├── tests
├── __init__.py
├── test_numerics.py
├── test_extension_of_sympy_functions.py
├── test_preparser.py
└── test_algebraic_equation.py
├── algebra_with_sympy
├── version.py
├── __init__.py
├── preparser.py
└── algebraic_equation.py
├── docs
├── logo art.odg
├── resources
│ ├── short_syntax.png
│ └── simple_example.png
├── index.html
├── intro.md
└── alg_w_sympy.svg
├── Developer Testing
├── Display_Math_Operations.py
├── expression made of multiple equations.ipynb
├── how does is play with solve?.ipynb
├── DMO plus SymPy Algebra.ipynb
├── Equation_OB_ver.py
├── Test ` importing ... as ...`.ipynb
├── Importing sympy into global namespace and then extending...ipynb
└── Algebra Scratch.ipynb
├── requirements.txt
├── .gitmodules
├── dotests.sh
├── setup.py
├── pyproject.toml
├── Development Notes.md
├── algebraic_equation_ex_func_old.py
└── ReadMe.md
/tests/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/algebra_with_sympy/version.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | __version__ = "1.1.3"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/logo art.odg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy/HEAD/docs/logo art.odg
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Developer Testing/Display_Math_Operations.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | /home/jonathan/GIT/Easy_Pretty_Math/Display_Math_Operations.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/resources/short_syntax.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy/HEAD/docs/resources/short_syntax.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/requirements.txt:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # For binder
2 | sympy-for-algebra>=1.12
3 | jupyter>=1.0.0
4 | jupyterlab>=4.0.0,<5
5 | notebook>=7.0.0,<8
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/resources/simple_example.png:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy/HEAD/docs/resources/simple_example.png
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/.gitmodules:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [submodule "algebra_with_sympy/sympy"]
2 | path = algebra_with_sympy/sympy
3 | url = https://github.com/sympy/sympy.git
4 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/index.html:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
7 |
8 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/dotests.sh:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!/usr/bin/env bash
2 |
3 | echo 'Core tests:'
4 | pytest --ignore='Developer Testing' --ignore-glob='*test_preparser.py' --ignore-glob='*test_numerics.py'
5 | echo 'Doc tests:'
6 | pytest --ignore='tests' --ignore='Developer Testing' --ignore-glob='*old*' --doctest-modules
7 | echo 'Preparser and numerics tests (require ipython environment):'
8 | ipython -m pytest tests/test_preparser.py tests/test_numerics.py
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/setup.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | import setuptools
2 |
3 | # Get current script folder path so works with build
4 | import os, sys
5 | csfp = os.path.abspath(os.path.dirname(__file__))
6 | if csfp not in sys.path:
7 | sys.path.insert(0, csfp)
8 |
9 | try:
10 | from algebra_with_sympy.version import __version__
11 | # f = open('algebra_with_sympy/version.py','w')
12 | # f.write("__version__ = \"" + str(__version__) + "\"")
13 | # f.close()
14 | except Exception as e:
15 | raise RuntimeError('Unable to find __version__') from e
16 |
17 | setuptools.setup(
18 | version=__version__,
19 | )
20 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/pyproject.toml:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | [build-system]
2 | requires = ["setuptools"]
3 | build-backend = "setuptools.build_meta"
4 |
5 | [project]
6 | dynamic = ['version']
7 | name="Algebra_with_SymPy"
8 | readme = 'ReadMe.md'
9 | description="Equations that can be algebraicly manipulated."
10 | authors=[{name = "Jonathan Gutow", email="gutow@uwosh.edu"}]
11 | keywords=["symbolic algebra",
12 | "computer algebra",
13 | "CAS",
14 | "calculations with units",
15 | "sympy"
16 | ]
17 | license="GPL-3.0+"
18 | dependencies = [
19 | "sympy-for-algebra ~= 1.13"
20 | ]
21 | classifiers=[
22 | 'Development Status :: 5 - Production/Stable',
23 | 'Intended Audience :: Developers',
24 | 'Intended Audience :: Education',
25 | 'Intended Audience :: End Users/Desktop',
26 | 'Programming Language :: Python :: 3',
27 | 'Operating System :: OS Independent'
28 | ]
29 | [project.urls]
30 | Homepage = "https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/"
31 | Repository = "https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy"
32 | Issues = "https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy/issues"
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_numerics.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!ipython
2 |
3 | from algebra_with_sympy.preparser import integers_as_exact
4 | from algebra_with_sympy.algebraic_equation import set_integers_as_exact, \
5 | unset_integers_as_exact, algwsym_config
6 | from IPython import get_ipython
7 | from pytest import raises
8 |
9 | if not(get_ipython()):
10 | raise EnvironmentError('This test module file must be run in an ipython '
11 | 'environment. Use `ipython -m pytest path-to-file`.'
12 | ' To avoid running this file in a general test '
13 | 'use `pytest --ignore-glob="*test_numerics.py"`')
14 |
15 | # Set up the global config object
16 | get_ipython().user_ns['algwsym_config'] = algwsym_config
17 | def test_set_integers_as_exact():
18 | set_integers_as_exact()
19 | assert integers_as_exact in get_ipython().input_transformers_post
20 | assert algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact == True
21 |
22 | def test_integers_as_exact():
23 | from sympy.core.symbol import symbols
24 | import __main__ as userns
25 | setattr(userns, 'x', symbols('x'))
26 | setattr(userns, 'y', symbols('y'))
27 | setattr(userns, 'z', symbols('z'))
28 | lines = []
29 | lines.append('1/2*x + 0.333*x')
30 | lines.append('2/3*z + 2.0*y + ln(3*x)')
31 | result = integers_as_exact(lines)
32 | splitlines = result.split('\n')
33 | expectedlines = ['Integer (1 )/Integer (2 )*x +0.333 *x ',
34 | 'Integer (2 )/Integer (3 )*z +2.0 *y +ln (Integer (3 )*x )']
35 | for k in range(len(splitlines)):
36 | assert splitlines[k] == expectedlines[k]
37 | delattr(userns, 'x')
38 | delattr(userns, 'y')
39 | delattr(userns, 'z')
40 |
41 | def test_unset_integers_as_exact():
42 | unset_integers_as_exact()
43 | assert algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact == False
44 | assert integers_as_exact not in get_ipython().input_transformers_post
45 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/algebra_with_sympy/__init__.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | .. include:: ../ReadMe.md
3 | .. include:: ../Development Notes.md
4 | """
5 | __docformat__ = "numpy"
6 | from warnings import warn
7 | proper_sympy = True
8 | try:
9 | from sympy import Equation
10 | except ImportError:
11 | proper_sympy = False
12 | warn('You need the extended version of Sympy to use Algebra_with_Sympy. '
13 | 'Algebra_with_Sympy will not be loaded. You can use your current '
14 | 'version of Sympy without the Algebra_with_Sympy features using '
15 | 'the command `from sympy import *`. To get the extended version '
16 | 'of sympy:\n'
17 | '1. Uninstall your current version `pip uninstall sympy`.\n'
18 | '2. If sympy-for-algebra is also installed, it must be uninstalled.\n'
19 | ' `pip uninstall sympy-for-algebra`.\n'
20 | '3. (Re)install extended sympy `pip install sympy-for-algebra`.\n'
21 | 'NOTE: an update to extended sympy is usually issued soon after '
22 | 'each 1.XX.1 release of standard sympy.')
23 |
24 | if proper_sympy:
25 | from algebra_with_sympy.algebraic_equation import *
26 |
27 | # Set up numerics behaviors
28 | try:
29 | from IPython import get_ipython
30 |
31 | if get_ipython():
32 | get_ipython().input_transformers_post.append(integers_as_exact)
33 | algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = True
34 | except ModuleNotFoundError:
35 | pass
36 |
37 | from algebra_with_sympy.preparser import *
38 |
39 | # Set the output formatting defaults
40 | algwsym_config.output.show_code = False
41 | algwsym_config.output.human_text = True
42 | algwsym_config.output.label = True
43 | algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = False
44 | algwsym_config.output.latex_as_equations = False
45 |
46 | # Set version number for internal access
47 | algwsym_version = 'unknown'
48 | try:
49 | from algebra_with_sympy.version import __version__ as algwsym_version
50 | except FileNotFoundError as e:
51 | UserWarning('Could not read the version.py file. Your installation'
52 | ' of algebra_with_sympy probably did not work correctly.')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Development Notes.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Development Notes
2 | [General](#general-notes) | [Make Docs](#constructing-the-documentation) |
3 | [Running Tests](#running-tests) |
4 | [Build PyPi Package](#building-pypi-package)|
5 |
6 | ## General Notes
7 |
8 | * TODOs
9 | * Test collect when there isn't an available _eval_collect (not sure how
10 | to get there).
11 | * Test for _binary_op NotImplemented error (not sure how to get there).
12 | * To consider
13 | * Include [Sympy Plot Backends](https://sympy-plot-backends.readthedocs.io/en/latest/)
14 | in the default setup.
15 | * Change `Equation` constructor to accept `Equality`, `Set`, `List` or
16 | `lhs, rhs`, rather than just `lhs, rhs`.
17 | * Extend `.subs` to accept `.subs(a=2*c, b = sin(q), ...)`.
18 | * [MathLive](https://cortexjs.io/mathlive/) on another web page as possible
19 | input engine.
20 |
21 | ## Constructing the Documentation
22 |
23 | 1. Make sure pdoc is installed and updated in the virtual environment `pip
24 | install -U pdoc`.
25 | 2. Update any `.md` files included in `_init_.py`.
26 | * Generally URLs should be absolute, not relative.
27 | 3. At the root level run pdoc
28 | `
29 | pdoc --logo https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/alg_w_sympy.svg
30 | --logo-link https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/
31 | --footer-text "Algebra with Sympy vX.X.X" --math -html -o docs
32 | ./algebra_with_sympy
33 | `
34 | where `X.X.X` is the version number.
35 |
36 | ### Tasks for Documentation
37 |
38 | * Readme.md & Development Notes.md
39 | * Use absolute path to github pages for more examples.
40 |
41 | ## Running Tests
42 |
43 | 1. Install updated pytest in the virtual environment:
44 | ```
45 | pipenv shell
46 | pip install -U pytest
47 | ```
48 | 2. Run standard tests:
49 | `pytest --ignore='Developer Testing' --ignore-glob='*test_preparser.py'`.
50 | 3. Run preparser tests:
51 | `ipython -m pytest tests/test_preparser.py`
52 | 4. Run doctests:
53 | `pytest --ignore='tests' --ignore='Developer Testing'
54 | --ignore-glob='*old*' --doctest-modules`
55 |
56 | You can run all the tests using the dotests script: `./dotests.sh`.
57 |
58 | **NOTE**: Some warnings about invalid escape characters are expected because
59 | raw strings are being passed with specialized LaTex escaped characters.
60 |
61 | ## Building PyPi package
62 |
63 | 1. Make sure to update the version number in setup.py first.
64 | 1. Install updated setuptools and twine in the virtual environment:
65 | ```
66 | pipenv shell
67 | pip install -U setuptools wheel twine
68 | ```
69 | 1. Build the distribution `python -m build`.
70 | 1. Test it on `test.pypi.org`.
71 | 1. Upload it (you will need an account on test.pypi.org):
72 | `python -m twine upload --repository testpypi dist/*`.
73 | 1. Create a new virtual environment and test install into it:
74 | ```
75 | exit # to get out of the current environment
76 | cd
77 | mkdir
78 | cd
79 | pipenv shell #creates the new environment and enters it.
80 | pip install -i https://test.pypi.org/..... # copy actual link from the
81 | # repository on test.pypi.
82 | ```
83 | There are often install issues because sometimes only older versions of
84 | some of the required packages are available on test.pypi.org. If this
85 | is the only problem change the version to end in `rc0` for release
86 | candidate and try it on the regular pypi.org as described below for
87 | releasing on PyPi.
88 | 1. After install test by running a jupyter notebook in the virtual
89 | environment.
90 |
91 | ### Releasing on PyPi
92 |
93 | Proceed only if testing of the build is successful.
94 |
95 | 1. Double check the version number in `algebra_with_sympy/version.py`.
96 | 1. Rebuild the release: `python -m build`.
97 | 1. Upload it: `python -m twine upload dist/*`
98 | 1. Make sure it works by installing it in a clean virtual environment. This
99 | is the same as on test.pypi.org except without `-i https://test.pypy...`. If
100 | it does not work, pull the release.
101 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Developer Testing/expression made of multiple equations.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 2,
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "outputs": [],
8 | "source": [
9 | "from algebra_with_sympy import *"
10 | ]
11 | },
12 | {
13 | "cell_type": "code",
14 | "execution_count": 5,
15 | "metadata": {},
16 | "outputs": [
17 | {
18 | "name": "stdout",
19 | "output_type": "stream",
20 | "text": [
21 | "a/b = c + d (eq1)\n",
22 | "d - e = a (eq2)\n"
23 | ]
24 | }
25 | ],
26 | "source": [
27 | "var('a b c d e')\n",
28 | "eq1=Eqn(a/b, c+d)\n",
29 | "eq2 = Eqn(d-e,a)\n",
30 | "print(eq1)\n",
31 | "print(eq2)"
32 | ]
33 | },
34 | {
35 | "cell_type": "code",
36 | "execution_count": 6,
37 | "metadata": {},
38 | "outputs": [
39 | {
40 | "data": {
41 | "text/latex": [
42 | "$\\displaystyle \\frac{a}{b} - d + e=- a + c + d$"
43 | ],
44 | "text/plain": [
45 | "Equation(a/b - d + e, -a + c + d)"
46 | ]
47 | },
48 | "execution_count": 6,
49 | "metadata": {},
50 | "output_type": "execute_result"
51 | }
52 | ],
53 | "source": [
54 | "(eq1-eq2)"
55 | ]
56 | },
57 | {
58 | "cell_type": "code",
59 | "execution_count": 7,
60 | "metadata": {},
61 | "outputs": [
62 | {
63 | "data": {
64 | "text/latex": [
65 | "$\\displaystyle \\frac{a}{b} - d + e$"
66 | ],
67 | "text/plain": [
68 | "a/b - d + e"
69 | ]
70 | },
71 | "execution_count": 7,
72 | "metadata": {},
73 | "output_type": "execute_result"
74 | }
75 | ],
76 | "source": [
77 | "(eq1-eq2).lhs"
78 | ]
79 | },
80 | {
81 | "cell_type": "code",
82 | "execution_count": 8,
83 | "metadata": {},
84 | "outputs": [
85 | {
86 | "data": {
87 | "text/latex": [
88 | "$\\displaystyle - a + c + d$"
89 | ],
90 | "text/plain": [
91 | "-a + c + d"
92 | ]
93 | },
94 | "execution_count": 8,
95 | "metadata": {},
96 | "output_type": "execute_result"
97 | }
98 | ],
99 | "source": [
100 | "(eq1-eq2).rhs"
101 | ]
102 | },
103 | {
104 | "cell_type": "code",
105 | "execution_count": 9,
106 | "metadata": {},
107 | "outputs": [
108 | {
109 | "data": {
110 | "text/latex": [
111 | "$\\displaystyle \\frac{a \\left(d - e\\right)}{b}=a \\left(c + d\\right)$"
112 | ],
113 | "text/plain": [
114 | "Equation(a*(d - e)/b, a*(c + d))"
115 | ]
116 | },
117 | "execution_count": 9,
118 | "metadata": {},
119 | "output_type": "execute_result"
120 | }
121 | ],
122 | "source": [
123 | "eq1*eq2"
124 | ]
125 | },
126 | {
127 | "cell_type": "code",
128 | "execution_count": 10,
129 | "metadata": {},
130 | "outputs": [
131 | {
132 | "data": {
133 | "text/latex": [
134 | "$\\displaystyle \\frac{a}{b \\left(d - e\\right)}=\\frac{c + d}{a}$"
135 | ],
136 | "text/plain": [
137 | "Equation(a/(b*(d - e)), (c + d)/a)"
138 | ]
139 | },
140 | "execution_count": 10,
141 | "metadata": {},
142 | "output_type": "execute_result"
143 | }
144 | ],
145 | "source": [
146 | "eq1/eq2"
147 | ]
148 | },
149 | {
150 | "cell_type": "code",
151 | "execution_count": 14,
152 | "metadata": {},
153 | "outputs": [
154 | {
155 | "data": {
156 | "text/latex": [
157 | "$\\displaystyle \\text{False}$"
158 | ],
159 | "text/plain": [
160 | "False"
161 | ]
162 | },
163 | "execution_count": 14,
164 | "metadata": {},
165 | "output_type": "execute_result"
166 | }
167 | ],
168 | "source": [
169 | "Eqn(1,2).check()"
170 | ]
171 | },
172 | {
173 | "cell_type": "code",
174 | "execution_count": null,
175 | "metadata": {},
176 | "outputs": [],
177 | "source": []
178 | }
179 | ],
180 | "metadata": {
181 | "kernelspec": {
182 | "display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
183 | "language": "python",
184 | "name": "python3"
185 | },
186 | "language_info": {
187 | "codemirror_mode": {
188 | "name": "ipython",
189 | "version": 3
190 | },
191 | "file_extension": ".py",
192 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
193 | "name": "python",
194 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
195 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
196 | "version": "3.10.4"
197 | }
198 | },
199 | "nbformat": 4,
200 | "nbformat_minor": 4
201 | }
202 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_extension_of_sympy_functions.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from pytest import raises
2 | from sympy import functions, FunctionClass, symbols
3 | from sympy import Equation
4 | import importlib
5 |
6 | #####
7 | # Testing that sympy functions work with Equations
8 | #####
9 |
10 | # Overridden elsewhere
11 | _extended_ = ('sqrt', 'cbrt', 'root')
12 |
13 | # Either not applicable to Equations or have not yet figured out a way
14 | # to systematically apply to an Equation.
15 | # TODO examine these more carefully (top priority: real_root, Ynm_c).
16 | _not_applicable_to_equations_ = ('Min', 'Max', 'Id', 'real_root',
17 | 'unbranched_argument', 'polarify', 'unpolarify',
18 | 'piecewise_fold', 'E1', 'Eijk', 'bspline_basis',
19 | 'bspline_basis_set', 'interpolating_spline', 'jn_zeros',
20 | 'jacobi_normalized', 'Ynm_c', 'piecewise_exclusive', 'Piecewise',
21 | 'motzkin', 'hyper','meijerg', 'chebyshevu_root', 'chebyshevt_root',
22 | 'betainc_regularized')
23 | _skip_ = _extended_ + _not_applicable_to_equations_
24 |
25 | temp = importlib.import_module('sympy', package=functions)
26 | for func in functions.__all__:
27 | globals()[func] = getattr(temp, func)
28 |
29 | # Needed for some tests so that extended functions are in the correct
30 | # namespace.
31 | for func in _extended_:
32 | globals()[func] = getattr(temp, func)
33 |
34 |
35 | def test_sympy_import():
36 | for func in functions.__all__:
37 | if func not in _skip_:
38 | assert(str(func) in globals())
39 | assert(isinstance(globals()[func],FunctionClass))
40 | pass
41 |
42 |
43 | def test_functions_extensions():
44 | from inspect import signature
45 | failures = []
46 | a, b , c = symbols('a b c')
47 | eq = Equation(a, b/c)
48 | n = symbols('n', positive = True, integer = True)
49 | for func in functions.__all__:
50 | if func not in _skip_ or func in _extended_:
51 | obj = globals()[func]
52 | sig = signature(obj).parameters
53 | if func == 'betainc' or func == 'betainc_regularized':
54 | # The signature is undefined need 4 complex numbers:
55 | # a, b, x1, x2.
56 | sig = {'arg1':'a','arg2':'b','arg3':'x1','arg4':'x2'}
57 | keylist = [key for key in sig]
58 | tempargs = [eq]
59 | largs = [eq.lhs]
60 | rargs = [eq.rhs]
61 | for key in sig:
62 | if (str(sig[key]).find("="))==-1 and (str(sig[key]).
63 | find("**"))==-1 and key != keylist[0]:
64 | tempargs.append(n)
65 | largs.append(n)
66 | rargs.append(n)
67 | try:
68 | tst = obj(*tempargs)
69 | if not (tst == Equation(obj(*largs),obj(*rargs))):
70 | failures.append(func + ' extended but did not work.')
71 | except Exception as e:
72 | failures.append(str(func) +': '+str(e))
73 | assert(failures == [])
74 | pass
75 |
76 | def test_functions_extensions_eqn_not_arg1():
77 | from inspect import signature
78 | failures = []
79 | a, b , c = symbols('a b c')
80 | eq = Equation(a, b/c)
81 | n = symbols('n', positive = True, integer = True)
82 | for func in functions.__all__:
83 | if func not in _skip_ or func in _extended_:
84 | obj = globals()[func]
85 | sig = signature(obj).parameters
86 | if func == 'betainc' or func == 'betainc_regularized':
87 | # The signature is undefined need 4 complex numbers:
88 | # a, b, x1, x2.
89 | sig = {'arg1':'a','arg2':'b','arg3':'x1','arg4':'x2'}
90 | keylist = [key for key in sig]
91 | for j in range(1, len(sig)):
92 | tempargs = [n]
93 | largs = [n]
94 | rargs = [n]
95 | for k in range(1,len(sig)):
96 | if ((str(sig[keylist[k]]).find("=")) == -1 and
97 | (str(sig[keylist[k]]).find("**")) == -1):
98 | if k == j:
99 | tempargs.append(eq)
100 | largs.append(eq.lhs)
101 | rargs.append(eq.rhs)
102 | else:
103 | tempargs.append(n)
104 | largs.append(n)
105 | rargs.append(n)
106 | try:
107 | tst = obj(*tempargs)
108 | if (isinstance(tst, Equation) and not
109 | (tst == Equation(obj(*largs), obj(*rargs)))):
110 | failures.append(func + '('+str(*tempargs)+ ') ' \
111 | 'extended but did not work.')
112 | except Exception as e:
113 | failures.append(str(func) +': '+str(e))
114 | assert(failures == [])
115 | pass
116 |
117 | def test_two_eqn():
118 | a, b, c = symbols('a b c')
119 | eq = Equation(a, b / c)
120 | obj = globals()['besselj']
121 | raises(NotImplementedError, lambda: obj(eq,eq))
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Developer Testing/how does is play with solve?.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "outputs": [],
8 | "source": [
9 | "from algebraic_equation import *"
10 | ]
11 | },
12 | {
13 | "cell_type": "code",
14 | "execution_count": 2,
15 | "metadata": {},
16 | "outputs": [
17 | {
18 | "data": {
19 | "text/latex": [
20 | "$\\displaystyle a=\\frac{b}{c}$"
21 | ],
22 | "text/plain": [
23 | "a=b/c"
24 | ]
25 | },
26 | "execution_count": 2,
27 | "metadata": {},
28 | "output_type": "execute_result"
29 | }
30 | ],
31 | "source": [
32 | "var('a b c')\n",
33 | "t=equ(a, b/c)\n",
34 | "t"
35 | ]
36 | },
37 | {
38 | "cell_type": "code",
39 | "execution_count": 3,
40 | "metadata": {},
41 | "outputs": [
42 | {
43 | "data": {
44 | "text/plain": [
45 | "[]"
46 | ]
47 | },
48 | "execution_count": 3,
49 | "metadata": {},
50 | "output_type": "execute_result"
51 | }
52 | ],
53 | "source": [
54 | "solve(t,b)"
55 | ]
56 | },
57 | {
58 | "cell_type": "code",
59 | "execution_count": 4,
60 | "metadata": {},
61 | "outputs": [
62 | {
63 | "data": {
64 | "text/plain": [
65 | ""
66 | ]
67 | },
68 | "execution_count": 4,
69 | "metadata": {},
70 | "output_type": "execute_result"
71 | }
72 | ],
73 | "source": [
74 | "solve"
75 | ]
76 | },
77 | {
78 | "cell_type": "code",
79 | "execution_count": 5,
80 | "metadata": {},
81 | "outputs": [
82 | {
83 | "data": {
84 | "text/latex": [
85 | "$\\displaystyle a$"
86 | ],
87 | "text/plain": [
88 | "a"
89 | ]
90 | },
91 | "execution_count": 5,
92 | "metadata": {},
93 | "output_type": "execute_result"
94 | }
95 | ],
96 | "source": [
97 | "t.lhs"
98 | ]
99 | },
100 | {
101 | "cell_type": "code",
102 | "execution_count": 6,
103 | "metadata": {},
104 | "outputs": [
105 | {
106 | "data": {
107 | "text/latex": [
108 | "$\\displaystyle \\frac{b}{c}$"
109 | ],
110 | "text/plain": [
111 | "b/c"
112 | ]
113 | },
114 | "execution_count": 6,
115 | "metadata": {},
116 | "output_type": "execute_result"
117 | }
118 | ],
119 | "source": [
120 | "t.rhs"
121 | ]
122 | },
123 | {
124 | "cell_type": "code",
125 | "execution_count": 7,
126 | "metadata": {},
127 | "outputs": [
128 | {
129 | "name": "stdout",
130 | "output_type": "stream",
131 | "text": [
132 | "a - b/c=0\n",
133 | "a - b/c=0\n"
134 | ]
135 | },
136 | {
137 | "data": {
138 | "text/plain": [
139 | "[b/a]"
140 | ]
141 | },
142 | "execution_count": 7,
143 | "metadata": {},
144 | "output_type": "execute_result"
145 | }
146 | ],
147 | "source": [
148 | "t2=t-t.rhs\n",
149 | "print(t2)\n",
150 | "pretty_print(t2)\n",
151 | "solve(t2.lhs,c)"
152 | ]
153 | },
154 | {
155 | "cell_type": "code",
156 | "execution_count": 8,
157 | "metadata": {},
158 | "outputs": [
159 | {
160 | "data": {
161 | "text/plain": [
162 | "[]"
163 | ]
164 | },
165 | "execution_count": 8,
166 | "metadata": {},
167 | "output_type": "execute_result"
168 | }
169 | ],
170 | "source": [
171 | "solve(t-t.rhs,c)"
172 | ]
173 | },
174 | {
175 | "cell_type": "code",
176 | "execution_count": 9,
177 | "metadata": {},
178 | "outputs": [
179 | {
180 | "data": {
181 | "text/plain": [
182 | "[b/a]"
183 | ]
184 | },
185 | "execution_count": 9,
186 | "metadata": {},
187 | "output_type": "execute_result"
188 | }
189 | ],
190 | "source": [
191 | "solve((t-t.rhs).lhs,c)"
192 | ]
193 | },
194 | {
195 | "cell_type": "code",
196 | "execution_count": 10,
197 | "metadata": {},
198 | "outputs": [
199 | {
200 | "data": {
201 | "text/latex": [
202 | "$\\displaystyle a - \\frac{b}{c}=0$"
203 | ],
204 | "text/plain": [
205 | "a - b/c=0"
206 | ]
207 | },
208 | "execution_count": 10,
209 | "metadata": {},
210 | "output_type": "execute_result"
211 | }
212 | ],
213 | "source": [
214 | "t2"
215 | ]
216 | },
217 | {
218 | "cell_type": "code",
219 | "execution_count": 14,
220 | "metadata": {},
221 | "outputs": [],
222 | "source": [
223 | "Equation?"
