |
70 | # Remove the near-duplicate entries
71 | filtered_json_data = [item for index, item in enumerate(json_data) if index not in indices_to_remove]
72 |
73 | return filtered_json_data, near_duplicates
74 |
75 |
76 | def find_print_and_remove_near_duplicates(json_data, remove_duplicates=False, threshold=0.75):
77 | """
78 | Searches each key in the first JSON object for duplicates across a list of JSON objects.
79 | Prints the duplicates if found.
80 | """
81 | for key in json_data[0].keys():
82 |
83 | if remove_duplicates:
84 | json_data, near_duplicates = find_near_duplicates(json_data, key=key, threshold=threshold)
85 | else:
86 | _, near_duplicates = find_near_duplicates(json_data, key=key, threshold=threshold)
87 | separator = 50 * '='
88 | print(f"\n\n{separator}\nSearching '{key}' for duplicates ...\n{separator}")
89 | if not near_duplicates:
90 | print("No duplicates found")
91 | else:
92 | for dup in near_duplicates:
93 | print(
94 | f"Duplicate pair found with similarity {dup[2]:.2f}:\n"
95 | f"1. {dup[0][key]}\n2. {dup[1][key]}\n"
96 | )
97 | return json_data
98 |
99 |
100 | if __name__ == "__main__":
101 | print("scikit-learn version:", sklearn_version)
102 |
103 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
104 | parser.add_argument(
105 | "--json_file",
106 | type=str,
107 | help=("Path to the dataset JSON file")
108 | )
109 | parser.add_argument(
110 | "--threshold",
111 | type=float,
112 | default=0.9,
113 | help=("A sensitivity threshold between 0 and 1 where 1 is strictest")
114 | )
115 | parser.add_argument(
116 | "--remove_duplicates",
117 | action='store_true',
118 | default=False,
119 | help=(
120 | "Removes duplicates based on the 'input' or 'output' keys "
121 | " (but not the 'instruction') and saves the cleaned JSON file as --json_output_file"
122 | )
123 | )
124 | parser.add_argument(
125 | "--json_output_file",
126 | type=str,
127 | help=("Path to the dataset JSON file")
128 | )
129 |
130 | args = parser.parse_args()
131 |
132 | if args.remove_duplicates and not args.json_output_file:
133 | raise ValueError(
134 | "Provide an output file via --json_output_file "
135 | "to save the cleaned JSON data."
136 | )
137 |
138 | if not args.json_file:
139 | json_data = example_data
140 |
141 | else:
142 | with open(args.json_file, "r") as file:
143 | json_data = json.load(file)
144 |
145 | json_data = find_print_and_remove_near_duplicates(
146 | json_data=json_data,
147 | remove_duplicates=args.remove_duplicates,
148 | threshold=args.threshold
149 | )
150 |
151 | if args.remove_duplicates:
152 | with open(args.json_output_file, "w") as file:
153 | json.dump(json_data, file, indent=4)
154 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch06/01_main-chapter-code/exercise-solutions.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "id": "ba450fb1-8a26-4894-ab7a-5d7bfefe90ce",
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "source": [
8 | "
97 |
98 |
99 |
100 |
101 | # Questions?
102 |
103 | If you have any questions, please don't hesitate to reach out via the [Discussions](https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/discussions) forum in this GitHub repository.
104 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch07/02_dataset-utilities/find-near-duplicates.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 | # Copyright (c) Sebastian Raschka under Apache License 2.0 (see LICENSE.txt).
3 | # Source for "Build a Large Language Model From Scratch"
4 | # - https://www.manning.com/books/build-a-large-language-model-from-scratch
5 | # Code: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch
6 |
7 | import argparse
8 | import json
9 | import re
10 | from sklearn import __version__ as sklearn_version
11 | from sklearn.feature_extraction.text import TfidfVectorizer
12 | from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
13 |
14 |
15 | # Sample JSON dataset
16 | example_data = [
17 | {"instruction": "What is the capital of Italy?",
18 | "input": "", "output": "The capital of Italy is Rome."
19 | },
20 | {"instruction": "What's the capital city of Italy?",
21 | "input": "", "output": "The capital city is Rome."
22 | },
23 | {"instruction": "Identify the main verb in the sentence: 'The cat sleeps on the couch.'",
24 | "input": "", "output": "The verb is 'sleeps'."
25 | },
26 | {"instruction": "Identify the verb in the following sentence: The cat sleeps on the couch.",
27 | "input": "", "output": "The verb in the sentence is \"sleeps.\""
28 | },
29 | # ...