224 | ]
225 | },
226 | {
227 | "cell_type": "code",
228 | "execution_count": null,
229 | "metadata": {},
230 | "outputs": [],
231 | "source": []
232 | }
233 | ],
234 | "metadata": {
235 | "kernelspec": {
236 | "display_name": "Python 3",
237 | "language": "python",
238 | "name": "python3"
239 | },
240 | "language_info": {
241 | "codemirror_mode": {
242 | "name": "ipython",
243 | "version": 3
244 | },
245 | "file_extension": ".py",
246 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
247 | "name": "python",
248 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
249 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
250 | "version": "3.6.9"
251 | }
252 | },
253 | "nbformat": 4,
254 | "nbformat_minor": 4
255 | }
256 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_preparser.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | #!ipython
2 | from algebra_with_sympy.preparser import algebra_with_sympy_preparser as parser
3 | from algebra_with_sympy.preparser import integers_as_exact, toIntegerInSympyExpr
4 | from IPython import get_ipython
5 | from pytest import raises
6 |
7 | if not(get_ipython()):
8 | raise EnvironmentError('This test module file must be run in an ipython '
9 | 'environment. Use `ipython -m pytest path-to-file`.'
10 | ' To avoid running this file in a general test '
11 | 'use `pytest --ignore-glob="*testpreparser.py"`')
12 |
13 | def test_install_preparser():
14 | assert(get_ipython())
15 | get_ipython().input_transformers_post.append(parser)
16 |
17 | def test_parsing():
18 | lines = []
19 | expected_out = []
20 | lines.append('# A comment.\n')
21 | expected_out.append('# A comment.\n')
22 | assert parser(lines) == expected_out
23 | lines.append('eq1 =@ a + b = c/d\n')
24 | expected_out.append('eq1 = Eqn( a + b , c/d)\n')
25 | assert parser(lines) == expected_out
26 | lines.append('obj?\n')
27 | expected_out.append('obj?\n')
28 | assert parser(lines) == expected_out
29 | lines.append('eq1 =@a + b=c/d\n')
30 | expected_out.append('eq1 = Eqn(a + b,c/d)\n')
31 | assert parser(lines) == expected_out
32 | lines.append('tst = (a\n')
33 | expected_out.append('tst = (a\n')
34 | lines.append(' +b)\n')
35 | expected_out.append(' +b)\n')
36 | assert parser(lines) == expected_out
37 | lines.append('@property\n')
38 | expected_out.append('@property\n')
39 | assert parser(lines) == expected_out
40 | lines.append('\n')
41 | expected_out.append('\n')
42 | assert parser(lines) == expected_out
43 | lines.append('eq1 =@ a + b = c/d # A trailing comment\n')
44 | expected_out.append('eq1 = Eqn( a + b , c/d )\n')
45 | assert parser(lines) == expected_out
46 |
47 | def test_parsing_errors():
48 | lines = []
49 | expected_out = []
50 | lines.append('# A comment.\n')
51 | expected_out.append('# A comment.\n')
52 | assert parser(lines) == expected_out
53 | lines.append('eq1 =@ a + b > c/d\n')
54 | raises(ValueError, lambda: parser(lines))
55 |
56 | def test_toIntegerInSympyExpr():
57 | from sympy.core.symbol import symbols
58 | import __main__ as userns
59 | setattr(userns,'a', symbols('a'))
60 | setattr(userns, 'b', symbols('b'))
61 | setattr(userns, 'c', symbols('c'))
62 | setattr(userns, 'x', symbols('x'))
63 | tststr ='z, d = symbols(\'z d\')\n'
64 | tststr +='DG = Symbol(r"\Delta G")\n'
65 | tststr += 'units("kg m s")\n'
66 | tststr += 'eq1 = Eqn(a*x**2 + b*x + c,\n'
67 | tststr += '0)\n'
68 | tststr += 's = 2*m/(3*s)\n'
69 | tststr += 'o = z+2/3*d\n'
70 | tststr += 'p = 2\n'
71 | tststr += 'n = 3.0\n'
72 | tststr += 'r = 2/3*p\n'
73 | tststr += 'l = 3*p + 3/4*d\n'
74 | tststr += 'k = 3*p + 3/4*n\n'
75 | tststr += 'y = [1, 2.0, 4, 5.6]\n'
76 | tststr += 'f = DG*5/2 + s\n'
77 | resultstr = 'z ,d =symbols (\'z d\')\n'
78 | resultstr += 'DG =Symbol (r"\Delta G")\n'
79 | resultstr += 'units ("kg m s")\n'
80 | resultstr += 'eq1 =Eqn (a *x **Integer (2 )+b *x +c ,\n'
81 | resultstr += 'Integer (0 ))\n'
82 | resultstr += 's =Integer (2 )*m /(Integer (3 )*s )\n'
83 | resultstr += 'o =z +Integer (2 )/Integer (3 )*d \n'
84 | resultstr += 'p =2 \n'
85 | resultstr += 'n =3.0 \n'
86 | resultstr += 'r =2 /3 *p \n'
87 | resultstr += 'l =Integer (3 )*p +Integer (3 )/Integer (4 )*d \n'
88 | resultstr += 'k =3 *p +3 /4 *n \n'
89 | resultstr += 'y =[1 ,2.0 ,4 ,5.6 ]\n'
90 | resultstr += 'f =DG *Integer (5 )/Integer (2 )+s \n'
91 | assert toIntegerInSympyExpr(tststr) == resultstr
92 | # Something with no sympy in it and indentation.
93 | tststr = '# Arbitrary functions can operate on both sides of an equation '
94 | tststr += 'using\n'
95 | tststr += '# .apply(funcname, *args, **kwargs))\n\n'
96 | tststr += 'def addsquare(expr):\n'
97 | tststr += ' return expr+expr**2\n\n'
98 | tststr += 'f2.apply(addsquare)'
99 | resultstr = '# Arbitrary functions can operate on both sides of an '
100 | resultstr +='equation using\n'
101 | resultstr += '# .apply(funcname, *args, **kwargs))\n\n'
102 | resultstr += 'def addsquare (expr ):\n'
103 | resultstr += ' return expr +expr **2 \n\n'
104 | resultstr += 'f2 .apply (addsquare )'
105 | print(toIntegerInSympyExpr(tststr))
106 | assert toIntegerInSympyExpr(tststr) == resultstr
107 | #cleanup
108 | delattr(userns,'a')
109 | delattr(userns, 'b')
110 | delattr(userns, 'c')
111 | delattr(userns, 'x')
112 |
113 | def test_integers_as_exact():
114 | from sympy.core.symbol import symbols
115 | import __main__ as userns
116 | setattr(userns, 'x', symbols('x'))
117 | setattr(userns, 'y', symbols('y'))
118 | setattr(userns, 'z', symbols('z'))
119 | lines = []
120 | lines.append('1/2*x + 0.333*x')
121 | lines.append('2/3*z + 2.0*y + ln(3*x)')
122 | result = integers_as_exact(lines)
123 | splitlines = result.split('\n')
124 | expectedlines = ['Integer (1 )/Integer (2 )*x +0.333 *x ',
125 | 'Integer (2 )/Integer (3 )*z +2.0 *y +ln (Integer (3 )*x )']
126 | for k in range(len(splitlines)):
127 | assert splitlines[k] == expectedlines[k]
128 | delattr(userns, 'x')
129 | delattr(userns, 'y')
130 | delattr(userns, 'z')
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/intro.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | ## Algebraic Equations with SymPy
2 |
3 | [Introduction](#introduction) | [Output Formatting](#controlling-the-format-of-interactive-outputs)
4 | | [Installation](#setupinstallation) |
5 | [Try Live](#try-in-binder) | [Issues or Comments](#issues-or-comments) |
6 | [Change Log](#change-log) |
7 | [License](#this-software-is-distributed-under-the-gnu-v3-licensehttpsgnuorglicenses)
8 | | [GIT Repository](https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy)
9 | | [PyPi Link](https://pypi.org/project/Algebra-with-SymPy/)
10 |
11 | #### [Website/Documentation (including API)](https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/)
12 |
13 | #### Introduction
14 |
15 | This tool defines relations that all high school and college students would
16 | recognize as mathematical equations.
17 | They consist of a left hand side (lhs) and a right hand side (rhs) connected by
18 | the relation operator "=".
19 |
20 | This tool applies operations to both sides of the equation simultaneously, just
21 | as students are taught to do when
22 | attempting to isolate (solve for) a variable. Thus the statement `Equation/b`
23 | yields a new equation `Equation.lhs/b = Equation.rhs/b`
24 |
25 | The intent is to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to rearrange
26 | equations and perform algebra
27 | in a stepwise fashion using as close to standard mathematical notation as
28 | possible. In this way more people can successfully perform
29 | algebraic rearrangements without stumbling
30 | over missed details such as a negative sign.
31 |
32 | A simple example as it would appear in a [Jupyter](https://jupyter.org)
33 | notebook is shown immediately below:
34 |
35 | 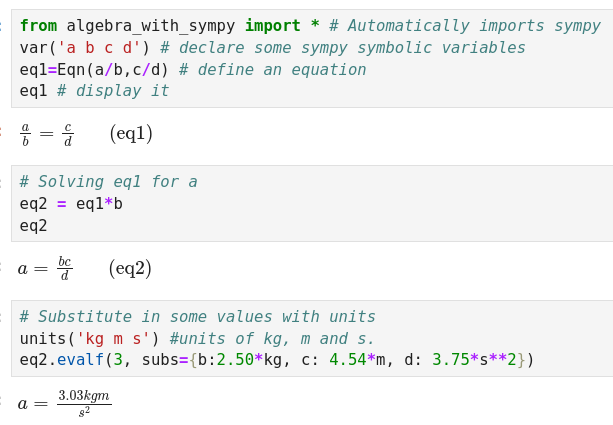
36 |
37 | Once the algebra is complete it is possible to substitute numbers with
38 | units into the solved equation to calculate a numerical solution with
39 | proper units.
40 |
41 | In IPython environments (IPython and Jupyter) there is also a shorthand
42 | syntax for entering equations provided through the IPython preparser. An
43 | equation can be specified as `eq1 =@ a/b = c/d`. If no Python name is
44 | specified for the equation (`eq1` left out in the previous example), the
45 | equation will still
46 | be defined, but will not be easily accessible for further computation. The
47 | `=@` symbol combination was chosen to avoid conflicts with reserved python
48 | symbols while minimizing impacts on syntax highlighting and autoformatting. A
49 | screenshot of an example in Jupyter is shown immediately below:
50 |
51 | 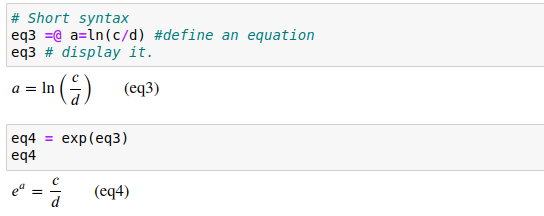
52 |
53 | [More examples of the capabilities of Algebra with Sympy are
54 | here](https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/Demonstration%20of%20equation%20class.html).
55 |
56 | Many math packages such as [SageMath](https://www.sagemath.org/)
57 | and [Maxima](http://maxima.sourceforge.net/) have similar capabilities,
58 | but require more knowledge of command syntax, plus they cannot easily be
59 | installed in a generic python environment.
60 |
61 | #### Controlling the Format of Interactive Outputs
62 |
63 | * **In graphical environments (Jupyter)** you will get rendered Latex such as
64 | $\frac{a}{b} = \frac{c}{d}$. To also see the code representation (what can
65 | be copied and pasted for
66 | additional computation) set `algwsym_config.output.show_code = True`.
67 | This will print the code version (e.g. `Equation(a,b/c)`) of the equation as
68 | well. This code version can be accessed directly by calling `repr()` on the
69 | equation.
70 |
71 | * **In interactive text environments (ipython and command line)** the
72 | representation (code version) is returned by default. Calling `print()`
73 | or `str()` on an equation will return the human readable version with an
74 | equals sign. To have the human readable version returned by default set
75 | `algwsym_config.output.human_text = True`. If combined with
76 | `algwsym_config.output.show_code = True`, both code and human readable
77 | versions will be shown.
78 |
79 | * **The equation label** can be turned off by setting
80 | `algwsym_config.output.label = False`.
81 |
82 | #### Setup/Installation
83 |
84 | 1. Use pip to install in your python environment:
85 | `pip install -U Algebra-with-SymPy`
86 | 2. To use in a running python session issue
87 | the following command : `from algebra_with_sympy import *`.
88 | This will also import the SymPy tools.
89 | 3. If you want to isolate this tool from the global namespace you are
90 | working with change the import statement
91 | to `import algebra_with_sympy as spa`, where
92 | `spa` stands for "SymPy Algebra". Then all calls would be made to `
93 | spa.funcname()`.
94 |
95 | #### Try in binder
96 |
97 | [](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy.git/master/?filepath=Demonstration%20of%20equation%20class.ipynb)
98 |
99 | #### Issues or Comments
100 |
101 | * Issues and bug reports should be [filed on
102 | github](https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy/issues).
103 | * Comments, questions, show and tell, etc. should go in the [project
104 | discussions](https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy/discussions).
105 |
106 | #### Change Log
107 |
108 | * 0.9.3
109 | * Added check for new enough version of IPython to use the preparser.
110 | * If IPython version too old issue, warning and do not accept `=@` shorthand.
111 | * 0.9.2
112 | * `=@` shorthand syntax for defining equations in IPython compatible
113 | environments.
114 | * Fixed bug where `root()` override called `sqrt()` on bare expressions.
115 | * 0.9.1
116 | * Equations labeled with their python name, if they have one.
117 | * Added flags to adjust human readable output and equation labeling.
118 | * Accept equation as function argument in any position.
119 | * First pass at `solve()` accepting equations.
120 | * Added override of `root()` to avoid warning messages.
121 | * More unit tests.
122 | * First pass at documentation.
123 | * 0.9.0 functionality equivalent to extension of SymPy in
124 | [PR#21333](https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/21333).
125 |
126 | ##### [This software is distributed under the GNU V3 license](https://gnu.org/licenses)
127 |
128 | This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
129 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
130 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
131 | (at your option) any later version.
132 | This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
133 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
134 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
135 | GNU General Public License for more details.
136 |
137 | Copyright - Jonathan Gutow 2021, 2022
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/algebra_with_sympy/preparser.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | def algebra_with_sympy_preparser(lines):
2 | """
3 | In IPython compatible environments (Jupyter, IPython, etc...) this supports
4 | a special compact input method for equations.
5 |
6 | The syntax supported is `equation_name =@ equation.lhs = equation.rhs`,
7 | where `equation_name` is a valid Python name that can be used to refer to
8 | the equation later. `equation.lhs` is the left-hand side of the equation
9 | and `equation.rhs` is the right-hand side of the equation. Each side of the
10 | equation must parse into a valid Sympy expression.
11 |
12 | **Note**: This does not support line continuation. Long equations should be
13 | built by combining expressions using names short enough to do this on one
14 | line. The alternative is to use `equation_name = Eqn(long ...
15 | expressions ... with ... multiple ... lines)`.
16 |
17 | **Note**: If the `equation_name` is omitted the equation will be formed,
18 | but it will not be assigned to a name that can be used to refer to it
19 | later. You may be able to access it through one of the special IPython
20 | underscore names. This is not recommended.
21 |
22 | **THIS FUNCTION IS USED BY THE IPYTHON ENVIRONMENT TO PREPARSE THE INPUT
23 | BEFORE IT IS PASSED TO THE PYTHON INTERPRETER. IT IS NOT MEANT TO BE USED
24 | DIRECTLY BY A USER**
25 | """
26 | new_lines = []
27 | if isinstance(lines,str):
28 | lines = [lines]
29 | for k in lines:
30 | if '=@' in k:
31 | drop_comments = k.split('#')
32 | to_rephrase = ''
33 | if len(drop_comments) > 2:
34 | for i in range(len(drop_comments)-1):
35 | to_rephrase += drop_comments[i]
36 | else:
37 | to_rephrase = drop_comments[0]
38 | linesplit = to_rephrase.split('=@')
39 | eqsplit = linesplit[1].split('=')
40 | if len(eqsplit)!=2:
41 | raise ValueError('The two sides of the equation must be' \
42 | ' separated by an \"=\" sign when using' \
43 | ' the \"=@\" special input method.')
44 | templine =''
45 | if eqsplit[0]!='' and eqsplit[1]!='':
46 | if eqsplit[1].endswith('\n'):
47 | eqsplit[1] = eqsplit[1][:-1]
48 | if linesplit[0]!='':
49 | templine = str(linesplit[0])+'= Eqn('+str(eqsplit[0])+',' \
50 | ''+str(eqsplit[1])+')\n'
51 | else:
52 | templine = 'Eqn('+str(eqsplit[0])+','+str(eqsplit[1])+')\n'
53 | new_lines.append(templine)
54 | else:
55 | new_lines.append(k)
56 | return new_lines
57 |
58 |
59 | def toIntegerInSympyExpr(string):
60 | """ This function takes a string of valid Python and wraps integers within Sympy expressions
61 | in `sympy.Integer()` to make them Sympy integers rather than Python `Int()`. The
62 | advantage of this is that calculations with `Integer()` types can be exact. This function
63 | is careful not to wrap `Int()` types that are not part of Sympy expressions, making it
64 | possible for this functionality to exist with operations (e.g. array and numpy indexing)
65 | that are not compatible with the `Integer()` type.
66 | """
67 | from tokenize import generate_tokens, NEWLINE, OP, untokenize
68 | from io import StringIO
69 | ###
70 | # Internally used functions
71 | ###
72 | def isSympy(tokens, newSymObj):
73 | """ Checks list of tokens to see if it contains a Sympy Object
74 |
75 | Parameters
76 | ==========
77 | tokens:list of tokens.
78 | newSymObj:list of string names of Sympy objects that have been declared
79 | in the current script/string being parsed.
80 | """
81 | from sympy import Basic
82 | from tokenize import NAME
83 | import __main__ as user_ns
84 | # print(dir(user_ns))
85 | sympy_obj = False
86 | for kind, string, start, end, line in tokens:
87 | if kind == NAME:
88 | # print('Checking: '+str(string))
89 | if hasattr(user_ns, string):
90 | if isinstance(getattr(user_ns, string), Basic):
91 | sympy_obj = True
92 | if string in newSymObj:
93 | sympy_obj = True
94 | return sympy_obj
95 |
96 | def toSympInteger(tokens):
97 | from tokenize import NUMBER, OP, NAME
98 | result = []
99 | for k in tokens:
100 | if k[0] != NUMBER:
101 | result.append((k[0], k[1]))
102 | else:
103 | if '.' in k[1] or 'j' in k[1].lower() or 'e' in k[1].lower():
104 | result.append((k[0], k[1]))
105 | else:
106 | result.extend([
107 | (NAME, 'Integer'),
108 | (OP, '('),
109 | (NUMBER, k[1]),
110 | (OP, ')')
111 | ])
112 | return result
113 |
114 | def checkforSymObjDecl(token):
115 | import re
116 | from tokenize import NAME
117 | syms = []
118 | for kind, string, start, end, line in token:
119 | if kind == NAME:
120 | if string == 'var':
121 | match = re.search(r'\".*?\"|\'.*?\'', line)
122 | if (match):
123 | syms = match.group().replace('\"', '').replace('\'',
124 | '').split(
125 | ' ')
126 | if string == 'units':
127 | match = re.search(r'\".*?\"|\'.*?\'', line)
128 | if (match):
129 | syms = match.group().replace('\"', '').replace('\'',
130 | '').split(
131 | ' ')
132 | if string == 'symbols':
133 | parts = line.split('=')
134 | syms = parts[0].replace(' ', '').split(',')
135 | if string == 'Symbol':
136 | parts = line.split('=')
137 | syms = parts[0].replace(' ', '').split(',')
138 | return syms
139 |
140 | ###
141 | # The parsing and substitution.
142 | ###
143 | g = generate_tokens(StringIO(string).readline)
144 | declaredSymObj = []
145 | result = []
146 | temptokens = []
147 | openleft = 0
148 | for k in g:
149 | declaredSymObj.extend(checkforSymObjDecl([k]))
150 | temptokens.append(k)
151 | if k[0] == OP and k[1] == '(':
152 | openleft += 1
153 | if k[0] == OP and k[1] == ')':
154 | openleft -= 1
155 | if k[0] == NEWLINE and openleft == 0:
156 | # This is where we check for sympy objects and replace int() with Integer()
157 | hasSympyObj = isSympy(temptokens, declaredSymObj)
158 | if hasSympyObj:
159 | converted = toSympInteger(temptokens)
160 | result.extend(converted)
161 | else:
162 | for j in temptokens:
163 | result.append((j[0],j[1]))
164 | temptokens = []
165 | return untokenize(result)
166 |
167 | def integers_as_exact(lines):
168 | """This preparser uses `sympy.interactive.session.int_to_Integer` to
169 | convert numbers without decimal points into sympy integers so that math
170 | on them will be exact rather than defaulting to floating point. **This
171 | should not be called directly by the user. It is plugged into the
172 | IPython preparsing sequence when the feature is requested.** The default for
173 | Algebra_with_sympy is to use this preparser. This can be turned on and
174 | off using the Algebra_with_sympy functions:
175 | * `set_integers_as_exact()`
176 | * `unset_integers_as_exact()`
177 | NOTE: This option does not work in plain vanilla Python sessions. You
178 | must be running in an IPython environment (Jupyter, Notebook, Colab,
179 | etc...).
180 | """
181 | #from sympy.interactive.session import int_to_Integer
182 | string = ''
183 | for k in lines:
184 | string += k + '\n'
185 | string = string[:-1] # remove the last '\n'
186 | return toIntegerInSympyExpr(string)
187 | try:
188 | from IPython import get_ipython
189 | if get_ipython():
190 | if hasattr(get_ipython(),'input_transformers_cleanup'):
191 | get_ipython().input_transformers_post.\
192 | append(algebra_with_sympy_preparser)
193 | else:
194 | import warnings
195 | warnings.warn('Compact equation input unavailable.\nYou will have ' \
196 | 'to use the form "eq1 = Eqn(lhs,rhs)" instead of ' \
197 | '"eq1=@lhs=rhs".\nIt appears you are running an ' \
198 | 'outdated version of IPython.\nTo fix, update IPython ' \
199 | 'using "pip install -U IPython".')
200 | except ModuleNotFoundError:
201 | pass
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Developer Testing/DMO plus SymPy Algebra.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "markdown",
5 | "metadata": {},
6 | "source": [
7 | "# Test of combining Equation class and DMO"
8 | ]
9 | },
10 | {
11 | "cell_type": "code",
12 | "execution_count": 1,
13 | "metadata": {},
14 | "outputs": [
15 | {
16 | "name": "stdout",
17 | "output_type": "stream",
18 | "text": [
19 | "Algebraic equations and Sympy successfully imported.\n",
20 | "Automatic typesetting of output disabled so output code can be copied into code cells.\n",
21 | " To enable automatic typesetting of output issue the command `init_printing(pretty_print=True)`.\n",
22 | "Automatic display of math operation activated for `dmo aware` operations.\n"
23 | ]
24 | }
25 | ],
26 | "source": [
27 | "from Display_Math_Operations import *"
28 | ]
29 | },
30 | {
31 | "cell_type": "code",
32 | "execution_count": 2,
33 | "metadata": {},
34 | "outputs": [
35 | {
36 | "data": {
37 | "text/html": [
38 | "$$t\\equiv a c=\\frac{b^{2}}{c}$$"
39 | ],
40 | "text/plain": [
41 | ""
42 | ]
43 | },
44 | "metadata": {},
45 | "output_type": "display_data"
46 | }
47 | ],
48 | "source": [
49 | "var('a b c')\n",
50 | "dmo(t=Eqn(a*c,b**2/c))"
51 | ]
52 | },
53 | {
54 | "cell_type": "code",
55 | "execution_count": 3,
56 | "metadata": {},
57 | "outputs": [
58 | {
59 | "data": {
60 | "text/plain": [
61 | "a=b**2/c**2"
62 | ]
63 | },
64 | "execution_count": 3,
65 | "metadata": {},
66 | "output_type": "execute_result"
67 | }
68 | ],
69 | "source": [
70 | "t/c"
71 | ]
72 | },
73 | {
74 | "cell_type": "code",
75 | "execution_count": 4,
76 | "metadata": {},
77 | "outputs": [
78 | {
79 | "data": {
80 | "text/html": [
81 | "$$a=\\frac{b^{2}}{c^{2}}$$"
82 | ],
83 | "text/plain": [
84 | ""
85 | ]
86 | },
87 | "metadata": {},
88 | "output_type": "display_data"
89 | }
90 | ],
91 | "source": [
92 | "dmo(t/c)"
93 | ]
94 | },
95 | {
96 | "cell_type": "code",
97 | "execution_count": 5,
98 | "metadata": {},
99 | "outputs": [
100 | {
101 | "data": {
102 | "text/plain": [
103 | "log(a)=log(b**2/c**2)"
104 | ]
105 | },
106 | "execution_count": 5,
107 | "metadata": {},
108 | "output_type": "execute_result"
109 | }
110 | ],
111 | "source": [
112 | "(t/c).applyfunc(log)"
113 | ]
114 | },
115 | {
116 | "cell_type": "code",
117 | "execution_count": 6,
118 | "metadata": {},
119 | "outputs": [
120 | {
121 | "data": {
122 | "text/html": [
123 | "$$\\log{\\left(a \\right)}=\\log{\\left(\\frac{b^{2}}{c^{2}} \\right)}$$"
124 | ],
125 | "text/plain": [
126 | ""
127 | ]
128 | },
129 | "metadata": {},
130 | "output_type": "display_data"
131 | },
132 | {
133 | "data": {
134 | "text/html": [
135 | "$$\\log{\\left(a \\right)}=\\log{\\left(\\frac{b^{2}}{c^{2}} \\right)}$$"
136 | ],
137 | "text/plain": [
138 | ""
139 | ]
140 | },
141 | "metadata": {},
142 | "output_type": "display_data"
143 | }
144 | ],
145 | "source": [
146 | "# Generates double display with DMO aware functions.\n",
147 | "dmo(log(t/c))"
148 | ]
149 | },
150 | {
151 | "cell_type": "code",
152 | "execution_count": 7,
153 | "metadata": {},
154 | "outputs": [
155 | {
156 | "data": {
157 | "text/html": [
158 | "$$lnt\\equiv \\log{\\left(a c \\right)}=\\log{\\left(\\frac{b^{2}}{c} \\right)}$$"
159 | ],
160 | "text/plain": [
161 | ""
162 | ]
163 | },
164 | "metadata": {},
165 | "output_type": "display_data"
166 | }
167 | ],
168 | "source": [
169 | "dmo(lnt=log(t,display_op=False))"
170 | ]
171 | },
172 | {
173 | "cell_type": "code",
174 | "execution_count": 8,
175 | "metadata": {},
176 | "outputs": [
177 | {
178 | "data": {
179 | "text/html": [
180 | "$$\\log{\\left(t \\right)}=\\log{\\left(a c \\right)}=\\log{\\left(\\frac{b^{2}}{c} \\right)}$$"
181 | ],
182 | "text/plain": [
183 | ""
184 | ]
185 | },
186 | "metadata": {},
187 | "output_type": "display_data"
188 | },
189 | {
190 | "data": {
191 | "text/plain": [
192 | "log(a*c)=log(b**2/c)"
193 | ]
194 | },
195 | "execution_count": 8,
196 | "metadata": {},
197 | "output_type": "execute_result"
198 | }
199 | ],
200 | "source": [
201 | "log(t)"
202 | ]
203 | },
204 | {
205 | "cell_type": "code",
206 | "execution_count": 9,
207 | "metadata": {},
208 | "outputs": [
209 | {
210 | "data": {
211 | "text/html": [
212 | "$$\\log{\\left(t \\right)}=\\log{\\left(a c \\right)}=\\log{\\left(\\frac{b^{2}}{c} \\right)}$$"
213 | ],
214 | "text/plain": [
215 | ""
216 | ]
217 | },
218 | "metadata": {},
219 | "output_type": "display_data"
220 | },
221 | {
222 | "data": {
223 | "text/html": [
224 | "$$lnt\\equiv \\log{\\left(a c \\right)}=\\log{\\left(\\frac{b^{2}}{c} \\right)}$$"
225 | ],
226 | "text/plain": [
227 | ""
228 | ]
229 | },
230 | "metadata": {},
231 | "output_type": "display_data"
232 | }
233 | ],
234 | "source": [
235 | "dmo(lnt=log(t))"
236 | ]
237 | },
238 | {
239 | "cell_type": "code",
240 | "execution_count": 10,
241 | "metadata": {},
242 | "outputs": [
243 | {
244 | "data": {
245 | "text/html": [
246 | "$$\\log{\\left(a \\right)}=\\log{\\left(\\frac{b^{2}}{c^{2}} \\right)}$$"
247 | ],
248 | "text/plain": [
249 | ""
250 | ]
251 | },
252 | "metadata": {},
253 | "output_type": "display_data"
254 | },
255 | {
256 | "data": {
257 | "text/plain": [
258 | "log(a)=log(b**2/c**2)"
259 | ]
260 | },
261 | "execution_count": 10,
262 | "metadata": {},
263 | "output_type": "execute_result"
264 | }
265 | ],
266 | "source": [
267 | "log(t/c)"
268 | ]
269 | },
270 | {
271 | "cell_type": "code",
272 | "execution_count": 11,
273 | "metadata": {},
274 | "outputs": [
275 | {
276 | "data": {
277 | "text/plain": [
278 | "b**2*log(c)"
279 | ]
280 | },
281 | "execution_count": 11,
282 | "metadata": {},
283 | "output_type": "execute_result"
284 | }
285 | ],
286 | "source": [
287 | "integrate(t,c,side='rhs')"
288 | ]
289 | },
290 | {
291 | "cell_type": "code",
292 | "execution_count": 18,
293 | "metadata": {},
294 | "outputs": [
295 | {
296 | "data": {
297 | "text/plain": [
298 | "b**2*log(c)"
299 | ]
300 | },
301 | "execution_count": 18,
302 | "metadata": {},
303 | "output_type": "execute_result"
304 | }
305 | ],
306 | "source": [
307 | "Integral(t,c,side='rhs')"
308 | ]
309 | },
310 | {
311 | "cell_type": "code",
312 | "execution_count": 13,
313 | "metadata": {},
314 | "outputs": [
315 | {
316 | "data": {
317 | "text/html": [
318 | "$$\\int t\\, dc=b^{2} \\log{\\left(c \\right)}$$"
319 | ],
320 | "text/plain": [
321 | ""
322 | ]
323 | },
324 | "metadata": {},
325 | "output_type": "display_data"
326 | },
327 | {
328 | "data": {
329 | "text/plain": [
330 | "b**2*log(c)"
331 | ]
332 | },
333 | "execution_count": 13,
334 | "metadata": {},
335 | "output_type": "execute_result"
336 | }
337 | ],
338 | "source": [
339 | "integ(t,c,side='rhs')"
340 | ]
341 | },
342 | {
343 | "cell_type": "code",
344 | "execution_count": 15,
345 | "metadata": {},
346 | "outputs": [
347 | {
348 | "data": {
349 | "text/html": [
350 | "$$\\int a c\\, dc=b^{2} \\log{\\left(c \\right)}$$"
351 | ],
352 | "text/plain": [
353 | ""
354 | ]
355 | },
356 | "metadata": {},
357 | "output_type": "display_data"
358 | }
359 | ],
360 | "source": [
361 | "dmo(t.integ(c))"
362 | ]
363 | },
364 | {
365 | "cell_type": "code",
366 | "execution_count": 16,
367 | "metadata": {},
368 | "outputs": [
369 | {
370 | "data": {
371 | "text/html": [
372 | "$$\\int t\\, dc=\\frac{a c^{2}}{2}$$"
373 | ],
374 | "text/plain": [
375 | ""
376 | ]
377 | },
378 | "metadata": {},
379 | "output_type": "display_data"
380 | },
381 | {
382 | "data": {
383 | "text/plain": [
384 | "a*c**2/2"
385 | ]
386 | },
387 | "execution_count": 16,
388 | "metadata": {},
389 | "output_type": "execute_result"
390 | }
391 | ],
392 | "source": [
393 | "integ(t,c,side='lhs')"
394 | ]
395 | },
396 | {
397 | "cell_type": "code",
398 | "execution_count": null,
399 | "metadata": {},
400 | "outputs": [],
401 | "source": []
402 | },
403 | {
404 | "cell_type": "code",
405 | "execution_count": null,
406 | "metadata": {},
407 | "outputs": [],
408 | "source": []
409 | }
410 | ],
411 | "metadata": {
412 | "kernelspec": {
413 | "display_name": "Python 3",
414 | "language": "python",
415 | "name": "python3"
416 | },
417 | "language_info": {
418 | "codemirror_mode": {
419 | "name": "ipython",
420 | "version": 3
421 | },
422 | "file_extension": ".py",
423 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
424 | "name": "python",
425 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
426 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
427 | "version": "3.6.9"
428 | }
429 | },
430 | "nbformat": 4,
431 | "nbformat_minor": 4
432 | }
433 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/algebraic_equation_ex_func_old.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | __Algebraic Equations with SymPy__
3 |
4 | author: Jonathan Gutow
5 | date: May 2020
6 | license: GPL V3+
7 |
8 | These tools define relations that all high school and college students would recognize as mathematical equations.
9 | They consist of a left hand side (lhs) and a right hand side (rhs) connected by a relation operator such as "=". At
10 | present only the "=" relation operator is recognized.
11 |
12 | This tool applies operations to both sides of the equation simultaneously, just as students are taught to do when
13 | attempting to isolate (solve for) a variable. Thus the statement `Equation/b` yields a new equation `Equation.lhs/b = Equation.rhs/b`
14 |
15 | The intent is to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to rearrange equations and perform algebra
16 | in a stepwise fashion. In this way more people can successfully perform algebraic rearrangements without stumbling
17 | over missed details such as a negative sign. This mimics the capabilities available in [SageMath]
18 | (https://www.sagemath.org/) and [Maxima](http://maxima.sourceforge.net/), but can be installed in a generic python
19 | environment.
20 |
21 | _Setup/Installation_: Currently this tool is not available as a pip installable package. The file `algebraic_equation.py`
22 | must be available for import in the directory space of the active Python, IPython or Jupyter notebook. To activate issue
23 | the command: `from algebraic_equation import *`. This will also import the SymPy tools. If you want to isolate this tool
24 | from the global namespace you are working with change the import statement to `import algebraic_equation as spa`, where
25 | `spa` stands for "SymPy Algebra". Then all calls would be made to `spa.funcname()`.
26 |
27 | Usage examples can be found in the docstrings and the demonstration Jupyter notebook `Demonstration of algebraic_equation.py.ipynb`.
28 | """
29 | from sympy import *
30 |
31 | class Equation(Expr):
32 | '''
33 | This class defines relations that all high school and college students would recognize as mathematical equations.
34 | They consist of a left hand side (lhs) and a right hand side (rhs) connected by a relation operator such as "=". At
35 | present only the "=" relation operator is recognized.
36 |
37 | This class is intended to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to rearrange equations and perform algebra
38 | in a stepwise fashion. In this way more people can successfully perform algebraic rearrangements without stumbling
39 | over missed details such as a negative sign.
40 |
41 | __Note__ that this module imports Sympy into its namespace so there is no need to import Sympy separately.
42 |
43 | Create an equation with the call `Equation(lhs,rhs,relation_operator)`, where `lhs` and `rhs` are any valid Sympy
44 | expression. `relation_operator` defaults to the string "=" if not supplied. Currently,"=" is the only valid option.
45 | `equ(...)` is a synonym for `Equation(...)`.
46 |
47 | Examples:
48 | >>> var('a b c')
49 | >>> equ(a,b/c)
50 | a=b/c
51 | >>> t=equ(a,b/c)
52 | >>> t
53 | a=b/c
54 | >>> t*c
55 | a*c=b
56 | >>> c*t
57 | a*c=b
58 | >>> exp(t)
59 | exp(a)=exp(b/c)
60 | >>> exp(log(t))
61 | a=b/c
62 |
63 | SymPy's solvers do not understand these equations. They expect an expression that the solver assumes = 0.
64 | Thus to use the solver the equation must be rearranged so that all non-zero symbols are on one side. Then
65 | just the non-zero symbolic side is passed to `solve()`.
66 | >>> t2 = t-t.rhs
67 | >>> t2
68 | a-b/c=0
69 | >>> solve(t2.lhs,c)
70 | [b/a]
71 | '''
72 | _op_priority = 11.0 # This makes sure the rules for equations are applied before those for expressions
73 | # which have _op_priority = 10.0
74 |
75 | def __init__(self,lhs,rhs,relop='='):
76 | if not(relop == '='):
77 | raise NotImplementedError('"=" is the only relational operator presently supported in Equations.')
78 | if (simplify(lhs).is_number) and (simplify(rhs).is_number) and not (lhs == rhs):
79 | print('WARNING: did your really mean to define unequal numbers as equal? ' + str(lhs) +'='+ str(rhs))
80 | self.lhs = lhs
81 | self.rhs = rhs
82 | self.relop=relop
83 |
84 | #####
85 | # Overrides of SymPy.Expr Arithmatic
86 | #####
87 | def __pos__(self):
88 | return self
89 |
90 | def __neg__(self):
91 | # Mul has its own __neg__ routine, so we just
92 | # create a 2-args Mul with the -1 in the canonical
93 | # slot 0.
94 | c = self.is_commutative
95 | lhs =Mul._from_args((S.NegativeOne, self.lhs), c)
96 | rhs =Mul._from_args((S.NegativeOne, self.rhs), c)
97 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
98 |
99 | def __abs__(self):
100 | from sympy import Abs
101 | lhs=Abs(self.lhs)
102 | rhs=Abs(self.rhs)
103 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
104 |
105 | def __add__(self, other):
106 | if (type(other) is Equation):
107 | raise NotImplementedError('Addition of equations not supported.')
108 | lhs = Add(self.lhs,other)
109 | rhs = Add(self.rhs,other)
110 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
111 |
112 | def __radd__(self, other):
113 | if (type(other) is Equation):
114 | raise NotImplementedError('Addition of equations not supported.')
115 | lhs = Add(other,self.lhs)
116 | rhs = Add(other,self.rhs)
117 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
118 |
119 | def __sub__(self, other):
120 | if (type(other) is Equation):
121 | raise NotImplementedError('Subtraction of equations not supported.')
122 | lhs = Add(self.lhs,-other)
123 | rhs = Add(self.rhs,-other)
124 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
125 |
126 | def __rsub__(self, other):
127 | if (type(other) is Equation):
128 | raise NotImplementedError('Subtraction of equations not supported.')
129 | lhs = Add(other,-self.lhs)
130 | rhs = Add(other,-self.rhs)
131 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
132 |
133 | def __mul__(self, other):
134 | if (type(other) is Equation):
135 | raise NotImplementedError('Multiplication of equations not supported.')
136 | lhs = Mul(self.lhs,other)
137 | rhs = Mul(self.rhs,other)
138 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
139 |
140 | def __rmul__(self, other):
141 | if (type(other) is Equation):
142 | raise NotImplementedError('Multiplication of equations not supported.')
143 | lhs = Mul(other,self.lhs)
144 | rhs = Mul(other,self.rhs)
145 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
146 |
147 | def _pow(self, other):
148 | if (type(other) is Equation):
149 | raise NotImplementedError('Raising to the power of an equation not supported.')
150 | lhs = Pow(self.lhs,other)
151 | rhs = Pow(self.rhs,other)
152 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
153 |
154 | def __rpow__(self, other):
155 | if (type(other) is Equation):
156 | raise NotImplementedError('Raising to the power of an equation not supported.')
157 | lhs = Pow(other,self.lhs)
158 | rhs = Pow(other,self.rhs)
159 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
160 |
161 | def __div__(self, other):
162 | if (type(other) is Equation):
163 | raise NotImplementedError('Division by equation not supported.')
164 | return self.__mul__(Pow(other, S.NegativeOne))
165 |
166 | def __rdiv__(self, other):
167 | raise NotImplementedError('Division by equation not supported.')
168 |
169 | __truediv__ = __div__
170 | __rtruediv__ = __rdiv__
171 |
172 | def __mod__(self, other):
173 | if (type(other) is Equation):
174 | raise NotImplementedError('Modulus by equation not supported.')
175 | lhs = Mod(self.lhs,other)
176 | rhs = Mod(self.rhs,other)
177 | return equ(lhs,rhs)
178 |
179 | def __rmod__(self, other):
180 | raise NotImplementedError('Modulus by equation not supported.')
181 |
182 | def __repr__(self):
183 | return(str(self.lhs)+self.relop+str(self.rhs))
184 |
185 | def _latex(self,obj,**kwargs):
186 | return(latex(self.lhs)+self.relop+latex(self.rhs))
187 |
188 | def __str__(self):
189 | return(self.__repr__())
190 |
191 | equ = Equation
192 |
193 | class Function(Function):
194 | def __new__(cls, *arg, **kwargs):
195 | if (type(arg[0]) is Equation):
196 | temptuple=(arg[0].lhs,)+arg[1:]
197 | lhs = super().__new__(cls, *temptuple, **kwargs)
198 | temptuple=(arg[0].rhs,)+arg[1:]
199 | rhs = super().__new__(cls, *temptuple, **kwargs)
200 | return (equ(lhs,rhs))
201 | else:
202 | return(super().__new__(cls, *arg, **kwargs))
203 |
204 | for func in functions.__all__:
205 | # listed in `skip` cannot be extended because of `mro` error or `metaclass conflict`.
206 | skip=('sqrt','root','Min','Max','Id','real_root','cbrt','unbranched_argument','polarify','unpolarify',
207 | 'piecewise_fold','E1','Eijk','bspline_basis','bspline_basis_set','interpolating_spline','jn_zeros',
208 | 'jacobi_normalized','Ynm_c')
209 | bare=('sqrt',)
210 | if func not in skip:
211 | execstr = 'class '+str(func)+'('+str(func)+',Function):\n pass\n'
212 | exec(execstr,globals(),locals())
213 | #####
214 | # Manual overrides of some bare functions. This is probably automatable with `inspect`.
215 | #####
216 | ###
217 | # override of sqrt
218 | ###
219 | from sympy import sqrt as spsqrt
220 | execstr='def sqrt(arg, evaluate=None):\n'
221 | execstr+=' """\n'
222 | # Since all we are doing is adding ability to handle Equations we will import the docstring
223 | execstr+=' '+spsqrt.__doc__+'\n'
224 | execstr+=' """\n'
225 | execstr+=' if (type(arg) is Equation):\n'
226 | execstr+=' lhs = spsqrt(arg.lhs,evaluate)\n'
227 | execstr+=' rhs = spsqrt(arg.rhs,evaluate)\n'
228 | execstr+=' return(Equation(lhs,rhs))\n'
229 | execstr+=' else:\n'
230 | execstr+=' return(spsqrt(arg,evaluate))\n'
231 | execstr+=' def __doc__():\n'
232 | execstr+=' return(spsqrt.__doc__())\n'
233 | exec(execstr,globals(),locals())
234 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/docs/alg_w_sympy.svg:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 |
2 |
3 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Developer Testing/Equation_OB_ver.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | __Algebraic Equations with SymPy__
3 |
4 | author: Jonathan Gutow
5 |
6 | Overrides of binary binary operations based on suggestions from [Oscar Benjamin](https://github.com/oscarbenjamin)
7 |
8 | date: May 2020
9 |
10 | license: GPL V3+
11 |
12 | These tools define relations that all high school and college students would recognize as mathematical equations.
13 | They consist of a left hand side (lhs) and a right hand side (rhs) connected by a relation operator such as "=". At
14 | present only the "=" relation operator is recognized.
15 |
16 | This class should not be confused with the Boolean class `Equality` (abbreviated `Eq`) which specifies
17 | that the equality of two expressions is `True`.
18 |
19 | This tool applies operations to both sides of the equation simultaneously, just as students are taught to do when
20 | attempting to isolate (solve for) a variable. Thus the statement `Equation/b` yields a new equation `Equation.lhs/b = Equation.rhs/b`
21 |
22 | The intent is to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to rearrange equations and perform algebra
23 | in a stepwise fashion. In this way more people can successfully perform algebraic rearrangements without stumbling
24 | over missed details such as a negative sign. This mimics the capabilities available in [SageMath]
25 | (https://www.sagemath.org/) and [Maxima](http://maxima.sourceforge.net/), but can be installed in a generic python
26 | environment.
27 |
28 | _Setup/Installation_: Currently this tool is not available as a pip installable package. The file `algebraic_equation.py`
29 | must be available for import in the directory space of the active Python, IPython or Jupyter notebook. To activate issue
30 | the command: `from algebraic_equation import *`. This will also import the SymPy tools. If you want to isolate this tool
31 | from the global namespace you are working with change the import statement to `import algebraic_equation as spa`, where
32 | `spa` stands for "SymPy Algebra". Then all calls would be made to `spa.funcname()`.
33 |
34 | Usage examples can be found in the docstrings and the demonstration Jupyter notebook `Demonstration of algebraic_equation.py.ipynb`.
35 |
36 | J.G 28-5-20
37 | """
38 | '''
39 | Selective import kept for incorporation into SymPy
40 | from sympy.core.basic import Basic
41 | '''
42 | from sympy.core.sympify import _sympify
43 | '''
44 | from sympy.simplify import simplify
45 | from sympy.core.relational import Equality
46 | from sympy.core import Function
47 | from sympy.functions import *
48 | from sympy import functions
49 | from sympy import factorial
50 | from sympy import latex
51 | '''
52 |
53 | from sympy import * # Replace with more selective import when folded into SymPy
54 |
55 | class Equation(Basic):
56 | '''
57 | This class defines relations that all high school and college students would recognize as mathematical equations.
58 | They consist of a left hand side (lhs) and a right hand side (rhs) connected by a relation operator such as "=". At
59 | present only the "=" relation operator is recognized.
60 |
61 | This class is intended to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to rearrange equations and perform algebra
62 | in a stepwise fashion. In this way more people can successfully perform algebraic rearrangements without stumbling
63 | over missed details such as a negative sign.
64 |
65 | __Note__ that this module imports Sympy into its namespace so there is no need to import Sympy separately.
66 |
67 | Create an equation with the call `Equation(lhs,rhs,relation_operator)`, where `lhs` and `rhs` are any valid Sympy
68 | expression. `relation_operator` defaults to the string "=" if not supplied. Currently,"=" is the only valid option.
69 | `Eqn(...)` is a synonym for `Equation(...)`.
70 |
71 | Examples:
72 | >>> var('a b c')
73 | >>> equ(a,b/c)
74 | a=b/c
75 | >>> t=equ(a,b/c)
76 | >>> t
77 | a=b/c
78 | >>> t*c
79 | a*c=b
80 | >>> c*t
81 | a*c=b
82 | >>> exp(t)
83 | exp(a)=exp(b/c)
84 | >>> exp(log(t))
85 | a=b/c
86 |
87 | Integration can only be performed on one side at a time.
88 | >>> q=Eqn(a*c,b/c)
89 | >>> integrate(q,b,side='rhs')
90 | b**2/(2*c)
91 | >>> integrate(q,b,side='lhs')
92 | a*b*c
93 |
94 | >>> # Make a pretty statement of integration from an equation
95 | ...: Eqn(Integral(q.lhs,b),integrate(q,b,side='rhs'))
96 | Integral(a*c, b)=b**2/(2*c)
97 | >>> # This is duplicated by the convenience function self.integ
98 | ...: q.integ(b)
99 | Integral(a*c, b)=b**2/(2*c)
100 |
101 | SymPy's solvers do not understand these equations. They expect an expression that the solver assumes = 0.
102 | Thus to use the solver the equation must be rearranged so that all non-zero symbols are on one side. Then
103 | just the non-zero symbolic side is passed to `solve()`.
104 | >>> t2 = t-t.rhs
105 | >>> t2
106 | a-b/c=0
107 | >>> solve(t2.lhs,c)
108 | [b/a]
109 | '''
110 |
111 | def __new__(cls, lhs, rhs, relop='='):
112 | if not(relop == '='):
113 | raise NotImplementedError('"=" is the only relational operator presently supported in Equations.')
114 | lhs = _sympify(lhs)
115 | rhs = _sympify(rhs)
116 | if (lhs.is_number) and (rhs.is_number) and not (lhs == rhs):
117 | print('WARNING: did your really mean to define unequal numbers as equal? ' + str(lhs) +'='+ str(rhs))
118 | return super().__new__(cls, lhs, rhs, relop)
119 |
120 | @property
121 | def lhs(self):
122 | return self.args[0]
123 |
124 | @property
125 | def rhs(self):
126 | return self.args[1]
127 |
128 | @property
129 | def relop(self):
130 | return self.args[2]
131 |
132 | def as_Boolean(self):
133 | return Equality(self.lhs, self.rhs)
134 |
135 | @property
136 | def reversed(self):
137 | return Equation(self.rhs, self.lhs)
138 |
139 | @property
140 | def free_symbols(self):
141 | ret =self.lhs.free_symbols
142 | ret.update(self.rhs.free_symbols)
143 | return ret
144 |
145 | def applyfunc(self, func, *args, **kwargs):
146 | return Equation(func(self.lhs, *args, **kwargs), func(self.rhs, *args, **kwargs))
147 |
148 | def applylhs(self, func, *args, **kwargs):
149 | return Equation(func(self.lhs, *args, **kwargs), self.rhs)
150 |
151 | def applyrhs(self, func, *args, **kwargs):
152 | return Equation(self.lhs, func(self.rhs, *args, **kwargs))
153 | #####
154 | # Overrides of binary math operations
155 | #####
156 |
157 | _op_priority = 11.0 # This makes sure the rules for equations are applied before those for expressions
158 | # which have _op_priority = 10.0
159 | @classmethod
160 | def _binary_op(cls, a, b, opfunc_ab):
161 | if isinstance(a, Equation) and not isinstance(b, Equation):
162 | return Equation(opfunc_ab(a.lhs, b), opfunc_ab(a.rhs, b))
163 | elif isinstance(b, Equation) and not isinstance(a, Equation):
164 | return Equation(opfunc_ab(a, b.lhs), opfunc_ab(a, b.rhs))
165 | elif isinstance(a, Equation) and isinstance(b, Equation):
166 | return Equation(opfunc_ab(a.lhs, b.lhs), opfunc_ab(a.rhs, b.rhs))
167 | else:
168 | raise TypeError('One of a or b should be an equation')
169 |
170 | def __add__(self, other):
171 | return self._binary_op(self, other, lambda a, b: a + b)
172 |
173 | def __radd__(self, other):
174 | return self._binary_op(other, self, lambda a, b: a + b)
175 |
176 | def __mul__(self, other):
177 | return self._binary_op(self, other, lambda a, b: a * b)
178 |
179 | def __rmul__(self, other):
180 | return self._binary_op(other, self, lambda a, b: a * b)
181 |
182 | def __sub__(self, other):
183 | return self._binary_op(self, other, lambda a, b: a - b)
184 |
185 | def __rsub__(self, other):
186 | return self._binary_op(other, self, lambda a, b: a - b)
187 |
188 | def __truediv__(self, other):
189 | return self._binary_op(self, other, lambda a, b: a / b)
190 |
191 | def __rtruediv__(self, other):
192 | return self._binary_op(other, self, lambda a, b: a / b)
193 |
194 | def __pow__(self, other):
195 | return self._binary_op(self, other, lambda a, b: a ** b)
196 |
197 | def __rpow__(self, other):
198 | return self._binary_op(other, self, lambda a, b: a ** b)
199 |
200 | def _eval_power(self, other):
201 | return self.__pow__(other)
202 |
203 | #####
204 | # Output helper functions
205 | #####
206 | def __repr__(self):
207 | return(str(self.lhs)+self.relop+str(self.rhs))
208 |
209 | def _latex(self,obj,**kwargs):
210 | return(latex(self.lhs)+self.relop+latex(self.rhs))
211 |
212 | def __str__(self):
213 | return(self.__repr__())
214 |
215 | #####
216 | # Operation helper functions
217 | #####
218 | def expand(self, *args, **kwargs):
219 | return Equation(self.lhs.expand(*args, **kwargs),self.rhs.expand(*args, **kwargs))
220 |
221 | def simplify(self, *args, **kwargs):
222 | return simplify(self, *args, **kwargs)
223 |
224 | def _eval_simplify(self, *args, **kwargs):
225 | return Equation(self.lhs.simplify(*args, **kwargs),self.rhs.simplify(*args, **kwargs))
226 |
227 | def factor(self, *args, **kwargs):
228 | # TODO: cancel out factors common to both sides.