30 | ]
31 |
32 |
33 | def preprocess_text(text):
34 | # Lowercase the text
35 | text = text.lower()
36 | # Remove punctuation
37 | text = re.sub(r'[^\w\s]', '', text)
38 | return text
39 |
40 |
41 | def find_near_duplicates(json_data, threshold=0.75, key="instruction"):
42 | """The higher the threshold, the more similar the texts have to be to match"""
43 |
44 | # Extract instructions
45 | text = [preprocess_text(item[key]) for item in json_data if item[key]]
46 | near_duplicates = []
47 | indices_to_remove = set()
48 |
49 | if not text:
50 | return {}, near_duplicates
51 |
52 | # Vectorize the text data
53 | vectorizer = TfidfVectorizer(stop_words=None, analyzer='char', ngram_range=(1, 3))
54 | tfidf_matrix = vectorizer.fit_transform(text)
55 |
56 | # Compute cosine similarity between each pair of entries
57 | cos_sim_matrix = cosine_similarity(tfidf_matrix)
58 |
59 | # Find pairs of near-duplicate instructions based on the threshold
60 |
61 | for i in range(len(cos_sim_matrix)):
62 | for j in range(i+1, len(cos_sim_matrix)):
63 | if cos_sim_matrix[i, j] > threshold:
64 | if len(json_data[i][key]) <= 1 or len(json_data[j][key]) <= 1:
65 | continue
66 | near_duplicates.append((json_data[i], json_data[j], cos_sim_matrix[i, j]))
67 | if key in ("input", "output"): # Don't remove duplicates based on the instruction
68 | indices_to_remove.add(j) # Mark the second entry for removal
69 |
70 | # Remove the near-duplicate entries
71 | filtered_json_data = [item for index, item in enumerate(json_data) if index not in indices_to_remove]
72 |
73 | return filtered_json_data, near_duplicates
74 |
75 |
76 | def find_print_and_remove_near_duplicates(json_data, remove_duplicates=False, threshold=0.75):
77 | """
78 | Searches each key in the first JSON object for duplicates across a list of JSON objects.
79 | Prints the duplicates if found.
80 | """
81 | for key in json_data[0].keys():
82 |
83 | if remove_duplicates:
84 | json_data, near_duplicates = find_near_duplicates(json_data, key=key, threshold=threshold)
85 | else:
86 | _, near_duplicates = find_near_duplicates(json_data, key=key, threshold=threshold)
87 | separator = 50 * '='
88 | print(f"\n\n{separator}\nSearching '{key}' for duplicates ...\n{separator}")
89 | if not near_duplicates:
90 | print("No duplicates found")
91 | else:
92 | for dup in near_duplicates:
93 | print(
94 | f"Duplicate pair found with similarity {dup[2]:.2f}:\n"
95 | f"1. {dup[0][key]}\n2. {dup[1][key]}\n"
96 | )
97 | return json_data
98 |
99 |
100 | if __name__ == "__main__":
101 | print("scikit-learn version:", sklearn_version)
102 |
103 | parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
104 | parser.add_argument(
105 | "--json_file",
106 | type=str,
107 | help=("Path to the dataset JSON file")
108 | )
109 | parser.add_argument(
110 | "--threshold",
111 | type=float,
112 | default=0.9,
113 | help=("A sensitivity threshold between 0 and 1 where 1 is strictest")
114 | )
115 | parser.add_argument(
116 | "--remove_duplicates",
117 | action='store_true',
118 | default=False,
119 | help=(
120 | "Removes duplicates based on the 'input' or 'output' keys "
121 | " (but not the 'instruction') and saves the cleaned JSON file as --json_output_file"
122 | )
123 | )
124 | parser.add_argument(
125 | "--json_output_file",
126 | type=str,
127 | help=("Path to the dataset JSON file")
128 | )
129 |
130 | args = parser.parse_args()
131 |
132 | if args.remove_duplicates and not args.json_output_file:
133 | raise ValueError(
134 | "Provide an output file via --json_output_file "
135 | "to save the cleaned JSON data."
136 | )
137 |
138 | if not args.json_file:
139 | json_data = example_data
140 |
141 | else:
142 | with open(args.json_file, "r") as file:
143 | json_data = json.load(file)
144 |
145 | json_data = find_print_and_remove_near_duplicates(
146 | json_data=json_data,
147 | remove_duplicates=args.remove_duplicates,
148 | threshold=args.threshold
149 | )
150 |
151 | if args.remove_duplicates:
152 | with open(args.json_output_file, "w") as file:
153 | json.dump(json_data, file, indent=4)
154 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ch06/01_main-chapter-code/exercise-solutions.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "id": "ba450fb1-8a26-4894-ab7a-5d7bfefe90ce",
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "source": [
8 | "| \n",
11 | "\n",
12 | "Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka \n", 13 | " Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 14 | "\n", 15 | " | \n",
16 | "\n",
17 | " \n",
18 | " \n",
18 | " | \n",
19 | "
| \n",
10 | "\n",
11 | "Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka \n", 12 | " Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 13 | "\n", 14 | " | \n",
15 | "\n",
16 | " \n",
17 | " \n",
17 | " | \n",
18 | "
| \n",
11 | "\n",
12 | "Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka \n", 13 | " Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 14 | "\n", 15 | " | \n",
16 | "\n",
17 | " \n",
18 | " \n",
18 | " | \n",
19 | "
| \n",
11 | "\n",
12 | "Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka \n", 13 | " Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 14 | "\n", 15 | " | \n",
16 | "\n",
17 | " \n",
18 | " \n",
18 | " | \n",
19 | "
| \n",
11 | "\n",
12 | "Supplementary code for the Build a Large Language Model From Scratch book by Sebastian Raschka \n", 13 | " Code repository: https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch\n", 14 | "\n", 15 | " | \n",
16 | "\n",
17 | " \n",
18 | " \n",
18 | " | \n",
19 | "