229 | return Equation(self.lhs.factor(*args, **kwargs),self.rhs.factor(*args, **kwargs))
230 |
231 | def evalf(self, *args, **kwargs):
232 | return Equation(self.lhs.evalf(*args, **kwargs),self.rhs.evalf(*args, **kwargs))
233 |
234 | def _eval_derivative(self, *args, **kwargs):
235 | # TODO Find why diff and Derivative do not appear to pass through kwargs to this.
236 | # Since we cannot set evaluation of lhs manually try to be intelligent about when
237 | # to do it.
238 | eval_lhs = False
239 | if not(isinstance(self.lhs,Derivative)):
240 | for sym in args:
241 | if sym in self.lhs.free_symbols and not(_sympify(sym).is_number):
242 | eval_lhs=True
243 | return Equation(self.lhs.diff(*args, **kwargs, evaluate=eval_lhs), self.rhs.diff(*args, **kwargs))
244 |
245 | def integ(self, *args, **kwargs):
246 | '''
247 | This function is a convenience function that returns a new equation consisting of an unevaluated
248 | integral of the lhs as the new lhs and the result of integrating the rhs as the new rhs.
249 | '''
250 | return Equation(Integral(self.lhs, *args, **kwargs), self.rhs.integrate(*args, **kwargs))
251 |
252 | def _eval_Integral(self, *args, **kwargs): # Make it require side specification?
253 | side = kwargs.pop('side',None)
254 | if (side is None):
255 | raise ValueError('You must specify `side="lhs"` or `side="rhs"` when integrating an Equation')
256 | else:
257 | try:
258 | return (getattr(self,side).integrate(*args, **kwargs))
259 | except AttributeError:
260 | raise AttributeError('`side` must equal "lhs" or "rhs".')
261 |
262 | Eqn = Equation
263 |
264 | #####
265 | # Extension of the Function class. For incorporation into SymPy this should become part of the class
266 | #####
267 | class Function(Function):
268 | def __new__(cls, *arg, **kwargs):
269 | if (hasattr(arg[0],'applyfunc')):
270 | return(arg[0].applyfunc(cls,*arg[1:],**kwargs))
271 | else:
272 | return(super().__new__(cls, *arg, **kwargs))
273 |
274 | for func in functions.__all__: # This will not be needed when incorporated into SymPy
275 | # listed in `skip` cannot be extended because of `mro` error or `metaclass conflict`. Seems to reflect
276 | # expectation that a helper function will be defined within the object (e.g. `_eval_power()` for
277 | # all the flavors of `root`).
278 | skip=('sqrt','root','Min','Max','Id','real_root','cbrt','unbranched_argument','polarify','unpolarify',
279 | 'piecewise_fold','E1','Eijk','bspline_basis','bspline_basis_set','interpolating_spline','jn_zeros',
280 | 'jacobi_normalized','Ynm_c')
281 | if func not in skip:
282 | execstr = 'class '+str(func)+'('+str(func)+',Function):\n pass\n'
283 | exec(execstr,globals(),locals())
284 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Developer Testing/Test ` importing ... as ...`.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "outputs": [],
8 | "source": [
9 | "import algebra_with_sympy as spa"
10 | ]
11 | },
12 | {
13 | "cell_type": "code",
14 | "execution_count": 2,
15 | "metadata": {},
16 | "outputs": [
17 | {
18 | "data": {
19 | "text/plain": [
20 | "(a, b, c)"
21 | ]
22 | },
23 | "execution_count": 2,
24 | "metadata": {},
25 | "output_type": "execute_result"
26 | }
27 | ],
28 | "source": [
29 | "spa.var('a b c')"
30 | ]
31 | },
32 | {
33 | "cell_type": "code",
34 | "execution_count": 3,
35 | "metadata": {},
36 | "outputs": [
37 | {
38 | "ename": "NameError",
39 | "evalue": "name 'Eqn' is not defined",
40 | "output_type": "error",
41 | "traceback": [
42 | "\u001b[0;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
43 | "\u001b[0;31mNameError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
44 | "Cell \u001b[0;32mIn[3], line 1\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m----> 1\u001b[0m t \u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[43mEqn\u001b[49m (c ,a \u001b[38;5;241m/\u001b[39mb )\n\u001b[1;32m 3\u001b[0m t \n",
45 | "\u001b[0;31mNameError\u001b[0m: name 'Eqn' is not defined"
46 | ]
47 | }
48 | ],
49 | "source": [
50 | "t=@c=a/b\n",
51 | "t"
52 | ]
53 | },
54 | {
55 | "cell_type": "code",
56 | "execution_count": 4,
57 | "metadata": {},
58 | "outputs": [
59 | {
60 | "data": {
61 | "text/latex": [
62 | "$c=\\frac{a}{b}$"
63 | ],
64 | "text/plain": [
65 | "Equation(c, a/b)"
66 | ]
67 | },
68 | "execution_count": 4,
69 | "metadata": {},
70 | "output_type": "execute_result"
71 | }
72 | ],
73 | "source": [
74 | "t =spa.Eqn (c ,a /b )\n",
75 | "t "
76 | ]
77 | },
78 | {
79 | "cell_type": "code",
80 | "execution_count": 5,
81 | "metadata": {},
82 | "outputs": [
83 | {
84 | "data": {
85 | "text/latex": [
86 | "$b c=a$"
87 | ],
88 | "text/plain": [
89 | "Equation(b*c, a)"
90 | ]
91 | },
92 | "execution_count": 5,
93 | "metadata": {},
94 | "output_type": "execute_result"
95 | }
96 | ],
97 | "source": [
98 | "t*b"
99 | ]
100 | },
101 | {
102 | "cell_type": "code",
103 | "execution_count": 6,
104 | "metadata": {},
105 | "outputs": [
106 | {
107 | "data": {
108 | "text/latex": [
109 | "$c=\\frac{a}{b}$"
110 | ],
111 | "text/plain": [
112 | "Equation(c, a/b)"
113 | ]
114 | },
115 | "execution_count": 6,
116 | "metadata": {},
117 | "output_type": "execute_result"
118 | }
119 | ],
120 | "source": [
121 | "spa.exp(spa.log(t))"
122 | ]
123 | },
124 | {
125 | "cell_type": "code",
126 | "execution_count": 7,
127 | "metadata": {},
128 | "outputs": [
129 | {
130 | "ename": "NameError",
131 | "evalue": "name 'exp' is not defined",
132 | "output_type": "error",
133 | "traceback": [
134 | "\u001b[0;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
135 | "\u001b[0;31mNameError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
136 | "Cell \u001b[0;32mIn[7], line 1\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m----> 1\u001b[0m \u001b[43mexp\u001b[49m (t )\n",
137 | "\u001b[0;31mNameError\u001b[0m: name 'exp' is not defined"
138 | ]
139 | }
140 | ],
141 | "source": [
142 | "exp(t)"
143 | ]
144 | },
145 | {
146 | "cell_type": "code",
147 | "execution_count": 8,
148 | "metadata": {},
149 | "outputs": [
150 | {
151 | "data": {
152 | "text/plain": [
153 | "'algebra_with_sympy'"
154 | ]
155 | },
156 | "execution_count": 8,
157 | "metadata": {},
158 | "output_type": "execute_result"
159 | }
160 | ],
161 | "source": [
162 | "spa.__name__"
163 | ]
164 | },
165 | {
166 | "cell_type": "code",
167 | "execution_count": 9,
168 | "metadata": {},
169 | "outputs": [
170 | {
171 | "ename": "AttributeError",
172 | "evalue": "module 'algebra_with_sympy' has no attribute '__parent__'",
173 | "output_type": "error",
174 | "traceback": [
175 | "\u001b[0;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
176 | "\u001b[0;31mAttributeError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
177 | "Cell \u001b[0;32mIn[9], line 1\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m----> 1\u001b[0m \u001b[43mspa\u001b[49m\u001b[43m \u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;241;43m.\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m__parent__\u001b[49m \n",
178 | "\u001b[0;31mAttributeError\u001b[0m: module 'algebra_with_sympy' has no attribute '__parent__'"
179 | ]
180 | }
181 | ],
182 | "source": [
183 | "spa.__parent__"
184 | ]
185 | },
186 | {
187 | "cell_type": "code",
188 | "execution_count": 10,
189 | "metadata": {},
190 | "outputs": [
191 | {
192 | "data": {
193 | "text/plain": [
194 | "['/home/jonathan/GIT/Algebra_with_SymPy/algebra_with_sympy']"
195 | ]
196 | },
197 | "execution_count": 10,
198 | "metadata": {},
199 | "output_type": "execute_result"
200 | }
201 | ],
202 | "source": [
203 | "spa.__path__"
204 | ]
205 | },
206 | {
207 | "cell_type": "code",
208 | "execution_count": 11,
209 | "metadata": {},
210 | "outputs": [
211 | {
212 | "data": {
213 | "text/plain": [
214 | "'algebra_with_sympy'"
215 | ]
216 | },
217 | "execution_count": 11,
218 | "metadata": {},
219 | "output_type": "execute_result"
220 | }
221 | ],
222 | "source": [
223 | "spa.__package__"
224 | ]
225 | },
226 | {
227 | "cell_type": "code",
228 | "execution_count": 12,
229 | "metadata": {},
230 | "outputs": [
231 | {
232 | "data": {
233 | "text/plain": [
234 | "ModuleSpec(name='algebra_with_sympy', loader=<_frozen_importlib_external.SourceFileLoader object at 0x7f8bee583d90>, origin='/home/jonathan/GIT/Algebra_with_SymPy/algebra_with_sympy/__init__.py', submodule_search_locations=['/home/jonathan/GIT/Algebra_with_SymPy/algebra_with_sympy'])"
235 | ]
236 | },
237 | "execution_count": 12,
238 | "metadata": {},
239 | "output_type": "execute_result"
240 | }
241 | ],
242 | "source": [
243 | "spa.__spec__"
244 | ]
245 | },
246 | {
247 | "cell_type": "code",
248 | "execution_count": 13,
249 | "metadata": {},
250 | "outputs": [
251 | {
252 | "data": {
253 | "text/plain": [
254 | "module"
255 | ]
256 | },
257 | "execution_count": 13,
258 | "metadata": {},
259 | "output_type": "execute_result"
260 | }
261 | ],
262 | "source": [
263 | "type(spa)"
264 | ]
265 | },
266 | {
267 | "cell_type": "code",
268 | "execution_count": 14,
269 | "metadata": {},
270 | "outputs": [
271 | {
272 | "ename": "AttributeError",
273 | "evalue": "module 'algebra_with_sympy' has no attribute '_'",
274 | "output_type": "error",
275 | "traceback": [
276 | "\u001b[0;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
277 | "\u001b[0;31mAttributeError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
278 | "Cell \u001b[0;32mIn[14], line 1\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m----> 1\u001b[0m \u001b[43mspa\u001b[49m\u001b[43m \u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;241;43m.\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m_\u001b[49m \n",
279 | "\u001b[0;31mAttributeError\u001b[0m: module 'algebra_with_sympy' has no attribute '_'"
280 | ]
281 | }
282 | ],
283 | "source": [
284 | "spa._"
285 | ]
286 | },
287 | {
288 | "cell_type": "code",
289 | "execution_count": 15,
290 | "metadata": {},
291 | "outputs": [
292 | {
293 | "ename": "RuntimeError",
294 | "evalue": "dictionary changed size during iteration",
295 | "output_type": "error",
296 | "traceback": [
297 | "\u001b[0;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
298 | "\u001b[0;31mRuntimeError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
299 | "Cell \u001b[0;32mIn[15], line 1\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m----> 1\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mfor\u001b[39;00m k \u001b[38;5;129;01min\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;28mglobals\u001b[39m ():\n\u001b[1;32m 3\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mif\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;28mhasattr\u001b[39m (\u001b[38;5;28mglobals\u001b[39m ()[k ],\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m__name__\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m):\n\u001b[1;32m 5\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28mprint\u001b[39m (k \u001b[38;5;241m+\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m:\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m,end \u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m)\n",
300 | "\u001b[0;31mRuntimeError\u001b[0m: dictionary changed size during iteration"
301 | ]
302 | }
303 | ],
304 | "source": [
305 | "for k in globals():\n",
306 | " if hasattr(globals()[k],'__name__'):\n",
307 | " print(k+':', end='')\n",
308 | " print(globals()[k].__name__)"
309 | ]
310 | },
311 | {
312 | "cell_type": "code",
313 | "execution_count": 16,
314 | "metadata": {},
315 | "outputs": [
316 | {
317 | "name": "stdout",
318 | "output_type": "stream",
319 | "text": [
320 | "__builtin__:builtins\n",
321 | "__builtins__:builtins\n",
322 | "get_ipython:get_ipython\n",
323 | "open:open\n",
324 | "_:module\n",
325 | "spa:algebra_with_sympy\n",
326 | "_13:module\n"
327 | ]
328 | }
329 | ],
330 | "source": [
331 | "for k in get_ipython().user_ns:\n",
332 | " if hasattr(get_ipython().user_ns[k],'__name__'):\n",
333 | " print(k+':', end='')\n",
334 | " print(get_ipython().user_ns[k].__name__)"
335 | ]
336 | },
337 | {
338 | "cell_type": "code",
339 | "execution_count": 17,
340 | "metadata": {},
341 | "outputs": [
342 | {
343 | "data": {
344 | "text/plain": [
345 | "False"
346 | ]
347 | },
348 | "execution_count": 17,
349 | "metadata": {},
350 | "output_type": "execute_result"
351 | }
352 | ],
353 | "source": [
354 | "'algwsym_config' in globals()"
355 | ]
356 | },
357 | {
358 | "cell_type": "code",
359 | "execution_count": 23,
360 | "metadata": {},
361 | "outputs": [],
362 | "source": [
363 | "spa.algwsym_config.output.show_code = True"
364 | ]
365 | },
366 | {
367 | "cell_type": "code",
368 | "execution_count": 25,
369 | "metadata": {},
370 | "outputs": [
371 | {
372 | "data": {
373 | "text/latex": [
374 | "$c=\\frac{a}{b}$"
375 | ],
376 | "text/plain": [
377 | "Equation(c, a/b)"
378 | ]
379 | },
380 | "execution_count": 25,
381 | "metadata": {},
382 | "output_type": "execute_result"
383 | }
384 | ],
385 | "source": [
386 | "t"
387 | ]
388 | },
389 | {
390 | "cell_type": "code",
391 | "execution_count": 26,
392 | "metadata": {},
393 | "outputs": [
394 | {
395 | "name": "stdout",
396 | "output_type": "stream",
397 | "text": [
398 | "Code version: Equation(c, a/b)\n"
399 | ]
400 | },
401 | {
402 | "data": {
403 | "text/latex": [
404 | "$c=\\frac{a}{b}\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,$(t)"
405 | ],
406 | "text/plain": [
407 | "Equation(c, a/b)"
408 | ]
409 | },
410 | "execution_count": 26,
411 | "metadata": {},
412 | "output_type": "execute_result"
413 | }
414 | ],
415 | "source": [
416 | "algwsym_config = spa.algwsym_config\n",
417 | "t"
418 | ]
419 | },
420 | {
421 | "cell_type": "code",
422 | "execution_count": 28,
423 | "metadata": {},
424 | "outputs": [],
425 | "source": [
426 | "Equation = spa.Equation\n",
427 | "Eqn = Equation\n",
428 | "tst2=@a/b=c"
429 | ]
430 | },
431 | {
432 | "cell_type": "code",
433 | "execution_count": 29,
434 | "metadata": {},
435 | "outputs": [
436 | {
437 | "name": "stdout",
438 | "output_type": "stream",
439 | "text": [
440 | "Code version: Equation(a/b, c)\n"
441 | ]
442 | },
443 | {
444 | "data": {
445 | "text/latex": [
446 | "$\\frac{a}{b}=c\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,$(tst2)"
447 | ],
448 | "text/plain": [
449 | "Equation(a/b, c)"
450 | ]
451 | },
452 | "execution_count": 29,
453 | "metadata": {},
454 | "output_type": "execute_result"
455 | }
456 | ],
457 | "source": [
458 | "tst2"
459 | ]
460 | },
461 | {
462 | "cell_type": "code",
463 | "execution_count": null,
464 | "metadata": {},
465 | "outputs": [],
466 | "source": []
467 | }
468 | ],
469 | "metadata": {
470 | "kernelspec": {
471 | "display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
472 | "language": "python",
473 | "name": "python3"
474 | },
475 | "language_info": {
476 | "codemirror_mode": {
477 | "name": "ipython",
478 | "version": 3
479 | },
480 | "file_extension": ".py",
481 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
482 | "name": "python",
483 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
484 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
485 | "version": "3.10.12"
486 | },
487 | "widgets": {
488 | "application/vnd.jupyter.widget-state+json": {
489 | "state": {},
490 | "version_major": 2,
491 | "version_minor": 0
492 | }
493 | }
494 | },
495 | "nbformat": 4,
496 | "nbformat_minor": 4
497 | }
498 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/ReadMe.md:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | # Algebraic Equations with SymPy
2 |
3 | [Introduction](#introduction) | [Output Formatting](#controlling-the-format-of-interactive-outputs)
4 | | [Installation](#setupinstallation) |
5 | [Try Live](#try-in-binder) | [Issues or Comments](#issues-or-comments) |
6 | [Change Log](#change-log) |
7 | [License](#licensed-under-gnu-v3-licensehttpsgnuorglicenses)
8 | | [GIT Repository](https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy)
9 | | [PyPi Link](https://pypi.org/project/Algebra-with-SymPy/)
10 |
11 | ## [Website/Documentation (including API)](https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/)
12 |
13 | ## Introduction
14 |
15 |
16 | This tool defines relations that all high school and college students would
17 | recognize as mathematical equations.
18 | They consist of a left hand side (lhs) and a right hand side (rhs) connected by
19 | the relation operator "=". In addition, it sets some convenient defaults and
20 | provides some controls of output formatting that may be useful even if
21 | you do not use the `Equation` class (see [Conveniences for
22 | SymPy](#convenience-tools-and-defaults-for-interactive-use-of-sympy)).
23 |
24 | This tool applies operations to both sides of the equation simultaneously, just
25 | as students are taught to do when
26 | attempting to isolate (solve for) a variable. Thus the statement `Equation/b`
27 | yields a new equation `Equation.lhs/b = Equation.rhs/b`
28 |
29 | The intent is to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to rearrange
30 | equations and perform algebra
31 | in a stepwise fashion using as close to standard mathematical notation as
32 | possible. In this way more people can successfully perform
33 | algebraic rearrangements without stumbling
34 | over missed details such as a negative sign.
35 |
36 | A simple example as it would appear in a [Jupyter](https://jupyter.org)
37 | notebook is shown immediately below:
38 |
39 | 
40 |
41 | The last cell illustrates how it is possible to substitute numbers with
42 | units into the solved equation to calculate a numerical solution with
43 | proper units. The `units(...)` operation is part this package, not Sympy.
44 |
45 | In IPython environments (IPython, Jupyter, Google Colab, etc...) there is
46 | also a shorthand syntax for entering equations provided through the IPython
47 | preparser. An equation can be specified as `eq1 =@ a/b = c/d`.
48 |
49 |
50 | 
51 |
52 | If no Python name is
53 | specified for the equation (no `eq_name` to the left of `=@`), the equation
54 | will still be defined, but will not be easily accessible for further
55 | computation. The `=@` symbol combination was chosen to avoid conflicts with
56 | reserved python symbols while minimizing impacts on syntax highlighting
57 | and autoformatting.
58 |
59 | [More examples of the capabilities of Algebra with Sympy are
60 | here](https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/Demonstration%20of%20equation%20class.html).
61 |
62 | Many math packages such as [SageMath](https://www.sagemath.org/)
63 | and [Maxima](http://maxima.sourceforge.net/) have similar capabilities,
64 | but require more knowledge of command syntax, plus they cannot easily be
65 | installed in a generic python environment.
66 |
67 | ## Convenience Tools and Defaults for Interactive Use of SymPy
68 |
69 | Even if you do not use the `Equation` class, there are some convenience
70 | tools and defaults that will probably make interactive use of SymPy in
71 | Jupyter/IPython environments easier:
72 |
73 | * By default, all numbers *in Sympy expressions* without decimal points are
74 | interpreted as integers (e.g. `2/3*x`, where x is a sympy symbol, ->
75 | `2*x/3` not `x*0.6666...`, but if x is just a plain Python object then `2/3*x`
76 | -> `x*0.66666...`). This can be turned off with `unset_integers_as_exact()`,
77 | which leads to standard Python behavior (`2/3*x` -> `x*0.6666...`) even for
78 | Sympy expressions. Turn on with `set_integers_as_exact()`. When on the flag
79 | `algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = True`.
80 | * Results of `solve()` are wrapped in `FiniteSet()` to force pretty-printing
81 | of all of a solution set. See [Controlling the Format of Interactive
82 | Outputs](#controlling-the-format-of-interactive-outputs).
83 | * It is possible to set the default display to show both the pretty-printed
84 | result and the code version simultaneously. See [Controlling the Format of Interactive
85 | Outputs](#controlling-the-format-of-interactive-outputs).
86 |
87 | ## Controlling the Format of Interactive Outputs
88 |
89 | * These controls impact all Sympy objects and the `Equation` class.
90 | * **In graphical environments (Jupyter)** you will get rendered Latex such as
91 | $\frac{a}{b} = \frac{c}{d}$ or $e^{\frac{-x^2}{\sigma^2}}$. To also see the
92 | code representation (what can be copied and pasted for
93 | additional computation) set `algwsym_config.output.show_code = True`.
94 | This will print the code version (e.g. `Equation(a,b/c)`) of equations
95 | and sympy expression in addition to the human readable version. This code
96 | version can be accessed directly by calling `repr()` on the
97 | equation or expression.
98 |
99 | * **In interactive text environments (IPython and command line)** The human
100 | readable string version of Sympy expressions are returned (for `Equations` a
101 | = b rather than Equation(a,b)). This is equivalent to Calling `print()`
102 | or `str()` on an expression.
103 | * To have the code version (can be copied and pasted as a
104 | Python statement) returned, set `algwsym_config.output.human_text = False`.
105 | * Setting both `algwsym_config.output.human_text = True`
106 | and `algwsym_config.output.show_code = True`, will return both the
107 | code and human readable versions.
108 |
109 | * **The equation label** can be turned off by setting
110 | `algwsym_config.output.label = False`.
111 |
112 | * **Automatic wrapping of `Equations` as Latex equations** can be activated
113 | by setting `algwsym_config.output.latex_as_equations` to `True`. The
114 | default is `False`. Setting this to `True` wraps output as LaTex equations,
115 | wrapping them in `\begin{equation}...\end{equation}`. Equations formatted
116 | this way will **not** be labeled with the internal name for the equation,
117 | independent of the setting of `algwsym_config.output.label`.
118 |
119 | * By default **solutions output by `solve()`** are returned as a SymPy
120 | `FiniteSet()` to force typesetting of the included solutions. To get Python
121 | lists instead you can override this for the whole session by setting
122 | `algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = True`. For a one-off, simply
123 | wrap the output of a solve in `list()` (e.g. `list(solve(...))`). One
124 | advantage of list mode is that lists can be ordered. When
125 | `algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = True` `solve()` maintains the
126 | solutions in the order the solve for variables were input.
127 |
128 | ## Setup/Installation
129 |
130 | 1. Use pip to install in your python environment:
131 | `pip install -U Algebra-with-SymPy`
132 | 2. To use in a running python session issue
133 | the following command : `from algebra_with_sympy import *`.
134 | This will also import the SymPy tools.
135 | 3. If you want to isolate this tool from the global namespace you are
136 | working with change the import statement
137 | to `import algebra_with_sympy as spa`, where
138 | `spa` stands for "SymPy Algebra". Then all calls would be made to `
139 | spa.funcname()`. WARNING: Doing this makes shorthand equation input and
140 | control of interactive output formats unavailable. To recover this
141 | functionality the following code must be run in the interactive session.
142 | ```
143 | Equation = spa.Equation
144 | Eqn = Equation
145 | algwsym_config = spa.algwsym_config
146 | ```
147 |
148 | ## Try in binder
149 |
150 | [](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy.git/master?labpath=Demonstration+of+equation+class.ipynb)
151 |
152 | ## Issues or Comments
153 |
154 | * Issues and bug reports should be [filed on
155 | github](https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy/issues).
156 | * Comments, questions, show and tell, etc. should go in the [project
157 | discussions](https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy/discussions).
158 |
159 | ## Change Log
160 |
161 | * 1.1.3 (September 7, 2025)
162 | * Better checking for an incompatible sympy installation and improved
163 | warning on how to solve the problem.
164 | * Shifting to more modern `pyproject.toml` packaging.
165 | * Updates to Developer documentation to reflect packaging changes.
166 | * Moved determination of equation (actually any sympy basic object) python
167 | name to this package from the equation object, thus simplifying what is
168 | included in sympy.
169 | * Minor test updates.
170 | * Added overrides of __repr__ and __str__ in preparation for inclusion of
171 | Equation class in Sympy.
172 | * 1.1.2 (August 13, 2024)
173 | * Test updates.
174 | * Verified compatibility with Sympy 1.13.2.
175 | * 1.1.1 (July 25, 2024)
176 | * BUG FIX accommodate empty re.search results in preparser. Prevents
177 | unnecessary error messages.
178 | * 1.1.0 (July 22, 2024)
179 | * Setting integers as exact (`set_integers_as_exact()`, the default) now
180 | only sets integers as exact within Sympy and Algebra_with_Sympy
181 | expressions. This increases compatibility with other packages that
182 | depend on integers being Python integers.
183 | * Refuse to import Algebra_with_Sympy if an incompatible
184 | version of Sympy is installed in the environment.
185 | * Added warning explaining how to install a compatible version of Sympy.
186 | * 1.0.2 (July 5, 2024)
187 | * Removed requirements for Jupyter and Jupyterlab as code will work in
188 | vanilla python or Google Colab.
189 | * Workaround for Google Colab's inconsistent handling of mixed Latex and
190 | plain text strings. This impacted display of equation labels in Colab.
191 | * BUG FIX: catch IPython not installed so that can run in plain vanilla
192 | python.
193 | * 1.0.1 (May 22, 2024)
194 | * BUG FIX: equation labels that include underscore characters "_" are now
195 | accepted.
196 | * BUG FIX: wrapping equations formatted as LaTex equation (ie. surrounded
197 | by `\begin{equation}...\end{equation}`) in the `$..$` code used to
198 | indicate markdown for MathJax was causing output errors in Quarto when
199 | outputing to .tex or .pdf. This is now fixed without negatively
200 | impacting MathJax rendering.
201 | * BUG FIX: Singleton results of solve unnecessarily wrapped by extra list
202 | or finiteset. No longer double nested.
203 | * BUG FIX: When returning lists make solve respect user order of solutions.
204 | * BUG FIX: Equation output threw error when Algebra_with_Sympy was
205 | imported as a submodule. Equation labeling turned off for this type of
206 | import to avoid error.
207 | * BUG FIX: Equation labels are now copyable even with the newer MathJax
208 | commonHTML rendering.
209 | * Updates to requirements.txt.
210 | * Documentation updates.
211 | * 1.0.0 (January 2, 2024)
212 | * Added convenience operation `units(...)` which takes a string of space
213 | separated symbols to use as units. This simply declares the symbols
214 | to be positive, making them behave as units. This does not create units
215 | that know about conversions, prefixes or systems of units. This lack
216 | is on purpose to provide units that require the user to worry about
217 | conversions (ideal in a teaching situation). To get units with built-in
218 | conversions see `sympy.physics.units`.
219 | * Fixed issue #23 where `cos()` multiplied by a factor was not the same
220 | type of object after `simplify()` acted on an expression. Required
221 | embedding the `Equation` type in the sympy library. Until `Equation` is
222 | incorporated into the primary Sympy repository a customized version of
223 | the latest stable release will be used.
224 | * Fixed issue where trailing comments (ie. `# a comment` at the end of a
225 | line) lead to input errors using compact `=@` notation.
226 | * `algwsym_config.output.latex_as_equations` has a default value of `False`.
227 | Setting this to `True` wraps output as LaTex equations wrapping them
228 | in `\begin{equation}...\end{equation}`. Equations formatted this way
229 | will not be labeled with the internal name for the equation.
230 | * 0.12.0 (July 12, 2023)
231 | * Now defaults to interpreting numbers without decimal points as integers.
232 | This can be turned off with `unset_integers_as_exact()` and on with
233 | `set_integers_as_exact()`. When on the flag
234 | `algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = True`.
235 | * 0.11.0 (June 5, 2023)
236 | * Formatting of `FiniteSets` overridden so that the contents always
237 | pretty-print. This removes the necessity of special flags to get
238 | pretty output from `solve`.
239 | * Sympy `solve()` now works reliably with equations and outputs
240 | pretty-printed solutions.
241 | * Added option `algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = True` which causes
242 | `solve()` to return solutions sets as Python lists. Using this option
243 | prevents pretty-printing of the solutions produced by `solve()`.
244 | * `algwsym_config.output.show_code` and
245 | `algwsym_config.output.human_text` now work for all sympy objects, not
246 | just `Equation` objects. This works
247 | in terminal, IPython terminal and Jupyter. This is achieved by hooking
248 | into the python `display_hook` and IPython `display_formatter`.
249 | * Added jupyter to requirements.txt so that virtual environment builds
250 | will include jupyter.
251 | * The way `__version__` was handled could break pip install. Changed to
252 | generating the internal version during setup. This means the version
253 | is now available as `algwsym_version`.
254 | * 0.10.0 (Sep. 5, 2022)
255 | * Documentation updates and fixes.
256 | * Significantly increased test coverage (~98%).
257 | * Support for `Eqn.rewrite(Add)`
258 | * Solving (e.g. `solve(Eqn,x)`) now supported fully. Still experimental.
259 | * Bug fix: latex printing now supports custom printer.
260 | * Substitution into an Equation using Equations is now
261 | supported (e.g. `eq1.subs(eq2, eq3, ...)`).
262 | * `algebra_with_sympy.__version__` is now available for version checking
263 | within python.
264 | * Bug fix: preparsing for `=@` syntax no longer blocks `obj?` syntax for
265 | getting docstrings in ipython.
266 | * More robust determination of equation names for labeling.
267 | * 0.9.4 (Aug. 11, 2022)
268 | * Update to deal with new Sympy function `piecewise_exclusive` in v1.11.
269 | * Added user warning if a function does not extend for use with `Equations`
270 | as expected. This also allows the package to be used even when a function
271 | extension does fail.
272 | * Simplification of documentation preparation.
273 | * Typo fixes in preparser error messages.
274 | * 0.9.3 (Aug. 9, 2022)
275 | * Added check for new enough version of IPython to use the preparser.
276 | * If IPython version too old, issue warning and do not accept `=@` shorthand.
277 | * 0.9.2 (Jun. 5, 2022)
278 | * `=@` shorthand syntax for defining equations in IPython compatible
279 | environments.
280 | * Fixed bug where `root()` override called `sqrt()` on bare expressions.
281 | * 0.9.1 (Mar. 24, 2022)
282 | * Equations labeled with their python name, if they have one.
283 | * Added flags to adjust human readable output and equation labeling.
284 | * Accept equation as function argument in any position.
285 | * First pass at `solve()` accepting equations.
286 | * Added override of `root()` to avoid warning messages.
287 | * More unit tests.
288 | * First pass at documentation.
289 | * 0.9.0 functionality equivalent to extension of SymPy in
290 | [PR#21333](https://github.com/sympy/sympy/pull/21333).
291 |
292 | ## [licensed under GNU V3 license](https://gnu.org/licenses)
293 |
294 | This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
295 | it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
296 | the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
297 | (at your option) any later version.
298 | This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
299 | but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
300 | MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
301 | GNU General Public License for more details.
302 |
303 | Copyright - Algebra with Sympy Contributors 2021, 2022, 2023, 2024
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/tests/test_algebraic_equation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | from sympy import symbols, integrate, simplify, expand, factor, Integral, Add
2 | from sympy import diff, FiniteSet, Function, Matrix, S, Eq
3 | from sympy import Equation, Eqn
4 | from sympy import sin, cos, log, exp, latex, Symbol, I, pi
5 | from sympy.core.function import AppliedUndef
6 | from sympy.printing.latex import LatexPrinter
7 | from algebra_with_sympy.algebraic_equation import solve, collect
8 | from algebra_with_sympy.algebraic_equation import Equality, units
9 | from sympy import sqrt, root, Heaviside
10 | from algebra_with_sympy.algebraic_equation import algwsym_config
11 |
12 |
13 | from pytest import raises
14 |
15 | #####
16 | # Testing that sympy functions work with Equations
17 | #####
18 |
19 | # Overridden elsewhere
20 | _extended_ = ('sqrt', 'cbrt', 'root')
21 |
22 | # Either not applicable to Equations or have not yet figured out a way
23 | # to systematically apply to an Equation.
24 | # TODO examine these more carefully (top priority: real_root, Ynm_c).
25 | _not_applicable_to_equations_ = ('Min', 'Max', 'Id', 'real_root',
26 | 'unbranched_argument', 'polarify', 'unpolarify',
27 | 'piecewise_fold', 'E1', 'Eijk', 'bspline_basis',
28 | 'bspline_basis_set', 'interpolating_spline', 'jn_zeros',
29 | 'jacobi_normalized', 'Ynm_c', 'piecewise_exclusive', 'Piecewise',
30 | 'motzkin', 'hyper','meijerg', 'chebyshevu_root', 'chebyshevt_root',
31 | 'betainc_regularized')
32 | _skip_ = _extended_ + _not_applicable_to_equations_
33 |
34 | class CustomLatexPrinter(LatexPrinter):
35 | """Print undefined applied functions without arguments"""
36 | def _print_Function(self, expr, exp=None):
37 | if isinstance(expr, AppliedUndef):
38 | return self._print(Symbol(expr.func.__name__))
39 | return super()._print_Function(expr, exp)
40 |
41 |
42 | def my_latex(expr, **settings):
43 | """Mimic latex()"""
44 | return CustomLatexPrinter(settings).doprint(expr)
45 |
46 |
47 | def test_define_equation():
48 | a, b, c = symbols('a b c')
49 | raises(TypeError, lambda: Equation(FiniteSet(a), FiniteSet(b, c)))
50 | assert(Equation(1, 0).check() == False)
51 | assert Eqn(1, 0) == Equation(1, 0)
52 | tsteqn = Equation(a, b/c)
53 | assert tsteqn.args == (a, b/c)
54 | assert tsteqn.lhs == a
55 | assert tsteqn.rhs == b/c
56 | assert tsteqn.free_symbols == {a, b, c}
57 |
58 | def test_convert_equation():
59 | a, b, c = symbols('a b c')
60 | tsteqn = Equation(a, b/c)
61 | assert tsteqn.as_Boolean() == Eq(a, b/c)
62 | assert tsteqn.reversed == Equation(b/c, a)
63 | assert tsteqn.swap == Equation(b/c, a)
64 |
65 |
66 | def test_binary_op():
67 | a, b, c = symbols('a b c')
68 | tsteqn = Equation(a, b/c)
69 | assert tsteqn + c == Equation(a + c, b/c + c)
70 | assert c + tsteqn == Equation(c + a, c + b/c)
71 | assert tsteqn*c == Equation(a*c, b)
72 | assert c*tsteqn == Equation(c*a, b)
73 | assert tsteqn - c == Equation(a - c, b/c - c)
74 | assert c - tsteqn == Equation(c - a, c - b/c)
75 | assert tsteqn/ c == Equation(a/c, b/c**2)
76 | assert c/tsteqn == Equation(c/a, c**2/b)
77 | assert tsteqn % c == Equation(a % c, (b/c) % c)
78 | assert c % tsteqn == Equation(c % a, c % (b/c))
79 | assert tsteqn**c == Equation(a**c, (b/c)**c)
80 | assert c**tsteqn == Equation(c**a, c**(b/c))
81 | assert tsteqn + tsteqn == Equation(2*a, 2*b/c)
82 | assert tsteqn*tsteqn == Equation(a**2, b**2/c**2)
83 | assert tsteqn - tsteqn == Equation(0, 0)
84 | assert tsteqn/tsteqn == Equation(1, 1)
85 | assert tsteqn % tsteqn == Equation(0, 0)
86 | assert tsteqn**tsteqn == Equation(a**a, (b/c)**(b/c))
87 | assert tsteqn**a == Equation(a**a, (b/c)**a)
88 | assert tsteqn._eval_power(tsteqn) == Equation(a**a, (b/c)**(b/c))
89 | assert tsteqn._eval_power(a) == Equation(a**a, (b/c)**a)
90 |
91 |
92 | def test_outputs(capsys):
93 | from algebra_with_sympy import algwsym_config
94 | from algebra_with_sympy.algebraic_equation import __latex_override__, \
95 | __command_line_printing__
96 |
97 | # check defaults
98 | assert algwsym_config.output.show_code == False
99 | assert algwsym_config.output.human_text == True
100 | assert algwsym_config.output.label == True
101 | assert algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list == False
102 |
103 | a, b, c = symbols('a b c')
104 | tsteqn = Eqn(a, b/c)
105 | assert tsteqn.__str__() == 'a = b/c'
106 | assert latex(tsteqn) == 'a=\\frac{b}{c}'
107 | assert tsteqn.__repr__() == 'Equation(a, b/c)'
108 | assert tsteqn.__repr__() == 'Equation(a, b/c)'
109 | assert tsteqn.__str__() == 'a = b/c'
110 | assert latex(tsteqn) == 'a=\\frac{b}{c}'
111 |
112 | import __main__ as gs
113 | vars(gs)['tsteqn'] = tsteqn
114 | assert tsteqn._get_eqn_name() == 'tsteqn'
115 | __command_line_printing__(tsteqn)
116 | captured = capsys.readouterr()
117 | assert captured.out == 'a = b/c (tsteqn)\n'
118 | # make sure sys.displayhook does not point to __command_line_printing__()
119 | import sys
120 | sys.displayhook = sys.__displayhook__
121 | assert __latex_override__(tsteqn) == ('$a=\\frac{b}{c}\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,\\,'
122 | '\\,\\,\\,\\,$(tsteqn)')
123 | algwsym_config.output.label = False
124 | __command_line_printing__(tsteqn)
125 | captured = capsys.readouterr()
126 | assert captured.out == 'a = b/c\n'
127 | assert __latex_override__(tsteqn) == '$a=\\frac{b}{c}$'
128 | algwsym_config.output.label = True
129 |
130 | f = Function("f")(a, b, c)
131 | eq = Eqn(f, 2)
132 | assert latex(eq) == "f{\\left(a,b,c \\right)}=2"
133 | # use custom printer
134 | assert my_latex(eq) == "f=2"
135 |
136 | x, y = symbols('x y', real=True)
137 | eq1 = Eqn(abs(2*x + y),3)
138 | eq2 = Eqn(abs(x + 2*y),3)
139 | B = solve([eq1,eq2],x,y)
140 | assert B.__repr__() == 'FiniteSet(FiniteSet(Equation(' \
141 | 'x, -3), ' \
142 | 'Equation(y, 3)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, ' \
143 | '-1), ' \
144 | 'Equation(y, -1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, ' \
145 | '1), ' \
146 | 'Equation(y, 1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 3),' \
147 | ' Equation(y, -3)))'
148 | assert B.__str__() == '{{x = -3, y = 3}, {x = -1, y = -1}, ' \
149 | '{x = 1, y = 1}, {x = 3, y = -3}}'
150 | __command_line_printing__(B)
151 | captured = capsys.readouterr()
152 | assert captured.out == \
153 | '{{x = -3, y = 3}, {x = -1, y = -1}, ' \
154 | '{x = 1, y = 1}, {x = 3, y = -3}}\n'
155 |
156 | algwsym_config.output.show_code = True
157 | __command_line_printing__(B)
158 | captured = capsys.readouterr()
159 | assert captured.out== \
160 | 'Code version: FiniteSet(FiniteSet(' \
161 | 'Equation(x, -3), Equation(y, 3)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, -1), ' \
162 | 'Equation(y, -1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 1), Equation(y, 1)), ' \
163 | 'FiniteSet(Equation(x, 3), Equation(y, -3)))' \
164 | '\n{{x = -3, y = 3}, {x = -1, y = -1}, {x = 1, y = 1}, {x = 3, y = -3}}\n'
165 | assert __latex_override__(B) == \
166 | '$\\left\\{\\left\\{x=-3, y=3\\right\\}, \\left\\{x=-1, ' \
167 | 'y=-1\\right\\}, \\left\\{x=1, y=1\\right\\}, ' \
168 | '\\left\\{x=3, y=-3\\right\\}\\right\\}$'
169 | captured = capsys.readouterr()
170 | assert captured.out == \
171 | 'Code version: FiniteSet(FiniteSet(' \
172 | 'Equation(x, -3), Equation(y, 3)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, -1), ' \
173 | 'Equation(y, -1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 1), Equation(y, 1)), ' \
174 | 'FiniteSet(Equation(x, 3), Equation(y, -3)))\n'
175 |
176 | algwsym_config.output.show_code = False
177 | algwsym_config.output.human_text = False
178 | __command_line_printing__(B)
179 | captured = capsys.readouterr()
180 | assert captured.out == 'FiniteSet(FiniteSet(Equation(x, -3), ' \
181 | 'Equation(y, 3)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, -1), ' \
182 | 'Equation(y, -1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 1), ' \
183 | 'Equation(y, 1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 3), ' \
184 | 'Equation(y, -3)))\n'
185 |
186 | def test_sympy_functions():
187 | a, b, c = symbols('a b c')
188 | tsteqn = Equation(a, b/c)
189 | assert sin(tsteqn) == Equation(sin(a),sin(b/c))
190 | assert log(tsteqn) == Equation(log(a),log(b/c))
191 | # Check matrix exponentiation is not overridden.
192 | assert exp(tsteqn) == Equation(exp(tsteqn.lhs),exp(tsteqn.rhs))
193 | tsteqn5 = Equation(a, Matrix([[1, 1], [1, 1]]))
194 | assert exp(tsteqn5).lhs == exp(a)
195 | assert exp(tsteqn5).rhs == exp(Matrix([[1, 1], [1, 1]]))
196 |
197 | def test_helper_functions():
198 | a, b, c, x= symbols('a b c x')
199 | tsteqn = Equation(a, b/c)
200 | raises(ValueError, lambda: integrate(tsteqn, c))
201 | raises(AttributeError, lambda: integrate(tsteqn, c, side='right'))
202 | assert tsteqn.evalf(4, {b: 2.0, c: 4}) == Equation(a, 0.5000).n(4)
203 | assert diff(tsteqn, c) == Equation(diff(a, c, evaluate=False), -b/c**2)
204 | tsteqn = Equation(a*c, b/c)
205 | assert diff(tsteqn, c) == Equation(a, -b/c**2)
206 | assert integrate(tsteqn, c, side='rhs') == integrate(tsteqn.rhs, c)
207 | assert integrate(tsteqn, c, side='lhs') == integrate(tsteqn.lhs, c)
208 |
209 | def adsq(eqn):
210 | # Arbitrary python function
211 | return eqn + eqn**2
212 |
213 | assert adsq(Equation(a*c, b/c)) == Equation(a**2*c**2 + a*c, b**2/c**2 +
214 | b/c)
215 | assert Equation((a - 1)*(a + 1), (2*b + c)**2).expand() == Equation(
216 | a**2 - 1, 4*b**2 + 4*b*c + c**2)
217 | assert expand(Equation((a - 1)*(a + 1), (2*b + c)**2)) == Equation(
218 | a**2 - 1, 4*b**2 + 4*b*c + c**2)
219 | assert Equation(a**2 - 1, 4*b**2 + 4*b*c + c**2).factor() == Equation(
220 | (a - 1)*(a + 1), (2*b + c)**2)
221 | assert factor(Equation(a**2 - 1, 4*b**2 + 4*b*c + c**2)) == Equation(
222 | (a - 1)*(a + 1), (2*b + c)**2)
223 | assert Equation(a**2 - 1, 4*b**2 + 4*b*c + c*a).collect(c) == Equation(
224 | a**2- 1, 4*b**2 + c*(a + 4*b))
225 | assert collect(Equation(a**2 - 1, 4*b**2 + 4*b*c + c*a), c) == Equation(
226 | a**2- 1, 4*b**2 + c*(a + 4*b))
227 | assert Equation((a + 1)**2/(a + 1), exp(log(c))).simplify() == Equation(
228 | a + 1, c)
229 | assert simplify(Equation((a + 1)**2/(a + 1), exp(log(c)))) == Equation(
230 | a + 1, c)
231 | assert root(Eqn(a,b/c),3) == Equation(a**(S(1)/S(3)), (b/c)**(S(1)/S(3)))
232 | assert root(b/c,3) == (b/c)**(S(1)/S(3))
233 | assert sqrt(Eqn(a,b/c)) == Equation(sqrt(a), sqrt(b/c))
234 |
235 | def test_units():
236 | units('J mol K')
237 | user_namespace = None
238 | import sys
239 | frame_num = 0
240 | frame_name = None
241 | while frame_name != '__main__' and frame_num < 50:
242 | user_namespace = sys._getframe(frame_num).f_globals
243 | frame_num += 1
244 | frame_name = user_namespace['__name__']
245 | J = user_namespace['J']
246 | mol = user_namespace['mol']
247 | K = user_namespace['K']
248 | assert sqrt((123.2*J/mol/K)**2) == 123.2*J/mol/K
249 | assert 1.0*J + 5.0*J == 6.0*J
250 | assert 1.0*J + 5.0*mol == 1.0*J + 5.0*mol
251 | assert J > 0 and mol > 0 and K > 0
252 |
253 | def test_solve():
254 | a, b, c, x = symbols('a b c x')
255 | assert Equation(x, ((b - sqrt(4*a*c + b**2))/(2*a)).expand()) in solve(
256 | Equation(a*x**2,b*x+c),x)
257 | assert Equation(x, ((b + sqrt(4*a*c + b**2))/(2*a)).expand()) in solve(
258 | Equation(a*x**2,b*x+c),x)
259 | assert len(solve(Equation(a*x**2,b*x+c), x)) == 2
260 | result = solve(a*x**2-b*x-c,x)
261 | solns = []
262 | for k in result:
263 | for key in k.keys():
264 | solns.append(k[key])
265 | assert ((b - sqrt(4*a*c + b**2))/(2*a)).expand() in solns
266 |
267 | x, y = symbols('x y', real = True)
268 | eq1 = Eqn(abs(2*x + y), 3)
269 | eq2 = Eqn(abs(x + 2*y), 3)
270 | assert solve([eq1,eq2], x, y) == FiniteSet(FiniteSet(Equation(x, -3),
271 | Equation(y, 3)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, -1),
272 | Equation(y, -1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 1),
273 | Equation(y, 1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 3),
274 | Equation(y, -3)))
275 | algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = True
276 | assert solve([eq1,eq2], x, y) == [[Equation(x, -3), Equation(y, 3)],
277 | [Equation(x, -1), Equation(y, -1)],
278 | [Equation(x, 1), Equation(y, 1)],
279 | [Equation(x, 3), Equation(y, -3)]]
280 |
281 | xi, wn = symbols("xi omega_n", real=True, positive=True)
282 | Tp, Ts = symbols("T_p, T_s", real=True, positive=True)
283 | e1 = Eqn(Tp, pi / (wn*sqrt(1 - xi**2)))
284 | e2 = Eqn(Ts, 4 / (wn*xi))
285 | algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = False
286 | assert solve([e1, e2], [xi, wn]) == FiniteSet(
287 | Eqn(xi, 4*Tp/sqrt(16*Tp**2 + pi**2*Ts**2)),
288 | Eqn(wn, sqrt(16*Tp**2 + pi**2*Ts**2)/(Tp*Ts)))
289 | algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = True
290 | assert solve([e1, e2], [xi, wn]) == [
291 | Eqn(xi, 4*Tp/sqrt(16*Tp**2 + pi**2*Ts**2)),
292 | Eqn(wn, sqrt(16*Tp**2 + pi**2*Ts**2)/(Tp*Ts))
293 | ]
294 | # order of symbols are swapped -> results are swapped as well
295 | assert solve([e1, e2], [wn, xi]) == [
296 | Eqn(wn, sqrt(16*Tp**2 + pi**2*Ts**2)/(Tp*Ts)),
297 | Eqn(xi, 4*Tp/sqrt(16*Tp**2 + pi**2*Ts**2))
298 | ]
299 |
300 | def test_Heaviside():
301 | a, b, c, x = symbols('a b c x')
302 | tsteqn = Equation(a, b / c)
303 | assert (Heaviside(tsteqn) ==
304 | Equation(Heaviside(tsteqn.lhs), Heaviside(tsteqn.rhs)))
305 | assert Heaviside(0) == S(1)/S(2)
306 |
307 | def test_equality_extension():
308 | a, b, c, x = symbols('a b c x')
309 | tstequal = Equality(a, b / c)
310 | assert(tstequal.to_Equation() == Equation(a, b / c))
311 | assert(tstequal.to_Eqn()== Equation(a, b / c))
312 |
313 | def test_apply_syntax():
314 | a, b, c, x = symbols('a b c x')
315 | tsteqn = Equation(a, b/c)
316 | assert tsteqn.apply(log) == Equation(log(a), log(b/c))
317 | assert tsteqn.applylhs(log) == Equation(log(a), b / c)
318 | assert tsteqn.applyrhs(log) == Equation(a, log(b / c))
319 | poly = Equation(a*x**2 + b*x + c*x**2, a*x**3 + b*x**3 + c*x)
320 | assert poly.applyrhs(collect, x) == Equation(poly.lhs, poly.rhs.collect(x))
321 |
322 |
323 | def test_do_syntax():
324 | a, b, c, x = symbols('a b c x')
325 | tsteqn = Equation(a, b/c)
326 | raises(AttributeError, lambda: tsteqn.do.log())
327 | poly = Equation(a*x**2 + b*x + c*x**2, a*x**3 + b*x**3 + c*x)
328 | assert poly.dorhs.collect(x) == Eqn(poly.lhs, poly.rhs.collect(x))
329 | assert poly.dolhs.collect(x) == Eqn(poly.lhs.collect(x), poly.rhs)
330 | assert poly.do.collect(x) == Eqn(poly.lhs.collect(x), poly.rhs.collect(x))
331 |
332 |
333 | def test_rewrite_add():
334 | b, x = symbols("x, b")
335 | eq = Equation(x + b, x - b)
336 | assert eq.rewrite(Add) == Equation(2 * b, 0)
337 | assert set(eq.rewrite(Add, evaluate=None).lhs.args) == set((b, x, b, -x))
338 | assert set(eq.rewrite(Add, evaluate=False).lhs.args) == set((b, x, b, -x))
339 | assert eq.rewrite(Add, eqn=False) == 2 * b
340 | assert set(eq.rewrite(Add, eqn=False, evaluate=False).args) == set((b, x, b, -x))
341 |
342 |
343 | def test_rewrite():
344 | x = symbols("x")
345 | eq = Equation(exp(I*x),cos(x) + I*sin(x))
346 |
347 | # NOTE: Must use `sexp` otherwise the test is going to fail.
348 | # This reflects the fact that rewrite pulls the fuction exp internally
349 | # from the definitions of functions in sympy and not from the globally
350 | # redefined functions that are Equation aware.
351 | from sympy import exp as sexp
352 | assert eq.rewrite(exp) == Equation(exp(I*x), sexp(I*x))
353 | assert eq.rewrite(Add) == Equation(exp(I*x) - I*sin(x) - cos(x), 0)
354 |
355 |
356 | def test_subs():
357 | a, b, c, x = symbols('a b c x')
358 | eq1 = Equation(x + a + b + c, x * a * b * c)
359 | eq2 = Equation(x + a, 4)
360 | assert eq1.subs(a, 2) == Equation(x + b + c + 2, 2 * x * b * c)
361 | assert eq1.subs([(a, 2), (b, 3)]) == Equation(x + c + 5, 6 * x * c)
362 | assert eq1.subs({a: 2, b: 3}) == Equation(x + c + 5, 6 * x * c)
363 | assert eq1.subs(eq2) == Equation(4 + b + c, x * a * b * c)
364 |
365 | # verify that proper errors are raised
366 | eq3 = Equation(b, 5)
367 | raises(TypeError, lambda: eq1.subs([eq2, eq3]))
368 | raises(ValueError, lambda: eq1.subs(eq2, {b: 5}))
369 |
370 | # verify that substituting an Equation into an expression is not supported
371 | raises(ValueError, lambda: eq1.dolhs.subs(eq2))
372 | raises(ValueError, lambda: eq1.dorhs.subs(eq2))
373 | raises(ValueError, lambda: (x + a + b + c).subs(eq2))
374 |
375 | # verify the effectiveness of `simultaneous`
376 | eq = Equation((x + a) / a, b * c)
377 | sd = {x + a: a, a: x + a}
378 | assert eq.subs(sd) == Equation(1, b * c)
379 | assert eq.subs(sd, simultaneous=True) == Equation(a / (x + a), b * c)
380 |
381 | def test_issue_23():
382 | # This gave a key error
383 | a, t = symbols('a t')
384 | assert simplify(a * cos(t) + sin(t)) == a * cos(t) + sin(t)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Developer Testing/Importing sympy into global namespace and then extending...ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": null,
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "outputs": [],
8 | "source": [
9 | "from sympy import *"
10 | ]
11 | },
12 | {
13 | "cell_type": "code",
14 | "execution_count": null,
15 | "metadata": {},
16 | "outputs": [],
17 | "source": [
18 | "var('a b c')\n",
19 | "t=a*b/c\n",
20 | "t"
21 | ]
22 | },
23 | {
24 | "cell_type": "code",
25 | "execution_count": null,
26 | "metadata": {},
27 | "outputs": [],
28 | "source": [
29 | "class Equation(Expr):\n",
30 | " \n",
31 | " _op_priority = 11.0\n",
32 | " \n",
33 | " def __init__(self,lhs,rhs,relop='='):\n",
34 | " if not(relop == '='):\n",
35 | " raise NotImplementedError('\"=\" is the only relational operator presently supported in Equations.') \n",
36 | " self.lhs = lhs\n",
37 | " self.rhs = rhs\n",
38 | " \n",
39 | "# def __init__(self,lhs,rhs,**kwargs):\n",
40 | "# pass\n",
41 | "#####\n",
42 | "# Overrides of sp.Expr Arithmatic\n",
43 | "#####\n",
44 | " def __pos__(self):\n",
45 | " return self\n",
46 | "\n",
47 | " def __neg__(self):\n",
48 | " # Mul has its own __neg__ routine, so we just\n",
49 | " # create a 2-args Mul with the -1 in the canonical\n",
50 | " # slot 0.\n",
51 | " c = self.is_commutative\n",
52 | " lhs =Mul._from_args((S.NegativeOne, self.lhs), c)\n",
53 | " rhs =Mul._from_args((S.NegativeOne, self.rhs), c) \n",
54 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
55 | "\n",
56 | " def __abs__(self):\n",
57 | " from sympy import Abs\n",
58 | " lhs=Abs(self.lhs)\n",
59 | " rhs=Abs(self.rhs)\n",
60 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
61 | "\n",
62 | " def __add__(self, other):\n",
63 | " lhs = Add(self.lhs,other)\n",
64 | " rhs = Add(self.rhs,other)\n",
65 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
66 | "\n",
67 | " def __radd__(self, other):\n",
68 | " lhs = Add(other,self.lhs)\n",
69 | " rhs = Add(other,self.rhs)\n",
70 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
71 | "\n",
72 | " def __sub__(self, other):\n",
73 | " lhs = Add(self.lhs,-other)\n",
74 | " rhs = Add(self.rhs,-other)\n",
75 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
76 | "\n",
77 | " def __rsub__(self, other):\n",
78 | " lhs = Add(other,-self.lhs)\n",
79 | " rhs = Add(other,-self.rhs)\n",
80 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
81 | "\n",
82 | " def __mul__(self, other):\n",
83 | " lhs = Mul(self.lhs,other)\n",
84 | " rhs = Mul(self.rhs,other)\n",
85 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
86 | " \n",
87 | " def __rmul__(self, other):\n",
88 | " lhs = Mul(other,self.lhs)\n",
89 | " rhs = Mul(other,self.rhs)\n",
90 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
91 | "\n",
92 | " def _pow(self, other):\n",
93 | " lhs = Pow(self.lhs,other)\n",
94 | " rhs = Pow(self.rhs,other)\n",
95 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
96 | "\n",
97 | " def __rpow__(self,other):\n",
98 | " lhs = Pow(other,self.lhs)\n",
99 | " rhs = Pow(other,self.rhs)\n",
100 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
101 | "\n",
102 | " def __div__(self, other):\n",
103 | " return self.__mul__(Pow(other, S.NegativeOne))\n",
104 | "\n",
105 | " def __rdiv__(self, other):\n",
106 | " raise NotImplemented('Division by equation not supported.')\n",
107 | "\n",
108 | " __truediv__ = __div__\n",
109 | " __rtruediv__ = __rdiv__\n",
110 | "\n",
111 | " def __mod__(self, other):\n",
112 | " lhs = Mod(self.lhs,other)\n",
113 | " rhs = Mod(self.rhs,other)\n",
114 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
115 | "\n",
116 | " def __rmod__(self, other):\n",
117 | " raise NotImplemented('Mod by equation not supported.')\n",
118 | " \n",
119 | " def __repr__(self):\n",
120 | " return(str(self.lhs)+' = '+str(self.rhs))\n",
121 | " \n",
122 | " def _latex(self,obj,**kwargs):\n",
123 | " return(latex(self.lhs)+'='+latex(self.rhs))\n",
124 | "\n",
125 | "equ = Equation\n",
126 | "\n",
127 | "class Function(Function):\n",
128 | " def __new__(cls, *arg, **kwargs):\n",
129 | " if (type(arg[0]) is Equation):\n",
130 | " temptuple=(arg[0].lhs,)+arg[1:]\n",
131 | " lhs = super().__new__(cls, *temptuple, **kwargs)\n",
132 | " temptuple=(arg[0].rhs,)+arg[1:]\n",
133 | " rhs = super().__new__(cls, *temptuple, **kwargs)\n",
134 | " return (equ(lhs,rhs))\n",
135 | " else:\n",
136 | " return(super().__new__(cls, *arg, **kwargs))\n",
137 | " \n",
138 | "for func in functions.__all__:\n",
139 | " # listed in `skip` cannot be extended because of `mro` error or `metaclass conflict`.\n",
140 | " skip=['sqrt','root','Min','Max','Id','real_root','cbrt','unbranched_argument','polarify','unpolarify',\n",
141 | " 'piecewise_fold','E1','Eijk','bspline_basis','bspline_basis_set','interpolating_spline','jn_zeros',\n",
142 | " 'jacobi_normalized','Ynm_c']\n",
143 | " if func not in skip:\n",
144 | " execstr = 'class '+str(func)+'(Function, '+str(func)+'):\\n pass\\n'\n",
145 | " exec(execstr,globals(),locals())"
146 | ]
147 | },
148 | {
149 | "cell_type": "code",
150 | "execution_count": null,
151 | "metadata": {},
152 | "outputs": [],
153 | "source": [
154 | "t=equ(a,b/c)\n",
155 | "t"
156 | ]
157 | },
158 | {
159 | "cell_type": "code",
160 | "execution_count": null,
161 | "metadata": {},
162 | "outputs": [],
163 | "source": [
164 | "log(t)"
165 | ]
166 | },
167 | {
168 | "cell_type": "code",
169 | "execution_count": null,
170 | "metadata": {},
171 | "outputs": [],
172 | "source": [
173 | "type(t)"
174 | ]
175 | },
176 | {
177 | "cell_type": "code",
178 | "execution_count": null,
179 | "metadata": {},
180 | "outputs": [],
181 | "source": [
182 | "c*t"
183 | ]
184 | },
185 | {
186 | "cell_type": "code",
187 | "execution_count": null,
188 | "metadata": {},
189 | "outputs": [],
190 | "source": [
191 | "t*c"
192 | ]
193 | },
194 | {
195 | "cell_type": "code",
196 | "execution_count": null,
197 | "metadata": {},
198 | "outputs": [],
199 | "source": [
200 | "t*c-b"
201 | ]
202 | },
203 | {
204 | "cell_type": "code",
205 | "execution_count": null,
206 | "metadata": {},
207 | "outputs": [],
208 | "source": [
209 | "b-t"
210 | ]
211 | },
212 | {
213 | "cell_type": "code",
214 | "execution_count": null,
215 | "metadata": {},
216 | "outputs": [],
217 | "source": [
218 | "equ(a,c/b,'>')"
219 | ]
220 | },
221 | {
222 | "cell_type": "code",
223 | "execution_count": null,
224 | "metadata": {},
225 | "outputs": [],
226 | "source": []
227 | },
228 | {
229 | "cell_type": "markdown",
230 | "metadata": {},
231 | "source": [
232 | "Try object creation and then extensions"
233 | ]
234 | },
235 | {
236 | "cell_type": "code",
237 | "execution_count": 1,
238 | "metadata": {},
239 | "outputs": [],
240 | "source": [
241 | "class A ():\n",
242 | " def __init__(self, arg1, arg2):\n",
243 | " self.arg1 = arg1\n",
244 | " self.arg2 = arg2\n",
245 | " \n",
246 | " def __repr__(self):\n",
247 | " return self.arg1+', '+self.arg2\n",
248 | " \n",
249 | "class B ():\n",
250 | " def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):\n",
251 | " self.arg=args[0]\n",
252 | " \n",
253 | " def __repr__(self):\n",
254 | " return 'B('+str(self.arg)+')'"
255 | ]
256 | },
257 | {
258 | "cell_type": "code",
259 | "execution_count": 2,
260 | "metadata": {},
261 | "outputs": [
262 | {
263 | "data": {
264 | "text/plain": [
265 | "Help, me"
266 | ]
267 | },
268 | "execution_count": 2,
269 | "metadata": {},
270 | "output_type": "execute_result"
271 | }
272 | ],
273 | "source": [
274 | "A1 = A(\"Help\",\"me\")\n",
275 | "A1"
276 | ]
277 | },
278 | {
279 | "cell_type": "code",
280 | "execution_count": 3,
281 | "metadata": {},
282 | "outputs": [
283 | {
284 | "data": {
285 | "text/plain": [
286 | "B(Help, me)"
287 | ]
288 | },
289 | "execution_count": 3,
290 | "metadata": {},
291 | "output_type": "execute_result"
292 | }
293 | ],
294 | "source": [
295 | "B1 = B(A1)\n",
296 | "B1"
297 | ]
298 | },
299 | {
300 | "cell_type": "code",
301 | "execution_count": 4,
302 | "metadata": {},
303 | "outputs": [],
304 | "source": [
305 | "class C(B):\n",
306 | " def __new__(self,value):\n",
307 | " self.arg = value\n",
308 | " return super().__new__(self)\n",
309 | " \n",
310 | " def __repr__(self):\n",
311 | " return 'C('+str(self.arg)+')'"
312 | ]
313 | },
314 | {
315 | "cell_type": "code",
316 | "execution_count": 5,
317 | "metadata": {},
318 | "outputs": [
319 | {
320 | "data": {
321 | "text/plain": [
322 | "12"
323 | ]
324 | },
325 | "execution_count": 5,
326 | "metadata": {},
327 | "output_type": "execute_result"
328 | }
329 | ],
330 | "source": [
331 | "C1 = C(12)\n",
332 | "C1.arg"
333 | ]
334 | },
335 | {
336 | "cell_type": "code",
337 | "execution_count": 6,
338 | "metadata": {},
339 | "outputs": [
340 | {
341 | "data": {
342 | "text/plain": [
343 | "C(Help, me)"
344 | ]
345 | },
346 | "execution_count": 6,
347 | "metadata": {},
348 | "output_type": "execute_result"
349 | }
350 | ],
351 | "source": [
352 | "C(A1)"
353 | ]
354 | },
355 | {
356 | "cell_type": "code",
357 | "execution_count": 28,
358 | "metadata": {},
359 | "outputs": [],
360 | "source": [
361 | "class B(B):\n",
362 | " def __new__(self,*args,**kwargs):\n",
363 | " return super().__new__(self)\n",
364 | " \n",
365 | " def __repr__(self):\n",
366 | " return str(self)+'!'"
367 | ]
368 | },
369 | {
370 | "cell_type": "code",
371 | "execution_count": 29,
372 | "metadata": {},
373 | "outputs": [
374 | {
375 | "data": {
376 | "text/plain": [
377 | "C(Help, me)"
378 | ]
379 | },
380 | "execution_count": 29,
381 | "metadata": {},
382 | "output_type": "execute_result"
383 | }
384 | ],
385 | "source": [
386 | "C(A1)"
387 | ]
388 | },
389 | {
390 | "cell_type": "code",
391 | "execution_count": 30,
392 | "metadata": {},
393 | "outputs": [
394 | {
395 | "ename": "RecursionError",
396 | "evalue": "maximum recursion depth exceeded",
397 | "output_type": "error",
398 | "traceback": [
399 | "\u001b[0;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
400 | "\u001b[0;31mRecursionError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
401 | "File \u001b[0;32m~/.local/share/virtualenvs/Algebra_with_SymPy-ZtpO9pAV/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/core/formatters.py:707\u001b[0m, in \u001b[0;36mPlainTextFormatter.__call__\u001b[0;34m(self, obj)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 700\u001b[0m stream \u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m StringIO()\n\u001b[1;32m 701\u001b[0m printer \u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m pretty\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mRepresentationPrinter(stream, \u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mverbose,\n\u001b[1;32m 702\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mmax_width, \u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mnewline,\n\u001b[1;32m 703\u001b[0m max_seq_length\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mmax_seq_length,\n\u001b[1;32m 704\u001b[0m singleton_pprinters\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39msingleton_printers,\n\u001b[1;32m 705\u001b[0m type_pprinters\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mtype_printers,\n\u001b[1;32m 706\u001b[0m deferred_pprinters\u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mdeferred_printers)\n\u001b[0;32m--> 707\u001b[0m \u001b[43mprinter\u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;241;43m.\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43mpretty\u001b[49m\u001b[43m(\u001b[49m\u001b[43mobj\u001b[49m\u001b[43m)\u001b[49m\n\u001b[1;32m 708\u001b[0m printer\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mflush()\n\u001b[1;32m 709\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mreturn\u001b[39;00m stream\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mgetvalue()\n",
402 | "File \u001b[0;32m~/.local/share/virtualenvs/Algebra_with_SymPy-ZtpO9pAV/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/lib/pretty.py:410\u001b[0m, in \u001b[0;36mRepresentationPrinter.pretty\u001b[0;34m(self, obj)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 407\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mreturn\u001b[39;00m meth(obj, \u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m, cycle)\n\u001b[1;32m 408\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mif\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;28mcls\u001b[39m \u001b[38;5;129;01mis\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;129;01mnot\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;28mobject\u001b[39m \\\n\u001b[1;32m 409\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;129;01mand\u001b[39;00m callable(\u001b[38;5;28mcls\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;18m__dict__\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mget(\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m__repr__\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m)):\n\u001b[0;32m--> 410\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mreturn\u001b[39;00m \u001b[43m_repr_pprint\u001b[49m\u001b[43m(\u001b[49m\u001b[43mobj\u001b[49m\u001b[43m,\u001b[49m\u001b[43m \u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;28;43mself\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m,\u001b[49m\u001b[43m \u001b[49m\u001b[43mcycle\u001b[49m\u001b[43m)\u001b[49m\n\u001b[1;32m 412\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mreturn\u001b[39;00m _default_pprint(obj, \u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m, cycle)\n\u001b[1;32m 413\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mfinally\u001b[39;00m:\n",
403 | "File \u001b[0;32m~/.local/share/virtualenvs/Algebra_with_SymPy-ZtpO9pAV/lib/python3.10/site-packages/IPython/lib/pretty.py:778\u001b[0m, in \u001b[0;36m_repr_pprint\u001b[0;34m(obj, p, cycle)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 776\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;124;03m\"\"\"A pprint that just redirects to the normal repr function.\"\"\"\u001b[39;00m\n\u001b[1;32m 777\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;66;03m# Find newlines and replace them with p.break_()\u001b[39;00m\n\u001b[0;32m--> 778\u001b[0m output \u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m \u001b[38;5;28;43mrepr\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m(\u001b[49m\u001b[43mobj\u001b[49m\u001b[43m)\u001b[49m\n\u001b[1;32m 779\u001b[0m lines \u001b[38;5;241m=\u001b[39m output\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39msplitlines()\n\u001b[1;32m 780\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mwith\u001b[39;00m p\u001b[38;5;241m.\u001b[39mgroup():\n",
404 | "Input \u001b[0;32mIn [28]\u001b[0m, in \u001b[0;36mB.__repr__\u001b[0;34m(self)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 5\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mdef\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;21m__repr__\u001b[39m(\u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m):\n\u001b[0;32m----> 6\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mreturn\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;28;43mstr\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m(\u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;28;43mself\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m)\u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;241m+\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m!\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\n",
405 | "Input \u001b[0;32mIn [28]\u001b[0m, in \u001b[0;36mB.__repr__\u001b[0;34m(self)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 5\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mdef\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;21m__repr__\u001b[39m(\u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m):\n\u001b[0;32m----> 6\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mreturn\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;28;43mstr\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m(\u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;28;43mself\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m)\u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;241m+\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m!\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\n",
406 | " \u001b[0;31m[... skipping similar frames: B.__repr__ at line 6 (984 times)]\u001b[0m\n",
407 | "Input \u001b[0;32mIn [28]\u001b[0m, in \u001b[0;36mB.__repr__\u001b[0;34m(self)\u001b[0m\n\u001b[1;32m 5\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mdef\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;21m__repr__\u001b[39m(\u001b[38;5;28mself\u001b[39m):\n\u001b[0;32m----> 6\u001b[0m \u001b[38;5;28;01mreturn\u001b[39;00m \u001b[38;5;28;43mstr\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m(\u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;28;43mself\u001b[39;49m\u001b[43m)\u001b[49m\u001b[38;5;241m+\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m!\u001b[39m\u001b[38;5;124m'\u001b[39m\n",
408 | "\u001b[0;31mRecursionError\u001b[0m: maximum recursion depth exceeded"
409 | ]
410 | }
411 | ],
412 | "source": [
413 | "\n",
414 | "B2 = B(A1)\n",
415 | "B2"
416 | ]
417 | },
418 | {
419 | "cell_type": "code",
420 | "execution_count": null,
421 | "metadata": {},
422 | "outputs": [],
423 | "source": []
424 | }
425 | ],
426 | "metadata": {
427 | "kernelspec": {
428 | "display_name": "Python 3 (ipykernel)",
429 | "language": "python",
430 | "name": "python3"
431 | },
432 | "language_info": {
433 | "codemirror_mode": {
434 | "name": "ipython",
435 | "version": 3
436 | },
437 | "file_extension": ".py",
438 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
439 | "name": "python",
440 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
441 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
442 | "version": "3.10.4"
443 | }
444 | },
445 | "nbformat": 4,
446 | "nbformat_minor": 4
447 | }
448 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/Developer Testing/Algebra Scratch.ipynb:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | {
2 | "cells": [
3 | {
4 | "cell_type": "code",
5 | "execution_count": 1,
6 | "metadata": {},
7 | "outputs": [
8 | {
9 | "name": "stdout",
10 | "output_type": "stream",
11 | "text": [
12 | "Automatic typesetting of output disabled so output code can be copied into code cells.\n",
13 | " To enable automatic typesetting of output issue the command `sp.init_printing(pretty_print=True)`.\n",
14 | "Automatic display of math operation activated for `dmo aware` operations.\n"
15 | ]
16 | }
17 | ],
18 | "source": [
19 | "from Display_Math_Operations import *"
20 | ]
21 | },
22 | {
23 | "cell_type": "code",
24 | "execution_count": 2,
25 | "metadata": {},
26 | "outputs": [
27 | {
28 | "data": {
29 | "text/html": [
30 | "$$RG\\equiv R T n - V p$$"
31 | ],
32 | "text/plain": [
33 | ""
34 | ]
35 | },
36 | "metadata": {},
37 | "output_type": "display_data"
38 | }
39 | ],
40 | "source": [
41 | "sp.var('p V n R T')\n",
42 | "dmo(RG=n*R*T-p*V)"
43 | ]
44 | },
45 | {
46 | "cell_type": "code",
47 | "execution_count": 3,
48 | "metadata": {},
49 | "outputs": [
50 | {
51 | "data": {
52 | "text/html": [
53 | "$$- V p$$"
54 | ],
55 | "text/plain": [
56 | ""
57 | ]
58 | },
59 | "metadata": {},
60 | "output_type": "display_data"
61 | },
62 | {
63 | "data": {
64 | "text/plain": [
65 | "-V*p"
66 | ]
67 | },
68 | "execution_count": 3,
69 | "metadata": {},
70 | "output_type": "execute_result"
71 | }
72 | ],
73 | "source": [
74 | "dmo(RG-R*T*n,code=True)"
75 | ]
76 | },
77 | {
78 | "cell_type": "code",
79 | "execution_count": 4,
80 | "metadata": {},
81 | "outputs": [
82 | {
83 | "data": {
84 | "text/html": [
85 | "$$V$$"
86 | ],
87 | "text/plain": [
88 | ""
89 | ]
90 | },
91 | "metadata": {},
92 | "output_type": "display_data"
93 | },
94 | {
95 | "data": {
96 | "text/plain": [
97 | "V"
98 | ]
99 | },
100 | "execution_count": 4,
101 | "metadata": {},
102 | "output_type": "execute_result"
103 | }
104 | ],
105 | "source": [
106 | "dmo((RG-R*T*n)/(-p),code=True)"
107 | ]
108 | },
109 | {
110 | "cell_type": "code",
111 | "execution_count": 5,
112 | "metadata": {},
113 | "outputs": [],
114 | "source": [
115 | "def Eq(lhs,rhs):\n",
116 | " print(str(lhs)+' = '+str(rhs))\n",
117 | " return([lhs,rhs])"
118 | ]
119 | },
120 | {
121 | "cell_type": "code",
122 | "execution_count": 6,
123 | "metadata": {},
124 | "outputs": [
125 | {
126 | "name": "stdout",
127 | "output_type": "stream",
128 | "text": [
129 | "V*p = R*T*n\n"
130 | ]
131 | },
132 | {
133 | "data": {
134 | "text/plain": [
135 | "[V*p, R*T*n]"
136 | ]
137 | },
138 | "execution_count": 6,
139 | "metadata": {},
140 | "output_type": "execute_result"
141 | }
142 | ],
143 | "source": [
144 | "Eq(p*V,n*R*T)"
145 | ]
146 | },
147 | {
148 | "cell_type": "code",
149 | "execution_count": 7,
150 | "metadata": {},
151 | "outputs": [
152 | {
153 | "name": "stdout",
154 | "output_type": "stream",
155 | "text": [
156 | "V*p = R*T*n\n"
157 | ]
158 | }
159 | ],
160 | "source": [
161 | "eq1=Eq(p*V,n*R*T)"
162 | ]
163 | },
164 | {
165 | "cell_type": "code",
166 | "execution_count": 8,
167 | "metadata": {},
168 | "outputs": [
169 | {
170 | "data": {
171 | "text/plain": [
172 | "[V*p, R*T*n]"
173 | ]
174 | },
175 | "execution_count": 8,
176 | "metadata": {},
177 | "output_type": "execute_result"
178 | }
179 | ],
180 | "source": [
181 | "eq1"
182 | ]
183 | },
184 | {
185 | "cell_type": "code",
186 | "execution_count": 9,
187 | "metadata": {},
188 | "outputs": [],
189 | "source": [
190 | "#eq1/V throws error"
191 | ]
192 | },
193 | {
194 | "cell_type": "code",
195 | "execution_count": 10,
196 | "metadata": {},
197 | "outputs": [],
198 | "source": [
199 | "sp.expr?"
200 | ]
201 | },
202 | {
203 | "cell_type": "code",
204 | "execution_count": 11,
205 | "metadata": {},
206 | "outputs": [
207 | {
208 | "data": {
209 | "text/plain": [
210 | "Eq(V*p, R*T*n)"
211 | ]
212 | },
213 | "execution_count": 11,
214 | "metadata": {},
215 | "output_type": "execute_result"
216 | }
217 | ],
218 | "source": [
219 | "eq3=sp.Eq(p*V,n*R*T,evaluate=False)\n",
220 | "eq3"
221 | ]
222 | },
223 | {
224 | "cell_type": "code",
225 | "execution_count": 12,
226 | "metadata": {},
227 | "outputs": [
228 | {
229 | "data": {
230 | "text/plain": [
231 | "'V p = R T n'"
232 | ]
233 | },
234 | "execution_count": 12,
235 | "metadata": {},
236 | "output_type": "execute_result"
237 | }
238 | ],
239 | "source": [
240 | "sp.latex(eq3)"
241 | ]
242 | },
243 | {
244 | "cell_type": "code",
245 | "execution_count": 13,
246 | "metadata": {},
247 | "outputs": [
248 | {
249 | "data": {
250 | "text/plain": [
251 | "(Eq(V*p, R*T*n))/V"
252 | ]
253 | },
254 | "execution_count": 13,
255 | "metadata": {},
256 | "output_type": "execute_result"
257 | }
258 | ],
259 | "source": [
260 | "eq3/V"
261 | ]
262 | },
263 | {
264 | "cell_type": "code",
265 | "execution_count": 14,
266 | "metadata": {},
267 | "outputs": [
268 | {
269 | "data": {
270 | "text/plain": [
271 | "Eq(V*p, R*T*n)"
272 | ]
273 | },
274 | "execution_count": 14,
275 | "metadata": {},
276 | "output_type": "execute_result"
277 | }
278 | ],
279 | "source": [
280 | "tstsymeq=sp.Eq(p*V,n*R*T)\n",
281 | "tstsymeq"
282 | ]
283 | },
284 | {
285 | "cell_type": "code",
286 | "execution_count": 15,
287 | "metadata": {},
288 | "outputs": [
289 | {
290 | "data": {
291 | "text/plain": [
292 | "'(Eq(V*p, R*T*n))/V'"
293 | ]
294 | },
295 | "execution_count": 15,
296 | "metadata": {},
297 | "output_type": "execute_result"
298 | }
299 | ],
300 | "source": [
301 | "str((tstsymeq/V))"
302 | ]
303 | },
304 | {
305 | "cell_type": "code",
306 | "execution_count": 16,
307 | "metadata": {},
308 | "outputs": [
309 | {
310 | "data": {
311 | "text/plain": [
312 | "sympy.core.relational.Equality"
313 | ]
314 | },
315 | "execution_count": 16,
316 | "metadata": {},
317 | "output_type": "execute_result"
318 | }
319 | ],
320 | "source": [
321 | "sp.Eq"
322 | ]
323 | },
324 | {
325 | "cell_type": "code",
326 | "execution_count": 17,
327 | "metadata": {},
328 | "outputs": [],
329 | "source": [
330 | "class equ(sp.Expr):\n",
331 | " \n",
332 | " def __init__(self,lhs,rhs):\n",
333 | " self.lhs = lhs\n",
334 | " self.rhs = rhs\n",
335 | "#####\n",
336 | "# Overrides of sp.Expr Arithmatic\n",
337 | "#####\n",
338 | " def __pos__(self):\n",
339 | " return self\n",
340 | "\n",
341 | " def __neg__(self):\n",
342 | " # Mul has its own __neg__ routine, so we just\n",
343 | " # create a 2-args Mul with the -1 in the canonical\n",
344 | " # slot 0.\n",
345 | " c = self.is_commutative\n",
346 | " lhs =sp.Mul._from_args((S.NegativeOne, self.lhs), c)\n",
347 | " rhs =sp.Mul._from_args((S.NegativeOne, self.rhs), c) \n",
348 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
349 | "\n",
350 | " def __abs__(self):\n",
351 | " from sympy import Abs\n",
352 | " lhs=Abs(self.lhs)\n",
353 | " rhs=Abs(self.rhs)\n",
354 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
355 | "\n",
356 | " def __add__(self, other):\n",
357 | " lhs = sp.Add(self.lhs,other)\n",
358 | " rhs = sp.Add(self.rhs,other)\n",
359 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
360 | "\n",
361 | " def __radd__(self, other):\n",
362 | " lhs = sp.Add(other,self.lhs)\n",
363 | " rhs = sp.Add(other,self.rhs)\n",
364 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
365 | "\n",
366 | " def __sub__(self, other):\n",
367 | " lhs = sp.Add(self.lhs,-other)\n",
368 | " rhs = sp.Add(self.rhs,-other)\n",
369 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
370 | "\n",
371 | " def __rsub__(self, other):\n",
372 | " lhs = sp.Add(other,-self.lhs)\n",
373 | " rhs = sp.Add(other,-self.rhs)\n",
374 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
375 | "\n",
376 | " def __mul__(self, other):\n",
377 | " lhs = sp.Mul(self.lhs,other)\n",
378 | " rhs = sp.Mul(self.rhs,other)\n",
379 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
380 | " \n",
381 | " def __rmul__(self, other):\n",
382 | " lhs = sp.Mul(other,self.lhs)\n",
383 | " rhs = sp.Mul(other,self.rhs)\n",
384 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
385 | "\n",
386 | " def _pow(self, other):\n",
387 | " lhs = sp.Pow(self.lhs,other)\n",
388 | " rhs = sp.Pow(self.rhs,other)\n",
389 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
390 | "\n",
391 | " def __rpow__(self, other):\n",
392 | " lhs = sp.Pow(other,self.lhs)\n",
393 | " rhs = sp.Pow(other,self.rhs)\n",
394 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
395 | "\n",
396 | " def __div__(self, other):\n",
397 | " return self.__mul__(sp.Pow(other, sp.S.NegativeOne))\n",
398 | "\n",
399 | " def __rdiv__(self, other):\n",
400 | " raise NotImplemented('Division by equation not supported.')\n",
401 | "\n",
402 | " __truediv__ = __div__\n",
403 | " __rtruediv__ = __rdiv__\n",
404 | "\n",
405 | " def __mod__(self, other):\n",
406 | " lhs = sp.Mod(self.lhs,other)\n",
407 | " rhs = sp.Mod(self.rhs,other)\n",
408 | " return equ(lhs,rhs)\n",
409 | "\n",
410 | " def __rmod__(self, other):\n",
411 | " raise NotImplemented('Mod by equation not supported.')\n",
412 | " \n",
413 | " def __repr__(self):\n",
414 | " return(str(self.lhs)+' = '+str(self.rhs))\n",
415 | " \n",
416 | " def _latex(self,obj,**kwargs):\n",
417 | " return(sp.latex(self.lhs)+'='+sp.latex(self.rhs))\n",
418 | "\n",
419 | "class Function2(sp.Function):\n",
420 | " def __new__(cls, *arg, **kwargs):\n",
421 | " if (type(arg[0]) is equ):\n",
422 | " temptuple=(arg[0].lhs,)+arg[1:]\n",
423 | " lhs = super().__new__(cls, *temptuple, **kwargs)\n",
424 | " temptuple=(arg[0].rhs,)+arg[1:]\n",
425 | " rhs = super().__new__(cls, *temptuple, **kwargs)\n",
426 | " return (equ(lhs,rhs))\n",
427 | " else:\n",
428 | " return(super().__new__(cls, *arg, **kwargs))\n",
429 | " \n",
430 | "class newlog(Function2,sp.log):\n",
431 | " pass\n",
432 | "\n",
433 | "#def newlog(arg, base=None):\n",
434 | "# if (base is None):\n",
435 | "# base=sp.exp(1)\n",
436 | "# if(type(arg) is equ):\n",
437 | "# lhs = log(arg.lhs,base)\n",
438 | "# rhs = log(arg.rhs,base)\n",
439 | "# return(equ(lhs,rhs))\n",
440 | "# else:\n",
441 | "# return(log(arg,base))\n",
442 | " "
443 | ]
444 | },
445 | {
446 | "cell_type": "code",
447 | "execution_count": 18,
448 | "metadata": {},
449 | "outputs": [
450 | {
451 | "data": {
452 | "text/html": [
453 | "$$tstequ\\equiv V p=R T n$$"
454 | ],
455 | "text/plain": [
456 | ""
457 | ]
458 | },
459 | "metadata": {},
460 | "output_type": "display_data"
461 | },
462 | {
463 | "data": {
464 | "text/plain": [
465 | "V*p = R*T*n"
466 | ]
467 | },
468 | "execution_count": 18,
469 | "metadata": {},
470 | "output_type": "execute_result"
471 | }
472 | ],
473 | "source": [
474 | "dmo(tstequ = equ(p*V,n*R*T))\n",
475 | "tstequ"
476 | ]
477 | },
478 | {
479 | "cell_type": "code",
480 | "execution_count": 19,
481 | "metadata": {},
482 | "outputs": [
483 | {
484 | "data": {
485 | "text/plain": [
486 | "T*V*p = R*T**2*n"
487 | ]
488 | },
489 | "execution_count": 19,
490 | "metadata": {},
491 | "output_type": "execute_result"
492 | }
493 | ],
494 | "source": [
495 | "tstequ*T"
496 | ]
497 | },
498 | {
499 | "cell_type": "code",
500 | "execution_count": 20,
501 | "metadata": {},
502 | "outputs": [
503 | {
504 | "data": {
505 | "text/plain": [
506 | "'V=\\\\frac{R T n}{p}'"
507 | ]
508 | },
509 | "execution_count": 20,
510 | "metadata": {},
511 | "output_type": "execute_result"
512 | }
513 | ],
514 | "source": [
515 | "sp.latex(tstequ/p)"
516 | ]
517 | },
518 | {
519 | "cell_type": "code",
520 | "execution_count": 21,
521 | "metadata": {},
522 | "outputs": [
523 | {
524 | "data": {
525 | "text/plain": [
526 | "V**2*p**2 = R**2*T**2*n**2"
527 | ]
528 | },
529 | "execution_count": 21,
530 | "metadata": {},
531 | "output_type": "execute_result"
532 | }
533 | ],
534 | "source": [
535 | "tstequ**2"
536 | ]
537 | },
538 | {
539 | "cell_type": "code",
540 | "execution_count": 22,
541 | "metadata": {},
542 | "outputs": [
543 | {
544 | "data": {
545 | "text/html": [
546 | "$$\\left|{V p}\\right|=\\left|{R T n}\\right|$$"
547 | ],
548 | "text/plain": [
549 | ""
550 | ]
551 | },
552 | "metadata": {},
553 | "output_type": "display_data"
554 | }
555 | ],
556 | "source": [
557 | "dmo(abs(tstequ))"
558 | ]
559 | },
560 | {
561 | "cell_type": "code",
562 | "execution_count": 23,
563 | "metadata": {},
564 | "outputs": [
565 | {
566 | "data": {
567 | "text/plain": [
568 | "V = 0.0244734726132267*J/Pa"
569 | ]
570 | },
571 | "execution_count": 23,
572 | "metadata": {},
573 | "output_type": "execute_result"
574 | }
575 | ],
576 | "source": [
577 | "sp.var('J mol K Pa')\n",
578 | "tsteq2=tstequ/p\n",
579 | "tsteq2.subs({R:8.314*J/mol/K,n:1.00*mol,T:298*K,p:101235*Pa})"
580 | ]
581 | },
582 | {
583 | "cell_type": "code",
584 | "execution_count": 24,
585 | "metadata": {},
586 | "outputs": [
587 | {
588 | "data": {
589 | "text/plain": [
590 | "Abs(V*p) = Abs(R*T*n)"
591 | ]
592 | },
593 | "execution_count": 24,
594 | "metadata": {},
595 | "output_type": "execute_result"
596 | }
597 | ],
598 | "source": [
599 | "_"
600 | ]
601 | },
602 | {
603 | "cell_type": "code",
604 | "execution_count": 25,
605 | "metadata": {},
606 | "outputs": [
607 | {
608 | "data": {
609 | "text/plain": [
610 | "V = 0.0244734726132267*m**3"
611 | ]
612 | },
613 | "execution_count": 25,
614 | "metadata": {},
615 | "output_type": "execute_result"
616 | }
617 | ],
618 | "source": [
619 | "sp.var('kg m s')\n",
620 | "tsteq2.subs({R:8.314*J/mol/K,n:1.00*mol,T:298*K,p:101235*Pa}).subs({J:kg*m**2/s**2,Pa:kg/m/s**2})"
621 | ]
622 | },
623 | {
624 | "cell_type": "code",
625 | "execution_count": 26,
626 | "metadata": {},
627 | "outputs": [
628 | {
629 | "data": {
630 | "text/plain": [
631 | "newlog(V*p)/newlog(10)"
632 | ]
633 | },
634 | "execution_count": 26,
635 | "metadata": {},
636 | "output_type": "execute_result"
637 | }
638 | ],
639 | "source": [
640 | "newlog(p*V,10)"
641 | ]
642 | },
643 | {
644 | "cell_type": "code",
645 | "execution_count": 27,
646 | "metadata": {},
647 | "outputs": [
648 | {
649 | "data": {
650 | "text/plain": [
651 | "newlog(V*p)/newlog(10) = newlog(R*T*n)/newlog(10)"
652 | ]
653 | },
654 | "execution_count": 27,
655 | "metadata": {},
656 | "output_type": "execute_result"
657 | }
658 | ],
659 | "source": [
660 | "newlog(tstequ,10)"
661 | ]
662 | },
663 | {
664 | "cell_type": "markdown",
665 | "metadata": {},
666 | "source": [
667 | "So will need to define overrides for all arithmatic and function calls on an expression...Does that mean making functions aware of equations? Can I use the `_is_distributive` property? I am not sure it is defined."
668 | ]
669 | },
670 | {
671 | "cell_type": "code",
672 | "execution_count": 28,
673 | "metadata": {},
674 | "outputs": [
675 | {
676 | "ename": "NameError",
677 | "evalue": "name '_50' is not defined",
678 | "output_type": "error",
679 | "traceback": [
680 | "\u001b[0;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
681 | "\u001b[0;31mNameError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
682 | "\u001b[0;32m\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m----> 1\u001b[0;31m \u001b[0m_50\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m",
683 | "\u001b[0;31mNameError\u001b[0m: name '_50' is not defined"
684 | ]
685 | }
686 | ],
687 | "source": [
688 | "_50"
689 | ]
690 | },
691 | {
692 | "cell_type": "code",
693 | "execution_count": 29,
694 | "metadata": {},
695 | "outputs": [
696 | {
697 | "data": {
698 | "text/plain": [
699 | "log(V*p)"
700 | ]
701 | },
702 | "execution_count": 29,
703 | "metadata": {},
704 | "output_type": "execute_result"
705 | }
706 | ],
707 | "source": [
708 | "sp.log(p*V)"
709 | ]
710 | },
711 | {
712 | "cell_type": "code",
713 | "execution_count": 30,
714 | "metadata": {},
715 | "outputs": [
716 | {
717 | "data": {
718 | "text/plain": [
719 | "Abs(V*p) = Abs(R*T*n)"
720 | ]
721 | },
722 | "execution_count": 30,
723 | "metadata": {},
724 | "output_type": "execute_result"
725 | }
726 | ],
727 | "source": [
728 | "_"
729 | ]
730 | },
731 | {
732 | "cell_type": "code",
733 | "execution_count": 31,
734 | "metadata": {},
735 | "outputs": [
736 | {
737 | "ename": "NameError",
738 | "evalue": "name '_50' is not defined",
739 | "output_type": "error",
740 | "traceback": [
741 | "\u001b[0;31m---------------------------------------------------------------------------\u001b[0m",
742 | "\u001b[0;31mNameError\u001b[0m Traceback (most recent call last)",
743 | "\u001b[0;32m\u001b[0m in \u001b[0;36m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0;32m----> 1\u001b[0;31m \u001b[0m_50\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0;34m\u001b[0m\u001b[0m\n\u001b[0m",
744 | "\u001b[0;31mNameError\u001b[0m: name '_50' is not defined"
745 | ]
746 | }
747 | ],
748 | "source": [
749 | "_50"
750 | ]
751 | },
752 | {
753 | "cell_type": "code",
754 | "execution_count": null,
755 | "metadata": {},
756 | "outputs": [],
757 | "source": [
758 | "_"
759 | ]
760 | },
761 | {
762 | "cell_type": "code",
763 | "execution_count": null,
764 | "metadata": {},
765 | "outputs": [],
766 | "source": []
767 | }
768 | ],
769 | "metadata": {
770 | "kernelspec": {
771 | "display_name": "Python 3",
772 | "language": "python",
773 | "name": "python3"
774 | },
775 | "language_info": {
776 | "codemirror_mode": {
777 | "name": "ipython",
778 | "version": 3
779 | },
780 | "file_extension": ".py",
781 | "mimetype": "text/x-python",
782 | "name": "python",
783 | "nbconvert_exporter": "python",
784 | "pygments_lexer": "ipython3",
785 | "version": "3.6.9"
786 | }
787 | },
788 | "nbformat": 4,
789 | "nbformat_minor": 4
790 | }
791 |
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
/algebra_with_sympy/algebraic_equation.py:
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1 | """
2 | This package uses a special version of sympy which defines an equation
3 | with a left-hand-side (lhs) and a right-
4 | hand-side (rhs) connected by the "=" operator (e.g. `p*V = n*R*T`).
5 |
6 | The intent is to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to rearrange
7 | equations and perform algebra in a stepwise fashion. In this way more people
8 | can successfully perform algebraic rearrangements without stumbling over
9 | missed details such as a negative sign. This mimics the capabilities available
10 | in [SageMath](https://www.sagemath.org/) and
11 | [Maxima](http://maxima.sourceforge.net/).
12 |
13 | This package also provides convenient settings for interactive use on the
14 | command line, in ipython and Jupyter notebook environments. See the
15 | documentation at https://gutow.github.io/Algebra_with_Sympy/.
16 |
17 | Explanation
18 | ===========
19 | This class defines relations that all high school and college students
20 | would recognize as mathematical equations. At present only the "=" relation
21 | operator is recognized.
22 |
23 | This class is intended to allow using the mathematical tools in SymPy to
24 | rearrange equations and perform algebra in a stepwise fashion. In this
25 | way more people can successfully perform algebraic rearrangements without
26 | stumbling over missed details such as a negative sign.
27 |
28 | Create an equation with the call ``Equation(lhs,rhs)``, where ``lhs`` and
29 | ``rhs`` are any valid Sympy expression. ``Eqn(...)`` is a synonym for
30 | ``Equation(...)``.
31 |
32 | Parameters
33 | ==========
34 | lhs: sympy expression, ``class Expr``.
35 | rhs: sympy expression, ``class Expr``.
36 | kwargs:
37 |
38 | Examples
39 | ========
40 | NOTE: All the examples below are in vanilla python. You can get human
41 | readable eqautions "lhs = rhs" in vanilla python by adjusting the settings
42 | in `algwsym_config` (see it's documentation). Output is human readable by
43 | default in IPython and Jupyter environments.
44 | >>> from algebra_with_sympy import *
45 | >>> a, b, c, x = var('a b c x')
46 | >>> Equation(a,b/c)
47 | Equation(a, b/c)
48 | >>> t=Eqn(a,b/c)
49 | >>> t
50 | Equation(a, b/c)
51 | >>> t*c
52 | Equation(a*c, b)
53 | >>> c*t
54 | Equation(a*c, b)
55 | >>> exp(t)
56 | Equation(exp(a), exp(b/c))
57 | >>> exp(log(t))
58 | Equation(a, b/c)
59 |
60 | Simplification and Expansion
61 | >>> f = Eqn(x**2 - 1, c)
62 | >>> f
63 | Equation(x**2 - 1, c)
64 | >>> f/(x+1)
65 | Equation((x**2 - 1)/(x + 1), c/(x + 1))
66 | >>> (f/(x+1)).simplify()
67 | Equation(x - 1, c/(x + 1))
68 | >>> simplify(f/(x+1))
69 | Equation(x - 1, c/(x + 1))
70 | >>> (f/(x+1)).expand()
71 | Equation(x**2/(x + 1) - 1/(x + 1), c/(x + 1))
72 | >>> expand(f/(x+1))
73 | Equation(x**2/(x + 1) - 1/(x + 1), c/(x + 1))
74 | >>> factor(f)
75 | Equation((x - 1)*(x + 1), c)
76 | >>> f.factor()
77 | Equation((x - 1)*(x + 1), c)
78 | >>> f2 = f+a*x**2+b*x +c
79 | >>> f2
80 | Equation(a*x**2 + b*x + c + x**2 - 1, a*x**2 + b*x + 2*c)
81 | >>> collect(f2,x)
82 | Equation(b*x + c + x**2*(a + 1) - 1, a*x**2 + b*x + 2*c)
83 |
84 | Apply operation to only one side
85 | >>> poly = Eqn(a*x**2 + b*x + c*x**2, a*x**3 + b*x**3 + c*x)
86 | >>> poly.applyrhs(factor,x)
87 | Equation(a*x**2 + b*x + c*x**2, x*(c + x**2*(a + b)))
88 | >>> poly.applylhs(factor)
89 | Equation(x*(a*x + b + c*x), a*x**3 + b*x**3 + c*x)
90 | >>> poly.applylhs(collect,x)
91 | Equation(b*x + x**2*(a + c), a*x**3 + b*x**3 + c*x)
92 |
93 | ``.apply...`` also works with user defined python functions
94 | >>> def addsquare(eqn):
95 | ... return eqn+eqn**2
96 | ...
97 | >>> t.apply(addsquare)
98 | Equation(a**2 + a, b**2/c**2 + b/c)
99 | >>> t.applyrhs(addsquare)
100 | Equation(a, b**2/c**2 + b/c)
101 | >>> t.apply(addsquare, side = 'rhs')
102 | Equation(a, b**2/c**2 + b/c)
103 | >>> t.applylhs(addsquare)
104 | Equation(a**2 + a, b/c)
105 | >>> addsquare(t)
106 | Equation(a**2 + a, b**2/c**2 + b/c)
107 |
108 | Inaddition to ``.apply...`` there is also the less general ``.do``,
109 | ``.dolhs``, ``.dorhs``, which only works for operations defined on the
110 | ``Expr`` class (e.g.``.collect(), .factor(), .expand()``, etc...).
111 | >>> poly.dolhs.collect(x)
112 | Equation(b*x + x**2*(a + c), a*x**3 + b*x**3 + c*x)
113 | >>> poly.dorhs.collect(x)
114 | Equation(a*x**2 + b*x + c*x**2, c*x + x**3*(a + b))
115 | >>> poly.do.collect(x)
116 | Equation(b*x + x**2*(a + c), c*x + x**3*(a + b))
117 | >>> poly.dorhs.factor()
118 | Equation(a*x**2 + b*x + c*x**2, x*(a*x**2 + b*x**2 + c))
119 |
120 | ``poly.do.exp()`` or other sympy math functions will raise an error.
121 |
122 | Rearranging an equation (simple example made complicated as illustration)
123 | >>> p, V, n, R, T = var('p V n R T')
124 | >>> eq1=Eqn(p*V,n*R*T)
125 | >>> eq1
126 | Equation(V*p, R*T*n)
127 | >>> eq2 =eq1/V
128 | >>> eq2
129 | Equation(p, R*T*n/V)
130 | >>> eq3 = eq2/R/T
131 | >>> eq3
132 | Equation(p/(R*T), n/V)
133 | >>> eq4 = eq3*R/p
134 | >>> eq4
135 | Equation(1/T, R*n/(V*p))
136 | >>> 1/eq4
137 | Equation(T, V*p/(R*n))
138 | >>> eq5 = 1/eq4 - T
139 | >>> eq5
140 | Equation(0, -T + V*p/(R*n))
141 |
142 | Substitution (#'s and units)
143 | >>> L, atm, mol, K = var('L atm mol K', positive=True, real=True) # units
144 | >>> eq2.subs({R:0.08206*L*atm/mol/K,T:273*K,n:1.00*mol,V:24.0*L})
145 | Equation(p, 0.9334325*atm)
146 | >>> eq2.subs({R:0.08206*L*atm/mol/K,T:273*K,n:1.00*mol,V:24.0*L}).evalf(4)
147 | Equation(p, 0.9334*atm)
148 |
149 | Substituting an equation into another equation:
150 | >>> P, P1, P2, A1, A2, E1, E2 = symbols("P, P1, P2, A1, A2, E1, E2")
151 | >>> eq1 = Eqn(P, P1 + P2)
152 | >>> eq2 = Eqn(P1 / (A1 * E1), P2 / (A2 * E2))
153 | >>> P1_val = (eq1 - P2).swap
154 | >>> P1_val
155 | Equation(P1, P - P2)
156 | >>> eq2 = eq2.subs(P1_val)
157 | >>> eq2
158 | Equation((P - P2)/(A1*E1), P2/(A2*E2))
159 | >>> P2_val = solve(eq2.subs(P1_val), P2).args[0]
160 | >>> P2_val
161 | Equation(P2, A2*E2*P/(A1*E1 + A2*E2))
162 |
163 | Combining equations (Math with equations: lhs with lhs and rhs with rhs)
164 | >>> q = Eqn(a*c, b/c**2)
165 | >>> q
166 | Equation(a*c, b/c**2)
167 | >>> t
168 | Equation(a, b/c)
169 | >>> q+t
170 | Equation(a*c + a, b/c + b/c**2)
171 | >>> q/t
172 | Equation(c, 1/c)
173 | >>> t**q
174 | Equation(a**(a*c), (b/c)**(b/c**2))
175 |
176 | Utility operations
177 | >>> t.reversed
178 | Equation(b/c, a)
179 | >>> t.swap
180 | Equation(b/c, a)
181 | >>> t.lhs
182 | a
183 | >>> t.rhs
184 | b/c
185 | >>> t.as_Boolean()
186 | Eq(a, b/c)
187 |
188 | `.check()` convenience method for `.as_Boolean().simplify()`
189 | >>> from sympy import I, pi
190 | >>> Equation(pi*(I+2), pi*I+2*pi).check()
191 | True
192 | >>> Eqn(a,a+1).check()
193 | False
194 |
195 | Differentiation
196 | Differentiation is applied to both sides if the wrt variable appears on
197 | both sides.
198 | >>> q=Eqn(a*c, b/c**2)
199 | >>> q
200 | Equation(a*c, b/c**2)
201 | >>> diff(q,b)
202 | Equation(Derivative(a*c, b), c**(-2))
203 | >>> diff(q,c)
204 | Equation(a, -2*b/c**3)
205 | >>> diff(log(q),b)
206 | Equation(Derivative(log(a*c), b), 1/b)
207 | >>> diff(q,c,2)
208 | Equation(Derivative(a, c), 6*b/c**4)
209 |
210 | If you specify multiple differentiation all at once the assumption
211 | is order of differentiation matters and the lhs will not be
212 | evaluated.
213 | >>> diff(q,c,b)
214 | Equation(Derivative(a*c, b, c), -2/c**3)
215 |
216 | To overcome this specify the order of operations.
217 | >>> diff(diff(q,c),b)
218 | Equation(Derivative(a, b), -2/c**3)
219 |
220 | But the reverse order returns an unevaulated lhs (a may depend on b).
221 | >>> diff(diff(q,b),c)
222 | Equation(Derivative(a*c, b, c), -2/c**3)
223 |
224 | Integration can only be performed on one side at a time.
225 | >>> q=Eqn(a*c,b/c)
226 | >>> integrate(q,b,side='rhs')
227 | b**2/(2*c)
228 | >>> integrate(q,b,side='lhs')
229 | a*b*c
230 |
231 | Make a pretty statement of integration from an equation
232 | >>> Eqn(Integral(q.lhs,b),integrate(q,b,side='rhs'))
233 | Equation(Integral(a*c, b), b**2/(2*c))
234 |
235 | Integration of each side with respect to different variables
236 | >>> q.dorhs.integrate(b).dolhs.integrate(a)
237 | Equation(a**2*c/2, b**2/(2*c))
238 |
239 | Automatic solutions using sympy solvers. THIS IS EXPERIMENTAL. Please
240 | report issues at https://github.com/gutow/Algebra_with_Sympy/issues.
241 | >>> tosolv = Eqn(a - b, c/a)
242 | >>> solve(tosolv,a)
243 | FiniteSet(Equation(a, b/2 - sqrt(b**2 + 4*c)/2), Equation(a, b/2 + sqrt(b**2 + 4*c)/2))
244 | >>> solve(tosolv, b)
245 | FiniteSet(Equation(b, (a**2 - c)/a))
246 | >>> solve(tosolv, c)
247 | FiniteSet(Equation(c, a**2 - a*b))
248 | """
249 | import sys
250 |
251 | import sympy
252 | from algebra_with_sympy.preparser import integers_as_exact
253 | from sympy import *
254 |
255 | class algwsym_config():
256 |
257 | def __init__(self):
258 | """
259 | This is a class to hold parameters that control behavior of
260 | the algebra_with_sympy package.
261 |
262 | Settings
263 | ========
264 | Printing
265 | --------
266 | In interactive environments the default output of an equation is a
267 | human readable string with the two sides connected by an equals
268 | sign or a typeset equation with the two sides connected by an equals sign.
269 | `print(Eqn)` or `str(Eqn)` will return this human readable text version of
270 | the equation as well. This is consistent with python standards, but not
271 | sympy, where `str()` is supposed to return something that can be
272 | copy-pasted into code. If the equation has a declared name as in `eq1 =
273 | Eqn(a,b/c)` the name will be displayed to the right of the equation in
274 | parentheses (eg. `a = b/c (eq1)`). Use `print(repr(Eqn))` instead of
275 | `print(Eqn)` or `repr(Eqn)` instead of `str(Eqn)` to get a code
276 | compatible version of the equation.
277 |
278 | You can adjust this behavior using some flags that impact output:
279 | * `algwsym_config.output.show_code` default is `False`.
280 | * `algwsym_config.output.human_text` default is `True`.
281 | * `algwsym_config.output.label` default is `True`.
282 | * `algwsym_config.output.latex_as_equations` default is `False`
283 |
284 | In interactive environments you can get both types of output by setting
285 | the `algwsym_config.output.show_code` flag. If this flag is true
286 | calls to `latex` and `str` will also print an additional line "code
287 | version: `repr(Eqn)`". Thus in Jupyter you will get a line of typeset
288 | mathematics output preceded by the code version that can be copy-pasted.
289 | Default is `False`.
290 |
291 | A second flag `algwsym_config.output.human_text` is useful in
292 | text-based interactive environments such as command line python or
293 | ipython. If this flag is true `repr` will return `str`. Thus the human
294 | readable text will be printed as the output of a line that is an
295 | expression containing an equation.
296 | Default is `True`.
297 |
298 | Setting both of these flags to true in a command line or ipython
299 | environment will show both the code version and the human readable text.
300 | These flags impact the behavior of the `print(Eqn)` statement.
301 |
302 | The third flag `algwsym_config.output.label` has a default value of
303 | `True`. Setting this to `False` suppresses the labeling of an equation
304 | with its python name off to the right of the equation.
305 |
306 | The fourth flag `algwsym_config.output.latex_as_equations` has
307 | a default value of `False`. Setting this to `True` wraps
308 | output as LaTex equations wrapping them in `\\begin{equation}...\\end{
309 | equation}`.
310 | """
311 | pass
312 |
313 | class output():
314 |
315 | def __init__(self):
316 | """This holds settings that impact output.
317 | """
318 | pass
319 |
320 | @property
321 | def show_code(self):
322 | """
323 | If `True` code versions of the equation expression will be
324 | output in interactive environments. Default = `False`.
325 | """
326 | return self.show_code
327 |
328 | @property
329 | def human_text(self):
330 | """
331 | If `True` the human readable equation expression will be
332 | output in text interactive environments. Default = `False`.
333 | """
334 | return self.human_text
335 |
336 | @property
337 | def solve_to_list(self):
338 | """
339 | If `True` the results of a call to `solve(...)` will return a
340 | Python `list` rather than a Sympy `FiniteSet`. This recovers
341 | behavior for versions before 0.11.0.
342 |
343 | Note: setting this `True` means that expressions within the
344 | returned solutions will not be pretty-printed in Jupyter and
345 | IPython.
346 | """
347 | return self.solve_to_list
348 |
349 | @property
350 | def latex_as_equations(self):
351 | """
352 | If `True` any output that is returned as LaTex for
353 | pretty-printing will be wrapped in the formal Latex for an
354 | equation. For example rather than
355 | ```
356 | $\\frac{a}{b}=c$
357 | ```
358 | the output will be
359 | ```
360 | \\begin{equation}\\frac{a}{b}=c\\end{equation}
361 | ```
362 | """
363 | return self.latex_as_equation
364 |
365 | class numerics():
366 |
367 | def __init__(self):
368 | """This class holds settings for how numerical computation and
369 | inputs are handled.
370 | """
371 | pass
372 |
373 | def integers_as_exact(self):
374 | """**This is a flag for informational purposes and interface
375 | consistency. Changing the value will not change the behavior.**
376 |
377 | To change the behavior call:
378 | * `unset_integers_as_exact()` to turn this feature off.
379 | * `set_integers_as_exact()` to turn this feature on (on by
380 | default).
381 |
382 | If set to `True` (the default) and if running in an
383 | IPython/Jupyter environment any number input without a decimal
384 | will be interpreted as a sympy integer. Thus, fractions and
385 | related expressions will not evalute to floating point numbers,
386 | but be maintained as exact expressions (e.g. 2/3 -> 2/3 not the
387 | float 0.6666...).
388 | """
389 | return self.integers_as_exact
390 |
391 | def __get_sympy_expr_name__(expr):
392 | """
393 | Tries to find the python string name that refers to a sympy object. In
394 | IPython environments (IPython, Jupyter, etc...) looks in the user_ns.
395 | If not in an IPython environment looks in __main__.
396 | :return: string value if found or empty string.
397 | """
398 | import __main__ as shell
399 | for k in dir(shell):
400 | item = getattr(shell, k)
401 | if isinstance(item, Basic):
402 | if item == expr and not k.startswith('_'):
403 | return k
404 | return ''
405 |
406 | def __latex_override__(expr, *arg):
407 | algwsym_config = False
408 | ip = False
409 | try:
410 | from IPython import get_ipython
411 | if get_ipython():
412 | ip = True
413 | except ModuleNotFoundError:
414 | pass
415 | colab = False
416 | try:
417 | from google.colab import output
418 | colab = True
419 | except ModuleNotFoundError:
420 | pass
421 | show_code = False
422 | latex_as_equations = False
423 | if ip:
424 | algwsym_config = get_ipython().user_ns.get("algwsym_config", False)
425 | else:
426 | algwsym_config = globals()['algwsym_config']
427 | if algwsym_config:
428 | show_code = algwsym_config.output.show_code
429 | latex_as_equations = algwsym_config.output.latex_as_equations
430 | if show_code:
431 | print("Code version: " + repr(expr))
432 | if latex_as_equations:
433 | return r'\begin{equation}'+latex(expr)+r'\end{equation}'
434 | else:
435 | tempstr = ''
436 | namestr = ''
437 | if isinstance(expr, Equation):
438 | namestr = __get_sympy_expr_name__(expr)
439 | if namestr != '' and algwsym_config and algwsym_config.output.label:
440 | tempstr += r'$'+latex(expr)
441 | # work around for colab's inconsistent handling of mixed latex and
442 | # plain strings.
443 | if colab:
444 | colabname = namestr.replace('_', r'\_')
445 | tempstr += r'\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,(' + colabname + ')$'
446 | else:
447 | tempstr += r'\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,$(' + namestr + ')'
448 | return tempstr
449 | else:
450 | return '$'+latex(expr) + '$'
451 |
452 | def __command_line_printing__(expr, *arg):
453 | # print('Entering __command_line_printing__')
454 | human_text = True
455 | show_code = False
456 | if algwsym_config:
457 | human_text = algwsym_config.output.human_text
458 | show_code = algwsym_config.output.show_code
459 | tempstr = ''
460 | if show_code:
461 | tempstr += "Code version: " + repr(expr) + '\n'
462 | if not human_text:
463 | return print(tempstr + repr(expr))
464 | else:
465 | labelstr = ''
466 | namestr = ''
467 | if isinstance(expr, Equation):
468 | namestr = __get_sympy_expr_name__(expr)
469 | if namestr != '' and algwsym_config.output.label:
470 | labelstr += ' (' + namestr + ')'
471 | return print(tempstr + str(expr) + labelstr)
472 |
473 | # Now we inject the formatting override(s)
474 | ip = None
475 | try:
476 | from IPython import get_ipython
477 | ip = get_ipython()
478 | except ModuleNotFoundError:
479 | ip = false
480 | formatter = None
481 | if ip:
482 | # In an environment that can display typeset latex
483 | formatter = ip.display_formatter
484 | old = formatter.formatters['text/latex'].for_type(Basic,
485 | __latex_override__)
486 | # print("For type Basic overriding latex formatter = " + str(old))
487 |
488 | # For the terminal based IPython
489 | if "text/latex" not in formatter.active_types:
490 | old = formatter.formatters['text/plain'].for_type(tuple,
491 | __command_line_printing__)
492 | # print("For type tuple overriding plain text formatter = " + str(old))
493 | for k in sympy.__all__:
494 | if k in globals() and not "Printer" in k:
495 | if isinstance(globals()[k], type):
496 | old = formatter.formatters['text/plain'].\
497 | for_type(globals()[k], __command_line_printing__)
498 | # print("For type "+str(k)+
499 | # " overriding plain text formatter = " + str(old))
500 | else:
501 | # command line
502 | # print("Overriding command line printing of python.")
503 | sys.displayhook = __command_line_printing__
504 |
505 | # Numerics controls
506 | def set_integers_as_exact():
507 | """This operation causes any number input without a decimal that is
508 | part of a Sympy expression to be interpreted as a sympy
509 | integer, by using a custom preparser to cast integers within Sympy
510 | expressions as Sympy integers (`Integer()`). It also sets the flag
511 | `algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = True` This is the default
512 | mode of algebra_with_sympy. To turn this off call
513 | `unset_integers_as_exact()`.
514 |
515 | NOTE: `2/3` --> `0.6666...` even when this is set, but `2*x/3` -->
516 | `Integer(2)/Integer(3)*x` if x is a sympy object. If `x` is just a Python
517 | object `2*x/3` --> `x*0.6666666666...`.
518 | """
519 | ip = False
520 | try:
521 | from IPython import get_ipython
522 | ip = True
523 | except ModuleNotFoundError:
524 | ip = False
525 | if ip:
526 | if get_ipython():
527 | get_ipython().input_transformers_post.append(integers_as_exact)
528 | algwsym_config = get_ipython().user_ns.get("algwsym_config", False)
529 | if algwsym_config:
530 | algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = True
531 | else:
532 | raise ValueError("The algwsym_config object does not exist.")
533 | return
534 |
535 | def unset_integers_as_exact():
536 | """This operation disables forcing of numbers input without
537 | decimals being interpreted as sympy integers. Numbers input without a
538 | decimal may be interpreted as floating point if they are part of an
539 | expression that undergoes python evaluation (e.g. 2/3 -> 0.6666...). It
540 | also sets the flag `algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = False`.
541 | Call `set_integers_as_exact()` to avoid this conversion of rational
542 | fractions and related expressions to floating point. Algebra_with_sympy
543 | starts with `set_integers_as_exact()` enabled (
544 | `algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = True`).
545 | """
546 | ip = False
547 | try:
548 | from IPython import get_ipython
549 | ip = True
550 | except ModuleNotFoundError:
551 | ip = False
552 | if ip:
553 | if get_ipython():
554 | pre = get_ipython().input_transformers_post
555 | # The below looks excessively complicated, but more reliably finds the
556 | # transformer to remove across varying IPython environments.
557 | for k in pre:
558 | if "integers_as_exact" in k.__name__:
559 | pre.remove(k)
560 | algwsym_config = get_ipython().user_ns.get("algwsym_config", False)
561 | if algwsym_config:
562 | algwsym_config.numerics.integers_as_exact = False
563 | else:
564 | raise ValueError("The algwsym_config object does not exist.")
565 |
566 | return
567 |
568 | Eqn = Equation
569 | if ip and "text/latex" not in formatter.active_types:
570 | old = formatter.formatters['text/plain'].for_type(Eqn,
571 | __command_line_printing__)
572 | # print("For type Equation overriding plain text formatter = " + str(old))
573 |
574 | def units(names):
575 | """
576 | This operation declares the symbols to be positive values, so that sympy
577 | will handle them properly when simplifying expressions containing units.
578 | Units defined this way are just unit symbols. If you want units that are
579 | aware of conversions see sympy.physics.units.
580 |
581 |
582 | :param string names: a string containing a space separated list of
583 | symbols to be treated as units.
584 |
585 | :return string list of defined units: calls `name = symbols(name,
586 | positive=True)` in the interactive namespace for each symbol name.
587 | """
588 | from sympy.core.symbol import symbols
589 | #import __main__ as shell
590 | user_namespace = None
591 | try:
592 | from IPython import get_ipython
593 | if get_ipython():
594 | user_namespace = get_ipython().user_ns
595 | except ModuleNotFoundError:
596 | pass
597 | syms = names.split(' ')
598 | retstr = ''
599 |
600 | if user_namespace==None:
601 | import sys
602 | frame_num = 0
603 | frame_name = None
604 | while frame_name != '__main__' and frame_num < 50:
605 | user_namespace = sys._getframe(frame_num).f_globals
606 | frame_num +=1
607 | frame_name = user_namespace['__name__']
608 | retstr +='('
609 | for k in syms:
610 | user_namespace[k] = symbols(k, positive = True)
611 | retstr += k + ','
612 | retstr = retstr[:-1] + ')'
613 | return retstr
614 |
615 |
616 | def solve(f, *symbols, **flags):
617 | """
618 | Override of sympy `solve()`.
619 |
620 | If passed an expression and variable(s) to solve for it behaves
621 | almost the same as normal solve with `dict = True`, except that solutions
622 | are wrapped in a FiniteSet() to guarantee that the output will be pretty
623 | printed in Jupyter like environments.
624 |
625 | If passed an equation or equations it returns solutions as a
626 | `FiniteSet()` of solutions, where each solution is represented by an
627 | equation or set of equations.
628 |
629 | To get a Python `list` of solutions (pre-0.11.0 behavior) rather than a
630 | `FiniteSet` issue the command `algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = True`.
631 | This also prevents pretty-printing in IPython and Jupyter.
632 |
633 | Examples
634 | --------
635 | >>> a, b, c, x, y = symbols('a b c x y', real = True)
636 | >>> import sys
637 | >>> sys.displayhook = __command_line_printing__ # set by default on normal initialization.
638 | >>> eq1 = Eqn(abs(2*x+y),3)
639 | >>> eq2 = Eqn(abs(x + 2*y),3)
640 | >>> B = solve((eq1,eq2))
641 |
642 | Default human readable output on command line
643 | >>> B
644 | {{x = -3, y = 3}, {x = -1, y = -1}, {x = 1, y = 1}, {x = 3, y = -3}}
645 |
646 | To get raw output turn off by setting
647 | >>> algwsym_config.output.human_text=False
648 | >>> B
649 | FiniteSet(FiniteSet(Equation(x, -3), Equation(y, 3)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, -1), Equation(y, -1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 1), Equation(y, 1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 3), Equation(y, -3)))
650 |
651 | Pre-0.11.0 behavior where a python list of solutions is returned
652 | >>> algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = True
653 | >>> solve((eq1,eq2))
654 | [[Equation(x, -3), Equation(y, 3)], [Equation(x, -1), Equation(y, -1)], [Equation(x, 1), Equation(y, 1)], [Equation(x, 3), Equation(y, -3)]]
655 | >>> algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list = False # reset to default
656 |
657 | `algwsym_config.output.human_text = True` with
658 | `algwsym_config.output.how_code=True` shows both.
659 | In Jupyter-like environments `show_code=True` yields the Raw output and
660 | a typeset version. If `show_code=False` (the default) only the
661 | typeset version is shown in Jupyter.
662 | >>> algwsym_config.output.show_code=True
663 | >>> algwsym_config.output.human_text=True
664 | >>> B
665 | Code version: FiniteSet(FiniteSet(Equation(x, -3), Equation(y, 3)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, -1), Equation(y, -1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 1), Equation(y, 1)), FiniteSet(Equation(x, 3), Equation(y, -3)))
666 | {{x = -3, y = 3}, {x = -1, y = -1}, {x = 1, y = 1}, {x = 3, y = -3}}
667 | """
668 | from sympy.solvers.solvers import solve
669 | from sympy.sets.sets import FiniteSet
670 | newf =[]
671 | solns = []
672 | displaysolns = []
673 | contains_eqn = False
674 | if hasattr(f,'__iter__'):
675 | for k in f:
676 | if isinstance(k, Equation):
677 | newf.append(k.lhs-k.rhs)
678 | contains_eqn = True
679 | else:
680 | newf.append(k)
681 | else:
682 | if isinstance(f, Equation):
683 | newf.append(f.lhs - f.rhs)
684 | contains_eqn = True
685 | else:
686 | newf.append(f)
687 | flags['dict'] = True
688 | result = solve(newf, *symbols, **flags)
689 | if len(symbols) == 1 and hasattr(symbols[0], "__iter__"):
690 | symbols = symbols[0]
691 | if contains_eqn:
692 | if len(result[0]) == 1:
693 | for k in result:
694 | for key in k.keys():
695 | val = k[key]
696 | tempeqn = Eqn(key, val)
697 | solns.append(tempeqn)
698 | if len(solns) == len(symbols):
699 | # sort according to the user-provided symbols
700 | solns = sorted(solns, key=lambda x: symbols.index(x.lhs))
701 | else:
702 | for k in result:
703 | solnset = []
704 | for key in k.keys():
705 | val = k[key]
706 | tempeqn = Eqn(key, val)
707 | solnset.append(tempeqn)
708 | if not algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list:
709 | solnset = FiniteSet(*solnset)
710 | else:
711 | if len(solnset) == len(symbols):
712 | # sort according to the user-provided symbols
713 | solnset = sorted(solnset, key=lambda x: symbols.index(x.lhs))
714 | solns.append(solnset)
715 | else:
716 | solns = result
717 | if algwsym_config.output.solve_to_list:
718 | if len(solns) == 1 and hasattr(solns[0], "__iter__"):
719 | # no need to wrap a list of a single element inside another list
720 | return solns[0]
721 | return solns
722 | else:
723 | if len(solns) == 1:
724 | # do not wrap a singleton in FiniteSet if it already is
725 | for k in solns:
726 | if isinstance(k, FiniteSet):
727 | return k
728 | return FiniteSet(*solns)
729 |
730 | def solveset(f, symbols, domain=sympy.Complexes):
731 | """
732 | Very experimental override of sympy solveset, which we hope will replace
733 | solve. Much is not working. It is not clear how to input a system of
734 | equations unless you directly select `linsolve`, etc...
735 | """
736 | from sympy.solvers import solveset as solve
737 | newf = []
738 | solns = []
739 | displaysolns = []
740 | contains_eqn = False
741 | if hasattr(f, '__iter__'):
742 | for k in f:
743 | if isinstance(k, Equation):
744 | newf.append(k.lhs - k.rhs)
745 | contains_eqn = True
746 | else:
747 | newf.append(k)
748 | else:
749 | if isinstance(f, Equation):
750 | newf.append(f.lhs - f.rhs)
751 | contains_eqn = True
752 | else:
753 | newf.append(f)
754 | result = solve(*newf, symbols, domain=domain)
755 | # if contains_eqn:
756 | # if len(result[0]) == 1:
757 | # for k in result:
758 | # for key in k.keys():
759 | # val = k[key]
760 | # tempeqn = Eqn(key, val)
761 | # solns.append(tempeqn)
762 | # display(*solns)
763 | # else:
764 | # for k in result:
765 | # solnset = []
766 | # displayset = []
767 | # for key in k.keys():
768 | # val = k[key]
769 | # tempeqn = Eqn(key, val)
770 | # solnset.append(tempeqn)
771 | # if algwsym_config.output.show_solve_output:
772 | # displayset.append(tempeqn)
773 | # if algwsym_config.output.show_solve_output:
774 | # displayset.append('-----')
775 | # solns.append(solnset)
776 | # if algwsym_config.output.show_solve_output:
777 | # for k in displayset:
778 | # displaysolns.append(k)
779 | # if algwsym_config.output.show_solve_output:
780 | # display(*displaysolns)
781 | # else:
782 | solns = result
783 | return solns
784 |
785 | class Equality(Equality):
786 | """
787 | Extension of Equality class to include the ability to convert it to an
788 | Equation.
789 | """
790 | def to_Equation(self):
791 | """
792 | Return: recasts the Equality as an Equation.
793 | """
794 | return Equation(self.lhs,self.rhs)
795 |
796 | def to_Eqn(self):
797 | """
798 | Synonym for to_Equation.
799 | Return: recasts the Equality as an Equation.
800 | """
801 | return self.to_Equation()
802 |
803 | Eq = Equality
804 |
805 | def __Equation__repr__override__(self):
806 | """Override of the default sympy representation to match normal python
807 | behavior and allow for a human readable string representation.
808 | """
809 | return 'Equation(%s, %s)' % (repr(self.lhs), repr(self.rhs))
810 |
811 | sympy.core.Equation.__repr__ = __Equation__repr__override__
812 |
813 | def __Equation__str__override__(self):
814 | """Override of the default sympy representation to match normal python
815 | behavior and allow for a human readable string representation.
816 | """
817 | return '%s = %s' % (repr(self.lhs), repr(self.rhs))
818 |
819 | sympy.core.Equation.__str__ = __Equation__str__override__
820 |
821 | def __FiniteSet__repr__override__(self):
822 | """Override of the `FiniteSet.__repr__(self)` to overcome sympy's
823 | inconsistent wrapping of Finite Sets which prevents reliable use of
824 | copy and paste of the code representation.
825 | """
826 | insidestr = ""
827 | for k in self.args:
828 | insidestr += k.__repr__() +', '
829 | insidestr = insidestr[:-2]
830 | reprstr = "FiniteSet("+ insidestr + ")"
831 | return reprstr
832 |
833 | sympy.sets.FiniteSet.__repr__ = __FiniteSet__repr__override__
834 |
835 | def __FiniteSet__str__override__(self):
836 | """Override of the `FiniteSet.__str__(self)` to overcome sympy's
837 | inconsistent wrapping of Finite Sets which prevents reliable use of
838 | copy and paste of the code representation.
839 | """
840 | insidestr = ""
841 | for k in self.args:
842 | insidestr += str(k) + ', '
843 | insidestr = insidestr[:-2]
844 | strrep = "{"+ insidestr + "}"
845 | return strrep
846 |
847 | sympy.sets.FiniteSet.__str__ = __FiniteSet__str__override__
848 |
849 | # Redirect python abs() to Abs()
850 | abs = Abs
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------